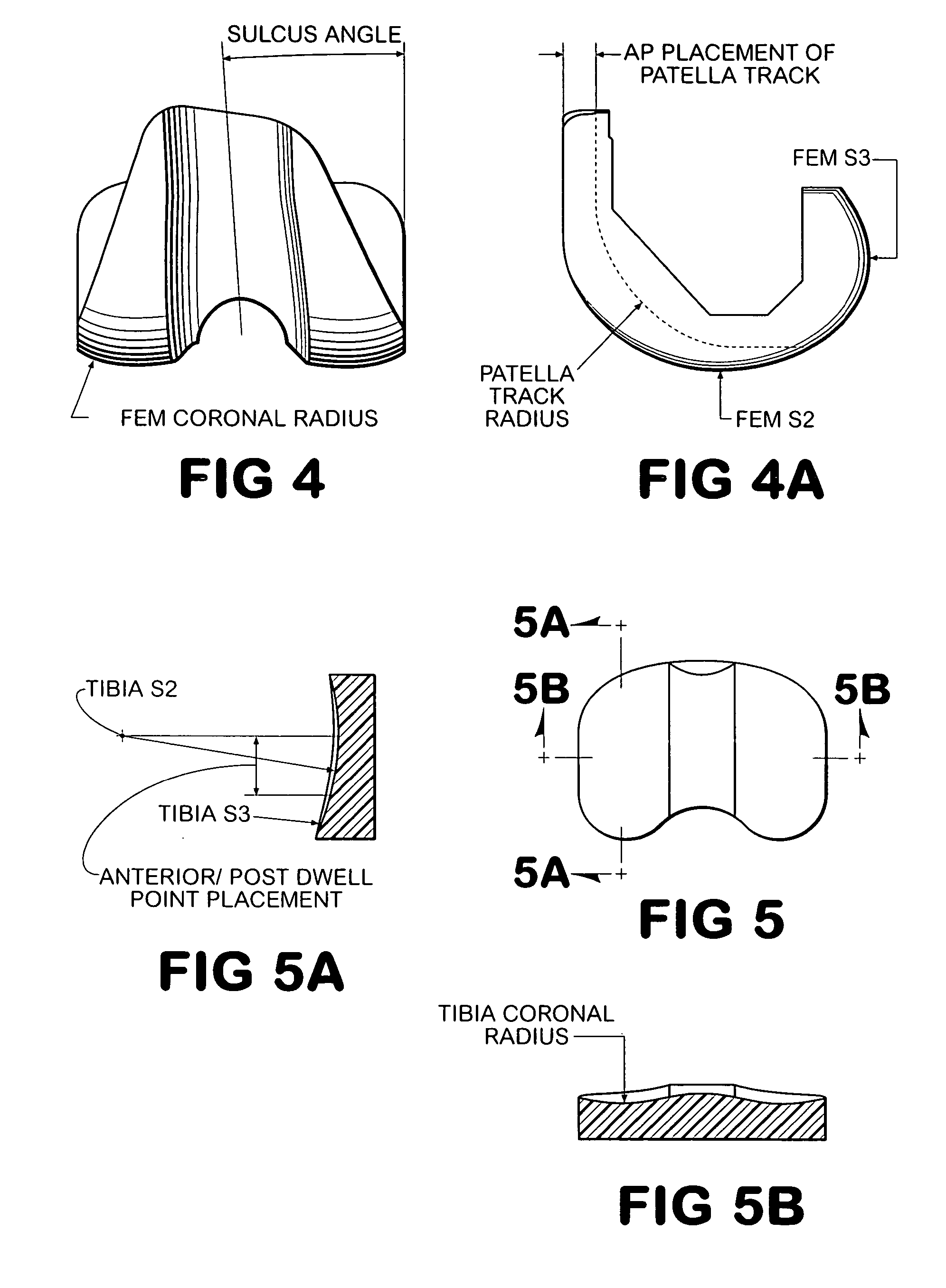
Patents
Literature
179 results about "Joints surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
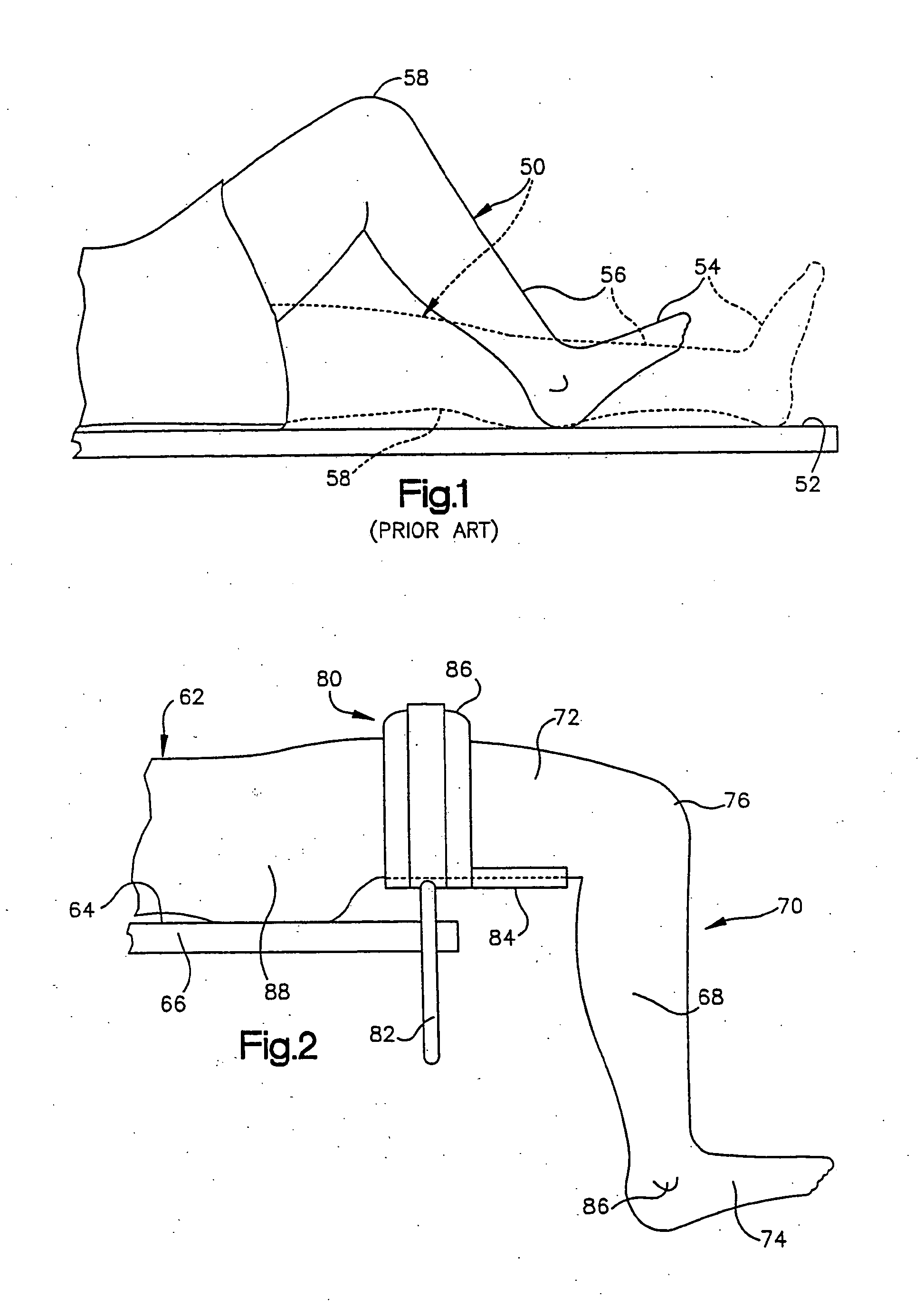
Replacement arthroplasty (from Greek arthron, joint, limb, articulate, + plassein, to form, mould, forge, feign, make an image of), or joint replacement surgery, is a procedure of orthopedic surgery in which an arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with an orthopedic prosthesis.
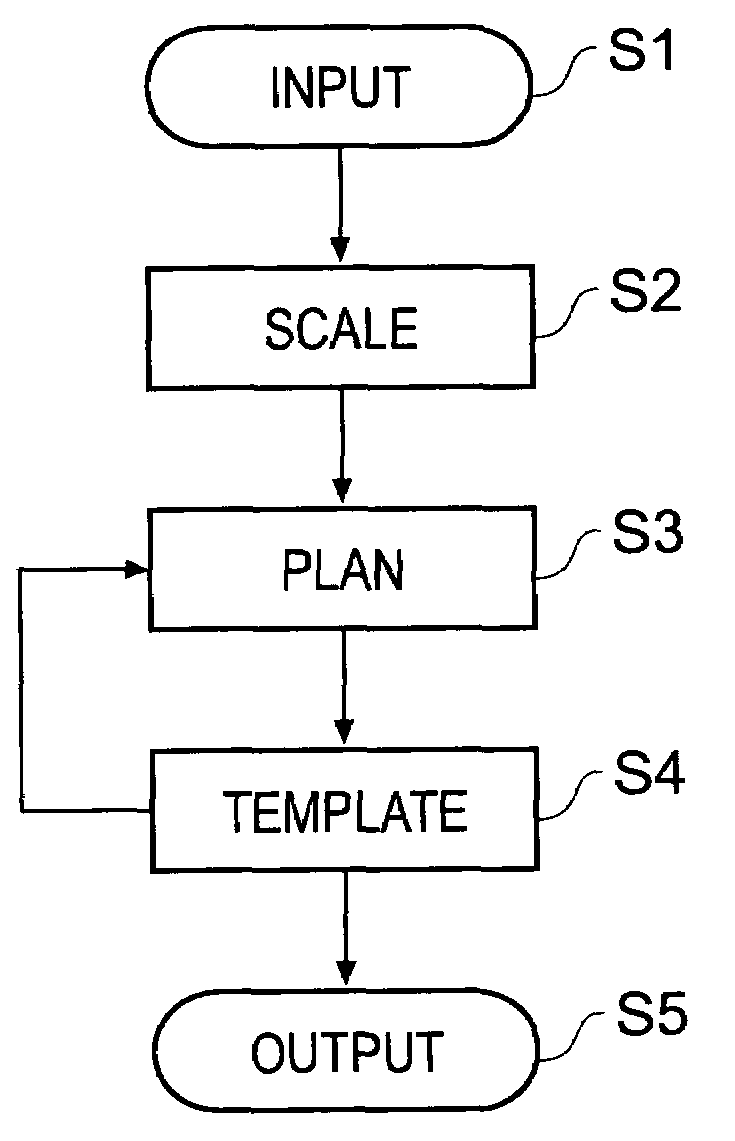
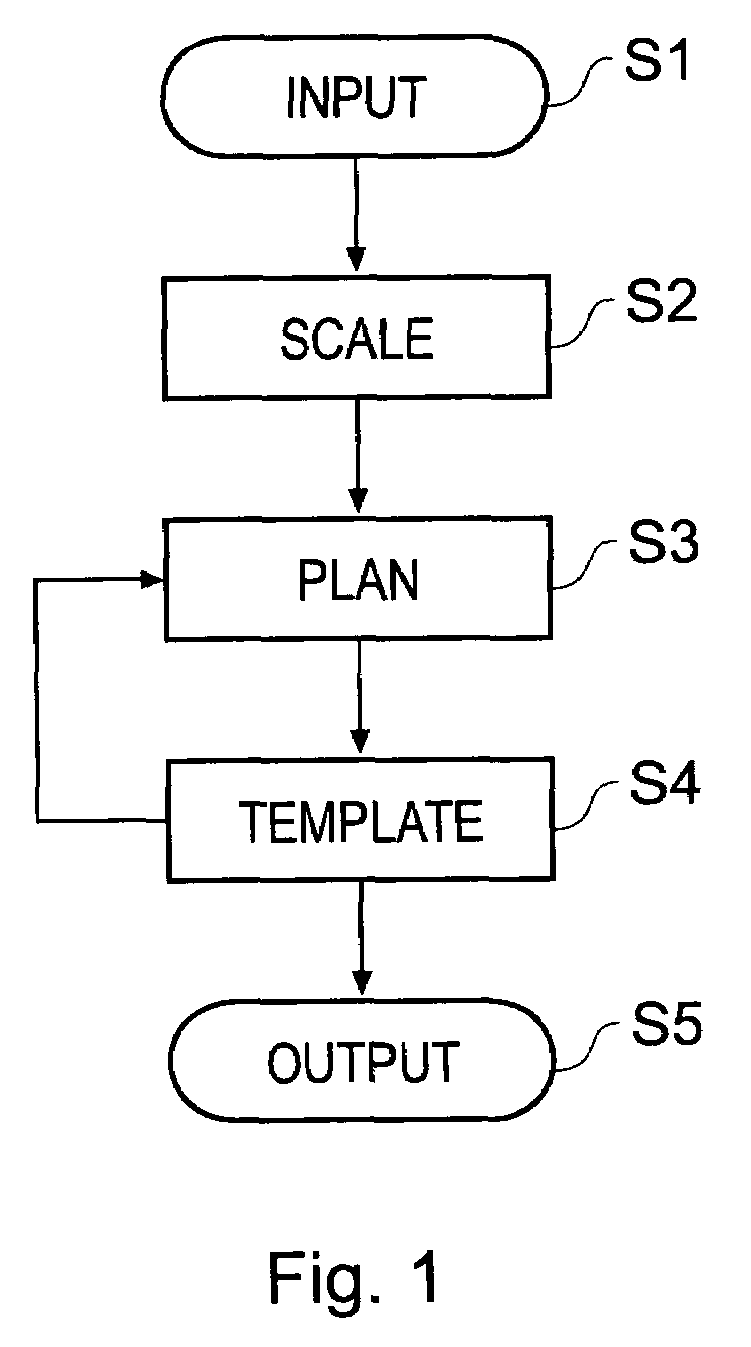
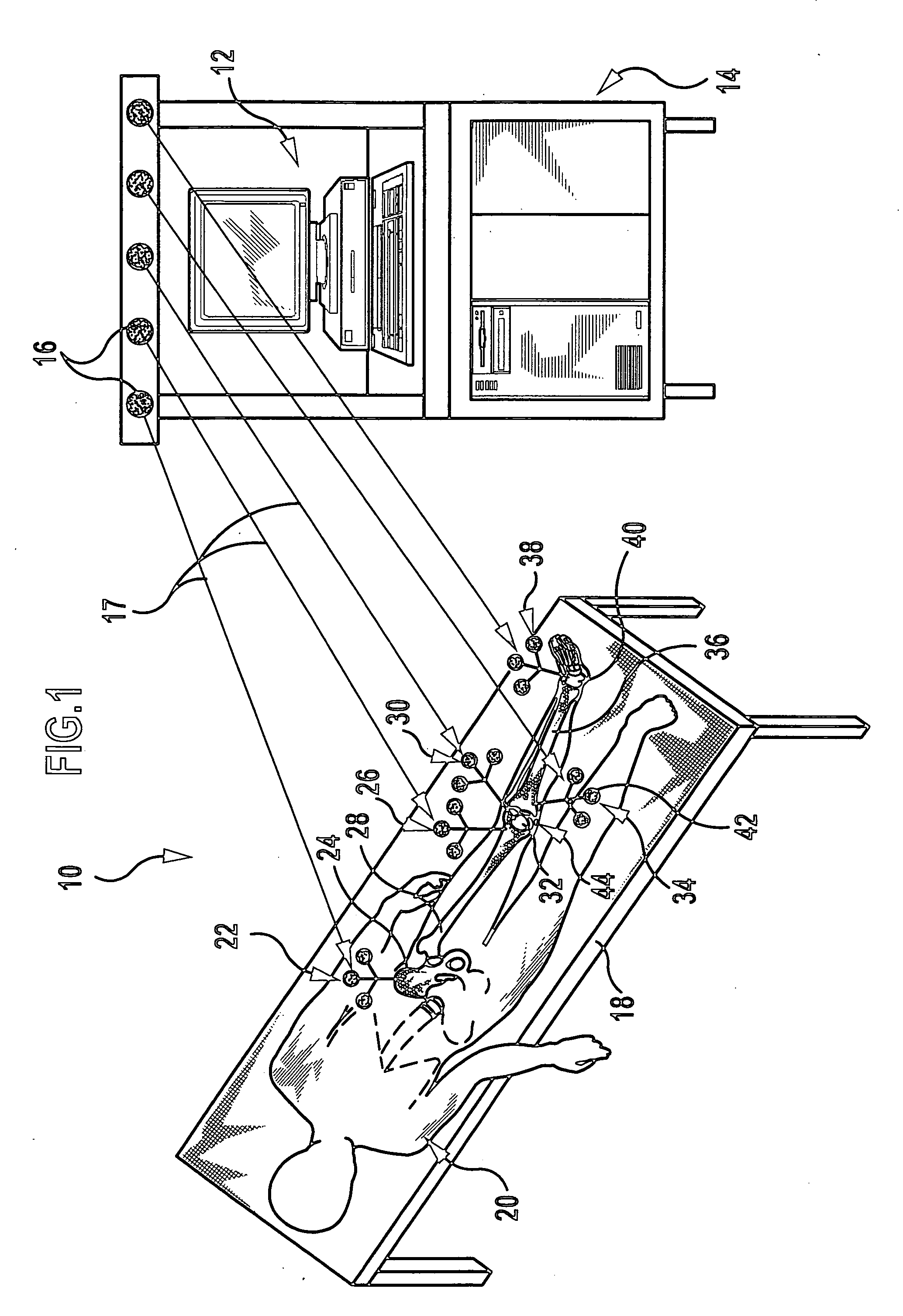
Orthopaedic surgery planning
Owner:MERIDIAN TECH LTD
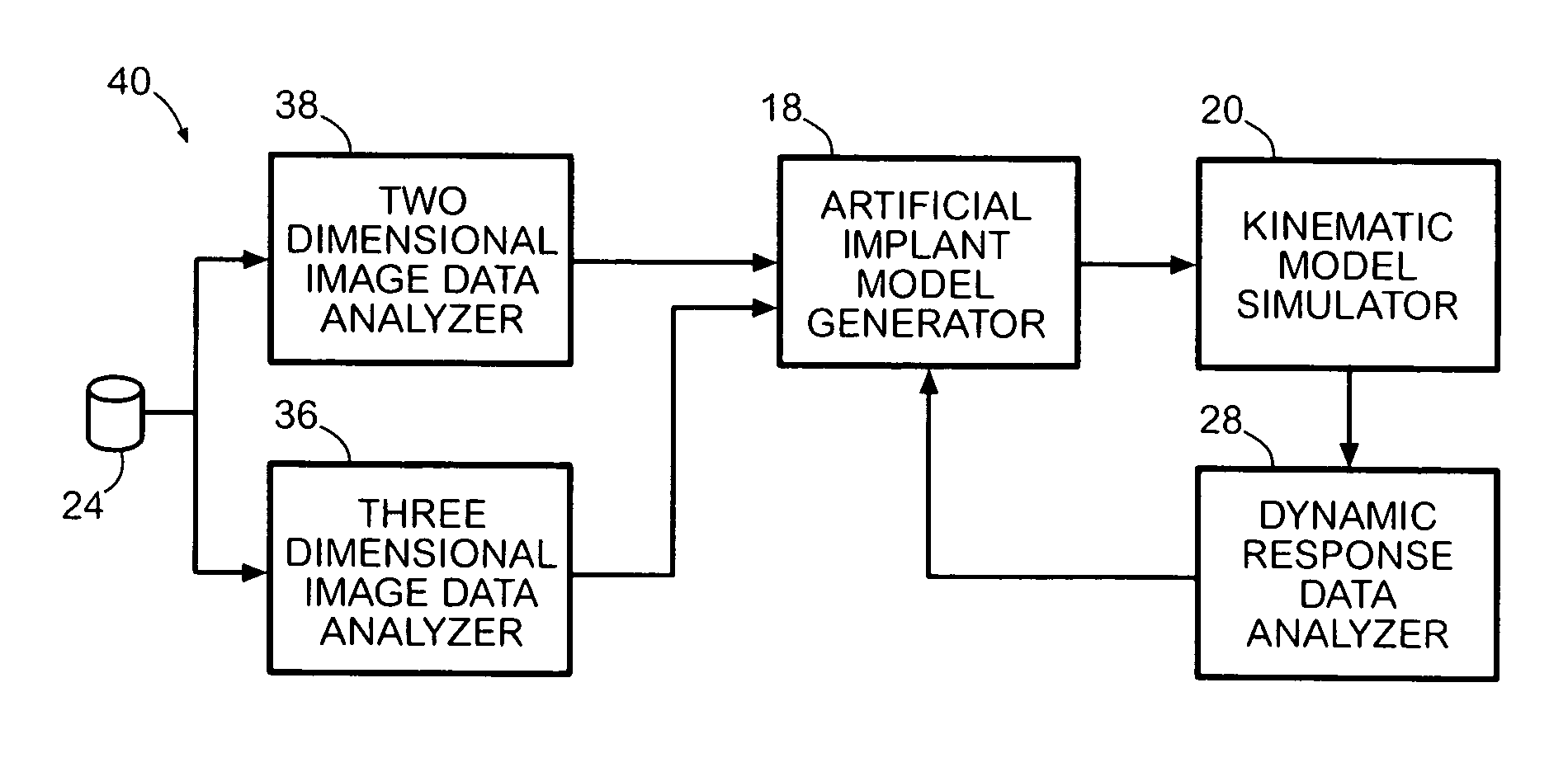
System and method for designing a physiometric implant system
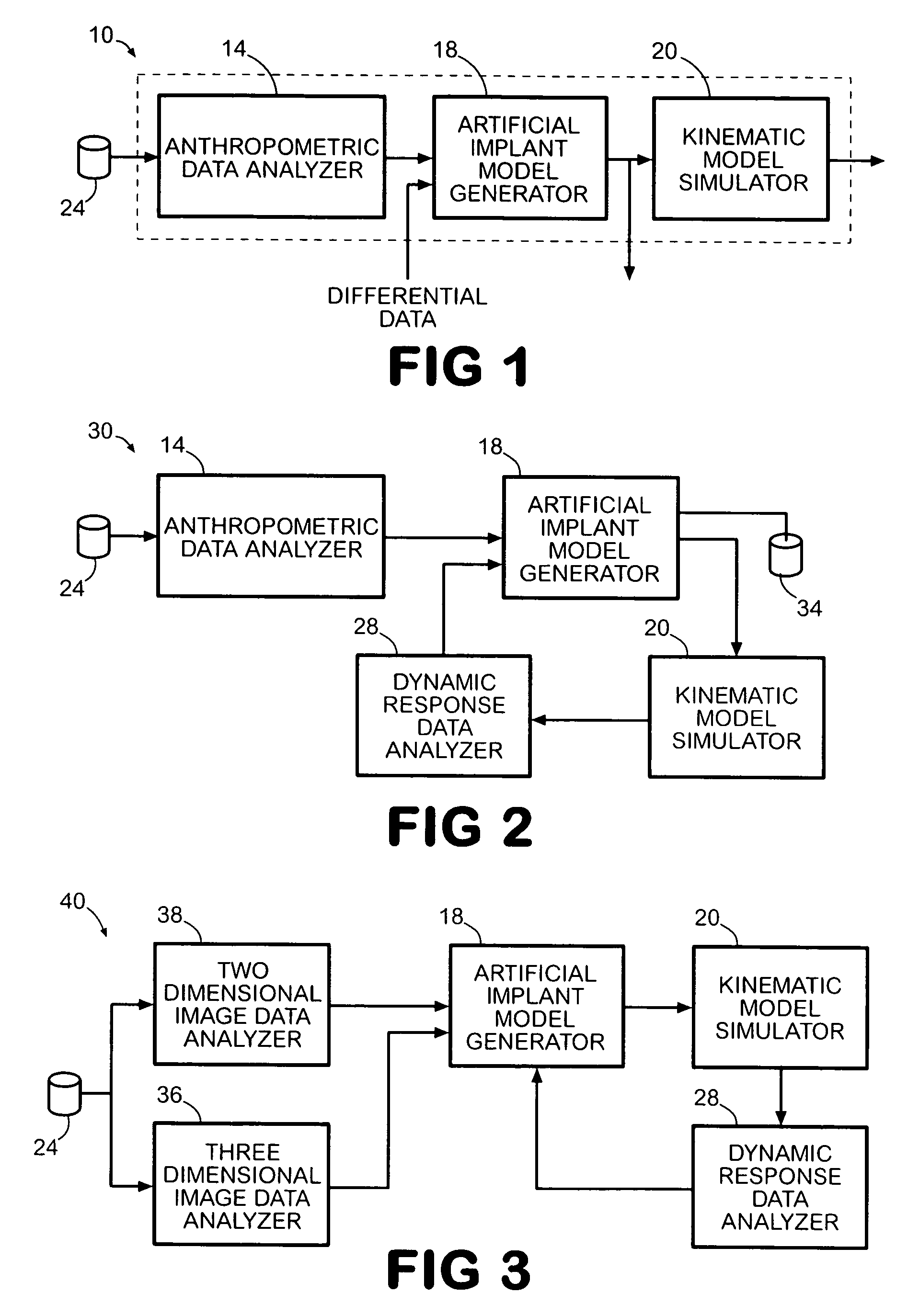
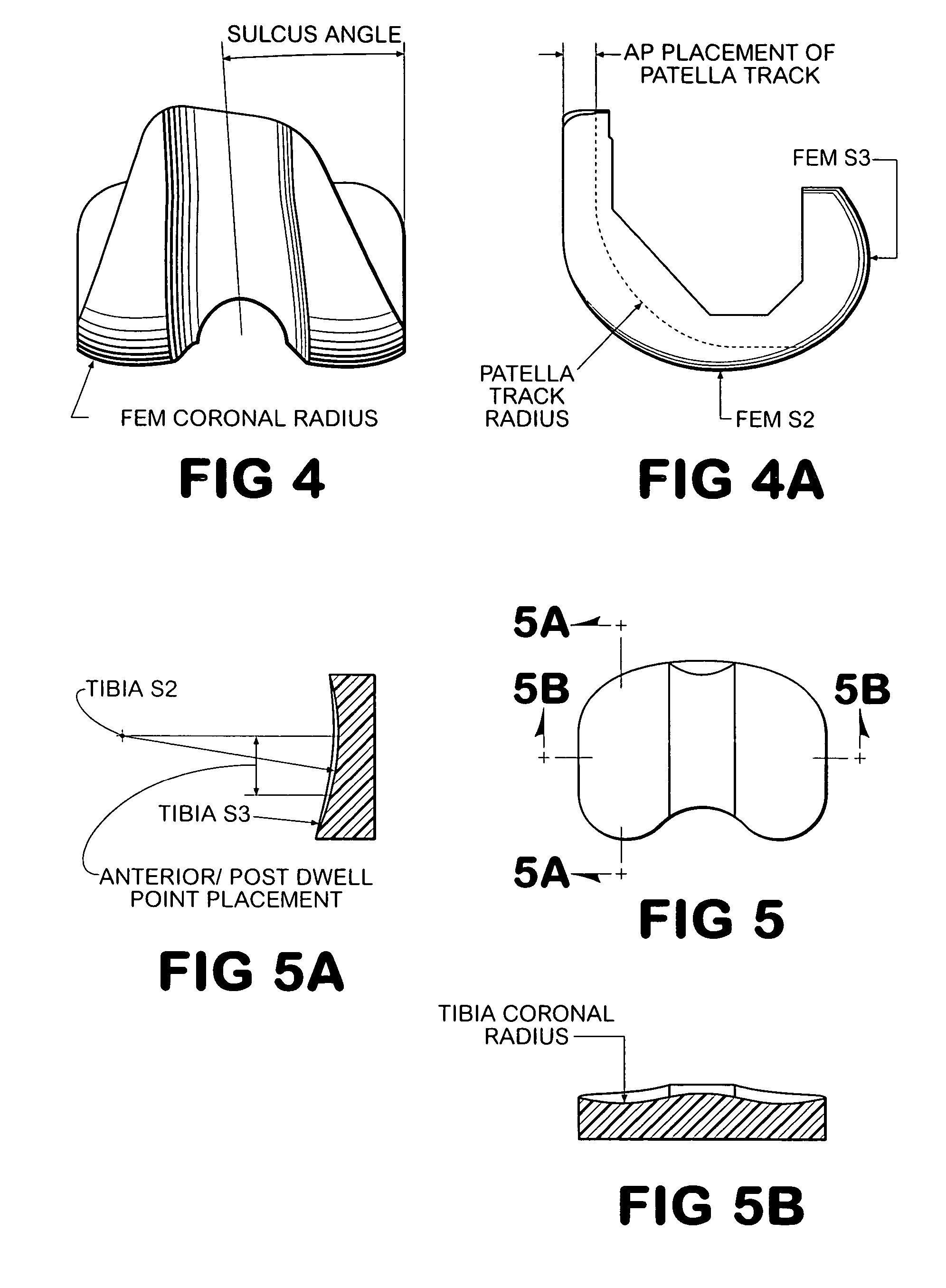
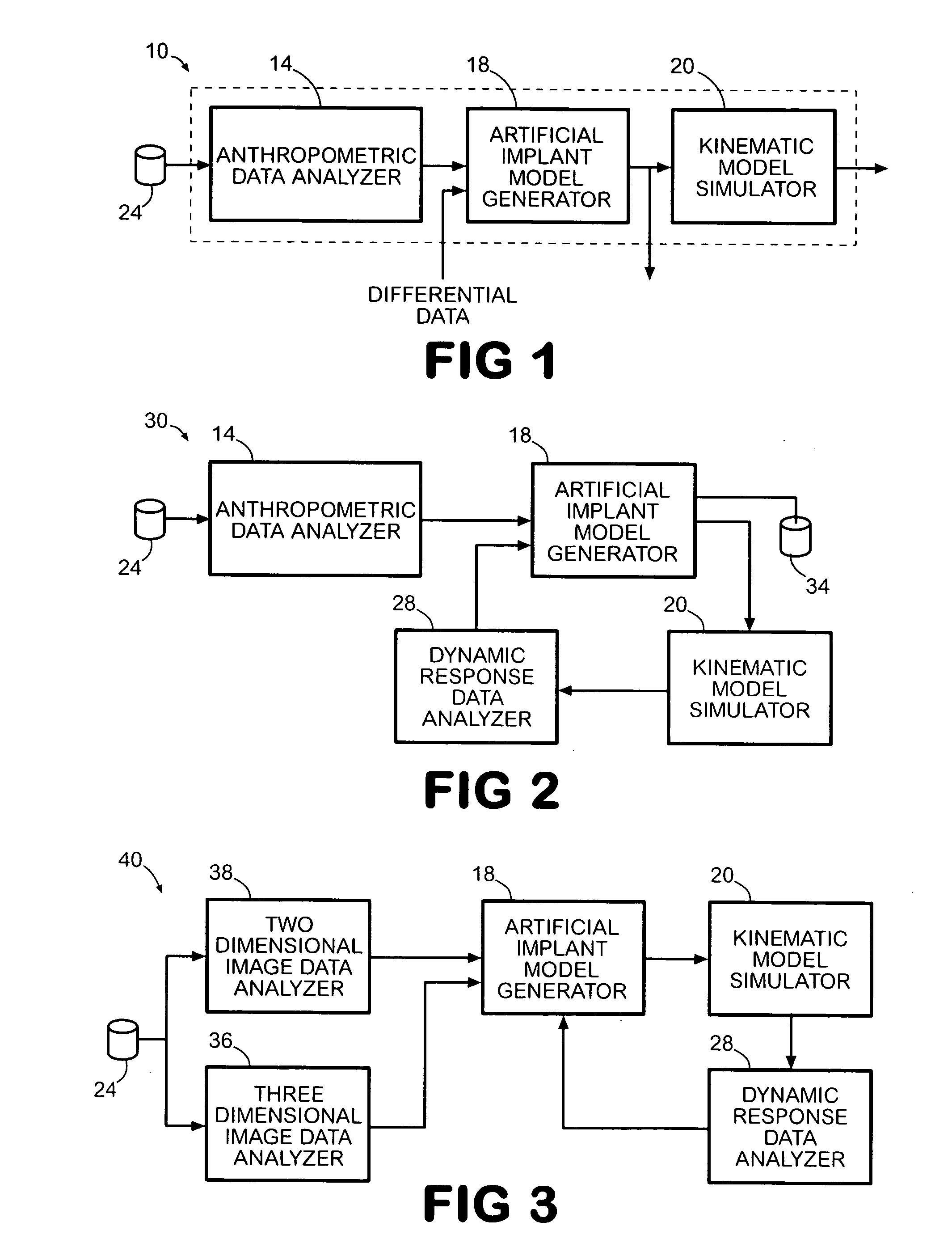
ActiveUS7383164B2Economy of motionReduction of jerkPerson identificationAnalogue computers for chemical processesDynamic modelsJoints surgery
A system improves the design of artificial implant components for use in joint replacement surgeries. The system includes an anthropometric static image data analyzer, an implant model data generator, a kinematic model simulator, and a dynamic response data analyzer. The implant model data generator may also use image data of a joint in motion for modification of the implant model data used in the kinematic simulation. Dynamic response data generated by the kinematic model simulation is analyzed by the dynamic response data analyzer to generate differential data that may be used to further refine the implant model data.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
System and method for designing a physiometric implant system
ActiveUS20050197814A1Economy of motionReduction of jerkPerson identificationAnalogue computers for chemical processesJoints surgeryImaging data
A system improves the design of artificial implant components for use in joint replacement surgeries. The system includes an anthropometric static image data analyzer, an implant model data generator, a kinematic model simulator, and a dynamic response data analyzer. The implant model data generator may also use image data of a joint in motion for modification of the implant model data used in the kinematic simulation. Dynamic response data generated by the kinematic model simulation is analyzed by the dynamic response data analyzer to generate differential data that may be used to further refine the implant model data.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
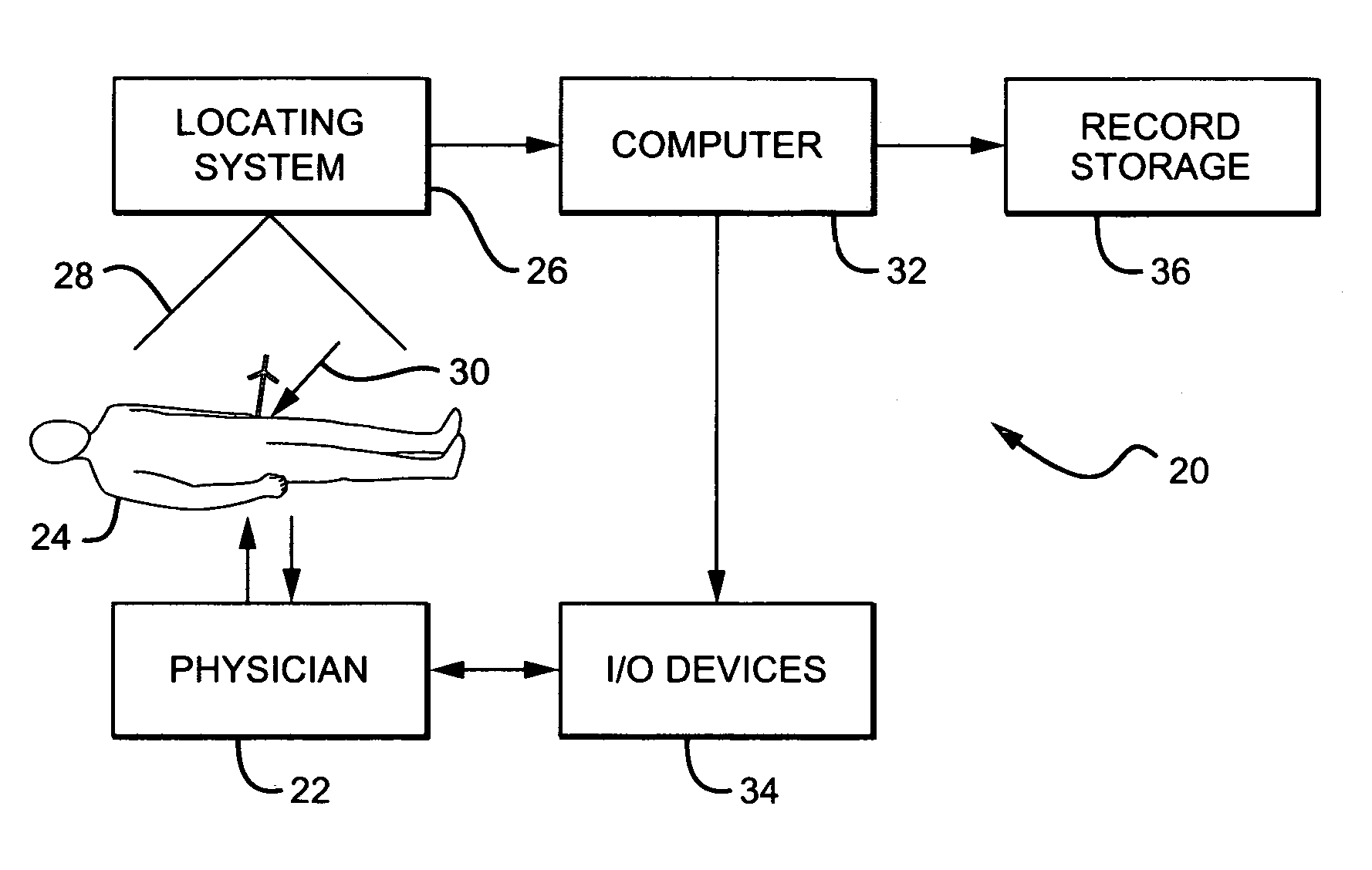
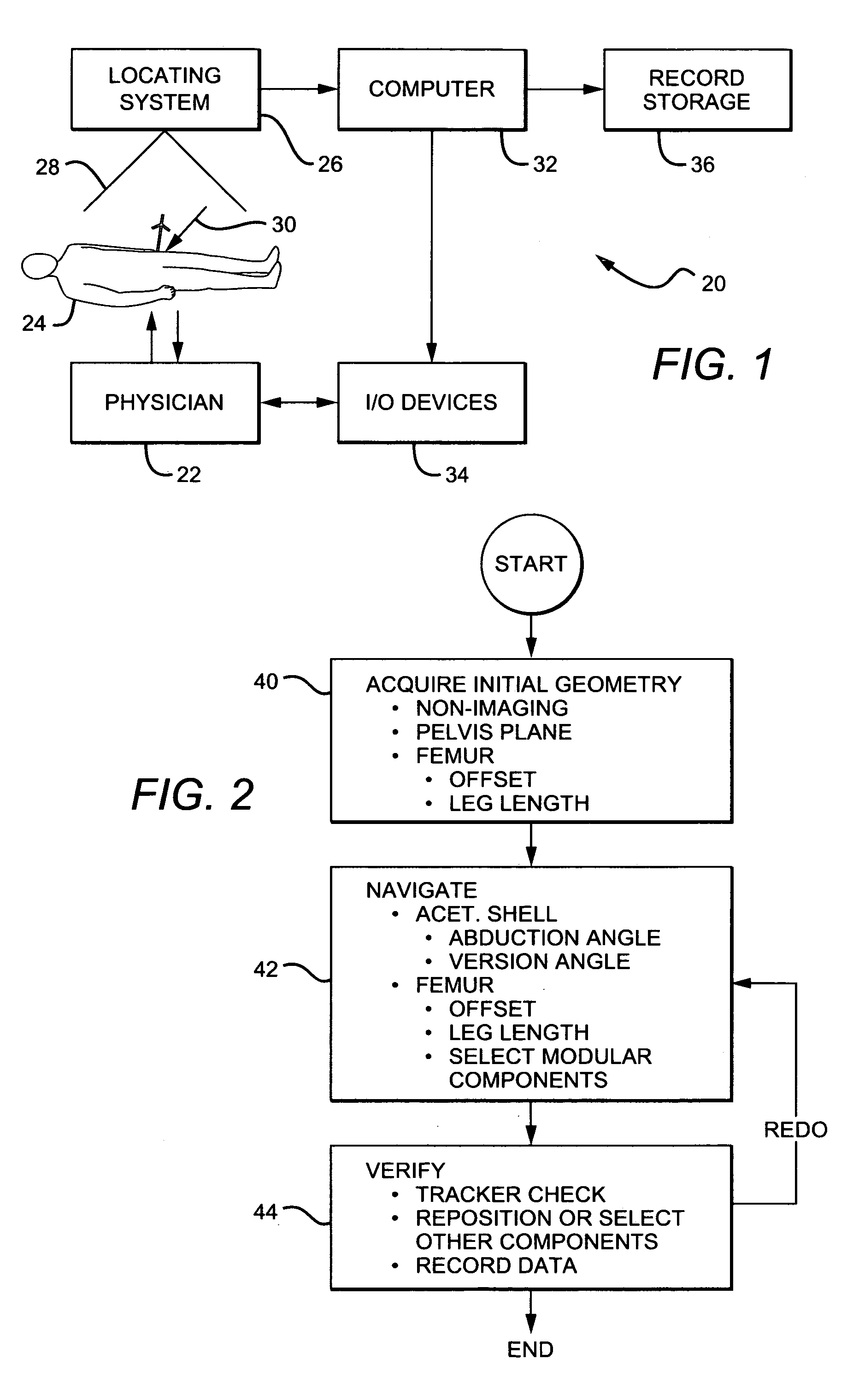
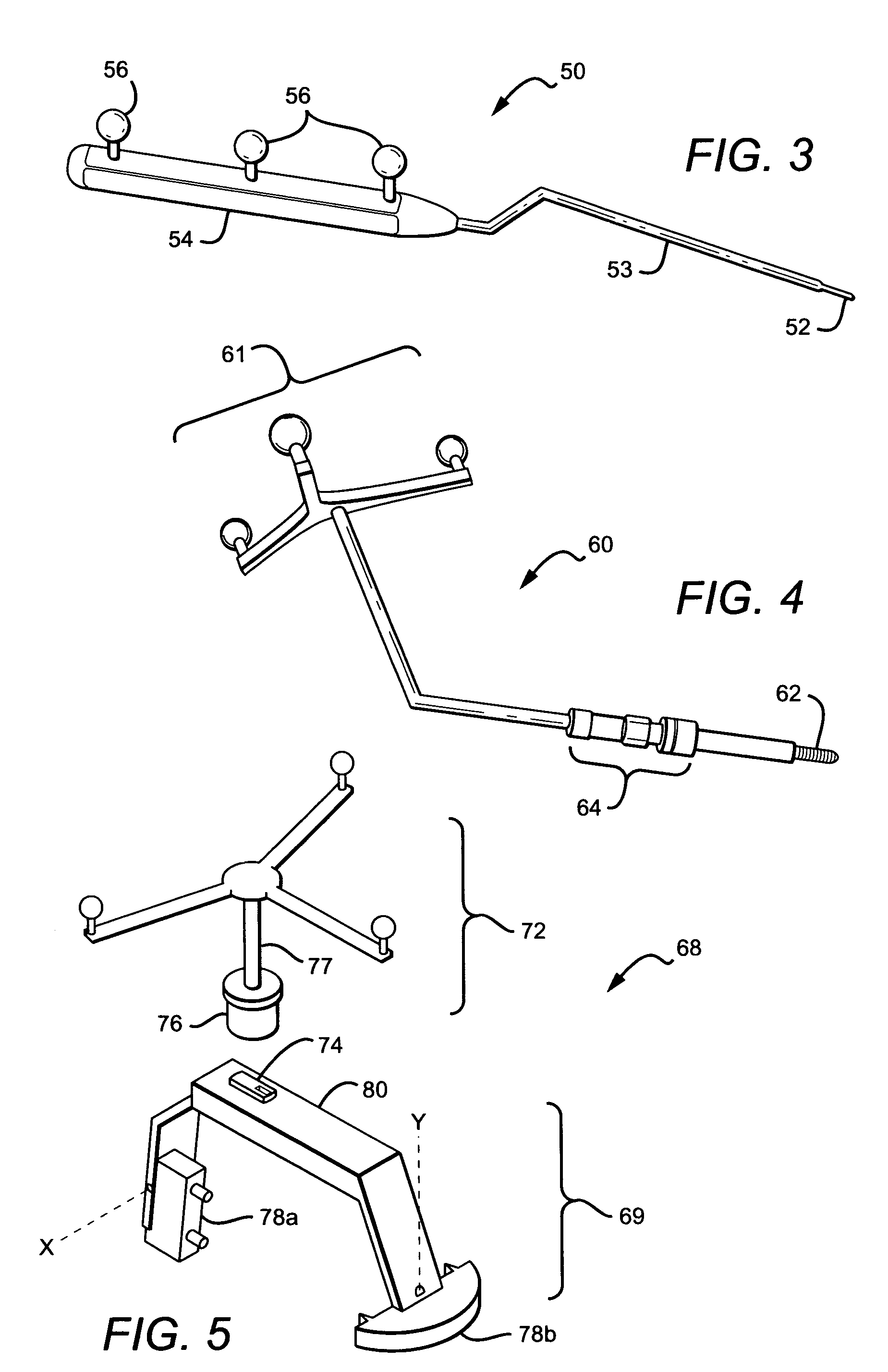
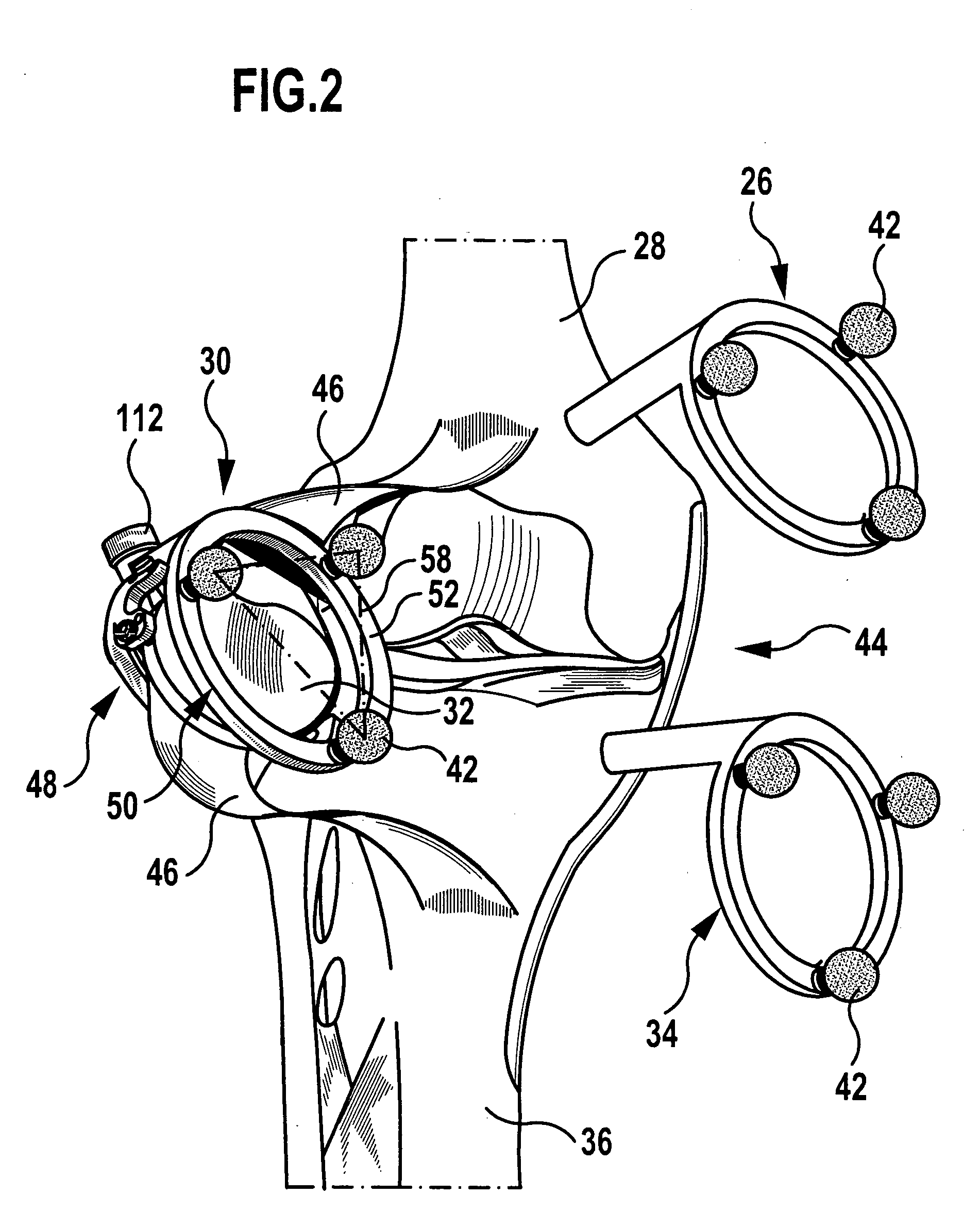
Non-image, computer assisted navigation system for joint replacement surgery with modular implant system
The invention includes a method and system for intra-operative navigation of a joint replacement operation, without recourse to pre-operative imagery of pre-operative computerized simulations. Trackable markers and a locating system are employed to track first and second bones. A computer receives positional information regarding the trackable markers and calculates (predicts) at least one suggested combination of components of a modular implant system to produce a desired post-operative skeletal relationship.
Owner:KINAMED
Tibial guide for knee surgery
InactiveUS20130237989A1Promote balance between supply and demandSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsTibiaKnee surgery
A joint replacement kit for use in a joint replacement procedure replacing a portion of a body joint. The kit includes a cutting guide and a trial component wherein the cutting guide and trial component are packaged together. There is also provided a method for replacing a portion of a body joint. The method includes providing a joint replacement kit having a cutting guide and a trial component, positioning the cutting guide against an end portion of a bone, cutting the end portion of the bone with a cutting instrument, positioning the trial component to the cut end portion of the bone, and disposing of the cutting guide and trial component.
Owner:BONUTTI SKELETAL INNOVATIONS
Patella reference device
InactiveUS20060052792A1Simple structureClearly definedSurgical navigation systemsPosition fixationKnee operationsKnee Joint
In order to conduct navigation-assisted knee operations in a simple and optimum manner, a patella reference device is proposed for the determination of the spatial position of a patella of a human knee joint during a navigation-assisted surgical procedure, comprising a base unit that can be secured on the patella, a reference element that can be detected by a detection device and a connecting device for the detachable connection of the base unit and the reference element in a first reference position and in at least one further second reference position differing from the first reference position.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
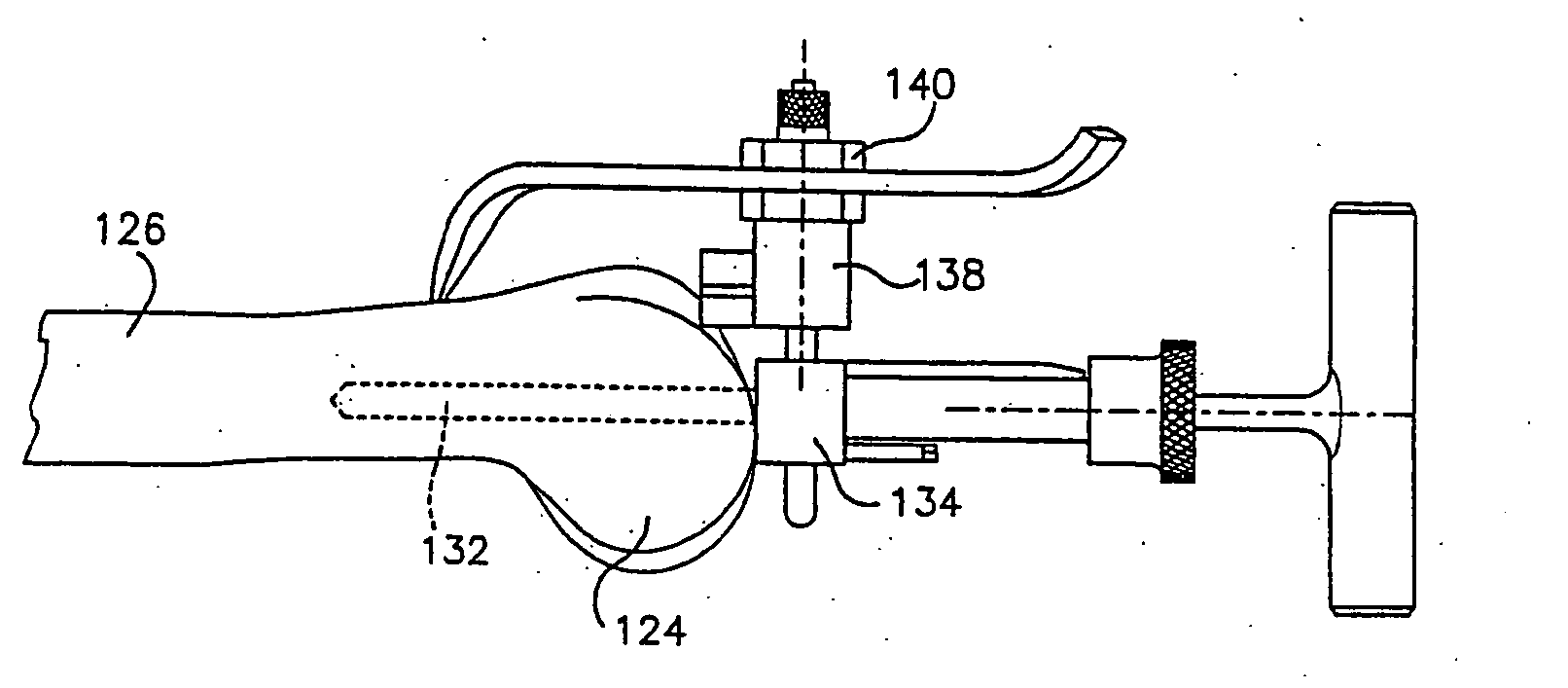
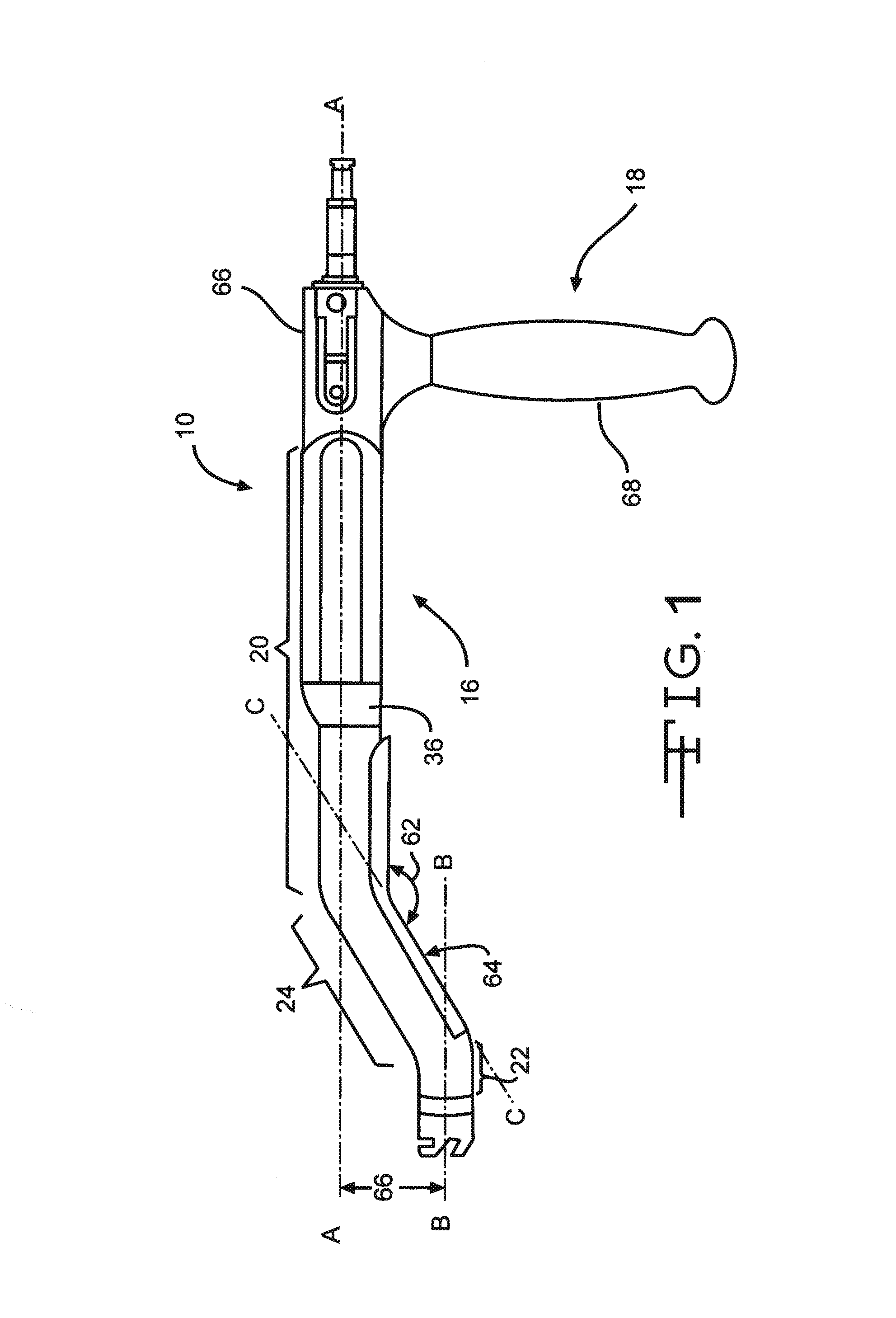
Broach handle for minimally invasive hip replacement surgery
A broach handle for attachment to a broach comprising a distal working end and a proximal connector end, the proximal connector end comprising a bore extending distally into the broach, and a finger comprising a recess and extending proximally away from the broach, the broach handle comprising: a body having a distal end and a proximal end, the distal end being longitudinally and laterally offset from the proximal end and comprising a finger for seating in the bore of the broach and a bore for receiving the finger of the broach; a linkage connected to the body and comprising a finger for selective disposition in the recess of the finger of the broach; and a lever connected to the body and arranged to manipulate the proximal end of the linkage so that manipulation of the proximal end of the lever can lock and unlock a broach to the handle.
Owner:ORTHOGROUP
Methods for manufacturing custom cutting guides in orthopedic applications
InactiveUS20130292870A1Additive manufacturing apparatusComputer-aided planning/modellingAnatomical structuresPhysical model
A patient specific system for joint replacement surgery that includes a custom cutting guide having an inner surface shaped to match the anatomy of a surface of a patient's joint to be resected. The custom cutting guide is designed for use with a corresponding prosthesis. A slot and guide holes are formed in the custom cutting guide corresponding to features protruding outwardly from a positive physical bone model. The slot guides a tool during resection of the femur to produce a first resected surface on the femur for mounting the prosthesis. The guide is formed from the positive physical model by applying a polymeric composition to the outer surface of the positive physical model including the features corresponding to the slot and guide holes of the custom cutting guide.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Intraoperative joint force measuring device, system and method
ActiveUS20070005145A1Optimal implant placementSmall sizeSurgical furniturePerson identificationMeasurement deviceEngineering
A surgical device for joint replacement surgery includes an intraoperative joint head having a stem attachment structure where the stem attachment structure may be removably attachable to a stem and a force sensor housed by the joint head for measuring in vivo forces during surgery. The in vivo forces may be generated by one or more of tension provided by soft tissue, load application during surgery, limb movement during surgery, and a combination thereof. Also, the joint head may provide a cavity where the stem attachment structure houses the force sensor and may be removably insertable in the joint head cavity. A method of performing joint replacement surgery includes installing an intraoperative joint head having a force sensor housed by the joint head and a stem attachment structure, the stem attachment structure being removably attachable to a stem, measuring joint forces, and adjusting an implant parameter based on the measured joint forces.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Femoral guide for knee surgery
InactiveUS20130226185A1Promote balance between supply and demandSuture equipmentsOperating tablesKnee surgeryBody joints
A joint replacement kit for use in a joint replacement procedure replacing a portion of a body joint. The kit includes a cutting guide and a trial component wherein the cutting guide and trial component are packaged together. There is also provided a method for replacing a portion of a body joint. The method includes providing a joint replacement kit having a cutting guide and a trial component, positioning the cutting guide against an end portion of a bone, cutting the end portion of the bone with a cutting instrument, positioning the trial component to the cut end portion of the bone, and disposing of the cutting guide and trial component.
Owner:BONUTTI SKELETAL INNOVATIONS
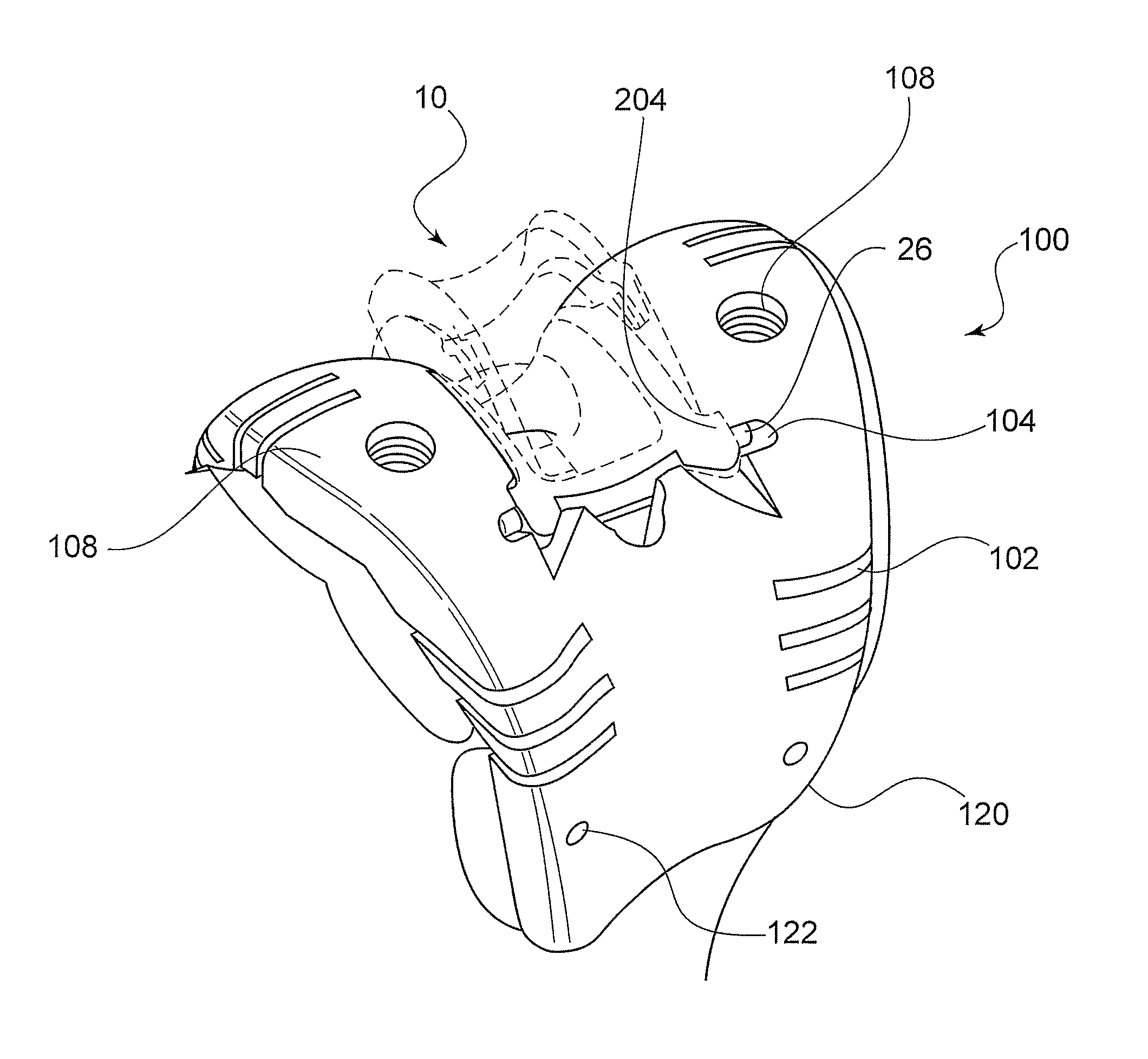
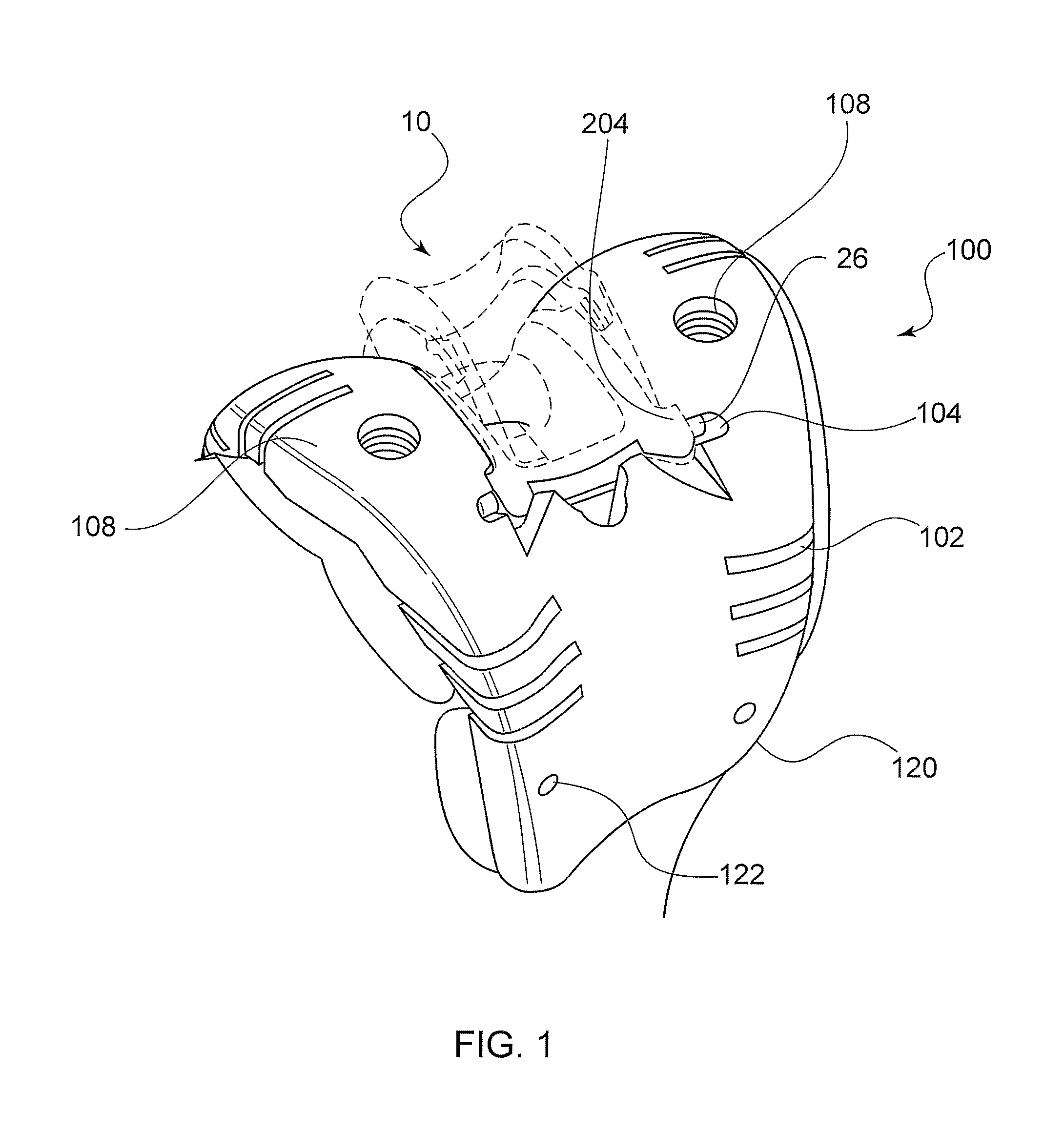
Trial femoral prosthesis and its use
Embodiments of the present application relate generally to provisional orthopedic components, and specifically, to a trial system including a cam module (10) and a trial femoral component (100) that can be used during joint replacement surgery. The systems and methods described help a surgeon prepare a patient's bone to receive a permanent implant by providing a system that can be used to guide preparatory box cuts, and that can then be completed with a cam module (10)—without removal from the patient's bone—so that the same component can be used for the trialing process.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Inserter for minimally invasive joint surgery
ActiveUS20060149285A1Easy to disassembleMinimize the numberJoint implantsAcetabular cupsLocking mechanismProsthesis
An acetabular impactor aids a surgeon in controlling the installation of an acetabular cup prosthesis having a central, female aperture. The impactor includes an impactor head, housing and a locking mechanism. The housing is attached to the impactor head, the housing enclosing a drive train having, at a far end, a prosthesis engaging thread, and at the opposite end, a handle which facilitates turning of the drive train by the operator. The locking mechanism is associated with the housing which selectively locks the drive train, and thus the prosthesis, in position. The opposite end of the drive train has a latch device which enables quick removal from the housing for cleaning and sterilization.
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
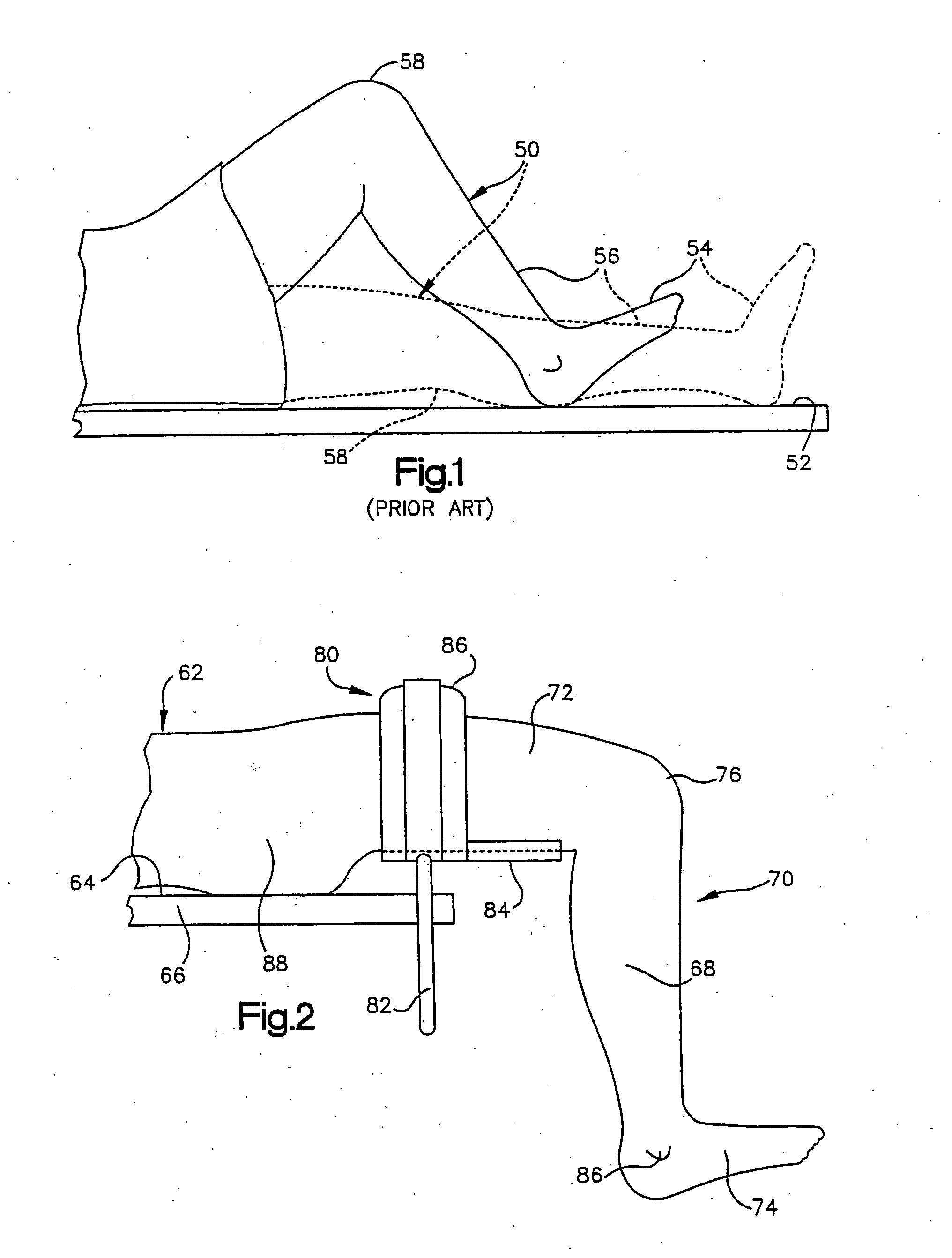
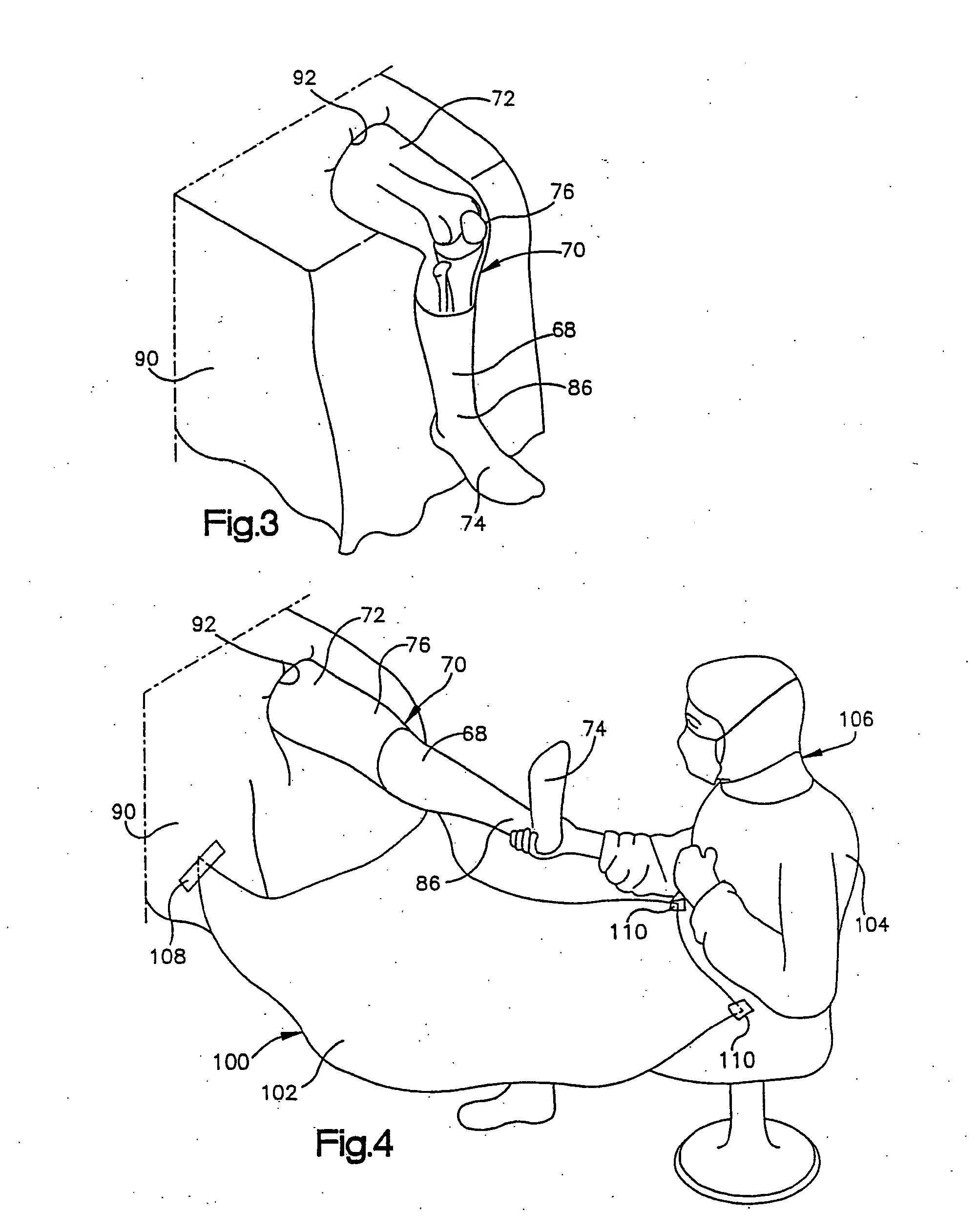
Method and system for determining resection guidelines for joint replacement surgical procedures
ActiveUS20070043375A1Easy to limitOvercome limitationsDiagnosticsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesGuidelineLight beam
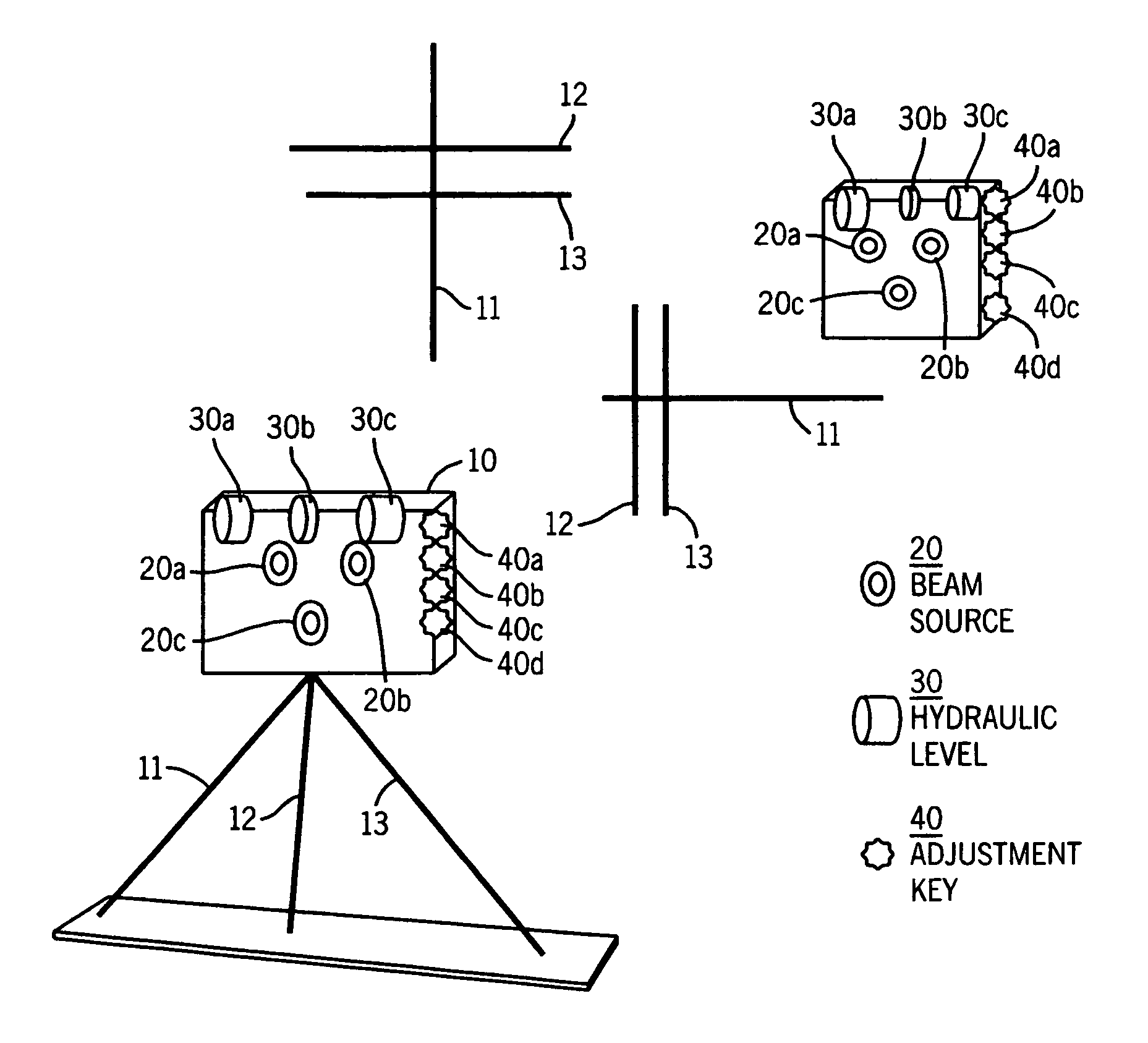
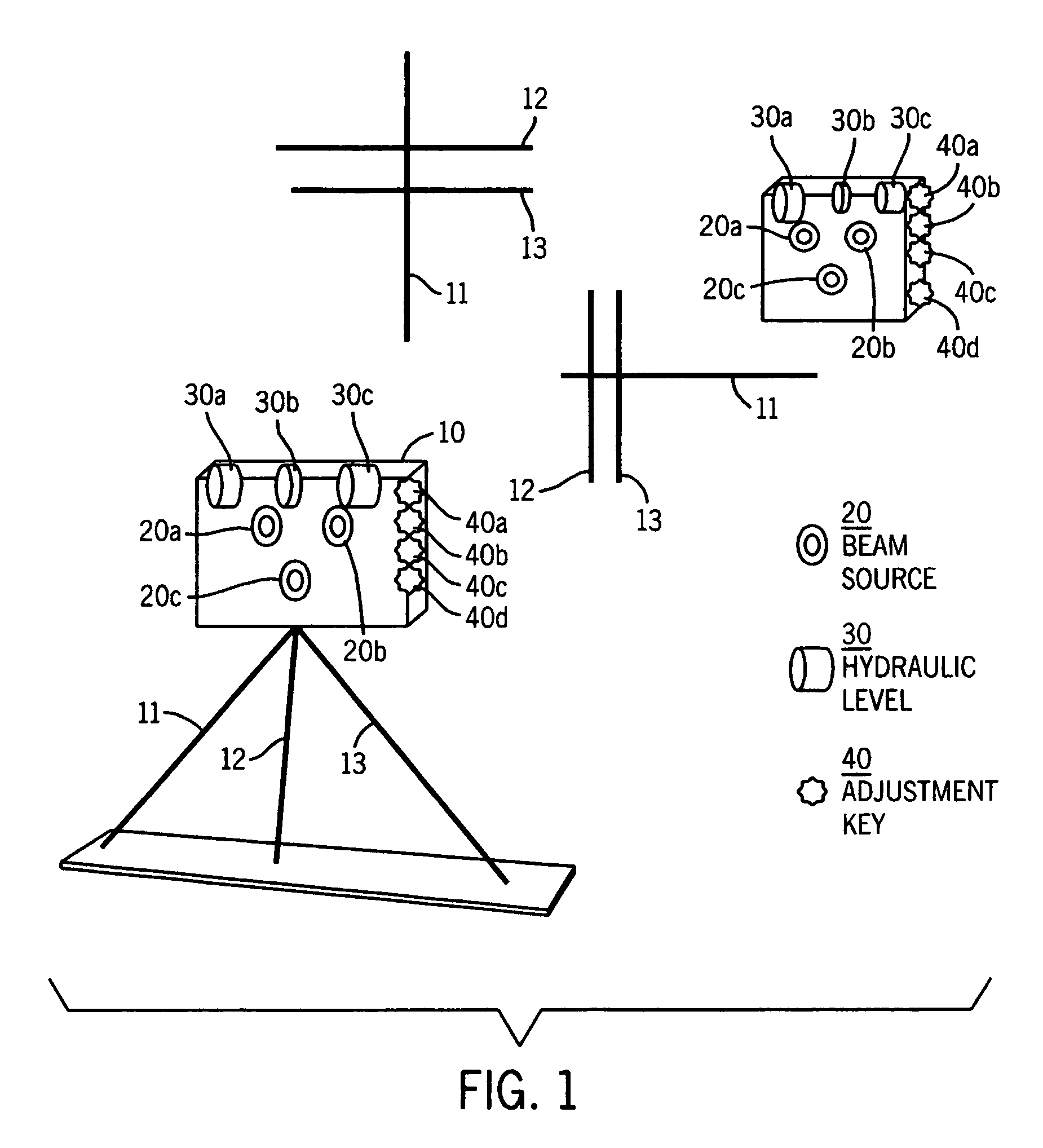
A method and system for utilizing a plurality of linear laser beams to project guidelines onto a skeletal joint for resection of the joint during surgical joint replacement procedures. The method comprises projecting a linear laser beam along the long axis of a limb at one end of the joint, utilizing the first beam as a benchmark for a second linear laser beam that is projected in an angular orientation to the first beam, and projecting a third beam in a parallel orientation to the second beam, which third beam provides the guideline for the resection procedure. The system comprises linear laser beam generating means with integrated leveling devices to allow for neutral positioning of the system prior to use. The system further includes a separate cutting block with a removable handle, wherein the handle includes its own integrated leveling devices. The cutting block is attached to the joint that is being resected in an orientation that is established by the linear laser beam guidelines.
Owner:ANISSIAN LUCAS
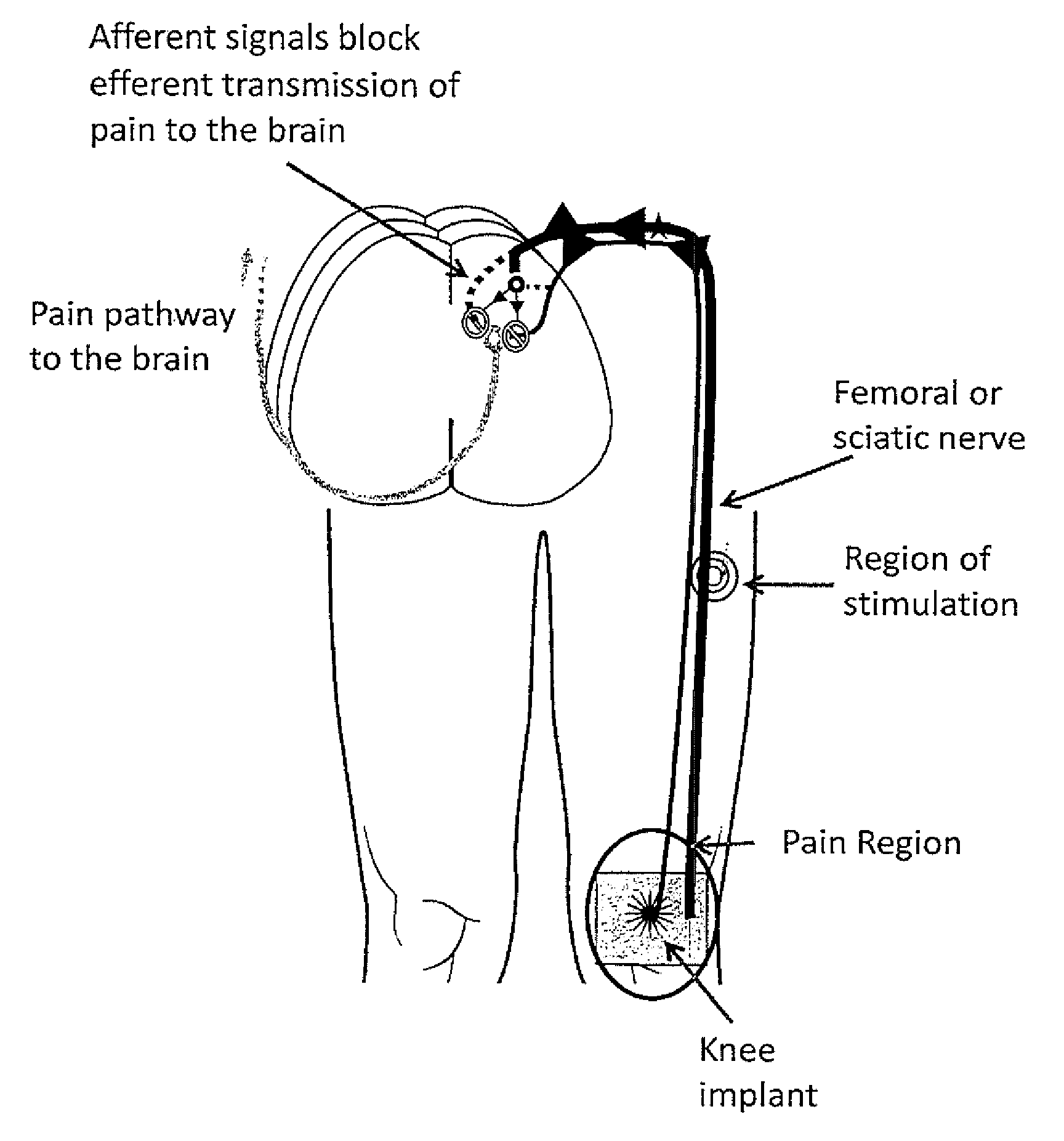
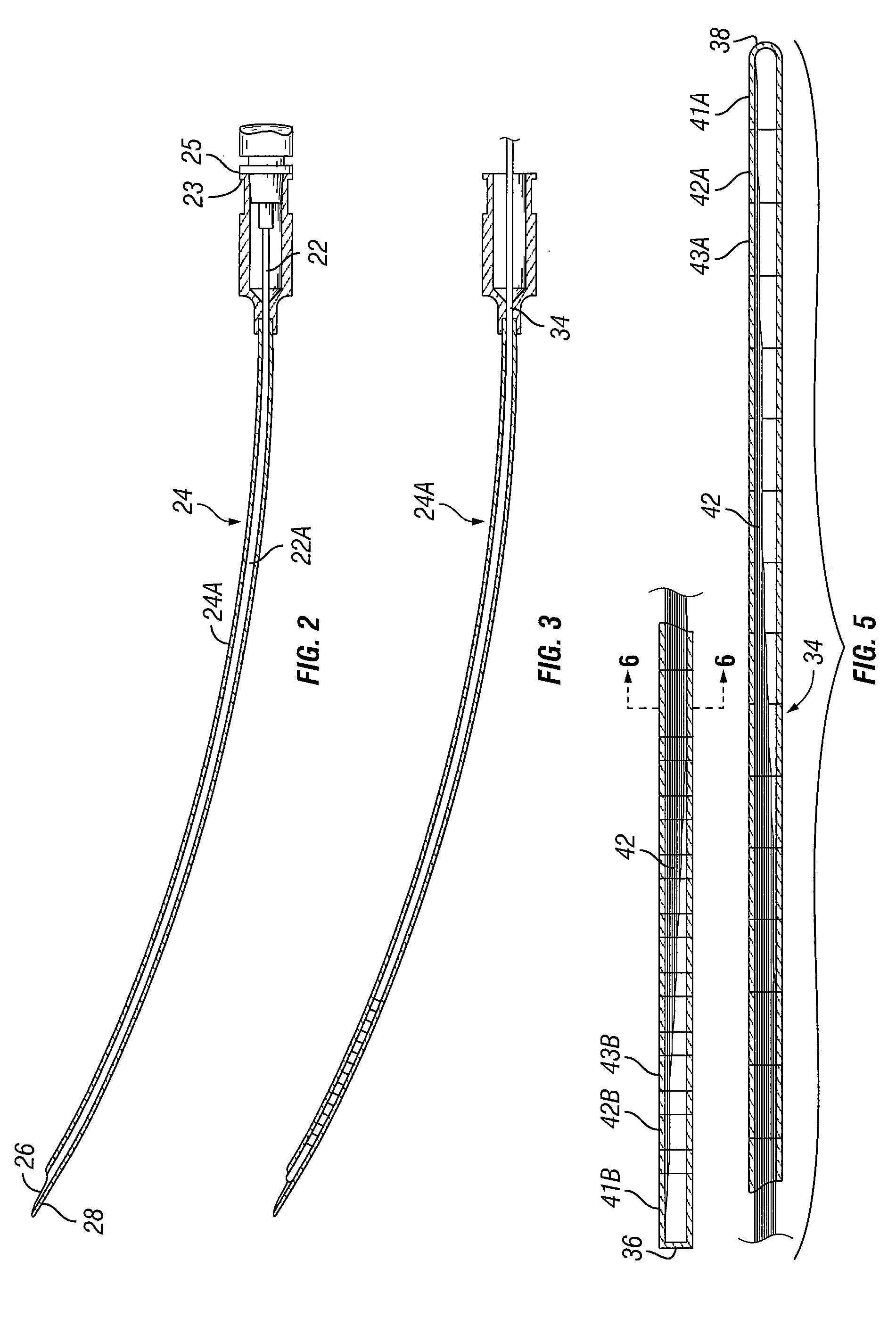
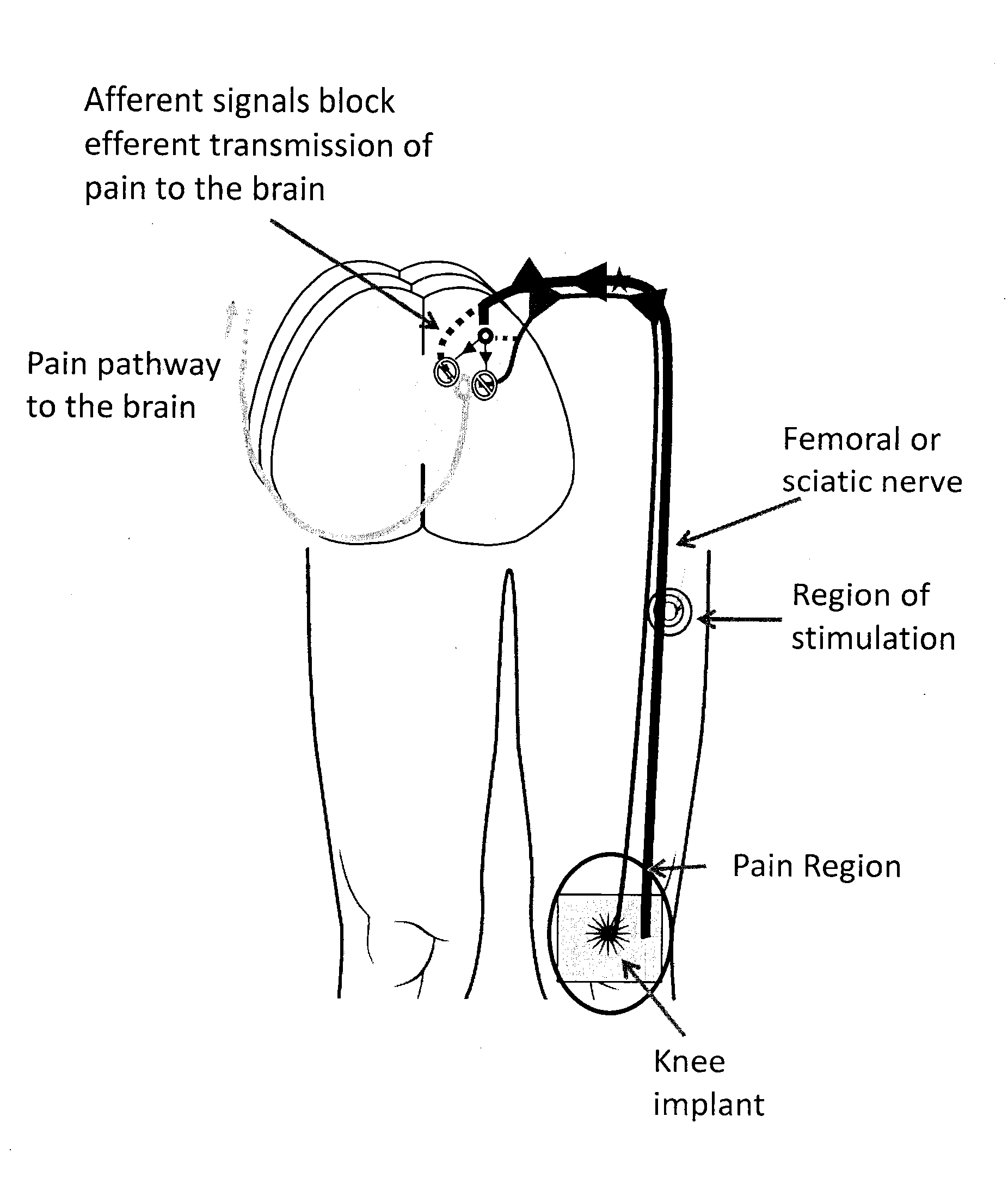
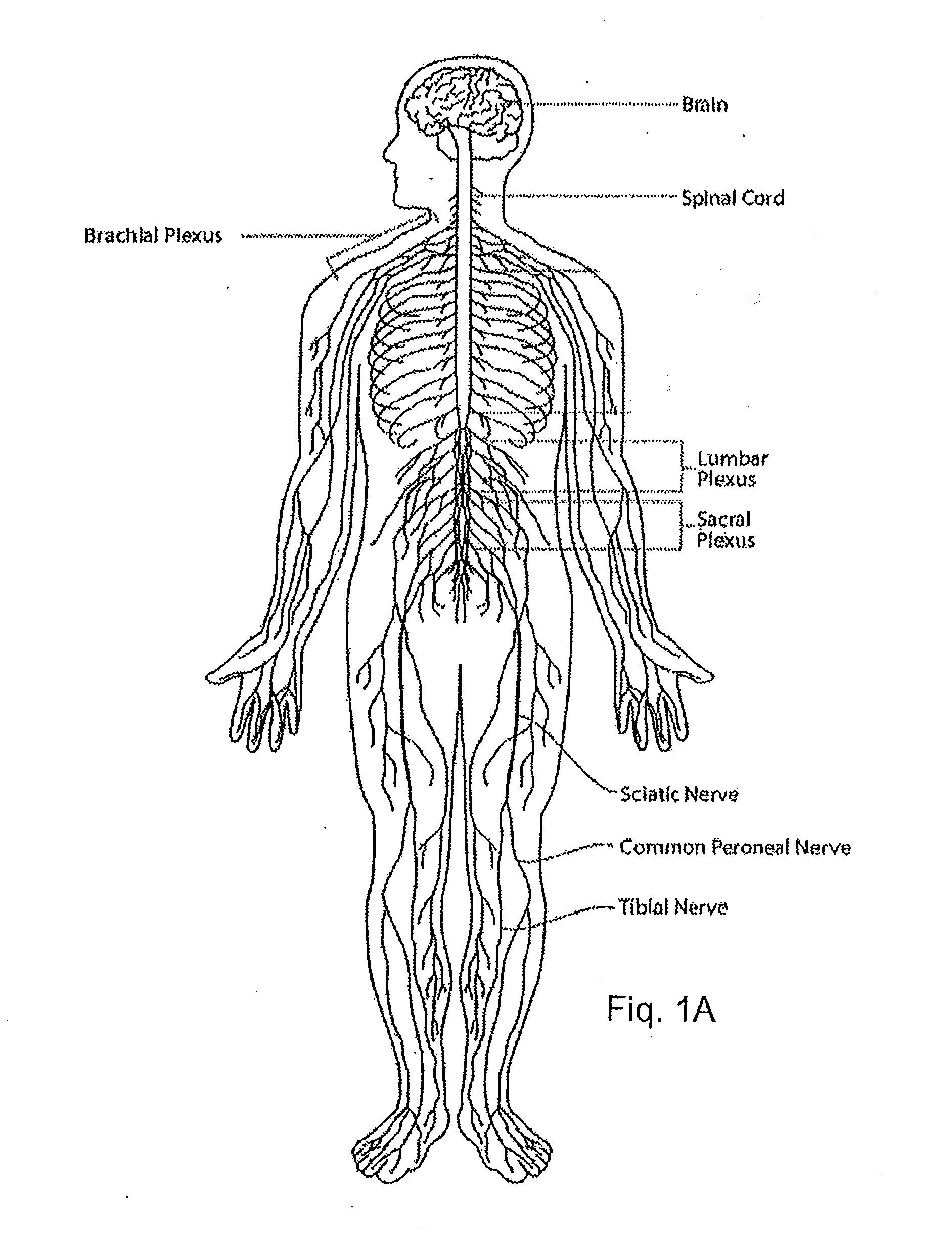
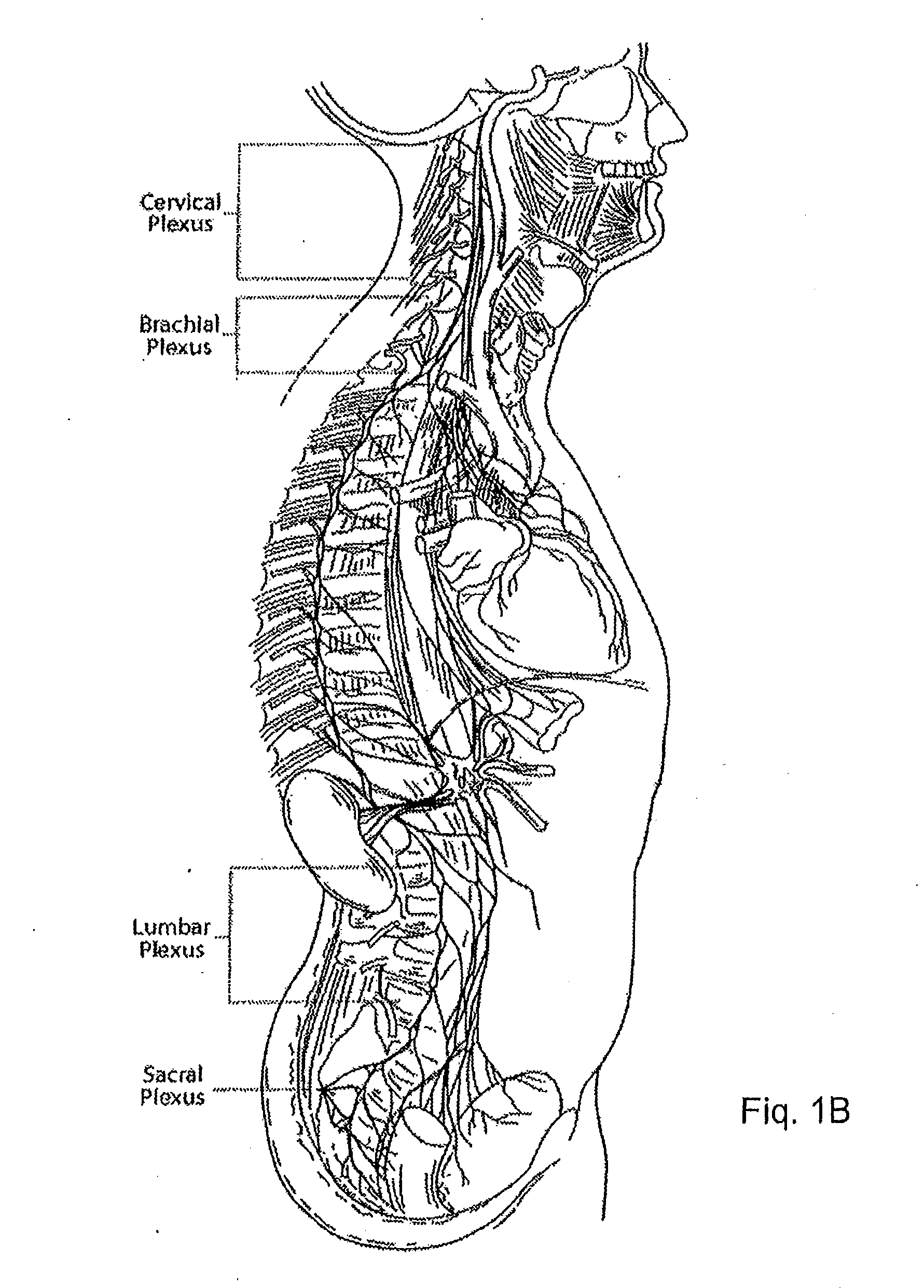
System and method for treatment of pain related to limb joint replacement surgery
It has been discovered that pain felt in a given region of the body can be treated by stimulating a peripheral nerve at a therapeutically effective distance from the region where pain is felt to generate a comfortable sensation (i.e., paresthesia) overlapping the regions of pain. A method has been developed to reduce pain in a painful region following limb joint replacement by stimulating a peripheral nerve innervating the painful region with an electrode inserted into tissue and spaced from the peripheral nerve. This method may be used to help alleviate postoperative pain in patients following total knee arthroplasty surgery or other limb joint replacement surgeries.
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
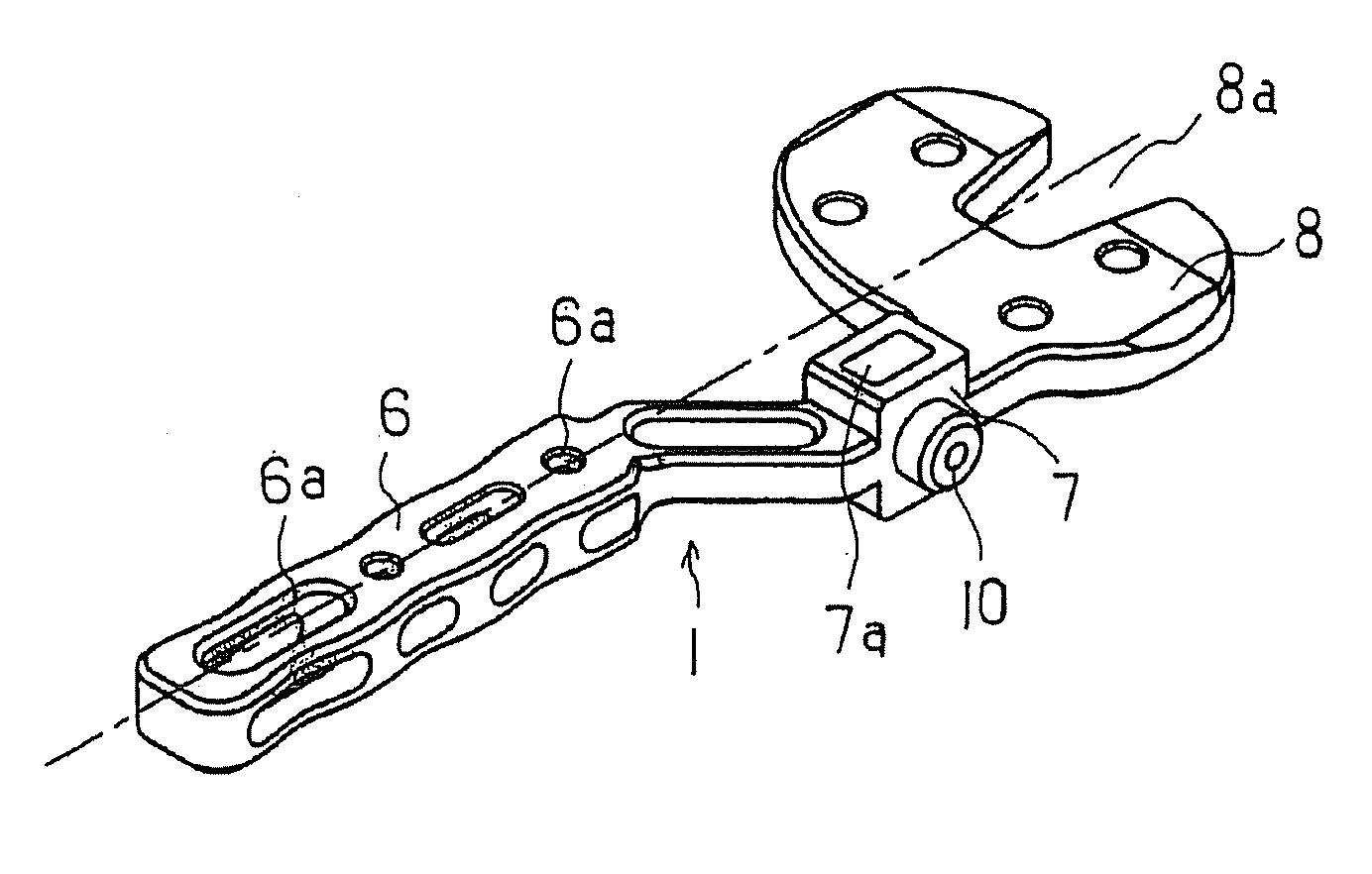
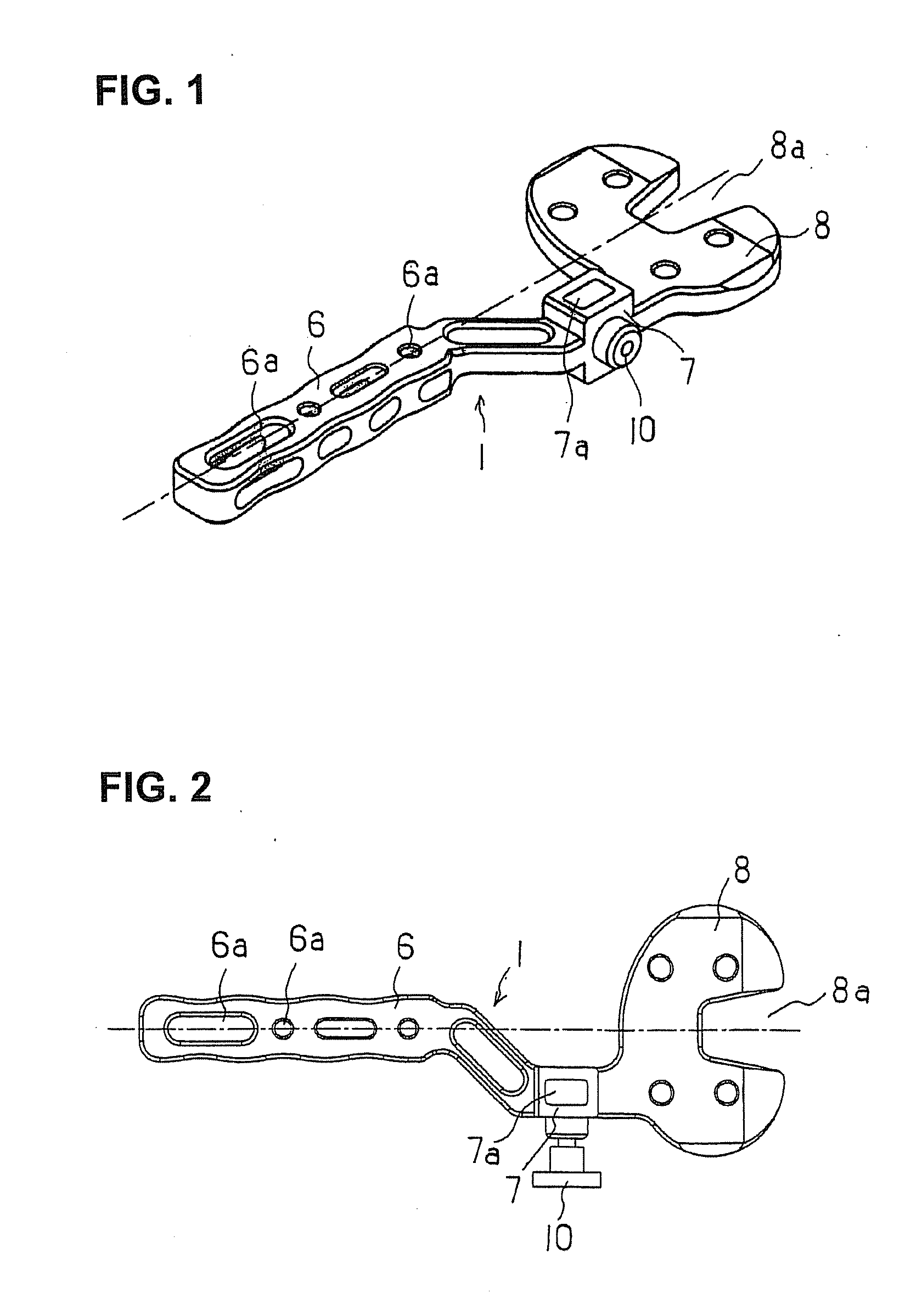
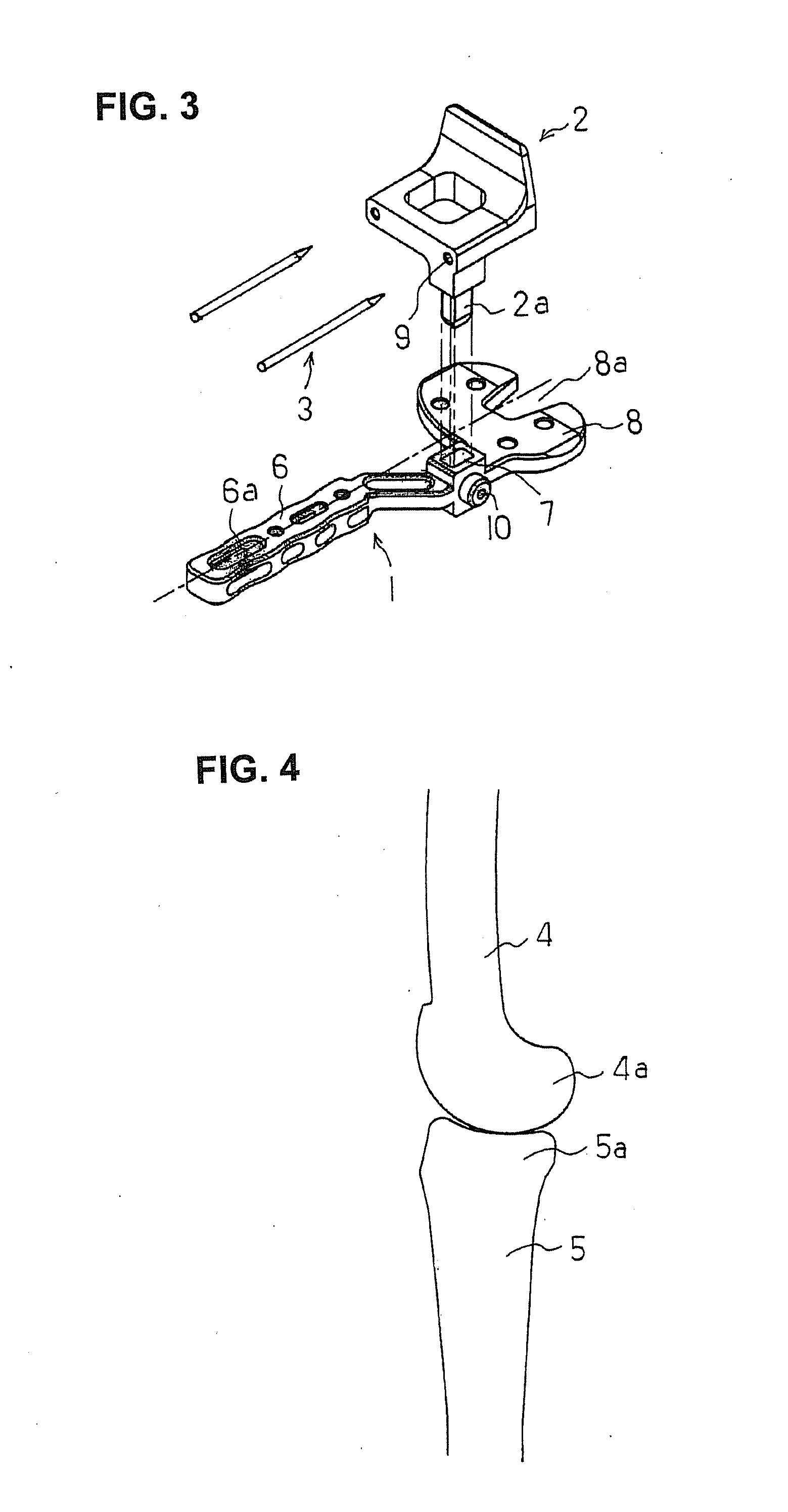
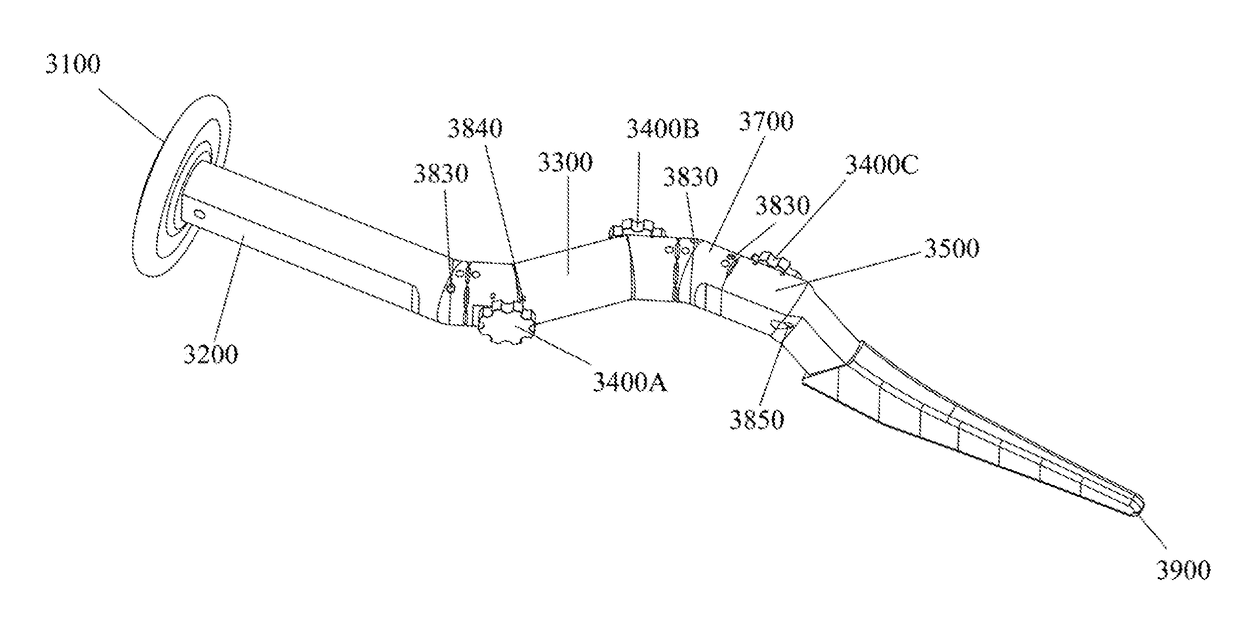
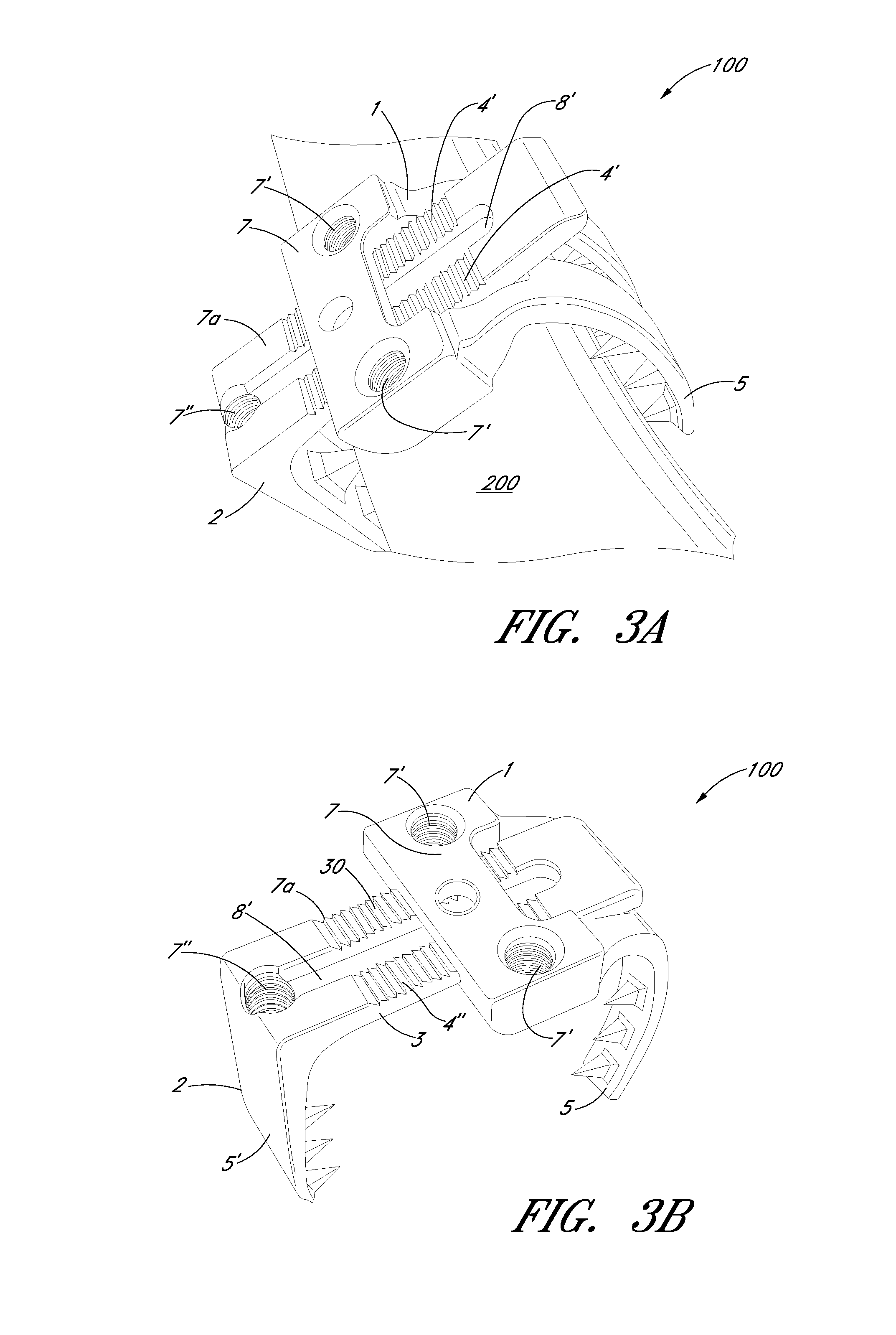
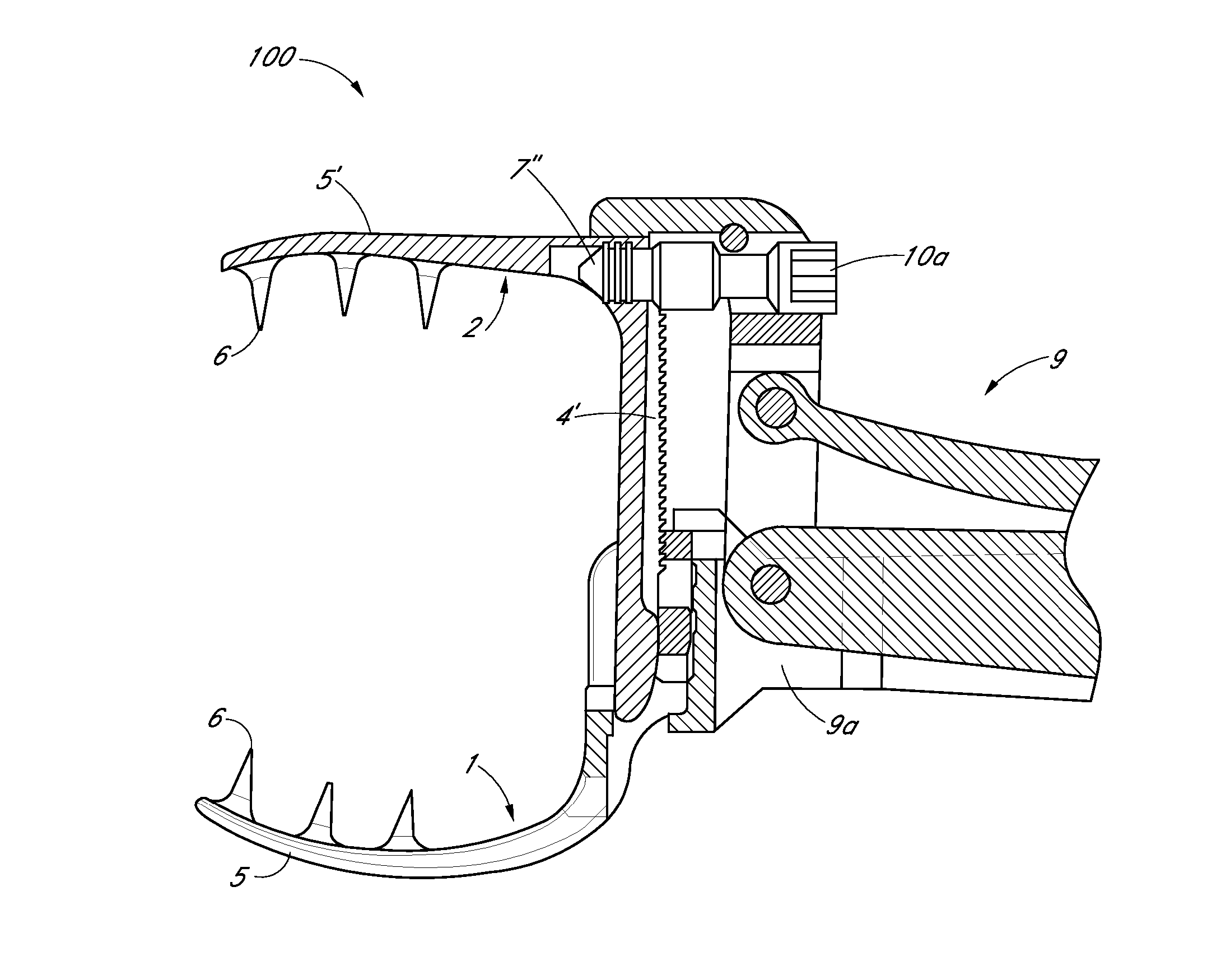
Bone Resection Jig Used in Artificial Knee Joint Replacement Surgery
A bone resection jig that can make ligament tension equal at extension and flexion positions without any actual measurements when resecting femur and tibia during artificial knee joint replacement surgery. The bone resection jig used in artificial knee joint replacement surgery includes a spacer block (1) comprised of a grip (6), a hollow box (7) that is provided on an other end side of the grip and has a vertical hole (7a) therein, and a reference spacer part (8) that extends out from the hollow box (7) and is adapted be inserted into the resection region between femur and tibia; a reference pin guide (2) which, when the femur and tibia are in the flexion position, is inserted into the vertical hole (7a) of the hollow box, extends on the reference spacer part (8) to the other end side of the grip so as to come into contact with a resection plane (FH) of the tip of the distal end of the femur, and is formed with guide holes (9) for guiding reference pins (3) to be installed from a front side into the resection plane (FH) of the tip of the distal end of the femur; and an aiming member (12) which is, after the spacer block (1) has been removed from a space between the femur and tibia leaving the reference pins (3), brought onto the reference pins (3) by being guided thereby, the aiming member being provided with an indicator (14) that indicates a resection plane (FR) at a back of the distal end of the femur when the aiming member (12) comes into contact with the resection plane (FH) of the tip of the distal end of the femur.
Owner:NAKASHIMA MEDICAL +1
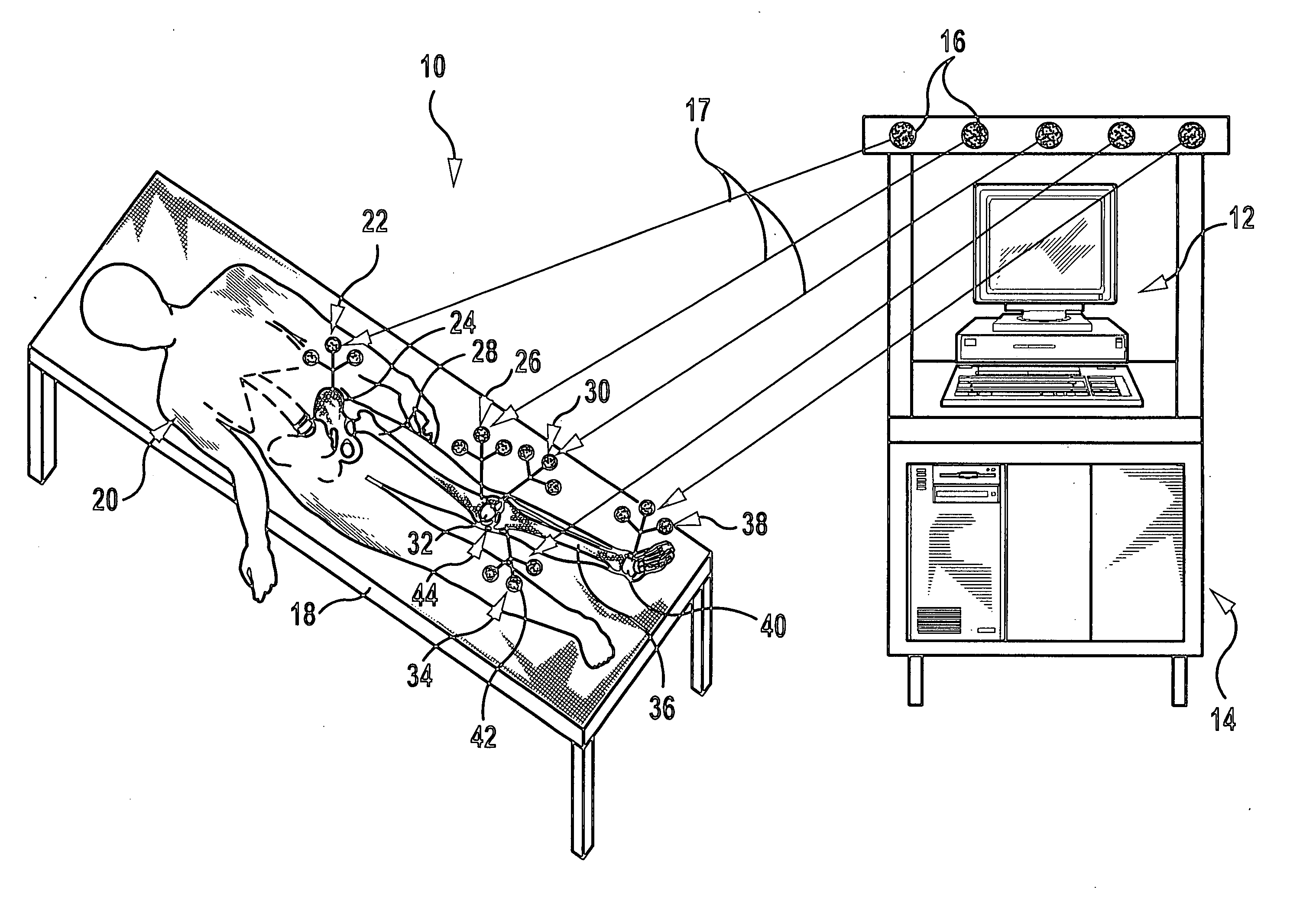
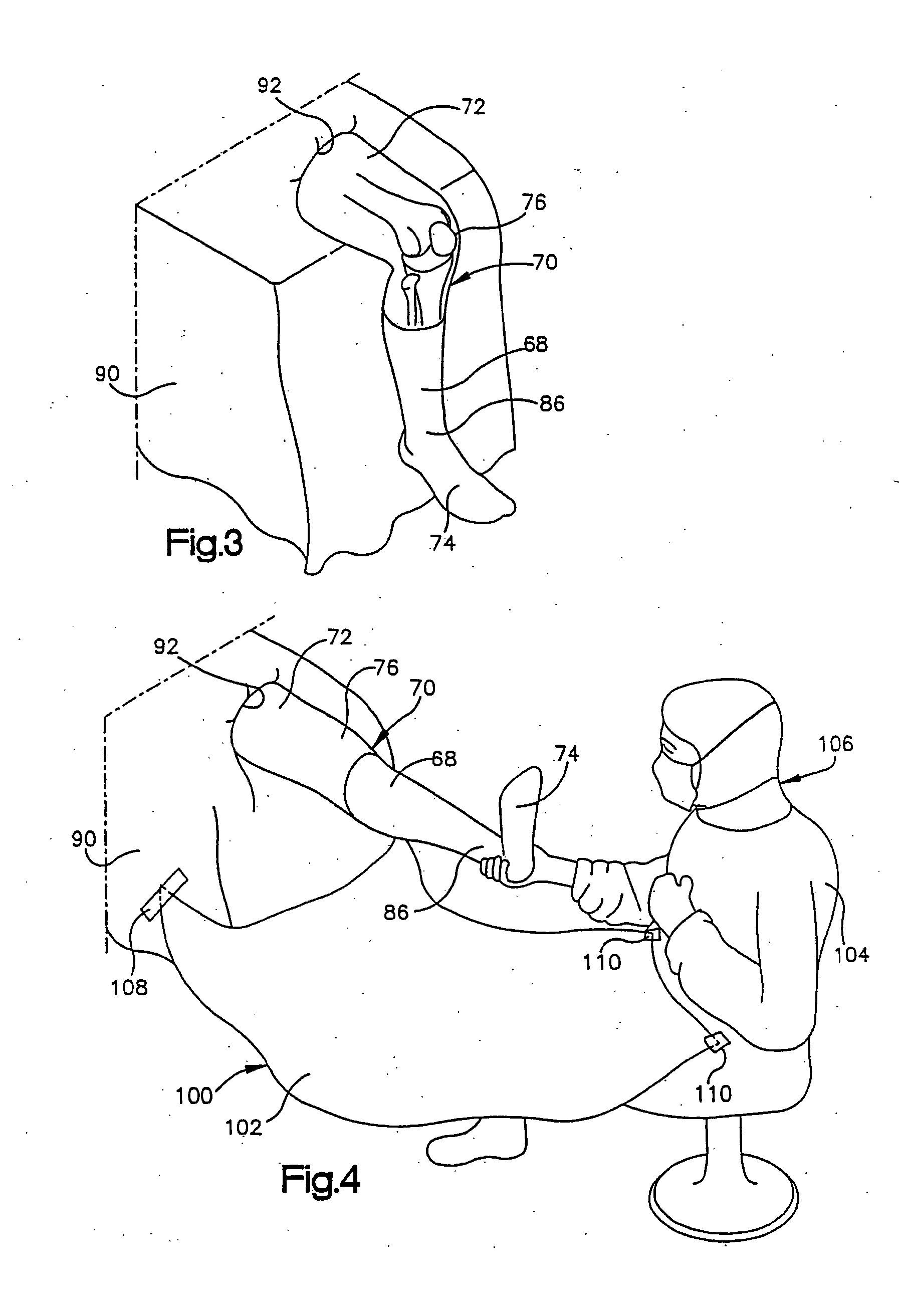
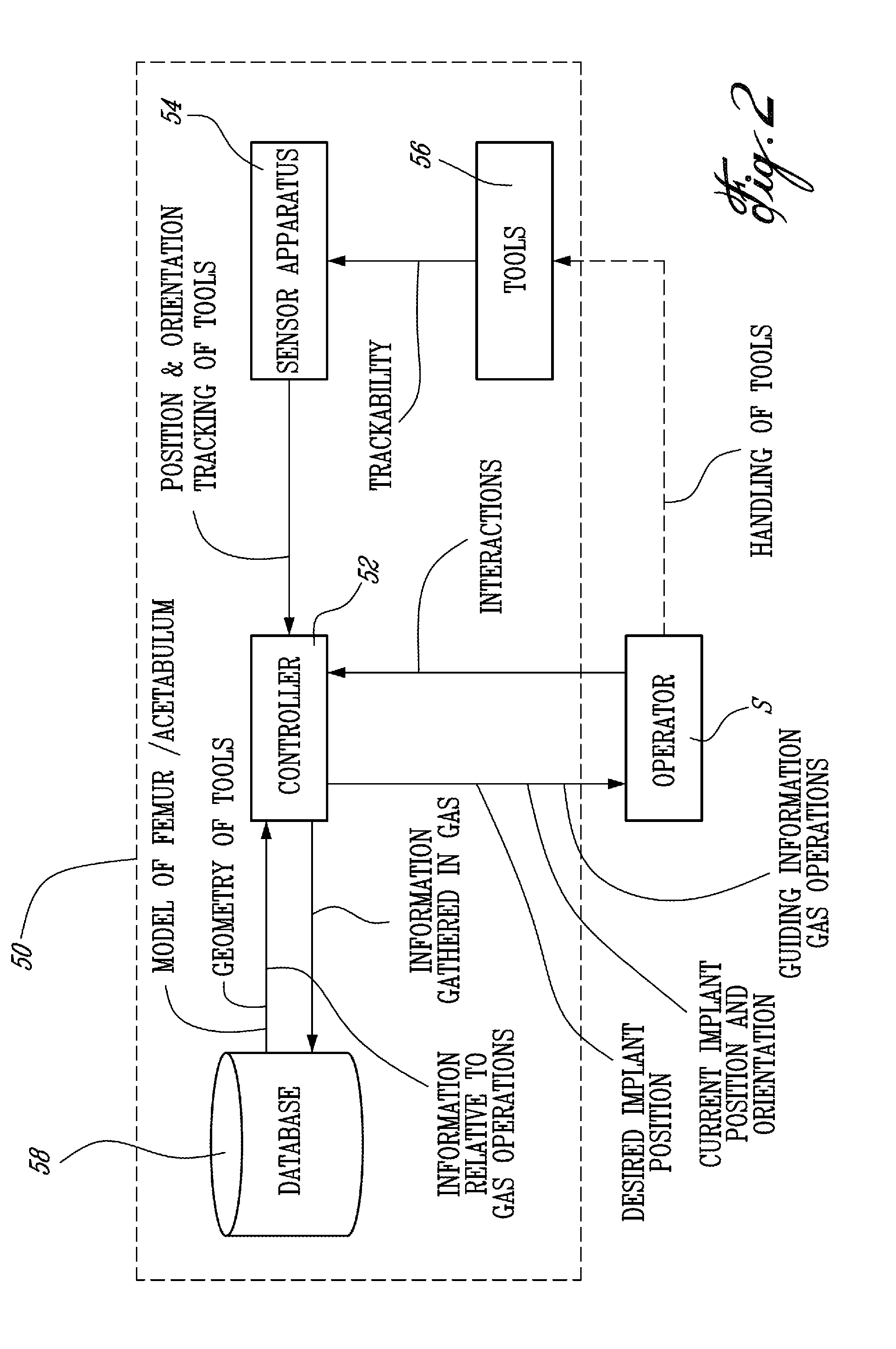
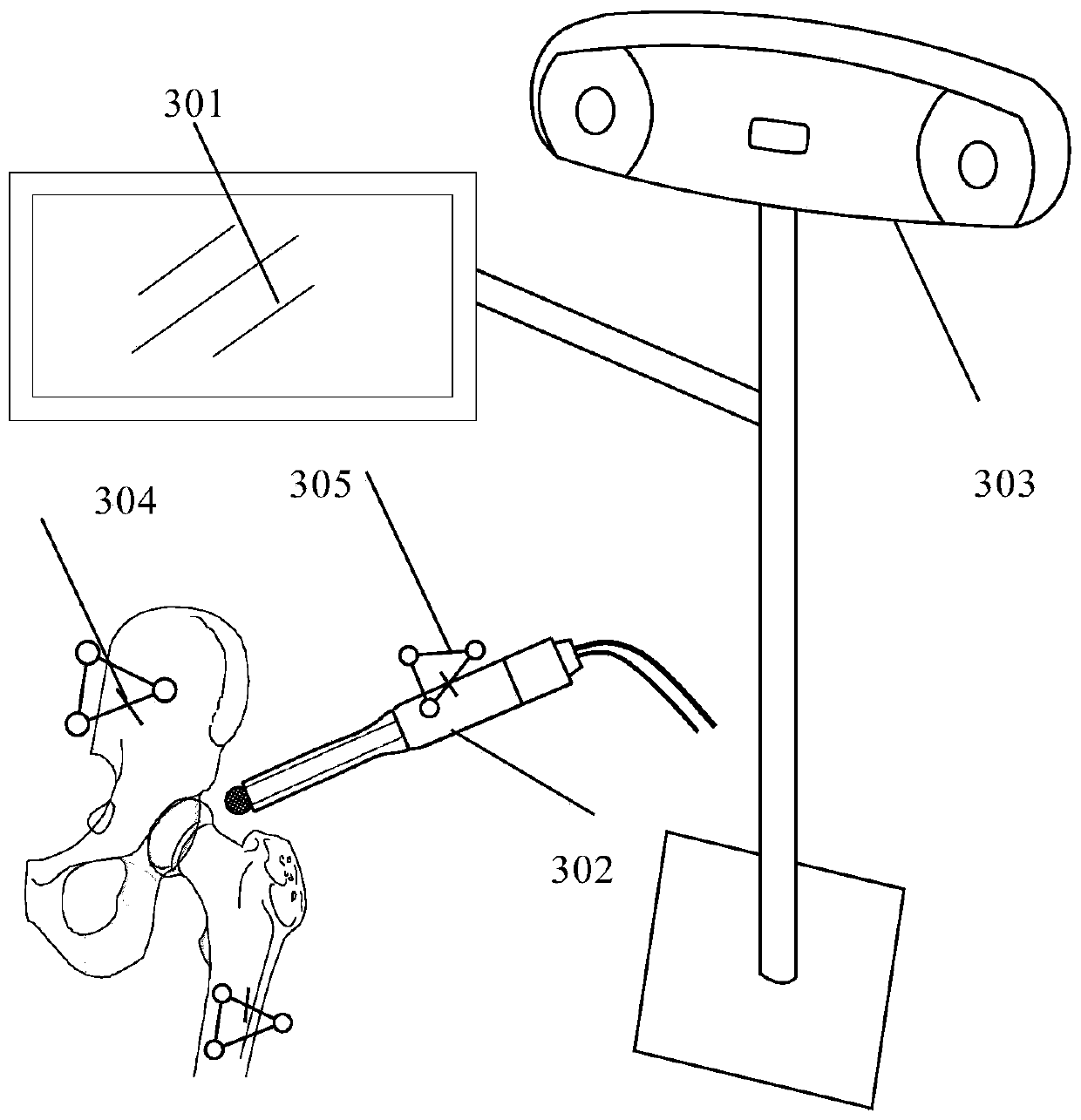
Operation assisting system
InactiveUS8400312B2Low costAccurate detectionSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationPelvisJoints surgery
An operation assisting system. When an operator manipulates an operation instrument to perform an operation for a joint surgery including a hip replacement, the operation assisting system provides the operator with information on the orientation of a bone such as a pelvis and an appropriate direction of the operation instrument relative to the bone to assist the operator so as to complete the operation in an easy and accurate manner, which ensures a high degree of operation accuracy and reduces the cost of the system.
Owner:SAGA UNIVERSITY
Biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material and a preparation method thereof. The material is applied to the bone surface or bone section of a human body or an animal, and is characterized in that the biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material is modified starch prepared by modifying natural starch serving as a raw material, and comprises one or more than two of modified starch granules, modified starch sponges, modified starch films, modified starch foams or modified starch glues, wherein the molecular weight of the modified starch is 15,000 to 10,000,000, and the water absorption rate is 1 to 100 times; in the natural starch serving as the raw material, the content of the amylopectin is at least no less than 70 percent of the total amount of the raw material. The invention fulfills the aim of stopping bleeding through direct spraying, daubing and pasting the biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material to touch the bone bleeding surface of wound; meanwhile, the biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material has a function of promoting bone healing, and can be used in the bleed stopping in the sternotomy of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, spinal surgeries and joint surgeries of orthopedics department, Craniotomy and maxillo-facial surgery and the bleed stopping in the process of trauma care.
Owner:纪欣
Intraoperative joint force measuring device, system and method
ActiveUS7458989B2Reduce sizeRisk of injurySurgical furniturePerson identificationMeasurement deviceEngineering
A surgical device for joint replacement surgery includes an intraoperative joint head having a stem attachment structure where the stem attachment structure may be removably attachable to a stem and a force sensor housed by the joint head for measuring in vivo forces during surgery. The in vivo forces may be generated by one or more of tension provided by soft tissue, load application during surgery, limb movement during surgery, and a combination thereof. Also, the joint head may provide a cavity where the stem attachment structure houses the force sensor and may be removably insertable in the joint head cavity. A method of performing joint replacement surgery includes installing an intraoperative joint head having a force sensor housed by the joint head and a stem attachment structure, the stem attachment structure being removably attachable to a stem, measuring joint forces, and adjusting an implant parameter based on the measured joint forces.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
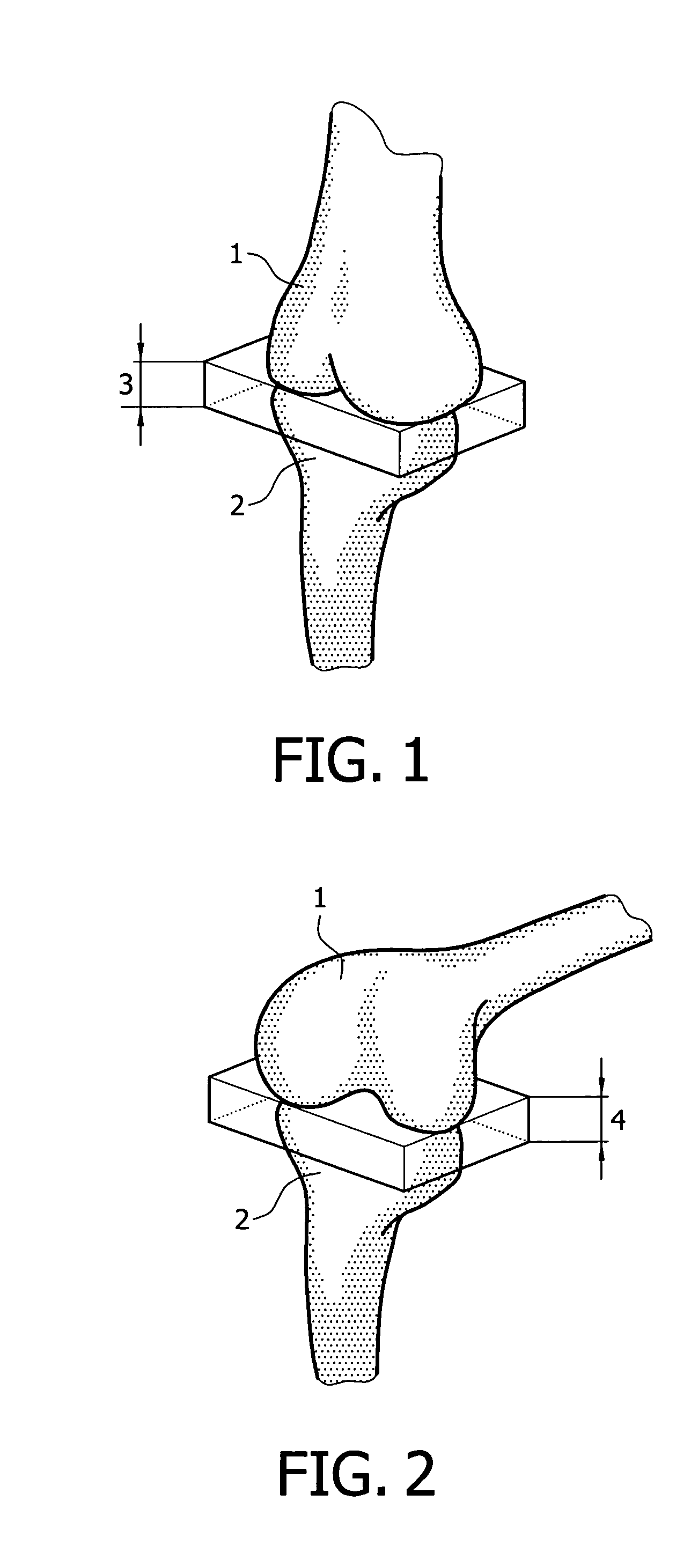
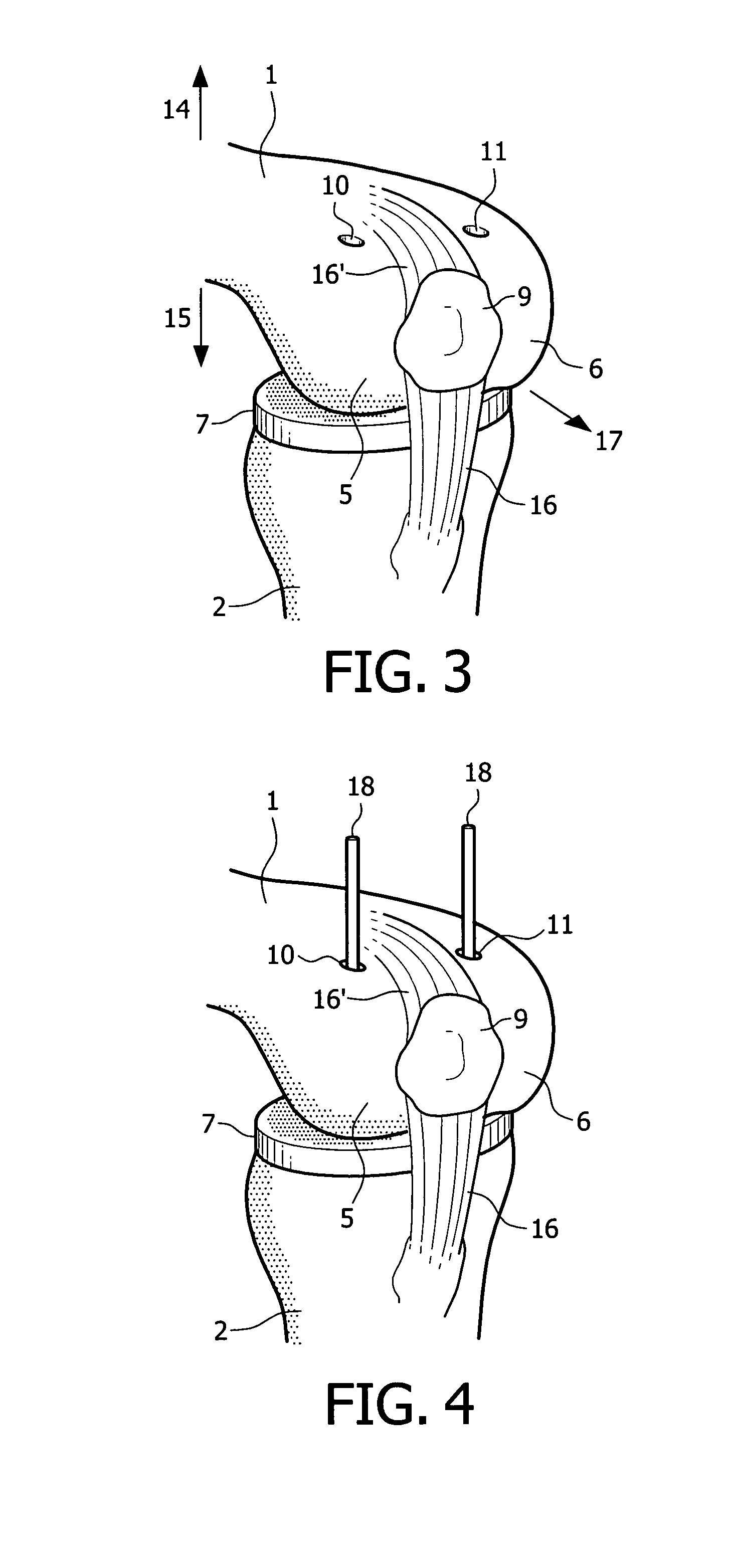
Device and method for installing femoral prosthetic knee joint
Devices and method for performing replacement prosthetic knee surgery are disclosed in which a spacing means is introduced between the femur (1) and tibia (2) while the patella (9) is in place. The spacing means separates the femur (1) from the tibia (2) by an amount essentially equal to or greater than the required flexion gap (4). An alignment device (26) is used for performing femoral bone cuts, which device attaches temporarily to a fitted tibial plate.
Owner:GHIJSELINGS IGNACE
Peripheral nerve field stimulator curved subcutaneous introducer needle with wing attachment specification
An apparatus for use in peripheral nerve field stimulation (PNFS) whereby a plurality of curved introducer needles, of varying curvatures, are provided to permit the physician to best locate the region of oligodendrocytes that contain the A Beta fibers by matching the lumbar lordosis. A wing device is also provided that is attachable to the hub of the curved needle introducer which gives the physician better ability to maneuver the needle during insertion as well as permitting tenting of the skin. The invention benefits a large number of painful disorders arising from pathology in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. In addition, this invention can also help a large number of other conditions including but not limited to failed back surgery syndrome / post-laminectomy pain, occipital / suboccipital headaches, scar pain, post herpetic neuralgia pain, mononeuritis multiplex, and pain following joint surgery (e.g., knee, hip, shoulder).
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
System and method for treatment of pain related to limb joint replacement surgery
It has been discovered that pain felt in a given region of the body can be treated by stimulating a peripheral nerve at a therapeutically effective distance from the region where pain is felt to generate a comfortable sensation (i.e., paresthesia) overlapping the regions of pain. A method has been developed to reduce pain in a painful region following limb joint replacement by stimulating a peripheral nerve innervating the painful region with an electrode inserted into tissue and spaced from the peripheral nerve. This method may be used to help alleviate postoperative pain in patients following total knee arthroplasty surgery or other limb joint replacement surgeries.
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
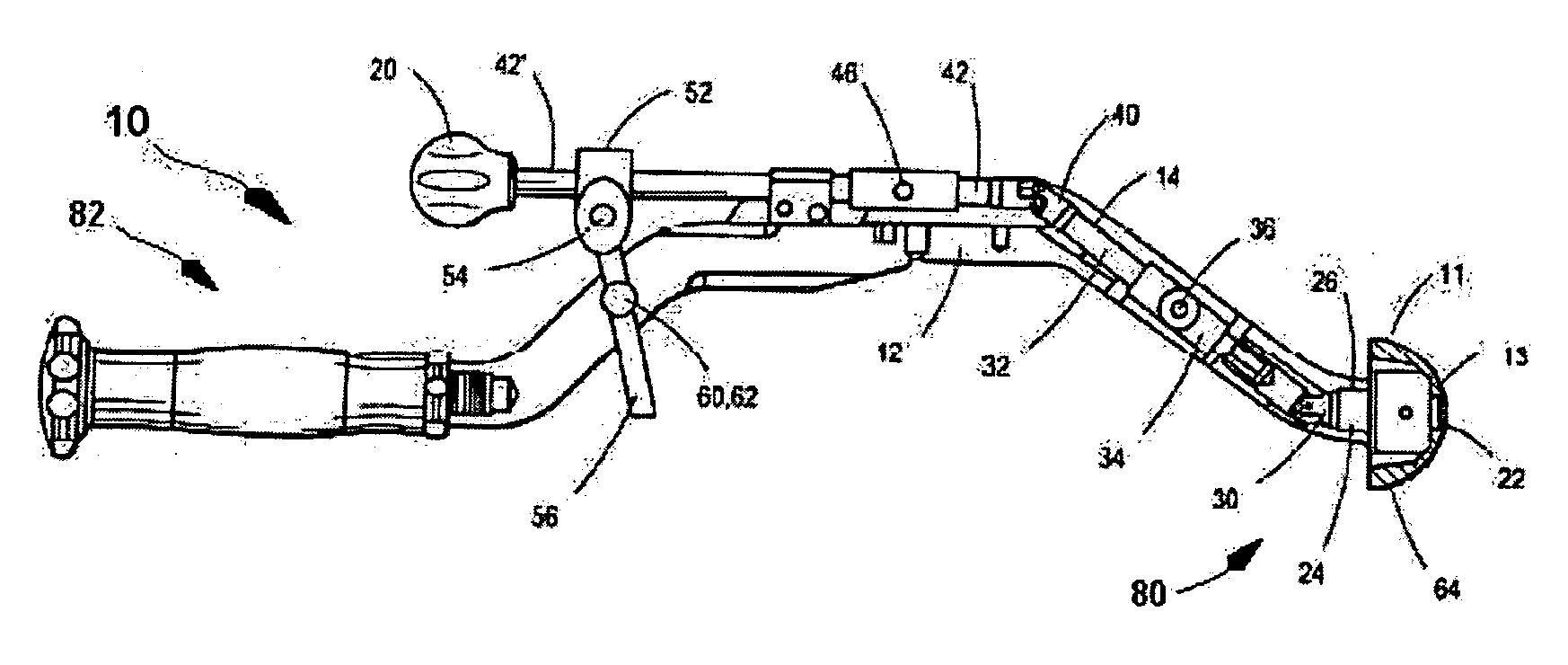
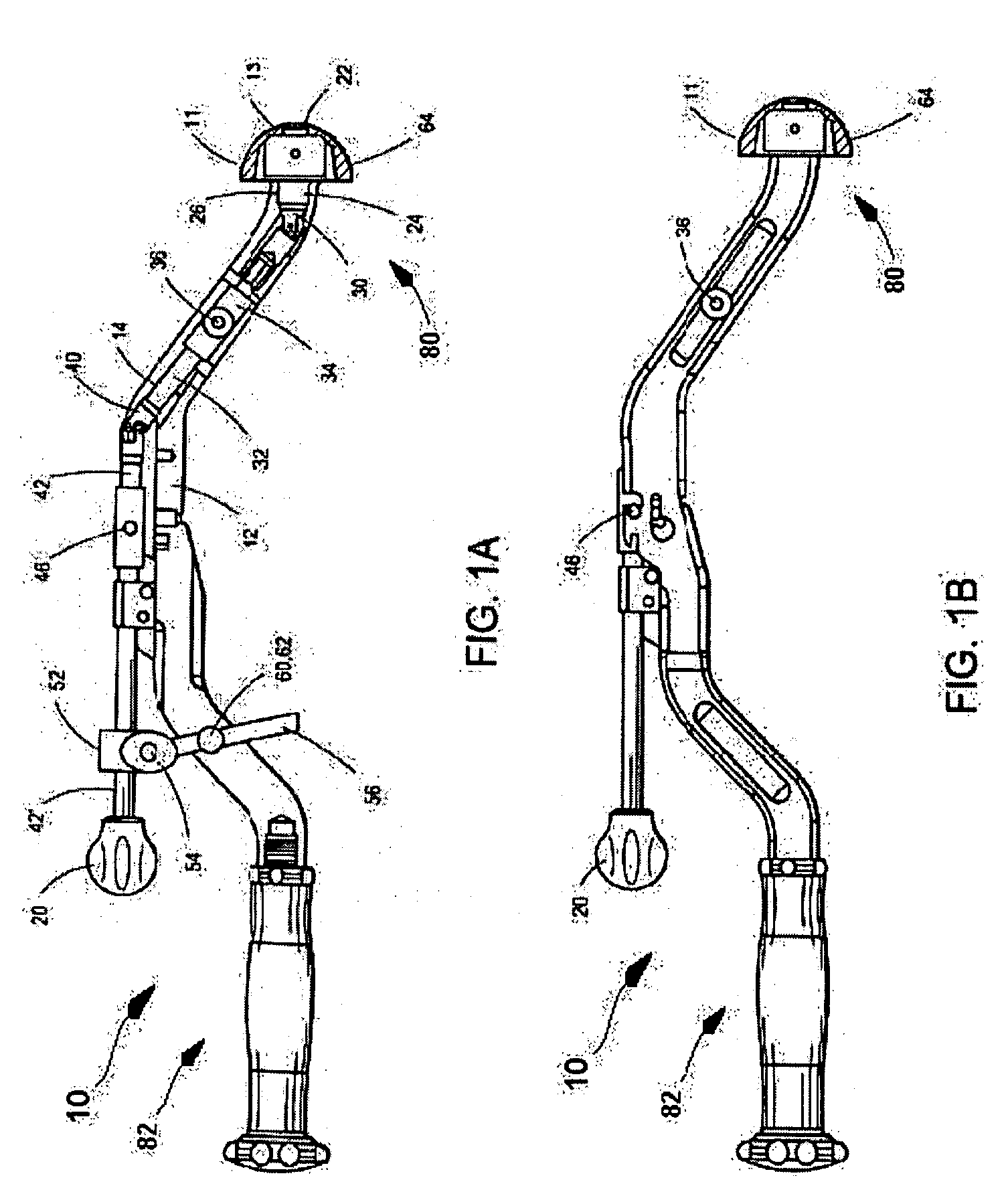
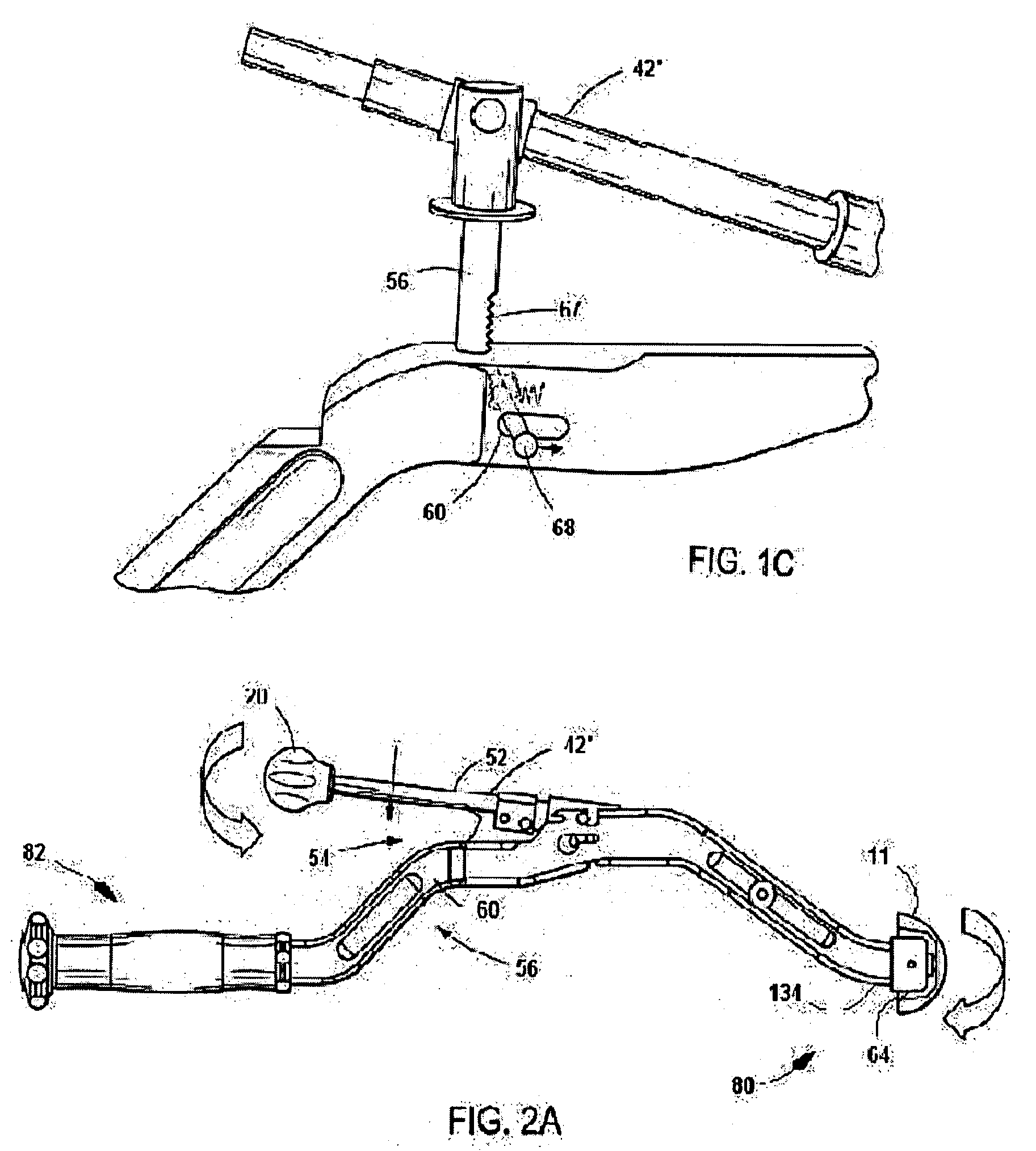
Inserter for minimally invasive joint surgery having interchangeable thread
ActiveUS20080021481A1Easy to disassembleReduce in quantityJoint implantsAcetabular cupsLocking mechanismProsthesis
An acetabular inserter (10) aids a surgeon in controlling the installation of an acetabular cup prosthesis (11) having a central, female aperture (13). The inserter includes an inserter head (20), a housing (12) and a locking mechanism. The housing (12) is attached to the inserter head, the housing enclosing a drive train (14) having, at a far end (134), a prosthesis engaging thread (124), and at the opposite end (42′), a handle (20) which facilitates turning of the drive train by the operator. The locking mechanism is associated with the housing which selectively locks the drive train, and thus the prosthesis, in position. The opposite end (42′) of the drive train has a latch device which enables quick removal from the housing for cleaning and sterilization.
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
Systems and methods for measuring parameters in joint replacement surgery
ActiveUS9456765B2Medical simulationSurgical navigation systemsComputer-assisted surgeryDisplay device
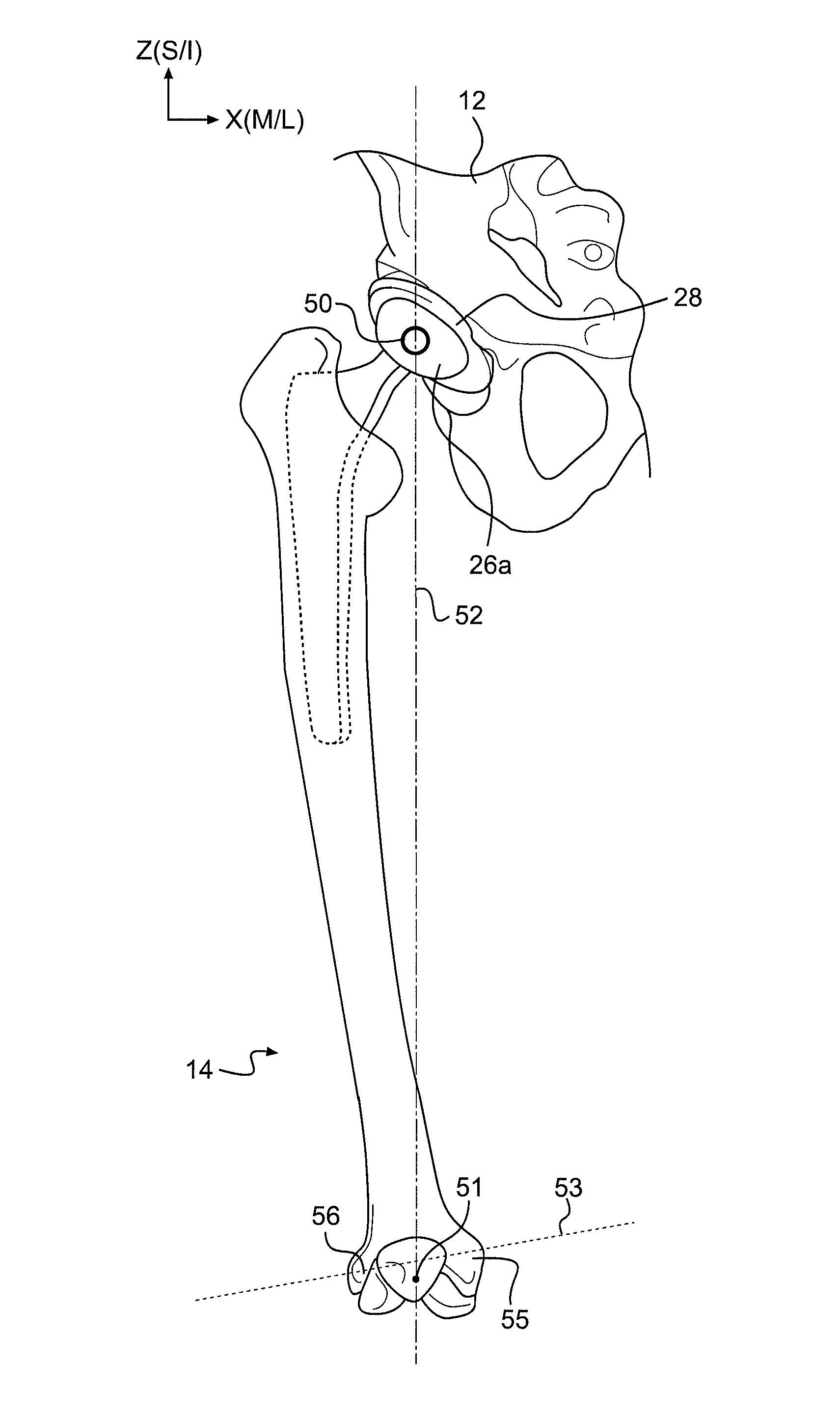
A computer-assisted surgery system includes a display, an input device configured to receive data input by a user, and a processor, coupled to the input device and the display. The processor is configured to establish a first position of a pre-operative center of rotation of a joint in a first coordinate space of a first bone and a second coordinate space of a second bone and establish a second position of the pre-operative center of rotation of the joint in the first coordinate space, wherein the second position is a projection into the first coordinate space of the position of the pre-operative center of rotation maintained in a constant position in the second coordinate space. The processor is further configured to determine a change in a parameter associated with the joint based on the first and second positions and output a result indicating the determined change to the display.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Computer-assisted hip replacement surgery
ActiveUS20160228192A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceMuscles of the hipComputer-aided
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Carbon reamer handle
A reamer for use in minimally invasive hip replacement surgical approaches is provided. The reamer spindle includes an offset elongate housing portion that extends from a proximal housing end portion a distal housing end portion. A handle assembly, preferably comprising a durable lightweight material such as carbon fiber that is removably connectable to the housing of the reamer spindle. A reamer head is removably connectable to the distal neck portion and has a surface configured to cut bone.
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
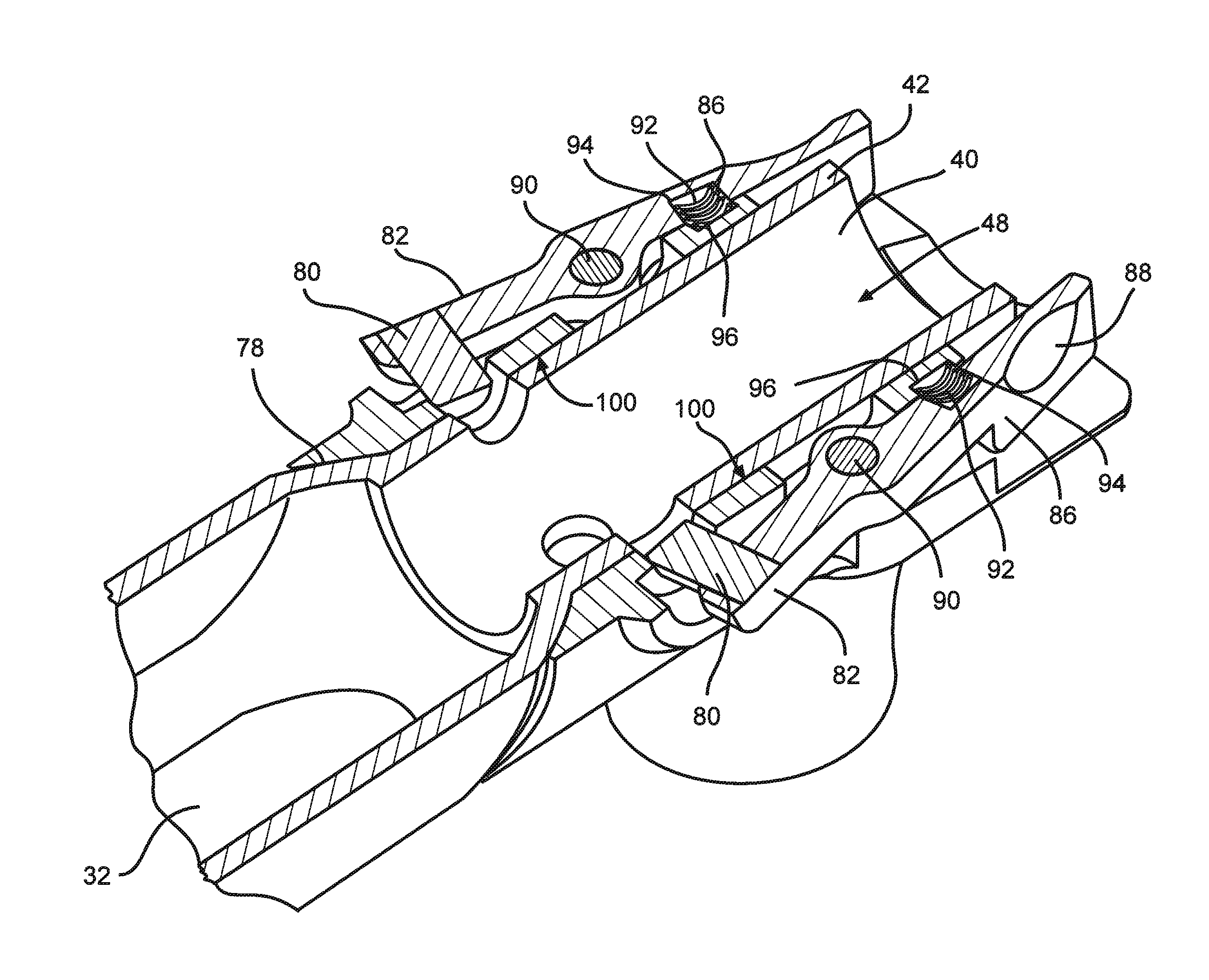
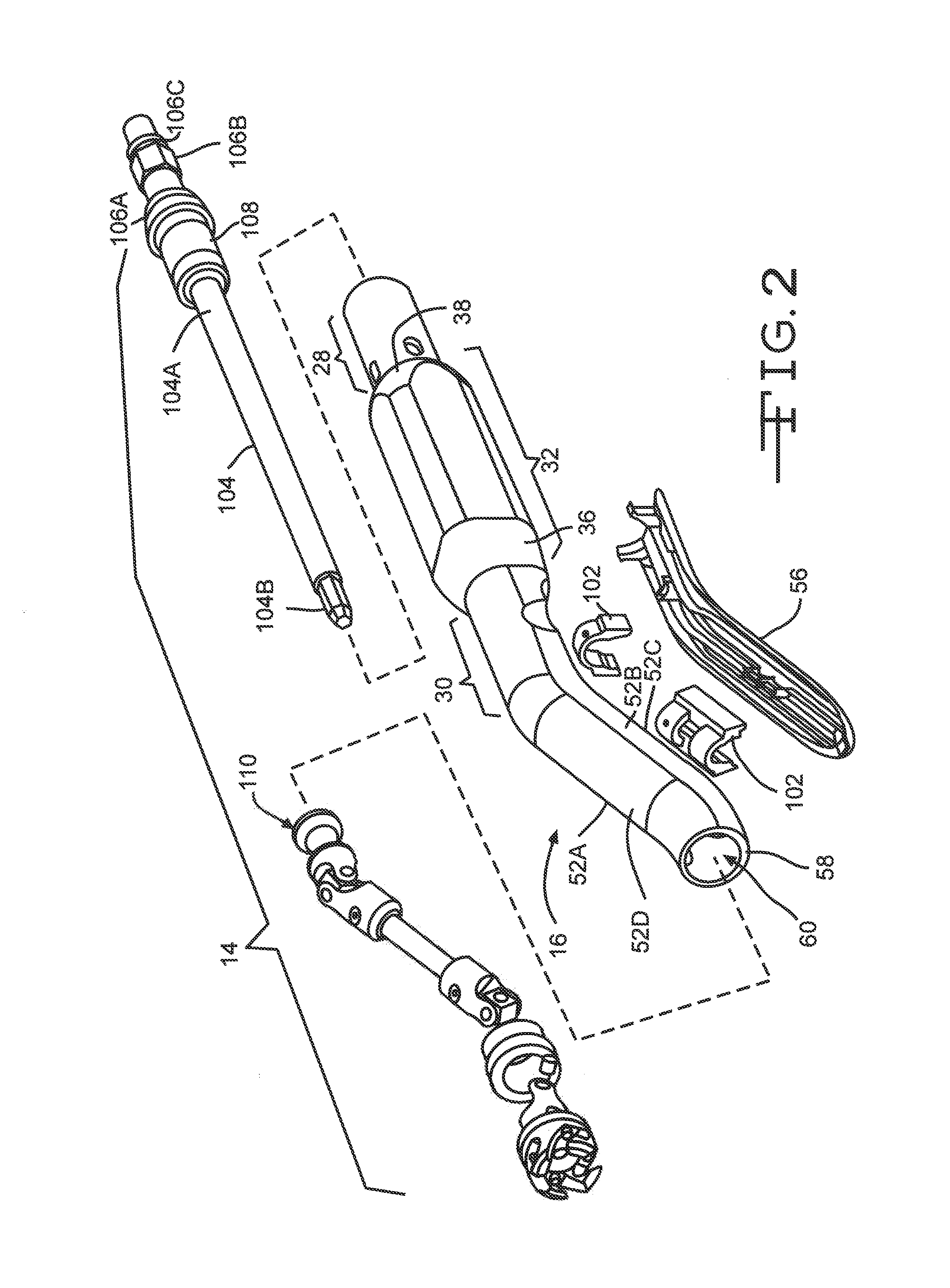
Articulating surgical tool
A surgical instrument for releasable connection to a surgical tool having two or more sections that are able to articulate 360 degrees in differing increments and directions. The articulation of the sections allows for the distal end to be spatially offset from the proximal, yet maintain parallel longitudinal axes. The surgical instrument includes a force disc at the proximal end upon which a surgeon can exert a linear force which is transmitted to the distal end having a second tool such as a broach firmly attached thereto.
Owner:INVICTUS ORTHOPAEDICS
Clamp for attaching surgical aids to bone during a surgical procedure and system for doing the same
InactiveUS20080027471A1Minimizing impairmentInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSURGICAL AIDSJoints surgery
A clamp for attaching surgical operating aids has at least two clamp members arranged so as to be movable relative to one another and a securing element for fixing the clamp members in at least one locked position. The clamp members have a connecting mechanism that allow the clamp members to be attached to a separate setting element actuatable for transmitting a setting force onto the clamp. A setting element, such as tongs, releasably connects to the clamp, and has a connecting mechanism connectible to the connecting mechanism of the clamp and has a spacing and / or aligning mechanism. A clamp and a setting element that is releasably joined to the clamp provide an arrangement for attachment of surgical operating aids to a bone during a surgical intervention, such as during a joint replacement surgery.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
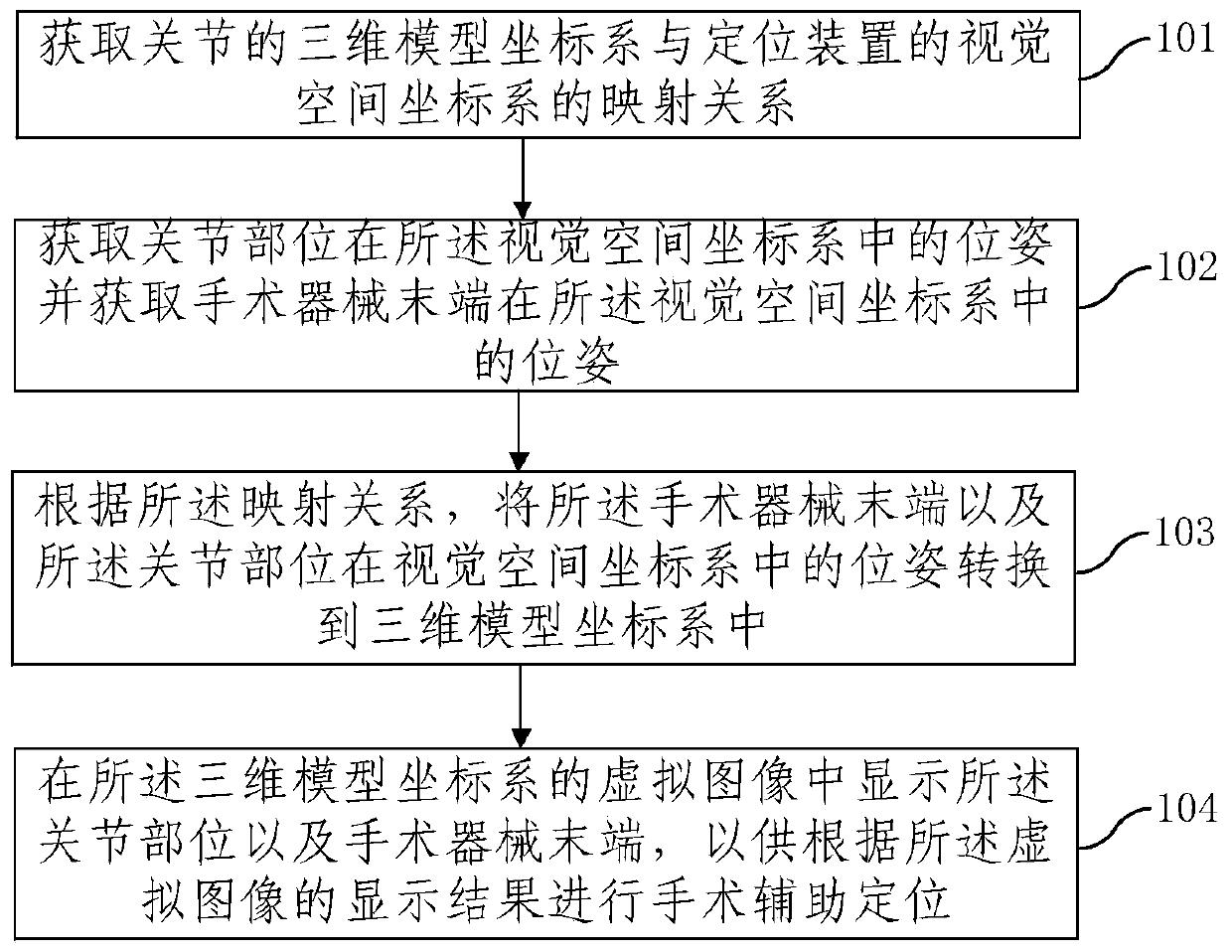
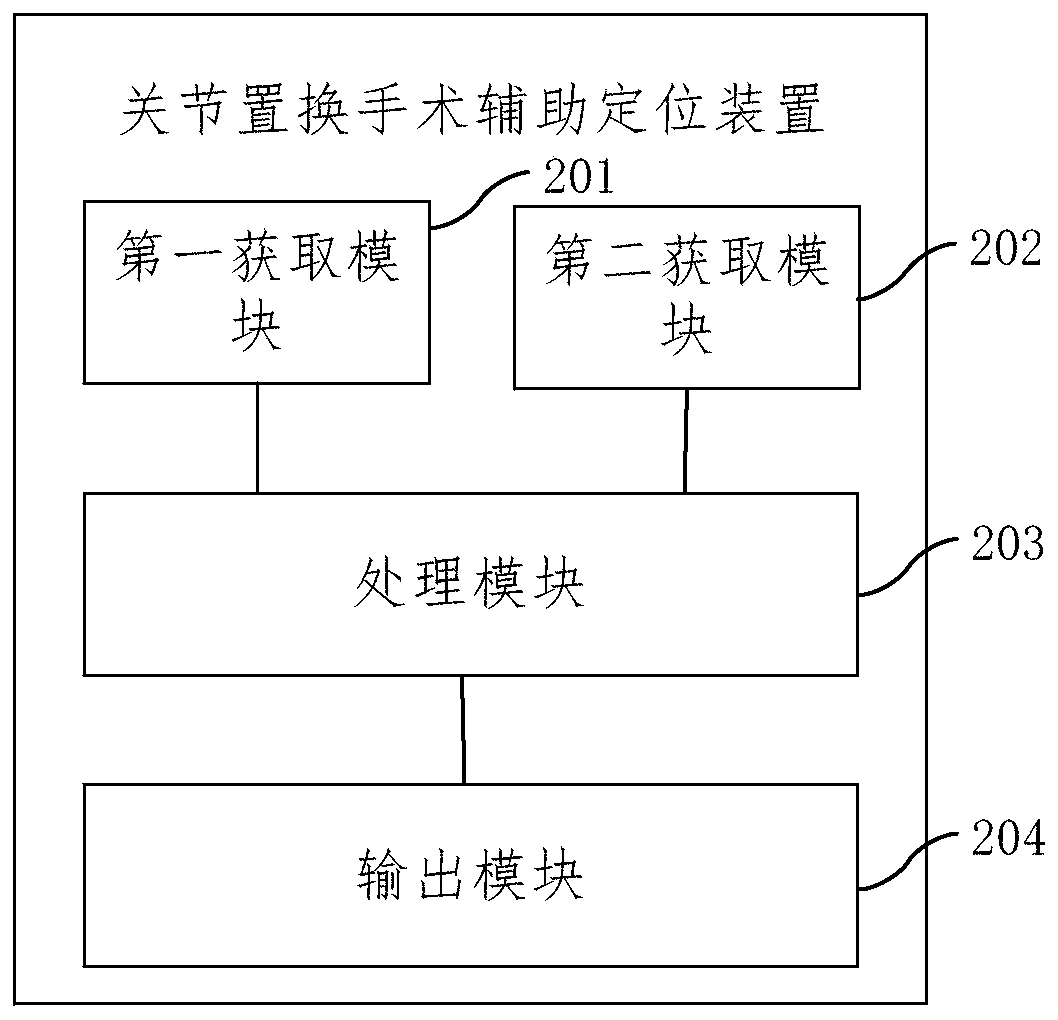
Auxiliary positioning method, positioning device and system for joint replacement
InactiveCN110037768AHigh precisionImprove matchSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingSurgical operationVisual space
The embodiment of the invention provides auxiliary positioning method, positioning device and system for joint replacement. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the mapping relation between a three-dimensional model coordinate system of a joint and a visual space coordinate system of the positioning device; acquiring the pose of the joint site in the visual space coordinate system,and acquiring the pose of the tail end of a surgical instrument in the visual space coordinate system; based on the mapping relation, converting the poses of the tail end of the surgical instrument and the joint site in the visual space coordinate system into the three-dimensional model coordinate system; and displaying the joint site and the tail end of the surgical instrument in a virtual imageof the three-dimensional model coordinate system, thereby performing surgery auxiliary positioning based on the display result of the virtual image. Because a doctor can visually observe the relativeposition relation between the joint site and the tail end of the surgical instrument during surgical operation, the osteotomy accuracy is high, operating risk is decreased, and further the accuracy and matching degree of the mounting position of a prosthesis are improved.
Owner:BEIJING YAKEBOT TECH CO LTD
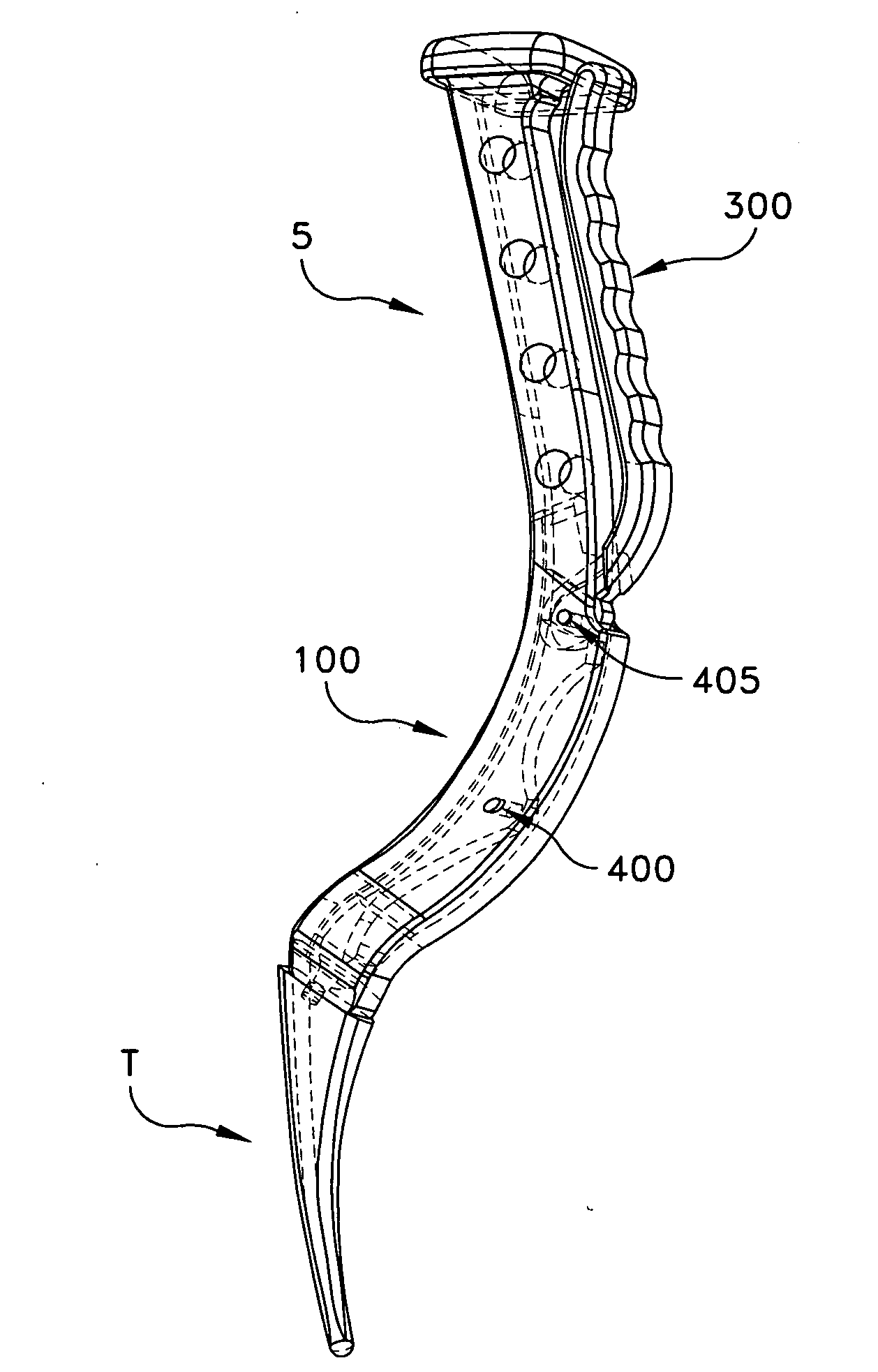
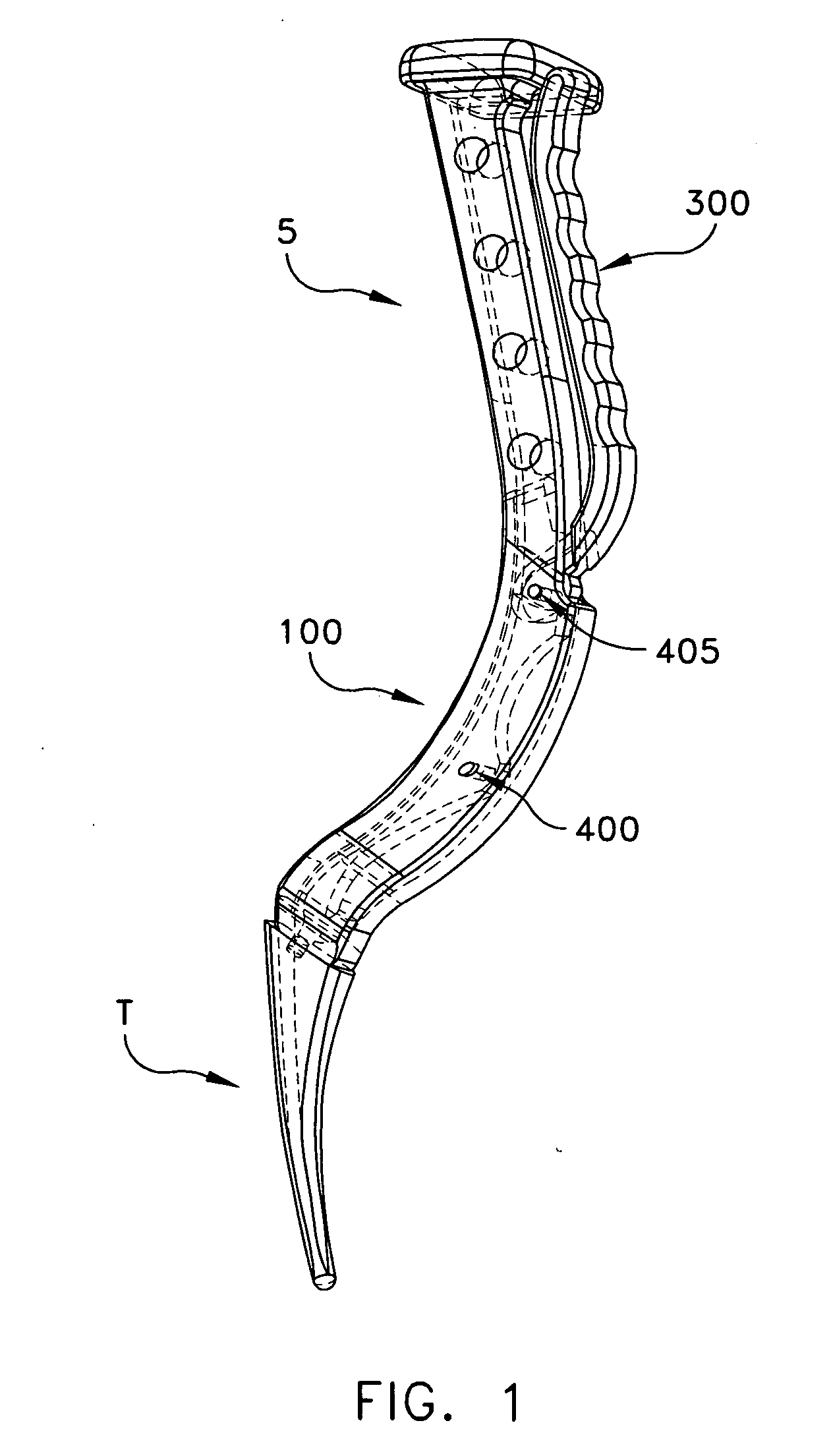
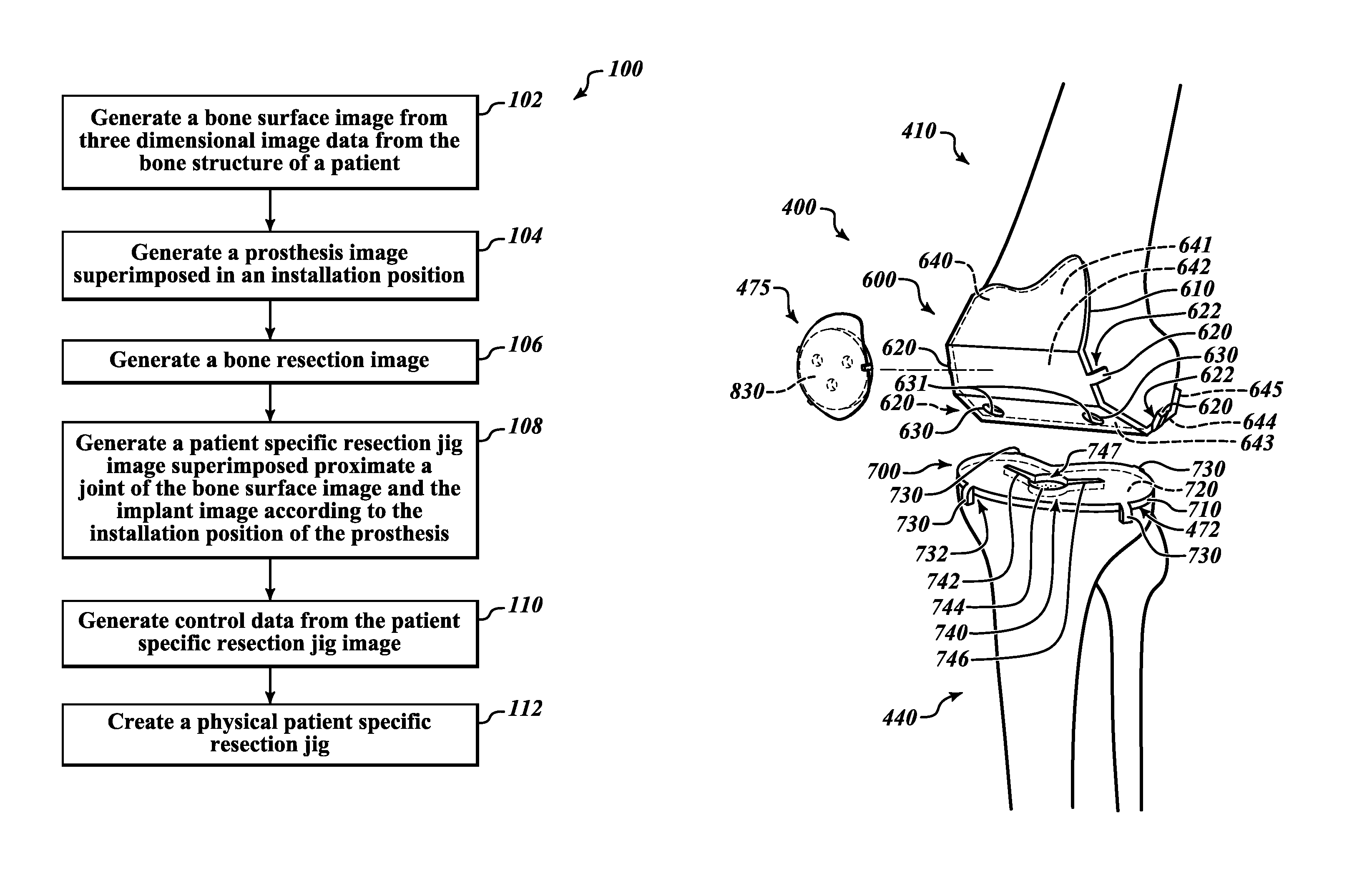
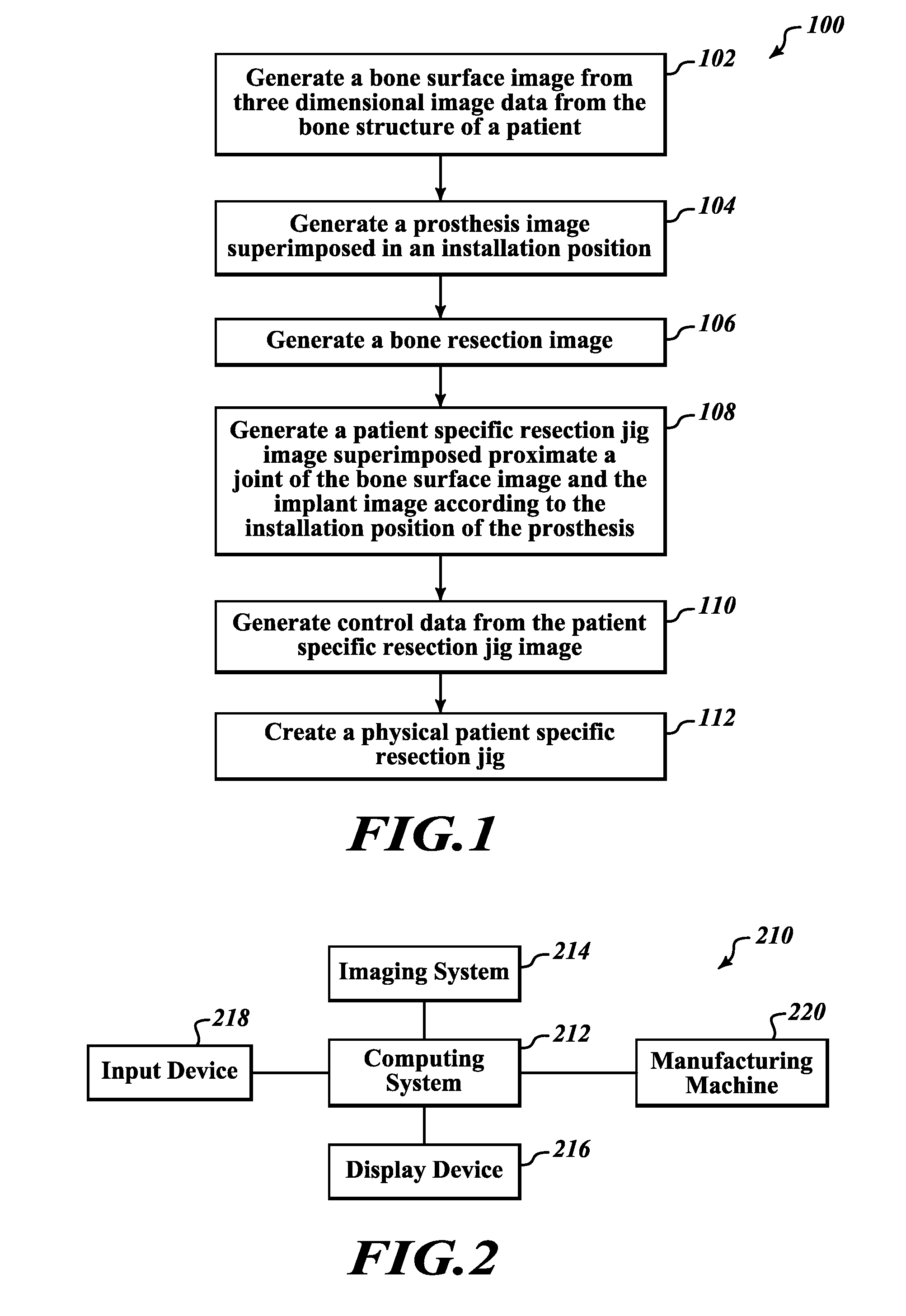
Devices and methods for knee replacement
A device for use in joint replacement surgery is disclosed, the device may comprise a patient-specific jig having a body formed using three dimensional data corresponding to a first resection surface of a bone of a patient according to a preoperative plan. The body may also include a first bone facing surface configured to match the first resection surface of the bone of the patient according to the three dimensional data and an alignment perimeter sized and shaped to match a perimeter of the resection surface of the bone of the patient according to the three dimensional data.
Owner:BULLSEYE HIP REPLACEMENT
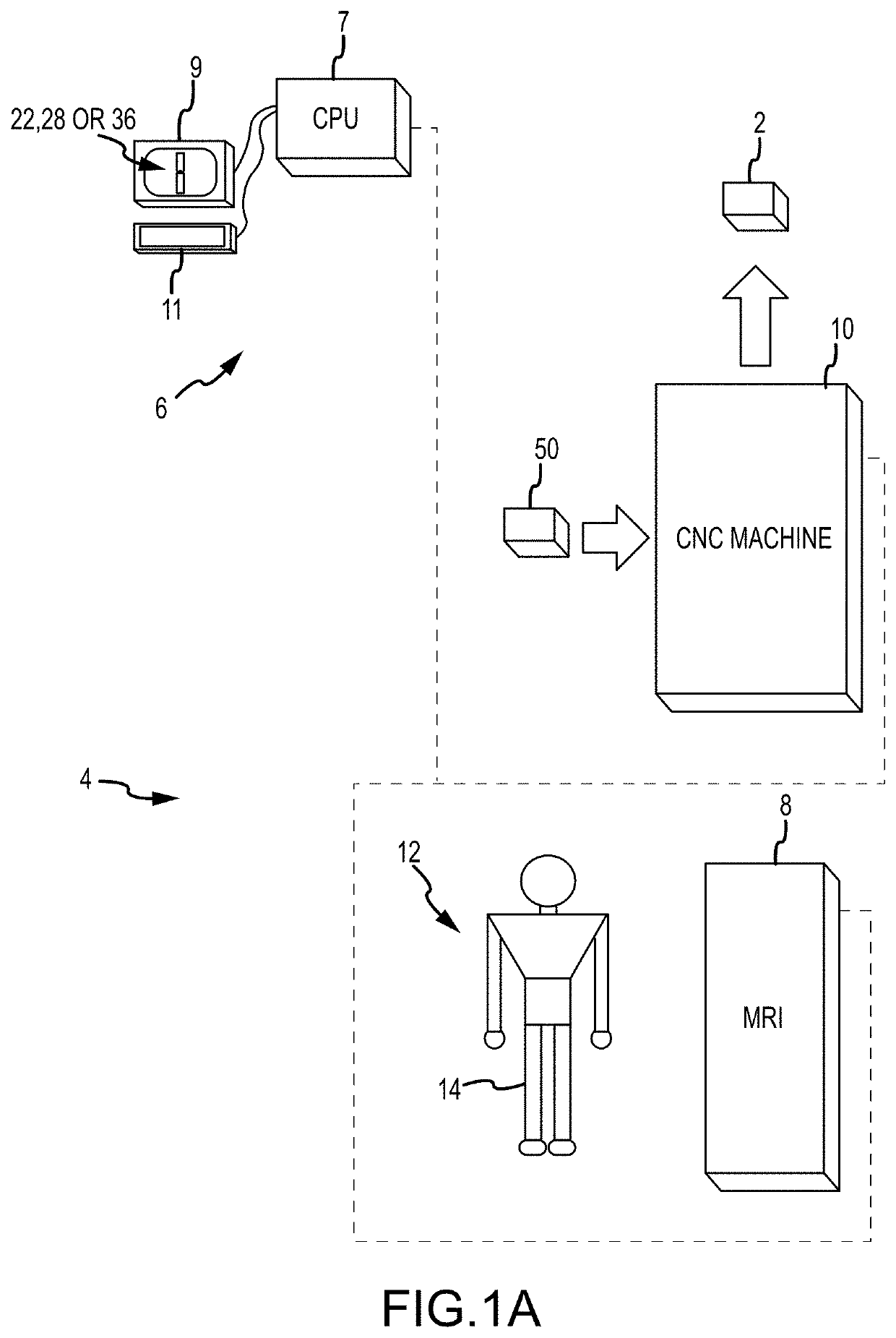
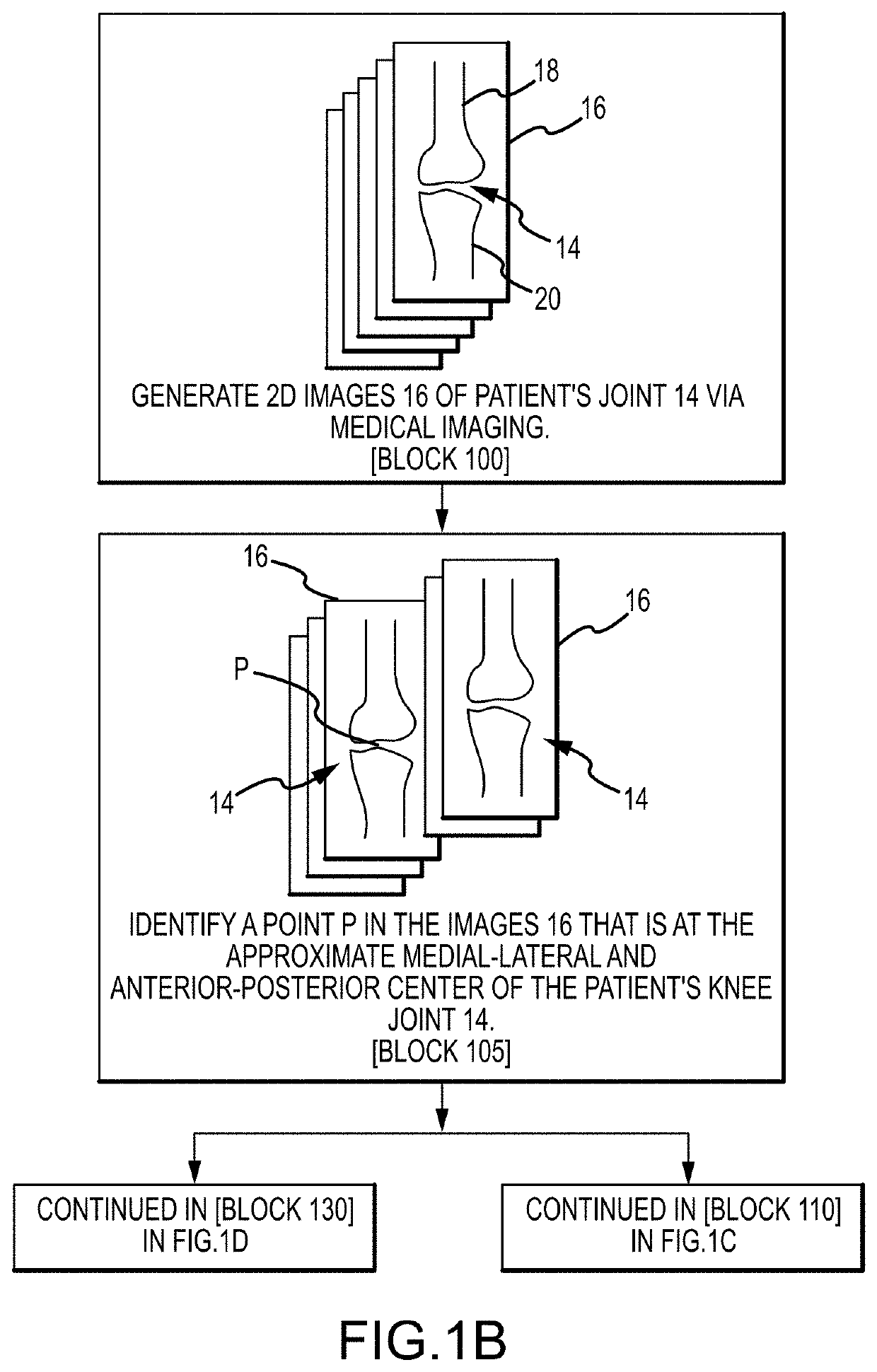
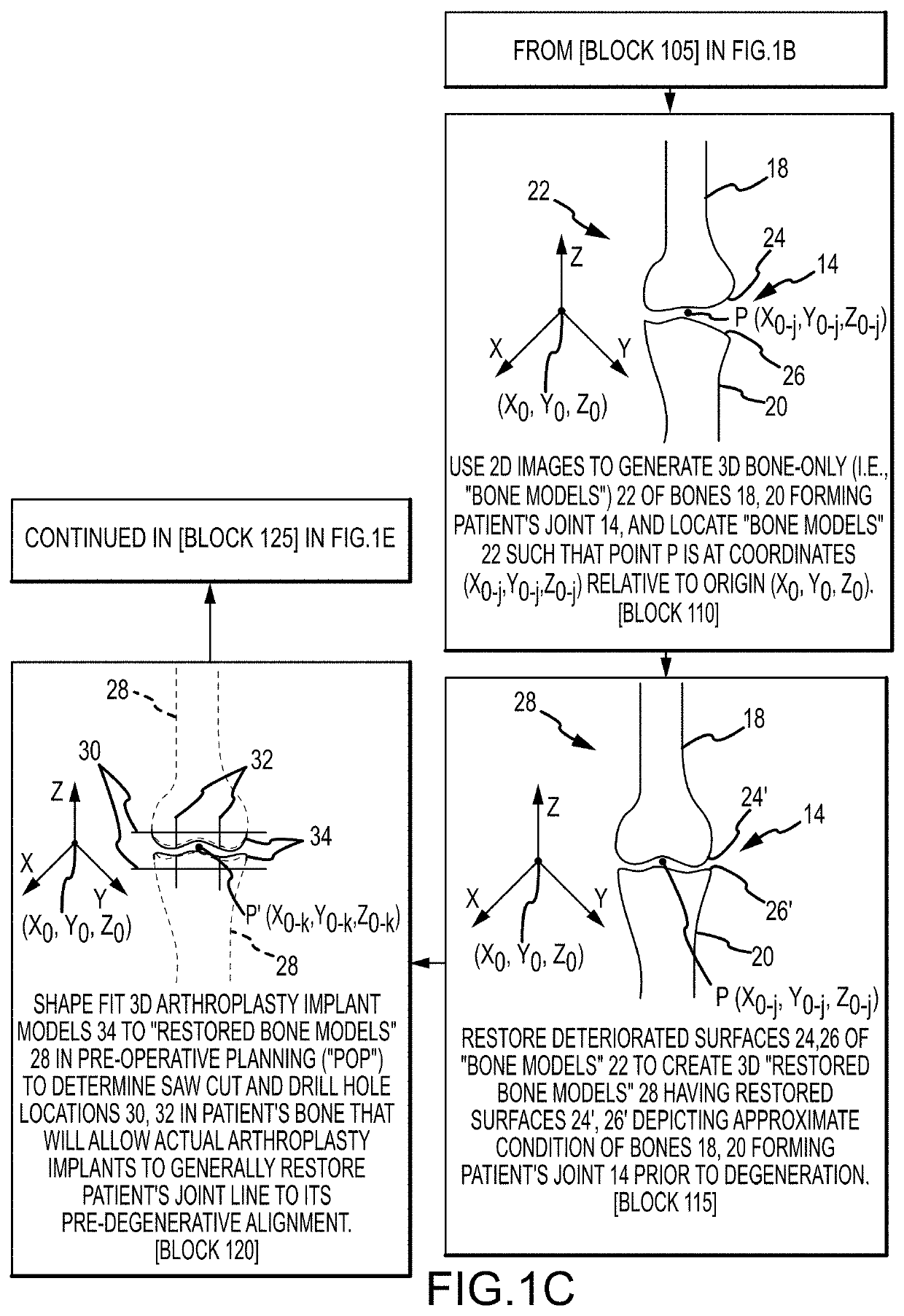
Systems and methods for surgical planning of arthroplasty procedures
ActiveUS20190388123A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMedical imaging dataBone tissue
A method for planning an arthroplasty procedure on a patient bone. The method may include accessing generic bone data stored in a memory of a computer, using the computer to generate modified bone data by modifying the generic bone data according to medical imaging data of the patient bone, using the computer to derive a location of non-bone tissue data relative to the modified bone data, and superimposing implant data and the modified bone data in defining a resection of an arthroplasty target region of the patient bone.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com