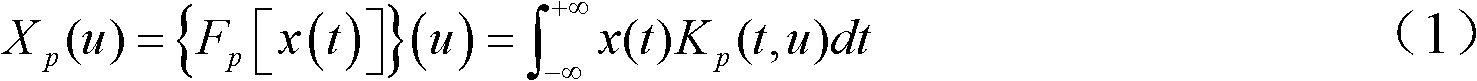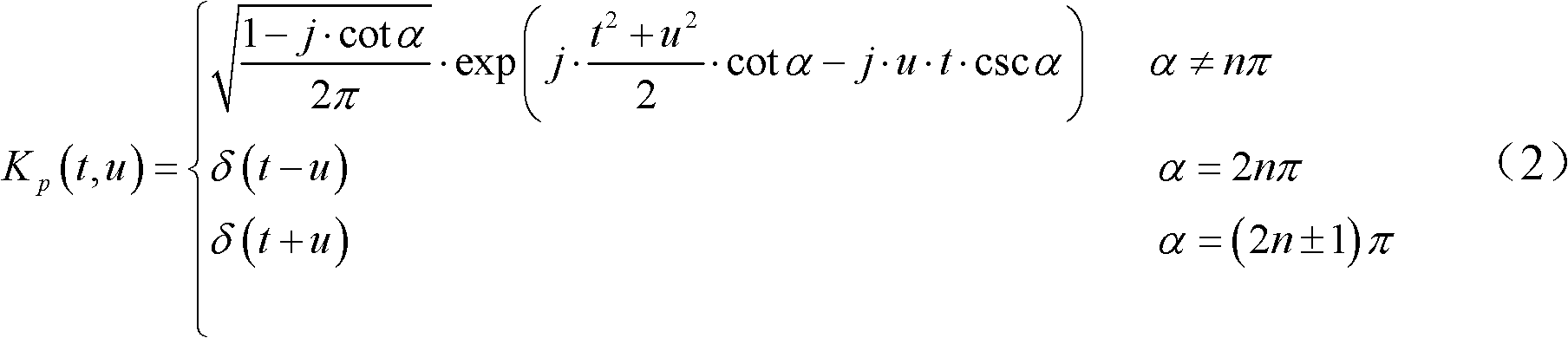Patents
Literature
369 results about "Dynamic motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
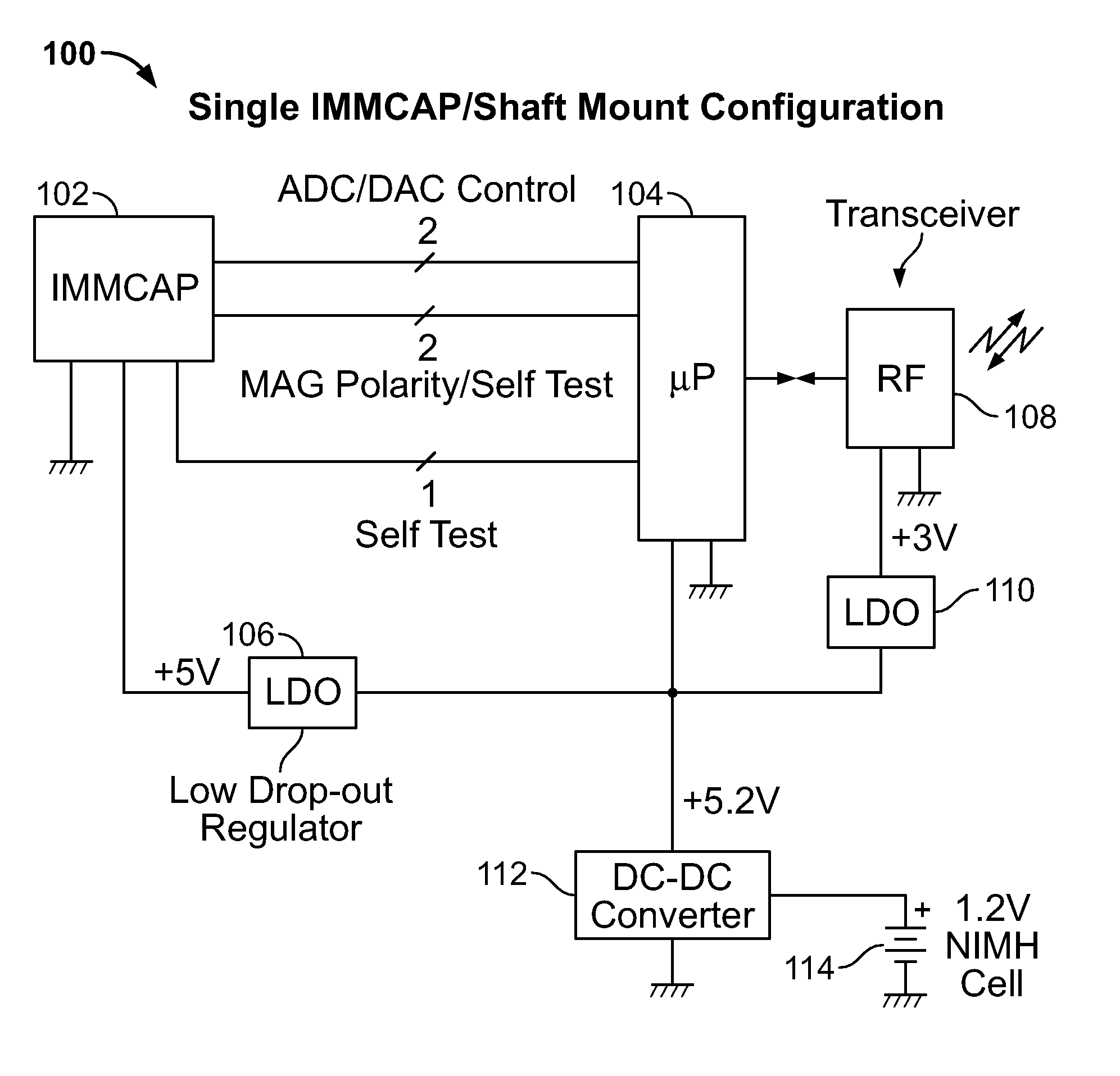
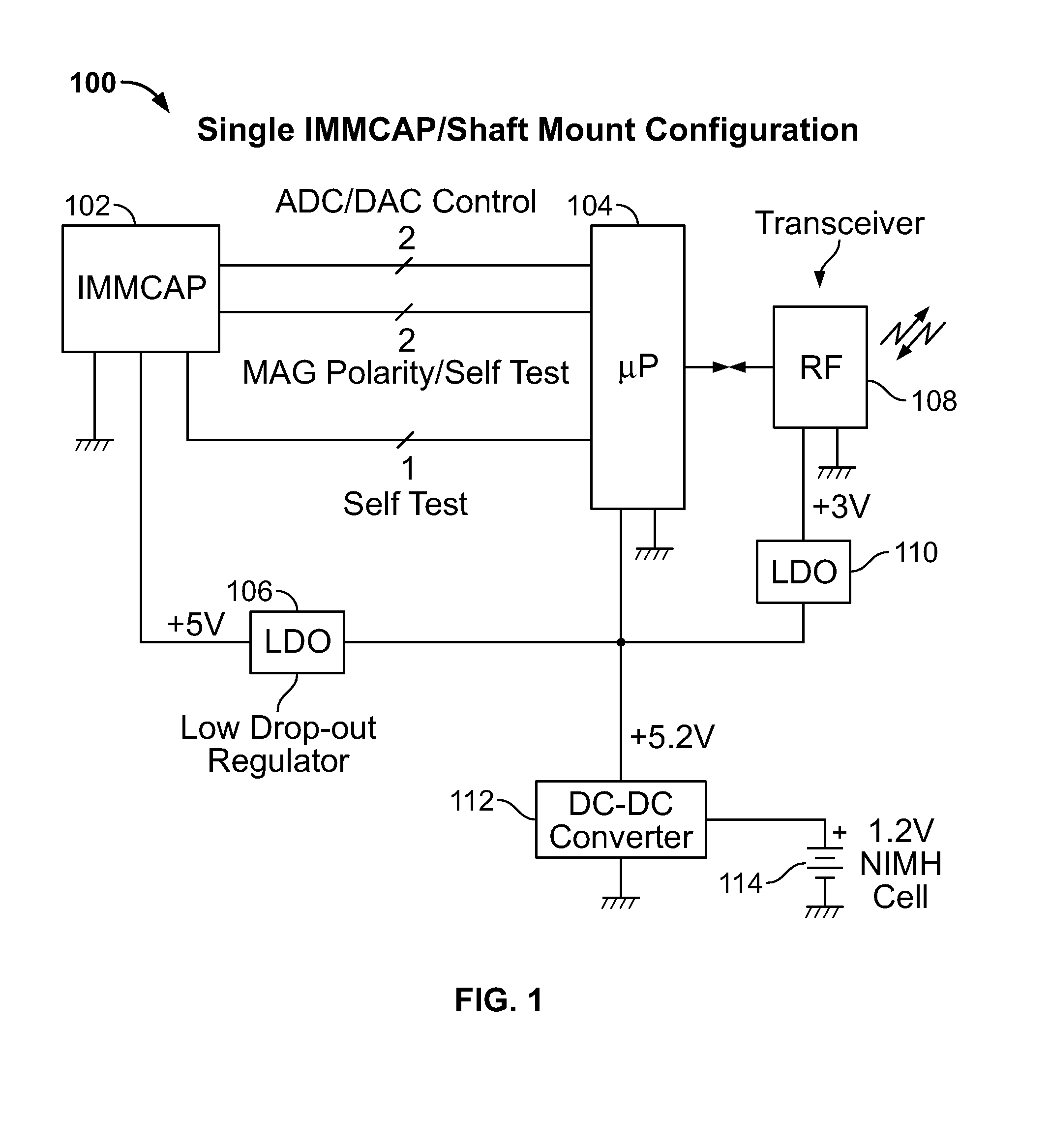
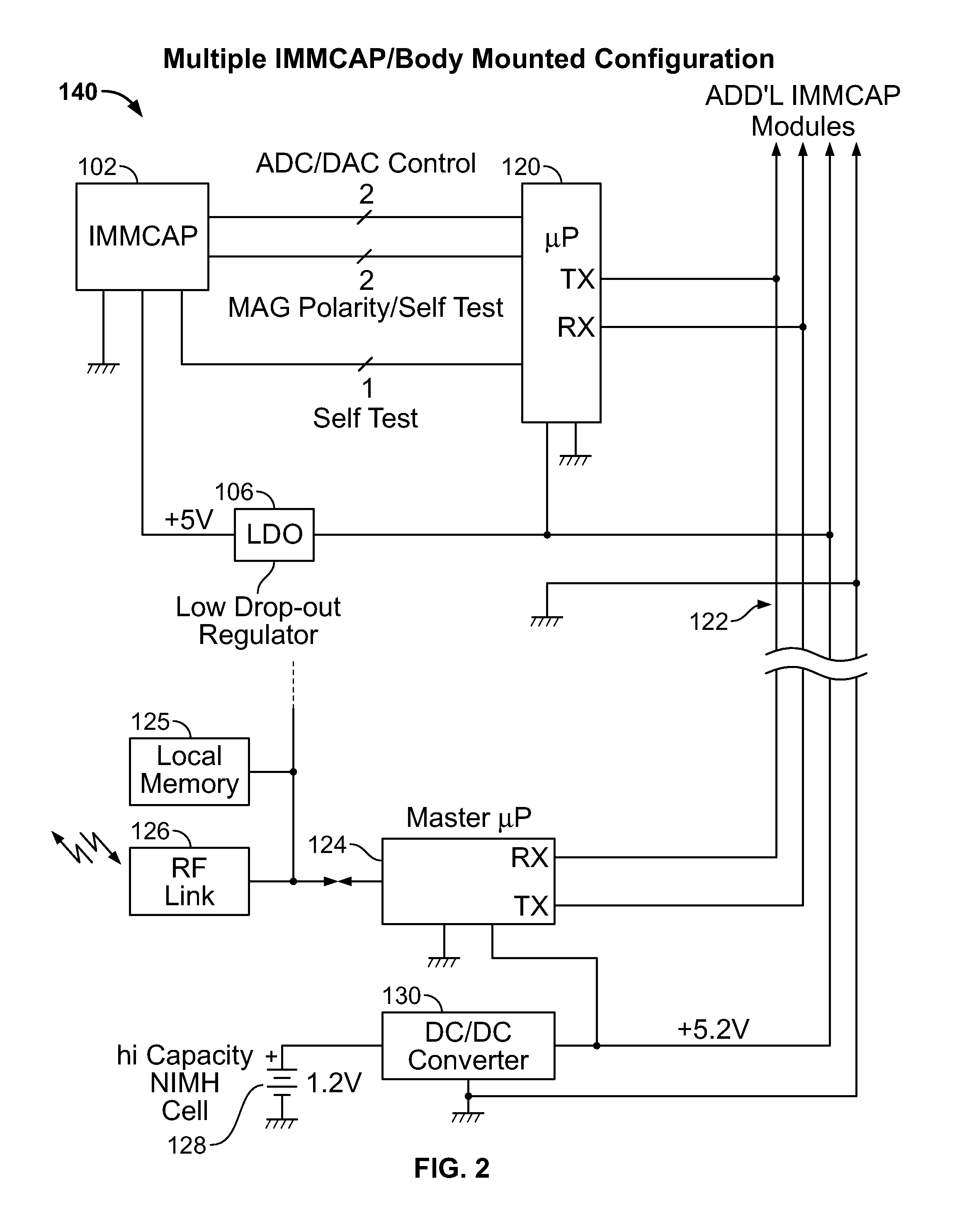
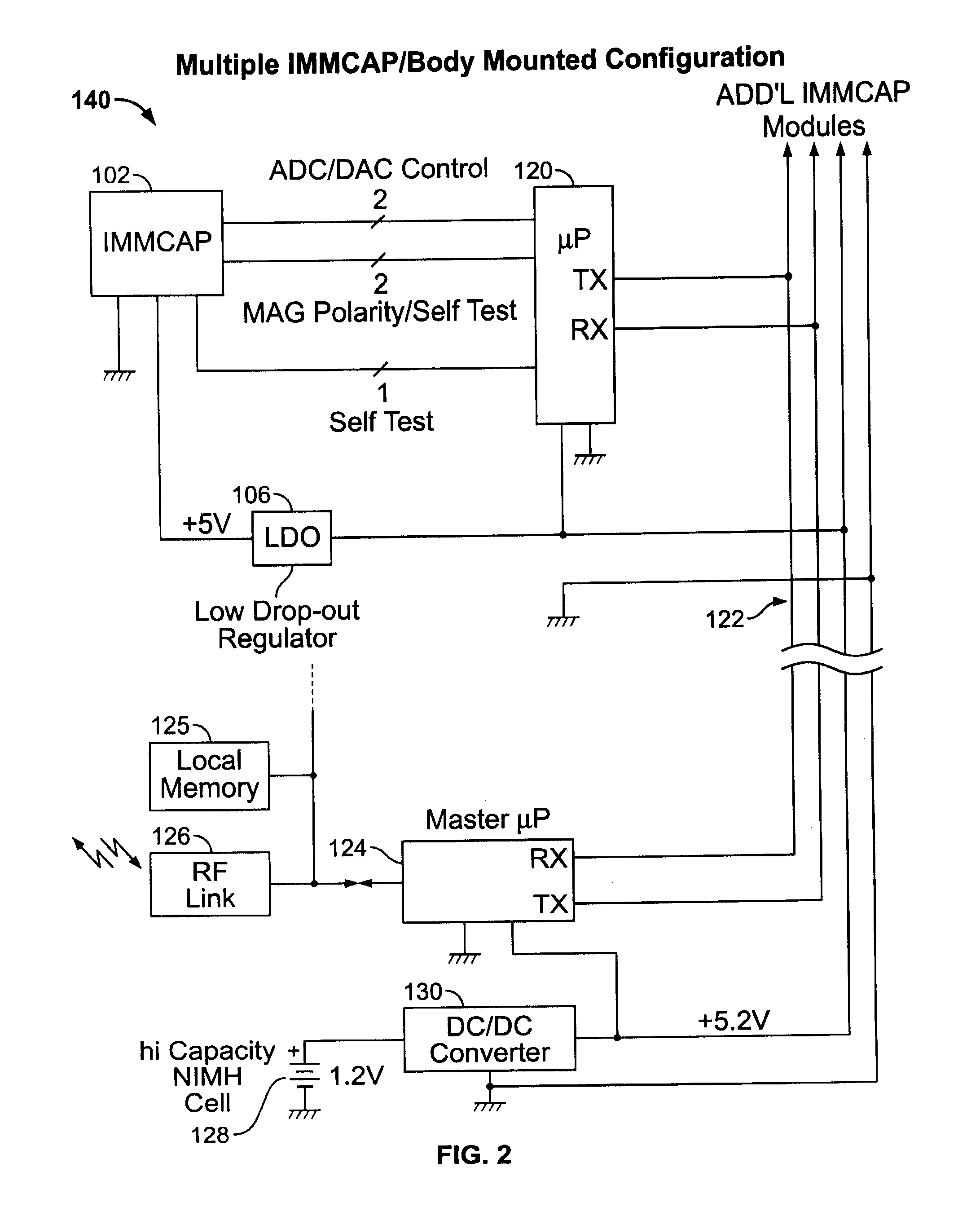
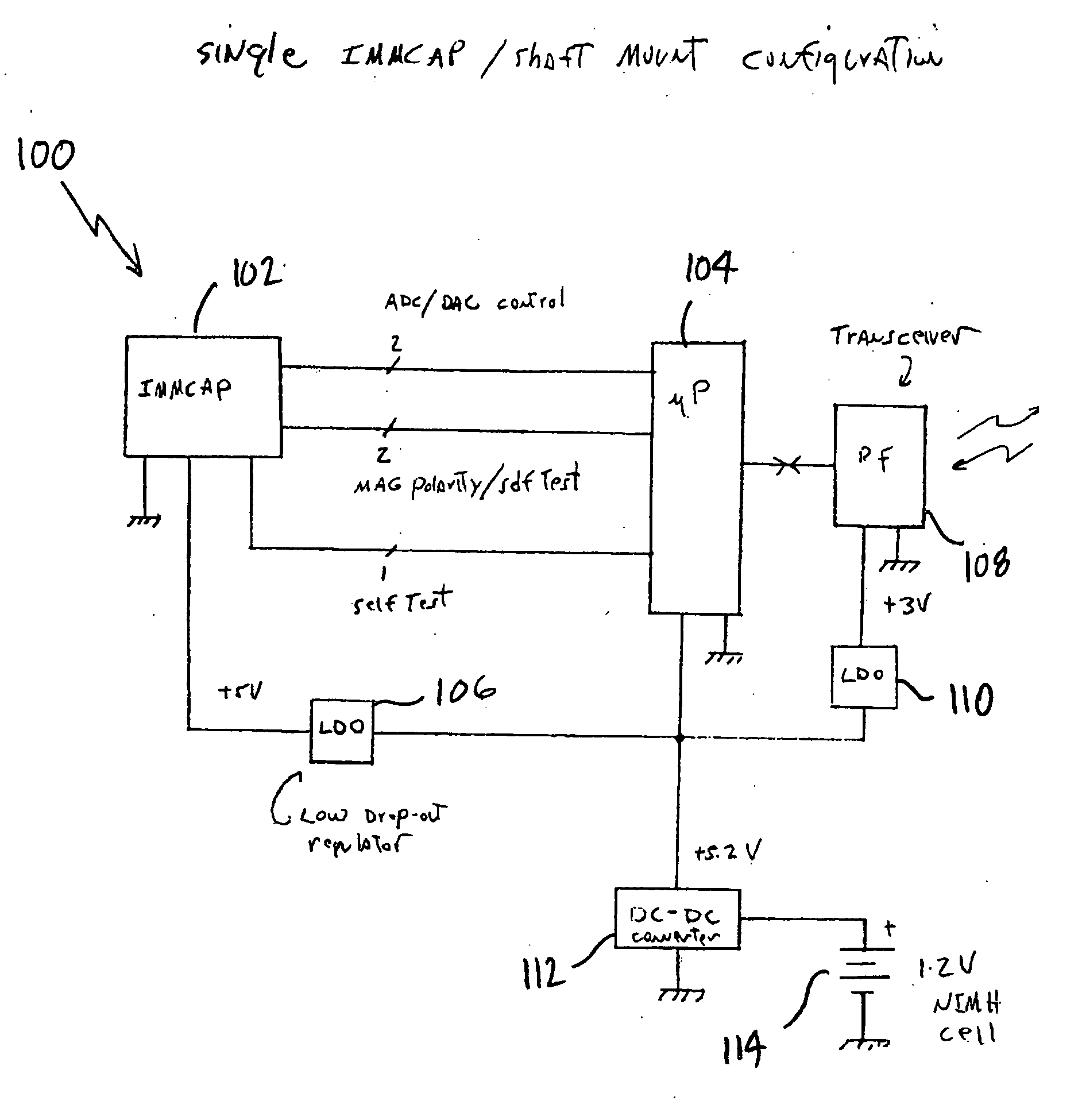
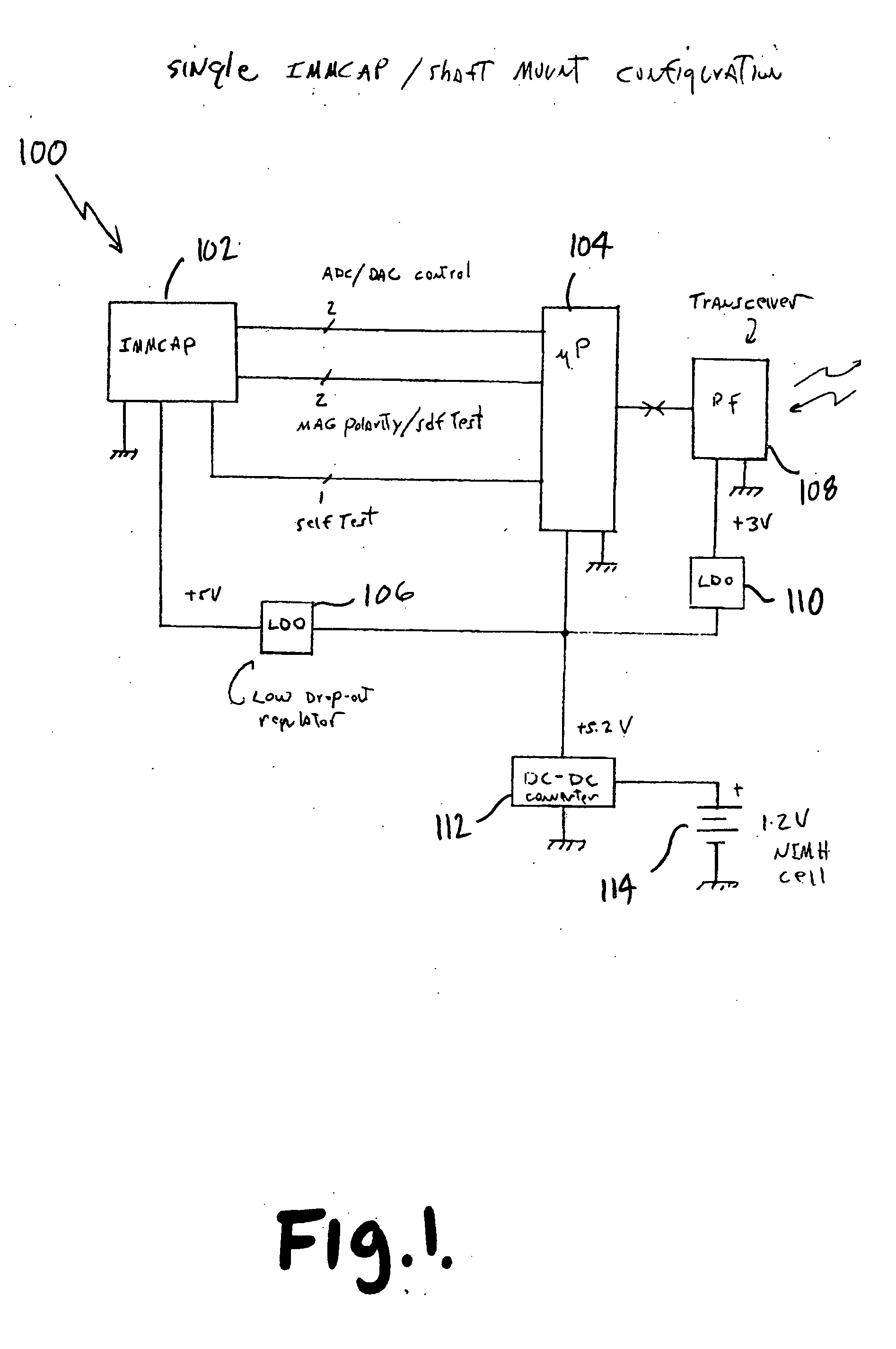
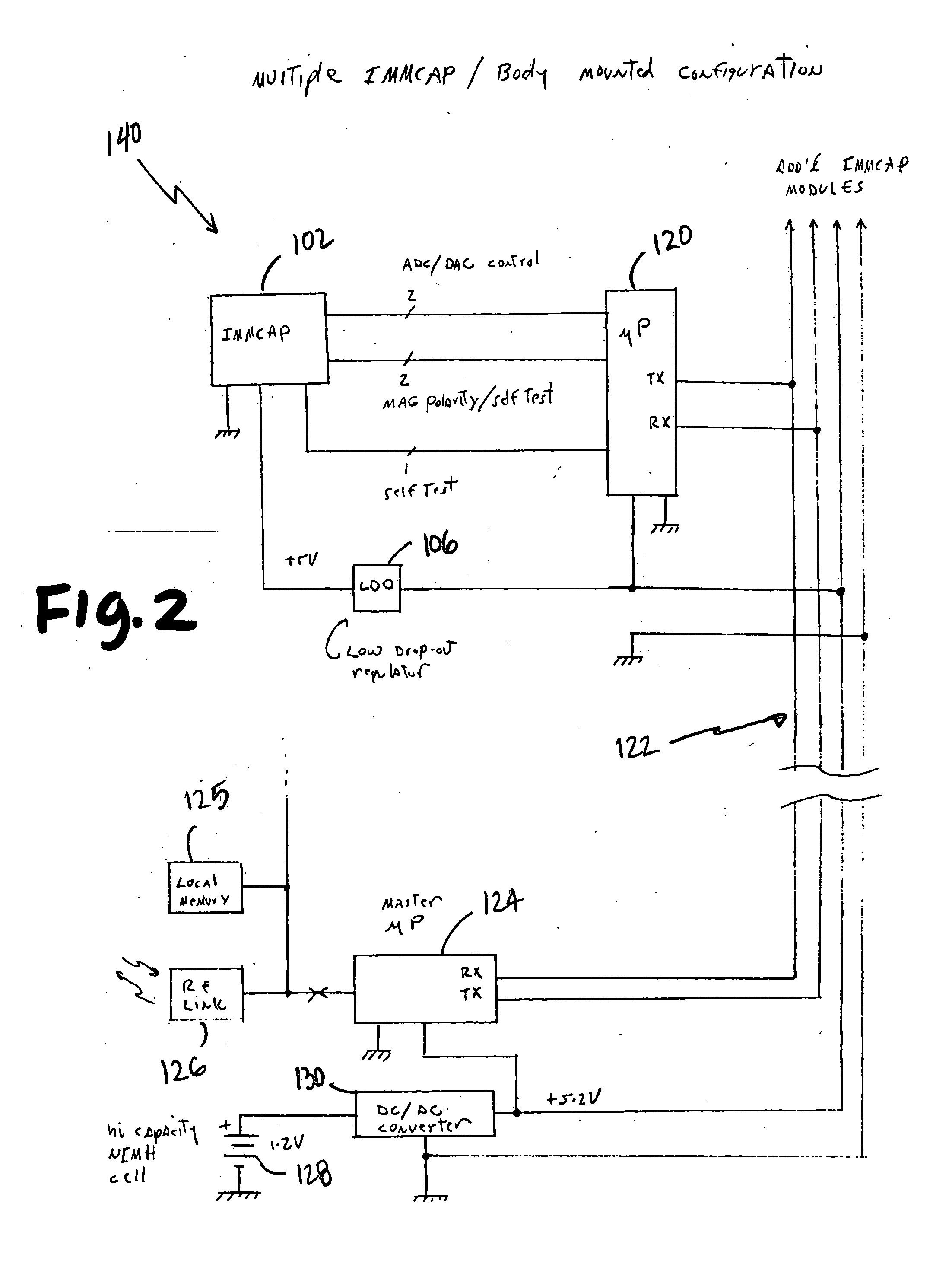
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
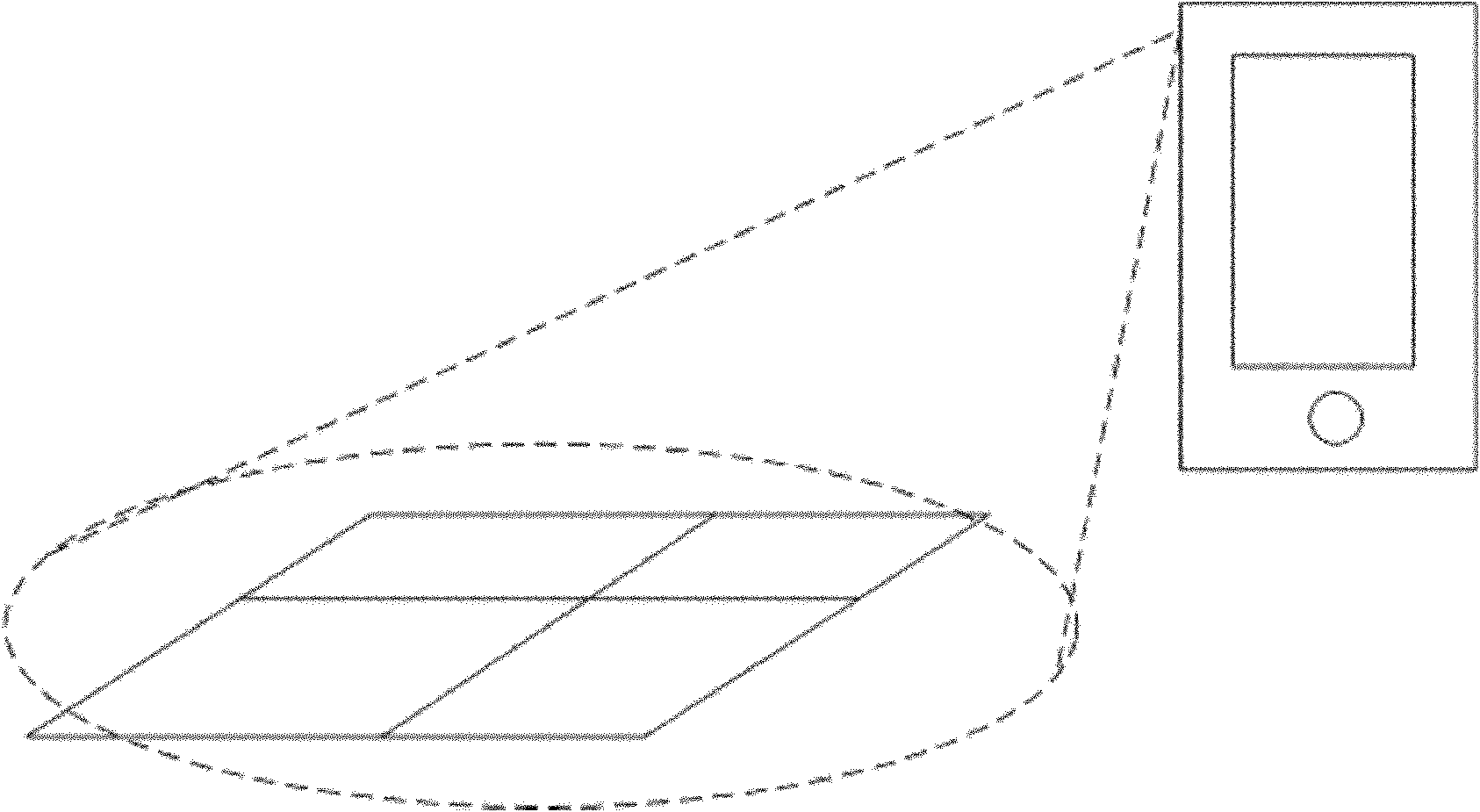
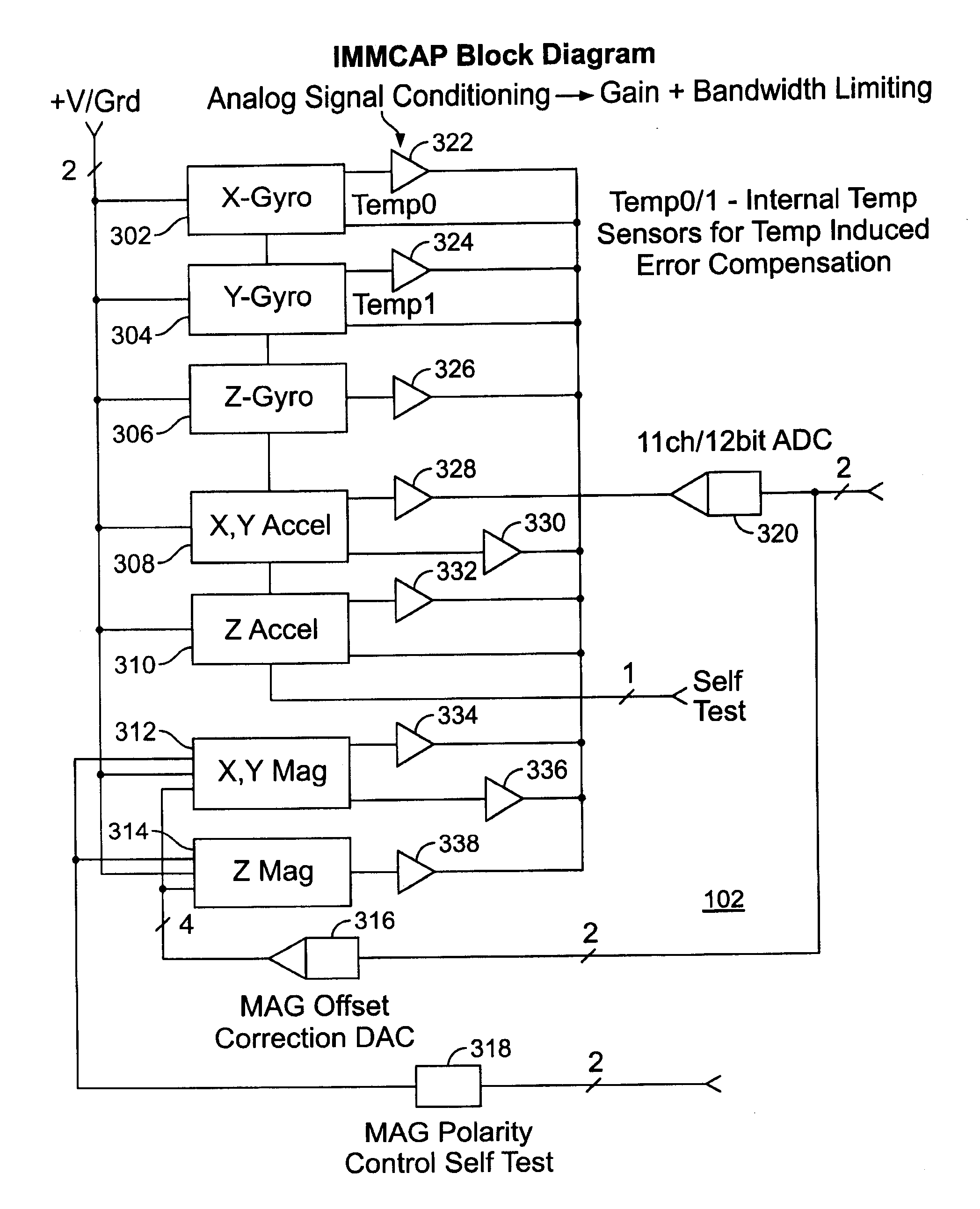
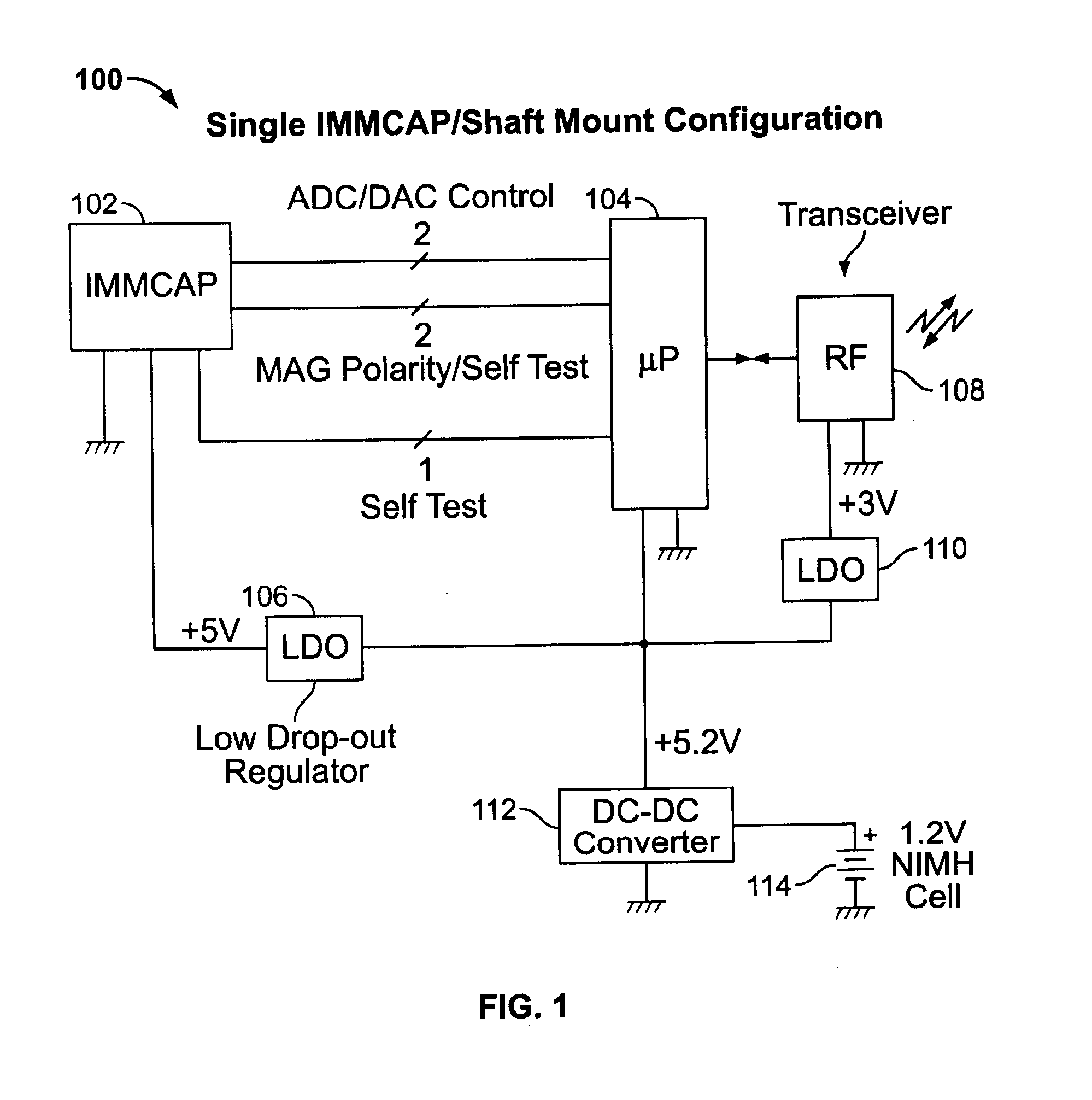
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
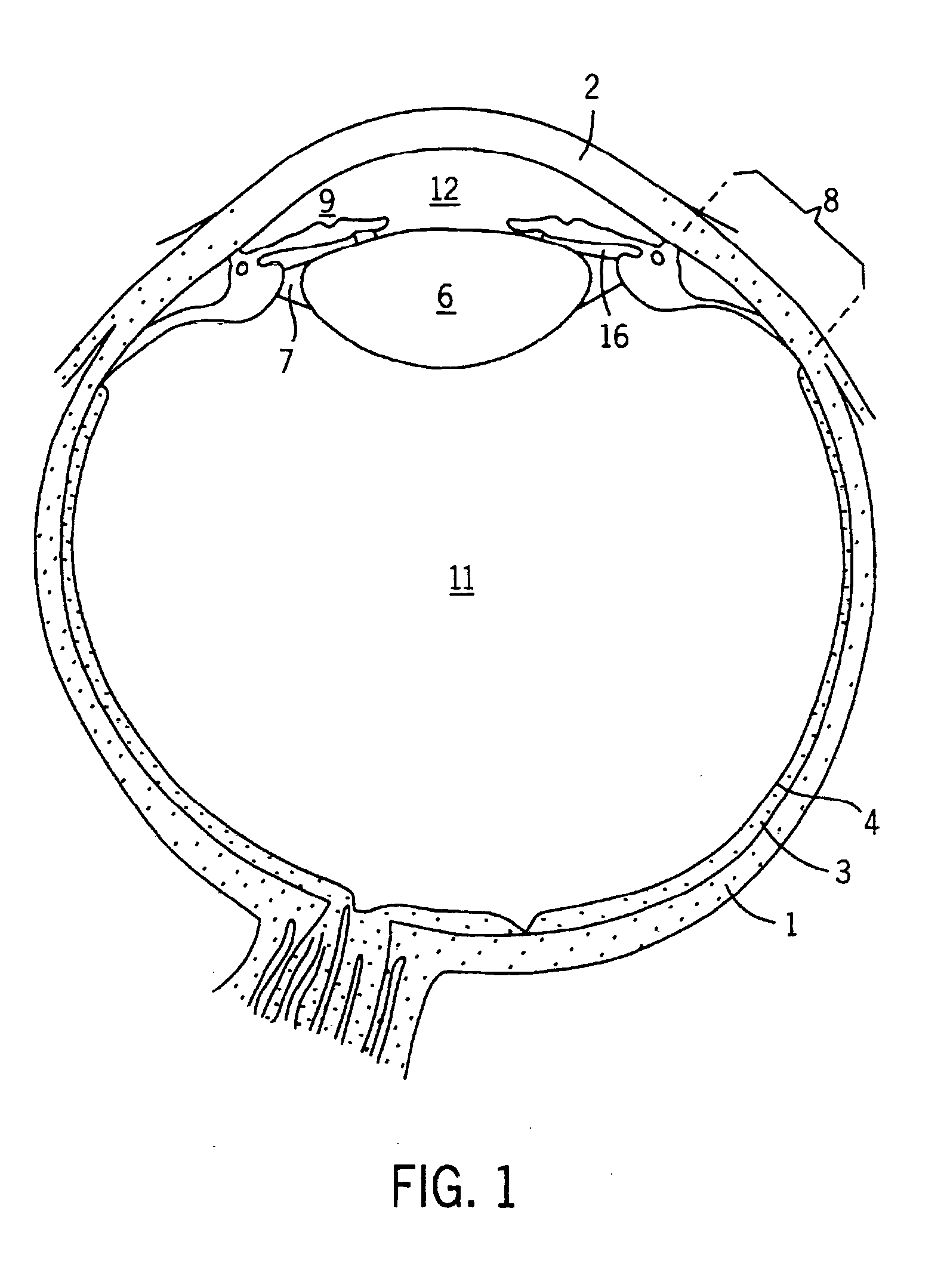
Device and method for medical training and evaluation
InactiveUS20050214727A1Accurate image generationSimulate the realEducational modelsAnatomical structuresRadiology
A training and / or evaluating device is provided particularly useful in performing laparoscopic procedures, radiological procedures, and precise surgeries that simulates the structure and dynamic motion of the corresponding anatomical structure on which the procedure takes place. The device includes an outer housing, which may be designed to mimic the body wall, in which one or more organs are located. Motion of the organ(s), as a result of respiration, pulmonary action, circulation, digestion and other factors present in a live body, is simulated in the device so as to provide accurate dynamic motion of the organs during a procedure.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Motion sensing apparatus, systems and techniques
InactiveUS20070219744A1Gymnastic exercisingNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDigital data3d print
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:C LAN WIRELESS
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
Color translating UV microscope
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:RICHARDSON TECH
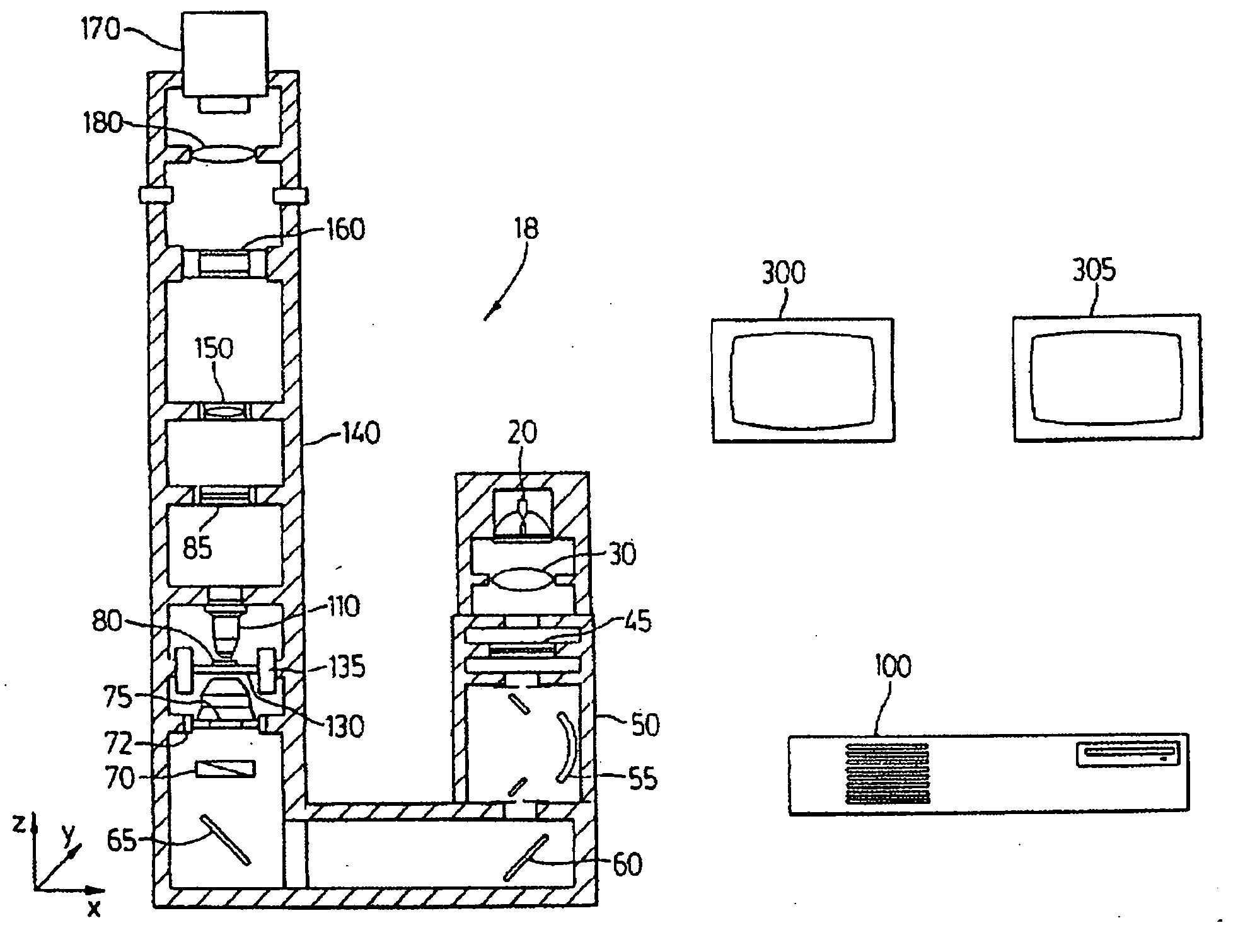
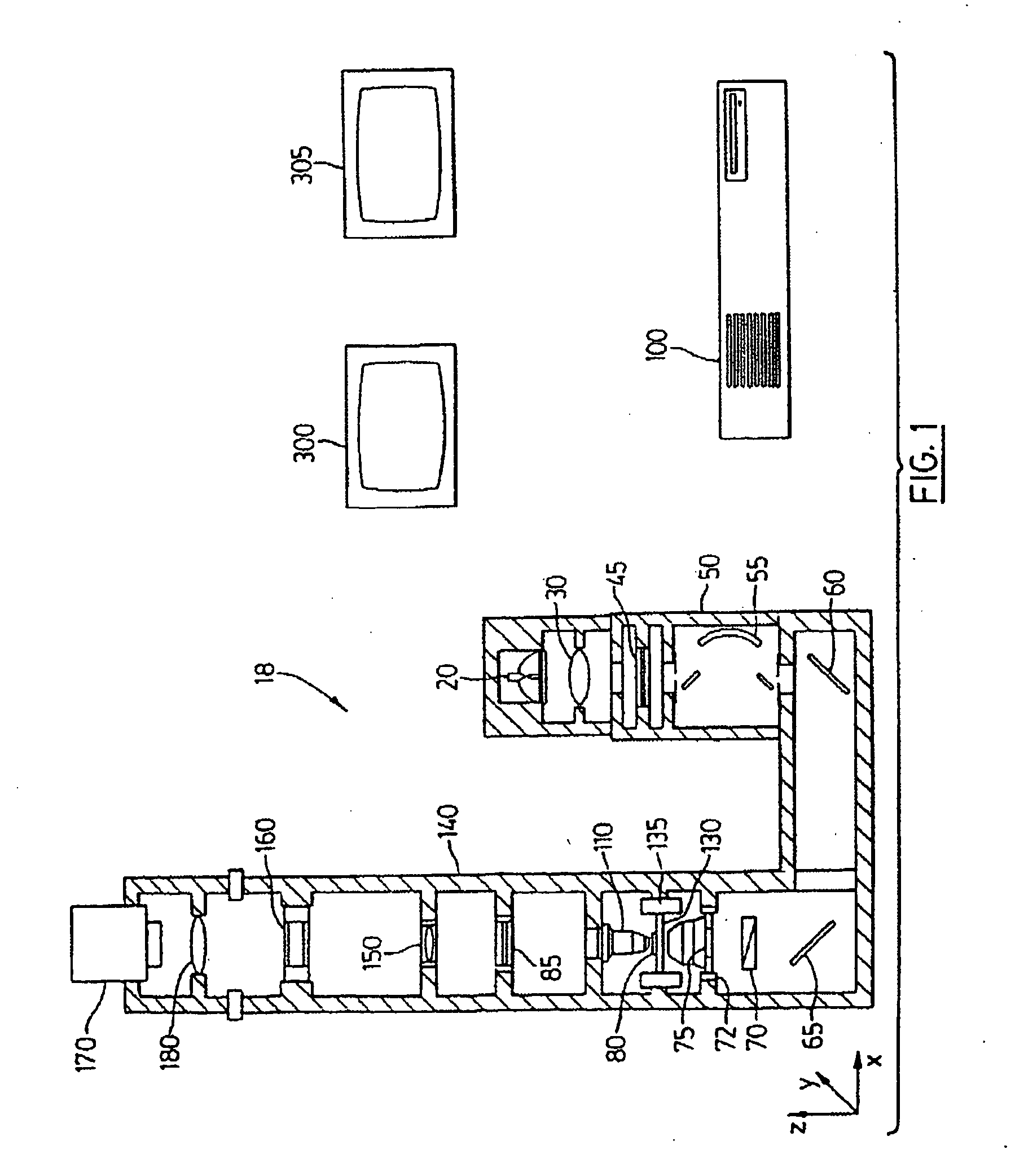
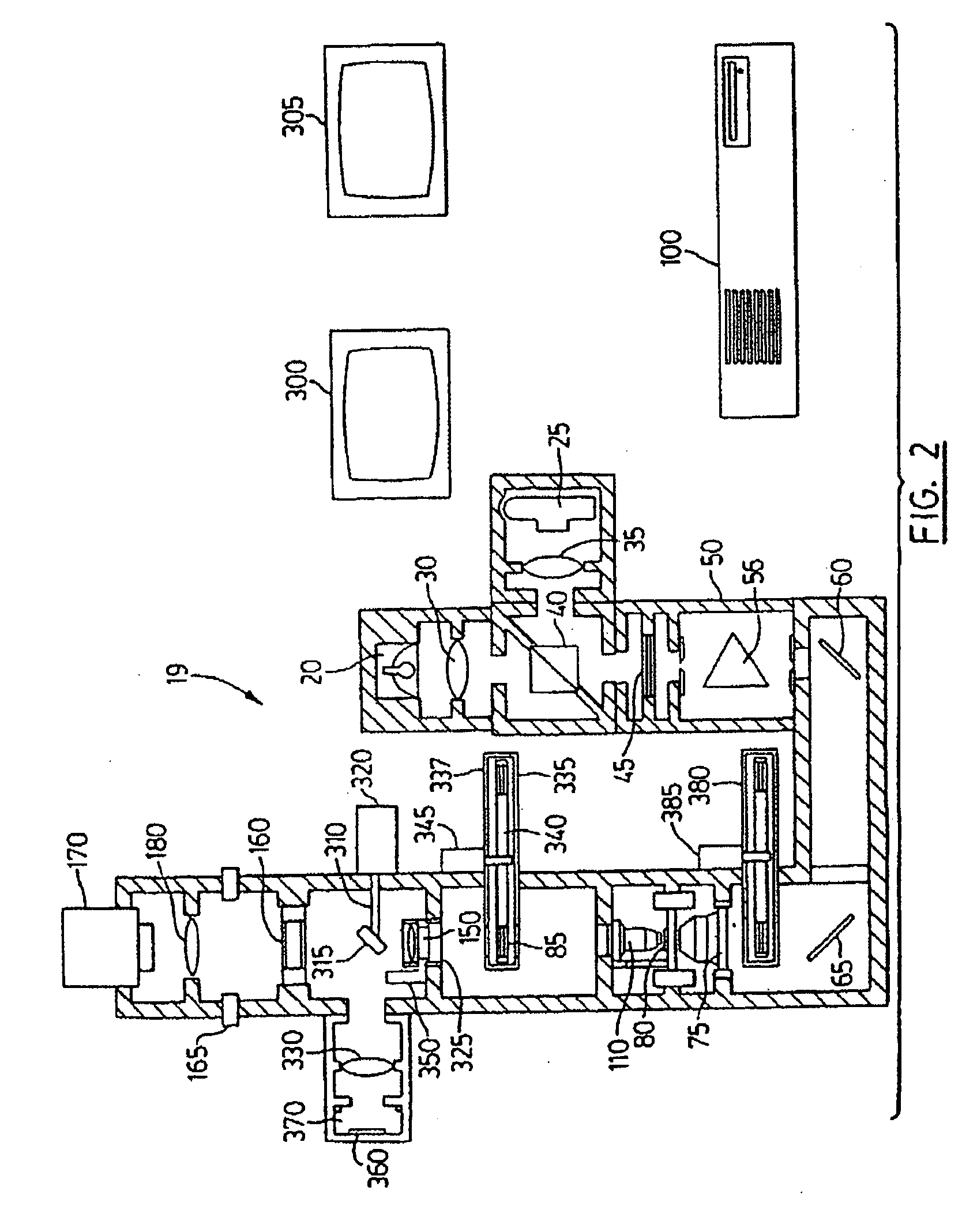
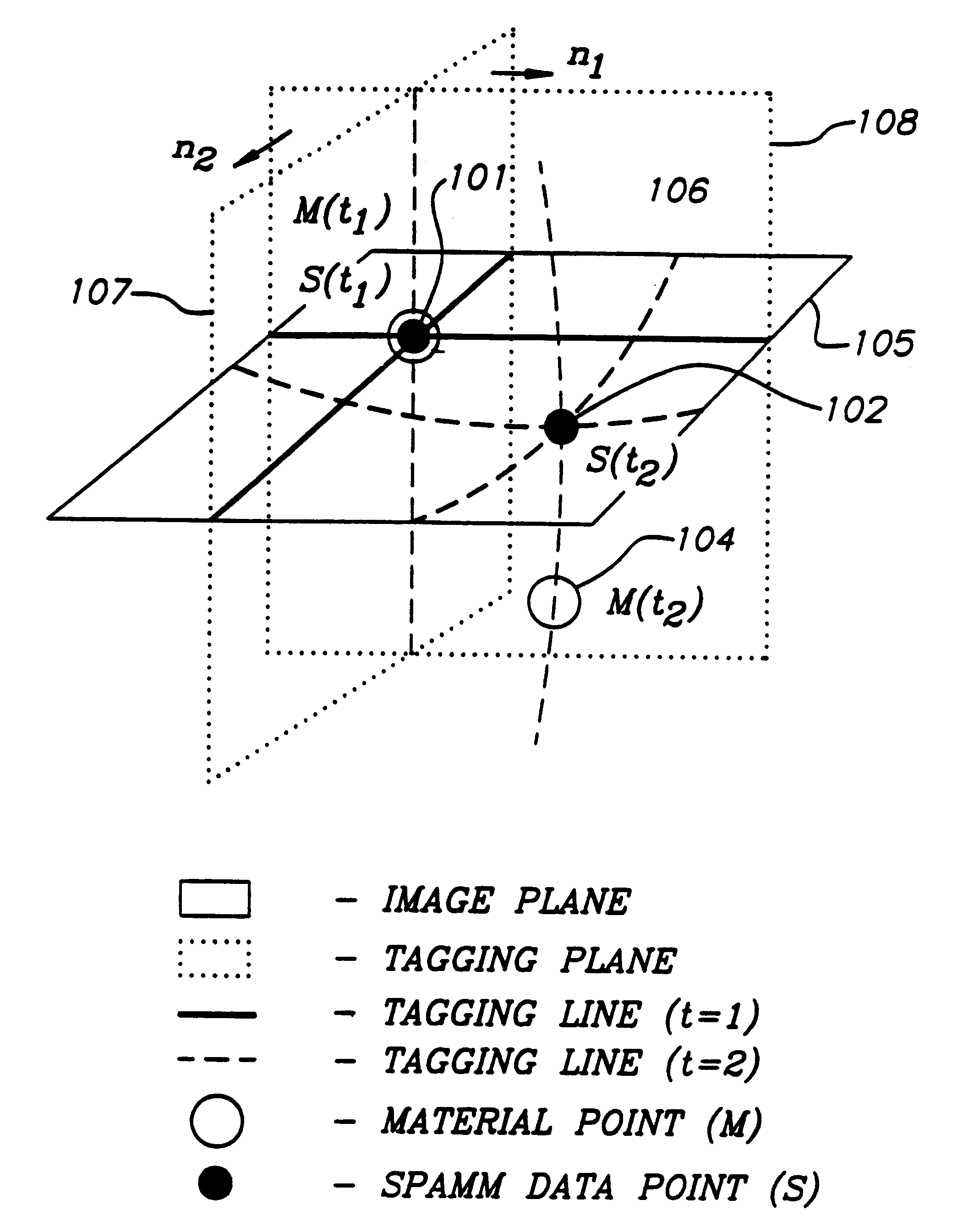
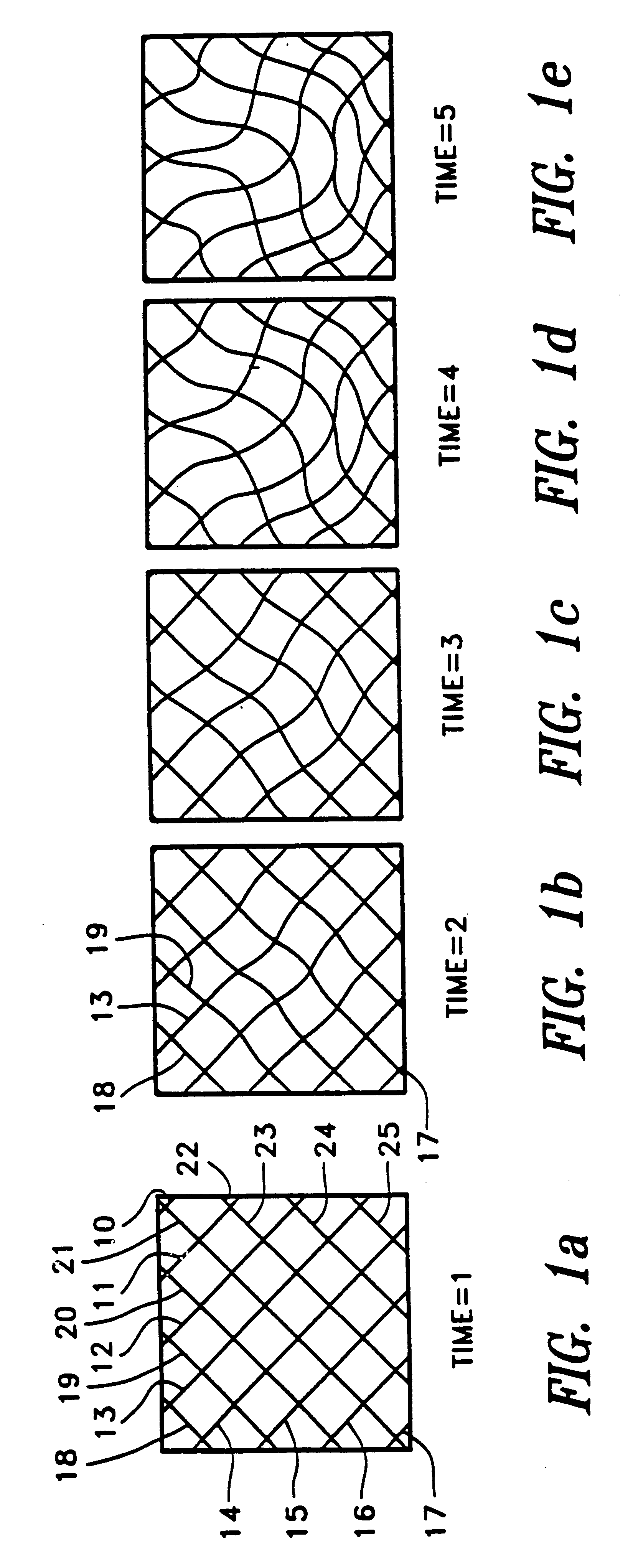
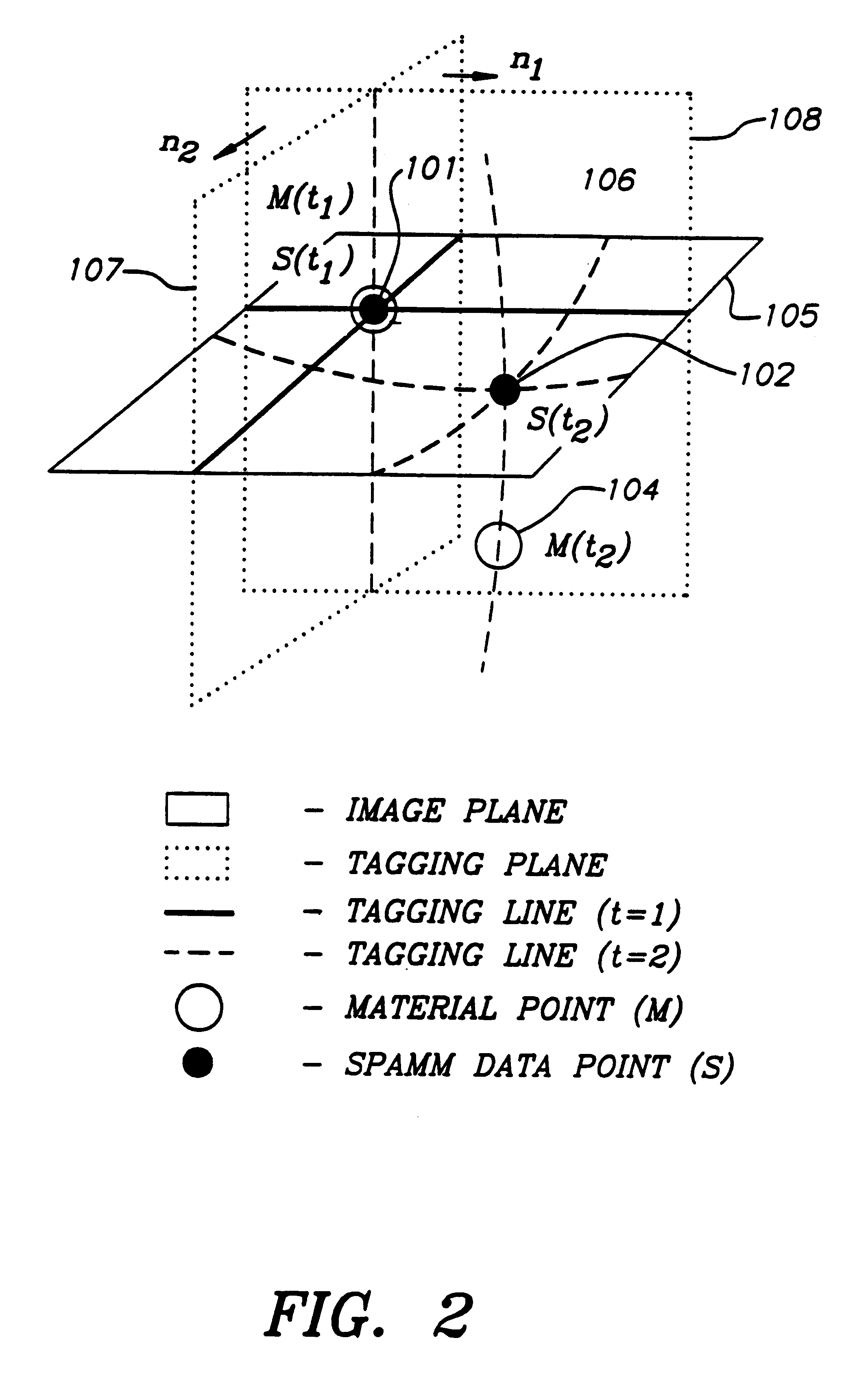
Apparatus and method for dynamic modeling of an object
InactiveUS6295464B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalogue computers for chemical processesModel dynamicsDynamic motion
A method and apparatus for dynamic modeling of an object having material points. The method includes receiving signals from a sensor which correspond to respective material points; providing a volumetric model, having functions as parameters, representative of the object; and adapting the parameters to fit a changing model shape. This method of dynamic shape modeling dynamic motion modeling or both includes shape estimation and motion analysis. The apparatus includes a signal processor for receiving signals from a sensor, a second signal processor for providing a volumetric model having functions as parameters representative of the object and a third signal processor for receiving sensed signals and adapting the model and providing a dynamic representation.
Owner:METAXAS DIMITRI
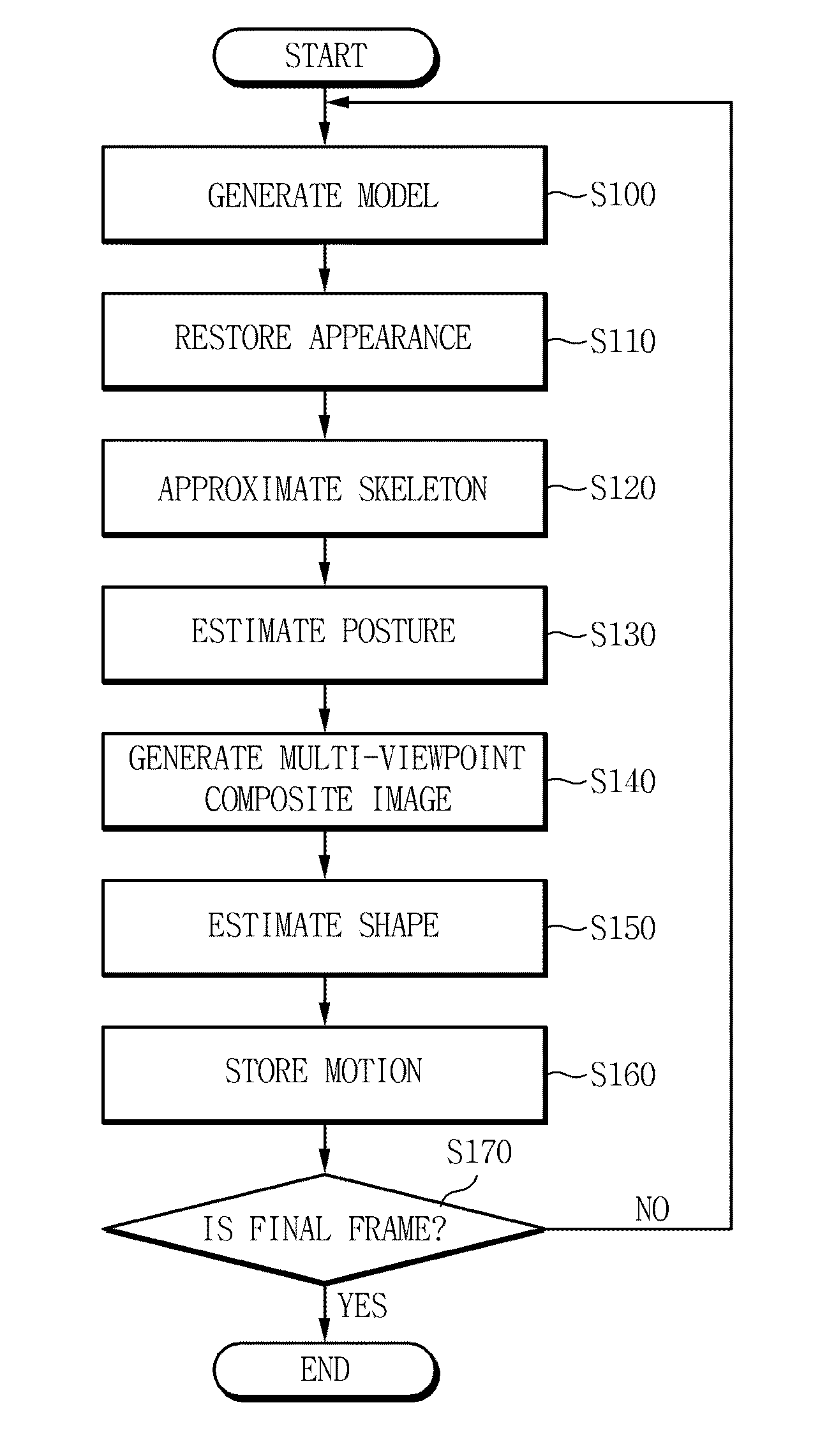
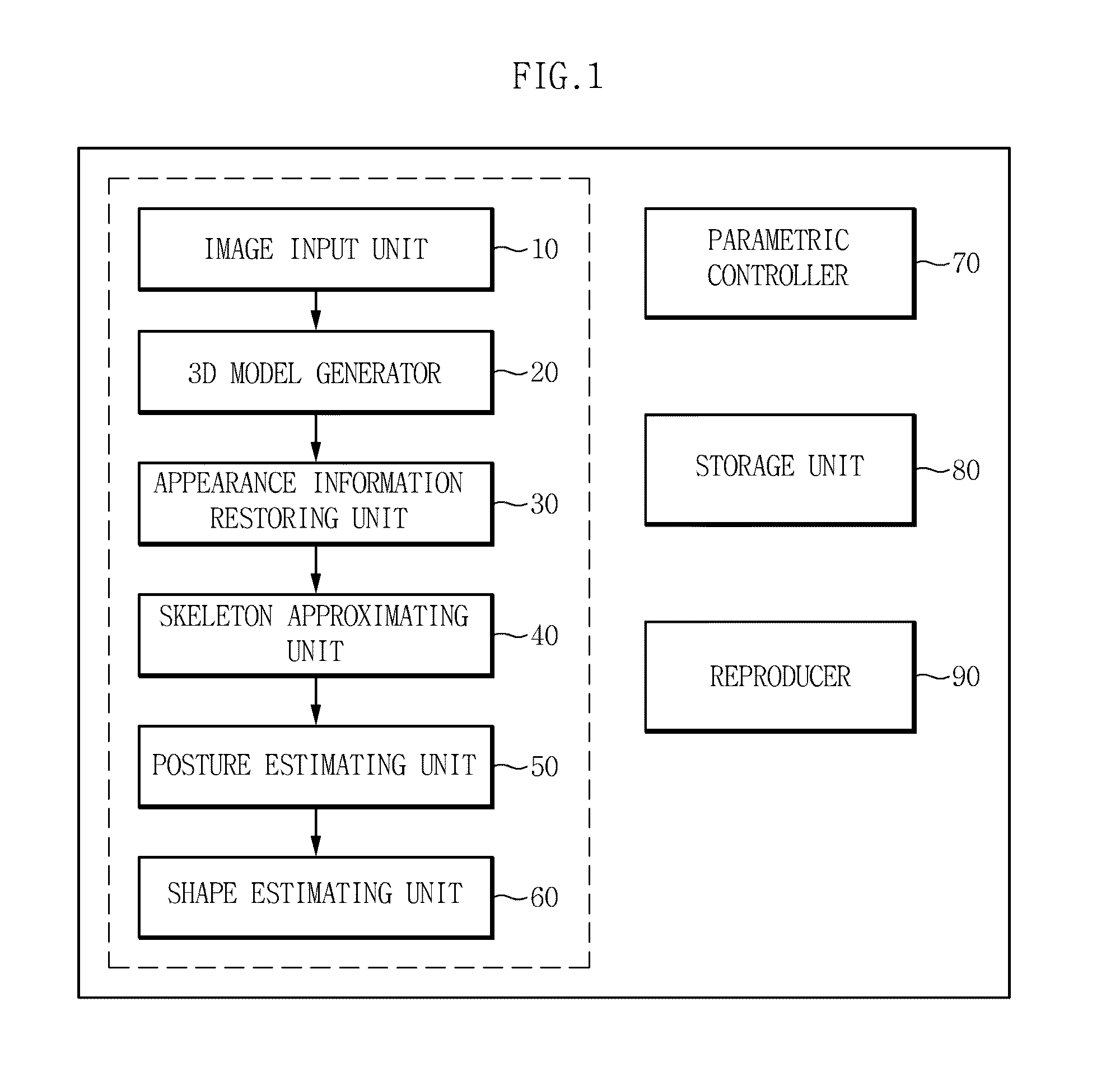
Method and apparatus for capturing motion of dynamic object
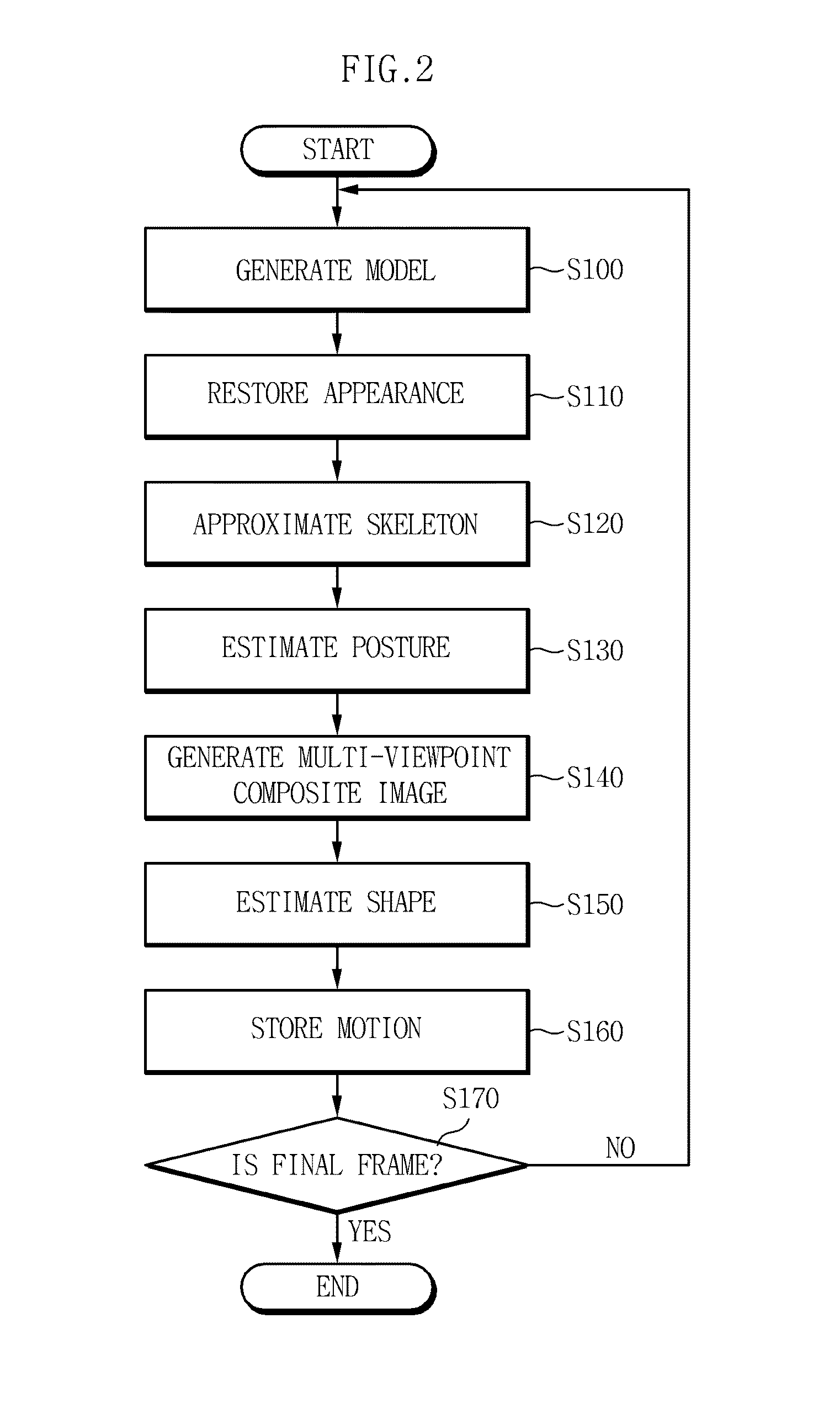
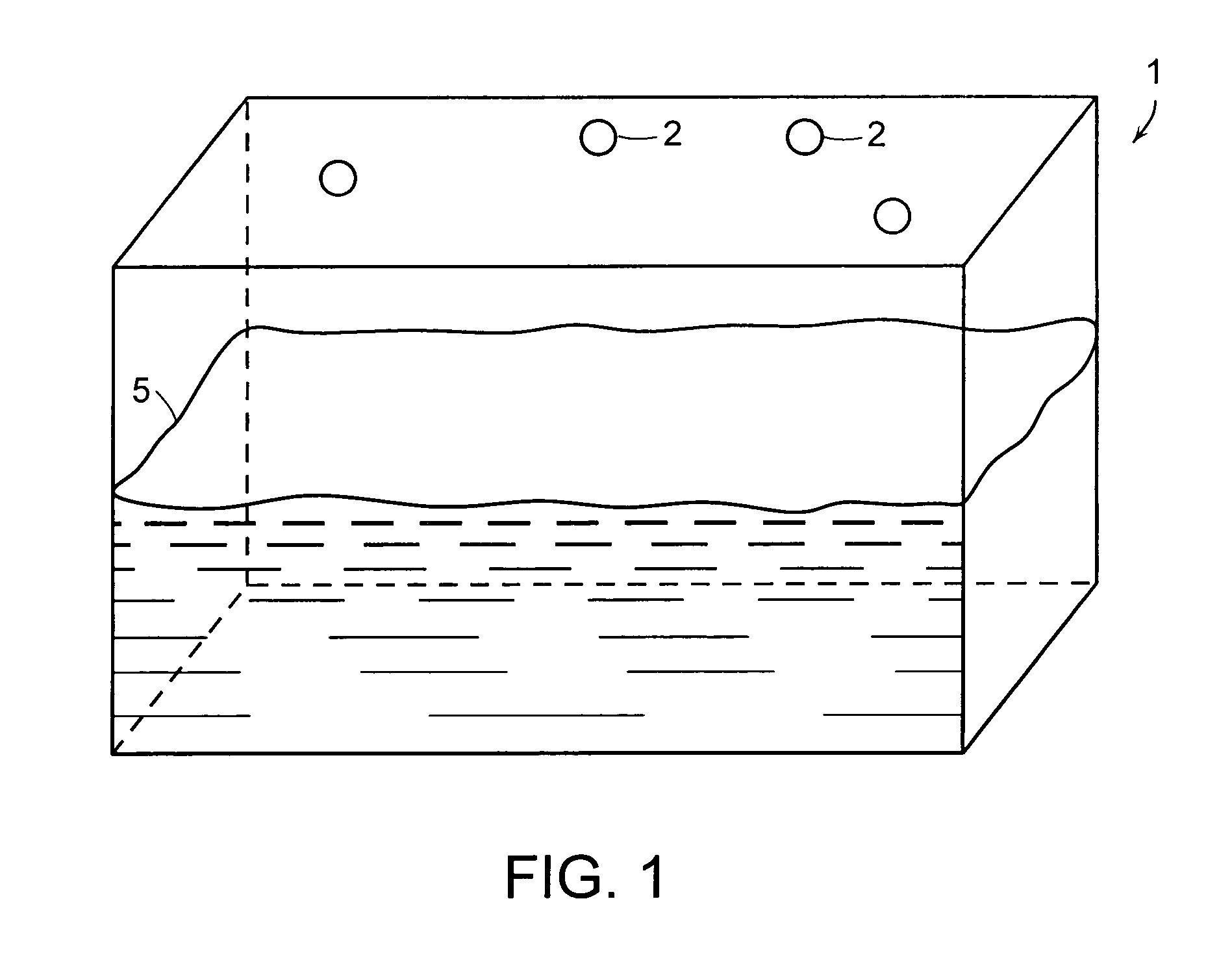
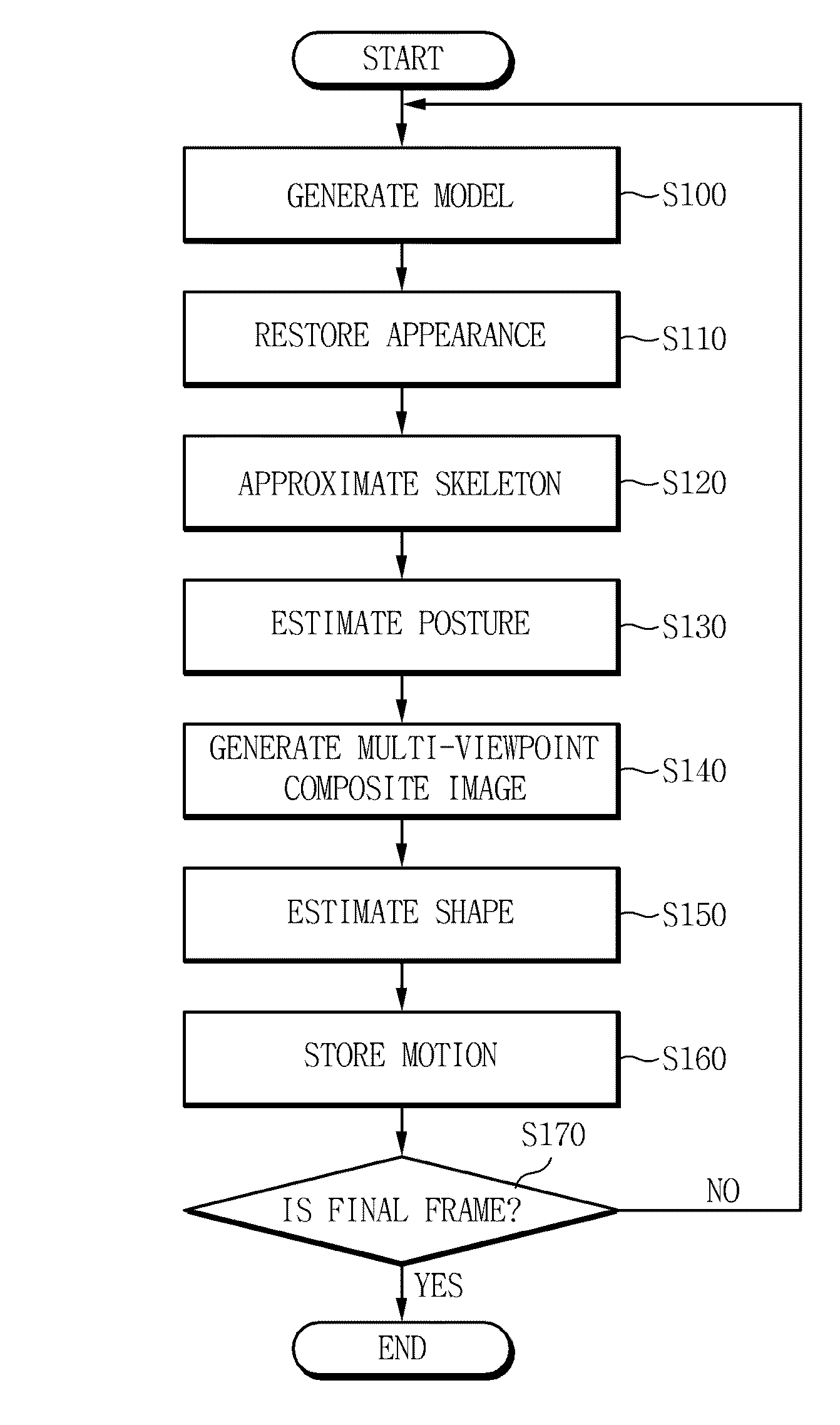
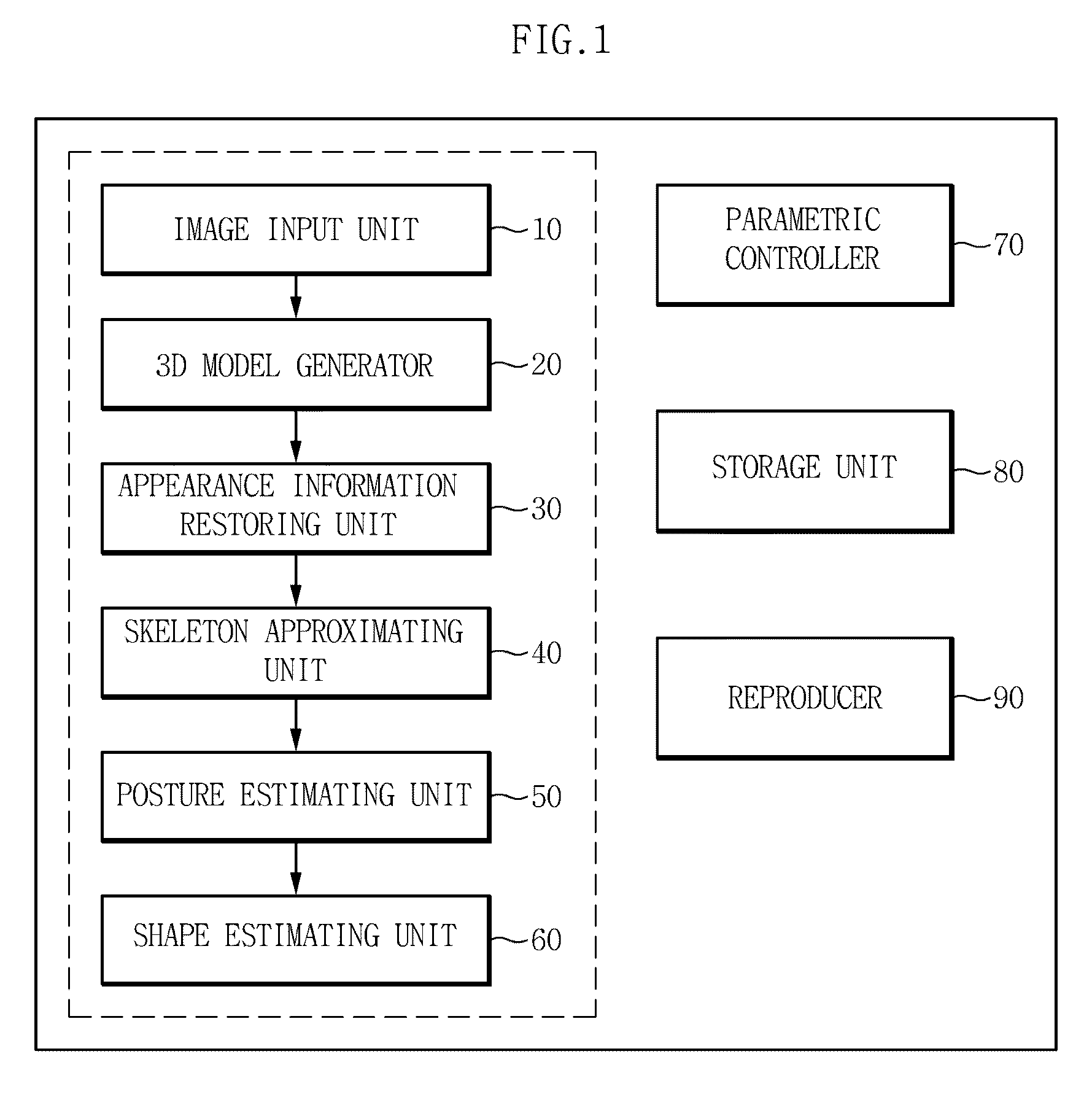
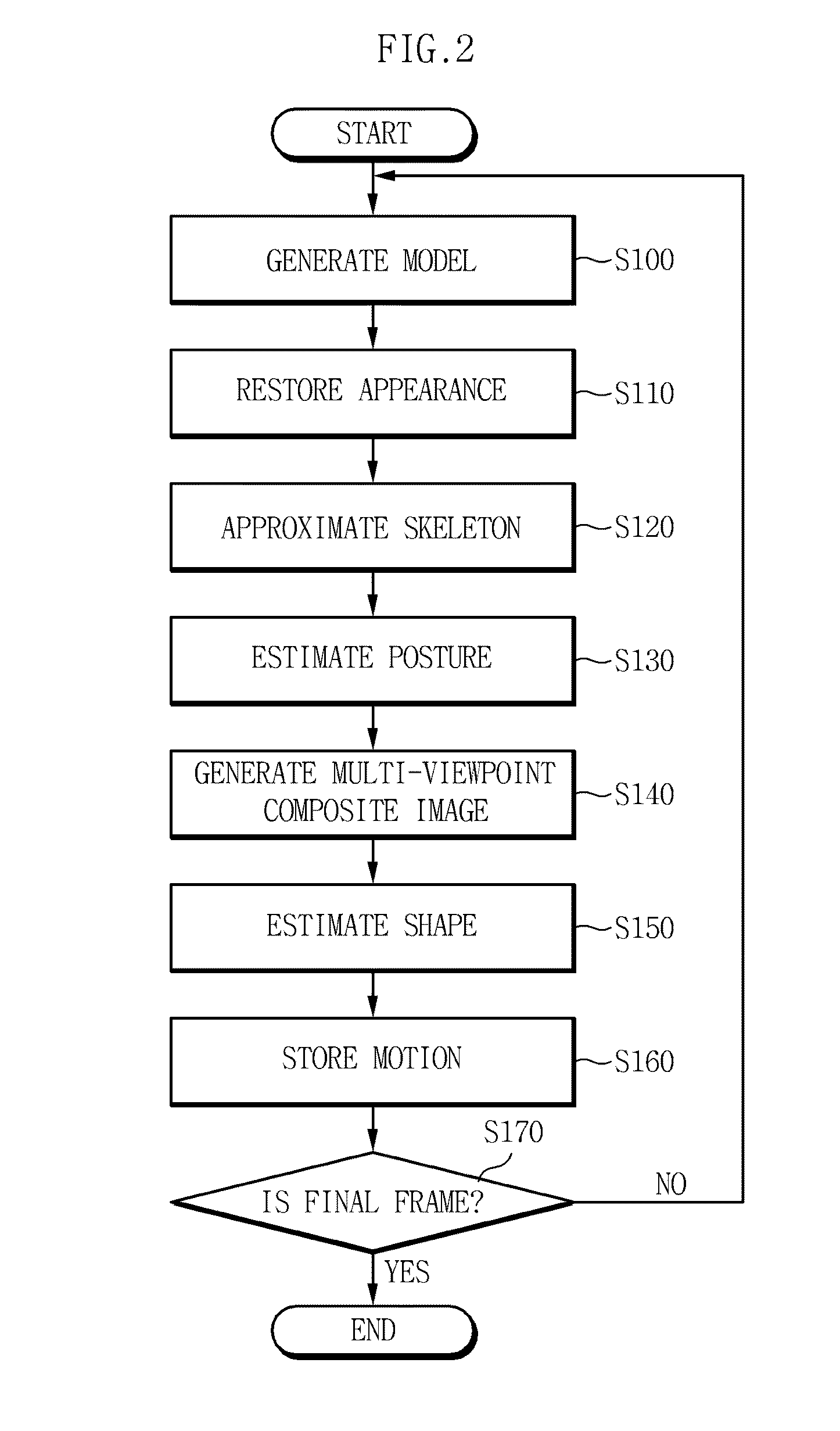
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for capturing a motion of a dynamic object, and restore appearance information of an object making a dynamic motion and motion information of main joints from multi-viewpoint video images of motion information of a dynamic object such as a human body, making a motion through a motion of a skeletal structure on the basis of the skeletal structure, acquired by using multiple cameras. According to the exemplary embodiments of the present invention, it is possible to restore motion information of the object making a dynamic motion by using only an image sensor for a visible light range and to reproduce a multi-viewpoint image by effectively storing the restored information. Further, it is possible to restore motion information of the dynamic object without attaching a specific marker.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
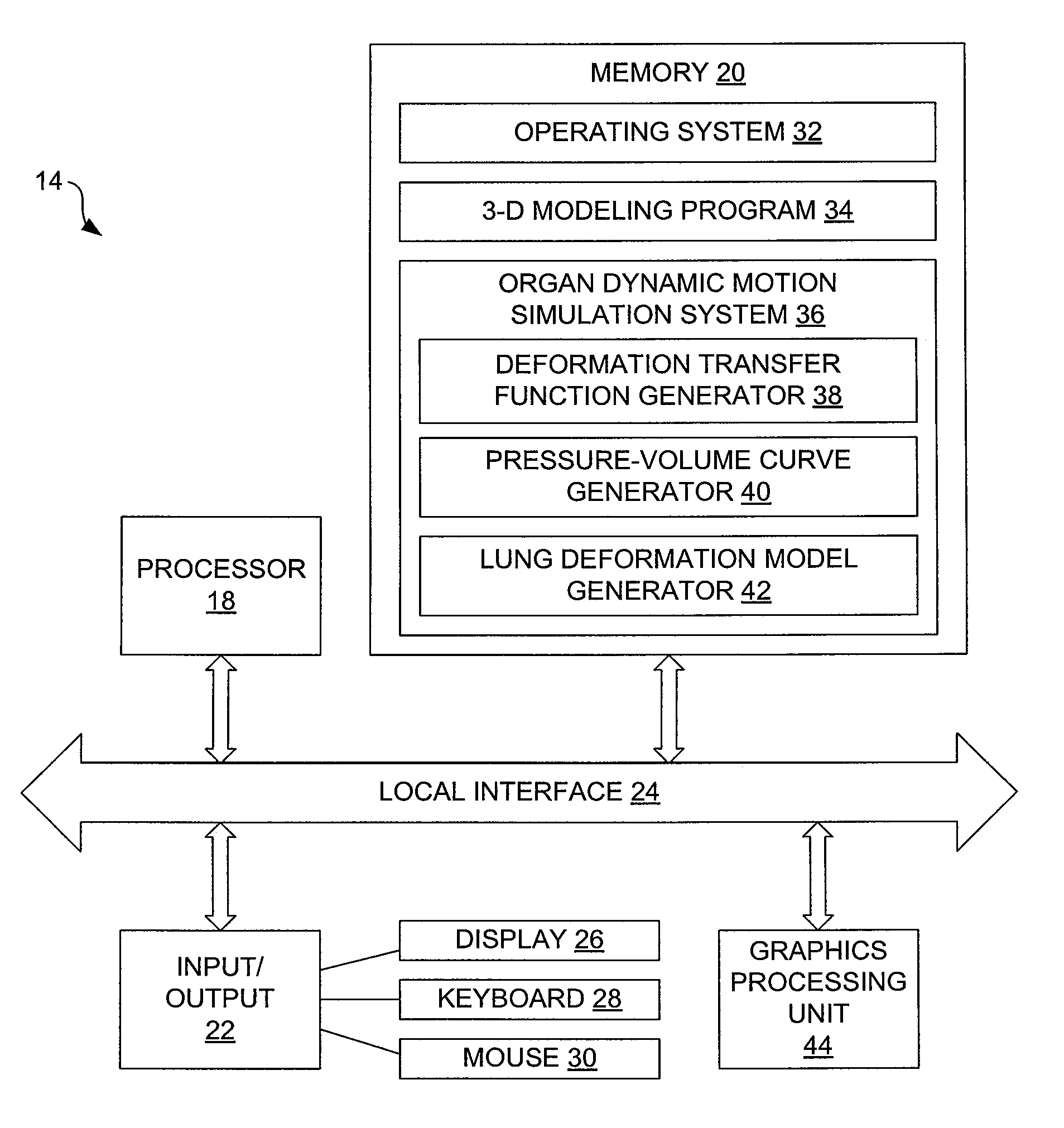
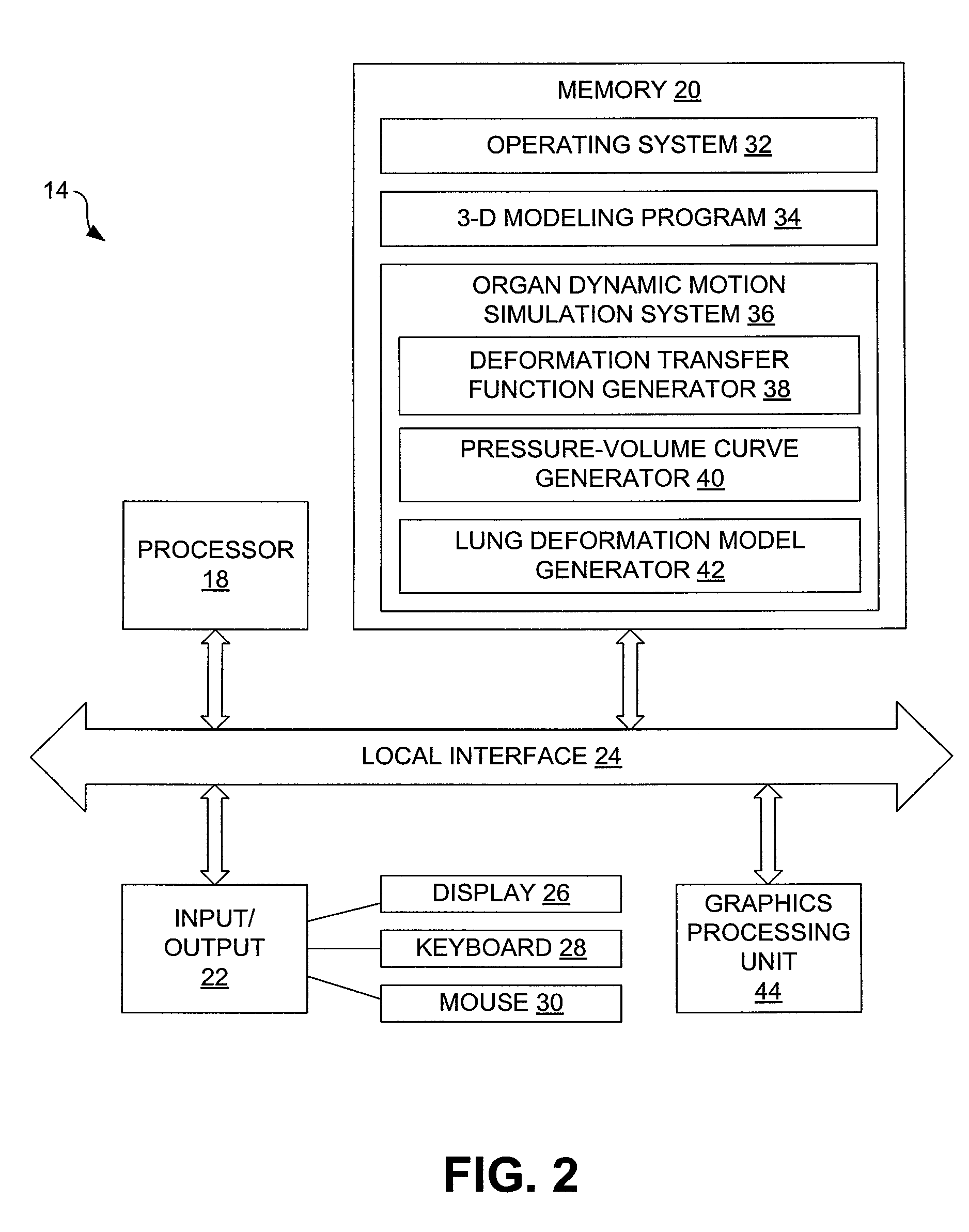
Systems and Methods for Simulation of Organ Dynamics
In one embodiment, a method for simulating organ dynamics includes generating a sequence of three-dimensional models of an organ during different stages of observed dynamic motion, generating a deformation transfer function from the sequence of three-dimensional models, generating a pressure-volume curve from the sequence of three-dimensional models, and generating an organ deformation model that simulates dynamic motion of the organ.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
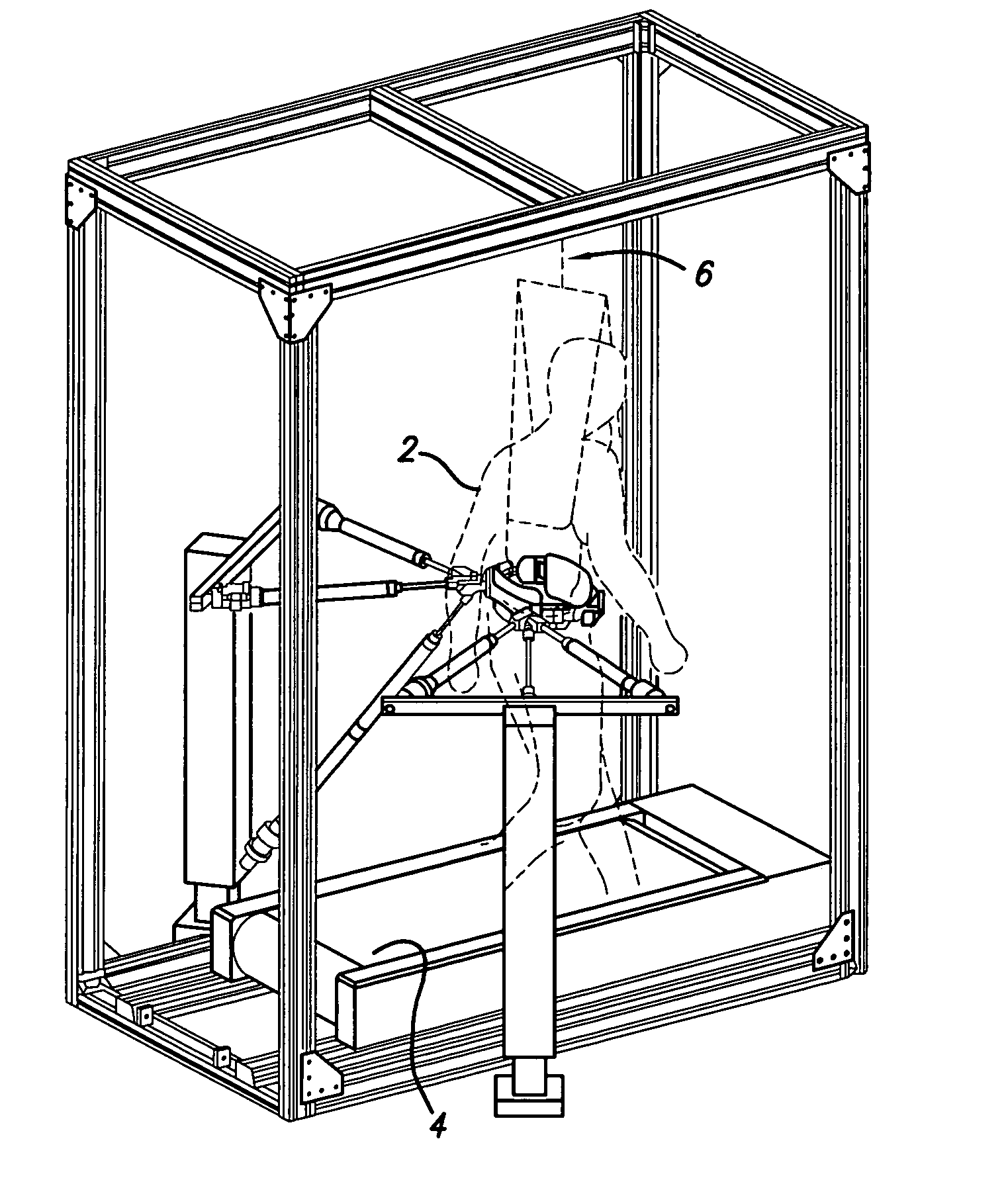
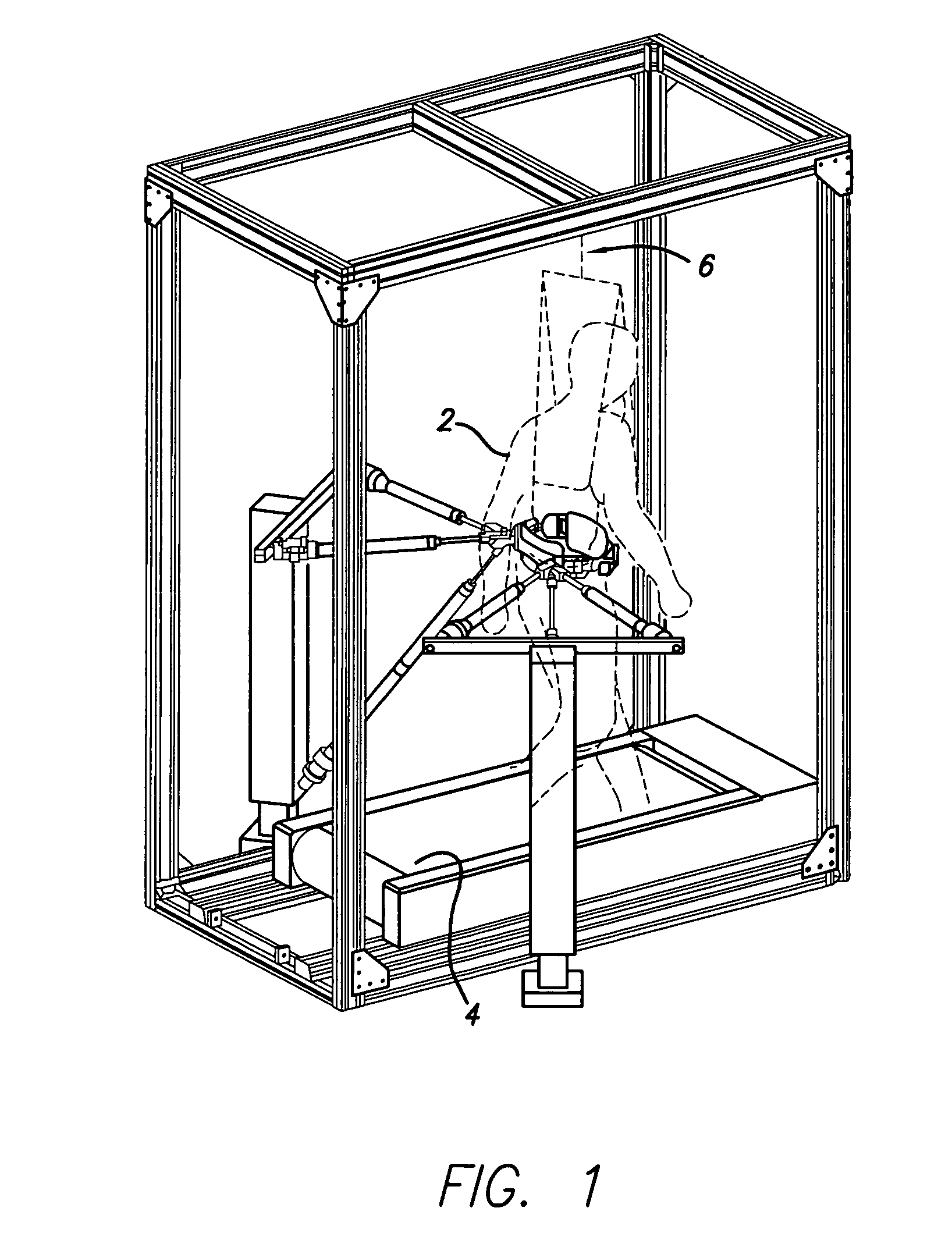
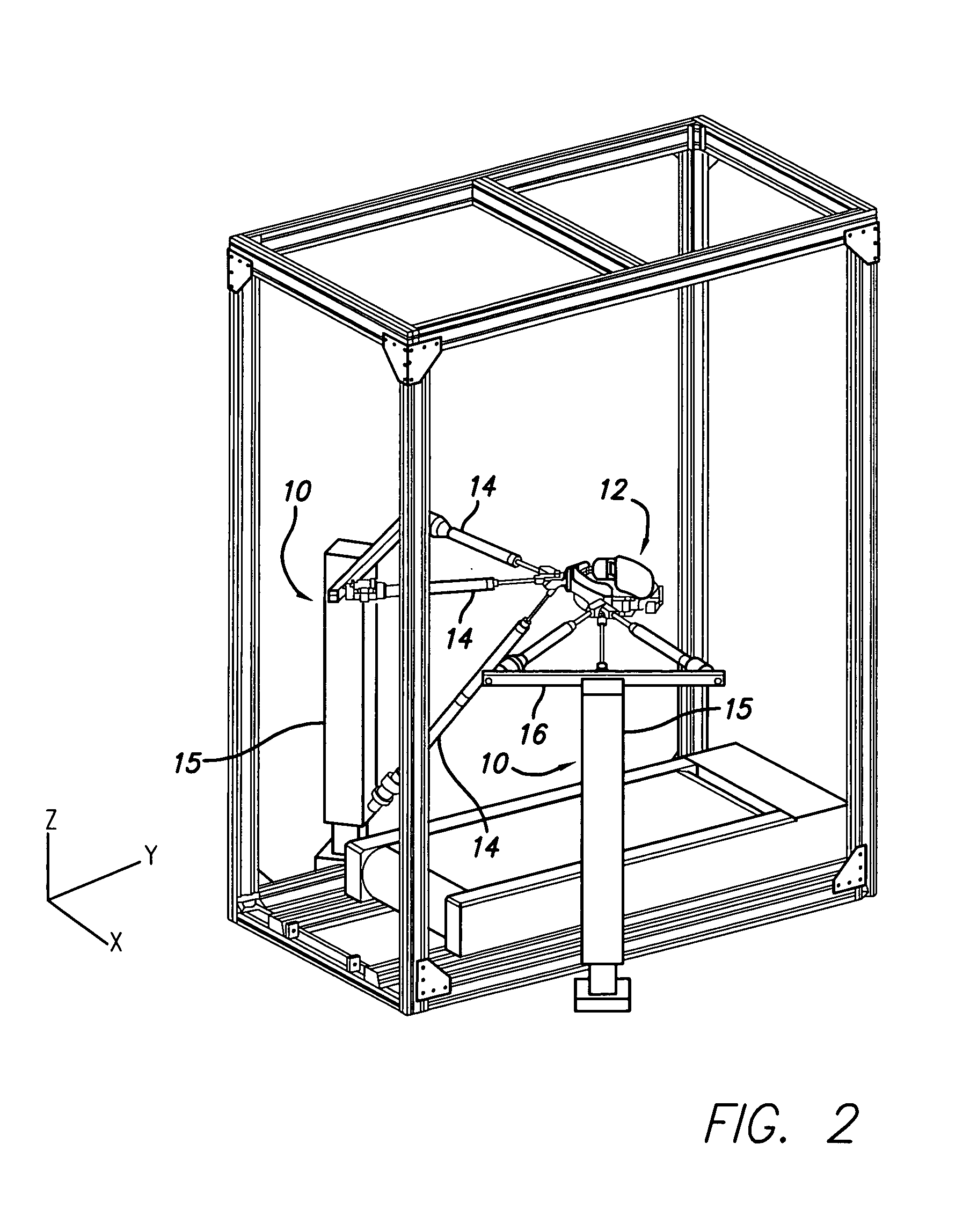
Robotic gait rehabilitation by optimal motion of the hip
A method and a robotic device for locomotion training. The method involves shifting a subject's pelvis without directly contacting the subject's leg, thereby causing the subject's legs to move along a moveable surface. The device comprises two backdriveable robots, each having three pneumatic cylinders that connect to each other at their rod ends for attachment to the subject's torso. Also provided is a method of determining a locomotion training strategy for a pelvic-shifting robot by incorporating dynamic motion optimization.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Implantable pump apparatuses
InactiveUS20070106199A1Harvesting energyControl flowEye surgeryFlexible member pumpsDynamic motionEngineering
Owner:SOLTANPOUR DAVID P
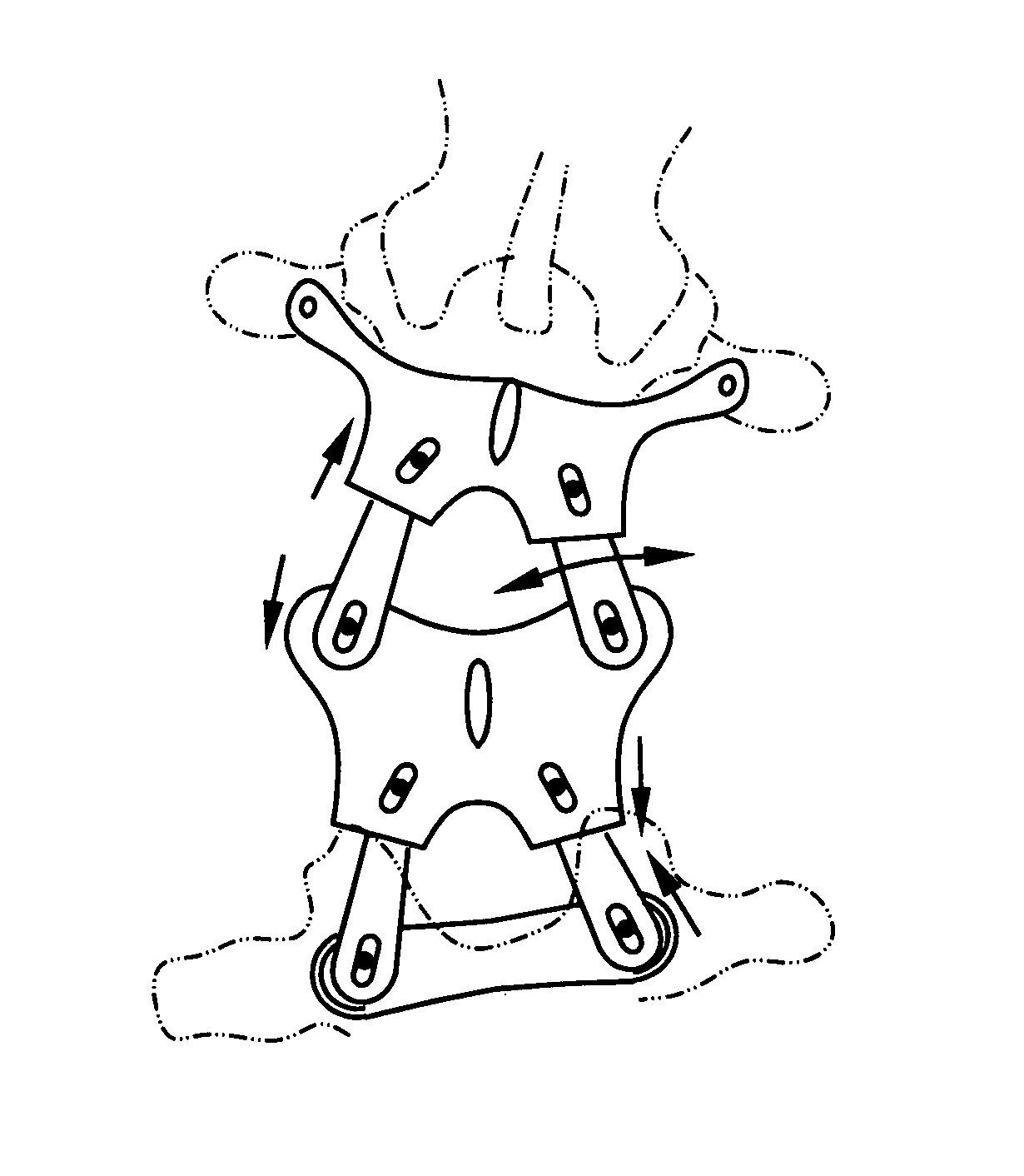
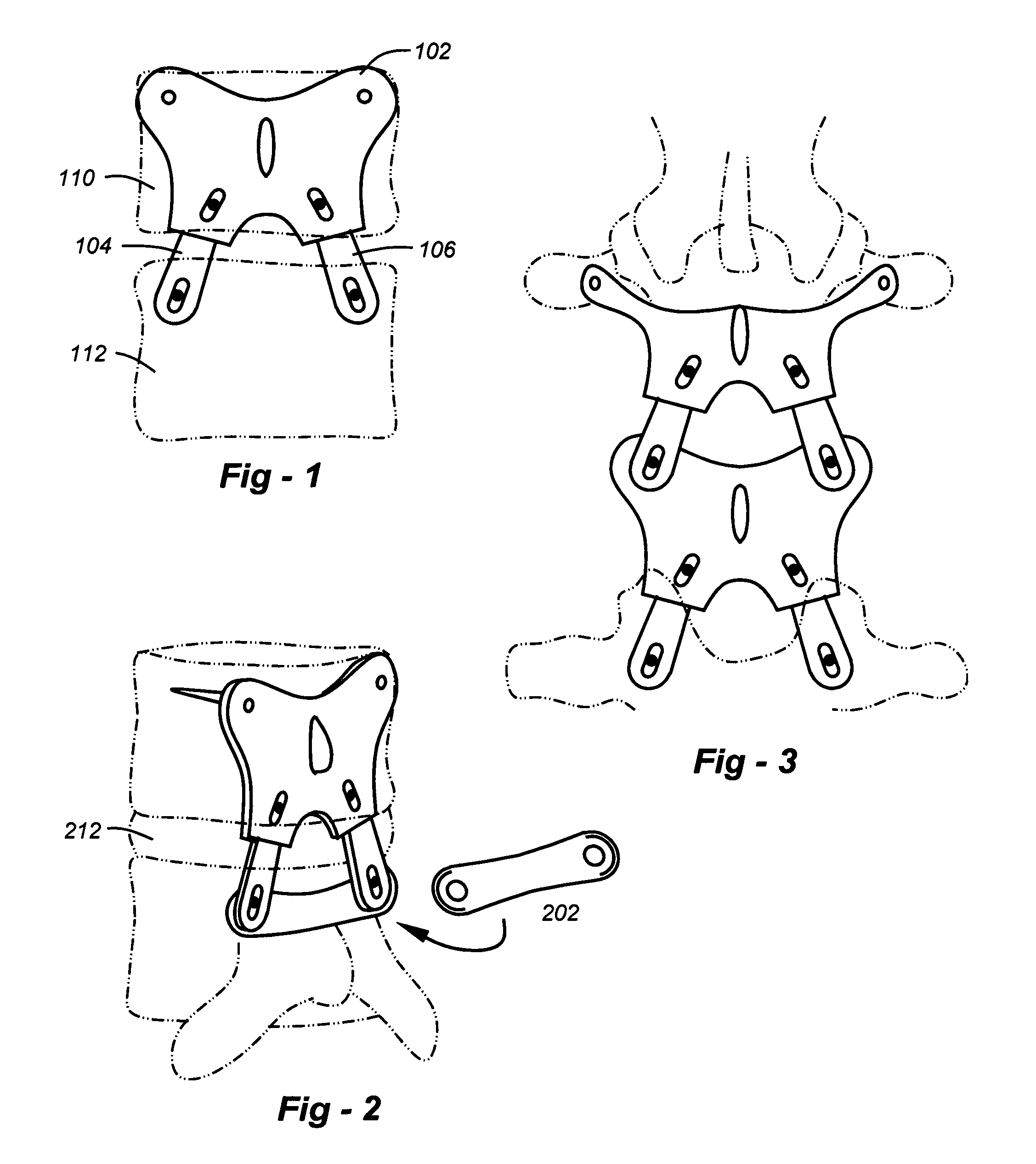
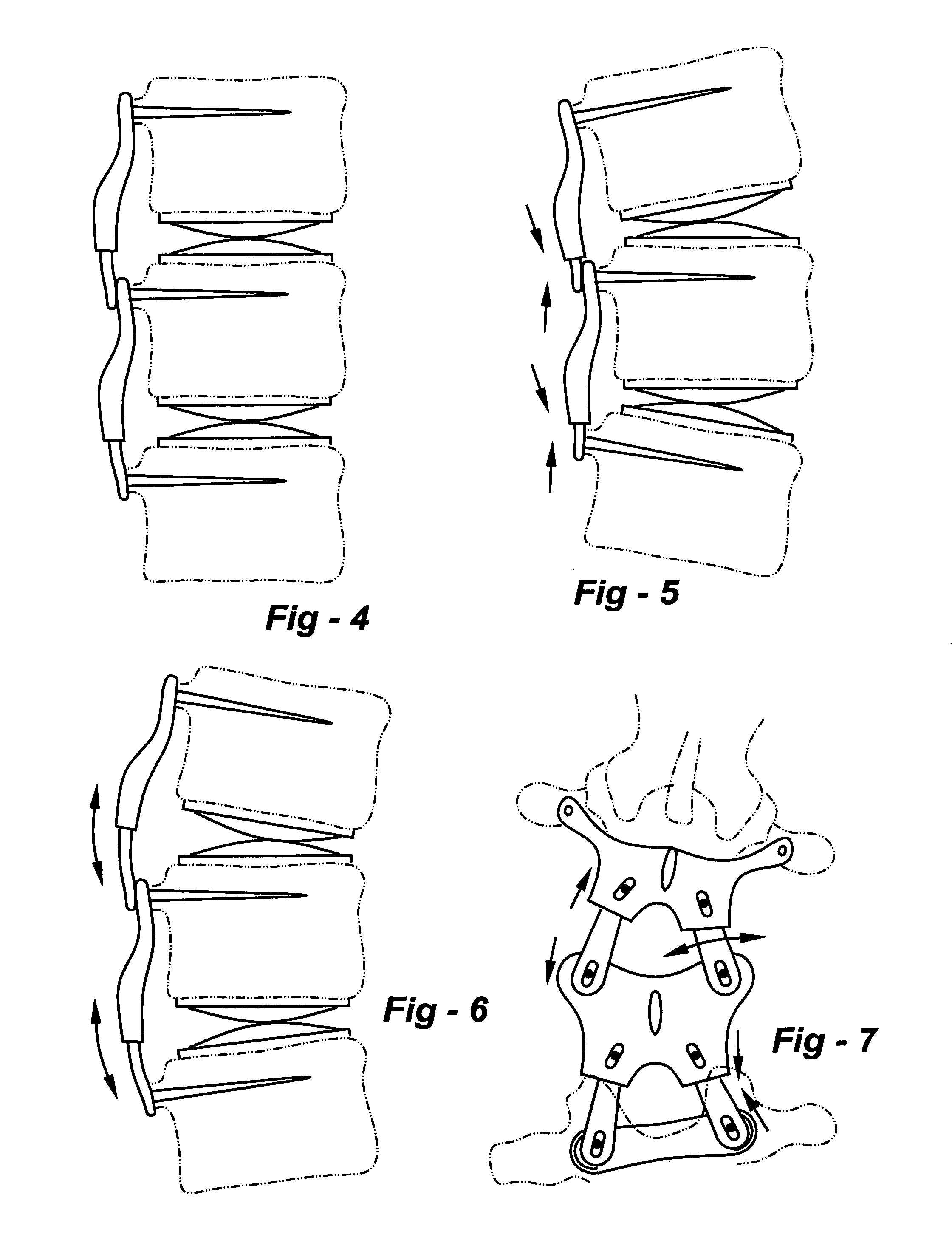
Posterior spinal reconstruction system
A system may be fixed in place to stabilize a spinal fusion, or released for dynamic motion, thereby providing stability with flexibility in conjunction with artificial mechanical or plasma discs, or normal physiologic discs. In terms of apparatus, the invention involves pedicle fixation utilizing a superior facet complex (SFC) with soft tissue attachment points. The SFC receives one or more inferior facet gliding arms (IFGAs) and associated joints which permit flexion, extension, lateral bending and / or other movements.
Owner:MEDICAL DESIGNS
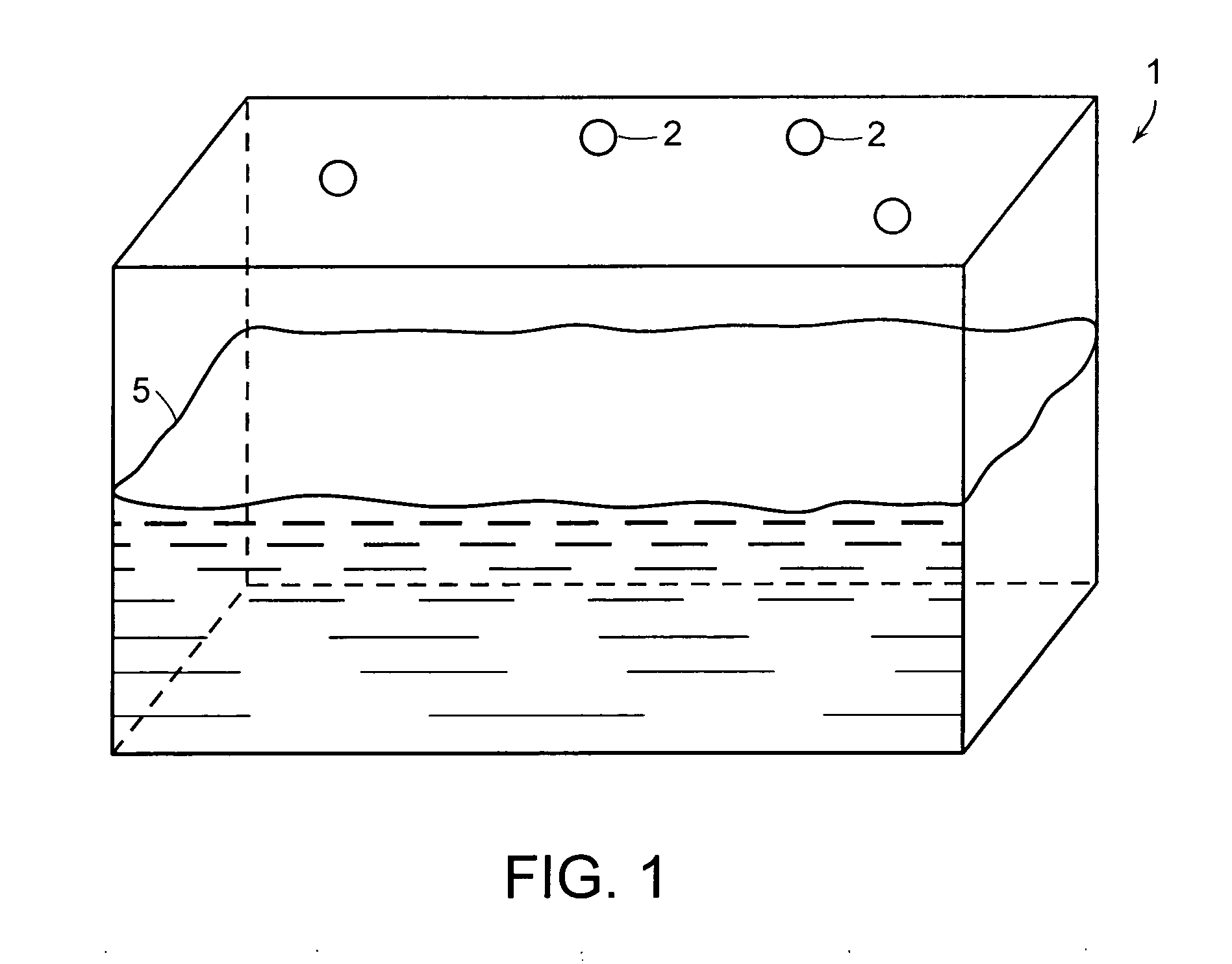
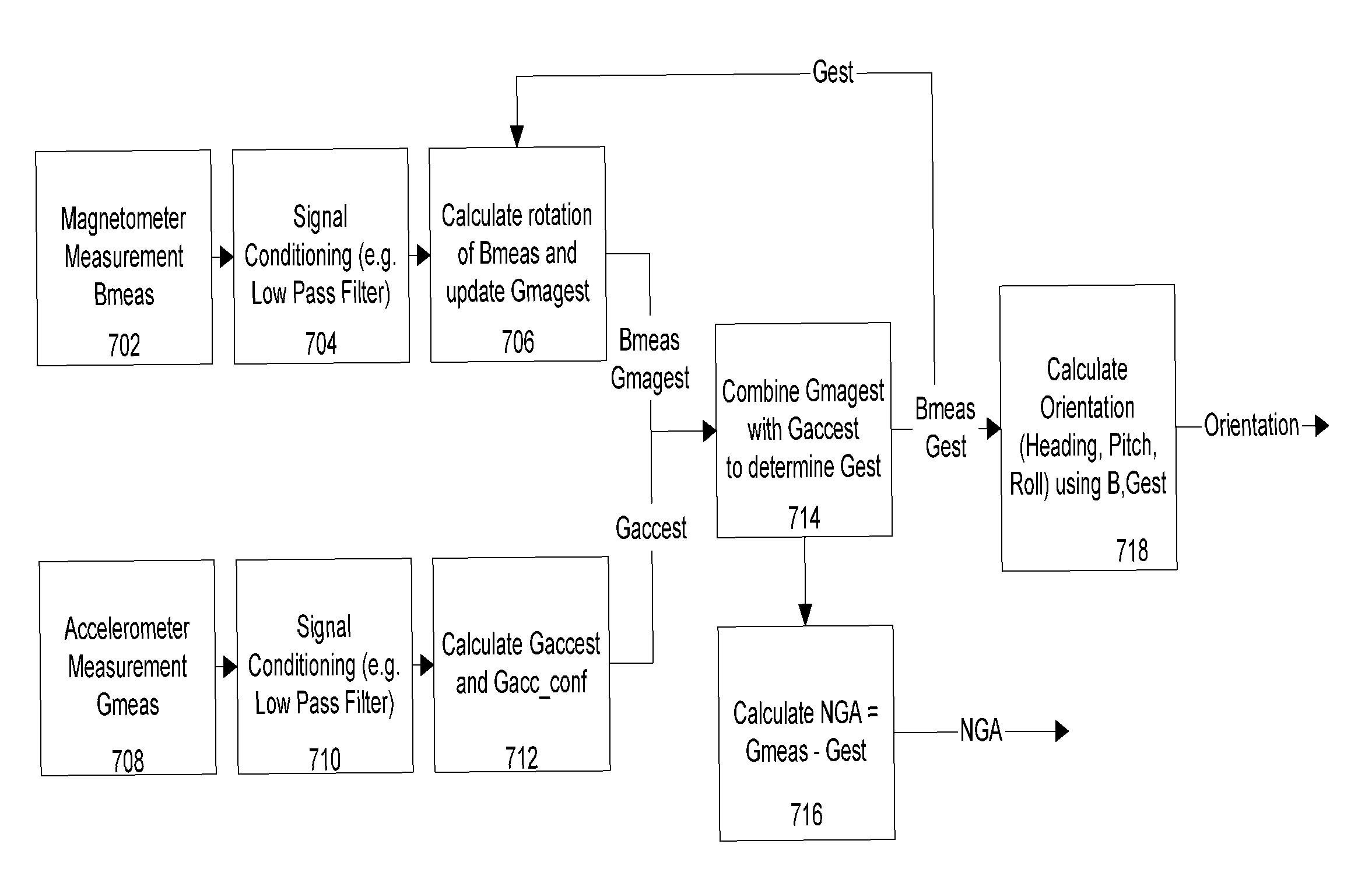
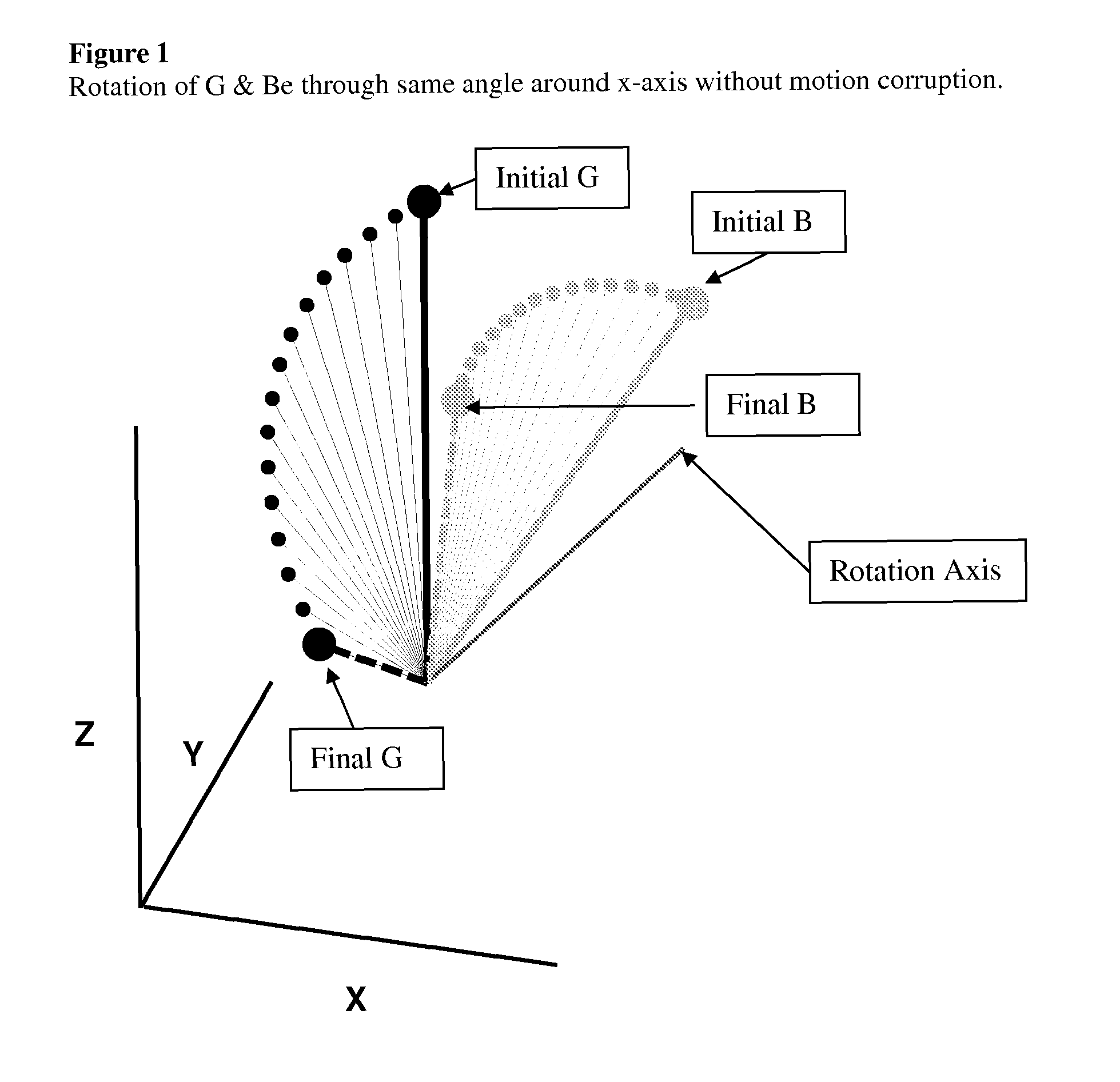
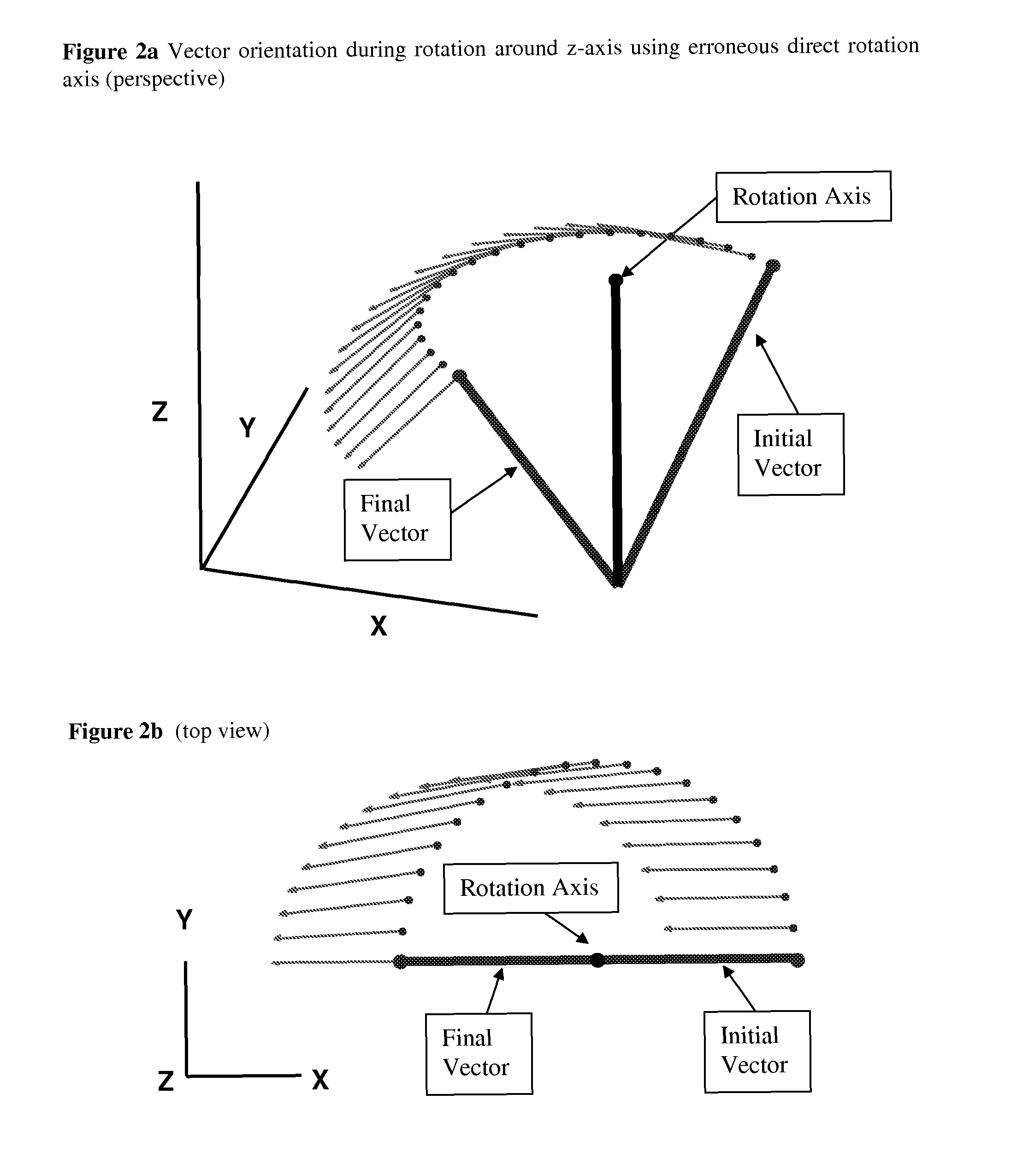
Dynamic motion compensation for orientation instrumentation
InactiveUS7844415B1Accurate readingDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsMeasuring instrumentDynamic motion
Owner:P&I
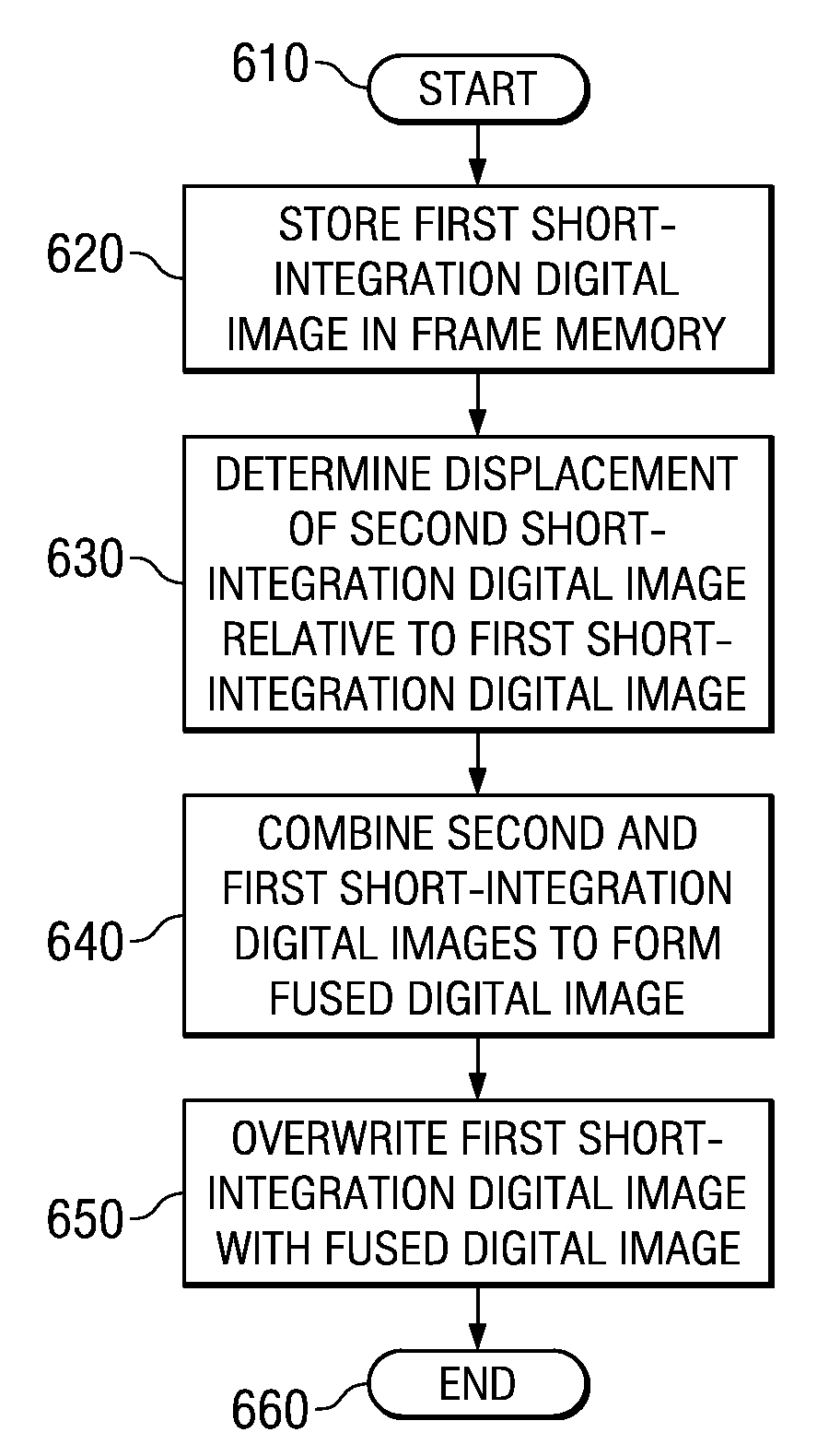
Image Stabilization System and Method for a Digital Camera
InactiveUS20080143840A1Television system detailsClosed circuit television systemsTime conditionDynamic motion
Deblurring digital camera images captured in low-light, long-integration-time conditions by capturing multiple short-integration images and fusing with on-the-fly motion estimation and alignment to limit the frame memory requirements. In one embodiment, an image stabilization system includes: (1) a frame memory and (2) a processor coupled to the frame memory and configured to store a first short-integration digital image in the frame memory, determine a displacement of a second short-integration digital image relative to the first short-integration digital image, combine the second short-integration digital image with the first short-integration digital image to form a fused digital image and overwrite the first short-integration digital image with the fused digital image.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Device and method for medical training and evaluation
InactiveUS8403675B2Generate accuratelySimulate the realEducational modelsAnatomical structuresDynamic motion
A training and / or evaluating device is provided particularly useful in performing laparoscopic procedures, radiological procedures, and precise surgeries that simulates the structure and dynamic motion of the corresponding anatomical structure on which the procedure takes place. The device includes an outer housing, which may be designed to mimic the body wall, in which one or more organs are located. Motion of the organ(s), as a result of respiration, pulmonary action, circulation, digestion and other factors present in a live body, is simulated in the device so as to provide accurate dynamic motion of the organs during a procedure.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method and apparatus for capturing motion of dynamic object
InactiveUS8659594B2Error minimizationMinimizing colorAnimation3D-image renderingViewpointsDynamic motion
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Fresnel solar concentrator with internal-swivel and suspended swivel mirrors
InactiveUS7568479B2Stability advantageSimpler and efficient alignmentSolar heating energyMirrorsVertical stabilityDynamic motion
This invention deals with novel method and apparatus for positioning and motion control of the elements (mirrors) of a Fresnel reflector solar concentrator tracking heliostat array wherein the elements are suspended with the center of mass below the swivel point, or have an internal-swivel. This achieves an advantageous natural vertical stability. The torque to produce angular deflection, and rotational motion is provided separately by an electric wind force due to electrons, ions, and / or neutrals; or in combination with an induced and / or permanent dipole coupling to an electronic grid. Thus forces and torques are produced without the use of internal moving parts such as in motors. The instant invention exceeds the capability of conventional systems. It is ideally suited for maximization of solar energy focused by a low-profile concentrator array onto a receiver. Since there are no internal moving parts, the instant invention provides less costly and greater ease of manufacture. Dynamic motion can be controlled over a wide range of dimensions from nanometers to decimeters.
Owner:RABINOWITZ MARIO
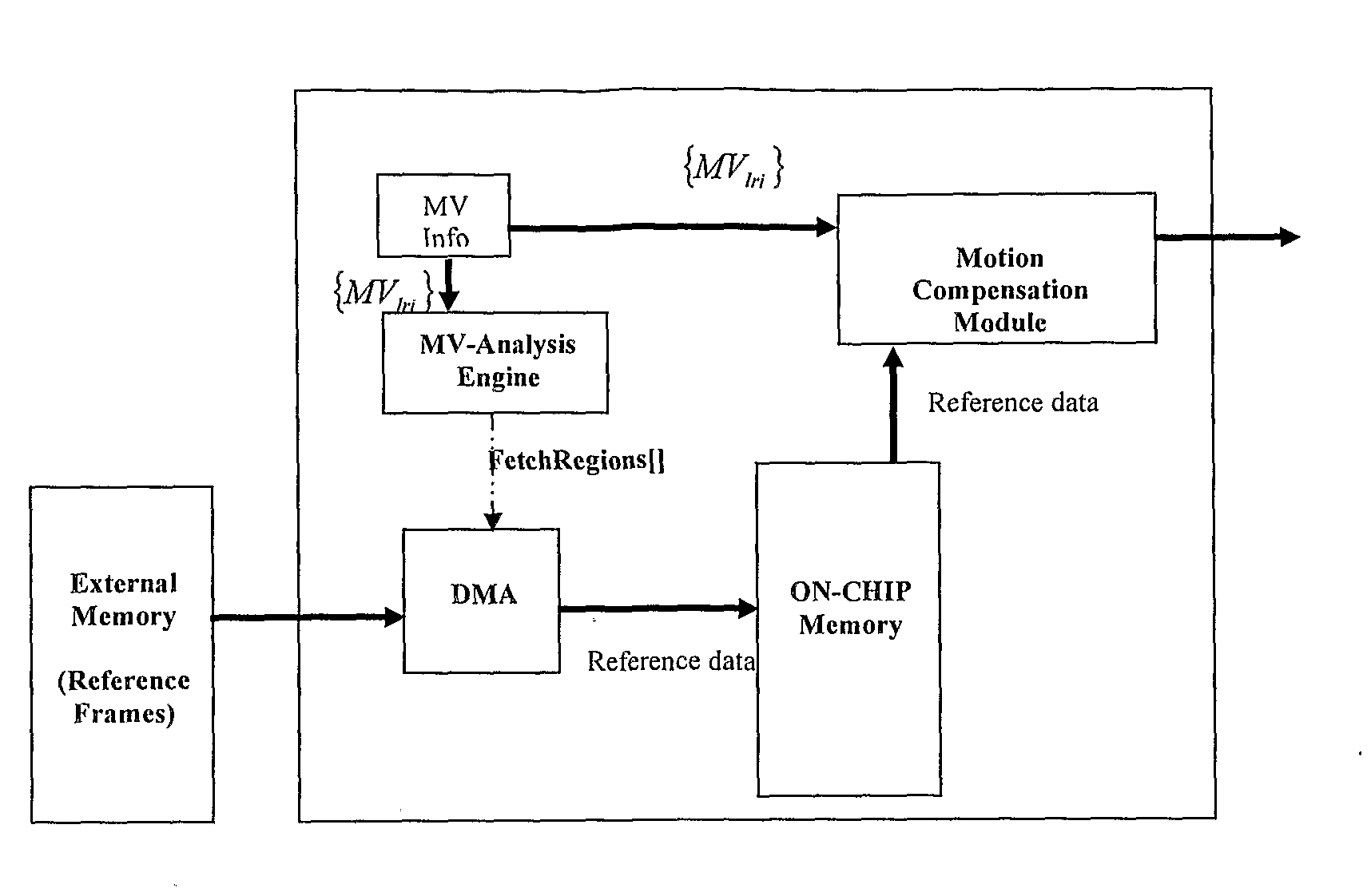
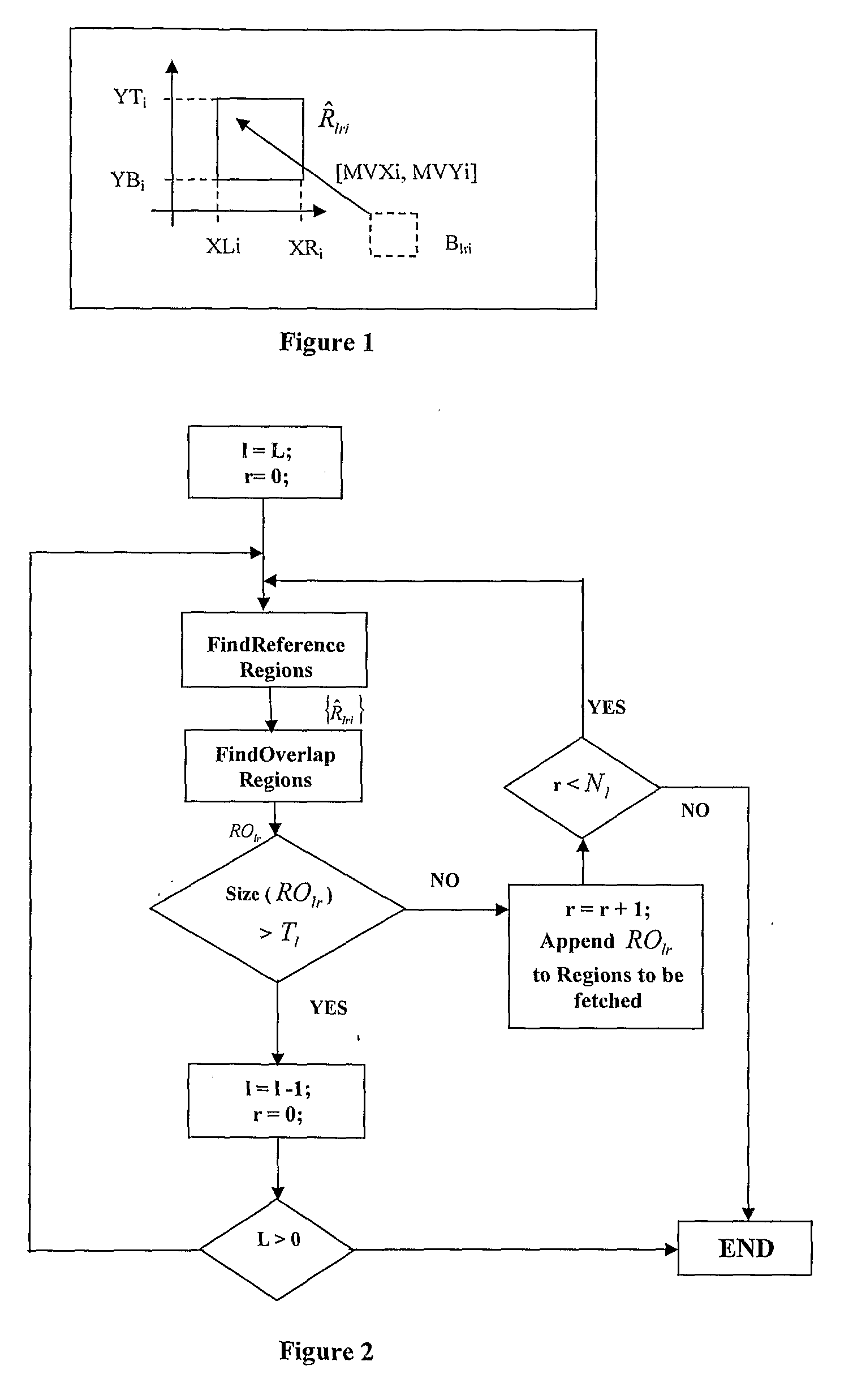
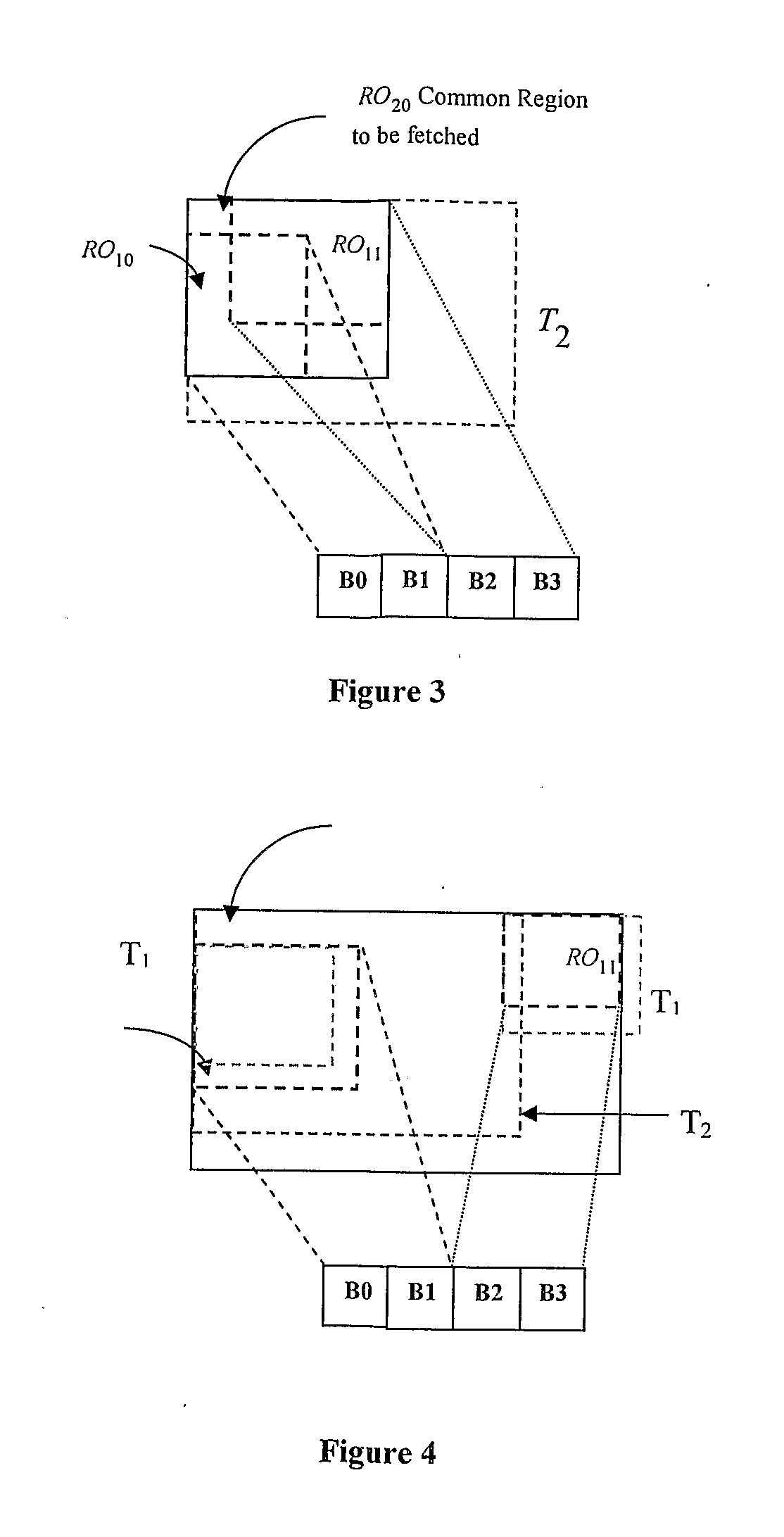
Dynamic motion vector analysis method
ActiveUS20100098165A1Reduce decreaseReduce redundant dataColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionExternal storageMotion vector
The proposed Dynamic Motion Vector Analysis method applies to the motion compensation module of a video decoder system. The method analyzes the motion-vectors of a given region of picture frame and outputs a set of regions to be fetched from the reference frames stored in the external memory. The size and number of regions are decided by a hierarchical method that uses a set of user-defined input thresholds. Pre-processing of the motion vectors associated with the given region allows the method to handle reference data to be fetched from multiple reference frames in the same framework. A complementary dynamic batch (region of operation) size strategy that works along with MV-analysis is also proposed to help utilize the on-chip memory resources more efficiently.
Owner:ALLGO EMBEDDED SYST PVT
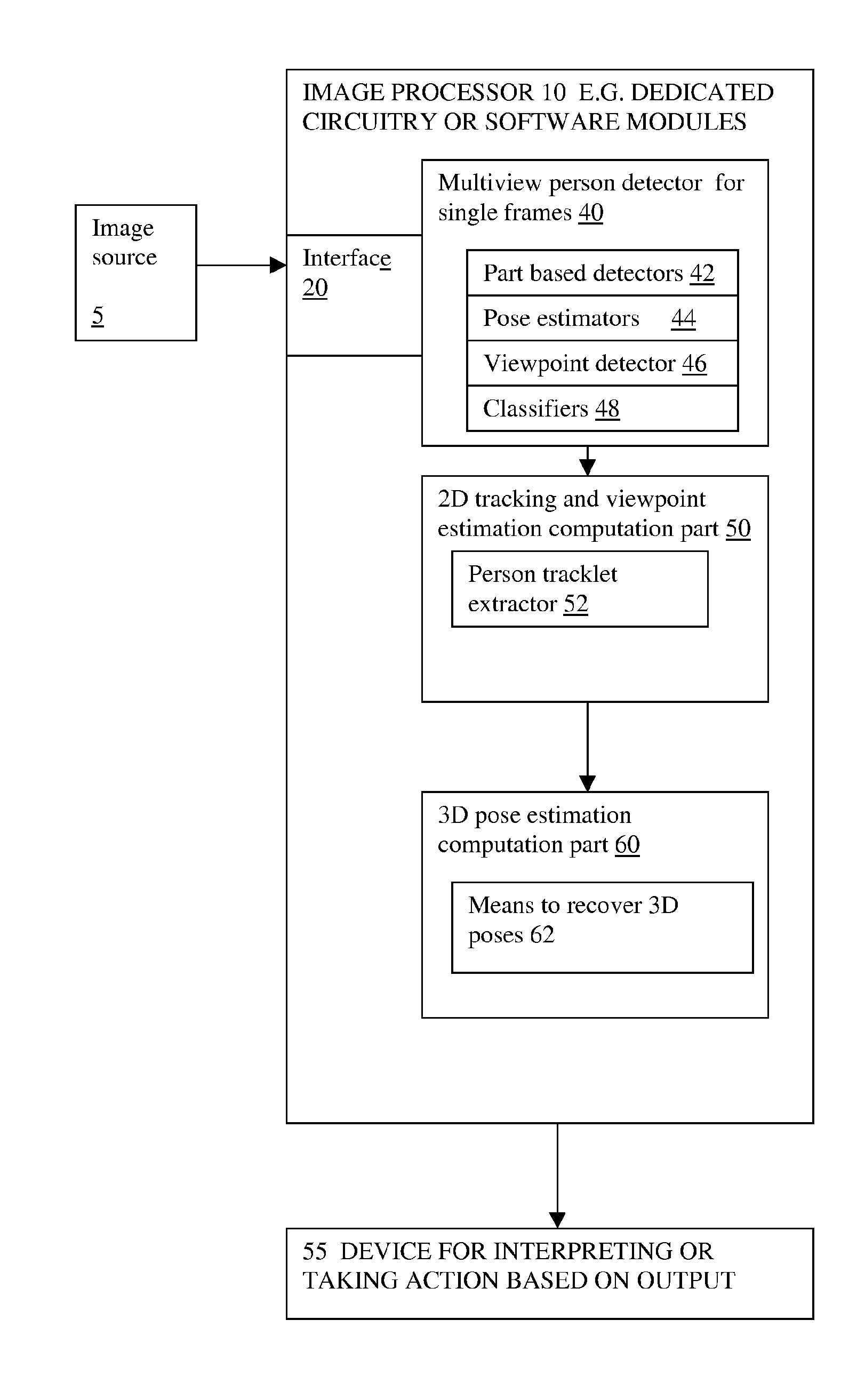
Monocular 3D pose estimation and tracking by detection
InactiveUS20130142390A1Low applicabilityReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisThree stageBayesian formulation
Methods and apparatus are described for monocular 3D human pose estimation and tracking, which are able to recover poses of people in realistic street conditions captured using a monocular, potentially moving camera. Embodiments of the present invention provide a three-stage process involving estimating (10, 60, 110) a 3D pose of each of the multiple objects using an output of 2D tracking-by detection (50) and 2D viewpoint estimation (46). The present invention provides a sound Bayesian formulation to address the above problems. The present invention can provide articulated 3D tracking in realistic street conditions.The present invention provides methods and apparatus for people detection and 2D pose estimation combined with a dynamic motion prior. The present invention provides not only 2D pose estimation for people in side views, it goes beyond this by estimating poses in 3D from multiple viewpoints. The estimation of poses is done in monocular images, and does not require stereo images. Also the present invention does not require detection of characteristic poses of people.
Owner:TECH UNIV DARMSTADT +1
Method and device for realizing interaction of augment reality (AR) and mobile terminal
ActiveCN102147658AAvoid operabilityAvoid stabilityInput/output for user-computer interactionSubstation equipmentDynamic motionInteraction device
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for realizing interaction of an augment reality (AR) and a mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring the information of a pattern, wherein the pattern is an interactive scene of the AR; determining the three-dimensional information of a virtual scene according to the information of the pattern; calculating an initial relative spatial position relationship among the virtual scene, the AR interaction device and the pattern according to the three-dimensional information; superposing the virtual scene and the pattern according to the initial relative spatial position relationship; acquiring a spatial position relationship of the AR interaction device, and determining a three-dimensional dynamic motion path of the AR interaction device; obtaining a current relative spatial position relationship among the virtual scene, the AR interaction device and the pattern according to the initial relative spatial position relationship and the three-dimensional dynamic motion path; and superposing the virtual scene and the pattern according to the current relative spatial position relationship. Therefore, the stability of the process of AR interaction is improved, and the operability of the AR interaction is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
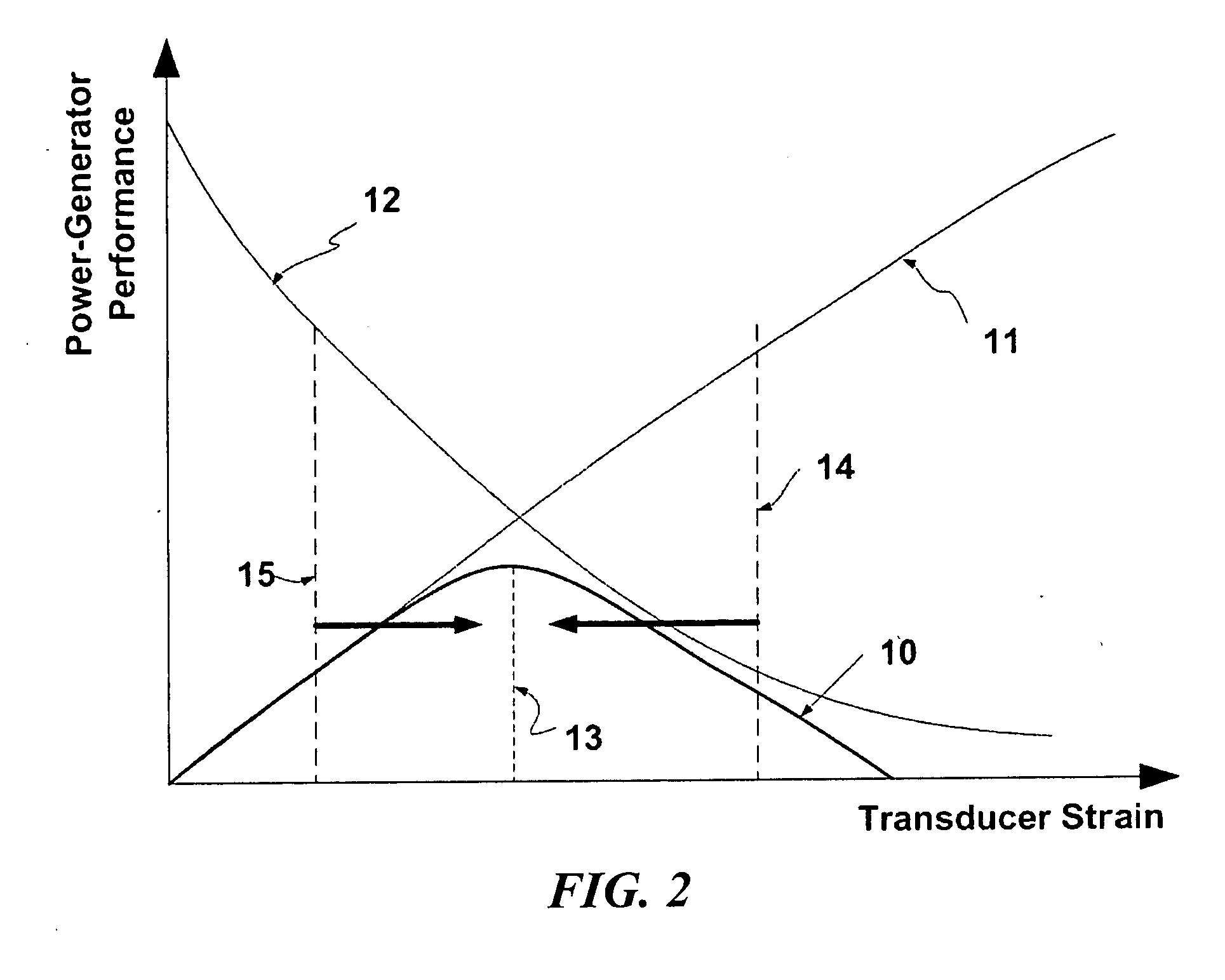
Robust piezoelectric power generation module
InactiveUS20050012434A1Easy to set upImprove performancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesElectricityTransducer
An electrical power generation system includes a transducer that generates electrical energy under dynamic mechanical loading. A buffer is mechanically coupled to the transducer and adapted to be mechanically coupled to a structure. The buffer facilitates the transducer to operate within a predetermined mechanical loading range to allow the system to provide electrical energy. An electricity generator module includes a transducer that generates electrical energy under dynamic motion conditions. A circuit coupled to the electrically transducer converts the electrical energy into usable electricity at a circuit output. A planar housing encloses the transducer and circuit and (i) allows the transducer to be exposed to the dynamic motion conditions and (ii) provides electrical contacts that facilitate delivery of the useable electricity for external circuitry.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP +1
Design of robotic gait rehabilitation by optimal motion of the hip
A method and a robotic device for locomotion training. The method involves shifting a subject's pelvis without directly contacting the subject's leg, thereby causing the subject's legs to move along a moveable surface. The device comprises two backdriveable robots, each having three pneumatic cylinders that connect to each other at their rod ends for attachment to the subject's torso. Also provided is a method of determining a locomotion training strategy for a pelvic-shifting robot by incorporating dynamic motion optimization.
Owner:REINKENSMEYER DAVID J +4
High-dynamic weak-signal rapid capture method for direct sequence spread spectrum system
InactiveCN102098074AImprove detection signal-to-noise ratioImprove detection rateTransmissionFast algorithmCarrier signal
The invention discloses a high-dynamic weak-signal rapid capture method for a direct sequence spread spectrum system, belonging to the field of radio communication. Because a spread spectrum carrier has a chirp signal characteristic under the condition of high-dynamic motion (high-speed and high-acceleration), the high-dynamic weak-signal rapid capture method comprises the steps of: firstly, carrying out carrier Doppler frequency compensation by using a time frequency focusing characteristic of fractional order Fourier transform; secondly, carrying out incoherent accumulation on a spread frequency signal by using an order resolving capacity of the fractional order Fourier transform; and finally, carrying out capture judgment on the signal in an order Fourier domain by using a constant false alarm rate detection technology. According to the invention, the difficulty of incapability of long-time coherent accumulation under the high-dynamic condition in the traditional Fourier transform based rapid capture method is solved; and under the condition of high dynamicity and low signal to noise ratio, the signal to noise ratio is effectively increased and the signal capture time is shortened. In addition, a rapid algorithm exists in the invention and is easy to realize on the engineering in real time.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Systems and methods for obtaining improved accuracy measurements of moving rolling stock components
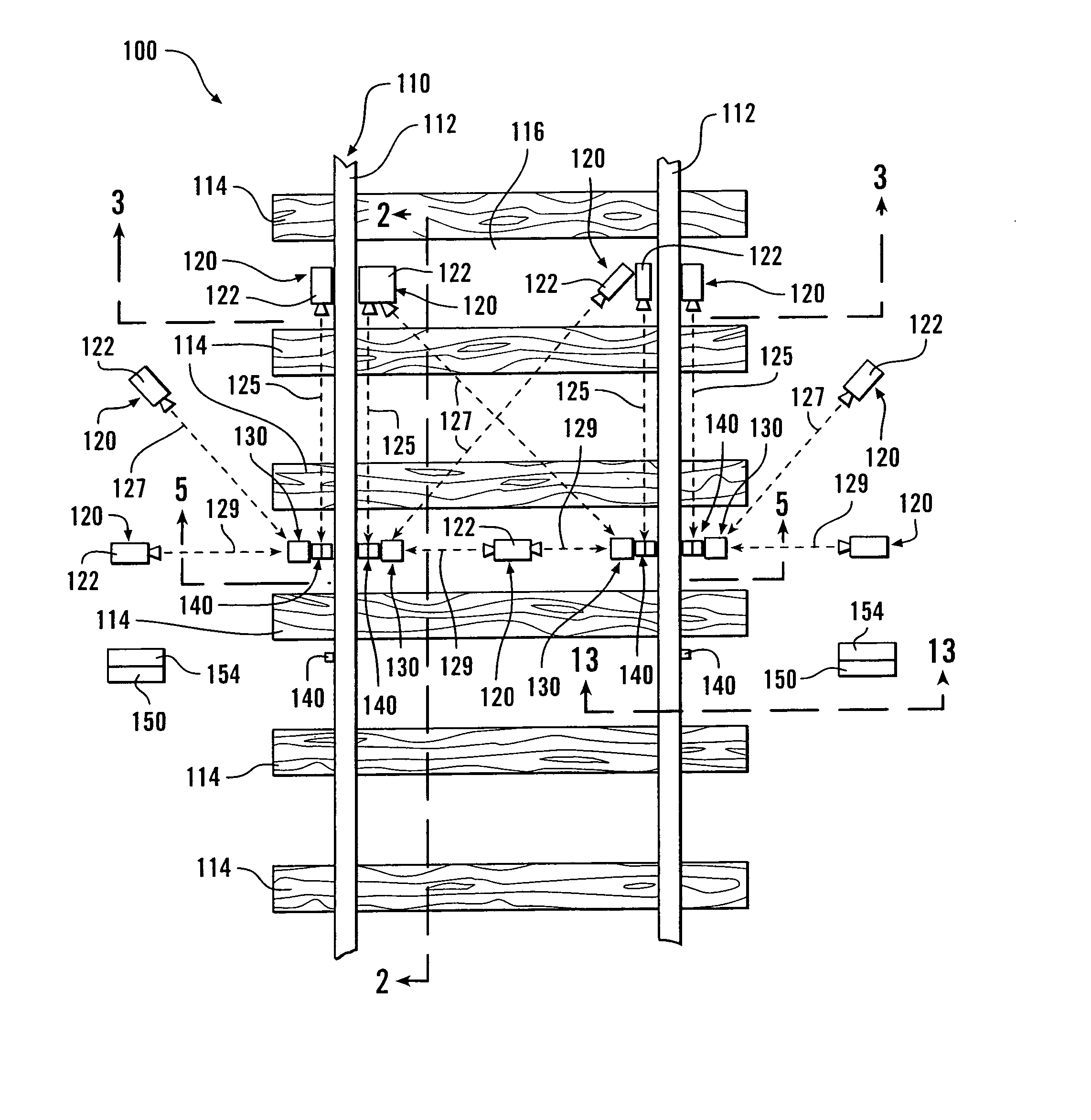
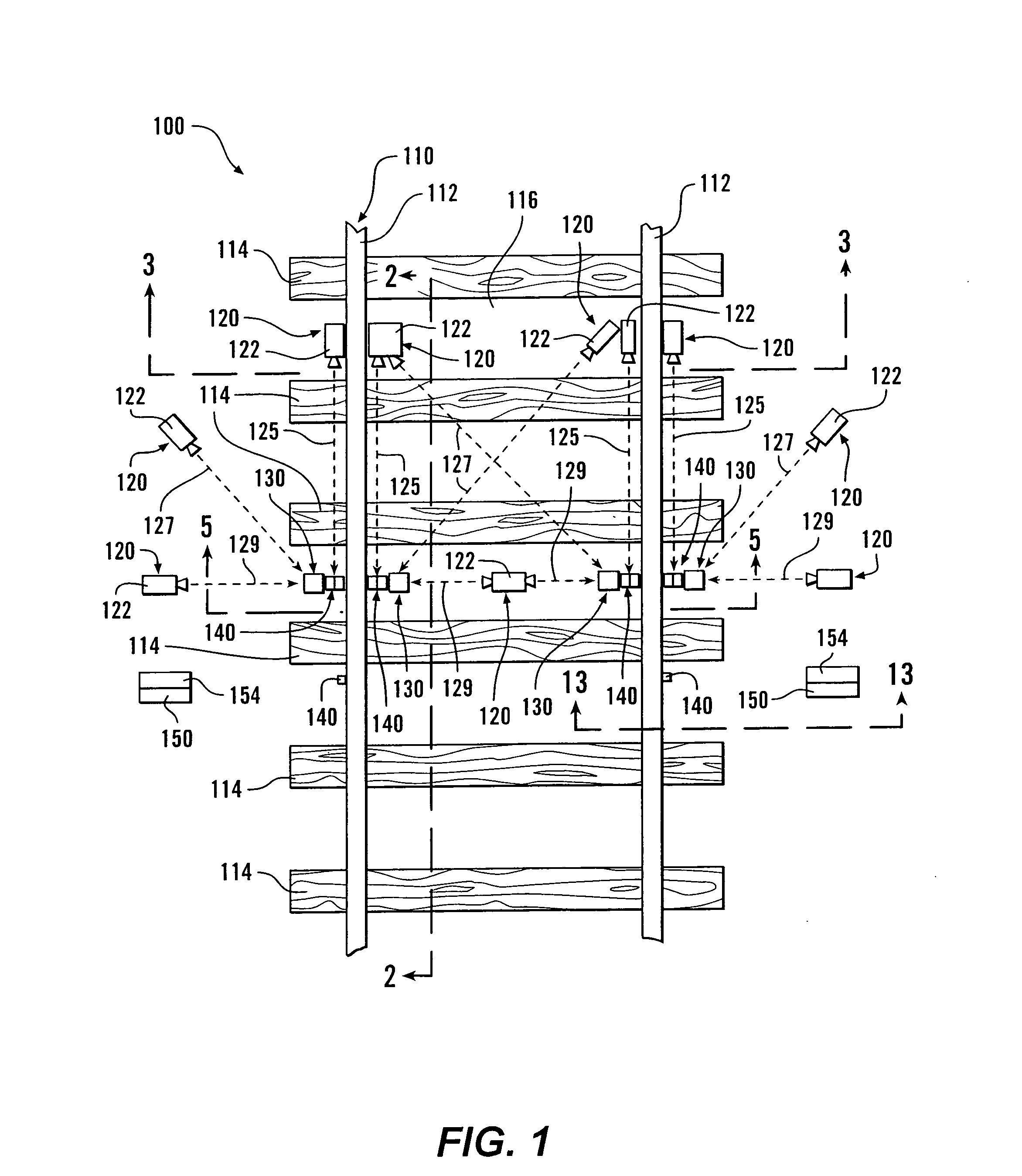
ActiveUS20070211145A1Low costGood delayWheel-rims surveying/measuringMaterial analysis by optical meansDynamic motionEngineering
Reference markers are attached to rails and / or other dynamically moving components of railroad tracks, and / or located at fixed and stationary positions adjacent to the track. When images of railway rolling stock are obtained, the reference marker(s) appear in the image. Accordingly, measurements of various aspects and parameters of various components of the railway rolling stock can be obtained at high precision and / or accuracy relative to the railroad track component to which the reference marker is attached and / or relative to the stationary position. The reference markers allow one or more images, obtained at some intervening time interval, to be accurately and precisely aligned relative to the reference marker(s) regardless of the dynamic motion of the railroad track component(s) and / or of the rolling stock that occurred as the images were captured. The reference markers can include optical, thermal or other indicia. The indicia have known dimensions and / or known distances from an image capture device.
Owner:WABTEC CONTROL SYST PTY LTD
Ultrasonic treatment chamber for particle dispersion into formulations
ActiveUS20090168591A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersFlow mixersUltrasonic cavitationDynamic motion
An ultrasonic mixing system having a particulate dispensing system to dispense particulates into a treatment chamber and the treatment chamber in which particulates can be mixed with one or more formulations is disclosed. Specifically, the treatment chamber has an elongate housing through which a formulation and particulates flow longitudinally from an inlet port to an outlet port thereof. An elongate ultrasonic waveguide assembly extends within the housing and is operable at a predetermined ultrasonic frequency to ultrasonically energize the formulation and particulates within the housing. An elongate ultrasonic horn of the waveguide assembly is disposed at least in part intermediate the inlet and outlet ports, and has a plurality of discrete agitating members in contact with and extending transversely outward from the horn intermediate the inlet and outlet ports in longitudinally spaced relationship with each other. The horn and agitating members are constructed and arranged for dynamic motion of the agitating members relative to the horn at the predetermined frequency and to operate in an ultrasonic cavitation mode of the agitating members corresponding to the predetermined frequency and the formulation and particulates being mixed in the chamber.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Ultrasonic treatment chamber having electrode properties
InactiveUS20090014377A1Electrolysis componentsSpecific water treatment objectivesElectrode potentialElectrolysis
A liquid treatment chamber having an elongate housing through which liquid flows longitudinally from an inlet port to an outlet port thereof is disclosed. An elongate ultrasonic waveguide assembly extends within the housing and is operable at a predetermined ultrasonic frequency and a predetermined electrode potential to ultrasonically energize and electrolyze liquid within the housing. An elongate ultrasonic horn of the waveguide assembly is disposed at least in part intermediate the inlet and outlet ports, and has a plurality of discrete agitating members in contact with and extending transversely outward from the horn intermediate the inlet and outlet ports in longitudinally spaced relationship with each other. The horn and agitating members are constructed and arranged for dynamic motion of the agitating members relative to the horn at the predetermined frequency and to operate in an ultrasonic cavitation mode of the agitating members corresponding to the predetermined frequency and the liquid being treated in the chamber.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
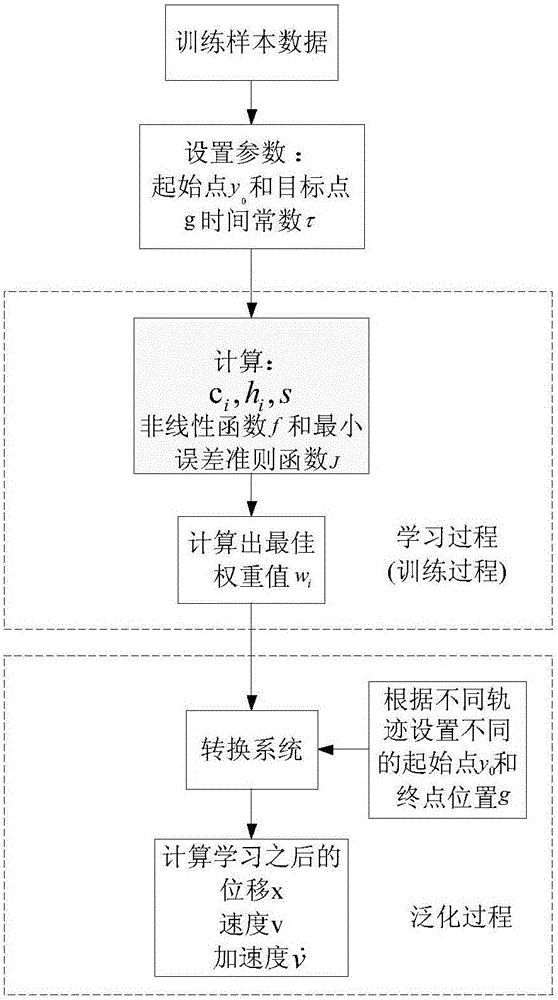
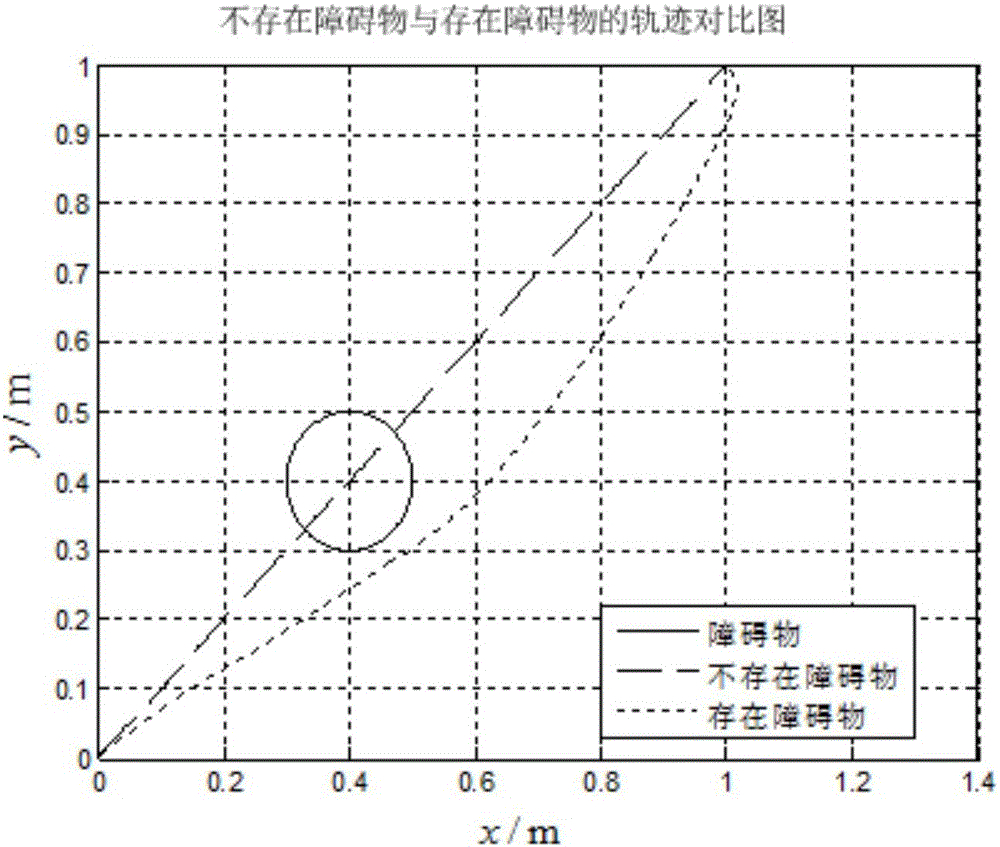
Mobile robot path planning method based on dynamic motion primitive learning model
ActiveCN106444738AAbility to generalizePosition/course control in two dimensionsPlanning approachDynamic motion
The invention discloses a mobile robot path planning method based on a dynamic motion primitive learning model. The method includes: controlling the motion of a robot through a handle, and recording the motion track of the robot; then regarding the recorded track as a sample of the dynamic motion primitive model, performing training by employing the track sample and establishing the dynamic motion primitive model to obtain dynamic motion primitive model parameters and realize autonomous path planning of the robot; and on the basis, changing a target position of the motion of the robot to complete generalized promotion of a new target. According to the path planning method, the intelligence level of the mobile robot is improved, when the target position of the motion of the robot is changed, the robot can autonomously arrive at the new target position, the robot can complete not just a certain specified task but has the capability of generalized promotion for other tasks, and the efficiency of path planning is improved with the combination of online learning characteristics of the dynamic motion primitive model and an autonomous obstacle-avoiding function thereof.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Earthquake and Displacement Early Warning System
Novel solutions, which can include devices, systems, methods, than can measure earthquakes and other displacement events. Some solutions feature the integration of real-time, high-rate global navigation satellite system (“GNSS”) displacement information with acceleration and / or velocity data within a single device to create very high-rate displacement records. The mating of these two instruments allows the creation of a new, very high-rate displacement measurement device that has the full-scale displacement characteristics of GNSS and high-precision dynamic motions of seismic technologies. Such a device can be used for earthquake early warning studies and other mission critical applications, such as volcano monitoring, building, bridge and dam monitoring systems.
Owner:TRIMBLE INC
Ultrasonic treatment chamber for preparing emulsions
InactiveUS20090166177A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersCircuit elementsUltrasonic cavitationEmulsion
An ultrasonic mixing system having a treatment chamber in which at least two separate phases can be mixed to prepare an emulsion is disclosed. Specifically, at least one phase is a dispersed phase and one phase in a continuous phase. The treatment chamber has an elongate housing through which the phases flow longitudinally from a first inlet port and a second inlet port, respectively, to an outlet port thereof. An elongate ultrasonic waveguide assembly extends within the housing and is operable at a predetermined ultrasonic frequency to ultrasonically energize the phases within the housing. An elongate ultrasonic horn of the waveguide assembly is disposed at least in part intermediate the inlet and outlet ports, and has a plurality of discrete agitating members in contact with and extending transversely outward from the horn intermediate the inlet and outlet ports in longitudinally spaced relationship with each other. The horn and agitating members are constructed and arranged for dynamic motion of the agitating members relative to the horn at the predetermined frequency and to operate in an ultrasonic cavitation mode of the agitating members corresponding to the predetermined frequency and the phases being mixed in the chamber.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
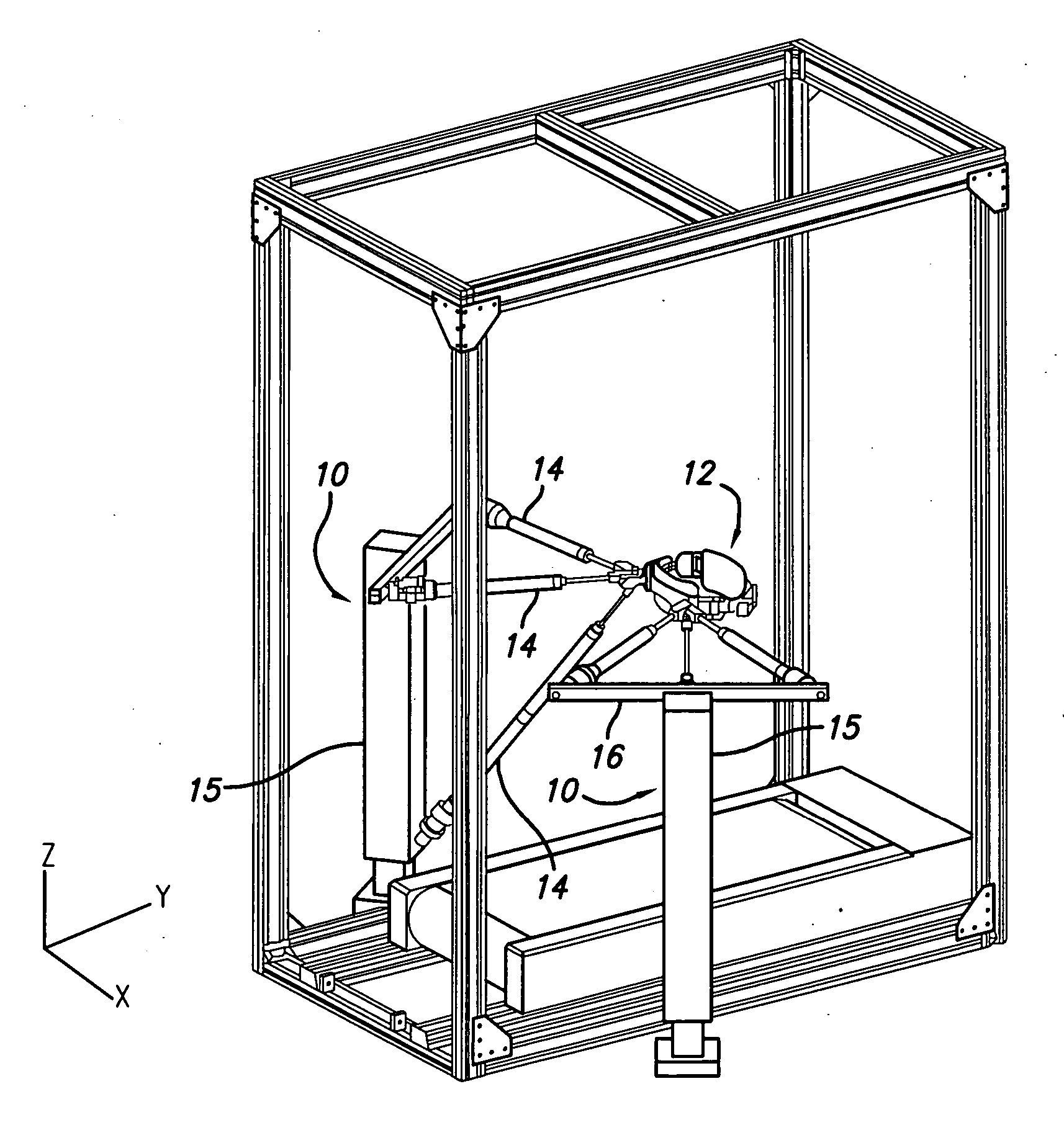
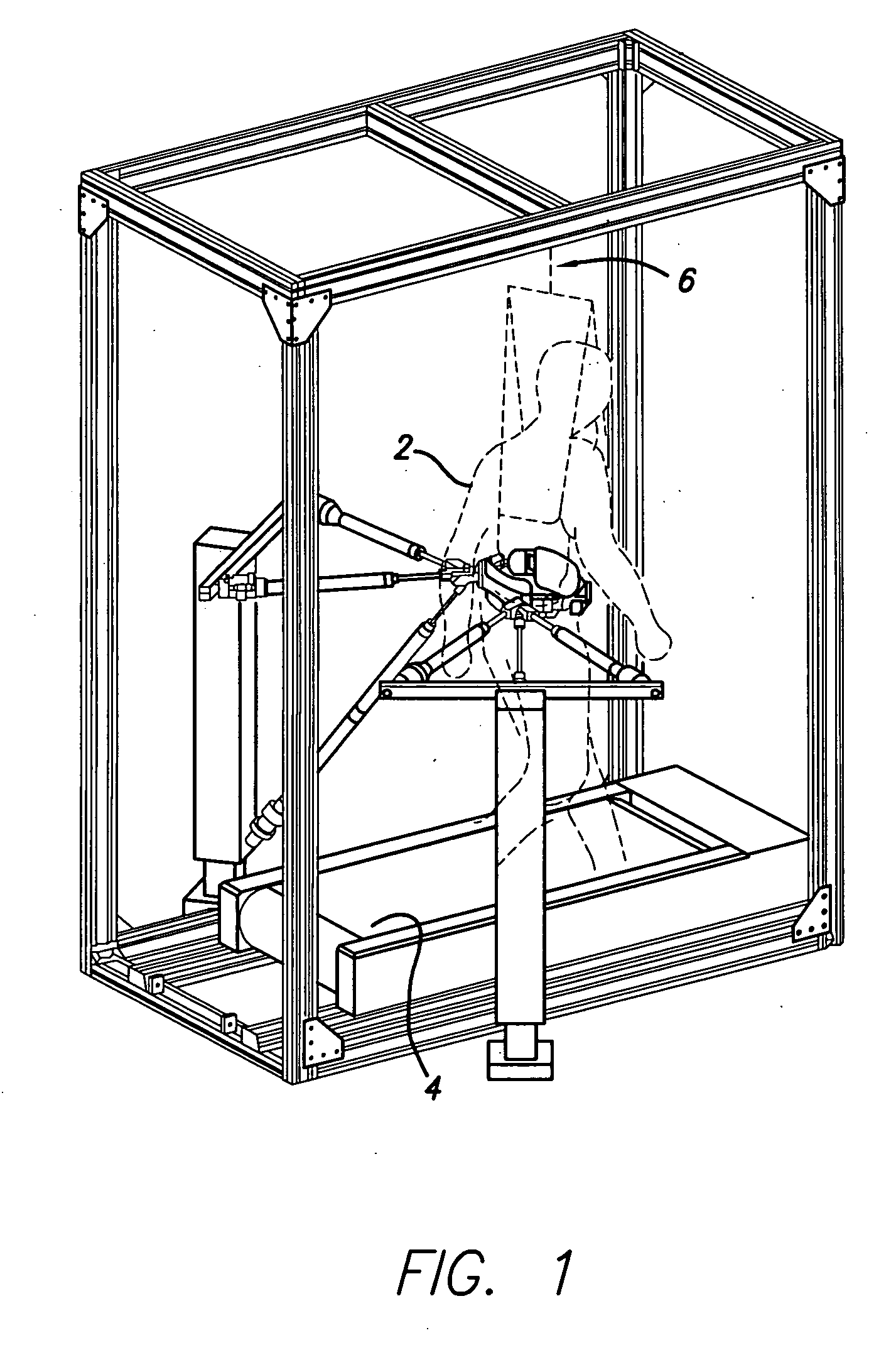
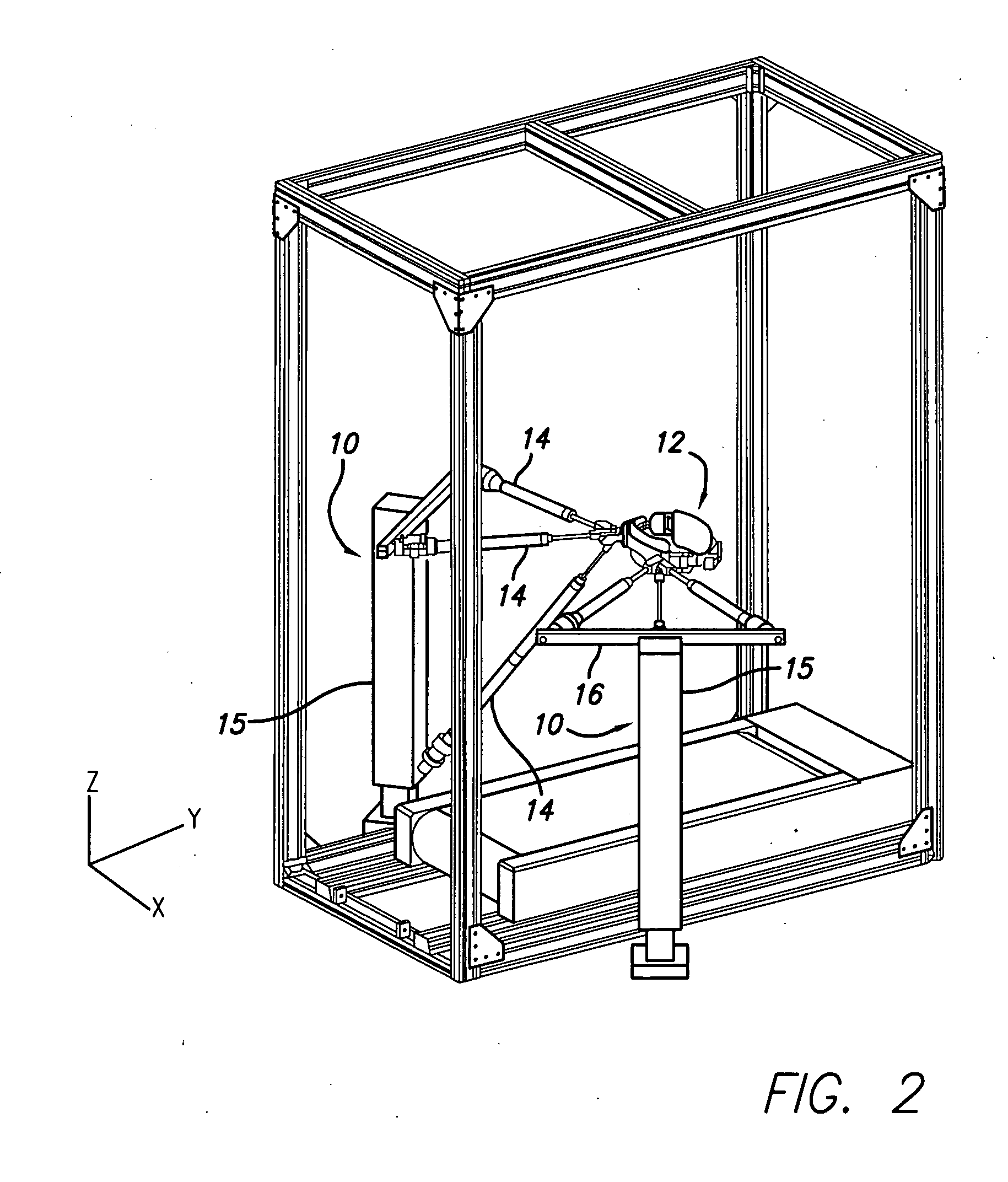
Method and apparatus for monitoring patient compliance during dynamic motion therapy
InactiveUS20070043310A1Decreasing and increasing transmissibilityReduce transmission ratePhysical therapies and activitiesData processing applicationsPatient complianceDynamic motion
A system and apparatus for remote monitoring of data related to therapeutic treatment of tissue are provided. The system and apparatus includes a platform configured to support a body of the patient; an oscillator connected to the platform and configured to impart an oscillating force at a predetermined frequency on the platform for transmitting mechanical vibration energy through the patient's body; and a processing device in operable communication with the platform for processing data related to the therapeutic treatment. The apparatus further includes a communication device in operative communication with the processing device.
Owner:AMERICAN MEDICAL INNOVATIONS LLC
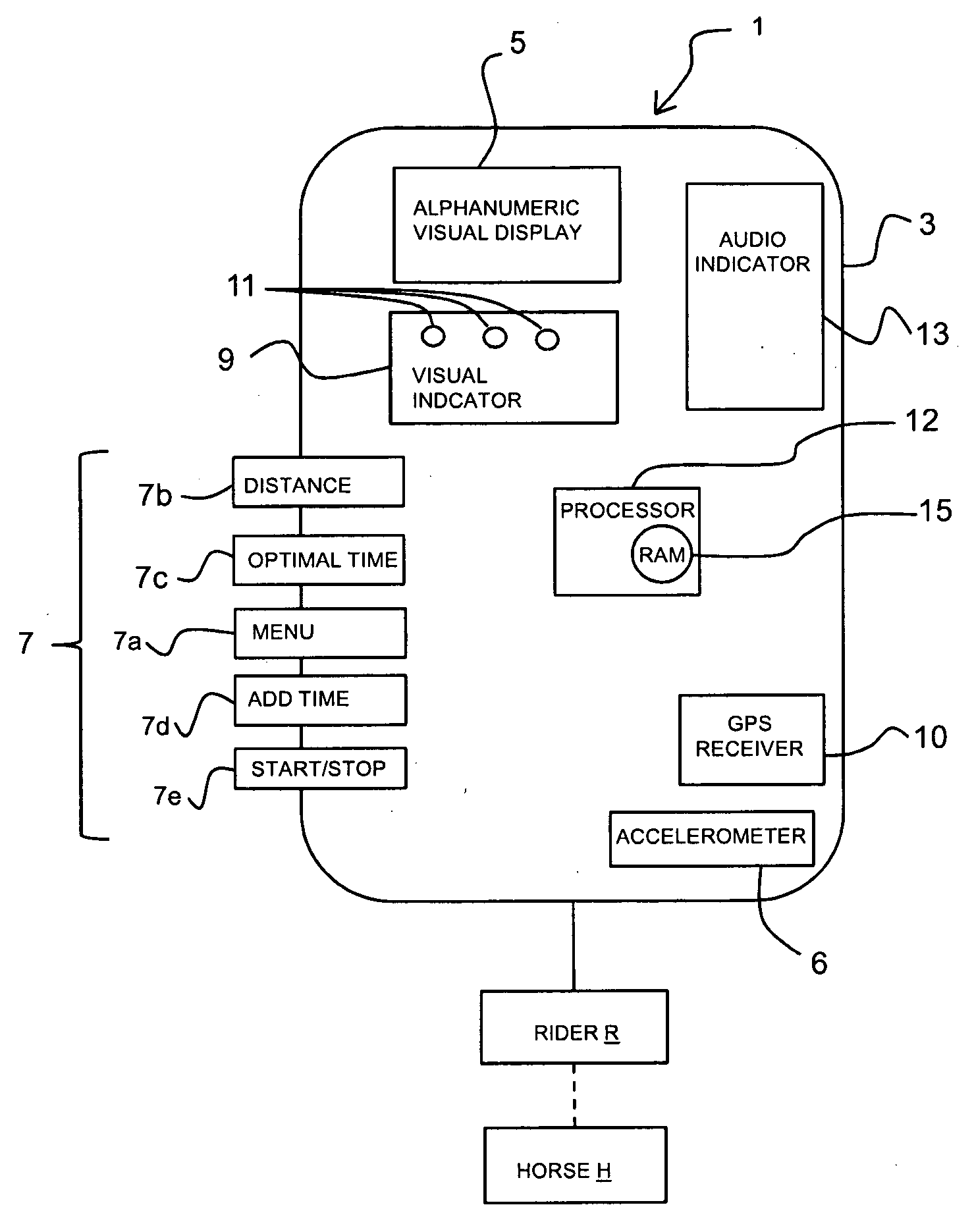
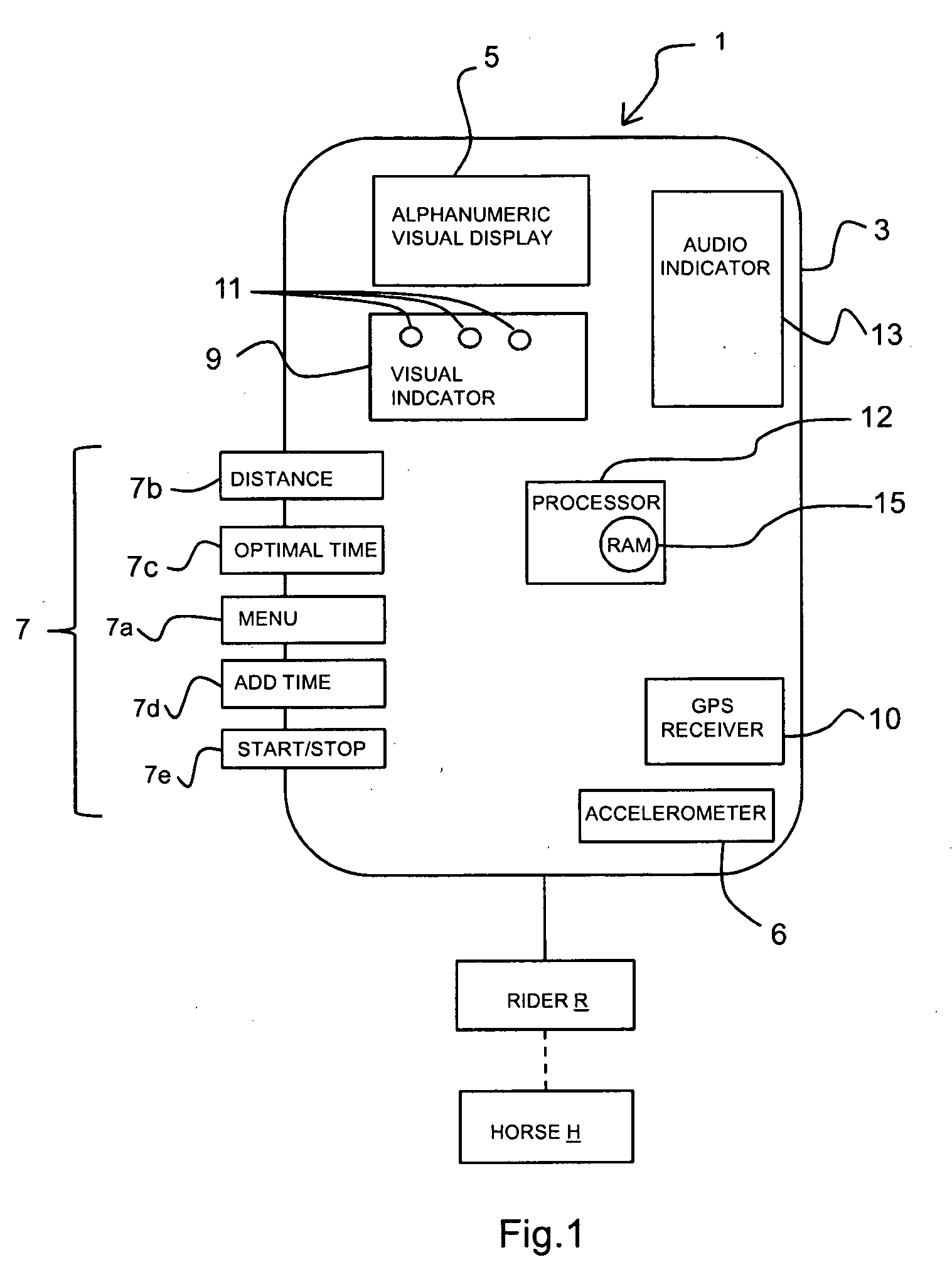
Method and apparatus for measuring and estimating subject motion in variable signal reception environments
InactiveUS20100250179A1Easy to viewLight weightRace-coursesAcceleration measurementTerrainDynamic motion
A dynamic motion and distance measuring device for estimating and measuring speed and distance covered by a subject engaged in an athletic endeavor and more particularly to measuring and estimating the speed and distance and providing a relative indication of a measured speed and distance to an optimal speed and distance and / or time including finish time of the subject engaged in an athletic event, even where the event is occurring in changing environment or terrain conditions where remote data collection and signal reception is inconsistent and variable.
Owner:MARIANO THOMAS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com