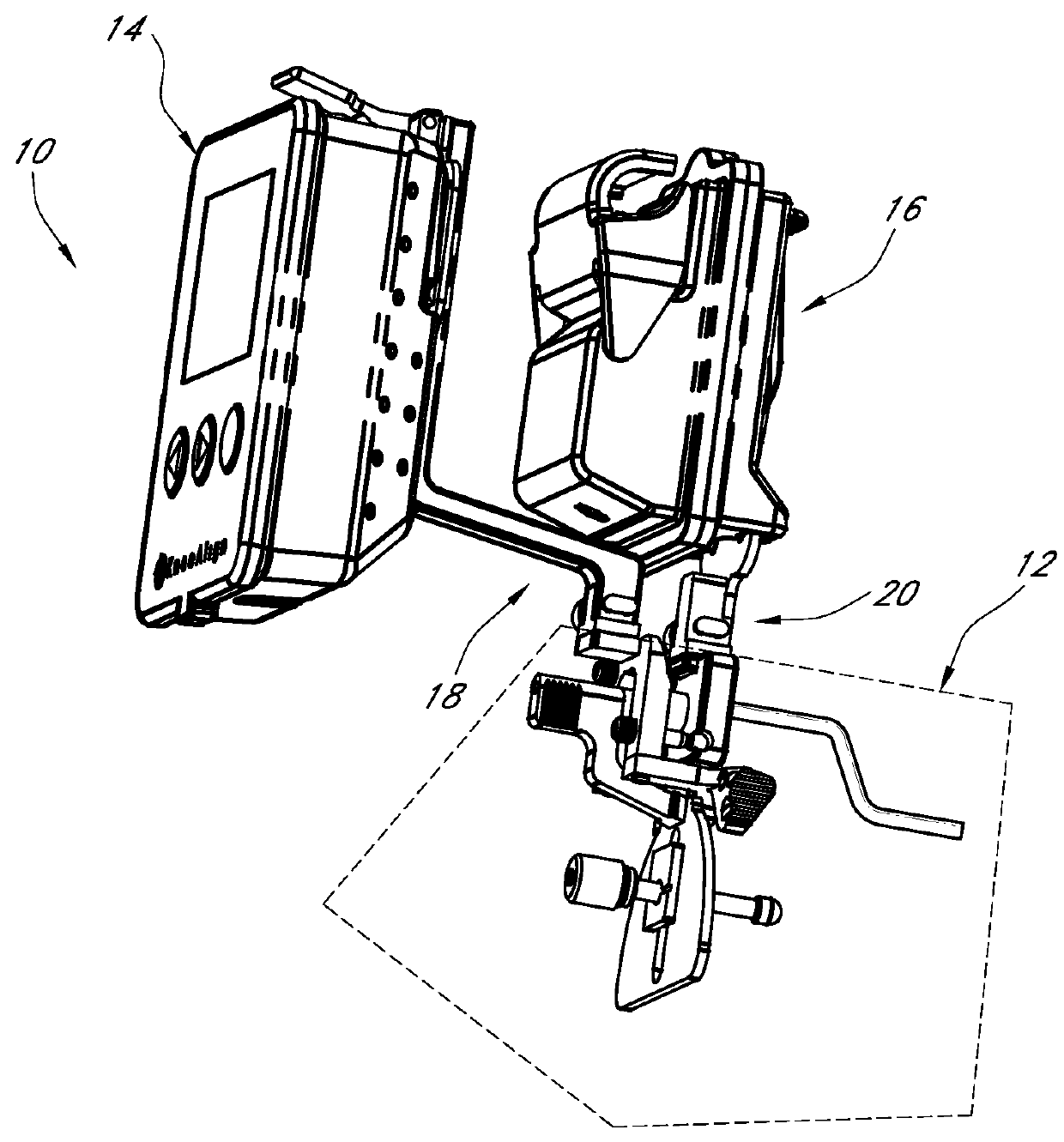
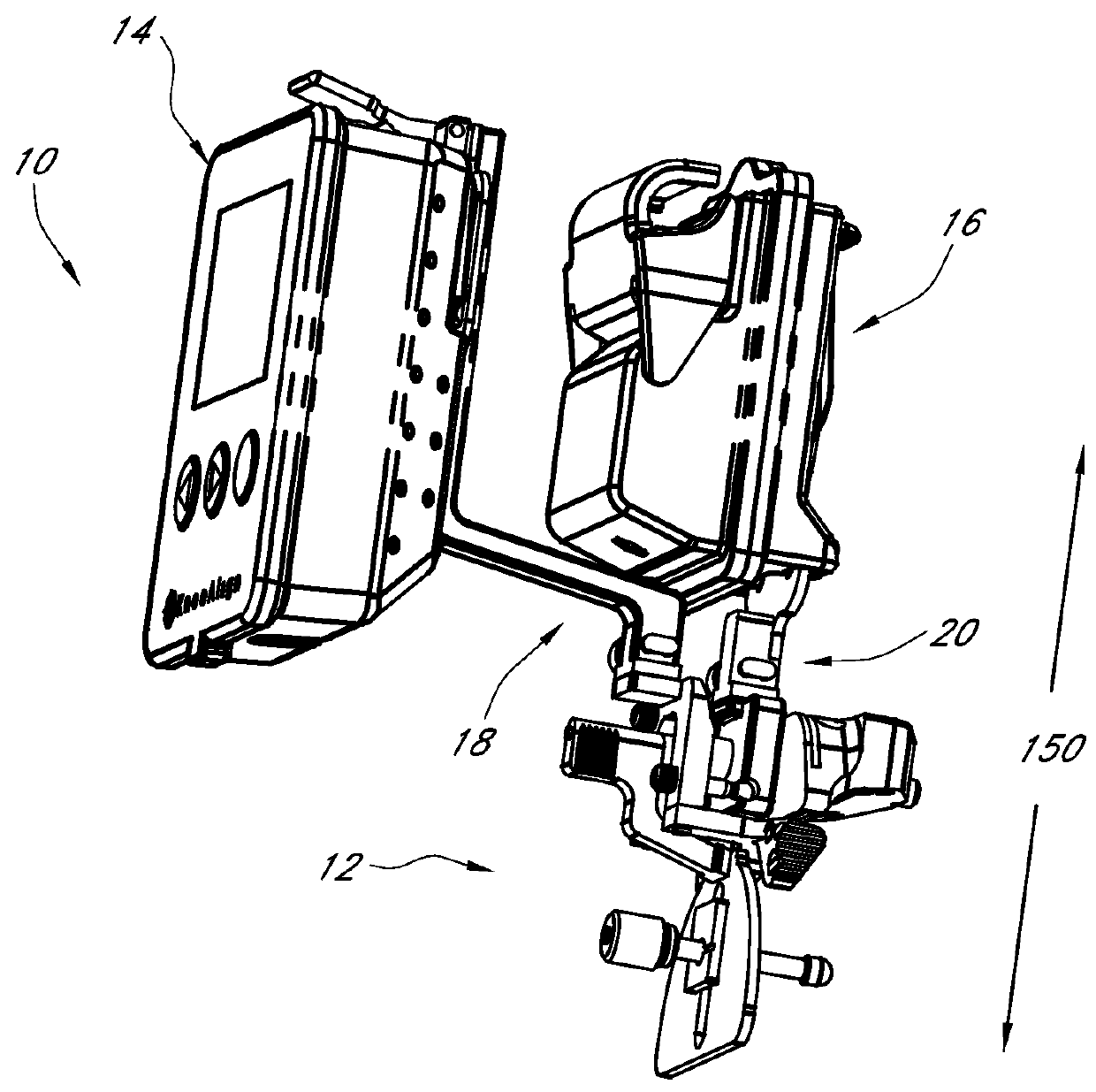
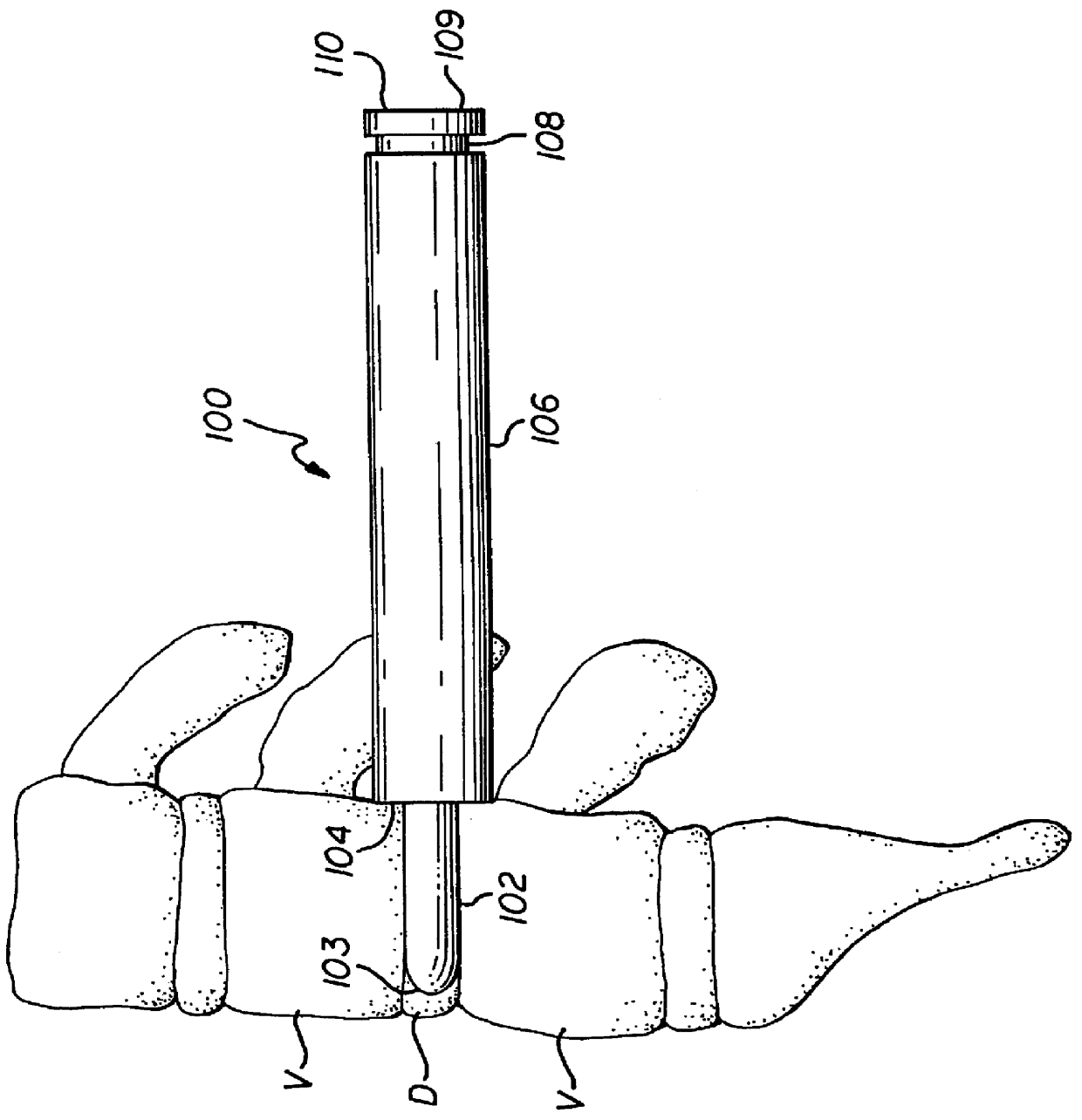
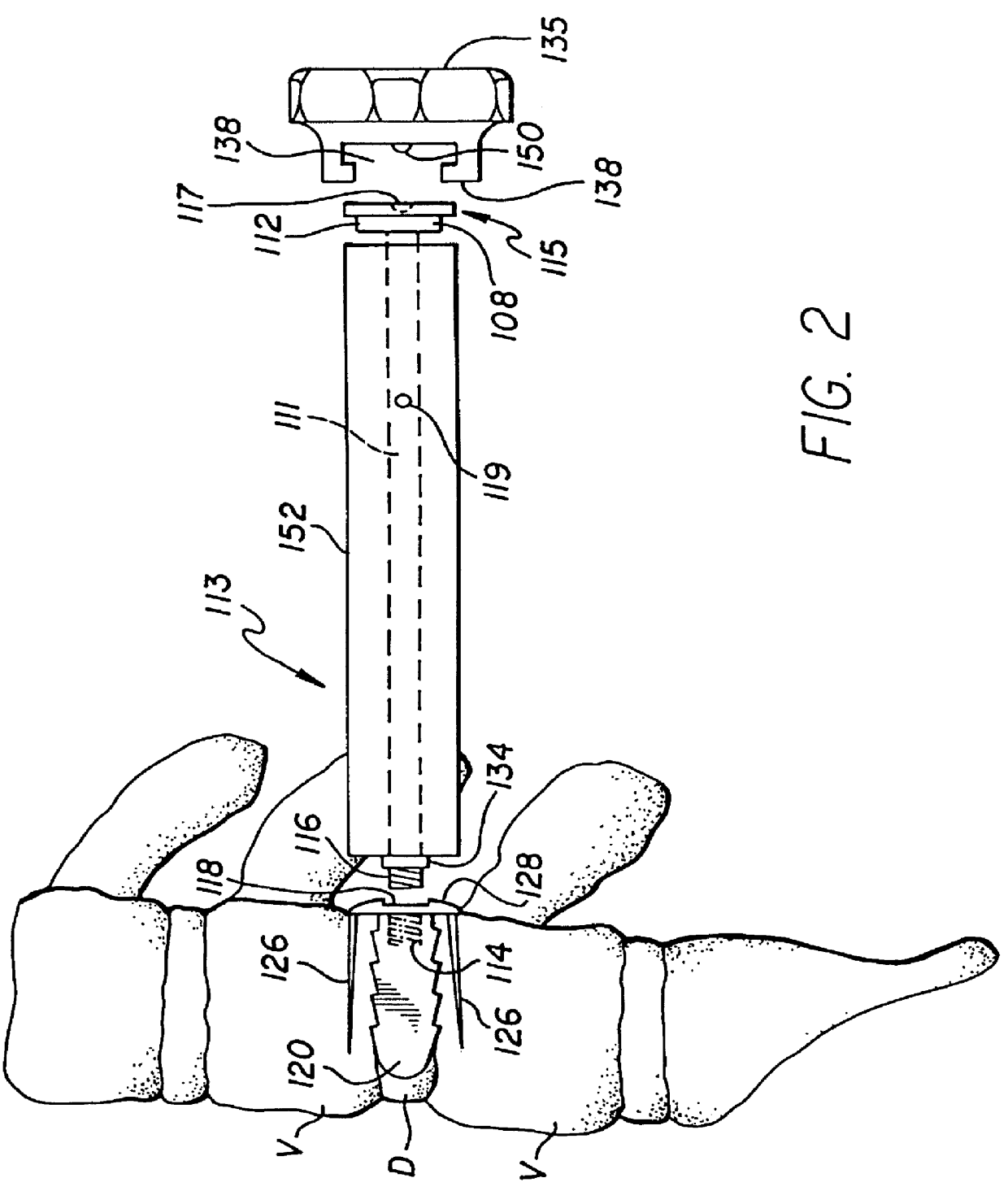
Patents
Literature
4639results about "Bone drill guides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
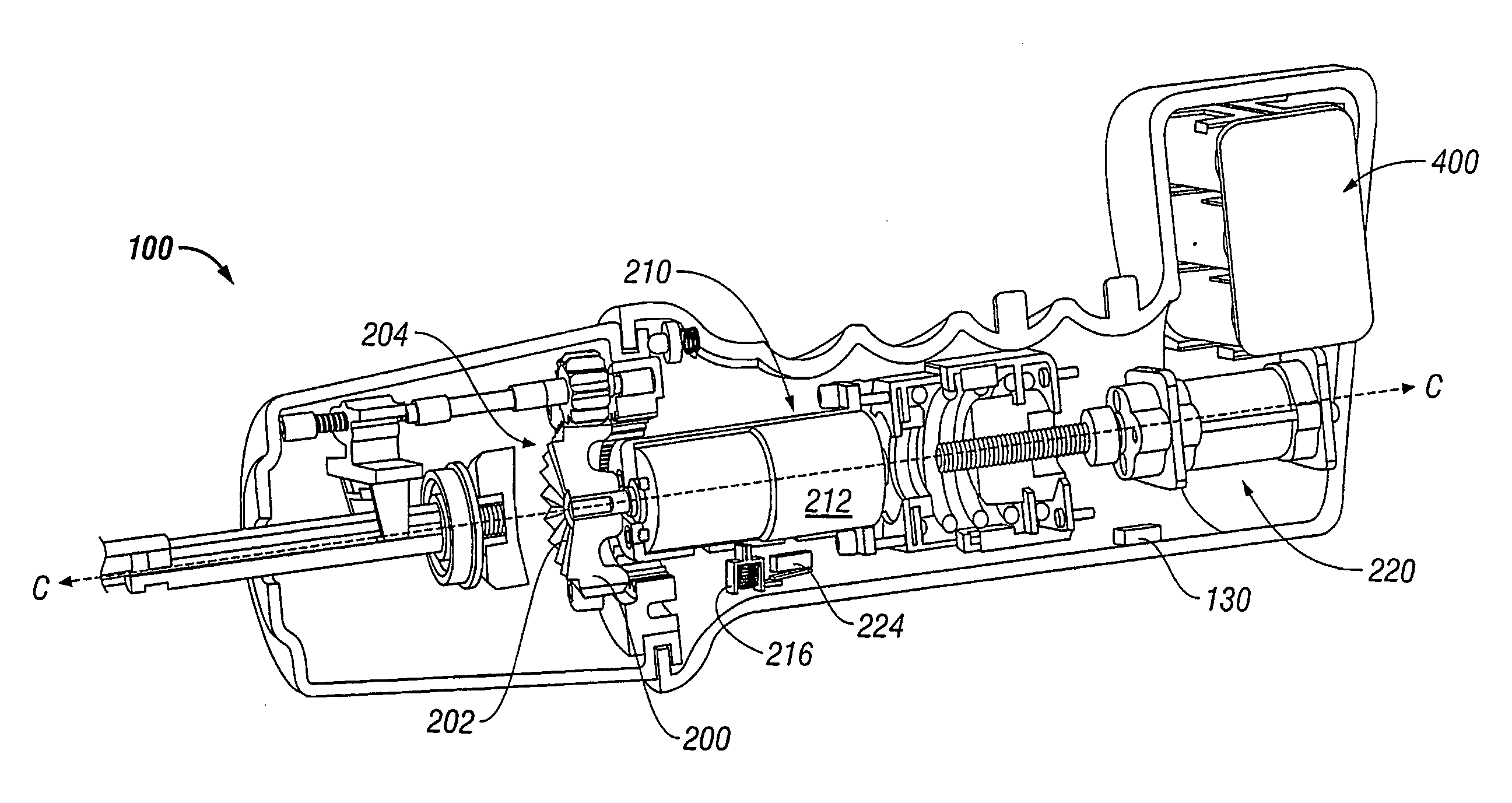
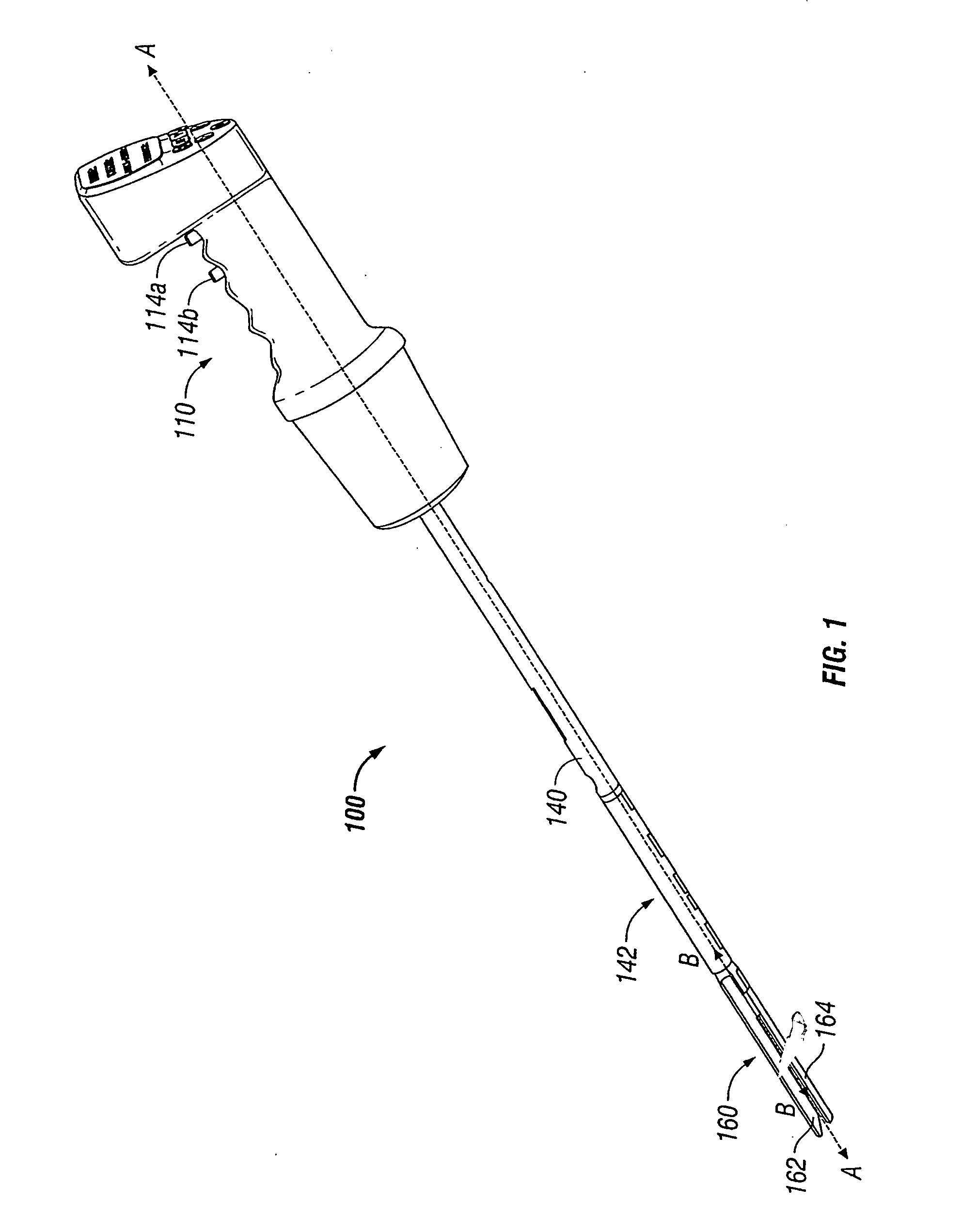
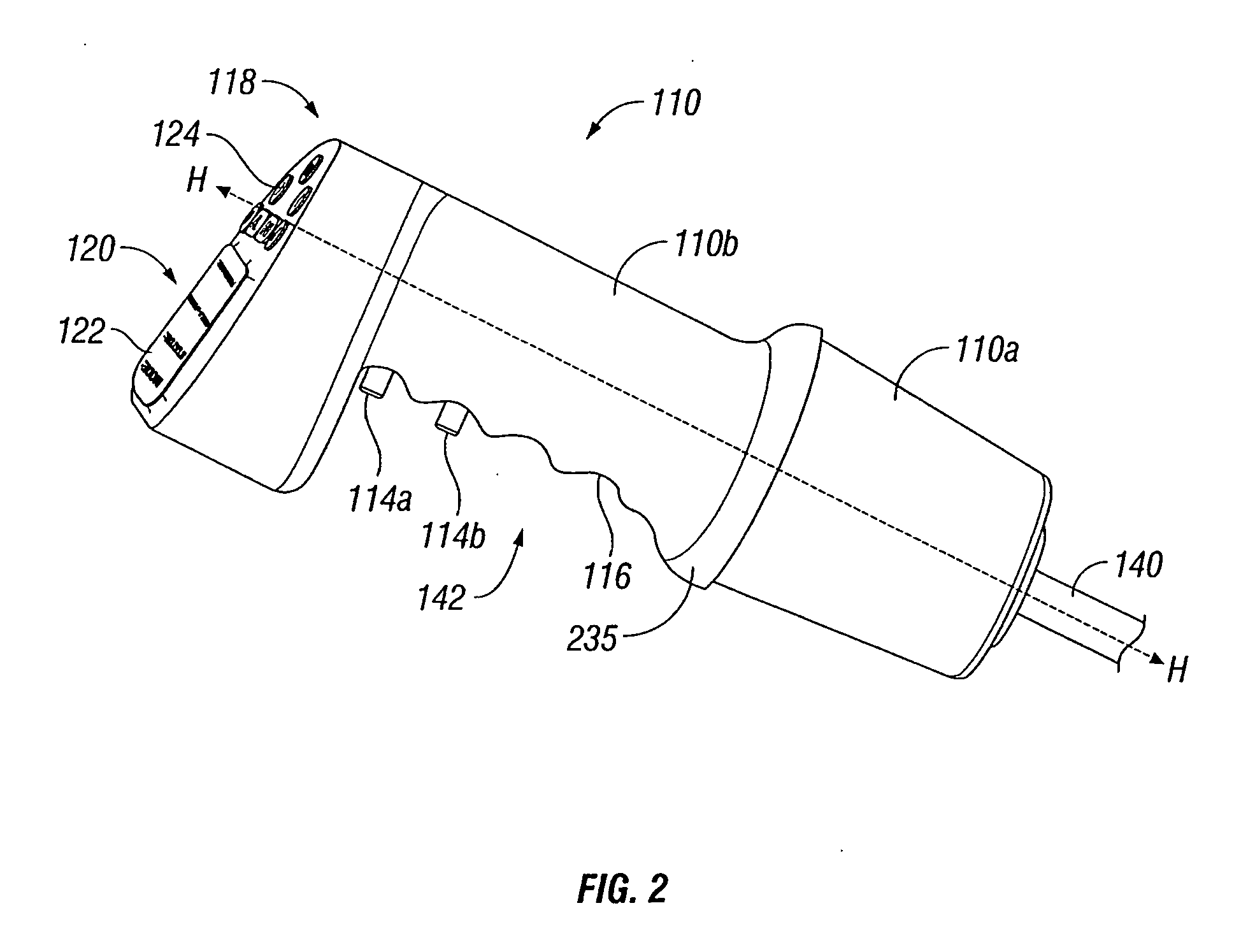
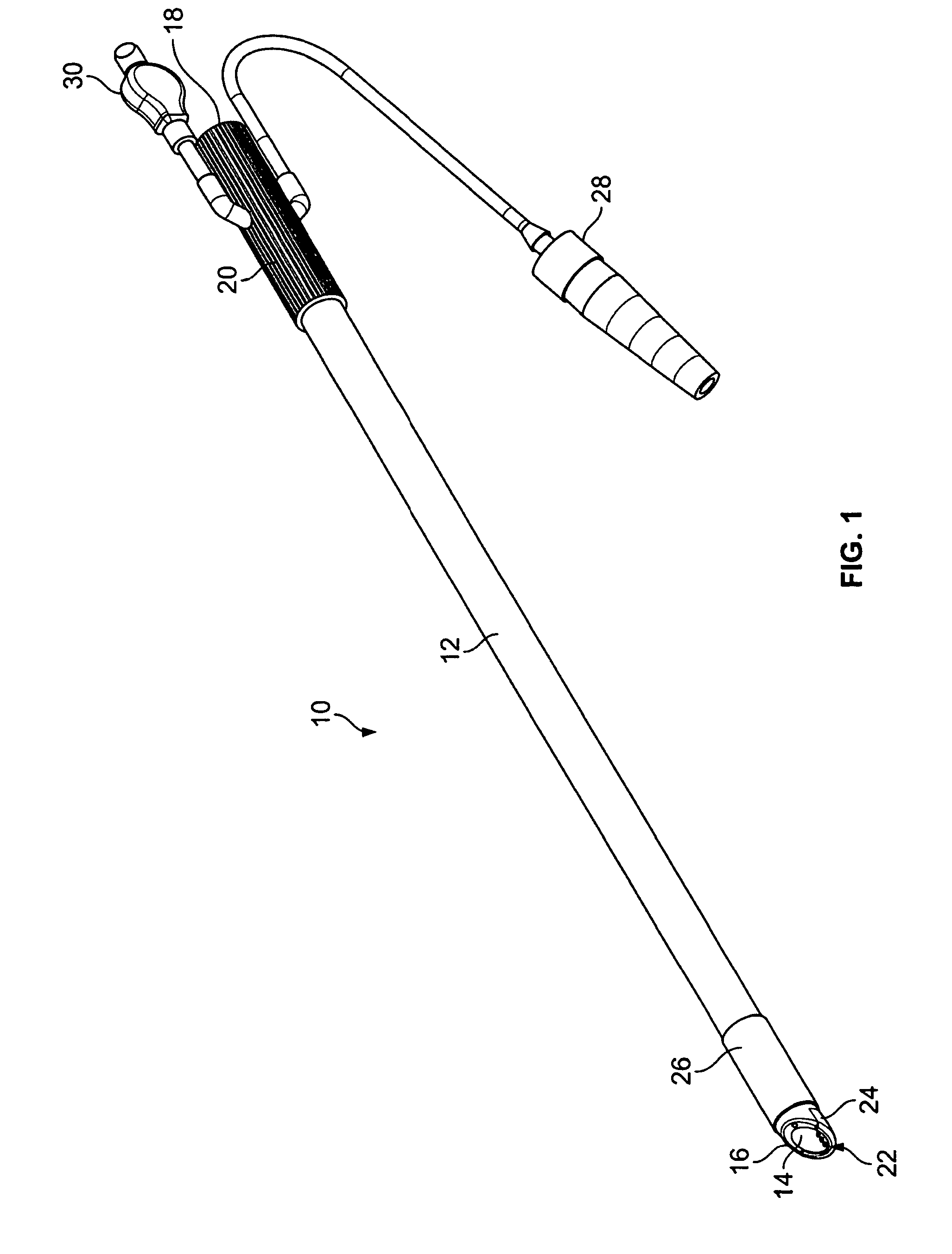
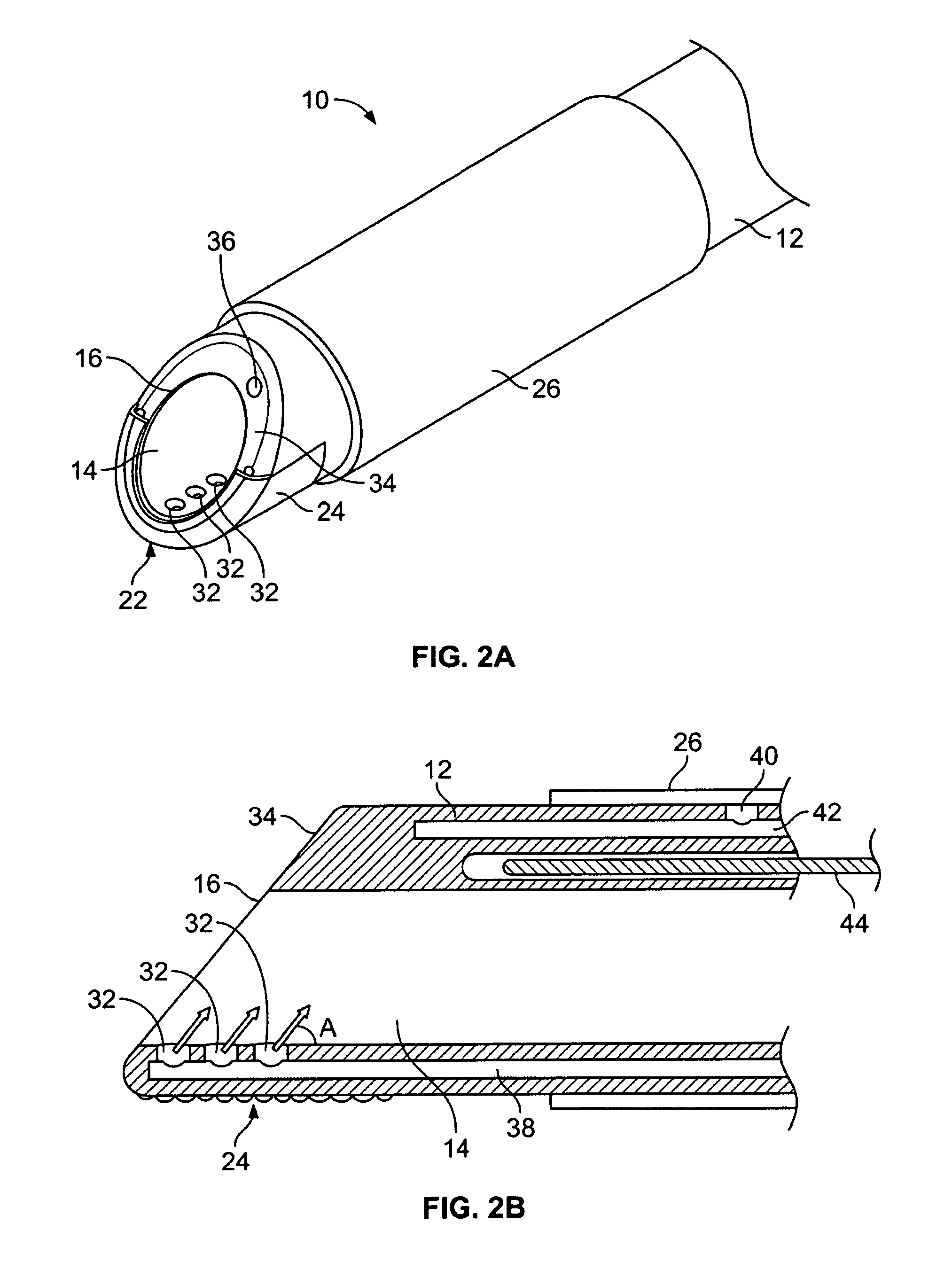
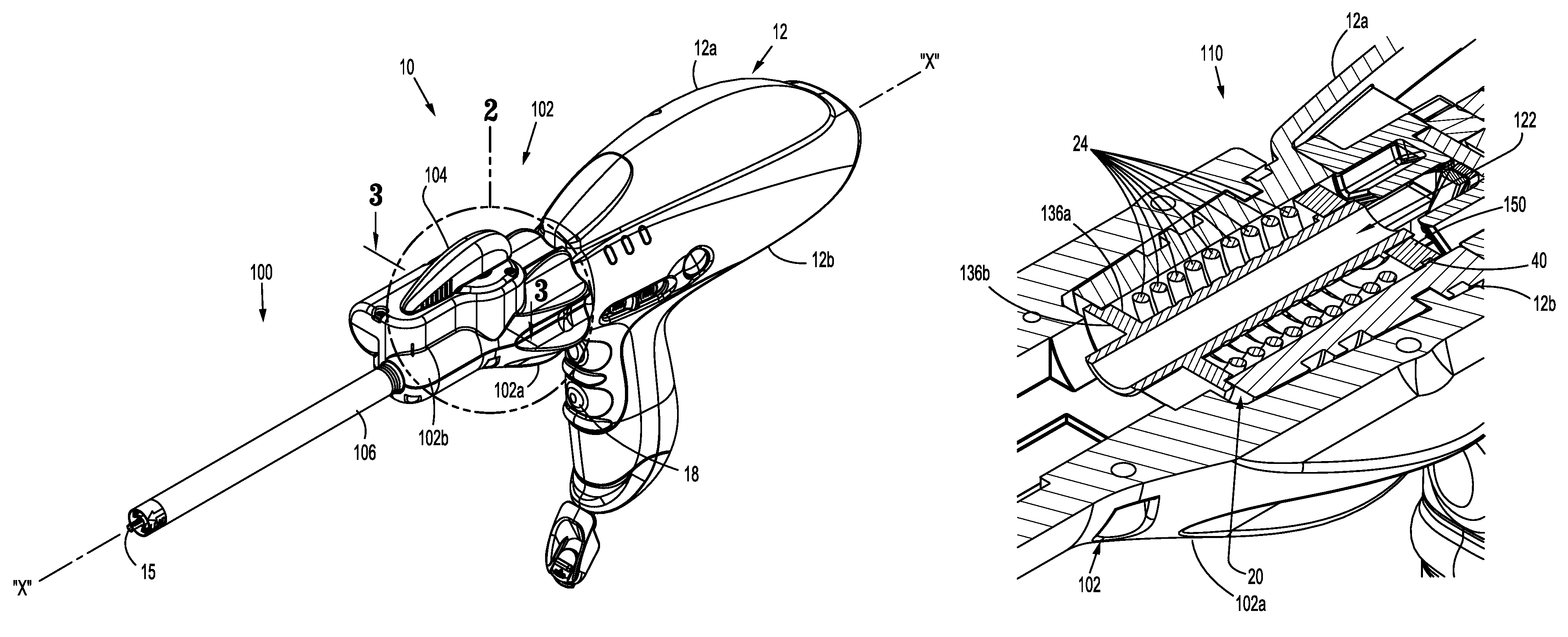
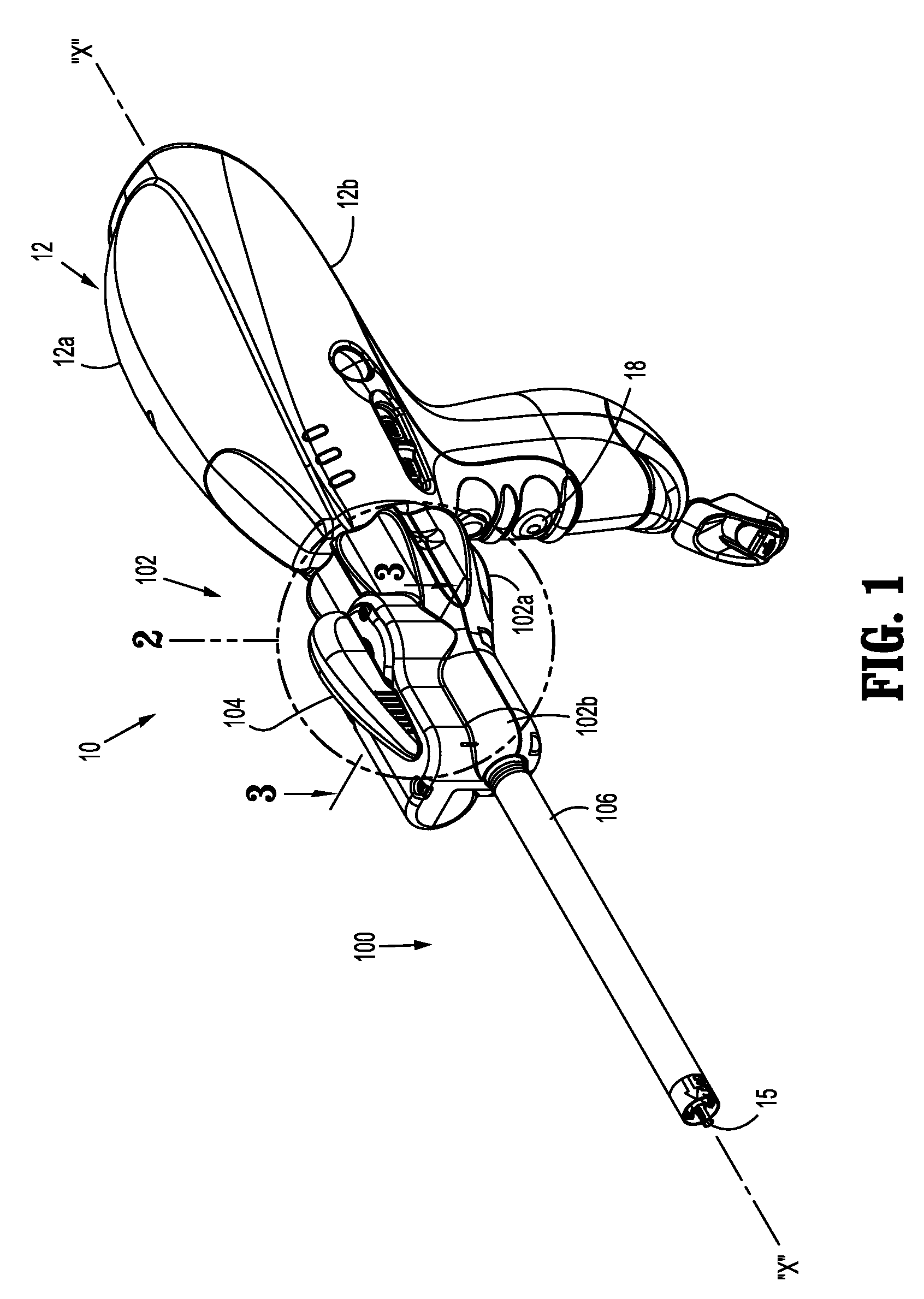
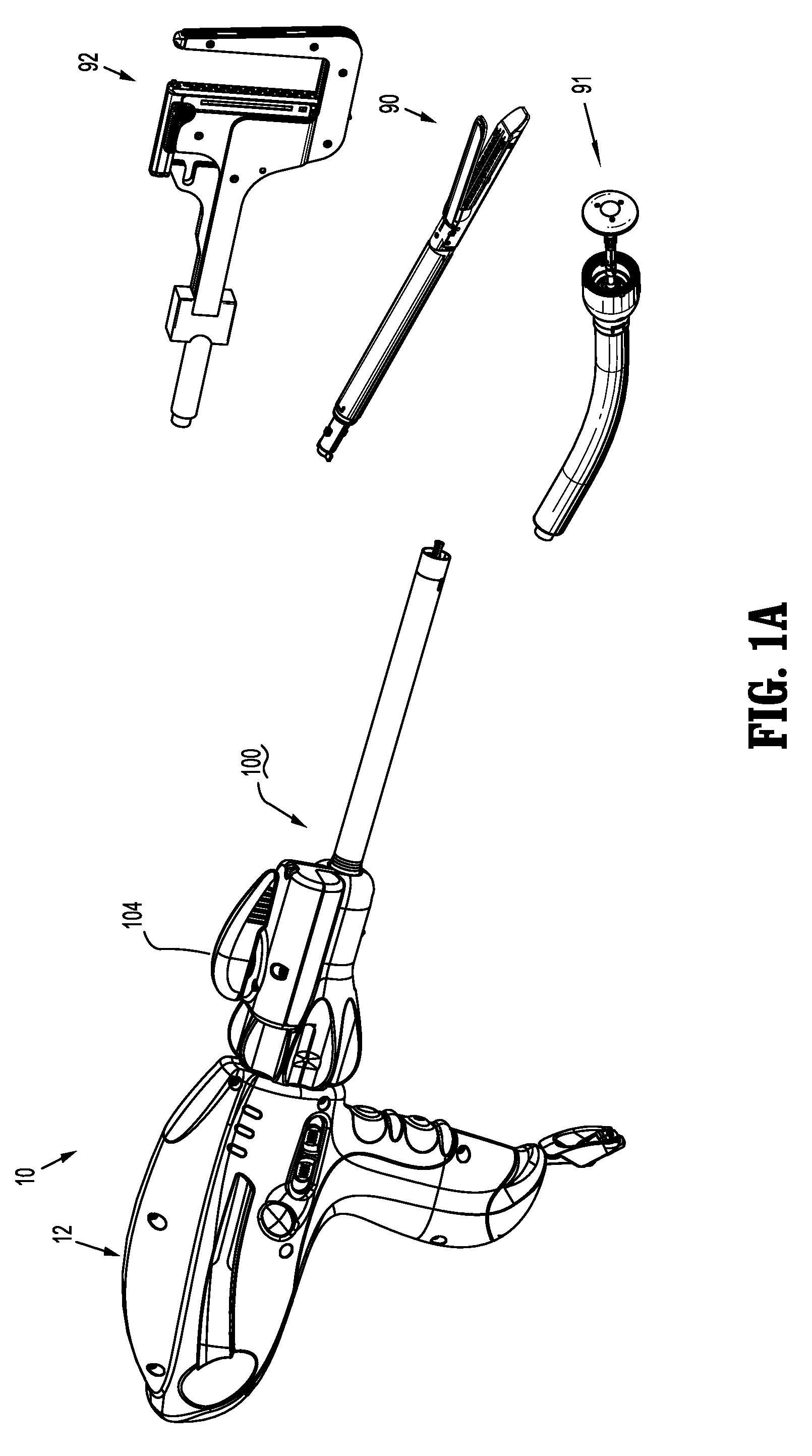
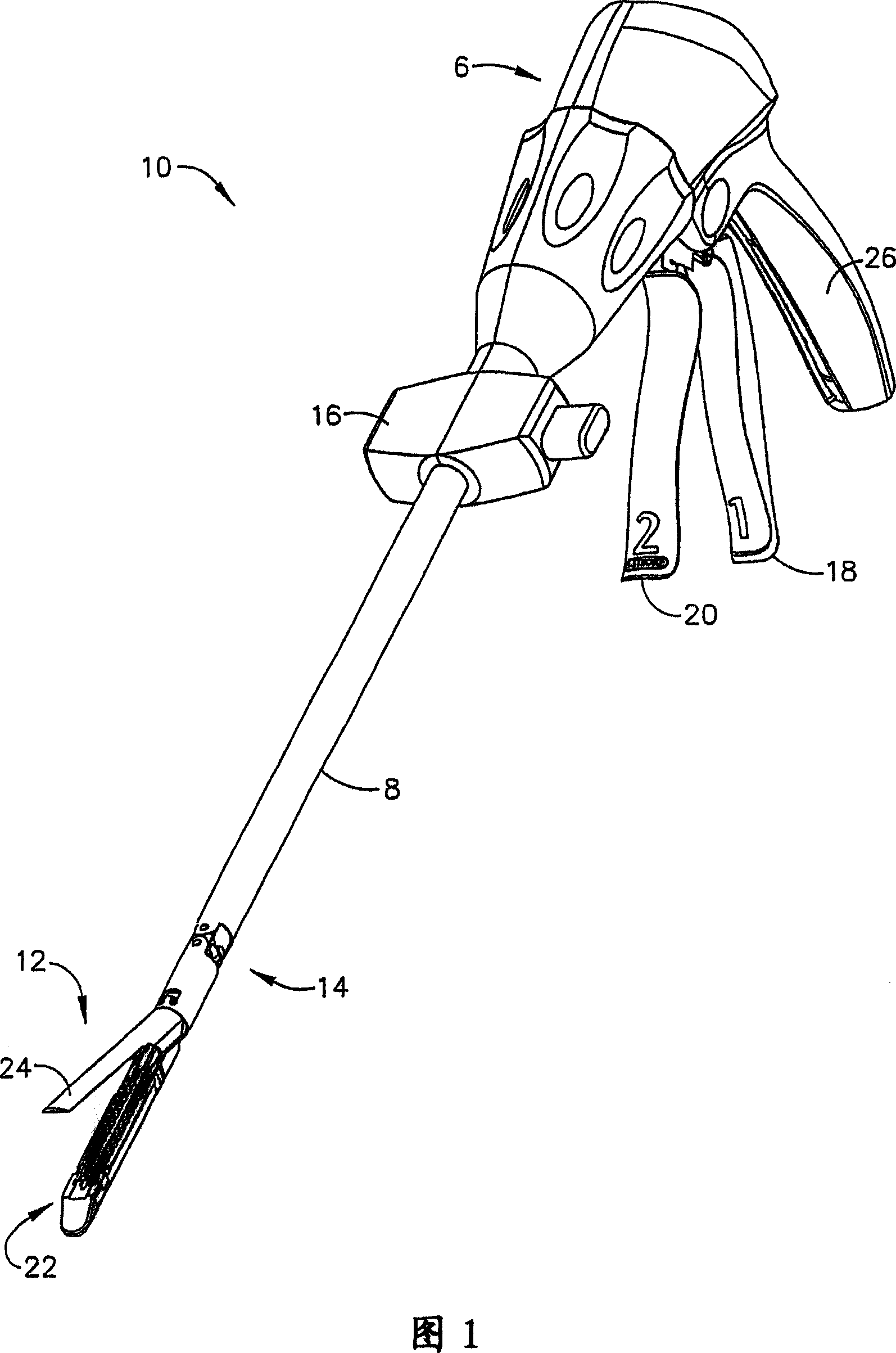
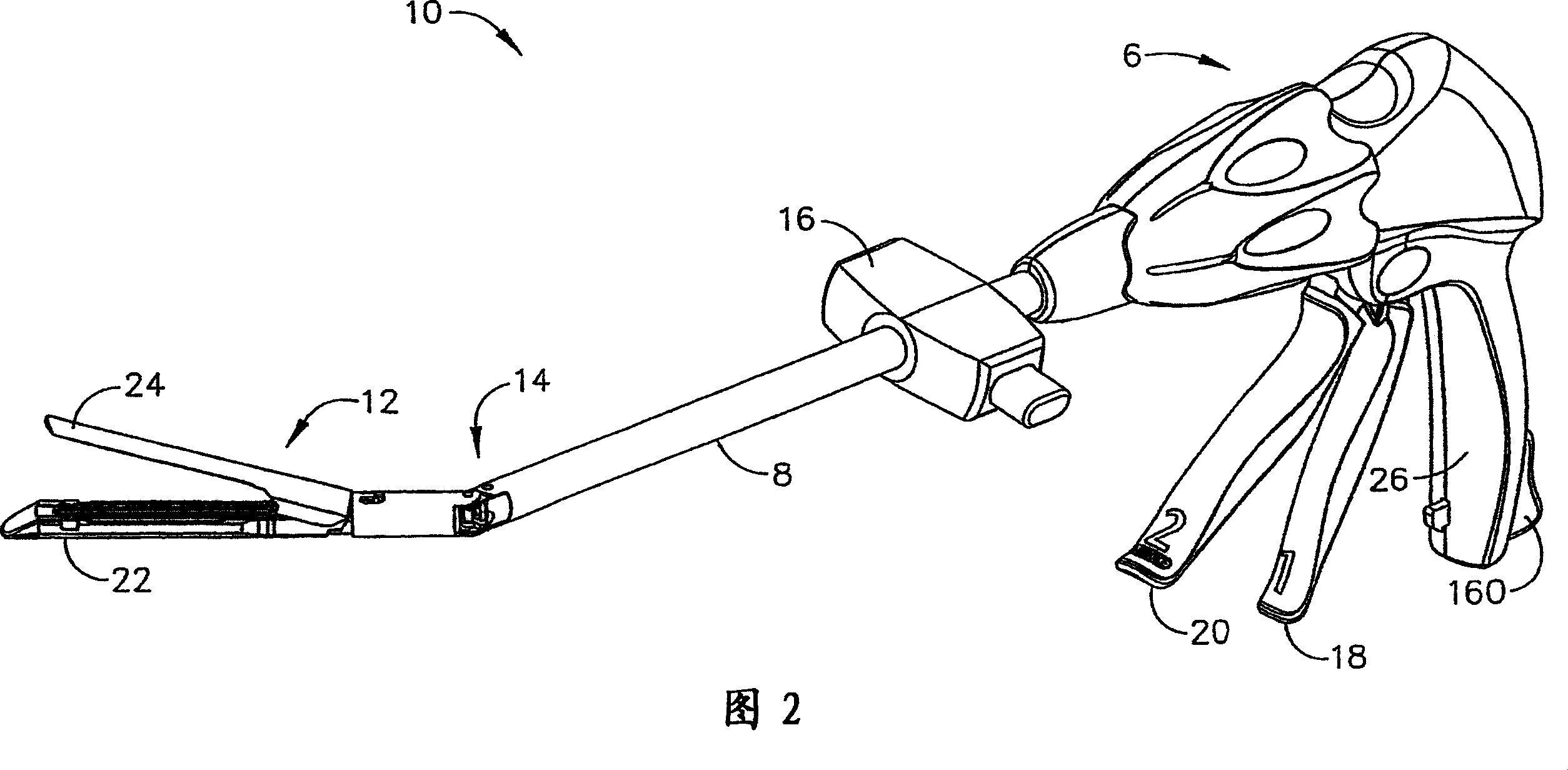
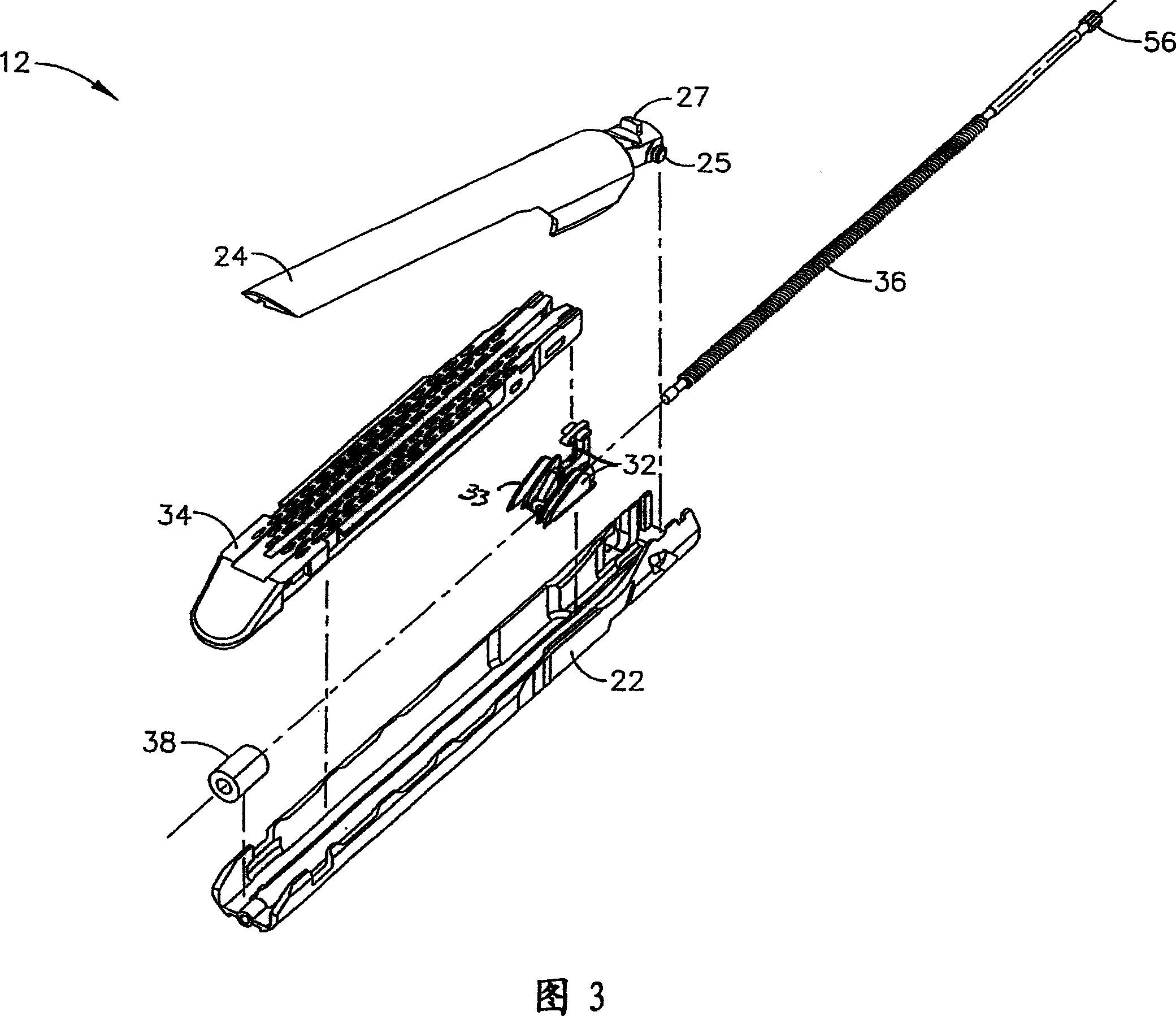
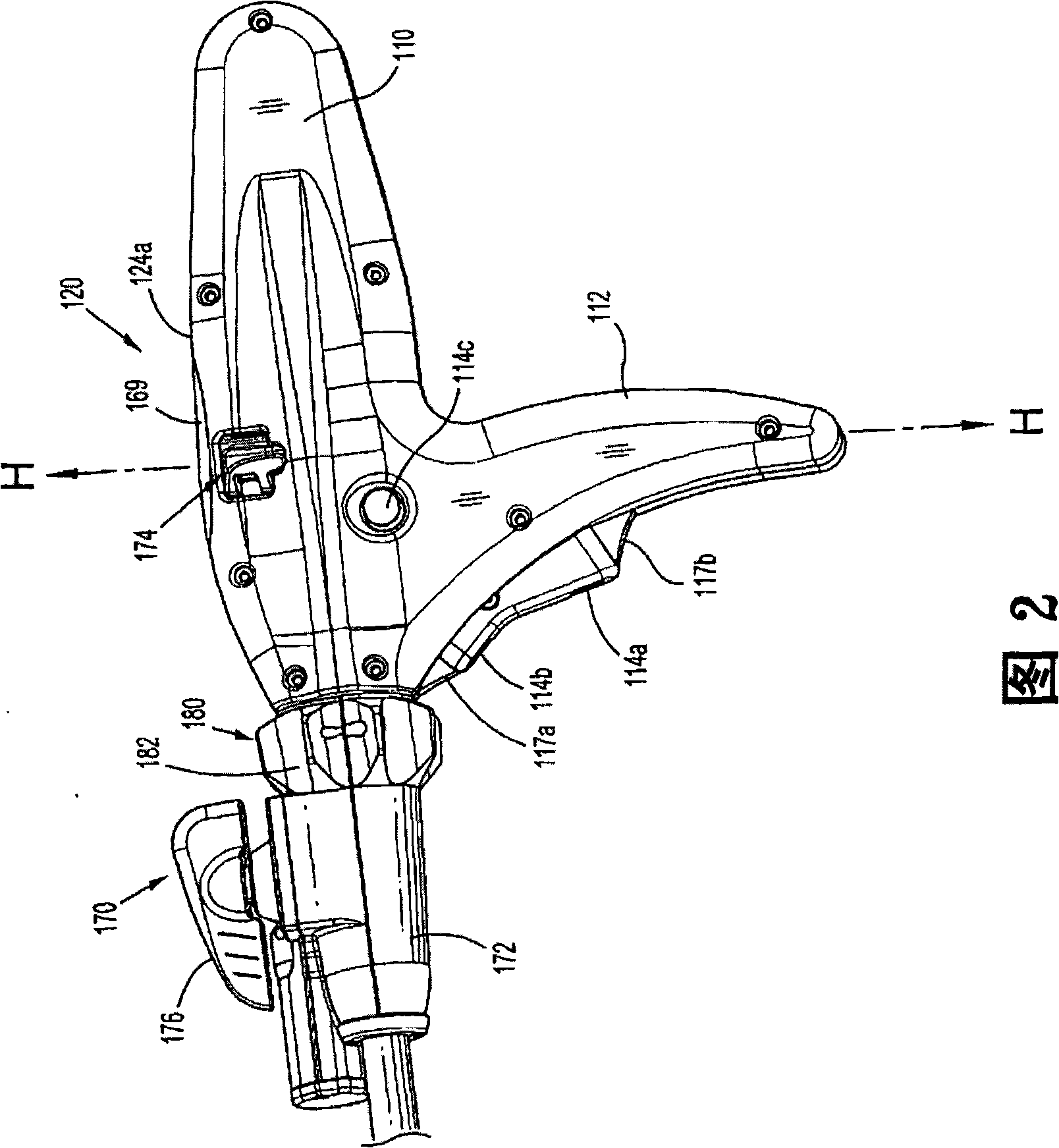
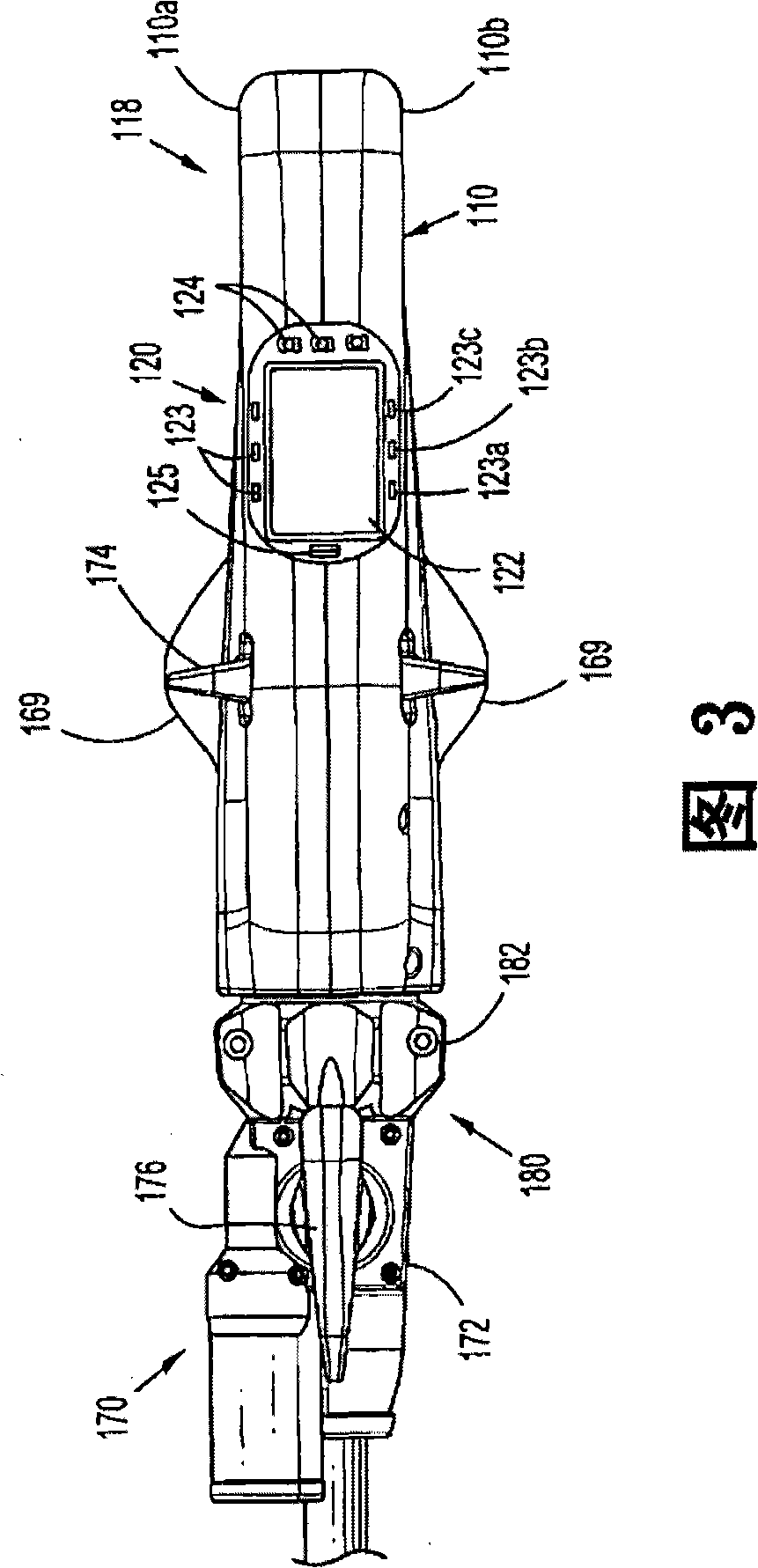
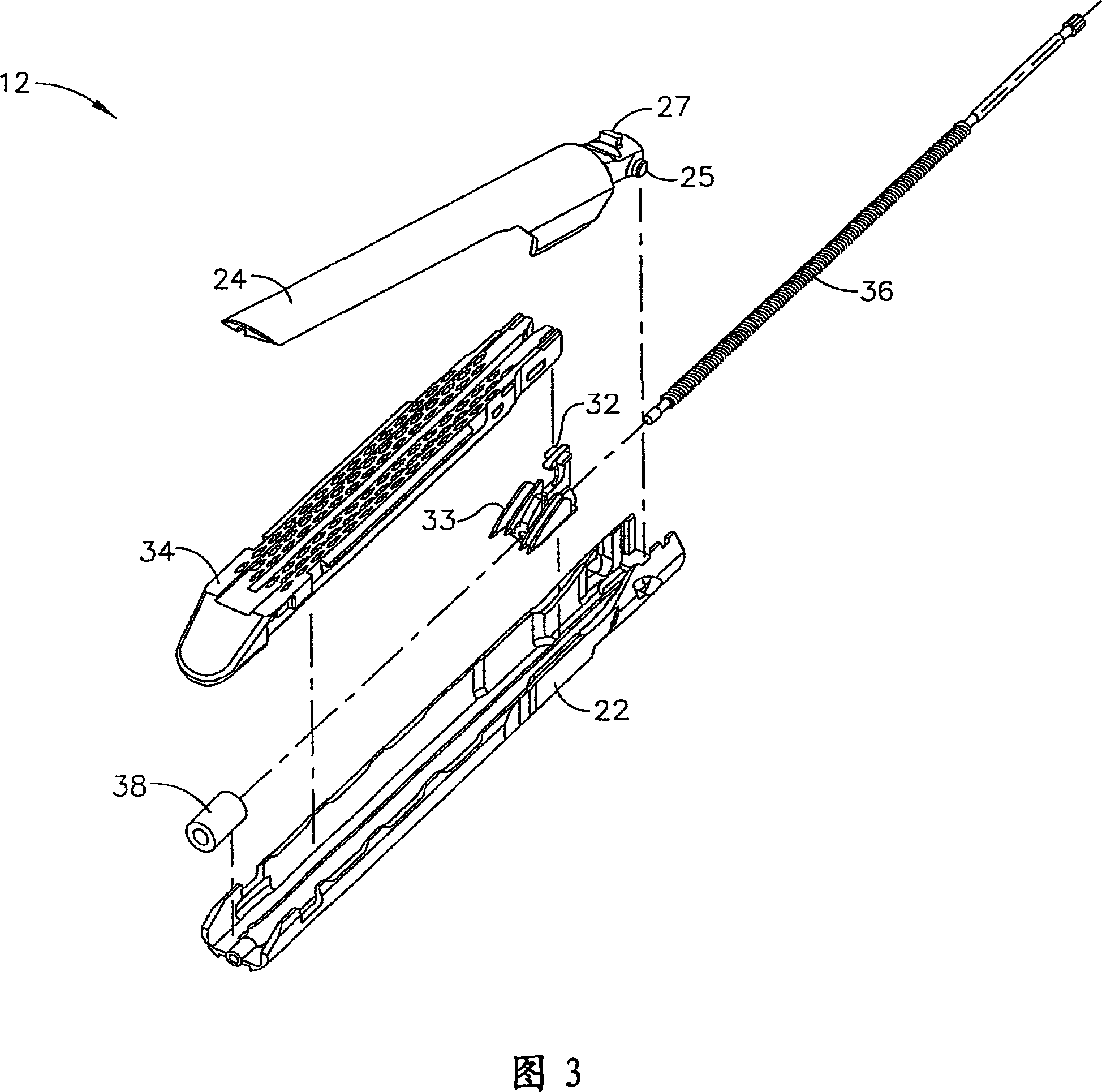
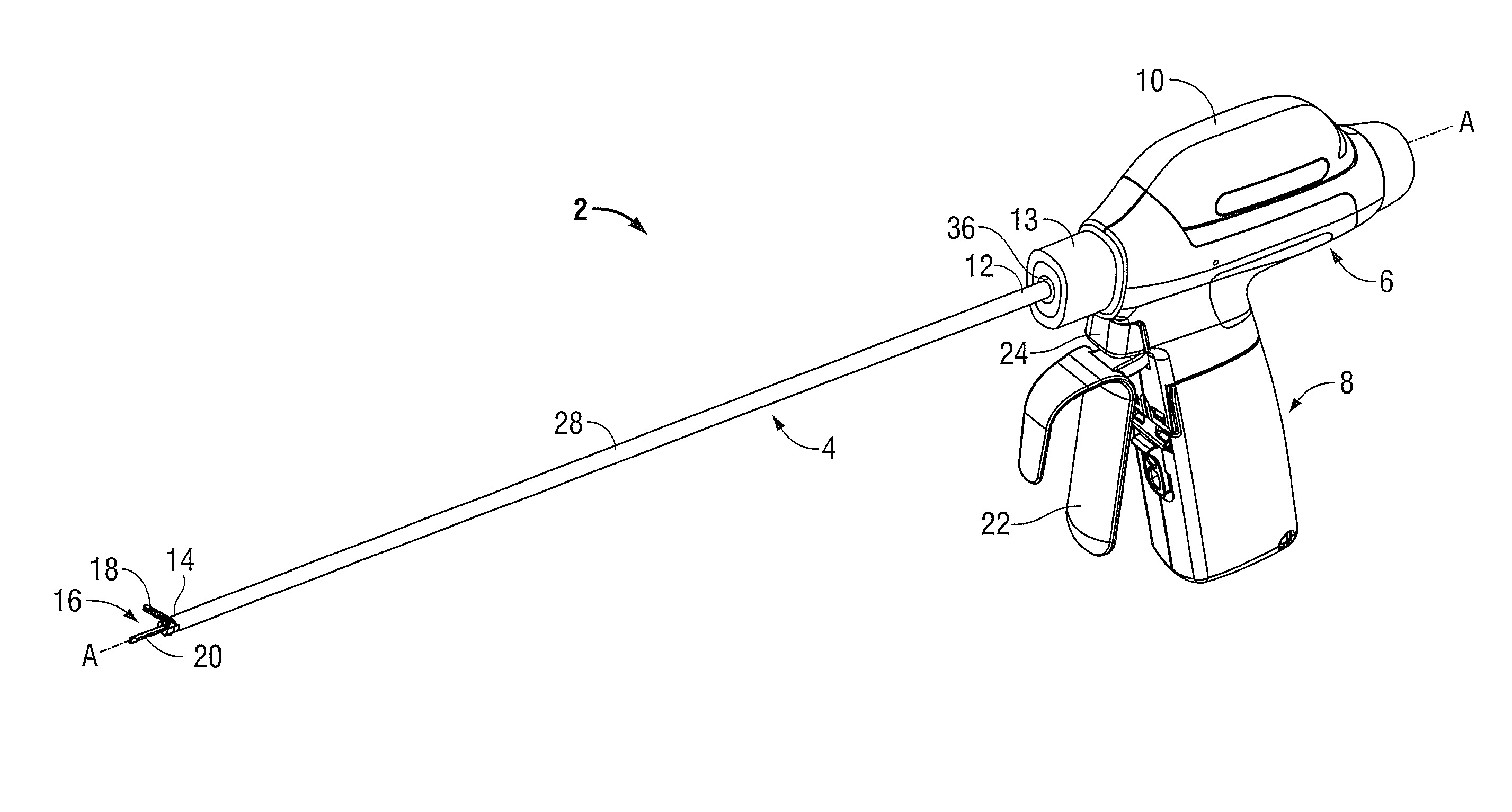
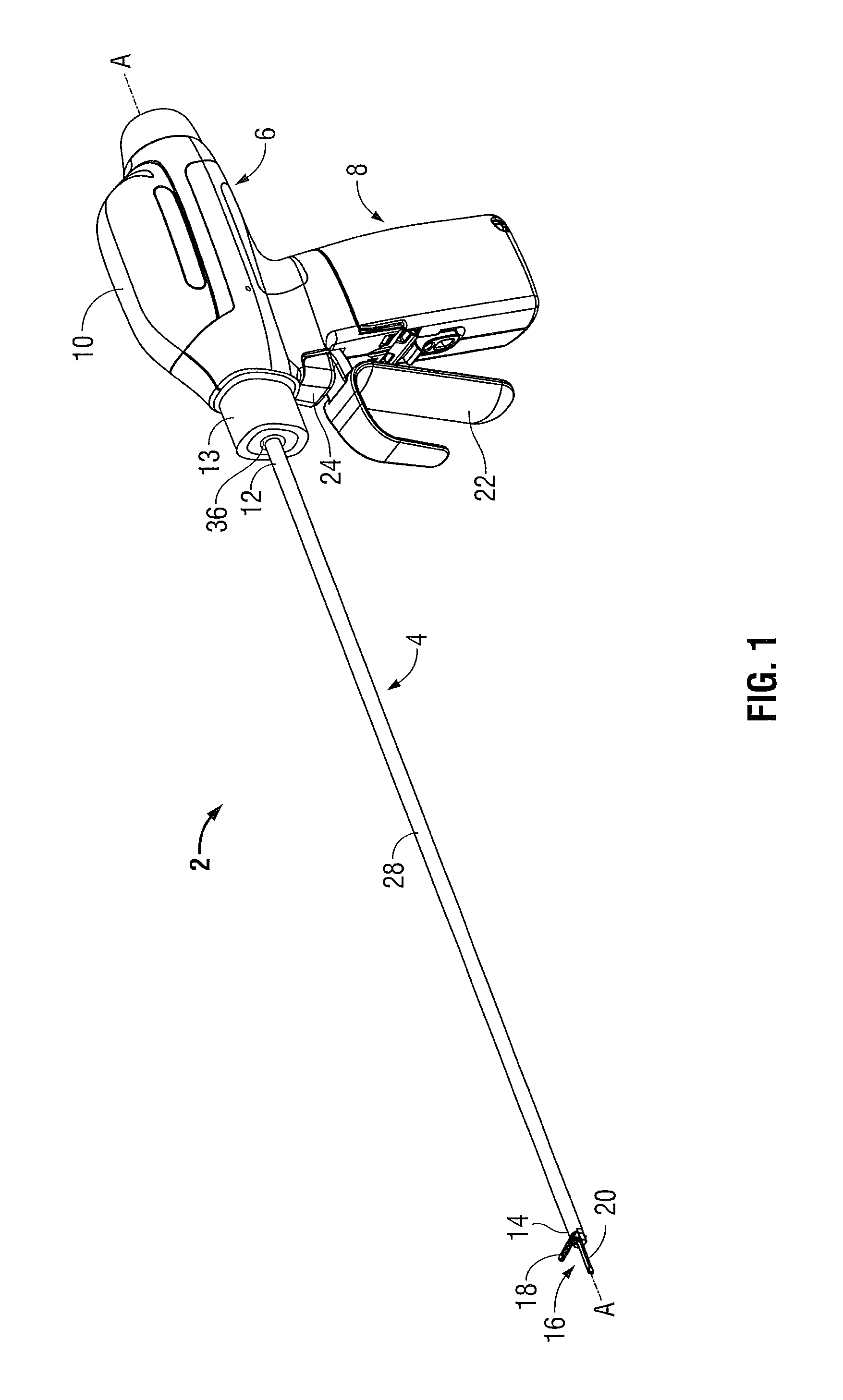
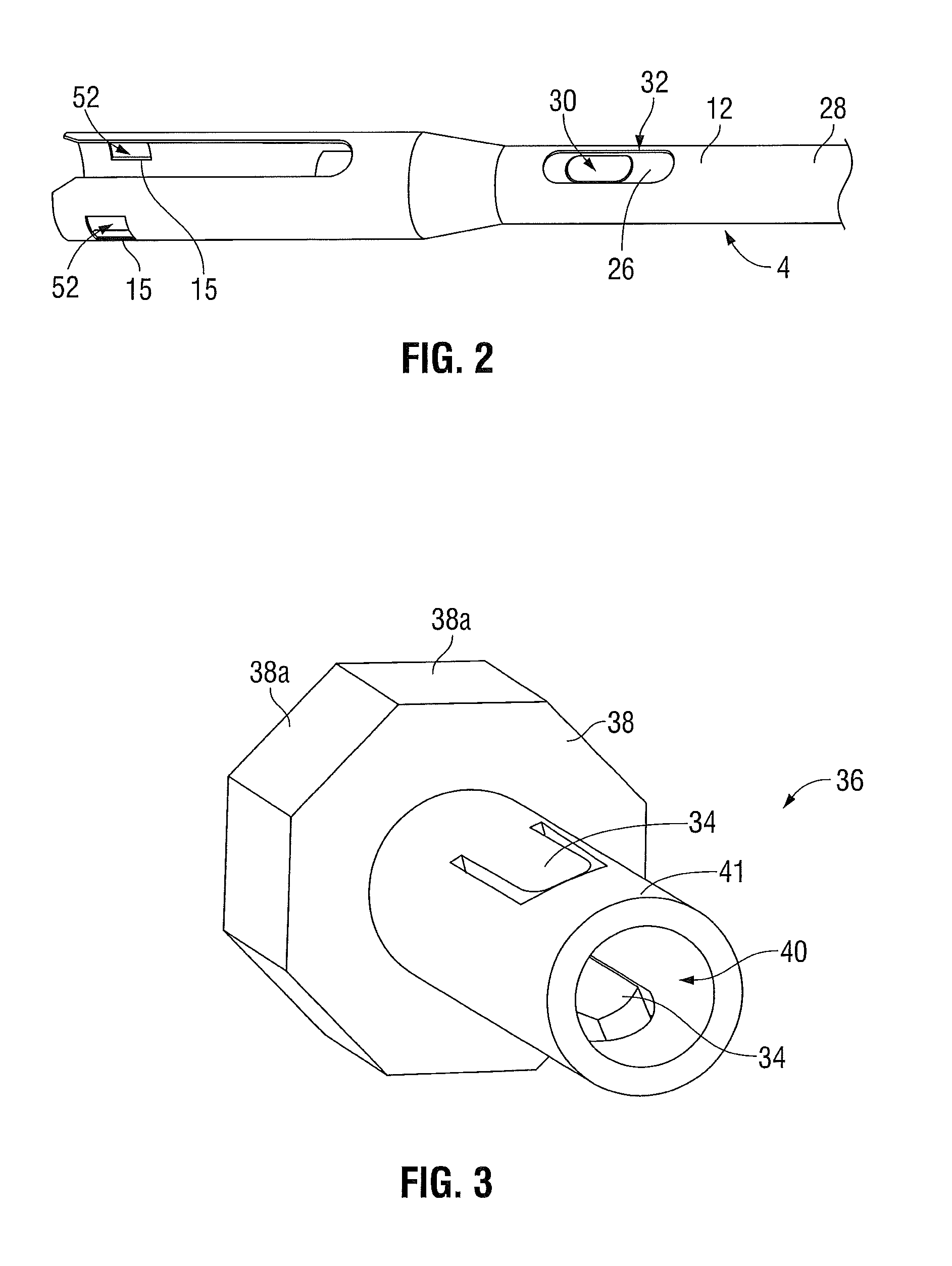
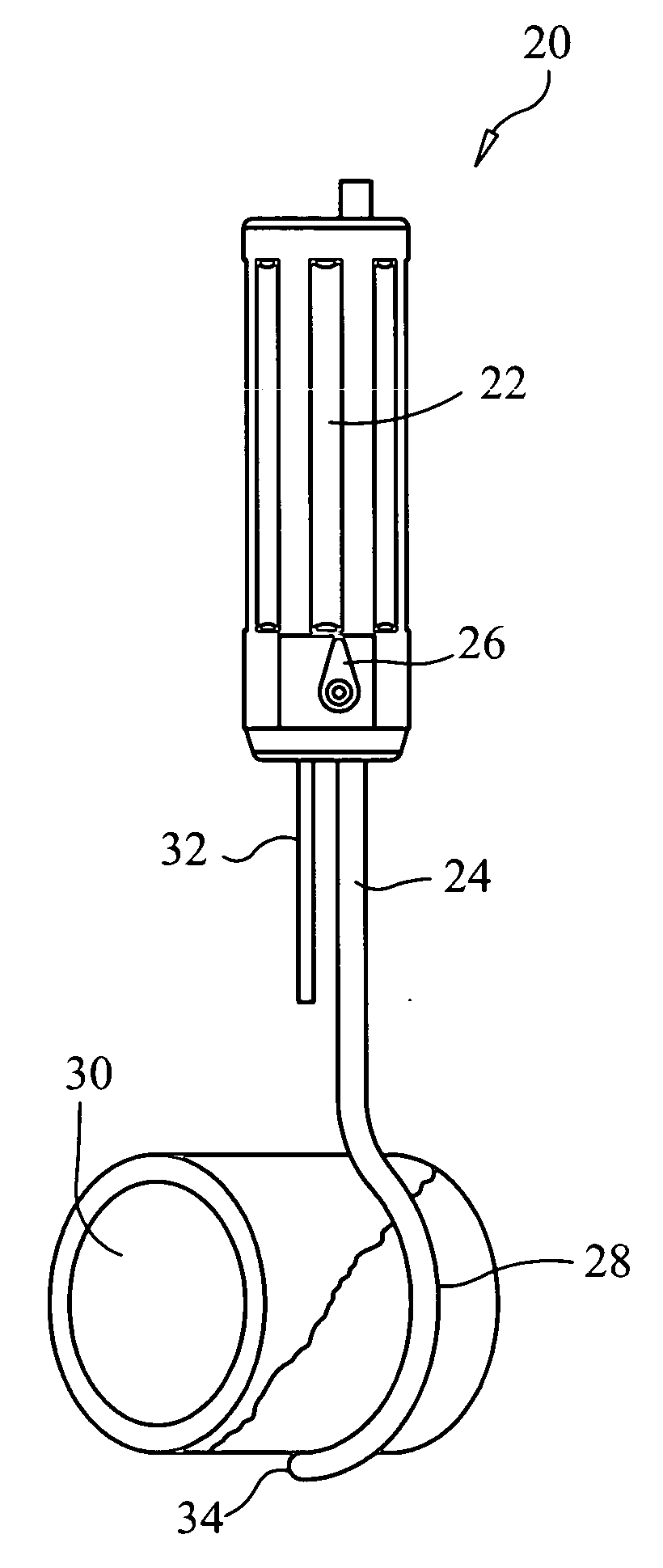
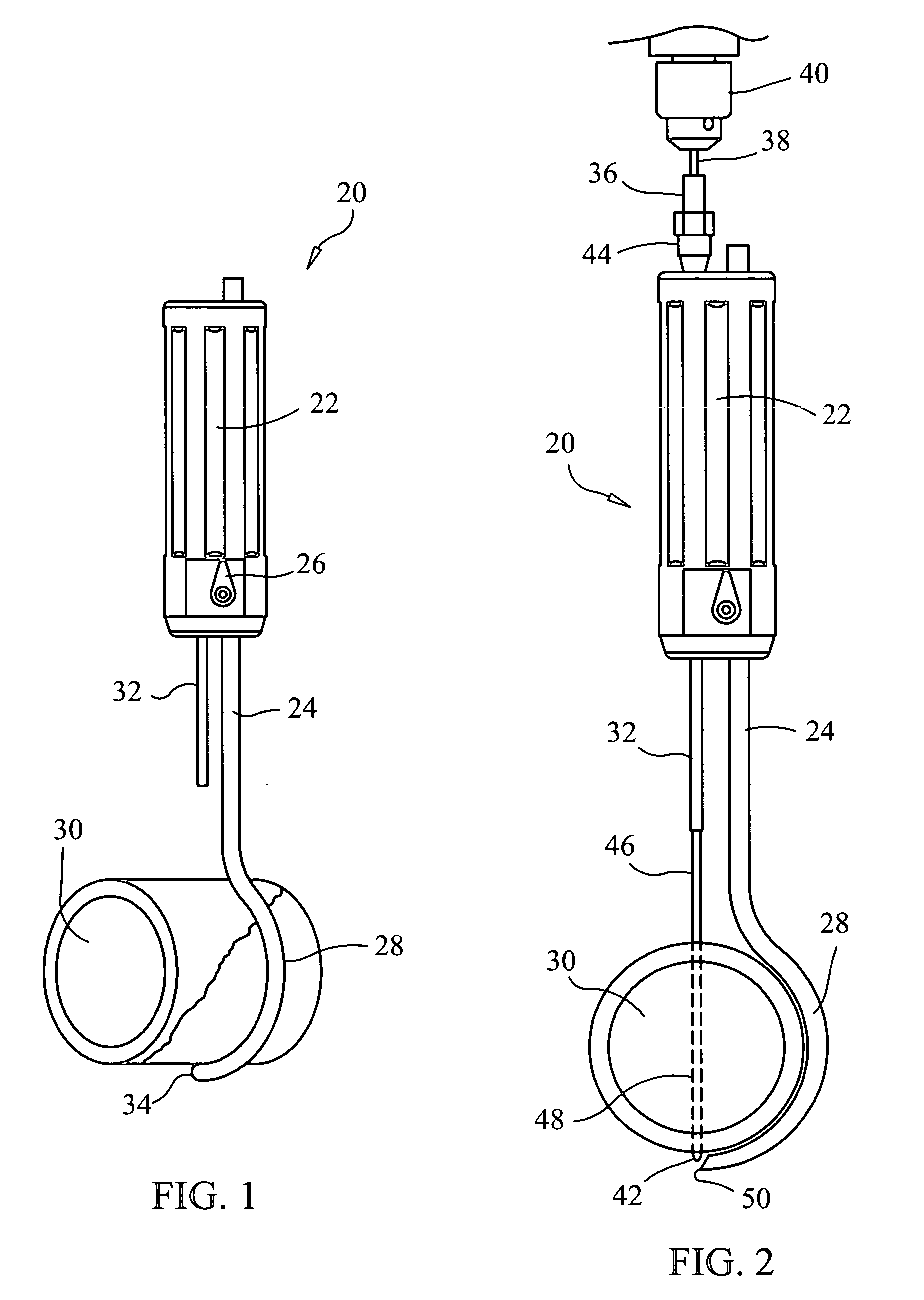
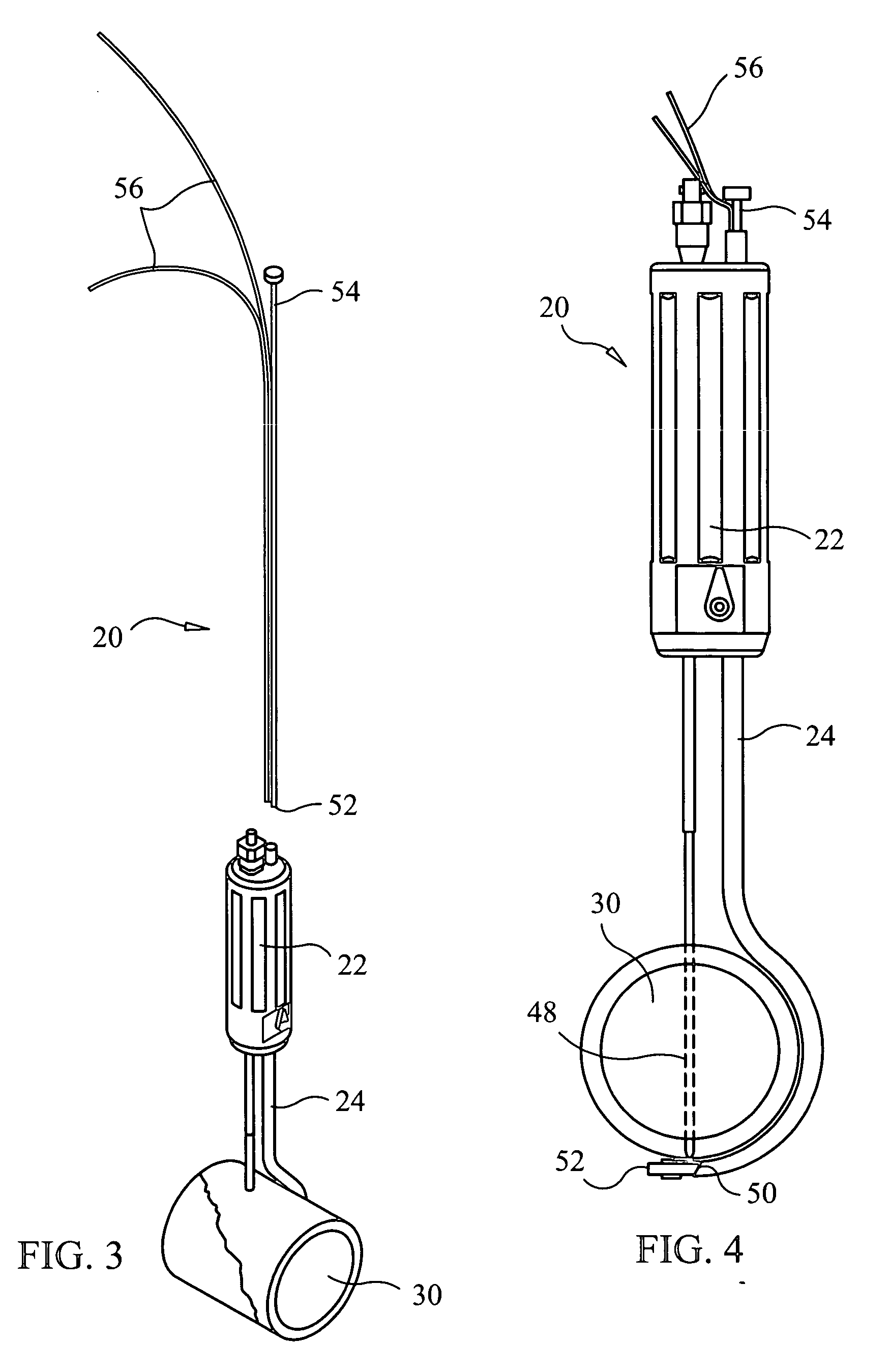
Powered surgical instrument
A surgical instrument including a housing, an endoscopic portion, a shaft portion and an end effector is disclosed. The endoscopic portion extends distally from the housing and defines a longitudinal axis. The shaft portion is selectively connectable to a distal end of the endoscopic portion. The end effector is selectively connectable to a distal end of the shaft portion.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Dissecting cannula and methods of use thereof
Methods and devices described herein facilitate improved access of locations within the body by providing a variety of dissection modes on a single access device.
Owner:ATRICURE
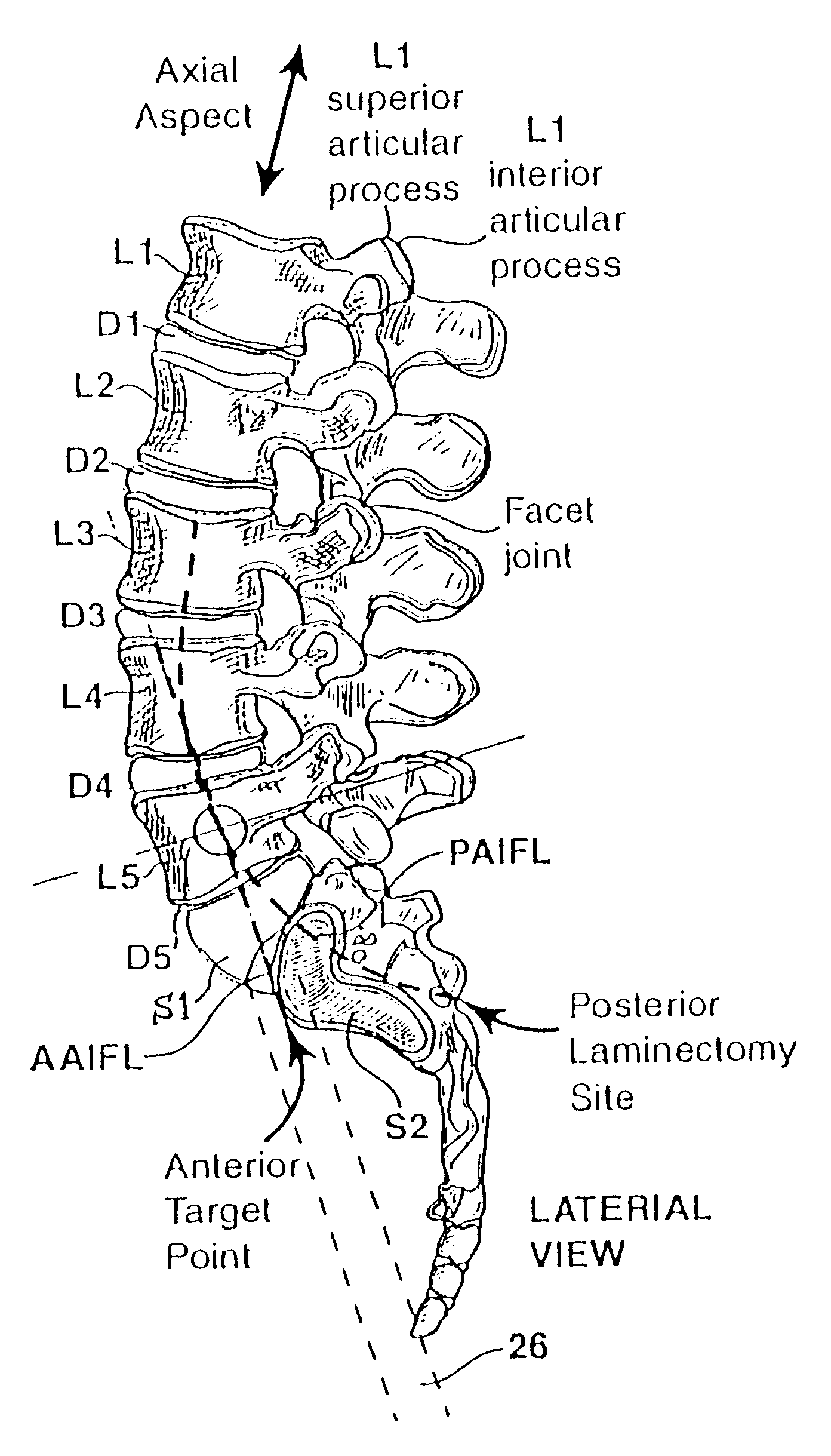
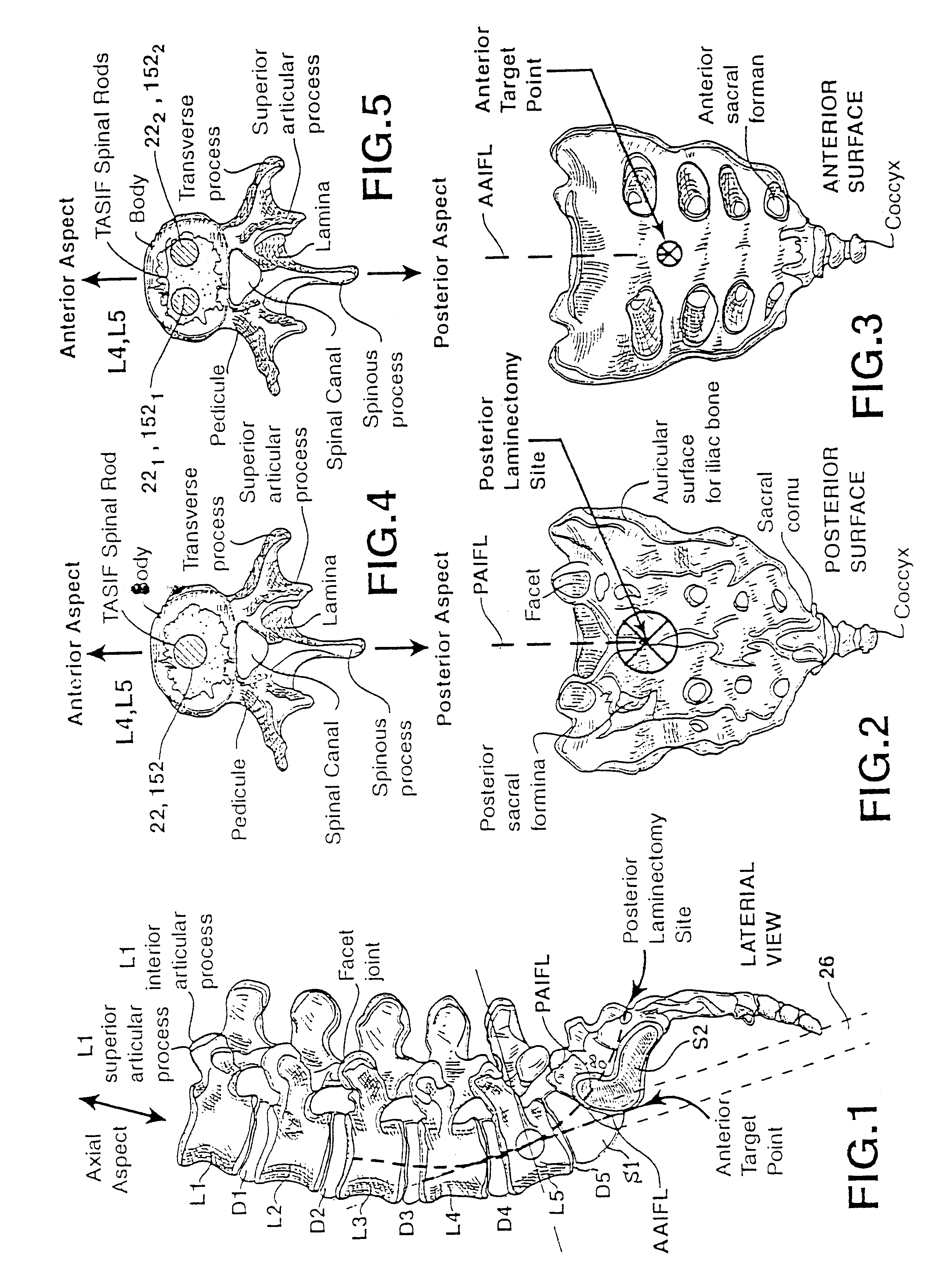
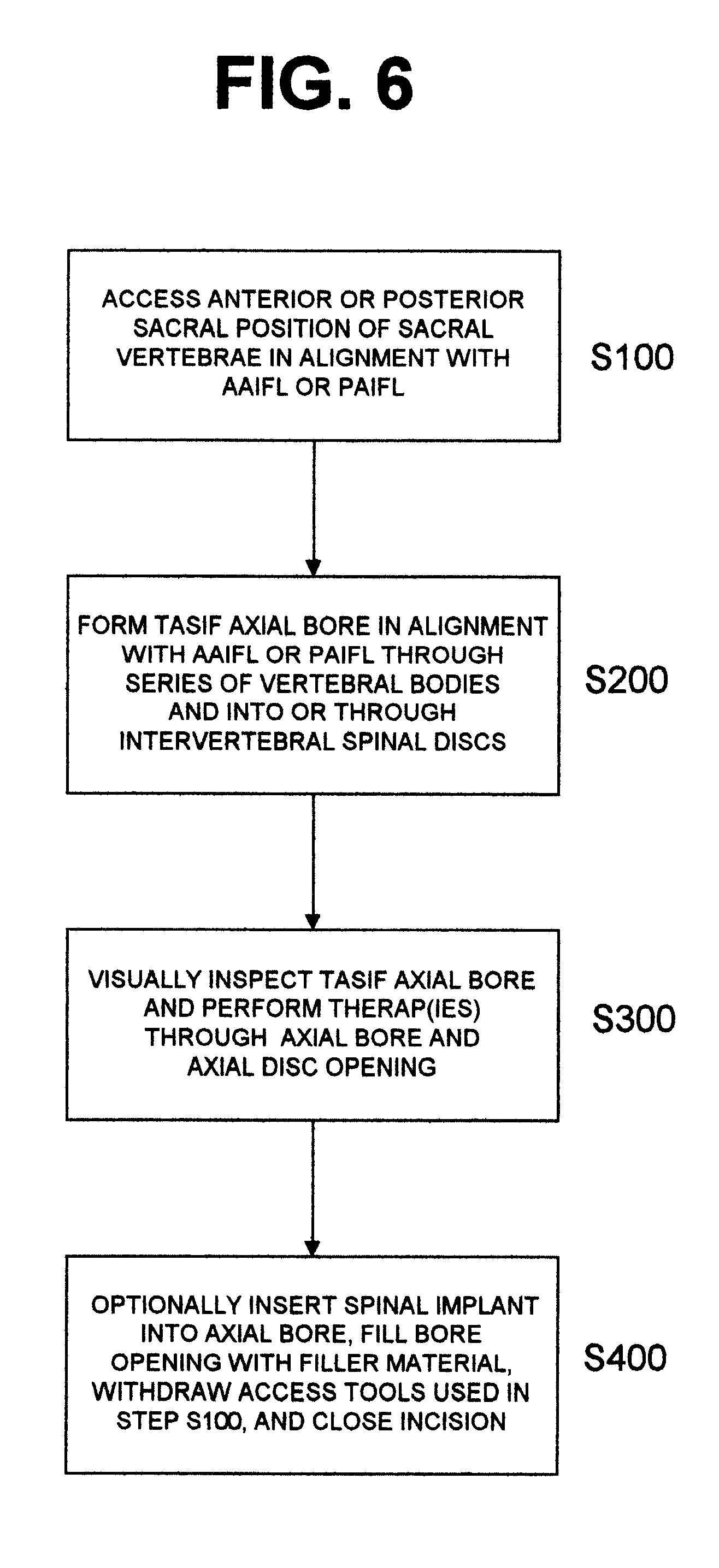
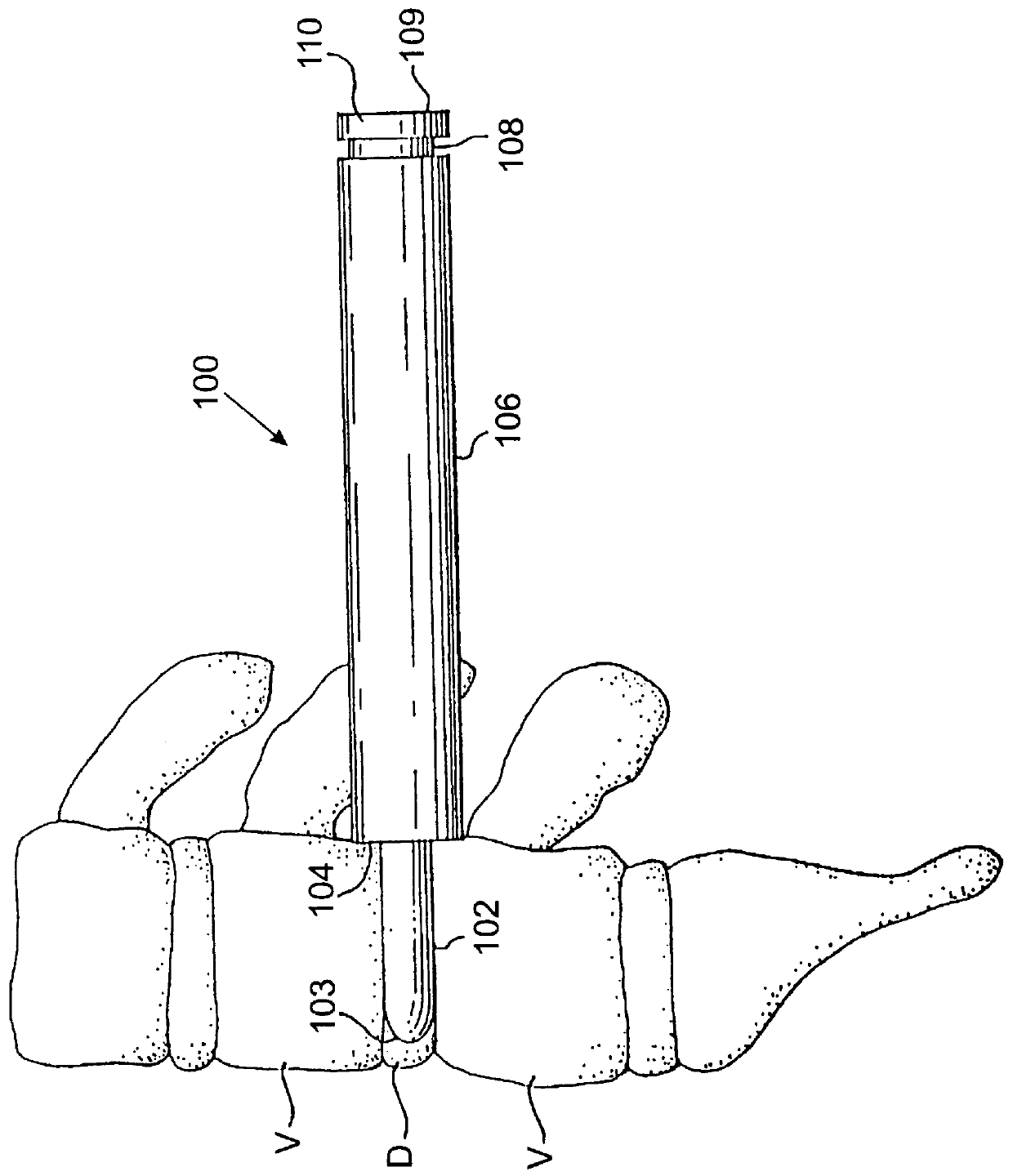
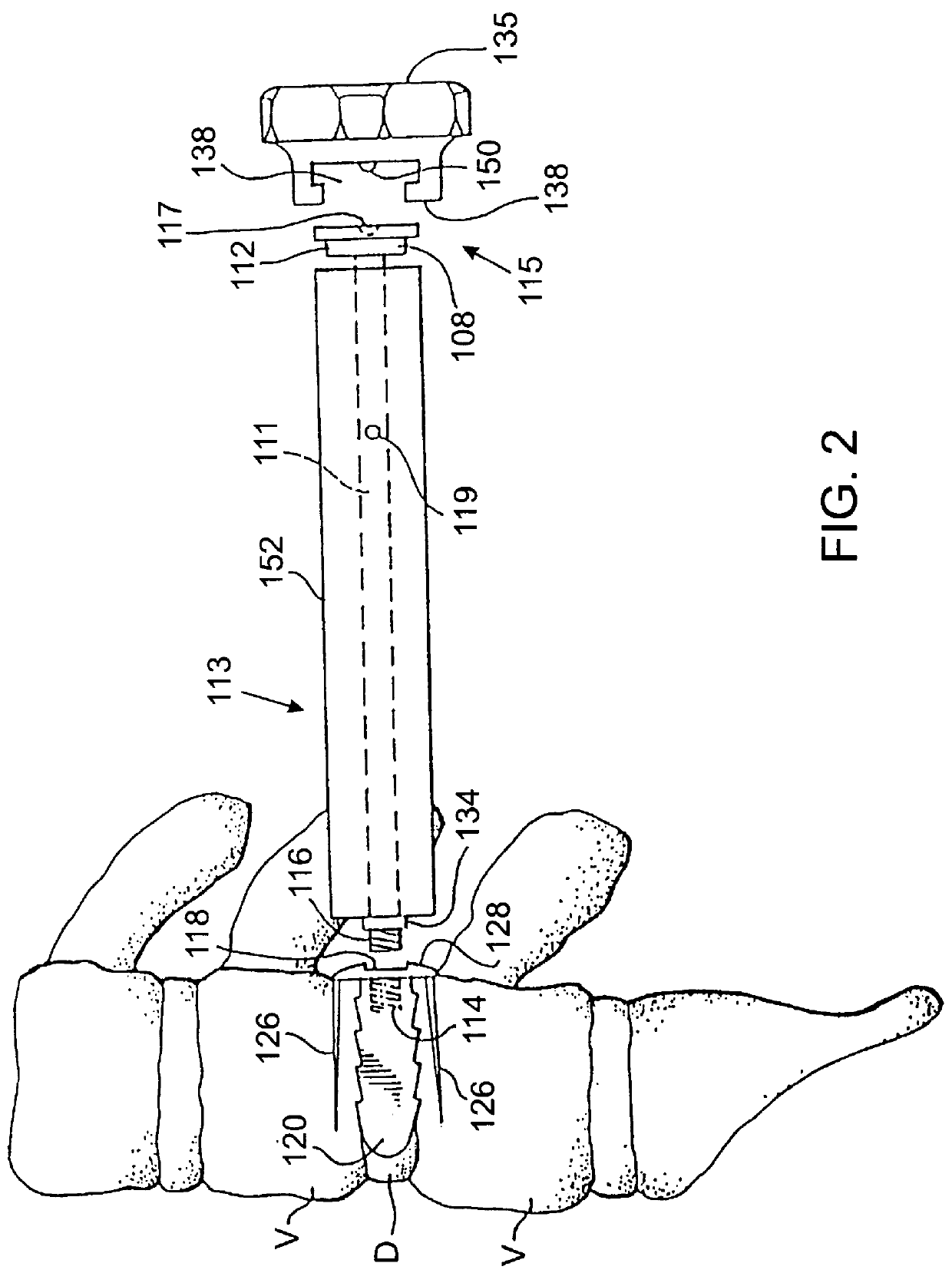
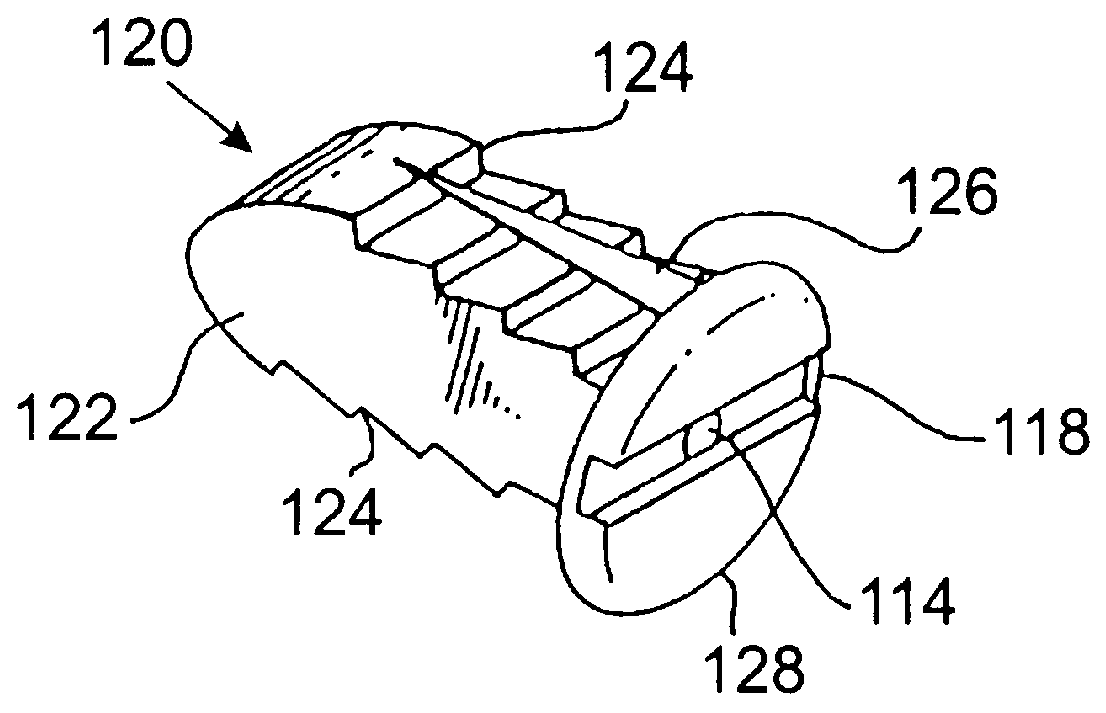
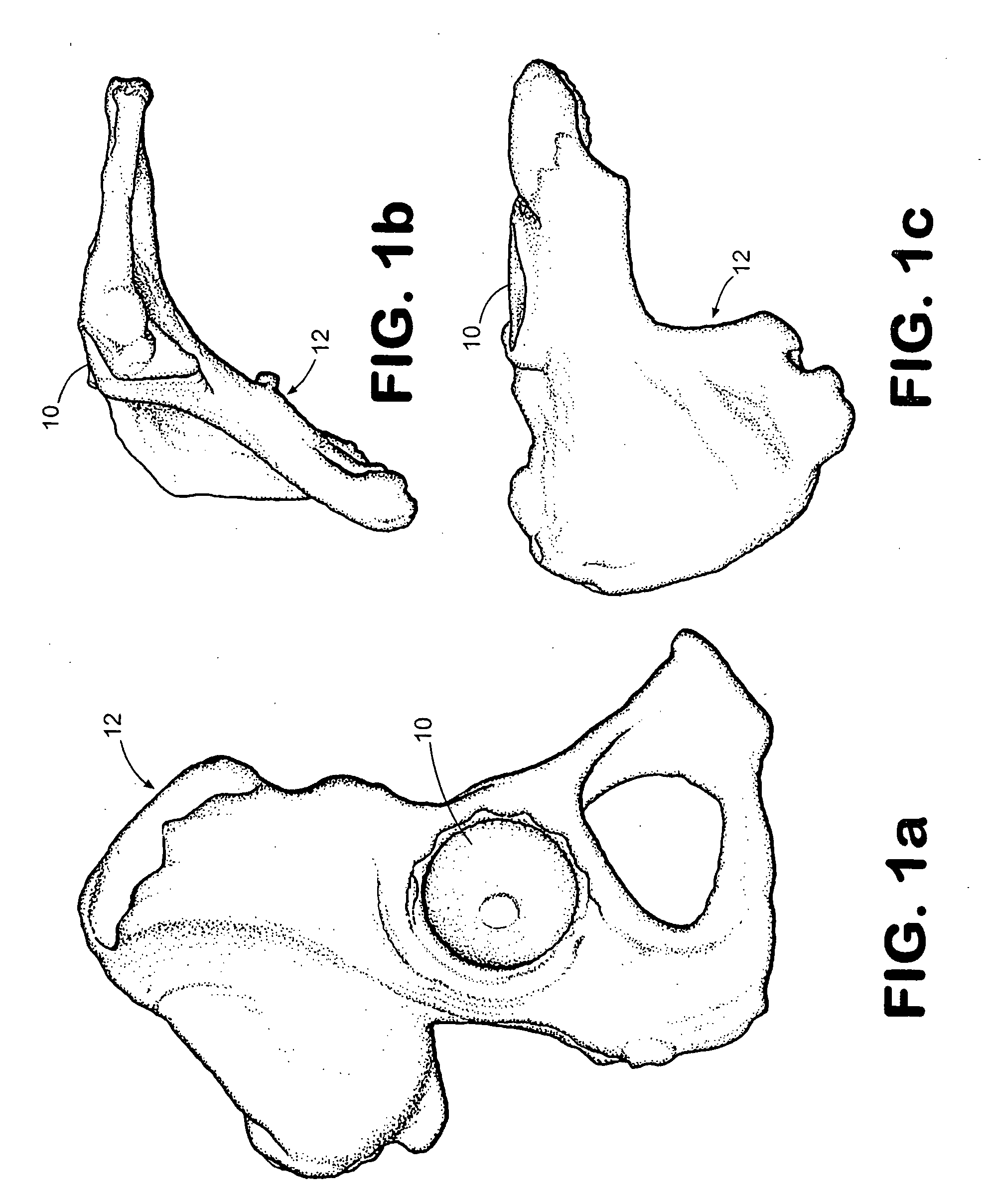
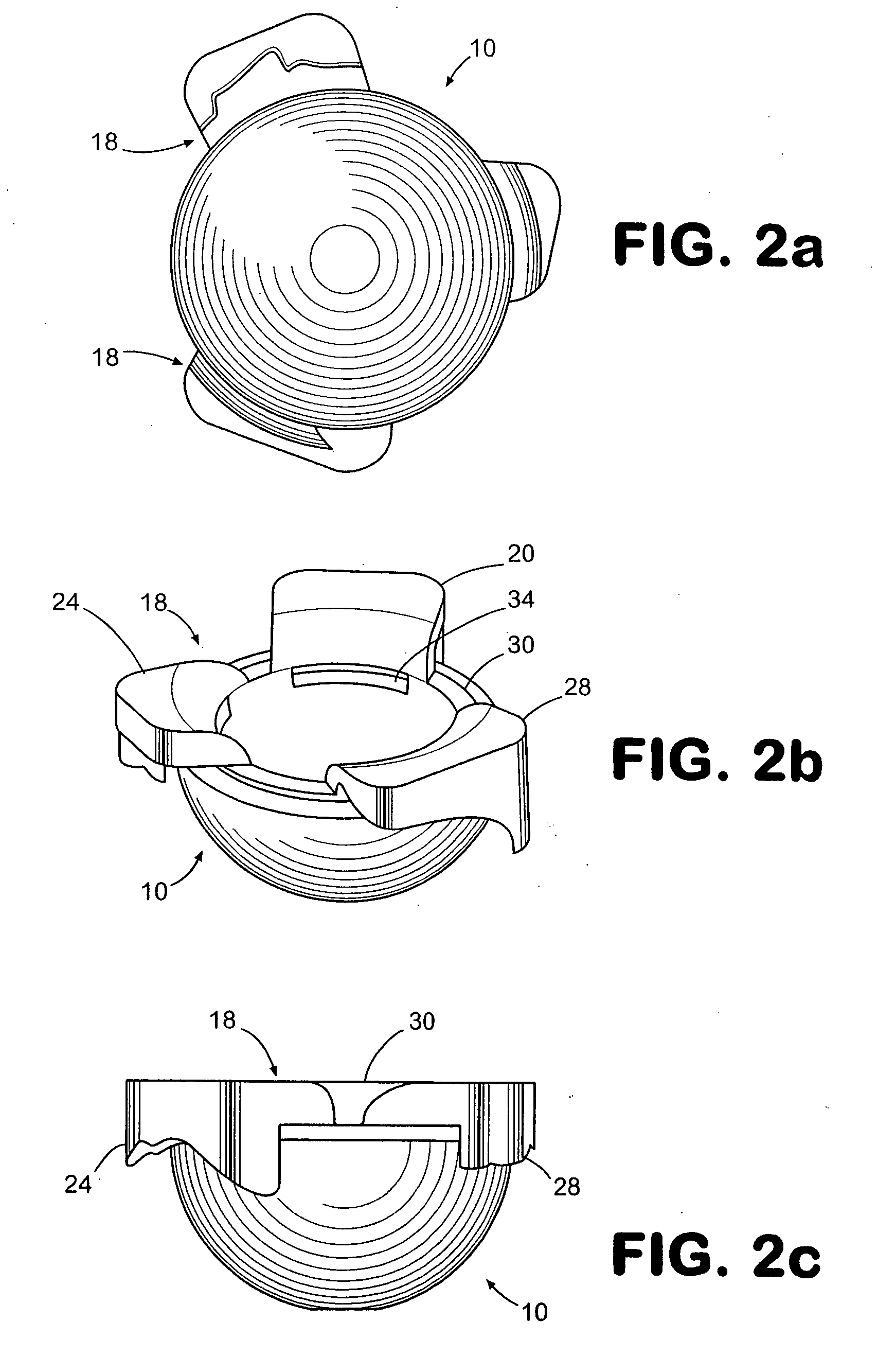
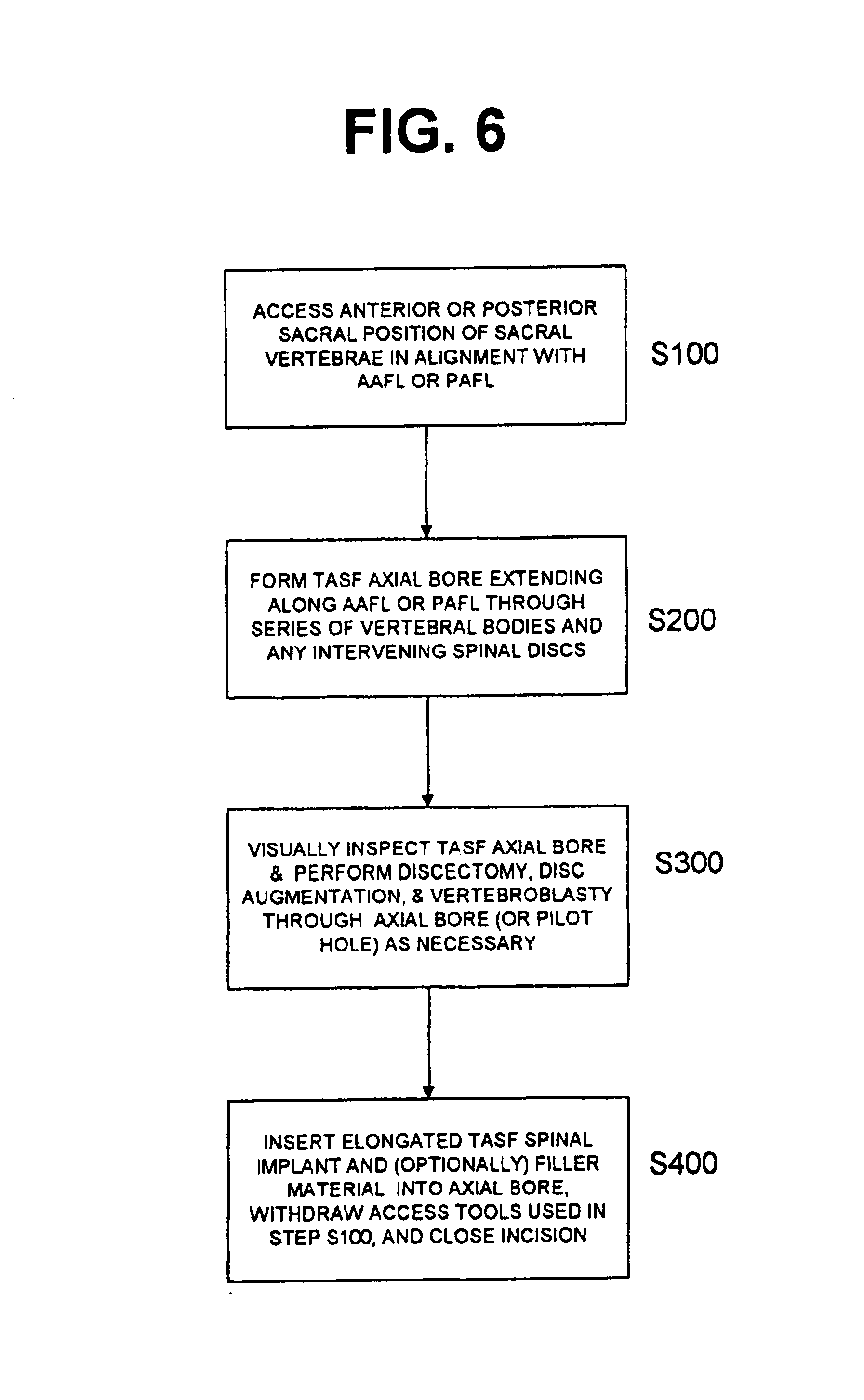
Methods and apparatus for performing therapeutic procedures in the spine
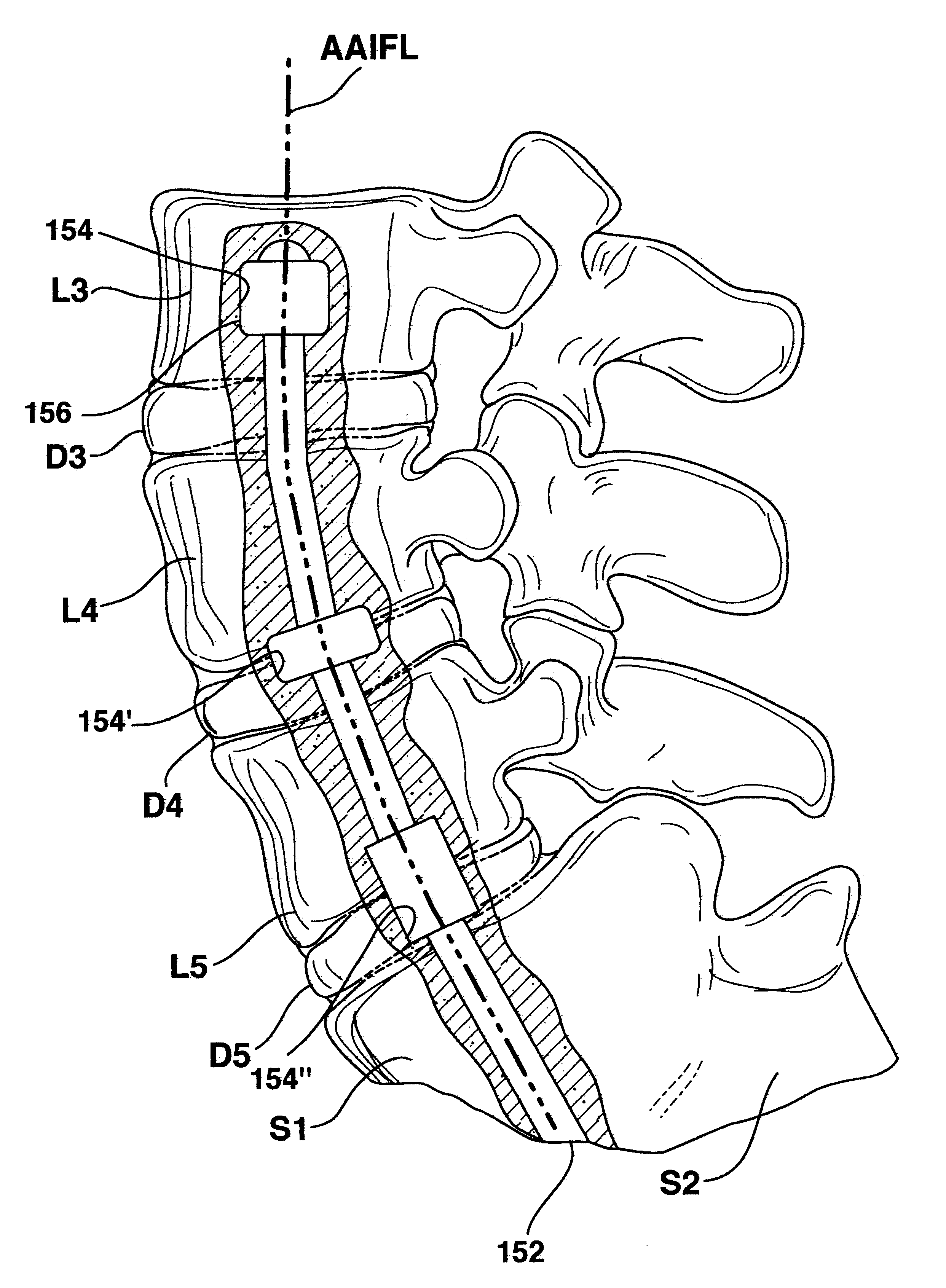
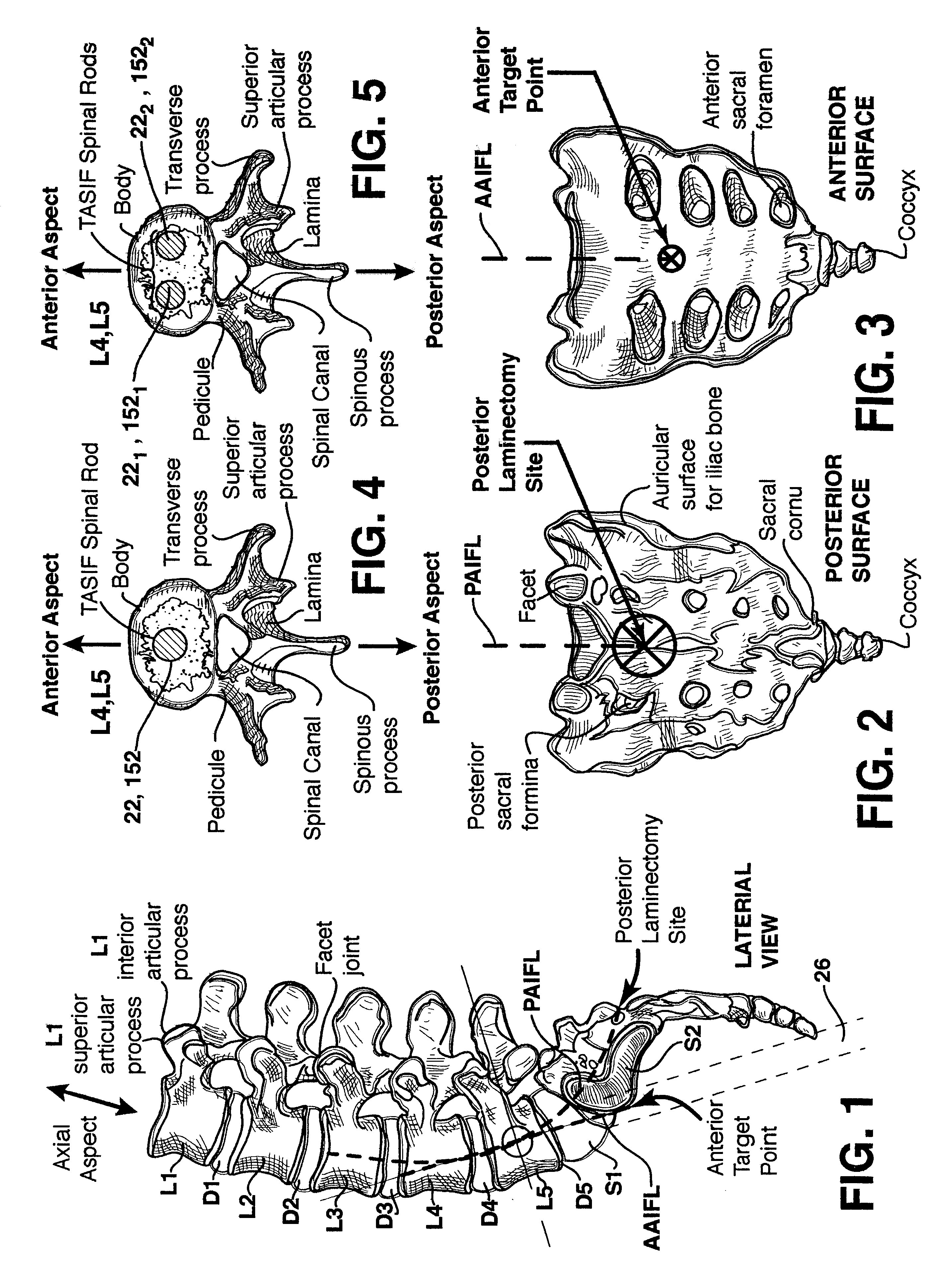
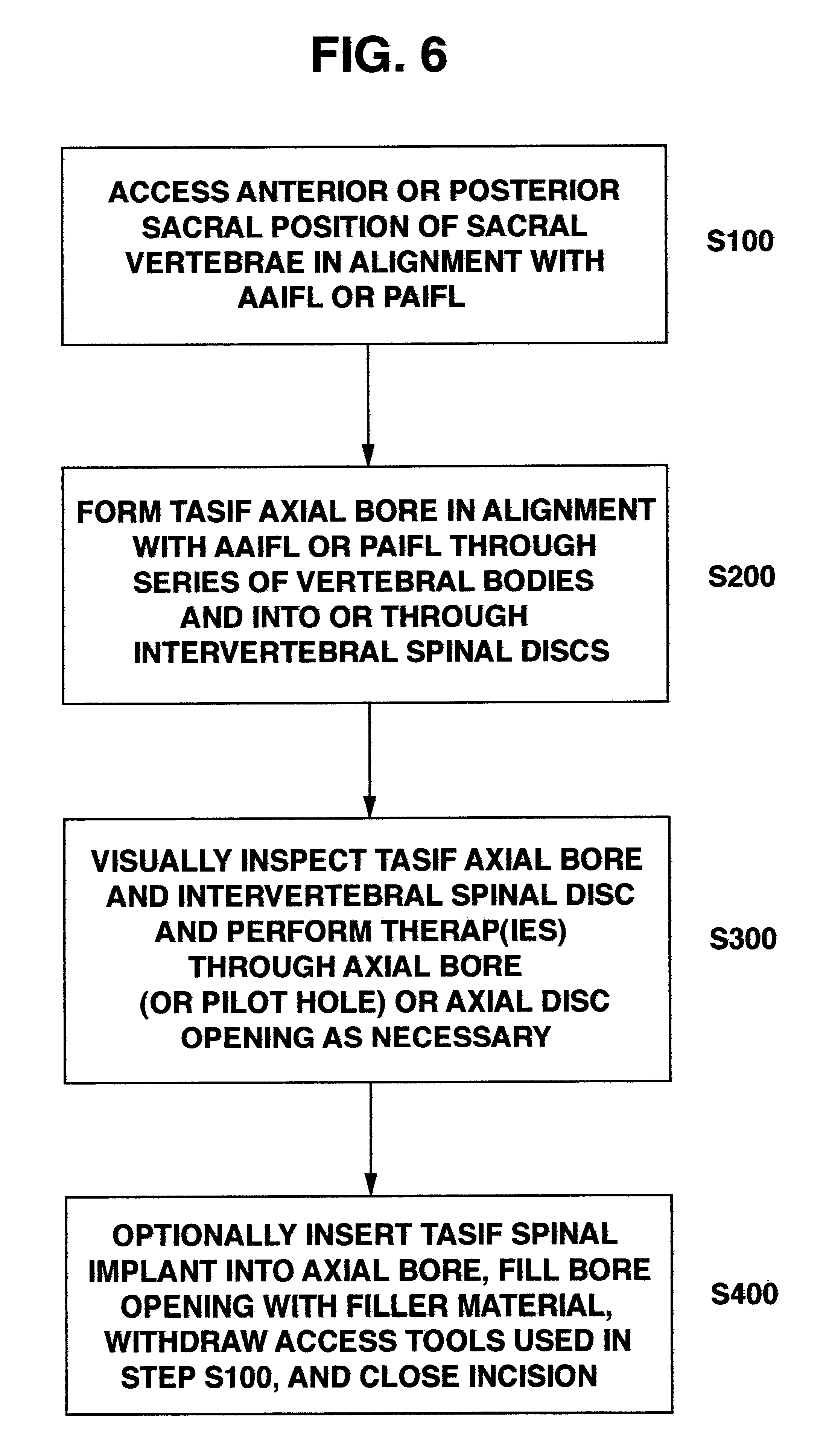
Methods and apparatus for forming one or more trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner and providing a therapy to the spine employing the axial bore. Anterior or posterior starting positions aligned with the AAIFL or PAIFL are accessed through respective anterior and posterior tracts. Curved or relatively straight anterior and curved posterior TASIF axial bores are formed from the anterior and posterior starting positions. The therapies performed through the TASIF axial bores include discoscopy, full and partial discectomy, vertebroplasty, balloon-assisted vertebroplasty, drug delivery, electrical stimulation and various forms of spinal disc cavity augmentation, spinal disc replacement, fusion of spinal motion segments and implantation of radioactive seeds. Axial spinal implants and bone growth materials can be placed into single or multiple parallel or diverging TASIF axial bores to fuse two or more vertebrae, or distract or shock absorb two or more vertebrae.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Method of inserting and preloading spinal implants
InactiveUS6080155ARestoring and maintaining normal angular relationshipFaster and safe and more efficaciousInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Wire spool for passing of wire through a rotational coupling
ActiveUS8568425B2Restrict movementPrevent further rotationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringElectric wire
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Systems and methods for joint replacement
Systems and methods for joint replacement are provided. The systems and methods include a surgical orientation device, a reference sensor device, and at least one orthopedic fixture. The surgical orientation device, reference sensor device, and orthopedic fixtures can be used to locate the orientation of an axis in the body, to adjust an orientation of a cutting plane or planes along a bony surface, or otherwise to assist in an orthopedic procedure(s).
Owner:ORTHALIGN
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6096038AEliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Medical manipulator system
ActiveUS8246608B2Easy to controlSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisWork unitBiological activation
A medical manipulator system includes a manipulator, an operating unit for entering operation commands, motors for actuating a working unit, and a controller for energizing the motors based on operation commands supplied from the operating unit. When an activation resetting switch and a resetting switch are operated according to a predetermined procedure, the controller performs a resetting process to return the motors to an origin. The controller is capable of controlling three manipulators. The activation resetting switch is shared by the three manipulators, and there are three resetting switches corresponding to the three manipulators.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
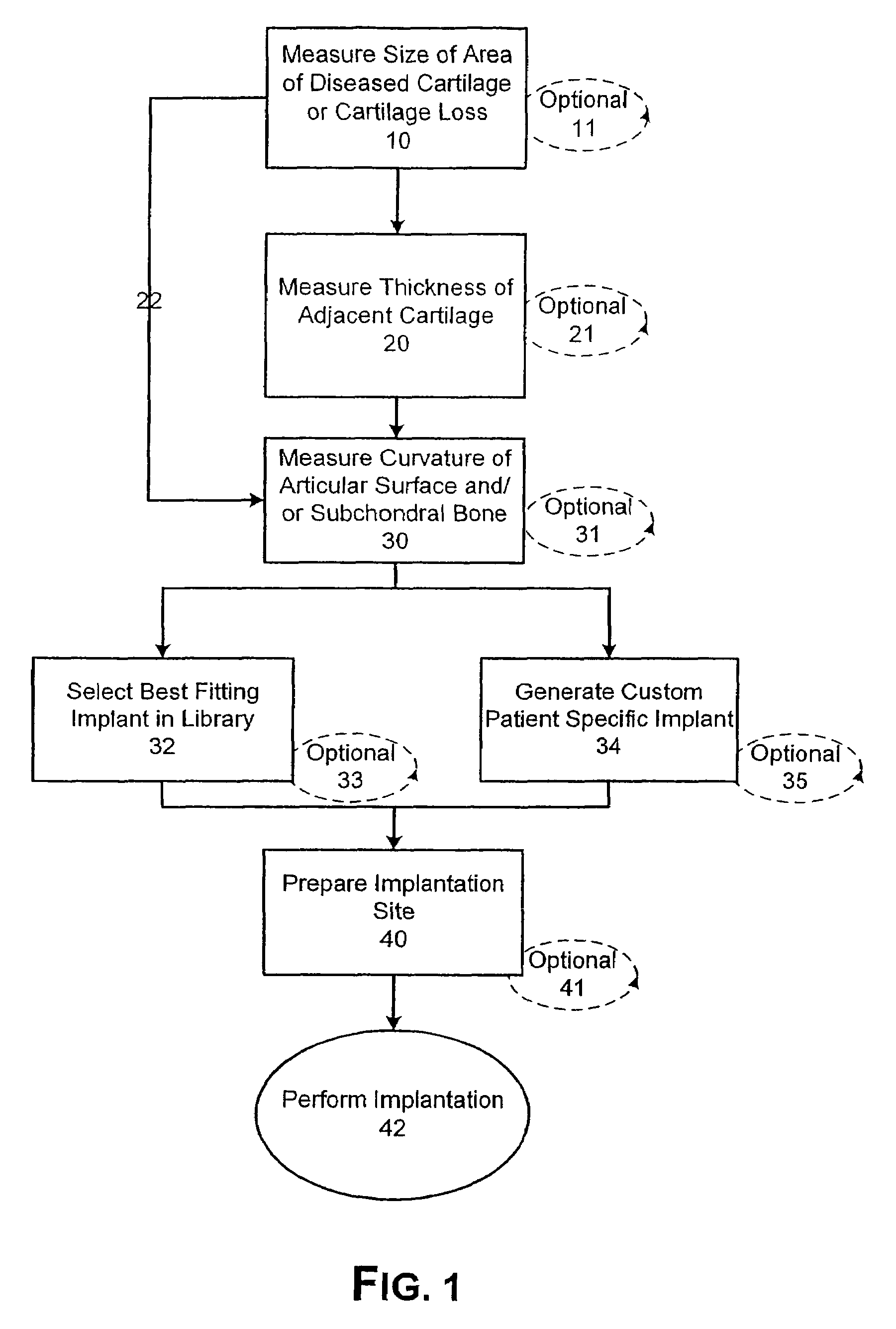
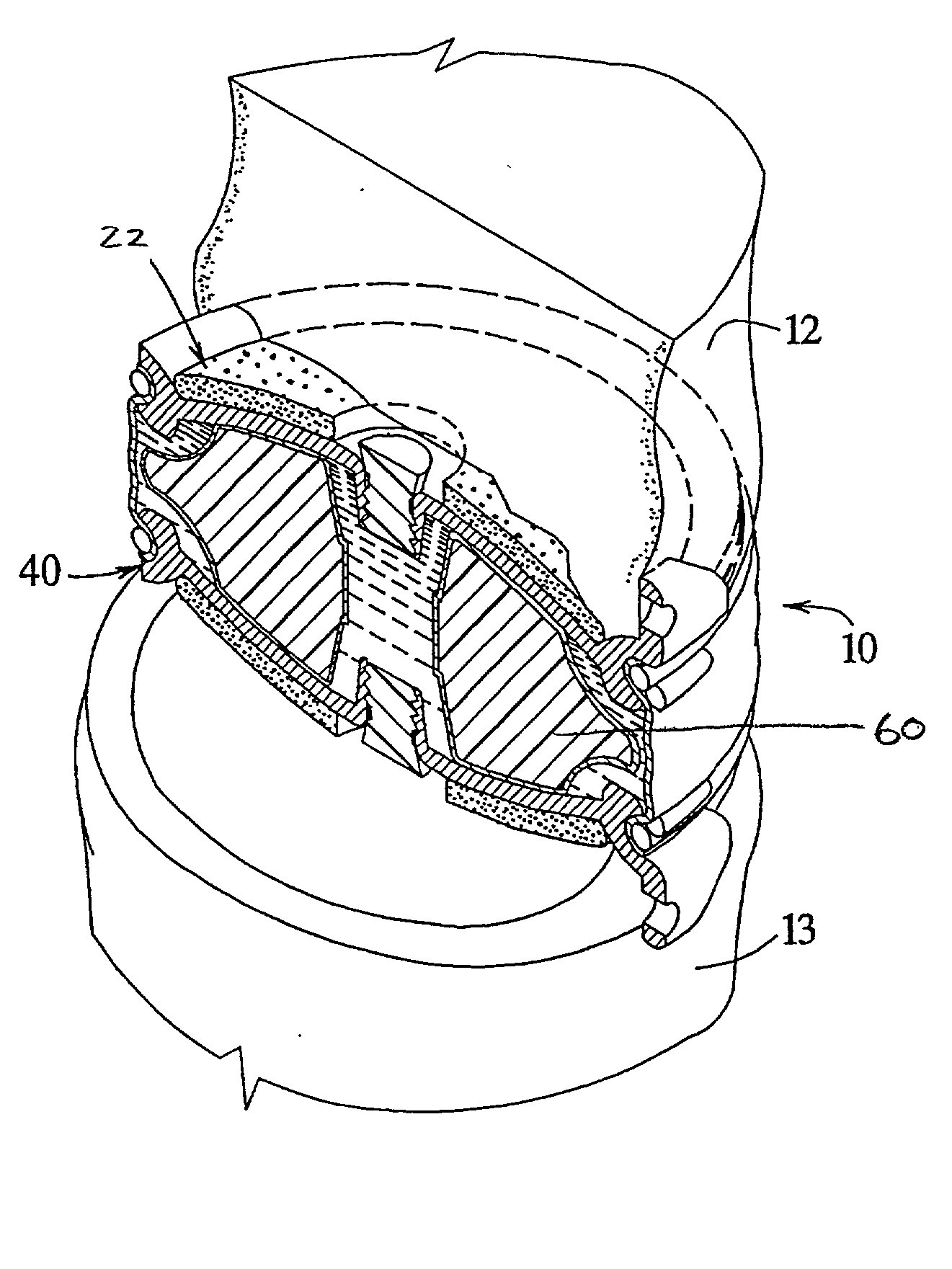
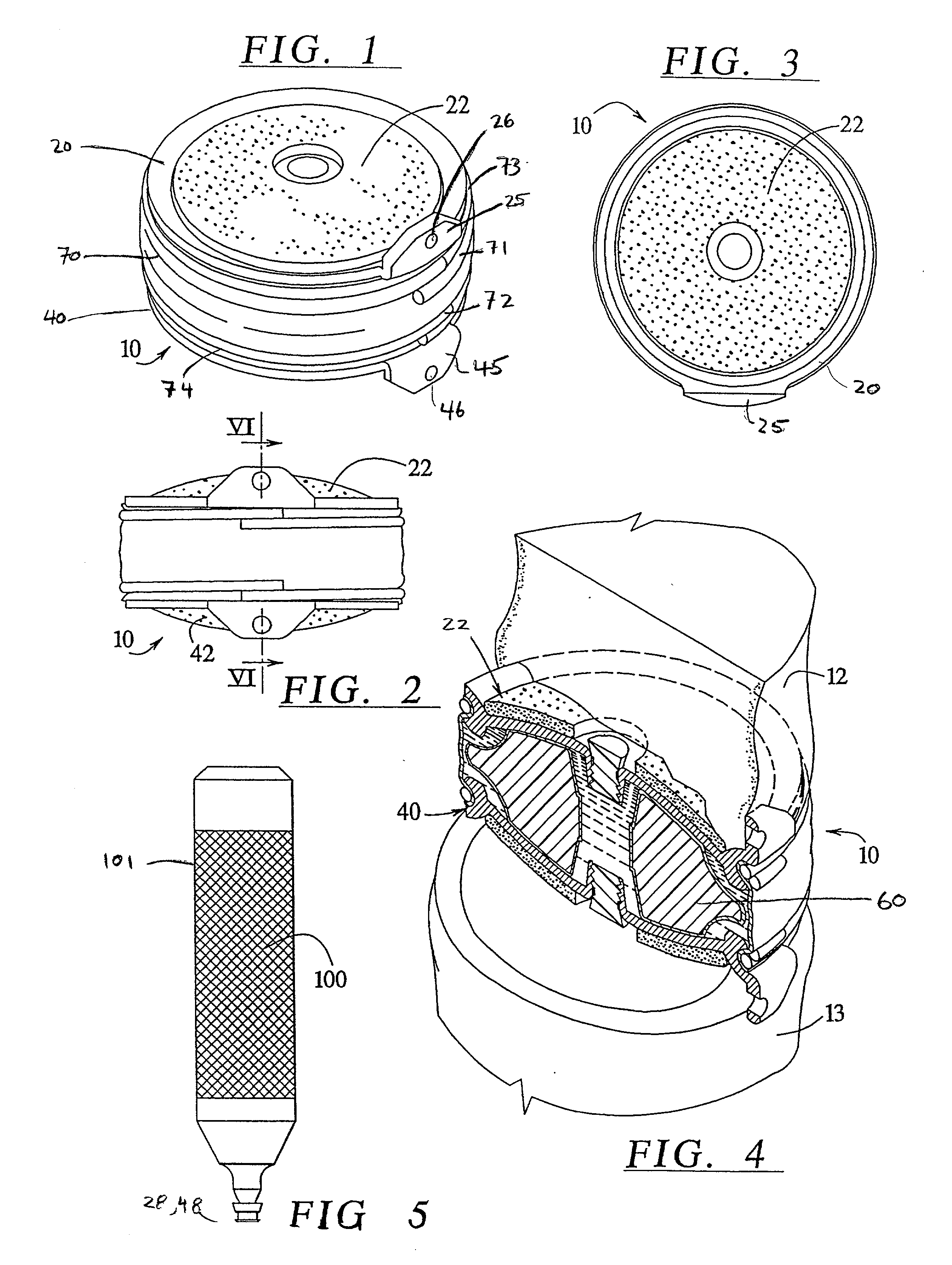
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
ActiveUS20070198022A1Accurate placementGeometric CADPerson identificationArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Spinal stabilization systems and methods
InactiveUS7250052B2Minimize damageProvide stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMinimally invasive proceduresSkin incision
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Detachable members may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The detachable members may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars.
Owner:HIGHRIDGE MEDICAL LLC
Manually driven surgical cutting and fastening instrument
A surgical cutting and fastening instrument that includes an elongate channel that is attached to a handle assembly by an elongate shaft assembly. The elongate channel is configured to receive a cartridge and has a pivotally translatable anvil attached thereto and a knife bar supported therein. The anvil may be selectively opened and closed by manipulating a closure trigger supported by the handle assembly. The knife bar may be distally advanced through the elongate channel by actuating a firing trigger that cooperates with a reversible rotary drive supported by the handle assembly. The knife bar may also be retracted to its starting position by actuating the firing trigger after the reversible rotary drive has been shifted to a retraction orientation.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
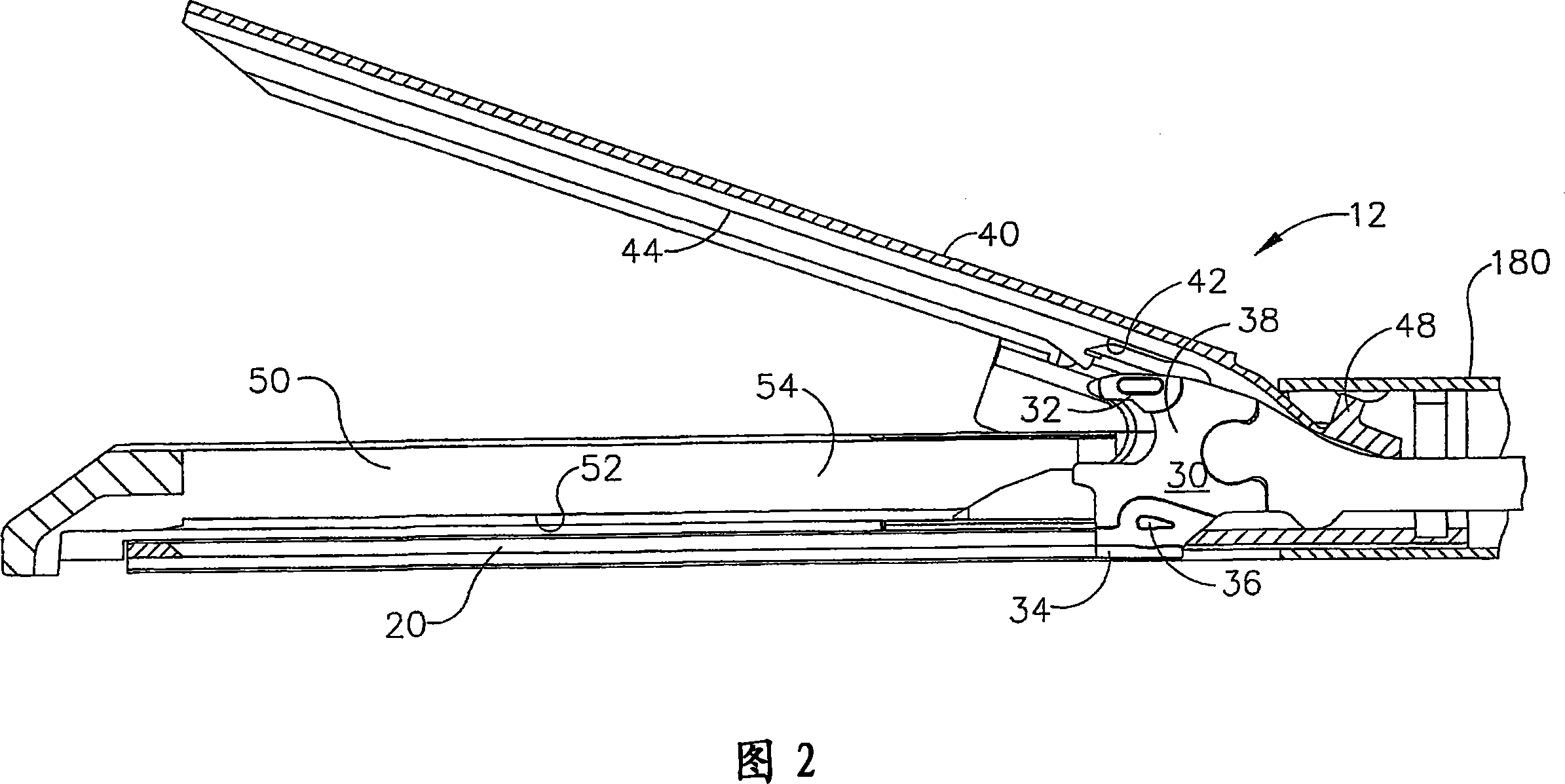
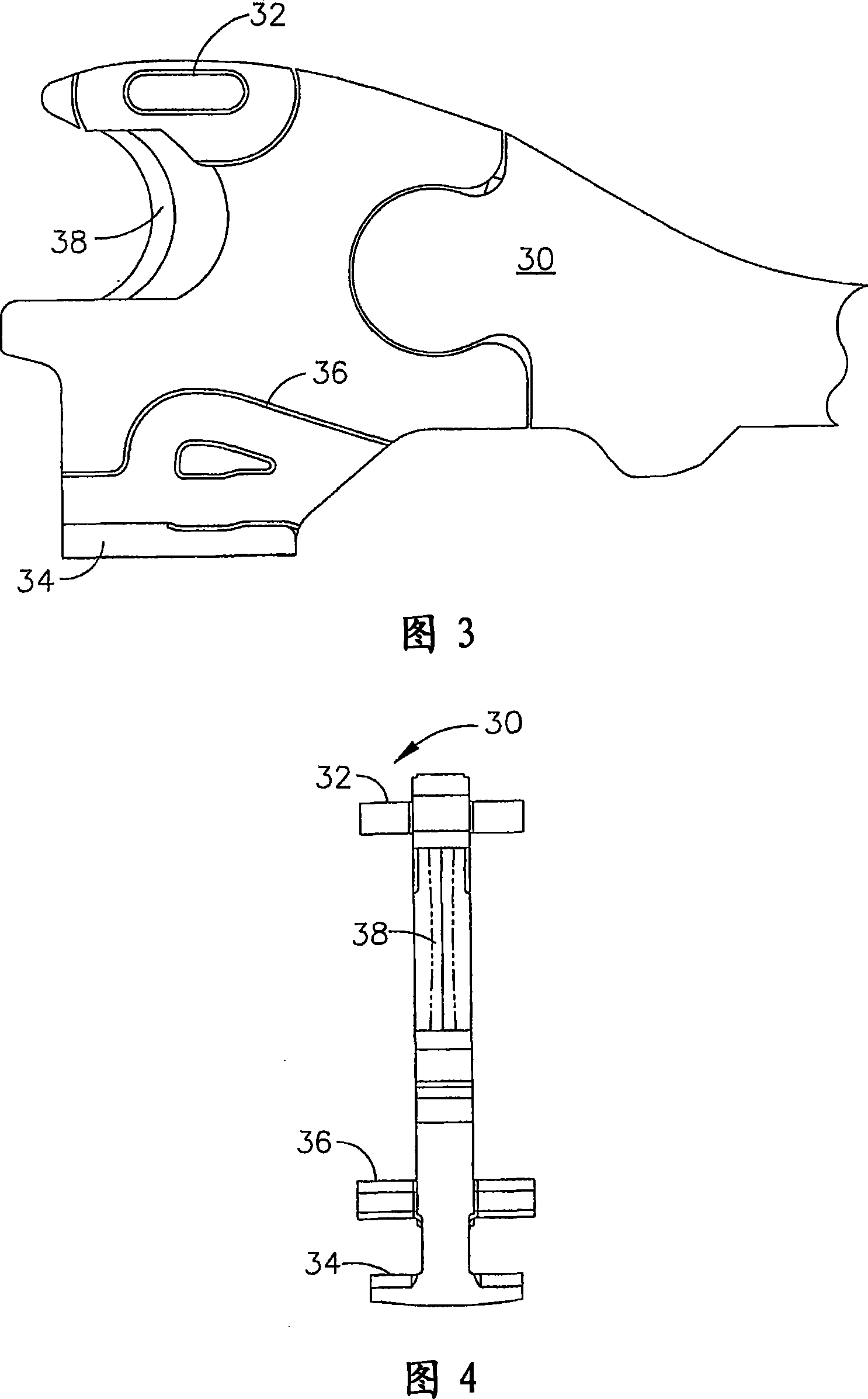
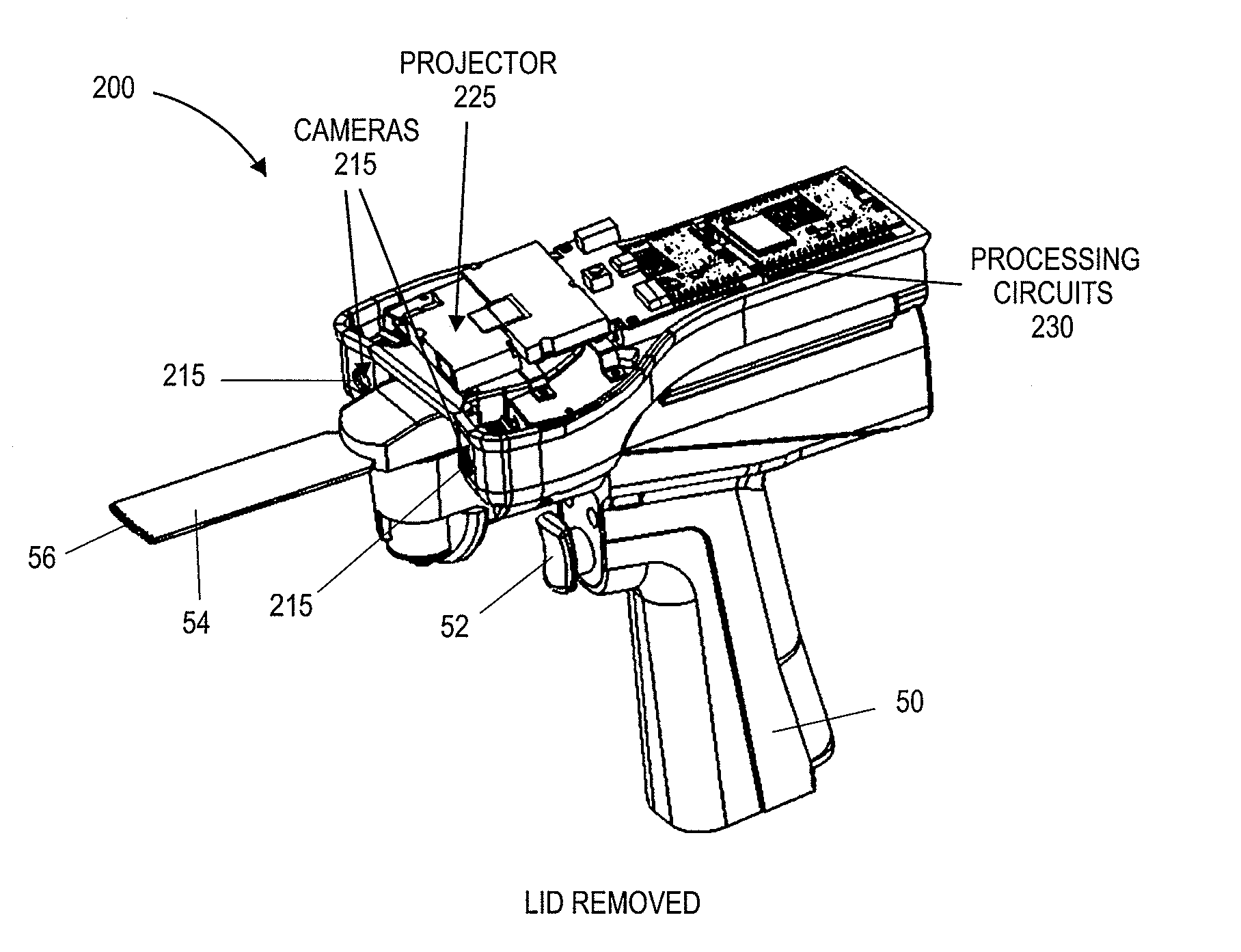
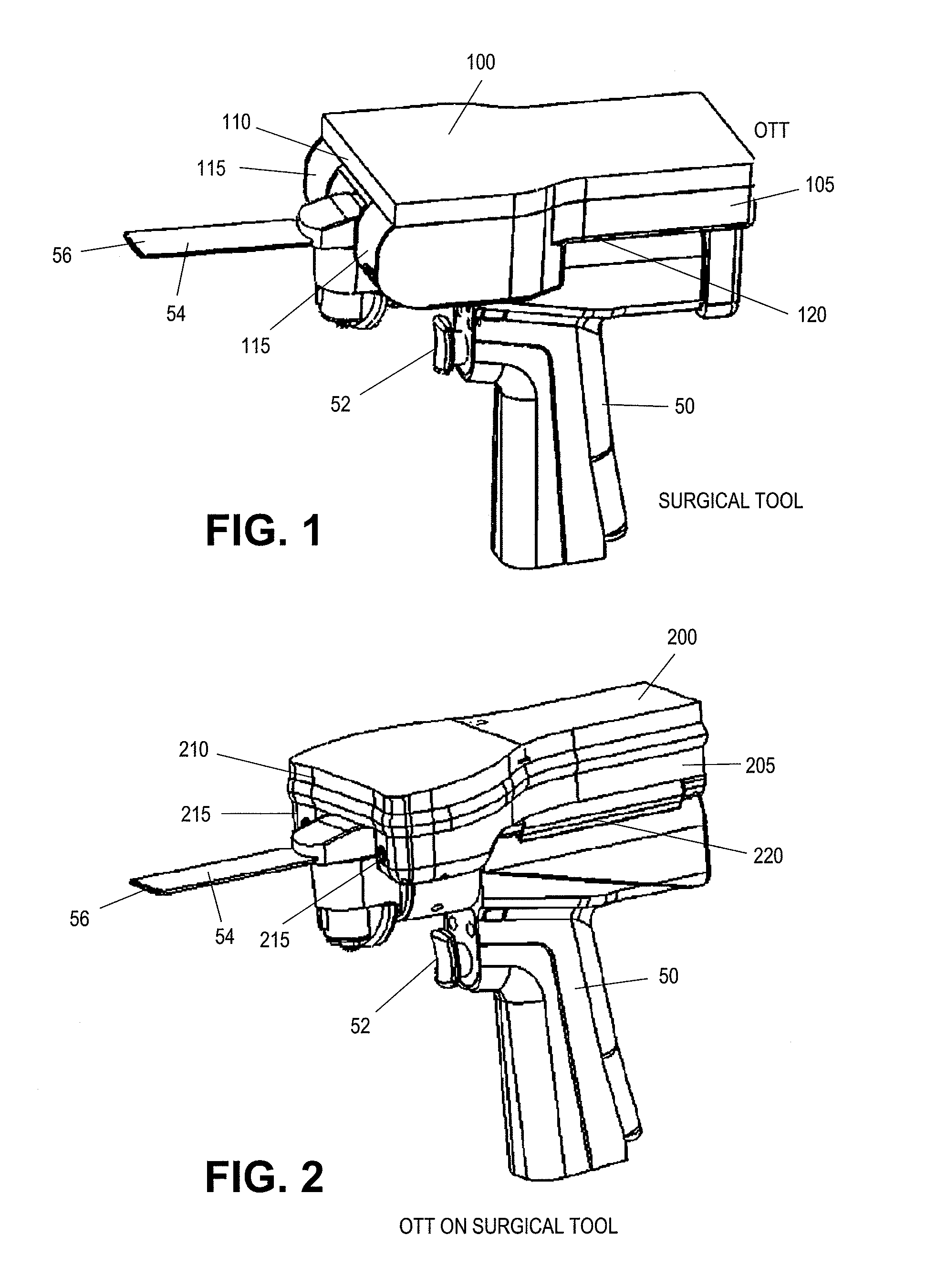
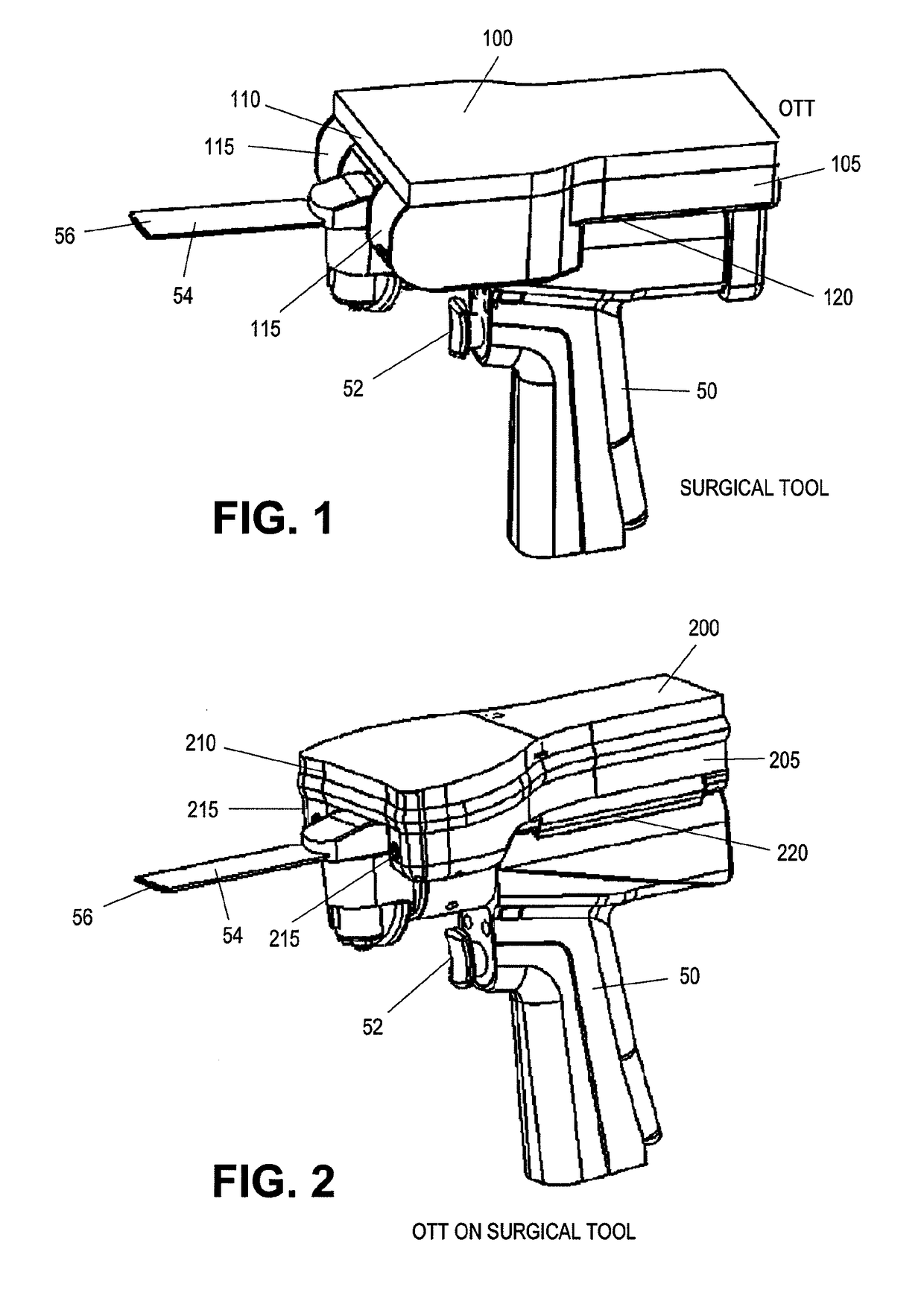
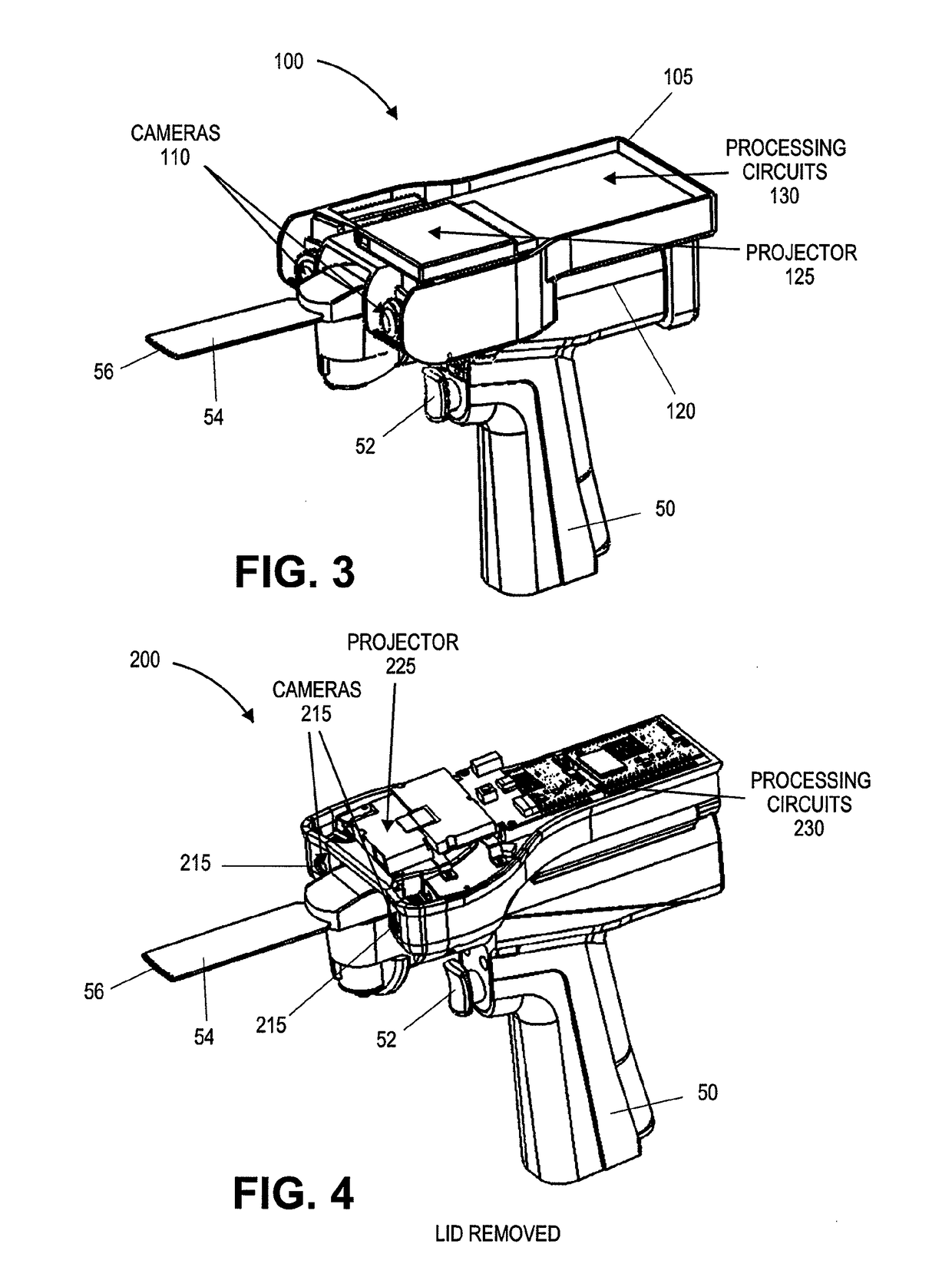
On-board tool tracking system and methods of computer assisted surgery
A number of improvements are provided relating to computer aided surgery utilizing an on tool tracking system. The various improvements relate generally to both the methods used during computer aided surgery and the devices used during such procedures. Other improvements relate to the structure of the tools used during a procedure and how the tools can be controlled using the OTT device. Still other improvements relate to methods of providing feedback during a procedure to improve either the efficiency or quality, or both, for a procedure including the rate of and type of data processed depending upon a CAS mode.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Articulating endoscopic instrument
ActiveUS8114017B2Possible injuries caused by tissue penetrating into intermediate spaces between the retractor fingers are minimizedSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringEndoscope
An endoscopic instrument comprises a shaft, comprising a proximal end and a distal end. A grip comprising a handle is arranged at said proximal end of said shaft and a tool having at least an open and a closed position is arranged at said distal end of said shaft. Said shaft comprises at least two sections, a first section and a second section, which can be articulated with respect to said first section. Said second section comprises said tool. Said instrument further comprises an actuating element, by means of which said handle is in operative connection with said second section and with which an articulation of said second section can be initiated. Said first section or said actuating element and said tool are connected by a control element, by means of which said tool can be moved back and forth between said closed position and said open position in the course of an articulation of said second section, such that both the articulation of said second section and an opening / closing of said tool can be accomplished by the movement of said actuating element.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Motor-driven surgical cutting and fastening instrument with tactile position feedback
A surgical cutting and fastening instrument is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the instrument includes an end effector, a main drive shaft assembly connected to the end effector, and a gear drive train connected to the main drive shaft assembly. The end effector comprises a movable cutting instrument for cutting an object positioned in the end effector. The instrument also includes a main motor for actuating the gear drive train and a firing trigger for actuating the main motor. The instrument also includes a tactile position feedback system for applying force to the firing trigger such that the position of the firing trigger is related to the position of the cutting instrument in the end effector.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Powered surgical stapling device
A powered surgical stapler is disclosed. The stapler includes a housing, an endoscopic portion extending distally from the housing and defining a first longitudinal axis, a drive motor disposed at least partially within a housing and a firing rod disposed in mechanical cooperation with the drive motor. The firing rod is rotatable by the motor about the first longitudinal axis extending therethrough. The stapler also includes an end effector disposed adjacent a distal portion of the endoscopic portion. The end effector is in mechanical cooperation with the firing rod so that the firing rod drives a surgical function of the end effector. The stapler further includes a control system having a plurality of sensors coupled to the drive motor, the firing rod, the loading unit and the end effector, the plurality of sensors configured to detect operating parameters thereof. The control system also includes a microcontroller coupled to the plurality of sensors and being configured to determine operating status of the powered surgical stapler as a function of the detected operating parameters.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical instrument having recording capabilities
A surgical instrument is disclosed. The surgical instrument has an end effector and a trigger in communication with the end effector. The surgical instrument also has a built-in memory system for recording the instrument condition during a use process. The recording system comprises: a first sensor located on or inside the instrument and an externally accessible built-in memory device in communication with the first sensor. The first sensor has an output that represents a first condition of either the trigger or the end effector. The memory device is configured to record the output of the first sensor. In various embodiments, memory device may include an output port and / or a removable storage medium.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Endoscopic instrument
An endoscopic instrument is provided and includes a housing including an elongated shaft assembly extending distally therefrom. The elongated shaft assembly includes inner and outer shaft members. The inner and outer shaft members are removably coupled to the housing and the outer shaft member is movable with respect to the inner shaft member. An end effector is operably supported at the distal end of the outer shaft member and includes a pair of jaw members configured for treating tissue. A bushing operably couples to the inner and outer shaft members of the shaft assembly and selectively and releasably couples to the housing. The bushing includes one or more mechanical interfaces configured to engage one or more slots defined through the inner shaft member and one or more slots defined through the outer shaft member to release the inner and outer shaft members from the housing.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Interbody fusion grafts and instrumentation
InactiveUS7479160B2Maintain disc heightMaintain distractionInternal osteosythesisBone implantMedicineDonor bone
This invention relates to implants formed from donor bone for use in lumbar interbody fusion procedures and instruments for performing such procedures. The implants are formed to include a concave surface formed from a portion of the medullary canal of a long bone. The concaved surface defines a recess in the implant that serves as a depot for osteogenic material. Specific instruments for inserting the implants prepared according to this invention and for preparing the intervertebral space to receive the implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Patient selectable joint arthroplasty devices and surgical tools facilitating increased accuracy, speed and simplicity in performing total and partial joint arthroplasty
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Implantable joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20020035400A1Improve wear resistanceImprove tribological propertiesDiagnosticsJoint implantsRange of motionIntervertebral disc
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:SPINAL DYNAMICS CORP
Custom replacement device for resurfacing a femur and method of making the same
InactiveUS6712856B1Joint implantsComputer-aided planning/modellingArticular surfacesRight femoral head
A replacement device for resurfacing a joint surface of a femur and a method of making and installing such a device is provided. The custom replacement device is designed to substantially fit the trochlear groove surface, of an individual femur. Thereby creating a "customized" replacement device for that individual femur and maintaining the original kinematics of the joint. The replacement device may be defined by four boundary points, and a first and a second surface. The first of four points is 3 to 5 mm from the point of attachment of the anterior cruciate ligament to the femur. The second point is near the bottom edge of the end of the natural articulatar cartilage. The third point is at the top ridge of the right condyle and the fourth point at the top ridge of the left condyle of the femur. The top surface is designed so as to maintain centrally directed tracking of the patella perpendicular to the plane established by the distal end of the femoral condyles and aligned with the center of the femoral head.
Owner:KINAMED
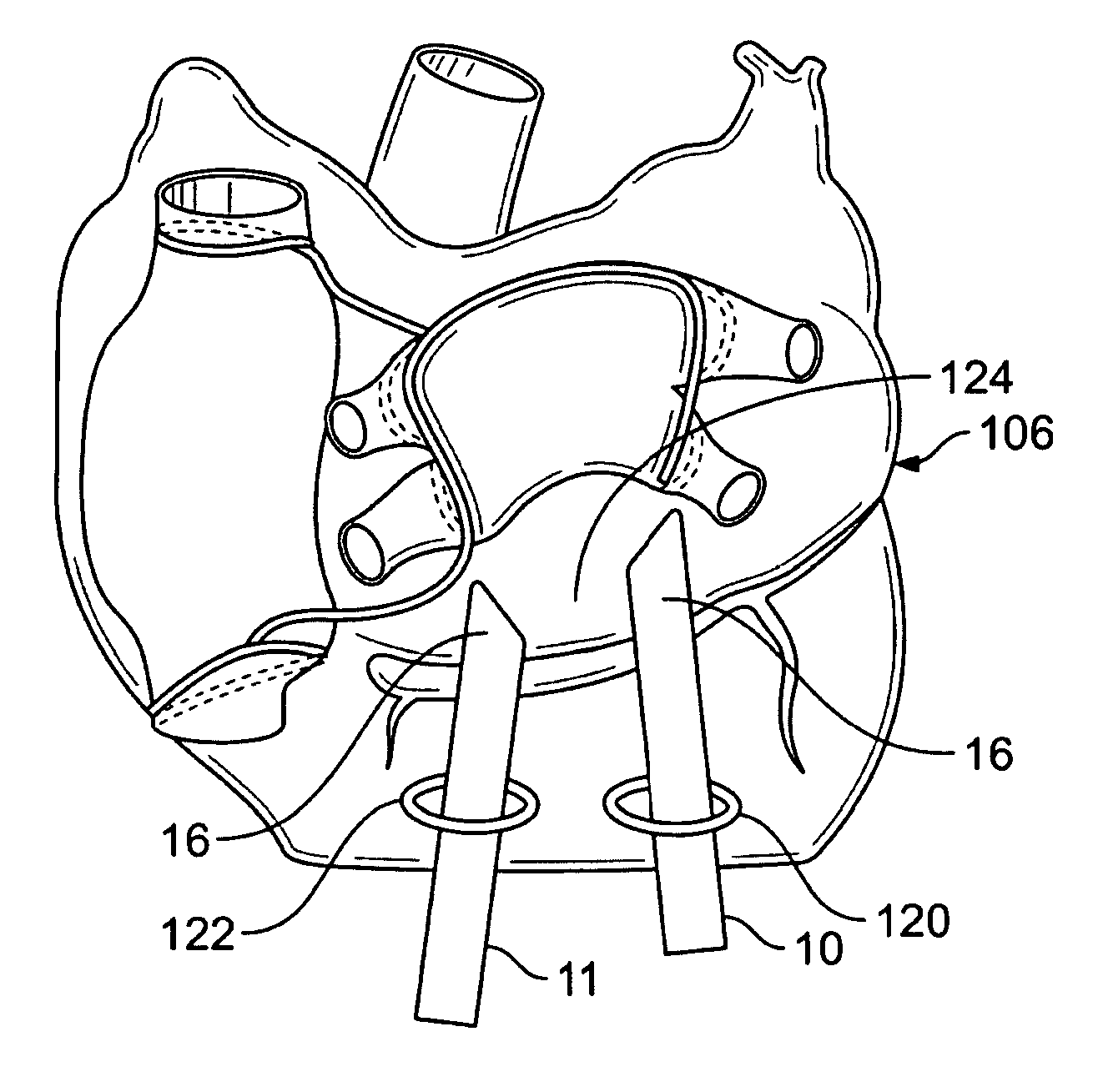
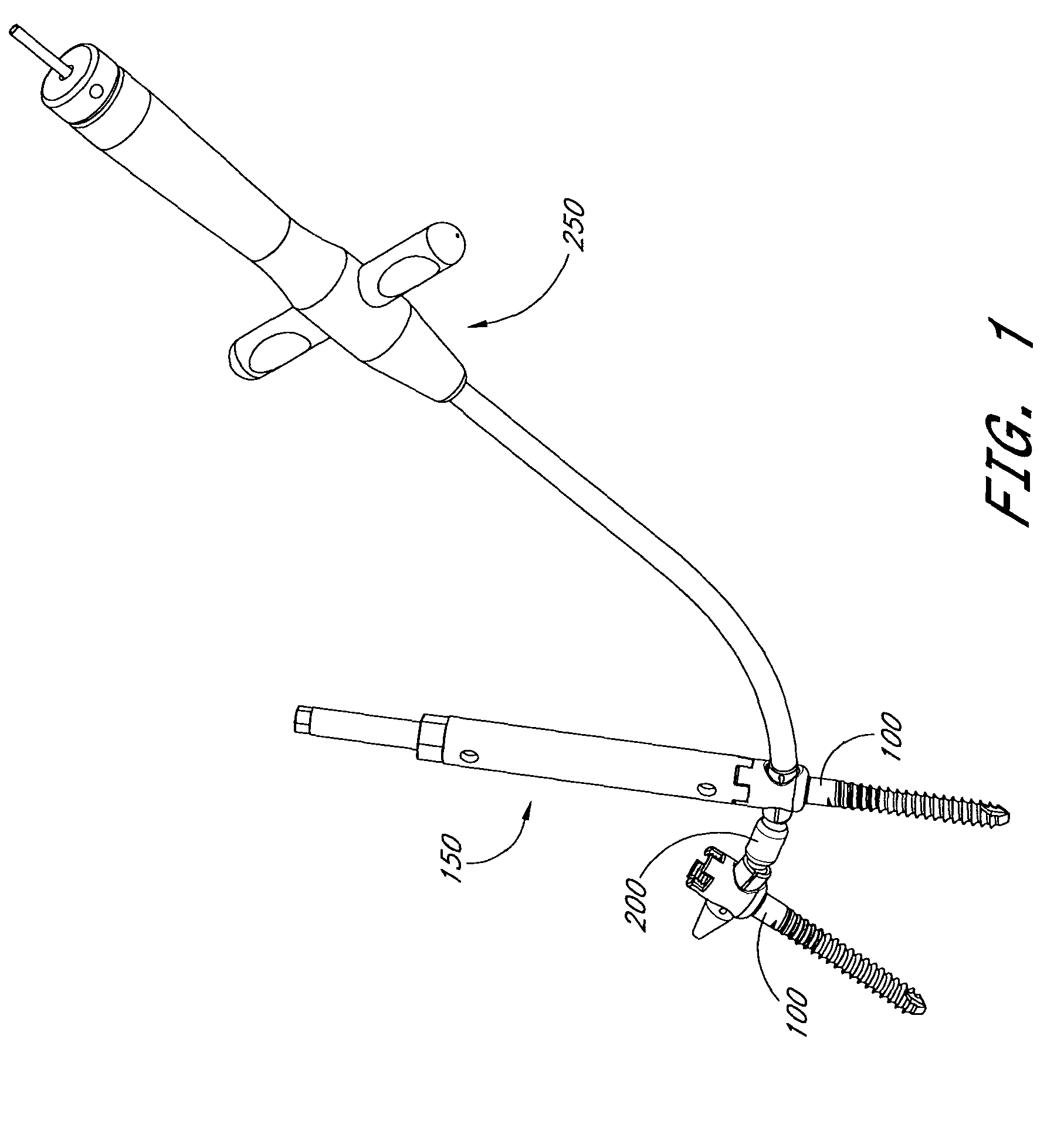
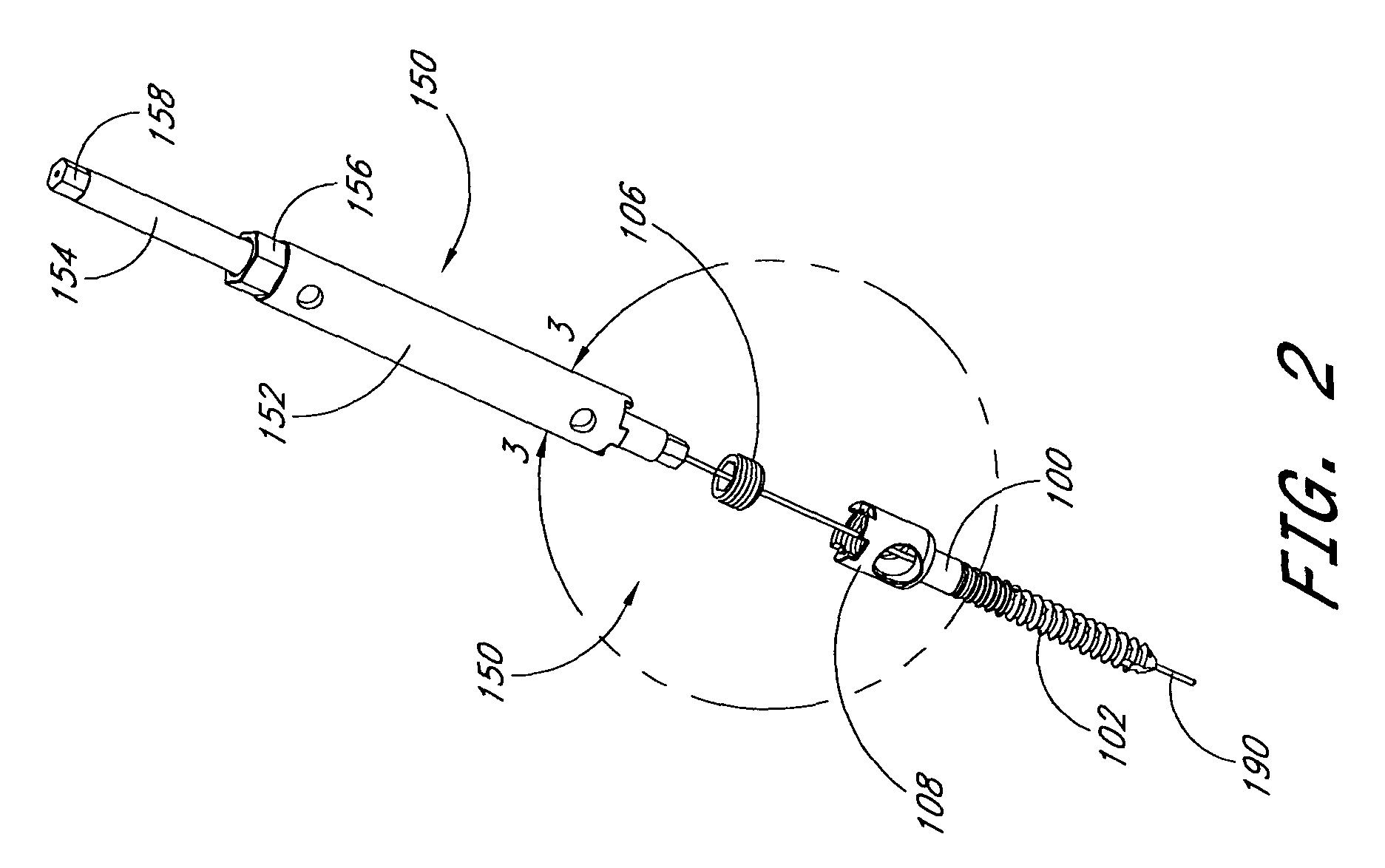
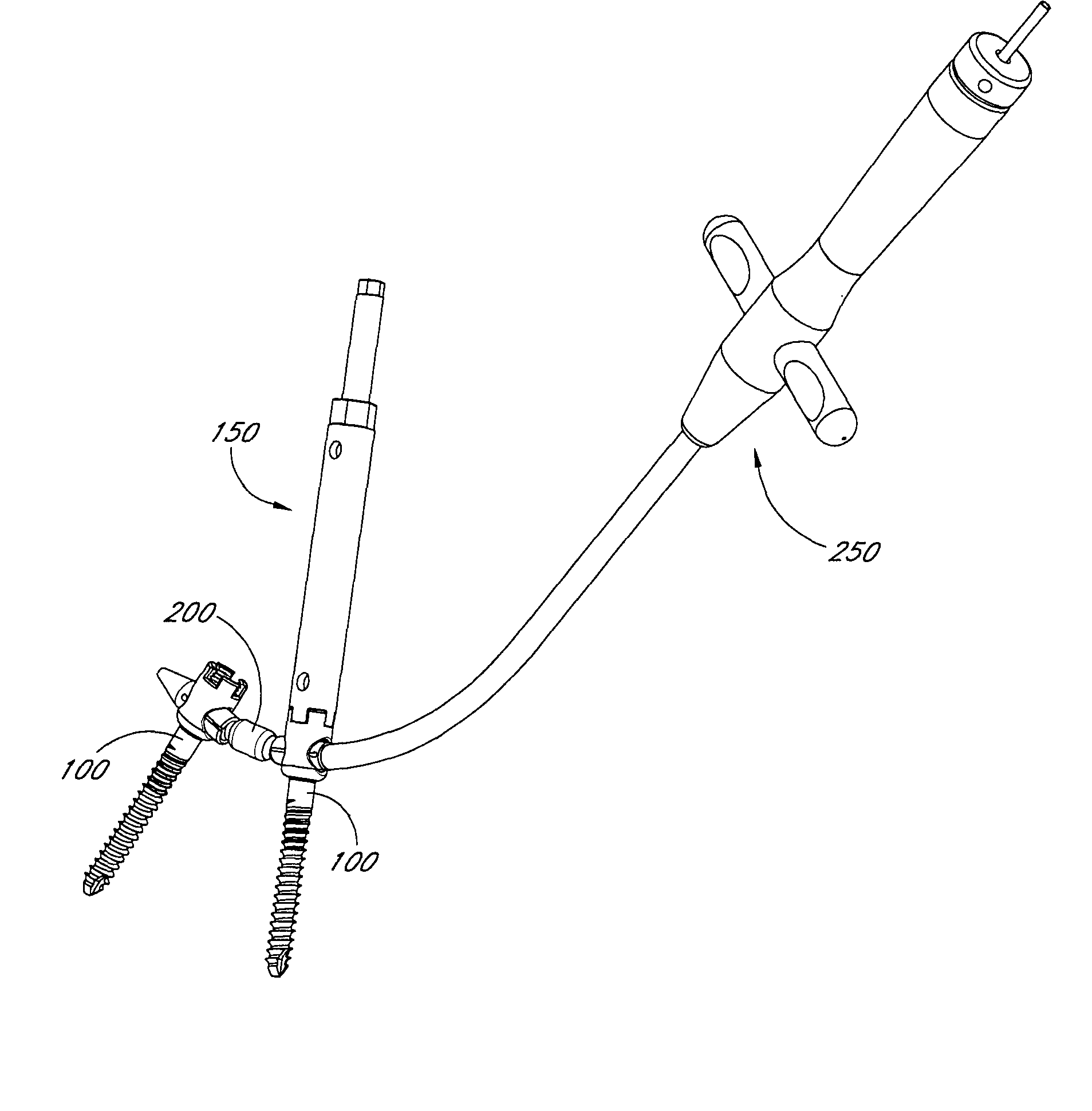
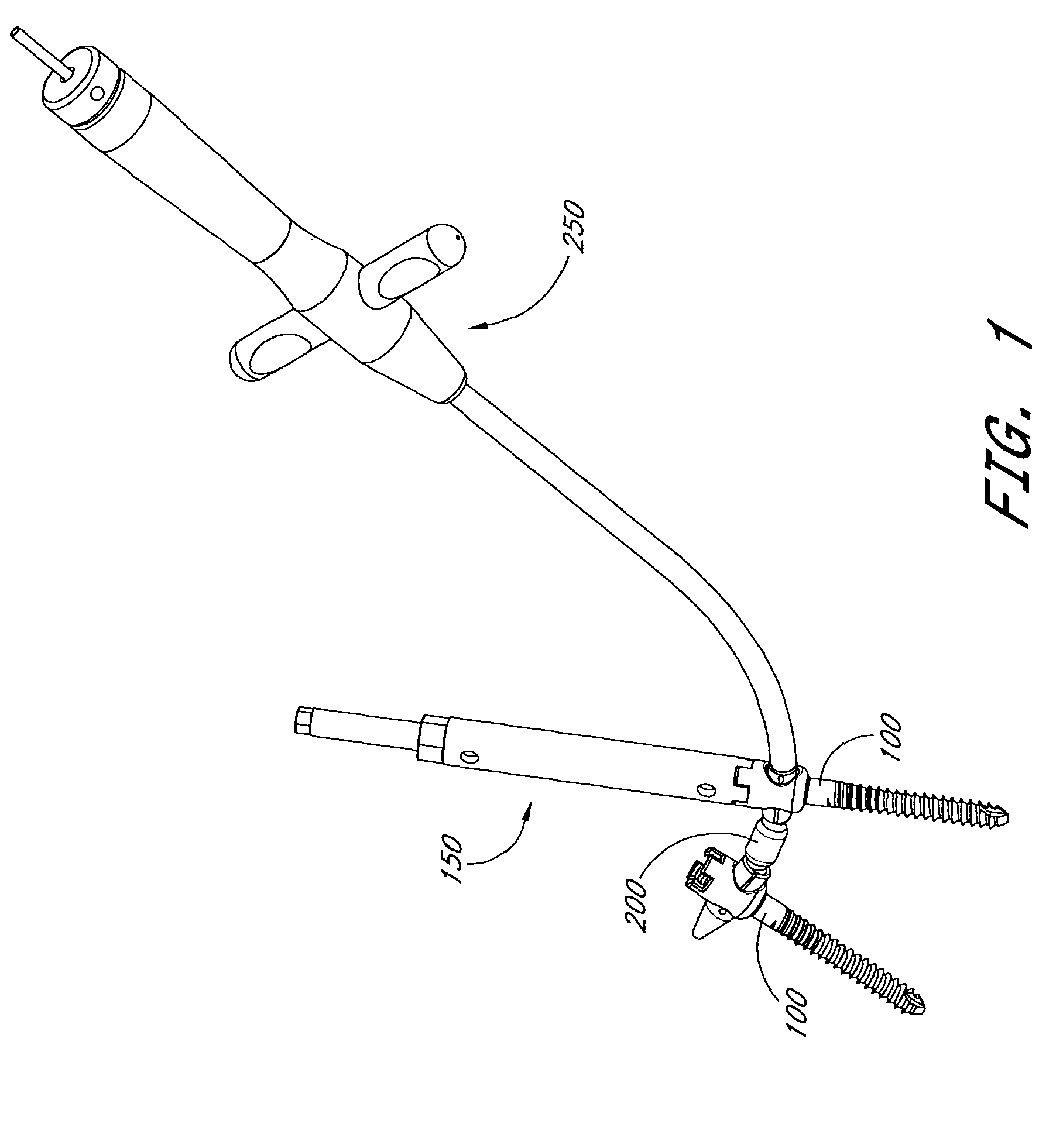
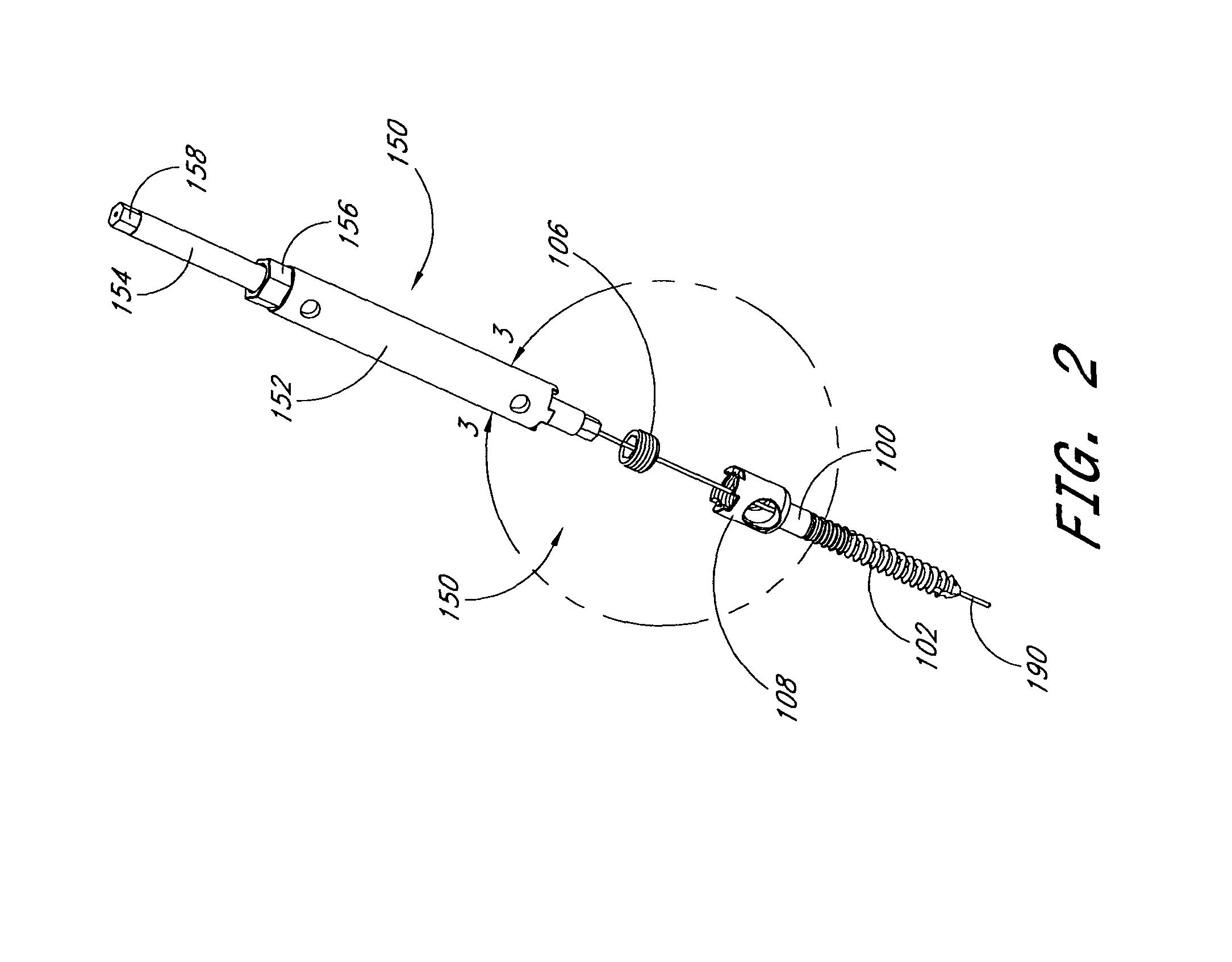
Articulating spinal fixation rod and system
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for aligning and implanting orthopedic fixation or stabilization implants within the body. In one embodiment, the system includes at least two bone anchors, at least one of which is provided with a transverse portal and a locking member. In one aspect, the system also includes at least one linkage rod, for linking two or more bone anchors through their respective locking members. The linking rod may include at least one angularly adjustable joint, which may be fixed by actuating the locking member. The bone anchors and the linkage rod may be locked into place to form a spinal fusion or fixation prosthesis.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
On-board tool tracking system and methods of computer assisted surgery
A number of improvements are provided relating to computer aided surgery utilizing an on tool tracking system. The various improvements relate generally to both the methods used during computer aided surgery and the devices used during such procedures. Other improvements relate to the structure of the tools used during a procedure and how the tools can be controlled using the OTT device. Still other improvements relate to methods of providing feedback during a procedure to improve either the efficiency or quality, or both, for a procedure including the rate of and type of data processed depending upon a CAS mode.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6270498B1Eliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
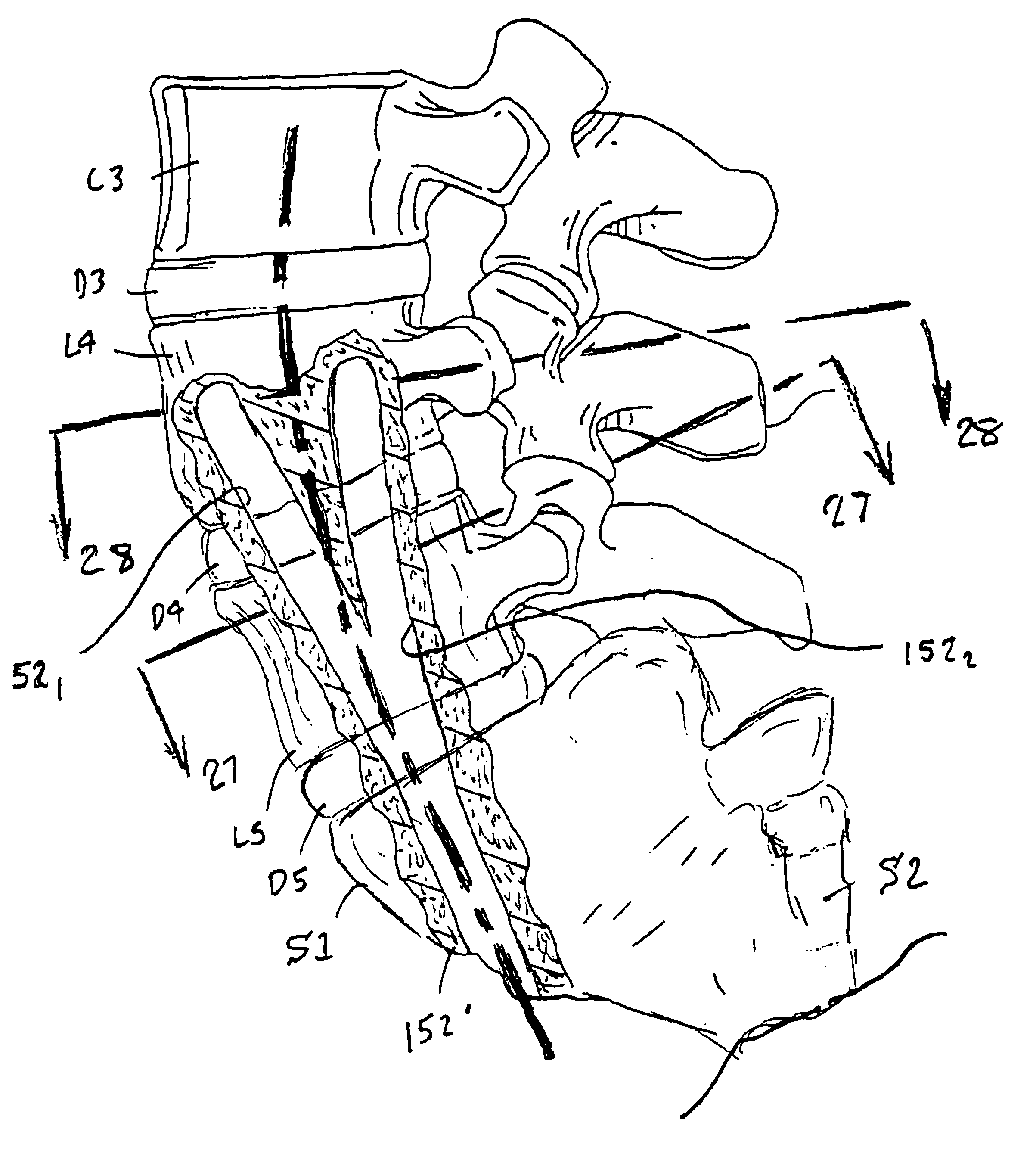
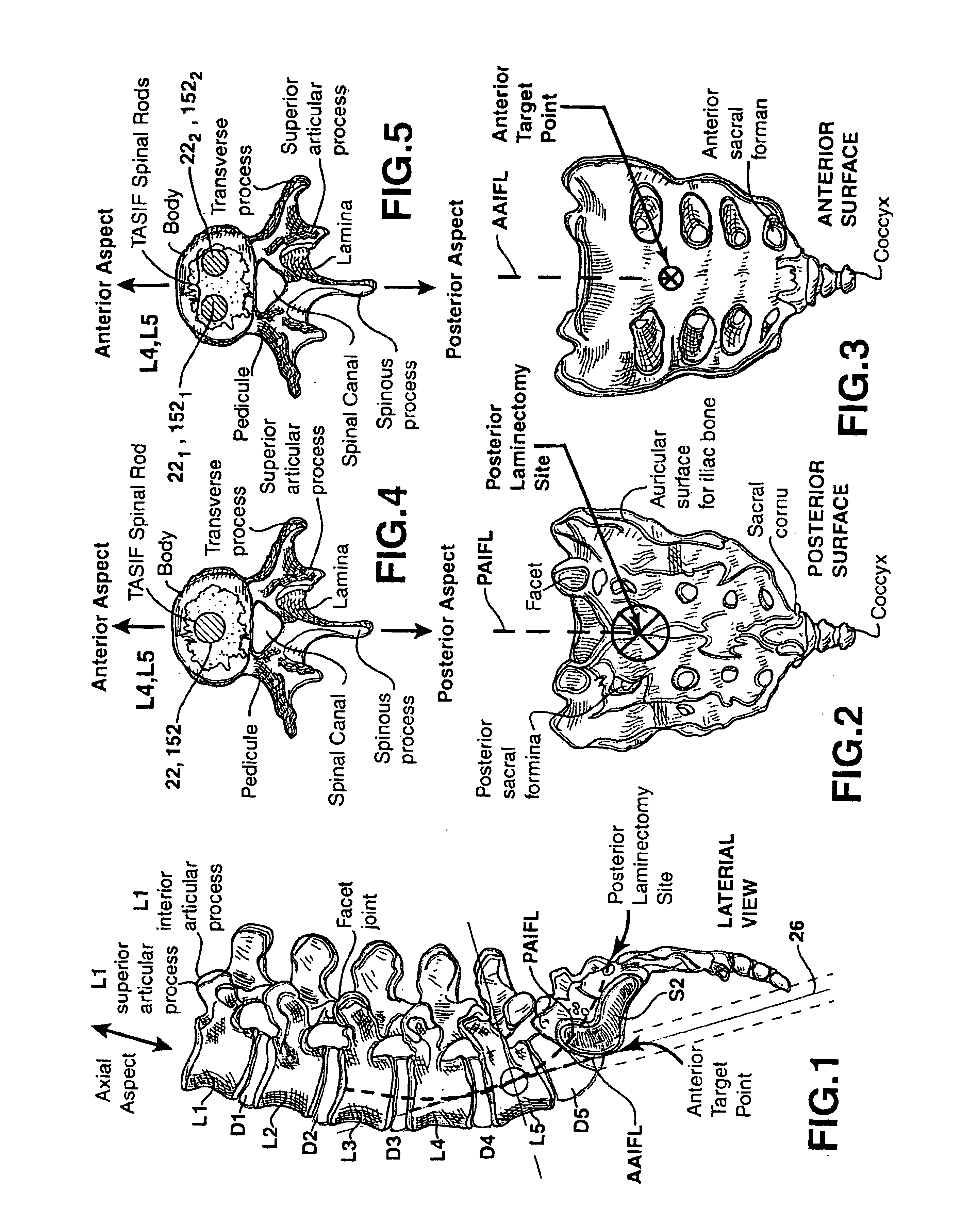
Methods and apparatus for forming shaped axial bores through spinal vertebrae
InactiveUS6740090B1Easy to understandInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal CurvaturesSpinal implant
One or more shaped axial bore extending from an accessed posterior or anterior target point are formed in the cephalad direction through vertebral bodies and intervening discs, if present, in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner. An anterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL) or a posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (PAIFL) that extends from the anterior or posterior target point, respectively, in the cephalad direction following the spinal curvature through one or more vertebral body is visualized by radiographic or fluoroscopic equipment. Preferably, curved anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores are formed in axial or parallel or diverging alignment with the visualized AAIFL or PAIFL, respectively, employing bore forming tools that can be manipulated from proximal portions thereof that are located outside the patient's body to adjust the curvature of the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores as they are formed in the cephalad direction. Further bore enlarging tools are employed to enlarge one or more selected section of the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bore(s), e.g., the cephalad bore end or a disc space, so as to provide a recess therein that can be employed for various purposes, e.g., to provide anchoring surfaces for spinal implants inserted into the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bore(s).
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
System and method of designing and manufacturing customized instrumentation for accurate implantation of prosthesis by utilizing computed tomography data
ActiveUS20050148843A1Quickly and accurately attachesPrecise positioningPerson identificationJoint implantsMedicineControl data
A method and system may be used to design and control the manufacture of a surgical guide for implanting a prosthetic component. The system includes a bone surface image generator, a surgical guide image generator, and a surgical guide image converter. The bone surface image generator receives three dimensional bone anatomical data for a patient's bone and generates a bone surface image. The surgical guide image generator generates a surgical guide image from the bone surface image and an image of a prosthesis imposed on the bone surface image. The supporting structure of the generated surgical guide image conforms to the surface features of the three dimensional bone surface image. The surgical guide image is converted by surgical guide image converter into control data for operating a machine to form a surgical guide that corresponds to the surgical guide image.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Methods and apparatus for forming curved axial bores through spinal vertebrae
One or more curved axial bore is formed commencing from an anterior or posterior sacral target point and cephalad through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner. An anterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL) or a posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (PAIFL) that extends from the anterior or posterior target point, respectively, in the cephalad direction following the spinal curvature through one or more vertebral body is visualized by radiographic or fluoroscopic equipment. Generally curved anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores are formed in axial or parallel or diverging alignment with the visualized AAIFL or PAIFL, respectively. The anterior and posterior TASIF axial bore forming tools can be manipulated from proximal portions thereof to adjust the curvature of the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores as they are formed in the cephalad direction. The boring angle of the distally disposed boring member or drill bit can be adjusted such that selected sections of the generally curved anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores can be made straight or relatively straight, and other sections thereof can be made curved to optimally traverse vertebral bodies and intervening disc, if present.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Total joint arthroplasty system
ActiveUS20090131941A1Precise alignmentImprove visualizationMedical simulationProgramme controlJoint arthroplastyTotal hip arthroplasty
A method and system for performing a total joint arthroplasty procedure on a patient's damaged bone region. A CT image or other suitable image is formed of the damaged bone surfaces, and location coordinate values (xn,yn,zn) are determined for a selected sequence of bone surface locations using the CT image data. A mathematical model z=f(x,y) of a surface that accurately matches the bone surface coordinates at the selected bone spice locations, or matches surface normal vector components at selected bone surface locations, is determined. The model provides a production file from which a cutting jig and an implant device (optional), each patient-specific and having controllable alignment, are fabricated for the damaged bone by automated processing. At this point, the patient is cut open (once), the cutting jig and a cutting instrument are used to remove a selected portion of the bone and to provide an exposed planar surface, the implant device is optionally secured to and aligned with the remainder of the bone, and the patient's incision is promptly repaired.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
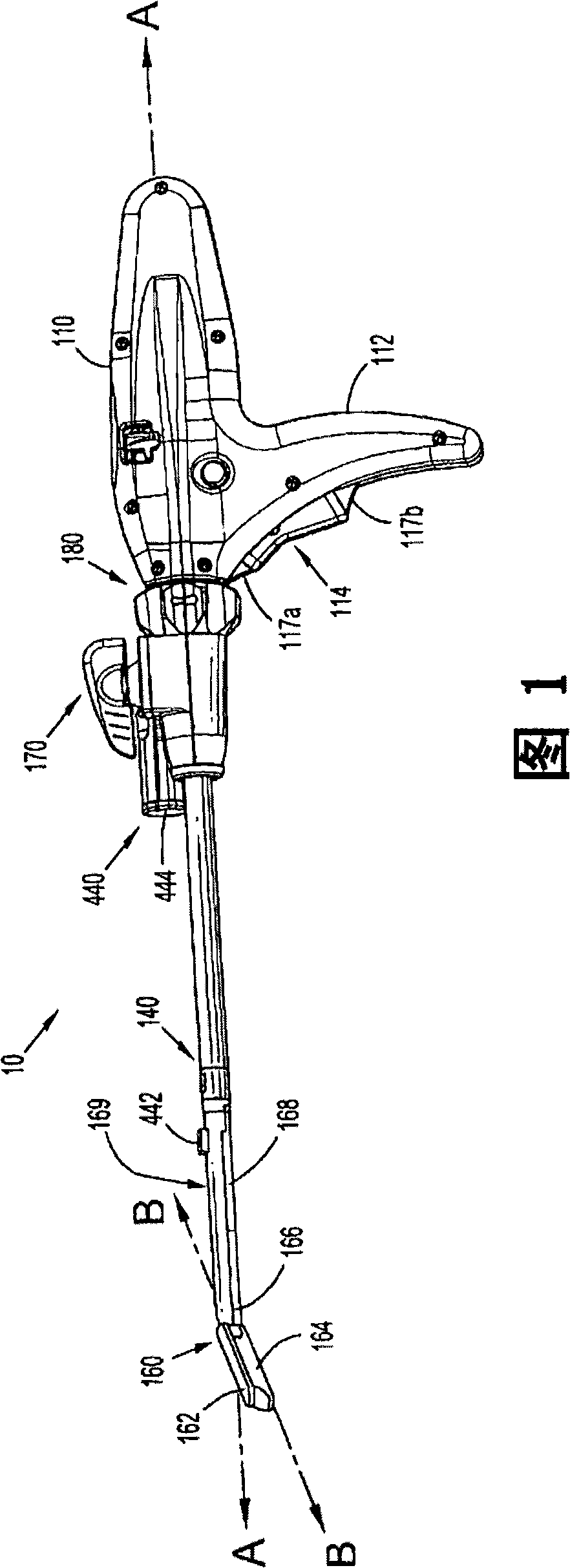
Apparatus and methods for surgery
An implant guidance and positioning device is provided for dynamic and rigid fixation of tissue or an implant. The device includes a handle and an elongated hook connected with the handle, which may have a lumen extending therethrough or may have a socket that can receive fasteners. The device also includes a guide channel or slot disposed in the handle. The longitudinal axis of the guide channel or slot may be generally aligned with or slightly offset from a distal end of the elongated hook or socket.
Owner:P TECH
Articulating spinal fixation rod and system
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for aligning and implanting orthopedic fixation or stabilization implants within the body. In one embodiment, the system includes at least two bone anchors, at least one of which is provided with a transverse portal and a locking member. In one aspect, the system also includes at least one linkage rod, for linking two or more bone anchors through their respective locking members. The linking rod may include at least one angularly adjustable joint, which may be fixed by actuating the locking member. The bone anchors and the linkage rod may be locked into place to form a spinal fusion or fixation prosthesis.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com