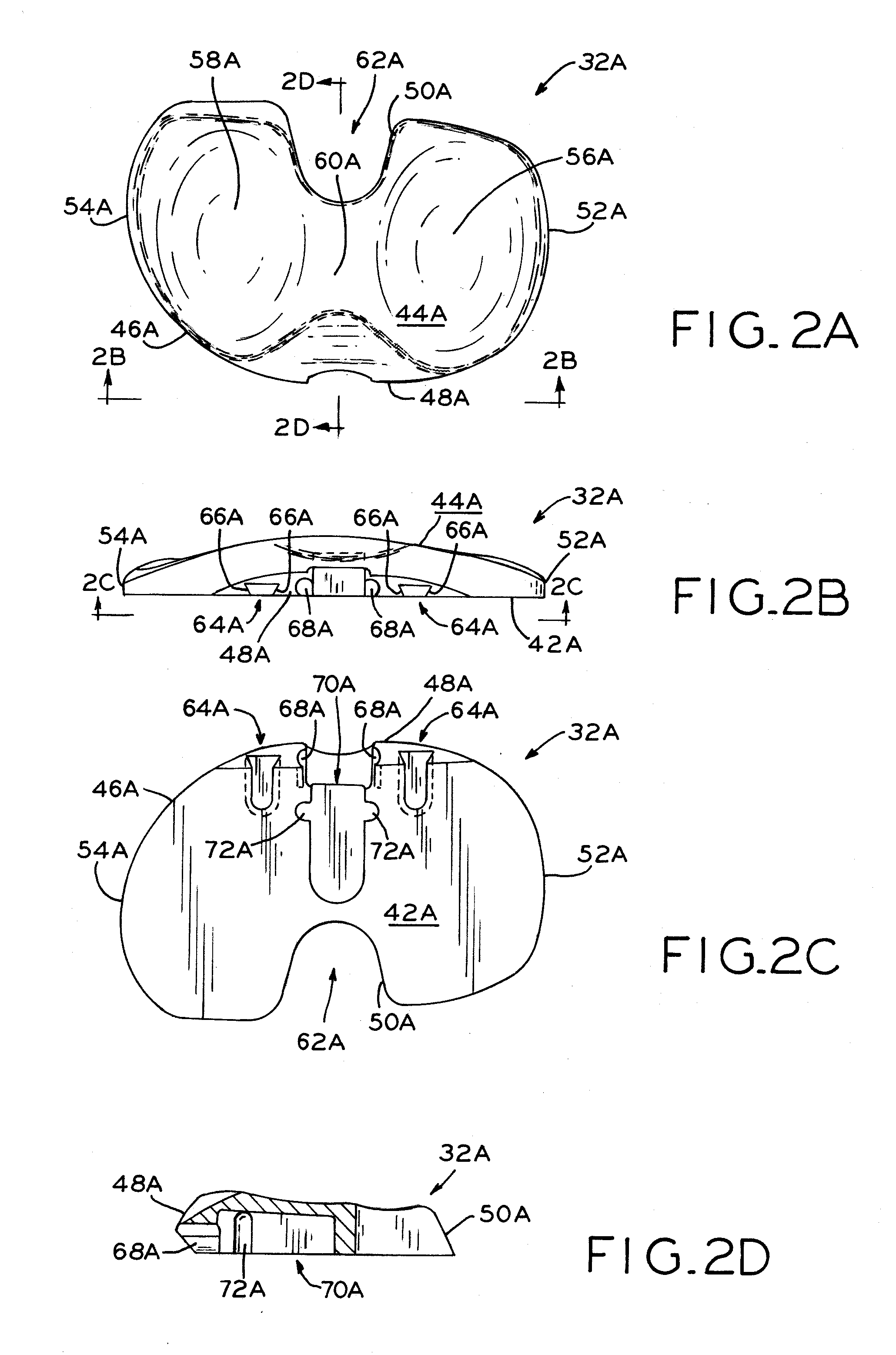
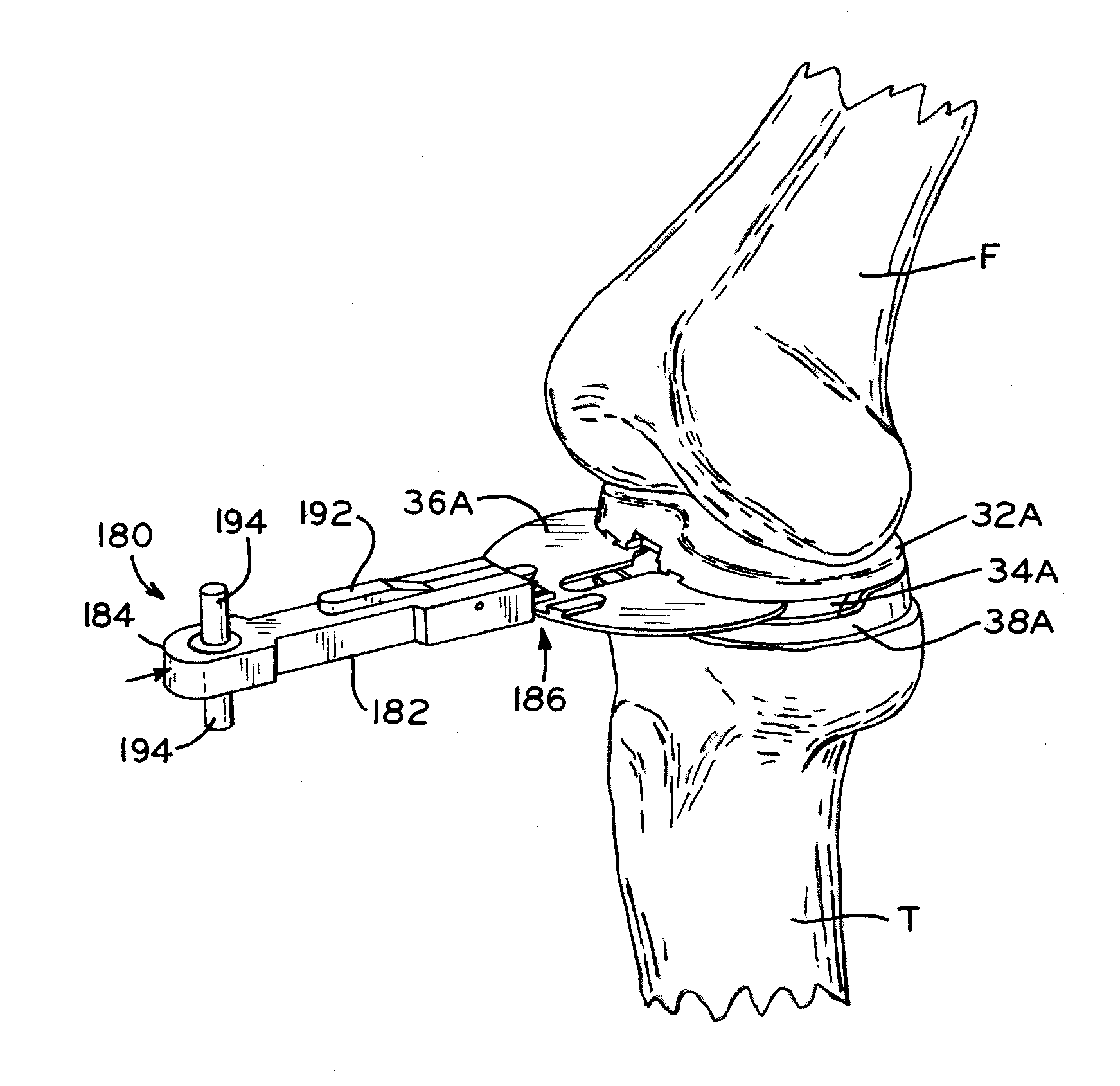
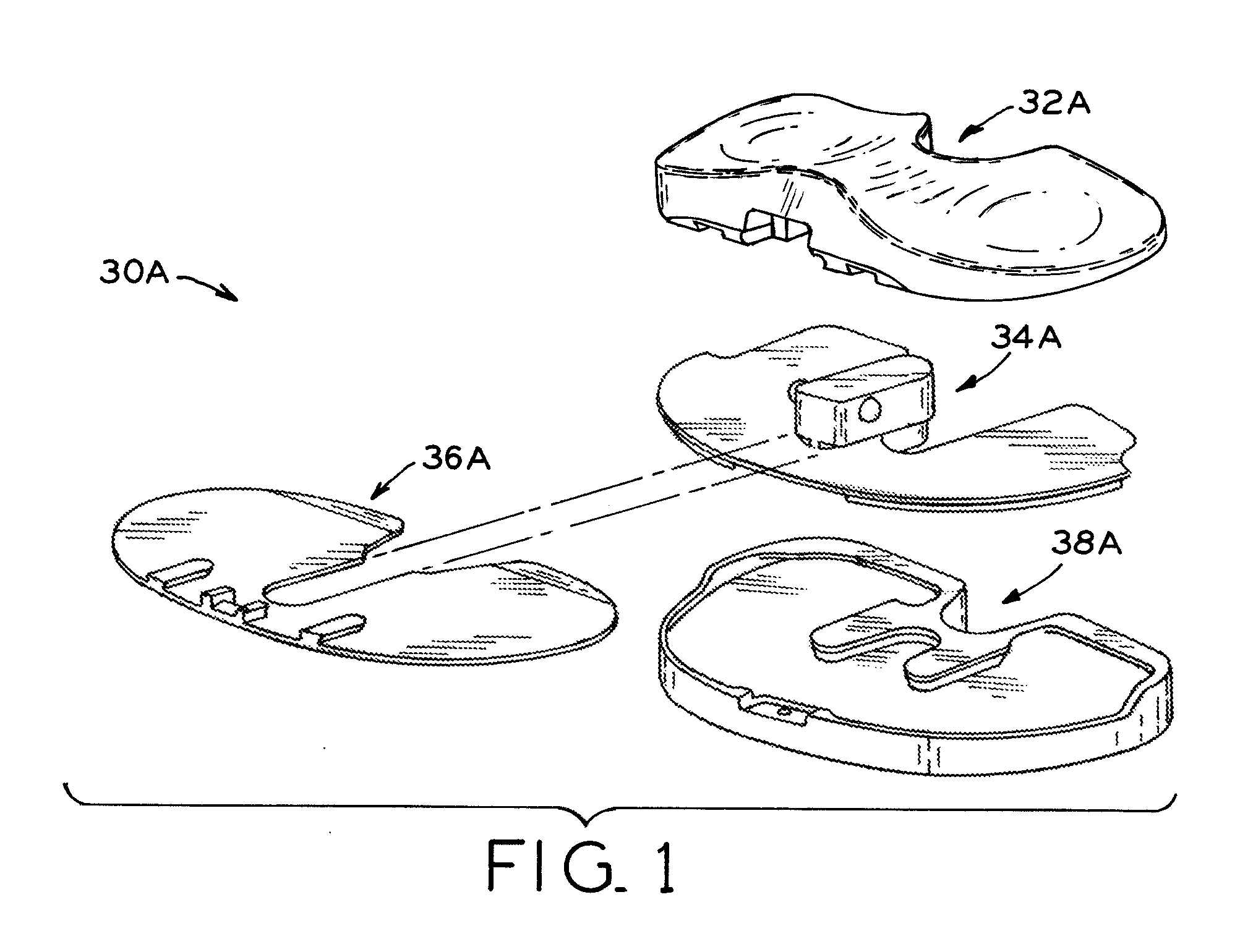
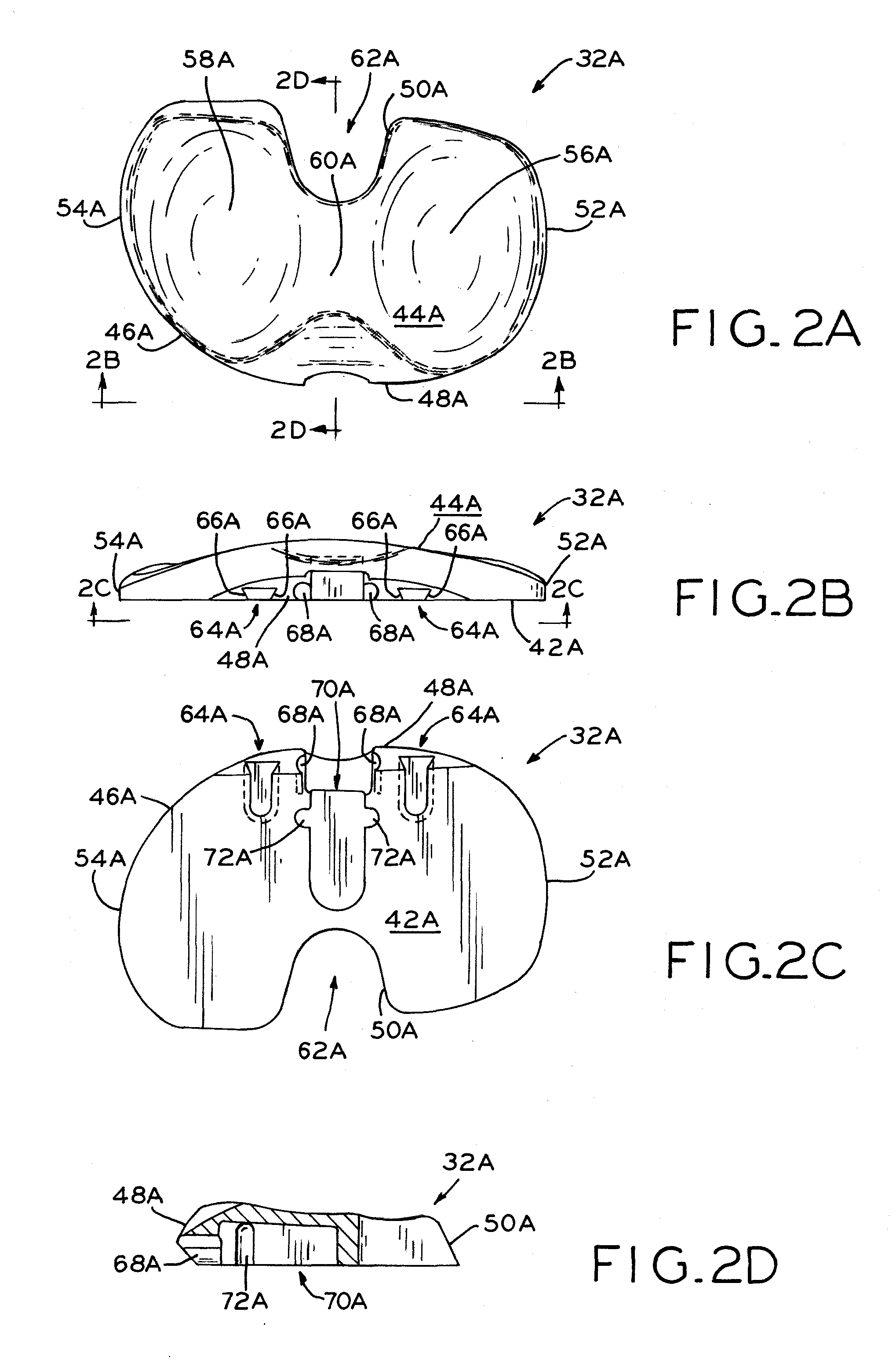
Patents
Literature
70 results about "Knee surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Orthopaedic surgery planning
Owner:MERIDIAN TECH LTD
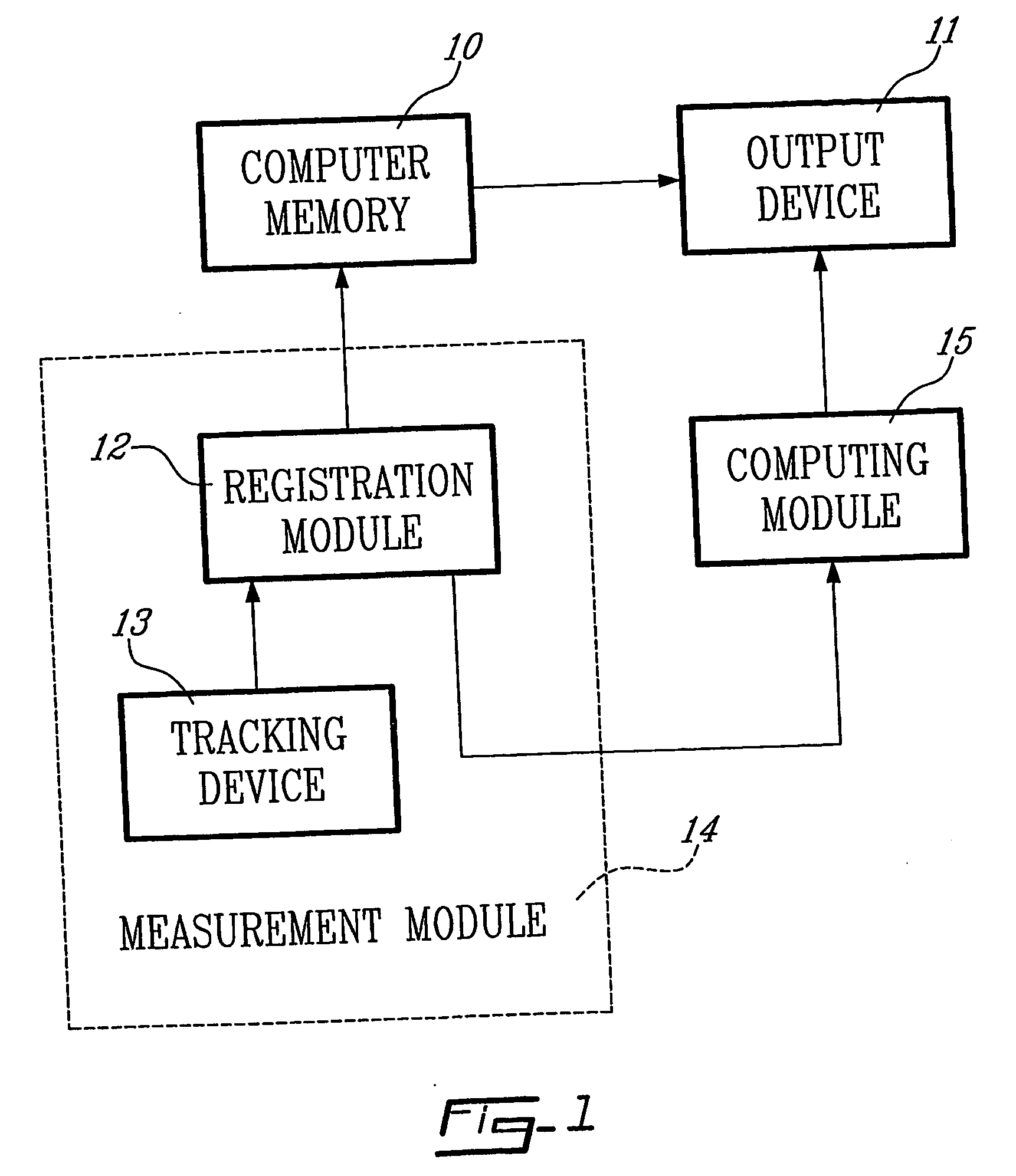
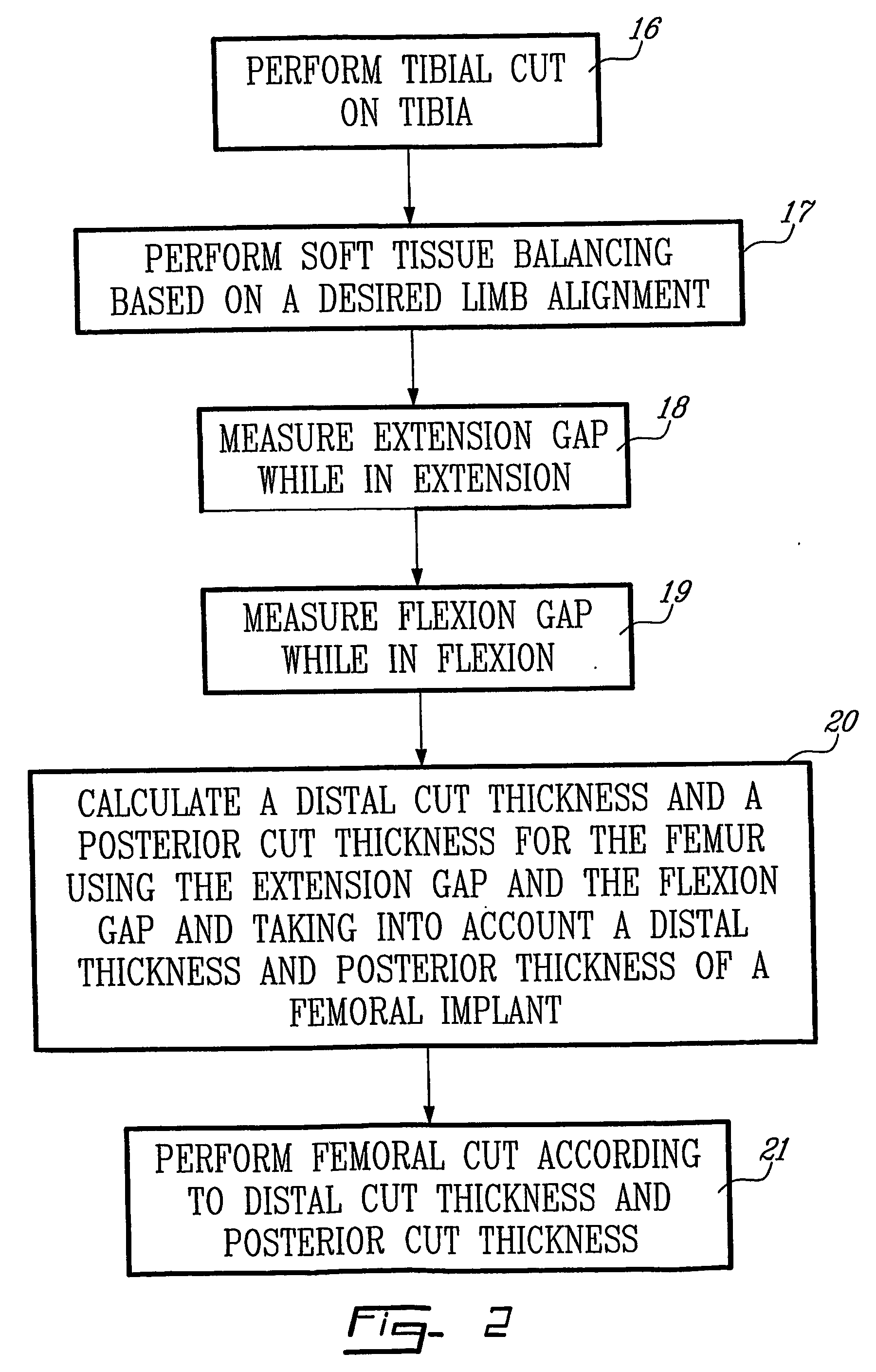
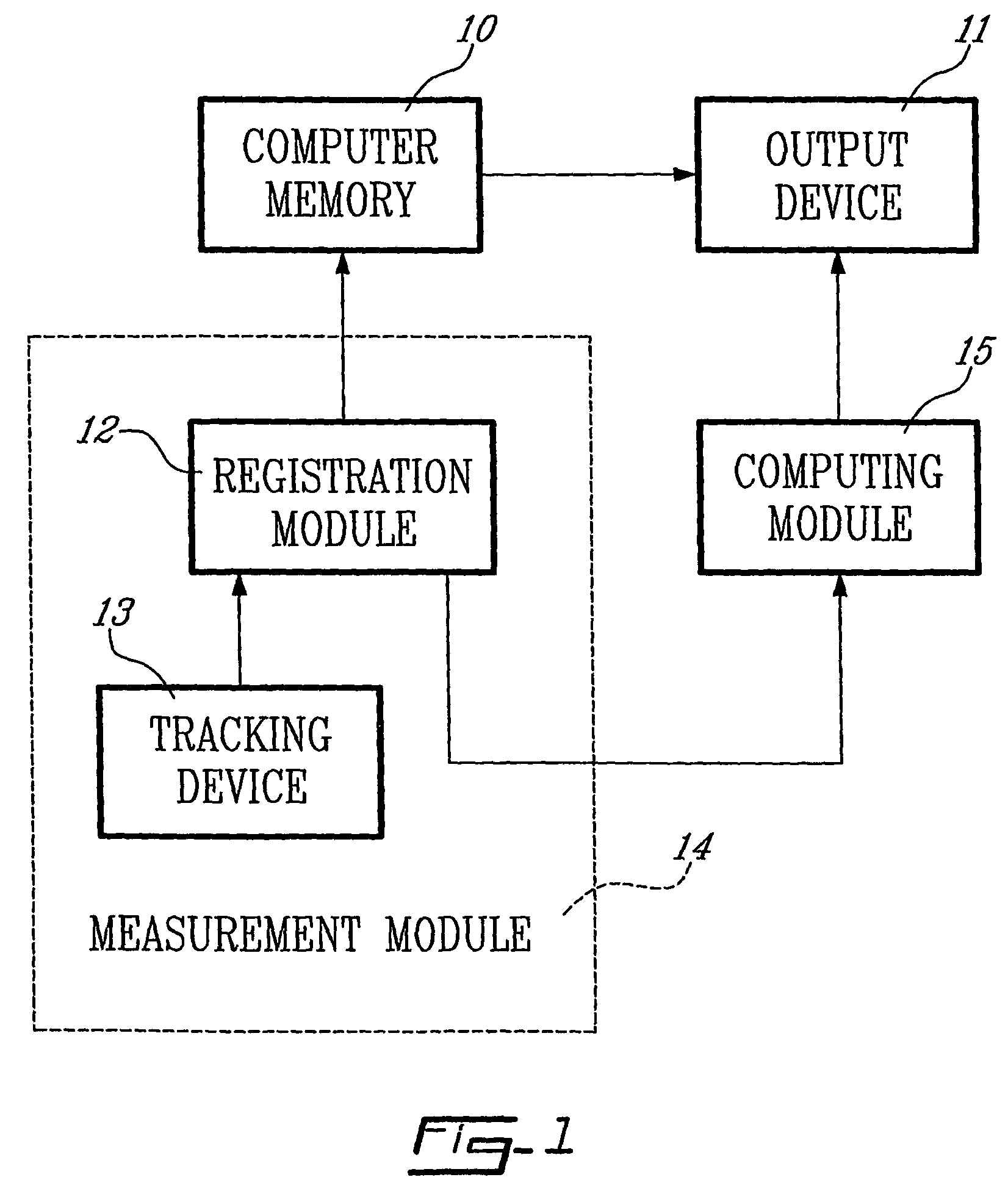
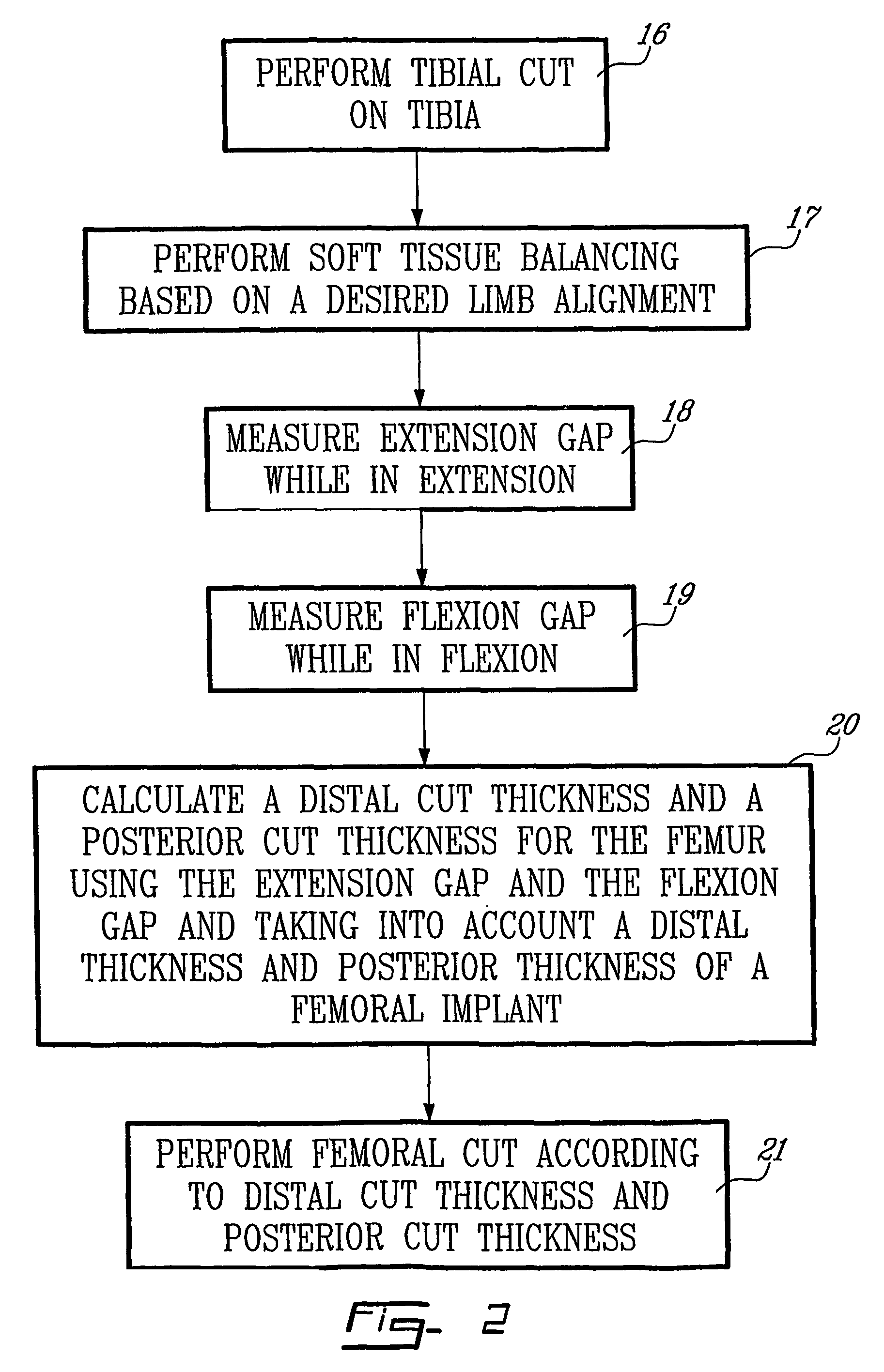
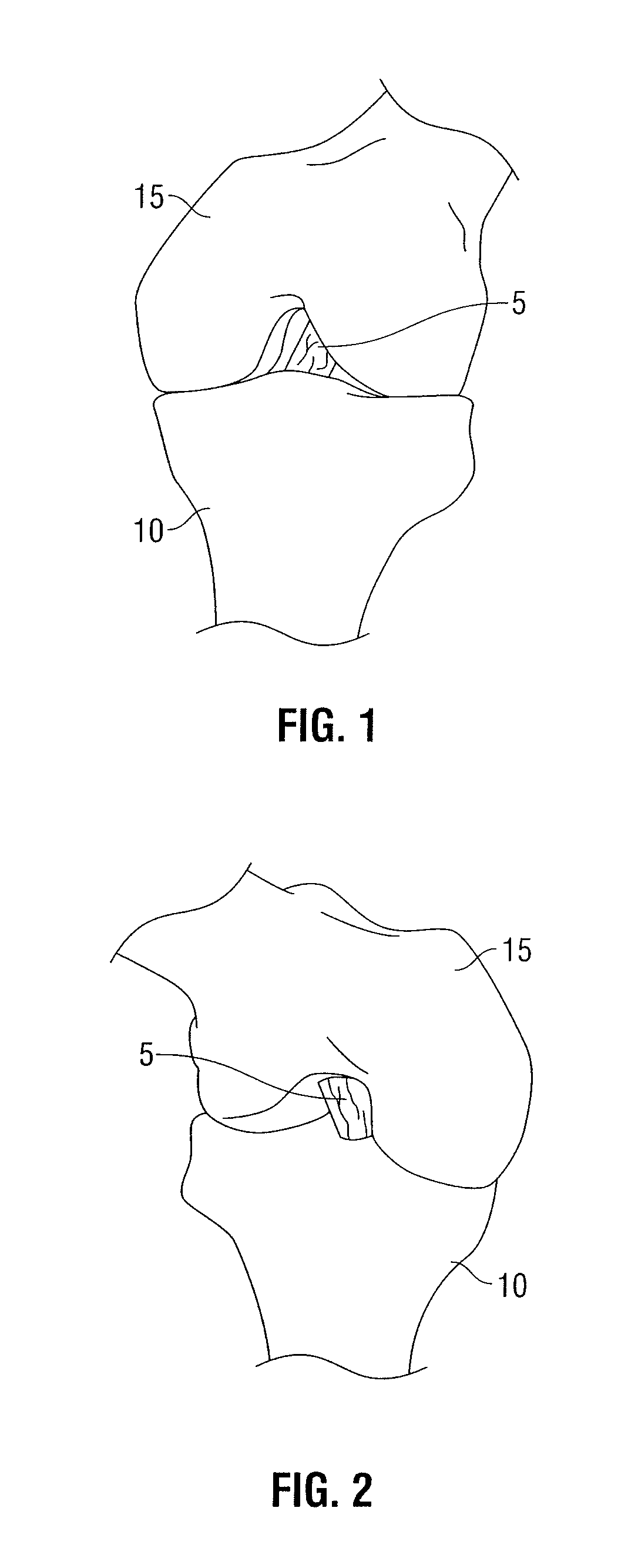
Determining femoral cuts in knee surgery
ActiveUS20060015120A1Extended service lifeEasy to placeDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsKnee surgeryTibia
There is provided a method and system for determining a distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness for a femur in a knee replacement operation, the method comprising: performing a tibial cut on a tibia; performing soft tissue balancing based on a desired limb alignment; measuring an extension gap between the femur and said tibial cut while in extension; measuring a flexion gap between the femur and the tibial cut while in flexion; calculating a distal cut thickness and a posterior cut thickness for the femur using the extension gap and the flexion gap and taking into account a distal thickness and posterior thickness of a femoral implant; and performing said femoral cut according to the distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
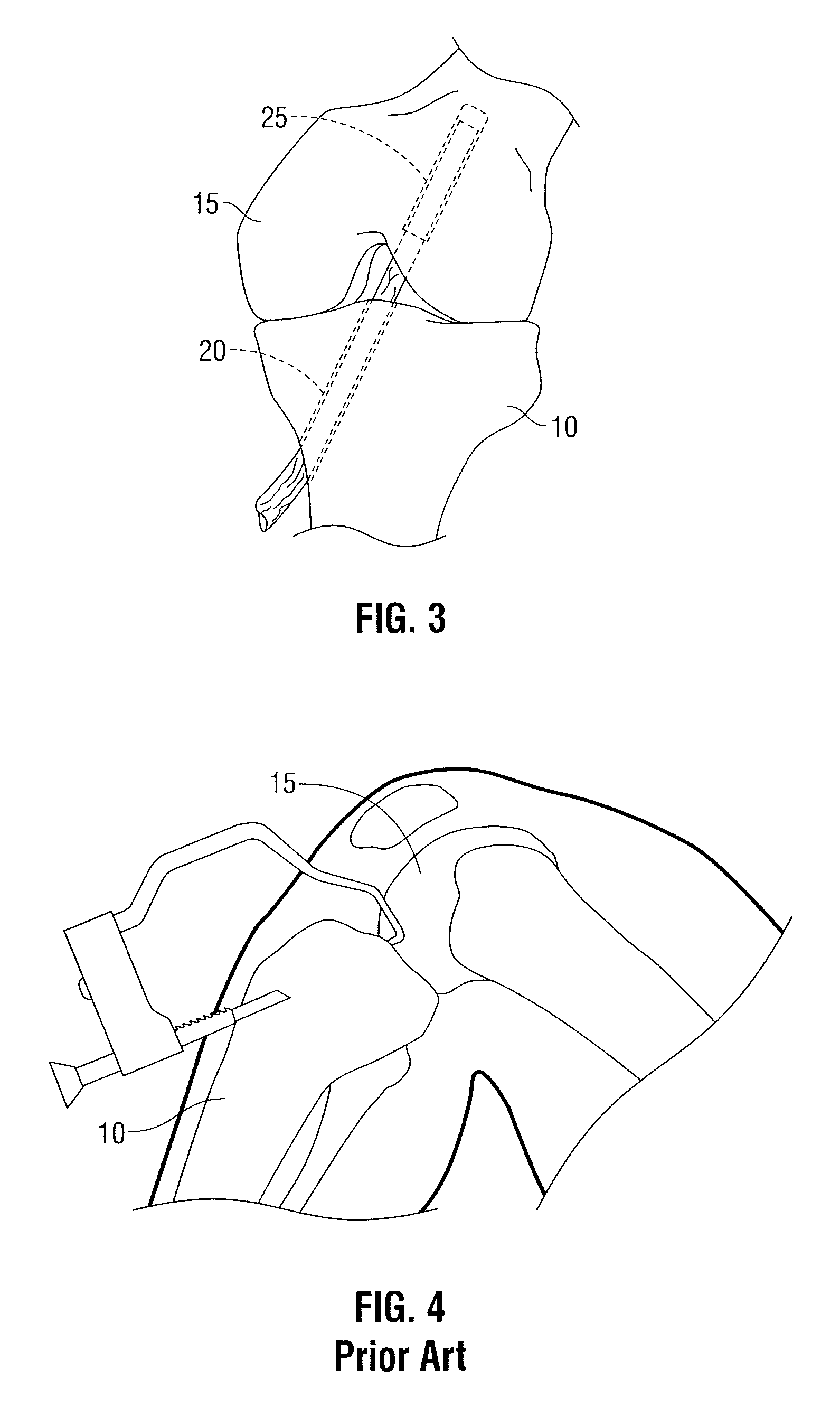
Instruments and methods for use in performing knee surgery
InactiveUS20050085920A1Avoid excessive bone removalJoint implantsKnee jointsKnee surgeryPatellar luxation
A system and method for aligning a patient's leg, for establishing the ultimate alignment of the leg prior to making a horizontal femoral cut or a horizontal tibial cut, for preparing the distal femur for receiving a femoral implant, and for making the horizontal, femoral and tibial cuts. The system and method incorporate a spacer, a cutting guide, and a template. The spacer is insertable between a distal femur and a proximal tibia to rotate the tibia with respect to the femur into the desired alignment. The cutting guide is engageable with the spacer, and can be fixed to the proximal tibia and the distal femur. The cutting guide has openings sized and shaped to guide a surgical saw to make the horizontal femoral cut and the horizontal tibial cut. The template is shaped to closely conform with the distal femur to allow the leg to be extended and to allow the procedure to be performed without dislocating a patella. Through one method of the present invention, the practitioner can select the desired ultimate alignment of the leg prior to making the horizontal, tibial and femoral cuts. As a result, when a replacement knee is implanted, the leg will be in the desired alignment.
Owner:WILLIAMSON RICHARD V
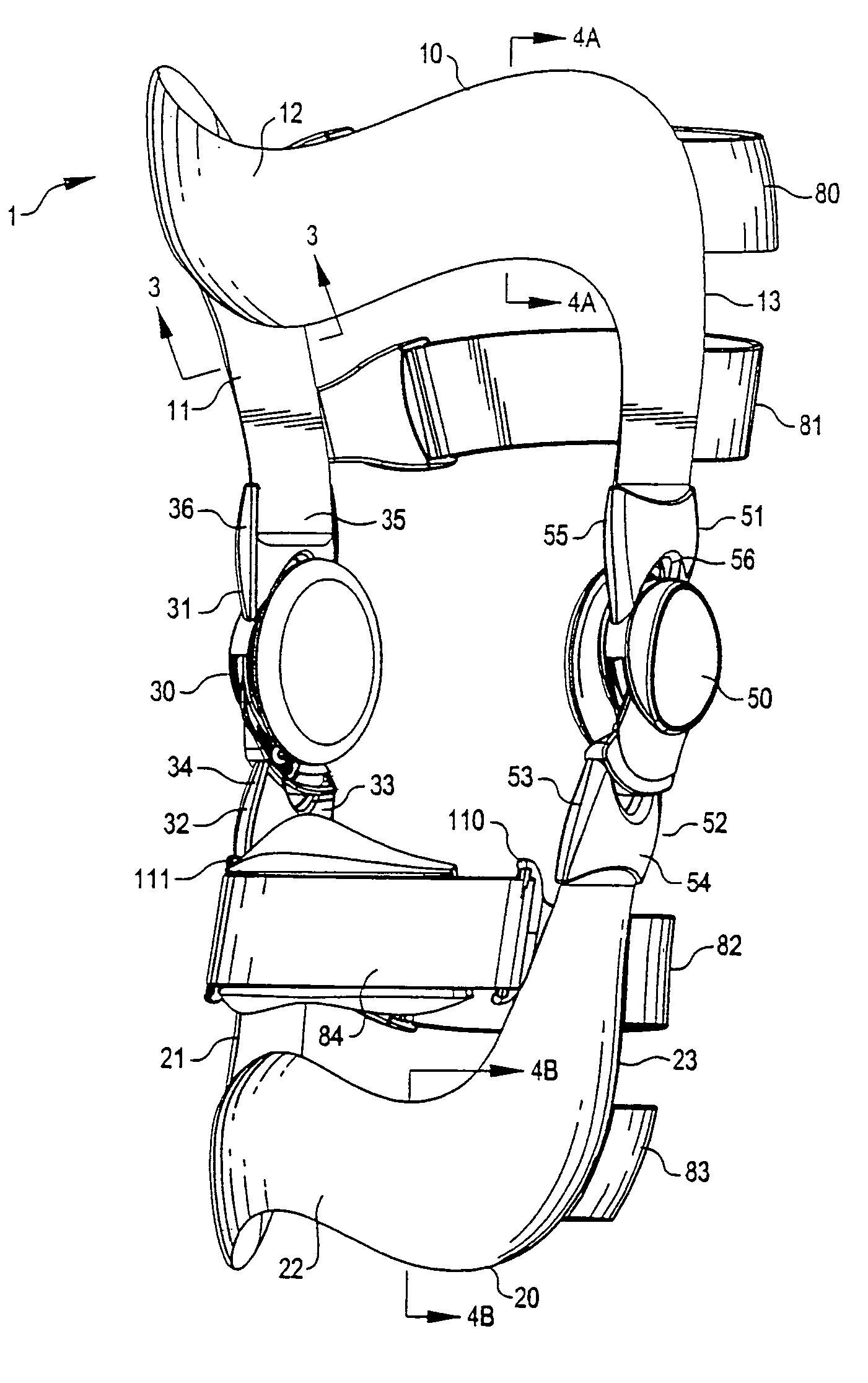
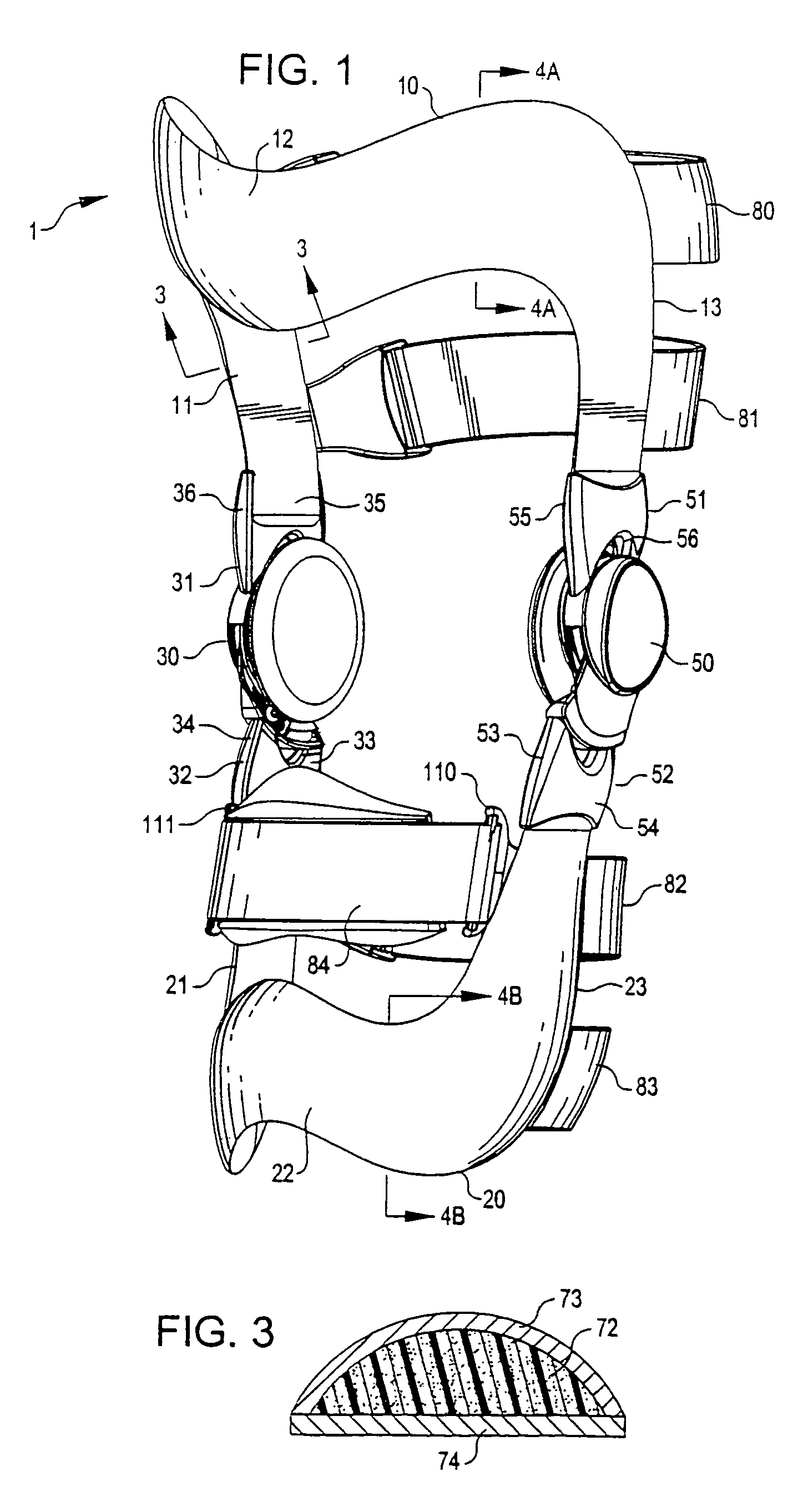
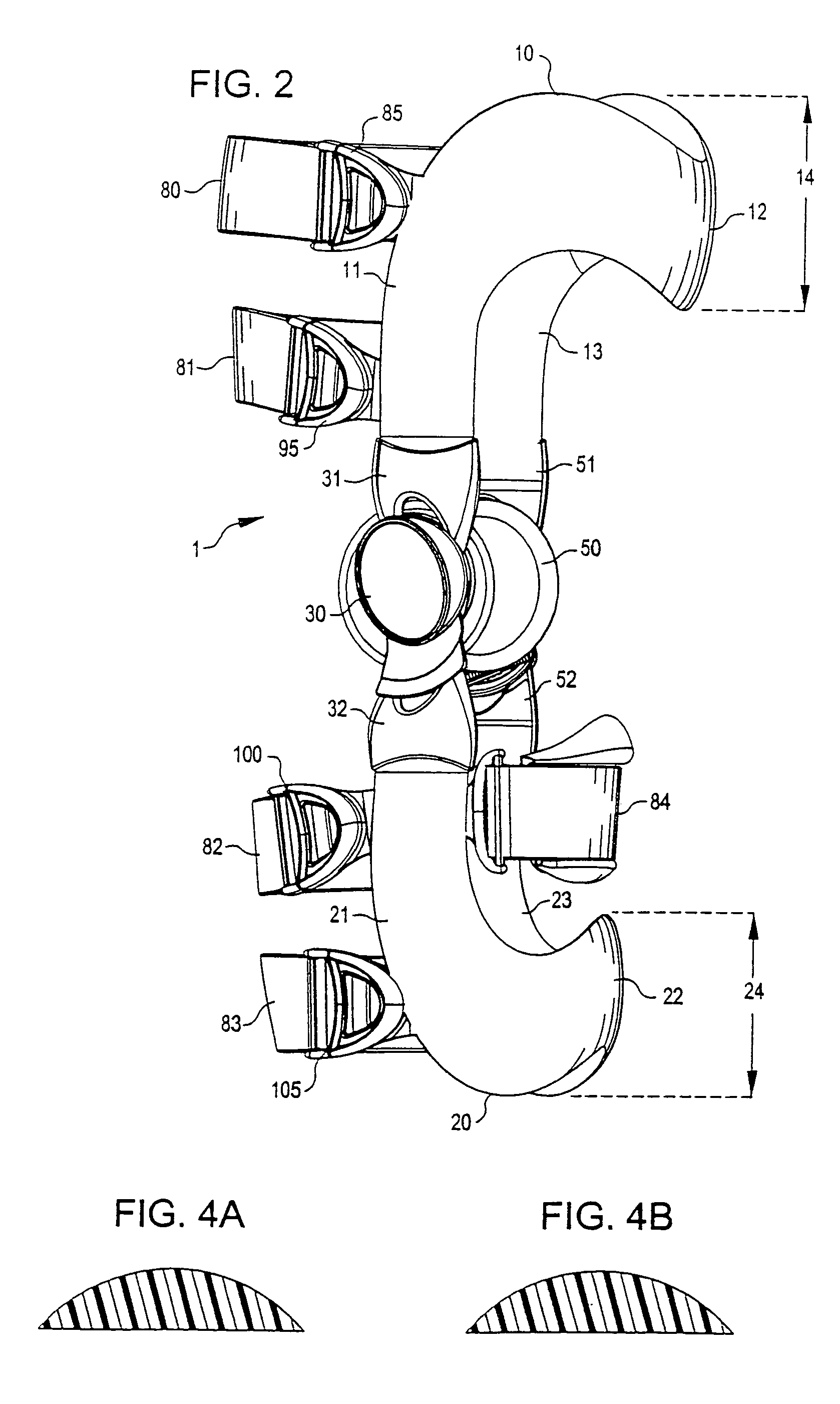
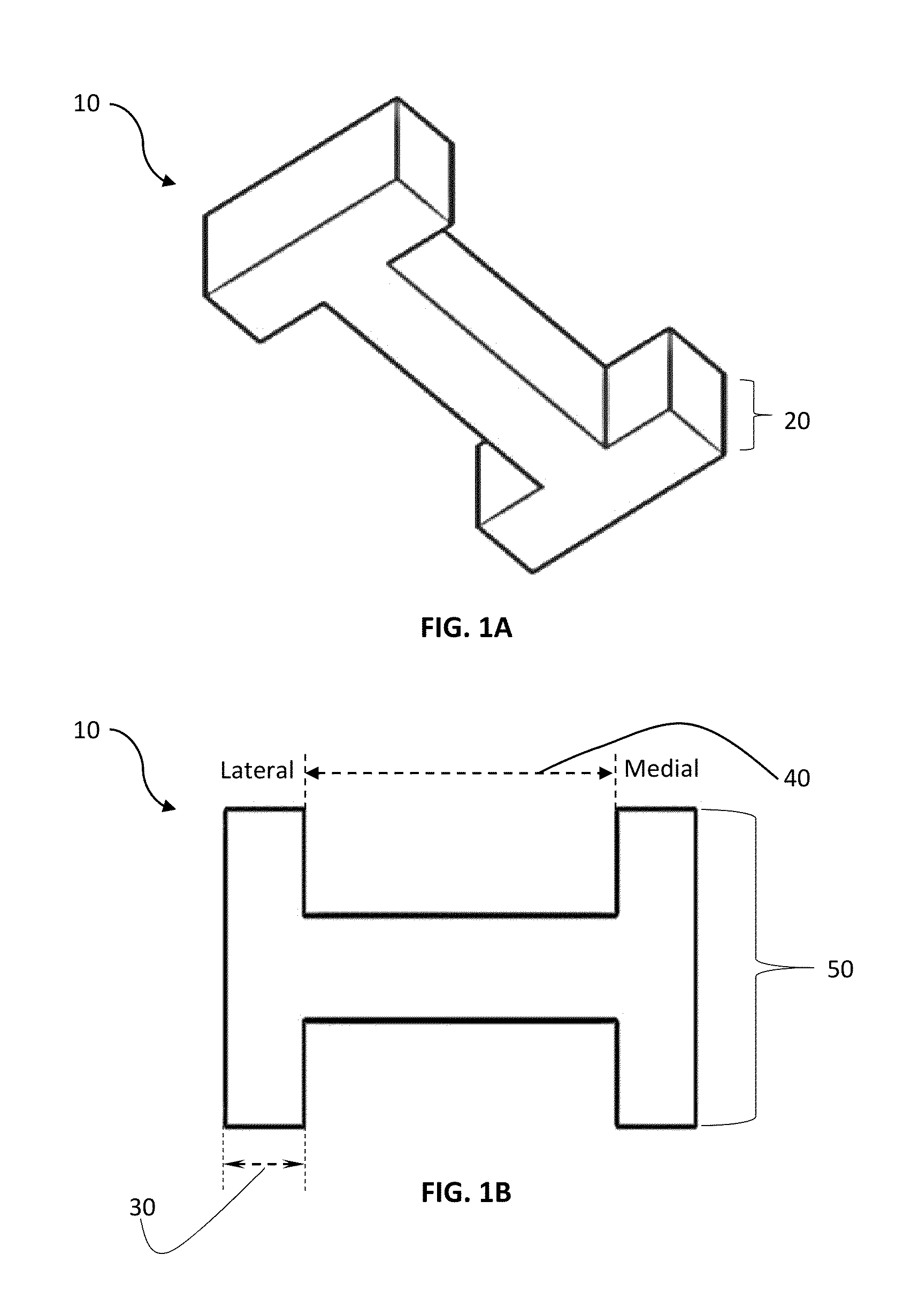
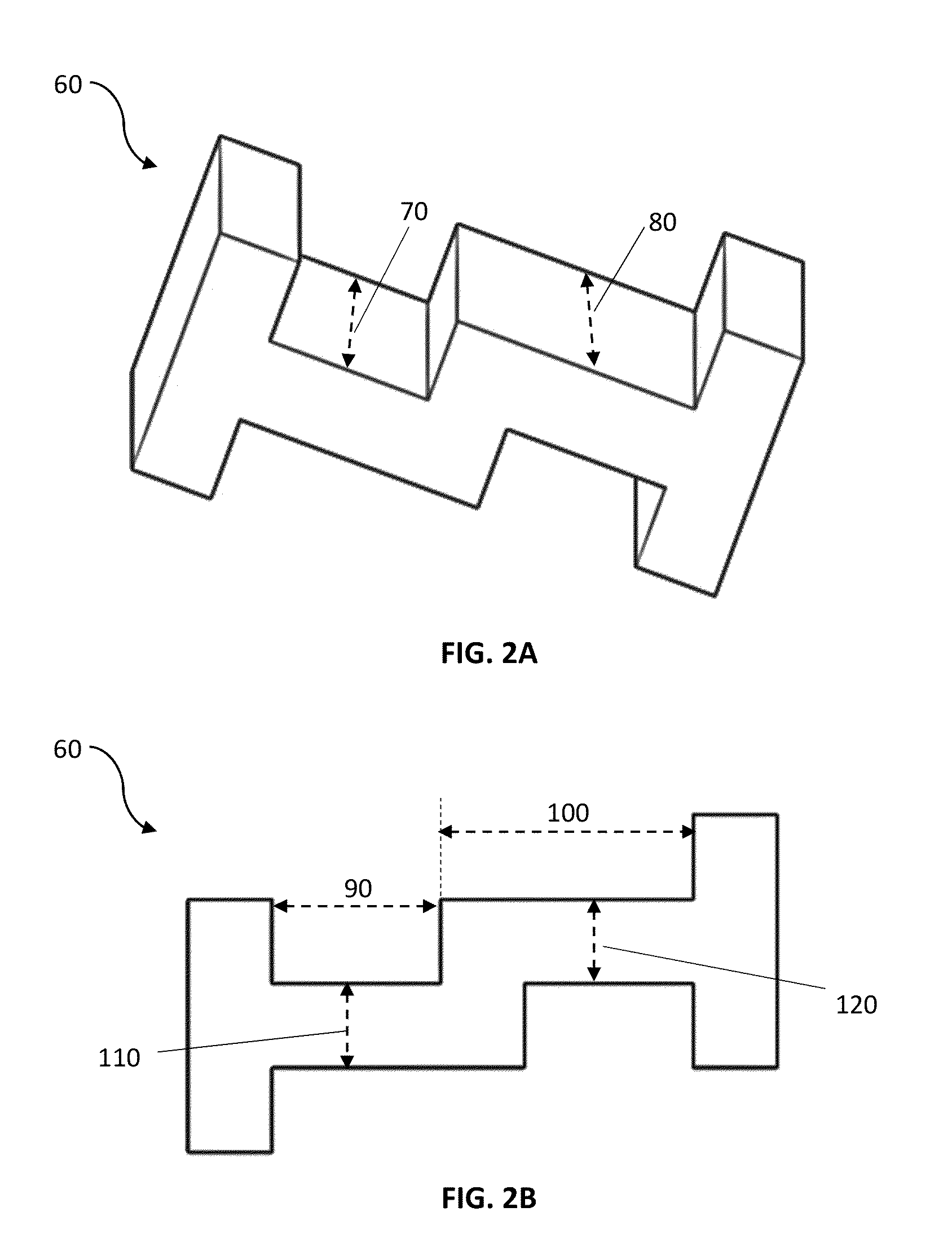
Anatomically designed orthopedic knee brace
InactiveUS7201728B2Novel and effectiveAccurately prescribingNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee proceduresTibia
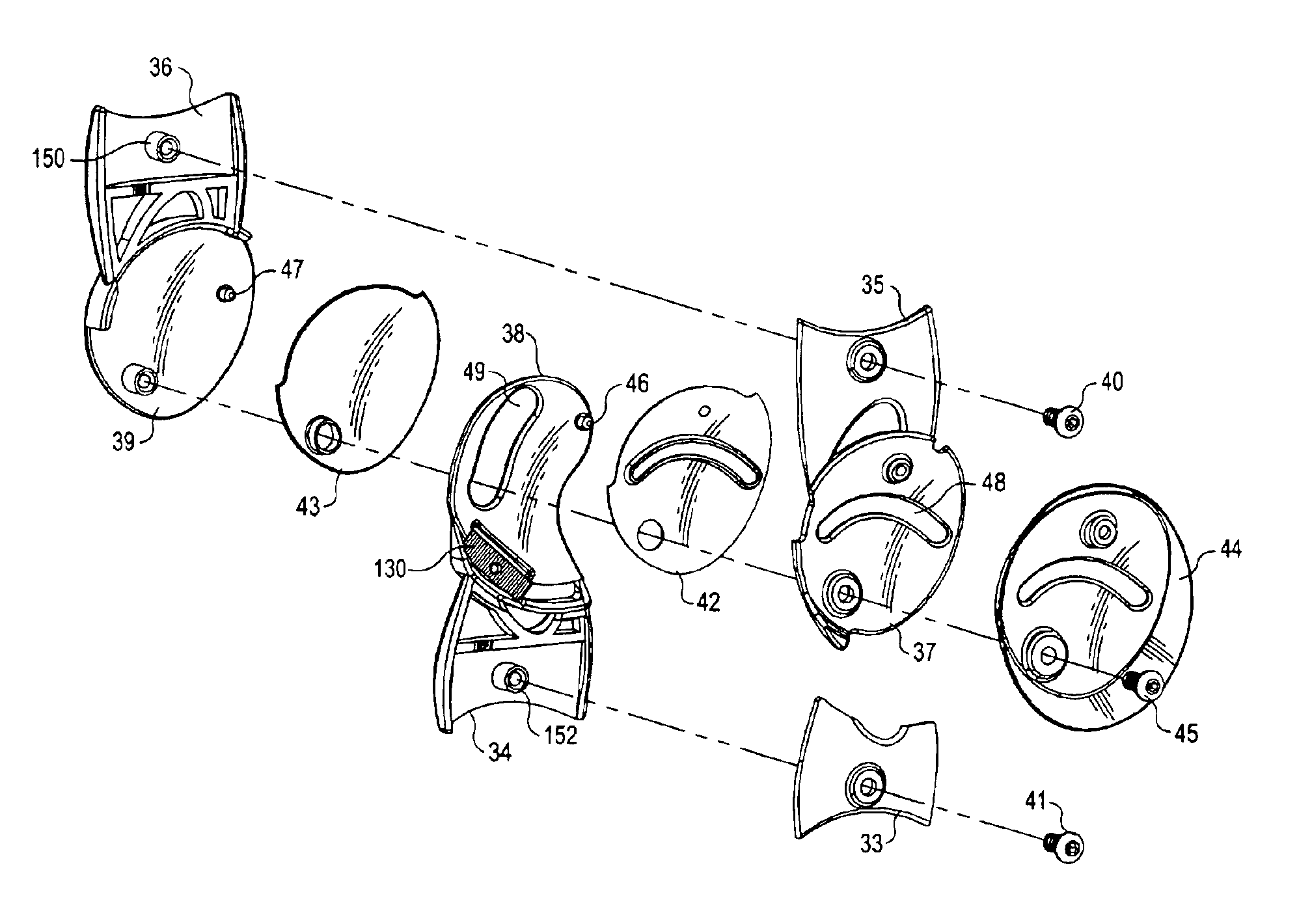
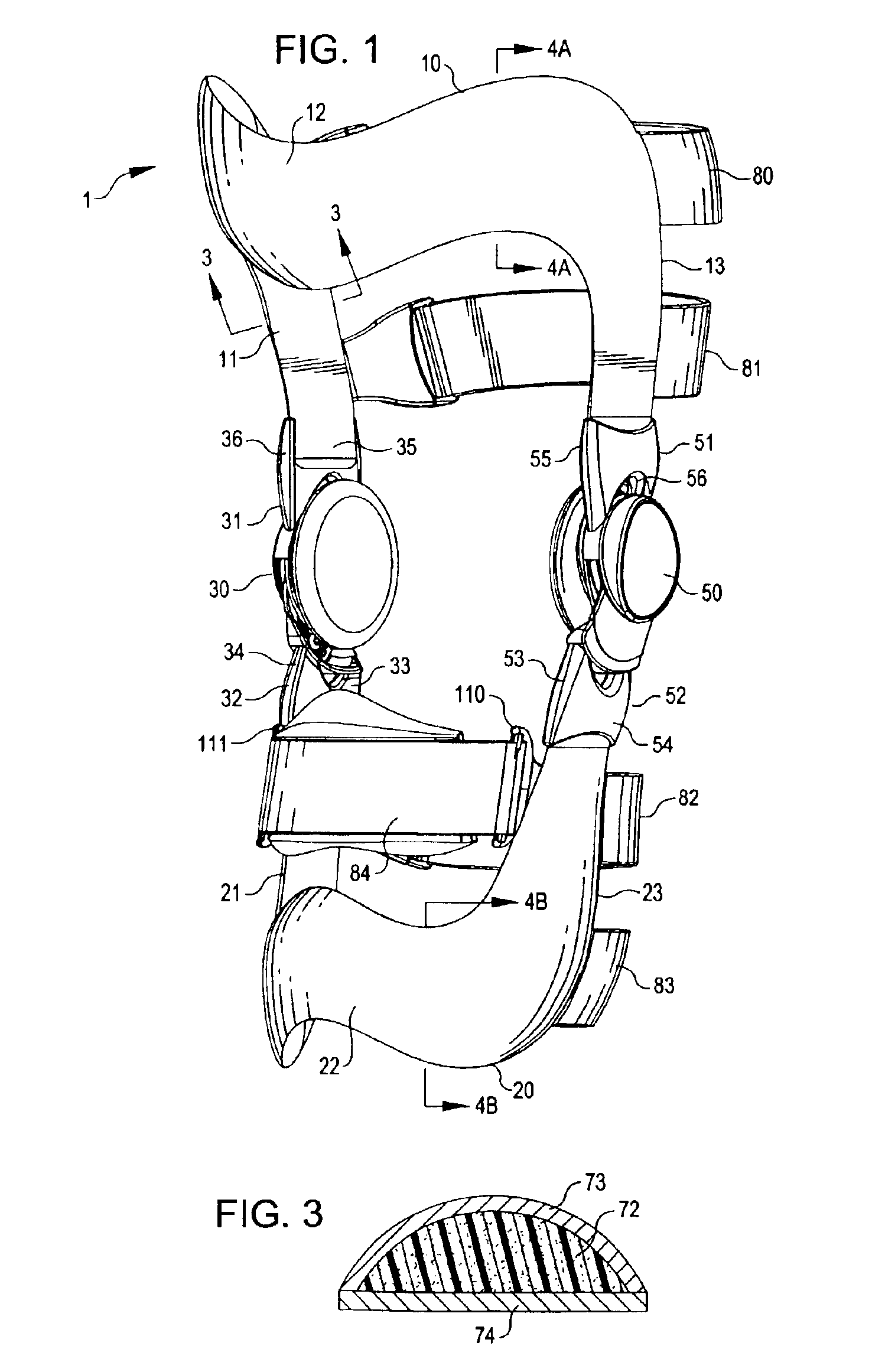
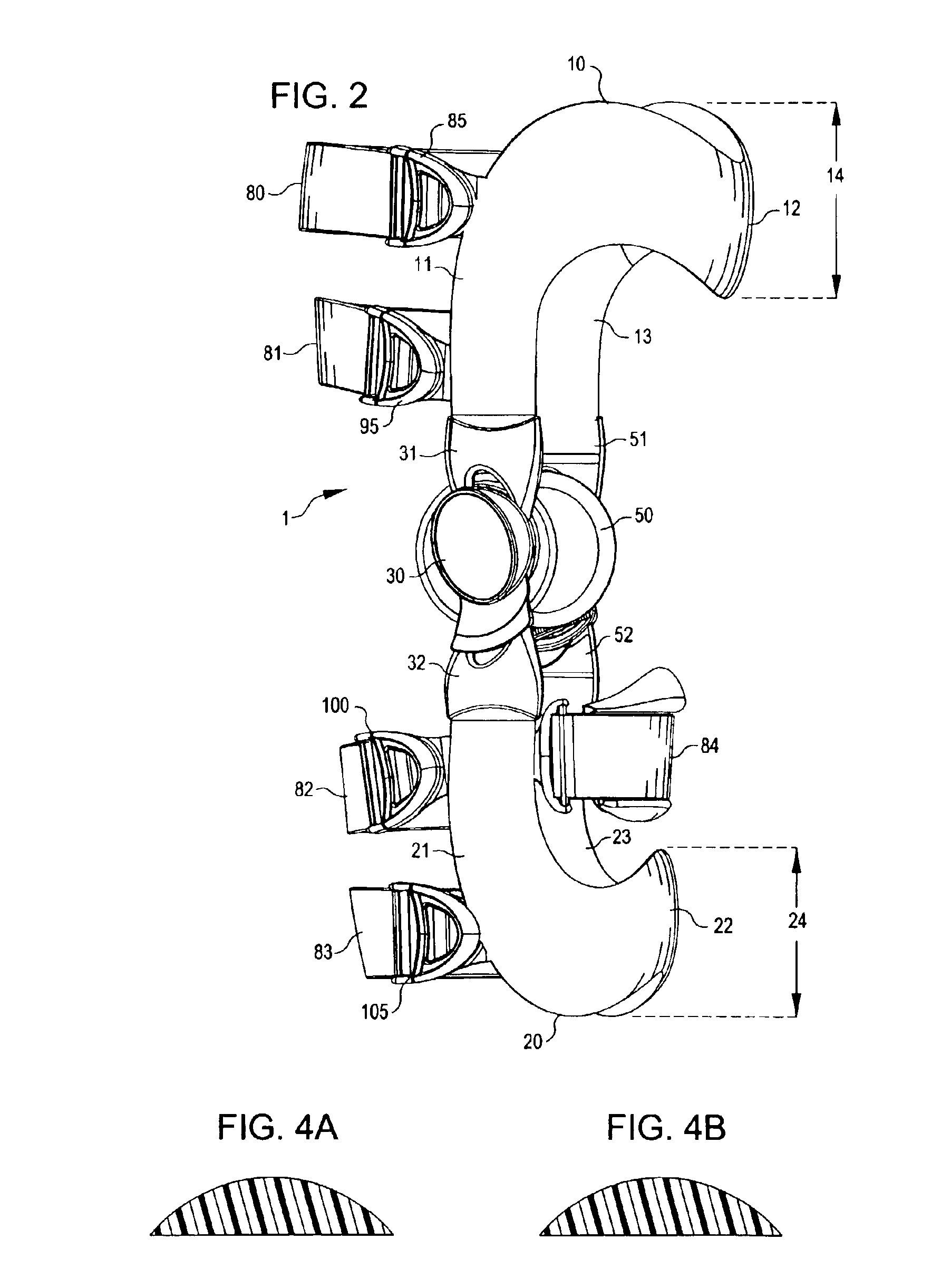
An orthopedic knee brace provides an apparatus for accurately prescribing the anatomical motion of the human knee. The orthopedic knee brace is used for treatment and rehabilitation following surgery to the knee, protection for a surgically repaired knee, and protection for an uninjured knee, among other applications. The orthopedic knee brace actively prescribes asymmetric three-dimensional anatomic motion in six degrees of freedom of the wearer's knee. The rigid connections between the thigh and calf engaging members and the medial and lateral hinges provide the ability of the orthopedic knee brace to prescribe asymmetric three-dimensional anatomic motion in six degrees of freedom by actively prescribing flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, internal / external rotation, anterior / posterior translation, medial / lateral translation, and proximal / distal translation between a femur and a tibia of a wearer's leg. In alternate embodiments a single-hinge brace design is provided for treatment and prevention of osteoarthritis and other joint diseases and conditions.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Tibial guide for knee surgery
InactiveUS20130237989A1Promote balance between supply and demandSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsTibiaKnee surgery
A joint replacement kit for use in a joint replacement procedure replacing a portion of a body joint. The kit includes a cutting guide and a trial component wherein the cutting guide and trial component are packaged together. There is also provided a method for replacing a portion of a body joint. The method includes providing a joint replacement kit having a cutting guide and a trial component, positioning the cutting guide against an end portion of a bone, cutting the end portion of the bone with a cutting instrument, positioning the trial component to the cut end portion of the bone, and disposing of the cutting guide and trial component.
Owner:BONUTTI SKELETAL INNOVATIONS
Determining femoral cuts in knee surgery
ActiveUS8257360B2Extended service lifeEasy to placeDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaKnee surgery
There is provided a method and system for determining a distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness for a femur in a knee replacement operation, the method comprising: performing a tibial cut on a tibia; performing soft tissue balancing based on a desired limb alignment; measuring an extension gap between the femur and said tibial cut while in extension; measuring a flexion gap between the femur and the tibial cut while in flexion; calculating a distal cut thickness and a posterior cut thickness for the femur using the extension gap and the flexion gap and taking into account a distal thickness and posterior thickness of a femoral implant; and performing said femoral cut according to the distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Provisional tibial prosthesis system
ActiveUS20120158152A1Reduce in quantityAdjustable spacingJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringTibiaKnee surgery
The present disclosure provides a provisional tibial prosthesis system for a set of prosthetic knee joints for implantation in a natural knee, the provisional tibial prosthesis system including a bearing component and a bearing support, the spacing of the bearing component from the bearing support is adjustable to allow for representation of a variety of different sized final tibial prostheses. In this system, only one provisional bearing component corresponding to each level of constraint is needed and shims are used to adjust the spacing of the bearing component from the bearing support. The shims are slidably insertable between the bearing component and the bearing support in an anterior / posterior direction to allow for adjustment of the spacing of the bearing component from the bearing support. The number of provisional components needed during knee surgery is reduced and adjustment of the system only requires the knee joint to be distracted by a distance equal to the height of a particular shim.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Provisional tibial prosthesis system
ActiveUS8603101B2Reduce in quantityAdjustable spacingJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringKnee surgeryTibia
The present disclosure provides a provisional tibial prosthesis system for a set of prosthetic knee joints for implantation in a natural knee, the provisional tibial prosthesis system including a bearing component and a bearing support, the spacing of the bearing component from the bearing support is adjustable to allow for representation of a variety of different sized final tibial prostheses. In this system, only one provisional bearing component corresponding to each level of constraint is needed and shims are used to adjust the spacing of the bearing component from the bearing support. The shims are slidably insertable between the bearing component and the bearing support in an anterior / posterior direction to allow for adjustment of the spacing of the bearing component from the bearing support. The number of provisional components needed during knee surgery is reduced and adjustment of the system only requires the knee joint to be distracted by a distance equal to the height of a particular shim.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Tools for femoral resection in knee surgery
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
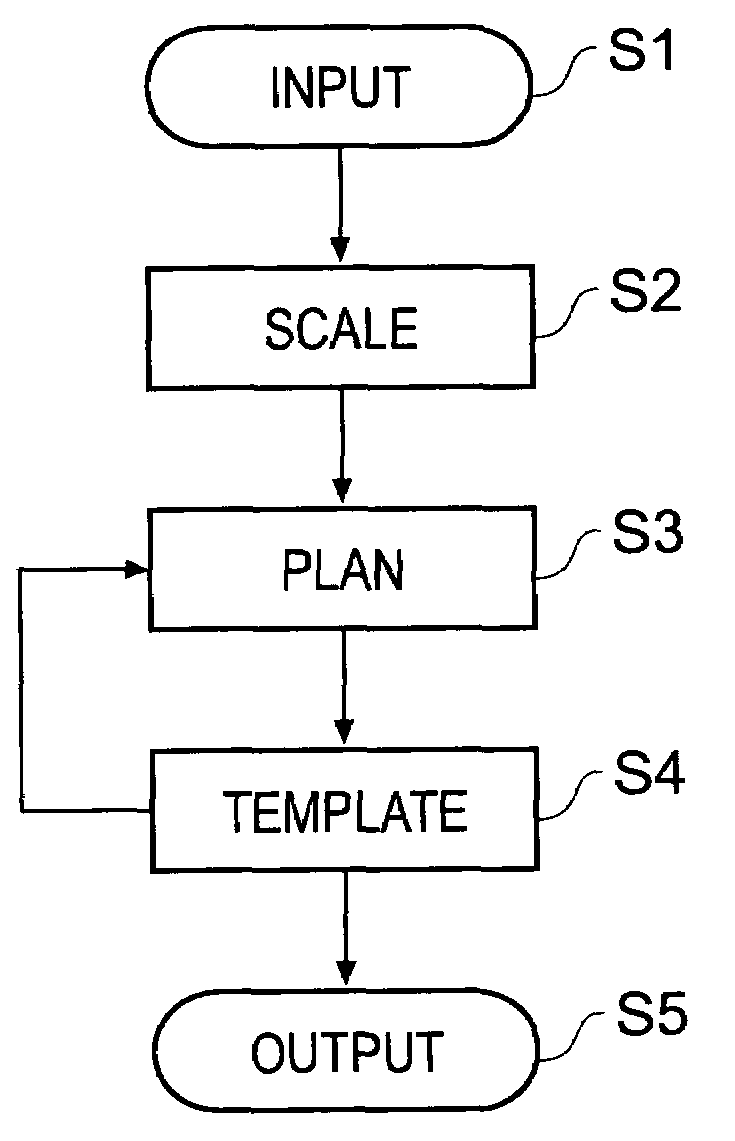
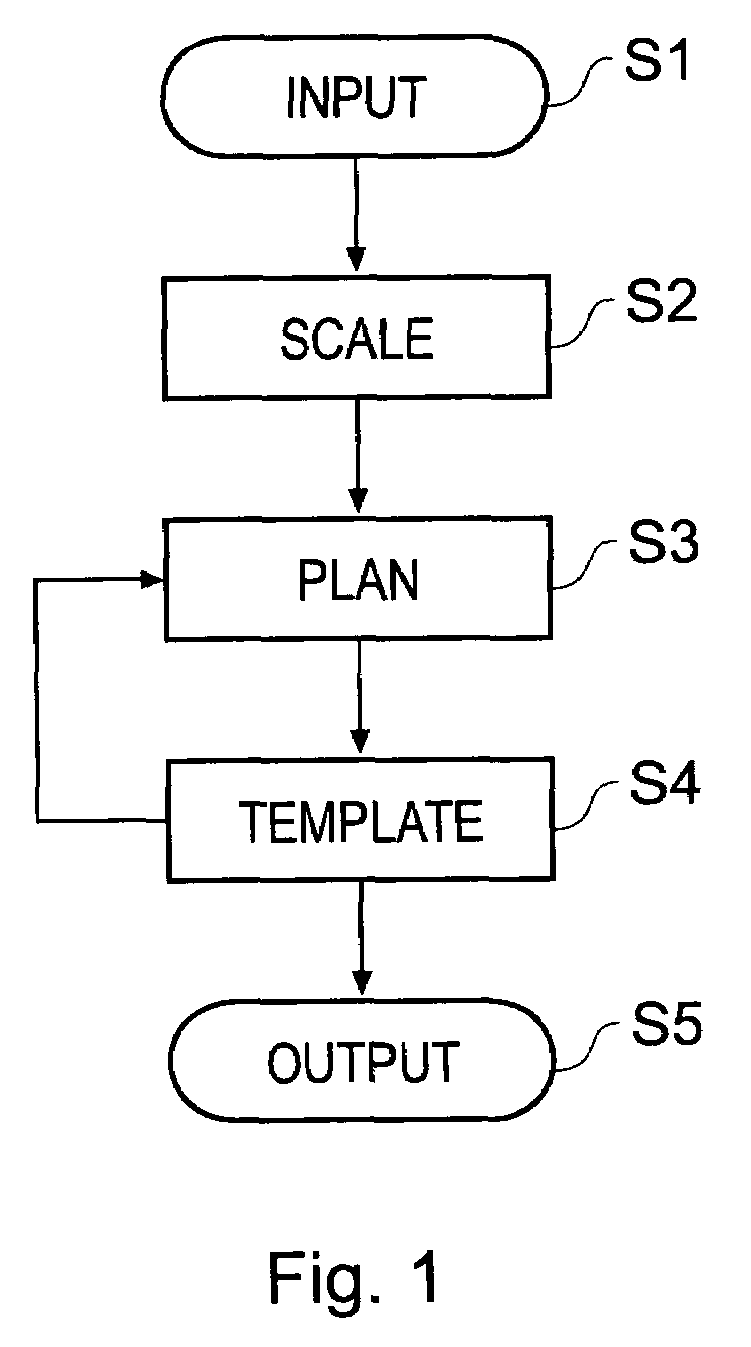
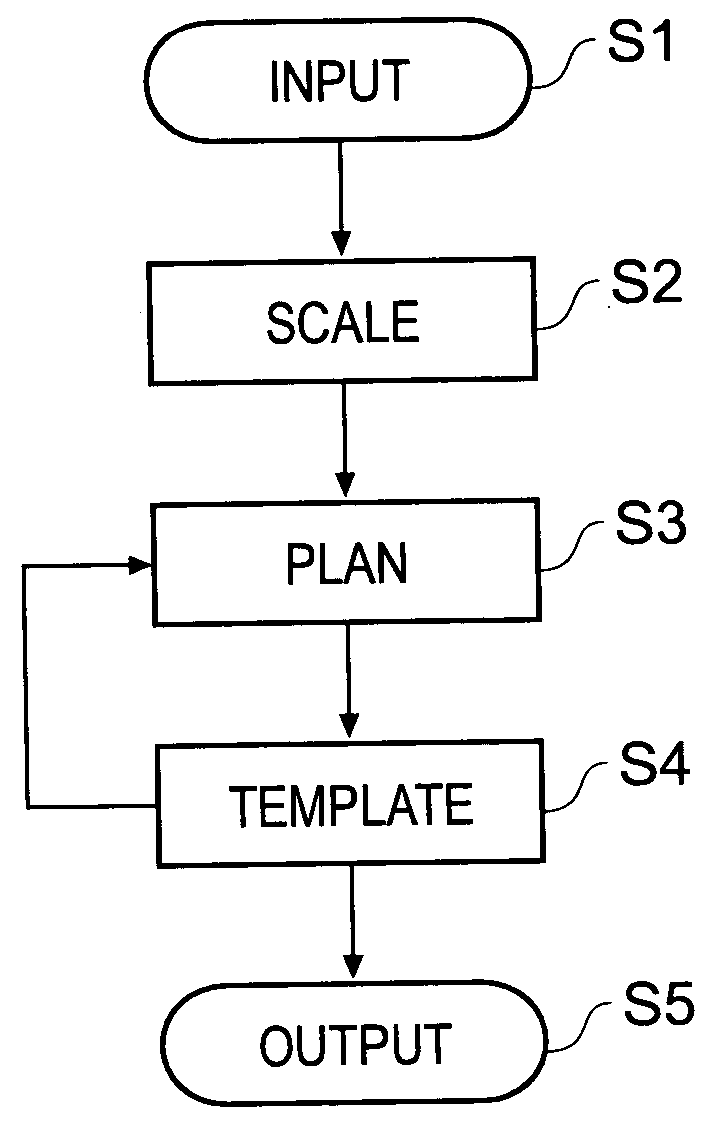
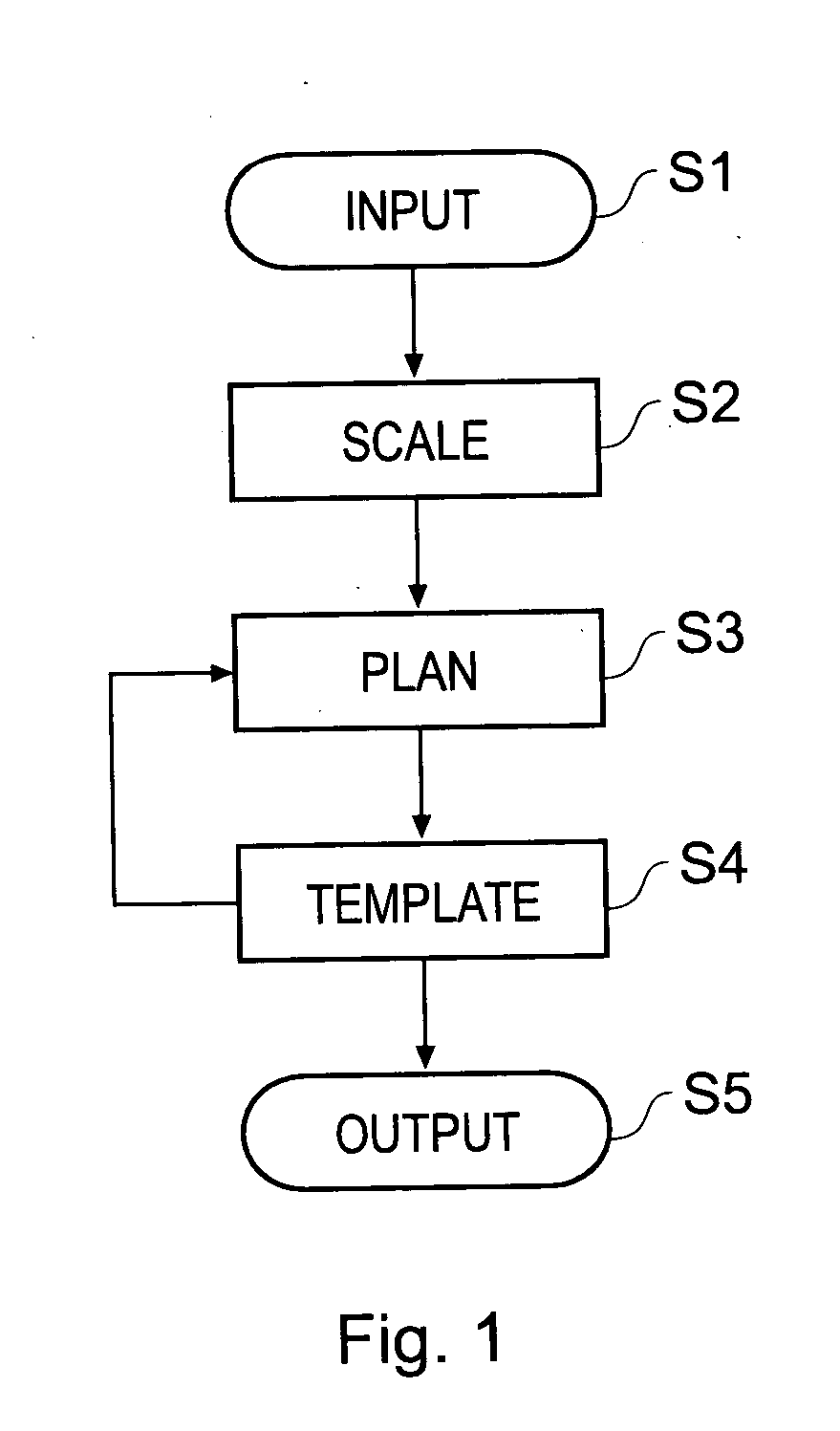
Orthopaedic surgery planning
ActiveUS20050054917A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsX-rayThe Internet
A computer-implemented method of planning orthopaedic surgery comprises providing a library of templates representing orthopaedic prostheses, displaying and scaling one or more patient images such as X-ray images, allowing a user to reconfigure geometrical constructs displayed over the images to match the construct to anatomical features shown in the image; and selecting one or more templates from the library in accordance with parameters of the reconfigured constructs. The templates correspond to the orthopaedic prosthesis or prostheses which are most suitable for the patient. Hip replacement surgery can be planned using a single patient image. Knee surgery can be planned using two patient images showing different views of the anatomical features, in which case geometrical constructs for use with each view are provided. The library of templates is accessible via the Internet so as to be accessible by users in any location and readily updateable.
Owner:MERIDIAN TECH LTD
Unicondylar knee instrument system
The present invention provides for an apparatus for cutting a tibia, a stylus, an apparatus for cutting a femur, an apparatus for aligning a femoral cutting guide, and an ankle clamp in support of a unicondylar knee surgery. The present invention further provides for a method of preparing a femoral condyle of a femur for the implantation of a unicondylar femoral knee implant. The apparatus for cutting a tibia includes a unicondylar tibial resection guide that is adjustably connectable to a unicondylar tibial alignment guide and configured to operate concurrently with the tibial alignment guide. The apparatus for cutting a femur includes a spacer block and a cutting guide configured to operate concurrently with the spacer block.
Owner:ARTHREX
Femoral guide for knee surgery
InactiveUS20130226185A1Promote balance between supply and demandSuture equipmentsOperating tablesKnee surgeryBody joints
A joint replacement kit for use in a joint replacement procedure replacing a portion of a body joint. The kit includes a cutting guide and a trial component wherein the cutting guide and trial component are packaged together. There is also provided a method for replacing a portion of a body joint. The method includes providing a joint replacement kit having a cutting guide and a trial component, positioning the cutting guide against an end portion of a bone, cutting the end portion of the bone with a cutting instrument, positioning the trial component to the cut end portion of the bone, and disposing of the cutting guide and trial component.
Owner:BONUTTI SKELETAL INNOVATIONS
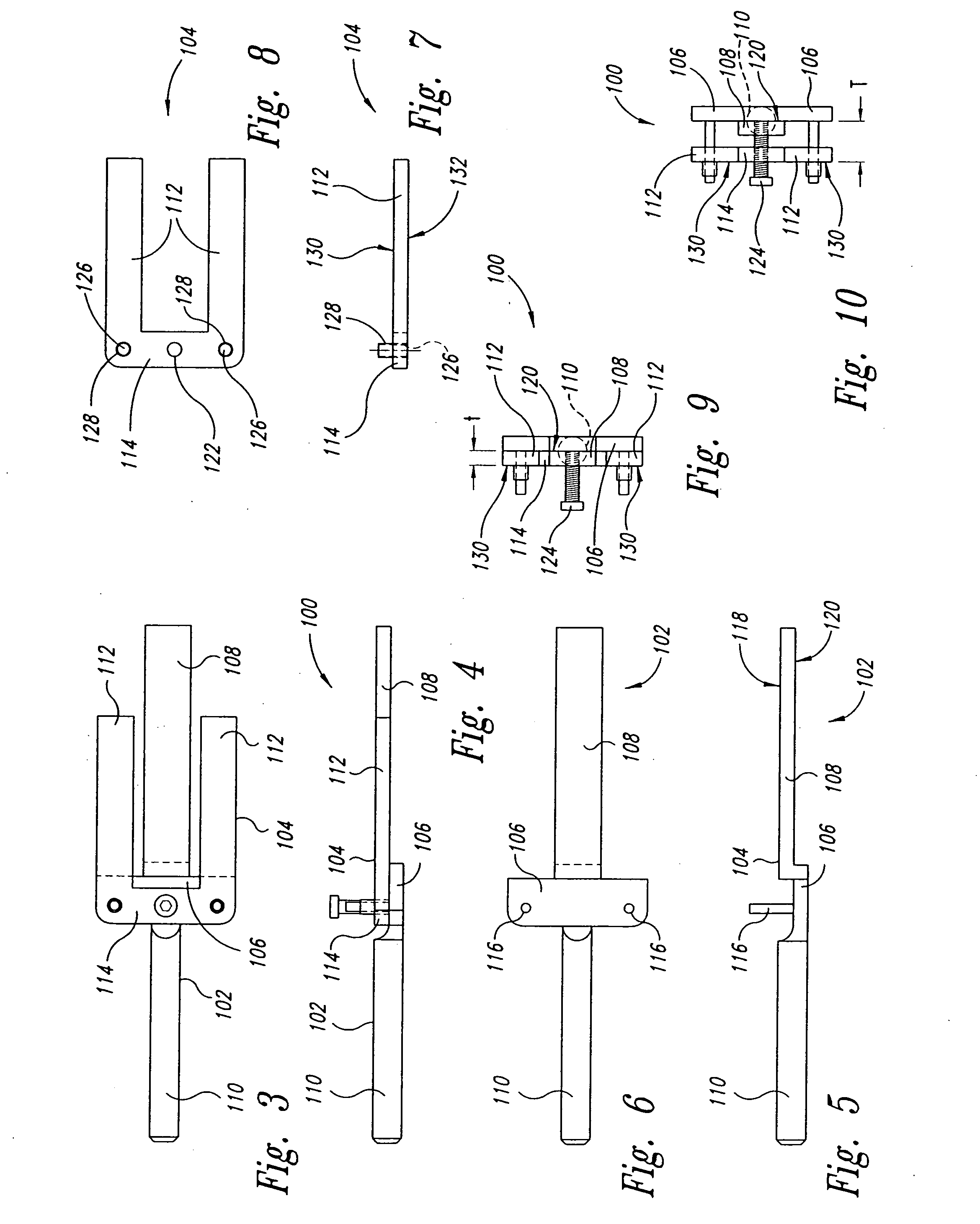
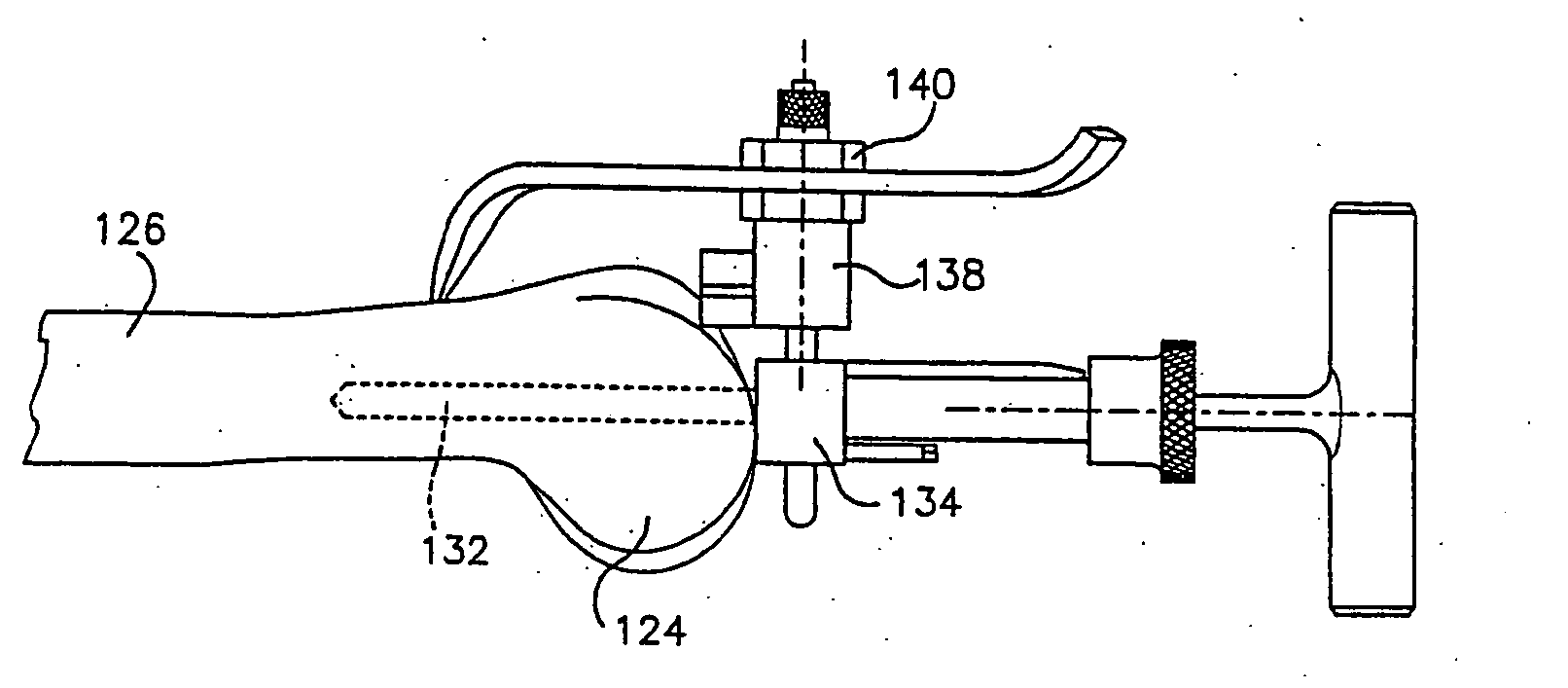
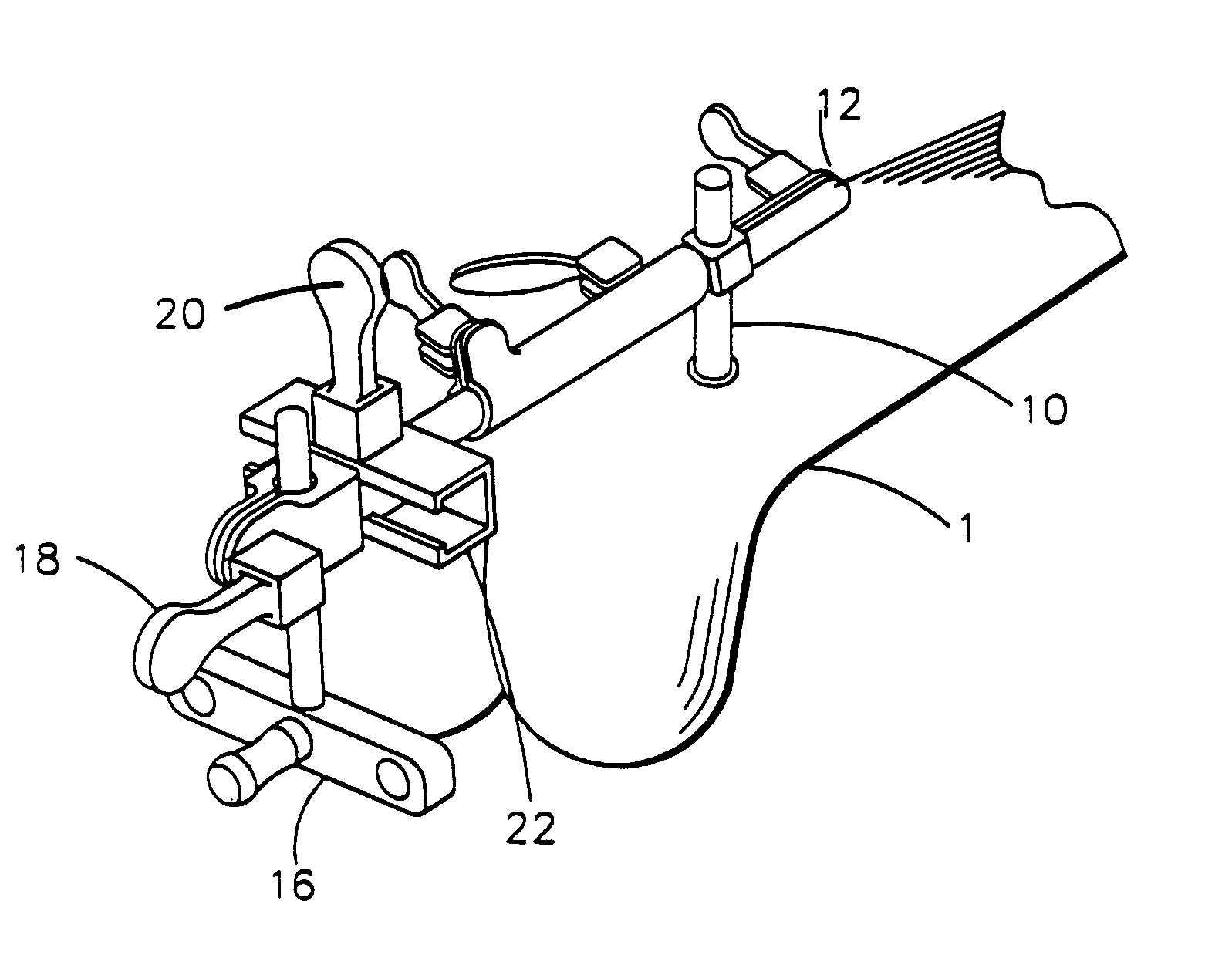
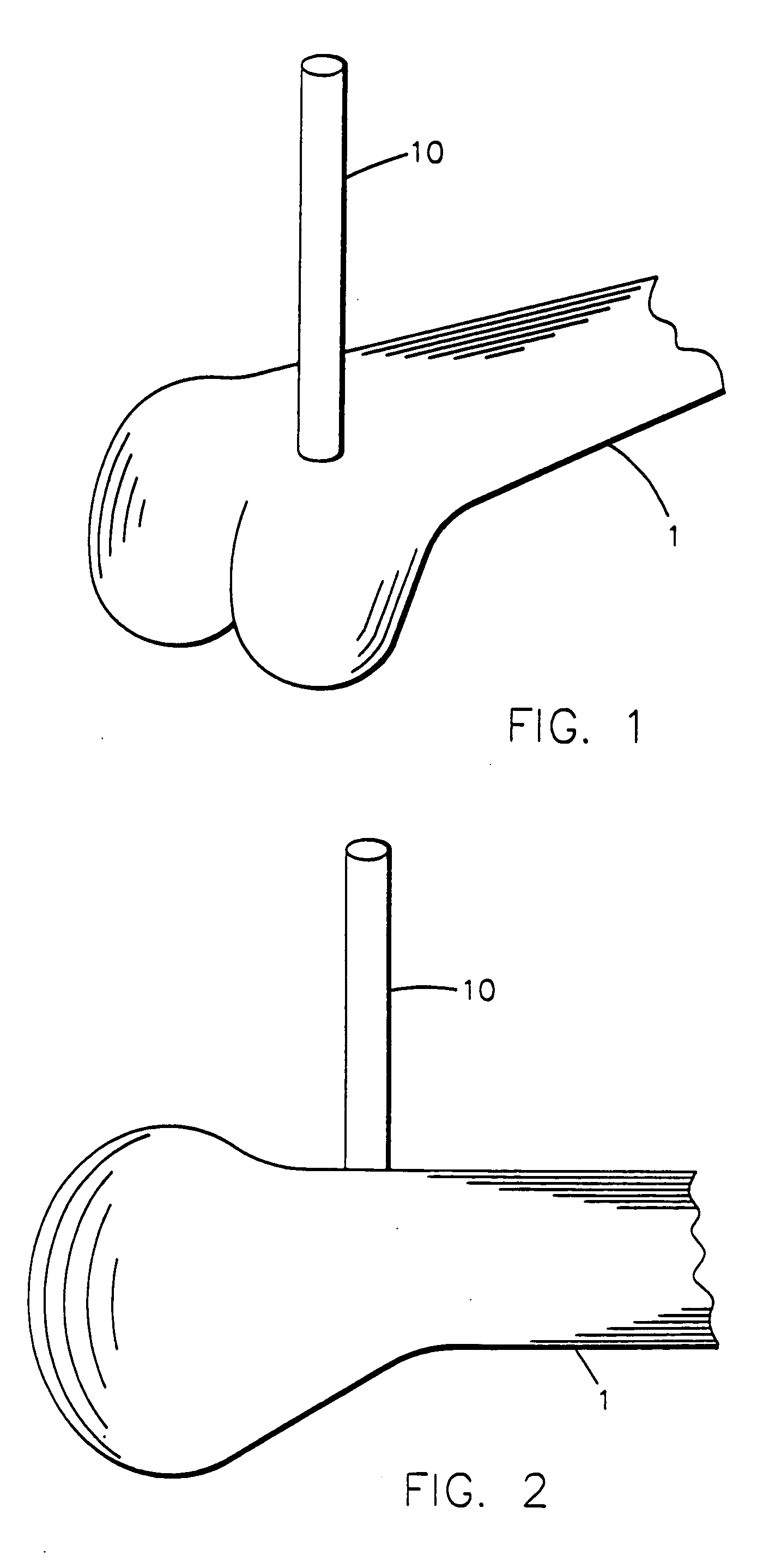
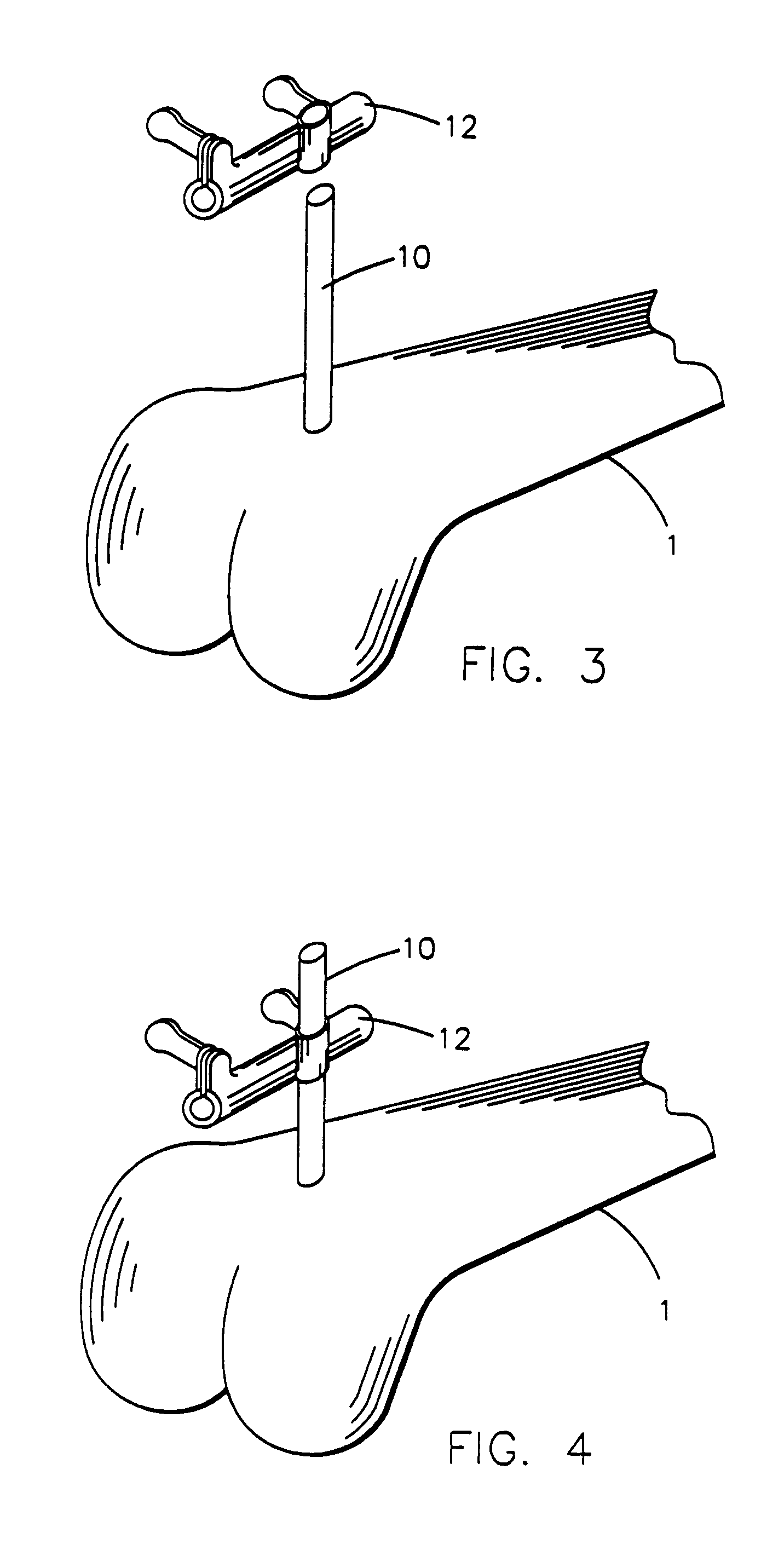
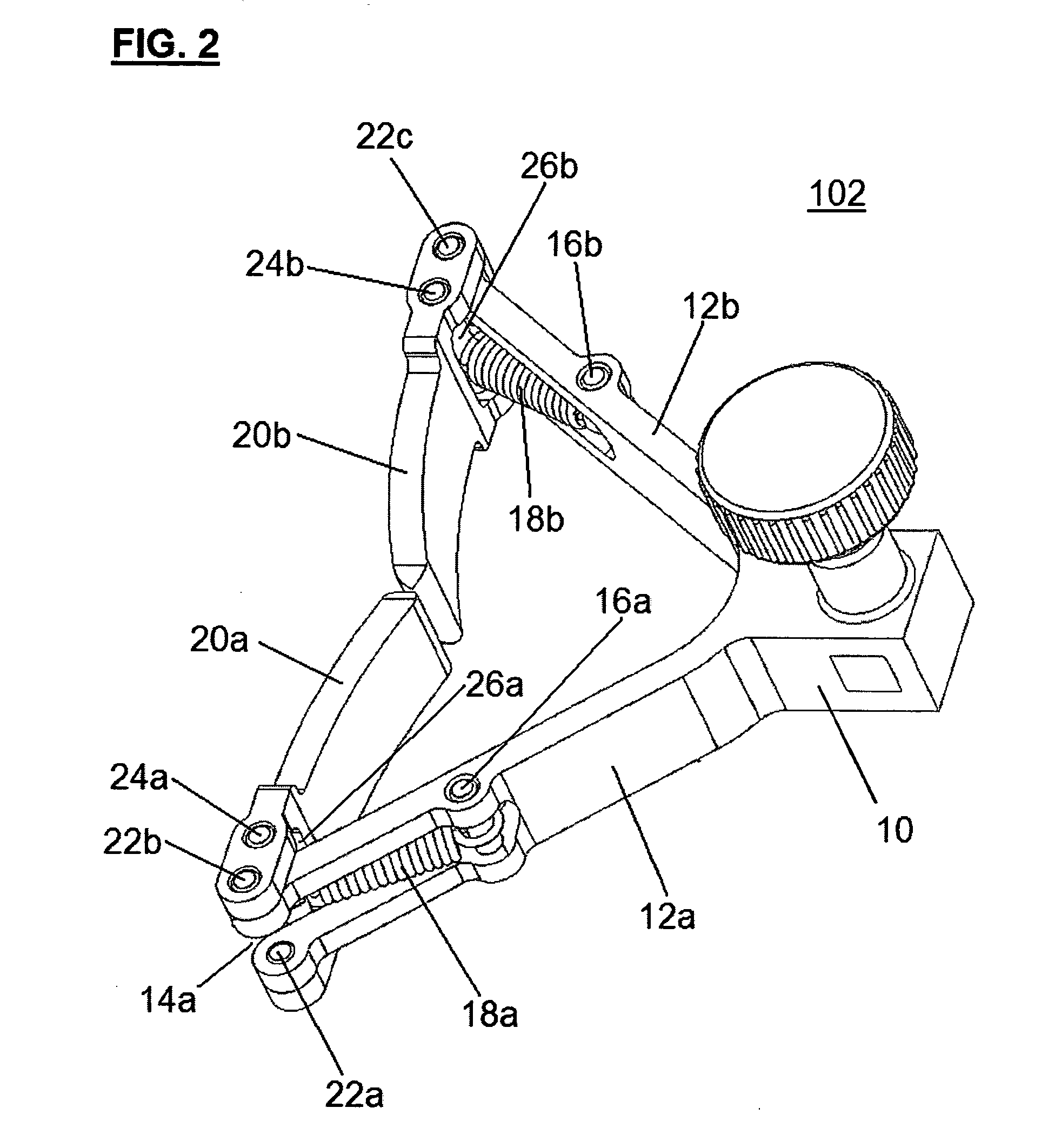
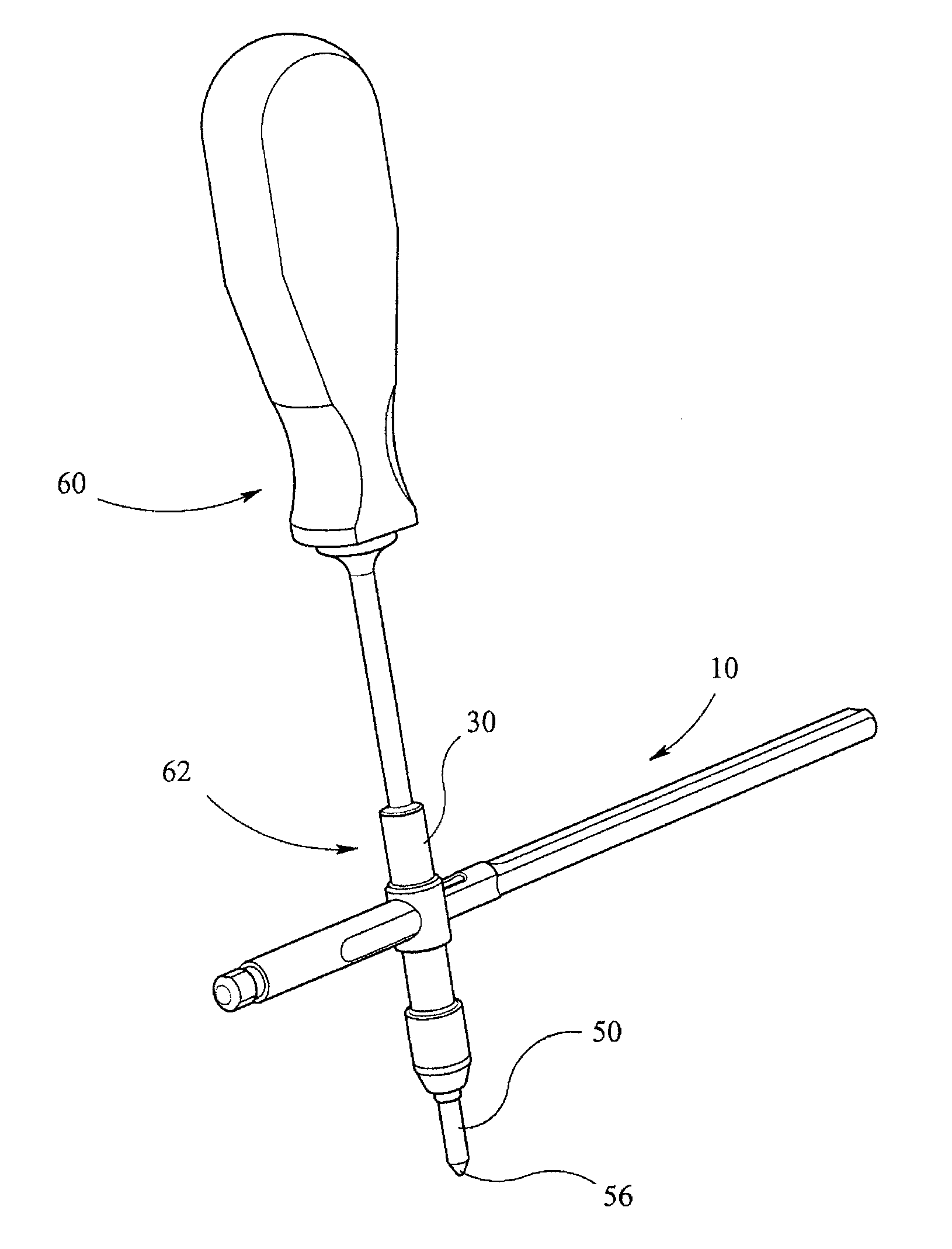
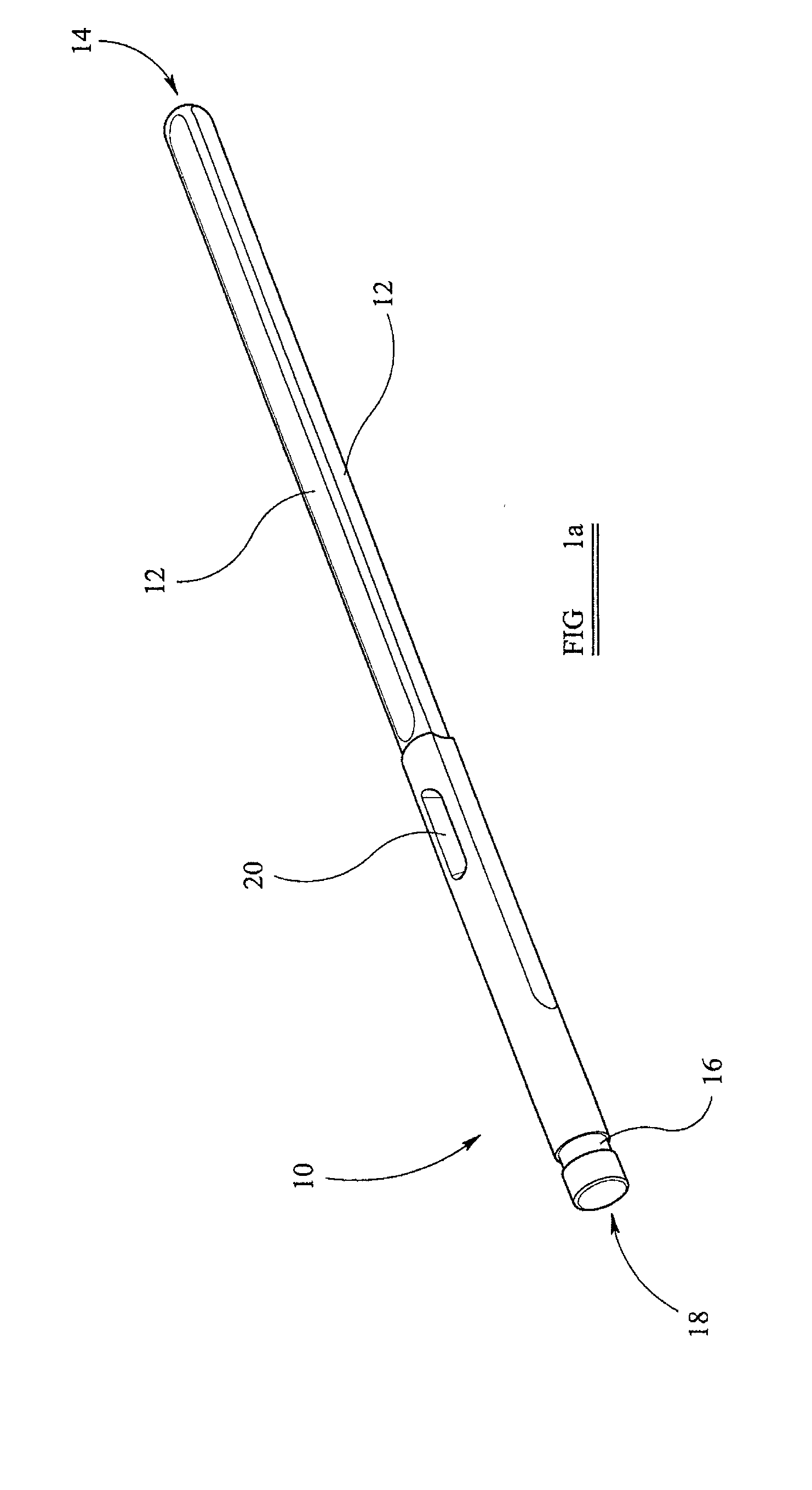
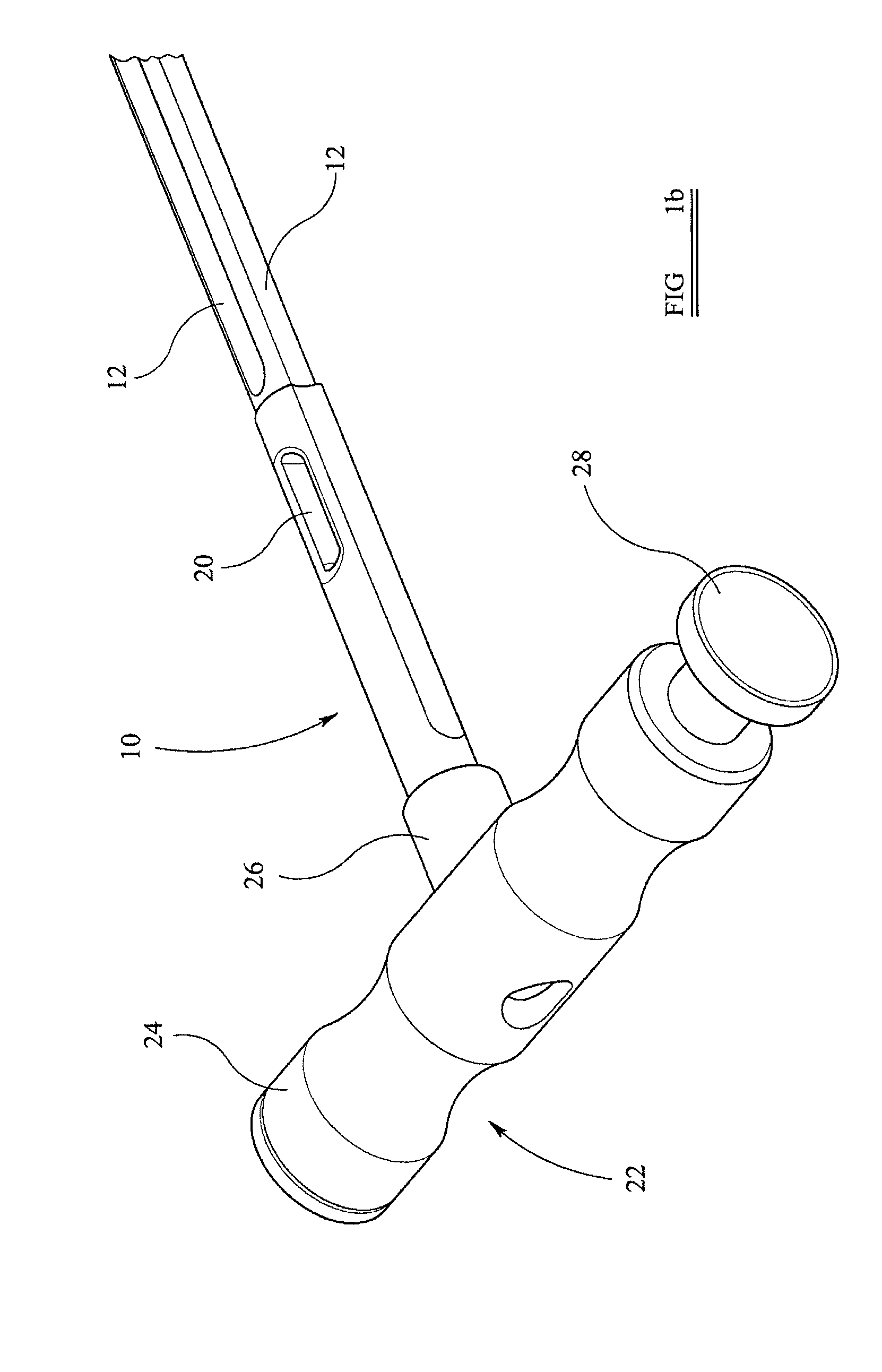
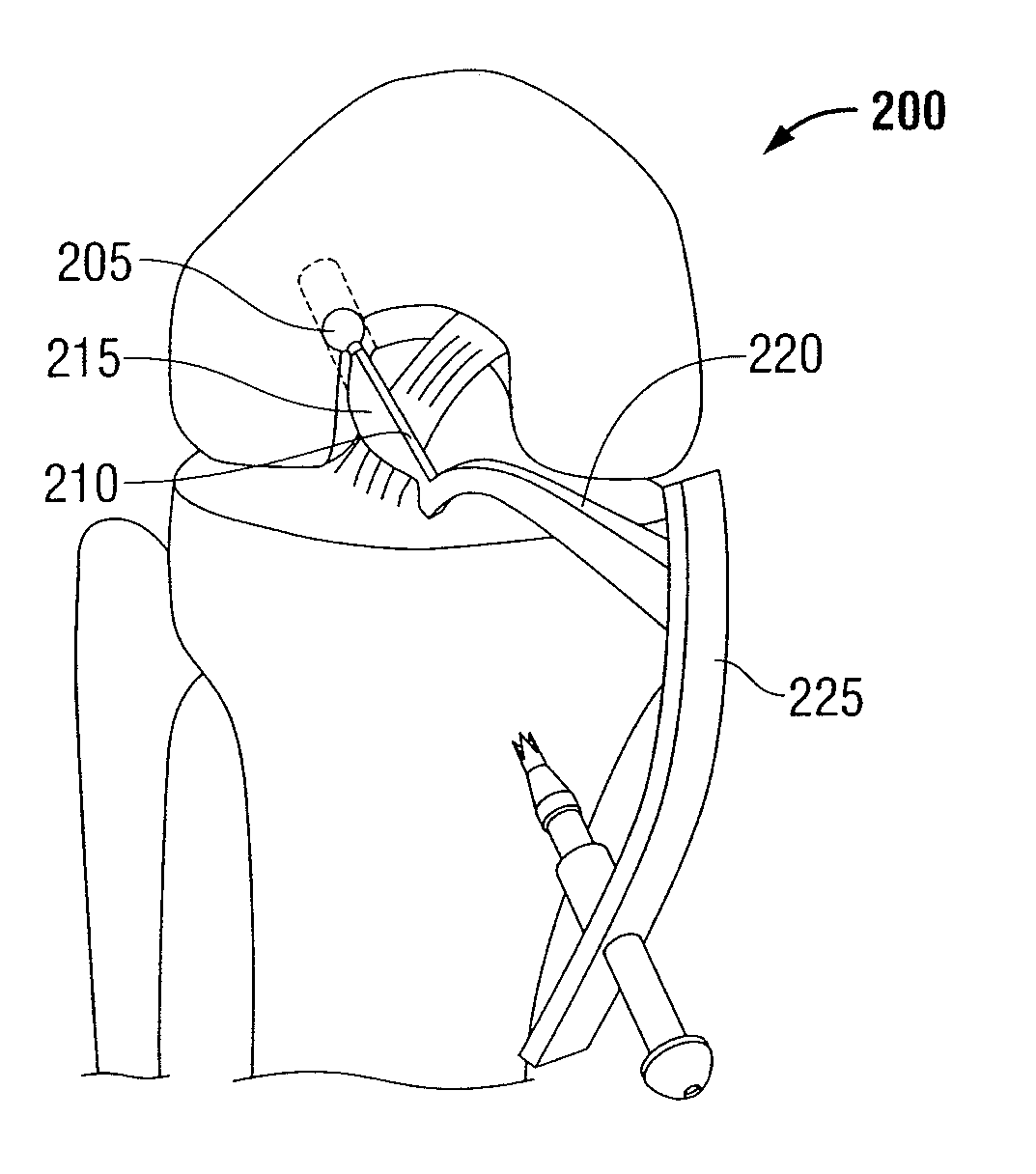
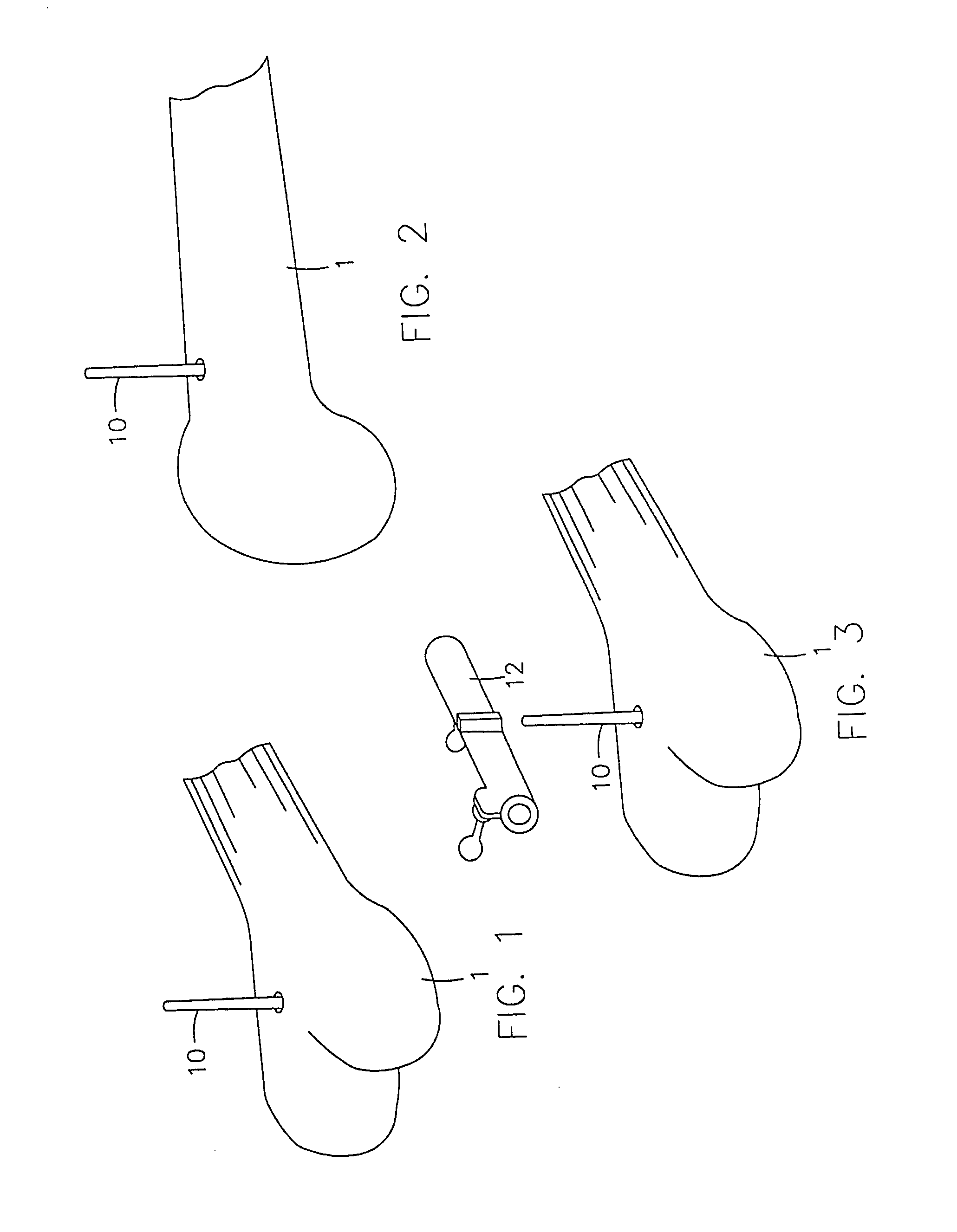
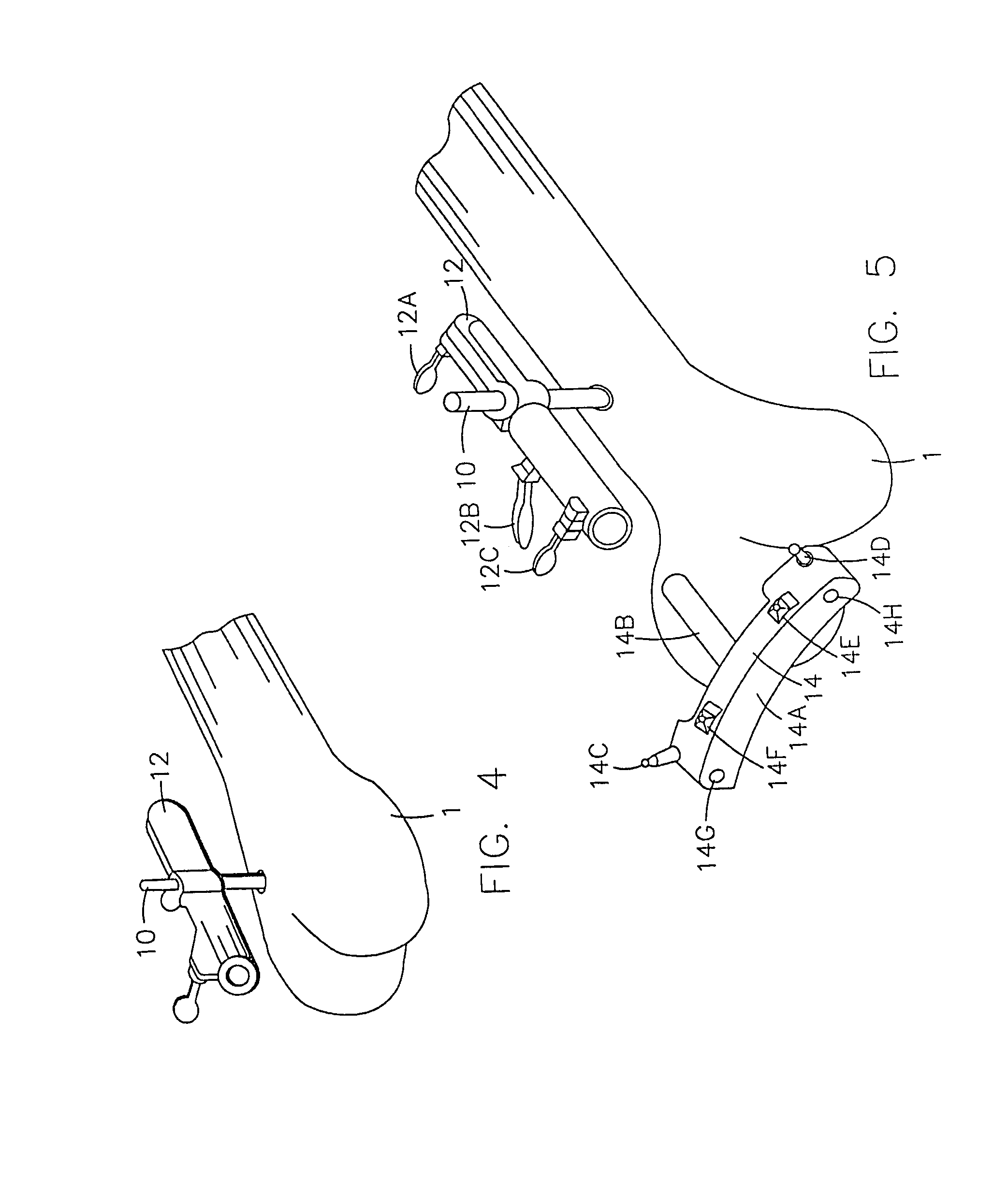
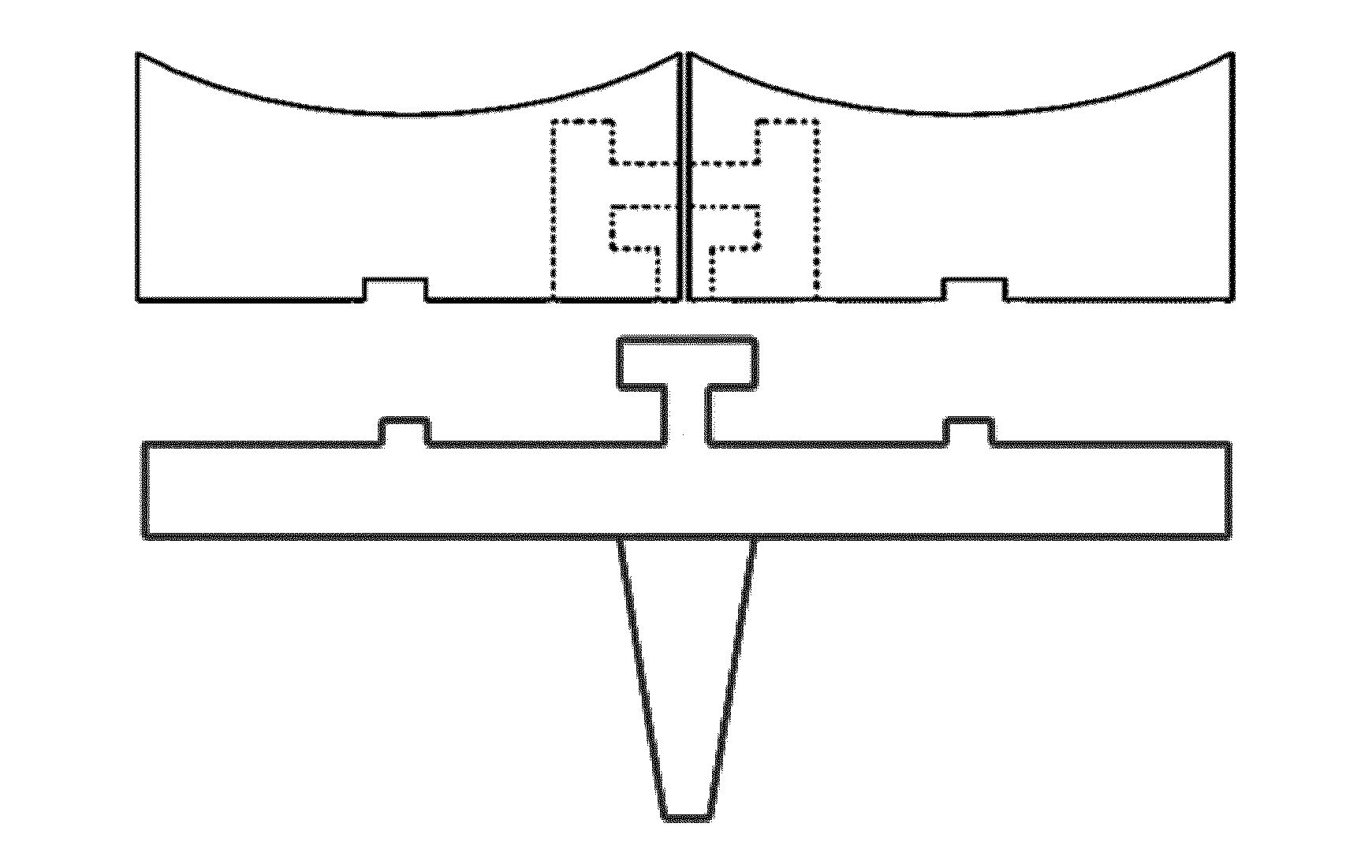
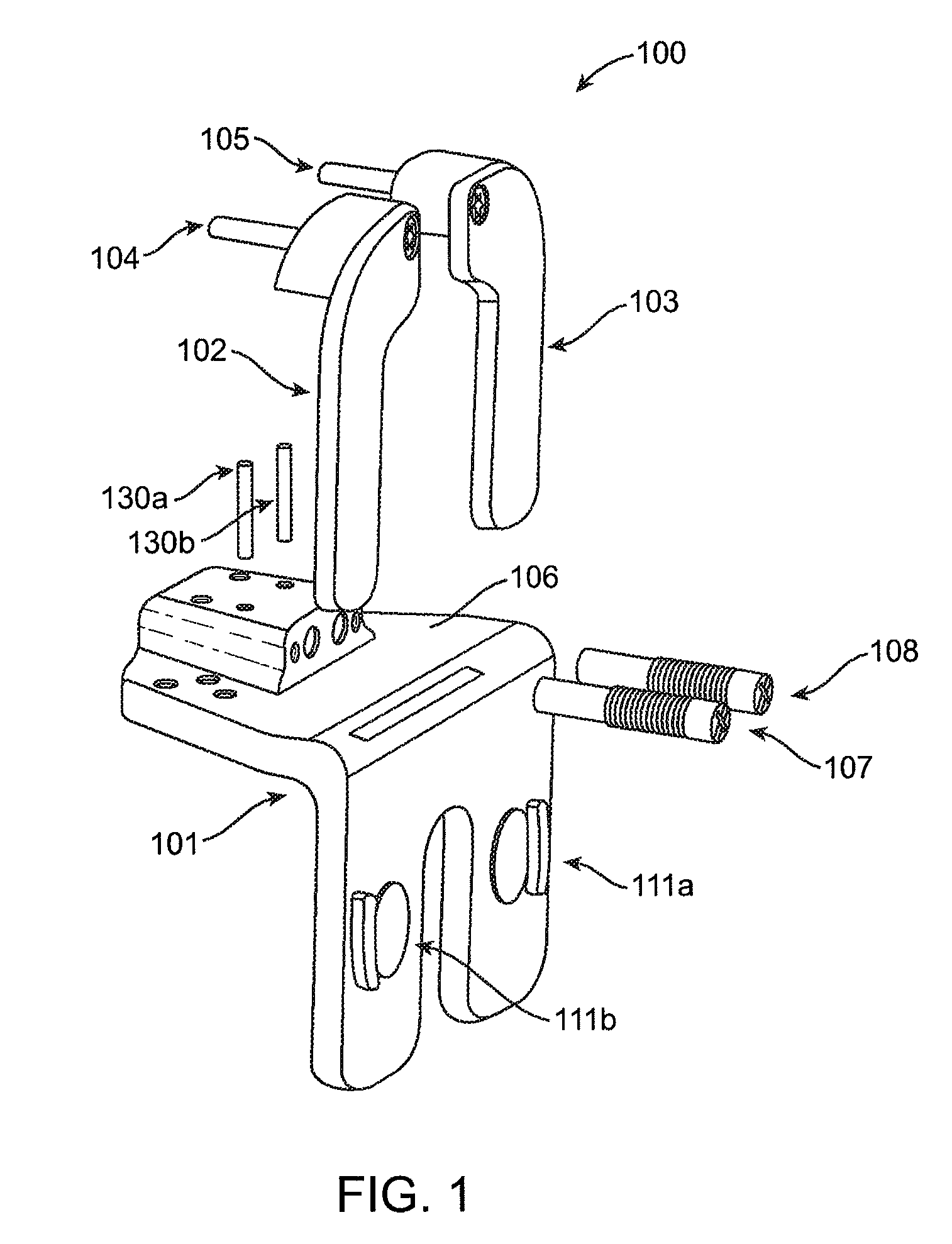
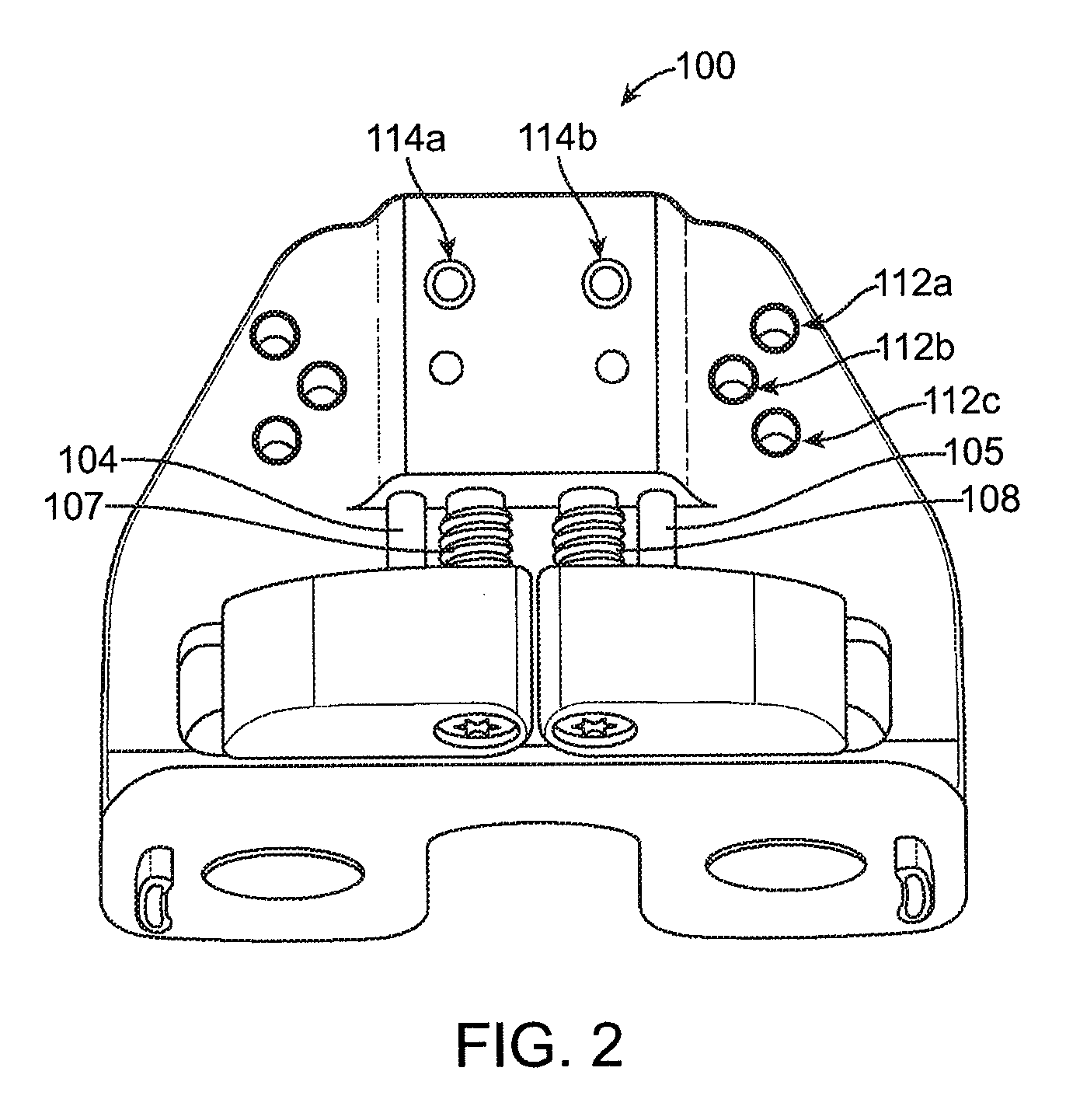
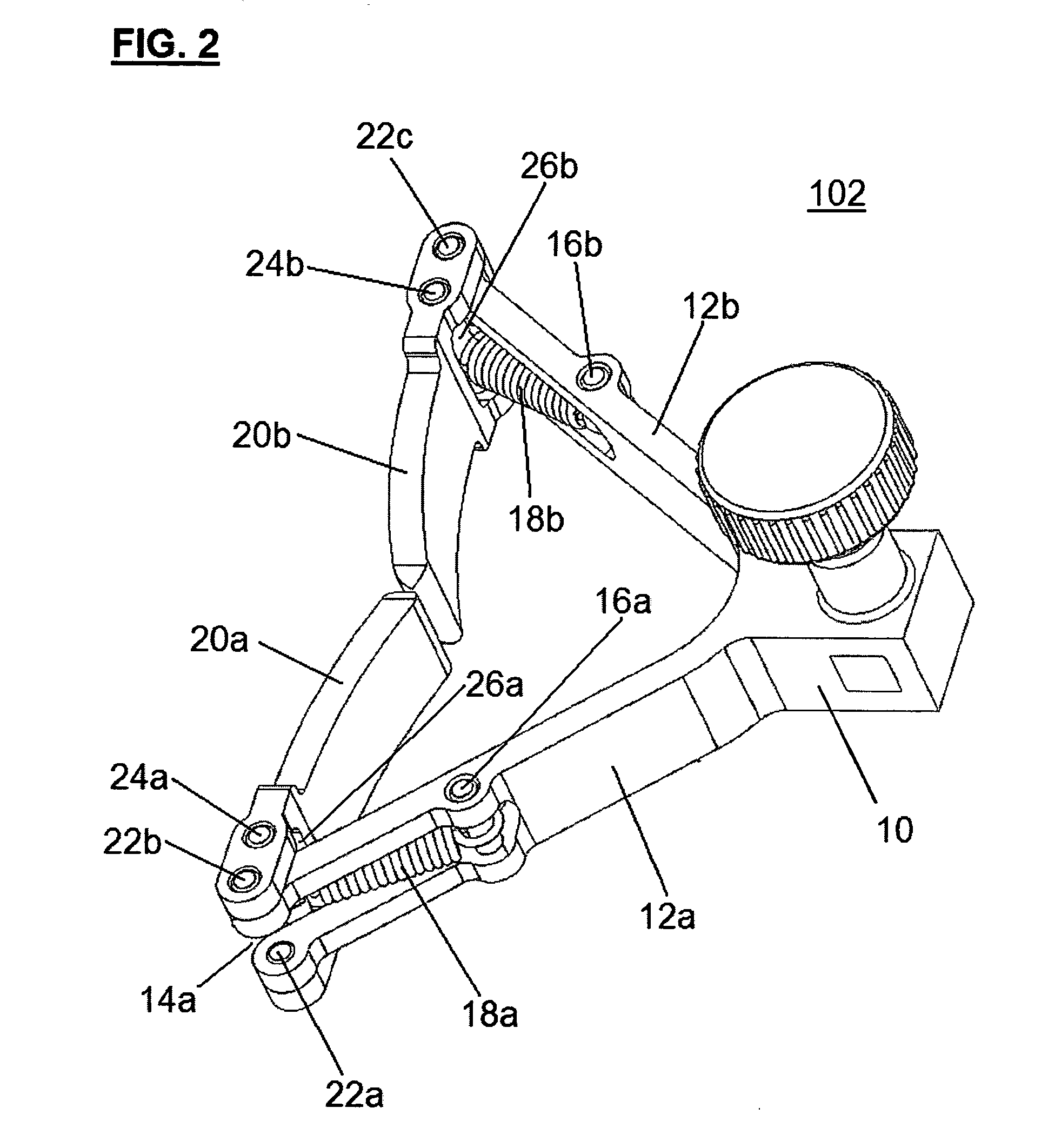
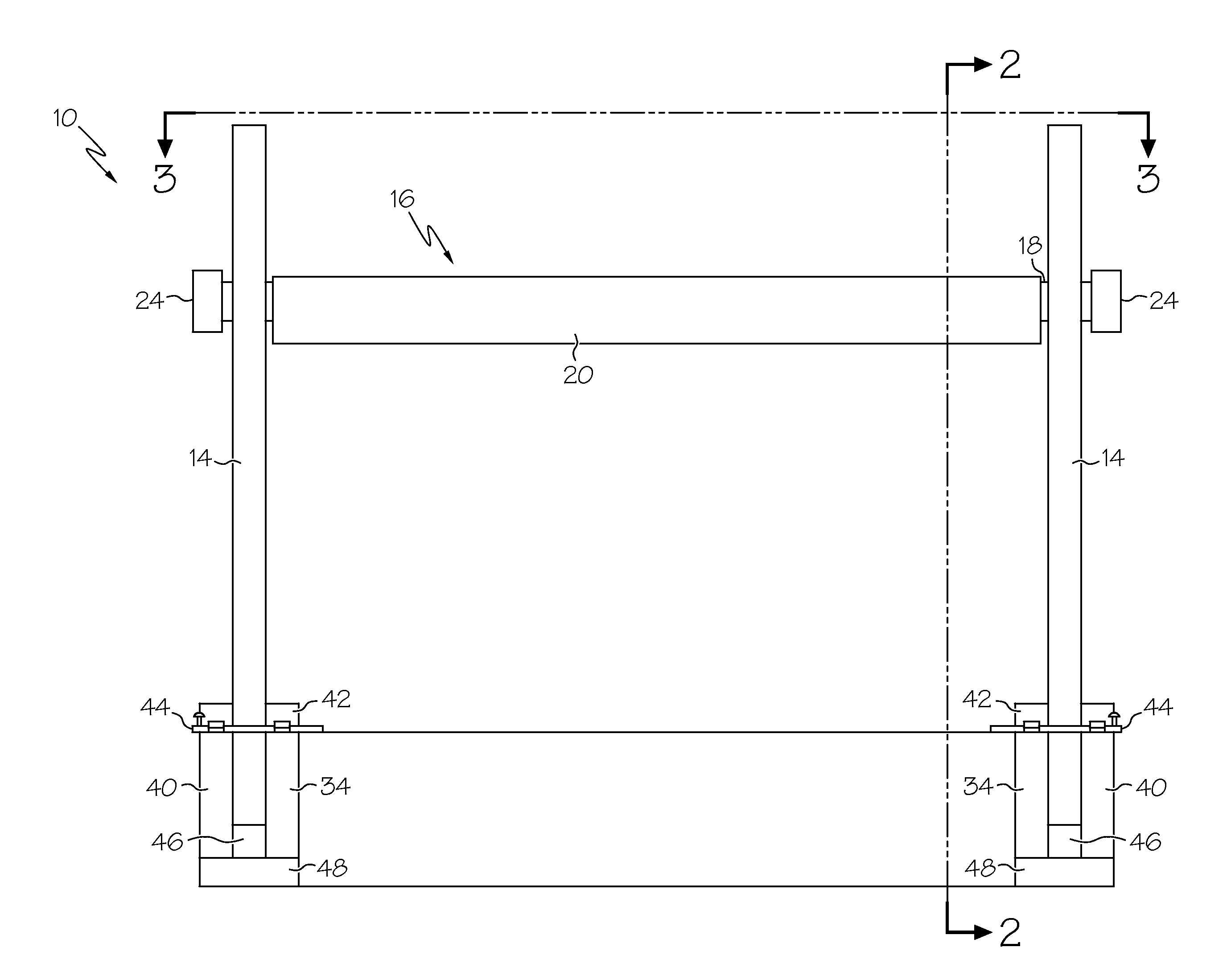
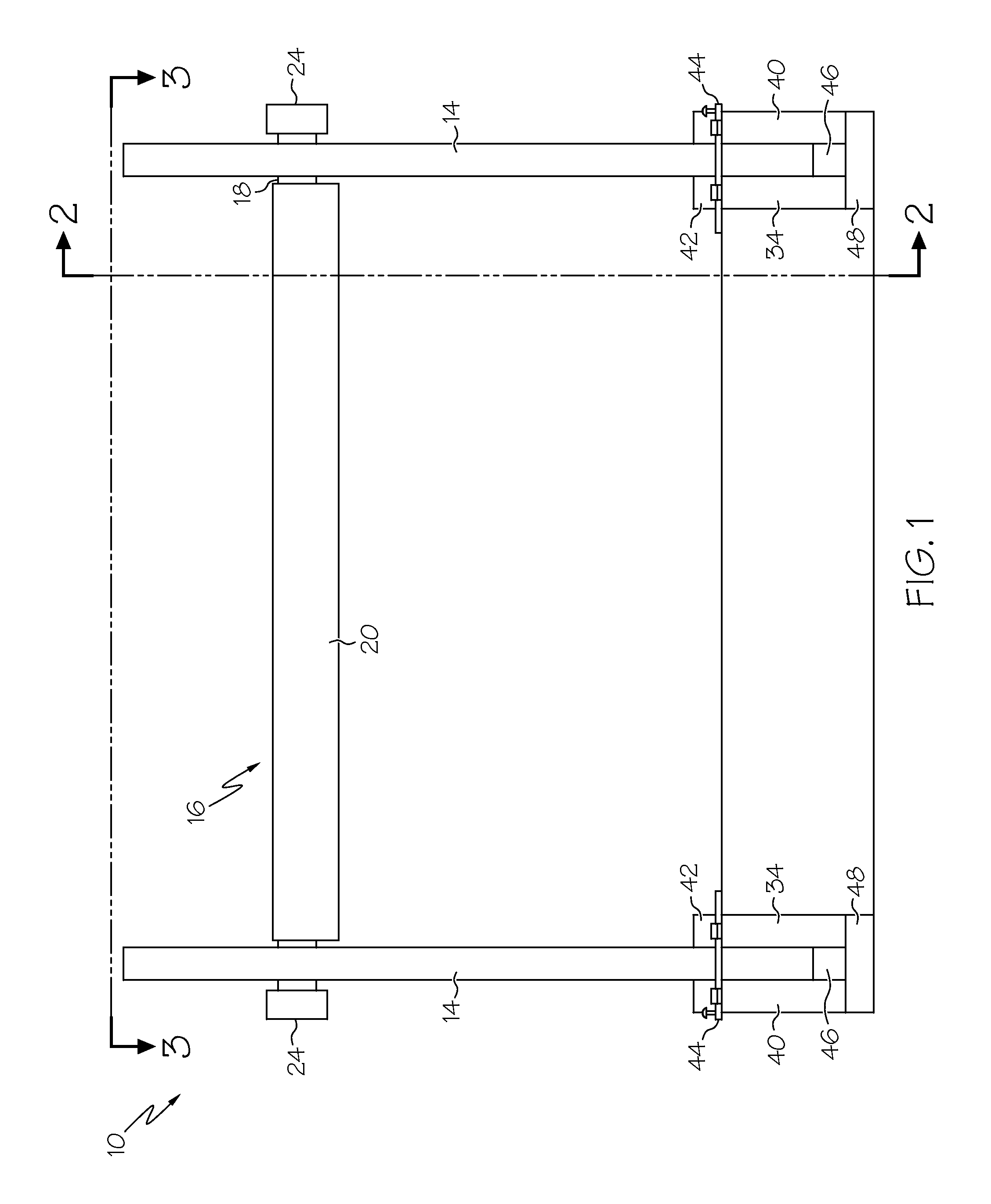
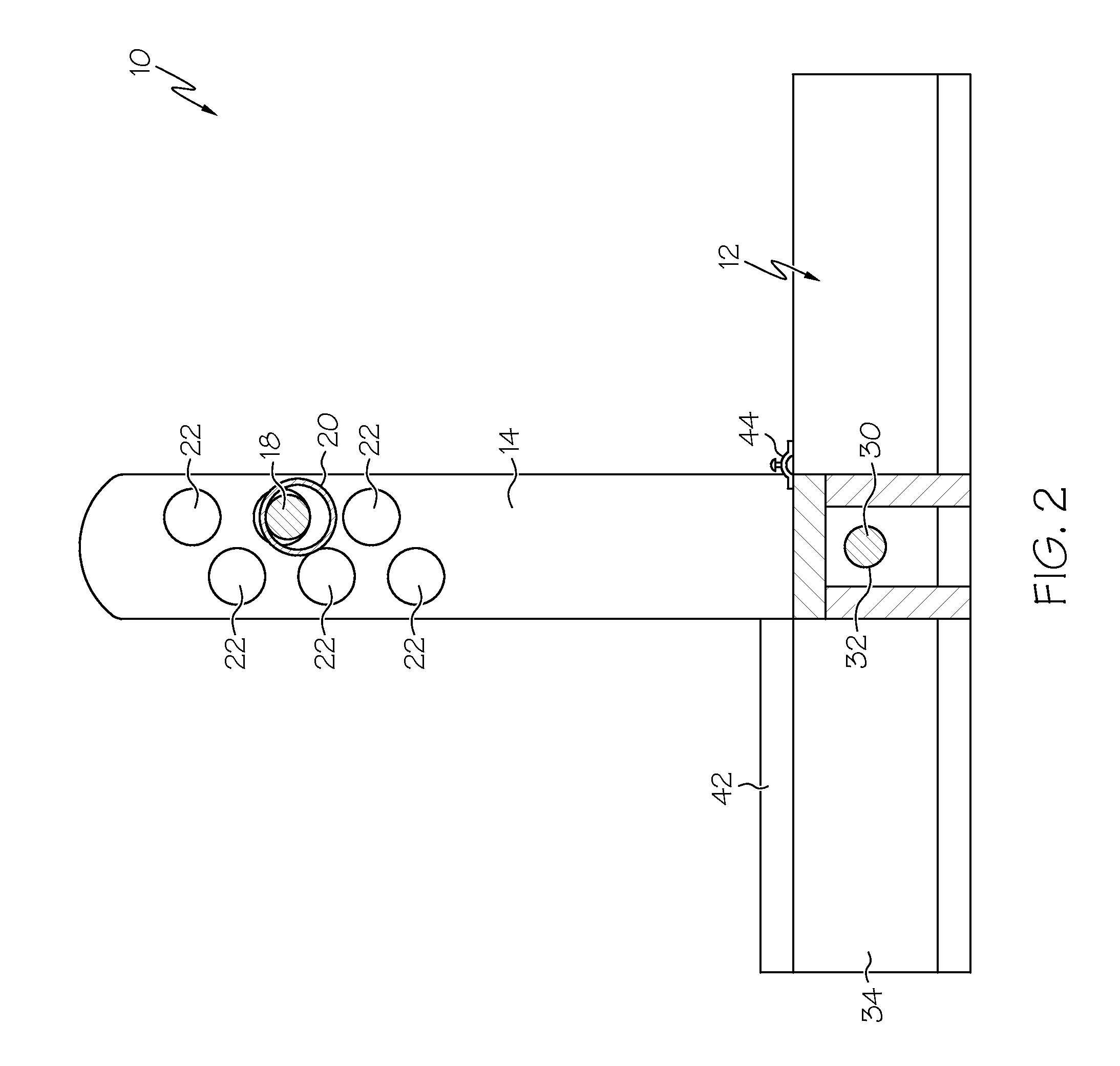
Instrumentation for knee surgery
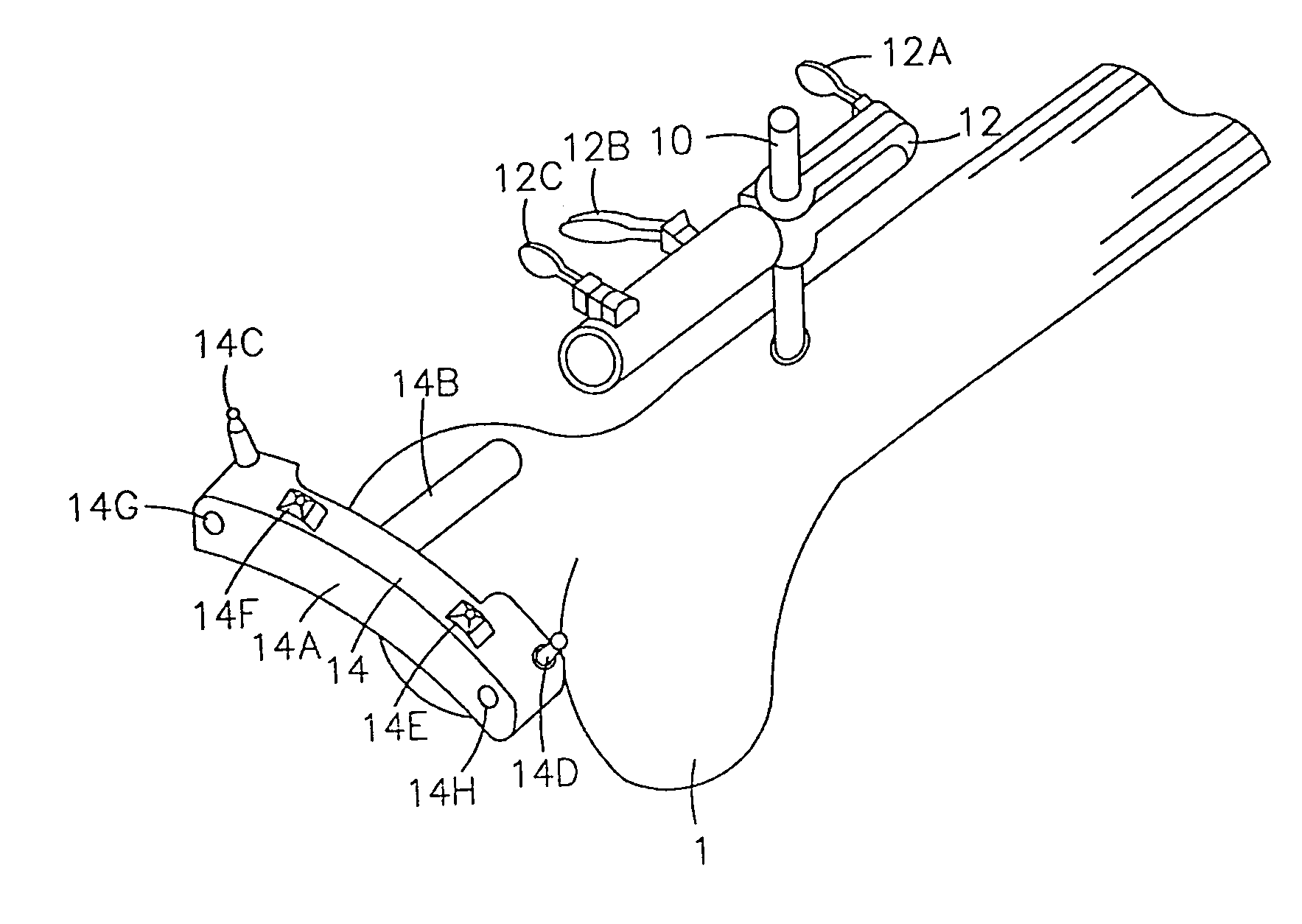
Instrumentation for use in knee surgery comprises an intramedullary rod (10) for insertion into an end of a femur (100) and a distraction device (62) coupleable to the intramedullary rod (10) and operable between the intramedullary rod (10) and the tibia for adjusting the tension of the collateral ligaments on either side of the knee. A cutting guide (70) is configured to locate over an intramedullary rod (10) that has been inserted into an end of a femur (100), such that the position of the cutting guide (70) relative to the intramedullary rod (10), and therefore the femur (100), is adjustable in at least the anterior-posterior direction. A kit for use in knee surgery is provided and a method of adjusting the tension of the collateral ligaments on either side of a knee is taught.
Owner:MCMINN DEREK JAMES WALLACE
Tibial guide for ACL repair having left/right docking configuration
A device for positioning a tibial tunnel during ACL reconstruction, the device that includes an elongated body having proximal and distal ends; and a distal arm extending from the distal end of the elongated body, a distal portion of the distal arm being configured for insertion into a pre-formed opening in a femur. The distal arm and the body are not aligned relative to each other when viewed from above. A pair of such devices, providing tunnel positioning for right and left knee surgeries, maybe provided in a set.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Porous Titanium Femoral Sleeves and Their Use in Revision Knee Surgery
The invention concerns monolithic foam sleeves that comprises titanium or titanium alloy foam having a porosity of 50 to 85% and possess a proximal end, a distal end, an interior wall that defines an interior channel and extends from the proximal end to the distal end; and a terraced outer surface that tapers such that said sleeve is widest at the distal end and most narrow at the proximal end.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
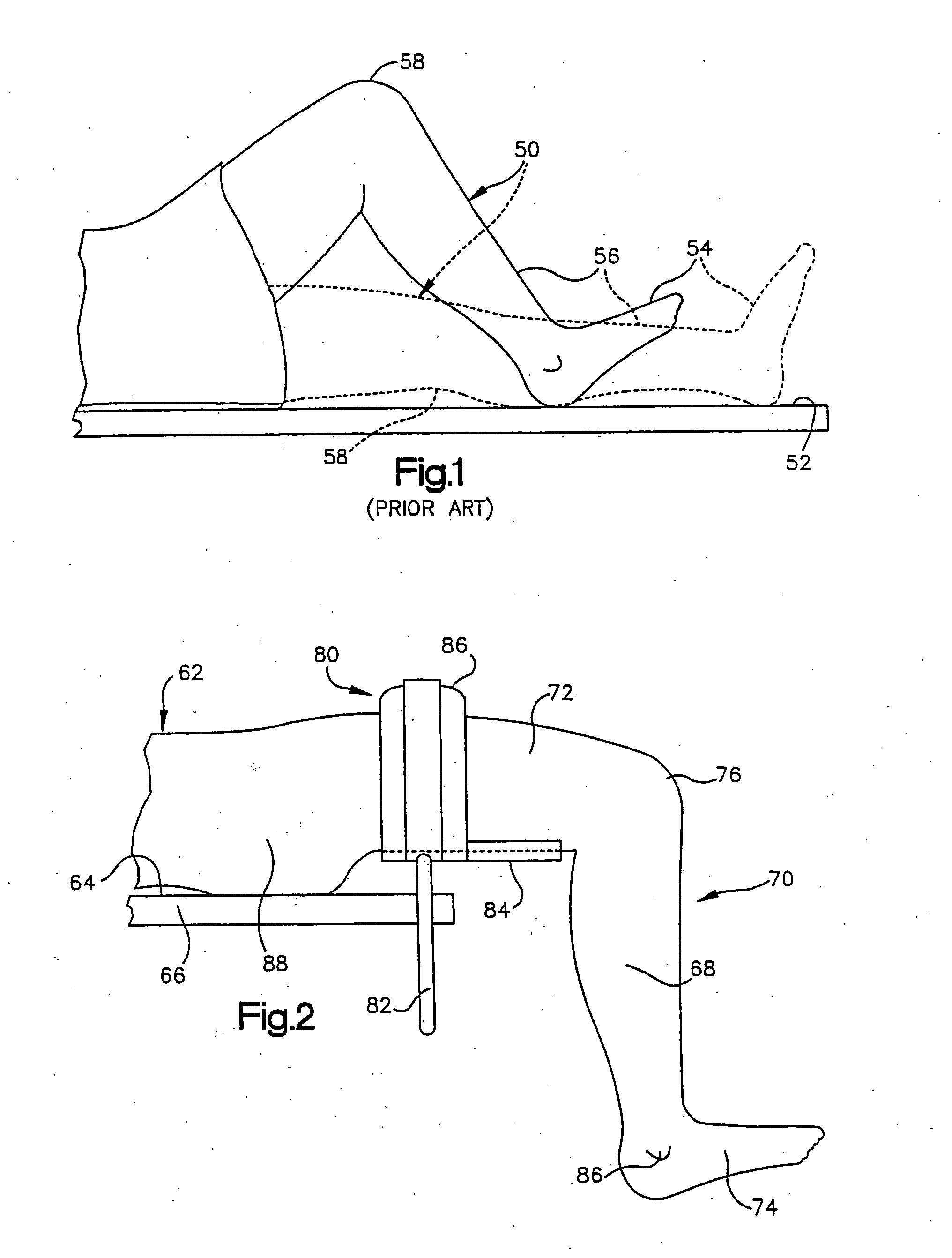
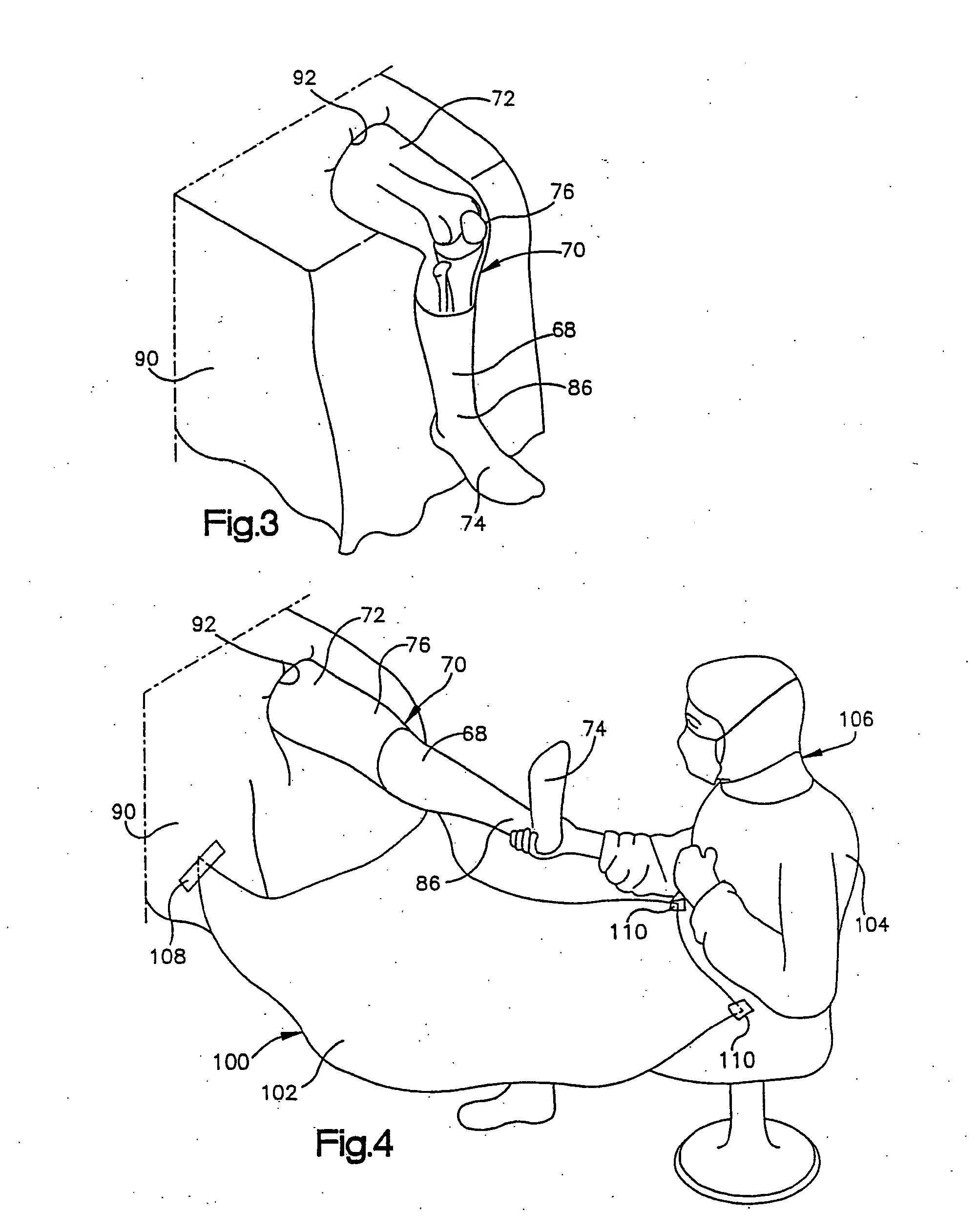
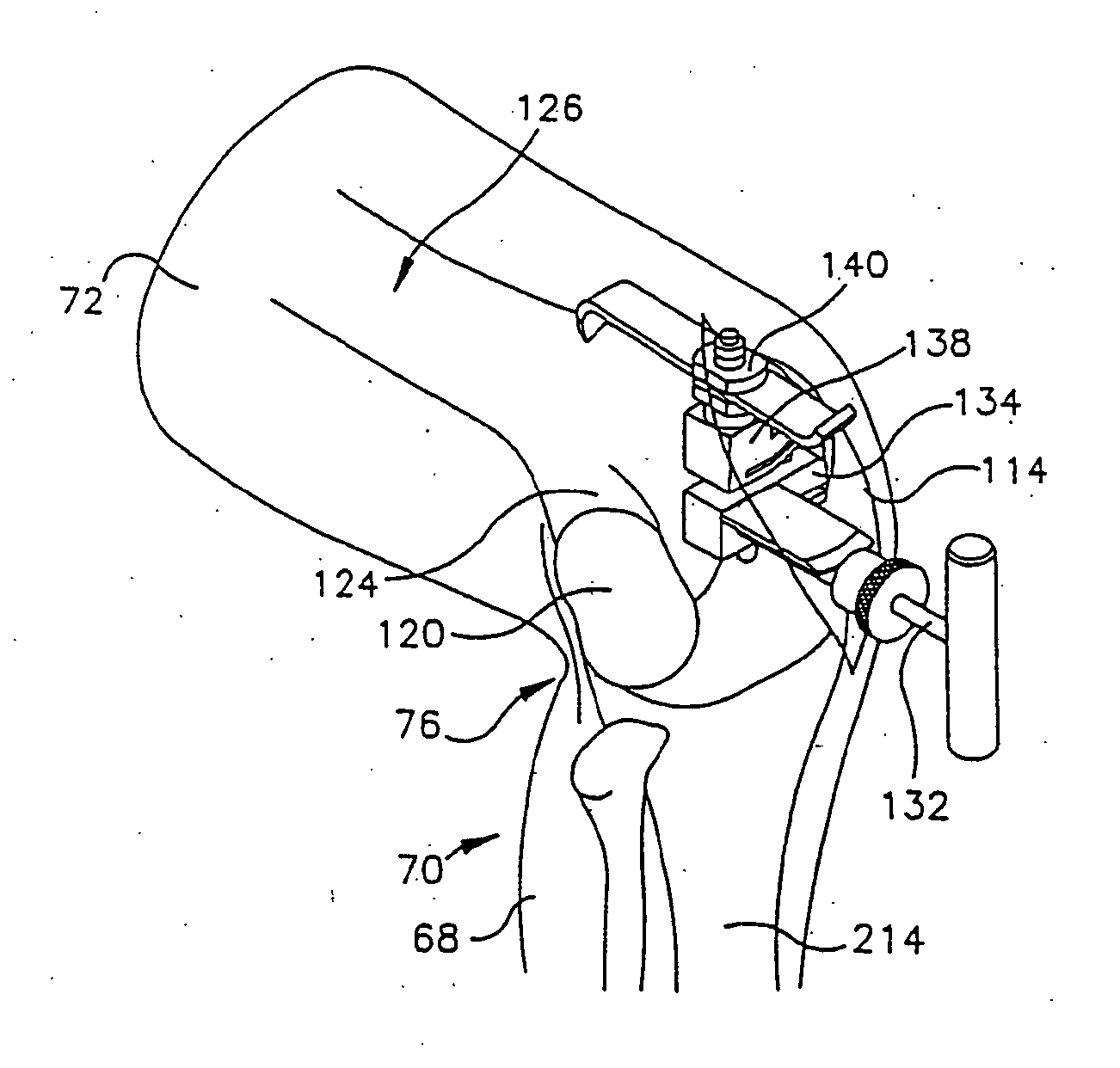
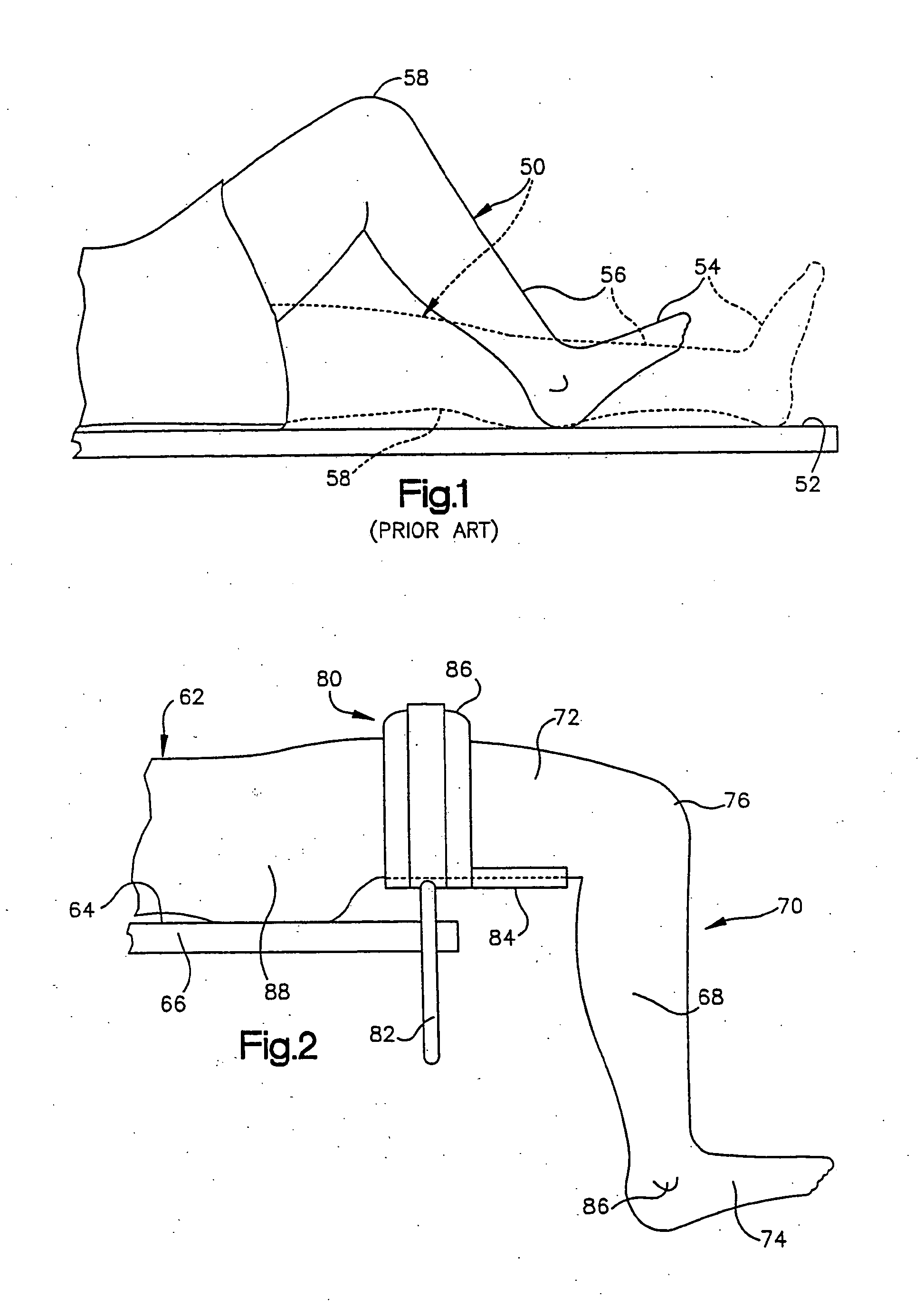
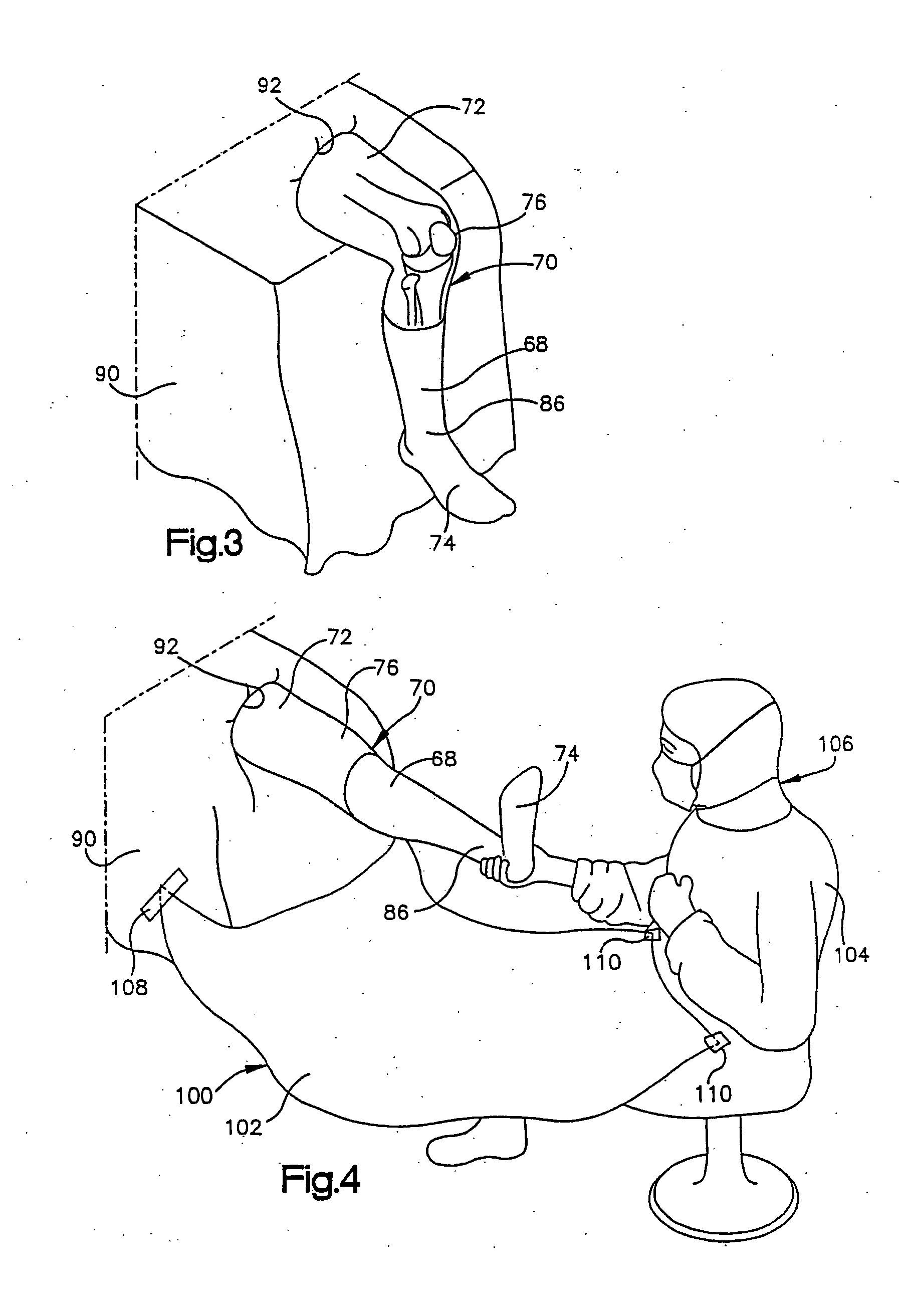
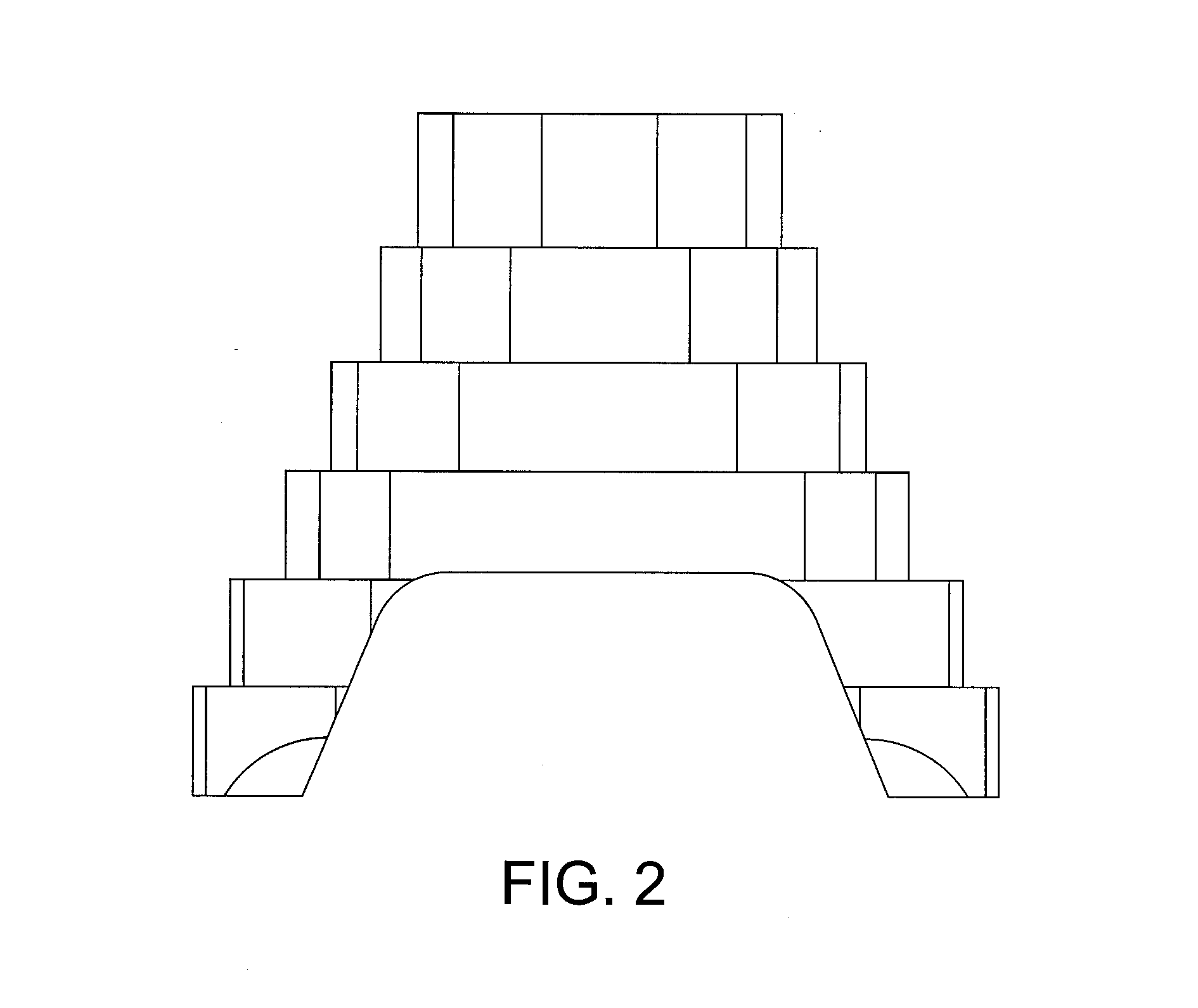
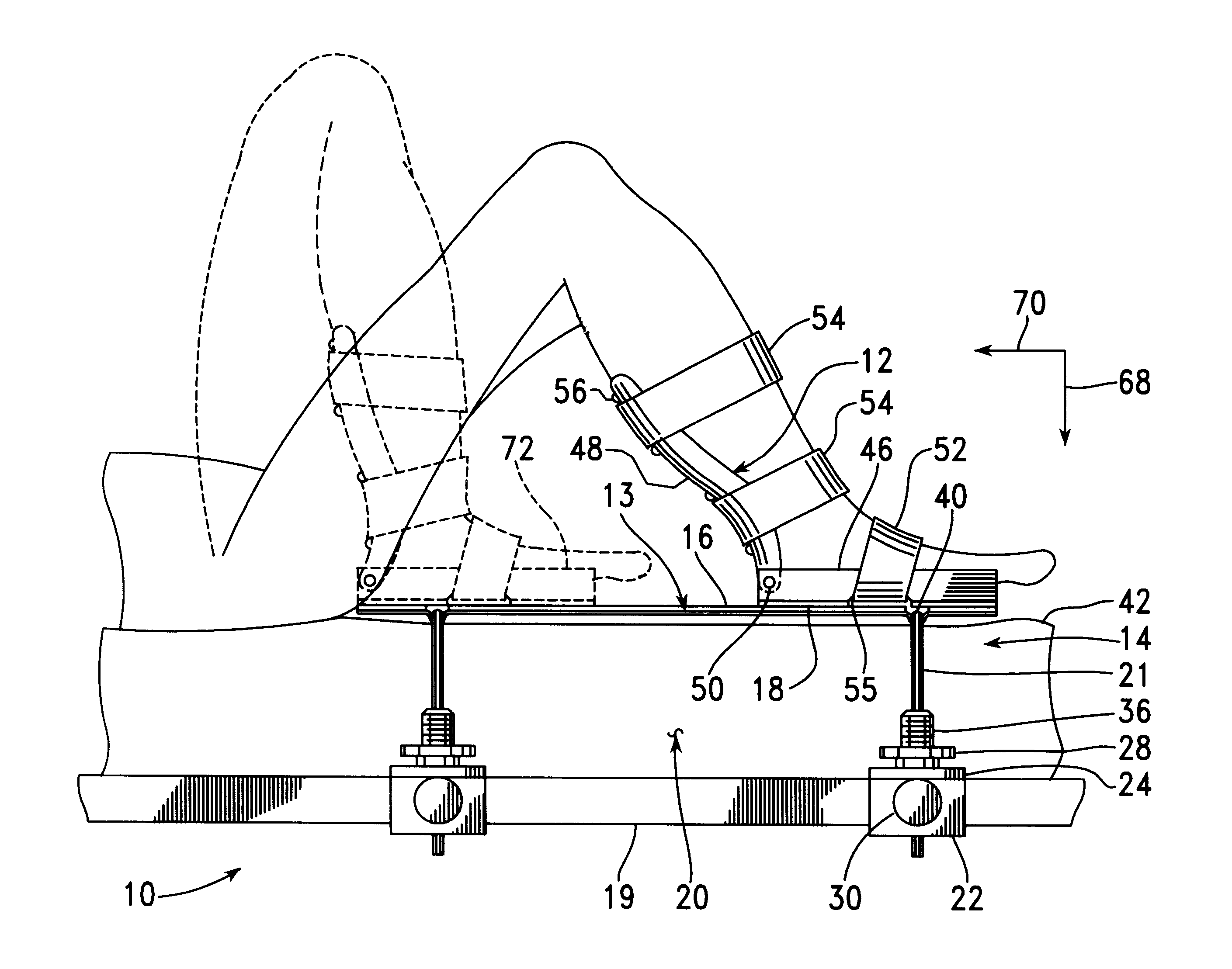
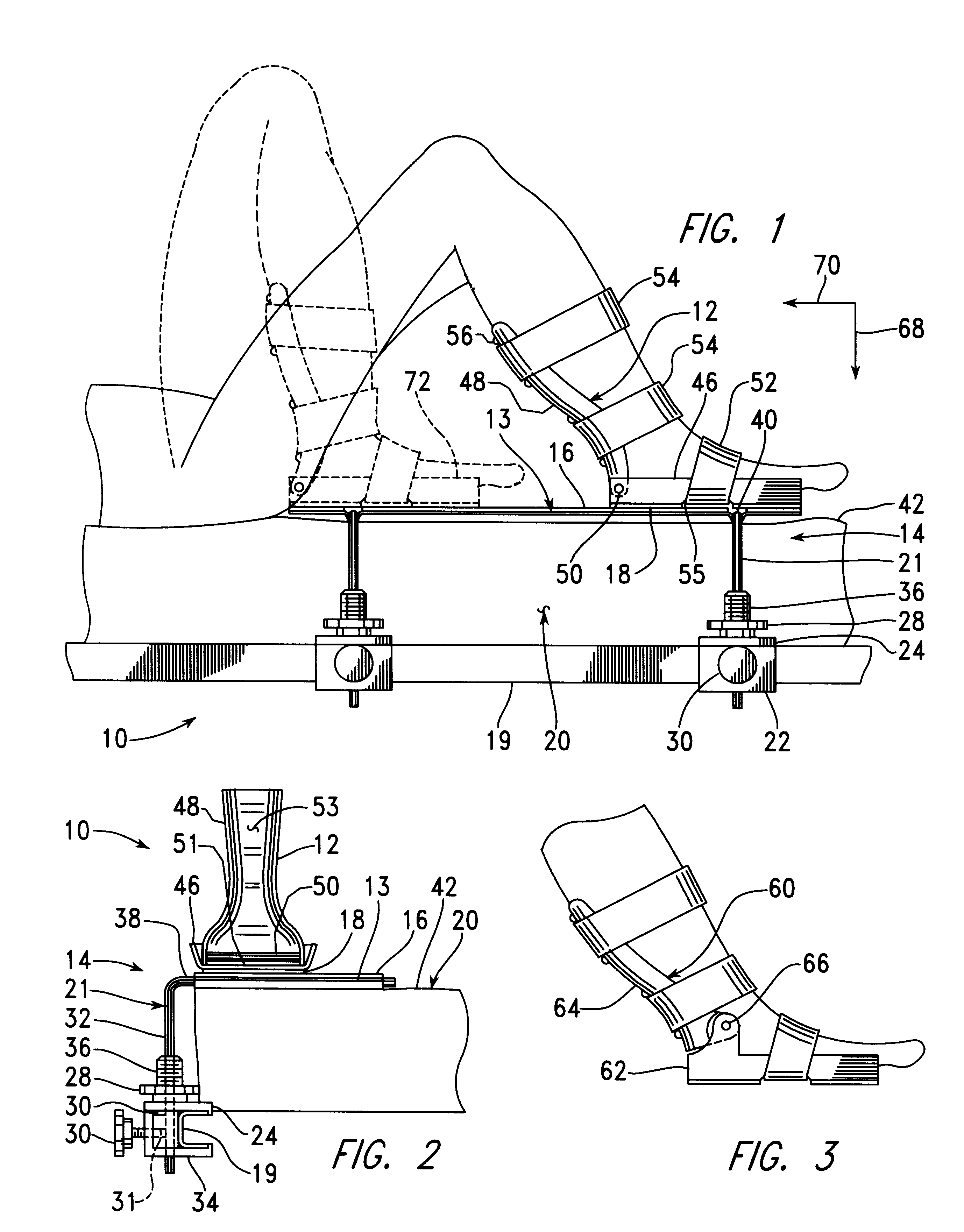
Foot restraint apparatus for holding a leg in place during knee surgery
InactiveUS6234173B1Easy to adjustPrevent lateral rotationOperating tablesDiagnosticsKnee surgeryKnee operations
A patient's leg is clamped into place for knee surgery by placement of the lower leg and foot in a leg receiving structure which is removably attached to a platform through the use of VELCRO closures. The platform is adjustably connected to a rail of an operating table. The leg receiving structure includes a foot holder, into which the foot is strapped, and a leg holder, into which a lower part of the leg is strapped. The leg holder is pivotally mounted on the foot holder, so that the foot may be flexed as the foot holder is moved among various positions on the platform.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
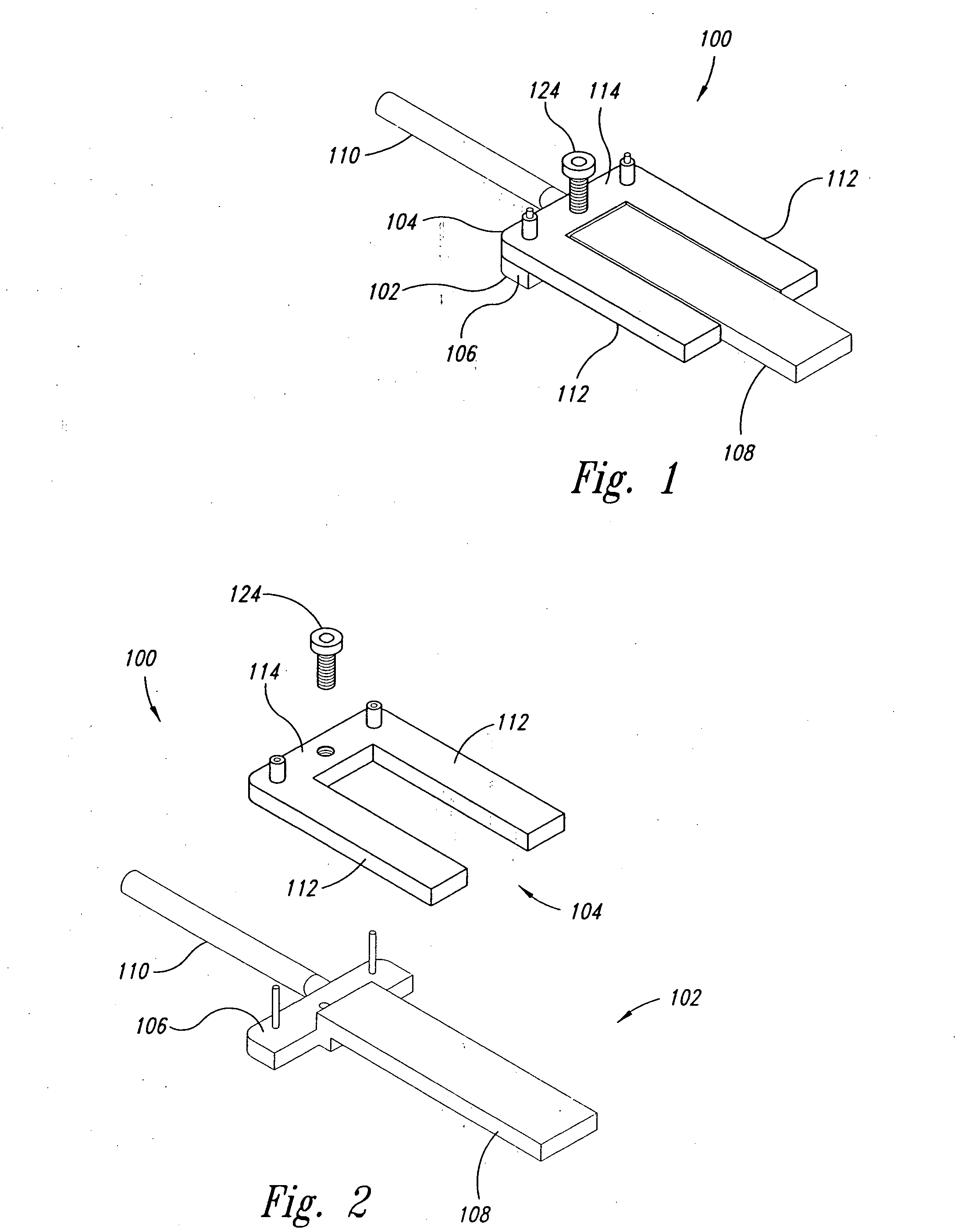
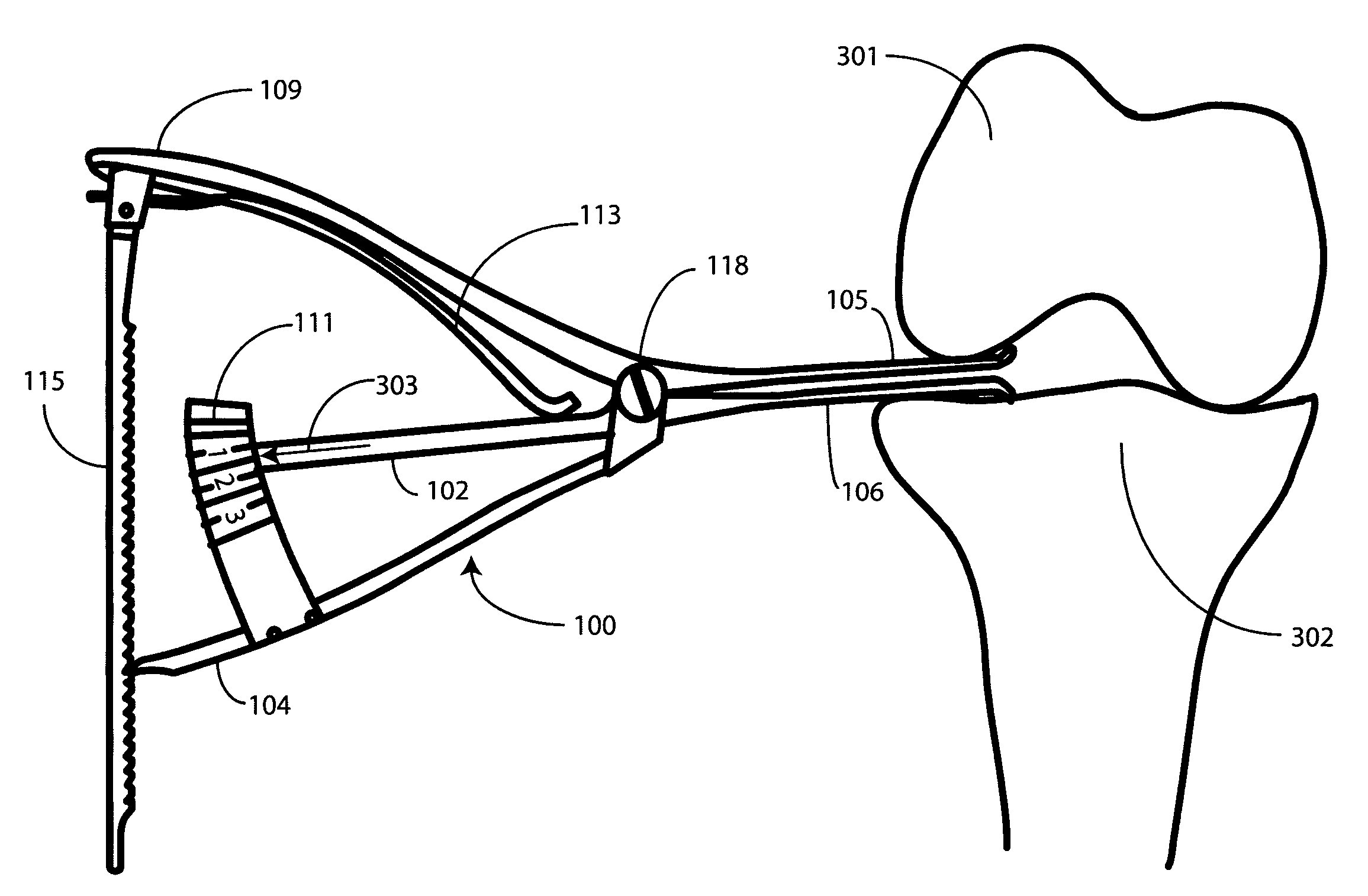
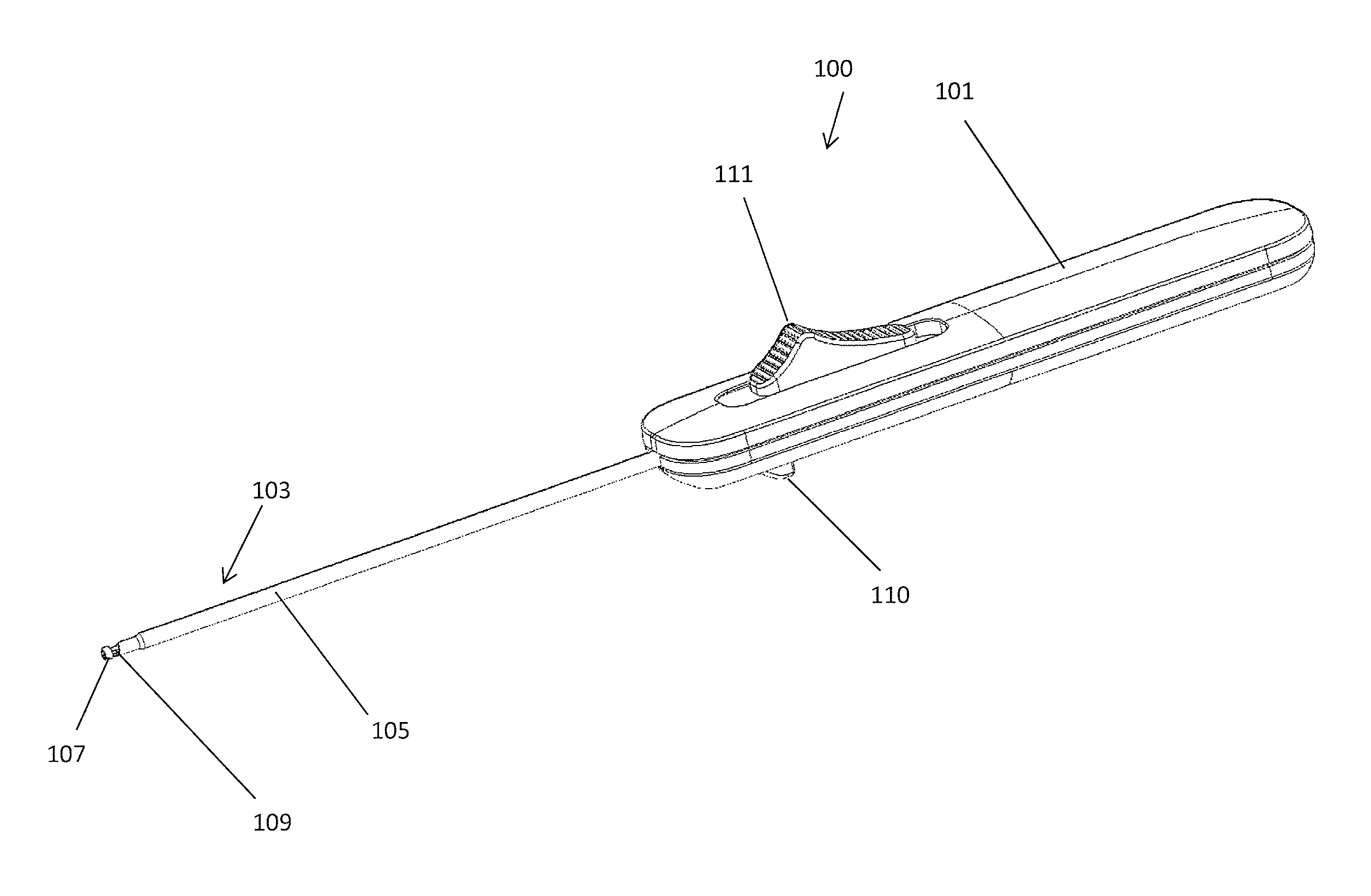
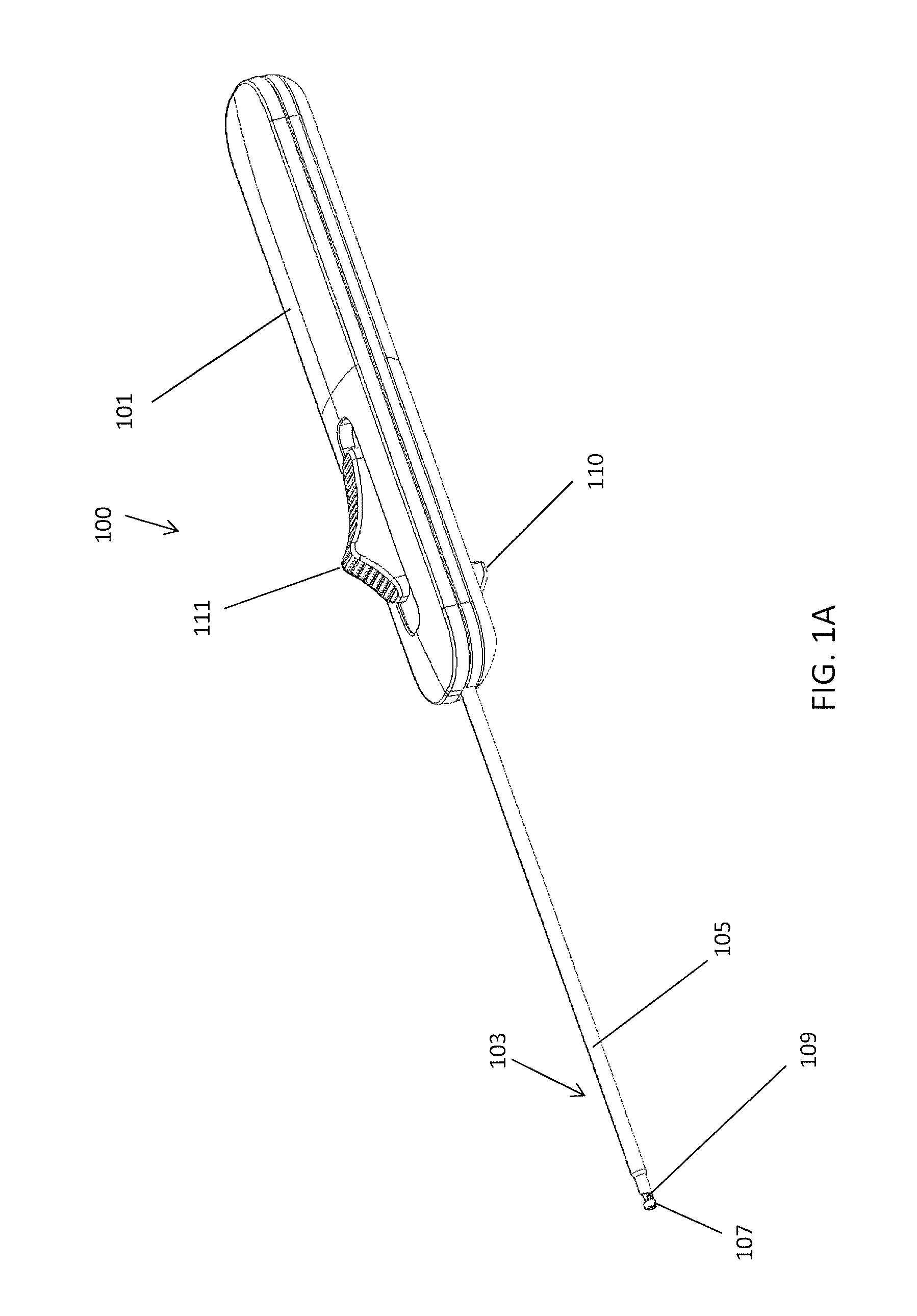
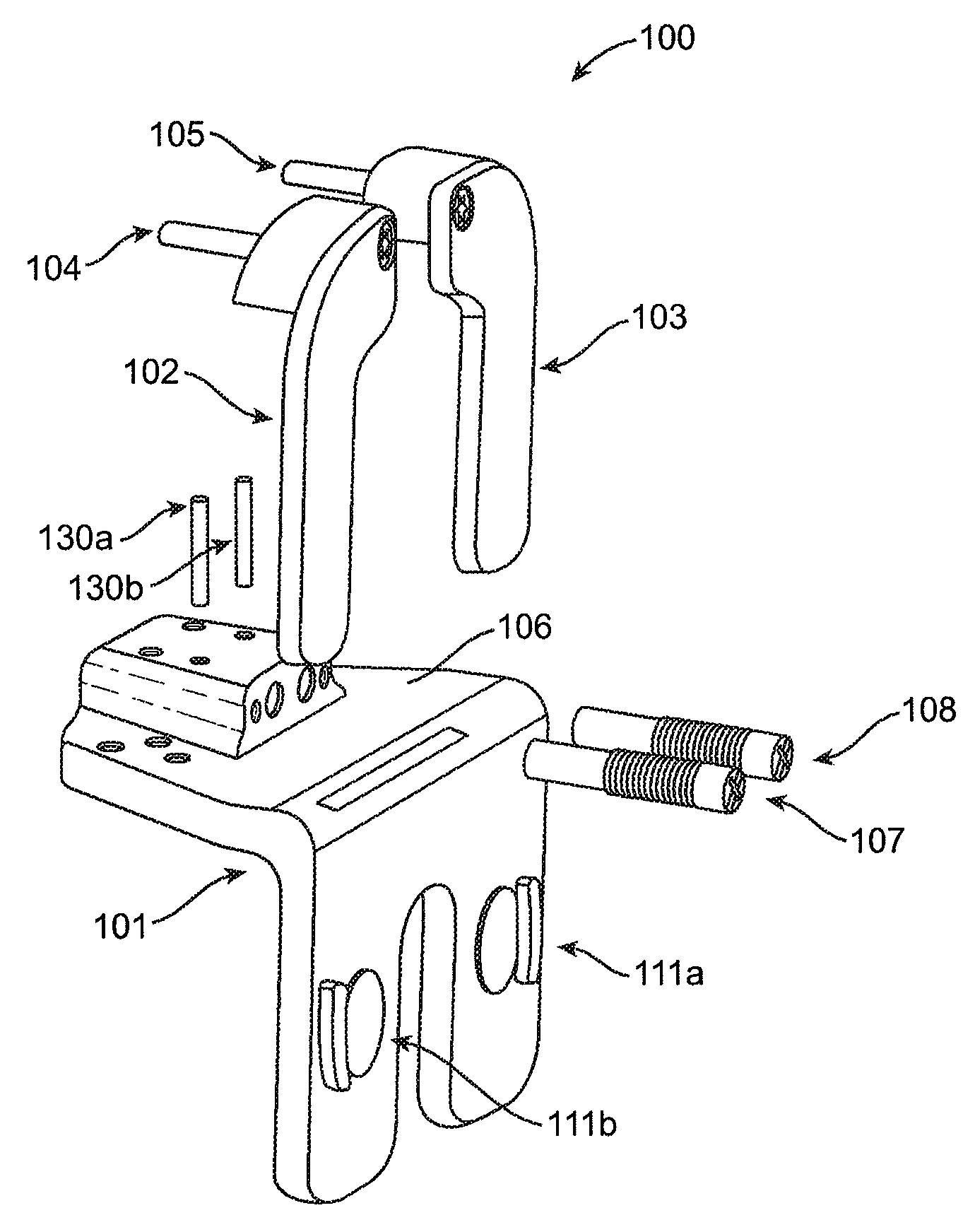
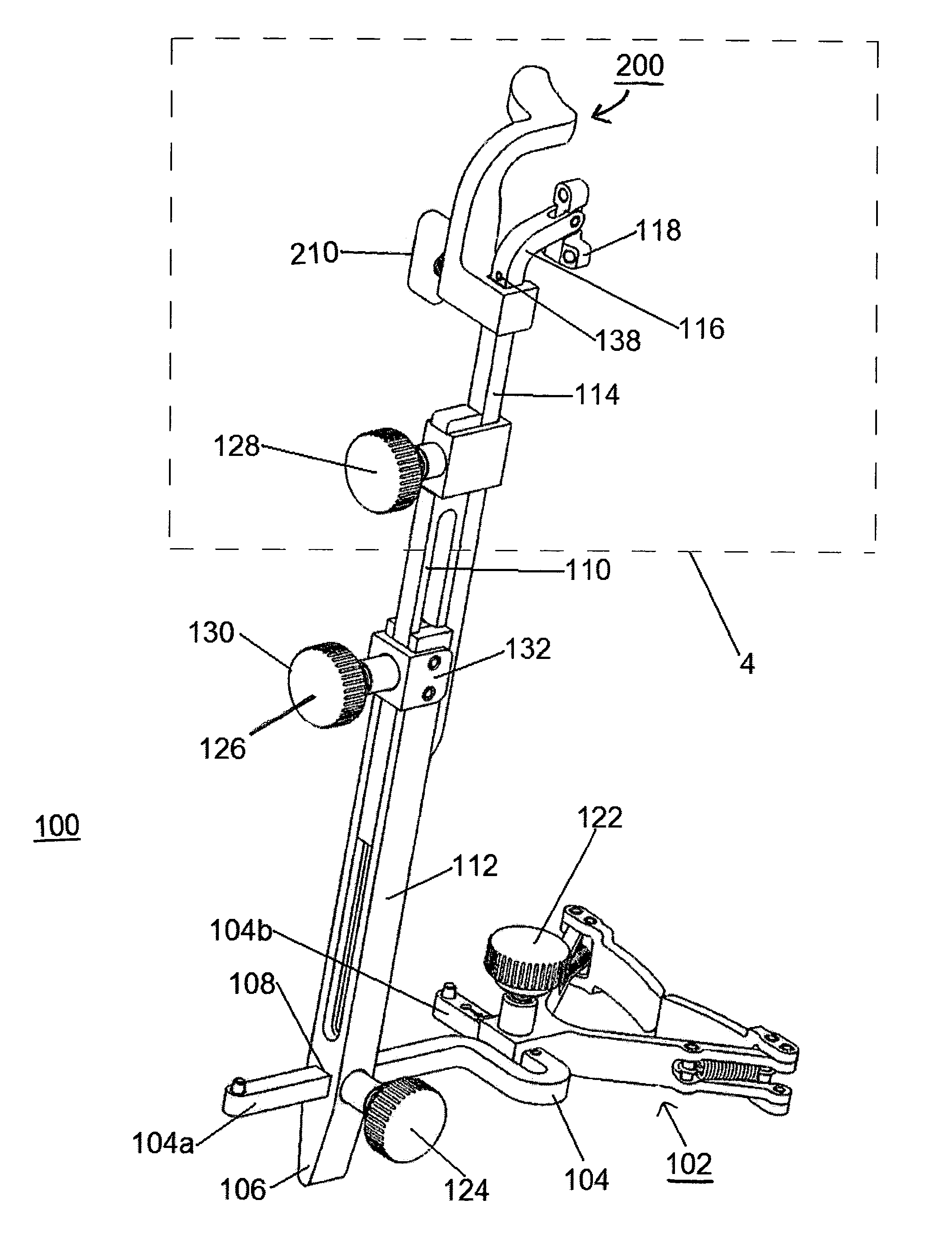
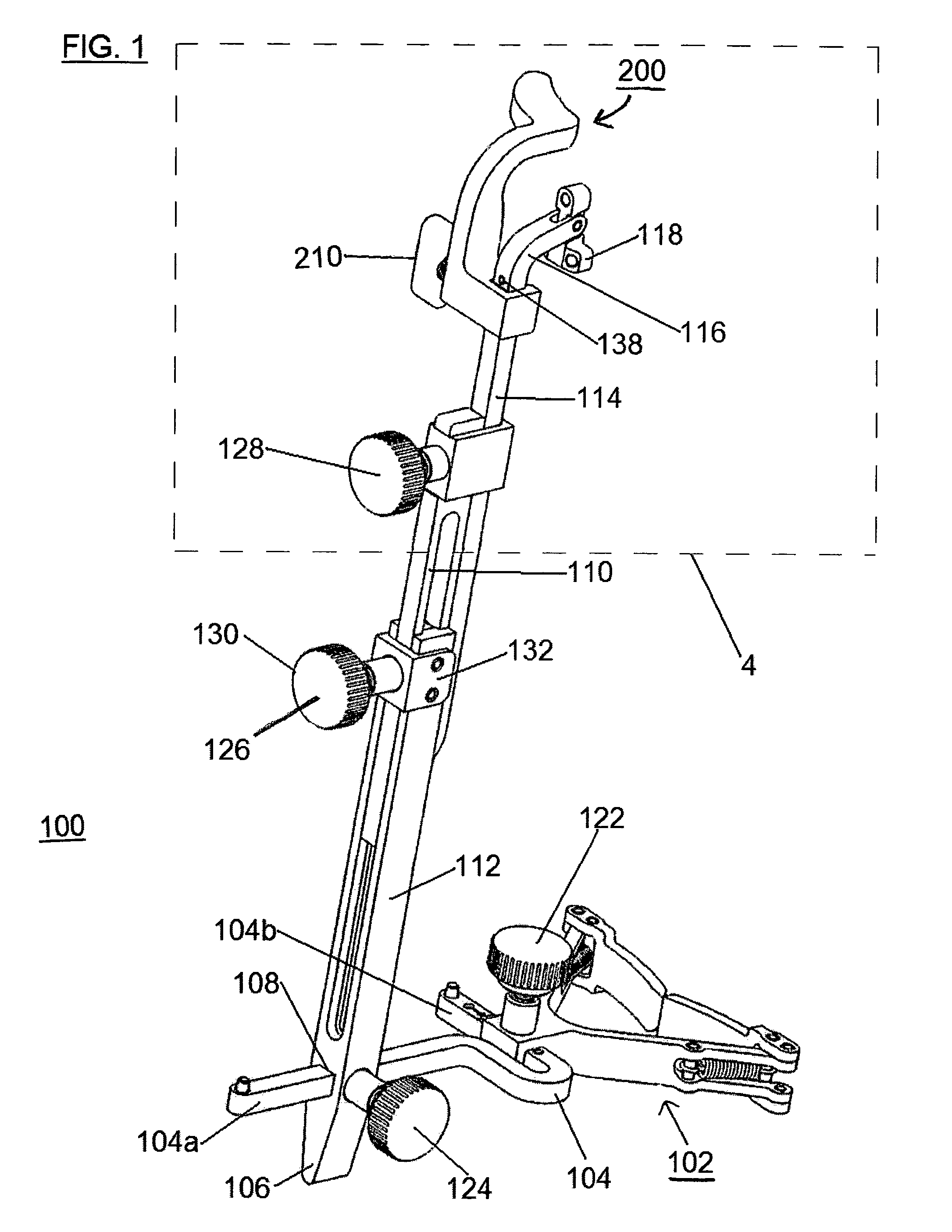
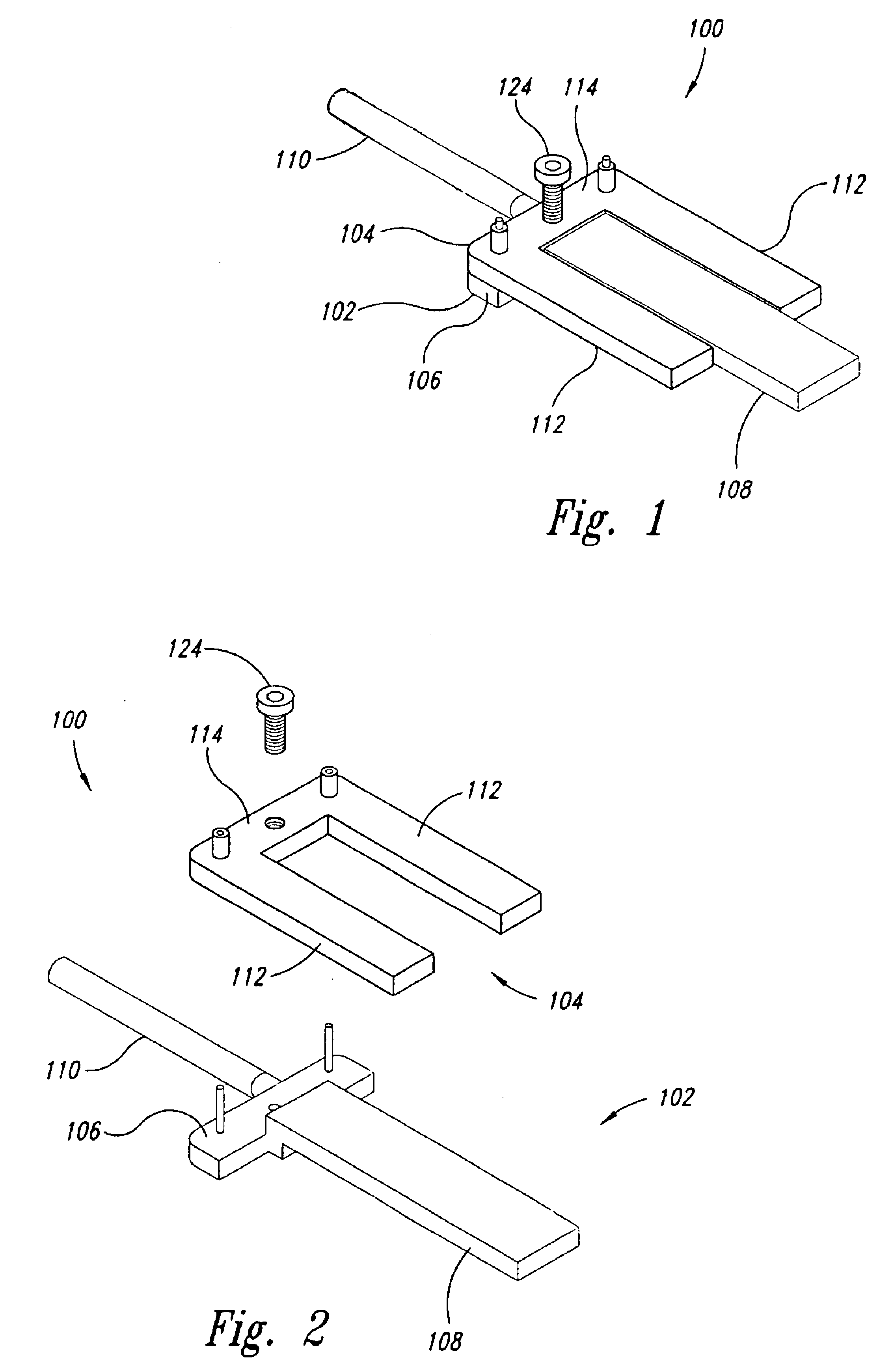
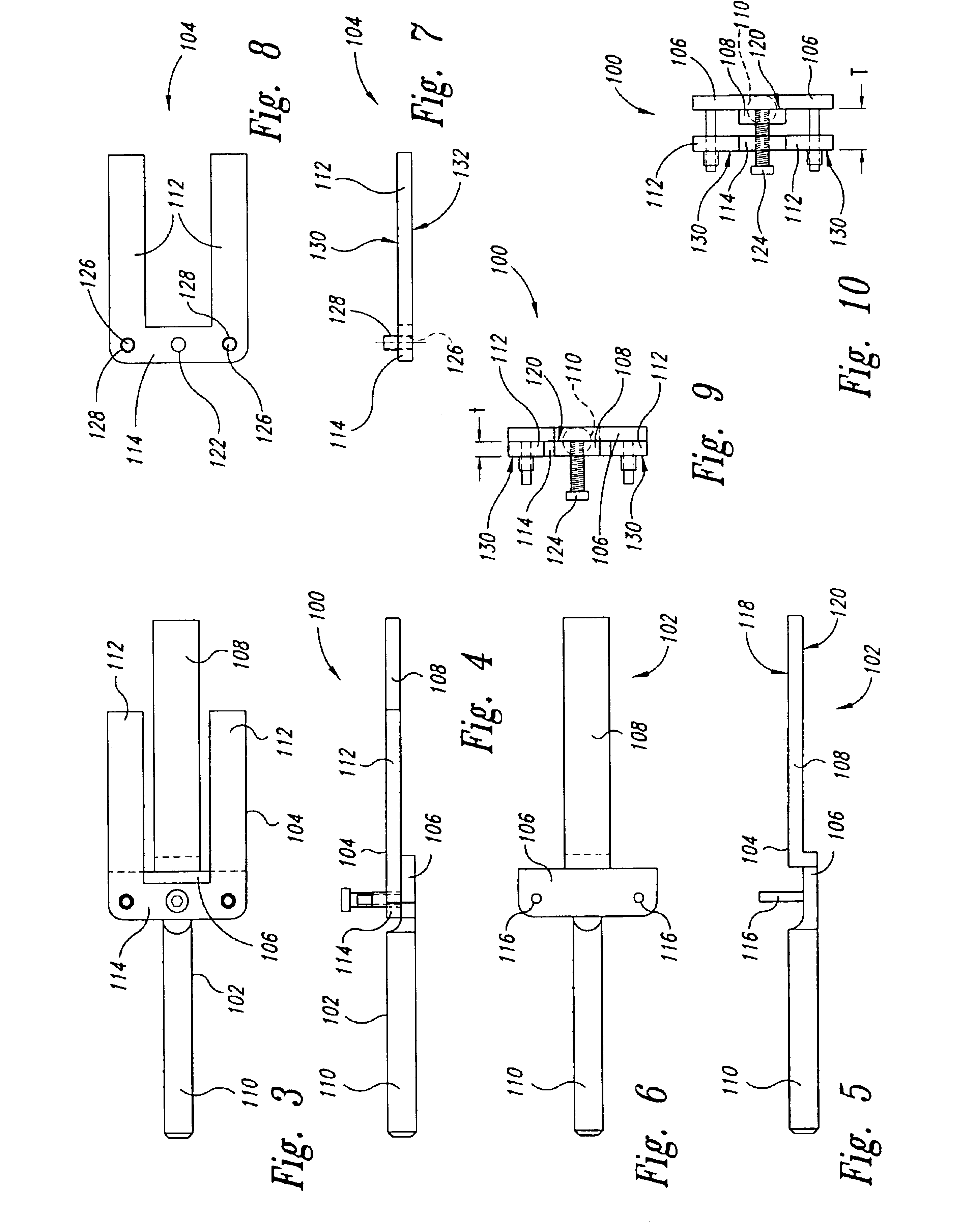
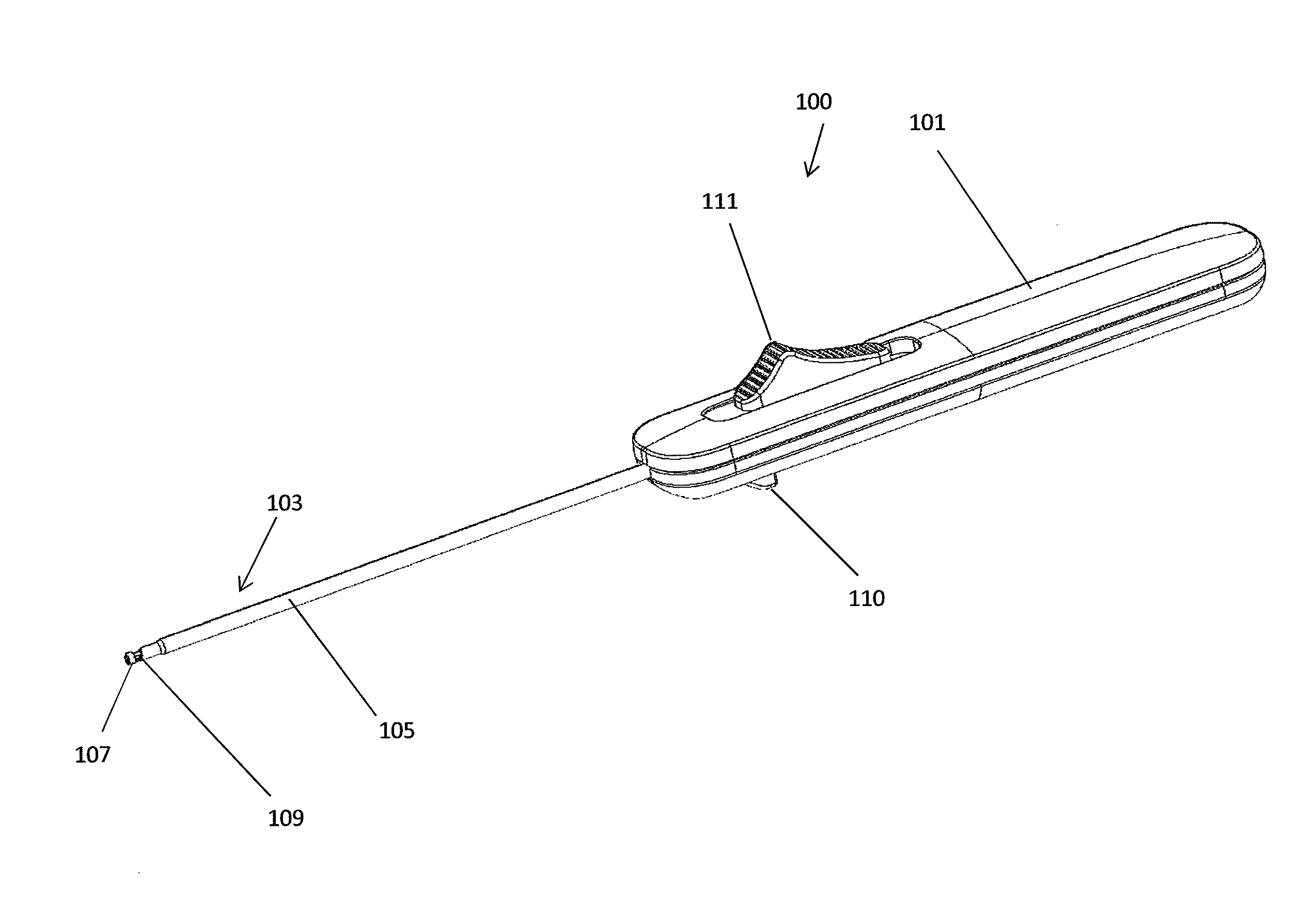
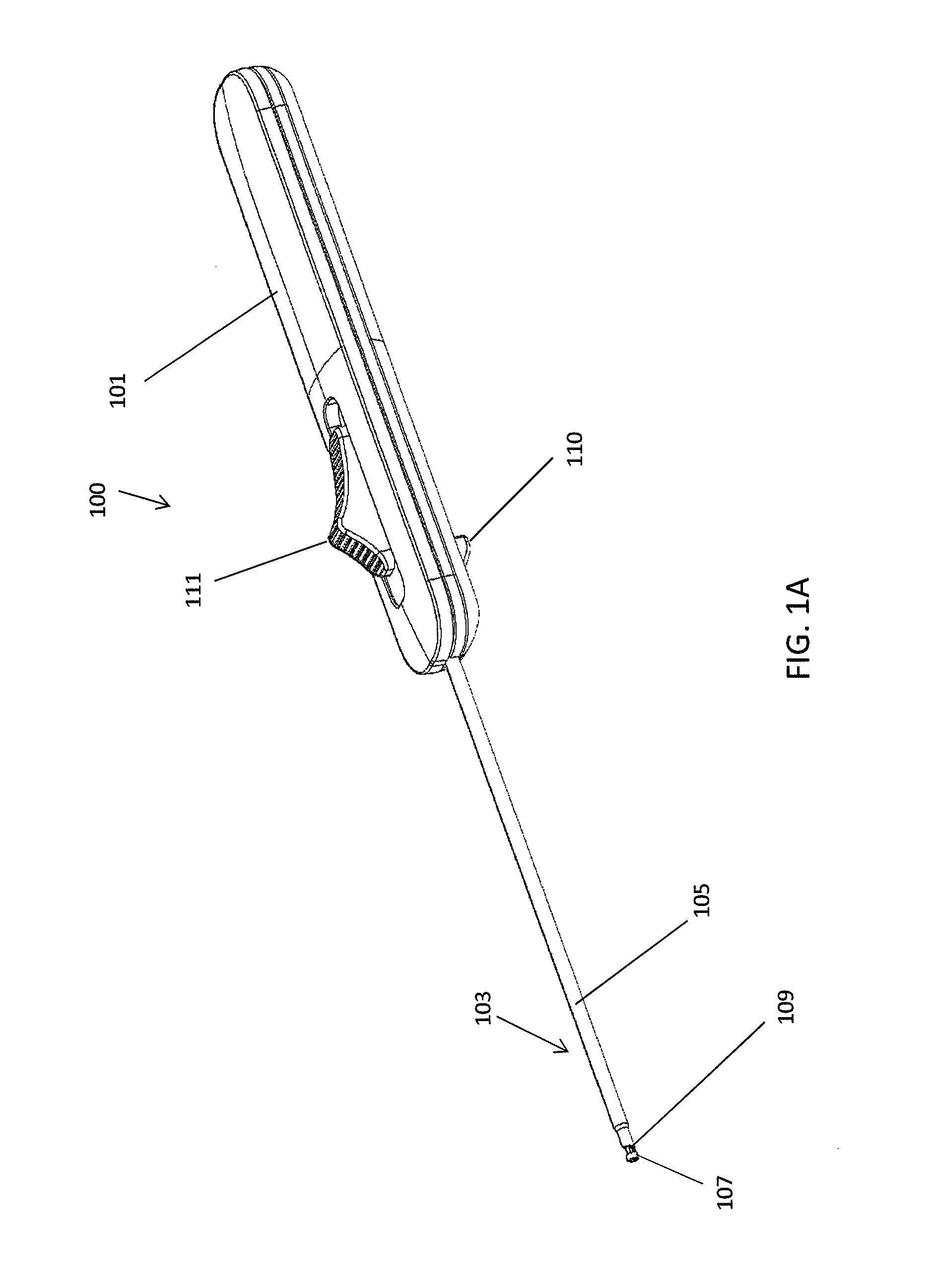
Femoral Tibial Spreader with Tensor Measurement
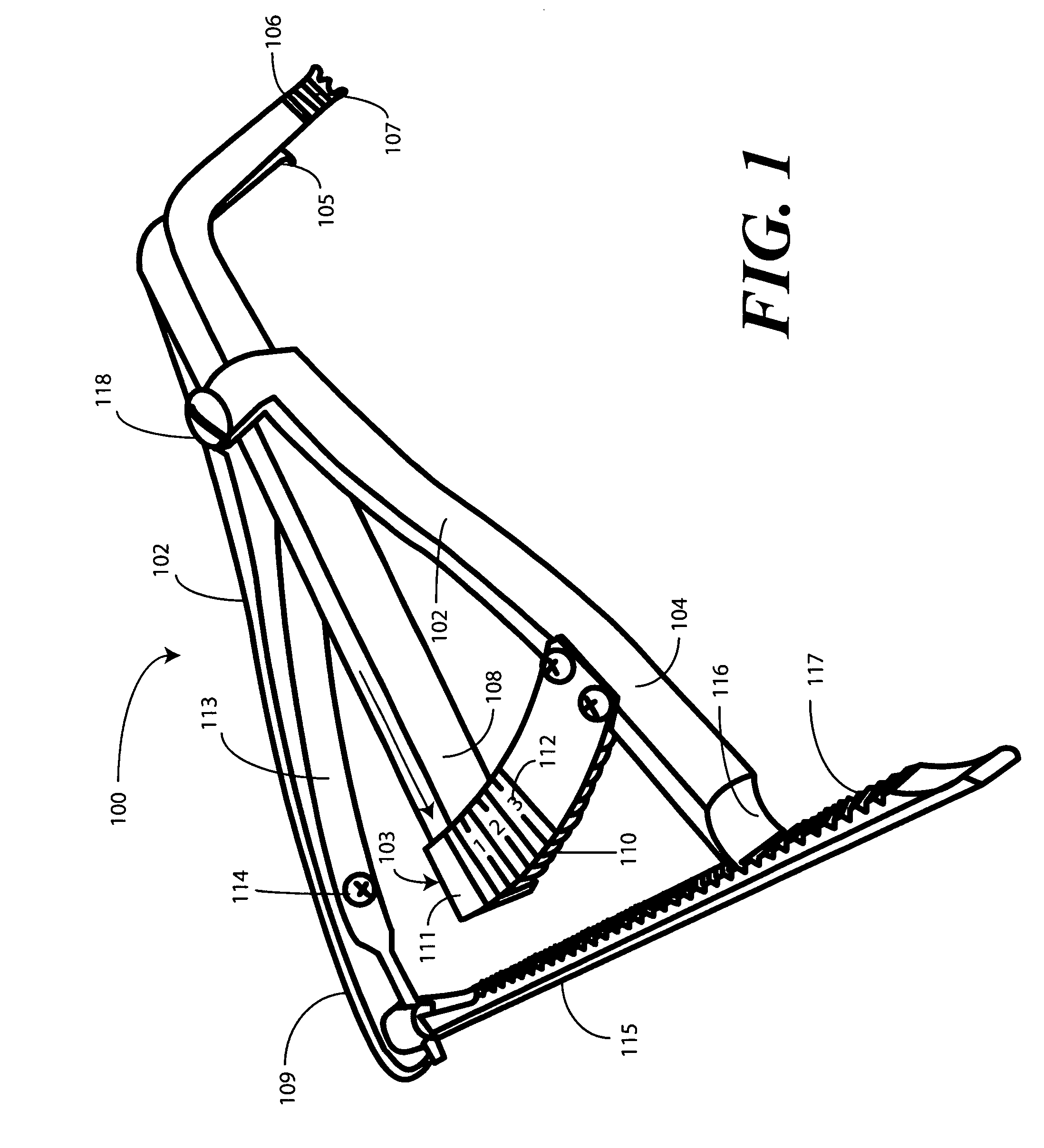
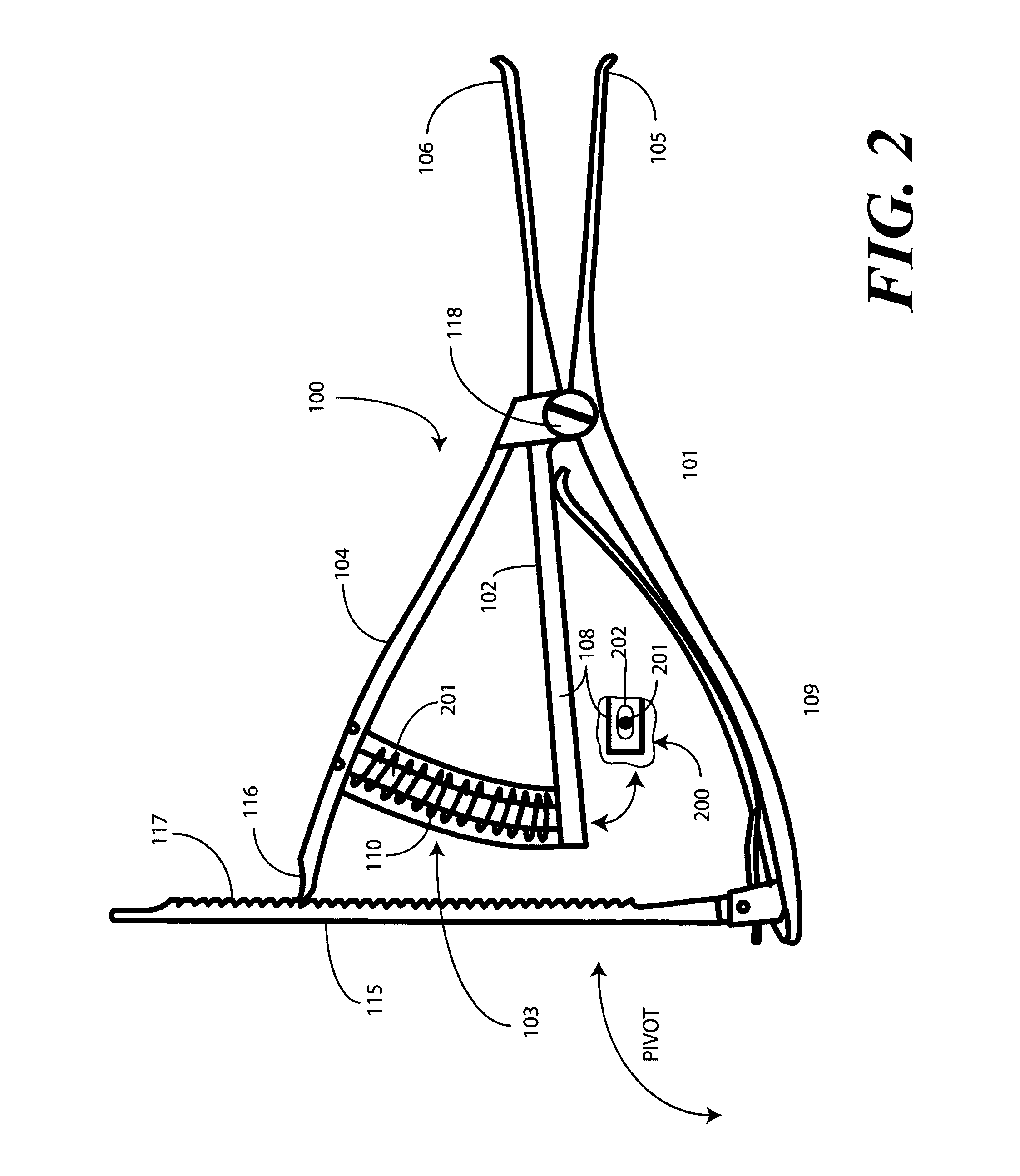
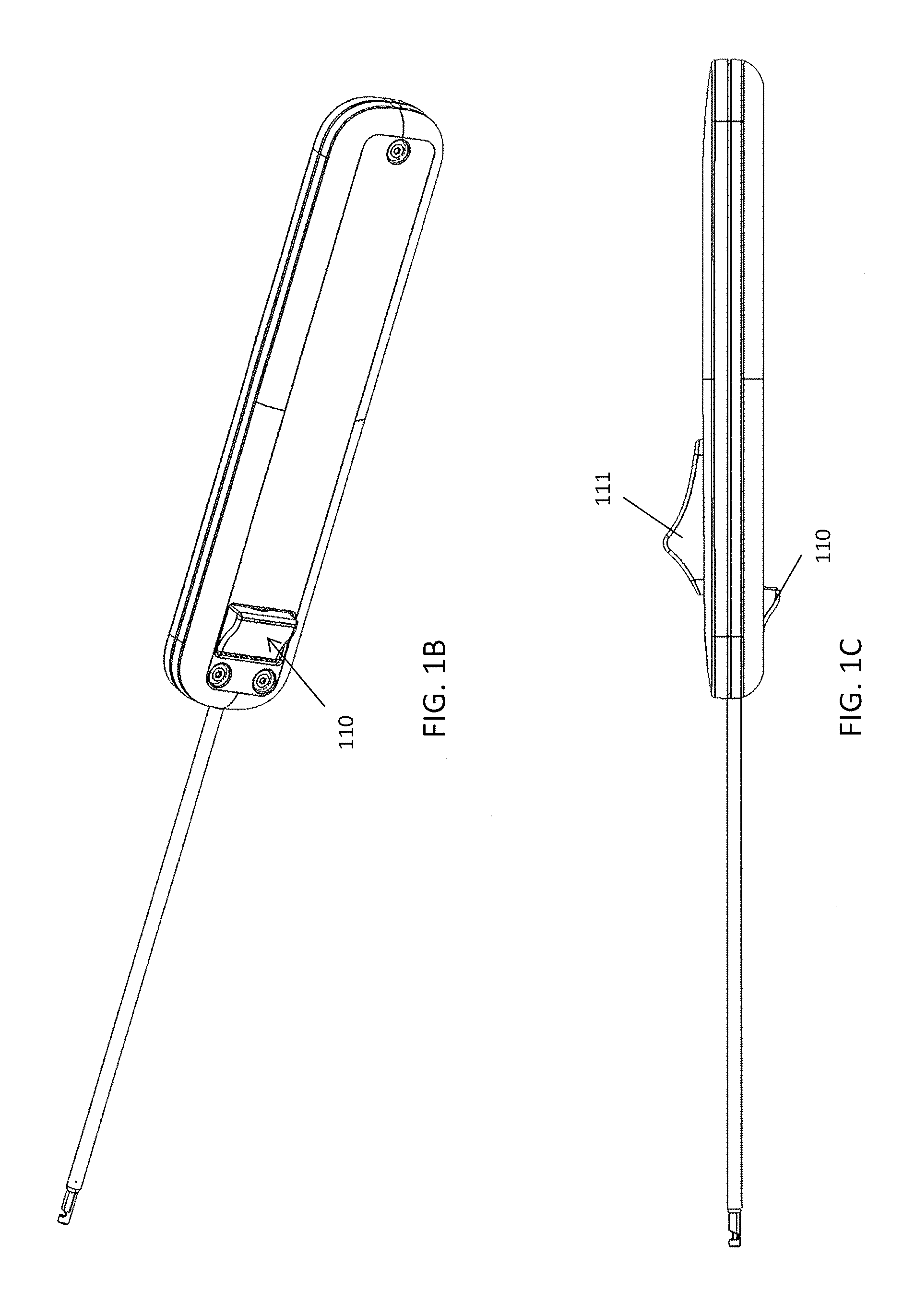
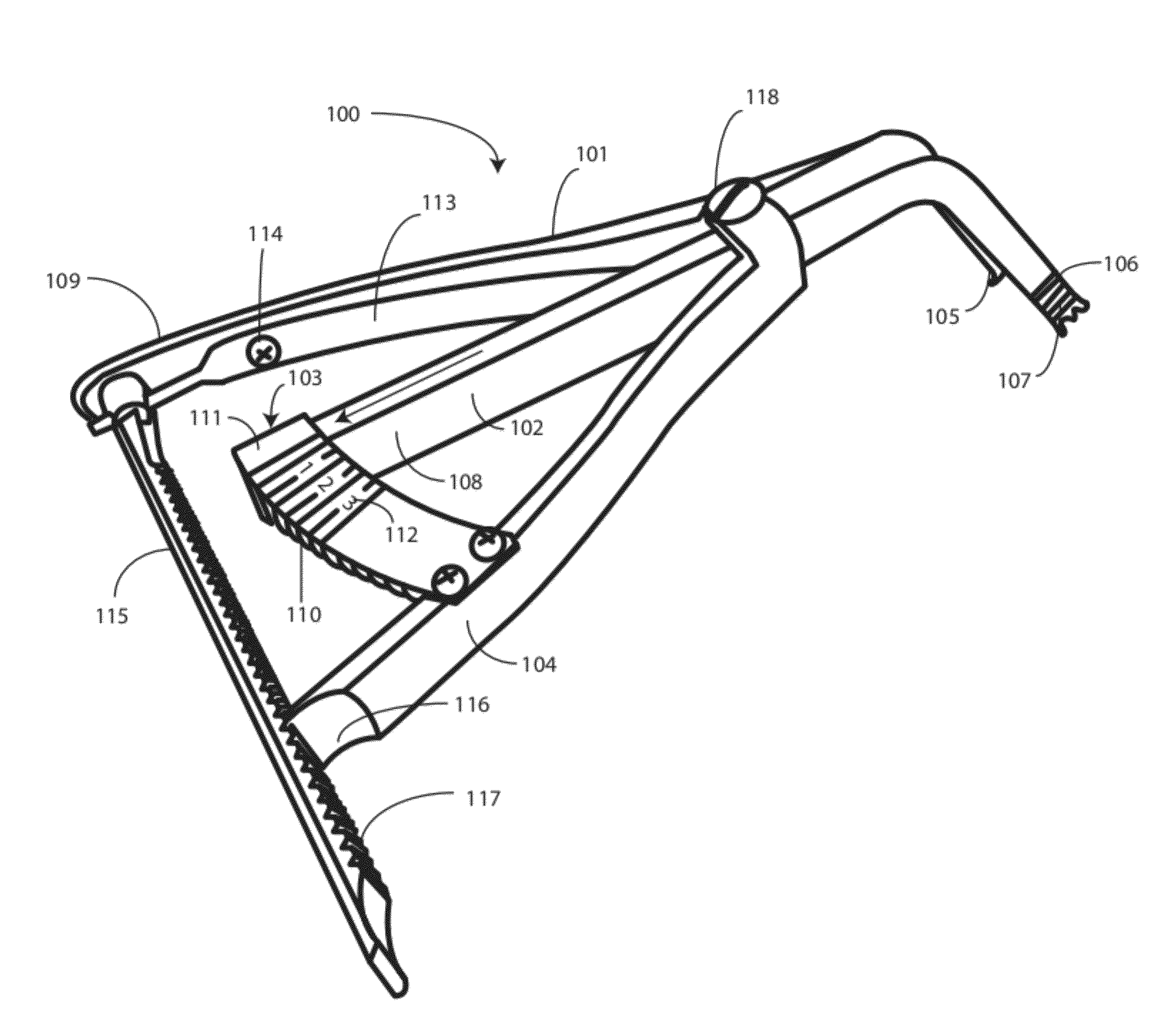
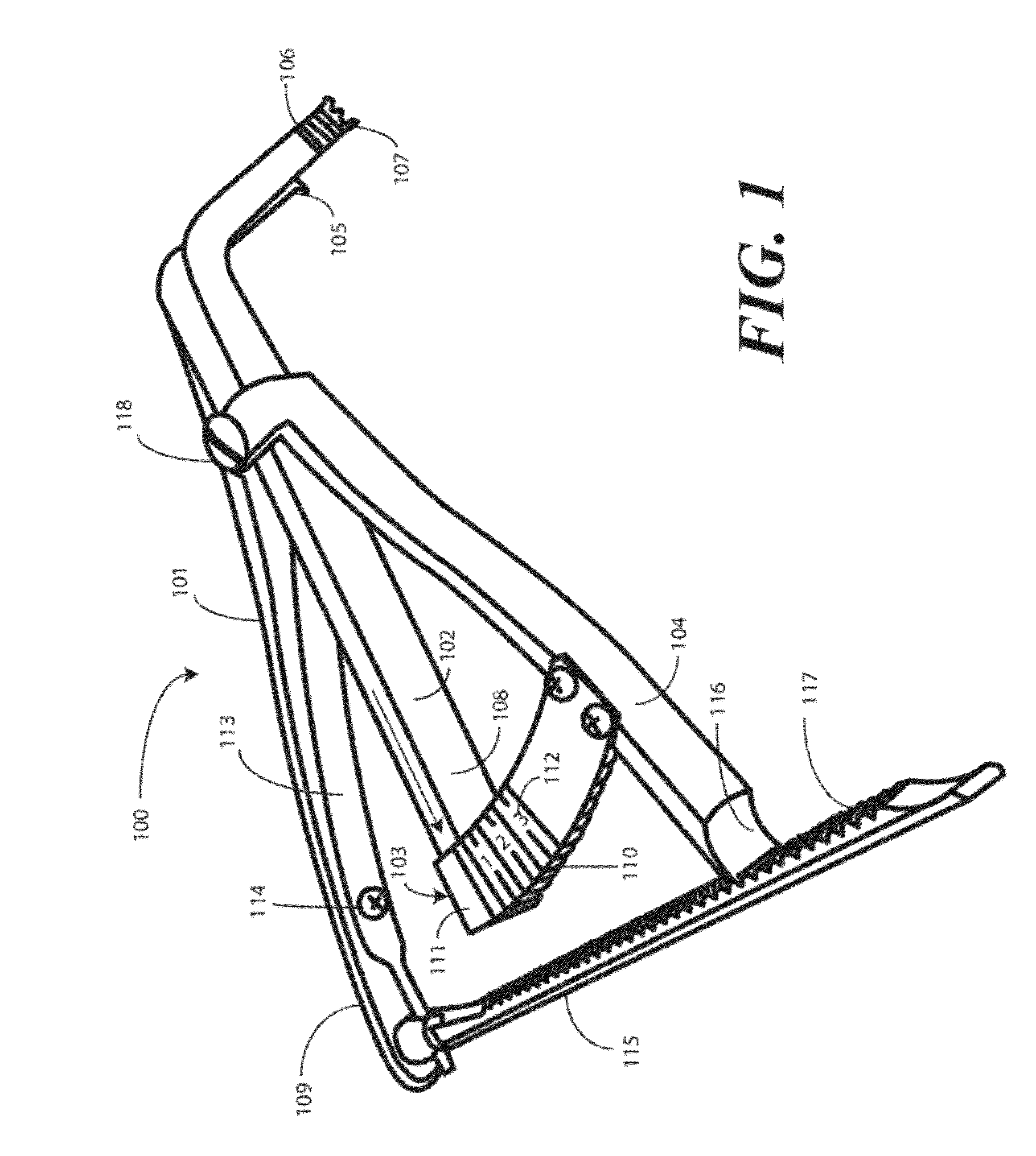
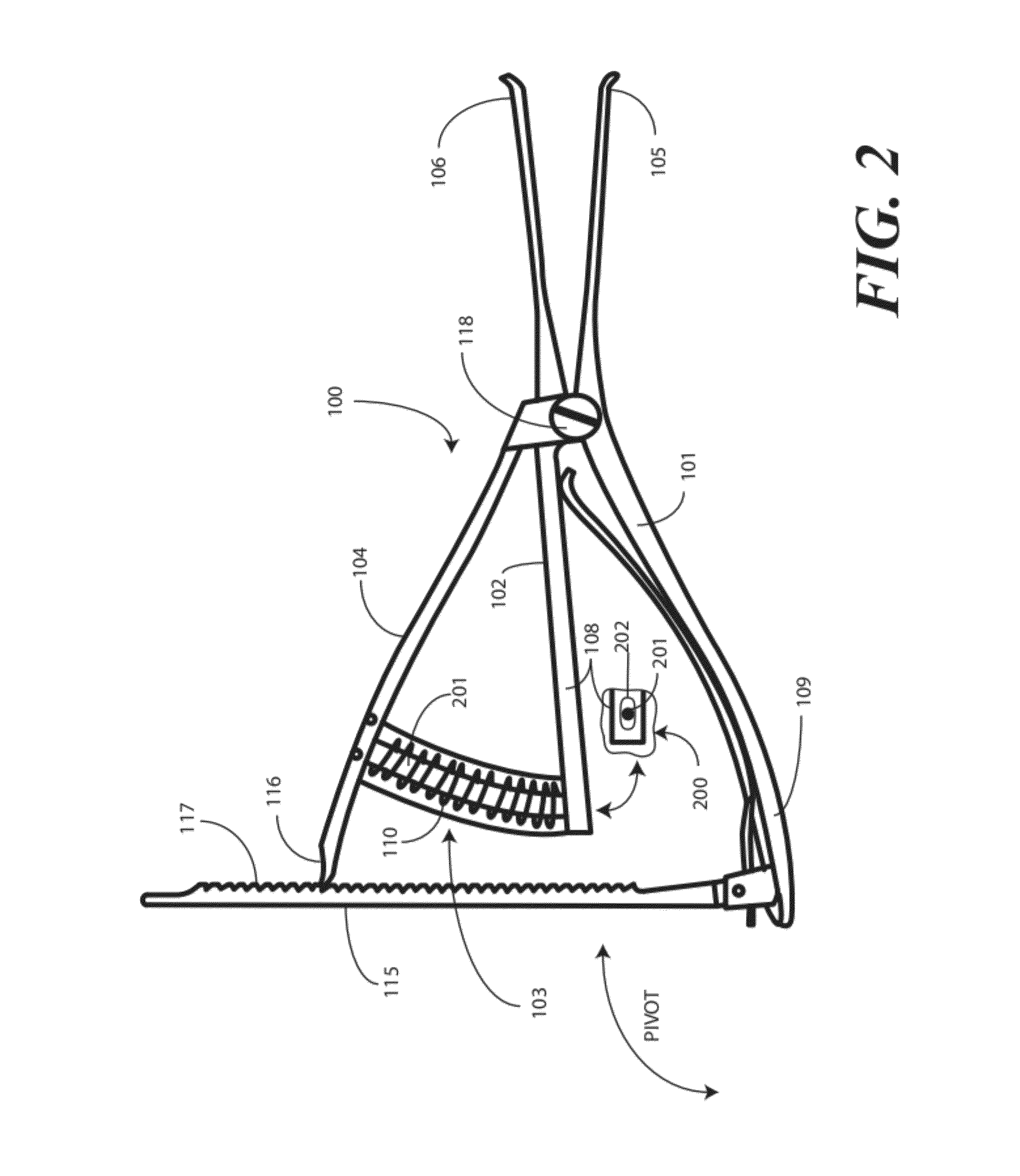
A femoral tibial spreader (100) for spreading adjacent bones includes a radial measurement gauge (111) for providing incidia corresponding to an amount of force being applied to the forward ends (105,106) of the femoral tibial spreader (100). The femoral tibial spreader (100) may be used, for example, to separate the femur (301) and tibia (302) during knee surgery. The radial measurement gauge (111) may be used to determine an amount of force being applied to the femur (301) and tibia (302), for example, by the medial and arterial ligaments. Two handle members (104,109) are squeezed together, which causes the forward ends (105,106) to open. A biasing member (110) allows a measurement extension (108) to pivot towards a handle member under tension, thereby providing a measurement of force applied by the ligaments.
Owner:INNOMED INC
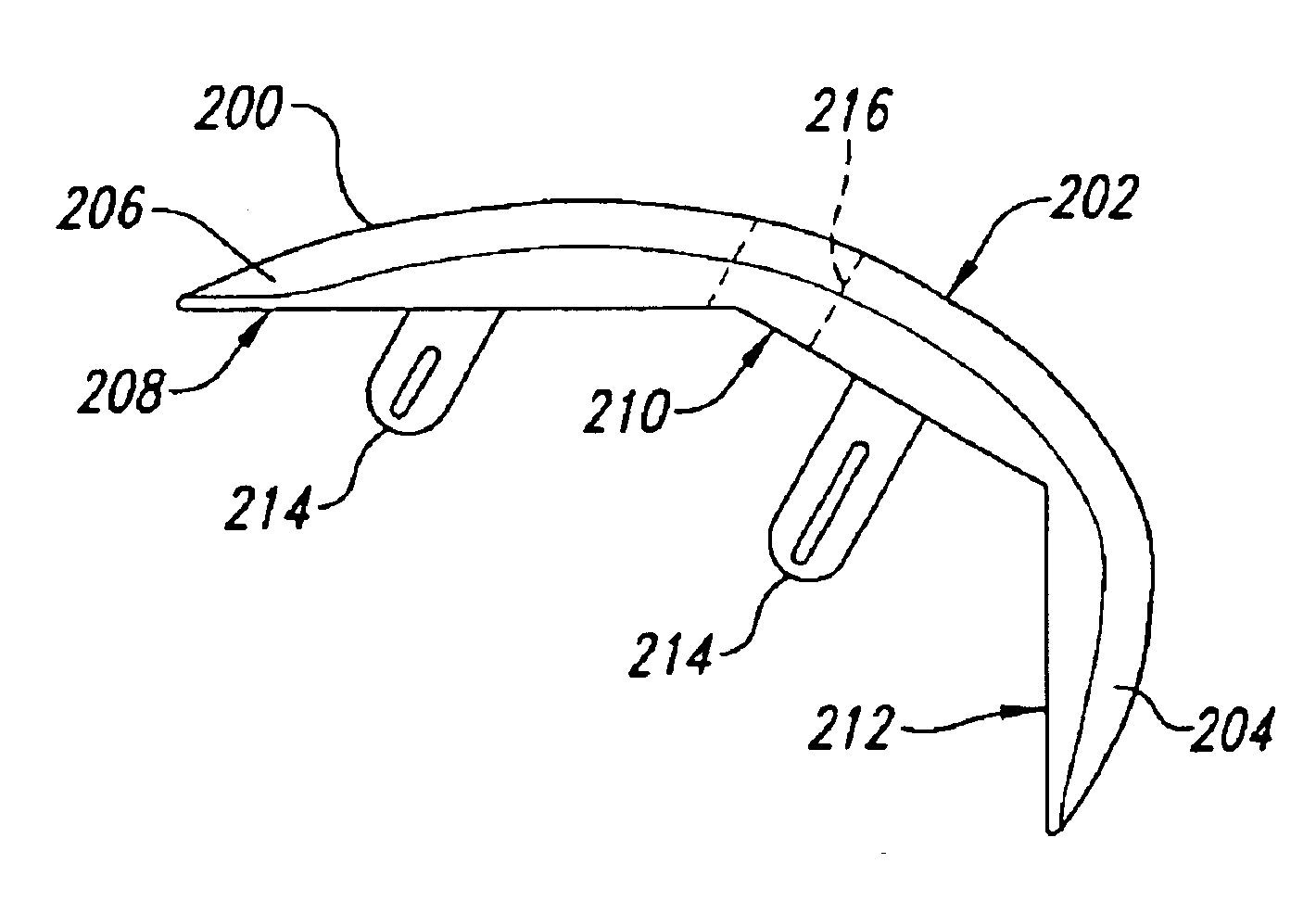
Tibial preparation apparatus and method
An apparatus and method for preparing a tibia for knee surgery. The apparatus includes a tibial base having a center axis, and a handle coupled to the base at an anterior base location that is offset relative to the center axis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Anatomically designed orthopedic knee brace
InactiveUS6969364B2Novel and effectiveAccurately prescribing anatomical motionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee proceduresTibia
An orthopedic knee brace provides an apparatus for accurately prescribing the anatomical motion of the human knee. The orthopedic knee brace is used for treatment and rehabilitation following surgery to the knee, protection for a surgically repaired knee, and protection for an uninjured knee, among other applications. The orthopedic knee brace actively prescribes asymmetric three-dimensional anatomic motion in six degrees of freedom of the wearer's knee. The rigid connections between the thigh and calf engaging members and the medial and lateral hinges provide the ability of the orthopedic knee brace to prescribe asymmetric three-dimensional anatomic motion in six degrees of freedom by actively prescribing flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, internal / external rotation, anterior / posterior translation, medial / lateral translation, and proximal / distal translation between a femur and a tibia of a wearer's leg.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Systems used in performing femoral and tibial resection in knee surgery
A system for resecting a tibia and femur during arthroplasty includes anchoring devices, a three-way alignnment guide attachable to an anchoring device. The alignment guide provides for locating a resection guide in three degrees of freedom, including one translation and two rotations. The resection guide is coupled to a computer navigation system.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Arthroscopic knot pusher and suture cutter
ActiveUS20150088163A1Prevent fallingPrevents the suture from fallingSuture equipmentsWound clampsKnee surgeryEngineering
Knot pushers and suture cutter apparatuses to be used arthroscopically, for example, in an arthroscopic knee surgery may be operated with a single control to both lock the suture within the distal end of the apparatus and cut the suture once the knot has been pushed to the appropriate location. The apparatus may include a safety lock preventing deployment of the cutter until the safety lock (e.g., cutter release) has been released.
Owner:CETERIX ORTHOPAEDICS
Femoral tibial spreader with tensor measurement
A femoral tibial spreader (100) for spreading adjacent bones includes a radial measurement gauge (111) for providing incidia corresponding to an amount of force being applied to the forward ends (105,106) of the femoral tibial spreader (100). The femoral tibial spreader (100) may be used, for example, to separate the femur (301) and tibia (302) during knee surgery. The radial measurement gauge (111) may be used to determine an amount of force being applied to the femur (301) and tibia (302), for example, by the medial and arterial ligaments. Two handle members (104,109) are squeezed together, which causes the forward ends (105,106) to open. A biasing member (110) allows a measurement extension (108) to pivot towards a handle member under tension, thereby providing a measurement of force applied by the ligaments.
Owner:INNOMED INC
Connecting Mechanism for Medial and Lateral Polyethylene Bearing Surfaces for Knee Replacement
InactiveUS20140039636A1Quick and strong lockingAvoid mechanical failureJoint implantsKnee jointsFixed bearingMobile bearing
Disclosed herein are improved methods, apparatus and / or systems for a tibial implant assembly that can facilitate balancing, positioning, insertion, locking and maneuvering of the modular tibial inserts during knee surgery. The system may include a plurality of modular tibial inserts with locking or engagement mechanisms that allow creation of a modular insert assembly, and a corresponding tibial tray and optional tray components. The system allows the quick and convenient mating and locking of the tibial insert assembly to the tibial tray. The various components can accommodate mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing designs for the tibial tray.
Owner:KURTZ WILLIAM B
System for positioning a cutting guide in knee surgery
A system is provided for positioning a cutting guide on a femur of a knee to make a cut along a distal end of the femur during knee surgery. The system may generally include an adjustable femoral attachment member configured to attach to a cut distal end of the femur, a cutting guide removably attachable to the femoral attachment member and configured to guide a surgical saw to make an additional cut on the distal end of the femur, and a force sensor for positioning between the femoral attachment member and a proximal end of a tibia of the knee. The force sensor may include a medial portion for sensing a medial force in the knee and a lateral portion for sensing a lateral force in the knee.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Unicondylar knee instrument system
The present invention provides for an apparatus for cutting a tibia, a stylus, an apparatus for cutting a femur, an apparatus for aligning a femoral cutting guide, and an ankle clamp in support of a unicondylar knee surgery. The present invention further provides for a method of preparing a femoral condyle of a femur for the implantation of a unicondylar femoral knee implant. The apparatus for cutting a tibia includes a unicondylar tibial resection guide that is adjustably connectable to a unicondylar tibial alignment guide and configured to operate concurrently with the tibial alignment guide. The apparatus for cutting a femur includes a spacer block and a cutting guide configured to operate concurrently with the spacer block.
Owner:ARTHREX
Instruments and methods for use in performing knee surgery
A system and method for aligning a patient's leg, for establishing the ultimate alignment of the leg prior to making a horizontal femoral cut or a horizontal tibial cut, for preparing the distal femur for receiving a femoral implant, and for making the horizontal, femoral and tibial cuts. The system and method incorporate a spacer, a cutting guide, and a template. The spacer is insertable between a distal femur and a proximal tibia to rotate the tibia with respect to the femur into the desired alignment. The cutting guide is engageable with the spacer, and can be fixed to the proximal tibia and the distal femur. The cutting guide has openings sized and shaped to guide a surgical saw to make the horizontal femoral cut and the horizontal tibial cut. The template is shaped to closely conform with the distal femur to allow the leg to be extended and to allow the procedure to be performed without dislocating a patella. Through one method of the present invention, the practitioner can select the desired ultimate alignment of the leg prior to making the horizontal, tibial and femoral cuts. As a result, when a replacement knee is implanted, the leg will be in the desired alignment.
Owner:WILLIAMSON RICHARD V
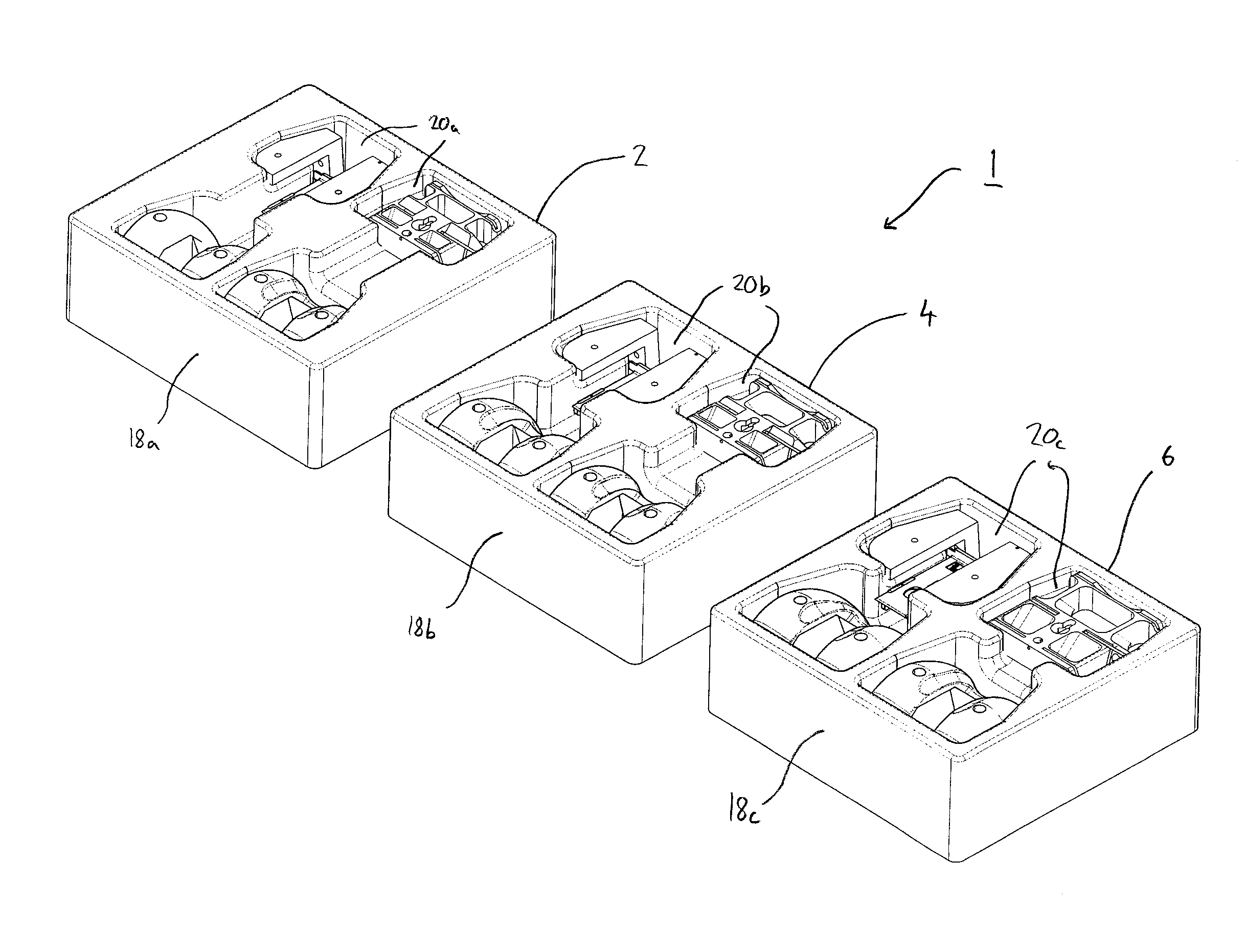
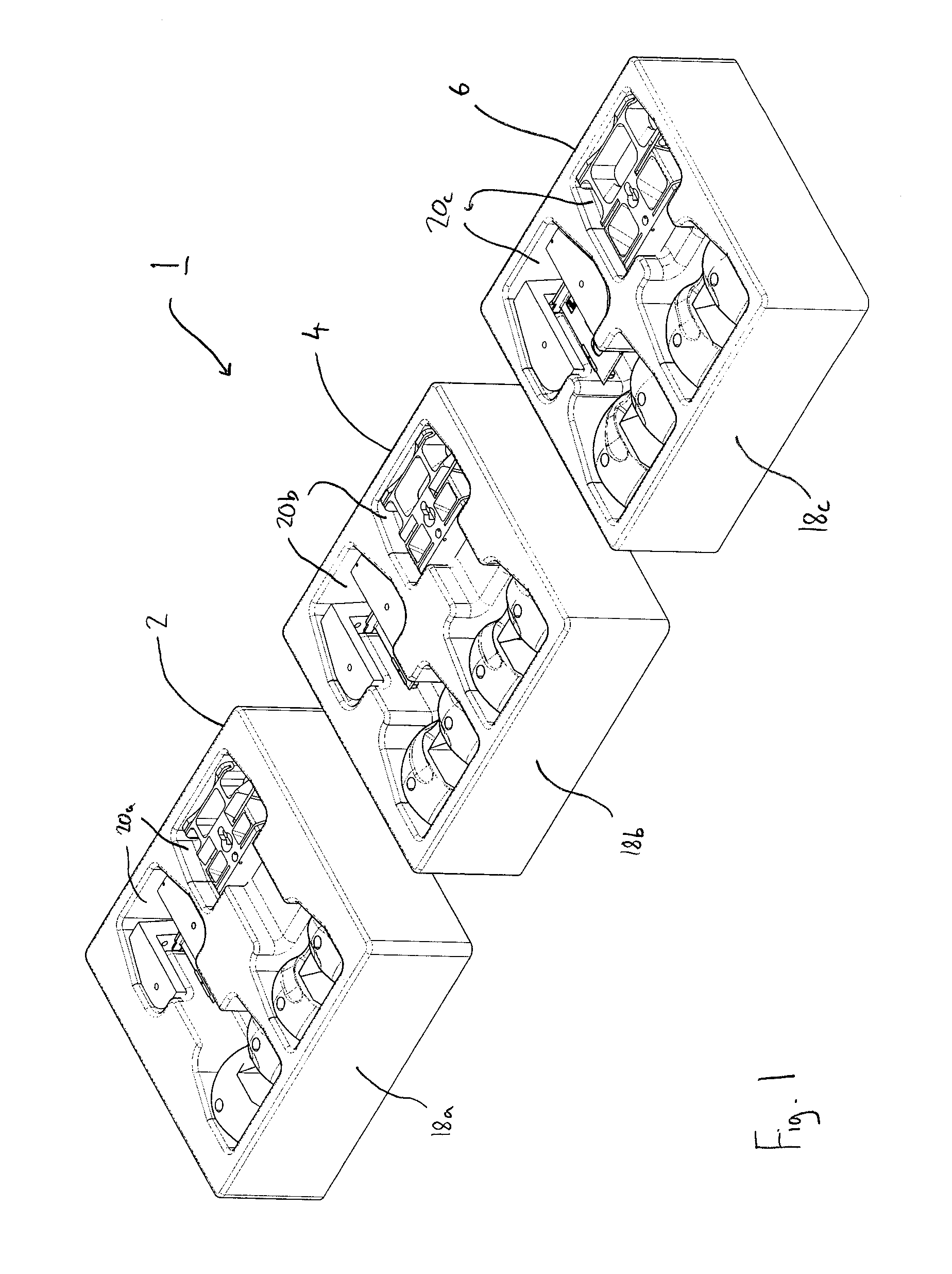
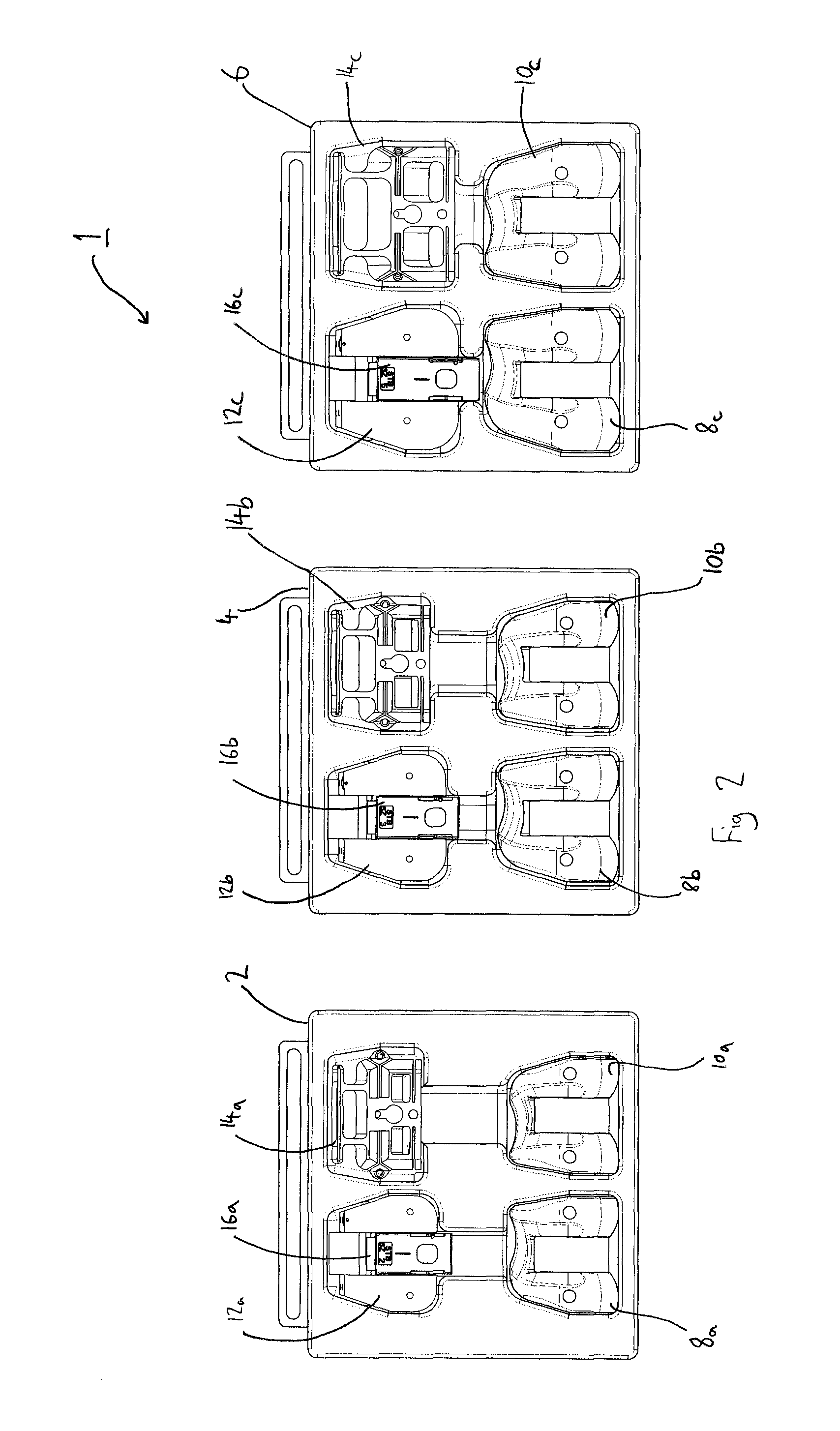
Container and system of containers of surgical instruments for knee surgery
ActiveUS8701890B2Reduce in quantityAvoid the needSurgical furnitureDispensing apparatusKnee surgeryKnee operations
A system of surgical instruments for use with at least a first implant and a second implant of the same type but different sizes is provided. The system includes a first container containing at least a first surgical instrument of a first type that is size specific and a second surgical instrument of a second type that is size specific; a second container containing at least a third surgical instrument of the first type and a fourth surgical instrument of the second type, wherein both the third and fourth instruments are of a second size that is different from the first size and that corresponds to the second implant; and a third container containing at least a fifth surgical instrument of a third type that is size independent.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
Portable knee rehabilitation device
InactiveUS20130110013A1Encourage useLimited rangeChiropractic devicesEye exercisersKnee surgeryKnee operations
A device for rehabilitating a knee after knee surgery includes a support adapted to support the leg at the popliteal fossa while allowing the knee to be bent about the support with little interference from the support. A method of knee rehabilitation includes the step of supporting the patient's leg on the support and allowing the patient to control to movement in order to overcome muscle guarding. The support is carried by uprights that are spaced apart far enough to allow the patient to be positioned on his back between the uprights with the knee to be rehabilitated disposed over the support and the other leg stretched straight under the support.
Owner:CARLSON DAVID LEE +1
Arthroscopic knot pusher and suture cutter
ActiveUS20150142022A1Prevents the suture from fallingPrevent fallingSuture equipmentsKnee surgeryEngineering
Knot pushers and suture cutter apparatuses to be used arthroscopically, for example, in an arthroscopic knee surgery may be operated with a single control to both lock the suture within the distal end of the apparatus and cut the suture once the knot has been pushed to the appropriate location. The apparatus may include a safety lock preventing deployment of the cutter until the safety lock (e.g., cutter release) has been released.
Owner:CETERIX ORTHOPAEDICS
Tools and methods for orthopedic surgery
InactiveUS20100023016A1Easy accessGuaranteed to workNon-surgical orthopedic devicesOsteosynthesis devicesTibiaRasp
Tools may be used individually and / or in combination to allow minimally invasive and safer orthopedic surgery. A femur adjustment tool lifts and lateralizes the proximal end of the femur during hip replacement surgery by pivoting on a ball temporarily placed in the acetabulum. A tissue protection and broach (rasp, cutting, drilling) guide tool may retract tissue at the incision, protect tendons and soft tissue, and provides a curved, elongated surface that cradles and guides the broaching tool. A tip of the main body of the protection and guide tool, and a hook protruding from the main body, may extend along opposite surfaces of the femur to help “capture” a portion of the femur for tool stability and to effectively and positively protect the piriformus tendon that will reside in the “V” between the hook and tip. A bone clamp is used when a generally transverse cut is made across a bone, for example, a knee surgery proximal tibial cut, wherein the clamp improves control of the bone portion for safer freeing of the bone portion from soft tissue and extracting the bone portion from the incision. A broad, flat plate of the bone clamp may be slid between the bone and the bone portion into the narrow space that has been created by cutting the bone, and a relatively narrow gripping member may be slid along / across the opposing surface of the bone portion, which allows the narrow gripping member to fit into the intercondylar notch of the femur.
Owner:BOTIMER GARY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com