Patents
Literature
296 results about "Femoral prosthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
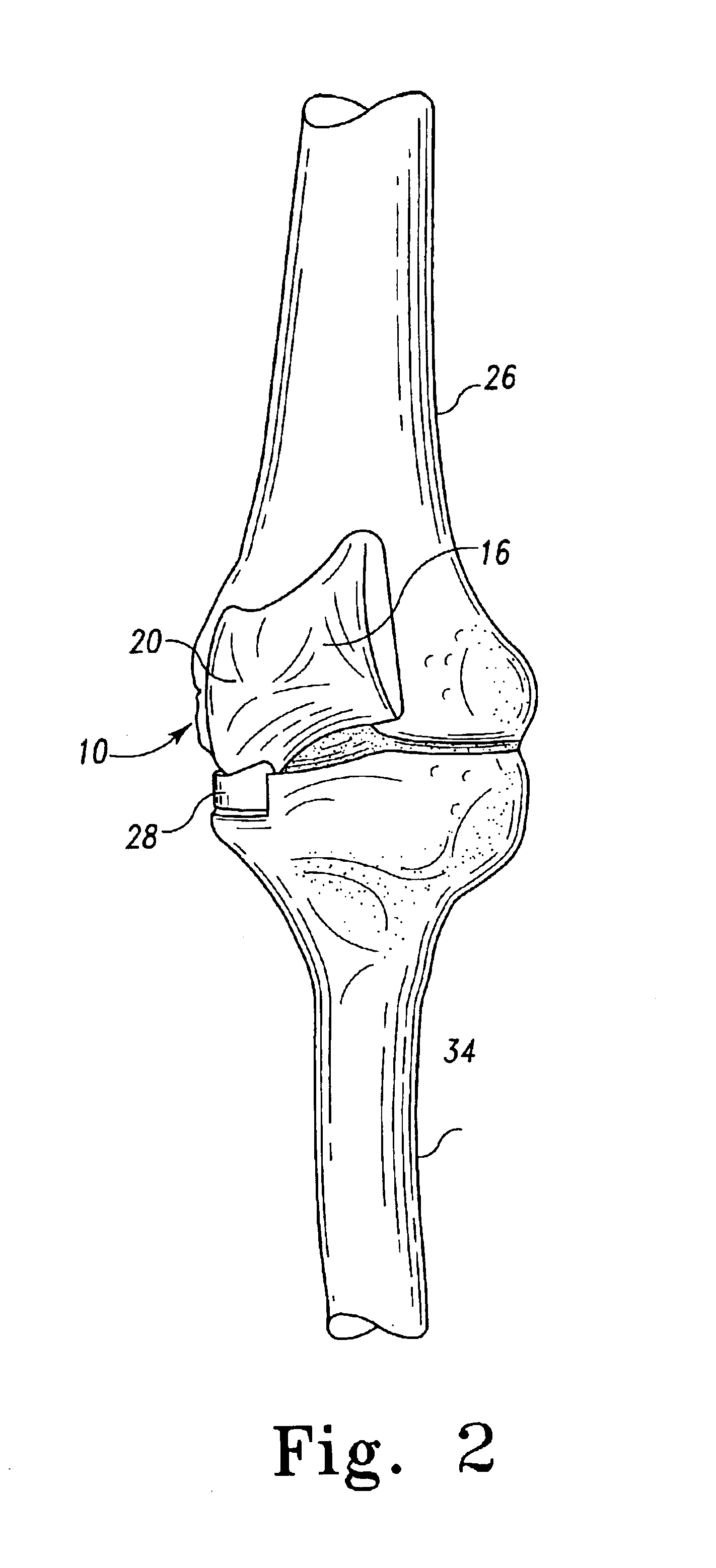
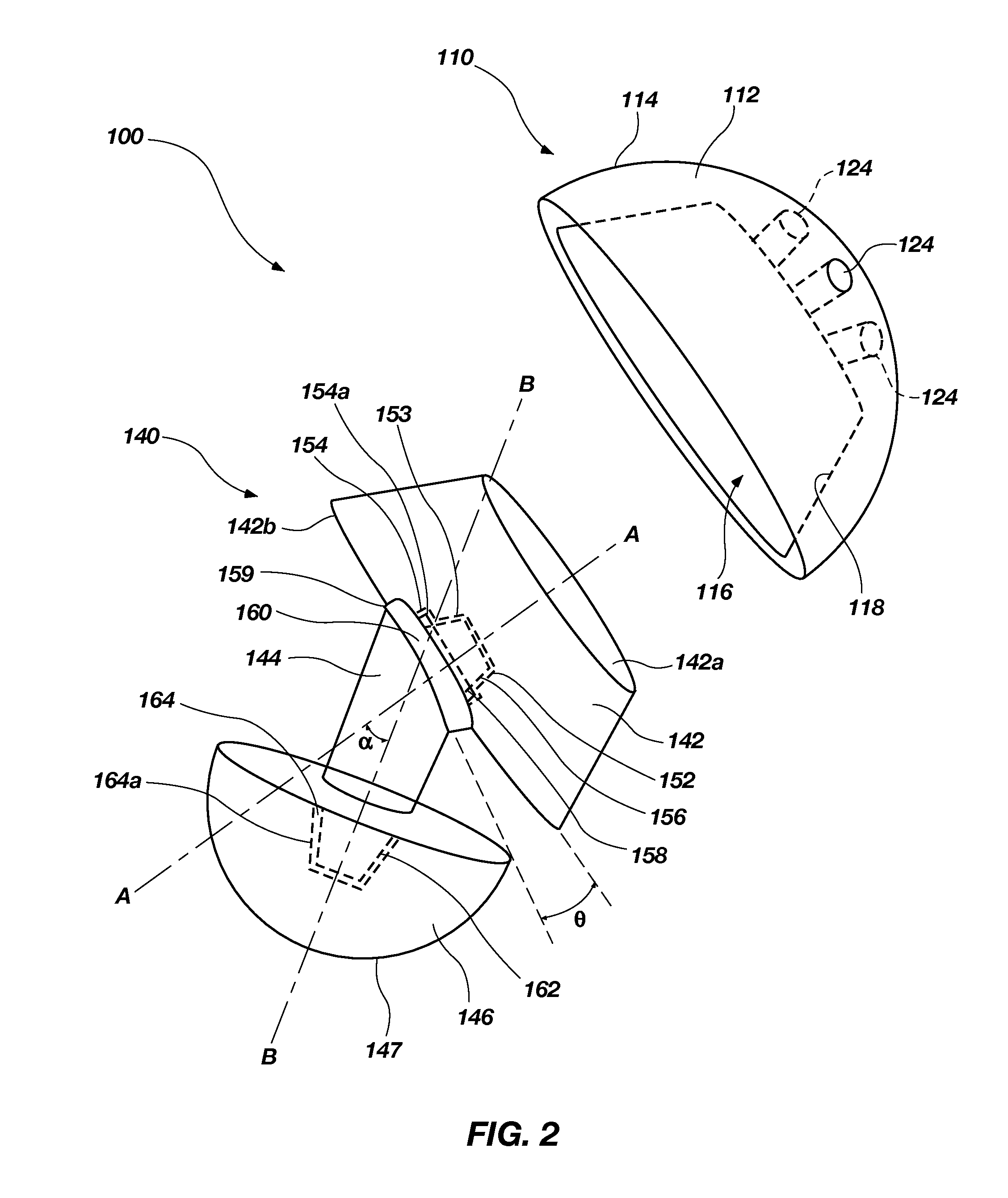
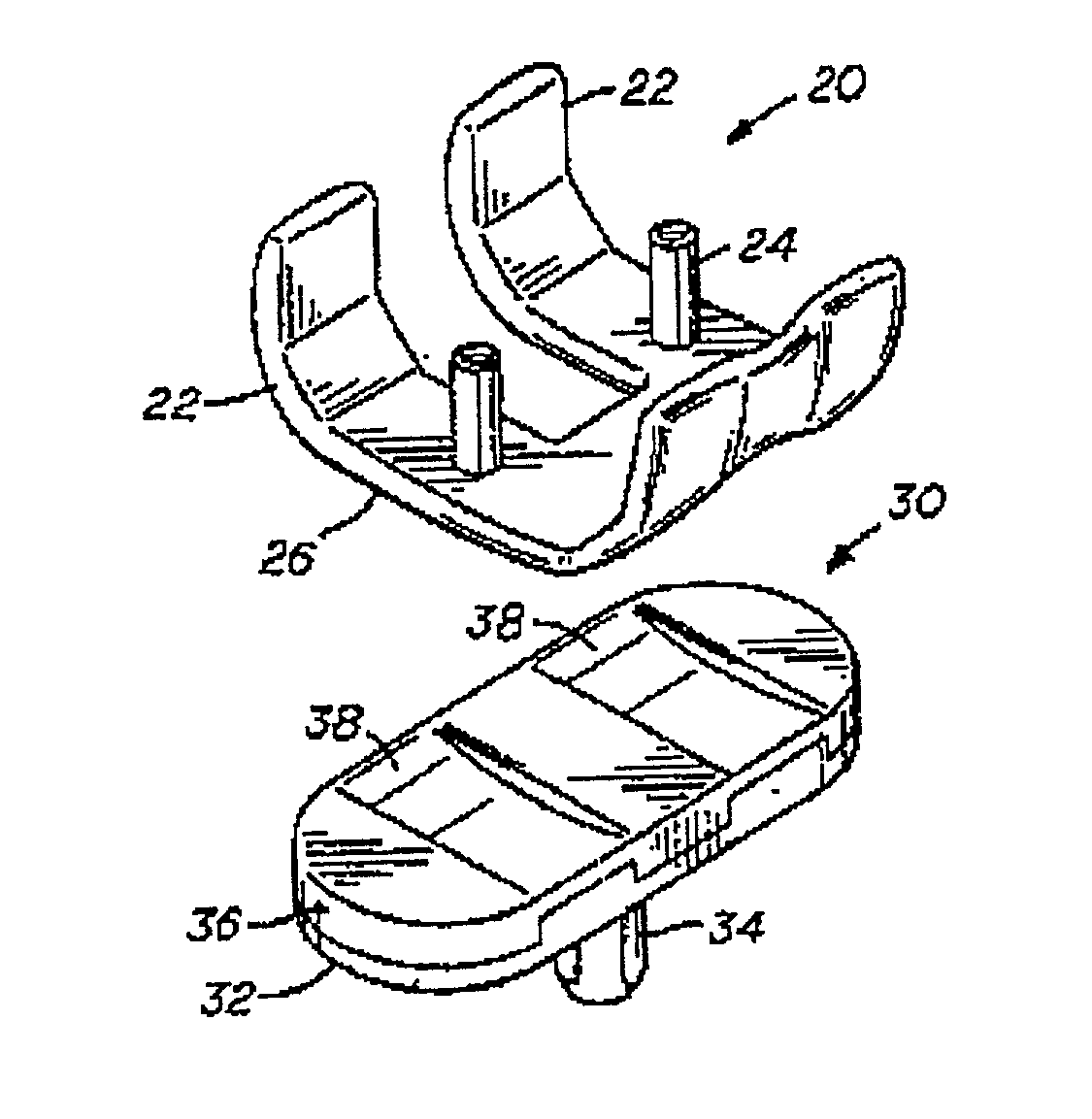
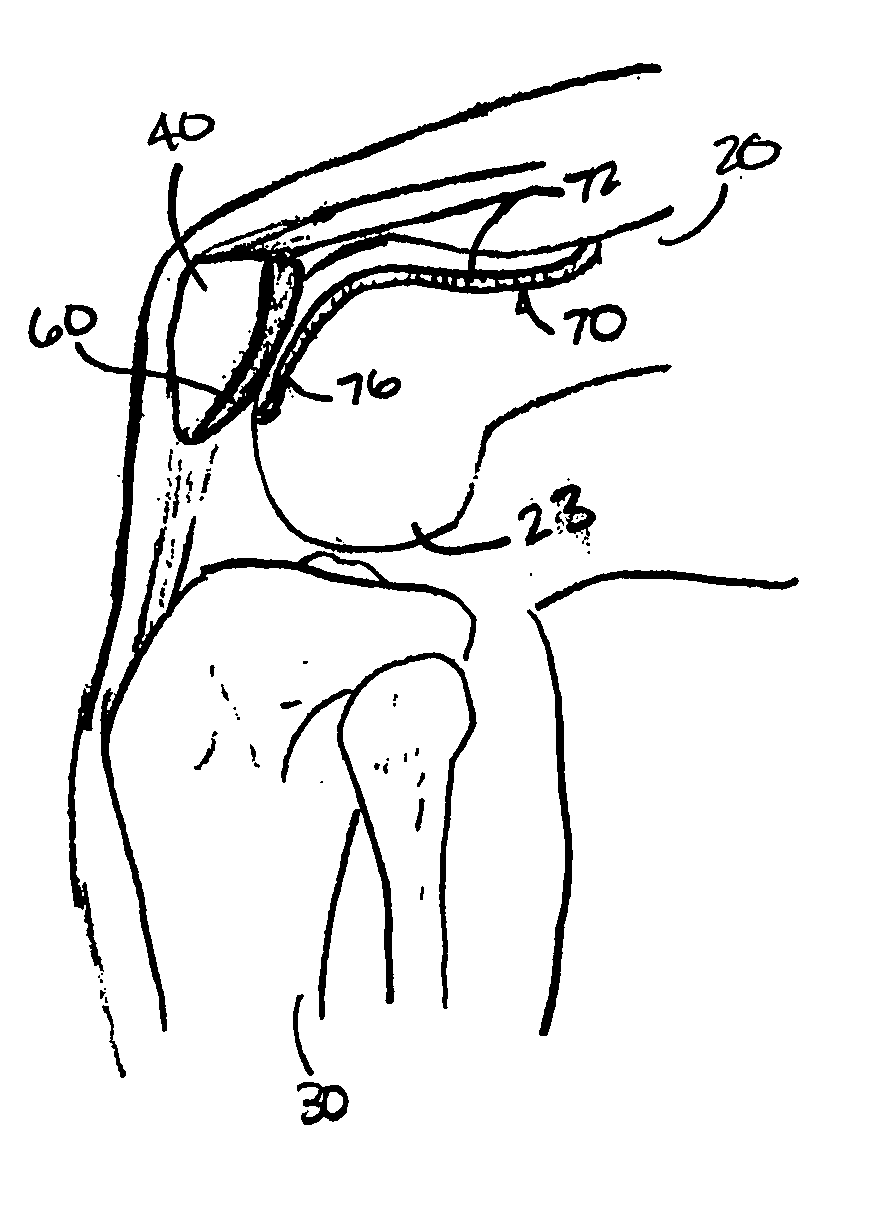
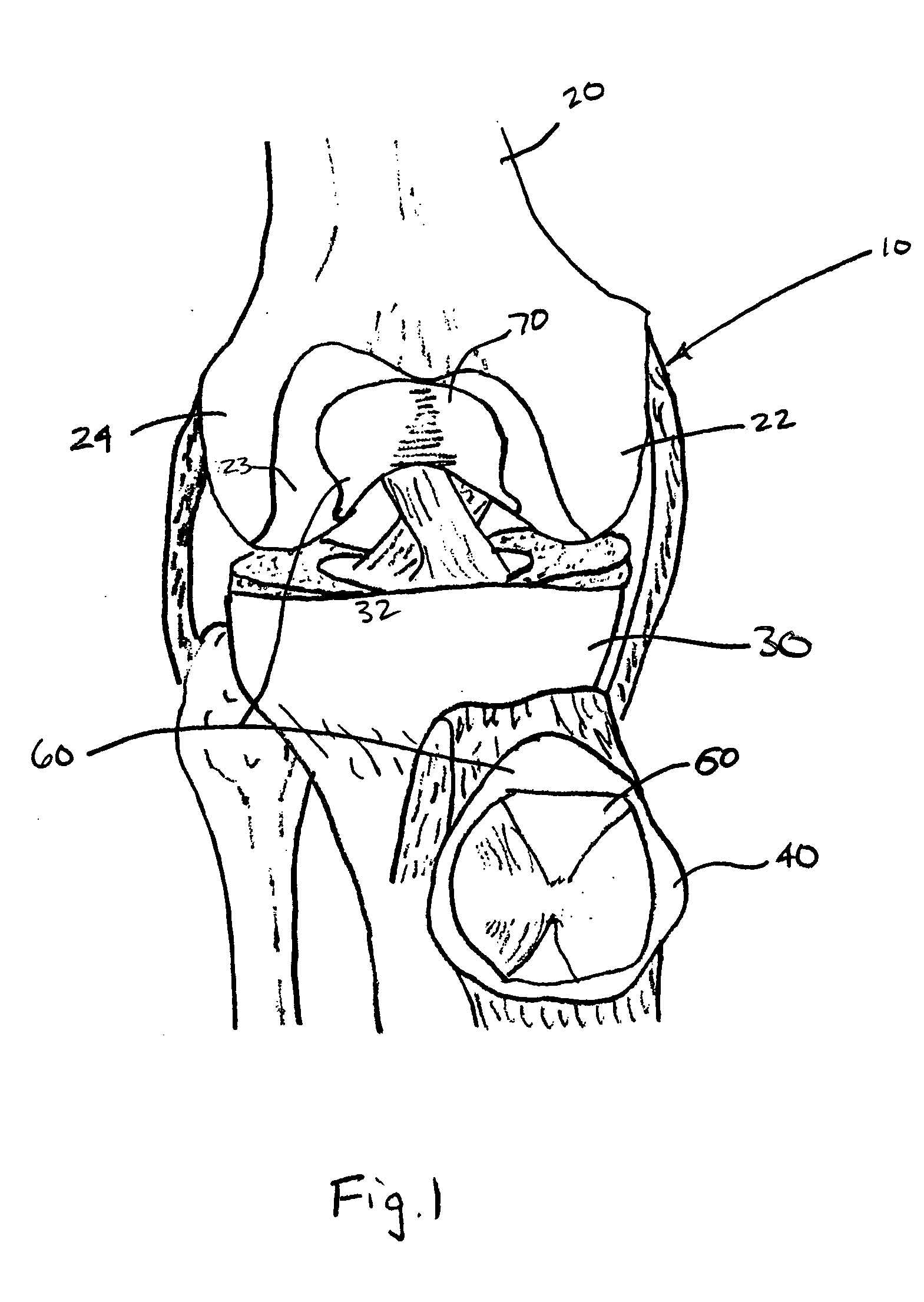
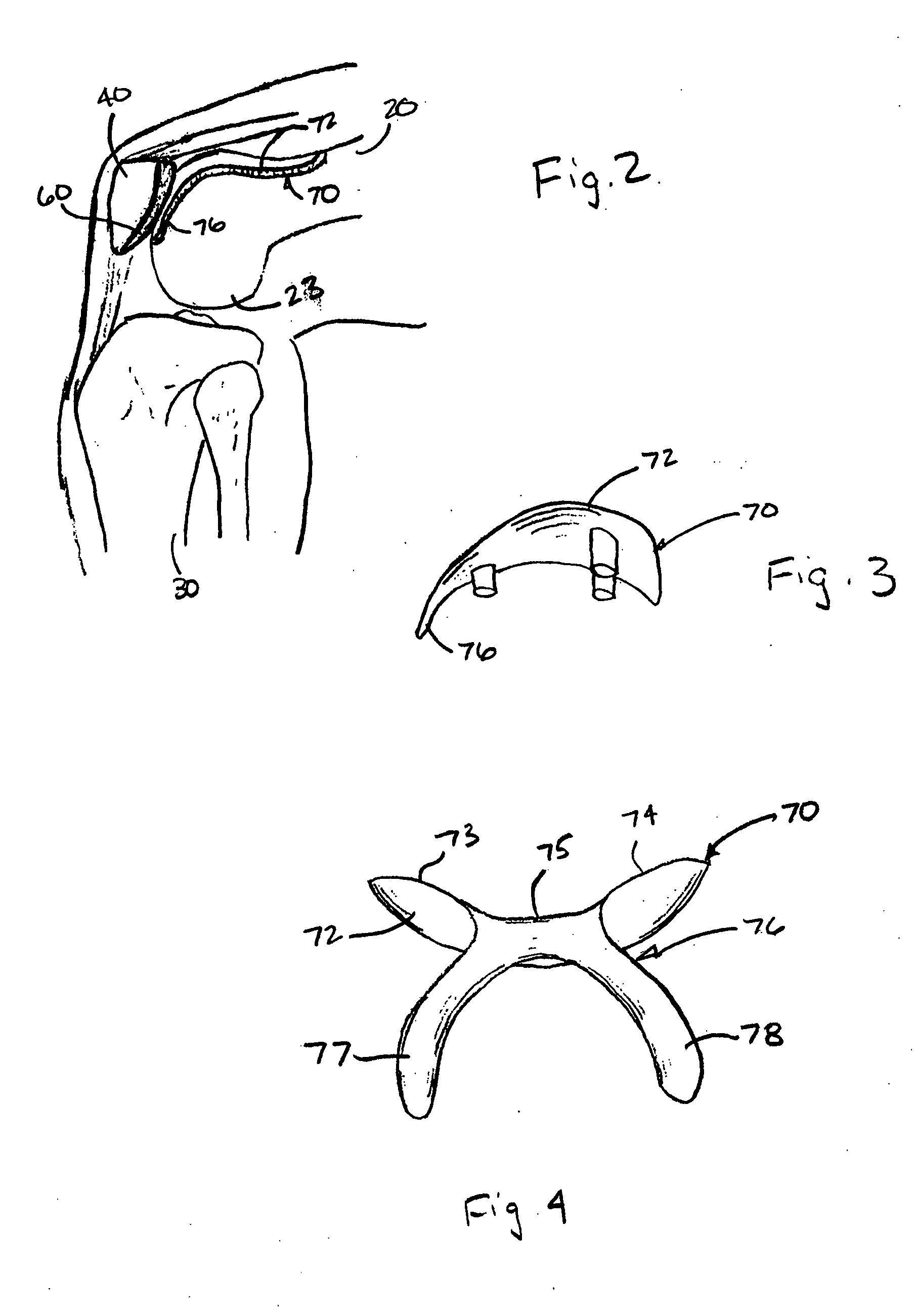
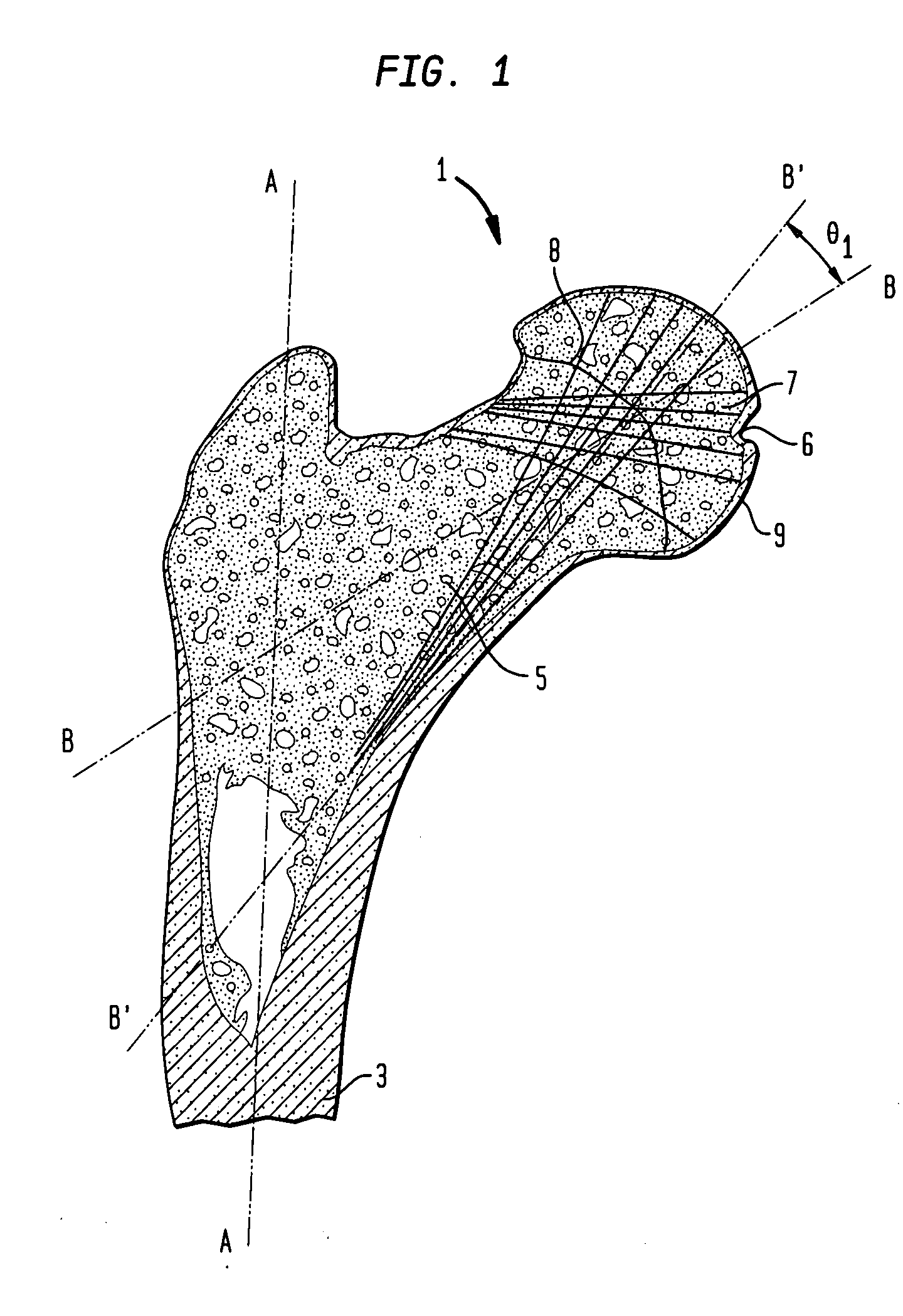
Trans-femoral prosthesis is an artificial limb, which replaces any amputated limb above the knee or AK (Above Knee). The prosthesis is made from high quality raw material known as polypropylene. It has several components, which fits together to construct the final piece.
Surgical device for implanting a total hip prosthesis
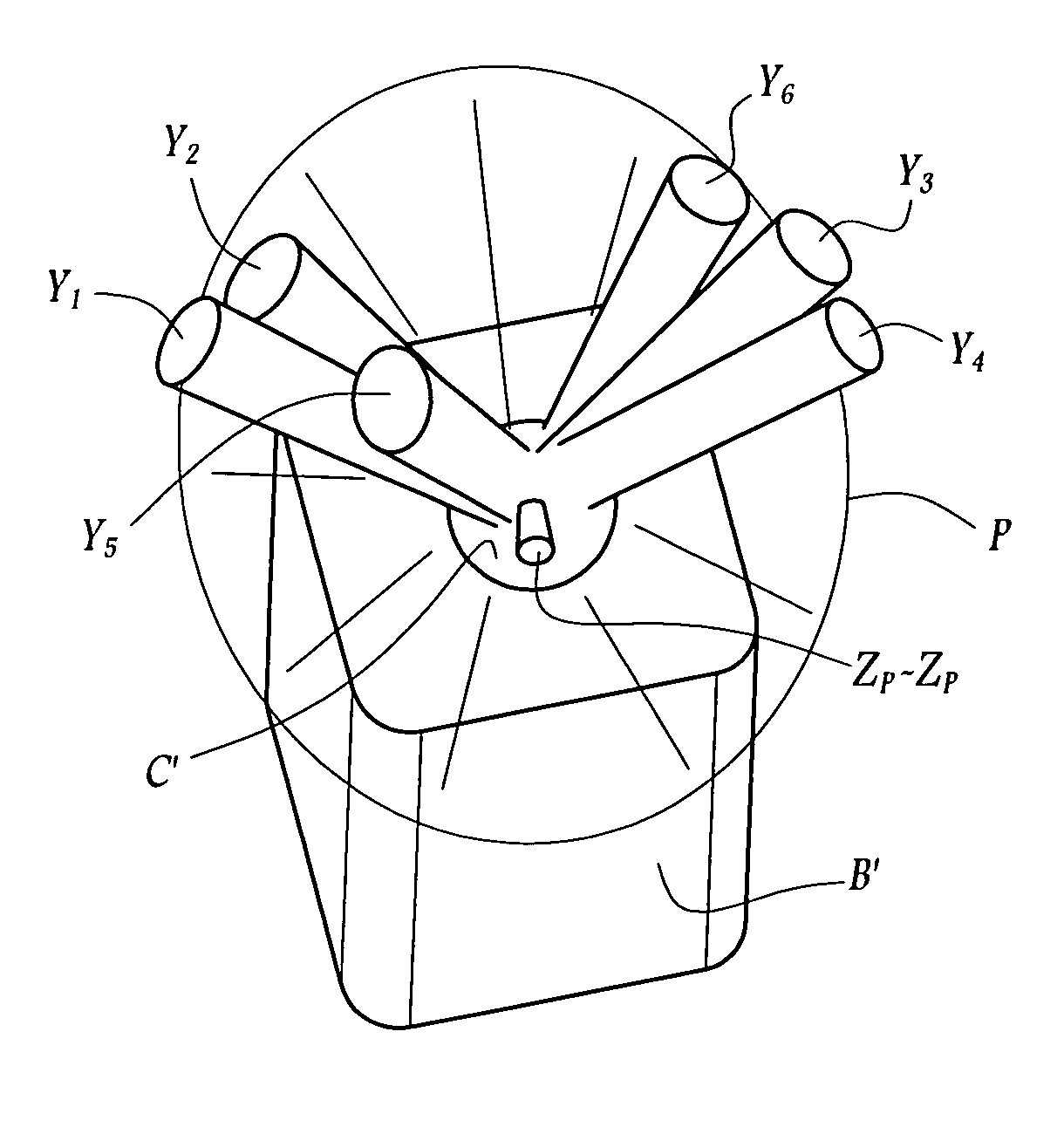
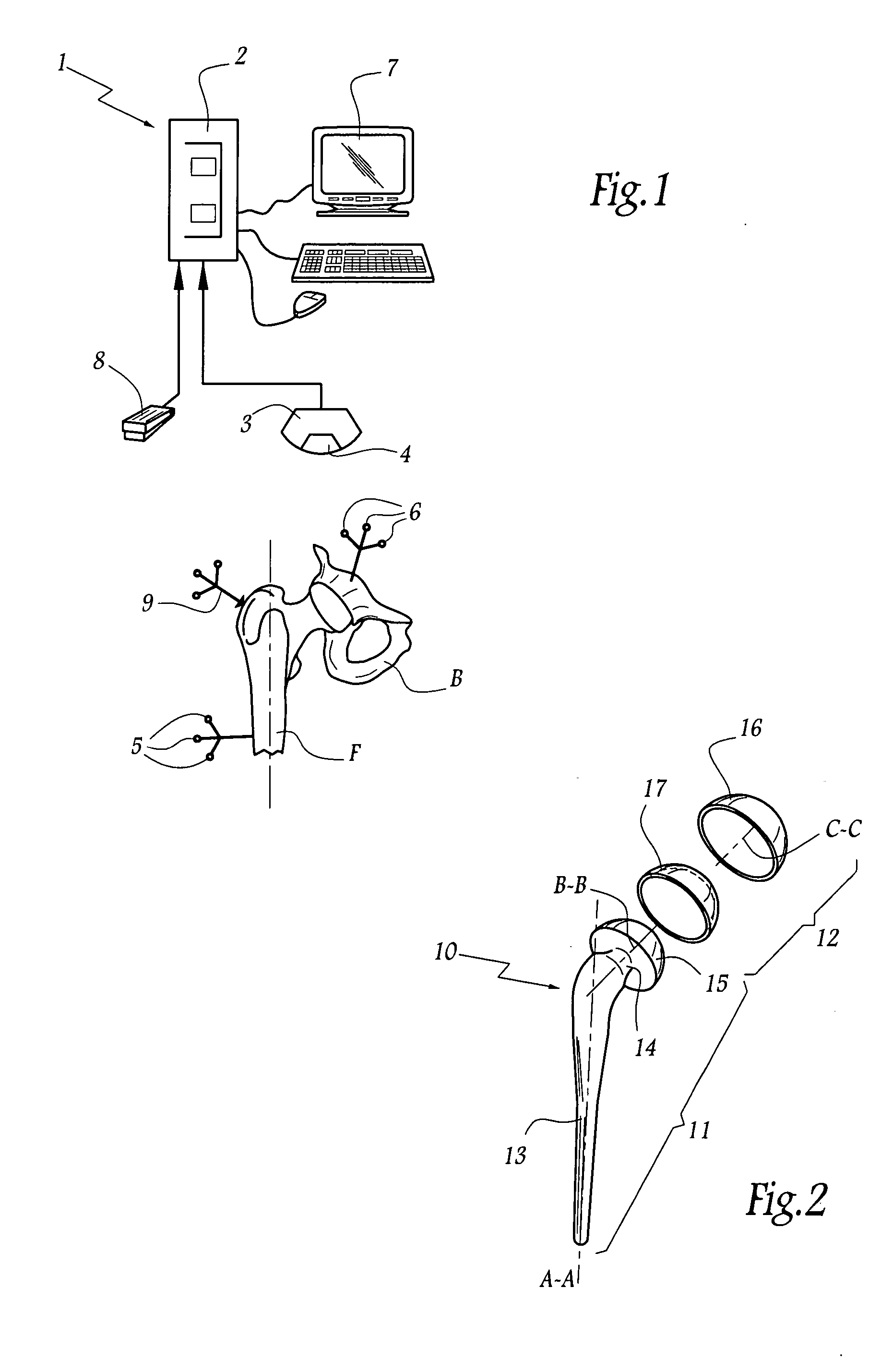
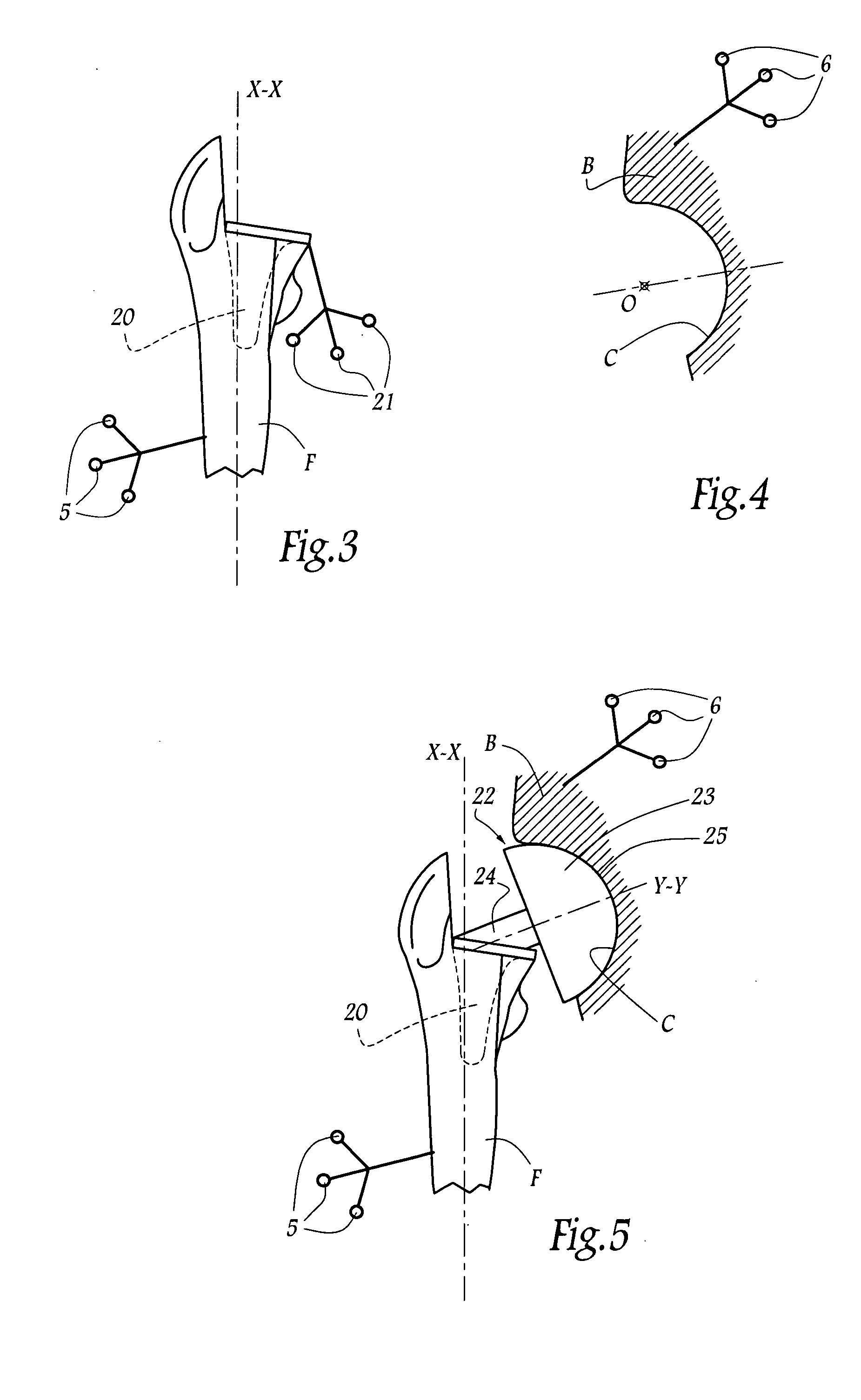
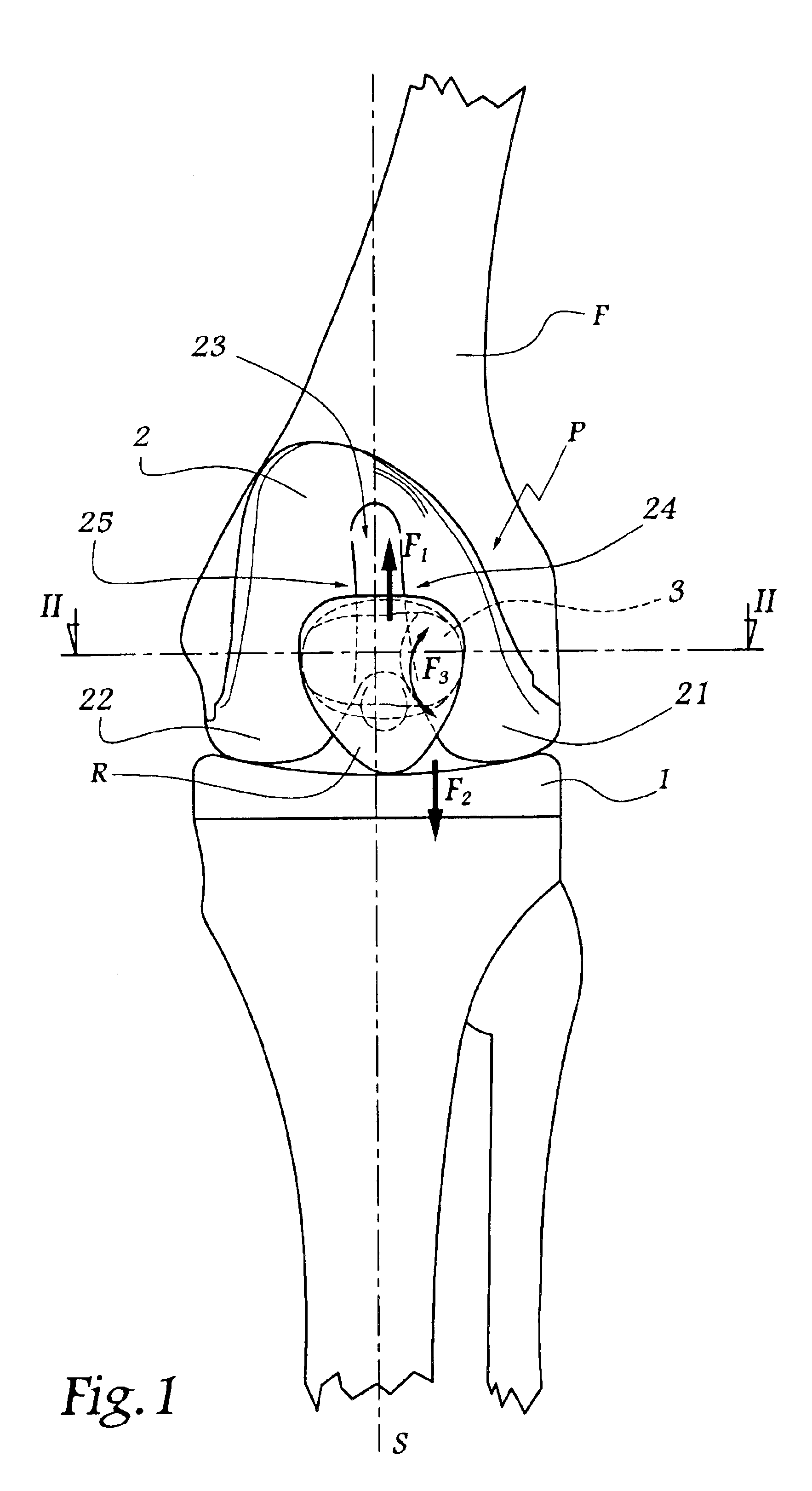
The surgical device according to the invention comprises both means for per-operative measurement and for memorization of a plurality of positions of a given femoral prosthetic direction and means for per-operative comparison of these positions with the cone of mobility of the prosthesis to be implanted, the position of the axis of revolution of this cone being, during the implantation of the prosthesis, adjustable with respect to the zone of the pelvis where the implantation of an acetabulum of the prosthesis is provided. By using this device, the surgeon can easily and rapidly determine, in the course of the surgical operation, a preferential direction for implanting the prosthetic acetabulum in order to reduce the subsequent risks of dislocations of the implanted prosthesis.
Owner:CORIN
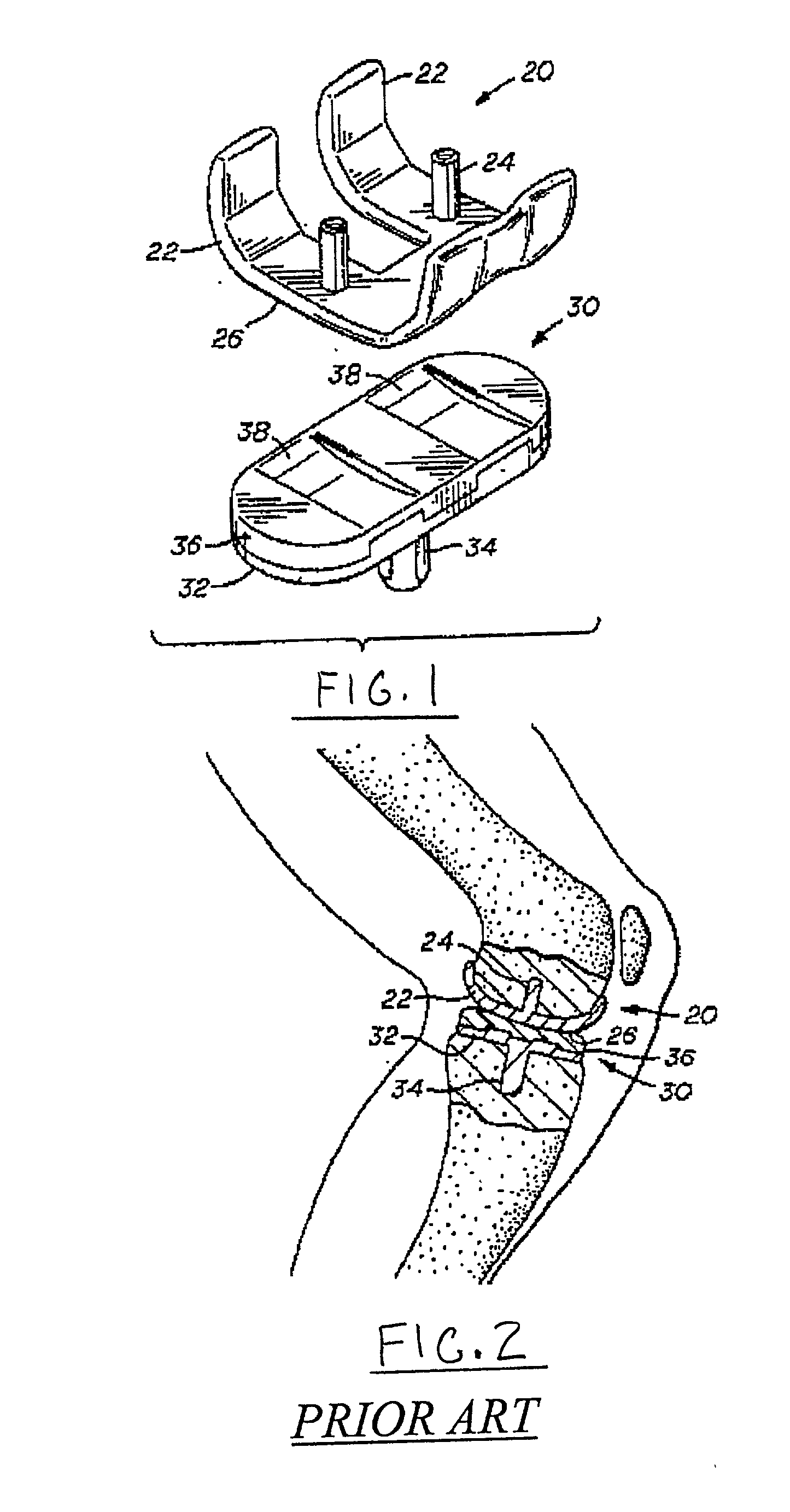
Dove tail total knee replacement unicompartmental
A knee joint prosthesis is provided for implanting on the tibial plateau and femoral condyle of the knee. The prosthesis includes a tibial prosthesis having a tibial fixation surface on the tibial prosthesis adapted to be positioned on the tibial plateau. The tibial fixation surface has at least one tibial attachment means for securing the tibial prosthesis to the tibial plateau. It further includes a femoral prosthesis having a femoral fixation surface adapted to be positioned on the femoral condyle. The femoral fixation surface has at least one femoral attachment means for securing the femoral prosthesis to the femoral condyle. The prosthesis further includes a bearing member supported by the tibial prosthesis for engaging the femoral prosthesis in weight bearing relationships.
Owner:OGDEN ORTHOPEDIC CLINIC
Device and method for bicompartmental arthroplasty
Disclosed is a device and method of bicompartmental arthroplasty of the knee. The device permits arthroplasty of the medial or lateral and patellofemoral compartments of the knee while leaving the opposite compartments and the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments intact. The device provides a femoral prosthesis component that includes a trochlear surface and a tibial prosthesis component which can be secured to the tibia. The femoral component is essentially “u” shaped having an anterior leg upon which the trochlear surface is positioned and a posterior leg which engages the posterior surface of the distal end of the femur. The femoral component also has a convex articulating surface which engages a concave articulating surface of the tibial prosthesis component to approximate the articulation of a healthy knee.
Owner:ROLSTON LINDSEY R
Tool
An alignment trial system for a hip prosthesis comprising: (a) a trial femoral prosthesis comprising a head component, a neck component and a stem component; and (b) a trial acetabular cup prosthesis wherein the head component of the trial femoral prosthesis and the trial acetabular cup prosthesis include interlocking engagement formations and wherein the trial acetabular cup prosthesis includes means to facilitate the formation of a bore in the pelvis. The invention also relates to a method of inserting an acetabular cup prosthesis comprising the steps of: (I) preparing the femur and pelvis for insertion of a femoral prosthesis and an acetabular cup prosthesis; (ii) inserting the alignment trial apparatus of the above first aspect such that the trial femoral prosthesis is located in the prepared femur; (iii) locating the patient's hip such that the trial cup prosthesis is seated in the prepared portion of the pelvis; (v) drilling a bore in the pelvis; (vi) removing the alignment trial apparatus; (vii)inserting the acetabular cup prosthesis into the pelvis using the mark as a guide.
Owner:FINSBURY DEV
Device and method for bicompartmental arthroplasty
Disclosed is a device and method of bicompartmental arthroplasty of the knee. The device permits arthroplasty of the medial or lateral and patellofemoral compartments of the knee while leaving the opposite compartments and the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments intact. The device provides a femoral prosthesis component that includes a trochlear surface and a tibial prosthesis component which can be secured to the tibia. The femoral component is essentially “u” shaped having an anterior leg upon which the trochlear surface is positioned and a posterior leg which engages the posterior surface of the distal end of the femur. The femoral component also has a convex articulating surface which engages a concave articulating surface of the tibial prosthesis component to approximate the articulation of a healthy knee. The patellar prosthesis is applied to the posterior surface of the patella and articulates with the trochlear exterior surface of the femur.
Owner:ROLSTON LINDSEY R
Elongated femoral component
A plurality of knee joint prostheses comprise a first femoral implant and a second femoral implant. The first femoral implant has a first maximum interior anterior to posterior dimension, a first maximum overall exterior anterior to posterior dimension, a first lateral condyle, and a first medial condyle. The second femoral implant has a second maximum interior anterior to posterior dimension that is substantially the same as the first maximum interior anterior to posterior dimension, a second maximum overall exterior anterior to posterior dimension that is different than the first maximum overall exterior anterior to posterior dimension, a second lateral condyle having a medial to lateral dimension that is substantially the same as a medial to lateral dimension of the first lateral condyle, and a second medial condyle having a medial to lateral dimension that is different than a medial to lateral dimension of the first medial condyle.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
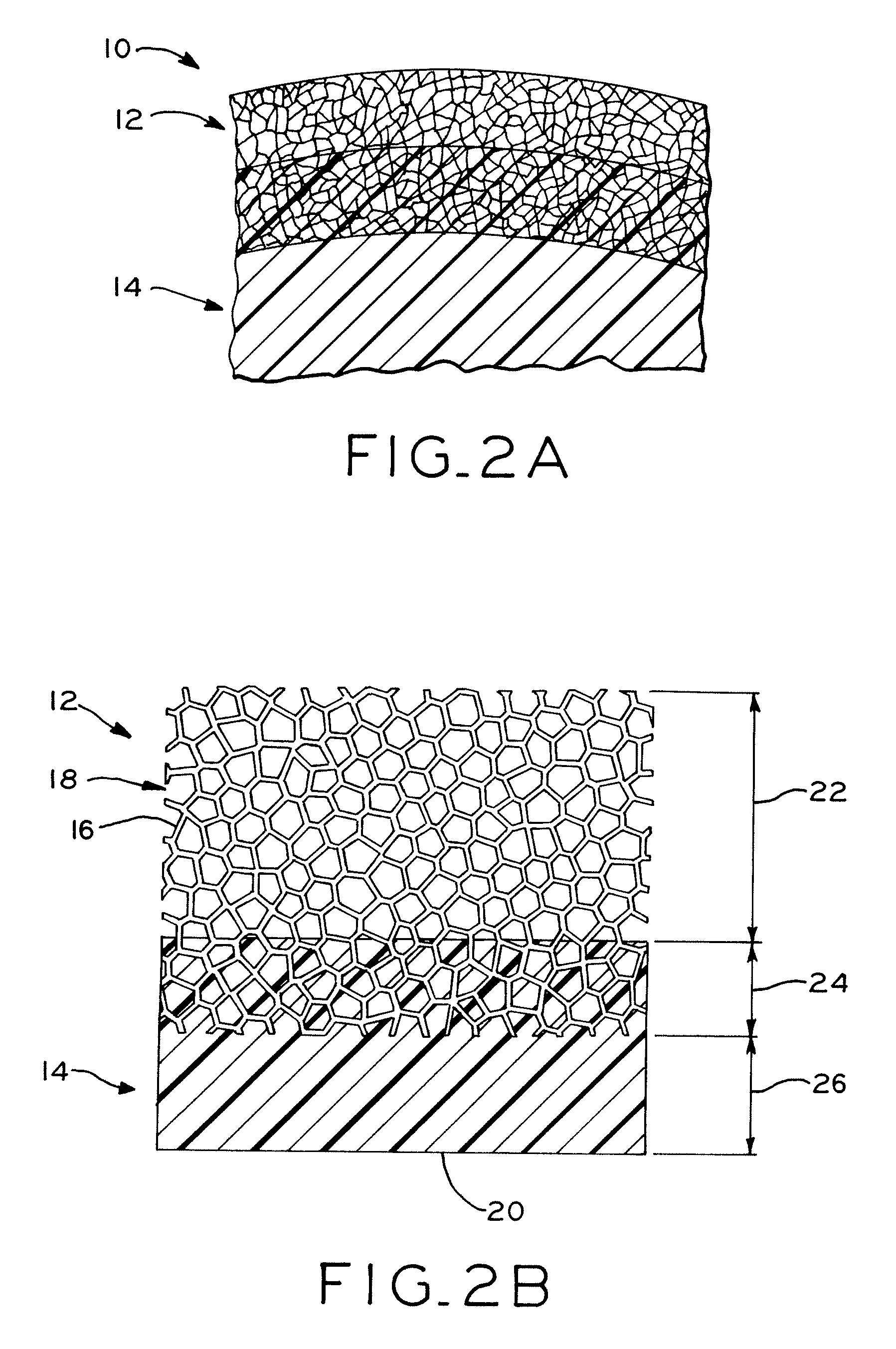
Method and apparatus for strengthening the biomechanical properties of implants
InactiveUS20050010231A1Add depthImproves Structural IntegrityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBiomechanicsSubject matter
A method for agitating a surgical fluid using a vibrating probe is disclosed. The agitation method drives entrapped air voids out of the surgical fluid and forces the fluid into a plurality of pores of various sizes in the adjacent bone. The vibrating apparatus in one embodiment includes a probe tip disposed upon a graspable elongate shaft and a series of fins extending into the fluid. The apparatus in one embodiment may include a set of probe tips of different shapes and sizes. The agitation and interdigitation method may facilitate any procedure involving any type of surgical fluid, with or without a prosthetic device such as an intramedullary nail or femoral prosthesis. This Abstract is provided to quickly inform a reader about the subject matter, and not for use interpreting the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:MYERS SURGICAL SOLUTIONS LLC
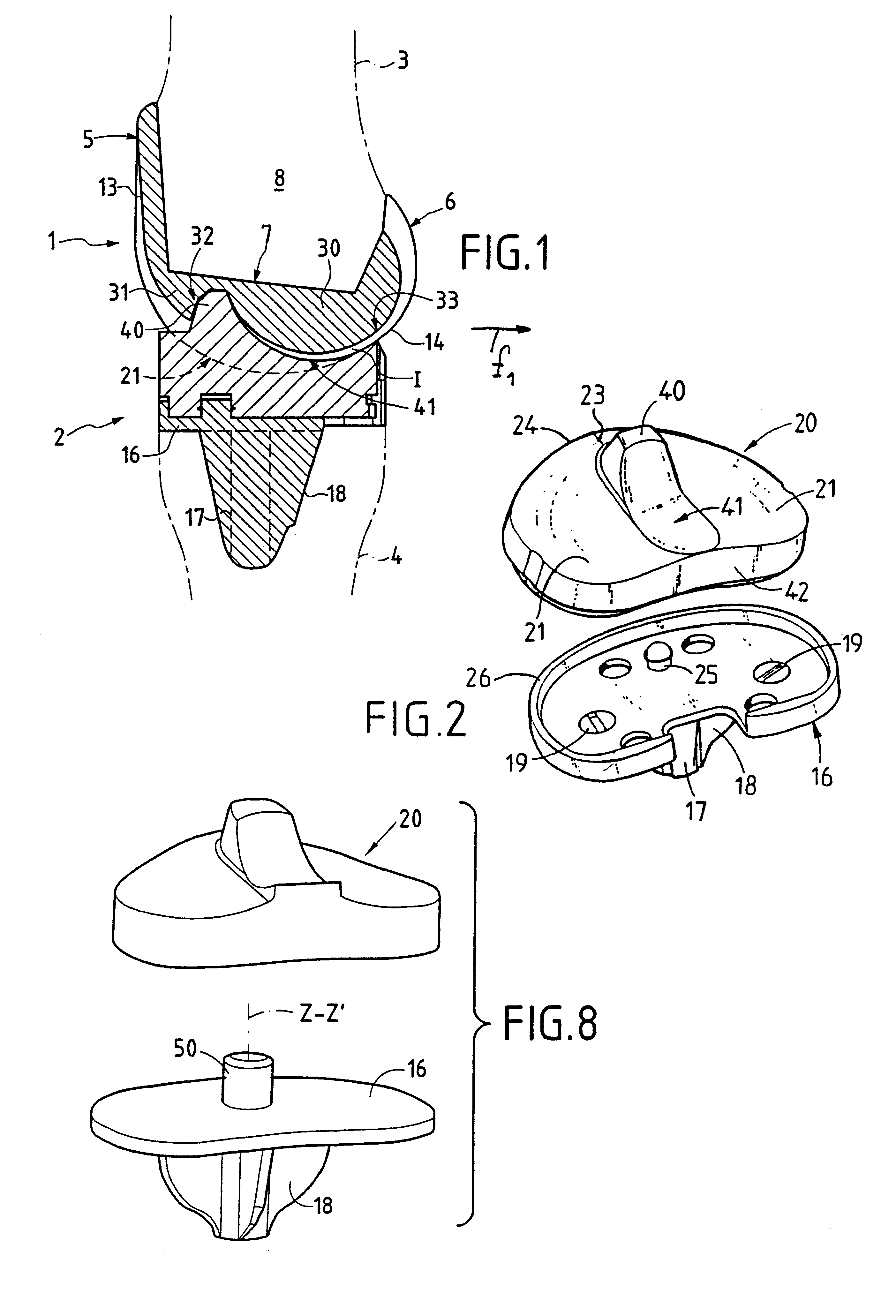
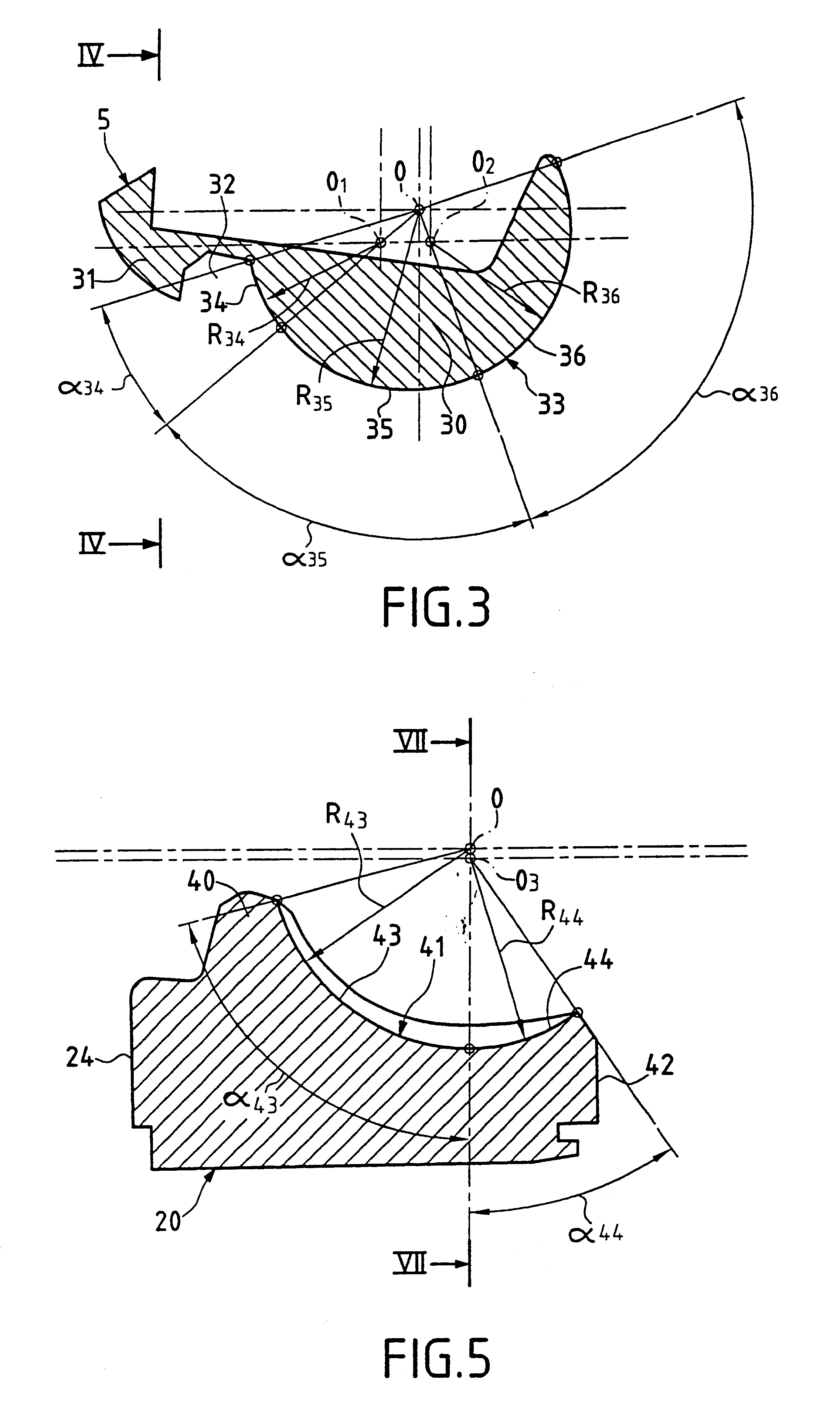
Patellar implant and knee prosthesis incorporating such an implant
InactiveUS6802864B2Improve contact stabilityReduce wearJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
A patellar implant for total or partial prosthesis of the knee joint incorporates an outer articular surface and an inner articular surface provided to cooperate respectively with an outer side and an inner side of a femoral trochlea or of a femoral prosthetic component. The inner and outer articular surfaces are separated by a transition ridge which is curved, as viewed from a front of the implant, so as to be concave facing the outer articular surface. The outer articular surface is concave in a plane parallel to a sagittal plane and in a transverse plane of the knee joint.
Owner:CORIN
Prosthetic revision knee system
The present invention provides a femoral component, and a method for surgical implantation of a femoral prosthesis, comprised of a revision knee implant and corresponding cutting block system. In particular, the revision knee implant, comprised of a femoral component having incremental markings thereon and a femoral stem, and corresponding cutting block system having corresponding incremental markings thereon, enables a surgeon maximally to position the cutting block adjacent as much area as possible of a distal femur of a patient and to infinitely position the femoral component in the exact position indicated by the cutting block.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Orthopedic component of low stiffness
ActiveUS20090192610A1Component can be removedReduce the impactBone implantSynthetic resin layered productsAcetabular linerPlastic surgery
An orthopedic component having multiple layers that are selected to provide an overall modulus that is substantially lower than the modulus of known orthopedic components to more closely approximate the modulus of the bone into which the orthopedic component is implanted. In one exemplary embodiment, the orthopedic component is an acetabular shell. For example, the acetabular shell may include an outer layer configured for securement to the natural acetabulum of a patient and an inner layer configured to receive an acetabular liner. The head of a femoral prosthesis articulates against the acetabular liner to replicate the function of a natural hip joint. Alternatively, the inner layer of the acetabular shell may act as an integral acetabular liner against which the head of the femoral prosthesis articulates.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Femoral component of an artificial knee joint
InactiveUS20090265011A1Add flexiblySimplify different cutJoint implantsKnee jointsFemoral prosthesisArtificial knee
A femoral component of an artificial knee joint is configured with multiple different facets which are similar in size and shape for many different sizes, to simplify an associated method for forming a distal end of the femur to receive the femoral component. Jig embodiments are provided to form surfaces on a distal end of a femur to correspond with facets of the femoral component, with the same jig usable for femoral components of differing size. The femoral component includes medial and lateral condylar legs with a posterior facet of the femoral component exhibiting a negative angle relative to a central axis of the femur, to maximize contact and increase flexion of the artificial knee joint.
Owner:MANDELL STEVEN L
Surface guided knee replacement
InactiveUS20070135925A1Reduce consistencyAvoid large displacementJoint implantsKnee jointsGonial angleTibial surface
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the motion and stability characteristics of the anatomic knee. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, more so on the lateral side than on the medial side. This is accomplished by the interaction of a projecting tibial post inside a cupola in the center of the femoral component, and by the saggital radius on the medial side being smaller than that on the lateral side. The prevention of anterior sliding of the femur on the tibia in early flexion is accomplished by the interaction between a distal-anterior recess on the medial side of the femur and an apposing raised pad on the tibial surface. Rotational laxity at all angles is allowed by the presence of only one recess pad and by non-conforming femoral-tibial surfaces on the lateral side.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Antero-postero-stabilized knee prosthesis
A prosthesis, such as a knee prosthesis, for the lower limb including a femur prosthetic element having a block presenting a lug running into the trochlea and adjacent to a notch from which a convex bearing surface extends, and a tibia prosthetic element having an insert with a sagittally oriented elevation defining a projection for antero-postero stabilization engaged in the notch when the prosthesis is in the extended position and which runs into a concave sliding ramp that extends to the rear edge of the insert.
Owner:MERCK BIOMATERIAL FRANCE
Reflex fixation geometry revision and reconstruction system reverse articulation
An orthopedic device is disclosed for restoring the normal or natural joint mechanics in, for example, a hip joint. The device includes a first component, such as an acetabular component in a hip implant, that includes a convex articulation surface and a second component, such as a femoral component in a hip implant, that includes a concave articulation surface. It will be appreciated that the convex articulation surface of the device disclosed herein articulates with the concave articulation surface in a mating engagement that may be reversed with respect to the traditional hip implant, in which the concave articulation surface is part of the acetabular component and the convex articulation surface is part of the femoral component.
Owner:GLOBAL ORTHOPAEDIC TECH
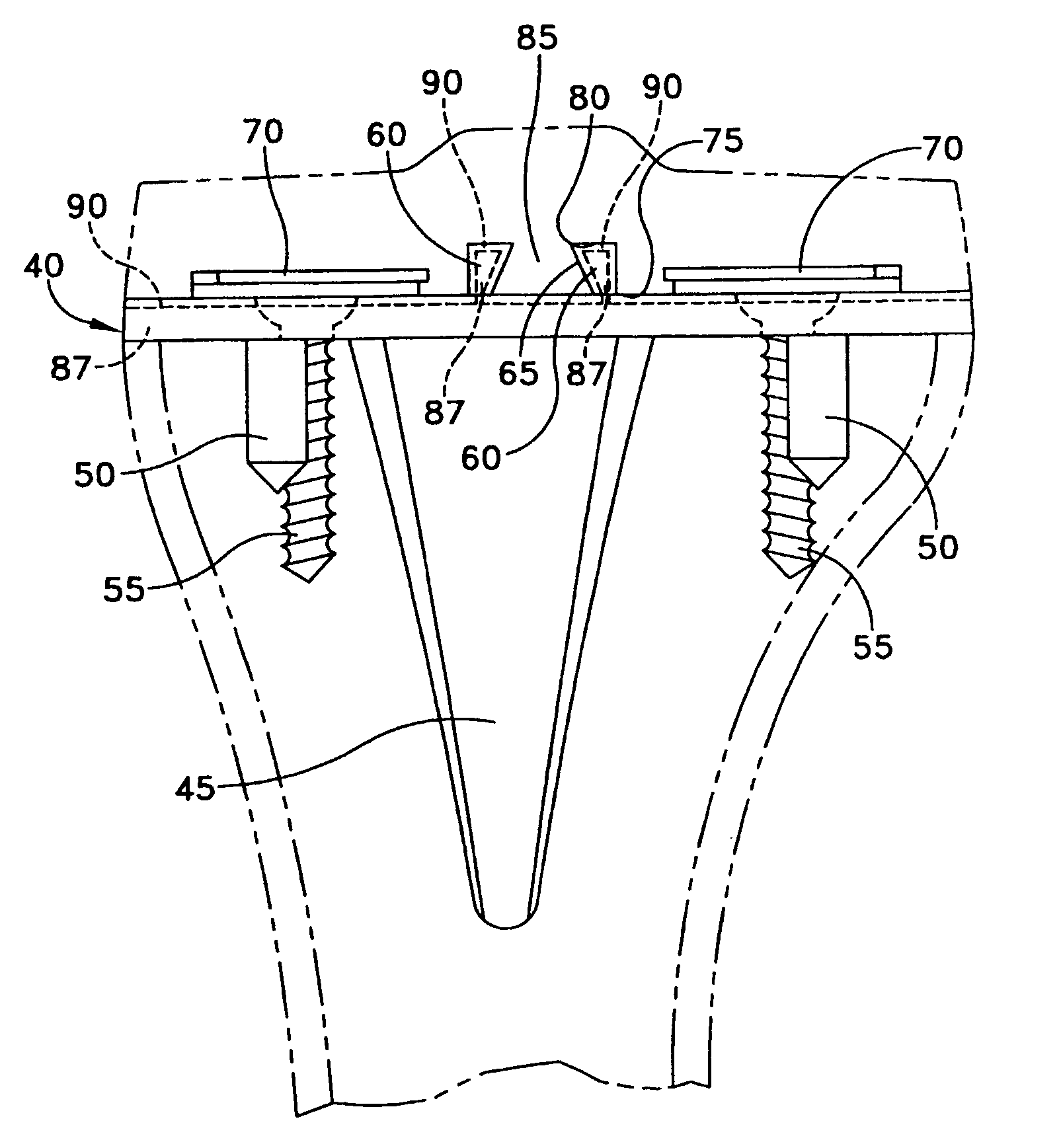
Knee balancing for revision procedures
ActiveUS20110093081A1Promote balance between supply and demandImprove balanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTibial Collateral LigamentsTotal knee replacement
Methods, systems and devices are provided for facilitating a surgical procedure on a knee, particularly, a revision total knee replacement procedure. Prior femoral and tibial prostheses are removed. A cut end of a distal femur is engaged with a femoral adjustment member, which will typically center itself about an intermedullary rod placed into the femur. The lateral and medial forces exerted by lateral and medial sides of the femoral adjustment member and the cut tibial plateau against each other are measured. The femoral adjustment member is adjusted to apply and / or adjust tension to the lateral collateral ligament and / or the medial collateral ligament based on the measured forces, for example, such that the measured lateral force and the measured medial force are matched. Based on the position of the adjusted femoral member, guided clean-up cuts for placement of a new femoral prostheses are made on the cut end of the distal femur.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Posterior stabilized knee system prosthetic devices employing diffusion-hardened surfaces
InactiveUS20030153979A1Restrict movementReduce frictionJoint implantsSolid state diffusion coatingOrthopedic departmentKnee Joint
An orthopedic implant with a diffusion-hardened surface on non-load bearing areas of the implant for interaction with non-load bearing surfaces of a polymeric bio-compatible material, such as UHMWPE. The orthopedic implant is a posterior stabilized knee prosthetic and system where a coating of oxidized zirconium is formed in the cam of the femoral prosthetic for interaction with the central post of a polymeric tibial insert. The diffusion-hardened surface of the orthopedic implant provides a strengthened cam and reduction in wear in the central post of the polymeric tibial insert.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
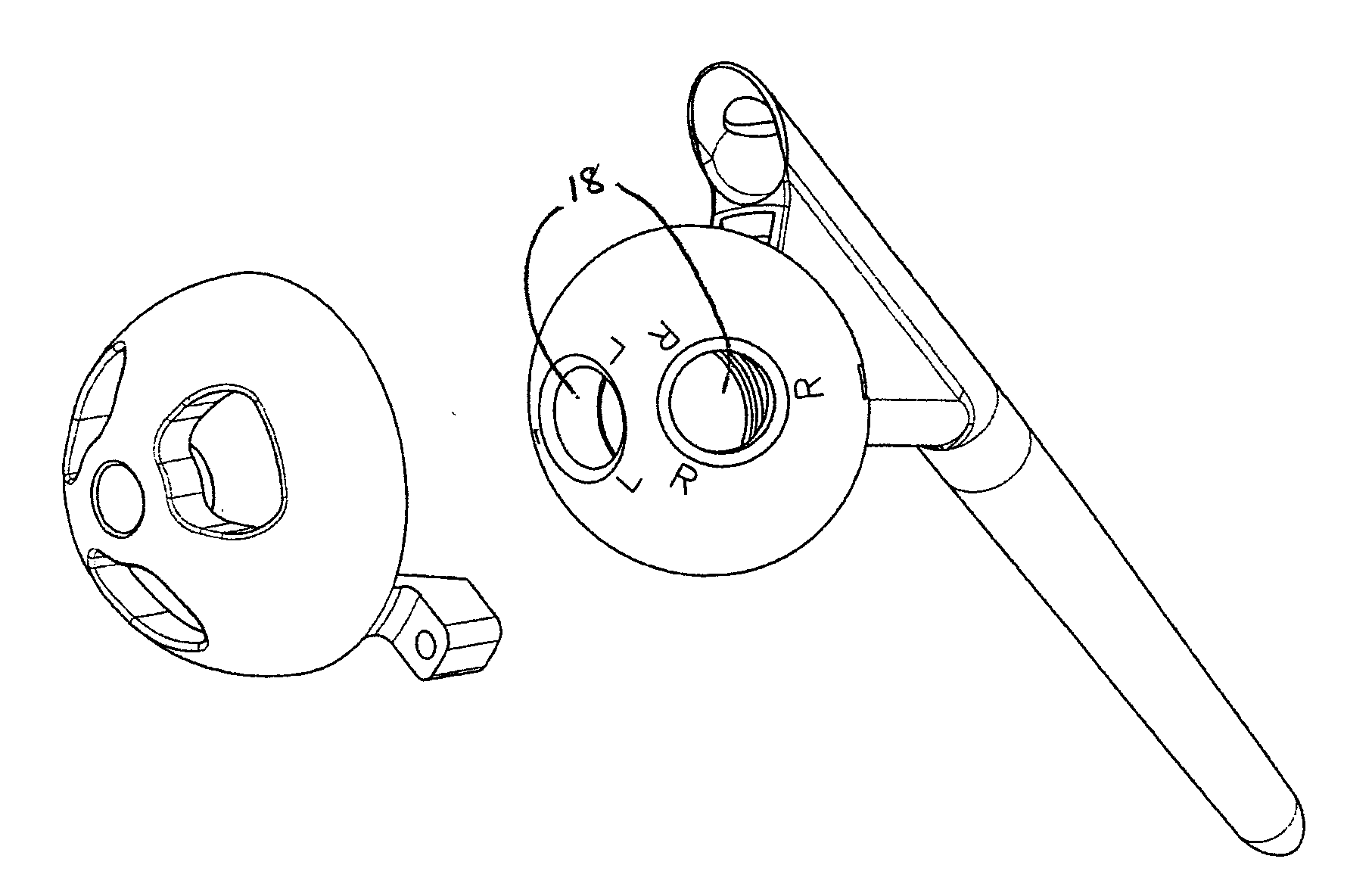
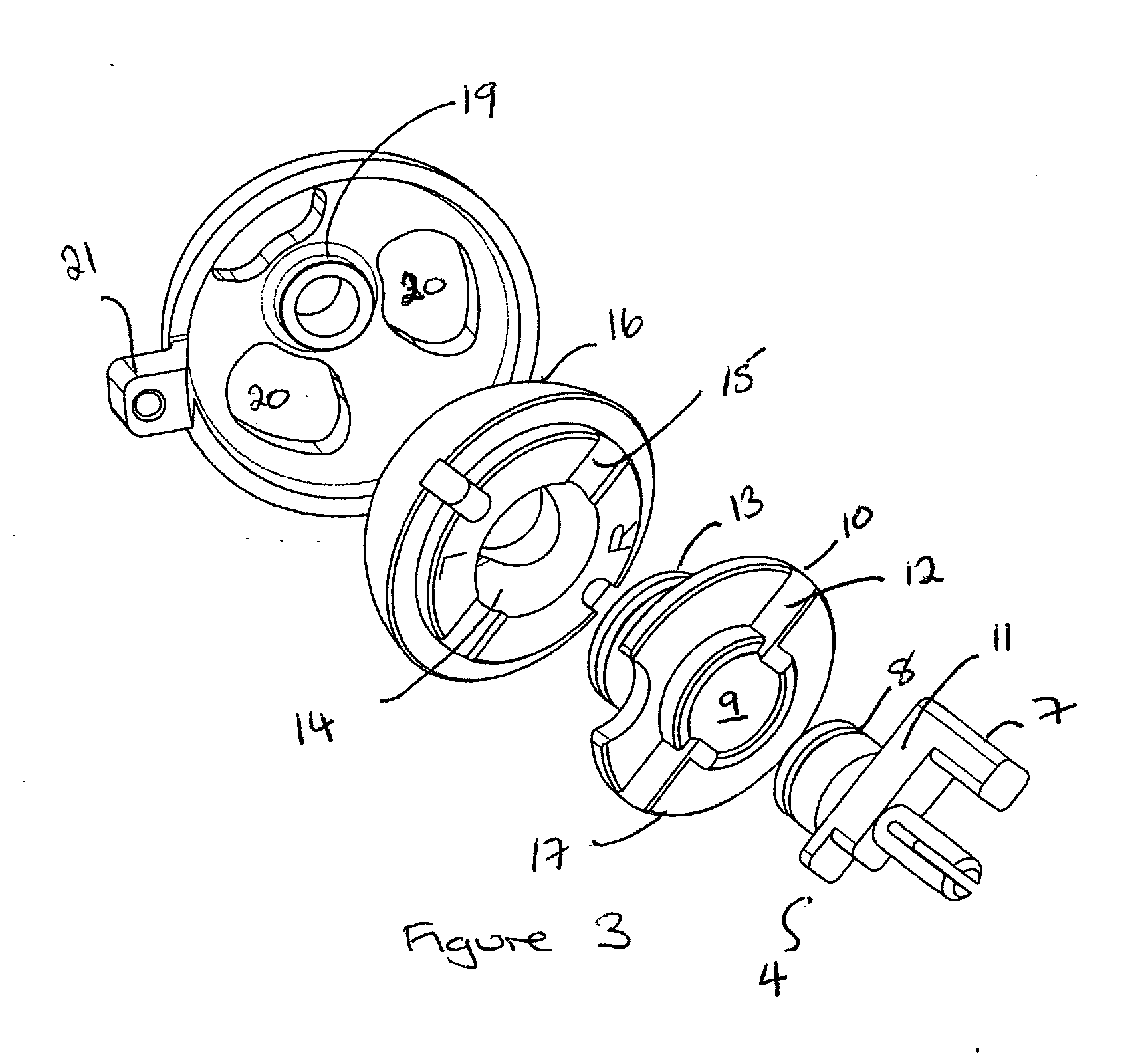
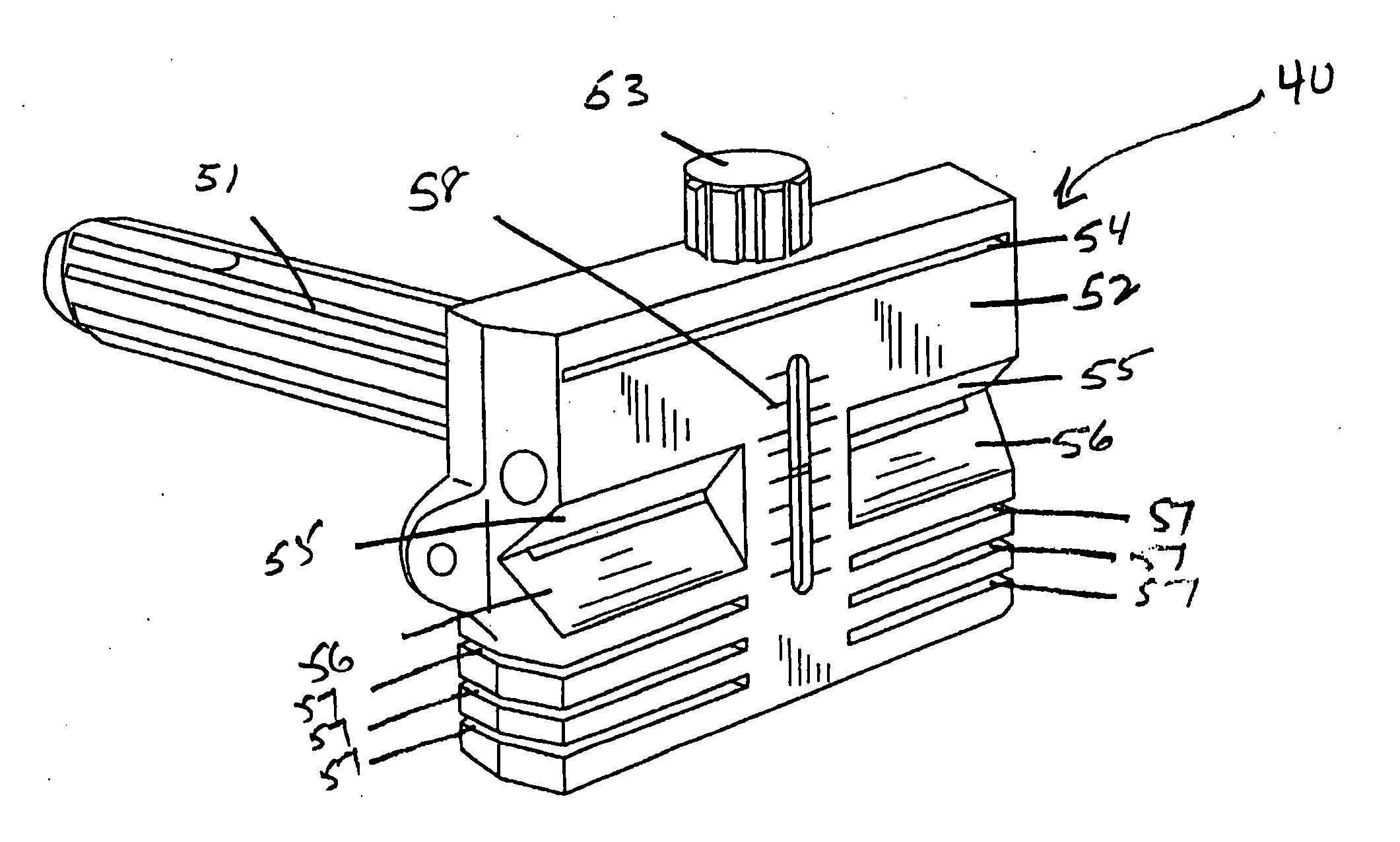
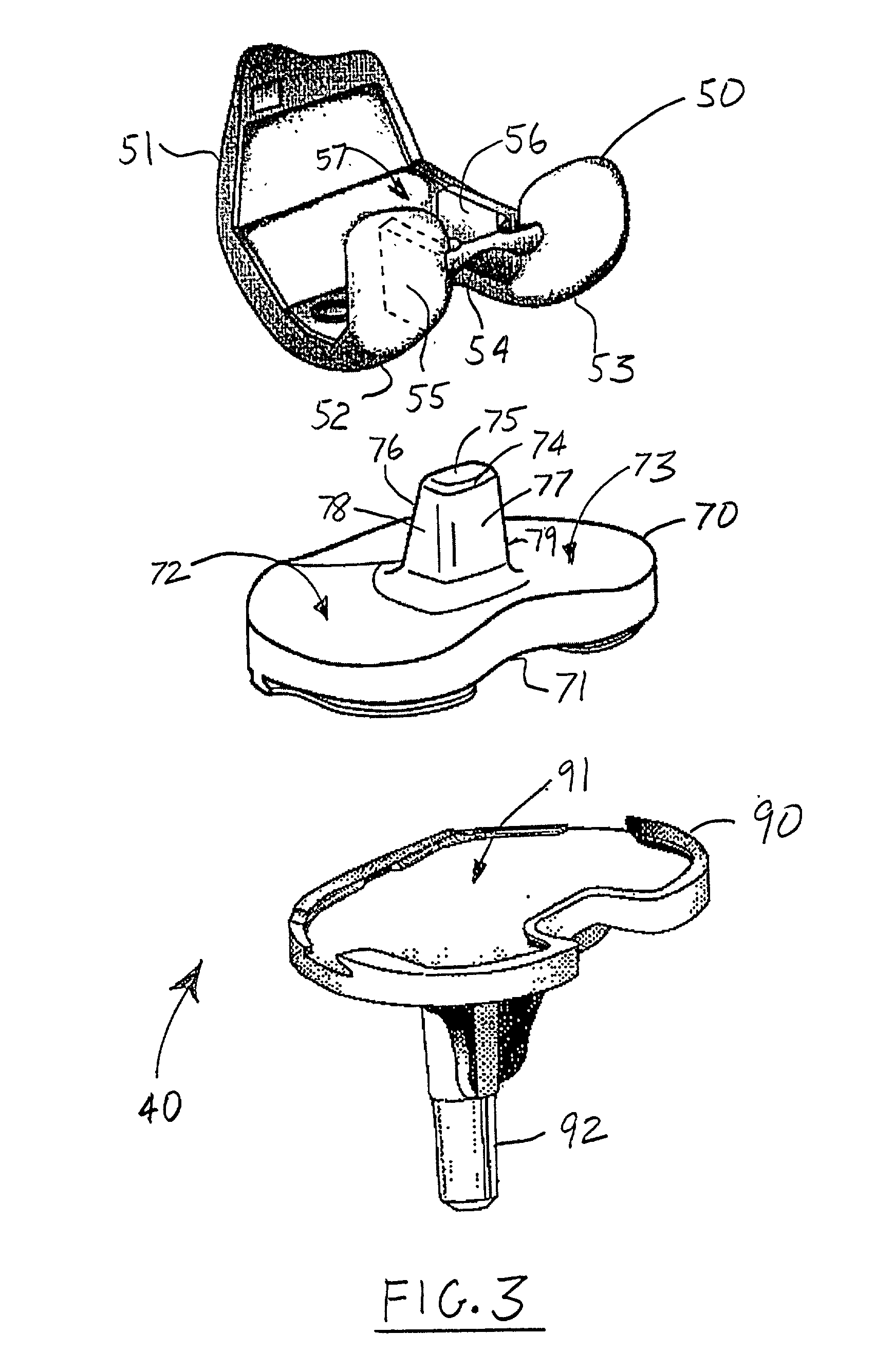
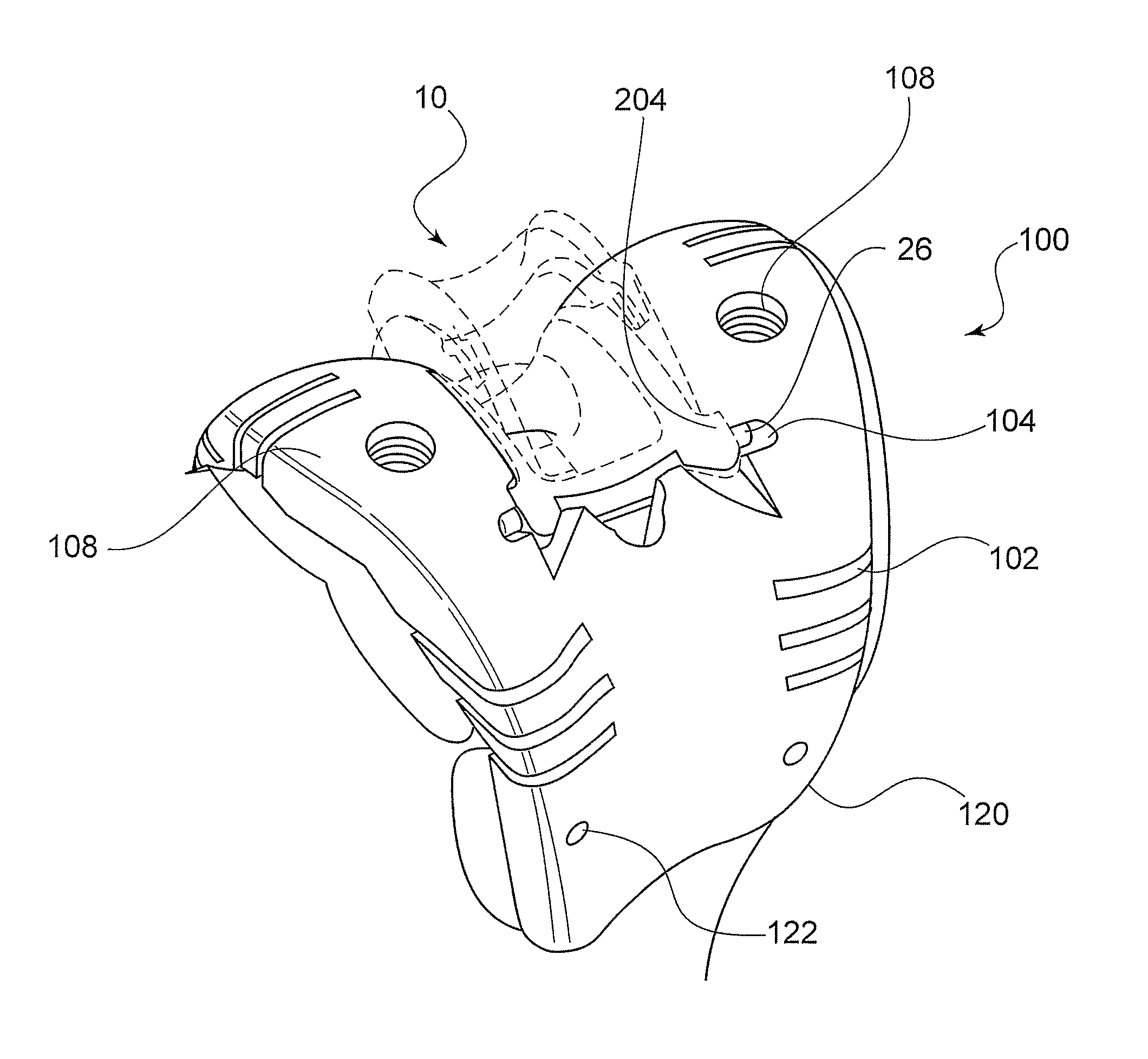
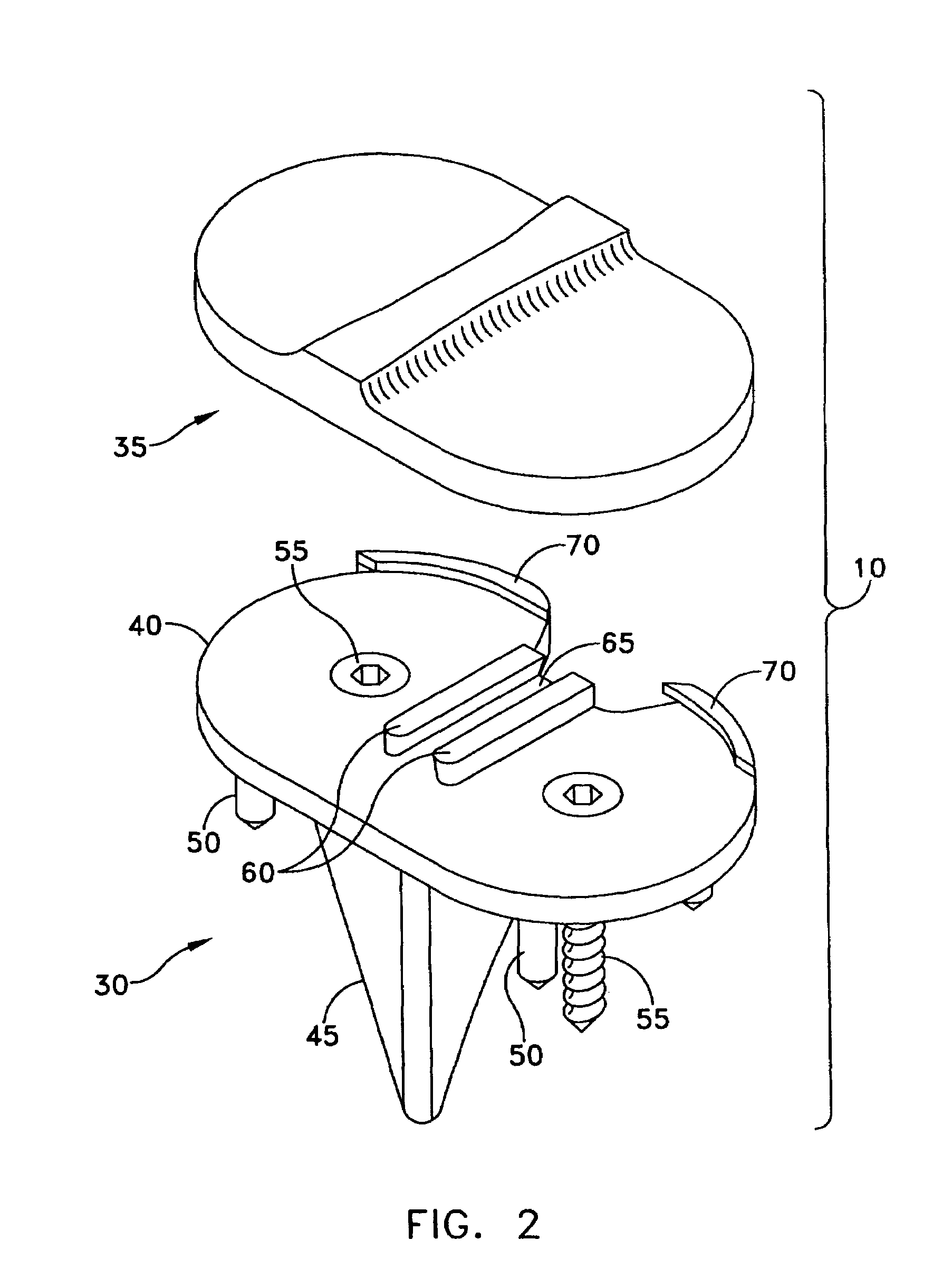
Trial femoral prosthesis and its use
Embodiments of the present application relate generally to provisional orthopedic components, and specifically, to a trial system including a cam module (10) and a trial femoral component (100) that can be used during joint replacement surgery. The systems and methods described help a surgeon prepare a patient's bone to receive a permanent implant by providing a system that can be used to guide preparatory box cuts, and that can then be completed with a cam module (10)—without removal from the patient's bone—so that the same component can be used for the trialing process.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Knee balancing for revision procedures
ActiveUS8506571B2Promote balance between supply and demandImprove balanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTibiaIntramedullary rod
Methods, systems and devices are provided for facilitating a surgical procedure on a knee, particularly, a revision total knee replacement procedure. Prior femoral and tibial prostheses are removed. A cut end of a distal femur is engaged with a femoral adjustment member, which will typically center itself about an intramedullary rod placed into the femur. The lateral and medial forces exerted by lateral and medial sides of the femoral adjustment member and the cut tibial plateau against each other are measured. The femoral adjustment member is adjusted to apply and / or adjust tension to the lateral collateral ligament and / or the medial collateral ligament based on the measured forces, for example, such that the measured lateral force and the measured medial force are matched. Based on the position of the adjusted femoral member, guided clean-up cuts for placement of a new femoral prostheses are made on the cut end of the distal femur.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
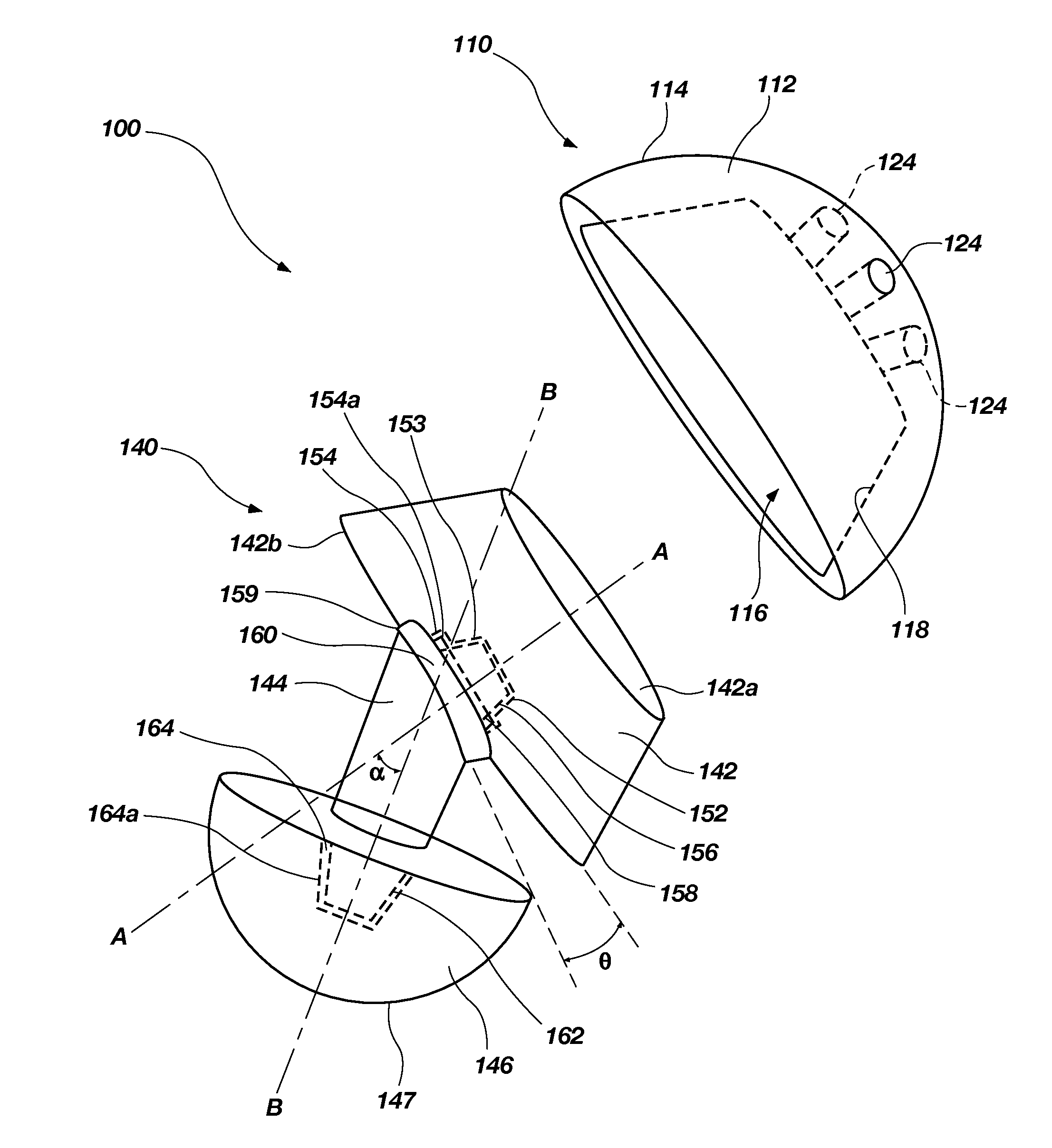
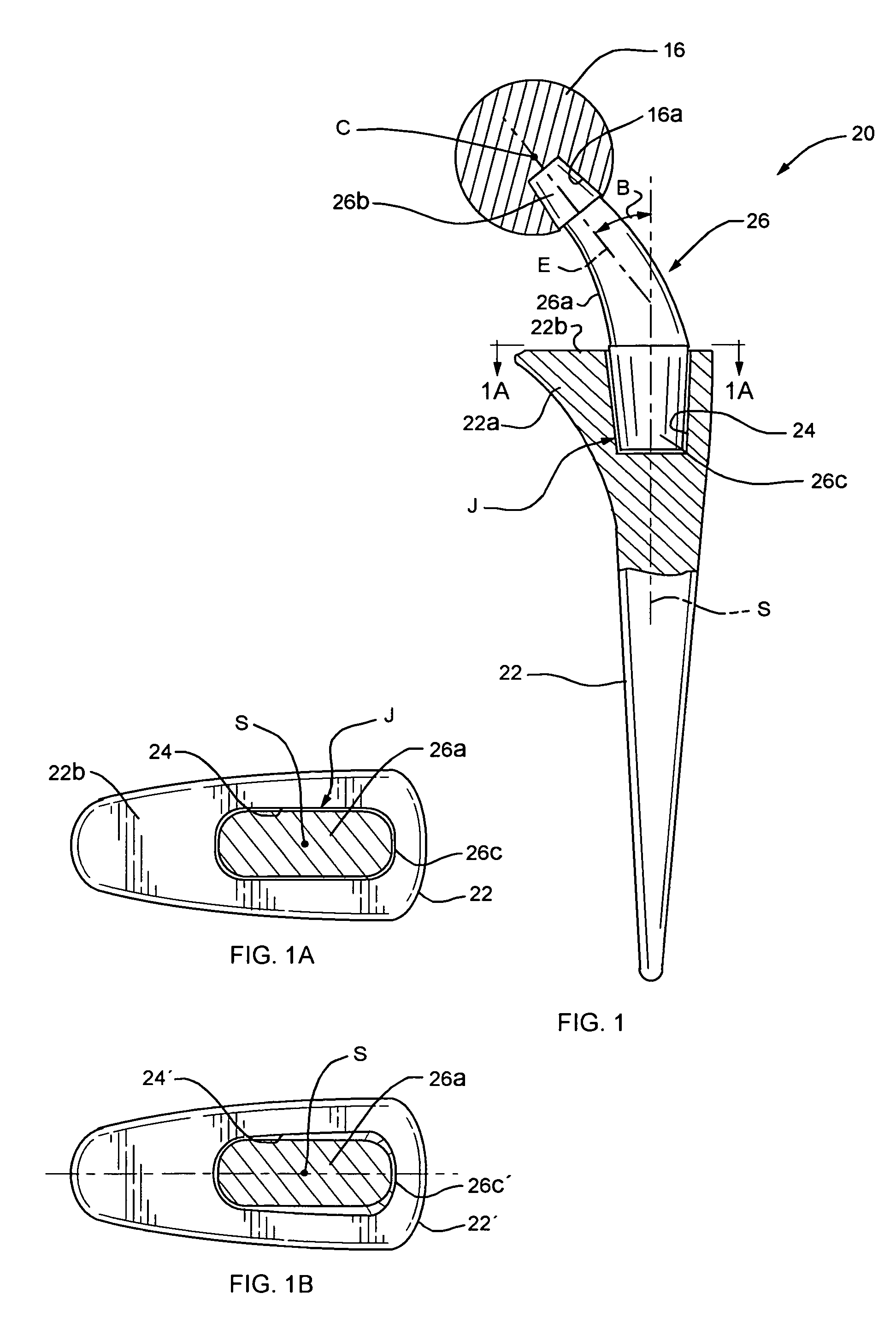
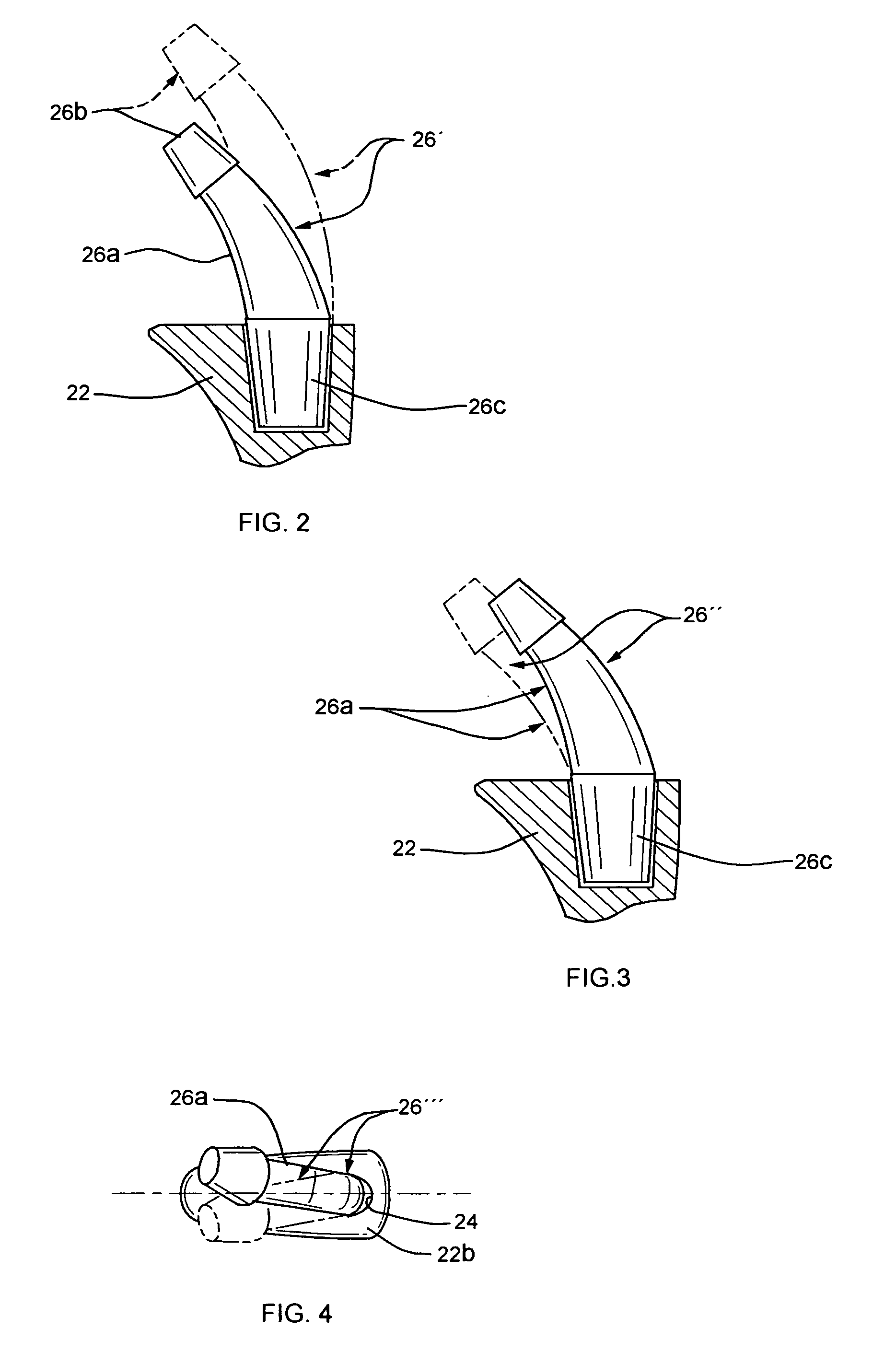
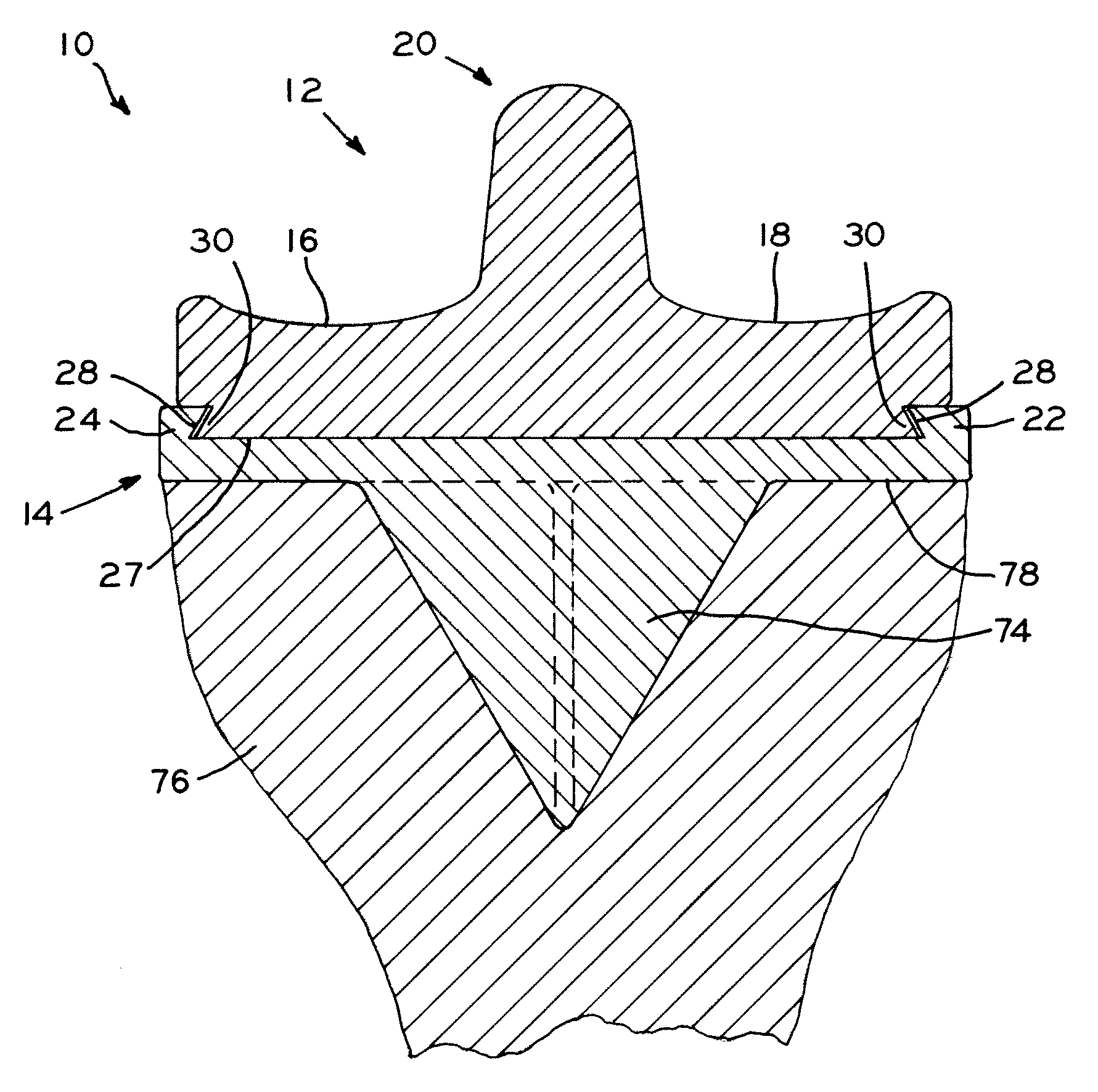
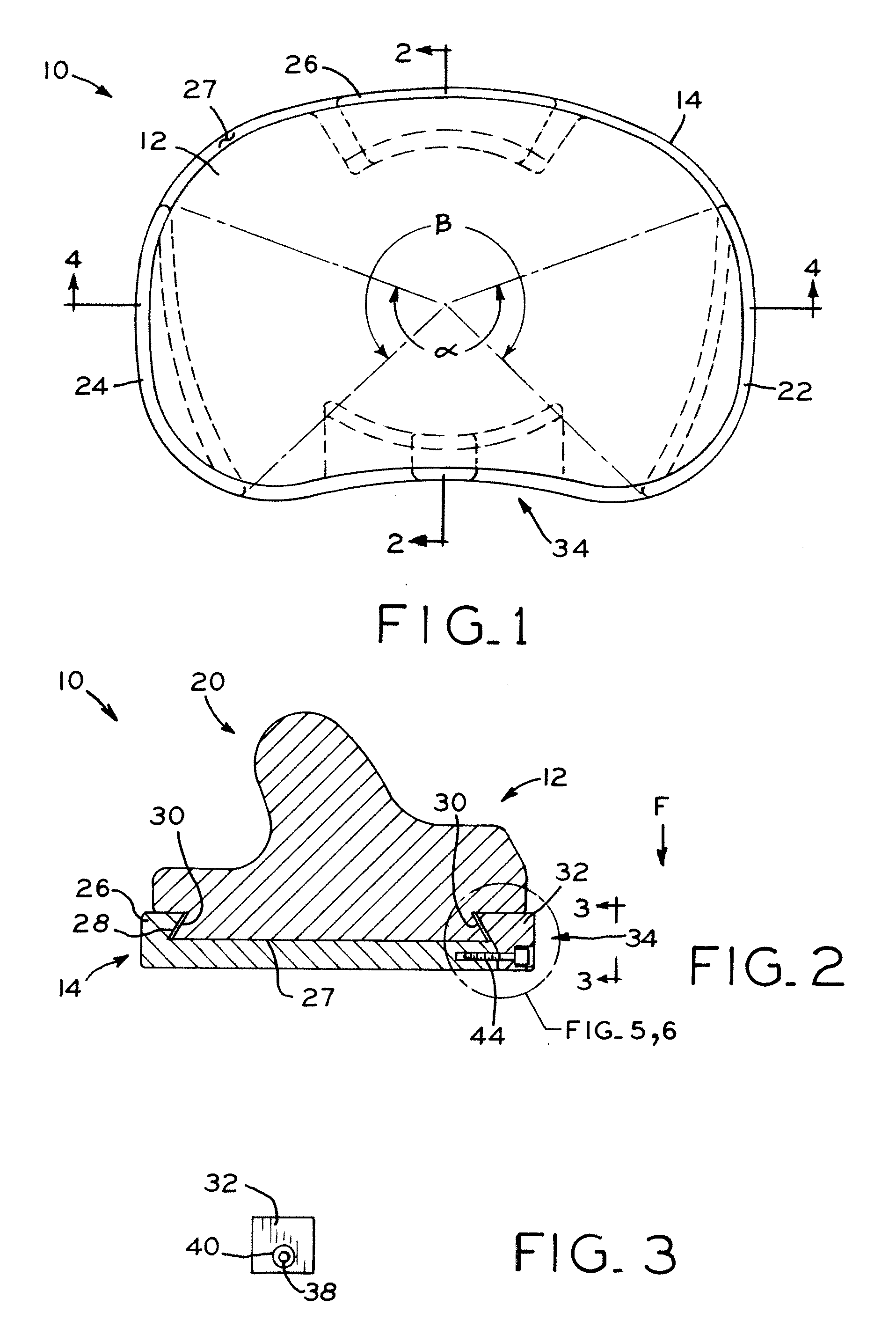
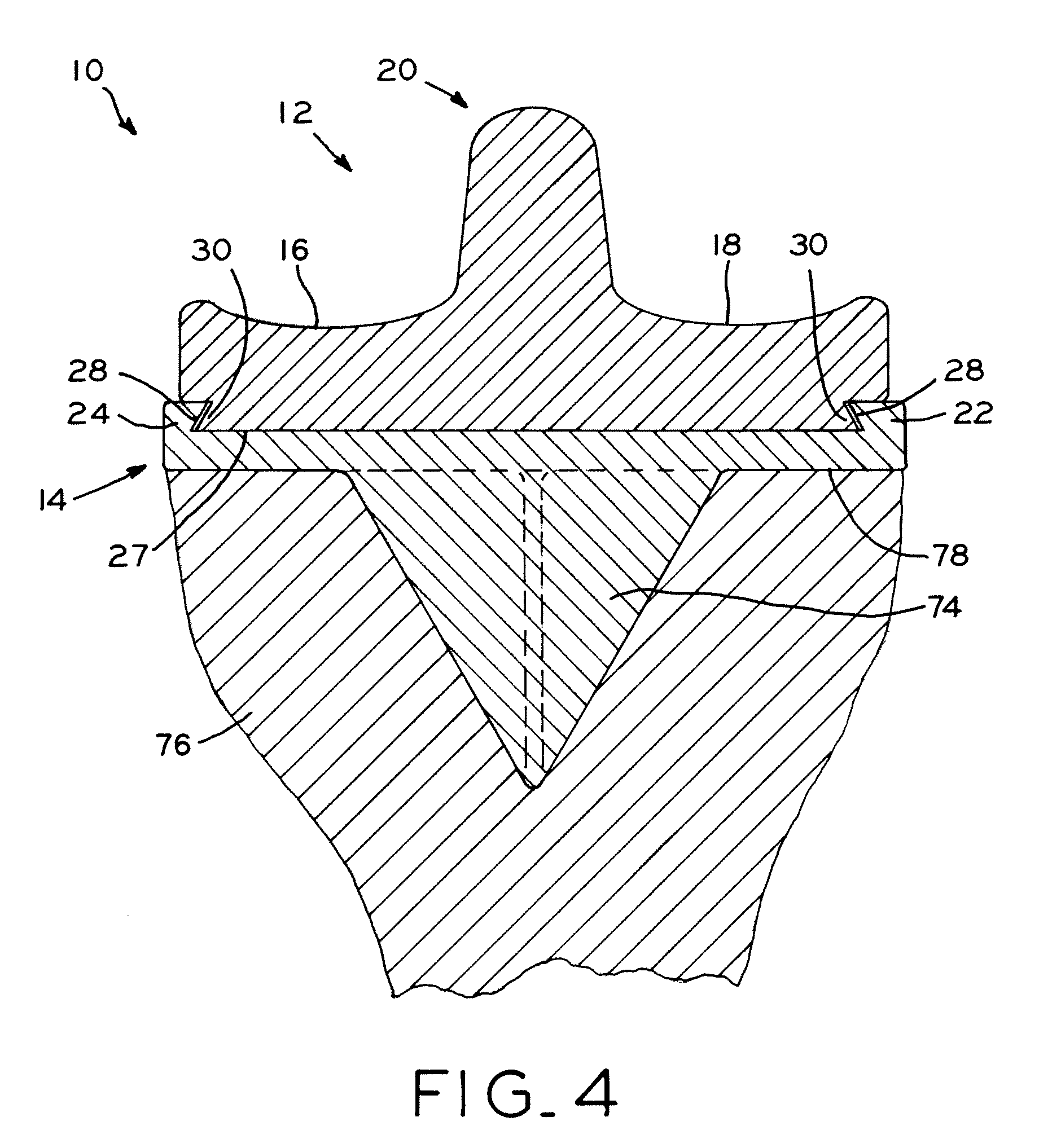
J-curve for a femoral prosthesis component
ActiveUS20110153026A1Improve stabilityClose approximationJoint implantsKnee jointsRange of motionKnee Joint
One or both of the condyles in a femoral component for a partial or total knee prosthesis includes a J-curve with a plurality of distinct radii, such as 5 or more radii. The centers of the radii are arranged along an arcuate path extending anteroposteriorly so that successively larger radii are serially arranged along the arcuate path from the posterior side of the femoral component to the anterior side. The femoral component provides a high degree of stability throughout the range of motion of the knee prosthesis, and facilitates a close approximation to the motion of a natural knee.
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
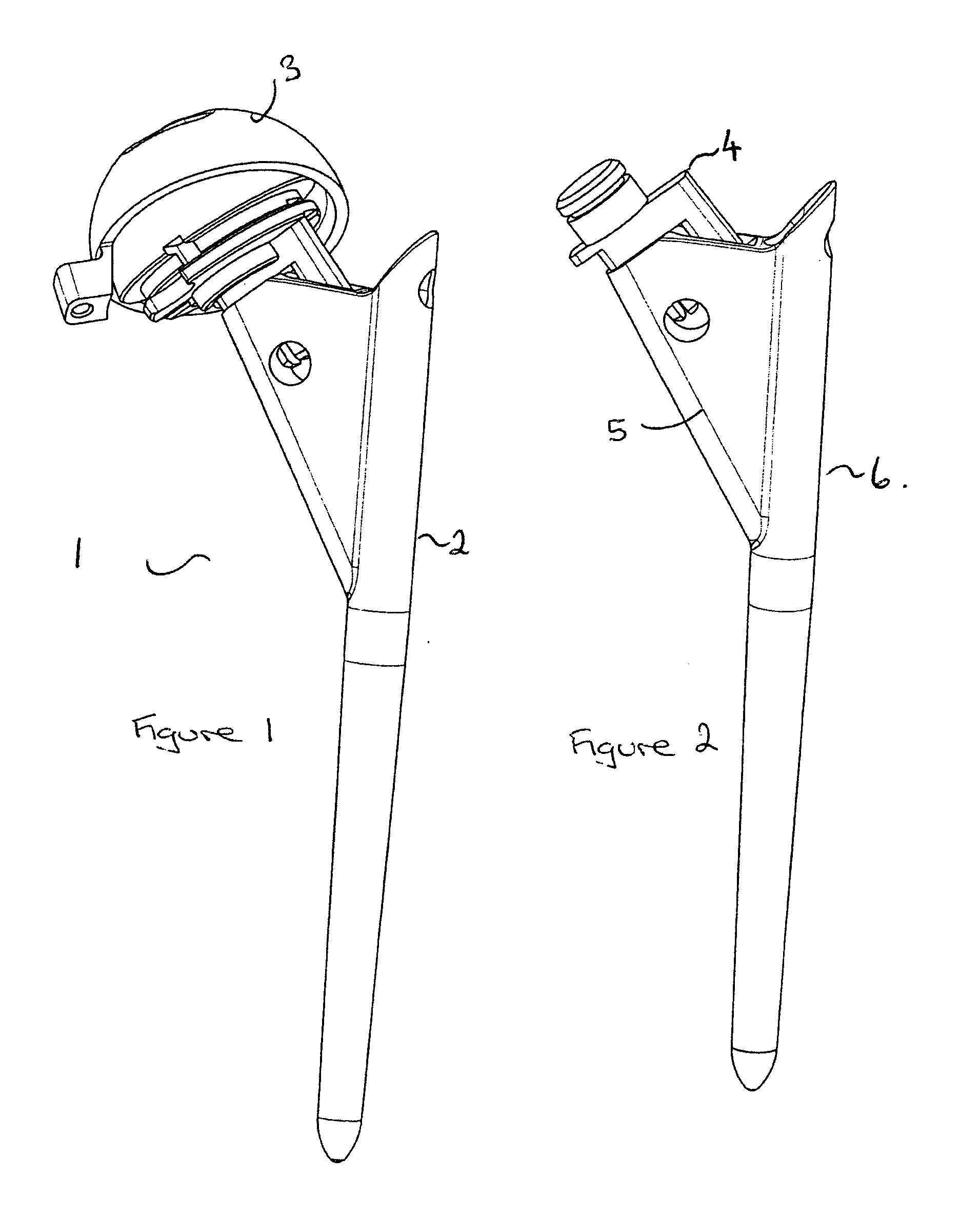
Modular femoral prosthesis with on-axis junction
ActiveUS7776098B2Easy and inexpensive to manufactureEasy to implantJoint implantsFemoral headsFemoral stemModularity
A modular hip prosthesis includes a femoral stem, a spherical head and a coupling member extending from the head defining a neck whose lower end forms a base which plugs into a socket at the top of the stem to form a tapered neck / stem junction. That junction is aligned with the stem axis and has a cross-section with opposite sides that extend generally parallel to the sides of the stem. With such an arrangement, that junction may be relatively long and have a relatively large cross-sectional area thus making a strong junction even in smaller femoral implants.
Owner:MURPHY STEPHEN B
Bimetal tibial component construct for knee joint prosthesis
InactiveUS7513912B2Superior bone-engaging faceSuperior polyethylene-engaging faceJoint implantsTissue regenerationMedicineKnee Joint
Owner:SHALBY ADVANCED TECH INC
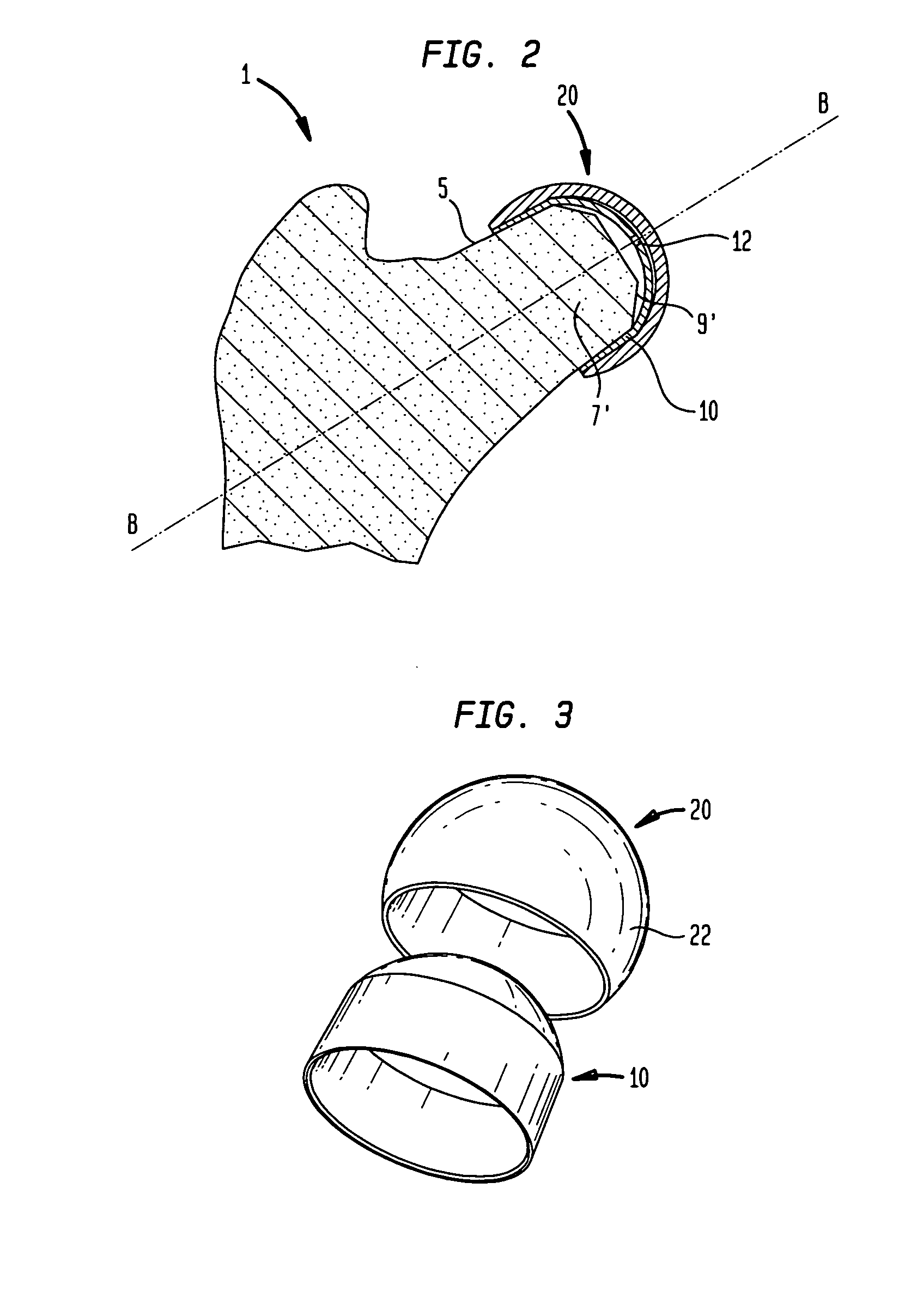
Patello-femoral prosthesis
A patello-femoral prosthesis is provided for replacing the engagement surfaces between the patella and the femur. The prosthesis is configured to cover the trochlear groove and extend into the intercondylar notch without extending onto the articulating surfaces of the condyles. A method is also provided for implanting a patello-femoral prosthesis in which a portion of the trochlear groove and intercondylar notch are resected and the prosthesis is implanted over the femur that had portions resected.
Owner:LOTKE PAUL A
Femoral sleeve for hip resurfacing
InactiveUS20080262626A1Maximizes retentionMinimize installation difficultyAnkle jointsJoint implantsRight femoral headCoxal joint
A hip resurfacing femoral prosthesis has a sleeve component with an internal bore adapted to receive a femoral head and a partially conical outer surface. The sleeve is for use with a mating partial ball component shaped to conform to an acetabular socket. The sleeve is slotted or segmented to enhance the engagement with the femoral head. The partial ball component may be translated proximally and distally to reposition the outer surface by selecting sleeves with varying geometries.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Bionic gradient knee femoral prosthesis structure and a production method thereof
ActiveCN103584931AImprove adaptabilityAdapt to exerciseAdditive manufacturing apparatusJoint implantsKnee JointFemoral prosthesis
The invention discloses a bionic gradient knee femoral prosthesis structure and a production method thereof. The prosthesis structure comprises a smooth curved-surface shell, a post-osteotomy completely-covering joint face, a gradient porous structure and a fixing device. The curved-surface shell is based on the shape of the distal end of a connate femur. The post-osteotomy completely-covering joint face reversely spreads to the distal-end curved surface of the connate femur. A solid more than 5mm distant from the curved surface is replaced by the gradient porous structure, and the fixing device is formed on the distal-end plane on the inner side of a femoral prosthesis. Compared with conventional standard prostheses, the prosthesis structure has the advantages that matching degree is high, and the prosthesis highly fits the bone shape of a connate knee and is adaptable to motions of a patient. The bionic gradient knee femoral prosthesis structure is easy to produce, and conventional production methods for conventional bionic gradient prostheses are complex; by the 3D (three-dimensional)-printing production method, prostheses can be customized according to individual differences of patients, production period is short, cost is low, and a possibility for application and development of individualized therapy is provided.
Owner:BEIJING NATON TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for hip femoral resurfacing tooling
InactiveUS20080109085A1Successful surface replacementSimple methodJoint implantsFemoral headsRight femoral headCoxal joint
Tools and methods for implanting hip resurfacing femoral prostheses along a path defined by the axis of a shaped femoral head surface are described. The prostheses are stemless partial ball components having an outer surface shaped to conform to an acetabular socket and may be a two part design having a mating sleeve component with an internal bore adapted to receive the shaped femoral head. The tools and methods are capable of accurately implanting both one and two piece ball components and sleeves without requiring the prosthesis to have a central stem or the preparation of a stem cavity in the femoral head and neck.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Transiently mobile tibial engagement
ActiveUS20100125339A1Maximum tibial bone coveragePrevent and minimizeJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaLocking mechanism
The present invention relates to a tibial prosthesis having an articulating component and a tray component. The articulating component is configured for attachment to the tray component. Additionally, the articulating component may be attached to the tray component in a first condition in which the articulating component is at least rotatable relative to the tray component. This allows for the tray component to be attached to the tibia in a position that provides for proper rotation of the tray component with respect to the tibia and / or prevents the tray component from overhanging the resected tibia. Then, the articulating component may be rotated and / or translated to a position that provides for proper alignment of the articulating component with a femoral prosthesis. Once in this positioned, a locking mechanism is used to rotationally fix the articulating component to the tray component.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Method and apparatus for hip femoral resurfacing tooling
ActiveUS20110004318A1Successful surface replacementAdditional toolJoint implantsFemoral headsMuscles of the hipFemoral prosthesis
Tools and methods for implanting hip resurfacing femoral prostheses along a path defined by the axis of a shaped femoral head surface are described. The prostheses are stemless partial ball components having an outer surface shaped to conform to an acetabular socket and may be a two part design having a mating sleeve component with an internal bore adapted to receive the shaped femoral head. The tools and methods are capable of accurately implanting both one and two piece ball components and sleeves without requiring the prosthesis to have a central stem or the preparation of a stem cavity in the femoral head and neck.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
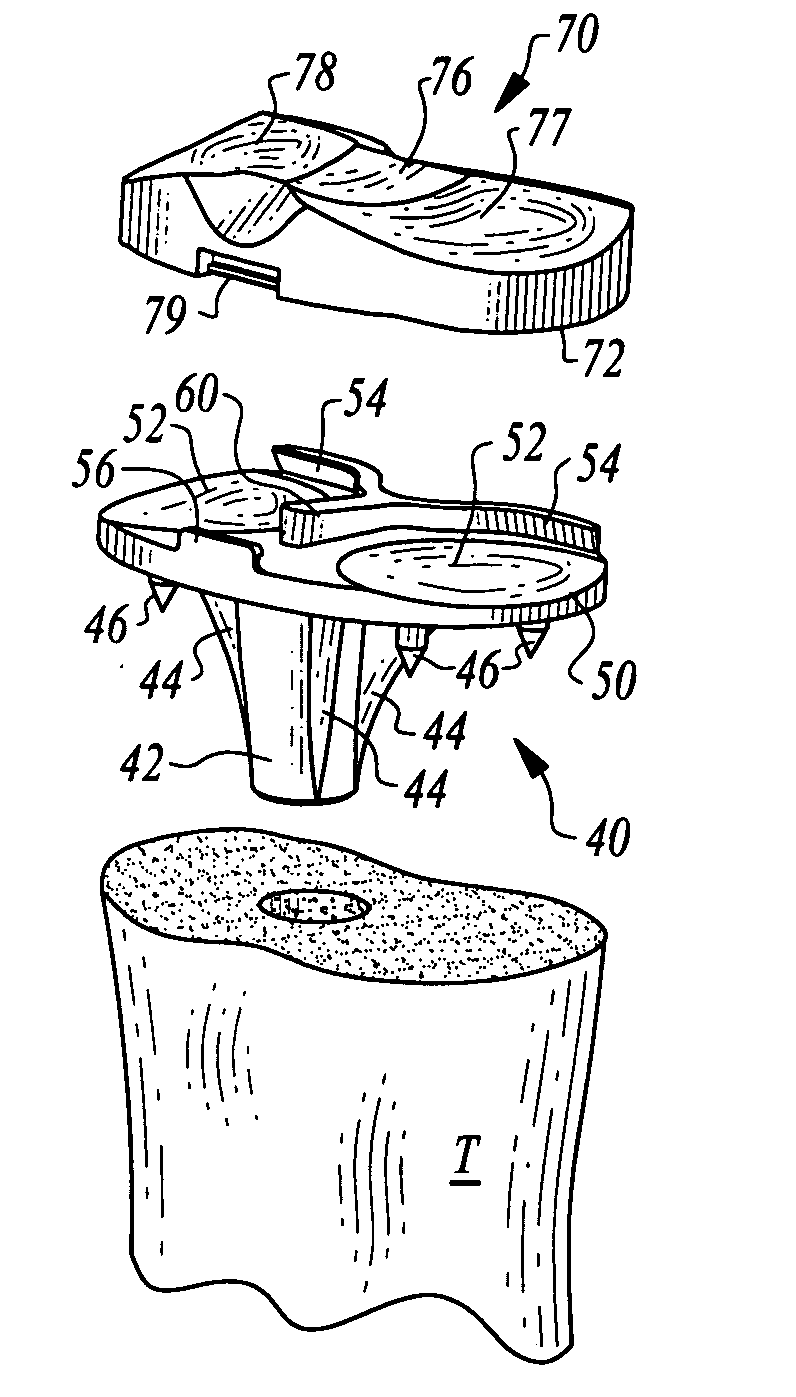
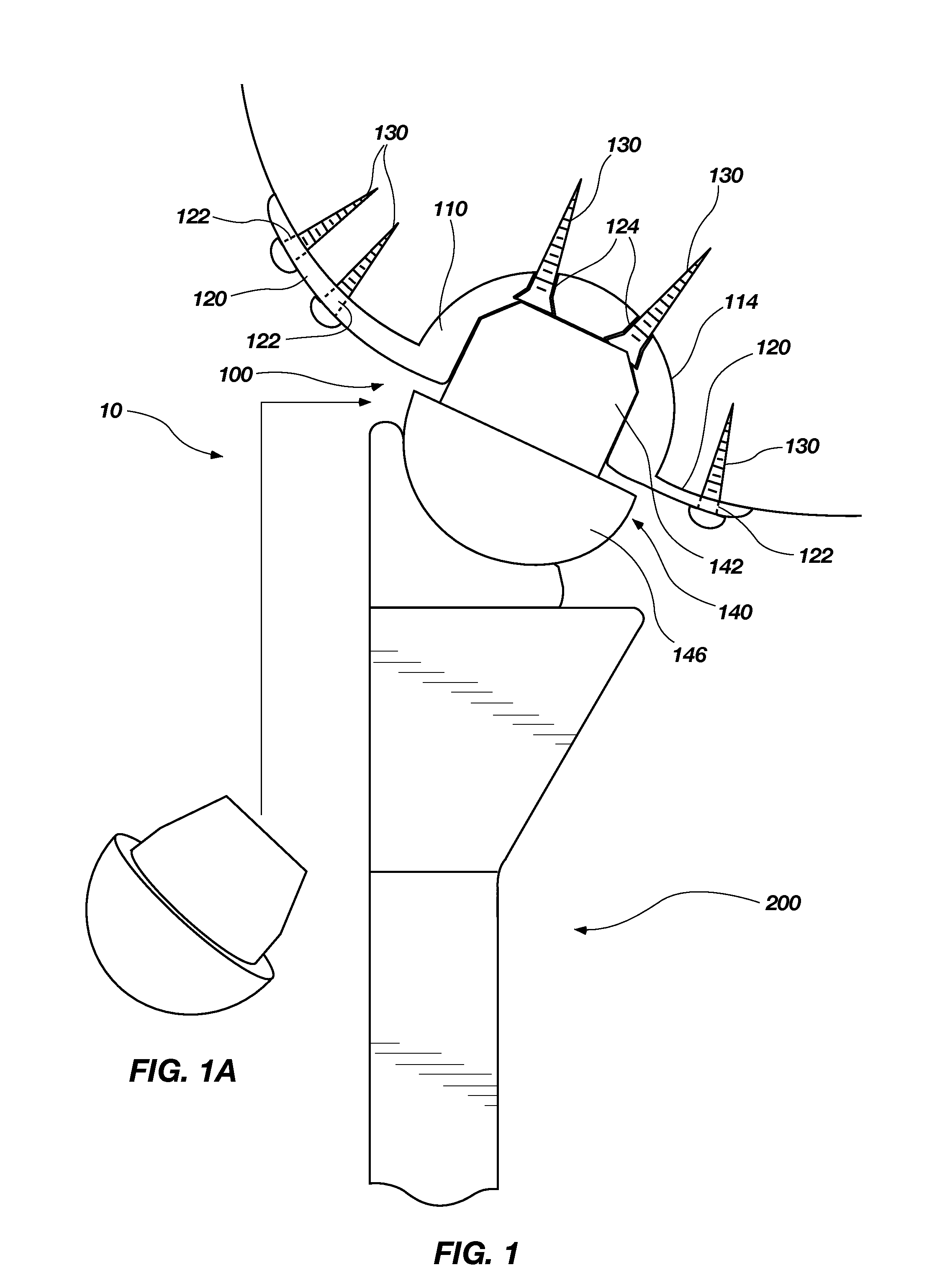
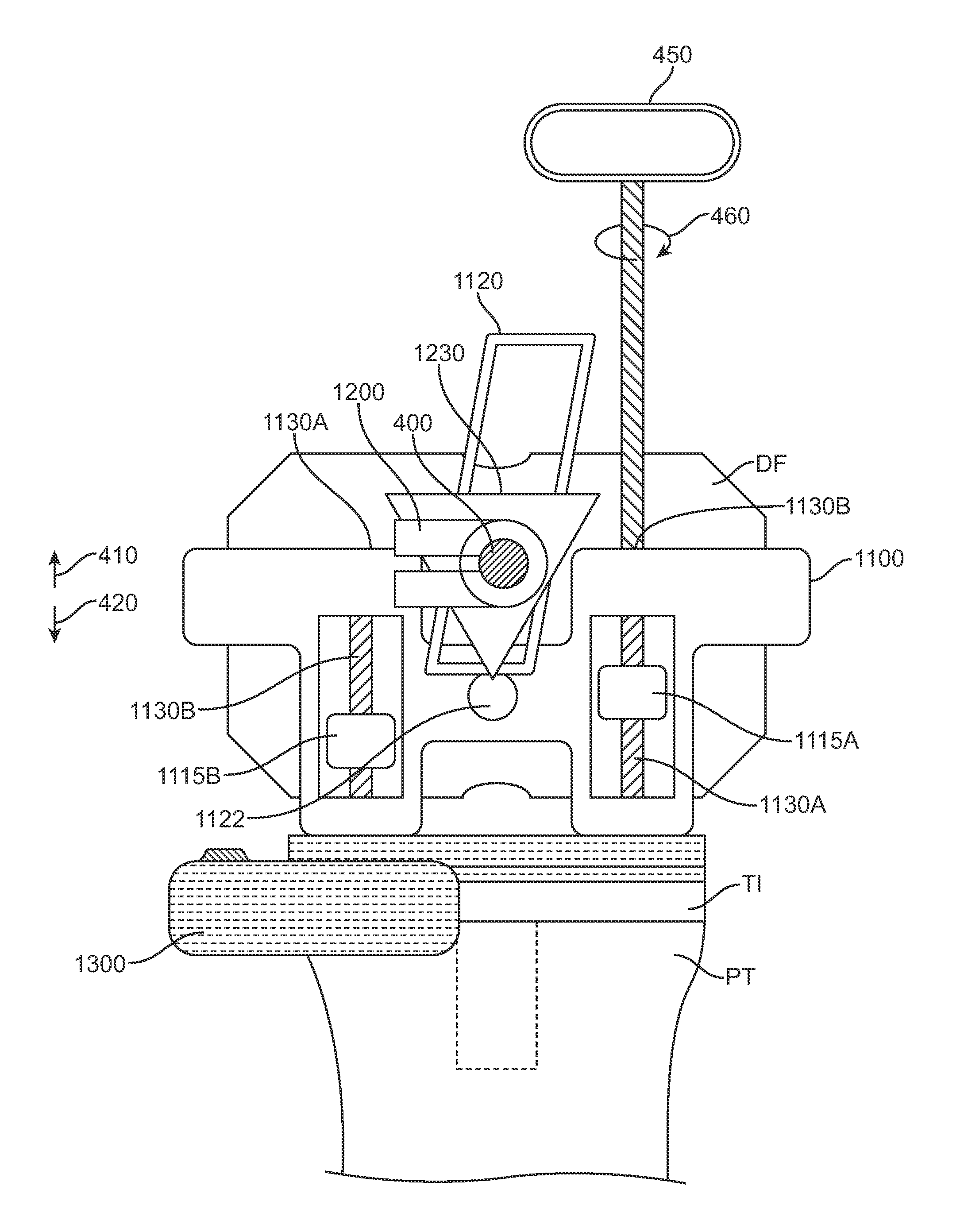
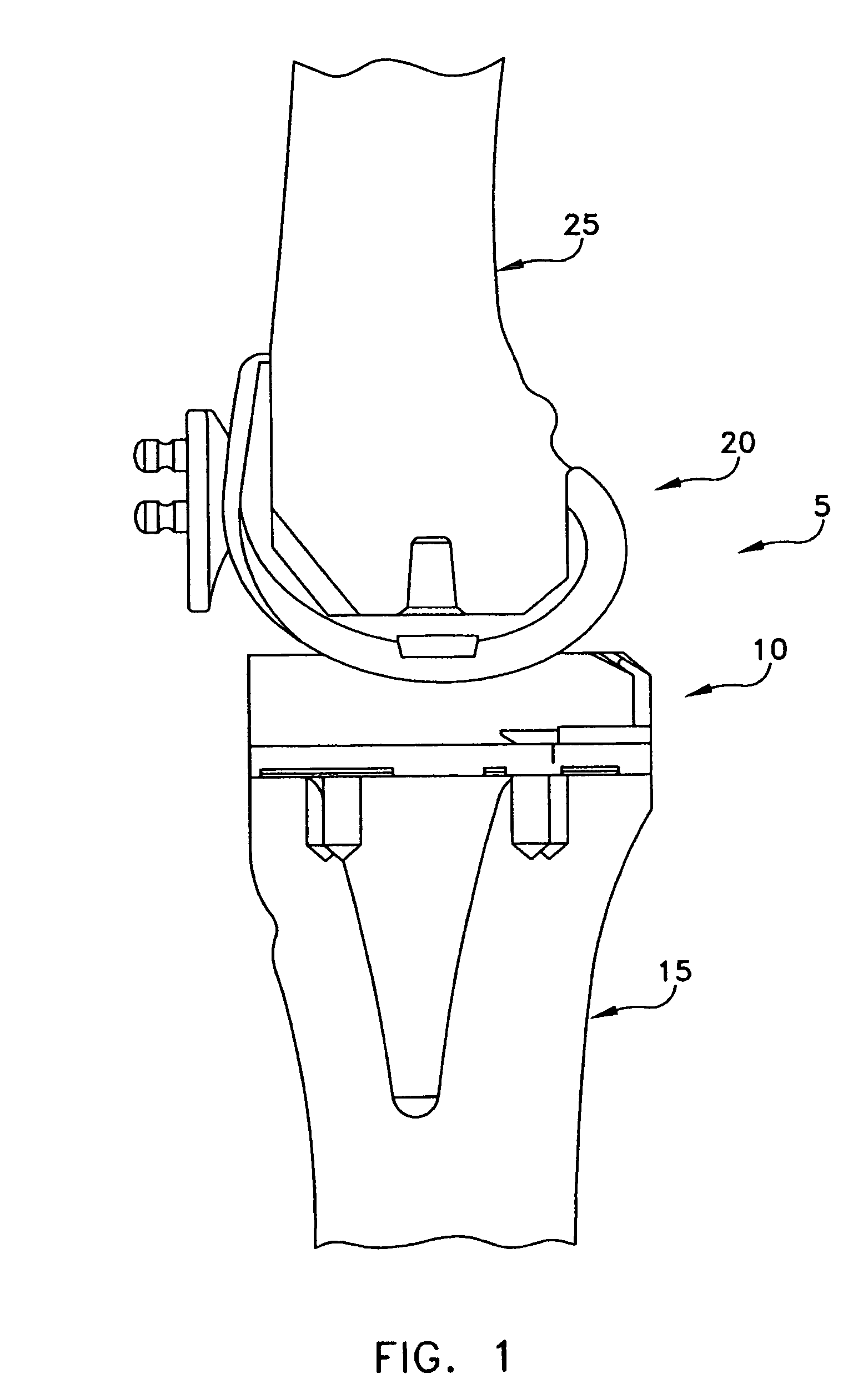
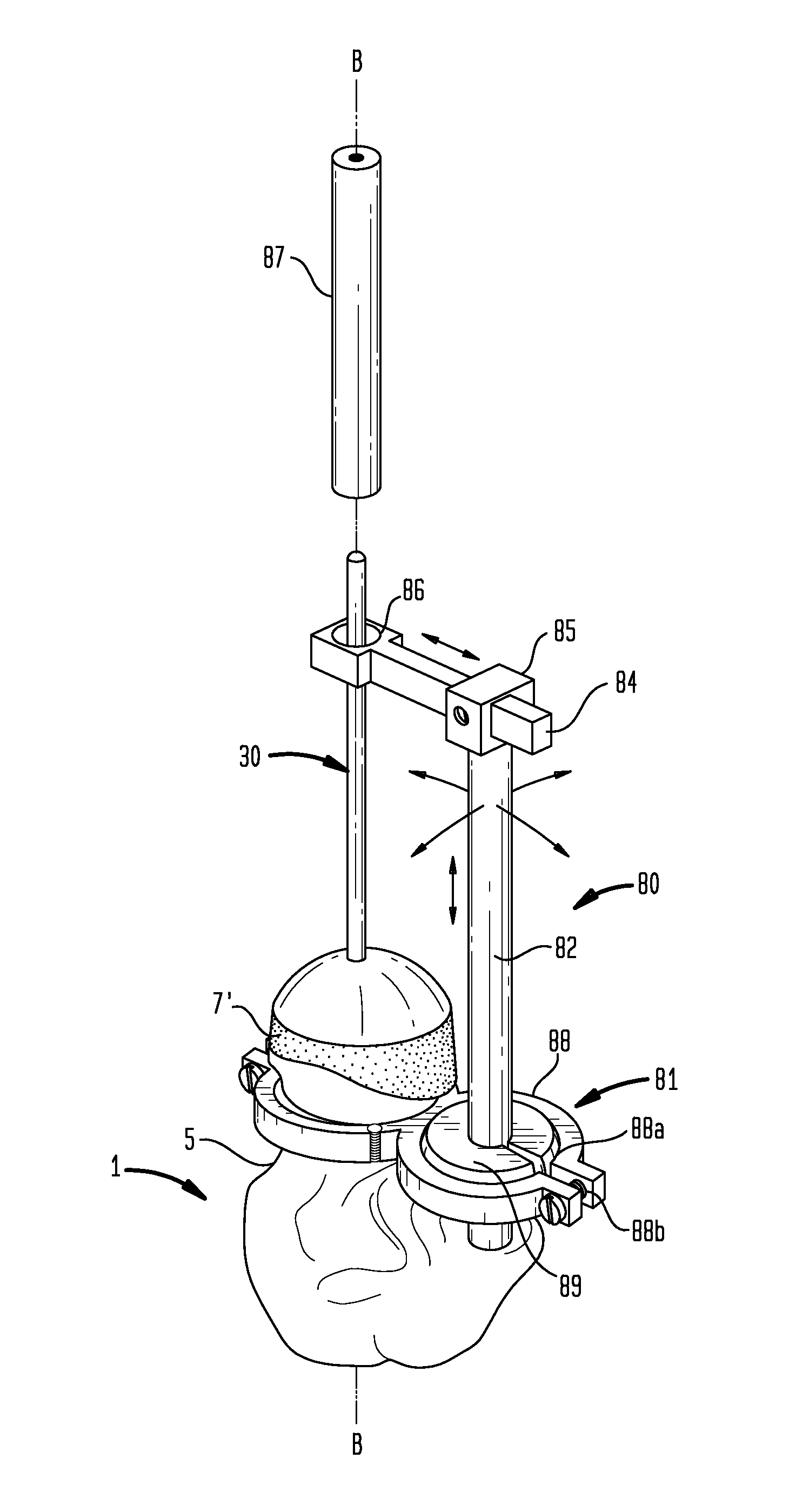
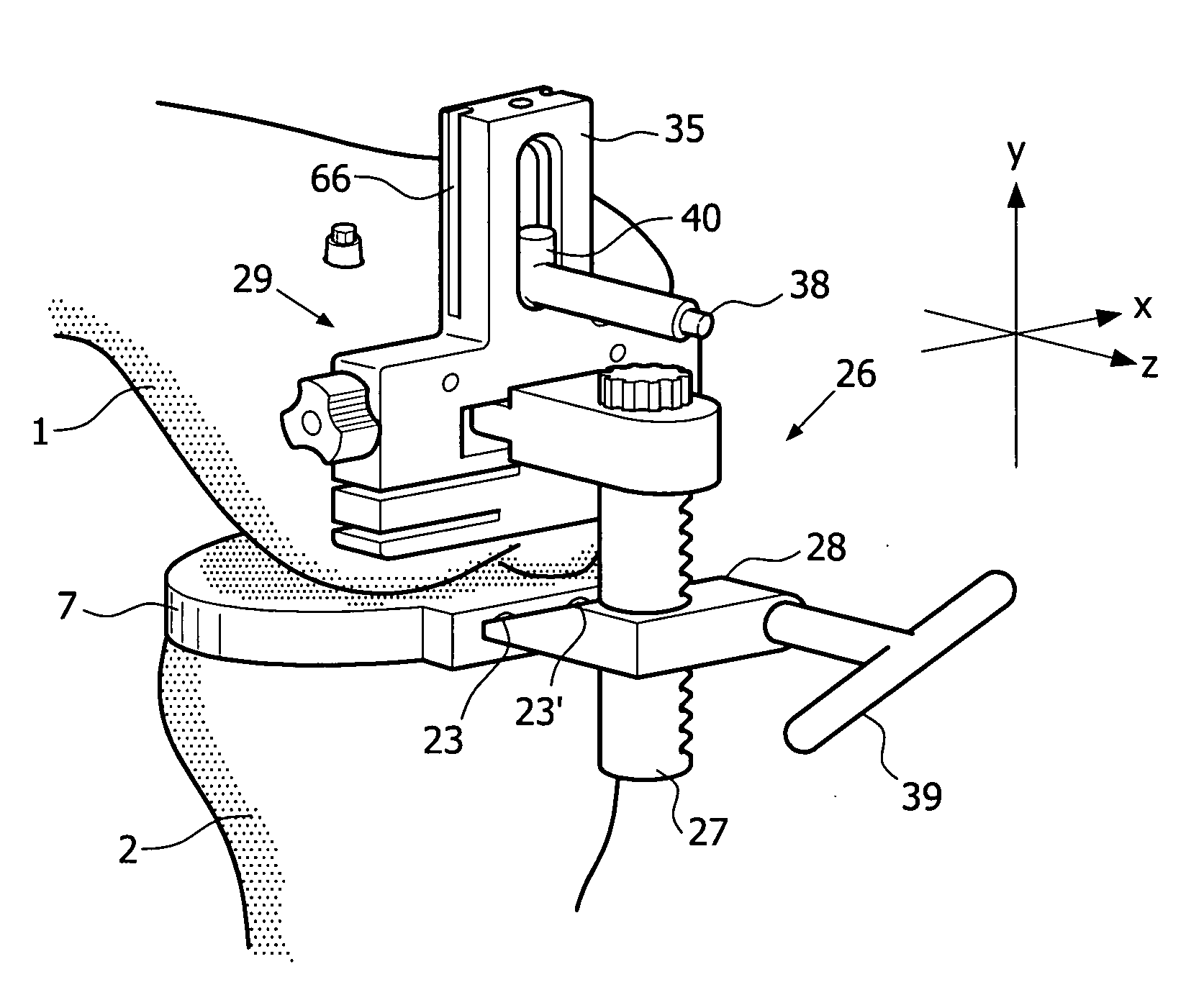
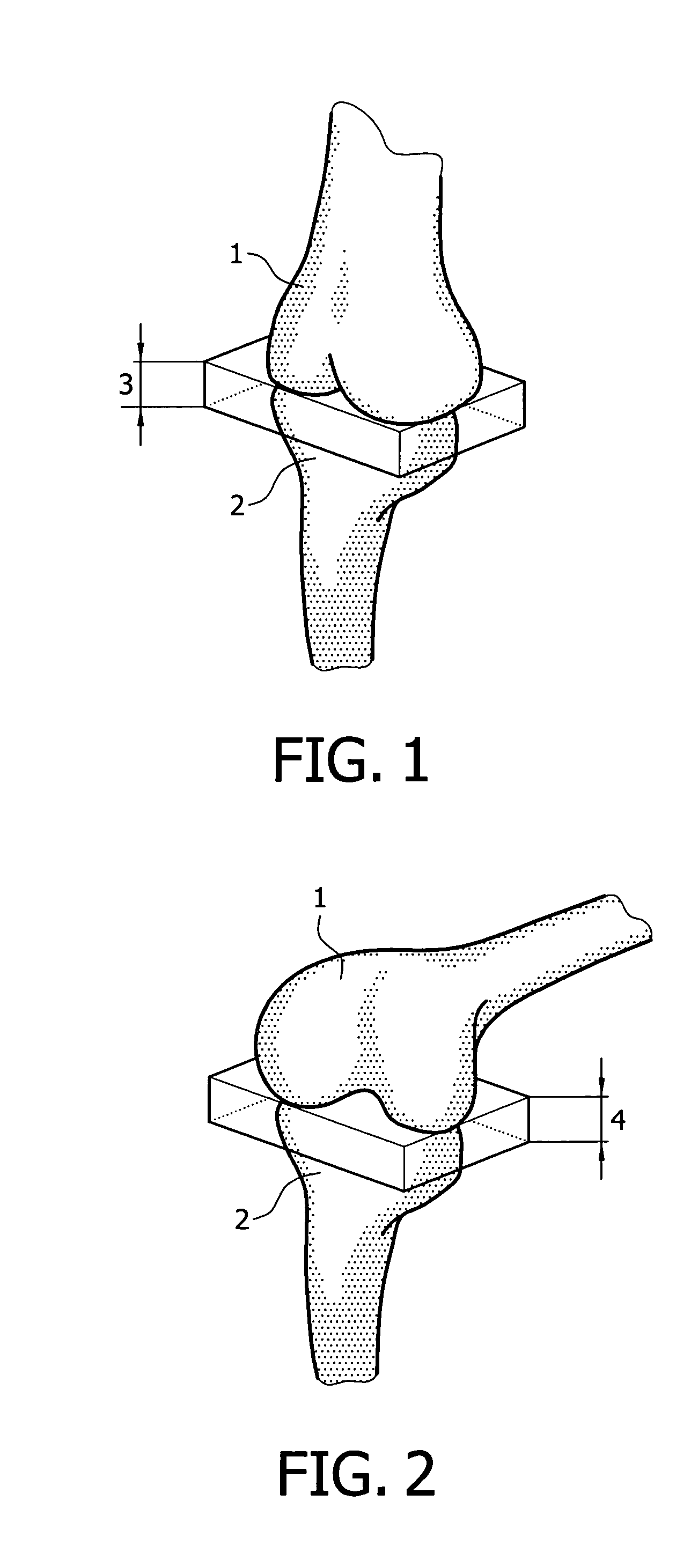
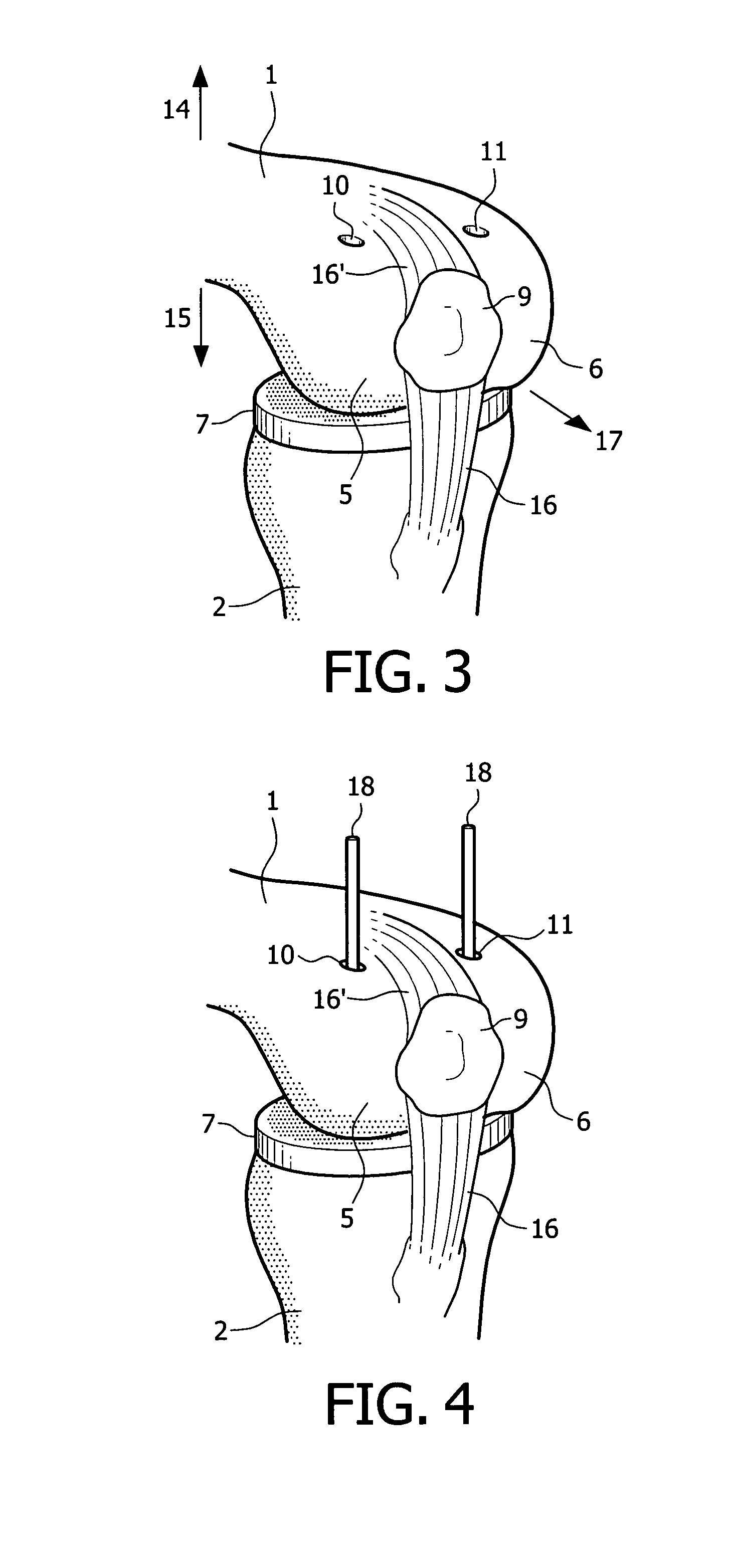
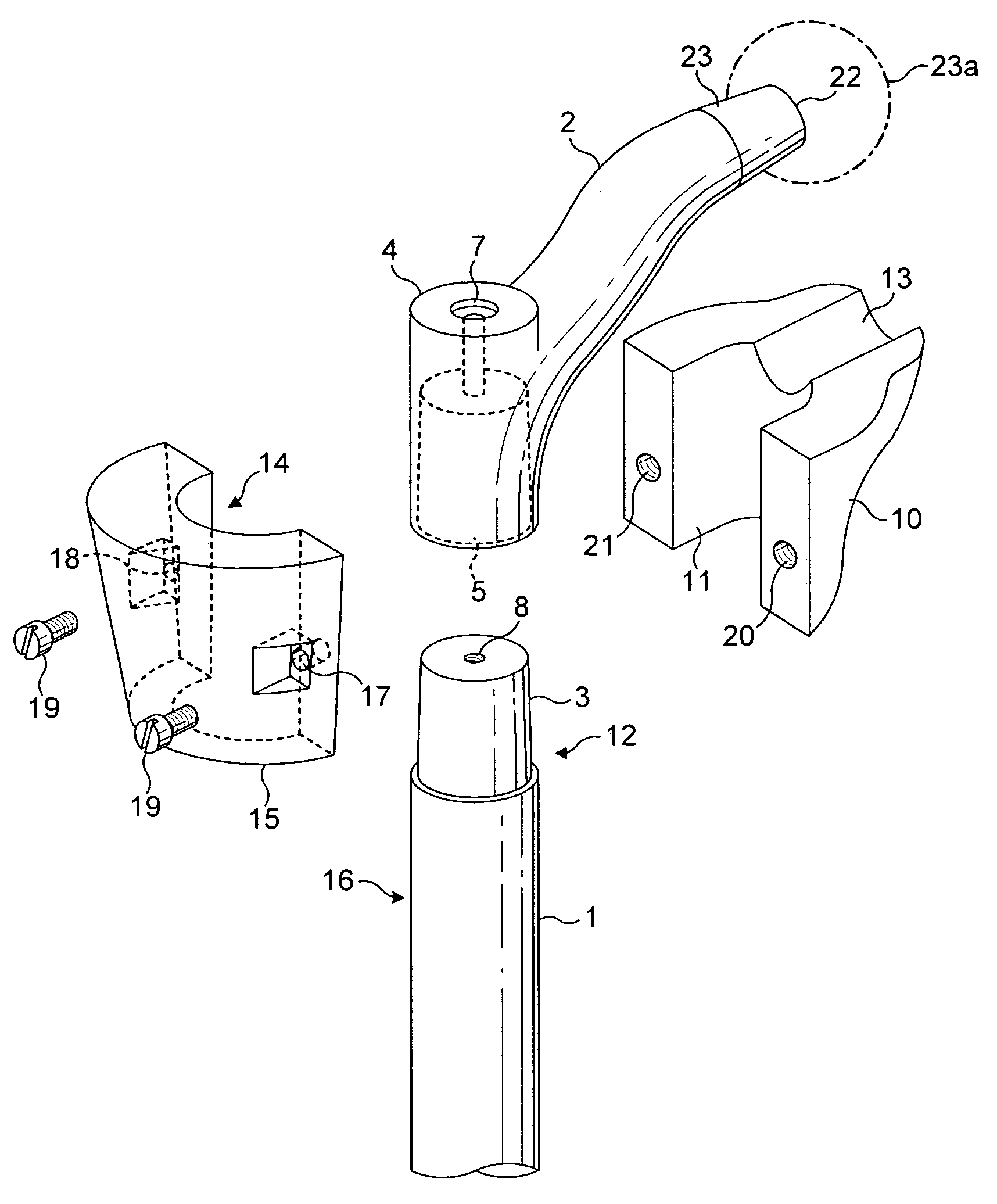
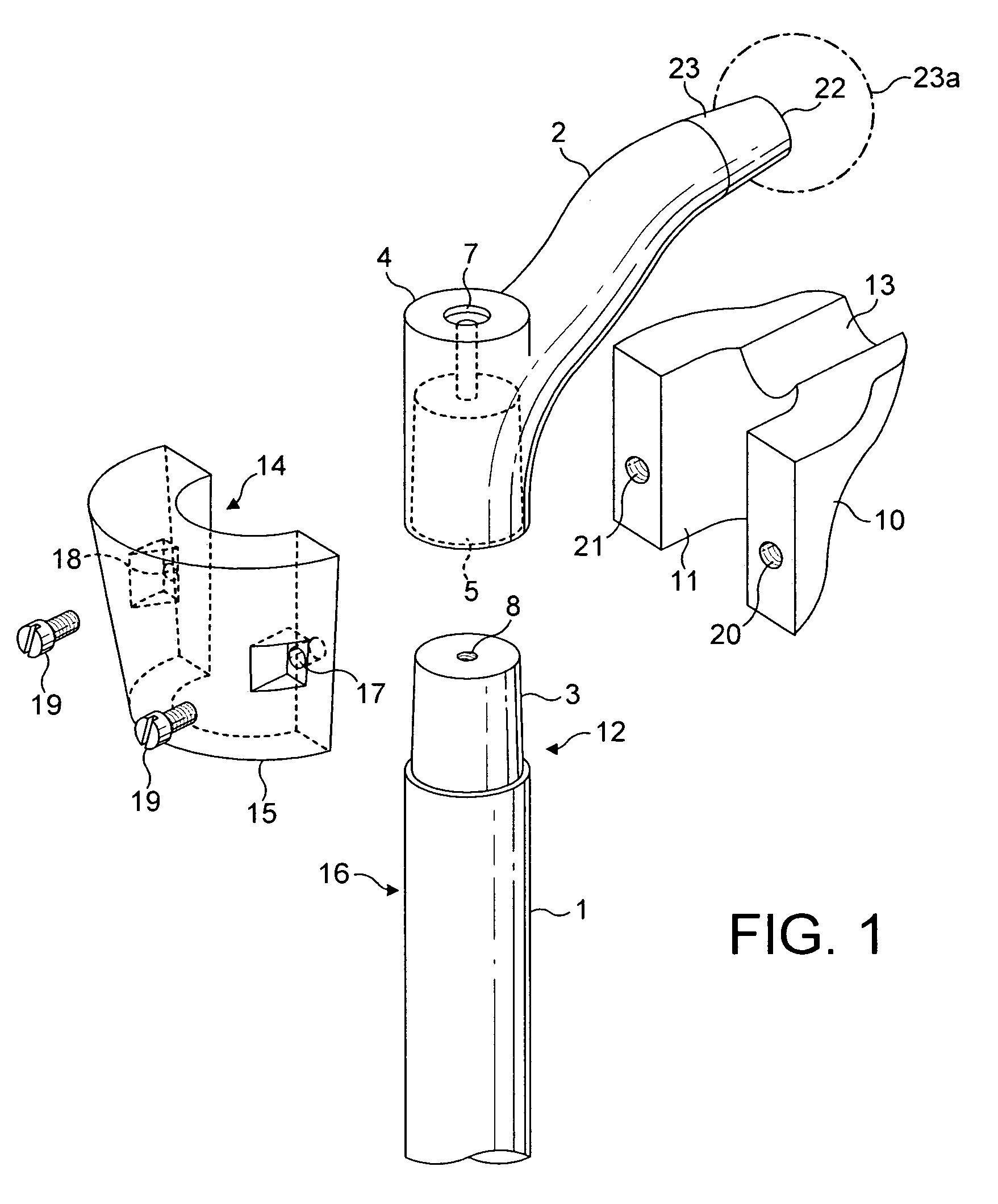
Device and method for installing femoral prosthetic knee joint
Devices and method for performing replacement prosthetic knee surgery are disclosed in which a spacing means is introduced between the femur (1) and tibia (2) while the patella (9) is in place. The spacing means separates the femur (1) from the tibia (2) by an amount essentially equal to or greater than the required flexion gap (4). An alignment device (26) is used for performing femoral bone cuts, which device attaches temporarily to a fitted tibial plate.
Owner:GHIJSELINGS IGNACE
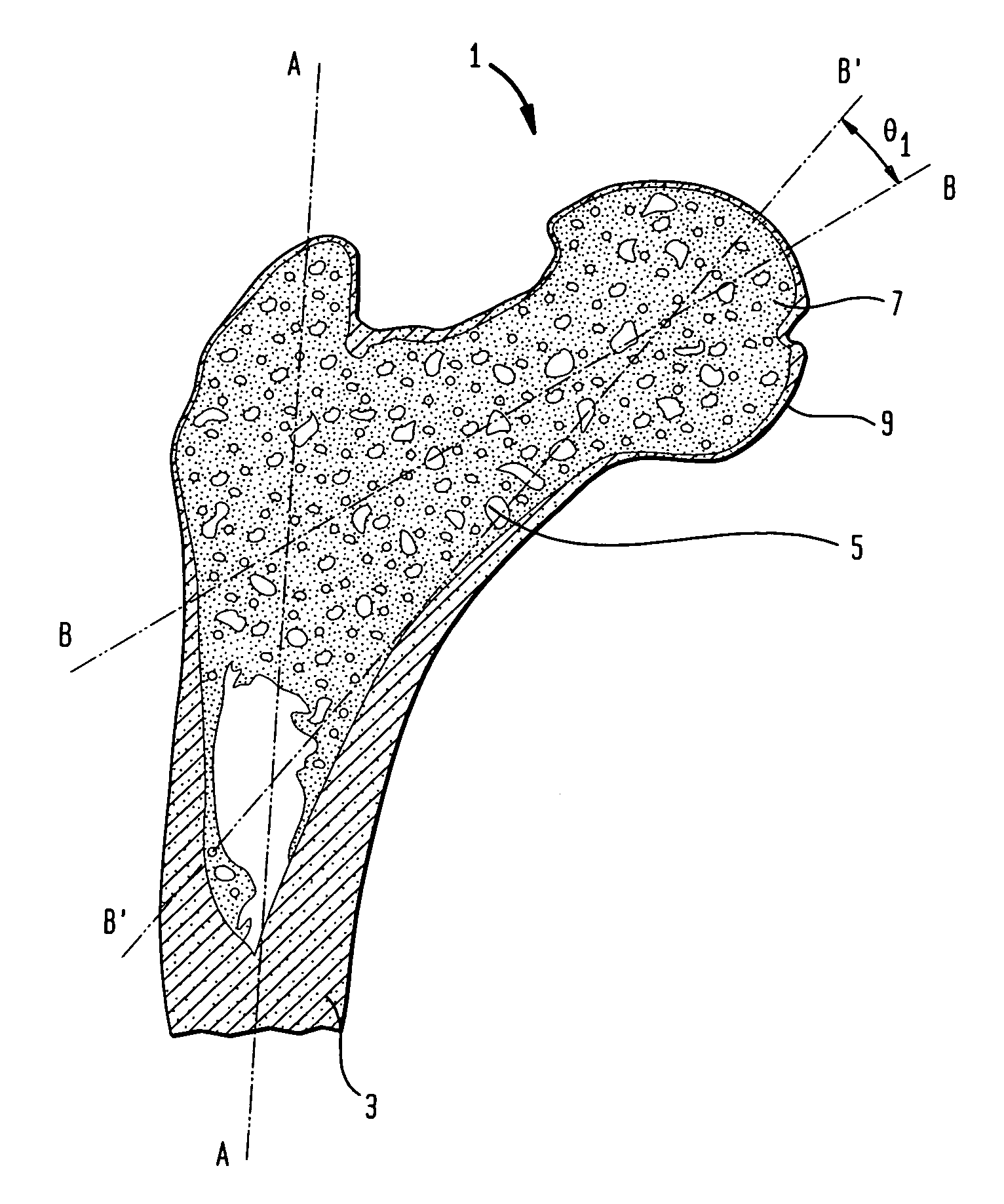
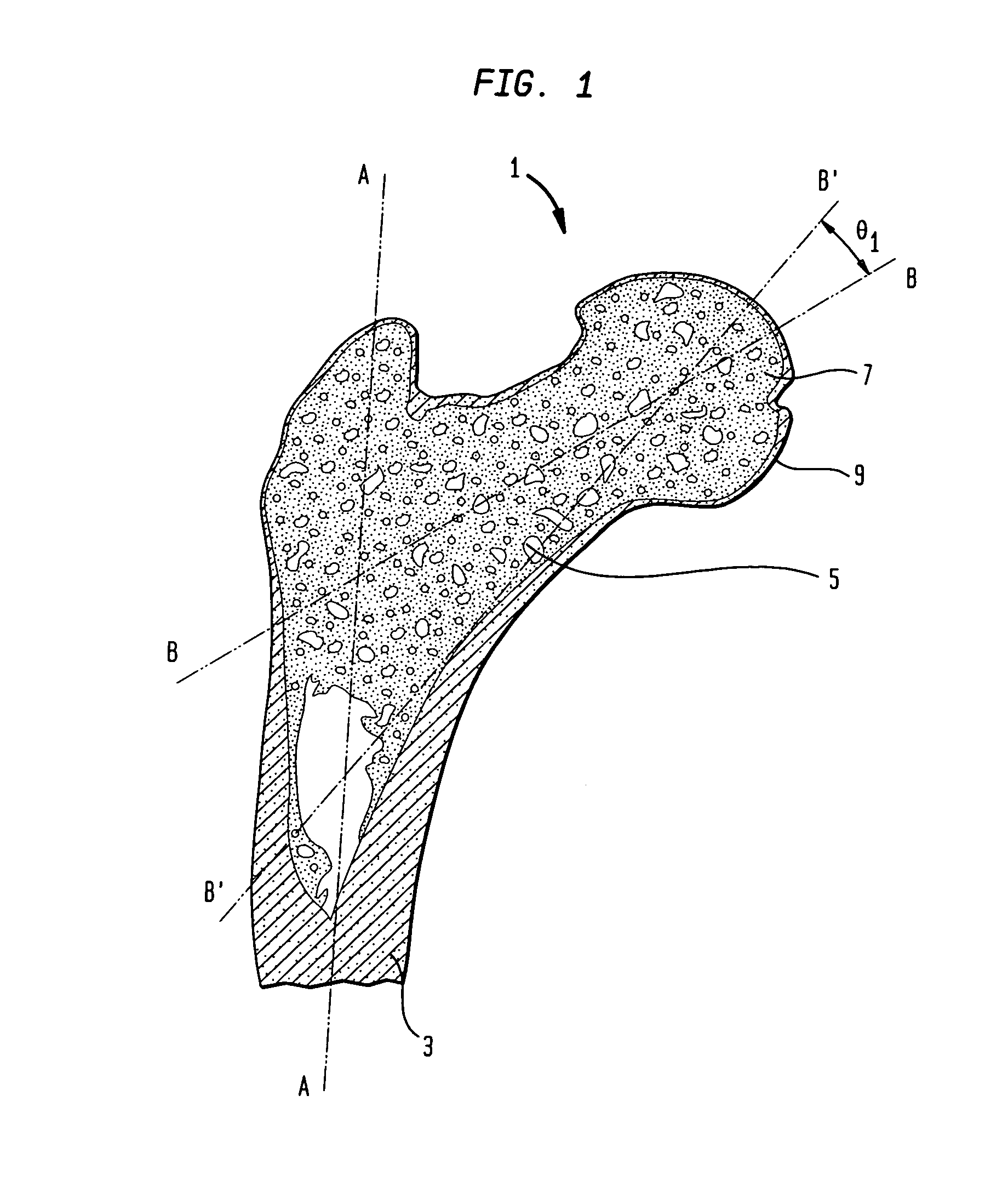
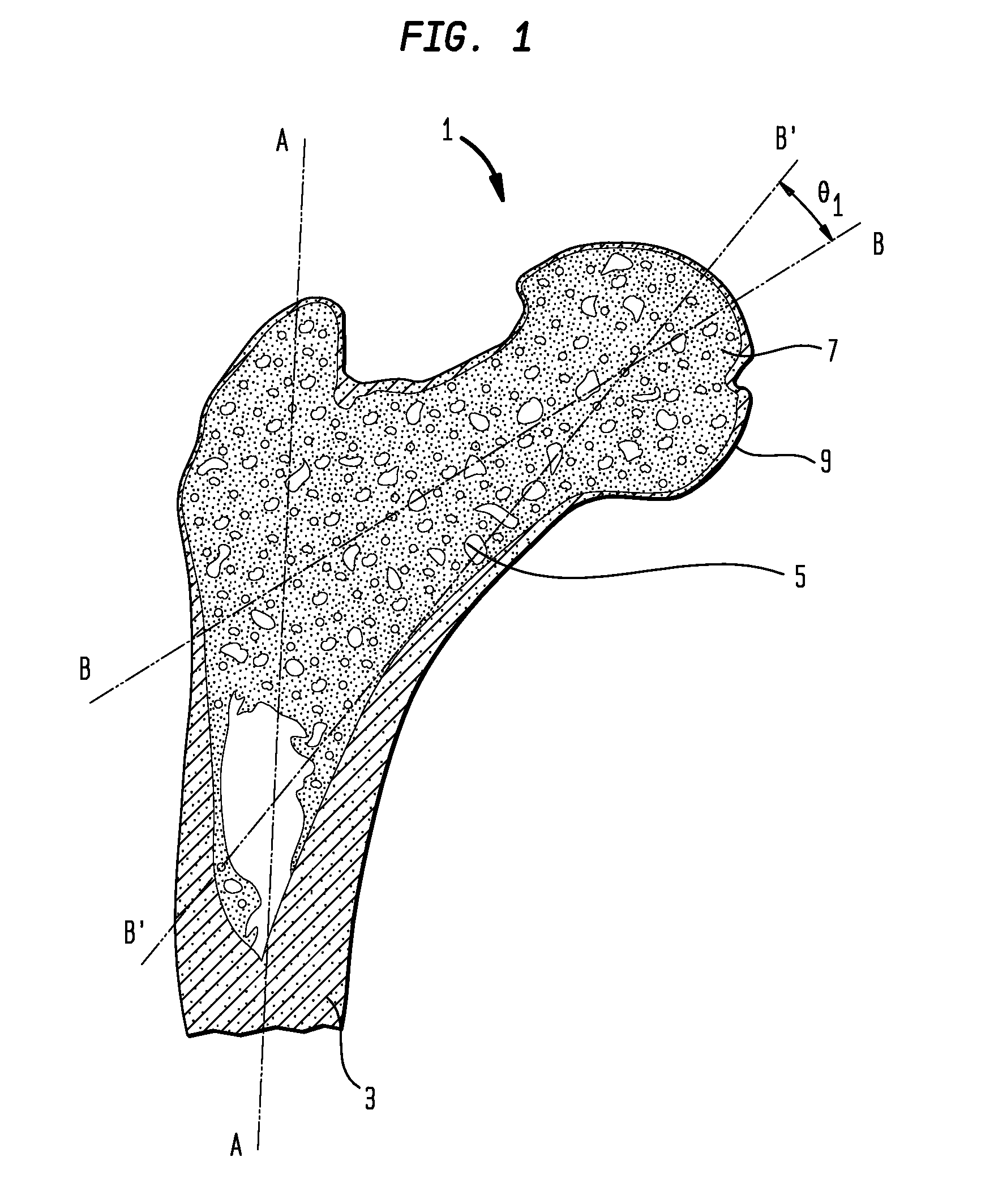
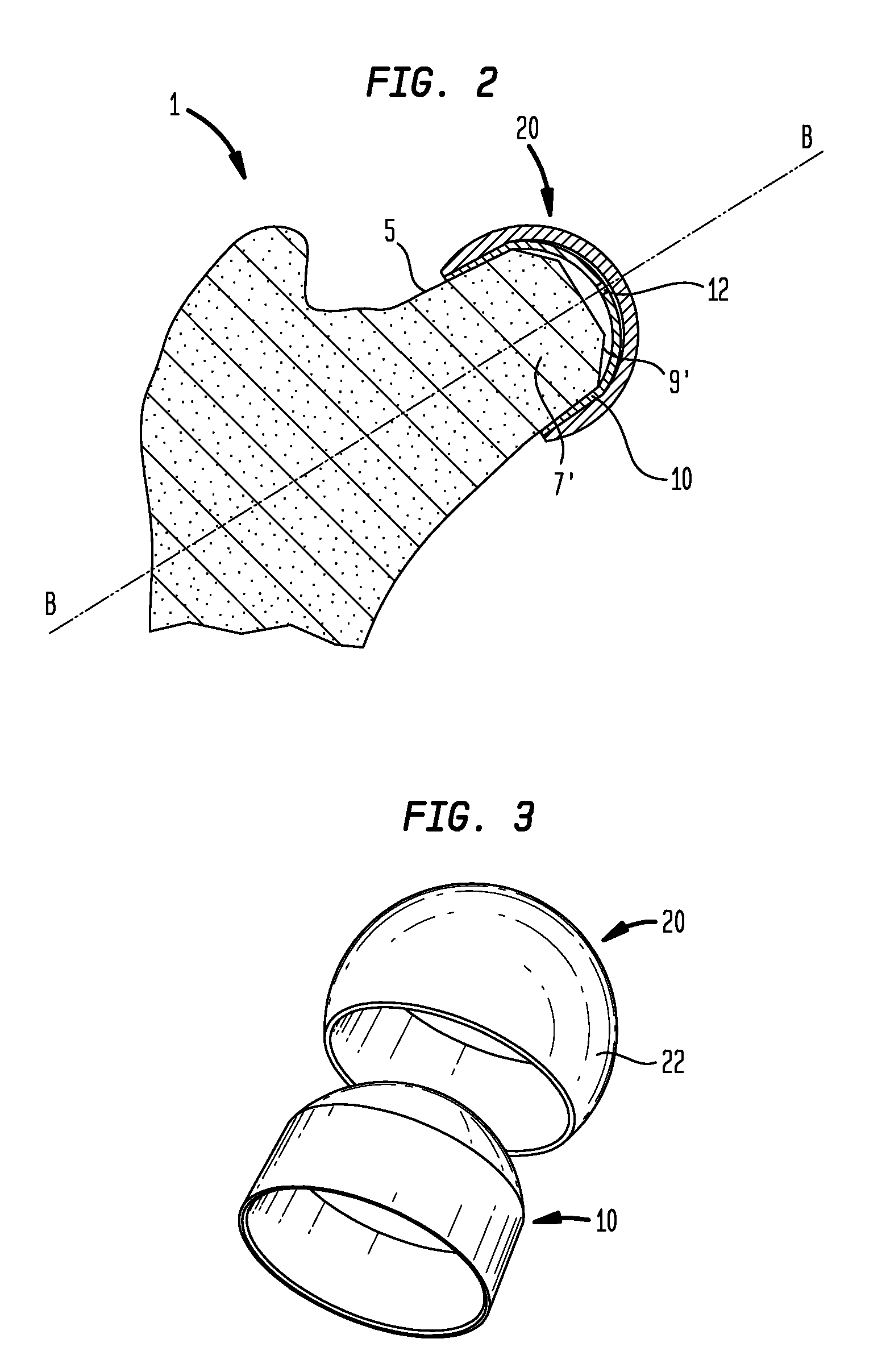
Femoral prosthesis
InactiveUS7491242B2Accurate shapeInternal osteosythesisBone implantRight femoral canalFemoral prosthesis
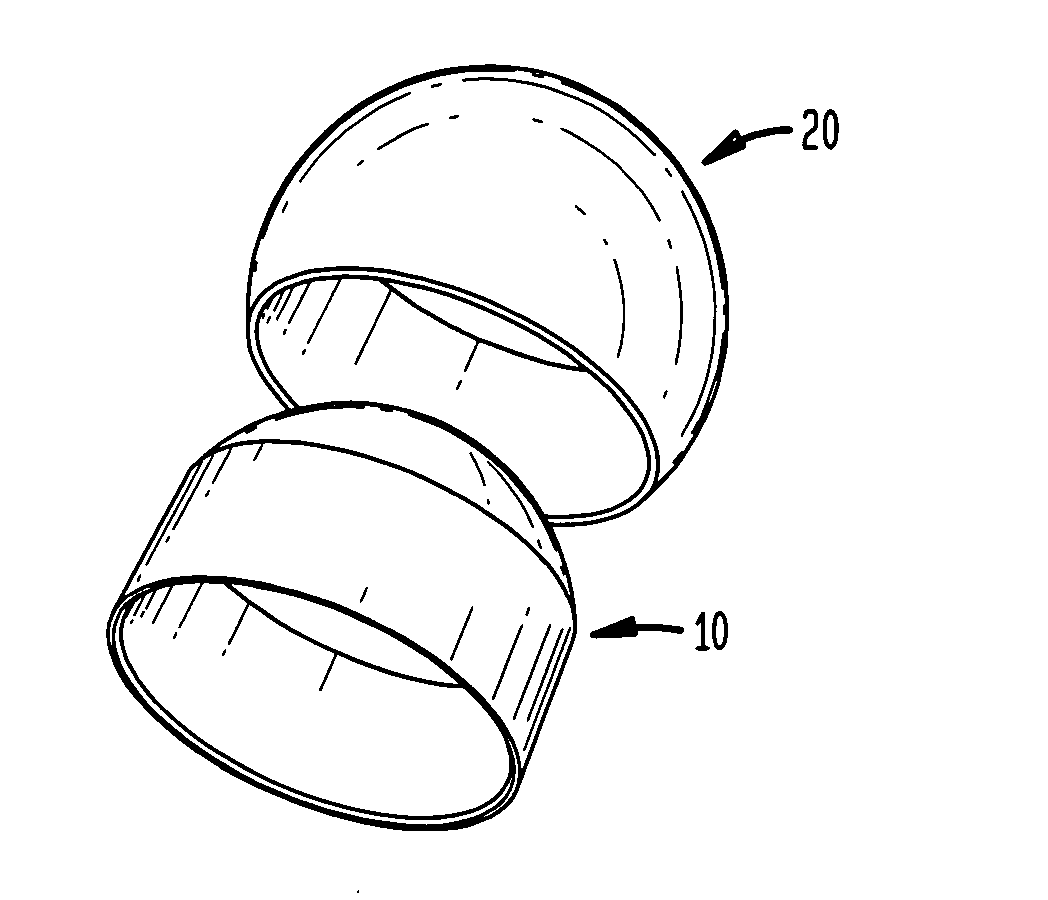
A femoral prosthesis including a stem for insertion in a femoral canal and a shoulder and / or neck portion characterized by a proximal sleeve having an outer circumferential wall and comprising two or more proximal sleeve components, each of which provides part of the circumferential outer surface of the sleeve, and means for securing the proximal sleeve components in position at the proximal end of the stem.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
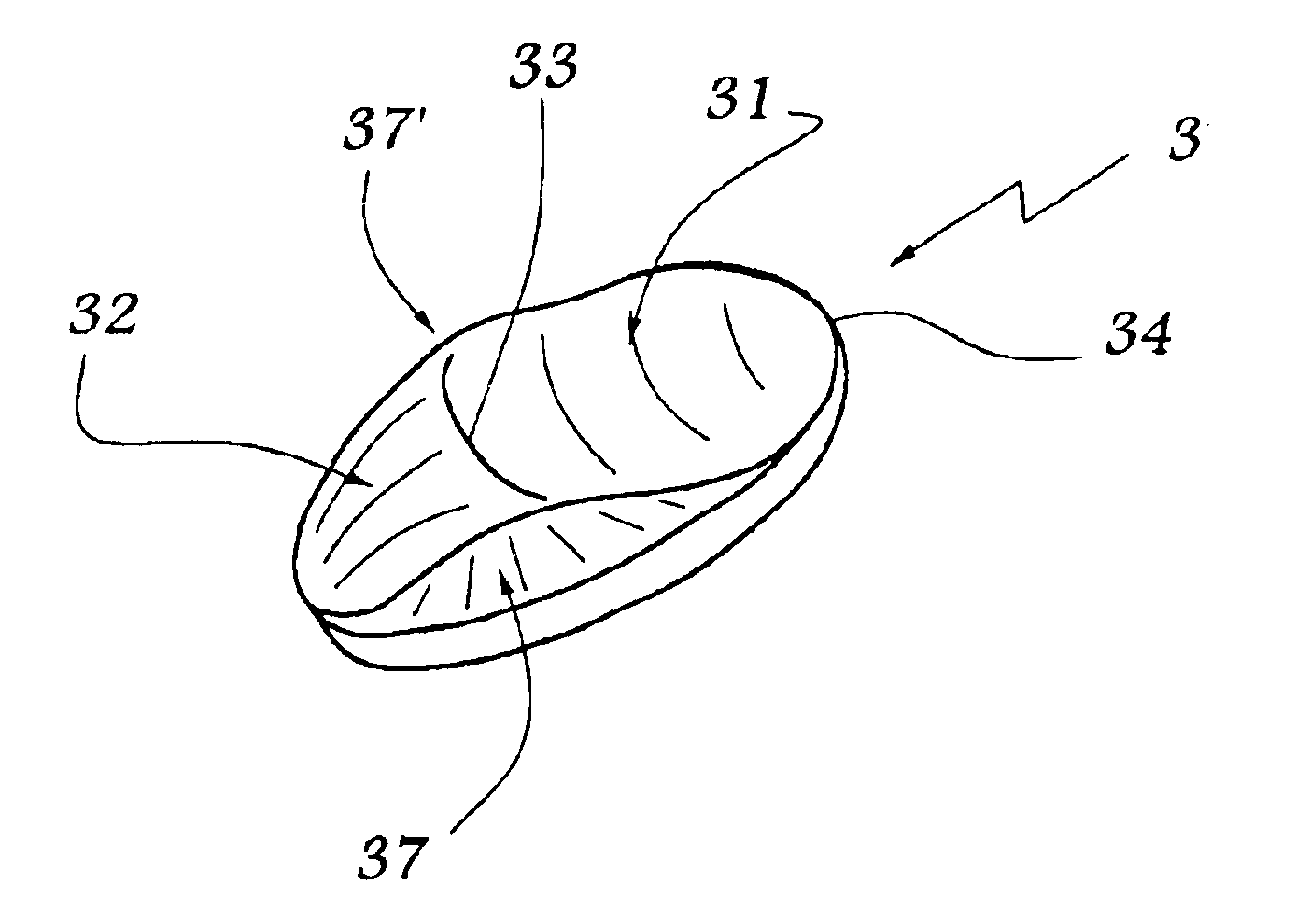
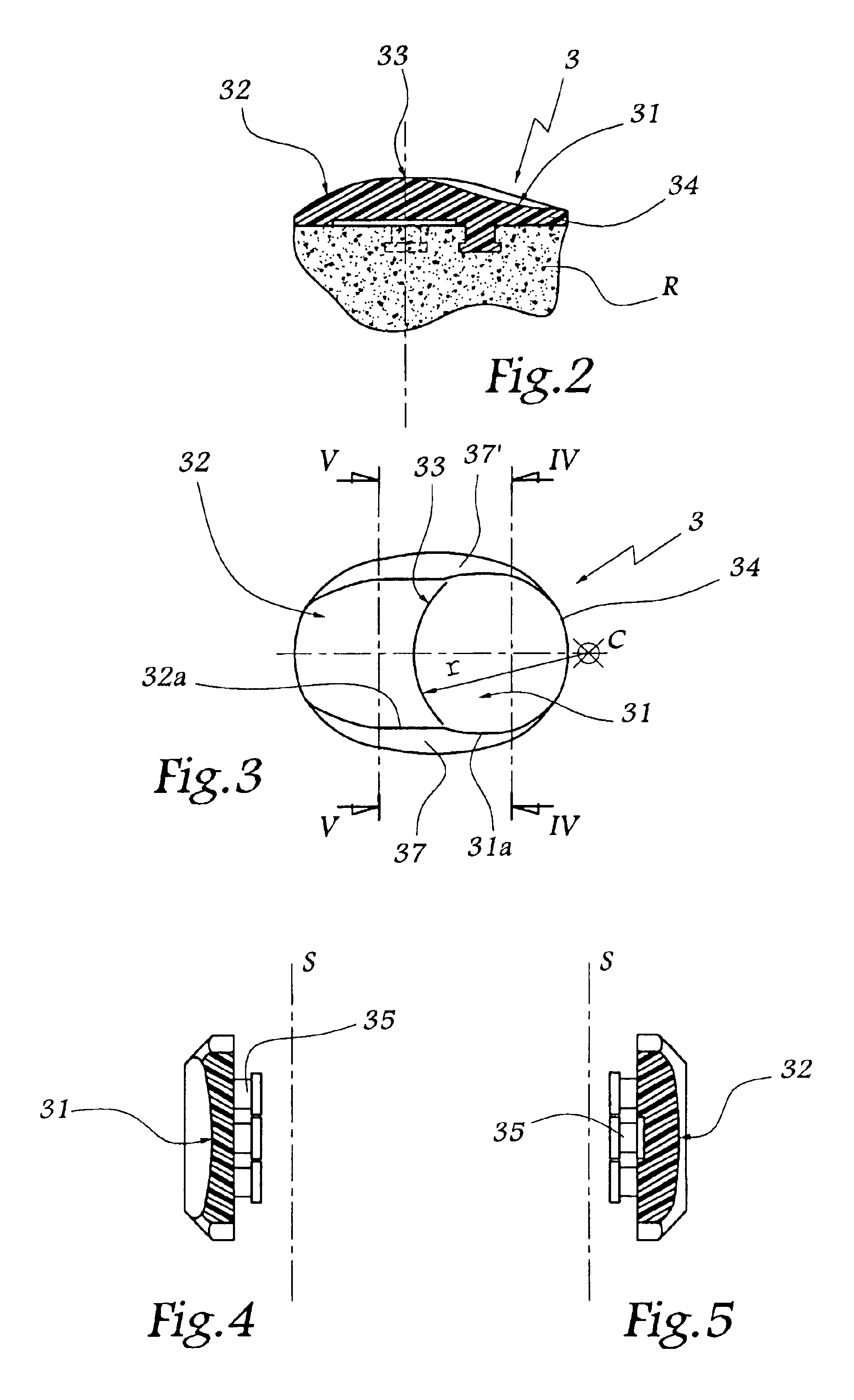
Femoral prosthesis with an offset head
InactiveUS20130211535A1Achieve regulationEasy to manufactureJoint implantsFemoral headsFemoral prosthesisBearing surface
A femoral prosthesis has a stem part and a head part, in which the stem part has a body section for location in the femur of a patient and a neck section including a trunion or spigot. The head part has a bearing surface formed as part of a sphere and a reverse side. The bearing surface has a polar axis extending through a center of the sphere formed thereby. A bore is provided in the reverse side adapted to receive the spigot wherein the bore comprise a bore axis, and in which the bore axis is oblique to the polar axis.
Owner:STRYKER IRELAND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com