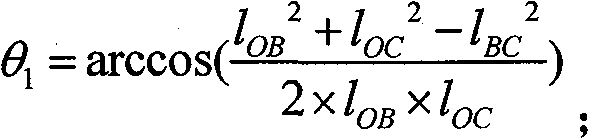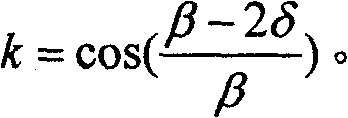Patents
Literature
36 results about "Zygomatic arch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
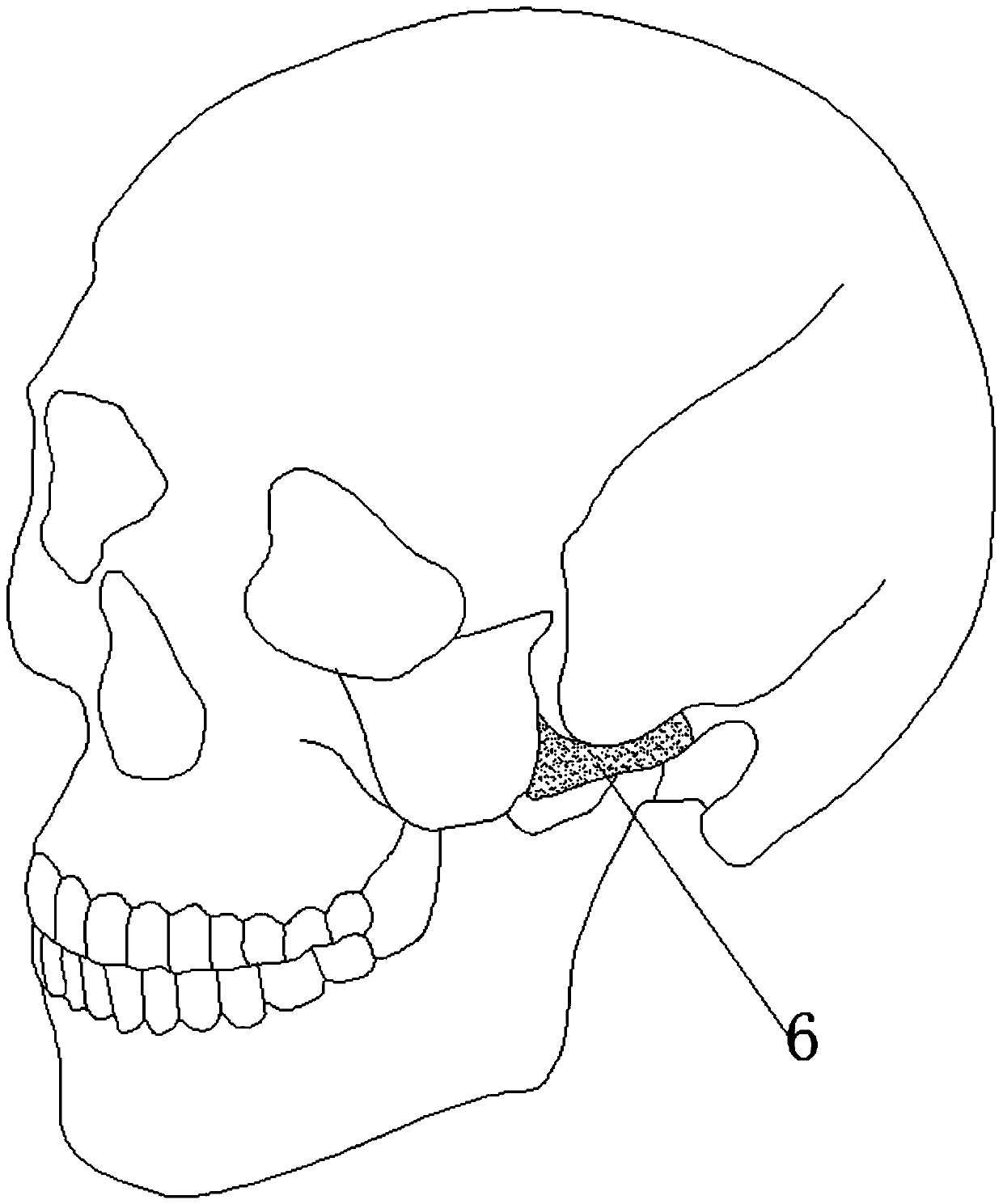
The zygomatic arch, or cheek bone, is formed by the zygomatic process of the temporal bone (a bone extending forward from the side of the skull, over the opening of the ear) and the temporal process of the zygomatic bone (the side of the cheekbone), the two being united by an oblique suture (zygomaticotemporal suture); the tendon of the temporalis passes medial to the arch to gain insertion into the coronoid process of the mandible. The jugal point is the point at the anterior end of the upper border of the zygomatic arch where the masseteric and maxillary edges meet at an angle. The jugal point is the anterior end of upper border of the zygomatic arch where it meets the process of the zygomatic bone.
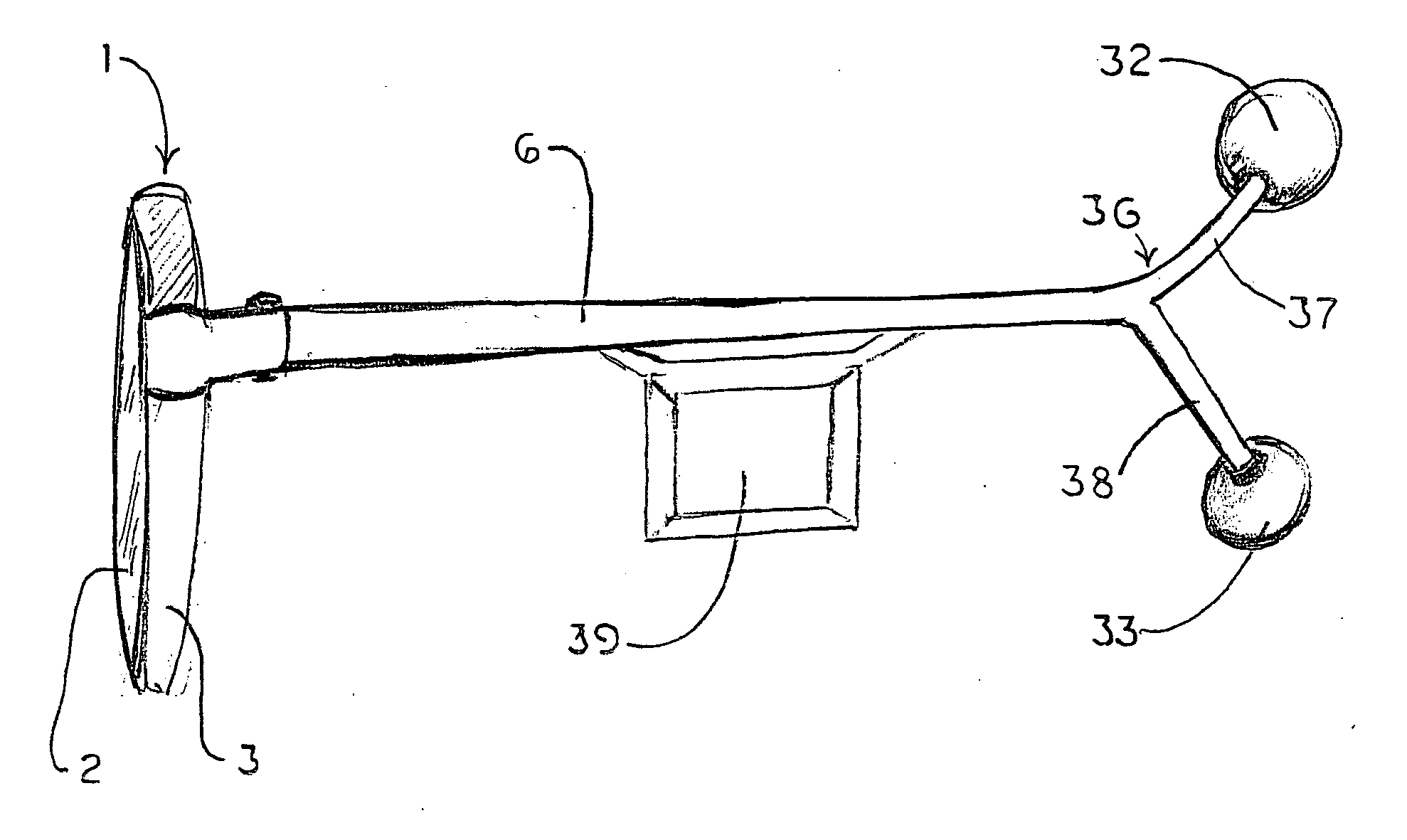
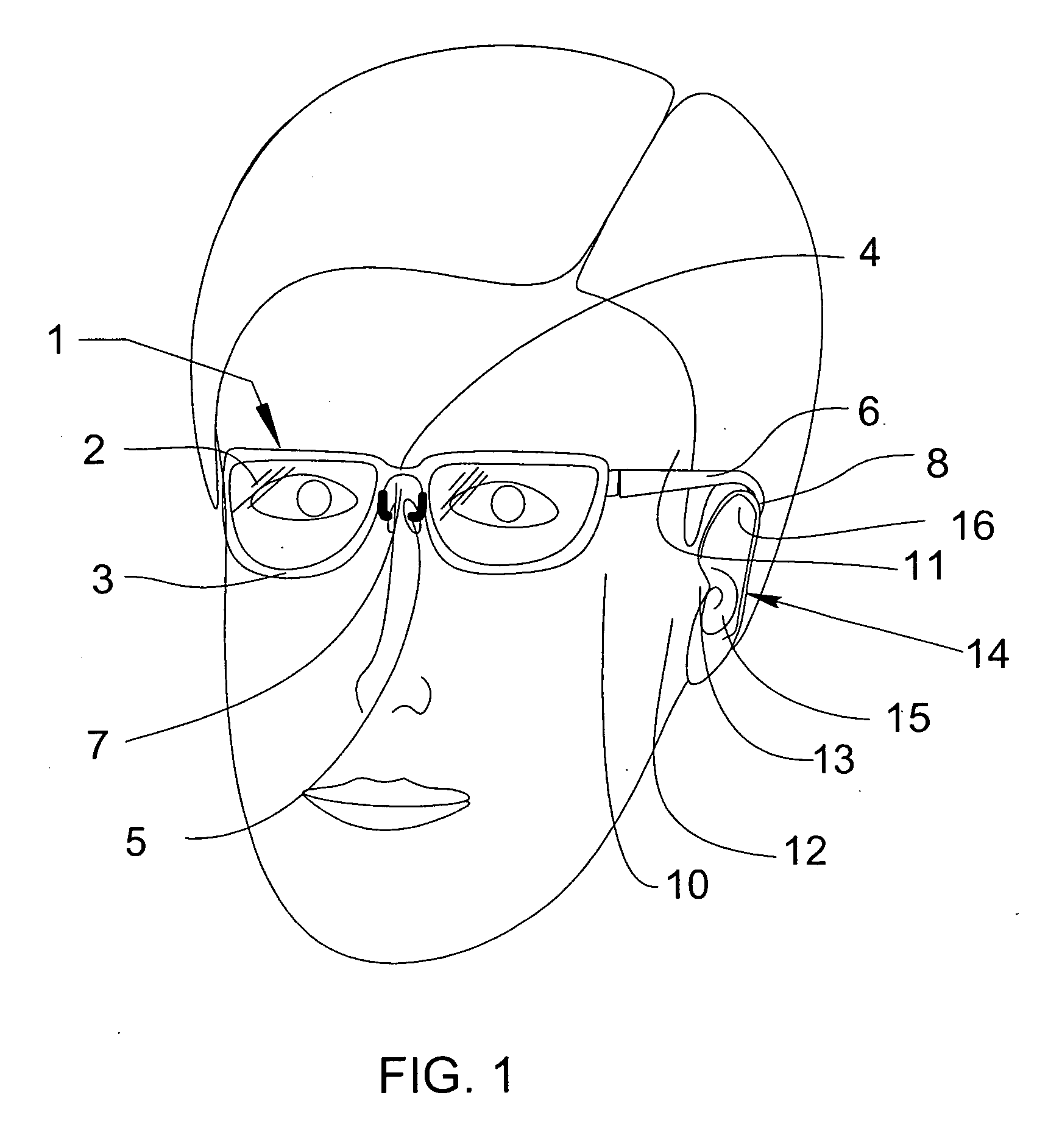
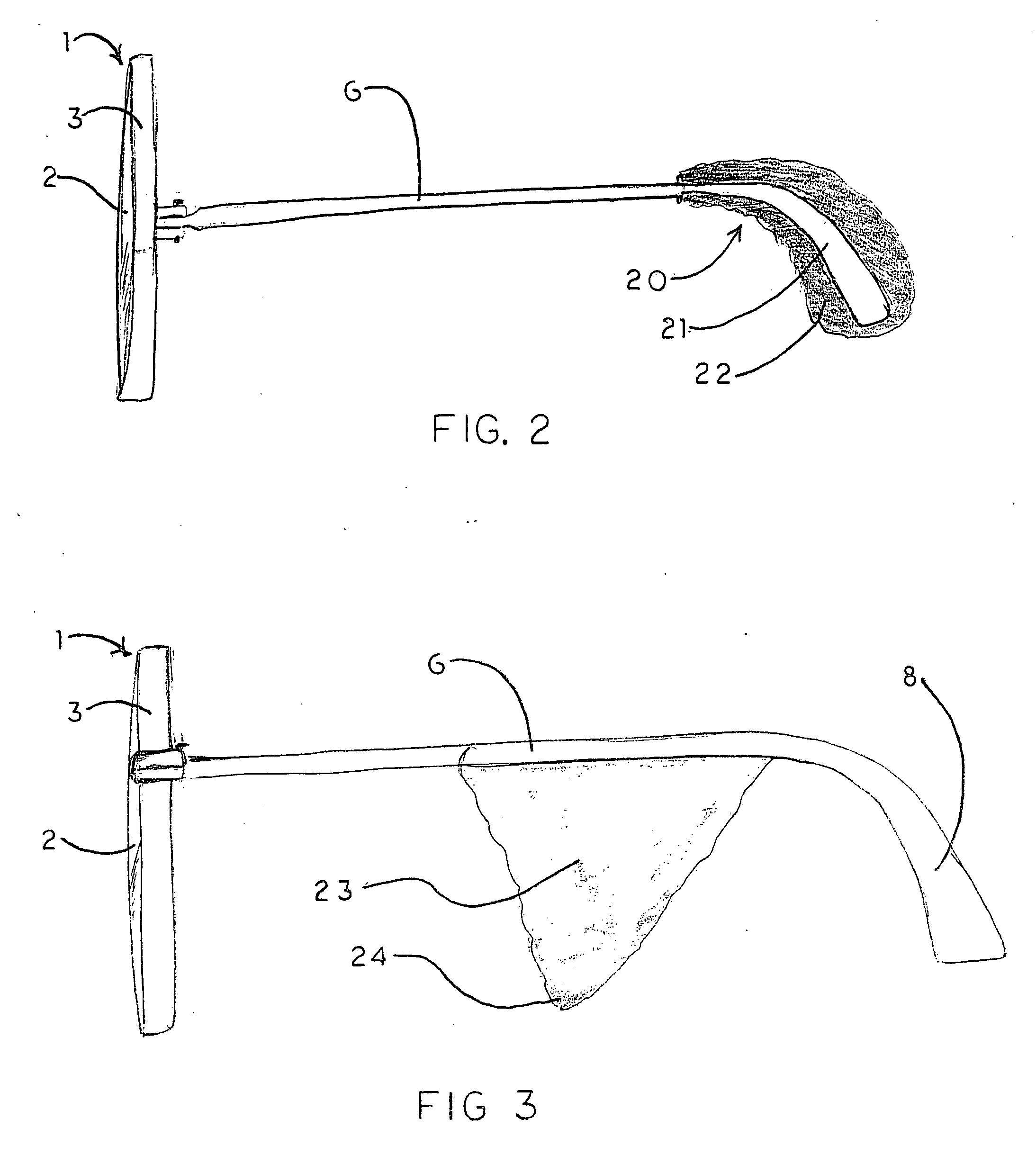
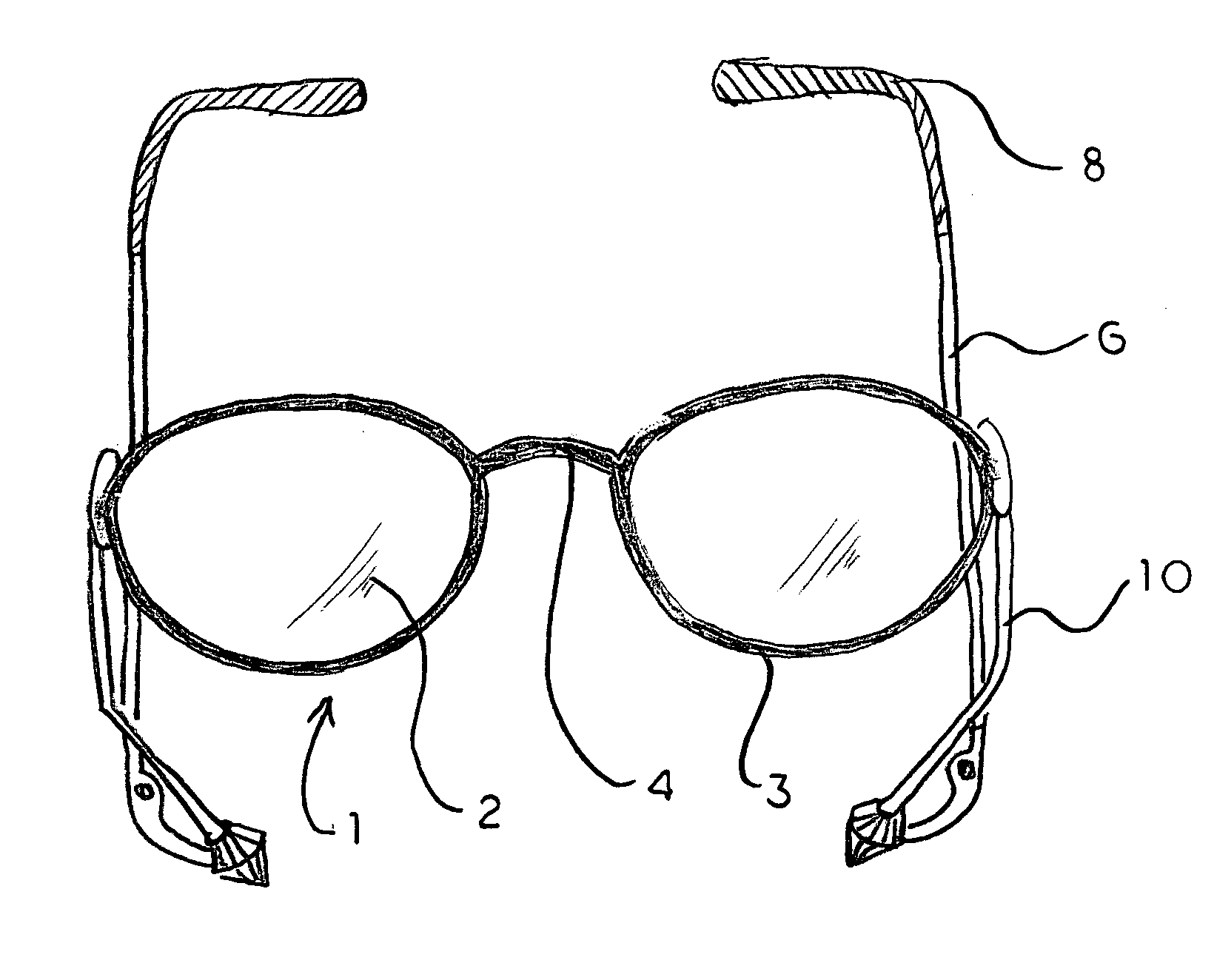
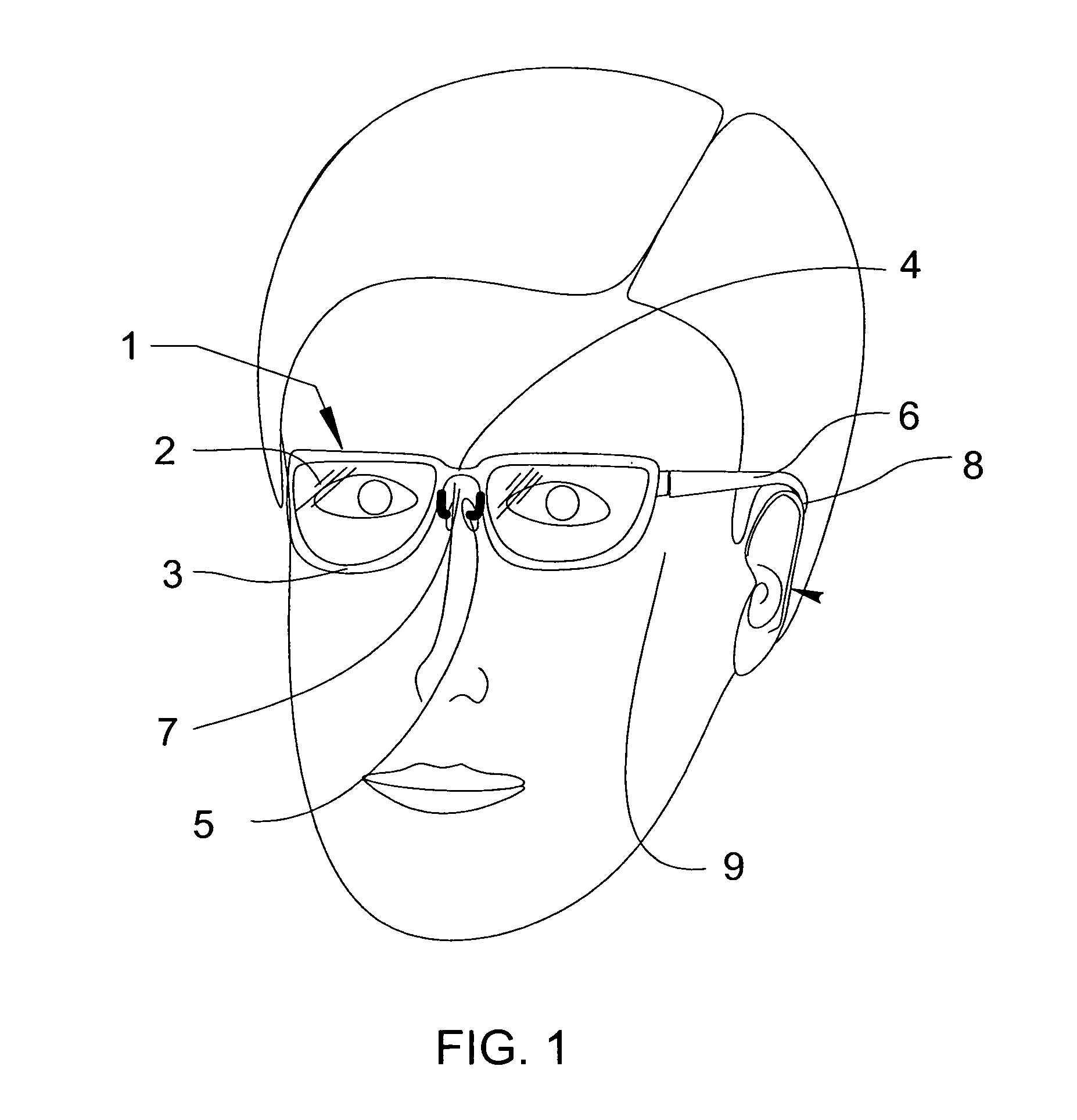
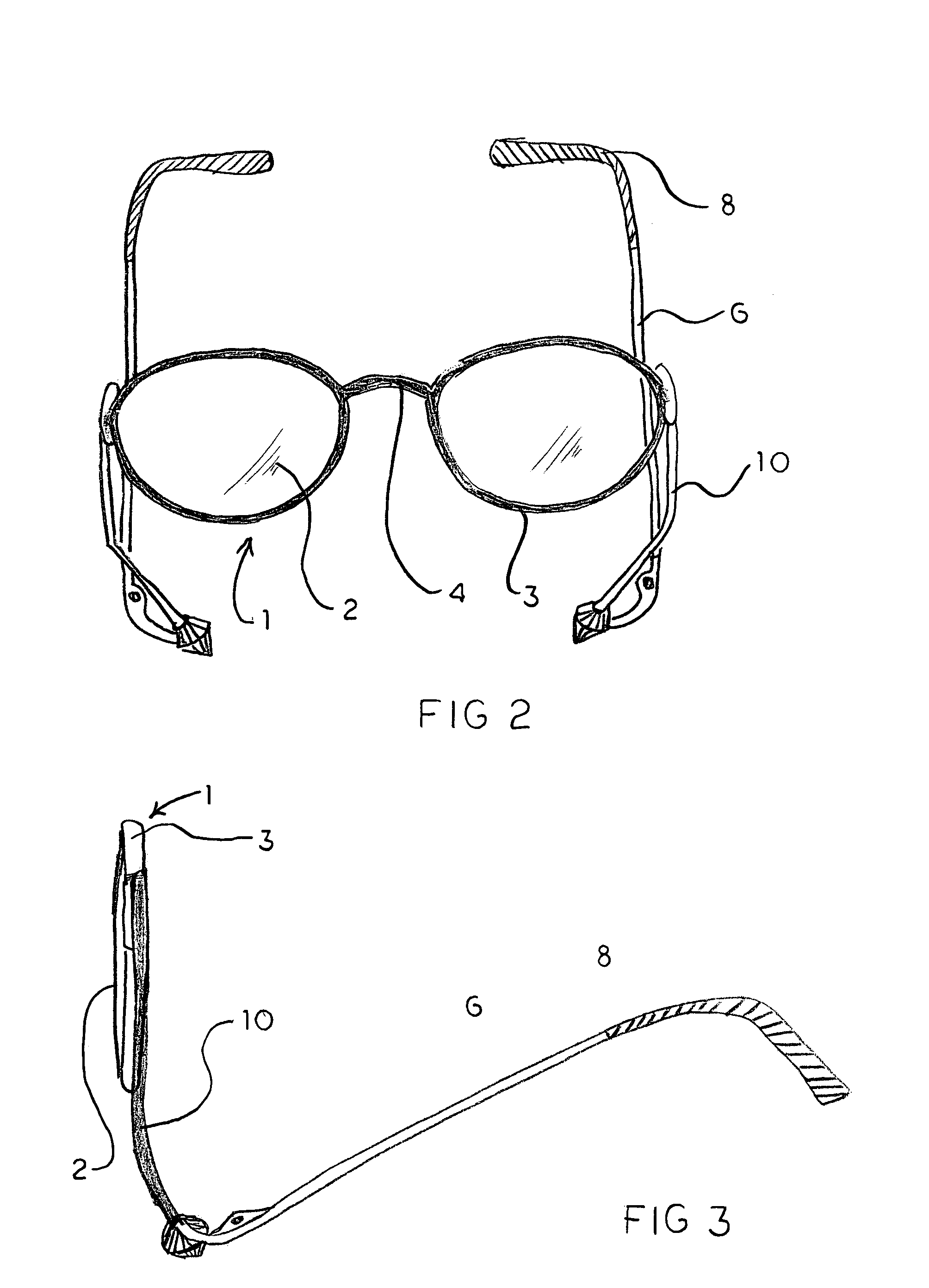
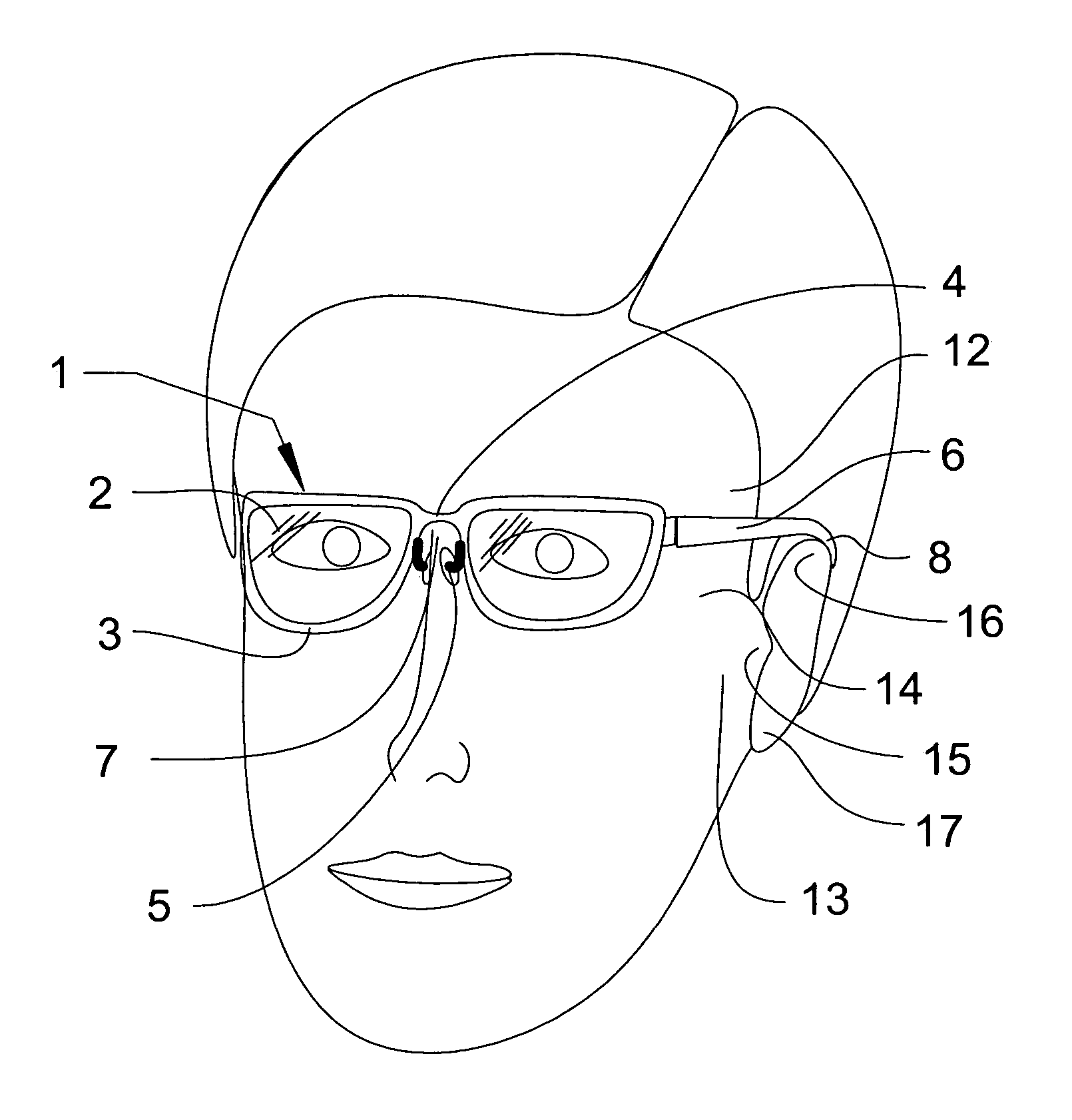
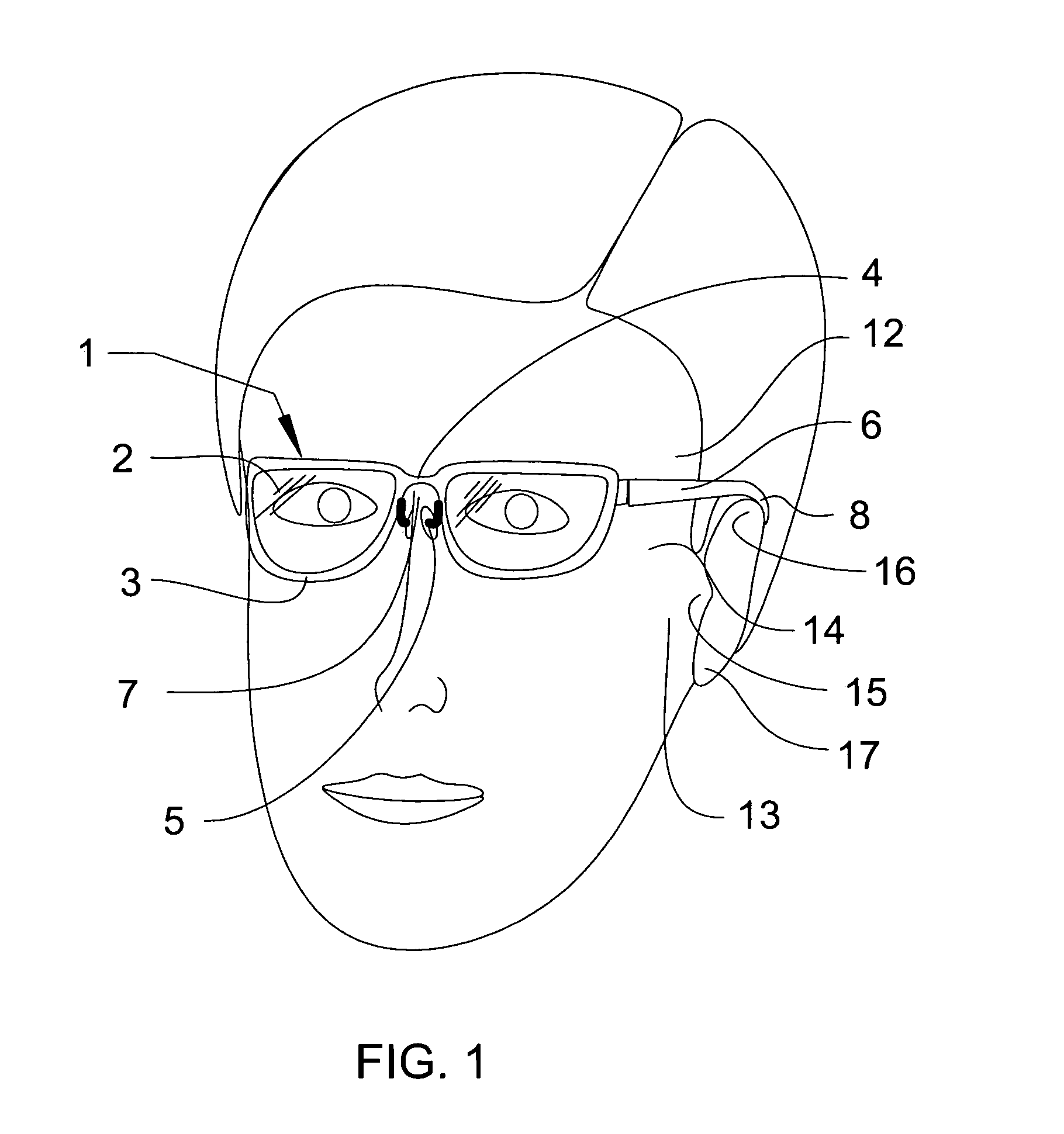
Eyeglasses with temple arm supports
InactiveUS20060098160A1Improve disadvantagesNon-optical adjunctsNon-optical partsNoseSurgery procedure
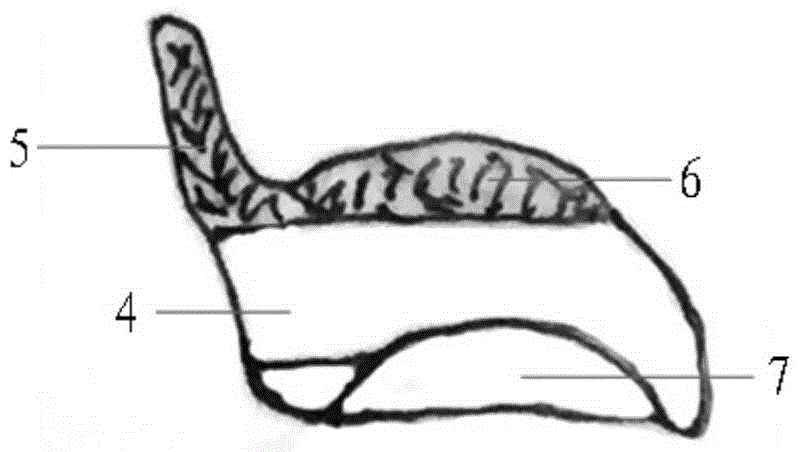
Eyeglasses with additional temple arm supports for supporting the frame of a pair of eyeglasses off of and above the nose and nasal bone. The glasses are used by patients recovering from rhinoplasty surgery but who must still have use of eyeglasses which do not contact the nasal bone or nose. In one embodiment, the frame is suspended above the nose by an enhanced counterweighed ear loop. In another embodiment, a stanchion is provided supported by the zygomatic arch to elevate the temple arm. Several embodiments support the temple arm with additional mandibular and temple rests extending orthogonally from the temple. Several additional embodiments replace the conventional ear loop with a pair of support pads at the end of a shortened temple arm. The support pads press against the two bony protuberances on the side of the wearer's head. These protuberances include the zygomatic arch, the mandibular condyle, and the temple. Pressure by the support pads against two of these protuberances provides sufficient support for the entire weight of the eyeglasses. Another embodiment is comprised of a support hoop disposed on the temple arm. The upper arc of the hoop is supported by the temple while the lower arc is supported by the mandible.
Owner:JAMIE SHAHROOZ S +1
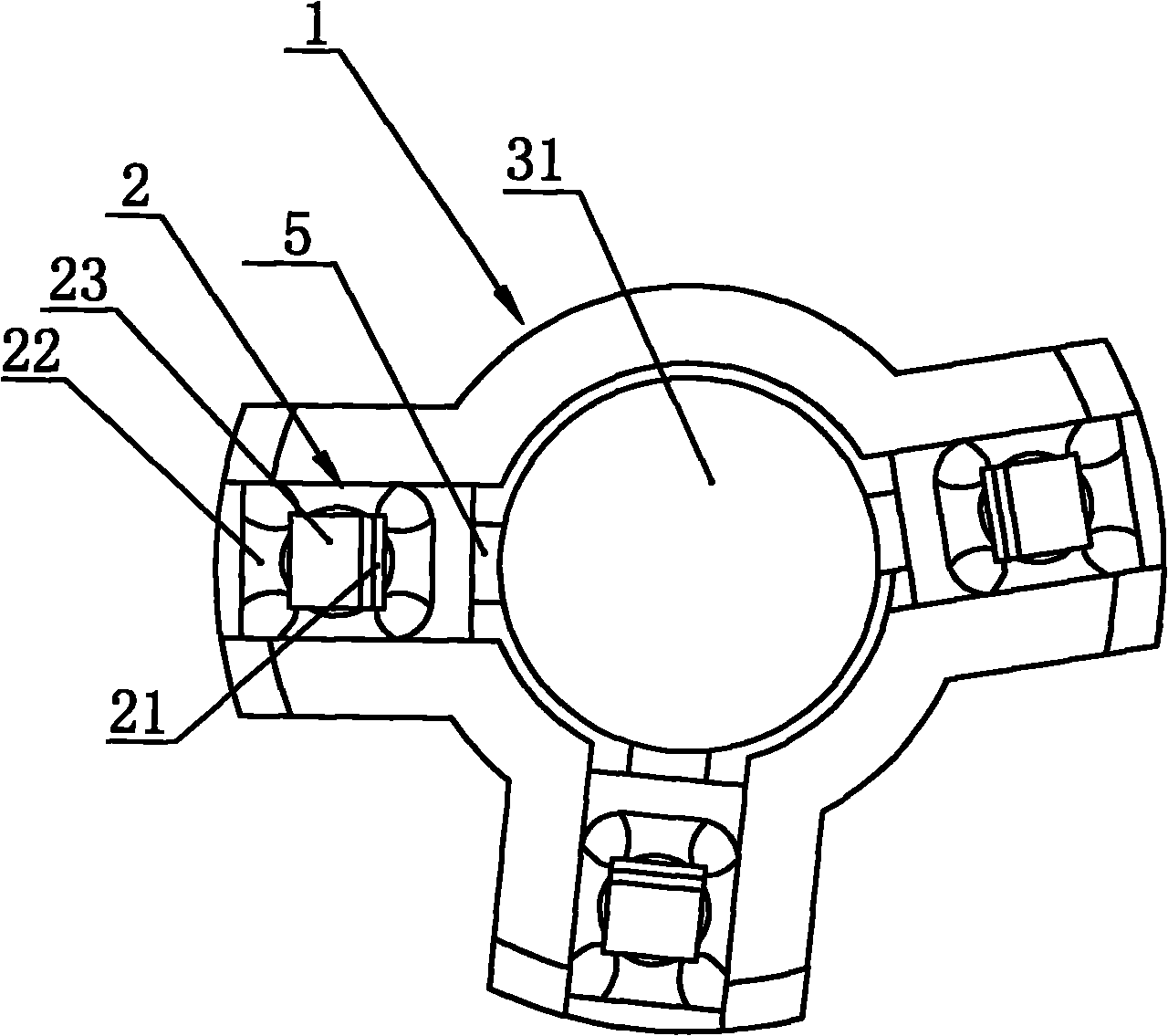
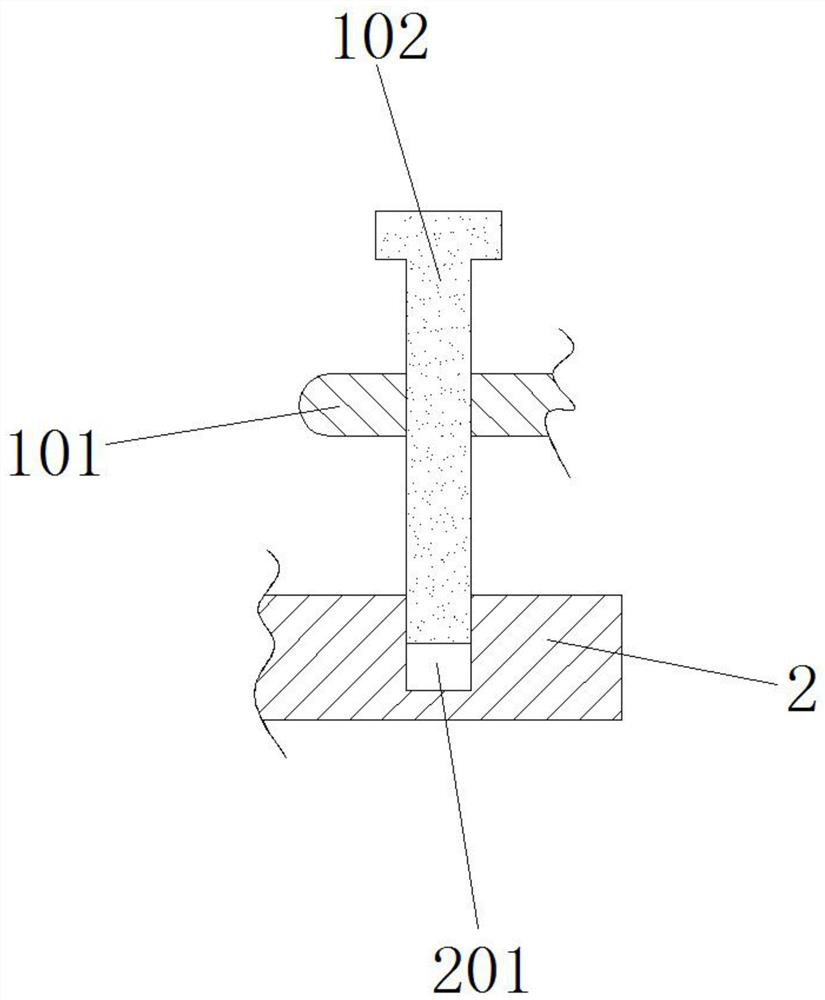
Artificial temporal-mandibular joint replacement bone trimming guide plate assembly
ActiveCN104939951AMake sure to implantGuaranteed application effectJoint implantsBone trimmingArticular tubercle
The invention discloses an artificial temporal-mandibular joint replacement bone trimming guide plate assembly. An articular tubercle guide plate is attached to the outer side face of the zygomatic arch, and the lower edge of the articular tubercle guide plate is in an edge shape or is provided with a shoulder. A zygomatic arch guide plate is attached to the outer surface of the zygomatic arch and is in a U shape, and the opening part of the U shape is in an edge shape. A condyle guide plate is attached to the outer surface of the condyle, and the upper edge of the condyle guide plate is in an edge shape or is provided with a shoulder. An ascending limb guide plate is attached to the outer surface of the mandible ascending limb, the upper portion of the ascending limb guide plate is hollowed out, and the hollowed-out part is in an edge shape. Bottom bone cutting of the maxilla articular tubercle, excision of the mandibular condyle and grinding of the outer surface of the zygomatic arch and the outer surface of the ascending limb are accurately guided, and the unnecessary bone loss is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
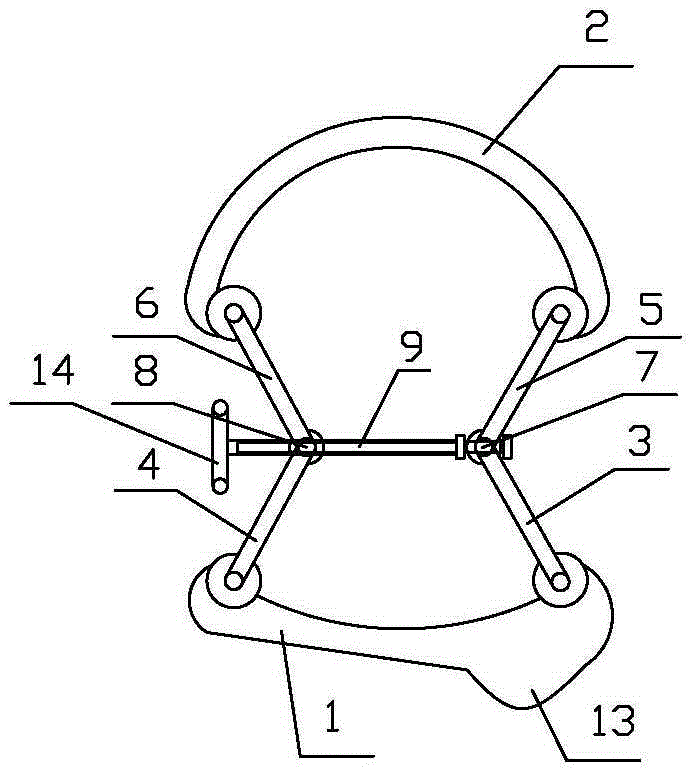
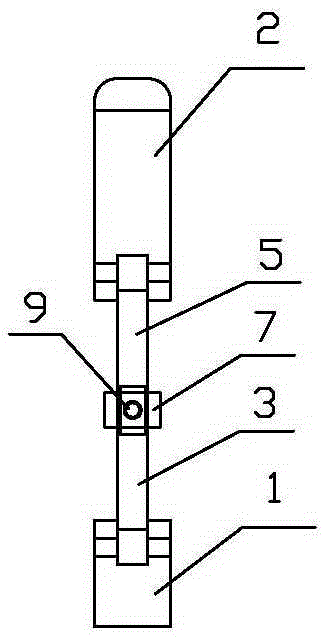
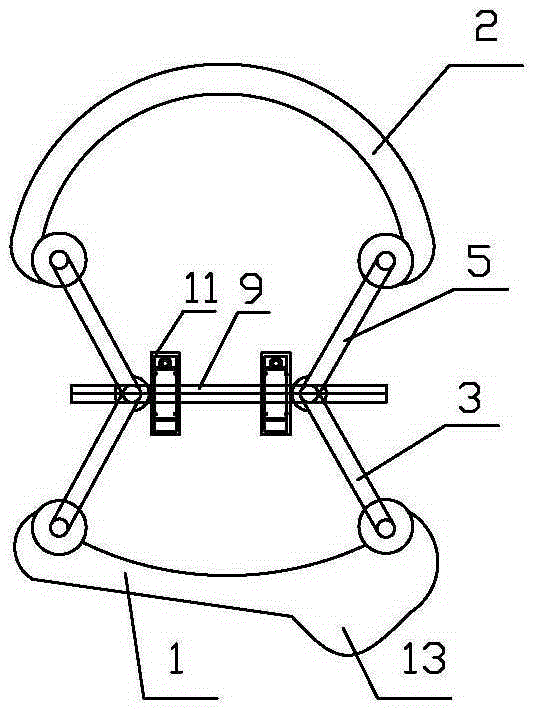
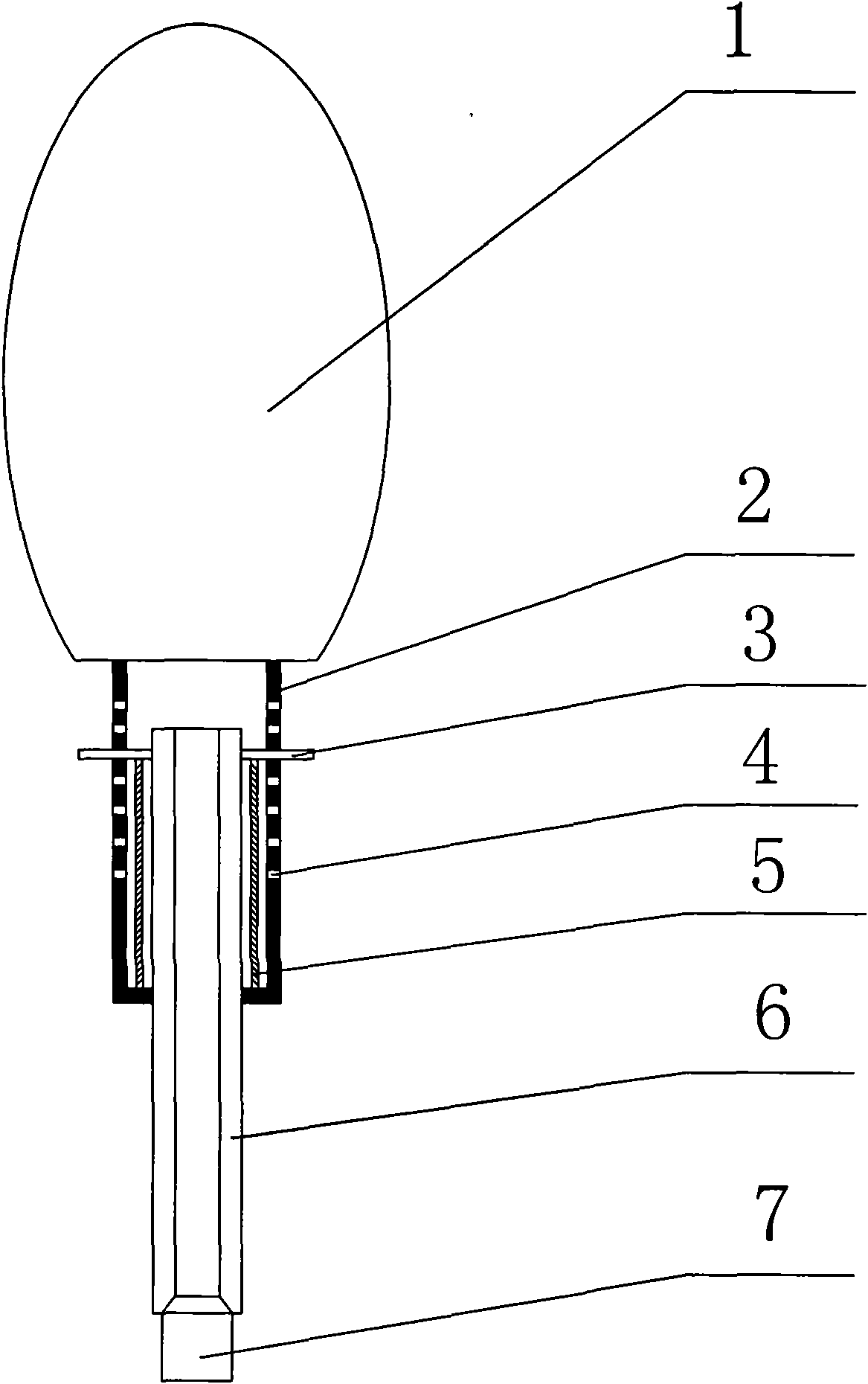
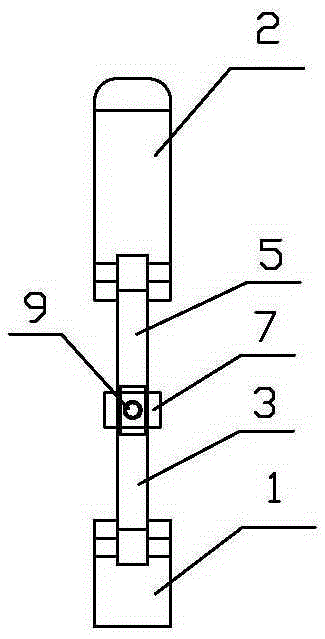
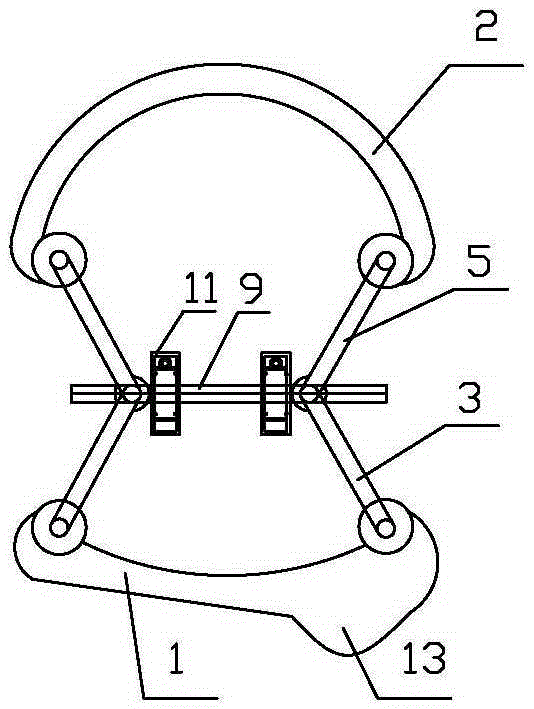
Mandibular condyle reposition expander
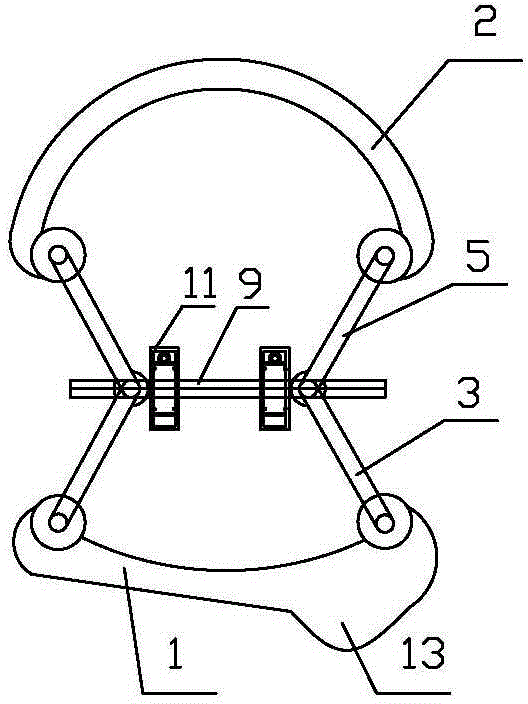
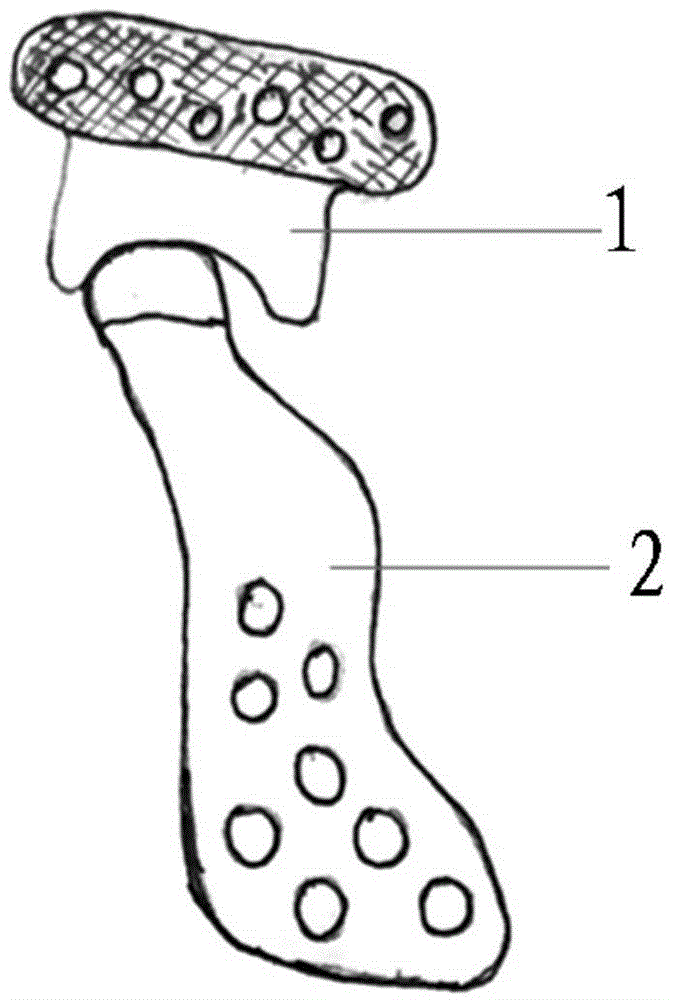
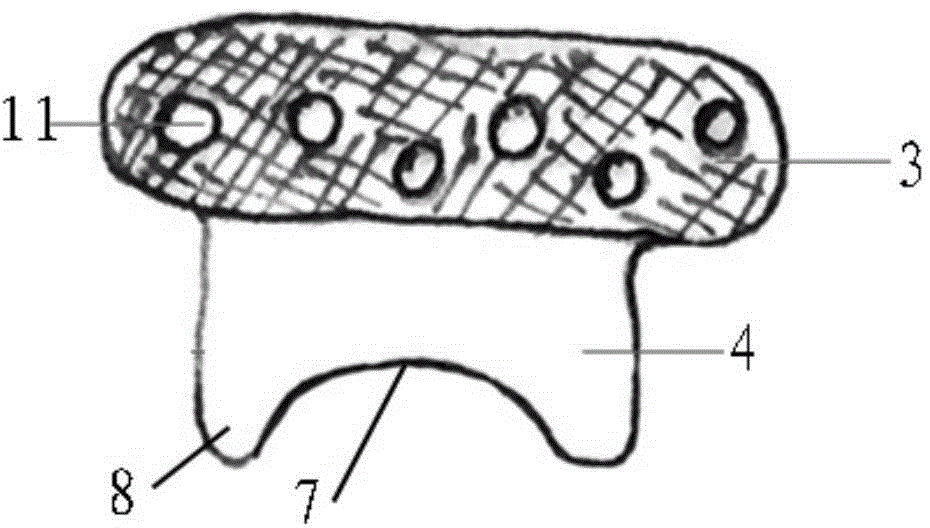
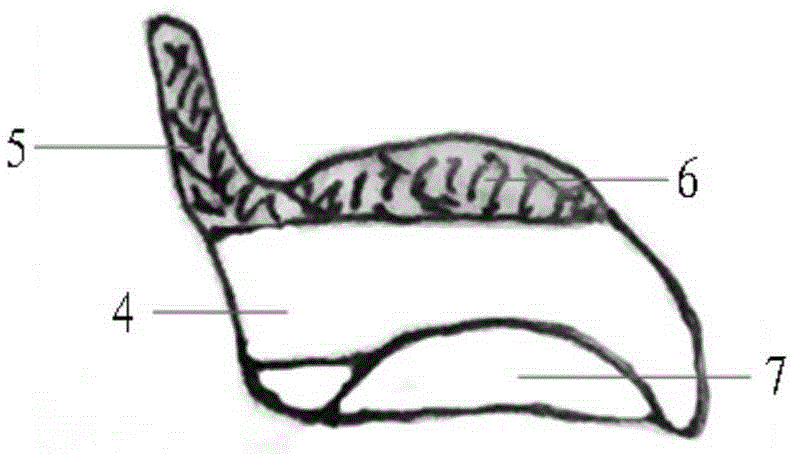
The invention relates to a medical instrument used for a dental operation, in particular to a mandibular condyle reposition expander. The mandibular condyle reposition expander comprises a lower supporting and combining portion and an upper supporting and combining portion. The lower supporting and combining portion corresponds to the incisura of the underjaw of the human body. The upper supporting and combining portion is matched with the zygomatic arch corresponding to the incisura of the underjaw of the human body. A lower supporting front rod and a lower supporting rear rod are hinged to the two ends of the lower supporting and combining portion respectively. An upper supporting front rod and an upper supporting rear rod are hinged to the two ends of the upper supporting and combining portion respectively. The upper end of the lower supporting front rod and the lower end of the upper supporting front rod are hinged to a front hinged shaft. The upper end of the lower supporting rear rod and the lower end of the upper supporting rear rod are hinged to a rear hinged shaft. Both the front hinged shaft and the rear hinged shaft are arranged on a middle shaft. The expander is compact in structure and convenient to use, the pains of patients are small, force is reasonably borne, mechanical deformation or breakage can not easily occur in the use process, and the mandibular condyle reposition expander can adapt to different individual differences.
Owner:郝宏
Artificial temporal-mandibular joint replacement prosthesis
The invention relates to an artificial temporal-mandibular joint replacement prosthesis. The replacement prosthesis comprises a glenoid fossa prosthesis and a mandible ramus prosthesis; the glenoid fossa prosthesis is made of supra polymer polyethylene polymer and comprises a tissue surface in contact with the glenoid fossa and a function surface in contact with the mandible ramus prosthesis, the tissue surface comprises a wing plate which is in contact with the zygomatic arch and is fixed to the zygomatic arch and a protrusion part in contact with the glenoid fossa, and the function surface comprises a sunken part in contact with the mandible ramus prosthesis and stopping plates arranged at the two ends of the sunken part; and the mandible ramus prosthesis comprises a condyloid process head and a mandible ramus fixing handle, the condyloid process head is cylindral and is in contact with the sunken part, the mandible ramus fixing handle is attached to the outer lateral face of the mandible ramus. By means of the artificial temporal-mandibular joint replacement prosthesis, the standard form artificial joint prosthesis is more suitable for the dissection appearance of the Chinese and is better attached to the jaw, complications in and after an operation are effectively reduced, the using effect of the standard form artificial joint prosthesis is improved, and the service life of the standard form artificial joint prosthesis is prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
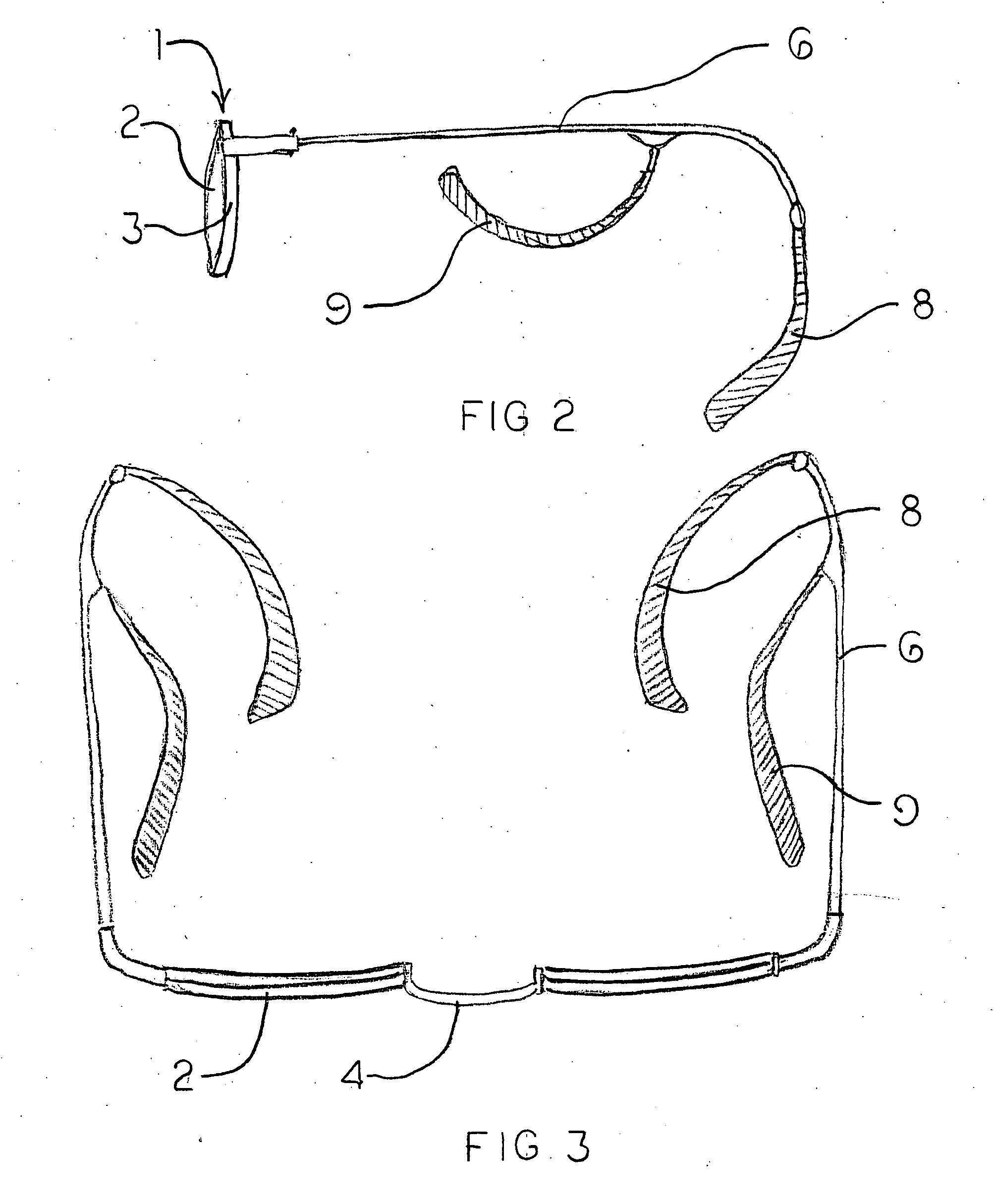
Eyeglasses with extension member supports
Eyeglasses with extension member supports, for supporting the eyeglass frame off of and above the nasal bone, comprised of an eyeglass frame having a pair of laterally aligned lens and, optionally, a pair of circuitous frames, each circuitous frame circumscribing and enclosing either lens; a bridge disposed medially between either lens, a pair of temple arms with distal and proximal ends, and a pair of extension members, each extension member having an upper end articulating with either lens, or its circuitous frame if provided, and a lower end articulating with the proximal end of either temple arm. Each temple arm articulates with the lower end of the extension member at an angle rotated in the parasagittal plane, downward from the traverse plane of the lenses. This rotation permits the temple arms to rest upon the zygomatic arch of the wearer's cranium, thereby supporting the frame off of and above the nasal bone of the wearer.
Owner:MIDDLEBROOK PHARMA
Eyeglass frames with lateral supports
A pair of eyeglasses with additional lateral supports for elevating the bridge of the eyeglasses above the nasal bone of the wearers. These supports permit the use of eyeglasses by persons recovering from rhinoplasty. In one embodiment, a support member attaches at one end to the underside of the rear portion of the temple arms, and courses anteriorly, superiorly and medially so that the distal section engages with the zygomatic arch. Another embodiment has a generally straight vertical support member which contacts with and is support by the temporal mandibular joint. A final embodiment is comprised of a support arm, separate from the temple arm, which articulates with the lens frame and which courses superiorly and medially at its distal end to engage with the zygomatic arch.
Owner:JAMIE SHAHROOZ S +1
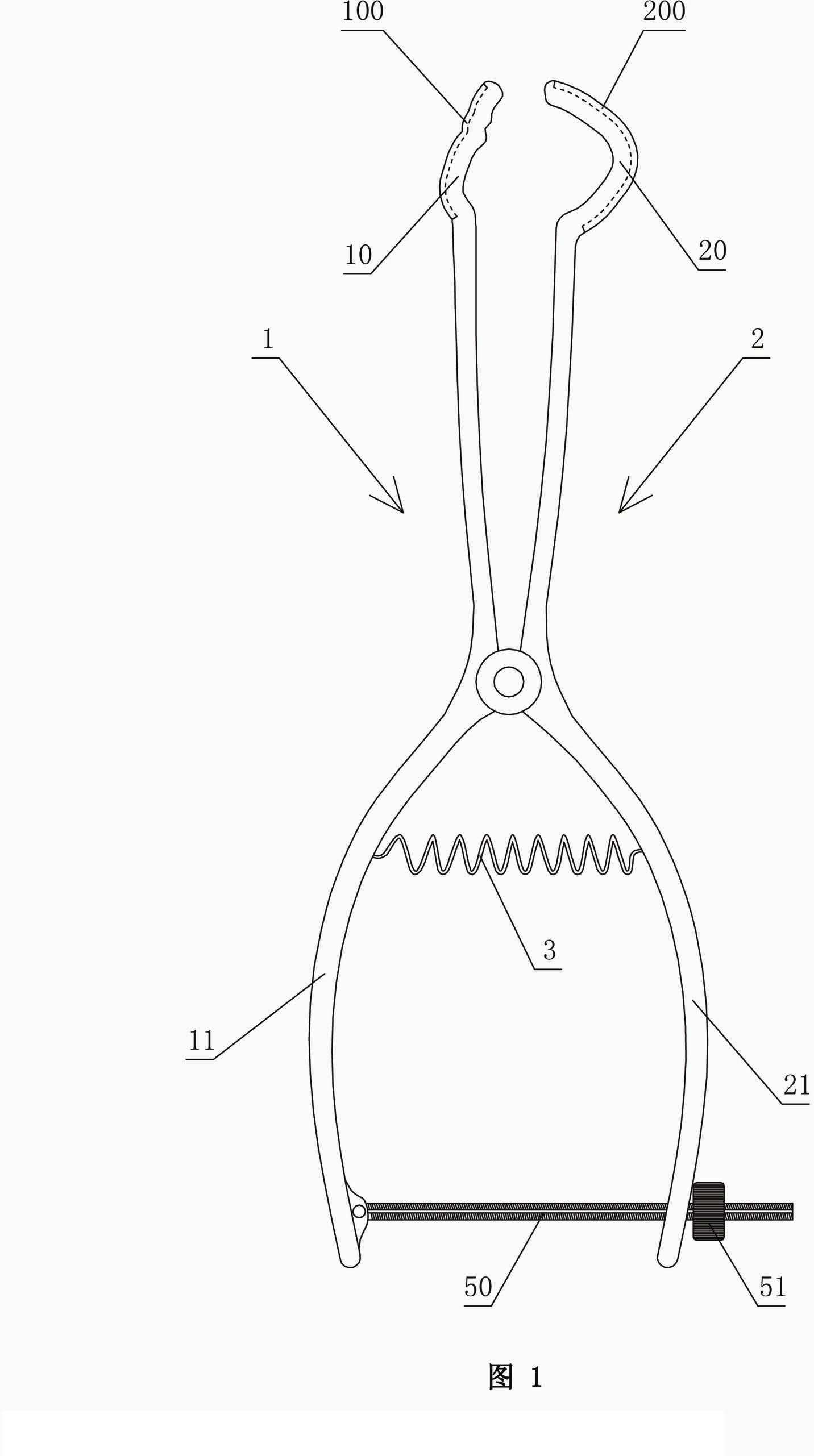
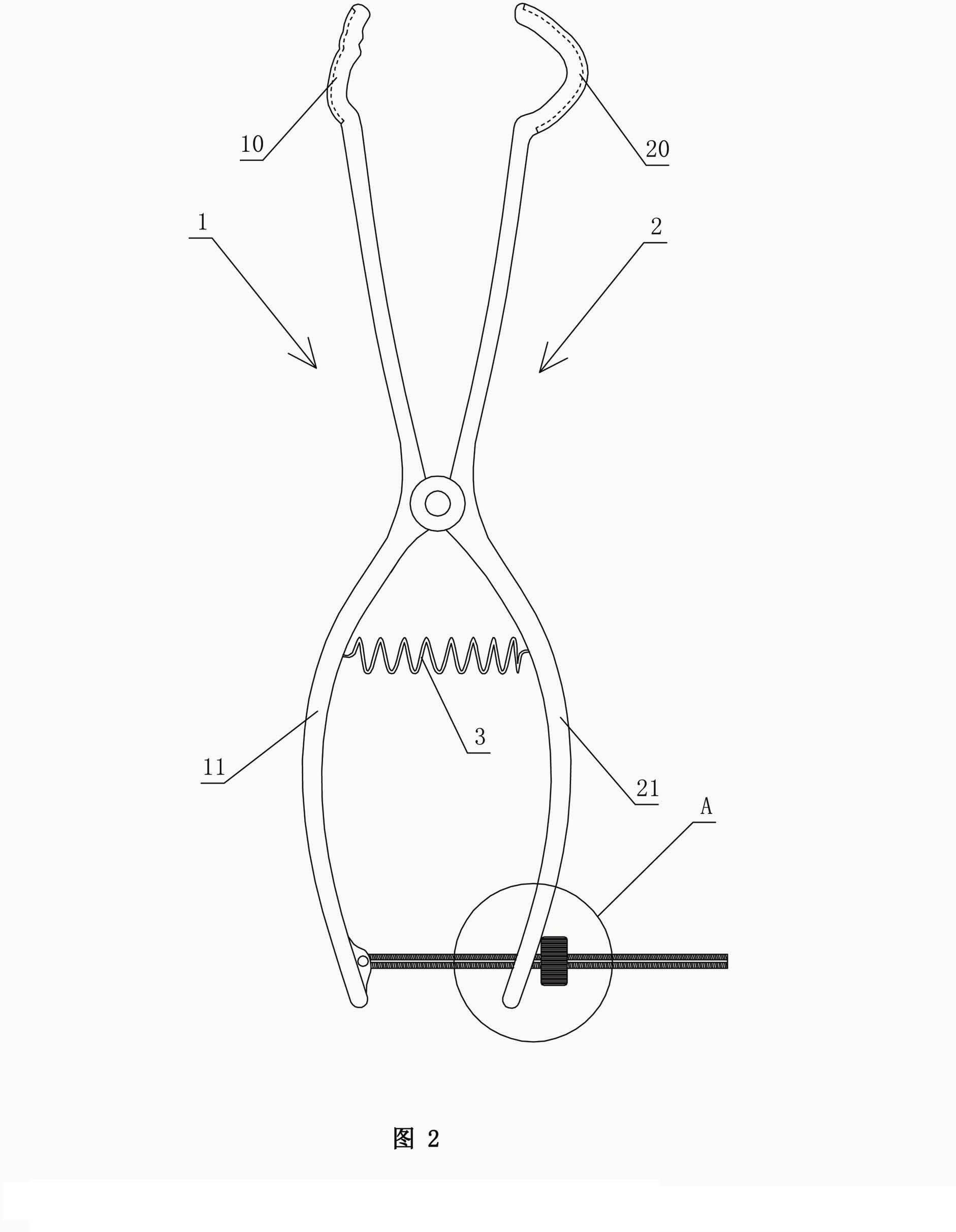
Mandibular condyle fracture reduction dilator
A mandibular condyle fracture reduction dilator comprises two forceps handles which are connected in a cross hub manner. Front ends of the two forceps handles are dilating portions while rear ends of the two forceps handles are holding portions, the dilating portions comprise a lower dilating portion and an upper dilating portion, the lower dilating portion matches with a mandibular incisura, and the upper dilating portion matches with a zygomatic arch corresponding to the mandibular incisura. The mandibular condyle fracture reduction dilator further comprises a positioning component for locking a gap between the upper dilating portion and the lower dilating portion, the positioning component comprises a screw stem and a nut matching with the screw stem, the screw stem is provided with a scale graduation area for displaying the size of the gap between the upper dilating portion and the lower dilating portion, the holding portions comprise an upper holding portion and a lower holding portion which match with each other, a perforated hole is arranged on the lower holding portion, one end of the screw stem penetrates through the perforated hole to be pivotally connected with the upper holding portion, and the nut is sleeved at the other end of the screw stem in a screwed manner, and is located on the outer side of the lower holding portion. The reduction dilator can be used for directly operating in a surgical site of the maxillofacial region of a patient, exerts force on the outside of the oral cavity of the patient, leads joint clearances to be exposed easily, and is convenient in operation, an additional incision is omitted, and tissue injury is low.
Owner:周剑虹
Method for controlling virtual human mouth motion
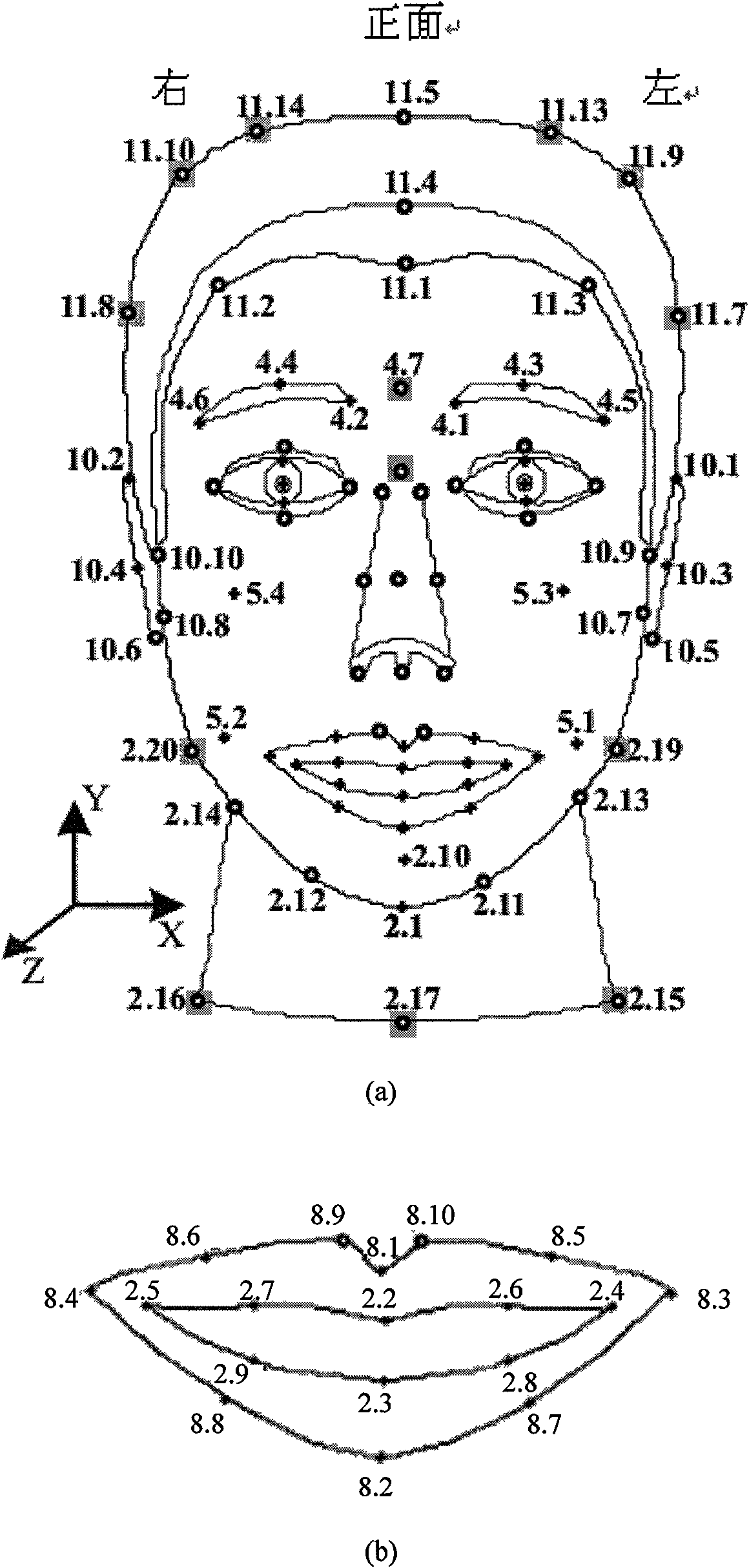
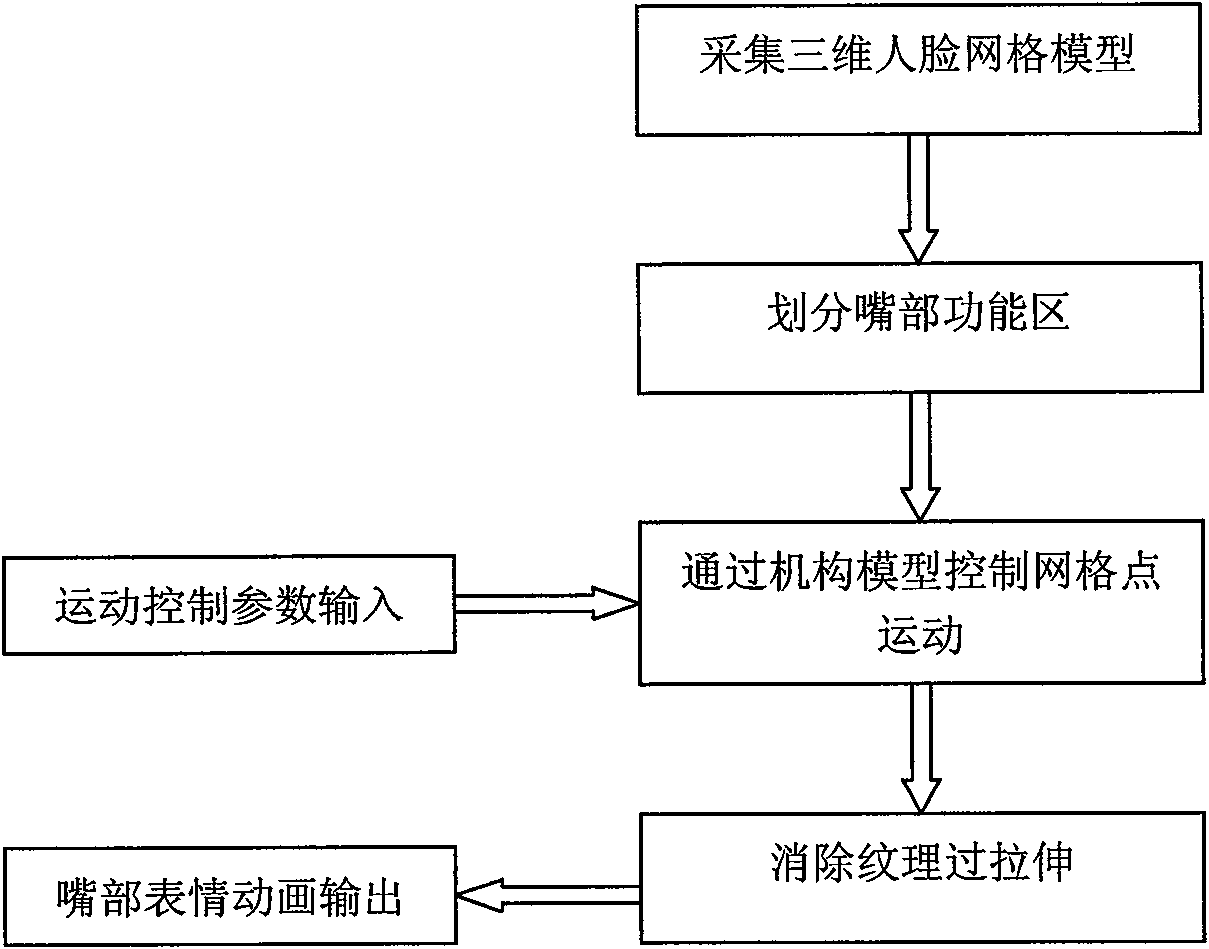
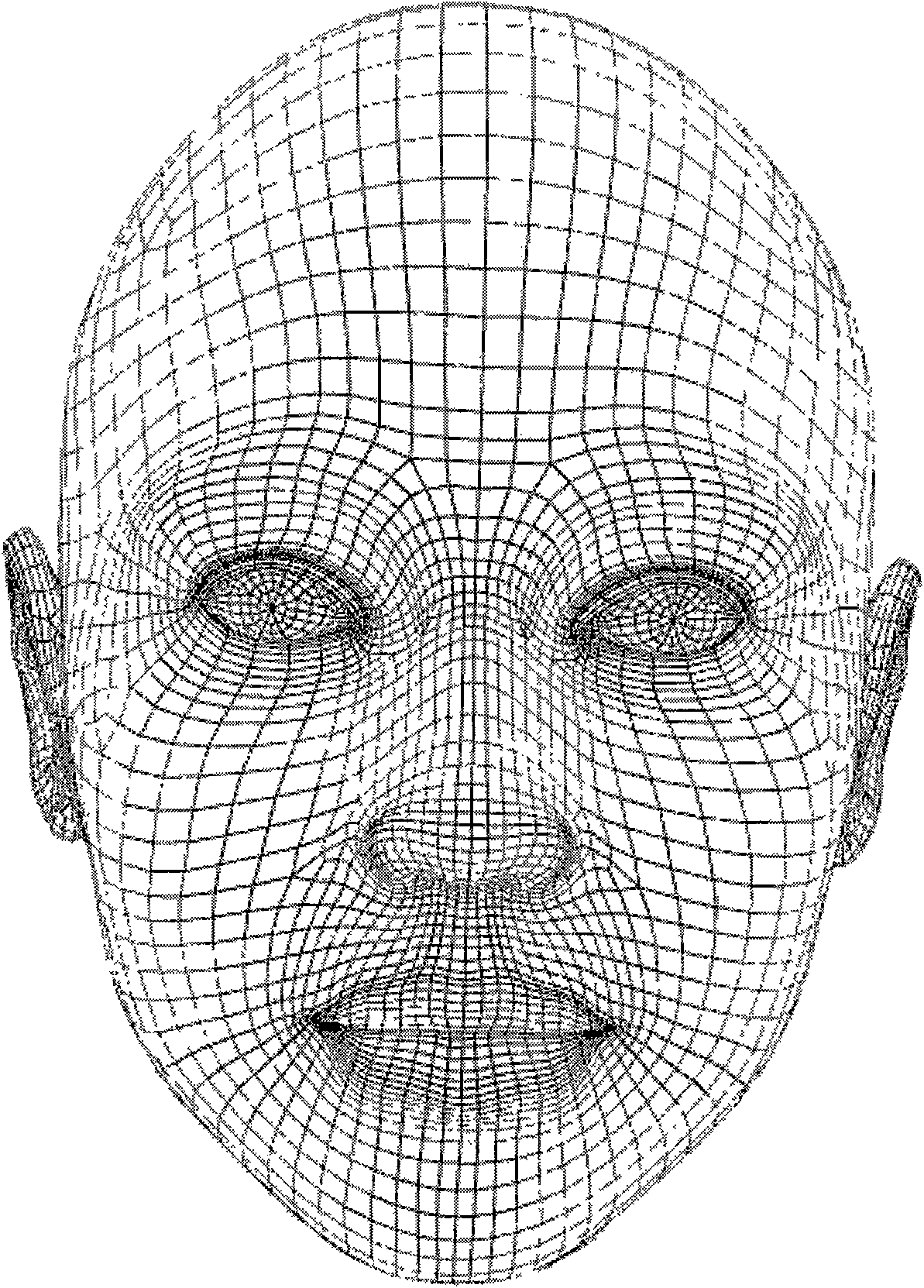
The invention discloses a method for controlling virtual human mouth motion, which comprises the following steps: after a three-dimensional human face grid model is acquired, consulting the definition for FDP characteristic points of a mouth area in MPEG-4 to select the characteristic points at the zygomatic arch, two mouth corners, upper boundary of lower lip and mandible boundary as boundary points of a mouth functional area, and finally determining the mouth functional area in the three-dimensional grid model according to the characteristic point coordinates of the zygomatic arch; and adopting an oscillating guide-bar mechanism model to drive grid points of the mouth functional area to move, simulating a real mouth opening-closing process, and eliminating the overstretching phenomenon at the boundary by processing a peak of a peak buffer area. The method can adopt the same mathematical model to realize opposite motion processes such as opening and closing of the human mouth under continuous condition, the mathematical model is simple, the physical significance is definite, the control is easy, and the simulation effect is vivid.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Implantable device for temporomandibular joint and method of production thereof
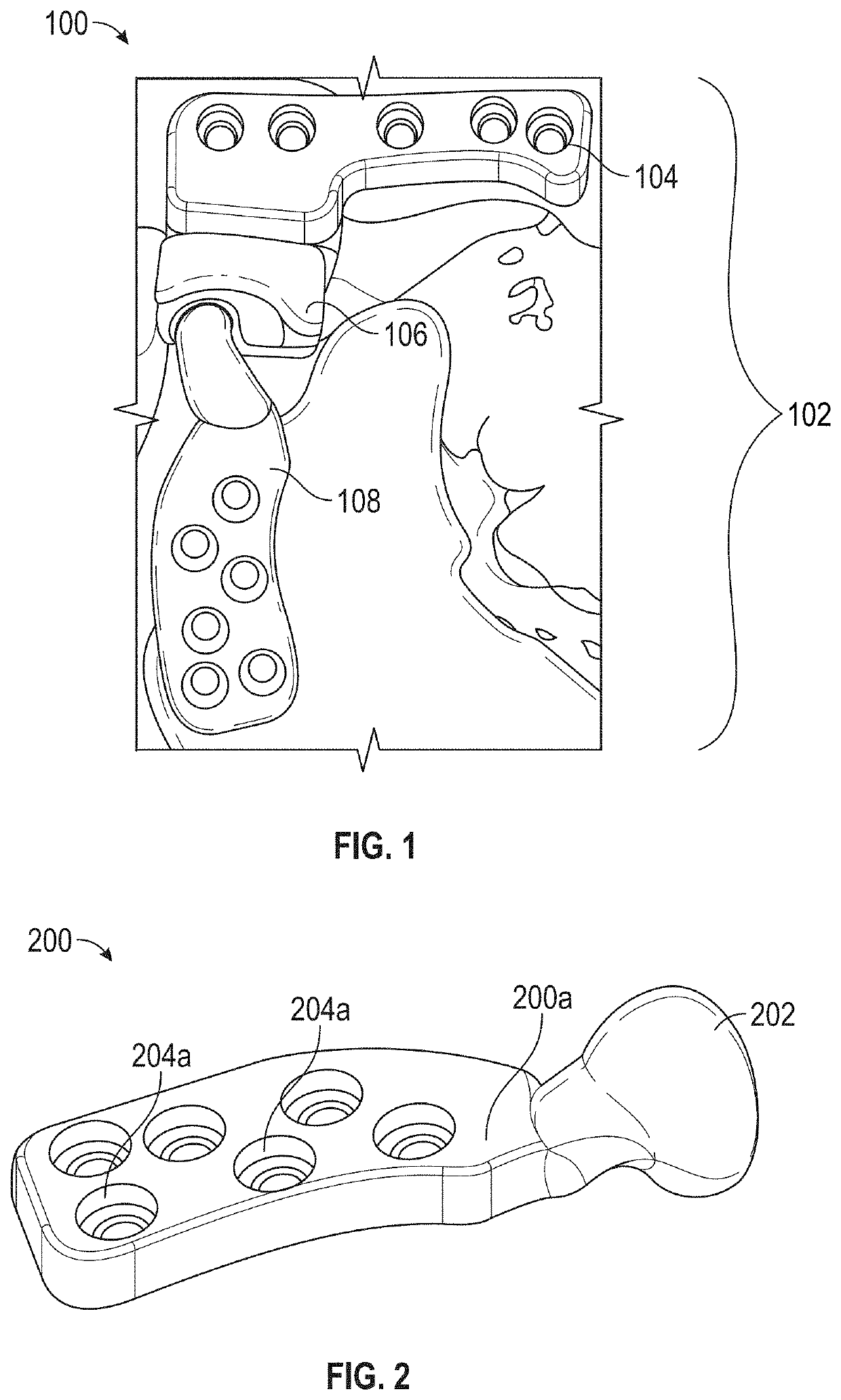
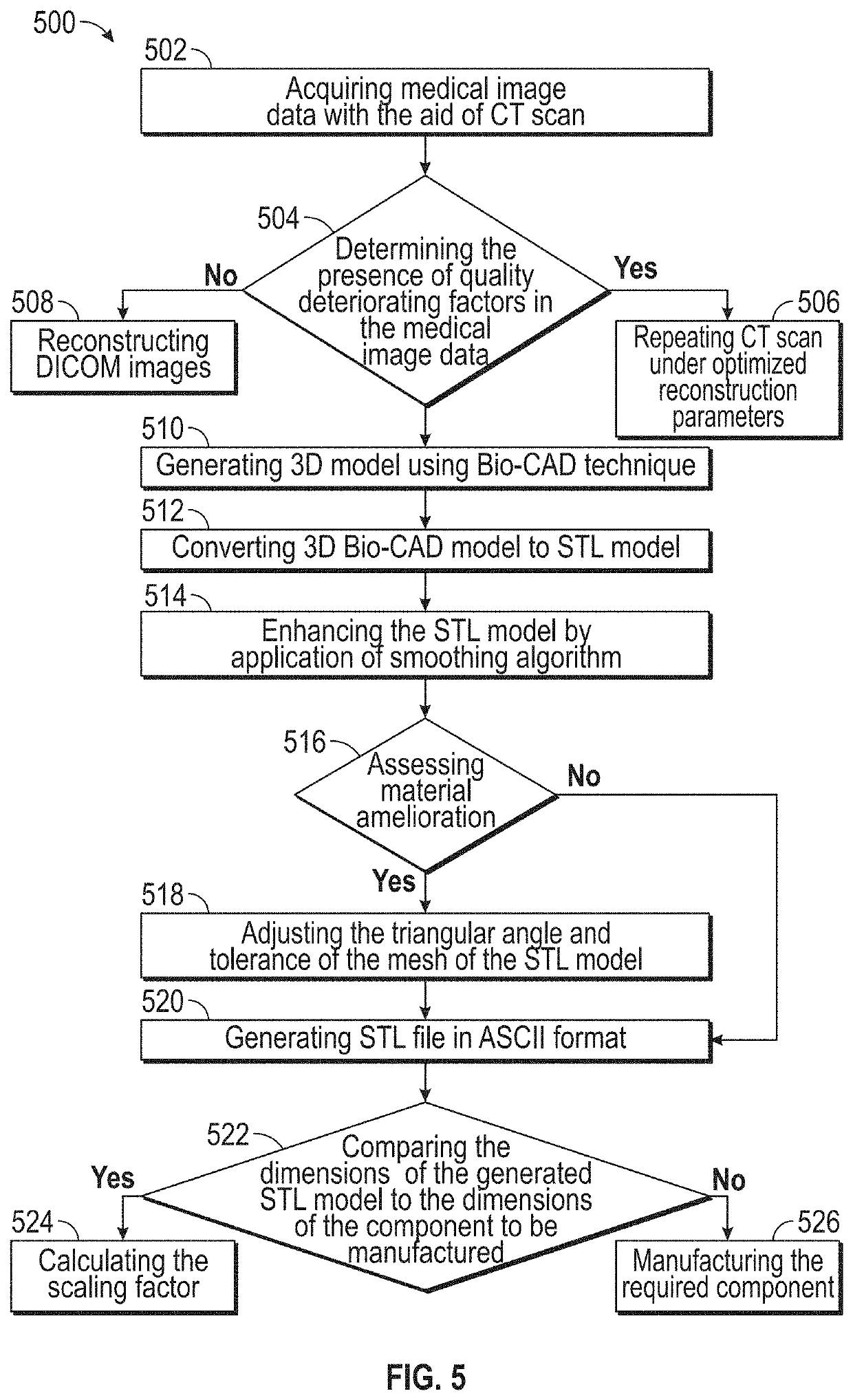
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure are directed towards an implantable device for complete replacement of temporomandibular joint comprising of a condyle component to reconstruct a mandibular end of the temporomandibular joint designed for movement within the implantable device with a plate; and a condyle surface where the plate is configured to mechanically secure the condyle component to a ramus surface of a patient undergoing implant with the aid of screws; and the condyle surface polished to generate a mirror effect to reduce the friction in the implantable device and infection rate; a zygomatic arch component to reconstruct a temporal bone (glenoid fossa) of the temporomandibular joint comprising at least one of: a plate; a plurality of multiple threaded counter sink holes; a plurality of conically tapered holes and a zygomatic arch surface, whereby the multiple threaded counter sink holes are structured within the plate; and a fossa component configured to be positioned between the condyle component and the zygomatic arch component to anchor the movement of the temporomandibular joint and the fossa component comprising of a low density biocompatible material made of a polycarbonate which is utilized in the additive manufacturing for the synthesis of implantable device for temporomandibular joint.
Owner:CHARY MANMADHA A +1
Personalized temporal-mandibular joint fossa implant
The invention discloses a personalized temporal-mandibular joint fossa implant which comprises an outer side retainer wing plate and a condyle process supporting surface, wherein the inner side face of the outer side retainer wing plate is in retaining fit with the outer side face of zygomatic arch of a patient; the lower edge of the outer side retainer wing plate and the condyle process supporting surface are connected into a whole; a top bulge is formed on the top surface of the condyle process supporting surface and positioned in a direction of the inner side face of the outer side retainer wing plate; the top surface of the condyle process supporting surface with the top bulge is attached to the temporal-mandibular joint fossa of the patient; the bottom surface of the condyle process supporting surface is attached to the lower condyle process head in a wrapped form; and the shape and size of the top bulge of the condyle process supporting surface and at least one of the width of the top surface and the width of the bottom surface of the condyle process supporting surface are in personalized matching according to the temporal-mandibular joint fossa and the lower condyle process head of the patient. The implant can be in close fit with the temporal-mandibular joint fossa of the patient, traumas and injuries of temporal-mandibular joint fossa implant surgery on peripheral tissues of the temporal-mandibular joint fossa can be reduced, and the joint fossa implant has high stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Zygomatic arch temporal-mandibular joint glenoid fossa combined remediation prosthesis
InactiveCN105943200AAvoid risk of injuryImprove accuracyJoint implantsExternal Auditory CanalsJaw bone
The invention discloses a zygomatic arch temporal-mandibular joint glenoid fossa combined remediation prosthesis, and the prosthesis comprises a zygomatic bone fixing pterygoid lamina which contacts with a zygomatic bone and is fixed on the zygomatic bone, a temporal bone fixing pterygoid lamina which contacts with the temporal bone and is fixed on the temporal bone, a zygomatic arch connection part, and a skull base projection part which contacts with a skull base. The zygomatic bone fixing pterygoid lamina, the temporal bone fixing pterygoid lamina and the zygomatic arch connection part are respectively connected with the zygomatic arch connection part. The skull base projection part is provided with a glenoid fossa recessed part and baffle plates disposed at two ends of the glenoid fossa recessed part. The prosthesis can be used for repairing the combined loss, caused by the temporal-mandibular joint tumour and congenital malformation, of the zygomatic arch and a temporal-mandibular joint fossa, is more attached to a jaw bone, reduces unnecessary bone grinding, avoids the risks of damages to a skull base and an external auditory canal, greatly reduces the operation time, improves the fixing accuracy and stability, and can achieve the precise restoration of the combine loss of a zygomatic arch temporal-mandibular joint glenoid fossa of a Chinese.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Zygomatic arch, skull base, top chin and submandibular top cephalometric positioning and shooting chair
InactiveCN102940504ASolve problems where quantitative measurements cannot be madeFunction increasePatient positioning for diagnosticsChinNose
The invention relates to a medical device. The invention discloses a zygomatic arch, skull base, top chin and submandibular top cephalometric positioning and shooting chair which comprises a skull positioning instrument, a supporting plate, a backrest, a seat and a seat supporting leg; the skull positioning instrument is fixed on the lower surface of the supporting plate by two chutes; the skull positioning instrument can slide relative to the supporting plate; the supporting plate is connected with the backrest by a rotating shaft; the backrest is connected with the seat by a regulating bolt; and the seat is connected with the seat supporting leg by a lifting regulating device. The zygomatic arch, skull base, top chin and submandibular top cephalometric positioning and shooting chair can be used for carrying out standard shooting of X-ray films on cranio maxillofacial region structures such as a zygomatic bone, upper and lower jawbones, a skull base, a nose and the like so as to carry out quantitative measurement; the zygomatic arch, skull base, top chin and submandibular top cephalometric positioning and shooting chair is convenient to use; the medical cost is saved; the accuracy and the objectivity of medical images are improved; and effects before and after the operative treatment can be accurately and objectively compared.
Owner:PLASTIC SURGERY HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for controlling virtual human mouth motion
InactiveCN101566828BEasy to controlHigh simulation3D-image renderingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationHuman mouth
The invention discloses a method for controlling virtual human mouth motion, which comprises the following steps: after a three-dimensional human face grid model is acquired, consulting the definitionfor FDP characteristic points of a mouth area in MPEG-4 to select the characteristic points at the zygomatic arch, two mouth corners, upper boundary of lower lip and mandible boundary as boundary points of a mouth functional area, and finally determining the mouth functional area in the three-dimensional grid model according to the characteristic point coordinates of the zygomatic arch; and adopting an oscillating guide-bar mechanism model to drive grid points of the mouth functional area to move, simulating a real mouth opening-closing process, and eliminating the overstretching phenomenon at the boundary by processing a peak of a peak buffer area. The method can adopt the same mathematical model to realize opposite motion processes such as opening and closing of the human mouth under continuous condition, the mathematical model is simple, the physical significance is definite, the control is easy, and the simulation effect is vivid.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Basis cranii-temporo-mandibular joint combination prosthesis
The invention discloses a basis cranii-temporo-mandibular joint combination prosthesis, which comprises a basis cranii portion, a zygomatic arch portion, an articular fossa portion, a condylar process head portion and a joint handle, wherein the basis cranii portion, which is in charge of repairing basis cranii defect, is made from a titanium alloy material; a plurality of fixing holes are formed in the edge of the basis cranii portion, so that the basis cranii portion is fixed to temporal bone; the zygomatic arch portion, which is in charge of repairing zygomatic arch defect, is made from a titanium alloy material; a plurality of fixing holes are formed in the front end of the zygomatic arch portion, so that the zygomatic arch portion is fixed to zygomatic arch; the articular fossa portion is an articular surface capable of simulating mandibular movements of a human body, and the articular fossa portion is made from an ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene material; the basis cranii portion, the zygomatic arch portion and the articular fossa portion are integrally connected; the condylar process head portion, which is made from a cobalt-chrome-molybdenum alloy material, is represented as a hollow cylindrical structure; the joint handle, which is made from a titanium alloy material, is used for repairing partial ascending limbs; a fixing hole is formed in the joint handle; and the condylar process head portion and the joint handle are integrally connected. The best effect can be achieved since different parts are made from different materials; and the individual basis cranii portion, zygomatic arch portion and articular fossa portion as well as the condylar process head portion and the joint handle, which are made from special materials, are integrally connected, so that the prosthesis is more stable and firmer and is better in fixing effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Oral and maxillofacial space infection incision and drainage virtual training method
PendingCN112002200AImprove practical abilityAddressing the Practice DisconnectCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsForcepsMandibular angle
The invention relates to an oral and maxillofacial space infection incision and drainage virtual training method and is used for knowing an anatomical part of space infection and selecting a correct incision and drainage part through the method. The method comprises the following steps of 1) establishing a skull three-dimensional model, and inputting the skull three-dimensional model into a computer simulation device; 2) inputting a muscle module used for simulating muscle, adding the muscle module to the three-dimensional model, adding an abscess module outside the mandibular ascending branchfor the clearance of the occlusal muscle, and covering the cheekbone zygomatic arch and the mandibular ascending branch mandibular angle area with the occlusal muscle on the abscess so as to determine the anatomical part of the clearance abscess of the occlusal muscle; (3) inputting an instrument module used for simulating the surgical knife so as to select the surgical knife and the incision part, and after incision, enabling vessel forceps to extend into a gap along the exterior of the mandible, and (4) selecting and operating the instrument module after abscess drainage. The method is advantaged in that the method operability is strong, and the method can be widely applied to the technical field of medical science.
Owner:湖南医药学院
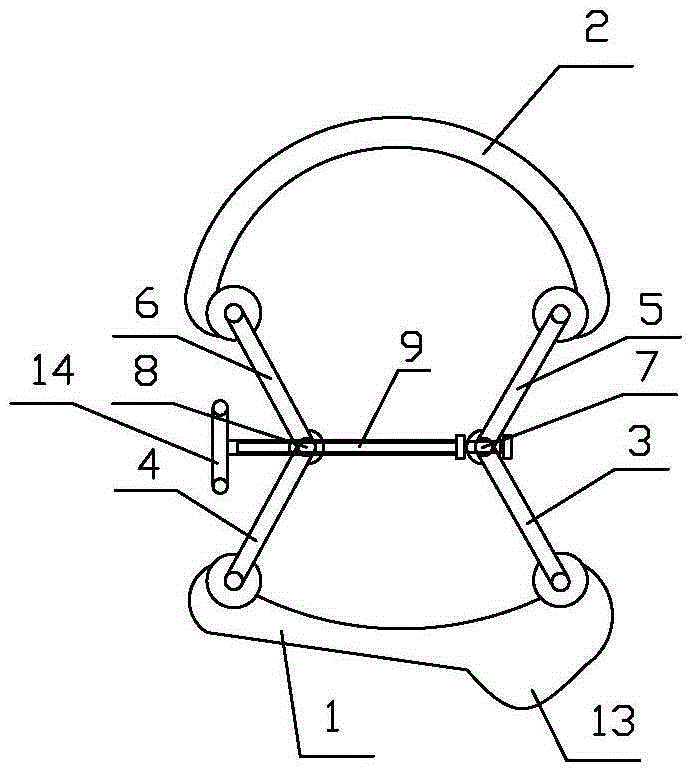
Clamping device special for zygomatic fracture reduction operation
The invention relates to a clamping device special for zygomatic fracture reduction operation, which comprises a fixing base and three clamping bodies. The fixing base is fixedly provided with a handle. The clamping bodies are hinged to the fixing base, and clamping ends of the clamping bodies are provided with clamping heads for realizing clamping action. Three clamping heads are correspondingly arranged on an inner side face of an external low edge of orbit, at the corner between an external edge of the orbit and the cheekbone, and at the corner between the cheekbone and a zygomatic crest support. An adjusting mechanism for clamping and loosening the clamping heads is arranged on the fixing base. Therefore, stable clamping force acts on three parts, namely an inner wall of the orbit, on the rear low part of the external edge of the orbit and at the zygomatic crest support, where the bone tissues are relatively firm, so that the maxillary process, the frontal process and the zygomatic process are integrally moved for reduction, and the problem that single prying or pulling is hard for the reduction of the cheekbone due to the complex shape of the cheekbone is solved. The clamping device special for the zygomatic fracture reduction operation can be used for large wound surface and minimally invasive zygomatic arch reduction, and has simple and reasonable structure and low cost.
Owner:温州医科大学附属口腔医院
Head hierarchical dissection three-dimensional scanning specimen manufacturing method
PendingCN113628517AEasy to compare and learnConserve anatomical materialsEducational modelsDura mater encephaliRectus muscle
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a head hierarchical dissection three-dimensional scanning specimen. The method comprises the following steps: selecting materials; sequentially removing skin, superficial fascia, latissimus jugular muscle, parotid gland, superficial vascular nerve, cap aponeurosis, masseter, periosteum and temporal muscle, opening zygomatic arch and mandible, removing sternoclavicular mastoid muscle, parietal bone of cranial top, frontal bone, temporal bone and occipital bone, cutting to open superior sagittal sinus, removing dura mater, brain, mandible, zygomatic major muscle, zygomatic minor muscle, orbiculus oculi muscle, trapezius muscle, capsid muscle, diabdominal muscle, deorbital horn muscle cheekbone, endocranium, and veins, removing styloid process tongue bone muscles, external rectus, arteries, styloid process pharynx muscles and styloid process tongue muscles, removing auricles, opening temporal bones, and performing median sagittal incision; then, trimming and cleaning the dissected specimen, and pasting specimen muscles, blood vessels and nerves to the original corresponding positions; and finally, combining and processing the 3D scanned images into a complete digital 3D model, so that the scanned specimen is complete in shape and structure, free switching can be realized, and observation and learning are facilitated.
Owner:河南中博科技有限公司
Mask for zygomatic fracture outer fixed healing and fixed healing system
PendingCN108542481AEasy to operateAvoid surgical incision scarsDiagnosticsExternal osteosynthesisComputed tomographyEngineering
The invention relates to a mask for zygomatic fracture outer fixed healing and a fixed healing system. The mask comprises a mask body worn on the face and a fixing bolt, wherein three threaded throughholes are formed in one side or two sides of the mask body, one of the threaded through holes is located at the position, corresponding to the lower portion of the front side of the facial cheekbone,of the mask body, another one of the threaded through holes is located at the position, corresponding to a combined position of the facial cheekbone and zygomatic arch, of the mask body, the rest oneof the threaded through holes is located at the position, corresponding to a combined position of the bottom of the outer edge of the facial eye socket and cheekbone, the threaded through holes are internally tightly screwed with fixing bolts used for positioning and fixing the cheekbone; the fixed healing system adopts the mask, and is provided with a CT scanning imaging device; the mask can effectively prevent the cheekbone from displacing, the wound of a patient is small when the mask is used, the appearance of the patient is not damaged, and the mask can be widely applied to the healing of zygomatic fracture.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
An artificial temporomandibular joint replacement prosthesis
The invention relates to an artificial temporal-mandibular joint replacement prosthesis. The replacement prosthesis comprises a glenoid fossa prosthesis and a mandible ramus prosthesis; the glenoid fossa prosthesis is made of supra polymer polyethylene polymer and comprises a tissue surface in contact with the glenoid fossa and a function surface in contact with the mandible ramus prosthesis, the tissue surface comprises a wing plate which is in contact with the zygomatic arch and is fixed to the zygomatic arch and a protrusion part in contact with the glenoid fossa, and the function surface comprises a sunken part in contact with the mandible ramus prosthesis and stopping plates arranged at the two ends of the sunken part; and the mandible ramus prosthesis comprises a condyloid process head and a mandible ramus fixing handle, the condyloid process head is cylindral and is in contact with the sunken part, the mandible ramus fixing handle is attached to the outer lateral face of the mandible ramus. By means of the artificial temporal-mandibular joint replacement prosthesis, the standard form artificial joint prosthesis is more suitable for the dissection appearance of the Chinese and is better attached to the jaw, complications in and after an operation are effectively reduced, the using effect of the standard form artificial joint prosthesis is improved, and the service life of the standard form artificial joint prosthesis is prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
Special clamping device for zygomatic fracture reduction surgery
The present invention and the special clamping device for zygomatic fracture reduction surgery include a fixing base and three clamping bodies, the fixing base is fixed with a handle, the clamping body is hinged on the fixing base, and the clamping end of the clamping body is provided with a The clamping head of the clamping action, the three clamping heads are respectively set corresponding to the inner surface of the outer and lower edge of the orbit, the corner between the outer edge of the orbit and the zygomatic bone, and the corner between the zygomatic bone and the zygomatic alveolar pillar. Adjustment mechanism for the clamping and releasing action of the clamping head. In this way, the stable clamping force acts on the inner wall of the orbit, the posterior lower part of the outer edge of the orbit, and the zygomatic alveolar pillar, which are relatively solid bone tissues, so that the zygomatic maxillary process, frontal process and zygomatic process move and reset together. It solves the problem of "due to the complex shape of the zygomatic bone, it is difficult to reset the zygomatic bone simply by prying or pulling", and can be used for large wounds and minimally invasive zygomatic arch reduction, with a simple and reasonable structure and low cost.
Owner:温州医科大学附属口腔医院
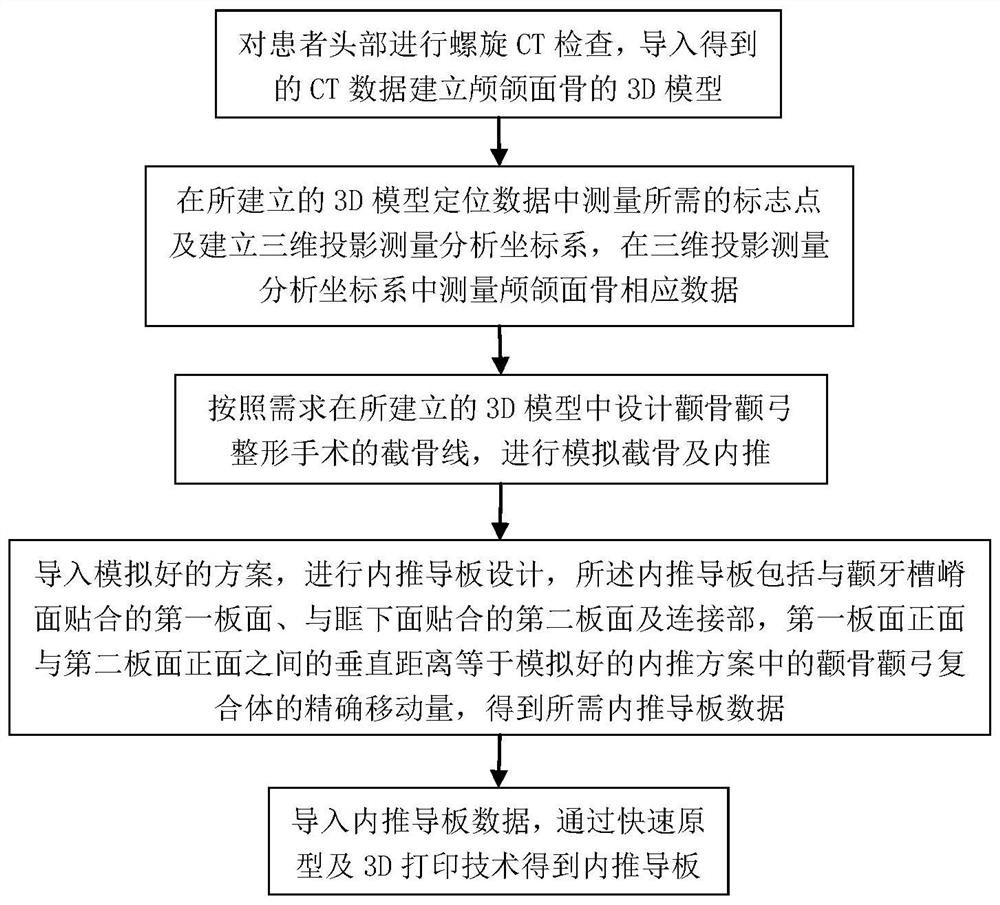
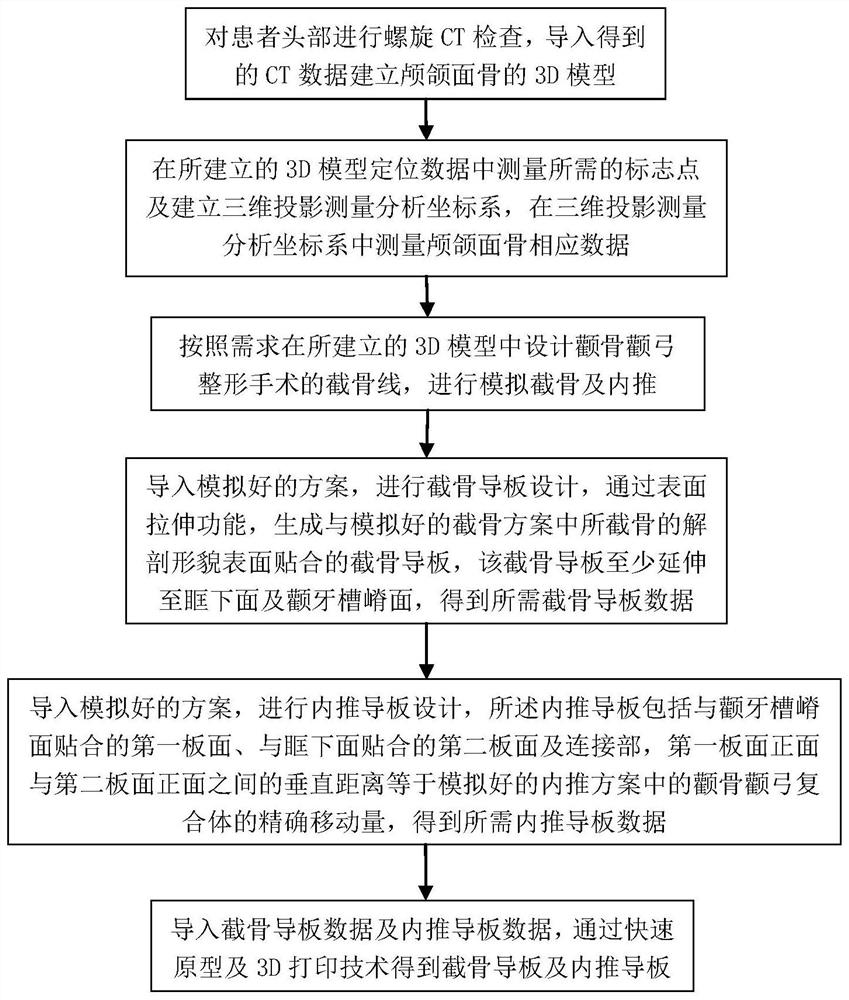
Osteotomy guide plate for zygomatic bone and zygomatic arch plastic surgery and method for generating inner push guide plate
ActiveCN113180776APromote generationAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone drill guidesPlastic surgeryRapid prototyping
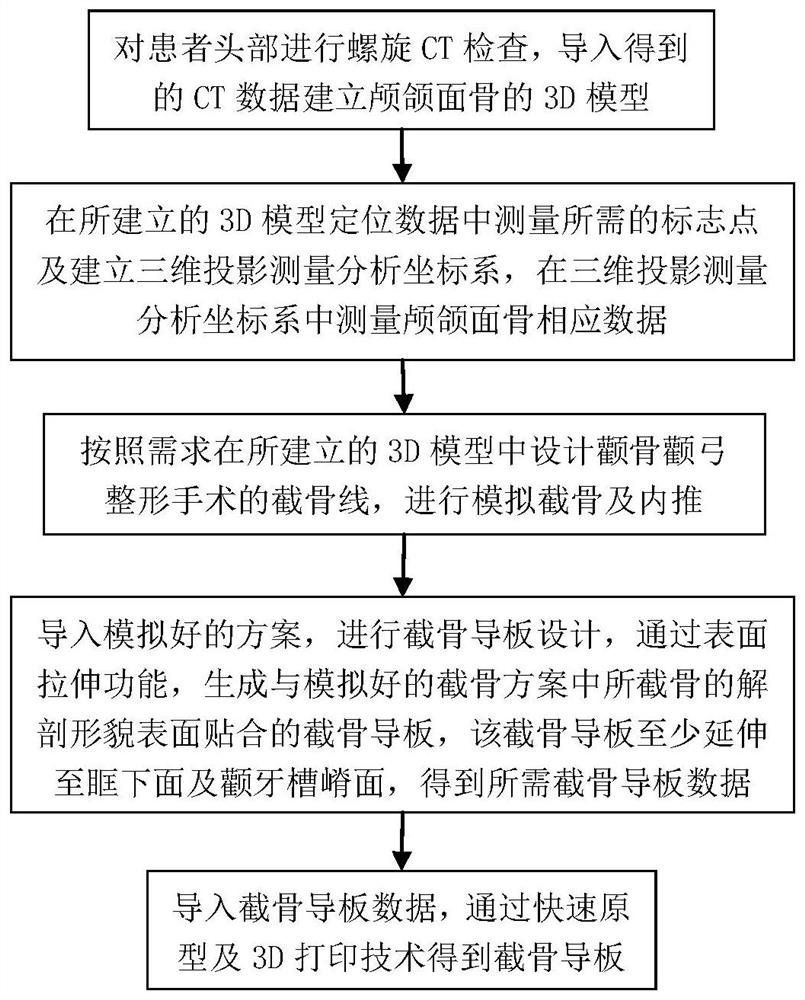
The invention relates to a template manufacturing technology, and provides an osteotomy guide plate for a cheekbone and zygomatic arch plastic surgery and an internal pushing guide plate generation method in order to solve the problem that no special osteotomy guide plate or internal pushing guide plate exists in the existing cheekbone and zygomatic arch plastic surgery. The technical scheme can be summarized as follows: establishing a 3D model of a cranio-maxillofacial bone according to the head of a patient; designing an osteotomy line, performing simulated osteotomy and inward pushing according to requirements to obtain a simulated scheme, importing the simulated scheme, and generating an osteotomy guide plate attached to the anatomical morphology surface of an osteotomy in the simulated osteotomy scheme through a surface stretching function; then enabling the osteotomy guide plate to at least extend to the lower surface of an orbital space and a zygomatic alveolar ridge surface to obtain required osteotomy guide plate data, and designing an internal pushing guide plate to obtain required internal pushing guide plate data, and obtaining the osteotomy guide plate and the internal pushing guide plate through rapid prototyping and a 3D printing technology. The method has the beneficial effects that the osteotomy guide plate and the inner pushing guide plate of a patient can be conveniently and quickly generated. The method is suitable for generating the osteotomy guide plate and the inner pushing guide plate for the zygomatic bone and zygomatic arch plastic surgery.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
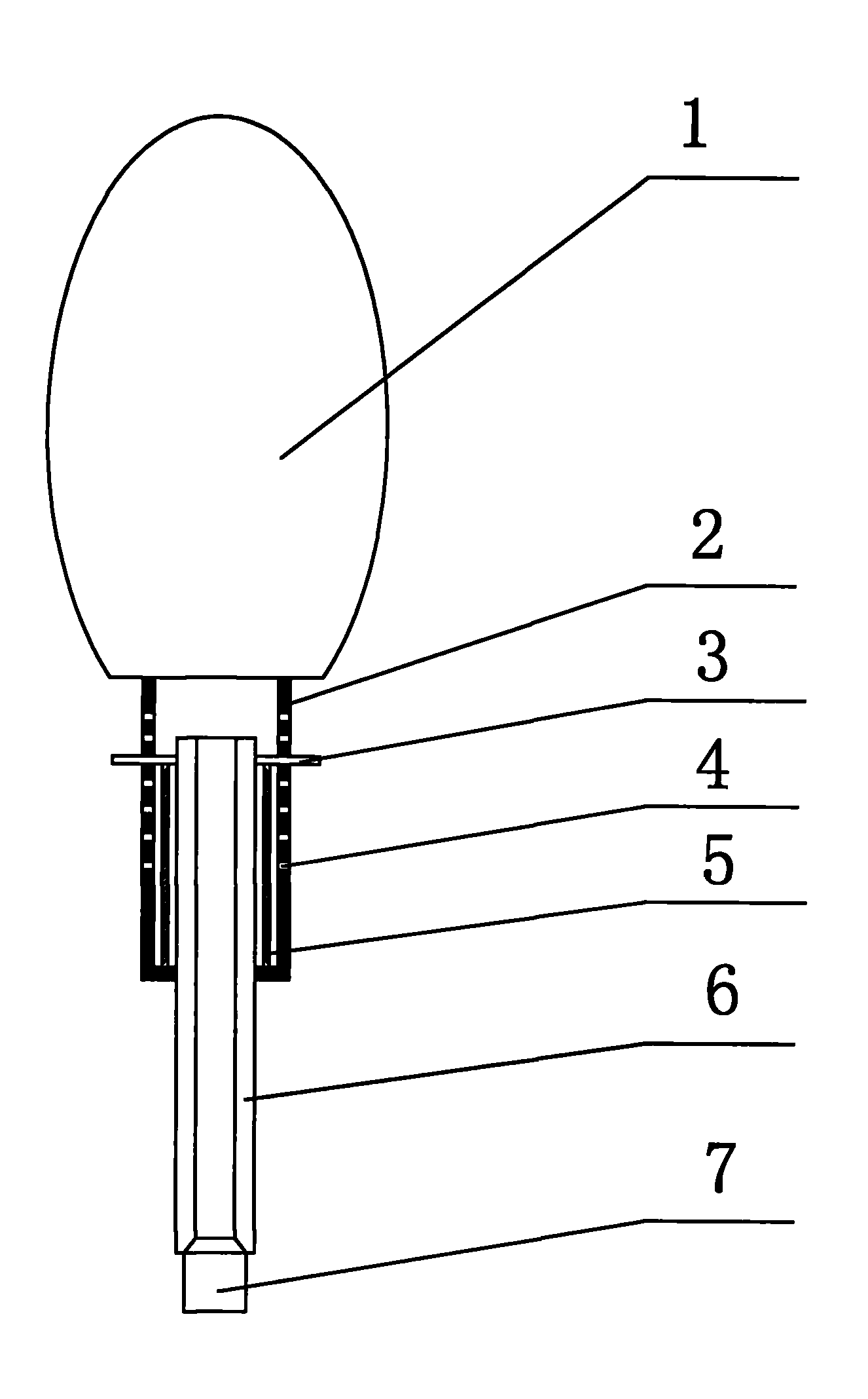
Surgical instrument for mandibular condyle
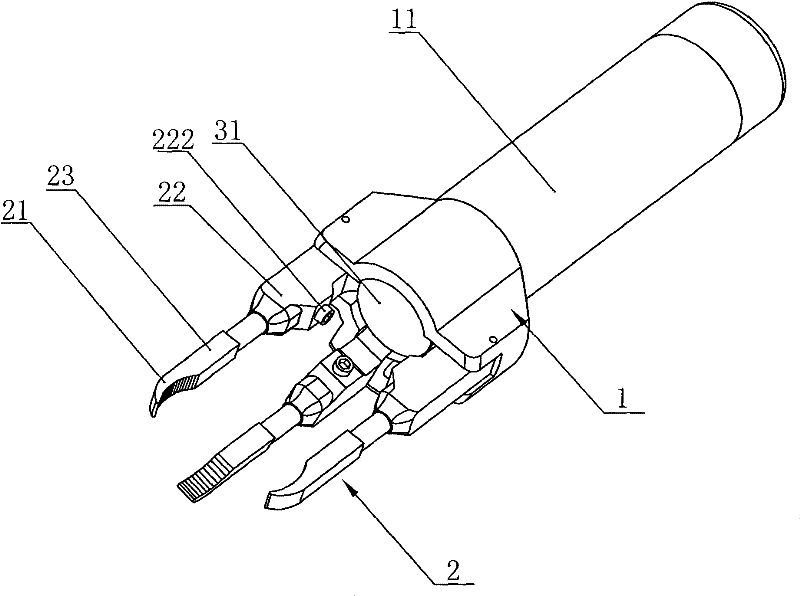
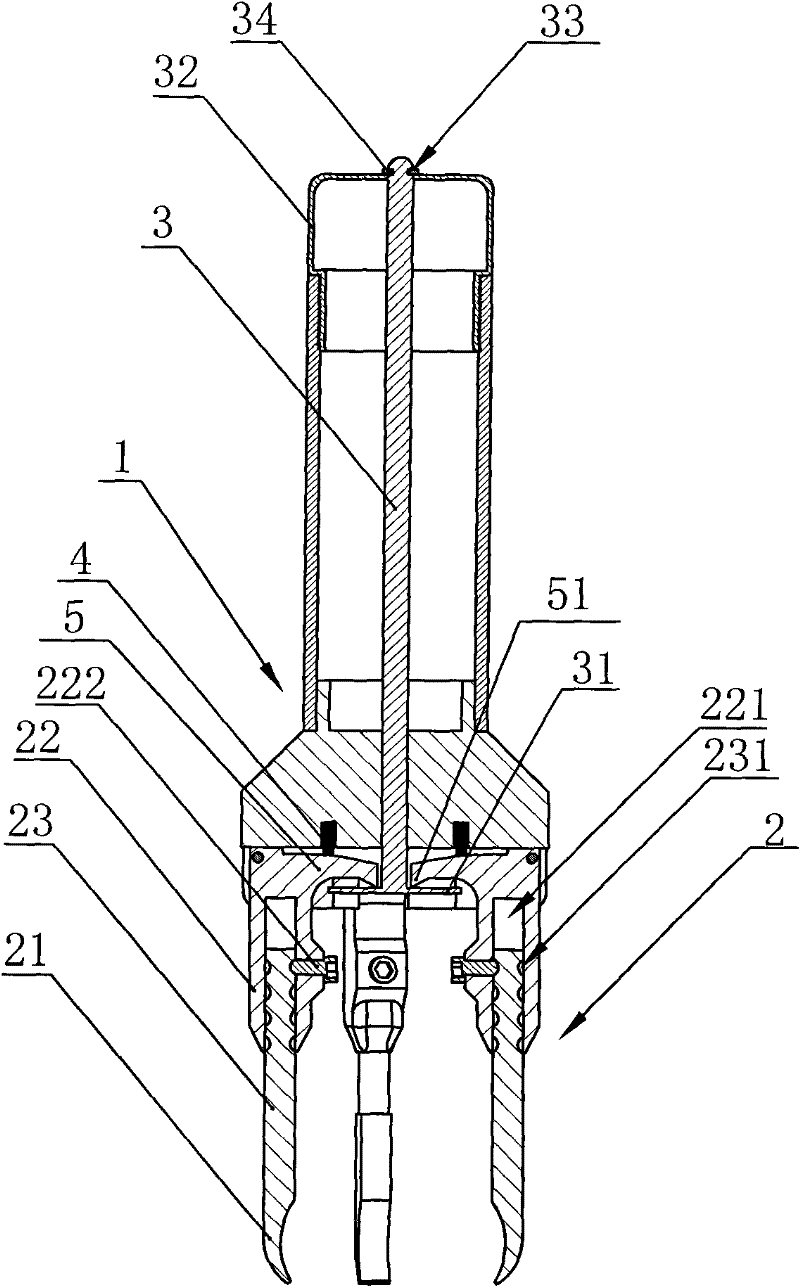
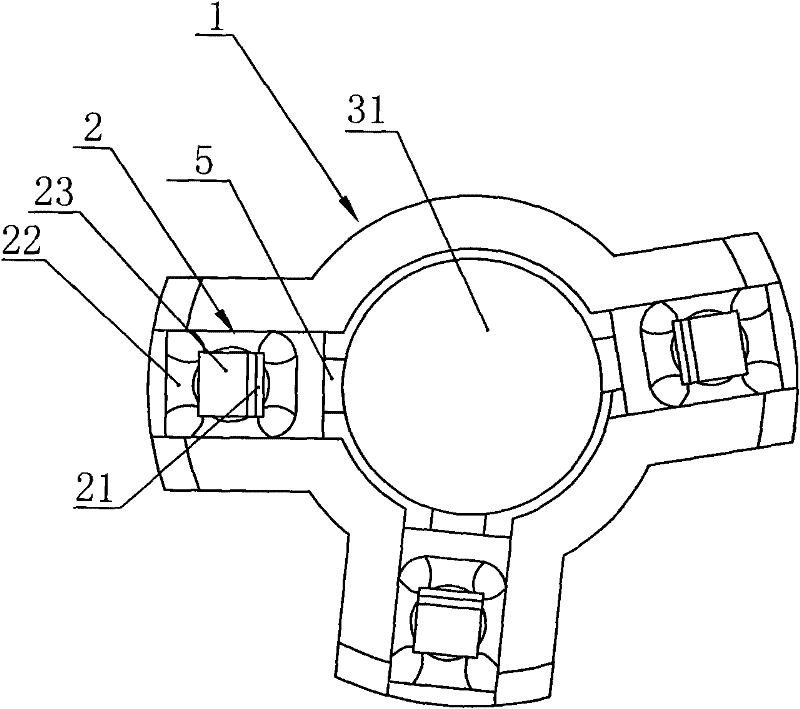
The invention relates to a medical instrument for maxillofacial surgery, in particular to a surgical instrument for mandibular condyle. The surgical instrument comprises a lower supporting and closing part corresponding to the mandibular incisure of a human body, an upper supporting and closing part matched with the zygomatic arch corresponding to the mandibular incisure of the human body, wherein two ends of the lower supporting and closing part are respectively hinged with a lower supporting front rod and a lower supporting rear rod; the two ends of the upper supporting and closing part are respectively hinged with an upper supporting front rod and an upper supporting rear rod; the upper end of the lower supporting front rod and the lower end of the upper supporting front rod are hinged on a front hinged shaft; the upper end of the lower supporting rear rod and the lower end of the upper supporting rear rod are hinged on a rear hinged shaft; the front hinged shaft and the rear hinged shaft are installed on a center shaft. A distracter is compact in structure, convenient to use, small in the pain of a patient and reasonable in force bearing, and the situation that mechanical deformation or fracture in use does not easily occur, and the surgical instrument is adaptable to different individual differences.
Owner:郝宏
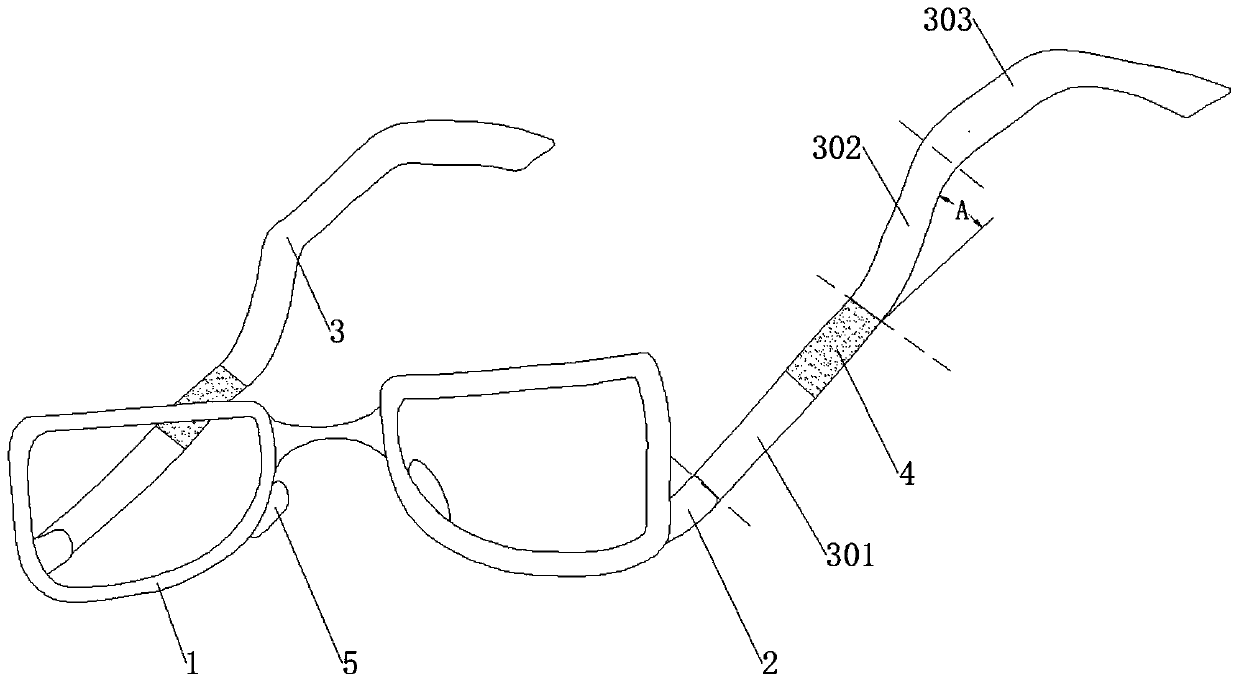
Antiskid glasses
PendingCN110515217AAvoid horizontal shiftSolve the technical problem that is easy to slide due to gravityNon-optical partsEngineeringGravitation
The invention provides antiskid glasses, and relates to the technical field of glasses equipment, solving the technical problem that in the prior art, pile heads of the glasses are positioned on the outer upper sides of a glass frame, glass legs only play a role in being connected with the glass frame, and thus the glass frame is easy to slide down under the effect of gravity. The antiskid glassescomprise the glass frame, the pile heads, the glass legs and nose pads, wherein one end of each pile head is fixedly arranged on the outer lower side of the glass frame, while the other end is connected with the corresponding lens leg; each glass leg comprises a support section connected with the corresponding pile head, a bent section arranged on the upper side of a corresponding auricle and a transition section connecting the support section and the bent section; and the support section is in contact with the upper side of a zygomatic arch part of a human face. According to the antiskid glasses, the downward sliding displacement of the glasses under the effect of the gravity is reduced.
Owner:格日勒图
Cheekbone lowering surgery
The invention discloses cheekbone lowering surgery. The cheekbone lowering surgery specifically comprises the following steps that first, a notch of about 1-1.5 cm is cut open in the position 1.0 cm in front of a temporal-mandibular joint on the front edges of temple hair lines in front of ears; second, a mosquito clamp is used for conducting blunt dissection deep into the zygomatic arch bone surface and the zygomatic arch deep surface, namely soft tissue on the two sides of a zygomatic arch can be separated. According to the cheekbone lowering surgery, operation is easy, an original method is high in difficulty and complex to operate, consequently, only small parts of physicians who are engaged in the plastic surgery industry can operate the surgery, and the generalization performance is limited; after change happens, most of physicians who are engaged in the plastic surgery industry can master and operate the surgery; surgery wounds are small, stripping is needed during surgery, the number of exposed parts is small, fixing by steel wires and steel plates is needless, and patients can get well quickly after surgery.
Owner:李雯
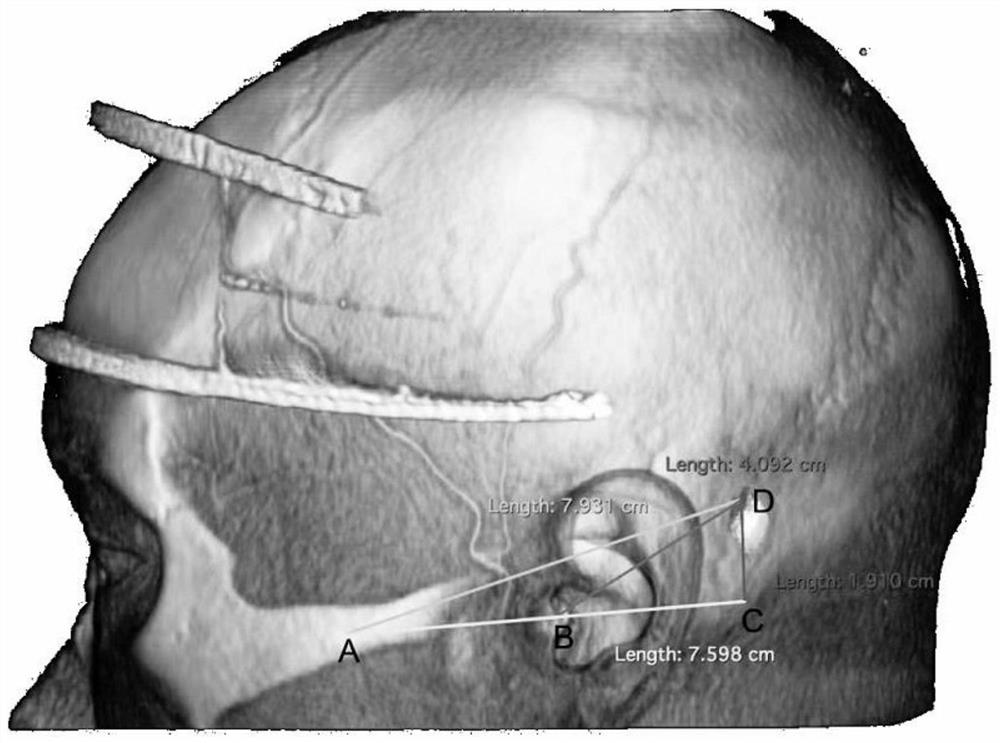
Method for positioning included angle between transverse sinus and sinus sigmoideus
PendingCN113520591AHigh speedImprove resection efficiencyComputer-aided planning/modellingExternal Auditory Canals3d image
The invention relates to an included angle between transverse sinus and sinus sigmoideus, which comprises the following steps of: (1) scanning a skull thin layer of a patient to obtain data; (2) importing the data into software to obtain a 3D image; (3) finding an included angle position of a transverse sinus and a sigmoid sinus on the inner side surface of the skull, and carrying out small hole positioning by utilizing a software tool; (4) adjusting the image to obtain images of the brain and skin muscles; (5) connecting the midpoint of the zygomatic arch and the midpoint of the external auditory canal and lengthening; (6) drawing a vertical line from the small hole as an original point to the extension lines of the midpoint of the zygomatic arch and the midpoint of the external auditory canal, and intersecting, wherein the intersection point is a point C; (7) respectively connecting the small hole with the midpoint of the zygomatic arch and the midpoint of the external auditory canal; and (8) measuring each included angle between transverse sinus and sinus sigmoideus by using software, and performing resection operation on the tumor. According to the method, the sinus sigmoideus-transverse sinus angle can be accurately positioned, the craniotomy speed and tumor excision efficiency of the bridge cerebellar horn tumor are remarkably improved, and technical support is provided for bridge cerebellar horn tumor excision.
Owner:赵彤
A bone modification guide plate assembly for artificial temporomandibular joint replacement
ActiveCN104939951BMake sure to implantGuaranteed application effectJoint implantsMaxillary OsteotomyEngineering
The invention discloses a bone trimming guide plate assembly for artificial temporomandibular joint replacement. The joint tubercle guide plate is attached to the outer surface of the zygomatic arch, the lower edge of the joint tubercle guide plate is blade-shaped or has a shoulder; the zygomatic arch guide plate is attached to On the outer side of the zygomatic arch, the zygomatic arch guide plate is U-shaped, and the U-shaped opening is blade-shaped; the condylar guide plate is attached to the outer surface of the condyle, and the upper edge of the condylar guide plate is blade-shaped or has a shoulder; the ascending branch guide plate Attached to the outer surface of the ascending ramus of the mandible, the upper part of the ascending ramus guide plate is hollowed out, and the hollowed out part is blade-shaped. Accurately guide the osteotomy of the bottom of the maxillary articular tubercle, the resection of the mandibular condyle, and the grinding of the lateral surface of the zygomatic arch and the lateral surface of the ascending ramus to reduce unnecessary bone loss.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Implantable device for temporomandibular joint and method of production thereof
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure are directed towards an implantable device for complete replacement of temporomandibular joint comprising of a condyle component to reconstruct a mandibular end of the temporomandibular joint designed for movement within the implantable device with a plate; and a condyle surface where the plate is configured to mechanically secure the condyle component to a ramus surface of a patient undergoing implant with the aid of screws; and the condyle surface polished to generate a mirror effect to reduce the friction in the implantable device and infection rate; a zygomatic arch component to reconstruct a temporal bone (glenoid fossa) of the temporomandibular joint comprising at least one of: a plate; a plurality of multiple threaded counter sink holes; a plurality of conically tapered holes and a zygomatic arch surface, whereby the multiple threaded counter sink holes are structured within the plate; and a fossa component configured to be positioned between the condyle component and the zygomatic arch component to anchor the movement of the temporomandibular joint and the fossa component comprising of a low density biocompatible material made of a polycarbonate which is utilized in the additive manufacturing for the synthesis of implantable device for temporomandibular joint.
Owner:CHARY MANMADHA A +1
U-shaped reducer for the treatment of zygomatic arch fracture
The invention discloses a U-shaped reducer for treating zygomatic arch fractures, comprising a support rod, a sliding rod, a rack, a guide groove, a sliding block, an arc rod, a guide rod, a connecting rod, a fixing plate, a connecting pin, a gear and a rotating plate , The U-shaped reducer for the treatment of zygomatic arch fractures has ingenious structure, powerful functions and simple operation. The device has the characteristics of large reduction force, little tissue damage, convenient operation and safe use. Fractures can also be applied, so it has a good value for promotion and use.
Owner:张曦
Traction reduction fixator handle
The invention relates to a medical instrument, in particular to a zygomatic bone and zygomatic arch bone traction reduction fixator handle which is used for clamping a hook. The traditional reduction fixator handle mainly adopts the principle of a spring clamp head. However, because the elasticity of a spring is limited during the use process of the spring clamp head, the elastic capability of the spring clamp head is reduced after multiple times of use, and the operation is influenced. The traction reduction fixator handle comprises a handle and a case sleeve, a locking socket is embedded in the case sleeve, and a clamp head is arranged in the locking socket. The traction reduction fixator handle is characterized in that both sides of the case sleeve are sequentially provided with a plurality of clamp slots, both sides of the upper end of the locking socket are provided with supporting bars, and the supporting bars are clamped into corresponding clamp slots. In the invention, the clamp head is tensioned and is then directly clamped and fixed on the clamp slots, and the fixation force is stable and reliable.
Owner:西安三才电子科技有限公司
Maxillofacial surgical instrument
The invention relates to a surgical instrument for maxillofacial surgery, in particular to a maxillofacial surgical instrument. The maxillofacial surgical instrument comprises a lower expanding part corresponding to a human body mandibular notch, and an upper expanding part matched with the zygoma corresponding to the human body mandibular notch. The two ends of the lower expanding part are provided with a lower expanding front rod and a lower expanding rear rod in a hinged mode respectively. The two ends of the upper expanding part are provided with an upper expanding front rod and an upper expanding rear rod in a hinged mode respectively. The upper end of the lower expanding front rod and the lower end of the upper expanding front rod are hinged to a front hinge shaft. The upper end of the lower expanding rear rod and the lower end of the upper expanding rear rod are hinged to a rear hinge shaft. The front hinge shaft and the rear hinge shaft are arranged on a middle shaft. The expander is compact in structure and convenient to use, pain of a patient is little, stress is reasonable, and the maxillofacial surgical instrument is not prone to mechanical deformation or breaking in use and can adapt to individual differences.
Owner:谭洪武 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com