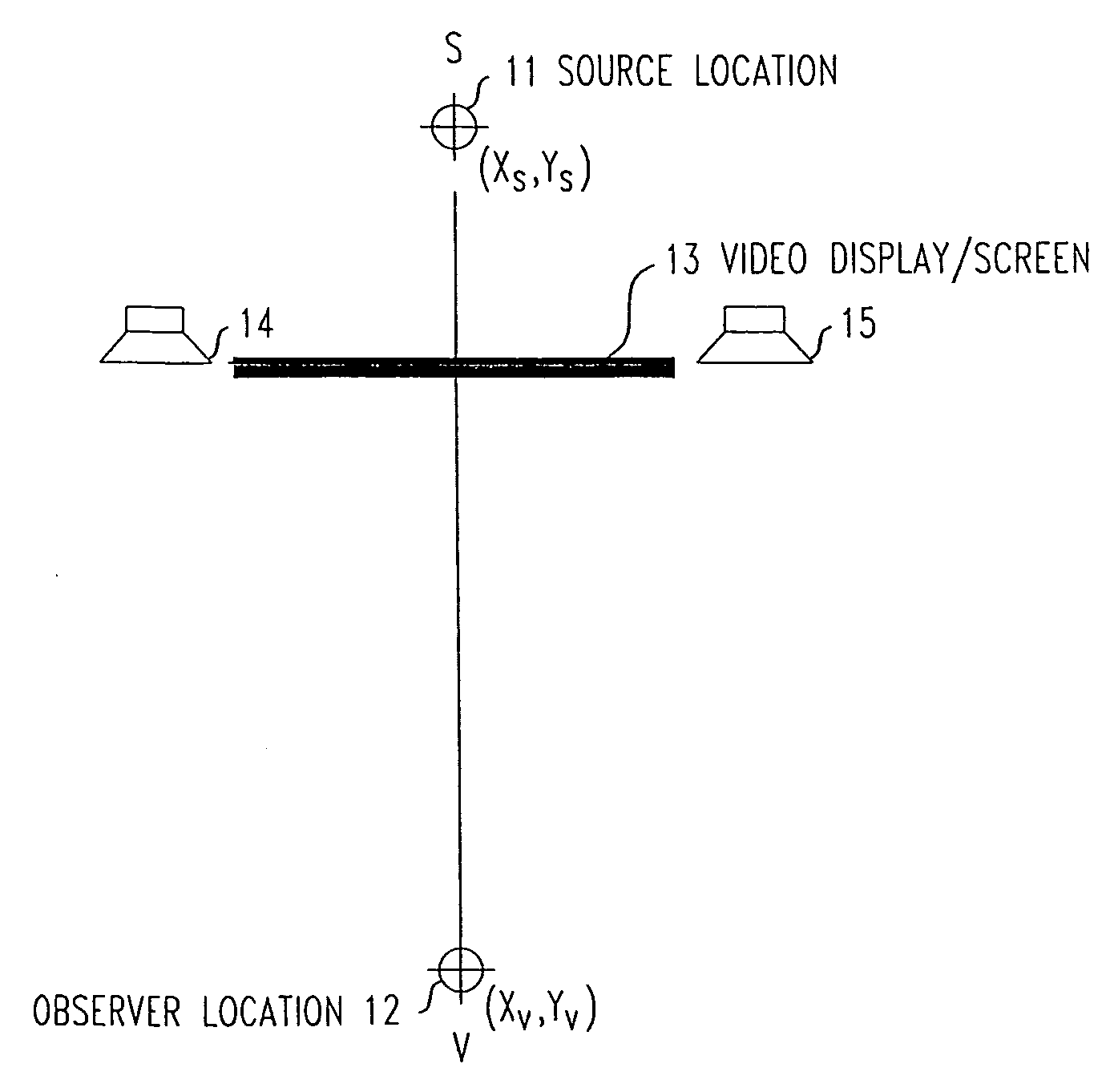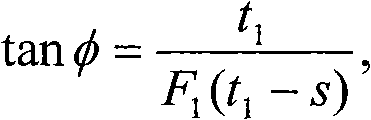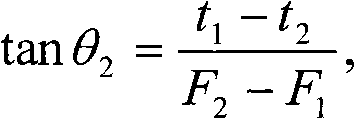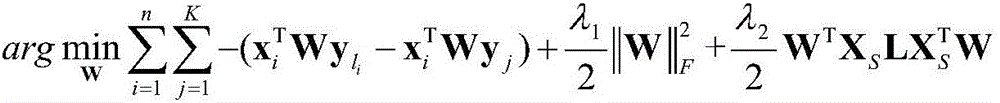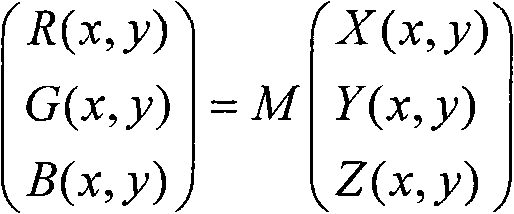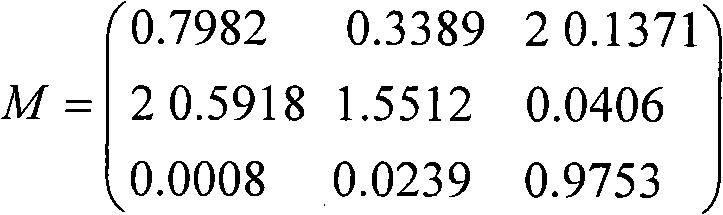Patents
Literature
148 results about "Visual space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
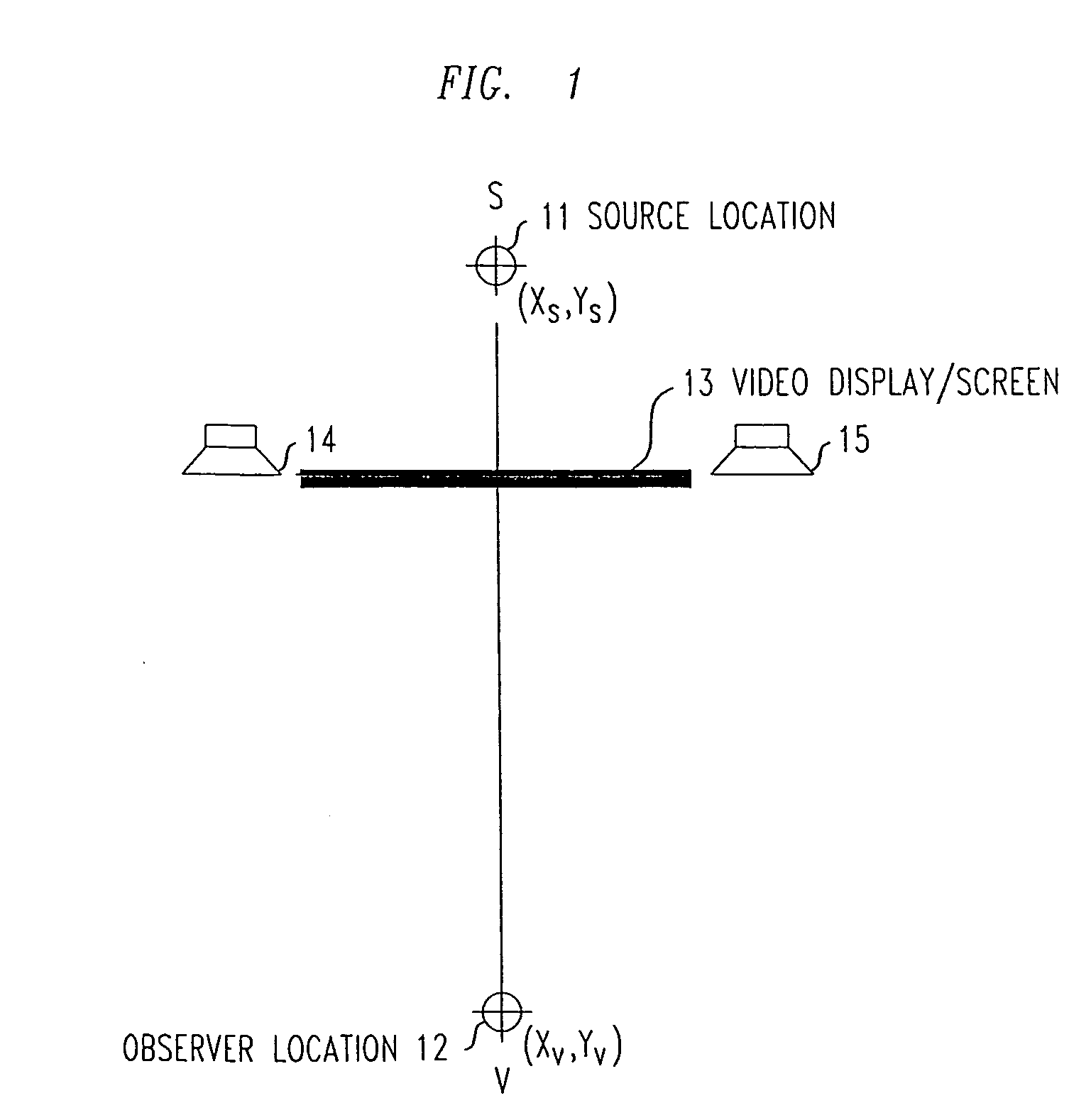
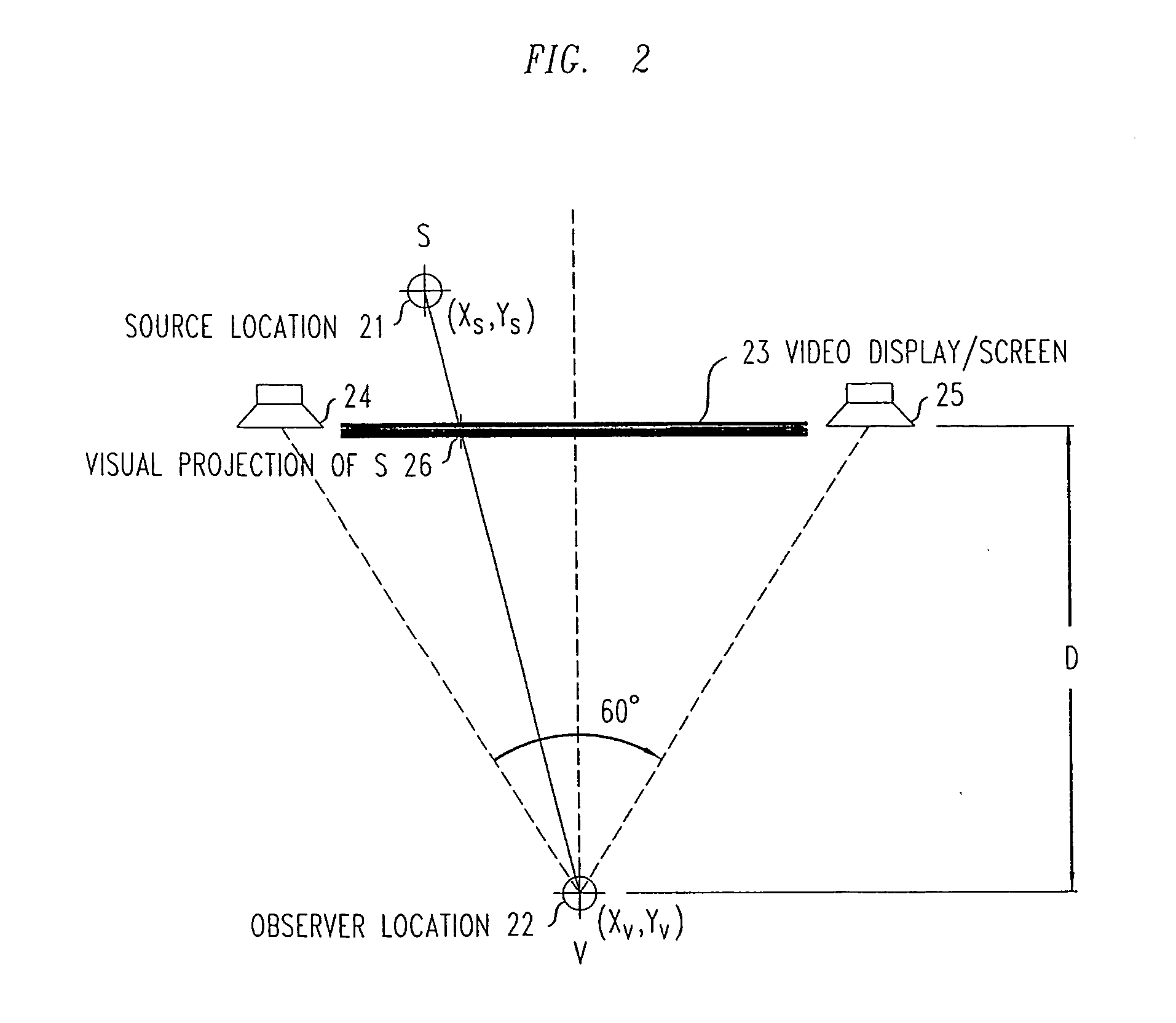
Visual space is the experience of space by an aware observer. It is the subjective counterpart of the space of physical objects. There is a long history in philosophy, and later psychology of writings describing visual space, and its relationship to the space of physical objects. A partial list would include René Descartes, Immanuel Kant, Hermann von Helmholtz, William James, to name just a few.
Method and apparatus for improved mactching of auditory space to visual space in video teleconferencing applications using window-based displays
ActiveUS20100328423A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsSound source locationVisual space
A method and apparatus for enabling an improved experience by better matching of the auditory space to the visual space in video viewing applications such as those that may be used in video teleconferencing systems using window-based displays. In particular, in accordance with certain illustrative embodiments of the present invention, one or more desired sound source locations are determined based on a location of a window in a video teleconference display device (which may, for example, comprise the image of a teleconference participant within the given window), and a plurality of audio signals which accurately locate the sound sources at the desired sound source locations (based on the location of the given window in the display) are advantageously generated.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
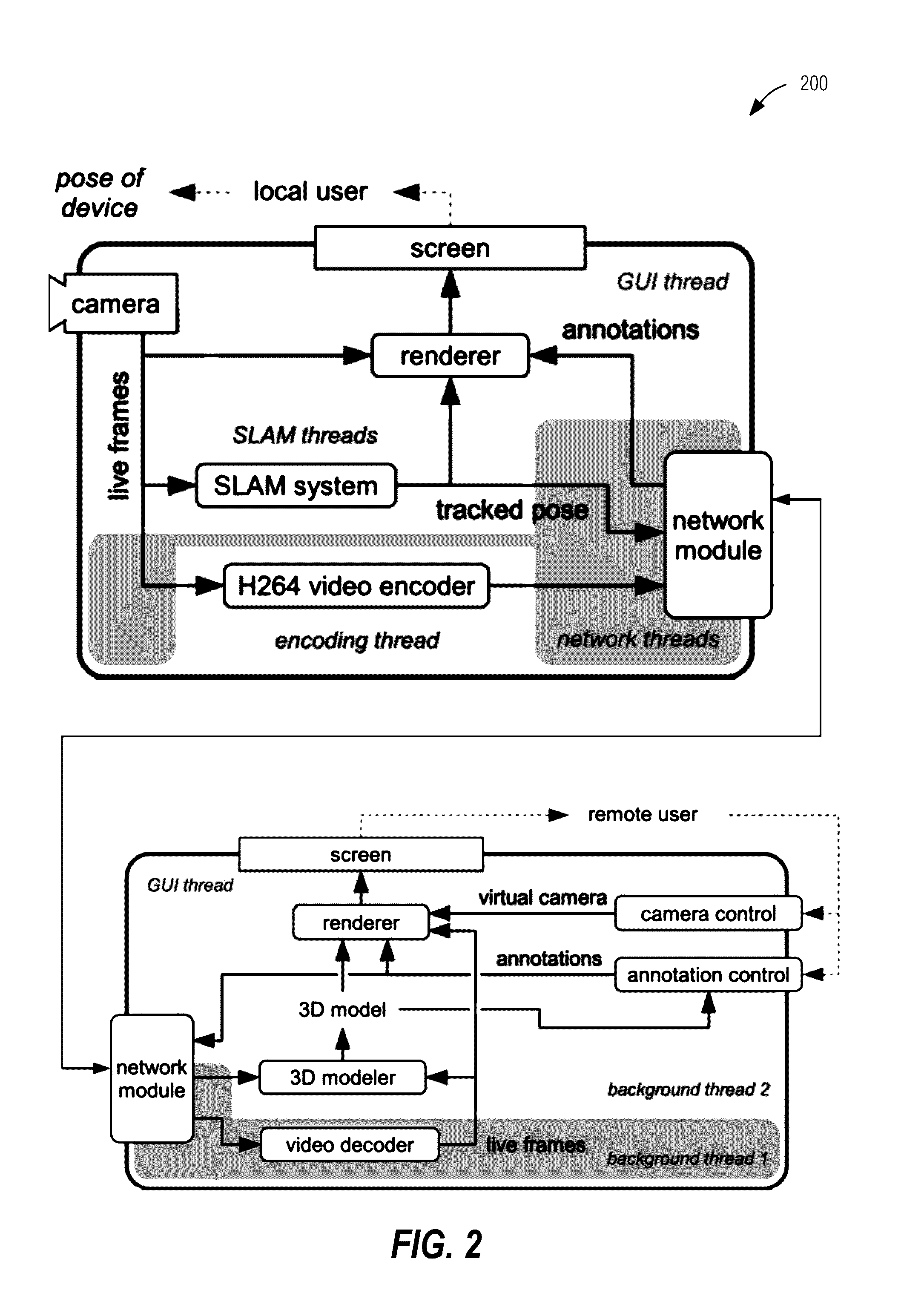
Systems and methods for augmented reality-based remote collaboration
InactiveUS20160358383A1Image analysisDetails involving 3D image dataVisual spaceDistance collaboration
Various embodiments each include at least one of systems, methods, devices, and software for an augmented shared visual space for live mobile remote collaboration on physical tasks. One or more participants in location A can explore a scene in location B independently of one or more local participants current camera position in location B, and can communicate via spatial annotations that are immediately visible to all other participants in augmented reality.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
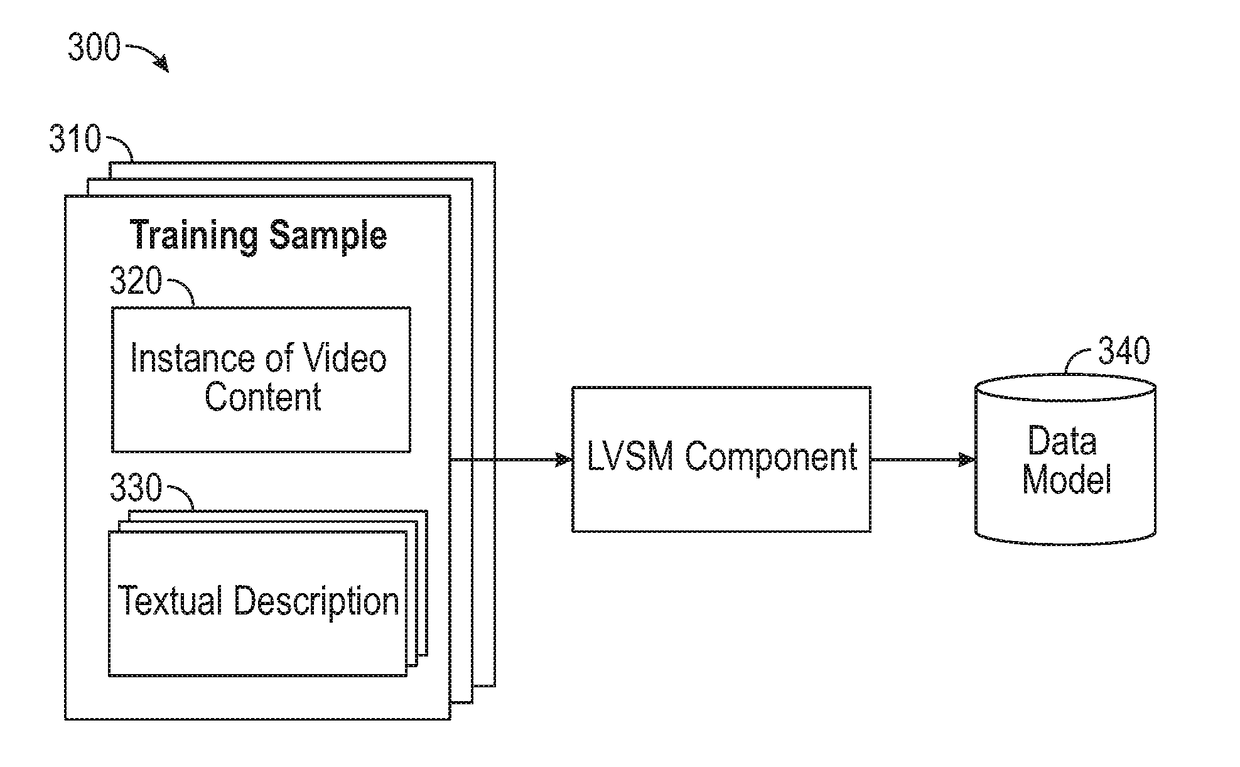
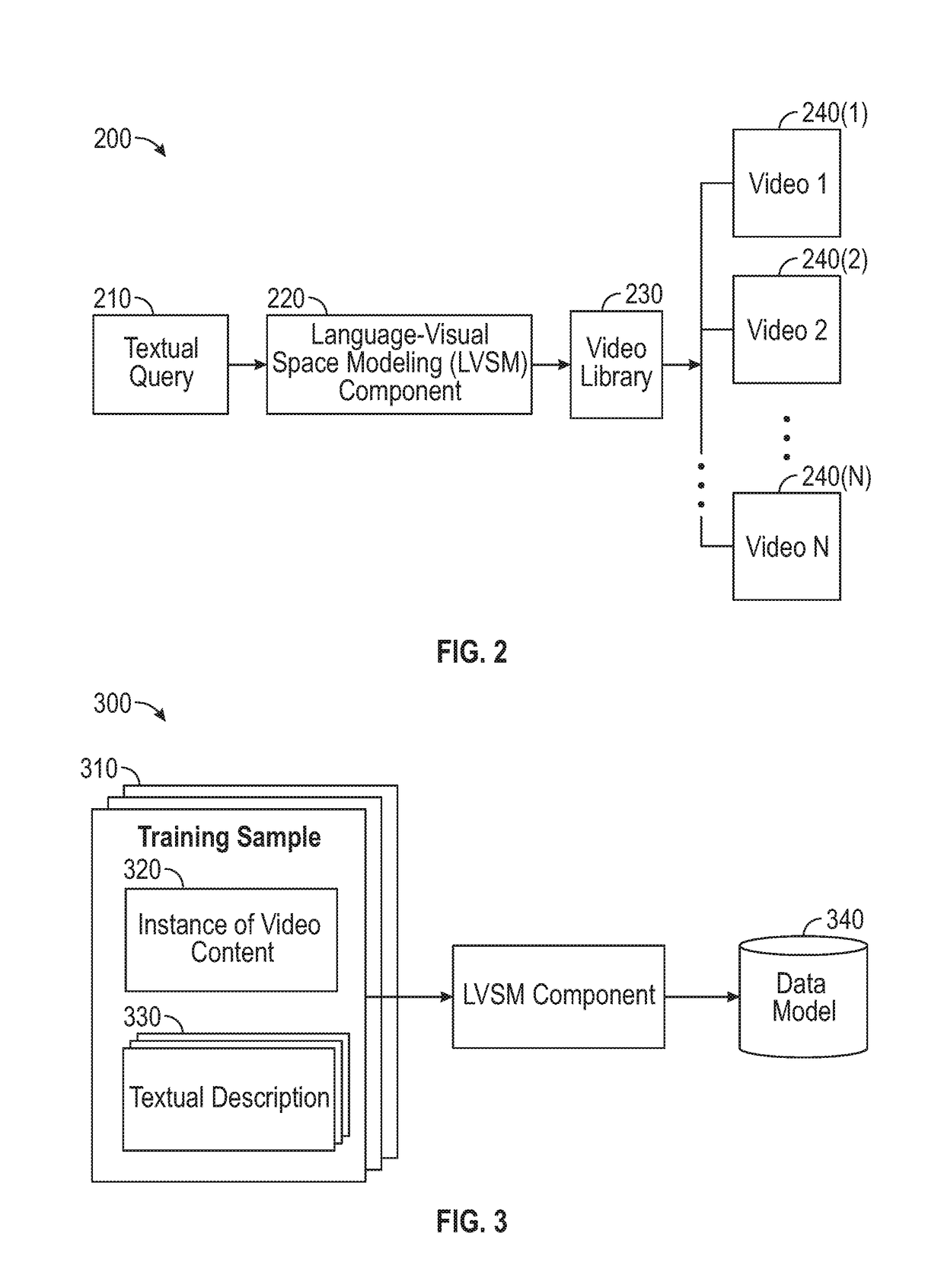
Joint heterogeneous language-vision embeddings for video tagging and search
ActiveUS20170357720A1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual spacePattern recognition
Systems, methods and articles of manufacture for modeling a joint language-visual space. A textual query to be evaluated relative to a video library is received from a requesting entity. The video library contains a plurality of instances of video content. One or more instances of video content from the video library that correspond to the textual query are determined, by analyzing the textual query using a data model that includes a soft-attention neural network module that is jointly trained with a language Long Short-term Memory (LSTM) neural network module and a video LSTM neural network module. At least an indication of the one or more instances of video content is returned to the requesting entity.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Stereo vision measuring apparatus based on binocular omnidirectional visual sense sensor
Disclosed is a stereo vision measuring device based on a binocular omni-directional vision sensor. Each ODVS composing the binocular omni-directional vision sensor adopts the design of mean angle resolution. The parameters of two image collection cameras are in complete accord and in possession of a pretty good symmetry, and can quickly realize the point-to-point matching. The device adopts a unified spherical coordinate in the process of data collection, processing, description and representation of space objects in terms of centering on human in visual space, and adopts the elements of distance sense, direction sense and color sense to express features of each characteristic point, thereby simplifying the complication of calculus, omitting the calibration of the cameras, facilitating the feature extraction and realizing the stereo image matching easily, finally realizing the purpose of high-effective, real-time, and accurate stereo vision measurement. The device can be applied in a plurality of fields of industrial detection, object identification, robot automatic guidance, astronautics, aeronautics, military affairs, etc.
Owner:汤一平
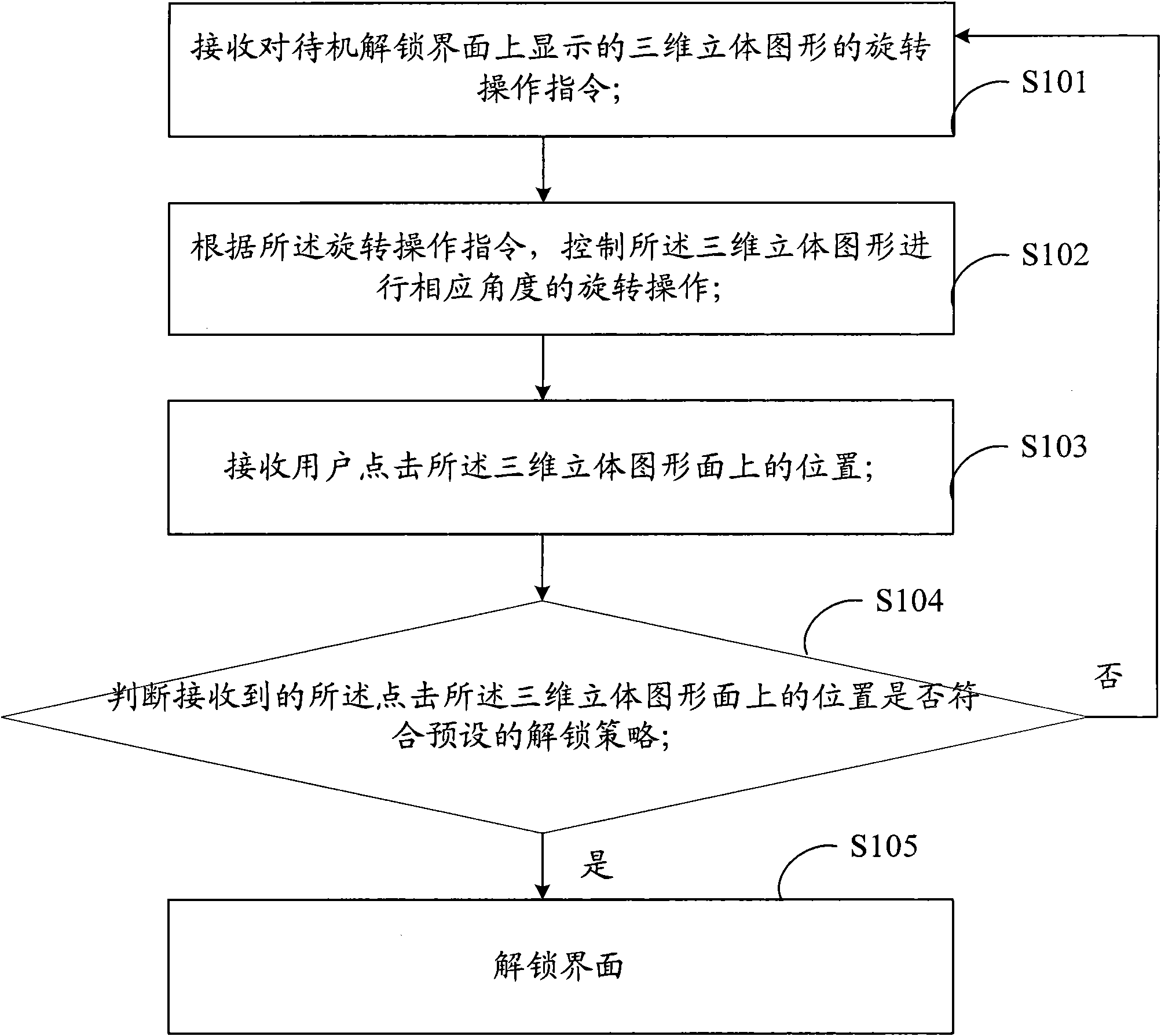
Method, system and touch terminal for unlocking touch terminal interface
ActiveCN101957715AIncrease the difficulty of crackingInput/output processes for data processingVisual spaceGraphics
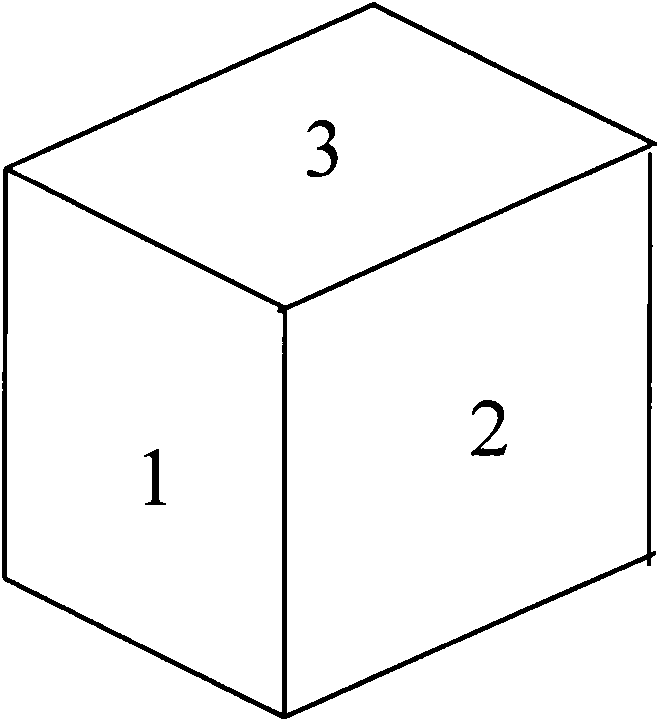
The invention is suitable for the field of touch technology, and provides a unlocking method, a system and a touch terminal for touch terminal interfaces. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a rotary operation command of a three-dimensional graph displayed on a standby unlocking interface; controlling the three-dimensional graph to perform rotary operation in corresponding angle according to the rotary operation command; receiving the position clicked by a user on the three-dimensional graph; and judging whether the position clicked on the three-dimensional graph conforms to the preset unlocking strategy or not, if so, the interface is unlocked. In the scheme for unlocking the multi-dimensional visual space interface in a single-face touch screen, the invention provides brand new operation experience and the unlocking scheme for multi-dimensional visual space interface for users, and the password setting is improved to a brand new breaking difficulty.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
System and method for clustering gene expression data based on manifold learning
InactiveCN102184349AAccurately discover co-regulatory relationshipsDiscovery of co-regulatory relationshipsSpecial data processing applicationsVisual spaceCluster algorithm
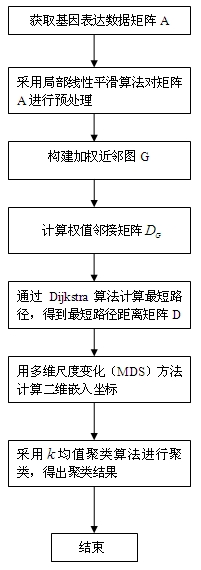
The invention discloses a method for clustering gene expression data based on manifold learning, and the method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: acquiring a gene expression data matrix A through an acquisition system, and preprocessing the gene expression data matrix A by using a local linear smoothing algorithm; introducing the preprocessed data matrix A, and constructing a weighted neighborhood figure G in a three-dimensional space; taking the shortest path between two points as the approximate geodesic distance between two points; calculating a two-dimensional embedded coordinate by using an MDS (minimum discernible signal), and mapping the three-dimensional data matrix A to a two-dimensional visual space; and carrying out clustering on the two-dimensional visual space subjected to mapping by using a k-mean clustering algorithm so as to obtain the clustering result. The clustering method has the characteristics of low calculating cost, capability of eliminating high-order redundancies, suitability for pattern classification tasks, and the like; and by using the method disclosed by the invention, the current states of cells, the effectiveness of medicaments to malignant cells, and the like can be discriminated effectively according to the clustering result. The invention also provides a system for clustering gene expression data based on manifold learning.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
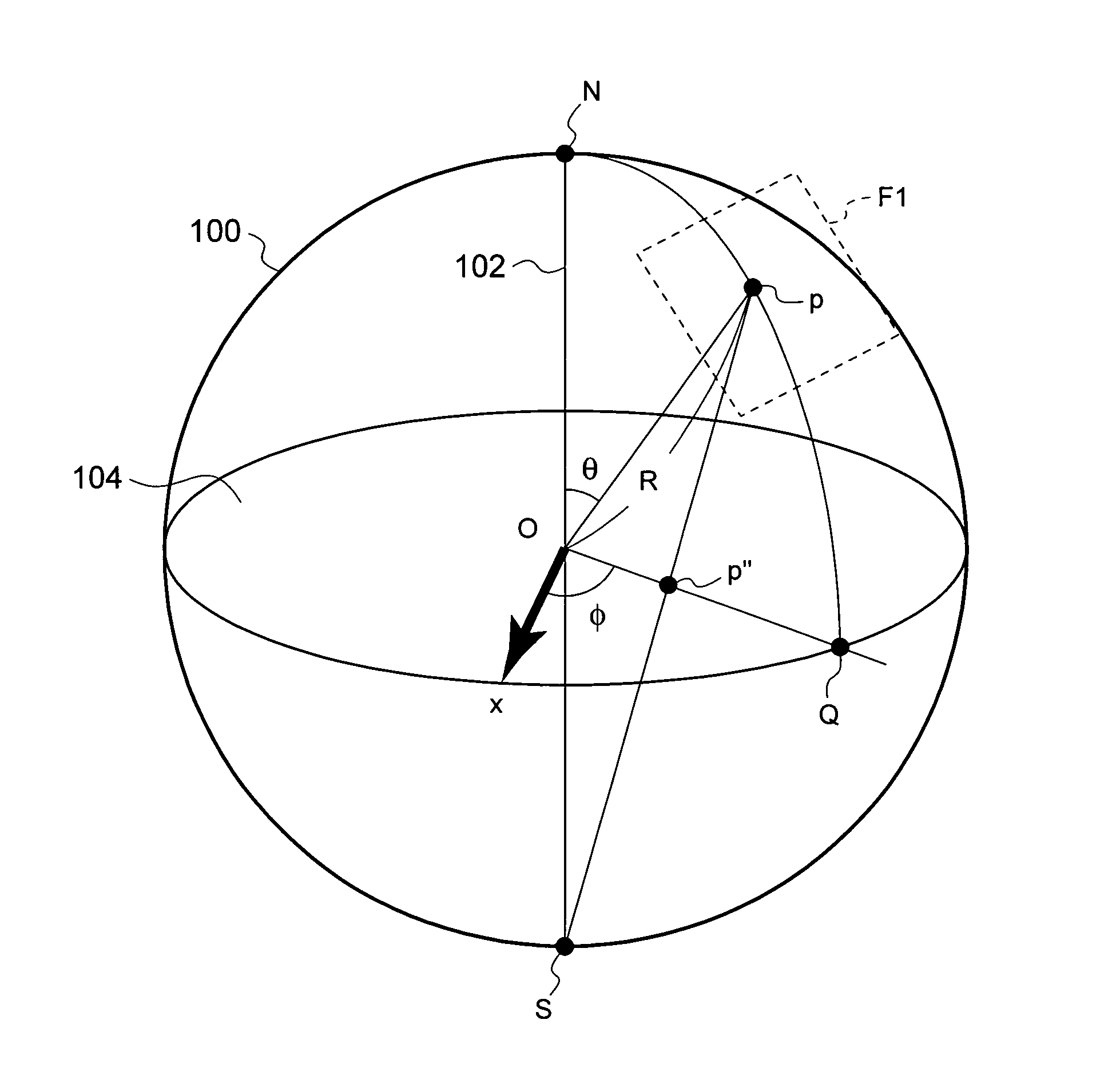
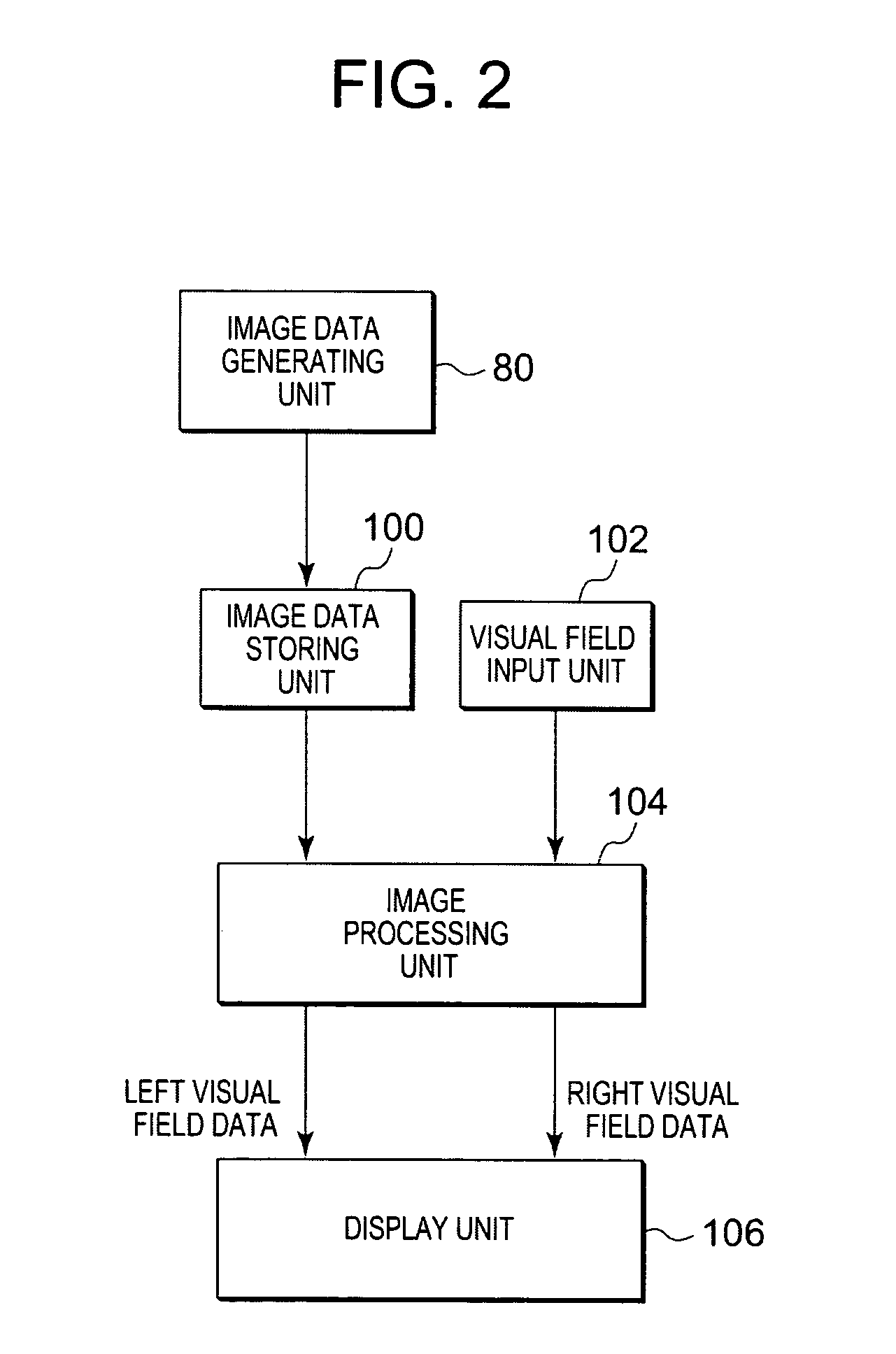
Method and system for simulating stereographic vision
A 3-D visual simulating system stores image data sets in a predetermined viewing space for right and left visual field and selects a portion of the stored image data corresponding to the current visual field for displaying it to an observer. The 3-D image stimulus changes according to the current visual field of the observer and the location of the observer in a predetermined visual space in a manner that undesirable perceptional effects are substantially eliminated. The image data sets are stored in a reduced space in an efficient manner for retrieval.
Owner:RICOH KK
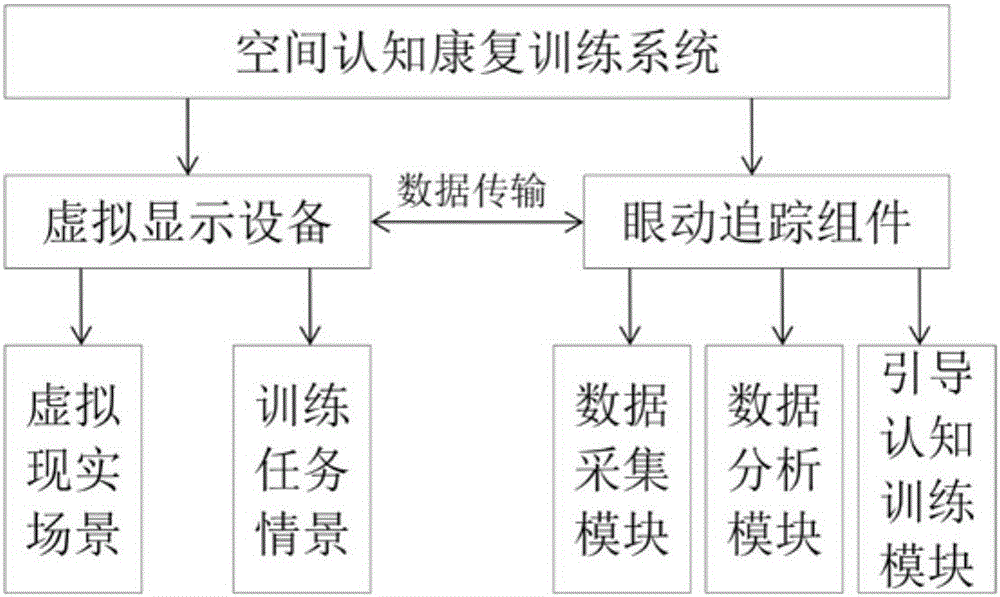
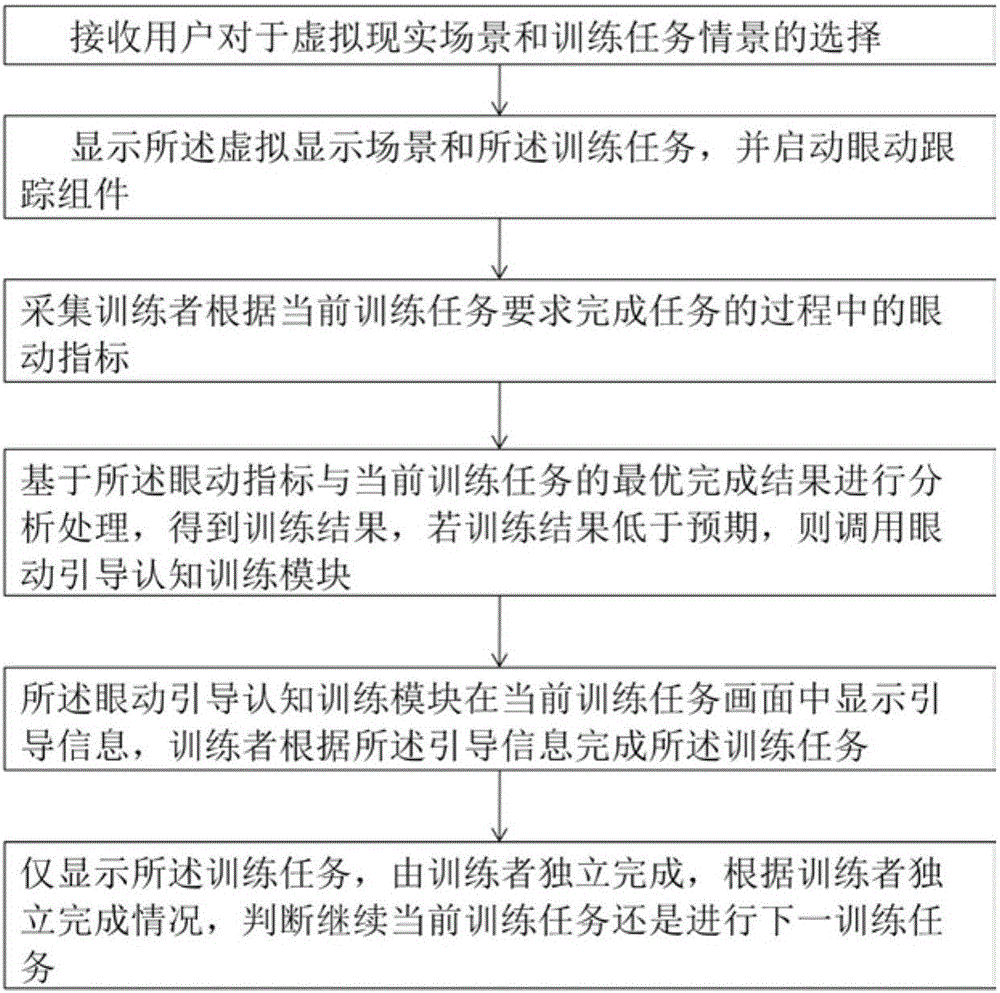
Spatial cognition rehabilitation training system and method based on virtual reality and eye tracking
The invention discloses a spatial cognition rehabilitation training system based on virtual reality and eye tracking. The system comprises a virtual reality device. The virtual reality device comprises a scene display assembly which is used for displaying a virtual reality scene and a training task scene, an infrared eye tracking assembly which obtains eye movement data in real time when a trainee completes the task according to training task requirements and transmits the eye movement data to a data analyzing module; a data analyzing module which analyzes eye movement indexes when the trainee completes the scene task according to the data obtained by the eye tracking assembly, evaluates the visual space processing characteristics of the trainee, and transmits the result to an eye movement guiding cognition training module, and the eye movement guiding cognition training module which calls different eye movement prompting modes for guiding machining according to the visual space processing characteristics. The spatial cognition training is conducted through the virtual reality scene, guiding processing is conducted in a targeted mode, and the method has more ecology, effectiveness and operability compared with the prior art.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Method for visualizing graphical data sets having a non-uniform graphical density for display
InactiveUS7046247B2Increase display areaHigh resolutionDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsVisual spaceGraphics
A method for visualizing high density graphical data sets for display is effectuated by determining the graphical density corresponding to an area of the display, where the graphical density is of a non-uniform nature. A non-linear visual space transformation corresponding to the graphical density is processed. Resolution in the area of the display is increased in response to the non-linear visual space transformation and the area is displayed with increased resolution.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
Human body characteristic visualization device and method
InactiveCN105534694AAcupoint labeling is intuitiveHigh precisionDevices for locating reflex pointsEducational modelsHuman bodyVisual space
The invention provides a human body characteristic visualization device. The human body characteristic visualization device is capable of visualizing non-dominant human body characteristics in the various parts of a human body and even in the whole body, so that the intuitive location of an observer is achieved and the position and morphology information of the non-dominant characteristics of the human body are mastered; specifically, the human body characteristic visualization device comprises a three-dimensional scanning device which, together with a visualization device, defines a visual space, and a data processing device which is stored with human body characteristic information and is used for processing the three-dimensional information in a human body detected part acquired by the three-dimensional scanning device, so that the visualization device is controlled within the visual space, and the matched visual human body characteristic information is released from the body surface region of the human body detected part.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAJUN TECH CO LTD
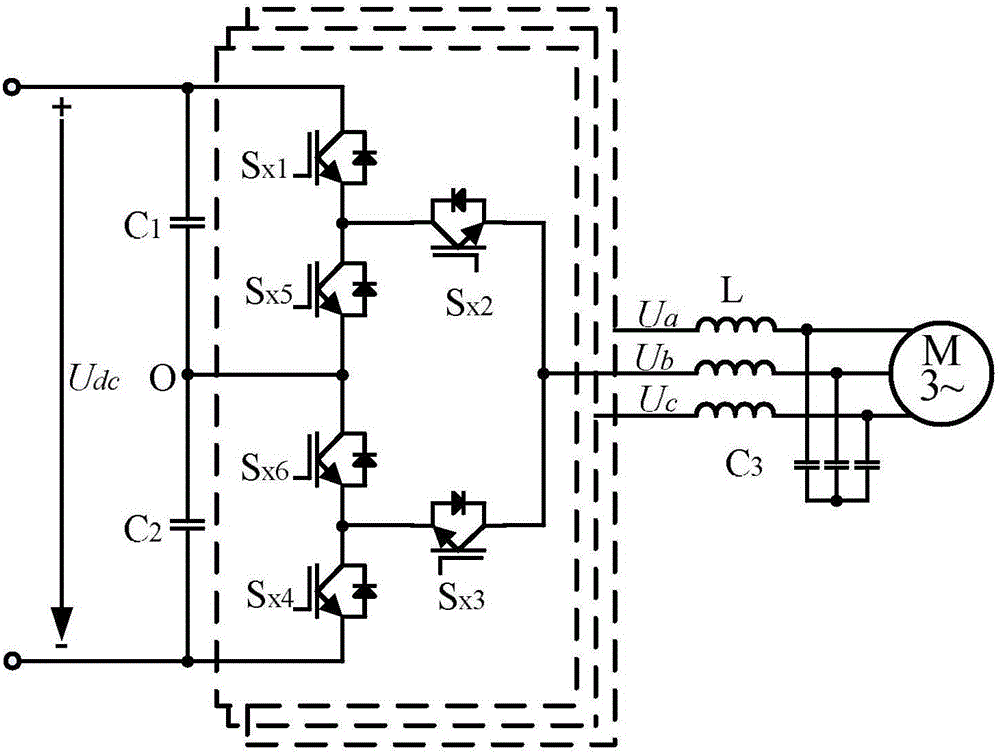
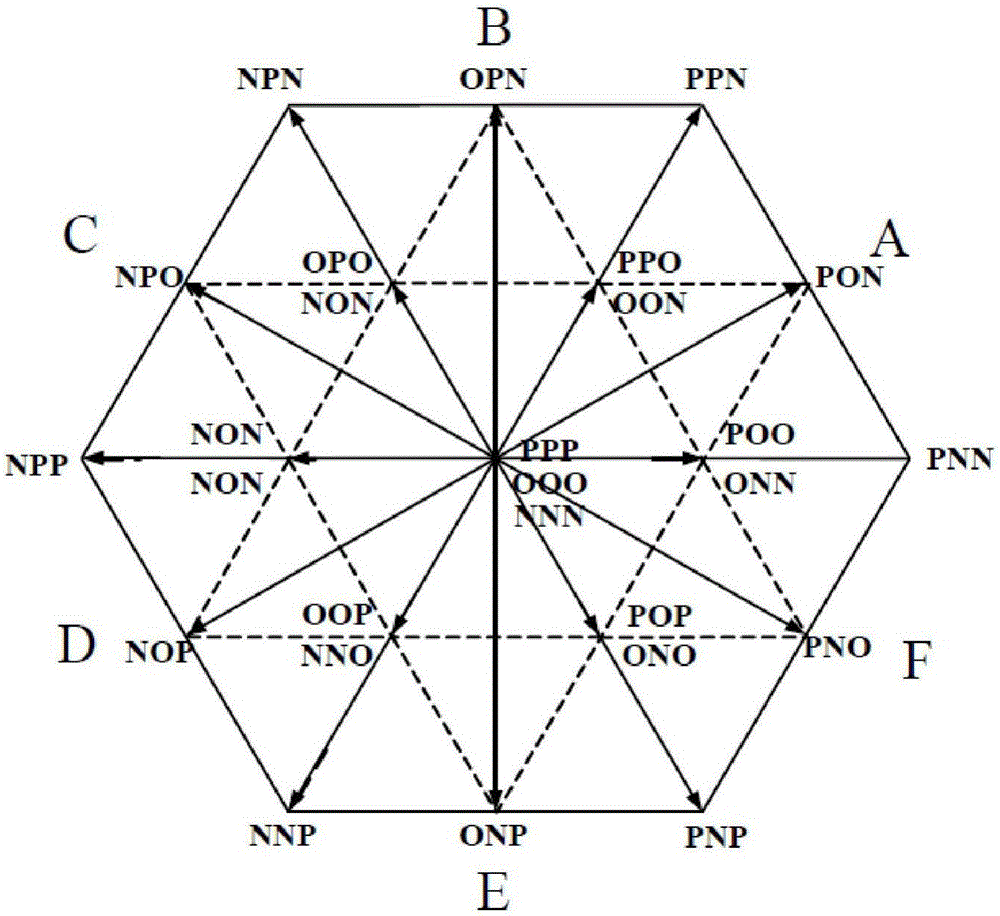
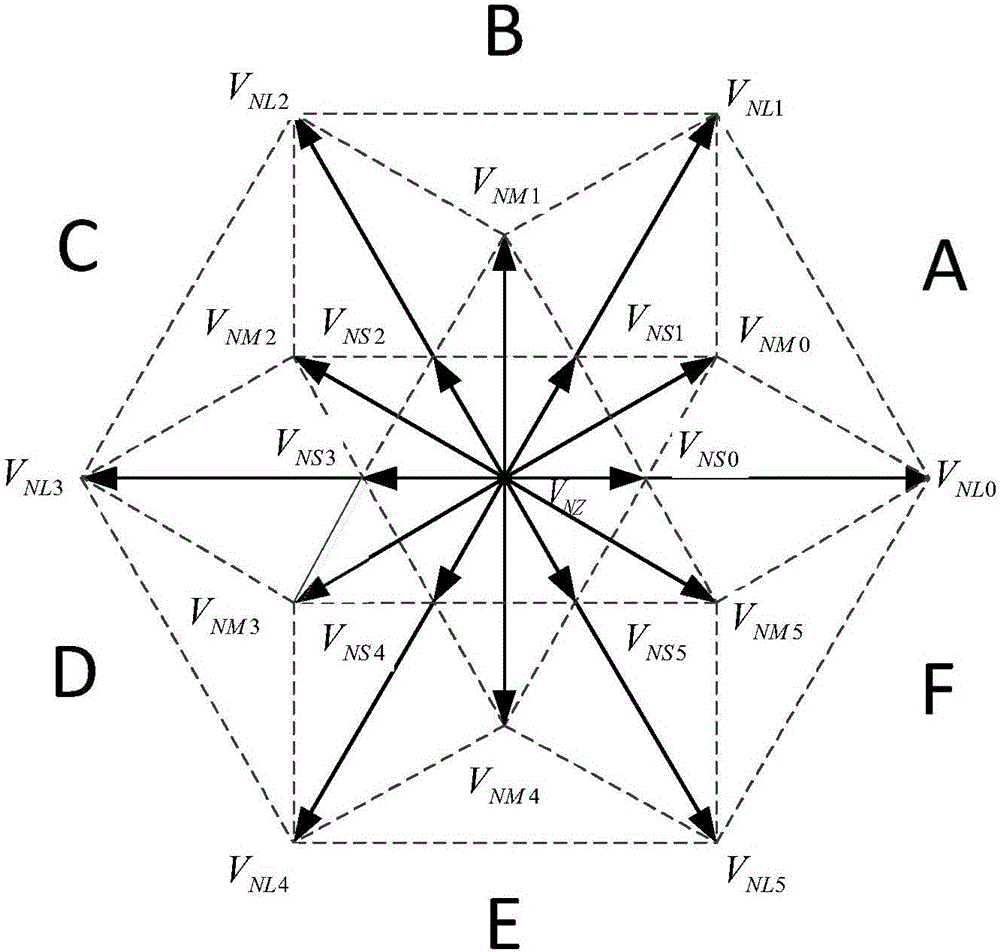
Neutral-point voltage balance and common-mode voltage suppression method for three-level inverter
ActiveCN105978374ASimple logical judgmentImprove work performanceAc-dc conversionVisual spaceVirtual space
The invention relates to a neutral-point voltage balance and common-mode voltage suppression method for a three-level inverter, and mainly provides a novel visual space vector modulation (VSVM) method. The method comprises the following steps: defining a new visual zero vector to just include zero vector 000; defining a novel visual small vector to be composed of an original negative small vector and two negative small vectors adjacent to the original negative small vector; and defining a new visual medium vector to be composed of an original medium vector and two medium vectors adjacent to the original medium vector. By using the space vector definition method, each composite vector cannot cause neutral-point voltage to be fluctuated, and basic vectors forming the novel visual space vector do not include positive small vectors and zero vector PPP and NNN, so that the output common-mode voltage is relatively small. When external nonlinear factors enable the neutral-point voltage to be fluctuated, on the basis of a new visual space vector modulation strategy, the action time distribution factors for each composite vector are appropriately adjusted by comparing the size of three-phase load current, so that neutral-point voltage balance is controlled.
Owner:丹阳博亚新材料技术服务有限公司
Auxiliary positioning method, positioning device and system for joint replacement
InactiveCN110037768AHigh precisionImprove matchSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingSurgical operationVisual space
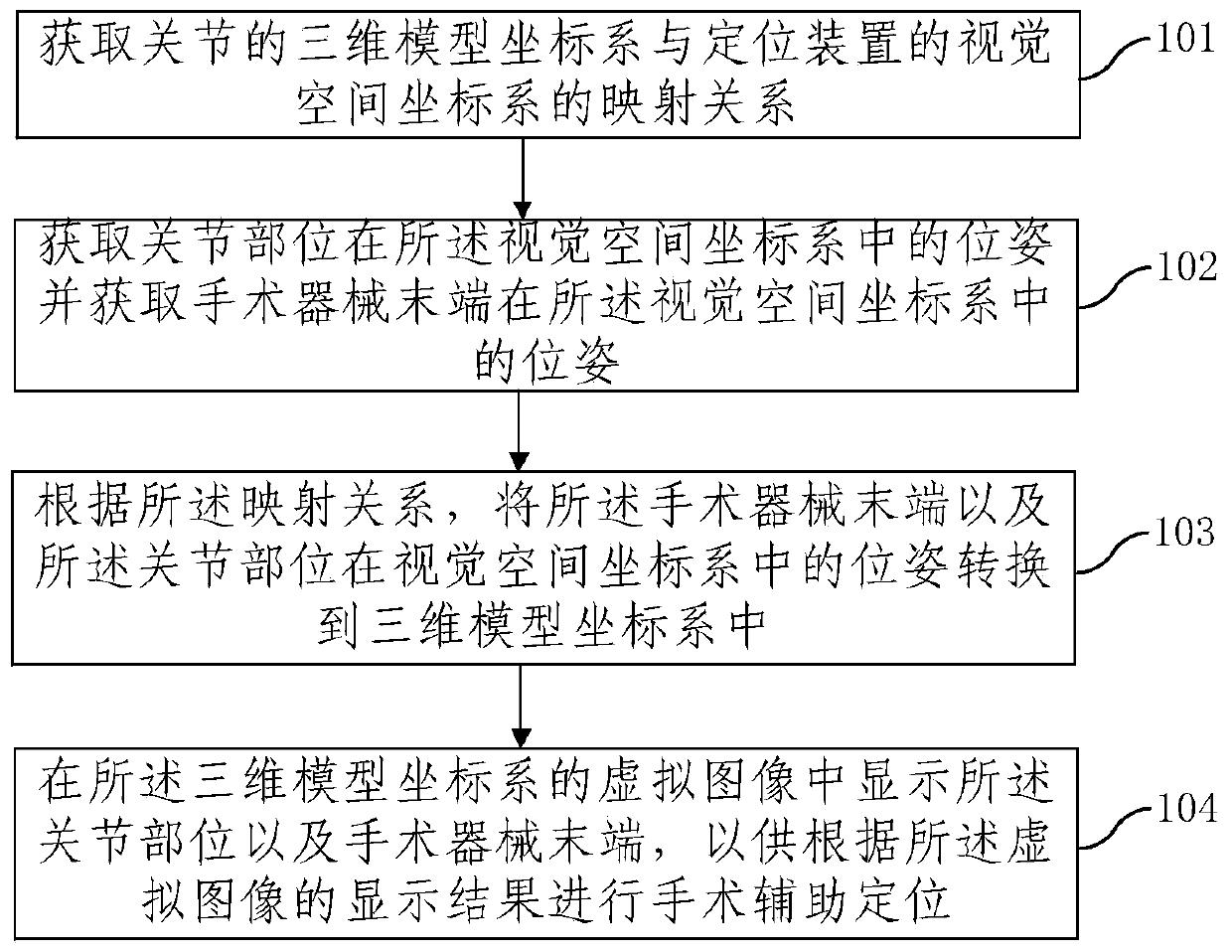
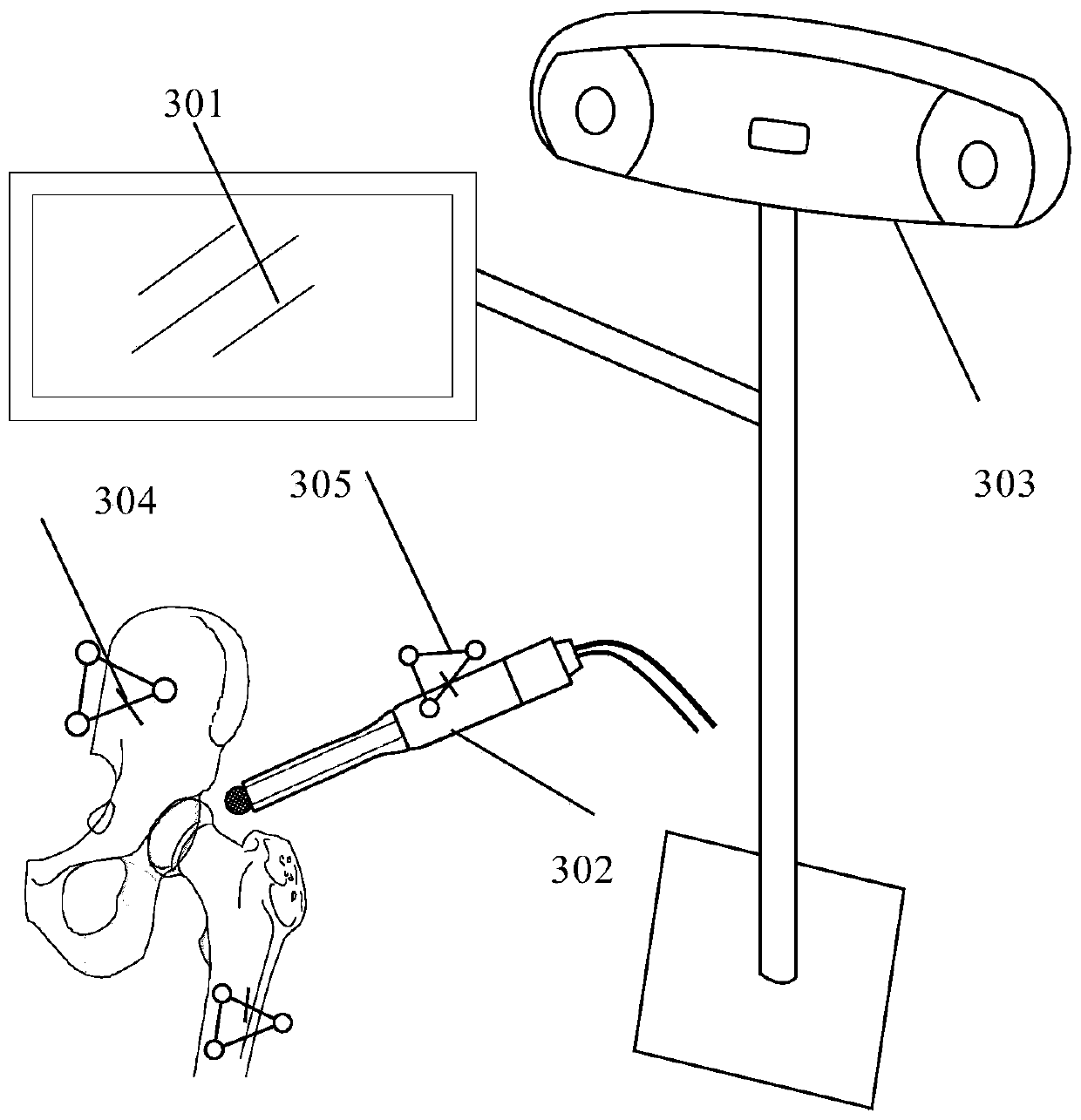
The embodiment of the invention provides auxiliary positioning method, positioning device and system for joint replacement. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the mapping relation between a three-dimensional model coordinate system of a joint and a visual space coordinate system of the positioning device; acquiring the pose of the joint site in the visual space coordinate system,and acquiring the pose of the tail end of a surgical instrument in the visual space coordinate system; based on the mapping relation, converting the poses of the tail end of the surgical instrument and the joint site in the visual space coordinate system into the three-dimensional model coordinate system; and displaying the joint site and the tail end of the surgical instrument in a virtual imageof the three-dimensional model coordinate system, thereby performing surgery auxiliary positioning based on the display result of the virtual image. Because a doctor can visually observe the relativeposition relation between the joint site and the tail end of the surgical instrument during surgical operation, the osteotomy accuracy is high, operating risk is decreased, and further the accuracy and matching degree of the mounting position of a prosthesis are improved.
Owner:BEIJING YAKEBOT TECH CO LTD
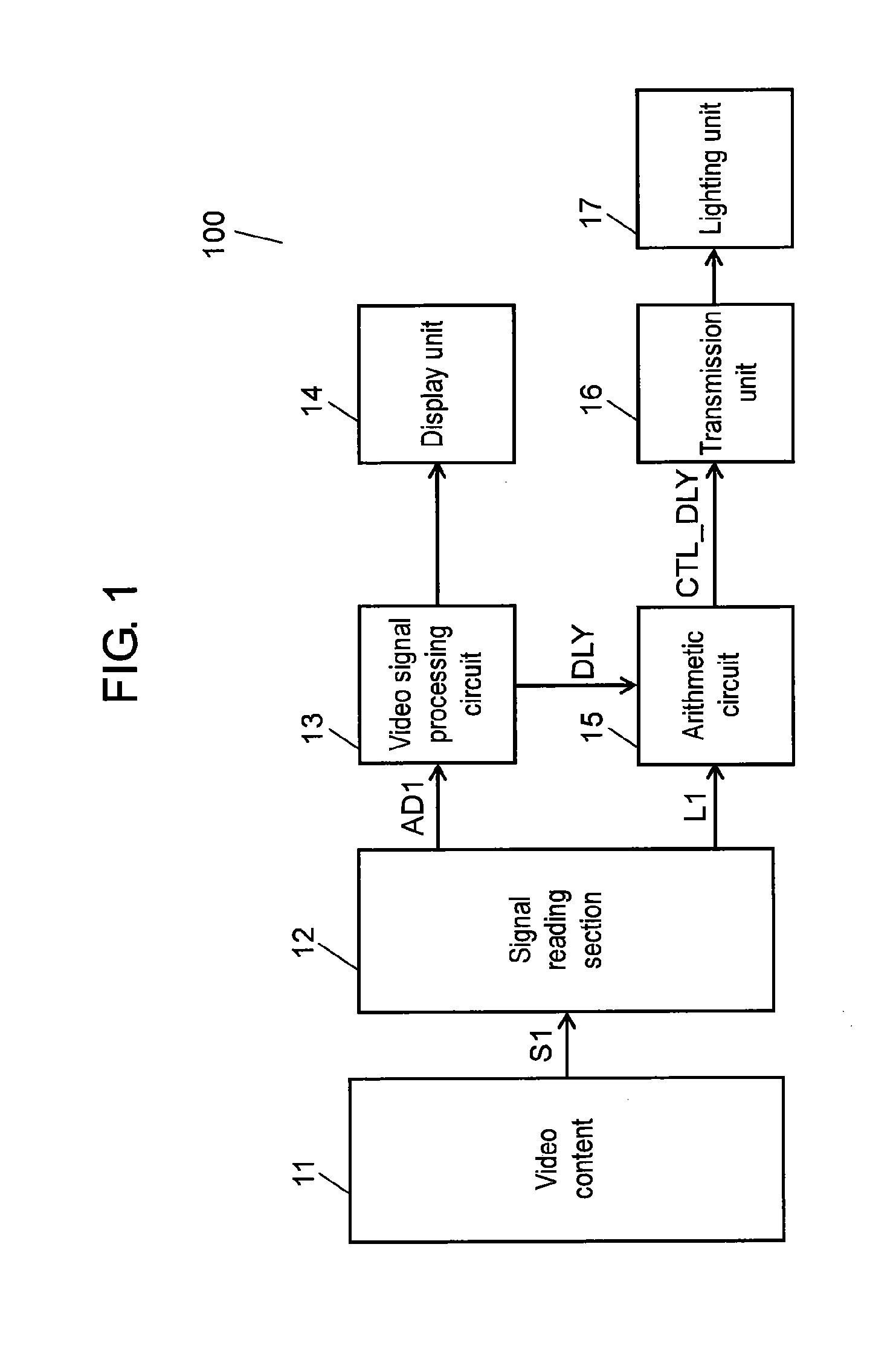
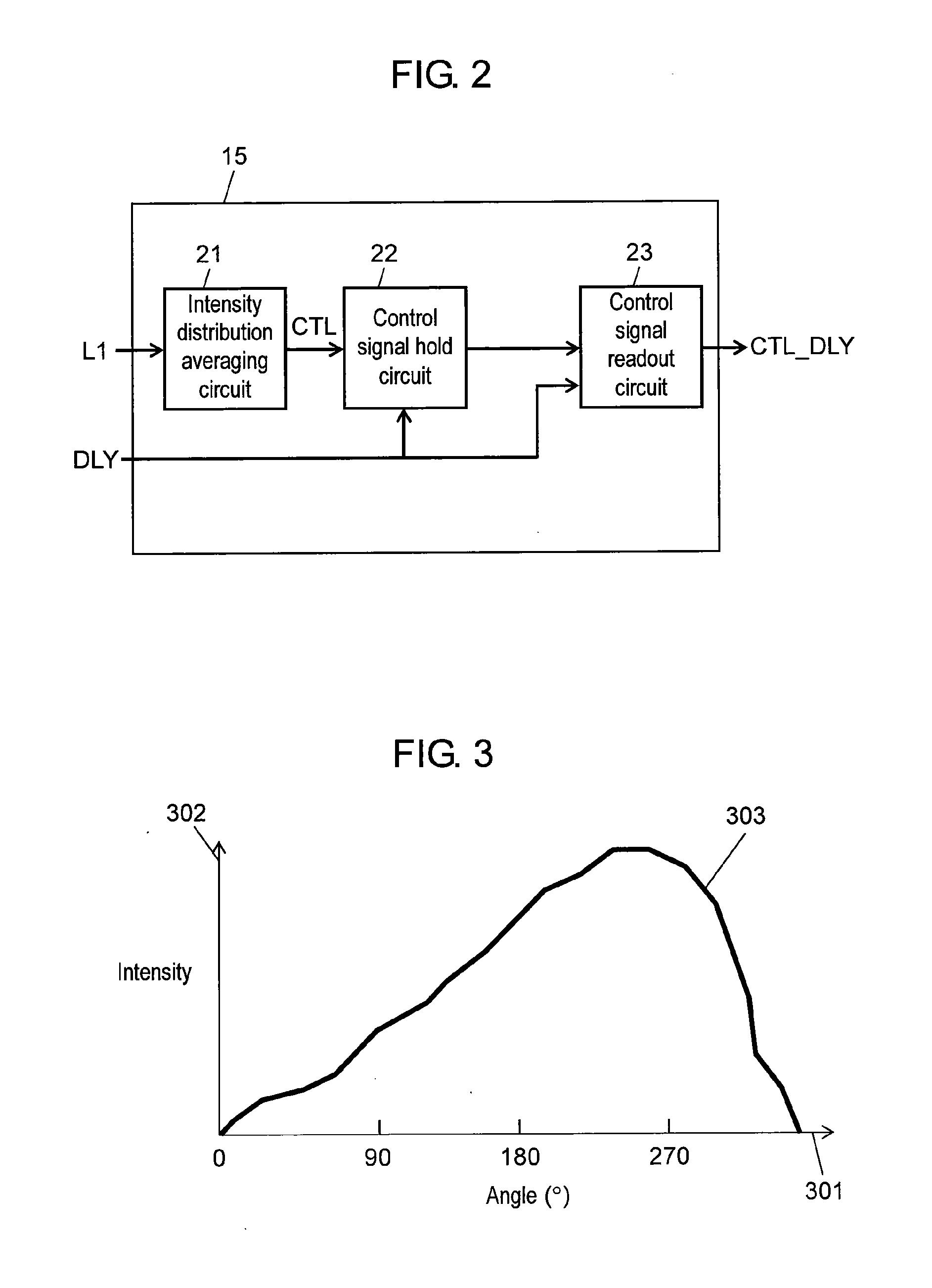
Video collaboration type illuminating control system and video collaboration type illuminating control method
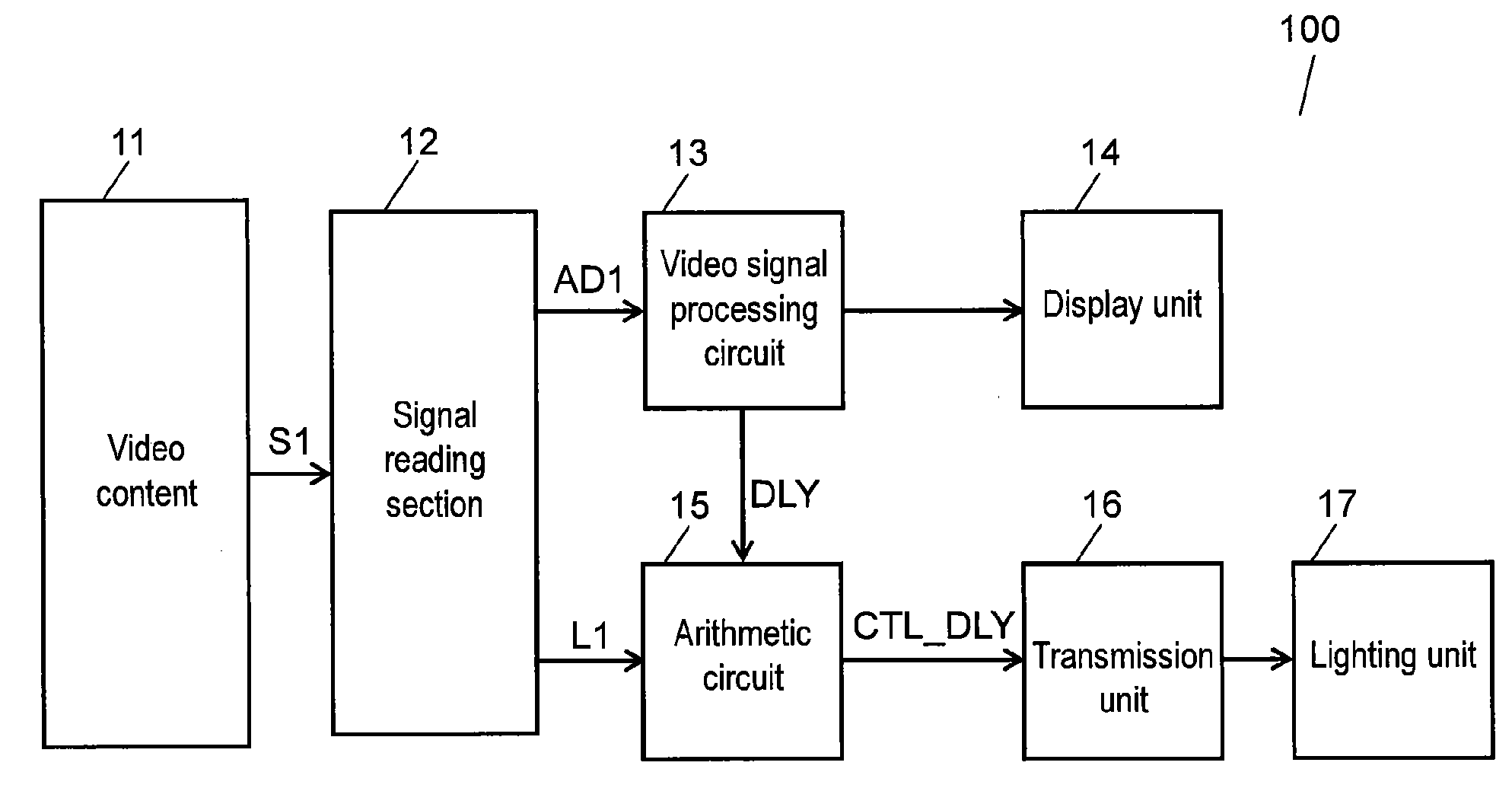
InactiveUS20120098960A1More realismFaithfully reproducedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisual spaceControl signal
A video link type illuminating control system and video link type illuminating control method allow a signal containing the idea of the content creator to be added to an airwave signal or a video content signal so that the audio-visual space is illuminated based on the control signal generated from the signal. As a result, illumination can be controlled in linkage with video, thus increasing visual realism.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
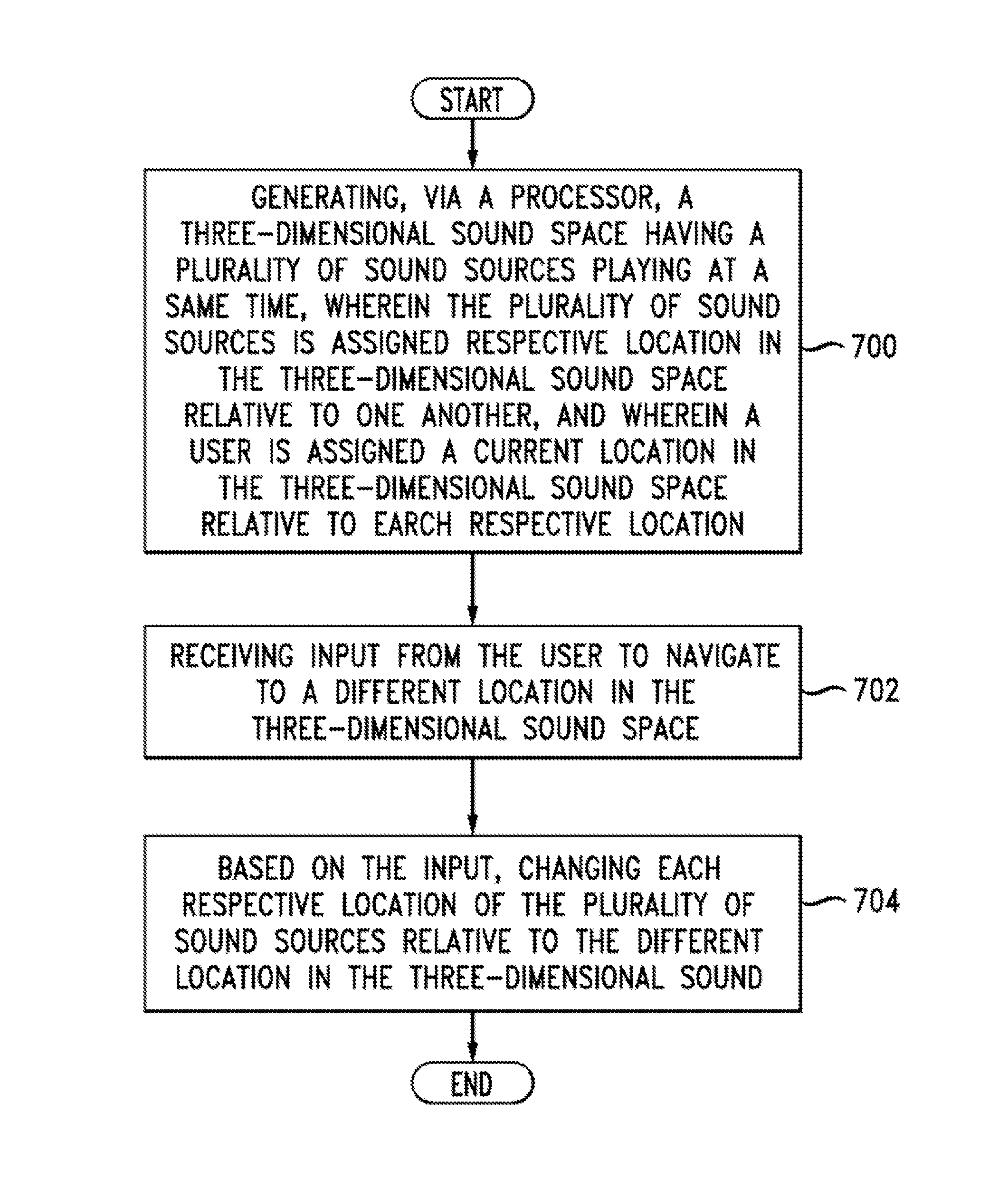
Three-dimensional generalized space
ActiveUS20170038943A1The process is convenient and fastPublic address systemsSound input/outputVisual spaceSound sources
According to one embodiment, audio and non-audio data can be represented as sound sources in a three-dimensional sound space adapted to also provide visual data. Non-audio data can be associated with audio sound sources presented in the sound space. Navigation within this combined three-dimensional audio / visual space can be based primarily on the audio aspects of the sound sources with the details of the non-audio data being presented on demand, for example, when the listener navigates through the combined three-dimensional audio / visual space to a particular sound source at which point the non-audio data associated with that sound source can be presented.
Owner:AVAYA INC
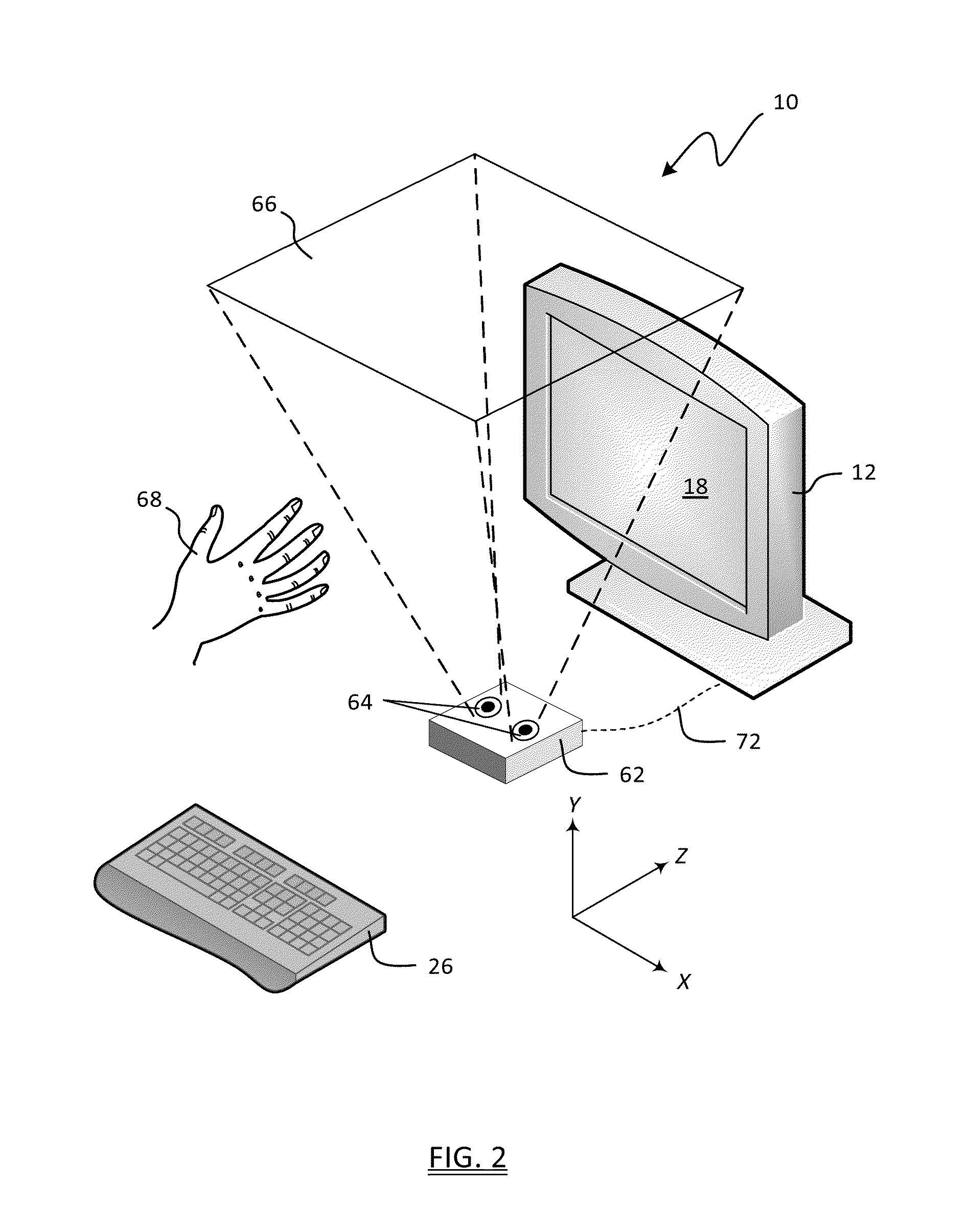
Dynamic tool control in a digital graphics system using a vision system
A system and method for controlling tool selection in a graphics application program executing on a computer are disclosed. The method includes the steps of connecting a vision system to the computer, wherein the vision system is adapted to monitor a visual space. The method further includes the steps of detecting, by the vision system, a tracking object in the visual space, and outputting, by the vision system to the computer, spatial coordinate data representative of the location of the tracking object within the visual space. The method further includes the steps of mapping a horizontal portion and a vertical portion of the spatial coordinate data to a display connected to the computer, and controlling a characteristic of a tool within the tool configuration utility user interface by mapping the spatial coordinate data to a tool control.
Owner:COREL CORP
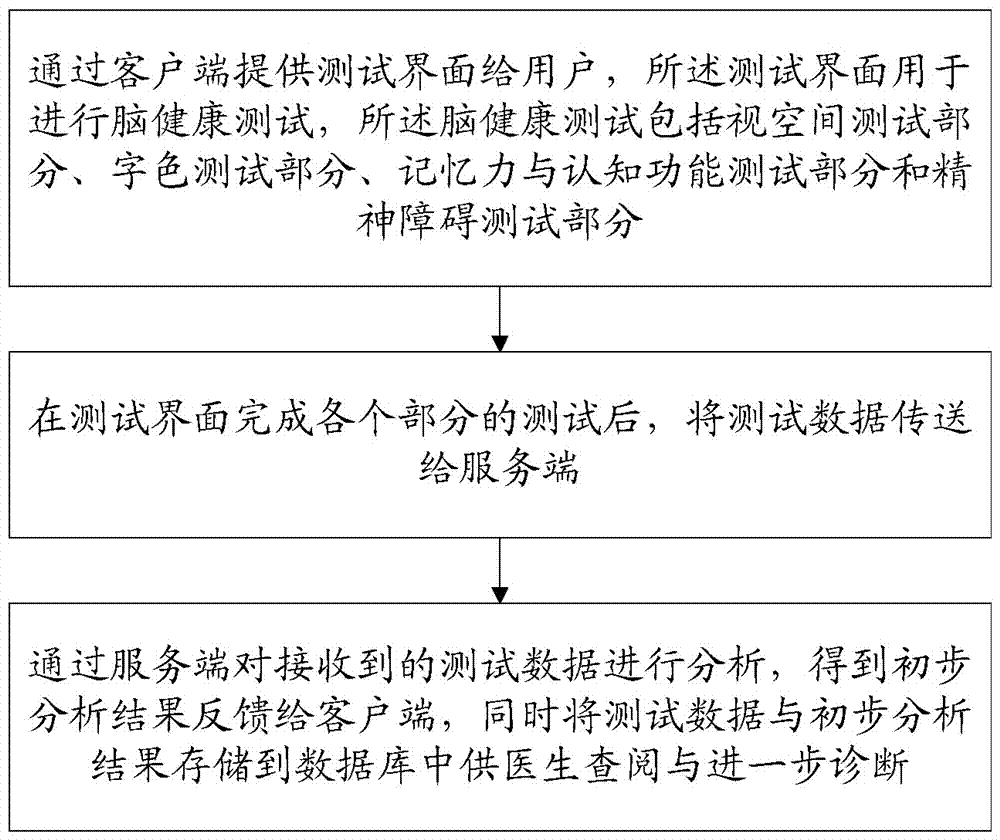
Method and system used for brain health cognitive disorder diagnosis and risk evaluation
InactiveCN107088051ATest UnityEasy to testDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTest efficiencyVisual space
The invention provides a method used for brain health cognitive disorder diagnosis and risk evaluation. A client-side and a server need to be provided, and the server is further provided with a database. The method comprises the steps of providing a test interface for a user through a client-side wherein the test interface is used for conducting a brain health test, and the brain health test comprises a visual space test part, a character color test part, a memory and cognitive function test part and a mental disorder test part; after the test interface completes tests of all the parts, using the test interface to transmit test data to the server; using the server to analyze the received test data to obtain a preliminary analysis result and feed the preliminary analysis result back to the server, and storing the test data and the preliminary analysis result into the database for a doctor to refer to and conduct further diagnosis at the same time. The invention further provides a system used for brain health cognitive disorder diagnosis and risk evaluation, the purpose that the user conducts an accurate brain function test at any time and any place is achieved, treatment is conveniently conducted timely, and the test efficiency is drastically improved.
Owner:潘晓东 +3
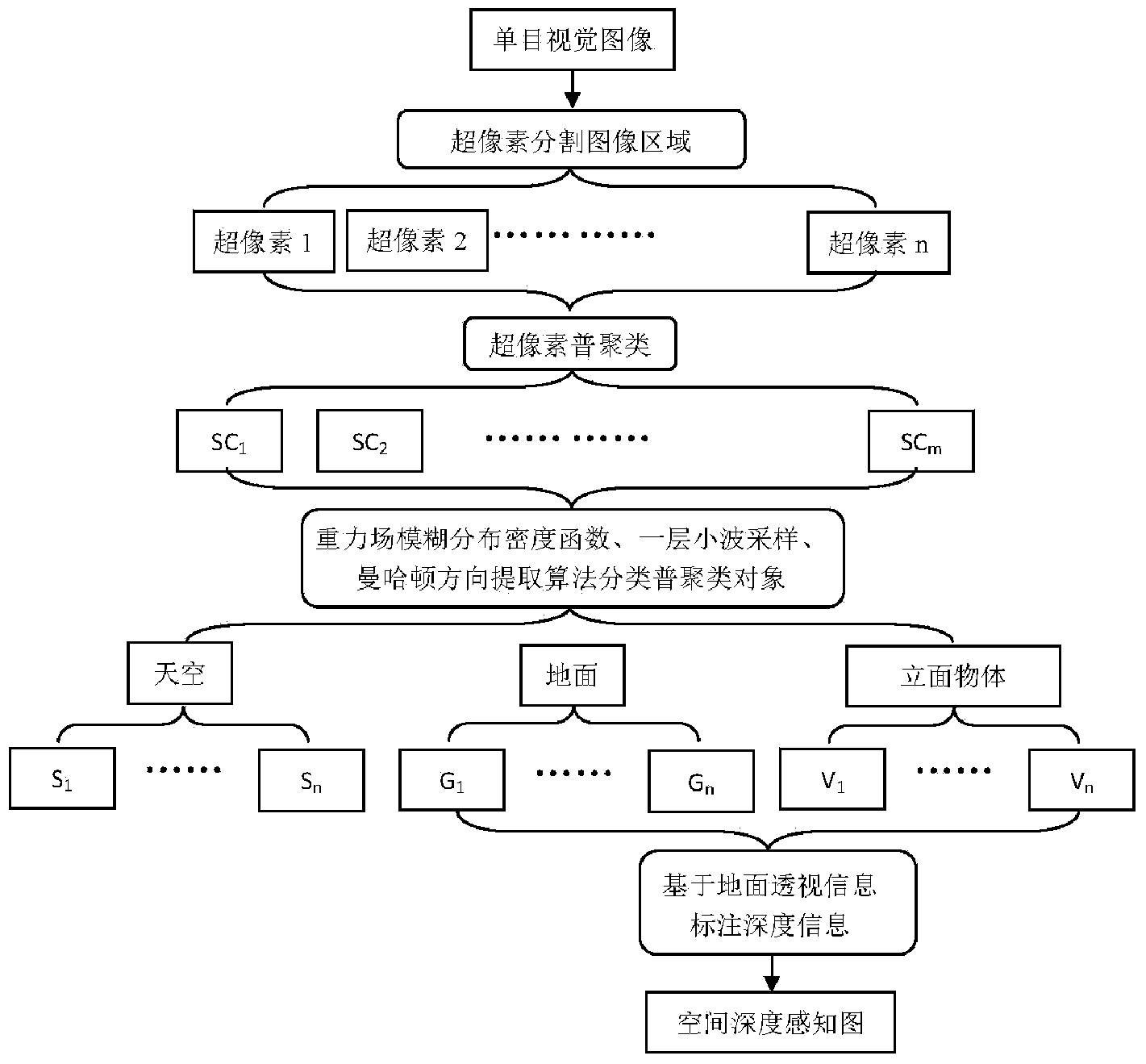
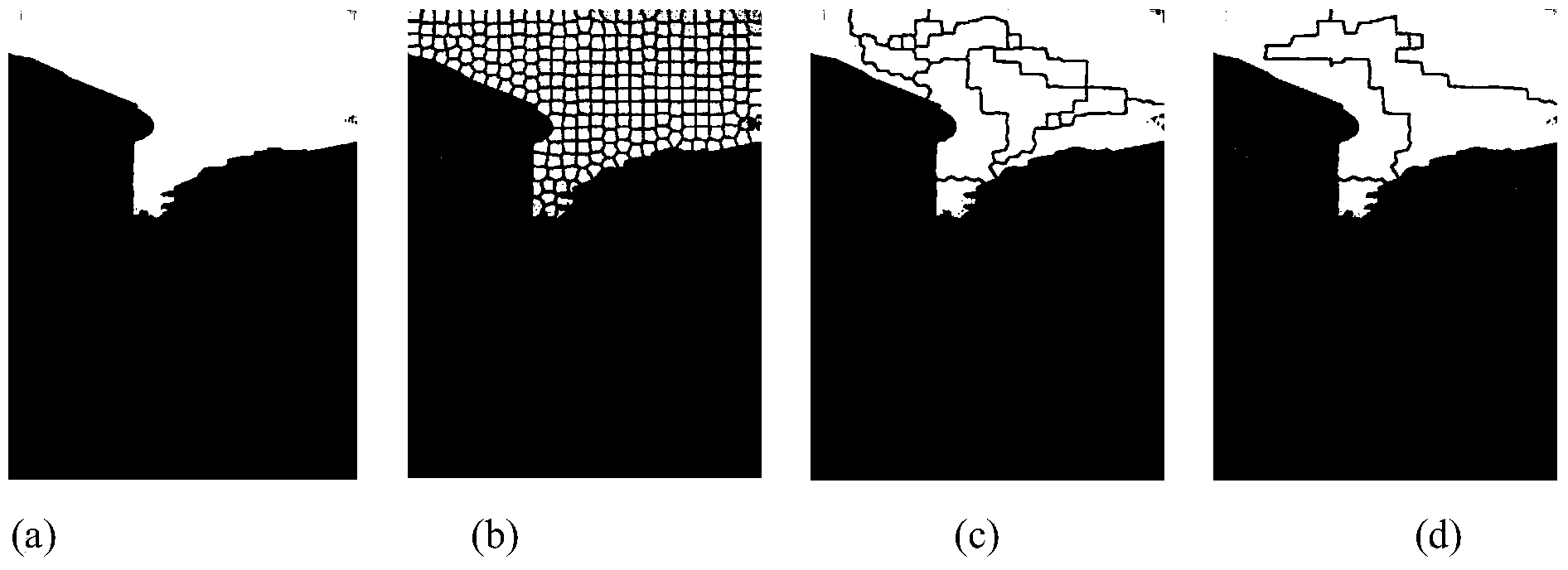
Method for identifying monocular visual spaces in terrestrial gravitational field environments
ActiveCN103632167AChange 3D reconstructionChange depthCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual spaceVisual perception
The invention discloses a method for identifying monocular visual spaces in terrestrial gravitational field environments. The method is characterized by comprising steps of firstly, dividing ultra-pixels of images on the basis of CIELAB color space values L, a and b of pixels and coordinate values x and y of the pixels to generate ultra-pixel images; secondly, reducing dimensions of the divided and formed ultra-pixel images by a general clustering algorithm on the basis of vector distances from color characteristics to feature characteristics of the ultra-pixels and adjacency relations, and generating large image blocks; thirdly, respectively multiplying pixels of the obtained large image blocks by fuzzy distribution density functions of gravitational fields and solving expected values of the large image blocks so as to initially classify the sky, the ground and vertical objects; fourthly, extracting classified images of the sky, the ground and the vertical objects by the aid of single-layer wavelet sampling and characteristics of the Manhattan direction; fifthly, generating spatial depth perception images on the basis of wavelet imaging models and ground linear perspective information. The fuzzy distribution density functions of the gravitational fields represent the sky, the ground and the vertical objects. The method has the advantages of simplicity, feasibility, high resolution and wide application range.
Owner:NANJING YUANJUE INFORMATION & TECH CO NANJING
Ambient light occlusion method for microstructural surface object of screen space
InactiveCN101615300AEfficient drawingFast and efficient drawing of ambient occlusion effects3D-image renderingVisual spaceScreen space
The invention provides an ambient light occlusion method for a microstructural surface object of screen space. The method comprises the following two steps: drawing a scene under a view point, drawing depth information of a scene vertex under visual space in a piece of floating texture; and drawing a full-screen quadrangle, quickly calculating a value of the ambient light occlusion in image space by using an occlusion angle of an object according to the obtained depth texture, and outputting the value of the ambient occlusion onto a screen. The method can quickly calculate the ambient light occlusion for the microstructural surface object, and has the advantages of high efficiency and verisimilitude.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and apparatus accounting for independent cognitive capacities in the right vs. left half of vision
ActiveUS20120308972A1Reduce in quantityInput/output processes for data processingTeaching apparatusVisual spaceLeft half
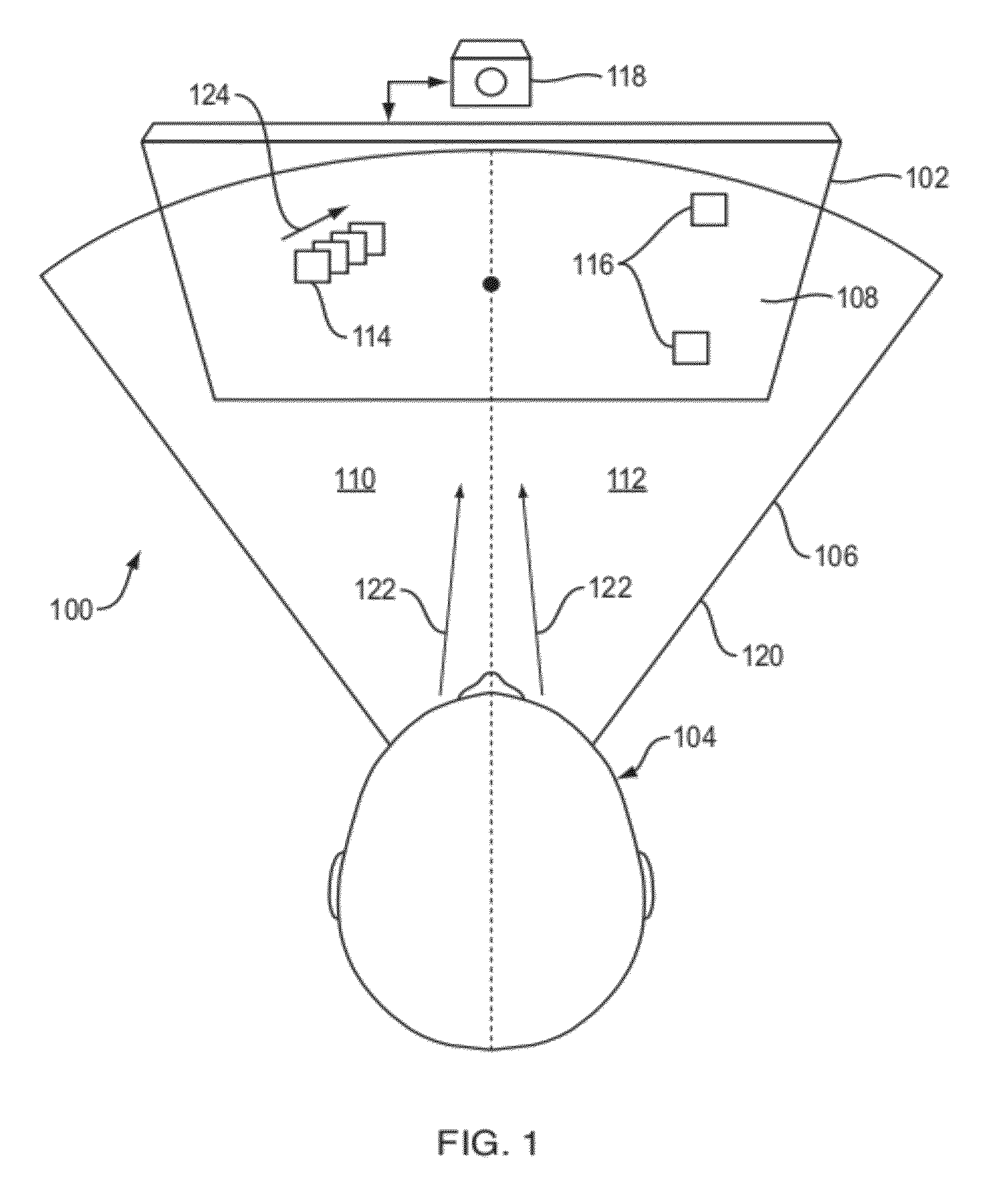
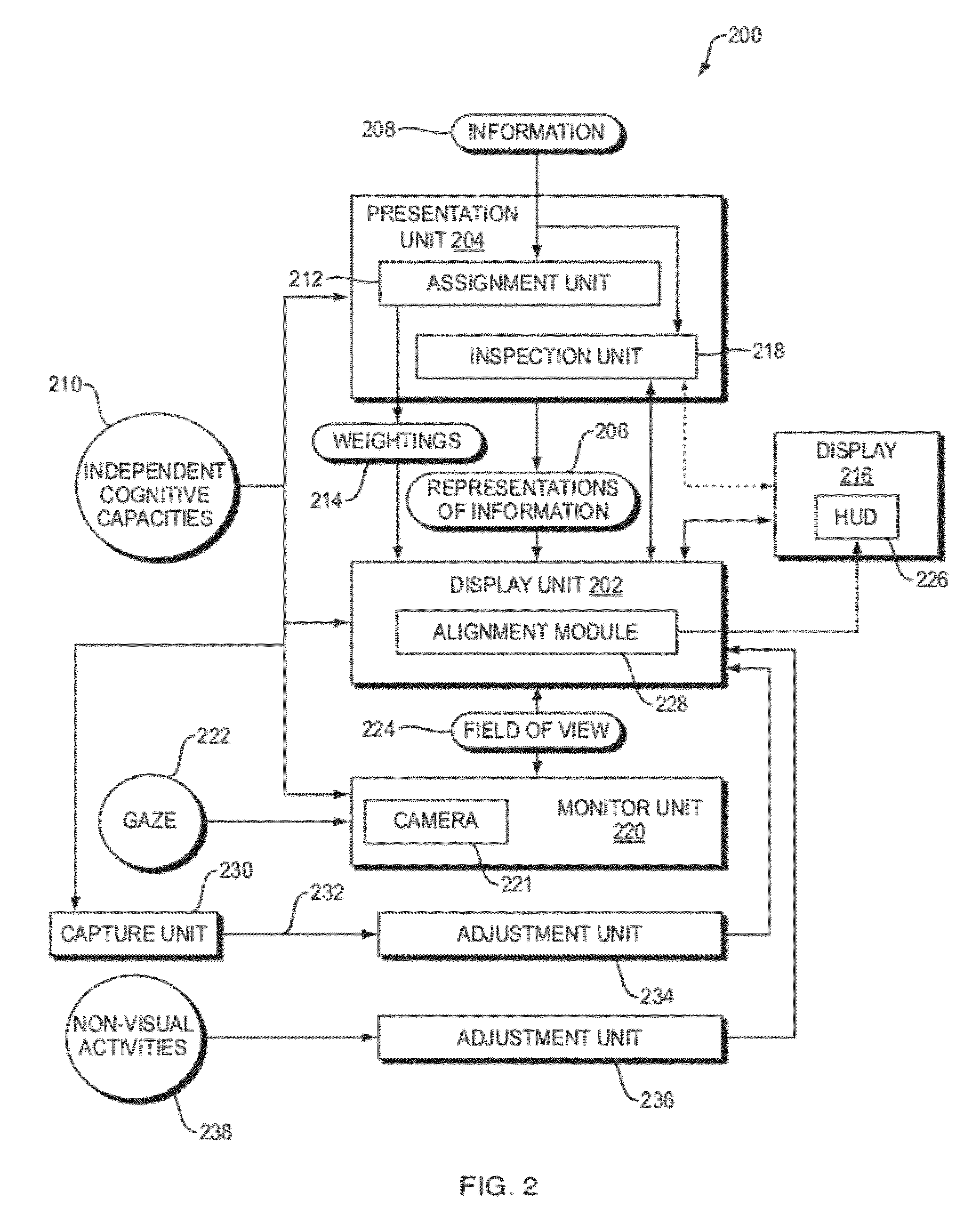
A method of displaying information includes presenting representations of information in a manner accounting for independent cognitive capacities corresponding to a subject's left and right halves of visual space. Weightings of importance may be assigned to the information and used to display the representations in the left half or the right half of the visual space with zero or few other representations. Presenting the representations can also include inspecting content of the information and determining a position on a display to present the content as a function of the information previously, currently, or in the future displayed on the display. In a display system, a presentation unit is configured to present, e.g. generate, representations of information in a manner accounting for the independent cognitive capacities, and a display unit is configured to display the representations. Displaying information can include arranging physical objects in locations of a subject's expected visual space.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Montreal cognitive assessment system
InactiveCN103886200ASimple and fast screening for mild cognitive impairmentSpecial data processing applicationsVisual spaceInformation finding
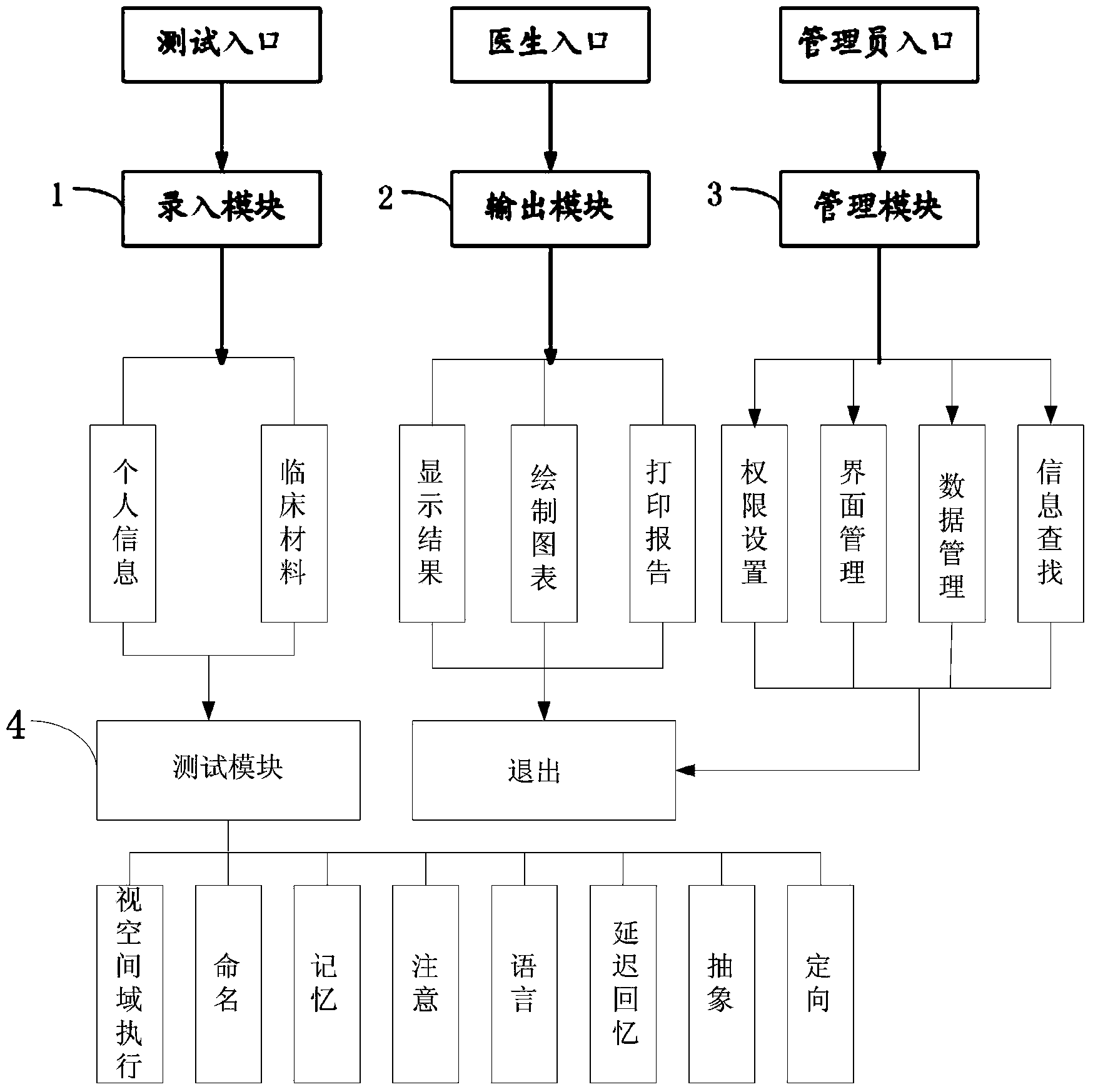
The invention discloses a Montreal cognitive assessment system. The Montreal cognitive assessment system comprises an input module, an output module, a management module and a test module. The input module is mainly used for input subject personal information and subject clinical data and establishing an integral cognition condition database. The test module is connected with the input module, and testing is divided into the eight fields including the visual space and executive function, nominating, memorizing, noticing, language, abstracting, memory delaying and directive force. An operator can check the test result through the output module after a measuring system finishes working, and the output module is used for generating and printing a corresponding analysis chart and an integral diagnosis report. The management module is mainly used for allocating permission setting, interface managing, data managing and information searching. The Montreal cognitive assessment system comprises the input module, the output module, the management module and the test module, and compared with a traditional assessment tool, the Montreal cognitive assessment system is easier, more convenient and faster to use and is close to clinic practicality for mild cognitive impairment screening.
Owner:郁可
Road condition analysis method based on meshing of visual space conversion
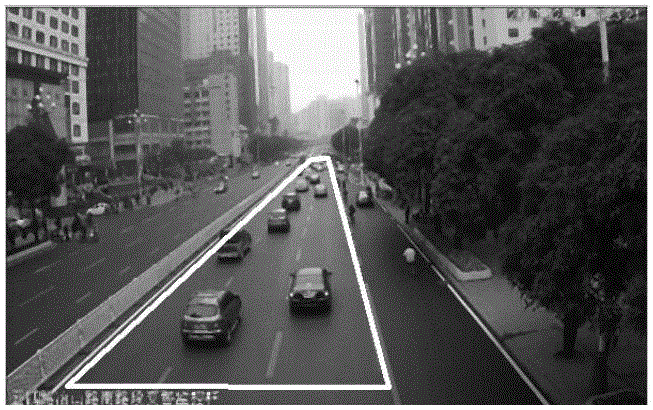
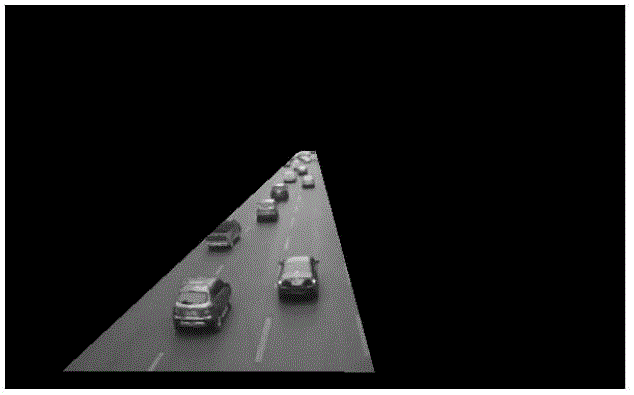
InactiveCN106548628AImprove detection accuracyFast recognitionDetection of traffic movementCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual spaceComputer graphics (images)
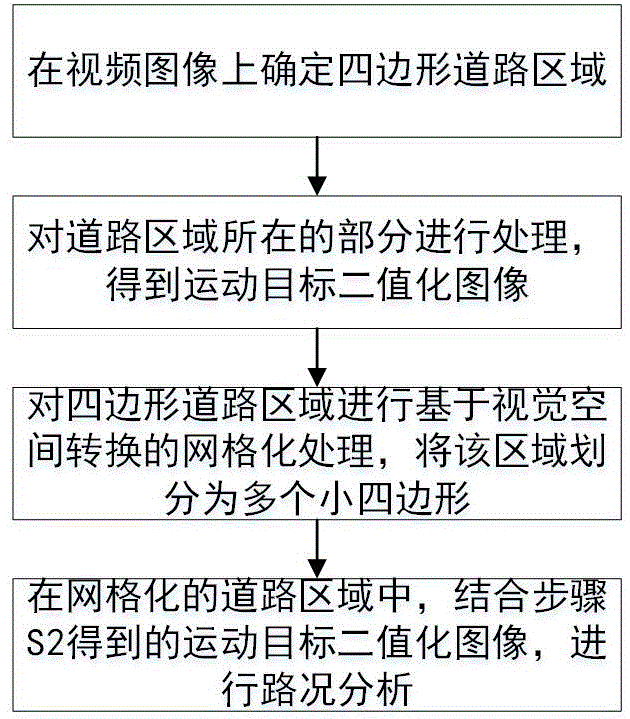
The invention relates to a road condition analysis method based on meshing of visual space conversion. A quadrangular road area is determined in a traffic video image; an image where the road area is positioned is processed, and a binary image of moving objects is obtained; visual space conversion based meshing is carried out on the quadrangular road area to divide the area into four small quadrangles; and in the meshed road area, the traffic road condition is analyzed by combining the binary image of the moving objects. The method can meet requirements for accuracy and timeliness in road condition analysis application, and is highly practical.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Object loading method and device, storage medium and electronic device
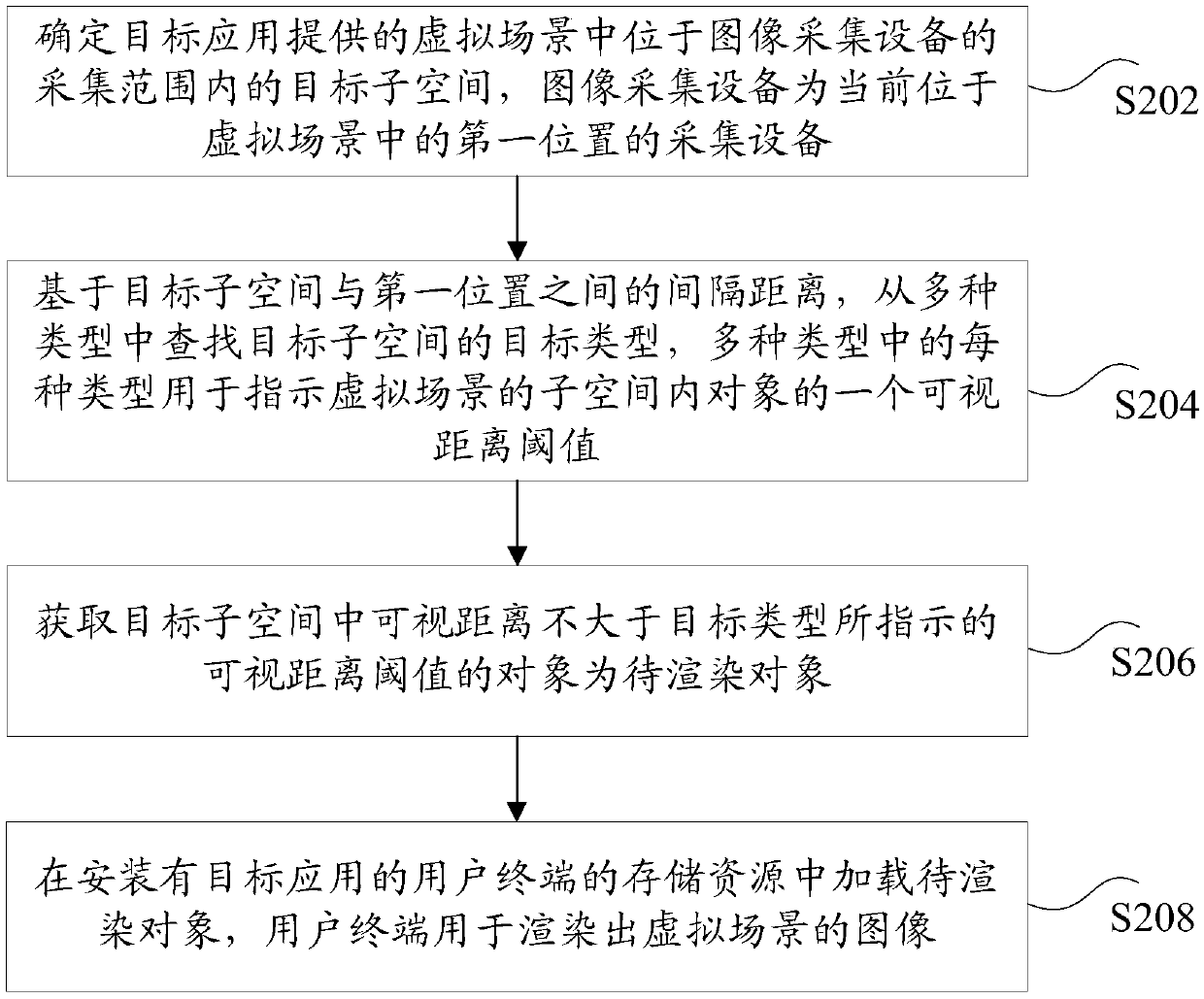
ActiveCN109523621ASolve technical problems that occupy more hardware resourcesReduce occupancyImage memory managementVideo gamesVisual spaceComputer terminal
The invention discloses an object loading method and device, a storage medium and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps of determining a visual space located in an acquisition range ofan image acquisition device in a virtual scene provided by a target application, the image acquisition device being an acquisition device currently located at a first position in the virtual scene; Determining a target subspace in the visual space within a visual distance threshold indicated by a target type in a plurality of types based on the first position, wherein each type in the plurality oftypes is used for indicating one visual distance threshold of an object in the subspace of the virtual scene; Obtaining an object of which the visual distance is not greater than a visual distance threshold indicated by the target type in the target subspace as a to-be-rendered object; And loading the to-be-rendered object in the storage resource of the user terminal installed with the target application, wherein the user terminal is used for rendering the image of the virtual scene. According to the method and the device, the technical problem that more hardware resources are occupied for rendering the object in the virtual scene in the related art is solved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
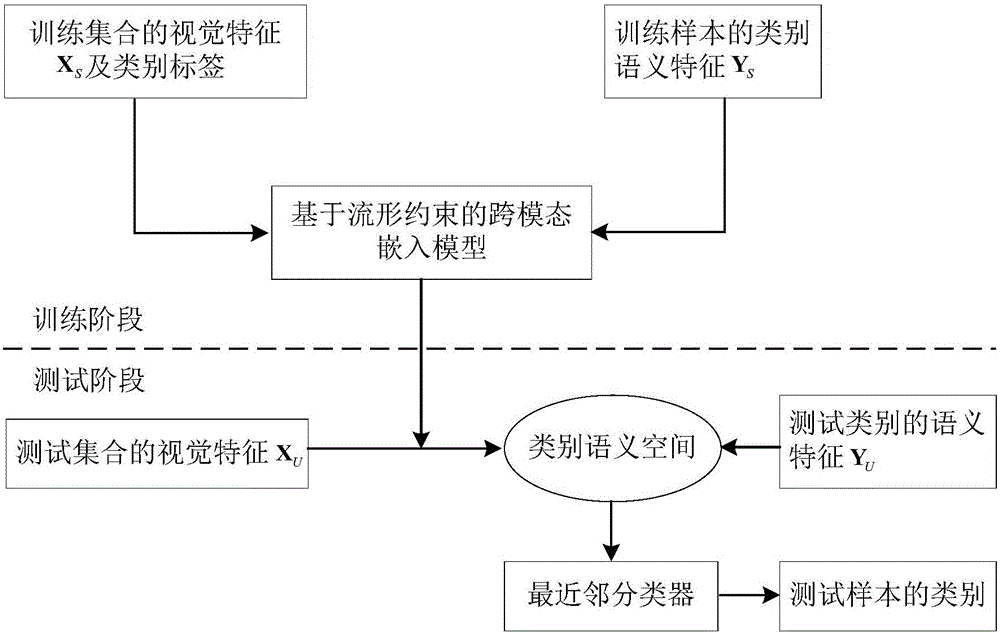
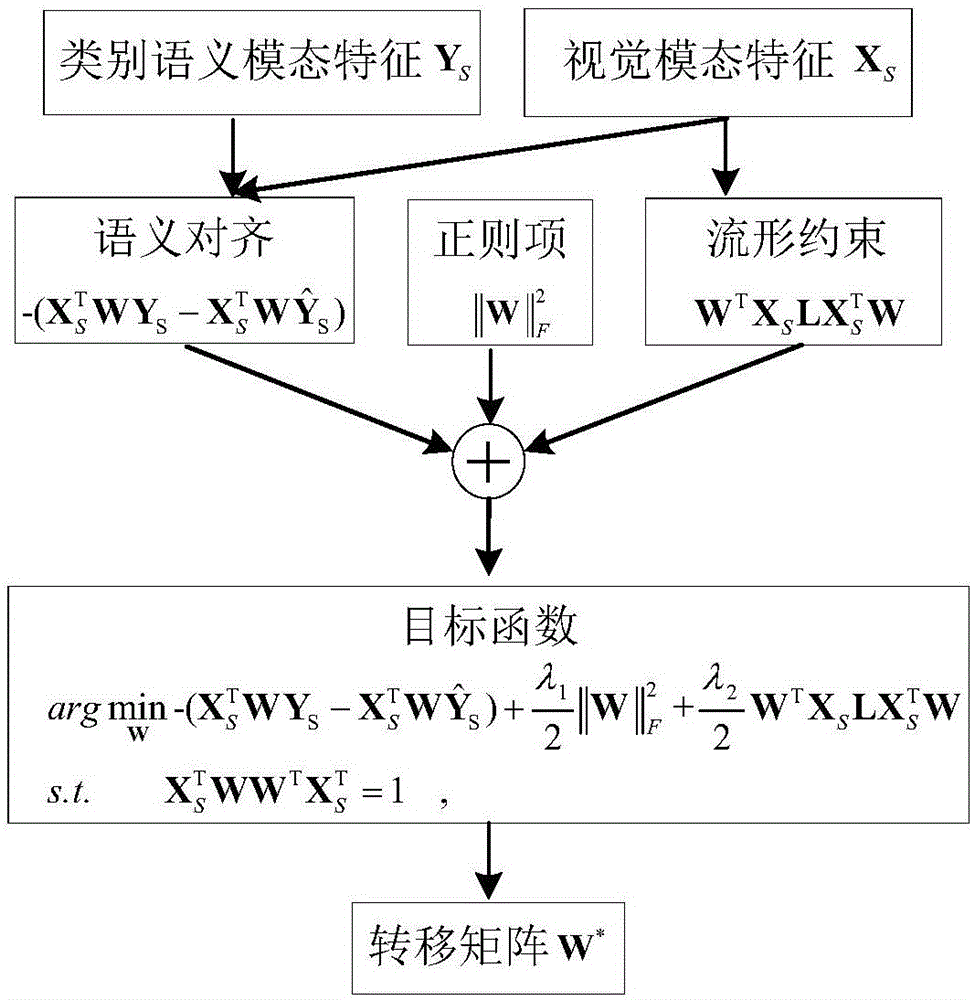
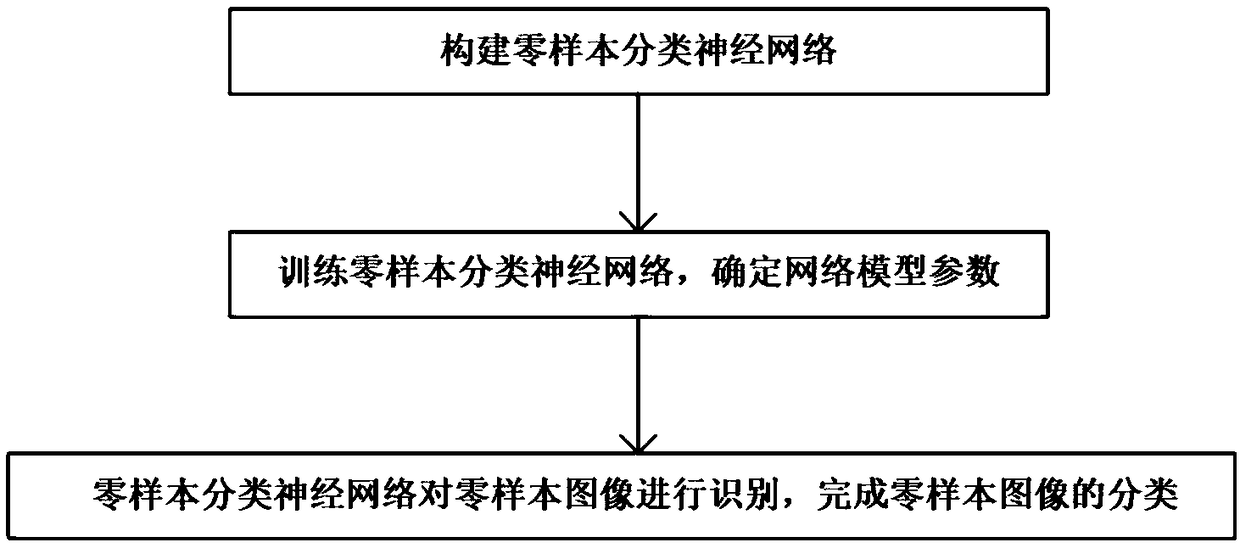
Zero sample classification method based on cross-modal embedding of manifold constraint
InactiveCN106485272AEasy to digAchieving the purpose of cross-modal transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual spaceAlgorithm
The invention discloses a zero sample classification method based on cross-modal embedding of a manifold constraint. The method comprises the steps of learning a conversion matrix of mapping from a visual space to a category semantic space by utilizing a cross-modal embedding model of the manifold constraint; mapping test samples to the category semantic space from the visual space by utilizing the learned conversion matrix to obtain embedding vectors of the test samples in the category semantic space; and calculating relationships between the embedding vectors of the test samples in the category semantic space and semantic features of test categories by utilizing a Euclidean distance, and classifying the test samples by utilizing a nearest neighbor classifier. According to the zero sample classification method based on the cross-modal embedding of the manifold constraint, semantic information among different modes and judgment information among different categories can be better mined, and local structure in the mode conversion process is kept by utilizing the manifold constraint.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Head surgery navigation method based on three-dimensional scanning
InactiveCN109498156AHigh precisionConvenient preoperative CT scanSurgical navigation systemsVisual spaceVisual perception
The invention relates to the field of medicine, in particular to a head surgery navigation method based on three-dimensional scanning. The method includes the following steps: (1) performing preoperative CT scanning on a patient's head; (2) mounting calibration reference frames, reference reference frames and stereo vision equipment; (3) acquiring three-dimensional models of the patient's head, the reference reference frames and all correction reference frames by adopting the three-dimensional scanning equipment, and fitting characteristic points; (4) acquiring spatial coordinates of the reference reference frames and all correction reference frames by adopting stereo vision; (5) correcting the visual space error through an error correction model; (6) performing point cloud registration ona CT model of the patient's head and a head model constructed by the three-dimensional scanning equipment; (7) acquiring coordinate systems of the target reference frames through stereo vision in real time, and displaying the position of the equipment in CT space in real time in navigation software. The method can avoid navigation deviation caused by mark deviation before operation and during operation, so that the accuracy of operation navigation is improved.
Owner:北京大华旺达科技有限公司
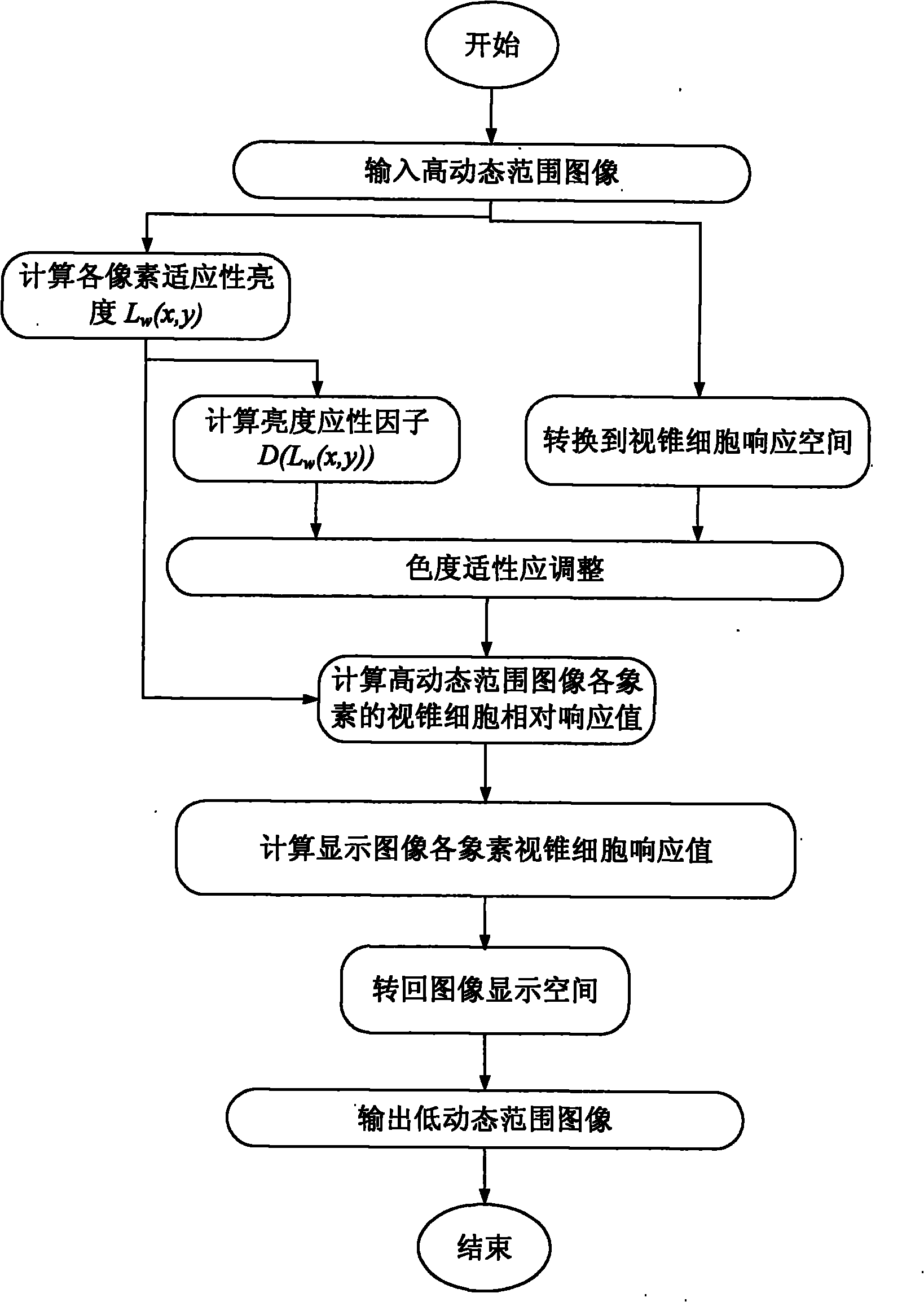
Method for displaying and reproducing high dynamic range images
InactiveCN101916555AMeet the requirements of effectivenessMeet the needs of high dynamic range image applicationsColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsHigh-dynamic-range imagingVisual space
The invention relates to a method for displaying and reproducing high dynamic range images. The dynamic range of the images is compressed through a principle of keeping relative visual perception of light sensing cells of human eyes under adaptive brightness, so the aim of copying scenes in the high dynamic range images to display equipment and paper of a low dynamic range, wherein a border phase resistance mechanism related to visual space and contrast is used to calculate the relatively perceptive adaptive brightness. By detecting the difference from the conventional high dynamic range images, compared with some conventional methods, the method has relatively good effect and meets the requirements for output and display of the high dynamic range images.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
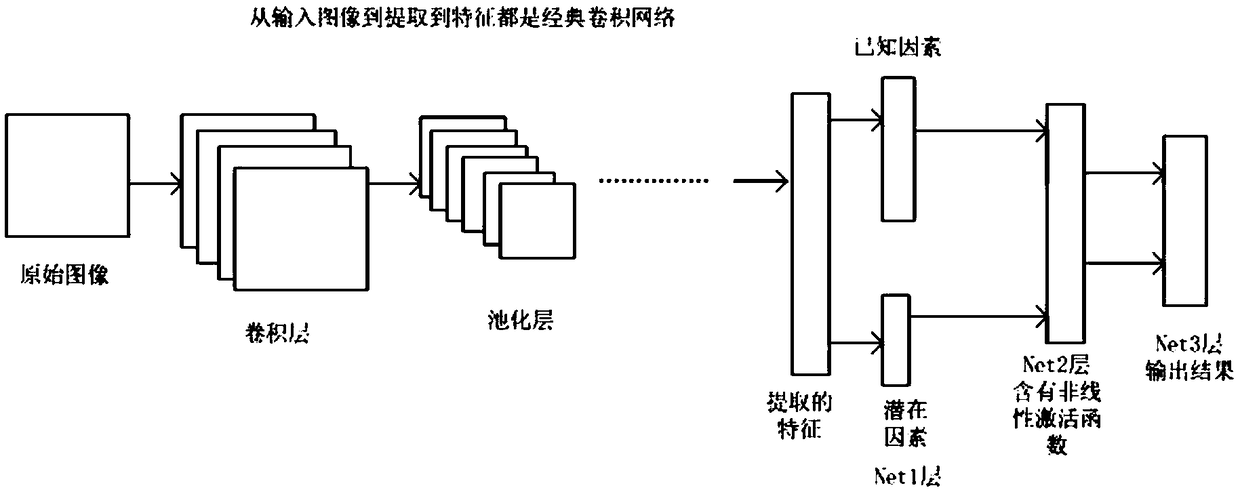
Zero sample image classification method and system based on a convolutional neural network and a factor space
ActiveCN109492750AEnhance expressive abilityImprove generalization abilityStill image data queryingNeural architecturesVisual spaceData set
The invention provides a zero sample image classification method and system based on a convolutional neural network and a factor space, and the method comprises the steps: building a unified zero-sample classification neural network: firstly, extracting image features in a data set through a classical convolutional neural network, and enabling the image features to serve as the input of the neuralnetwork; the dimensionality of known factors is reduced by using a factor pressure reduction technology, and the known factors and potential factors are embedded into a network to serve as an intermediate layer to jointly determine a final classification result; the network enables image input to final category output. And training a zero sample classification network, and iteratively determiningnetwork model parameters. And identifying the image by using the zero sample classification neural network to finish classification of the zero sample image. According to the method, a convolutionalneural network model is used for uniformly processing the relationship among the visual space, the factor space and the category space, the problem that the generalization ability of specific linear or nonlinear function expression is not high is solved, and the factors serving as auxiliary knowledge are embedded into the network and are easy to understand, train and use.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF LAUNCH VEHICLE TECH
Zero sample classification method based on dual-triple deep metric learning network
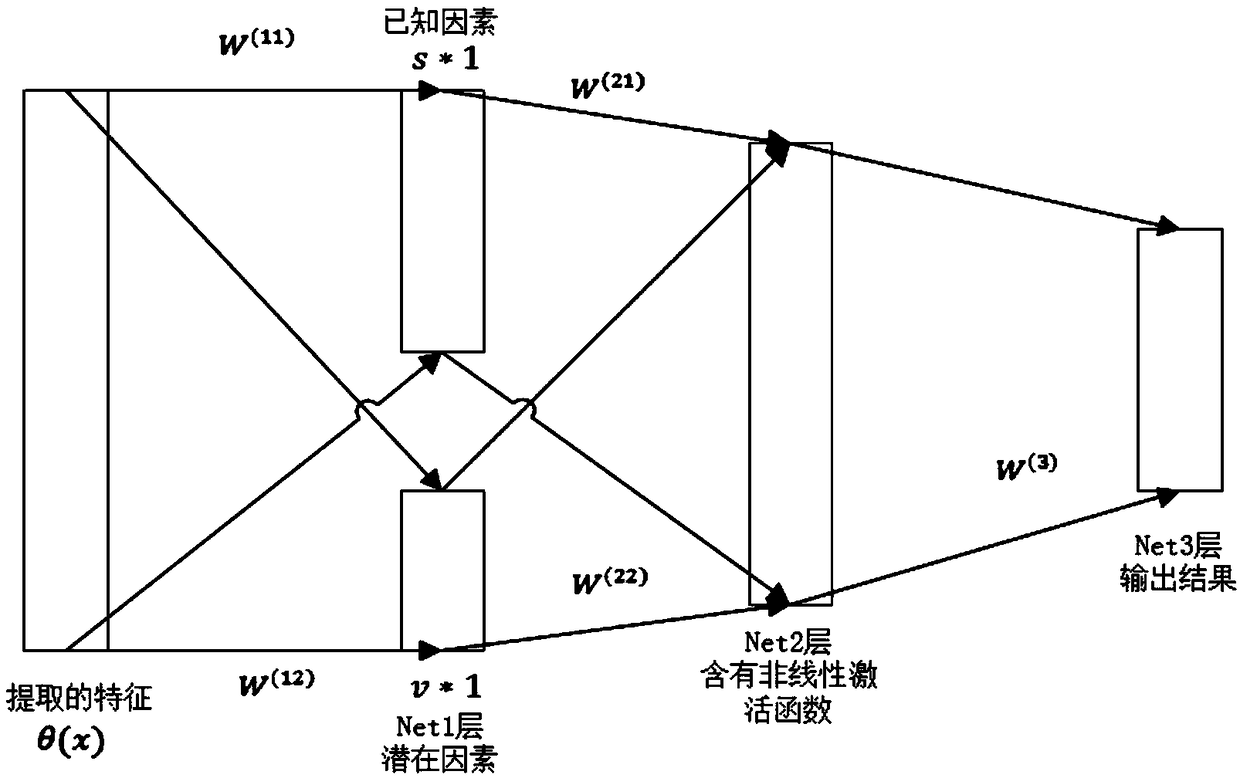
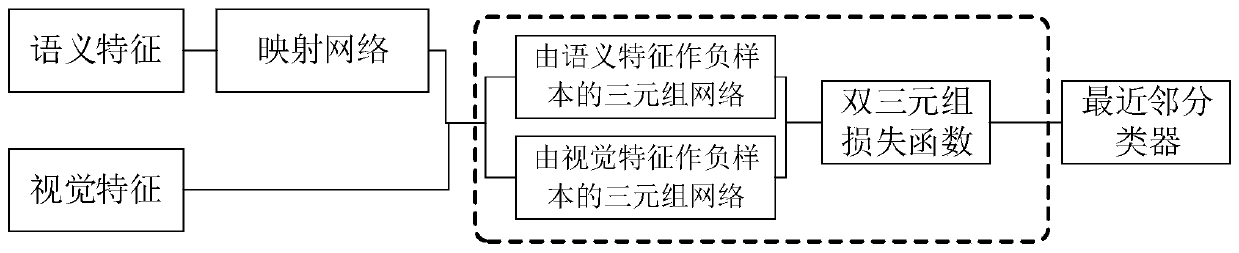
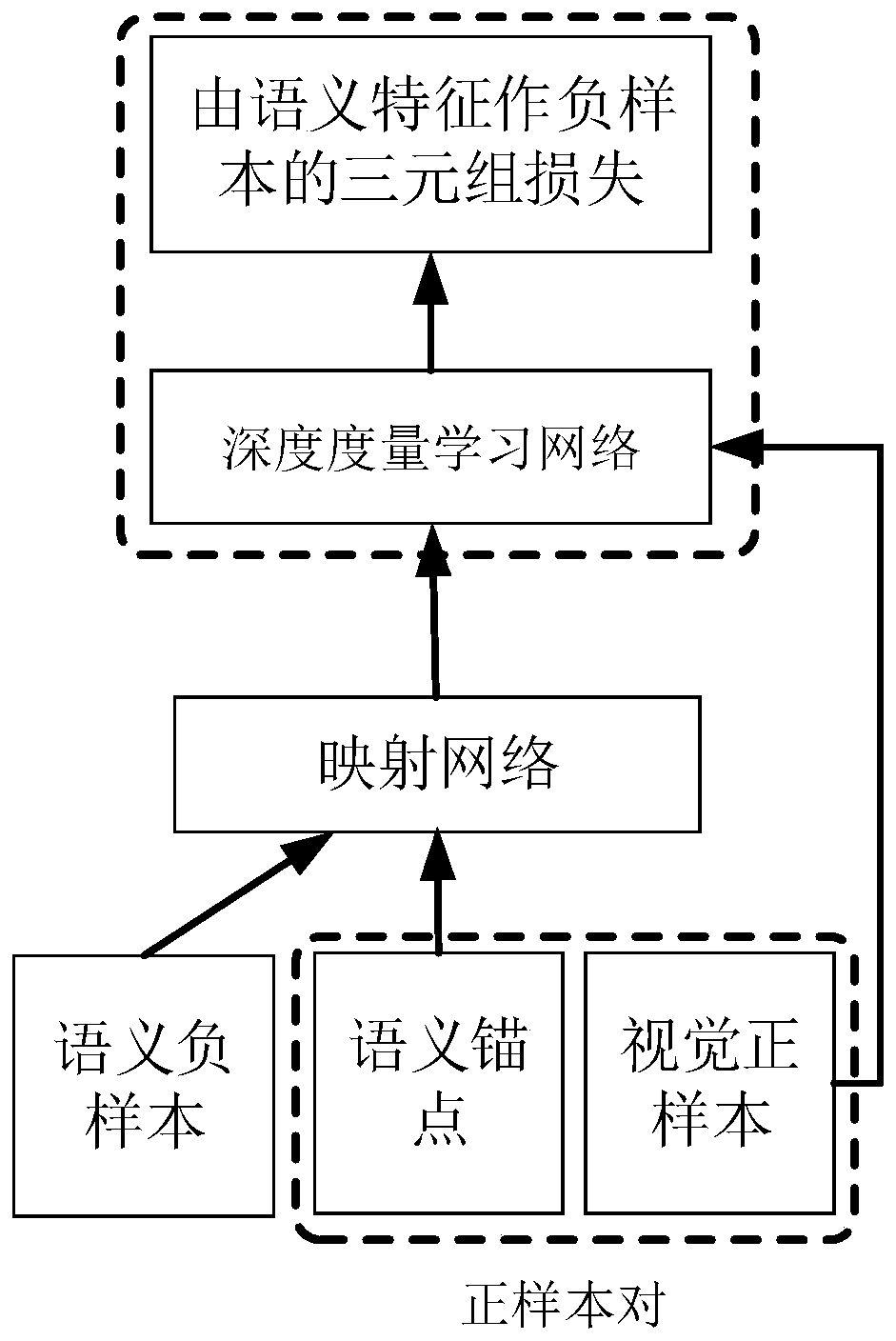
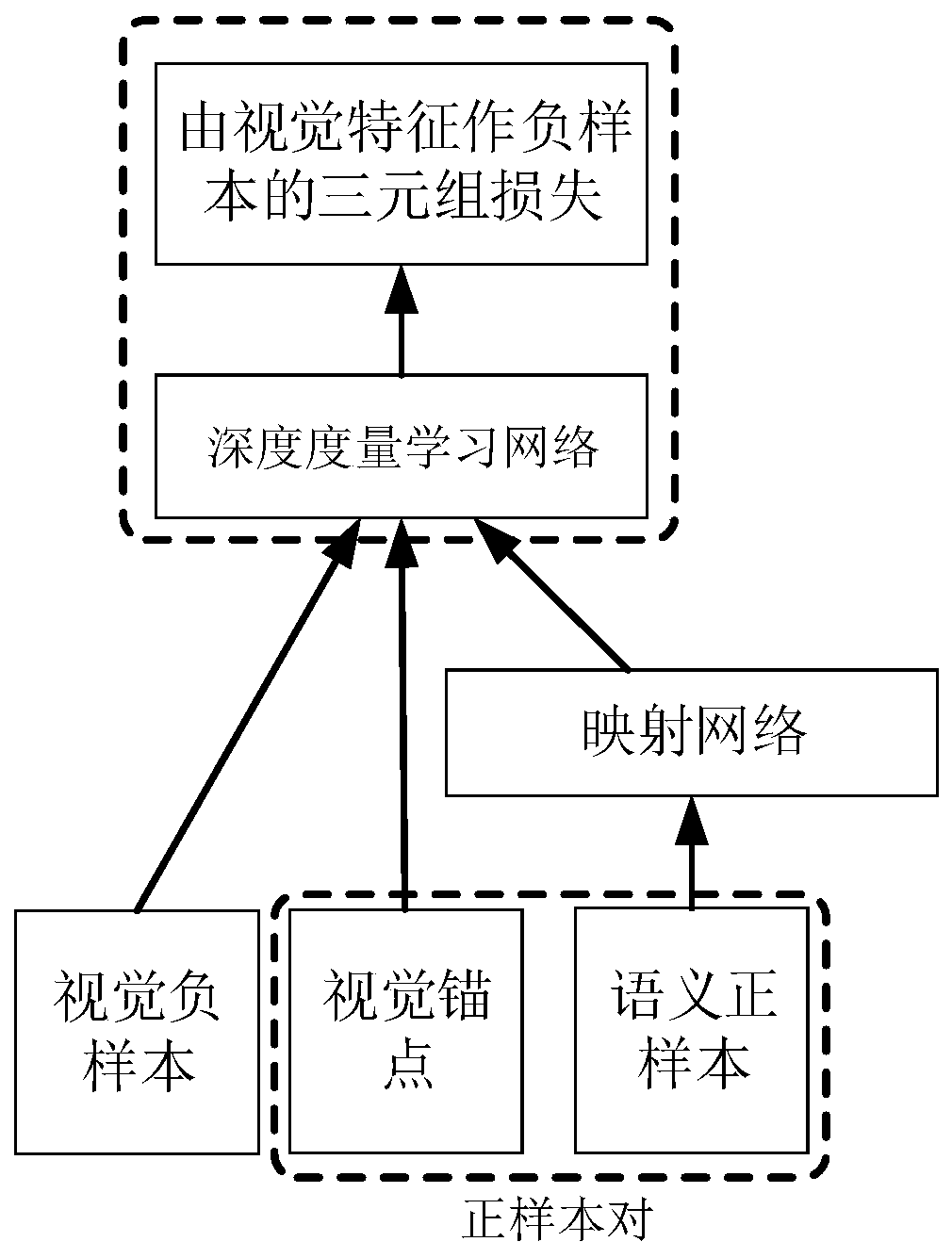
ActiveCN110135459ARich learningSimple structureCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual spacePositive sample
The invention relates to a zero sample classification method based on a double-triple deep metric learning network, which comprises the following steps of: inputting semantic features of samples intoa mapping network, and outputting the semantic features to a visual space; in a visual space, selecting a pair of semantic features and visual features belonging to the same category to form a positive sample pair, then selecting a semantic feature different from the positive sample pair to form a triple, and inputting the triple into a semantic-guided triple network; selecting a pair of semanticfeatures and visual features belonging to the same category are selected to form a positive sample pair, then a visual feature different from the positive sample pair in category to form a triple, andinputting the triple into a visual guidance triple network; inputting the output of the semantic-guided triple network and the output of the visual-guided triple network into a double-triple loss function for calculation; and finally, classifying the test samples by using a nearest neighbor classifier. The structure is easy to realize, the training method is simpler, the training parameters are fewer, and training can still be carried out under the condition that computer hardware equipment is poorer.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
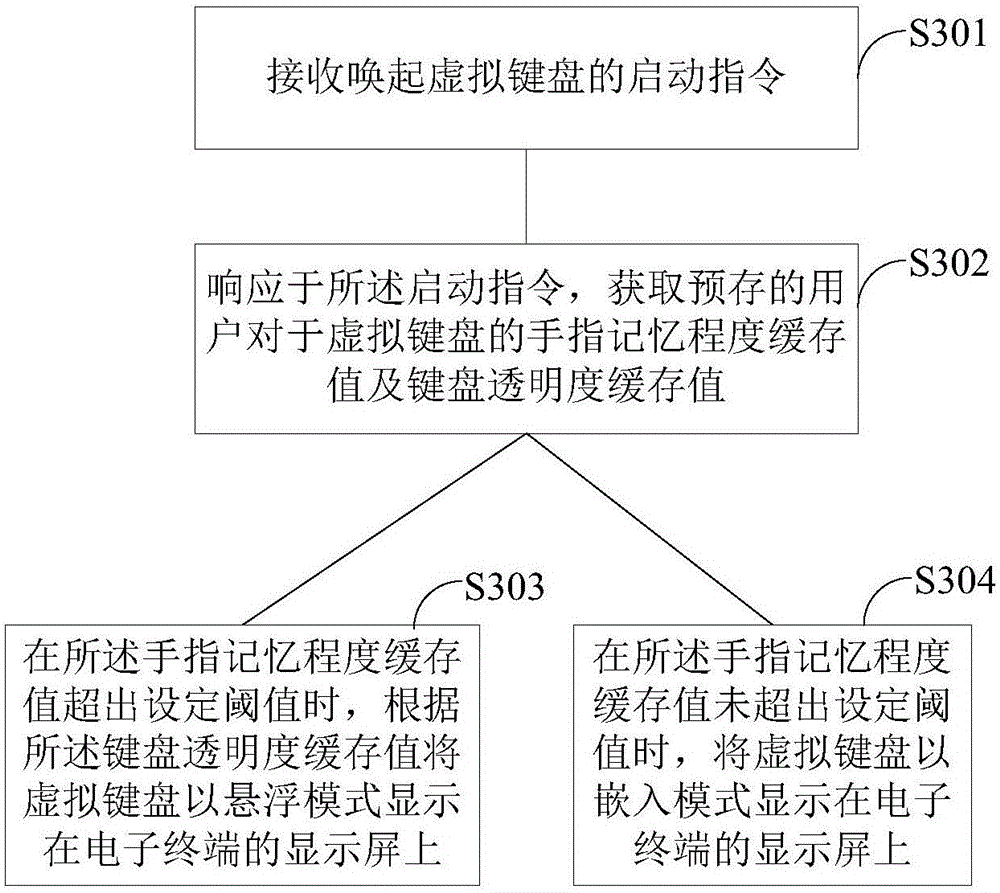
Virtual keyboard display method and display device
ActiveCN106708411AImprove experiencePreserve visual space requirementsInput/output processes for data processingVisual spaceDisplay device
The invention relates to the technical field of communication, and discloses a virtual keyboard display method and display device and an electronic terminal. The display method includes the steps: receiving a startup instruction for calling a virtual keyboard; responding to the startup instruction and acquiring pre-stored keyboard transparency cache values and finger memory degree cache values of a user for the virtual keyboard; displaying the virtual keyboard on a display screen of the electronic terminal in a suspension mode according to the keyboard transparency cache values when the finger memory degree cache values exceed set threshold values. According to the virtual keyboard display method and display device, the virtual keyboard in the suspension mode is selectively provided for the user according to the finger memory degree of the user, an original view scene of the electronic terminal cannot be damaged, and visual space requirements of other contents can be reserved as far as possible, so that user experience is improved.
Owner:北京万方数据股份有限公司 +1
Idea page system and method
InactiveUS7958080B2Digital computer detailsWebsite content managementVisual spaceDocument preparation
Ideas, groups of ideas, projects, documents, and related materials may be depicted, organized, modified, and shared according to Idea Page systems, methods, and user interfaces. Published workflow templates may additionally be copied into a user context, modified, and depicted in a multi-level visual space, including first-level ideas organized and visually arranged in a first-level idea page, and second-level ideas organized and visually arranged in a second-level idea page.
Owner:KERIKA
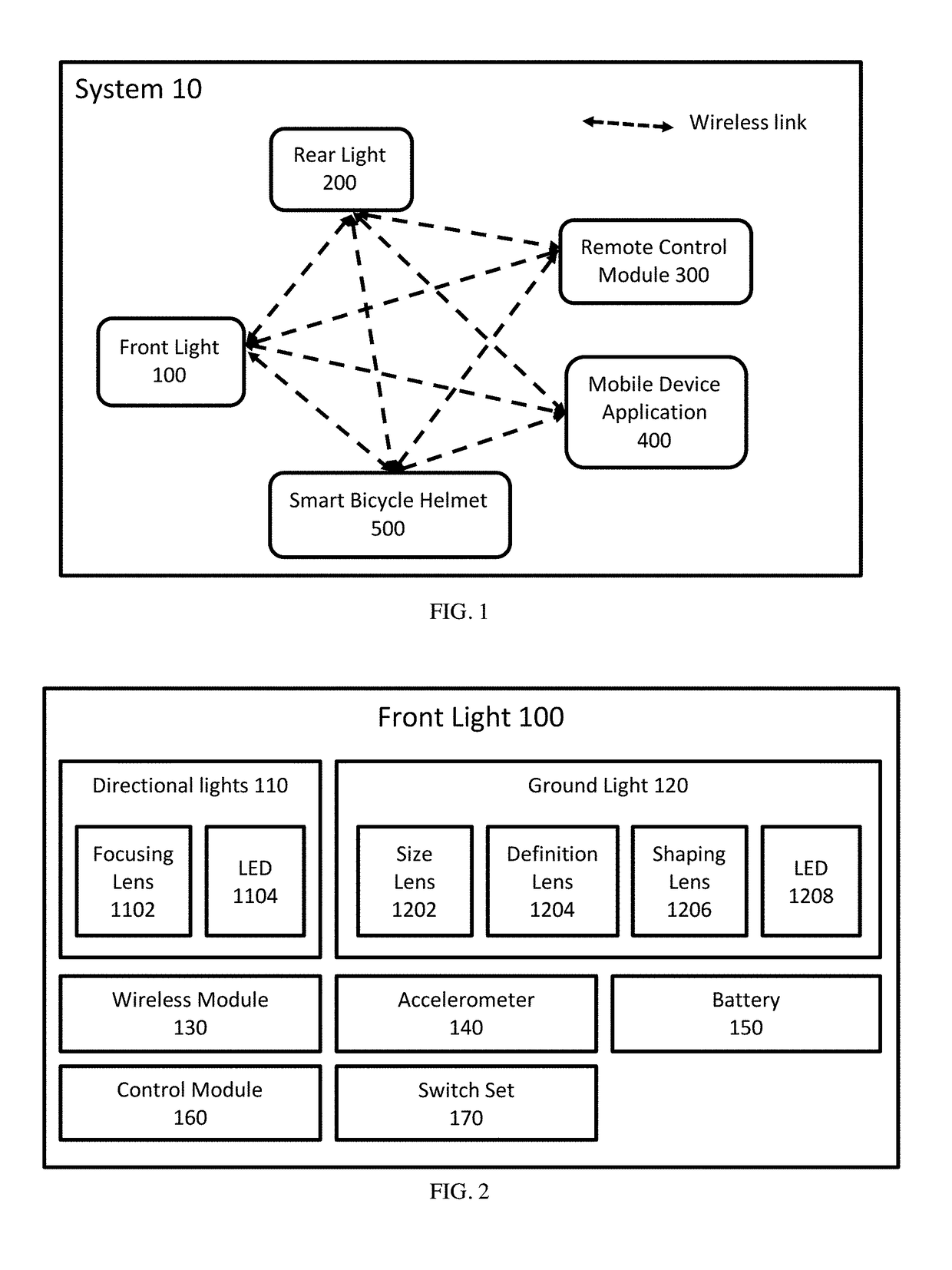
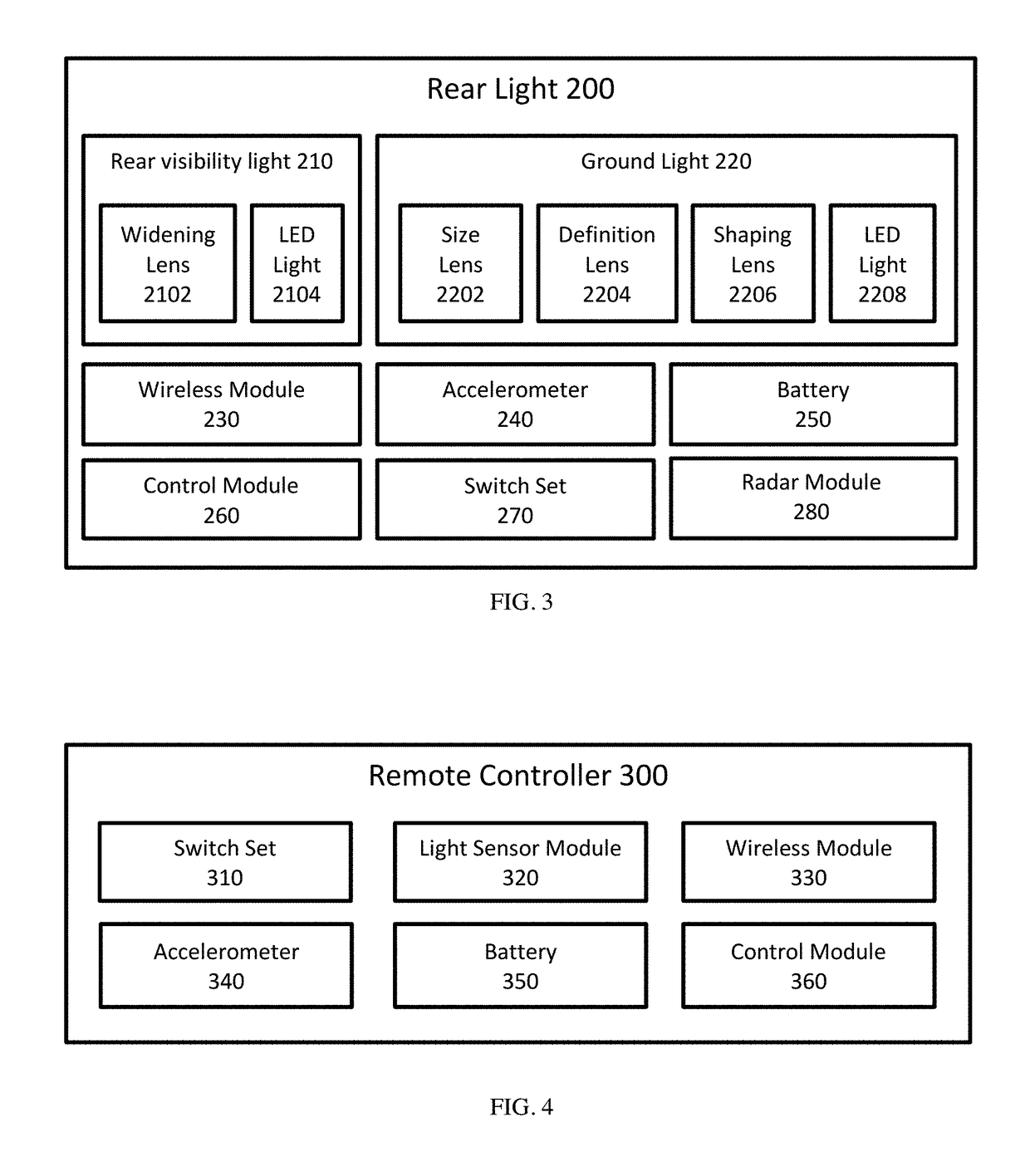
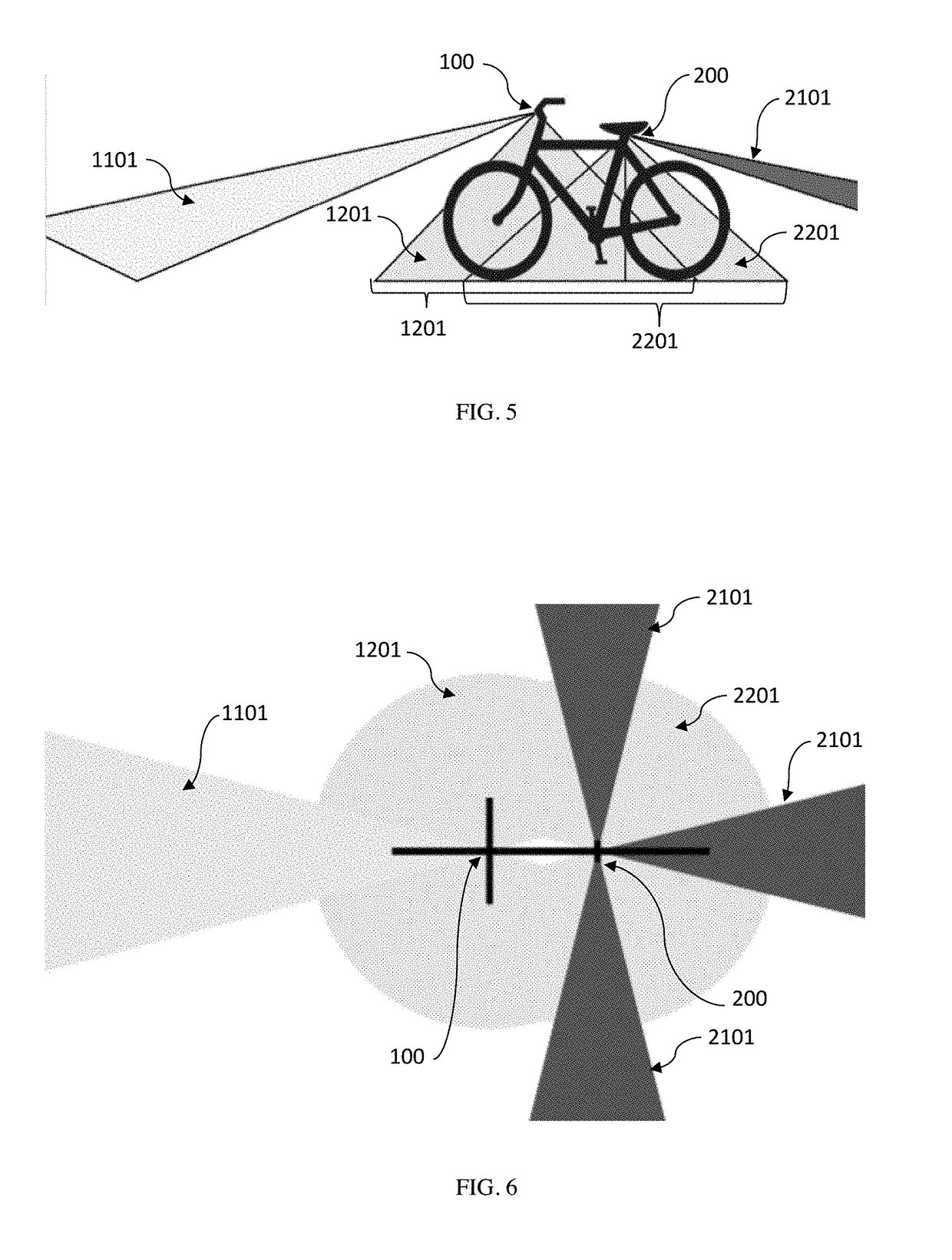
Light Projected Visual Space and Safety System For Bicycles
InactiveUS20190002052A1Increasing cyclist ' visibilityIncrease awarenessOptical signalOptical signallingVisual spaceLuminous flux
A light projection system for bicycles that comprises a front light and a rear light that act in tandem to emit light on the sides and beneath the cycle to visually indicate the ‘safety space’ of the cyclist; and to use such lights to indicate cyclists' intention to other commuters. Individually, both the front and rear light can project light as wide as 330°, with sharply defined patterns and objects. The front and rear lights act in concert that allows the projection of light on a surface that is demonstrably more visible, brighter, better defined, which allows the user of such lights signal intentions to other commuters. Moreover, the lights are synchronized so the shape and outline of the projected light field is malleable, thus different shapes can be projected with no loss of luminous flux and / or sharpness.
Owner:LUMEN LABS HK LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com