Patents
Literature
2151 results about "Takeoff" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
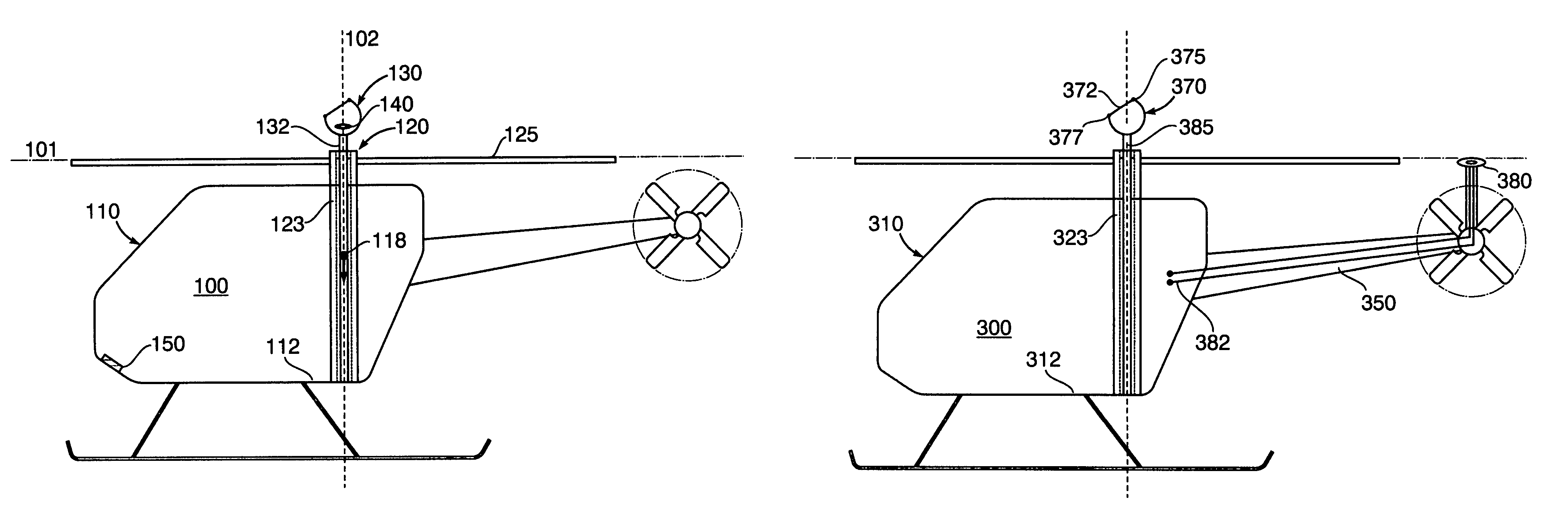
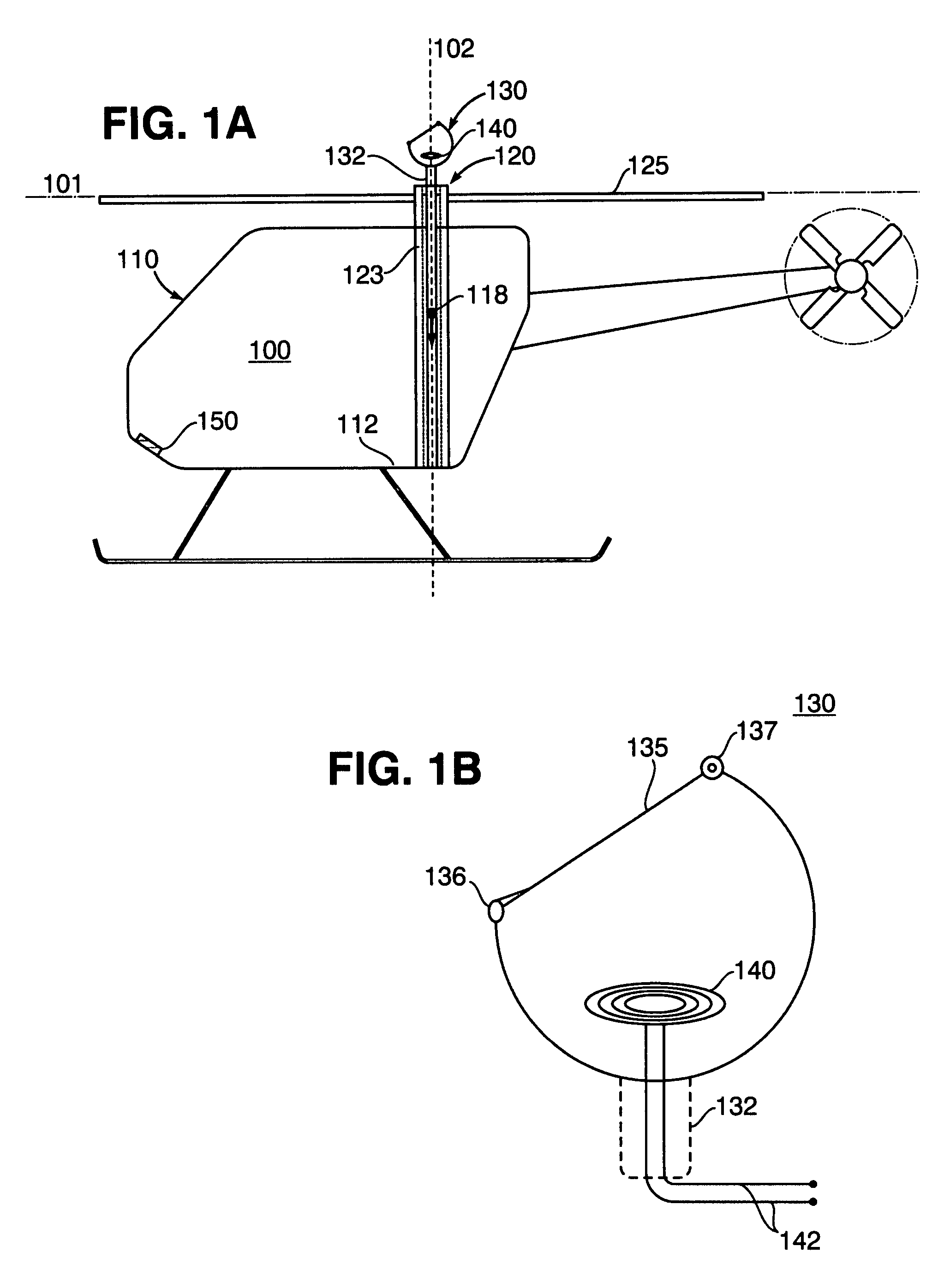
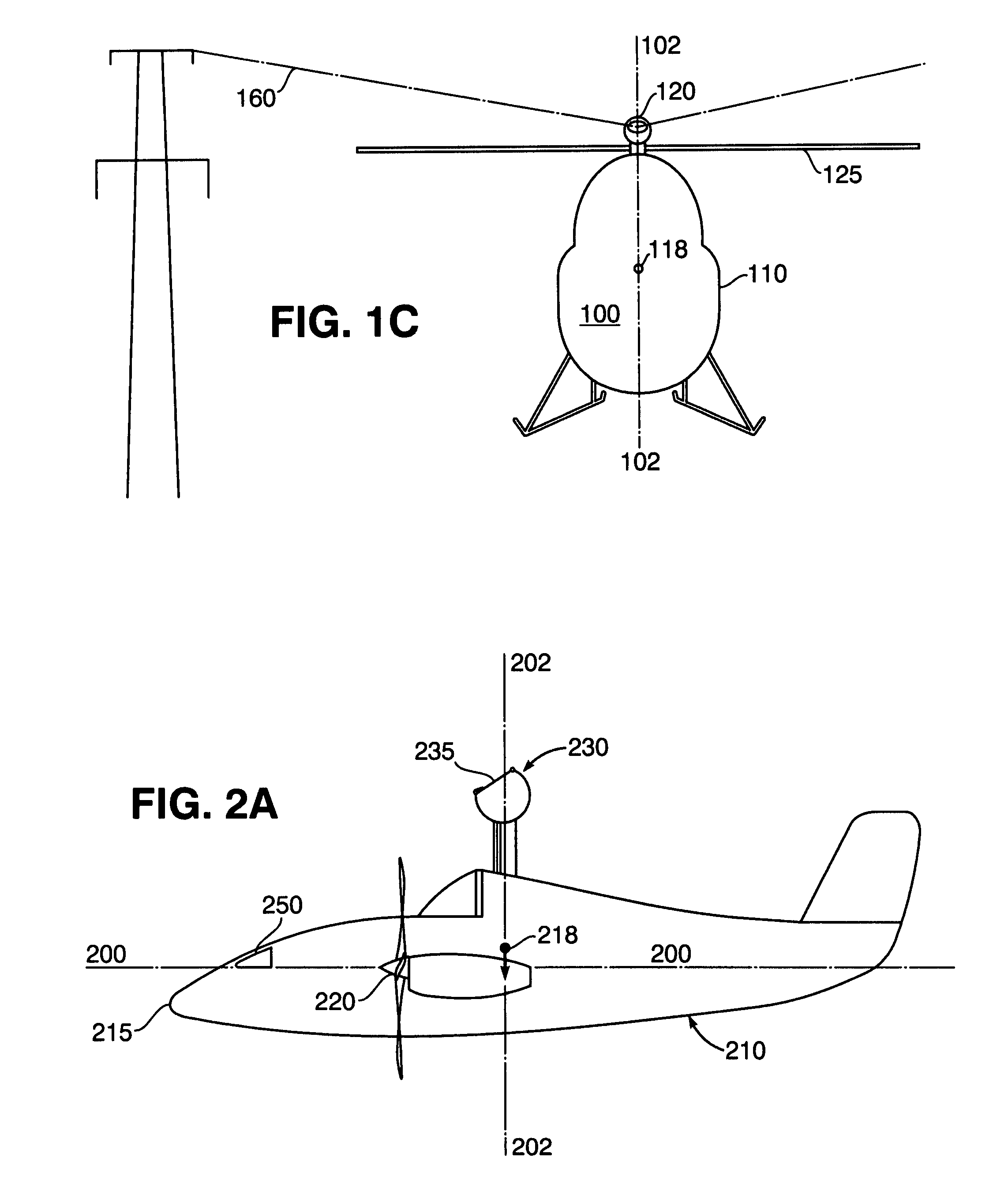
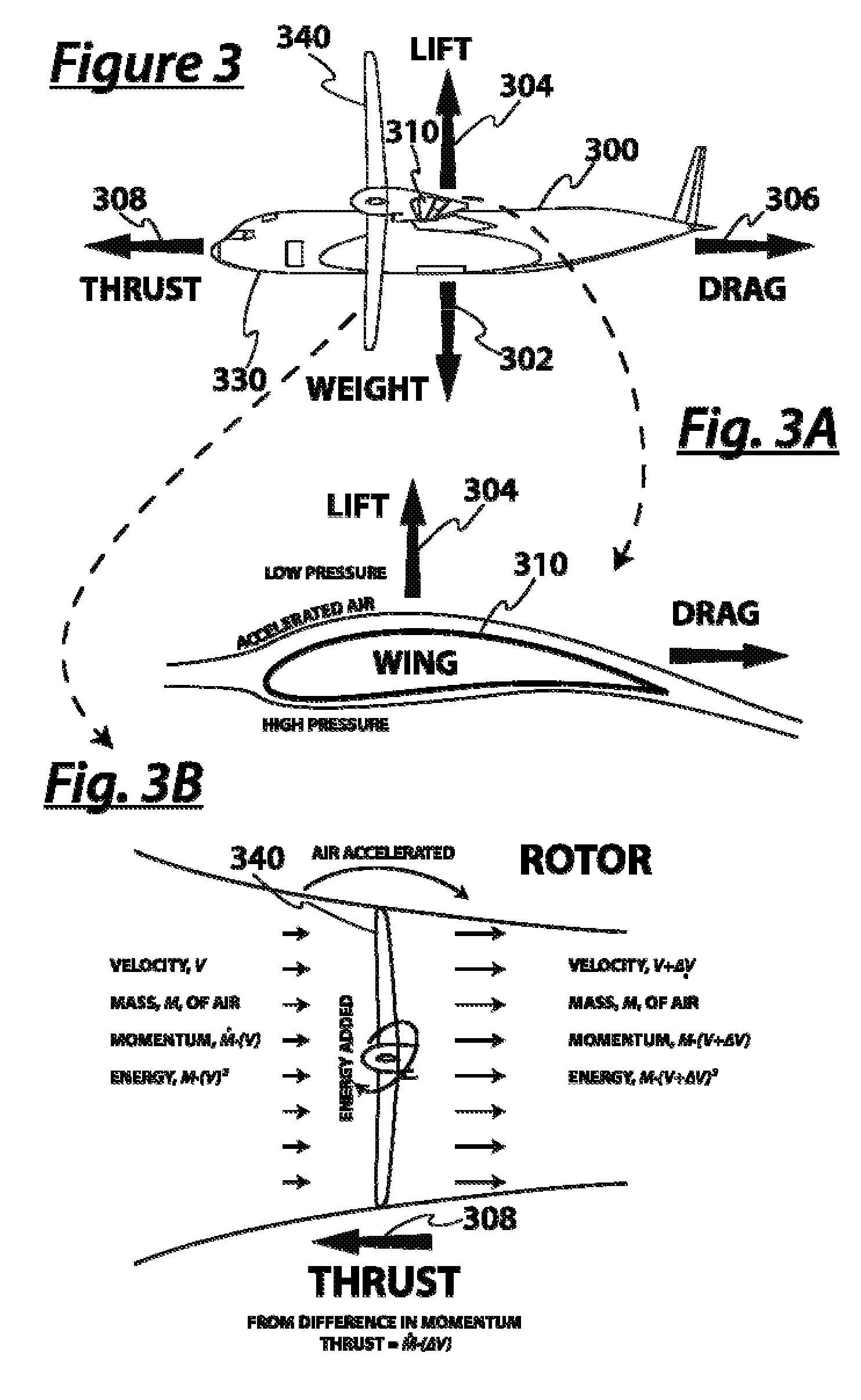
Takeoff is the phase of flight in which an aerospace vehicle leaves the ground and become airborne. For aircraft that take off horizontally, this usually involves starting with a transition from moving along the ground on a runway. For balloons, helicopters and some specialized fixed-wing aircraft (VTOL aircraft such as the Harrier), no runway is needed. Takeoff is the opposite of landing.
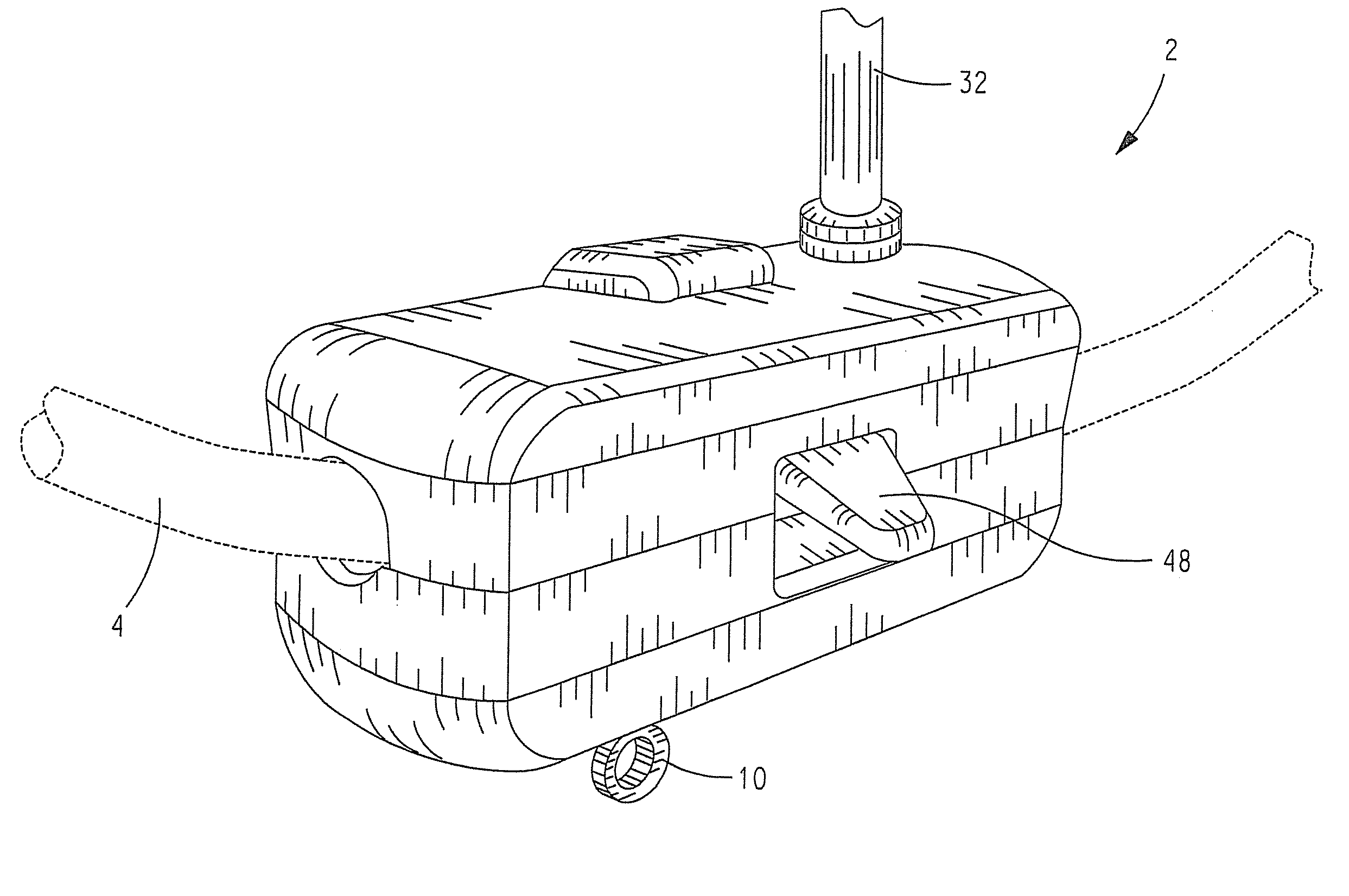
Battery charging arrangement for unmanned aerial vehicle utilizing the electromagnetic field associated with utility power lines to generate power to inductively charge energy supplies
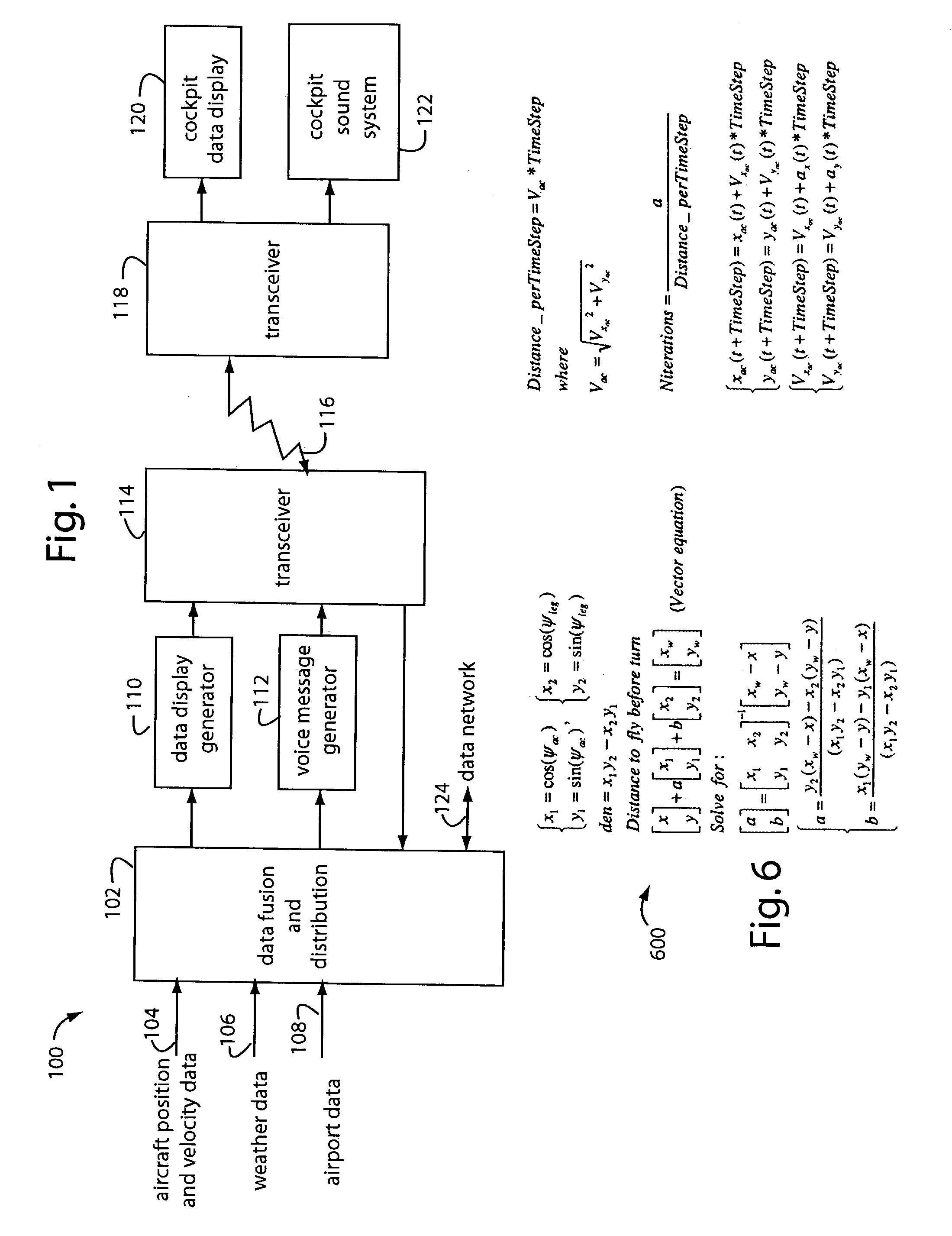
A method and apparatus for charging energy supplies in an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). The present invention relates to a UAV that comprises an inductive charging device that utilizes the electromagnetic field emanated by overhead / utility power lines, to charge the energy supplies. The UAV also includes a releasable latch for holding power lines to allow for the perching of the UAV on power lines during the charging process. The latch and the inductive charging device may be provided on a single device, a battery augmentation trap (BAT). The UAV may be perched in an upright orientation to allow for takeoff after the charging of energy supplies on the power line.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
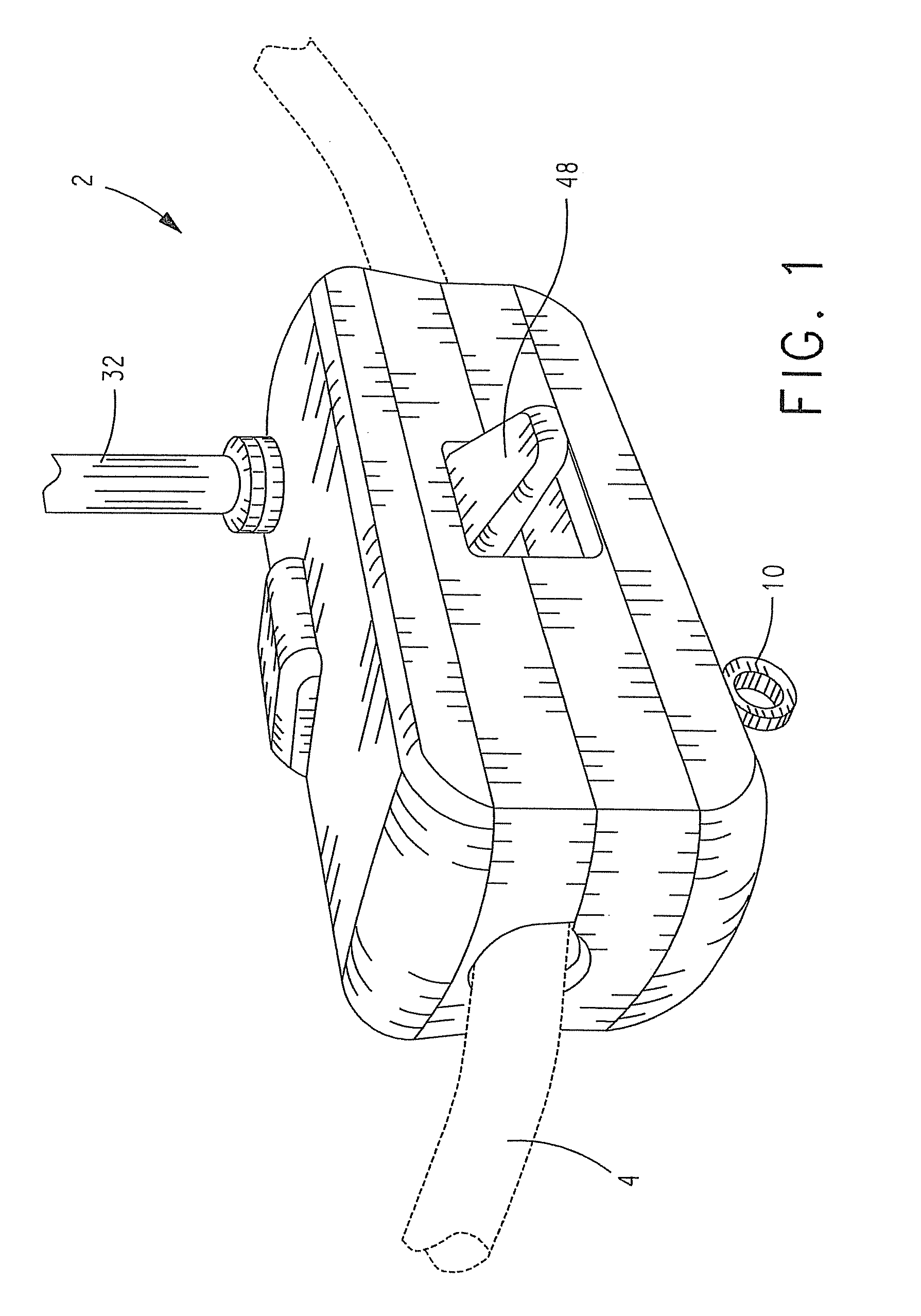
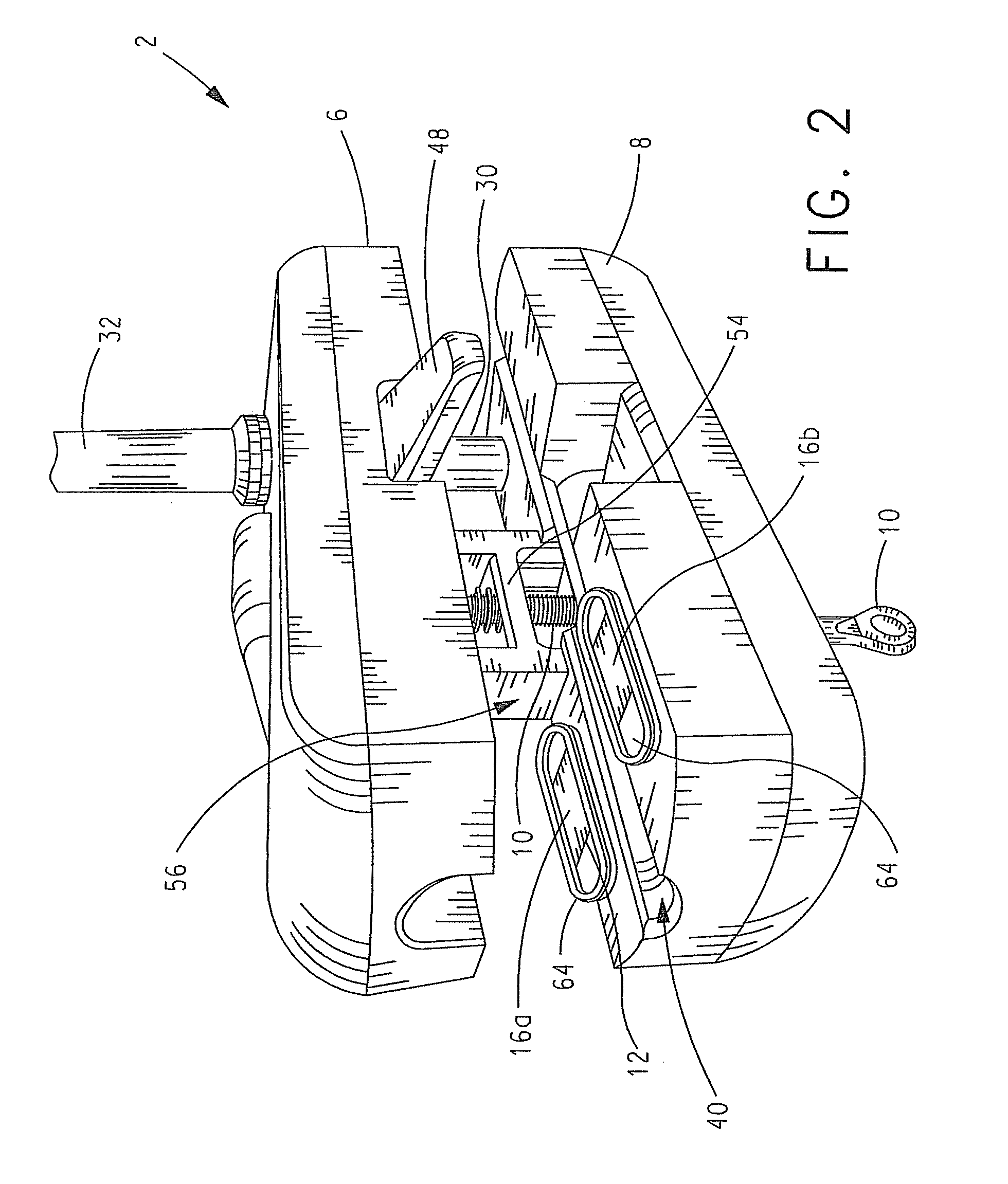
Power line takeoff clamp assembly
ActiveUS8536857B2Measurement using ac-dc conversionBase element modificationsTransceiverWireless transceiver
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
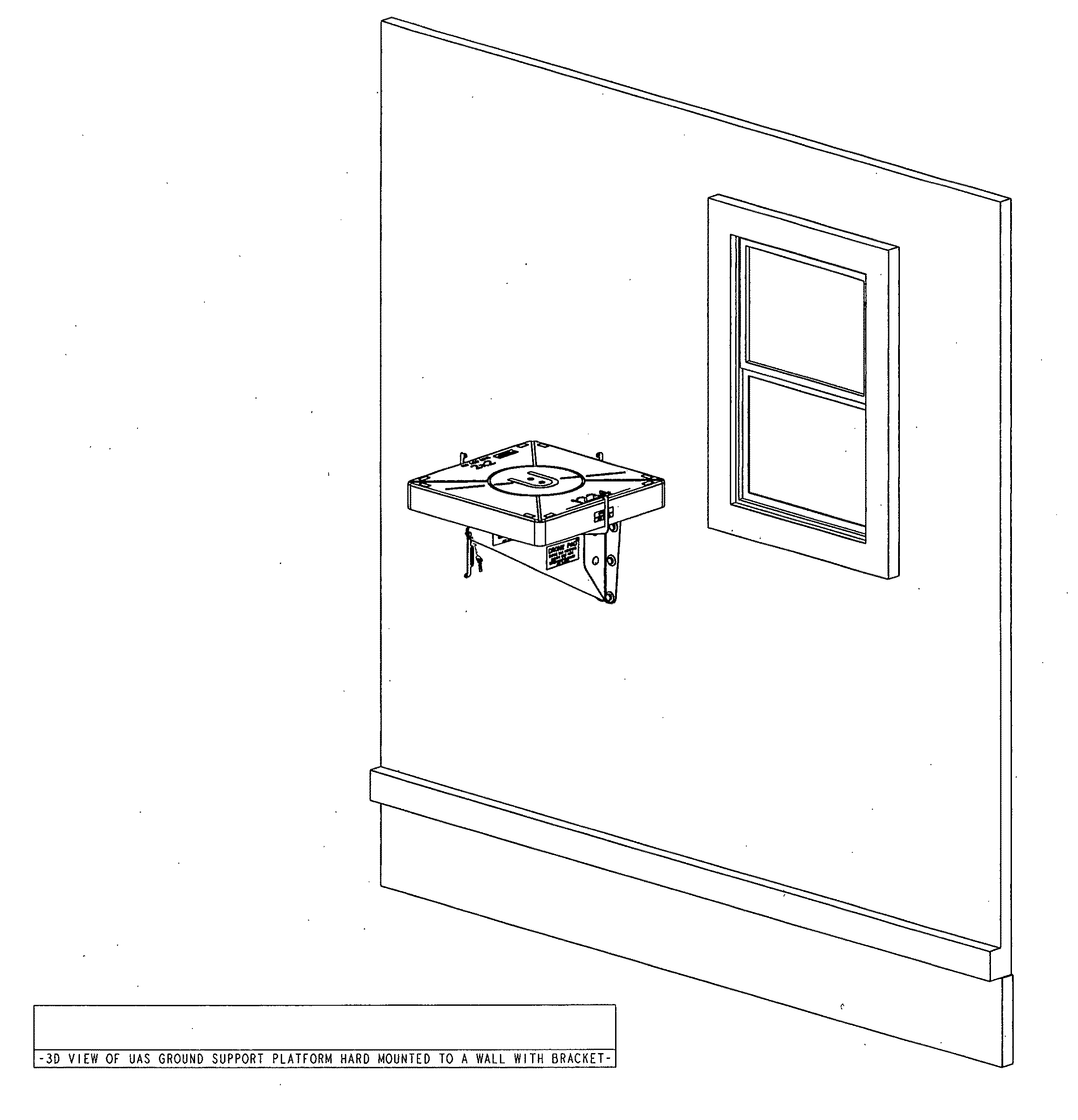
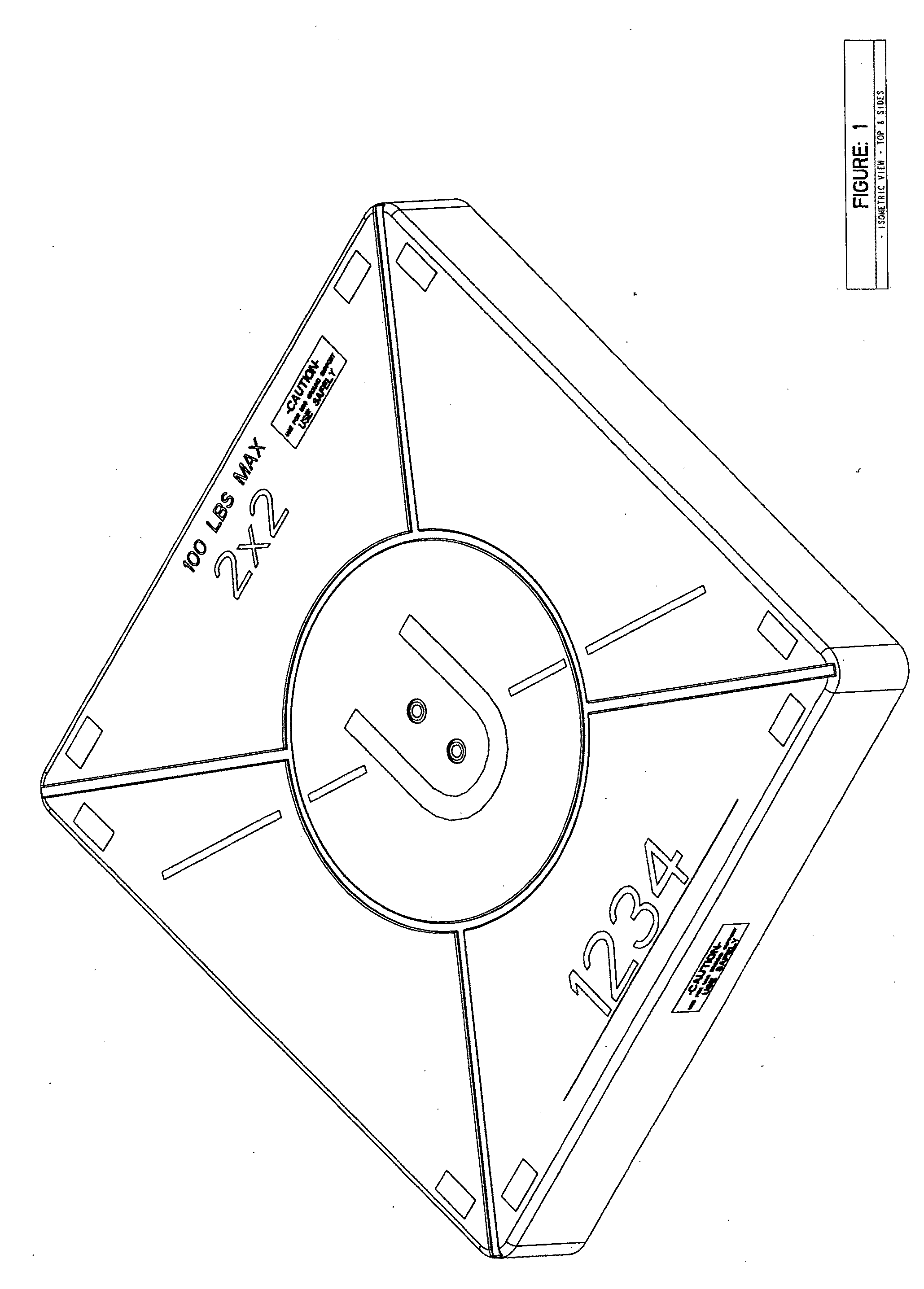
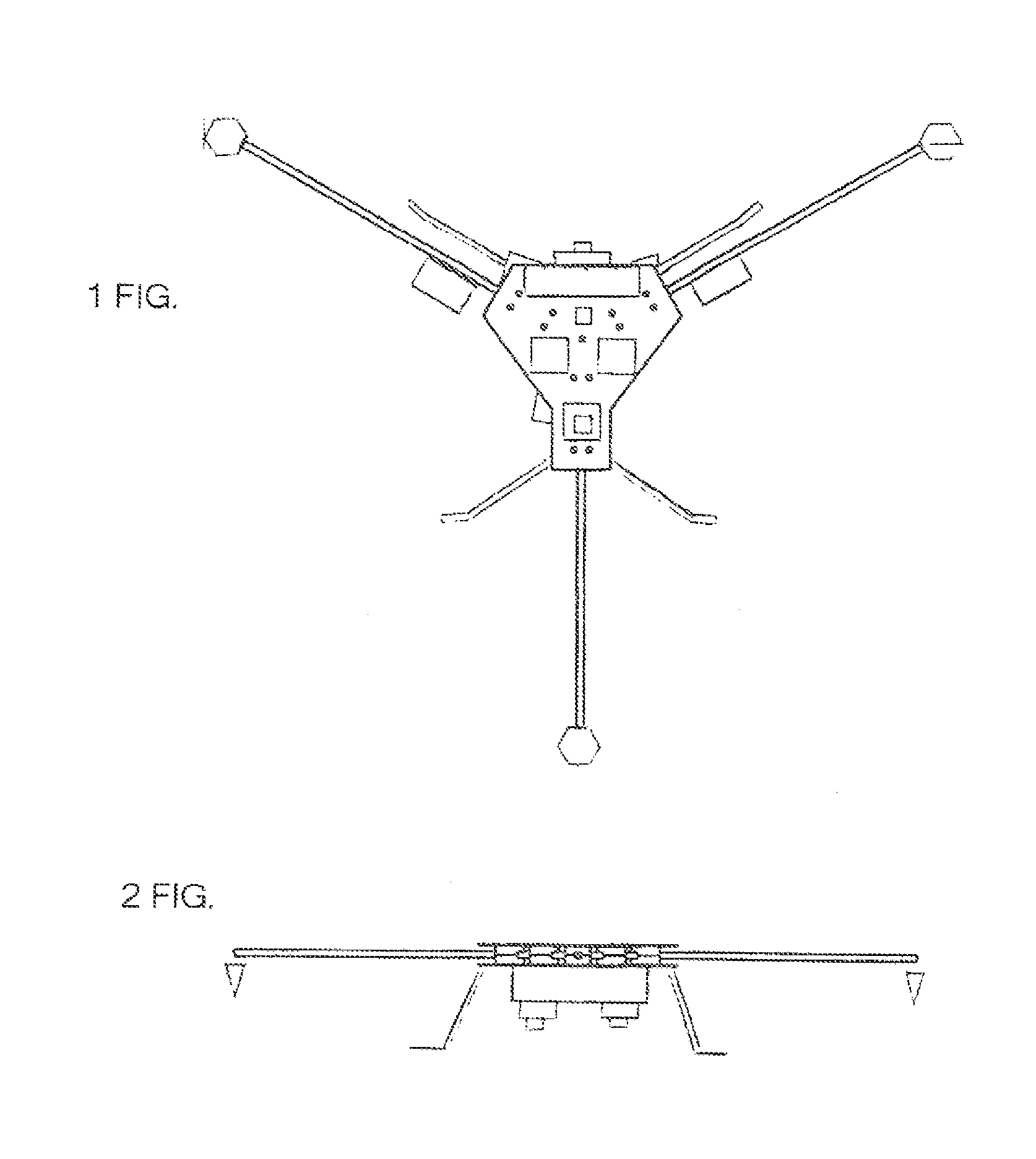
Unmanned Aircraft Systems Ground Support Platform
InactiveUS20160068277A1Small footprintPromotes personal safetyHelicopter landing platformRemote controlled aircraftUncrewed vehicleAirplane
The Unmanned Aircraft Systems ground support platform is a portable, multifunctional apparatus to accommodate UAS (Drone, UAV) landings, takeoffs, idle time, maintenance, retail merchandise product display and package delivery support within the UAS recreational and business industry. The Unmanned Aircraft Systems ground support platform will provide stability and cleanliness of a Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Ownership identification is intergraded into the base platform.
Owner:MANITTA SALVATORE
Helicopter
ActiveUS20110301784A1Reduce problem sizeEasy to flyPropellersUnmanned aerial vehiclesMission planGround station
The present invention relates to a reduced scale industrial helicopter, with an integrated automatic flight control system, that includes core autopilot functions, GPS management, and full-function navigation systems. The autopilot technology includes rapid launch capability, real-time in-flight switching between one or more of a) remote control, b) autopilot-directed, c) ground station controlled, and d) home modes, and is upgradeable. The helicopter is used for high or low altitude surveillance, and can handle various payloads, including photographic missions. The helicopter may include onboard batteries and / or a unique battery unit disposed beneath the helicopter, and includes autonomous features such as automatic takeoff, automatic landing, safety return to home base, and predetermined mission plans.
Owner:GEOTECH ENVIRONMENTAL EQUIP
Controlled take-off and flight system using thrust differentials
InactiveUS20110042508A1Aircraft navigation controlUnmanned aerial vehiclesLevel flightFlight vehicle
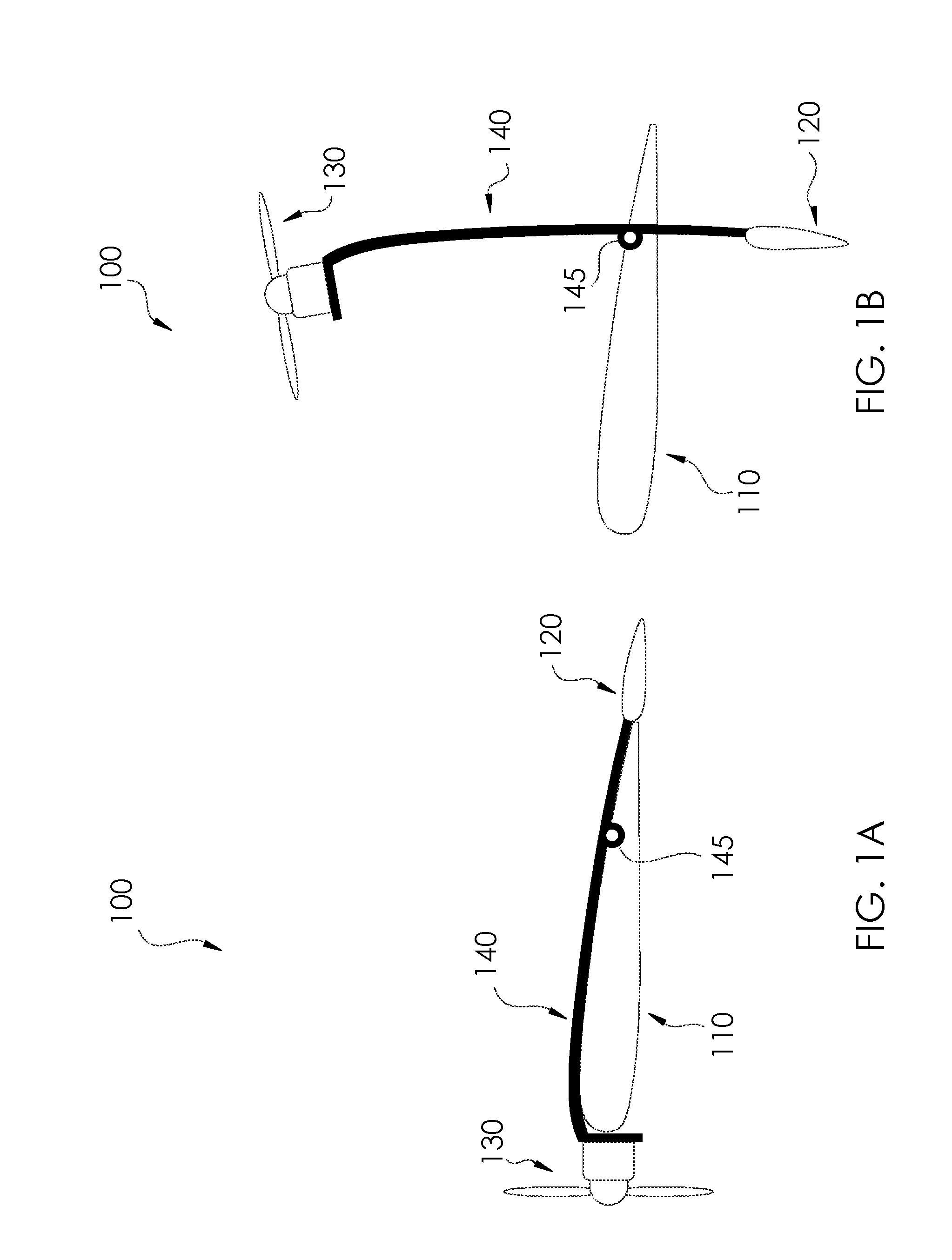
A manned / unmanned aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using the same set of engines for takeoff and landing as well as for forward flight. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to takeoff with the wings in a vertical as opposed to horizontal flight attitude which takes off in this vertical attitude and then transitions to a horizontal flight path. An aerial vehicle which controls the attitude of the vehicle during takeoff and landing by alternating the thrust of engines, which are separated in least two dimensions relative to the horizontal during takeoff. An aerial vehicle which uses a rotating platform of engines in fixed relationship to each other and which rotates relative to the wings of the vehicle for takeoff and landing.
Owner:TRANSITION ROBOTICS INC
Aerodynamically efficient lightweight vertical take-off and landing aircraft with pivoting rotors and stowing rotor blades
ActiveUS20150266571A1Reduce resistanceReduce drag in all flight modesPropellersEfficient propulsion technologiesLevel flightFlight vehicle
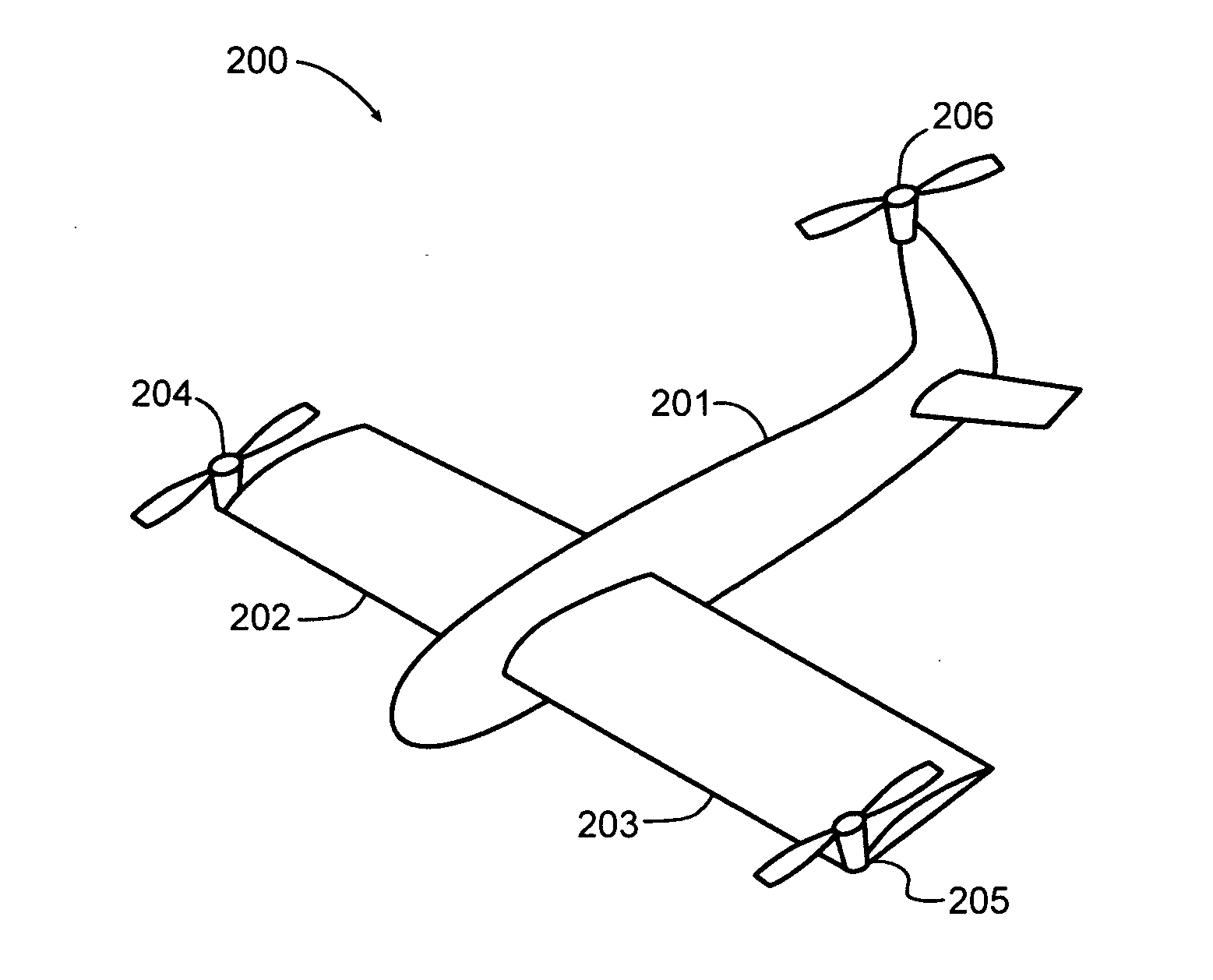
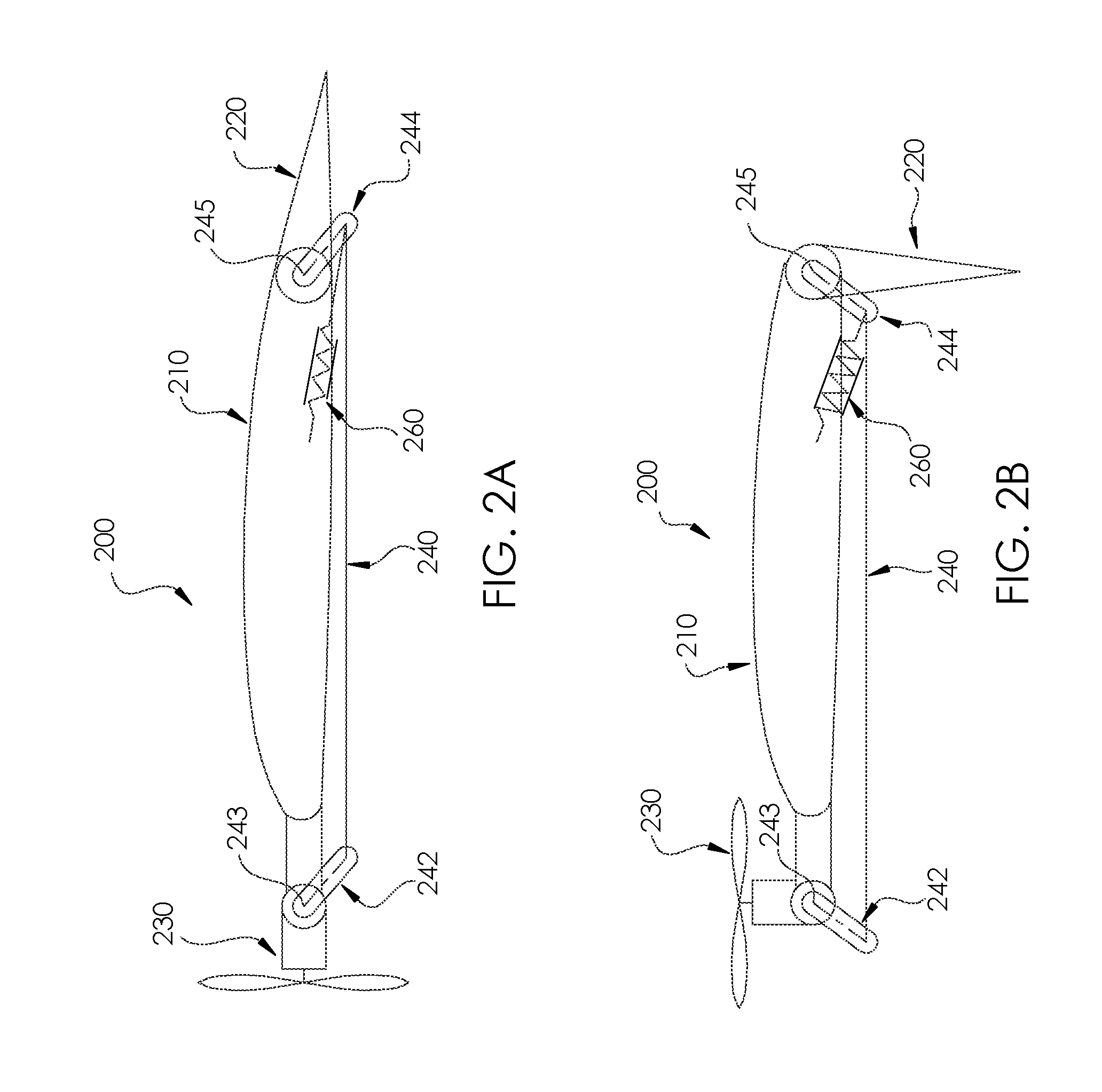
An aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using a set of wing mounted thrust producing elements and a set of tail mounted rotors for takeoff and landing. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to vertical takeoff with the rotors in a rotated, take-off attitude then transitions to a horizontal flight path, with the rotors rotated to a typical horizontal configuration. The aerial vehicle uses different configurations of its wing mounted rotors and propellers to reduce drag in all flight modes.
Owner:JOBY AERO INC
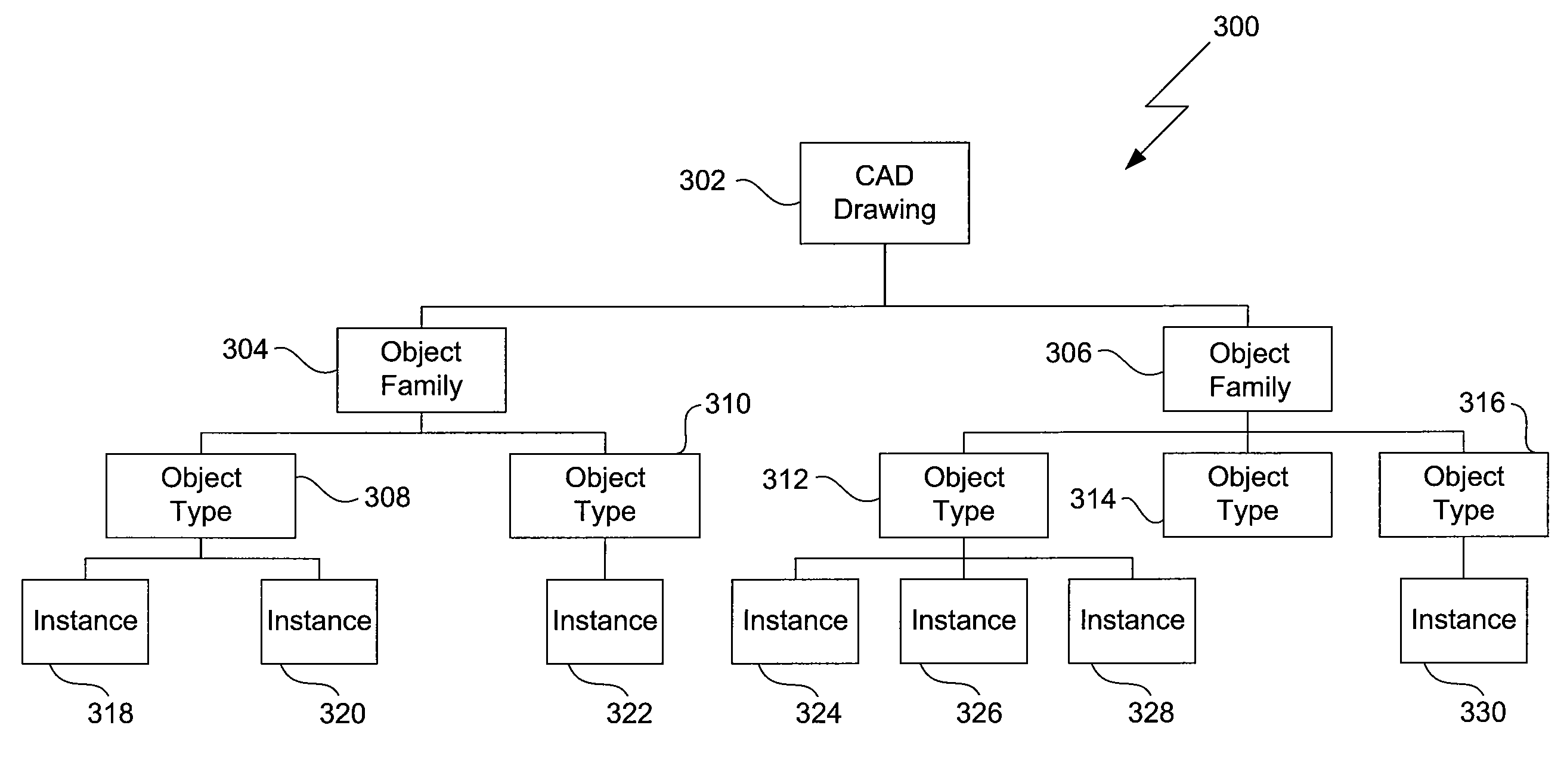
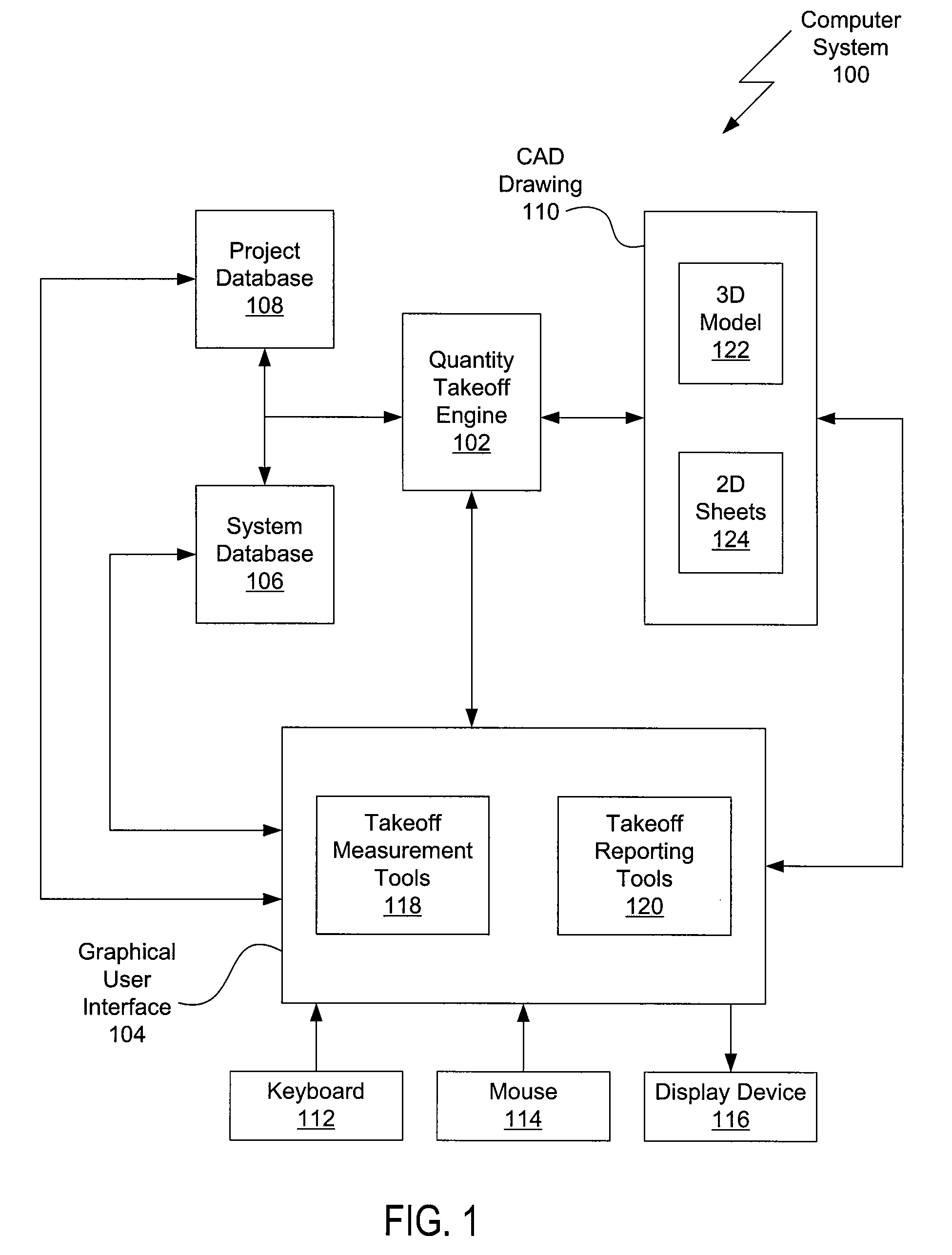
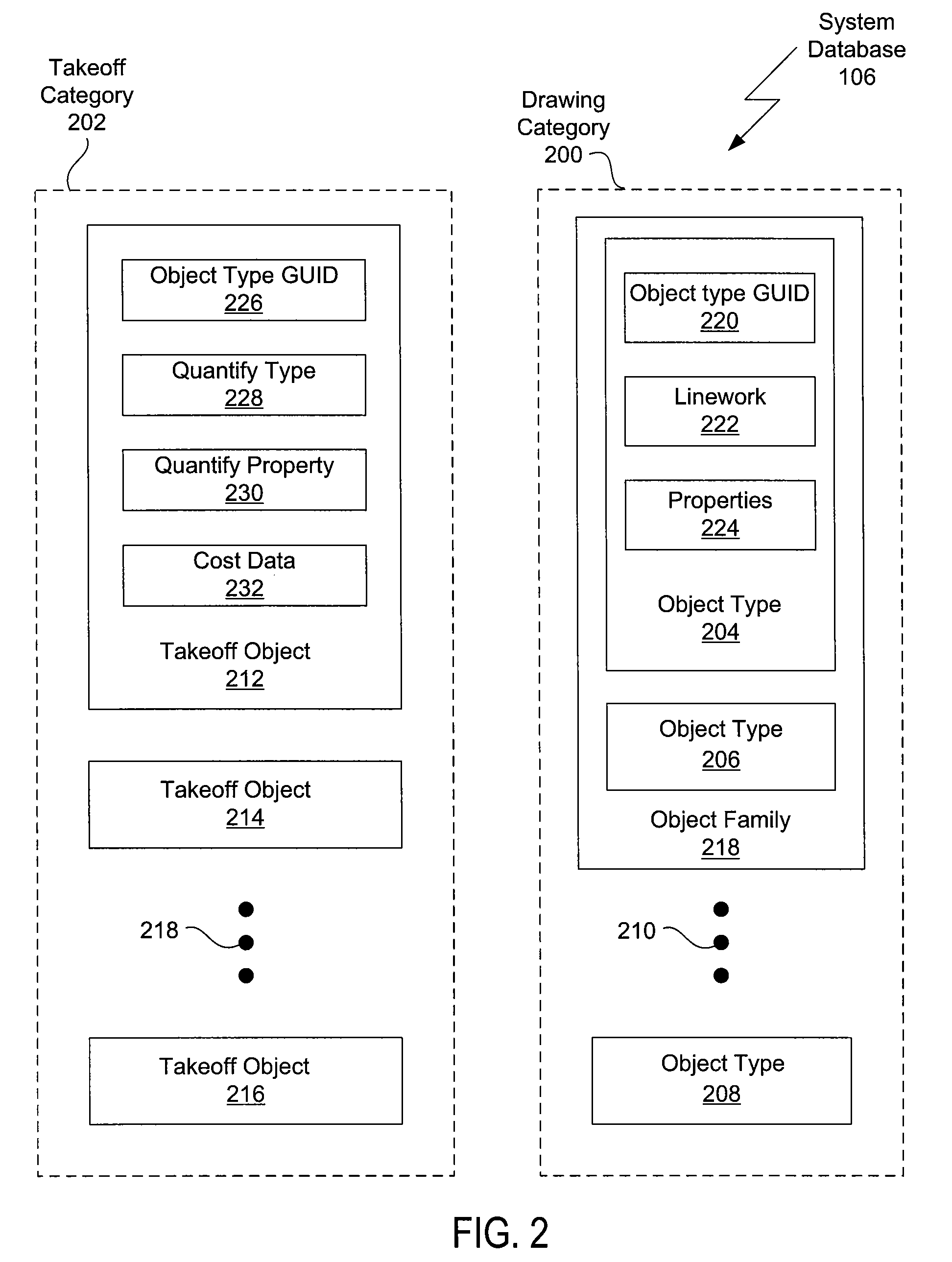
Selective quantity takeoff from computer aided design drawings
ActiveUS20090240730A1Estimated costQuickly and easily costObject oriented databasesSpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignApplication software
One embodiment of the invention sets forth a CAD application configured to perform quantity takeoff computations. The CAD application is further configured to organize a CAD drawing into a hierarchical representation of object families and associated object types, where instances of the object types represent drawing objects present in the CAD drawing. The CAD application is further configured to receive a selection of an object family and to parse the selection to determine the object types associated with the selection. The CAD application then creates a takeoff object for each of the object types associated with the selection and identifies instances, associated with object properties, of each of the object types of the selection. The CAD application quantifies the instances and associated properties to produce a quantity takeoff value. Advantageously, users are able to more quickly and easily estimate the cost of a design project associated with the CAD drawing.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
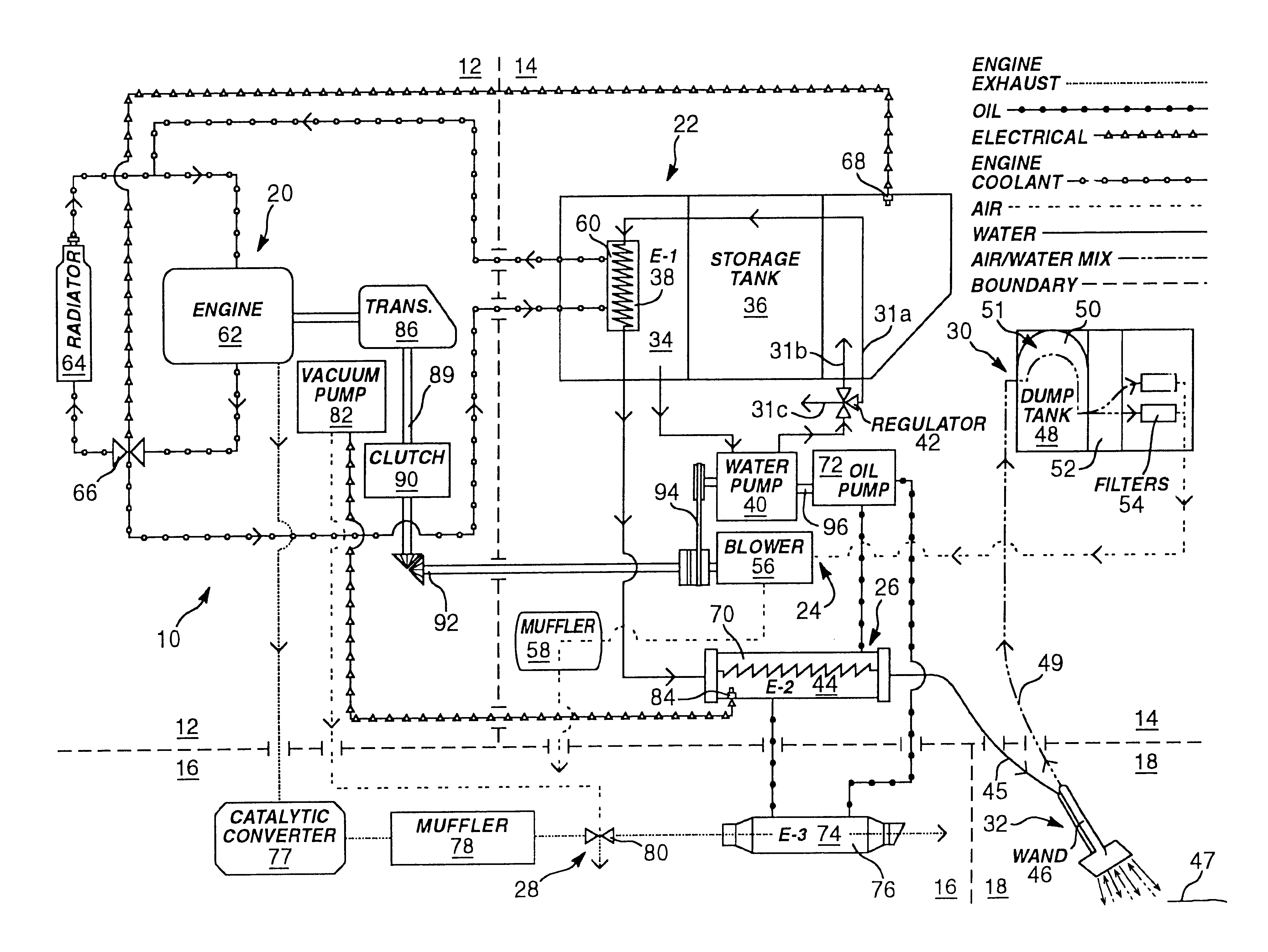
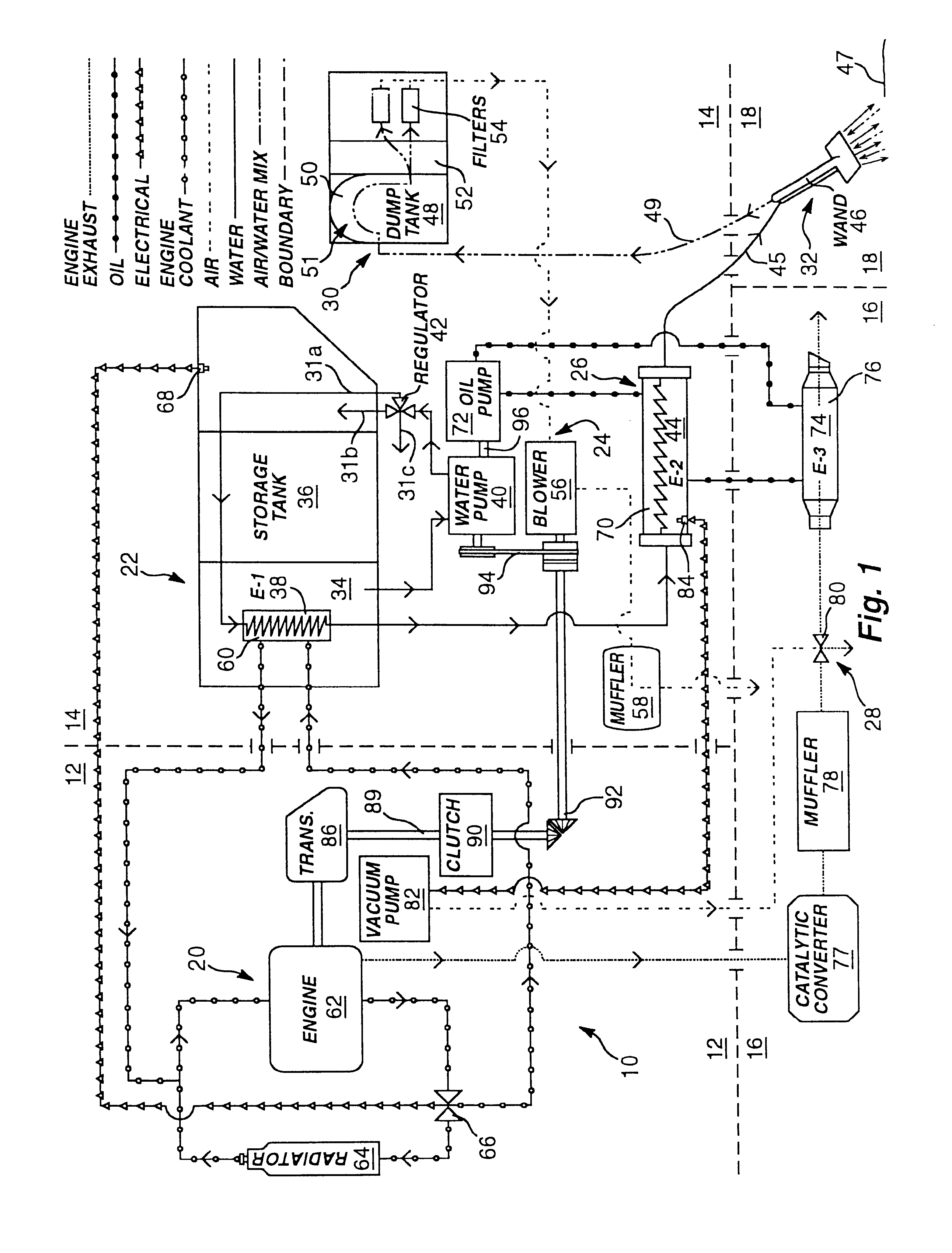
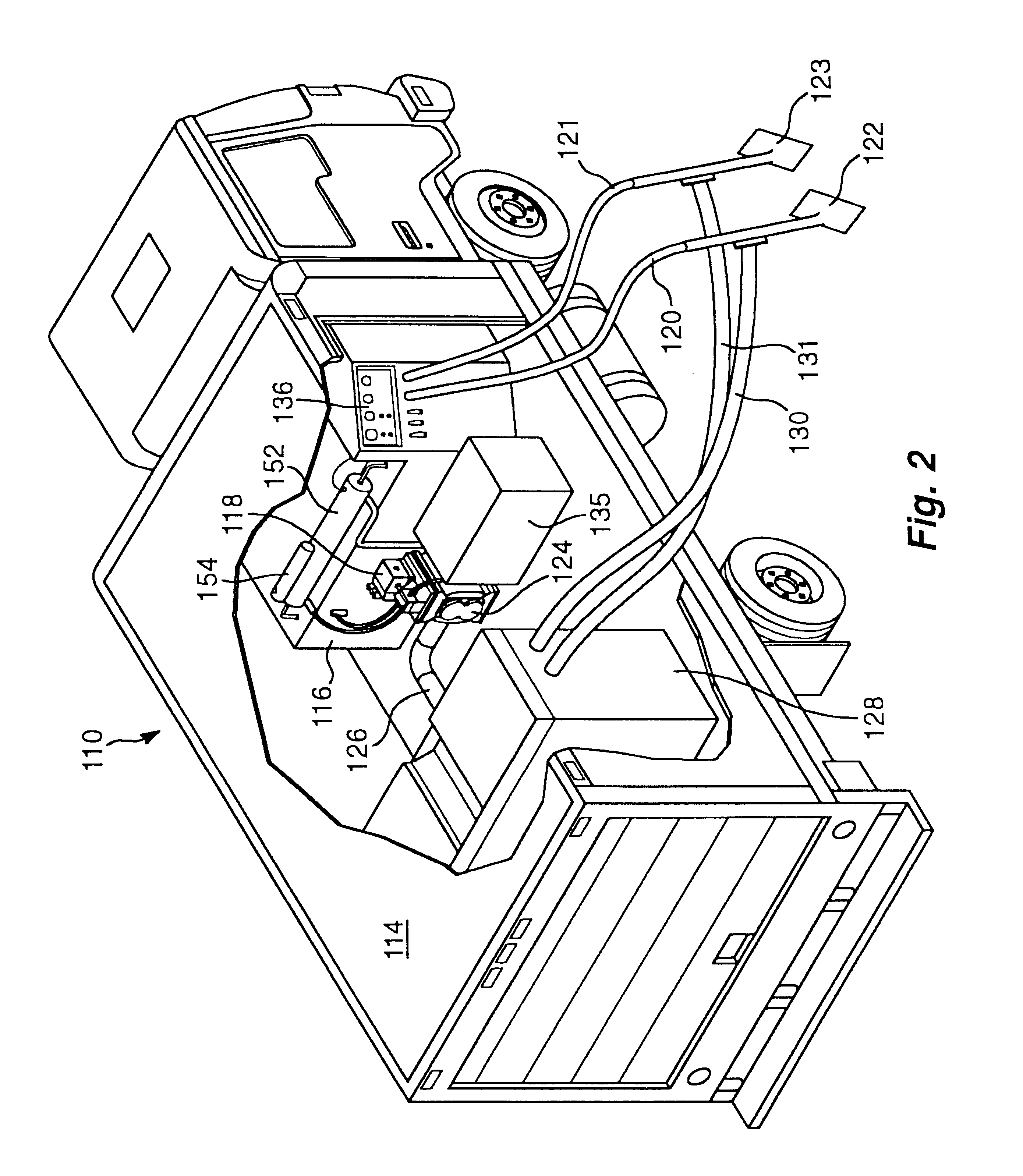
Portable high-temperature, high-pressure washing plant
InactiveUS6675437B1Reliable outputIncrease temperatureInternal combustion piston enginesRecuperative heat exchangersProcess engineeringThermal contact
A washing system for high temperature cleaning applications, such as carpet-cleaning, is disclosed that provides a consistent cleaning fluid temperature. The washing system utilizes multiple heat exchangers and multiple heat paths. The heating and power source is provided by a medium duty, diesel cycle engine. Multi-stage heating involves heat transfer from the engine's coolant to the cleaning fluid and heat transfer from the exhaust of the engine to the cleaning fluid via an intermediate medium. The system also includes a fluid clutch used to engage a power takeoff from the engine to operate the pump and blower of the washing plant. A failsafe source cutoff diverts the exhaust flow from thermal contact with an intermediate heat transfer oil.
Owner:BLUE LINE EQUIP
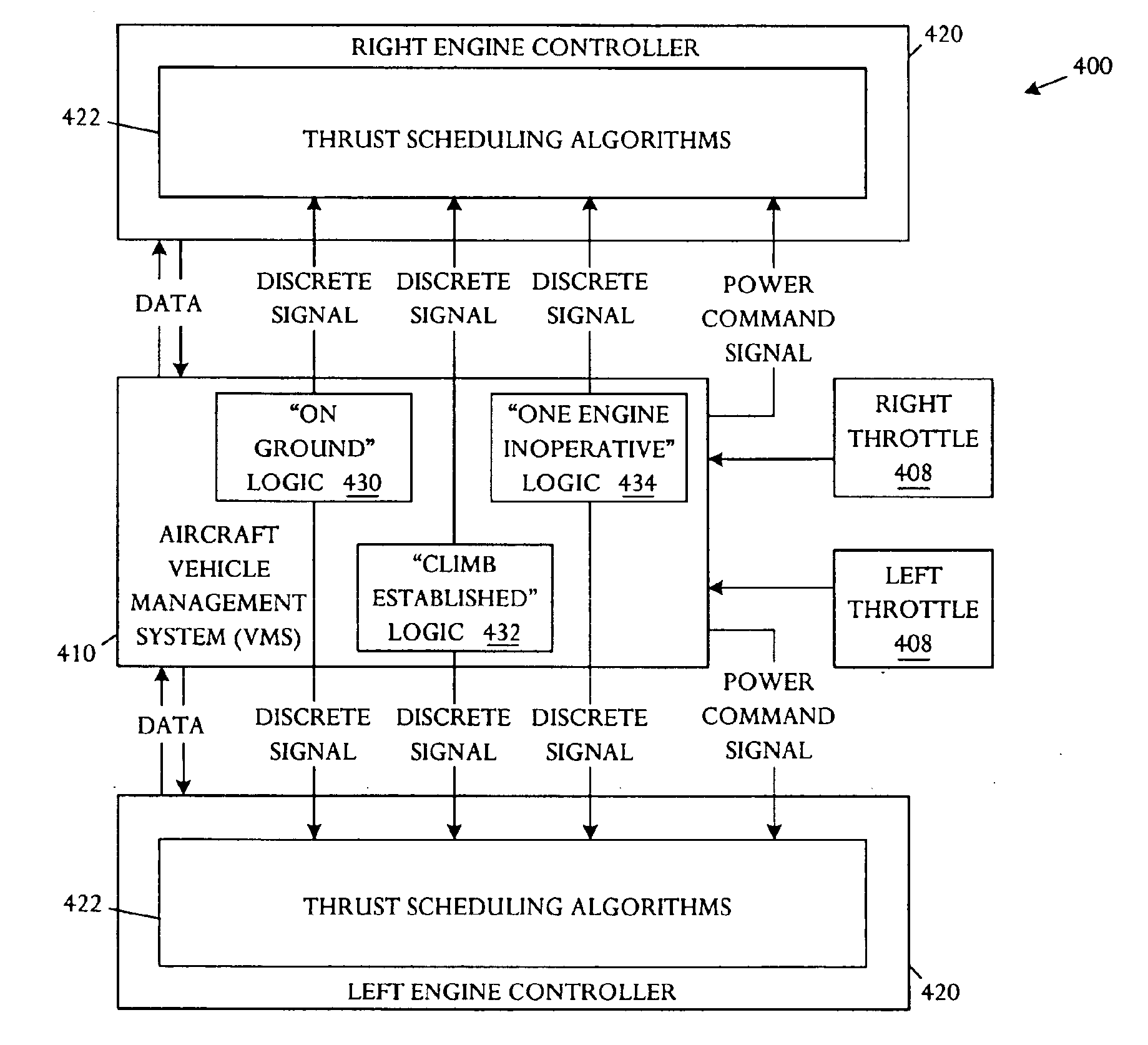
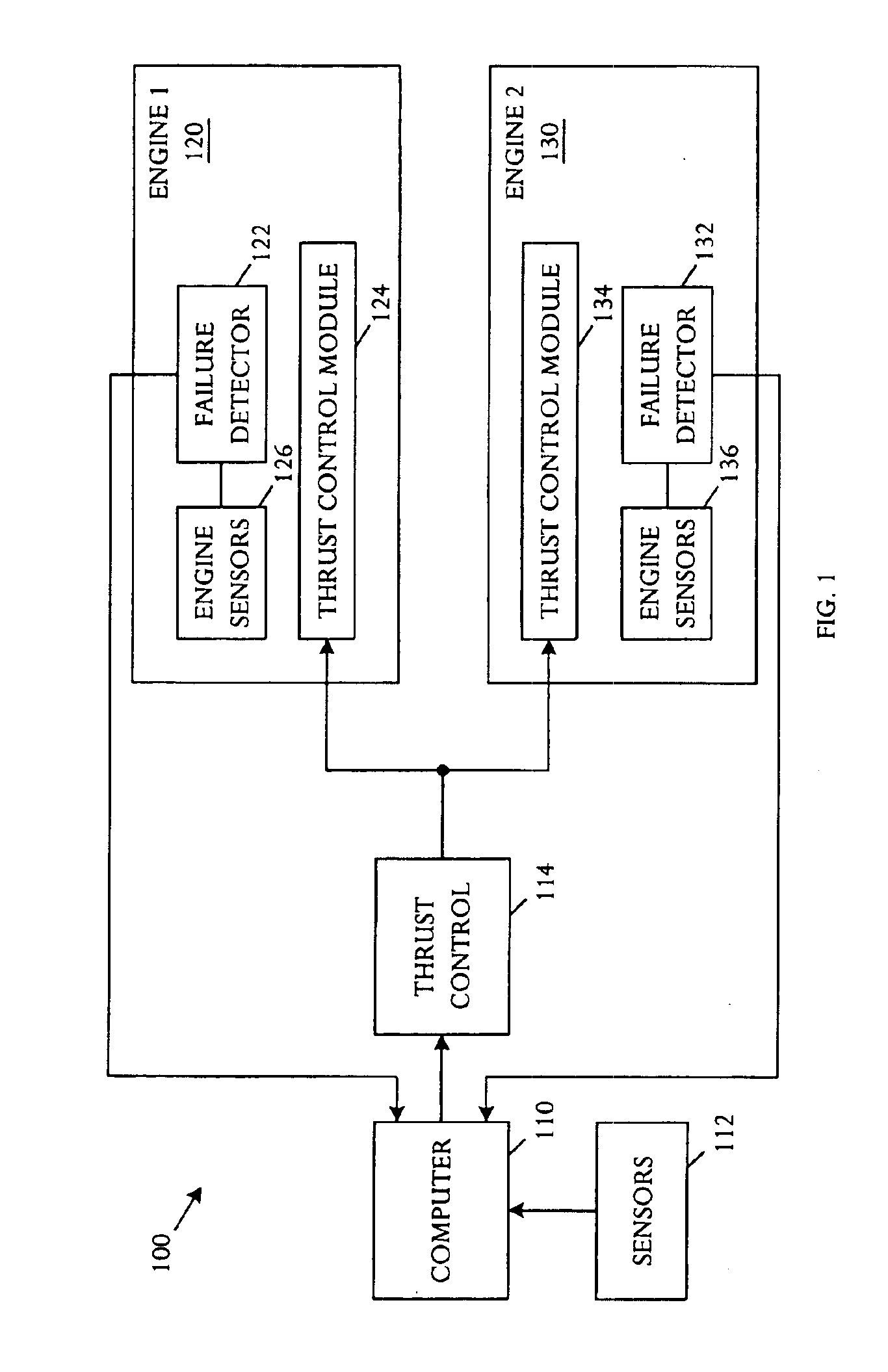
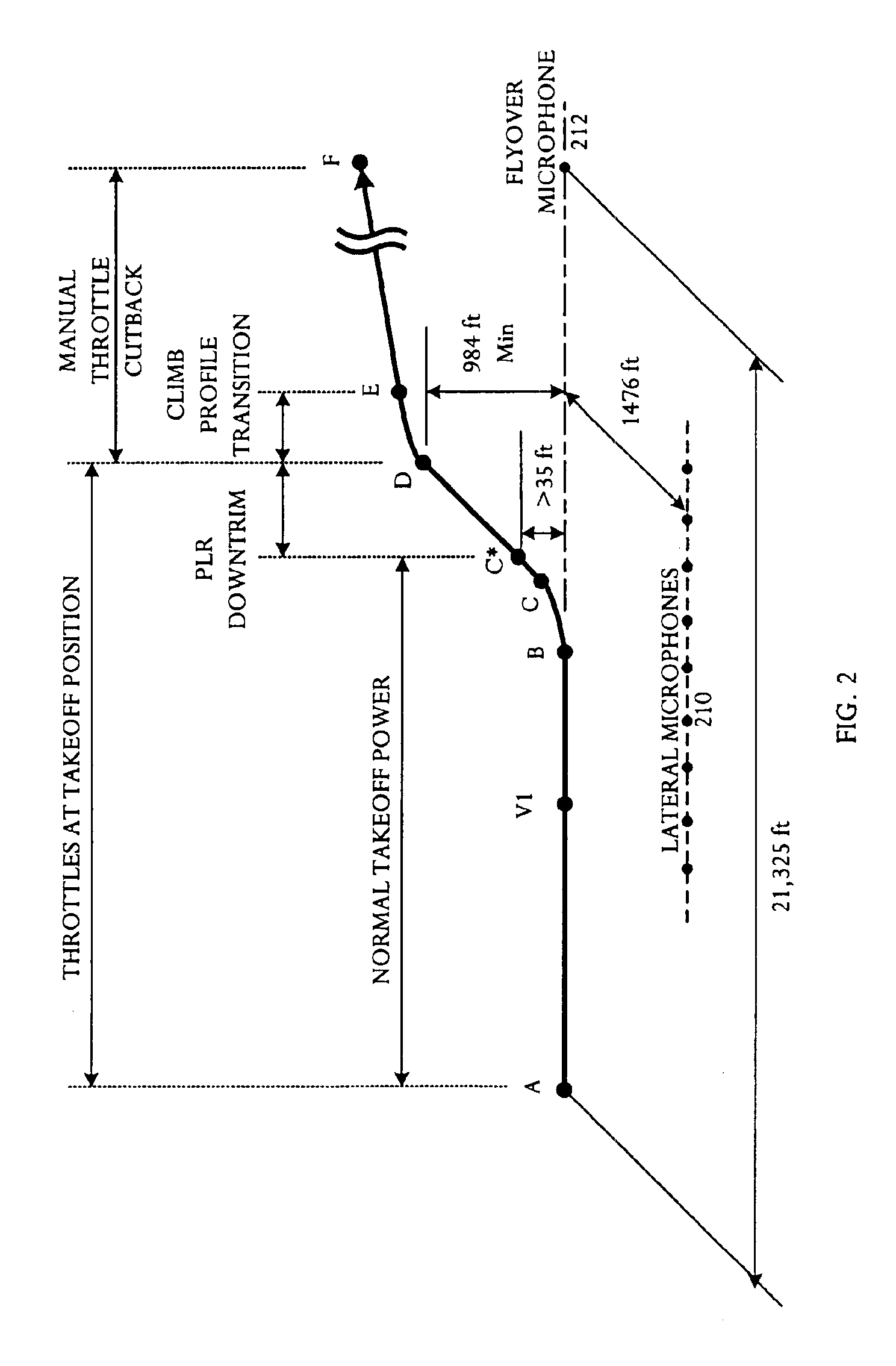
Automatic takeoff thrust management system
InactiveUS6880784B1Reduce and minimize takeoff noiseReduce thrustAircraft power plantsAircraft stabilisationFlight vehicleManagement system
An automatic takeoff thrust management system can be used in an aircraft with at least two engines. The management system comprises an aircraft status sensor or set of sensors capable of detecting establishment of takeoff climb conditions, and engine failure detectors respectively coupled to the at least two engines and capable of detecting engine failure. The management system further comprises thrust control modules respectively coupled to the at least two engines and capable of controlling the thrust of the engines, and a controller coupled to the aircraft status sensors, the engine failure detectors, and the thrust control modules. The controller reduces thrust by a selected amount upon detecting establishment of takeoff climb conditions and, if engine failure is detected, restoring thrust to an initial or a higher schedule.
Owner:SUPERSONIC AEROSPACE INT
Aerodynamically efficient lightweight vertical take-off and landing aircraft with pivoting rotors and stowing rotor blades
ActiveUS9694911B2Reduce drag in all flight modesPropellersEfficient propulsion technologiesJet aeroplaneVertical take off and landing
An aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using a set of wing mounted thrust producing elements and a set of tail mounted rotors for takeoff and landing. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to vertical takeoff with the rotors in a rotated, take-off attitude then transitions to a horizontal flight path, with the rotors rotated to a typical horizontal configuration. The aerial vehicle uses different configurations of its wing mounted rotors and propellers to reduce drag in all flight modes.
Owner:JOBY AERO INC
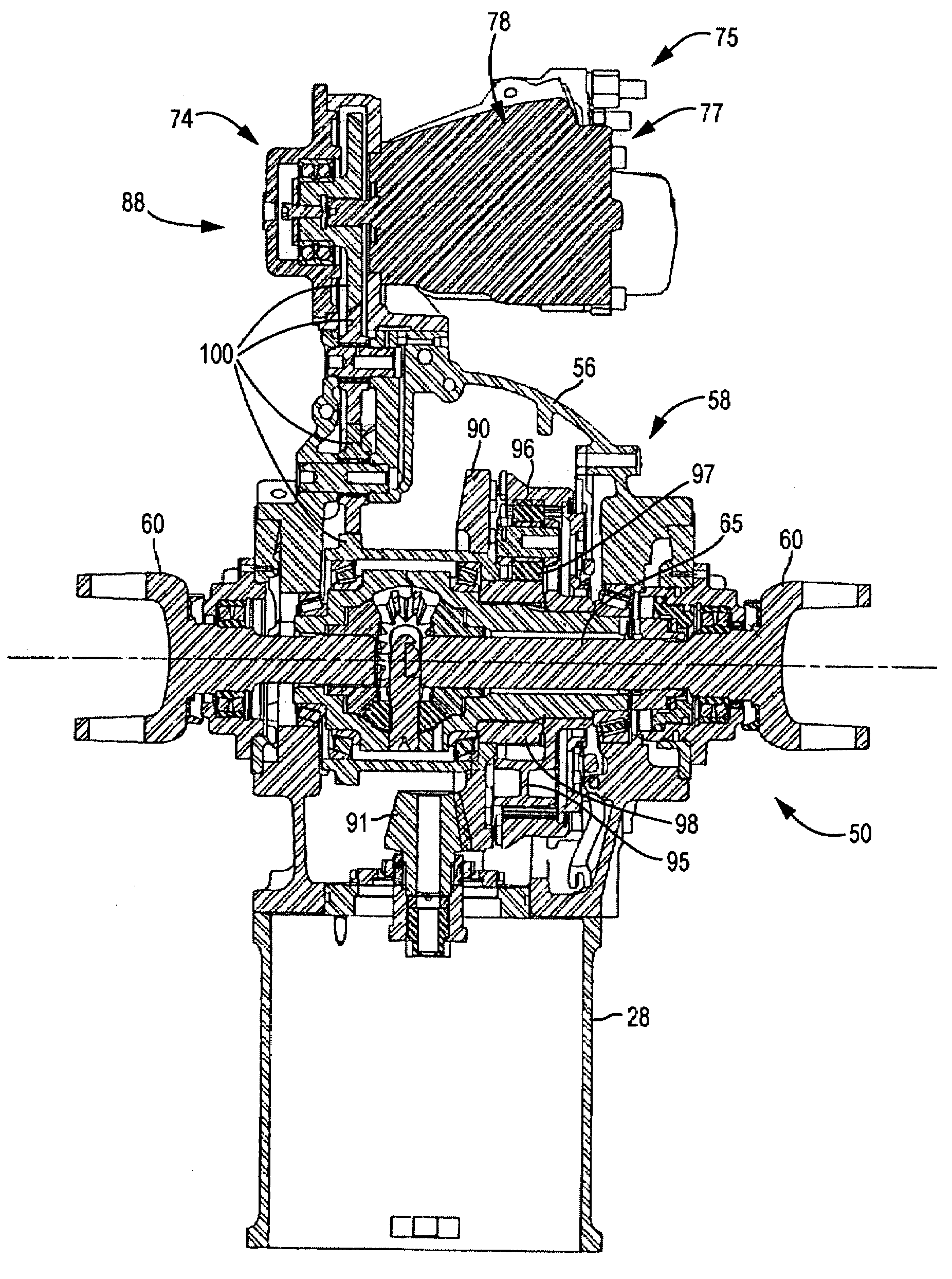
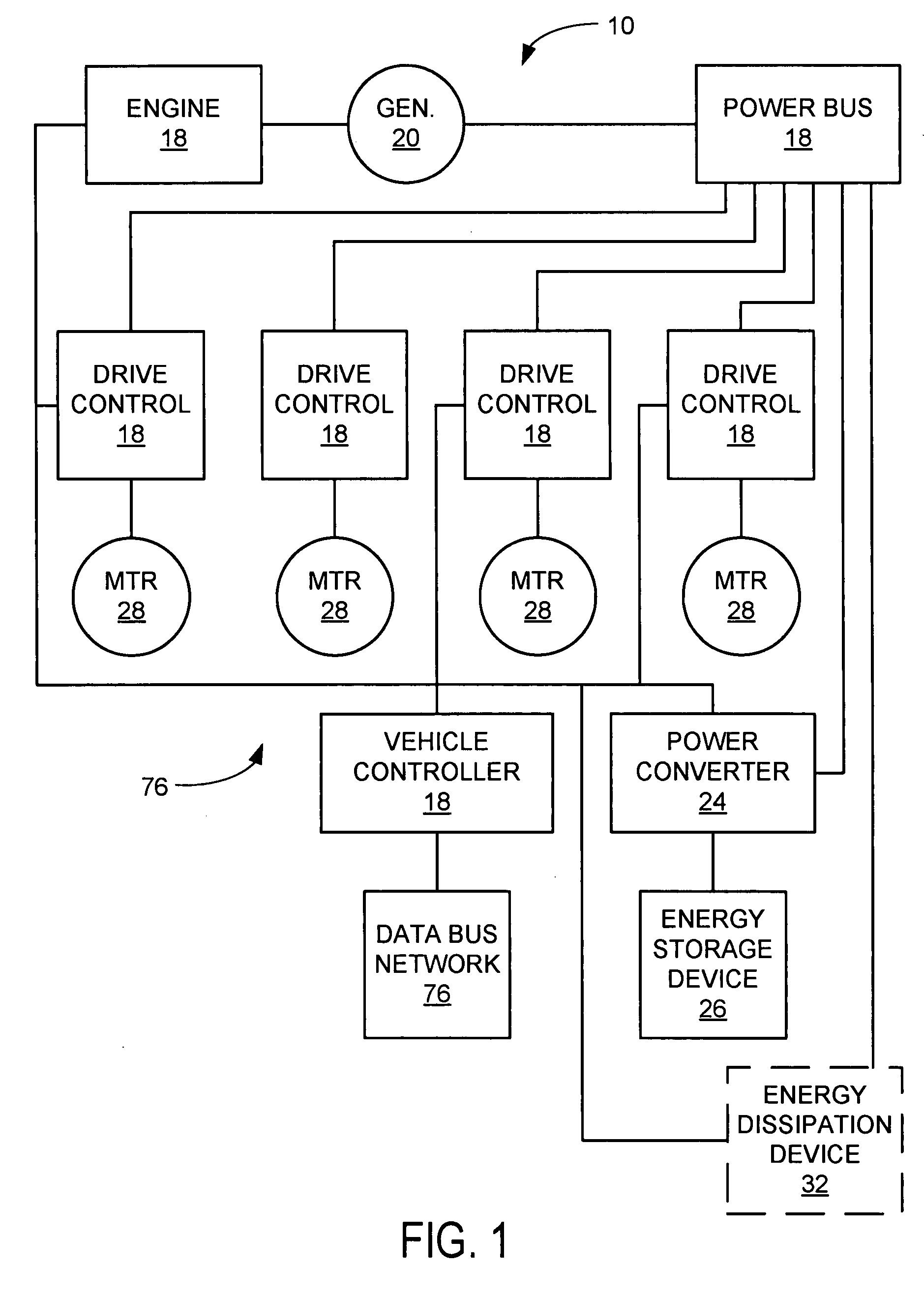
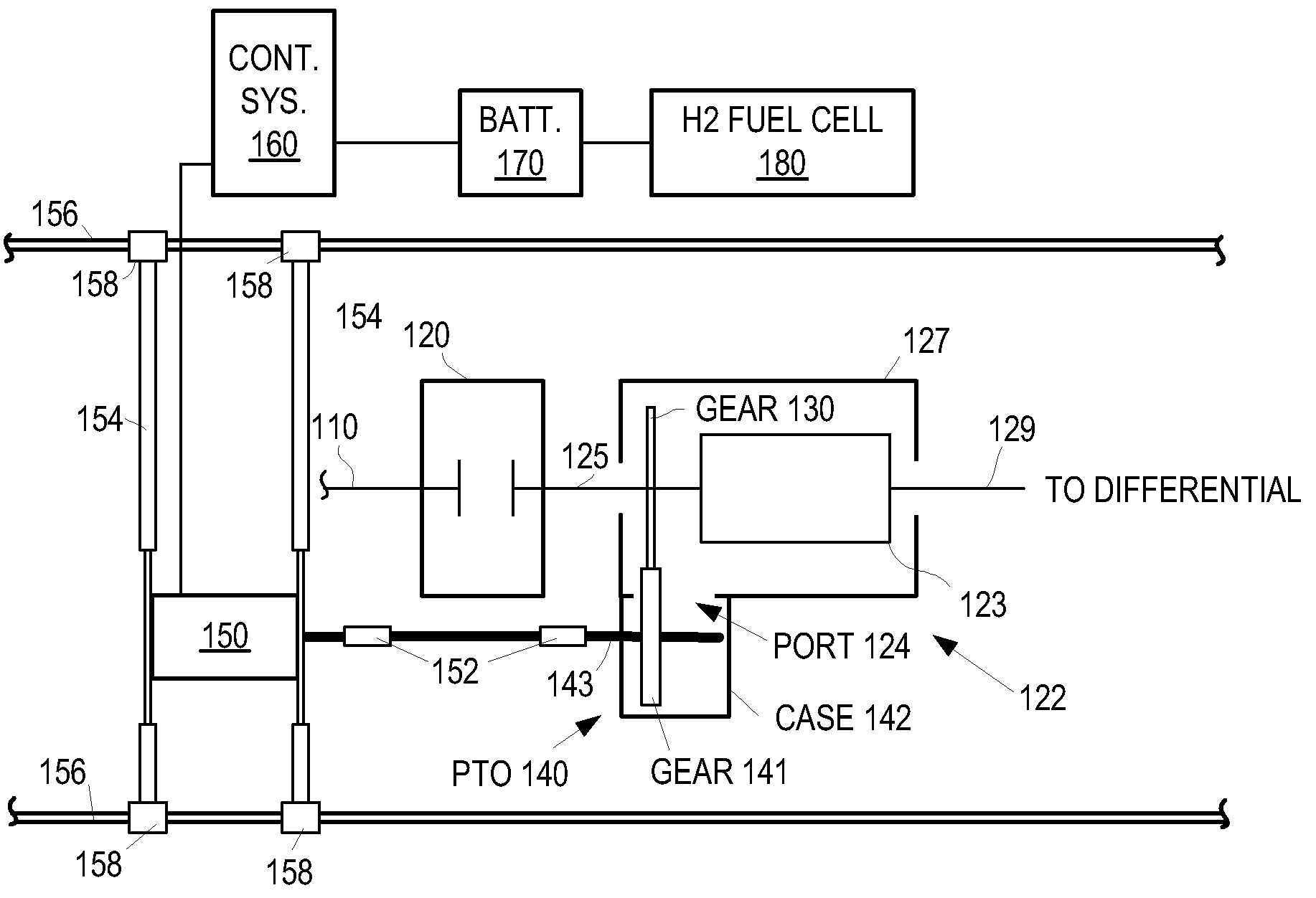
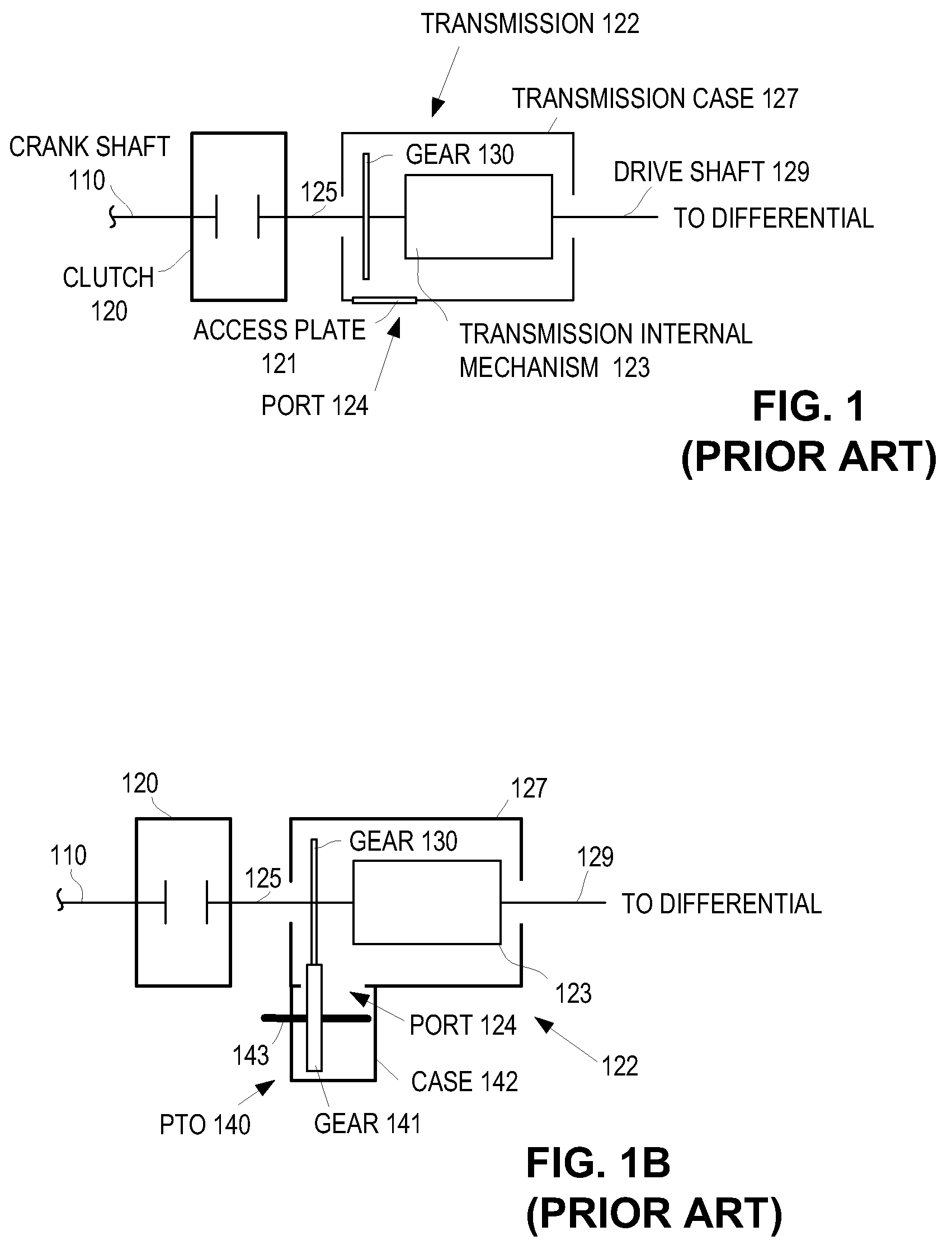
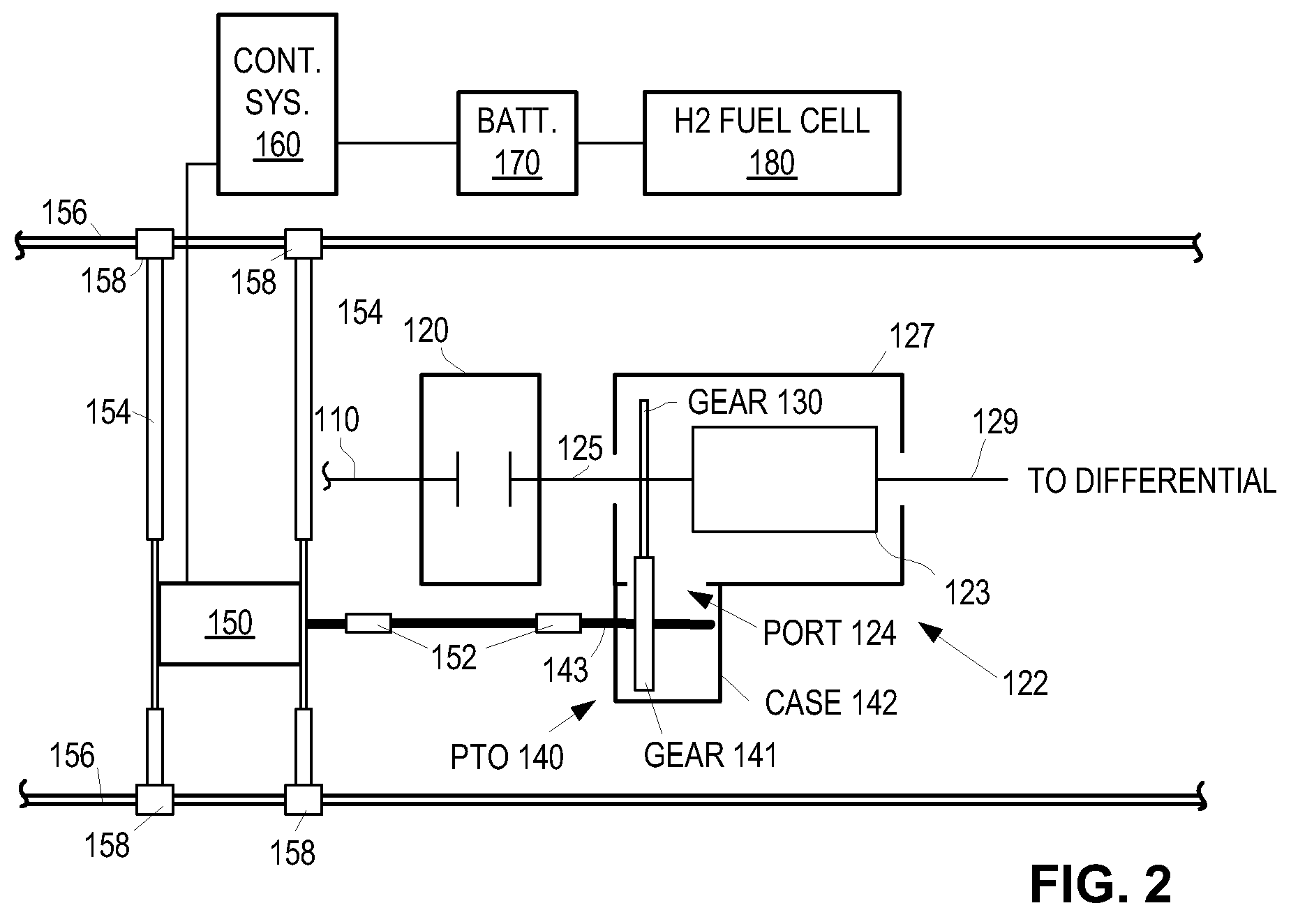
Power takeoff for an electric vehicle
A power take-off for an electric vehicle. The power take-off includes a variable speed electric motor for driving at least one wheel of the vehicle. A transmission, including a neutral state, coupled to the electric motor. An auxiliary output shaft is coupled to the transmission. When the transmission is in the neutral state, the auxiliary output shaft will operate at a speed independent of wheel speed and dependent on the electric motor speed. When the transmission is operably engaged in other than the neutral state, the auxiliary output shaft will operate at a speed related to both the electric motor speed and the wheel speed.
Owner:OSHKOSH CORPORATION
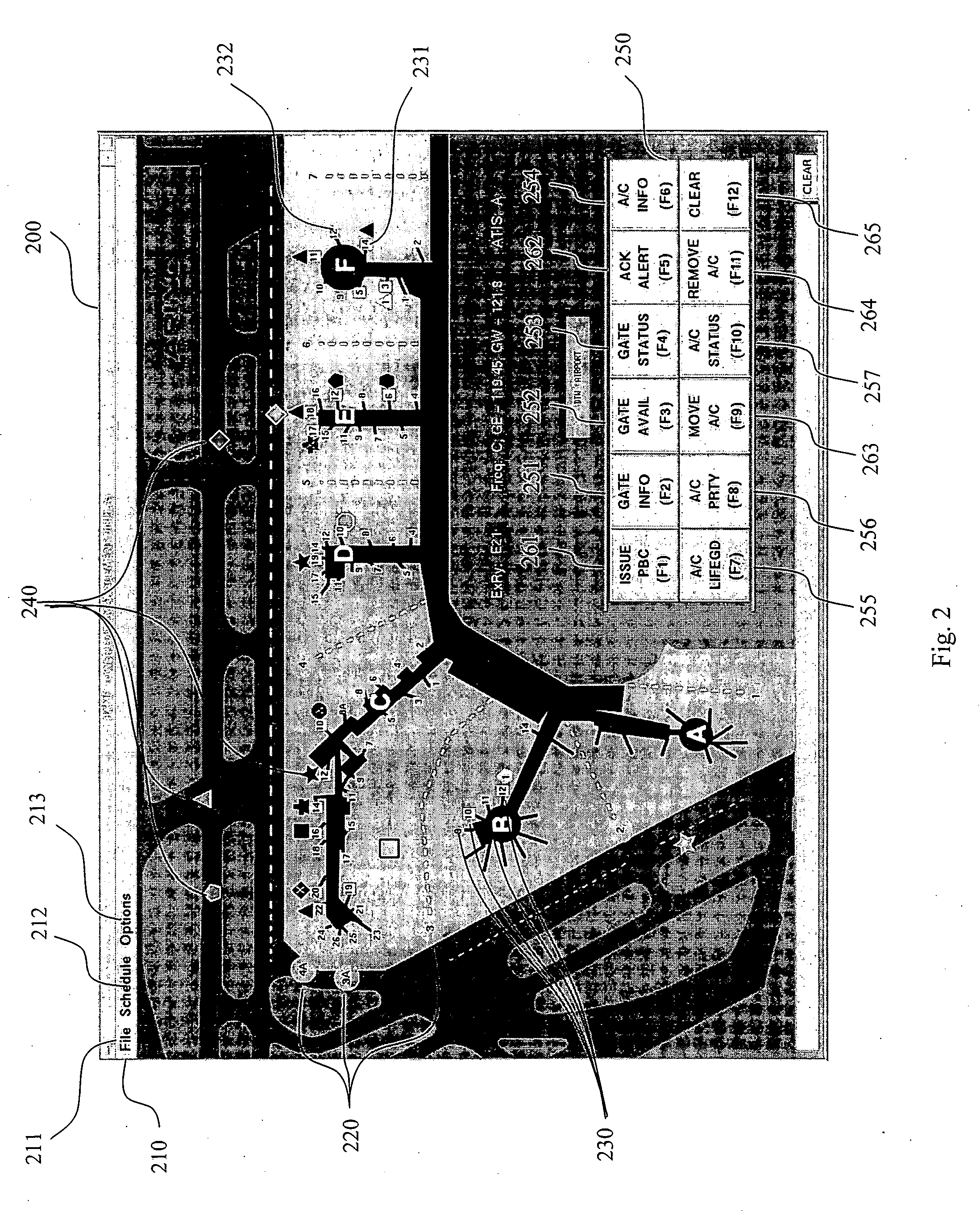
System and methods for automated airport air traffic control services
InactiveUS20180061243A1Extension of timeMaximized situational awarenessNatural language translationTelevision system detailsNetwork operations centerAirplane
A system and method for automating Air Traffic Control operations at or near an airport. as a complete standalone automated system replacing the need for a human controller to make aircraft movement decisions nor the need communicate with pilots, or as semi-automated, where a controller controls how the system operates. The system with related methods and computer hardware and computer software package, automatically manages manned aircraft, remote controlled UAV and airborne-able vehicles traffic at or near an airport, eliminates ATC-induced and reduce pilot-induced runway incursions and excursions, processes control messages related to aircraft or Pilots, communicates with Pilot over ATC radio frequency, receives aircraft positions, communicates control messages with the aircraft avionics, provides pilots a dynamic map with continuous display of nearby traffic operations, shows clearance and information related to runway operations, warns pilot of runway conditions and turbulence from other operations, warns when landing gear is not locked, displays the pilot emergency exits during takeoff roll, shows the pilot when and where to exit from the runway, shows the pilot where and when to cross a junction, calculates and displays pilot optimal speed and timing on taxiways and junctions for saving fuel, calculates congestions, calculates best taxiway routes, calculates when aircraft can cross a runway, provides directives and information to pilot over CPDLC display or dynamic map for airside operations, alerts and triggers breaks of the aircraft on wrong path or when hold-short bar is breached, displays emergency personnel with routing map and final aircraft resting position for emergency operations, takes over an aircraft operation when aircraft is hijacked or deviates from the flight plan, provide standalone or manned Remote Tower functionality, Records and retains all information related to airport airside operations including aircraft positions and conditions from sensors and reports for runways, junctions and taxiways, Records and retains aircraft data and cockpit voice to ground-based servers to eliminate black-box requirements, calculate future weather and airport capacity from aircraft at or nearby airport, coordinates handoff operations with other ATC positions, interfaces with ACDM systems, airport operations center, flow center and network operations center.
Owner:IATAS AUTOMATIC AIR TRAFFIC CONTROL
System, method, and apparatus for hybrid dynamic shape buoyant, dynamic lift-assisted air vehicle, employing aquatic-like propulsion
InactiveUS20080087762A1Economic securityEasy to operateNon-rigid airshipsDrag reductionMorphingMarine propulsion
A method and system for air flight is shown. The blended lifting body system includes a lift module, a propulsion module, a payload module and a control system. A conventional control system morphs the other modules through variable buoyant lift, internal structures and a flexible exterior, and varies bio-inspired oscillation in the propulsion module in order to facilitate takeoff, flight and landing. The hybrid dynamic / morphing shape buoyant, dynamic lift-assisted (hybrid) air vehicle, employing aquatic-like (e.g. fin) propulsion was discussed, with many variations and examples.
Owner:HOLLOMAN RICHARD +1
Remotely controlled vtol aircraft, control system for control of tailless aircraft, and system using same
A manned / unmanned aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using the same set of engines for takeoff and landing as well as for forward flight. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to takeoff with the wings in a vertical as opposed to horizontal flight attitude which takes off in this vertical attitude and then transitions to a horizontal flight path. An aerial vehicle which controls the attitude of the vehicle during takeoff and landing by alternating the thrust of engines, which are separated in at least two dimensions relative to the horizontal during takeoff, and which may also control regular flight in some aspects by the use of differential thrust of the engines. A tailless airplane which uses a control system that takes inputs for a traditional tailed airplane and translates those inputs to provide control utilizing non-traditional control methods.
Owner:SINHA PRANAY +5
System for automatic takeoff and landing by interception of small uavs
ActiveUS20150266575A1Facilitate automatic capture and launchPrecise positioningArrester hooksArresting gearLifting capacityFlight vehicle
A system for facilitating automated landing and takeoff of an autonomous or pilot controlled hovering air vehicle with a cooperative underbody at a stationary or mobile landing place and an automated storage system used in conjunction with the landing and takeoff mechanism that stores and services a plurality of UAVs is described. The system is primarily characterized in that the landing mechanism is settable with 6 axes in roll, pitch, yaw, and x, y and z and becomes aligned with and intercepts the air vehicle in flight and decelerates the vehicle with respect to vehicle's inertial limits. The air vehicle and capture mechanism are provided with a transmitter and receiver to coordinate vehicle priority and distance and angles between landing mechanism and air vehicle. The landing and takeoff system has means of tracking the position and orientation of the UAV in real time. The landing mechanism will be substantially aligned to the base of the air vehicle. With small UAVs, their lifting capacity is limited. Reducing sensing and computation requirements by having the landing plate perform the precision adjustments for the landing operation allows for increased flight time and / or payload capacity.
Owner:BORKO BRANDON
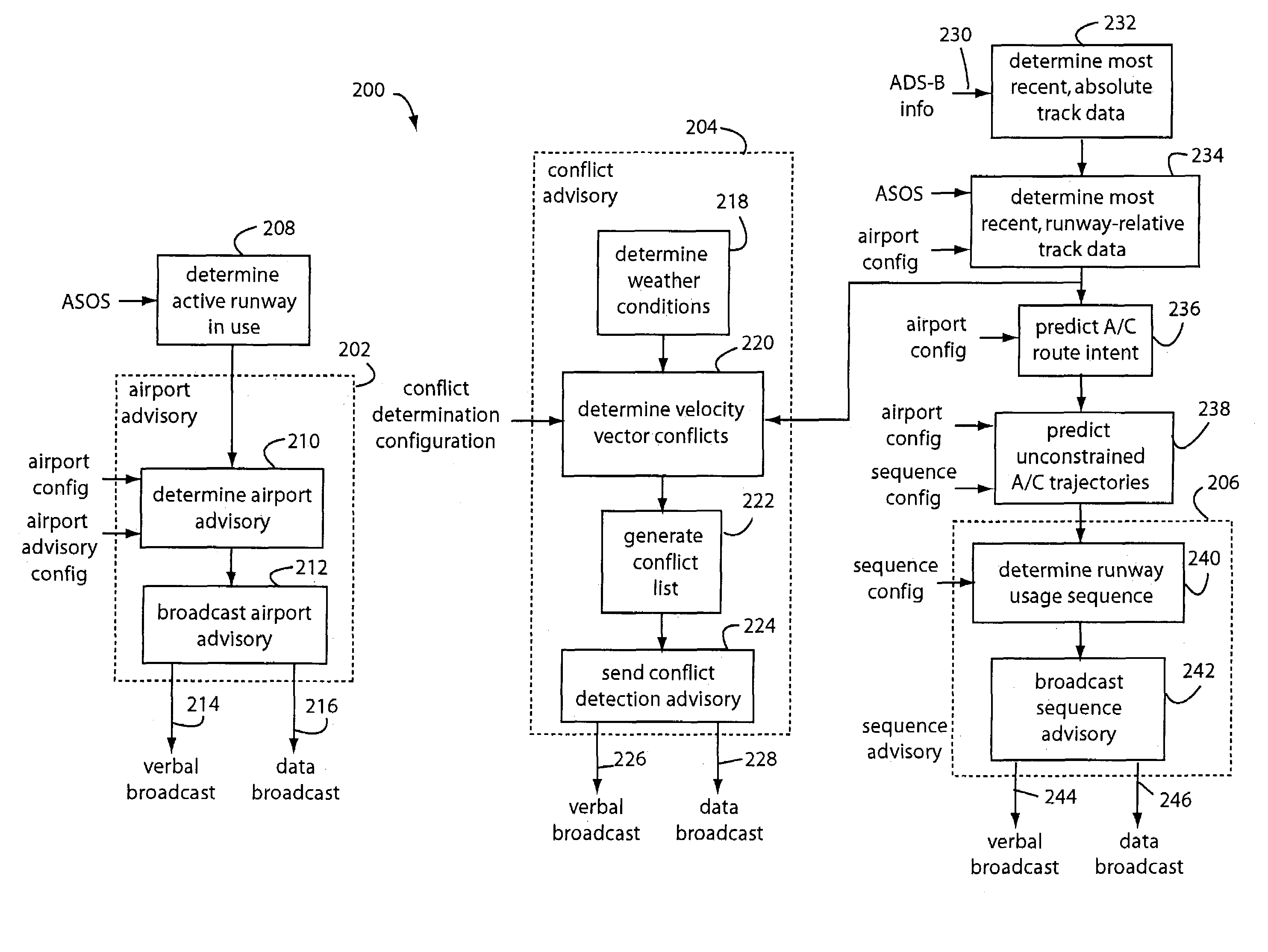
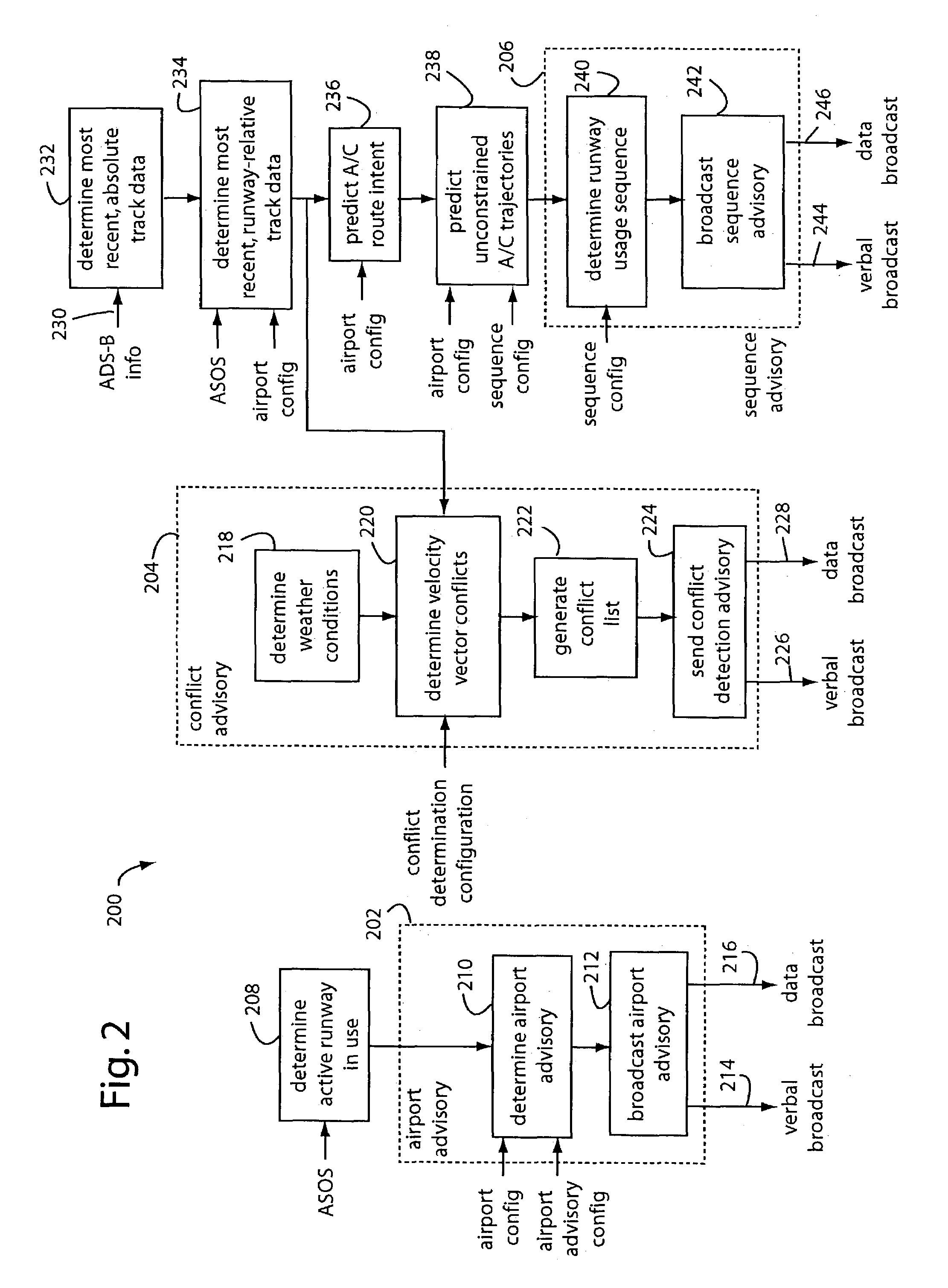
Smart airport automation system
InactiveUS6950037B1Enhances pilot situation awarenessIncrease awarenessAnalogue computers for trafficNavigation instrumentsObjective informationLighting system
A smart airport automation system includes a subsystem that inputs weather and airport configuration data to determine an active runway in use and an airport state. Another subsystem inputs aircraft position and velocity data from available surveillance sources, known flight-intent information, and past aircraft trajectories to project future aircraft unconstrained trajectories. A third subsystem uses the projected trajectories and aircraft intent to determine desired landing and takeoff sequences, and desired adjacent aircraft spacing. A fourth subsystem uses such information to predict potential aircraft conflicts, such as a loss of acceptable separation between adjacent aircraft. A fifth subsystem packages the weather, airport configuration, aircraft state, desired landing / takeoff sequence, and potential conflict detection into a verbal advisory message that is broadcast on a local common radio frequency. A sixth subsystem uses the projected trajectory information to control the runway and taxiway lighting system.
Owner:ARCHITECTURE TECH +1
Power Line Takeoff Clamp Assembly
ActiveUS20100013457A1Measurement using ac-dc conversionBase element modificationsWireless transceiverTransceiver
In a power line takeoff clamp assembly and method of use thereof an electrical power distribution line is clamped to a body of the clamp assembly. A power takeoff supported by the body clamped to the power line generates direct current from alternating current flowing in the power line. One or more sensors supported by the body clamped to the power line sense one or more values related to an electrical current flowing in a power line. A wireless transceiver supported by the body clamped to the power line communicates data regarding the one or more sensed values. Each sensor and the wireless transceiver utilize direct current generated by the power takeoff for the operation thereof.
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
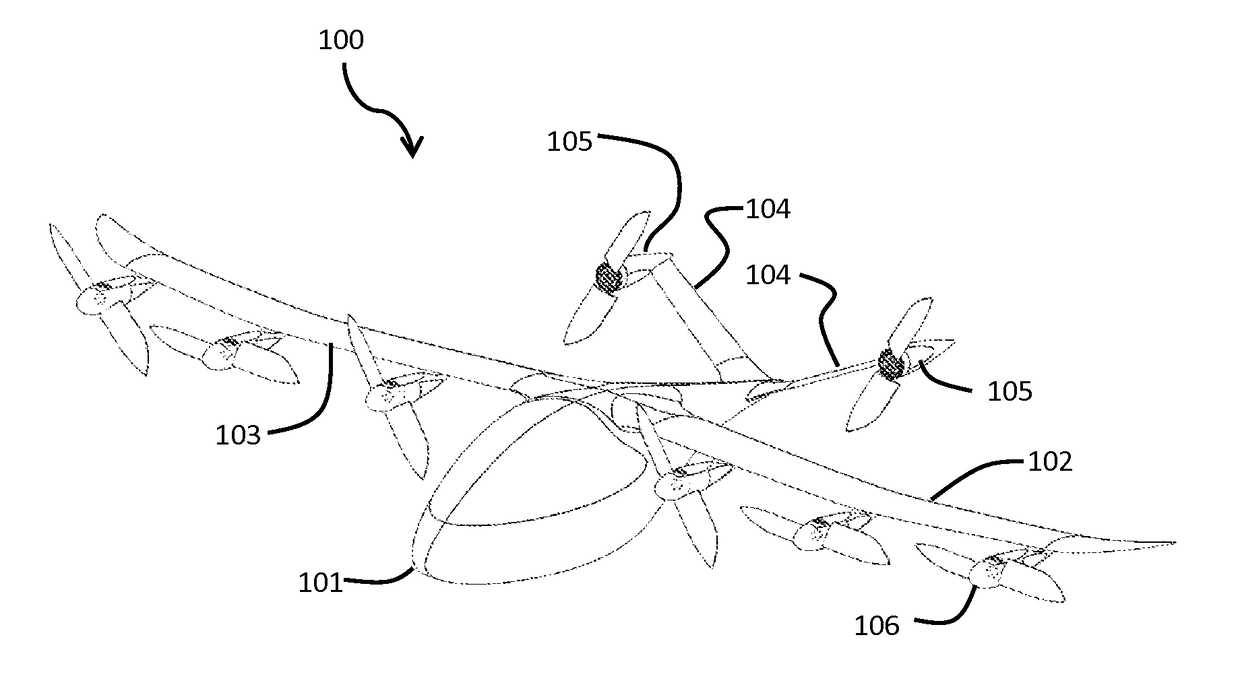
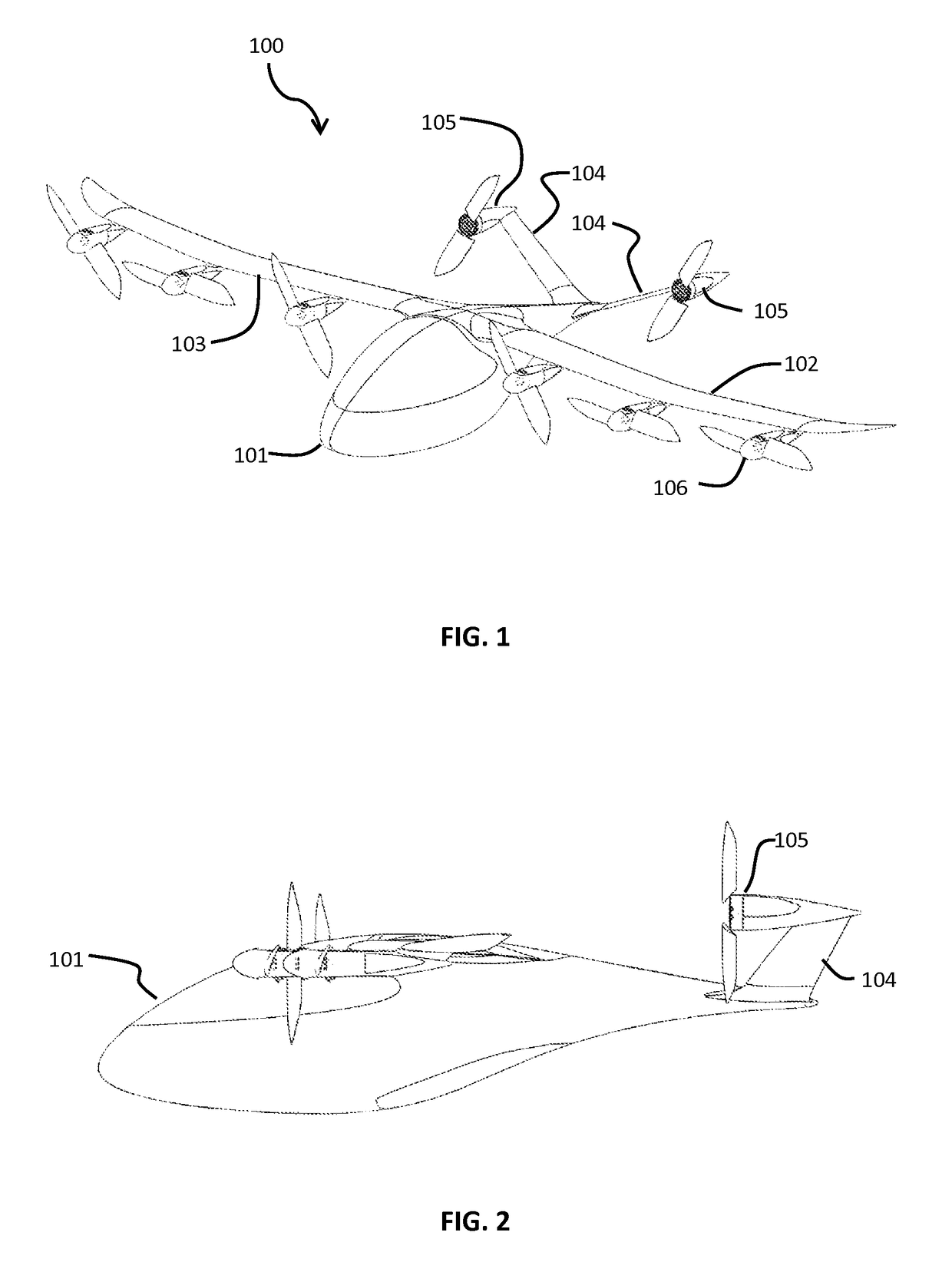
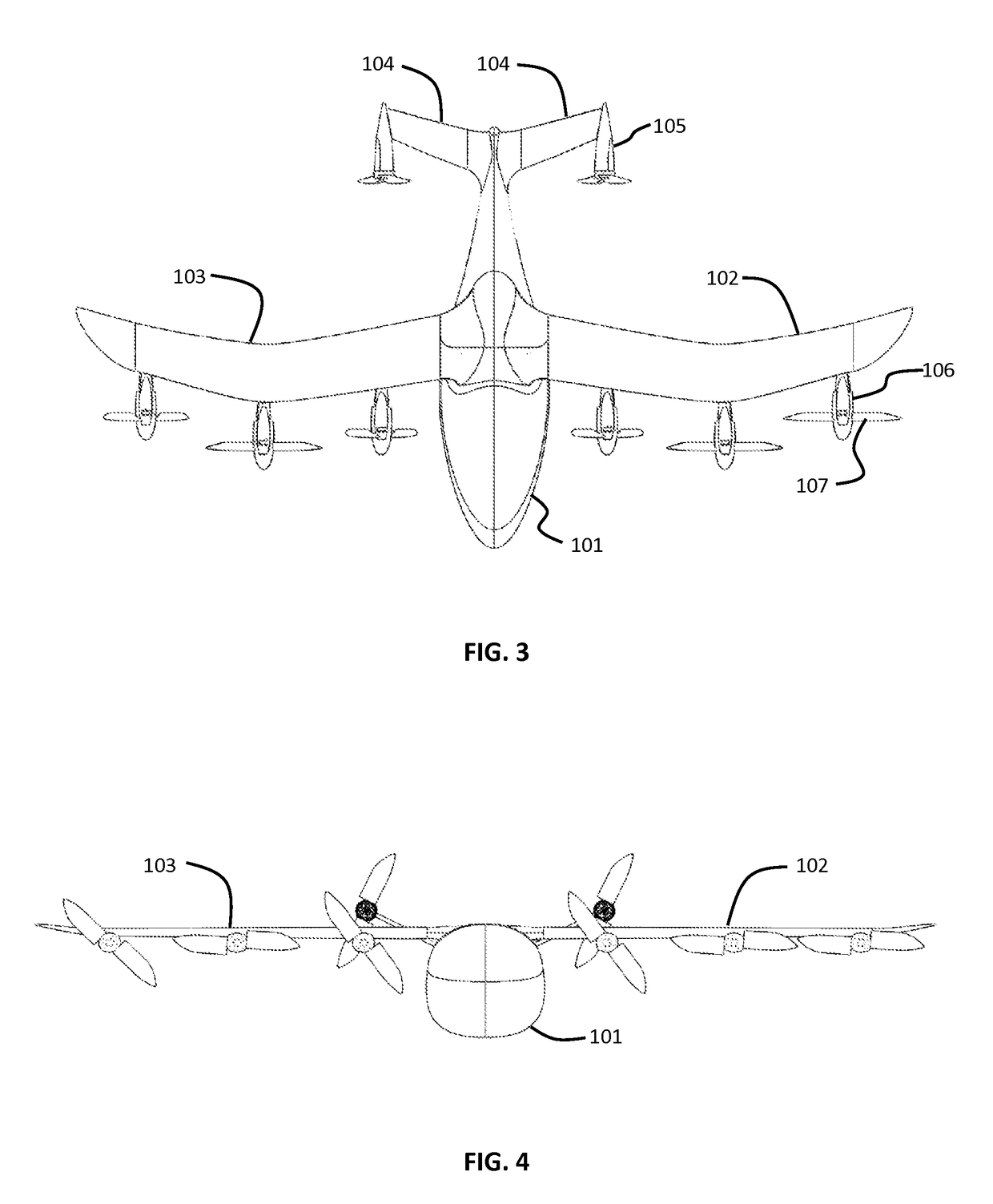
High Performance VTOL Aircraft
ActiveUS20150344134A1Maximize effective thrustMaximize useRemote controlled aircraftWing adjustmentsJet aeroplaneEngineering
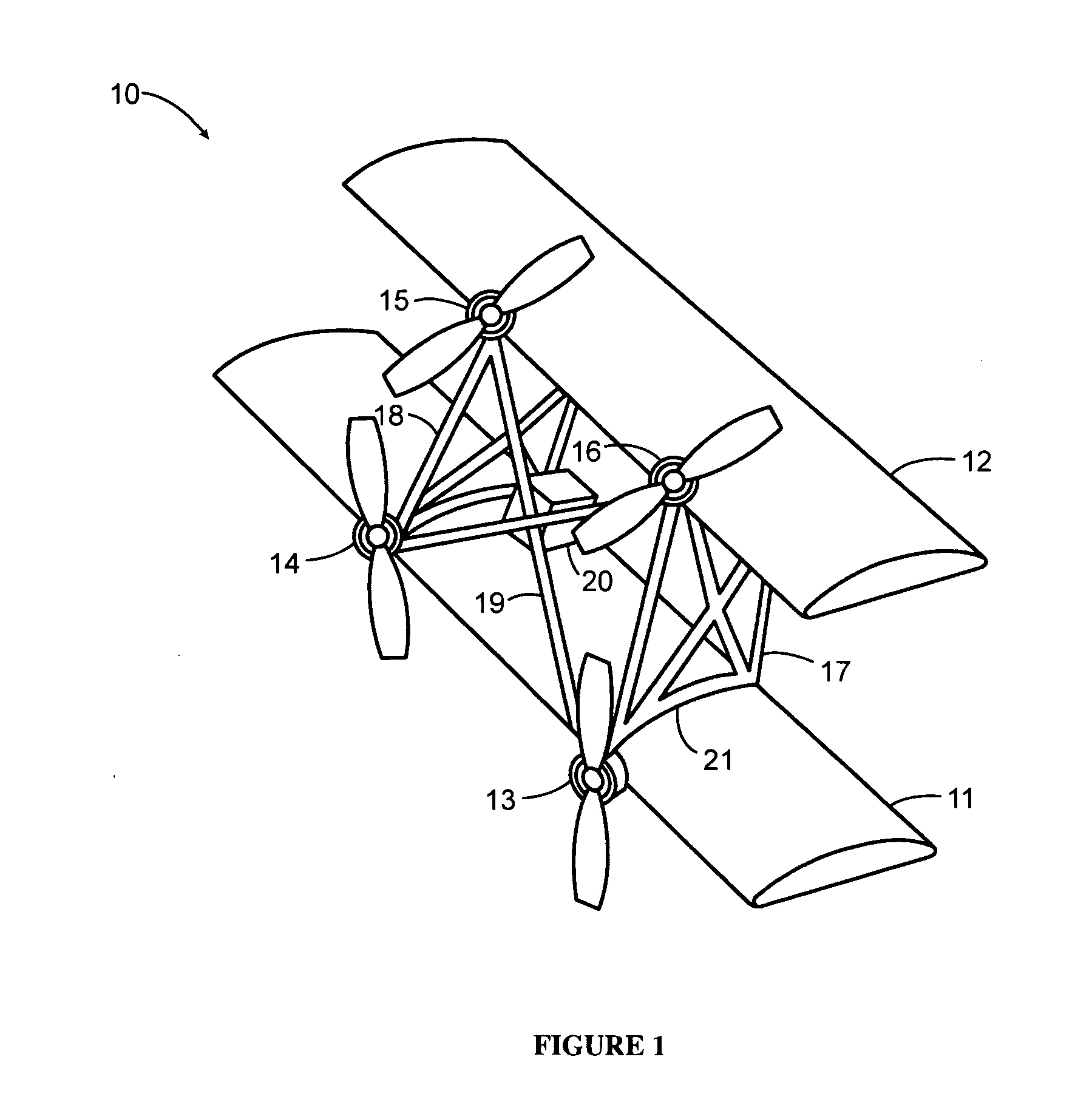
The present disclosure relates to a high performance Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL) aircraft for executing hovering flight, forward flight, and transitioning between the two in a stable and efficient manner. The VTOL aircraft provides a highly stable, controllable and efficient VTOL aircraft. The preferred comprises: (1) a pusher propeller configuration with strategic placement which maximizes the effective use of thrust, (2) four propellers which allow for the highly-controllable and mechanically simple control methods used in multirotor aircraft, (3) electric motors which create mechanically simple, lightweight and reliable operation, (4) and a tandem wing configuration which is stable, controllable and efficient in both hovering and forward flight. The VTOL aircraft is capable of full runway, short runway or vertical takeoffs or landings, having unobstructed forward view for camera and sensor placement; and providing a compact, mechanically simple and low-maintenance VTOL aircraft design.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Aircraft capable of vertical takeoff
ActiveUS20160236774A1Good hovering characteristicHigh travel flight speedUnmanned aerial vehiclesPower plant typeJet aeroplanePropeller
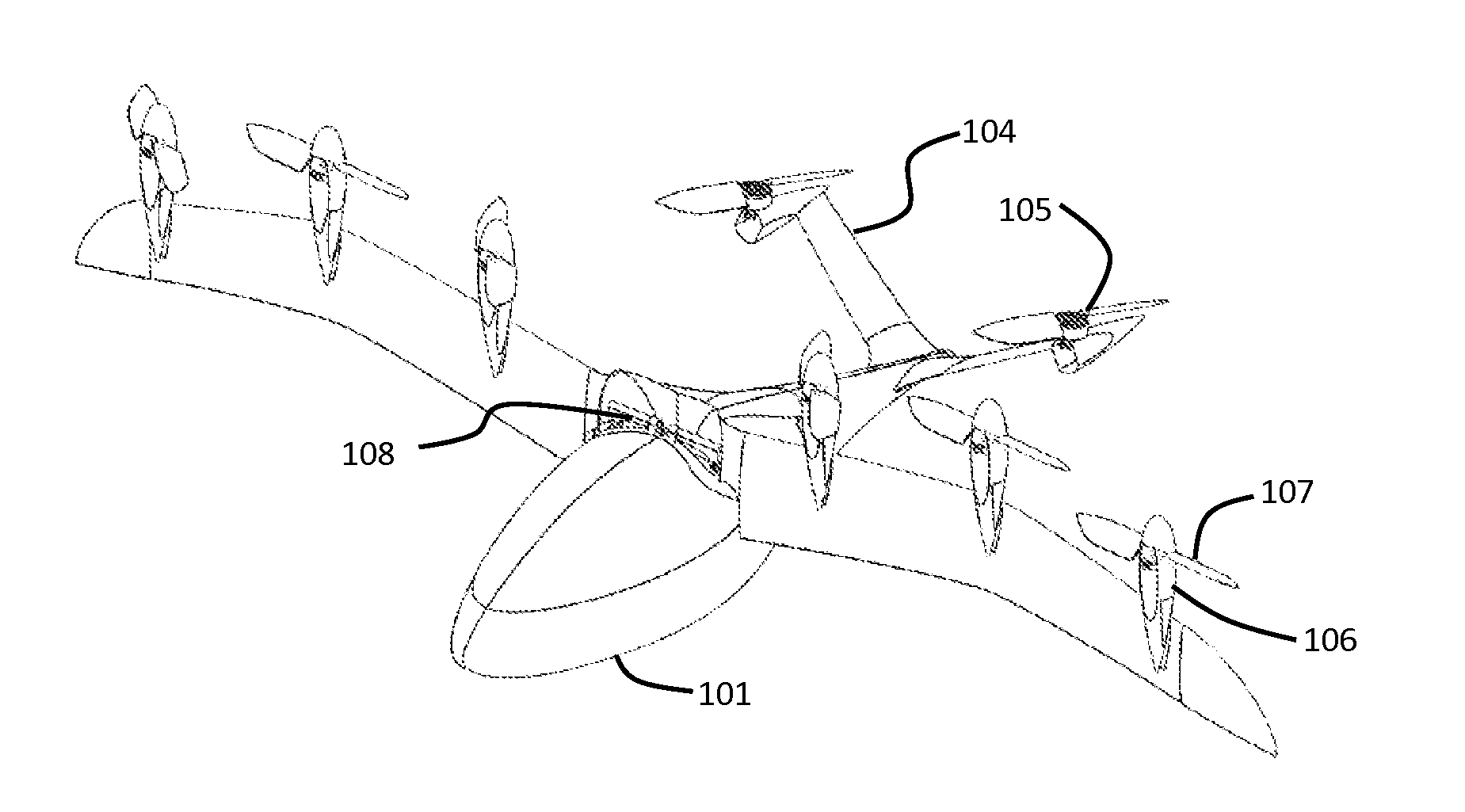
An aircraft has a bearing structure, the bearing structure having at least one central fuselage and two pylons each situated at a distance laterally from the fuselage. In addition, the aircraft has a wing structure, at least four hub rotors, and at least one thrust drive. Each hub rotor is fastened to the bearing structure, has a propeller having two propeller blades, and produces, through rotation of the propeller, an upward drive force acting in the vertical direction on the aircraft. The thrust drive is produces a thrust force acting in the horizontal direction on the bearing structure. The pylons each have two hub rotors, the hub rotors being configured to arrest respective propeller blades of a hub rotor in a position relative to the pylons. In the arrested position, the propeller blades of a hub rotor do not extend beyond the outer dimensions of the pylons.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Counter-quad tilt-wing aircraft design
InactiveUS20050230519A1Halved in cross-sectionReduced wake turbulence hazardVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftAviationLevel flight
The invention consists of a specific, matched arrangement of aeronautical elements which (1) eliminates aerodynamic interference of, and (2) adds variable-cycle propulsion to, the level flight mode of a four-propulsor tilt-wing VTOL (vertical takeoff & landing) aircraft, without an additional element of variable geometry. This is achieved by configuring the components such that the rotor planes on either side pass through each other in the transition maneuver to form adjacent, close-coupled, counter-rotating pairs in level flight.
Owner:HURLEY FRANCIS X
Aircraft kinetic landing energy conversion system
ActiveUS20080258014A1Increase braking powerAvoid heatArresting gearRailway vehiclesElectric potential energyElectric generator
A kinetic energy system which transfers the kinetic landing into recoverable electric energy for an aircraft. The system incorporates at least one wheel supporting the aircraft for landing and takeoff coupled with a dynamic functioning motor / generator mounted to and operated by rotation of the wheel to create electrical energy from kinetic energy. An induction shoe structurally connected to the aircraft and electrically connected to the motor / generator, which shoe draws the converted energy from the generator which supplies the load created by the inductively coupled induction shoe to the an ancillary load provided by the resistive heat sink on by the capacitor storage bank. This provides the generator circuit for conversion of the rotational energy of the wheel to electrical energy and creates braking drag. In exemplary embodiments, the system employs an energy storage system acting as the load to store electrical potential energy created by the generator. Additionally, the generator is employable as a motor, receiving energy from the storage system for traction power to the associated aircraft wheel. An induction grid or a surface mounted conductive layer mounted into or onto a runway is employed for transferring energy to and from the motor / generator.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
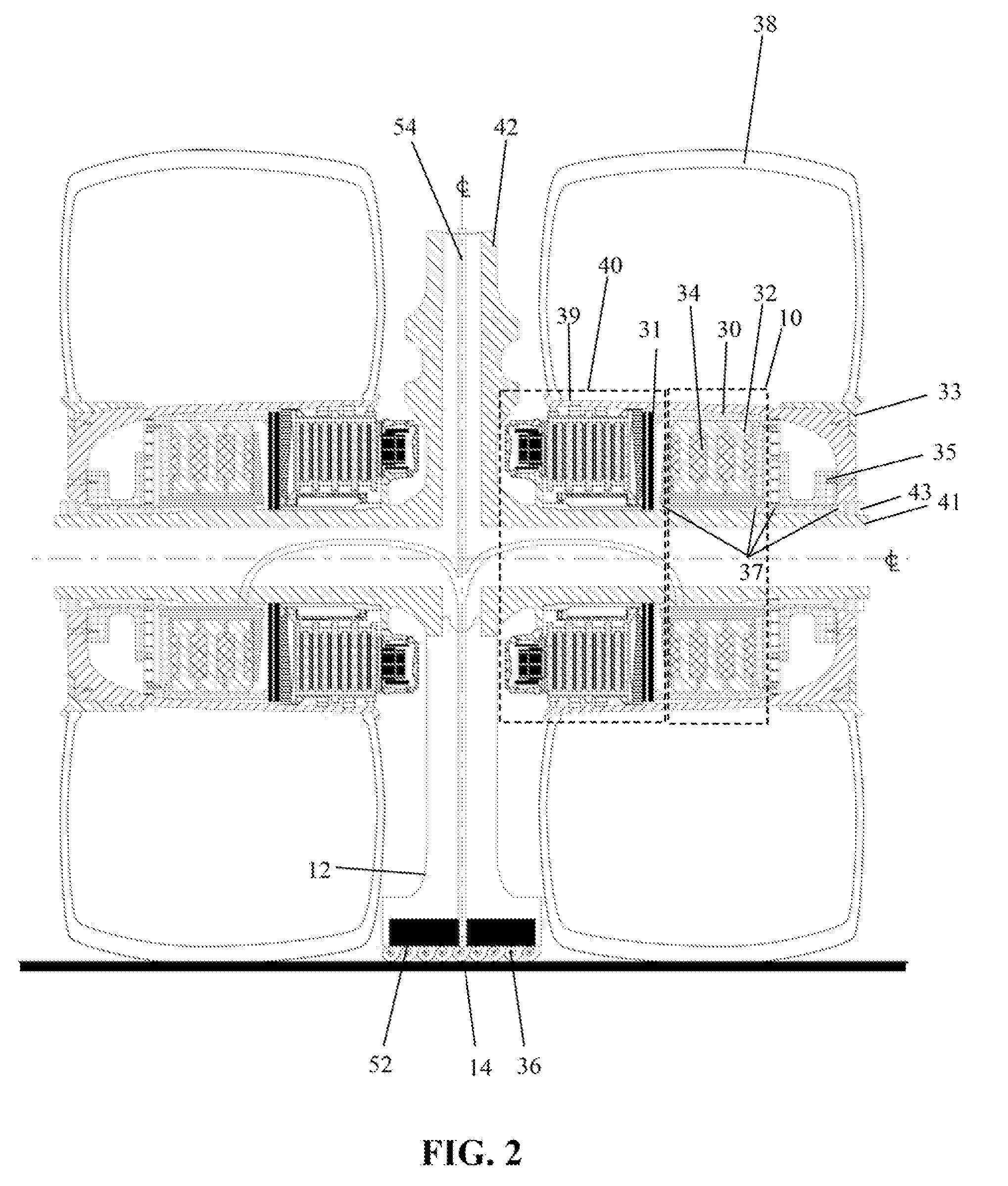
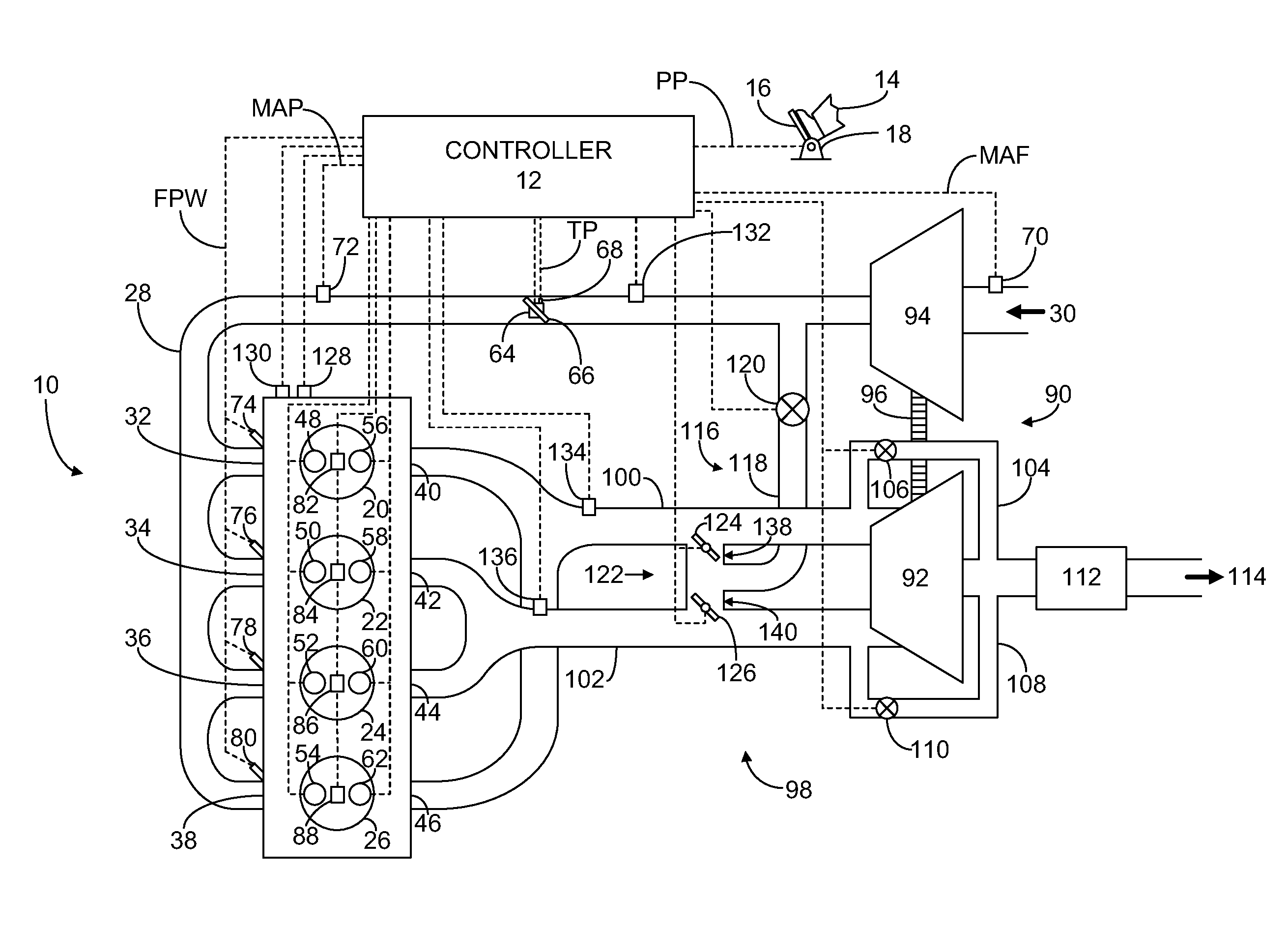
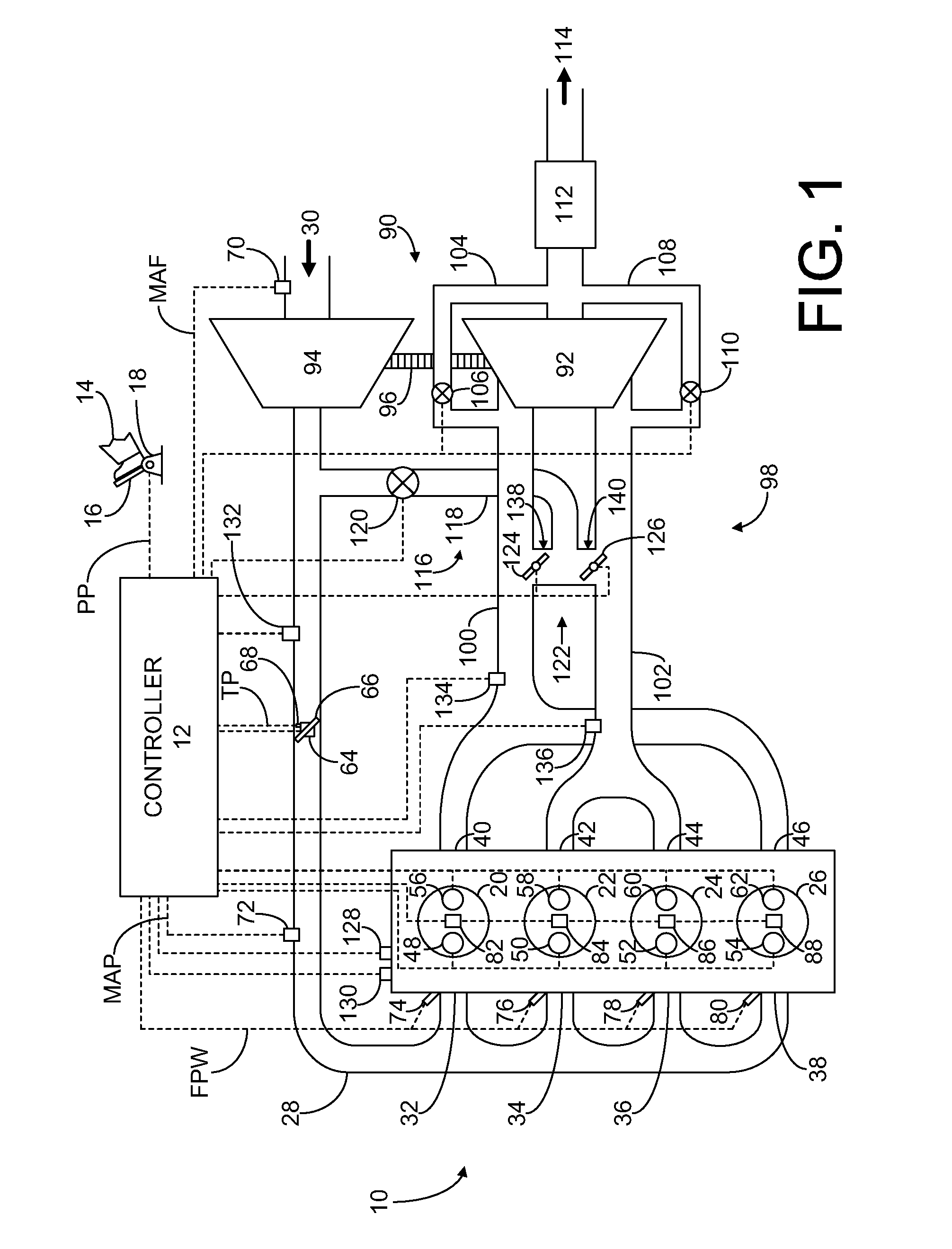
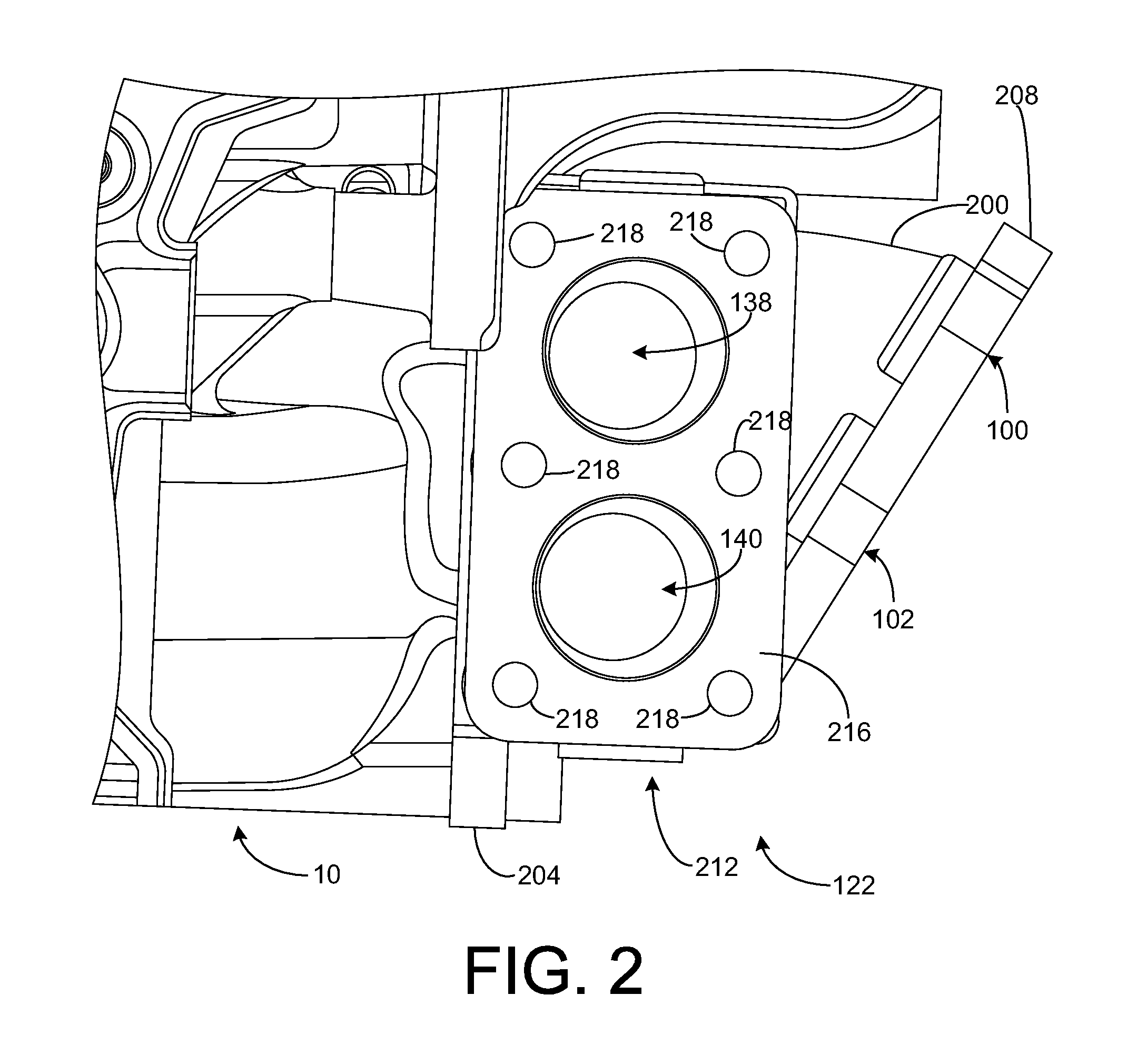
Twin scroll turbocharger with egr takeoffs
ActiveUS20110302917A1Improve efficiencyLow efficiencyValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust fumesExhaust gas recirculation
Systems and methods for operating a twin scroll turbocharged engine with a junction configured to selectively control exhaust gas delivery to an exhaust gas recirculation system and a twin scroll turbine are provided.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Aircraft with Integrated Lift and Propulsion System
ActiveUS20100193644A1Reduce the amount requiredAircraft navigation controlWing shapesVertical take off and landingAirplane
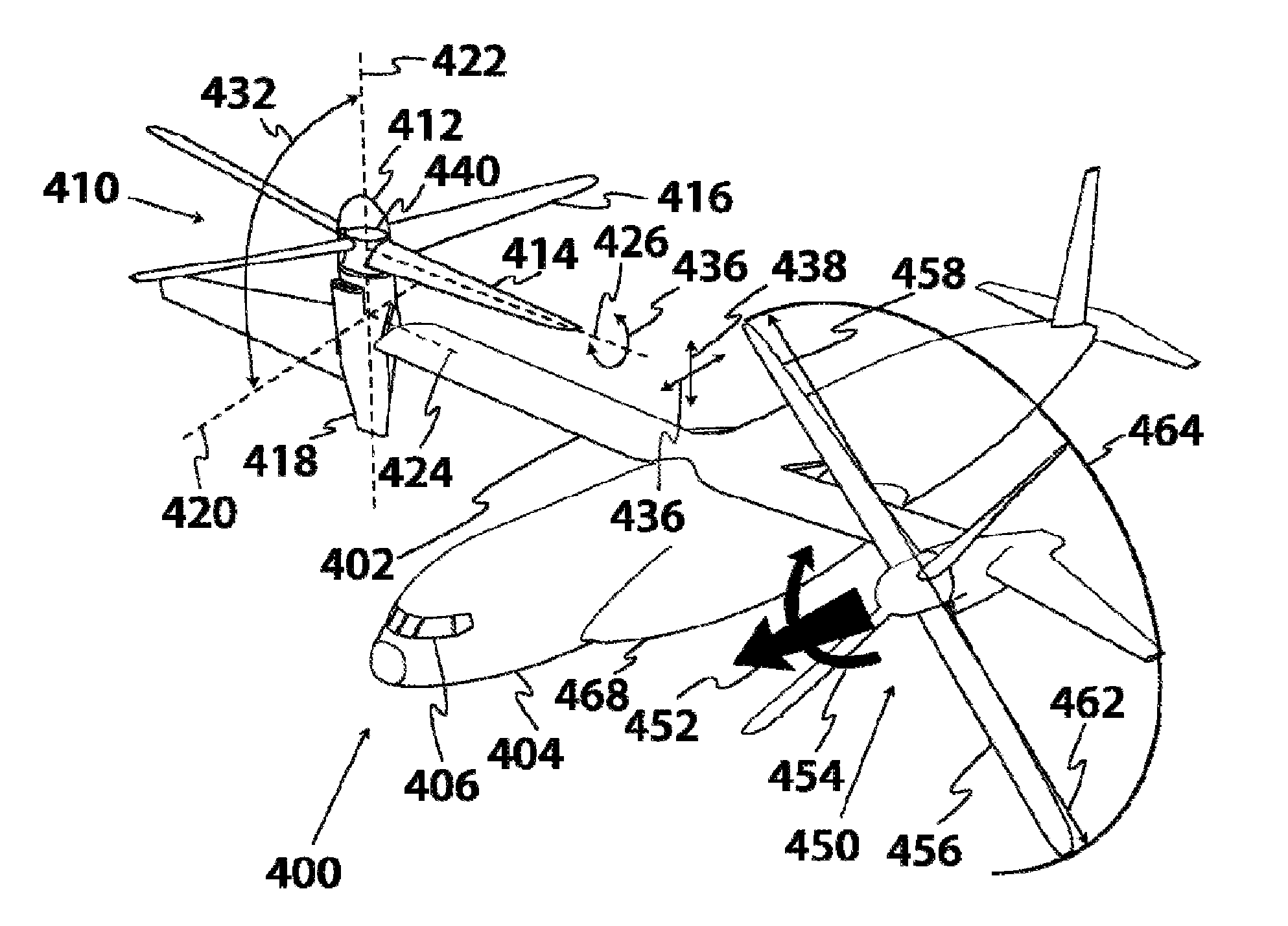
A vertical take off and landing (VTOL) aircraft is designed to be so efficient that it can be commercially competitive with runway dependent aircraft operating in a range of 100 to 1000 miles. Improvements include a high efficiency tilting rotor and wing design that enable both vertical takeoff and efficient high speed cruising, a high aspect ratio wing, and a variable speed propulsion system that is efficient in both hover and cruise flight. Preferred aircraft use thin inboard and outboard wings, thin rotor blades, and use efficient lightweight design to achieve unusually low empty weight fraction. Inventive methods include utilization of advanced design and analysis techniques, which allow for accurate prediction of an aircraft's physical behavior.
Owner:KAREM ABE
Vertical take off and landing autonomous/semiautonomous/remote controlled aerial agricultural sensor platform
InactiveUS20140263822A1The process is fast and accurateInherent costsAircraft componentsUnmanned aerial vehiclesCrop managementFlight vehicle
The invention provides for a vertical takeoff and landing capable aerial vehicle with multiple rotors that is designed to carry agricultural sensors and telemetry allowing for real time control of agricultural equipment in accord with sensor data. The ability to carry a suite of agricultural sensors combined with multiple rotors will allow the craft to operate quickly in hovering and longitudinal flight over rows of farm fields and other vegetation and use an NDVI imager and other sensors to take data readings and real time imagery which will allow farmers and other personnel to determine vegetation type, need for chemical applications, plant fertilization, irrigation requirements, and other vegetation features including types of vegetation present. This will allow for precision agricultural, vegetation, and crop management and for farmers it will increase the efficiency of precision agriculture operations.
Owner:MALVEAUX CHESTER CHARLES
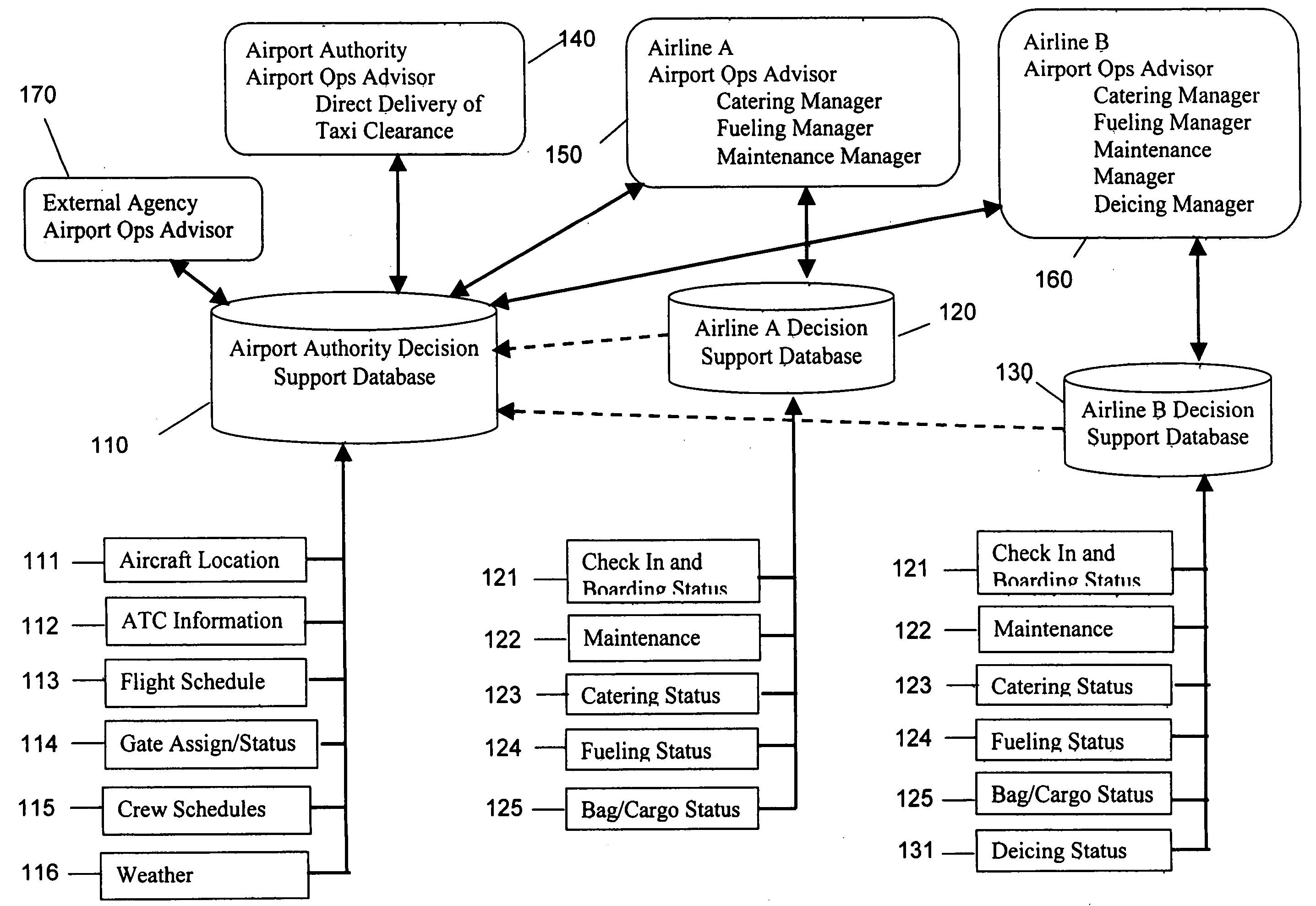
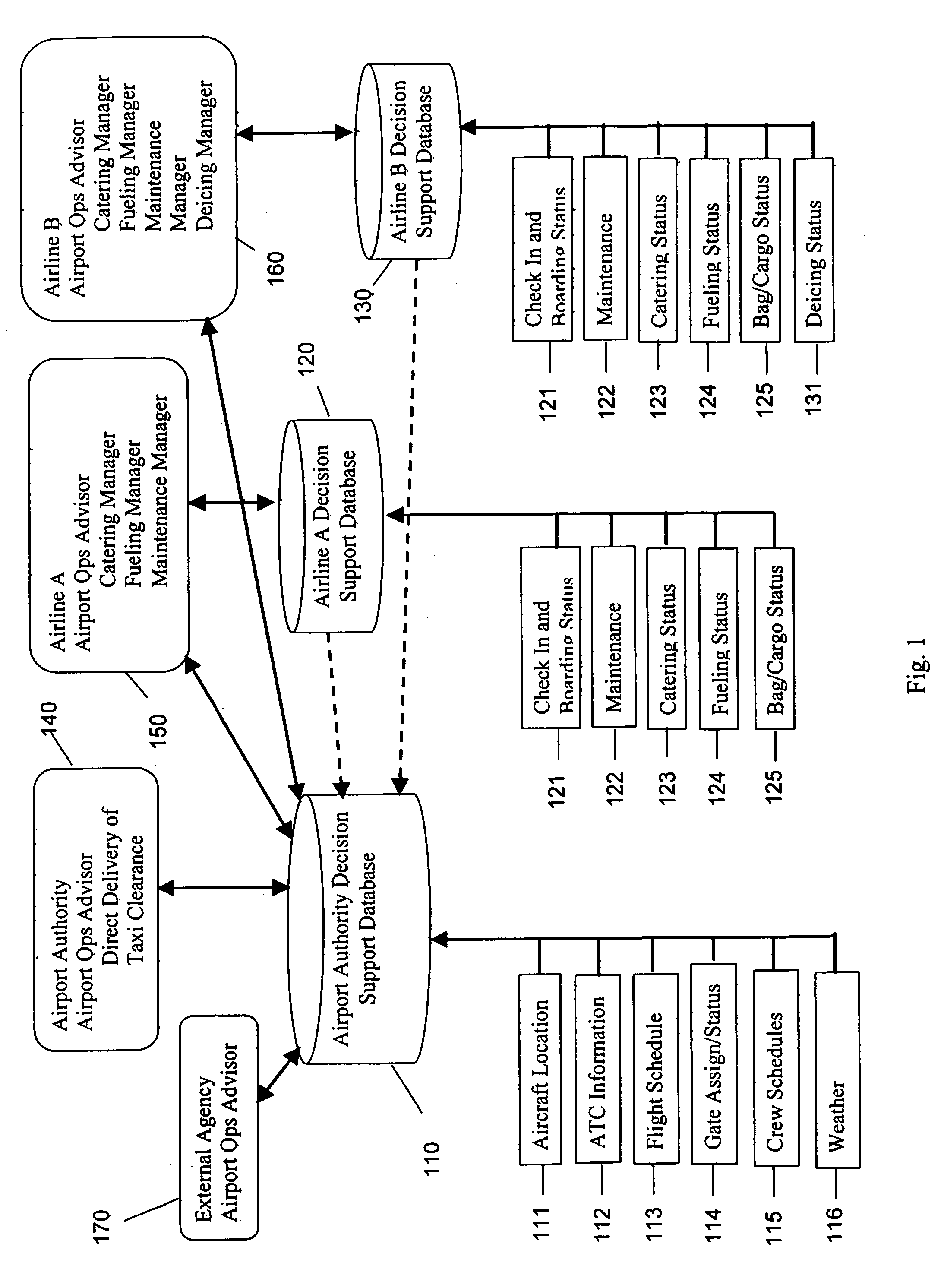
Systems and methods for managing airport operations
InactiveUS20050090969A1Reduce operating costsEnhanced Situational AwarenessAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficAviationInformation sharing
Status information on plane, passenger, cargo, crew, fuel, food, baggage, maintenance, weather and any other process used to manage airport operations, including expediting aircraft turnaround time for takeoff, is gathered into a common decision support database. The system includes decision support tools to increase the sharing of information between airline, airport, contractors and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), to more efficiently and safely manage the service, maintenance and operations of aircraft.
Owner:ARINC
Brake for hoist assembly
InactiveUS6889958B2Effective weight reductionReduce riskStage arrangementsWinding mechanismsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A lift assembly having a drum rotatably mounted to a frame and linearly translatable with respect to the frame. A plurality of head blocks are connected to the frame along a helical mounting path, wherein linear translation of the drum during takeoff or take-up maintains a predetermined fleet angle between a take off point from the drum and the head block.
Owner:ELECTRONIC THEATRE CONTROLS
Cross-flow fan propulsion system
InactiveUS20120111994A1Improve mobilityIncrease propulsionPropellersWave amplification devicesPower stationTrailing edge
The present invention includes improvements to cross-flow fans and cross-flow fan propelled aircraft including improved control, a dynamically adjustable vortex wall and internal housing, a vortex tube, vertical takeoff and landing rotorcraft configurations, the inclusion of an optimized oscillating blade fan, a wavy vortex wall, power plant refinements, dual leading and trailing edge configurations, stability improvements, tip plates, tapered wings, tapered fans, a fan construction method, and underwater applications.
Owner:PROPULSIVE WING
Aerodynamically Actuated Thrust Vectoring Devices
A vehicle includes a wing and a control surface pivotably coupled to the wing and configured to pivot about a range of motion. A propulsor is coupled to the control surface and configured to rotate between a first position associated with a hover flight mode and a second position associated with a forward flight mode. The propulsor is aerodynamically actuated between the first position and the second position due to aerodynamics about the wing. The propulsor may rotate from an initial flight mode, such as a takeoff mode, to a second flight mode, such as a forward flight mode.
Owner:NASA
Electric traction
ActiveUS20070181355A1Auxillary drivesPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingInternal combustion engineElectric traction
A drive train includes an internal combustion engine (“ICE”) coupled to a transmission having a power takeoff port. A transfer device couples an electric motor to the transmission via the port. The electric motor is enabled in a certain configuration to selectively power the drive train during at least certain intervals when the ICE is powered off.
Owner:AKIN RICK
Vertical-takeoff aircraft
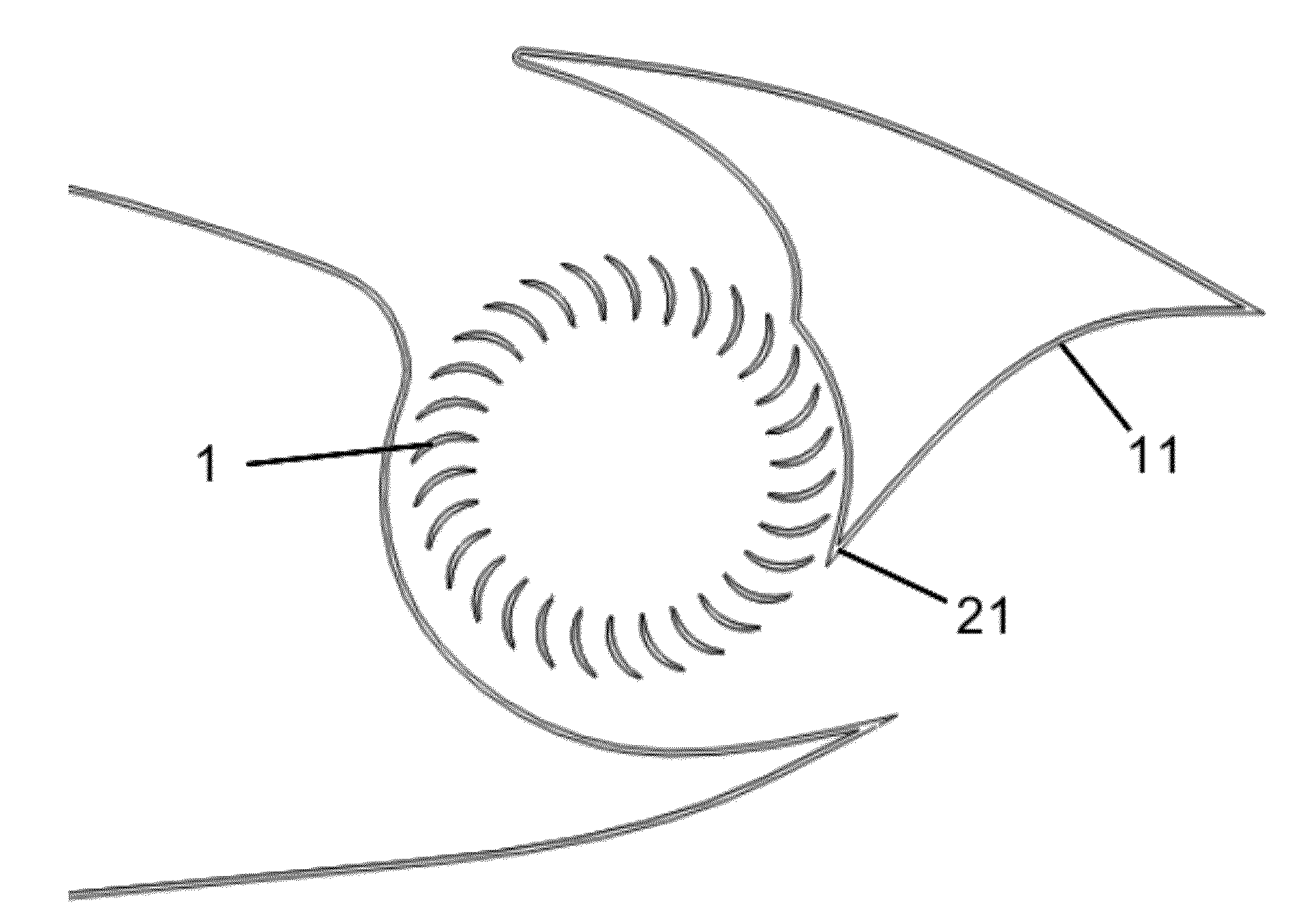
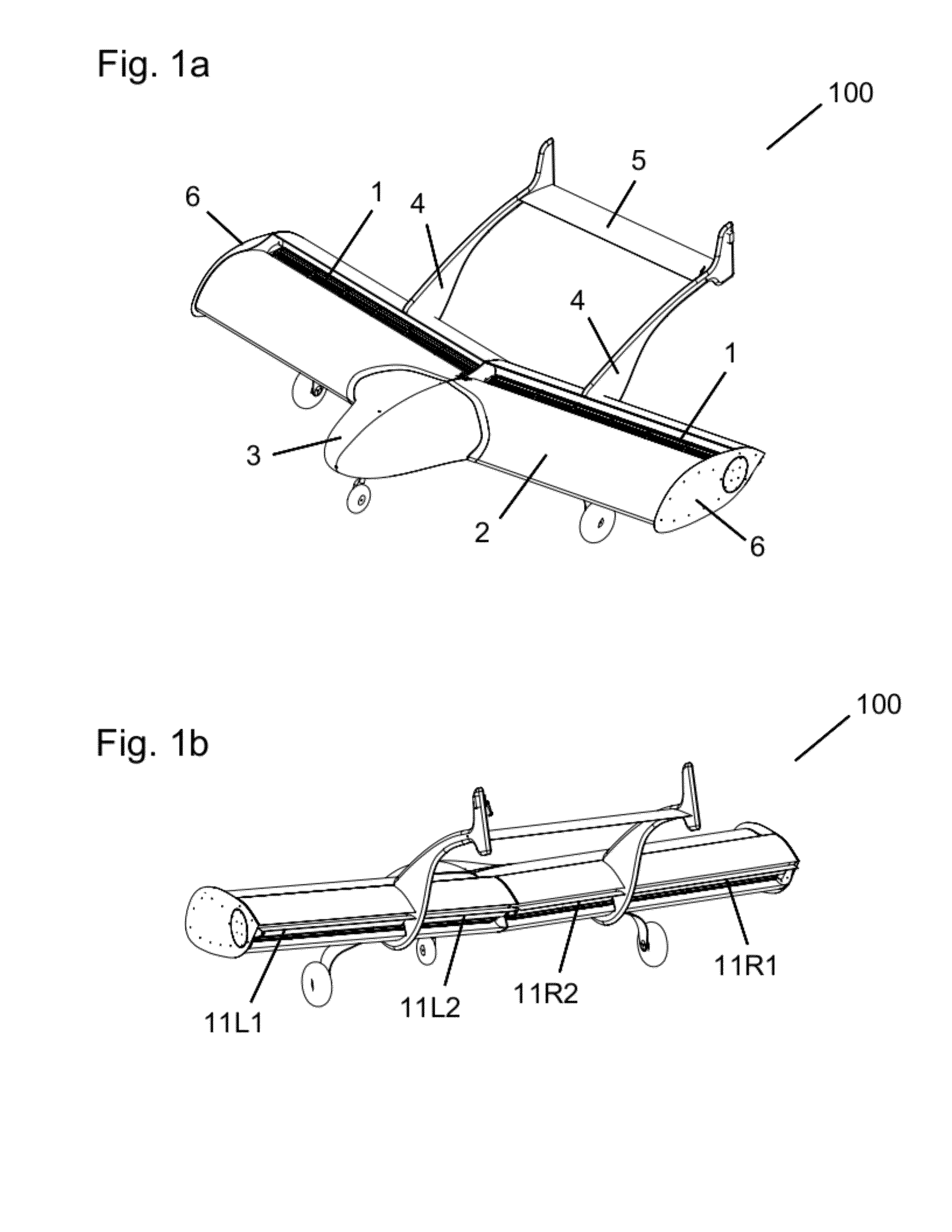
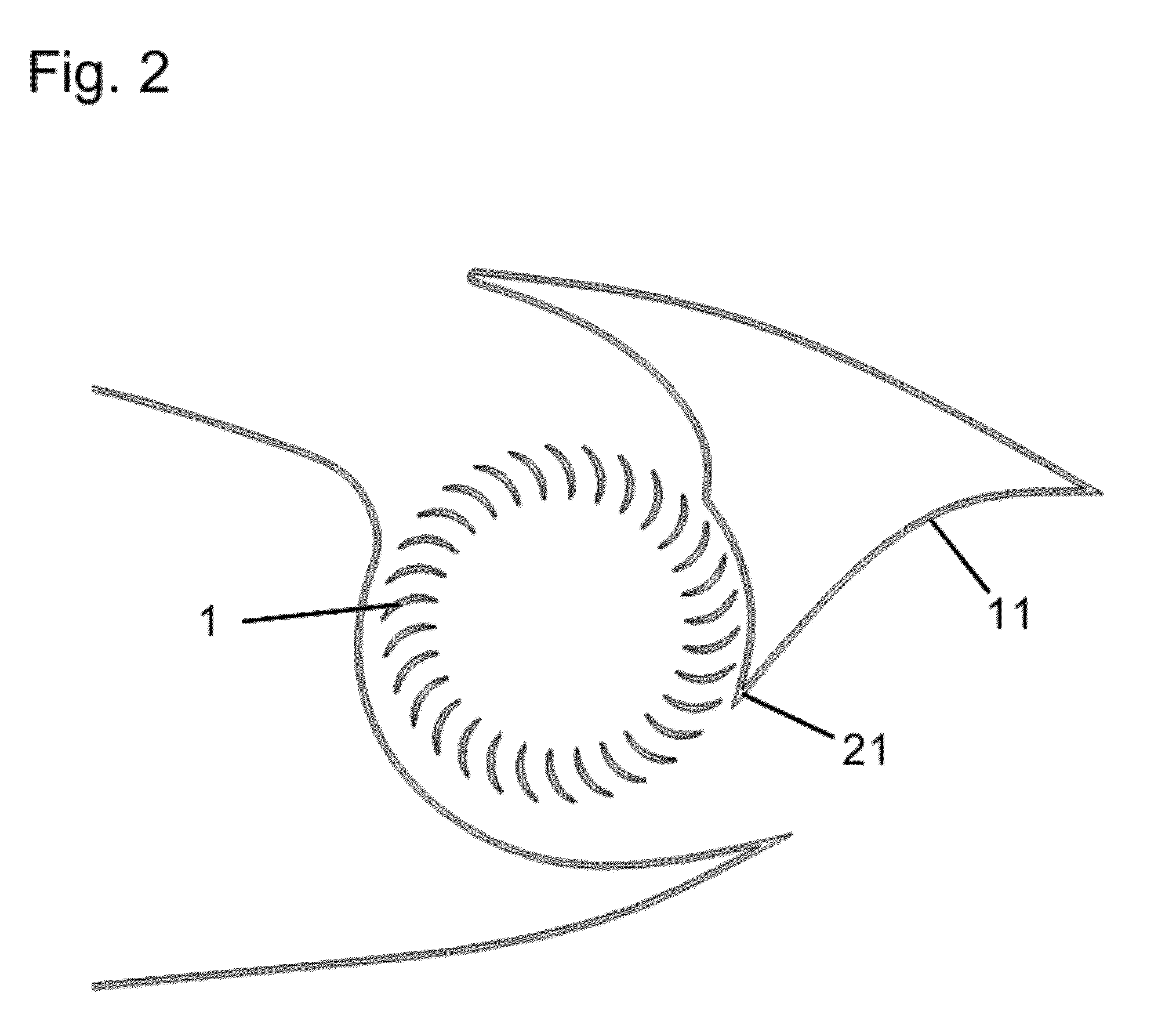
ActiveUS9643720B2Effective positioningImprove efficiencyPropellersPower plant constructionFlight vehicleAirplane
A vertical-takeoff aircraft with a wing. A first drive unit and a second drive unit are swivellably mounted on the wing. The first drive unit and the second drive unit are arranged on the wing at a distance from a wing-end of the wing. A first distance between the first drive unit and a longitudinal axis of the aircraft is approximately equal to a second distance between the second drive unit and the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The first drive unit and the second drive unit are swivellable into a horizontal flying position and a vertical flying position. In the horizontal flying position the first drive unit is arranged above a wing surface and the second drive unit below the wing surface on the wing. In the vertical flying position the first drive unit and the second drive unit are arranged in an approximately horizontal plane. The first drive unit and the second drive unit each have a swivel arm, wherein the swivel arms are swivellably mounted on the wing.
Owner:WINGCOPTER GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com