Patents
Literature
41 results about "Trochlear groove" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
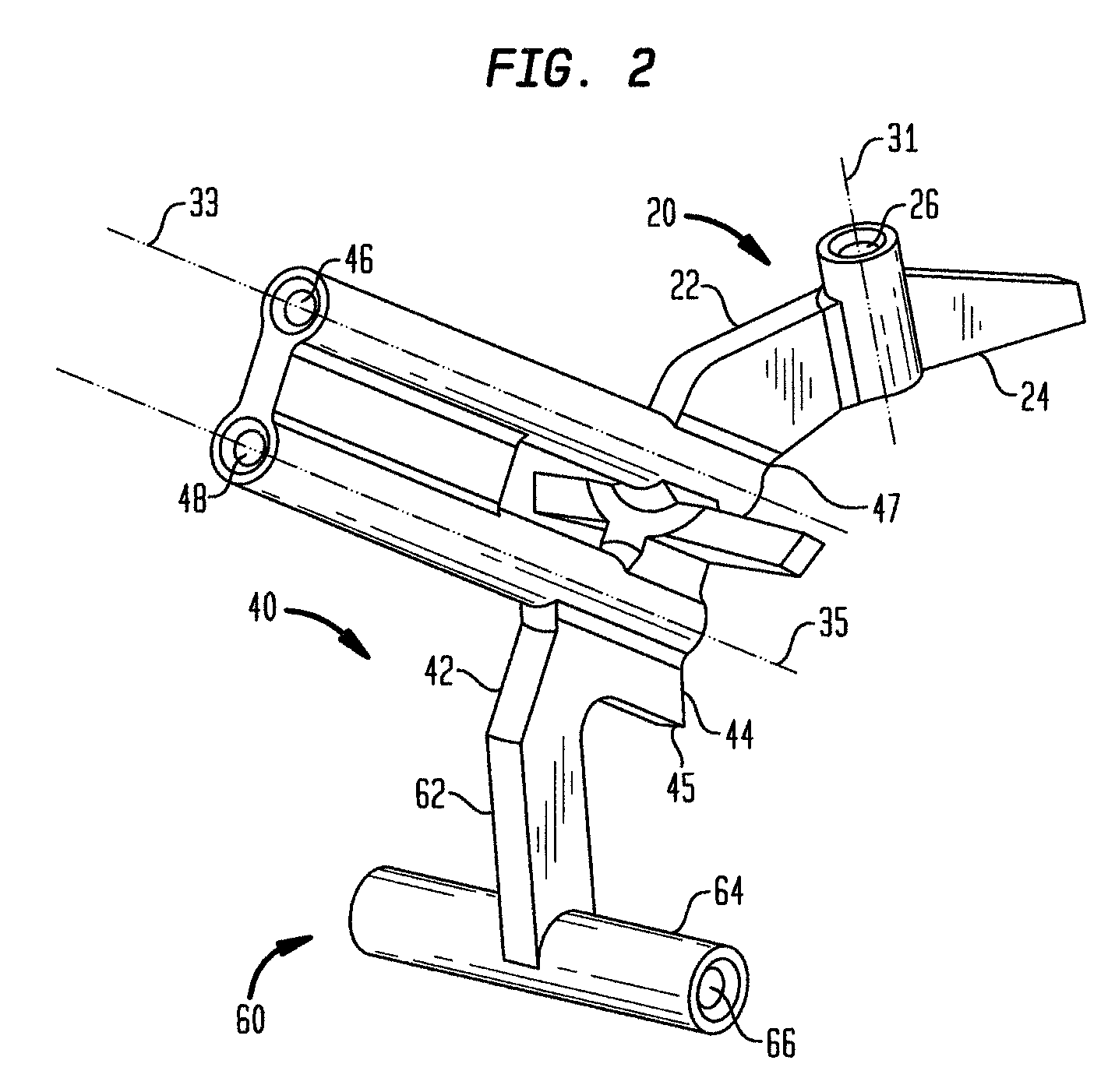
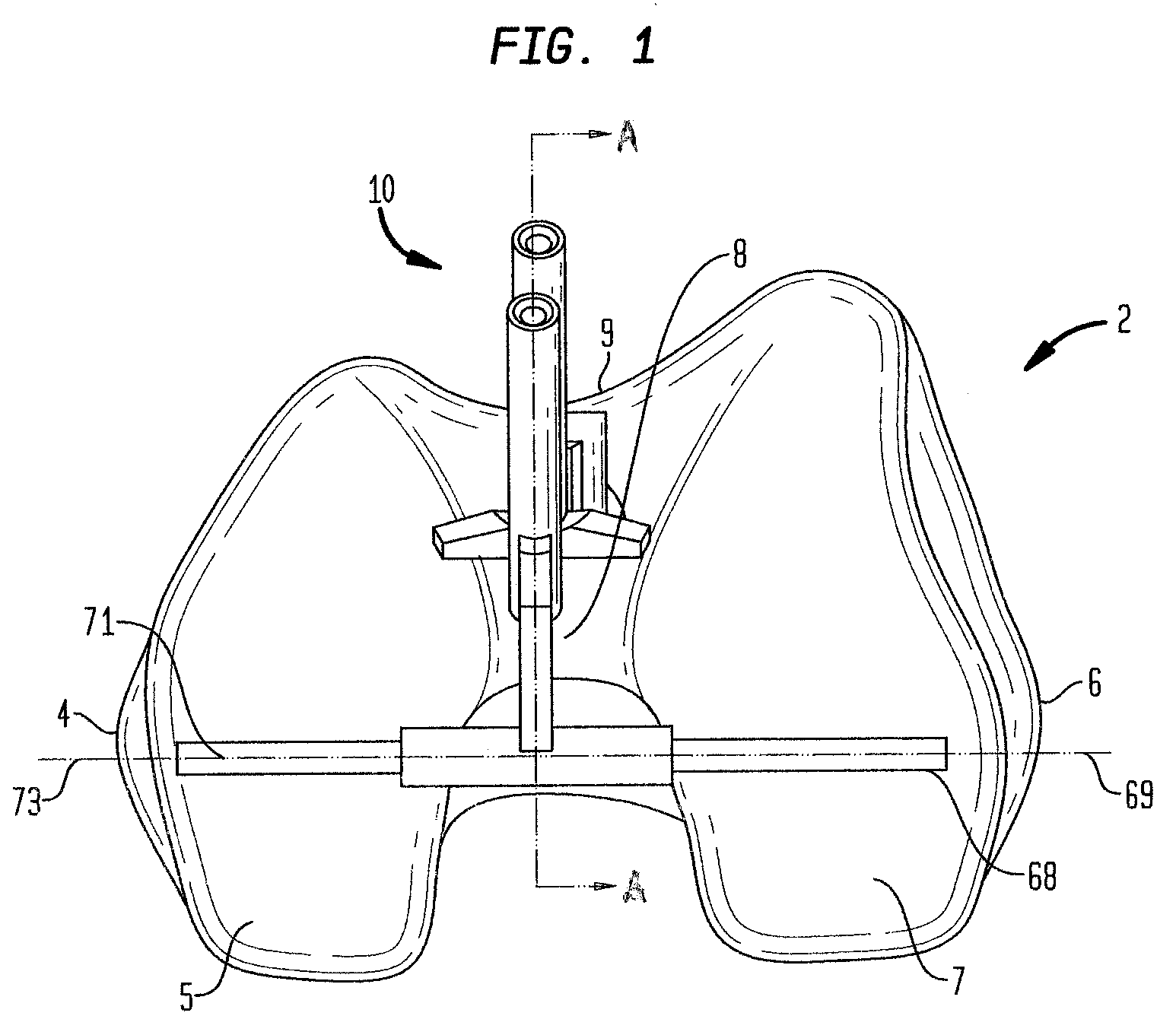
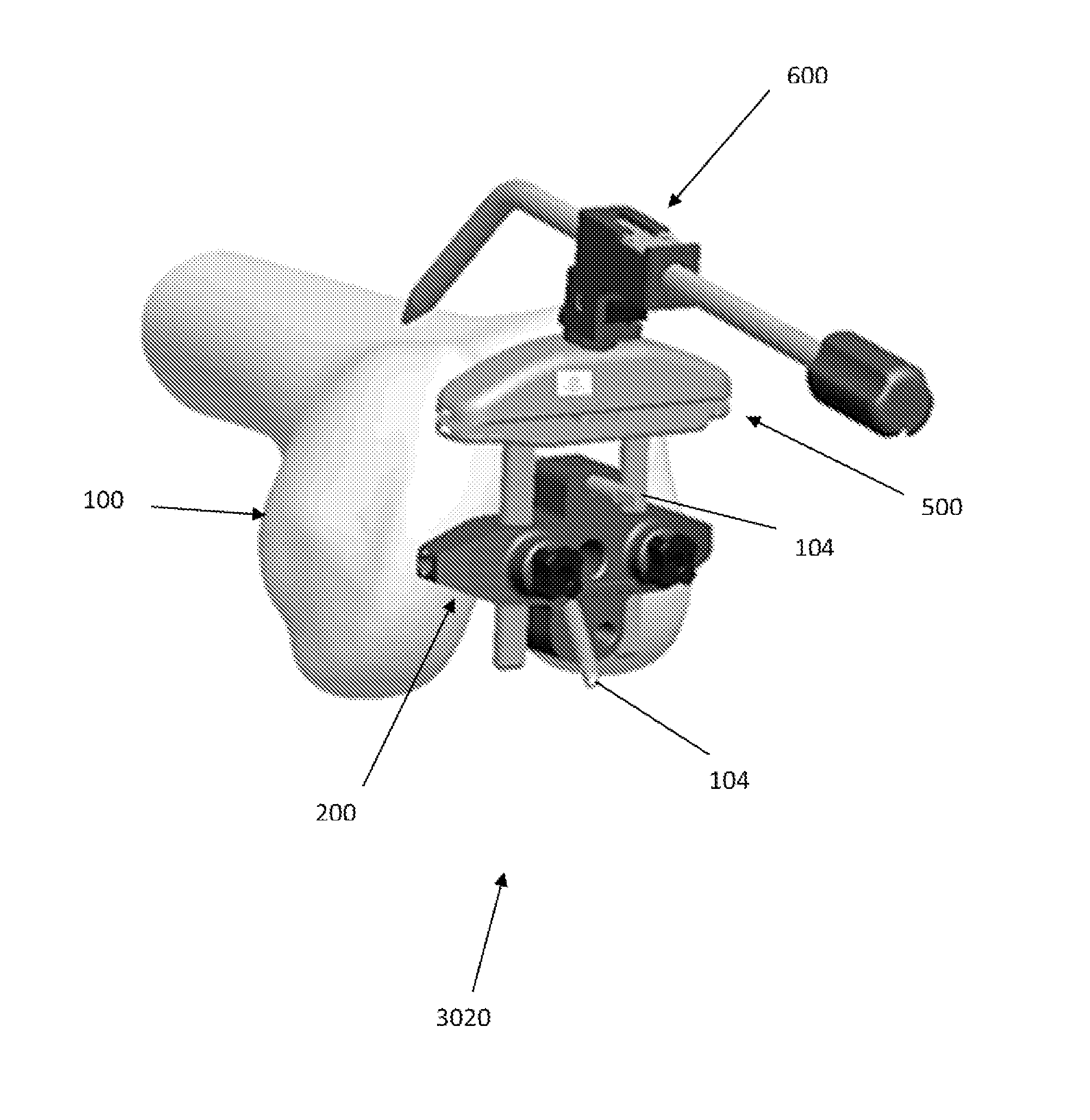
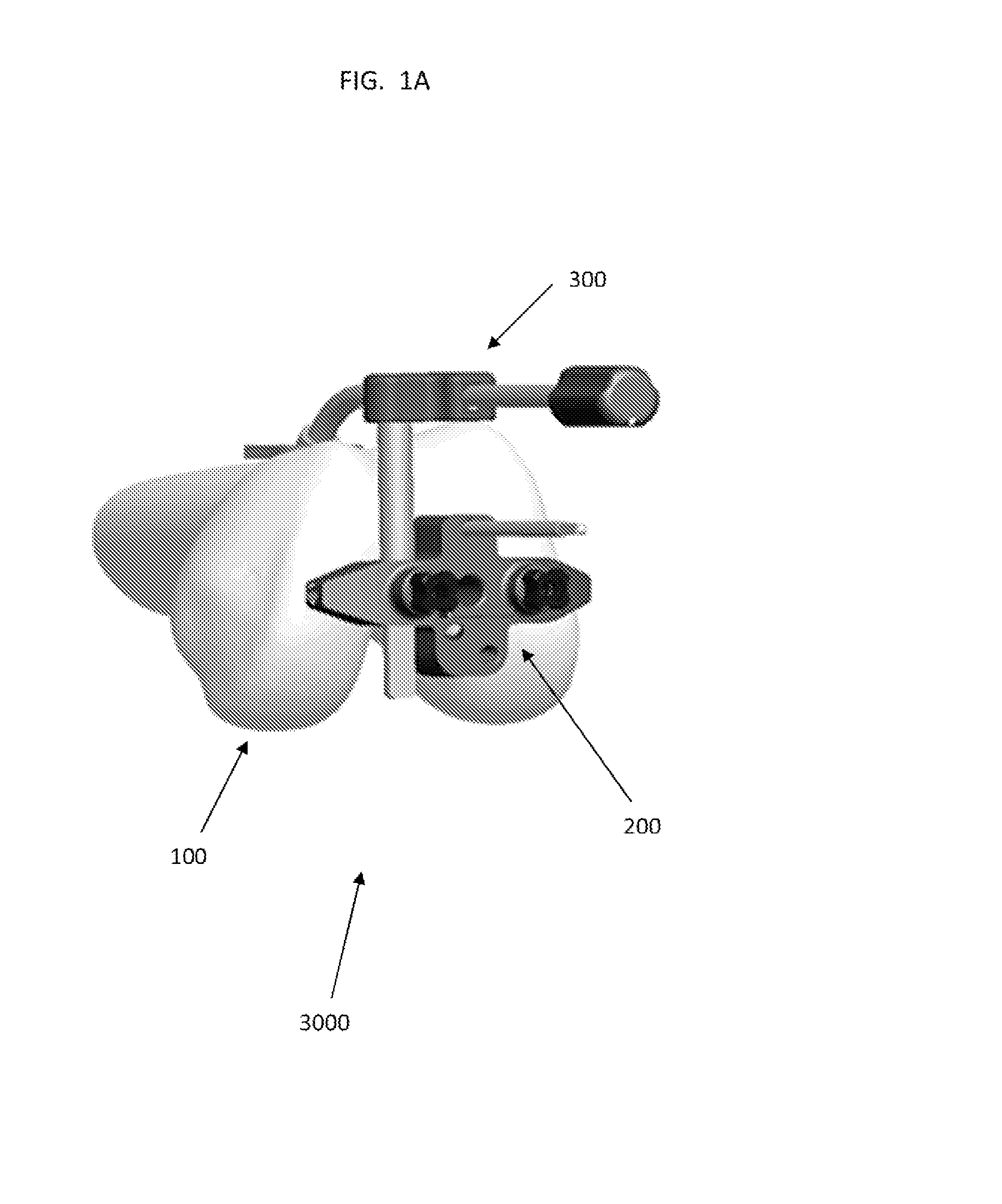
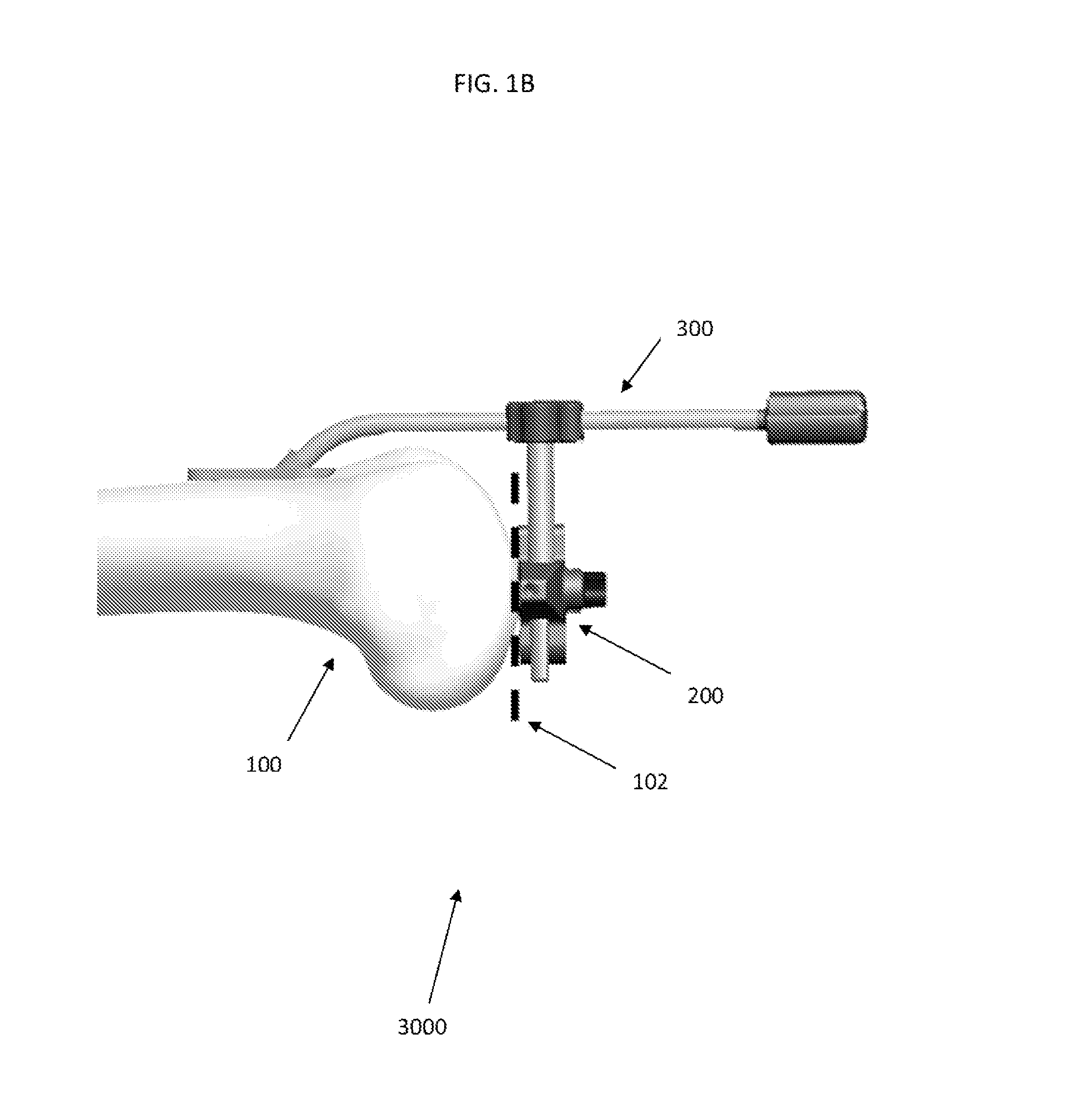
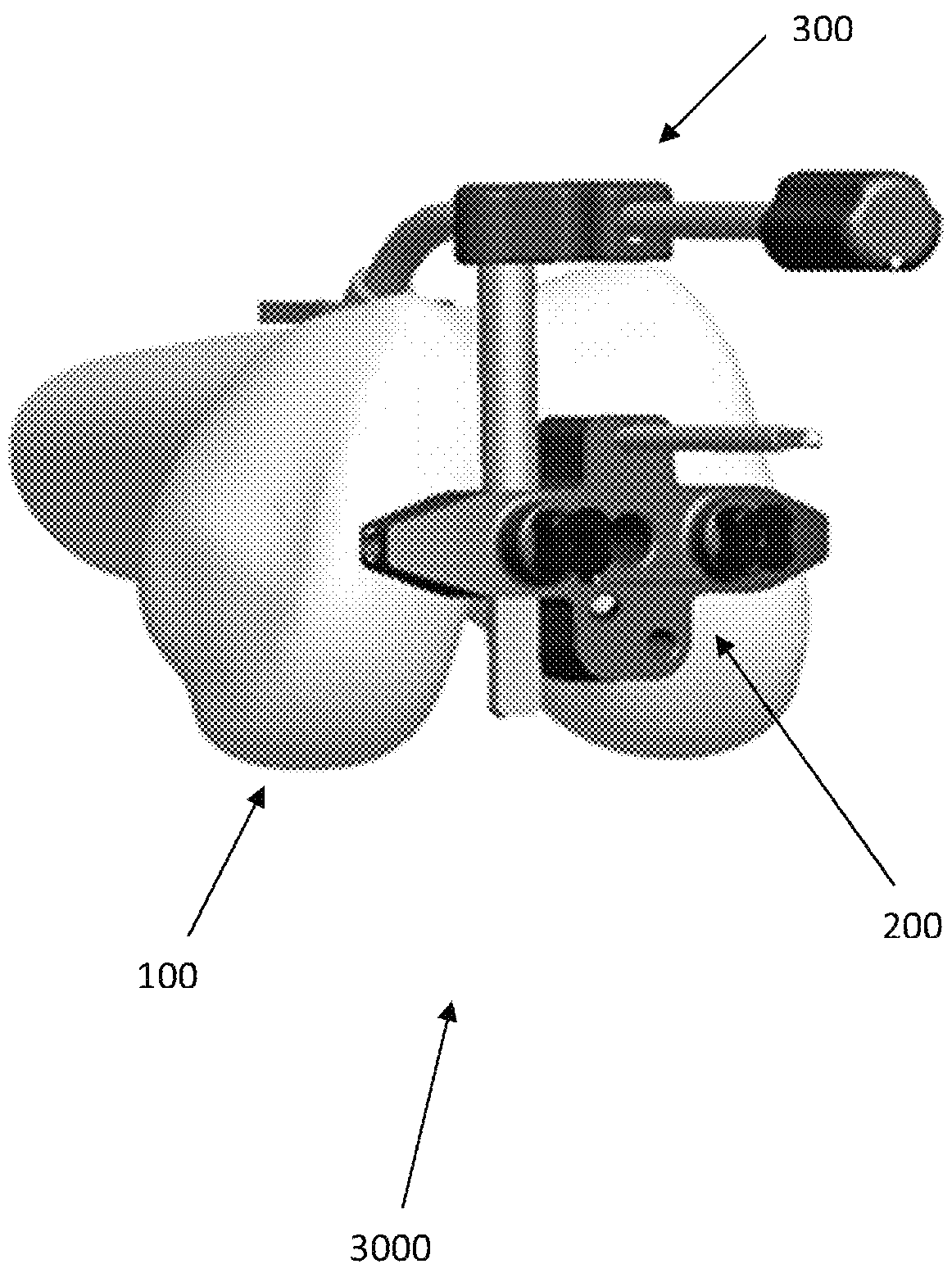
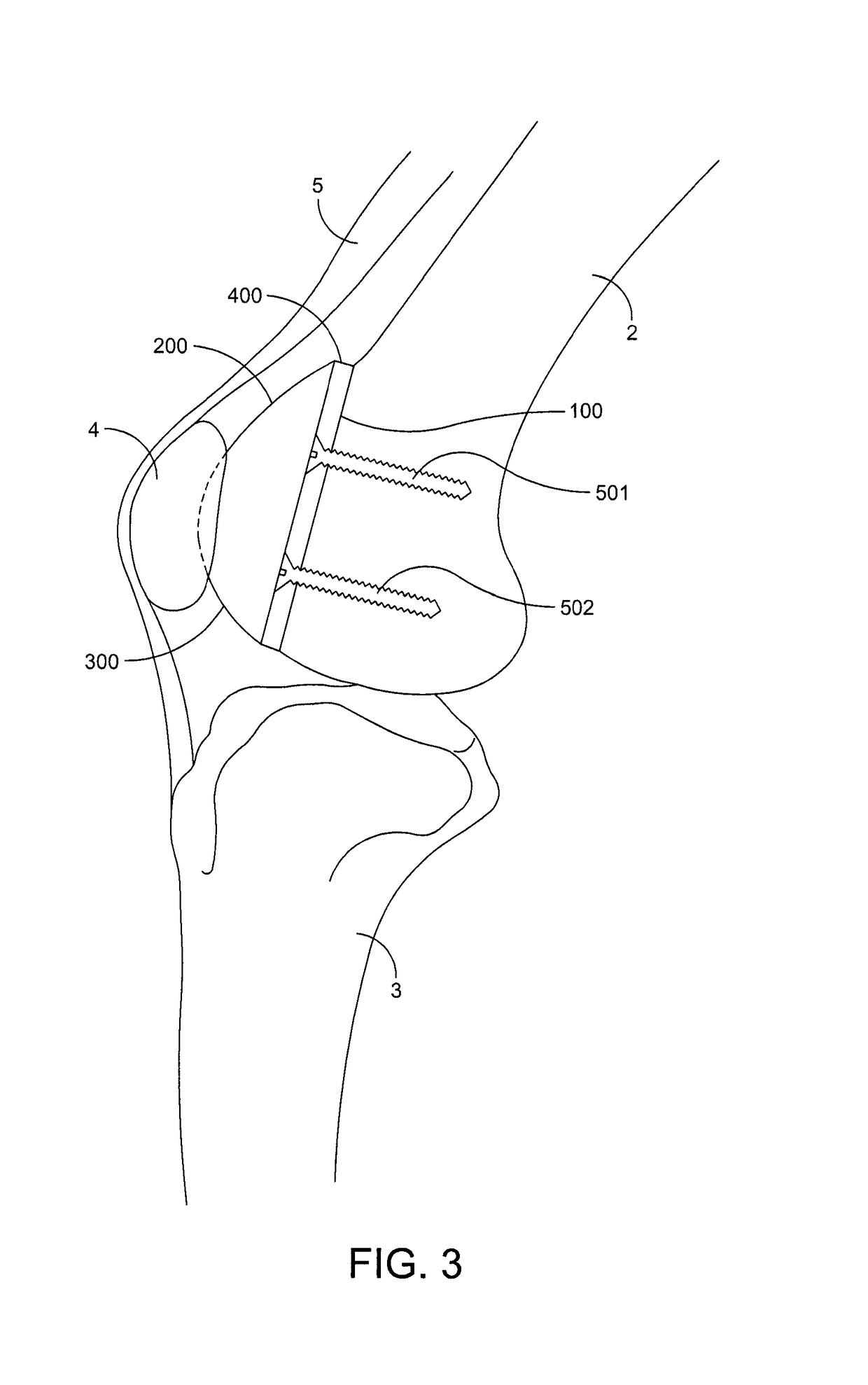
Trochlear groove. The trochlear groove is the concave surface where the patella (kneecap) makes contact with the femur (thighbone). Also called the 'trochlea'.
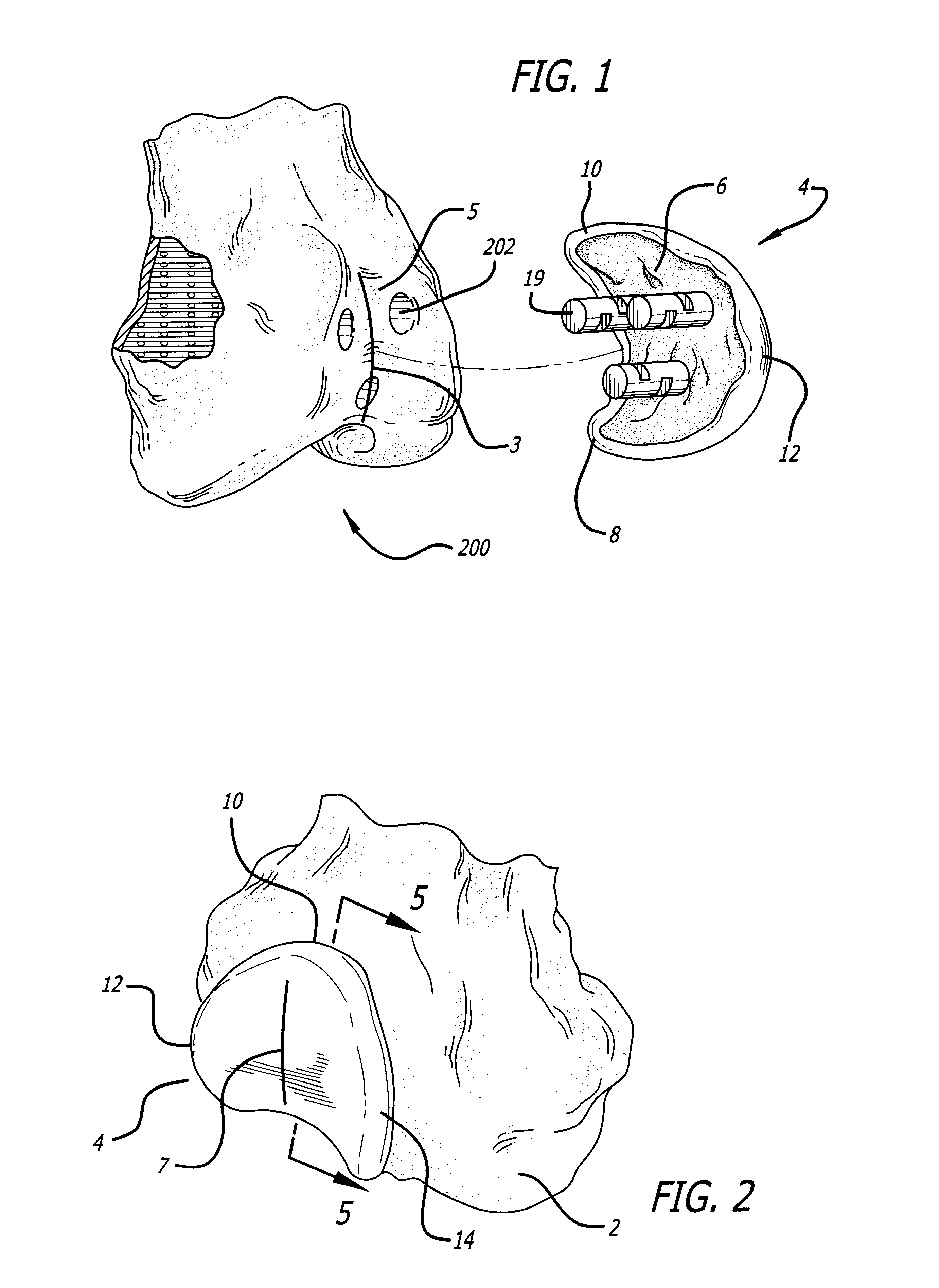
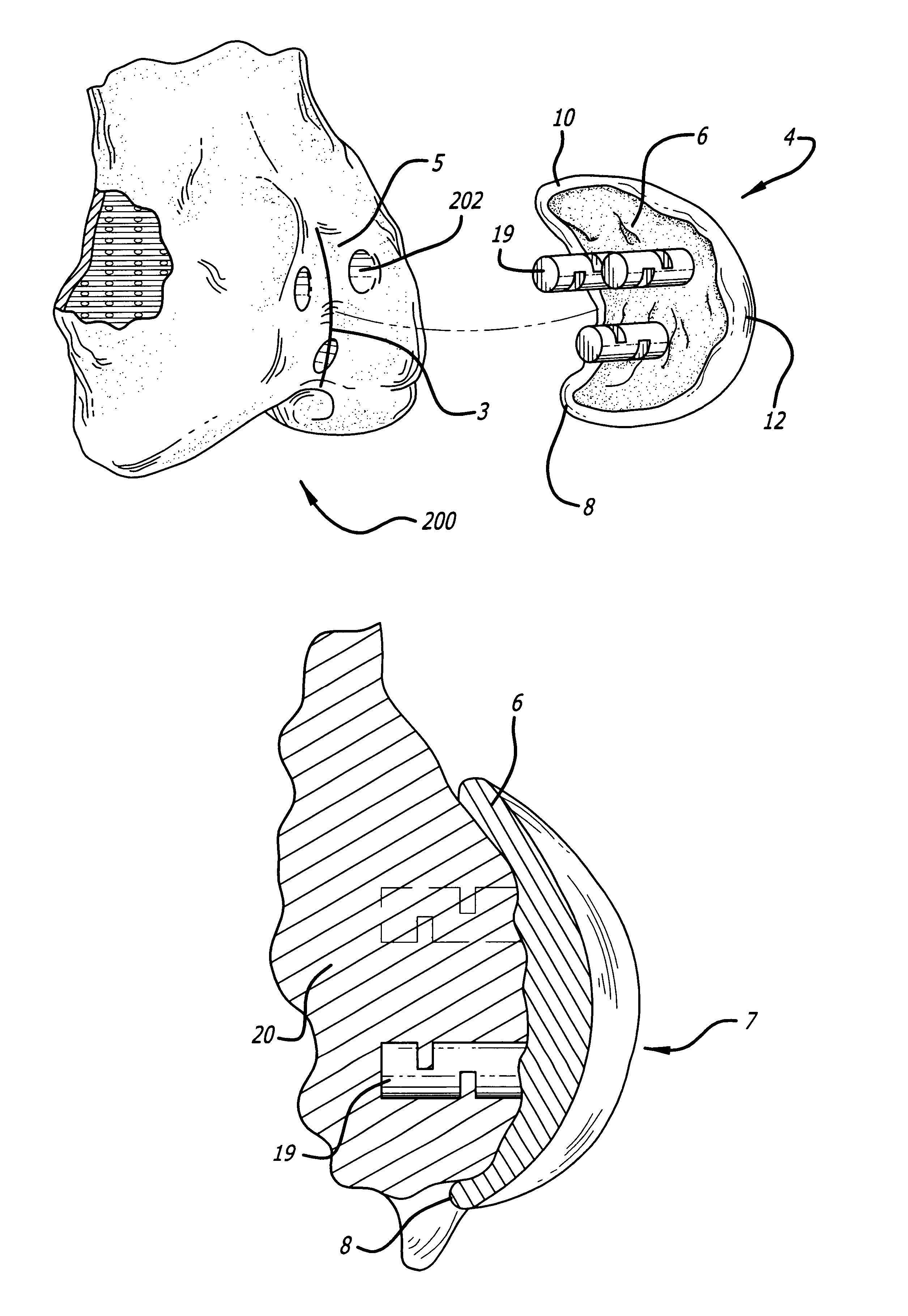
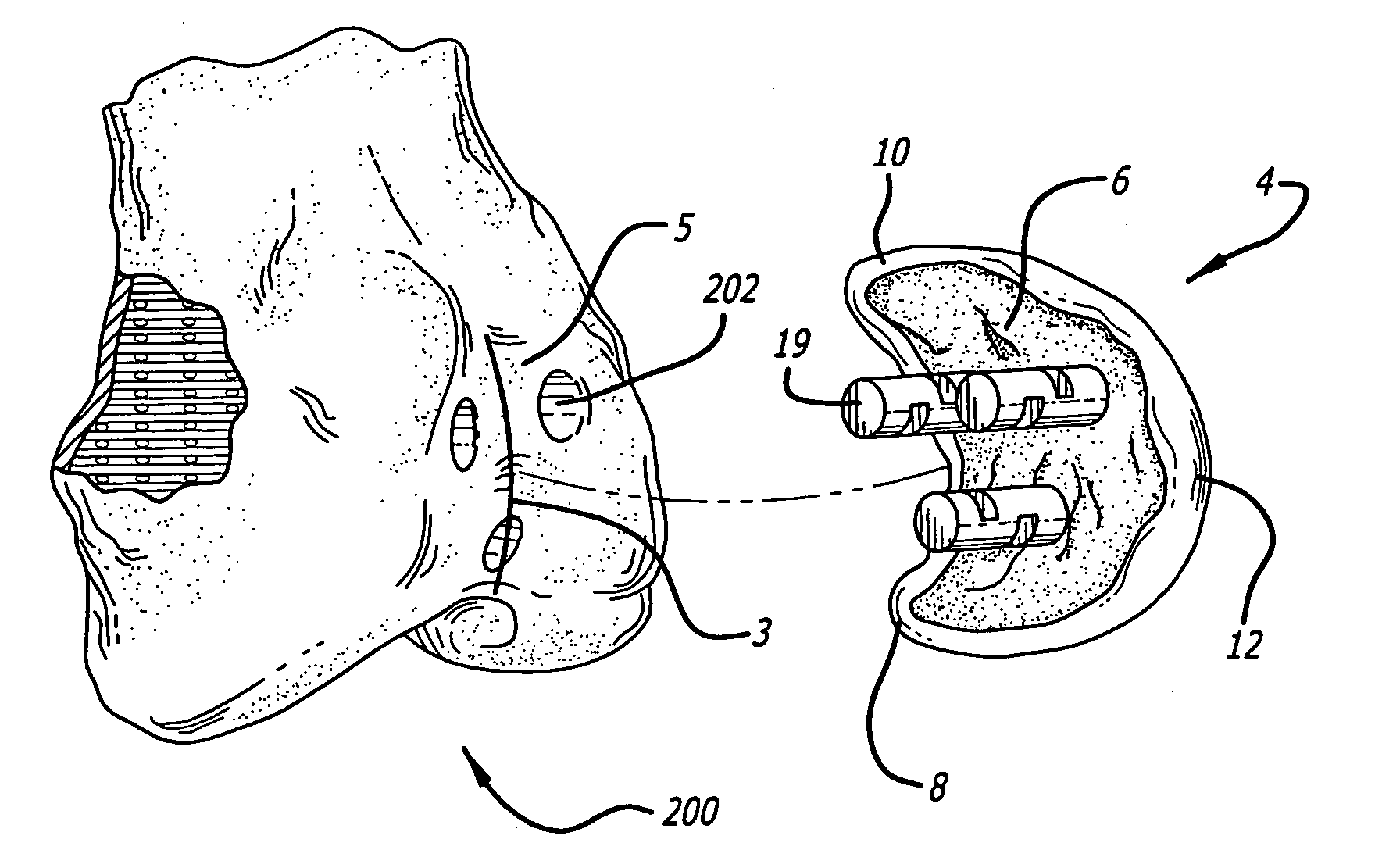
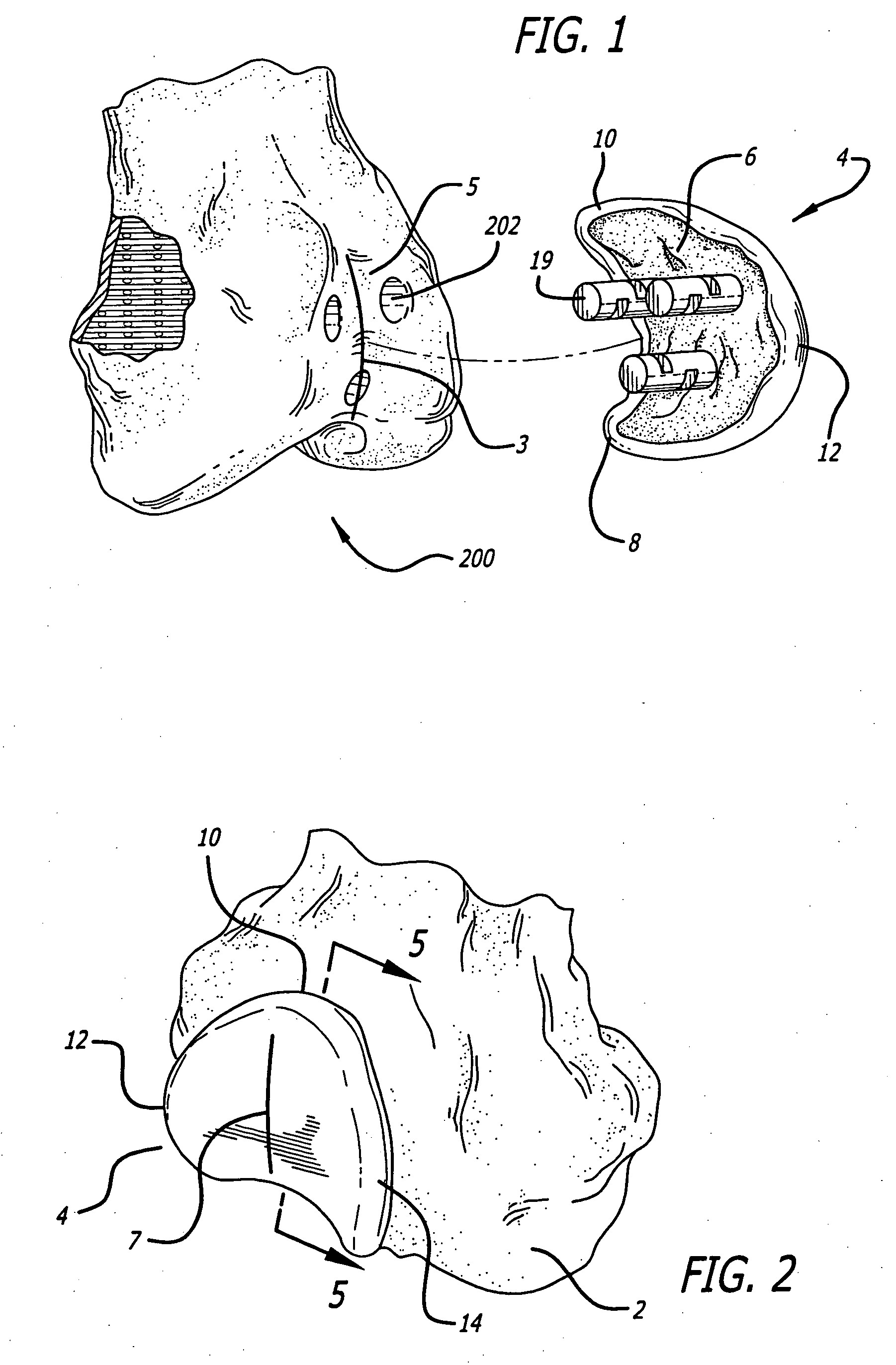
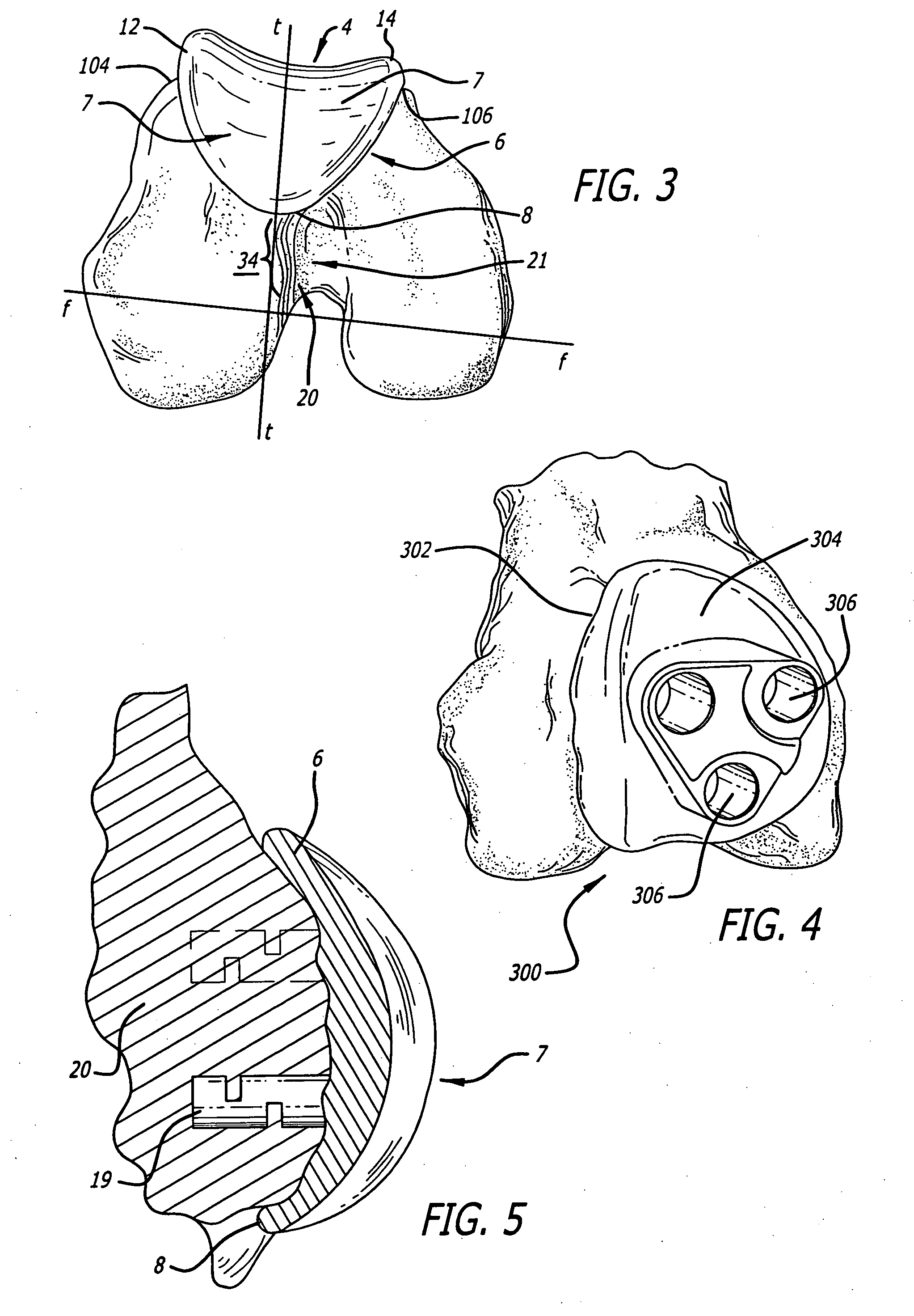
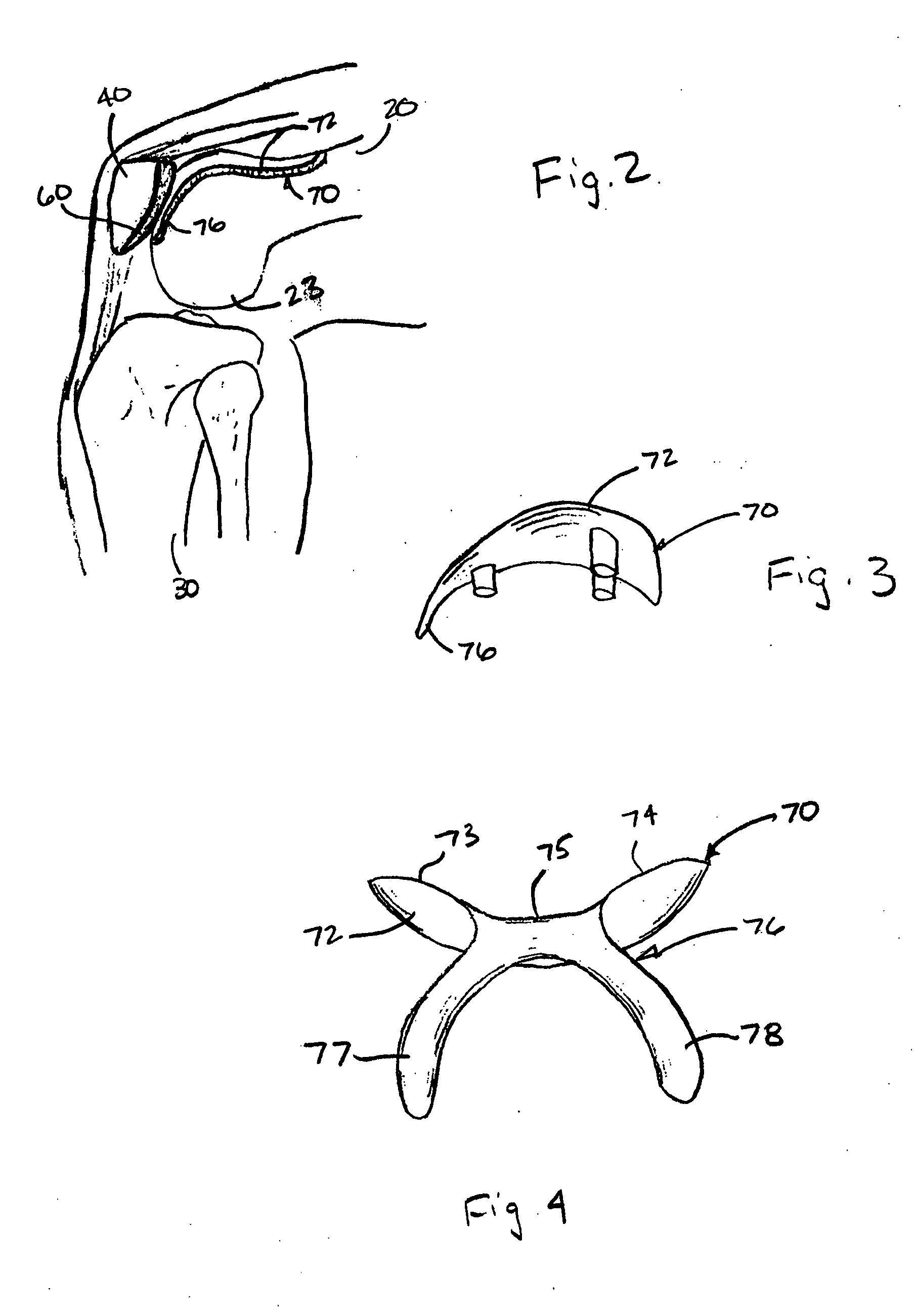
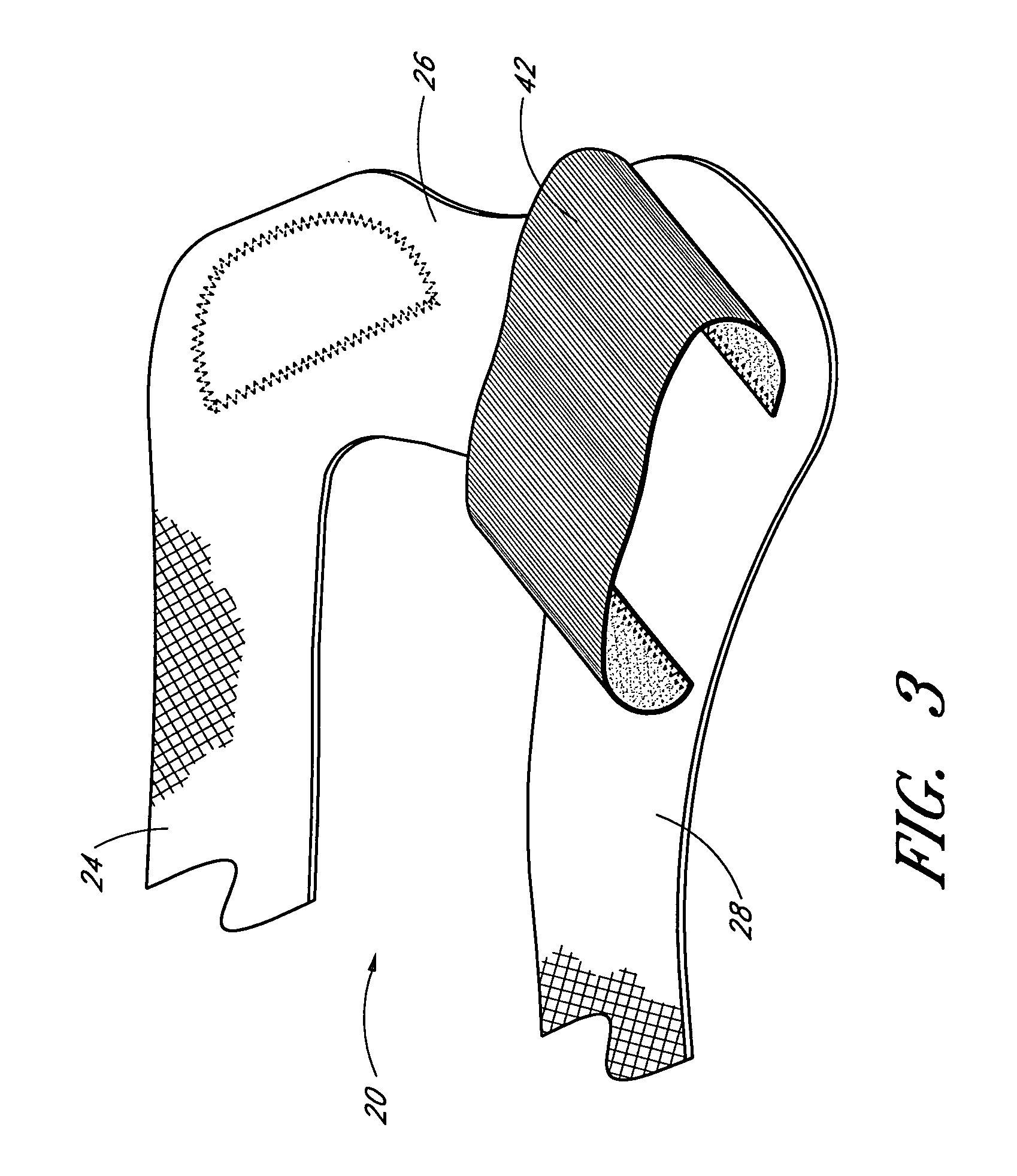
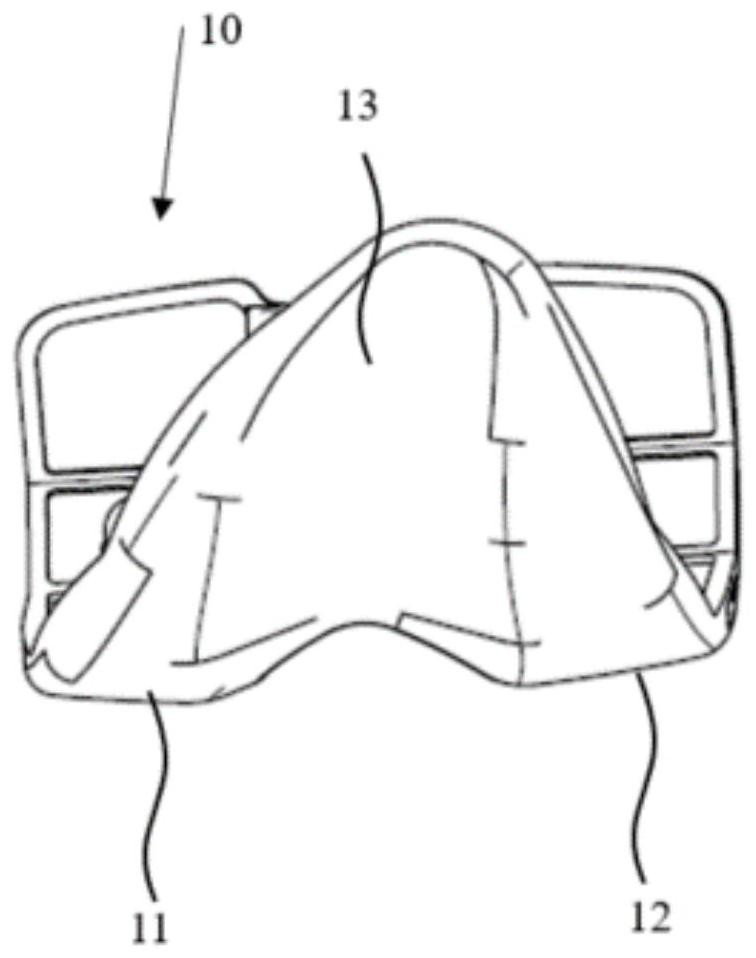
Custom replacement device for resurfacing a femur and method of making the same
InactiveUS6712856B1Joint implantsComputer-aided planning/modellingArticular surfacesRight femoral head
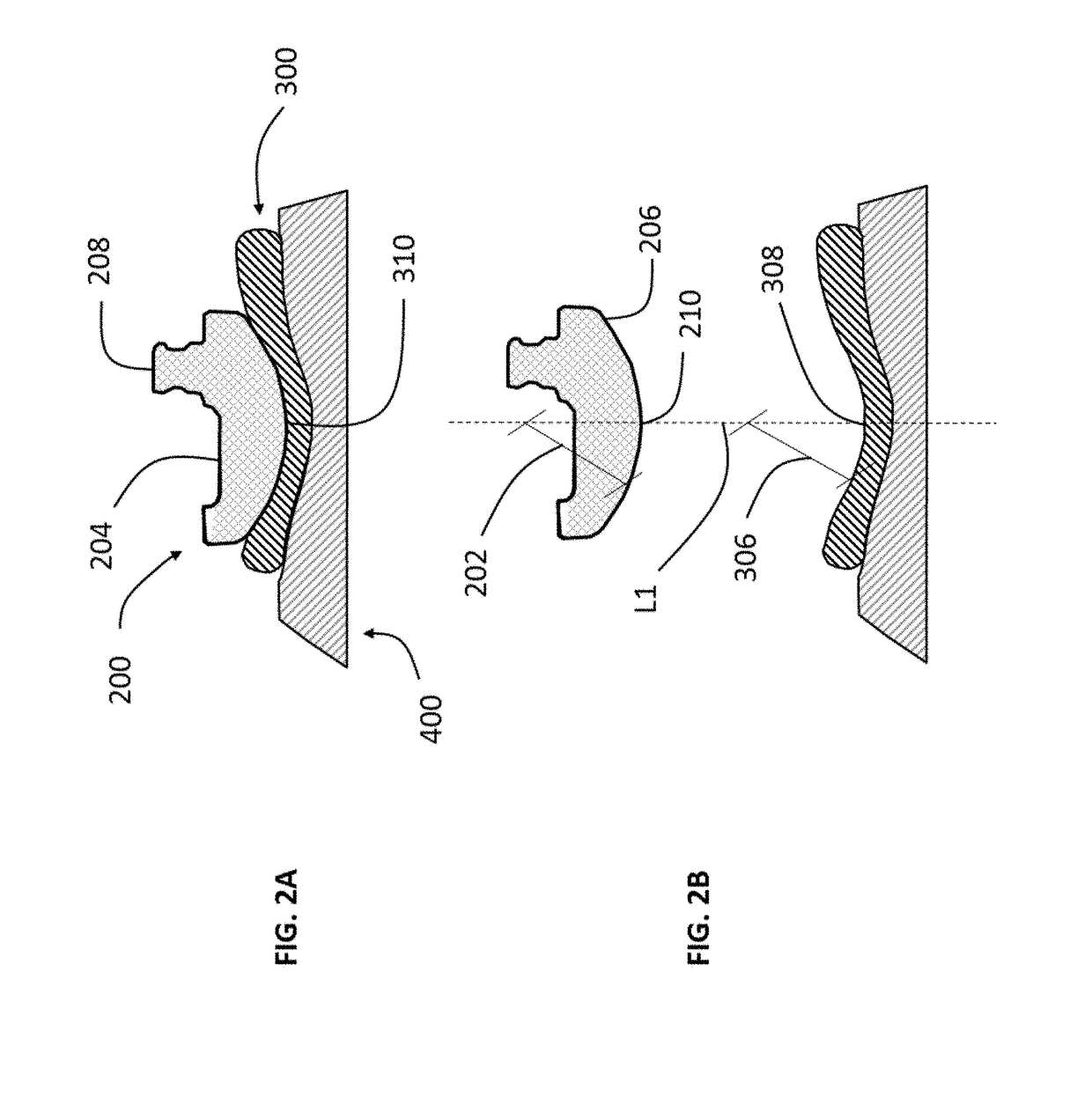
A replacement device for resurfacing a joint surface of a femur and a method of making and installing such a device is provided. The custom replacement device is designed to substantially fit the trochlear groove surface, of an individual femur. Thereby creating a "customized" replacement device for that individual femur and maintaining the original kinematics of the joint. The replacement device may be defined by four boundary points, and a first and a second surface. The first of four points is 3 to 5 mm from the point of attachment of the anterior cruciate ligament to the femur. The second point is near the bottom edge of the end of the natural articulatar cartilage. The third point is at the top ridge of the right condyle and the fourth point at the top ridge of the left condyle of the femur. The top surface is designed so as to maintain centrally directed tracking of the patella perpendicular to the plane established by the distal end of the femoral condyles and aligned with the center of the femoral head.
Owner:KINAMED
Custom replacement device for resurfacing a femur and method of making the same
InactiveUS20040098133A1Joint implantsComputer-aided planning/modellingArticular surfacesRight femoral head
Owner:KINAMED
Two-thirds prosthetic arthroplasty
A two-thirds prosthetic arthroplasty having a trochlear groove, a patello-femoral component, and either a lateral condyle or a medial condyle. The arthroplasty may be configured to be a prosthetic for either a right or left knee. The condyle and patello-femoral component are separated by a modified intercondylar notch that is blended to avoid protrusions or sharp angles. The prosthetic arthroplasty is inserted after preoperative MRI mapping of articular cartilage damage. The prosthetic arthroplasty may be cemented during surgery and the two-thirds design of the present invention obviates the problem of cement retrieval from remote parts of the prosthesis.
Owner:WOOD DAVID JOHN
Implant designs, apparatus and methods for total knee resurfacing
A ligament and bone conserving prosthesis for total knee resurfacing includes a distal femoral component which resurfaces the weight bearing portions of both femoral condyles and the trochlear groove. The prosthesis also includes implants to independently resurface the medial and lateral tibial plateaus in an inset manner. Also disclosed are apparatus and methods for performing the total knee resurfacing utilizing a minimally invasive, bone and ligament conserving manner.
Owner:REMIA LEONARD
Patello-femoral prosthesis
A patello-femoral prosthesis is provided for replacing the engagement surfaces between the patella and the femur. The prosthesis is configured to cover the trochlear groove and extend into the intercondylar notch without extending onto the articulating surfaces of the condyles. A method is also provided for implanting a patello-femoral prosthesis in which a portion of the trochlear groove and intercondylar notch are resected and the prosthesis is implanted over the femur that had portions resected.
Owner:LOTKE PAUL A
Patient match instrument
InactiveUS20140018813A1Good repeatabilityGood reproducibilitySurgical sawsProsthesisTangential contactTrochlear groove
A patient matched instrument for a patient's femur is disclosed. The instrument includes a body having a cutting slot and a patient matched surface that mates with the patient's trochlear groove, a first leg portion extending from the body, a second leg portion extending from the body; and each leg portion has a contacting pad for tangential contact with the patient's femoral medial and lateral condyles.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Device and method for externally rotating the femur
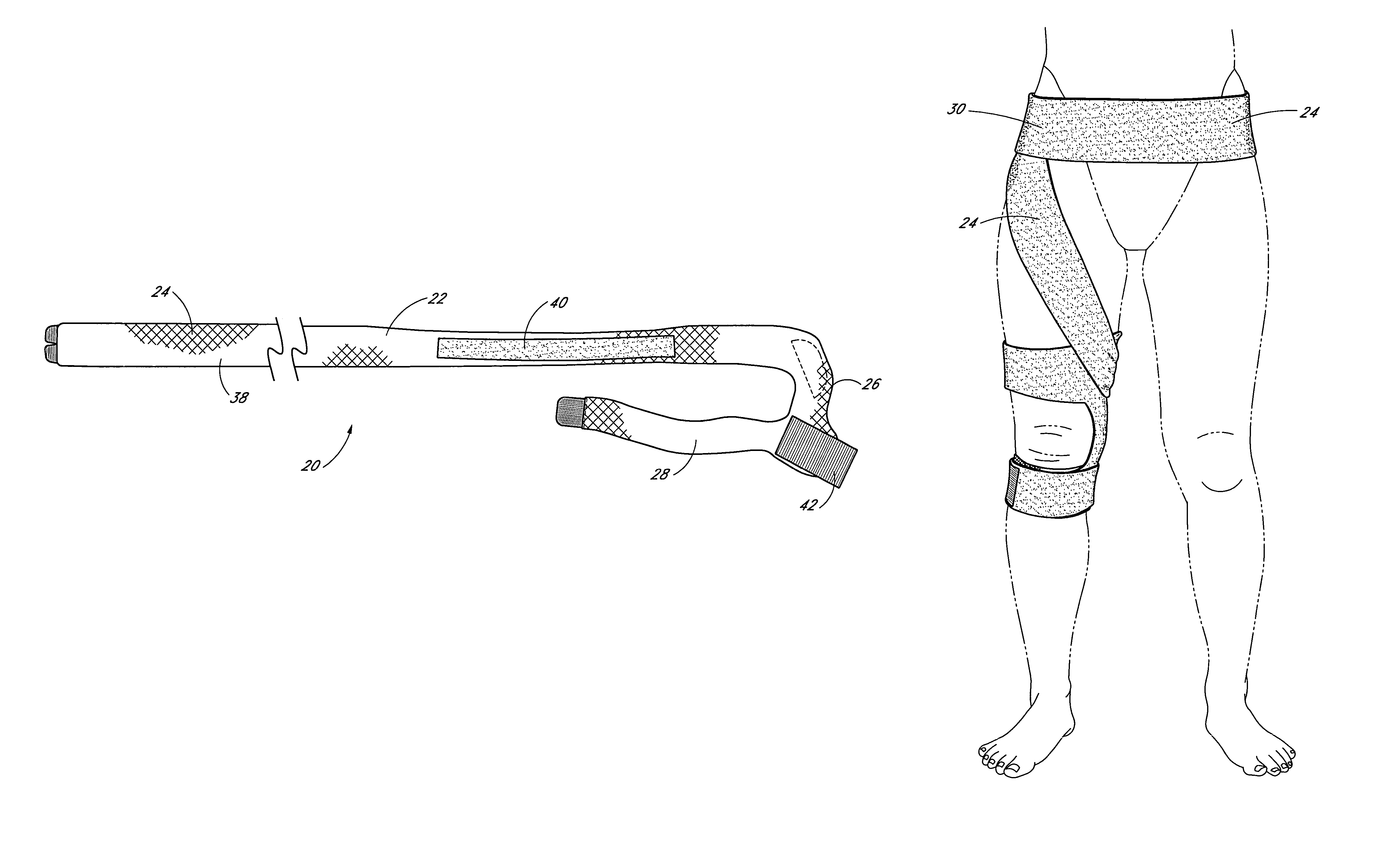
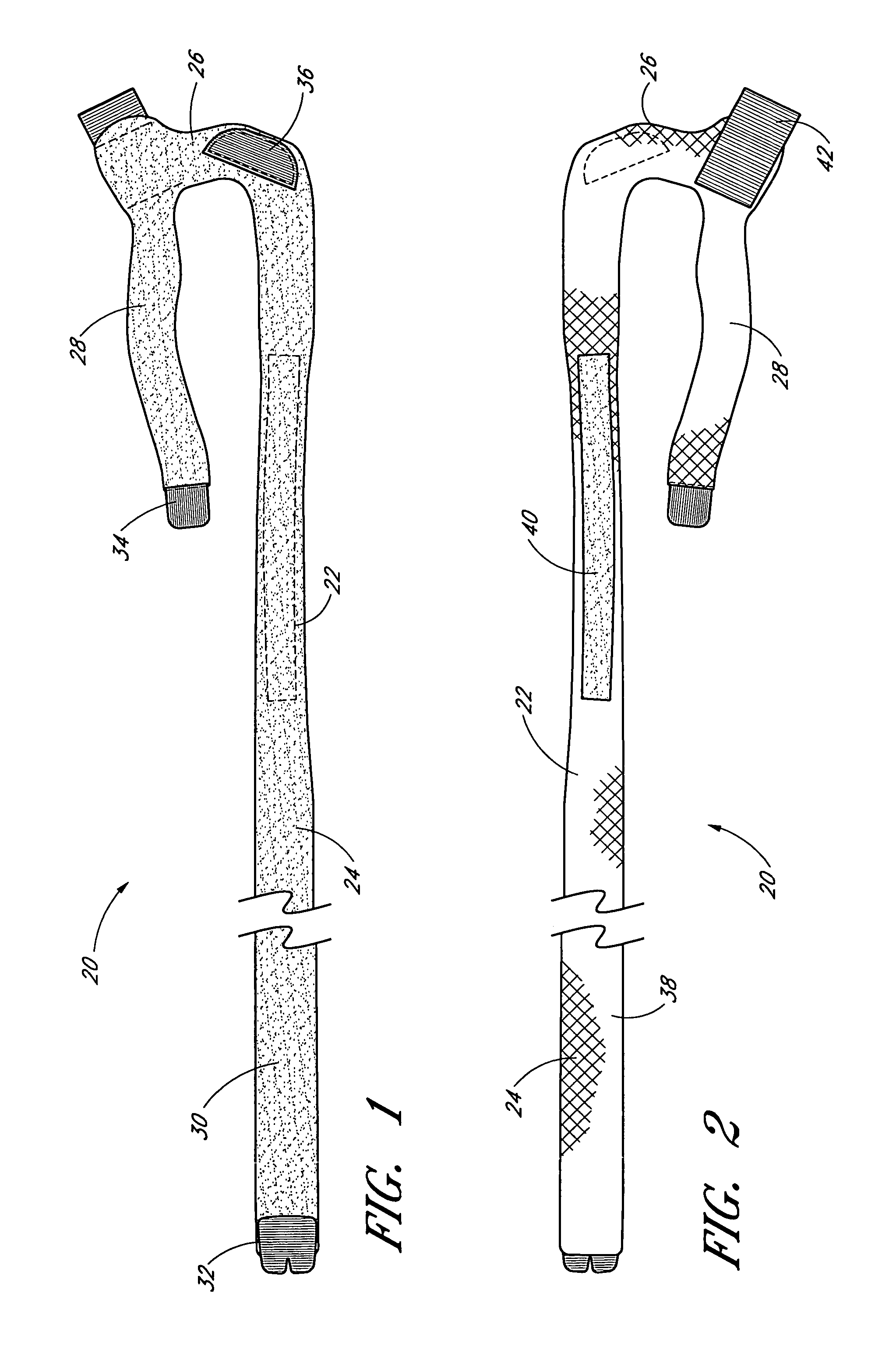
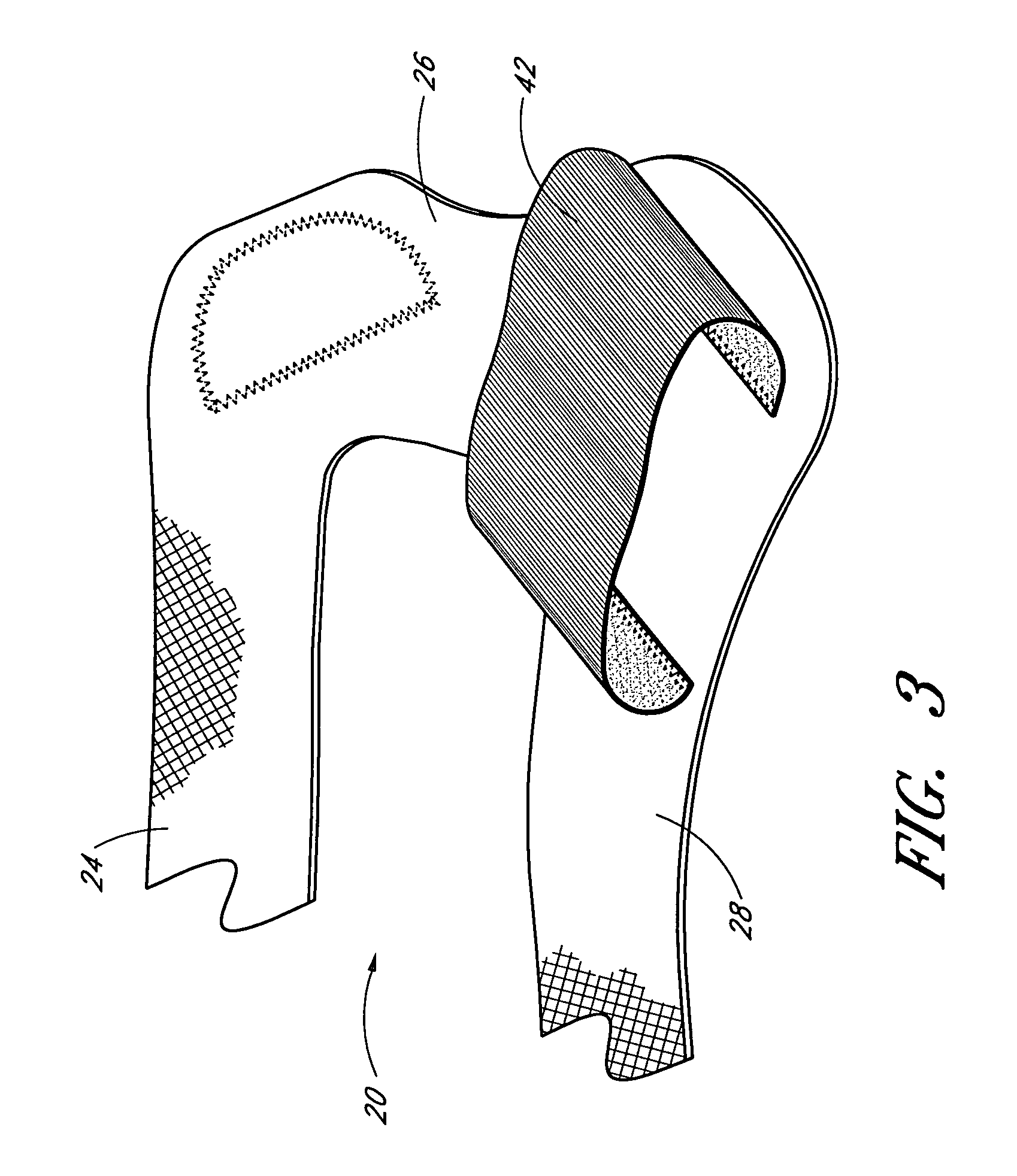
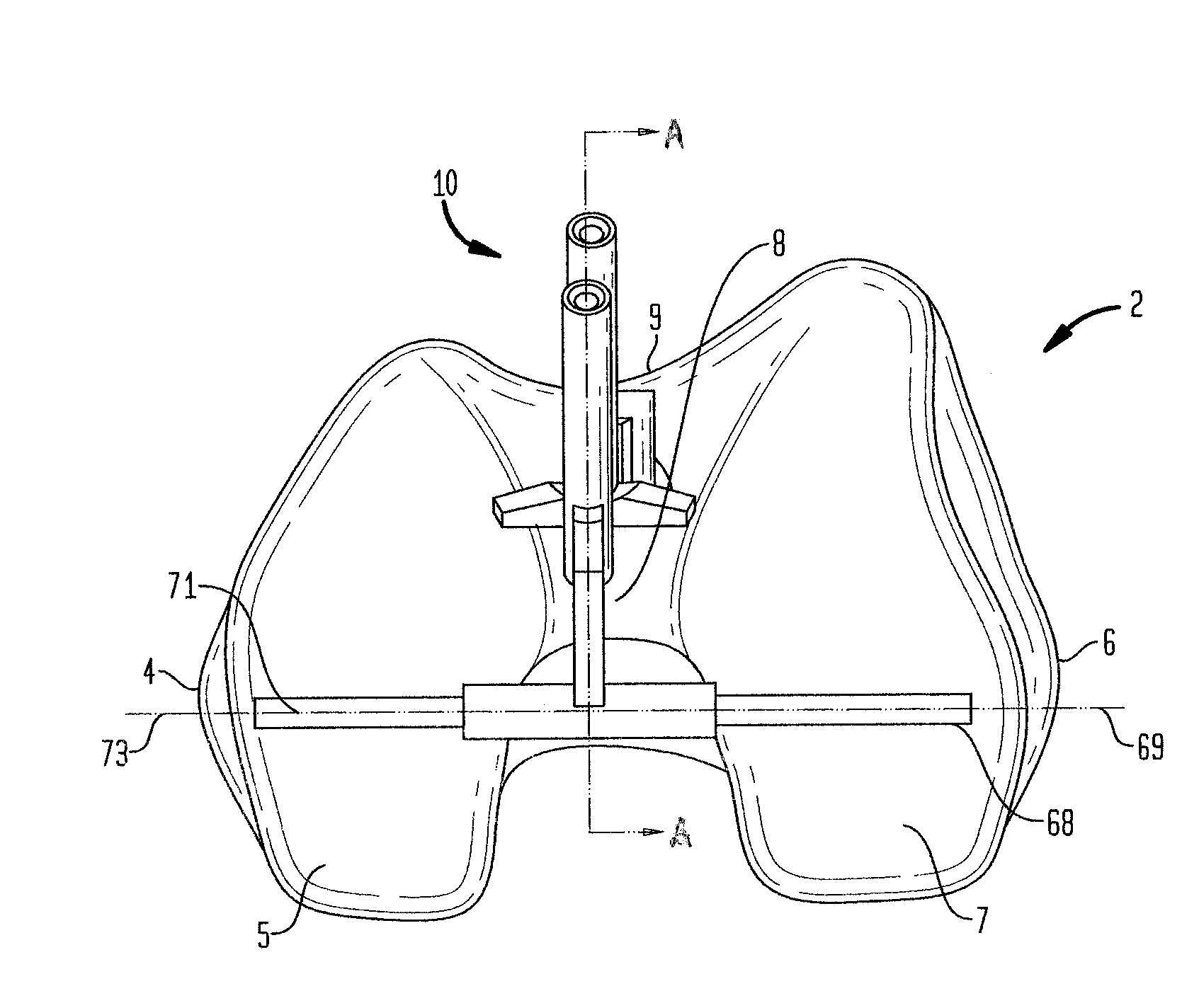
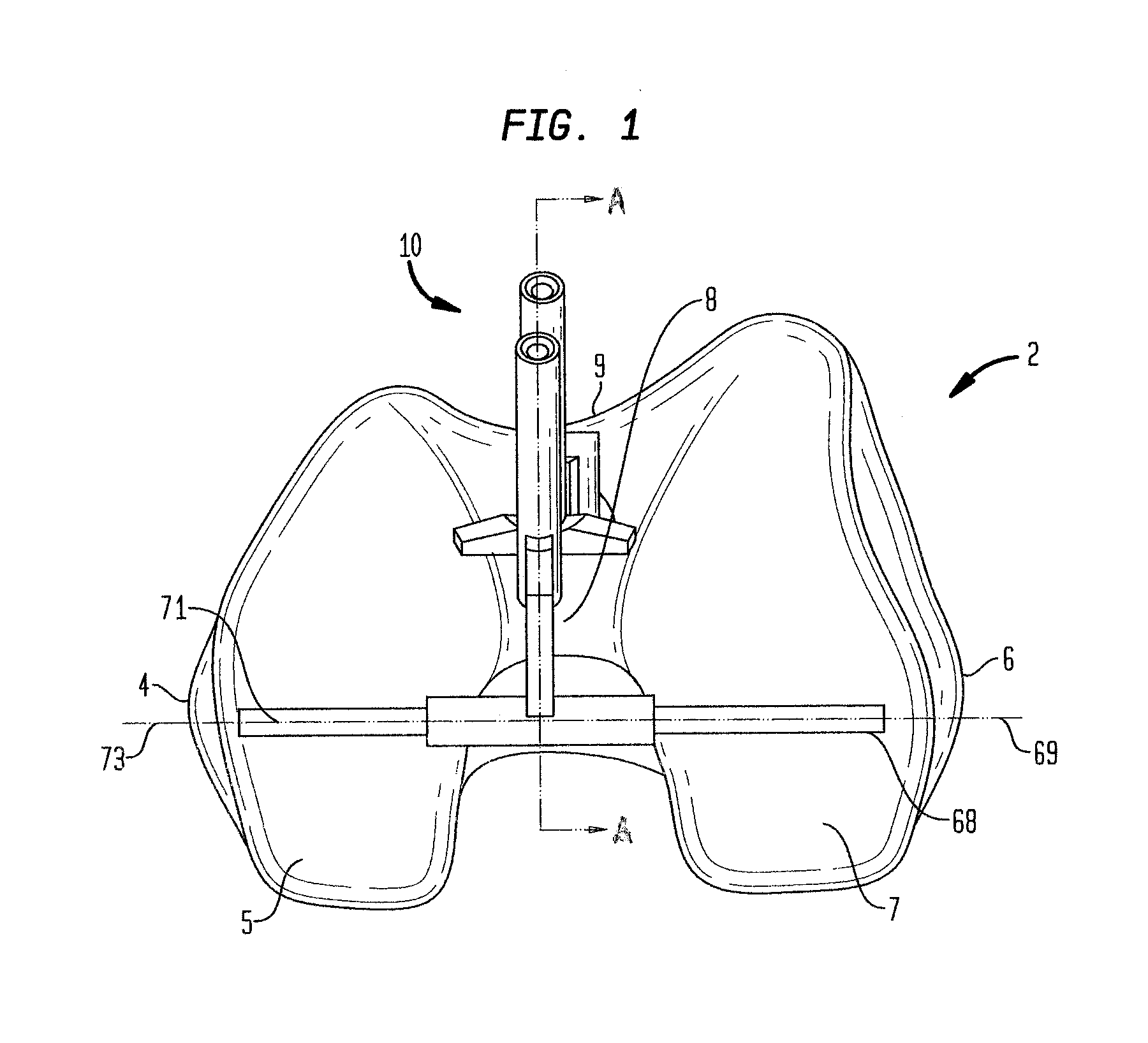
ActiveUS7959591B2Light weightImprove lower-extremity mechanicsRestraining devicesDiagnosticsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPelvis
Owner:DJO
Apparatus for and method of diagnosing and treating patello-femoral misalignment
An apparatus for, and method of, diagnosing and treating patello-femoral misalignment, which includes an inward tracking member that operatively fits over, and provides direct inward pressure against, a patella; wherein the inward tracking member provides a compressive force against the patella, thereby increasing the contact surface area between the patellofemoral articular tissue and an associated femoral trochlear groove; is disclosed.
Owner:CROPPER DEAN E
Apparatus for and method of diagnosing and treating patello-femoral misalignment
InactiveUS20090163842A1Increased contact surface areaNon-surgical orthopedic devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringSacroiliac jointTrochlear groove
An apparatus for, and method of, diagnosing and treating patello-femoral misalignment, which includes an inward tracking member that operatively fits over, and provides direct inward pressure against, a patella; wherein the inward tracking member provides a compressive force against the patella, thereby increasing the contact surface area between the patellofemoral articular tissue and an associated femoral trochlear groove; is disclosed.
Owner:CROPPER DEAN E
Patello-femoral prosthesis
Owner:LOTKE PAUL A
Spot facing trochlear groove
InactiveUS20100222782A1Restore accuratelyPrecise positioningKnee jointsOsteosynthesis devicesProsthesisReamer
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
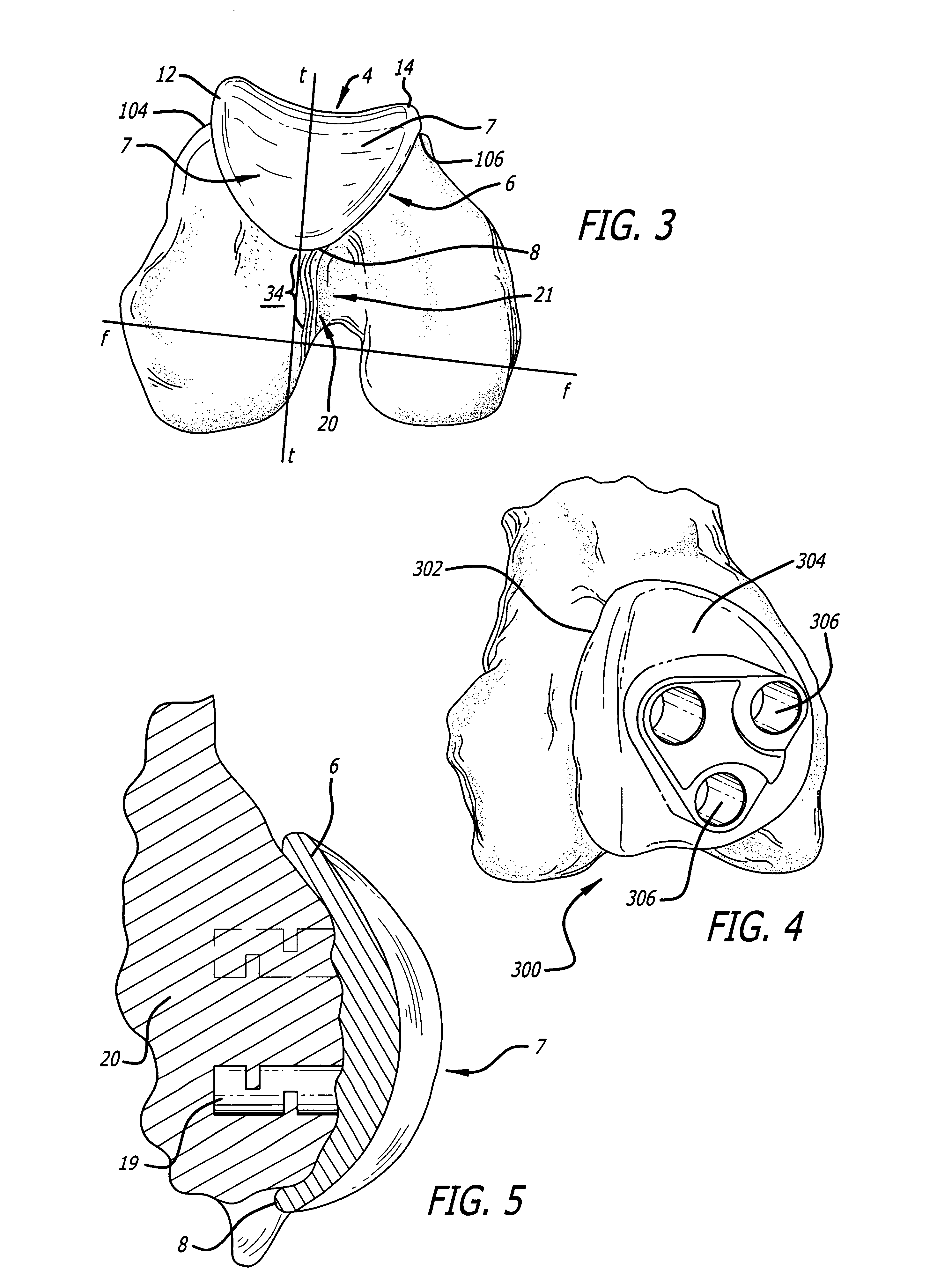
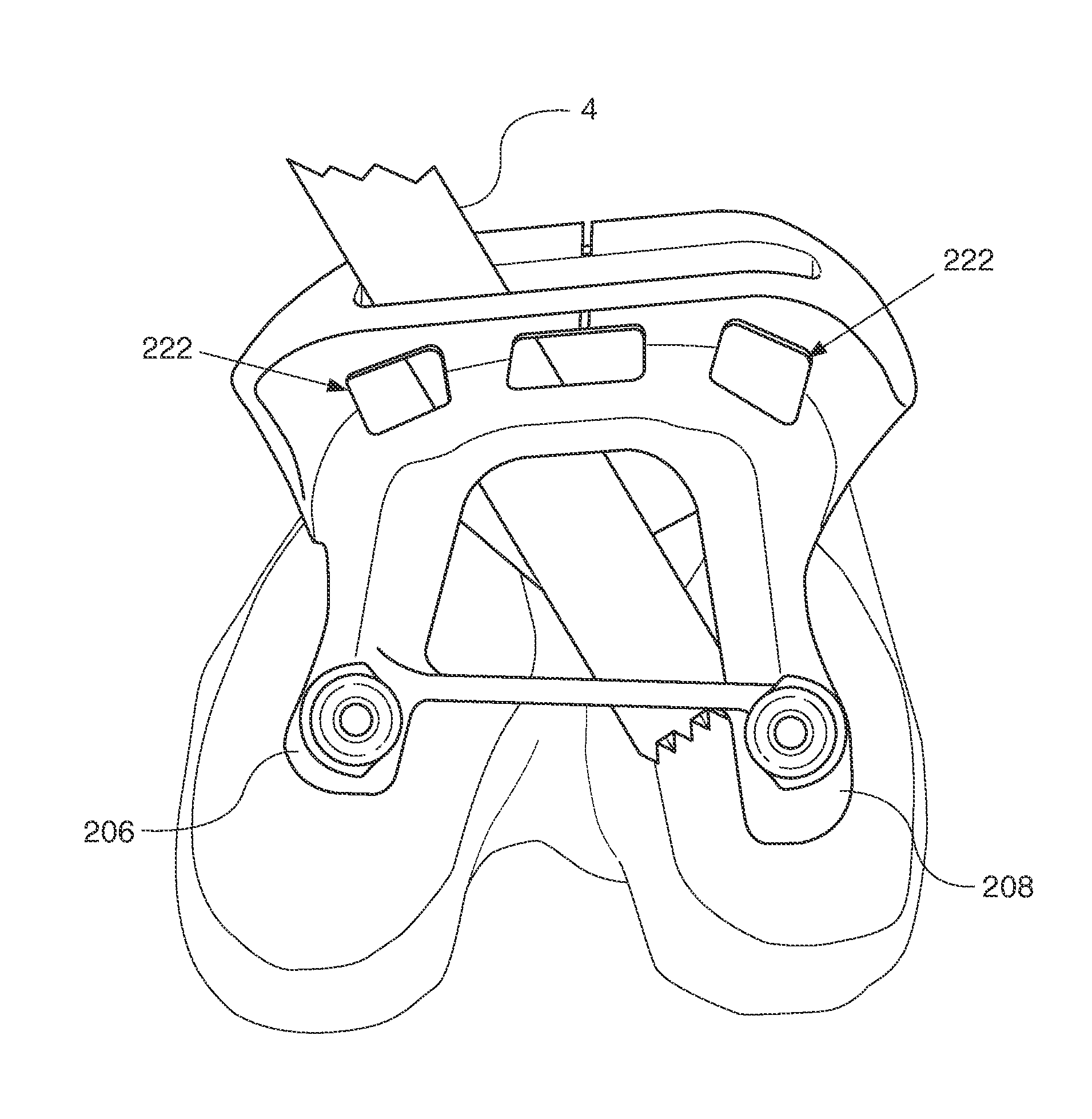
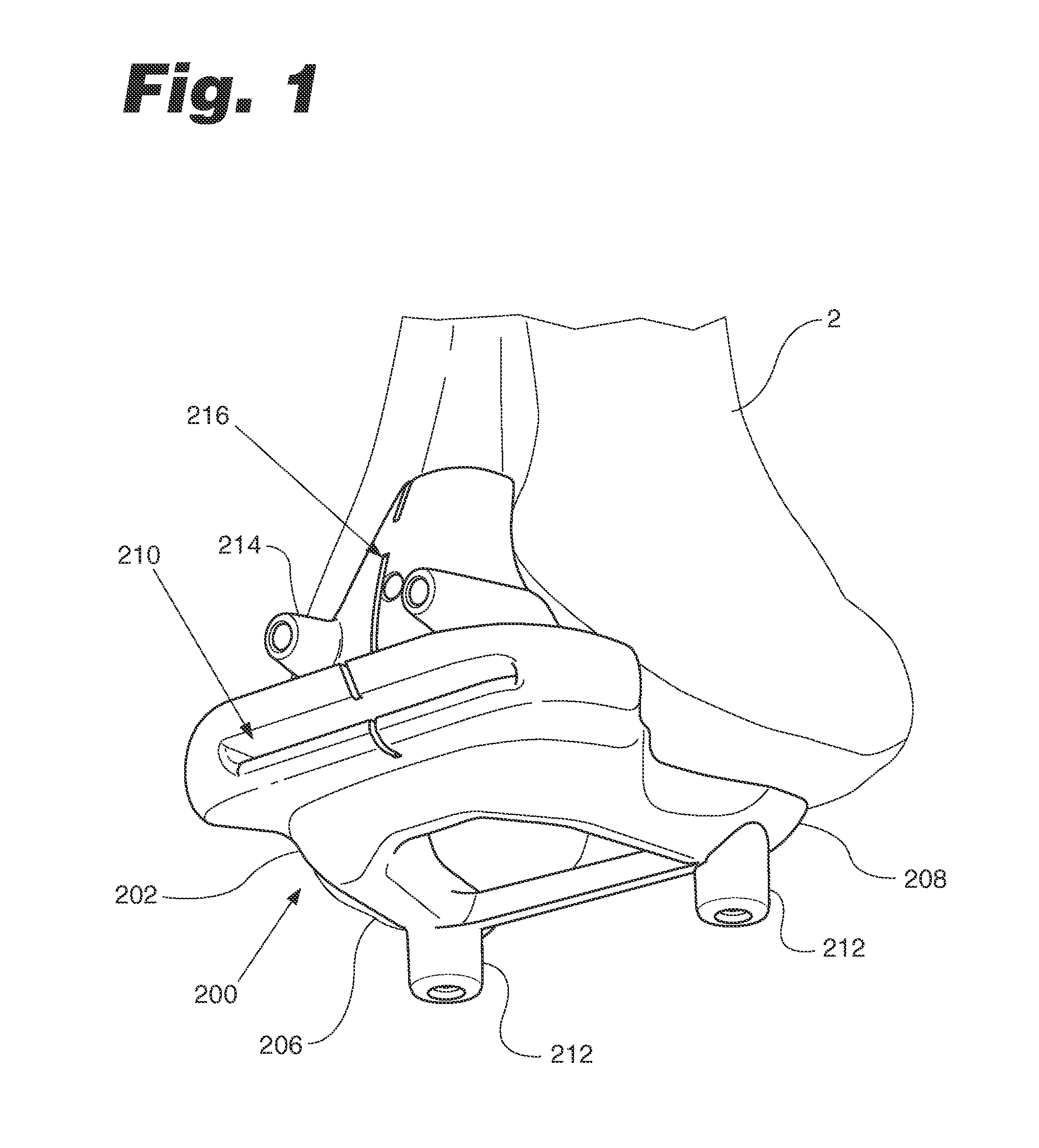
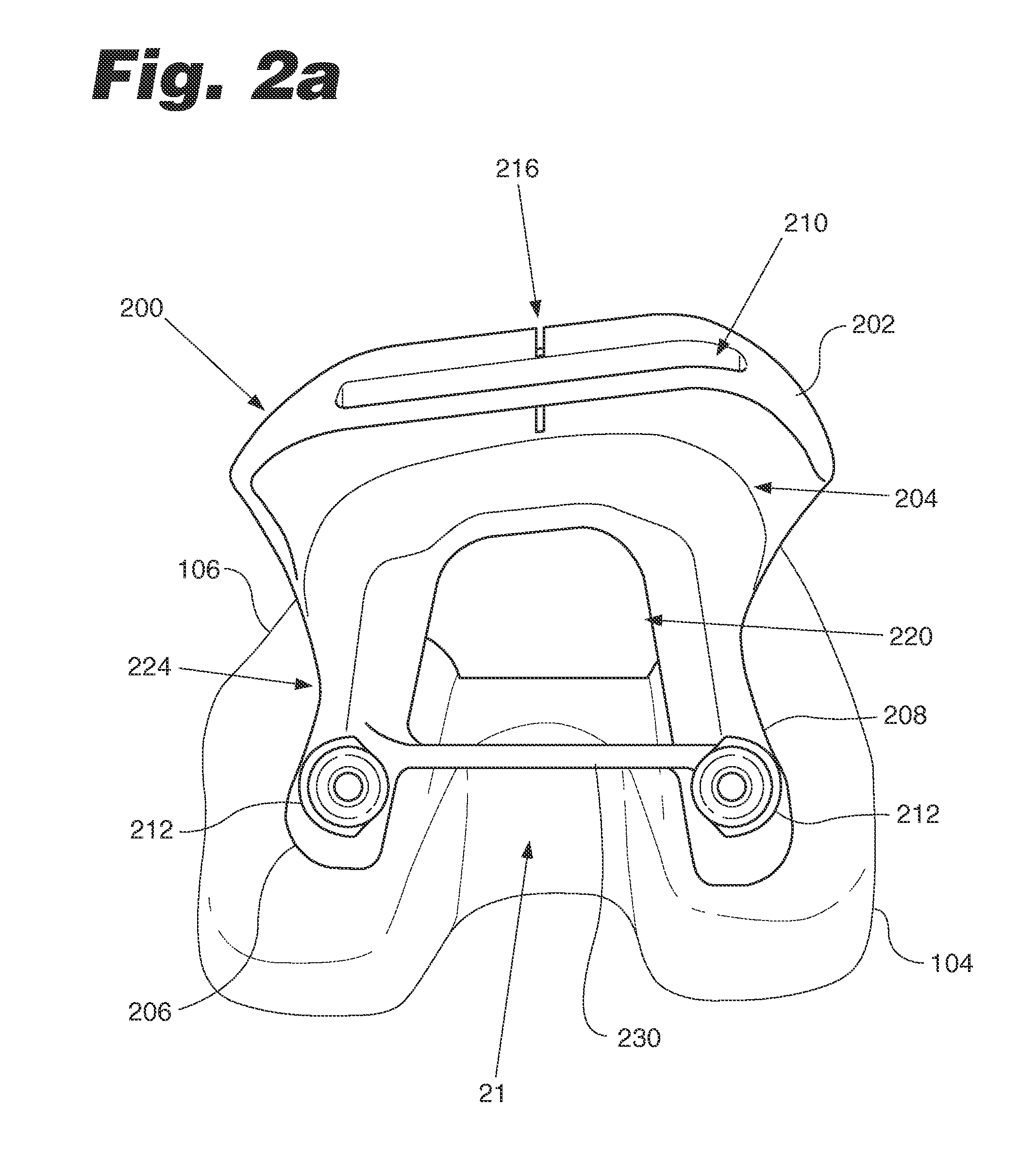
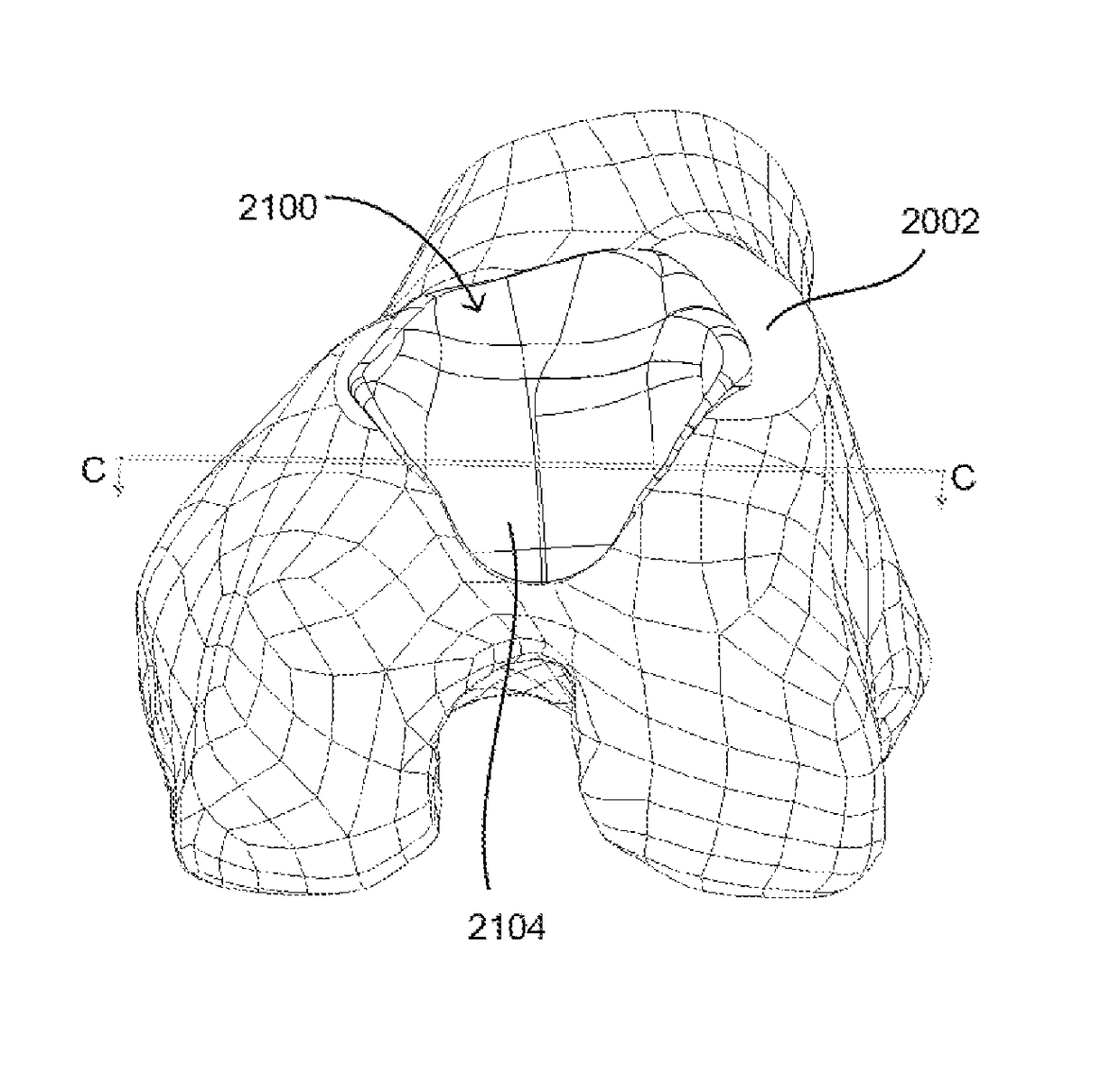
Anatomically guided instrumentation for trochlear groove replacement
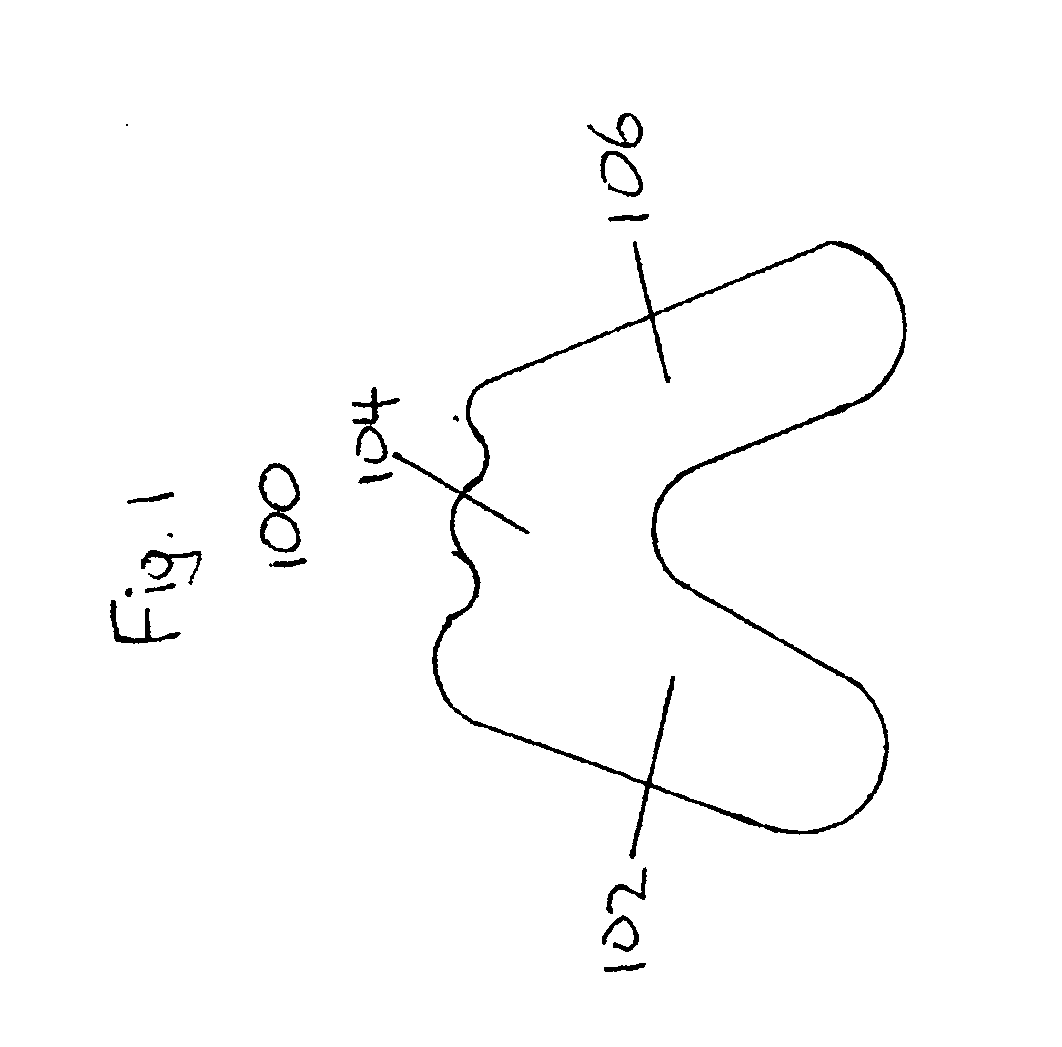
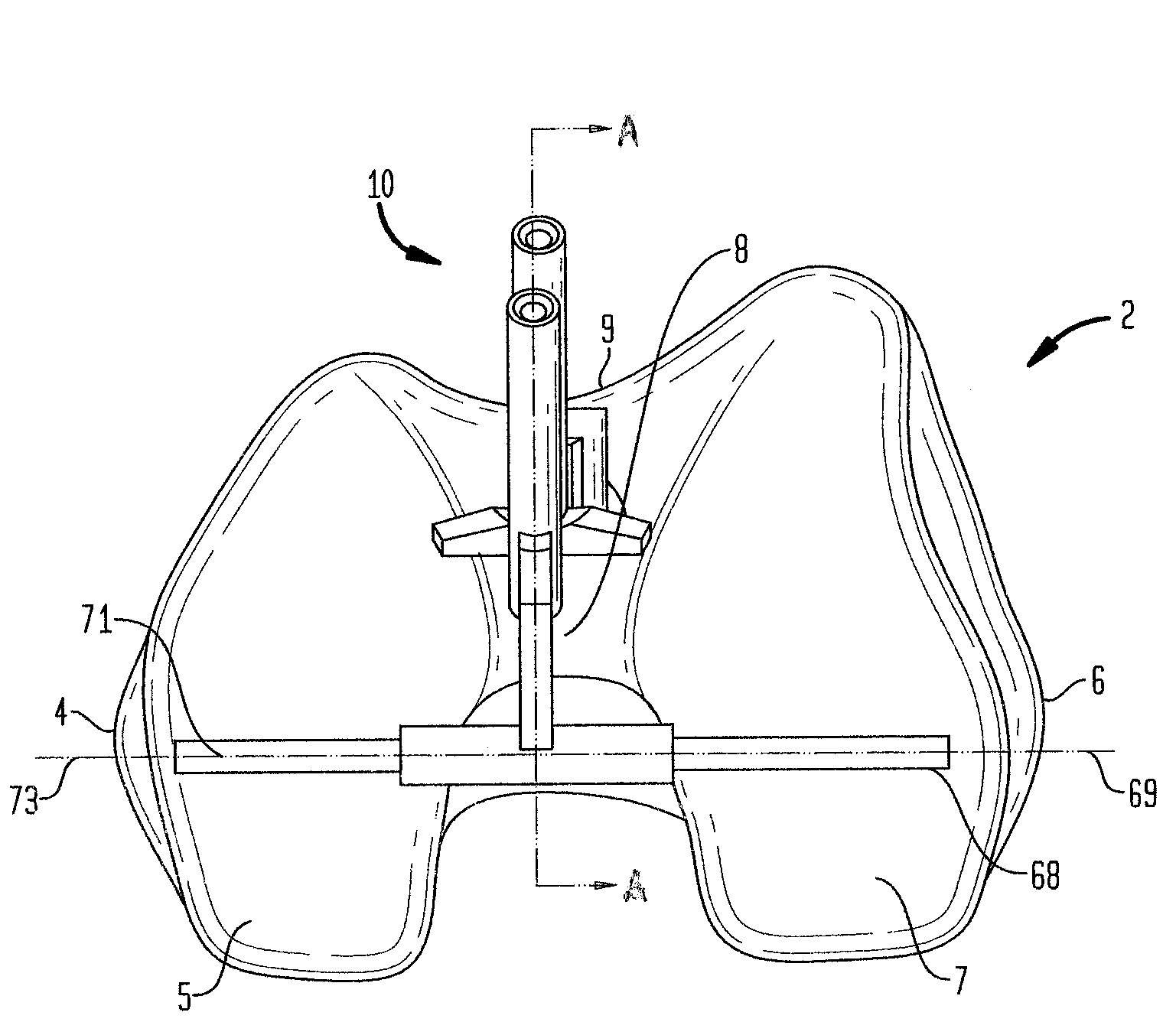
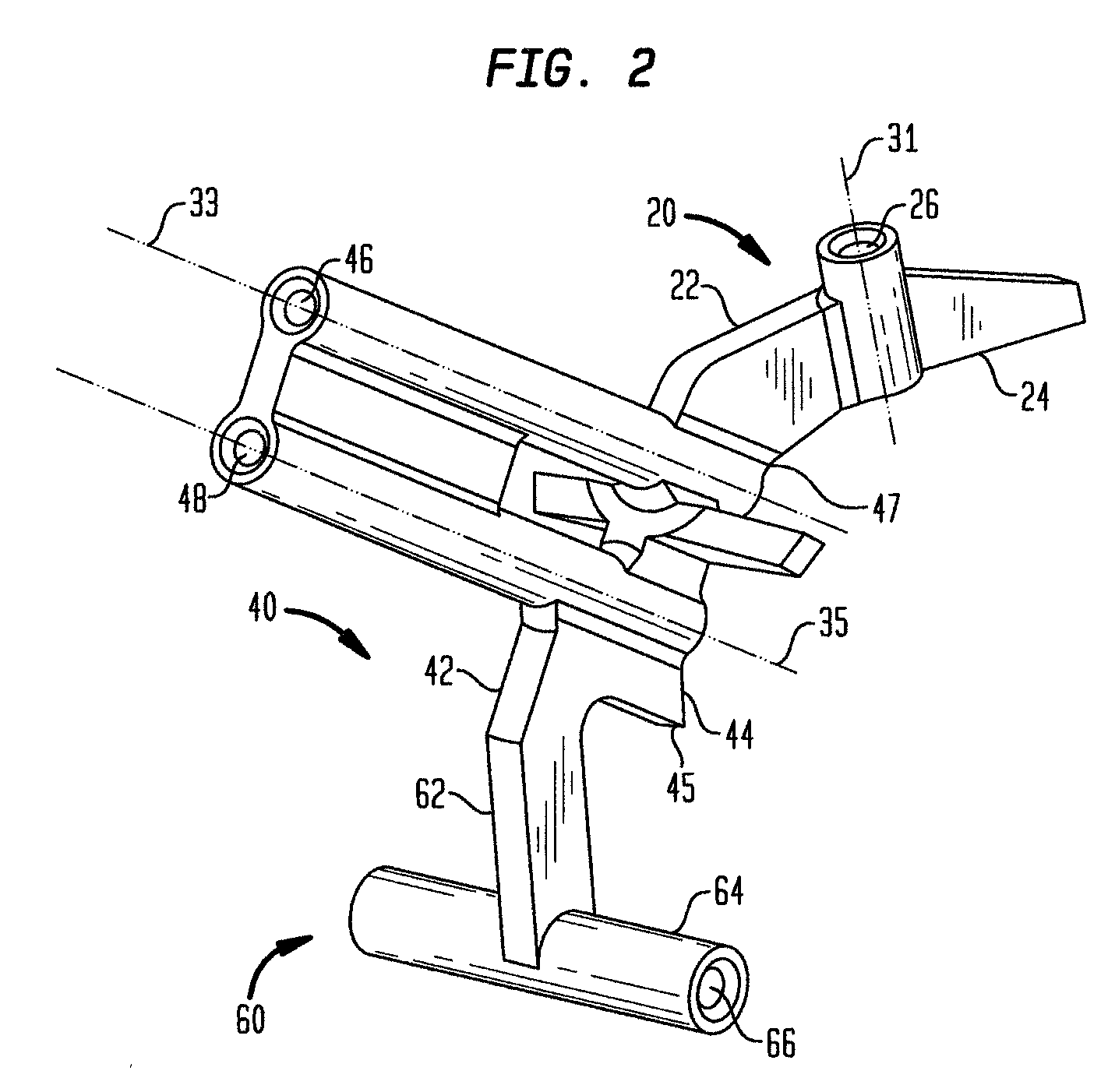
A method for replacing a joint surface, which includes resecting a first portion of the joint surface to create a wall surface and inner resected surface. The wall surface (2006) separates the inner resected surface and a non-resected portion of the joint surface. Further included in the method is cutting a concave groove having a first radius into the wall surface, and engaging the concave groove with a periphery of a joint prosthesis. The periphery includes a second radius that is substantially the same as the first radius of the concave groove.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Spot facing trochlear groove
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Spot facing trochlear groove
The present invention relates to systems and methods for preparing the trochlear groove of a patient's femur to receive a prosthesis thereon. In the system, a combination drill-and-alignment guide includes at least a proximal and intermediate section, and preferably also includes a distal section. Guide holes for receiving guide pins therein are located in the proximal and distal sections of the guide. After the guide is positioned using at least one of several visual and / or tactile references in the system, the guides pins are placed through the guide holes of the guide and into bone. The guide may then be removed and replaced by cannulated reamers that are rotated and used to resect a predetermined amount of bone around the guide pins. A prosthesis having at least a portion of an outer surface that substantially matches the trochlear groove of the patient in a pre-degenerated state is then implanted on the resected bone.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
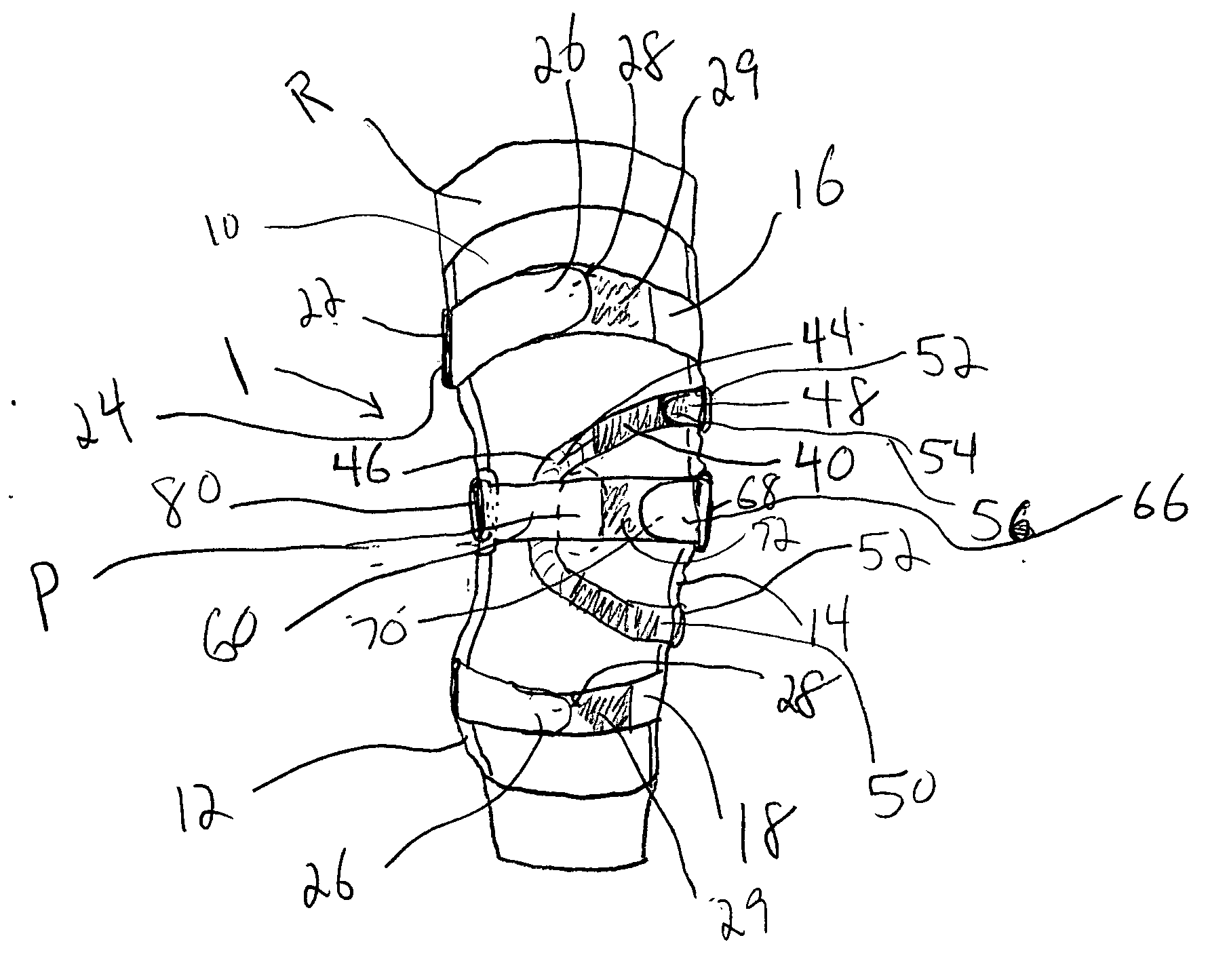
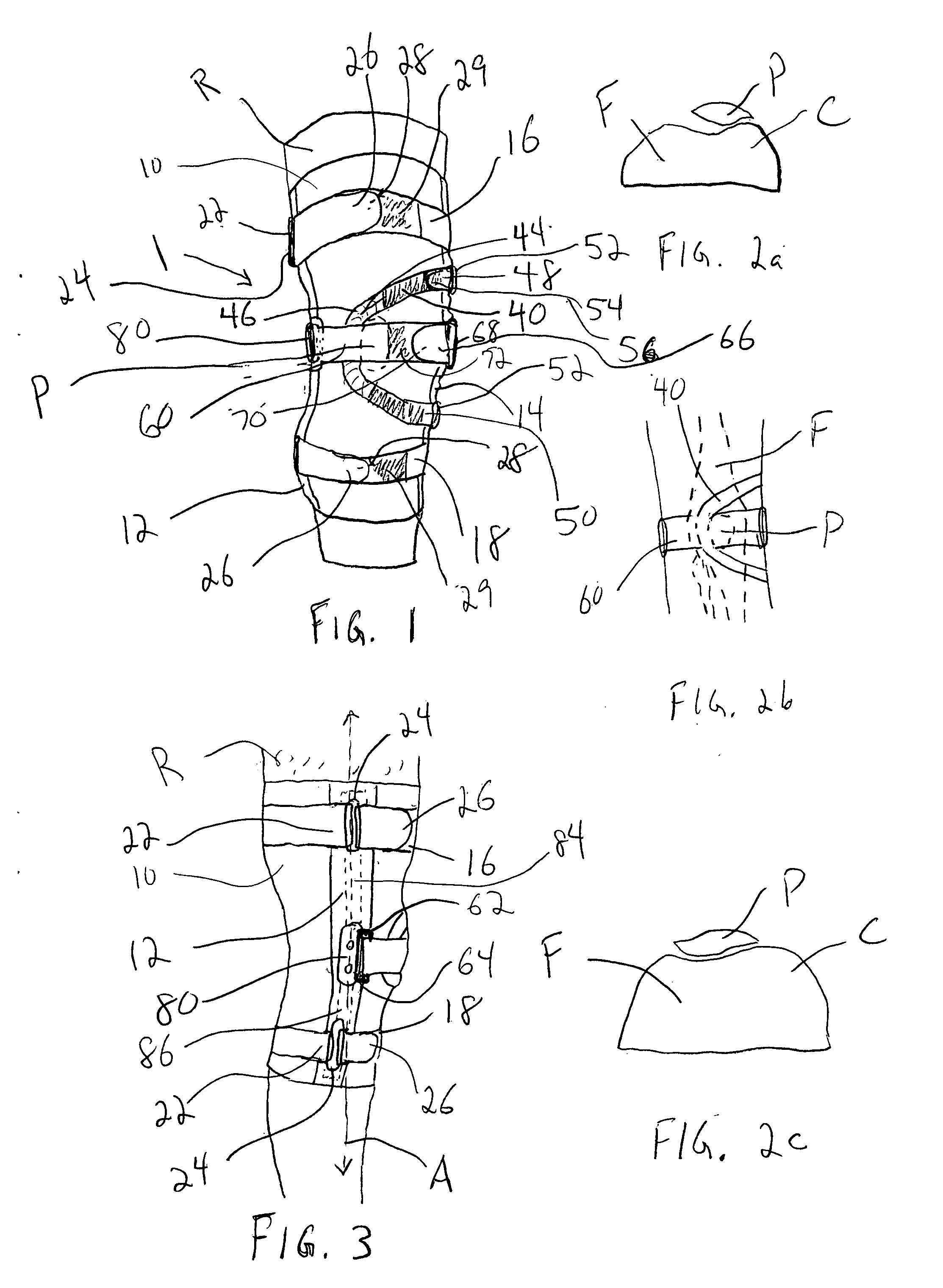
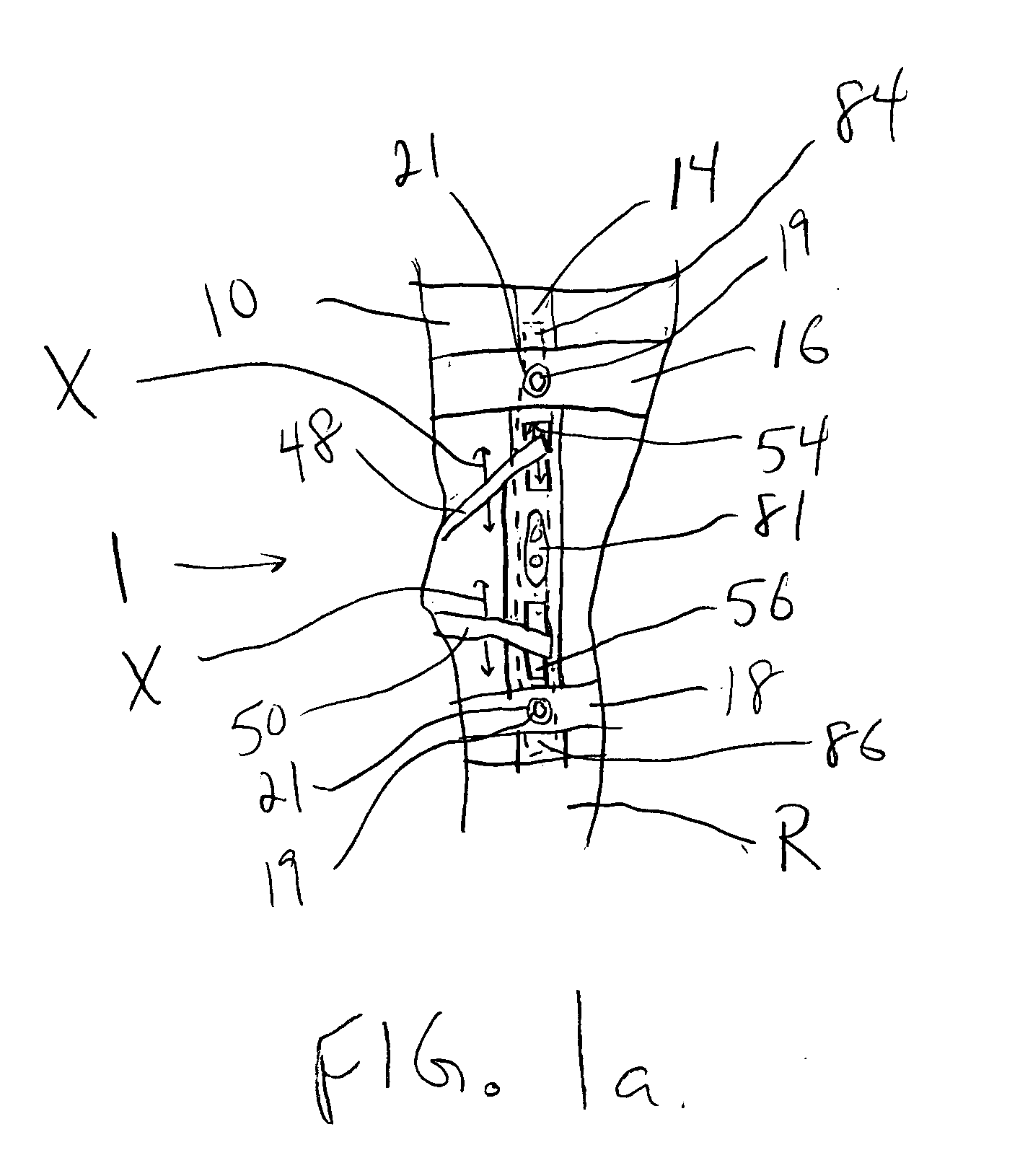
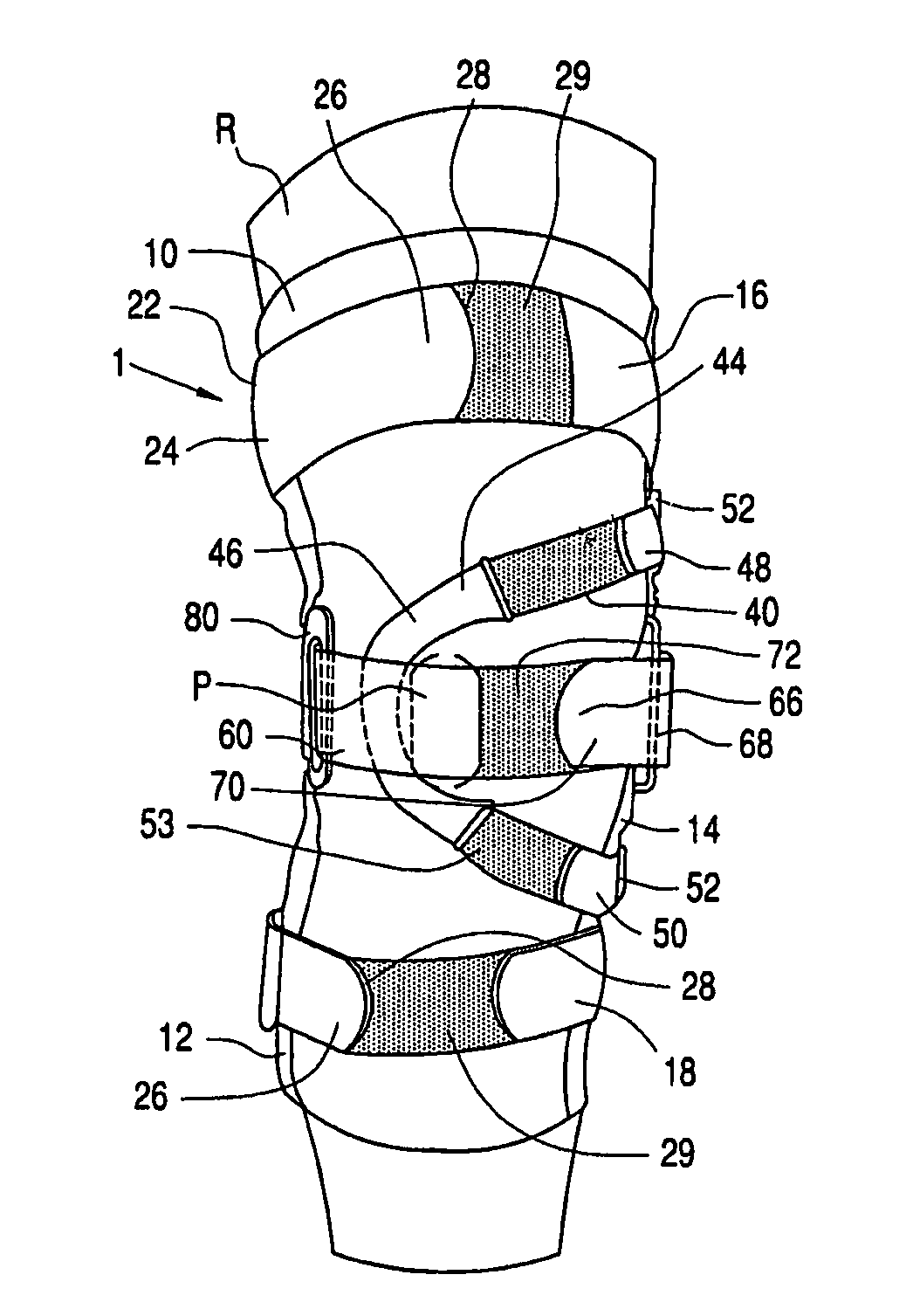
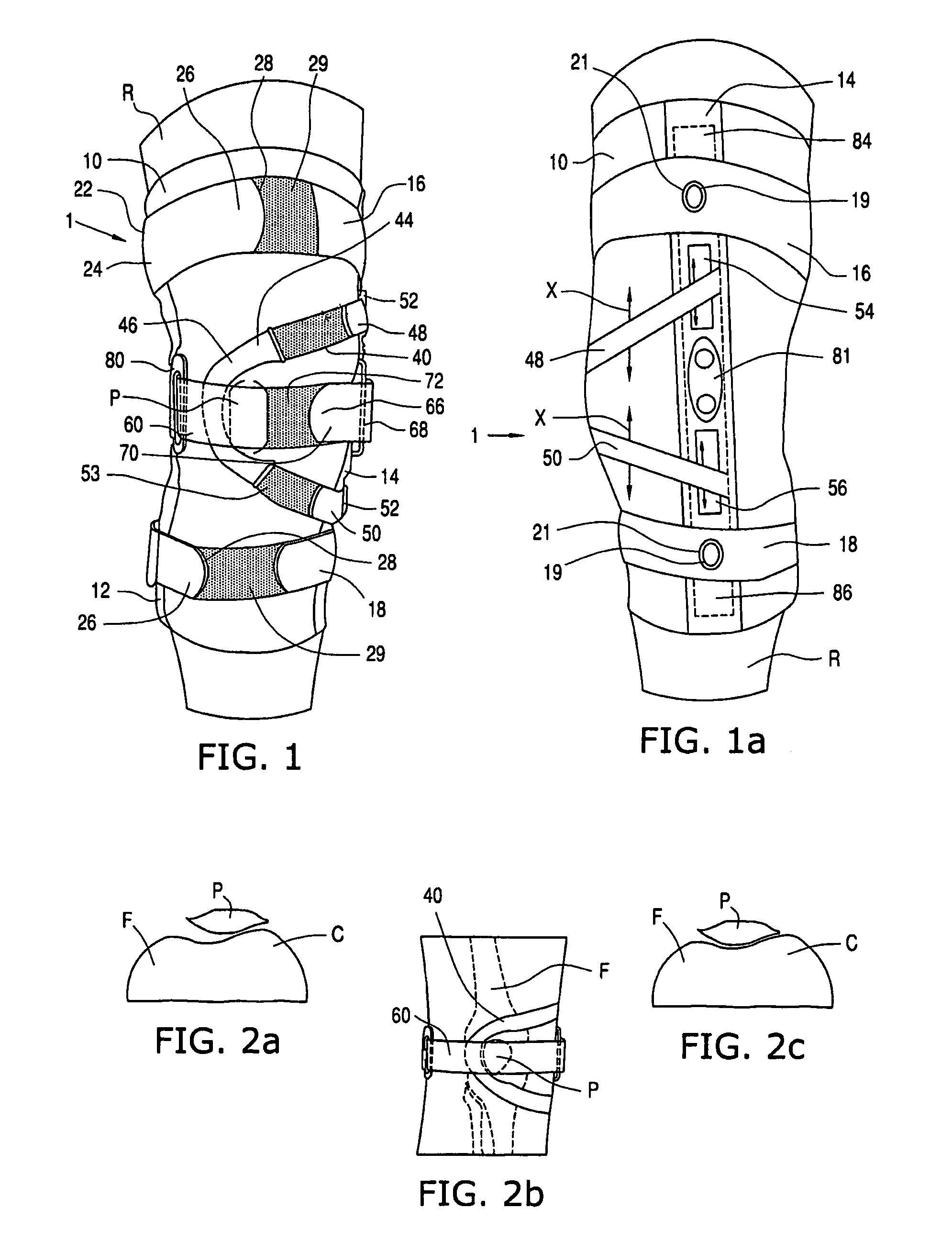
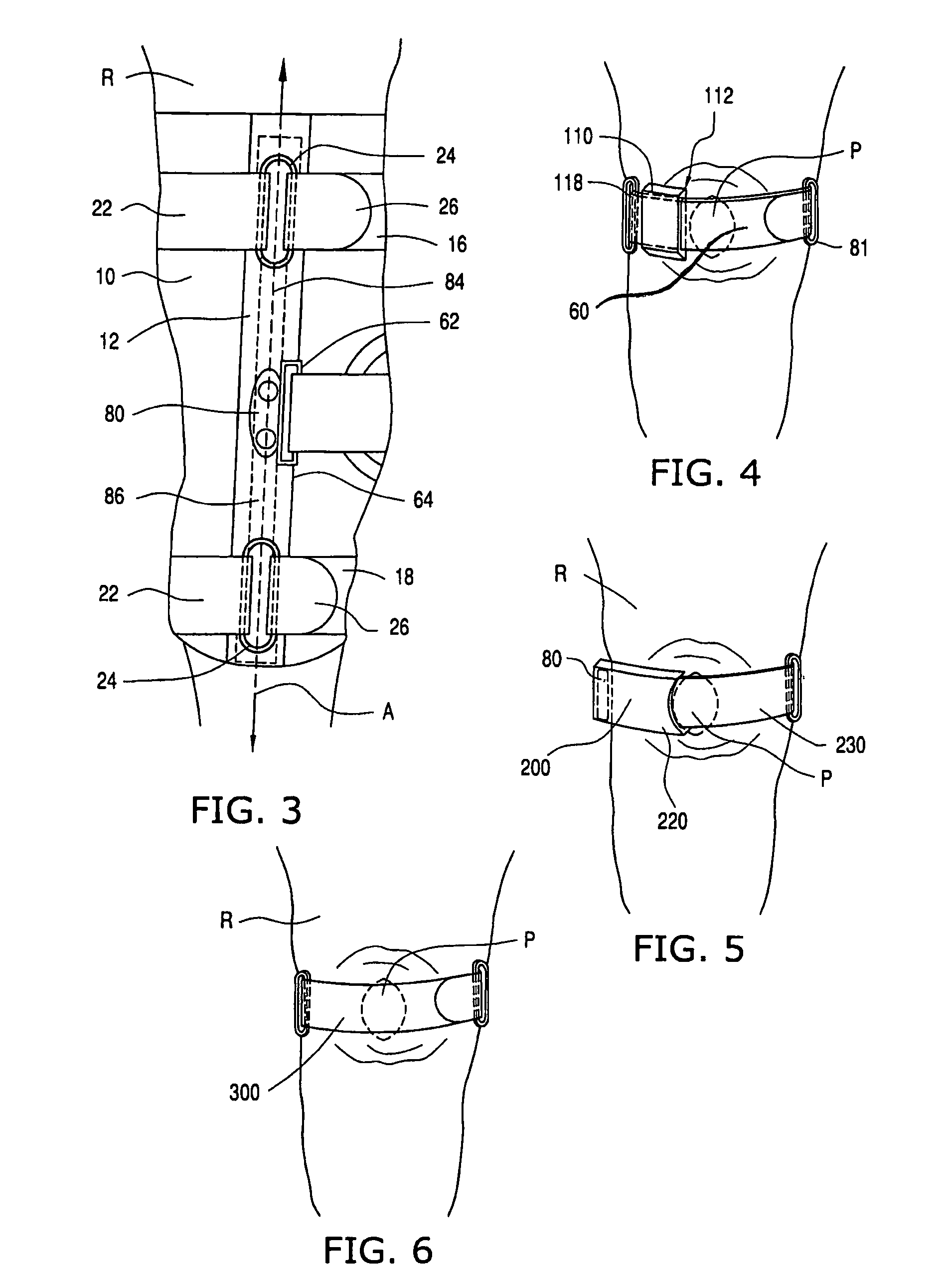
Knee orthosis and orthotic method
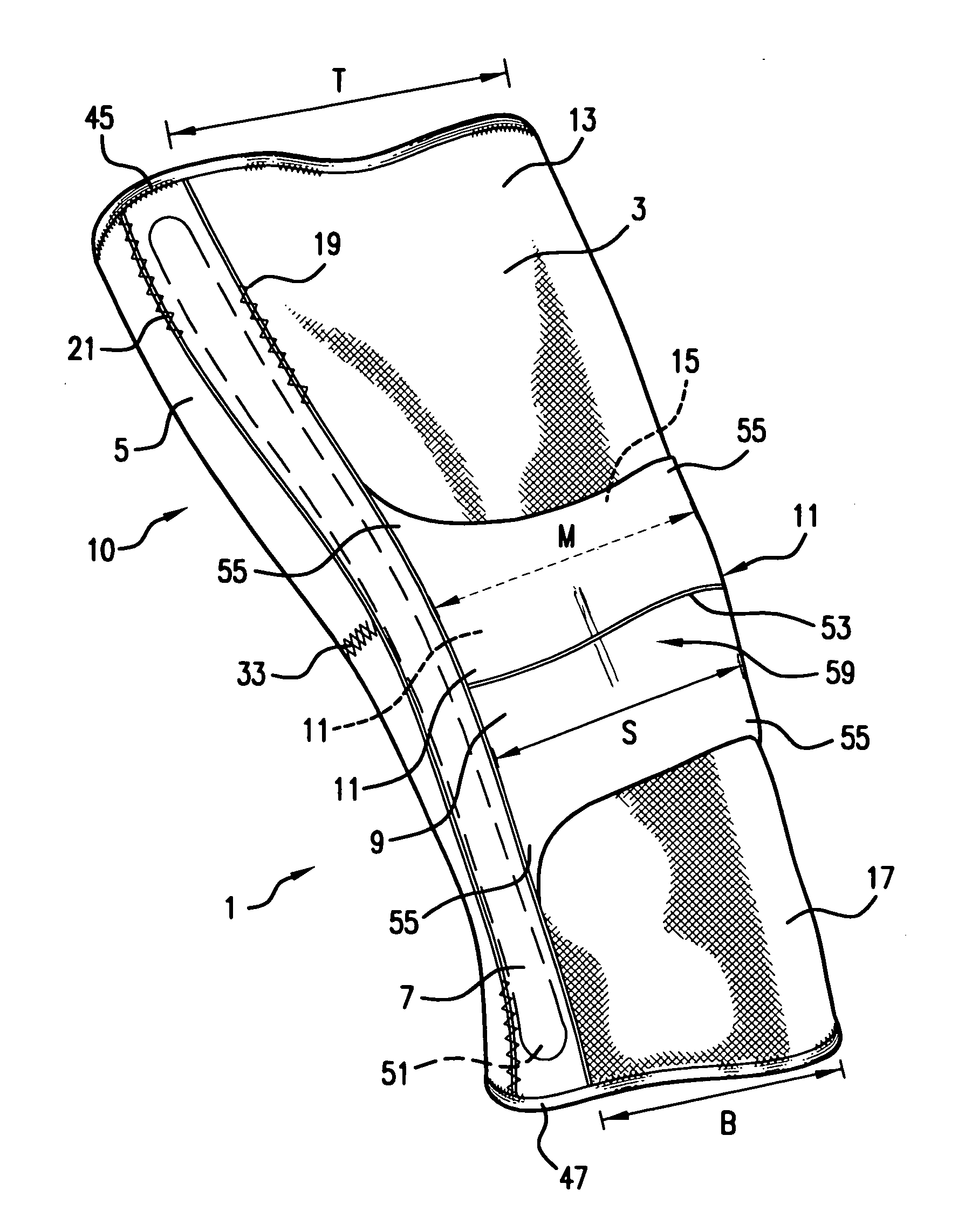
ActiveUS20050203455A1Increased contact surface areaNon-surgical orthopedic devicesStretch exerciseConnective tissue fiber
A knee orthosis that includes a medial tracking member that operatively fits along a lateral side of, and provides medial traction to, a patella having patellofemoral articular tissue; an inward tracking member that operatively fits over, and provides inward pressure against, the patella; wherein the inward tracking member provides a compressive force against the patella, thereby increasing the contact surface area between the patellofemoral articular tissue and an associated femoral trochlear groove. The inward tracking member overlays the patella and the medial tracking member so that medial traction can be placed on the patella. The inward tracking member provides continued compressive force against the patella to stretch lateral connective tissue, throughout a full extension motion of an associated knee, and the continuous compressive force is substantially the same throughout the extension motion. An orthotic method for correcting patellofemoral joint disorders is also disclosed.
Owner:CROPPER DEAN E
Anatomically guided instrumentation for trochlear groove replacement
A system for replacing a trochlear groove region of a femur. The system includes a prosthesis that includes a bone contact surface and a periphery that defines an outer perimeter. The bone contact surface has a plurality of protrusions and a spatial configuration with respect to one another. Additionally, the system includes a first template that has a plurality of guide holes and a first periphery that defines an outer perimeter that substantially corresponds with the periphery of the prosthesis. Also, included in the system is a second template that has a plurality of guide holes and a second periphery that defines an outer perimeter that substantially corresponds with the periphery of the prosthesis. The plurality of guide holes of the second template are spatially arranged with respect to the second periphery to substantially match the spatial configuration of the plurality of protrusions of the prosthesis.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Device and method for externally rotating the femur
ActiveUS20070219478A1Light weightImprove lower-extremity mechanicsDiagnosticsRestraining devicesPelvic regionPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An elongate flexible strap is adapted to be wrapped about a wearer's leg and pelvic region. The strap applies a torque to the leg, rotating the leg into a desired degree of external rotation. In a leg having an improperly aligned patella, it is believed that the external rotation improves lower extremity mechanics by aligning the patella within the trochlear groove.
Owner:DJO
Posterior cruciate ligament protection device for total knee replacement
The invention relates to a posterior cruciate ligament protection device for total knee replacement. The posterior cruciate ligament protection device is characterized by comprising a handle, wherein one end of the handle is fastened and connected with an auxiliary plate; the inner surface of the auxiliary plate is of an arc-shaped structure; one end, far away from the handle, of the auxiliary plate is fastened and connected with a fixed protection plate; the inner surface of the fixed protection plate is provided with a groove structure; and the end part, far away from the auxiliary plate, of the fixed protection plate is provided with a cutting edge. One end of the handle is fastened and connected with the auxiliary plate for covering a thighbone trochlear groove, and the fixed protection plate inserted into the tibial plateau sclerotin is fastened and connected into a position, far away from the handle, of the auxiliary plate, so that in the use process, the tibial plateau can be forwards pushed out relative to the thighbone by using the lever principle; and the convenience is brought to osteotomy. The inner surface of the fixed protection plate is provided with the groove structure, so that the posterior cruciate ligament and the posterior cruciate ligament bottom dead center can be covered and protected, and the posterior cruciate ligament tibial lateral bottom dead center avulsion fracture in and after the operation can be prevented.
Owner:BEIJING CHAOYANG HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Knee orthosis and orthotic method
ActiveUS8926539B2Increased contact surface areaFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisPatellofemoral Joints
A knee orthosis that includes a medial tracking member that operatively fits along a lateral side of, and provides medial traction to, a patella having patellofemoral articular tissue; an inward tracking member that operatively fits over, and provides inward pressure against, the patella; wherein the inward tracking member provides a compressive force against the patella, thereby increasing the contact surface area between the patellofemoral articular tissue and an associated femoral trochlear groove. The inward tracking member overlays the patella and the medial tracking member so that medial traction can be placed on the patella. The inward tracking member provides continued compressive force against the patella to stretch lateral connective tissue of the patella, throughout a full extension or flexion motion of an associated knee, and the continuous compressive force is substantially the same throughout the extension or flexion motion. An orthotic method for correcting patellofemoral joint disorders is also disclosed.
Owner:CROPPER DEAN E
Patellofemoral joint prosthesis and manufacture method thereof
PendingCN108403263AHigh activityAvoid collisionJoint implantsKnee jointsPatella prosthesisPatellofemoral joint prosthesis
The invention relates to the field of medical devices, and discloses a patellofemoral joint prosthesis and a manufacture method thereof. The patellofemoral joint prosthesis comprises a femur trochleaprosthesis body and a patella prosthesis body, wherein the femur trochlea prosthesis body comprises an internal condyle, an external condyle and a trochlear groove. The internal condyle and the external condyle are located on the two sides of the femur trochlea prosthesis body, and the trochlear groove is connected with the internal condyle and the external condyle, wherein the internal condyle and the external condyle are in cambered connection with the trochlear groove at different curvature radii, so that the junction surface formed by the internal condyle, the external condyle and the trochlear groove together forms a cooperative curved surface which cooperates with the patella prosthesis body. The femur trochlea prosthesis body further comprises a fixing surface which is formed on thefemur trochlea prosthesis body and is opposite to the cooperative curved surface, and a fixing assembly is formed on the fixing surface. The patella prosthesis body comprises a curved joint surface which cooperates with the cooperative curved surface, the top view of the section of the curved joint surface is elliptical, the front view of the section is in an unsymmetrical parabolic shape, and aconnection column is formed on the face, opposite to the curved joint surface, of the patella prosthesis body. The patellofemoral joint prosthesis is more suitable for Chinese in use.
Owner:BEIJING CHUNLIZHENGDA MEDICAL INSTR +1
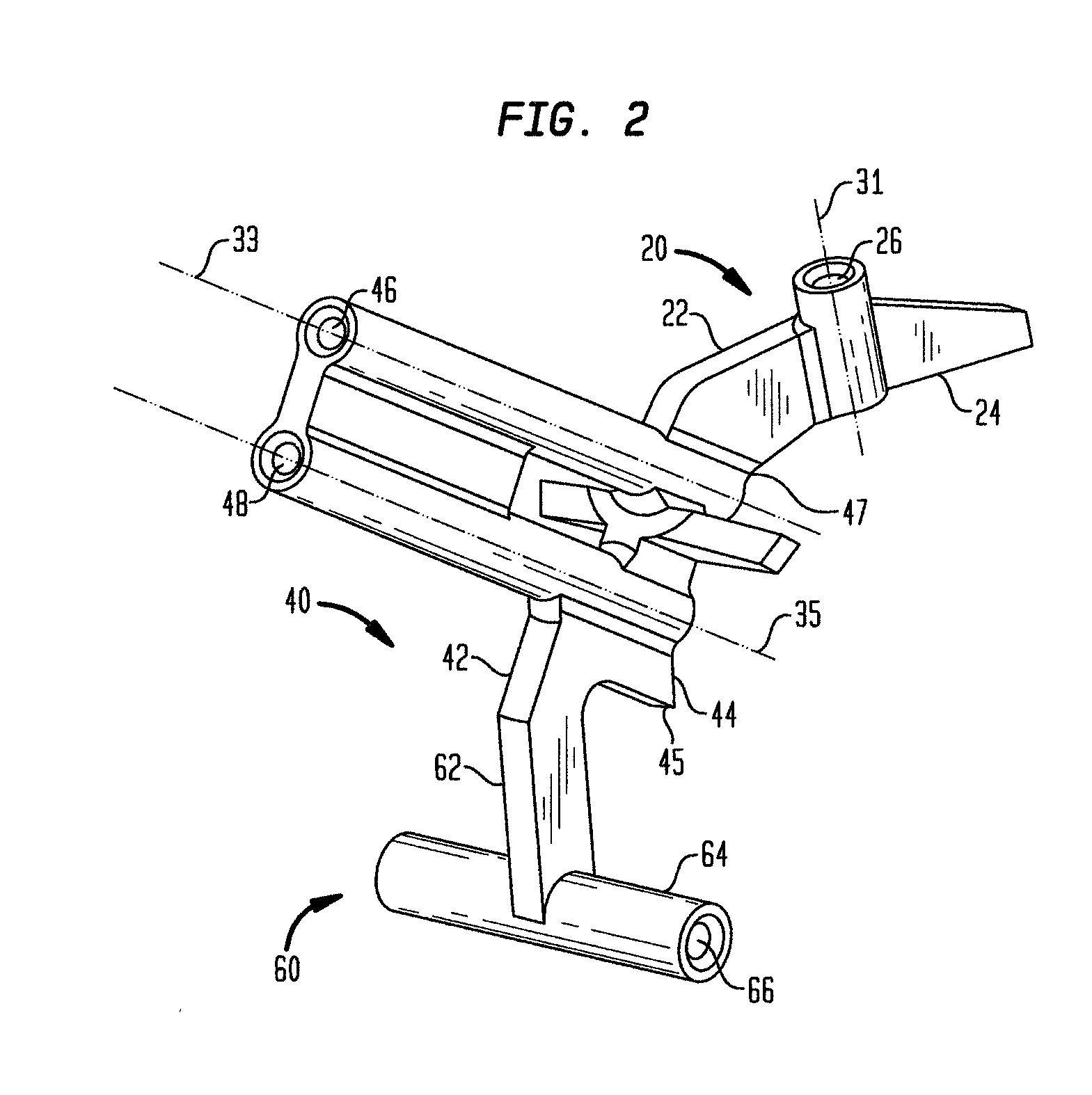
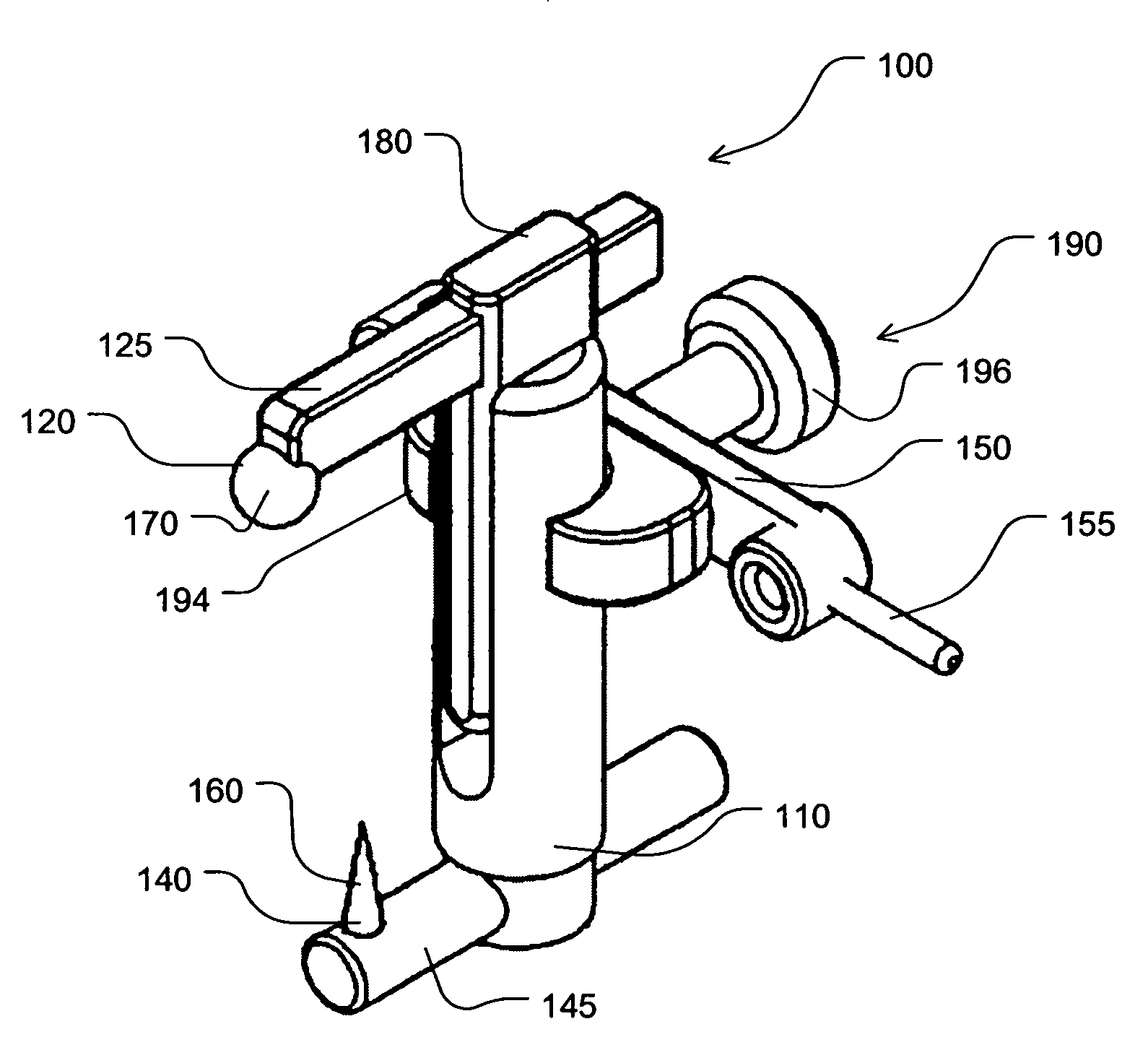
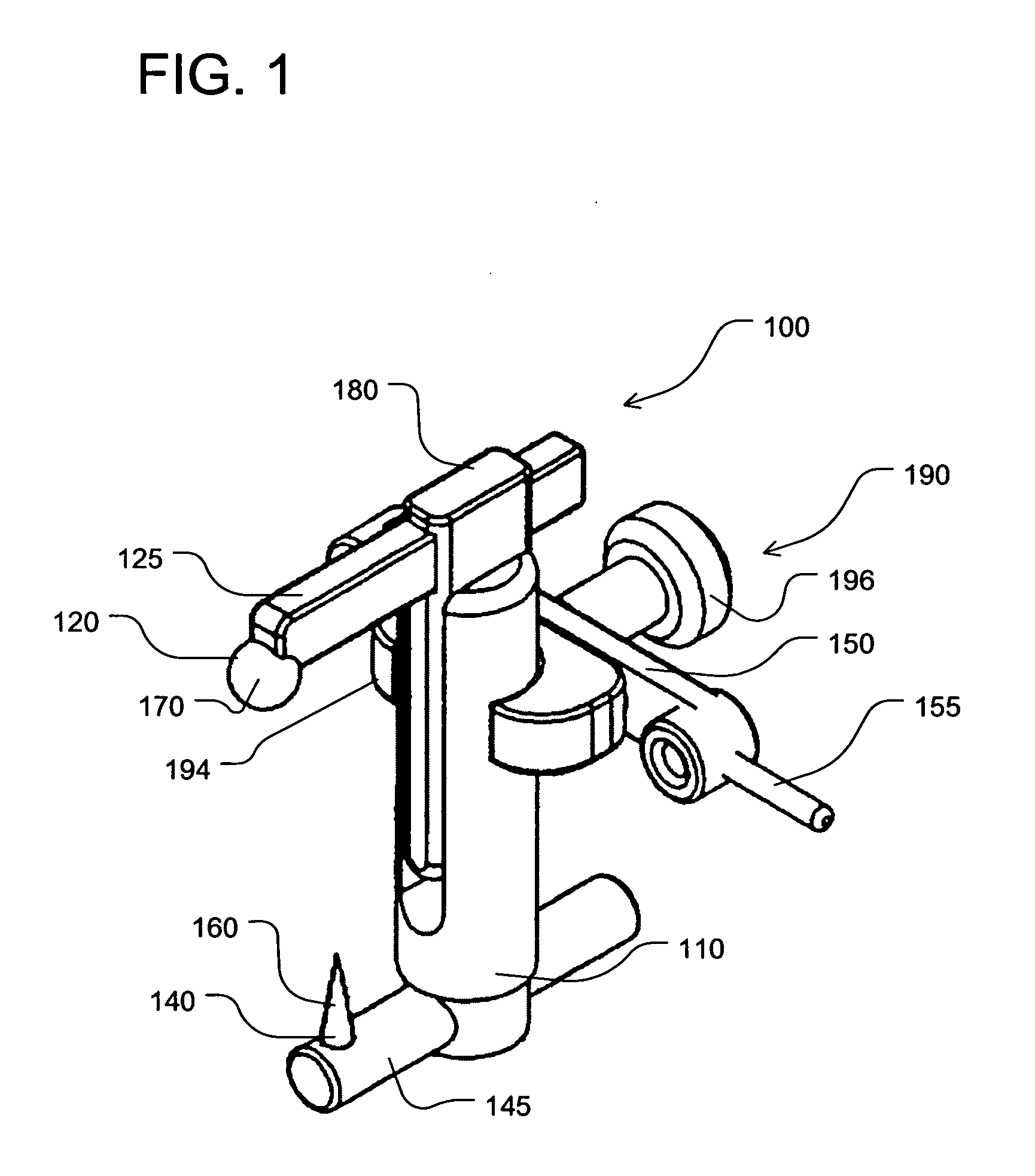
Device and method for locating the anteroposterior femoral axis to determine proper femoral component rotation in knee replacement
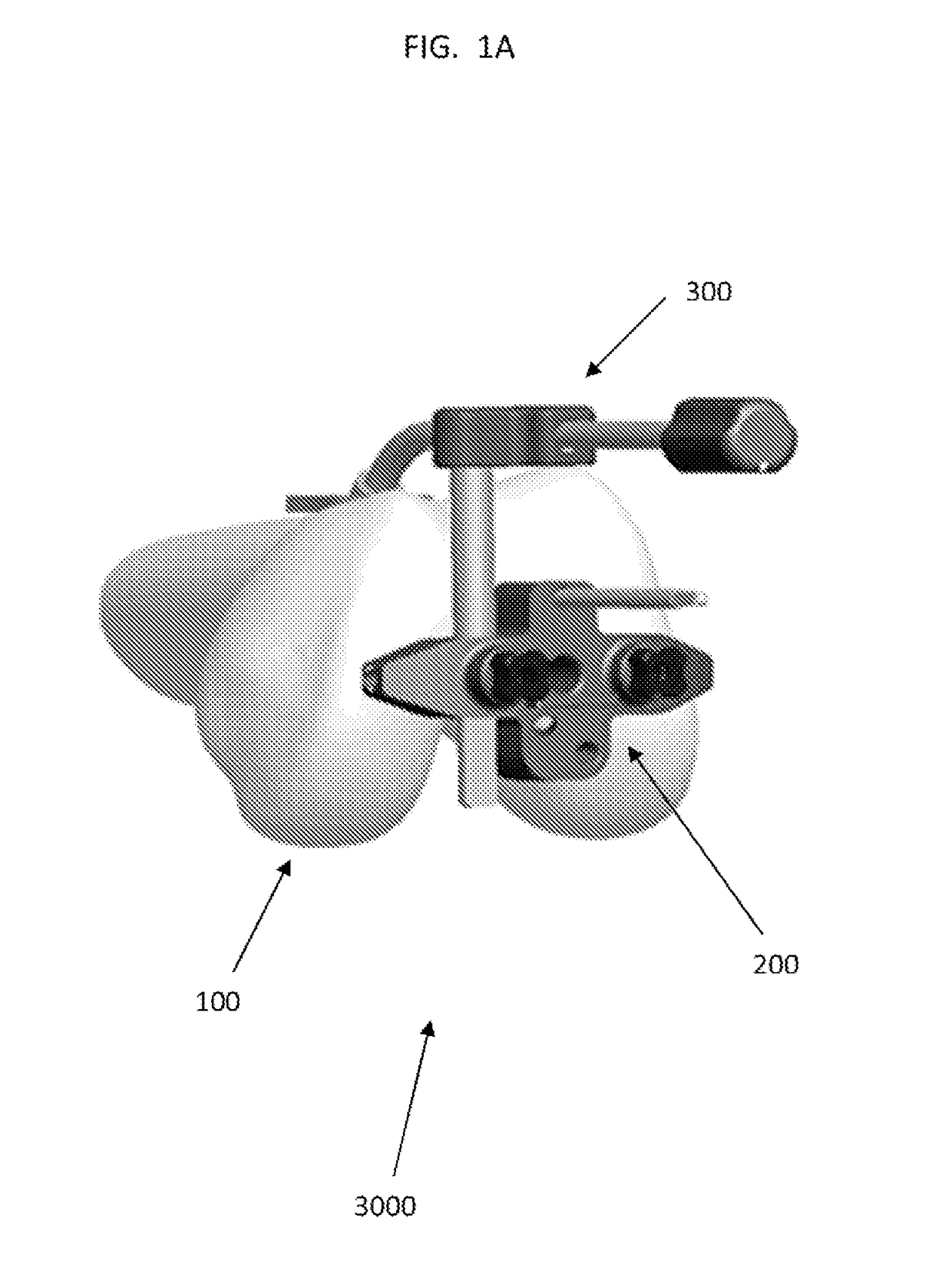
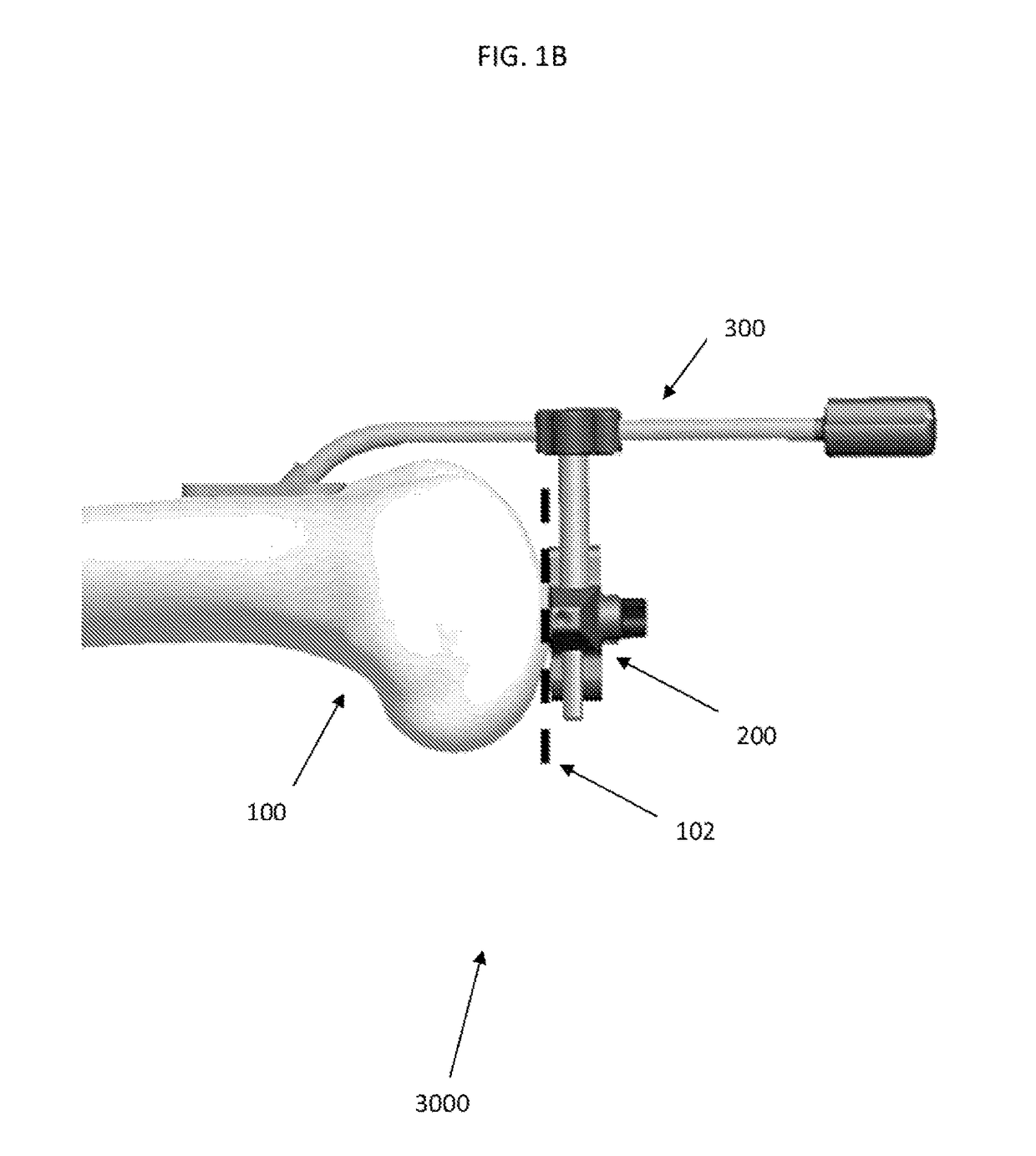
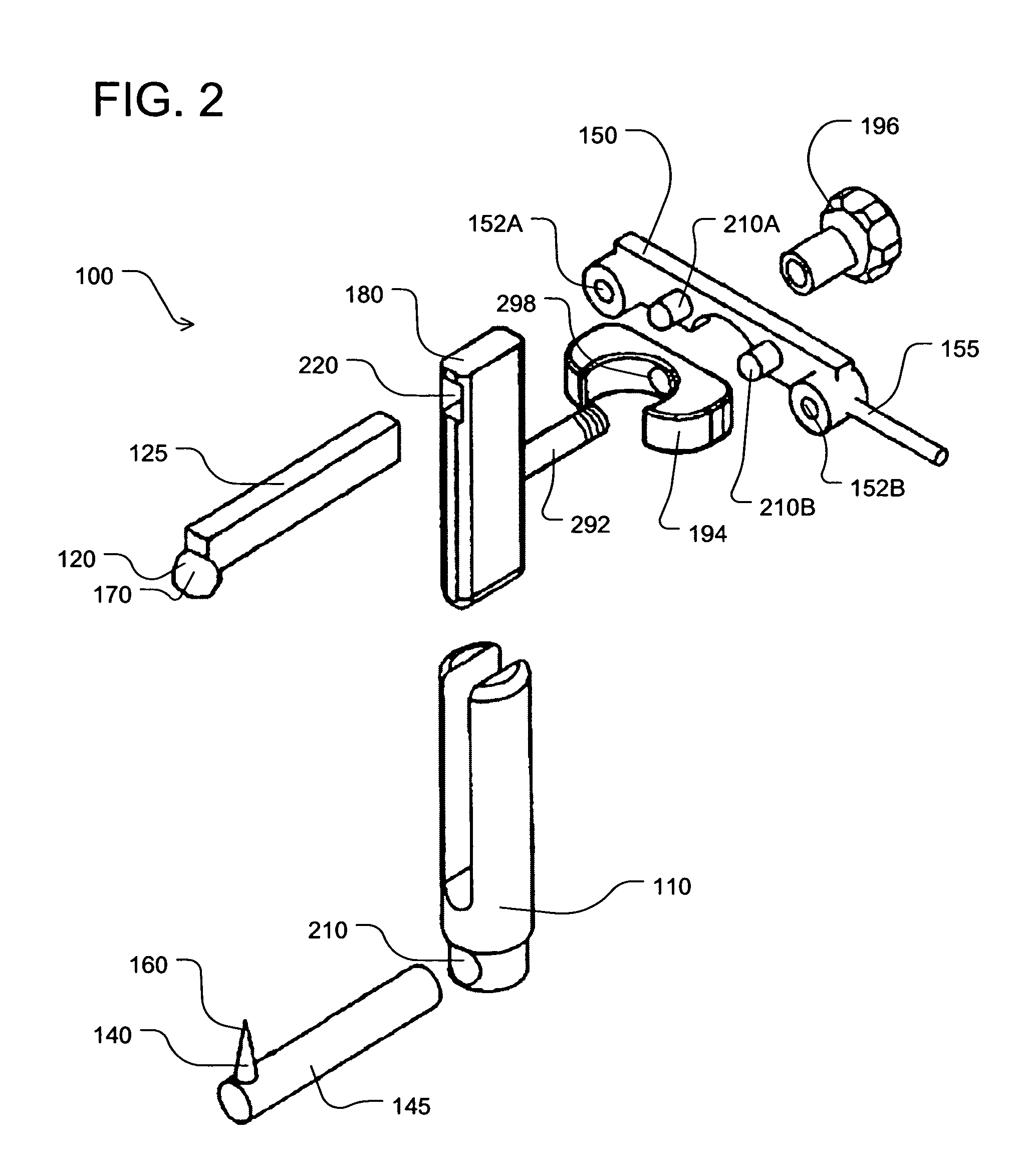
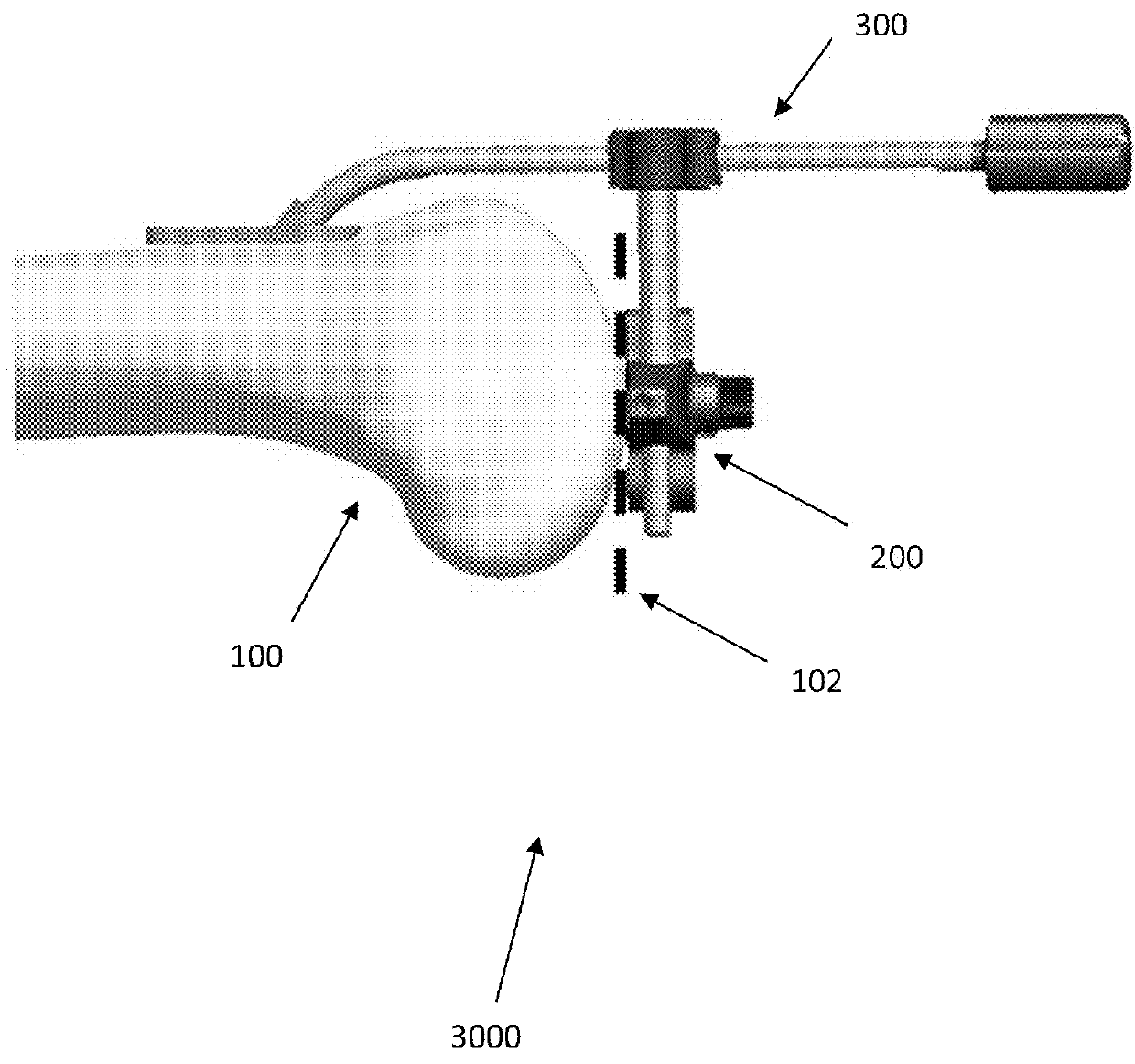
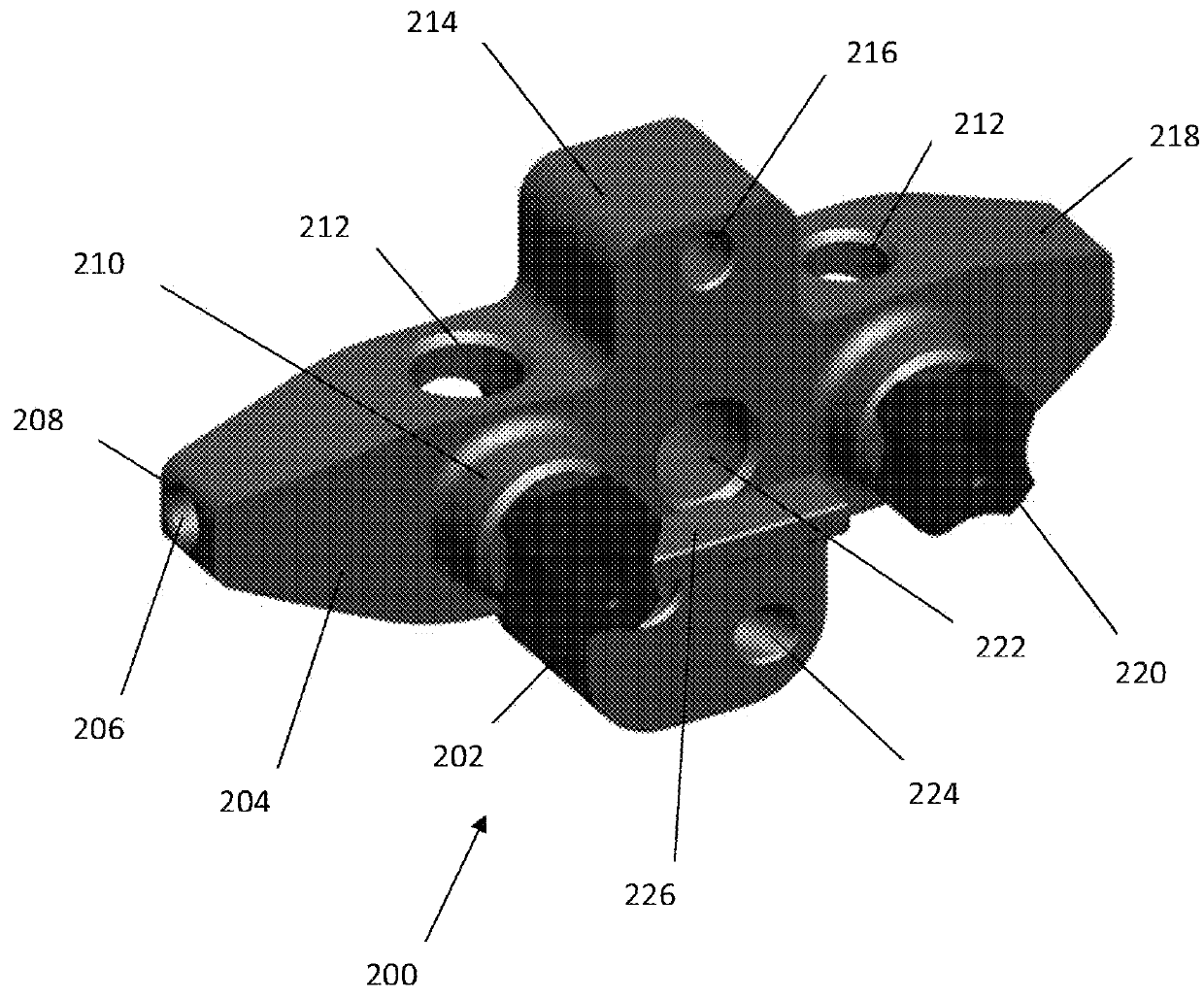
A device for indicating the location of the anteroposterior femoral axis has a spike or needle that engages the anterior-most point in the intercondylar notch and a rounded or spherical surface is placed on the trochlear groove of the femur and urged in a posterior direction. That is, the rounded surface or ball is urged toward the bottom of the trochlear groove. This causes the rounded surface or ball to self-locate into the deepest point of the trochlear groove. The anterior-most point in the intercondylar notch and the deepest part of the trochlear groove anteriorly are points that accurately determine the anteroposterior femoral axis, and the device includes a marking device or guide member that is fixed perpendicular to this axis. A surgeon, therefore, has an accurate indication of the correct femoral component rotation for proper implant position in a knee replacement or other surgical procedure.
Owner:ARTHROPLASTY INNOVATIONS
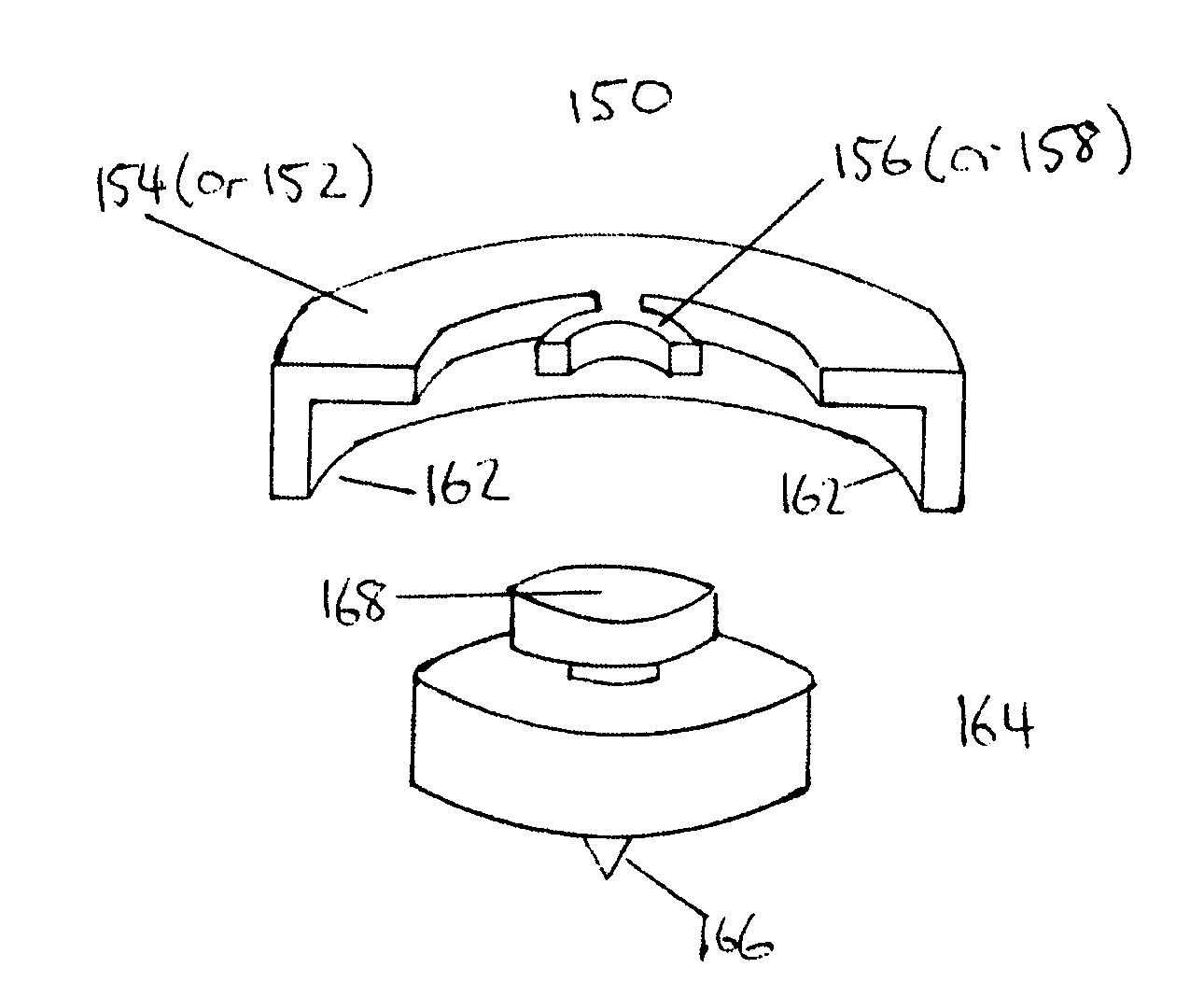
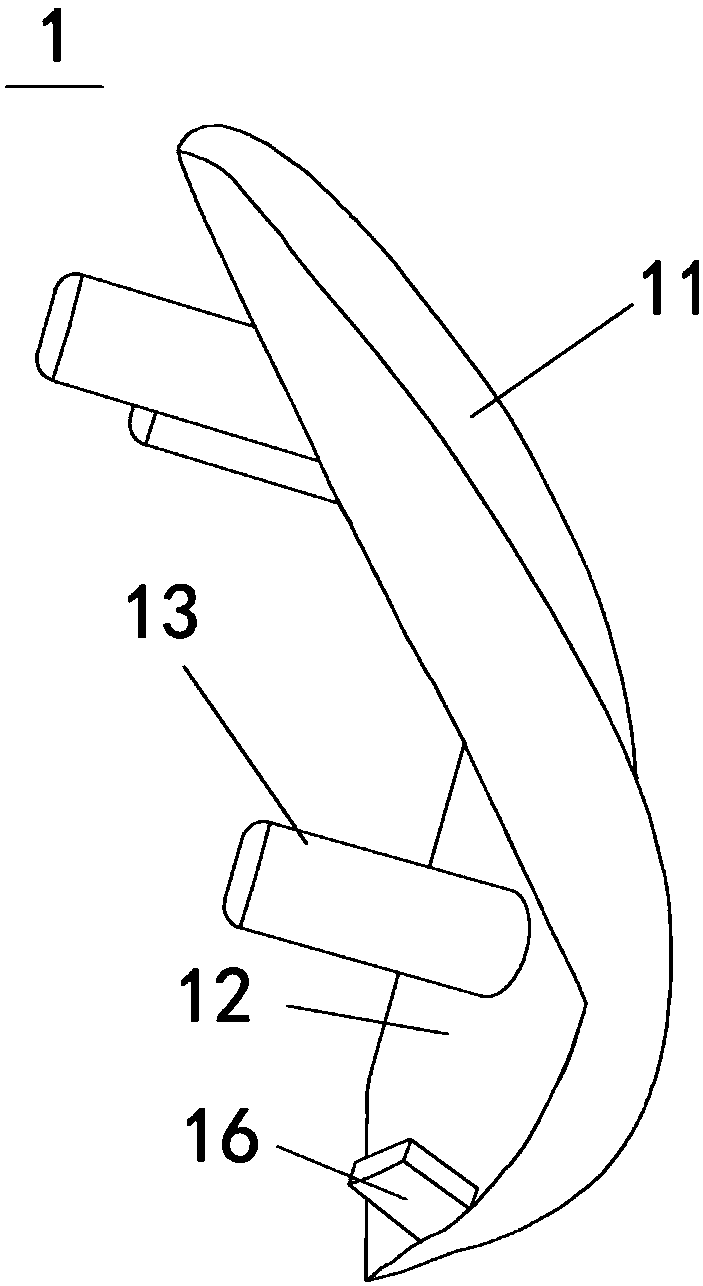
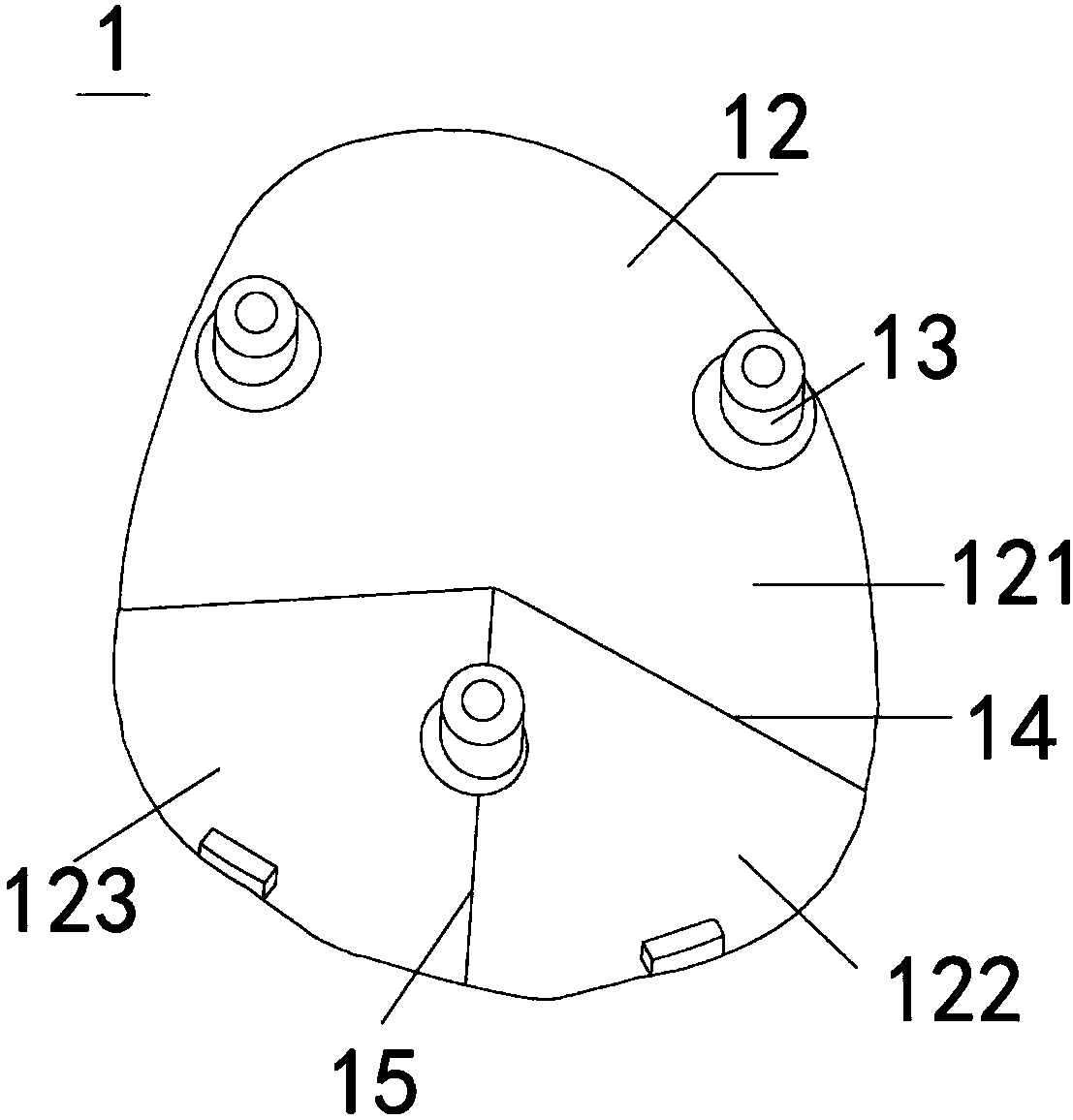
Trochlear groove prosthesis
A trochlear groove prosthesis includes a base plate and cap. The base plate and cap are shaped to correspond to the shape of the trochlear groove. A cut is made in the femur to remove the worn or damaged trochlear groove. The base plate is attached to the cut portion of the femur. The cap is mated with the base plate. The prosthesis and procedure provide a properly shaped prosthesis with a single planar cut of the femur.
Owner:KYON
Anatomically guided instrumentation for trochlear groove replacement
A method for replacing a joint surface, which includes resecting a first portion of the joint surface to create a wall surface and inner resected surface. The wall surface (2006) separates the inner resected surface and a non-resected portion of the joint surface. Further included in the method is cutting a concave groove having a first radius into the wall surface, and engaging the concave groove with a periphery of a joint prosthesis. The periphery includes a second radius that is substantially the same as the first radius of the concave groove.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Anatomically guided instrumentation for trochlear groove replacement
A system for replacing a trochlear groove region of a femur. The system includes a prosthesis that includes a bone contact surface and a periphery that defines an outer perimeter. The bone contact surface has a plurality of protrusions and a spatial configuration with respect to one another. Additionally, the system includes a first template that has a plurality of guide holes and a first periphery that defines an outer perimeter that substantially corresponds with the periphery of the prosthesis. Also, included in the system is a second template that has a plurality of guide holes and a second periphery that defines an outer perimeter that substantially corresponds with the periphery of the prosthesis. The plurality of guide holes of the second template are spatially arranged with respect to the second periphery to substantially match the spatial configuration of the plurality of protrusions of the prosthesis.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Trochlear groove prosthesis
Owner:KYON
Osteotomy device
The invention relates to an osteotomy device, which comprises an osteotomy plate, a fixing plate and an adjusting structure. The osteotomy plate is mounted on the femur through the fixing plate, and two ends of the adjusting structure are respectively connected with the fixing plate and the osteotomy plate. The osteotomy plate slides to the left and right by the adjustment structure relative to the fixing plate; and the osteotomy plate has a femur osteotomy groove for four-sided osteotomy and a femur trochlear osteotomy groove for the femur trochlear osteotomy. By using the osteotomy device, the femur trochlear osteotomy can be continued without replacing the osteotomy plate after the four-sided osteotomy operation, which effectively reduces the number of instruments, avoids repeated disassembly and assembly, and simplifies the operation steps; the osteotomy device can conveniently adjust the left and right sliding of the osteotomy plate relative to the fixing plate by using the adjustment structure, and then adjust the osteotomy plate to the femur trochlear groove facing to the femur trochlear. The osteotomy accuracy of the femur trochlear is increased, and the influence of the abnormal sliding trajectory of the kneecap after the restoration of the prosthesis due to the inaccurate osteotomy position of the femur trochlear can be avoided.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROPORT ORTHORECON CO LTD
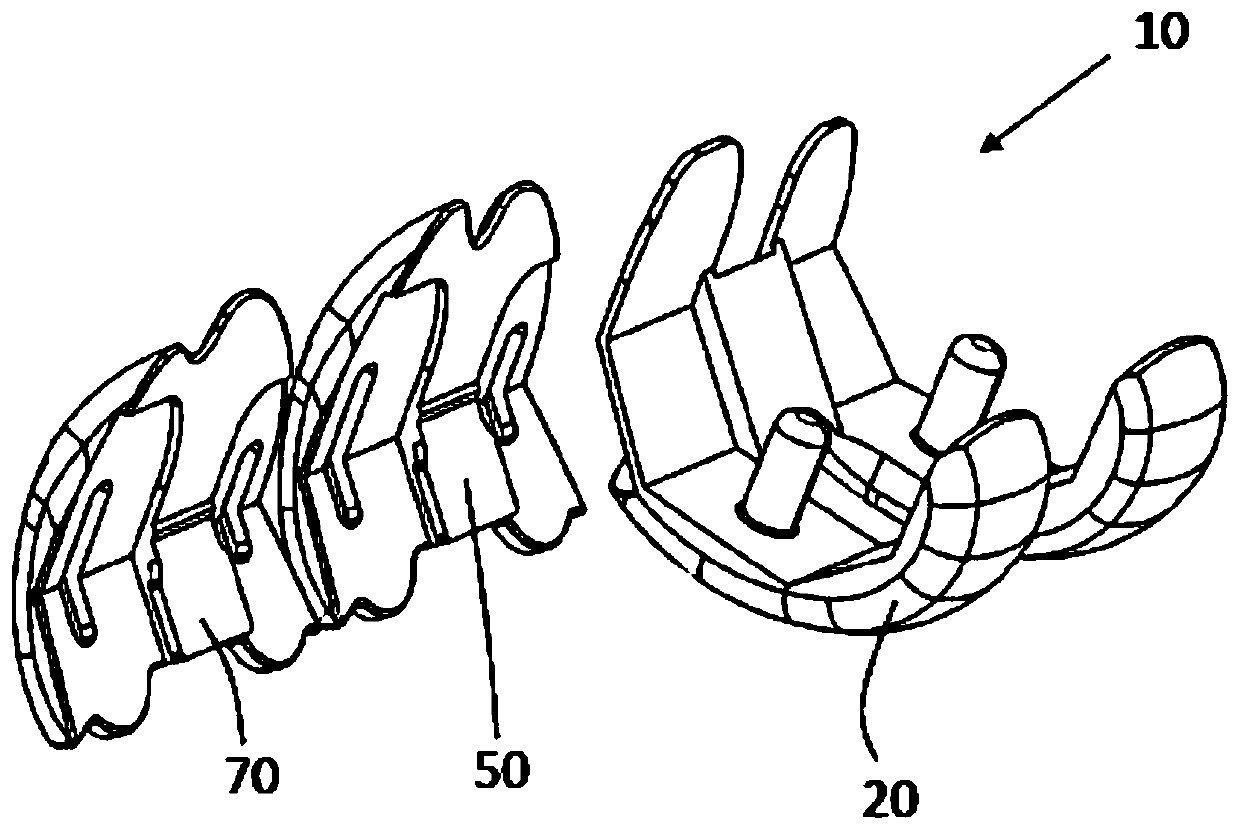
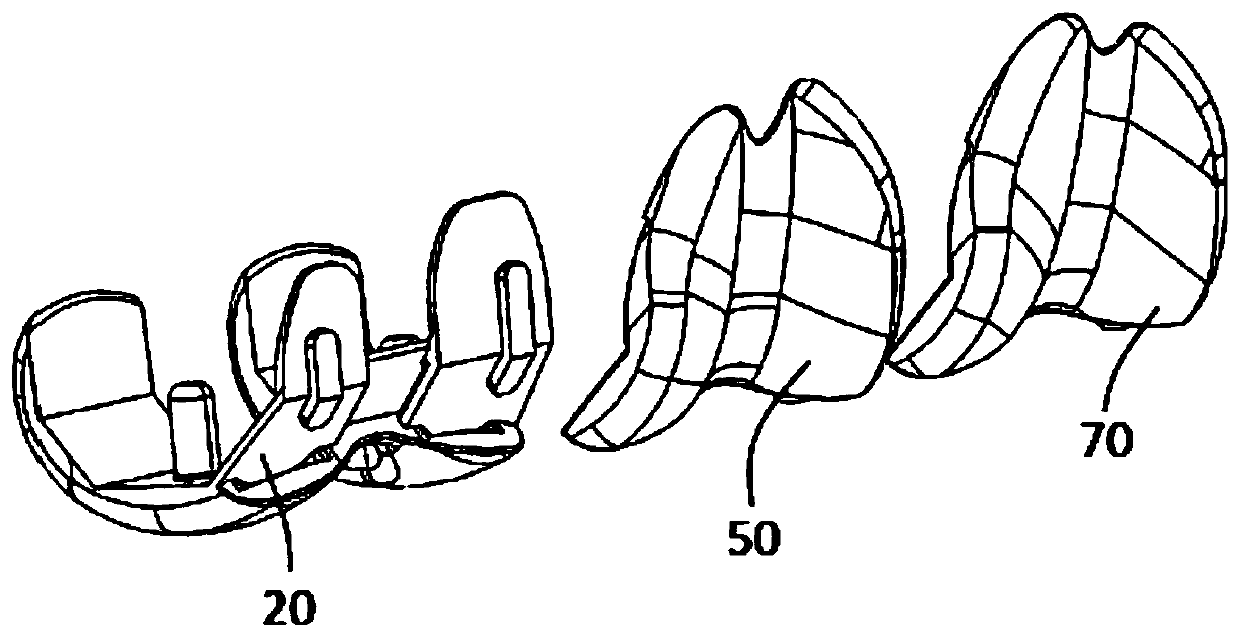
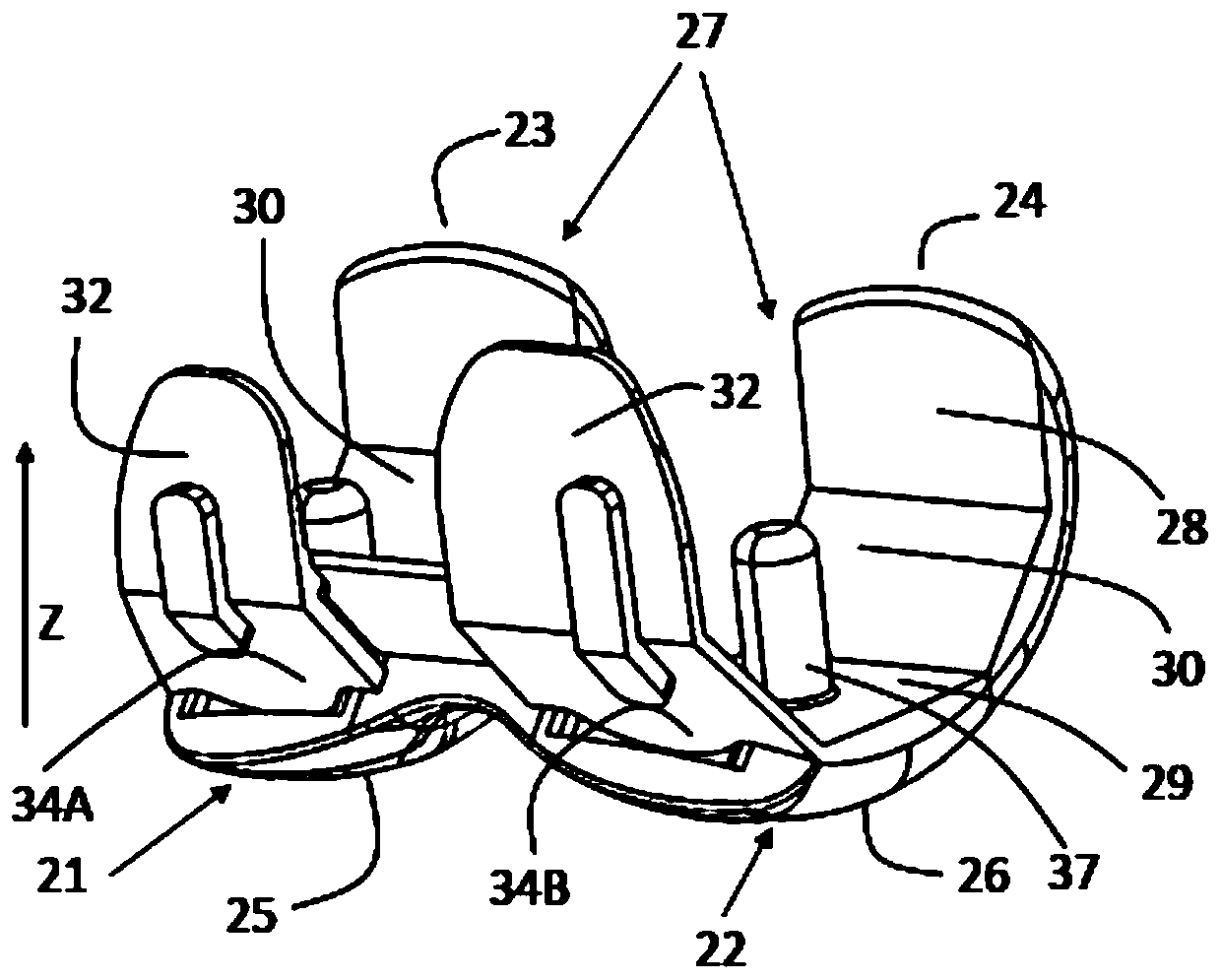
Modular knee prosthesis
The present invention relates to a modular knee prosthesis assembly kit (10) for replacement of resected articular surfaces of a distal femur of a first patient side. The kit (10) comprises (a) at least one bi-condylar component (20) sized and shaped to substantially replace resected posterior and distal condylar bone portions; and (b) at least a first trochlear groove component (50) and a secondtrochlear groove component (70), each sized and shaped to replace a resected trochlear groove bone portion. The first trochlear groove component (50) comprises a first patella articulation path defining a first trochlear groove direction angle. The second trochlear groove component (70) comprises a second patella articulation path defining a second trochlear groove direction angle. An assembly ofthe bi-condylar component (20) and one of the first and second trochlear groove components (50; 70) forms a substantially complete femoral knee prosthesis. The second trochlear groove direction angleis different from the first trochlear groove direction angle.
Owner:斯蒂芬埃格利
Femoral prosthesis
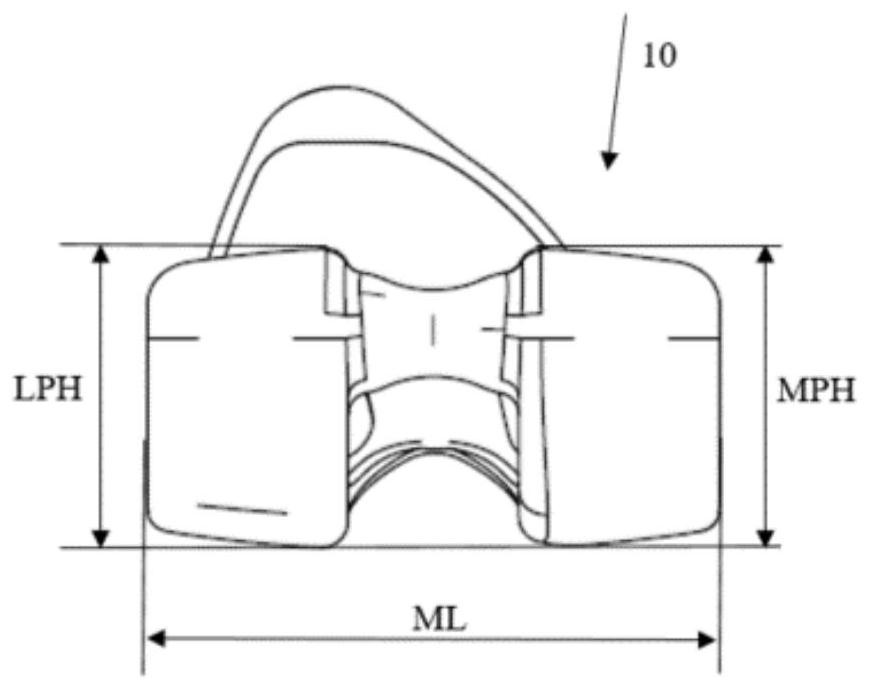
The invention provides a femoral prosthesis, which comprises a medial condyle, an external condyle and a trochlear groove arranged between the medial condyle and the external condyle, wherein the front-back diameter of the femoral prosthesis is AP, the left-right diameter of the femoral prosthesis is ML, the height of the paracondyloid of the femoral prosthesis is AH, the height of the hypocondyle of the medial condyle of the femoral prosthesis is MPH, and the height of the hypocondyle of the external condyle of the femoral prosthesis is LPH. The range of the ratio of the left-right diameter ML to the front-back diameter AP of the knee joint femoral prosthesis is 1.0-1.3, and the ratio is linearly decreased progressively along with increasing of the front-back diameter AP. The relation between the front-back diameter AP and the left-right diameter ML can be approximately fitted as ML / AP =-0.002 * AP + 1.25. According to the femoral prosthesis provided by the invention, the femoral prosthesis conforms to the anatomical structure of the human body, the coverage rate of the femoral prosthesis can be increased, and the probability of postoperative looseness and pain of the femoral prosthesis is reduced.
Owner:杭州蓝心医疗科技有限公司
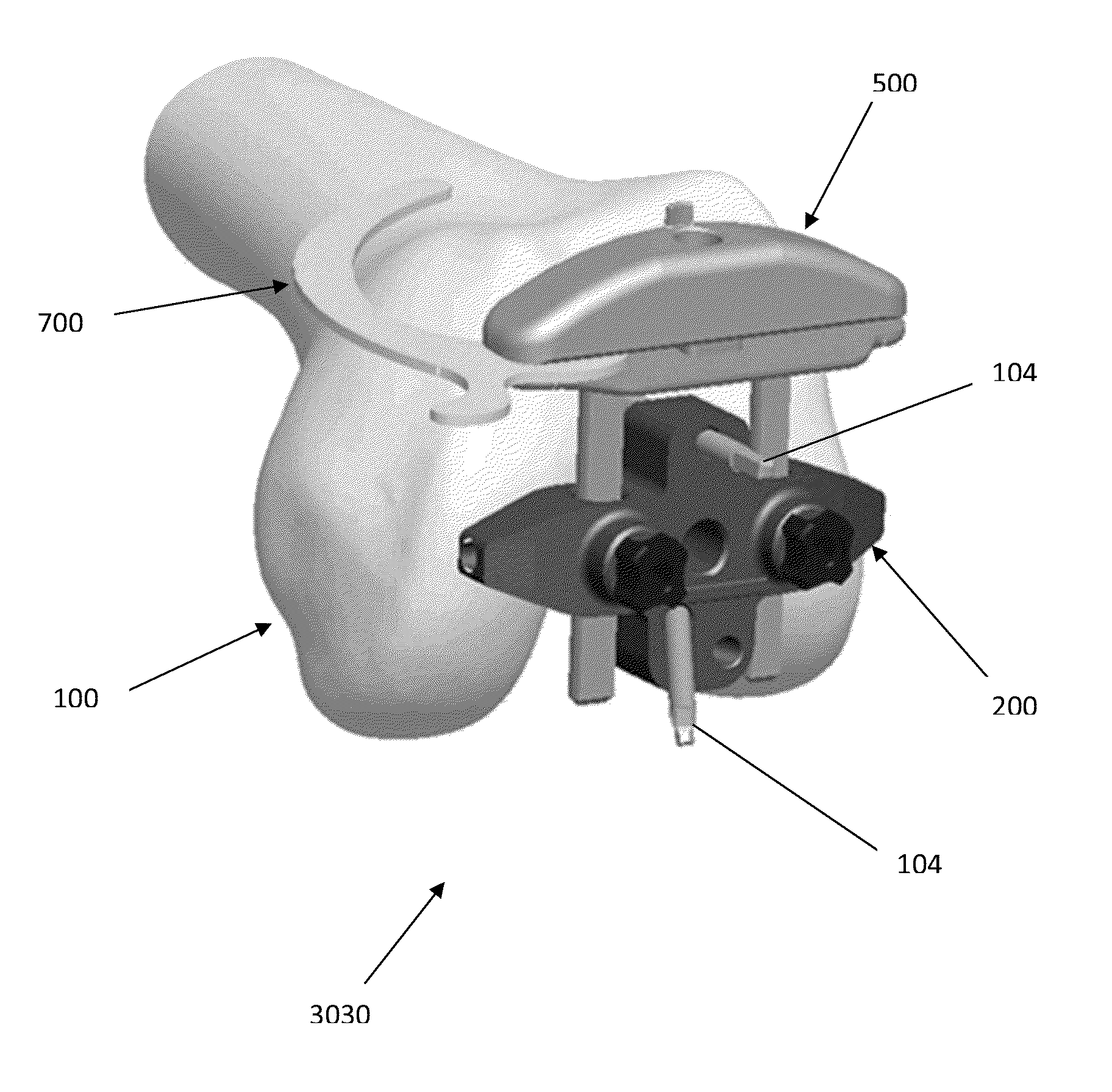
Patellofemoral implant
A femoral implant for articulation with a patella or a patellar implant includes a body having an articular surface defining a trochlear groove. The trochlear groove is defined by a first trochlear radius at a first location along the trochlear groove and by a second trochlear radius at a second location along the trochlear groove, the first radius being different than the second radius. The configuration of the trochlear groove is such that it narrows as a patella or patellar implant moves from an extension configuration to a flexion configuration. A kit includes the femoral implant along with a patellar implant. A method of trialing involves use of the femoral implant or kit to ensure a smooth transition of the patella or the patellar implant from the femoral component to the adjacent bone.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
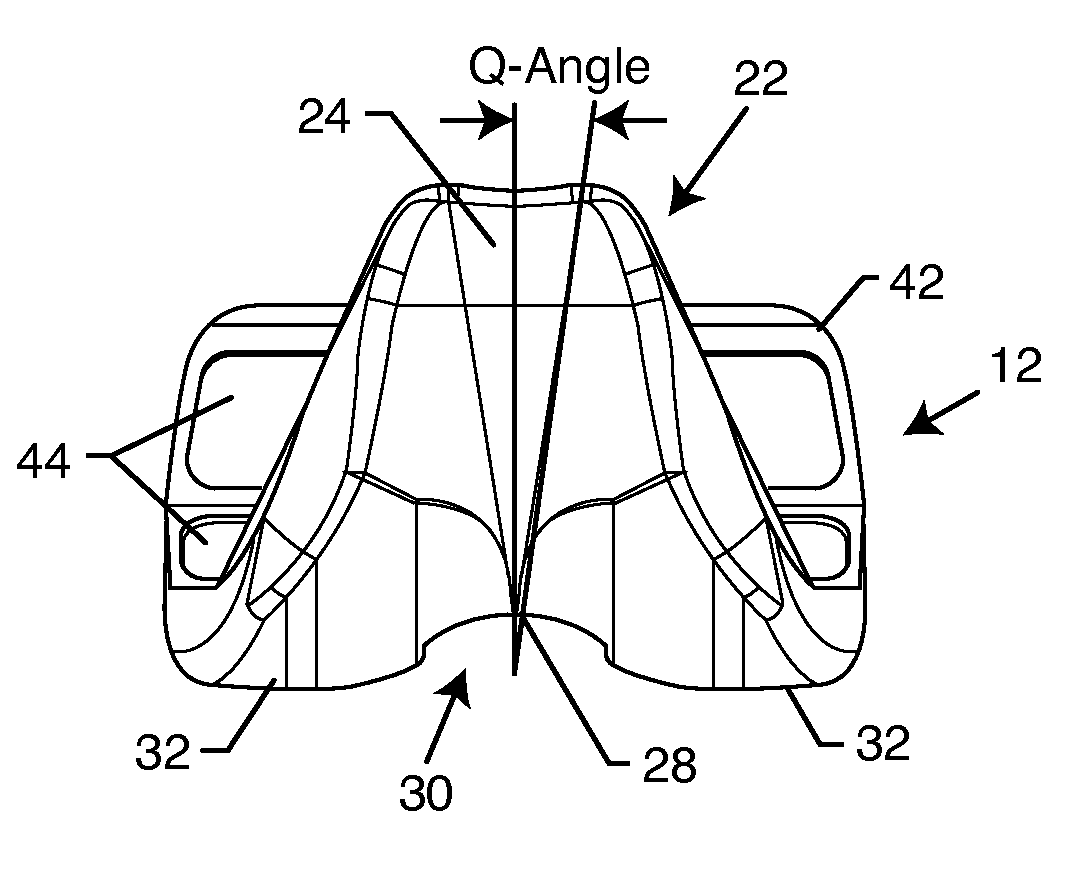
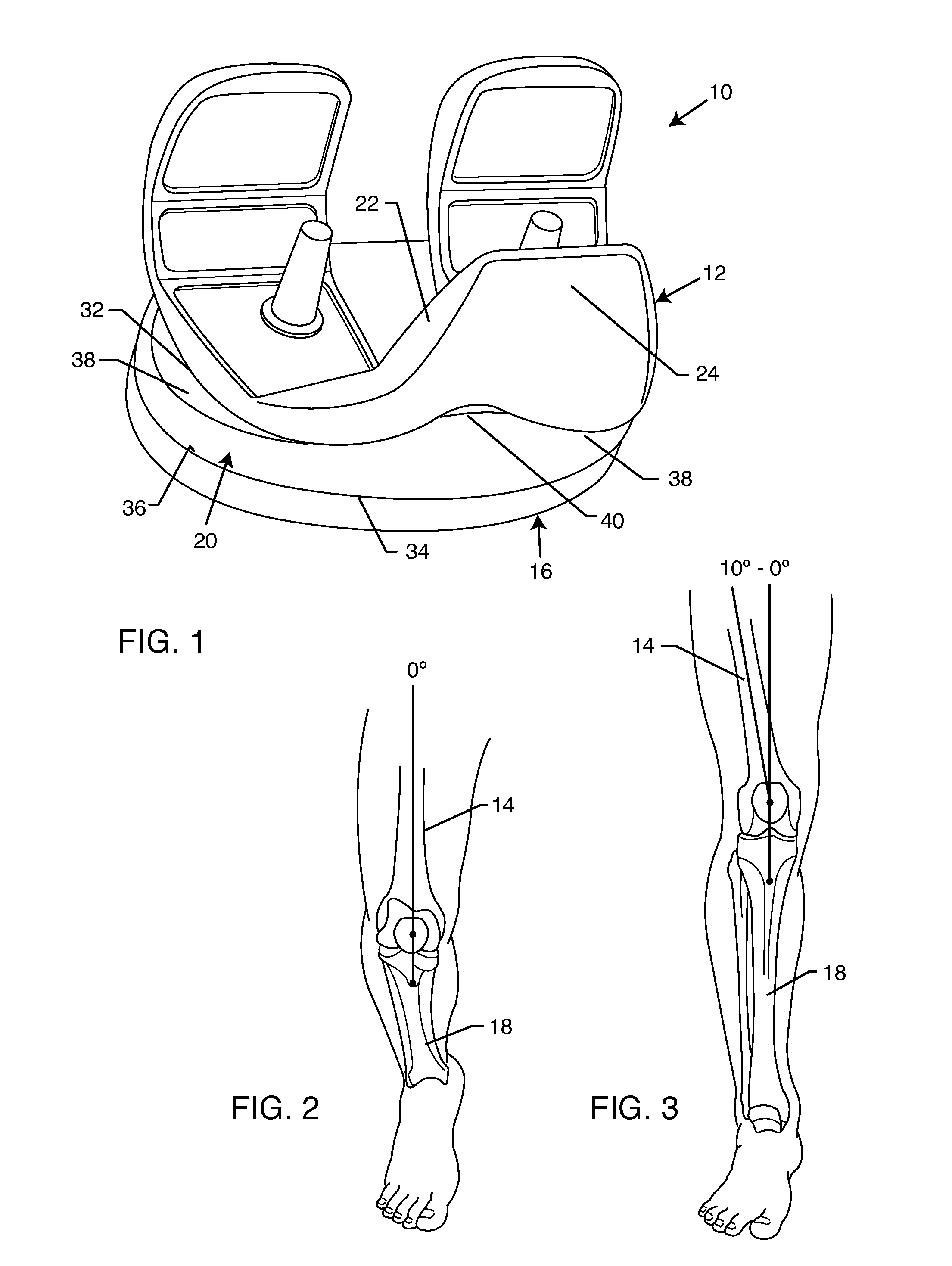
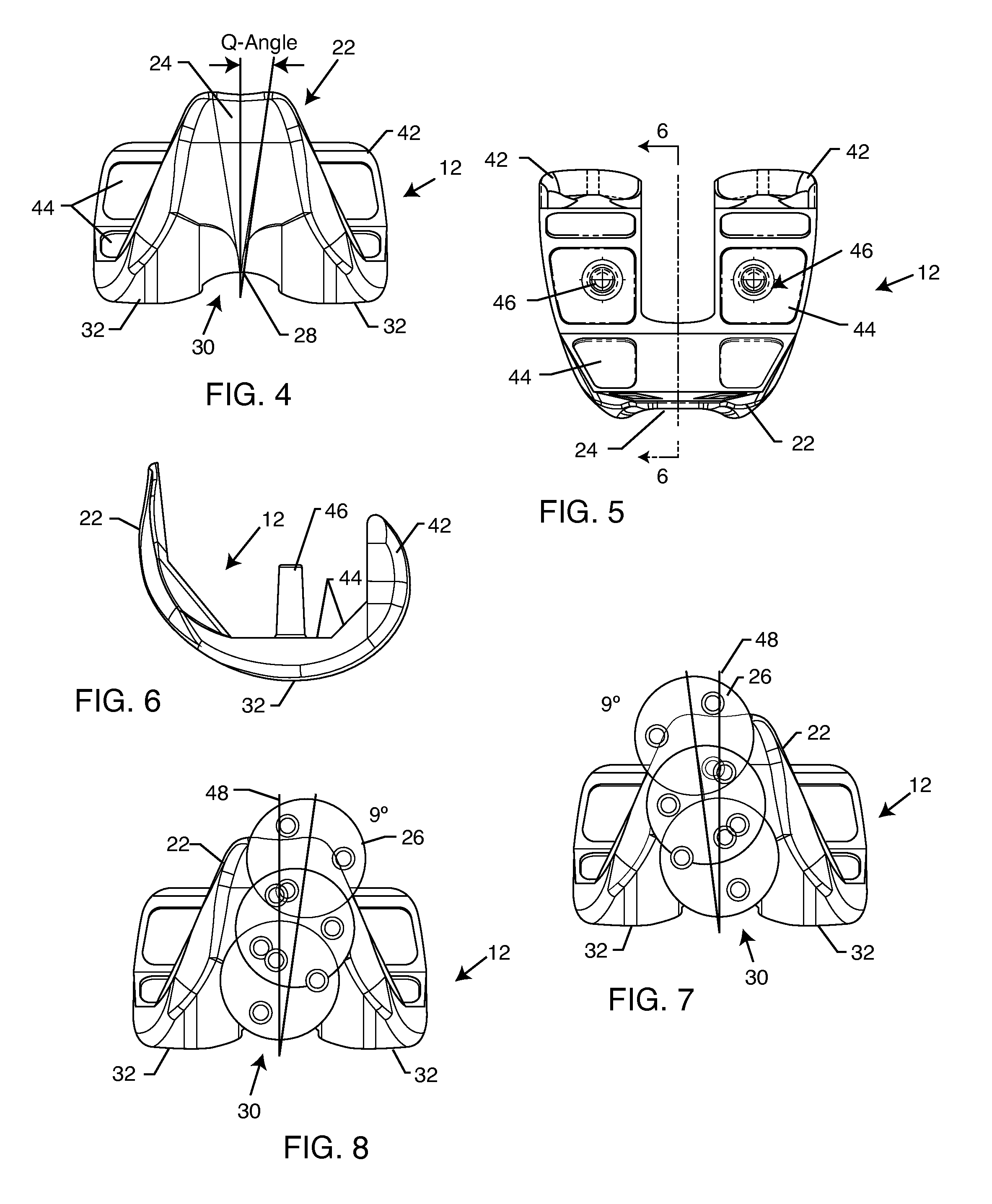
Total knee arthroplasty with symmetric femoral implant having double Q-angle trochlear groove
A total knee arthroplasty includes a symmetric femoral prosthesis for articulating with a tibial prosthesis in the left or right leg of a patient. The symmetric femoral prosthesis includes an anterior flange having a symmetric and upwardly diverging, generally V-shaped, double Q-angle trochlear groove formed in an anterior side thereof for accommodating natural Q-angle tracking of a natural or prosthetic patella when the symmetric femoral component is surgically implanted in either the left or right leg of a patient. In a preferred form, the double Q-angle trochlear groove is formed with an angle of + or − about 10°, for a total groove angle of about 20°.
Owner:JOINT DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com