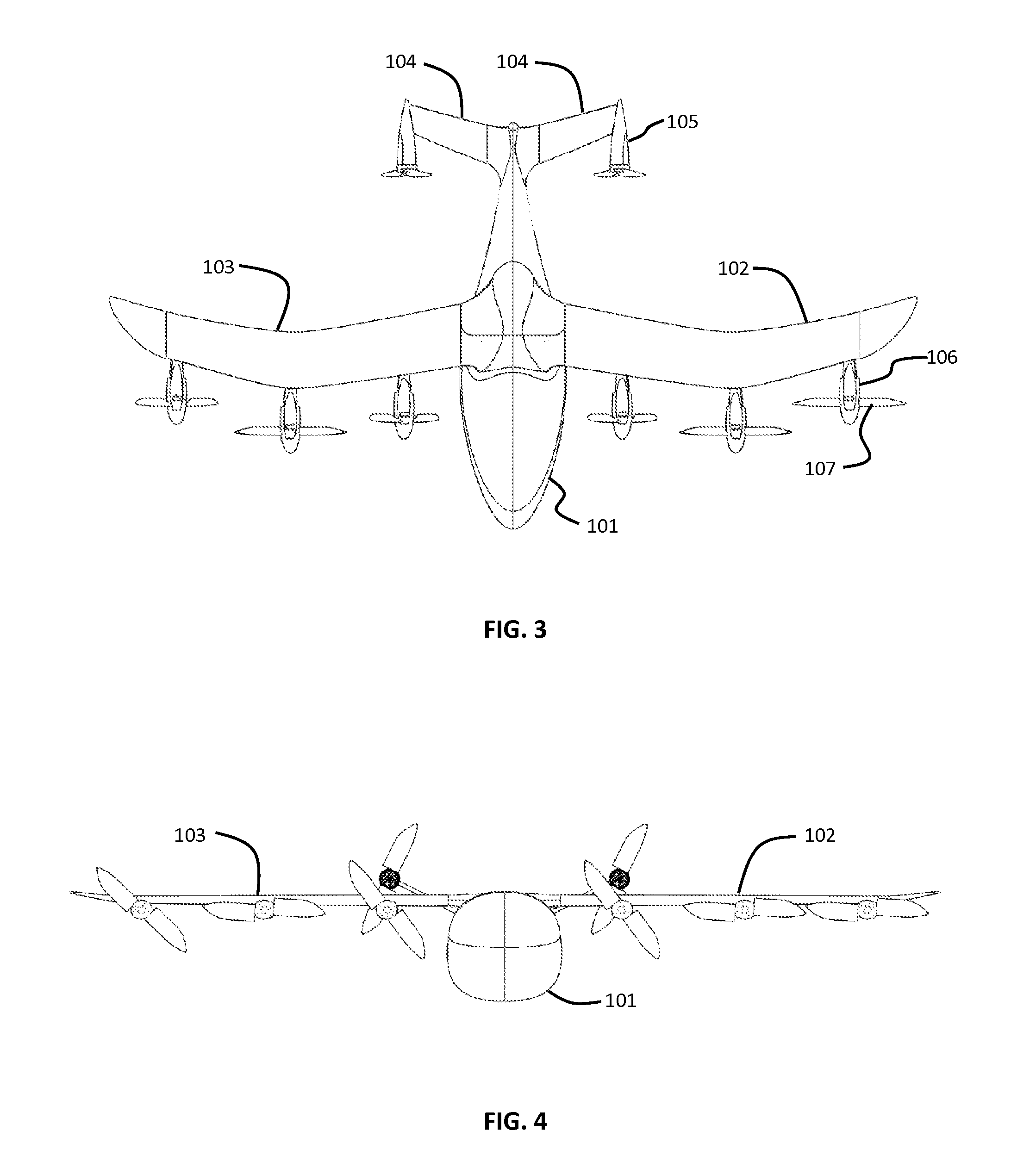
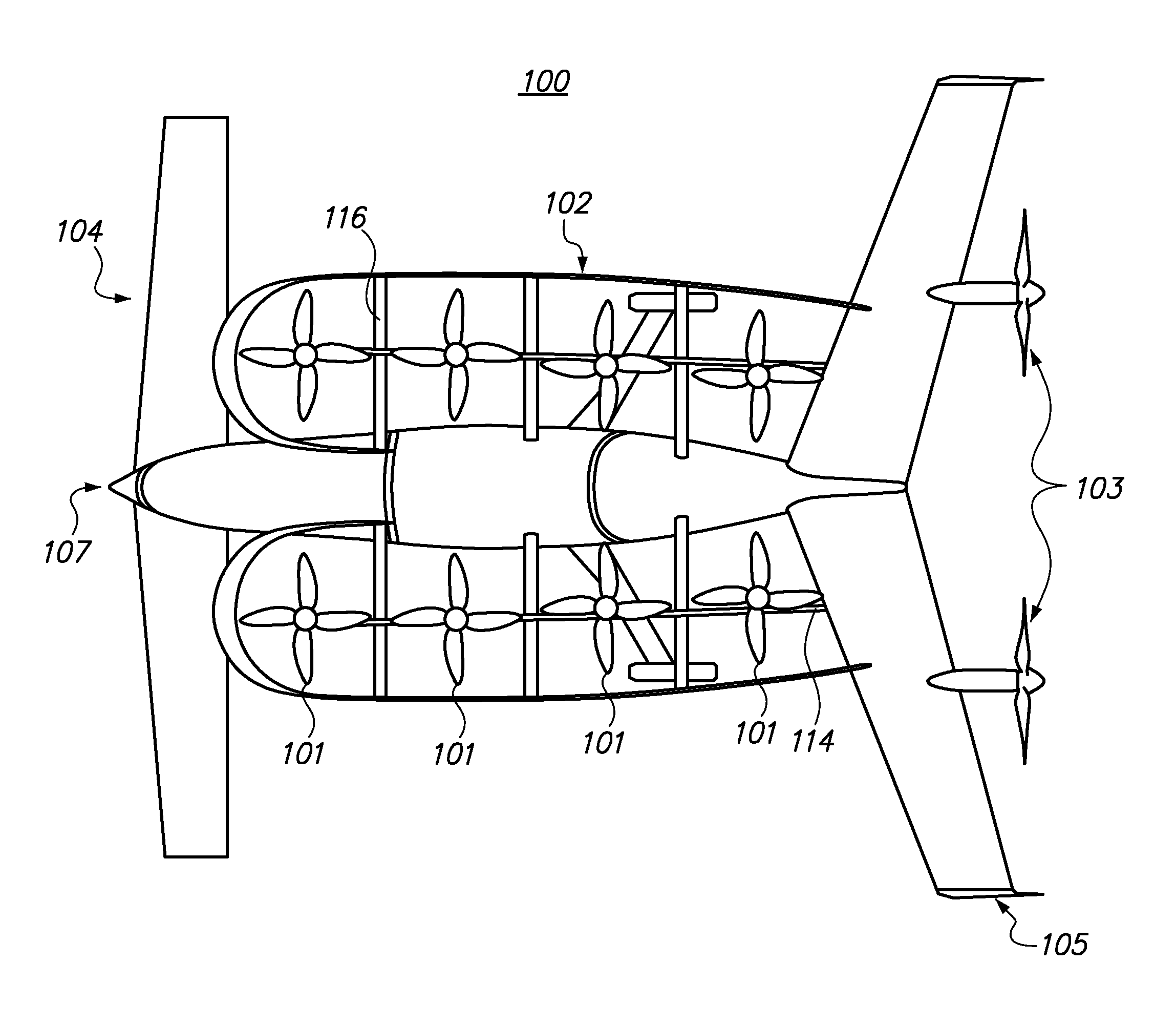
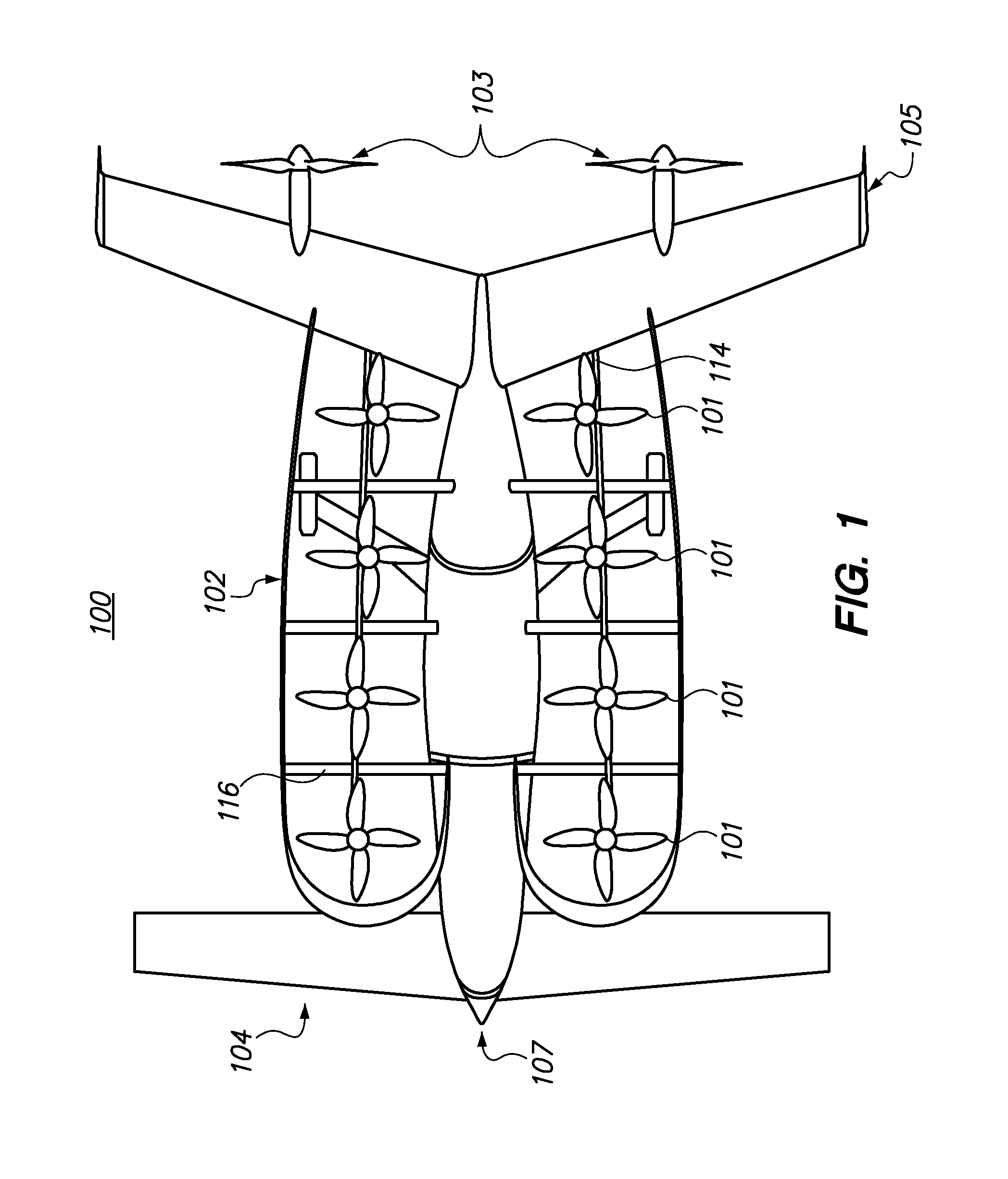
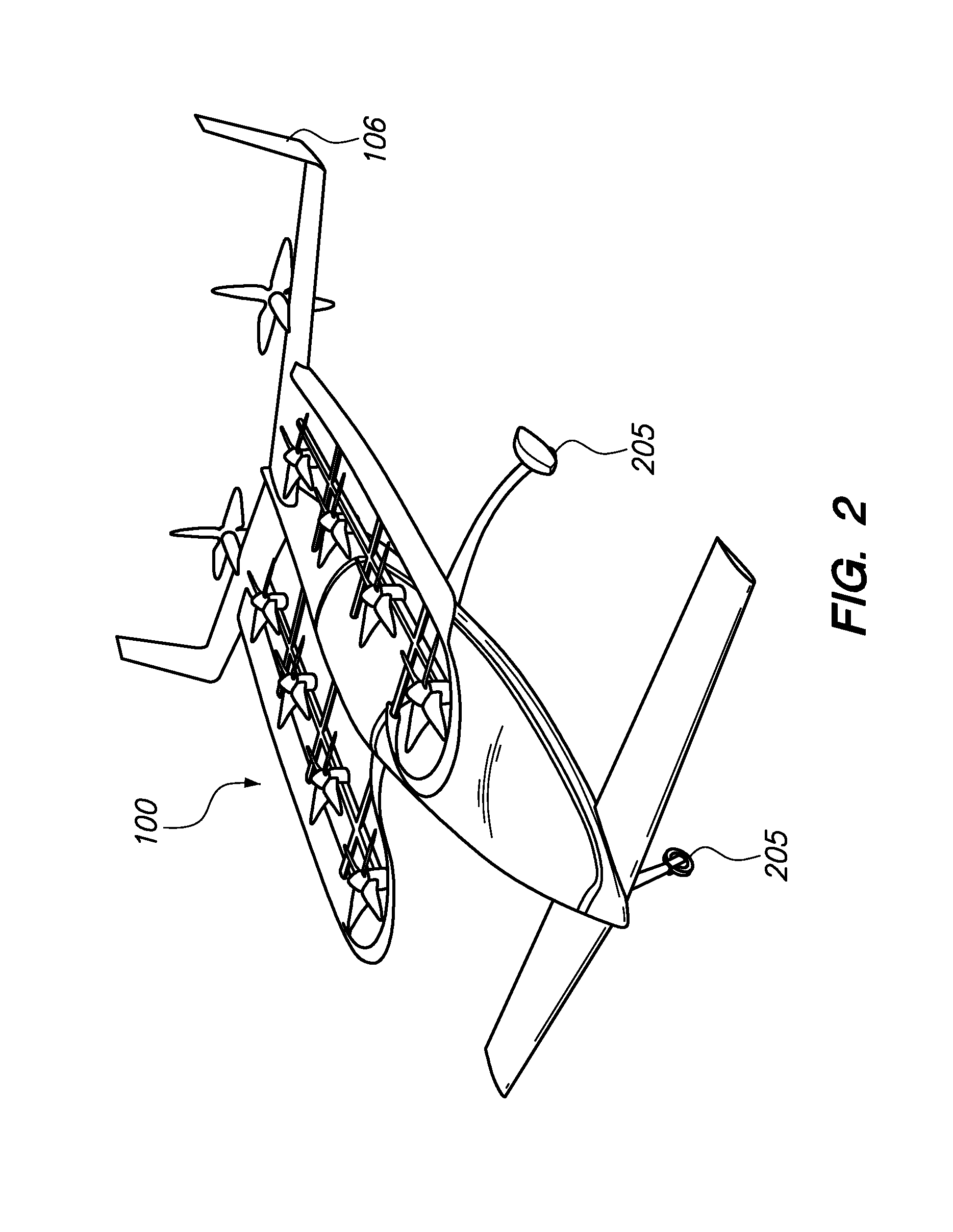
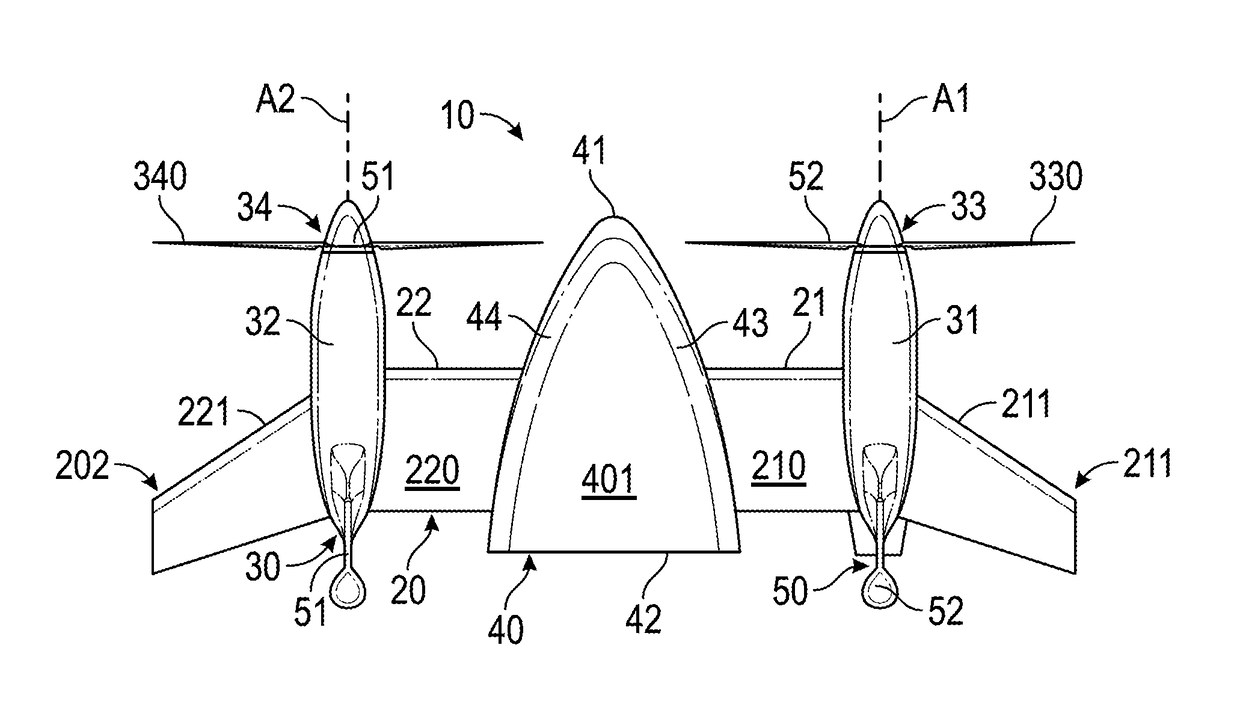
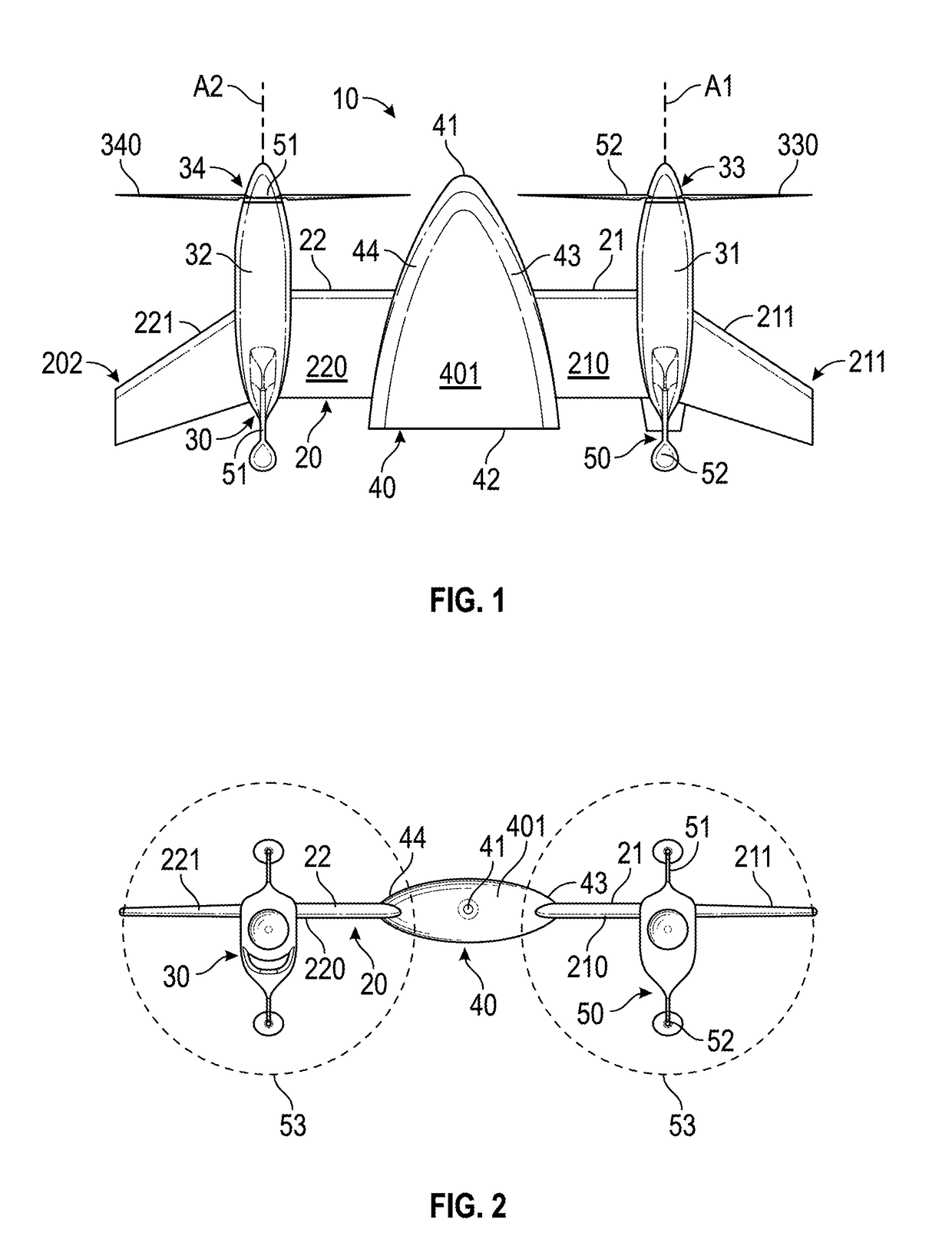
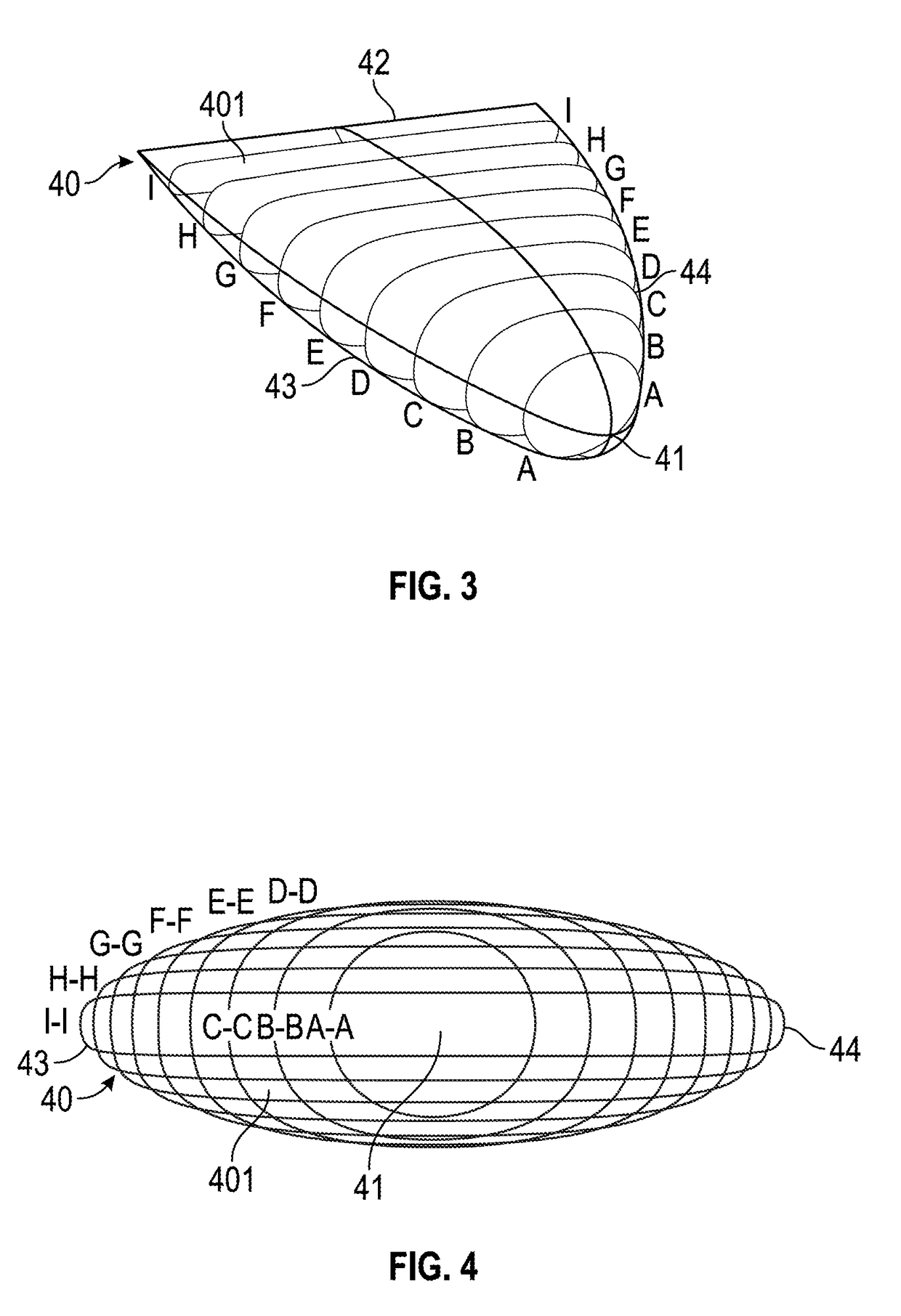
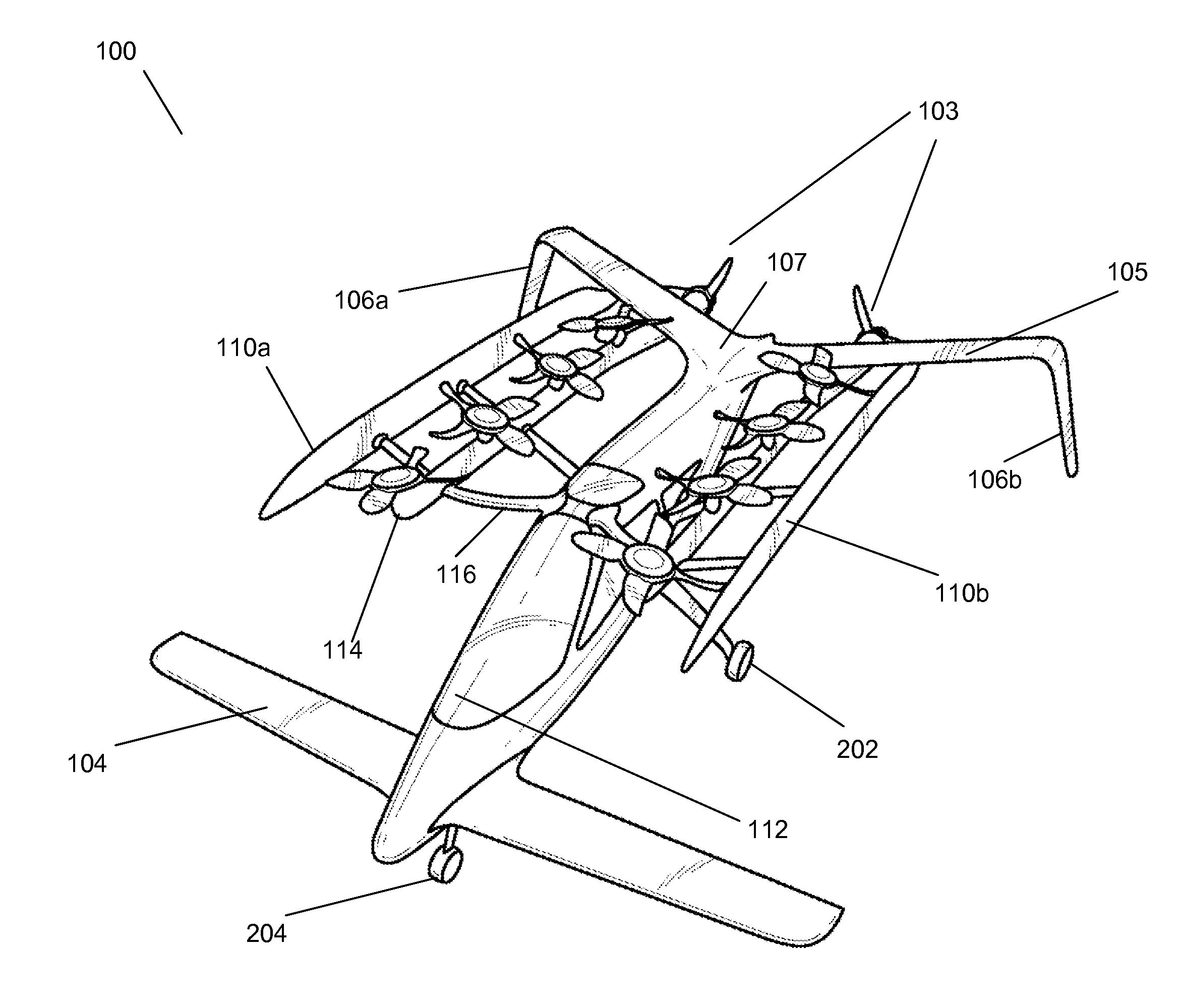
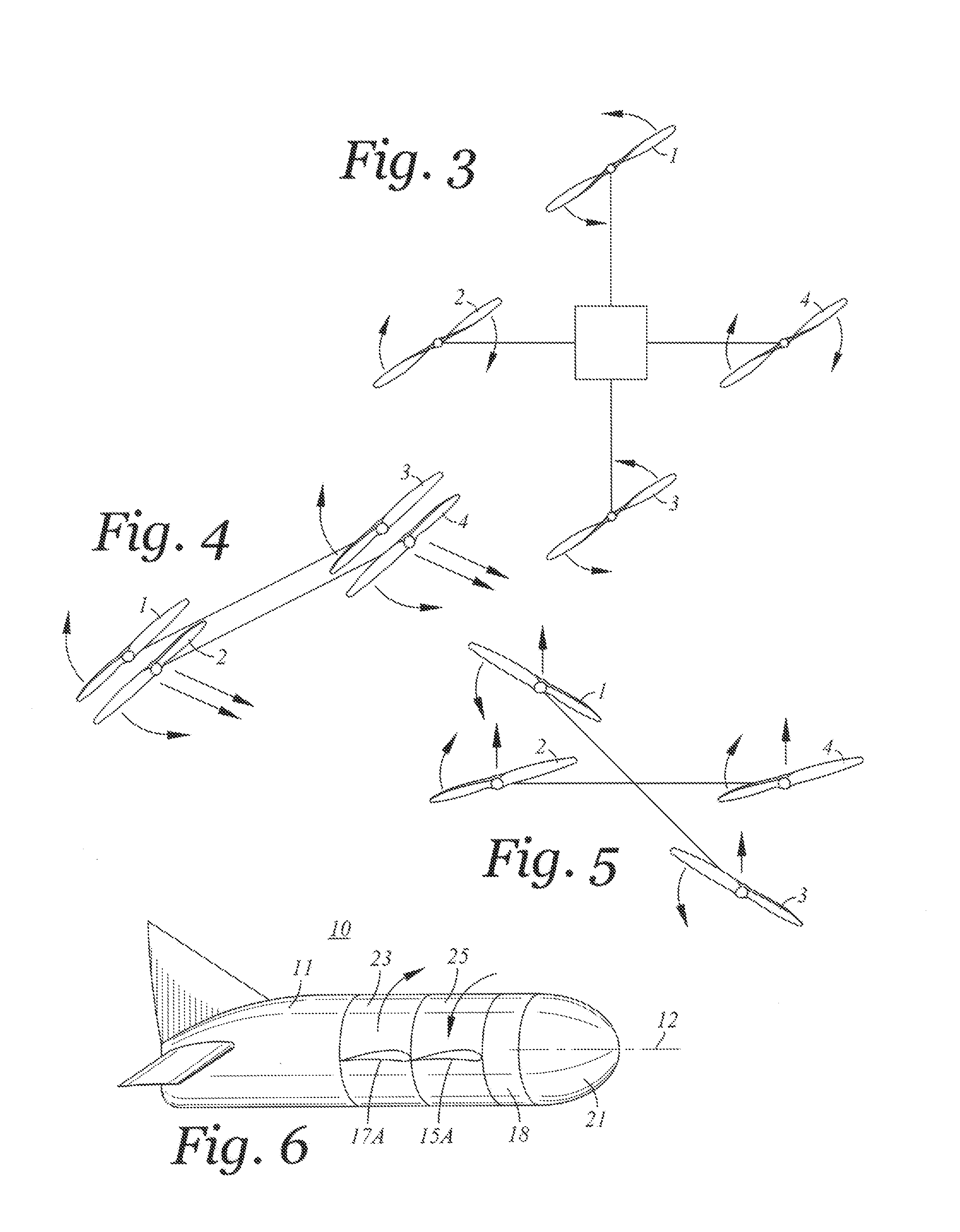
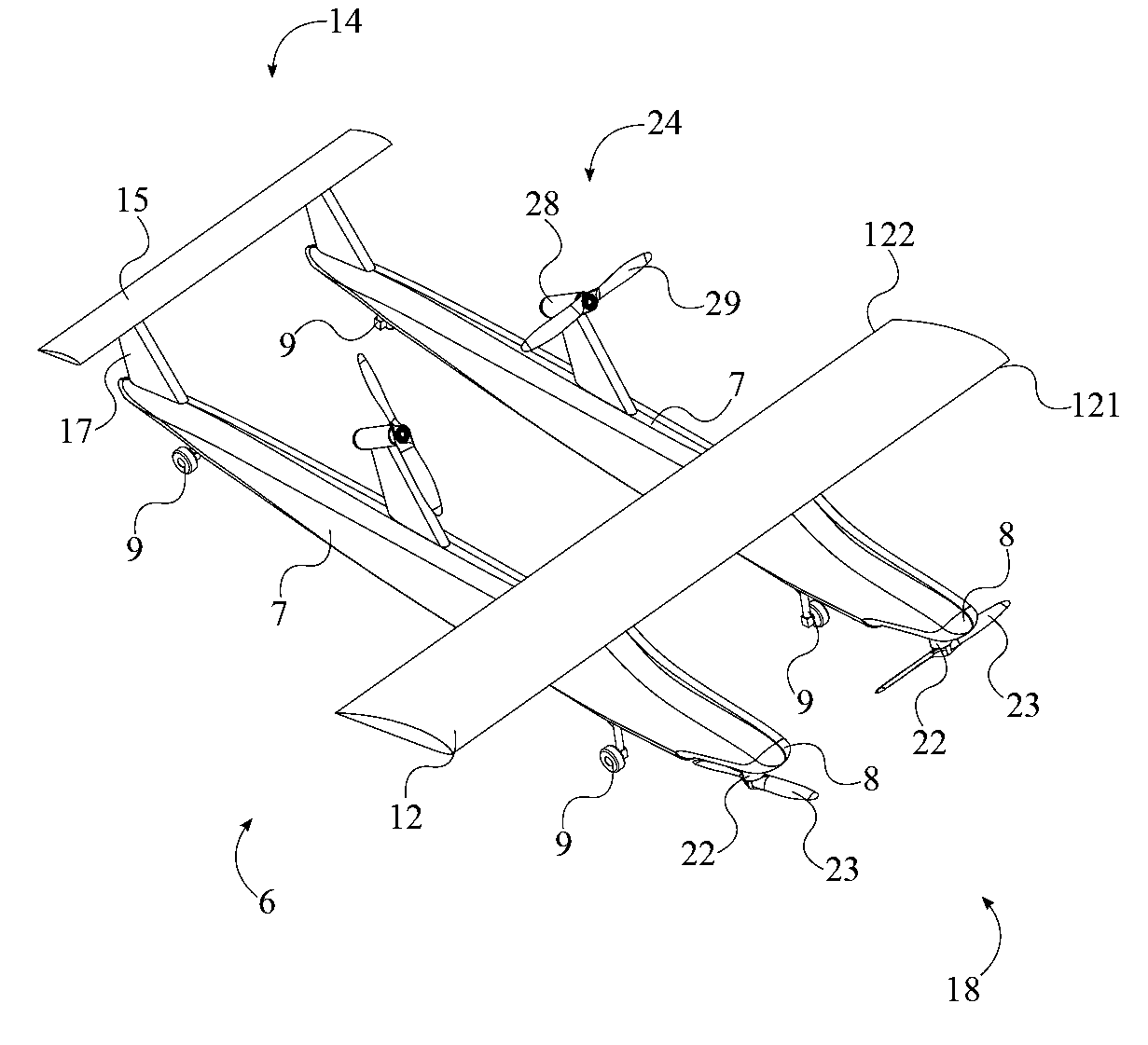
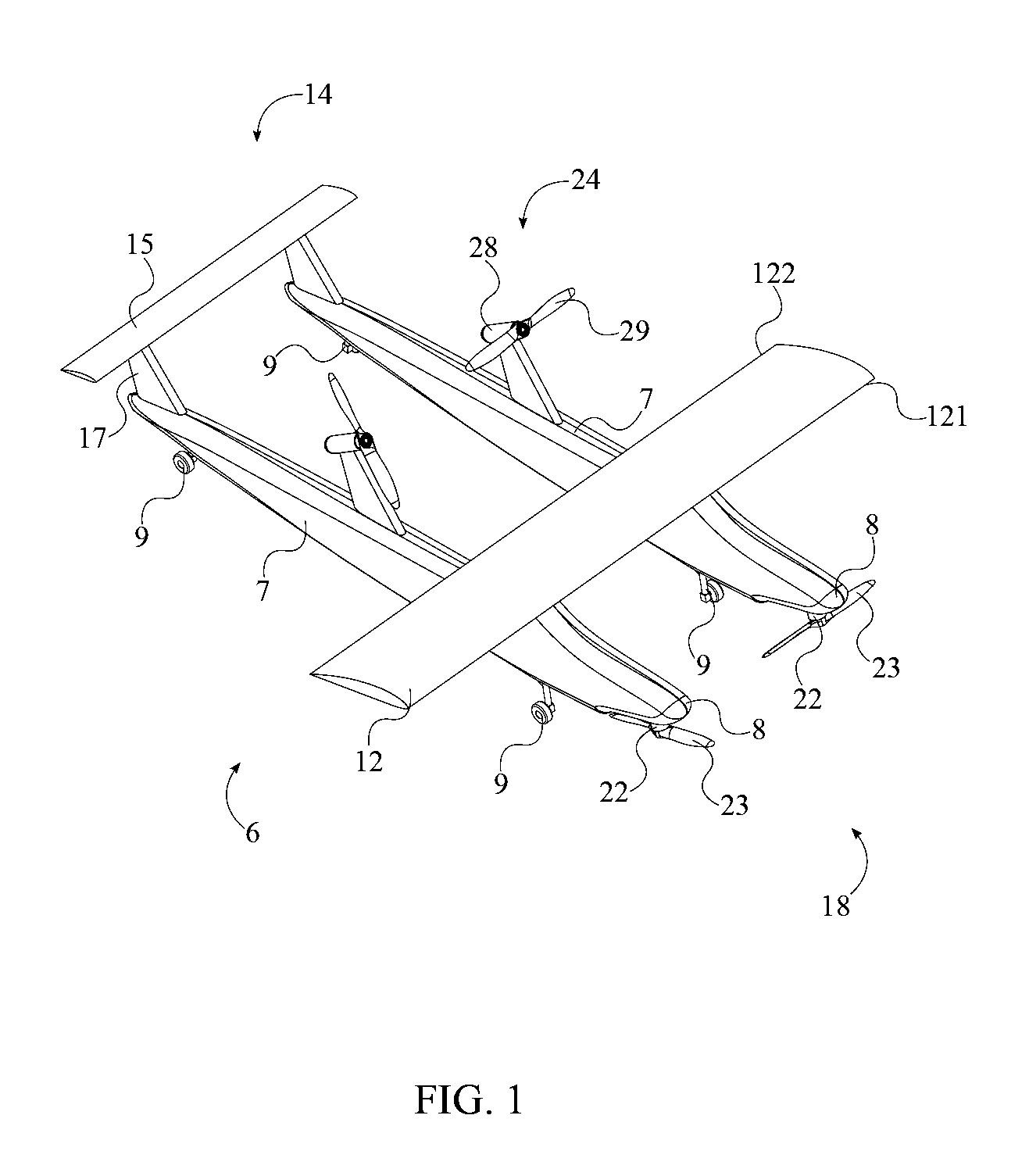
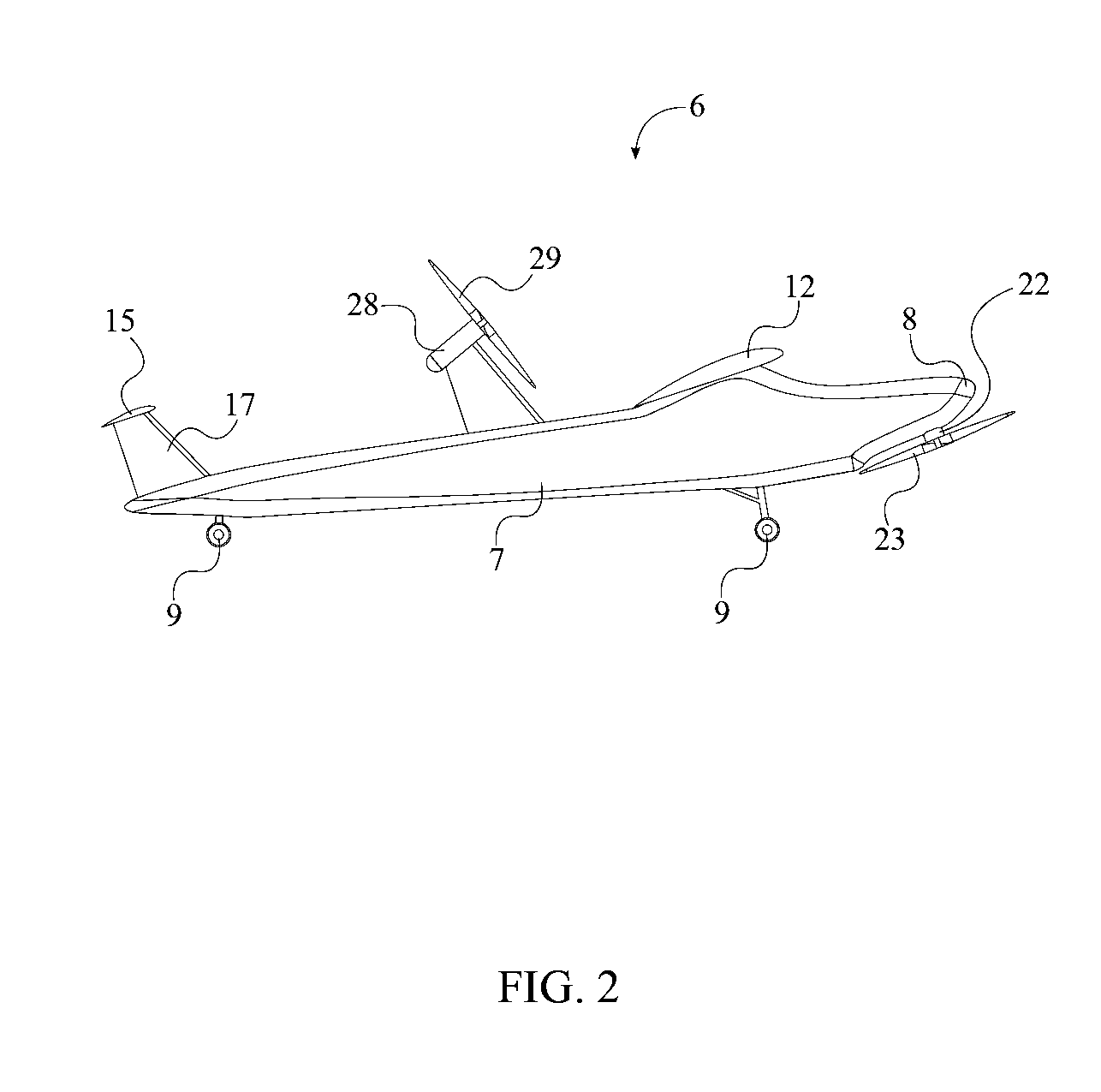
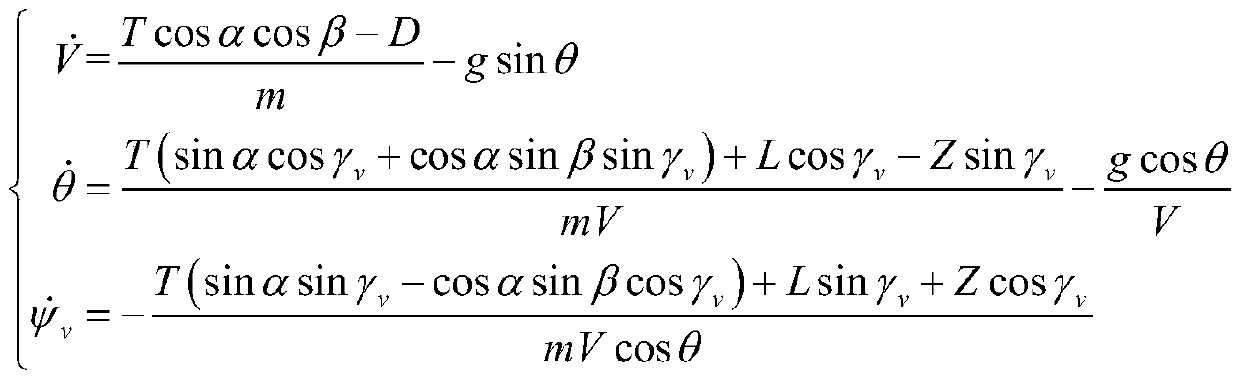Patents
Literature
458 results about "Level flight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
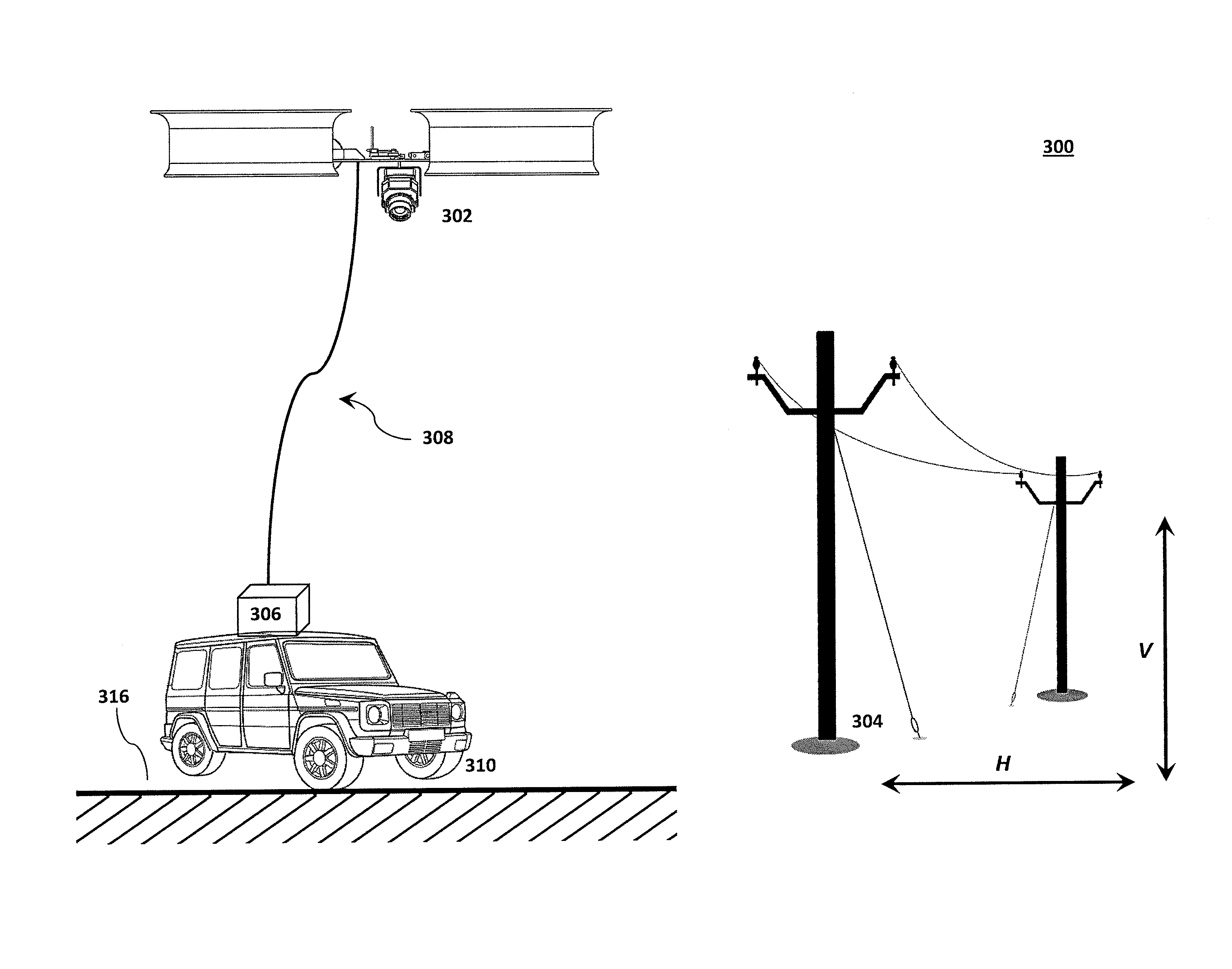
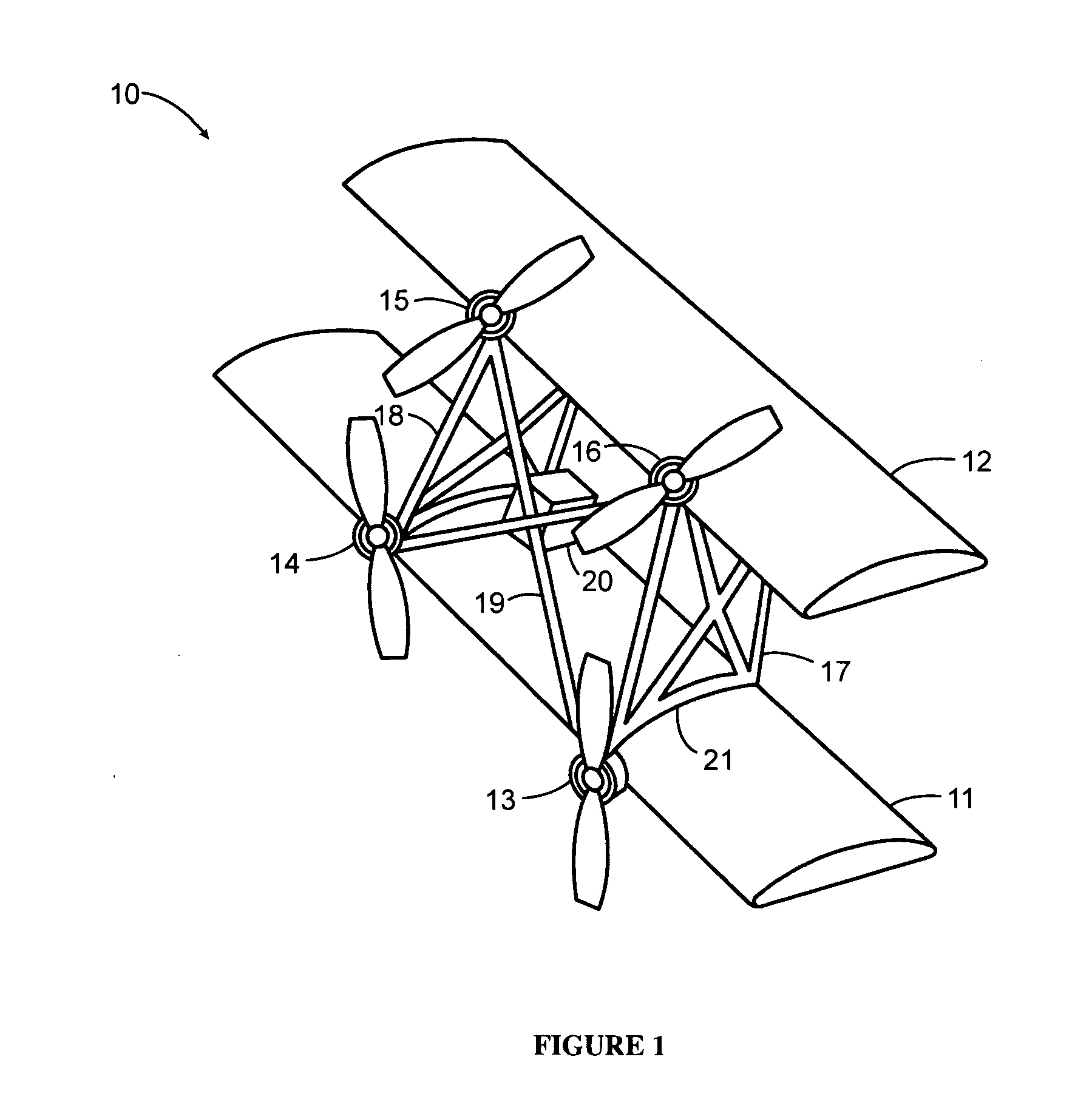
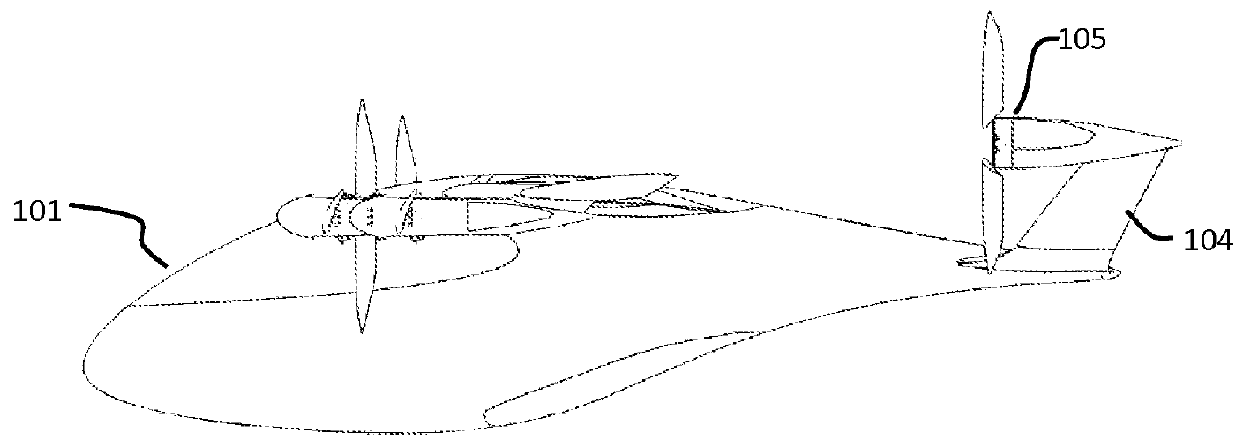
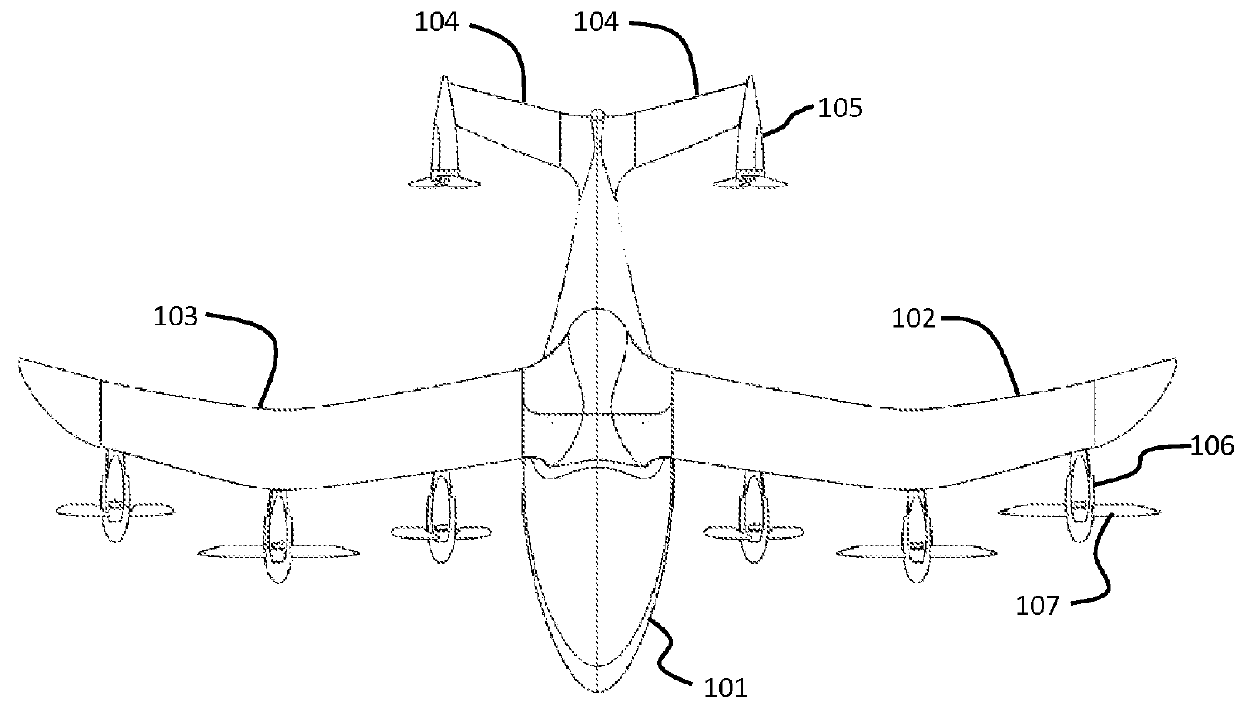
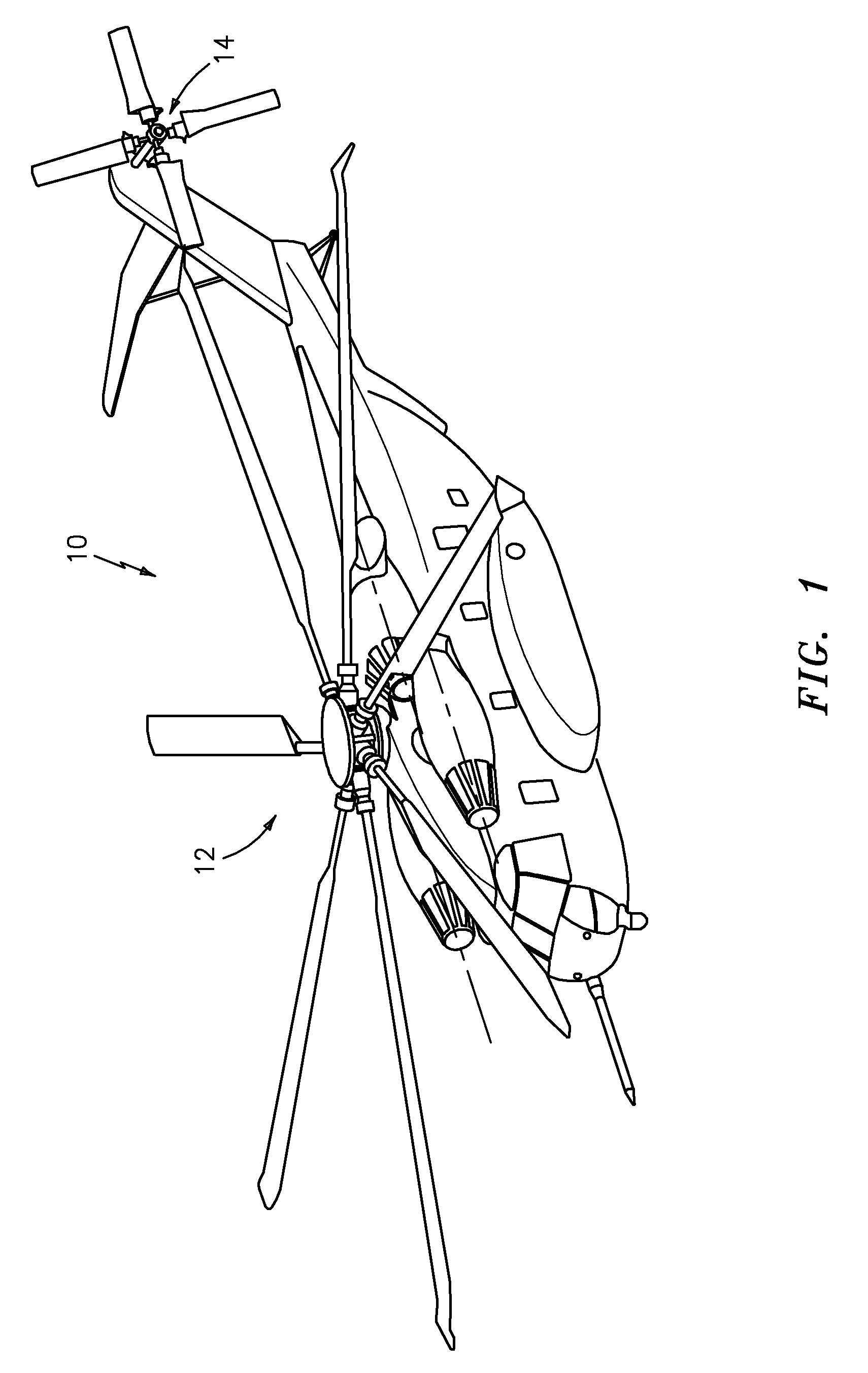
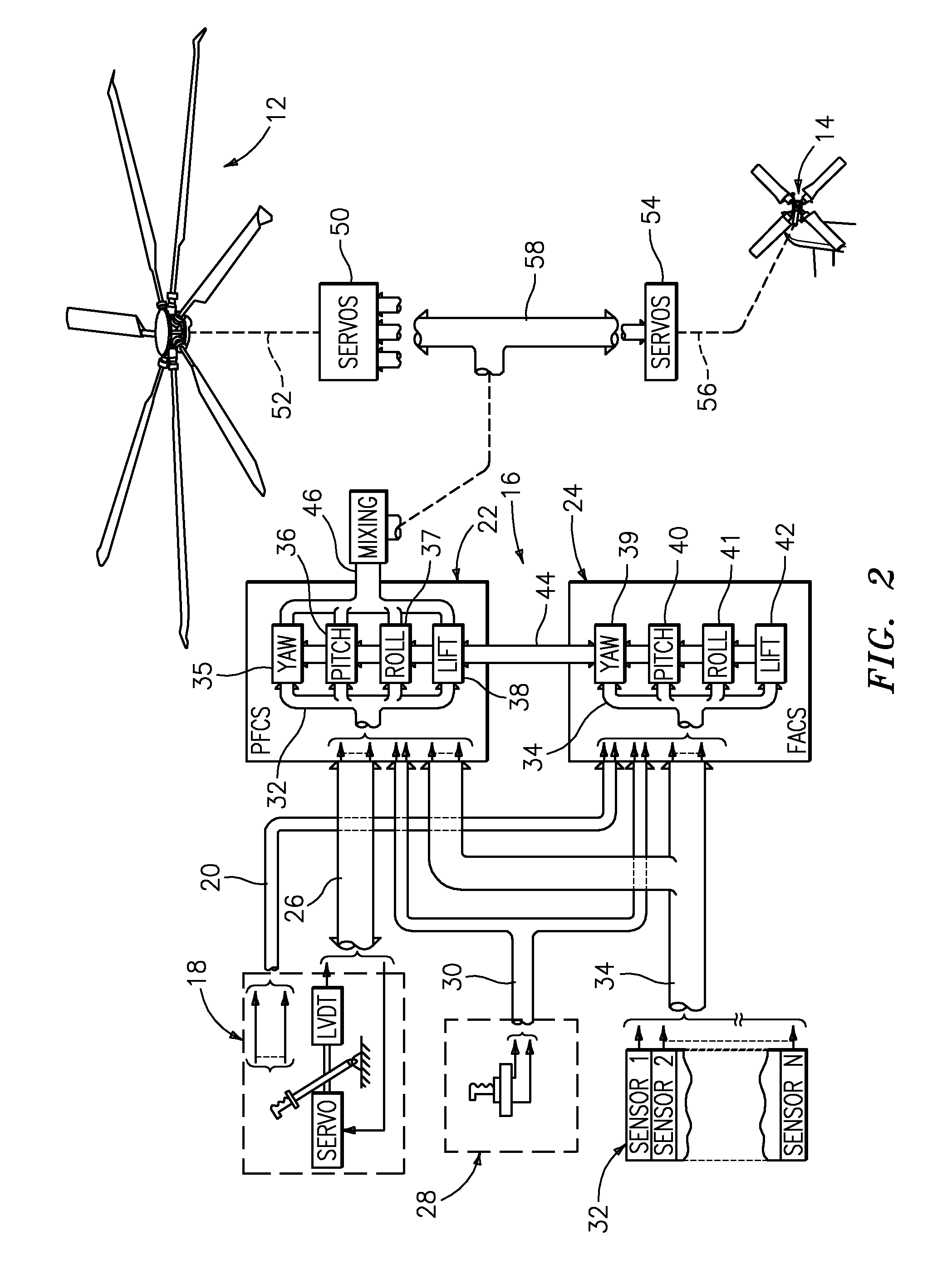
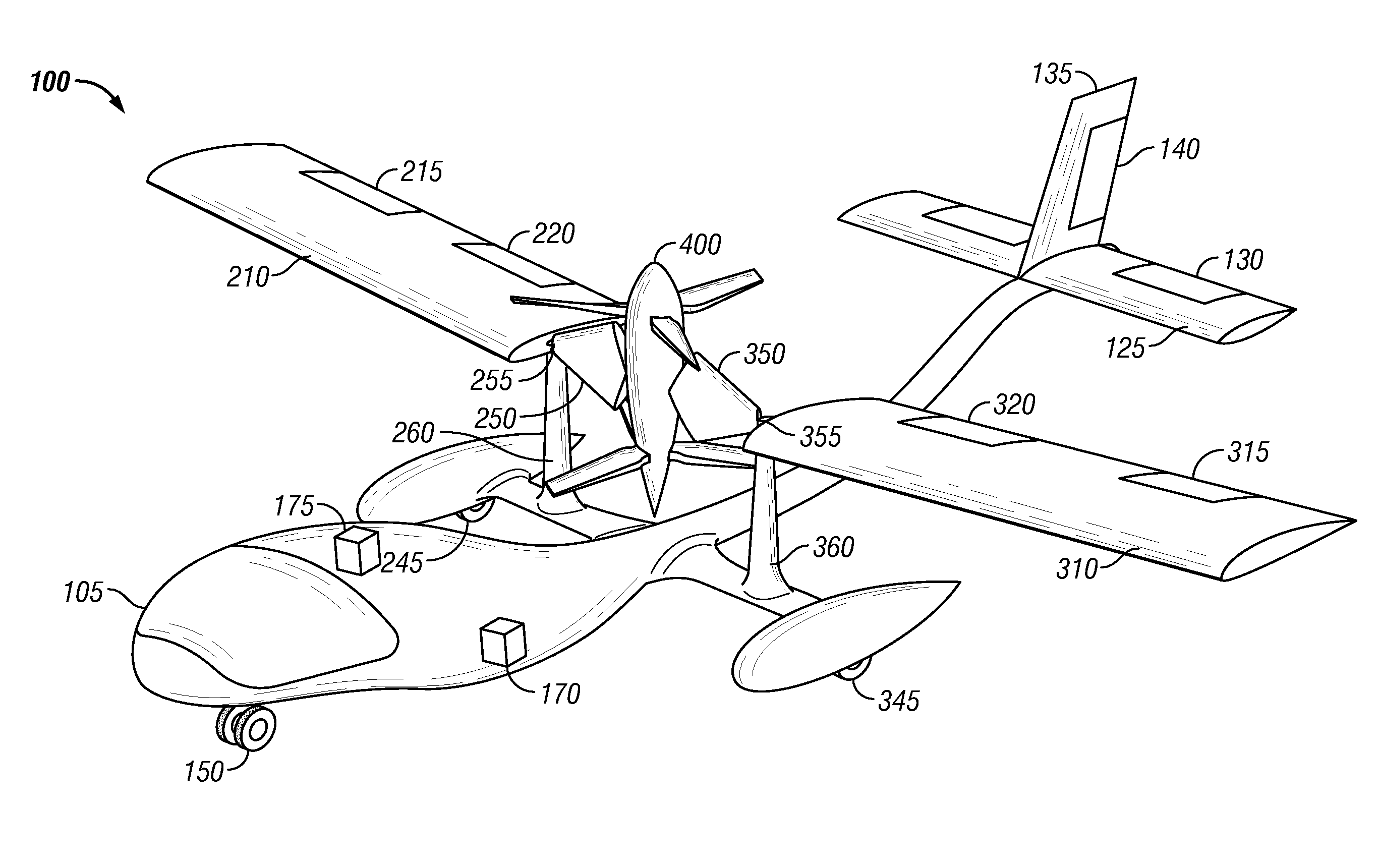
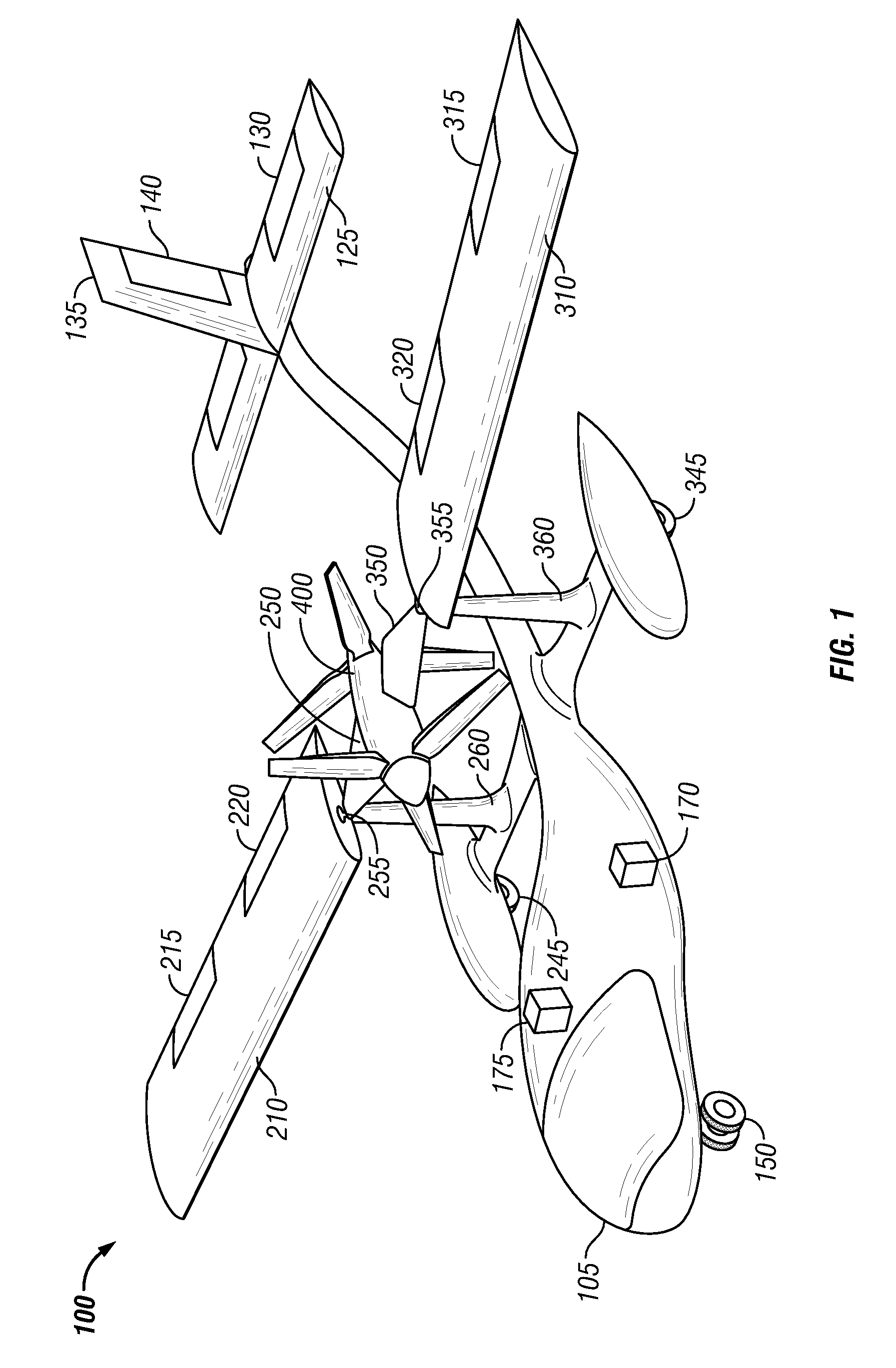
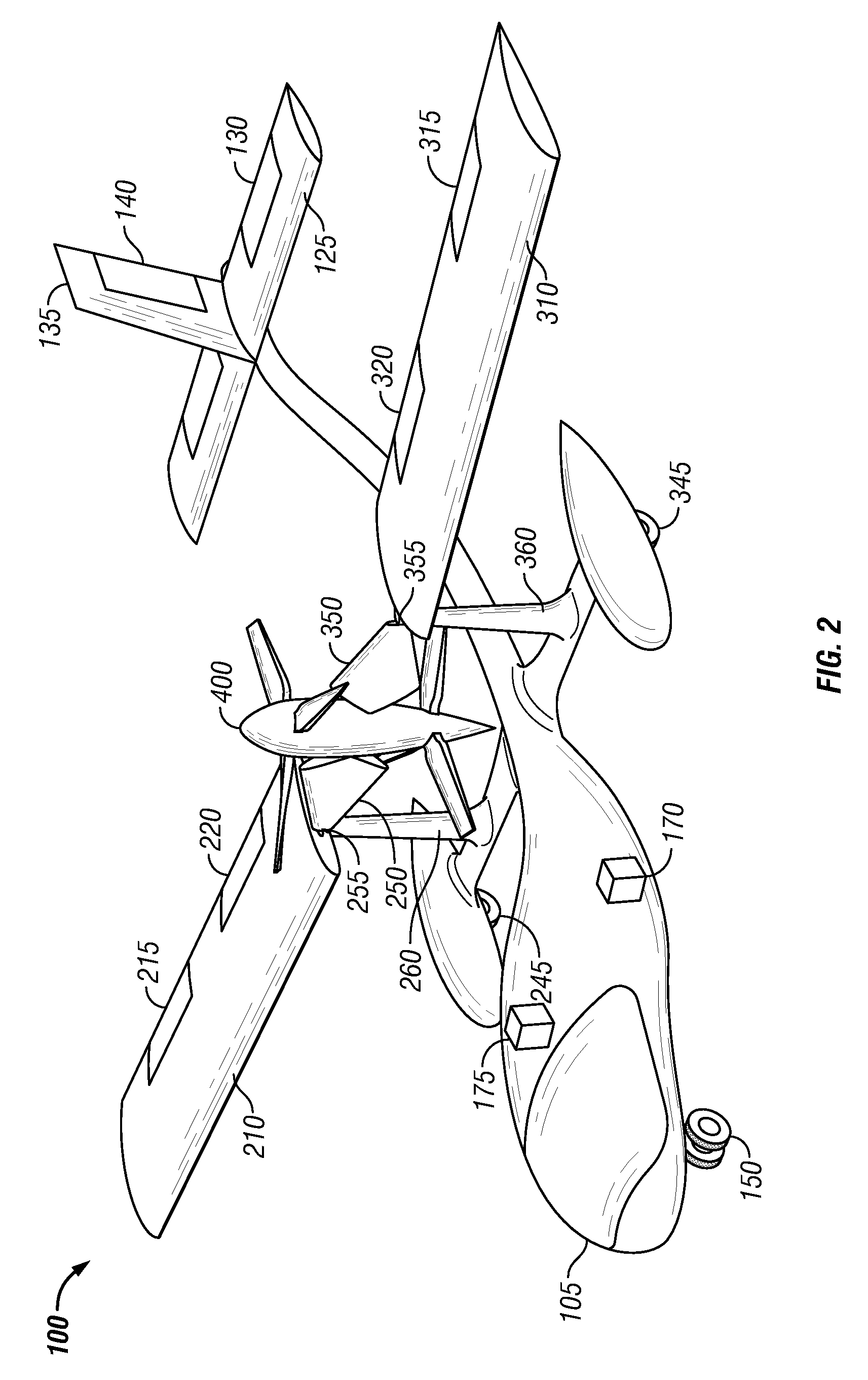
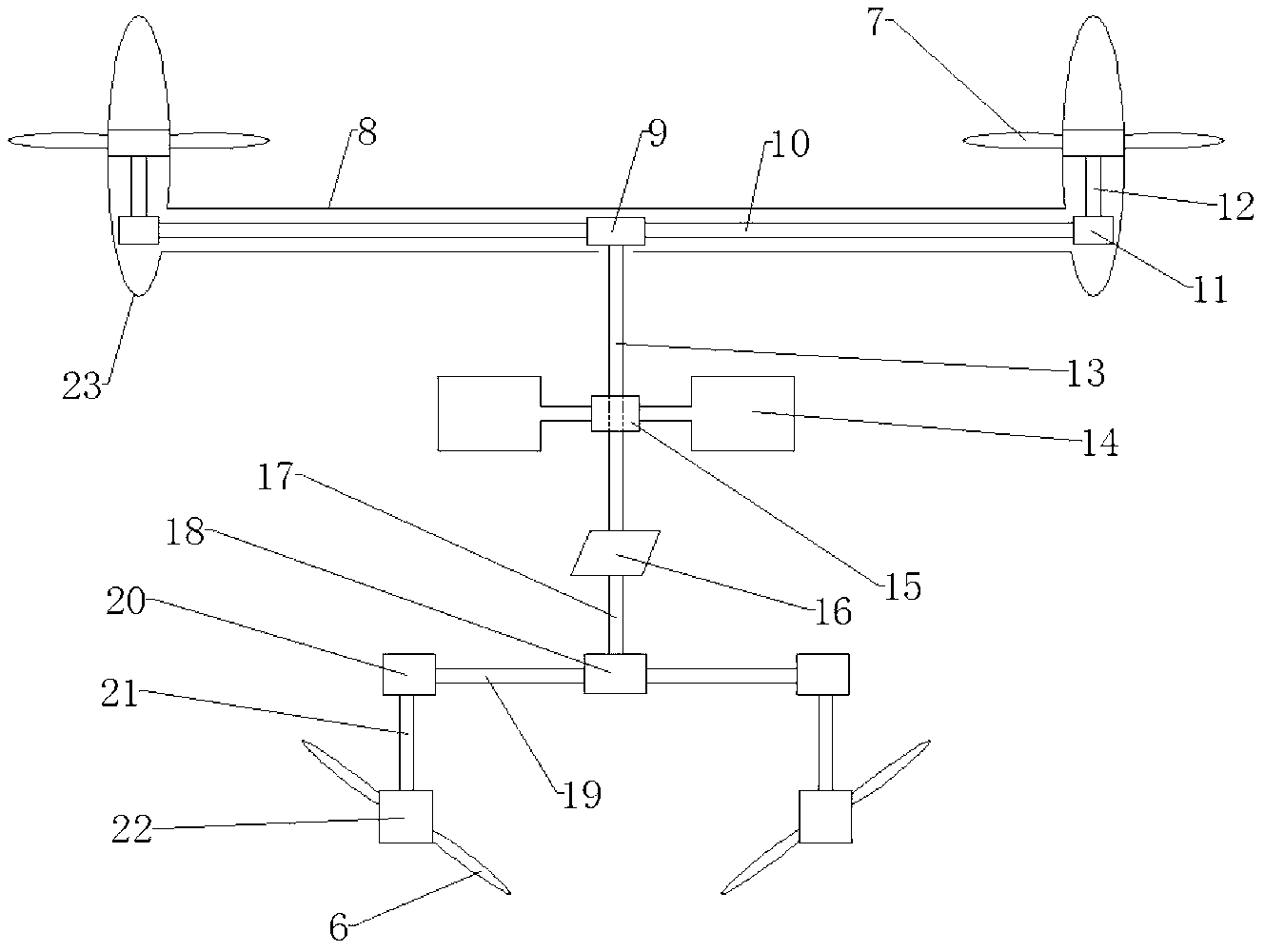
Tethered aerial system for data gathering
InactiveUS20130233964A1Increase horizontal rangeExtending flight spaceTethered aircraftActuated automaticallyLevel flightFlight vehicle
A tethered unmanned aerial vehicle (“UAV”) may be outfitted with a sensor payload for data gathering. The tethered UAV may be tethered to a ground station for constricting the flight space of the UAV while also providing the option for power delivery and / or bidirectional communications. The tethered UAV's flight path may be extended by introducing one or more secondary UAVs that cooperate to extend the horizontal flight path of a primary UAV. The ground station, which may be coupled with the tethered aerial vehicle, may comprise a listening switch configured to determine a condition of the tether such that the supply of power to the tether may be terminated when tether damage or a tether severance is detected.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
Controlled take-off and flight system using thrust differentials
InactiveUS20110042508A1Aircraft navigation controlUnmanned aerial vehiclesLevel flightFlight vehicle
A manned / unmanned aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using the same set of engines for takeoff and landing as well as for forward flight. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to takeoff with the wings in a vertical as opposed to horizontal flight attitude which takes off in this vertical attitude and then transitions to a horizontal flight path. An aerial vehicle which controls the attitude of the vehicle during takeoff and landing by alternating the thrust of engines, which are separated in least two dimensions relative to the horizontal during takeoff. An aerial vehicle which uses a rotating platform of engines in fixed relationship to each other and which rotates relative to the wings of the vehicle for takeoff and landing.
Owner:TRANSITION ROBOTICS INC
Aerodynamically efficient lightweight vertical take-off and landing aircraft with pivoting rotors and stowing rotor blades
ActiveUS20150266571A1Reduce resistanceReduce drag in all flight modesPropellersEfficient propulsion technologiesLevel flightFlight vehicle
An aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using a set of wing mounted thrust producing elements and a set of tail mounted rotors for takeoff and landing. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to vertical takeoff with the rotors in a rotated, take-off attitude then transitions to a horizontal flight path, with the rotors rotated to a typical horizontal configuration. The aerial vehicle uses different configurations of its wing mounted rotors and propellers to reduce drag in all flight modes.
Owner:JOBY AERO INC
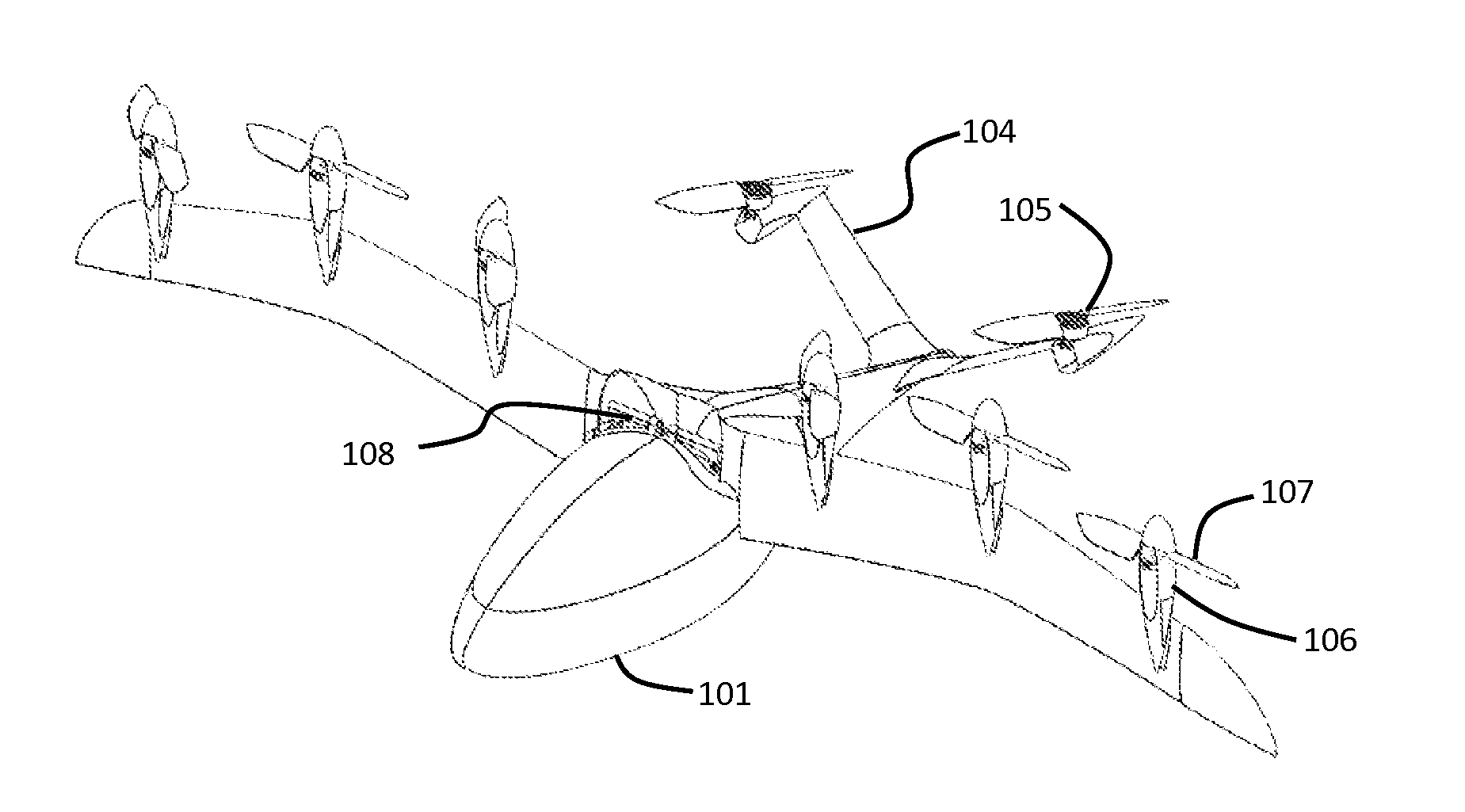
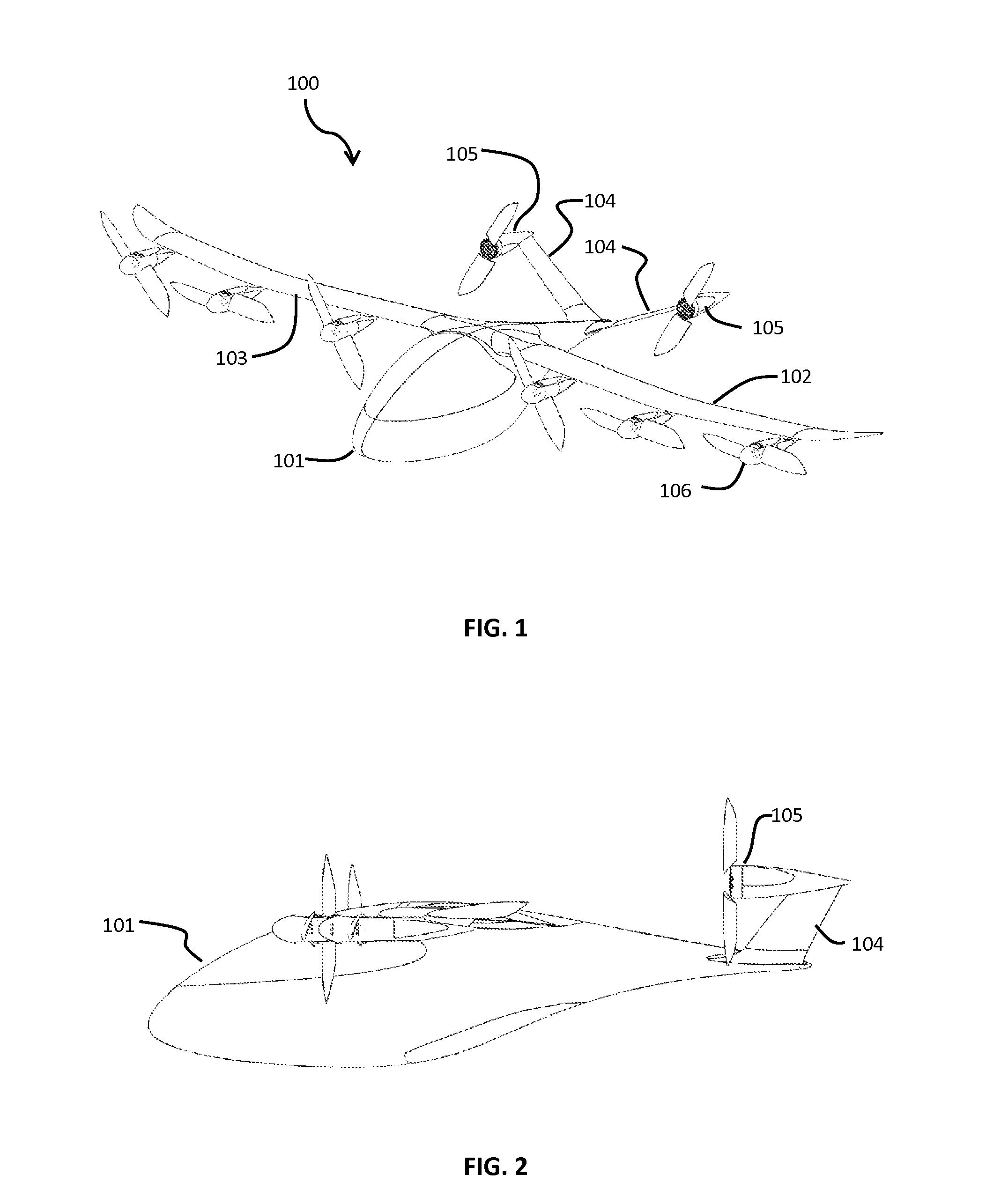
Personal Aircraft
ActiveUS20120012692A1Easy to controlImprove compactnessPower installationsEfficient propulsion technologiesLevel flightPropeller
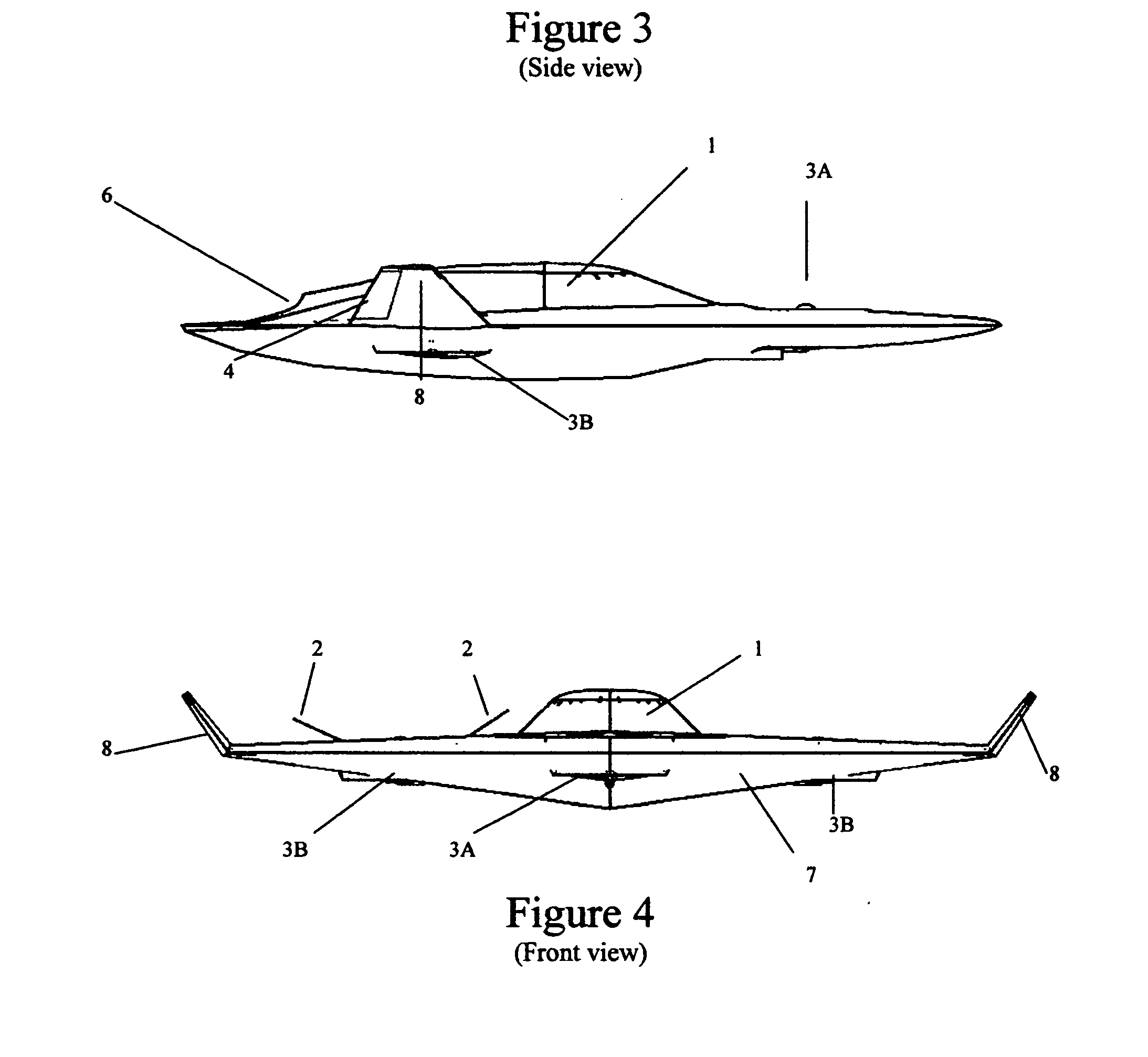
A safe, quiet, easy to control, efficient, and compact aircraft configuration is enabled through the combination of multiple vertical lift rotors, tandem wings, and forward thrust propellers. The vertical lift rotors, in combination with a front and rear wing, permits a balancing of the center of lift with the center of gravity for both vertical and horizontal flight. This wing and multiple rotor system has the ability to tolerate a relatively large variation of the payload weight for hover, transition, or cruise flight while also providing vertical thrust redundancy. The propulsion system uses multiple lift rotors and forward thrust propellers of a small enough size to be shielded from potential blade strike and provide increased perceived and real safety to the passengers. Using multiple independent rotors provides redundancy and the elimination of single point failure modes that can make the vehicle non-operable in flight.
Owner:WISK AERO LLC
Tailboom-stabilized VTOL aircraft
InactiveUS6845939B1Drag minimizationStable controlUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftNacelleLevel flight
A disclosed flying craft includes a suspension structure having a first end and a second end, a lift unit, and a payload unit. The lift unit includes a nacelle and a tailboom, and pivotally couples to the first end of the suspension structure, and a payload unit couples to the structure's second end. Thus the tailboom can pivotally couple with respect to the payload unit, which advantageously permits the tailboom to assume an orientation desirable for a particular mode of flight. During vertical flight or hover, the tailboom can hang from the lift unit in an orientation that is substantially parallel to the suspension structure and that minimizes resistance to downwash from the lift unit. During horizontal flight, the tailboom can be orthogonal to the suspension structure, extending rearward in an orientation where it can develop pitching and yawing moments to control and stabilize horizontal flight. Advantageous variations and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:BALDWIN G DOUGLAS
Hybrid Propulsion Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft
A hybrid propulsion aircraft is described having a distributed electric propulsion system. The distributed electric propulsion system includes a turbo shaft engine that drives one or more generators through a gearbox. The generator provides AC power to a plurality of ducted fans (each being driven by an electric motor). The ducted fans may be integrated with the hybrid propulsion aircraft's wings. The wings can be pivotally attached to the fuselage, thereby allowing for vertical take-off and landing. The design of the hybrid propulsion aircraft mitigates undesirable transient behavior traditionally encountered during a transition from vertical flight to horizontal flight. Moreover, the hybrid propulsion aircraft offers a fast, constant-altitude transition, without requiring a climb or dive to transition. It also offers increased efficiency in both hover and forward flight versus other VTOL aircraft and a higher forward max speed than traditional rotorcraft.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
Manned/unmanned V.T.O.L. flight vehicle
A manned / unmanned, autotonomously or remotely directed, horizontal, or vertical take-off and landing (HOVTOL) aircraft. This air vehicle incorporates multiple vertical facing ducted fans (shrouded propellers) driven by at least one power plant. Control authority of said air vehicle when in vertical flight mode is maintained through varying and vectoring the thrust produced by said ducted fans. When in a conventional horizontal flight mode, the aircraft would rely on aerodynamic control surfaces. In one embodiment this air vehicle would have the ability to transition from vertical helicopter type flight to a conventional horizontal aircraft mode of flight and back again. In another embodiment, this aircraft would perform similar to a helicopter—using only its ducted fans to produce vertical lift and maneuver in three dimensions.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Remotely controlled vtol aircraft, control system for control of tailless aircraft, and system using same
A manned / unmanned aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using the same set of engines for takeoff and landing as well as for forward flight. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to takeoff with the wings in a vertical as opposed to horizontal flight attitude which takes off in this vertical attitude and then transitions to a horizontal flight path. An aerial vehicle which controls the attitude of the vehicle during takeoff and landing by alternating the thrust of engines, which are separated in at least two dimensions relative to the horizontal during takeoff, and which may also control regular flight in some aspects by the use of differential thrust of the engines. A tailless airplane which uses a control system that takes inputs for a traditional tailed airplane and translates those inputs to provide control utilizing non-traditional control methods.
Owner:SINHA PRANAY +5
Counter-quad tilt-wing aircraft design
InactiveUS20050230519A1Halved in cross-sectionReduced wake turbulence hazardVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftAviationLevel flight
The invention consists of a specific, matched arrangement of aeronautical elements which (1) eliminates aerodynamic interference of, and (2) adds variable-cycle propulsion to, the level flight mode of a four-propulsor tilt-wing VTOL (vertical takeoff & landing) aircraft, without an additional element of variable geometry. This is achieved by configuring the components such that the rotor planes on either side pass through each other in the transition maneuver to form adjacent, close-coupled, counter-rotating pairs in level flight.
Owner:HURLEY FRANCIS X
Aerodynamically efficient lightweight vertical take-off and landing aircraft with pivoting rotors and stowing rotor blades
ActiveUS20160031555A1Reduce resistanceReduce drag in all flight modesPropellersAircraft stabilisationLevel flightFlight vehicle
An aerial vehicle adapted for vertical takeoff and landing using a set of wing mounted thrust producing elements and a set of tail mounted rotors for takeoff and landing. An aerial vehicle which is adapted to vertical takeoff with the rotors in a rotated, take-off attitude then transitions to a horizontal flight path, with the rotors rotated to a typical horizontal configuration. The aerial vehicle uses different configurations of its wing mounted rotors and propellers to reduce drag in all flight modes.
Owner:JOBY AERO INC
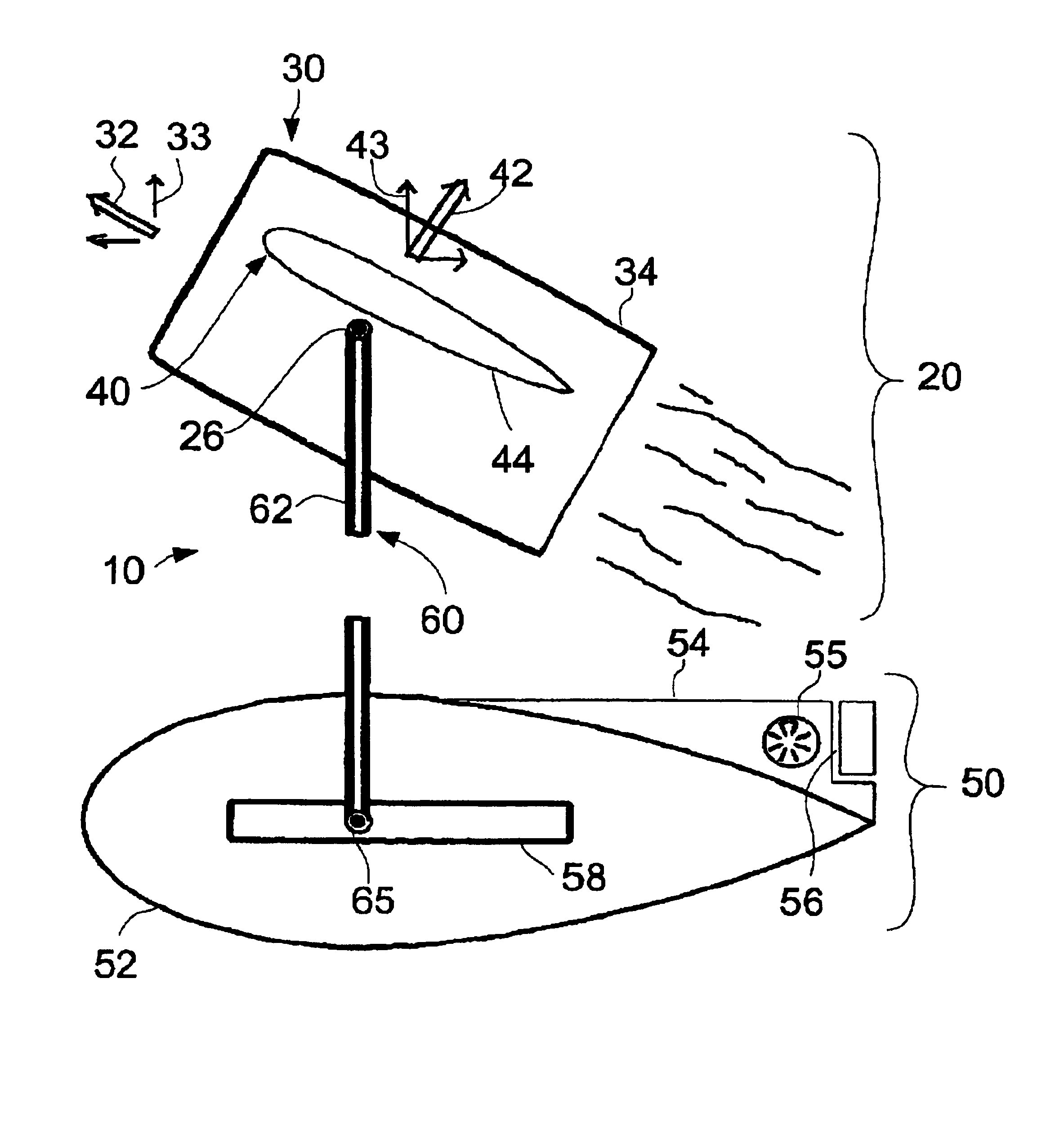
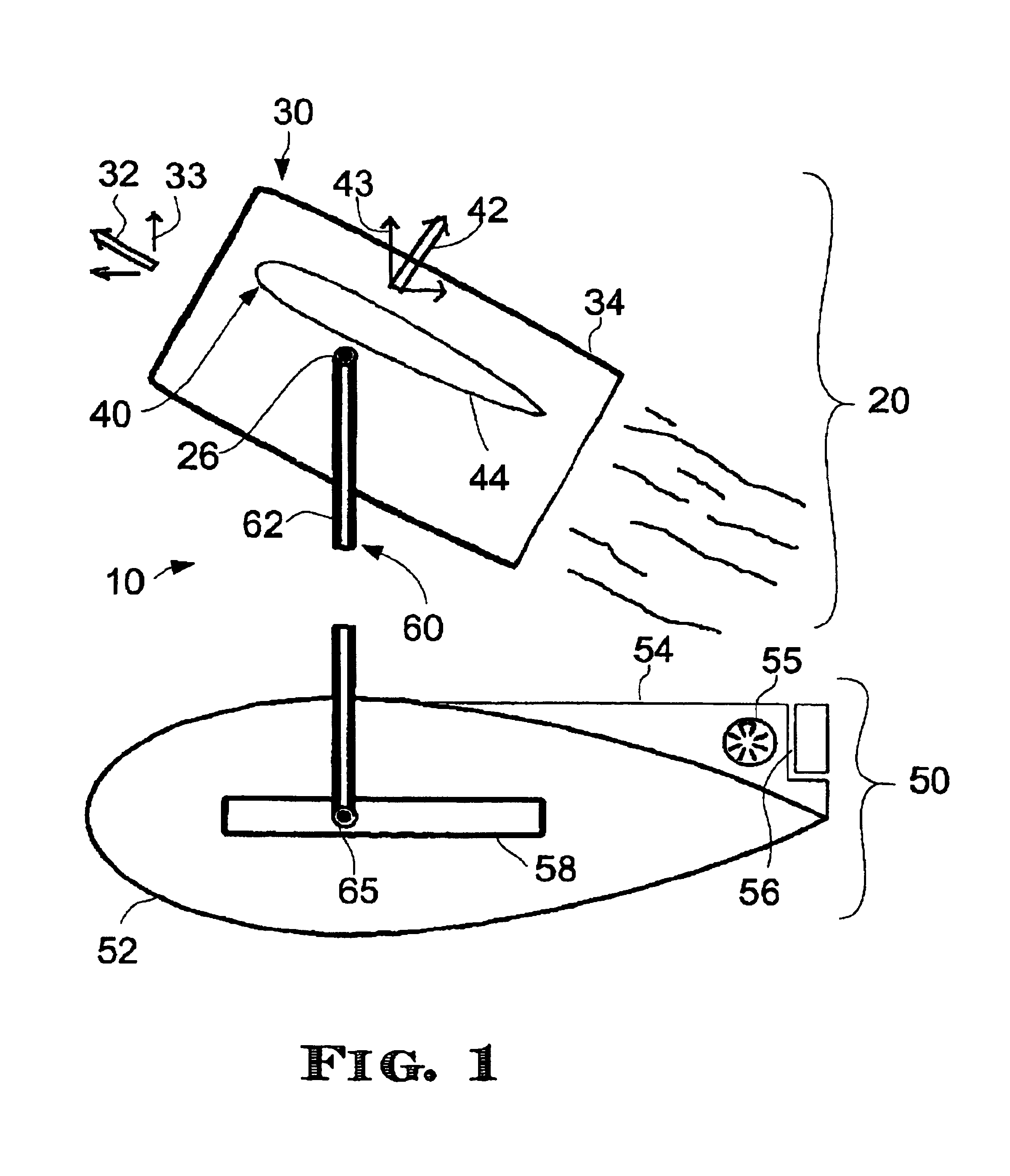
Vertical lift flying craft
InactiveUS7059562B2Avoid developmentReduce wind resistanceAircraft navigation controlPropellersLevel flightFlight vehicle
Owner:BALDWIN G DOUGLAS
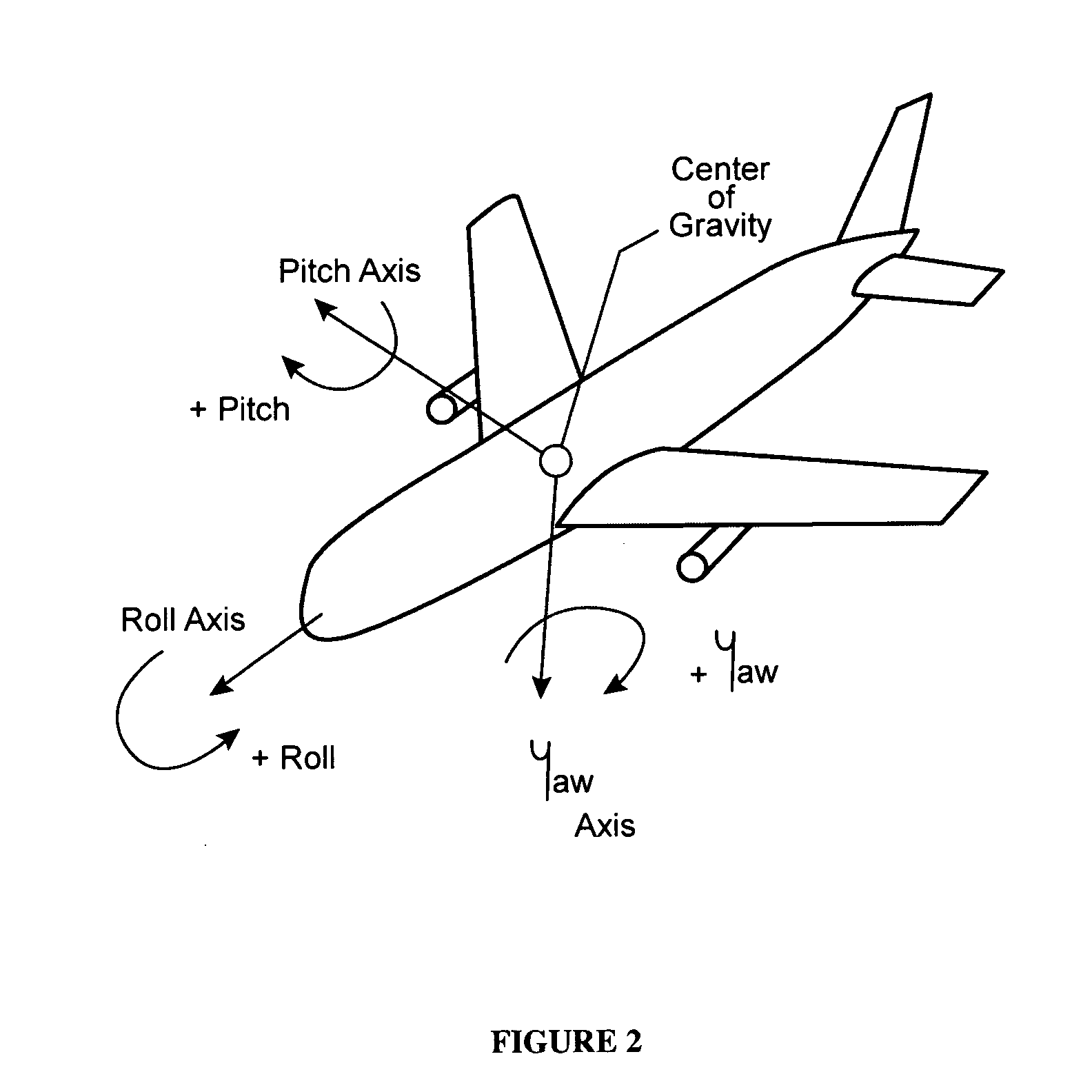
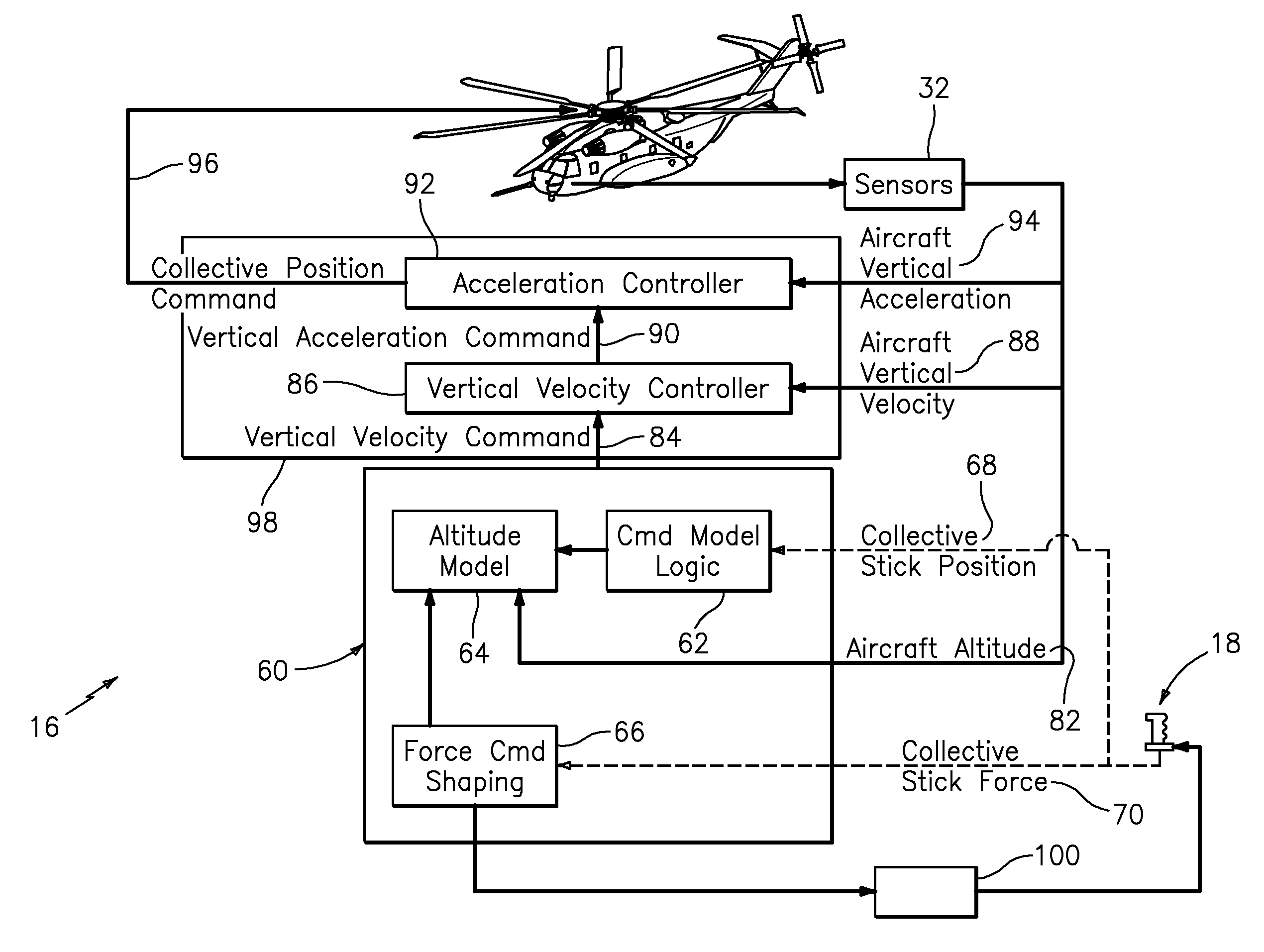
Vertical speed and flight path command algorithm for displacement collective utilizing tactile cueing and tactile feedback
ActiveUS20080234881A1Improve processing qualityEnhanced Situational AwarenessAircraft controlDigital data processing detailsLevel flightDetent
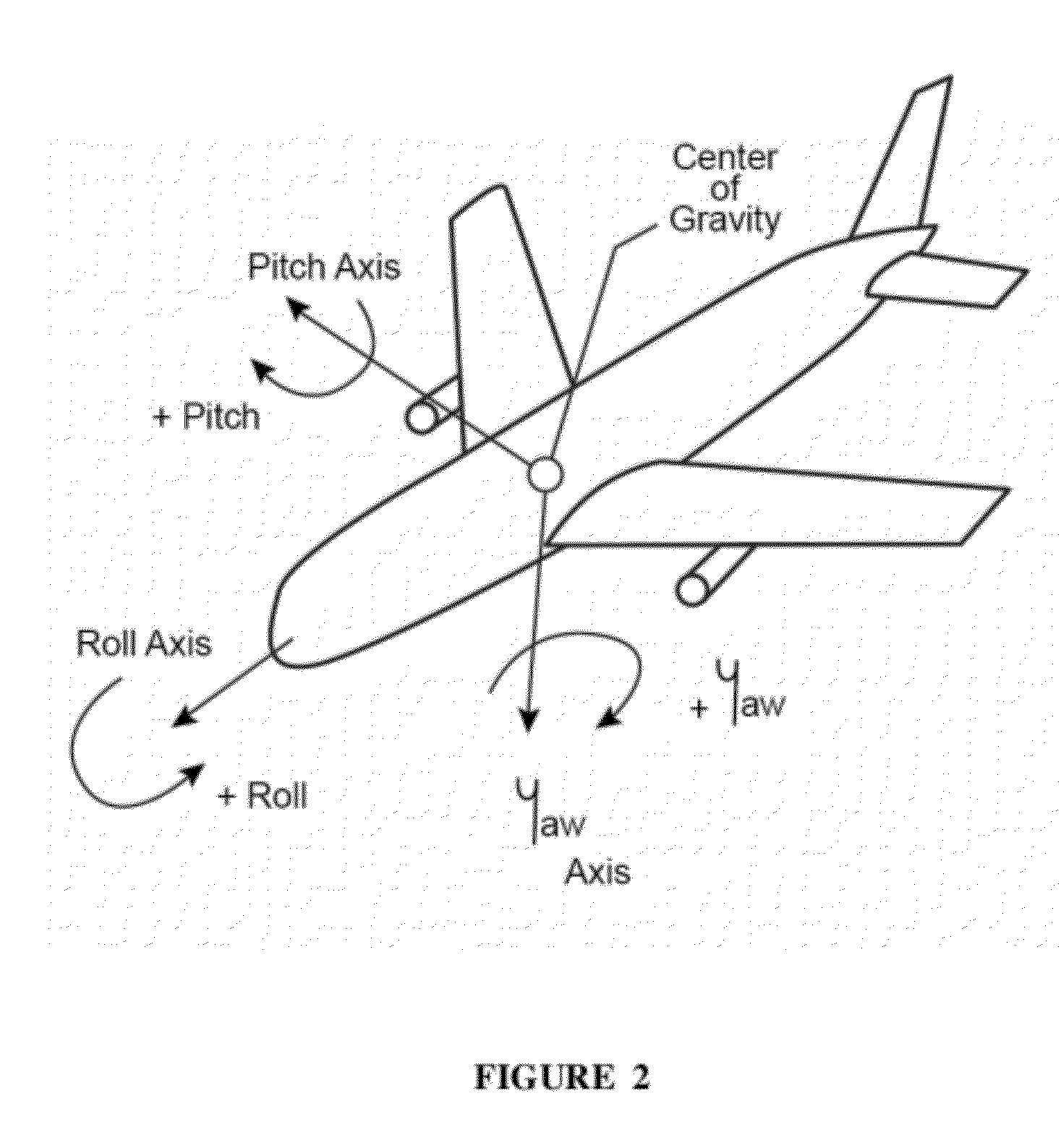
A flight control system includes a collective position command algorithm for a lift axis (collective pitch) which, in combination with an active collective system, provides a force feedback such that a pilot may seamlessly command vertical speed, flight path angle or directly change collective blade pitch. The collective position command algorithm utilizes displacement of the collective controller to command direct collective blade pitch change, while a constant force application to the collective controller within a “level flight” detent commands vertical velocity or flight path angle. The “level flight” detent provides a tactile cue for collective position to reference the aircraft level flight attitude without the pilot having to refer to the instruments and without excessive collective controller movement.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Delta fuselage for vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft is provided. The aircraft includes a wing, nacelles supportively disposed at opposite ends of the wing, proprotors respectively attached to each of the nacelles with each of the proprotors being rotatable to generate lift in vertical flight and thrust in horizontal flight and a delta-wing shaped fuselage disposed along the wing between the nacelles.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Personal aircraft
ActiveUS8485464B2Easy to controlMinimize disturbanceAircraft power plantsPropellersLevel flightPropeller
A safe, quiet, easy to control, efficient, and compact aircraft configuration is enabled through the combination of multiple vertical lift rotors, tandem wings, and forward thrust propellers. The vertical lift rotors, in combination with a front and rear wing, permits a balancing of the center of lift with the center of gravity for both vertical and horizontal flight. This wing and multiple rotor system has the ability to tolerate a relatively large variation of the payload weight for hover, transition, or cruise flight while also providing vertical thrust redundancy. The propulsion system uses multiple lift rotors and forward thrust propellers of a small enough size to be shielded from potential blade strike and provide increased perceived and real safety to the passengers. Using multiple independent rotors provides redundancy and the elimination of single point failure modes that can make the vehicle non-operable in flight.
Owner:WISK AERO LLC
Tilt Wing Aerial Vehicle
ActiveUS20150225071A1Improve translationAircraft navigation controlRemote controlled aircraftLevel flightFlight vehicle
A multi-engine aircraft is disclosed which is convertible from horizontal flight mode to a vertical flight mode. The aircraft comprises an aircraft fuselage defining a fuselage longitudinal axis, and the first and second wing attached to the fuselage. Each wing defines first and second wing segments. The first segments are translatable about the fuselage longitudinal axis, from a horizontal mode position adjacent the second wing segments to vertical fight mode wherein the first wing segment are substantially offset from the second wing segments. An aircraft propulsion unit is attached to each of the first and second wing segments. The propulsion units attached to a common wing being disposed in substantial axial alignment when the aircraft operates in a horizontal flight mode, and being substantially offset when the aircraft operates in a vertical flight mode. A senor unit is connected to a forward portion of the fuselage.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Zero Transition Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft
InactiveUS20140158815A1Stable levelOptimize both vertical and forward flightAircraft navigation controlVertical landing/take-off aircraftsNacelleLevel flight
A zero transition vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft, which is stable in all levels of flight, especially the transition phase from vertical to horizontal flight. The zero transition VTOL aircraft is capable of achieving both vertical and horizontal flight without changing the positioning of thrusters, such as through the use of tiltable or rotatable nacelles or wings. Rather a front thruster assembly and a rear thruster assembly are positioned at specific angles in relation to each other along at least one fuselage in order to generate the desired ratio of vertical to horizontal thrust. At least one wing is also positioned at a specific wing angle in order to achieve a desired angle of attack when in horizontal flight. The attitude of the zero transition VTOL aircraft can be controlled through the use of differential thrust alone, or in conjunction with control surfaces.
Owner:RENTERIA JOSEPH RAYMOND
System and method for improving transition lift-fan performance
ActiveUS20130140404A1Reduce air resistanceImprove efficiencyPropellersVehicle position/course/altitude controlLevel flightThrottle
A system and method enabled to increase efficiency during a VTOL aircraft's transition. A VTOL aircraft enabled to operate multiple lift fans arranged into separately controllable groups, wherein the VTOL aircraft initially has vertical flight but transitions to horizontal flight. A first group of lift fans may be kept at full throttle, a second group of lift fans may be throttled to balance thrust and / or weight, and a third group of lift fans may be shut off.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
Vertical speed and flight path command module for displacement collective utilizing tactile cueing and tactile feedback
ActiveUS7930074B2MoreImprove handling qualityAircraft controlDigital data processing detailsLevel flightConstant force
A flight control system includes a collective position command module for a lift axis (collective pitch) which, in combination with an active collective system, provides a force feedback such that a pilot may seamlessly command vertical speed, flight path angle or directly change collective blade pitch. The collective position command module utilizes displacement of the collective controller to command direct collective blade pitch change, while a constant force application to the collective controller within a “level flight” detent commands vertical velocity or flight path angle. The “level flight” detent provides a tactile cue for collective position to reference the aircraft level flight attitude without the pilot having to refer to the instruments and without excessive collective controller movement.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
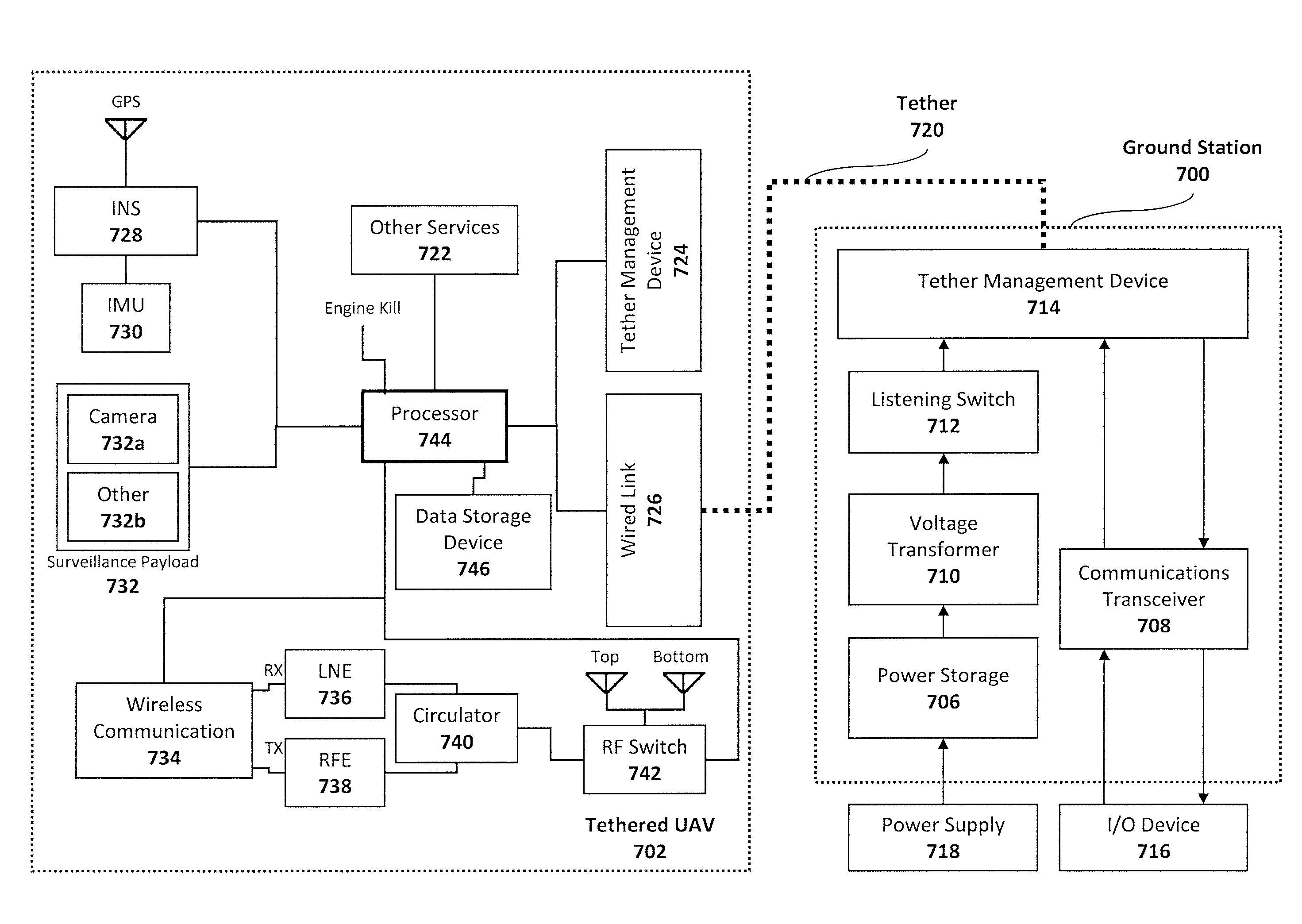
Tethered aerial systems for data gathering
InactiveUS20160144958A1Improve securityIncrease rangeTethered aircraftConvertible aircraftsLevel flightFlight vehicle
A tethered unmanned aerial vehicle (“UAV”) may be outfitted with a sensor payload for data gathering. The tethered UAV may be tethered to a ground station for constricting the flight space of the UAV while also providing the option for power delivery and / or bidirectional communications. The tethered UAV's flight path may be extended by introducing one or more secondary UAVs that cooperate to extend the horizontal flight path of a primary UAV. The ground station, which may be coupled with the tethered aerial vehicle, may comprise a listening switch configured to determine a condition of the tether such that the supply of power to the tether may be terminated when tether damage or a tether severance is detected.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
Slotting duct propeller systems and hovercar applying same
InactiveCN103395491AEasy to liftPropellersAircraft convertible vehiclesLocking mechanismVertical take off and landing
The invention discloses slotting duct propeller systems. In each slotting duct propeller system, the upper portion of a duct is provided with a seam communicated with an inner wall surface and an outer wall surface of the duct, the inner wall of the duct is provided with a controllable mechanism for controlling closing and opening of the seam, so that the seam is closed when the duct is in an approximately horizontal posture and vertical take-off and landing are carried out, so as to reduce a friction resistance of a propeller slipstream in the inner wall and reduce the loss of a direct lift force; the seam is opened when the duct tilts to an approximately perpendicular beneficial incidence angle posture and horizontal flight is carried out, lift augmentation of power is carried out, so as to increase a duct lift force. A hovercar applying the slotting duct propeller systems is provided with folding mechanisms, locking mechanisms and tilting mechanisms, so that the hovercar can be changed between a car status and an aircraft status, and the hovercar can perform vertical take-off and landing in the aircraft status and flies at a high speed.
Owner:李凤
Method and apparatus for managing flight planning
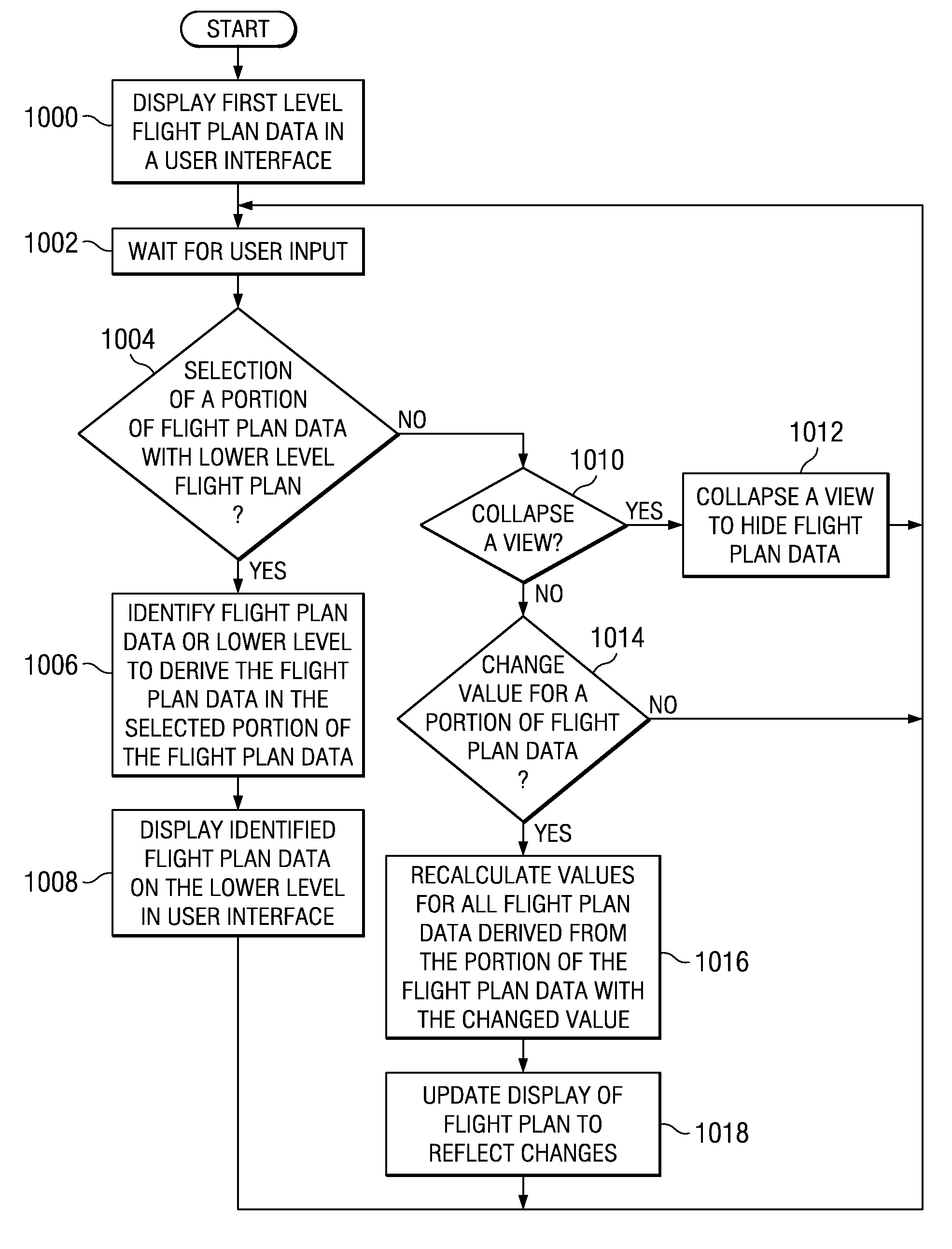
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer usable program code for displaying flight plan data. First level flight plan data is displayed and user input is received selecting a selection of a portion of the first level flight plan data. In response to receiving the selection of the portion of the first level flight plan data, second level flight plan data is displayed, wherein the second level flight plan data displayed is used to derive the selected portion of the first level flight plan data selected by the user input.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Tailless layout single tail seat type vertical take-off and landing aircraft
InactiveCN103287576ACapable of vertical take-off and landingVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftLevel flightLow speed
The invention provides a single aircraft with vertical take-off and landing capacity. The single aircraft comprises a body (1), wings (2), rotor wings (5 and 13) which are arranged on the wings (2) on two sides, and elevons (7) which are arranged at the rear edges of the two wings (2), wherein rolling and pitching can be stabilized and controlled through deflection of the elevons (7); in a vertical take-off and landing period, the head of the aircraft is upward; the aircraft takes off and / or lands in a tail seat manner; the gravity is overcome through elevating force generated by rotation of the rotor wing (5); vertical take-off and landing can be realized. The single aircraft has the advantages that (1) through a tailless layout, the air resistance is effectively reduced, and the flight speed is increased; (2) the advantages of a helicopter and a fixed wing aircraft are taken into consideration, and high efficiency can be maintained in both high-speed level flight and low-speed hovering periods; (3) a rotary mechanism is eliminated, and the single aircraft is simple in structure, high in reliability and low in cost; (4) the aircraft can be stabilized and controlled under low-speed and large-incidence conditions, and is applied to city airspace; (5) an emergency is handled in an engine connecting shaft and full-aircraft parachute-opening manner, and the aircraft is high in safety.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
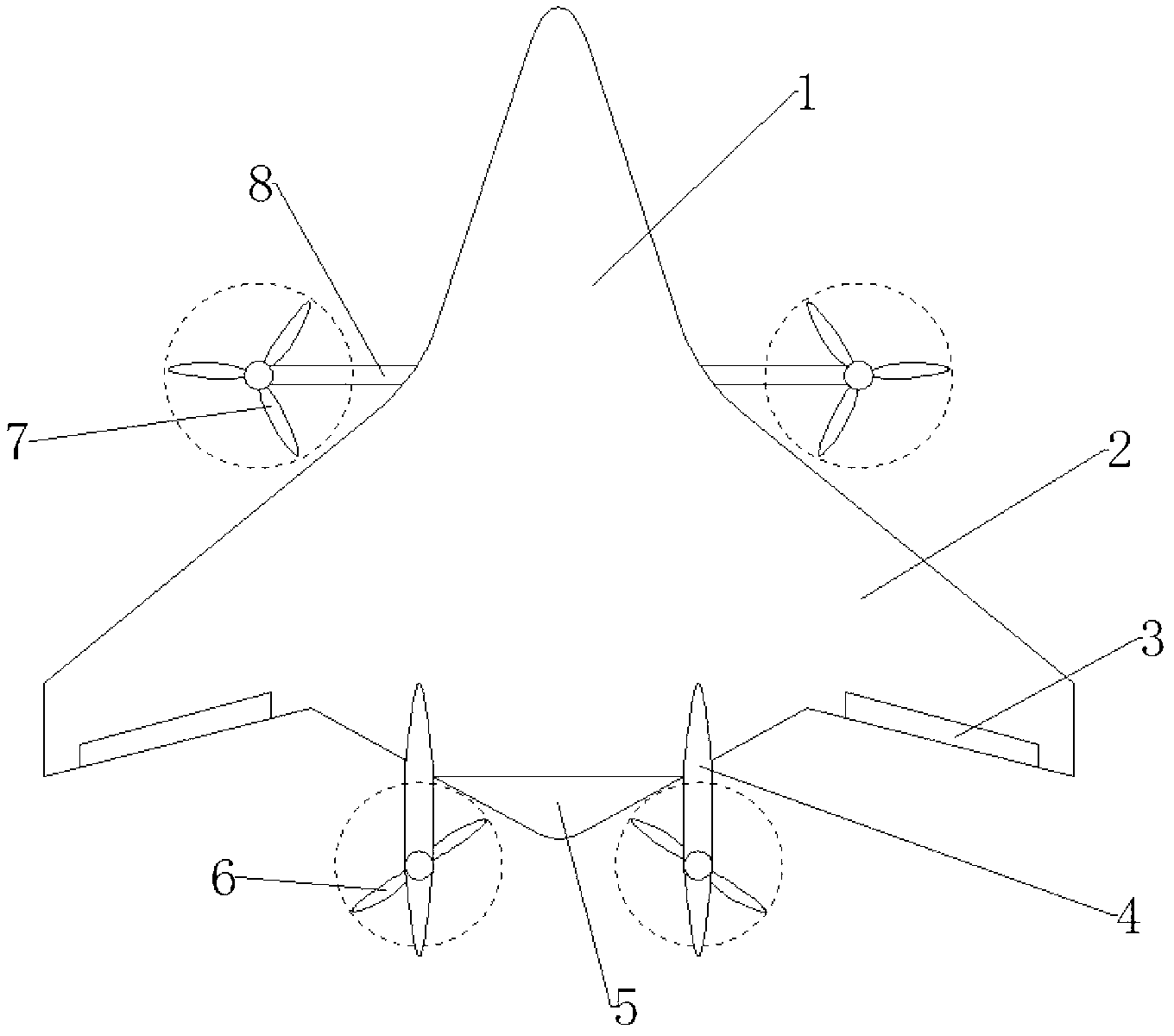
Vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle with foldable fixed wings based on dual-duct fan power system
ActiveCN107176286AImprove aerodynamic performanceBarrier formationPropellersRemote controlled aircraftLow speedTrailing edge
The invention discloses a vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle with foldable fixed wings based on a dual-duct fan power system. A dual-duct fan power system which is horizontally arranged at the tail of the body of the unmanned aerial vehicle in a tail-driving arrangement is adopted, so that lifting force for vertical takeoff and landing and thrust for horizontal flying are provided for an aircraft; a control surface which is arranged at the exit of each duct in a deflected manner is used for providing vector thrust, so that quick attitude change is realized; wings adopt a folding wing configuration, when the aircraft vertically takes off and lands / flies at a low speed, the wings are folded to decrease the frontal area of cross wind, and when the aircraft flies horizontally, the wings are unfolded to obtain large lifting force; and combined optimization of ducts and the wings is adopted, the wings are arranged in a specific duct air flow region, the duct suction generates a Coanda effect at a wing edge, so that the properties of the wings are improved. Multi-mold flight tasks such as vertical takeoff and landing, high-speed cruise, and the like of the aircraft are realized; the vertical takeoff and landing aircraft is high in aerodynamic efficiency during hanging in the air / flying at a low speed; and the vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle is high in anti-disturbance capacity during takeoff and landing / hanging in the air. The vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle is low in energy consumption, small in noise and high in safe reliability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
VTOL Aircraft with Propeller tiltable around two Axes and a retractable Rotor
InactiveUS20140084114A1Reduce weightReduce the space requiredVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftAerodynamic dragFlight direction
A VTOL aircraft has a rotor, wings, and a propeller providing thrust for take-off and landing and horizontal flight. The propeller, attached through a joint mechanism to the aircraft, is continuously tiltable around to axes, providing the anti-torque forces for the rotor and thrust forces for lifting the aircraft and for horizontal flight. The hubs of rotor blade sets are rotatable to each other for alignment. The rotor assembly, attached to a moveable linkage mechanism, is tiltable in or against the direction of flight and movable towards to or into the fuselage. The folded and retracted rotor reduces the air drag and the high thrust of the propeller increase the speed of winged flight. The flexibility and lower weight of the drive are preferably achieved with an advanced hydrostatic drivetrain.
Owner:VALENTIN INGO
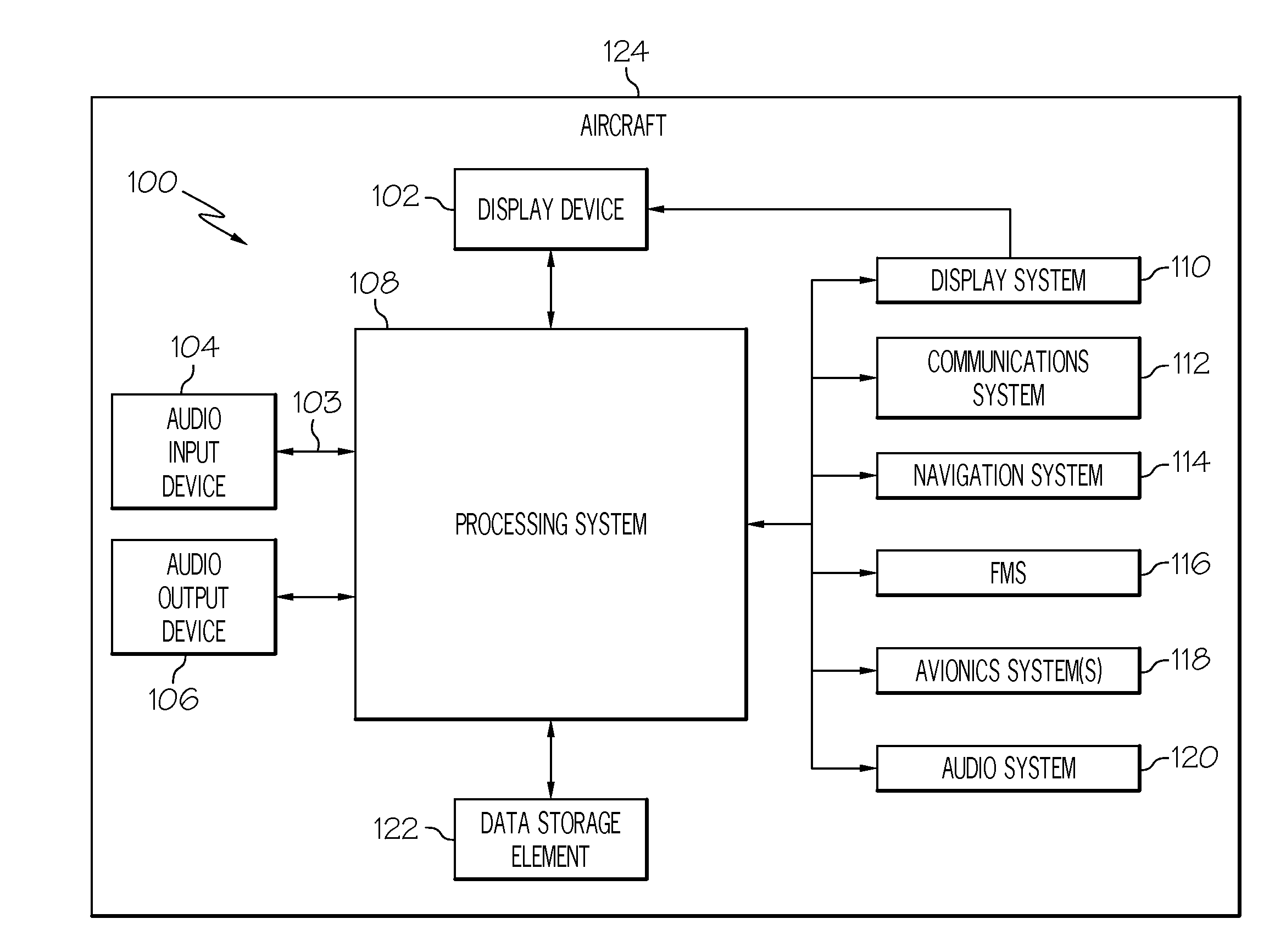
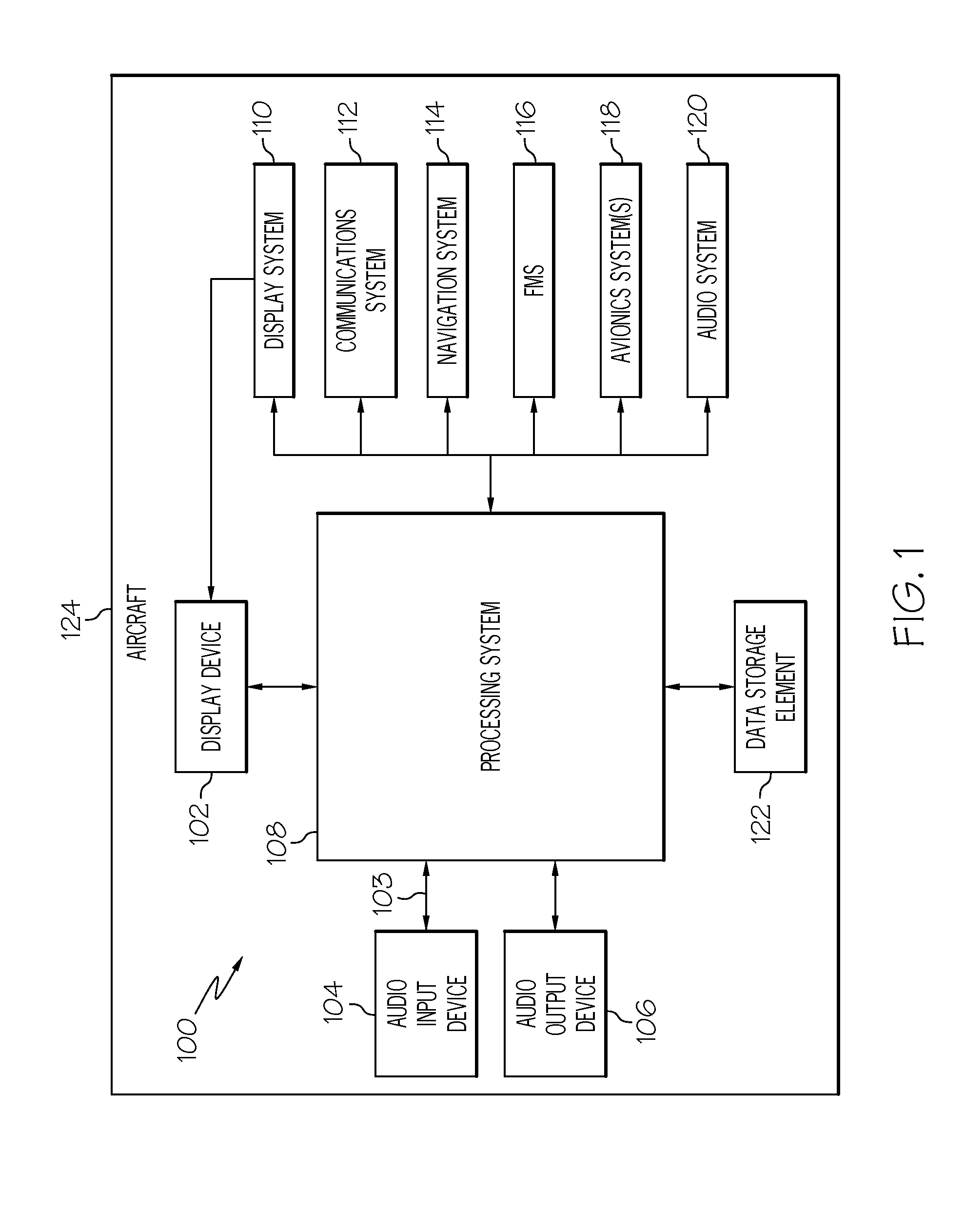
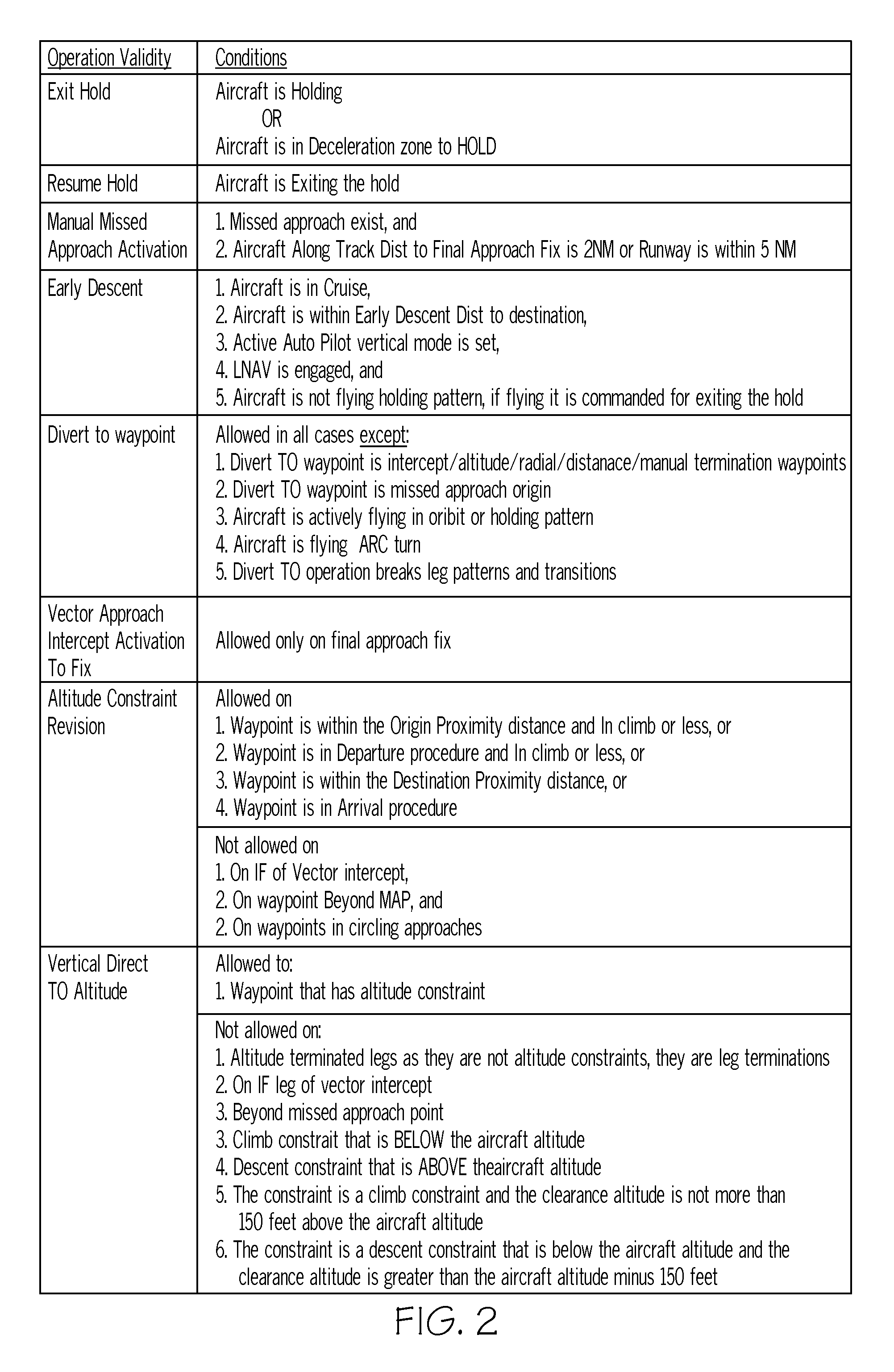
Systems and methods for utilizing voice commands onboard an aircraft
A system and method are provided for programming a flight management system in response to a voice input. The voice input is validated (the pilot spoken vocabulary is thereby filtered (e.g., adapted) to improve recognition accuracy and reduce false positives) by comparing the current operational state of the aircraft (for example, climb, level flight, descent, speed, altitude, and heading), operation validities and availabilities (for example, operations allowed and not allowed) based on the flight management system planned and predicted lateral and vertical trajectory of the flight route (flight plan) from origin / present position to destination, and the requested action being taken.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Tilt-rotor fixed wing aircraft with vertical take-off and landing function
ActiveCN106143898AStable flightExtended flight timeAircraft stabilisationVertical landing/take-off aircraftsJet aeroplaneAviation
Owner:北京奇正数元科技股份有限公司
Land and air double-used aircraft
InactiveCN101885295AGood for air flightShorten the lengthVertical landing/take-off aircraftsAircraft convertible vehiclesGratingLevel flight
The invention relates to a land and air double-used aircraft, comprising an aircraft body, an aircraft controller, an engine and an undercarriage, wherein a front ducted fan which faces the wind at upper front is connected with the lower part of the front end of the aircraft body; a rear ducted fan which faces the wind at upper front is connected with the upper part of the rear end of the aircraft body; the front ducted fan and the rear ducted fan form a Z-shaped structure with the aircraft body; the front ducted fan and the rear ducted fan are respectively connected with a guide plate and a stream guiding grating; a pull rod pulling the stream guiding grating is connected with a pull rod electric motor; the undercarriage comprises a front support and a rear support which are respectively arranged at the frond end and at the rear end of the aircraft body; a front wheel is connected with the lower end of the front support; a rear wheel is connected with the lower end of the rear support; and the front wheel and the rear wheel are driven by a wheel-and-axle electric motor or a motorcycle engine. The invention discloses a land and air double-used light aircraft which can take off and land vertically, flies horizontally and can run on the ground normally, effectively solves the problem that the existing aircraft has complicated structure, heavy weight and low safety performance, and is beneficial for the aircraft to be used early and safely.
Owner:杨朝习
Aircraft full-section control method based on anti-interference technology
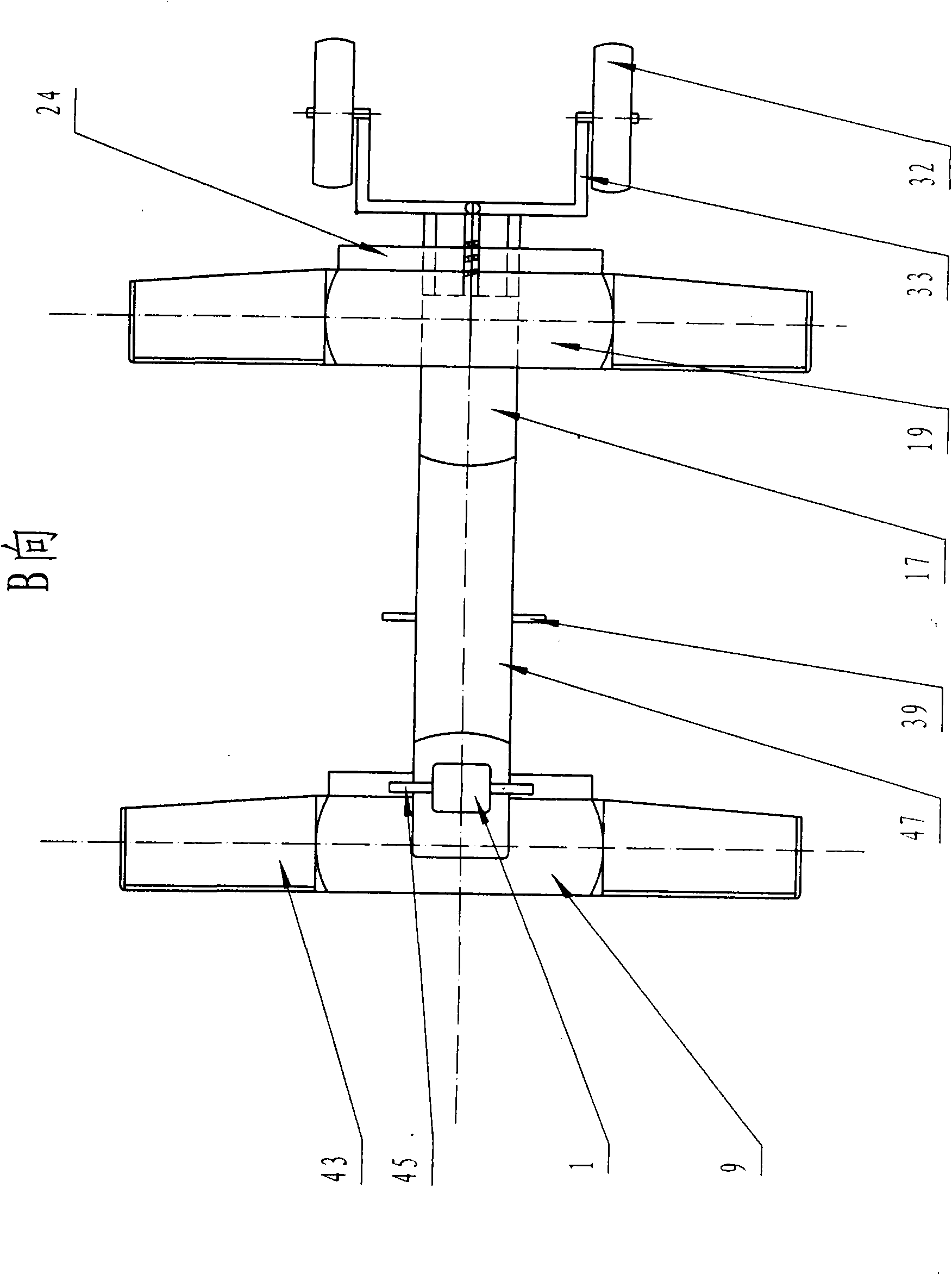
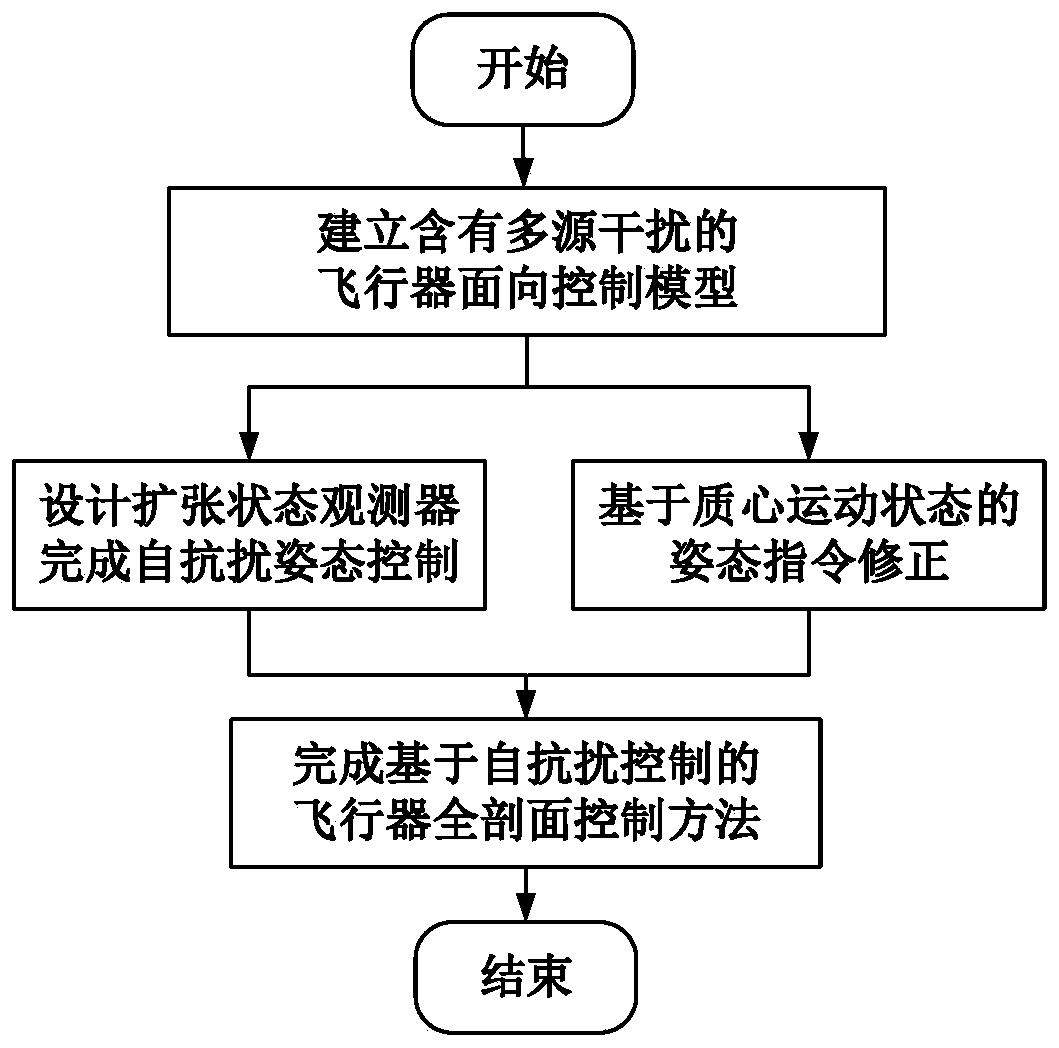
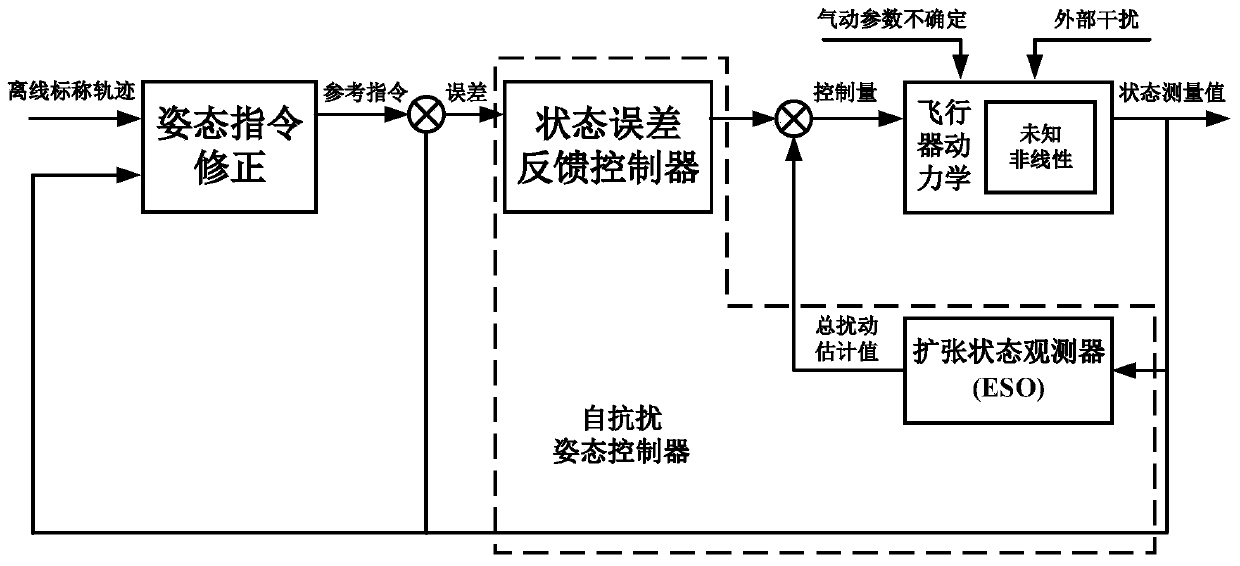
ActiveCN110377045AHigh precisionAchieve strong robustnessAutonomous decision making processAttitude controlLevel flightDynamic models
The invention relates to an aircraft full-section control method based on the anti-interference technology. For an aircraft full-section control problem under unknown nonlinear dynamics, aerodynamic parameter uncertainty and external disturbance, the method comprises a step of establishing an aircraft six-degree-freedom model containing the above multi-source interference, converting an attitude dynamics model into an integral series type by linear state transformation and calling the uncertainty, the external disturbance and the unknown nonlinear dynamics as total disturbance, and representing with an expansion state, a step of designing an extended state observer to quickly estimate the aircraft total disturbance to obtain an interference estimation value, a step of designing an aircraftattitude controller based on active disturbance rejection control, and a step of designing attitude command correction based on a centroid motion state to complete the aircraft full-section control method based on the active disturbance rejection control. The invention realizes the full-section control of a level flight section and a going down section of an unpowered reentry vehicle, and the method has the characteristics of high robustness and easy engineering realization and is suitable for various types of flight systems requiring unpowered reentry.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Vertical/short take-off and landing aircraft
InactiveUS8256704B2Easy to buildEasy maintenanceUnmanned aerial vehiclesDigital data processing detailsLevel flightPropeller
A vertical / short take-off and landing aircraft with a single proprotor assembly that has a pair of inline counter-rotating rotors. Two inline counter-rotating engines are directly connected to the rotors. One engine is shut down in horizontal flight to improve efficiency. Gimbal mounting the proprotor assembly permits thrust to be directed forward to back and left to right to control pitch and roll when hovering. Varying the relative engine speeds controls yaw. The aircraft is adaptable as an unmanned vehicle.
Owner:LAPCAD ENG
Vertical/short take-off and landing flying wing layout aircraft
InactiveCN103192990ALarge internal spaceReasonable weight distributionDepending on number of propellersRotocraftFlight directionLevel flight
The invention provides a flying wing layout aircraft which comprises an aircraft body (1), aircraft wings (2), ailerons, an elevator (5) and double vertical fins (4), wherein the aircraft body (1) and the aircraft wings (2) are integrated; the ailerons (3) are positioned on the outer sections of the aircraft wings (2), and are used for rolling control in level flight; the elevator (5) is positioned at the rearmost part of the aircraft body (1), and is used for pitching control in level flight; and the dual vertical fins (4) are positioned at the rear part of the aircraft body (1), and are used for enhancing the flight direction safety in level flight. The flying wing layout aircraft provided by the invention has the advantages that the aircraft body integration technique inherits the excellent pneumatic property of the flying wings, and larger internal space is provided; the weight distribution is more reasonable, and the structure is lighter, so that the load and the voyage are increased; front air screws which are arranged in an engine and tilt and rear air screws which are fixed and can be accommodated in the vertical fins achieve the capability of vertical / short take-off and landing, and the interference to the whole pneumatic appearance of the aircraft is lowered greatly; and the connection shaft design among engines greatly improves the reliability of a dynamic system, avoids the dangerous situation of invalidity after taking off, and guarantees the flight safety in vertical / short take-off and landing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com