Patents
Literature
1017 results about "Rotational degrees of freedom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
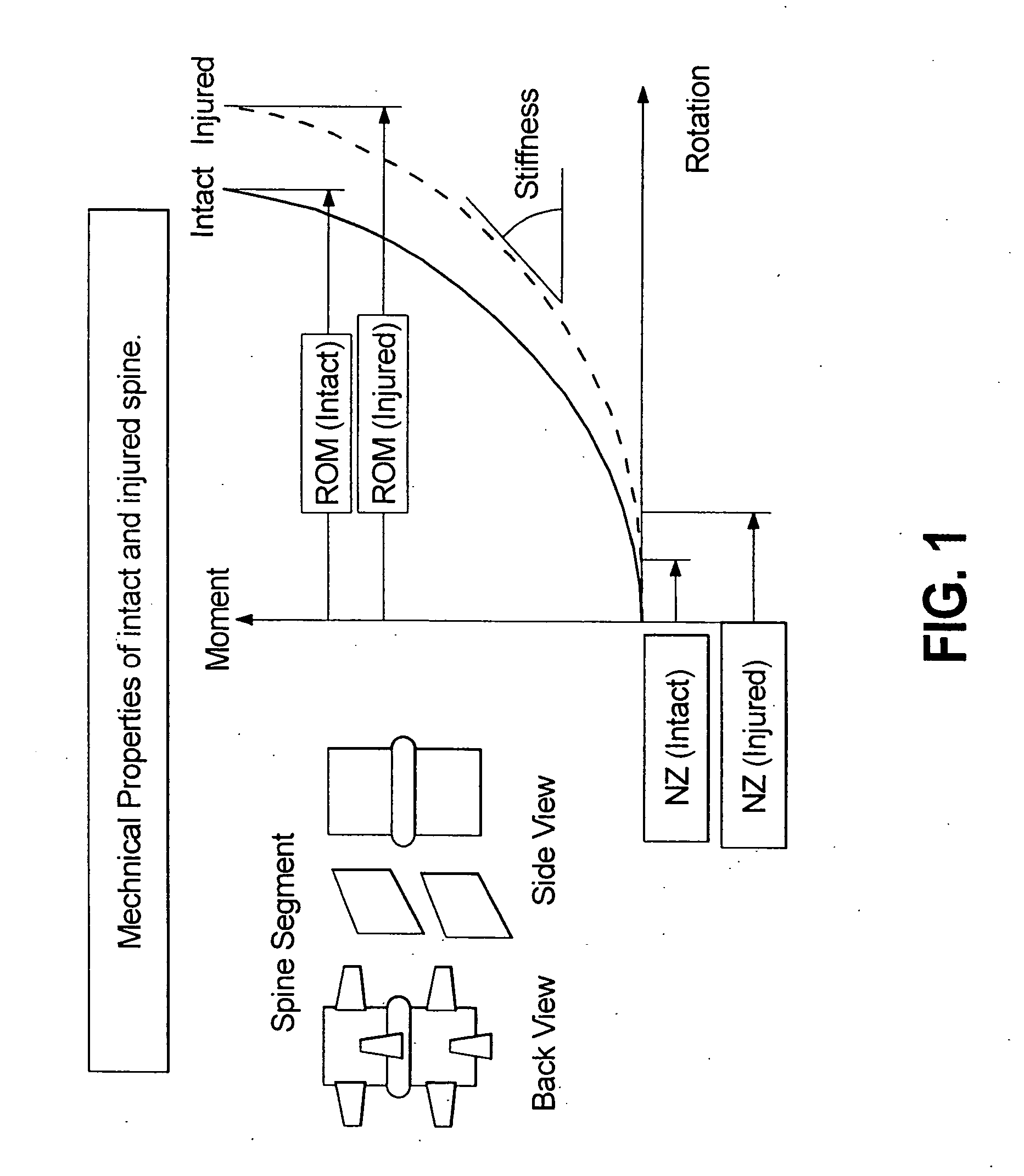
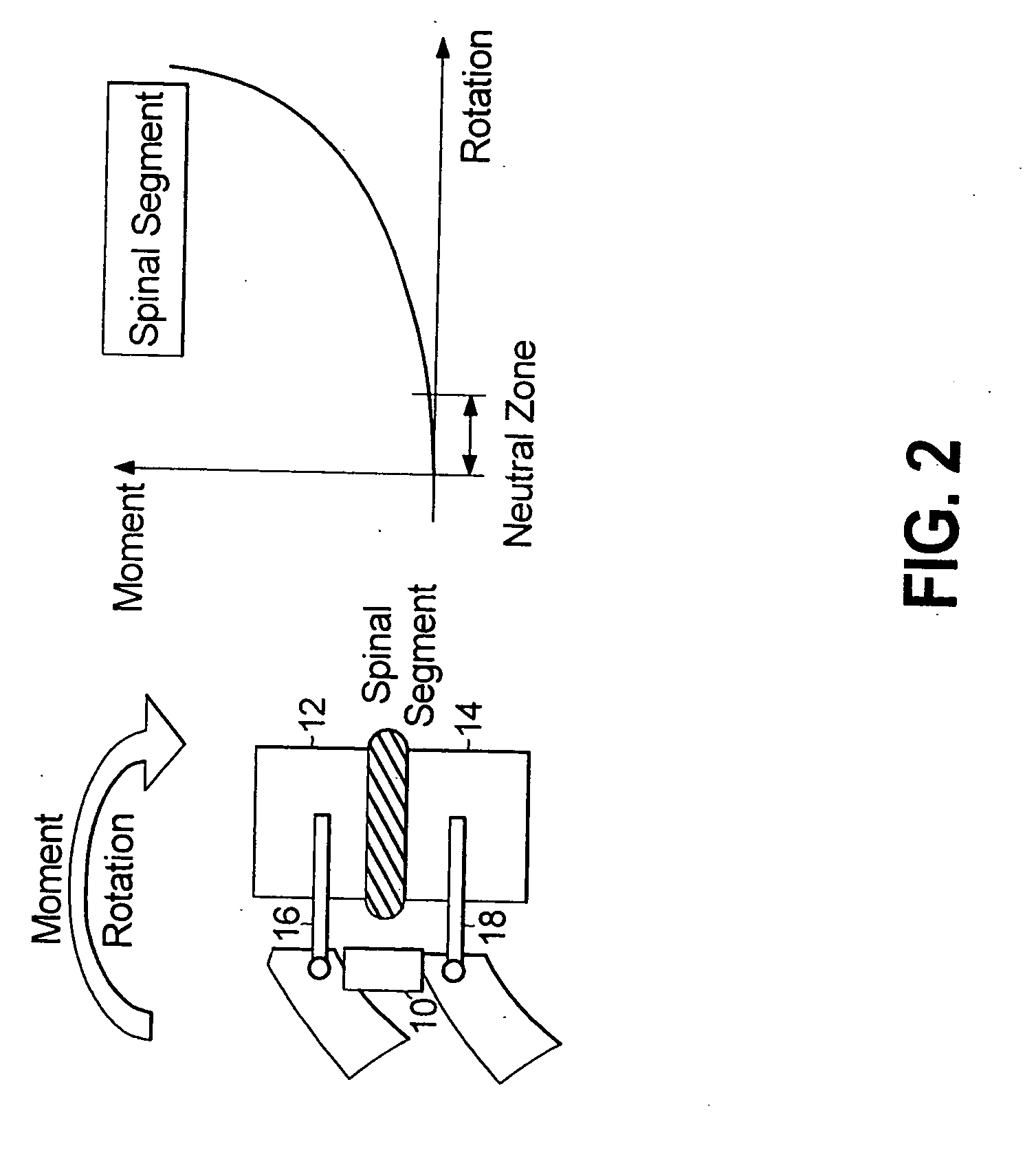
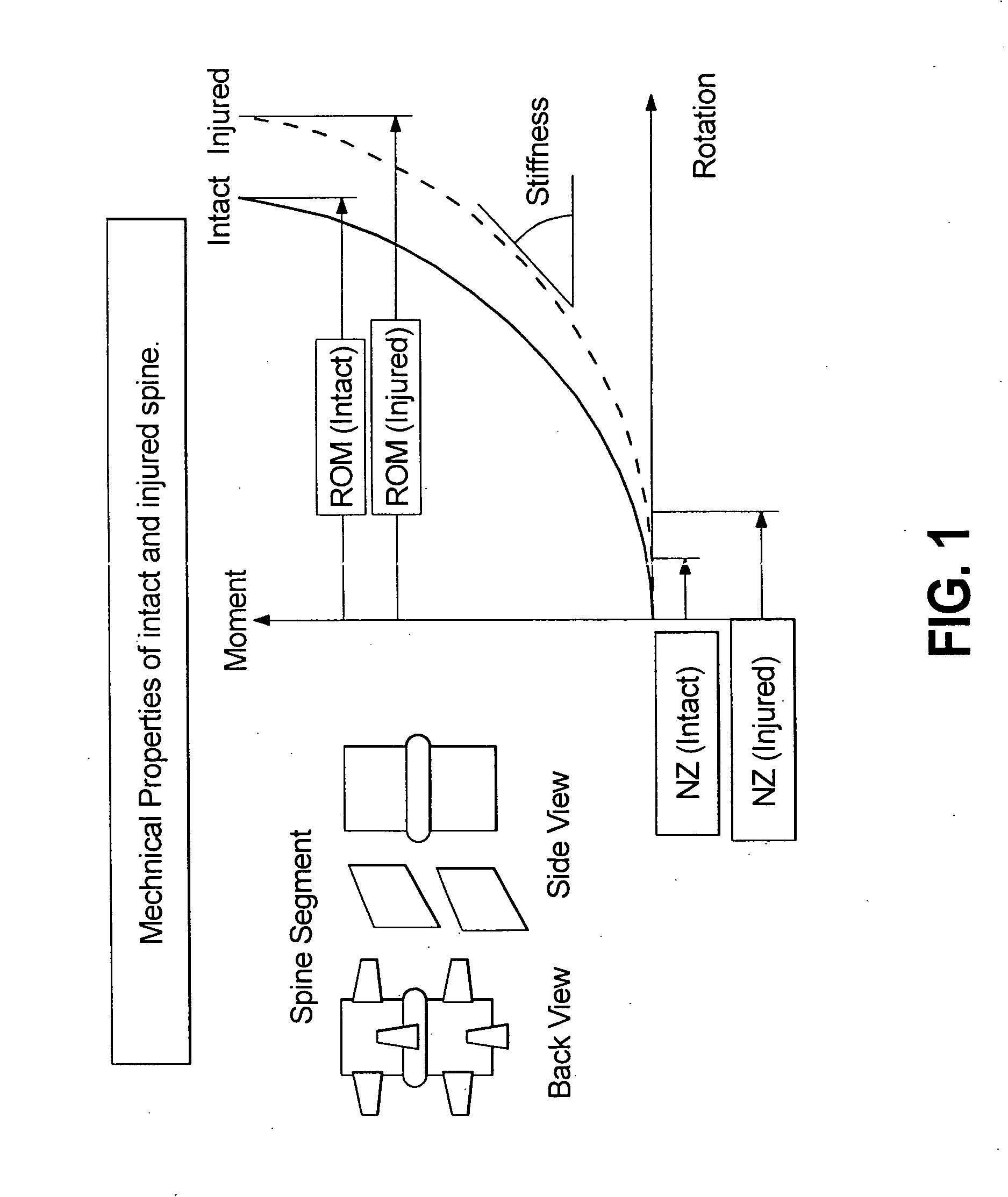
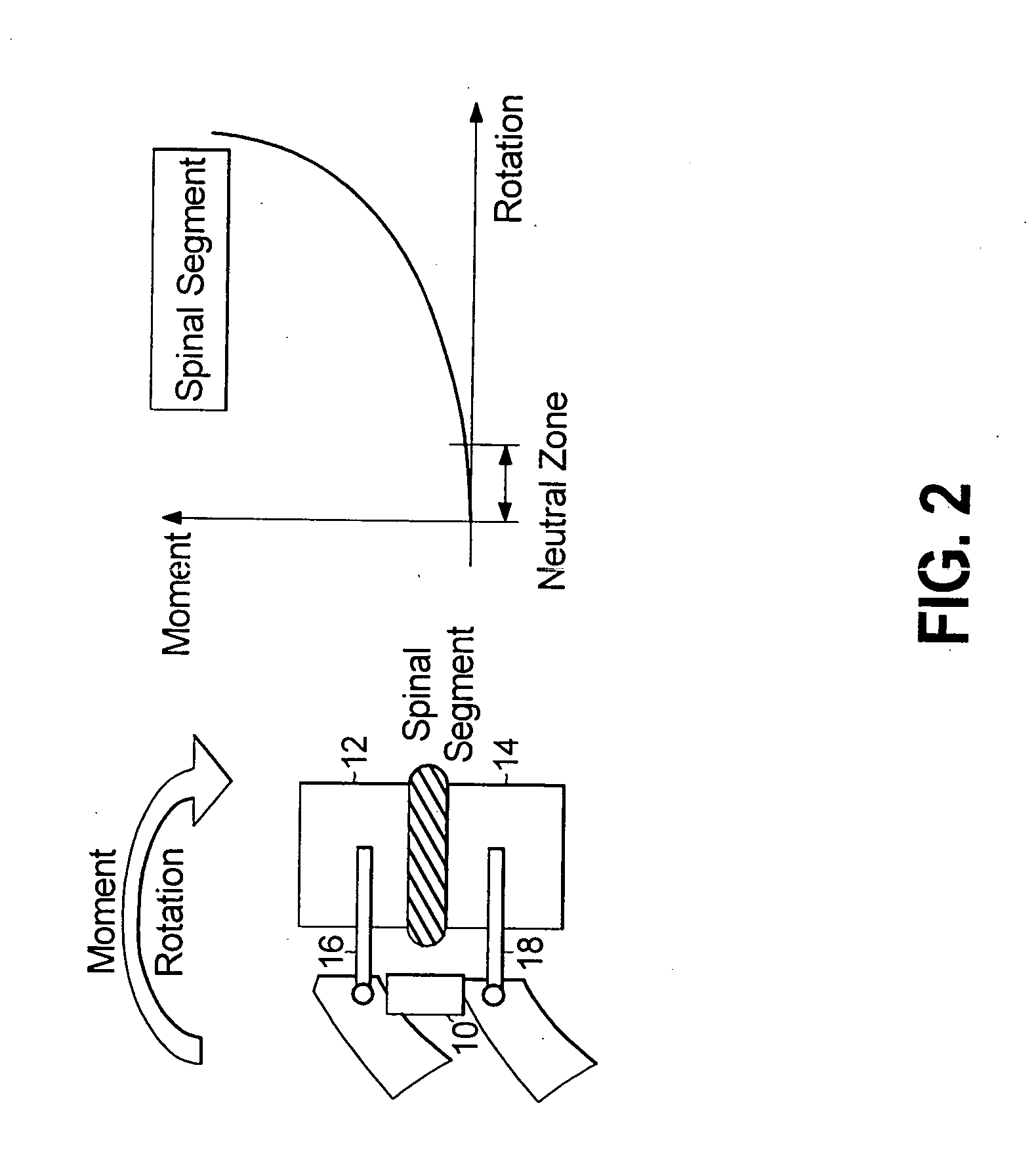
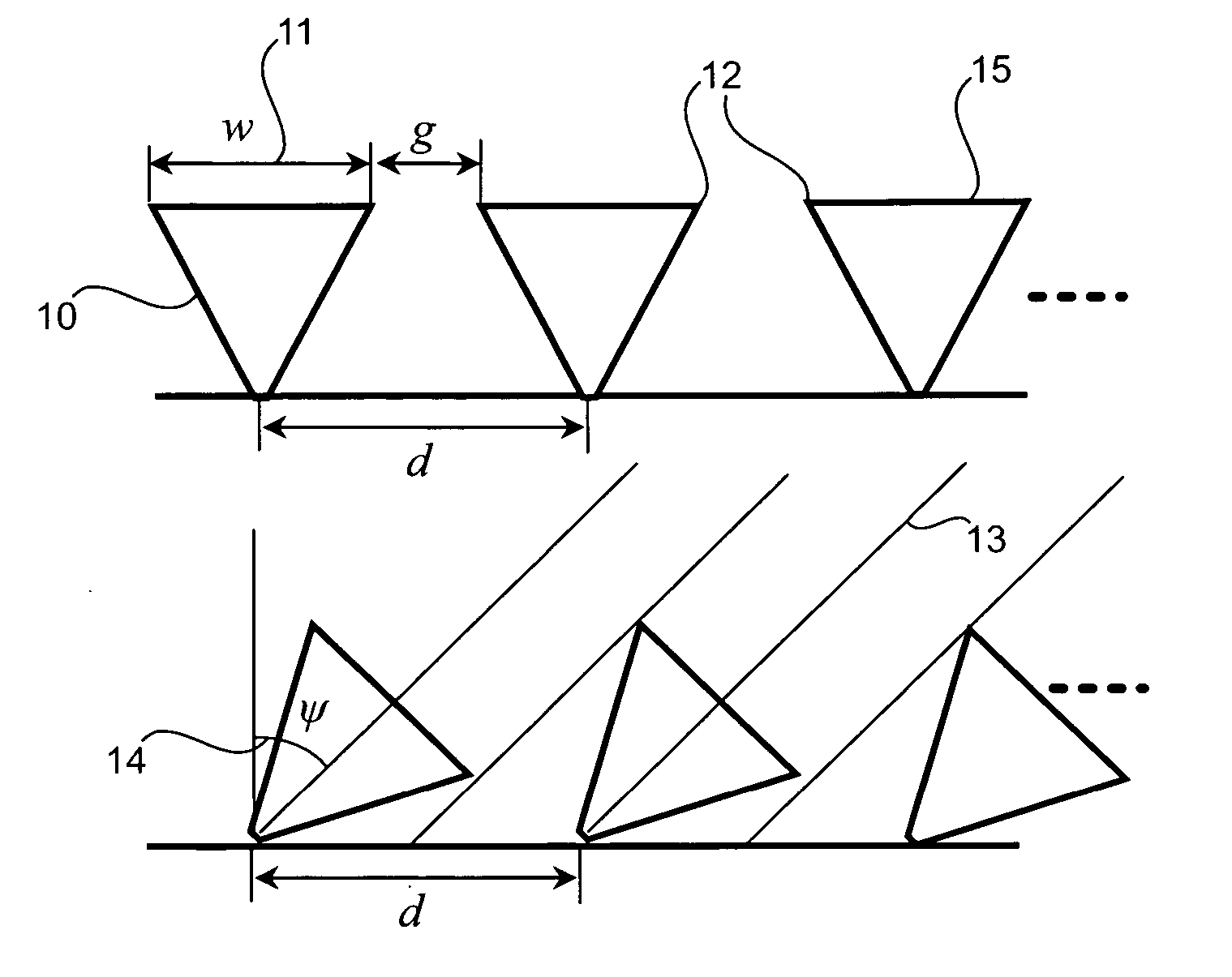
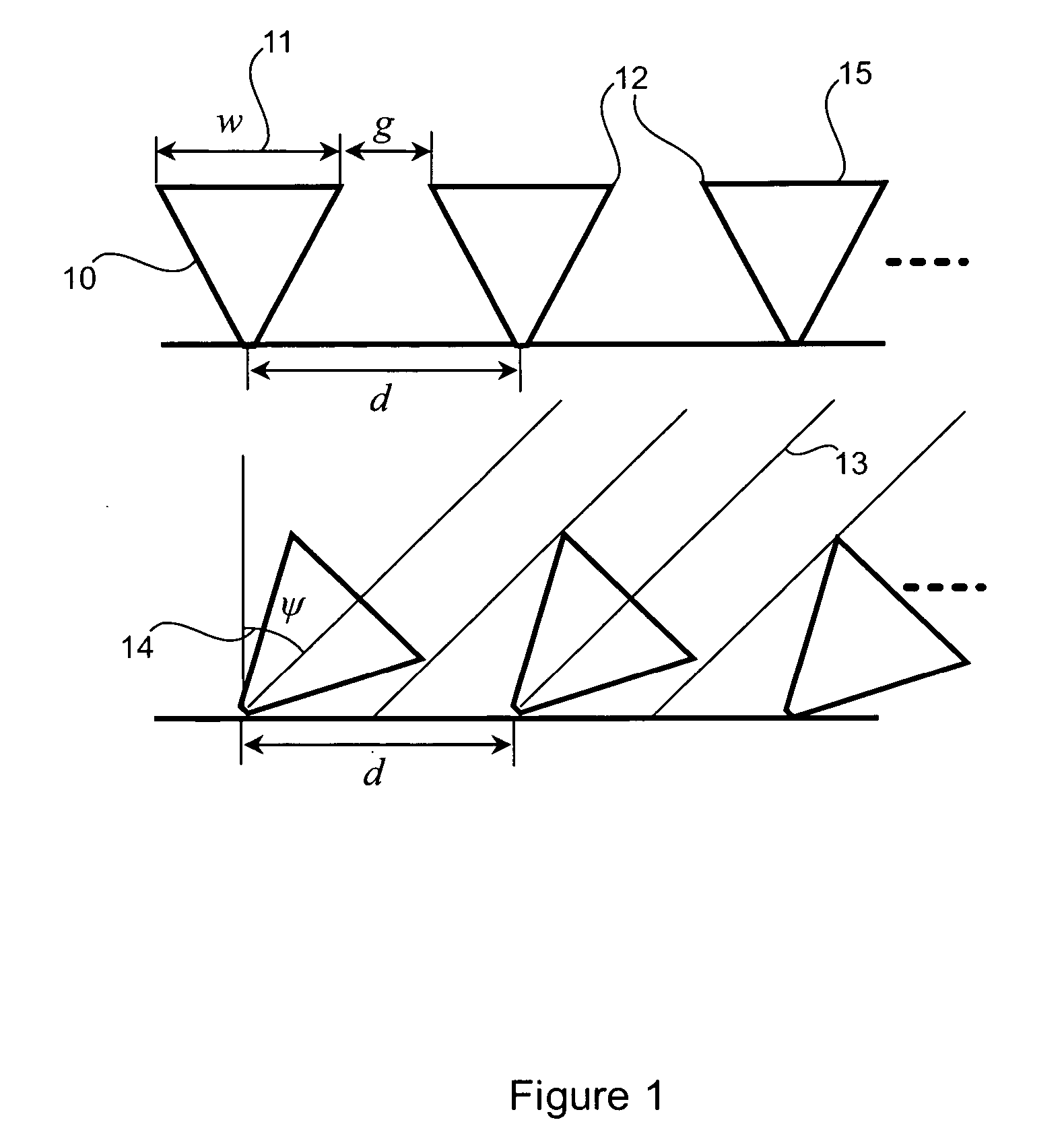
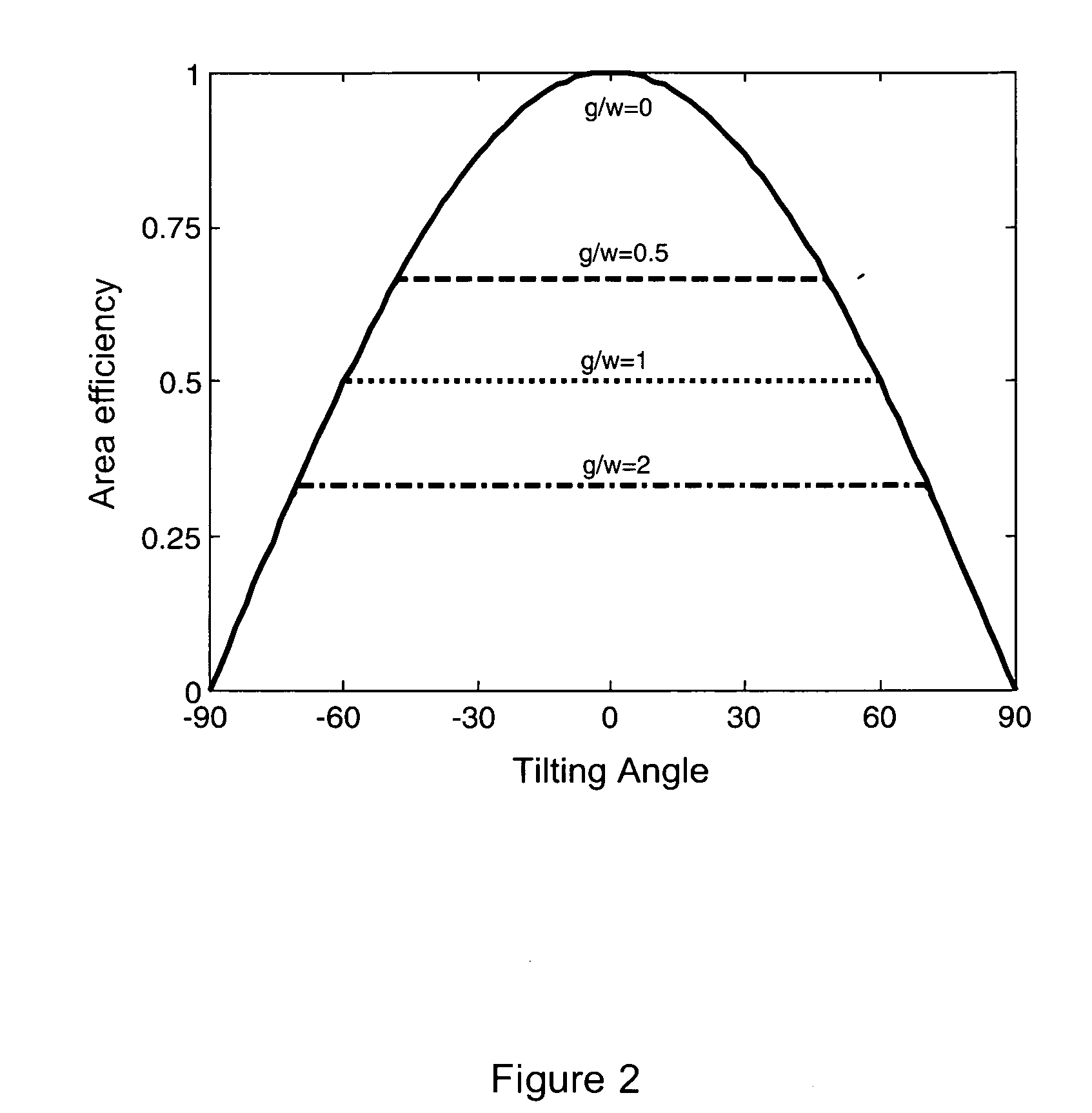
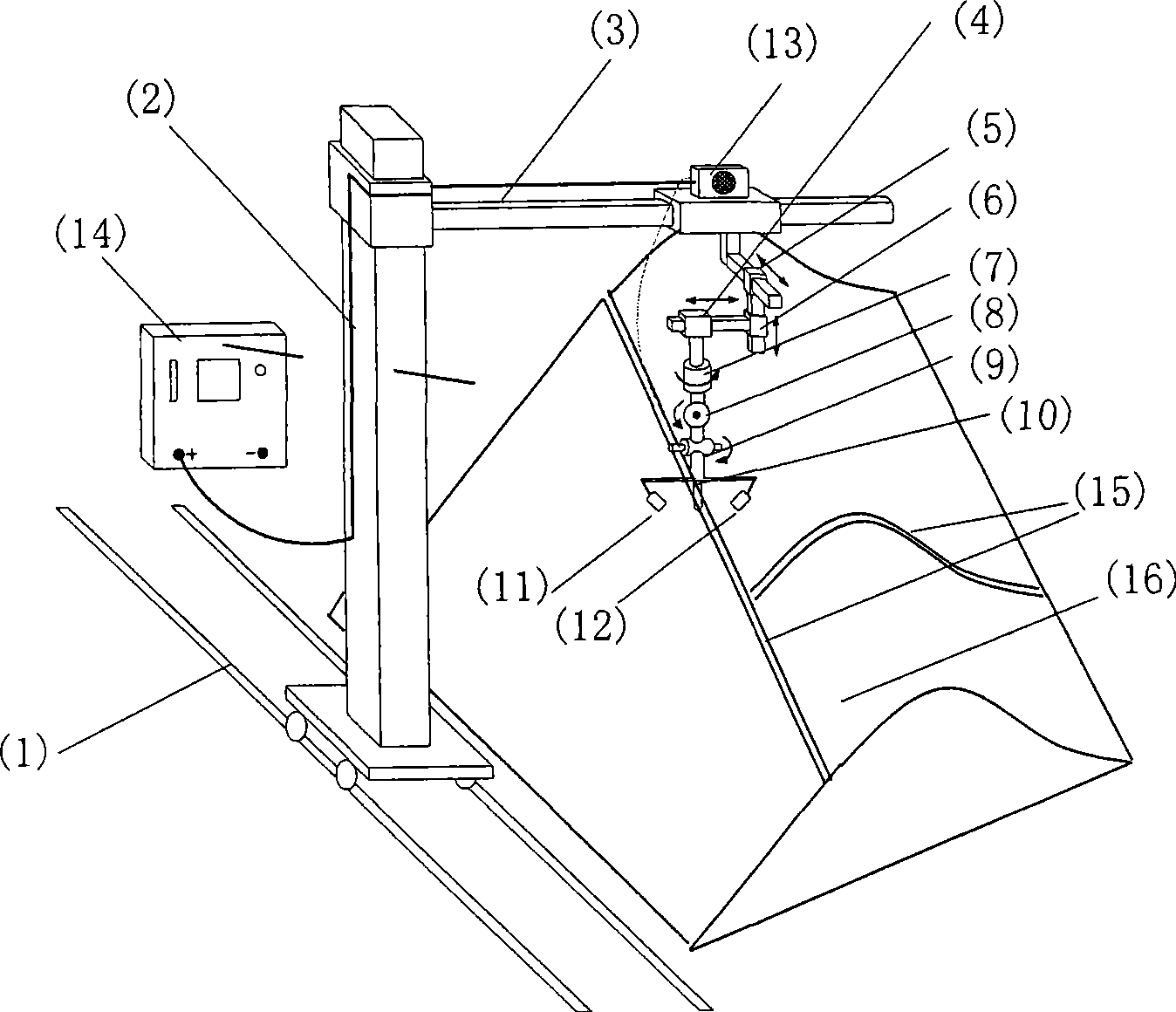
A degree of freedom corresponds to a translation or a rotation at each node of an element. There can be up to 6 degrees of freedom per node depending on the element type.
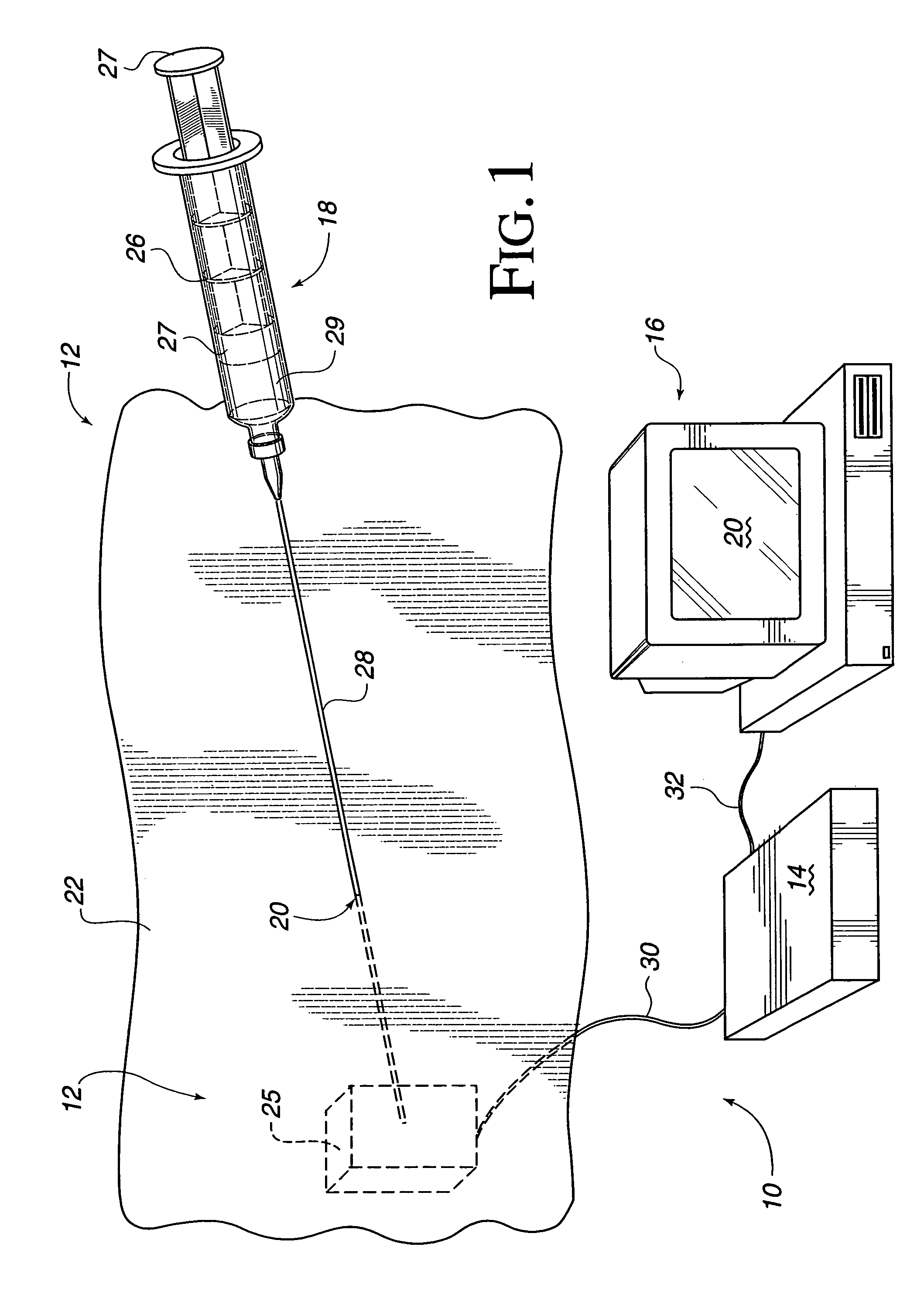
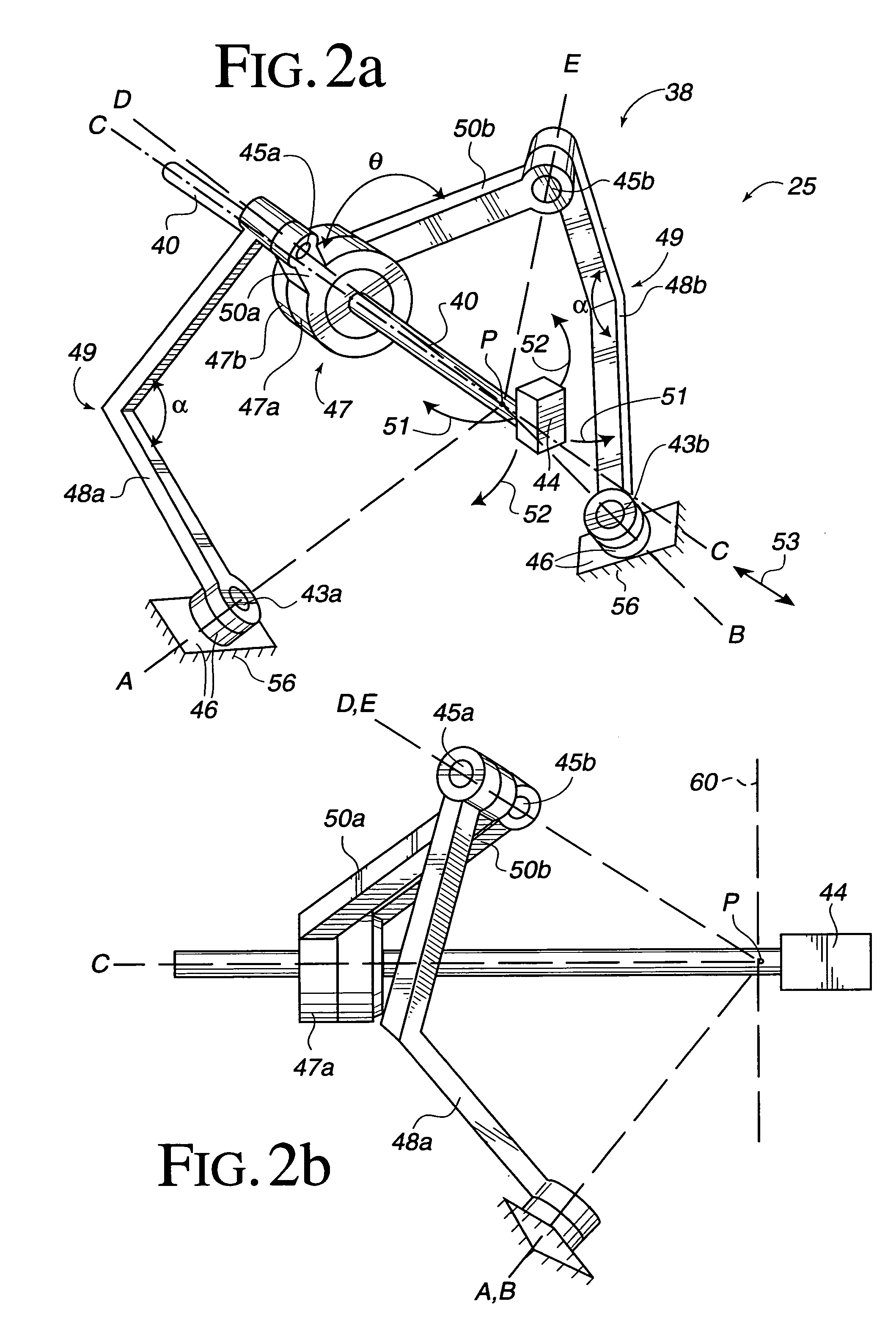
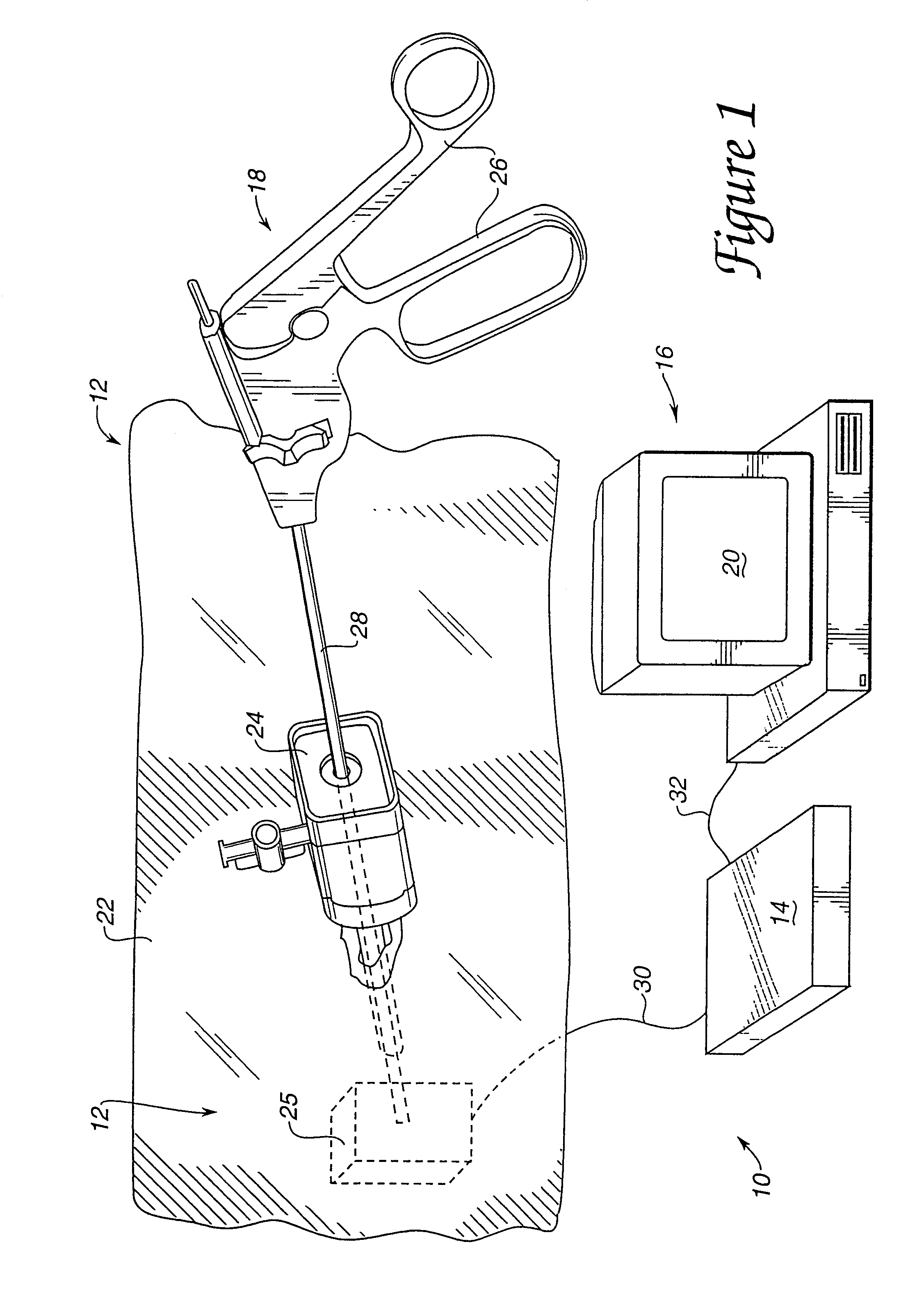
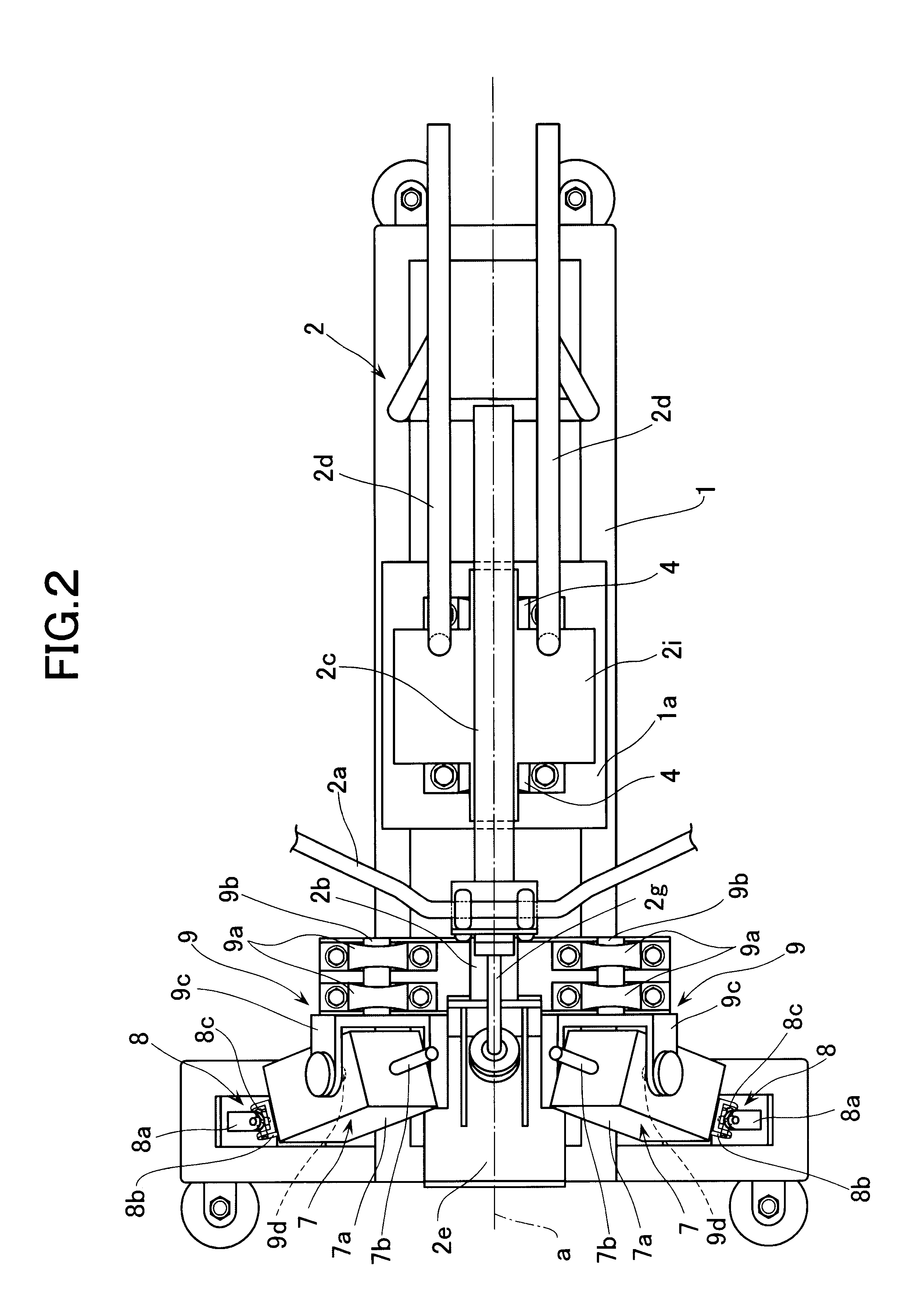
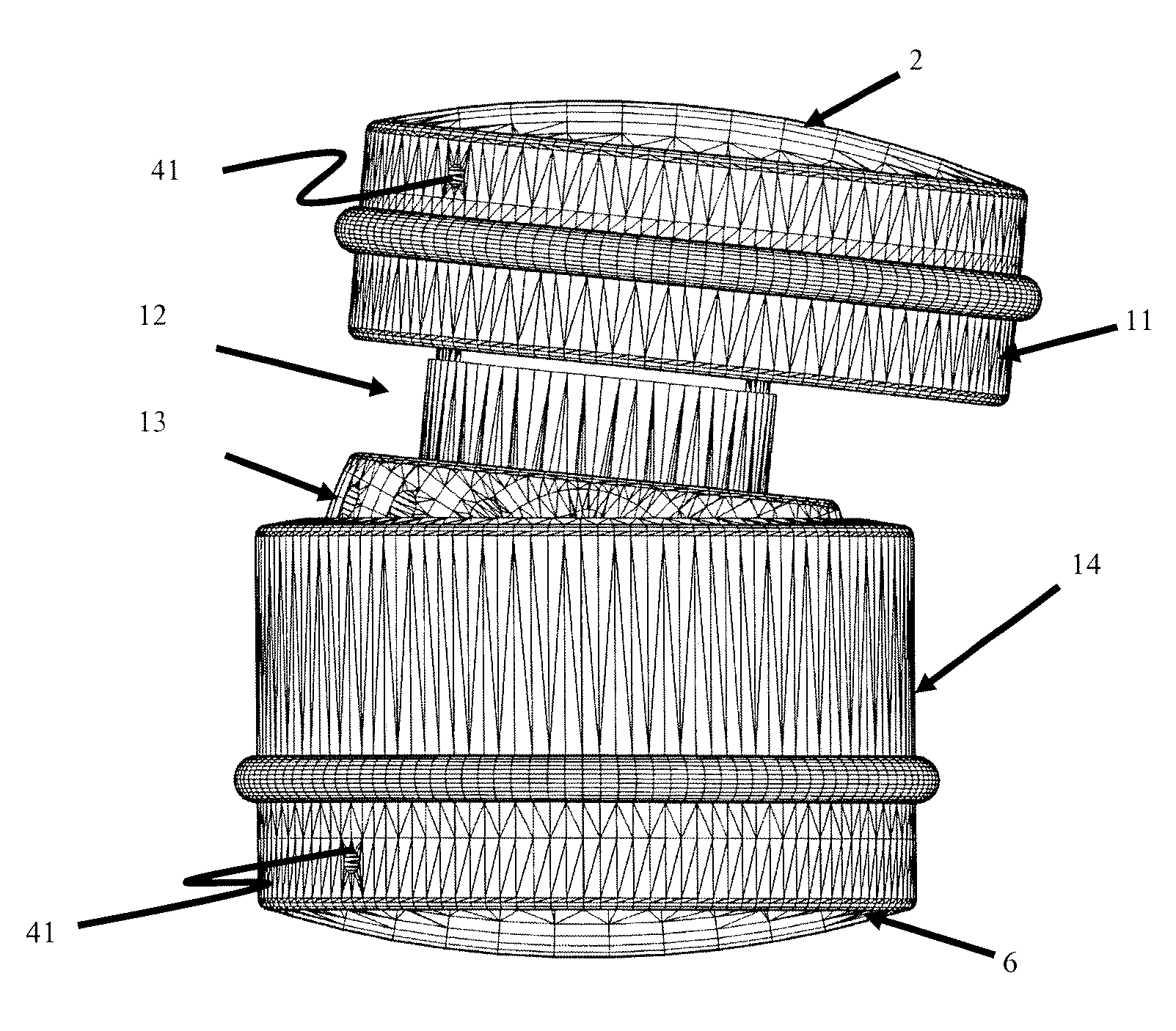
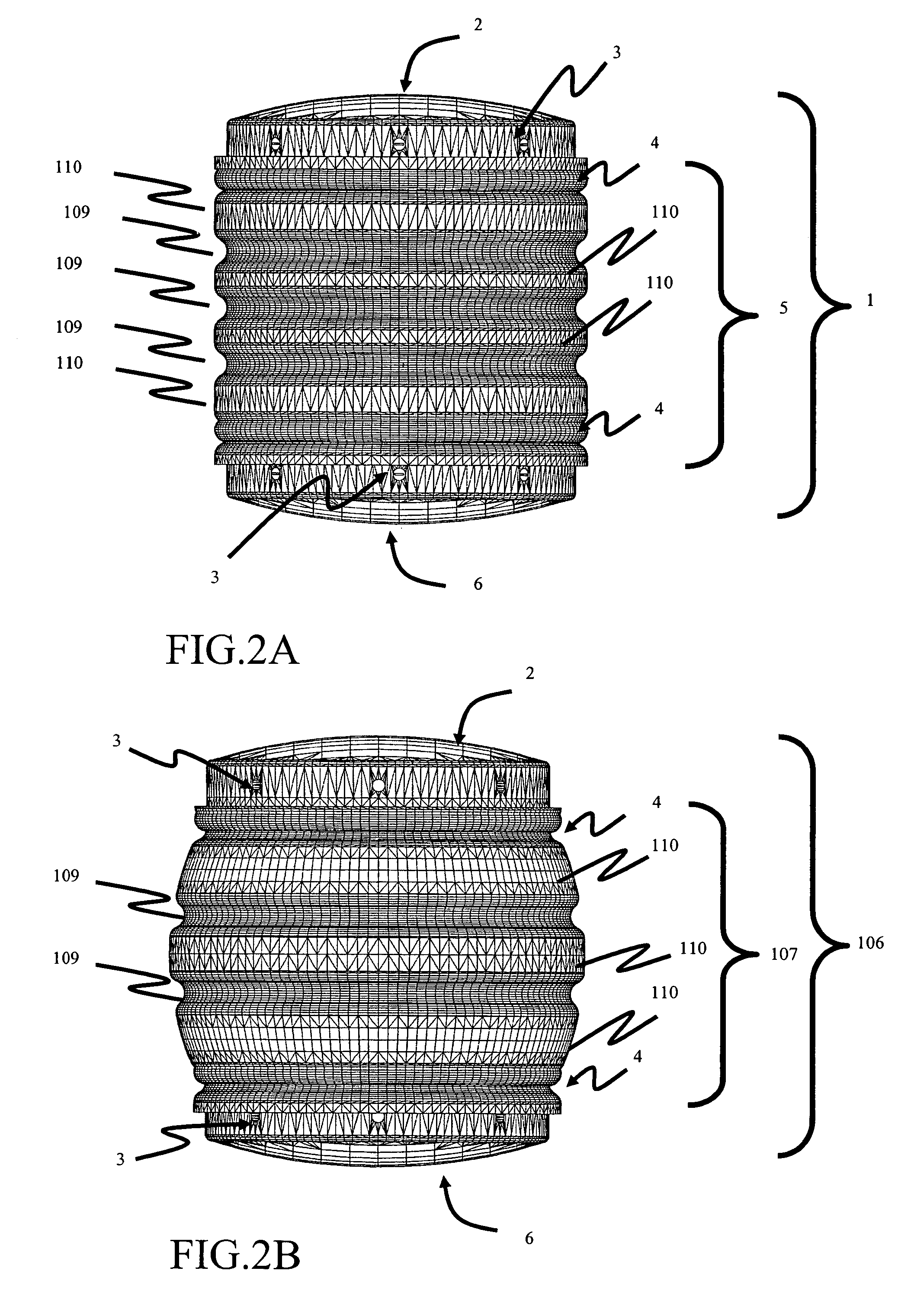
Sterile drape interface for robotic surgical instrument
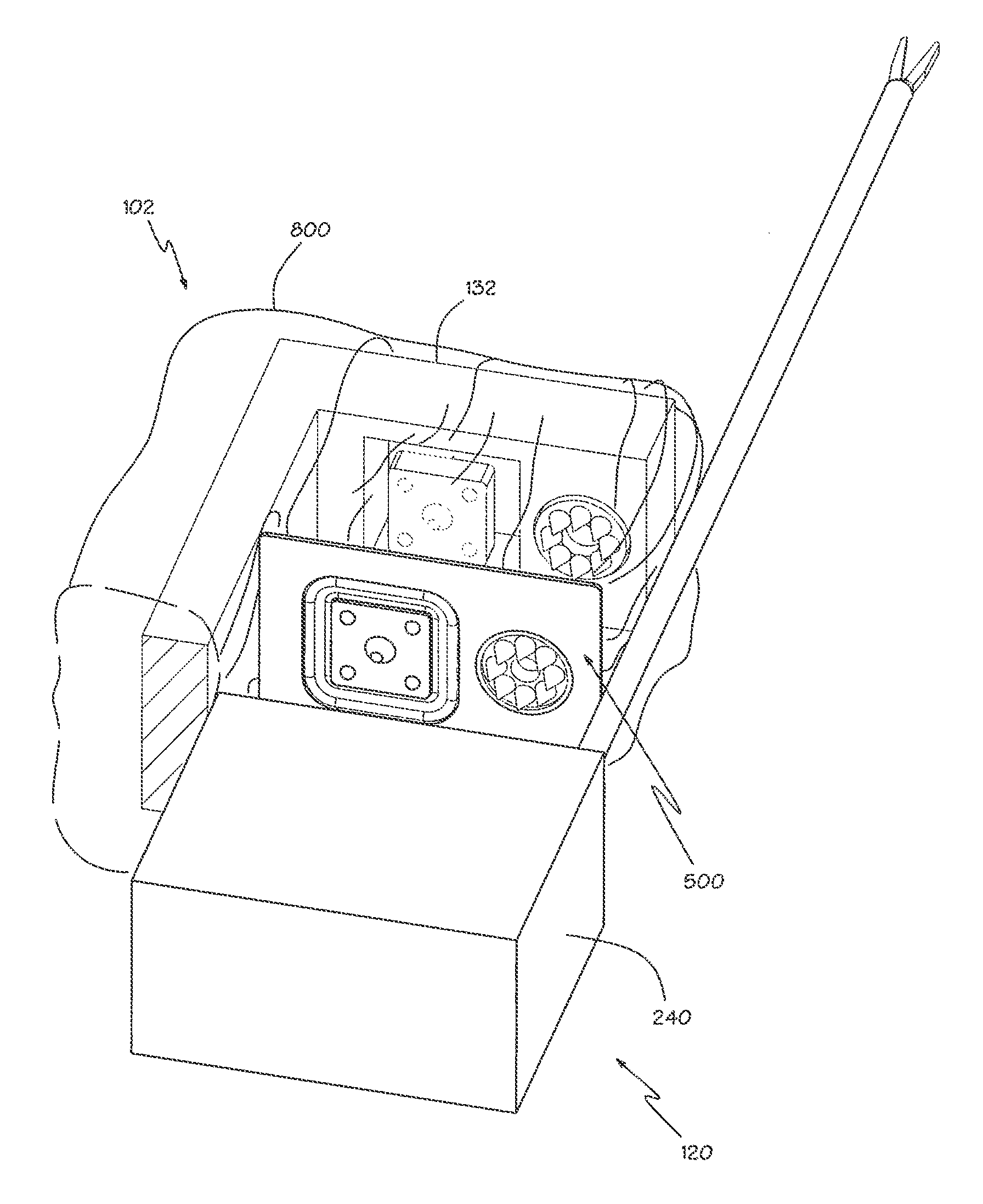
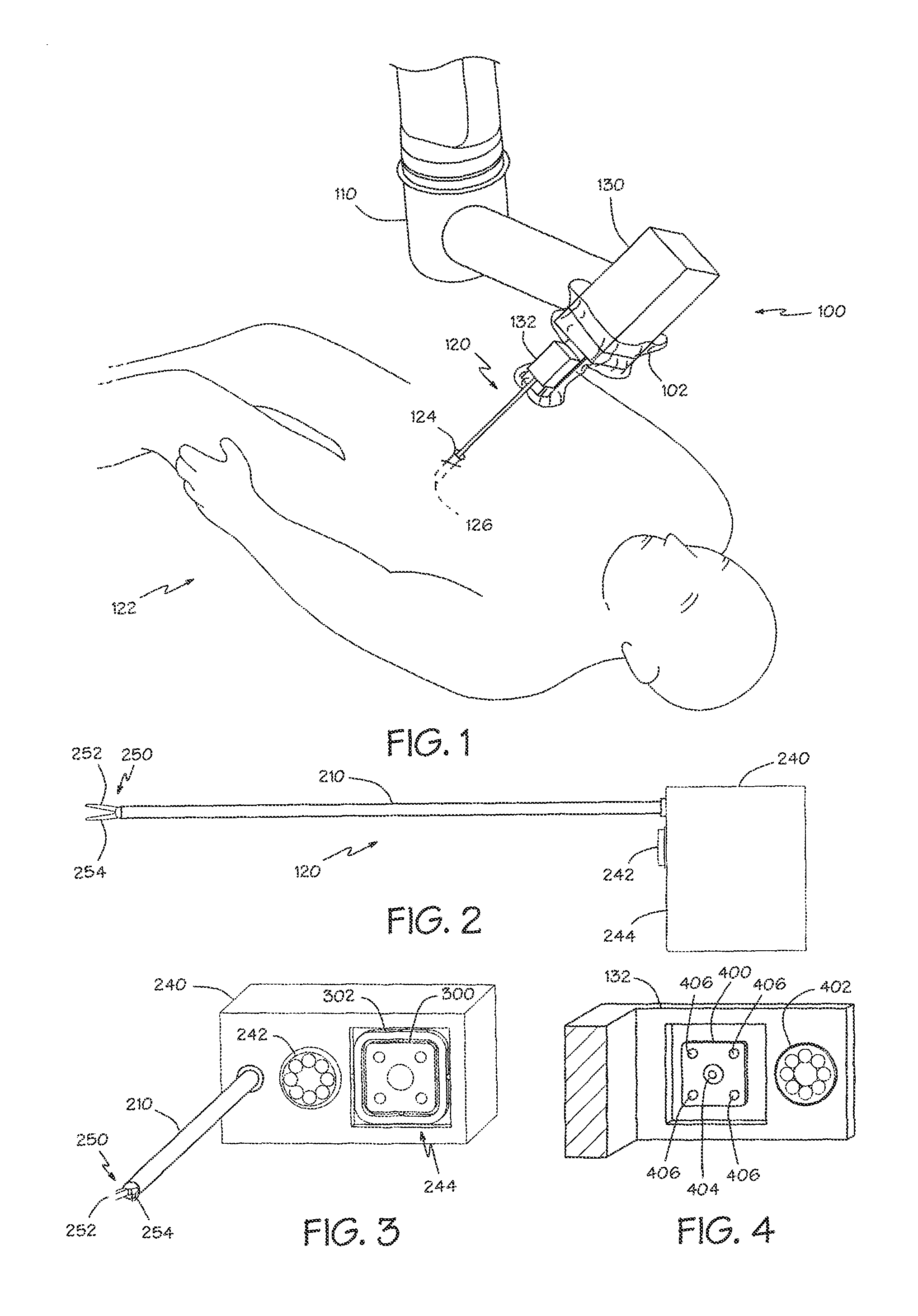
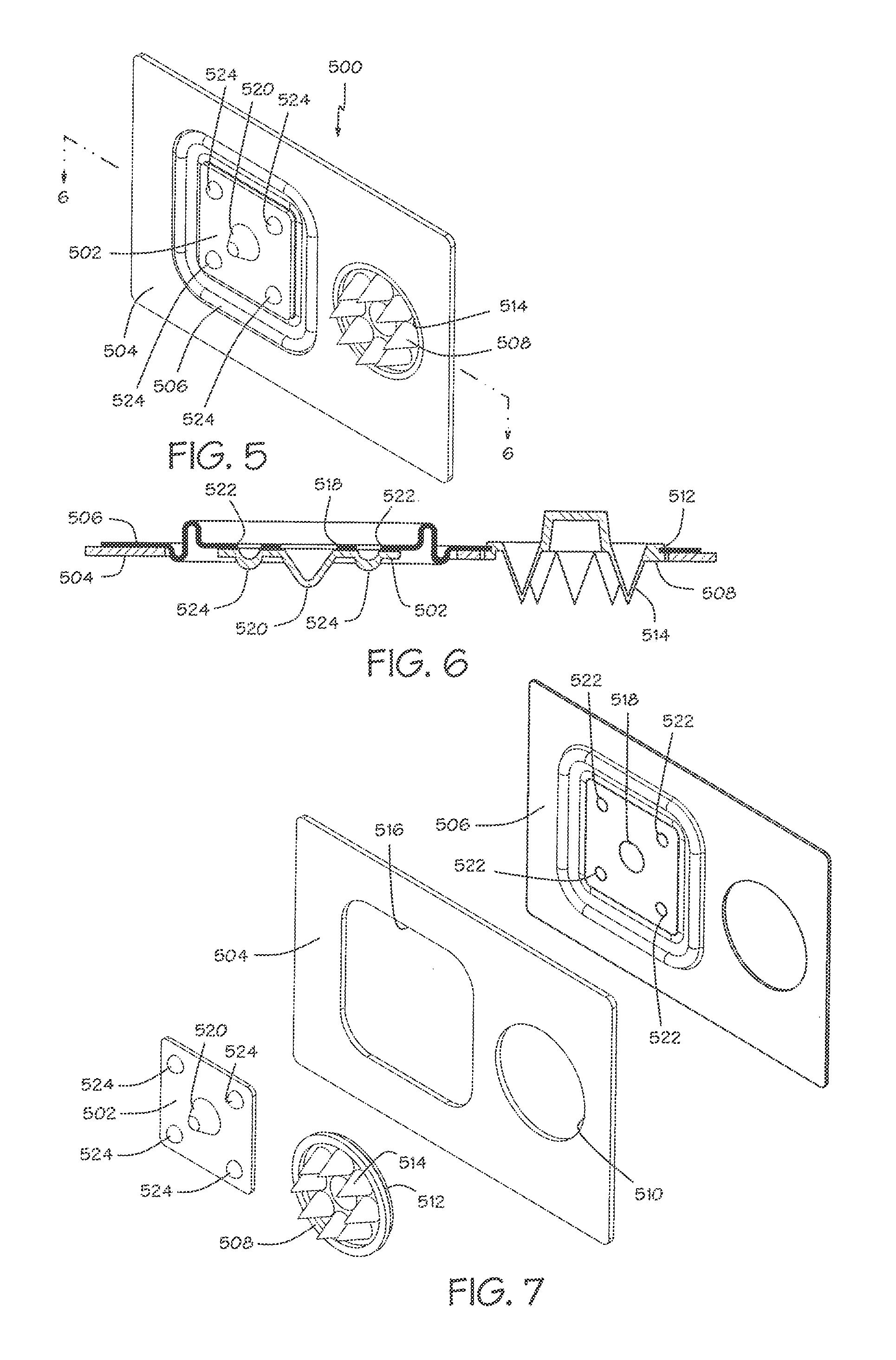
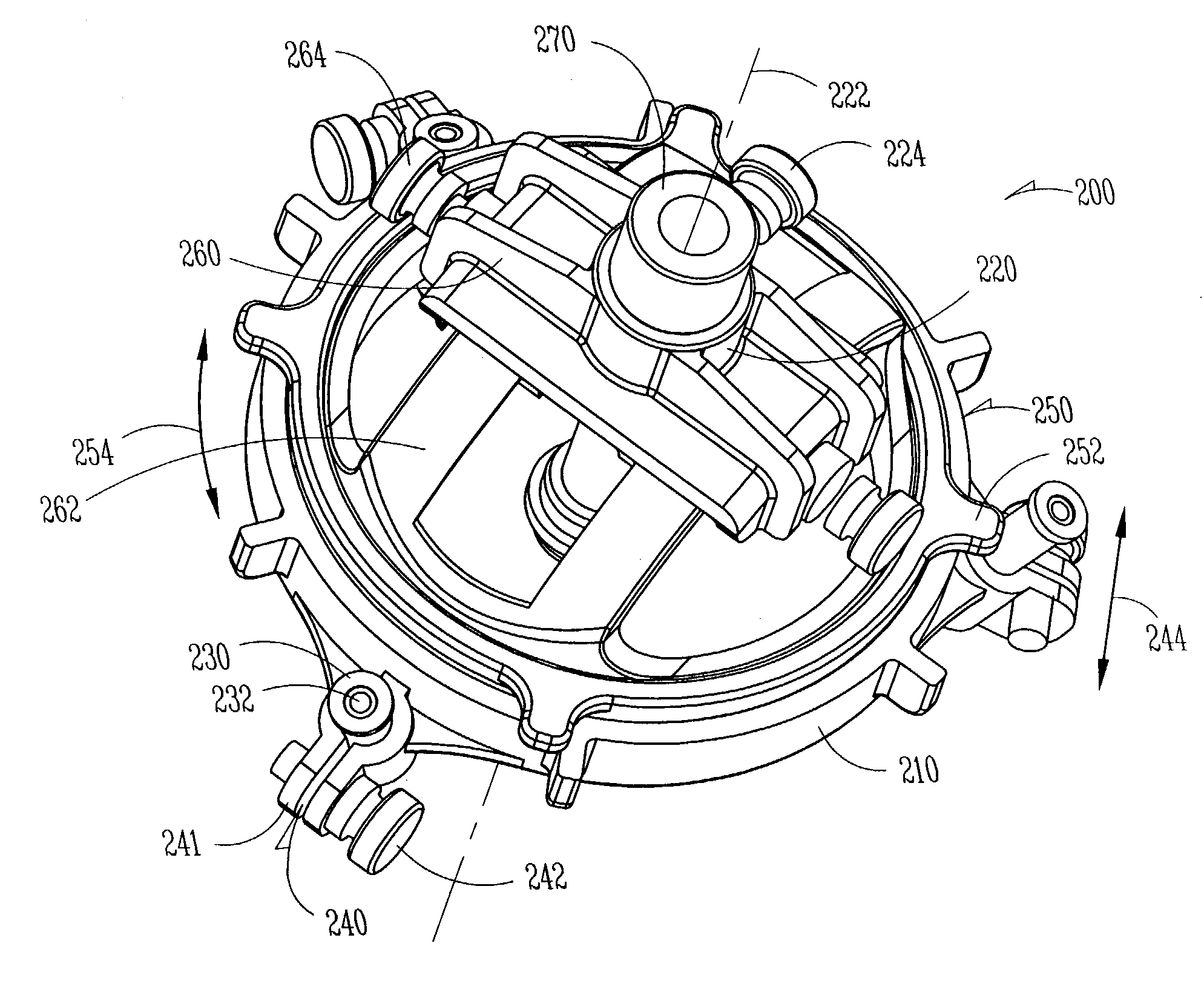
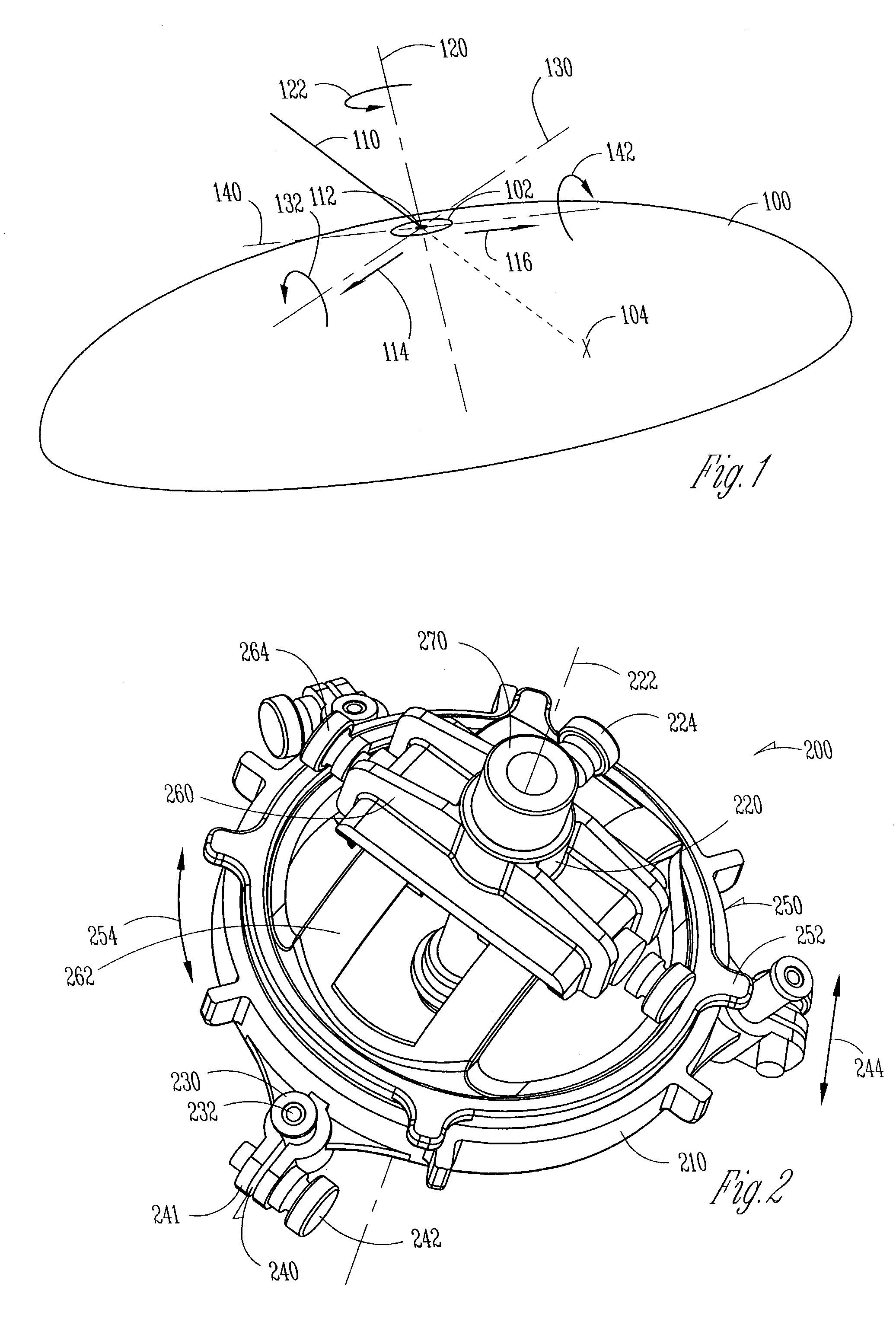
A robotic surgical system includes a sterile surgical instrument, a robotic surgical manipulator, and a sterile drape covering at least a portion of the robotic surgical manipulator. The surgical instrument has a proximal interface and a distal end effector. The proximal interface includes a gimbal assembly with two intersecting rotational axes coupled to the distal end effector. The robotic surgical manipulator has a drive plate that bears against the gimbal assembly. The drive plate has two degrees of rotational freedom about a center of motion that is coincident with an intersection of the axes of the gimbal assembly. The sterile drape includes a sterile sheet covers at least a portion of the robotic surgical manipulator, a frame bonded to the sterile sheet, an instrument interface that covers the drive plate of the robotic surgical manipulator, and a diaphragm that connects the instrument interface to the frame.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
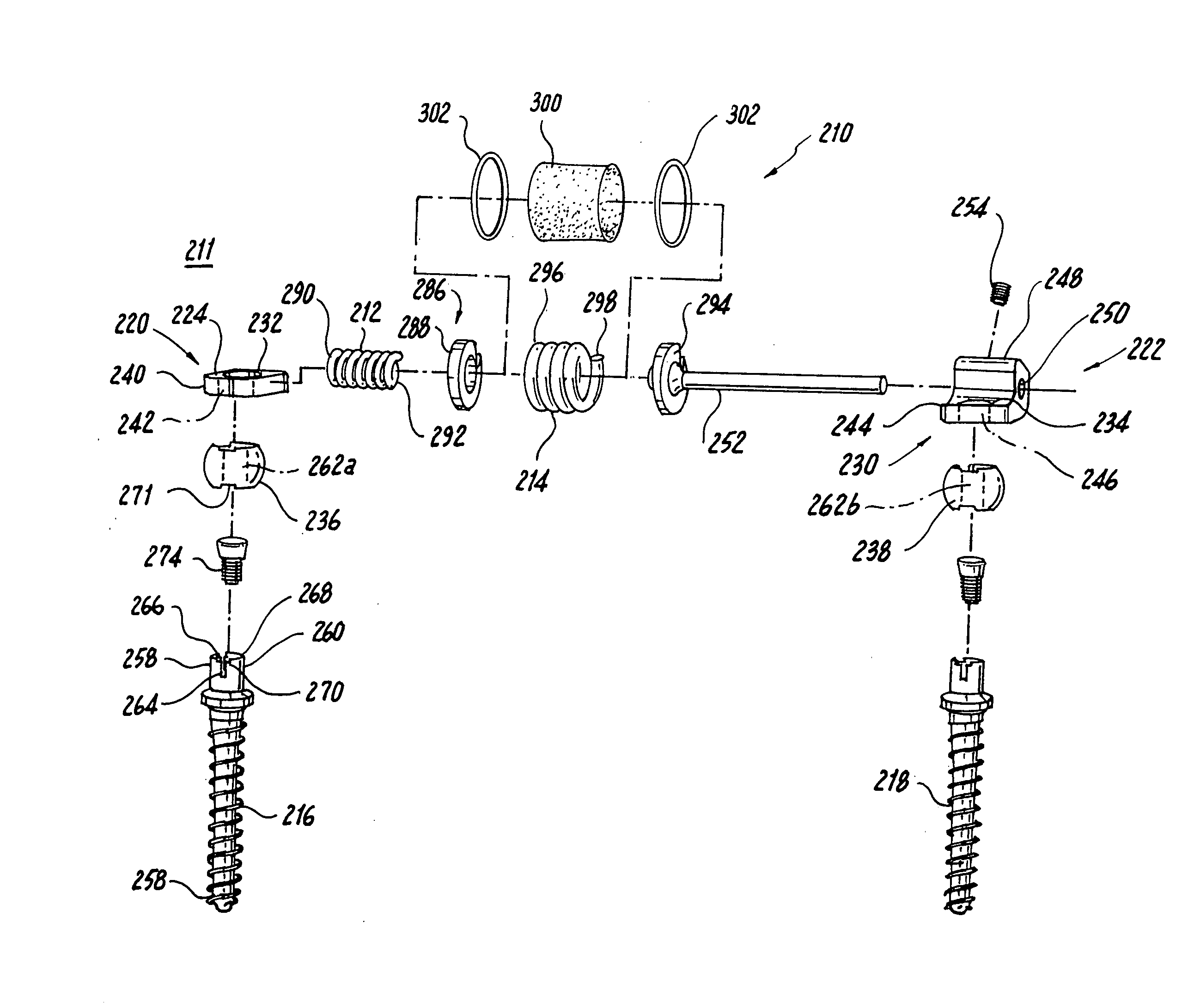
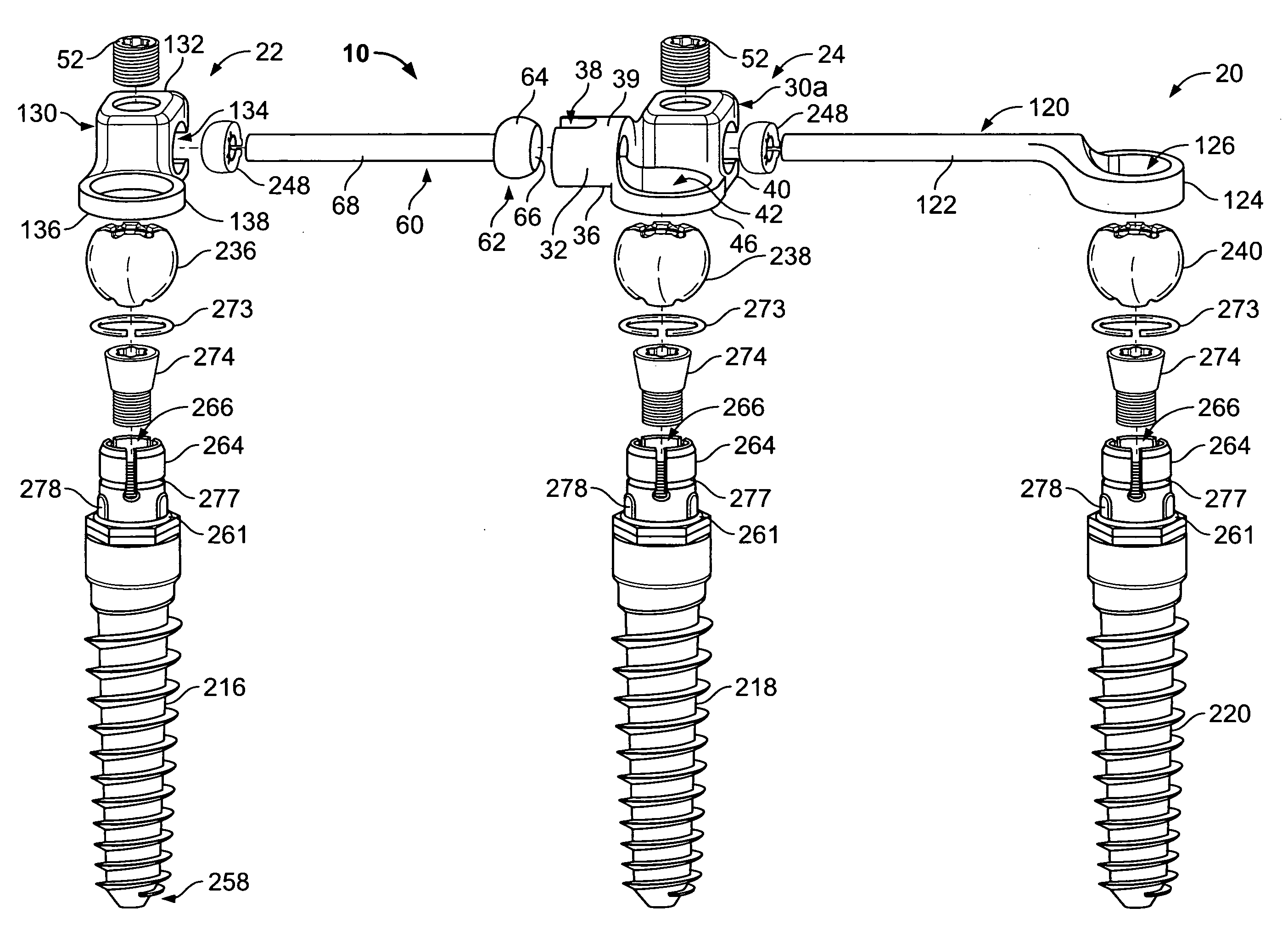
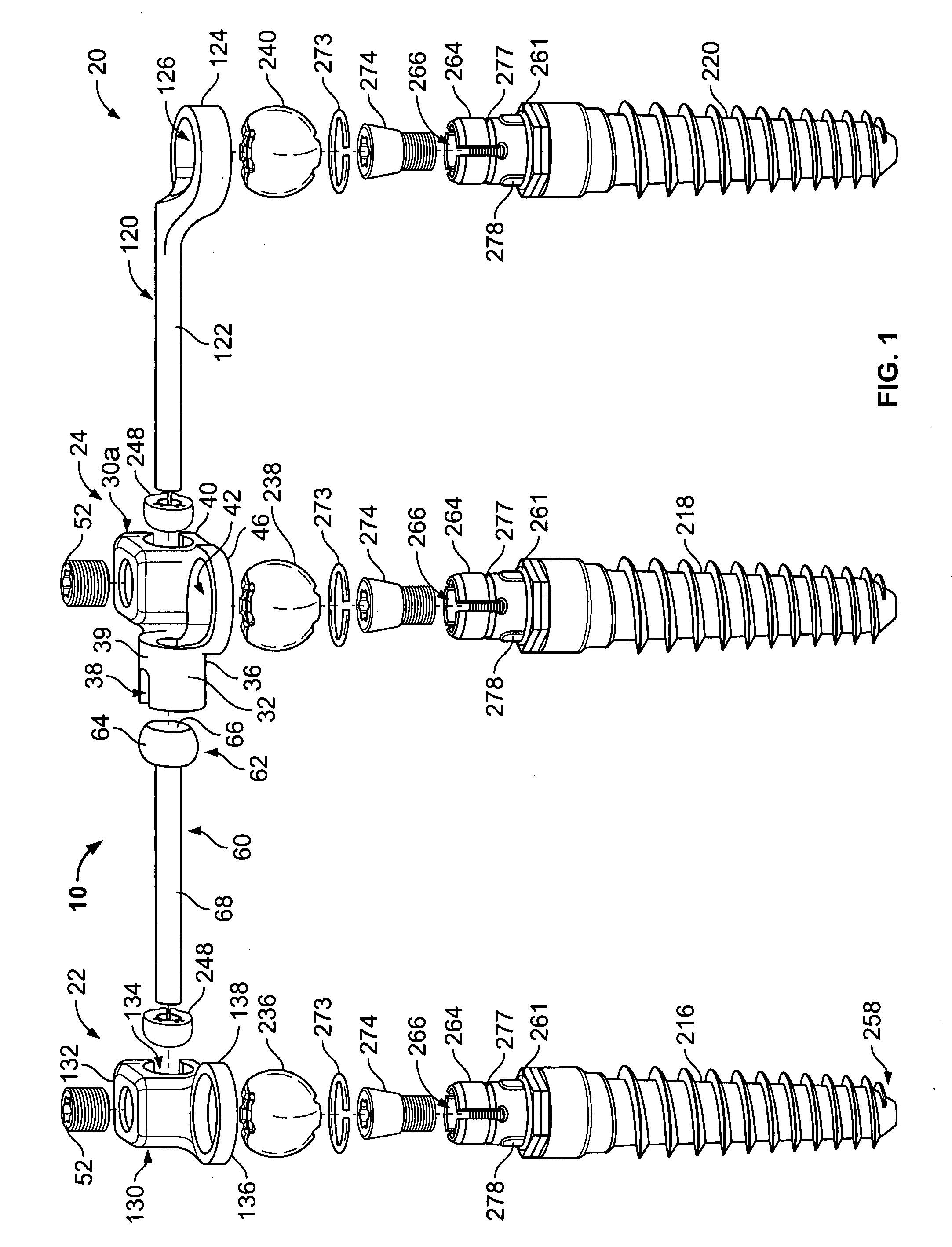
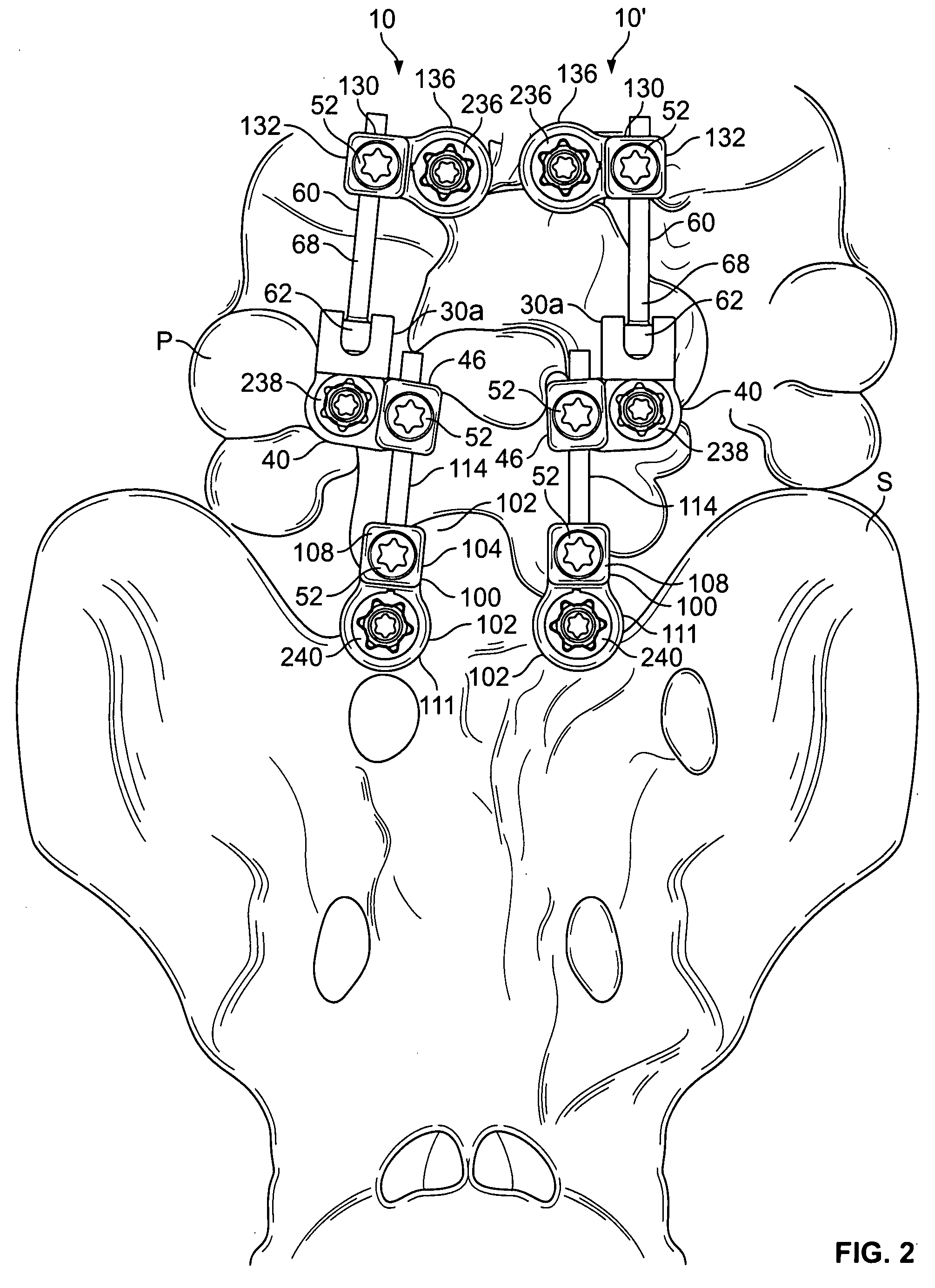
Spine stabilization systems and associated devices, assemblies and methods
InactiveUS20050171543A1Easy to installImprove clinical outcomesInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRotational freedomReady to use
A system and method for effecting multi-level spine stabilization is provided. The system includes a plurality of pedicle screws which are joined relative to each other by elongated members, e.g., rods. At least one of the rods includes a dynamic stabilizing member. The pedicle screw junctions are dynamic, i.e., free relative movement of a socket member is permitted relative to a fixed spherical element. Placement of the spherical element may be facilitated using a guidewire system that includes a guidewire and a tapered guide member. A spine stabilization assembly is also provided that includes an attachment member that includes an opening. At least one spherical element that includes a rod-receiving channel is movably mounted within the opening with three degrees of rotational freedom. The spherical element generally defines an elliptical rod-receiving channel that is deformable to a circular opening to firmly engage a rod positioned therein. Multi-level stabilization systems that combine / mix dynamic and non-dynamic stabilization modalities are also provided. The multi-level spine stabilization system offers efficacious clinical results at least in part due to the inclusion of dynamic stabilizing member(s).
Owner:APPLIED SPINE TECH
Systems and methods for spine stabilization including a dynamic junction
InactiveUS20050182401A1Easy to installImprove clinical outcomesSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisRotational freedomUniversal joint
Spinal stabilization devices, systems and methods are provided that include at least one pedicle screw and at least one mechanism that supports three degrees of rotational freedom relative to the pedicle screw. The mechanism may include a universal joint mechanism or a ball and socket mechanism. In the case of the ball and socket mechanism, at least one spherical element is mounted with respect to the at least one pedicle screw and a socket member cooperates with the spherical element. The spherical element and the socket member cooperate to define a dynamic junction that allows the socket member to move relative to the ball element while remaining engaged therewith. The dynamic junction is advantageously incorporated into a spinal stabilization system that includes additional pedicle screw(s), spherical element(s) and socket member(s). The spinal stabilization system may incorporate dynamic stabilizing member(s) to so as to provide clinically efficacious results.
Owner:APPLIED SPINE TECH
Deriving input from six degrees of freedom interfaces
ActiveUS20120038549A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingMixed realityVirtual space
The present invention relates to interfaces and methods for producing input for software applications based on the absolute pose of an item manipulated or worn by a user in a three-dimensional environment. Absolute pose in the sense of the present invention means both the position and the orientation of the item as described in a stable frame defined in that three-dimensional environment. The invention describes how to recover the absolute pose with optical hardware and methods, and how to map at least one of the recovered absolute pose parameters to the three translational and three rotational degrees of freedom available to the item to generate useful input. The applications that can most benefit from the interfaces and methods of the invention involve 3D virtual spaces including augmented reality and mixed reality environments.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Multi-level spinal stabilization system
ActiveUS20080312692A1Clinically efficacious resultEasy to installSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisRotational freedomUniversal joint
Multi-level spinal stabilization devices, systems and methods are provided that include at least one multi-level connector, one elongated member with an enlarged head, at least one pedicle screw, and at least one mechanism that supports three degrees of rotational freedom relative to both the elongated member and the pedicle screw each. The mechanism may include universal joint mechanisms or ball and socket mechanisms. In the case of the ball and socket mechanisms, the enlarged head of the elongated member cooperates with a first socket member of the multi-level connector to define a dynamic junction that allows the socket member to move relative to the enlarged head of the elongated member while remaining engaged therewith.
Owner:RACHIOTEK
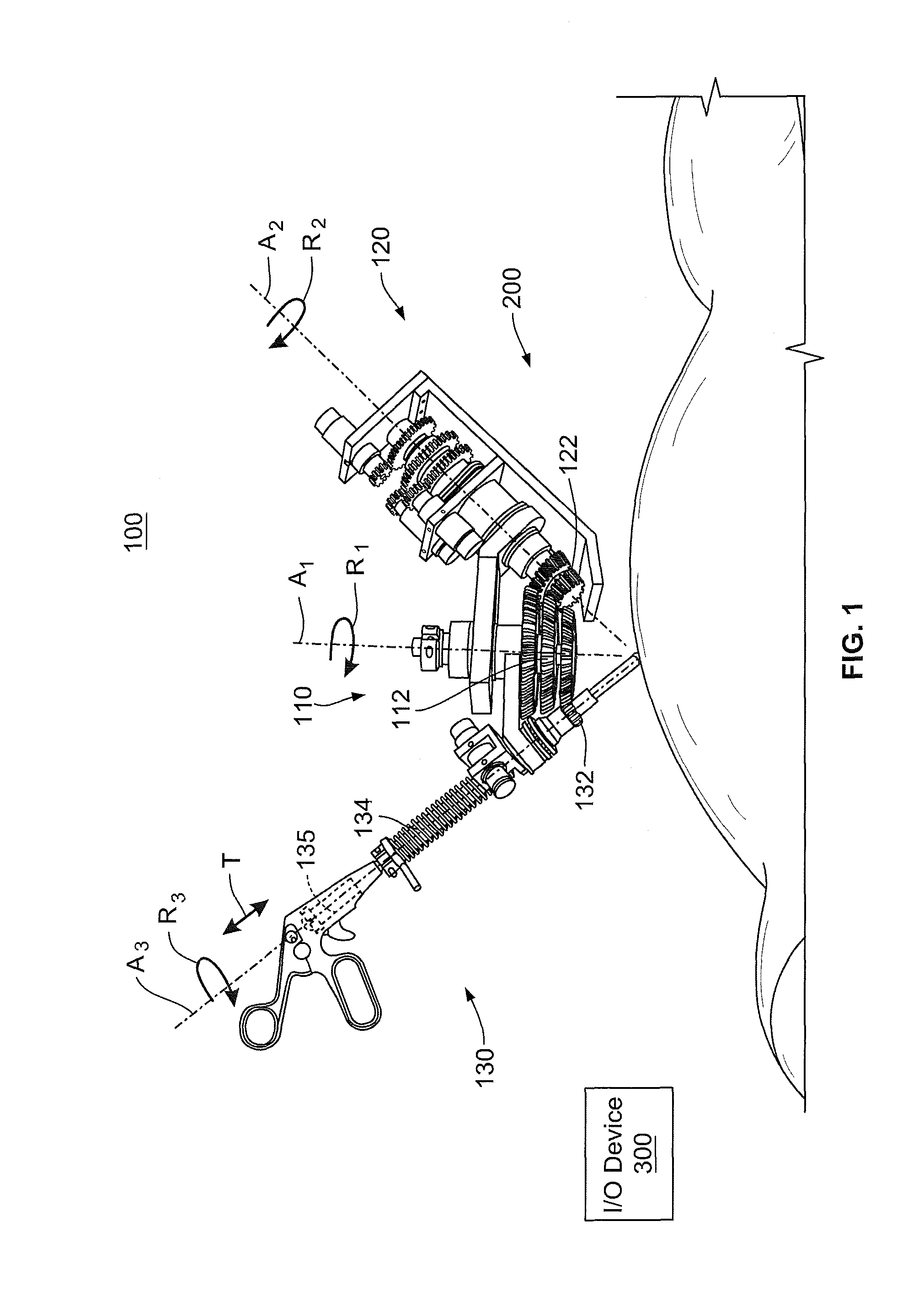
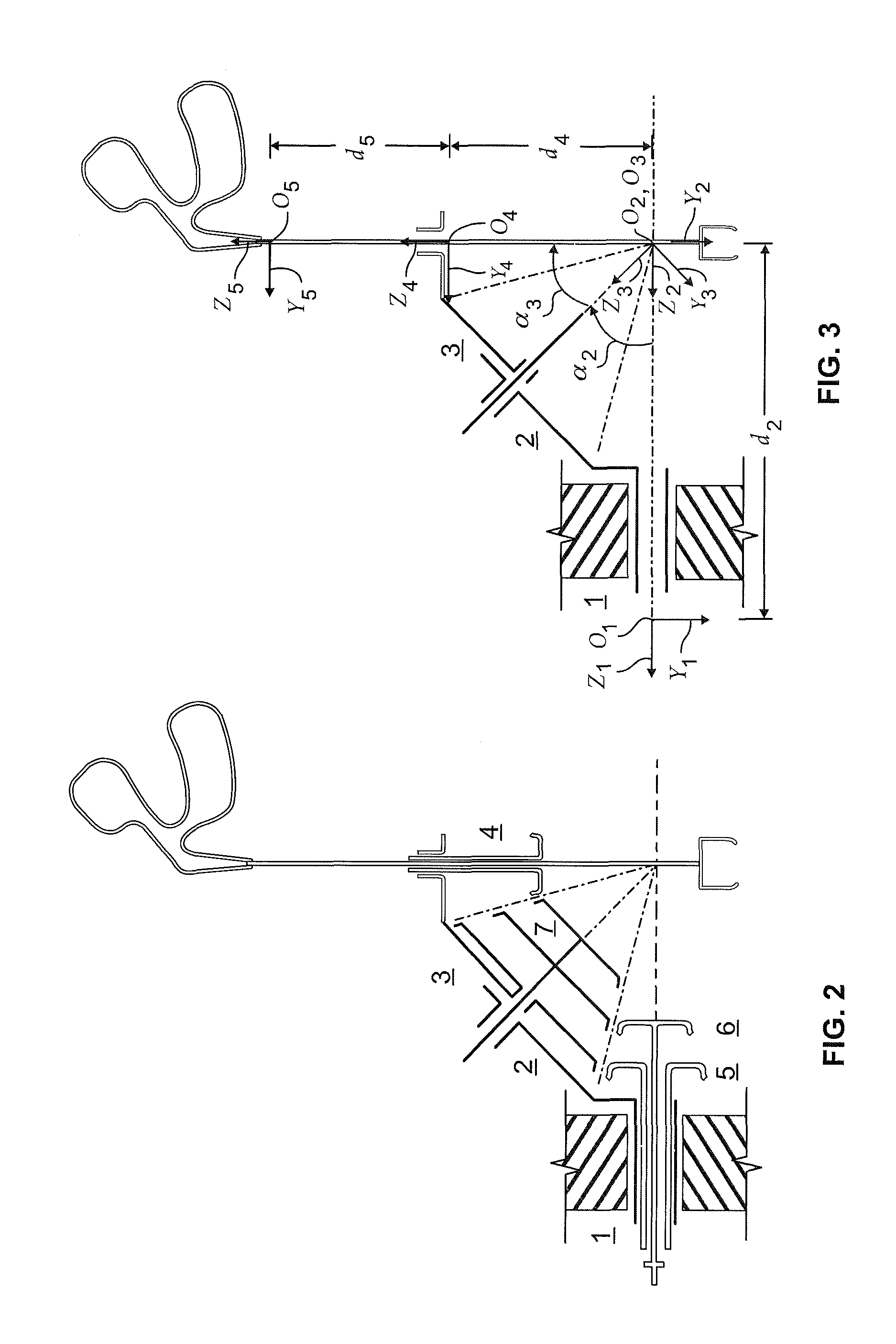
Surgical instrument
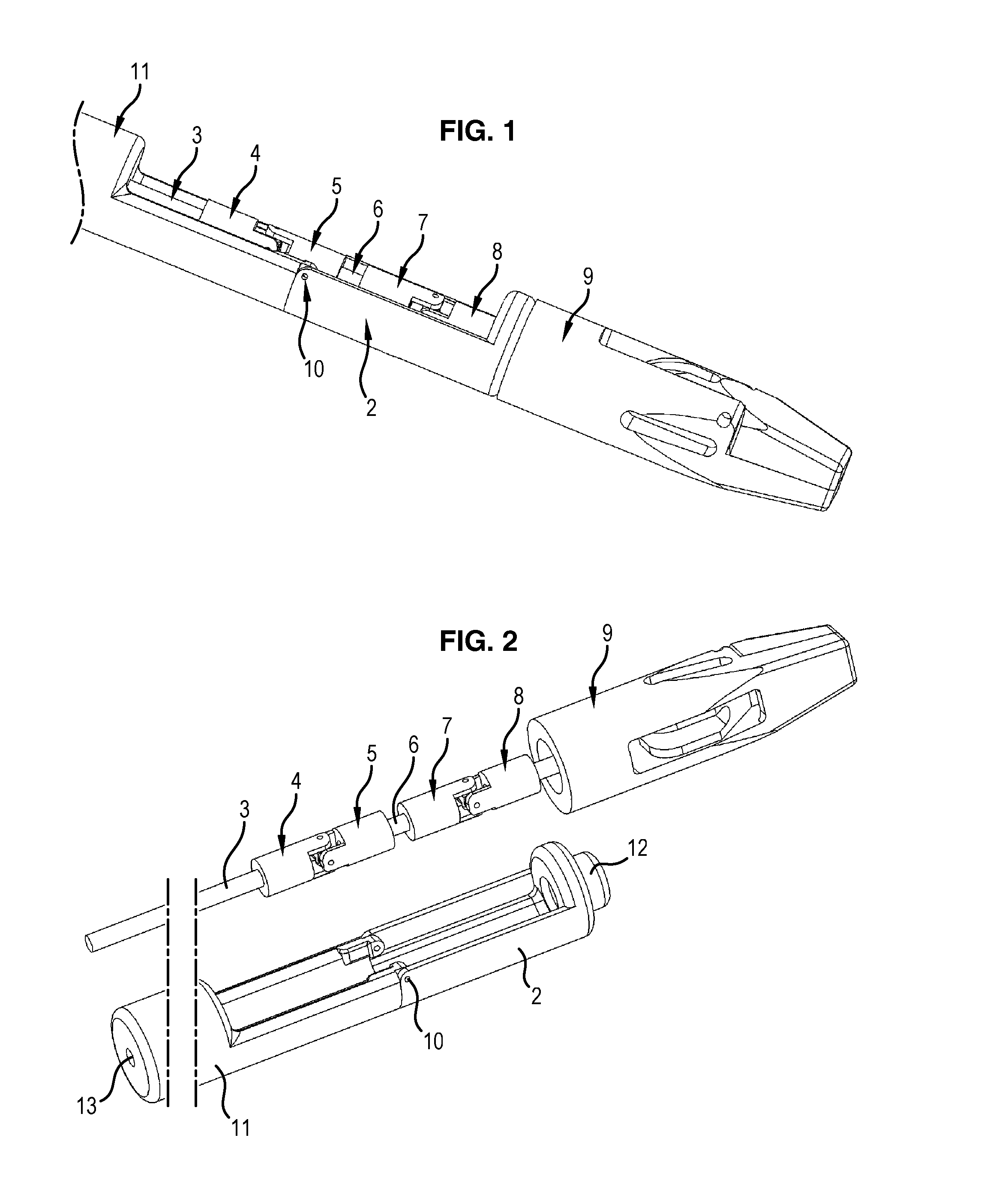
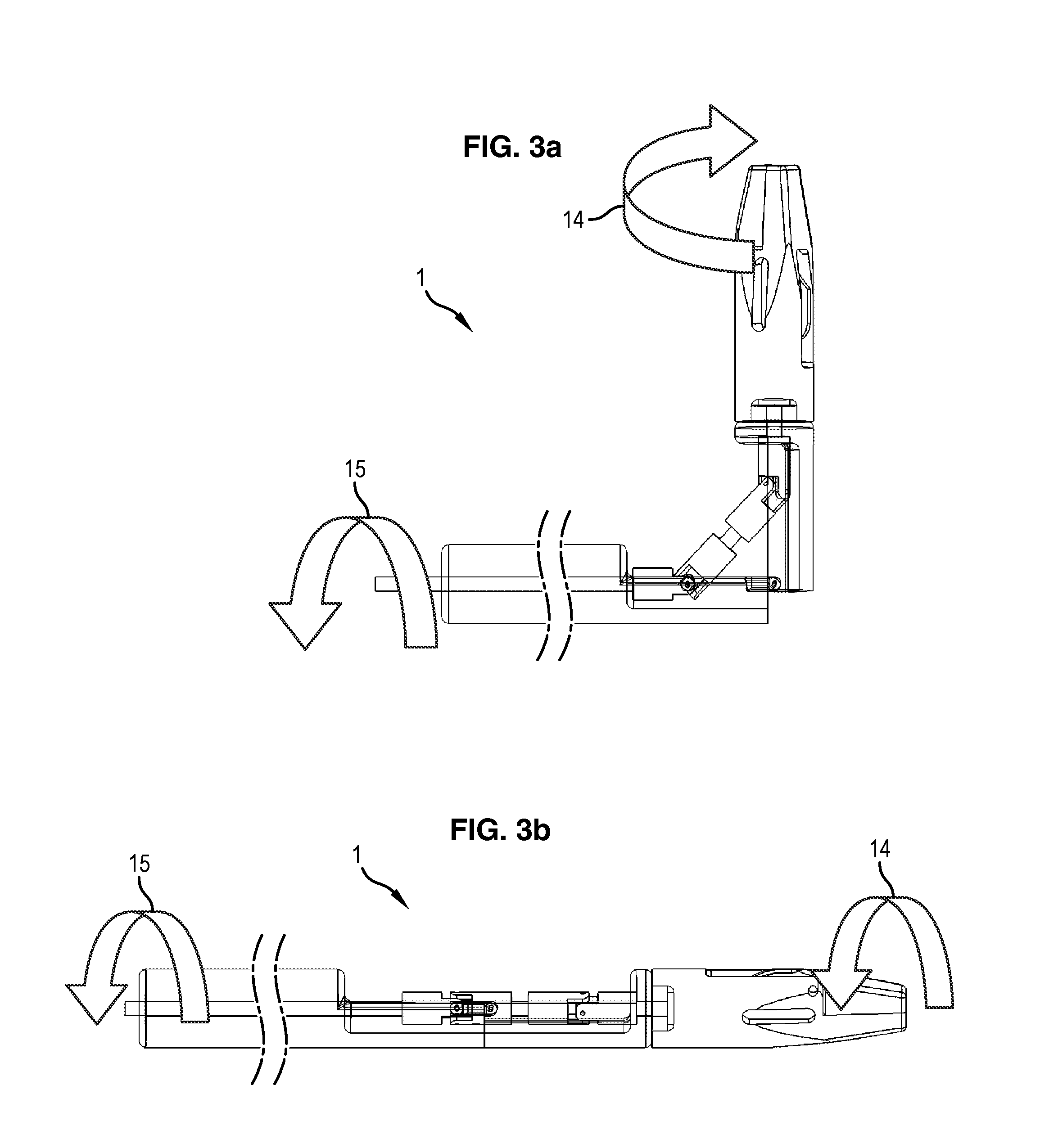
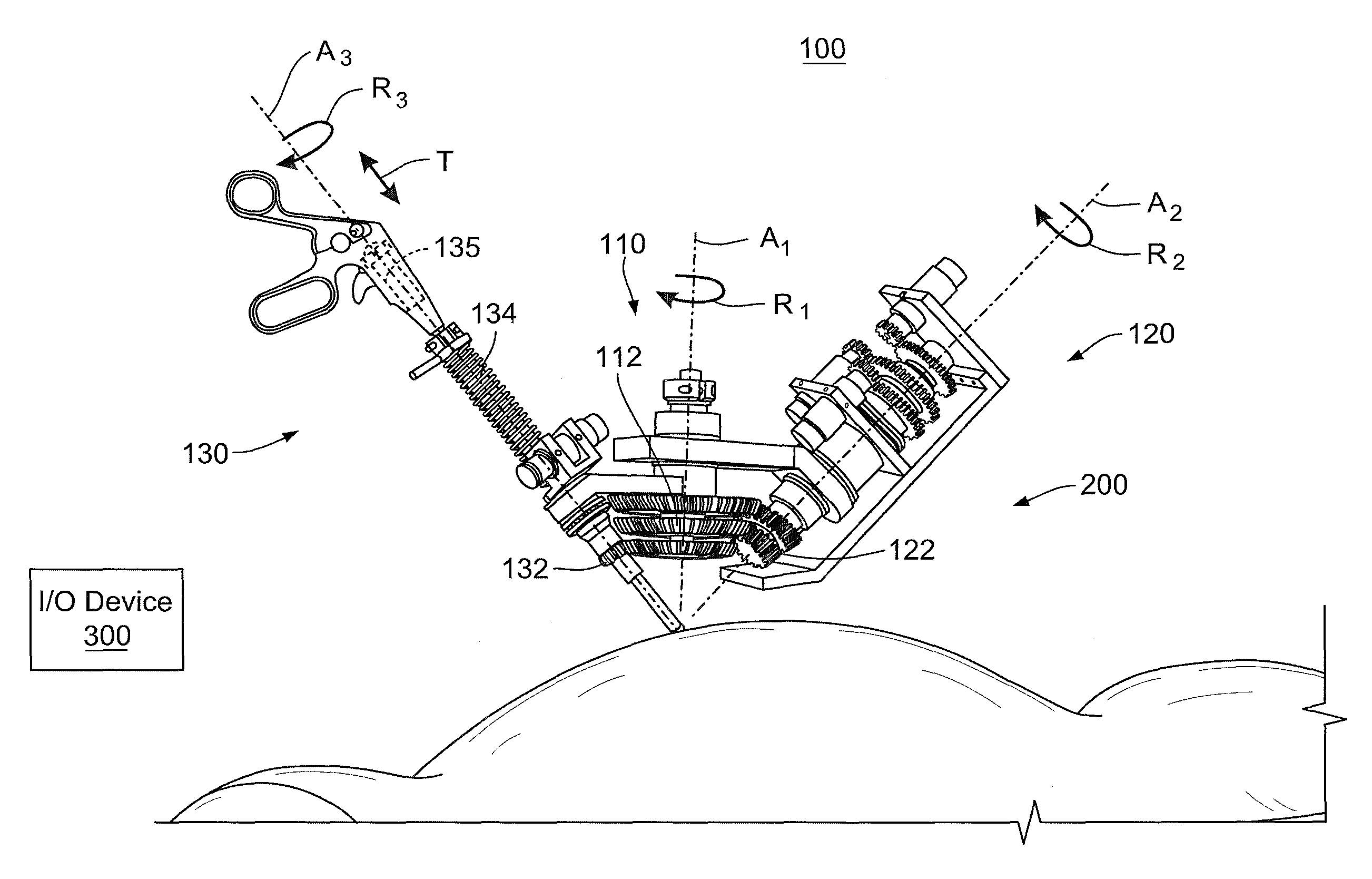
ActiveUS8845622B2Easy to controlEasy to manufactureDiagnosticsSurgical forcepsUniversal jointDrive shaft
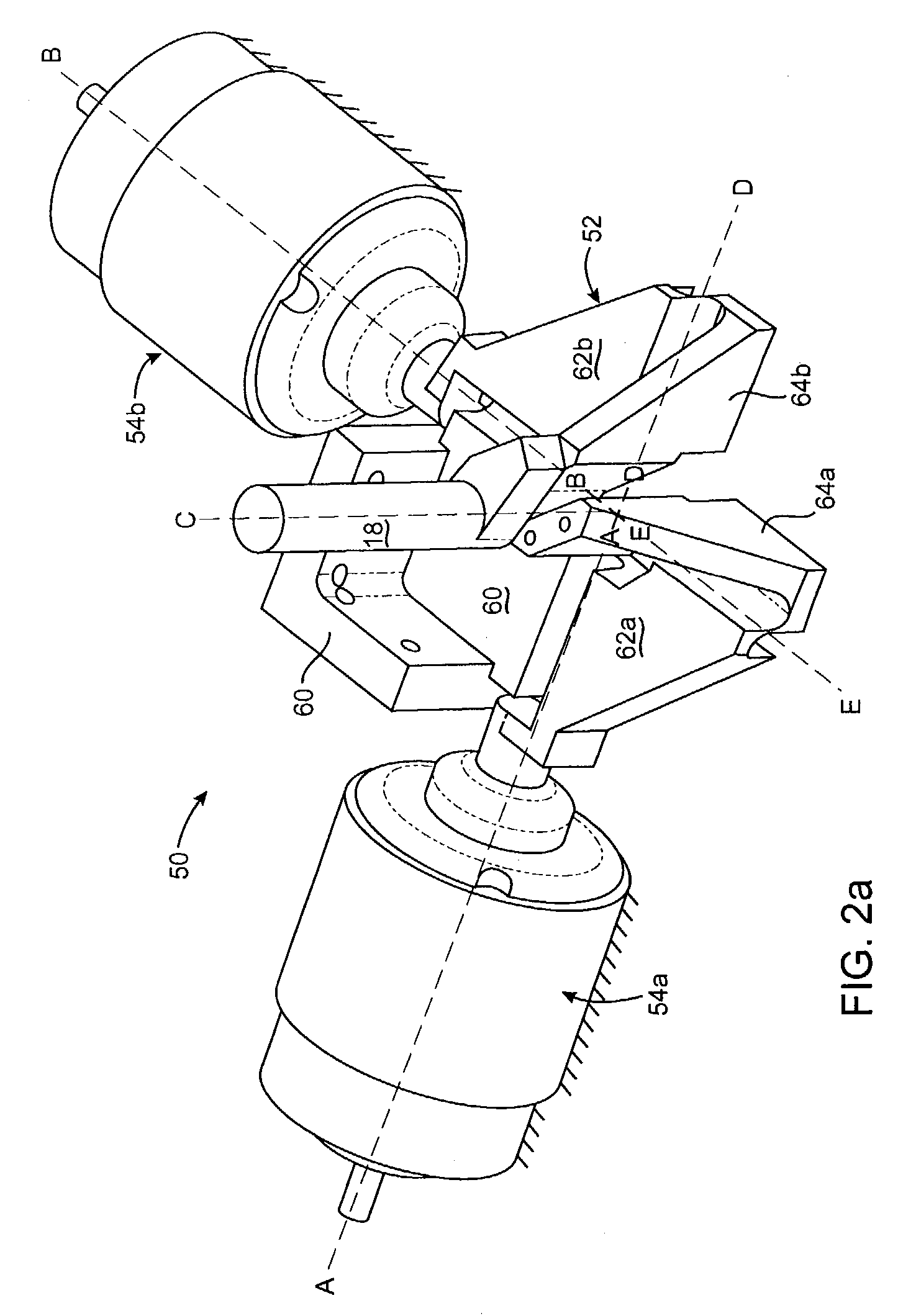
The invention relates to a surgical instrument (100; 200) comprising:an elongated arm (111; 207) according to a longitudinal axis and having a distal end (105; 204) mounted with a pivot joint on the elongated arm according to an axis substantially orthogonal to the longitudinal axis;a drive shaft (103; 3), substantially coaxial with the elongated arm, comprising means forming a universal joint (104; 206) facing the pivot joint; and,distal tool (9) securely fastened on the drive shaft and rotatively mounted on and in the extension of the distal end of the elongated arm, such that the distal tool has two rotational degrees of freedom, distinct and independent of each other, one being around an axis substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the elongated arm and the other being around an axis substantially collinear to an own axis of the distal tool, characterized in that the means forming a universal joint comprise a flexible drive sleeve (104; 206).
Owner:UNIV PIERRE & MARIE CURIE +1
Rotary blood pump and control system therefor
Owner:TC1 LLC +1
Solar modules with tracking and concentrating features
InactiveUS20070251569A1Reduce in quantityImprove photovoltaic efficiencyPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectricityRotational freedom
Disclosed are fixed solar-electric modules having arrays of solar concentrator assemblies capable of separately tracking movements through one or two degrees of rotational freedom to follow the movement of the sun daily and / or seasonally. The concentrators can include optical elements to direct and concentrate light onto photovoltaic and / or thermoelectric receivers for generation of electric current.
Owner:INTEMATIX
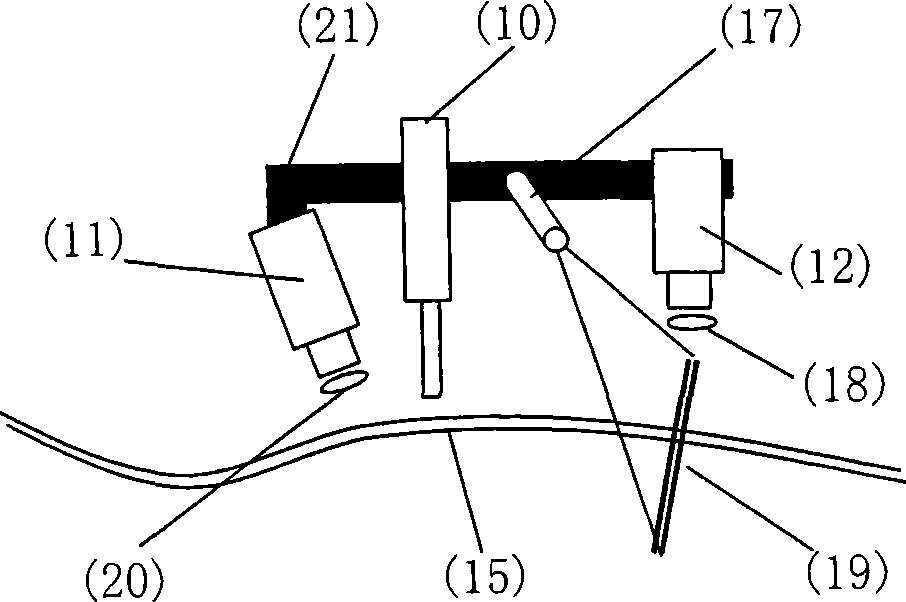
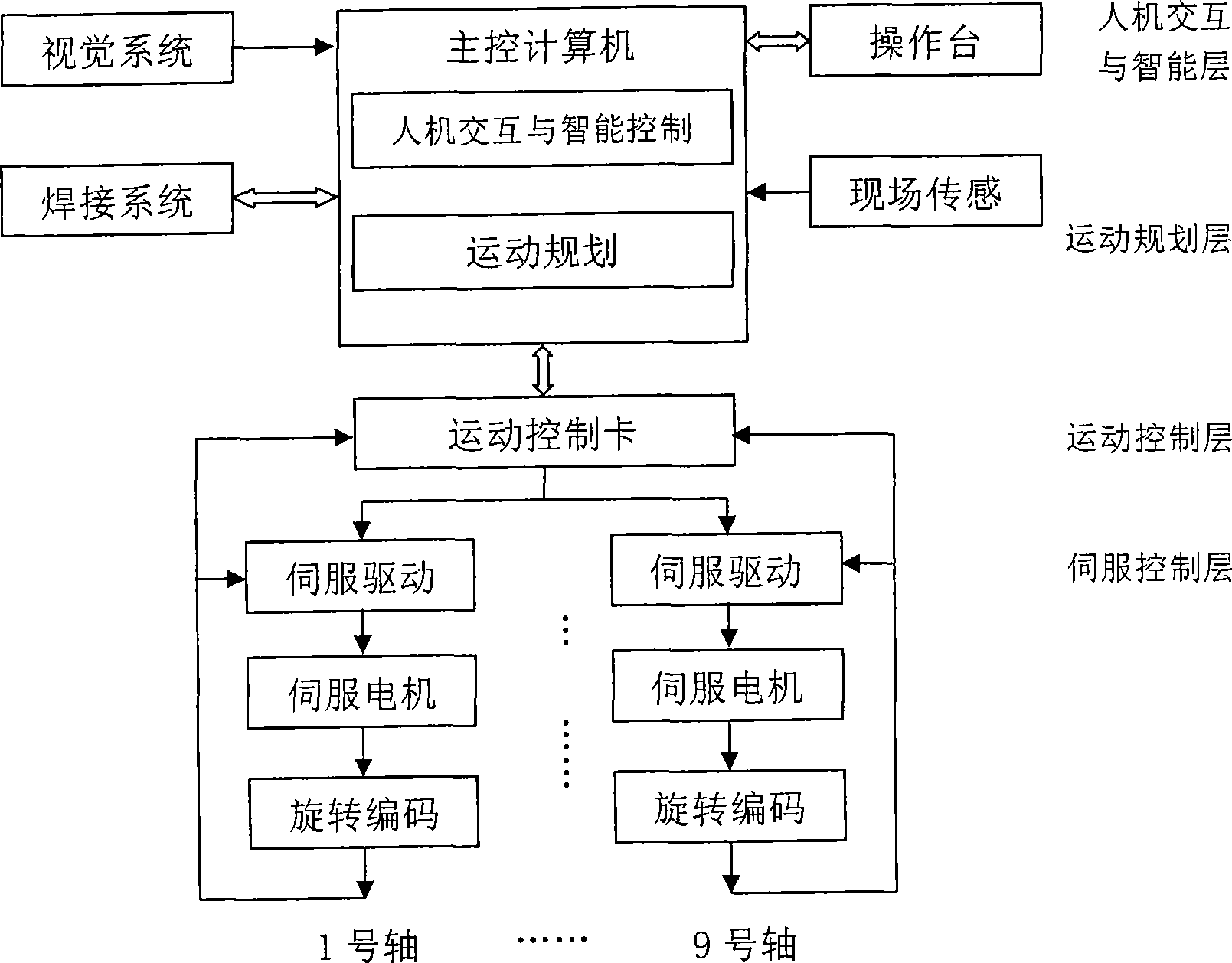
Intelligent robot welding device using large-scale workpiece
InactiveCN101456182AWith visual functionSimple motion controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorArc welding apparatusRotational axisRotational degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a large-sized workpiece welded intelligent robot device, relates to robot technology, in particular to the robot device based on visual control technology. The device consists of a robot body, a sensing system, a robot controller and a welding auxiliary mechanism. The welded robot is provided with nine moving shafts, including three macrographic moving translational moving shafts, three microscopic moving translational moving shafts and three rotating shafts. The robot body comprises a robot frame and a robot head which is arranged on a transverse arm of the robot frame, and the robot frame consists of the three macrographic moving translational moving shafts, namely a horizontal lead rail, an upright post and the transverse arm. The robot head consists of the three microscopic moving translational moving shafts, the three rotating shafts and a welding gun. The robot frame provides the large-scale three-dimensional movement of the robot; the precision of macrographic moving movement is compensated by the microscopic moving mechanisms of the robot head which also provides rotating freedom of motion. The robot device can meet the movement requirements of large scale and precise positioning for the welding operation of large-sized workpieces. Through the visual sensing technology and intelligent visual controlling technology, the device can improve the automatic welding quality and efficiency of the welded robot.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Drive roller control for toric-drive transmission
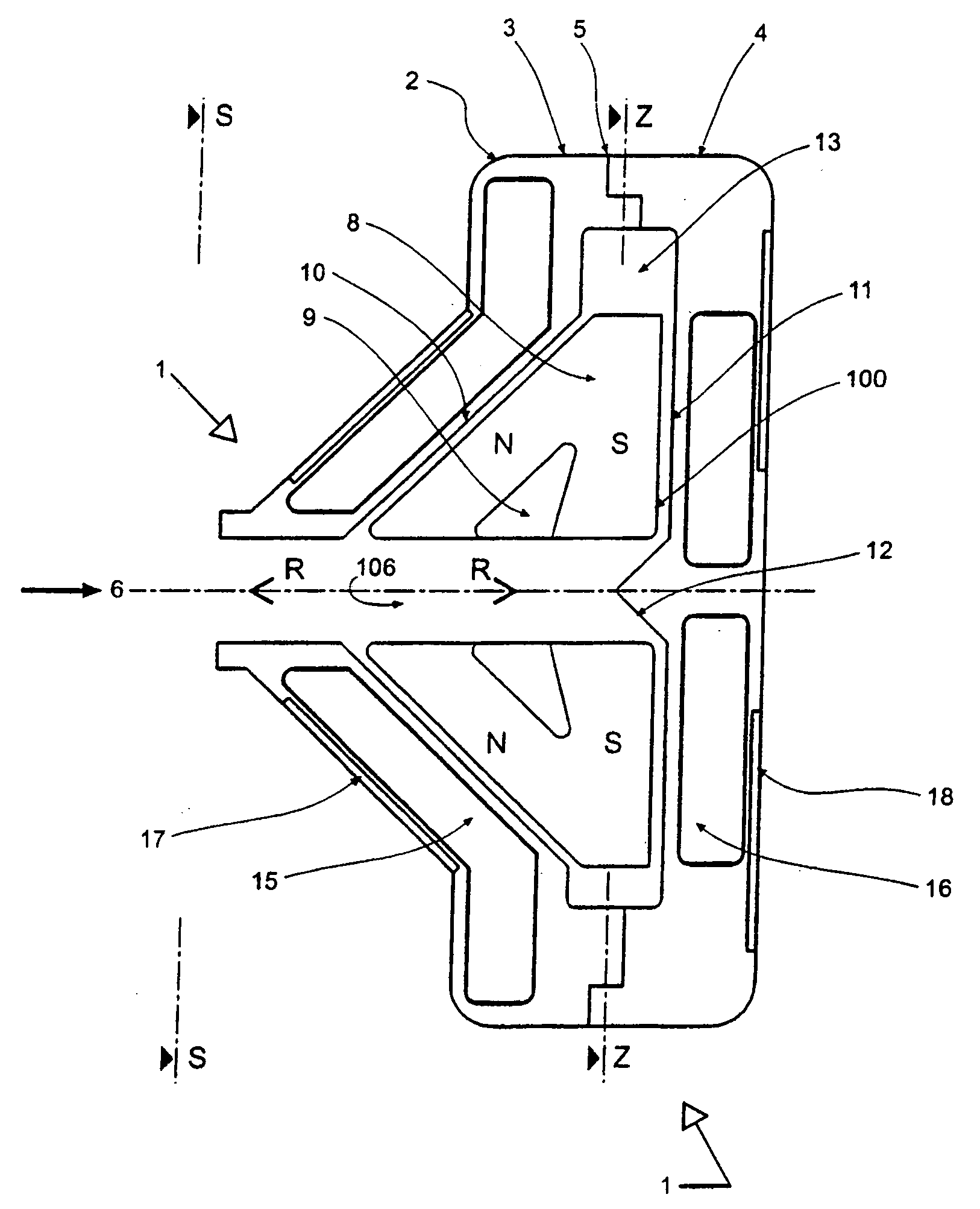
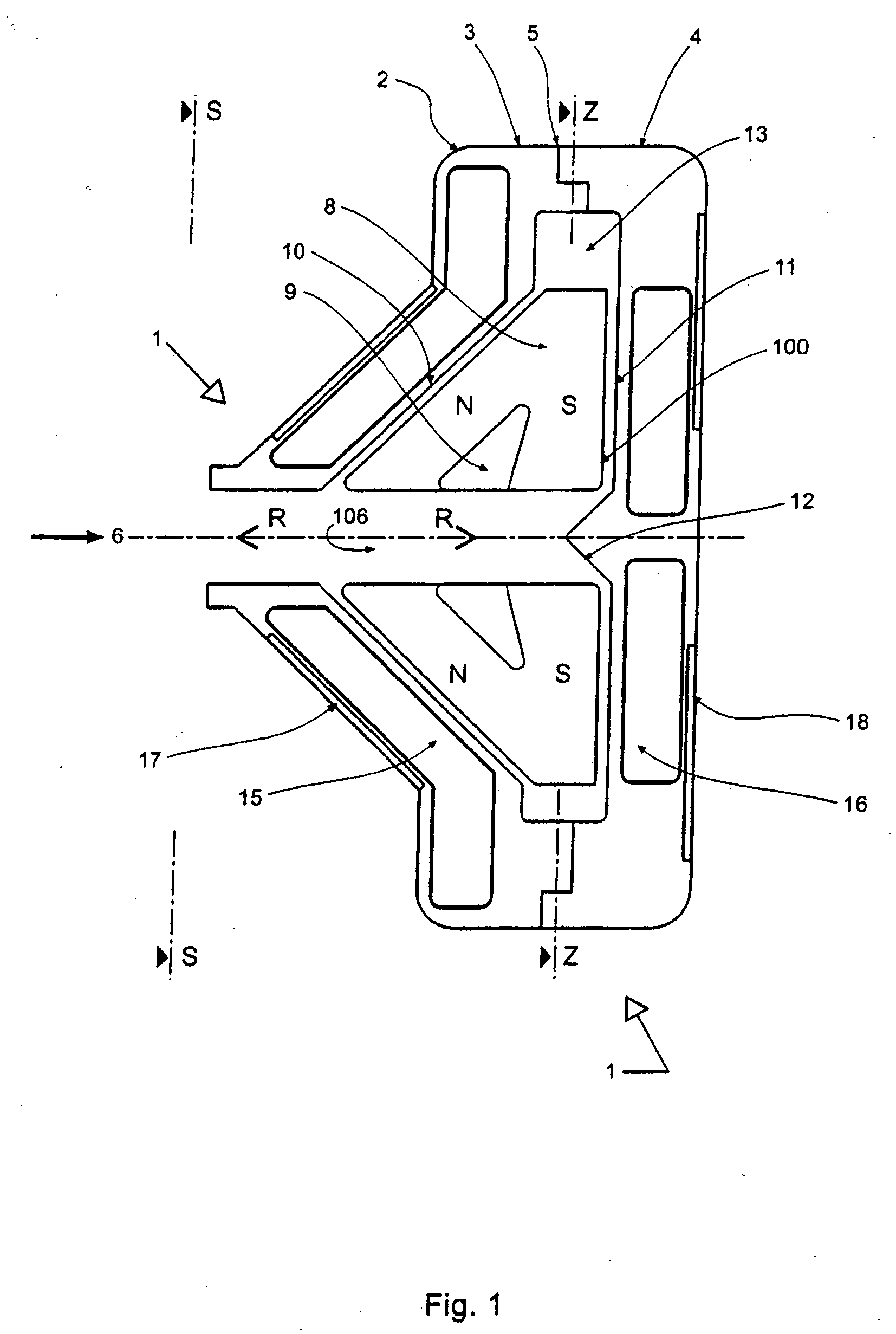
ActiveUS7217220B2Improve energy efficiencyReduce the amount requiredGearing controlFriction gearingsDegrees of freedomRotational degrees of freedom
A toric-drive transmission comprising a drive disk for receiving a power input. A driven disk transmits a power output. A roller device has a roller displaceably mounted between the drive disk and the driven disk. The roller has three rotational degrees of freedom. A first degree of freedom transmits motion from the drive disk to the driven disk to convert the power input to the power output. A second degree of freedom varies a ratio of the power output to the power input as a function of an orientation of the roller along the second degree of freedom. A third degree of freedom initiates a rotation of the roller about the second degree of freedom. A controller system is operatively connected to the roller device for changing the orientation of the roller in the second degree of freedom by actuating a displacement of the roller in the third degree of freedom.
Owner:S O E TECH
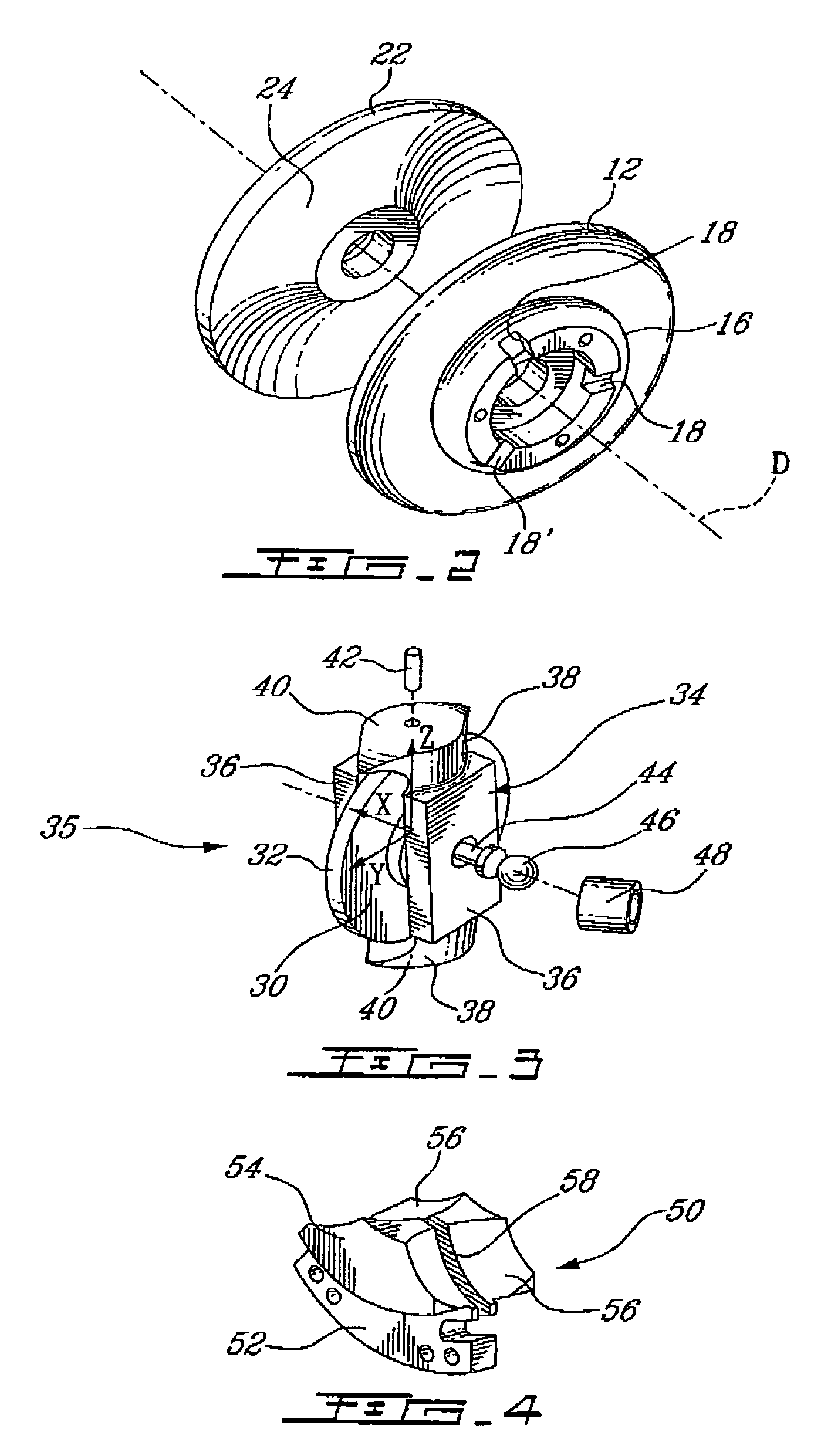
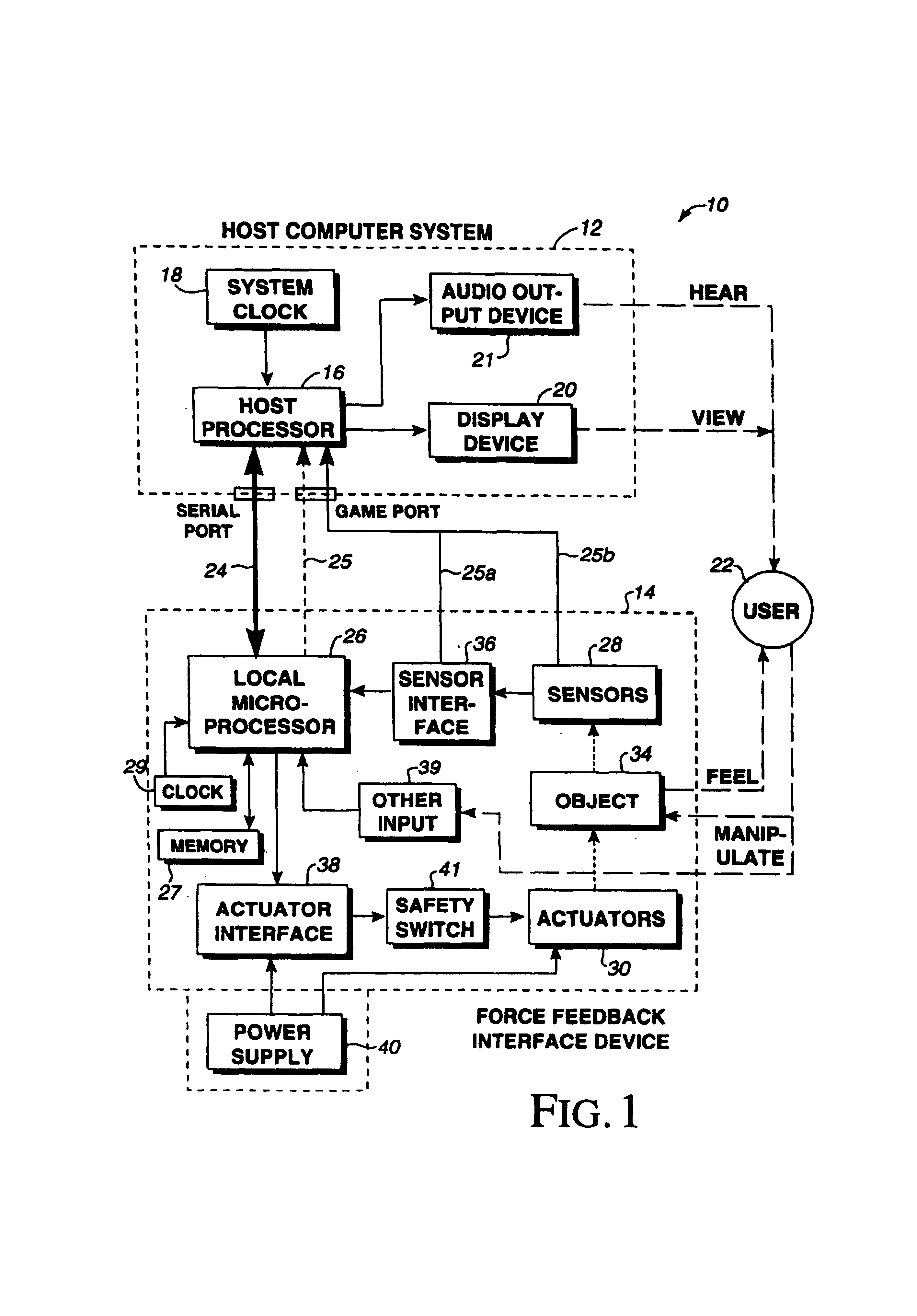
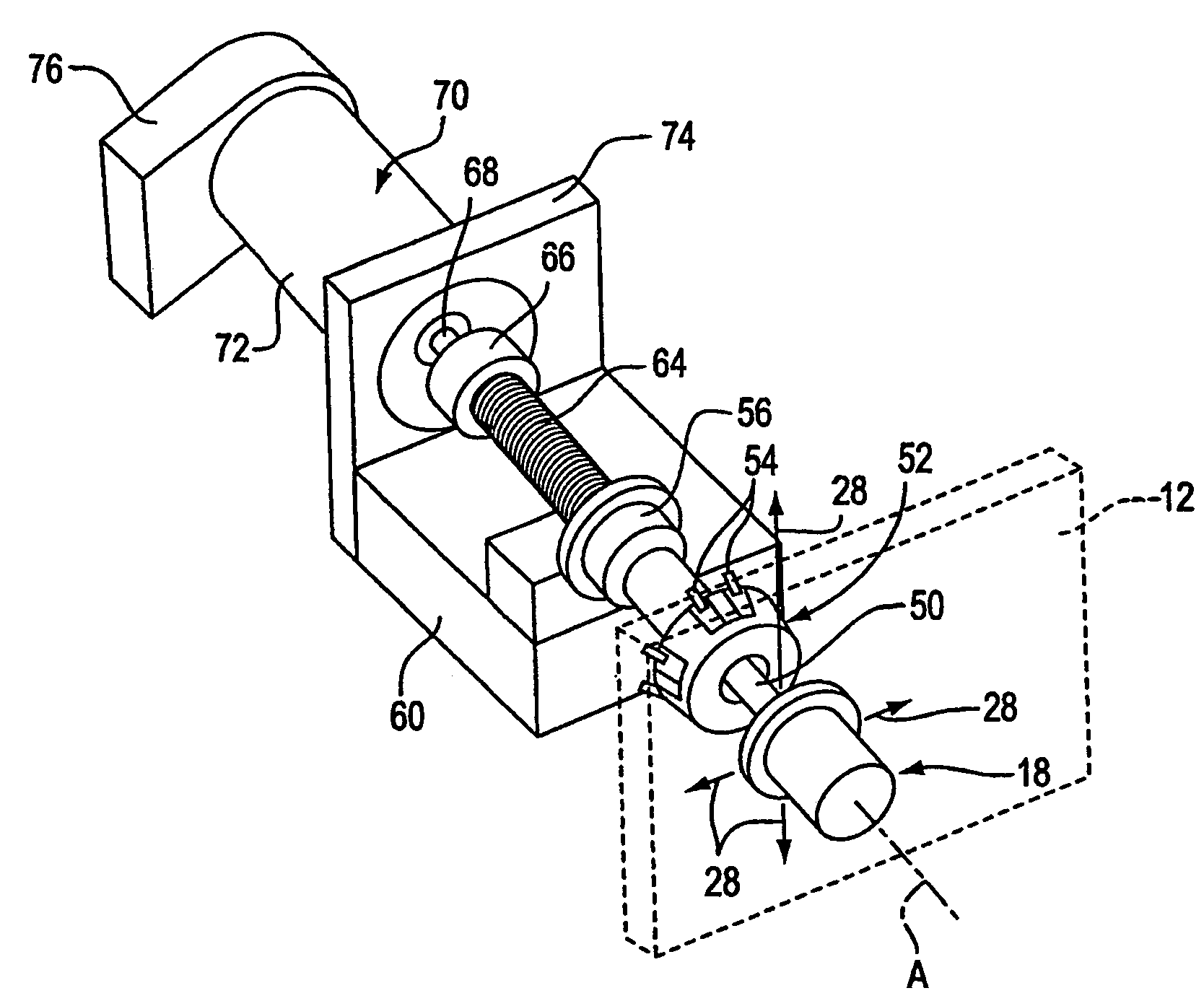
Method for providing high bandwidth force feedback with improved actuator feel
InactiveUS7236157B2Improve realismEliminate the effects ofInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersHigh bandwidthJoystick
A method and apparatus for providing low-cost, realistic force feedback including an improved actuator. The invention provides force sensations to a user and includes an interface device coupled to a host computer and allowing a user to interact with a host application program. A user object, such as a joystick, is moveable by a user in at least one rotary degree of freedom. A sensor reports a locative signal to the host computer to indicate a position of the user object. An actuator outputs forces on the user object in response to signals from the host computer and program. The actuator includes a housing, a set of grounded magnets provided on opposing surfaces of the housing and creating a magnetic field, and a rotor coupled to the user object positioned between the magnets. The rotor rotates about an axis of rotation and includes a shaft and teeth spaced around the shaft. An electric current flows through one or more coils on the teeth to cause the rotor to rotate. The teeth and the magnets are provided in a skewed, helical arrangement relative to each other so that, as the rotor rotates, a first tooth gradually exits the magnetic field as the next consecutive tooth gradually enters the magnetic field, thereby significantly reducing a cogging effect of the rotor when the user object is moved by the user and increasing the fidelity of forces experienced by the user.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
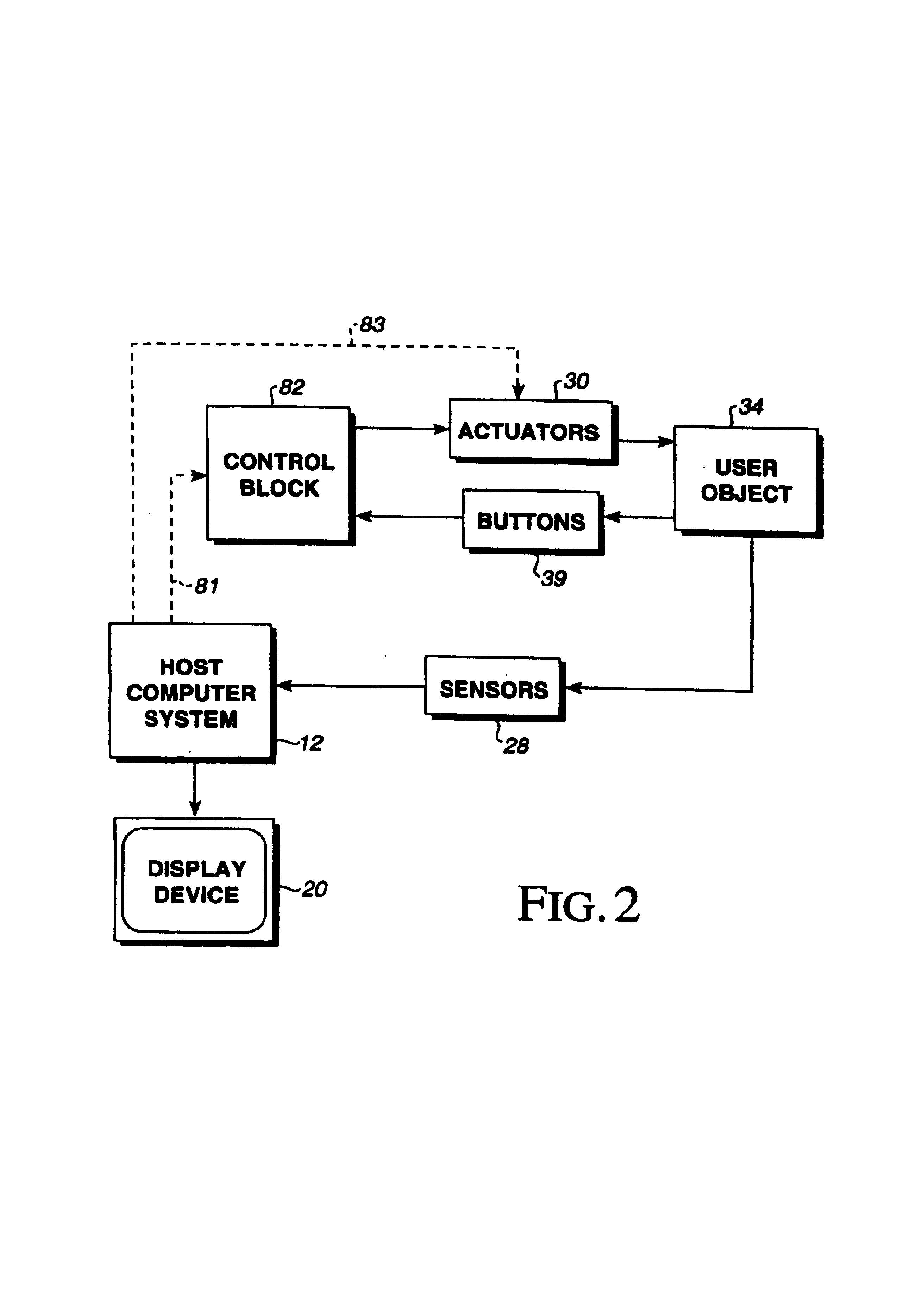
Method and apparatus for providing an interface mechanism for a computer simulation
InactiveUS7249951B2Highly realistic feedbackHighly realistic motionManual control with multiple controlled membersDiagnosticsHigh bandwidthComputerized system
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
System and methods for controlling surgical tool elements
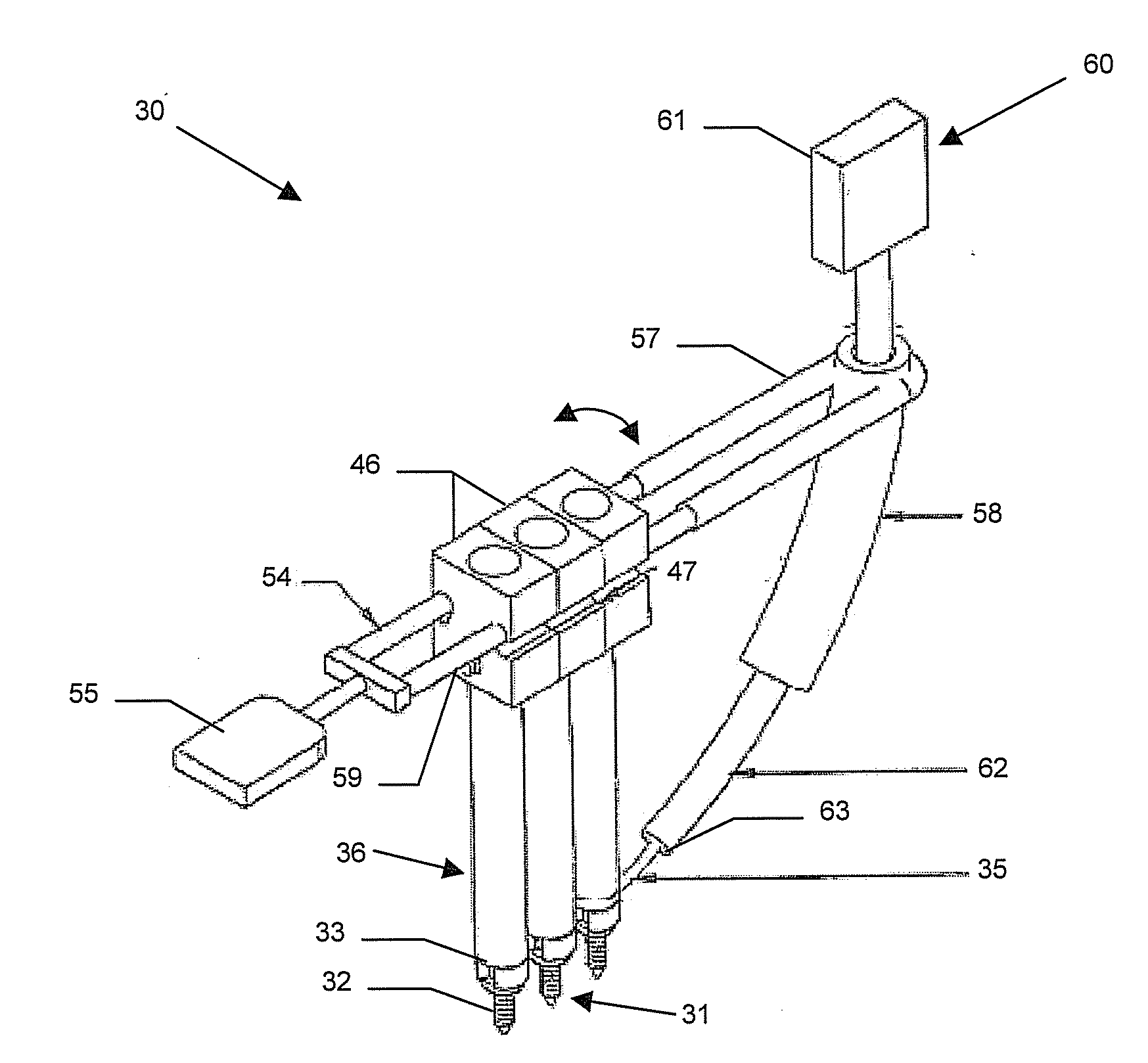
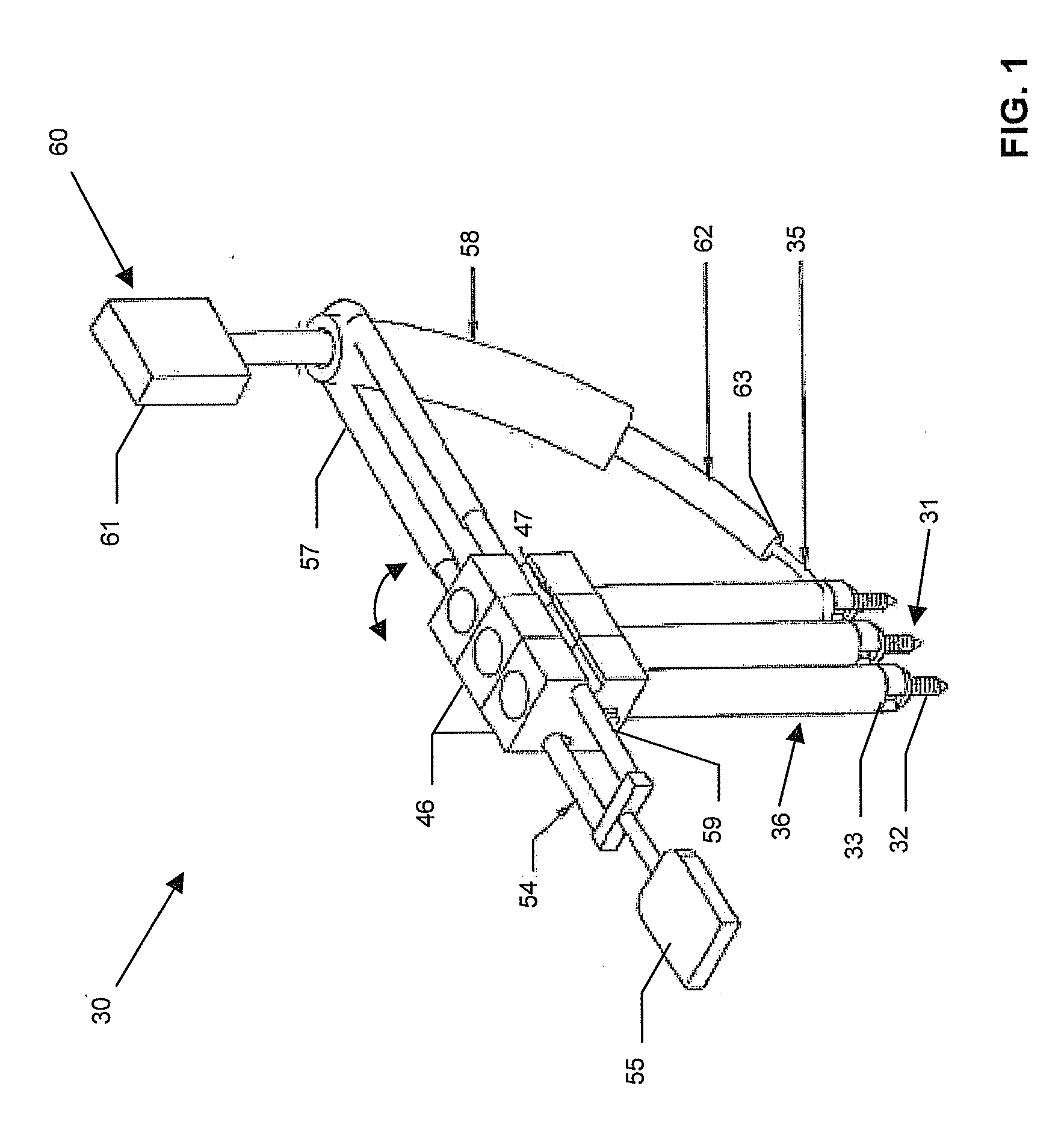
InactiveUS8282653B2Efficient implementationMechanical apparatusJointsSurgical operationLess invasive surgery
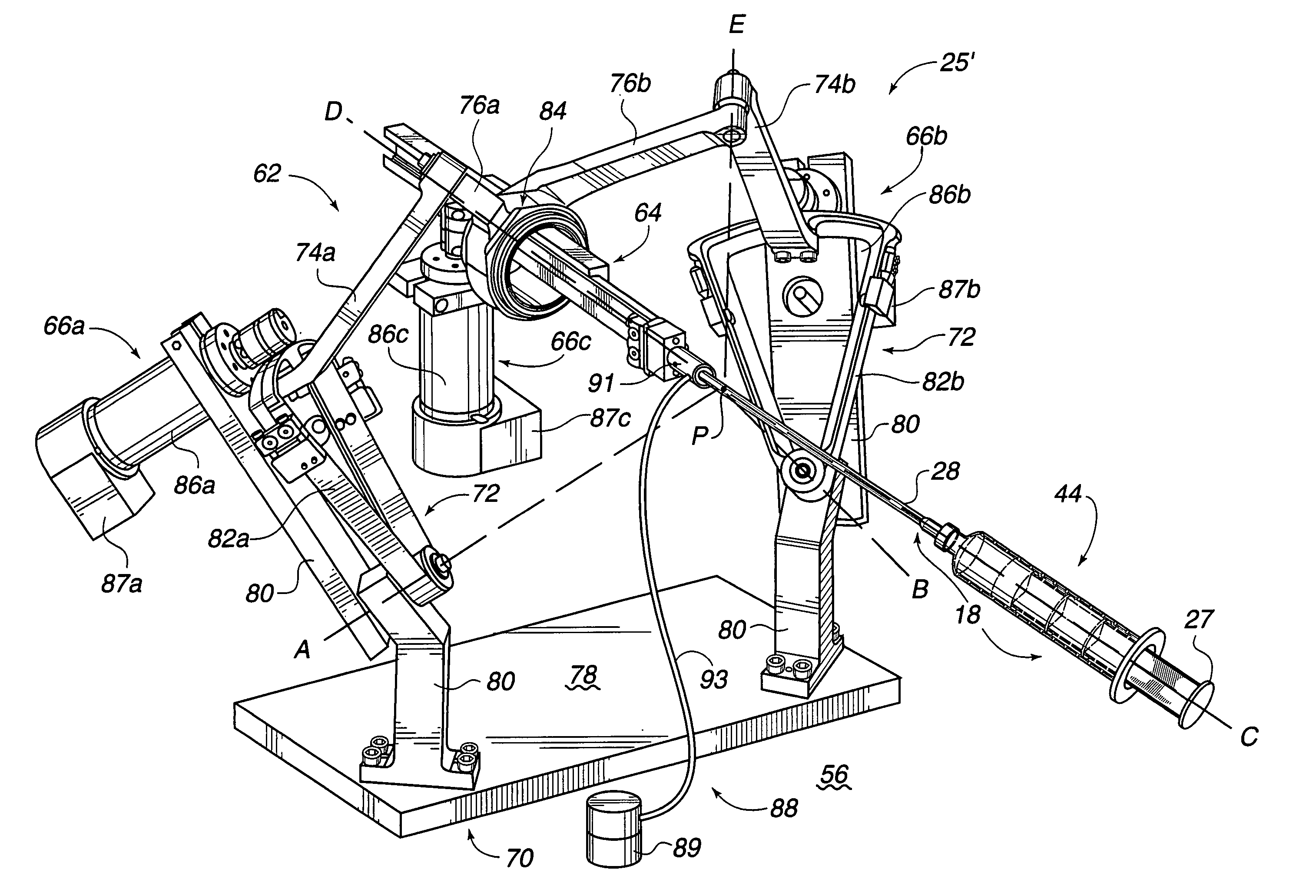
A light-weight, compact, highly dexterous surgical robot system for performing in vivo minimally invasive surgeries that allows precise control of position and orientation of surgical tools. The surgical robot system has three rotational degrees of freedom and one translational degree of freedom and is composed of seven links joined by three gear pairs and six turning pairs. The surgical robot system maintains an open space where a surgical tool element enters the patient to avoid self-collisions within the robot system during surgeries.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Flexure mechanism for interface device
InactiveUS7193607B2Low costEasy to manufactureInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersCouplingClosed loop
A flexure mechanism for an interface device that interfaces a user with a computer system. An interface device includes a manipulandum physically contacted by the user. A five-bar closed-loop mechanism is coupled to the manipulandum to provide two rotary degrees of freedom to the manipulandum. The mechanism includes members coupled to each other by flexible couplings allowing rotation of the members. In preferred embodiments, four or five of the members are coupled together by flexible couplings that allow bending, thereby forming a unitary piece, where the couplings are oriented along axes of rotation of the mechanism. A senor senses a position of the manipulandum outputs a sensor signal, and in some embodiments actuators are coupled to the mechanism to output a force to the manipulandum in particular degrees of freedom. The manipulandum can be a joystick handle or portion of a sphere, where the device in one embodiment can be a handheld gamepad or similar controller.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Camera based six degree-of-freedom target measuring and target tracking device with rotatable mirror
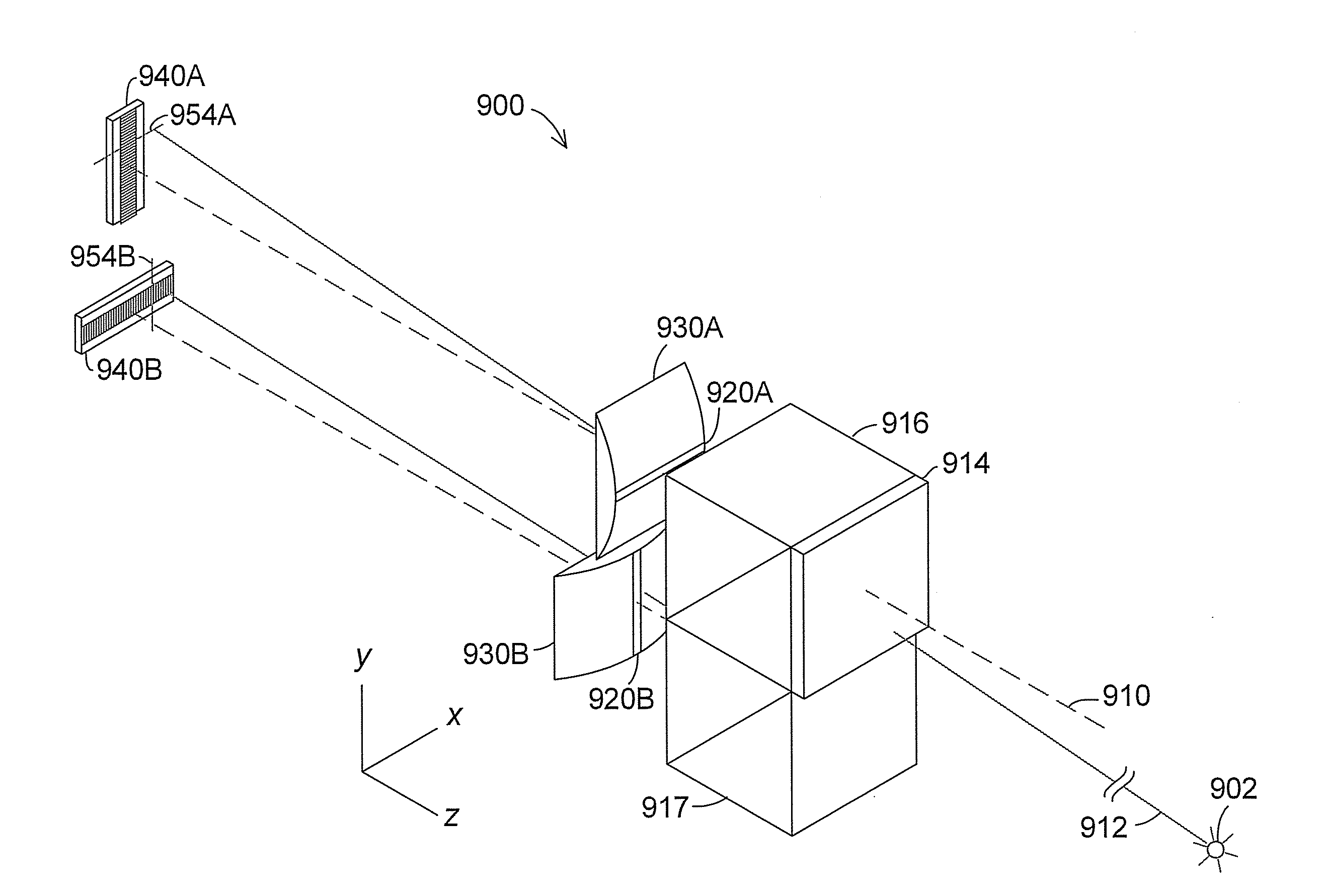
An embodiment may comprise a camera based target coordinate measuring system or apparatus for use in measuring the position of objects in manner that preserves a high level of accuracy. This high level of measurement accuracy is usually only associated with more expensive laser based devices. Many different arrangements are possible. Other embodiments may comprise related methods of using a camera based target coordinate measuring method for use in measuring the position of objects. Many variations on the methods are possible. For example, a camera based coordinate measuring system for use in measuring the position of a target relative to at least one frame of reference without requiring use of a laser range finder for measuring distance may comprise at least three or more light sources located on a target wherein the light sources are located on the target at known three-dimensional coordinates relative to each other; at least one rotatable mirror rotatable on about a first axis and a second axis; a camera located to receive light emitted by the light sources that is reflected off the minor; two angular measuring devices to measure the angles of rotation of the mirror about the first and second axes; and a processor for determining up to three positional degrees of freedom and up to three rotational degrees of freedom of the target.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
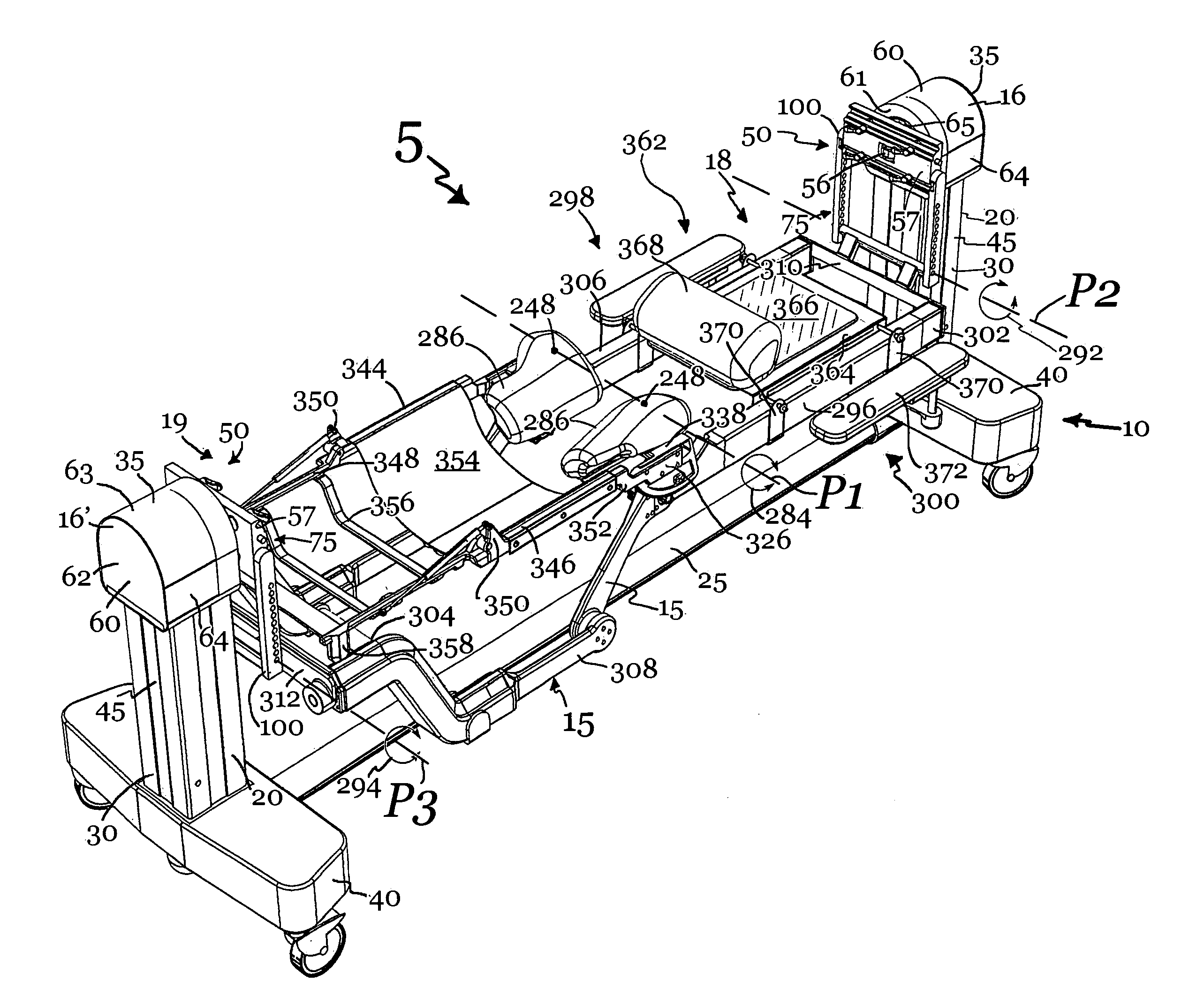
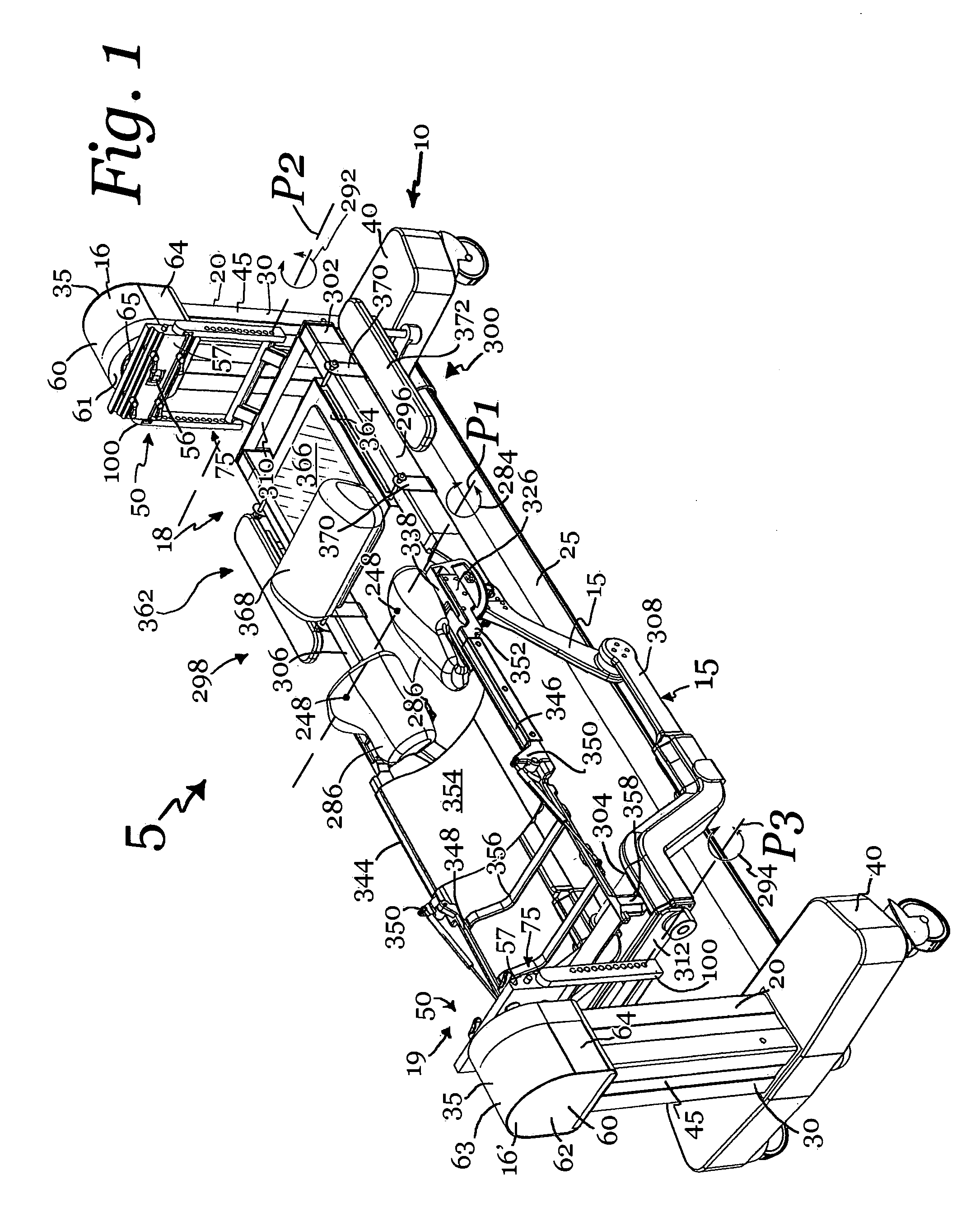
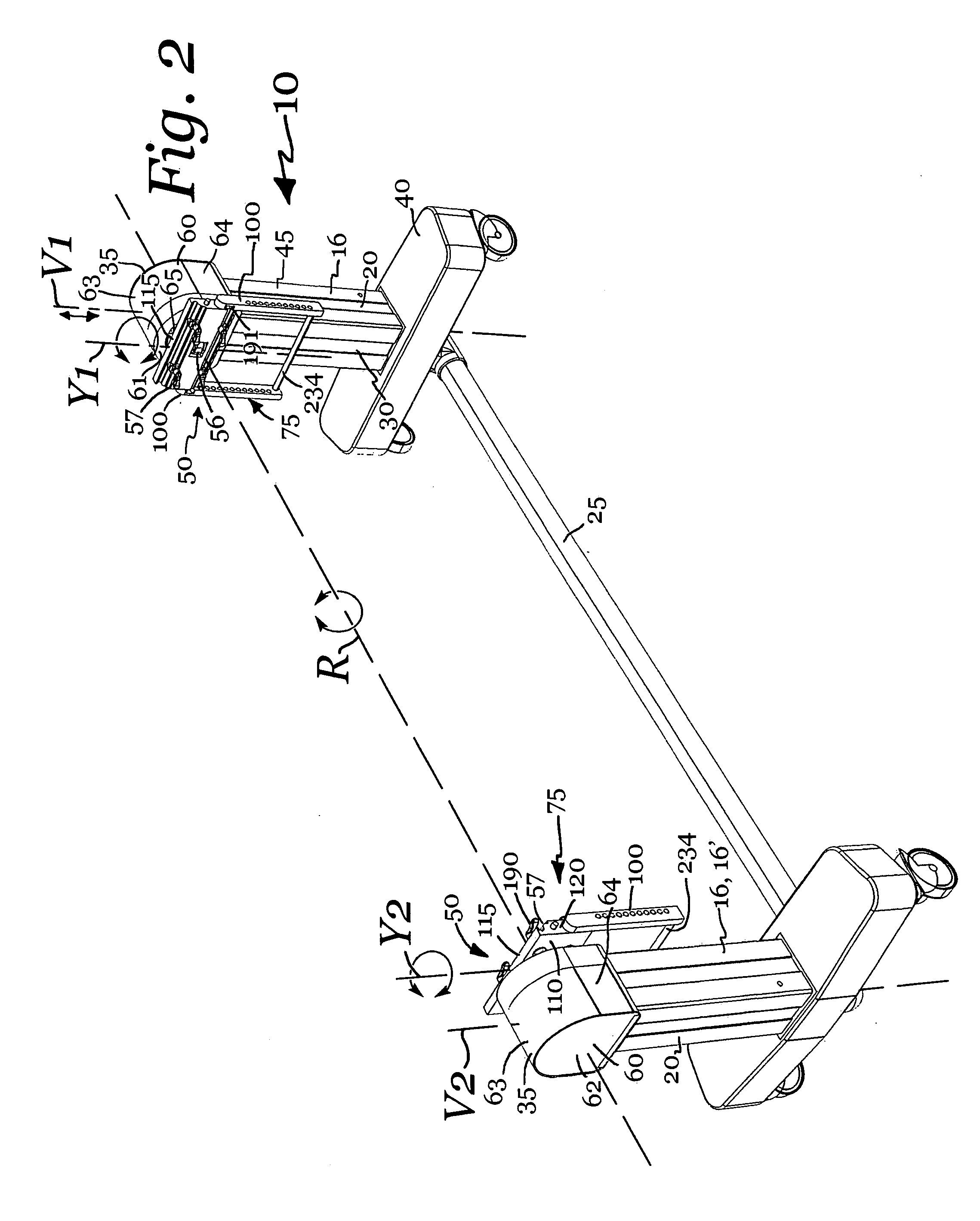
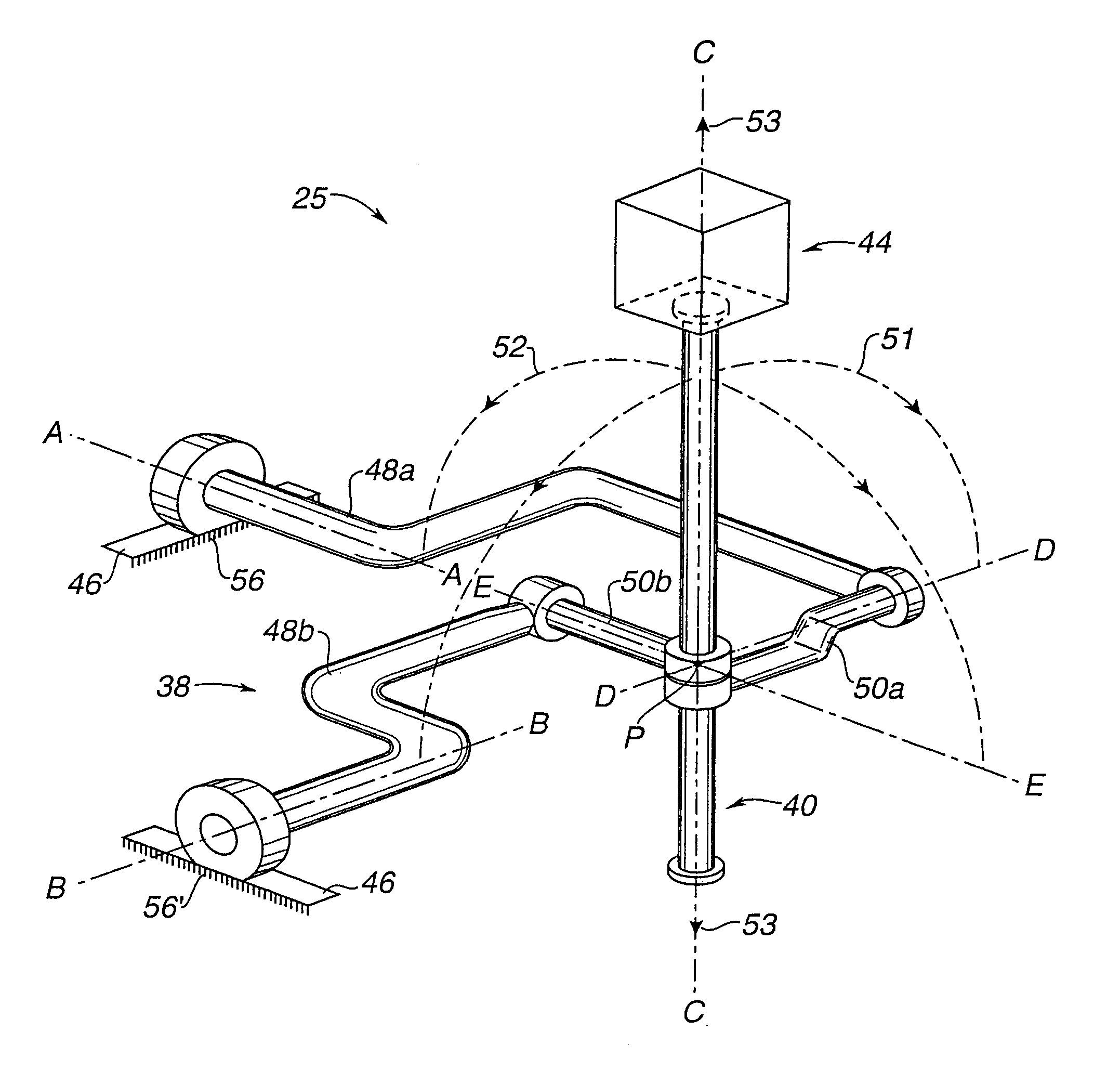
Patient positioning support apparatus with virtual pivot-shift pelvic pads, upper body stabilization and fail-safe table attachment mechanism
ActiveUS20140068861A1Preventing vertical and horizontal translationAvoid injuryMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOperating tablesRotational freedomFixed frame
A patient support apparatus for supporting a patient in a prone position during a surgical procedure is provided, including an open fixed frame suspended above a floor and a pair of spaced opposed radially sliding joints cooperating with the frame, each joint including a virtual pivot point and an arc of motion spaced from the virtual pivot point, the joints being movable along the arc providing a pivot ship mechanism for a pair of pelvic pads attached to the joints. A base for supporting and suspending a patient support structure above the floor, for supporting a patient during a surgical procedure, the base including a pair of spaced opposed vertical translation subassemblies reversibly attachable to a patient support structure, a cross-bar, and a rotation subassembly having two degrees of rotational freedom; wherein a location of each vertical translation subassembly is substantially constant during operation of the patient support structure.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
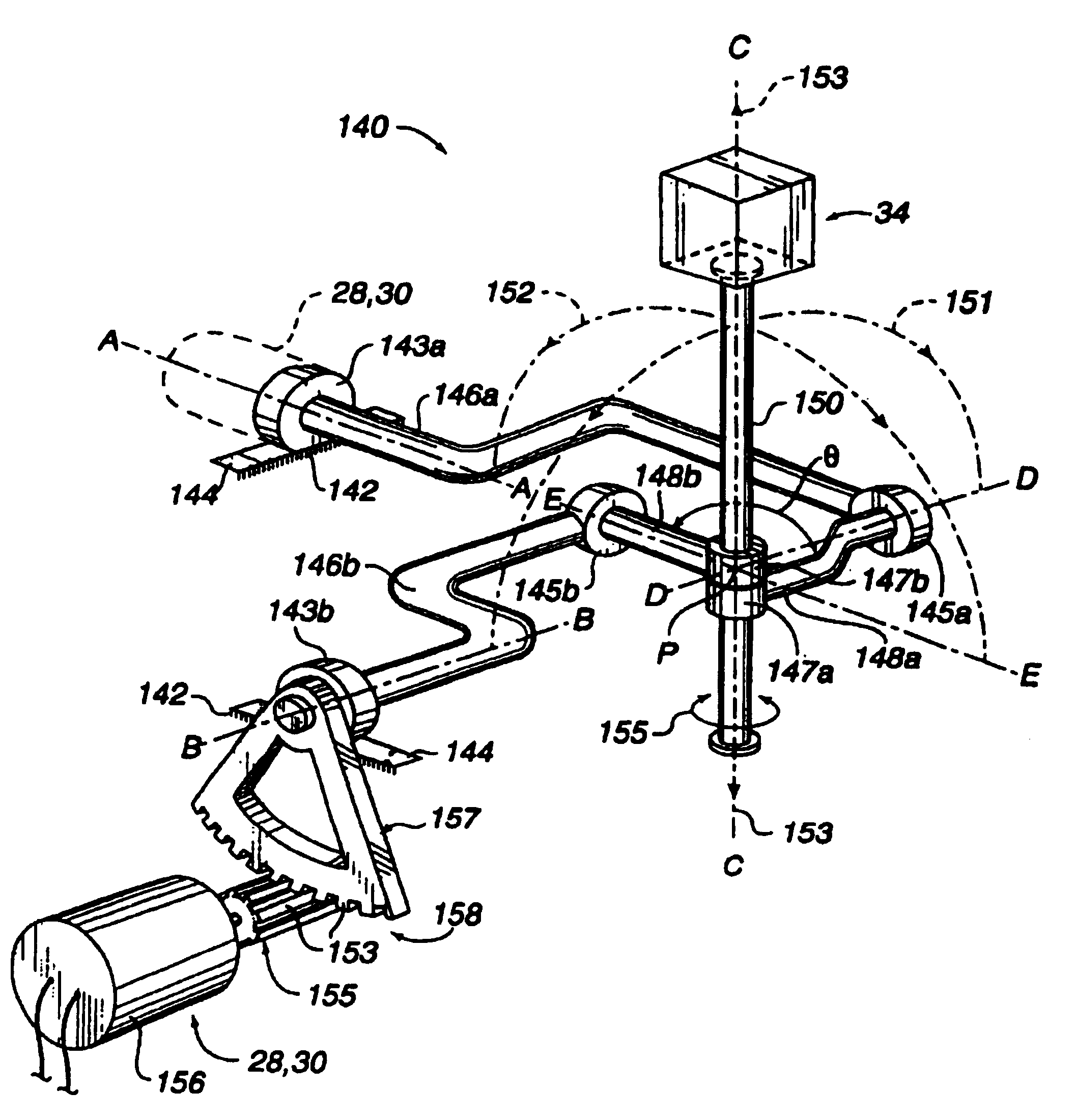
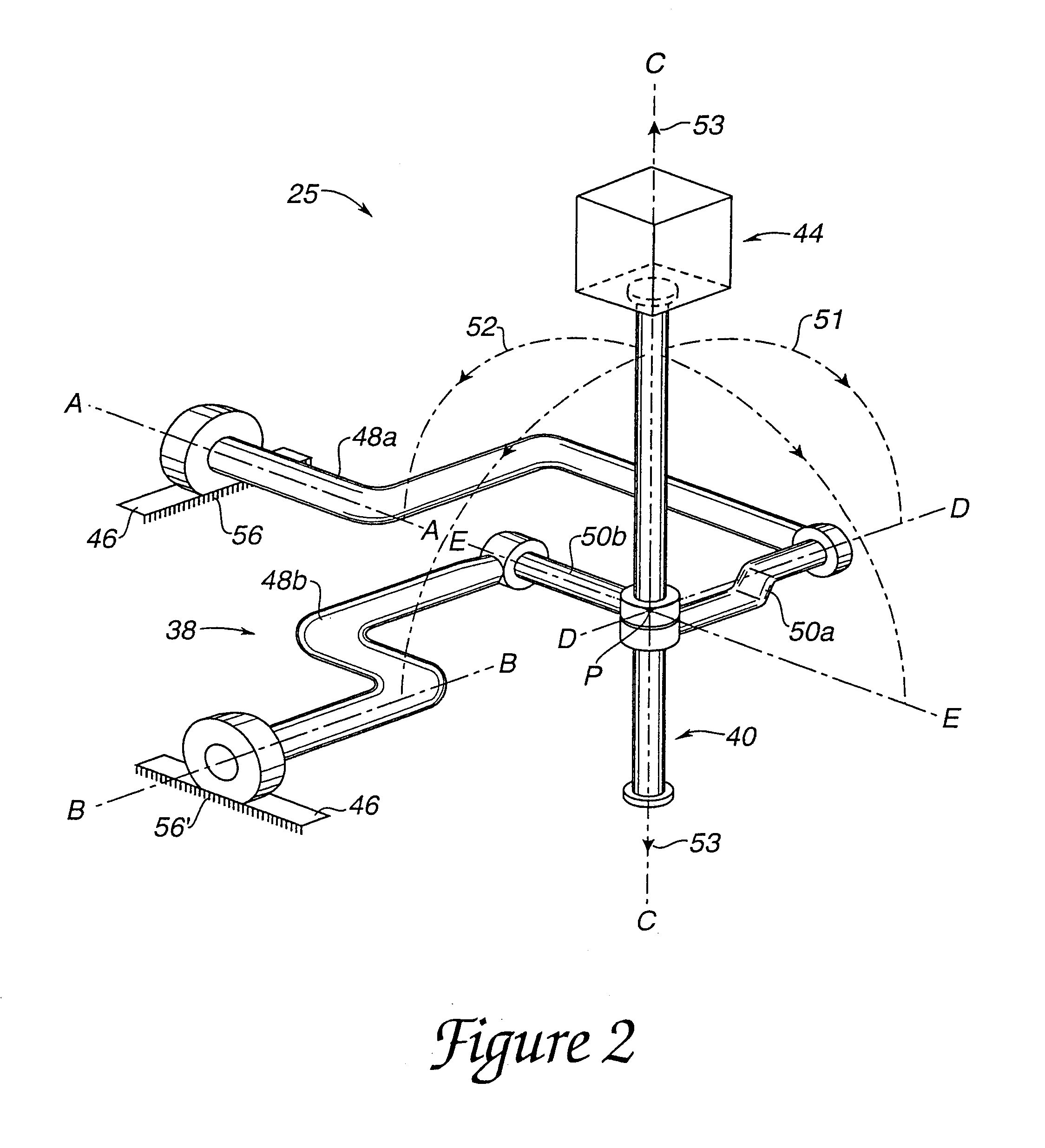
Laparoscopic simulation interface
InactiveUS7023423B2Highly realistic force feedbackReduction of friction and compliance and backlashInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersHigh bandwidthJoystick
A method and apparatus for providing high bandwidth and low noise mechanical input and output for computer systems. A gimbal mechanism provides two revolute degrees of freedom to an object about two axes of rotation. A linear axis member is coupled to the gimbal mechanism at the intersection of the two axes of rotation. The linear axis member is capable of being translated along a third axis to provide a third degree of freedom. The user object is coupled to the linear axis member and is thus translatable along the third axis so that the object can be moved along all three degrees of freedom. Transducers associated with the provided degrees of freedom include sensors and actuators and provide an electromechanical interface between the object and a digital processing system. Capstan drive mechanisms transmit forces between the transducers and the object. The linear axis member can also be rotated about its lengthwise axis to provide a fourth degree of freedom, and, optionally, a floating gimbal mechanism is coupled to the linear axis member to provide fifth and sixth degrees of freedom to an object. Transducer sensors are associated with the fourth, fifth, and sixth degrees of freedom. The interface is well suited for simulations of medical procedures and simulations in which an object such as a stylus or a joystick is moved and manipulated by the user.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Spinal disc prosthesis and methods of use
Spinal disc prosthetic devices are provided having up to six-degrees-of-freedom with three rotational and three translational degrees-of-freedom within the entire workspace of a Functional Spinal Unit (FSU). Certain embodiments of the prosthetic disc mechanisms attach to upper and lower plates anchored between vertebrae of an FSU allowing modularity of the devices. Scaling, conjoined mechanical programmability allow the devices to realize almost any nominal required spinal articulation, from the cervical to lumbar regions.
Owner:DOTY KEITH L
Organ access device and method
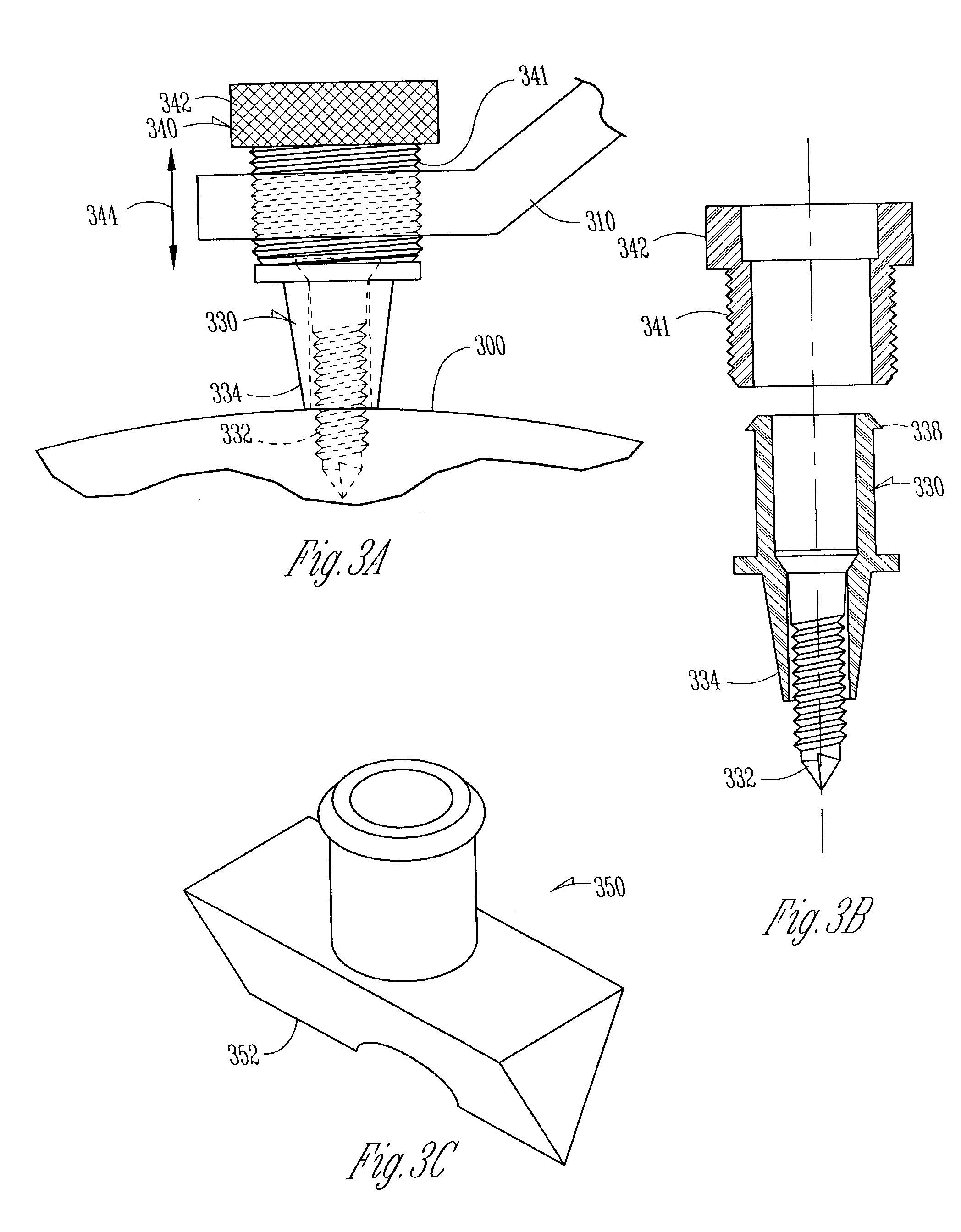
ActiveUS7636596B2Improve accuracyImprove ease of useAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical needlesRotational freedomBurr holes
An insertion guide is shown that includes at least one insertion point adjustment device. A user such as a surgeon is able to adjust a lateral position of an insertion point to more precisely center the insertion point within an opening in a subject, such as a burr hole. Selected insertion guide devices further include a centering guide that easily indicates to a user when the insertion point is substantially centered within the opening in the subject. Selected insertion guide devices include adjustability of multiple degrees of rotational freedom of an insertion axis. Selected insertion guide devices further permit a user to fix multiple degrees of rotational freedom of an insertion axis using a single locking device. Tissue damage due to an attachment procedure of an insertion guide device is reduced using selected configurations described herein.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Percutaneous spinal rod insertion system and related methods
InactiveUS20090326586A1Increase flexibilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnRotational freedom
A spinal rod implantation system may be used with pedicle screws to be secured to respective pedicles of a patient's spine, each pedicle screw having a spinal rod channel therethrough. The system may include extenders each including an inner member having a distal end, and an outer member surrounding the inner member and being slidable relative thereto to permit removable coupling of the distal end to a respective pedicle screw. The inner and outer members may include respective features defining a first joint permitting at least partial relative rotation to provide a first degree of rotational freedom. The system may further include extender heads each pivotally coupled to a proximal end of a respective outer member to define a second joint providing a second degree of rotational freedom. A spinal rod insertion assembly may be coupled to the extender heads for guiding the spinal rod through the spinal rod channels.
Owner:DUARTE LUIS E
Rotary blood pump and control system therefor
A pump assembly and estimation and control system therefor, the pump adapted for continuous flow pumping of blood. In a particular form, the pump is a centrifugal pump wherein the impeller is entirely sealed within the pump housing and is exclusively hydrodynamically suspended therein against movement in three translational and two rotational degrees of freedom as the impeller rotates within the fluid urged by electromagnetic means external to the pump cavity. Hydrodynamic suspension is assisted by the impeller having deformities therein such as blades with surfaces tapered from the leading edges to the trailing edges of bottom and top surfaces thereof.
Owner:THORATEC CORPORTION +1
Tactile feedback interface device including display screen
InactiveUS7151527B2Effective and convenient mannerImprove efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsControl signalRotational degrees of freedom
A control device including a housing and a carrier moveable with respect to the housing in a first rotary degree of freedom. A first sensor senses the movement of the carrier and outputs a first control signal. A roller rotatably coupled to the carrier rotates with the carrier in the first degree of freedom and rotates independently of the carrier in a second rotary degree of freedom. A second sensor senses rotary motion of the roller and outputs a second control signal. Preferably, an arm member coupled between carrier and housing pivots about an axis. A third sensor, such as a switch, can be used to detect when the carrier has been pushed in a direction substantially orthogonal to a plane of rotation of the arm member. Force feedback can also be provided in the rotary degrees of freedom of the control device.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
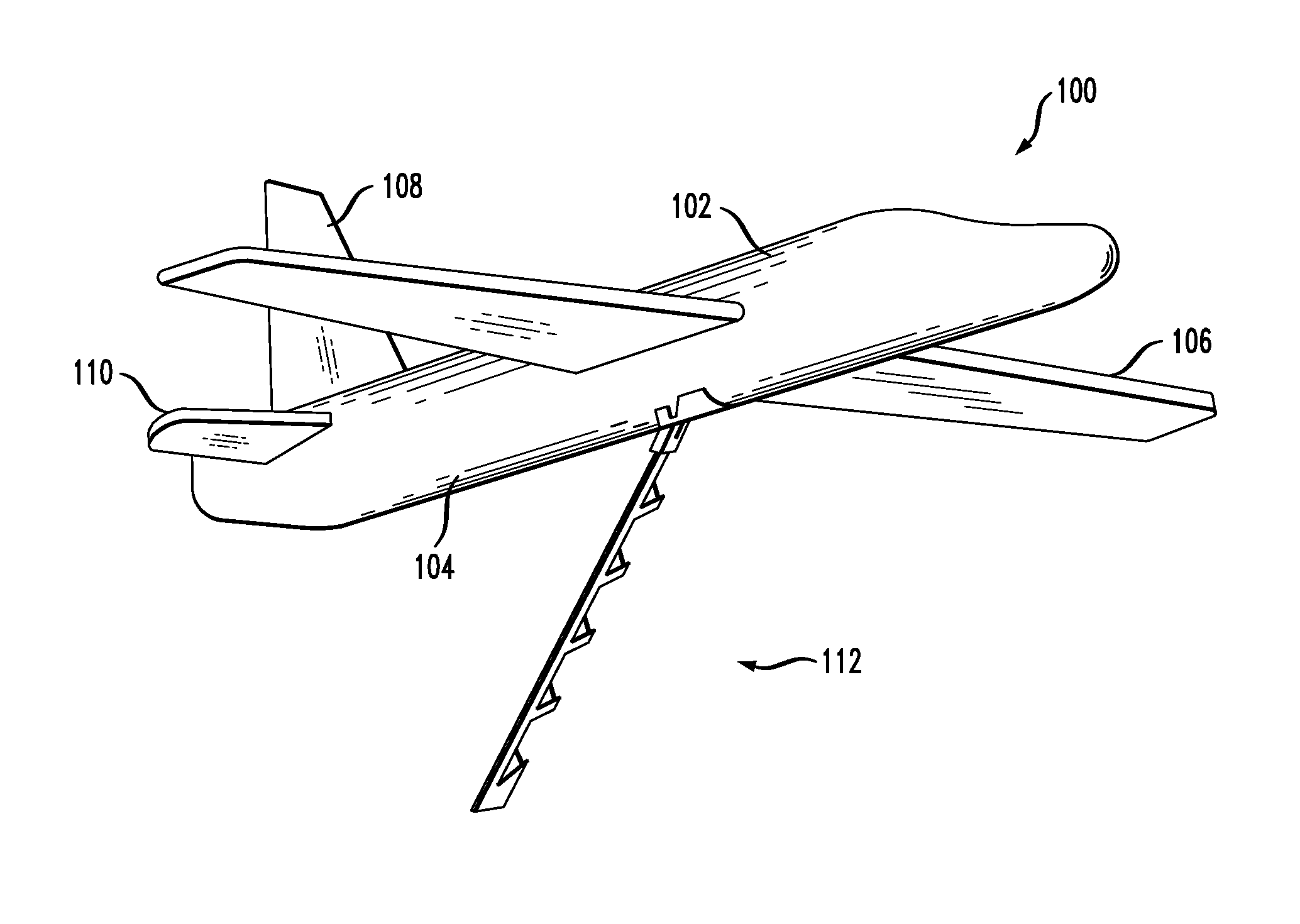
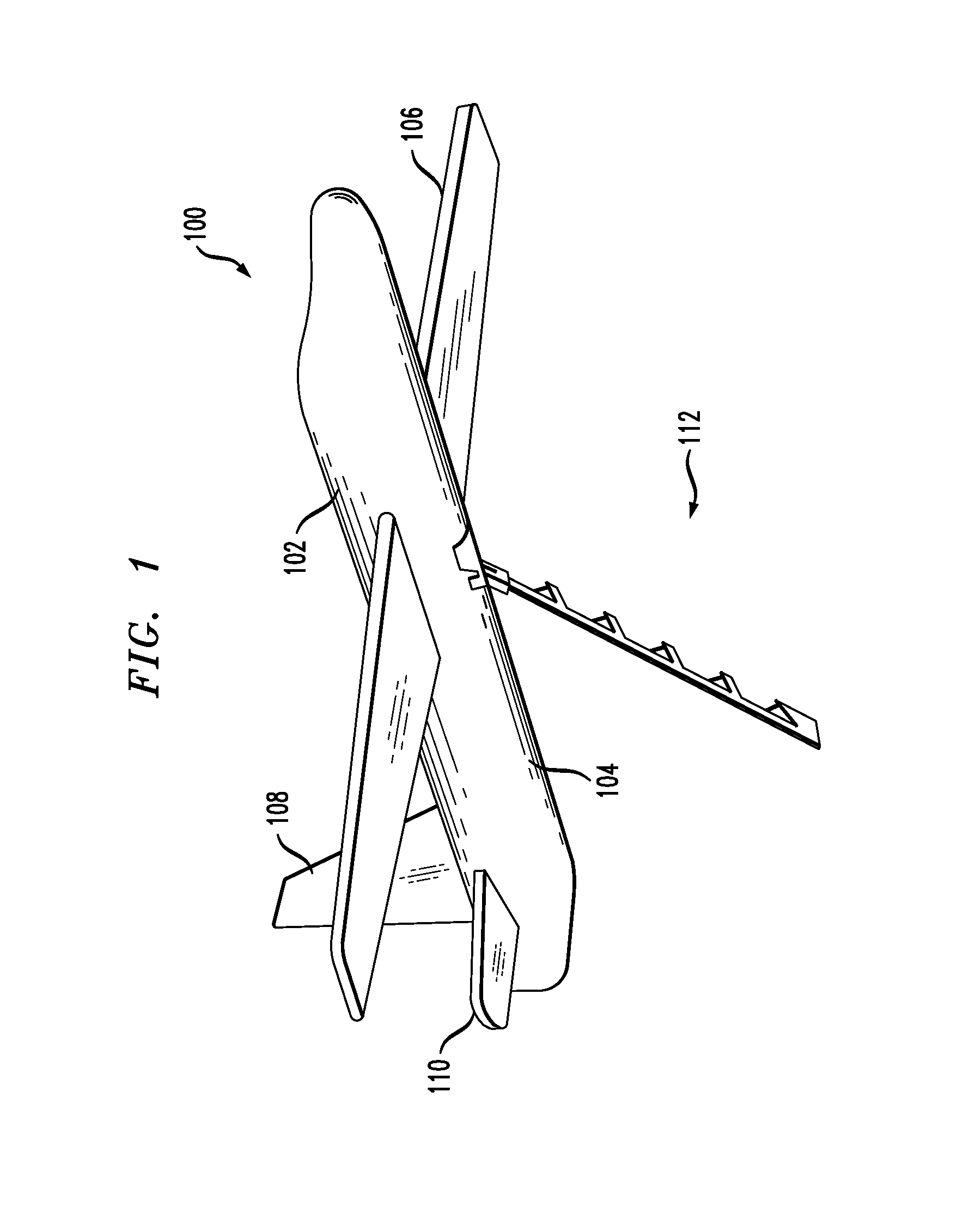
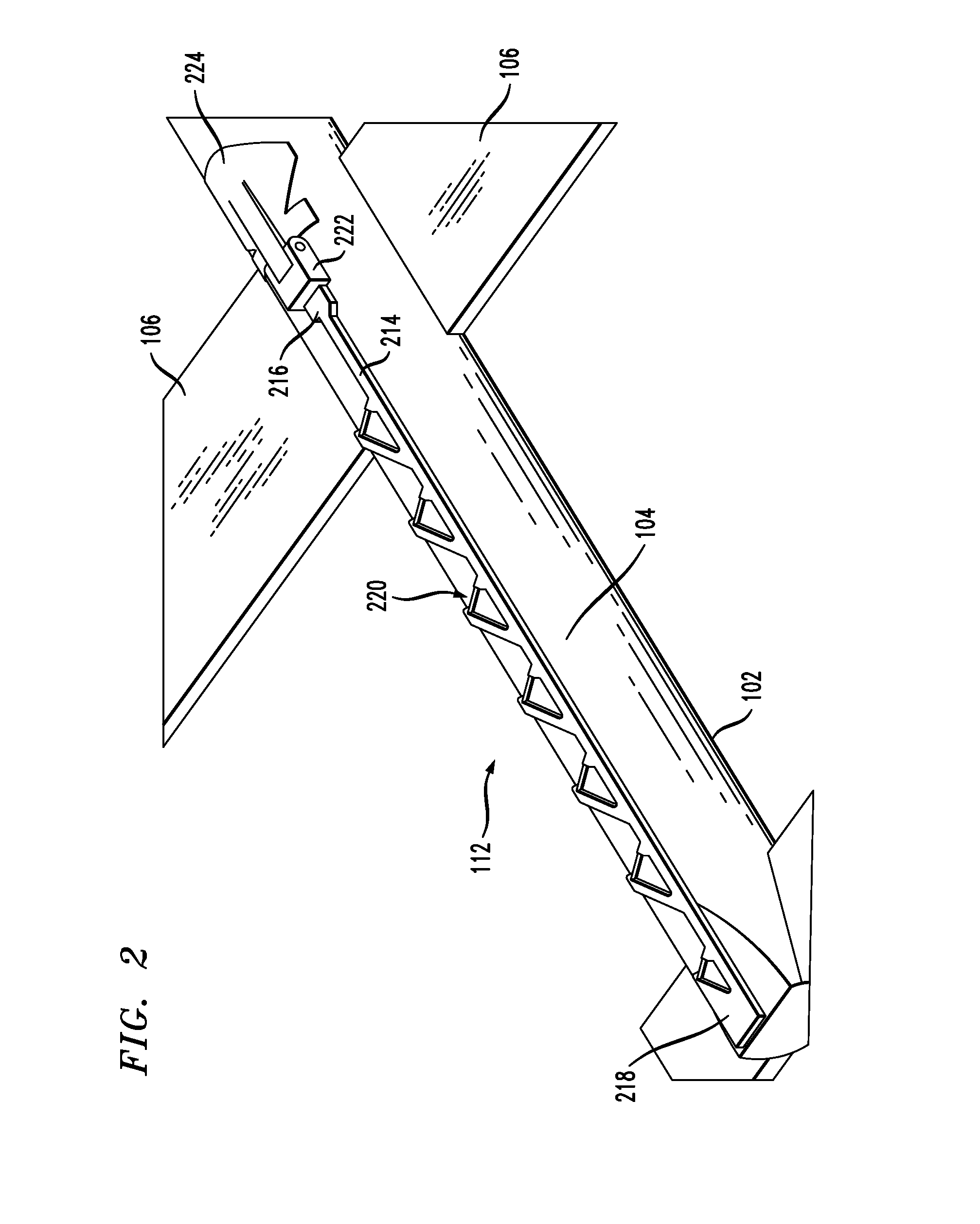
UAV arresting hook for use with UAV recovery system
A UAV arresting hook is disclosed. The arresting hook facilitates the capture of a UAV via a UAV recovery system. In the illustrative embodiment, the arresting hook has a rotation block, an arm, and a plurality of latches that are disposed on the arm. The arm is coupled to the UAV via the rotation block, which provides two rotational degrees of freedom to the arm. In a stowed position, the arm is flush against the surface of the UAV. To deploy the arm, a free end of the arm is rotated away from the surface of the UAV. The arm is additionally biased to rotate about its longitudinal axis as it rotates away from the surface of the UAV. This rotation positions the latches to capture an arresting line that is part of a UAV recovery system.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Spinal disc prosthesis and methods of use
ActiveUS20060241767A1Promote sportsSmooth movementSpinal implantsCoatingsFunctional spinal unitLumbar vertebrae
The subject invention provides a modular six-degrees-of-freedom spatial mechanism for spinal disc prosthesis, with three rotational and three translational degrees-of-freedom within the entire workspace of a Functional Spinal Unit (FSU). The prosthetic disc mechanism attaches to upper and lower plates anchored between vertebrae of an FSU. Scaling, conjoined with motion limit stops, allows the device to realize almost any nominal spinal articulation, from the cervical to lumbar regions.
Owner:DOTY KEITH L
Apparatus for simulating ride on vehicle
InactiveUS6764310B1Improve aestheticsCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsUniversal jointRotational degrees of freedom
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Control knob with multiple degrees of freedom and force feedback
InactiveUS7233313B2Strong control functionGreat caseInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersDetentDisplay device
The present invention provides a control knob on a device that allows a user to control functions of the device. In one embodiment, the knob is rotatable in a rotary degree of freedom and moveable in at least one transverse direction approximately perpendicular to the axis. An actuator is coupled to the knob to output a force in the rotary degree of freedom about the axis, thus providing force feedback. In a different embodiment, the knob is provided with force feedback in a rotary degree of freedom about an axis and is also moveable in a linear degree of freedom approximately parallel to the axis, allowing the knob to be pushed and / or pulled by the user. The device controlled by the knob can be a variety of types of devices, such as an audio device, video device, etc. The device can also include a display providing an image updated in response to manipulation of the knob. Detent forces can be provided for the knob by overlapping and adjusting ranges of closely-spaced detents in the rotary degree of freedom of the knob.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Spinal disc prosthesis and methods of use
The subject invention provides a modular six-degrees-of-freedom spatial mechanism for spinal disc prosthesis, with three rotational and three translational degrees-of-freedom within the entire workspace of a Functional Spinal Unit (FSU). The prosthetic disc mechanism attaches to upper and lower plates anchored between vertebrae of an FSU. Scaling, conjoined with motion limit stops, allows the device to realize almost any nominal spinal articulation, from the cervical to lumbar regions.
Owner:DOTY KEITH L
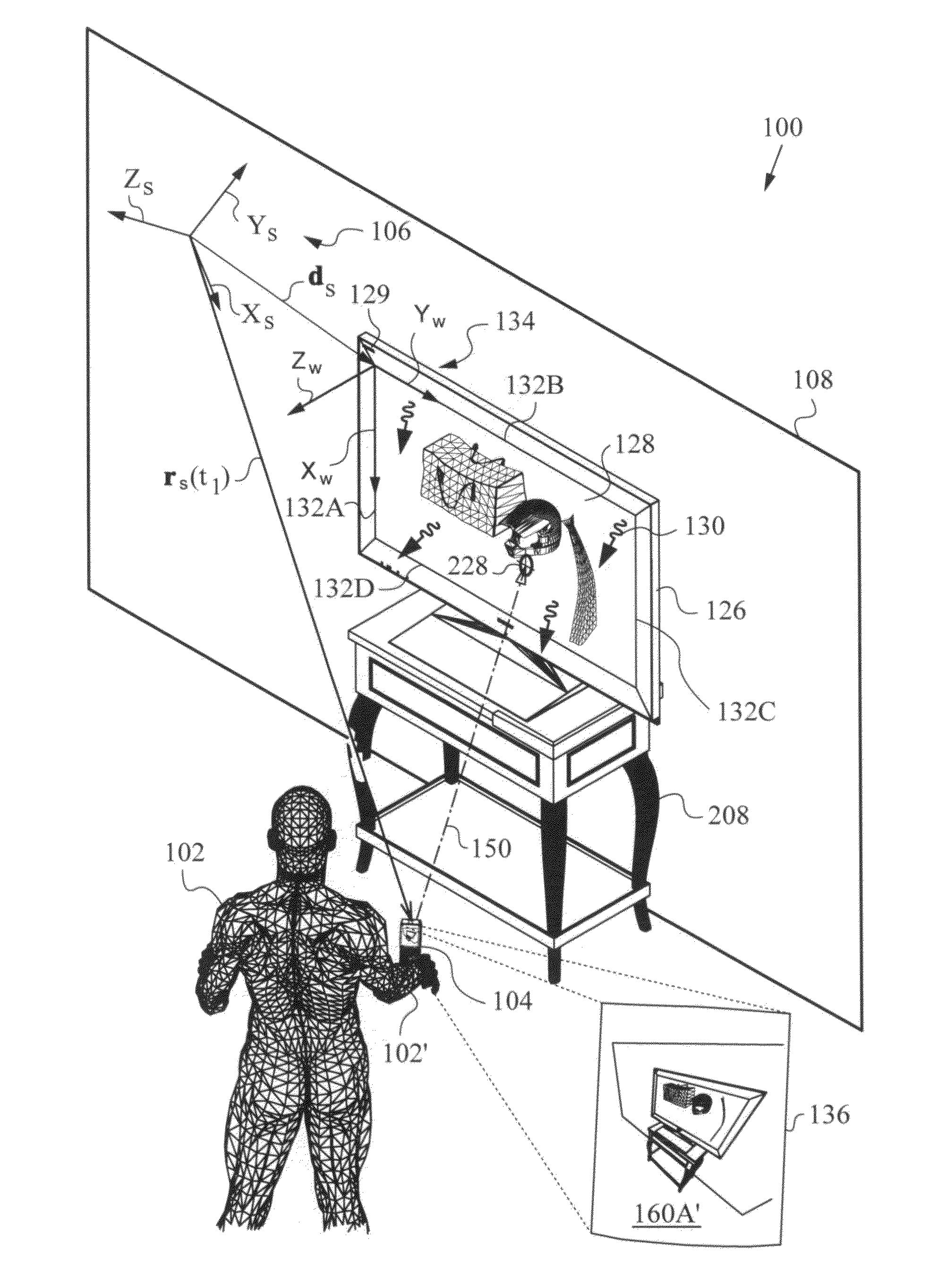
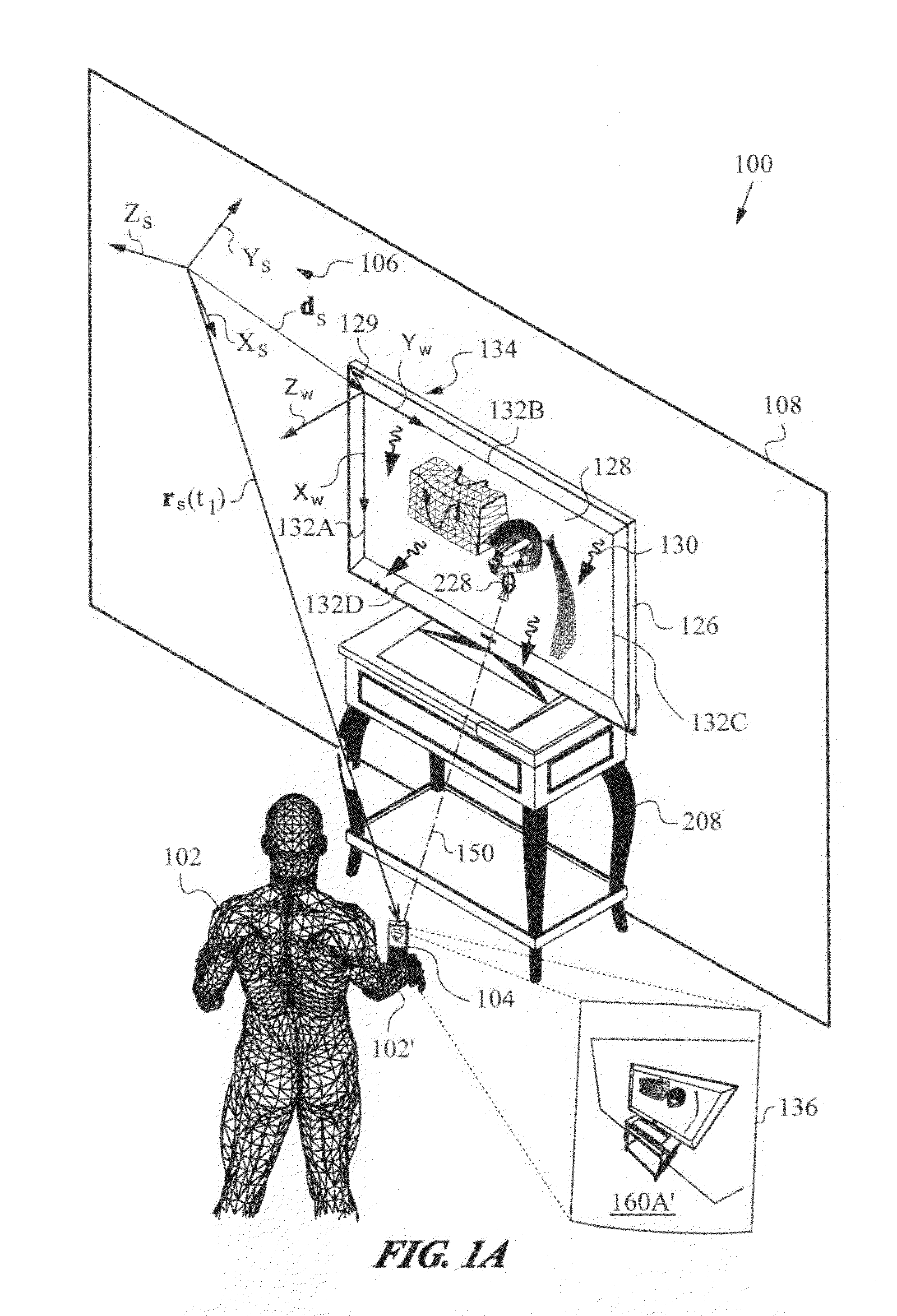
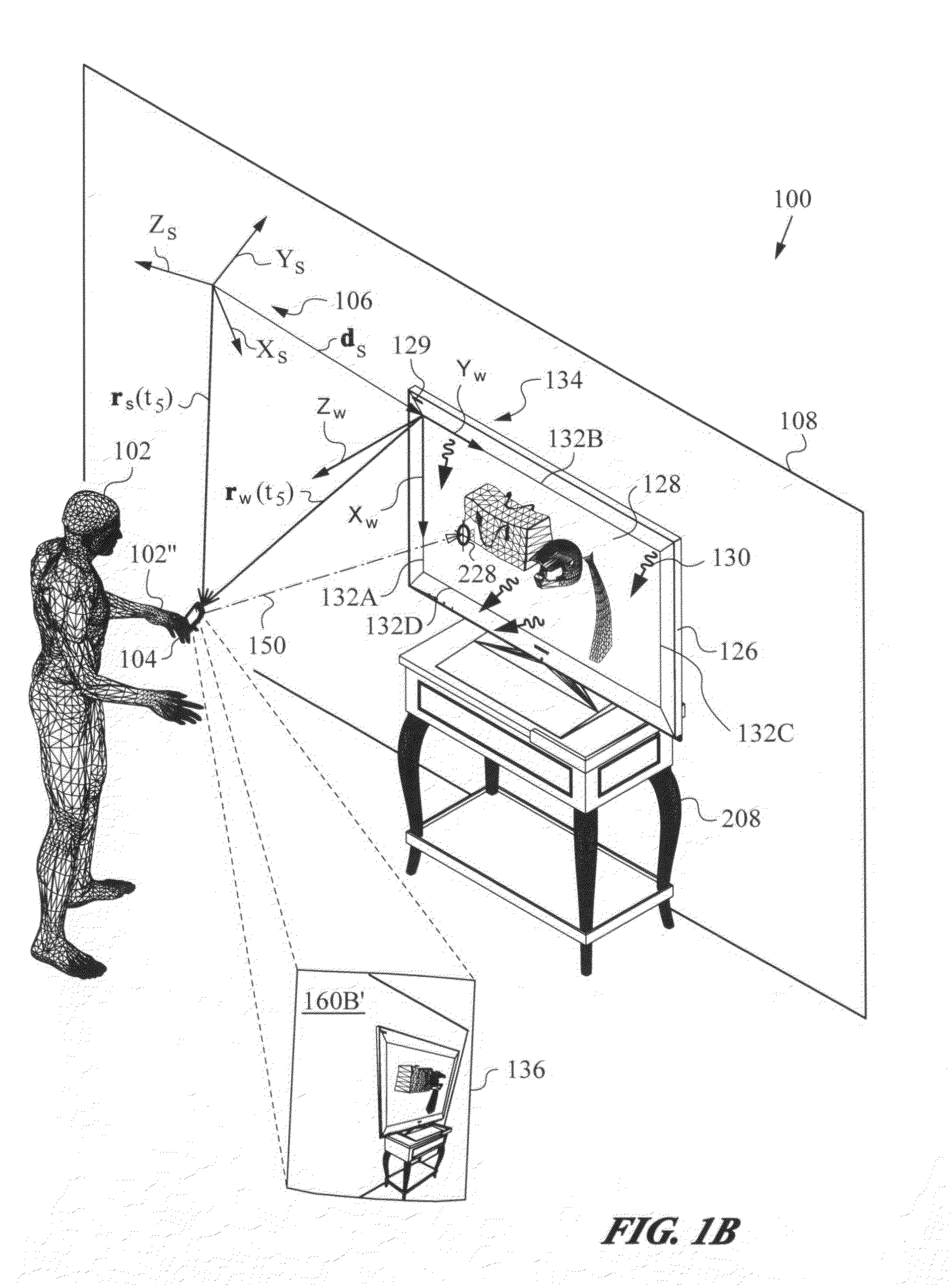
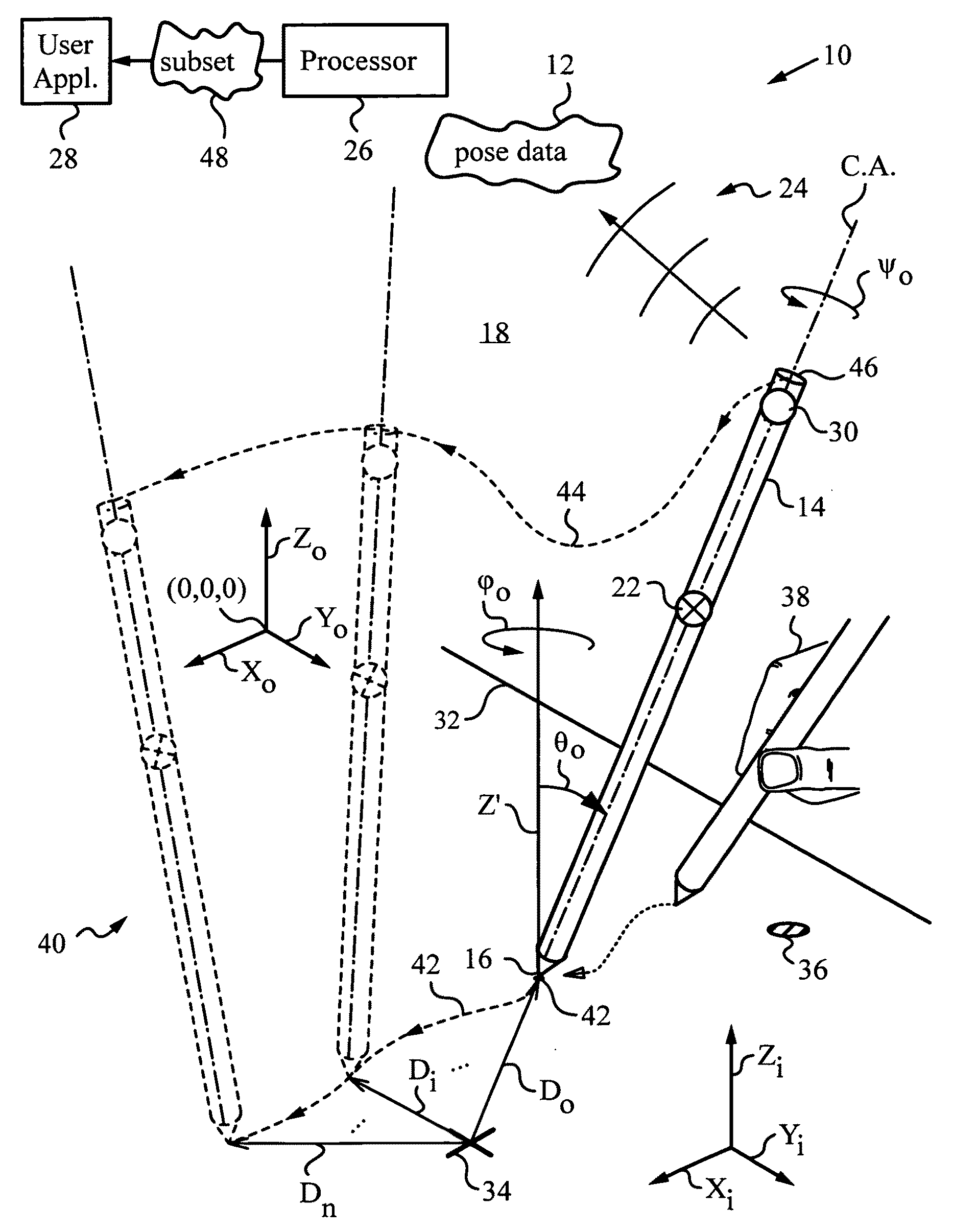
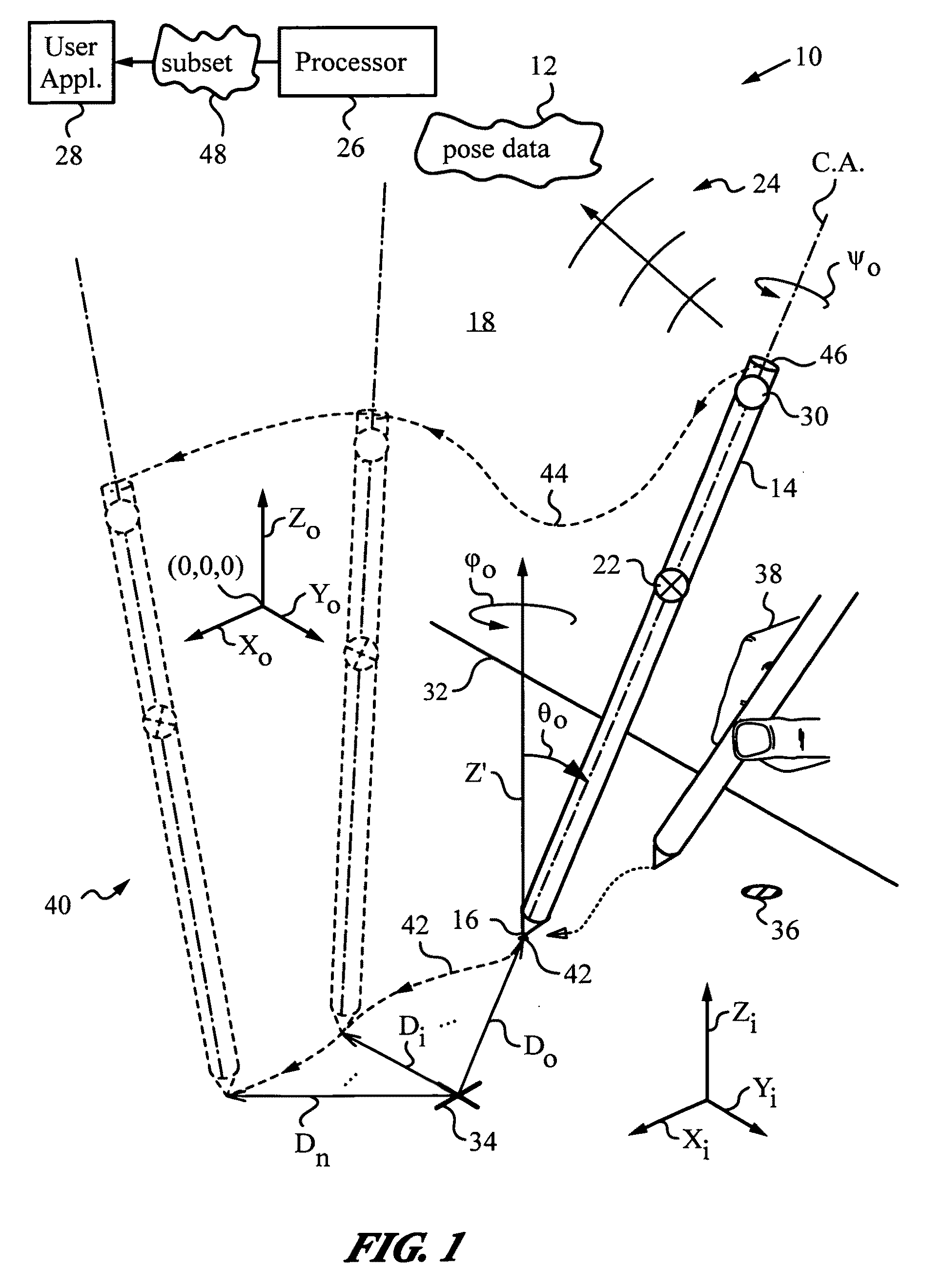
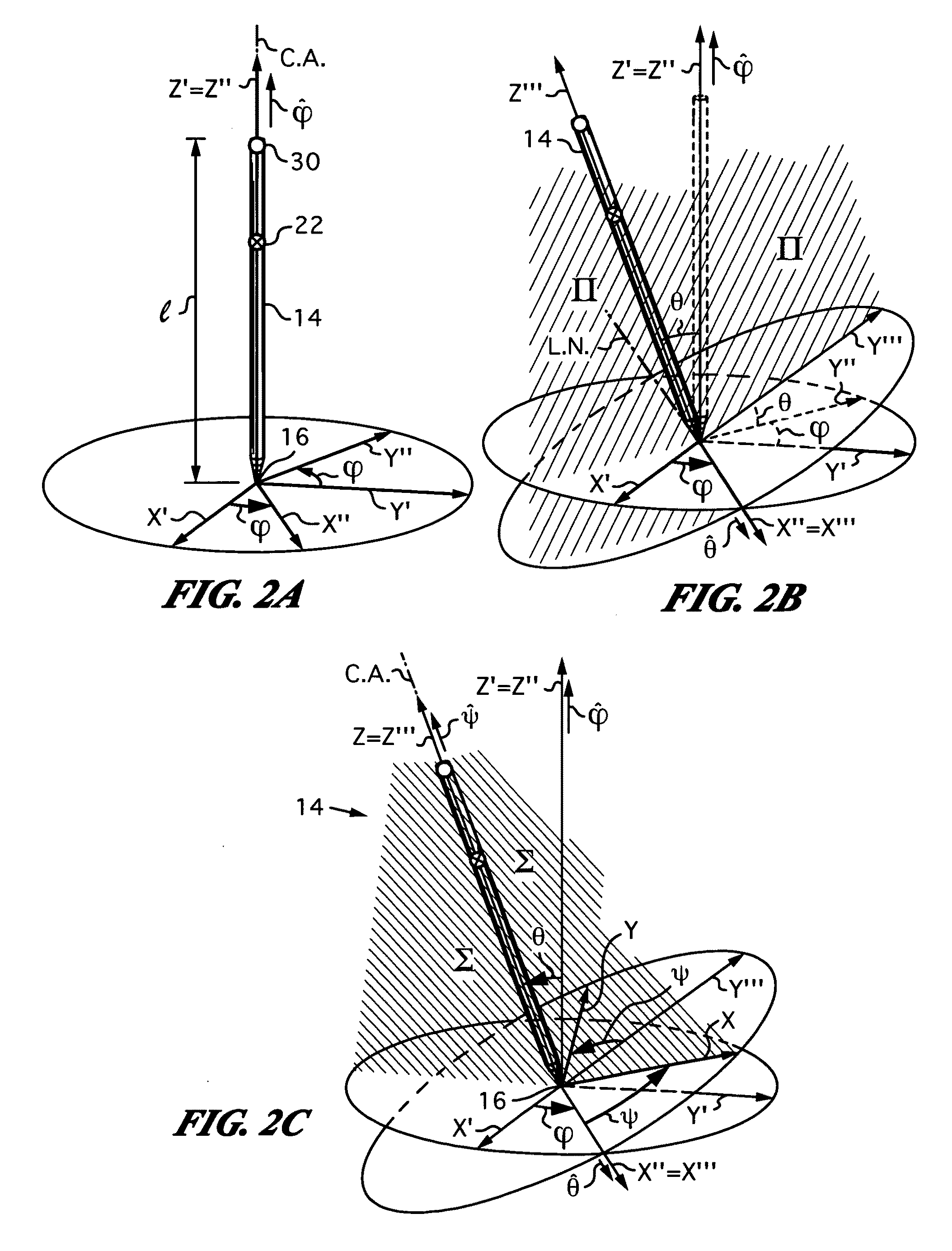
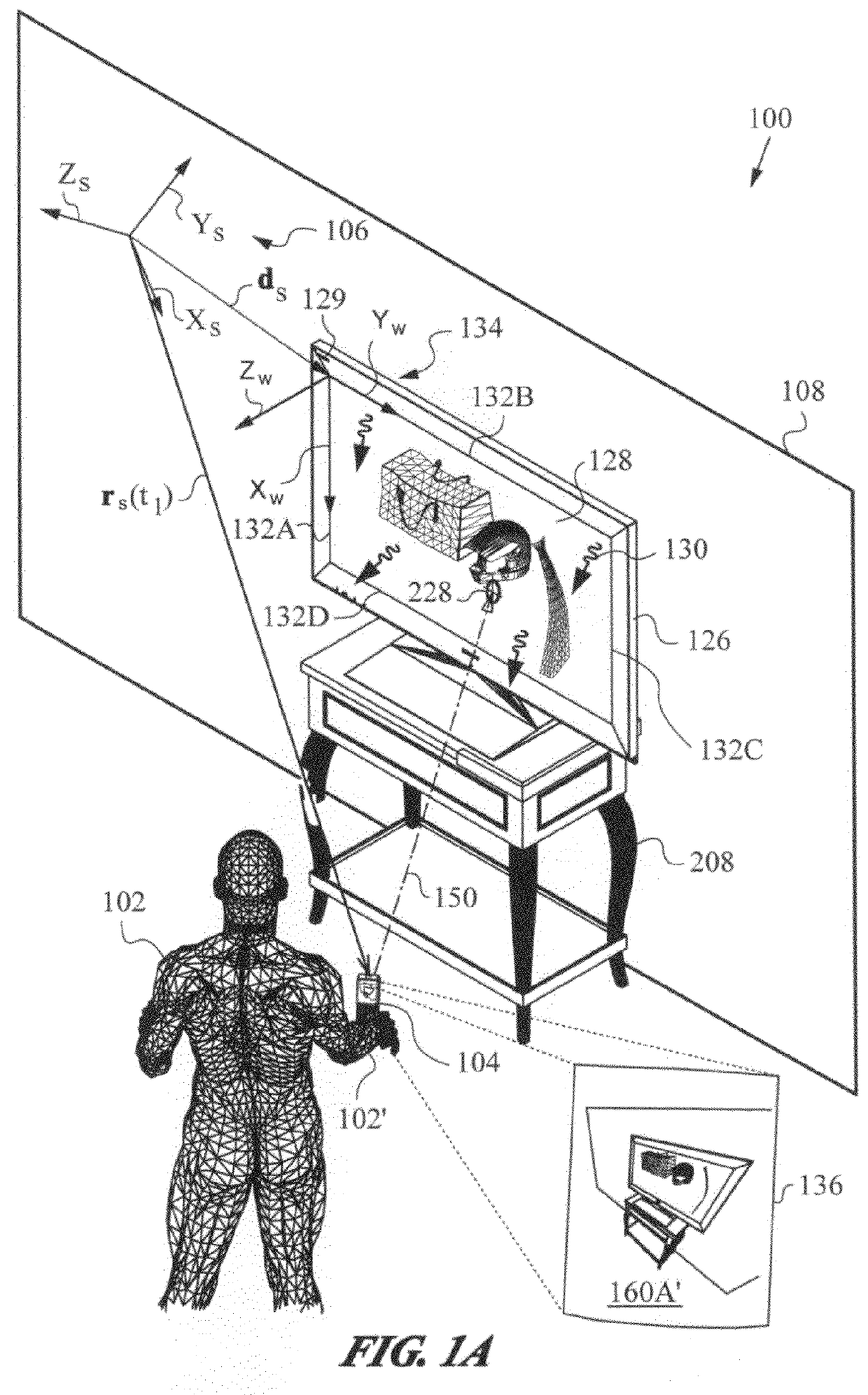
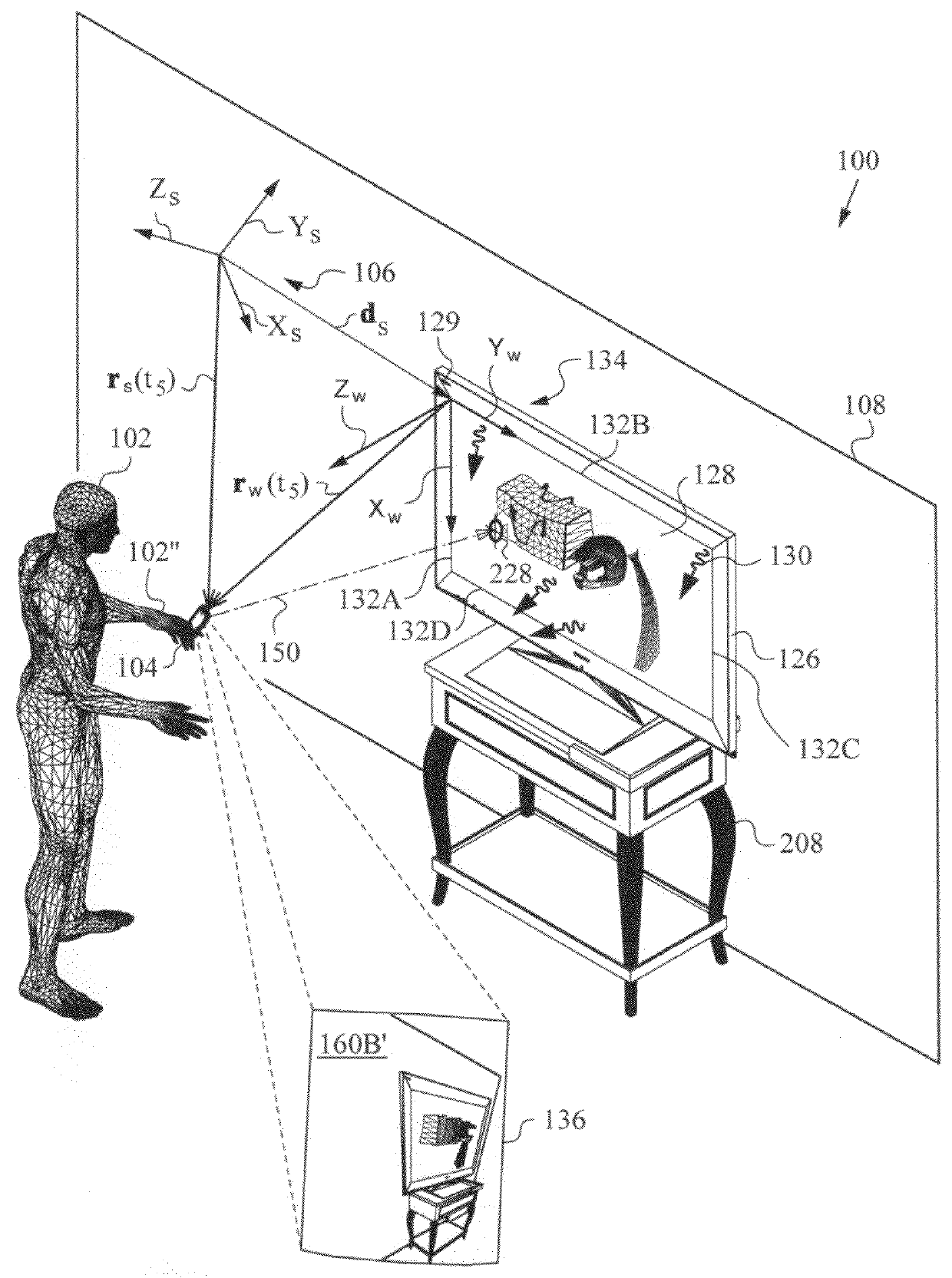
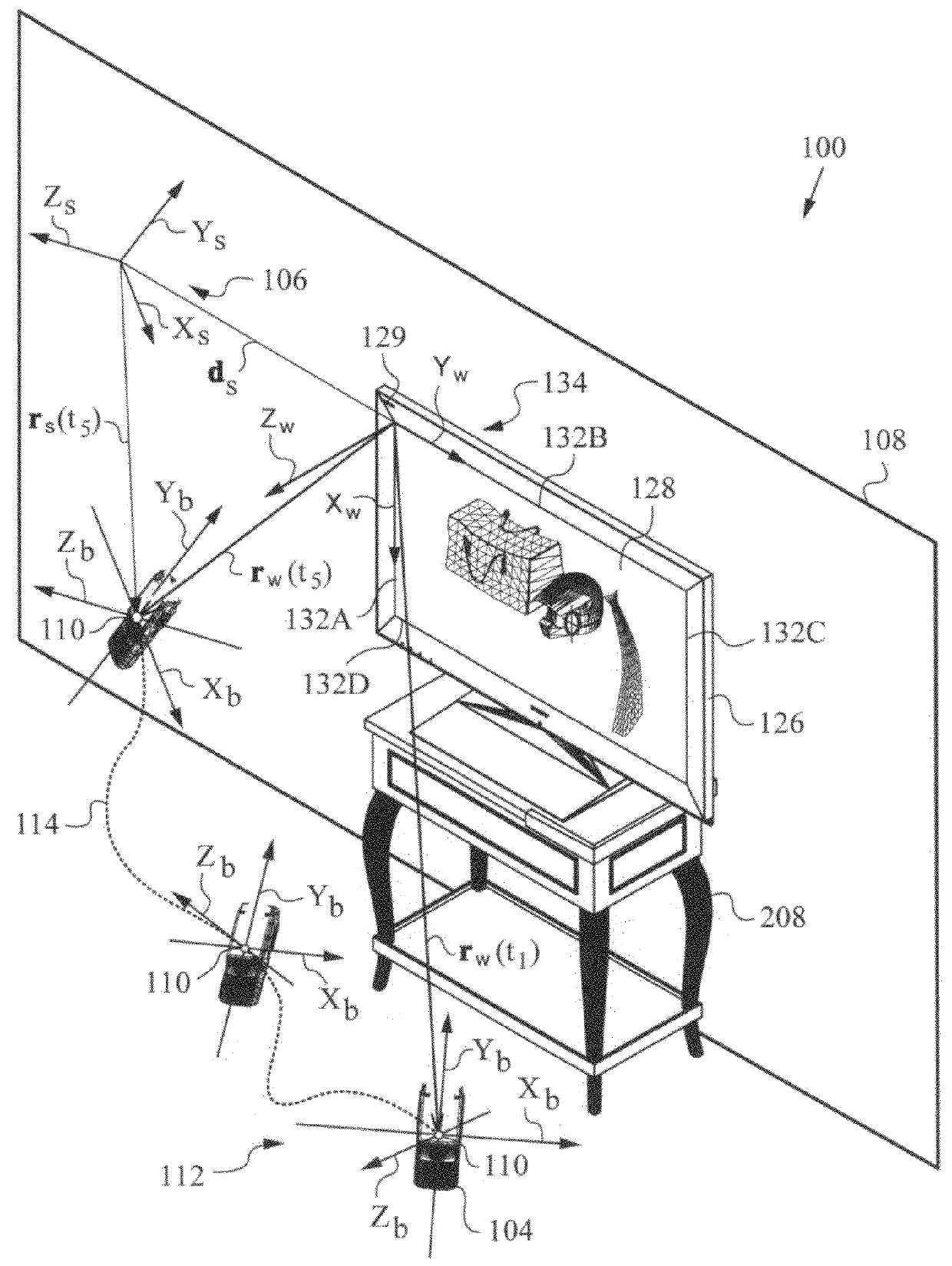
Apparatus and method for determining an absolute pose of a manipulated object in a real three-dimensional environment with invariant features
InactiveUS20100001998A1High optical contrastImproved signal-to-noise ratio performanceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurement deviceTelecommunications link
An apparatus and method for optically inferring an absolute pose of a manipulated object in a real three-dimensional environment from on-board the object with the aid of an on-board optical measuring arrangement. At least one invariant feature located in the environment is used by the arrangement for inferring the absolute pose. The inferred absolute pose is expressed with absolute pose data (φ,θ,ψ,x,y,z) that represents Euler rotated object coordinates expressed in world coordinates (Xo,Yo,Zo) with respect to a reference location, such as, for example, the world origin. Other conventions for expressing absolute pose data in three-dimensional space and representing all six degrees of freedom (three translational degrees of freedom and three rotational degrees of freedom) are also supported. Irrespective of format, a processor prepares the absolute pose data and identifies a subset that may contain all or fewer than all absolute pose parameters. This subset is transmitted to an application via a communication link, where it is treated as input that allows a user of the manipulated object to interact with the application and its output.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
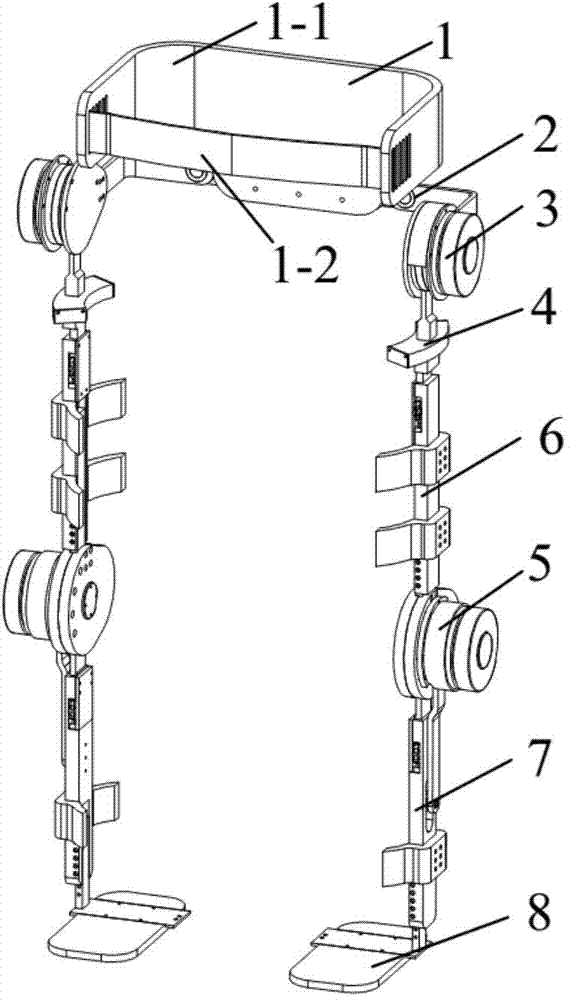
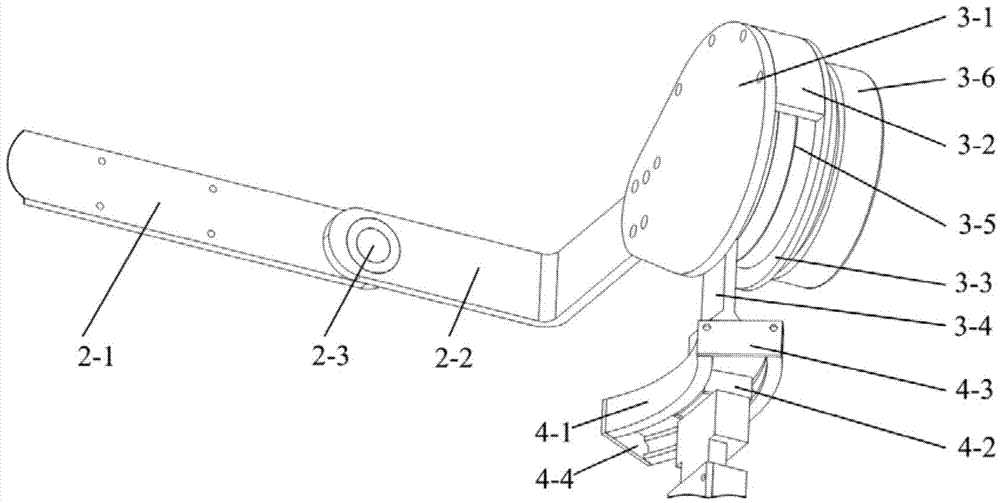
Lower limb rehabilitation training exoskeleton with bionics design
ActiveCN103932870AAvoid damageCompact structureChiropractic devicesWalking aidsMedial rotationCoxal joint
The invention relates to a lower limb rehabilitation training exoskeleton with bionics design. An existing lower limb rehabilitation training exoskeleton is complex in driving structure, low in the response speed and not ideal in rehabilitation training effect, and lacks bionic consideration. The lower limb rehabilitation training exoskeleton comprises a waist tightening mechanism and lower limb exoskeleton leg rods, wherein the waist tightening mechanism is connected with the waist of a wearer, the left lower limb exoskeleton leg rod and the right lower limb exoskeleton leg rod respectively have four degrees of freedom and achieve three degrees of freedom of hip joints through a hip joint adduction and abduction mechanism, a hip joint bending and stretching mechanism and a hip joint medial rotation and lateral rotation mechanism. The axes of the three rotation degrees of freedom are orthogonal at the motion center of the hip joints of the human body. The rotation center of a knee joint bending and stretching mechanism moves along with the rotation center of the knee joints of the human body, so that the exoskeleton and the rotation center of the knee joints of the human body are always kept in the same axis. The hip joint bending and stretching mechanism and the knee joint bending and stretching mechanism are directly driven by a motor in cooperation with a speed reducer. The lower limb rehabilitation training exoskeleton is compact and portable in structure, man-machine interference force is avoided, damage caused by rehabilitation training to the knee joints is reduced, and the whole rehabilitation training becomes more natural and easier.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Deriving input from six degrees of freedom interfaces
ActiveUS9229540B2Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsMixed realityVirtual space
The present invention relates to interfaces and methods for producing input for software applications based on the absolute pose of an item manipulated or worn by a user in a three-dimensional environment. Absolute pose in the sense of the present invention means both the position and the orientation of the item as described in a stable frame defined in that three-dimensional environment. The invention describes how to recover the absolute pose with optical hardware and methods, and how to map at least one of the recovered absolute pose parameters to the three translational and three rotational degrees of freedom available to the item to generate useful input. The applications that can most benefit from the interfaces and methods of the invention involve 3D virtual spaces including augmented reality and mixed reality environments.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com