Rotary blood pump and control system therefor
a blood pump and control system technology, applied in the direction of piston pumps, positive displacement liquid engines, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of rotors of motors providing shaft torque that remain to be supported, seals that may leak, and many of these characteristics are difficult to meet in a conventional pump configuration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
third embodiment
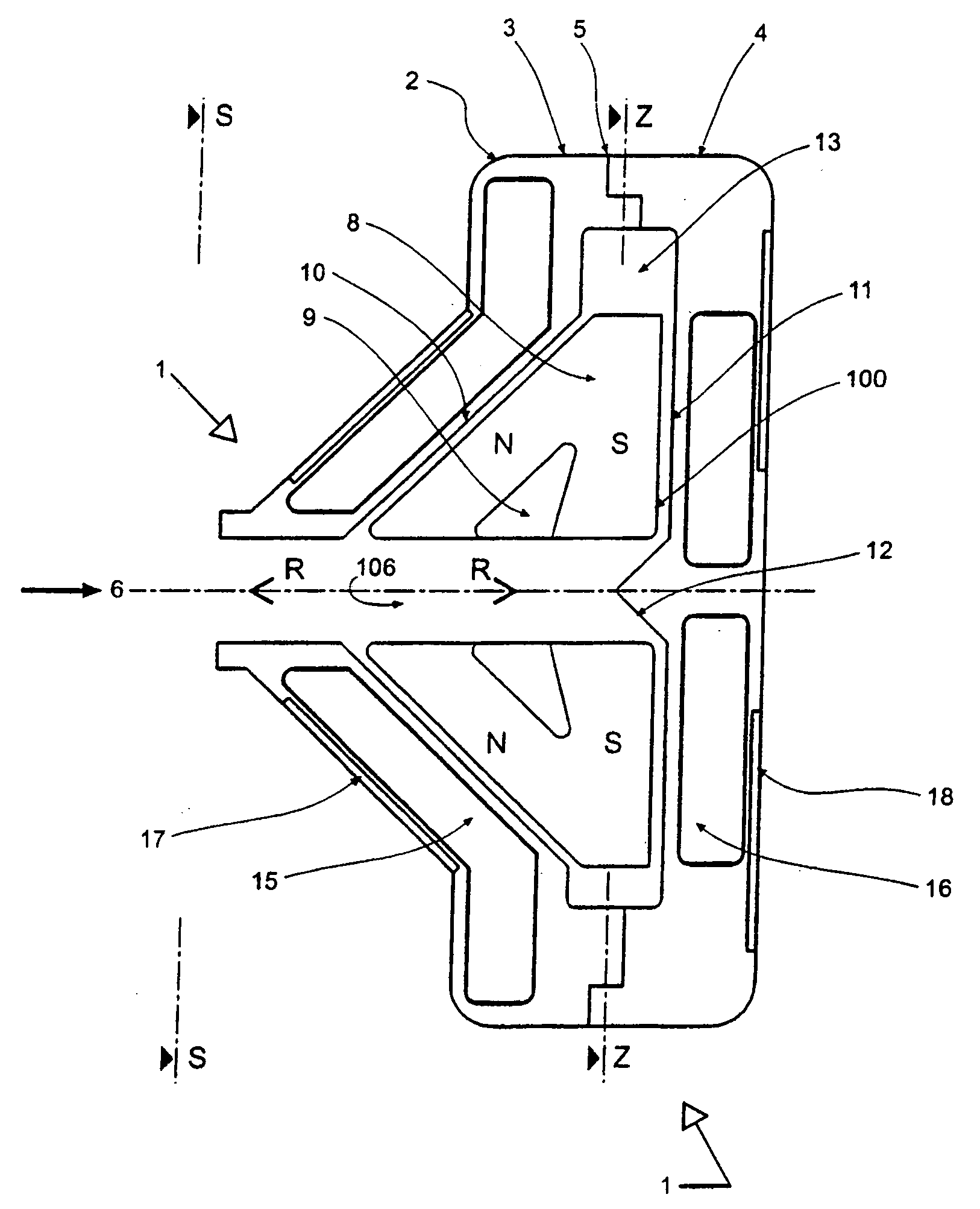
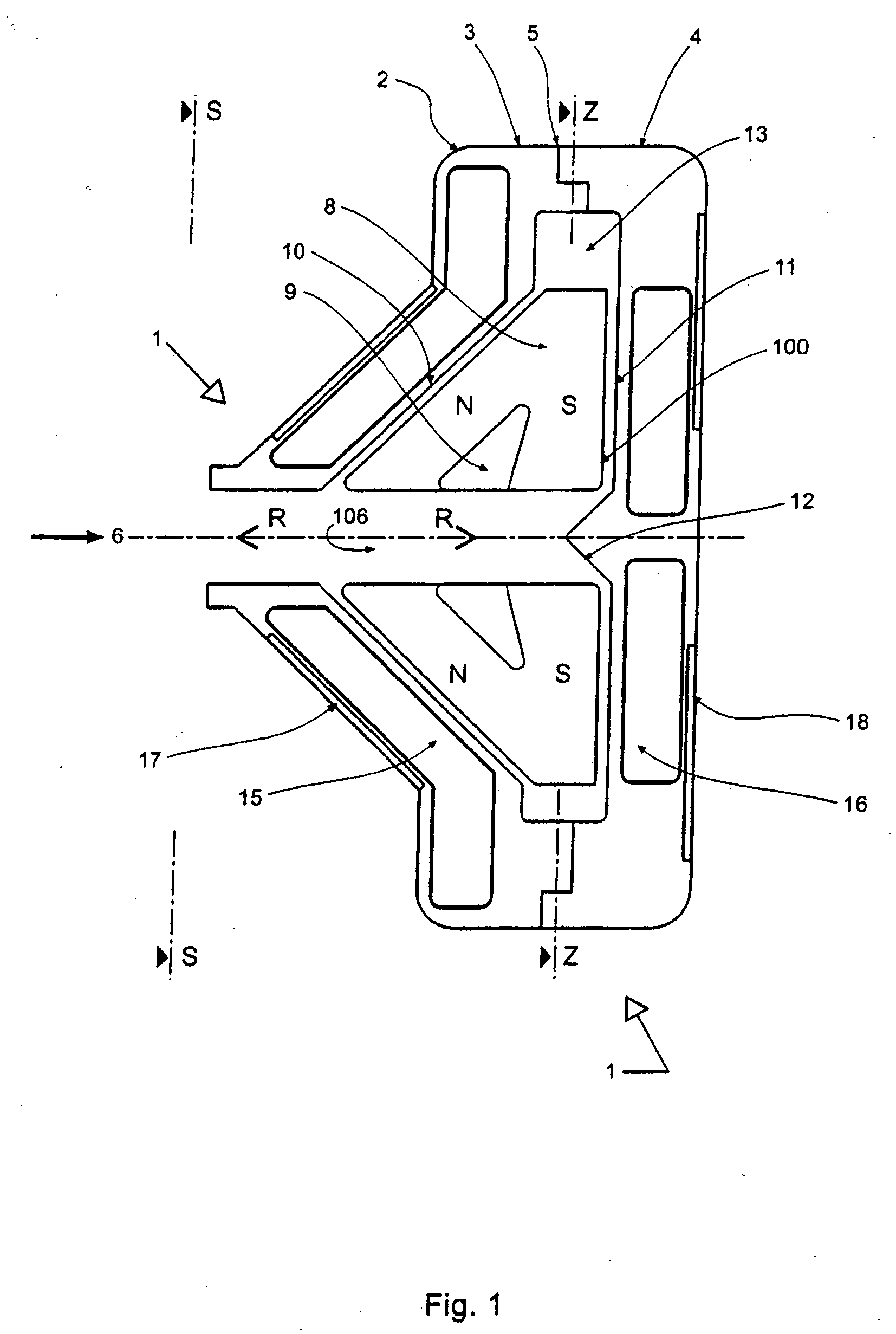
With reference to FIGS. 7 to 15 inclusive there is shown a further preferred embodiment of the pump assembly 200.
With particular reference initially to FIG. 7 the pump assembly 200 comprises a housing body 201 adapted for bolted connection to a housing cover 202 and so as to define a centrifugal pump cavity 203 therewithin.
The cavity 203 houses an impeller 204 adapted to receive magnets 205 within cavities 206 defined within blades 207. As for the first embodiment the blades 207 are supported from a support 208.
Exterior to the cavity 203 but forming part of the pump assembly 200 there is located a body winding 209 symmetrically mounted around inlet 210 and housed between the housing body 201 and a body yoke 211.
Also forming part of the pump assembly 200 and also mounted external to pump cavity 203 is cover winding 212 located within winding cavity 213 which, in turn, is located within housing cover 202 and closed by cover yoke 214.
The windings 212 and 209 are supplied fro...
fourth embodiment
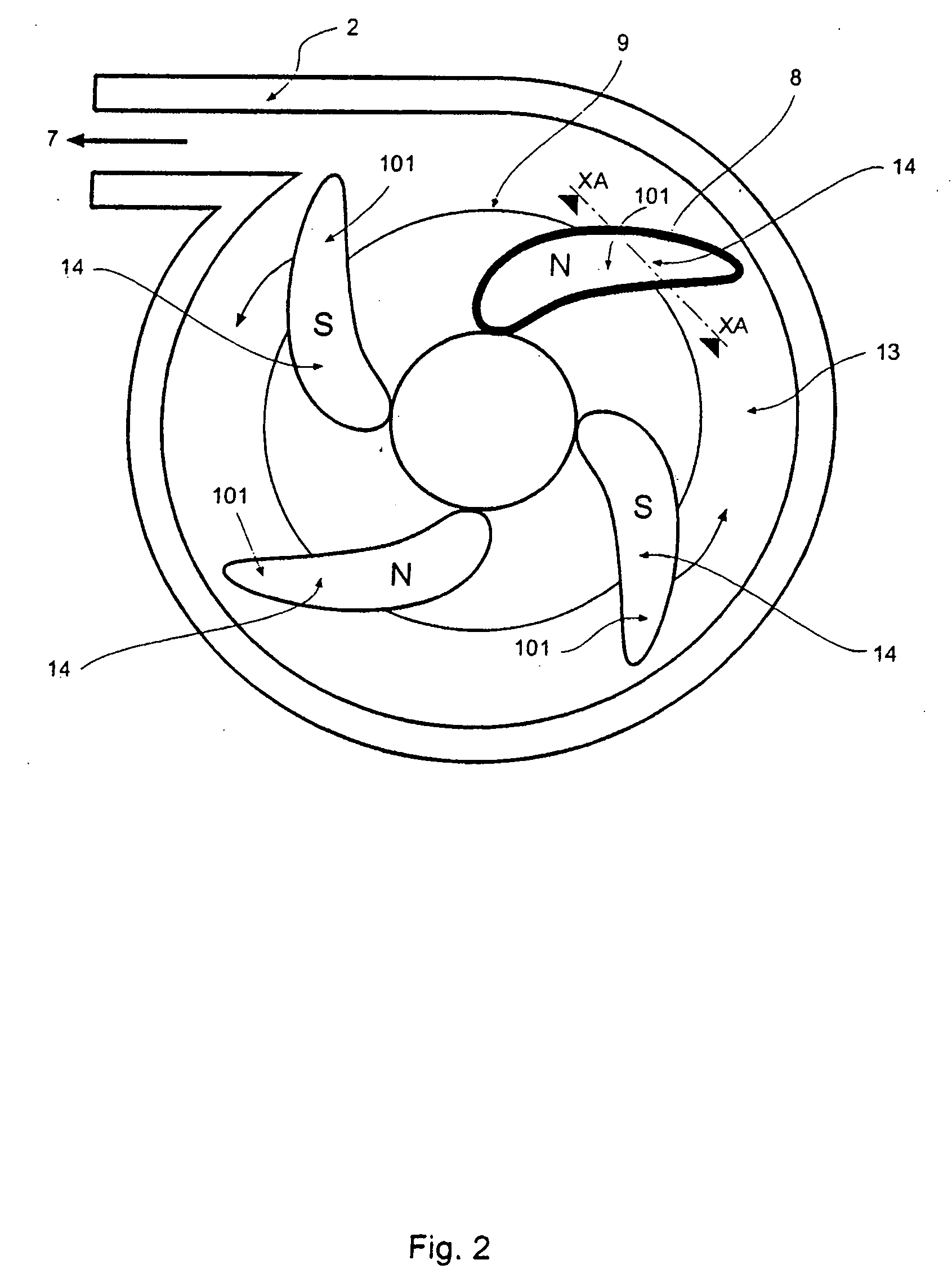
With reference to FIG. 18 a further embodiment of the invention is illustrated comprising a plan view of the impeller 300 forming part of a “channel” pump. In this embodiment the blades 301 have been widened relative to the blades 207 of the third embodiment to the point where they are almost sector-shaped and the flow gaps between adjacent blades 301, as a result, take the form of a channel 302, all in communication with axial cavity 303.
A further modification of this arrangement is illustrated in FIG. 19 wherein impeller 304 includes secter-shaped blades 305 having curved leading and trailing −38 portions 306, 307 respectively thereby defining channels 308 having fluted exit portions 309.
As with the first and second embodiments the radial and axial hydrodynamic forces are generated by appropriate profiling of the top and bottom faces of the blades 301, 305 (not shown in FIGS. 18 and 19).
FIG. 20 illustrates a perspective view of an impeller 304 which follows the theme of the ...
fifth embodiment
A fifth embodiment of a pump assembly according to the invention comprises an impeller 410 as illustrated in FIG. 21 where, conceptually, the upper and lower surfaces of the blades of previous embodiments are interconnected by a top shroud 411 and a bottom shroud 412. In this embodiment the blades 413 can be reduced to a very small width as the hydrodynamic behaviour imparted by their surfaces in previous embodiments is now given effect by the profiling of the shrouds 411, 412 each of which, in this instance, comprise a series of smoothed wedges 414 with the leading edge of one wedge directly interconnected to the trailing edge of the preceding wedge.
As for previous embodiments the top shroud 411 is of overall conical shape thereby to impart both radial and axial thrust forces whilst the bottom shroud 412 is substantially planar thereby to impart substantially only axial thrust forces.
It is to be understood that, whilst the example of FIG. 21 shows the surfaces of the shroud 41...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com