Patents
Literature
4005 results about "Six degrees of freedom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
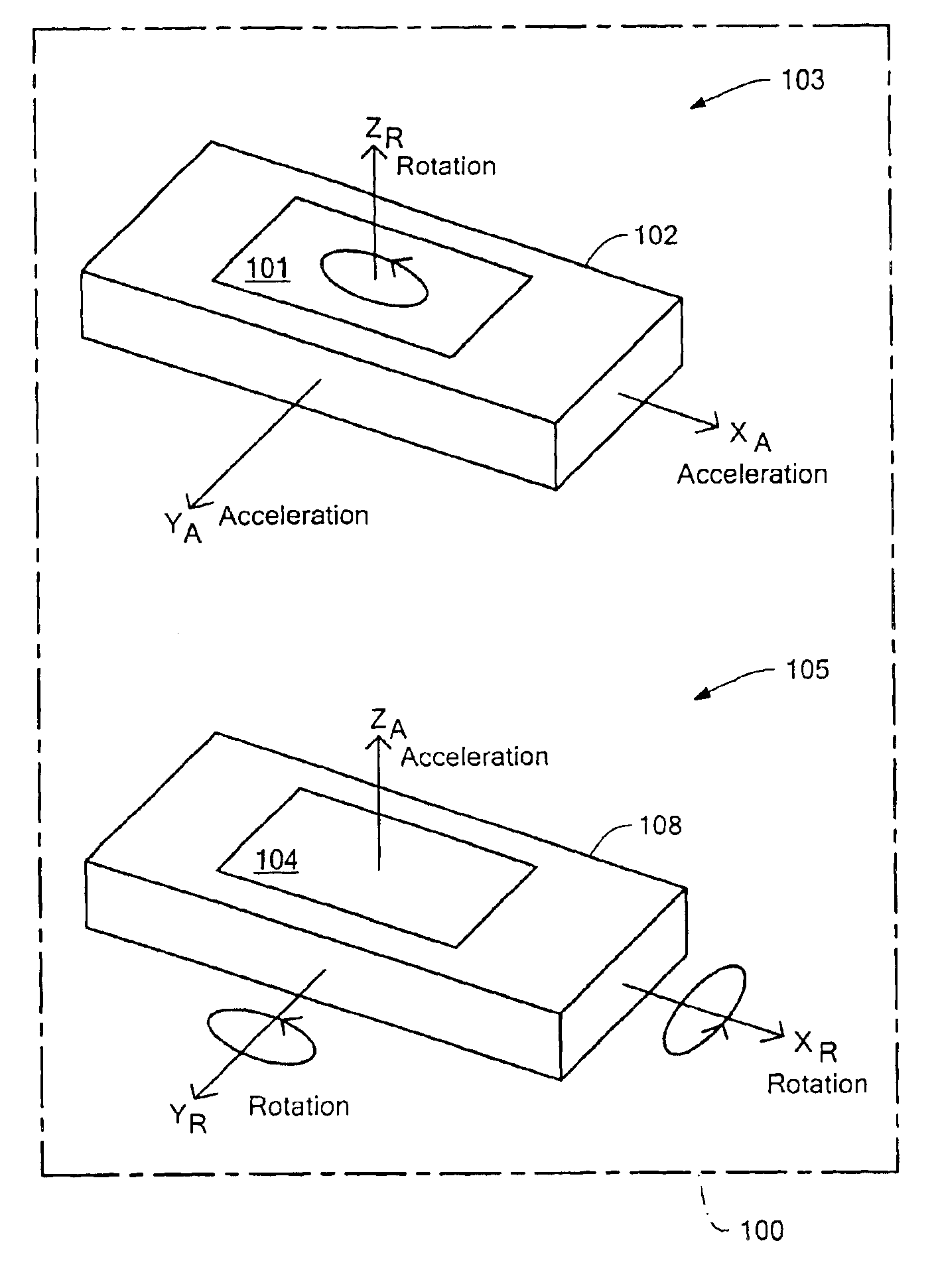
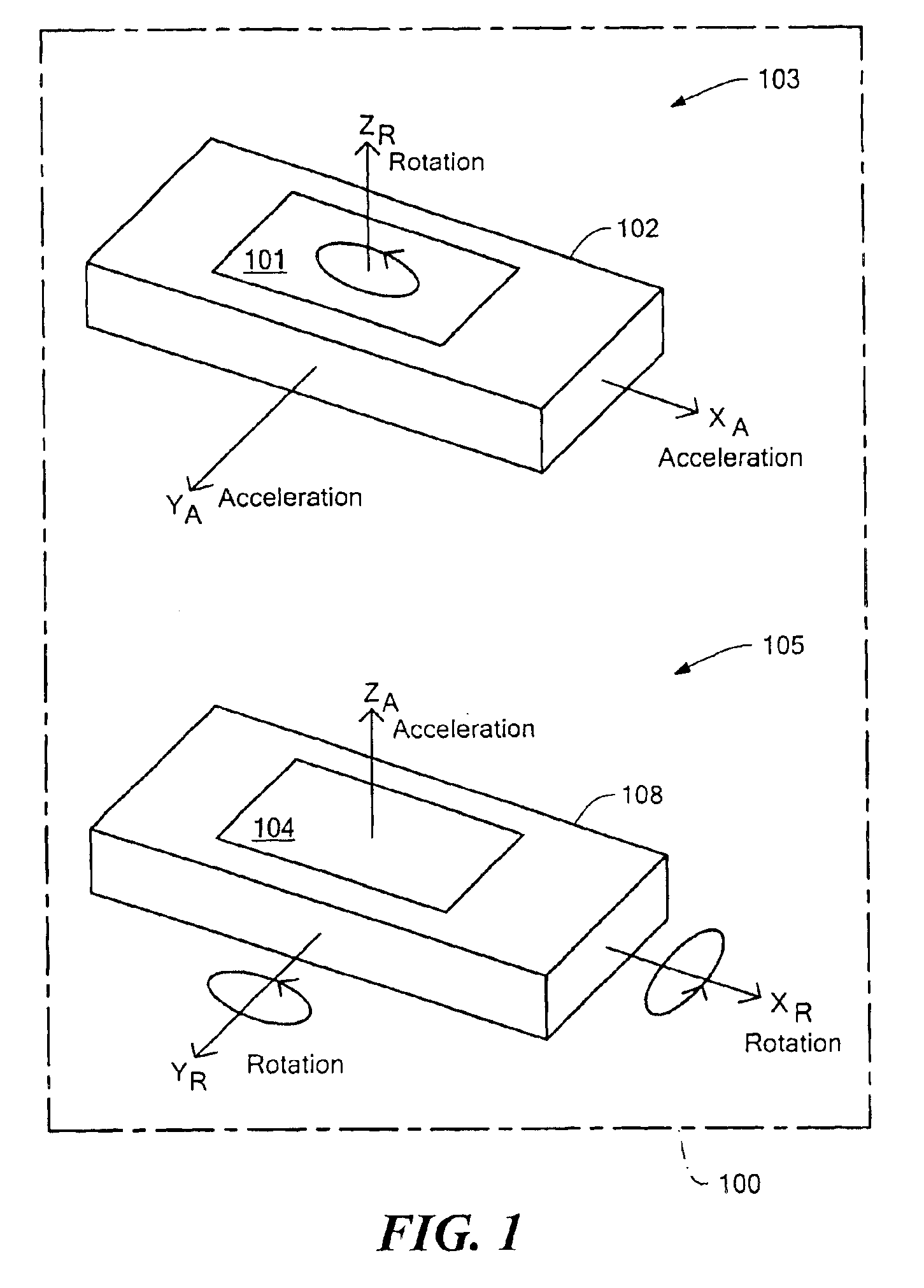
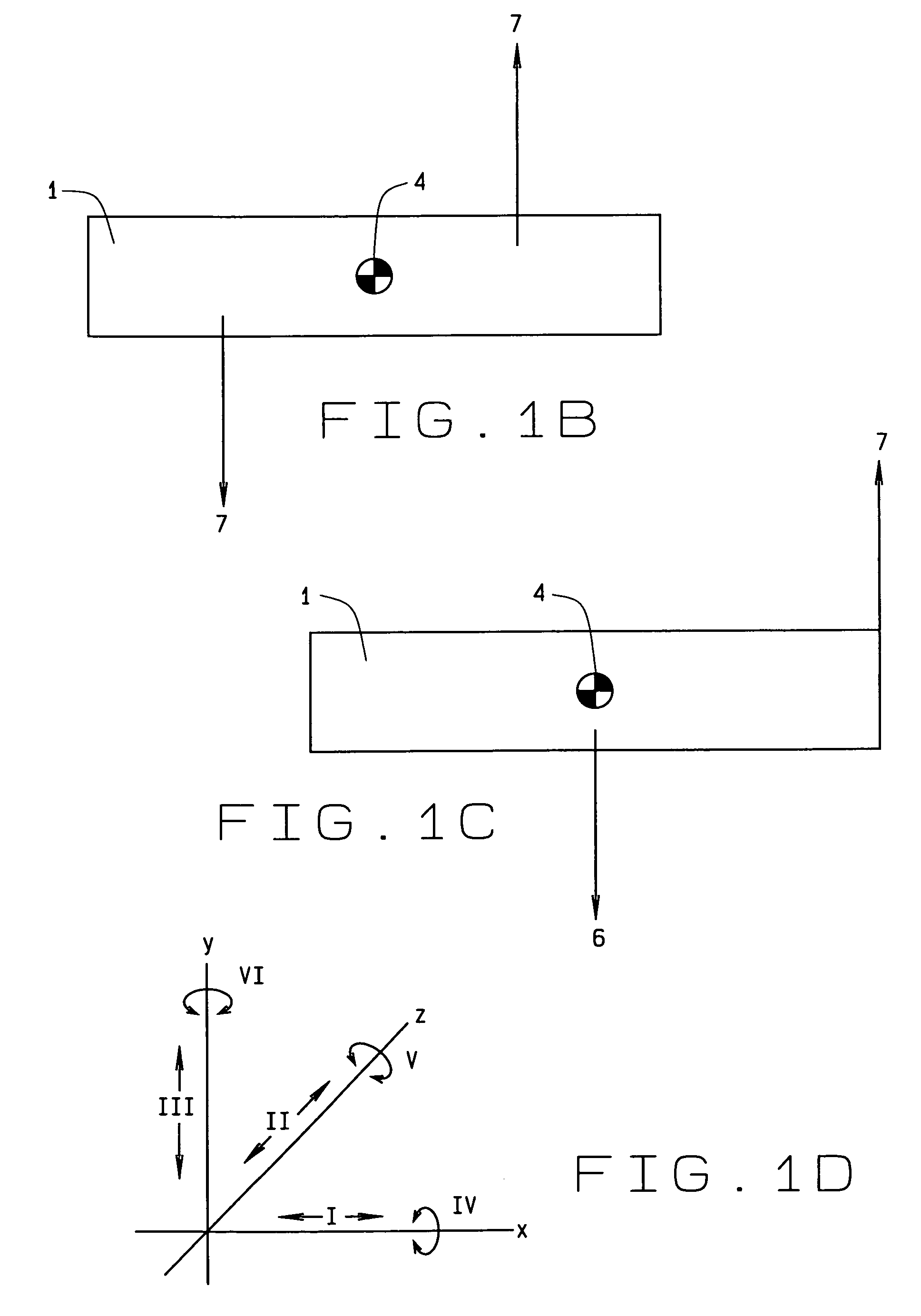
Six degrees of freedom (6DoF) refers to the freedom of movement of a rigid body in three-dimensional space. Specifically, the body is free to change position as forward/backward (surge), up/down (heave), left/right (sway) translation in three perpendicular axes, combined with changes in orientation through rotation about three perpendicular axes, often termed yaw (normal axis), pitch (transverse axis), and roll (longitudinal axis).
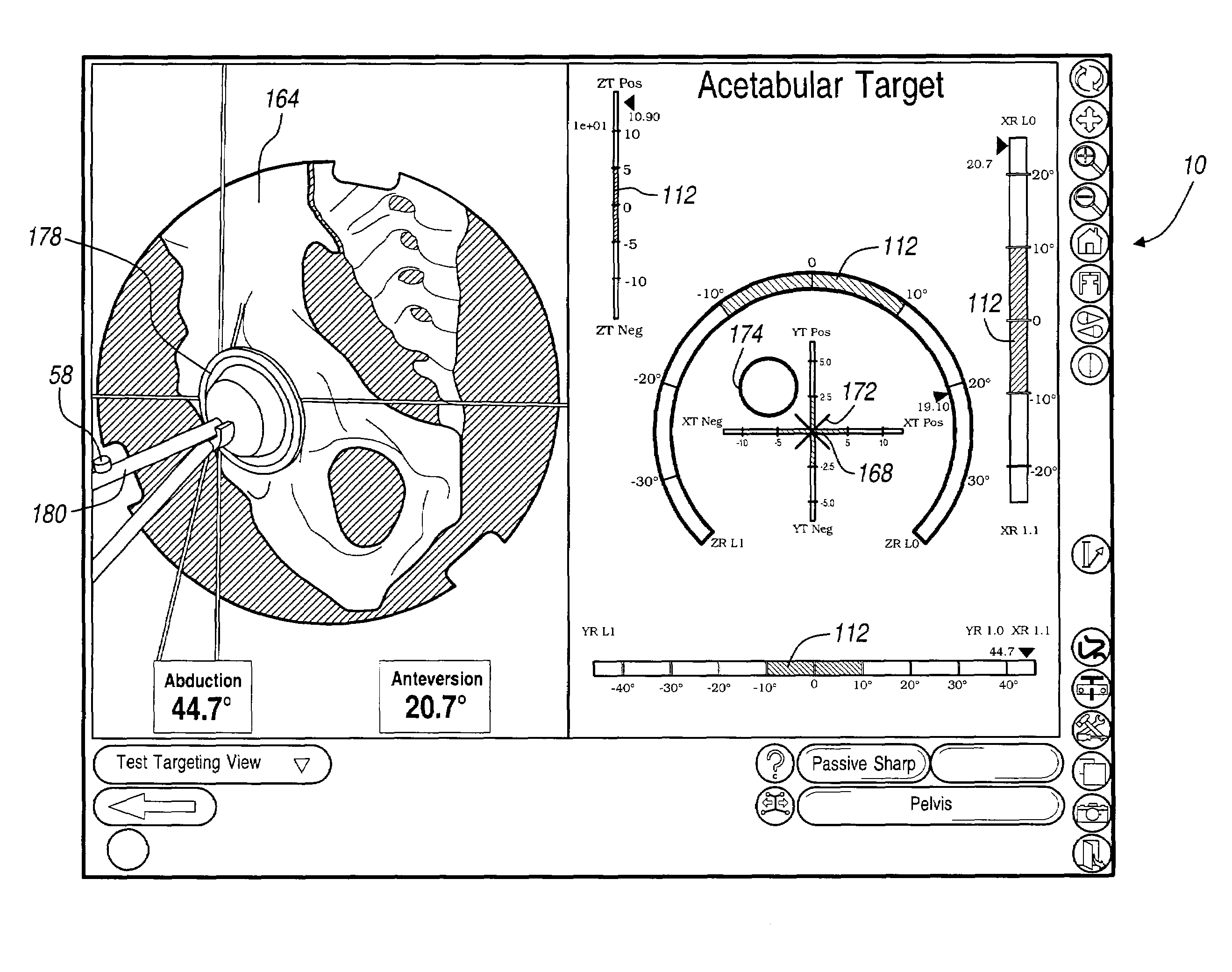
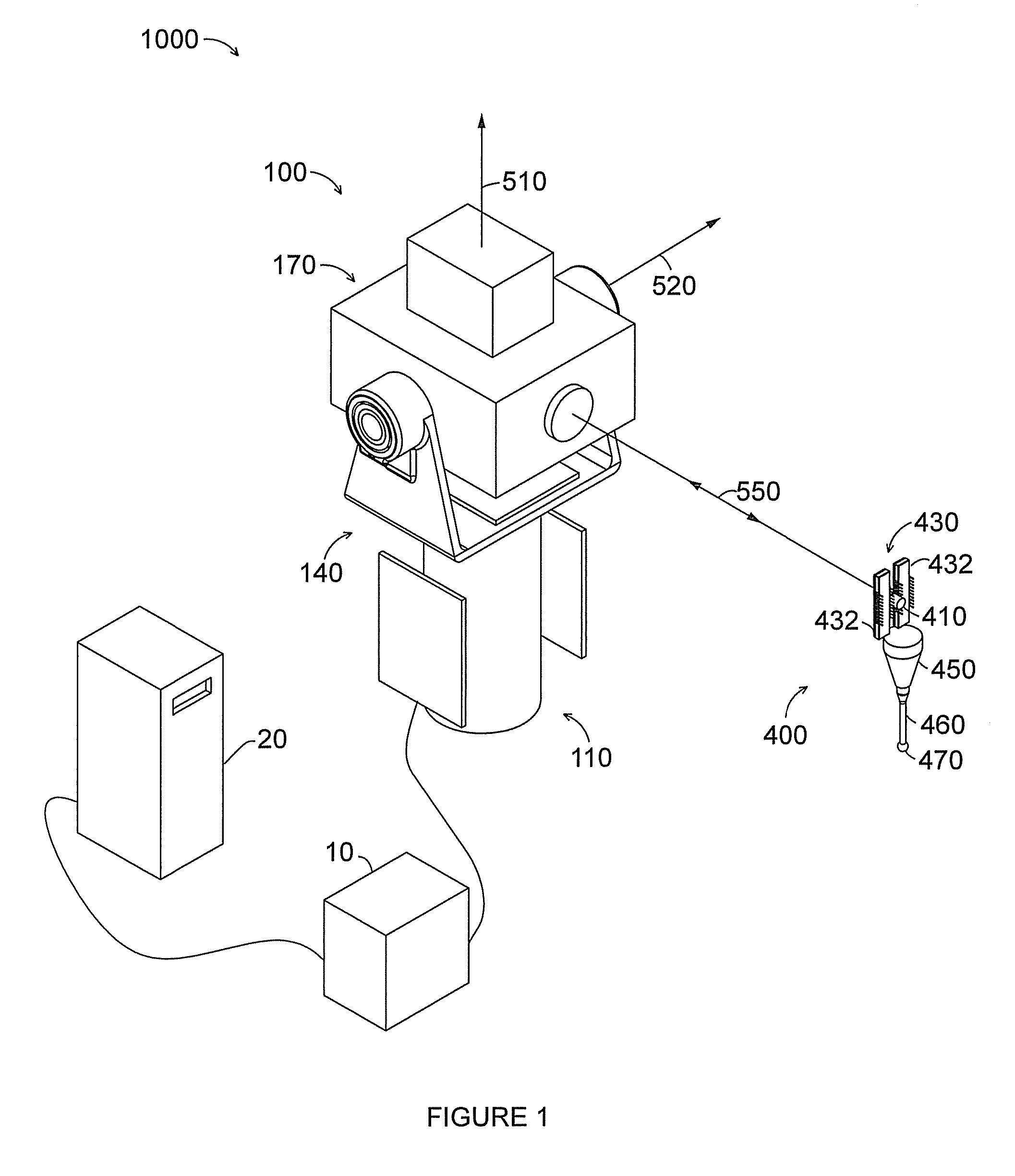
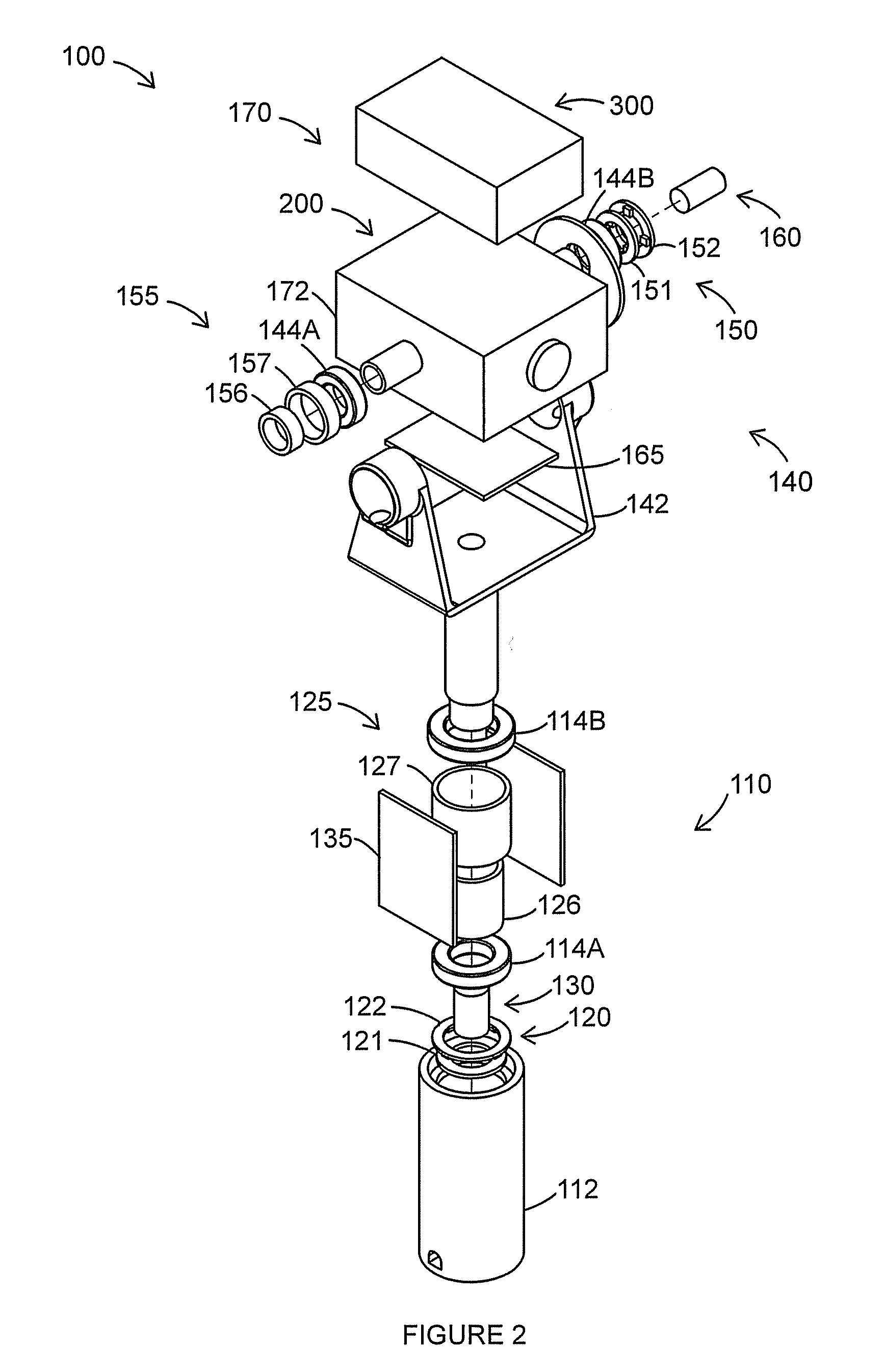
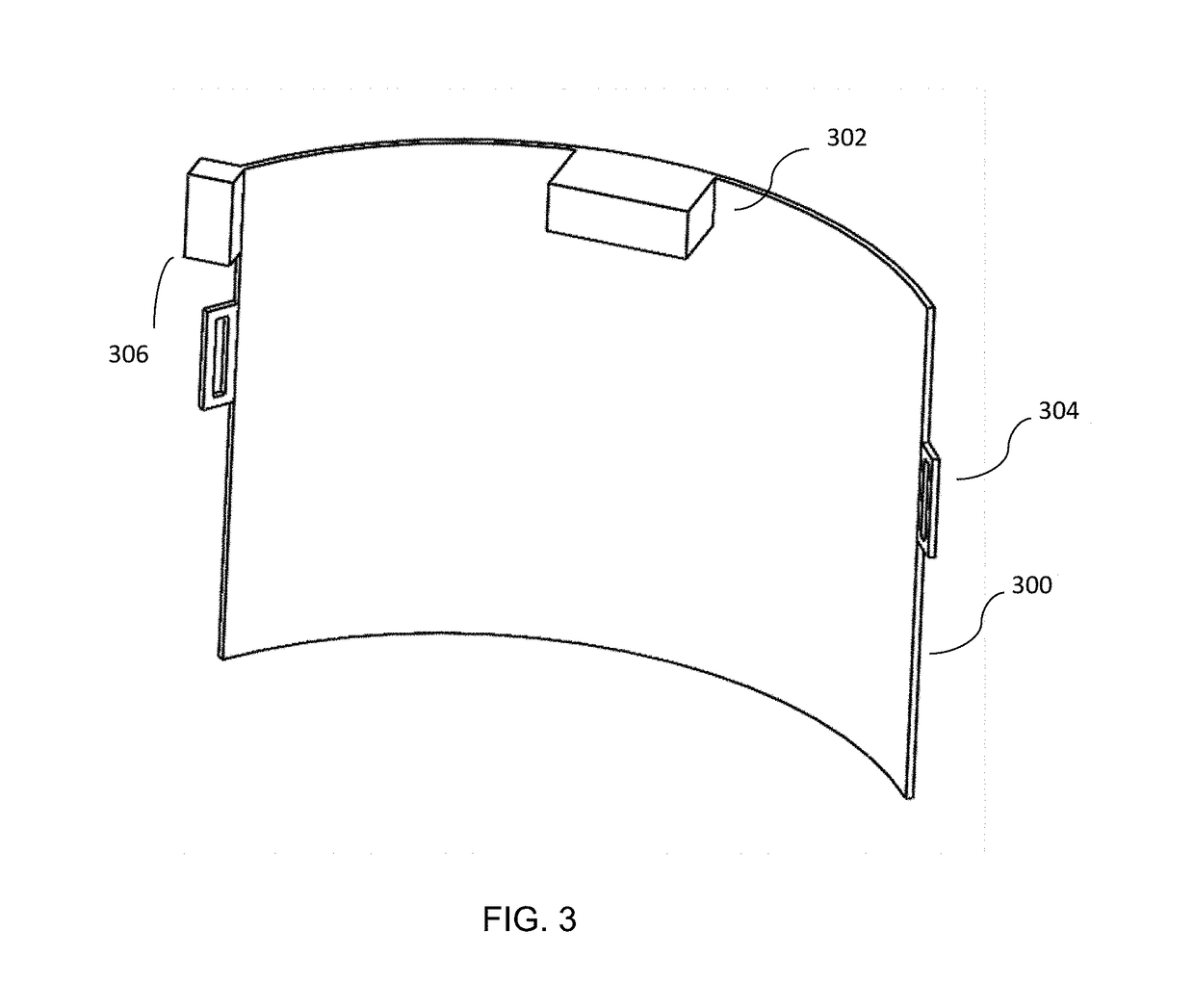
Six degree of freedom alignment display for medical procedures
A display and navigation system for use in guiding a medical device to a target in a patient includes a tracking sensor, a tracking device and display. The tracking sensor is associated with the medical device and is used to track the medical device. The tracking device tracks the medical device with the tracking sensor. The display includes indicia illustrating at least five degree of freedom information and indicia of the medical device in relation to the five degree of freedom information.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
Motion Tracking System
ActiveUS20080285805A1High precisionAccurate recordProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationMovement trackingKalman filter
Owner:XSENS HLDG BV
Deriving input from six degrees of freedom interfaces
ActiveUS20120038549A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingMixed realityVirtual space
The present invention relates to interfaces and methods for producing input for software applications based on the absolute pose of an item manipulated or worn by a user in a three-dimensional environment. Absolute pose in the sense of the present invention means both the position and the orientation of the item as described in a stable frame defined in that three-dimensional environment. The invention describes how to recover the absolute pose with optical hardware and methods, and how to map at least one of the recovered absolute pose parameters to the three translational and three rotational degrees of freedom available to the item to generate useful input. The applications that can most benefit from the interfaces and methods of the invention involve 3D virtual spaces including augmented reality and mixed reality environments.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Multibody aircrane
InactiveUS20090152391A1Precise and timely point to point transferEfficient powerCargo handling apparatusPassenger handling apparatusLow speedControl line
The MULTIBODY AIRCRANE performs relative positioning, predictive control, and ballast control to achieve very heavy-lifting tasks on land or sea. Such tasks allow station keeping and precise transfer of very heavy payloads between ships underway. This scalable multibody system features three subcomponents: AIRSHIP, SKYCRANE and LOADFRAME. This semi-autonomous system combines aerodynamic (kinetic) and aerostatic (buoyancy force) lift with efficient power and propulsion. During low-speed flight, the Airship and Skycrane are decoupled but linked via a reelable Tether Control Line. Beneath the Skycrane, centered on its hull, a patented NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) RoboCrane (featuring a computer controlled six degrees of freedom (DoF) cabling system,) is attached, to precisely suspend and control a Loadframe, with or without payload. During subsonic forward flight, these Airship and Skycrane are coupled as a single airframe (fuselage and delta wing.)
Owner:MCWHIRK BRUCE KIMBERLY
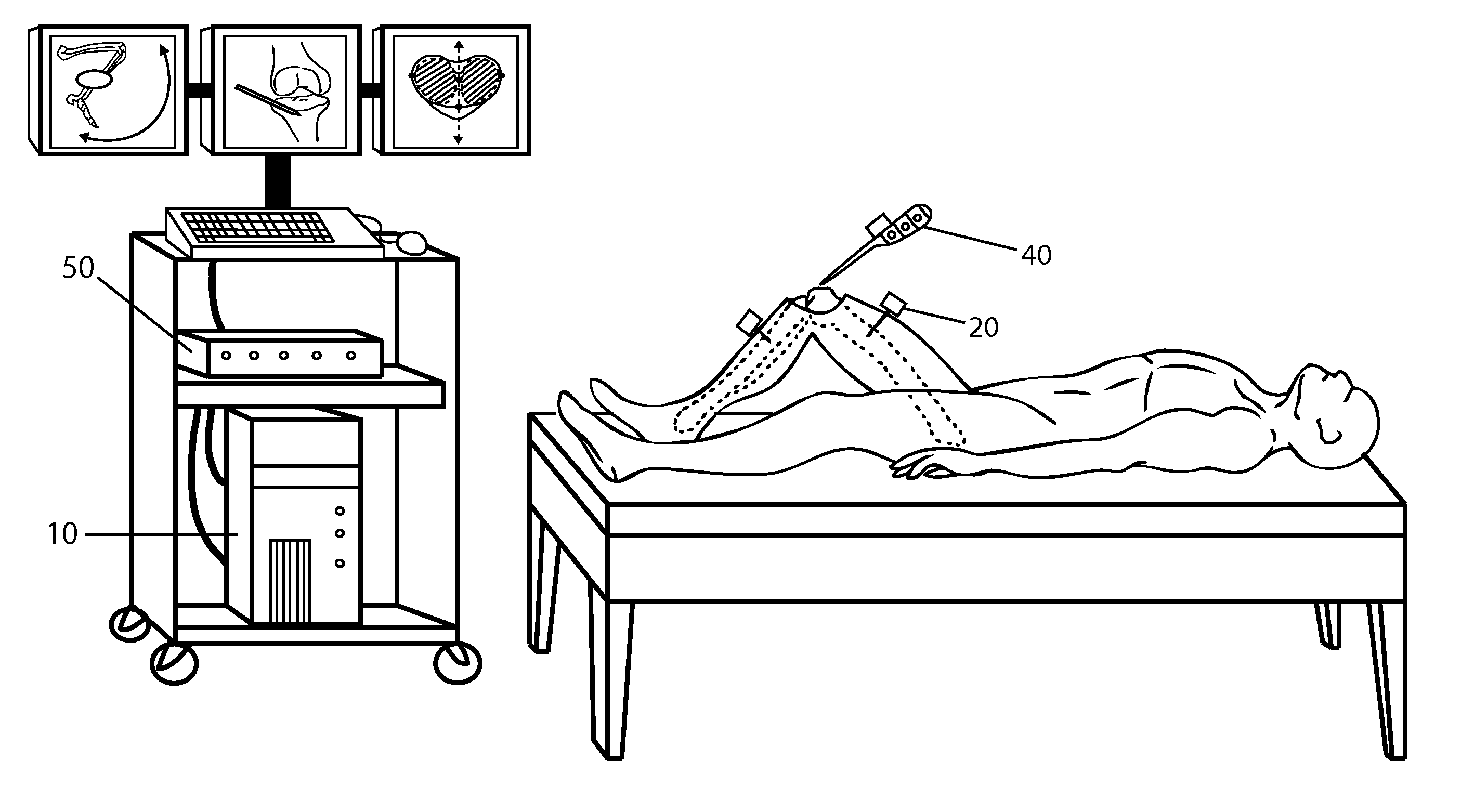
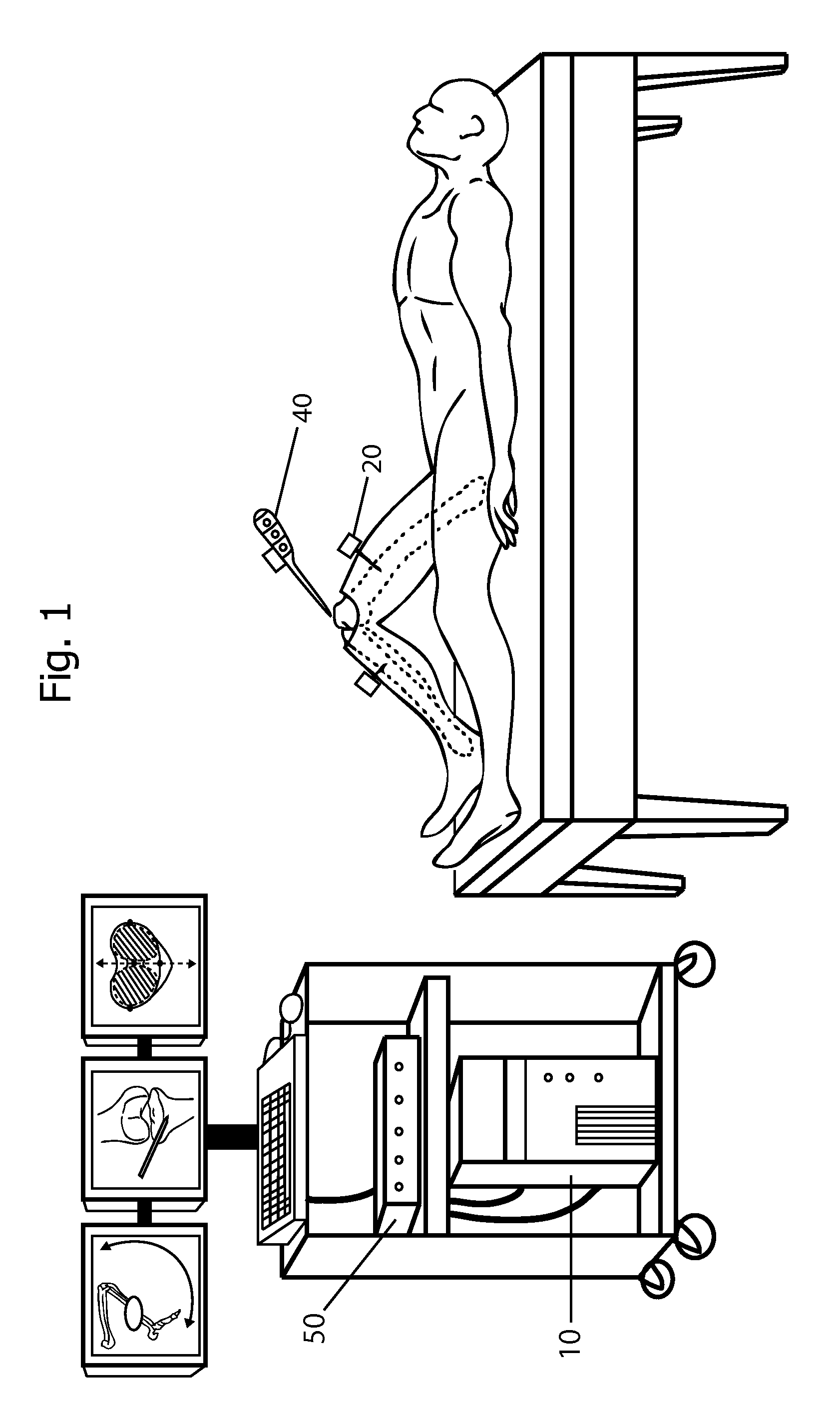
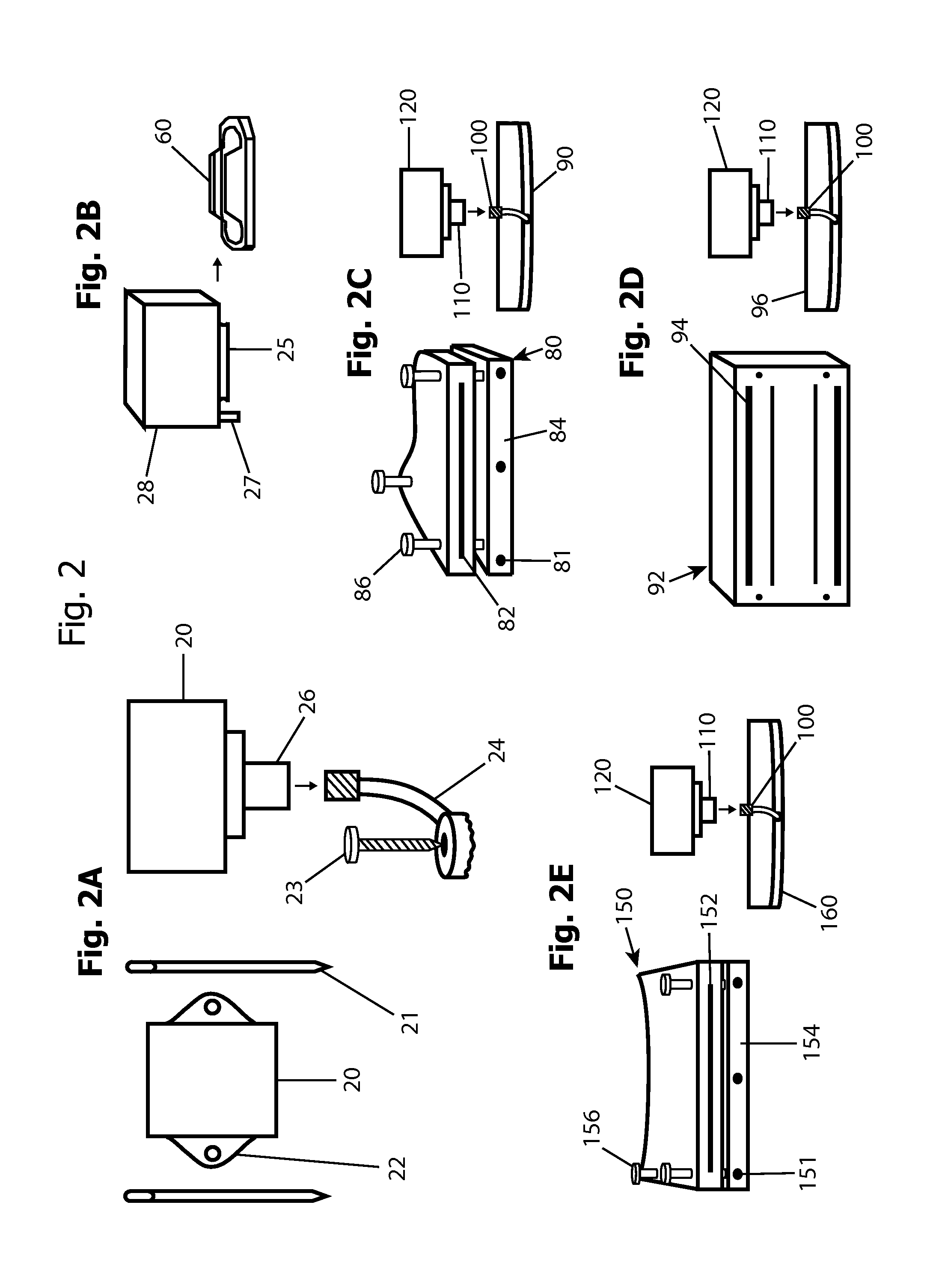
Inertial Sensor Based Surgical Navigation System for Knee Replacement Surgery
ActiveUS20110275957A1Improve accuracyGood precisionSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationKnee JointNavigation system
An inertial sensor based surgical navigation system for knee replacement surgery is disclosed. Inertial sensors composed of six-degree-of-freedom inertial chips, whose measurements are processed through a series of integration, quaternion, and kalman filter algorithms, are used to track the position and orientation of bones and surgical instruments. The system registers anatomically significant geometry, calculates joint centers and the mechanical axis of the knee, develops a visualization of the lower extremity that moves in real time, assists in the intra-operative planning of surgical cuts, determines the optimal cutting planes for cut guides and the optimal prosthesis position and orientation, and finally navigates the cut guides and the prosthesis to their optimal positions and orientations using a graphical user interface.
Owner:BHANDARI SACHIN
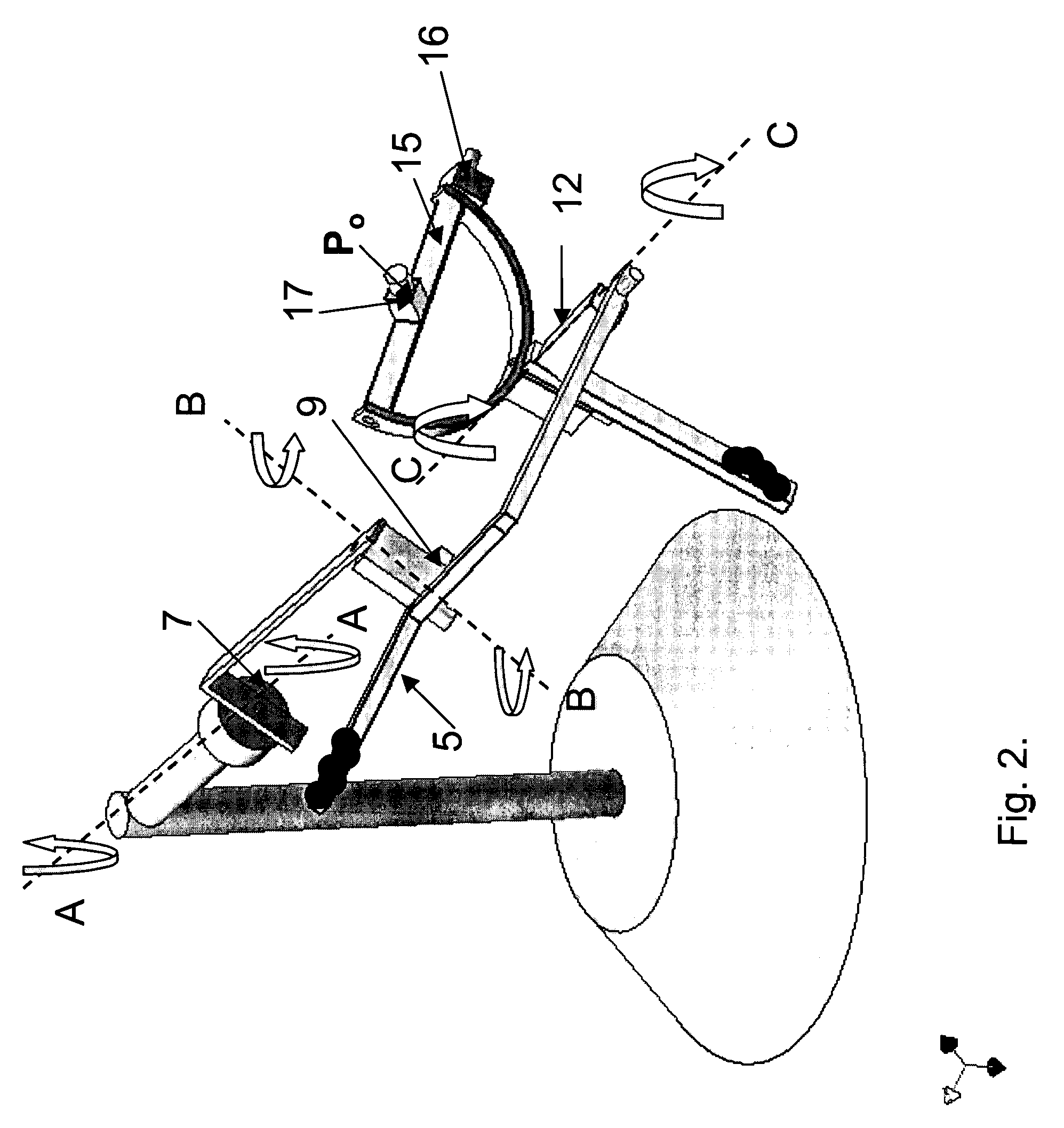
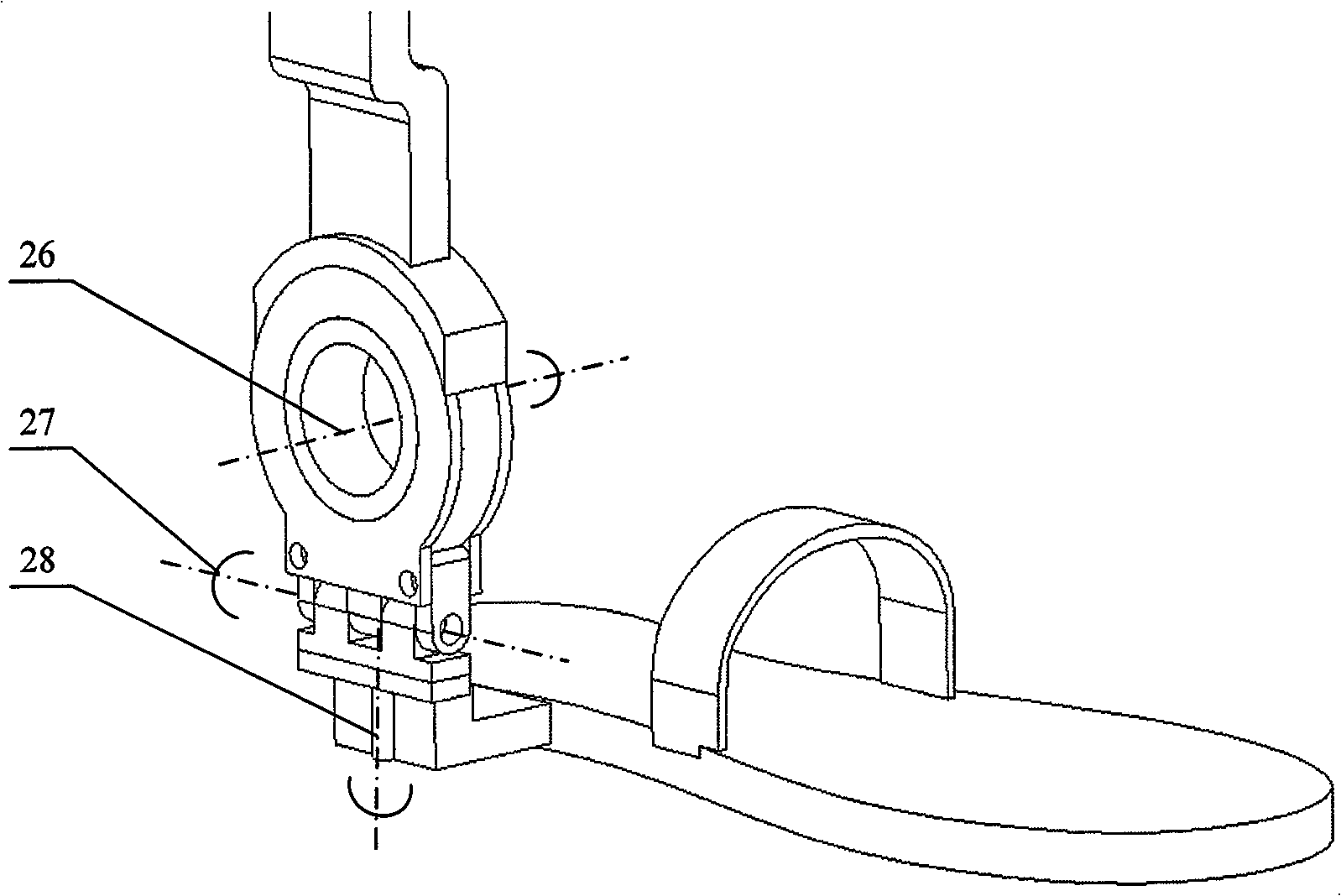
Device and method for measuring six degrees of freedom
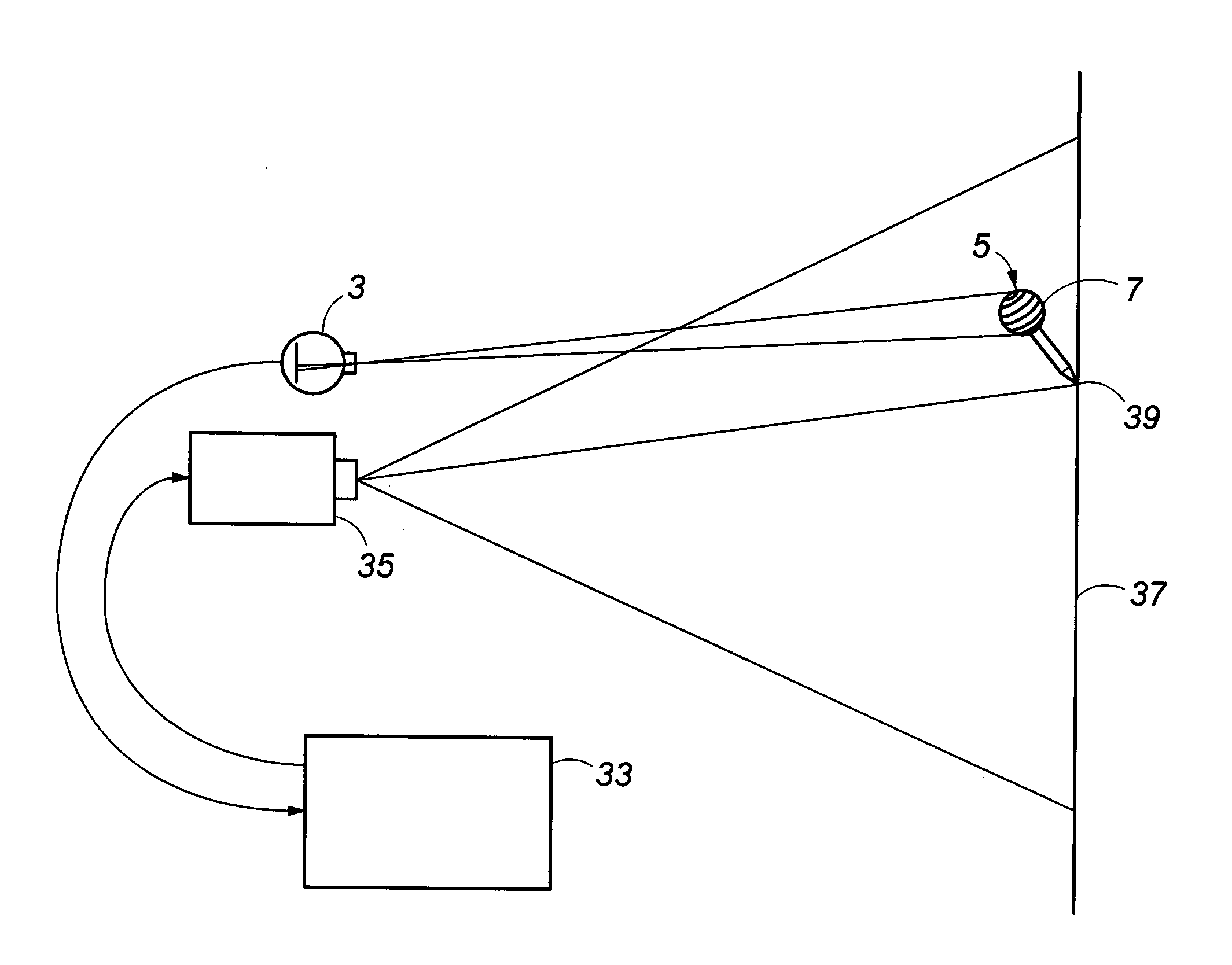
InactiveUS20100128259A1Angle measurementBeacon systems using electromagnetic wavesLight beamDegrees of freedom
A laser tracker system for measuring six degrees of freedom may include a main optics assembly structured to emit a first laser beam, a pattern projector assembly structured to emit a second laser beam shaped into a two-dimensional pattern, and a target. The target may include a retroreflector and a position sensor assembly. A center of symmetry of the retroreflector may be provided on a different plane than a plane of the position sensor assembly. A method of measuring orientation of a target may include illuminating the target with a laser beam comprising a two-dimensional pattern, recording a position of the two-dimensional pattern on a position sensor assembly to create a measured signature value of the two-dimensional pattern, and calculating an orientation of the target based on the measured signature value.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Device and process for manipulating real and virtual objects in three-dimensional space
InactiveUS7466303B2Rapid localizationAccurate detectionManual control with multiple controlled membersSurgeryRest positionThree-dimensional space
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
To a combined fingerprint acquisition and control device
The present invention combines the functionality of a computer pointing device with a fingerprint authentication system, In the preferred embodiment, by regularly scanning fingerprints acquired from the pointing device touch pad, fingerprint features may be extracted and compared to stored data on authorized users for passive authentication. Furthermore, calculations based upon the acquired fingerprint images and associated features allows the system to determine six degrees of freedom of the finger, allowing the user to control a variety of functions or to manipulate a three-dimensional model or virtual reality system.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
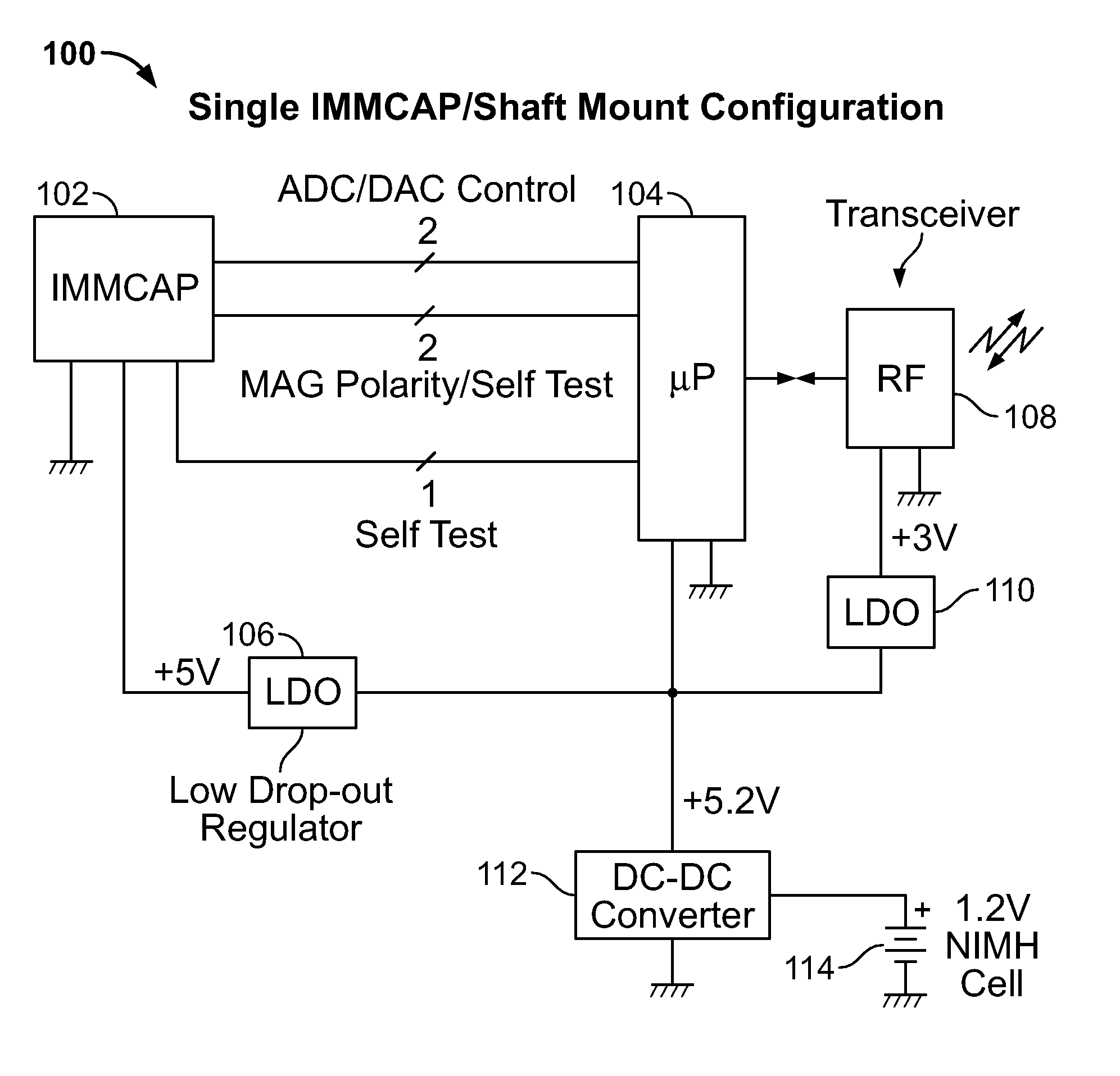
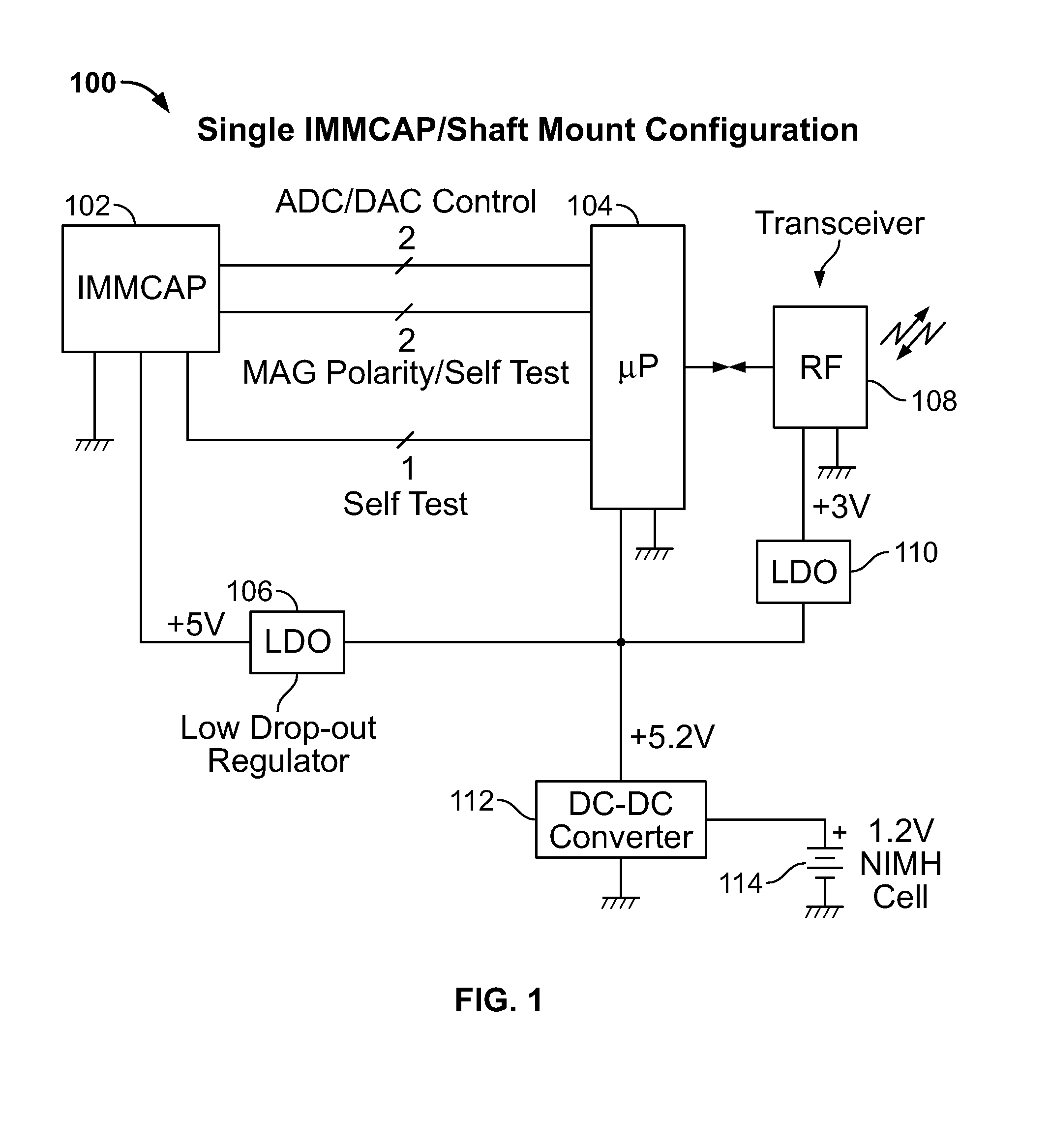
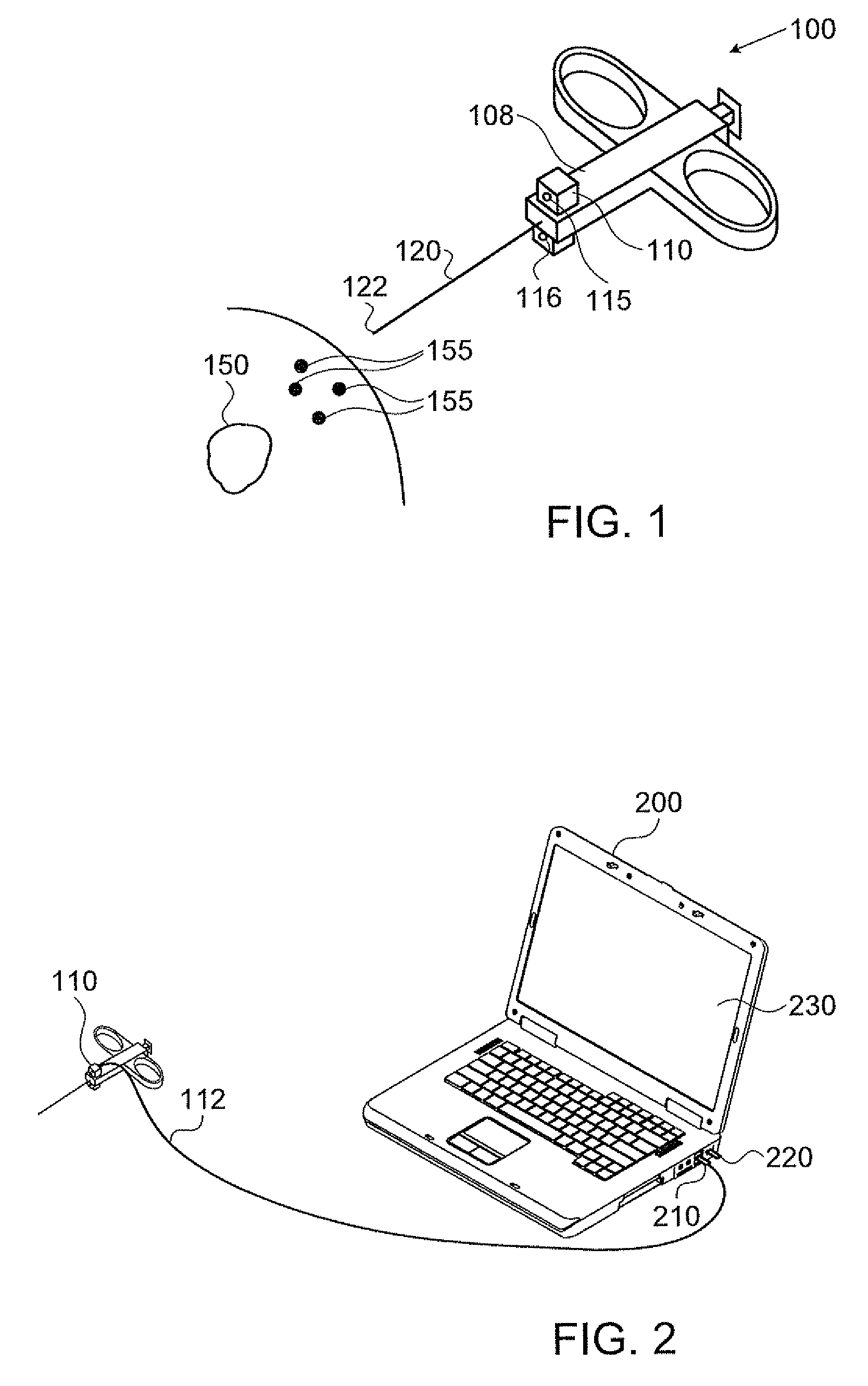
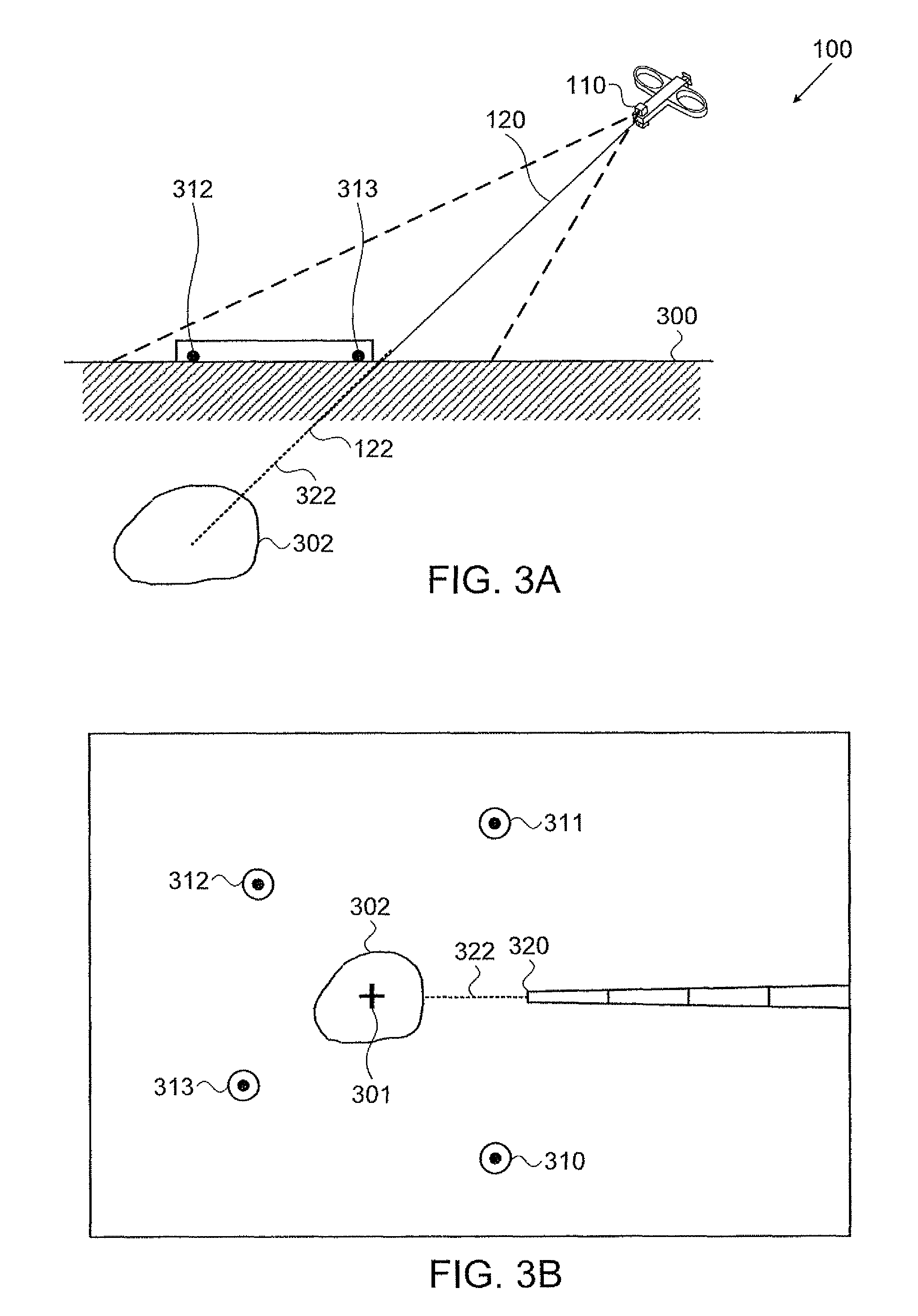
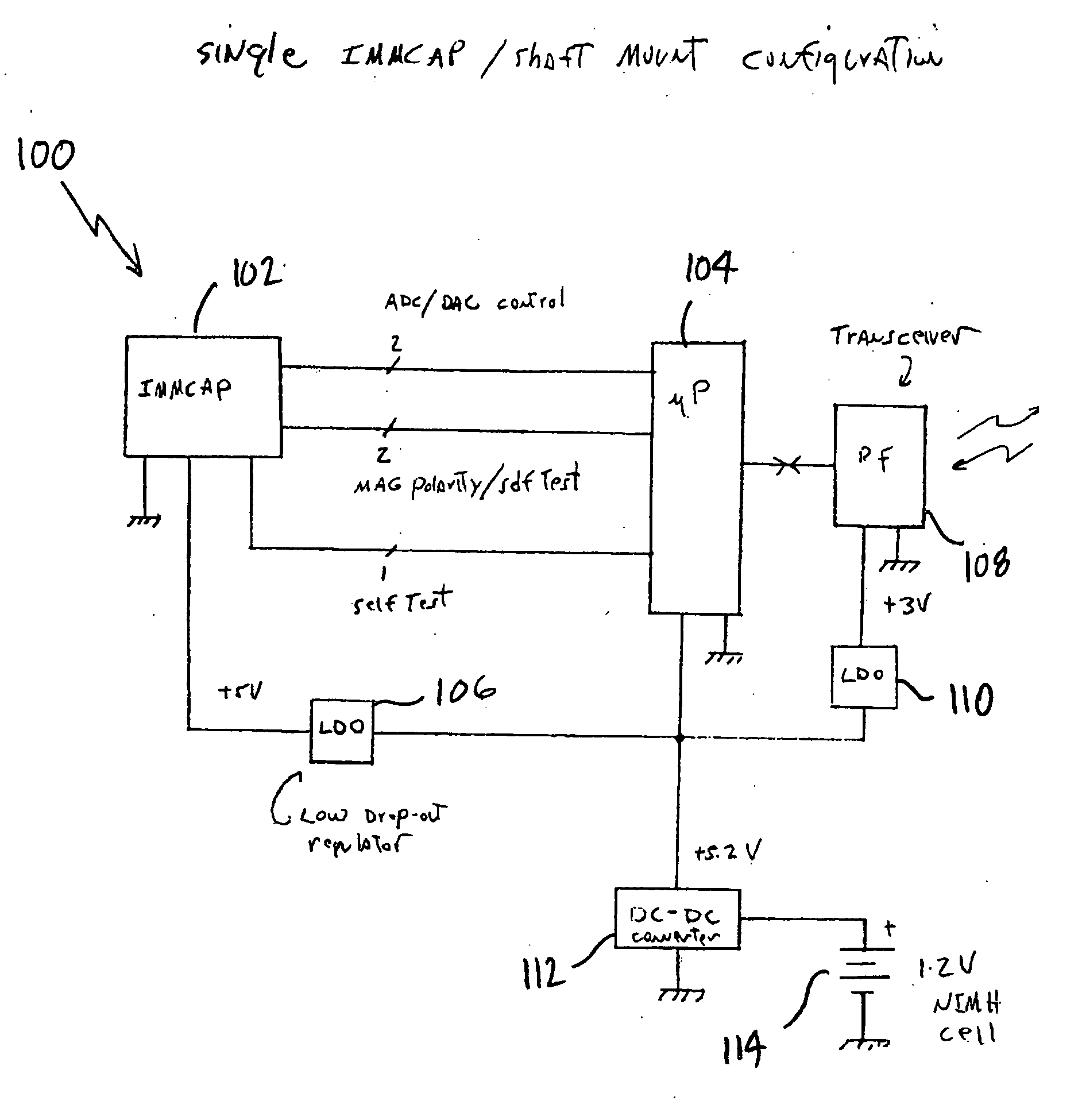
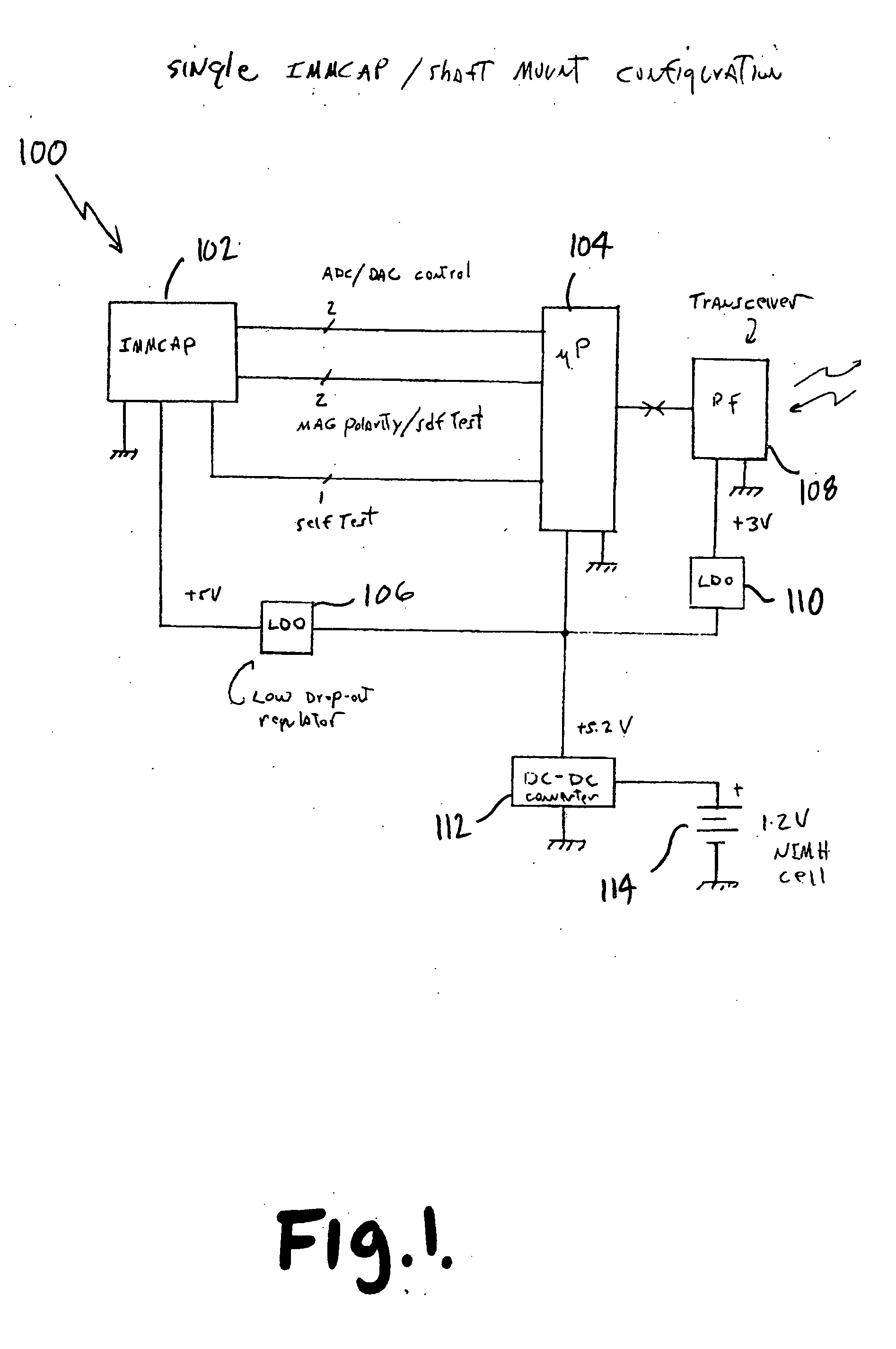
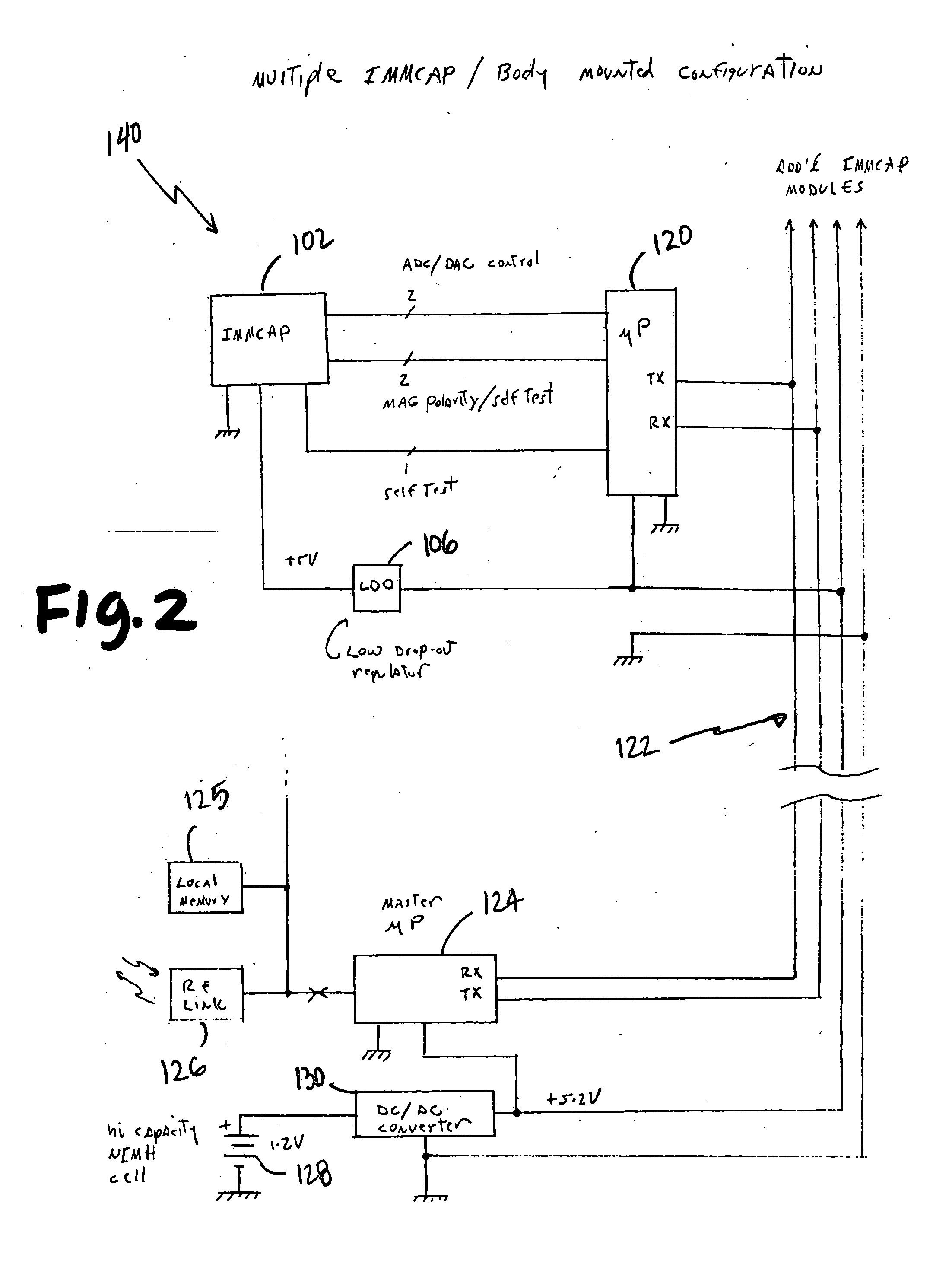
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
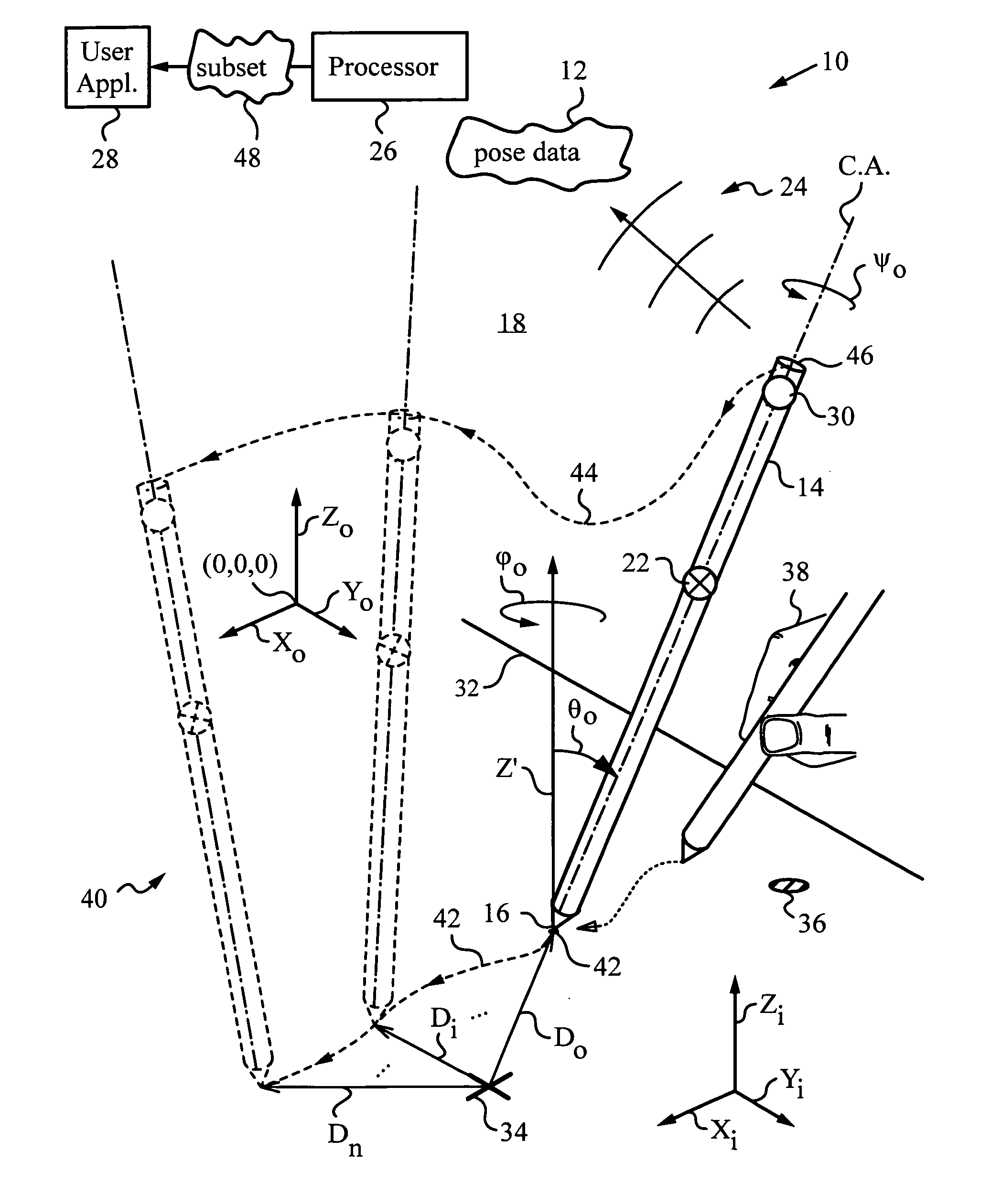
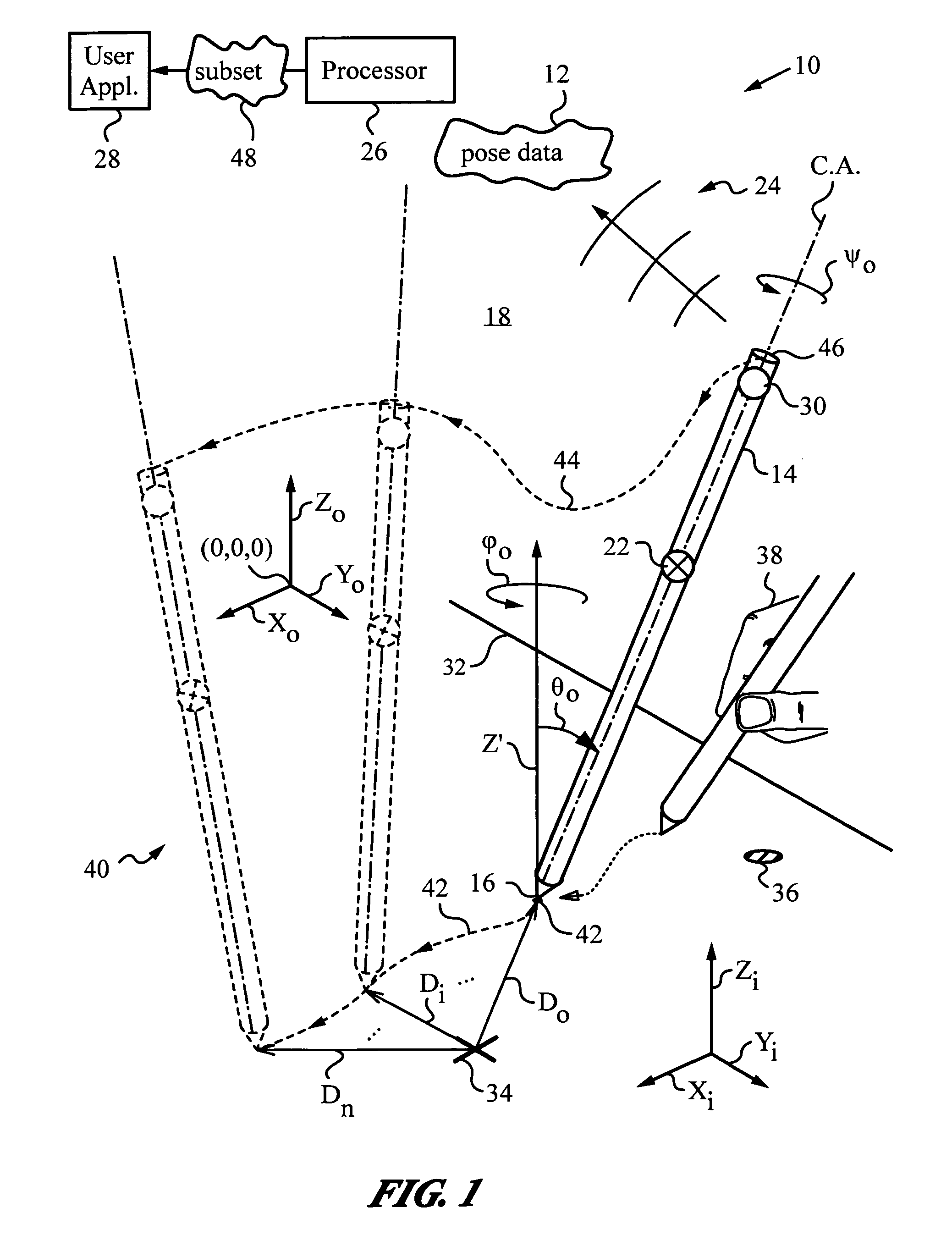
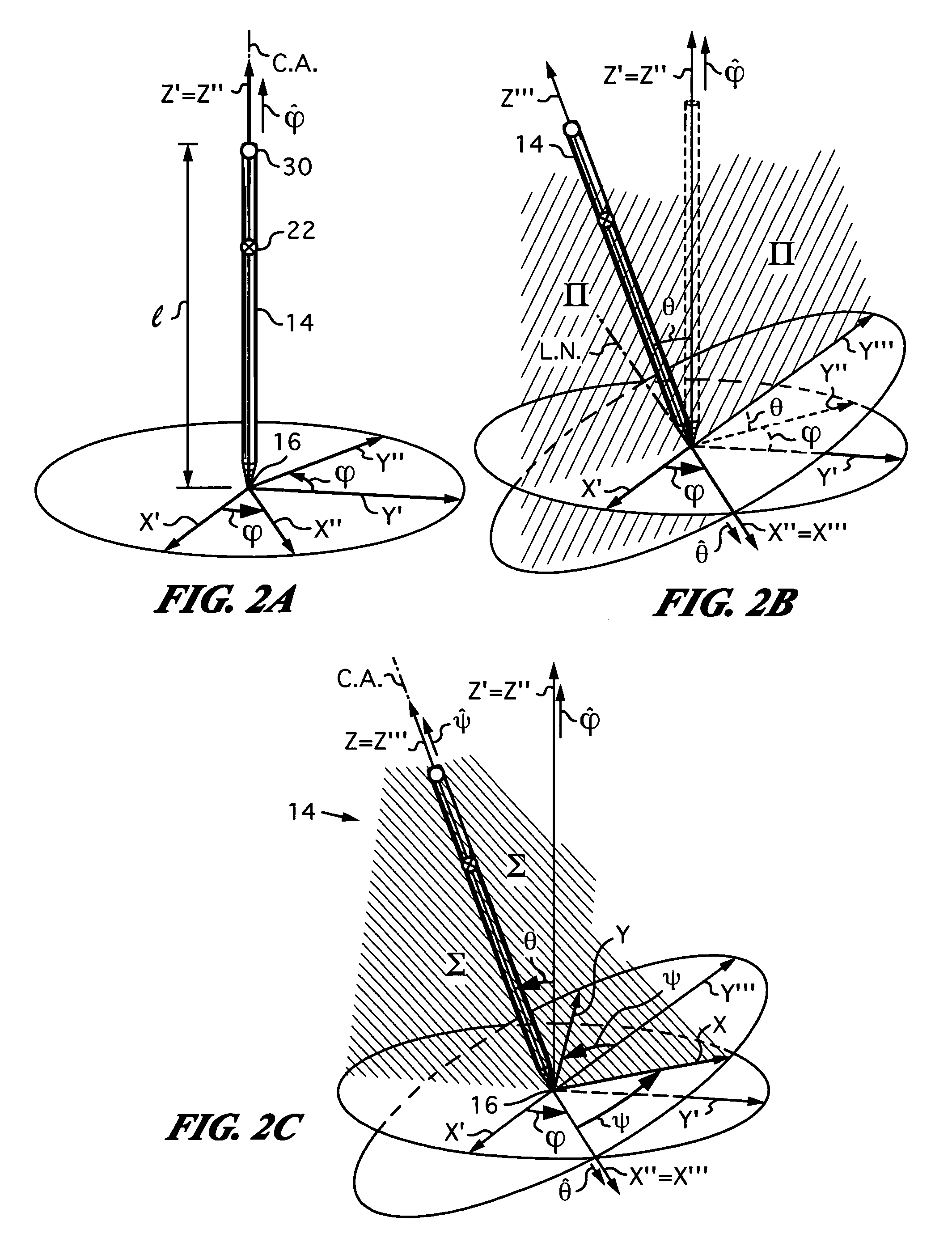
Apparatus and method for determining an absolute pose of a manipulated object in a real three-dimensional environment with invariant features
An apparatus and method for optically inferring an absolute pose of a manipulated object in a real three-dimensional environment from on-board the object with the aid of an on-board optical measuring arrangement. At least one invariant feature located in the environment is used by the arrangement for inferring the absolute pose. The inferred absolute pose is expressed with absolute pose data (φ, θ, ψ, x, y, z) that represents Euler rotated object coordinates expressed in world coordinates (Xo, Yo, Zo) with respect to a reference location, such as, for example, the world origin. Other conventions for expressing absolute pose data in three-dimensional space and representing all six degrees of freedom (three translational degrees of freedom and three rotational degrees of freedom) are also supported. Irrespective of format, a processor prepares the absolute pose data and identifies a subset that may contain all or fewer than all absolute pose parameters. This subset is transmitted to an application via a communication link, where it is treated as input that allows a user of the manipulated object to interact with the application and its output.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
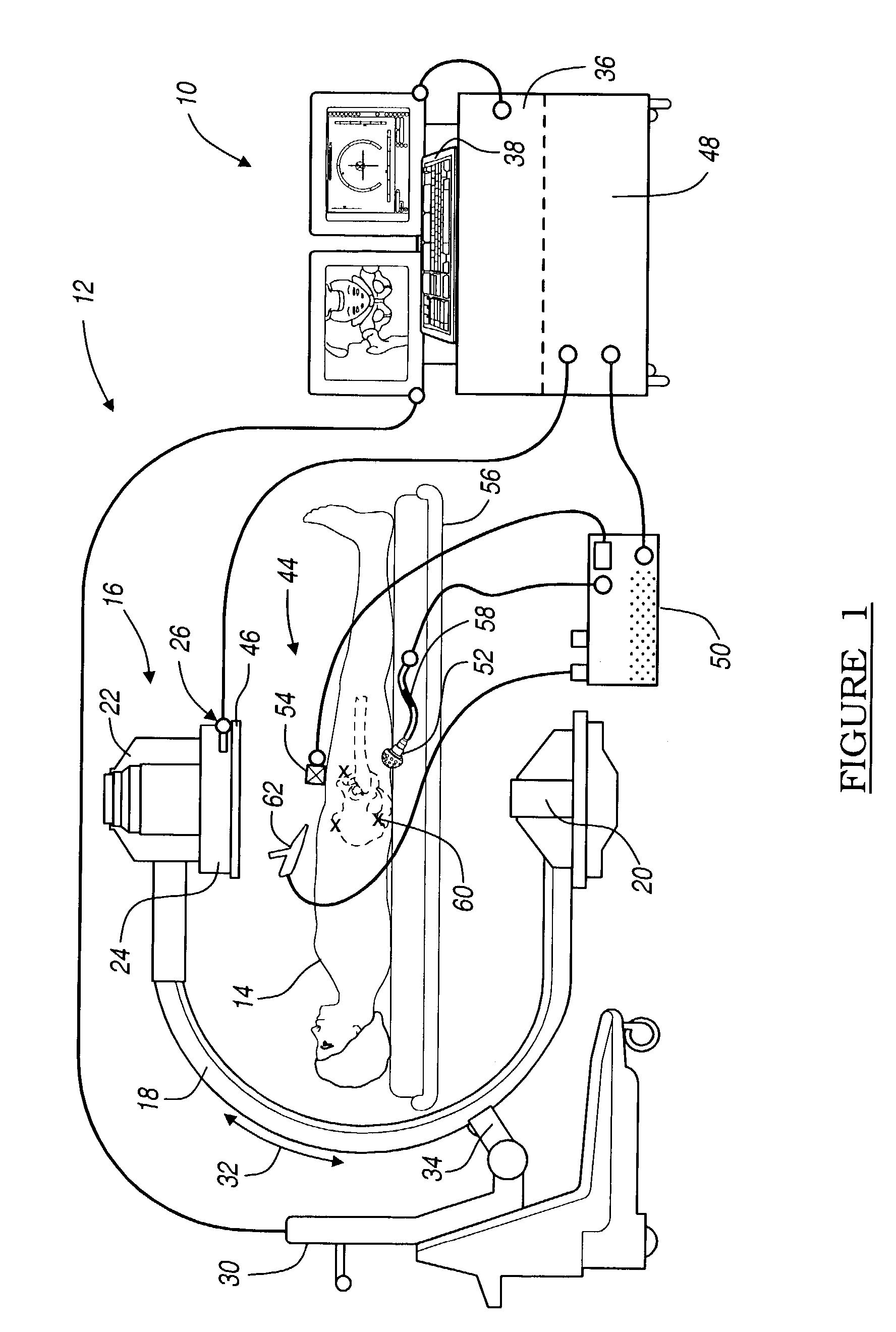
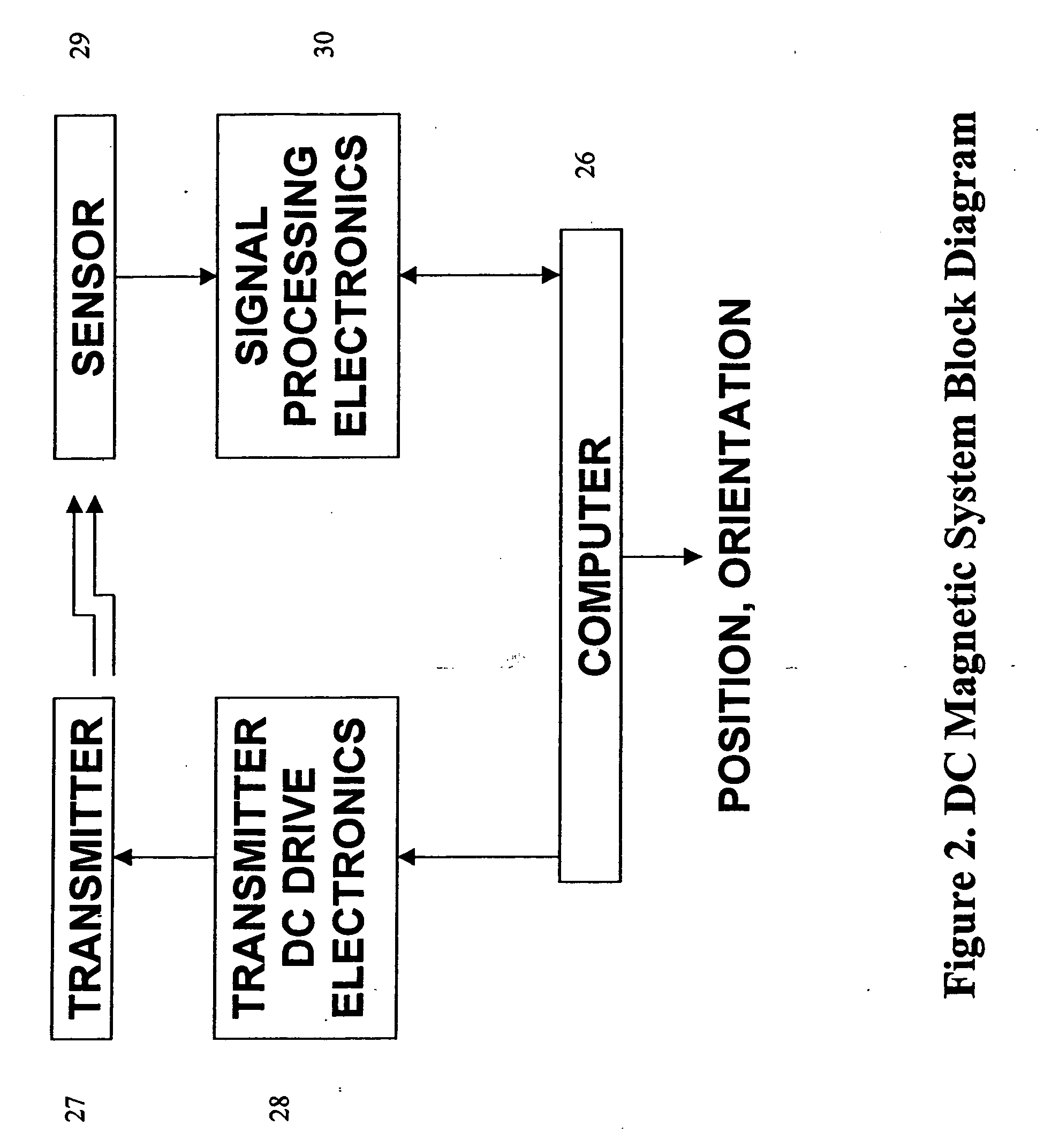
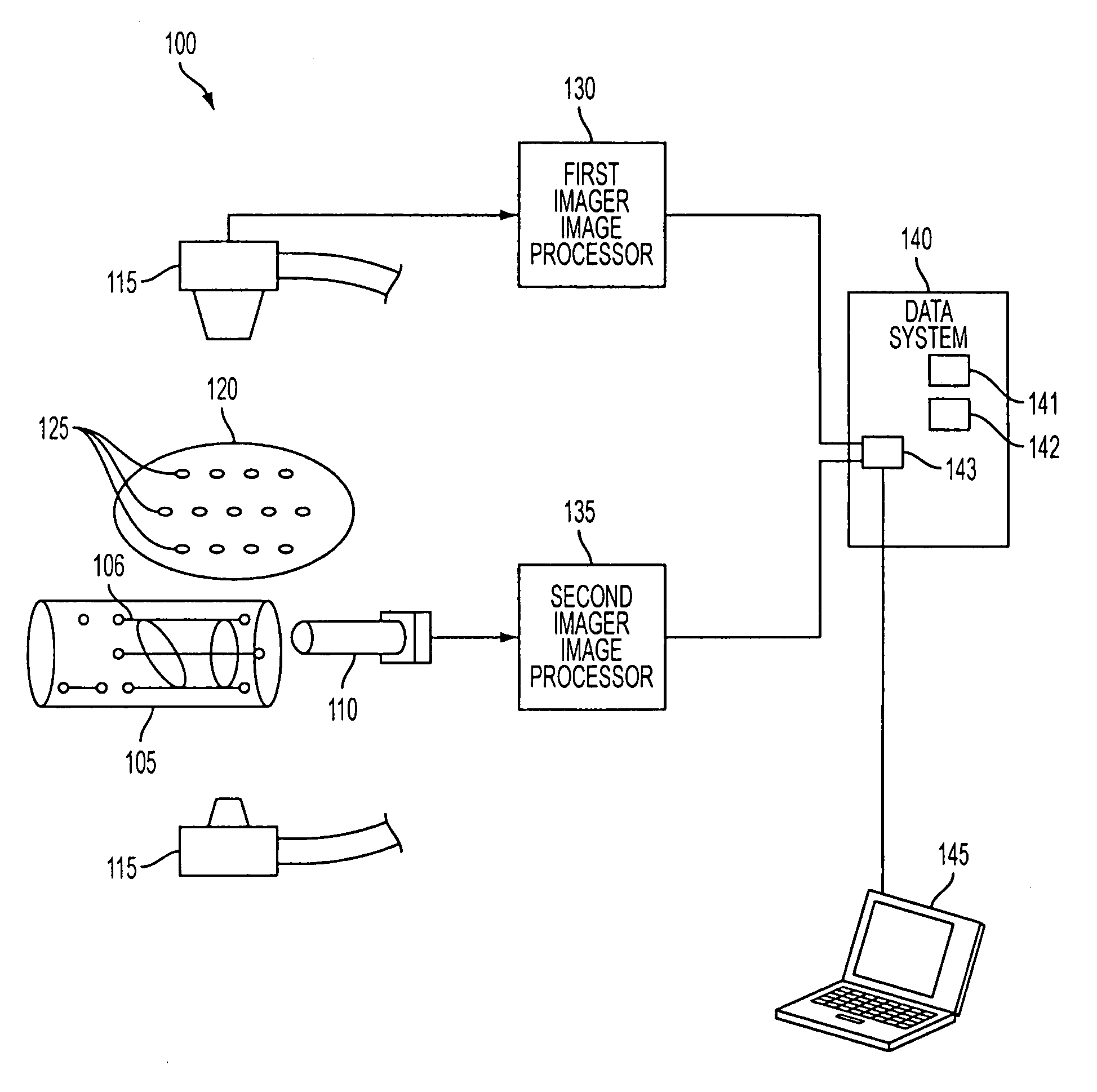
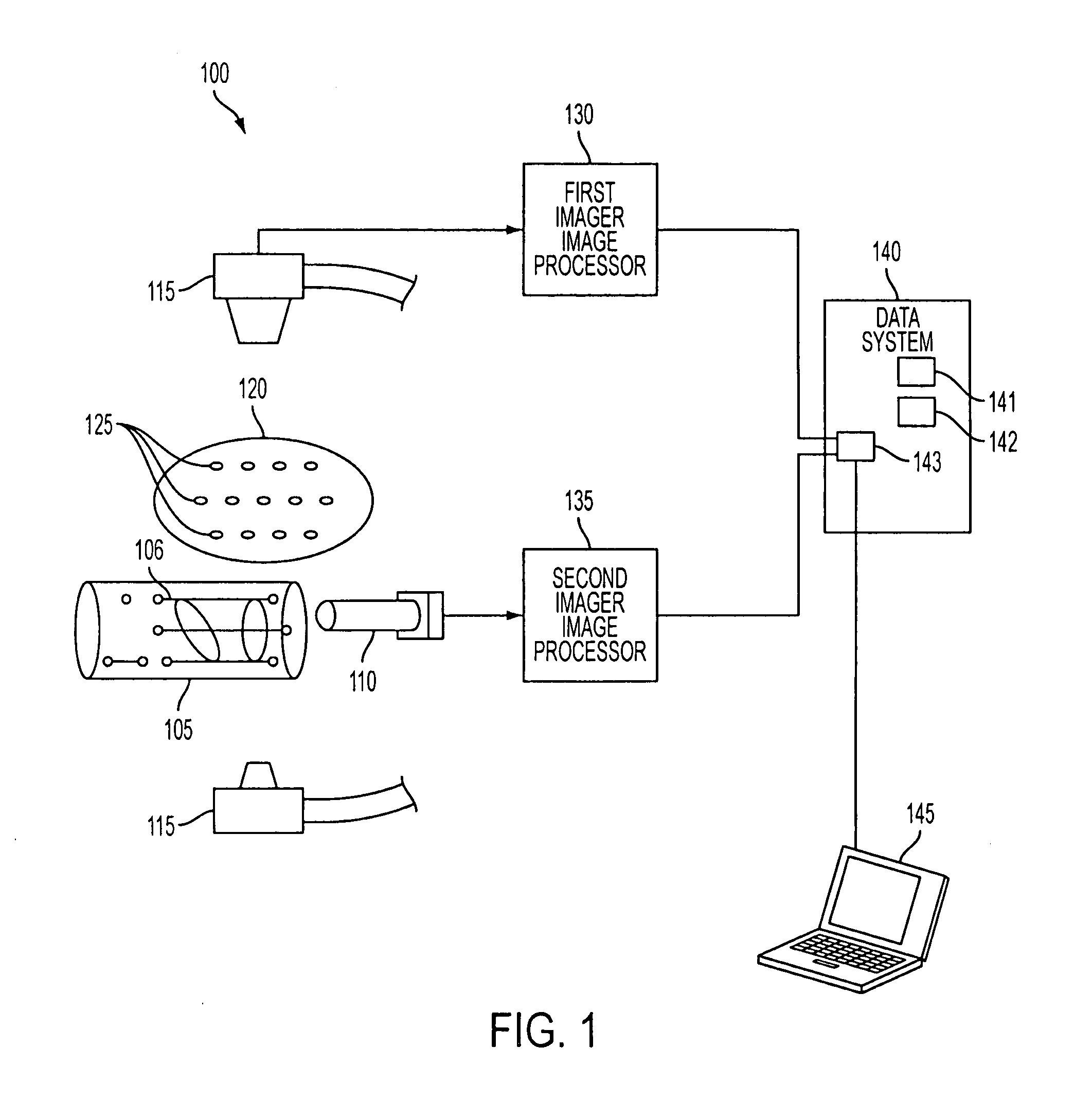
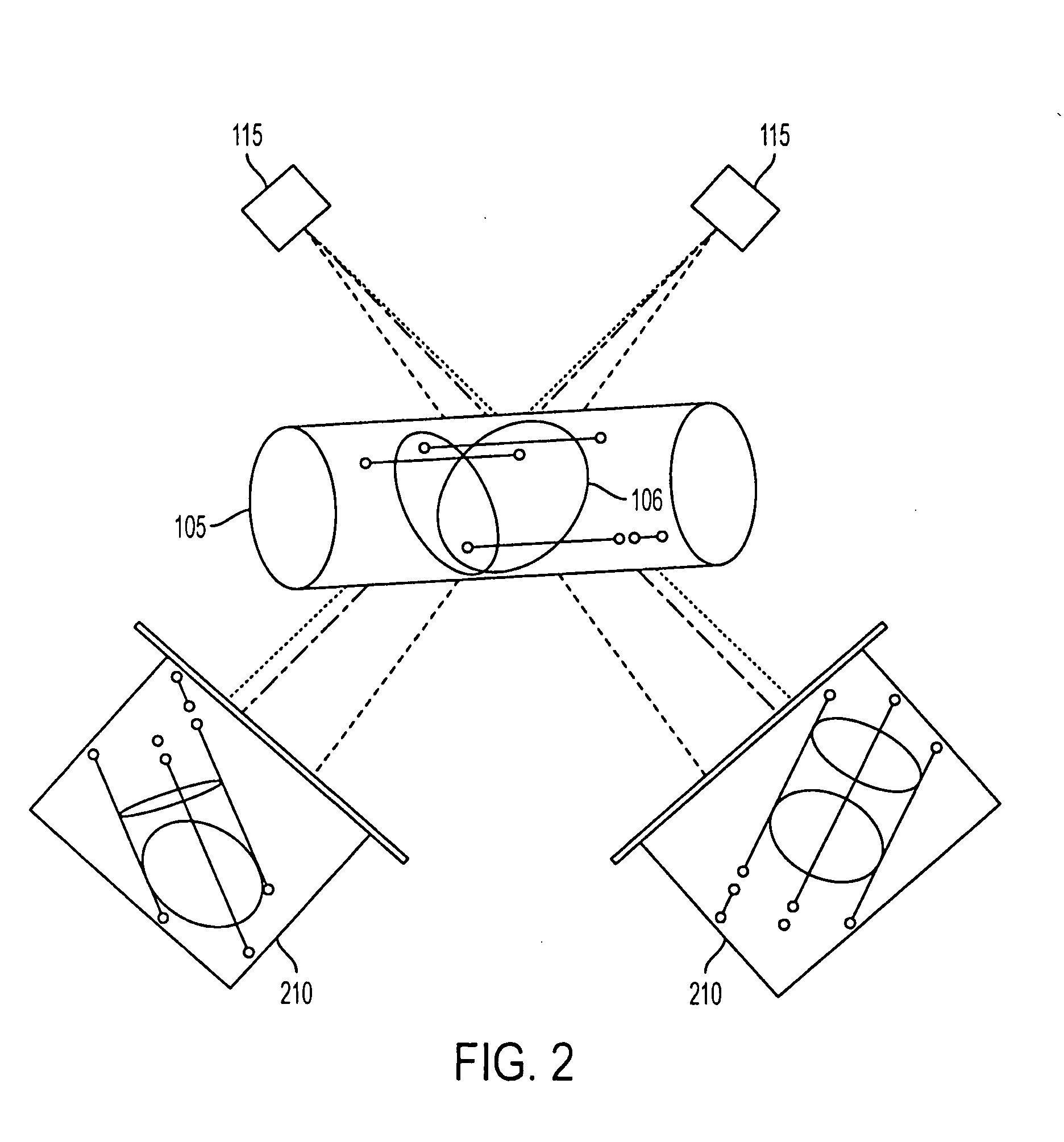
DC magnetic-based position and orientation monitoring system for tracking medical instruments
ActiveUS20070078334A1Overcome disposabilityOvercome cost issueDiagnostic recording/measuringSensors3d sensorEngineering
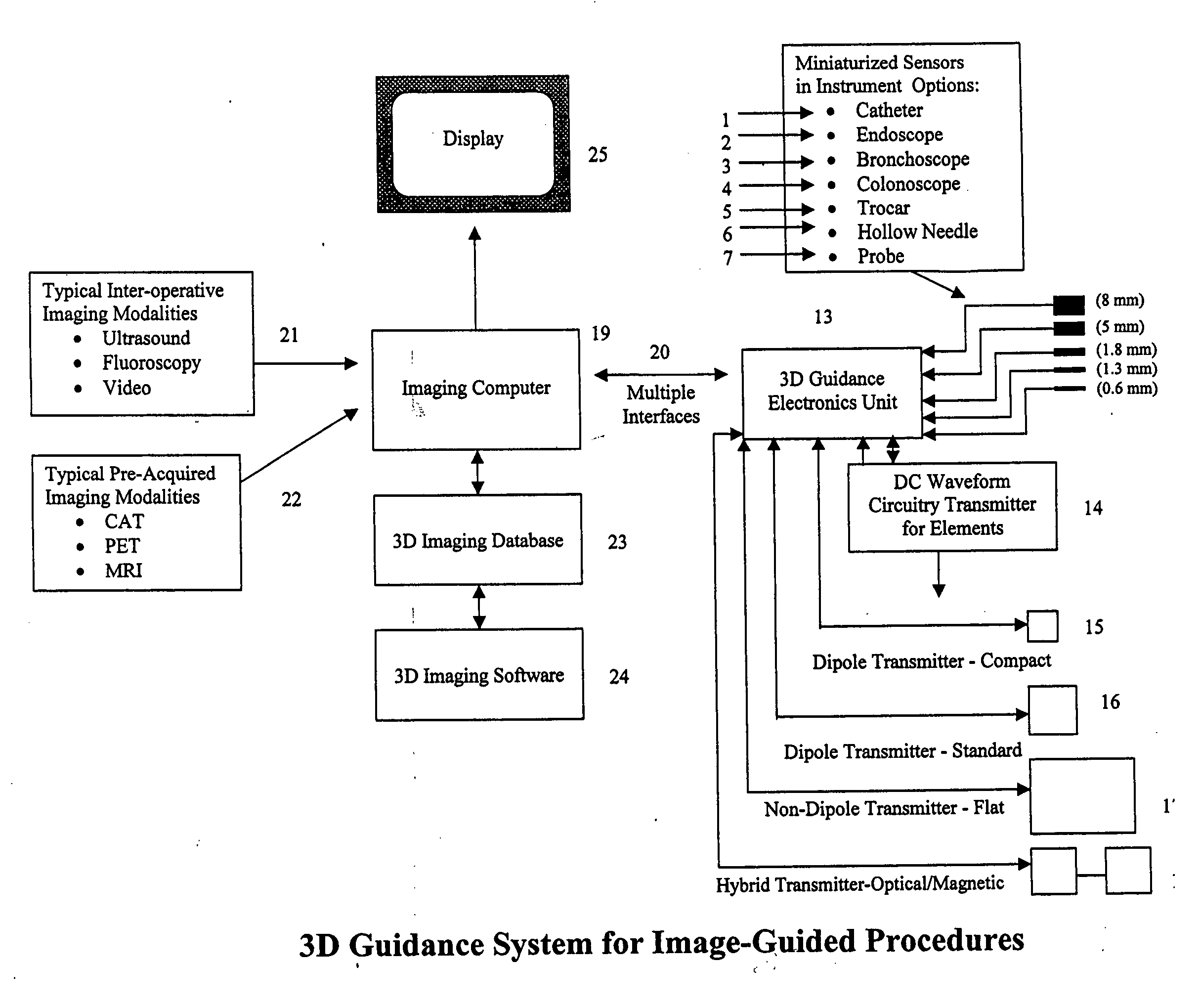
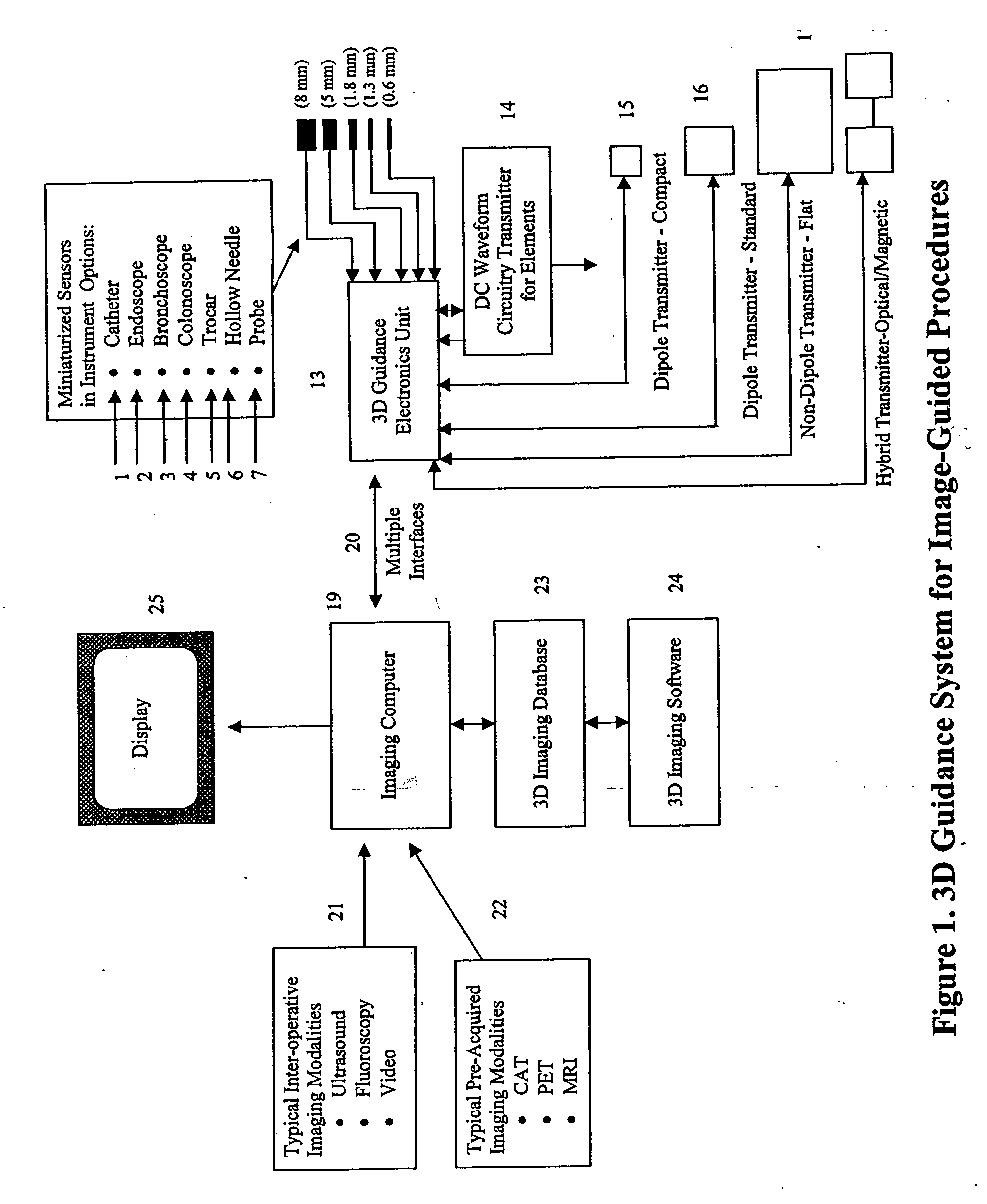
Miniaturized, five and six degrees-of-freedom magnetic sensors, responsive to pulsed DC magnetic fields waveforms generated by multiple transmitter options, provide an improved and cost-effective means of guiding medical instruments to targets inside the human body. The end result is achieved by integrating DC tracking, 3D reconstructions of pre-acquired patient scans and imaging software into a system enabling a physician to internally guide an instrument with real-time 3D vision for diagnostic and interventional purposes. The integration allows physicians to navigate within the human body by following 3D sensor tip locations superimposed on anatomical images reconstructed into 3D volumetric computer models. Sensor data can also be integrated with real-time imaging modalities, such as endoscopes, for intrabody navigation of instruments with instantaneous feedback through critical anatomy to locate and remove tissue. To meet stringent medical requirements, the system generates and senses pulsed DC magnetic fields embodied in an assemblage of miniaturized, disposable and reposable sensors functional with both dipole and co-planar transmitters.
Owner:NORTHERN DIGITAL
Method and apparatus for computer input using six degrees of freedom
InactiveUS6844871B1Keep the environmentImprove user interactionInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A mouse is provided that uses a camera as its input sensor. A real-time vision algorithm determines the six degree-of-freedom mouse posture, consisting of 2D motion, tilt in the forward / back and left / right axes, rotation of the mouse about its vertical axis, and some limited height sensing. Thus, a familiar 2D device can be extended for three-dimensional manipulation, while remaining suitable for standard 2D Graphical User Interface tasks. The invention includes techniques for mouse functionality, 3D manipulation, navigating large 2D spaces, and using the camera for lightweight scanning tasks.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Object position and orientation detection system
ActiveUS20100091112A1Image be preventEfficient detectionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionWhiteboardDisplay device
An object position and orientation detection system and in particular one which is capable of describing observed movement in 3 dimensions. In one example, a spherical patterned marker with concentric rings is imaged using one or more digital cameras, and the resulting images are processed to determine the position and orientation of an object to which the patterned marker is attached. The method of optical tracking employed by the system allows motion to be determined in six degrees of freedom. In conjunction with a suitable display, such as a projector, an interactive white board or similar application can be realised.
Owner:CARL ZEISS IND MESSTECHN GMBH +1
System and method for optical position measurement and guidance of a rigid or semi-flexible tool to a target
A system for measuring the position of a hand-held tool relative to a body in six degrees of freedom employs a camera attached via a mechanical linkage to the tool so that the camera moves together with the proximal portion of the tool and has a field of view including the distal end of the tool. A processing system processes images from the camera to determine a position of at least part of the tool. By employing optically identifiable fiducial reference points defined on the external surface of the body, a projection of the tool tip position onto a plane containing the target can be derived and displayed together with the target position, thereby facilitating guiding the tool to the target.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
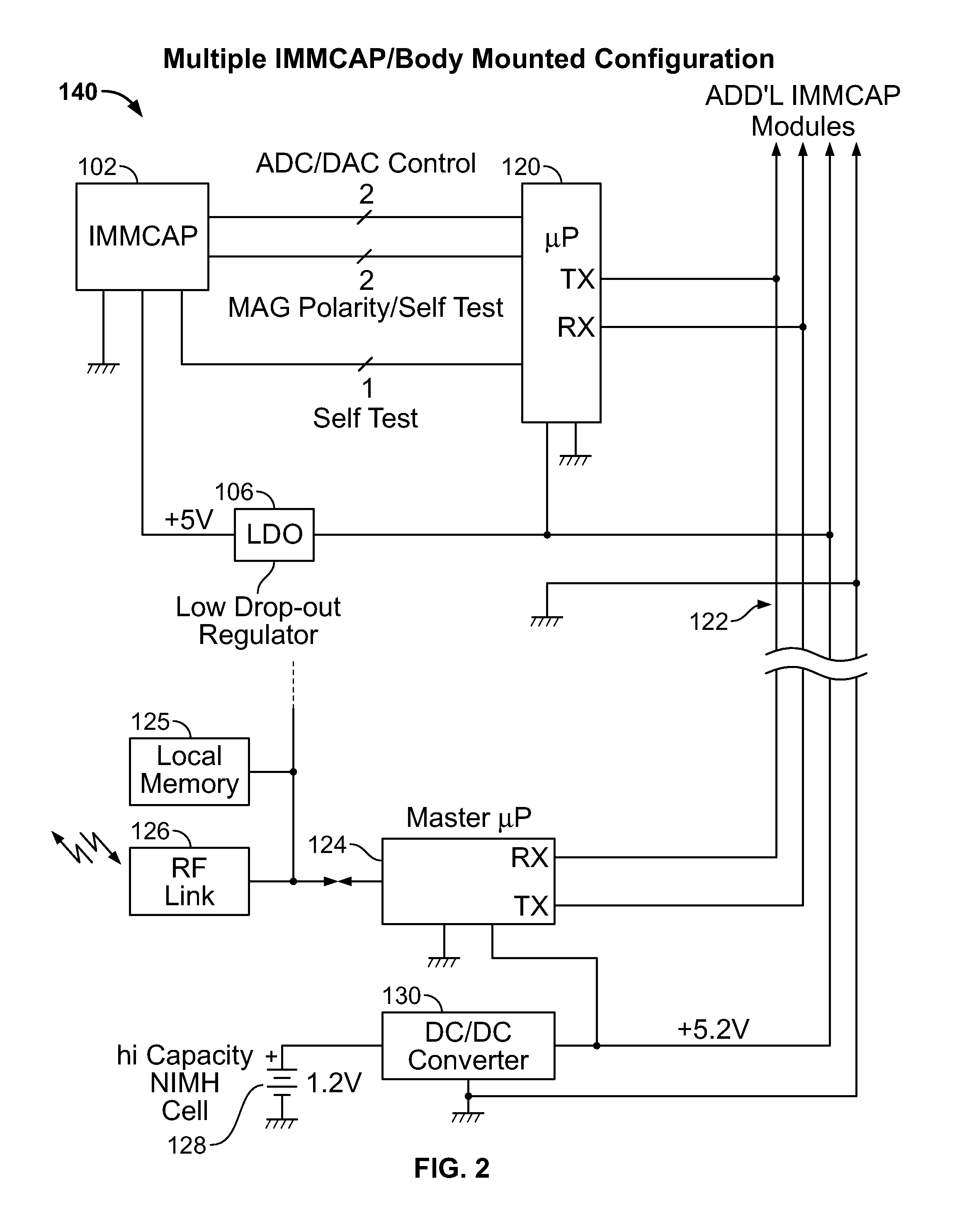
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
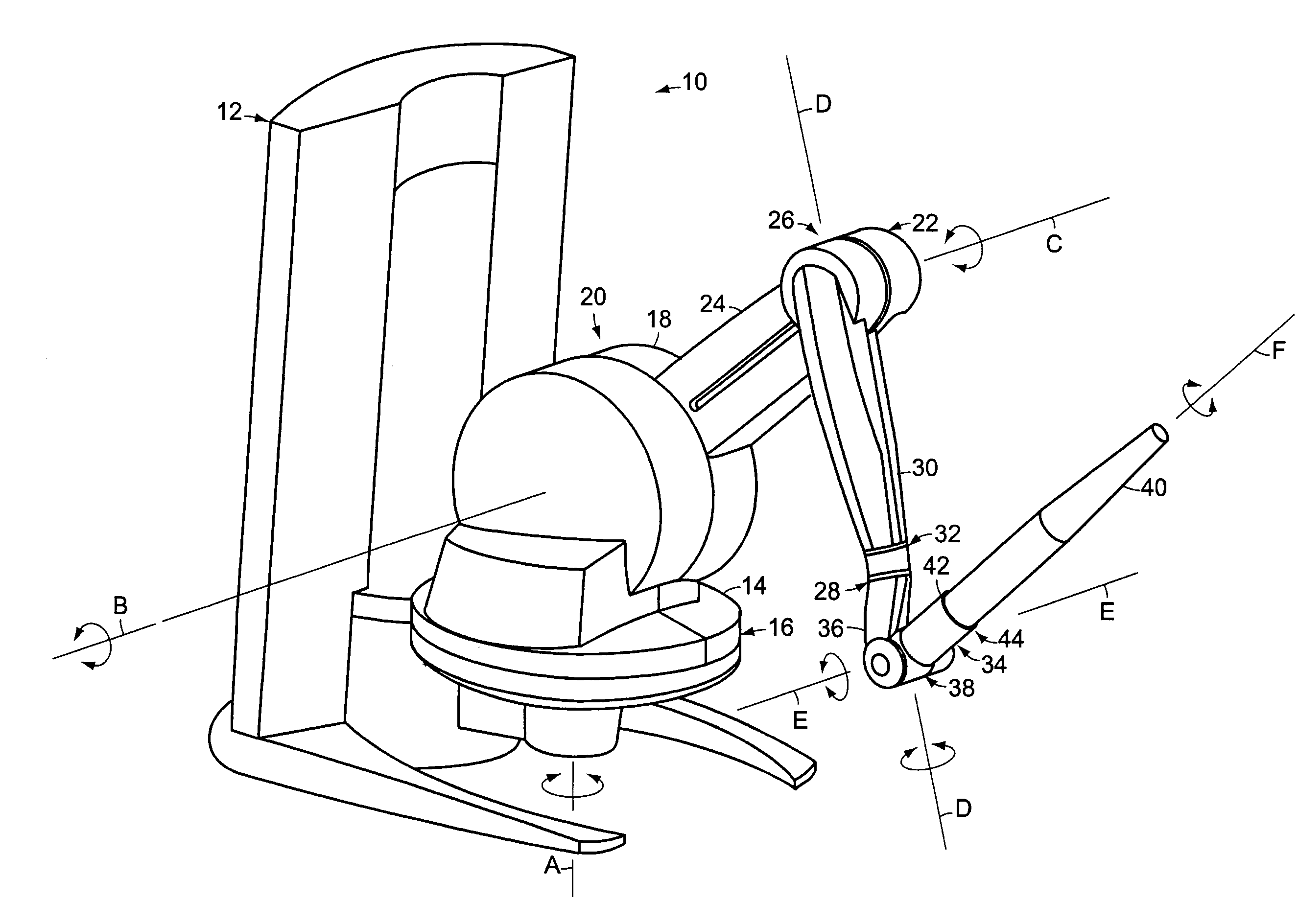
Multi-axis joystick and transducer means therefore
InactiveUS20050162389A1Reduce noiseLow costProgramme controlManual control with multiple controlled membersJoystickTransducer
The invention relates to improved multi-axis joysticks and associated multi-axis optical displacement measurement means. The displacement measuring means may include one or more light emitters and one or more light detectors, preferably mounted in a planar hexagonal array. The relative position of an adjacent movable reflector assembly can be measured in six degrees of freedom by variations in detected light amplitude. Various ergonomic configurations of six axis joystick embodiments which may be facilitated by the compact design of the transducer means are disclosed. Means for dynamically adjusting coordinate transformations for construction machinery control are also disclosed.
Owner:OBERMEYER HENRY K +1
Six degree-of-freedom micro-machined multi-sensor
InactiveUS6848304B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsDegrees of freedomSubstructure
A six degree-of-freedom micro-machined multi-sensor that provides 3-axes of acceleration sensing, and 3-axes of angular rate sensing, in a single multi-sensor device. The six degree-of-freedom multi-sensor device includes a first multi-sensor substructure providing 2-axes of acceleration sensing and 1-axis of angular rate sensing, and a second multi-sensor substructure providing a third axis of acceleration sensing, and second and third axes of angular rate sensing. The first and second multi-sensor substructures are implemented on respective substrates within the six degree-of-freedom multi-sensor device.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
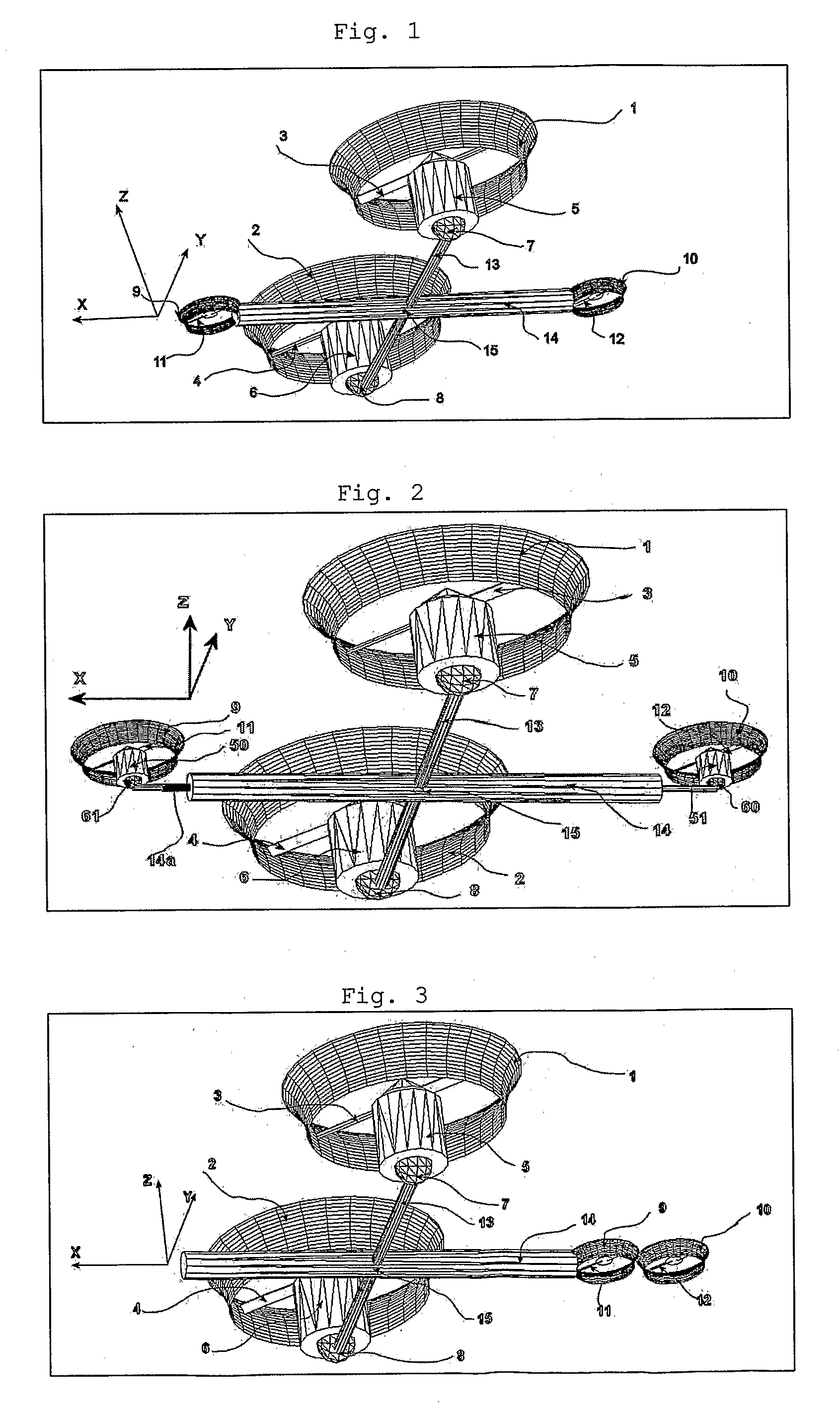
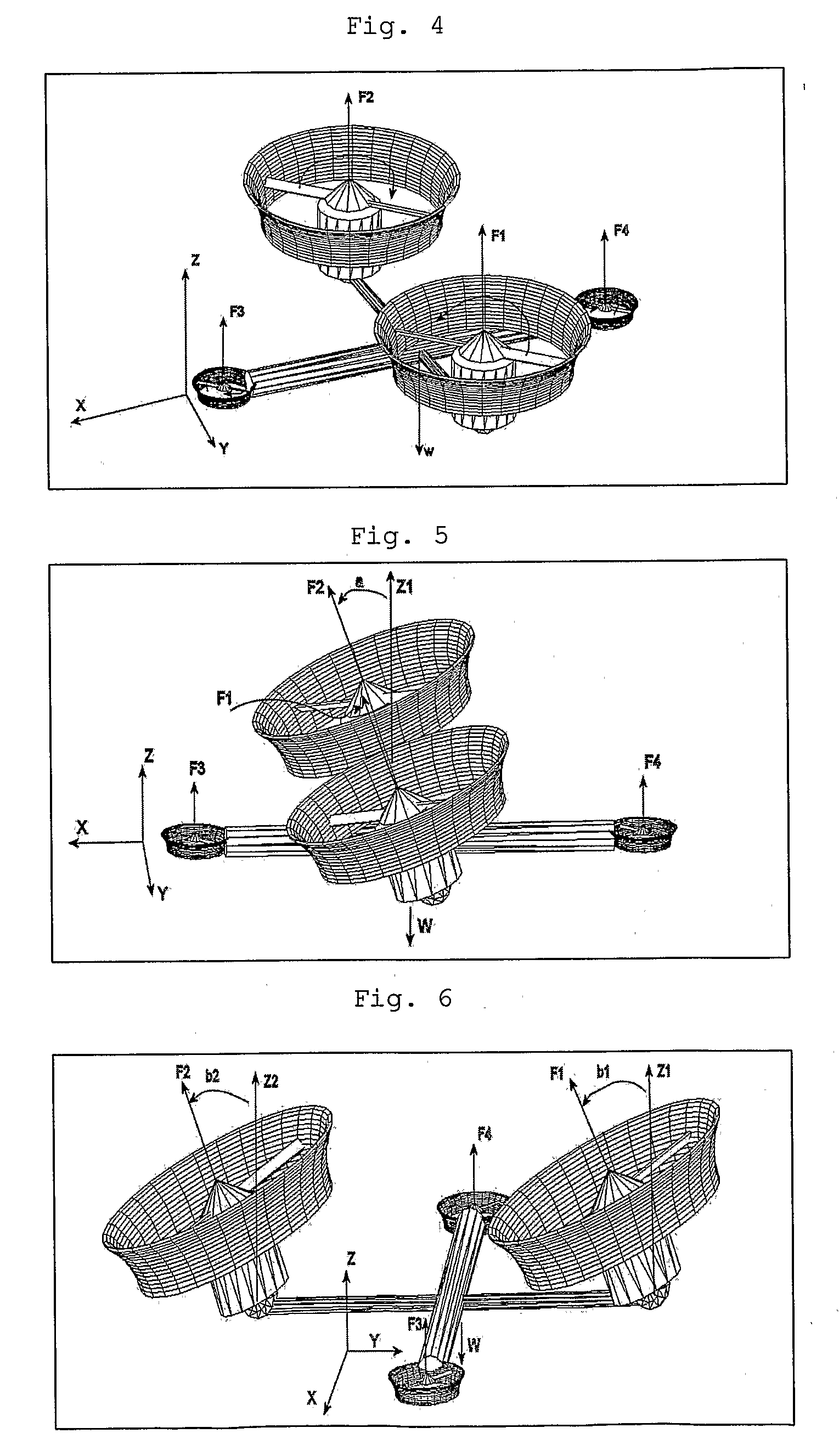
System and Process of Vector Propulsion with Independent Control of Three Translation and Three Rotation Axis
ActiveUS20100301168A1Reduces the passenger's discomfortEasy to controlCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsControl systemVector control system
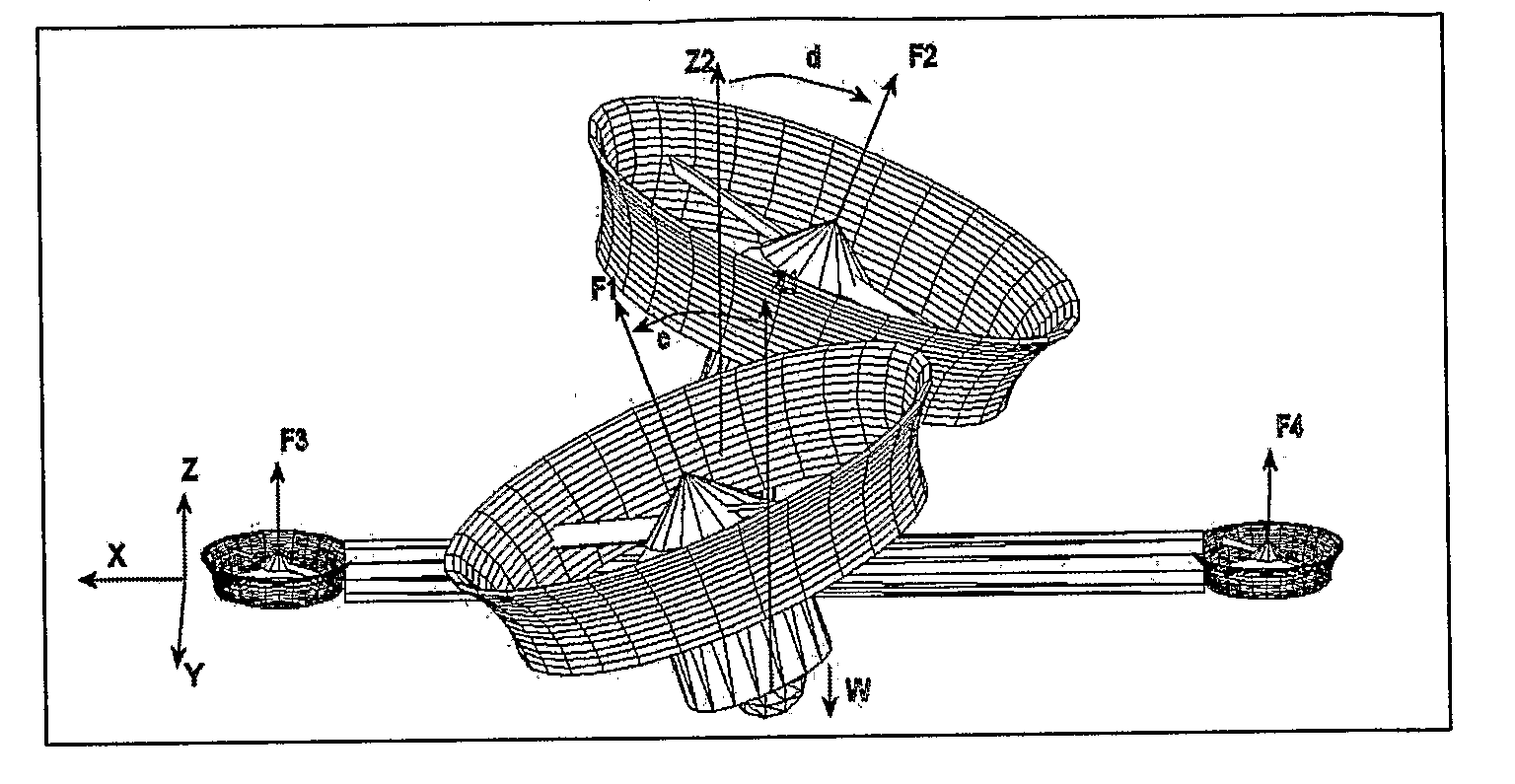
The present invention relates to a propulsion system of a vertical takeoff and landing aircraft or vehicle moving in any fluid or vacuum and more particularly to a vector control system of the vehicle propulsion thrust allowing an independent displacement with six degrees of freedom, three degrees of translation in relation to its centre of mass and three degrees of rotation in relation to its centre of mass. The aircraft displacement ability using the propulsion system of the present invention depends on two main thrusters or propellers and which can be tilted around pitch is (I) by means of tilting mechanisms and, used to perform a forward or backward movement, can be tilted around roll axis (X) by means of tilting mechanisms and, used to perform lateral movements to the right or to the left and to perform upward or downward movements (Z), the main thrusters being further used to perform rotations around the vehicle yaw axis (Z) and around the roll is (X). The locomotion function also uses one or two auxiliary thrusters or propellers and mainly used to control the rotation around the pitch axis, these thrusters or propellers and being fixed at or near the longitudinal is of the vehicle, with there thrust perpendicular or nearly perpendicular to the roll and pitch axis of the vehicle.
Owner:RAPOSO SEVERINO
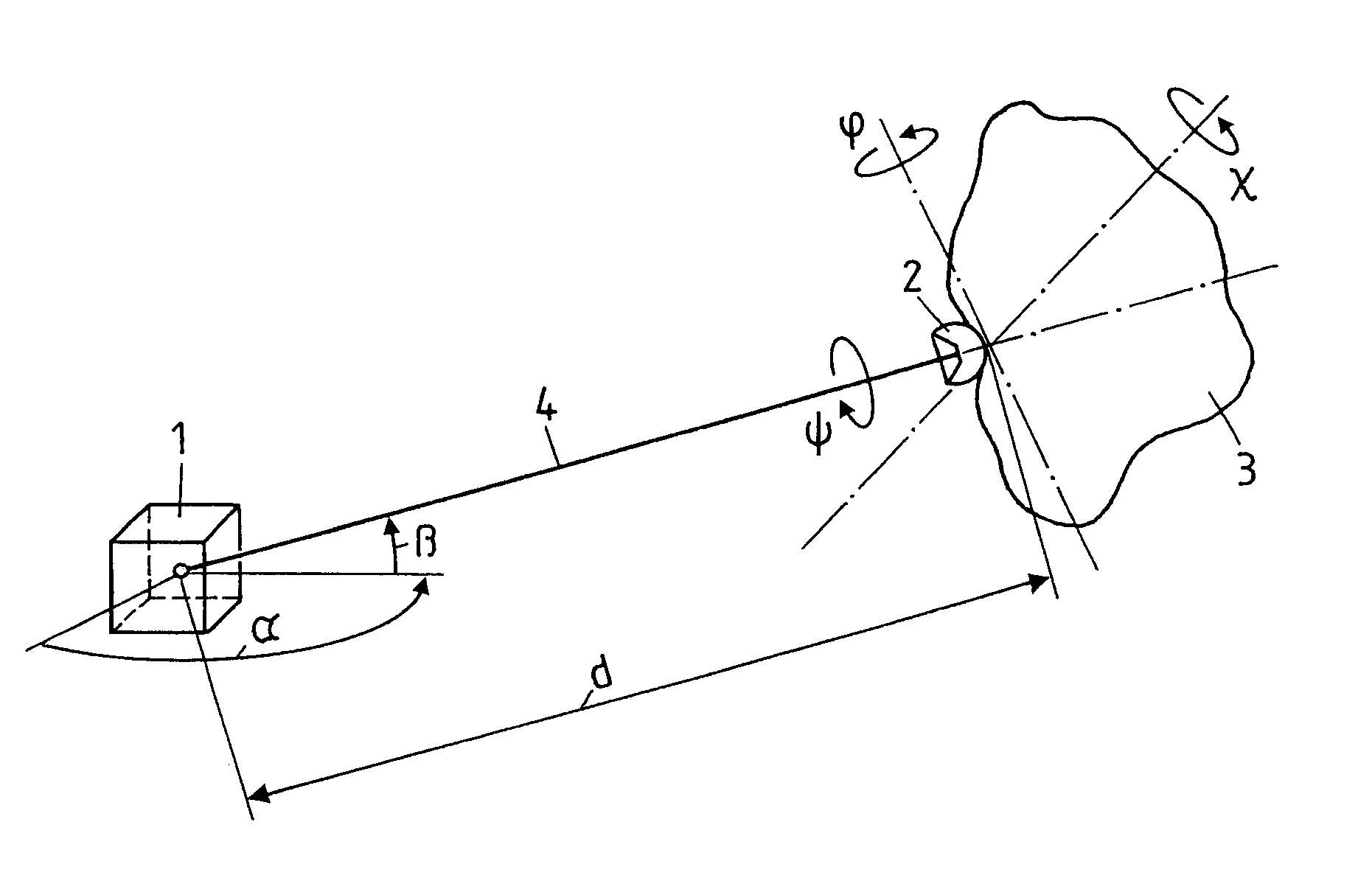
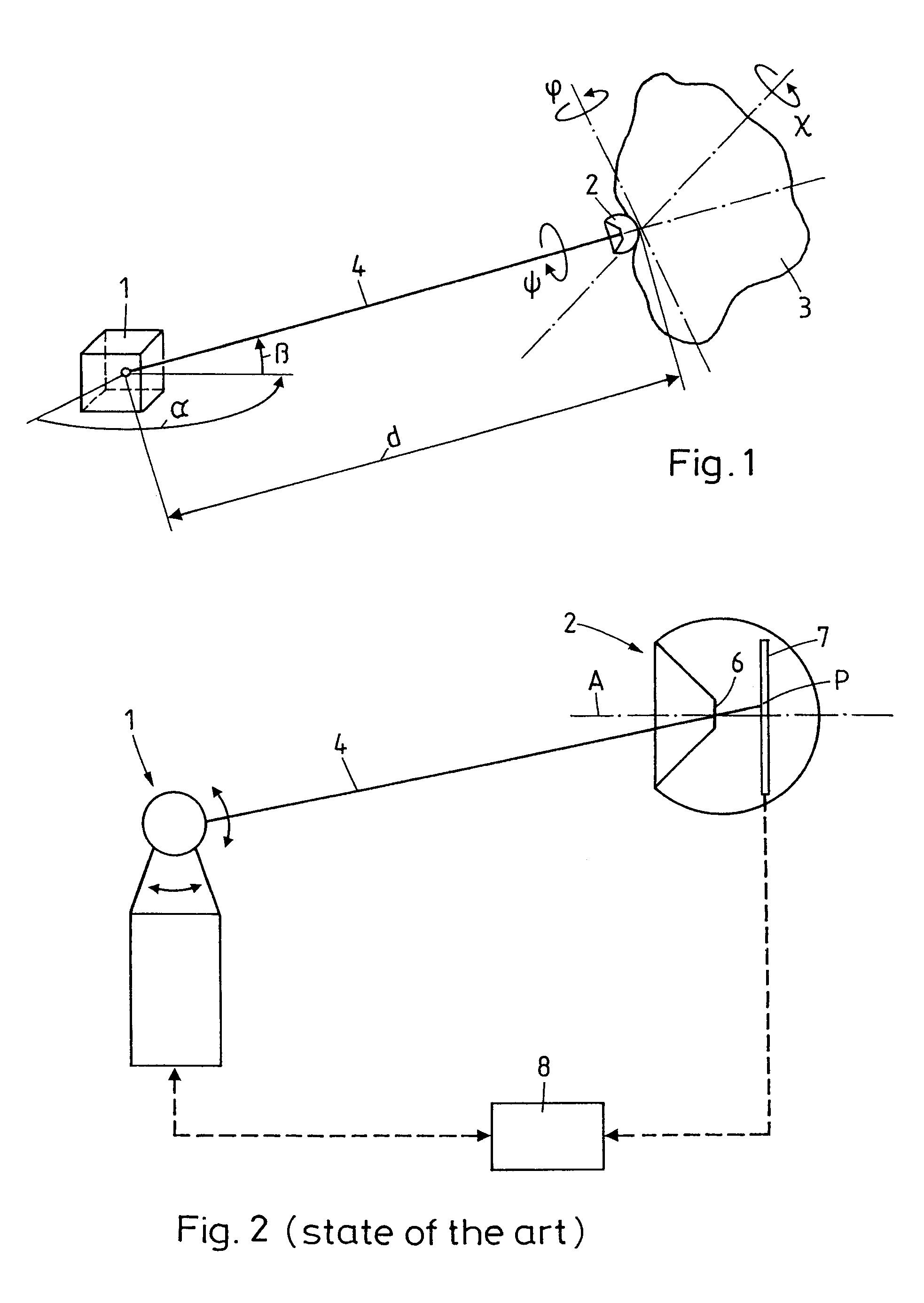
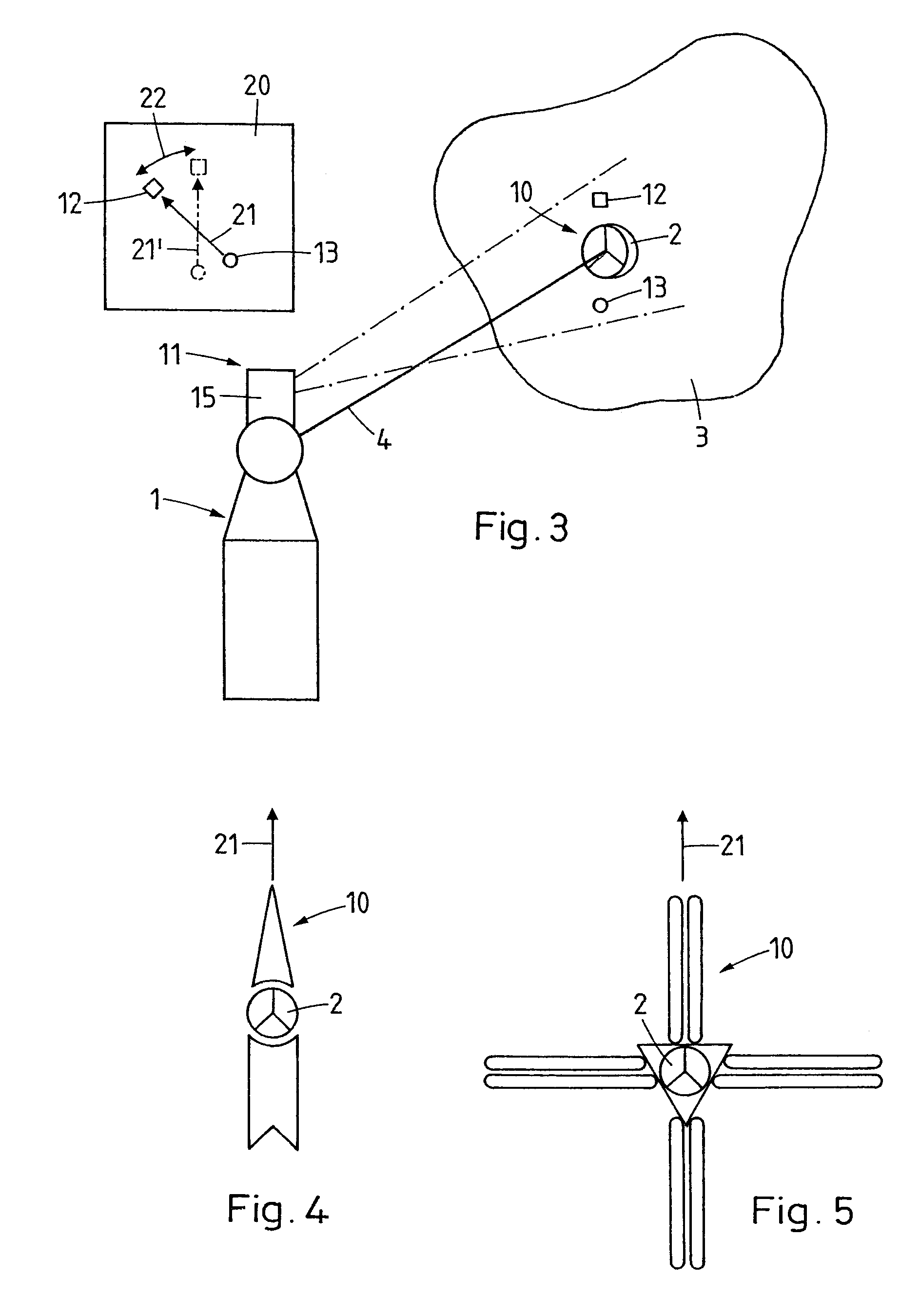
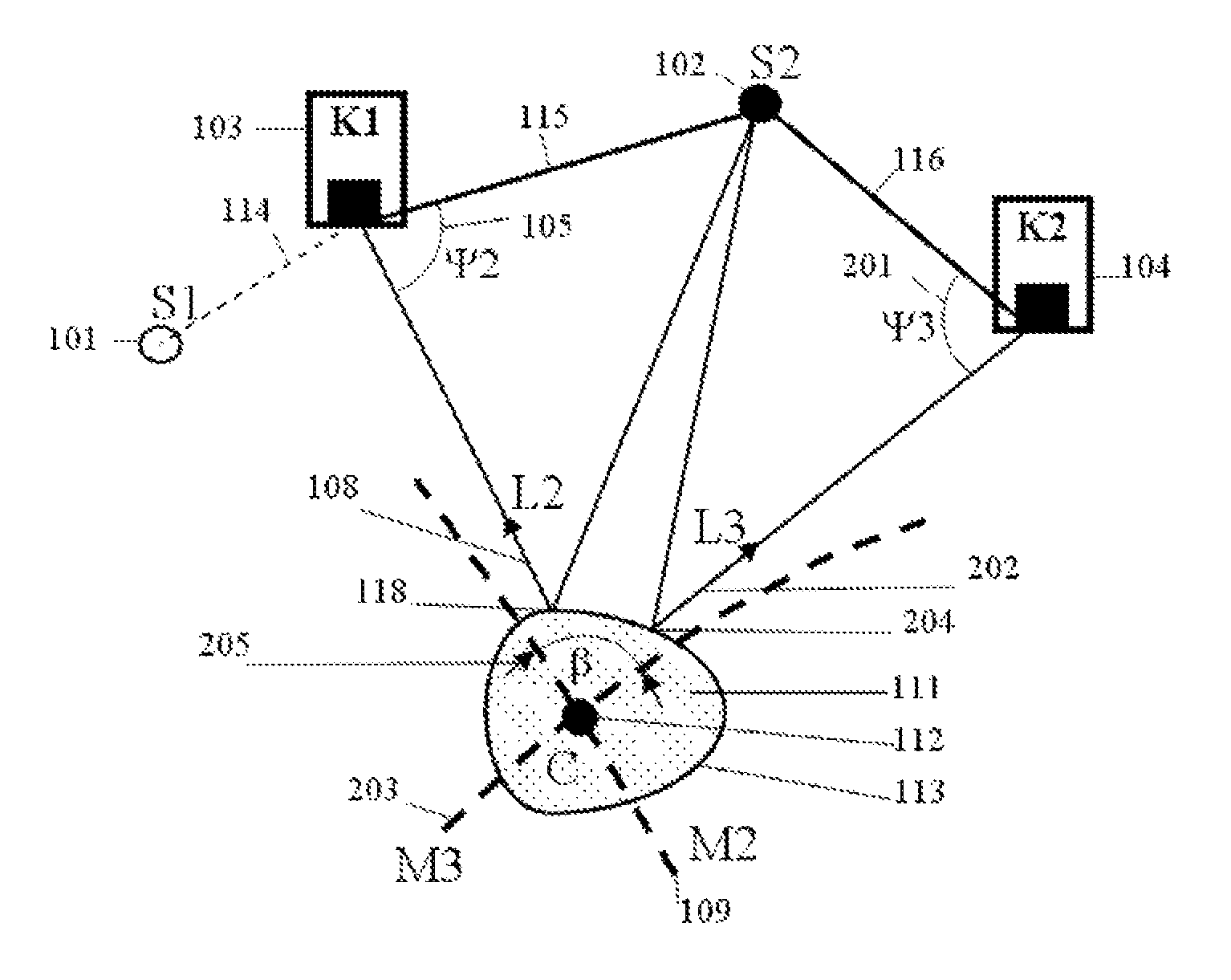
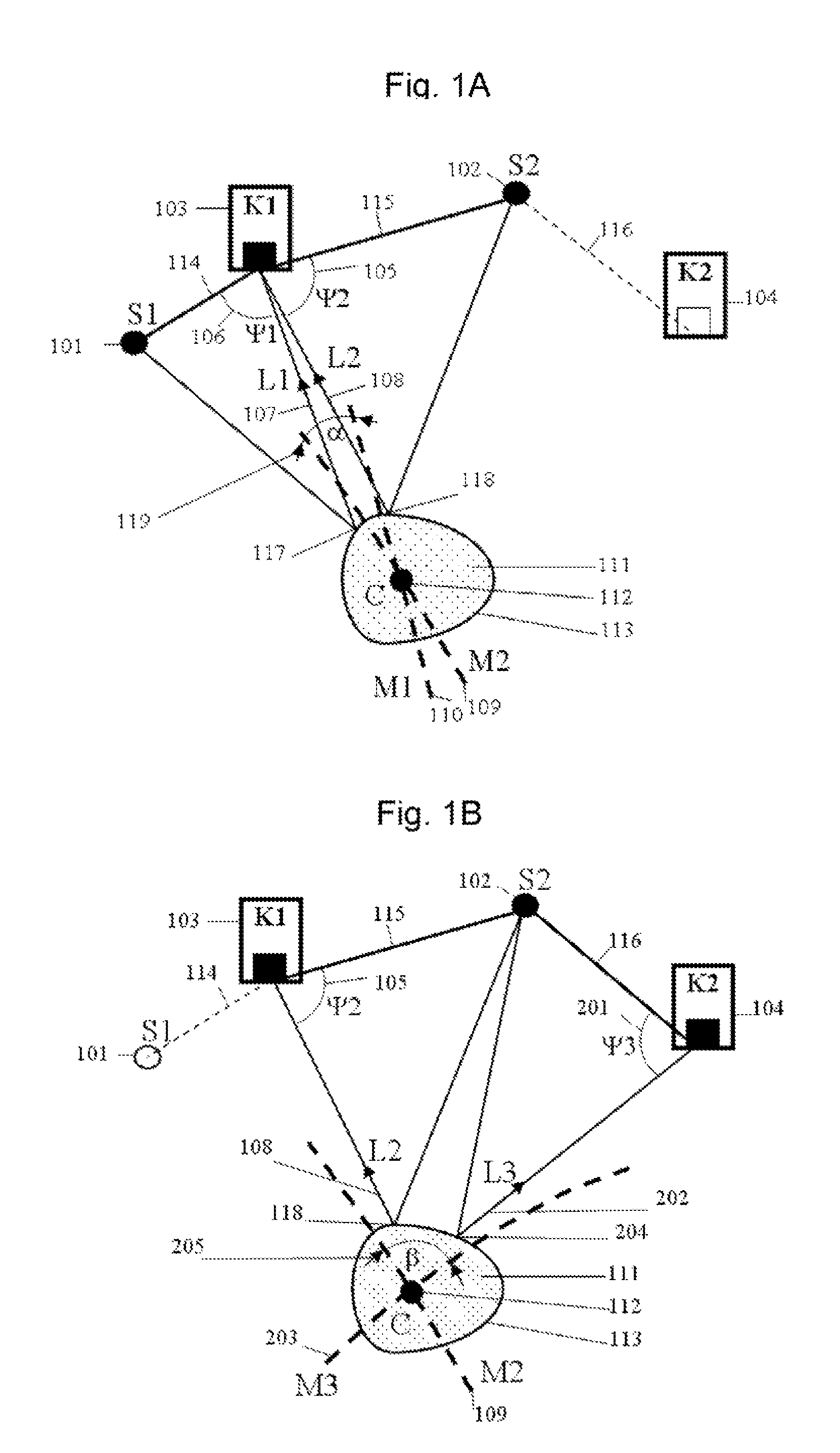
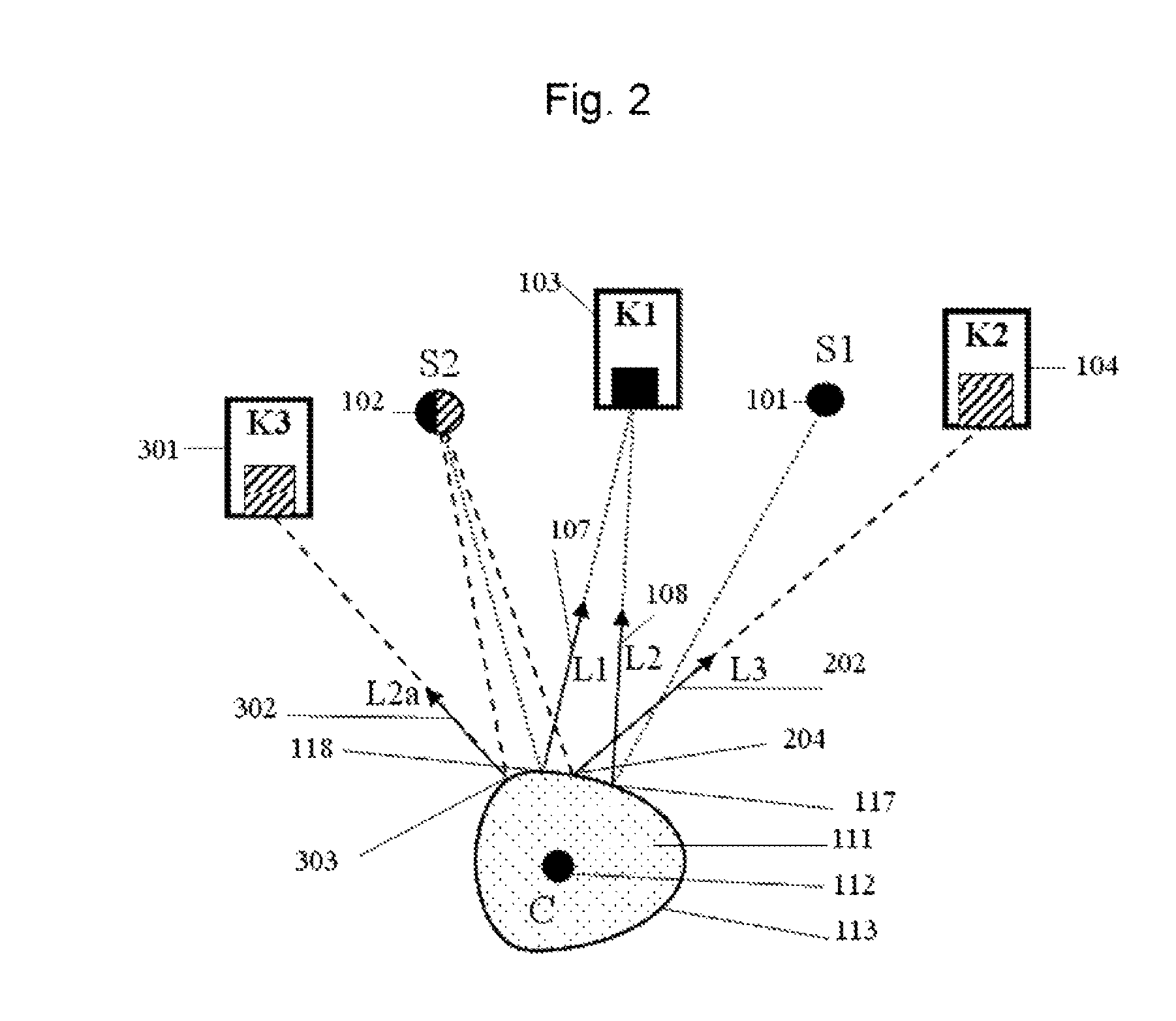
Measurement system for determining six degrees of freedom of an object
A measurement system for determining six degrees of freedom (α, β, d, φ, χ, ψ) of a reflector (2) or of an object (3) on which the reflector is arranged, comprises an angle- and distance measurement apparatus (1), e.g. a laser tracker, operating with a laser beam as a measurement beam (4). The reflector (2) is designed for a parallel reflection of the measurement beam (4) and has an apical opening or surface (6), in a manner such that a part of the measurement beam (4) directed onto the reflector (2), passes through the apical opening or surface (6), and is incident on a light-sensitive surface (7) arranged behind the reflector apex. Five degrees of freedom (α, β, d, φ, χ) of the reflector (2) or the object (3) are computed from measurement data produced by the angle- and distance measurement apparatus (1) and by the light-sensitive surface (7).
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
System and method for improved control of tooth movement with elastic repositioning appliances
InactiveUS20060223022A1Easy to controlGood tooth alignmentOthrodonticsDental toolsElectrical resistance and conductanceCoupling
Micro-regional force application improves the control of the orthodontic movement of teeth in all six degrees of freedom. Micro regional force application utilizes an elastic repositioning appliance, a tooth positioner, a polymeric shell, or preprogrammed series of polymeric shells. The key components of the invention are the envelope of freedom, the force applicators, force couplers, counterpart coupling, vector modifiers, seating guides, decouplers, and forced balance points. Further, computerized finite element analysis determines the center of resistance and the center of rotation for each tooth to be moved. The present invention gently rotates and translates one or more teeth to a desired straight position within a treatment plan.
Owner:SOLOMON FREDERICK
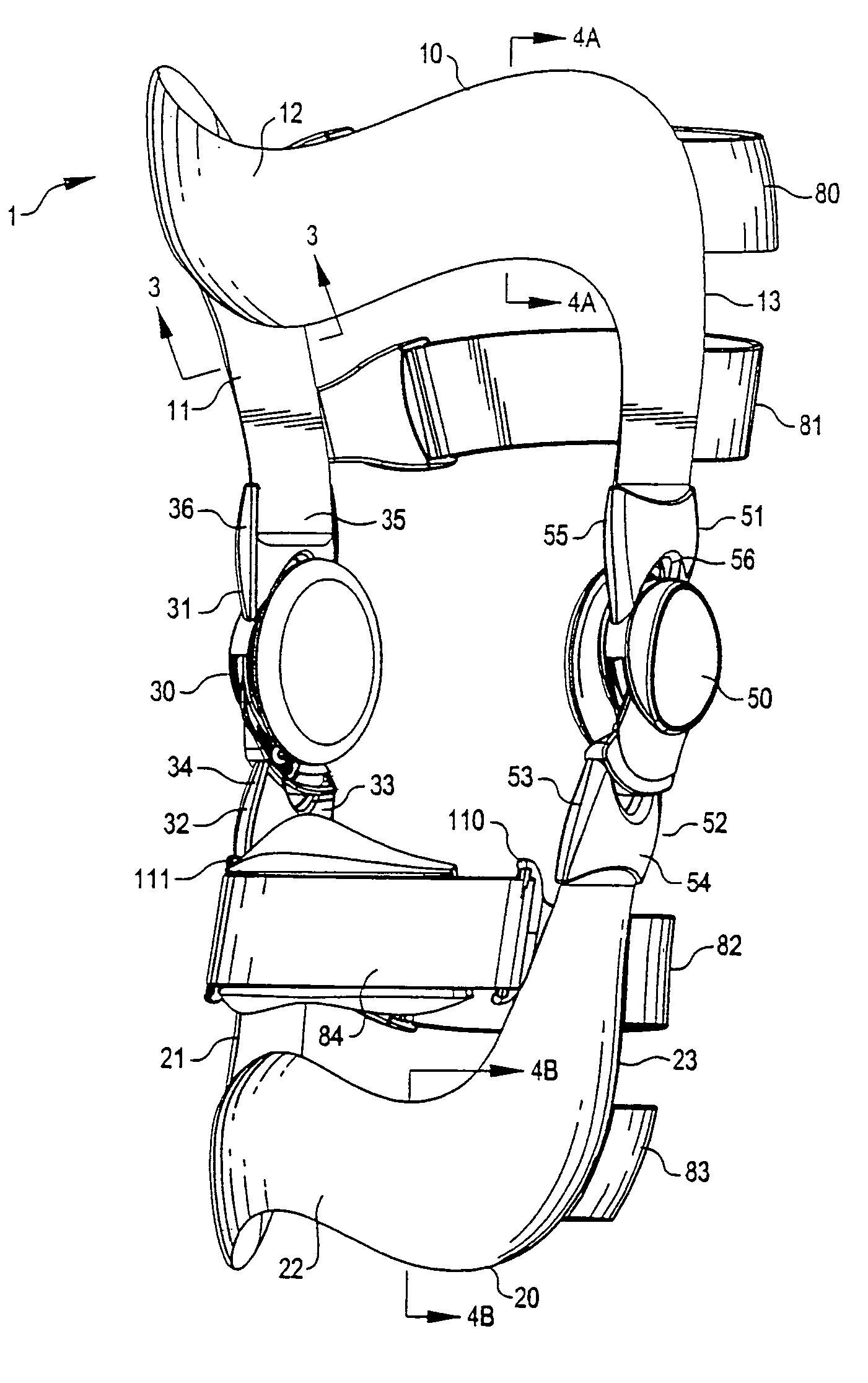
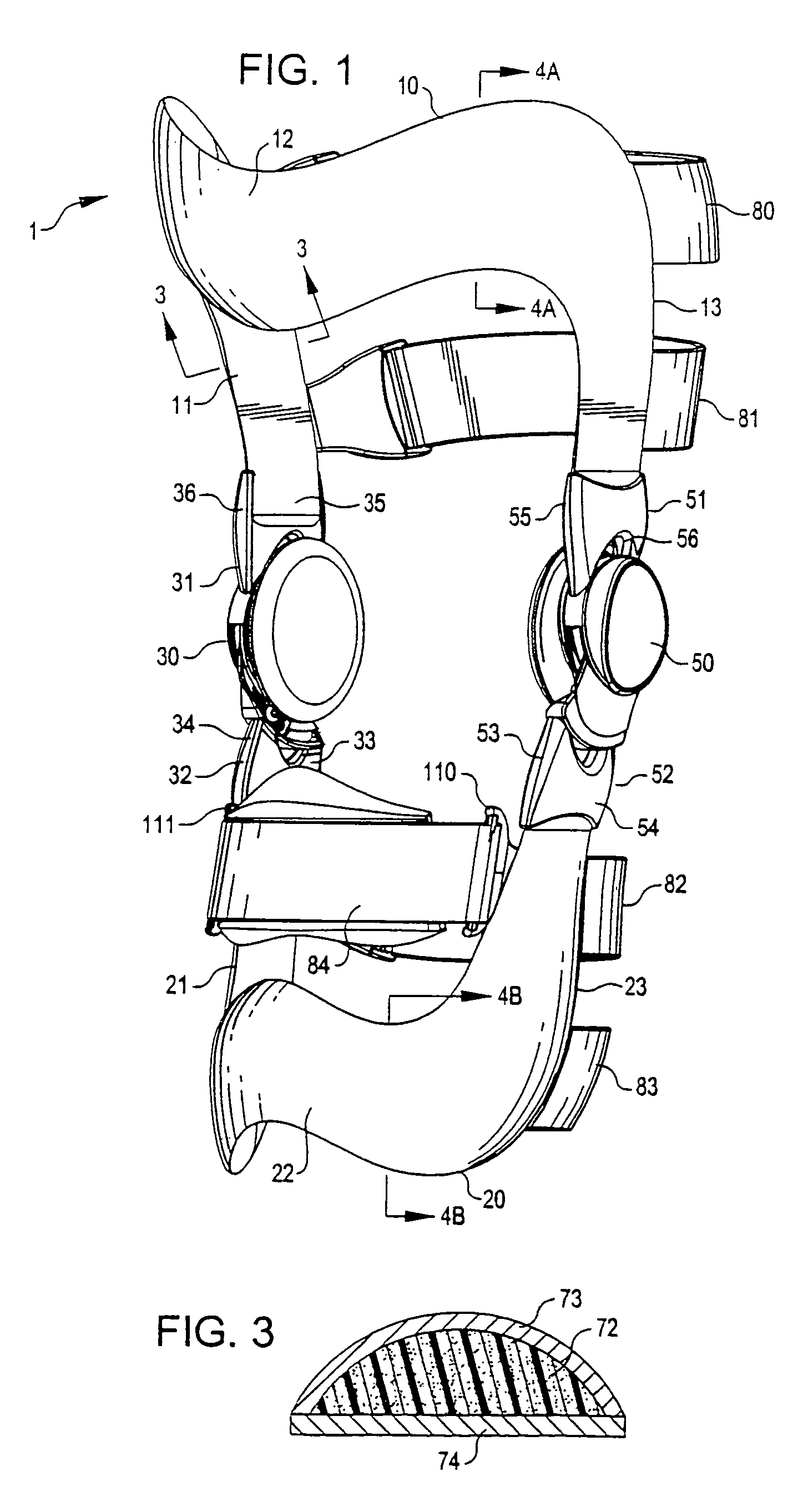
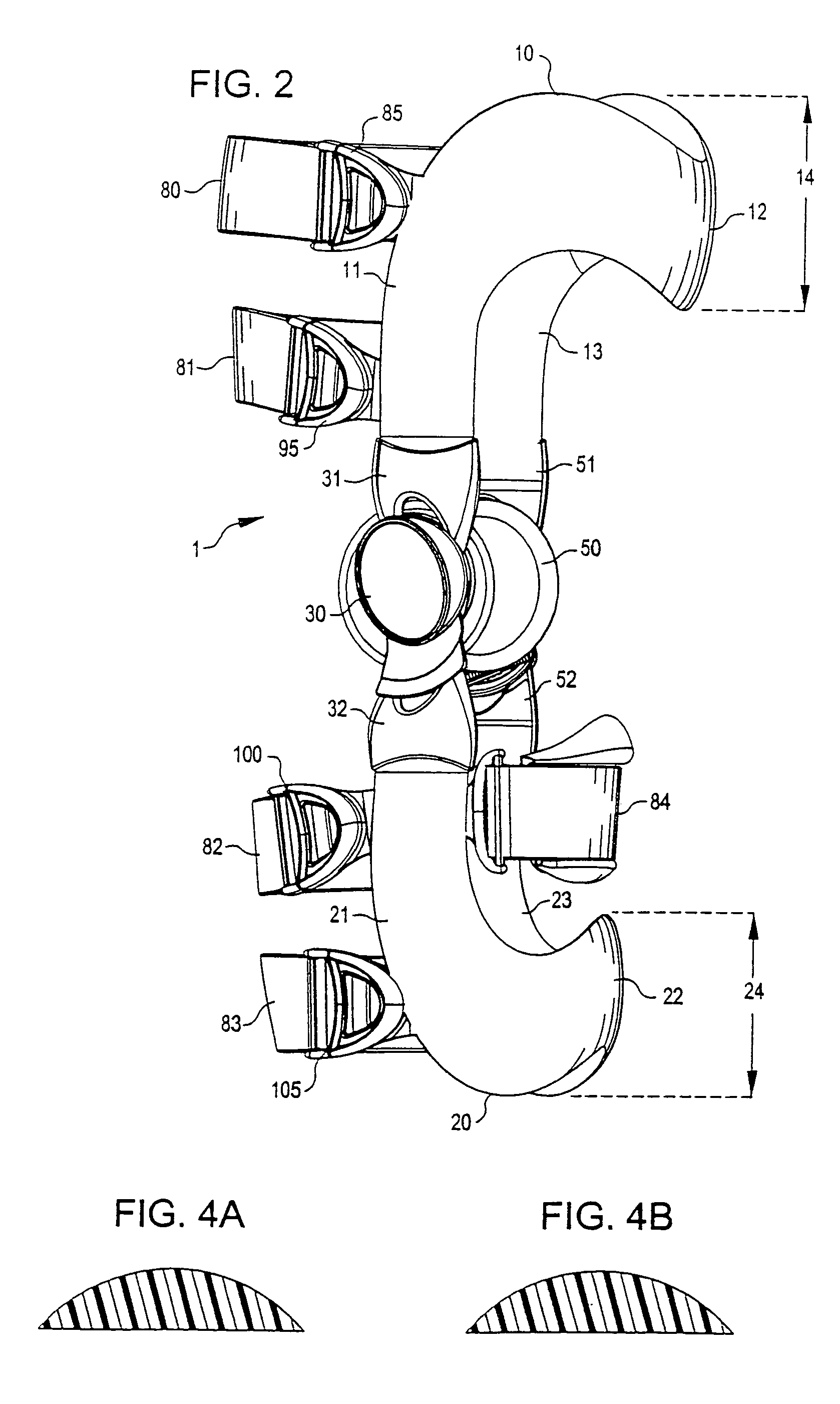
Anatomically designed orthopedic knee brace
InactiveUS7201728B2Novel and effectiveAccurately prescribingNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee proceduresTibia
An orthopedic knee brace provides an apparatus for accurately prescribing the anatomical motion of the human knee. The orthopedic knee brace is used for treatment and rehabilitation following surgery to the knee, protection for a surgically repaired knee, and protection for an uninjured knee, among other applications. The orthopedic knee brace actively prescribes asymmetric three-dimensional anatomic motion in six degrees of freedom of the wearer's knee. The rigid connections between the thigh and calf engaging members and the medial and lateral hinges provide the ability of the orthopedic knee brace to prescribe asymmetric three-dimensional anatomic motion in six degrees of freedom by actively prescribing flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, internal / external rotation, anterior / posterior translation, medial / lateral translation, and proximal / distal translation between a femur and a tibia of a wearer's leg. In alternate embodiments a single-hinge brace design is provided for treatment and prevention of osteoarthritis and other joint diseases and conditions.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Multi-beam multi-column electron beam inspection system
InactiveUS6844550B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSystems designData stream
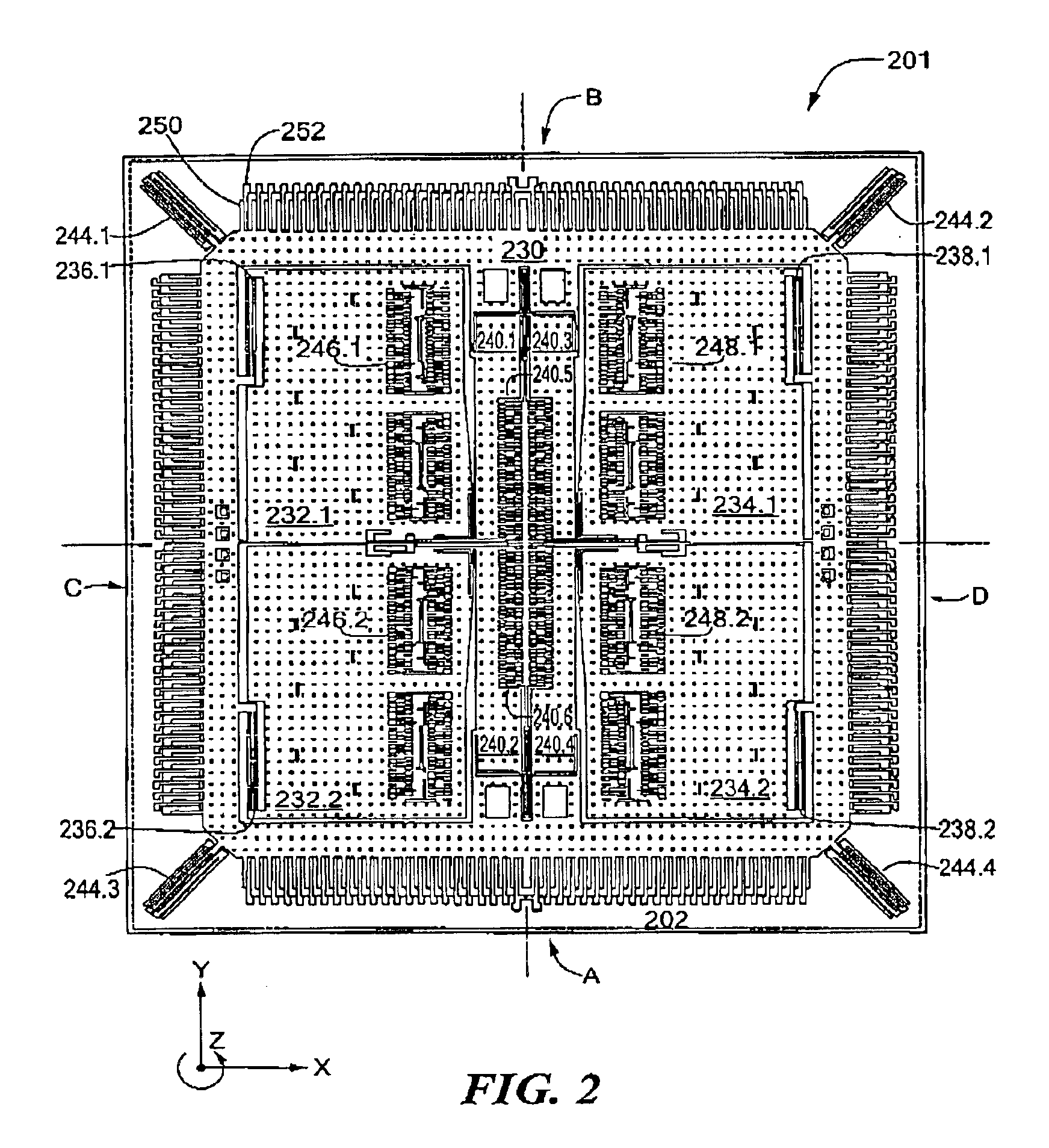
A multi-column electron beam inspection system is disclosed herein. The system is designed for electron beam inspection of semiconductor wafers with throughput high enough for in-line use. The system includes field emission electron sources, electrostatic electron optical columns, a wafer stage with six degrees of freedom of movement, and image storage and processing systems capable of handling multiple simultaneous image data streams. Each electron optical column is enhanced with an electron gun with redundant field emission sources, a voltage contrast plate to allow voltage contrast imaging of wafers, and an electron optical design for high efficiency secondary electron collection.
Owner:MULTIBEAM CORP
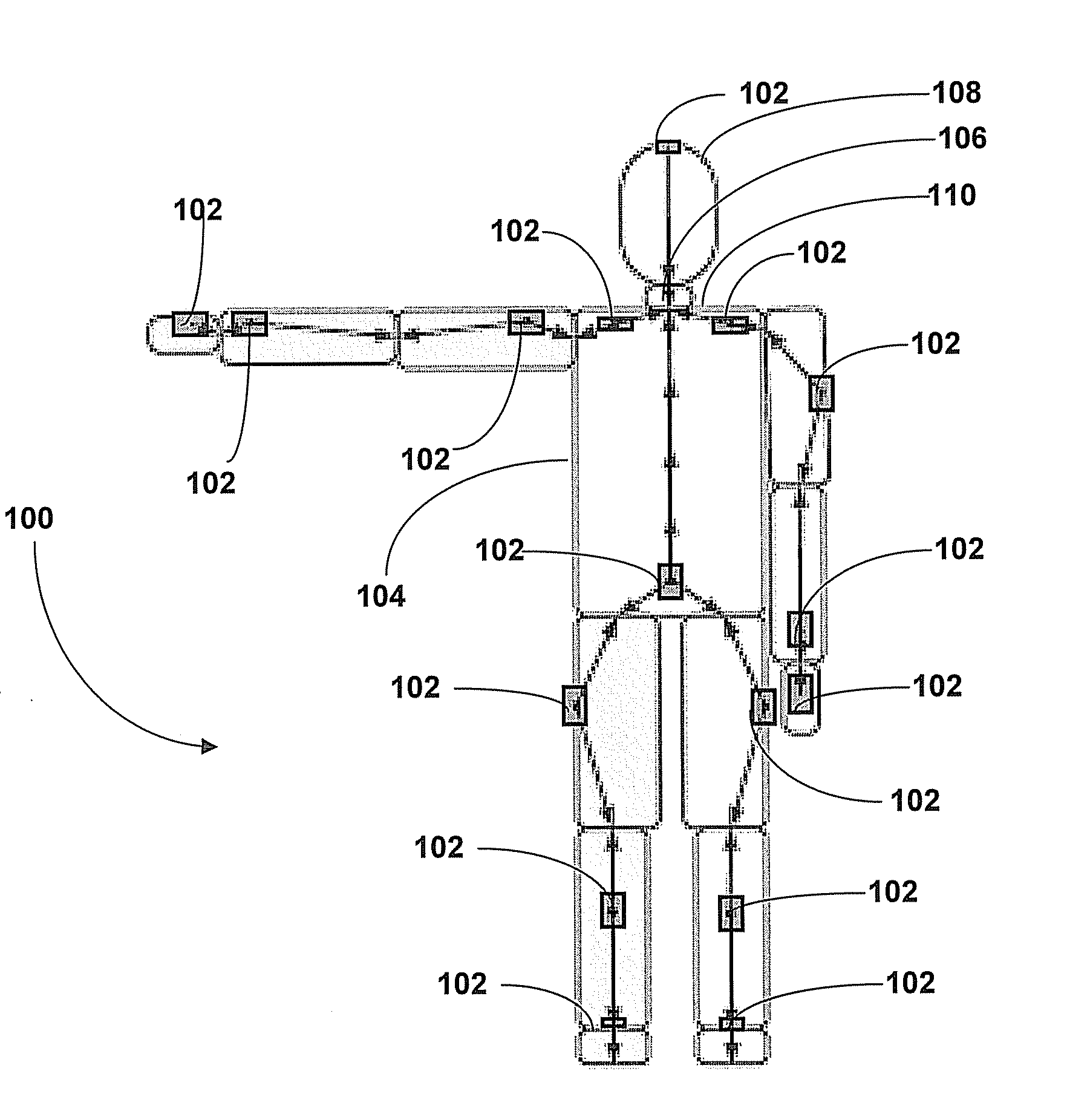
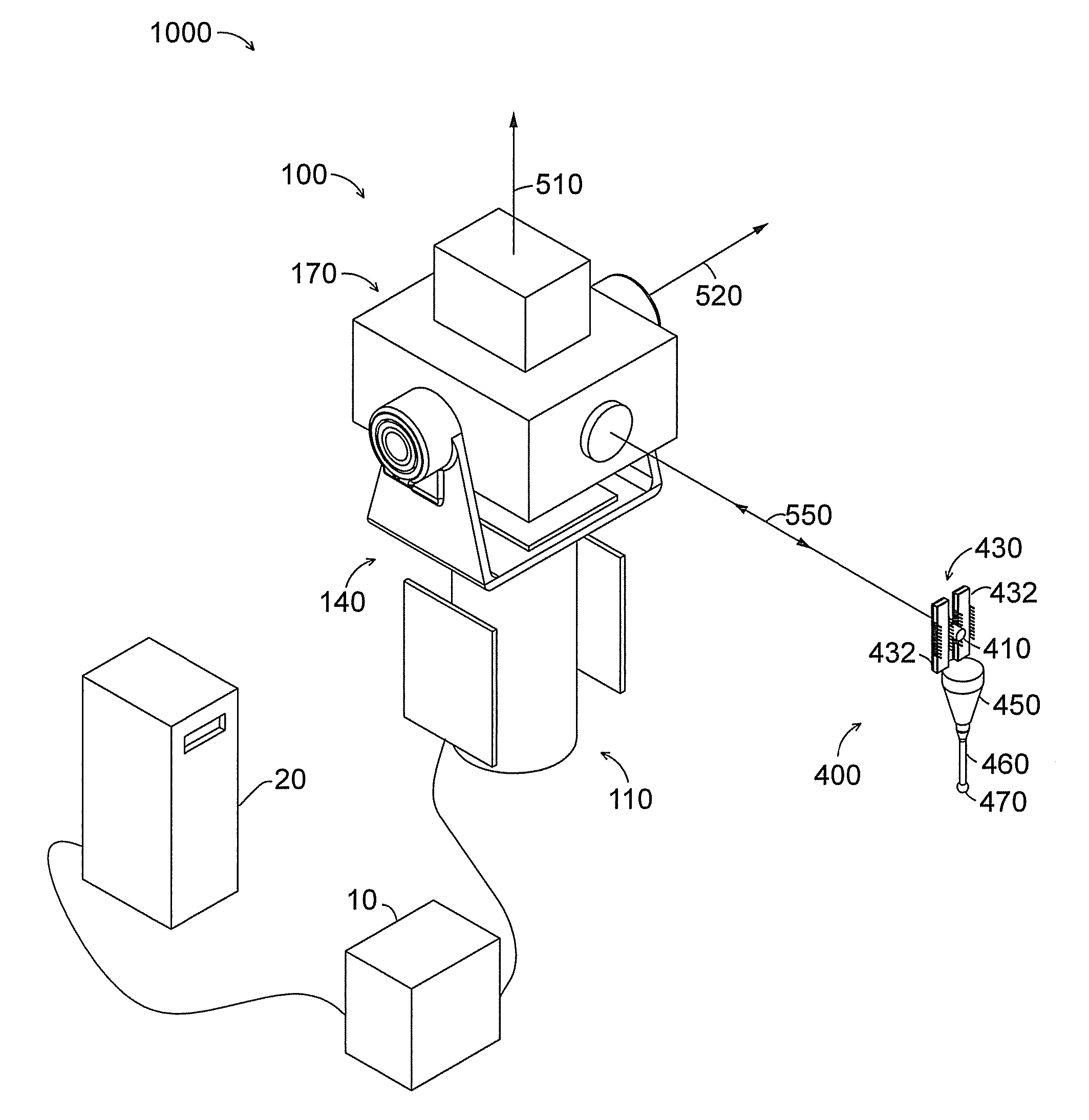
Systems and methods for sensory augmentation in medical procedures
InactiveUS20180049622A1Minimizes line of site obscuration issuePrecise positioningEndoscopesJoint implantsMixed realityGNSS augmentation
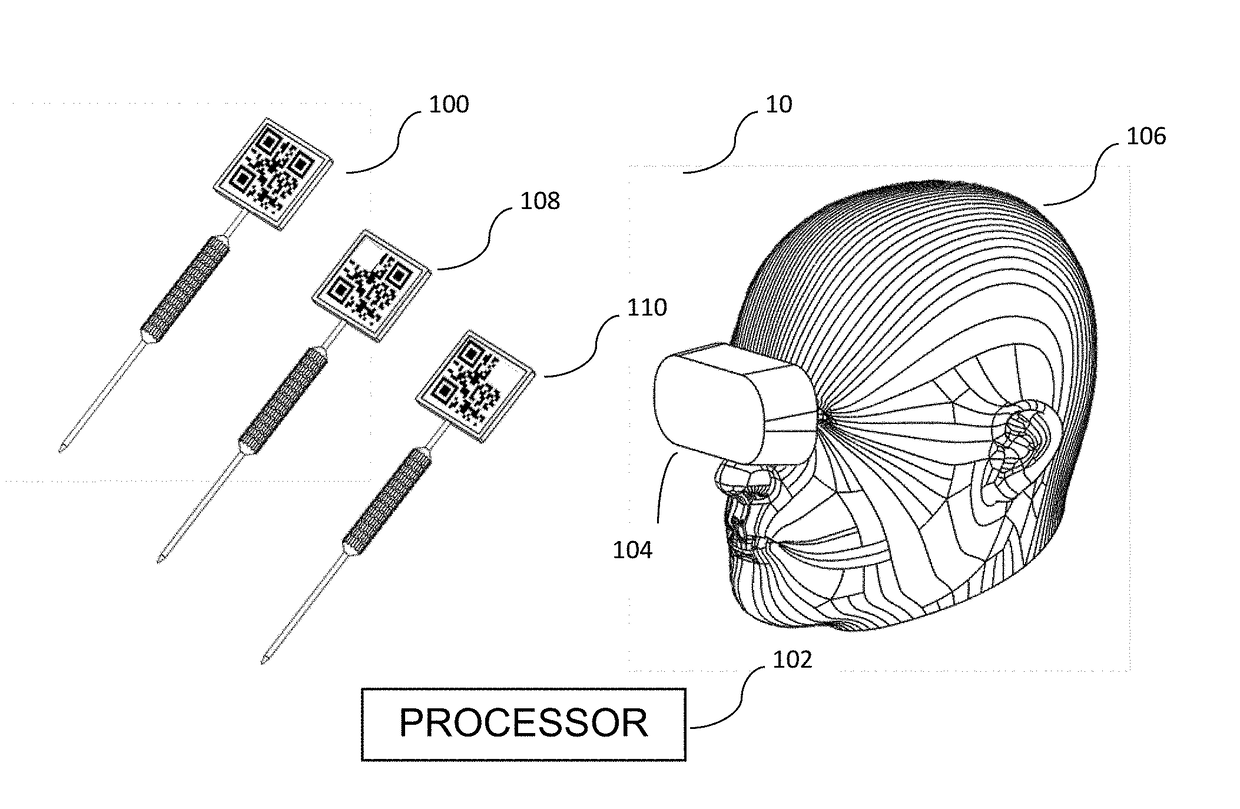
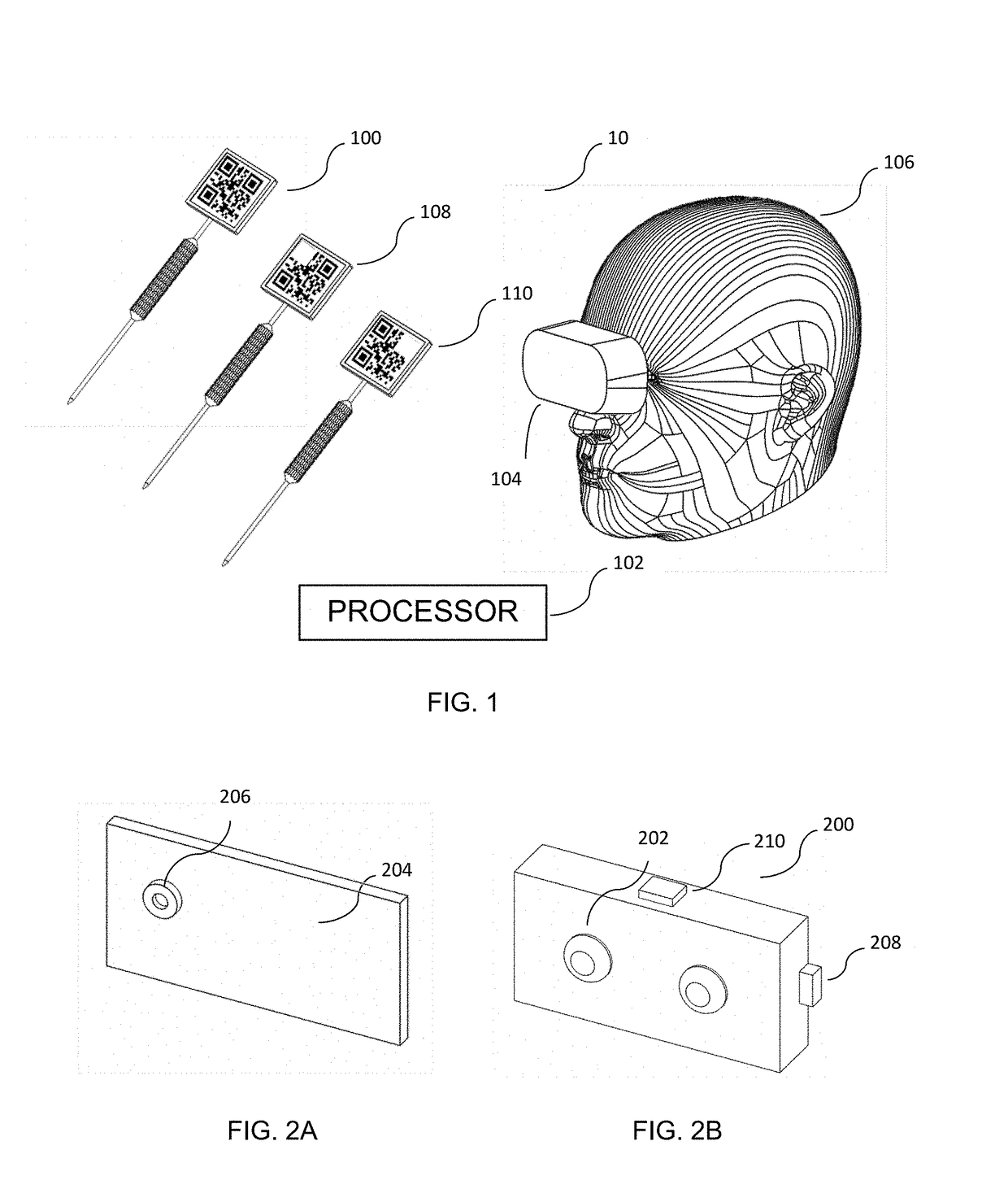
The present invention provides a mixed reality surgical navigation system (10) comprising: a display device (104) comprising a processor unit (102), a display generator (204), a sensor suite (210) having at least one camera (206); and at least one marker (600) fixedly attached to a surgical tool (608); wherein the system (10) maps three-dimensional surfaces of partially exposed surfaces of an anatomical object of interest (604); tracks a six-degree of freedom post of the surgical tool (608), and provides a mixed reality user interface comprising stereoscopic virtual images of desired features of the surgical tool (608) and desired features of the anatomical object (604) in the user's (106) field of view. The present invention also provides methods of using the system in various medical procedures.
Owner:INSIGHT MEDICAL SYST INC
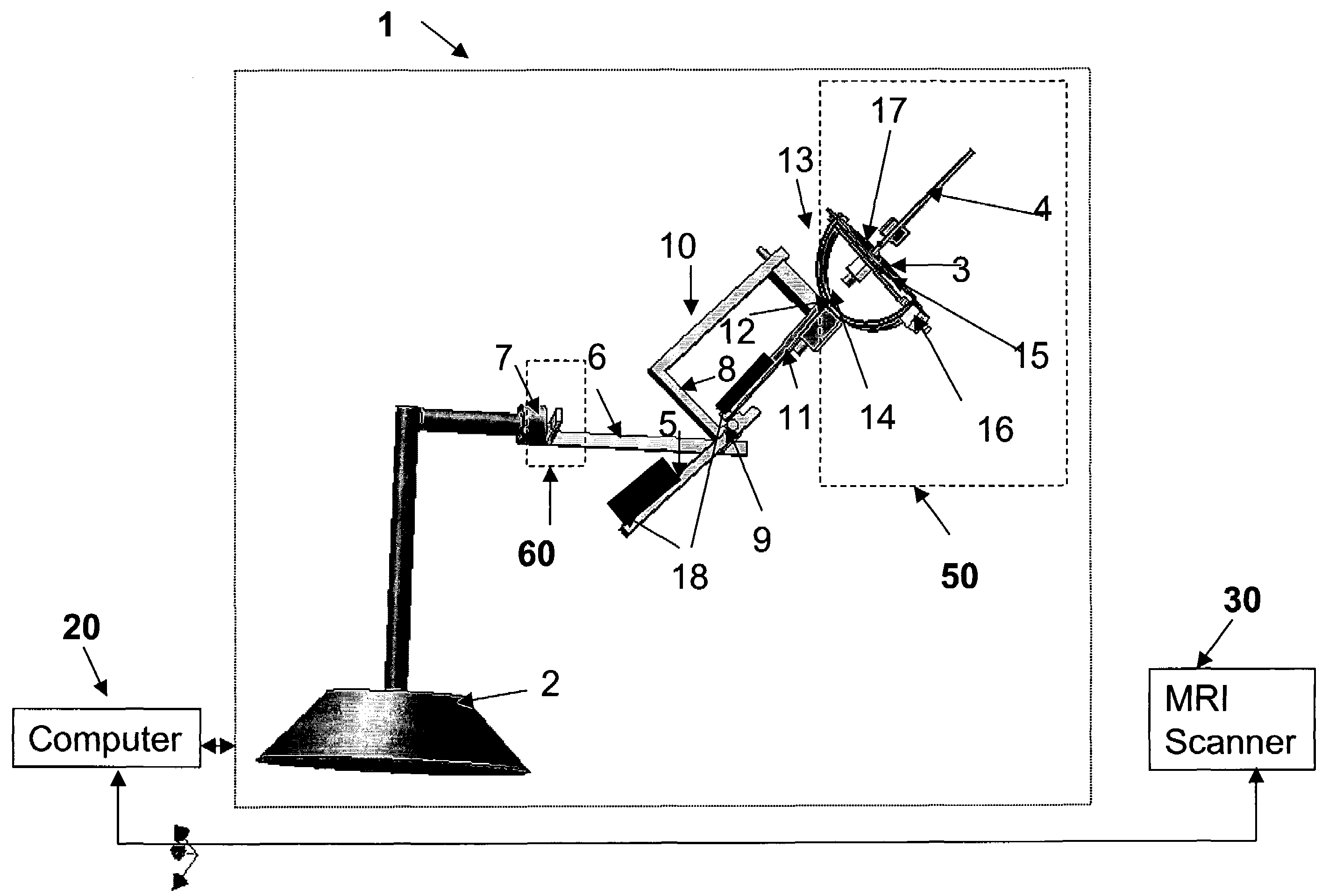
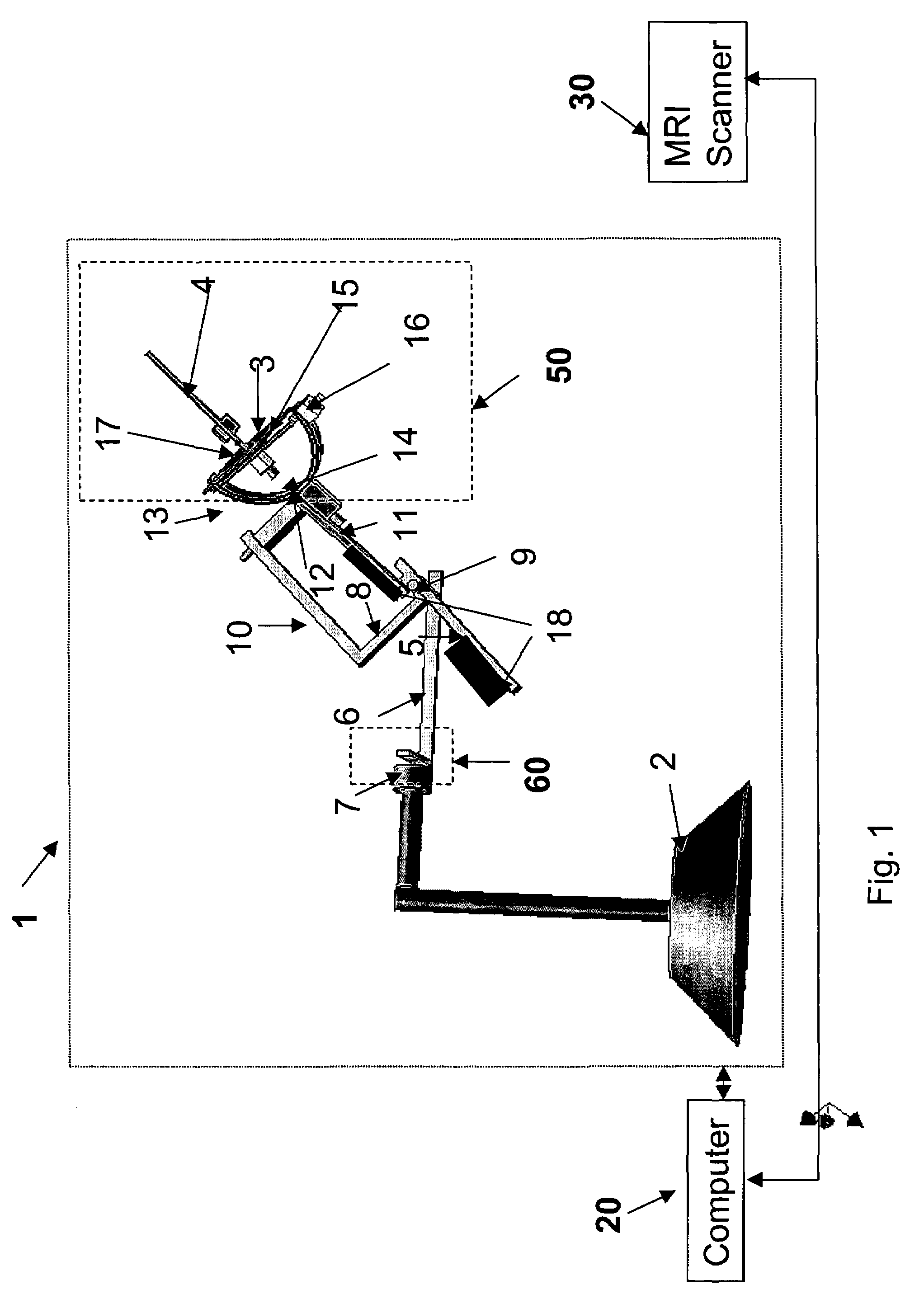
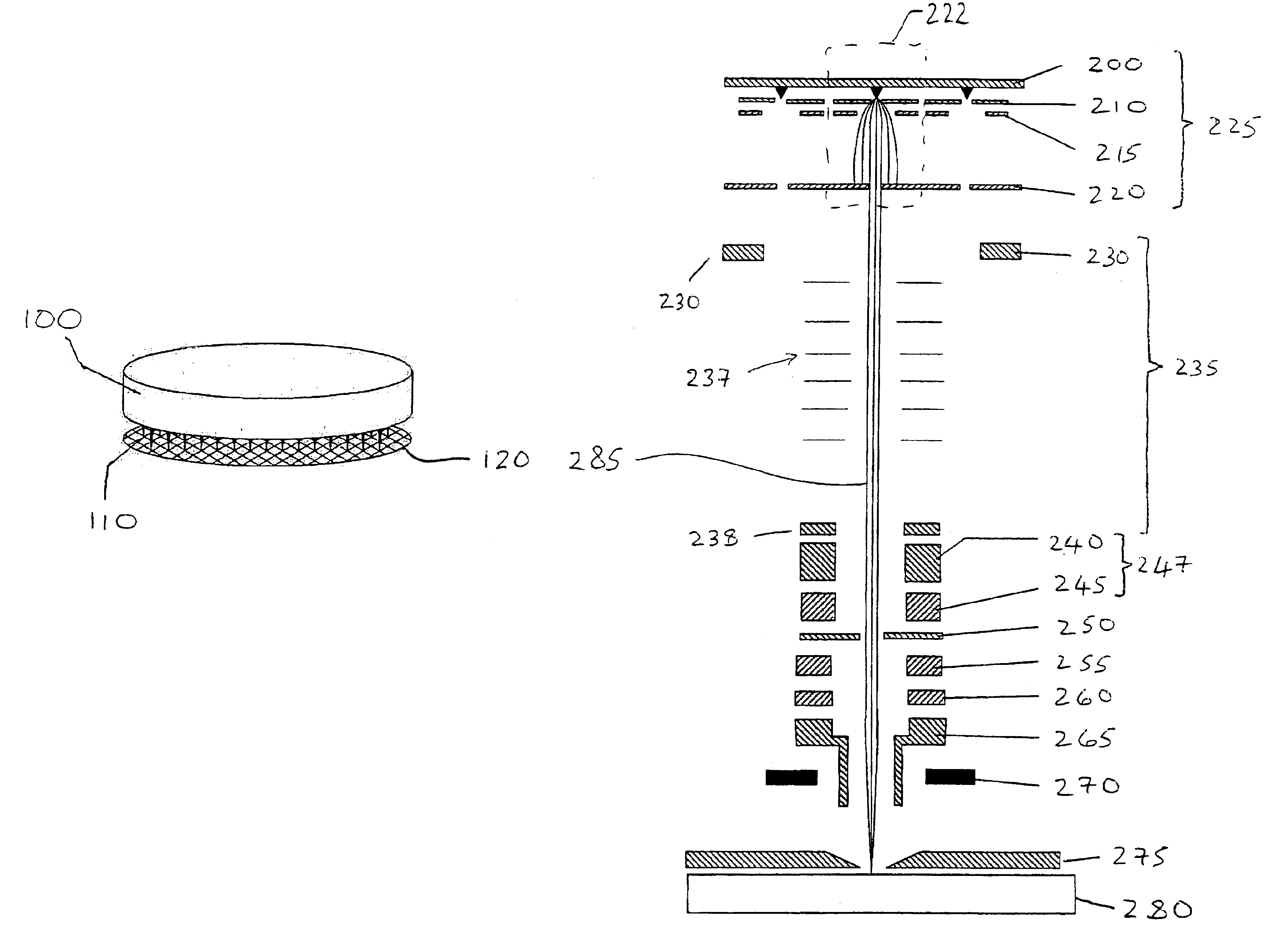
Image registration of multiple medical imaging modalities using a multiple degree-of-freedom-encoded fiducial device
ActiveUS20080262345A1Easy to controlImprove visualizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityX-ray
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Optical tracking apparatus using six degrees of freedom
InactiveUS8077914B1Improve robustnessAccurate trackingAcquiring/recognising eyesEye diagnosticsAngular degreesLight-emitting diode
This invention discloses an optical object tracking method and system with to up to six degrees of freedom: three translational and three angular coordinates. In the preferred embodiment, the system includes two near-infra-red light sources (e.g., light emitting diode), two cameras, and a digital signal processor. The system performs to tasks: object locking and tracking. For object locking and tracking, a single camera and two off-axis light sources are engaged. For more precise object tracking, two spatially-separate cameras and a single diode are used. In another embodiment, a third camera may be used to separate the locking and tracking tasks. The light sources may have different light wavelengths and may operate in a sequential mode. The cameras may be sensitive over different spectral ranges and may also differ in terms of field-of-view and resolution. The invention describes a method based on capturing images of light reflections at the camera focal plane and analyzing them, through mathematical mapping, for known locations of light sources and cameras. Invention can be adopted for the tracking of an eyeball. The related method determines an object location and orientation or a gaze vector and a point-of-regard.
Owner:KAPLAN ARKADY
Force reflecting haptic interface
InactiveUS6985133B1Prevent reboundIncrease stiffnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringActuator
A six degree of freedom force reflecting haptic interface includes three powered axes and three free axes, all of which are tracked so that the position of a user connection element in the work volume can be determined. The interface includes cable drives with polymer composite or metallic cables, automatic cable tensioning devices, and grounded actuator capstans. A nested hub and transfer drive provide a compact, weight balanced interface. User comfort and safety features are also provided.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Wearable lower limb exoskeleton device
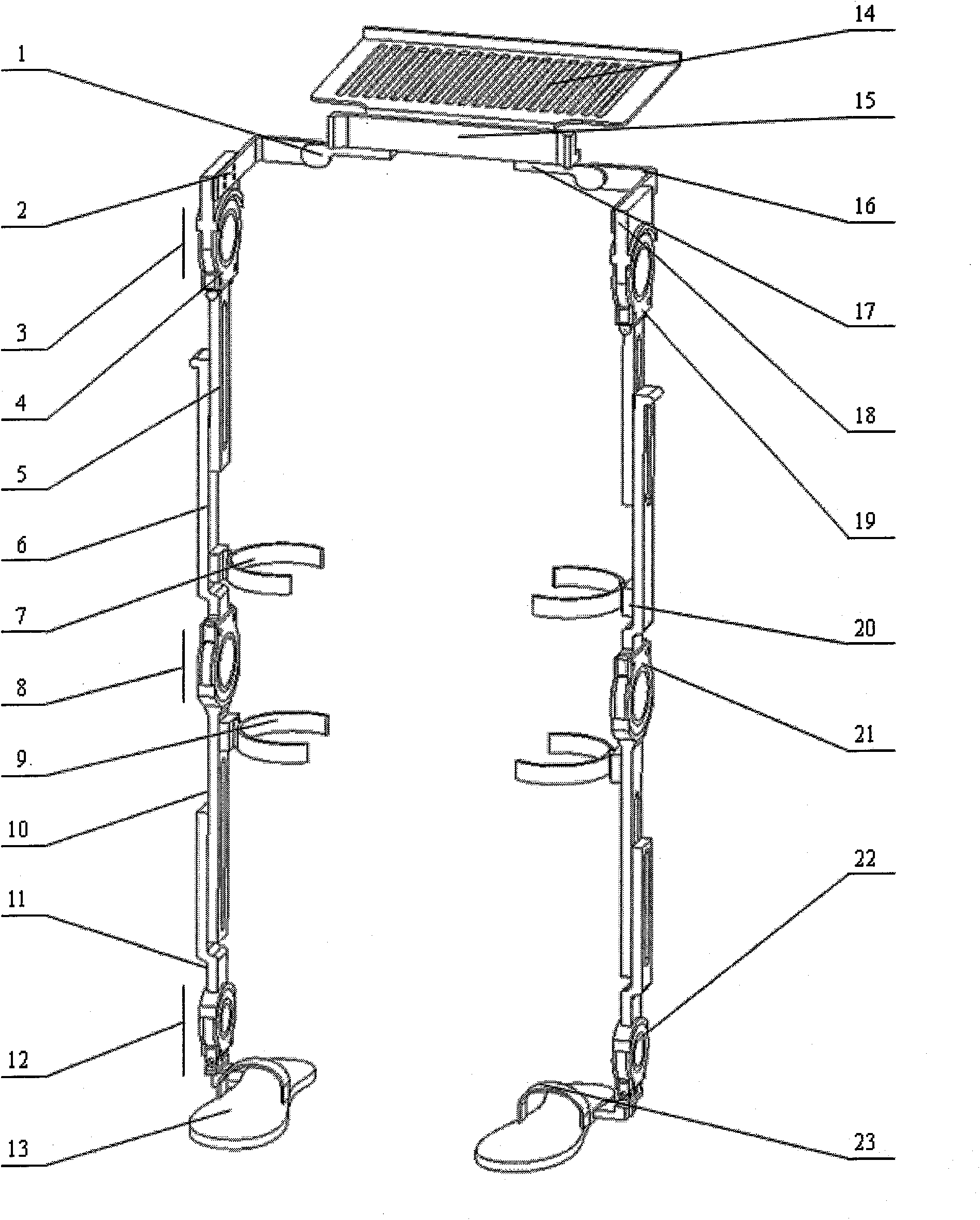
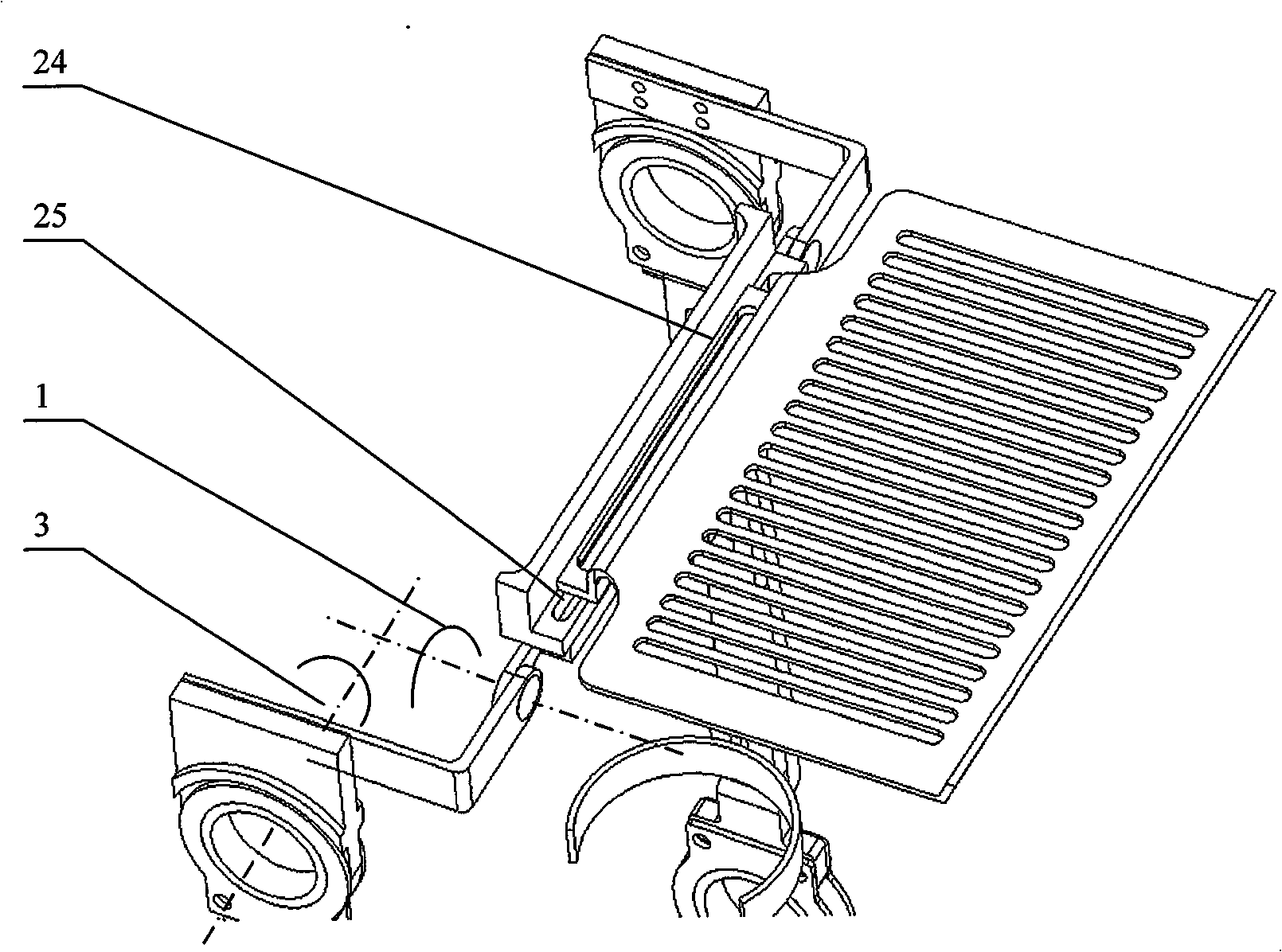
InactiveCN101589983AImprove consistencySmall coaxialityWalking aidsInvalid friendly devicesHuman bodyKnee Joint
The invention discloses a wearable lower limb exoskeleton device, which comprises a waist supporting frame, a waist object carrier, an adjustable hip mechanism, a connecting rod adjustable knee joint mechanism, a connecting rod adjustable ankle joint mechanism, pressure detection shoes, a leg connecting rod, a constraint part and various connecting pieces. Both lower limbs have twelve rotational freedoms, the single lower limb has six degrees of freedom respectively, a hip has two degrees of freedom which finish bending and stretching as well as adduction and abduction movements of a hip joint, two joint axes always intersects at the center of the hip joint of a human body through the adjustment of the hip mechanism, and a knee joint has one degree of freedom which is coaxial with the knee joint of the human body and corresponds to the bending and stretching movement of the knee joint of the human body; and an ankle joint has three degrees of freedom. The device has good consistency of the movement of the hip joint and the movement of the human body during the walking of people; human-machine knee joints have small coaxality and position deviation; and the ankle joint has a compact structure. The device can be used for strengthening the abilities of walking with load and walking for a long time of wearers and detecting walking information of the wearers, and can also be used for helping people with slight obstacle of lower limb movement to normally walk and gradually rehabilitate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
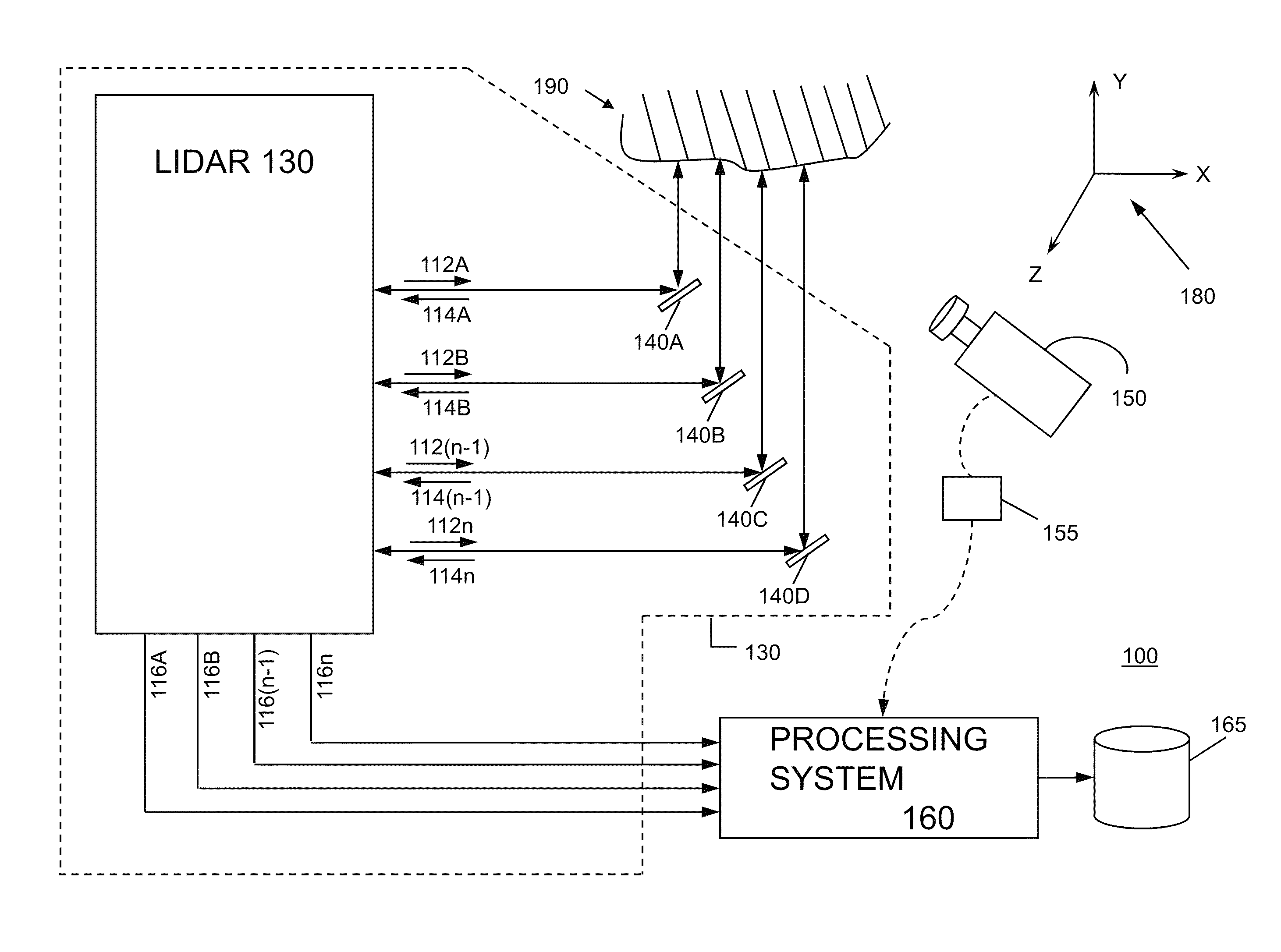
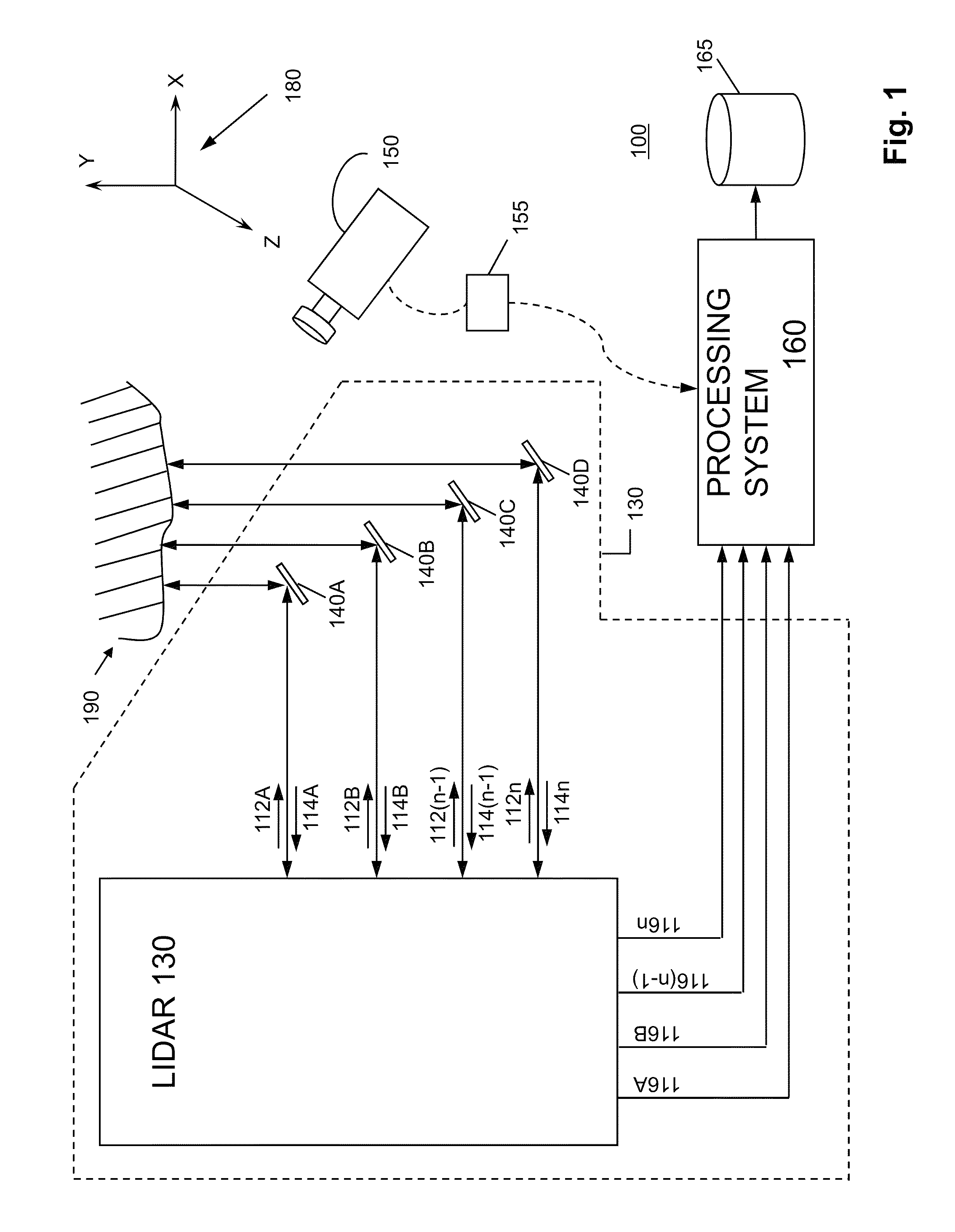
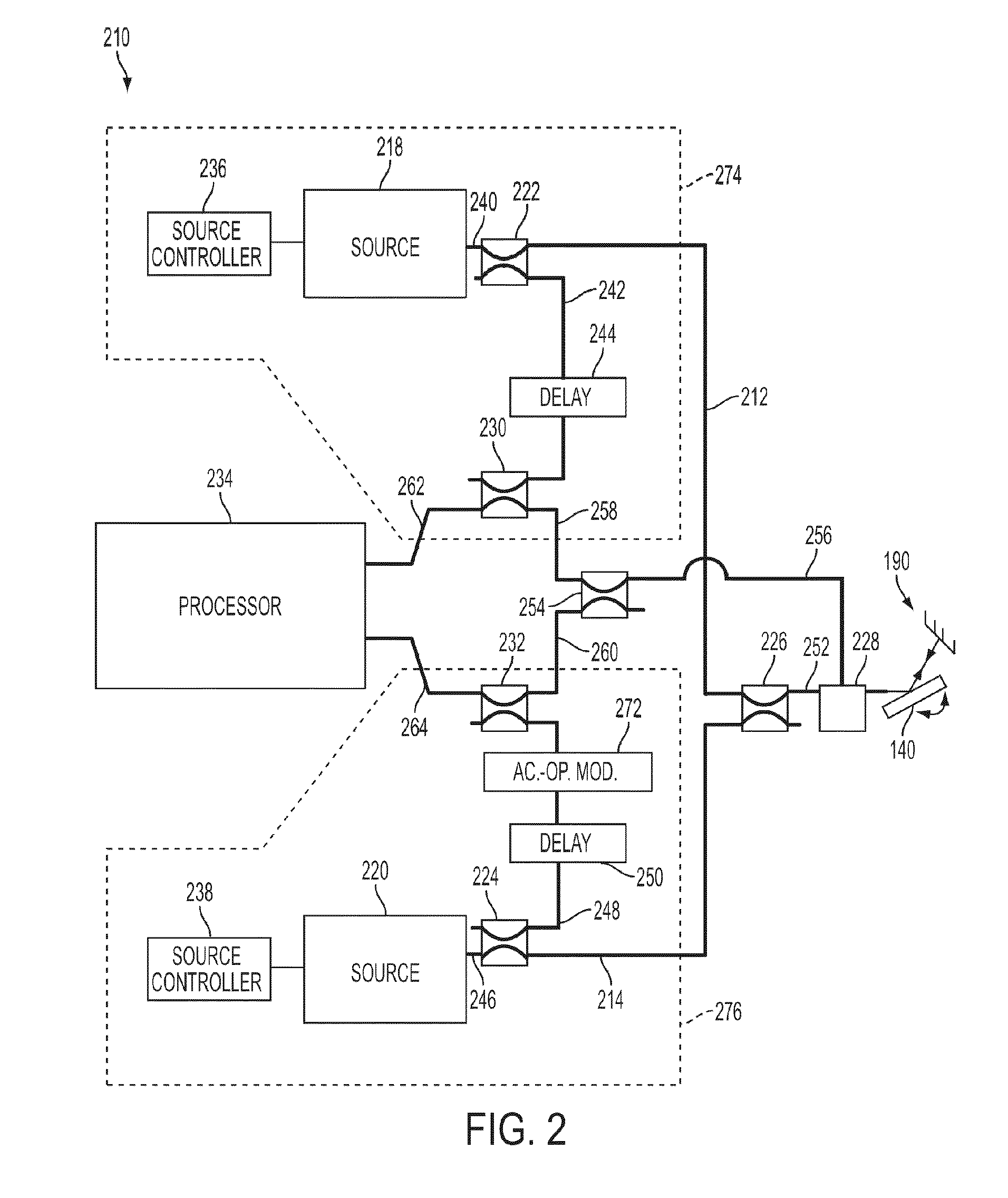
System and method for calibrating video and lidar subsystems
A system uses range and Doppler velocity measurements from a lidar system and images from a video system to estimate a six degree-of-freedom trajectory of a target. The system calibrates the lidar subsystem with the video subsystem in two stages. In a first stage, the system calibrates the lidar subsystem so that lidar measurements provide 3D lidar coordinates. In a second stage, the system relates the 3D lidar coordinates with a video image obtained from the video subsystem.
Owner:AEVA INC
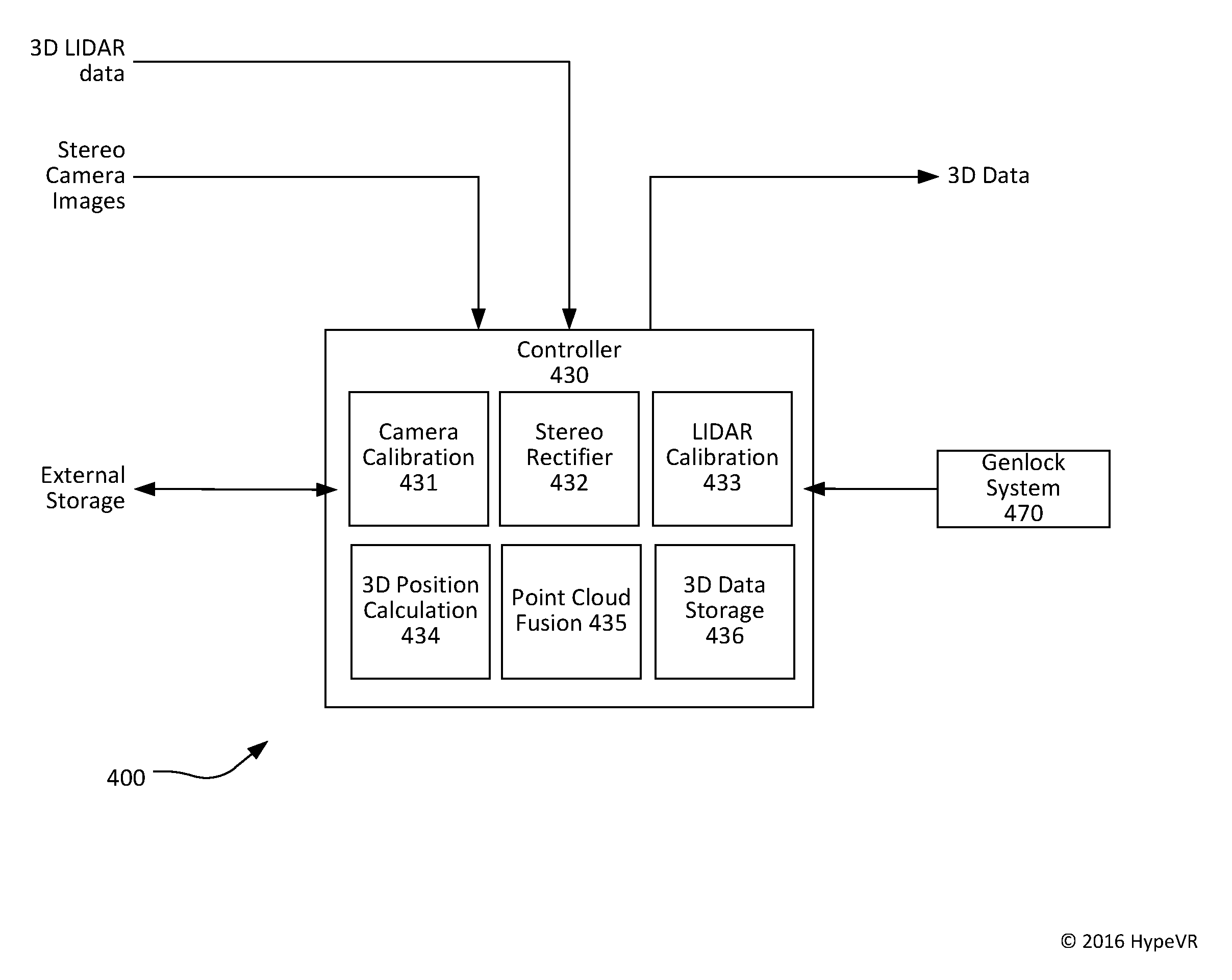
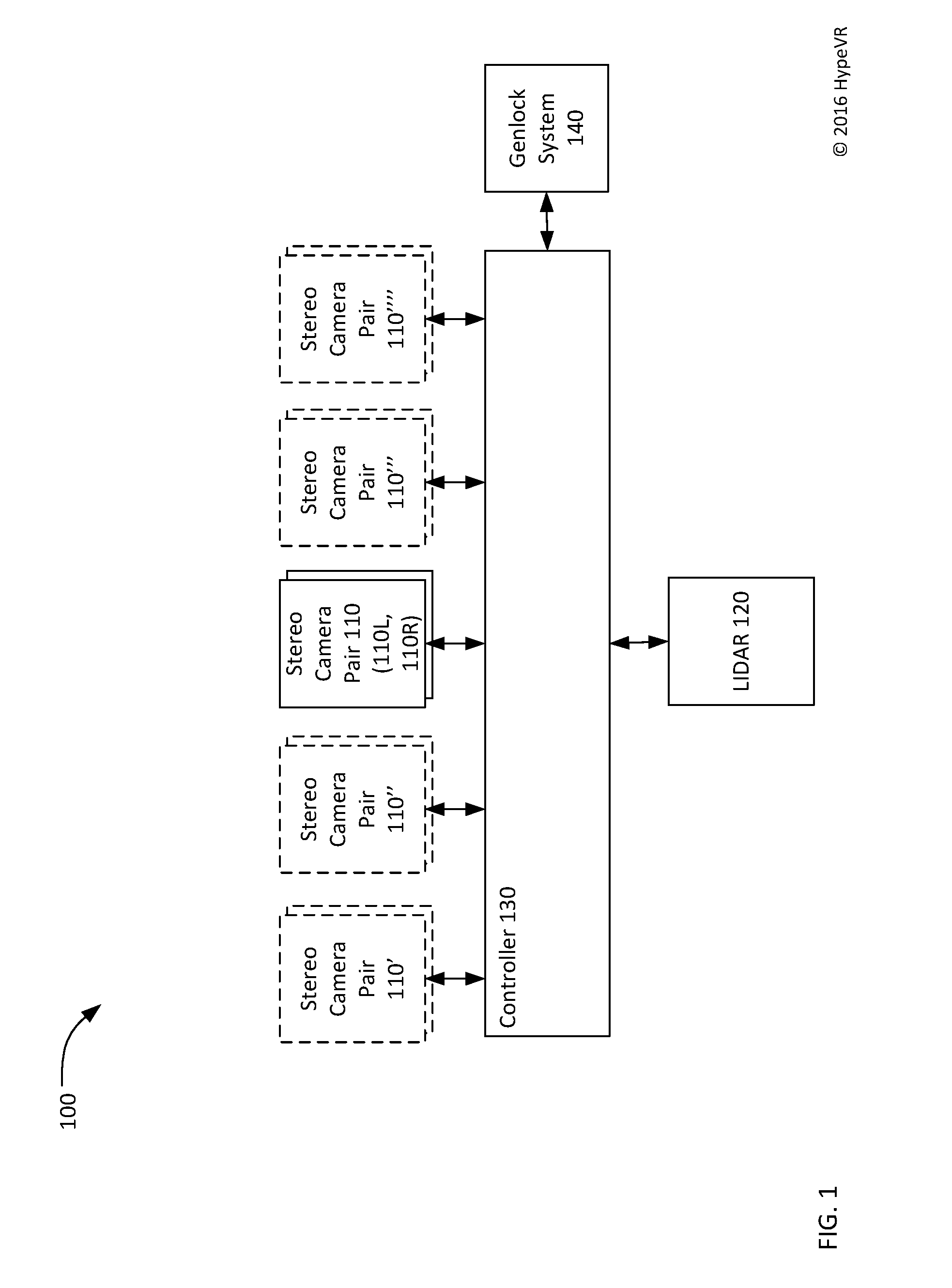
Lidar stereo fusion live action 3D model video reconstruction for six degrees of freedom 360° volumetric virtual reality video
A system for capturing live-action three-dimensional video is disclosed. The system includes pairs of stereo cameras and a LIDAR for generating stereo images and three-dimensional LIDAR data from which three-dimensional data may be derived. A depth-from-stereo algorithm may be used to generate the three-dimensional camera data for the three-dimensional space from the stereo images and may be combined with the three-dimensional LIDAR data taking precedence over the three-dimensional camera data to thereby generate three-dimensional data corresponding to the three-dimensional space.
Owner:HYPEVR
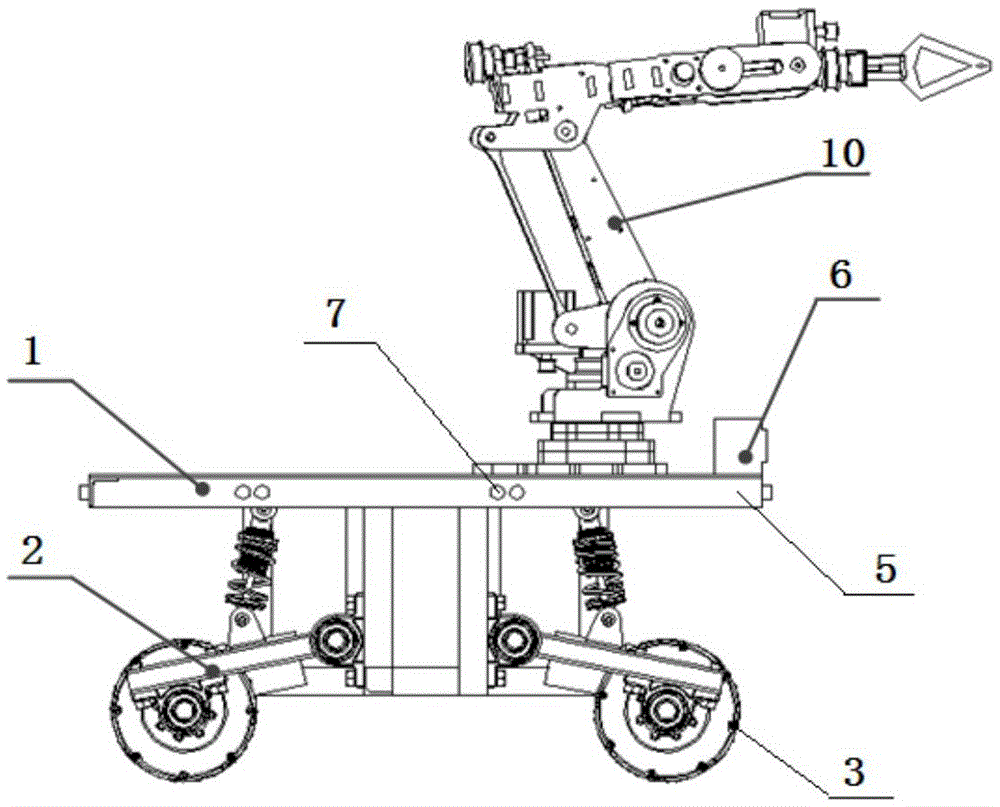
Omnidirectional moving transfer robot with Mecanum wheels
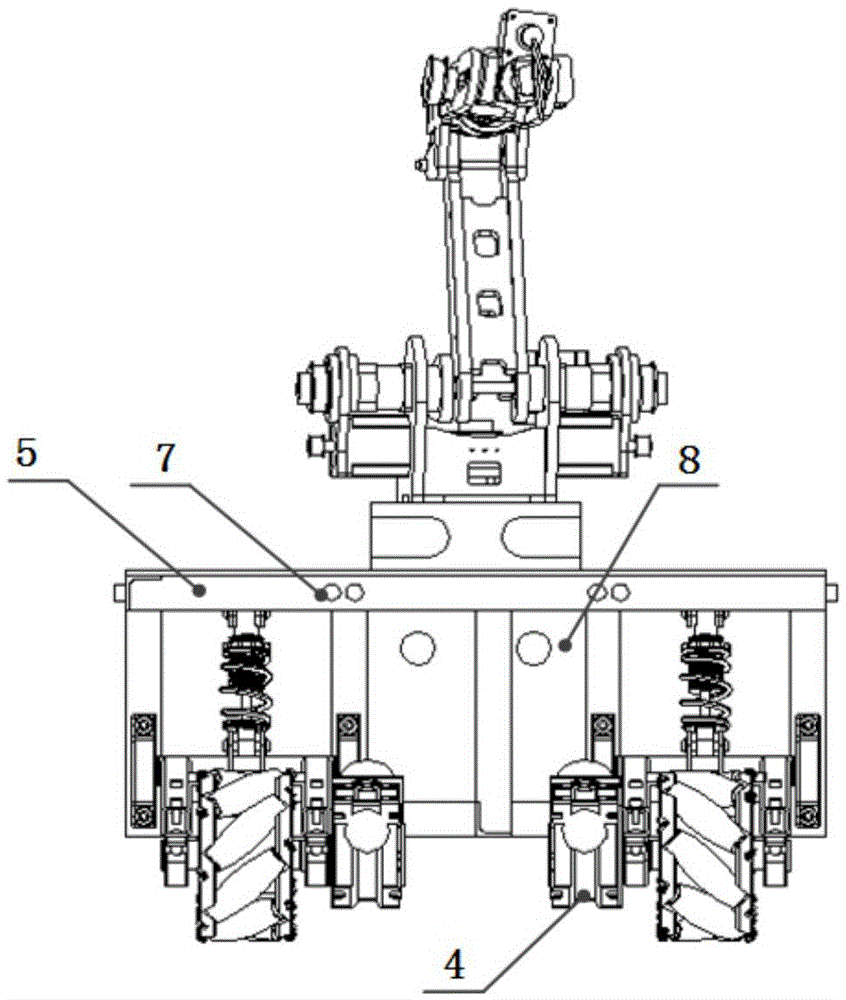
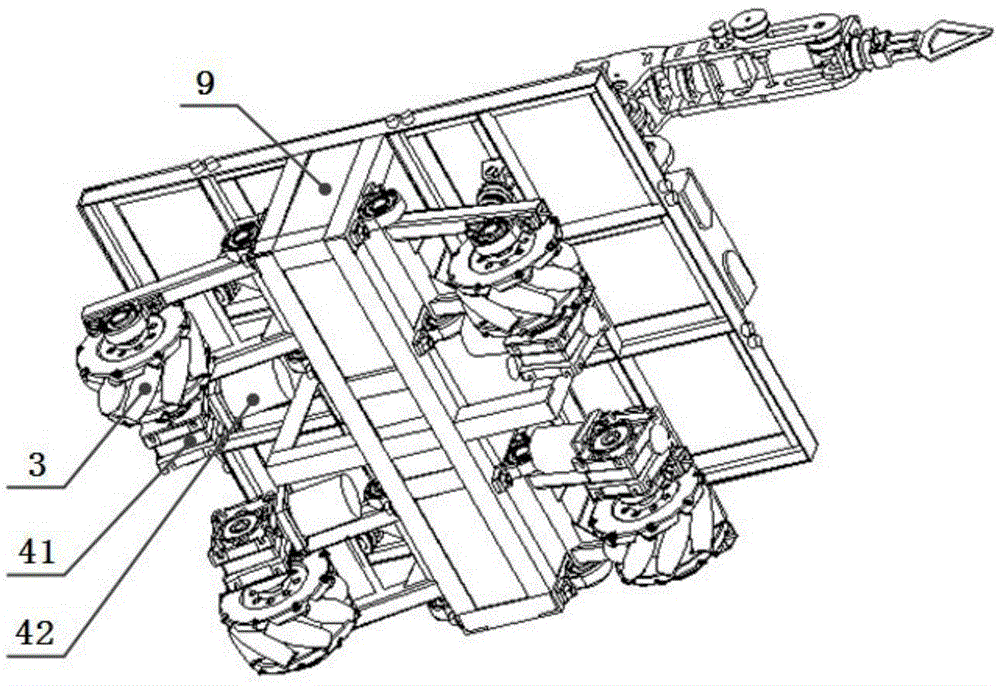
InactiveCN105479433AImprove motor flexibilityHigh degree of intelligenceManipulatorVehicle frameDrive wheel
The invention discloses an omnidirectional moving transfer robot with Mecanum wheels. The omnidirectional moving transfer robot comprises a mechanical arm with six degrees of freedom, an omnidirectional moving base plate, a binocular vision device, a master control box and a remote monitoring device. The omnidirectional moving base plate comprises a frame and the multiple Mecanum wheels arranged below the frame. Each Mecanum wheel is a drive wheel. A plurality of distance measuring sensors are arranged on the periphery of the frame. Each distance measuring sensor is fixedly connected with the frame through an independent suspending module. By means of the structure, the rotating speeds and the steering direction of all the wheels are matched so that a moving platform can move in any direction in the plane, and the moving flexibility of the whole transfer device is remarkably improved; in addition, it can also be ensured that the Mecanum wheels are in full contact with the ground, and operation stability and control precision are improved; and furthermore, the binocular vision device is used for guiding the robot to move and conduct the object carrying and conveying task, the whole process is completed by the robot independently, and the intelligence degree is higher.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com