Patents
Literature
94 results about "Slipstream" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A slipstream is a region behind a moving object in which a wake of fluid (typically air or water) is moving at velocities comparable to the moving object, relative to the ambient fluid through which the object is moving. The term slipstream also applies to the similar region adjacent to an object with a fluid moving around it. "Slipstreaming" or "drafting" works because of the relative motion of the fluid in the slipstream.
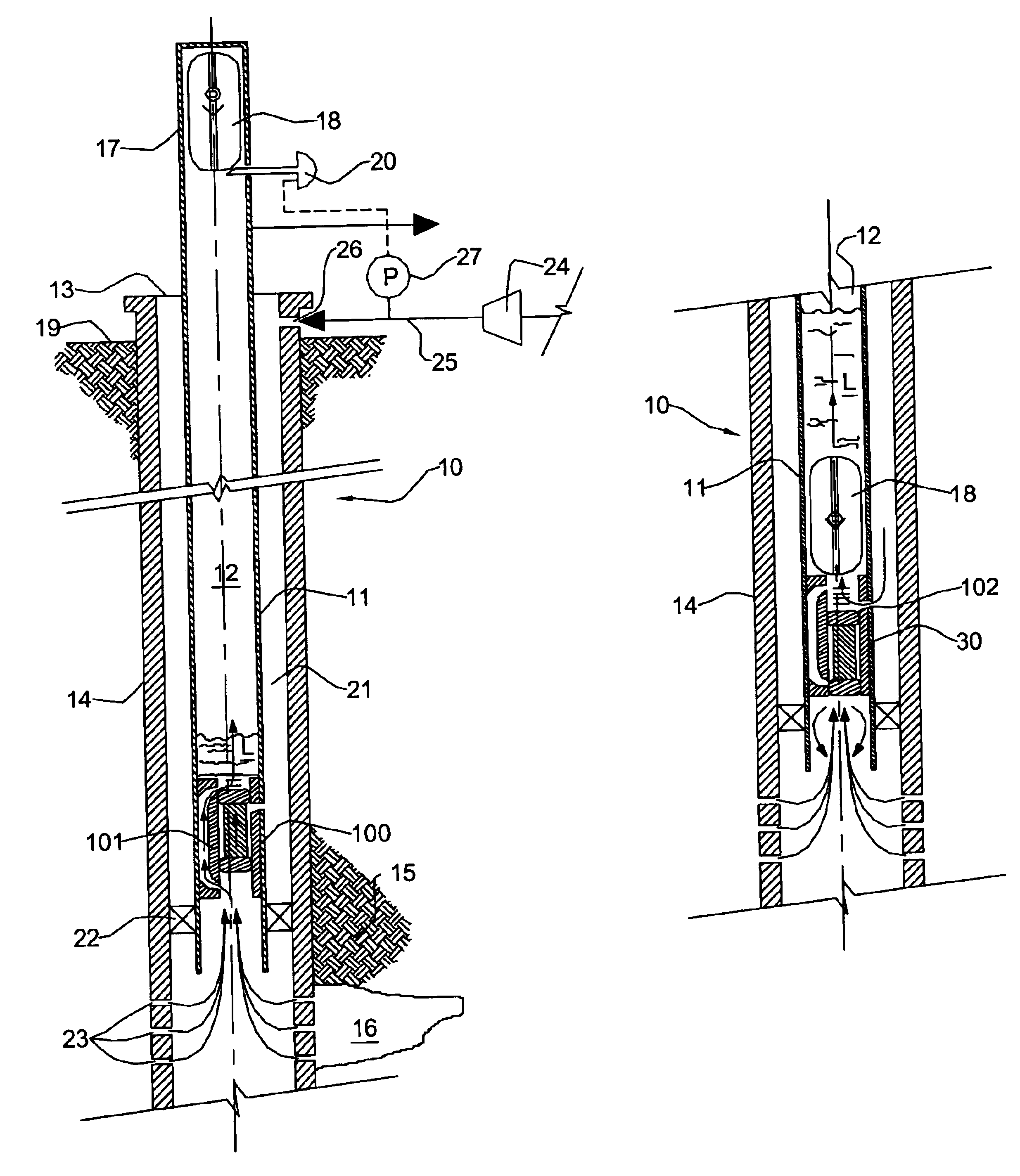
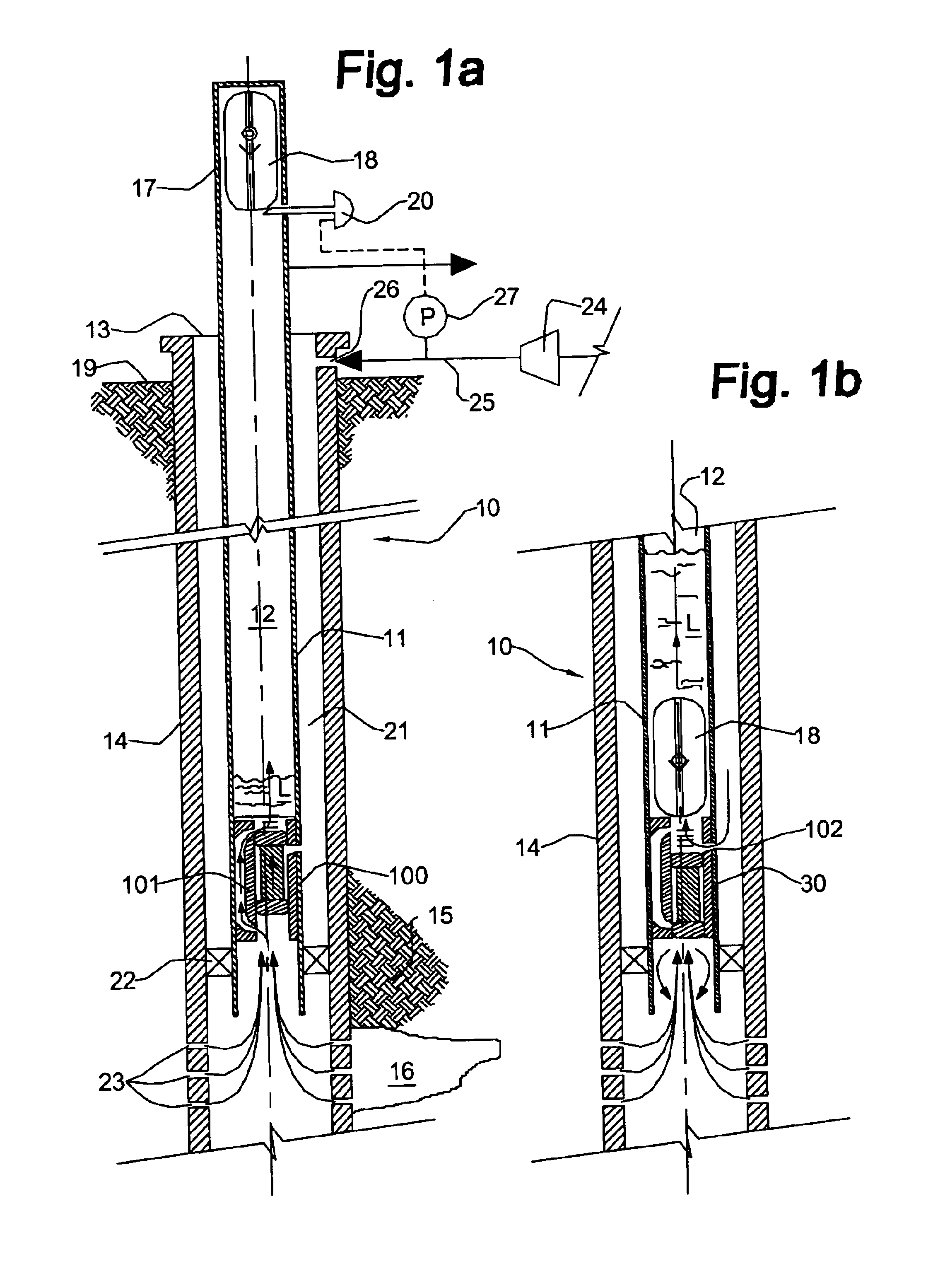
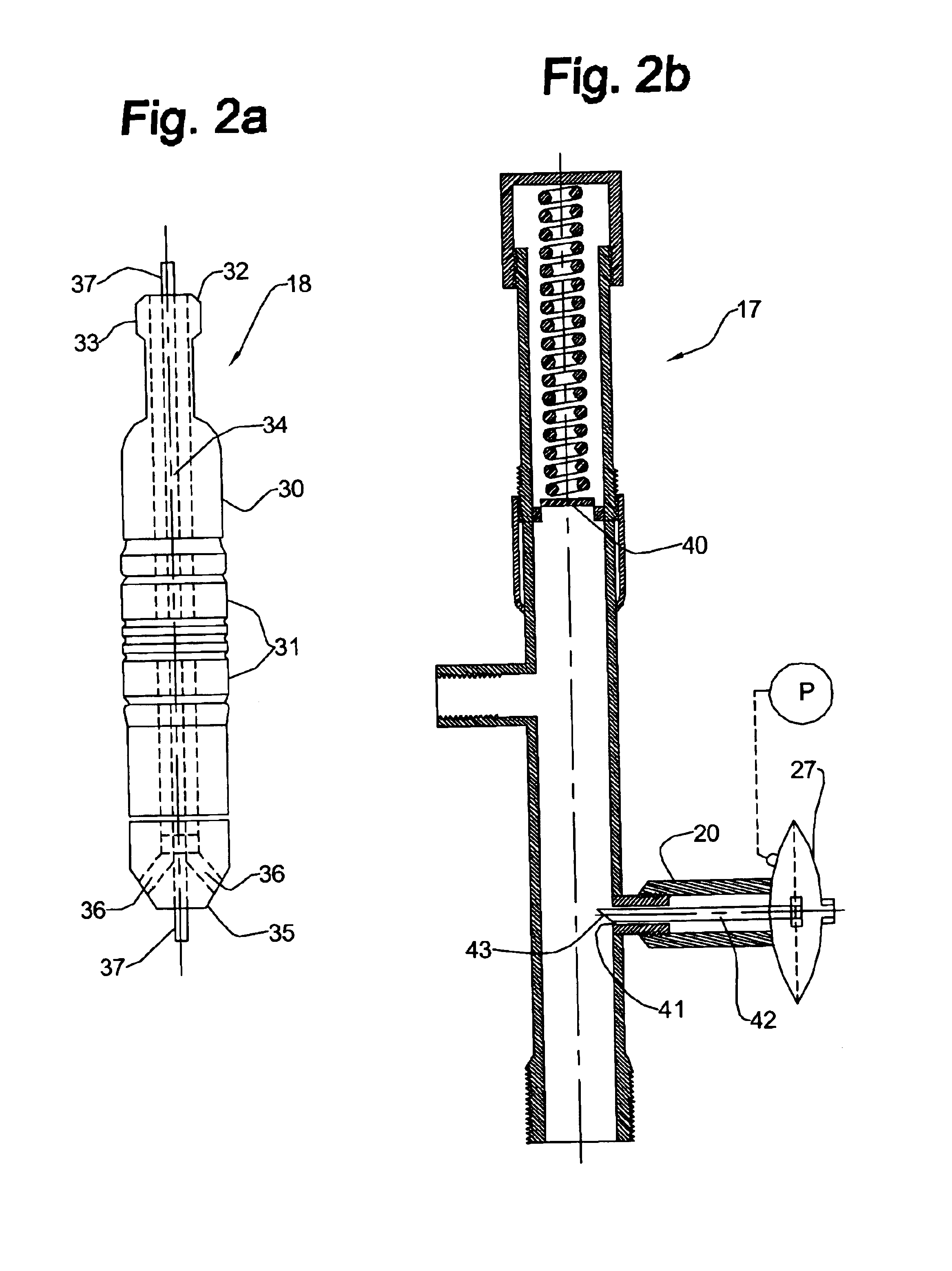
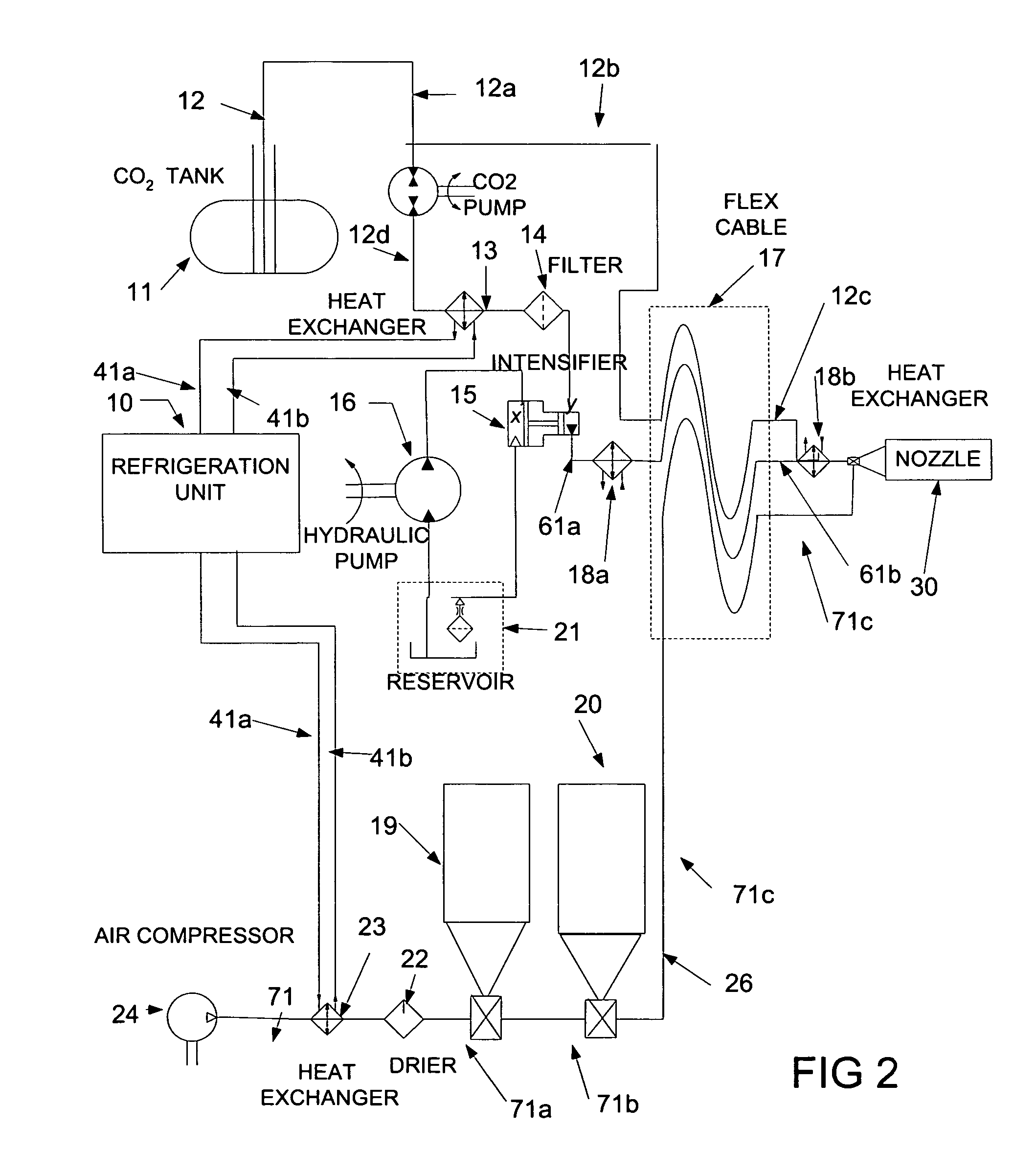
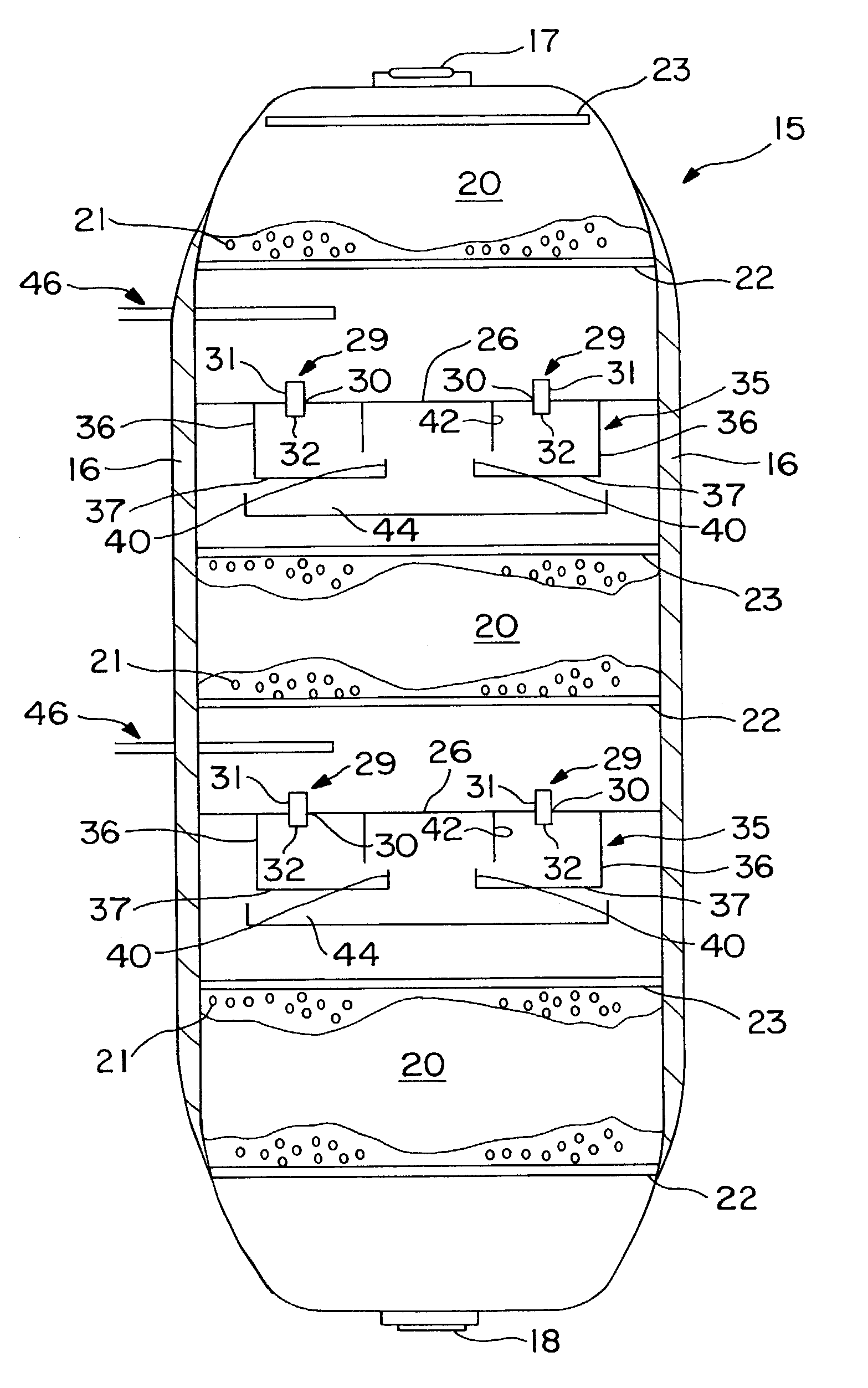
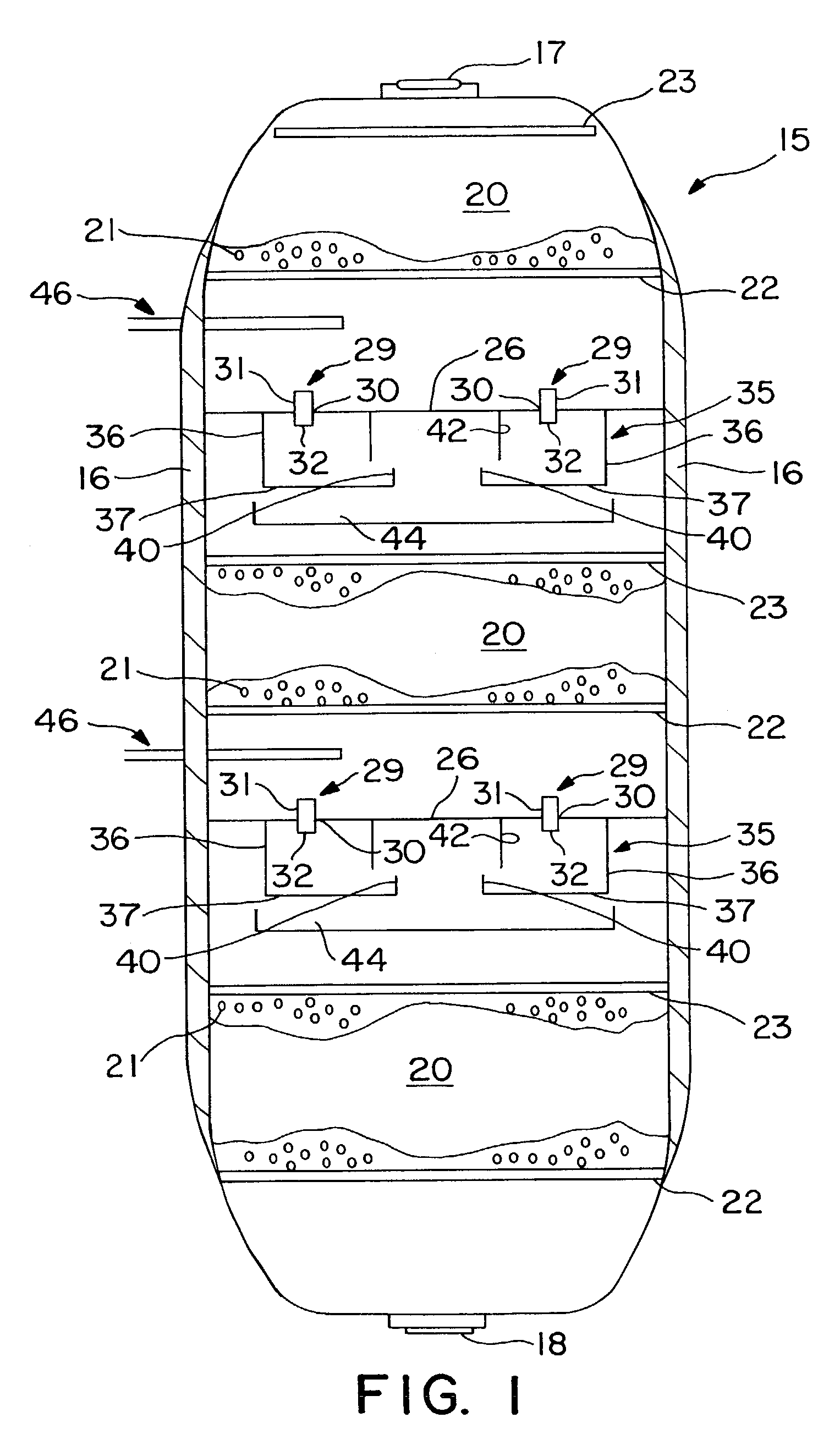
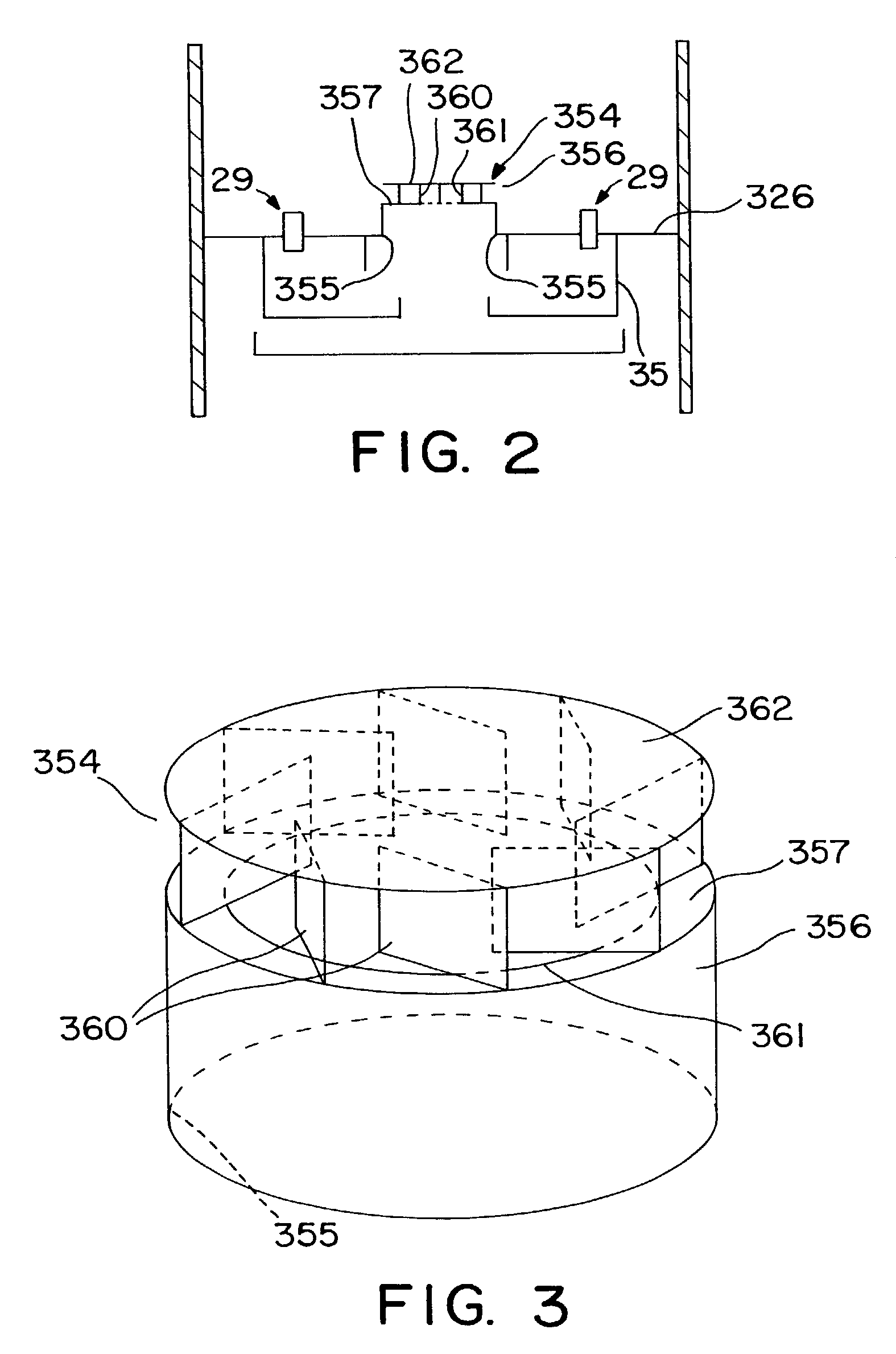
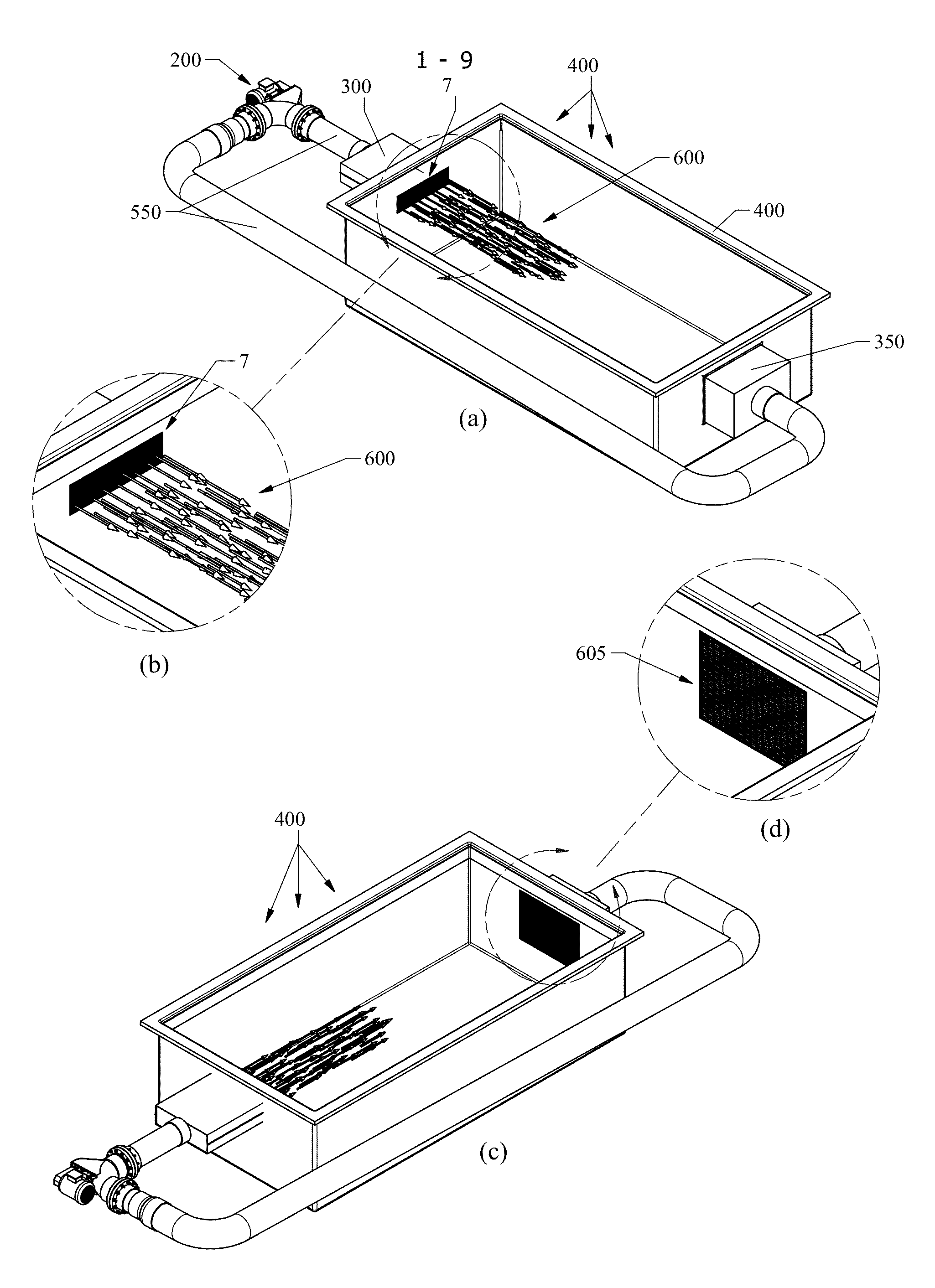
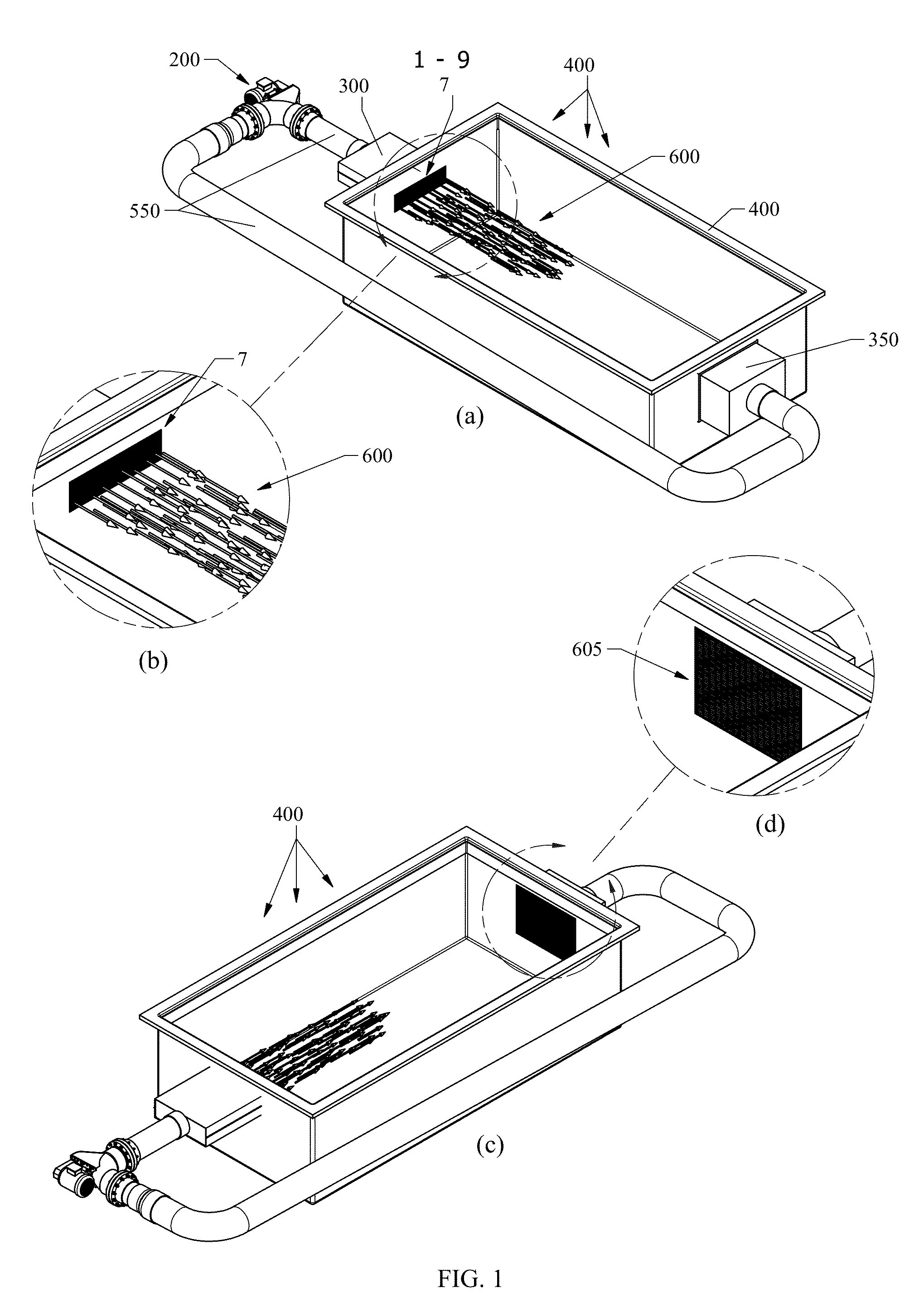
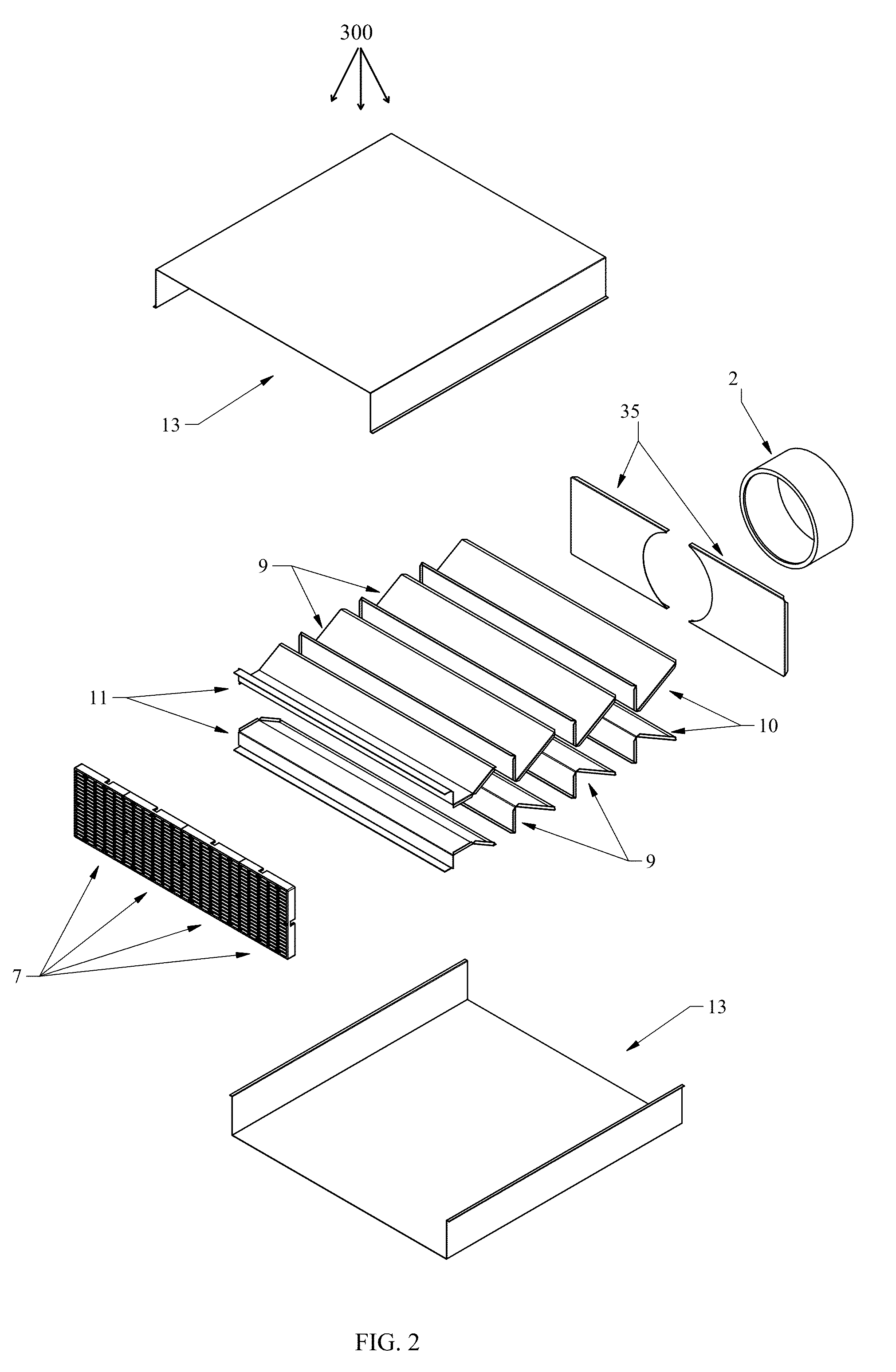
Open well plunger-actuated gas lift valve and method of use
InactiveUS6907926B2Increase gas productionReduce hydrostatic pressureFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringHigh pressure
A system is provided for unloading accumulated liquids and enhancing the recovery of gas from a reservoir having diminished pressure. An annulus between a tubing string and casing is isolated by a packer and continually pressurized with a slipstream of compressed gas while the well continues to produce. A unique valve positioned in the tubing string is shuttled between a production position in which production fluids are permitted to bypass the valve to the surface and a lift position in which the bypass is blocked and an unloading port is opened to vent high pressure annulus gas to the tubing string above the valve, lifting accumulated liquids with it. Preferably, the valve is actuated to the lift position by the impact of a plunger dropped from a lubricator at the wellhead, when the pressure in the annulus has reached a predetermined threshold. When the gas has been vented and the pressure in the annulus drops, the valve is actuated to the uphole production position as a result of the higher reservoir pressure.
Owner:G BOSLEY OILFIELD SERVICES
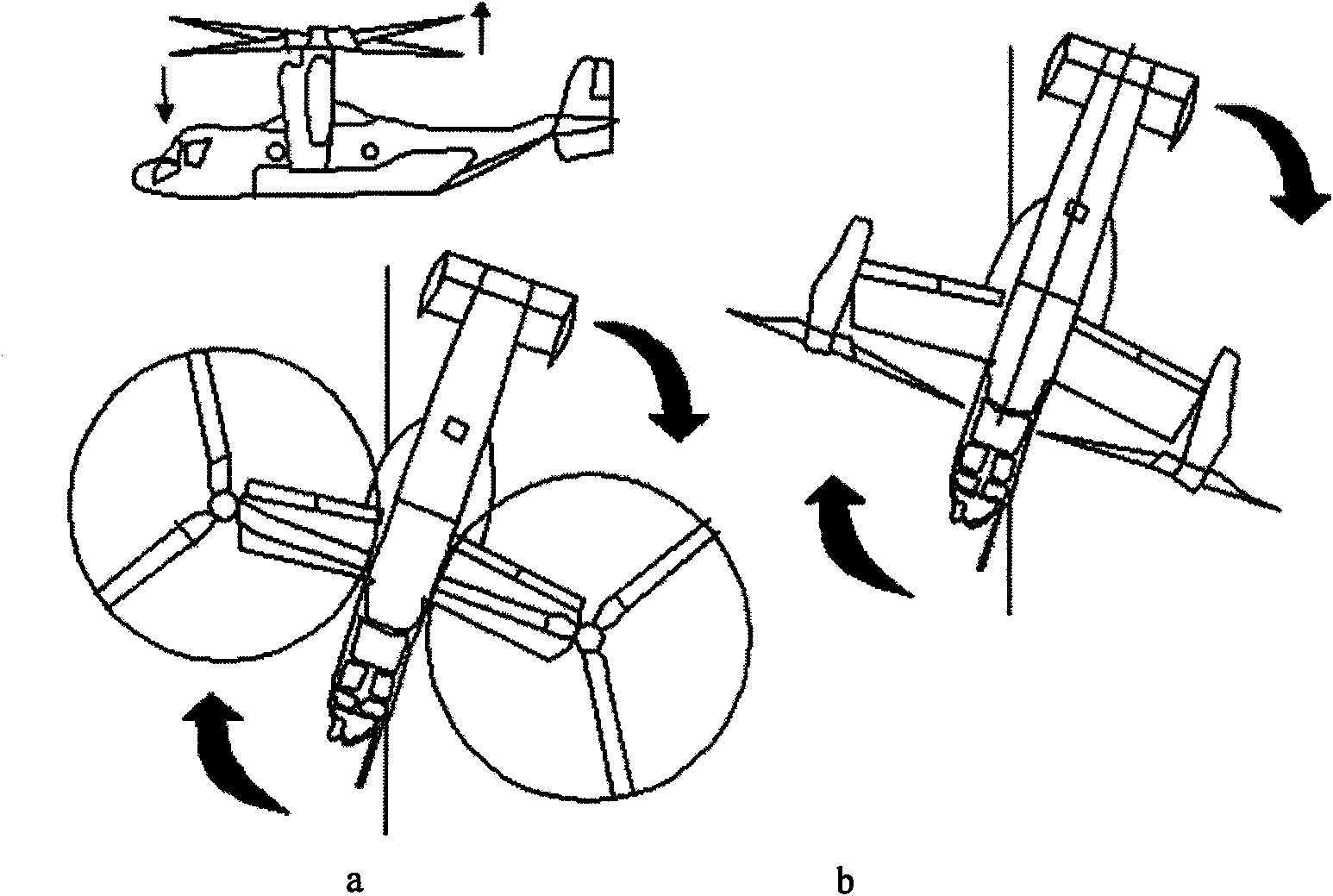
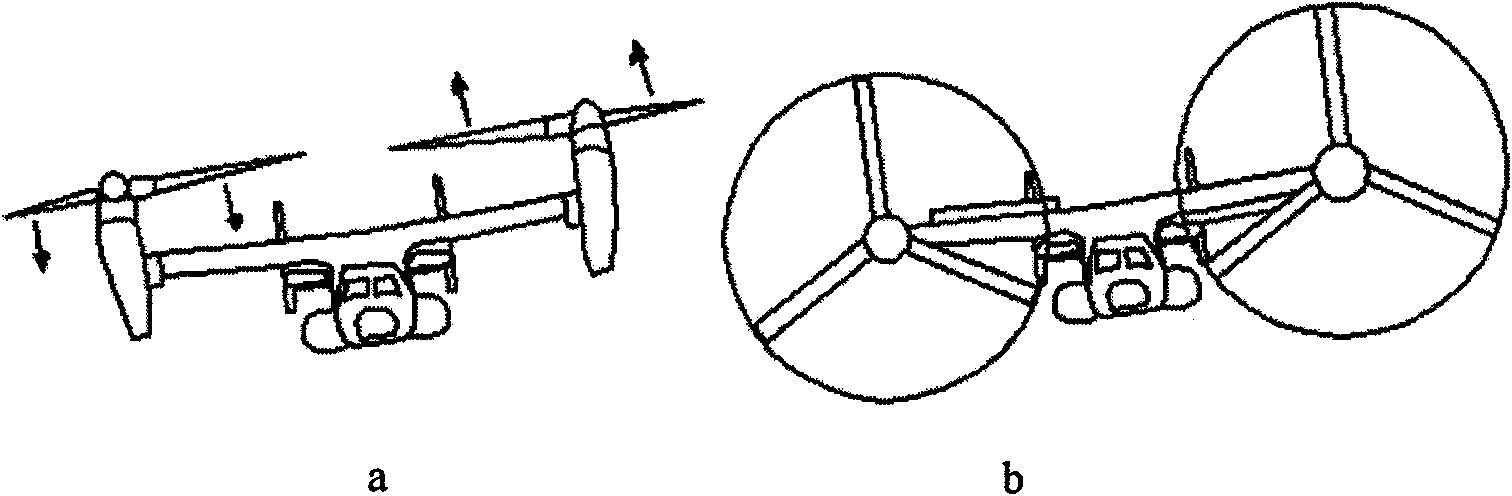
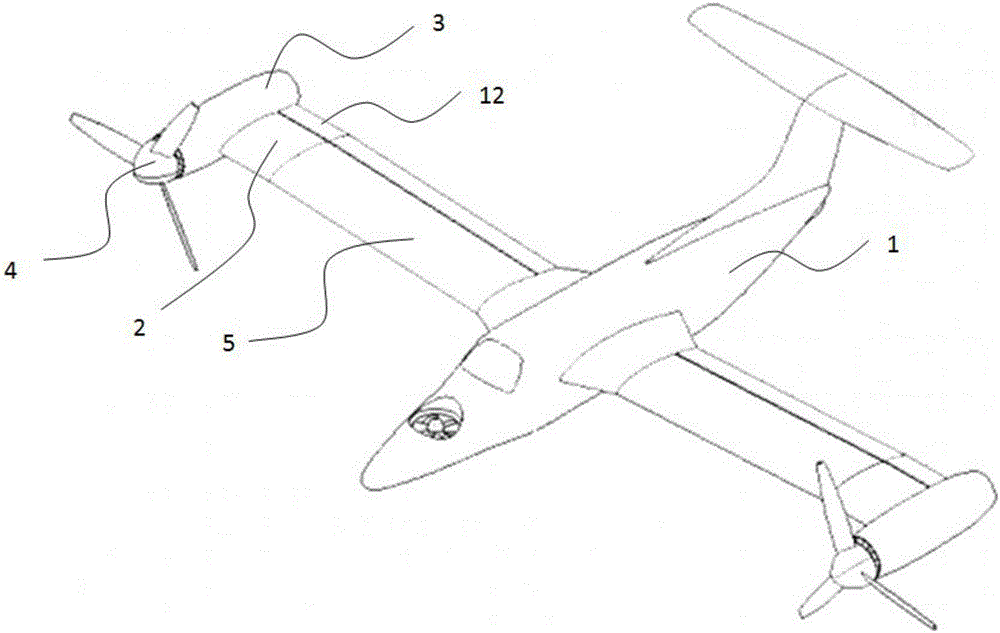
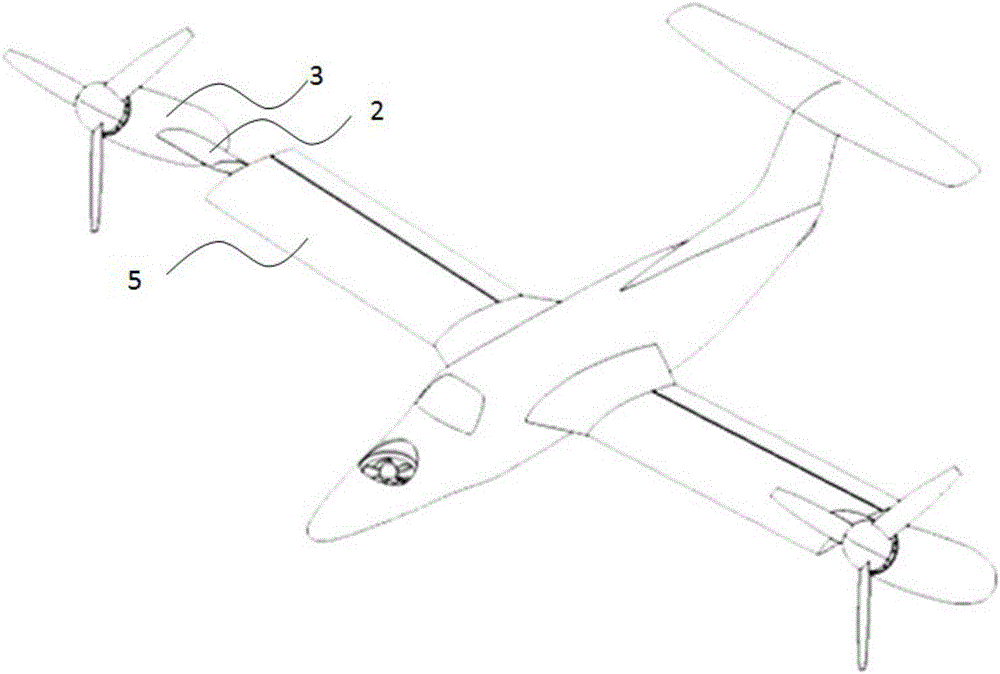
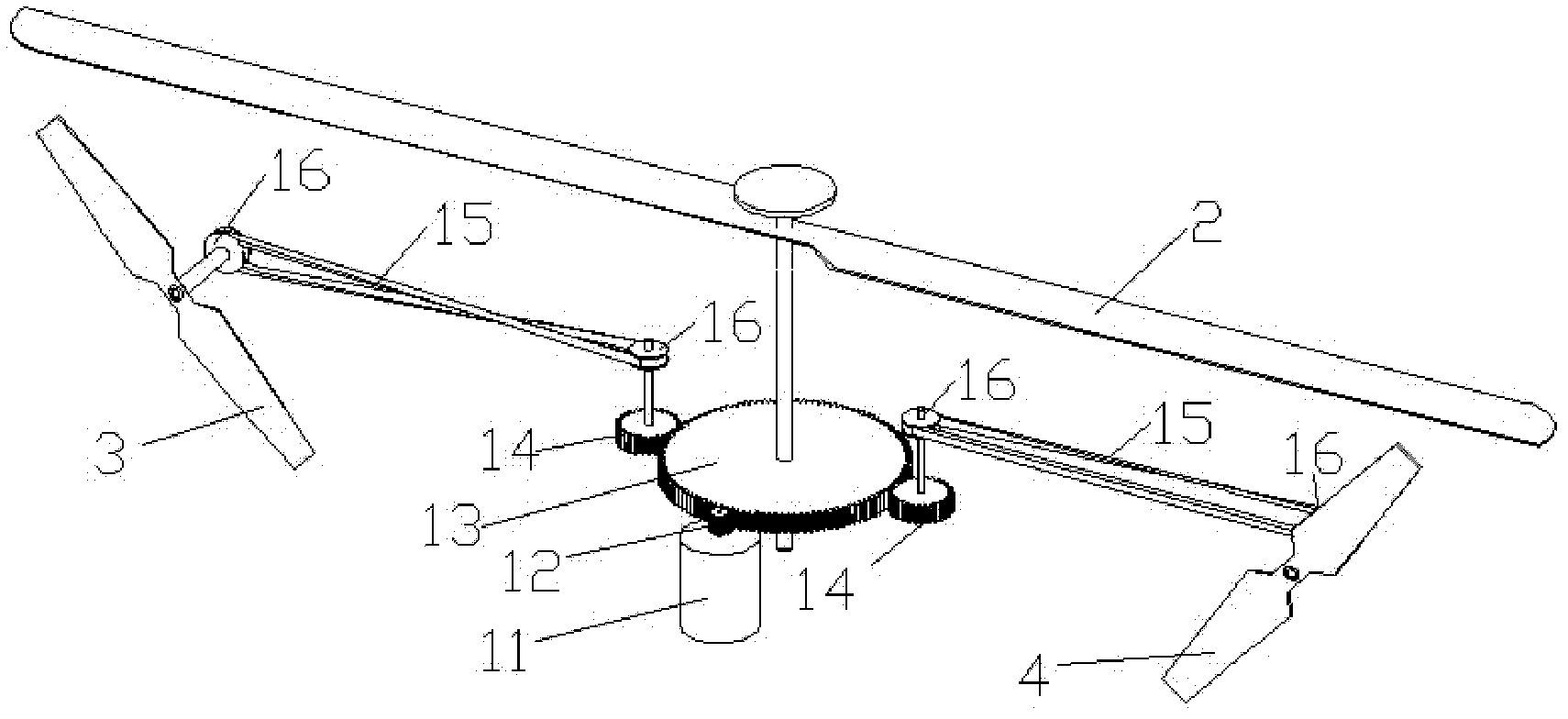
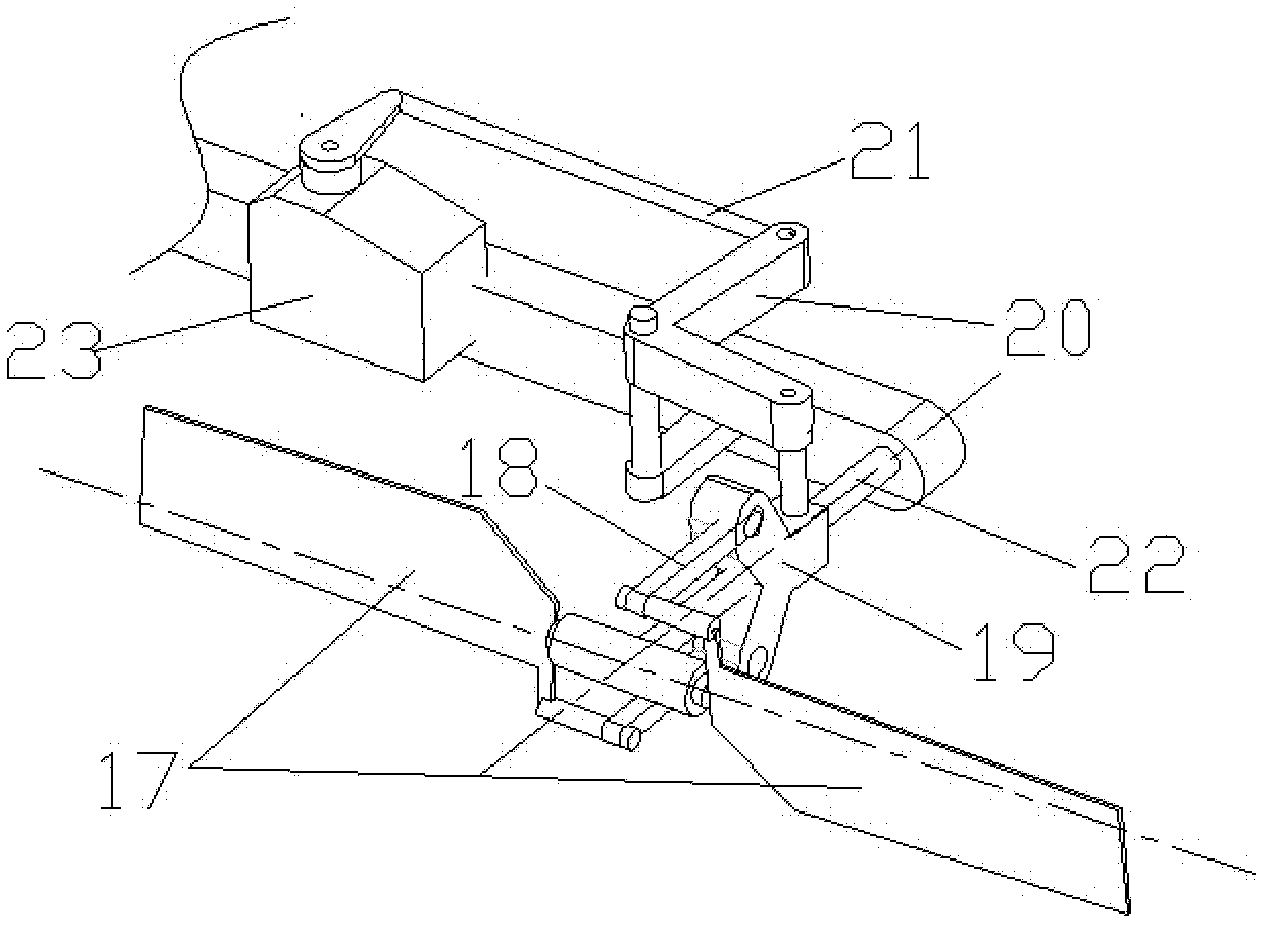
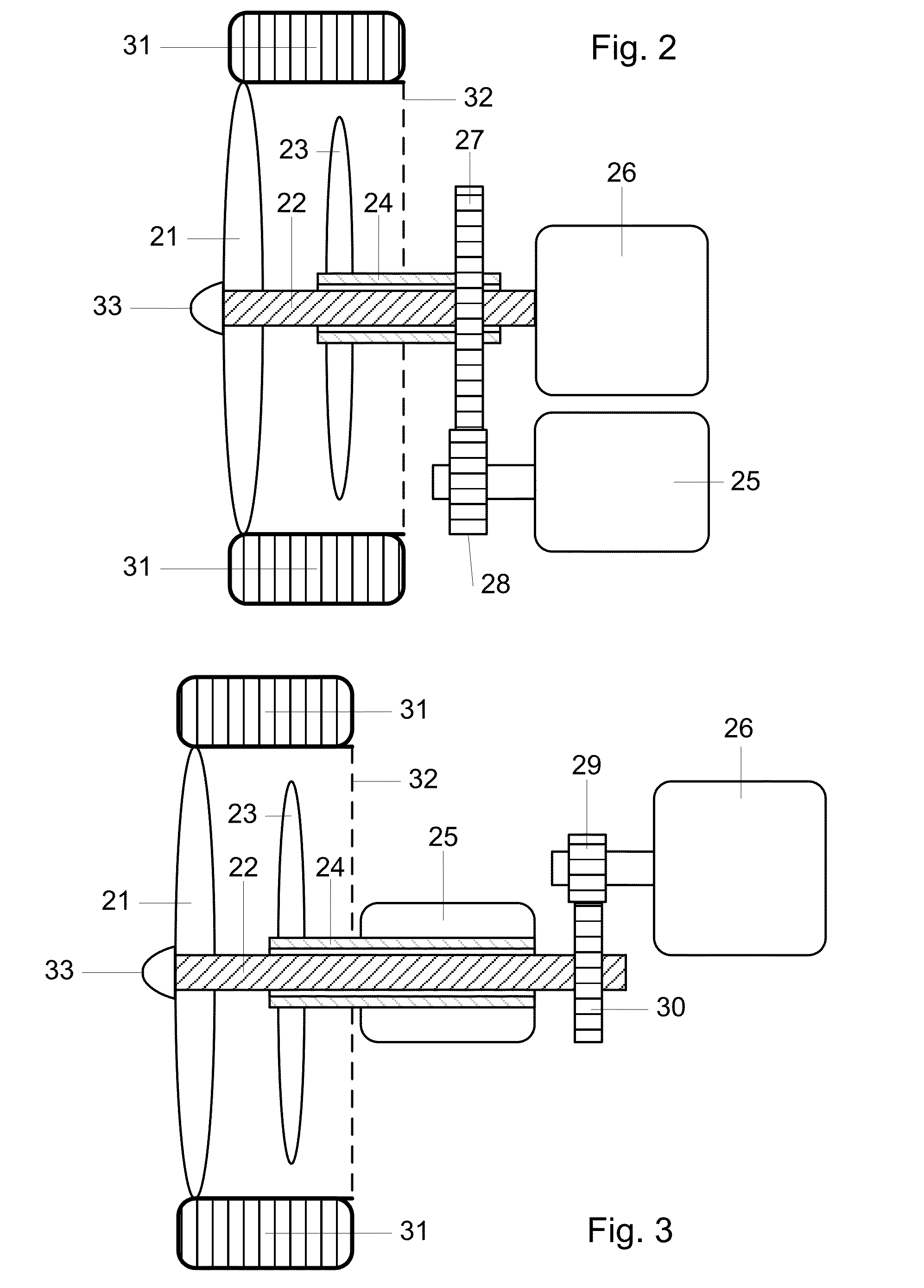
Tiltrotor controlled by double-propeller vertical duct
The invention provides a tiltrotor controlled by a double-propeller vertical duct. The tiltrotor, using the design of parallel twin-rotor and conventional aerodynamic configuration, consists of a fuselage, straight wings, rotors, a nacelle, an aileron, a vertical empennage, a rudder, an elevator, a horizontal empennage, a duct end cover, a vertical duct, an undercarriage, a power and decelerationsystem, a propeller power input shaft, a lower propeller, an upper propeller, louver-type slipstream sheets, a propeller gearing and collective-pitch controlling device, a propeller gear box supporting structure, a duct end cover driving device, a duct end cover motion slide rail and a slipstream sheet controlling device. Compared with the cyclic pitch control mode, the tiltrotor of the inventionsimplifies the operations during the vertical flight and the flight conversion and improves the reliability by using the structure of the double-propeller vertical duct to control the vertical flightand the conversion of the flight mode, and the tiltrotor has the advantages of long control force arm, high control efficiency and simple structure. Therefore, the tiltrotor constitutes a novel aircraft with significant development potential and promising future.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High pressure cleaning and decontamination system
InactiveUS7140954B2Suitable protectionClean effectAbrasive feedersAbrasive machine appurtenancesTriple pointRoom temperature
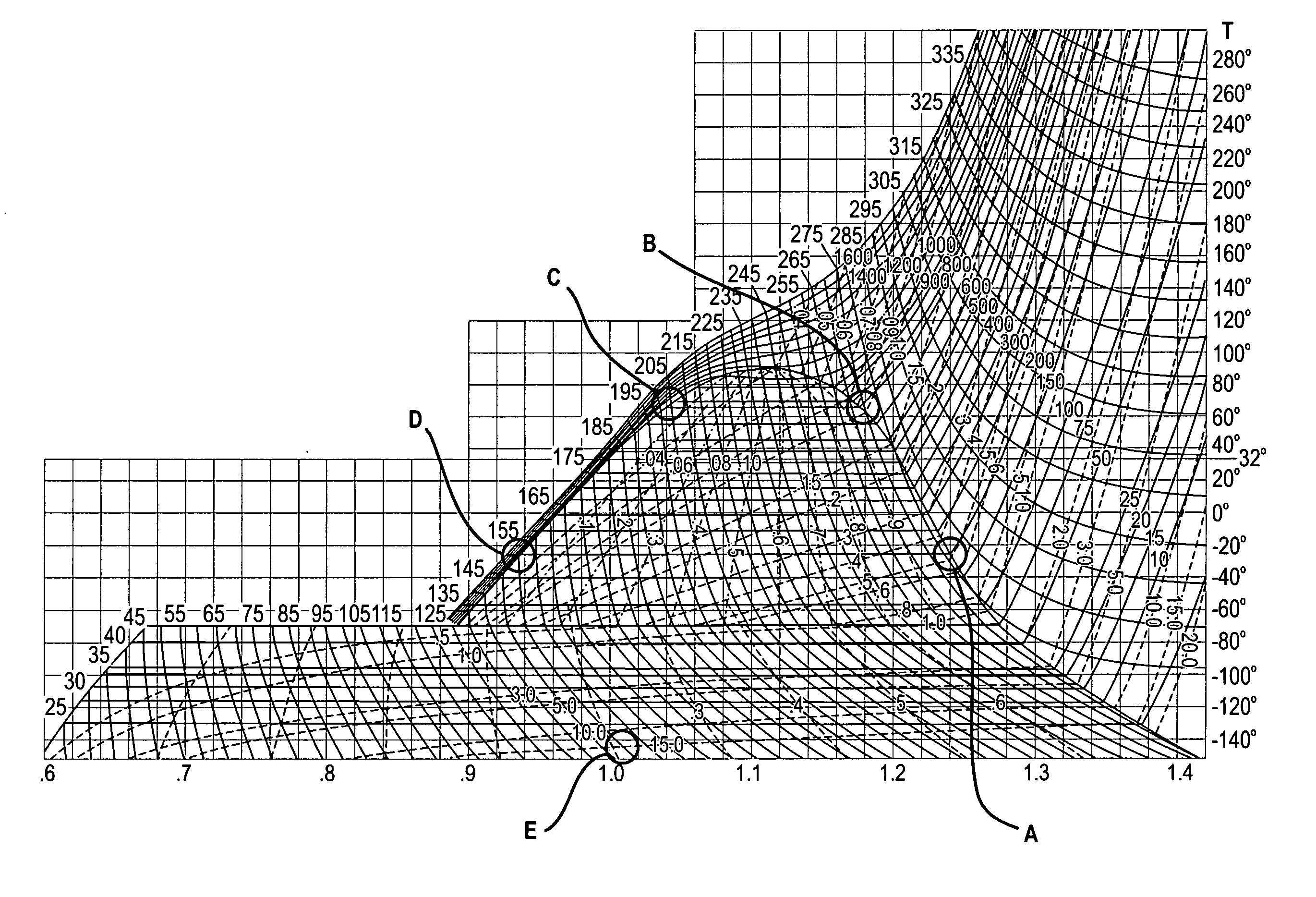
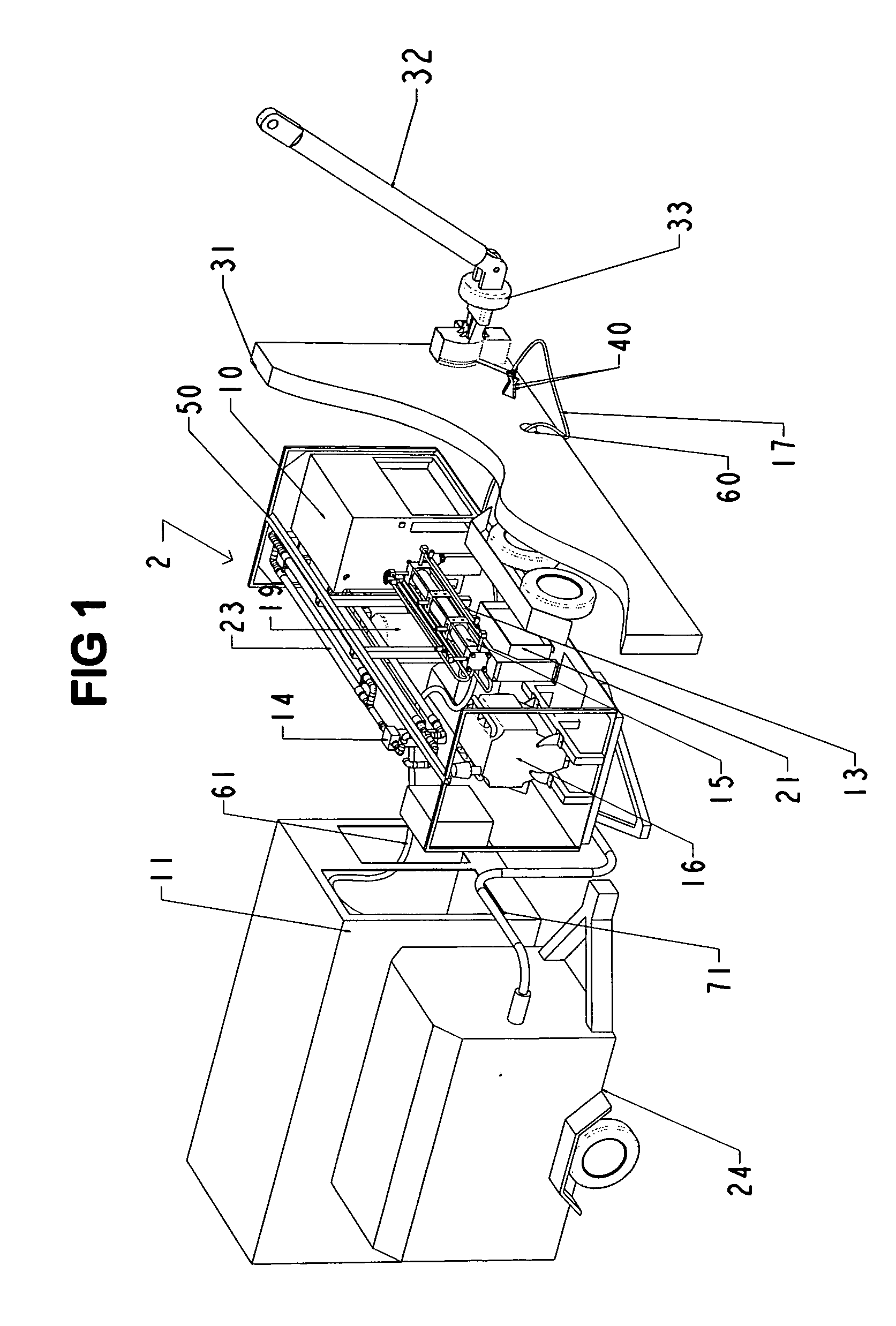
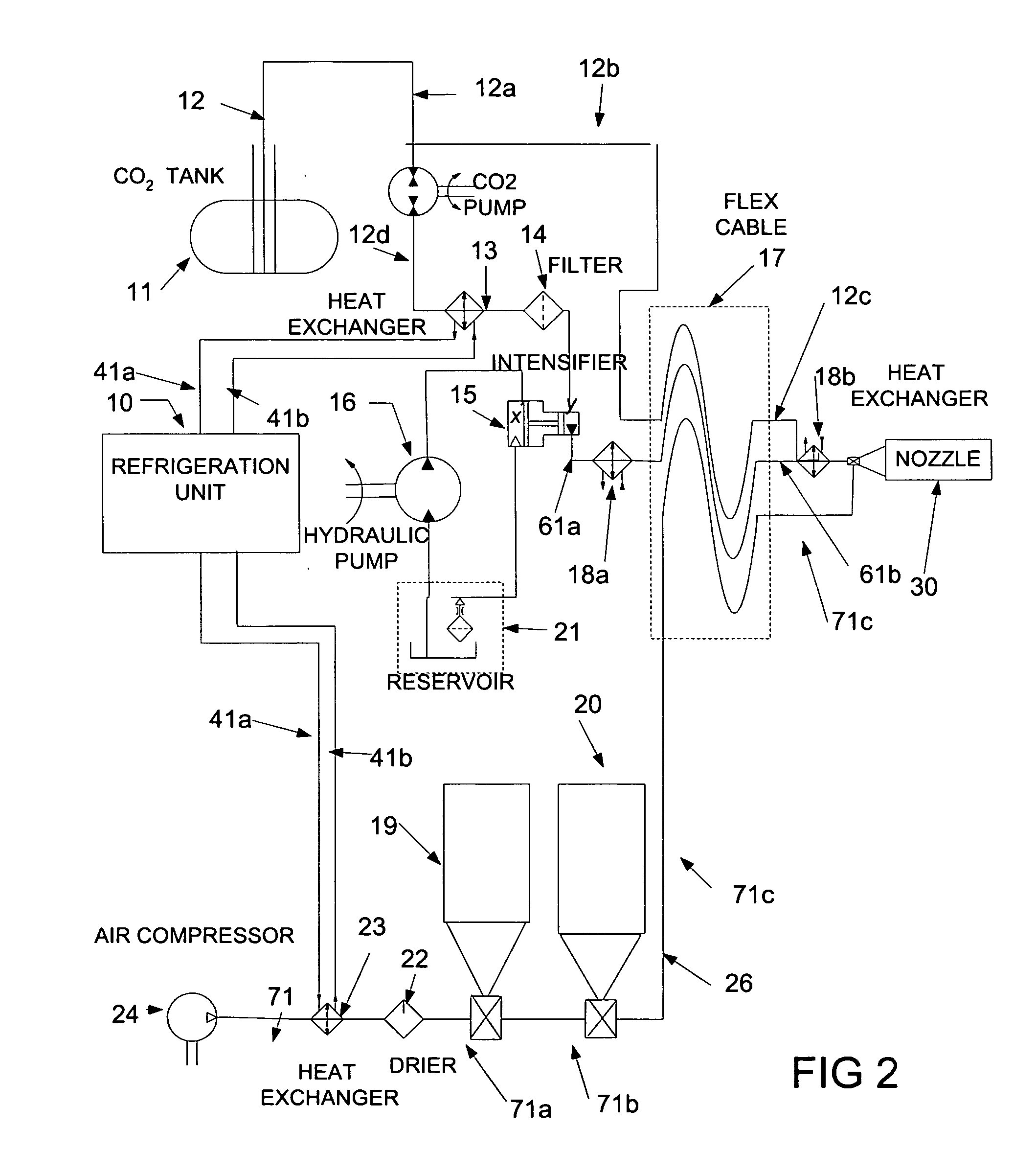
Abrasive cleaning and decontamination methods and systems are disclosed. The methods and systems use a high pressure liquefied gas, such as carbon dioxide, which produces insignificant quantities of secondary waste. These principles of the invention exploit the properties of the relatively high triple point of CO2 in order to first pressurize it to 35,000 to 60,000 PSI from a pressurized liquid. In the pressurized state, such a fluid can be at or above room temperature, allowing for transport over long distances in a flexible high pressure hose. At a point of use, a heat exchanger may subsequently chill the liquid, so that after expansion through a small high pressure orifice, a significant fraction of the liquid is converted to solid phase crystals exiting at high velocity to effectively clean and decontaminate. For more aggressive cleaning, abrasive particles and / or small diameter solid CO2 pellets can be entrained into the high pressure CO2 slipstream.
Owner:KURION INC
Multiphase mixing device with staged gas introduction
InactiveUS7052654B2Lower overall pressure dropImprove efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPhase mixingHybrid system
The present invention comprises a mixing system that provides improved mixing of quench gas and process fluids in a height constrained interbed space while not increasing pressure drop. In particular, the device improves the effectiveness of an existing mixing volume in mixing the gas phase of two-phase systems. The mixing system includes a horizontal collection tray, a mixing chamber positioned below the collection tray, at least one passageway extending through the collection tray into the mixing chamber, and a vapor slipstream passageway extending through the collection tray into the mixing chamber for directing a vapor slipstream from above the collection tray into the mixing chamber. The mixing chamber and the collection tray define a two-phase mixing volume. The passageway conducts fluid containing at least some vapor from above the collection tray into the mixing chamber. The mixing chamber preferably includes at least one outlet opening for the downward passage of fluid. The vapor slipstream passageway, optionally, comprises a plurality of inlets arranged to impart rotational movement to the vapor phase at a location within the mixing chamber where the vapor phase has substantially expended the kinetic energy of its initial entry into the mixing chamber. As a result of providing at least one additional passageway for a vapor slipstream, and optionally, including one or more baffles as described above, significant re-acceleration of the vapor phase is achieved in the mixing chamber resulting in improvements in mixing efficiency of both the vapor and liquid phases.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Slotting duct propeller systems and hovercar applying same
InactiveCN103395491AEasy to liftPropellersAircraft convertible vehiclesLocking mechanismVertical take off and landing
The invention discloses slotting duct propeller systems. In each slotting duct propeller system, the upper portion of a duct is provided with a seam communicated with an inner wall surface and an outer wall surface of the duct, the inner wall of the duct is provided with a controllable mechanism for controlling closing and opening of the seam, so that the seam is closed when the duct is in an approximately horizontal posture and vertical take-off and landing are carried out, so as to reduce a friction resistance of a propeller slipstream in the inner wall and reduce the loss of a direct lift force; the seam is opened when the duct tilts to an approximately perpendicular beneficial incidence angle posture and horizontal flight is carried out, lift augmentation of power is carried out, so as to increase a duct lift force. A hovercar applying the slotting duct propeller systems is provided with folding mechanisms, locking mechanisms and tilting mechanisms, so that the hovercar can be changed between a car status and an aircraft status, and the hovercar can perform vertical take-off and landing in the aircraft status and flies at a high speed.
Owner:李凤
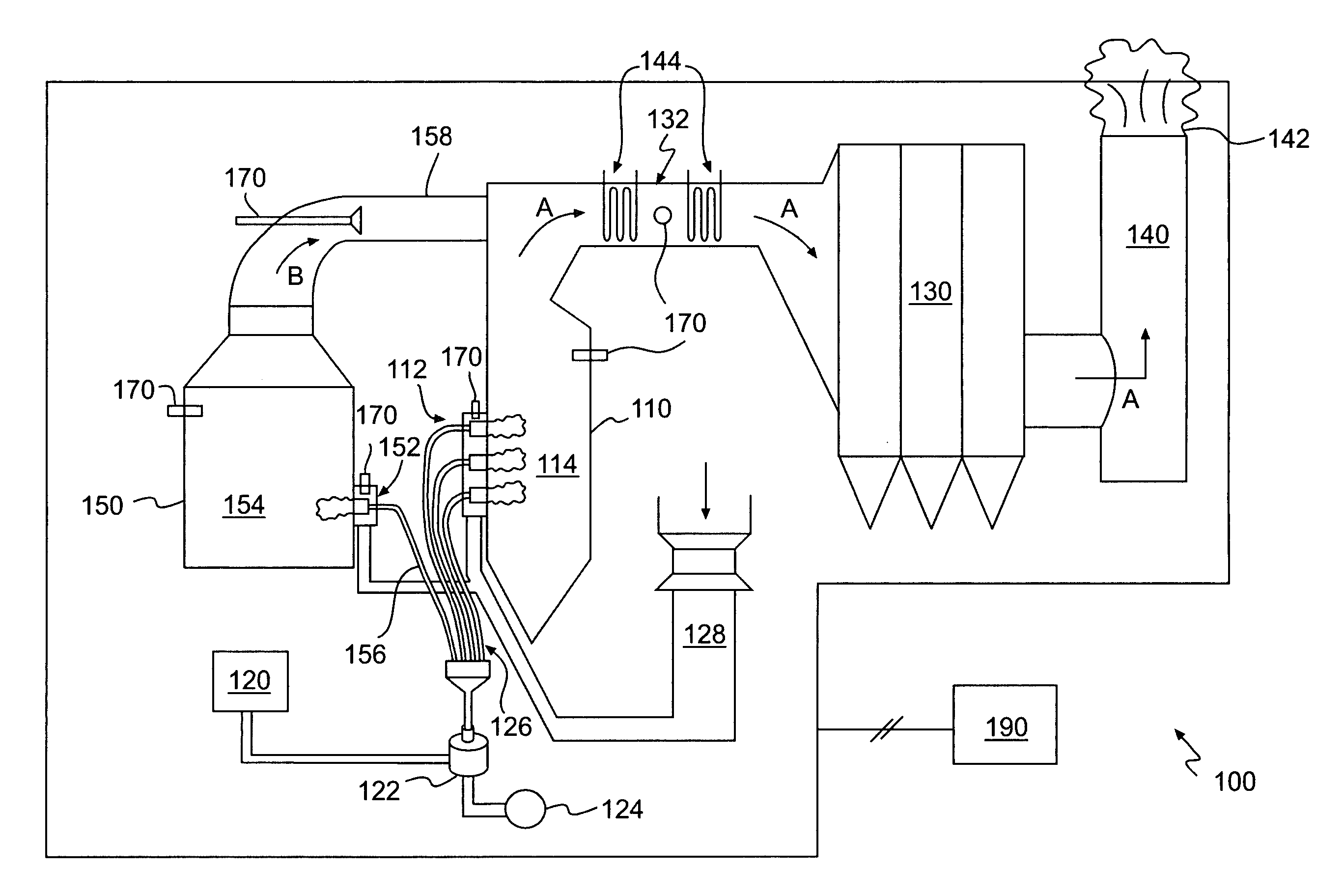
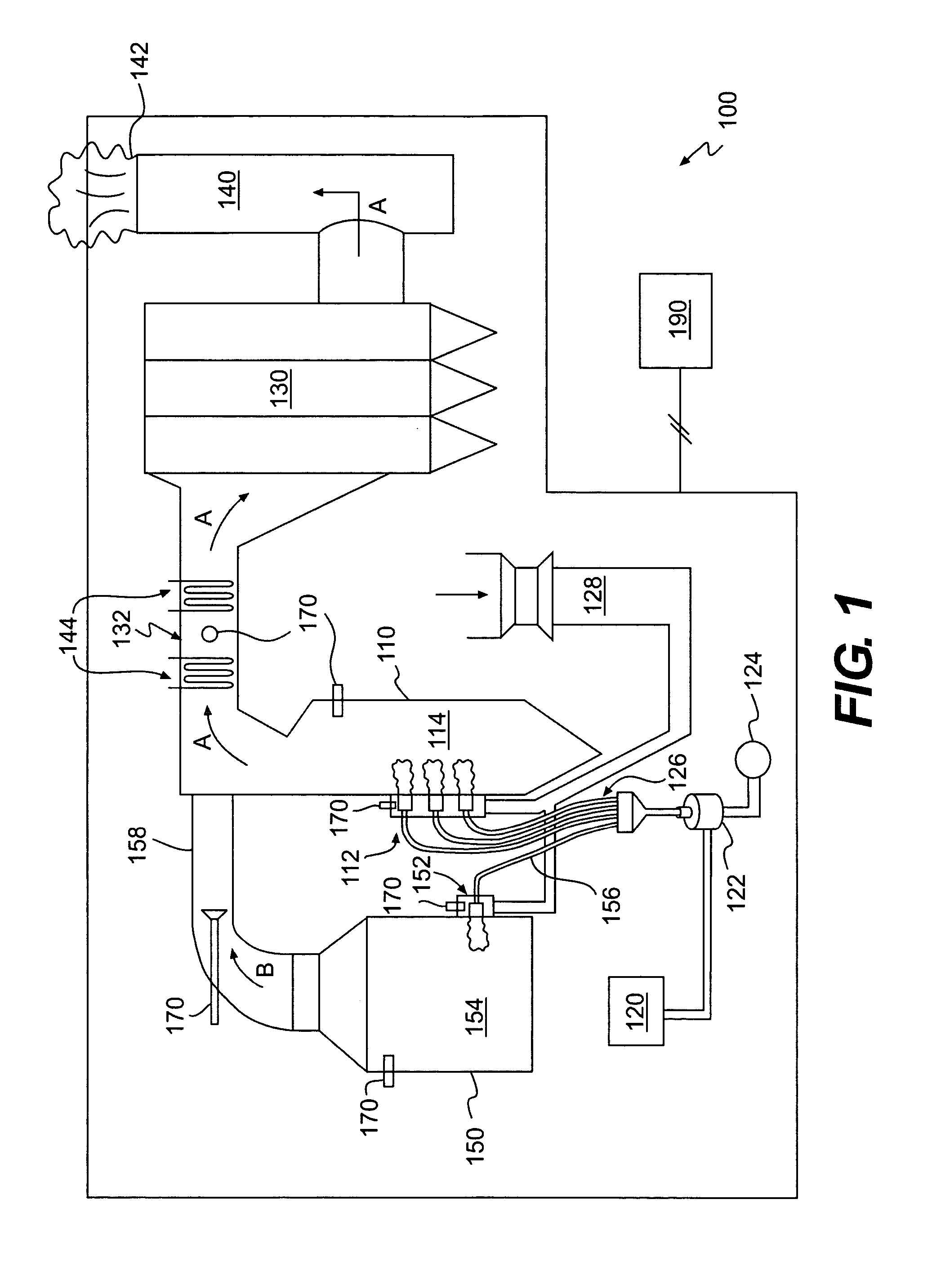
Methods and apparatuses for removing mercury-containing material from emissions of combustion devices, and flue gas and flyash resulting therefrom
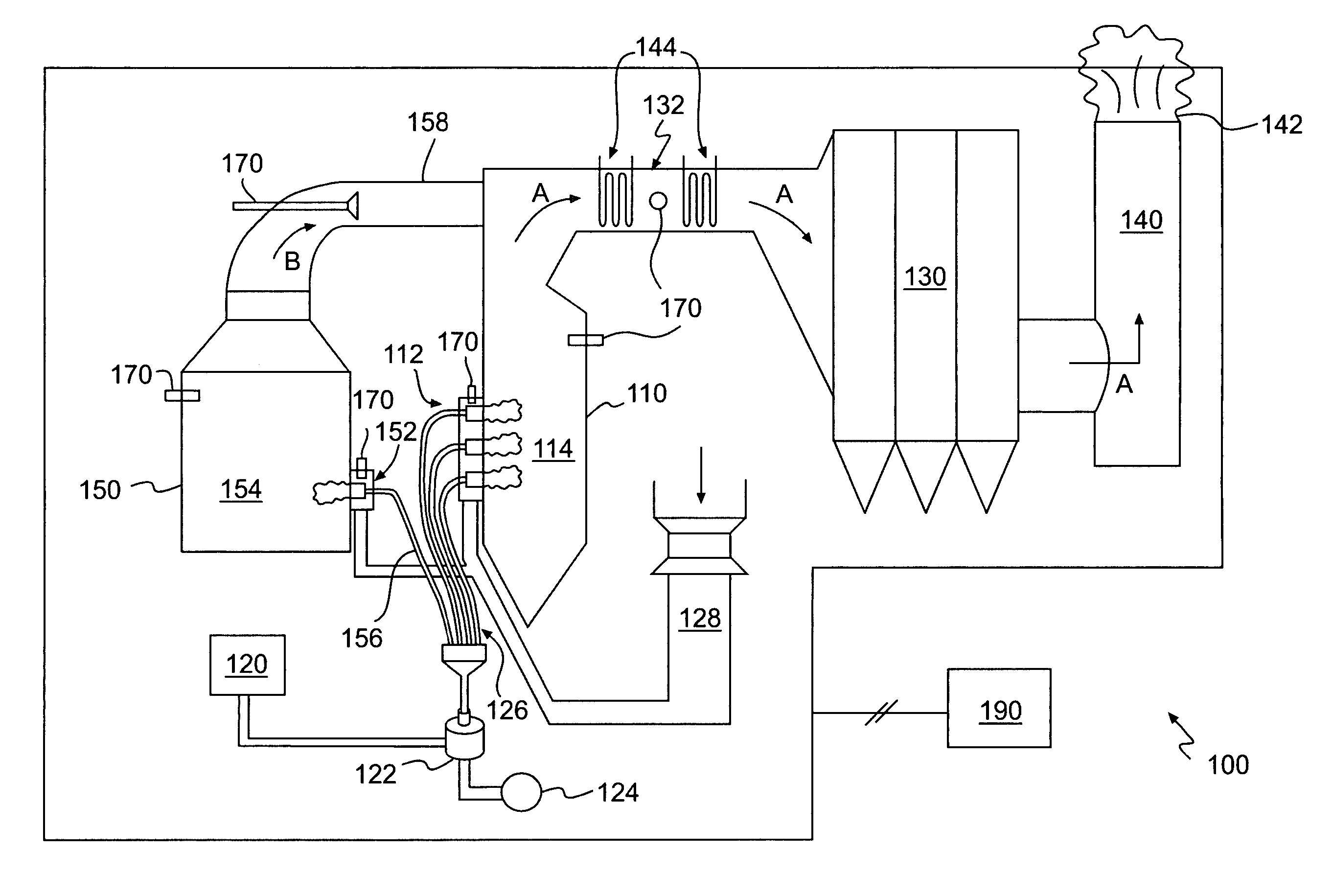
A method of removing mercury or mercury-containing material from flue gas produced by a coal-burning main furnace includes feeding coal, which contains mercury or mercury-containing material, to a main furnace which produces flue gas. The method further includes feeding the coal to an auxiliary burner which produces a slipstream of flyash, feeding the slipstream of flyash from the auxiliary burner into the flue gas produced by the main furnace, and introducing a mercury-active oxidant to the coal being fed to the auxiliary burner, the combustion air fed to the auxiliary burner, and / or the flyash.
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
Vehicle spoiler with spinner mechanism
A mechanism for producing turbulent flow of the air moving over the rear deck of a vehicle is an air flow control apparatus comprising a vehicle spoiler of a typical and well known type having a horizontal portion joined integrally with spaced apart vertical standoffs. Mounted between the standoffs is a rotating spinner held in bearing sets. The spinner provides blades configured for rotating the spinner when the vehicle moves using its slipstream.
Owner:GARCIA MARTIN LEE
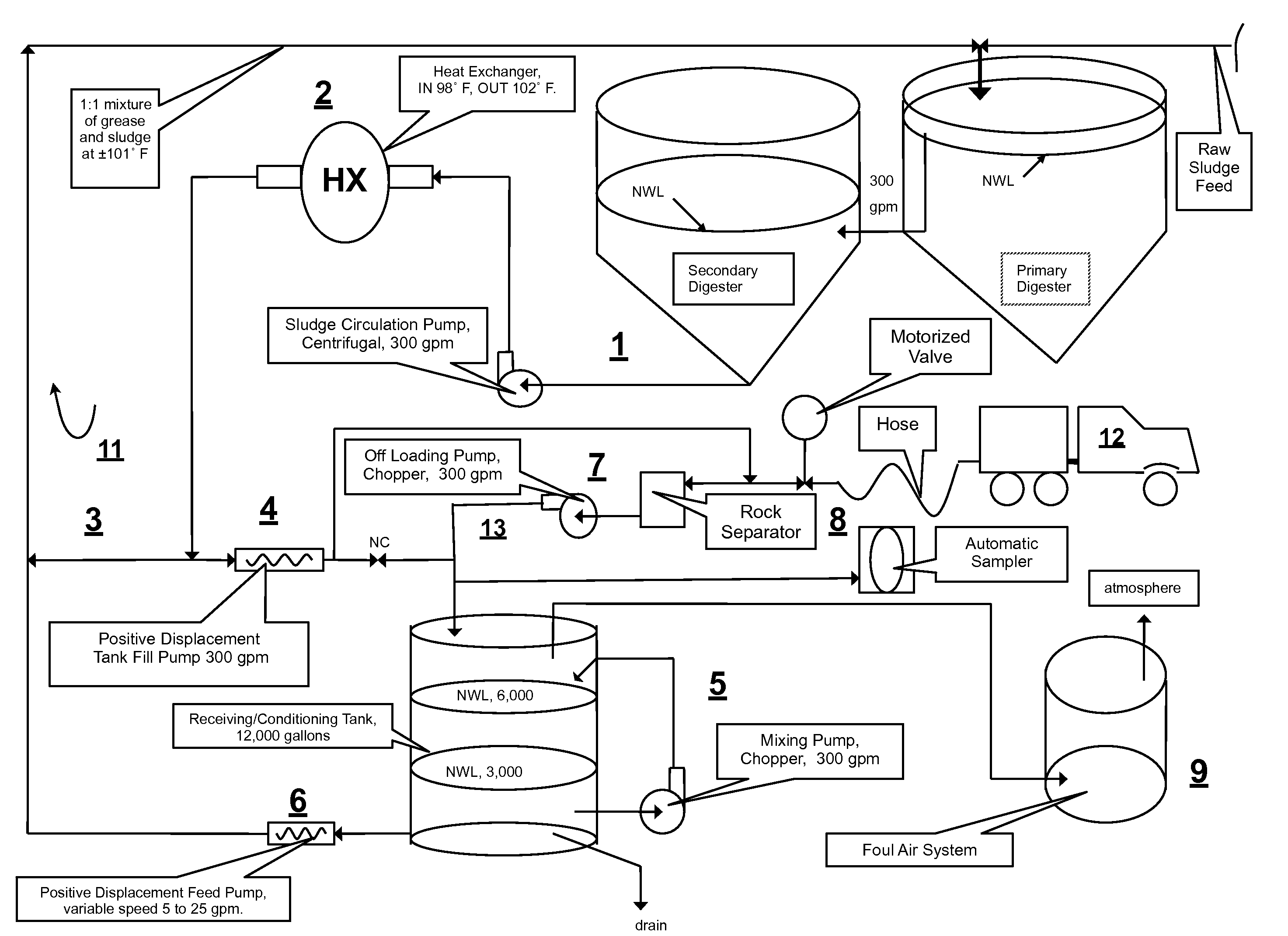
Integrated cogeneration wastewater sewage and waste polar fats/ oils/ greases/waxes (FOG) waste treatment method and facility
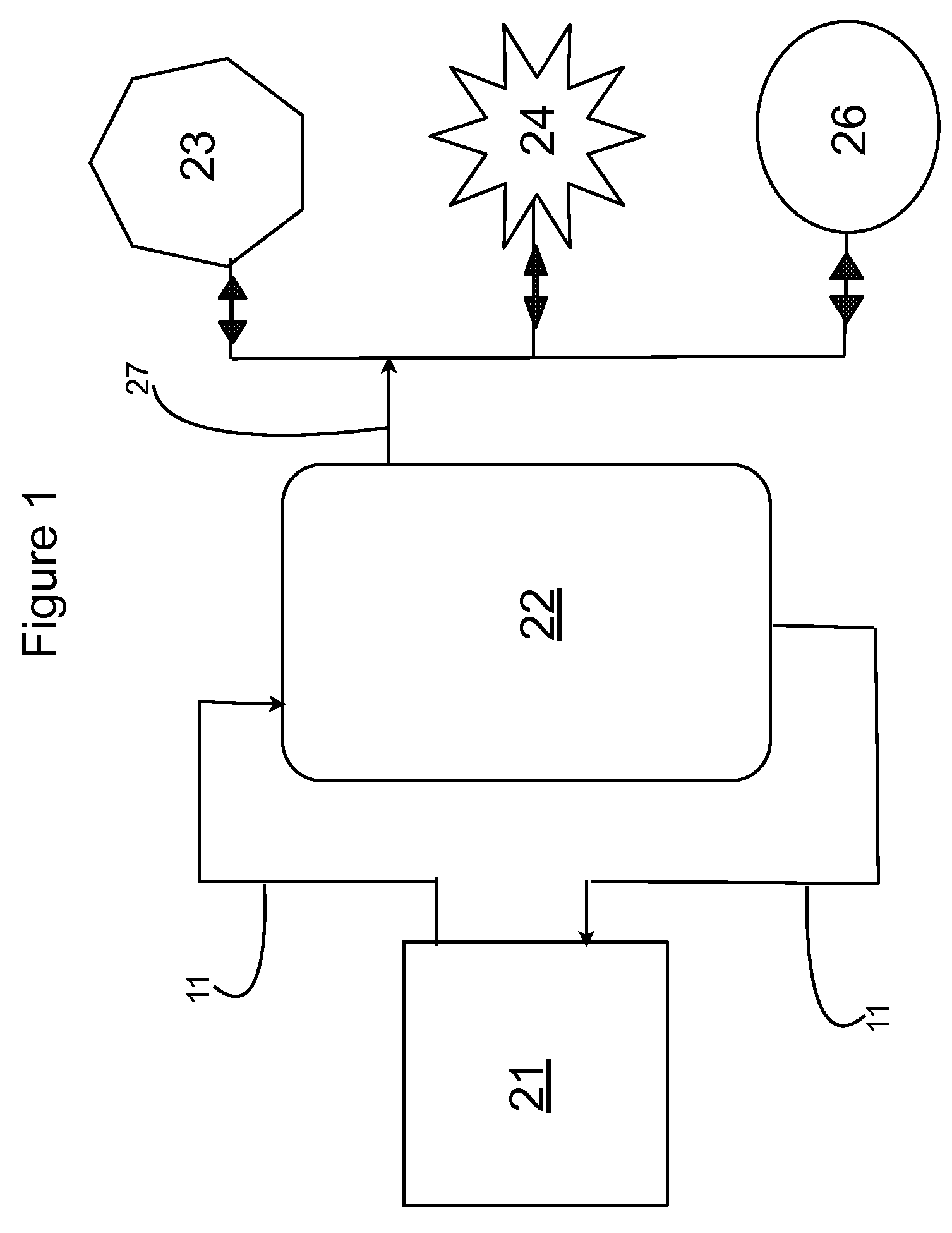
InactiveUS20080203014A1Rule out the possibilityLow solidsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGeneral water supply conservationOil and greaseVolatile fatty acids
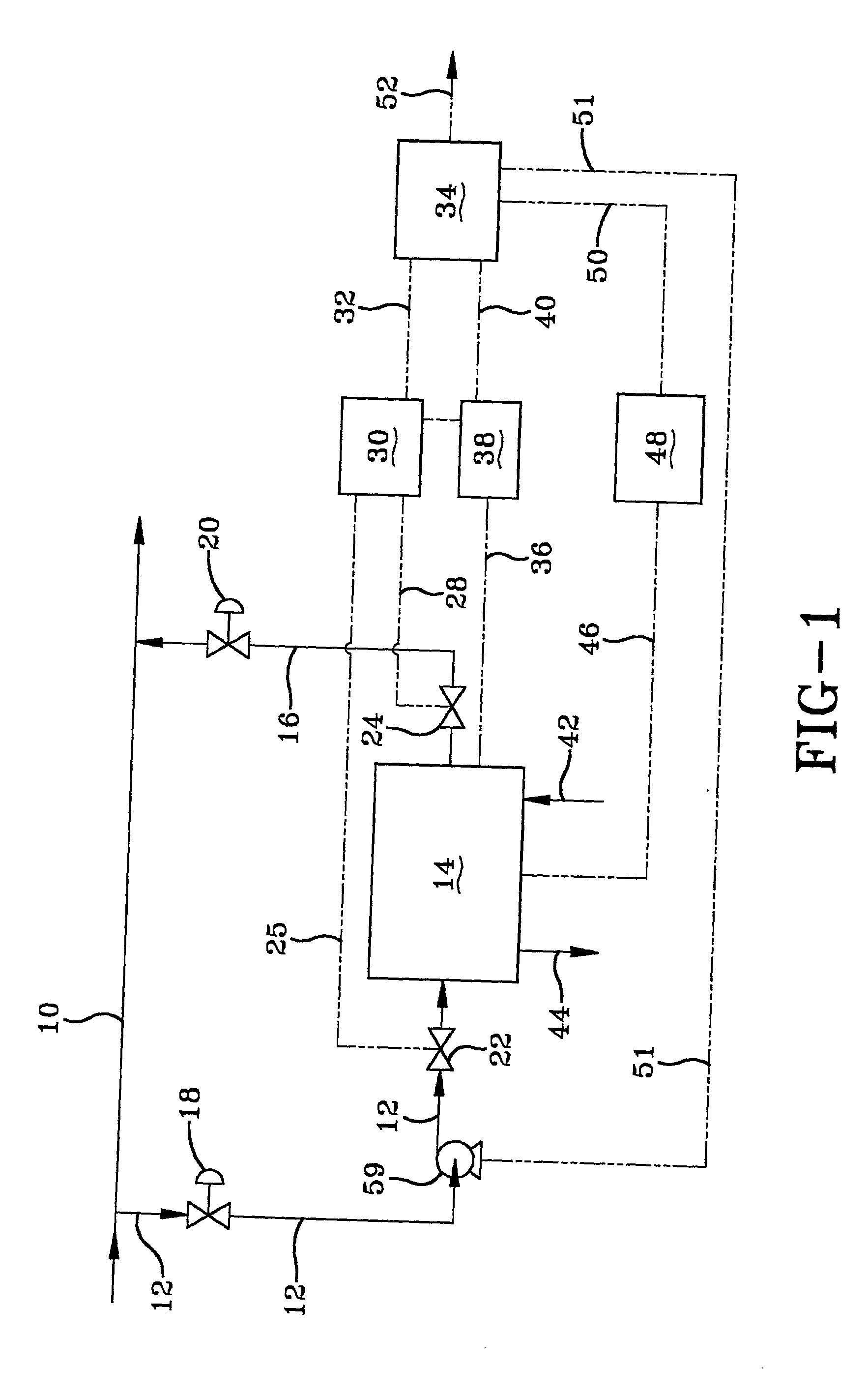
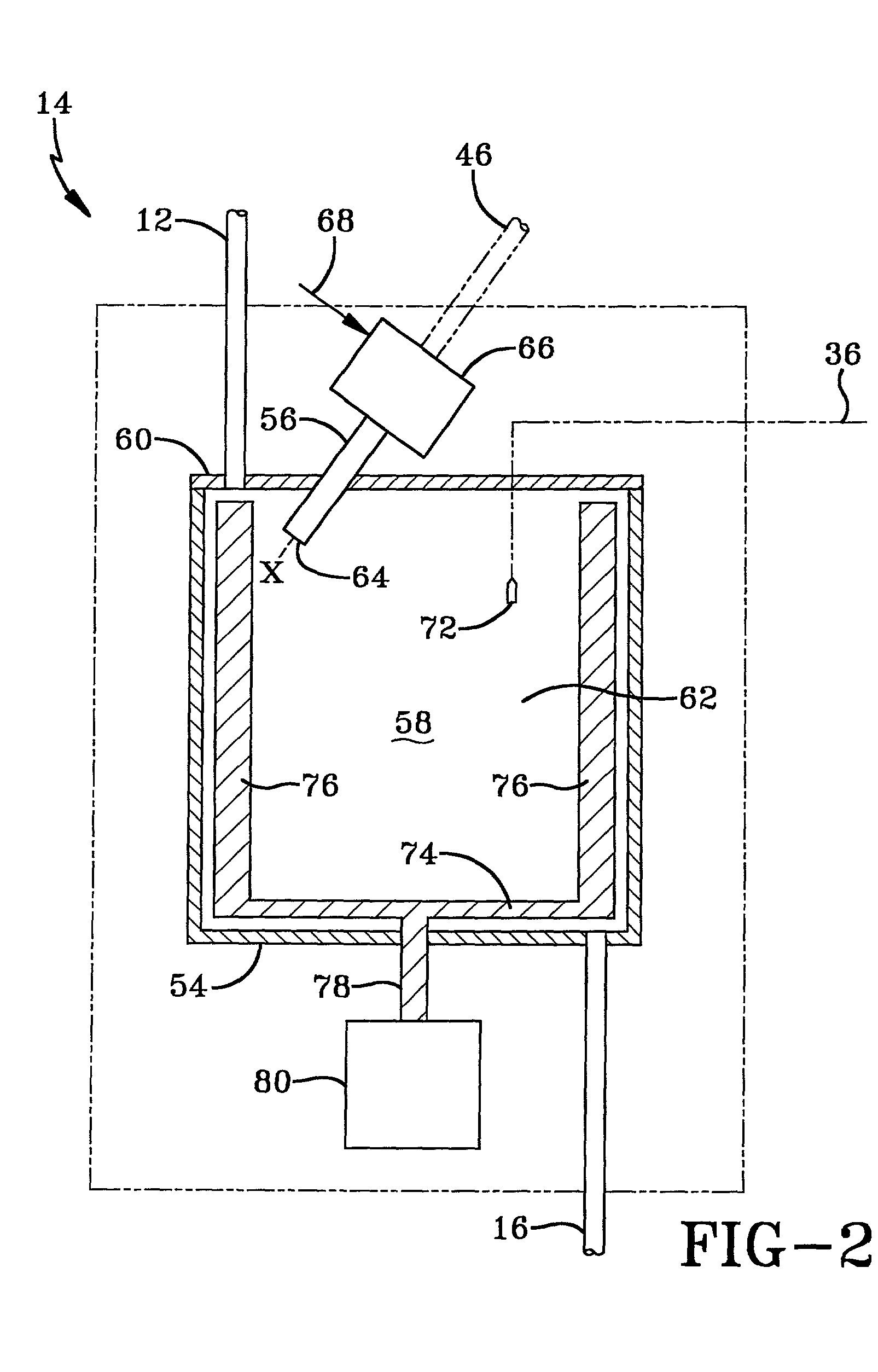
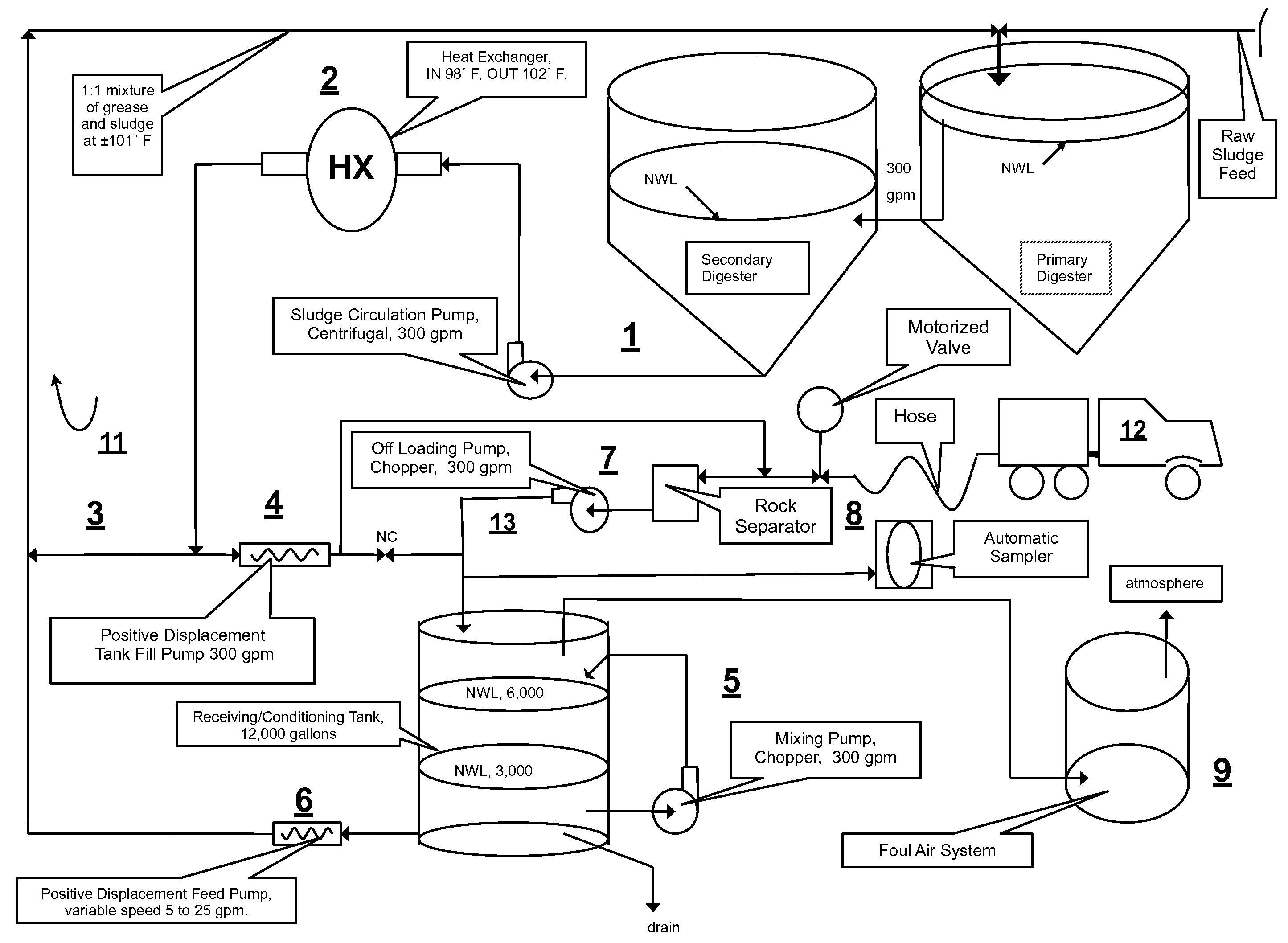
Integrated sewage or digestible wastes, and fats, oils, greases and waxes (FOG) waste treatment methods, systems and facilities include a slipstream loop incorporating circulation pumps, hot water heat exchangers and conventional anaerobic digesters for continuously circulating actively digesting sludge at a rate to preclude solid settlement accumulation as a warm flowable slurry source. The warmed actively digesting sludge is pumped from the slipstream loop through a rock trap into a delivery / input loop both for aiding transport or delivery of FOG waste to, and for partially filing a closed receiving / conditioning holding tank, where the warmed actively digesting sludge softens and liquefies the FOG wastes offloaded into the holding tank for further treatment at a desired treatment temperature range (whether psychrophilic, mesophilic, or thermophilic). The contents of the closed receiving / conditioning holding tank are continuously mixed by a bottom-top recirculation chopper pump to pre-treat the FOG wastes, liquefying and decreasing solids particle size allowing acidogens in the actively digesting sludge to pre-digest such wastes producing volatile fatty acids, some biogas and a highly bioreactive, flowable feedstock slurry. The produced highly bioreactive, flowable feedstock slurry can then injected back into the actively digesting sludge slipstream loop at a controlled rate where the resultant mixture then is introduced, together with raw sewage or other digestible wastes, into input or head ends of waste treatment systems having anaerobic digesters for digestion of solids and steady-state methane production. Advantages of the integrated system relate to a partial digestion of the FOG in the reaction / holding tank generating volatile fatty acids that suppress expression of methane producing methagens in the holding tank, increased steady-state methane production and significantly reduced solids volume of treated digestible wastes (sewage) and FOG wastes.
Owner:MAGNER JOSEPH A +1
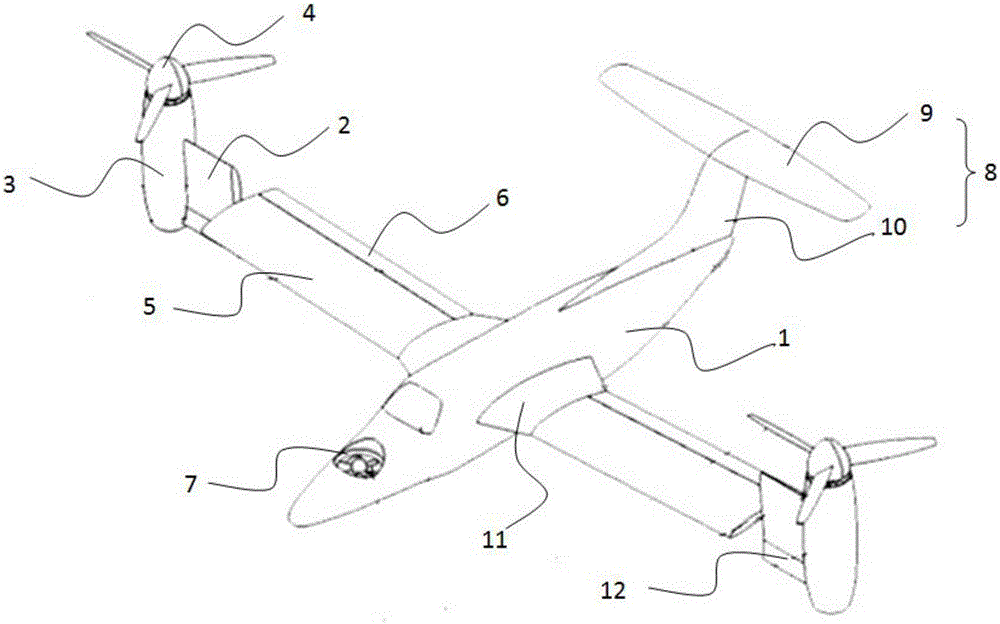
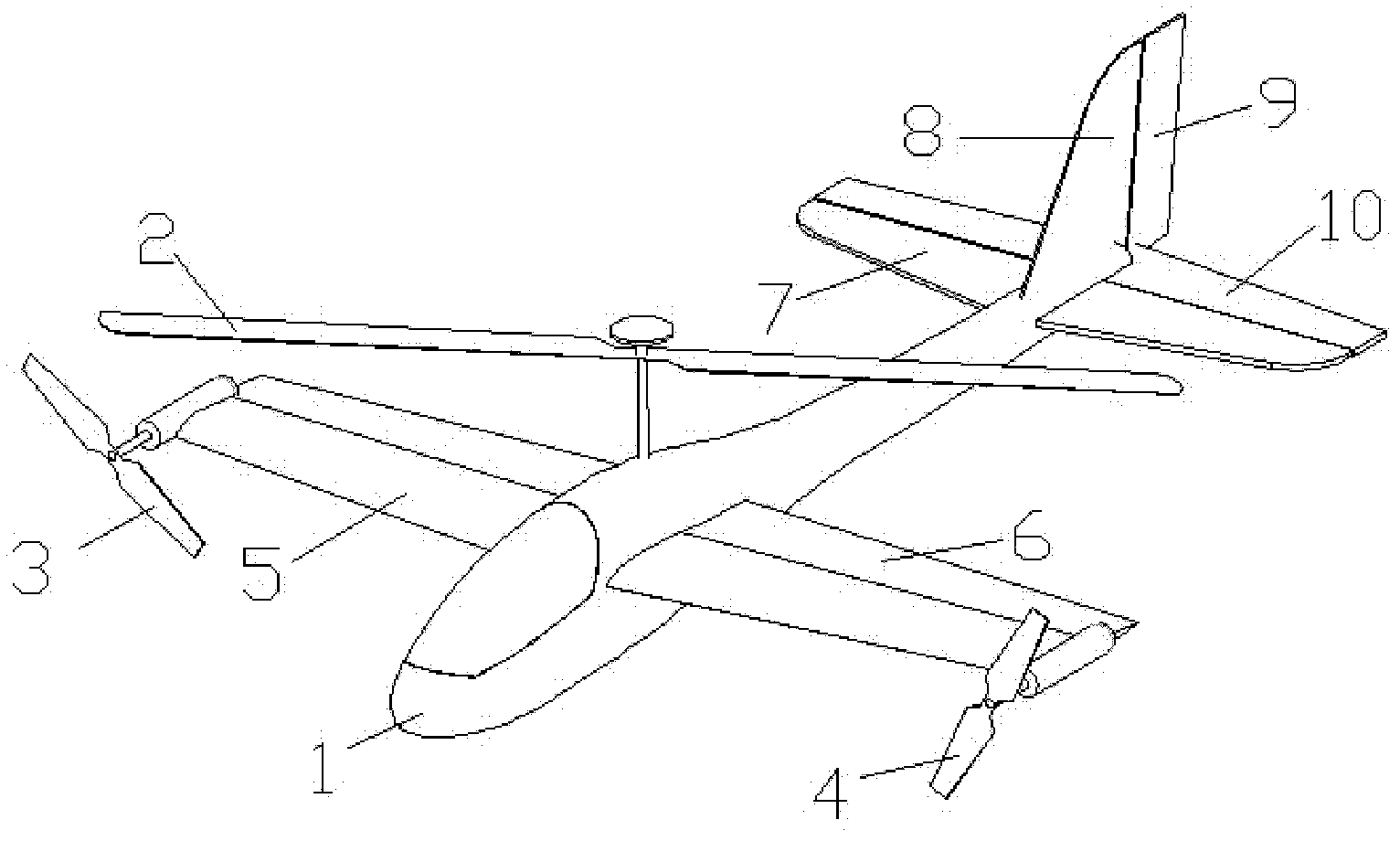
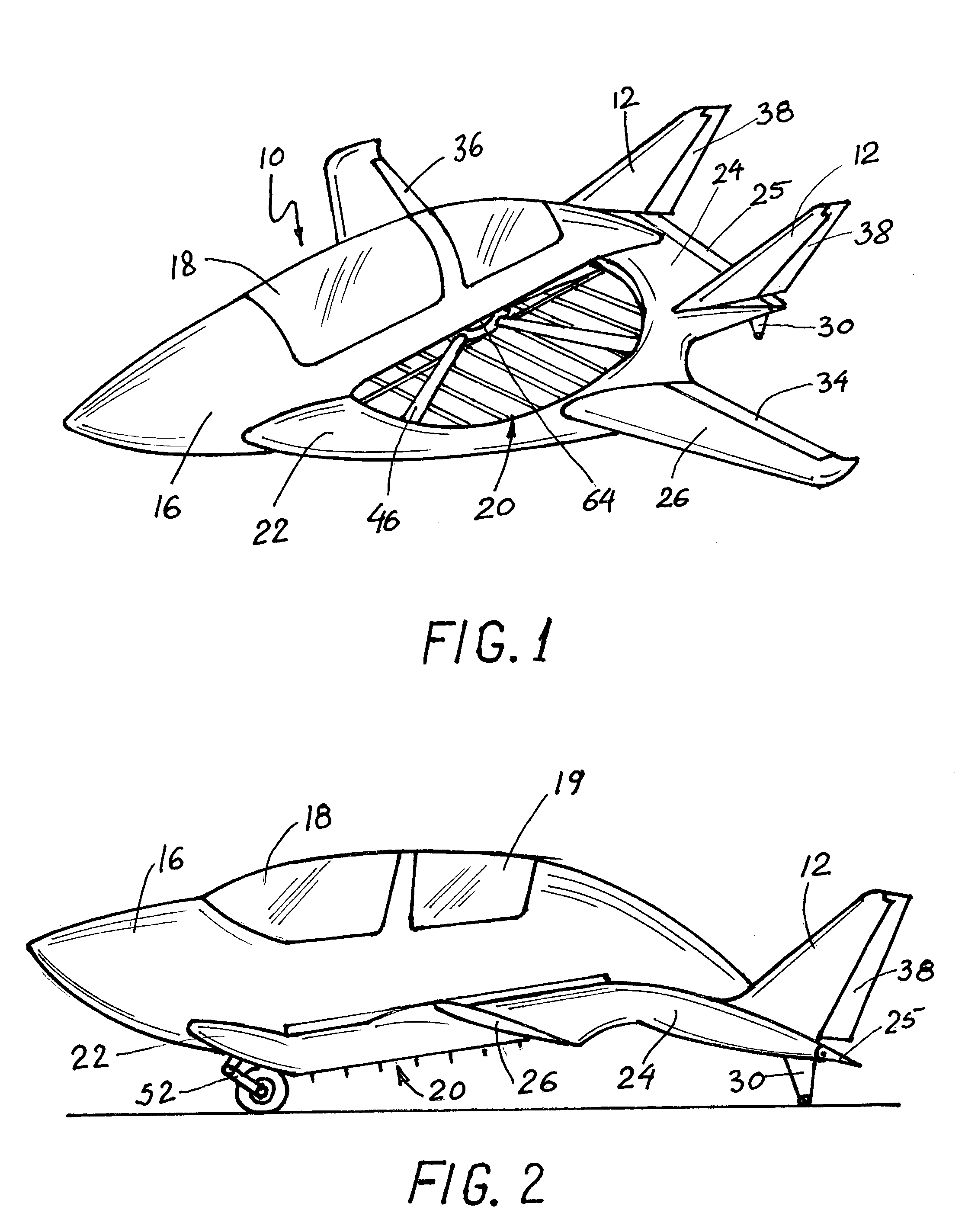
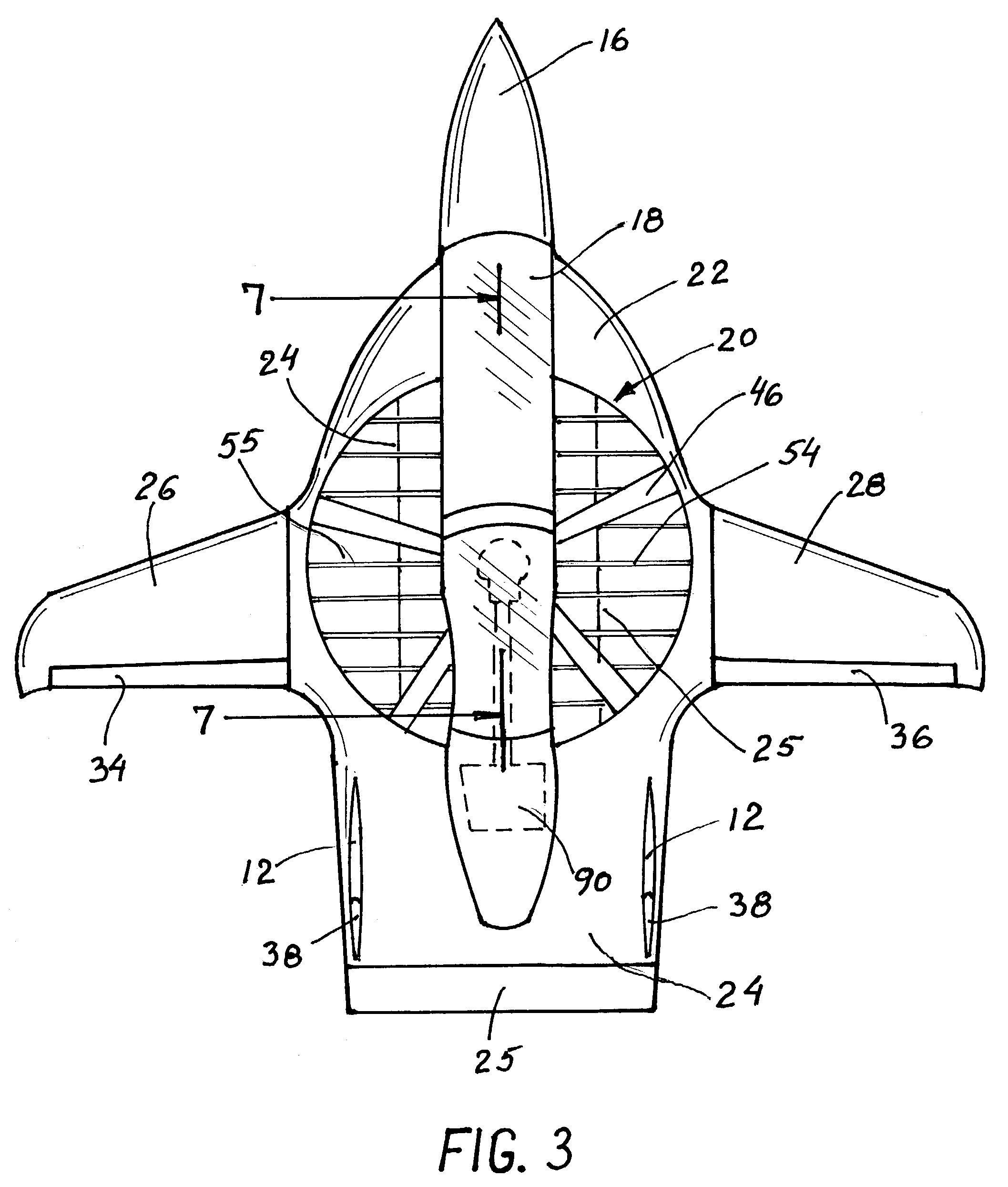
Fixed-wing aircraft realizing vertical take-off and landing
The invention provides a fixed-wing aircraft realizing vertical take-off and landing. The fixed-wing aircraft comprises an aircraft body, a tail and power devices provided with tilting mechanisms, wherein each power device provided with the tilting mechanism comprises a fixed-pitch propeller, an engine, an engine cabin, a slipstream rudder, a wing, a tilting wing and a steering engine, the engine is mounted in the engine cabin, the fixed-pitch propeller is connected with an output shaft of the engine, one end of the tilting wing is fixedly connected onto the engine cabin, the other end is rotationally mounted onto the wing, the slipstream rudder is movably connected onto the tilting wing, and the steering engine drives the slipstream rudder; the power devices provided with the tilting mechanisms are symmetrically arranged on two sides of the aircraft body, the wings are horizontally arranged, a through hole is formed in the head of the aircraft body, and a ducted fan is arranged in the through hole. The size of the aircraft rotor wings and the aircraft is smaller, a complex automatic tilting device and a periodic pitch-variable device are omitted, the structure is simple, the trim difficulty and flight control system complexity are reduced, the system reliability is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:HUNAN AIRTOPS INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Single-power horizontal tractor type high-speed high-mobility helicopter
An embodiment of the invention discloses a helicopter. The helicopter is characterized in that 1), the helicopter is provided with a single engine, power for propulsion devices is outputted by the central engine in a mechanical transmission manner; 2), a tail rotor is omitted, and the variable-pitch propeller horizontal propulsion devices are mounted at the outer ends of stub wings; 3), the propulsion devices on two sides of the helicopter realize same-direction propulsion so that the helicopter flies at a high speed, and the propulsion devices realize differential propulsion in reverse directions so that the heading direction of the helicopter deflects; 4), the lift force compensating stub wings are arranged on two sides of a helicopter body to increase lift force; 5), broad ailerons are disposed at the rear edges of the stub wings, and rolling mobility is improved; and 6), the helicopter is provided with empennages, and pitching and yawing mobility is enhanced. The high-speed helicopter is further characterized by comprising the streamline helicopter body with a single tail boom, a main rotor disposed on the upper side of the helicopter body, the lift force stub wings arranged on the two sides of the helicopter body, the propeller horizontal propulsion devices mounted at the outer ends of the stub wings, horizontal stabilizers positioned out of slip flow of a rear rotor of the helicopter body and a single vertical stabilizer, wherein elevators are arranged at the rear edges of the horizontal stabilizers, and a rudder is disposed at the rear edge of the vertical stabilizer.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
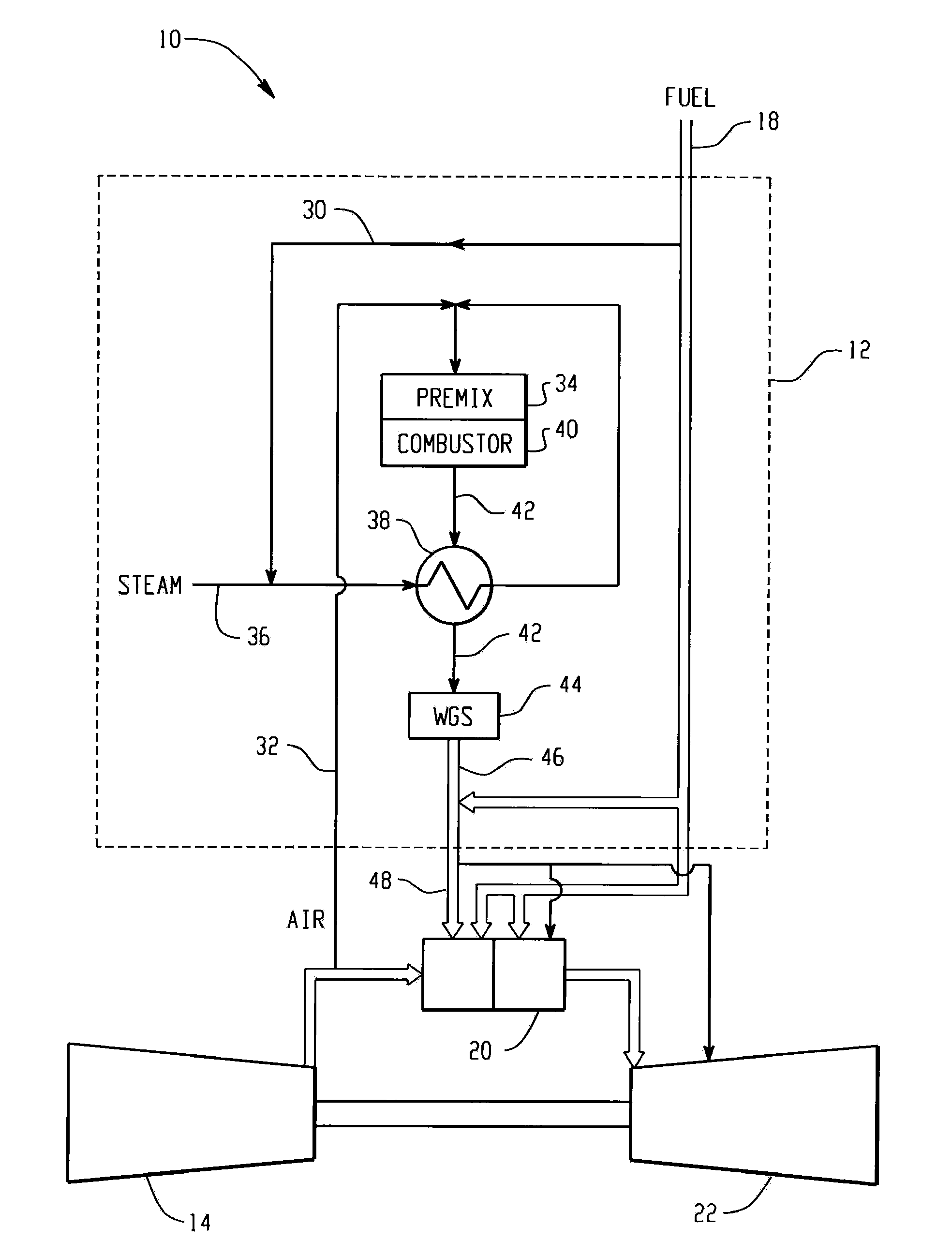
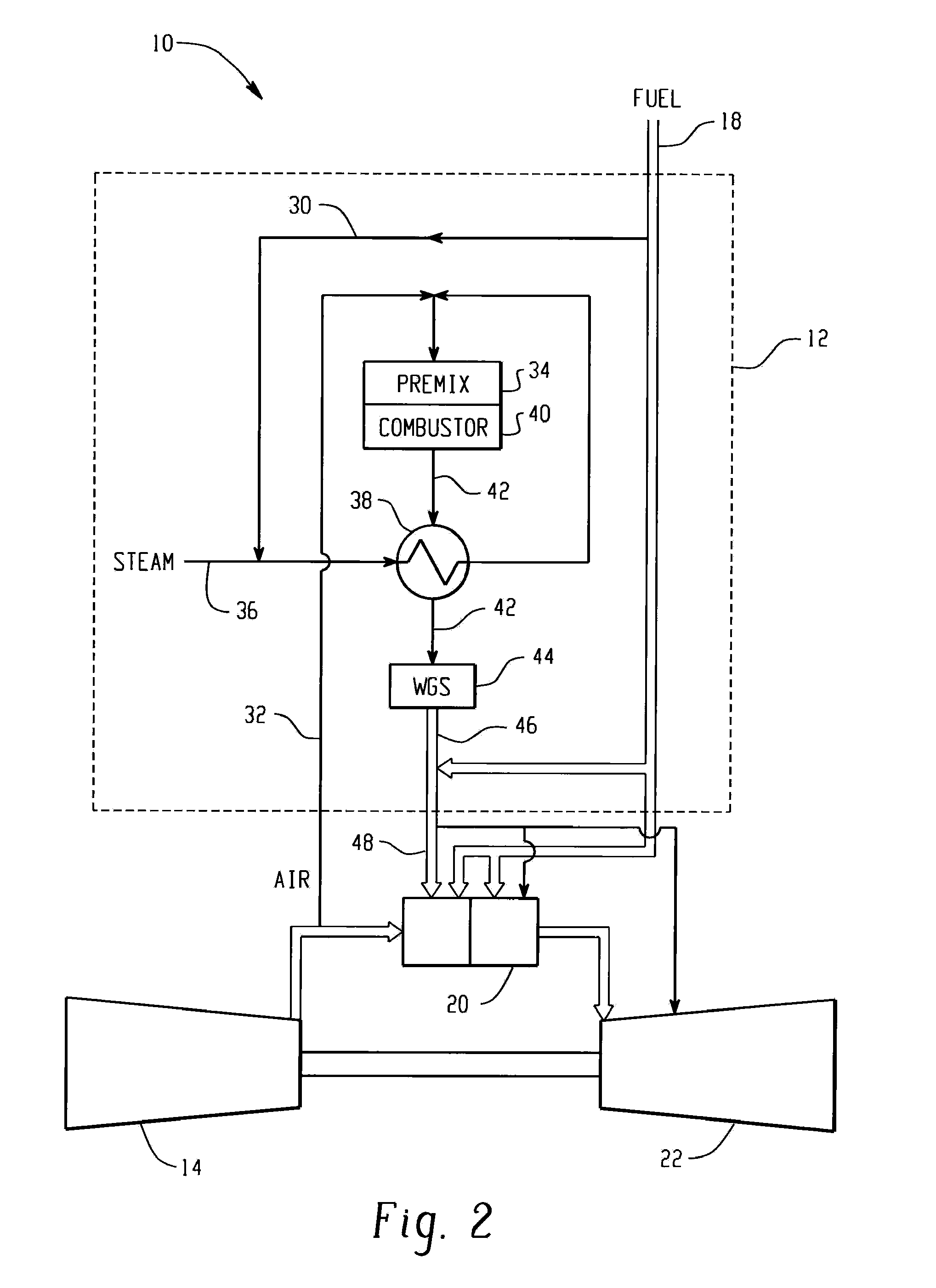
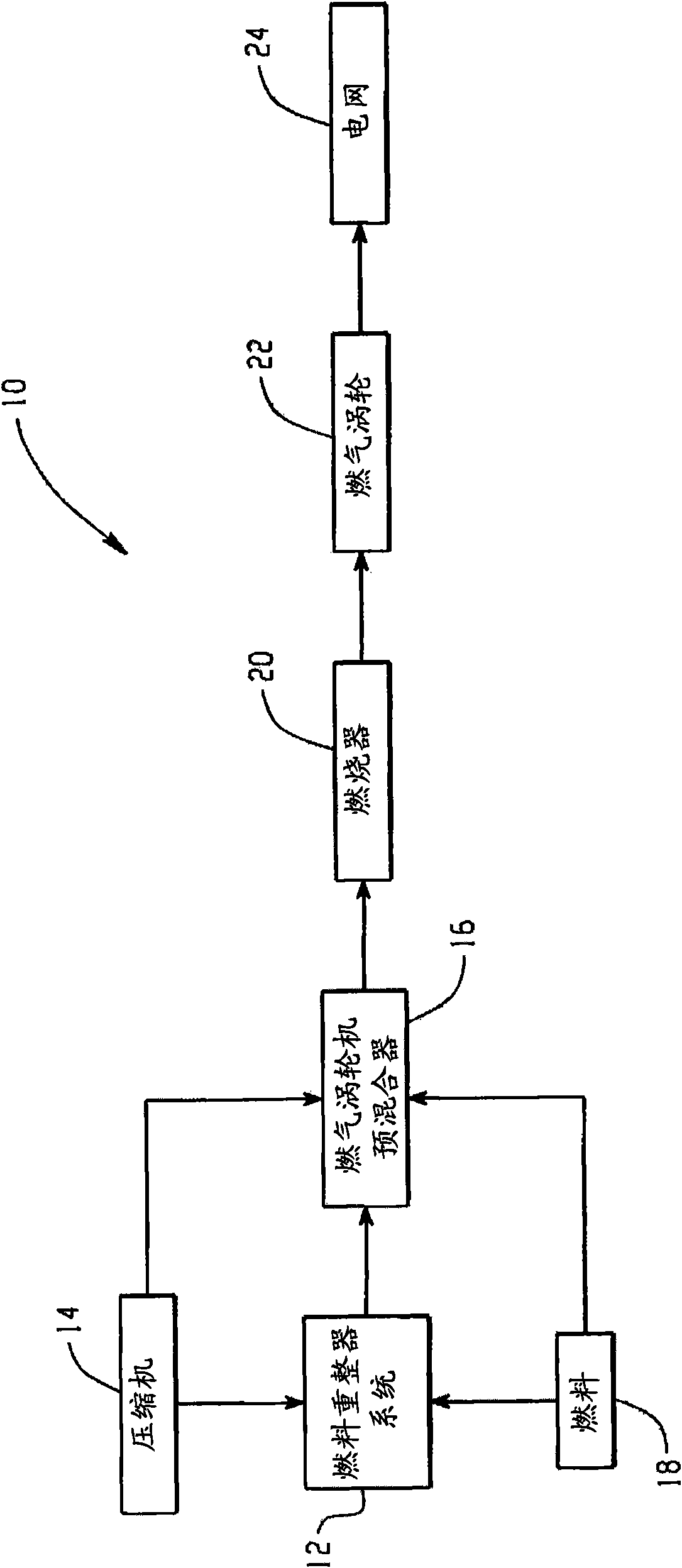
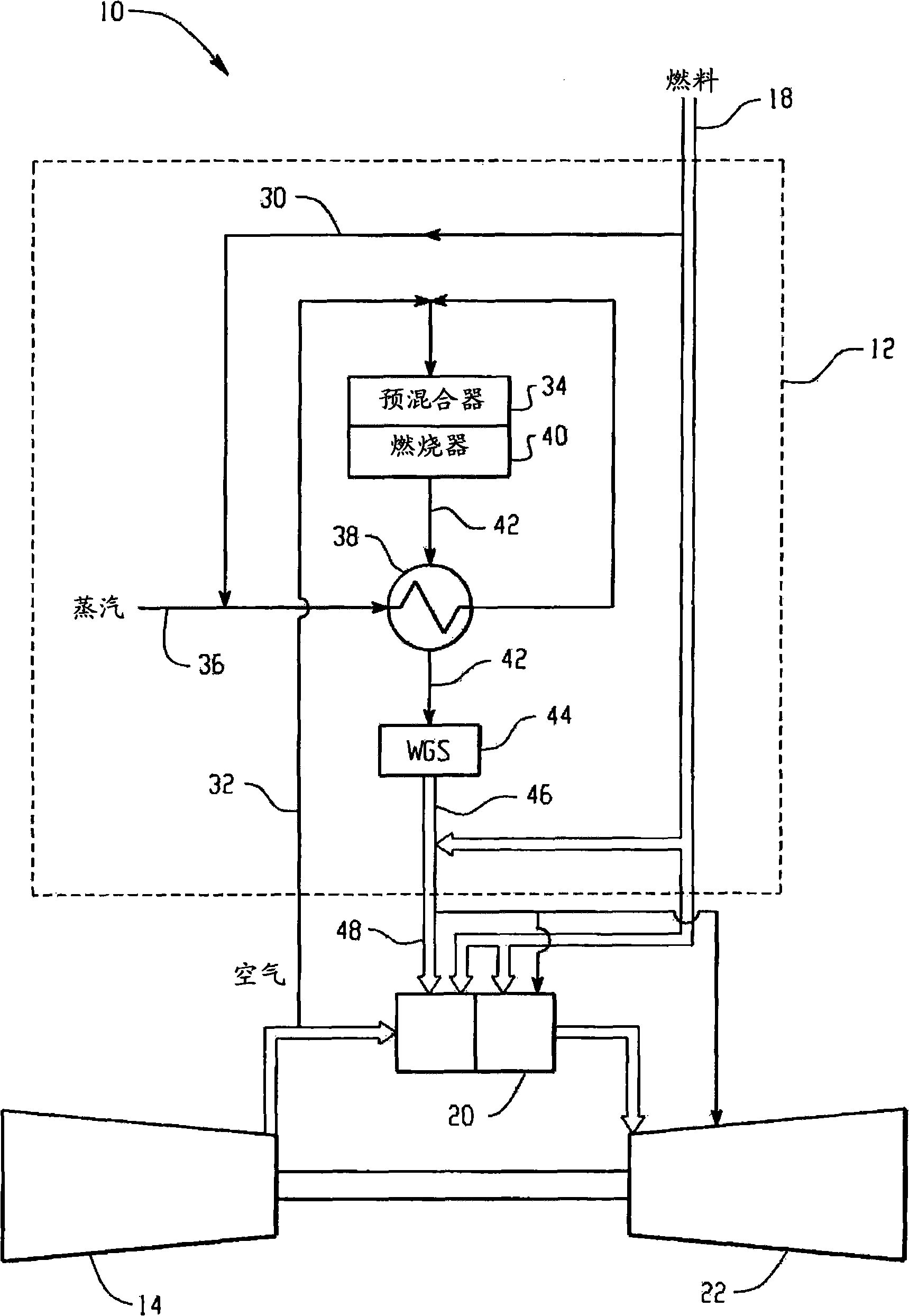
Premixed partial oxidation syngas generation and gas turbine system
InactiveUS20100175386A1Well mixedTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberSyngasPartial oxidation
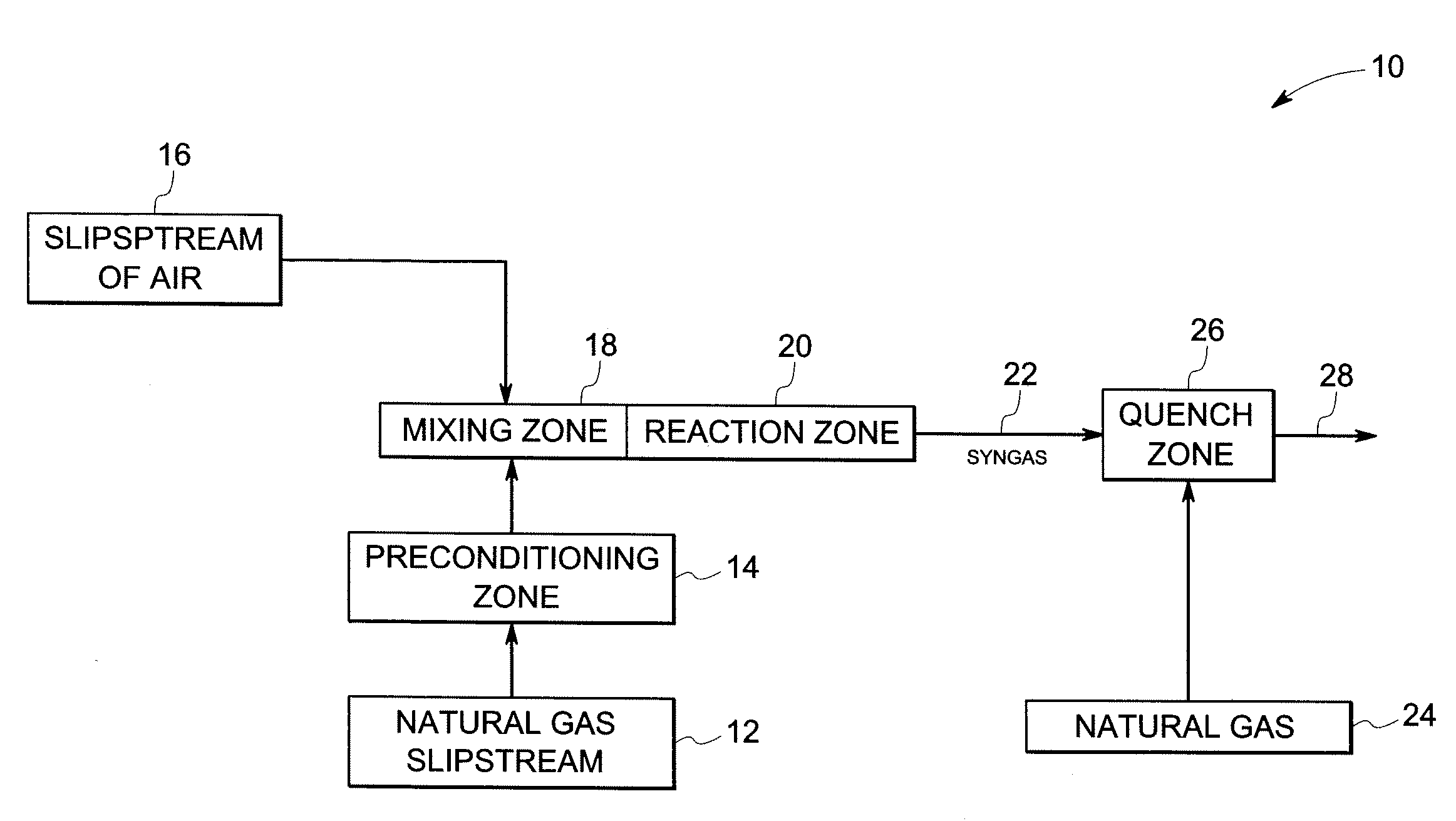
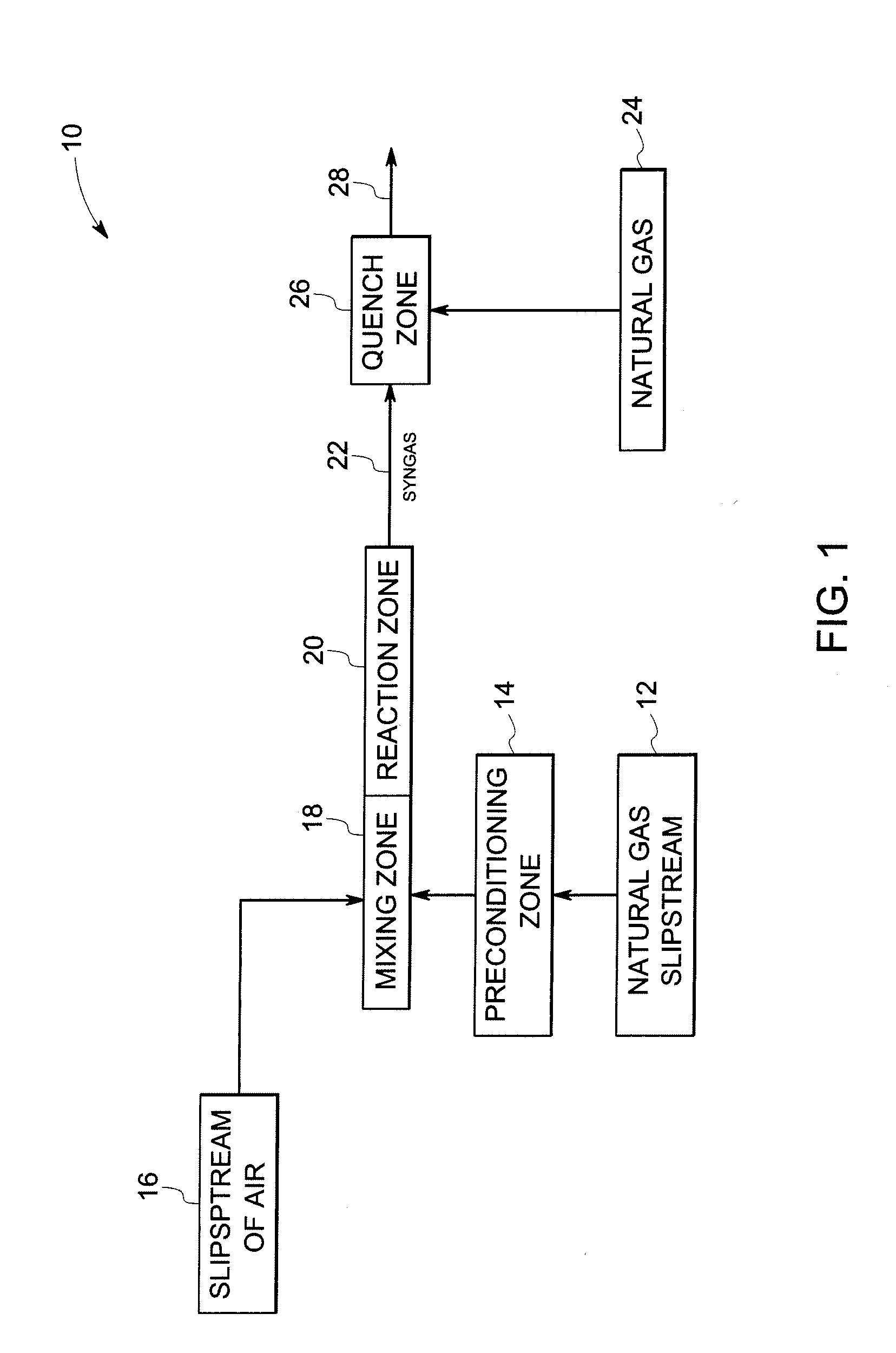
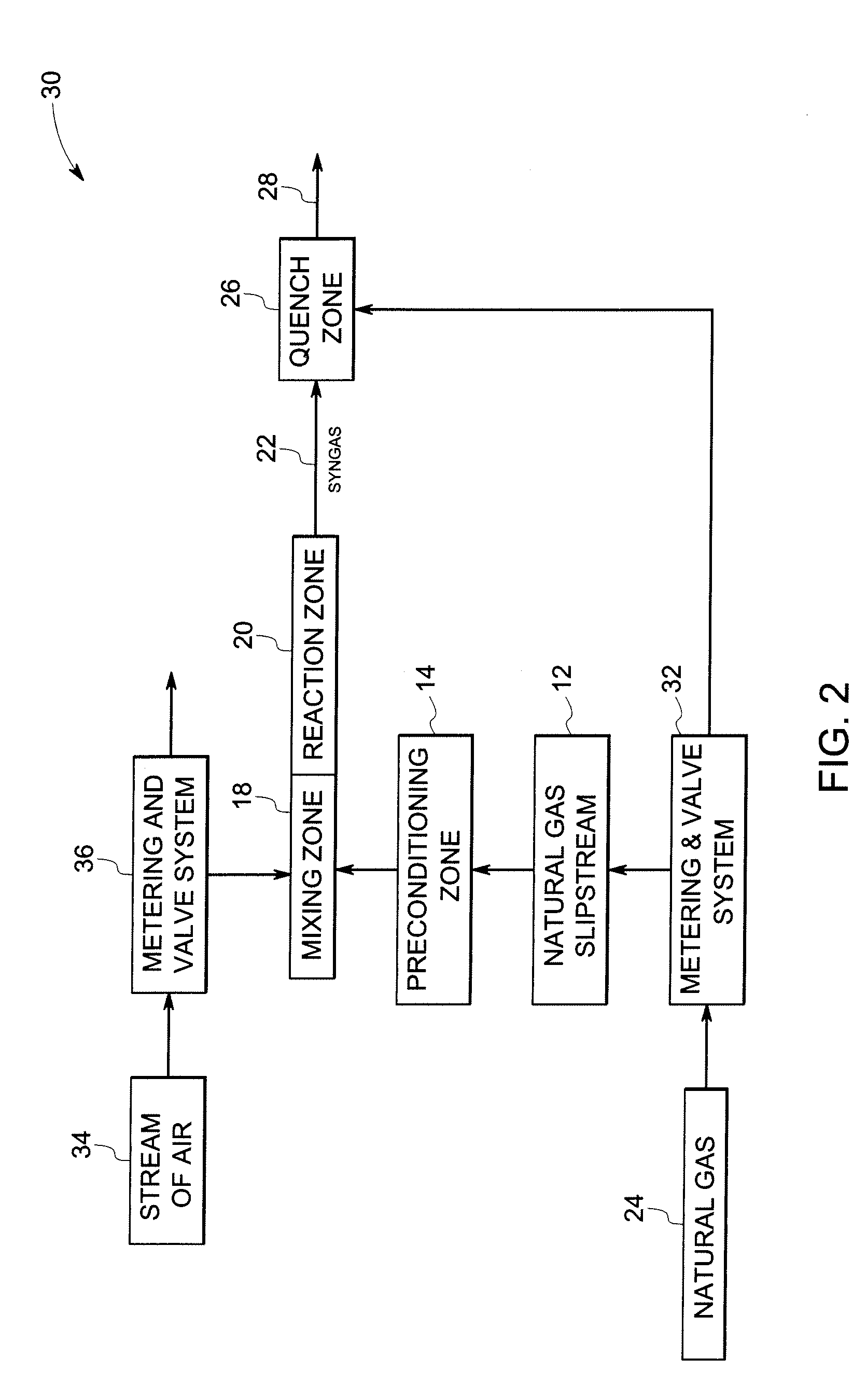
A gas turbine system includes a fuel reformer system comprising a fuel inlet configured to receive a fuel slipstream; an oxygen inlet configured to introduce an oxygen slipstream; a preconditioning zone configured to pretreat the fuel slipstream; a mixing zone comprising a premixing device configured to facilitate mixing of the fuel slipstream and the oxygen slipstream to form a gaseous premix; a reaction zone configured to generate a syngas from the gaseous premix; a quench zone configured to mix a fuel stream into the syngas to form a hydrogen-enriched fuel mixture; and a gas turbine configured to receive the fuel mixture.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wing assembly and aircraft
ActiveUS7510143B1Easy to reachPermit adjustmentAircraft stabilisationEfficient propulsion technologiesFlight vehicleEngineering
An aircraft is provided with a wing assembly mounted in a slipstream of a source of propulsion of the aircraft. The aircraft includes a body having a longitudinal axis, a wing assembly carried by the body and including a moveable portion moveable relative to the body and a wing carried by the moveable portion. A first actuator is coupled to the moveable portion to move it relative to the body in a direction generally parallel to the axis of the body. A second actuator is coupled to the wing to move the wing relative to the moveable portion and between first and second positions. The second actuator at least selectively permits uninhibited pivoted movement of the wing relative to the body in response to aerodynamic forces acting on the wing so that the wing may pivot to a position wherein the forces acting on the wing are balanced.
Owner:BERTELSEN DEISGN
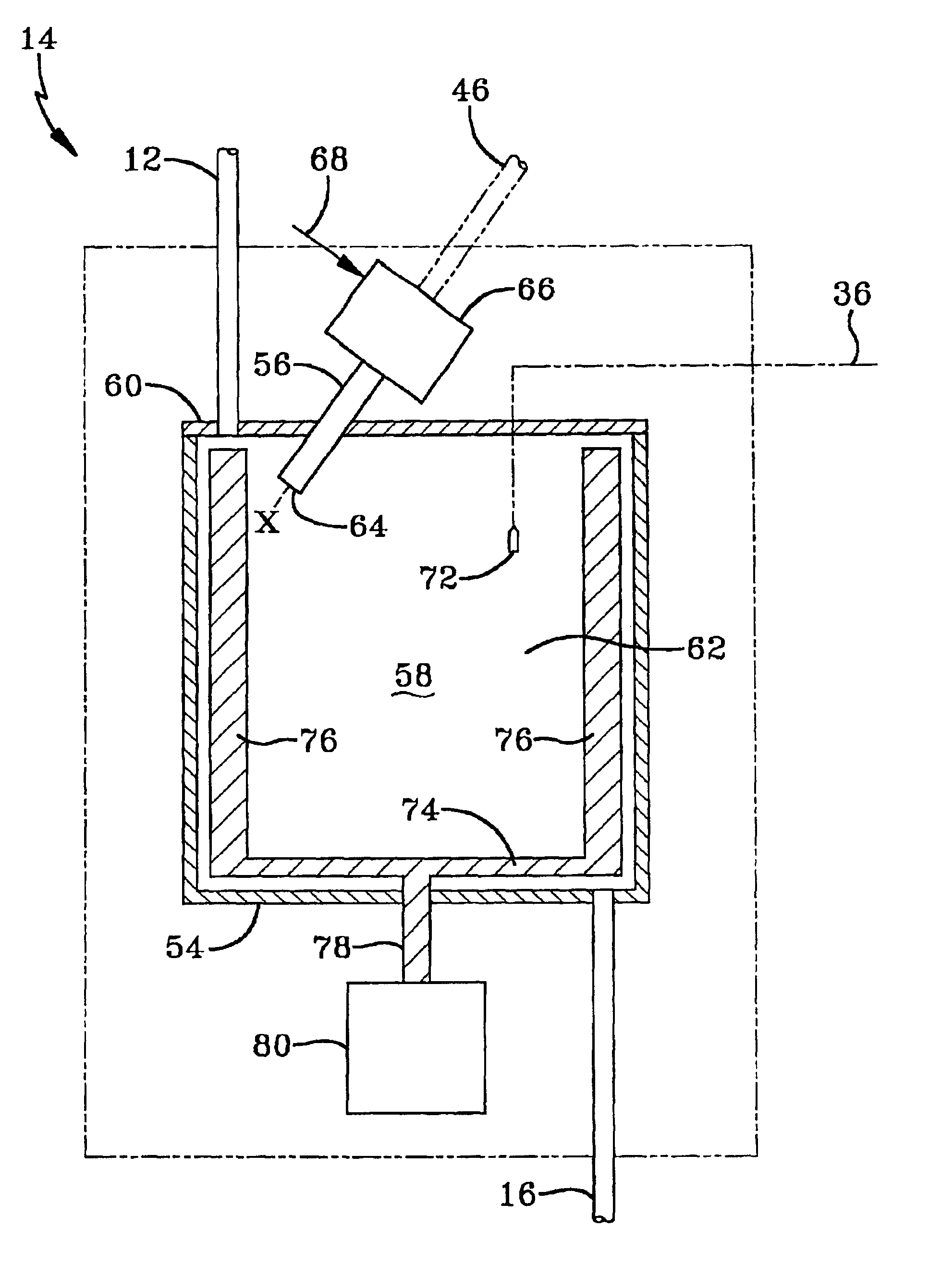
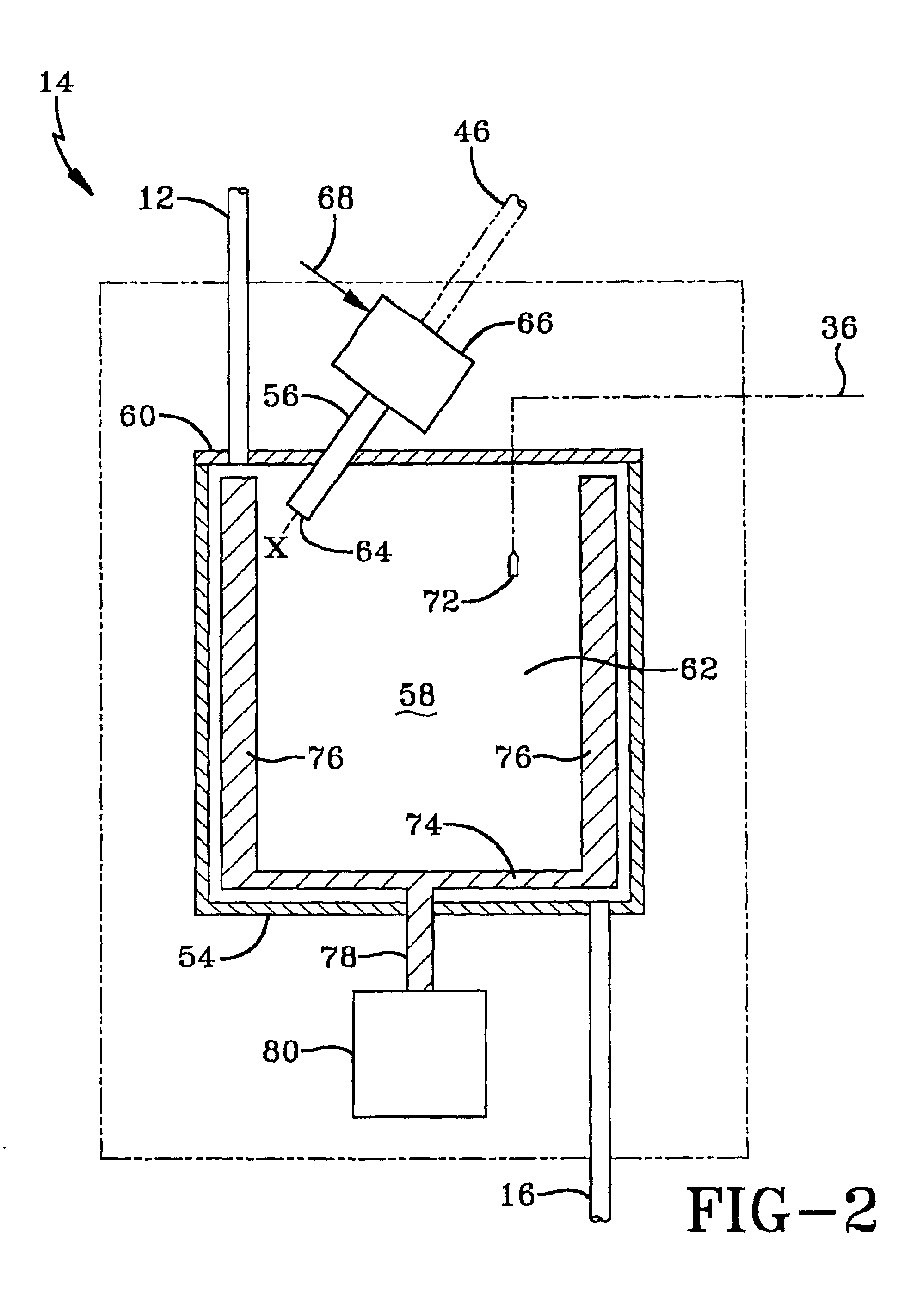
VTOL/STOL ducted propeller aircraft
InactiveUS7281680B2Avoid vibrationPrevent flutteringAircraft navigation controlVertical landing/take-off aircraftsLouverDucted propeller
The aircraft incorporates a single ducted propeller. The fuselage Bridges over the ducted propeller assembly, and is shaped in a way that the incoming air can smoothly flow into the propeller area. The duct has an aerodynamically shaped frontal area, and an aft extension, which forms the tail section. The wings are attached to the side of the duct. The ducted propeller assembly also contains louvers, which run span wise, to redirect the outgoing air in horizontal direction. During vertical take-off or landing, the propeller has a horizontal plane of rotation, after take-off the whole craft entirely tilts forward approximately 26 degrees to transition into horizontal wing born flight. During vertical flight, the aircraft is controlled by control louvers installed inside the ducted propeller assembly in the propeller slipstream.
Owner:MELKUTI ATTILA
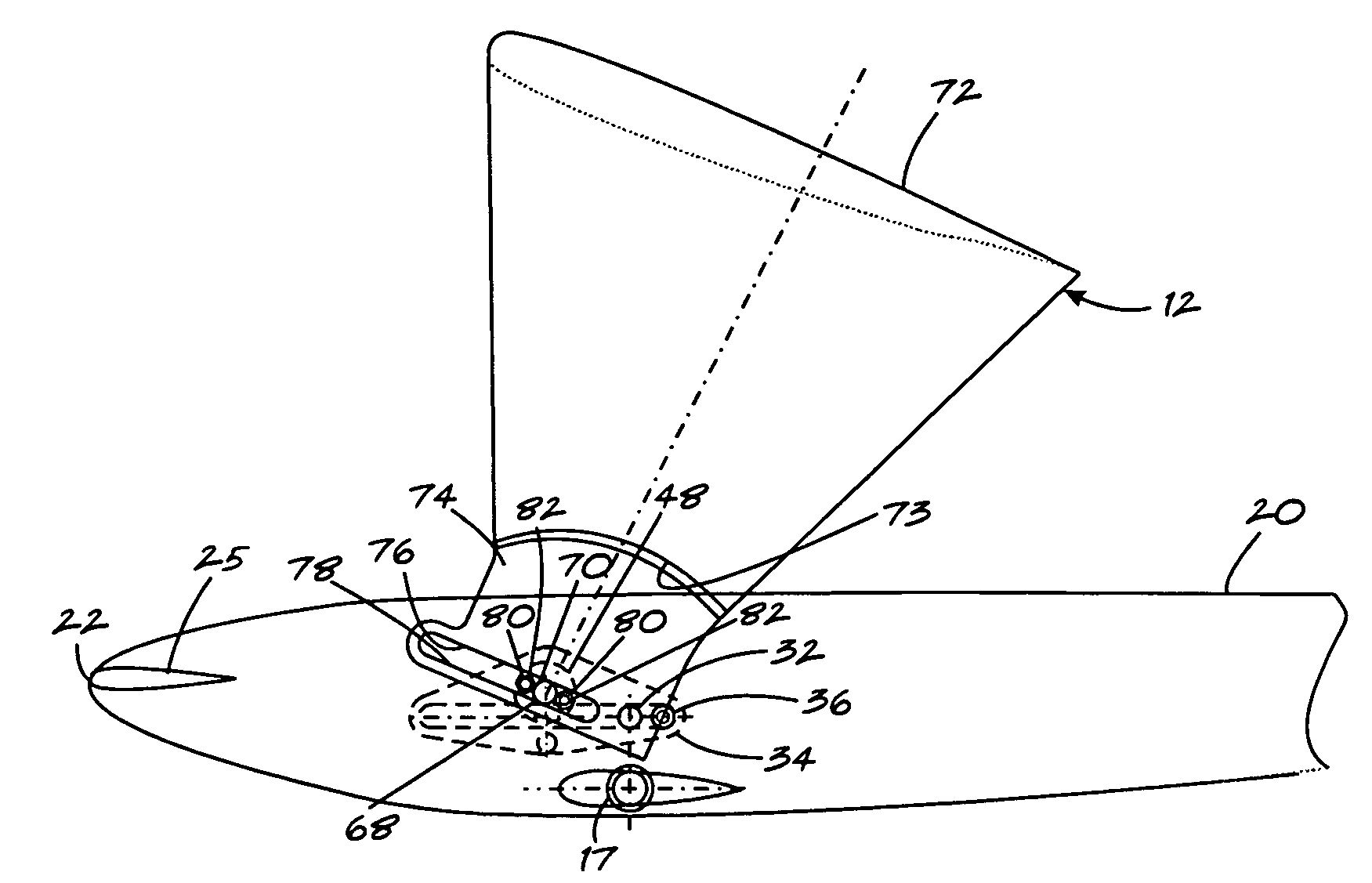
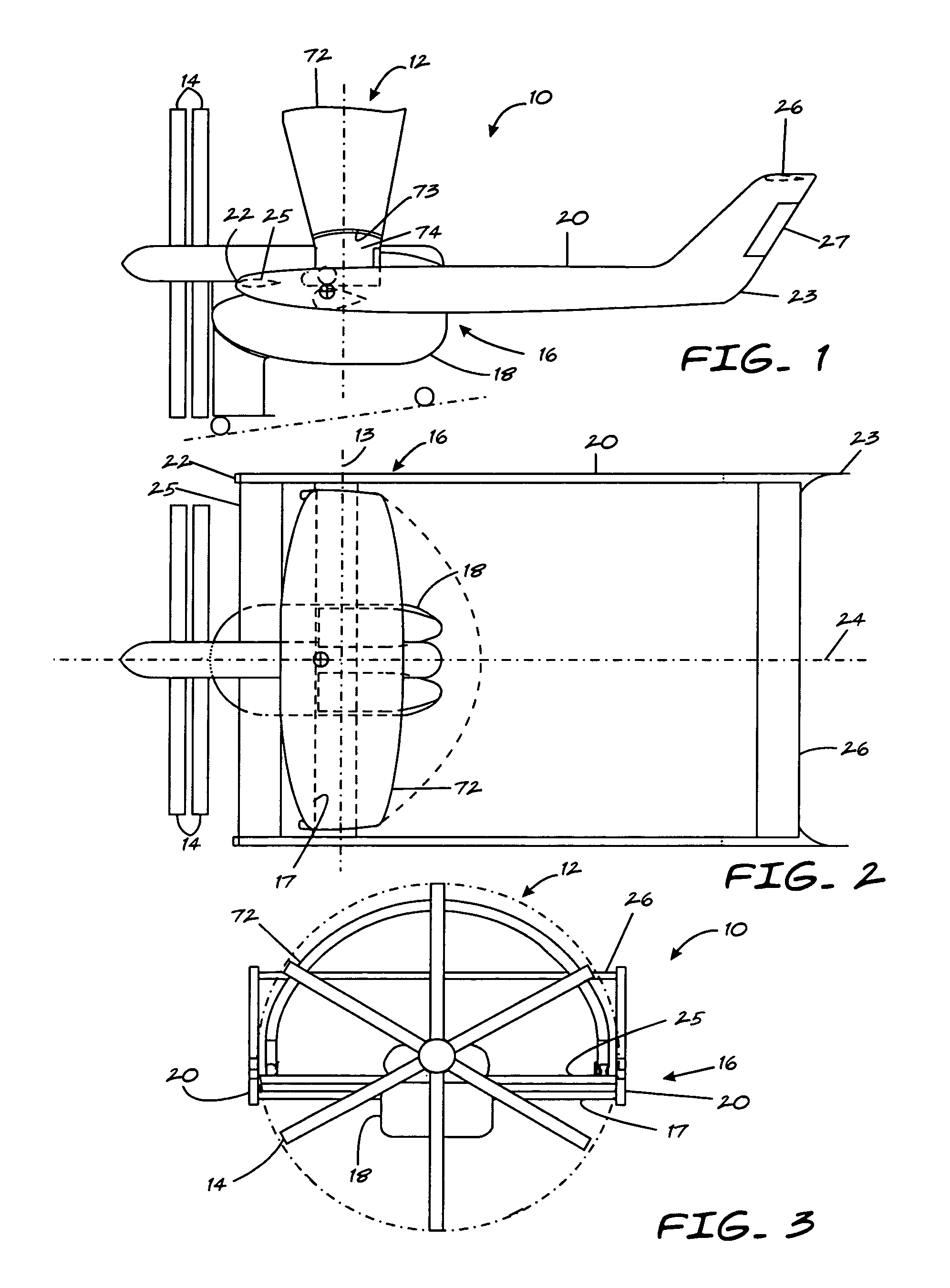
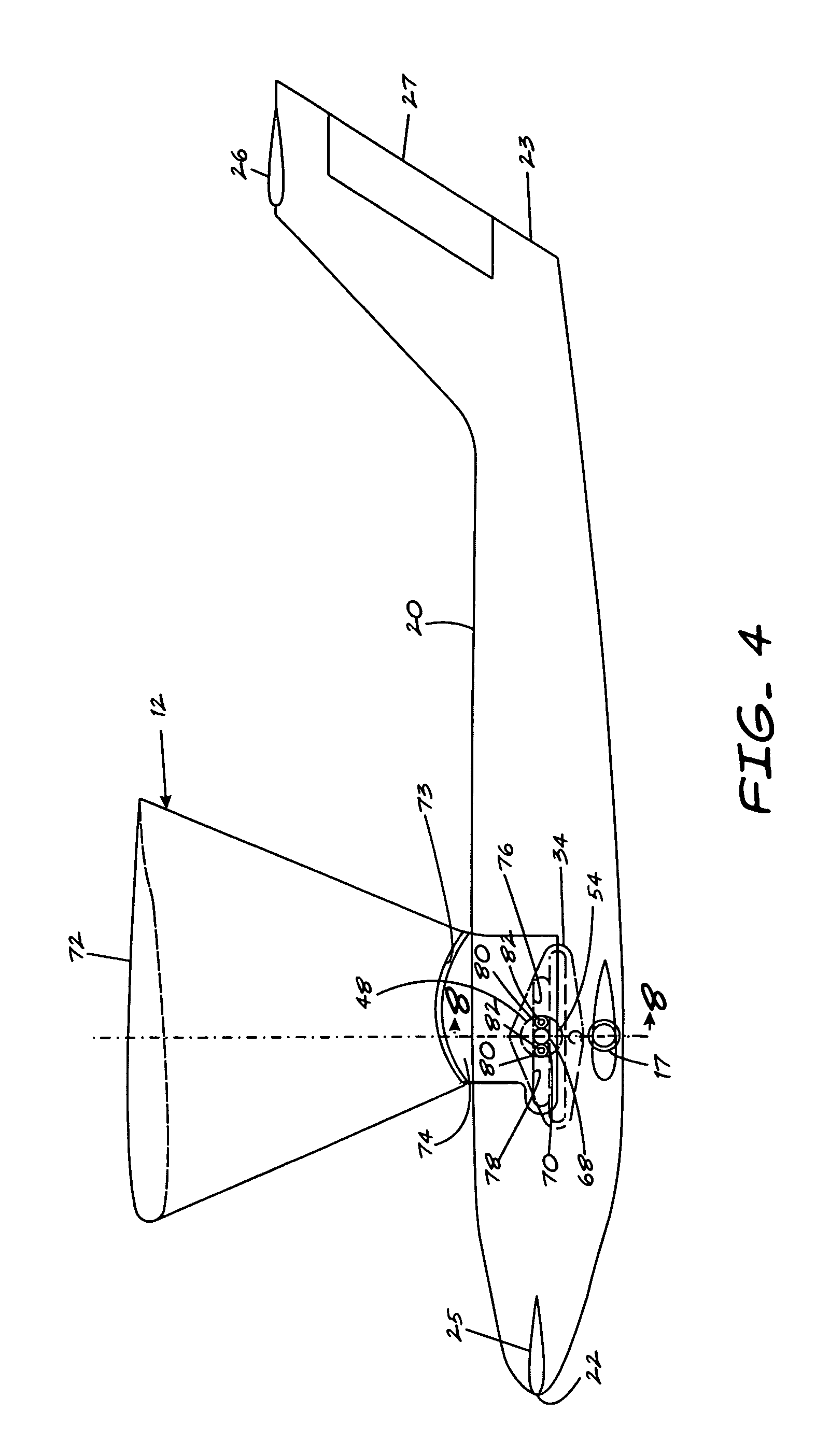
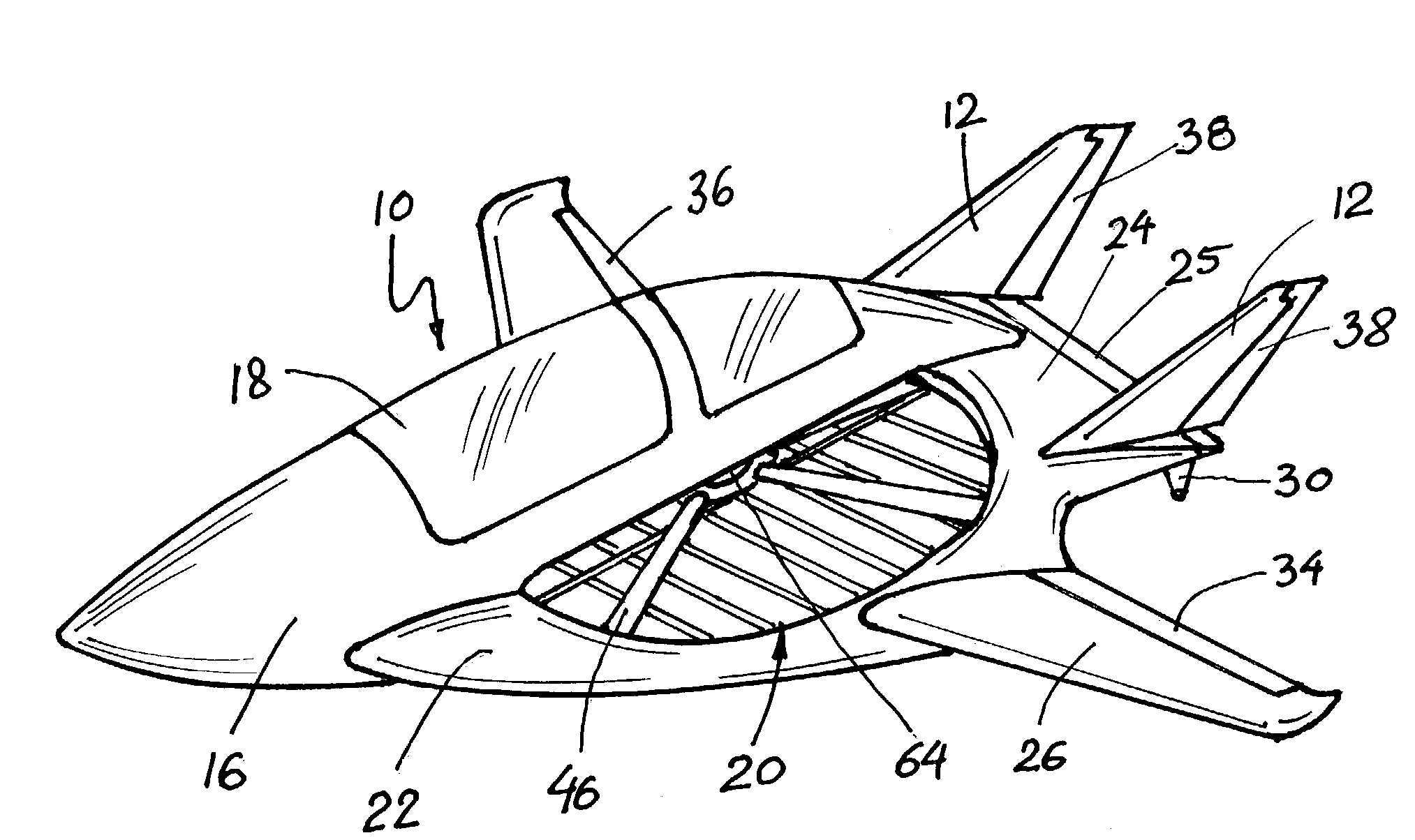
Aircraft wheels having vanes
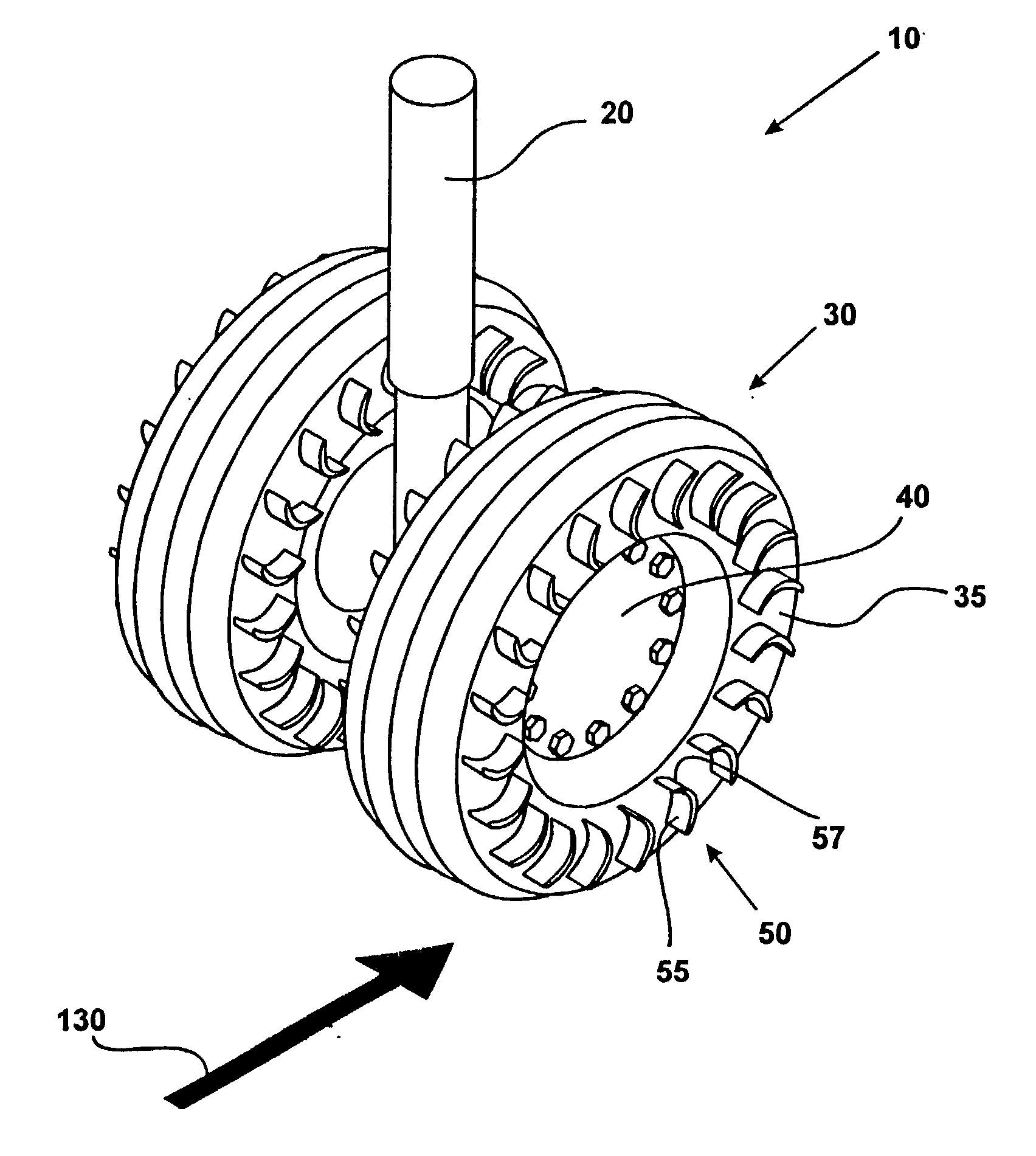
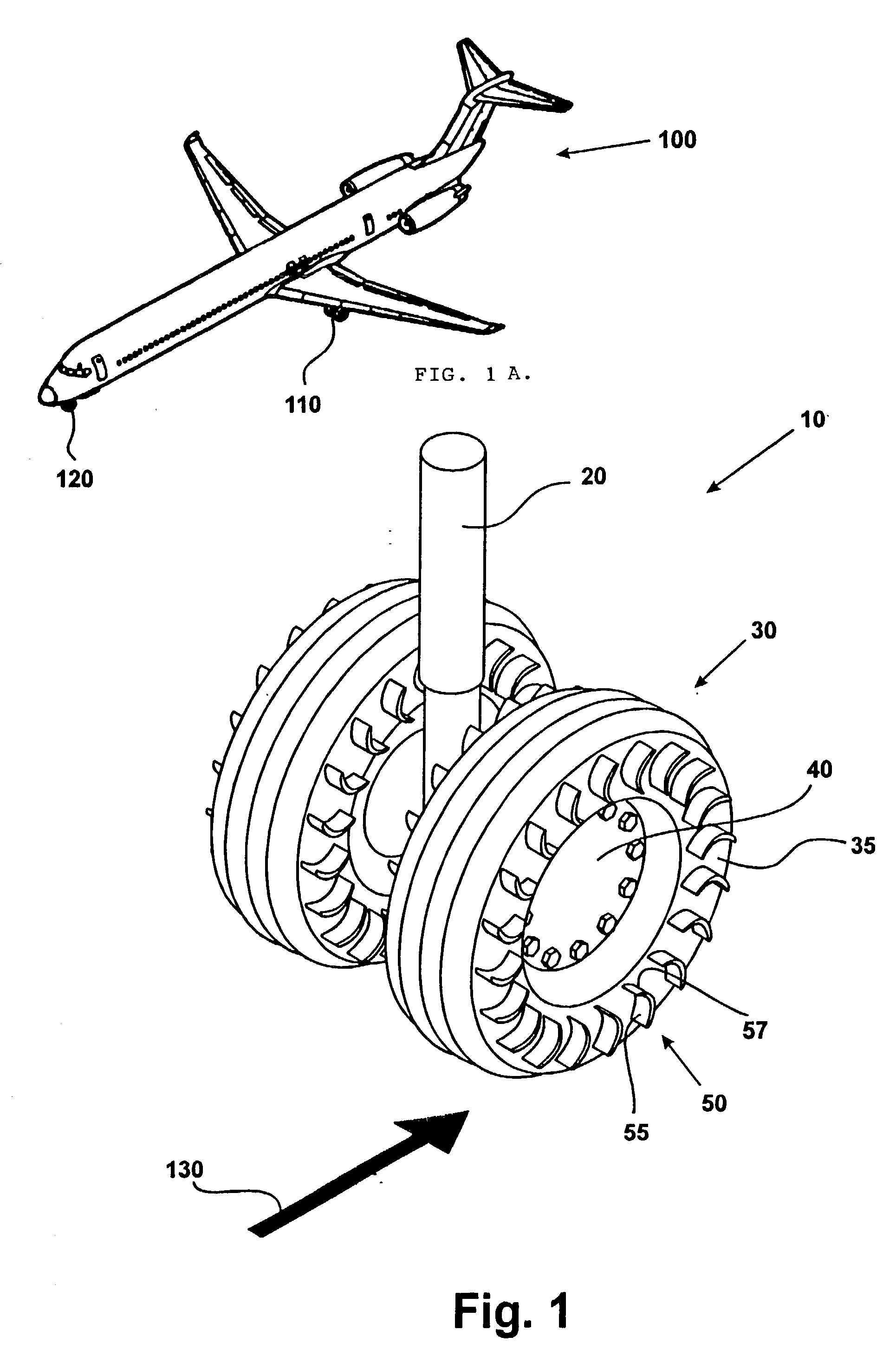
The present invention utilizes a new aircraft tire or wheel which employs specially shaped vanes protruding from the tire or wheel. These vanes capture the slipstream, and cause the tire and wheel to rotate in the direction of aircraft travel. Another embodiment of the invention employs a ring with cast or molded vanes, which may be mounted to the wheel of existing landing gear without changing to the new type of tire. The desired rotational speed of the tire will determine the number, size, and shape of the vanes, as well as how far they are mounted from the rotational axis of the tire / wheel combination.
Owner:SNYDER ARNOLD J
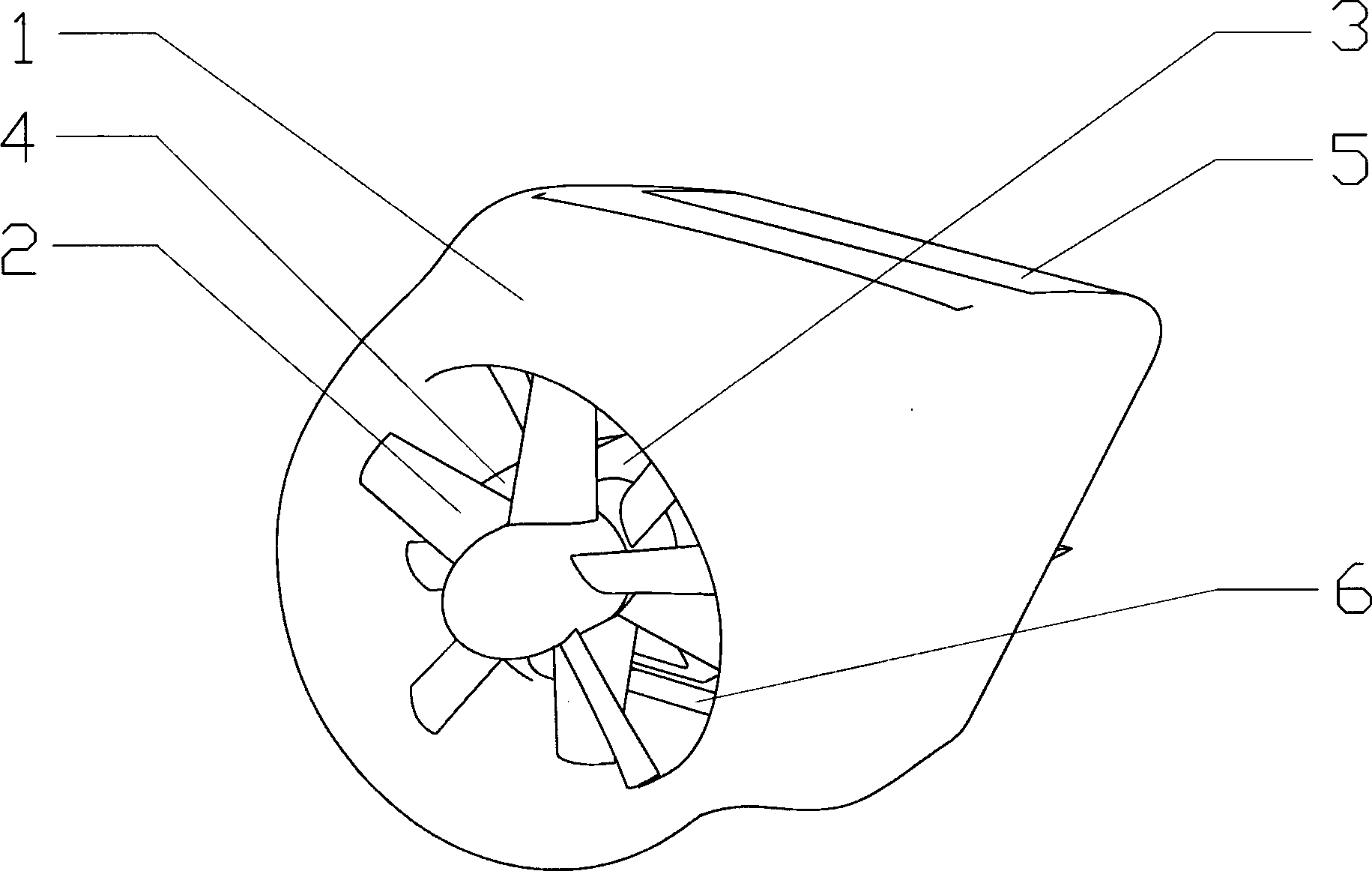
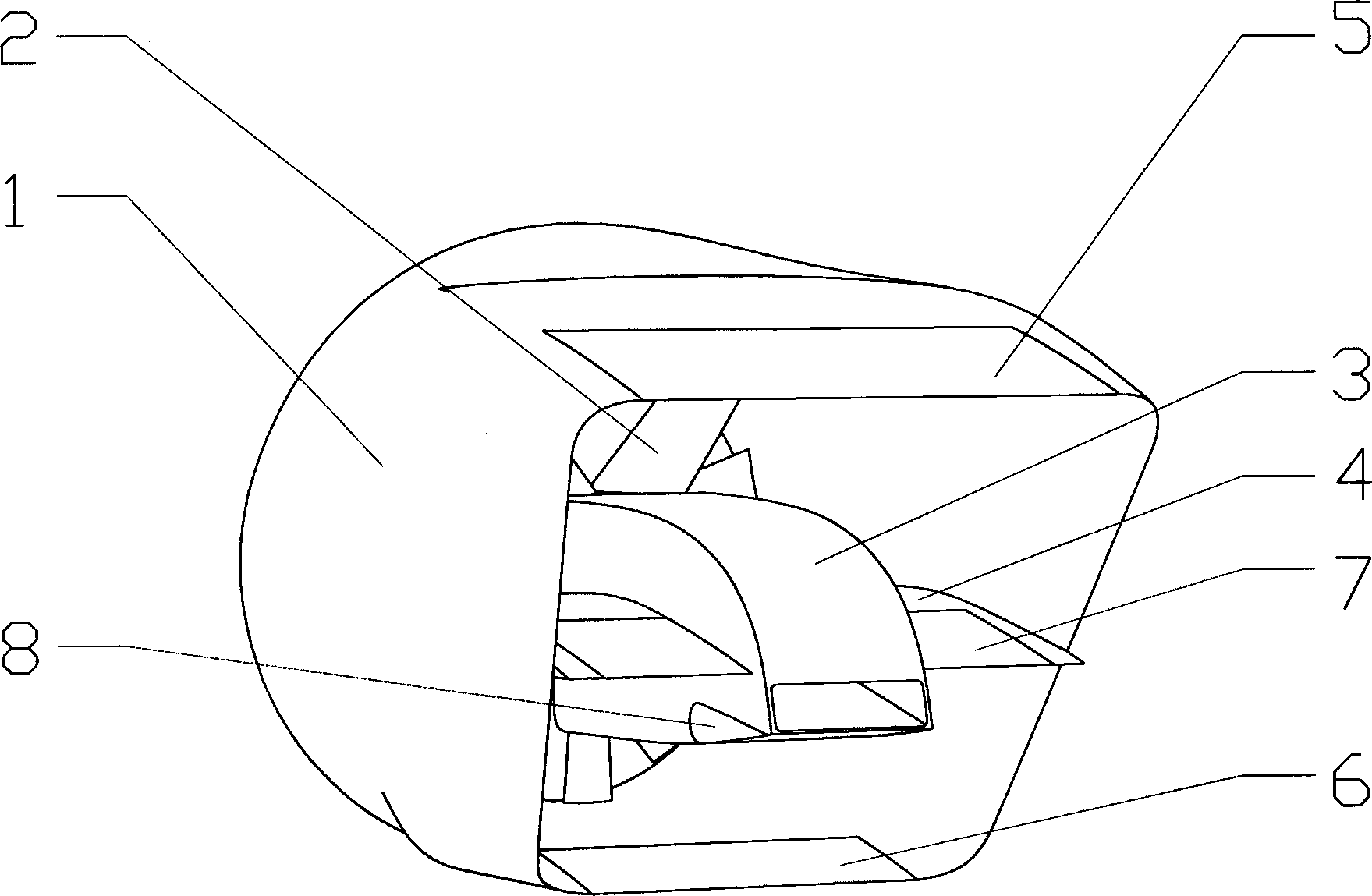
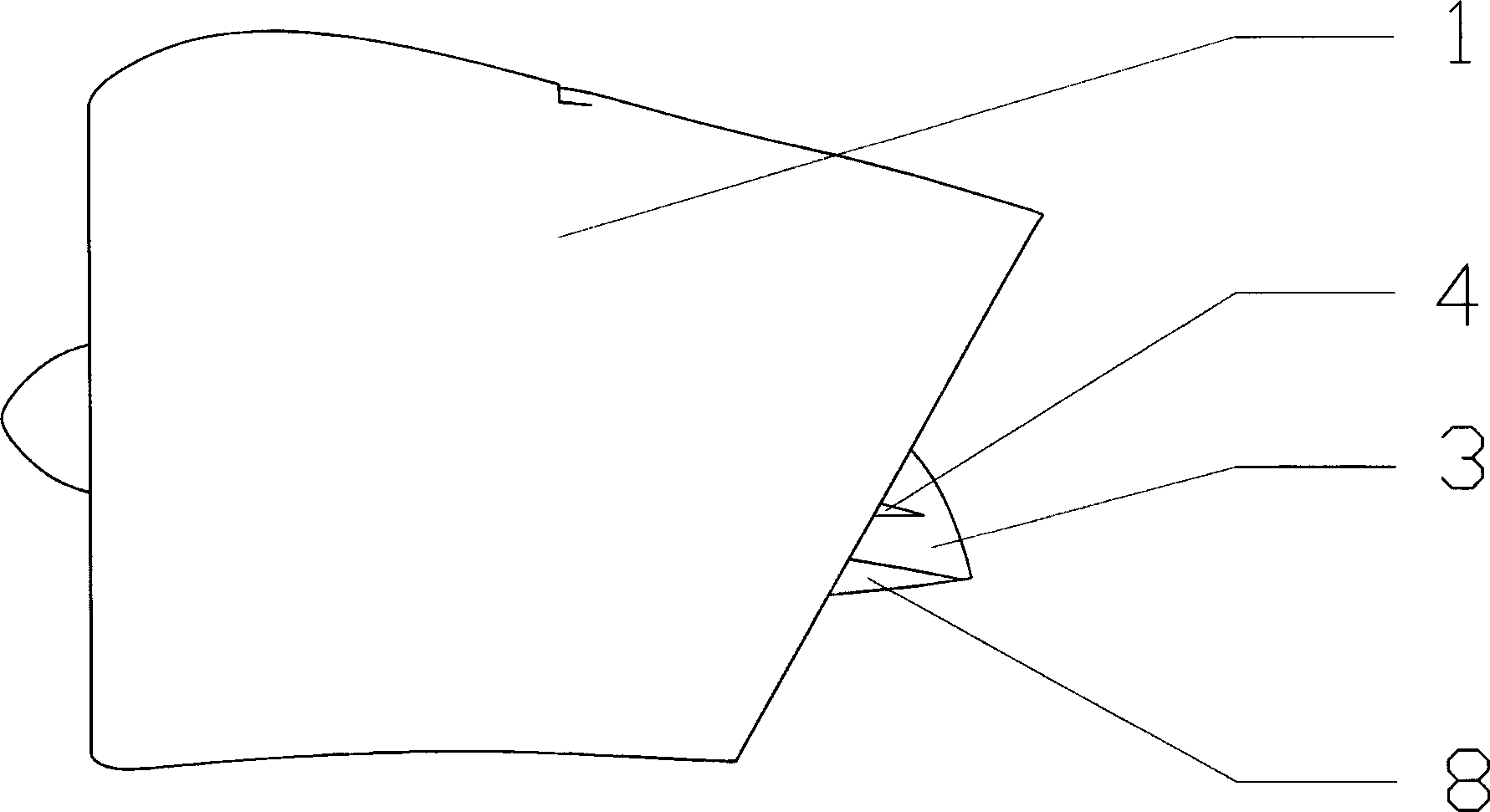
Duct wing system and aircraft using same
InactiveCN103921931AEasy to liftEliminate swirl twistAircraft controlWing adjustmentsFlight vehicleTrailing edge
The invention discloses a duct wing system comprising a duct wing, and a fan arranged at the front edge part of the duct wing, wherein the front edge part of the duct wing is shaped like a ring; the rear edge part of the duct wing is shaped like a trapezoid which is wide in upper part and narrow in lower part; the ring of the front edge part of the duct wing is in smooth connection with the trapezoid which is wide in upper part and narrow in lower part with and arranged at the rear edge part; the fan is a coaxial counter rotating fan and free of race rotation; the inner wall of the ring-shaped front edge part of the duct wing completely wraps the fan to reduce a tip vortex of the fan; meanwhile, the noise is shielded; the duct wing system is relatively safe. A gap communicated with the inner wall surface and the outer wall surface of the duct wing is formed in the upper part of the duct wing; the fan slip flow can enable power of the duct wing to be increased according to the groove wing effect and the gap wing effect. An aircraft using the duct wing system, disclosed by the invention, can vertically take off and land and horizontally fly, the vertical taking off and landing states and the horizontal flight state are stably converted, the duct wing system is good in safety, and good in economical efficiency, and the sight of a pilot is good.
Owner:龙川
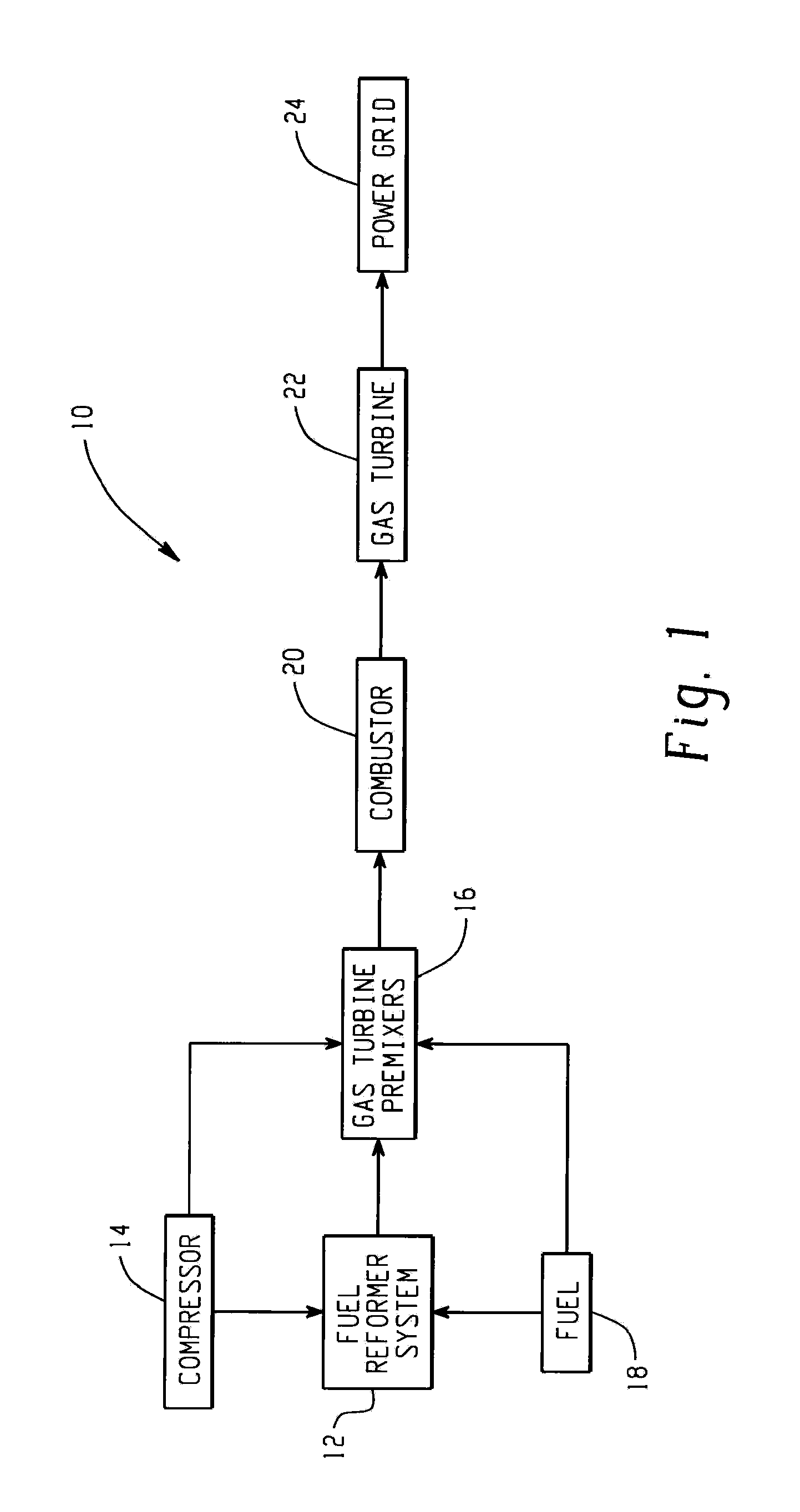
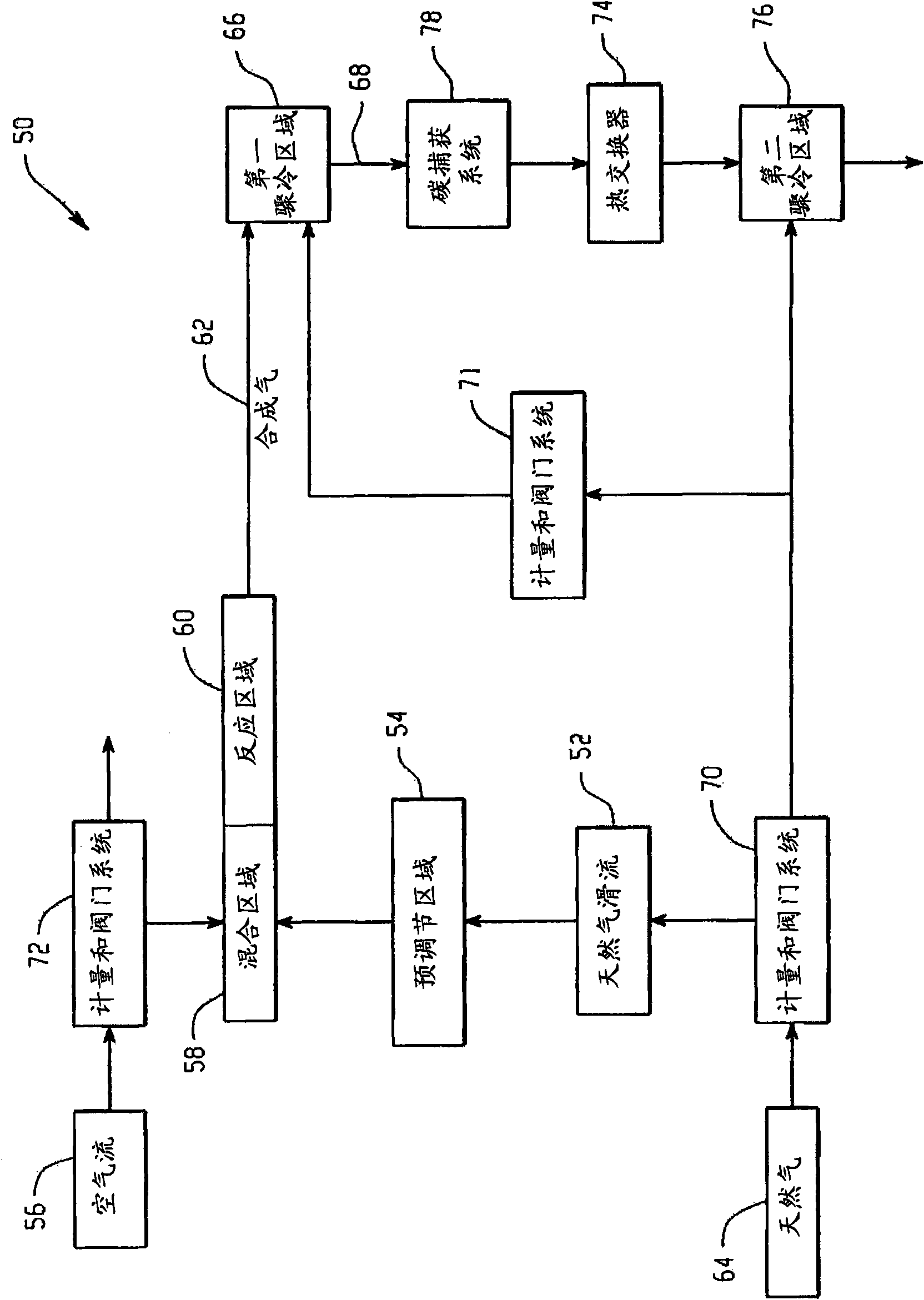
Fuel reformer system and a method for operating the same
A natural gas reformer system is provided. The natural gas reformer system includes a natural gas inlet configured to receive a natural gas slipstream. The natural gas reformer system also includes an air inlet configured to introduce a slip stream of air. The natural gas reformer system further includes a preconditioning zone configured to pretreat the natural gas slipstream. The natural gas reformer system also includes a mixing zone configured to mix the natural gas slipstream and the air in a rich proportion. The natural gas reformer system further includes a reaction zone configured to combust the natural gas and air to generate a syngas. The natural gas reformer system also includes a quench zone configured to mix the natural gas back into the syngas.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Radial counterflow muffler for no reduction and pollutant collection
ActiveUS20120193221A1Efficient separationCombination devicesCellsWorkspaceInternal combustion engine
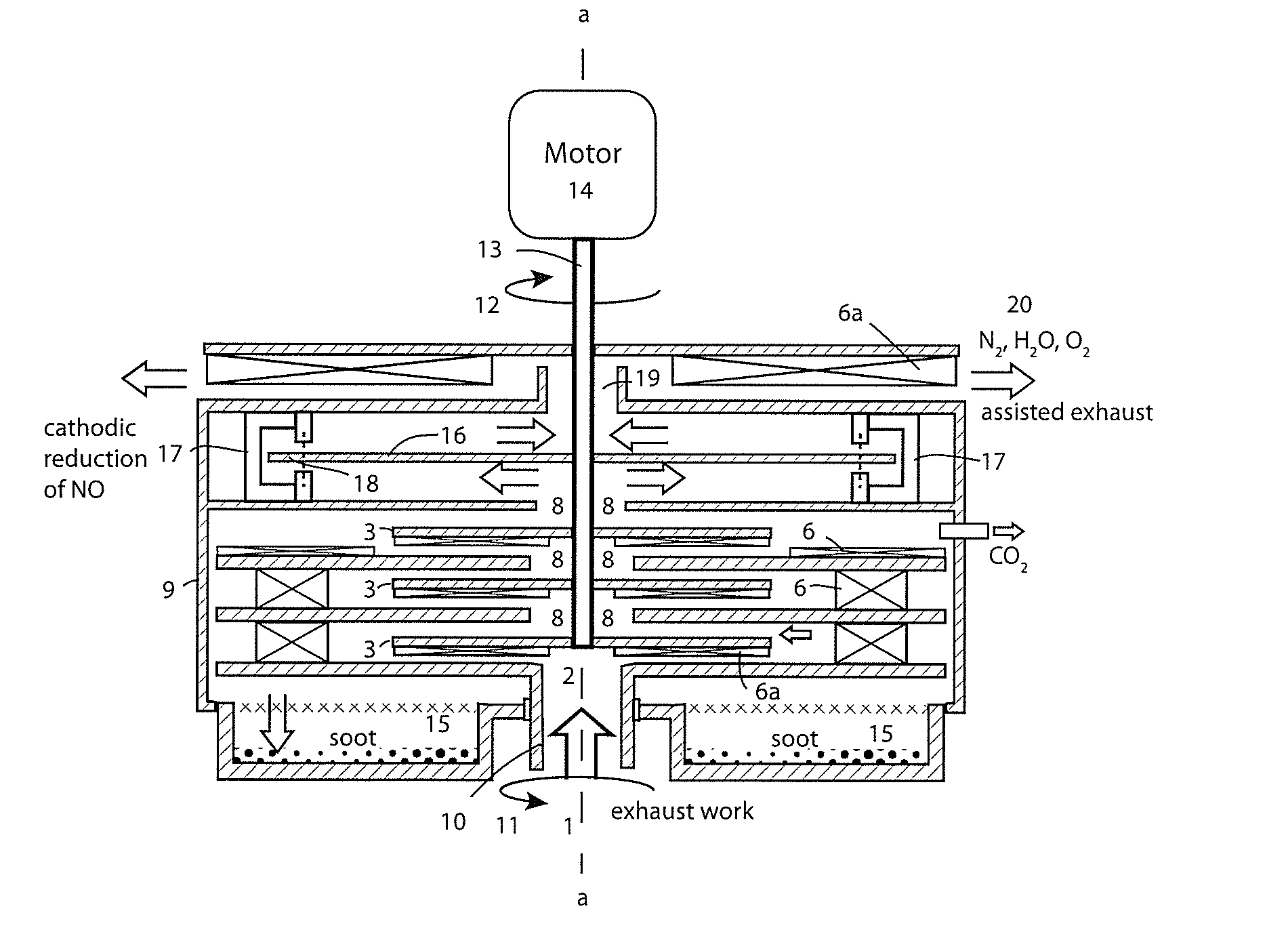
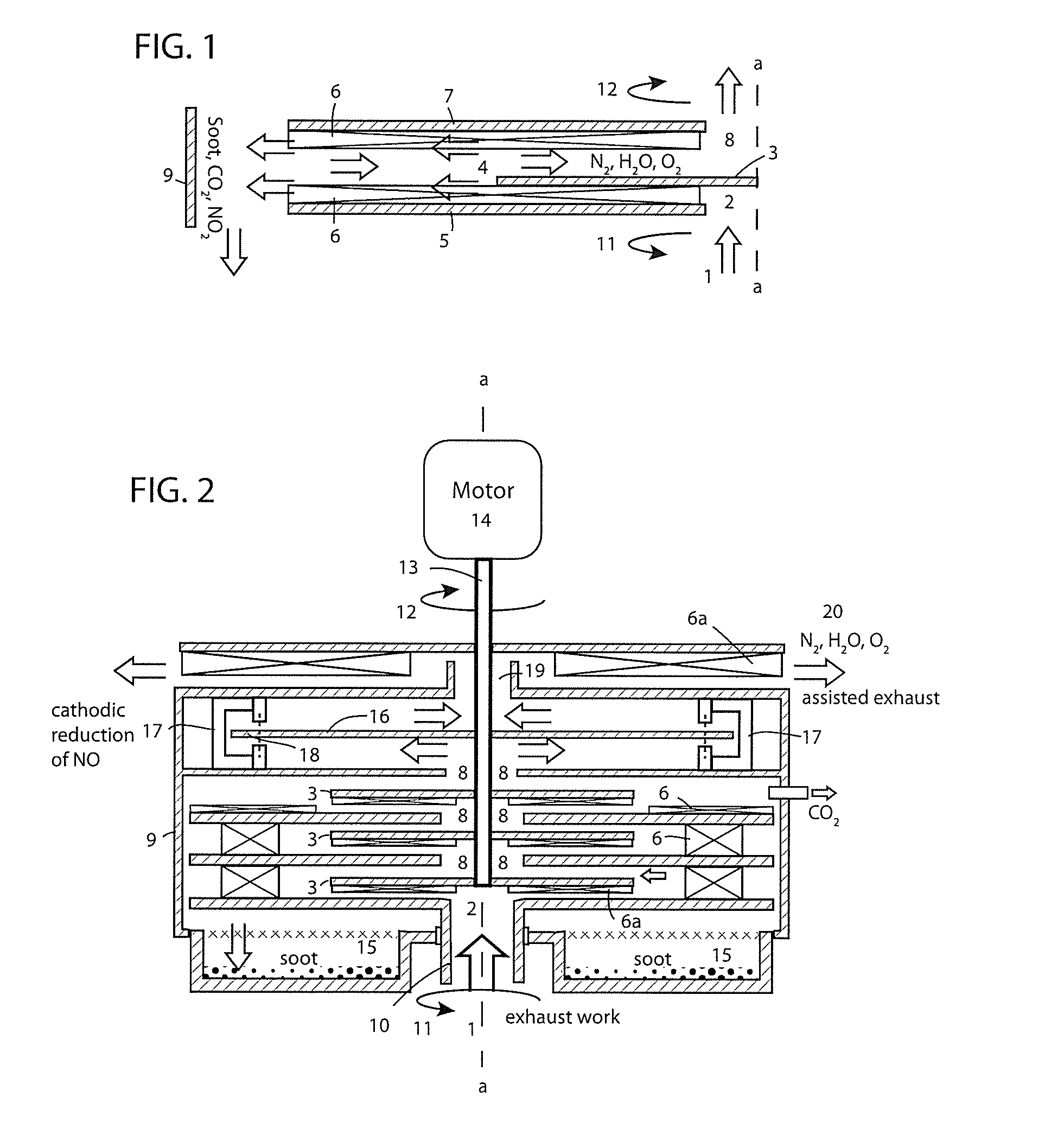
A scrubbing muffler for internal combustion engines comprises coaxial counter-rotating disk pairs stacked in a cascade. Acoustic pulses are attenuated by doing work and dissipated by the circuitous path through the dynamic cascade. A motor and / or Venturi effect from slipstream over a vehicle assists exhaust and reduces backpressure for greater fuel economy. Exhaust gas fed at the axis is sheared between the disks of the first stage of the cascade as it passes radially outward into a shrouding tank disposed about the cascade. Vortex rebound at the tank wall advects flow radially inward back through the workspace between the first stage disks to axial extraction as feed for the second stage of the cascade. N2 and H2O, along with CO and NO, can pass radially inward to successive stages. Soot and CO2 stay in the tank. NO and CO are reduced at a Faraday disk cathode.
Owner:VORSANA INC
Optimal wing planforms for reducing the induced or total drag of the wing of an aircraft driven by wing-mounted tractor propellers/rotors
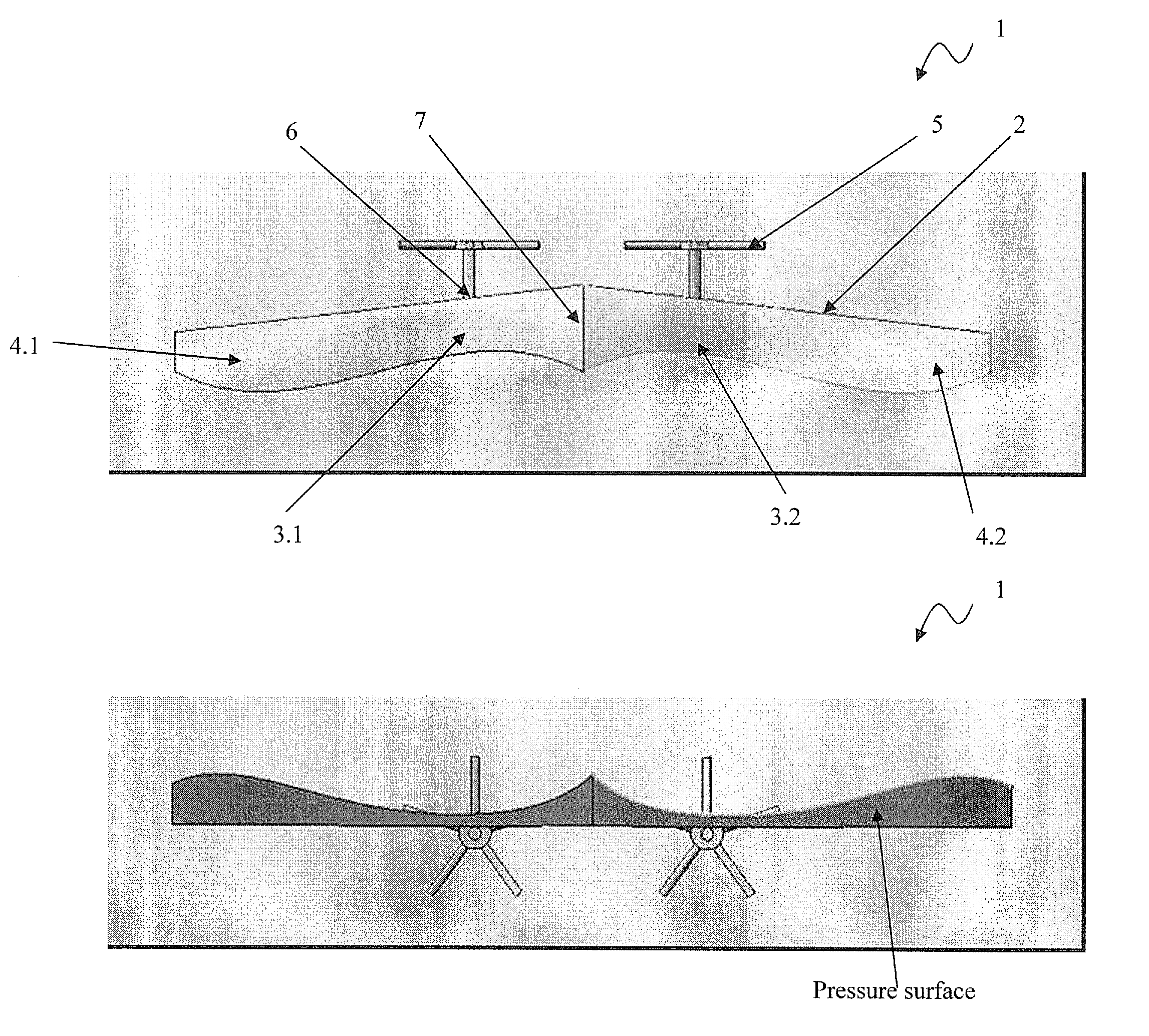
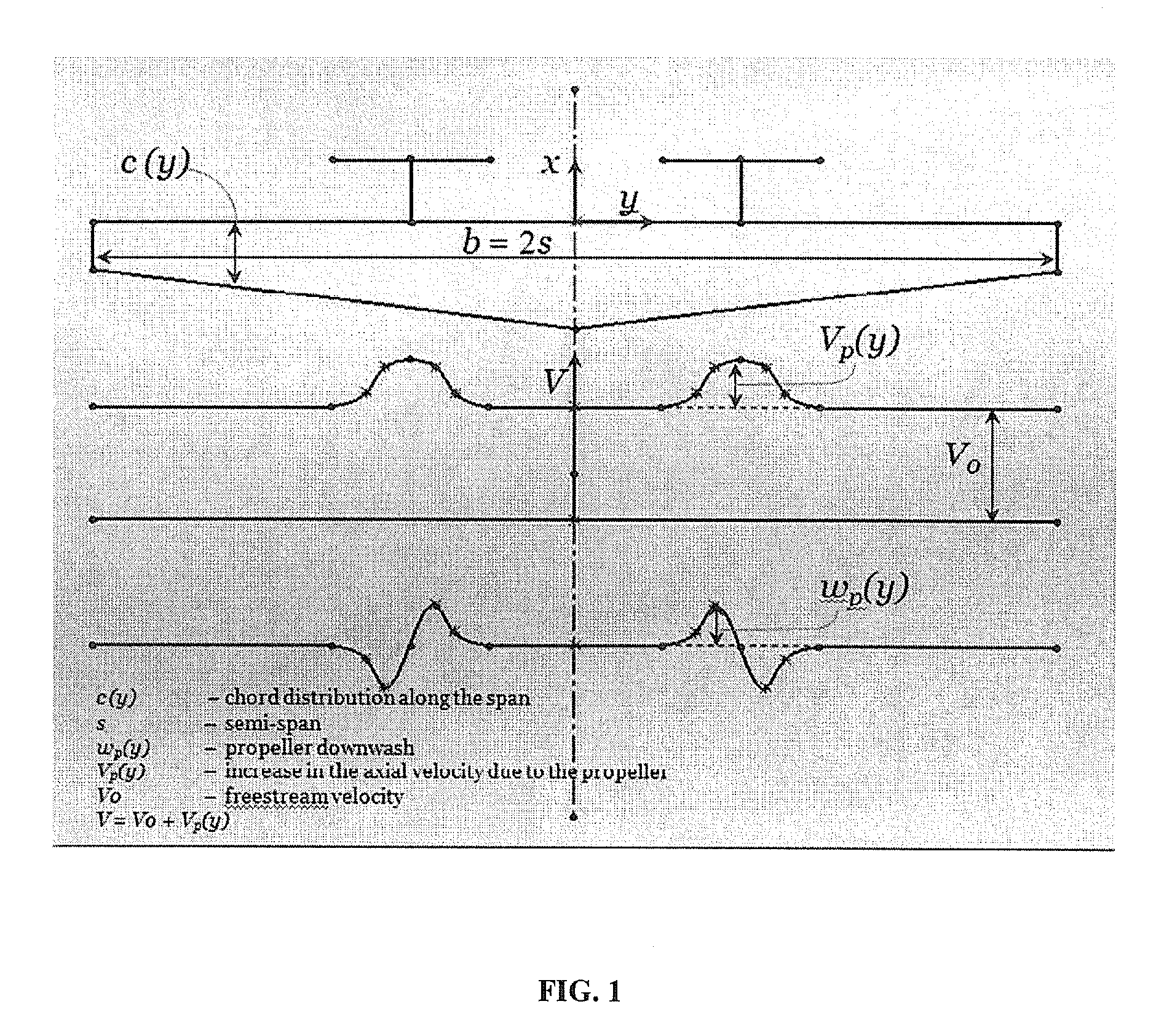
The disclosure relates to Aeronautics, more particularly relating to wing planforms that reduce wing drag substantially in aircraft driven by propellers or other rotors in tractor configuration. An aircraft comprising a wing and propeller system (1), said system comprising wing planform (2) characterized into wing chord regions (3) behind each propeller / rotor (5) whose length is relatively varied with respect to length of wing chord regions (4) at outboard of the propeller / rotor (5) towards wing tip and / or at inboard of the propeller (5) towards fuselage, and plurality of propellers (5) fixed ahead of wing leading edge such that induced drag is reduced by exploiting the velocity field generated by the slipstream of the propeller (5). Also, provides for a method of optimizing wing and propeller system and a method reducing induced drag, among other possible parameters of interest.
Owner:JAWAHARLAL NEHRU CENT FOR ADVANCED SCI RES
On-line determination of wax crystallization temperature of waxy solvent stream
InactiveUS20030075478A1Material crystallisationScattering properties measurementsRemote controlCrystallization temperature
A laser beam reflected by wax crystals is used in determining the wax crystallization temperature of a hot dewaxing solvent upstream of solvent chillers. This is automatically achieved by an on-line method from a remote control point, in which a slipstream of solvent is passed through an attached solvent loop into a sample chamber in the loop, without being exposed to ambient conditions. As the sample is cooled, the beam reflections are detected and indicate the wax to crystallization temperature. Corrective measures can then be taken to prevent fouling of the chillers, if need be.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
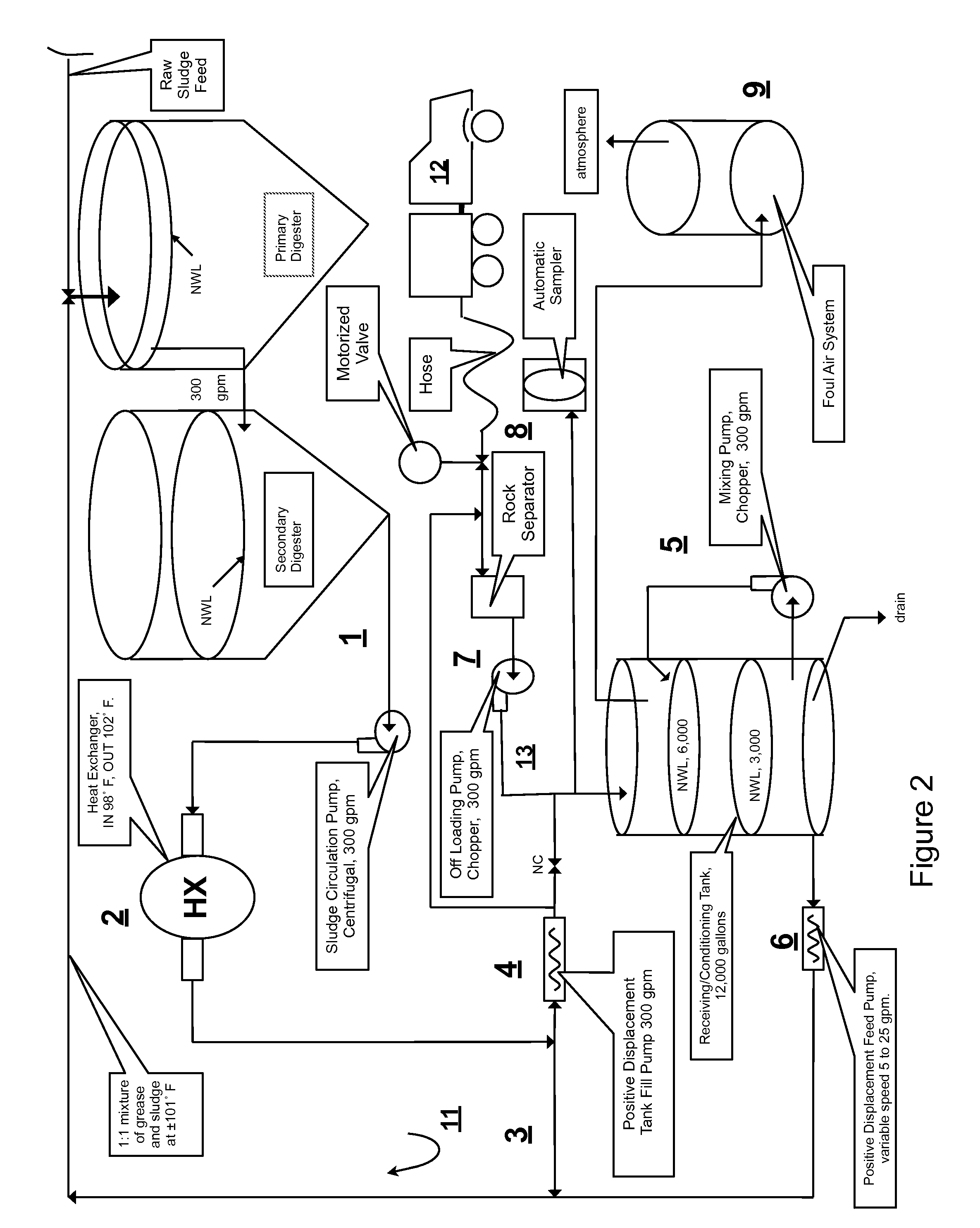
Integrated cogeneration wastewater sewage and waste polar fats/ oils/ greases/waxes (FOG) waste treatment method and facility
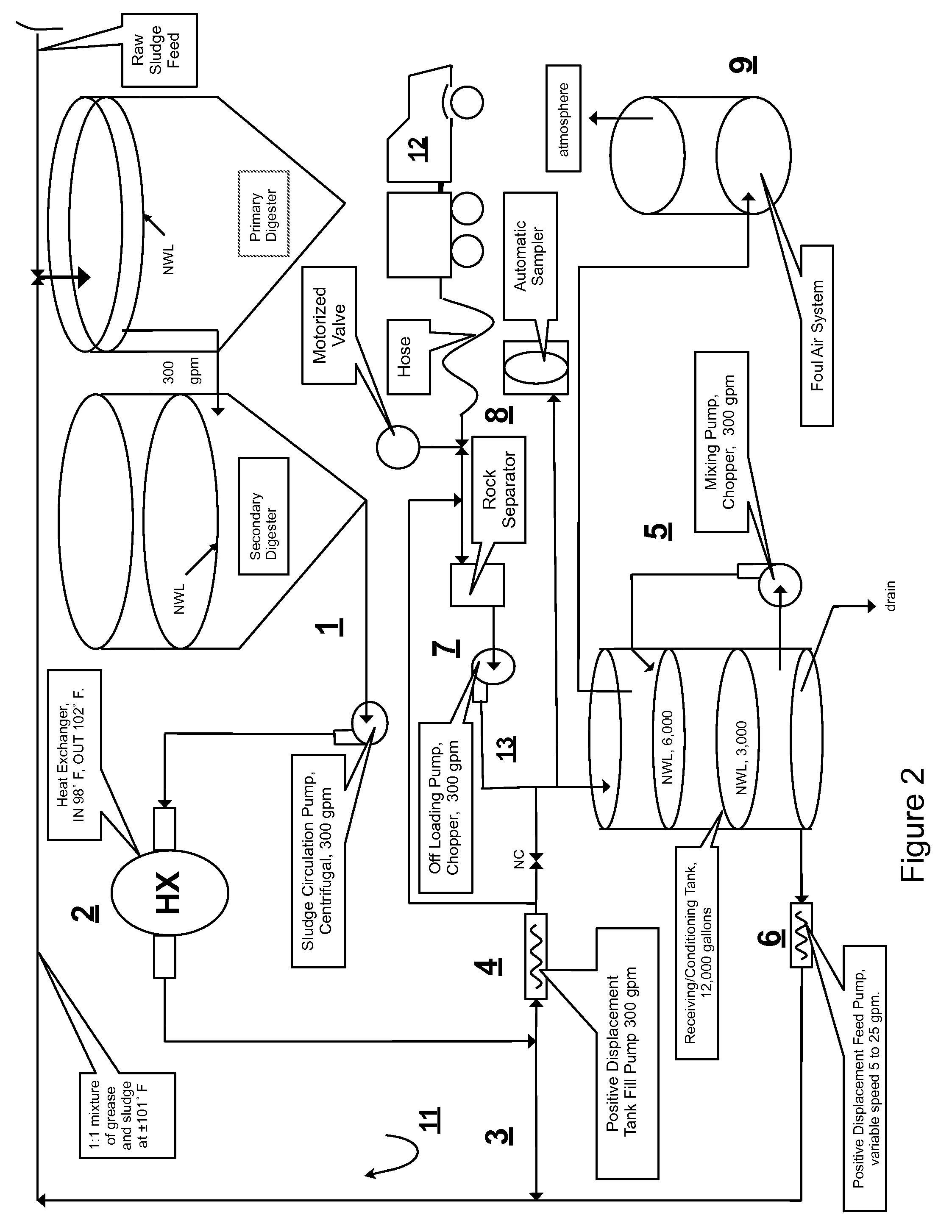
InactiveUS7485230B2Low solidsHigh energyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGeneral water supply conservationVolatile fatty acidsCogeneration
A system and method integrating treatment of waste, polar Fats / Oils / Greases (FOG) with conventional anaerobic wastewater treatment facilities for biologically fueling digestion of solids in, and steady state production of methane from treated wastewater streams that includes a slipstream loop circulating warmed, actively digesting sludge from the base to the head of the anaerobic wastewater treatment facility, a conditioning tank with input screened by a rock trap, actively digesting sludge pumped from the slipstream loop into the tank via the rock trap, before and after FOG wastes are pumped from a hauler tank via a hose connecting to the rock trap into the conditioning tank and mixed with actively digesting sludge in the tank to produce a feedstock slurry rich in volatile fatty acids for injection at a metered rate back into the actively digesting sludge slipstream loop for introduction at the head of the anaerobic wastewater treatment facility.
Owner:MAGNER JOSEPH A +1
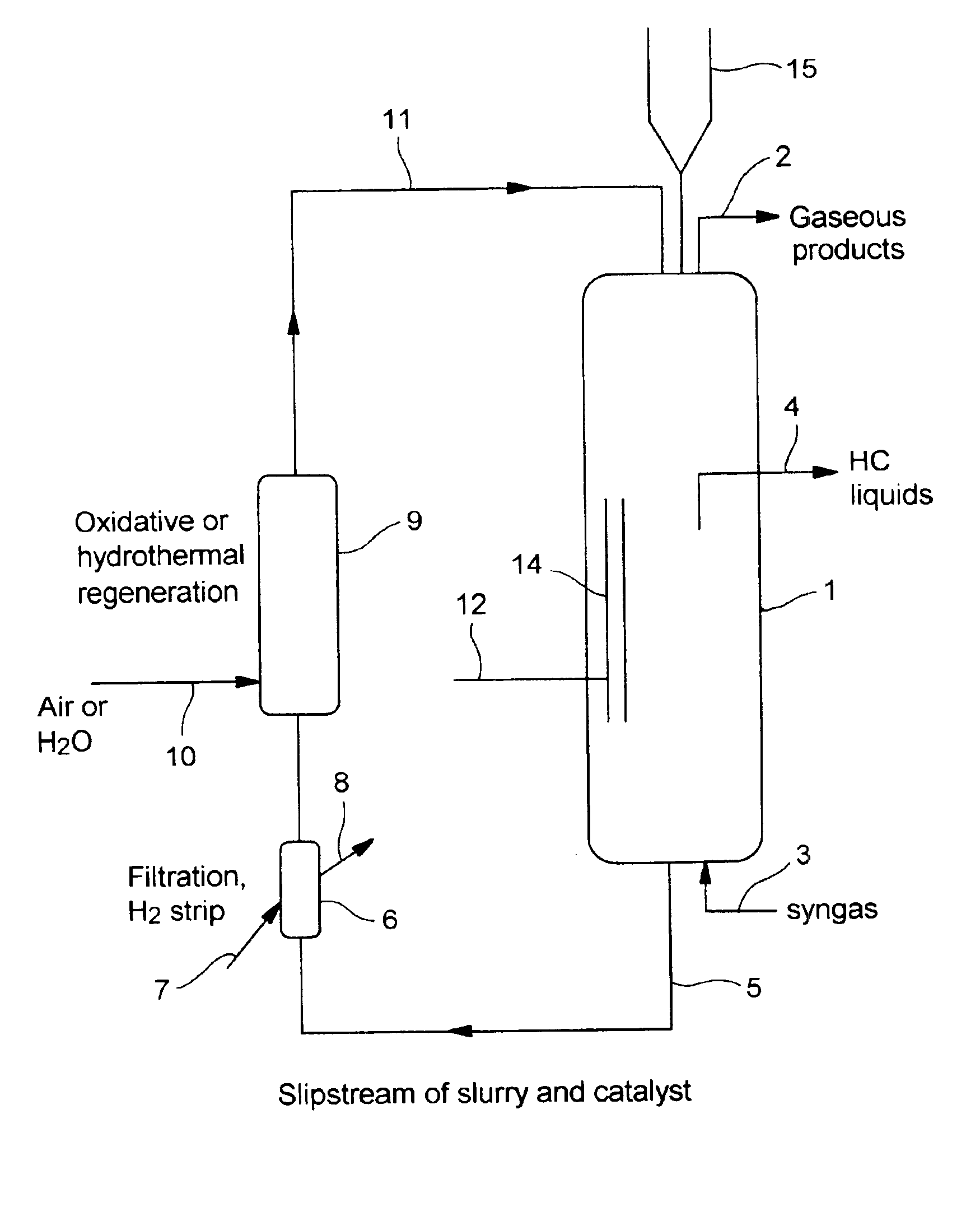
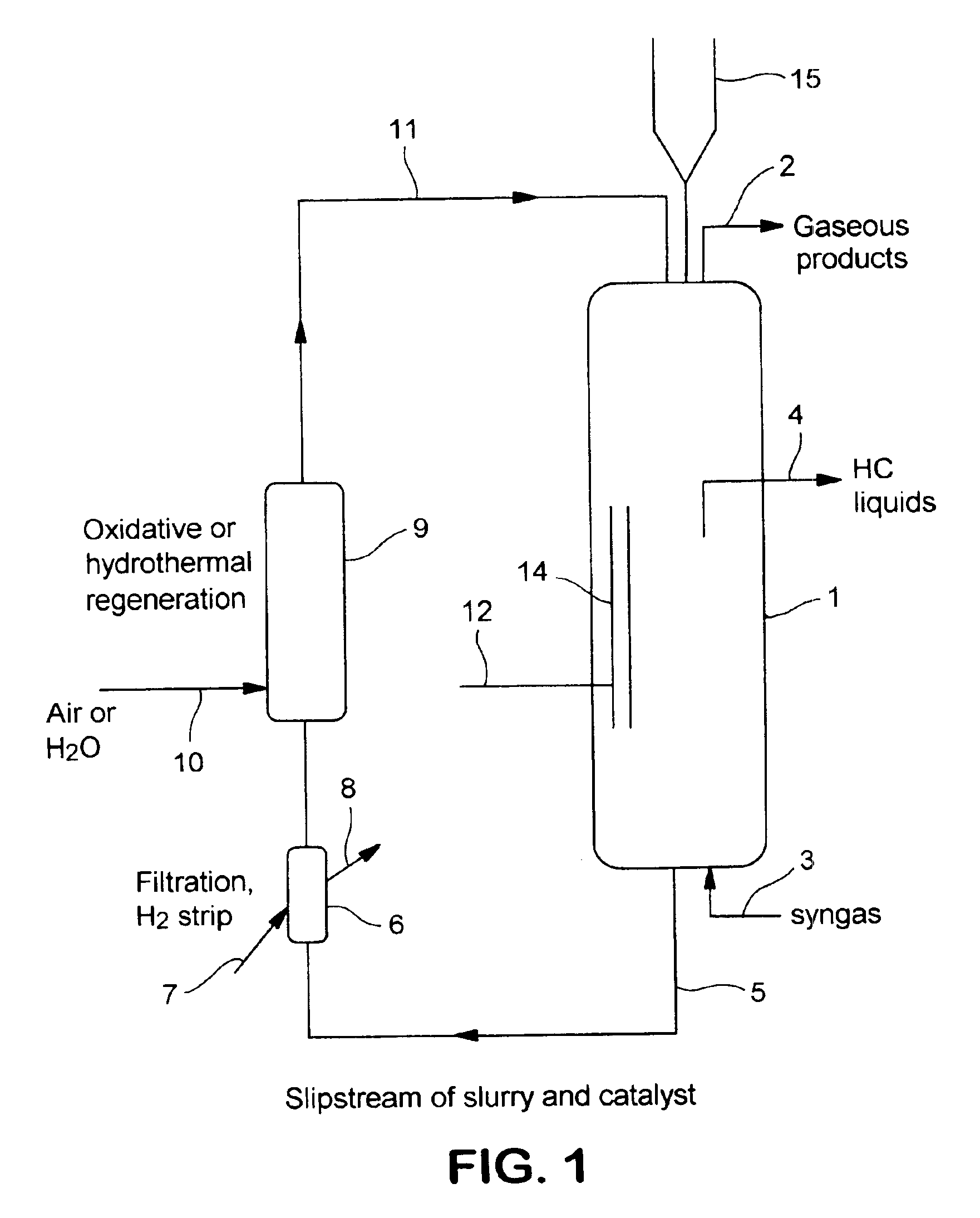
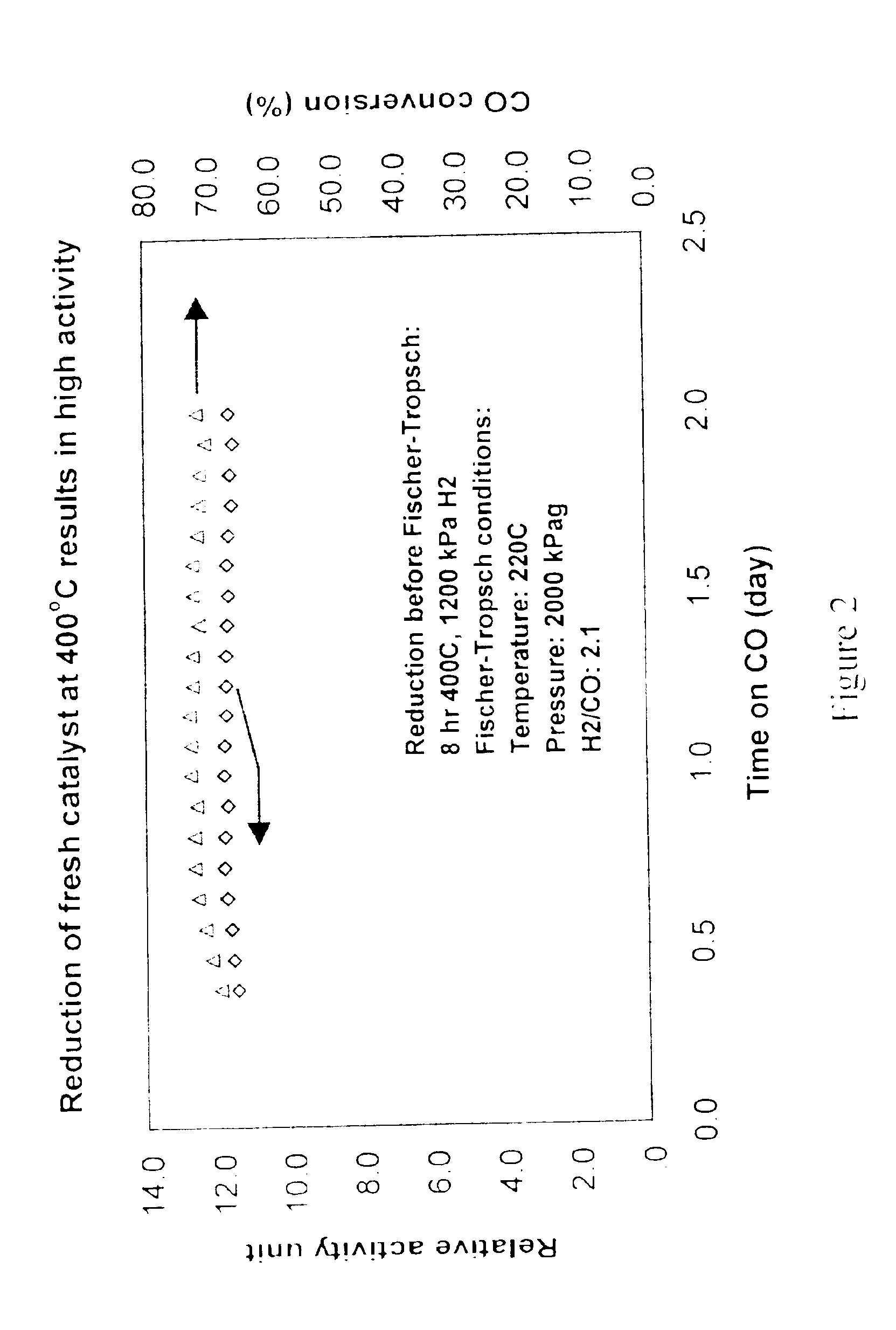
In situ catalyst regeneration/activation process
An in situ process for conducting regeneration of spent hydrocarbon synthesis catalyst. Regenerated, but not yet re-activated, catalyst (15) may be introduced into an operating HCS reactor (1) that has catalyst rejuvenation means (14). Any combination of a fresh, activated catalyst, a fresh, passivated catalyst or short-term or long-term deactivated catalysts may already be present in the HCS reactor (1). The regenerated, but not yet re-activated catalyst is activated in the HCS reactor (1) with rejuvenation means (14) at normal process conditions. The HCS reactor (1) receives syngas through the inlet line (3) and releases liquid hydrocarbons through outlet line (4) and gaseous hydrocarbon and unreacted syngas through the offgas line (2). Catalyst is removed from the HCS reactor (1) through the slipstream line (5) and into a filtration unit (6) which is fed with a stripping fluid (7). The filtered catalyst proceeds to the regeneration unit (9) which is fed a regenerative fluid (10). The regenerated catalyst is returned to the HCS Reactor (1) through the catalyst return line (11) where it is reactivated.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Power-operated tail-sitting type mixed layout vertical take-off and landing aircraft
InactiveCN106240814AStable and efficient vertical take-off and landingStable and efficient hoveringVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftRotary wingDihedral angle
The invention discloses a power-operated tail-sitting type mixed layout vertical take-off and landing aircraft. The power-operated tail-sitting type mixed layout vertical take-off and landing aircraft is composed of a fuselage, airfoils, motors, propellers and landing gears; the fuselage axis coincides with the OX axis of a body axial system, the projections of the fuselage axis and the OX axis in an XOY plane of the body axial system are distributed in an X shape; each airfoil on the fuselage is divided into several sections, sweepback angles and dihedral angles of all the sections are different from one another, and excellent pneumatic performance and maneuvering performance are achieved through positively-curved airfoil profiles and negatively-curved airfoil profiles; four sets of propeller-motor power systems are installed on the four airfoils correspondingly, and the distances between the positions where the propeller-motor power systems are located and the OX axis of the body axial system are the same; and four power devices take off in an X-shaped quad-rotor mode in the vertical take-off and landing processes and complete conversion operation to enter a cruising state through different tensile forces of the motors or by being matched with maneuvering surfaces, and required maneuvering is completed through tensile force changing of the motors in the whole process. The power devices of the aircraft are simple, the control mode is reliable, propeller slipstreams can be effectively utilized, and the aircraft is suitable for serving as flying platforms of a tail-sitting type vertical take-off and landing unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
High pressure cleaning and decontamination system
InactiveUS20060089090A1Suitable protectionClean effectAbrasive feedersAbrasive machine appurtenancesTriple pointRoom temperature
Abrasive cleaning and decontamination methods and systems are disclosed. The methods and systems use a high pressure liquefied gas, such as carbon dioxide, which produces insignificant quantities of secondary waste. These principles of the invention exploit the properties of the relatively high triple point of CO2 in order to first pressurize it to 35,000 to 60,000 PSI from a pressurized liquid. In the pressurized state, such a fluid can be at or above room temperature, allowing for transport over long distances in a flexible high pressure hose. At a point of use, a heat exchanger may subsequently chill the liquid, so that after expansion through a small high pressure orifice, a significant fraction of the liquid is converted to solid phase crystals exiting at high velocity to effectively clean and decontaminate. For more aggressive cleaning, abrasive particles and / or small diameter solid CO2 pellets can be entrained into the high pressure CO2 slipstream.
Owner:KURION INC
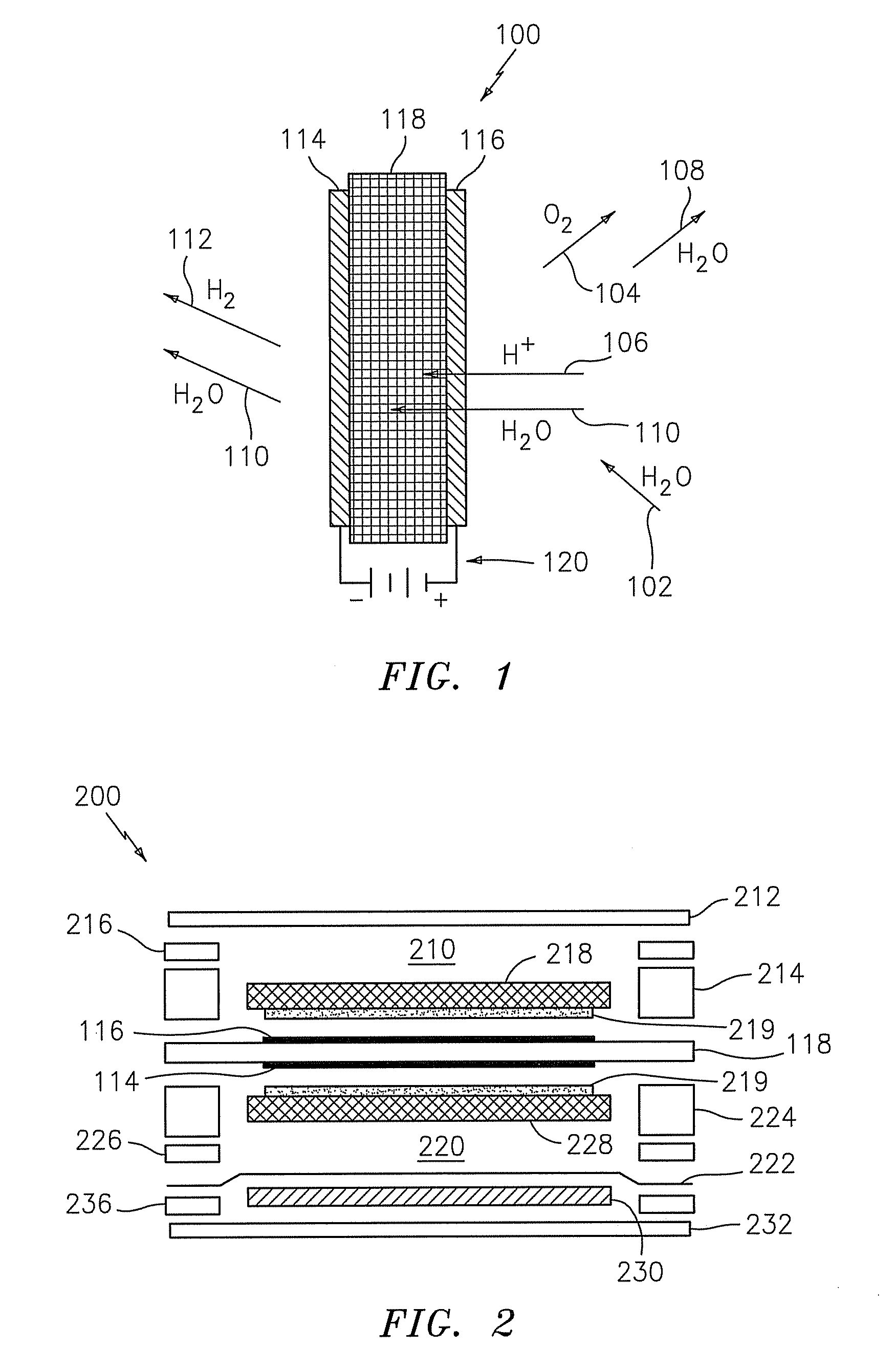
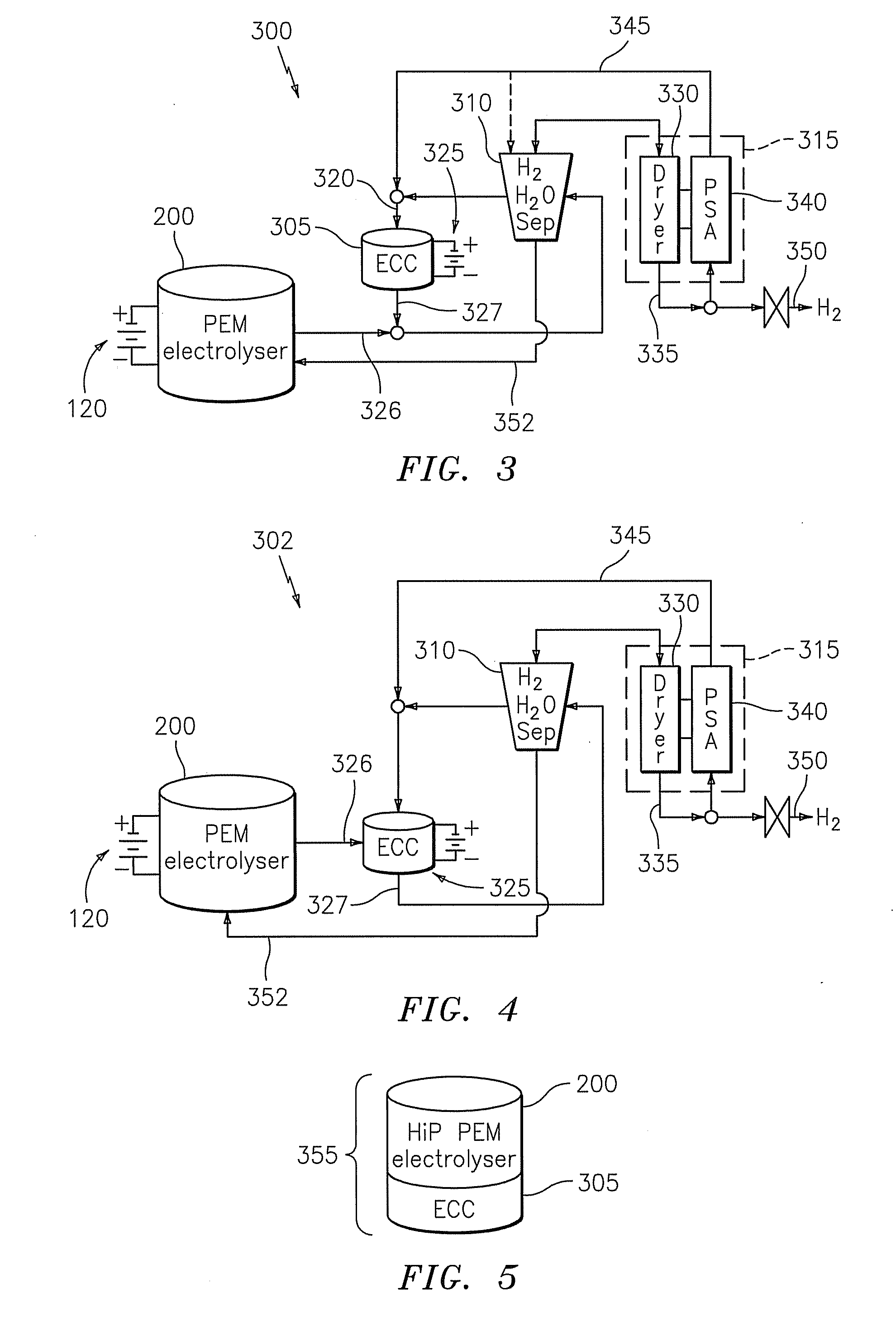
Gas recovery system
InactiveUS20080236396A1Improve gas production efficiencyIncrease productivityCellsGas treatmentProduct gasProcess engineering
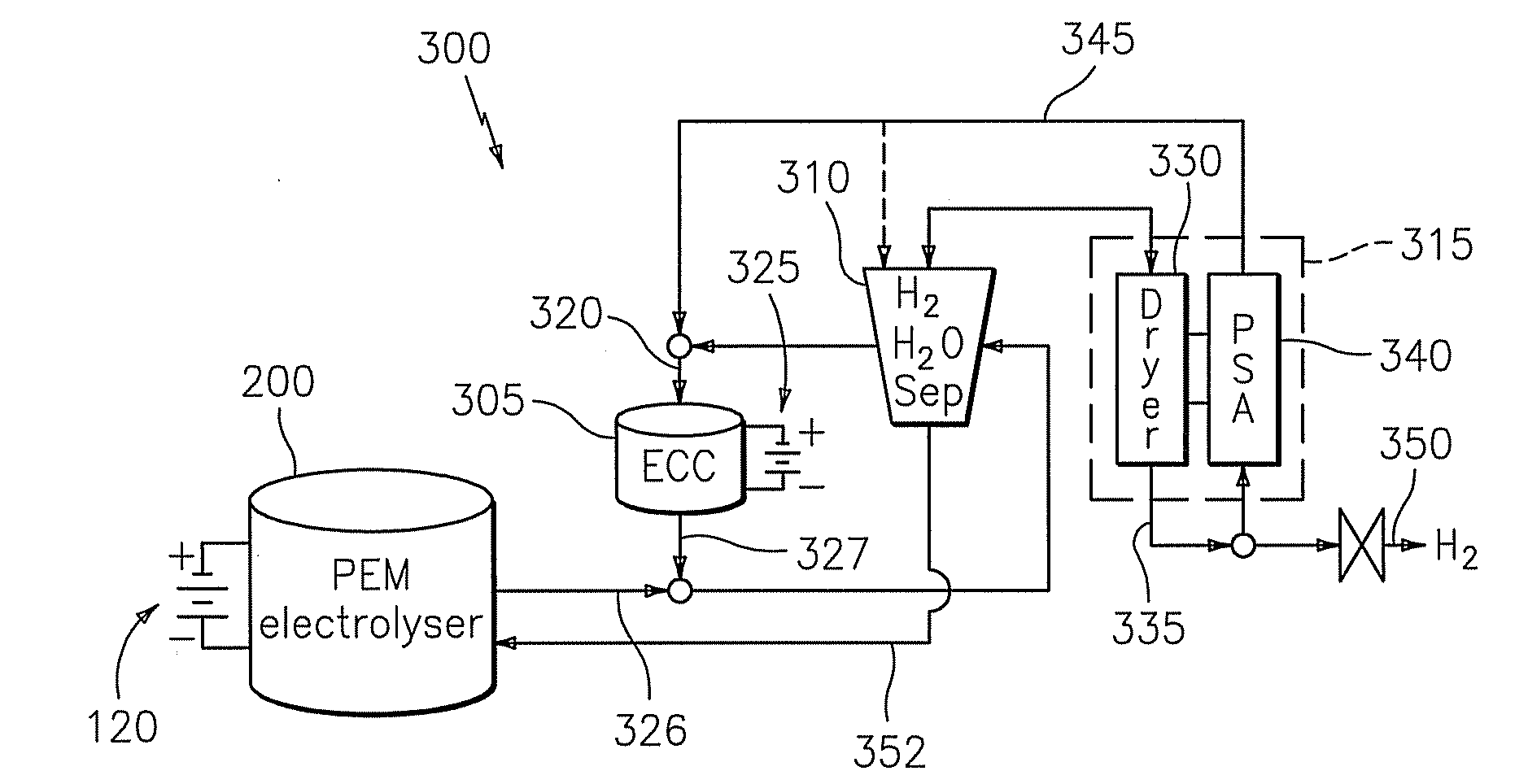
A gas recovery system is disclosed. The gas recovery system includes a gas source productive of a gaseous stream comprising moisture, a gas dryer in fluid communication with and downstream of the gas source, and an electrochemical compressor in fluid communication with and downstream of the gas dryer. The gas dryer is disposed to receive the gaseous stream and produce a delivery stream absent moisture and a slipstream comprising moisture. The electrochemical compressor is disposed to receive the slipstream at a first pressure and produce a compressed stream at a second pressure greater than the first pressure.
Owner:PROTON ENERGY SYST
Methods and apparatuses for removing mercury-containing material from emissions of combustion devices, and flue gas and flyash resulting therefrom
InactiveUS20060102057A1Increasing mercury contentUsing liquid separation agentPulverulent fuel combustion burnersCombustorFlue gas
A method of removing mercury or mercury-containing material from flue gas produced by a coal-burning main furnace includes feeding coal, which contains mercury or mercury-containing material, to a main furnace which produces flue gas. The method further includes feeding the coal to an auxiliary burner which produces a slipstream of flyash, feeding the slipstream of flyash from the auxiliary burner into the flue gas produced by the main furnace, and introducing a mercury-active oxidant to the coal being fed to the auxiliary burner, the combustion air fed to the auxiliary burner, and / or the flyash.
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
Propulsion system
ActiveUS8702387B2Energy efficiencyExcessive velocityFlow mixersPump componentsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityWater velocity
The present invention relates generally to propulsion systems, and, more particularly, to a propulsion system including an axial flow water pump assembly and a laminar flow box assembly for generating a streamline laminar slipstream of water velocity that is used in aquatic therapy, aquatic sport fitness rehabilitation, aquatic rehabilitation, swimming, and a variety of other functional therapy and training modalities.
Owner:VISION AQUATICS
Premixed partial oxidation syngas generation and gas turbine system
InactiveCN101776015ATurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberSyngasPartial oxidation
The invention relates to a premixed partial oxidation syngas generation and a gas turbine system. The gas turbine system includes a fuel reformer system comprising a fuel inlet configured to receive a fuel slipstream; an oxygen inlet configured to introduce an oxygen slipstream; a preconditioning zone configured to pretreat the fuel slipstream; a mixing zone comprising a premixing device configured to facilitate mixing of the fuel slipstream and the oxygen slipstream to form a gaseous premix; a reaction zone configured to generate a syngas from the gaseous premix; a quench zone configured to mix a fuel stream into the syngas to form a hydrogen-enriched fuel mixture; and a gas turbine configured to receive the fuel mixture.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
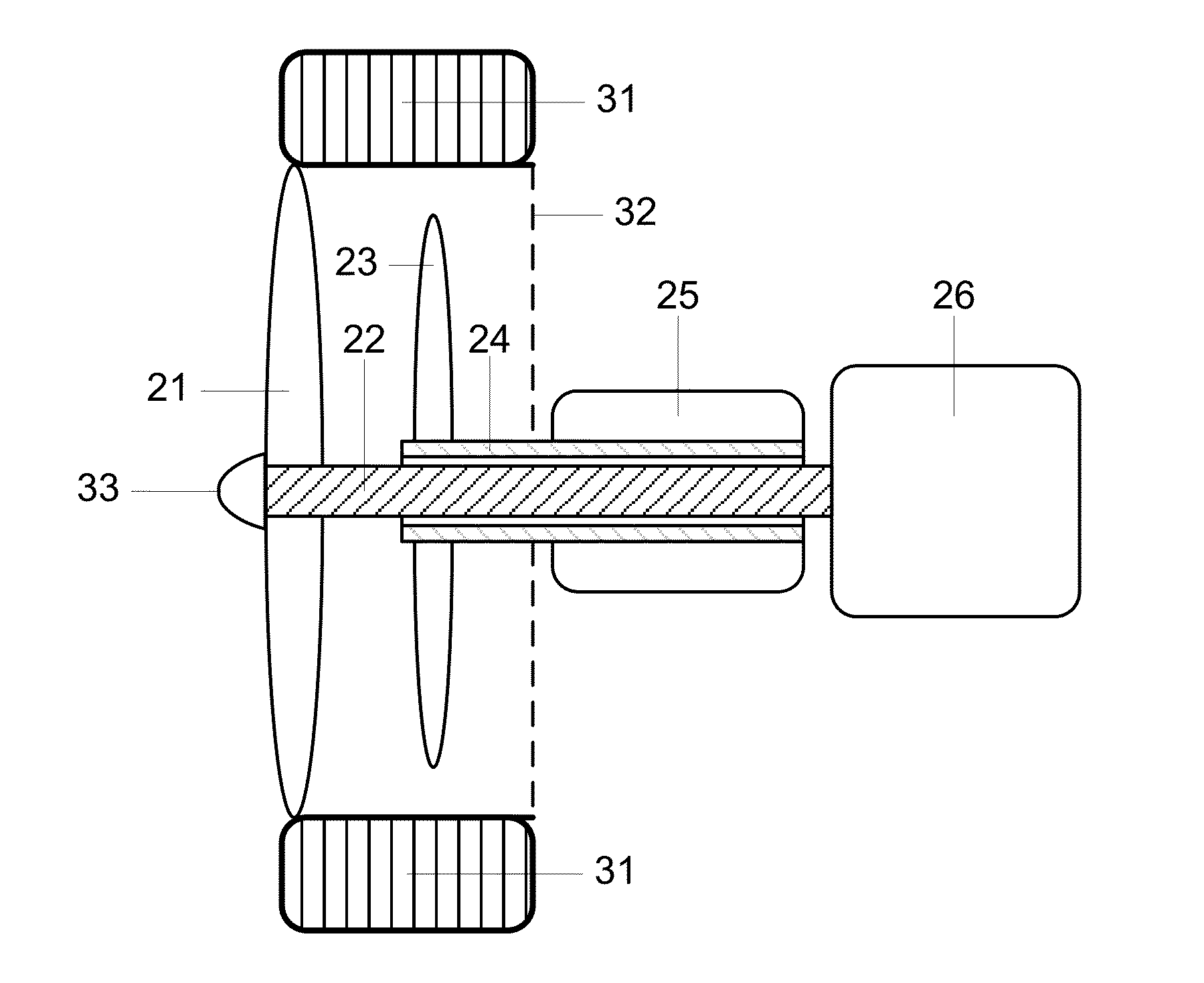
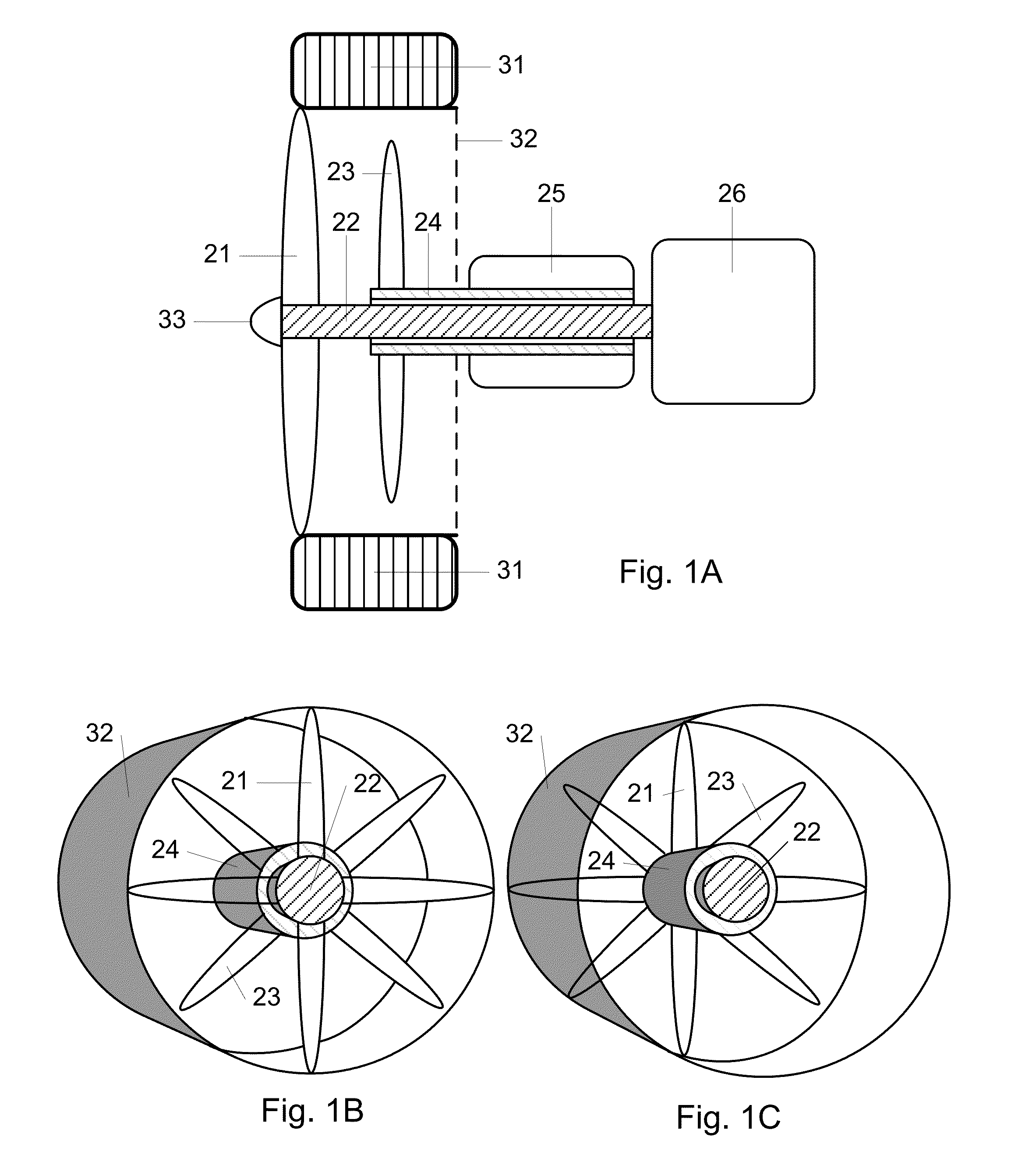
Wind Energy Recovery in the Wheels of Vehicles
One embodiment of an apparatus for wheel slipstream energy recovery in wheeled vehicles comprising a plurality of wheel spokes (21) of a wheel attached to a rotatable motoring shaft (22) which in turn is connected to a motor (26) and a generating propeller (23) attached to a rotatable generating shaft (24) which in turn is connected to a generator (25). Operation of the motor (26) results in the motoring propeller (21) to rotate and generate an accelerating slipstream towards the generating propeller (23) which results in the generator (25) rotating to convert recovered rotational energy into other forms of useable energy. The motor (26) may be an electric motor or an internal combustion engine. The generator (25) output is available for charging batteries or powering electrical loads in either electric or conventional vehicles. Both motor (26) and generator (25) are motoring and generating simultaneously.
Owner:THOMAZIOS KEVIN
On-line determination of wax crystallization temperature of waxy solvent stream
InactiveUS6827842B2Material crystallisationScattering properties measurementsRemote controlCrystallization temperature
A laser beam reflected by wax crystals is used in determining the wax crystallization temperature of a hot dewaxing solvent upstream of solvent chillers. This is automatically achieved by an on-line method from a remote control point, in which a slipstream of solvent is passed through an attached solvent loop into a sample chamber in the loop, without being exposed to ambient conditions. As the sample is cooled, the beam reflections are detected and indicate the wax to crystallization temperature. Corrective measures can then be taken to prevent fouling of the chillers, if need be.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
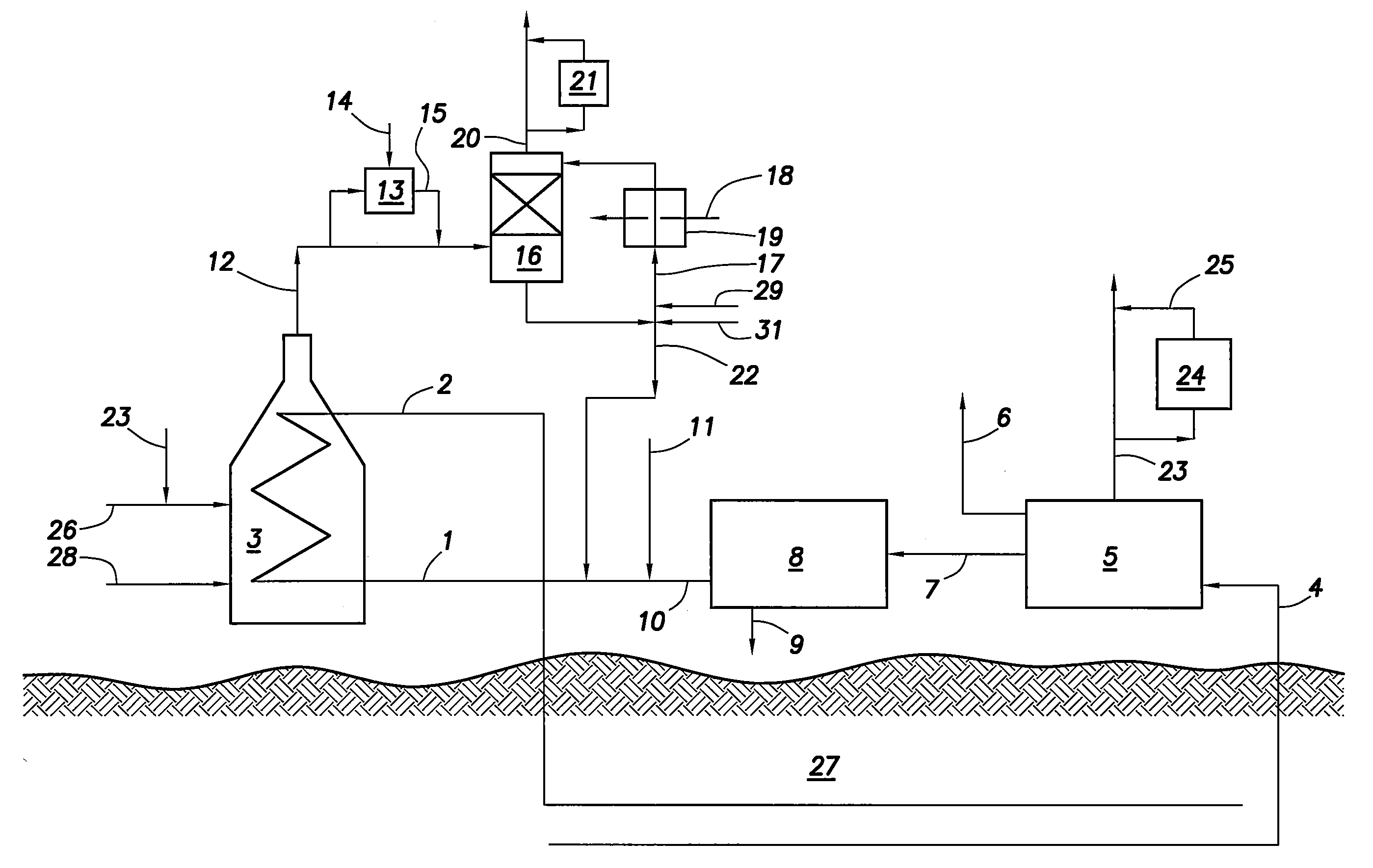
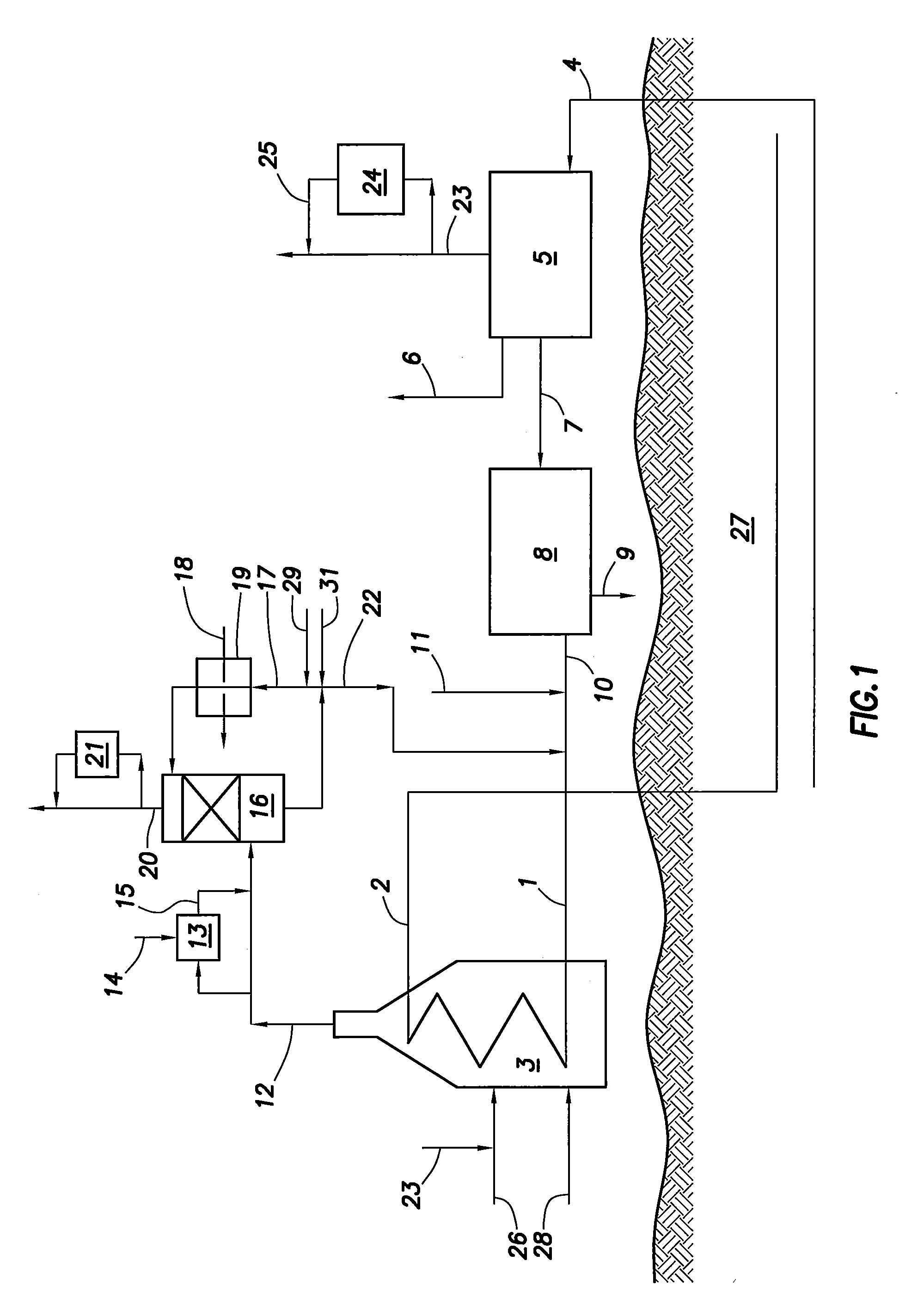
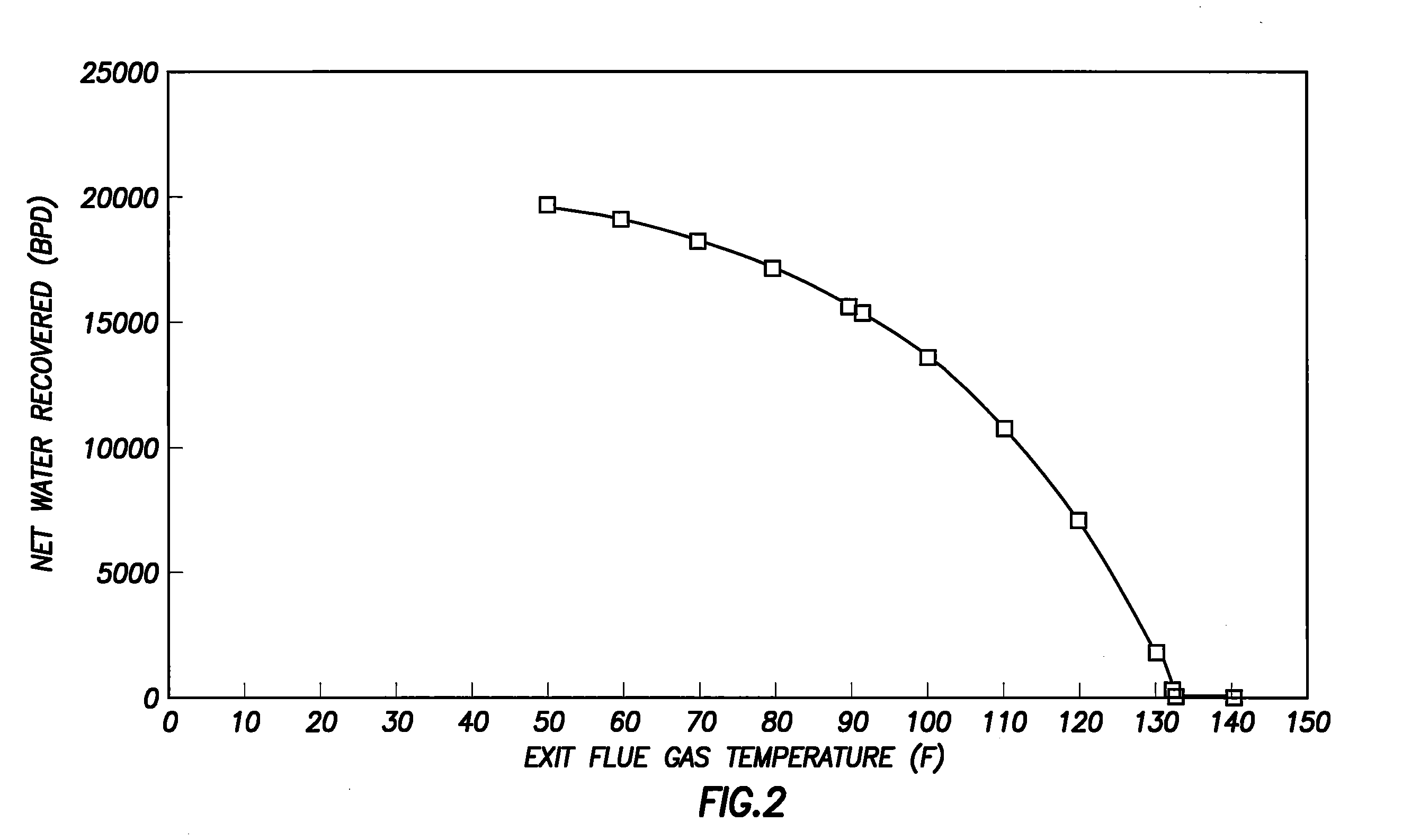
Water recovery from flue gas in steam-assisted production
InactiveUS20110067610A1Reduce sulfur contentGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentVapor liquidWater vapor
A method for introducing flue gas in a steam-assisted production facility into a vapor-liquid contactor. In this method the flue gas comprises boiler combustion products selected from at least one of commercial pipeline natural gas and produced gas. The flue gas is cooled with the vapor-liquid contactor to condense a portion of the water vapor in the flue gas to produce a water stream. The water stream is then recirculated and cooled in an air cooler to produce recirculating water exiting the bottom of the vapor-liquid contactor. A water slipstream is then taken off the recirculating water to be used as make-up water.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com