Patents
Literature
788 results about "Aileron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
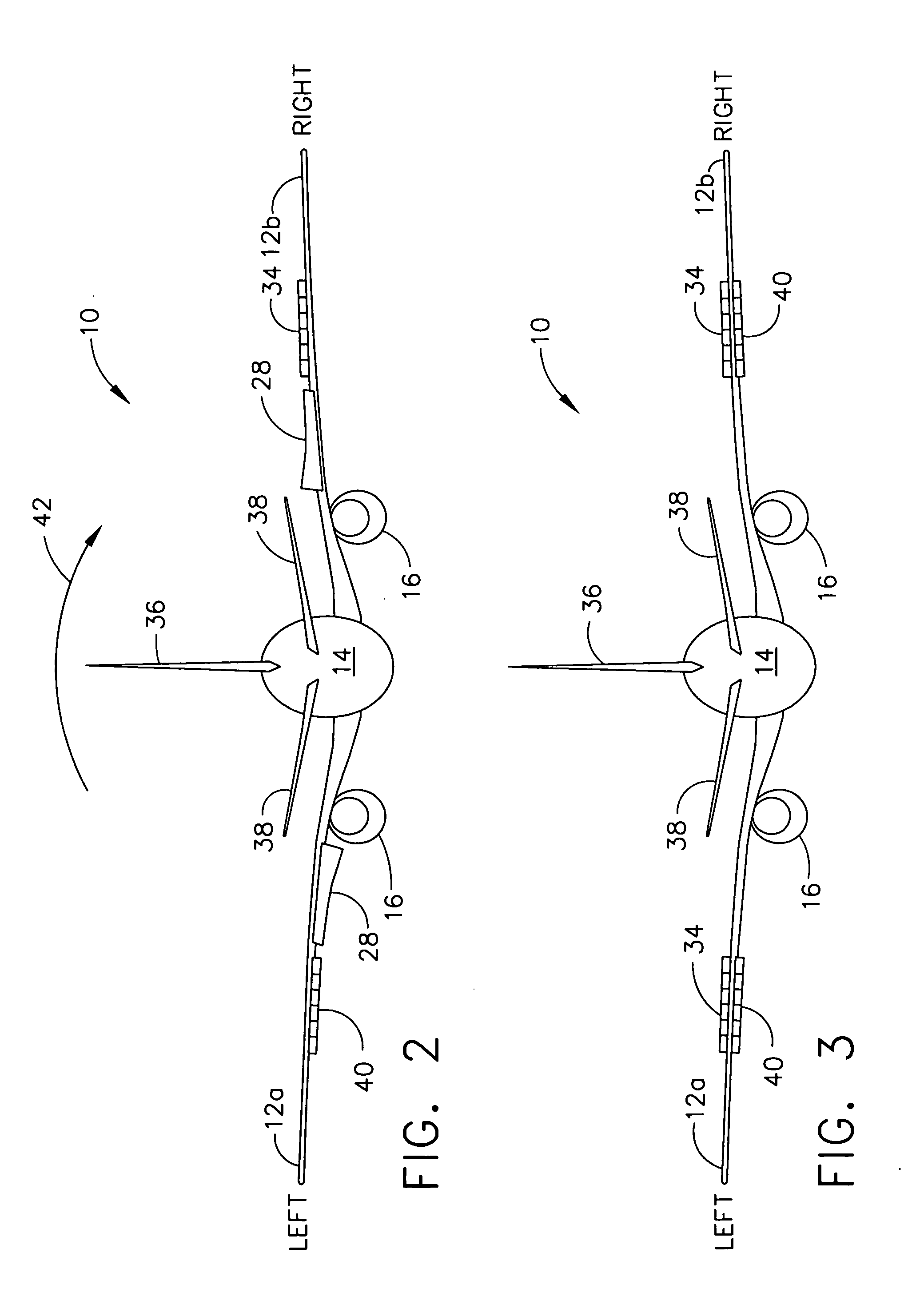
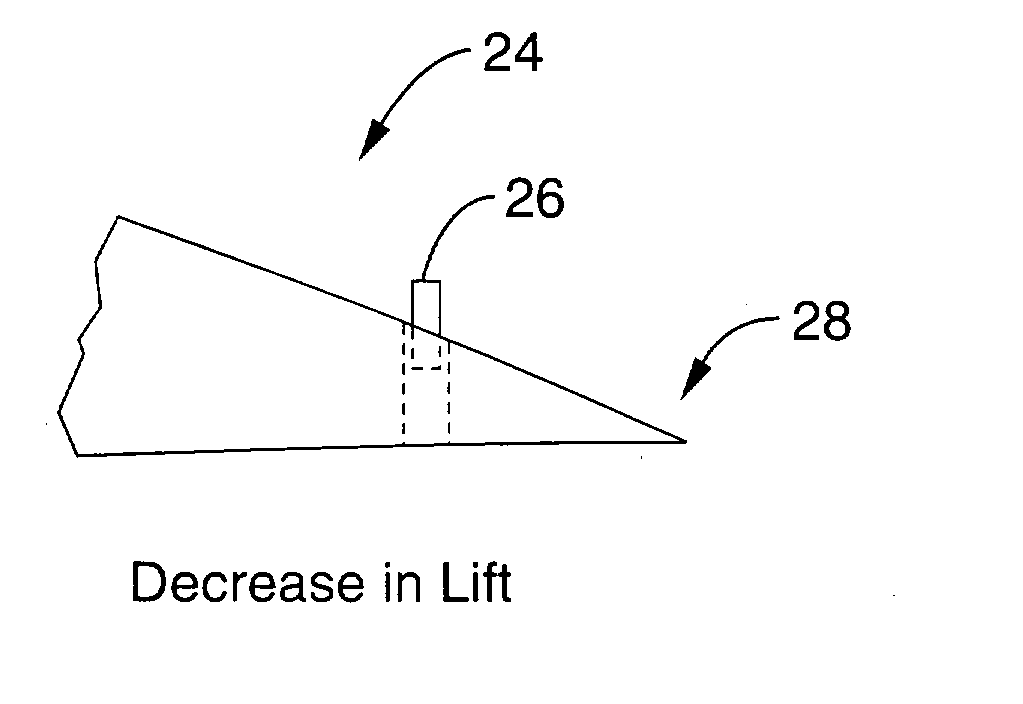
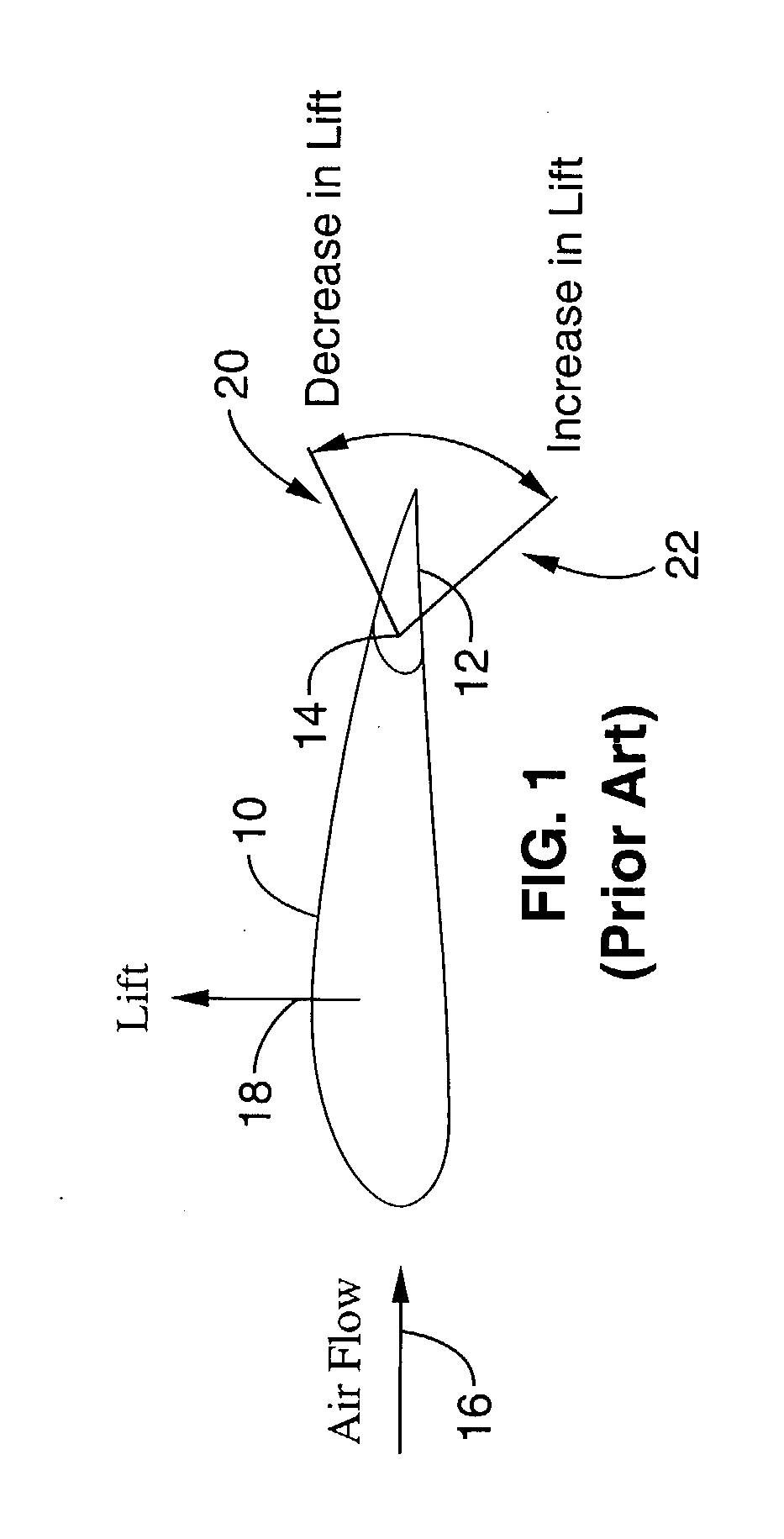
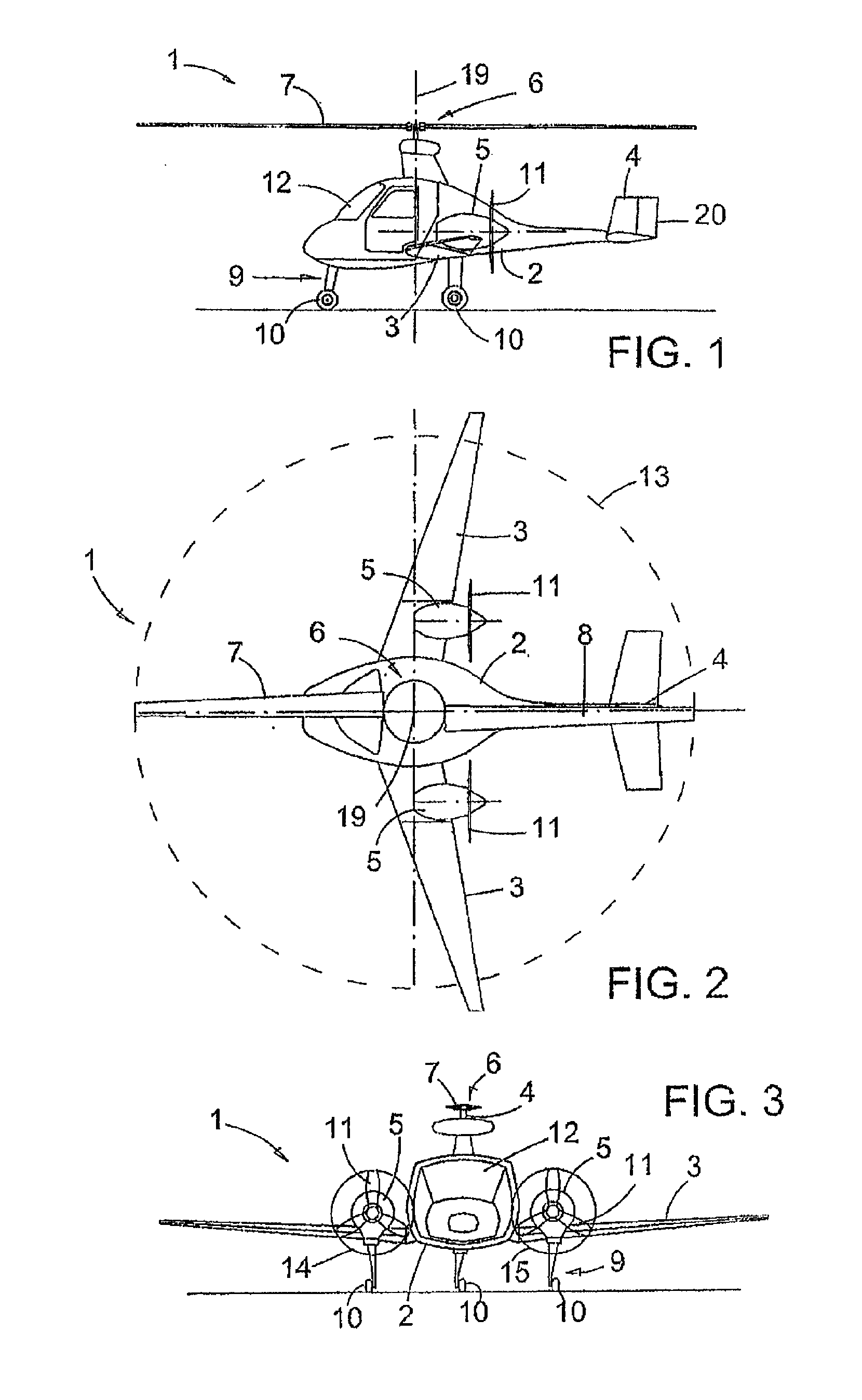
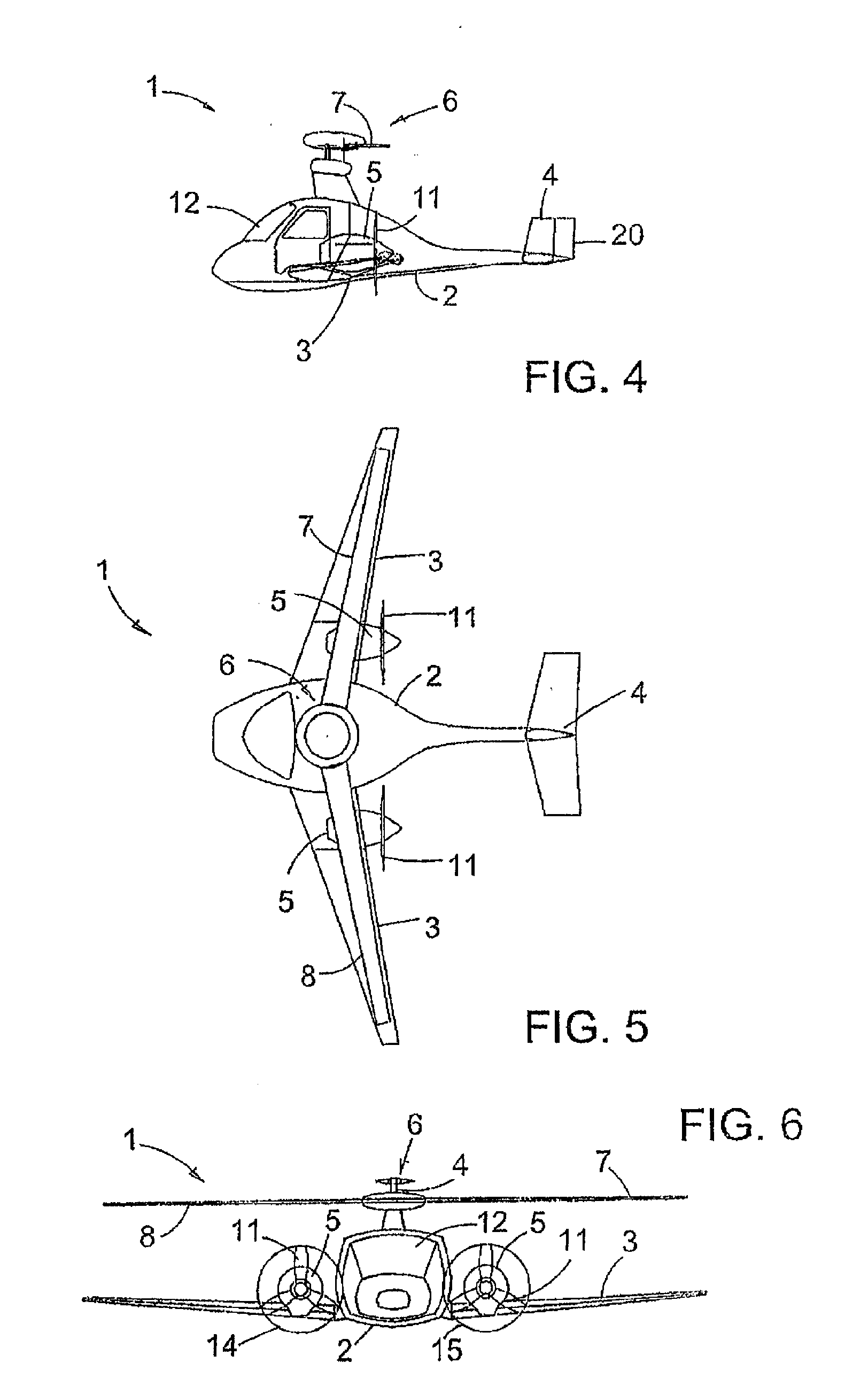
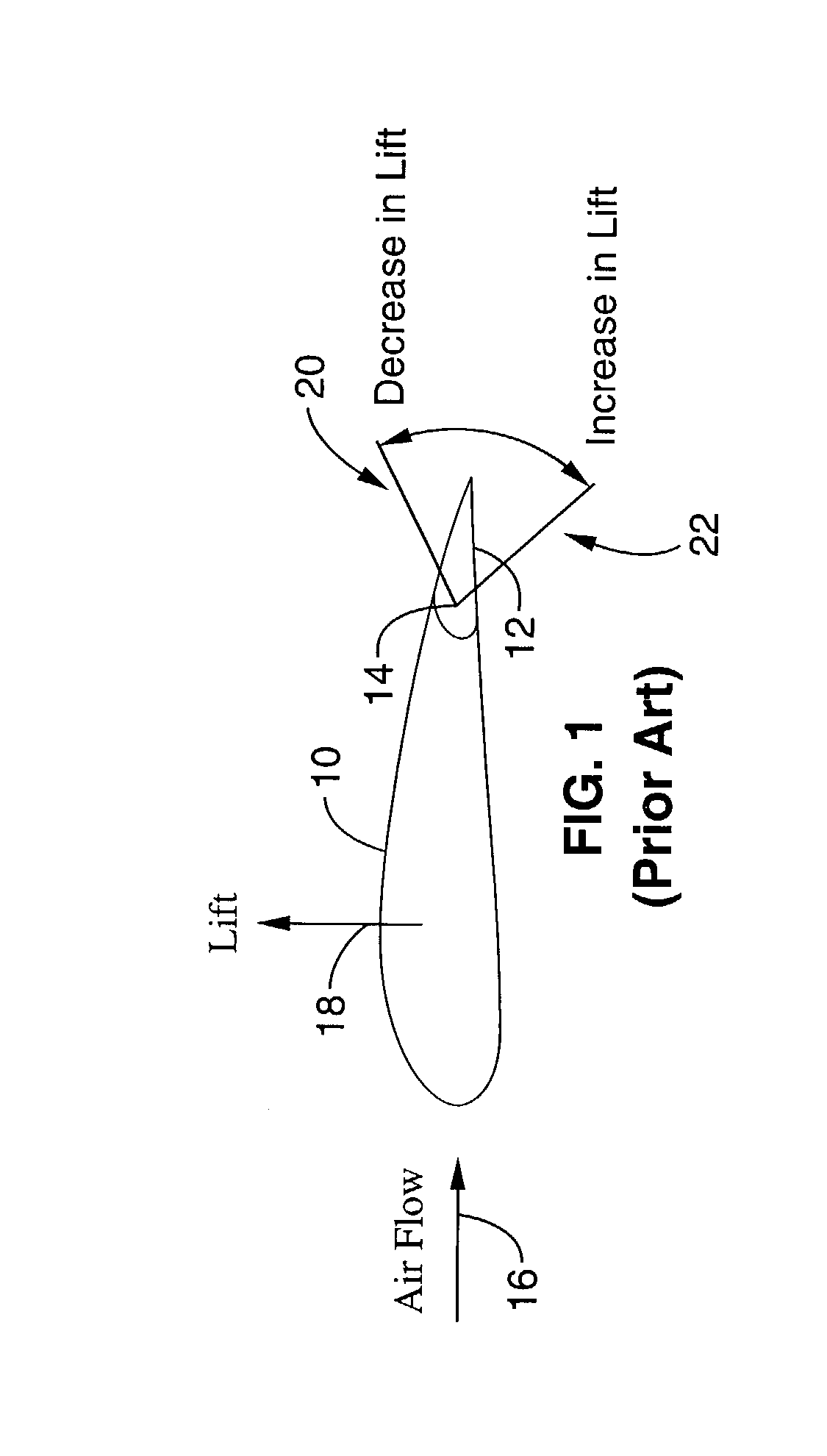
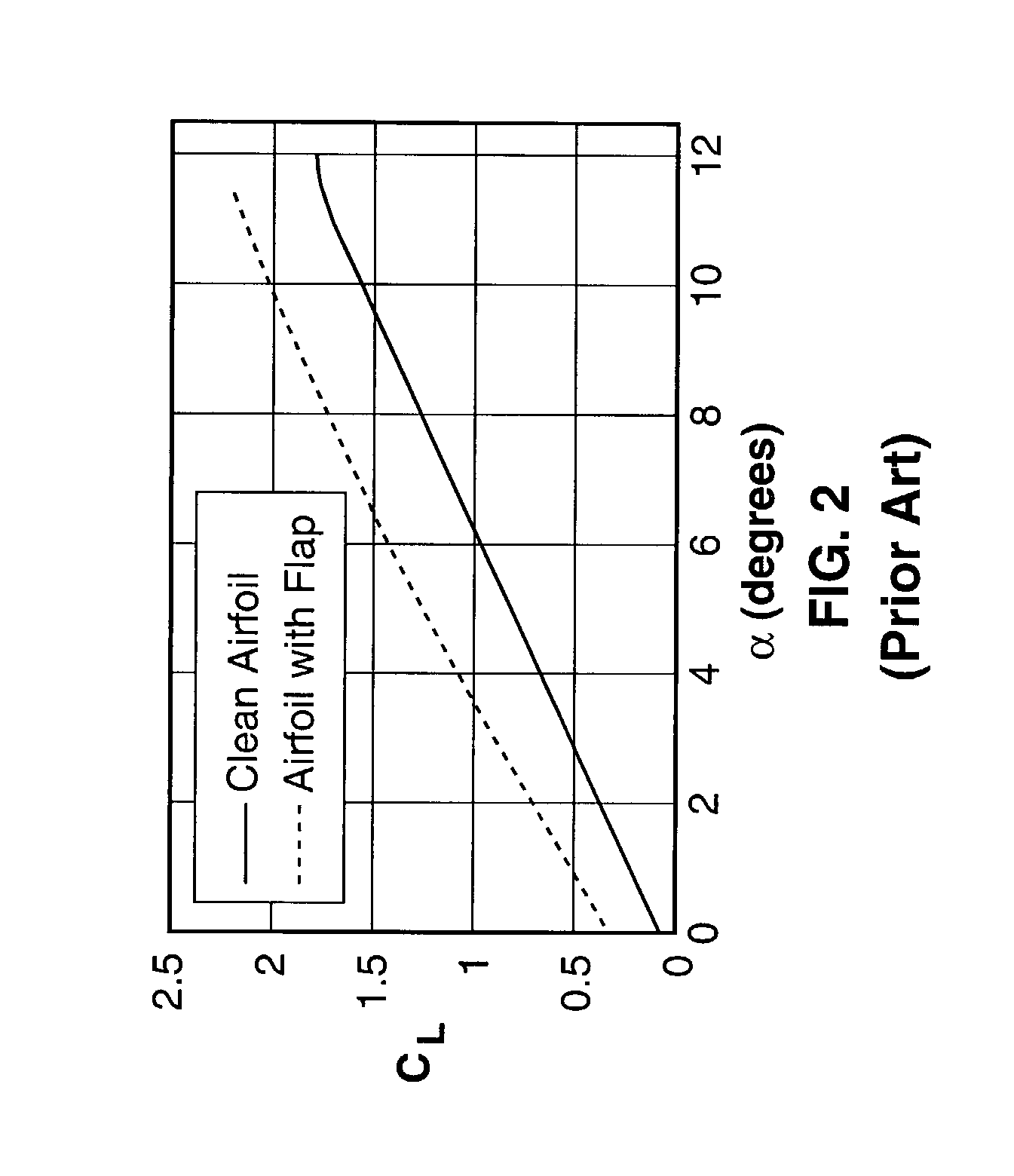
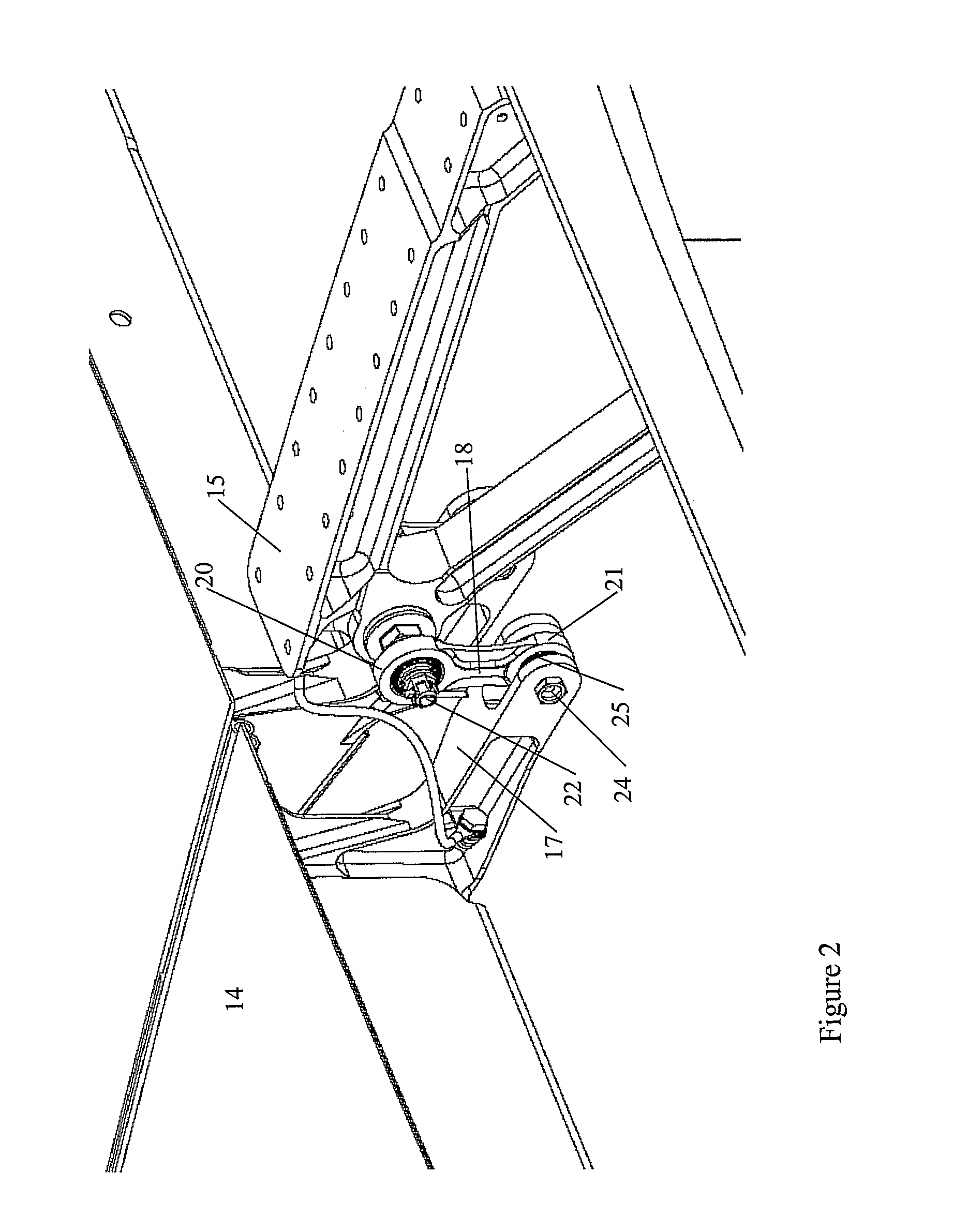
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called 'rolling' or 'banking'.
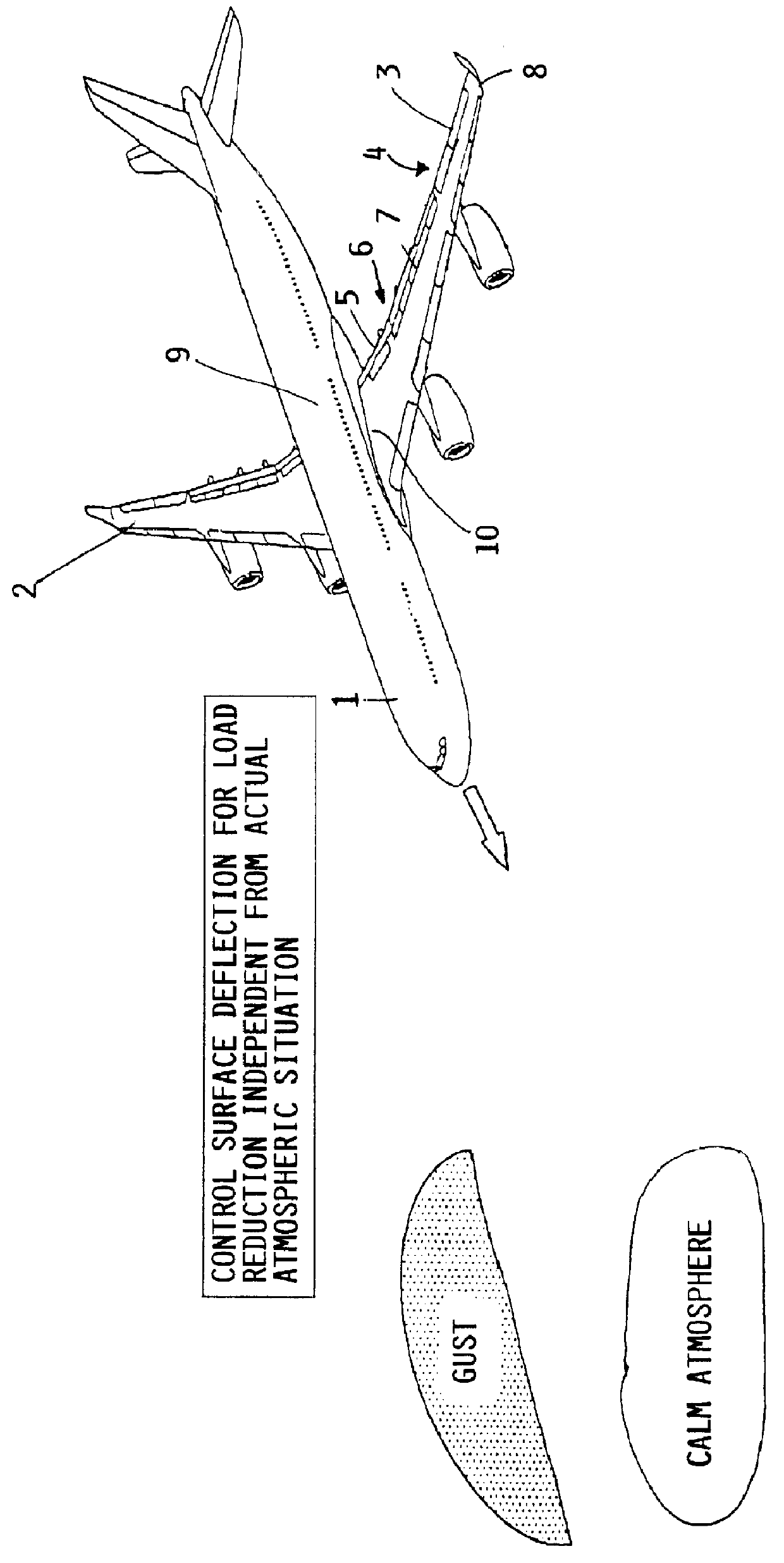
Method of reducing wind gust loads acting on an aircraft
InactiveUS6161801AReduce wing load of wingReduce loadEnergy saving arrangementsActuated automaticallyWing configurationRolling moment
A method of reducing the bending moment effect of wind gust loads acting on the wing of an aircraft involves adjusting the aerodynamic configuration of the wing so as to alter the distribution of lift generated by the wing during phases of flight in which critical wind gusts are expected to occur. Particularly, during climb and descent phases of flight below cruise altitude, the lift generated by outboard portions of the wings is reduced while the lift generated by inboard portions of the wings is increased. Thereby, the 1 g basis load acting on the outboard portions of the wings is reduced, and consequently the total load applied to the outboard portions of the wings, resulting from the 1 g basis load plus the additional wind gust load, is correspondingly reduced. This leads to a reduction of the bending moments effective on the wings, and of any rolling moment effective on the aircraft. The required adjustment of the lift distribution is preferably achieved by deflecting the ailerons of both wings symmetrically upward and / or deflecting the flaps of both wings symmetrically downward during climb and descent. The adjustment of the wing configuration is carried out dependent only on flight parameters such as the altitude, speed and gross weight, and does not require rapid sensing of the occurrence of a wind gust and rapid actuation of control surfaces to try to instantaneously counteract a wind gust as it occurs.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER AEROSPACE AIRBUS
Unmanned air vehicle
InactiveUS20100051741A1Easy to moveEasy to startArrester hooksArresting gearLeading edgeTrailing edge
An unmanned air vehicle for military, land security and the like operations includes a fuselage provided with foldable wings having leading edge flaps and trailing edge ailerons which are operable during ascent from launch to control the flight pattern with the wings folded, the wings being deployed into an open unfolded position when appropriate. The vehicle is contained within a pod from which it is launched and a landing deck is provided to decelerate and arrest the vehicle upon its return to land.
Owner:ISMAILOV ANVAR +1
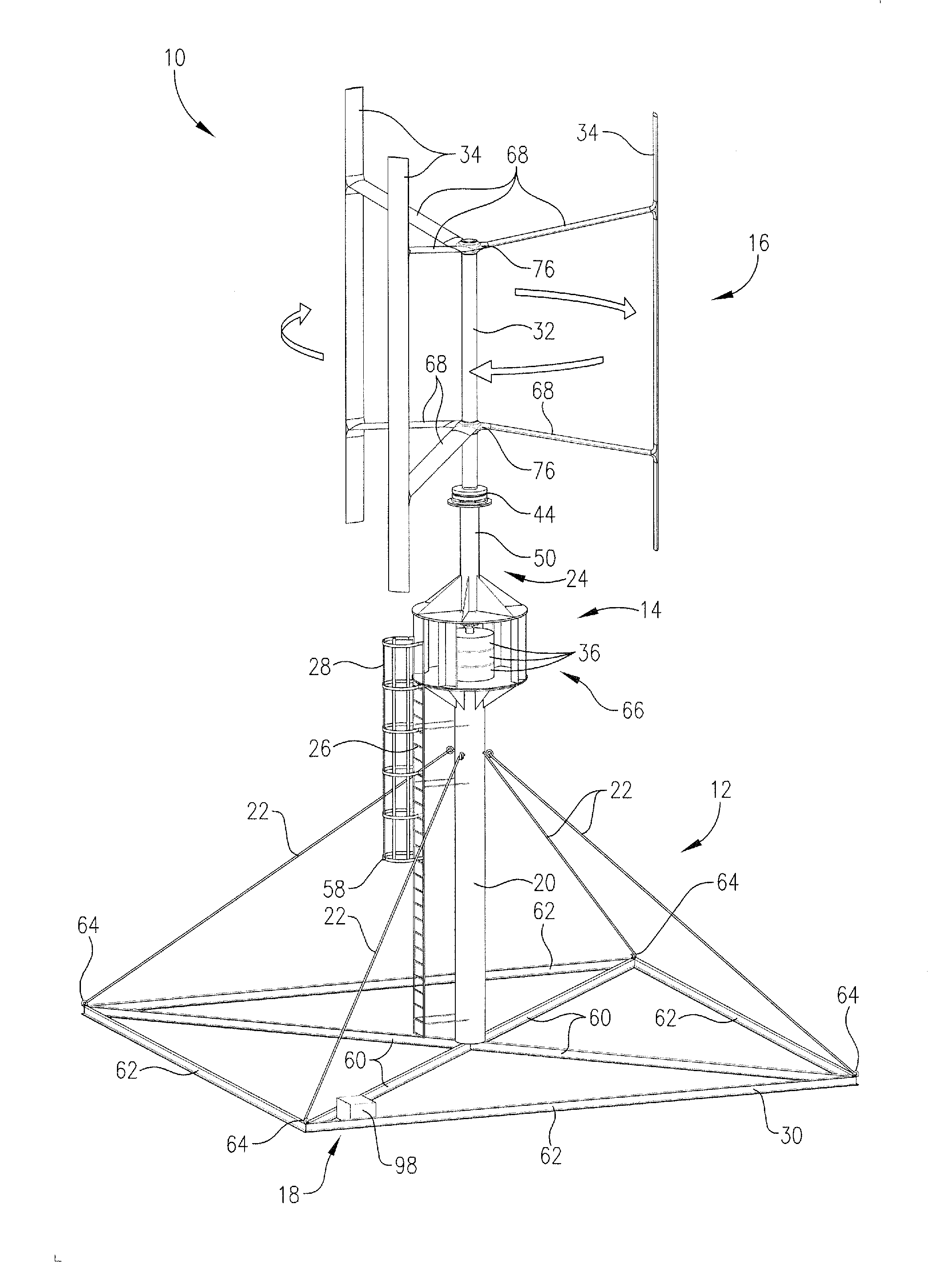
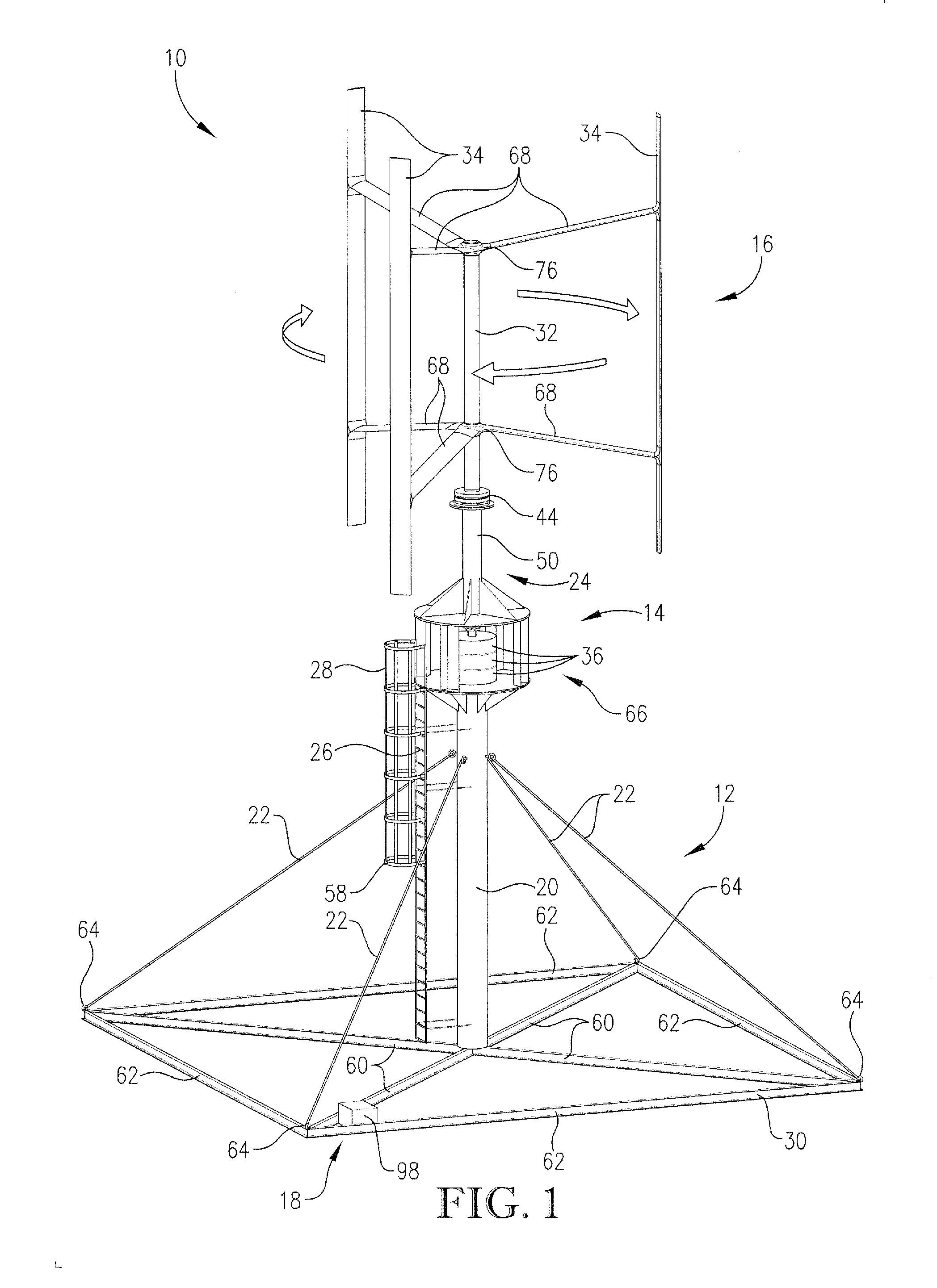
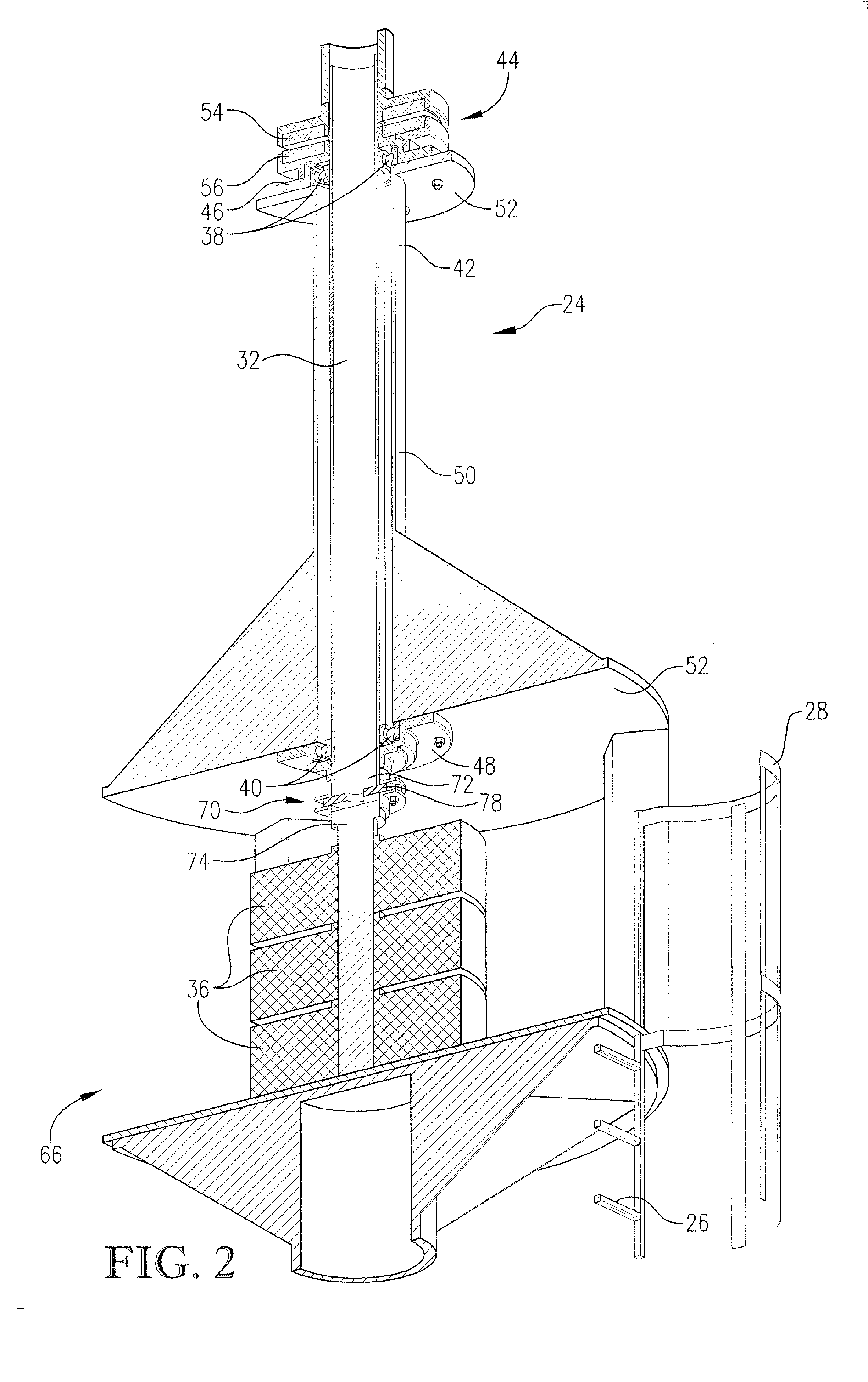
Vertical axis wind turbine
ActiveUS20110133474A1Increase torqueReduce resistanceWind motor controlRenewable energy generationVertical axis wind turbineVertical axis
A vertical axis wind turbine includes an upstanding support structure, a plurality of generators disposed on the support structure, a central shaft in rotatable communication with the generators and positioned along a central axis of the vertical-axis wind turbine, a plurality of struts extending from the central shaft, and a plurality of blades, each blade positioned at an end of a corresponding strut and oriented substantially vertically. The vertical axis wind turbine optionally includes strut ailerons, blade extension elements, or blade ailerons to increase the efficiency and duty cycle of the wind turbine.
Owner:JONATHAN HAAR
A composite rotating fixed-wing aircraft and its design method
InactiveCN101549754APrevent rolloverPrevent sideslipVehicle position/course/altitude controlGround installationsStarter generatorMotor drive
The composite rotating fixed-wing aircraft consists of the coaxial counter-paddle, reverse gear, engine output shaft, engine with a starter-generator, wings, tail blades, landing device, culvert, steering gear, fairing, fuselage, motor, motor drive shaft, wing control unit of small angle of attack, aileron rudder surface, and tailplane rudder surface. Co-axial counter-blade is located in the upper part of the aircraft, which connects with the engine output shaft; the reverse gear is installed between the co-axial counter-propellers; the motor connects with motor drive shaft powered by the starter-generator of the engine; the wings are located on both sides of aircraft and connect with the fuselage; the tail blades are located at the aircraft tail, which are installed behinde motor drive shaft; the landing device is located under the lower part of the fuselage and fixed with it; the culvert connects with the landing device; the fairing is installed in the culvert and connects with the steering gear; the wing control unit of small angle of attack is installed on the wing. The aircraft design method has six steps with strict scientific idea; this invention has a wide range of practical value and application prospect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Lifters, methods of flight control and maneuver load alleviation
InactiveUS20050242234A1Shorten speedWith power amplificationAir braking surfacesSupersonic speedAirplane
The present invention provides a flight control system and method for various models of aircraft, including thin-winged, long range, transonic and low supersonic aircraft, and may be beneficial on supersonic and hypersonic aircraft as well. One embodiment of the flight control system comprises a plurality of lifters for generating lift or drag, the plurality of lifters mechanically associated with a lower surface of each wing in a pair of wings. During operation, the lifters may be selectively deployed alone or in combination with other flight control devices, such as ailerons and spoilers, to provide various operative benefits such as improved roll control, speed braking functionality, and maneuver load alleviation.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
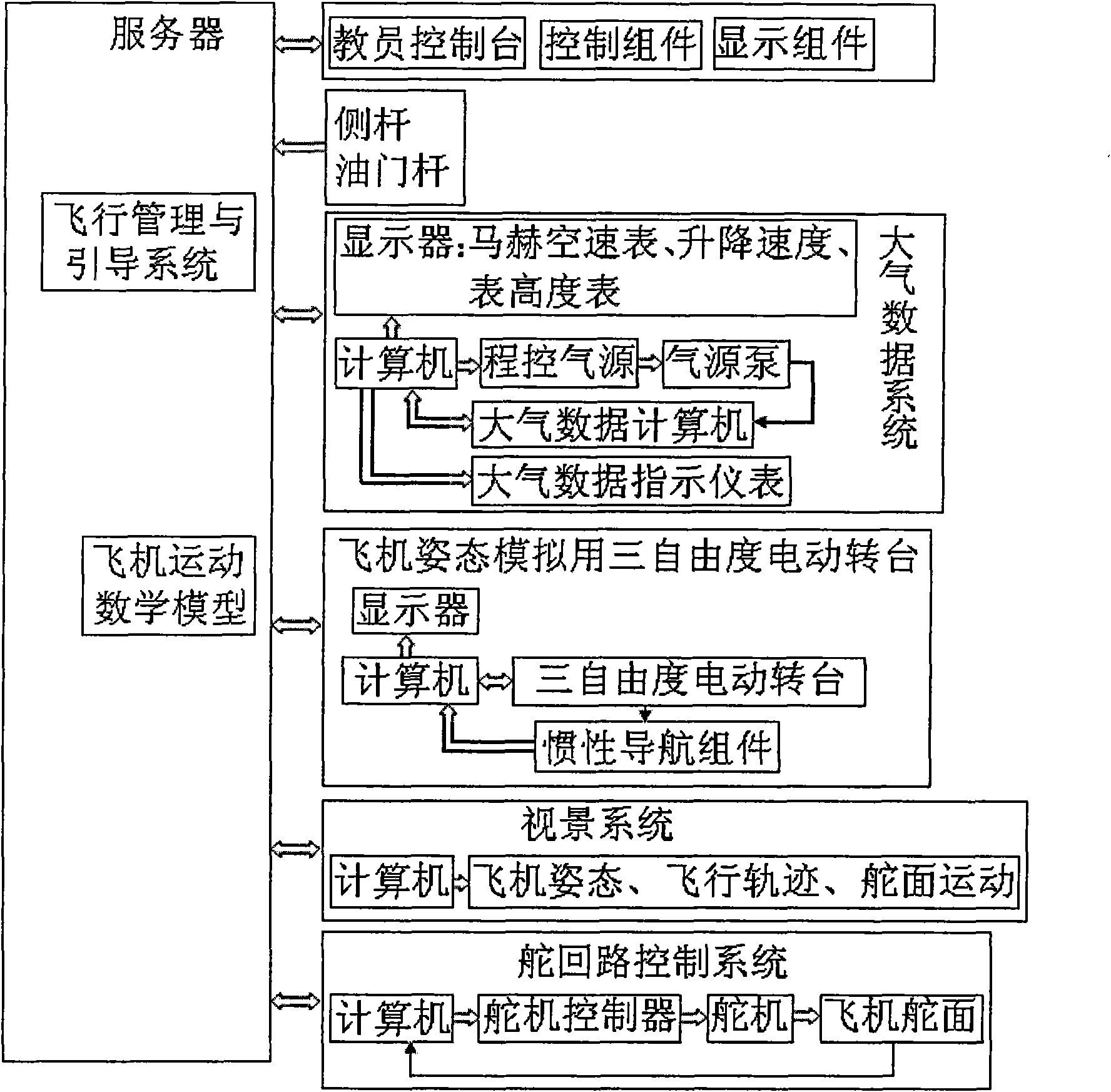
Aircraft hardware-in-the-loop simulation device
InactiveCN101794523ANovel structureCompact assemblyCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsLoop controlTest fixture
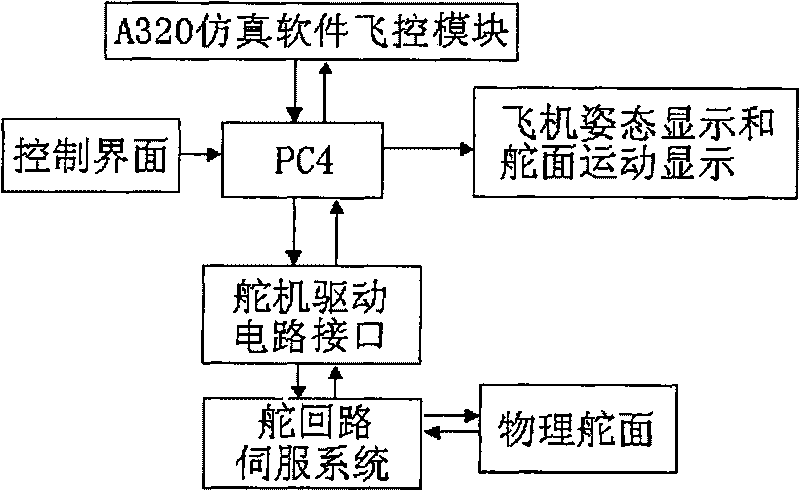
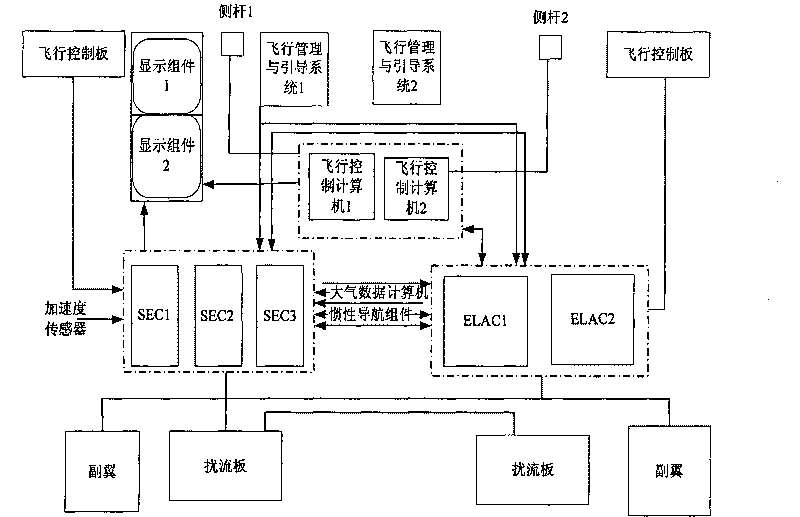
The invention relates to an aircraft hardware-in-the-loop simulation device, belonging to the technical field of simulation. The aircraft hardware-in-the-loop simulation device comprises a flight training device, a control surface control mechanism, a flight scene system, an atmospheric data testing device, a three-degree-of-freedom electric turntable and an inertial navigation system, which are all integrated as a whole through network; the flight training device is provided with a server, a central console, a sidebar and a display mechanism; the control surface control mechanism is provided with an aircraft physical mode, an aileron, a rudder, an elevating rudder and a rudder loop control system; the flight scene system displays flight attitude, data or trajectory; the atmospheric data testing device comprises a computer, a direct current power supply module, a power supply control module, an adaptor module and a signal conditioning box module; the three-degree-of-freedom electric turntable comprises an inner frame, a middle frame, an outer frame as well as a turntable pedestal and a control system thereof; and the inertial navigation system is provided with a sensor assembly mounted on the three-degree-of-freedom electric turntable and a computer. The aircraft hardware-in-the-loop simulation device has the advantages of novel structure, compact assembly, good dynamic performance, high simulation degree and being visual and convenient, etc.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Tiltrotor controlled by double-propeller vertical duct
The invention provides a tiltrotor controlled by a double-propeller vertical duct. The tiltrotor, using the design of parallel twin-rotor and conventional aerodynamic configuration, consists of a fuselage, straight wings, rotors, a nacelle, an aileron, a vertical empennage, a rudder, an elevator, a horizontal empennage, a duct end cover, a vertical duct, an undercarriage, a power and decelerationsystem, a propeller power input shaft, a lower propeller, an upper propeller, louver-type slipstream sheets, a propeller gearing and collective-pitch controlling device, a propeller gear box supporting structure, a duct end cover driving device, a duct end cover motion slide rail and a slipstream sheet controlling device. Compared with the cyclic pitch control mode, the tiltrotor of the inventionsimplifies the operations during the vertical flight and the flight conversion and improves the reliability by using the structure of the double-propeller vertical duct to control the vertical flightand the conversion of the flight mode, and the tiltrotor has the advantages of long control force arm, high control efficiency and simple structure. Therefore, the tiltrotor constitutes a novel aircraft with significant development potential and promising future.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Unmanned air vehicle
InactiveUS8146855B2Easy to moveEasy to startPropellersPower plant arrangements/mountingLeading edgeUncrewed vehicle
An unmanned air vehicle for military, land security and the like operations includes a fuselage provided with foldable wings having leading edge flaps and trailing edge ailerons which are operable during ascent from launch to control the flight pattern with the wings folded, the wings being deployed into an open unfolded position when appropriate. The vehicle is contained within a pod from which it is launched and a landing deck is provided to decelerate and arrest the vehicle upon its return to land.
Owner:ISMAILOV ANVAR +1
Unmanned supply delivery aircraft
ActiveUS20170001724A1Safe and accurate deliveryQuick and easy retrievalAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesDrogue parachuteAirplane
A heavy payload, autonomous UAV able to deliver supply by way of airdrop with more precision and at a lower cost. The UAV can be equipped with a movable wing system. The UAV can include a removable storage box. The UAV can be equipped with a drogue parachute for deploying the wings upon jettison of the UAV from a mothership. The UAV can be controlled remotely or it can operate autonomously. The UAV can include canard wings. The canard wings and the movable wings can include ailerons to effectuate flight control of the UAV. The UAV can be reusable or can be an expandable UAV. The UAV's wings can be configured to automatically separate from the UAV during the landing sequence.
Owner:W MORRISON CONSULTING GRP
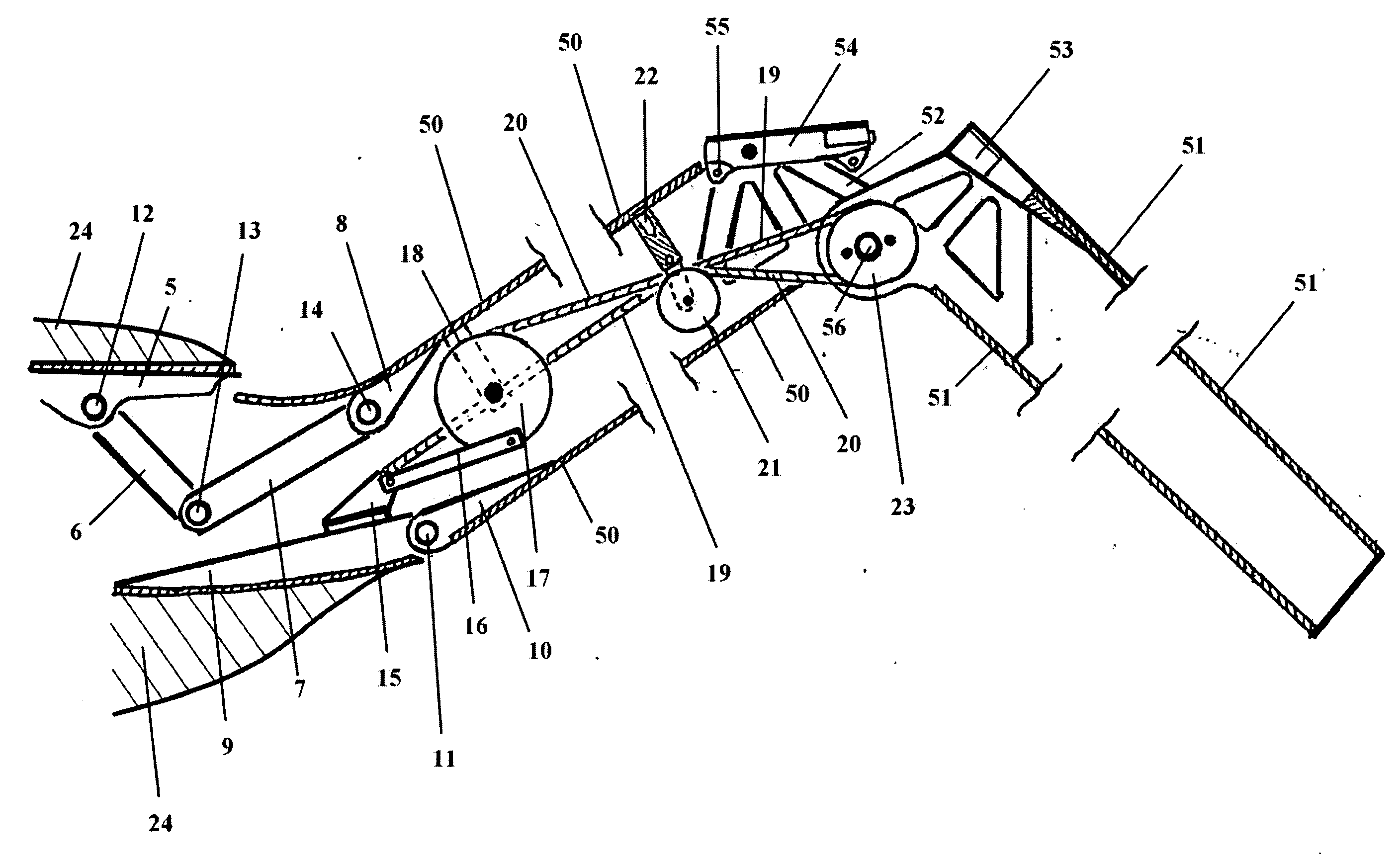
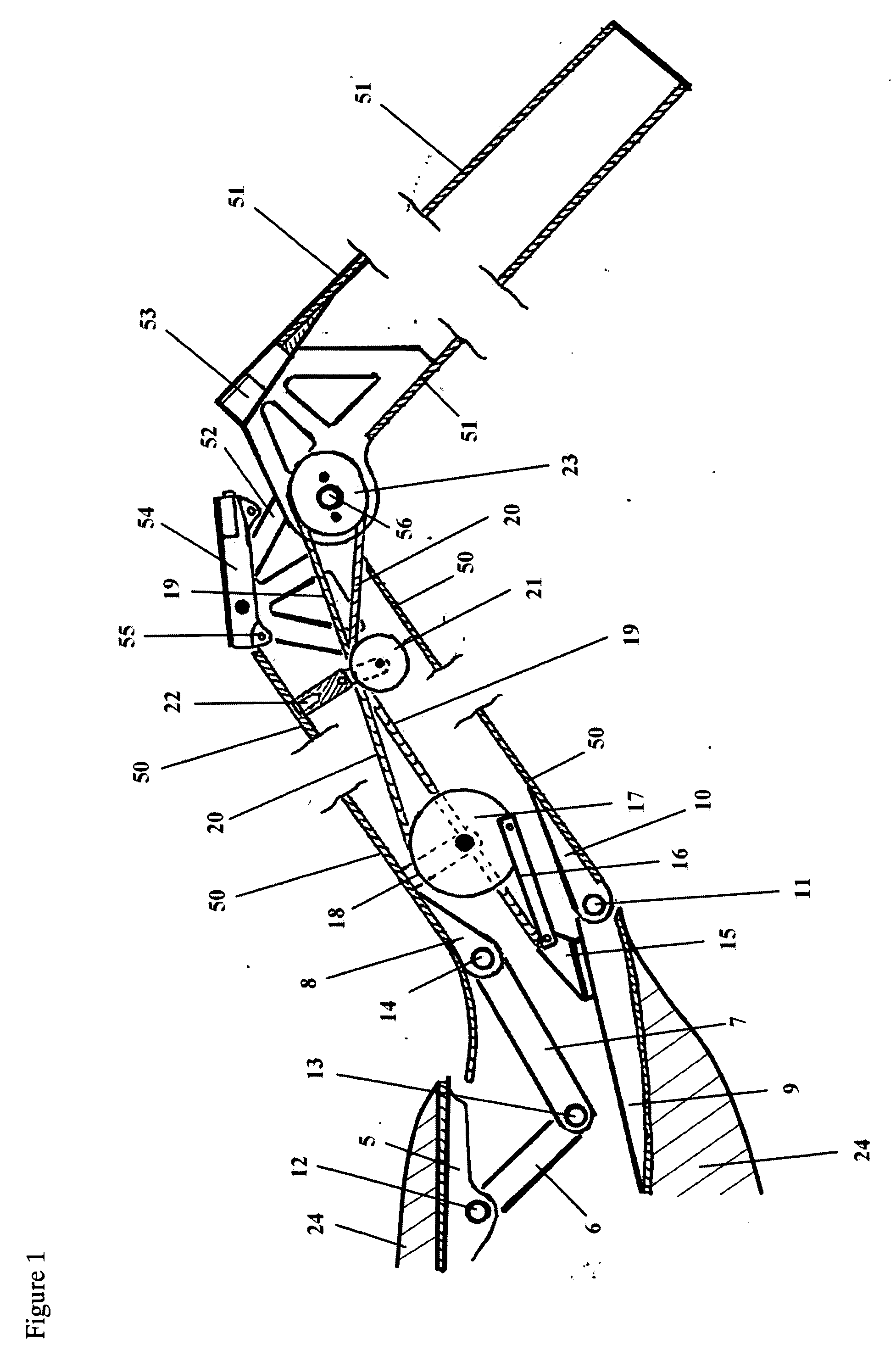
Aileron rotary retractable flapping wing device
The invention relates to an aileron rotary folding and unfolding type flapping wing device, which includes aileron rotary folding and unfolding type flapping wings and a related drive device, wherein the wings are divided into main wings and ailerons along the wingspan direction, exterior edges of the main wings and exterior edges of the ailerons which are connected via butt hinge can relatively rotate on the wings plane with the butt hinge as an axis, and the aileron plane can be folded under the main wings plane, the drive device comprises a main wings drive device and an aileron drive device which are driven to be connected via a main drive shaft, the main wings drive device is positioned in the head section, and composed of two symmetrical crank rocker mechanisms which respectively drive the left wing and the right wing, and the aileron drive device is positioned in the middle-rear portion of the wings chordwise direction. The aileron rotary folding and unfolding type flapping wing device employs a bevel gear pair to realize rotation shaft changes, thereby multi-degree-of-freedom motion can be driven by single power, approximately saving one main drive shaft and related motors, and greatly reducing weight.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Microfabricated translational stages for control of aerodynamic loading
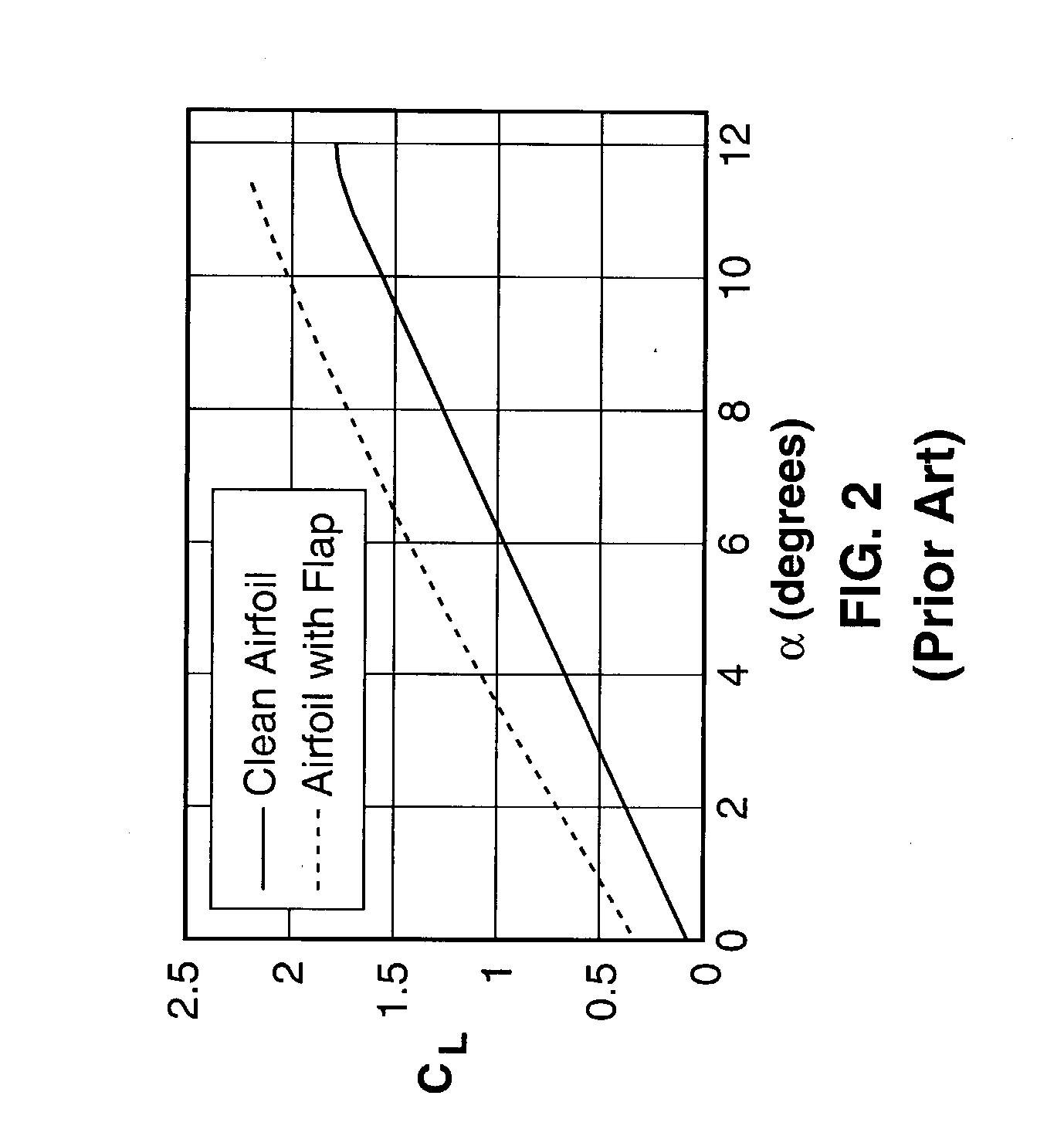
Micro-electro-mechanical (MEM) translational tabs are introduced for enhancing and controlling aerodynamic loading of lifting surfaces. These microtabs are mounted at or near the trailing edge of lifting surfaces, deploy approximately normal to the surface, and have a maximum deployment height on the order of the boundary layer thickness. Deployment of this type of device effectively changes the camber, thereby affecting the lift generated by the surface. The effect of these microtabs on lift is as powerful as conventional control surfaces such as ailerons. Application of this simple yet innovative lift enhancement and control device will permit the elimination of some of the bulky conventional high-lift and control systems and result in an overall reduction in system weight, complexity and cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Convertible aircraft operating method
The invention relates to a convertible aircraft operating method. According to the invention, the aircraft comprises: a fuselage, standard fixed wings which are equipped with ailerons, a tail unit with flight-control surfaces, engines, a rotor with blades, a transmission which is placed between the engines and the rotor and which is equipped with rotor clutch and braking means, a landing gear, means for transition from helicopter mode to gyroplane mode and vice versa, and means for direct or reverse transition from gyroplane / helicopter mode to aeroplane mode. The lift for a range of low speeds is produced by means of the rotor, while the lift for a range of high speeds is produced by means of the wings. In addition, the lift for a range of intermediate speeds can be produced using the wings and the rotor in gyroplane mode simultaneously, and take-off and landing can be performed in gyroplane mode or in helicopter mode with the engines coupled to the rotor. The aircraft comprises a hybrid helicopter / gyroplane / aeroplane aircraft and, as such, can perform the direct or reverse transition to aeroplane mode from both helicopter mode and gyroplane mode.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD +1
Folding Wing & Locking Mechanism
InactiveUS20100051742A1Reduce changesPrevent rotationWing adjustmentsControl systemLocking mechanism
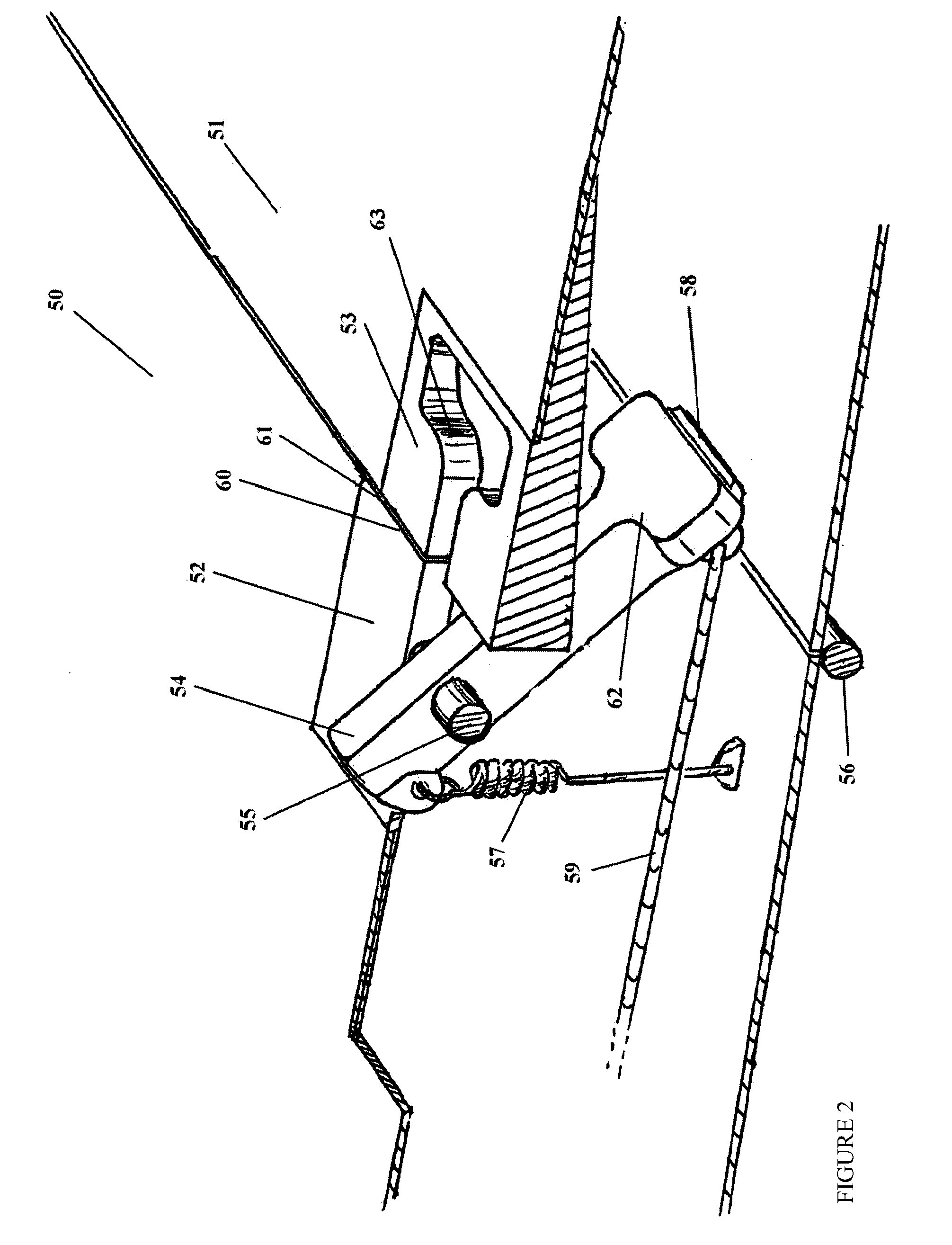
Improved mechanisms for folding and locking an aircraft wing and controlling the wing's aileron through a wing fold have been motivated by development of a roadable aircraft. Applicable to a broader class of aircraft, these mechanisms allow for a safer, lighter-weight solution to the wing-folding challenge than currently available. The cable control system allows an outer wing section to be moved in concert with an actuated inner wing section. The locking mechanism allows for automated operation and visual inspection. The aileron control mechanism provides centering and locking in addition to flight control through the hinge axis.
Owner:TERRAFUGIA
Microfabricated translational stages for control of aerodynamic loading
Micro-electro-mechanical (MEM) translational tabs are introduced for enhancing and controlling aerodynamic loading of lifting surfaces. These microtabs are mounted at or near the trailing edge of lifting surfaces, deploy approximately normal to the surface, and have a maximum deployment height on the order of the boundary layer thickness. Deployment of this type of device effectively changes the camber, thereby affecting the lift generated by the surface. The effect of these microtabs on lift is as powerful as conventional control surfaces such as ailerons. Application of this simple yet innovative lift enhancement and control device will permit the elimination of some of the bulky conventional high-lift and control systems and result in an overall reduction in system weight, complexity and cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
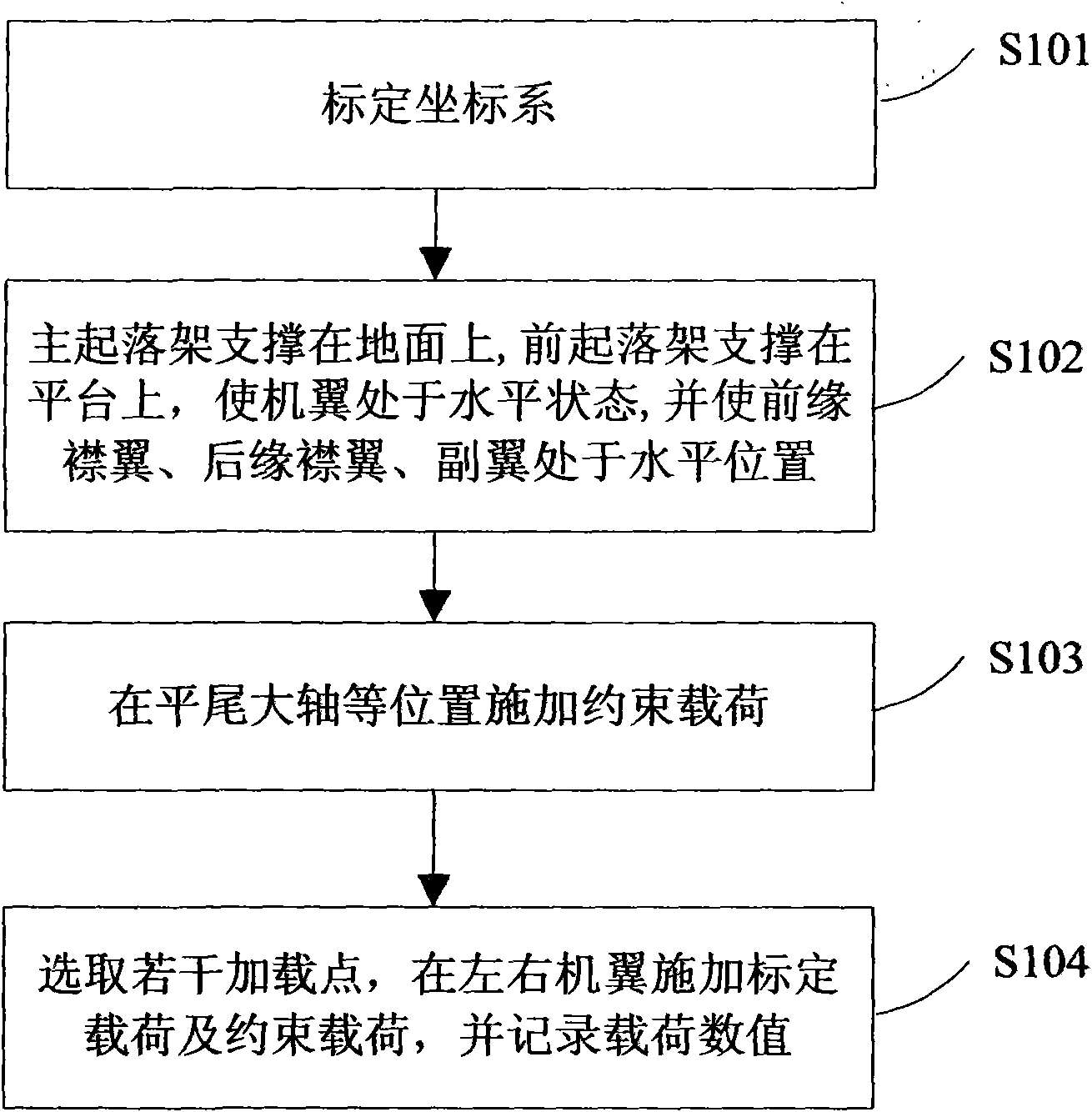
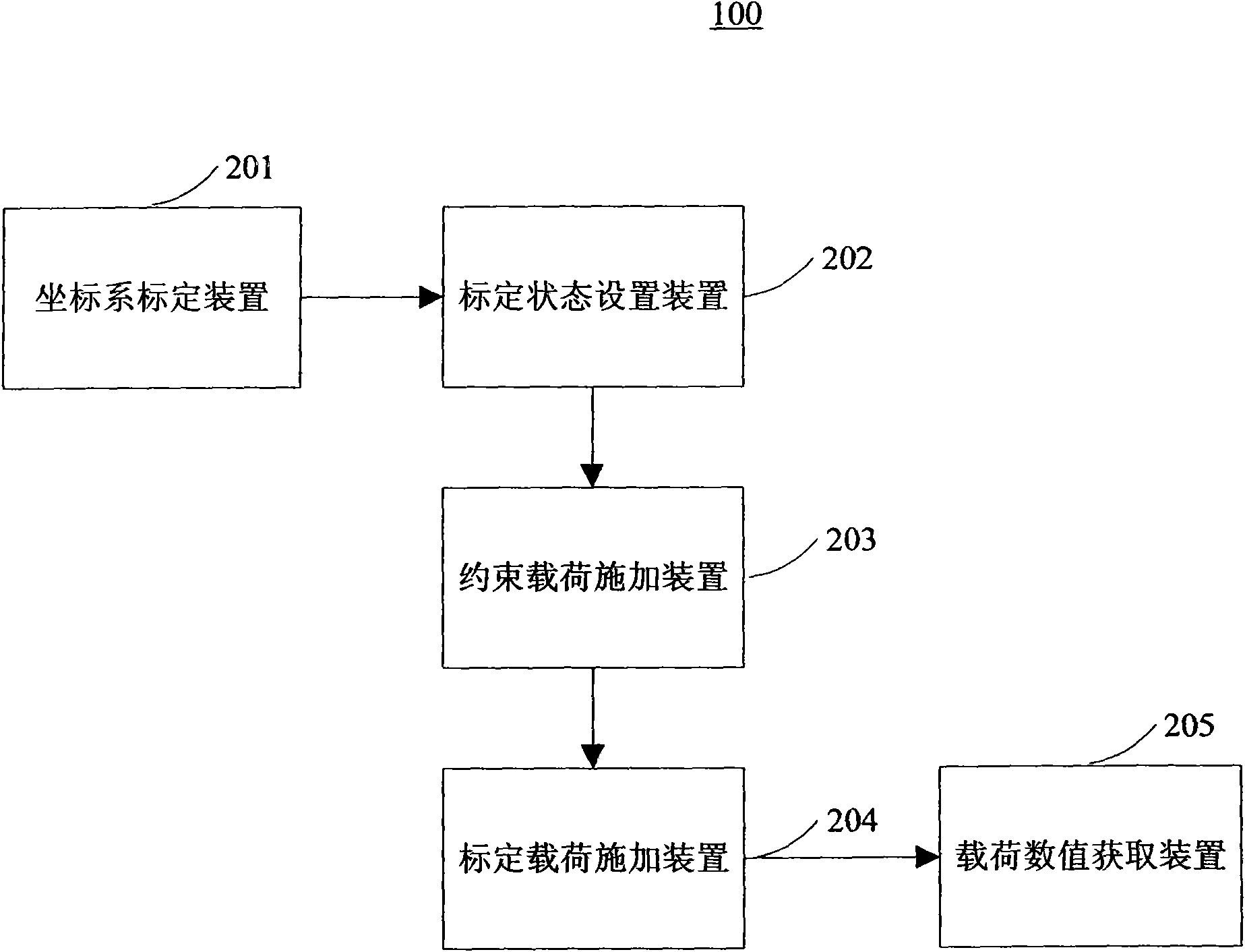
Method for testing field ground load calibration of airplane wing and calibration device thereof
ActiveCN101685039AHigh precisionEnsure safetyForce measurementElasticity measurementBit lineTrailing edge
The invention discloses a method for testing ground load calibration of an airplane wing and a special device for ground load calibration of the airplane wing. The method comprises the following steps: 1, calibrating a coordinate system, setting an intersection point of a horizontal line of an airframe structure of the airplane and a zero bit line as the original point of the coordinate system toensure that an X axis is coincided with the horizontal line of the airframe structure of the airplane and is positive afterwards, an Y axis is in a symmetric surface of the airplane and is positive upwards, and a Z axis points at the left wing of the airplane and forms a right-handed system with the X axis and the Y axis; 2, supporting a main undercarriage of the airplane on the ground, supportinga front undercarriage of the airplane on a platform, maintaining the wing in a horizontal state, and leading a fore flap, a tailing flap and a flap to be in the horizontal state; 3, applying restraint load to left and right horizontal stabilizer shafts of the airplane; and 4, selecting load points of the wing, applying calibration load to the selected load point of the wing, and acquiring the value of the calibration load. The method realizes field ground load calibration of the airplane wing.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI MECHANIZATION SCI
Novel hybrid vertical/short take-off and landing (V/STOL) unmanned aerial vehicle
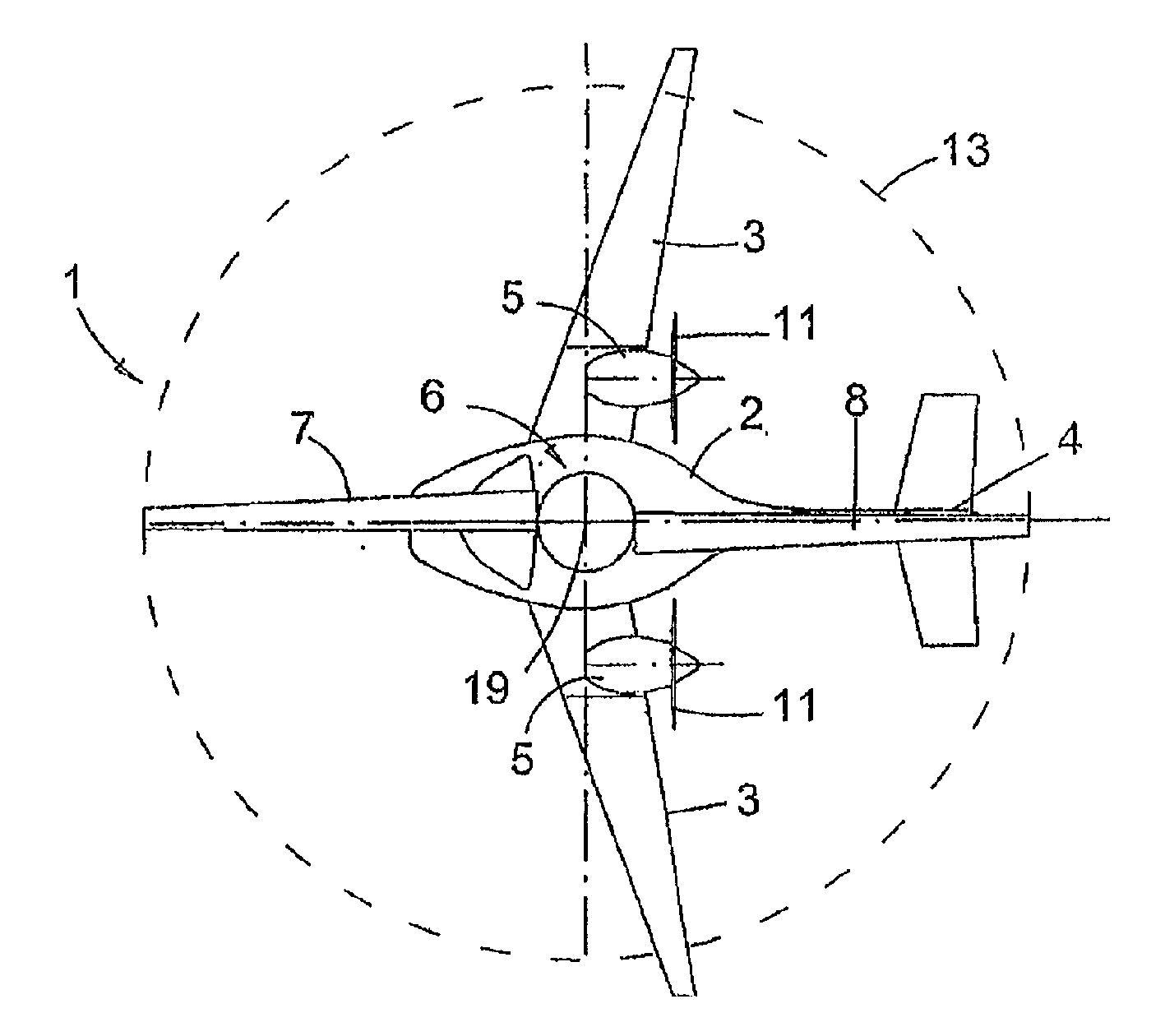
The invention discloses a novel hybrid vertical / short take-off and landing (V / STOL) unmanned aerial vehicle, aiming at solving the problems of complicated structure, high cost and the like of the existing aerial vehicles. The unmanned aerial vehicle comprises a body, a main wing, take-off and landing auxiliary wings arranged on the main wing, canards arranged at the front part of the body, a vertical tail arranged at the rear part of the body, a landing gear, an accumulator battery, a control system, a power supply management system and the like, wherein the landing gear, the accumulator battery, the control system, the power supply management system and the like are arranged below the body. The unmanned aerial vehicle adopts a ducted fan to provide a lift and assist balance during vertical take off and landing, and adopts an engine to provide the main push force and to automatically generate electricity so as to effectively utilize oil-electricity complement, simultaneously the reasonable hybrid use of fuel oil and electric energy is achieved through the structure and aerodynamic configuration design of the aerial vehicle, thereby achieving vertical and short take-off and landing, reducing the control difficulty of the aerial vehicle and solving the problem of inconsistence between difficult control and short voyage of the existing V / STOL unmanned aerial vehicles; the novel hybrid vertical / short take-off and landing (V / STOL) unmanned aerial vehicle disclosed by the invention can achieve vertical / short take-off and landing, and has the advantages of flexible and steady flight, wide application range and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
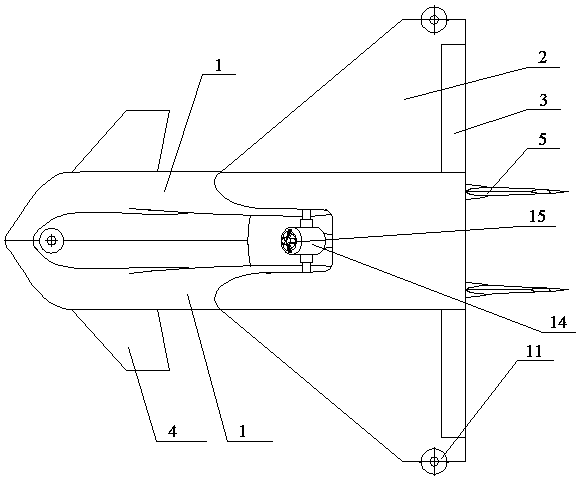
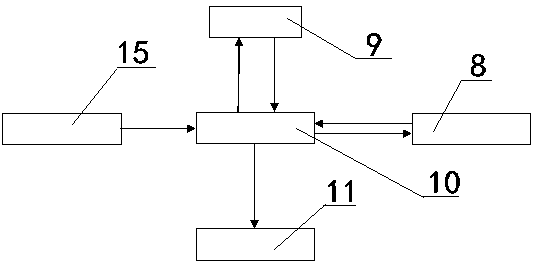
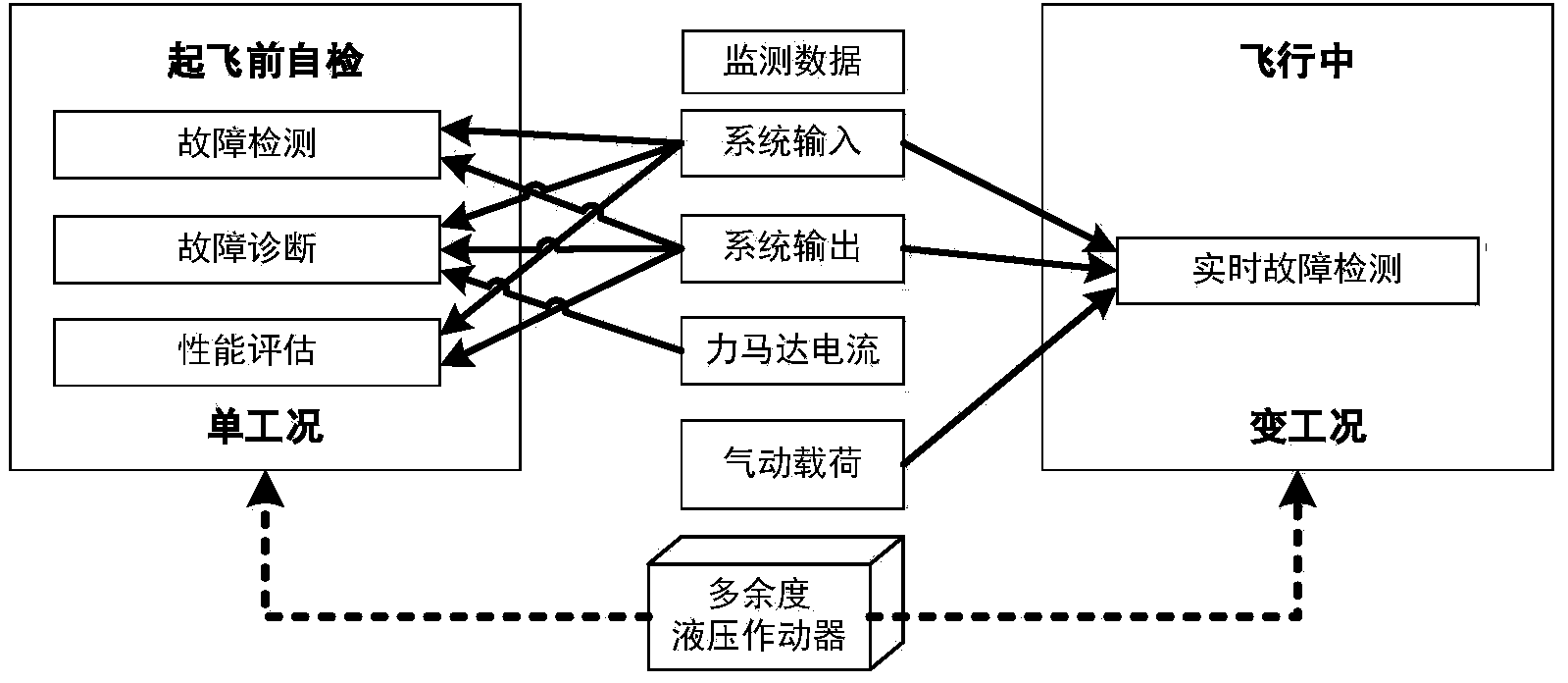
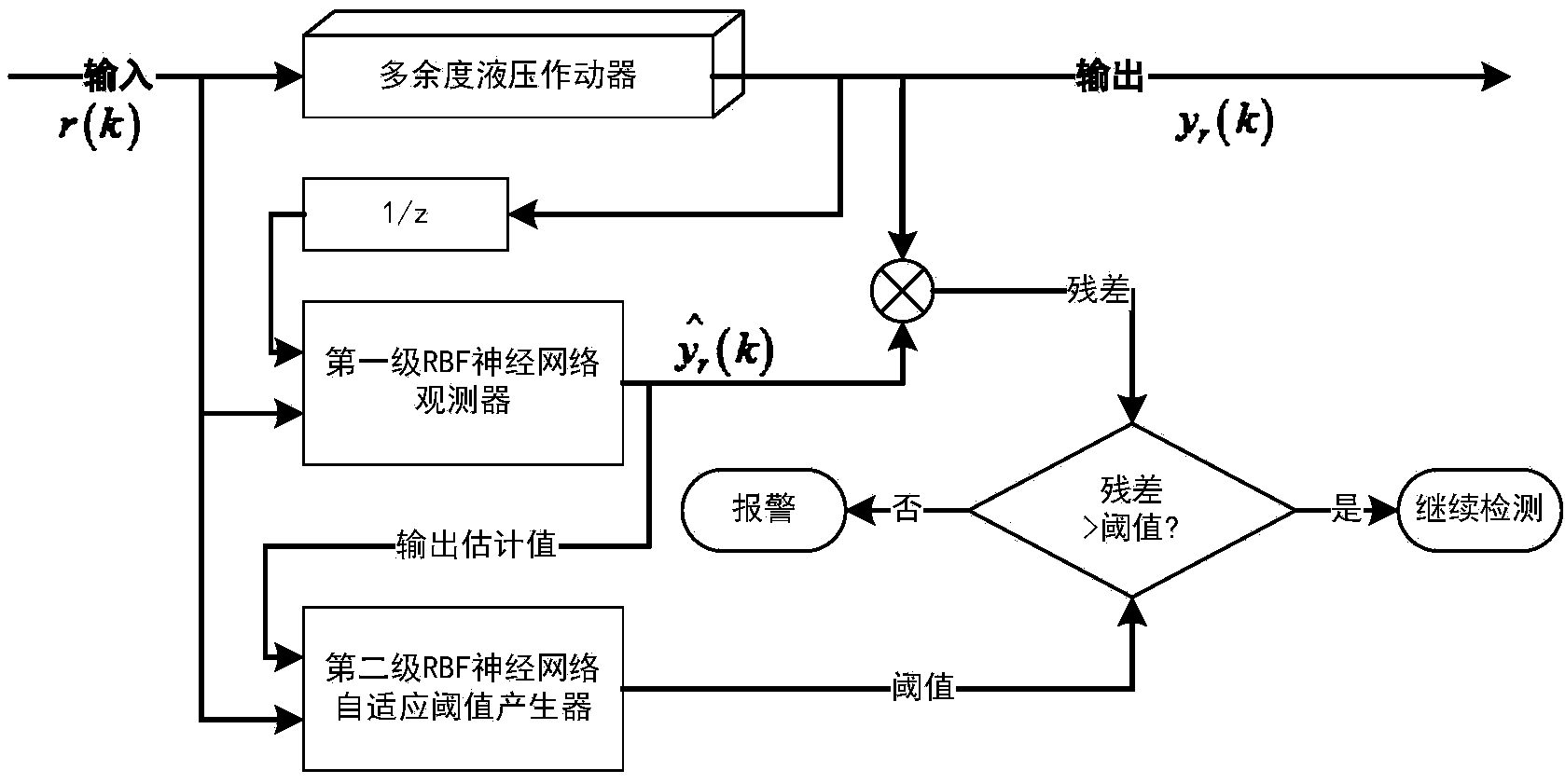
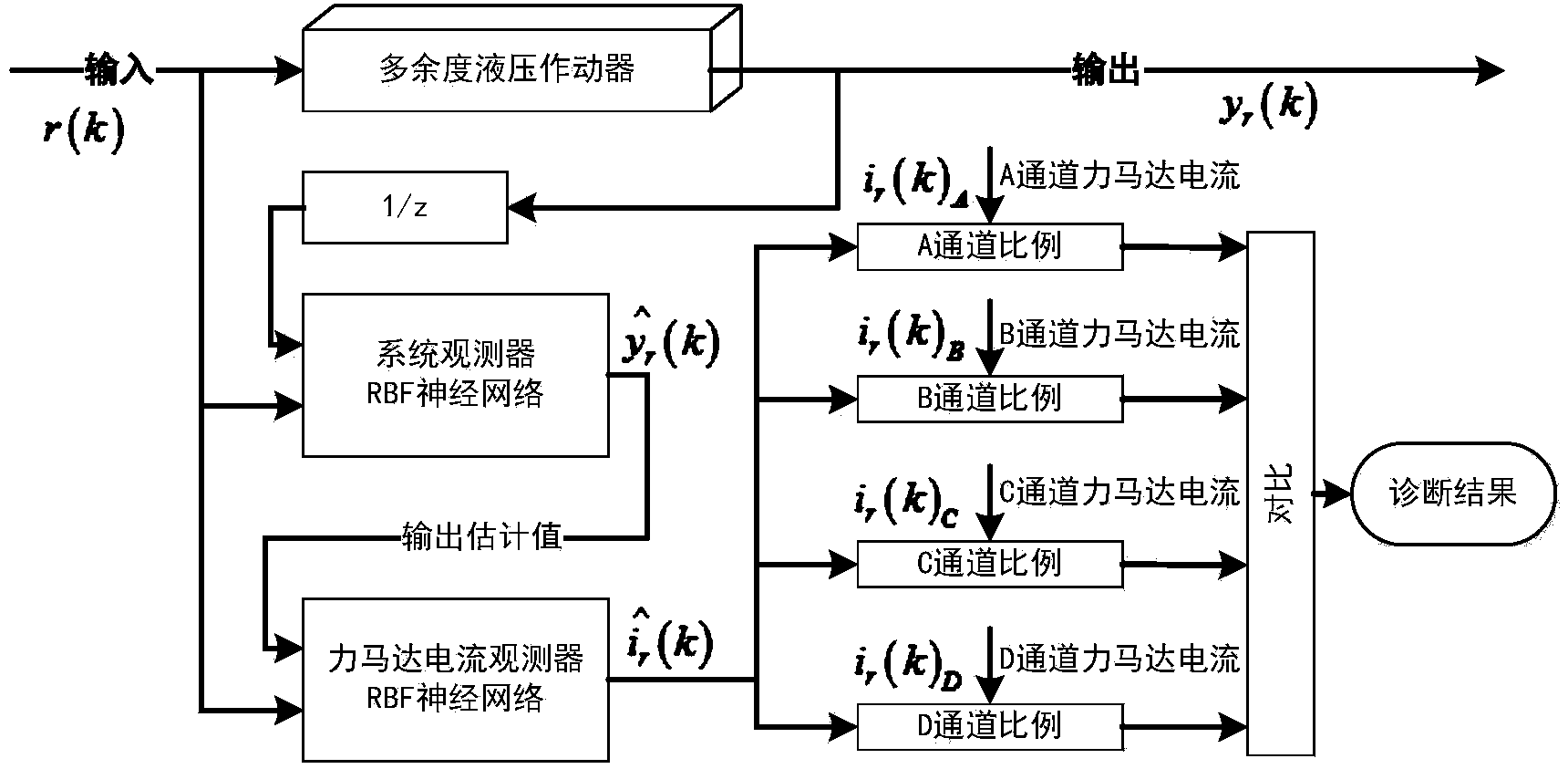
Fault detection, diagnosis and performance evaluation method for redundant aileron actuator
ActiveCN104390776AImprove accuracyReduce the false alarm rate of detectionMachine part testingFluid-pressure actuator testingTime domainNetwork output
The invention discloses a fault detection, diagnosis and performance evaluation method for a redundant aileron actuator. According to the method, fault detection, diagnosis, evaluation and real-time detection of the actuator are performed by means of an input order signal, an output displacement signal, a force motor current signal and aerodynamic loading data of the actuator; the fault detection is realized by a two-stage neural network, a first neural network is used as a system observer and is matched with actual output to acquire a residual error, and a second neural network outputs a self-adaptive threshold value synchronously; the fault detection is realized by the system observer and a force motor current observer; a time domain feature is extracted from a residual error signal and output to a self-organizing mapping neural network, and a minimum quantization error is acquired and normalized to a health degree, so that the actuator performance is evaluated; and on the basis of fault detection, the aerodynamic loading data is introduced, by means of a specific input order spectrum, the system observer and the neural network with the self-adaptive threshold value are trained, and the real-time fault detection is realized.
Owner:北京恒兴易康科技有限公司
Vorticity cancellation at trailing edge for induced drag elimination
InactiveUS7134631B2More suction powerGood power savingPropellersInfluencers by generating vorticesPropellerFan blade
Wing tip vortices are evident from airliner vapor trails, and helicopter blade slap. Elliptically loaded high aspect ratio tapered wings have minimum induced drag but cannot eliminate it. Different methods are disclosed herein, for upper and lower surface boundary layers to cancel their opposing vorticity upon shedding from the trailing edge, thereby eliminating wake vorticty, induced drag and associated noise. This requires wing-rotor-propeller or fan blades with a platform designed for uniform bound circulation and with boundary layer control near the tip. In addition this requires special techniques to counter span-wise pressure gradients, such as tip circulation control blowing or an upwind small propeller or wind turbine on each tip. These techniques can eliminate wake vorticity with its induced drag, noise, flying on the backside of the power curve and the option for asymmetric loading by pneumatic means to eliminate need for cyclic pitch control or conventional ailerons.
Owner:LOTH JOHN L
Dynamic Adjustment of Wing Surfaces for Variable Camber
ActiveUS20080255713A1Increase the burdenRaise the ratioAircraft controlDigital data processing detailsFlaperonFlight control surfaces
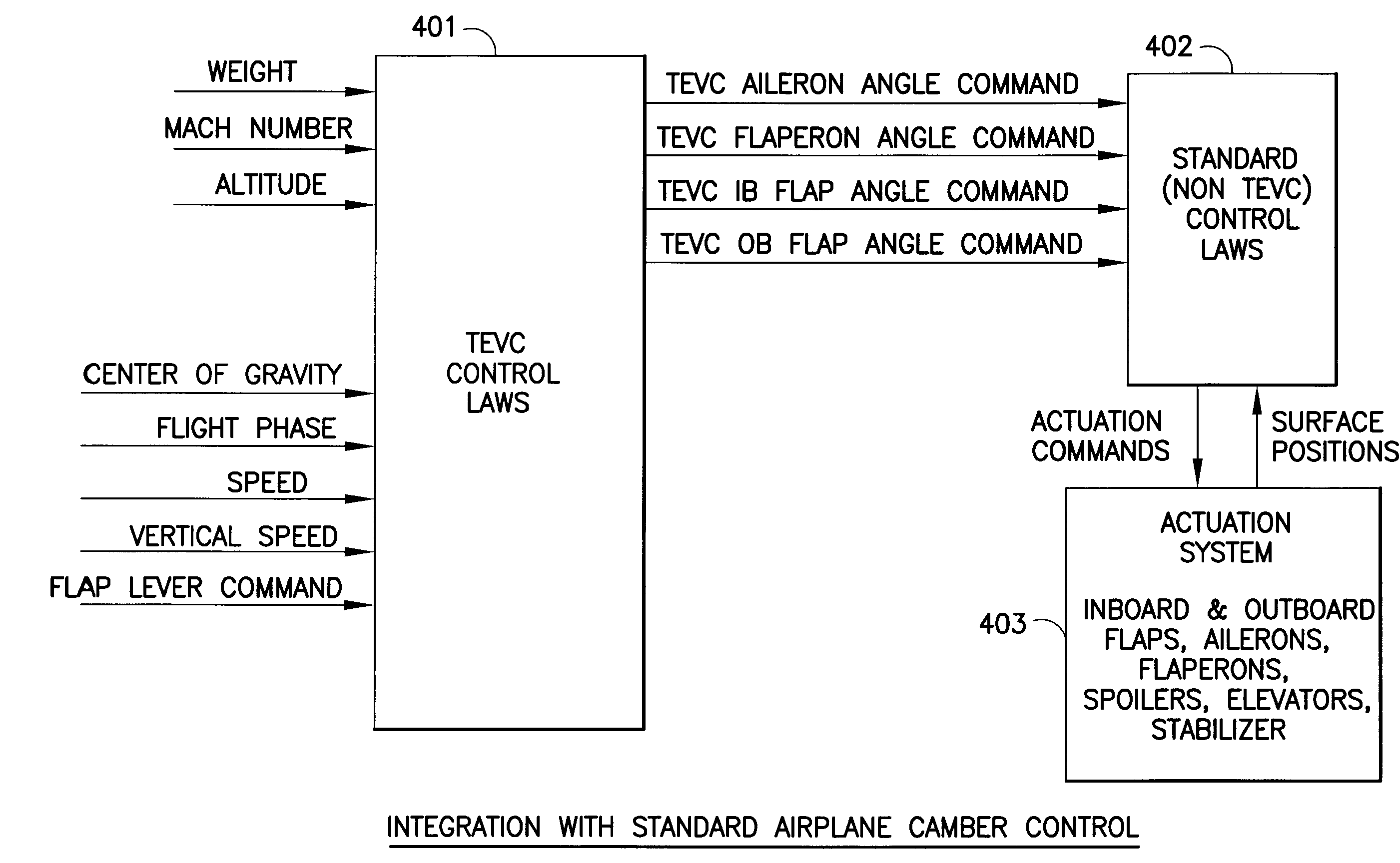
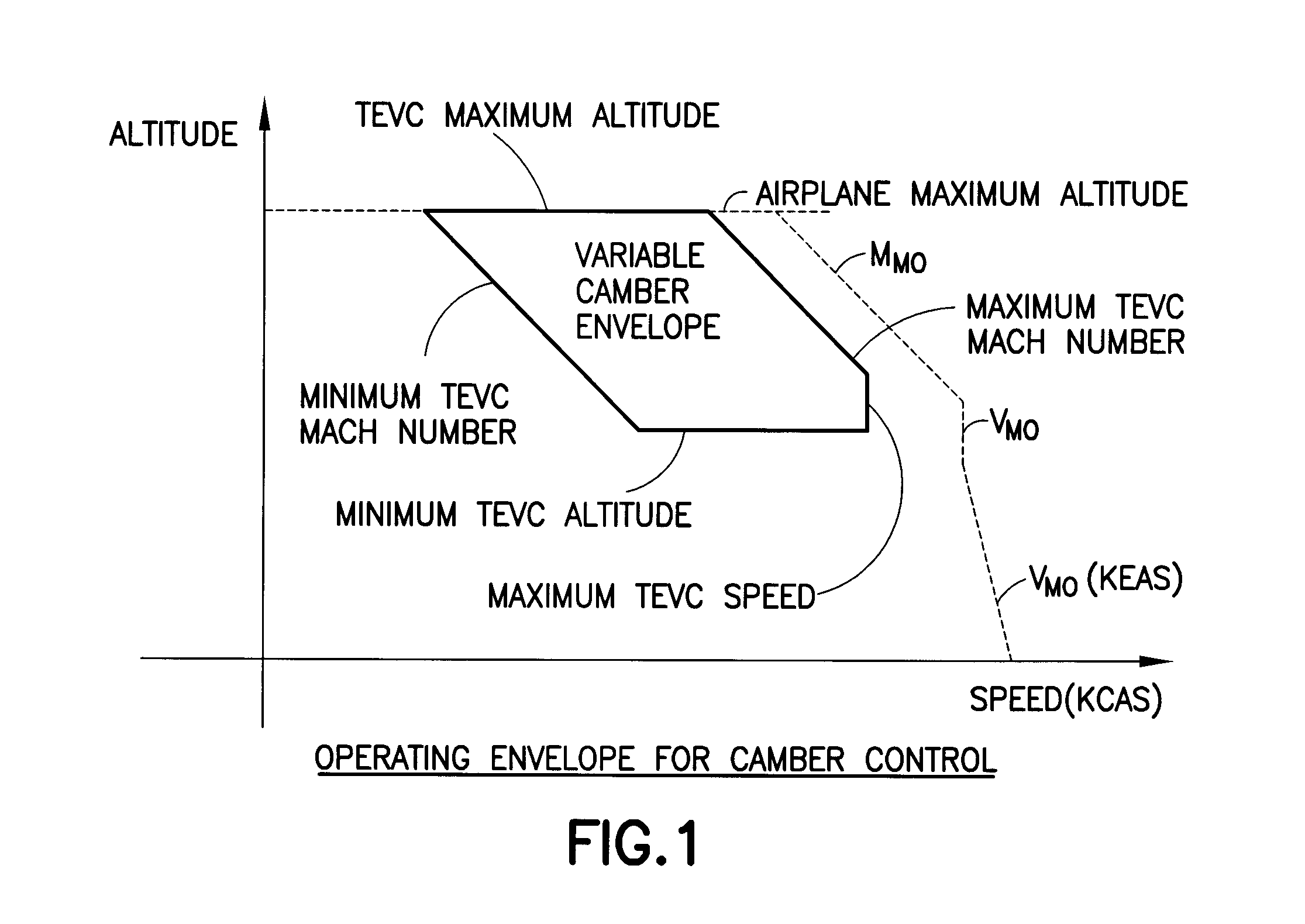
The movable surfaces affecting the camber of a wing are dynamically adjusted to optimize wing camber for optimum lift / drag ratios under changing conditions during a given flight phase. In a preferred embodiment, an add-on dynamic adjustment control module provides command signals for optimum positioning of trailing edge movable surfaces, i.e., inboard flaps, outboard flaps, ailerons, and flaperons, which are used in place of the predetermined positions of the standard flight control system. The dynamic adjustment control module utilizes inputs of changing aircraft conditions such as altitude, Mach number, weight, center of gravity, vertical speed and flight phase. The dynamic adjustment control module's commands for repositioning the movable surfaces of the wing are transmitted through the standard flight control system to actuators for moving the flight control surfaces.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
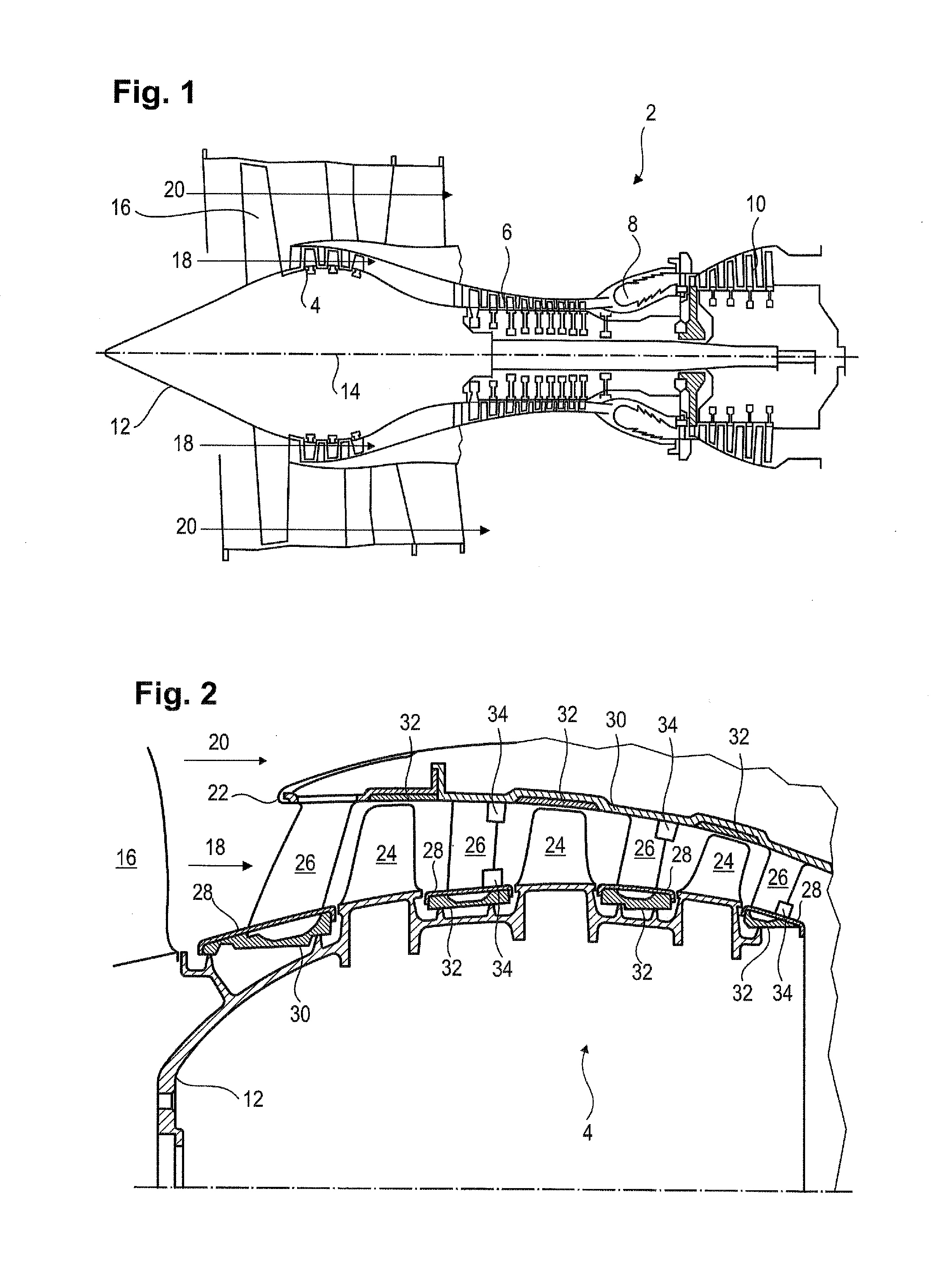
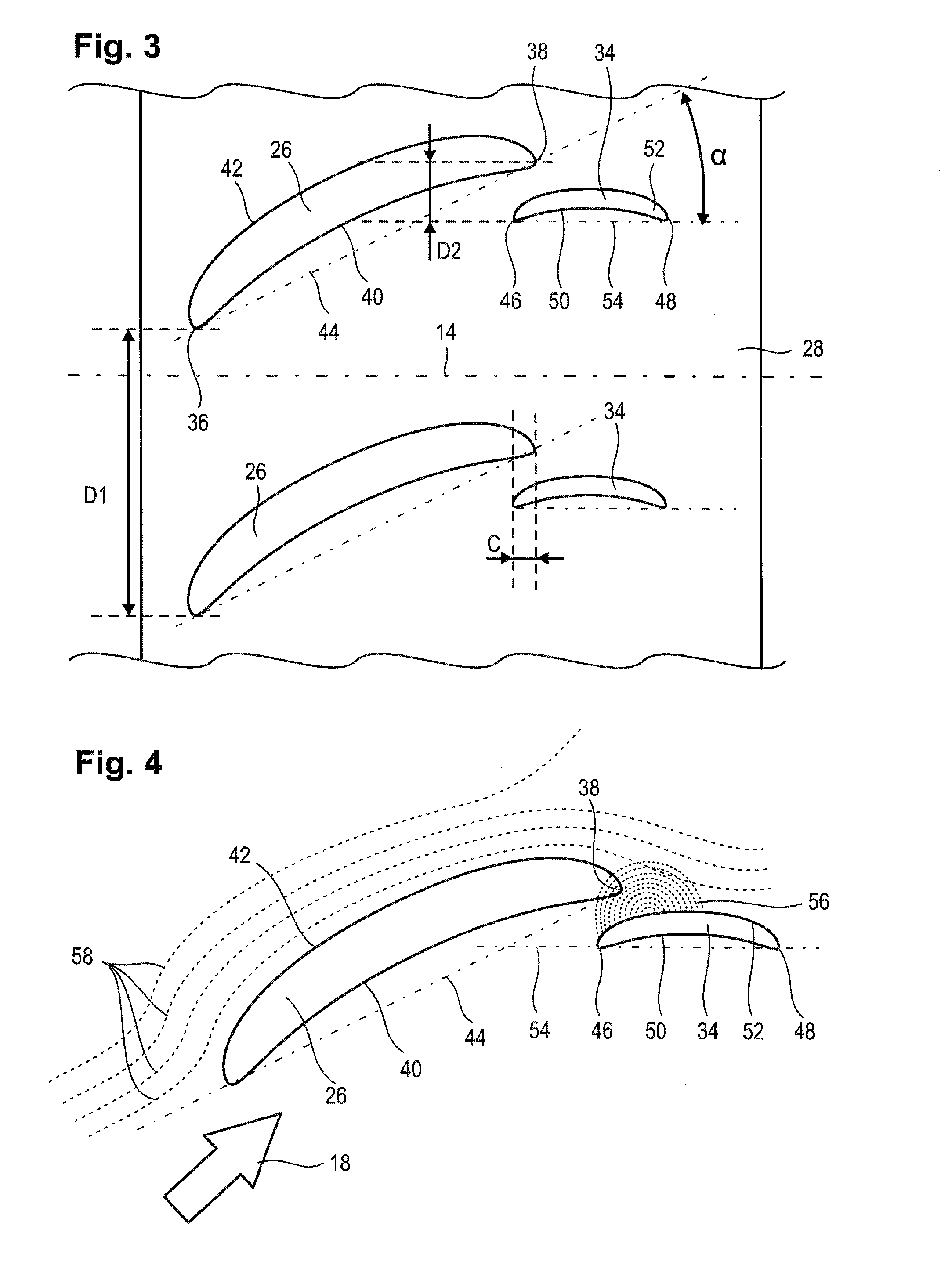
Axial Turbomachine Stator with Ailerons at the Blade Roots
ActiveUS20140328675A1Improve abilitiesStalling can be eliminatedPump componentsReaction enginesLow-pressure areaTrailing edge
The present application relates to the compressor stator of an axial turbomachine. The stator comprises an annular row of main stator blades and auxiliary blades each of which are associated with a main blade. The auxiliary blades are located at the trailing edges of the main blades and are in the vicinity of the pressure faces of the main blades. The auxiliary blades are aligned to generate a low-pressure area at the trailing edges of the main blades. Thus, a flow bypassing a main blade by its suction face is sucked in by the low-pressure area when it approaches the trailing edge of the main blade. Stalling is thus avoided and the efficiency of the machine is improved.
Owner:TECHSPACE AERO
Tailless layout single tail seat type vertical take-off and landing aircraft
InactiveCN103287576ACapable of vertical take-off and landingVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftLevel flightLow speed
The invention provides a single aircraft with vertical take-off and landing capacity. The single aircraft comprises a body (1), wings (2), rotor wings (5 and 13) which are arranged on the wings (2) on two sides, and elevons (7) which are arranged at the rear edges of the two wings (2), wherein rolling and pitching can be stabilized and controlled through deflection of the elevons (7); in a vertical take-off and landing period, the head of the aircraft is upward; the aircraft takes off and / or lands in a tail seat manner; the gravity is overcome through elevating force generated by rotation of the rotor wing (5); vertical take-off and landing can be realized. The single aircraft has the advantages that (1) through a tailless layout, the air resistance is effectively reduced, and the flight speed is increased; (2) the advantages of a helicopter and a fixed wing aircraft are taken into consideration, and high efficiency can be maintained in both high-speed level flight and low-speed hovering periods; (3) a rotary mechanism is eliminated, and the single aircraft is simple in structure, high in reliability and low in cost; (4) the aircraft can be stabilized and controlled under low-speed and large-incidence conditions, and is applied to city airspace; (5) an emergency is handled in an engine connecting shaft and full-aircraft parachute-opening manner, and the aircraft is high in safety.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Hypersonic speed aircraft control method capable of suppressing constant deviation influence of sideslip angle signal
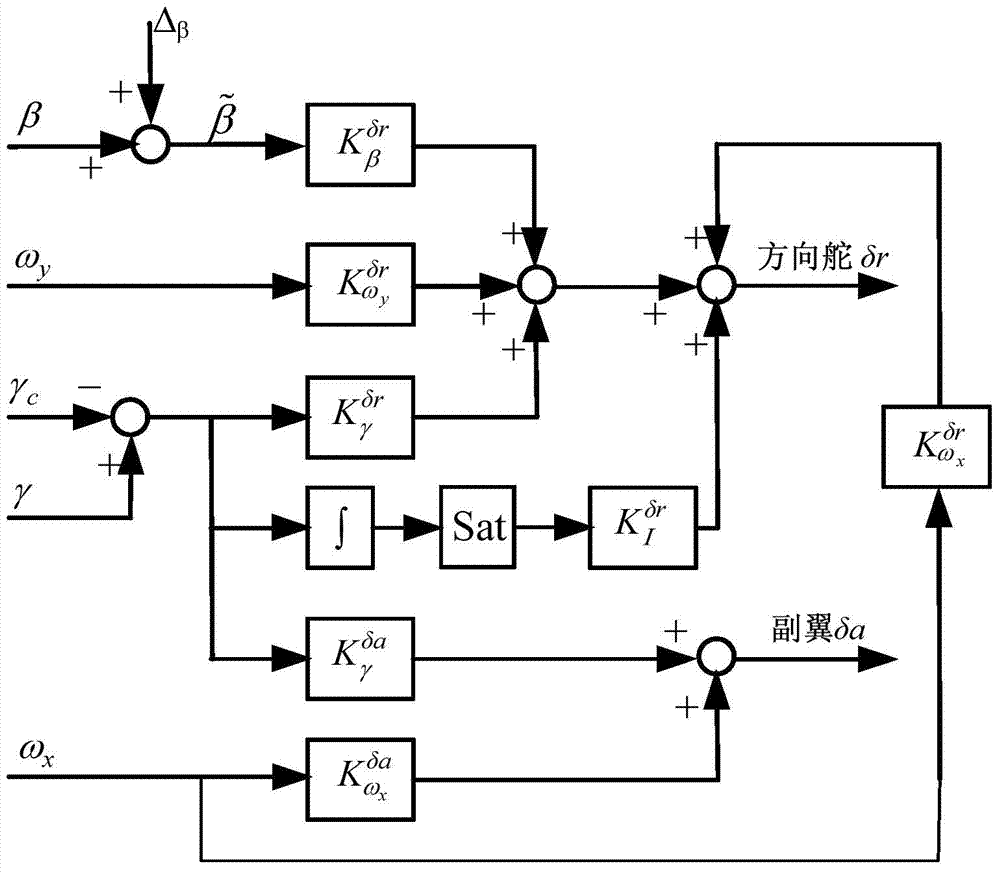
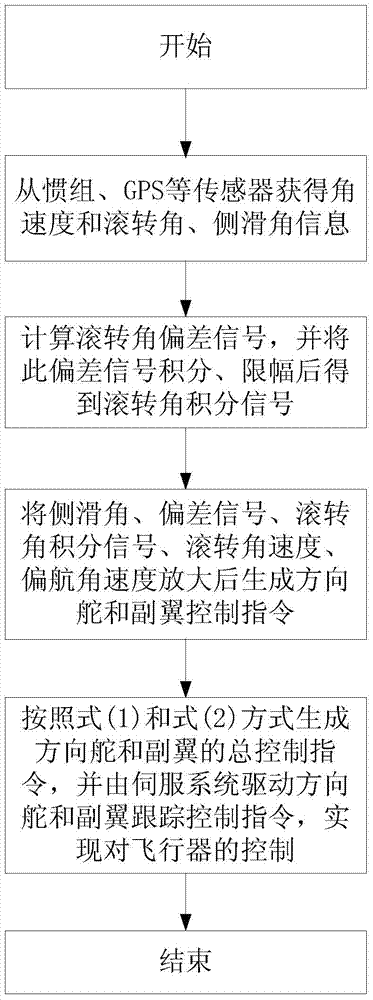
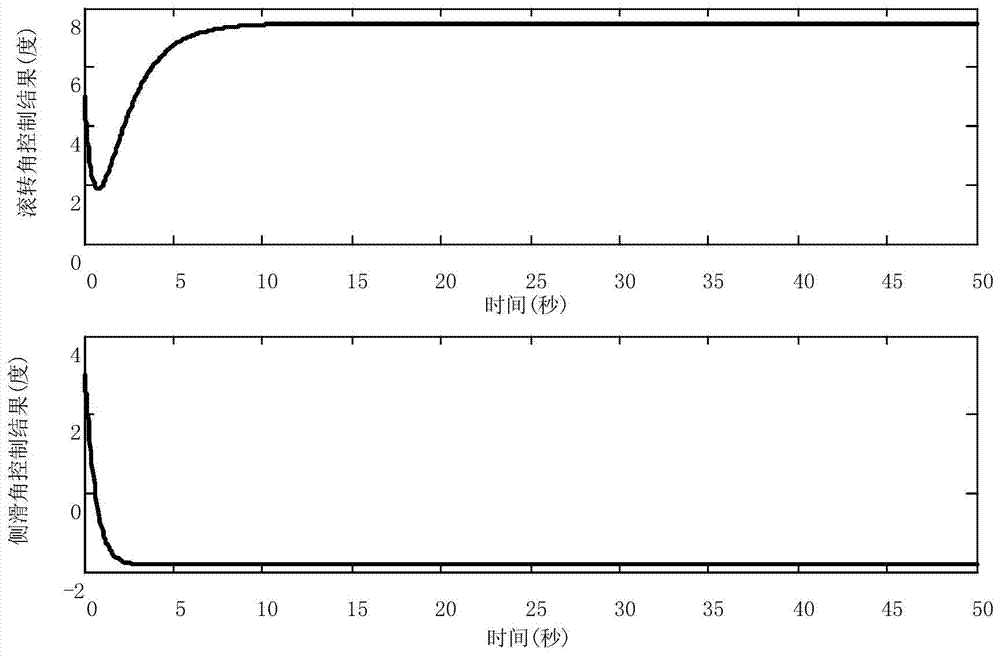
ActiveCN103587681ASteady state error zeroHigh control precisionActuated automaticallyAdaptive controlEngineeringOmega
The invention discloses a hypersonic speed aircraft control method capable of suppressing the constant deviation influence of a sideslip angle signal. The method comprises the following steps: (1) measuring the yaw angle speed omega y and the roll angle speed omega x of an aircraft in real time by utilizing an inertial measurement unit, and acquiring a roll angle gamma and a sideslip angle by utilizing the inertial measurement unit and a sensor; (2) calculating a deviation signal of the gamma and a roll angle instruction gamma c, integrating a deviation signal Delta gamma, and performing the amplitude limiting on the deviation signal, so as to obtain a roll angle integrated signal; (3) amplifying the roll angle integrated signal and the omega y, generating a control instruction, and feeding the control instruction back to a rudder of the aircraft; amplifying the omega x, generating a control instruction I and feeding the control instruction I back to an aileron of the aircraft; amplifying the Delta gamma, generating a control instruction II and feeding the control instruction II back to the rudder / aileron of the aircraft; (4) adding all the control instructions which are fed back to the rudder to serve as a general control instruction of the rudder, and controlling the rudder to track the general control instruction through a servo system on the aircraft; adding all the control instructions I fed back to the aileron to serve as a general control instruction I of the aileron, and controlling the aileron to track the general control instruction through the servo system on the aircraft.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF LAUNCH VEHICLE TECH
Automatic-piloting simulator of aeroplane
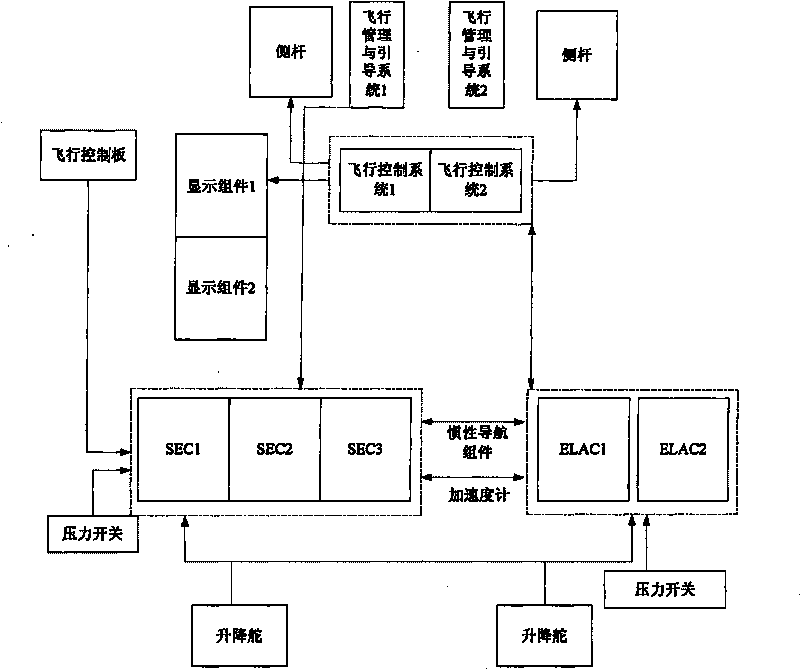
InactiveCN101714302ASimple structureCompact assemblyCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsJet aeroplaneLoop control
The invention relates to an automatic-piloting simulator of an aeroplane, and belongs to the field of simulation technique. The automatic-piloting simulator of the aeroplane is characterized by comprising a flight trainer, a model airplane rudder control mechanism and a flight vision system which are connected into a whole by a computer network, wherein the flight trainer is provided with a server, a central control platform, a side pole and a display mechanism; the model airplane rudder control mechanism is provided with a semi-physical model, ailerons, a rudder, an elevator and a rudder loop control system of the aeroplane; and the flight vision system is driven by aeroplane motion data generated by the flight trainer, and displays a flight attitude, flight data and a flight trajectory image of the aeroplane. The automatic-piloting simulator of the invention has the advantages of simple structure, compact assembly, economy, practicality, accurate data, high simulation degree, good automatic and manual piloting dynamic performance of the simulated airplane and the like.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Inverted-landing aircraft
ActiveUS20140350748A1Free from damageAircraft componentsAnalogue computers for vehiclesJet aeroplaneControl system
An aircraft defining an upright orientation and an inverted orientation, a ground station; and a control system for remotely controlling the flight of the aircraft. The ground station has an auto-land function that causes the aircraft to invert, stall, and controllably land in the inverted orientation to protect a payload and a rudder extending down from the aircraft. In the upright orientation, the ground station depicts the view from a first aircraft camera. When switching to the inverted orientation: (1) the ground station depicts the view from a second aircraft camera, (2) the aircraft switches the colors of red and green wing lights, extends the ailerons to act as inverted flaps, and (3) the control system adapts a ground station controller for the inverted orientation. The aircraft landing gear is an expanded polypropylene pad located above the wing when the aircraft is in the upright orientation.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
Control surface failsafe drop link
ActiveUS20100032520A1Reduce weightEliminate needAircraft stabilisationWithout power ampliicationFlight vehicleAirplane
An aircraft control surface failsafe hinge configuration is disclosed. The arrangement comprises a drop link configuration which is adapted to attach a control surface to an aircraft structure where the drop link additionally incorporates a failsafe hinge means which provides a backup hinge connection between the control surface and the aircraft structure to which it is attached. The improved failsafe hinge construction may be applied to any aircraft control surface such as an aileron, elevator, vertical tail plane and the like.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
GPS-guided unmanned aerial vehicle automatic carrier-landing adaptive control system and method
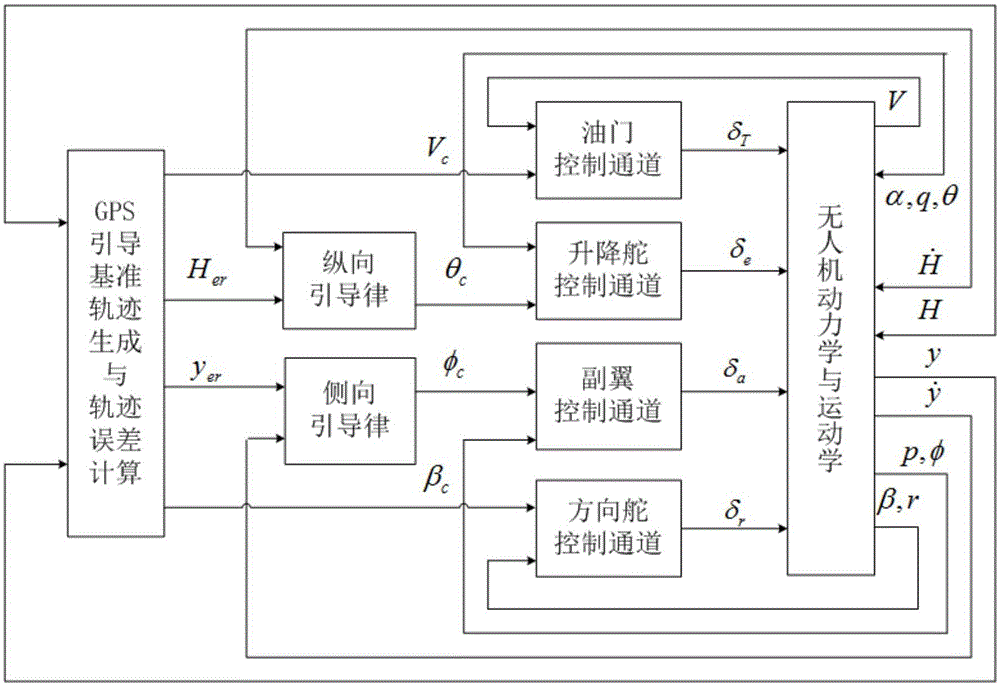
InactiveCN105138012AGood landing trajectory tracking performanceAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsFlight heightControl system
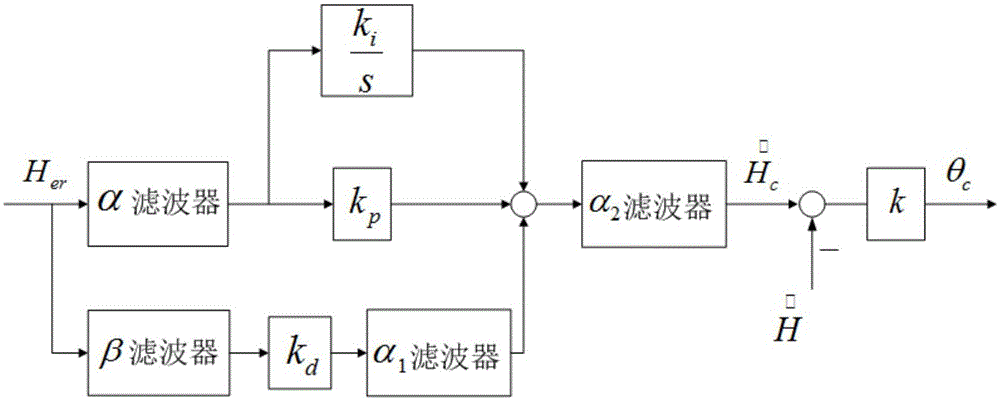
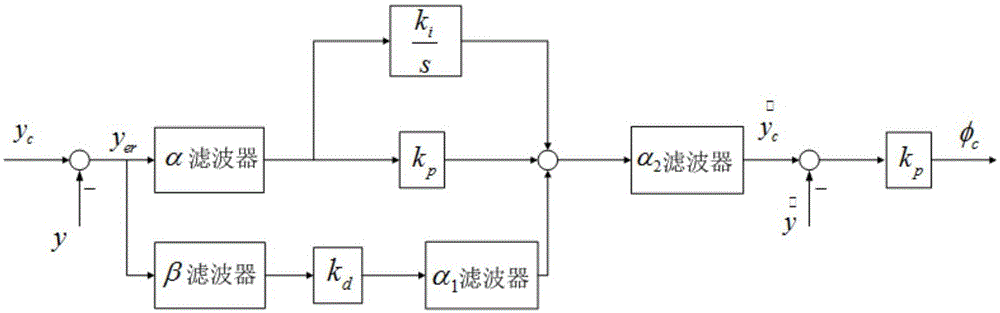
The invention discloses a GPS-guided unmanned aerial vehicle automatic carrier-landing adaptive control system and method. The system includes: a GPS guidance reference trajectory generation and trajectory error calculation module which is used for inputting signals detected by a GPS, establishing a reference trajectory in a ground coordinate system with an ideal carrier-landing point being an original point, and finally outputting the signals; a longitudinal guidance law module which uses a pitch attitude as an internal loop, and realizes control of flight height by suppression of a height error; a lateral guidance law module used for subtracting an actual lateral position signal from a designated lateral position signal to obtain an error signal and eliminating the error signal; and a flight control loop includes control law modules of four channels of accelerator, elevator, aileron and rudder. The GPS-guided unmanned aerial vehicle automatic carrier-landing adaptive control system provided by the invention realizes conversion of a trajectory tracking error signal into an attitude tracking command signal, solves the problem of attitude tracking through adaptive control, and an unmanned aerial vehicle automatic carrier-landing guidance and control system is formed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Cross-medium aircraft with changeable shape like flying fish
ActiveCN104589938AAdvanced gas-hydraulic layoutGood structural variant abilityAircraft convertible vehiclesRotational axisMode control
Provided is a cross-medium aircraft with a changeable shape like a flying fish. A pair of machine wings (2) are movably installed on the two sides of the middle of a machine body (1) respectively. A pair of duck wings (3) are installed below the middle rear portion of the machine body (1). The machine wings (2) and the duck wings (3) can rotate around rotating shafts to change the tapping angle. A flap and an aileron are distributed on the inner side and the outer side of each machine wing (2) respectively. An air-propulsion foldable spiral paddle (4) is installed at the head portion of the machine body (1). A V-shaped tail wing (5) is arranged at the middle rear section of the machine body (1). An underwater-propulsion spiral paddle (6) is installed at the tail portion of the machine body (1). A rectifying cover (7) is arranged at the lower middle portion of the head of the machine body (1). The cross-medium aircraft has the advantages that the air-water dynamic layout of two different media including air and water and the light pressure-resistant shape-changeable structure are taken into consideration, multi-mode control and water sealing can be easily achieved, and the various military and civilian requirements can be met.
Owner:CHINA SPECIAL TYPE FLIER RES INST
Hypersonic aircraft
A supersonic aircraft having unique structural, geometrical, electromagnetic, mechanical, thermal and aerodynamic configuration is described. Its design characteristics maximize aerodynamic performance, speed, efficiency, comfort and range in the operational affect of carrying passengers over long distances at very high flight speeds and Mach numbers, generally above Mach 4.0+. It has fully integrated-mated fuselage twin engine nacelle structures which reduce and stabilize wave drag, wherein engines sit forward of the sonic boom electrode swept aerospace but are integrated right through the sub-wing, the aero-spike and inlet just above the top surface of the central wing, and above and the major wing mating join, attached via a massive composite titanium keel structure, through the central wing box and fuselage.
Owner:HYPERMACH AEROSPACE INDS
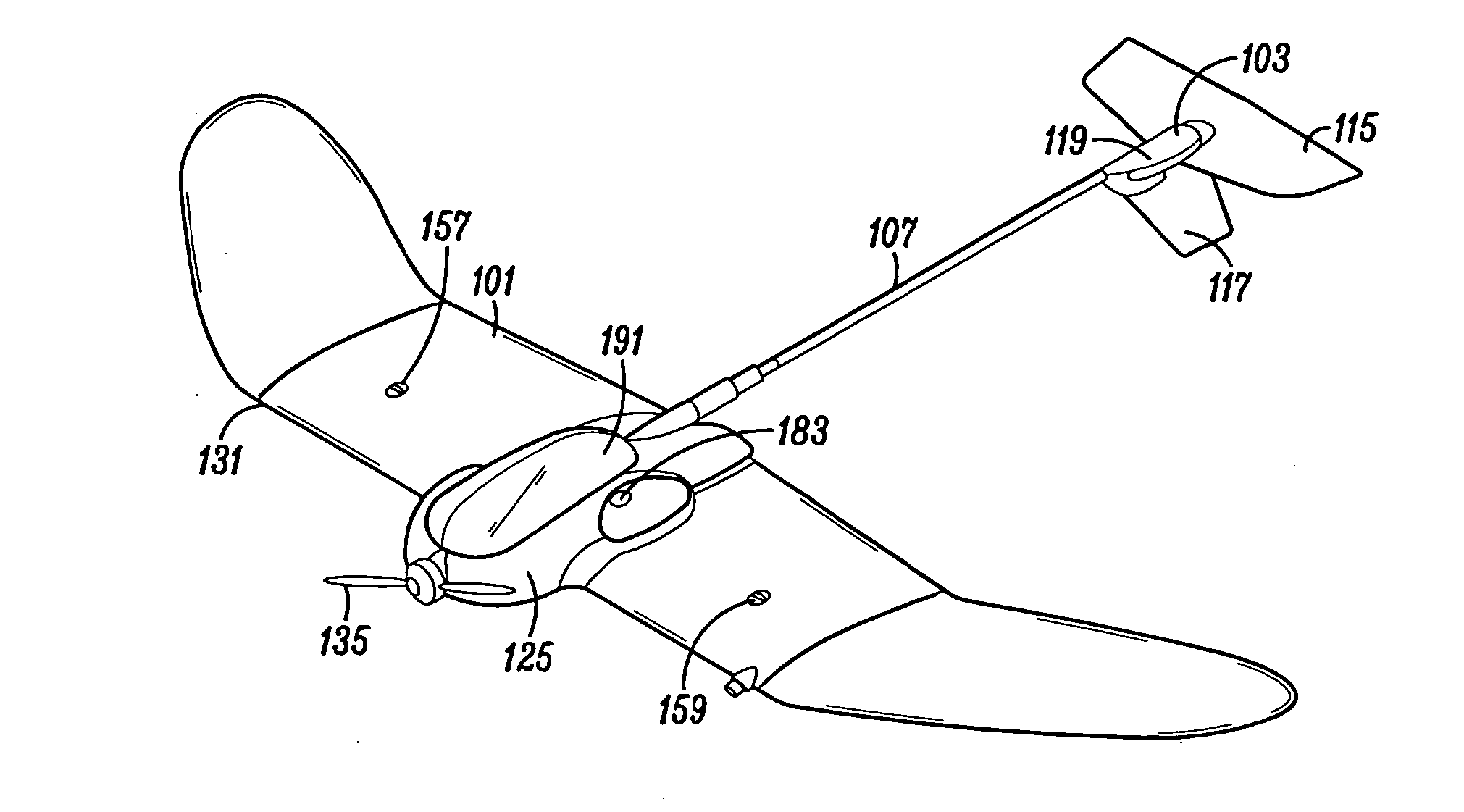
Delta Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and Method of Manufacture of the Same
This disclosure pertains to the field of small-unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The delta wing vehicle consists of an isosceles triangular shaped lifting body milled from Styrofoam. The longitudinal axis is approximately 65% of the lateral axis. The horizontal wing projections, or tiplets, are attached to the main lifting body at an approximately 10 degree upward angle from horizontal, have a 30 degree sweep back leading edge, and each one comprises 5% of the total wing area. The airfoil is a rhomboid or diamond shape. The chord is swept back at a 45-degree angle from the longitudinal centerline. The airfoil is symmetrical about the longitudinal center. The aircraft is controlled by a set of combined elevator / aileron surfaces (elevons) at the rear as well as a vertical stabilizer / rudder combination. This resulting lightweight UAV can make flat (unbanked) unbanked turns, fly in high winds, and has superior flexibility in payload capability.
Owner:SMITH DONALD EARL +1
Simulation device for steering wheel of airplane flight simulator
ActiveCN102157089AImprove versatilityAvoid Mechanical Transmission ErrorsCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsJet aeroplaneSteering wheel
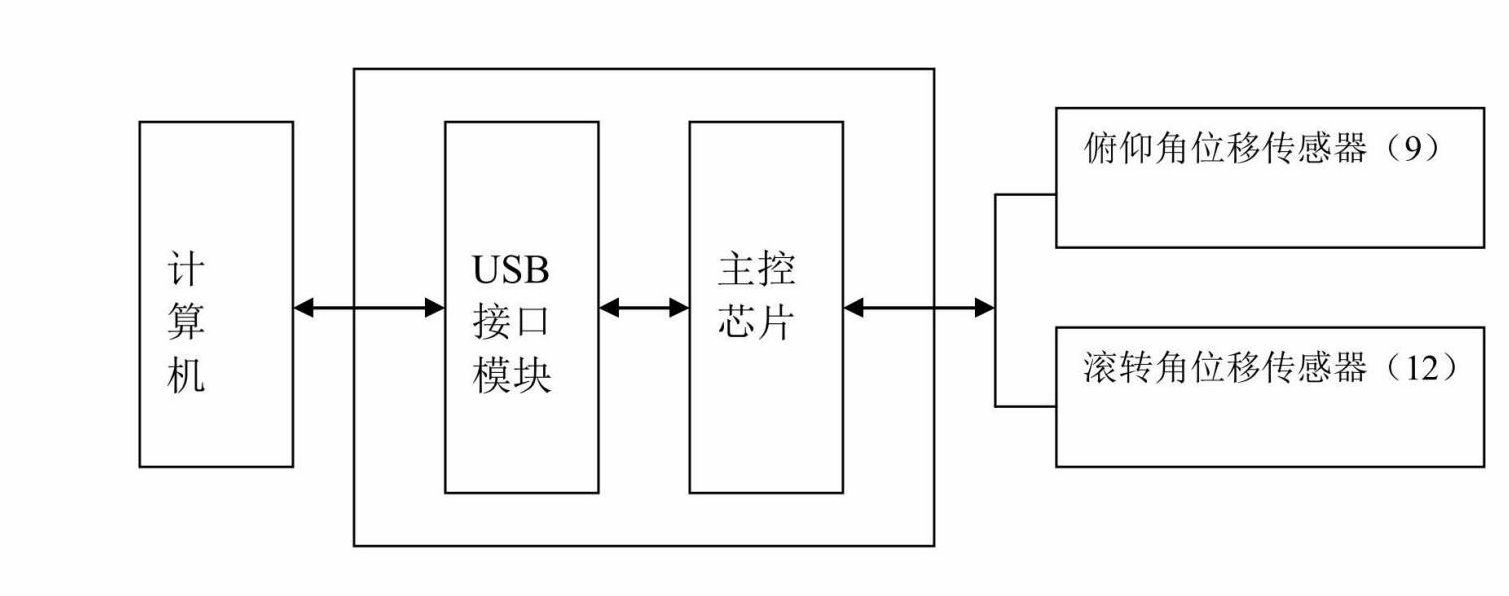
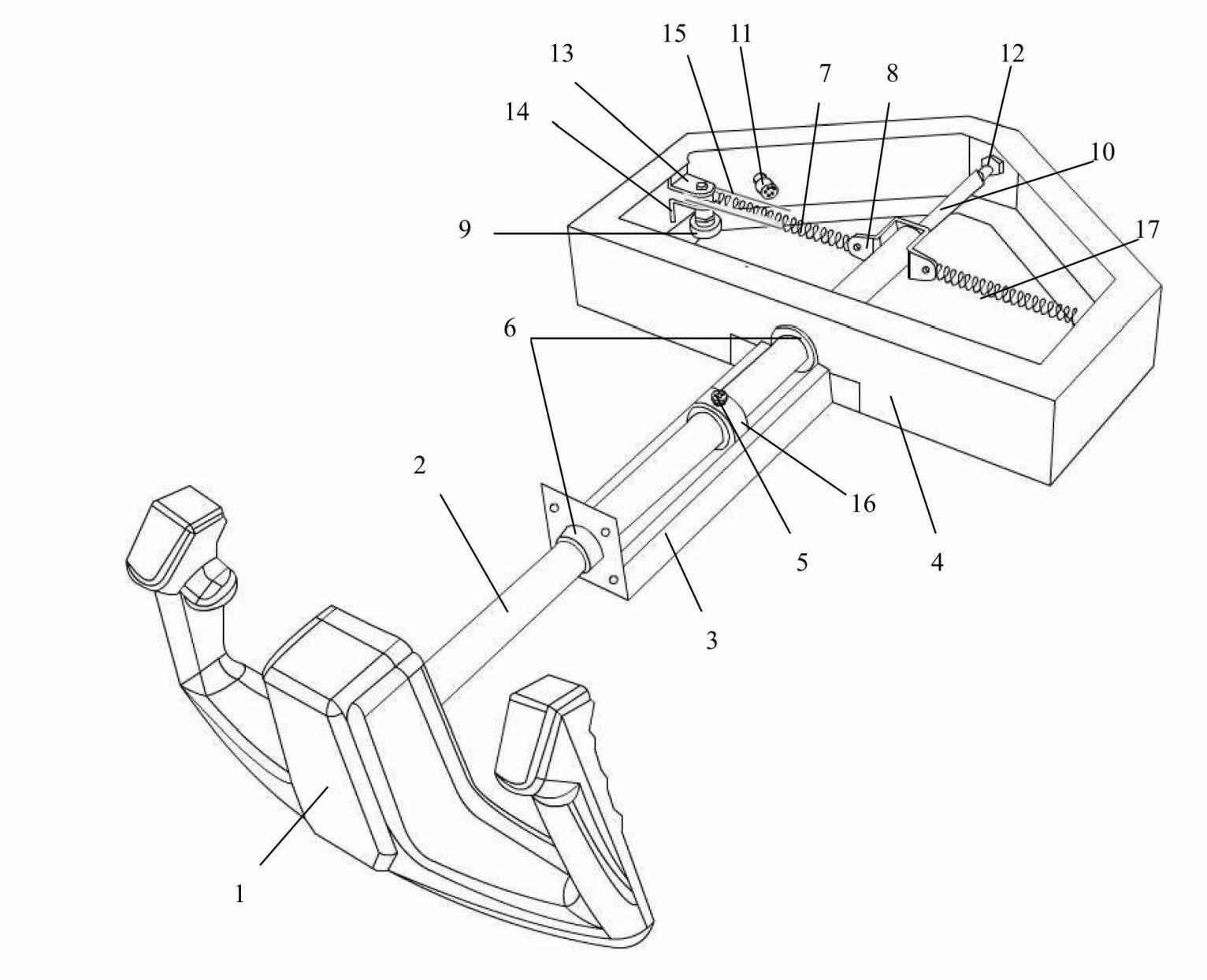
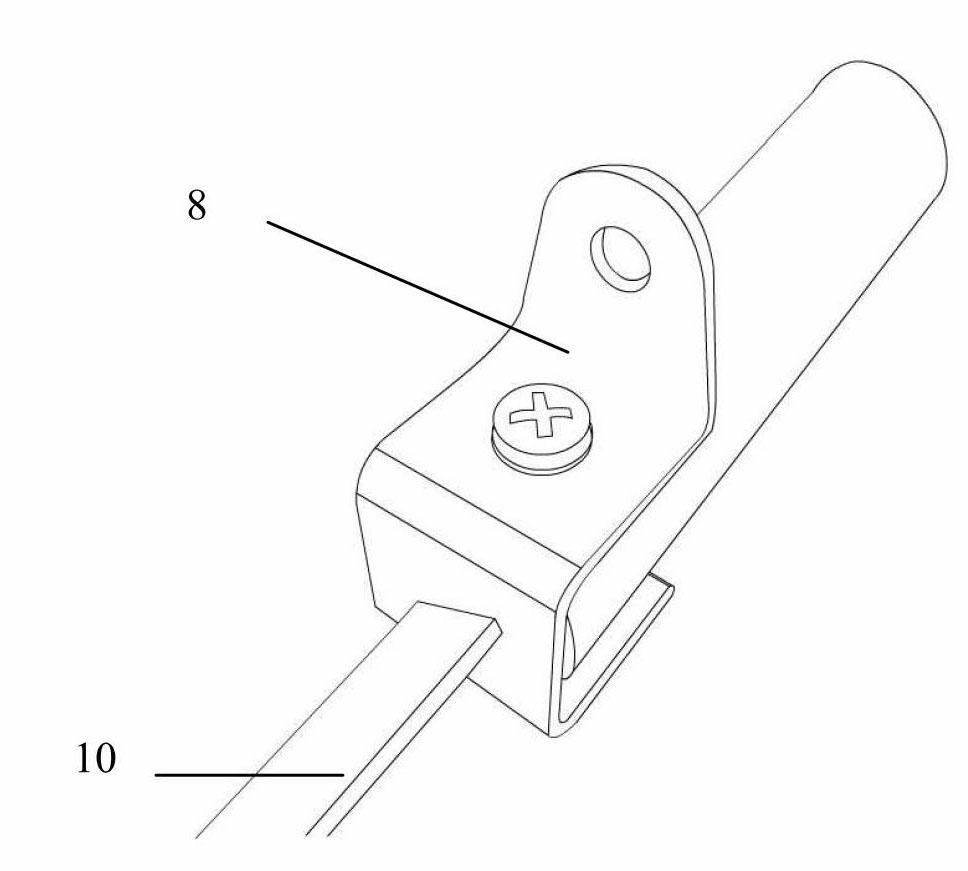
The invention relates to a simulation device for a steering wheel of an airplane flight simulator. The device mainly consists of a steering wheel surface, a transmission mechanism, angular displacement sensors, a mechanical structure, a serial bus (USB), an HID (Human Interface Device), and the like. By controlling the steering wheel to make longitudinal displacement and rotary displacement around a vertical shaft, the device controls the state of elevators and the state of ailerons of the flight simulator, thus controlling the flight attitude; and the device simulates the operating force of an airplane through a spring and the structural frictional force. The device has a simple structure and high simulation degree, and directly measures the displacement value of the steering wheel by adopting an aileron angular displacement sensor and an elevator angular displacement sensor, thus avoiding the error of mechanical transmission of indirect measurement and achieving high measurement accuracy. The device adopts a universal interface so that a driver does not need to be installed on a computer of a host machine, and the device can be applied to different types of flight simulators.
Owner:TIANJIN ZHONGTIAN XIANGYI AVIATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com