Patents
Literature
47 results about "Tibial insert" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
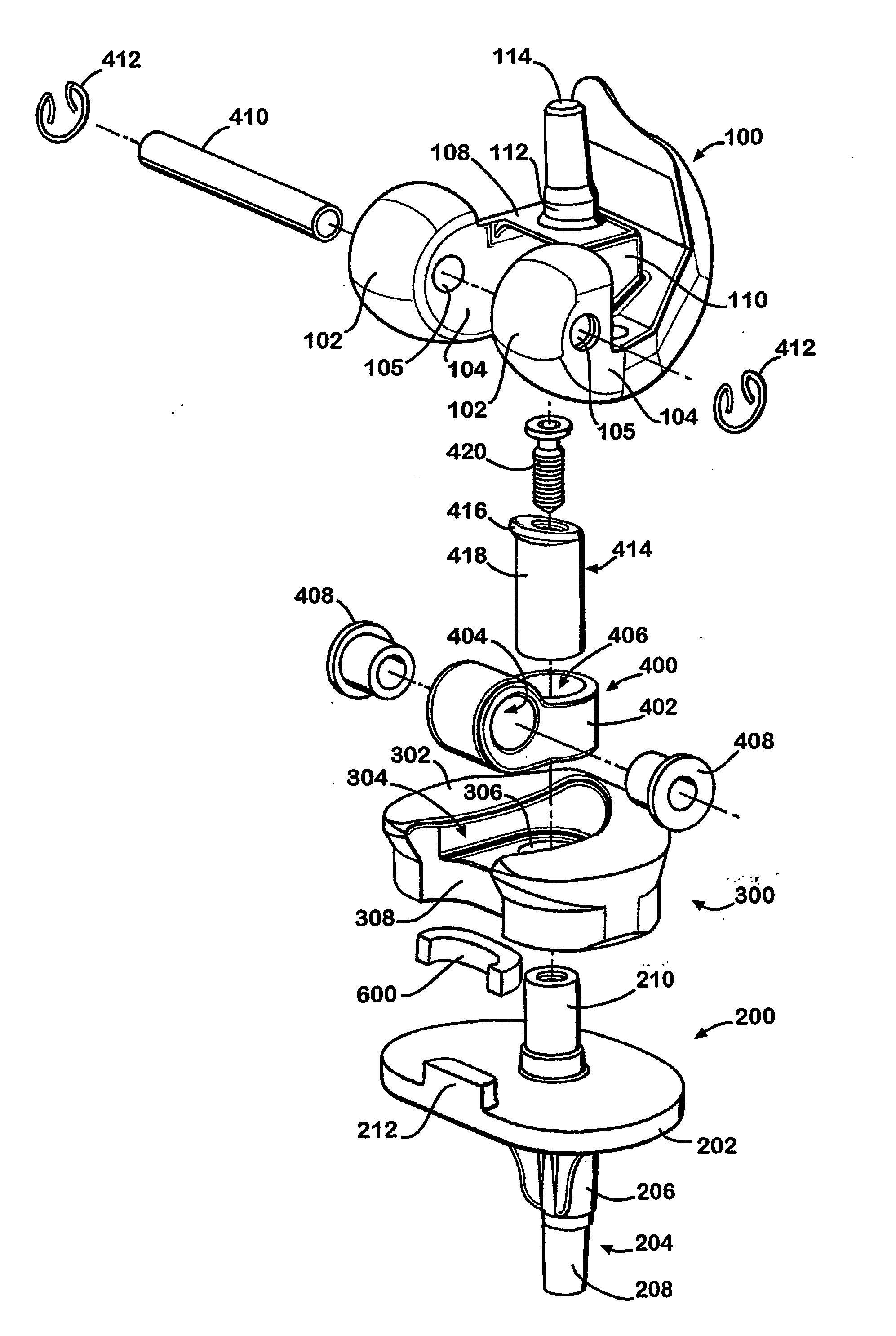
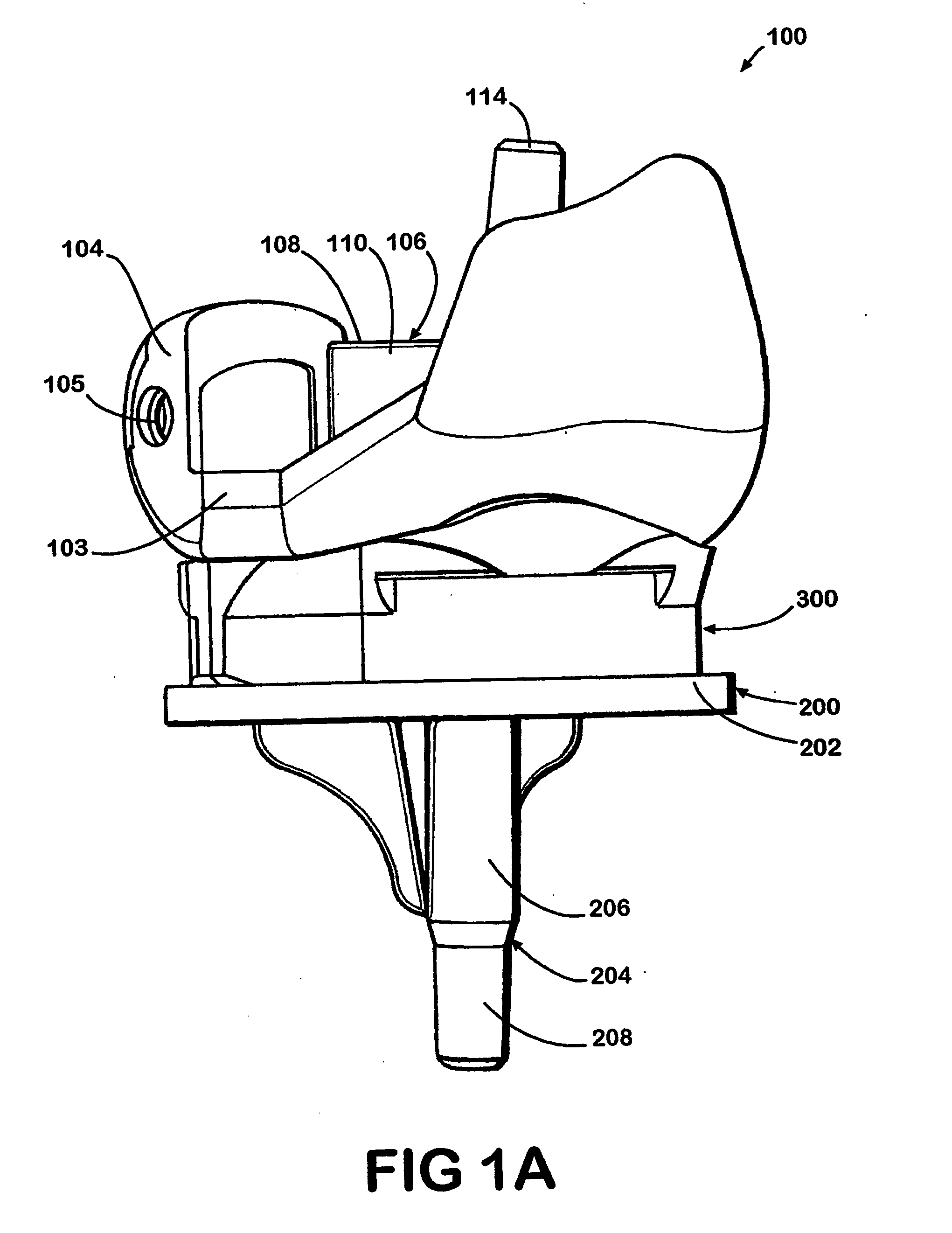
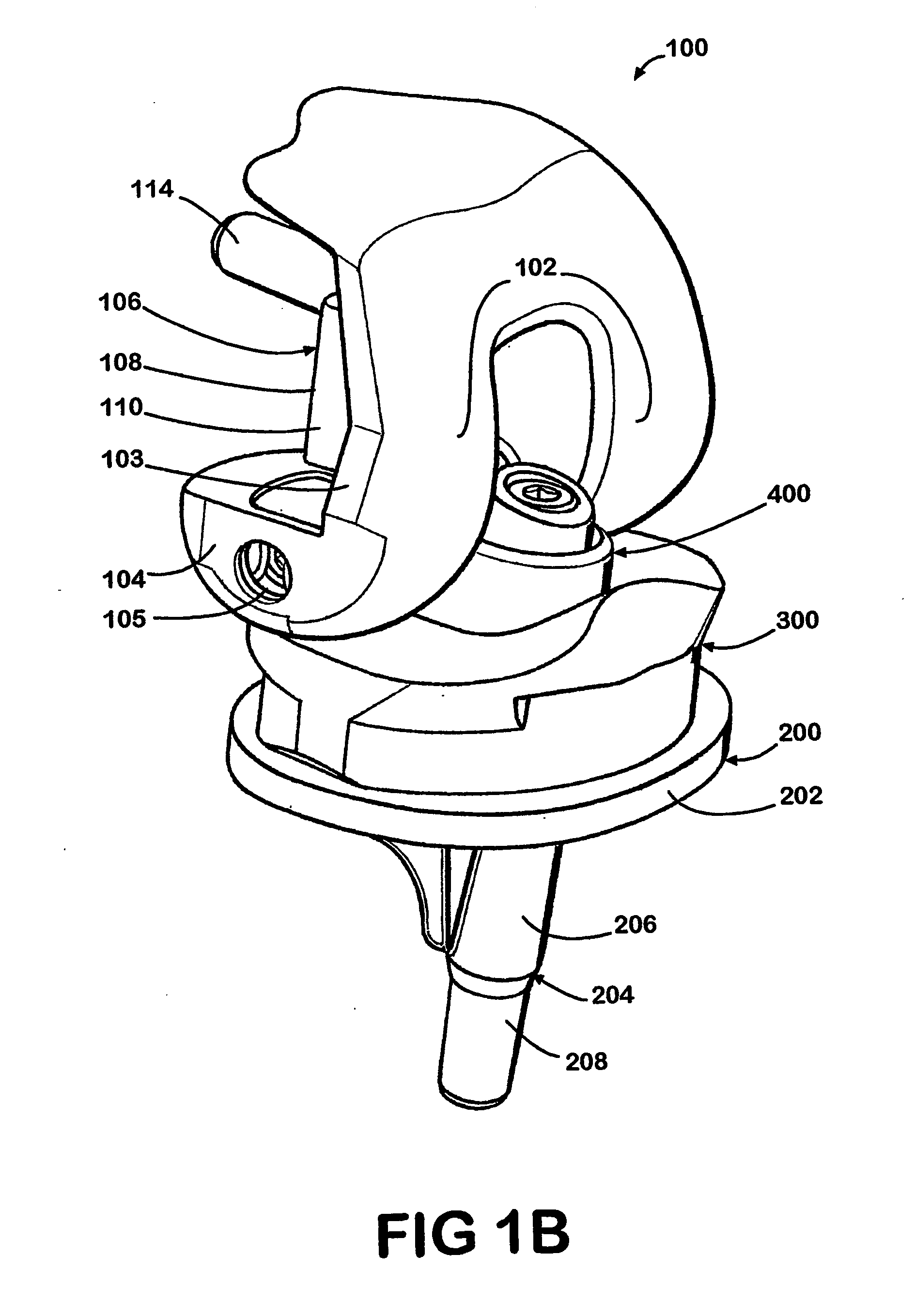
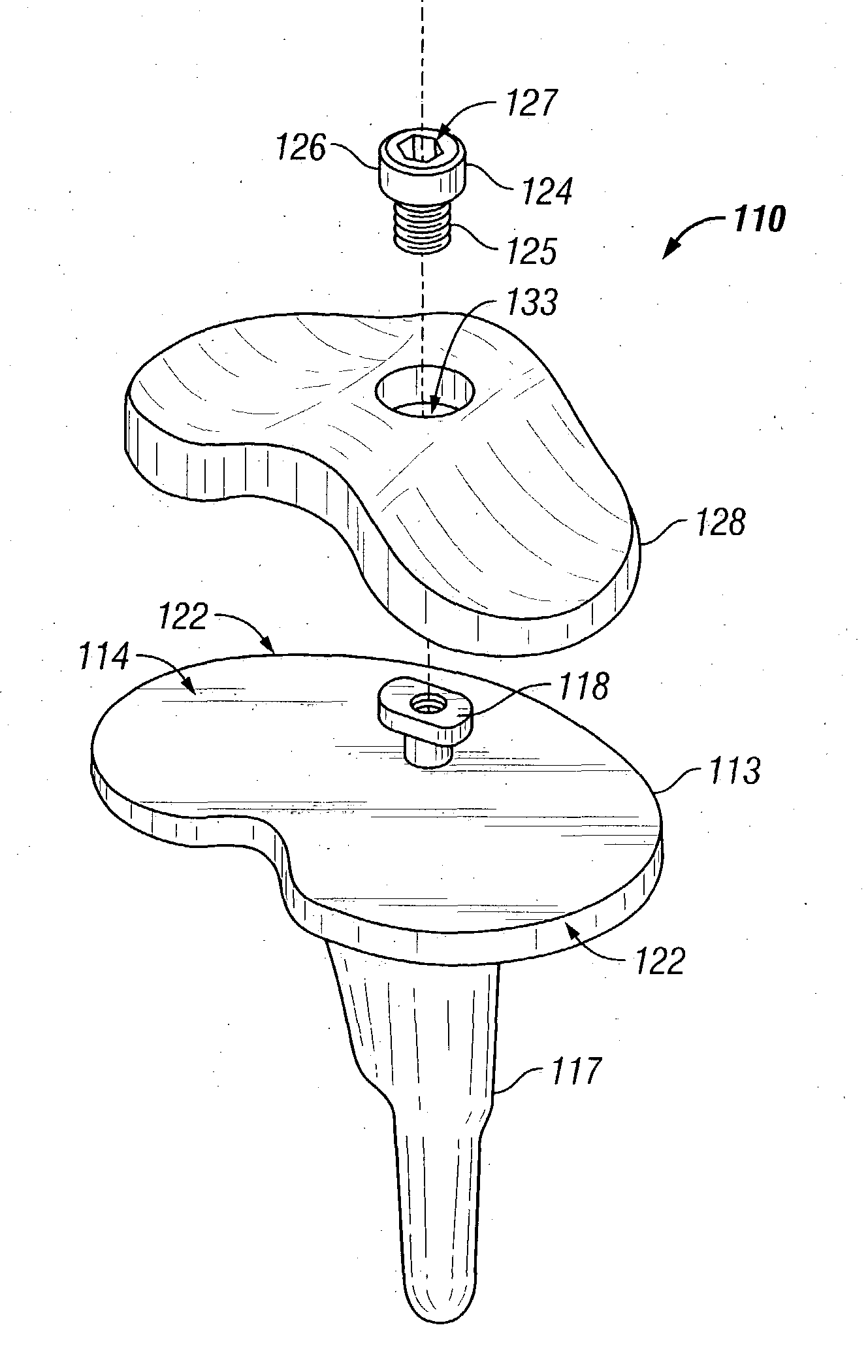
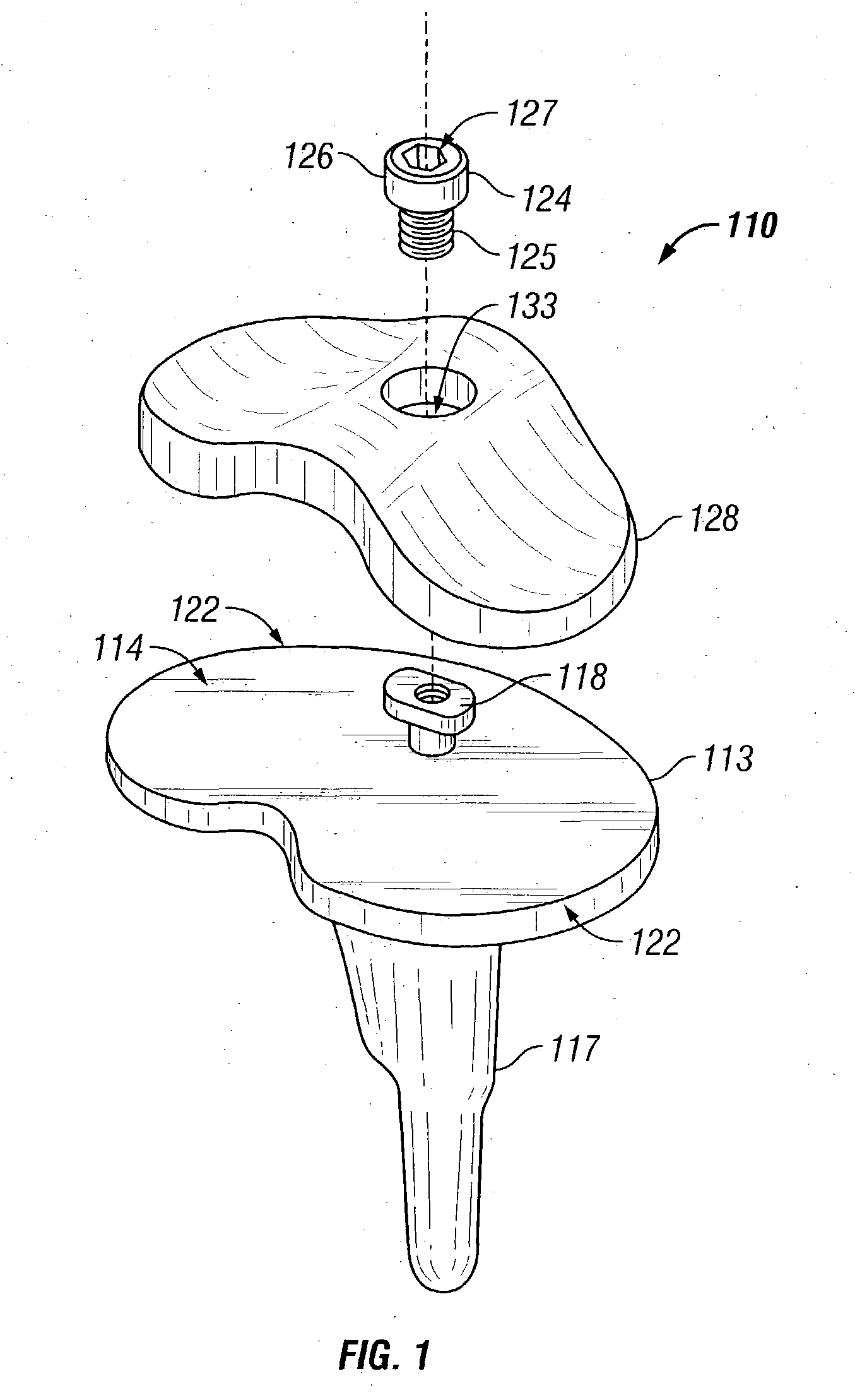
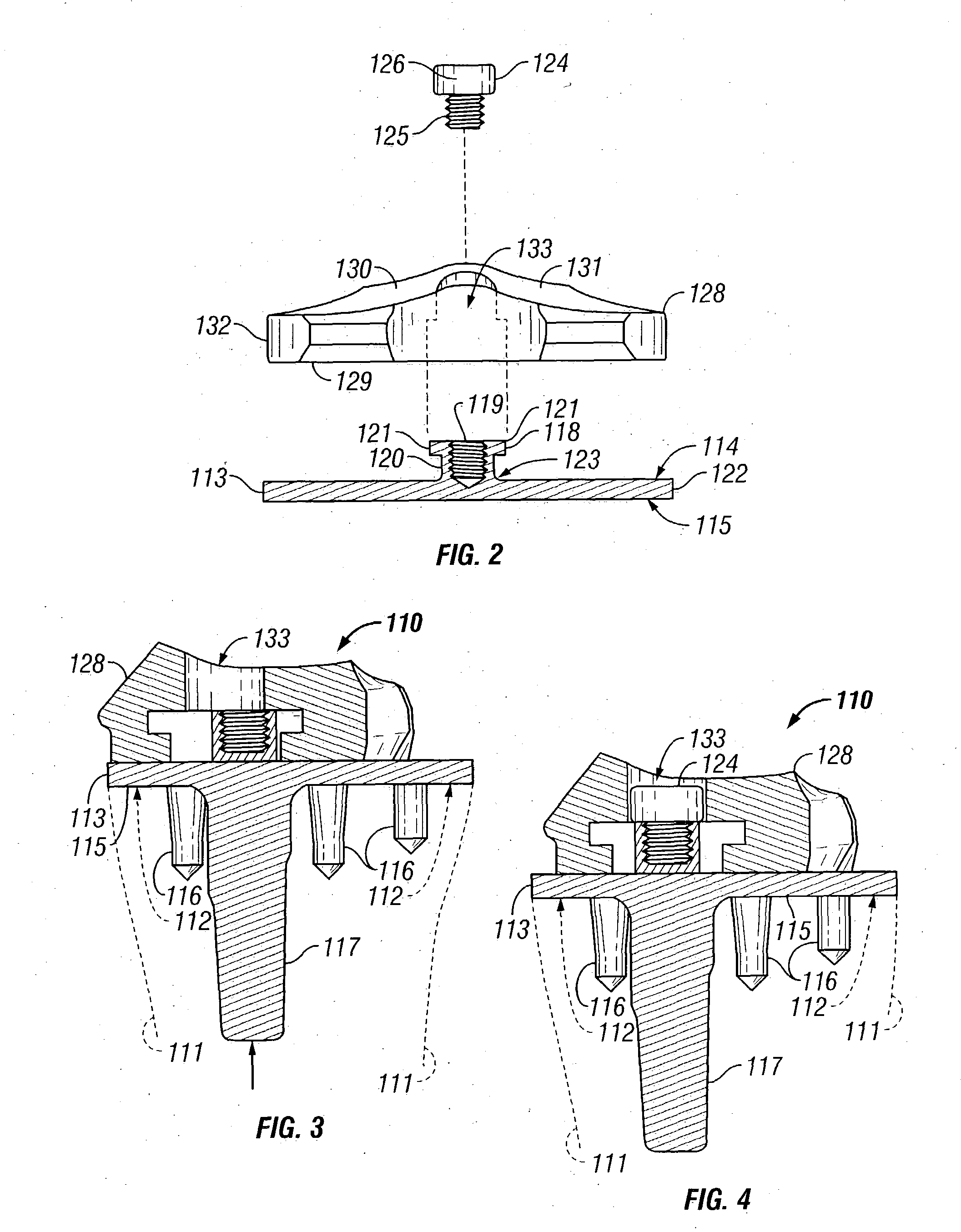
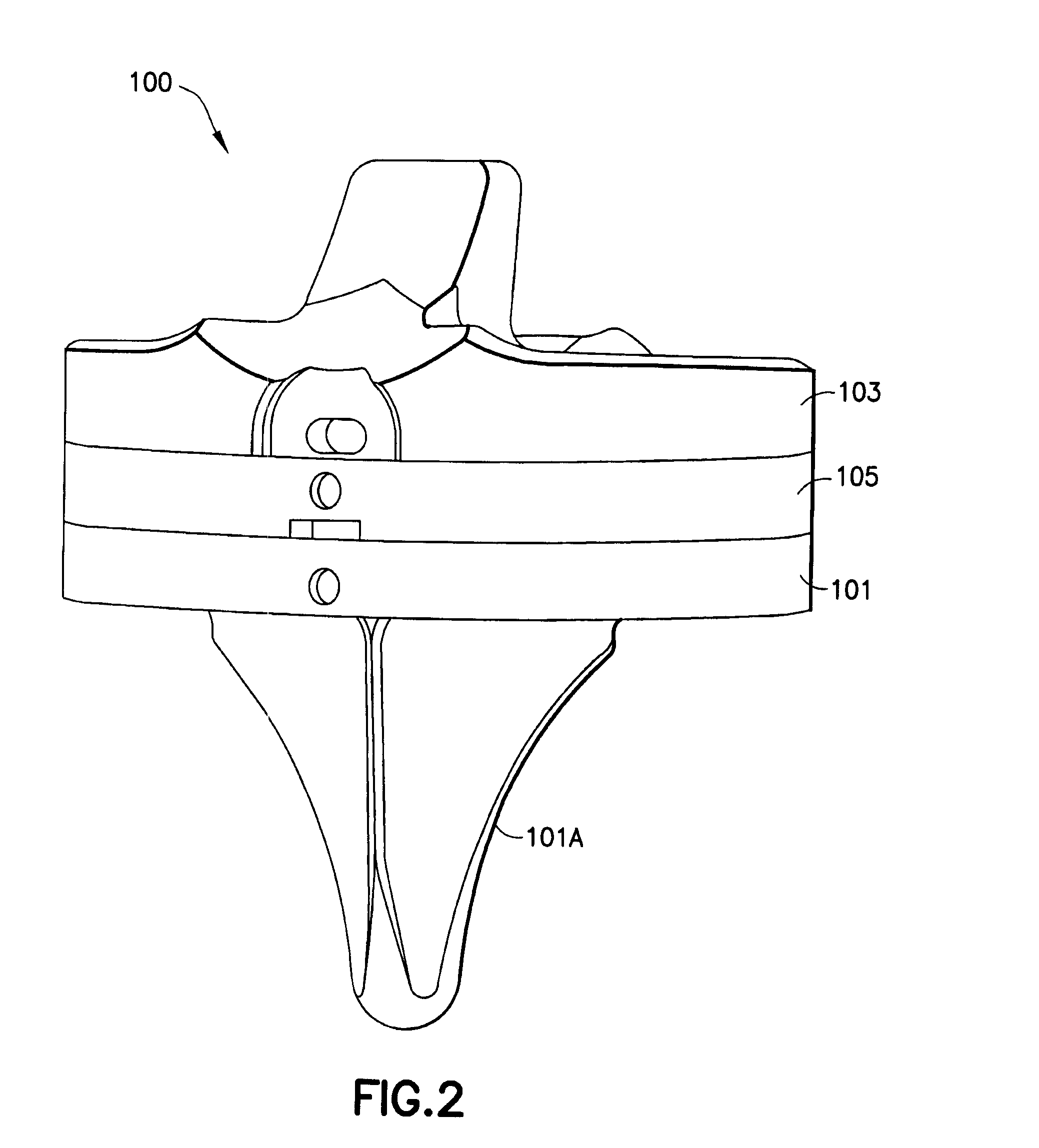
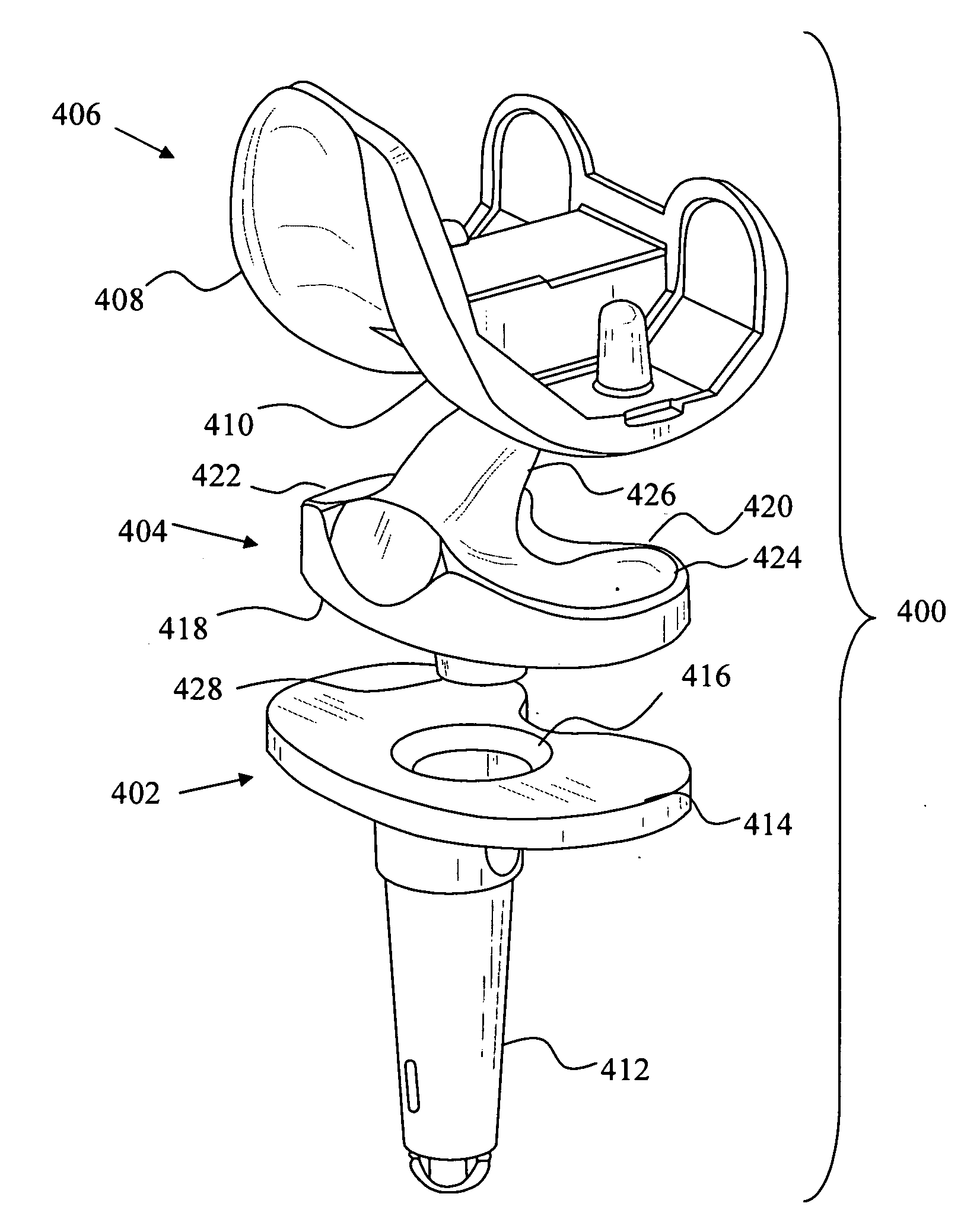
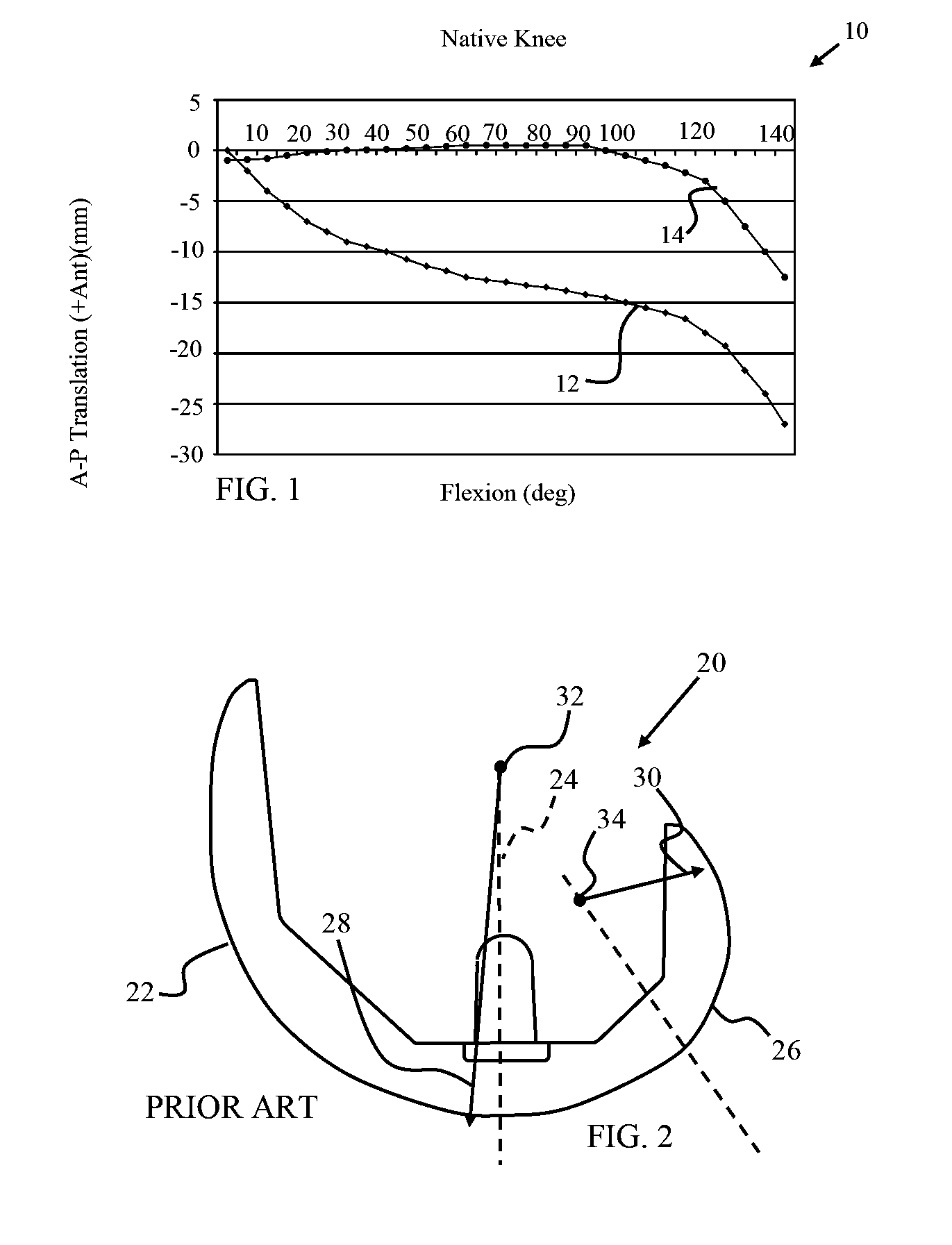
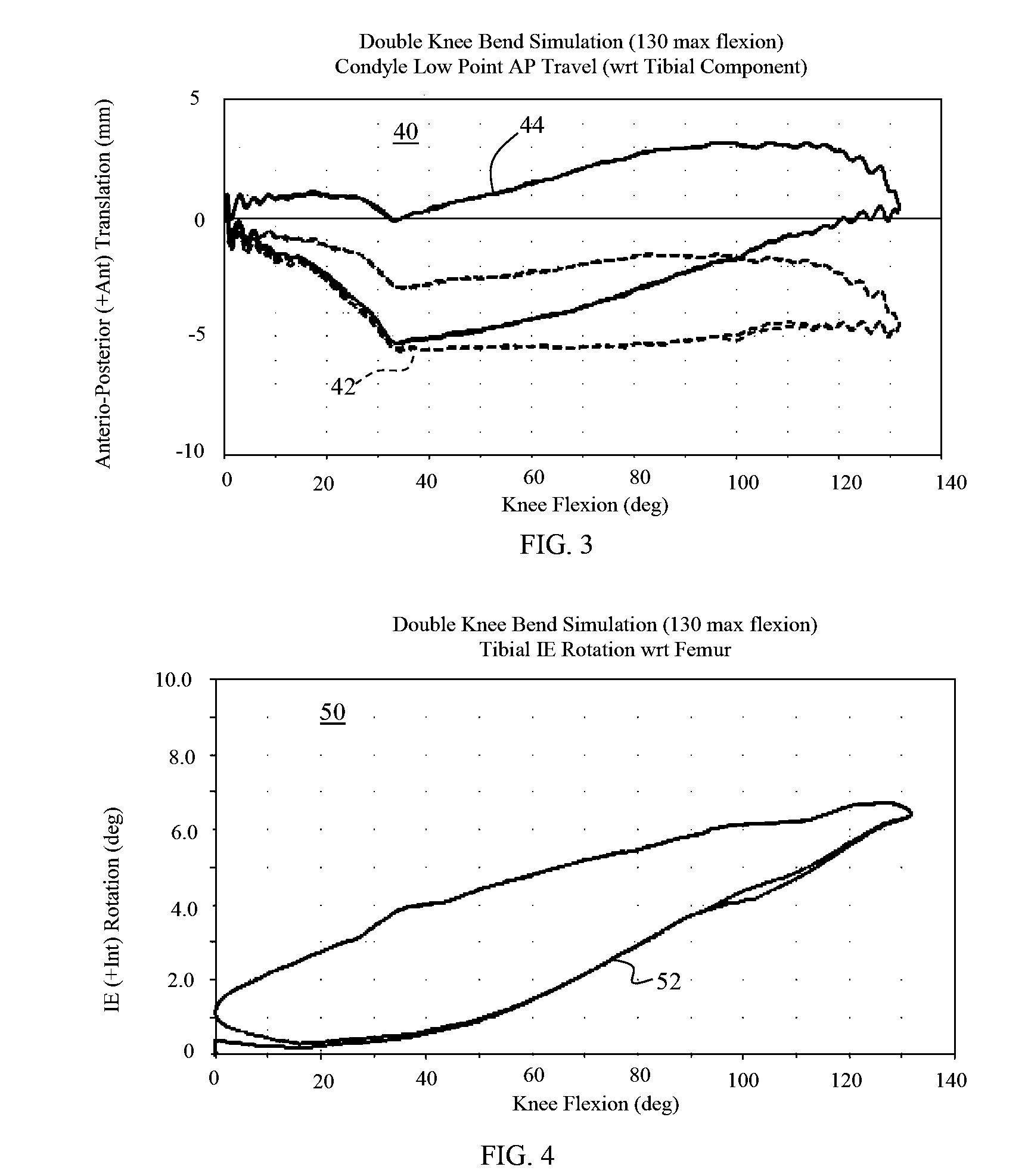
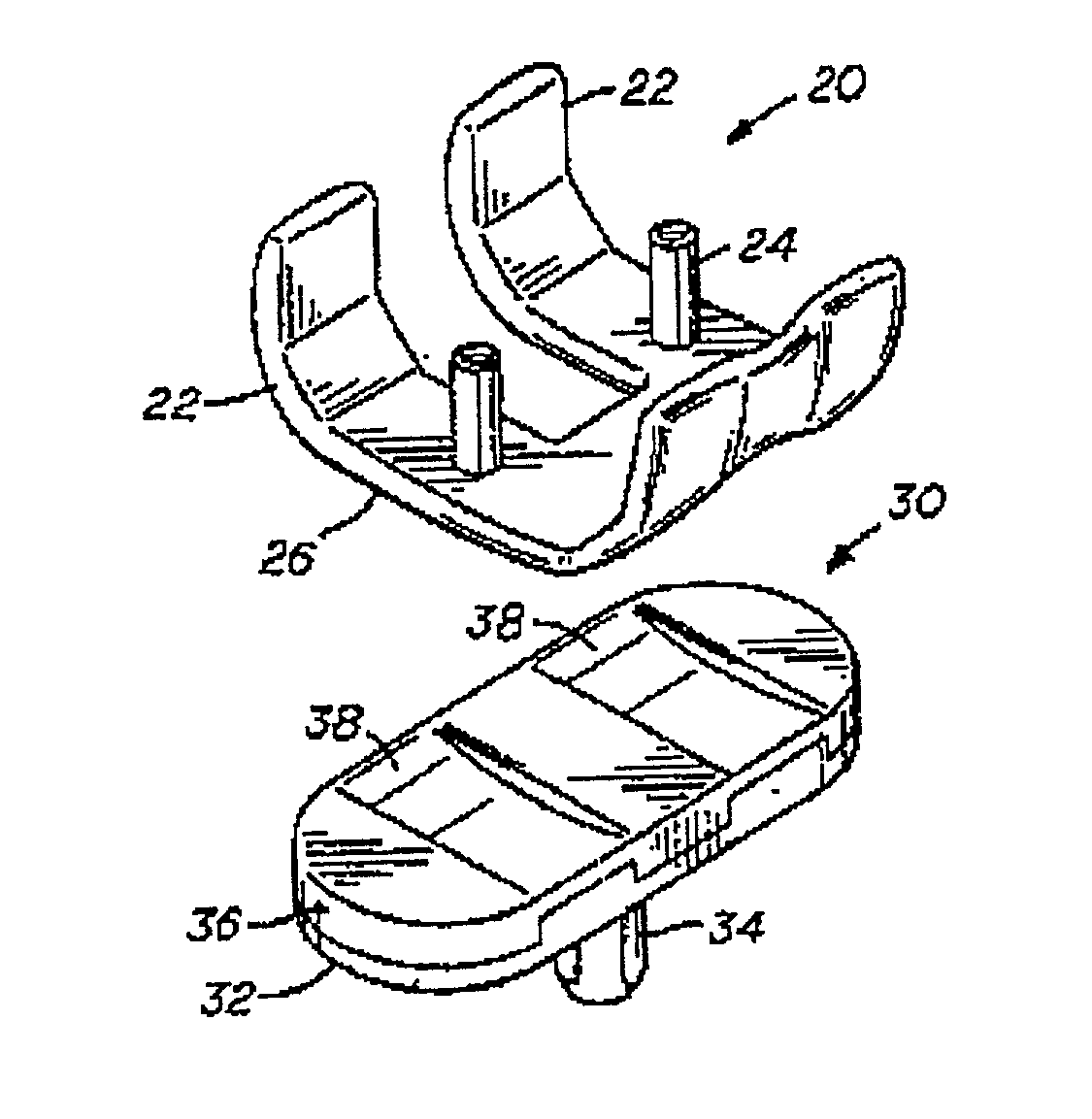
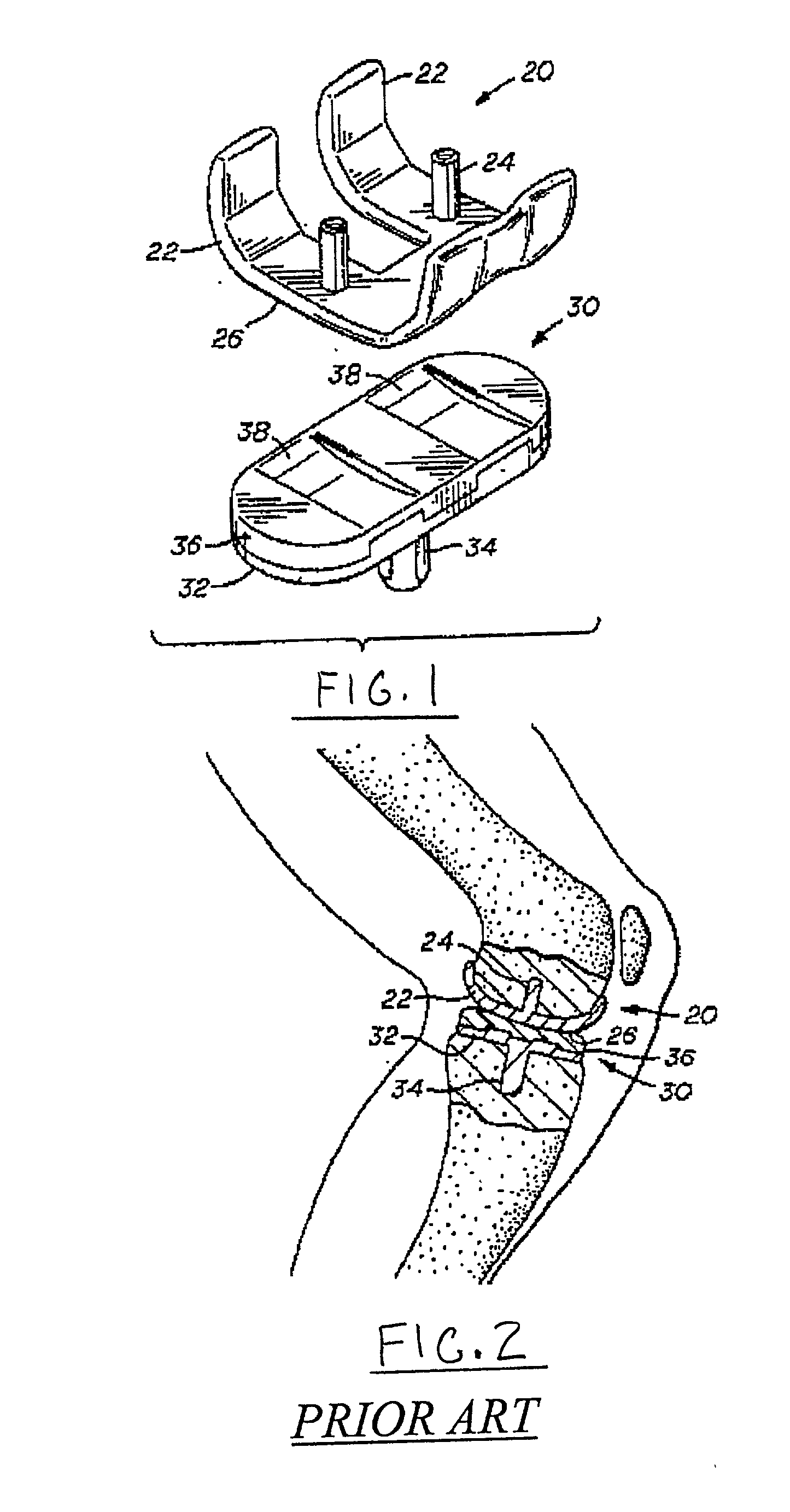
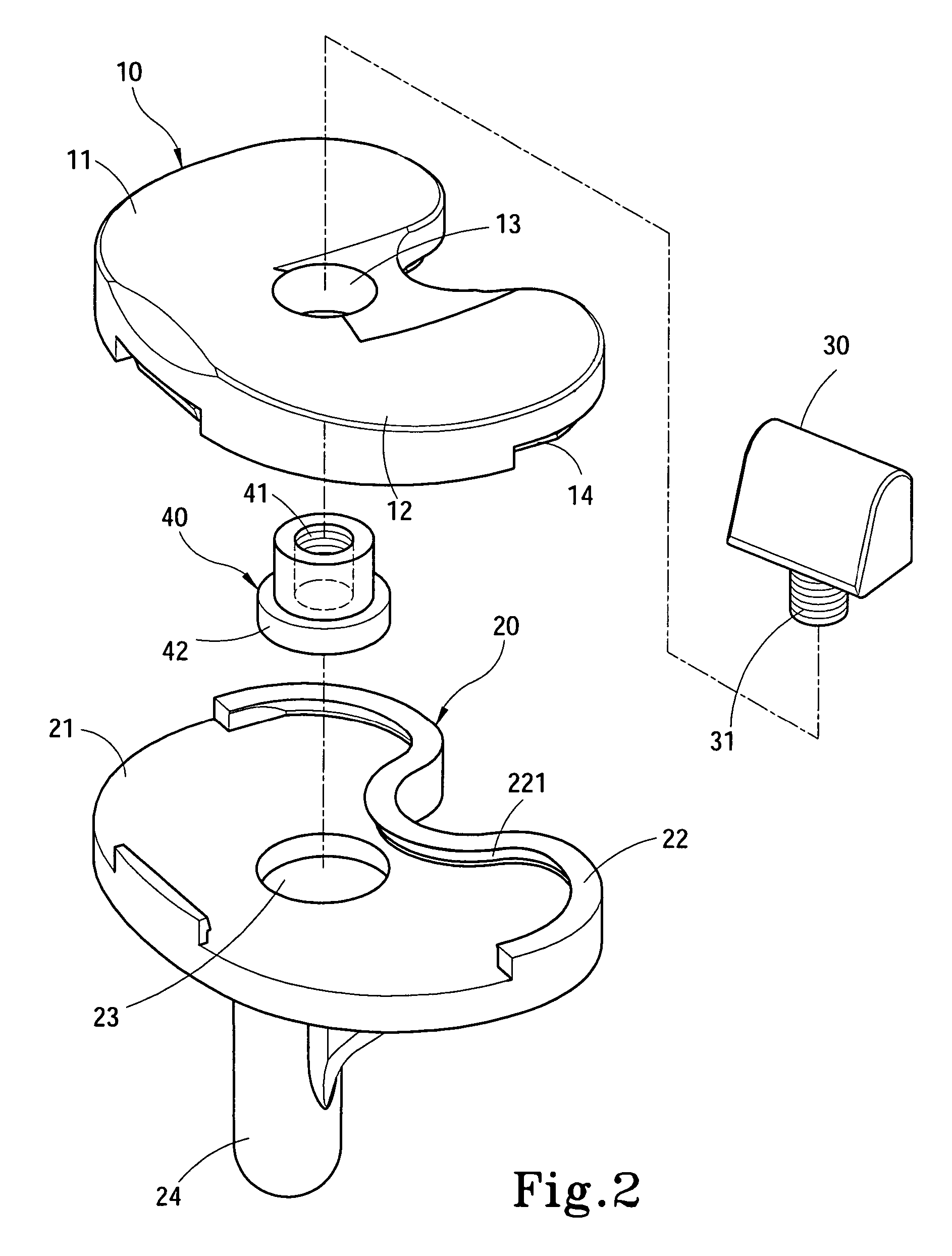
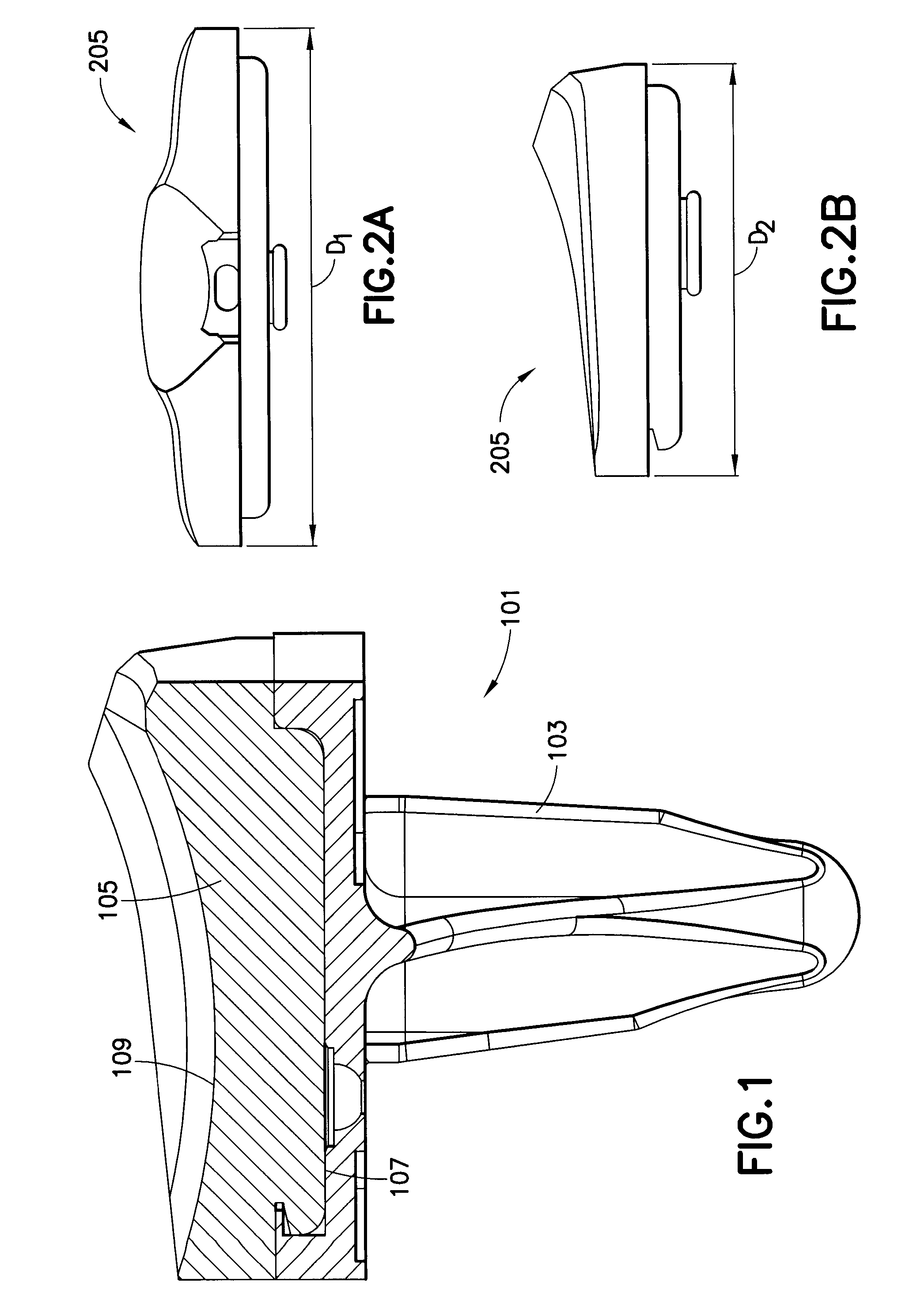
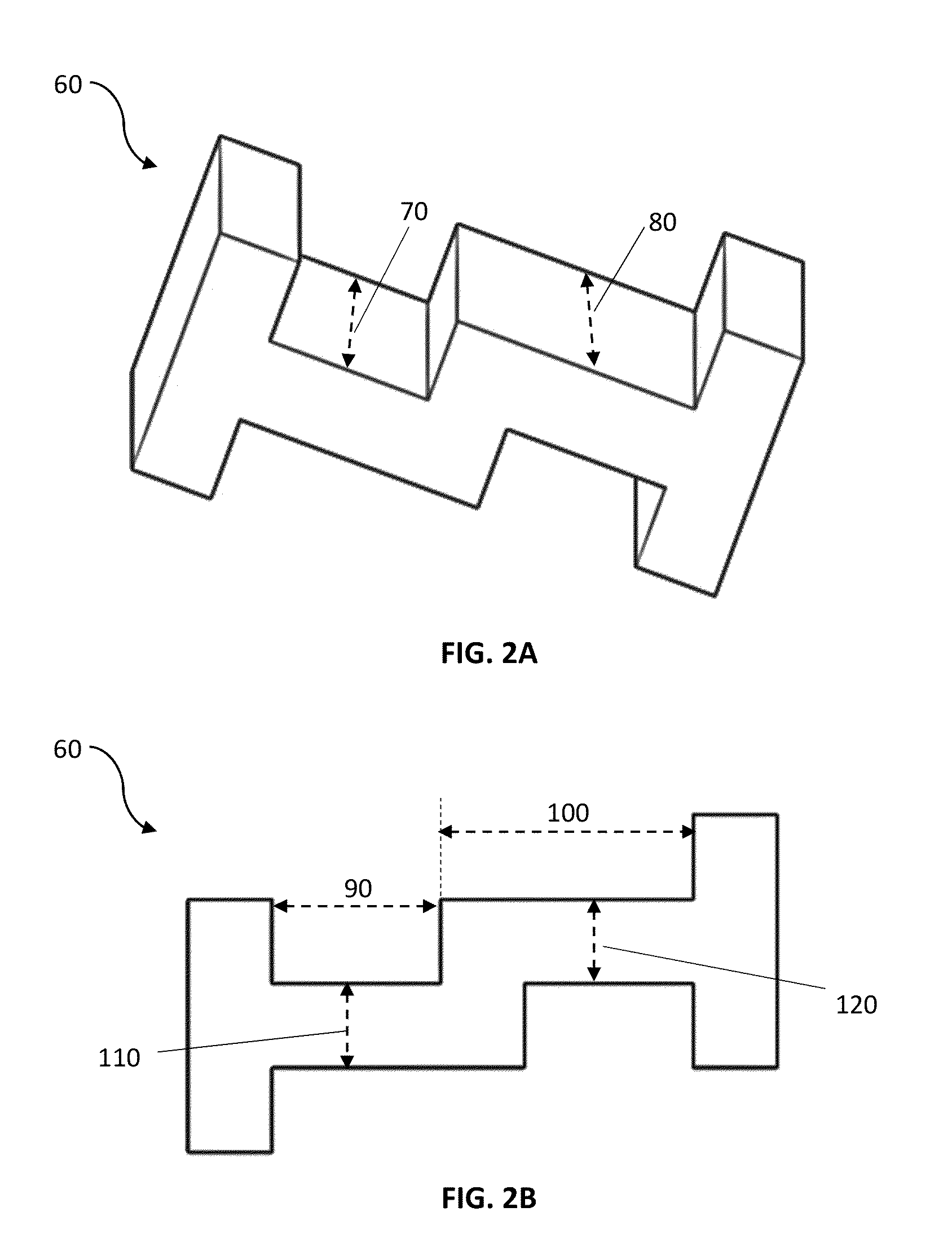
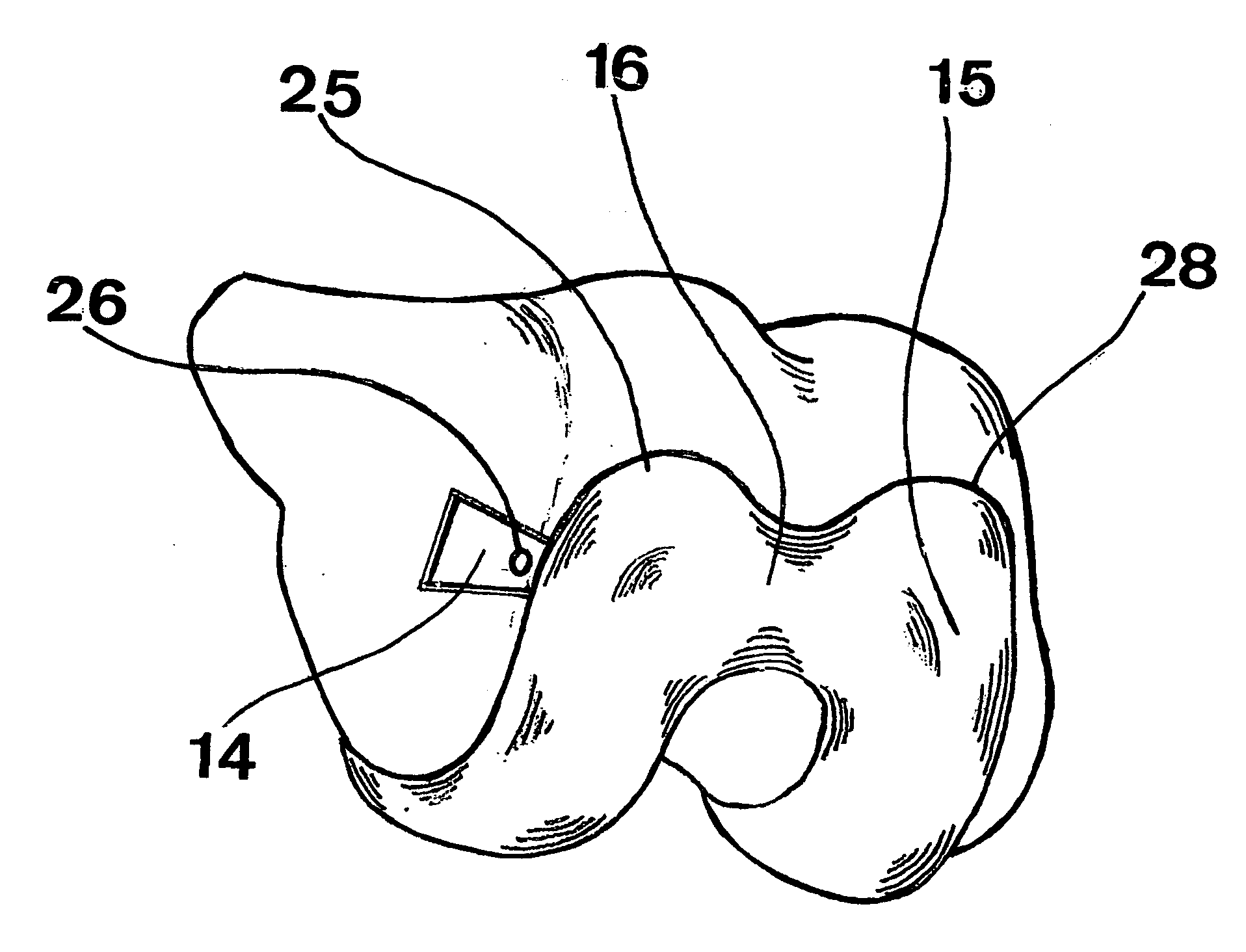
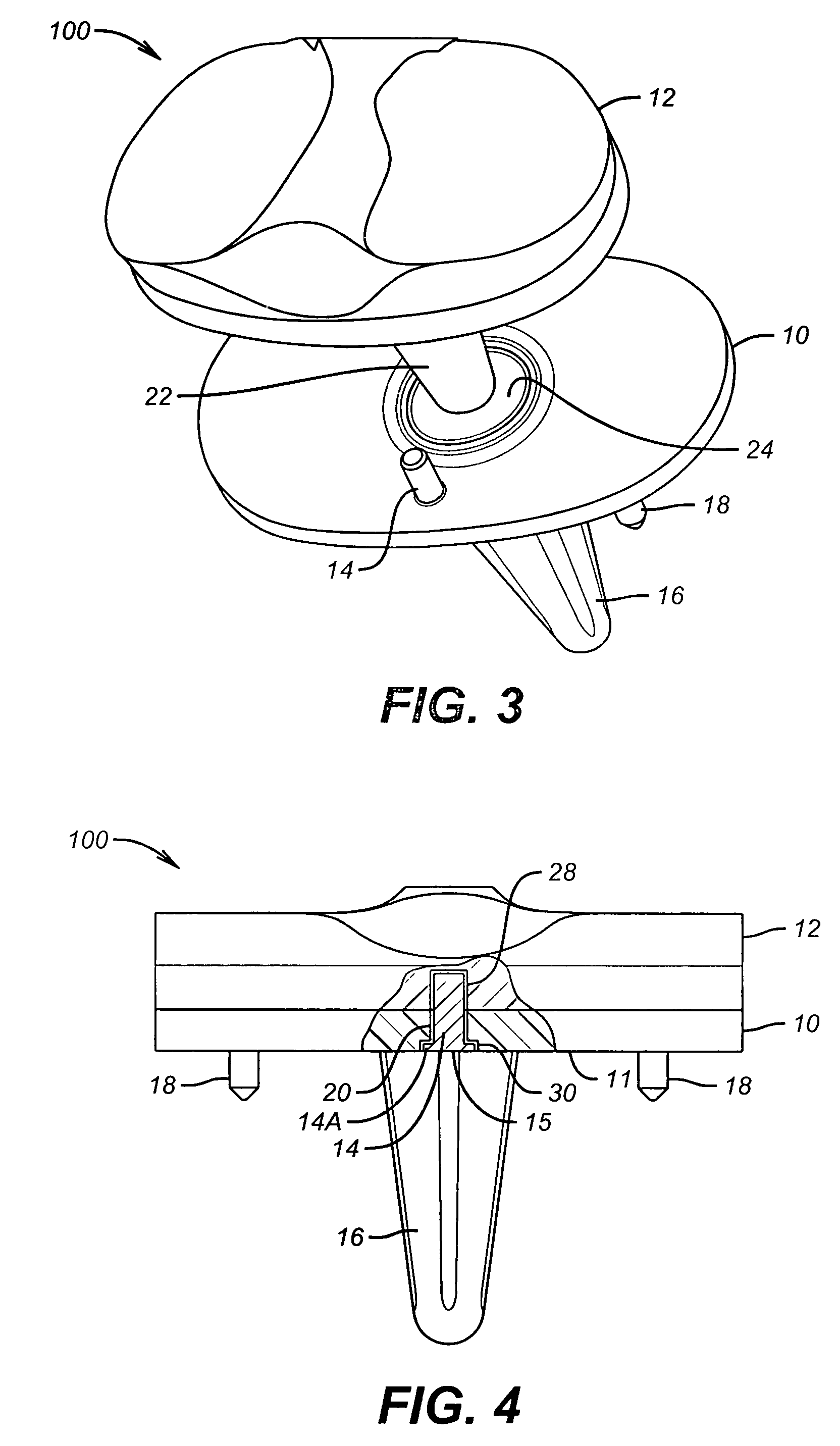
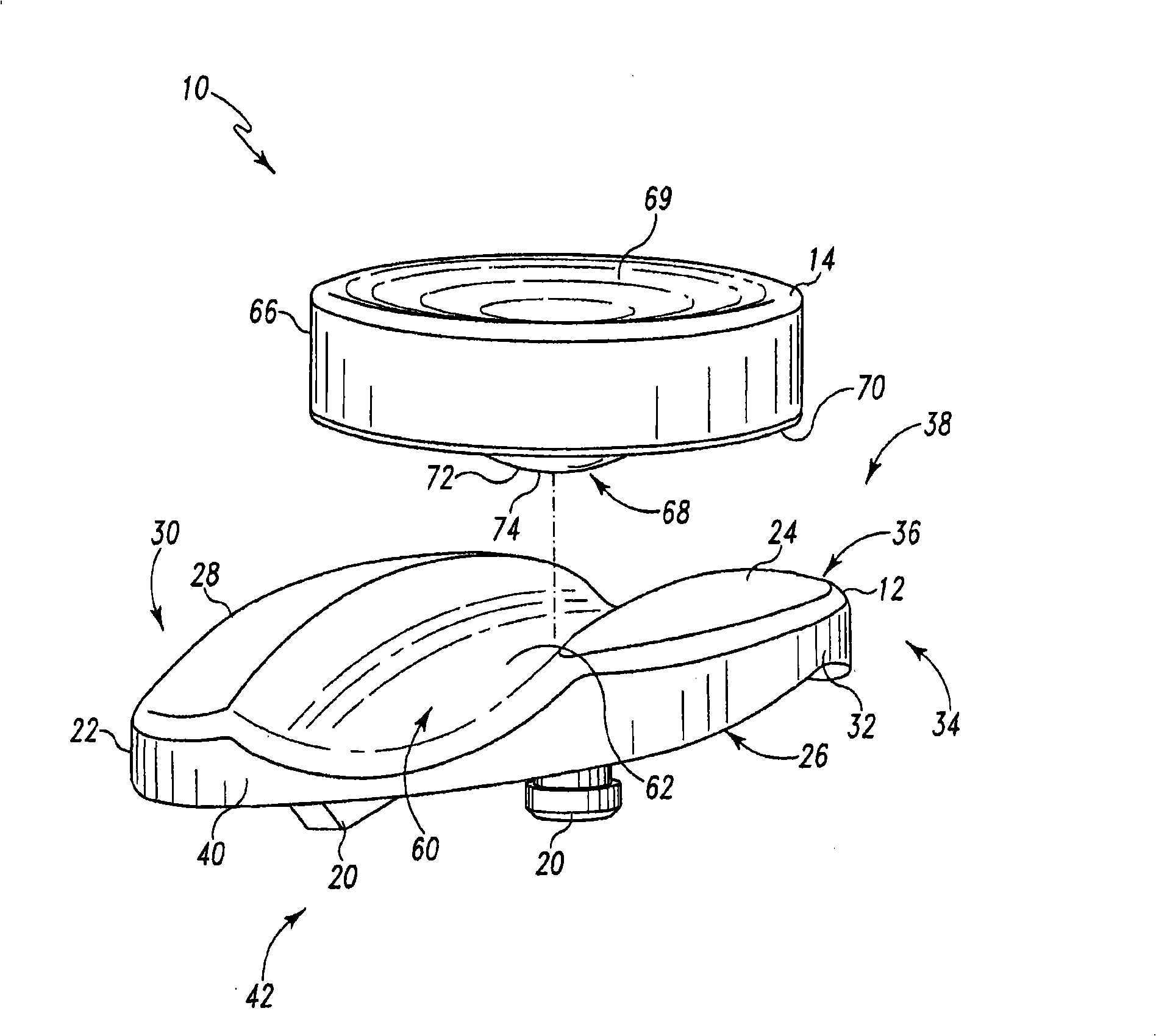
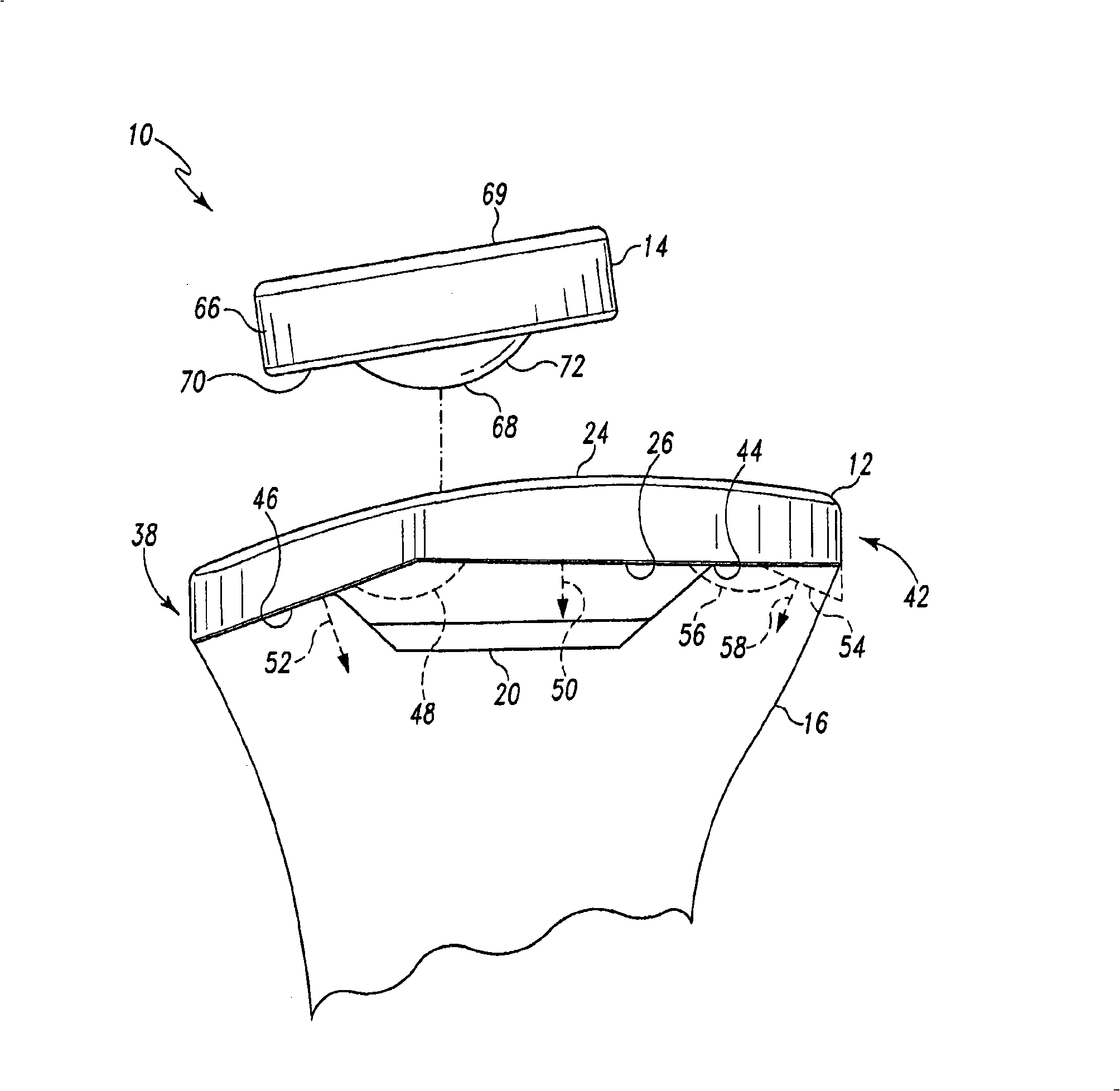
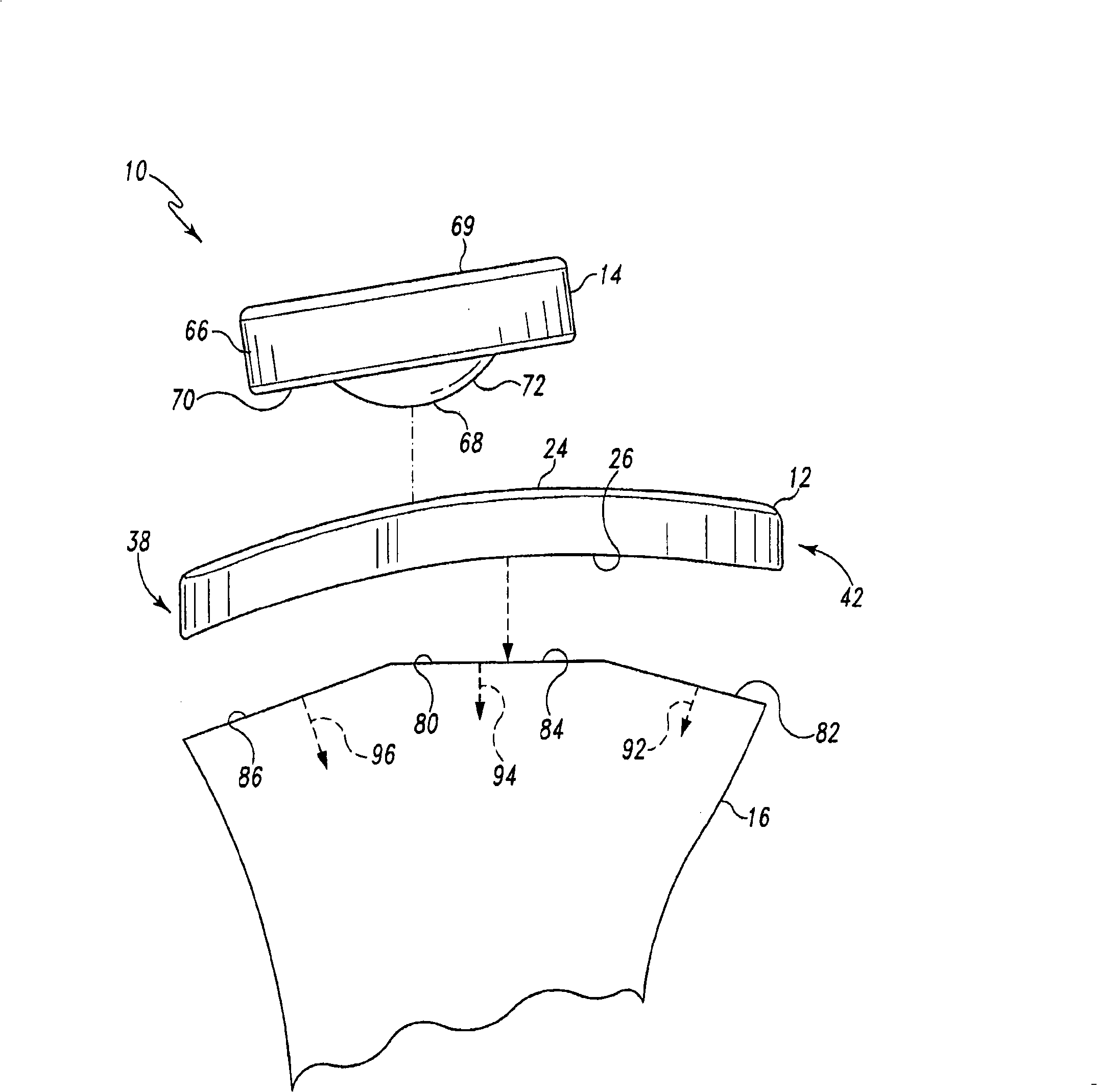
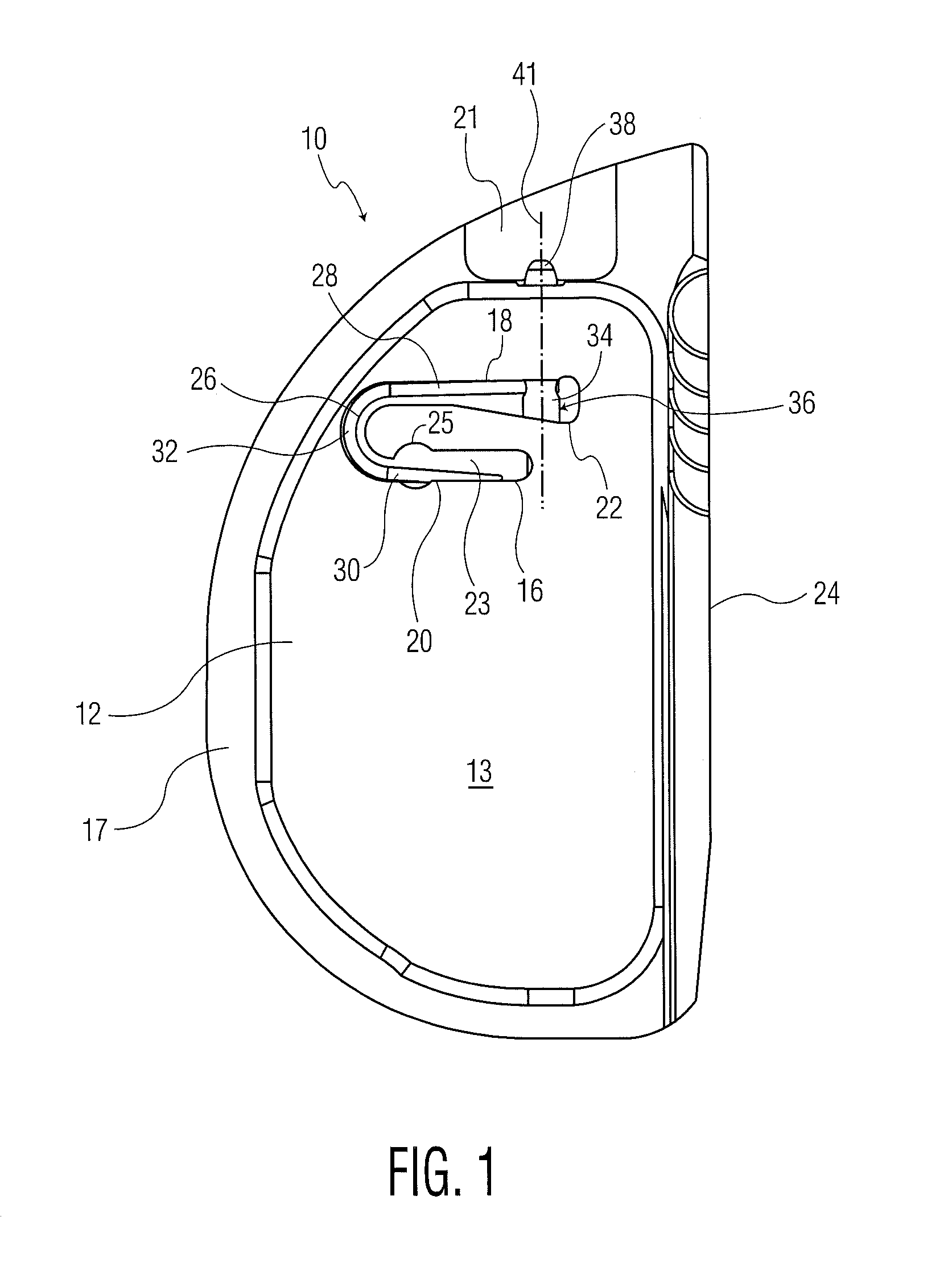
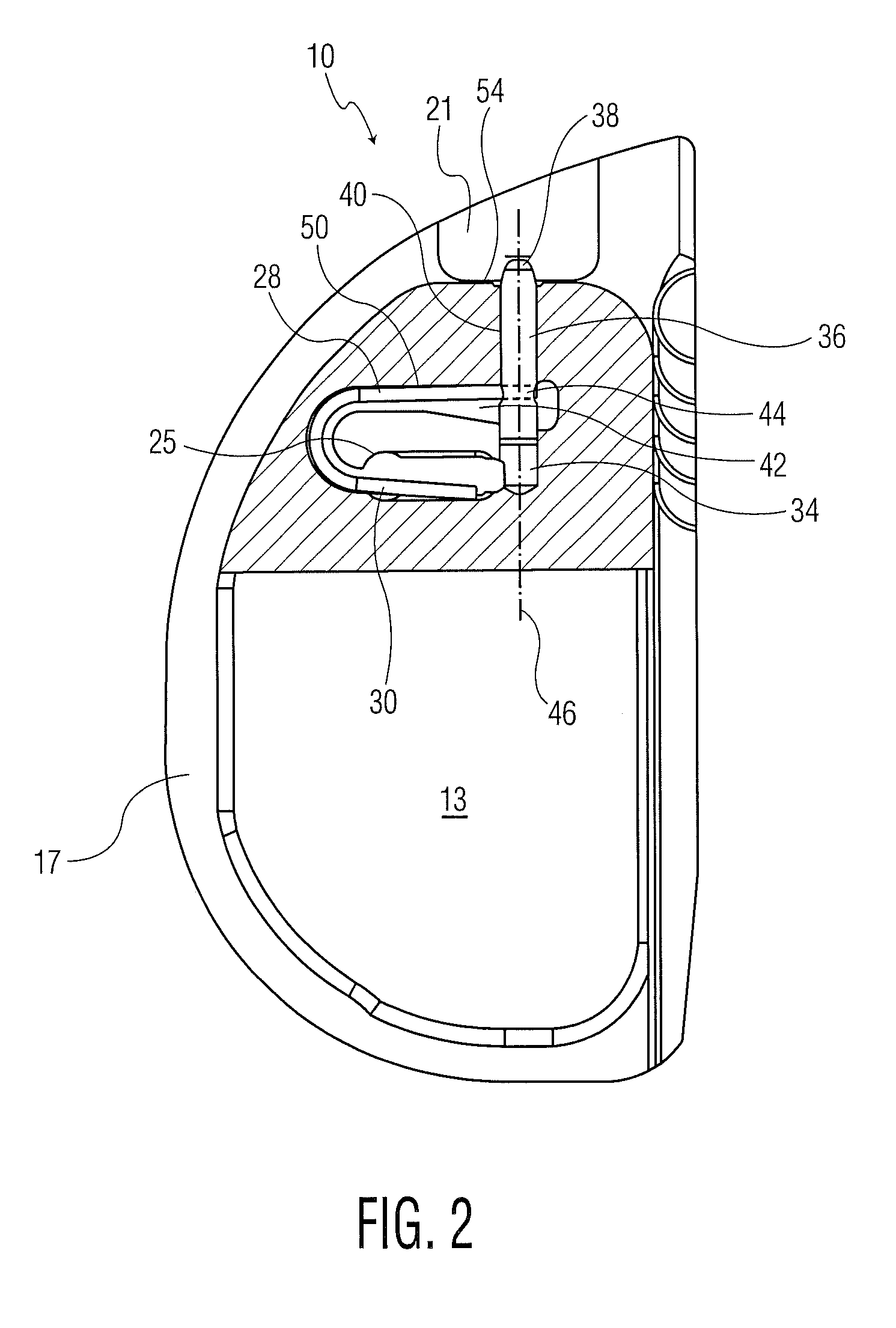
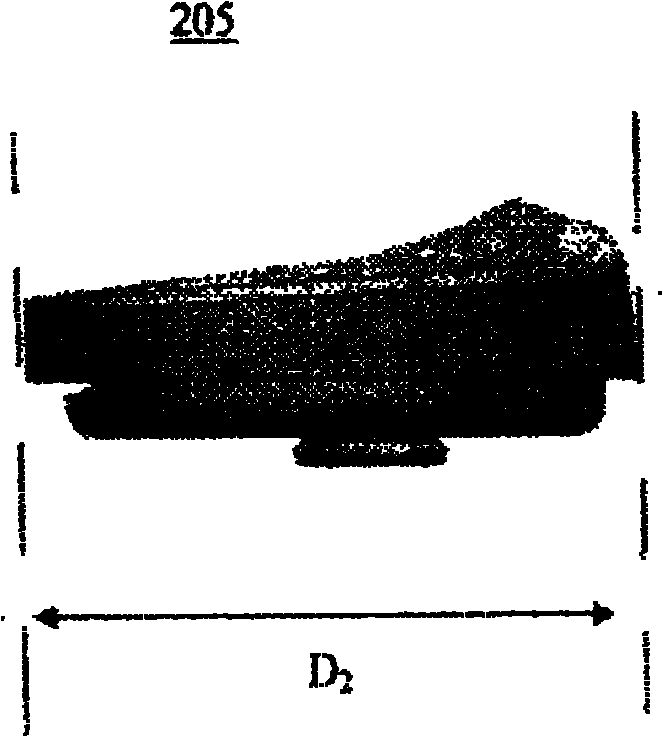
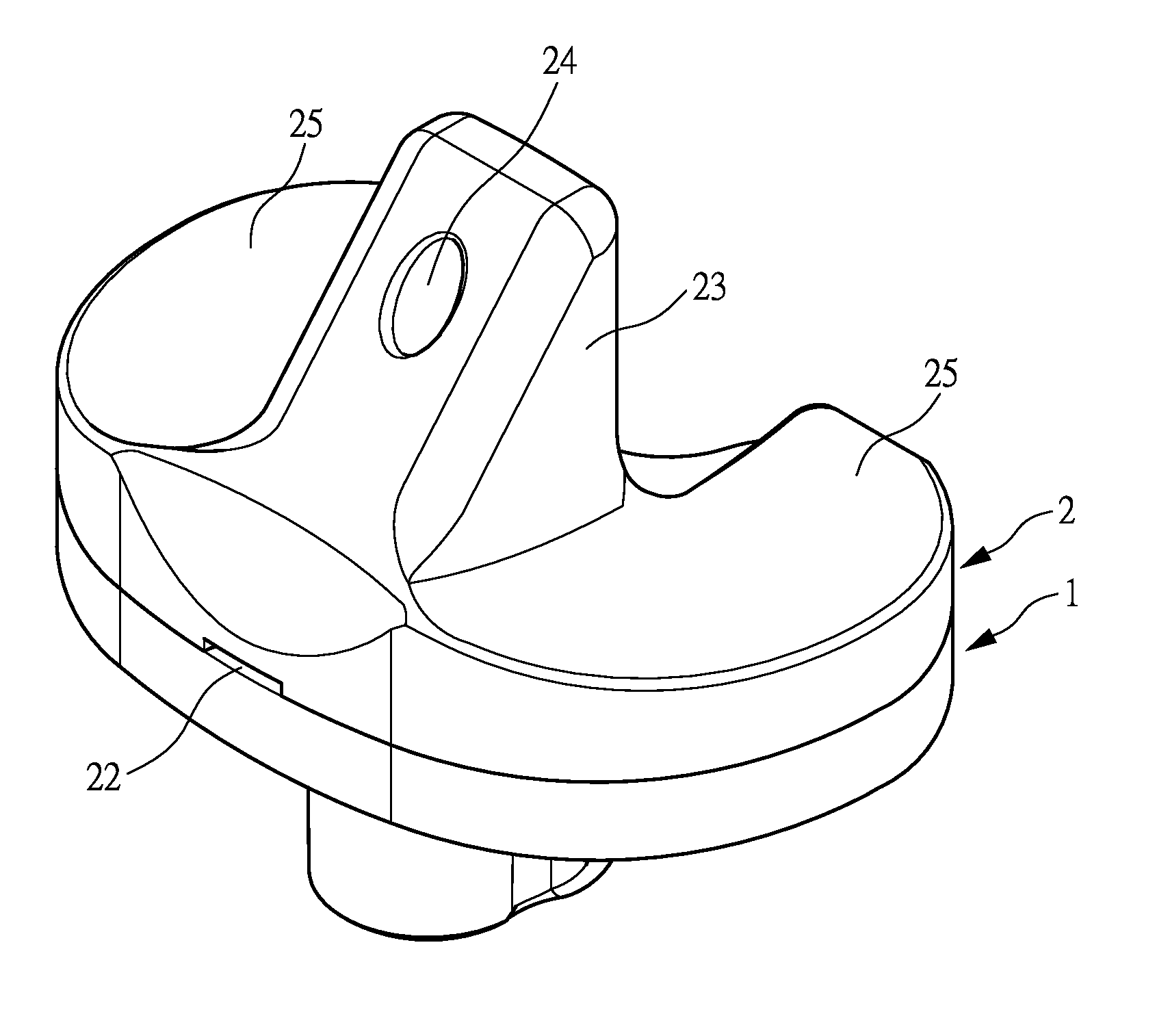
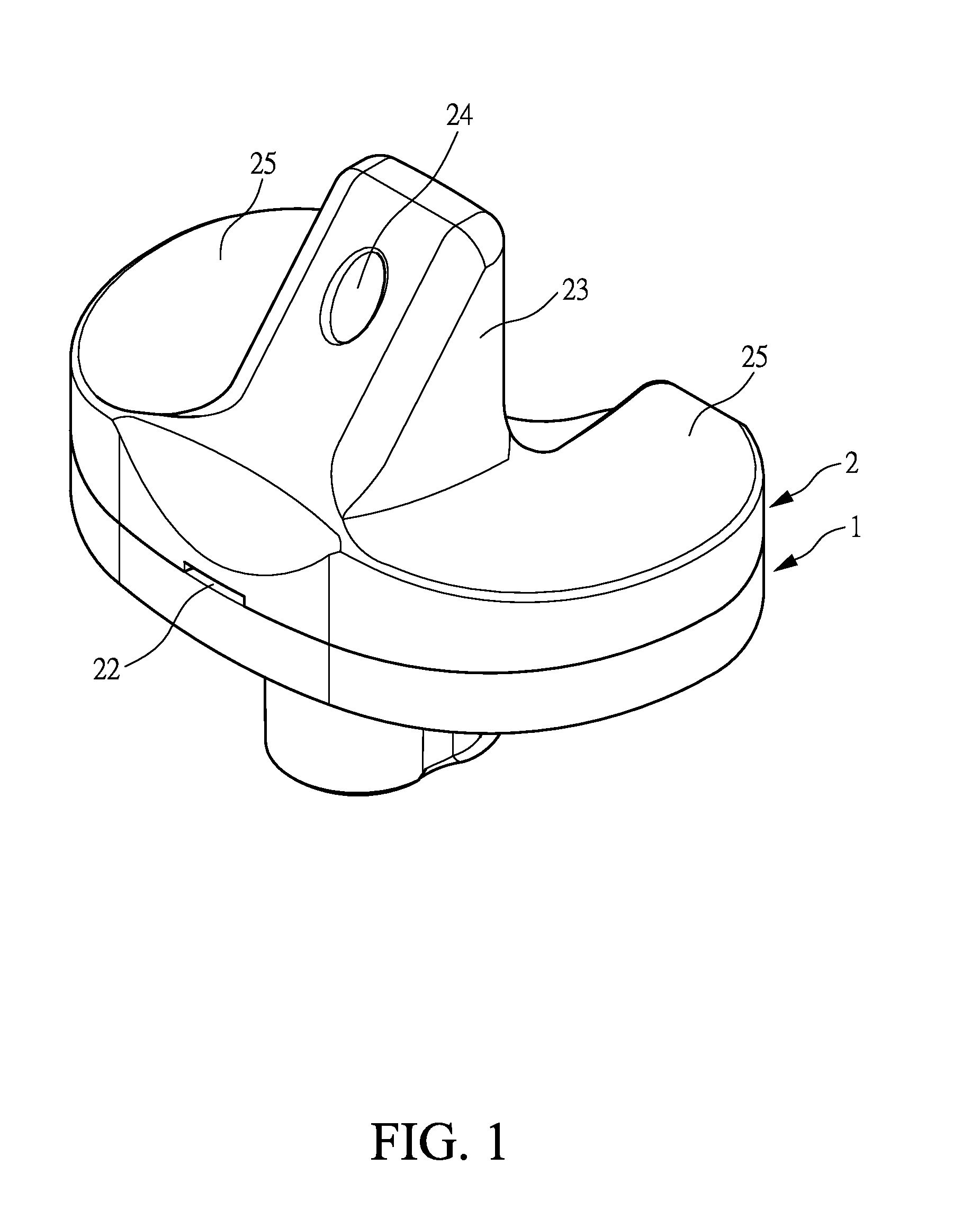
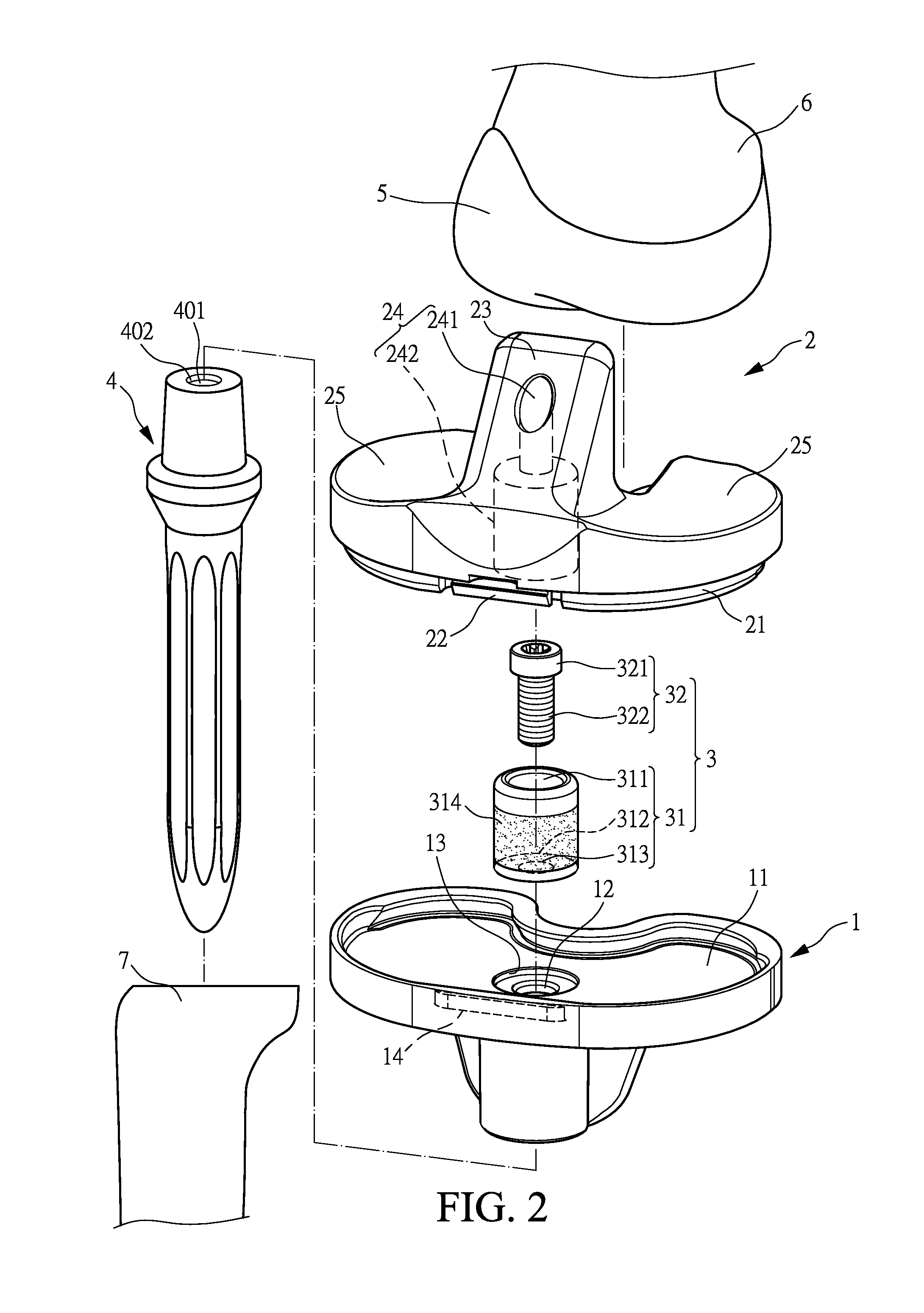
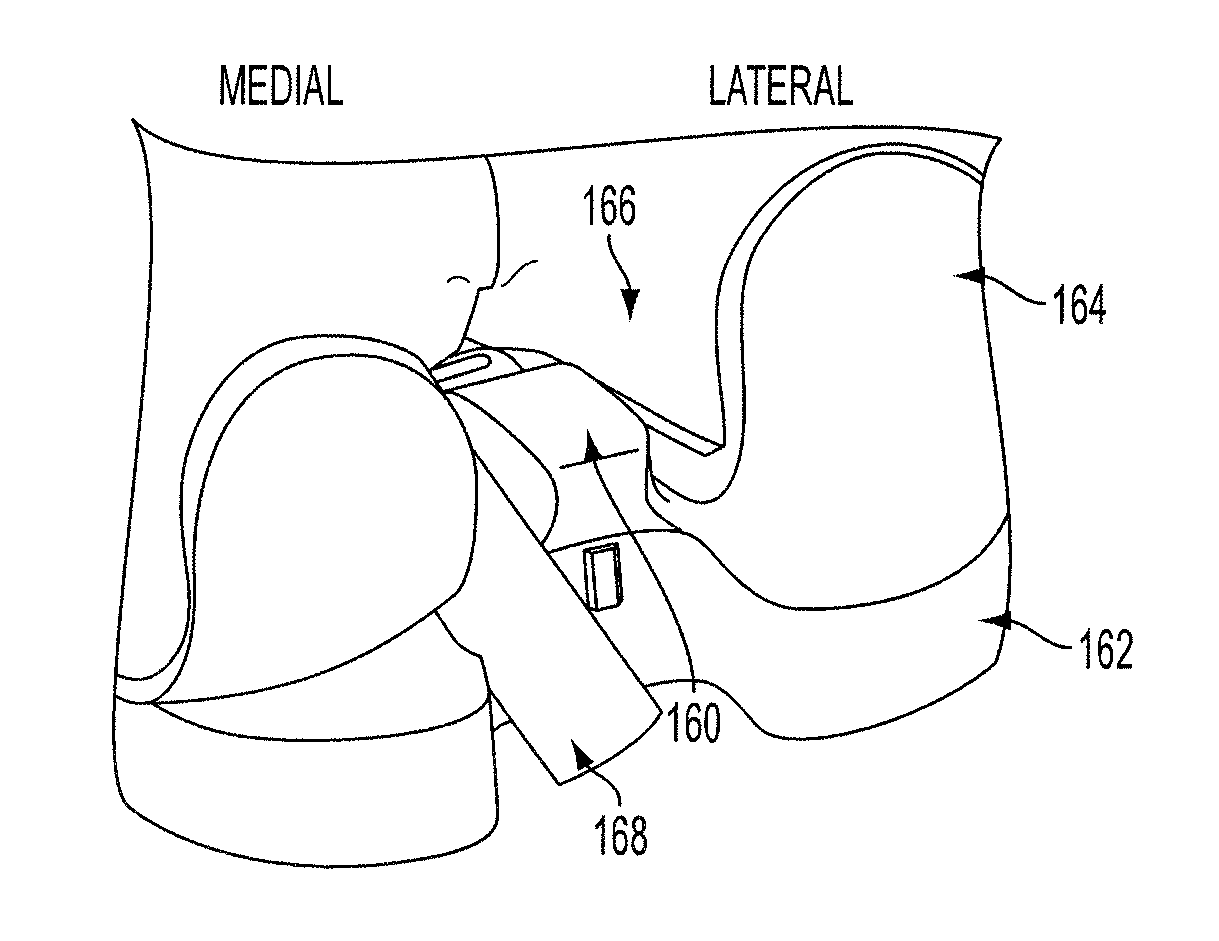
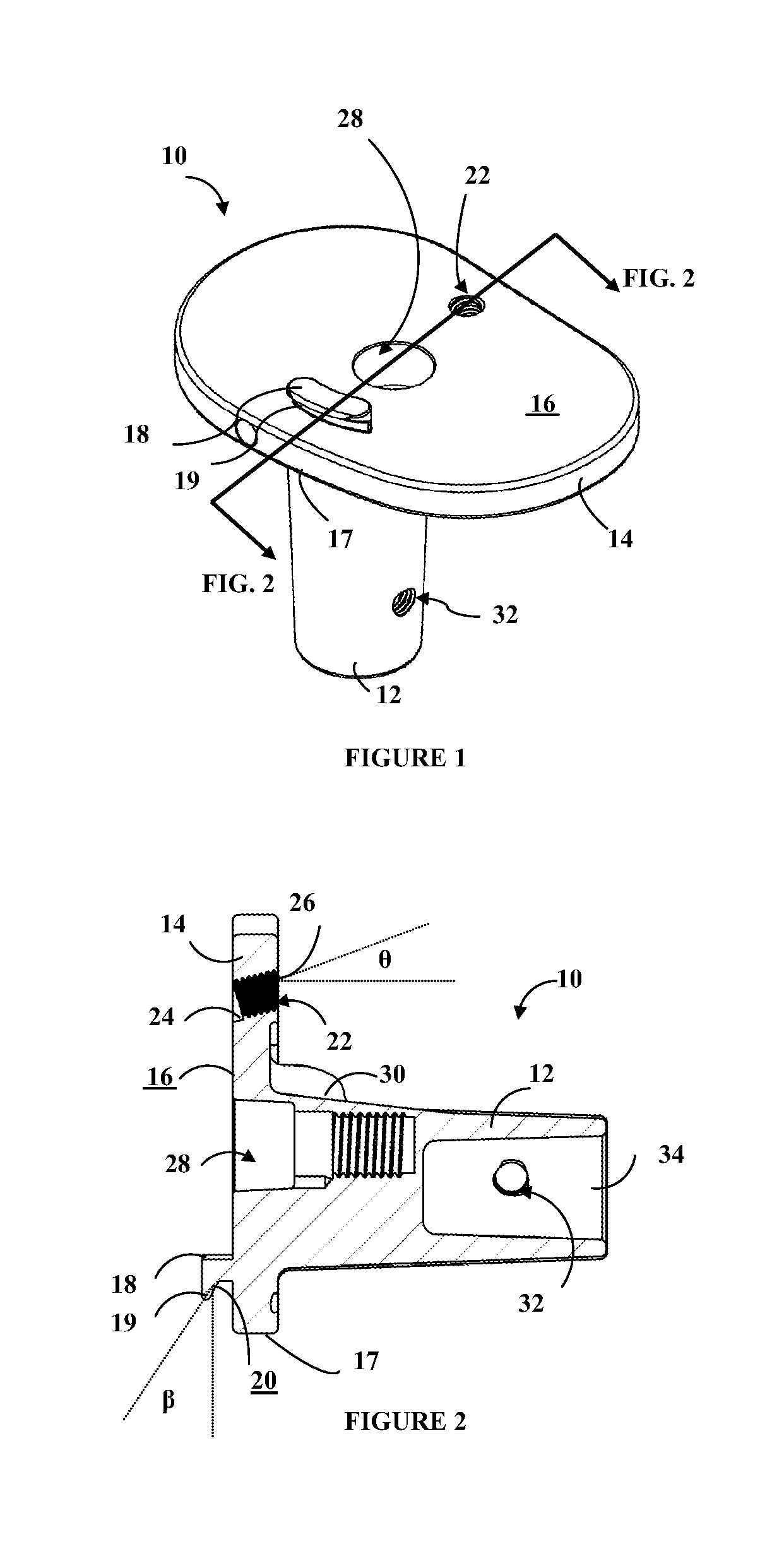
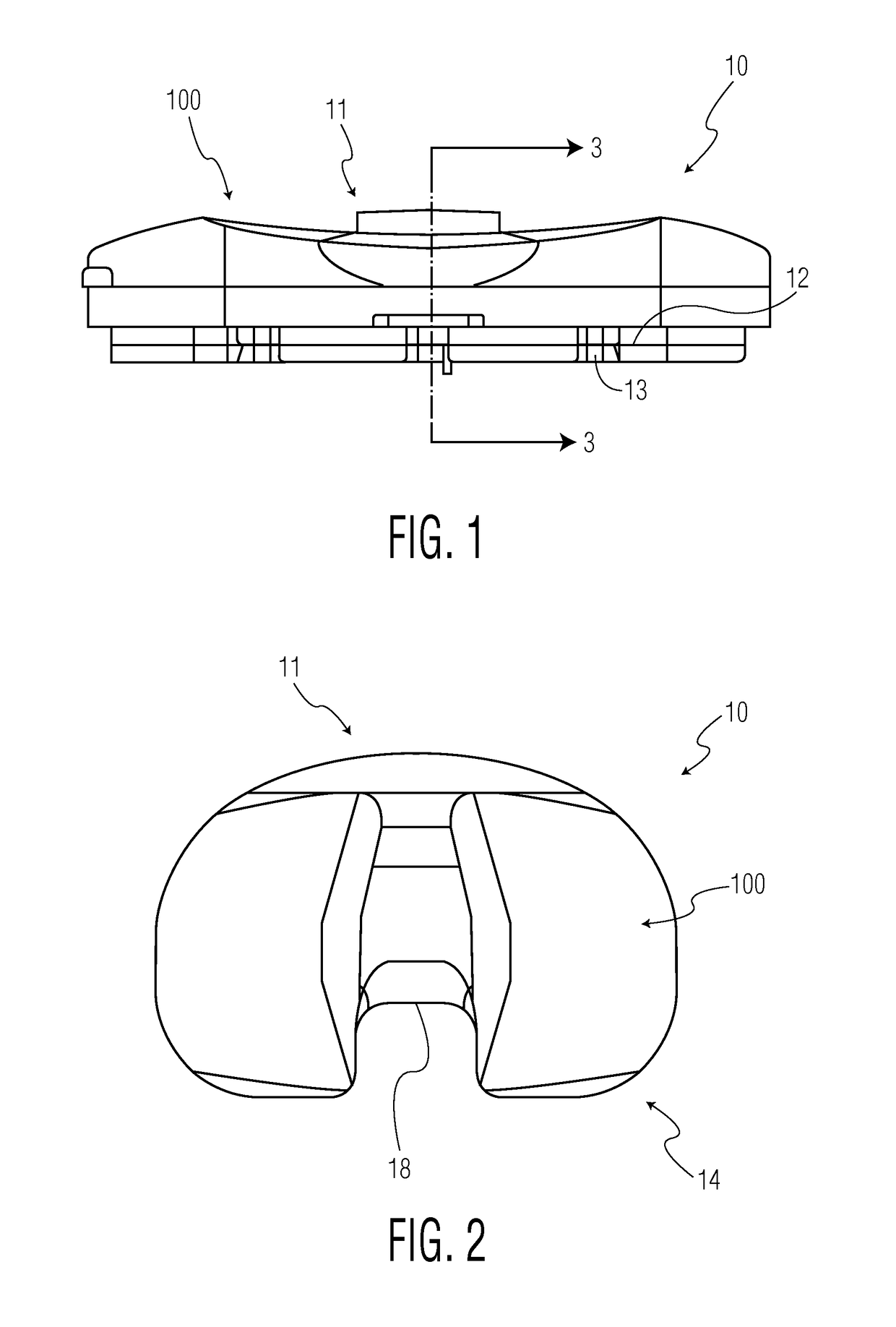
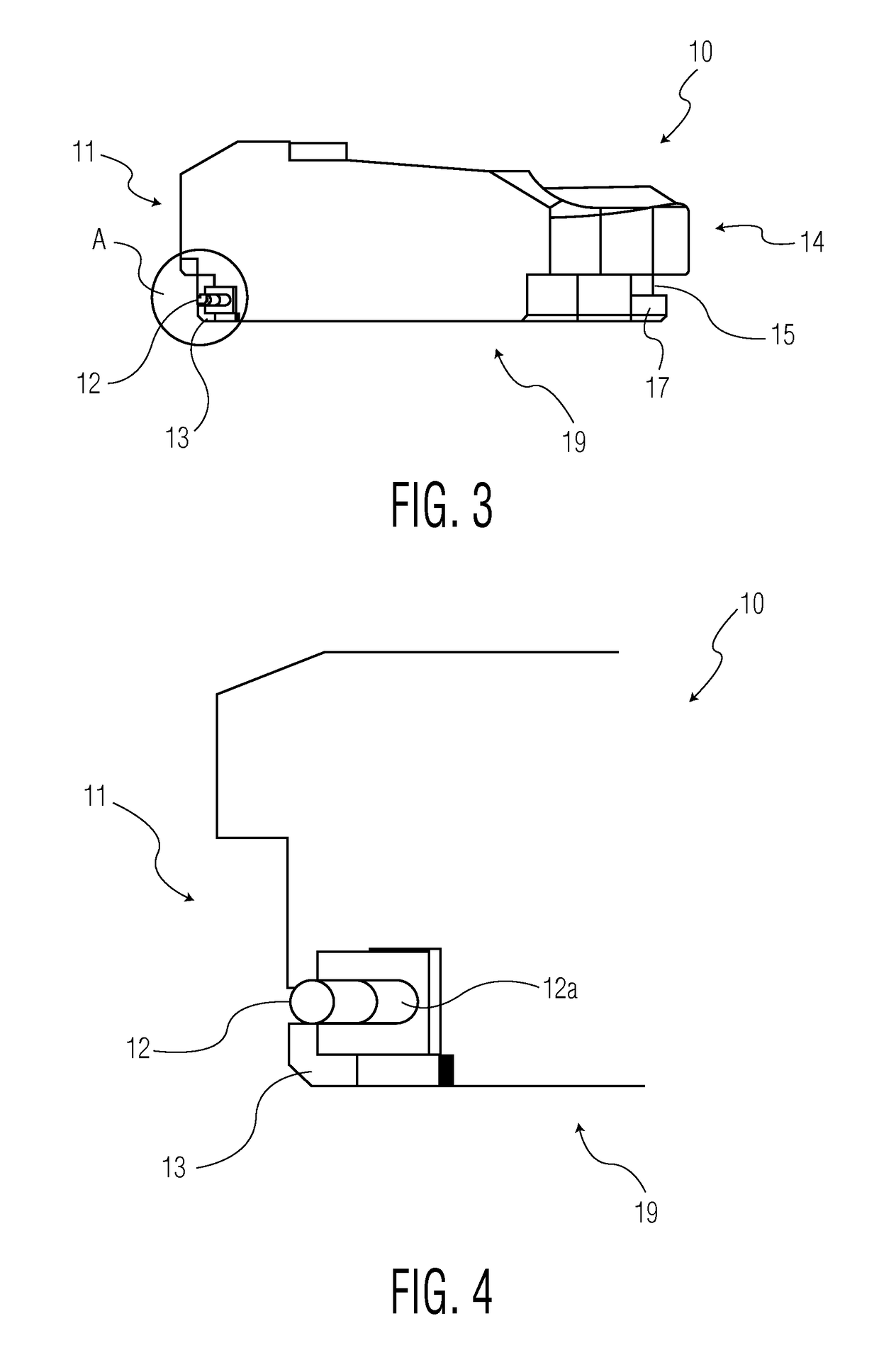
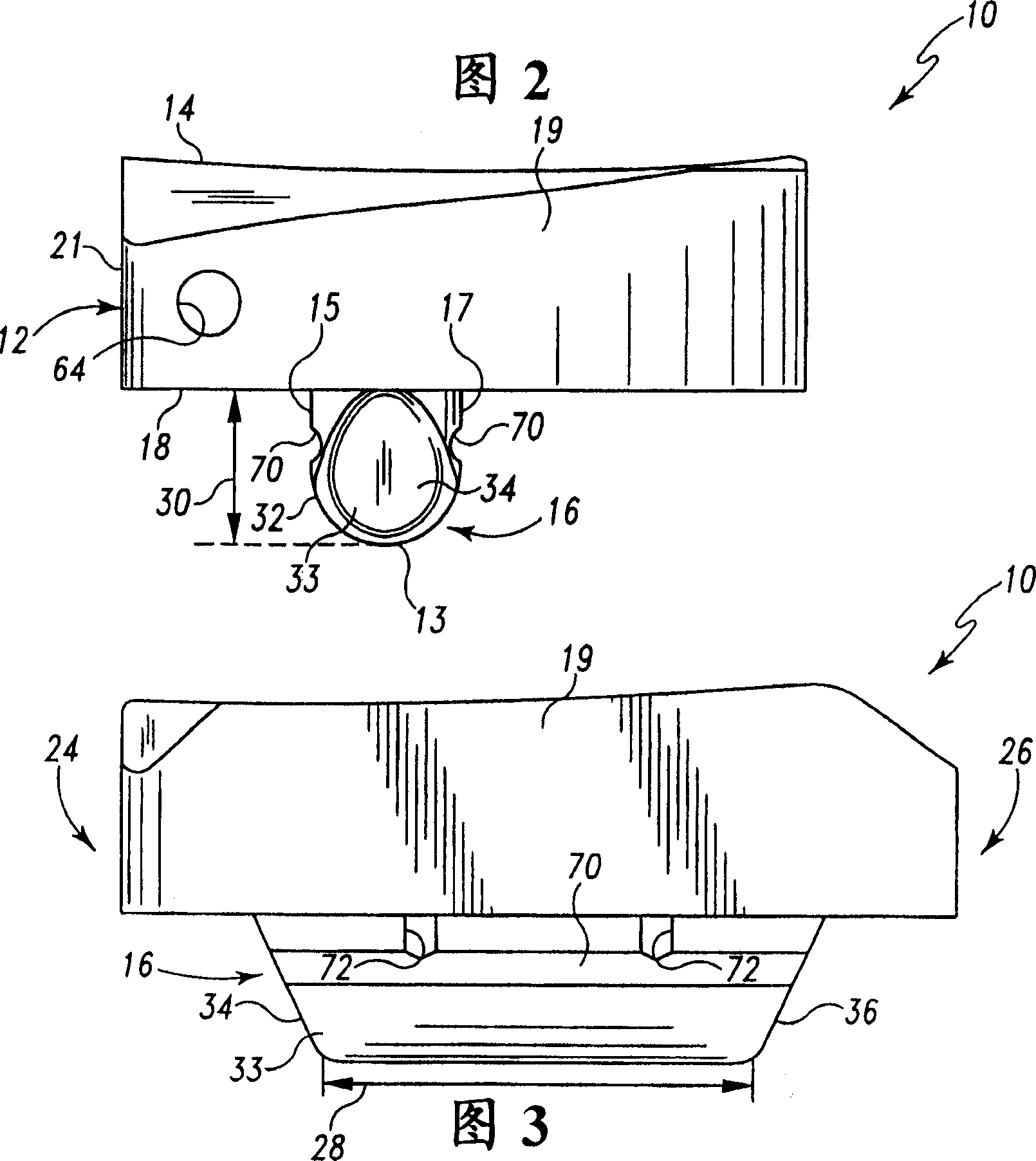
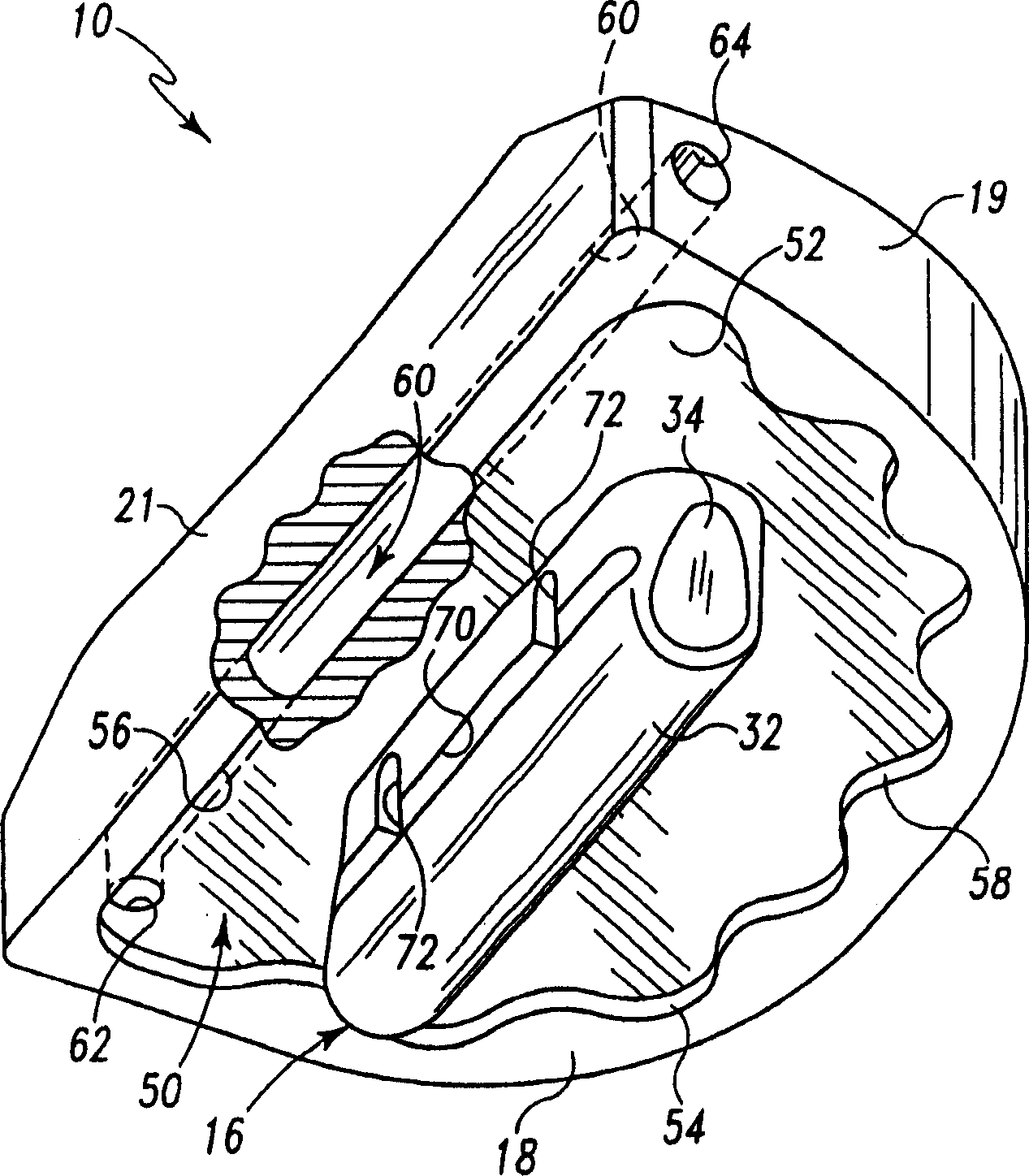
Hinged joint system
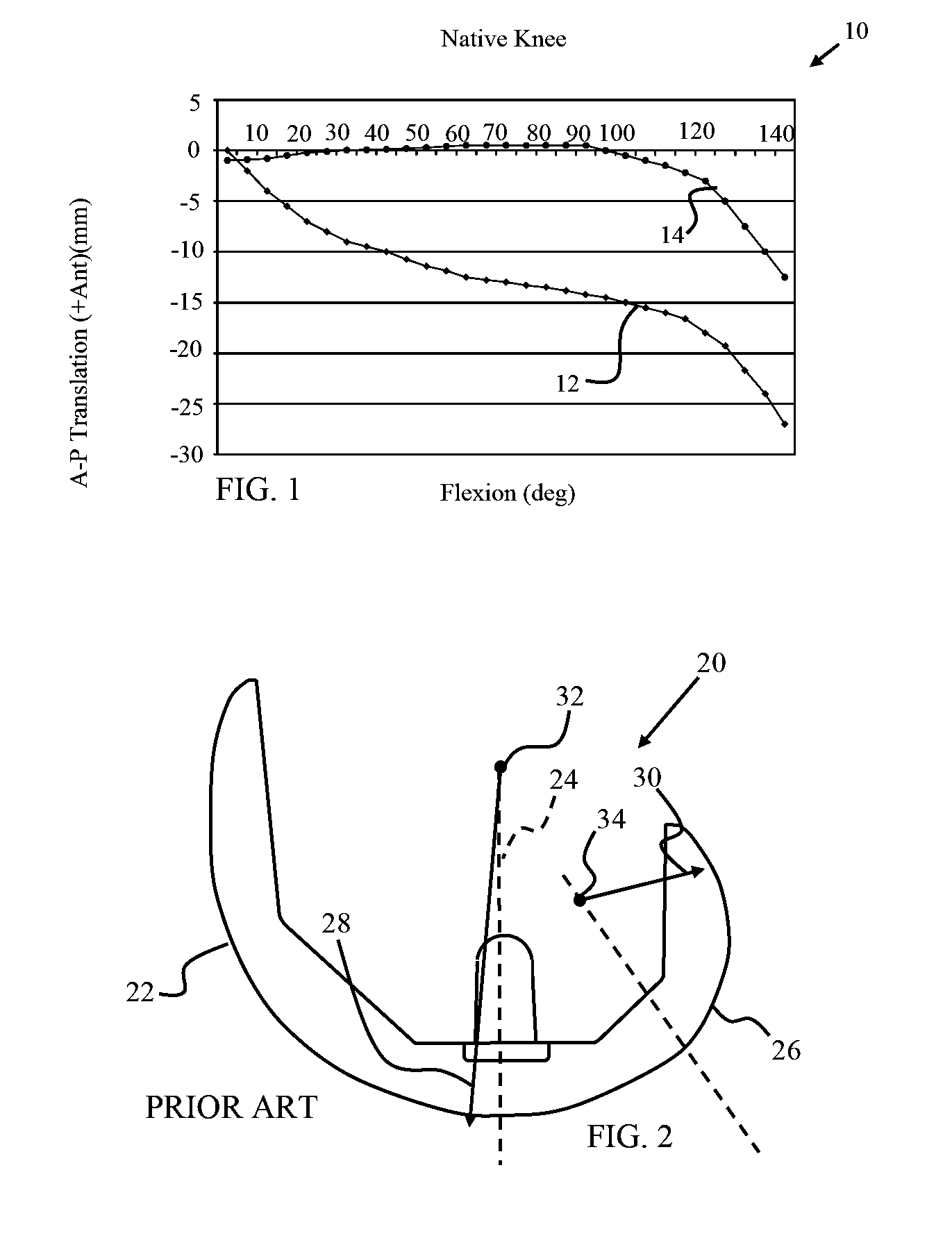
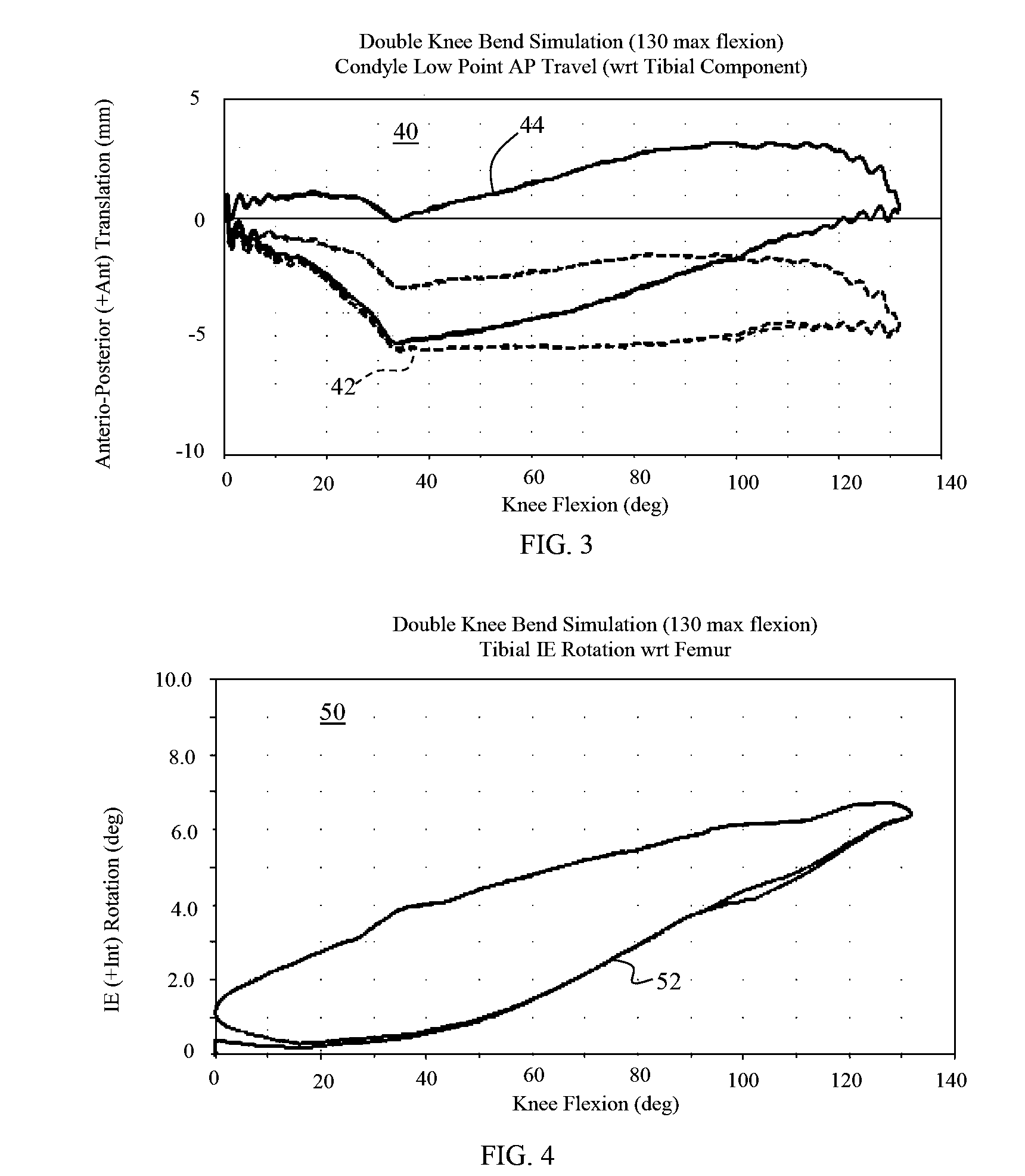
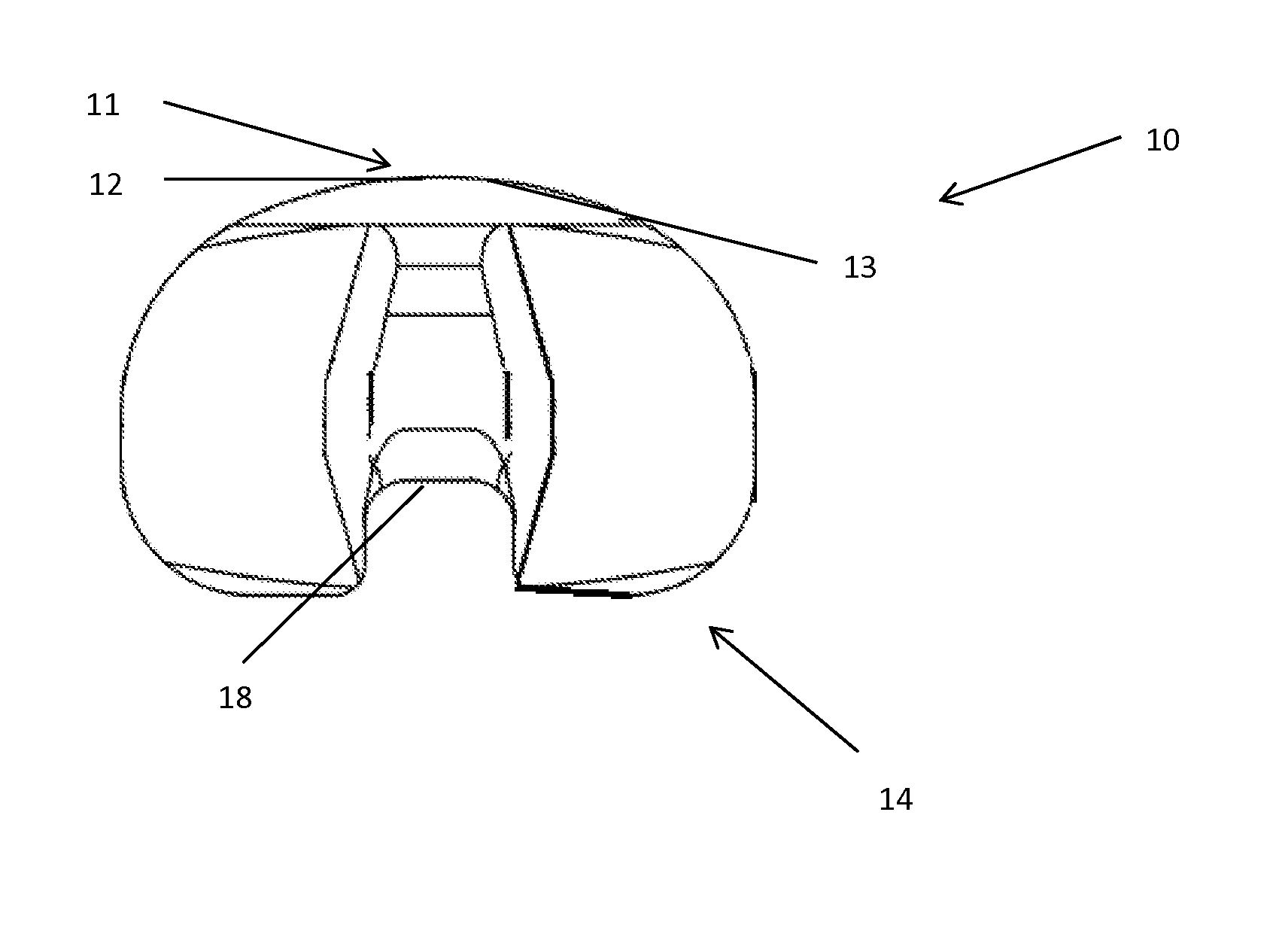
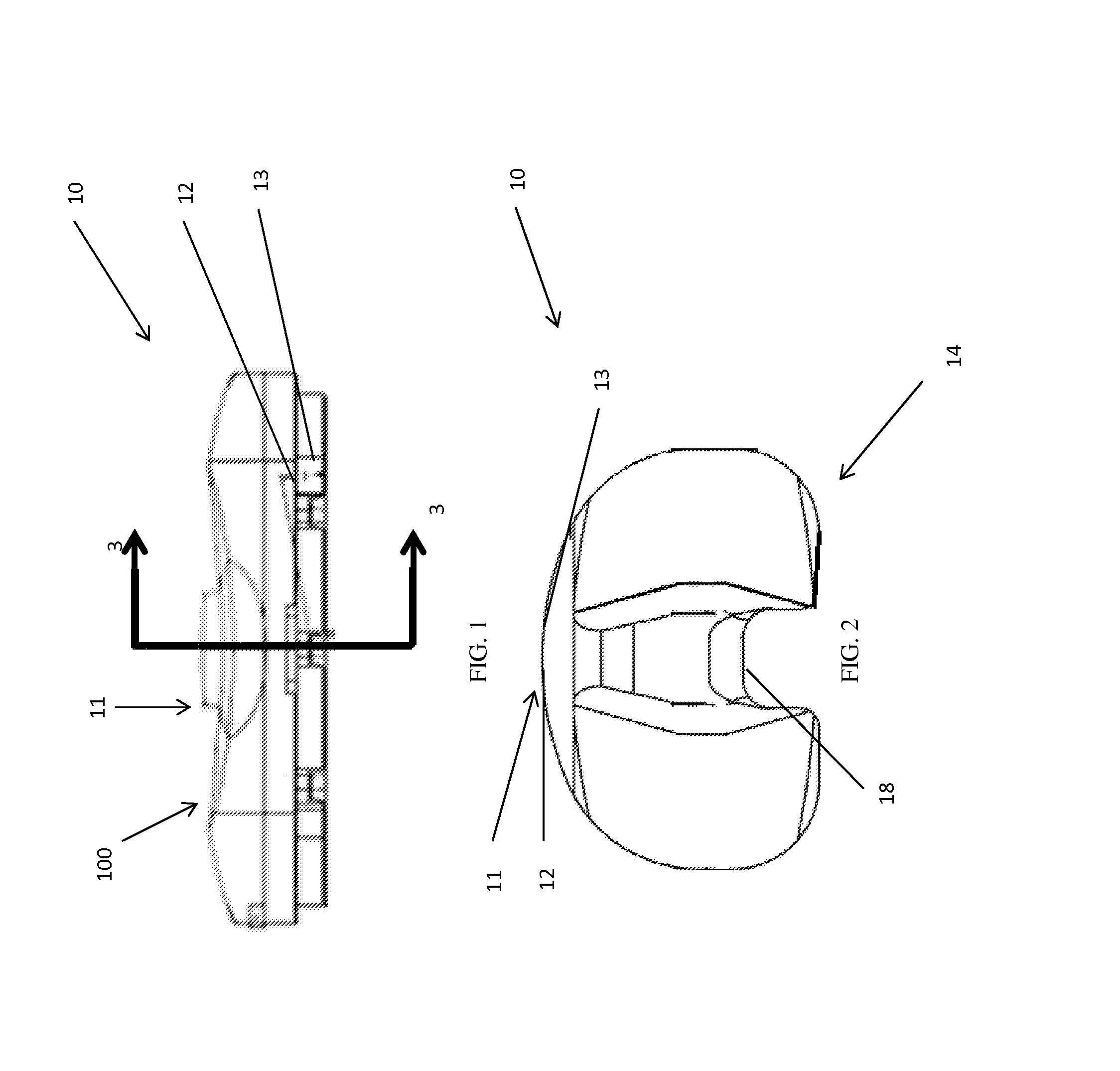
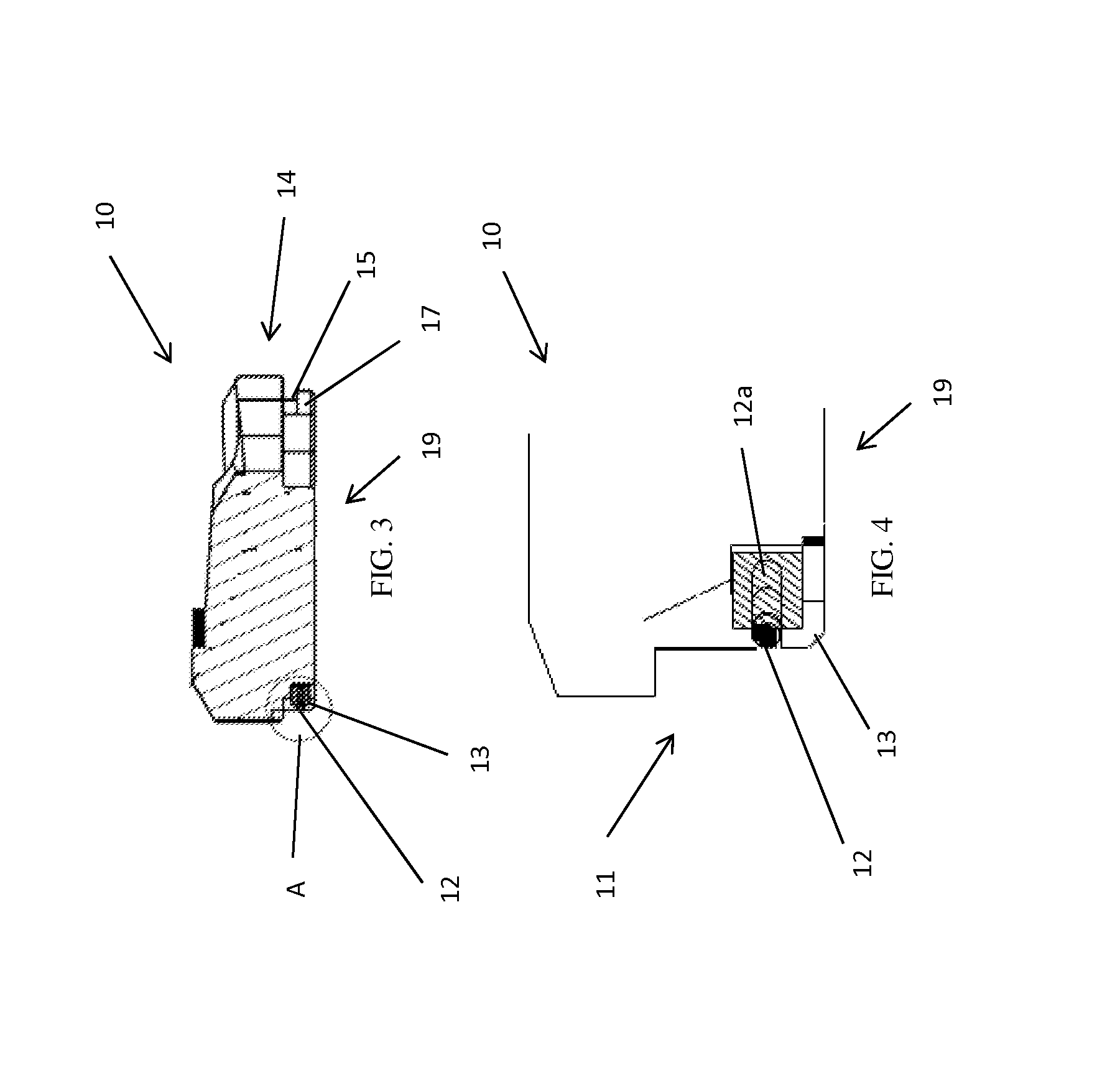
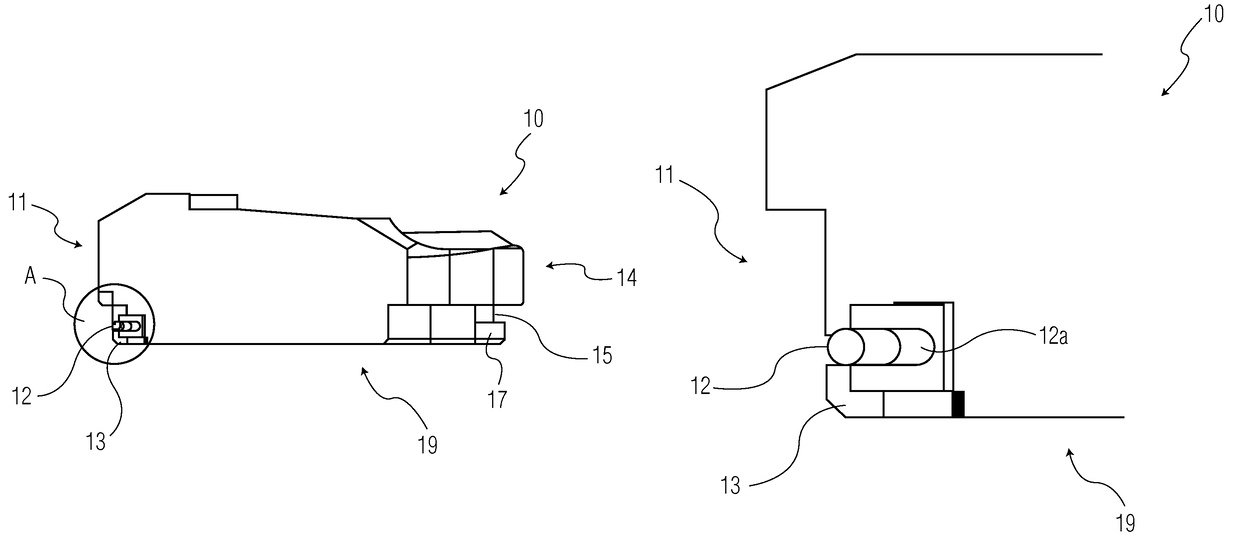
Methods, systems, and devices for replacement of a joint with a prosthetic system that replicates the natural kinematics of the joint is disclosed. A prosthetic system according to one embodiment includes a tibial component having a tibial plateau and a tibial stem portion, the tibial plateau having a top side and a bottom side, a tibial insert, with a bearing surface, adapted to be positioned on the top side of the tibial plateau, a femoral component having a base portion and a central housing, the femoral component having an axis of extension-flexion rotation, the base portion having a pair of condyles, a mechanical linkage component linking the tibial component with the femoral component and with the tibial insert in between the tibial component and the femoral component, so that there is a center of contact between the condyles and the bearing surface, the mechanical linkage component adapted to allow the center of contact to move posteriorly during flexion, provide for the movement of the axis of extension-flexion rotation in the superior-inferior direction, and allow rotation of the tibial component, the bearing surface, and the femoral component about a superior-inferior axis in order to provide and control the natural kinematics of the knee joint.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Mobile bearing tibial base prosthetic devices employing oxidized zirconium surfaces
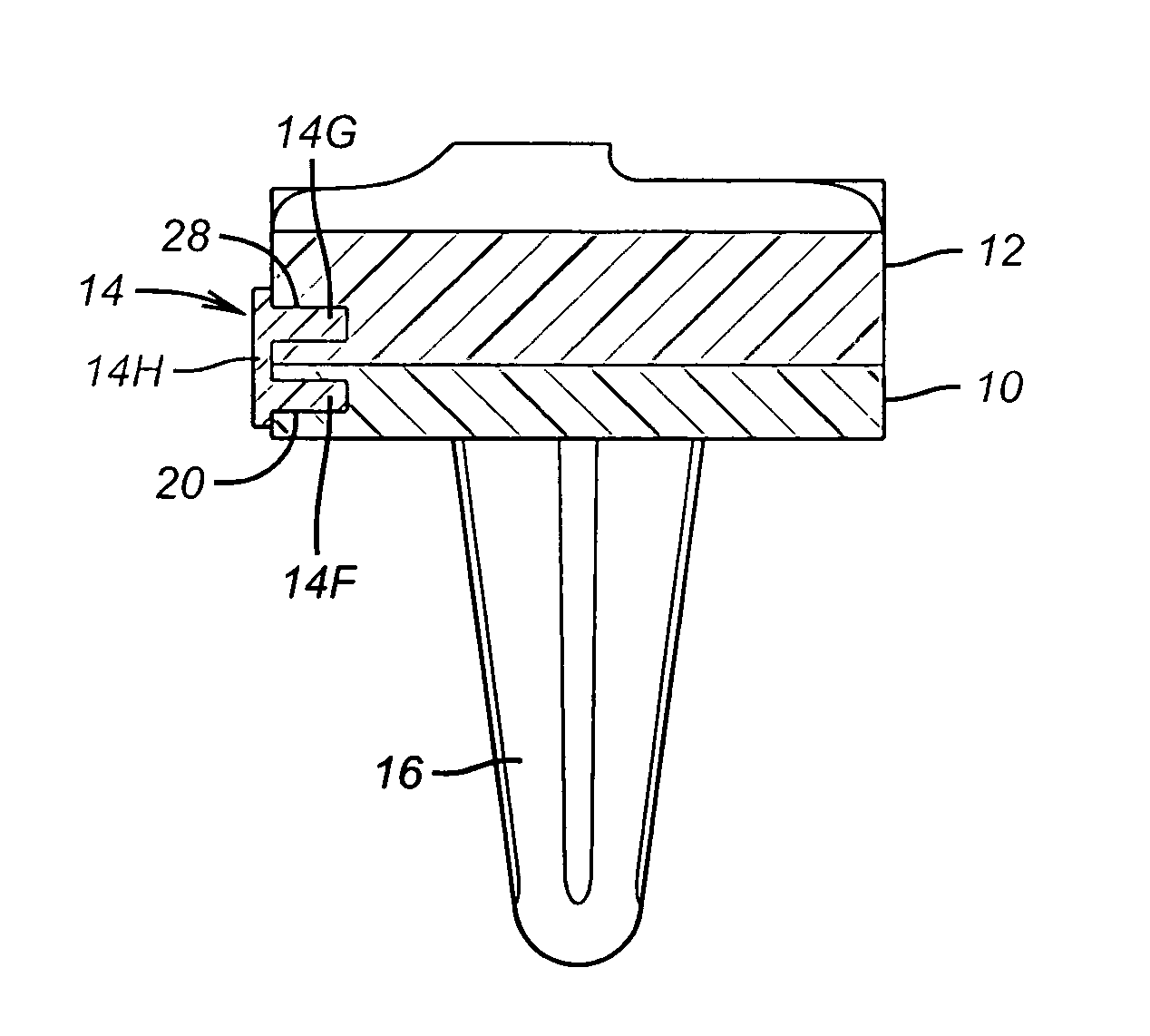
An orthopedic implant with a diffusion-hardened surface on non-load bearing areas of the implant for interaction with non-load bearing surfaces of a polymeric bio-compatible material, such as UHMWPE (ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene). The orthopedic implant is a mobile-bearing knee prosthetic and system where a coating of oxidized zirconium is formed on the post of the tibial tray of the prosthetic for interaction with an opening of a polymeric tibial insert. The diffusion-hardened surface of the orthopedic implant provides a strengthened post and reduction in wear in the opening of the polymeric insert.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
System and method for adjusting the thickness of a prosthesis
The present invention relates to a system and method for adjusting a thickness of a prosthesis (e.g., a knee implant). In one embodiment, a knee prosthesis for implantation in a patient is provided, comprising: a tibial tray, wherein the tibial tray comprises an upper surface and a lower surface, and the lower surface of the tibial tray is disposed adjacent a tibia of the patient; a tibial insert, wherein the tibial insert comprises an upper surface and a lower surface; a tibial spacer, wherein the tibial spacer comprises an upper surface and a lower surface, and wherein the tibial spacer is disposed between the tibial tray and the tibial insert such that the lower surface of the tibial spacer is adjacent the upper surface of the tibial tray and the upper surface of the tibial spacer is adjacent the lower surface of the tibial insert; and at least one locking mechanism, wherein the locking mechanism locks the tibial spacer to the tibial tray to form a locked spacer / tray assembly such that the locking mechanism substantially prohibits at least relative up-down movement between the tibial spacer and the tibial tray when the locked spacer / tray assembly is implanted in the patient. In one example, the locking mechanism may further lock the tibial spacer to the tibial insert to form a locked insert / spacer / tray assembly such that the locking mechanism substantially prohibits at least relative up-down movement between the tibial spacer and the tibial insert when the locked insert / spacer / tray assembly is implanted in the patient. In another embodiment, a method for implanting a knee prosthesis in a patient is provided, comprising: providing a tibial tray, wherein the tibial tray comprises an upper surface and a lower surface, and the lower surface of the tibial tray is disposed adjacent a tibia of the patient; providing a tibial insert which has a shelf life and which is not readily re-sterilizable after the shelf life has expired, wherein the tibial insert comprises an upper surface and a lower surface; and providing a tibial spacer which has a shelf life and which is re-sterilizable after the shelf life has expired, wherein the tibial spacer comprises an upper surface and a lower surface, and wherein the tibial spacer is disposed between the tibial tray and the tibial insert such that the lower surface of the tibial spacer is adjacent the upper surface of the tibial tray and the upper surface of the tibial spacer is adjacent the lower surface of the tibial insert.
Owner:EXACTECH INC
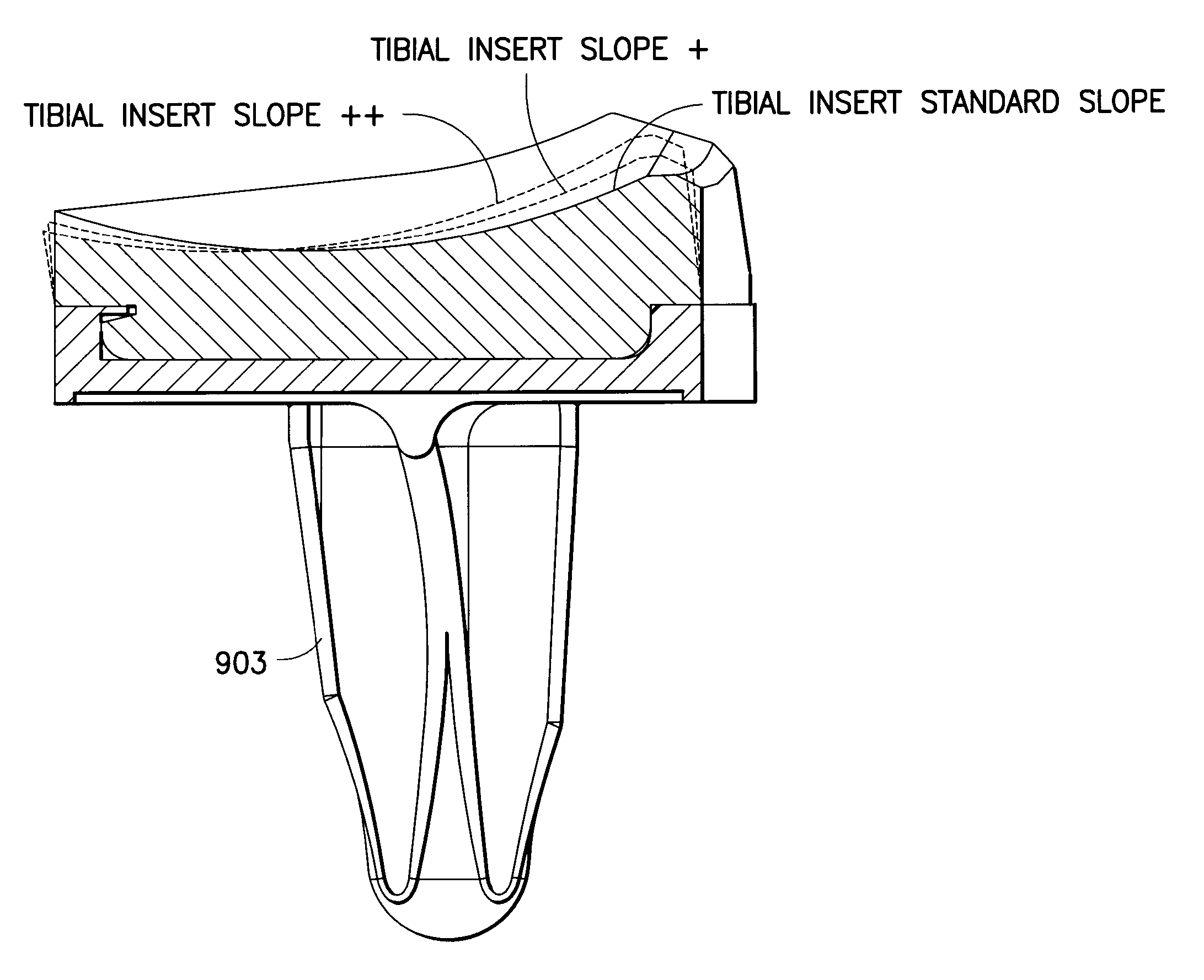
Knee prosthesis system with at least a first tibial portion element (a tibial insert or tibial trial) and a second tibial portion element (a tibial insert or tibial trial), wherein each of the first tibial portion element and the second tibial portion element has a different slope
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a knee prosthesis system with at least a first tibial portion element (a tibial insert or a tibial insert trial) and a second tibial portion element (a tibial insert or a tibial insert trial), wherein each of the first tibial portion element and the second tibial portion element has a different slope. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a method of implanting a knee prosthesis, wherein the method utilizes at least a first tibial portion element (a tibial insert or a tibial insert trial) and a second tibial portion element (a tibial insert or a tibial insert trial), wherein each of the first tibial portion element and the second tibial portion element has a different slope.
Owner:EXACTECH INC
Antero-posterior placement of axis of rotation for a rotating platform
A knee replacement system includes a femoral component including a lateral condylar articulating portion and a medial condylar articulating portion, a tibial tray including an upper articulating surface, and a tibial insert including (i) a first articulating portion for articulating with the lateral condylar articulating portion with a first condylar dwell point, (ii) a second articulating portion for articulating with the medial condylar articulating portion with a second condylar dwell point, (iii) a lower articulating surface for articulating with the upper articulating surface, and (iv) a coupling member for coupling with the tibial tray and defining an axis of rotation about which the tibial insert rotates with respect to the tibial tray, the axis of rotation intersecting the upper articulating surface at a location posterior to a dwell axis including the condylar dwell points when the dwell axis is projected onto the upper articulating surface.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
Posterior stabilized knee system prosthetic devices employing diffusion-hardened surfaces
InactiveUS20030153979A1Restrict movementReduce frictionJoint implantsSolid state diffusion coatingOrthopedic departmentKnee Joint
An orthopedic implant with a diffusion-hardened surface on non-load bearing areas of the implant for interaction with non-load bearing surfaces of a polymeric bio-compatible material, such as UHMWPE. The orthopedic implant is a posterior stabilized knee prosthetic and system where a coating of oxidized zirconium is formed in the cam of the femoral prosthetic for interaction with the central post of a polymeric tibial insert. The diffusion-hardened surface of the orthopedic implant provides a strengthened cam and reduction in wear in the central post of the polymeric tibial insert.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
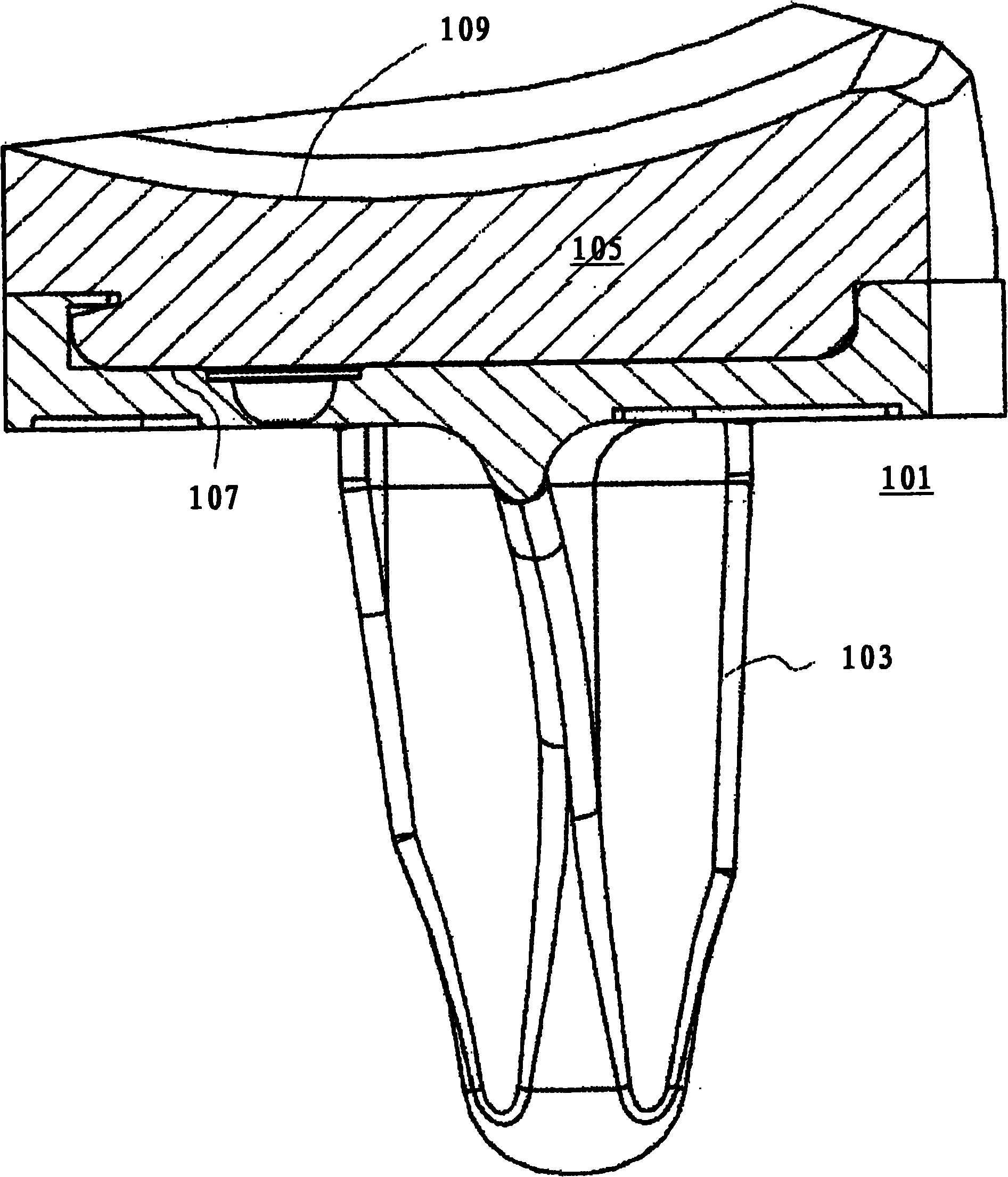
Knee joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20060161259A1Life span of the prosthetic knee joint increasesExtend your lifeJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaThigh
An improved knee joint prosthesis located between a thighbone and a tibia to couple with a femur implanted component to allow a patient to resume normal movement and exercise. The knee joint prosthesis adopts a separate design, and includes a tibial insert which has a moving aperture to hold a bracing member coupled with the femur implanted member and a tibial baseplate which has a retaining member. The bracing member and the retaining member are swivelable in the moving aperture, and the bracing member is made from wearing resistant material, so that sliding and wearing that might otherwise occur to the tibial insert may be prevented. Therefore the life span of the posterior stabilized knee joint prosthesis increases.
Owner:CHENG CHENG KUNG
System and method for adjusting the thickness of a prosthesis
The present invention relates to a system and method for adjusting a thickness of a prosthesis. A knee prosthesis for implantation may be provided, comprising: a tibial tray, wherein the tibial tray comprises an upper surface and a lower surface, and the lower surface of the tibial tray is disposed adjacent a tibia of the patient; a tibial insert, with an upper surface and a lower surface; a tibial spacer, with an upper surface and a lower surface. The spacer is disposed between the tibial tray and the tibial insert such that the lower surface of the tibial spacer is adjacent the upper surface of the tibial tray and the upper surface of the tibial spacer is adjacent the lower surface of the tibial insert; and at least one locking mechanism, wherein the locking mechanism locks the tibial spacer to the tibiat tray to form a locked spacer / tray assembly.
Owner:EXACTECH INC
Tibia cutter
InactiveUS20070233137A1Precise positioningNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsTibiaEngineering
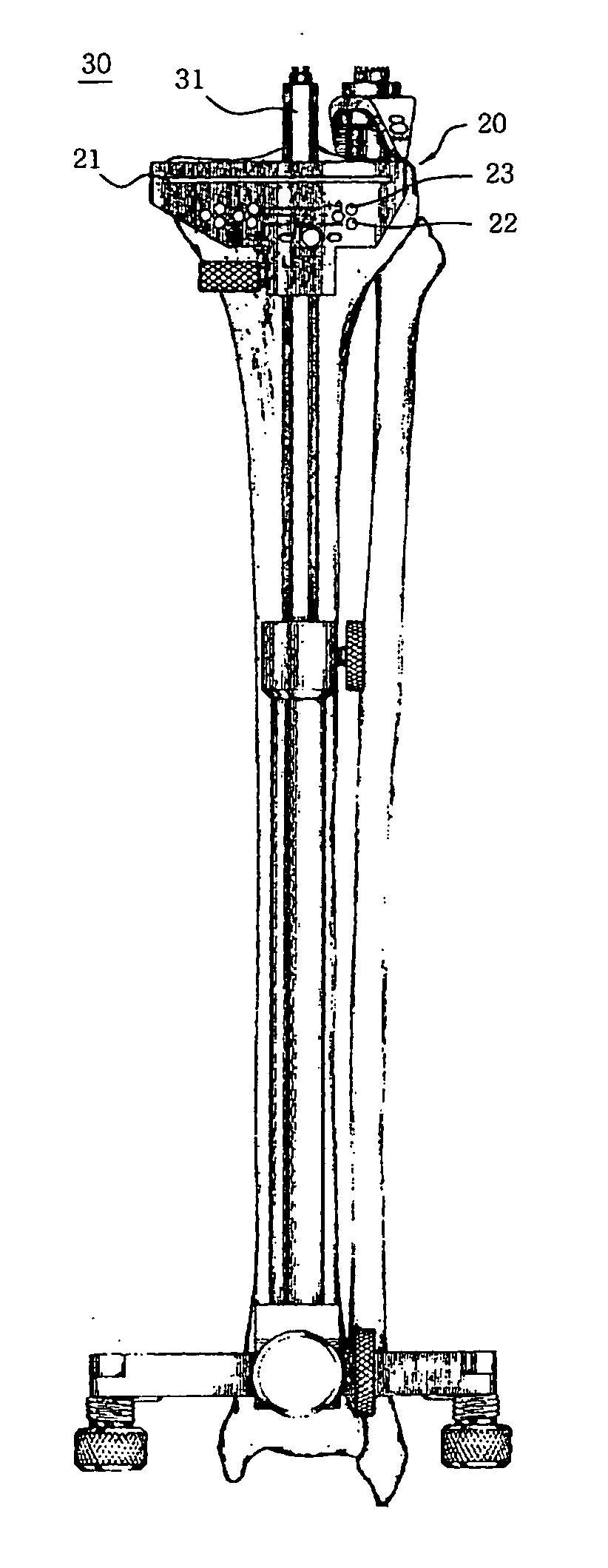
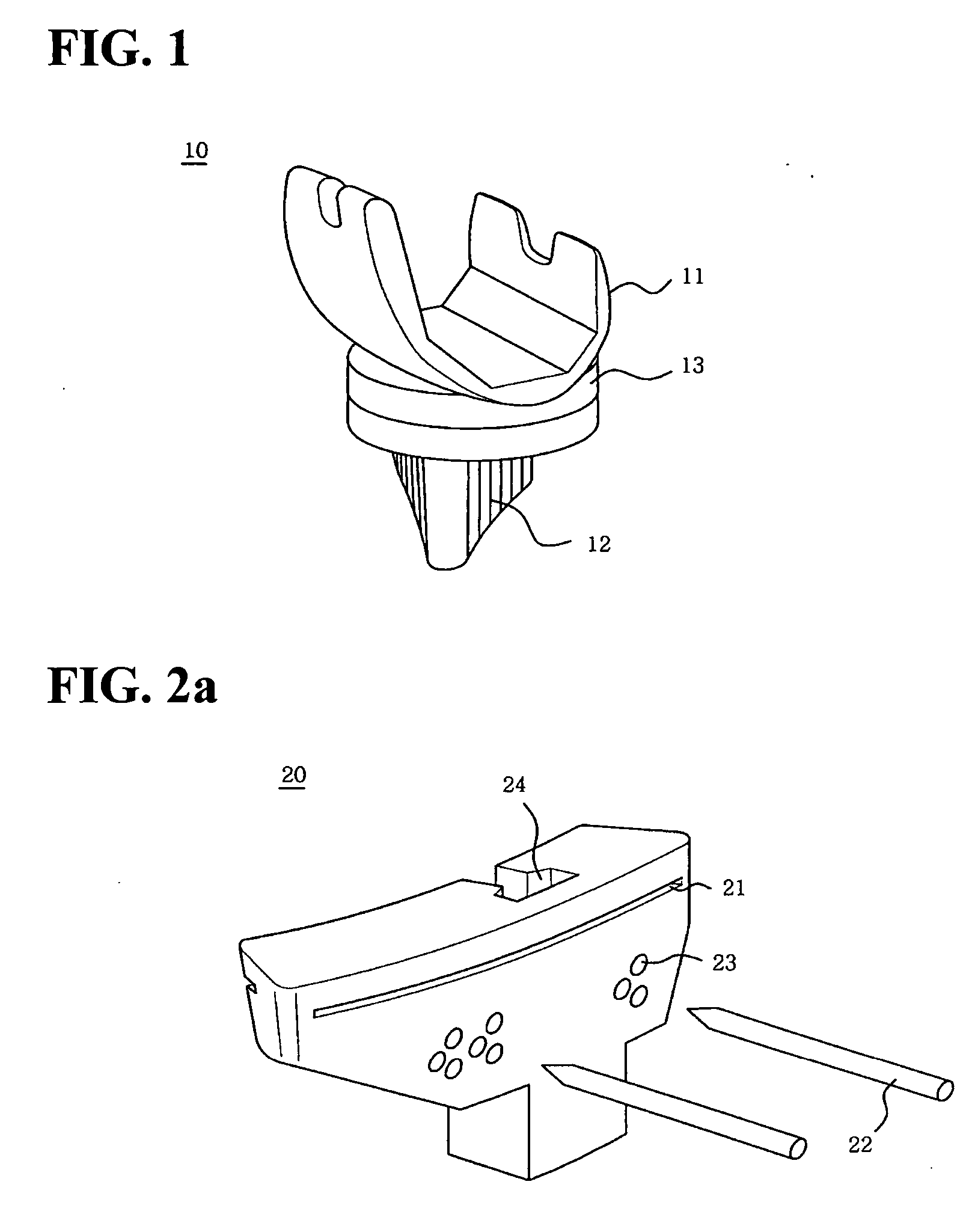
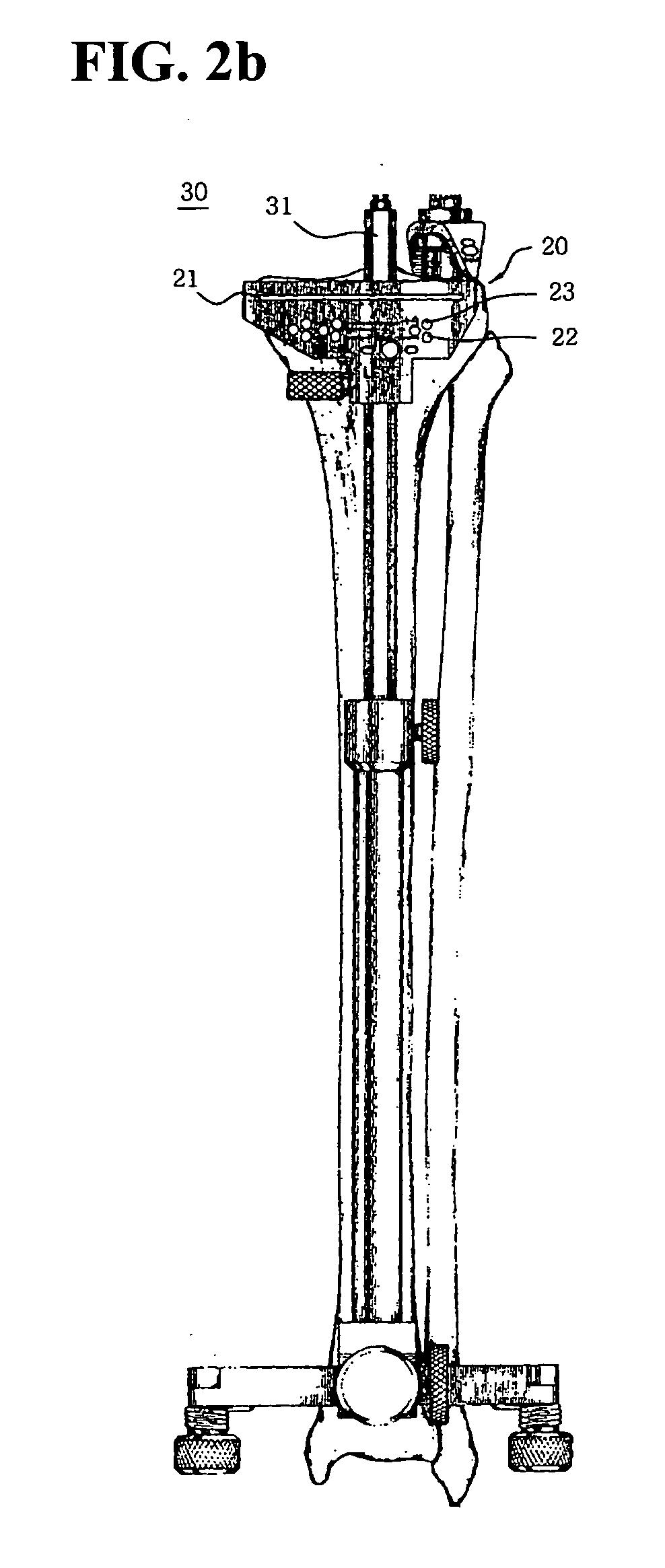
A tibia cutter, which enables the artificial tibia insert to be installed at the exact position by indicating information about the fitting position of the artificial tibia insert on the cut section of the tibia, is disclosed. The tibia cutter comprises a body including a bone cutting slot horizontally formed at the upper portion of the body, a plurality of pinholes horizontally formed under the bone cutting slot of the body, an alignment groove vertically formed at the rear side of the body, and an indication hole formed forward and backward along the bone cutting slot in said bone cutting slot; and an indication pin which is inserted into said indication hole to indicate information about the fitting position of artificial tibia insert on the cut section of the tibia that is cut by electric saw.
Owner:SEO JAI GON +1
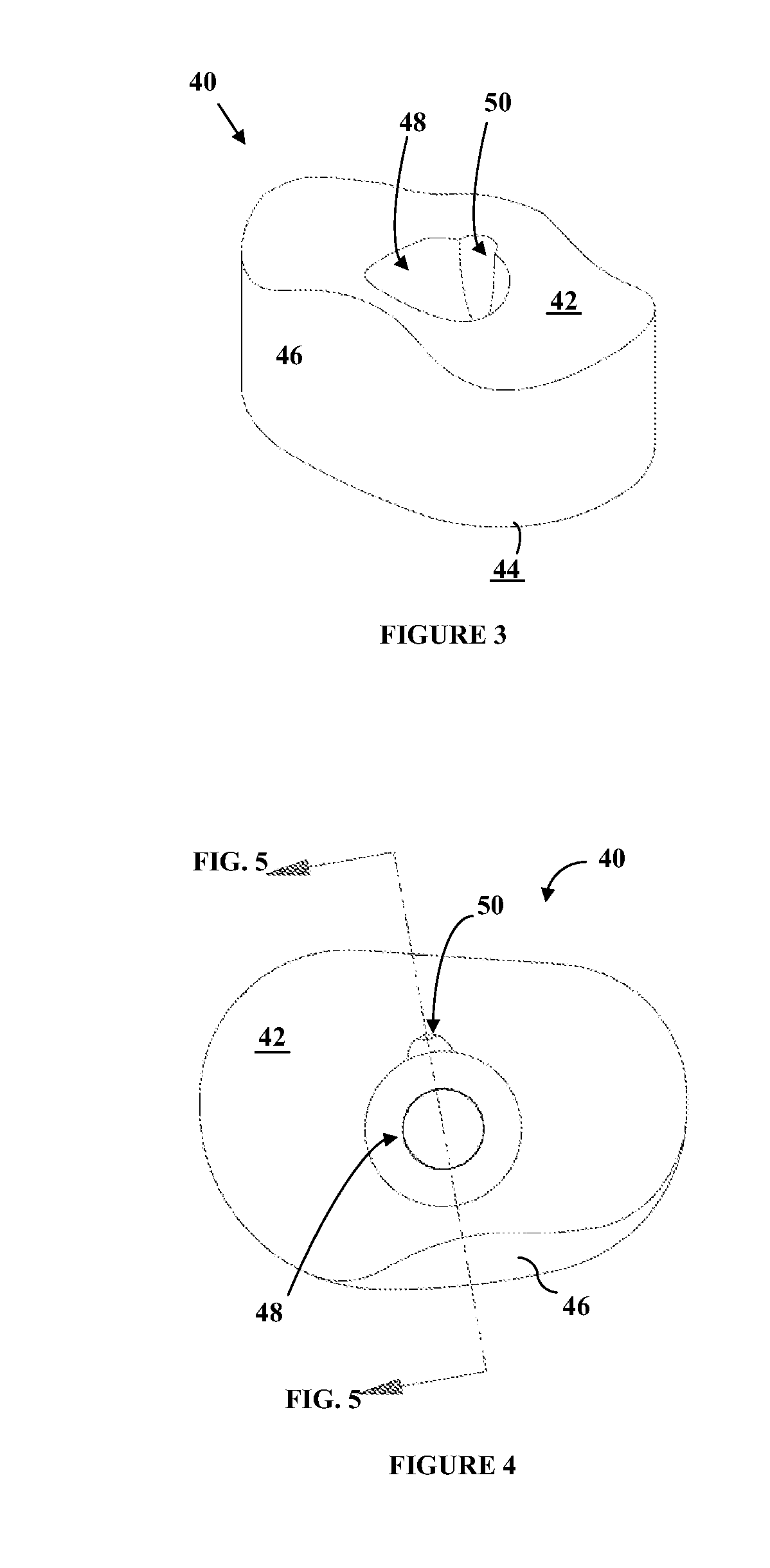
Connecting Mechanism for Medial and Lateral Polyethylene Bearing Surfaces for Knee Replacement
InactiveUS20140039636A1Quick and strong lockingAvoid mechanical failureJoint implantsKnee jointsFixed bearingMobile bearing
Disclosed herein are improved methods, apparatus and / or systems for a tibial implant assembly that can facilitate balancing, positioning, insertion, locking and maneuvering of the modular tibial inserts during knee surgery. The system may include a plurality of modular tibial inserts with locking or engagement mechanisms that allow creation of a modular insert assembly, and a corresponding tibial tray and optional tray components. The system allows the quick and convenient mating and locking of the tibial insert assembly to the tibial tray. The various components can accommodate mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing designs for the tibial tray.
Owner:KURTZ WILLIAM B
Hinged joint system
Methods, systems, and devices for replacement of a joint with a prosthetic system that replicates the natural kinematics of the joint is disclosed. A prosthetic system according to one embodiment includes a tibial component having a tibial plateau and a tibial stem portion, the tibial plateau having a top side and a bottom side, a tibial insert, with a bearing surface adapted to be positioned on the top side of the tibial plateau, a femoral component having a base portion and a central housing, the femoral component having an axis of extension-flexion rotation, the base portion having a pair of condyles, a mechanical linkage component linking the tibial component with the femoral component and with the tibial insert in between the tibial component and the femoral component, so that there is a center of contact between the condyles and the bearing surface, the mechanical linkage component adapted to allow the center of contact to move posteriorly during flexion, provide for the movement of the axis of extension-flexion rotation in the superior-inferior direction, and allow rotation of the tibial component, the bearing surface, and the femoral component about a superior-inferior axis in order to provide and control the natural kinematics of the knee joint.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
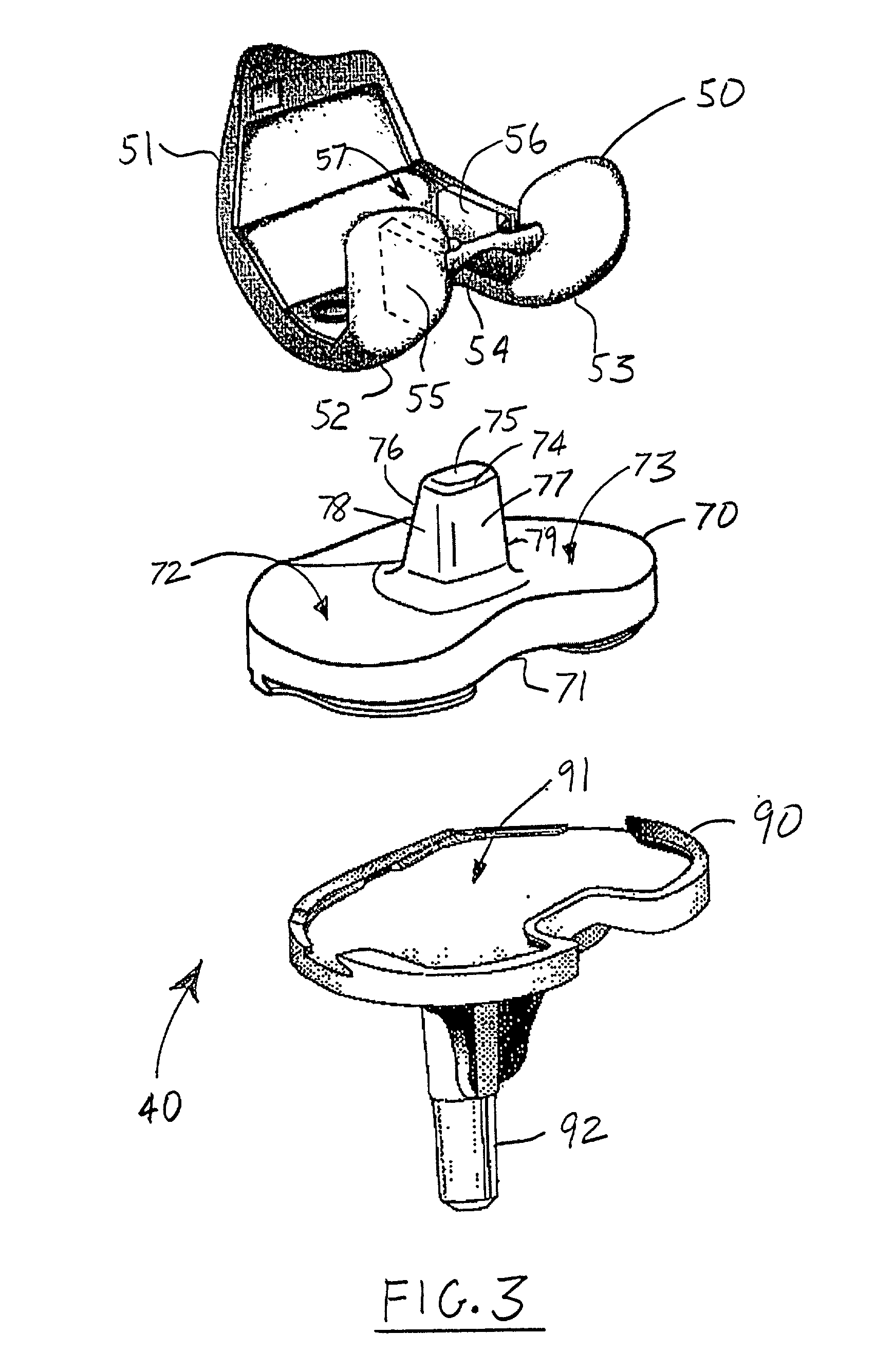
Bicondylar knee resurfacing prosthesis
A bicondylar knee resurfacing prosthesis for limited knee resurfacing procedure inserted through a direct mini lateral approach, which avoid disruption of the extensor mechanism or damage to the quadriceps tendon. The inventive device includes a reduced femoral component, a metallic tibial tray and a polyethylene tibial insert.A metallic reduced femoral component having a thin polished convex articular surface in a form of two condyles, medial and lateral, connected with an intercondylar bridge. The concave surface having a metallic dovetail transverse ridge across the entire width of the femoral component precisely positioned at the level of maximum weight bearing contact in full extension. The concave surface provides fine asperities and voids to allow bone ingrowth or can be cemented using conventional methyl methacrylate bone cement.The tibial tray provides a dovetail recess along the superior surface and transversely across its entire width, which will slidingly receive the polyethylene tibial insert. The bottom surface of the metallic tibial tray in contact with the tibial plateau has a dovetail ridge, which extends transversely along the entire width of the tibial component securing the tibial component to the resected tibial plateau.The tibial insert is made of polyethylene and has the same shape and size of the tibial metallic tray. It provides a dovetail that matches the one on the tibial tray so it can be easily driven in and locked in place. The surface of the tray provides two shallow condylar grooves that conformably match the condylar convex surfaces of the metallic femoral component.
Owner:TERMANINI ZAFER
Antero-posterior placement of axis of rotation for a rotating platform
A knee replacement system includes a femoral component including a lateral condylar articulating portion and a medial condylar articulating portion, a tibial tray including an upper articulating surface, and a tibial insert including (i) a first articulating portion for articulating with the lateral condylar articulating portion with a first condylar dwell point, (ii) a second articulating portion for articulating with the medial condylar articulating portion with a second condylar dwell point, (iii) a lower articulating surface for articulating with the upper articulating surface, and (iv) a coupling member for coupling with the tibial tray and defining an axis of rotation about which the tibial insert rotates with respect to the tibial tray, the axis of rotation intersecting the upper articulating surface at a location posterior to a dwell axis including the condylar dwell points when the dwell axis is projected onto the upper articulating surface.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
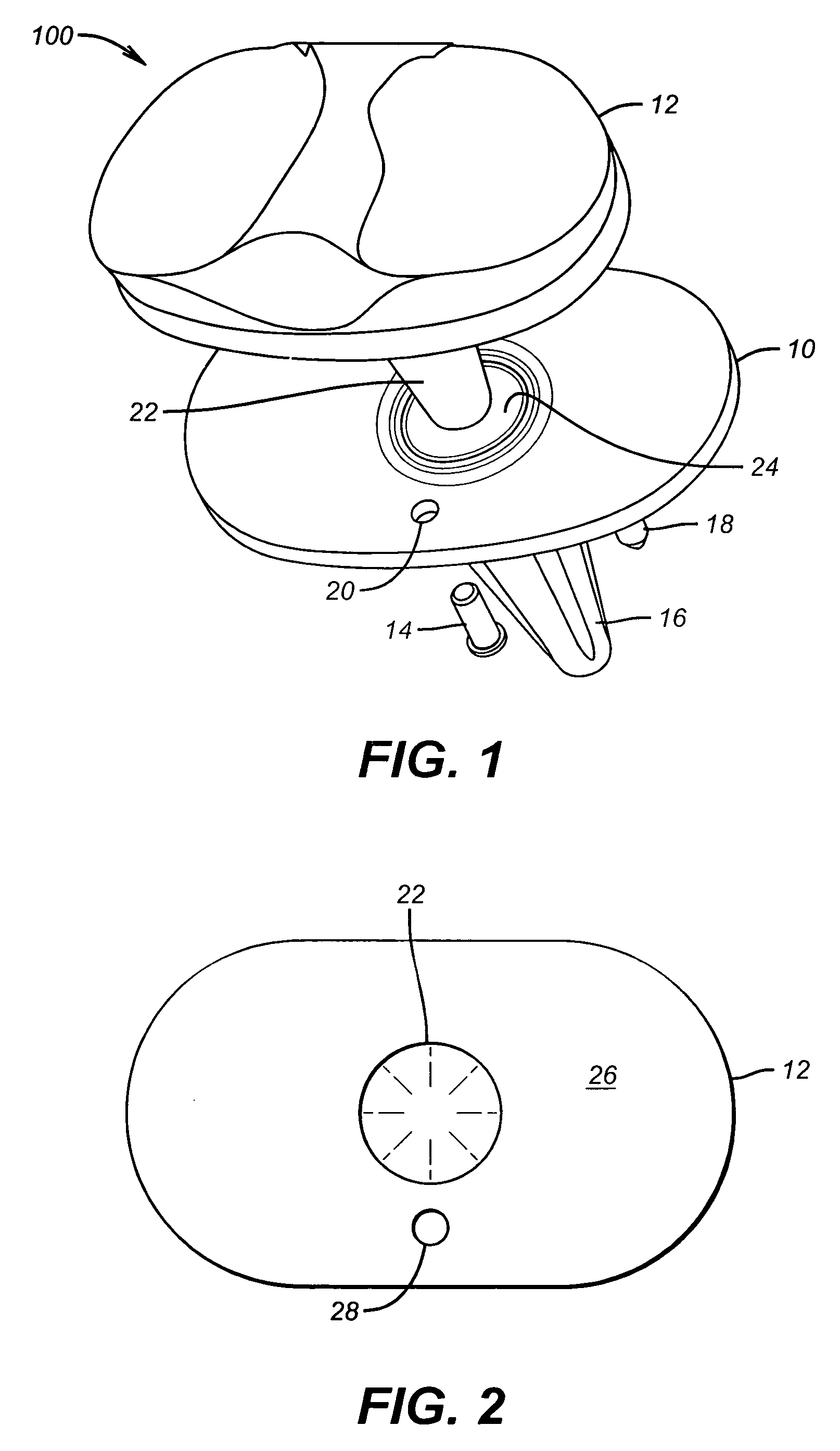
Rotating/non-rotating tibia base plate/insert system
The present invention is directed to a rotating / non-rotating tibia base plate / insert system. In one illustrative embodiment, the device comprises a tibia base plate, an insert adapted to be positioned above the base plate, and at least one removable pin that, when installed, engages at least a portion of the insert and the base plate to thereby prevent relative rotation between the insert and the base plate. In one illustrative embodiment, the method comprises obtaining a prosthetic knee assembly comprised of a tibia base plate, a tibia insert and a removable pin, the assembly being adapted to be configured in a first state such that the tibia insert may rotate relative to the base plate or in a second state such that said tibia insert cannot rotate relative to said base plate, making at least one incision adjacent a patient's knee, installing the prosthetic knee assembly in the patient, wherein the removable pin is removed such that the assembly is in the first state wherein the tibia insert may rotate relative to the tibia base plate, and closing the incision.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Stack-up assembly for tibial insert trial
A stack-up assembly for tibial insert trial is provided. The stack-up assembly for tibial insert trial is inserted between a femoral component and a tibial component of an artificial knee joint. The stack-up assembly for tibial insert trial includes an insert trial body and a plurality of first augments. The insert body is operatively connected with the femoral component. The first augments are stacked between the tibial component and the insert trial body.
Owner:UNITED ORTHOPEDIC CORP
Mobile bearing assembly having a non-planar interface
The invention relates to a mobile bearing assembly having a non-planar interface, specifically provides a unicompartmental mobile tibial assembly which includes a tibial tray and a tibial insert. The tibial tray includes an upper surface and a bottom surface configured to contact a portion of a surgically-prepared surface of the proximal end of a tibia. The tibial insert includes an upper bearing surface configured to contact a surgically-prepared surface of the distal end of a femur and a bottom bearing surface configured to contact the upper surface of the tibial tray when the tibial insert is coupled to the tibial tray. Any one or more of the upper surface of the tibial tray, the bottom surface of the tibial tray, and / or the bottom bearing surface of the tibial insert may be non-planar.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
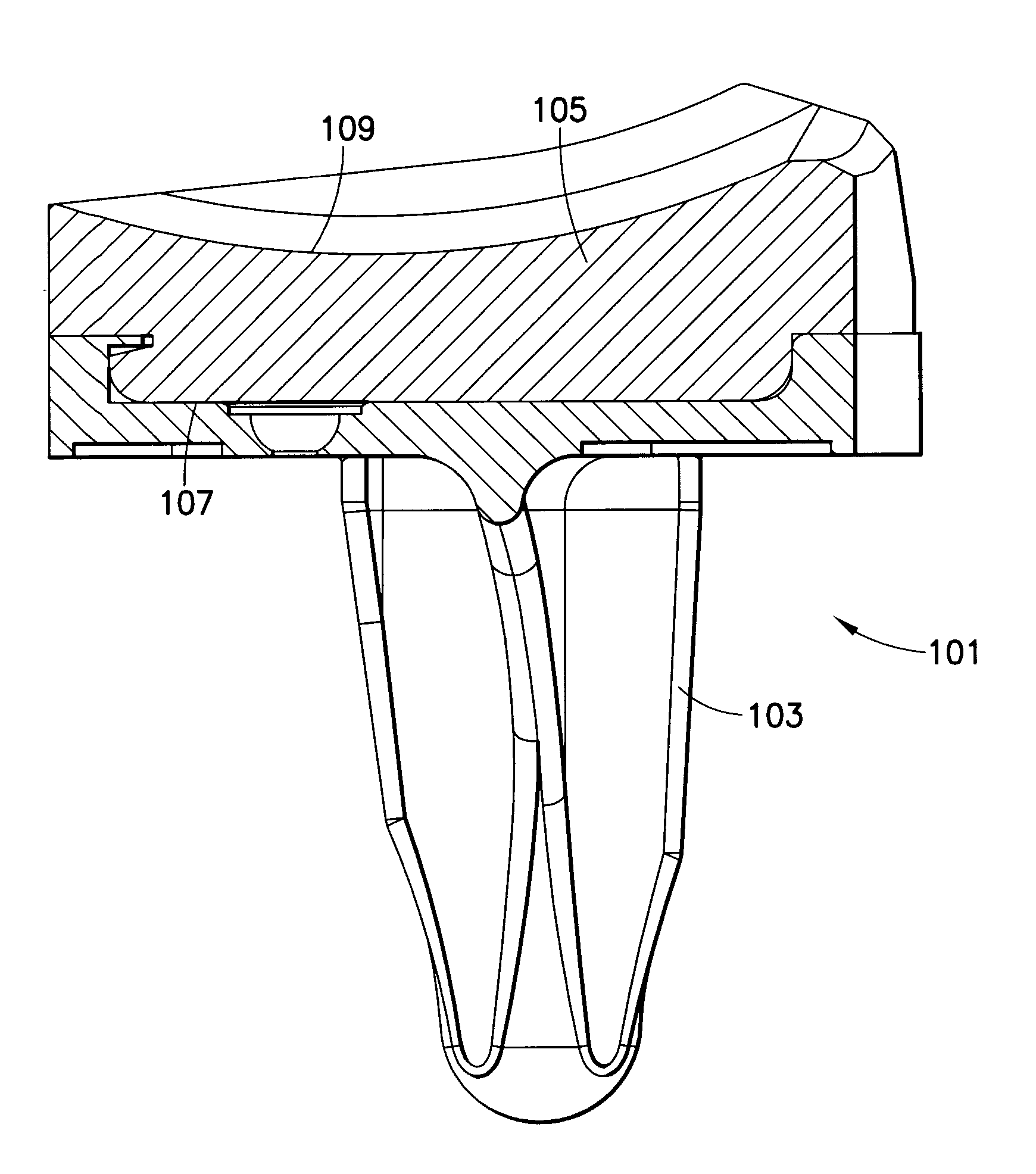
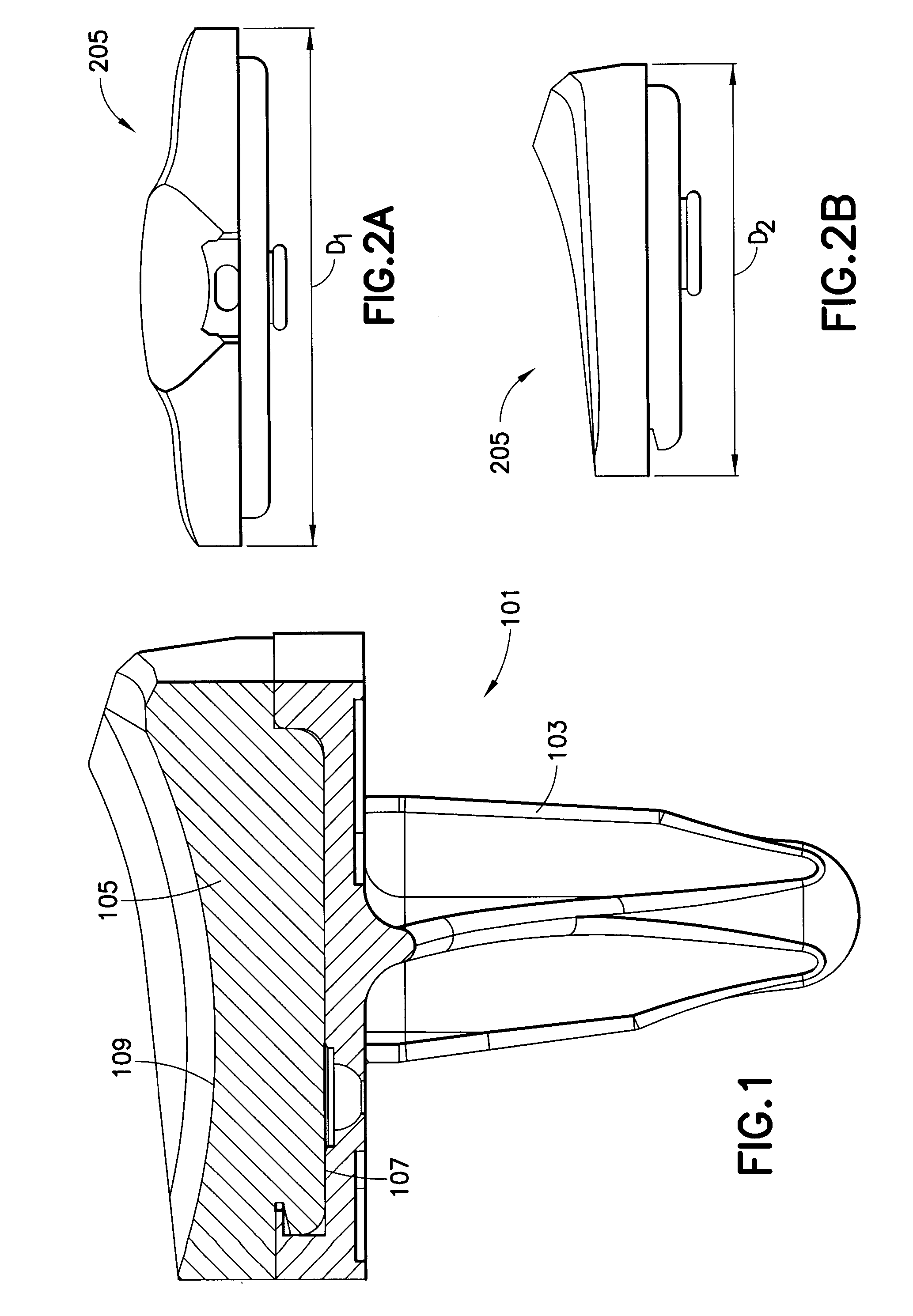
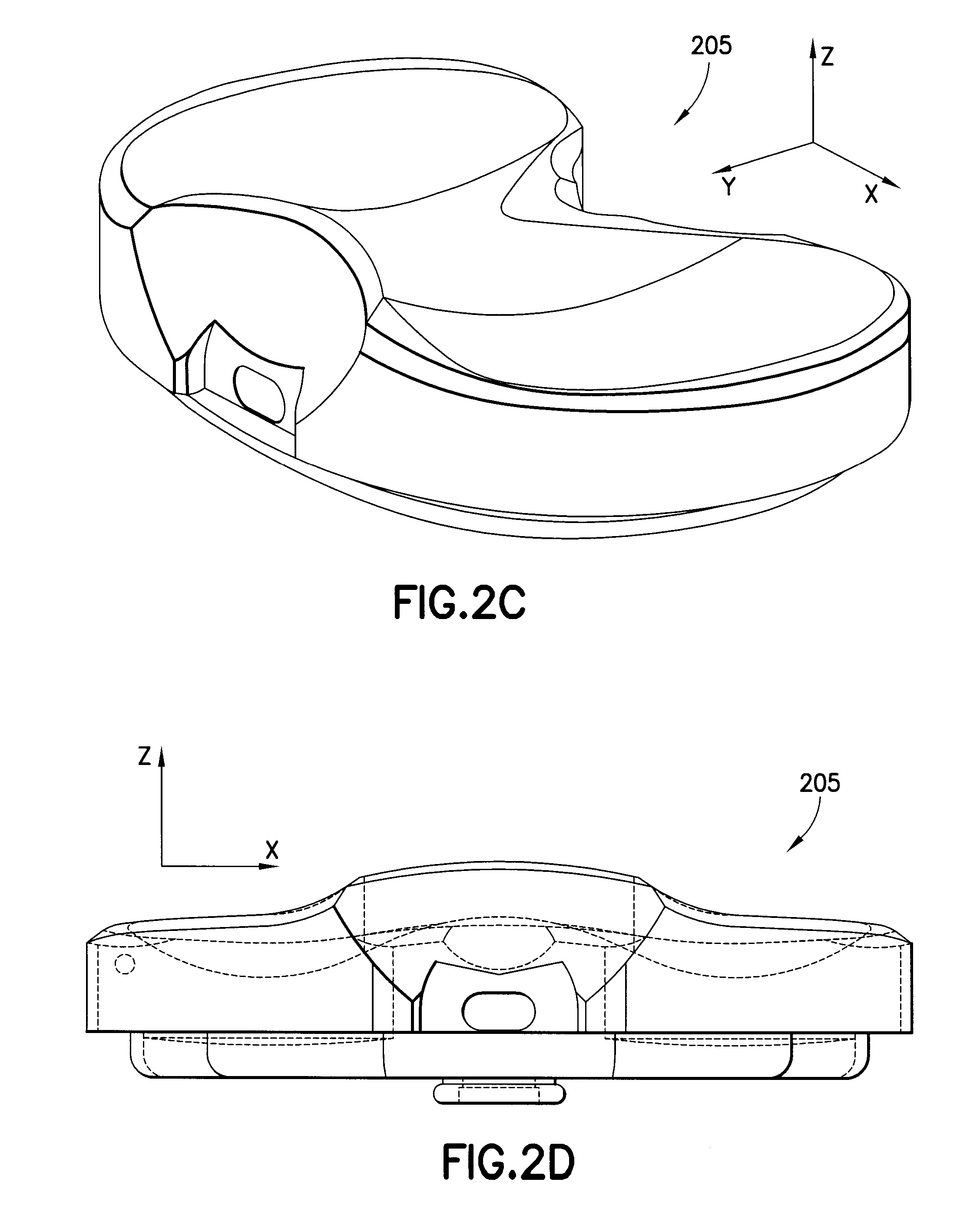
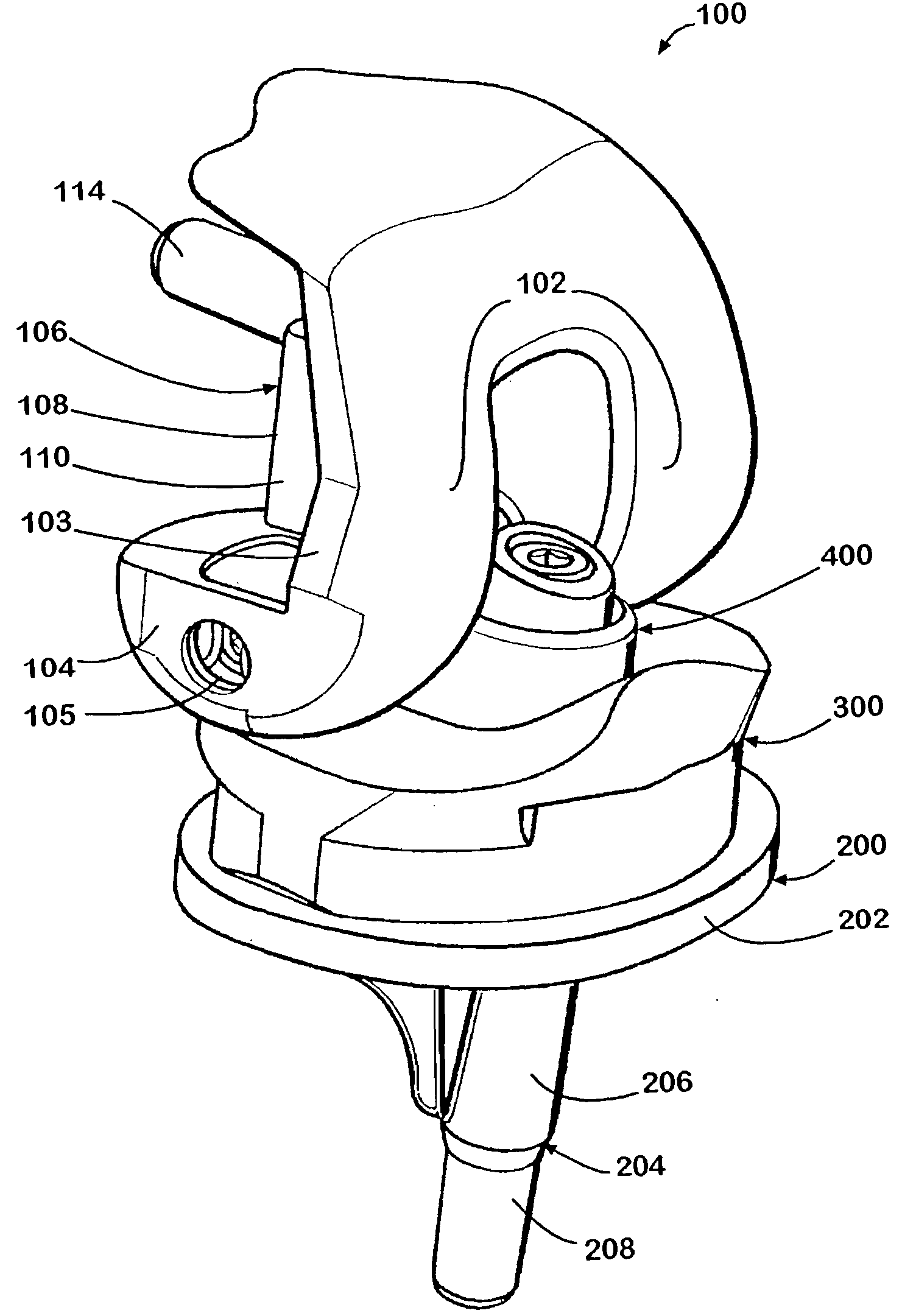
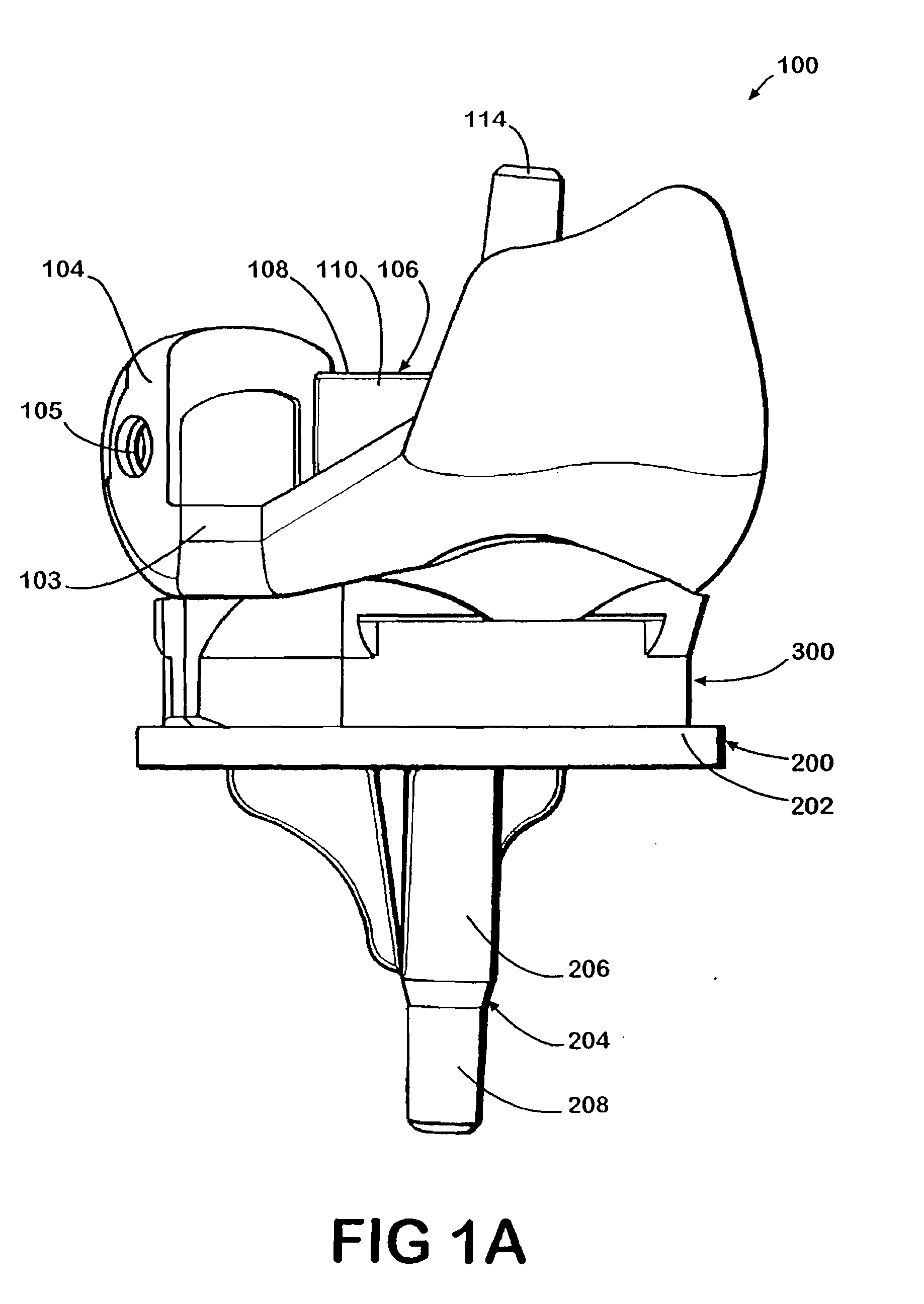
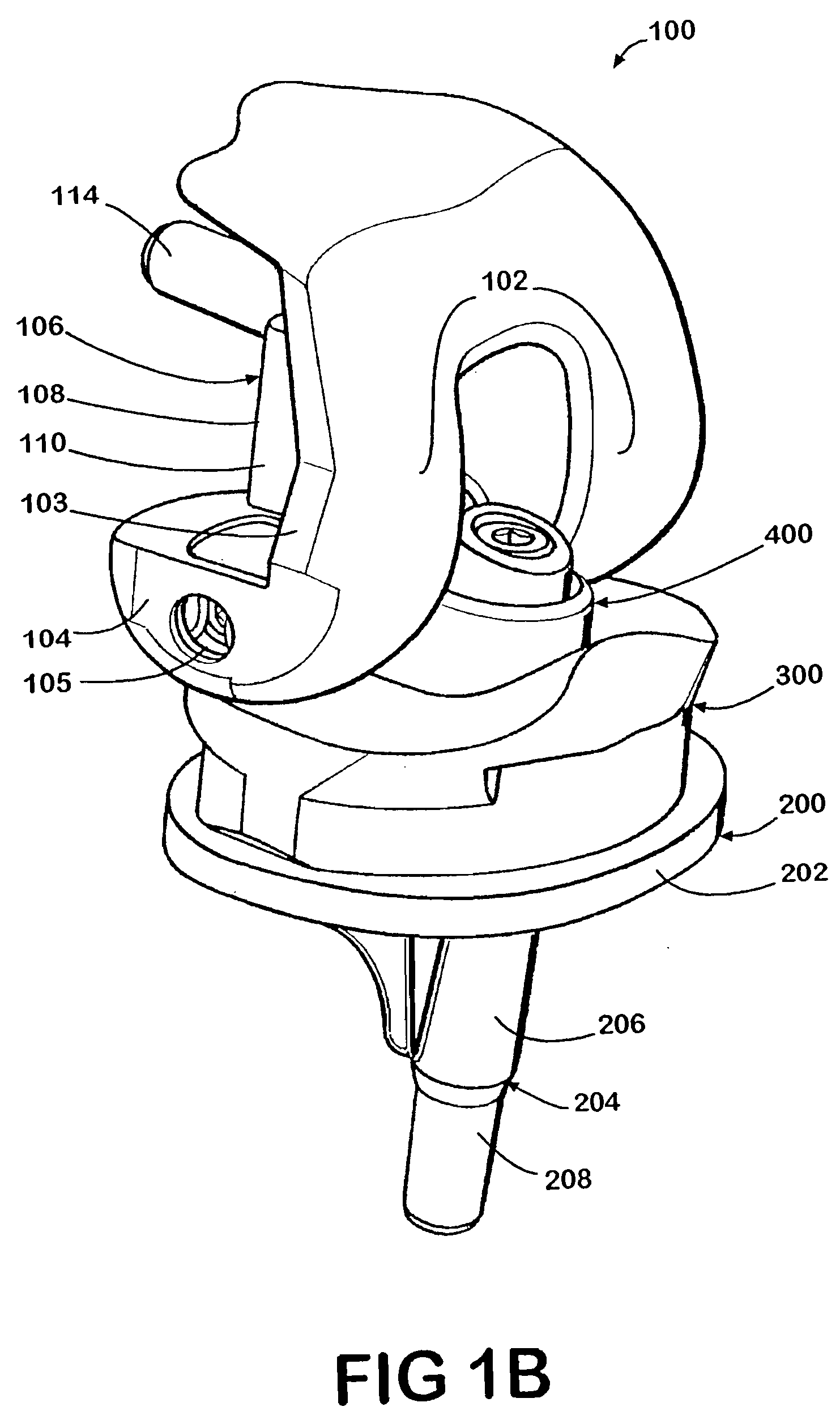
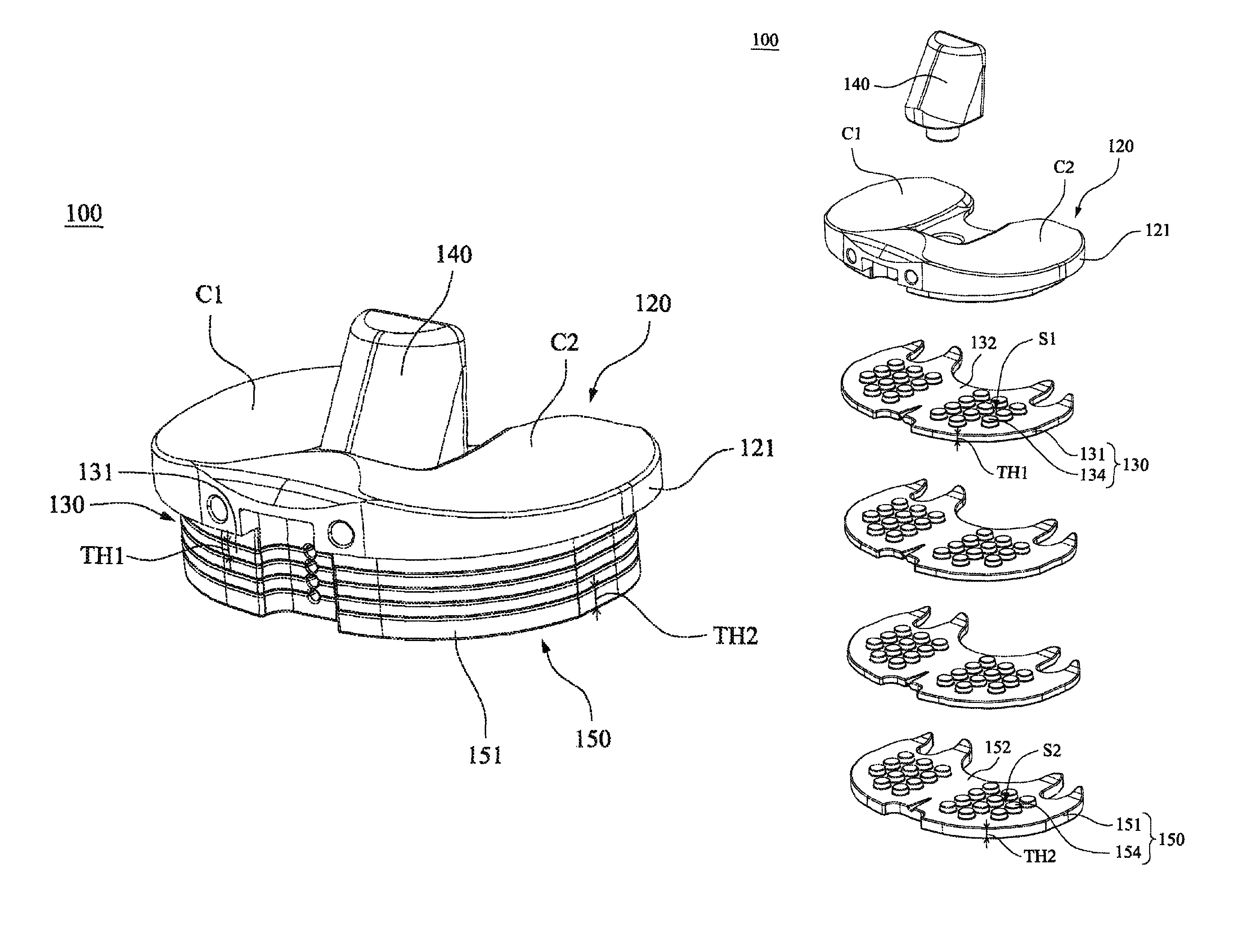
Tibial insert locking mechanism
ActiveUS20140067076A1Avoid separationReduce usageJoint implantsKnee jointsBiomedical engineeringImplant
A tibial implant includes a baseplate having a proximally facing surface surrounded at least in part by a proximally extending wall. The wall has a ramp surface extending from the wall towards the baseplate proximally facing baseplate surface and a bore located distally of the ramp. A polyethylene bearing insert is mounted on the baseplate and has a distally facing surface engaging the proximally facing surface of the baseplate. The distally facing bearing insert surface has a recess and the insert has a side surface with a passageway extending from the recess through the insert side surface. A spring detent is mounted in the bearing insert recess and has a moveable pin biased outwardly of the bearing insert side surface and into the bore of the baseplate.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Knee prosthesis system with slope
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a knee prosthesis system with at least a first tibial portion element (a tibial insert or a tibial insert trial) and a second tibial portion element (a tibial insert or a tibial insert trial), wherein each of the first tibial portion element and the second tibial portion element has a different slope. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a method of implanting a knee prosthesis, wherein the method utilizes at least a first tibial portion element (a tibial insert or a tibial insert trial) and a second tibial portion element (a tibial insert or a tibial insert trial), wherein each of the first tibial portion element and the second tibial portion element has a different slope.
Owner:EXACTECH INC
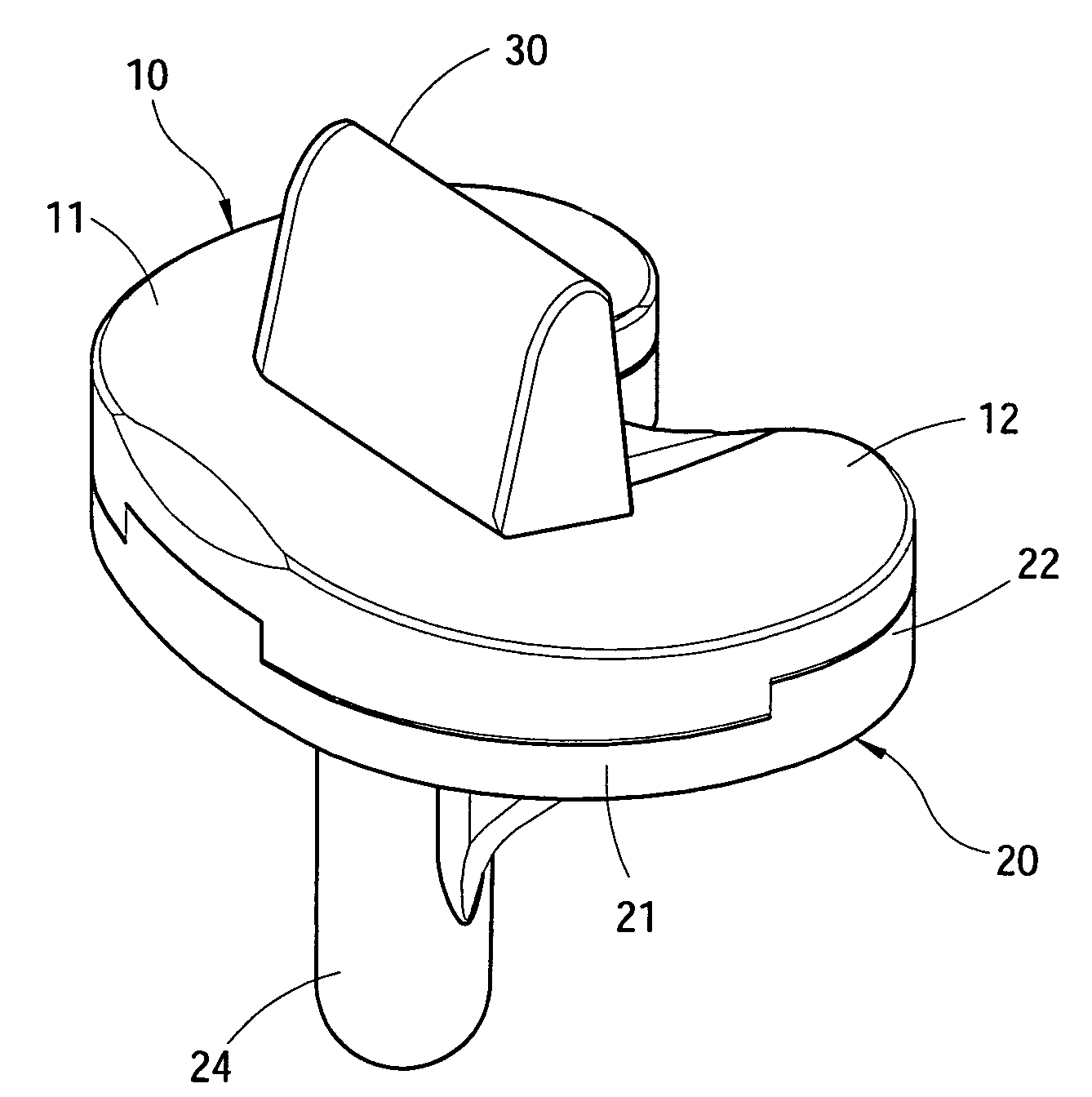
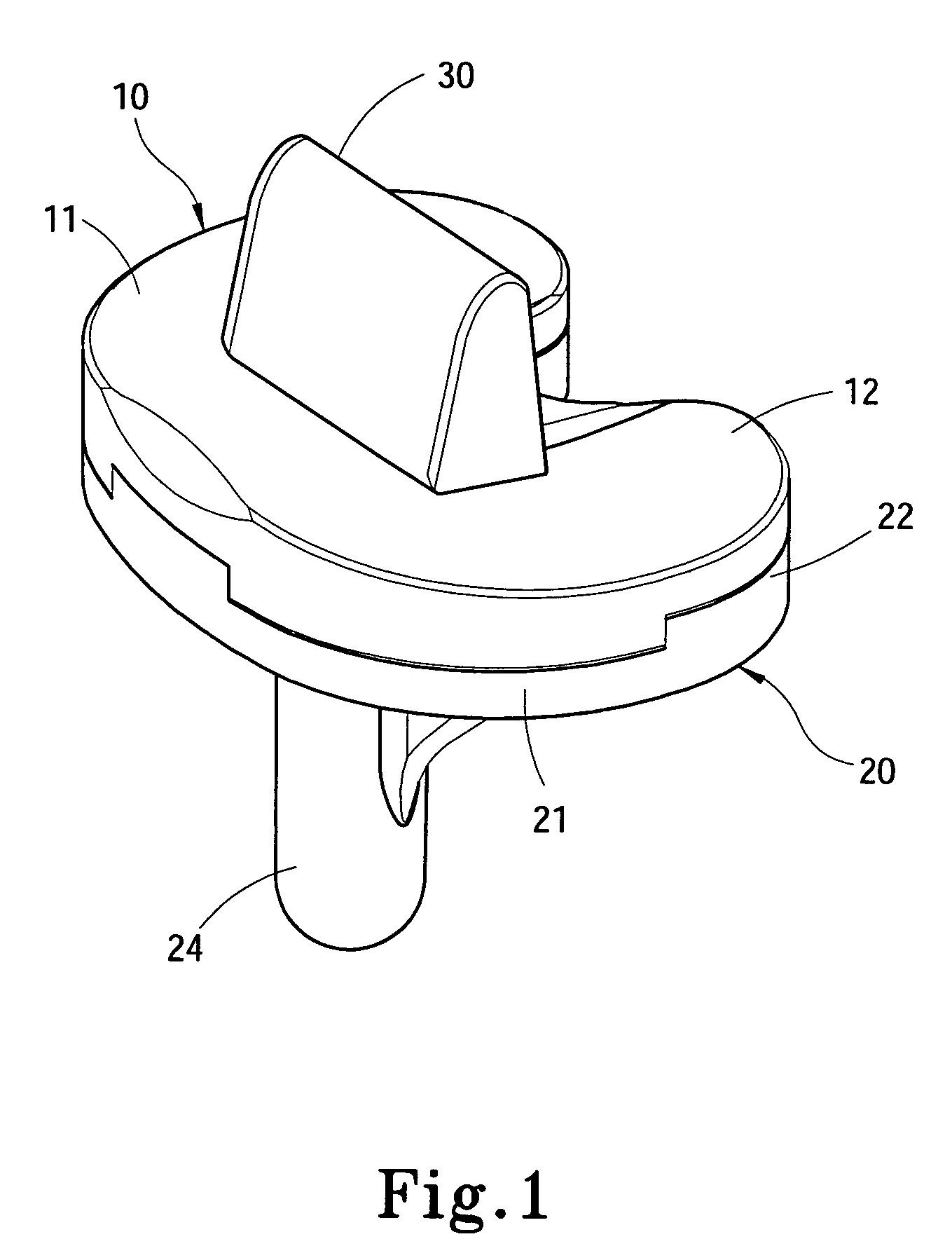
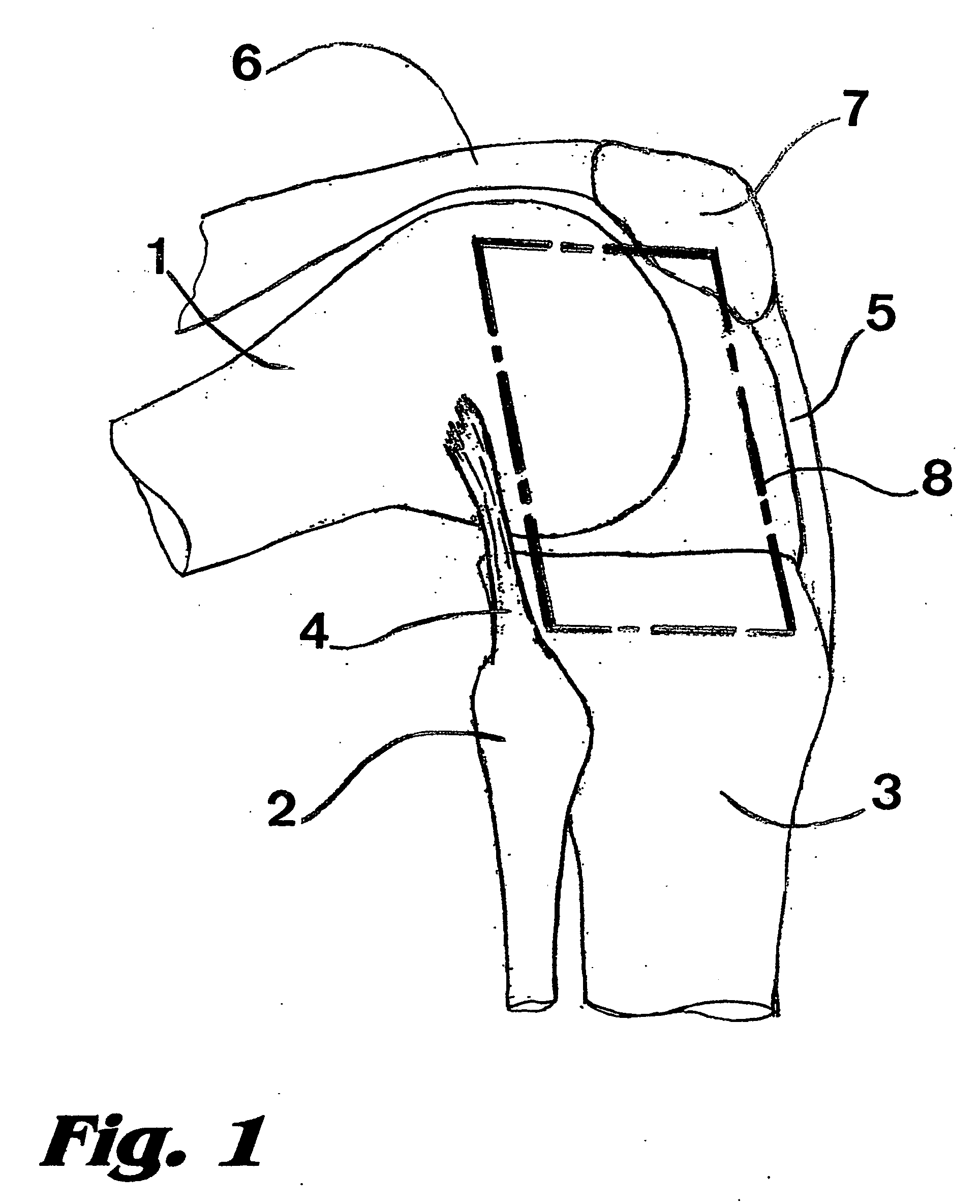
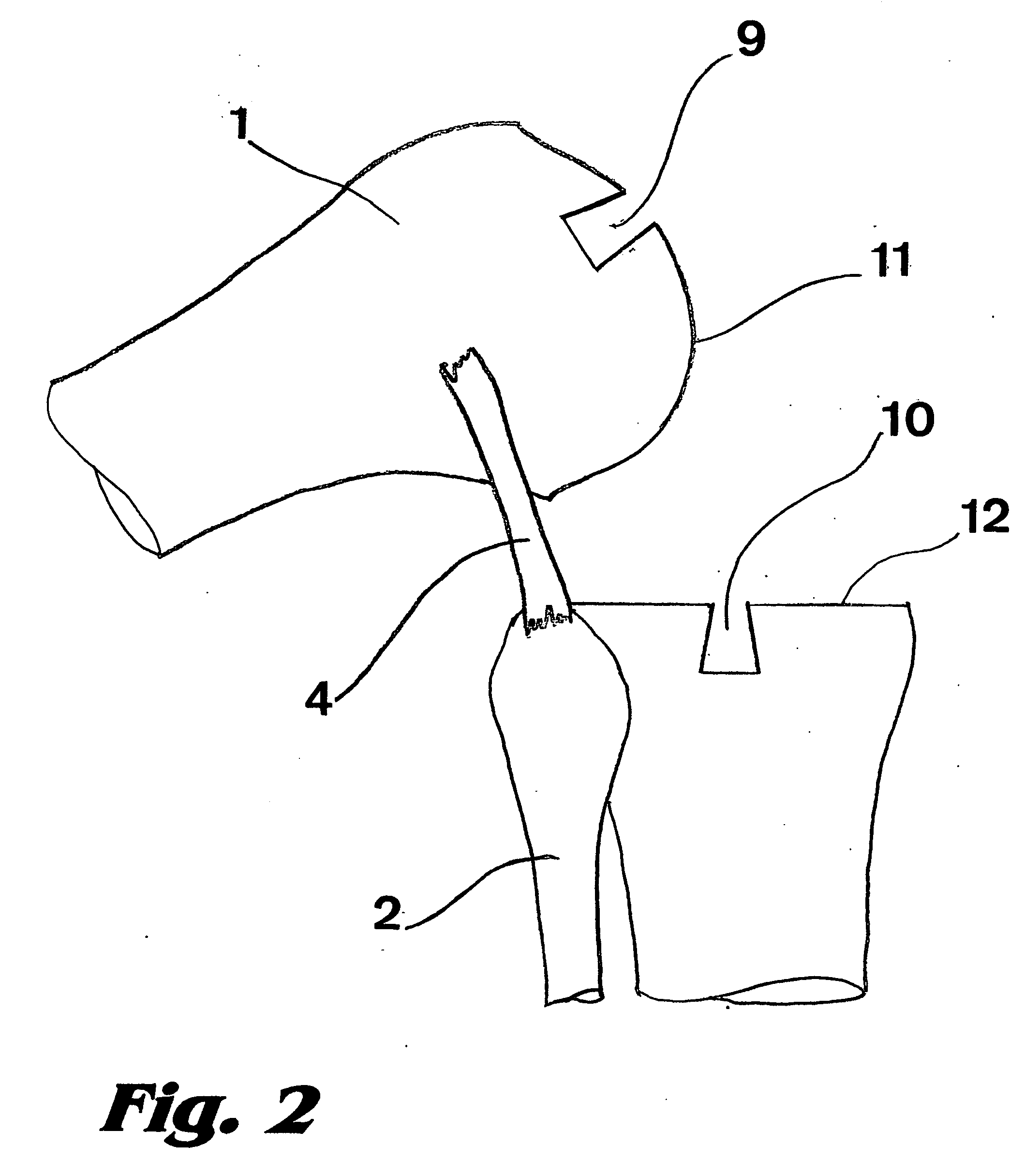
Structure Improvement Of Orthopaedic Implant
A structure improvement of orthopaedic implant for connecting a distal femur and a proximal tibia, and a stem was implanted into the proximal tibia, inwhich formed to allow inter-engagement between the stem of the tibia and the structure improvement of orthopaedic implant. The structure improvement of orthopaedic implant includes a tibial baseplate, a tibial insert, and a reinforcement. The tibial baseplate forms a recess having a bottom that has a central portion defining a through hole extending through the tibial baseplate. The tibial insert includes a support, a through region, and a projection, wherein an end of the tibial insert forming the projection corresponding to the recess of the tibial baseplate for press-fitting to the tibial baseplate. The reinforcement is inset in the tibial insert and includes a sleeve and a bolt. As such, the advantages of stable coupling includes force resistance, avoids insert loosening then extends prosthetic longevity.
Owner:UNITED ORTHOPEDIC CORP
Methods and devices for knee joint replacement with anterior cruciate ligament substitution
Methods and devices are provided for knee joint replacement with anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) substitution. Generally, the methods and devices can allow a knee joint to be partially or totally replaced in conjunction with substitution of the knee joint's ACL. In one embodiment, a knee replacement prosthesis can include a medial or lateral femoral implant, a femoral intercondylar notch structure, a medial or lateral tibial insert, and an ACL-substitution member. The ACL-substitution member can be configured to engage with the femoral intercondylar notch structure during a full range of knee motion and / or during only early knee flexion.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Orthopaedic implant system and fasteners for use therein
Orthopaedic assemblies including a tibial component and one of a fixed tibial insert or a rotatable tibial insert. The assemblies may include structure to prevent undesired movement between the tibial component and insert. For example, a retaining tab may be provided on the tibial component that couples to a tab opening on a surface of the tibial insert (either the fixed or rotatable insert). When assembled, the retaining tab may be covered to avoid possible irritation to the patient's surrounding anatomy. The fixed tibial insert may be provided with a tab opening that provides a minimal amount clearance with the retaining tab to help prevent rotation of the fixed tibial insert. The rotatable tibial insert may be provided with a tab opening with more clearance with the retaining tab to allow at least some rotation with the tibial component.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Methods and Devices for Knee Joint Replacement with Anterior Cruciate Ligament Substitution
Methods and devices are provided for knee joint replacement with anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) substitution. Generally, the methods and devices can allow a knee joint to be partially or totally replaced in conjunction with substitution of the knee joint's ACL. In one embodiment, a knee replacement prosthesis can include a medial or lateral femoral implant, a femoral intercondylar notch structure, a medial or lateral tibial insert, and an ACL-substitution member. The ACL-substitution member can be configured to engage with the femoral intercondylar notch structure during a full range of knee motion and / or during only early knee flexion.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
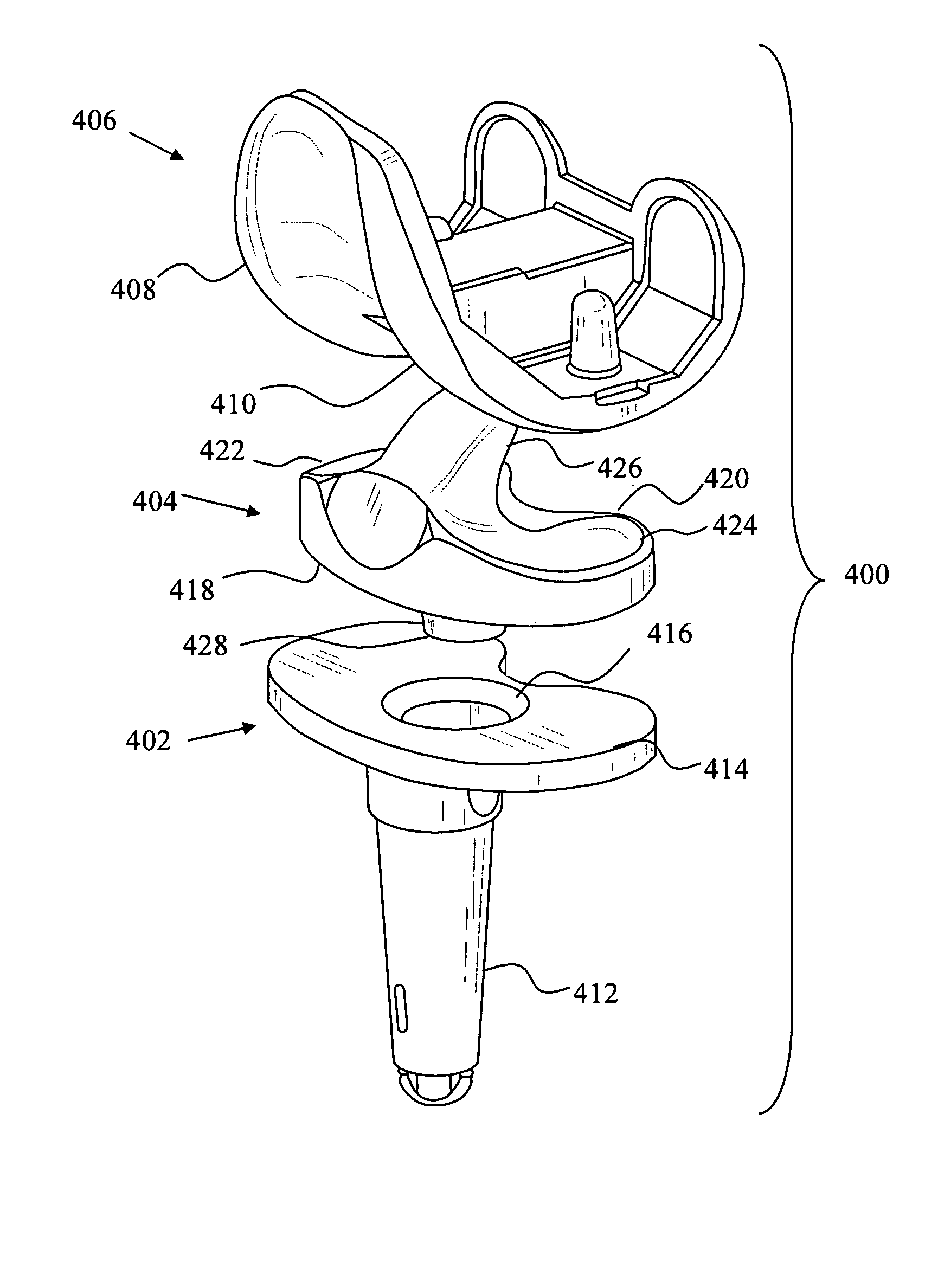
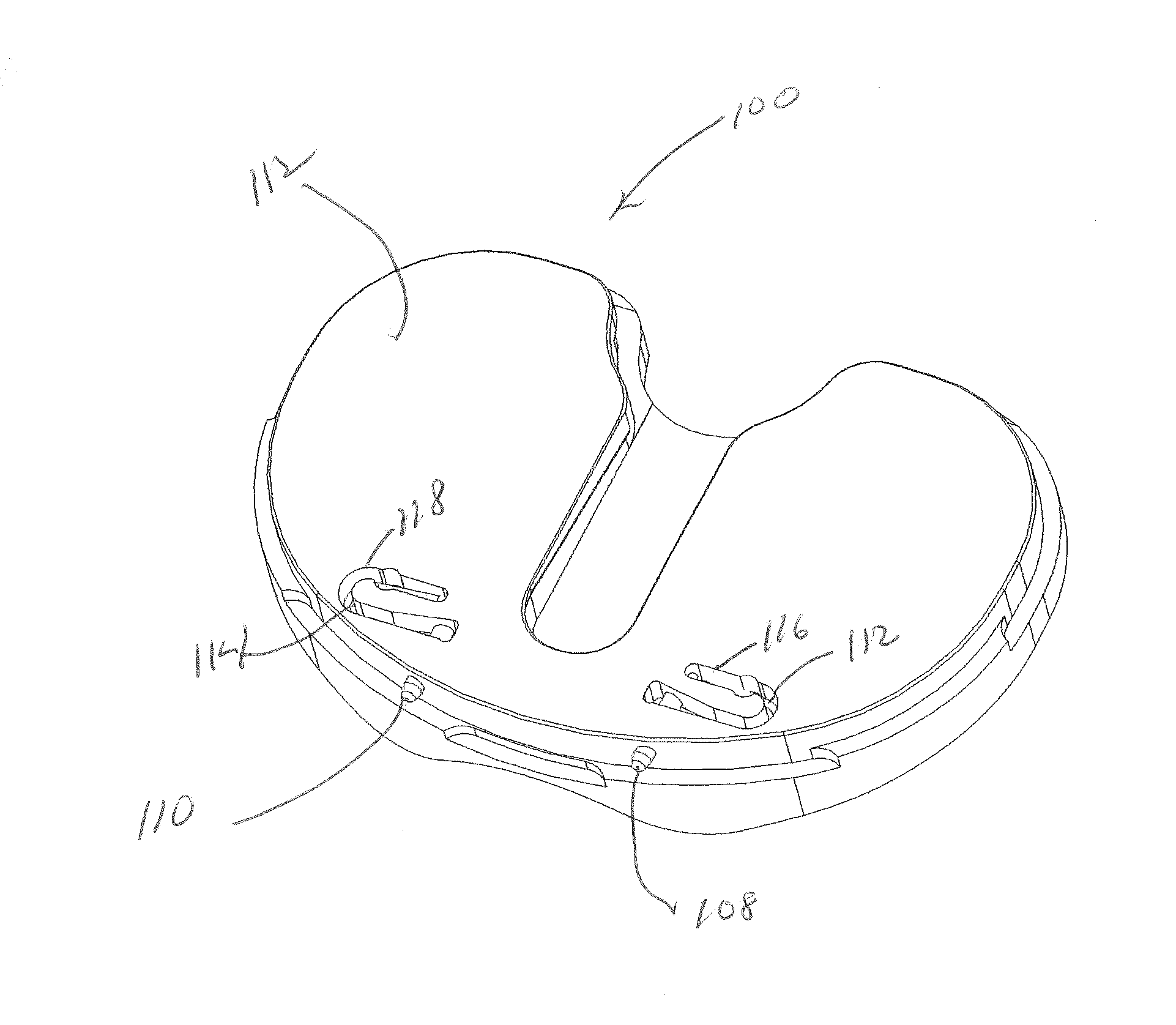
Implant Set Having Modularity with Conformity for Total Knee Replacement
ActiveUS20160228254A1Proper conformityProper conservationJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaLocking mechanism
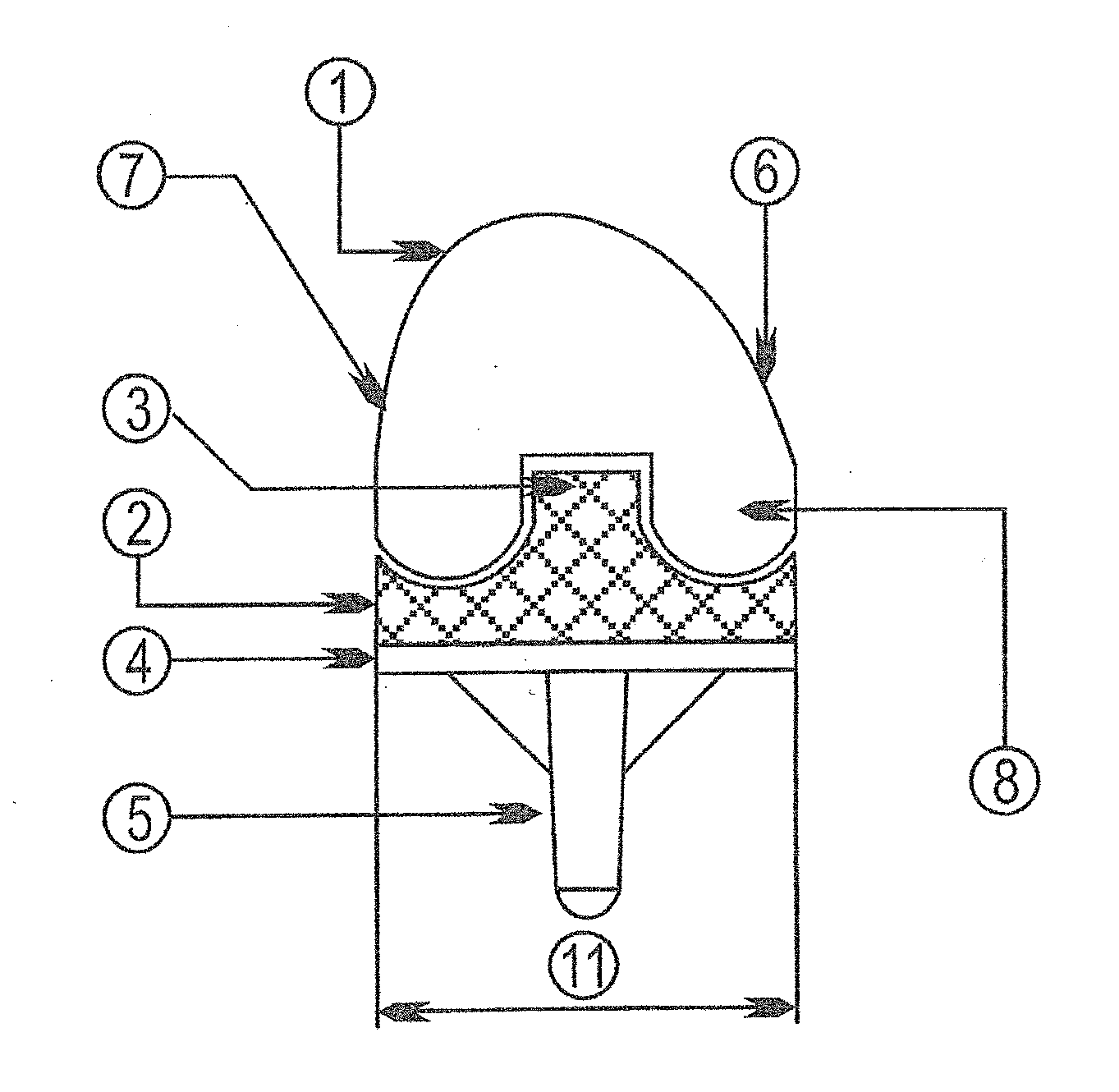
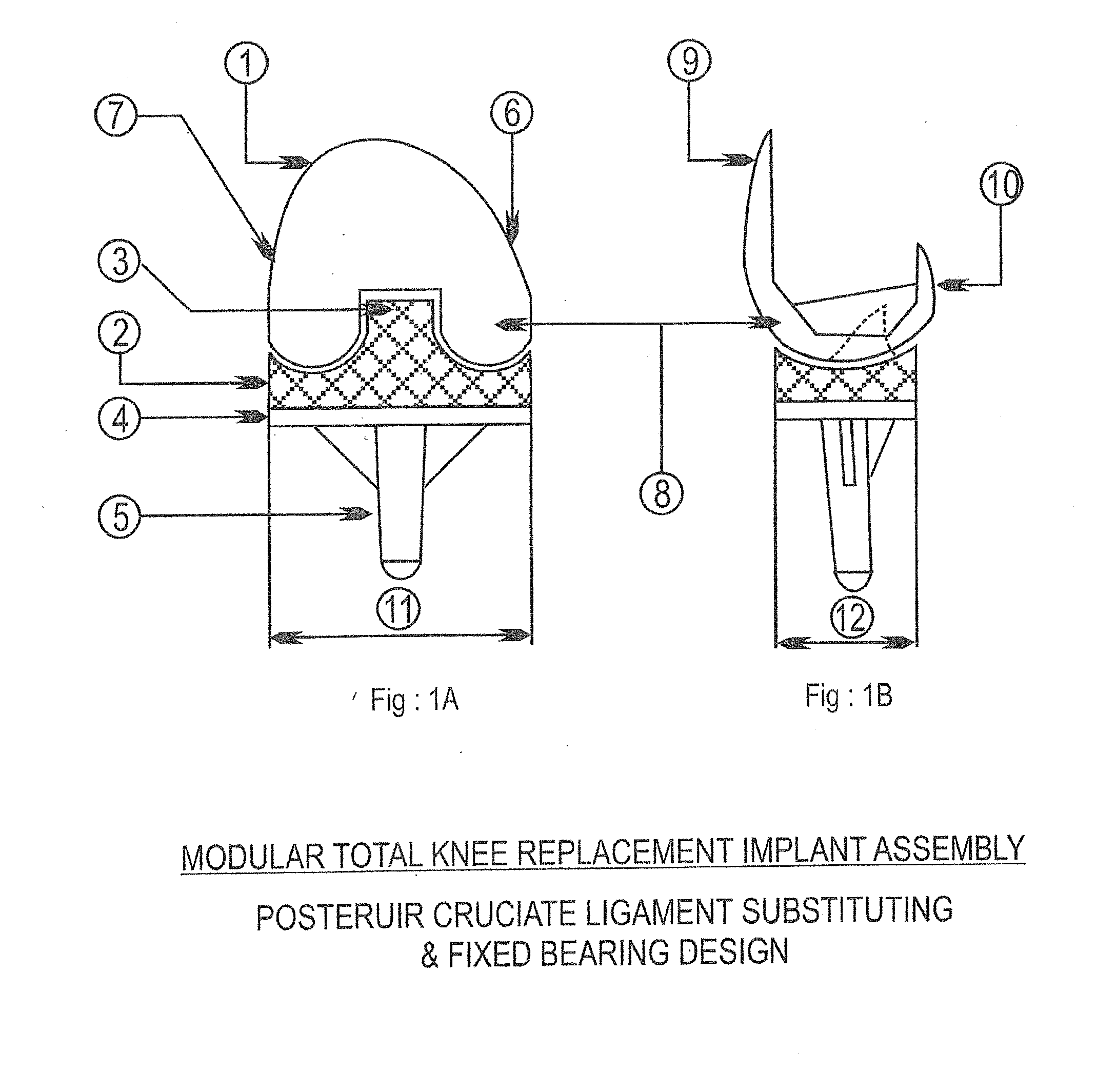
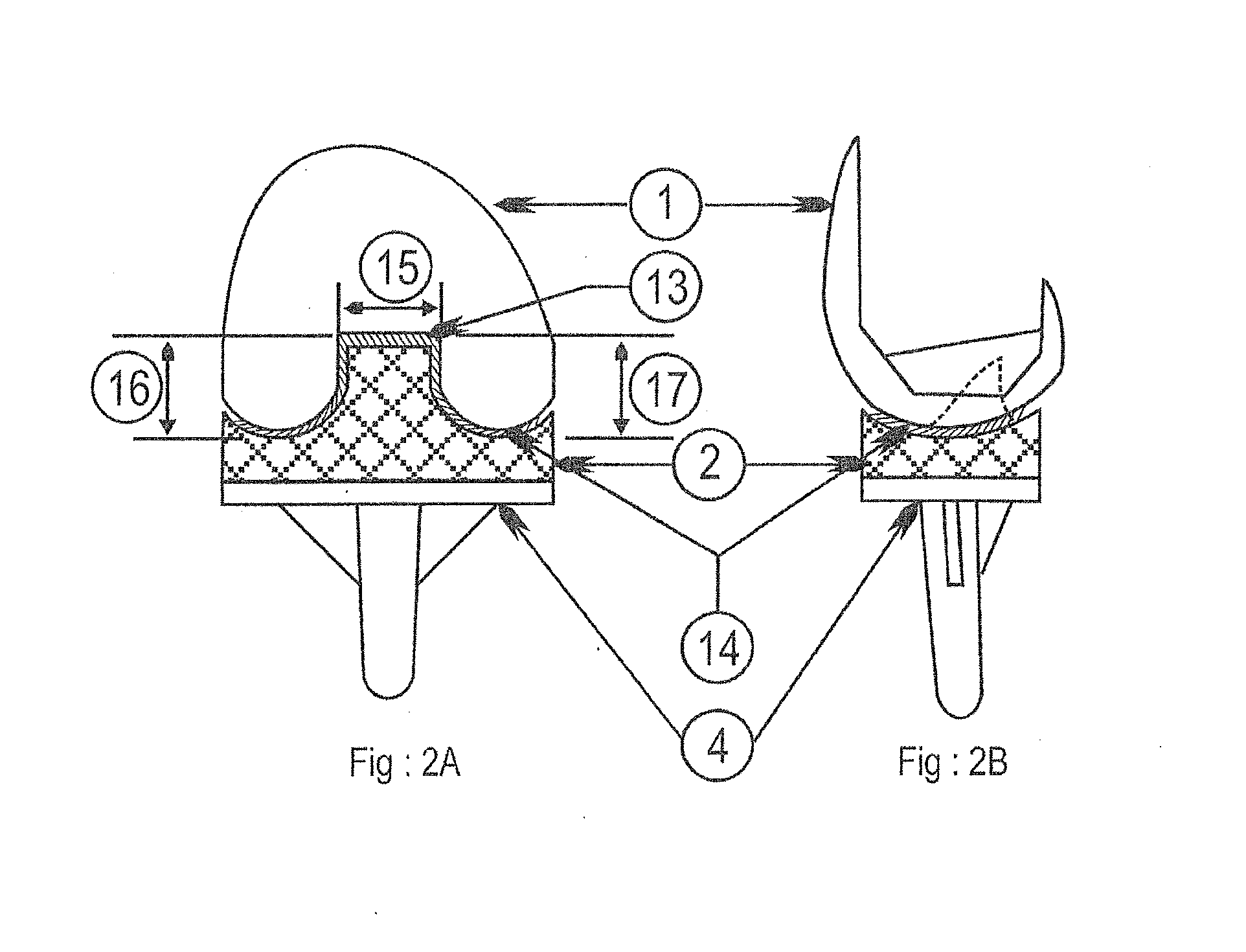
An implant set having modularity with conformity for total knee replacement. The set having a femoral metal component, Tibial Component (4) with locked tibial Insert (2) therein and Patella to provide the exact conformity of combination of femoral component (1) and tibial component (4). The improvement involves such way that each of the Femoral component (1) to tibial insert (2) pair, there will be at least three sizes of tibial components (4) available, namely, a minus size tibial component (4), a standard tibial component (4), and a plus size tibial component (4); the dimensions of the locking mechanism will be same on all the three sizes, i.e. on minus size, standard size, and plus size.
Owner:DAMLE NARENDRA +1
Implant system with pe insert and two tray options
A tibial implant system has an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene tibial insert which can engage with either one of two tibial trays through differing means of engagement. The tibial insert includes a locking wire and locking tab disposed along an anterior surface and a locking recess disposed along a posterior surface. A first polymeric tibial tray includes a bead along an anterior wall and an undercut area along a posterior wall. A second metallic tibial tray includes a plurality of barbs along an anterior wall and an undercut area along a posterior wall.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Implant system with polymeric insert and two tray options
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Torque-introducing full joint replacement prosthesis
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
Orthopaedic implant system and fasteners for use therein
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
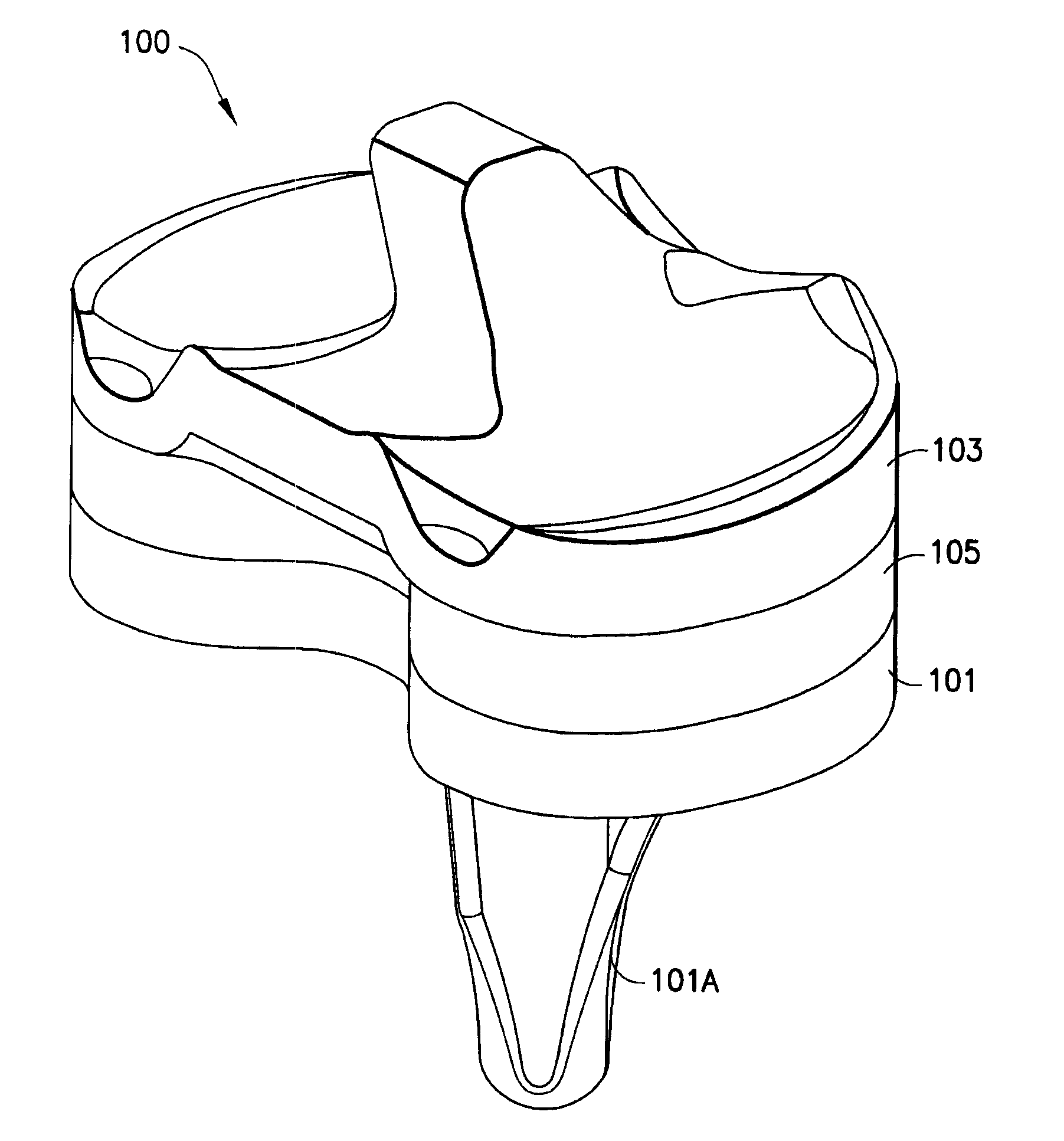
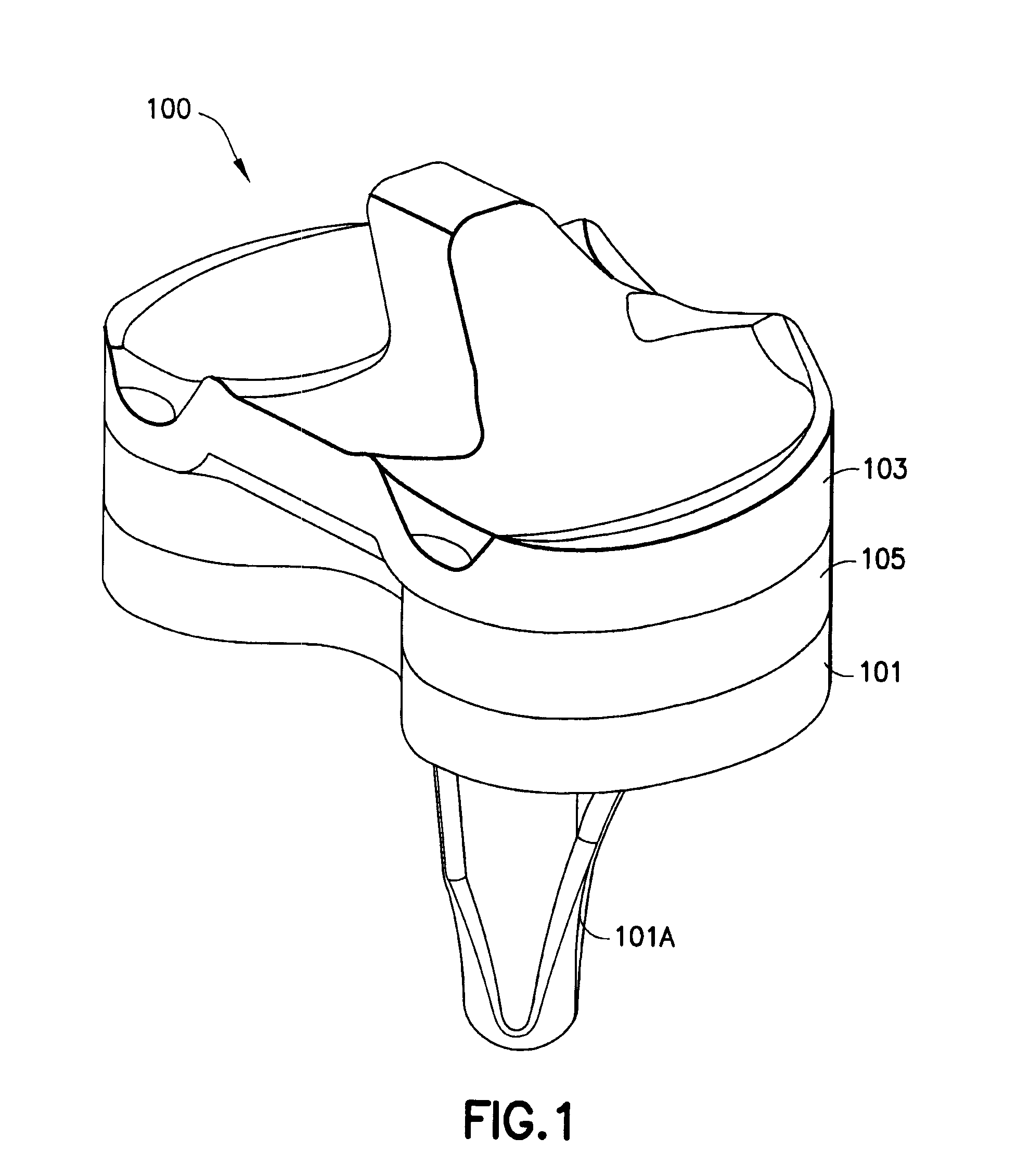
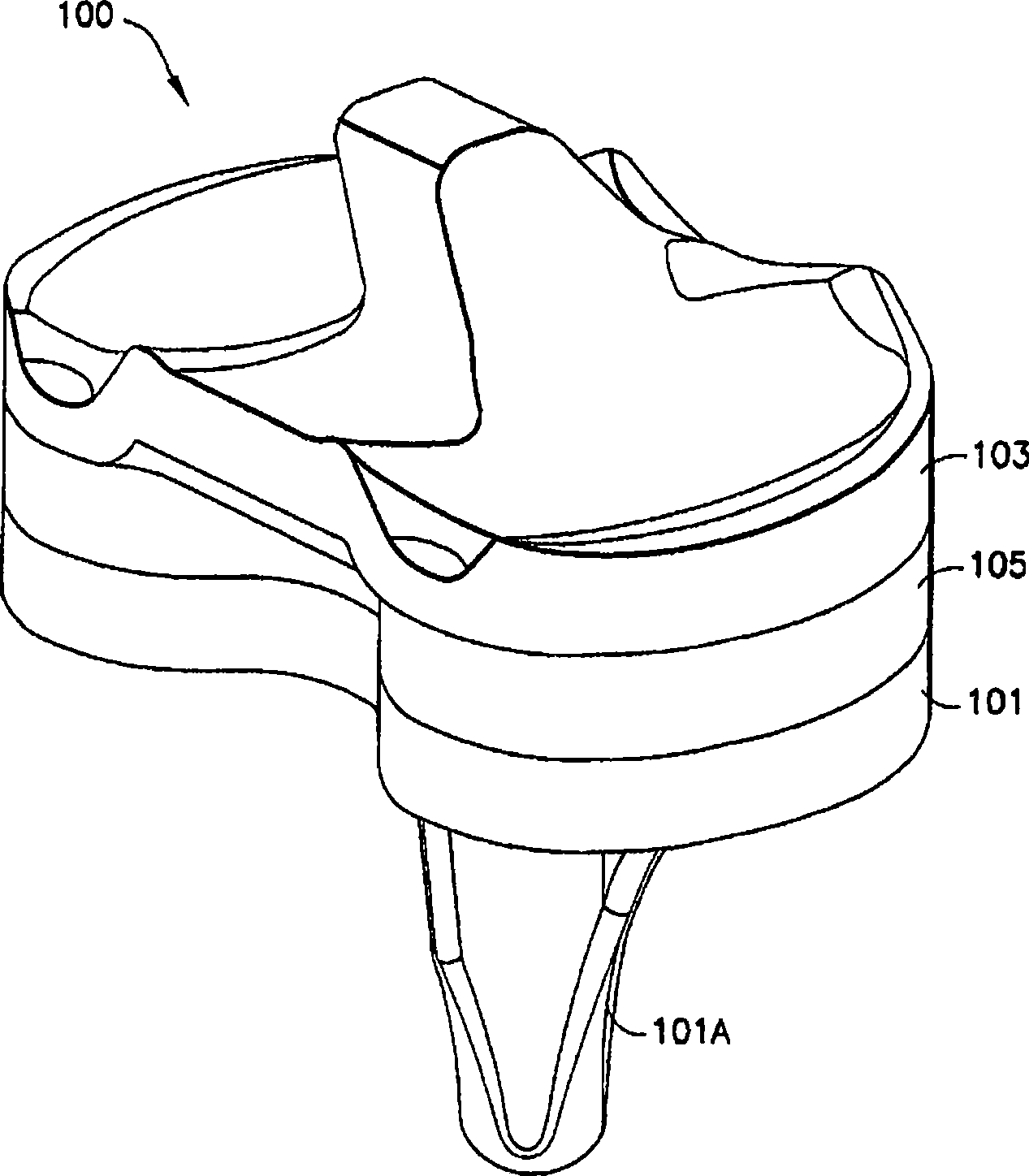
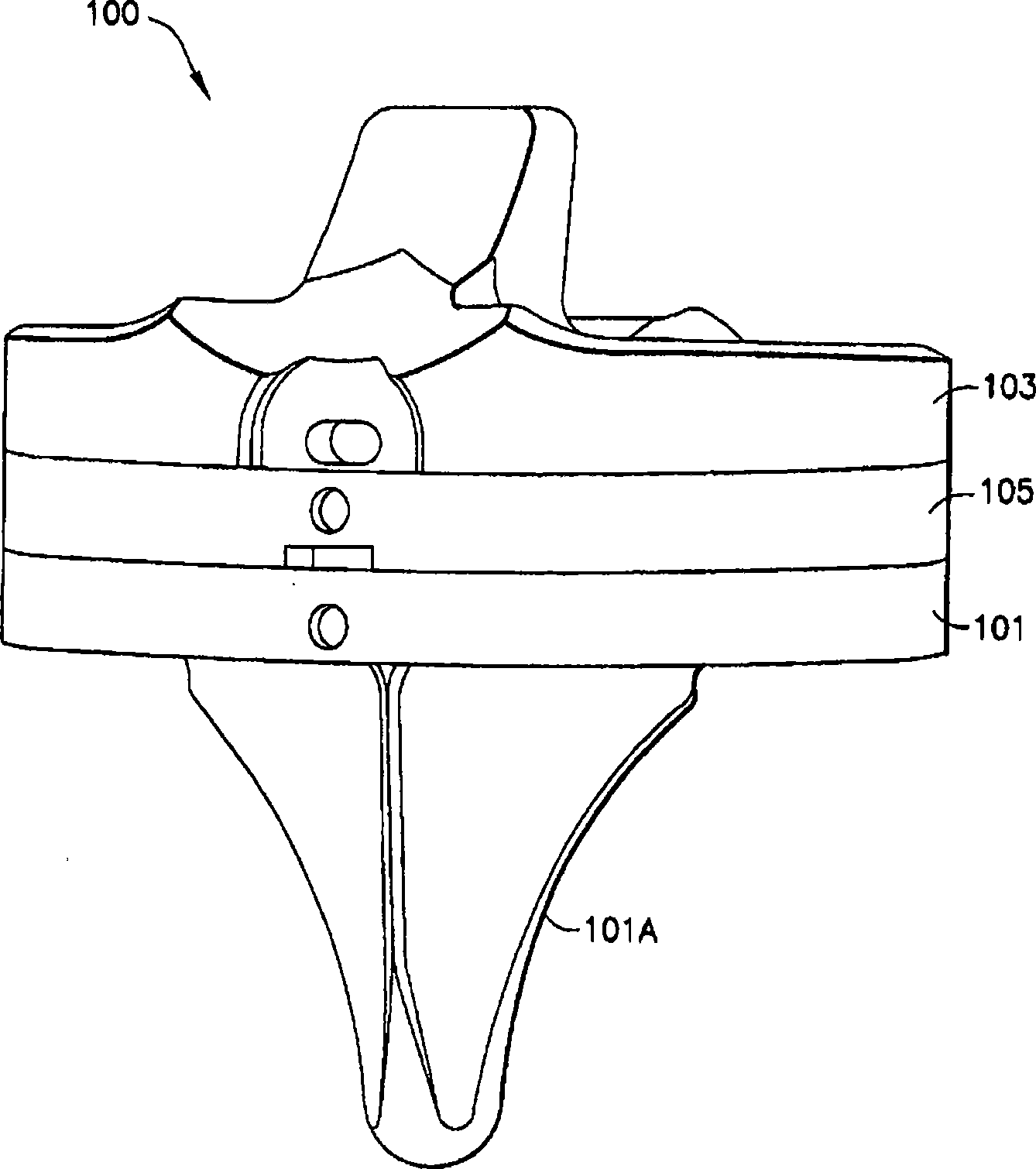
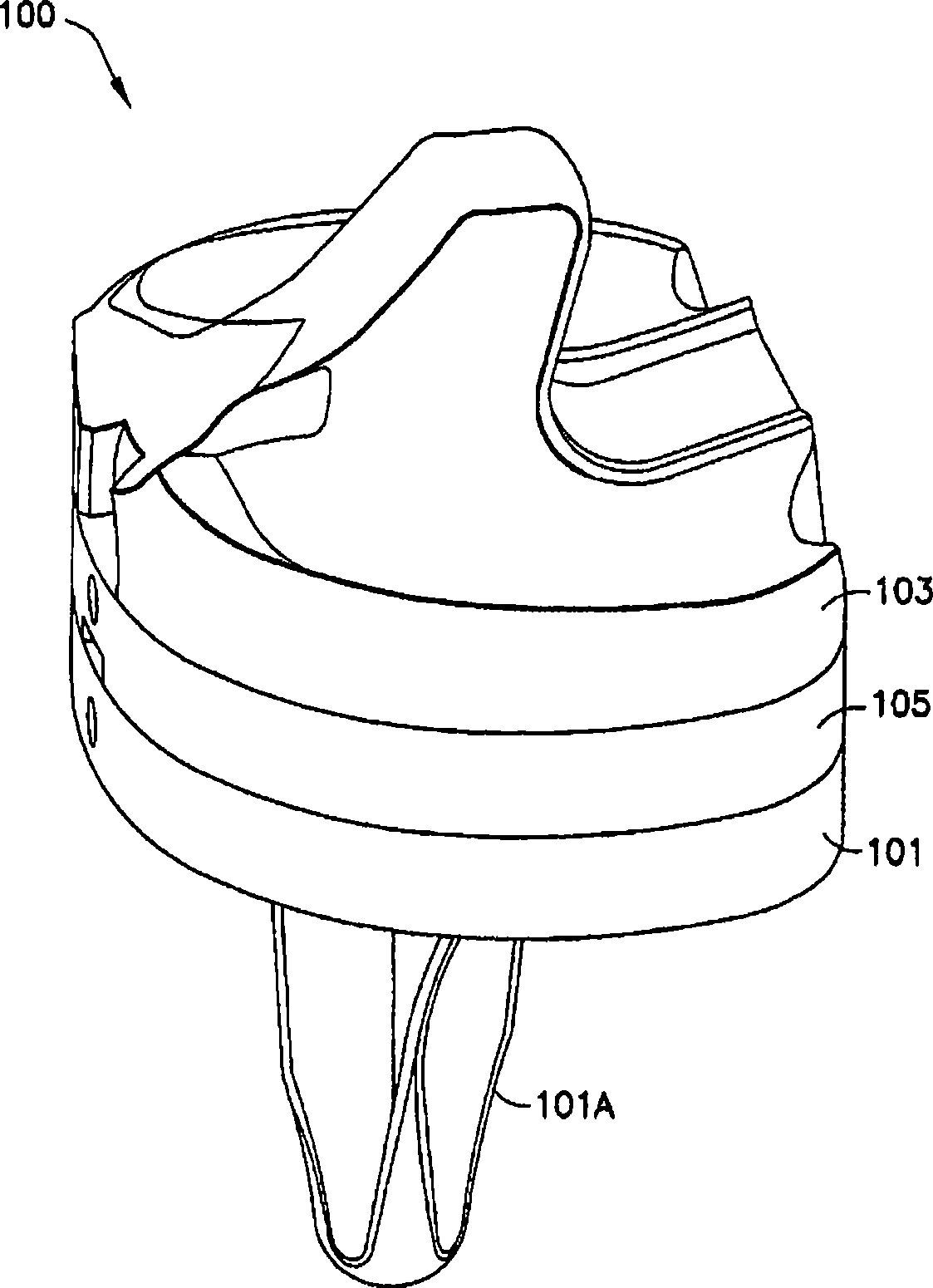
Constrained knee prosthesis
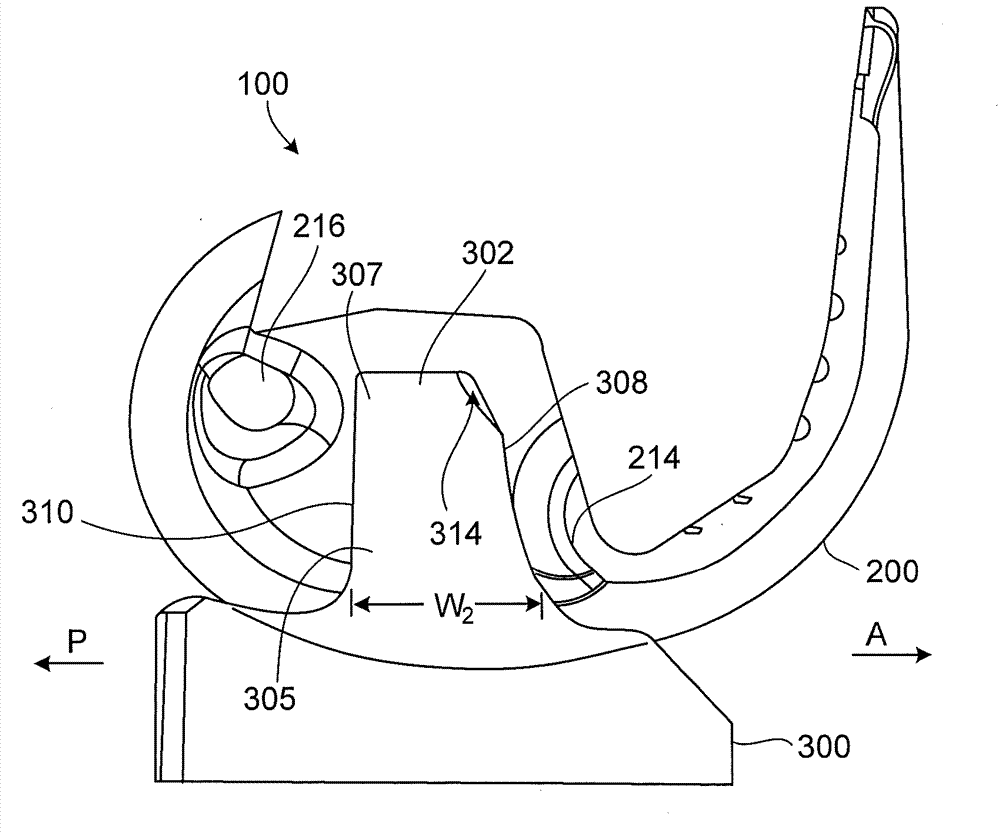
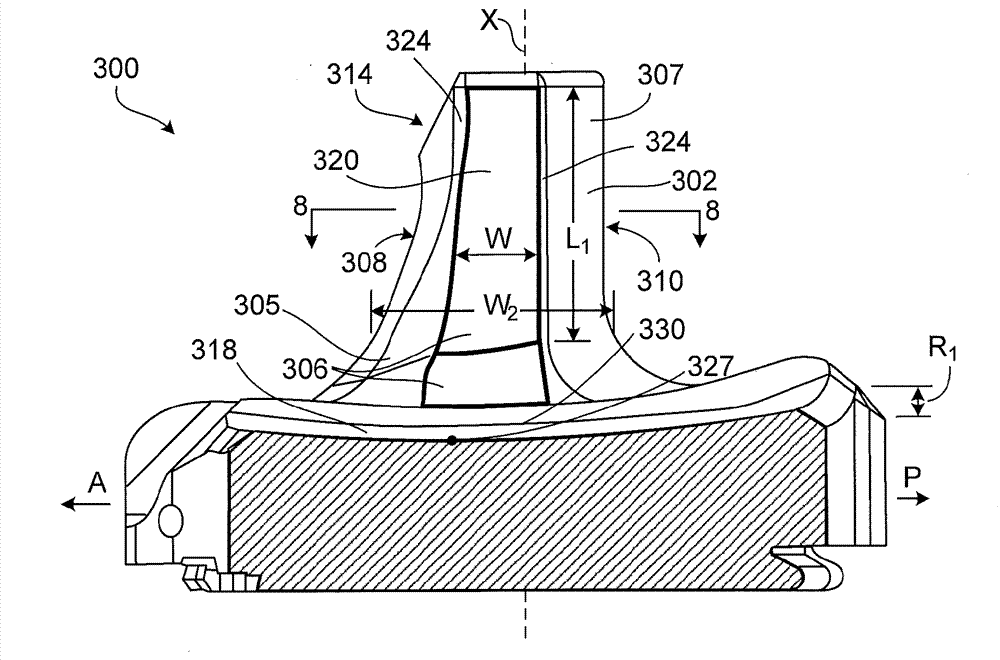
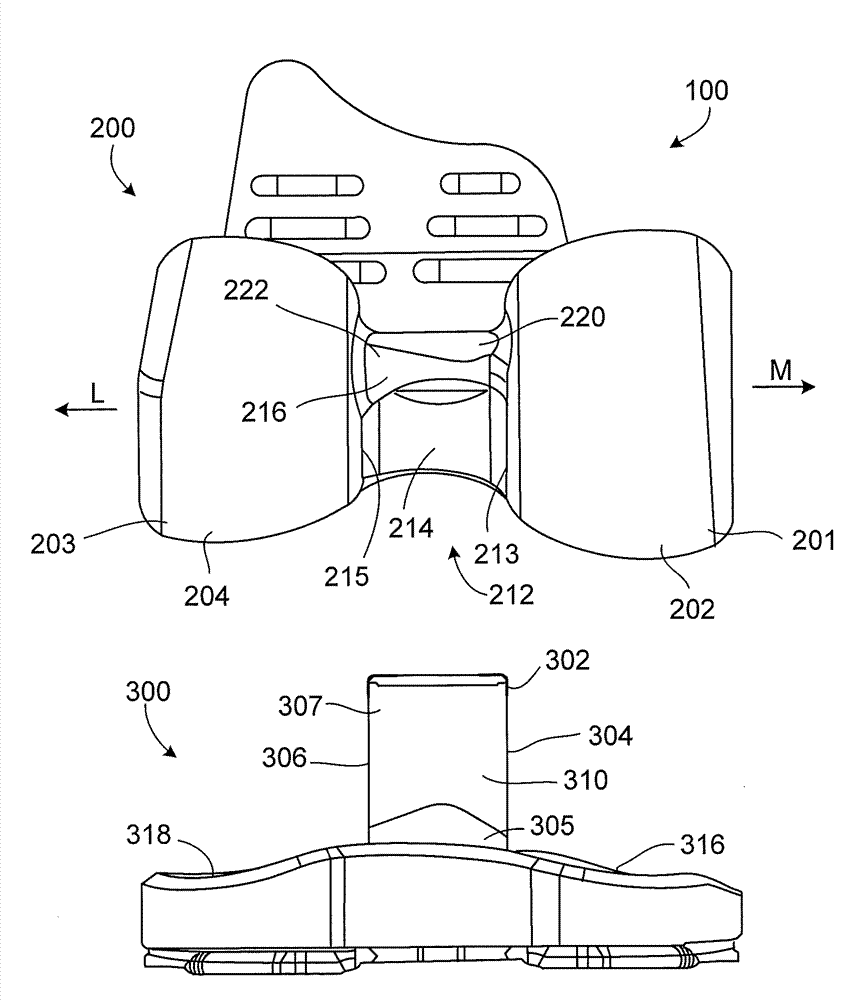
A tibial insert includes a base and a post extending from the base along a longitudinal axis. The post has a medial surface, a lateral surface, and a height along the longitudinal axis. The medial surface has a medial section, and the lateral surface has a lateral section oriented substantially parallel to the medial section. The medial section and the lateral section each have a width in a substantially anterior-posterior direction that is sufficient to enable varus / valgus constraint over a flexion / extension range from extension to about 90 to 120 degrees of flexion when the tibial insert is mated with a femoral component.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com