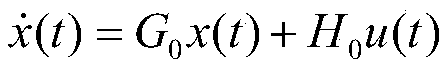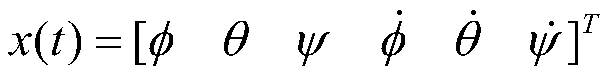Patents
Literature
84 results about "Steady flight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
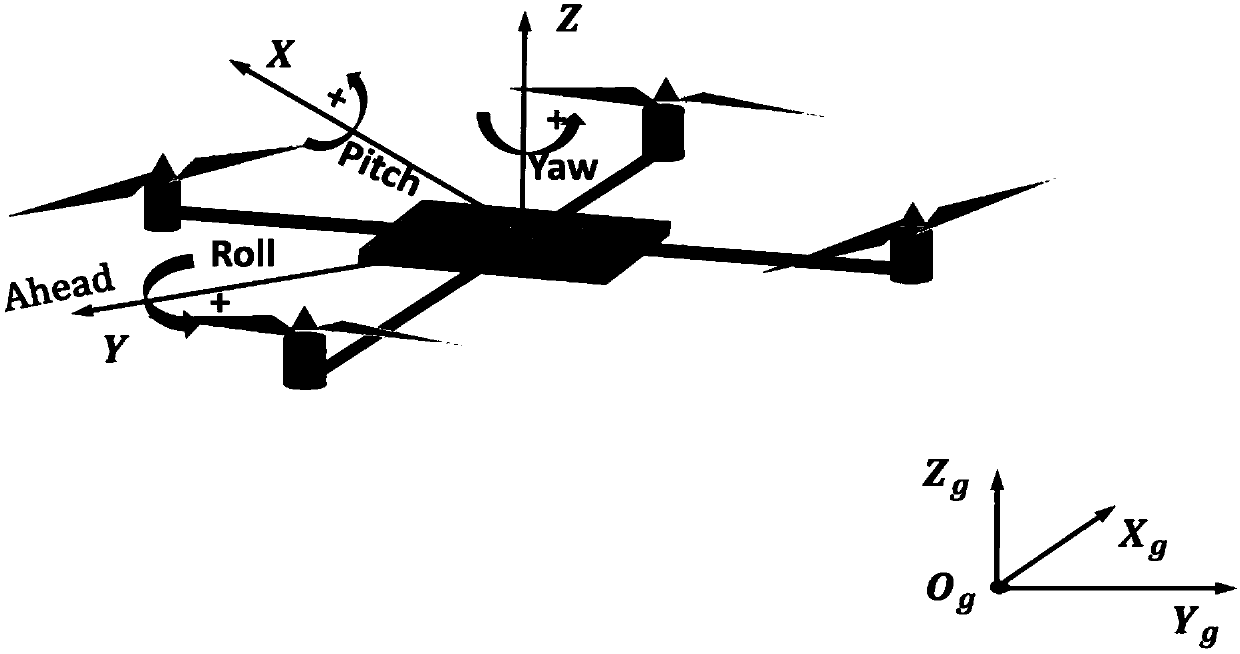
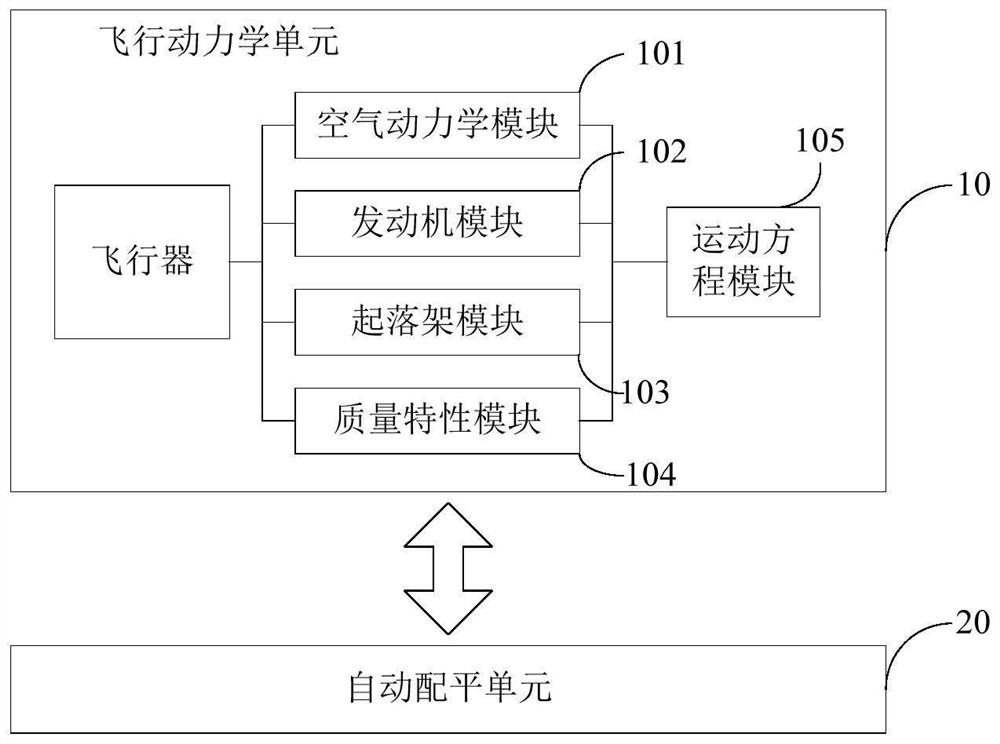
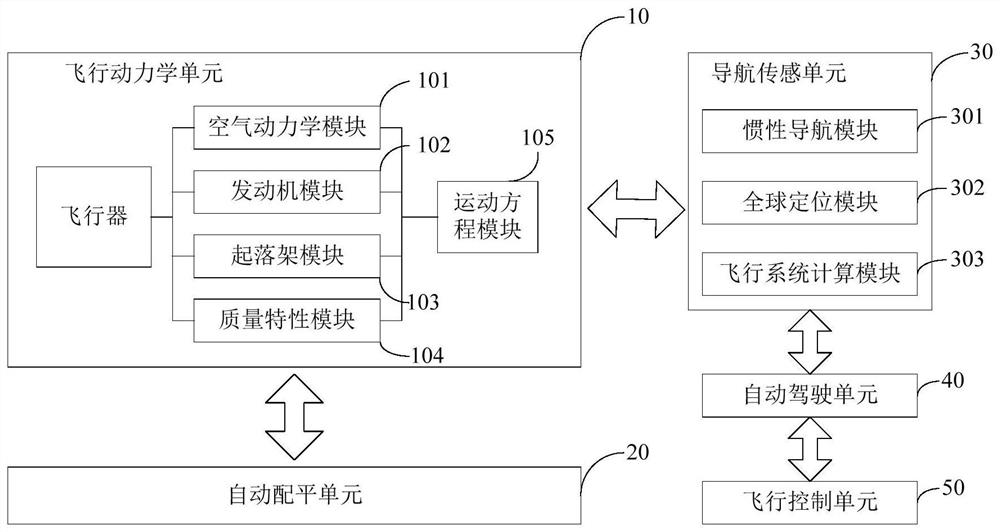
Steady flight, unaccelerated flight, or equilibrium flight is a special case in flight dynamics where the aircraft's linear and angular velocity are constant in a body-fixed reference frame. Basic aircraft maneuvers such as level flight, climbs and descents, and coordinated turns can be modeled as steady flight maneuvers. Typical aircraft flight consists of a series of steady flight maneuvers connected by brief, accelerated transitions. Because of this, primary applications of steady flight models include aircraft design, assessment of aircraft performance, flight planning, and using steady flight states as the equilibrium conditions around which flight dynamics equations are expanded.
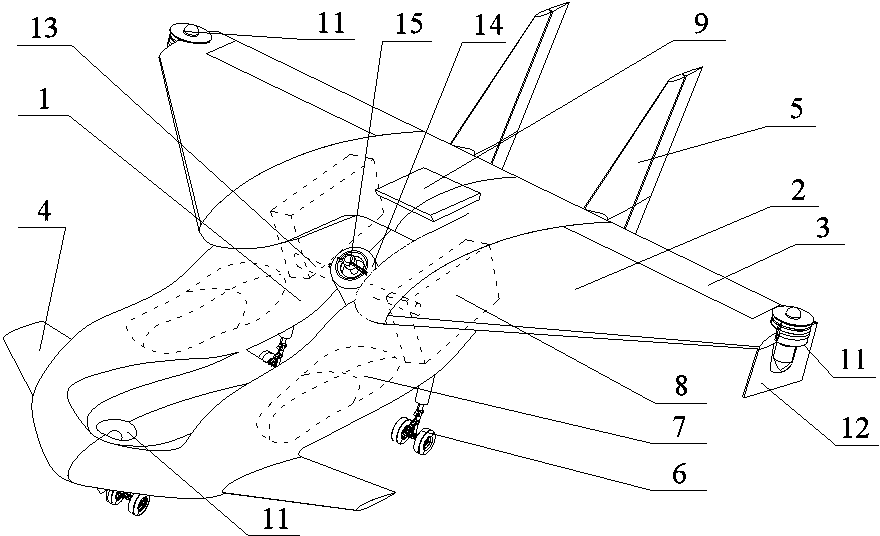
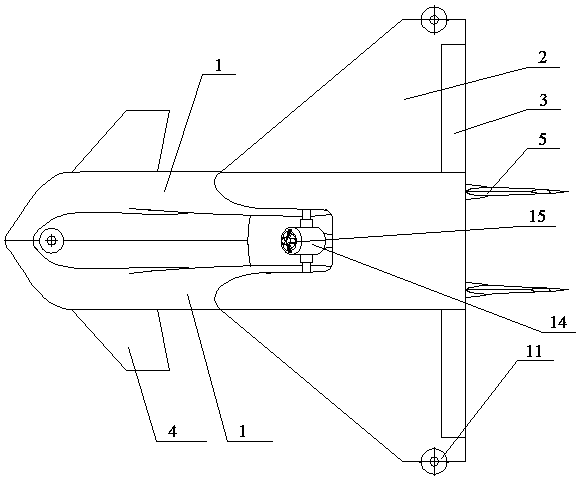
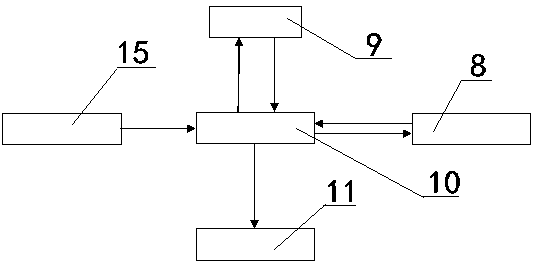
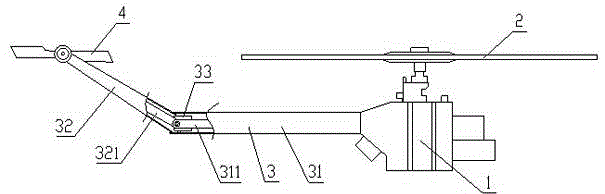
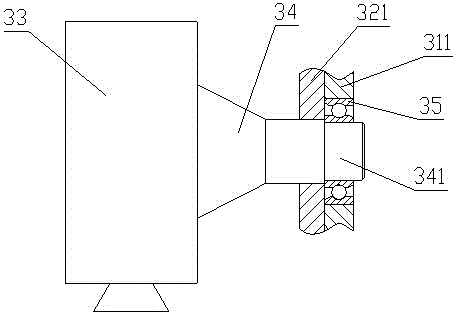
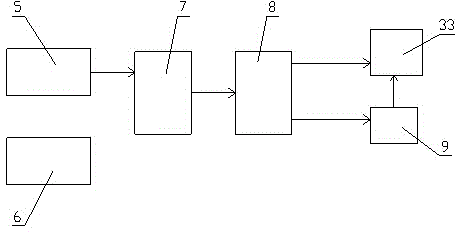
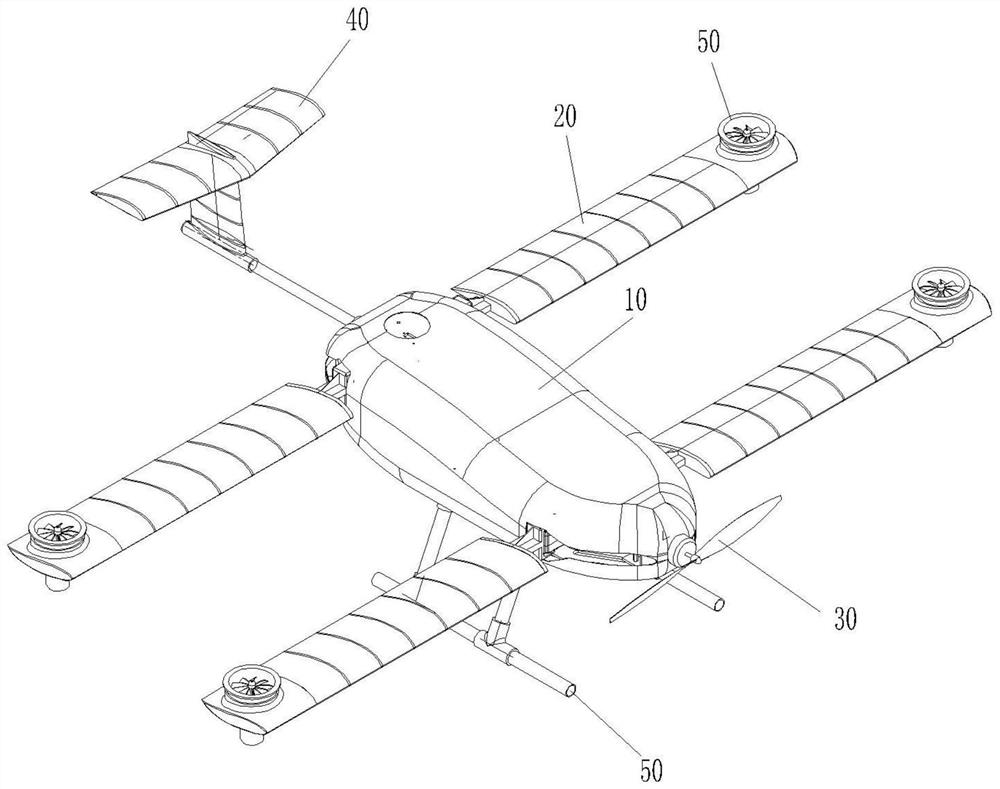
Novel hybrid vertical/short take-off and landing (V/STOL) unmanned aerial vehicle
The invention discloses a novel hybrid vertical / short take-off and landing (V / STOL) unmanned aerial vehicle, aiming at solving the problems of complicated structure, high cost and the like of the existing aerial vehicles. The unmanned aerial vehicle comprises a body, a main wing, take-off and landing auxiliary wings arranged on the main wing, canards arranged at the front part of the body, a vertical tail arranged at the rear part of the body, a landing gear, an accumulator battery, a control system, a power supply management system and the like, wherein the landing gear, the accumulator battery, the control system, the power supply management system and the like are arranged below the body. The unmanned aerial vehicle adopts a ducted fan to provide a lift and assist balance during vertical take off and landing, and adopts an engine to provide the main push force and to automatically generate electricity so as to effectively utilize oil-electricity complement, simultaneously the reasonable hybrid use of fuel oil and electric energy is achieved through the structure and aerodynamic configuration design of the aerial vehicle, thereby achieving vertical and short take-off and landing, reducing the control difficulty of the aerial vehicle and solving the problem of inconsistence between difficult control and short voyage of the existing V / STOL unmanned aerial vehicles; the novel hybrid vertical / short take-off and landing (V / STOL) unmanned aerial vehicle disclosed by the invention can achieve vertical / short take-off and landing, and has the advantages of flexible and steady flight, wide application range and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Position attitude control method of four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle with unbalance loads
InactiveCN108375988AImprove recognition accuracyPrecise Flight Status DataAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsDynamic modelsAttitude control
The invention relates to a position attitude control method of a four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle with unbalance loads, and belongs to the technical field of control of unmanned aerial vehicles, which aims at solving the problem of the unmanned aerial vehicle failing to continue to stably run due to unknown center of gravity and uncertainty in installation position in the process of loading unbalanced load. The position attitude control method comprises the following steps of firstly, deriving a kinematics model and a dynamics model before and after the unbalance load is loaded on the four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle by coordinate conversion and dynamics analysis; obtaining the measuring data of a sensor in the flight process, utilizing a Kalman filtering method to obtain the high-precision and non-lagging flight state, and distinguishing the approximate location of center of gravity by the flight states; designing a position attitude controller and a position controller of the four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle, and improving the controller by compensating the rotation speed of a propeller, so as to offset the additional rotary movement and linear movement due to location change of center of gravity. The position attitude control method is suitable for estimating the location of the center of gravity in the takeoff and hovering process of the four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle, and establishing a compensation controller.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Aircraft control method and device
ActiveCN104536453AControl precise controlStable controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsNegative feedbackClosed loop
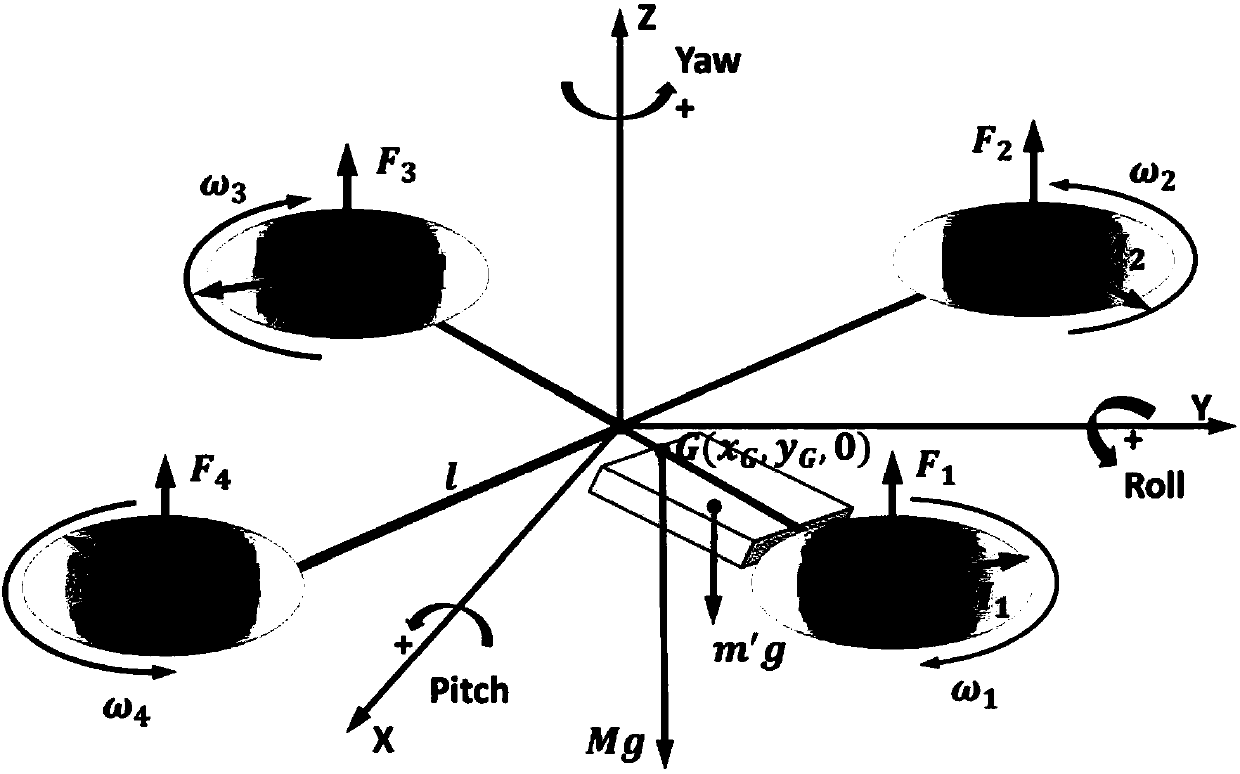
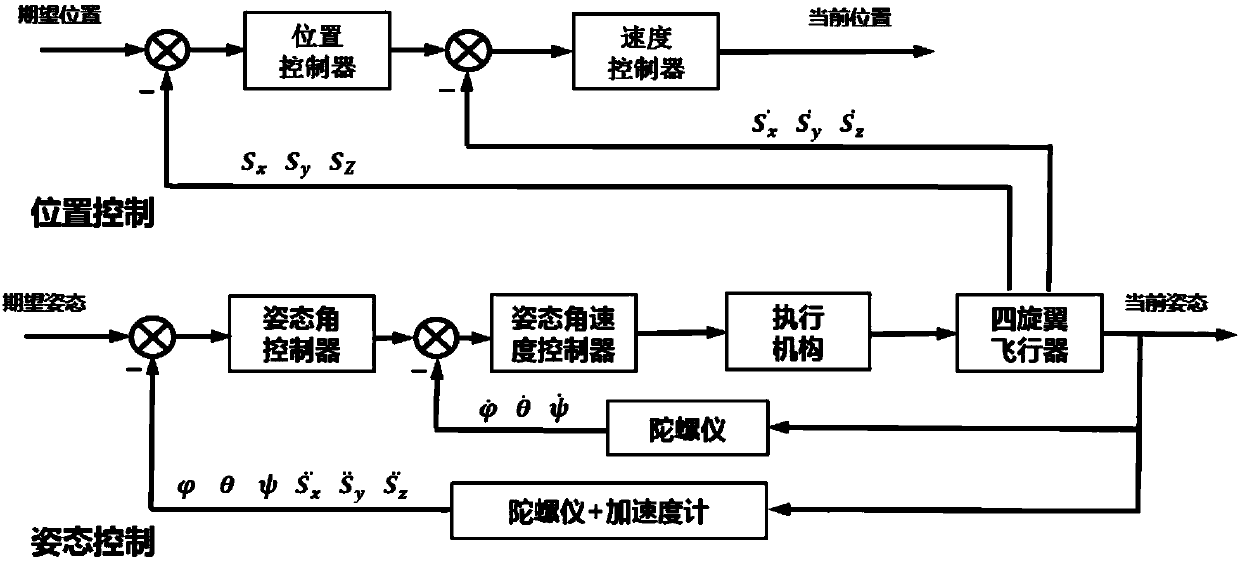
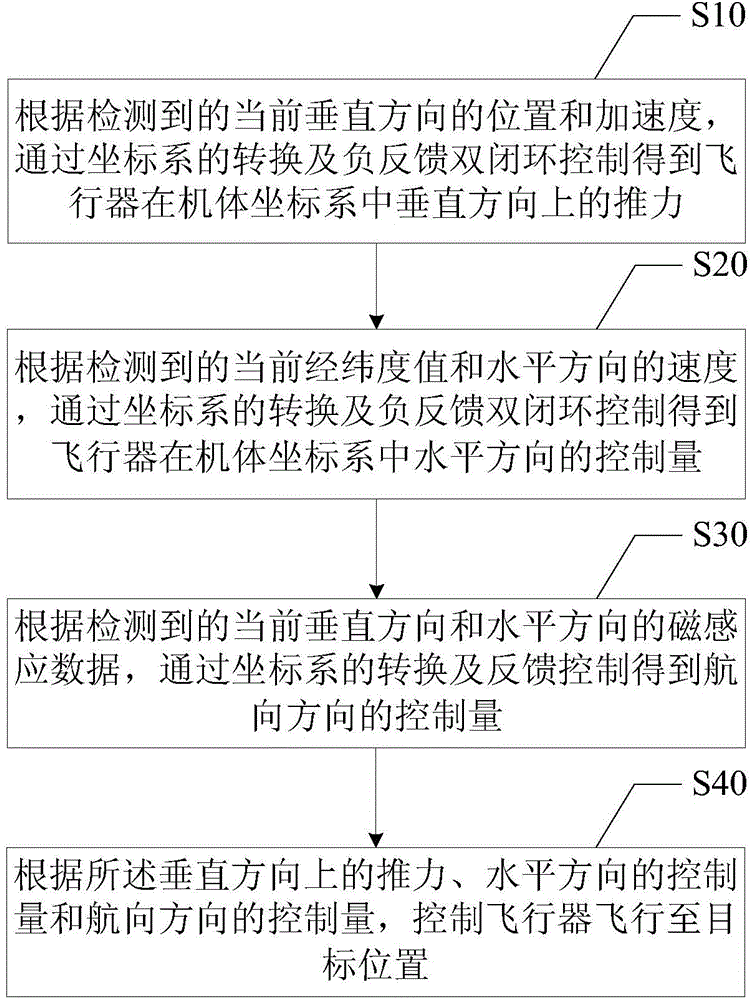
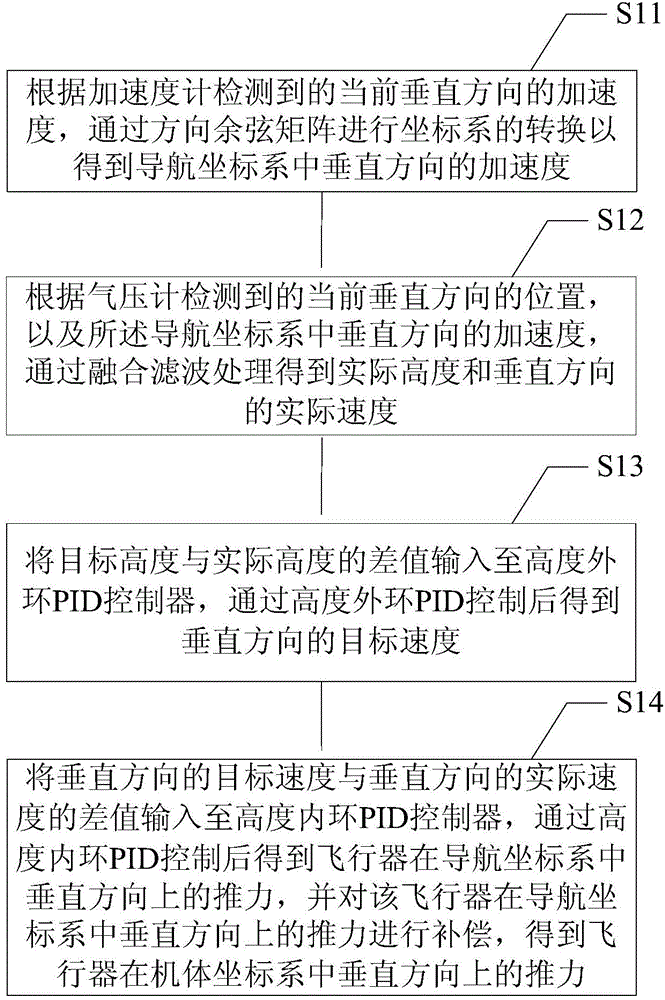
The invention discloses an aircraft control method comprising the following steps: obtaining the vertical thrust of an aircraft in an aircraft body coordinate system through coordinate system transformation and negative feedback double closed loop control according to detected current vertical position and acceleration; obtaining the horizontal controlled quantity of the aircraft in the aircraft body coordinate system through coordinate system transformation and negative feedback double closed loop control according to detected current latitude and longitude values and horizontal acceleration; obtaining the controlled quantity in the heading direction through coordinate system transformation and negative feedback double closed loop control according to detected current vertical and horizontal magnetic induction data; and controlling the aircraft to fly to a target position according to the vertical thrust, the horizontal controlled quantity and the controlled quantity in the heading direction. Aircraft control in the vertical, horizontal and heading directions can be realized, so that an aircraft can be controlled accurately to fly at a set height, and stable flight of an aircraft under complex conditions is ensured.
Owner:SICHUAN AEE AVIATION TECH CO LTD
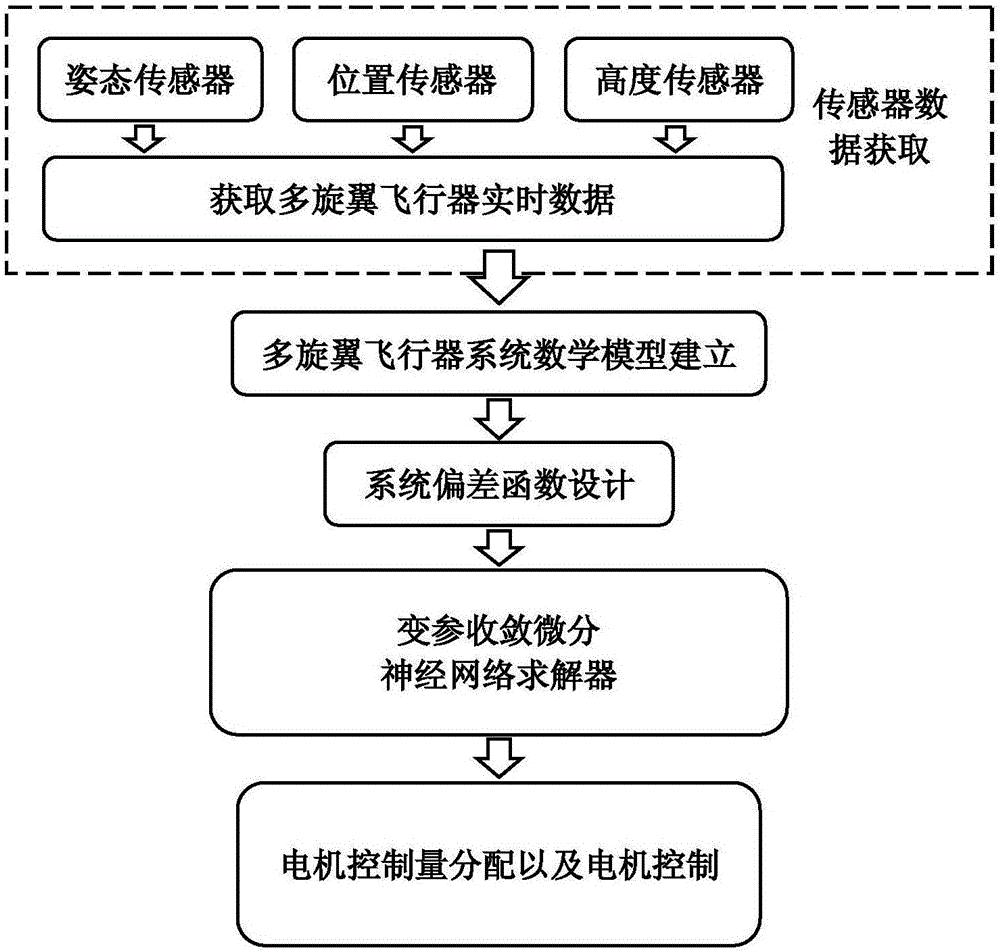
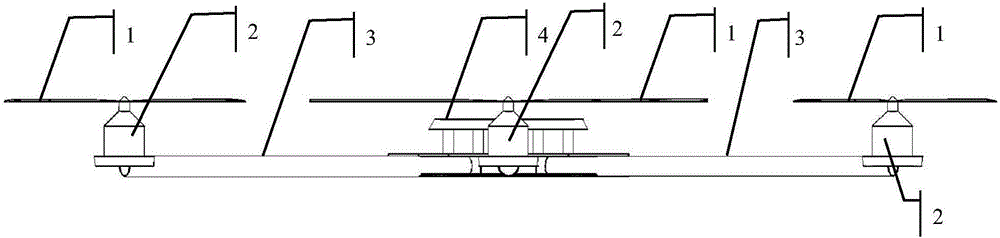
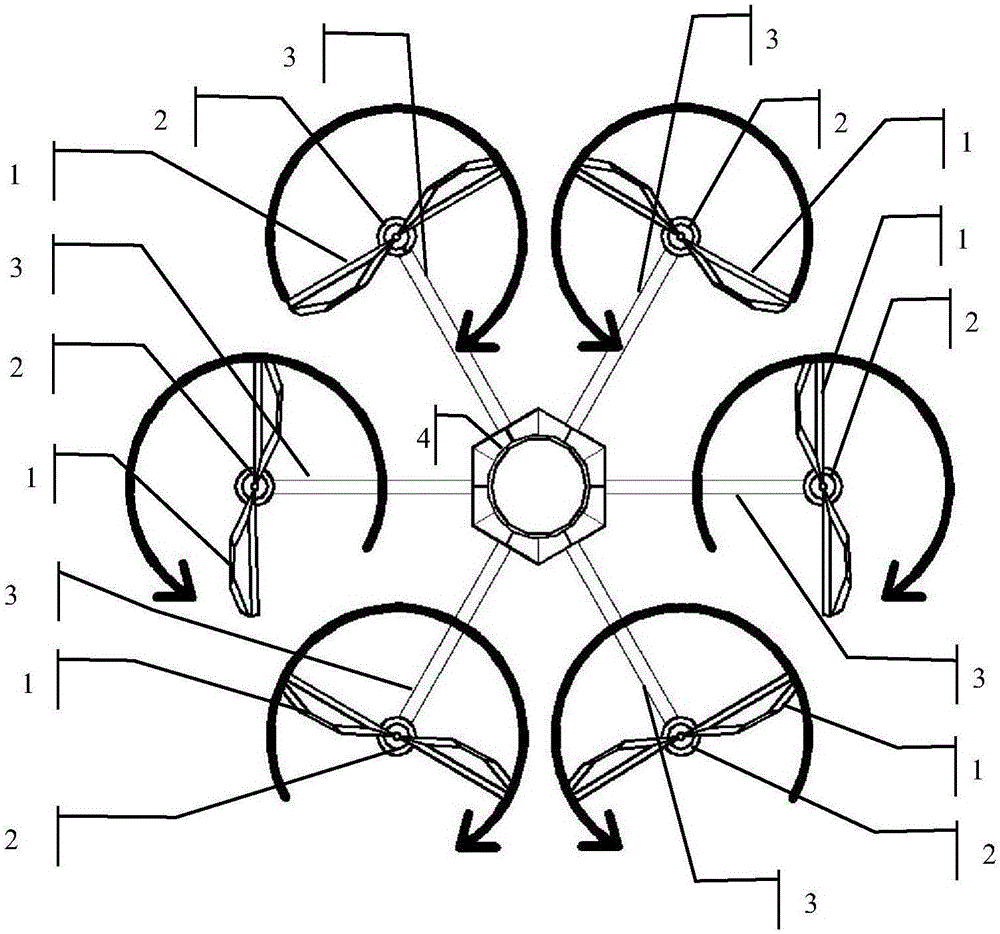
Steady flight control method of multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle
The invention provides a steady flight control method of a multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle. The method comprises the following steps: 1), obtaining flight real-time operation data of the aerial vehicle through an airborne sensor, performing corresponding analytical processing on kinematic problems of the aerial vehicle through an airborne processor, and establishing an aerial vehicle dynamical model; 2), designing a variable parameter convergence differential neural network solver of the multi-rotor aerial vehicle dynamical model according to a variable parameter convergence differential neural dynamical design method; 3), solving the output control variable of an aerial vehicle motor through the variable parameter convergence differential neural network solver by utilizing obtained flight real-time operation data and target attitude data of the aerial vehicle; 4), transmitting solving results of the third step to an aerial vehicle motor speed regulator to control the motion of the unmanned aerial vehicle. The method is based on the variable parameter convergence differential neural dynamical method, can rapidly and accurately approach the correct resolution of the problems in real time, and can properly solve various time dependent problems, such as matrixes, vectors, algebra and optimization.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
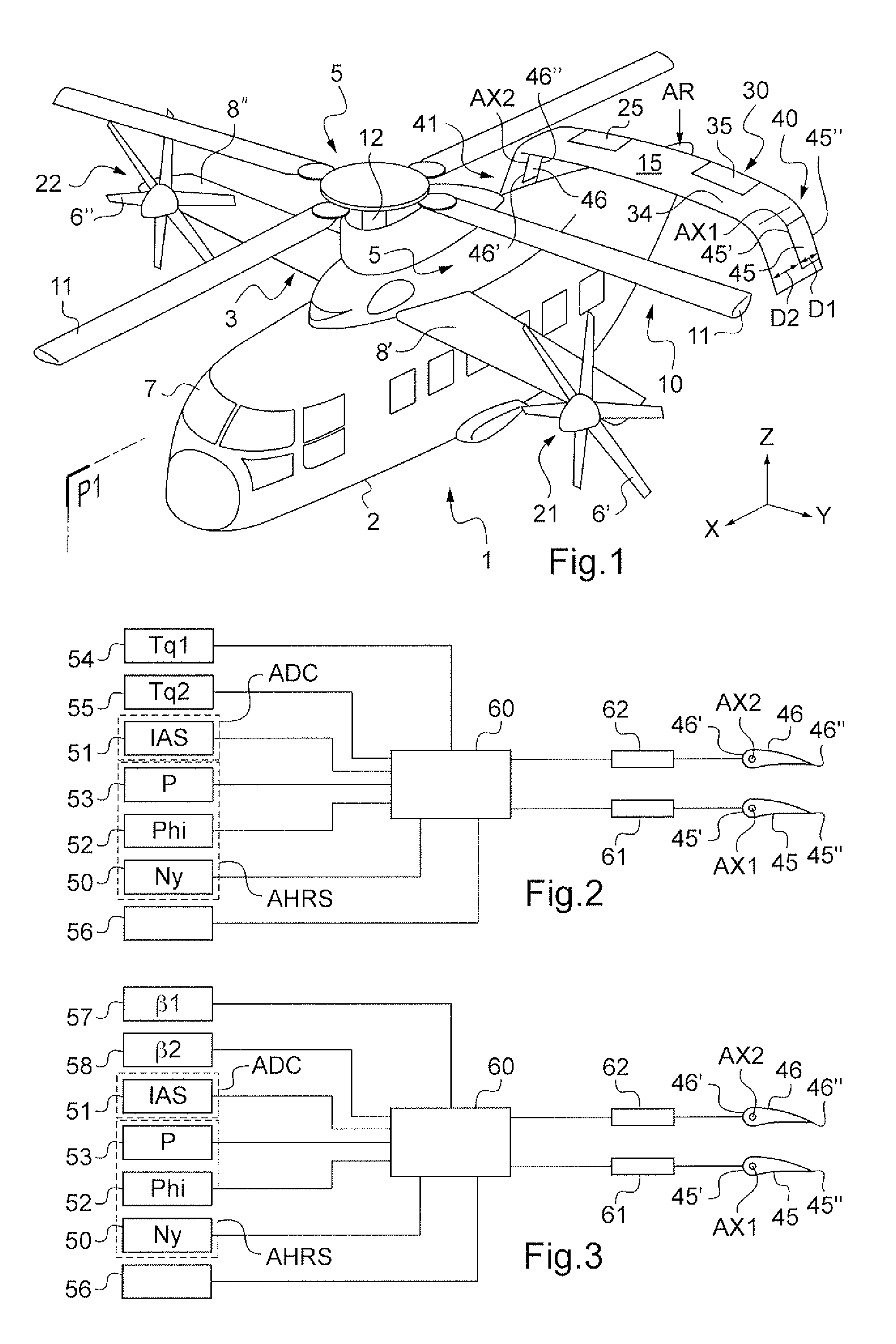
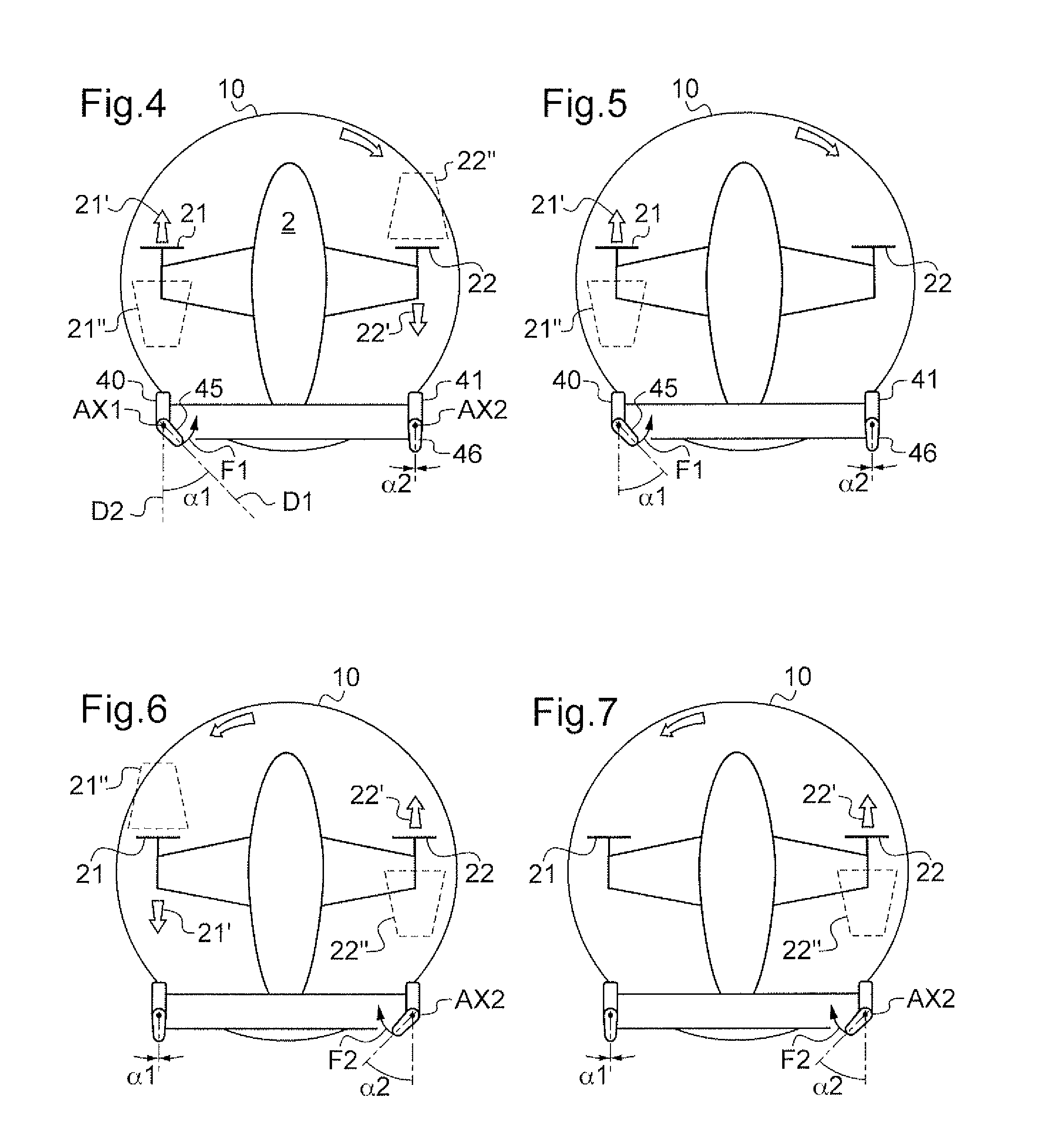
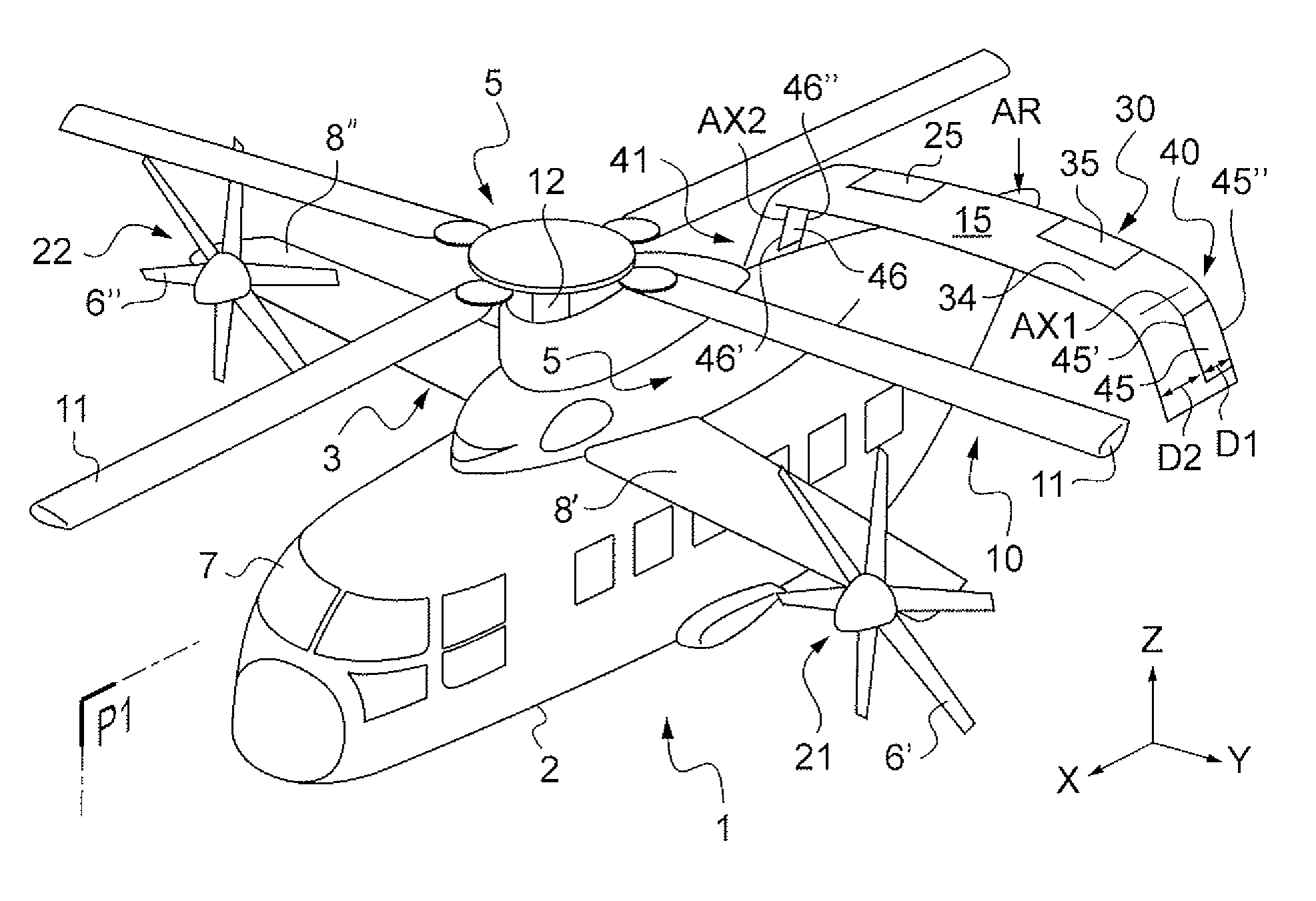
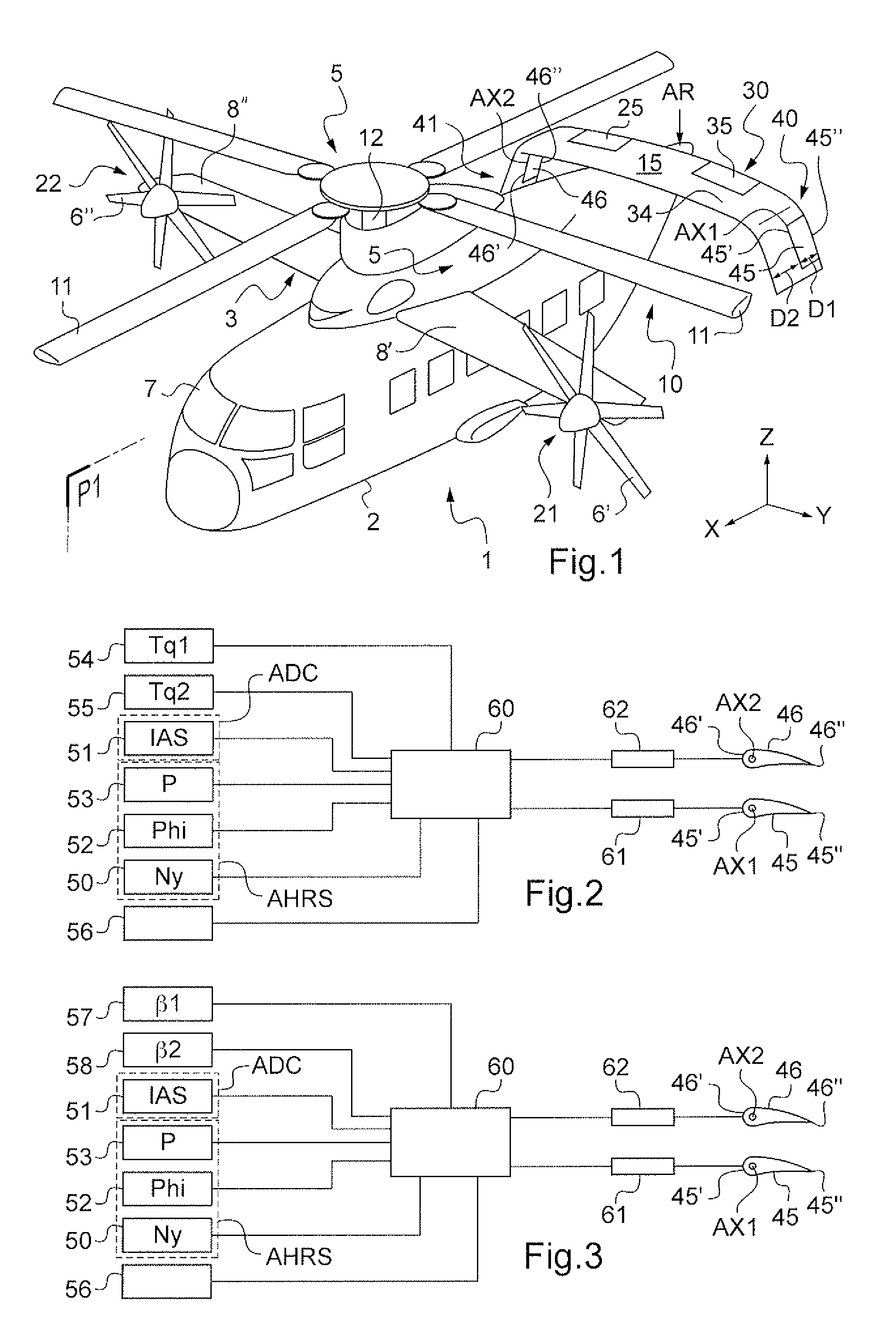
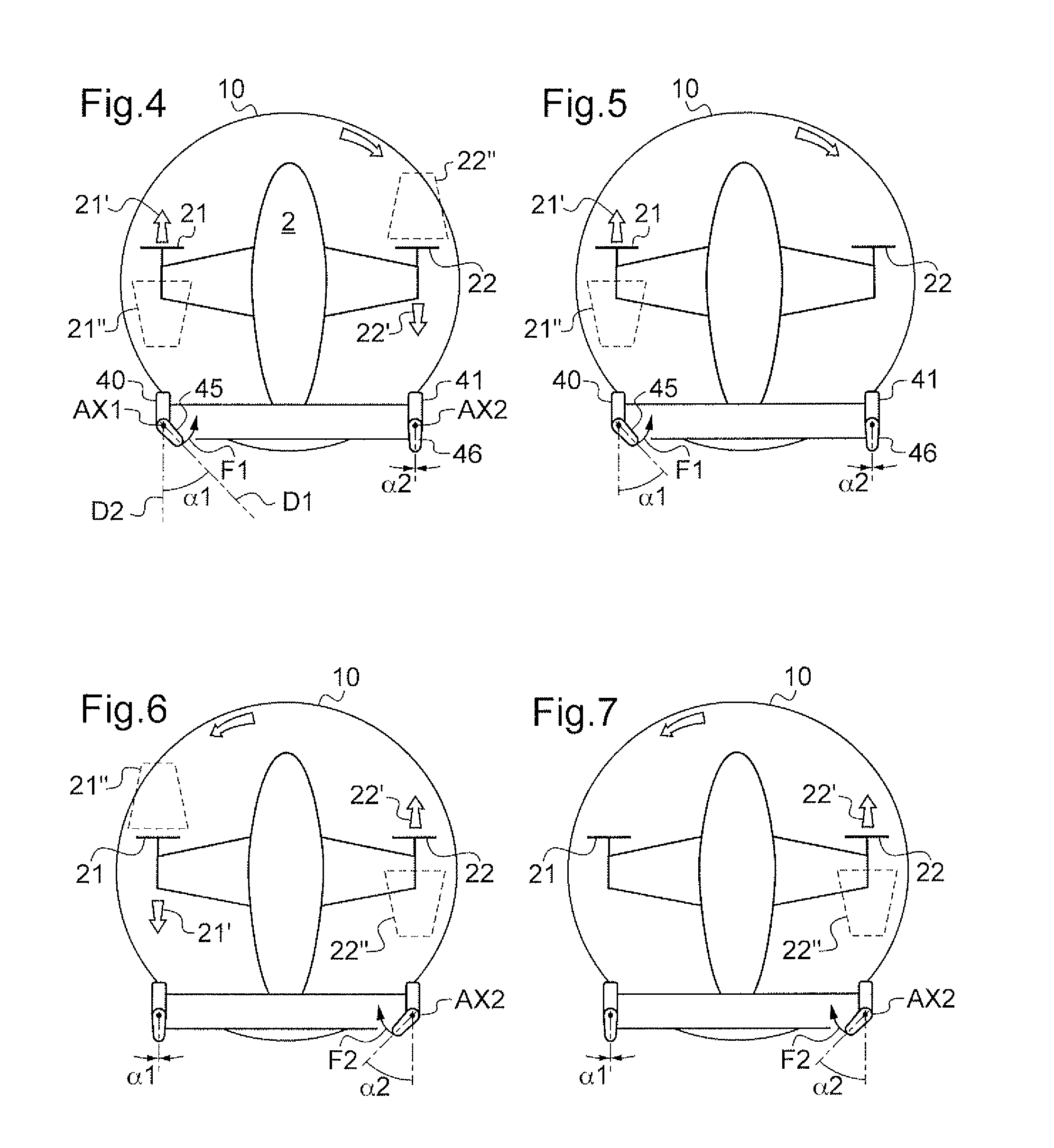
Method and a device for optimizing the operation of propulsive propellers disposed on either side of a rotorcraft fuselage
A method of optimizing the operation of left and right propellers disposed on either side of the fuselage of a rotorcraft including a main rotor. Left and right aerodynamic surfaces include respective left and right flaps suitable for being deflected, yaw stabilization of the rotorcraft being achieved via first and second pitches respectively of the left and right propellers, and the deflection angles of the left and right flaps are adjusted solely during predetermined stages of flight in order to minimize a differential pitch of the left and right propellers so as to optimize the operation of the left and right propellers, the predetermined stages of flight including stages of flight at low speed performed at an indicated air speed (IAS) of the rotorcraft that is below a predetermined threshold, and stages of yaw-stabilized flight at high speed performed at an indicated air speed of the rotorcraft greater than the predetermined threshold.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Method and a device for optimizing the operation of propulsive propellers disposed on either side of a rotorcraft fuselage
A method of optimizing the operation of left and right propellers disposed on either side of the fuselage of a rotorcraft including a main rotor. Left and right aerodynamic surfaces include respective left and right flaps suitable for being deflected, yaw stabilization of the rotorcraft being achieved via first and second pitches respectively of the left and right propellers, and the deflection angles of the left and right flaps are adjusted solely during predetermined stages of flight in order to minimize a differential pitch of the left and right propellers so as to optimize the operation of the left and right propellers, the predetermined stages of flight including stages of flight at low speed performed at an indicated air speed (IAS) of the rotorcraft that is below a predetermined threshold, and stages of yaw-stabilized flight at high speed performed at an indicated air speed of the rotorcraft greater than the predetermined threshold.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
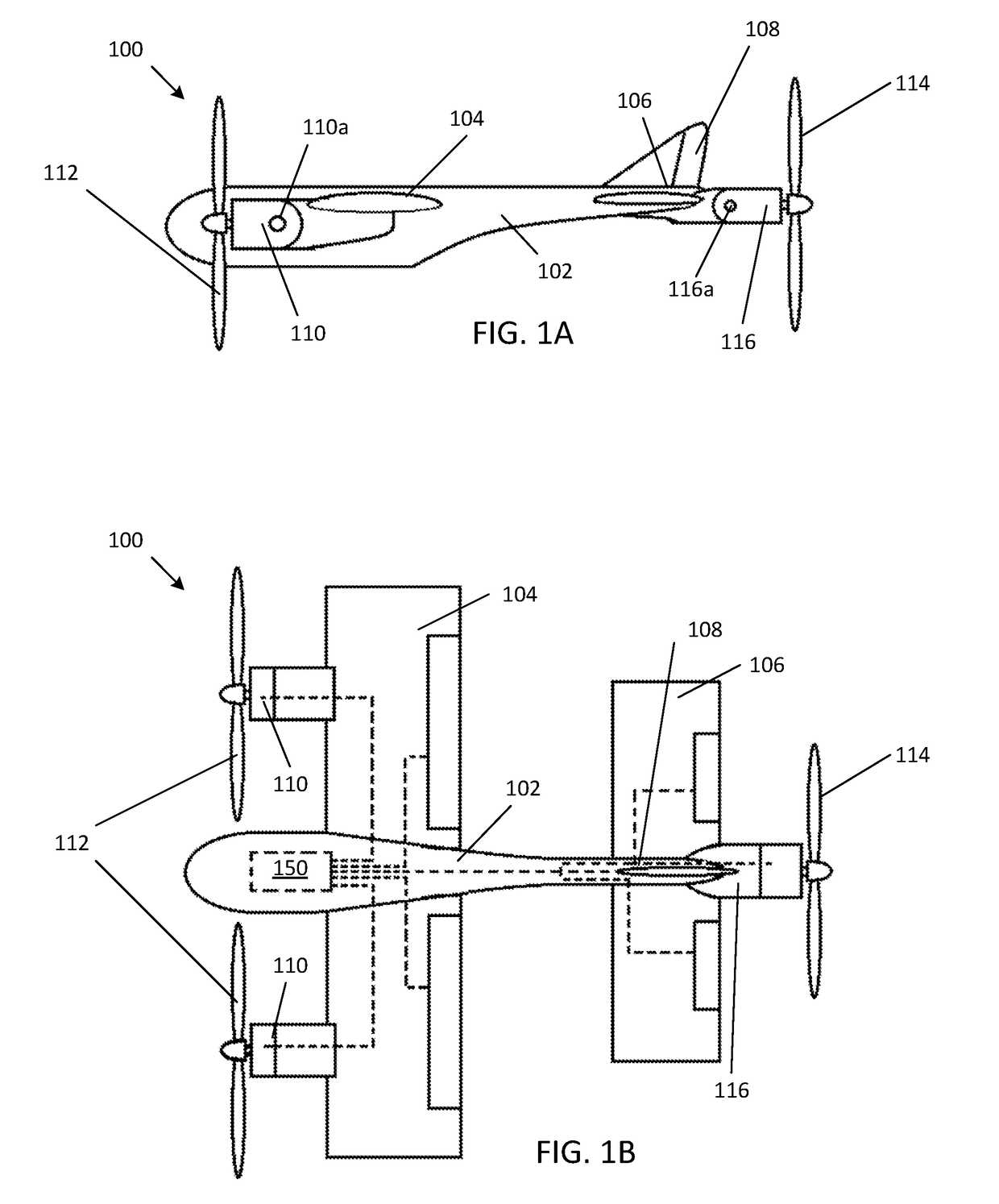
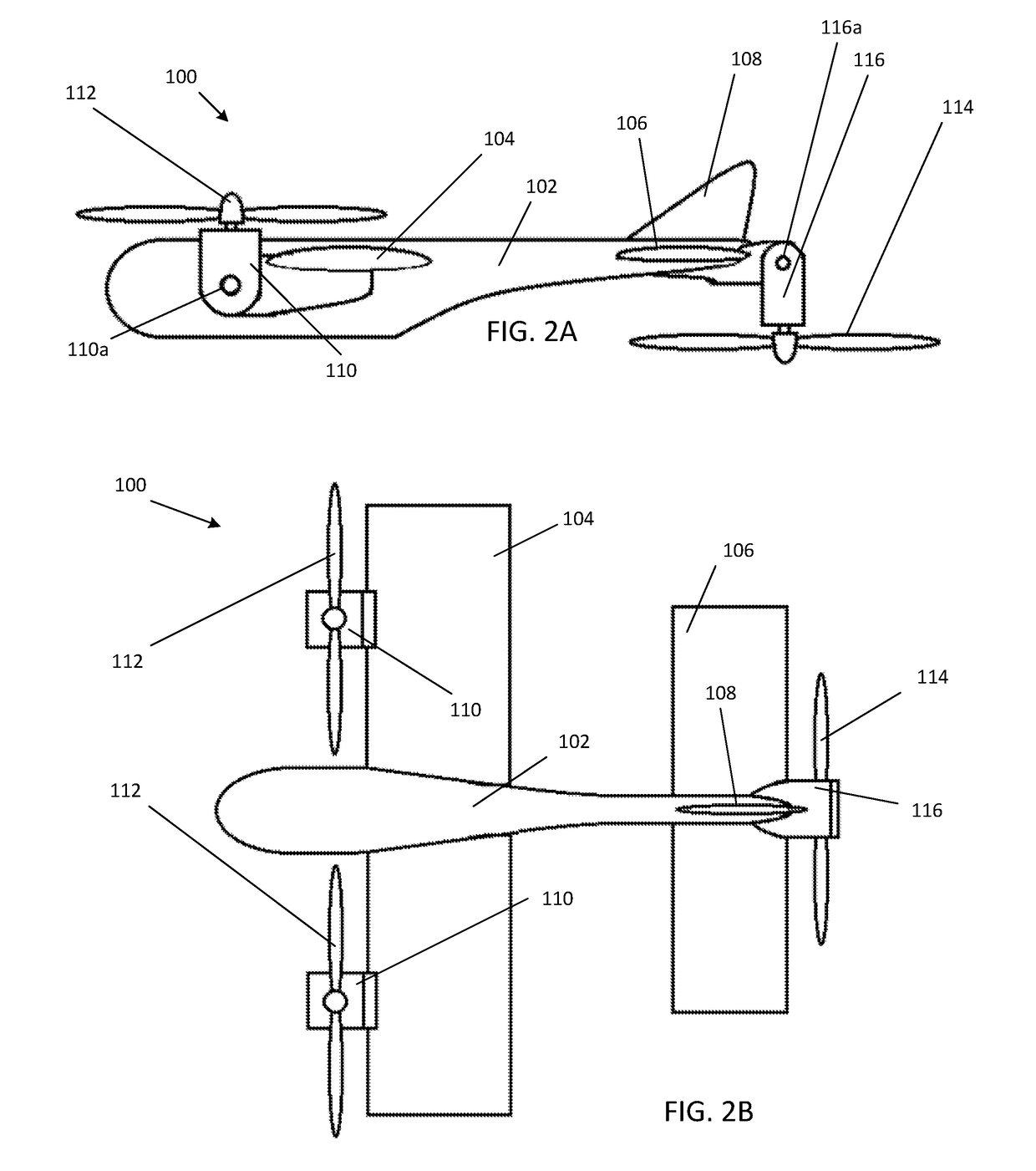
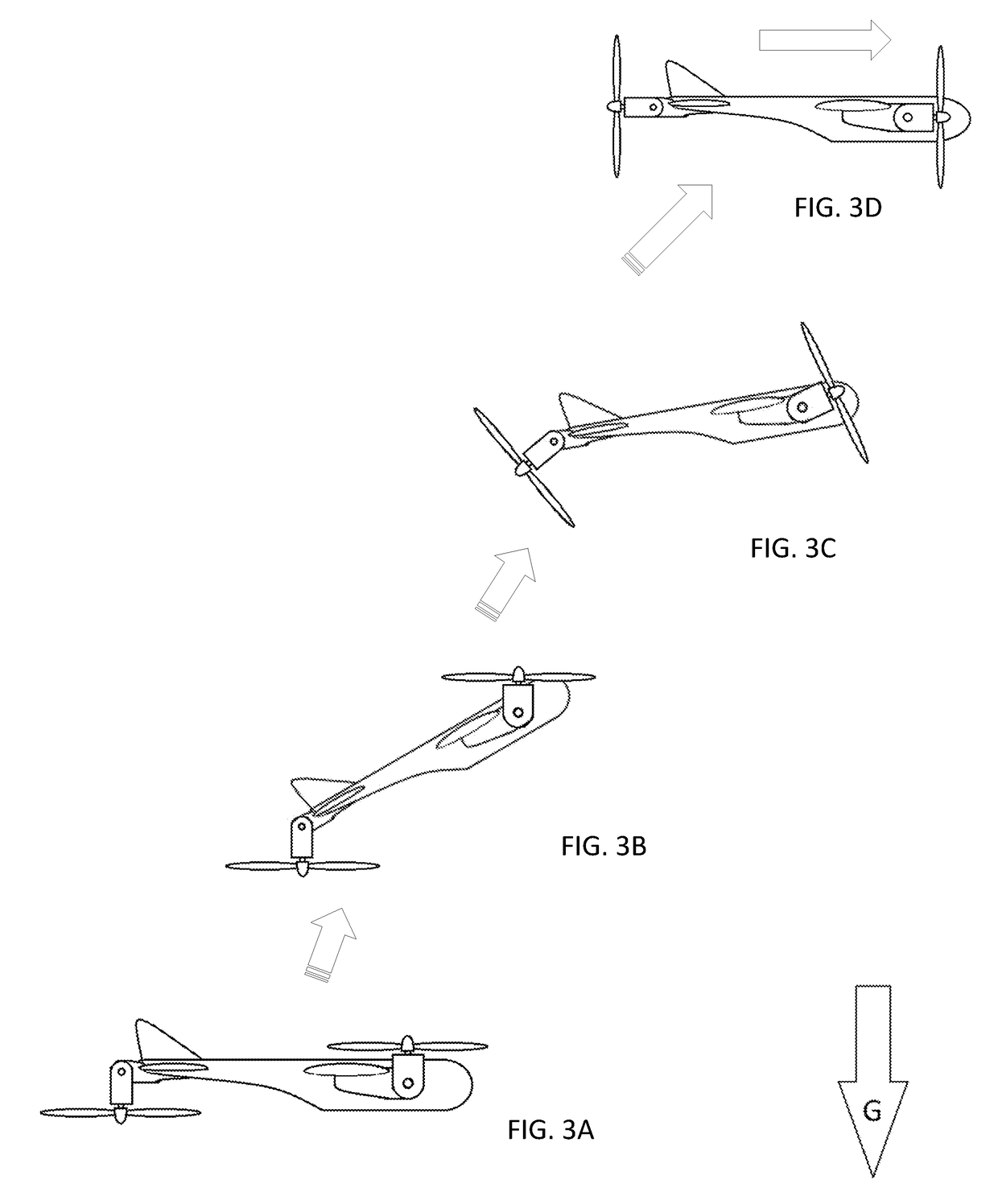
Vertical take off and landing (VTOL) aircraft with vectored thrust having continuously variable pitch attitude in hover
ActiveUS20190061936A1Constant altitudeContinuous regulationPropellersVertical landing/take-off aircraftsFlight vehicleSteady flight
The presently disclosed embodiments relate to vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft that have the capability of hovering in both a “nose forward” and a “nose up” orientation, and any orientation between those two. The disclosed aircraft can also transition into wing born (non-hovering) flight from any of the hovering orientations. In addition, certain of the disclosed embodiments can, if desired, use only vectored thrust control to maintain stable flight in both hover and forward flight. No control surfaces (e.g. ailerons, elevators, rudders, flaps) are required to maintain a stable vehicle attitude. However, the disclosure contemplates aircraft both with and without such control surfaces.
Owner:NASA
Power planning method for flight control of small unmanned helicopter
ActiveCN107272408AReduce total power demandReduce consumptionAdaptive controlControl engineeringSteady flight
The invention discloses a power planning method for flight control of a small unmanned helicopter. In the power planning method, on the premise of keeping the stable flight state of the small unmanned helicopter unchanged, the total demand power is analyzed and optimized; through optimizing match between a rotor rotation speed and a manipulated variable, the total demand power is minimized, and the corresponding best engine rotation speed under the minimum demand power is obtained; an engine constant speed controller is designed to track the best rotation speed under the corresponding stable flight in real time, the engine thus constantly works at the best working point under the current stable state, the mobility of the helicopter is ensured, the flight duration time is increased, fuel oil consumption is reduced, and the target for power planning of the engine is achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Methods of optimizing the location of an aircraft on the ground and in the take-off and landing phases
ActiveUS20090201197A1Easy to calculateAnalogue computers for vehiclesBeacon systemsSteady flightPositioning system
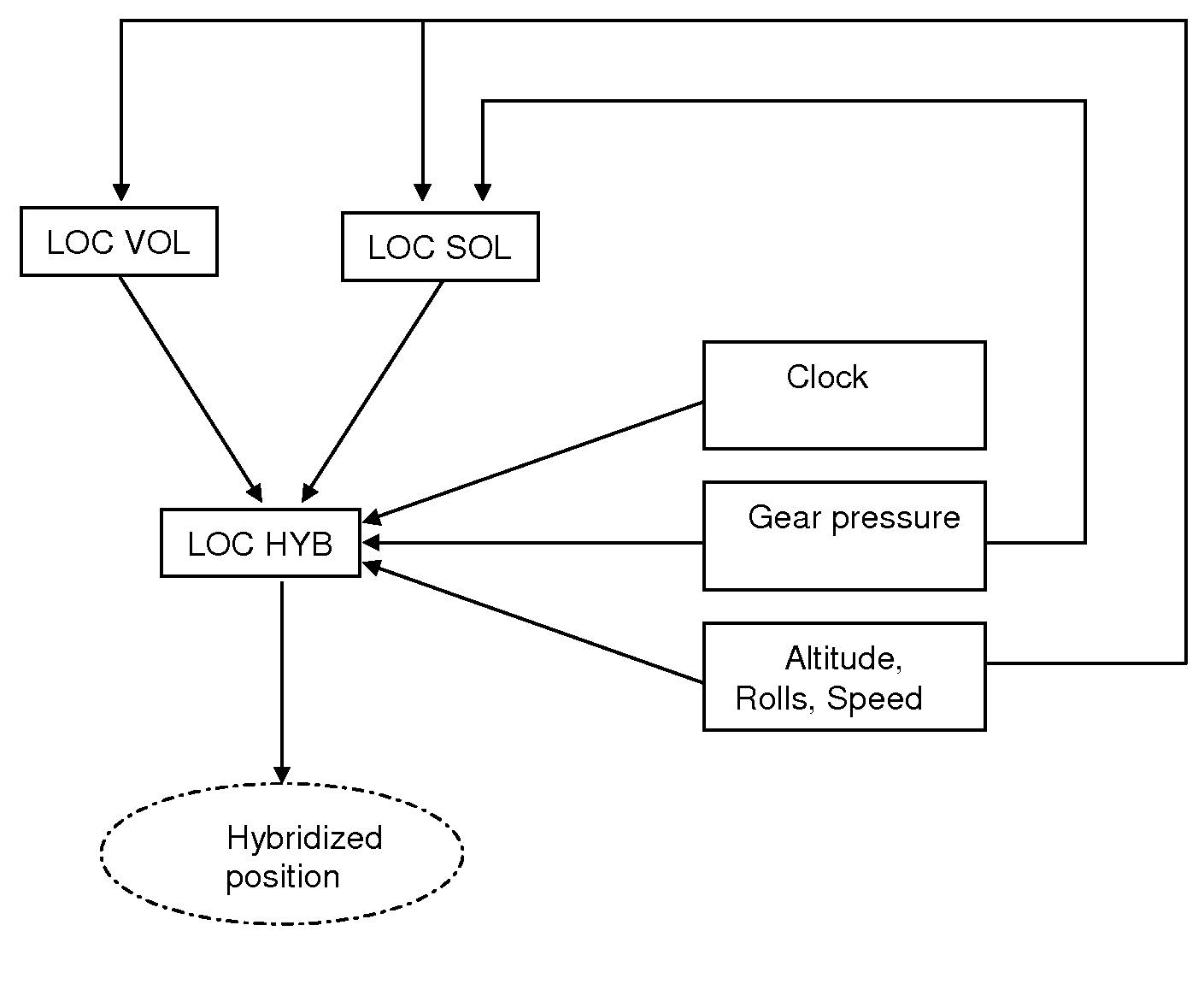
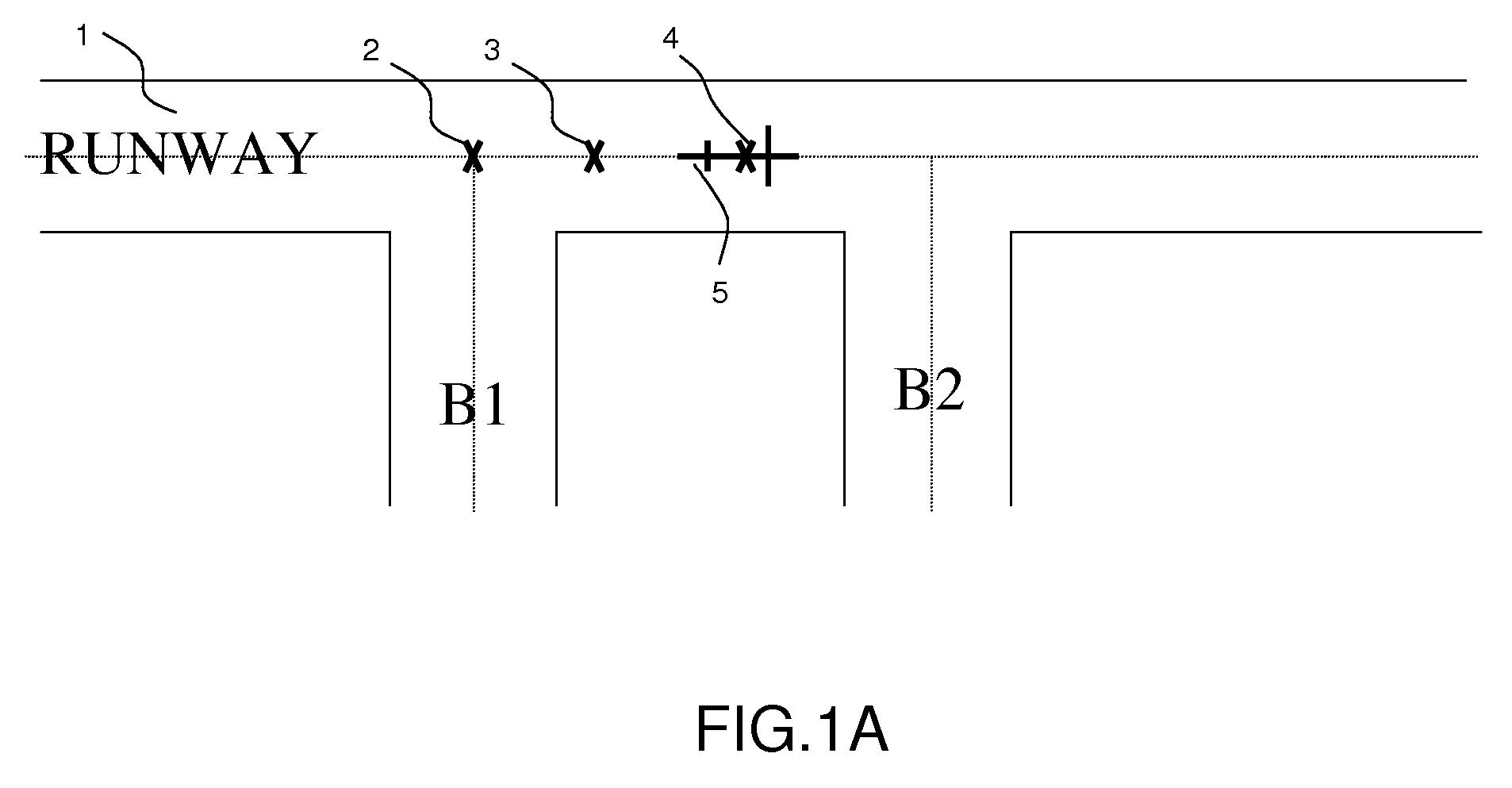
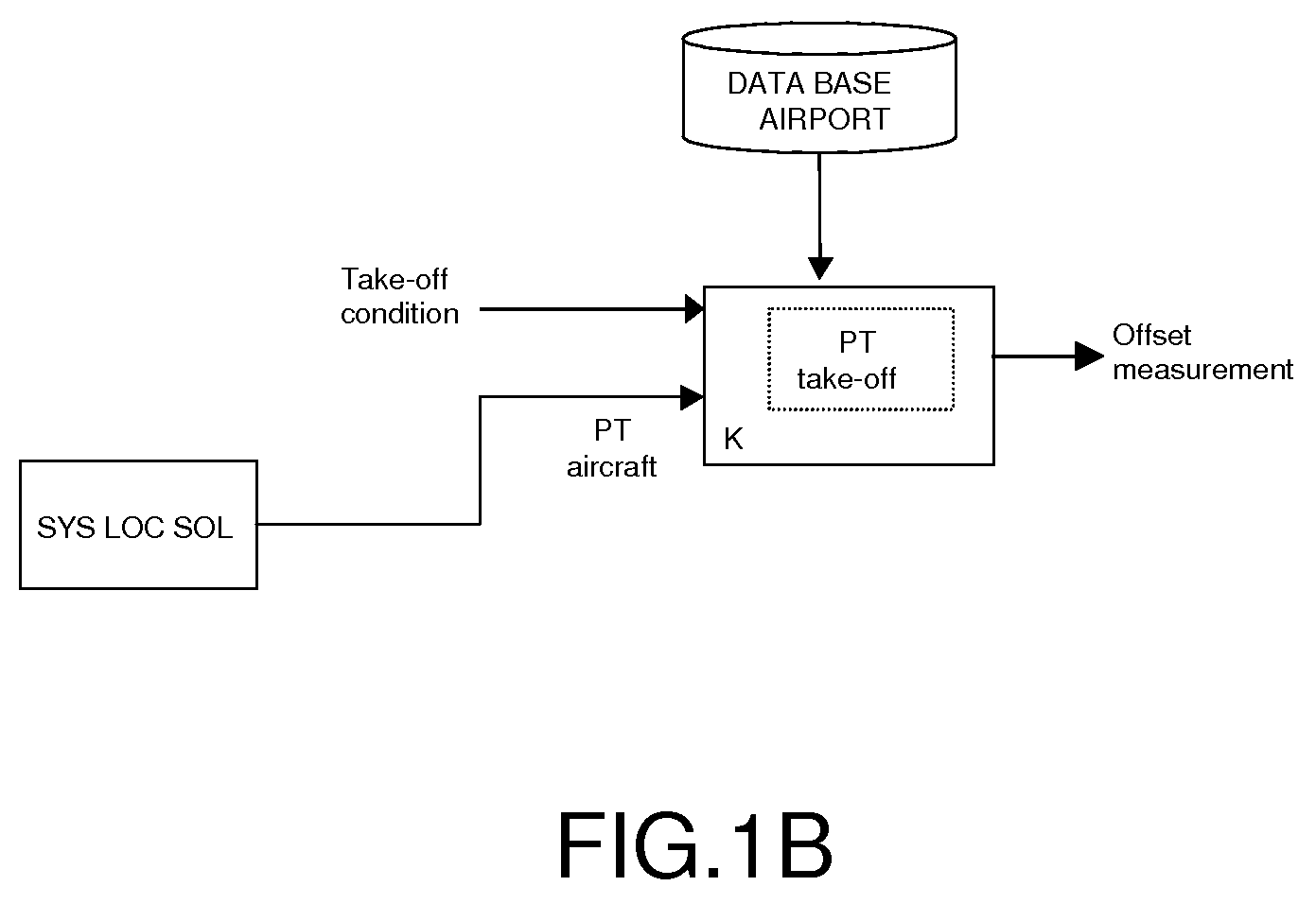
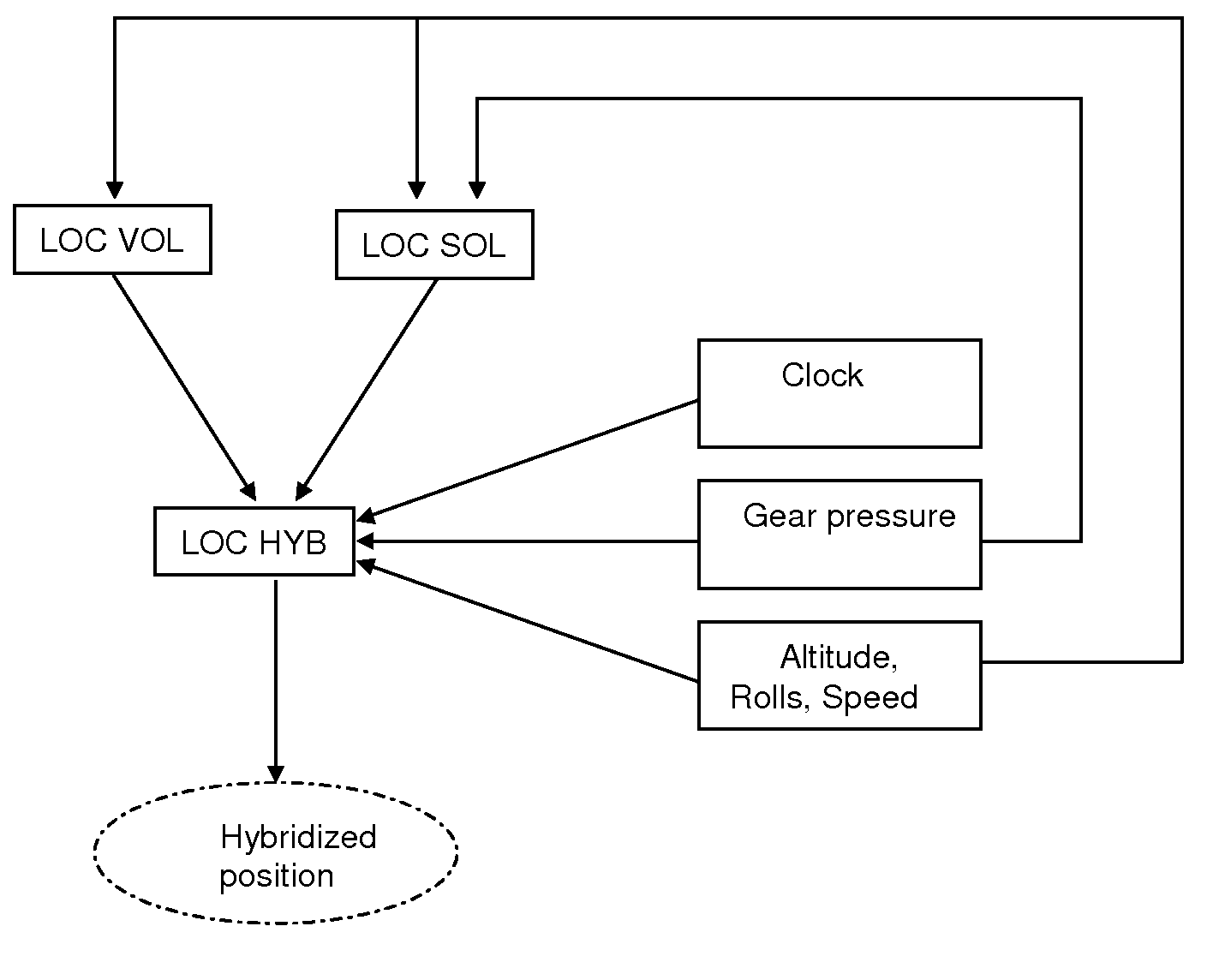
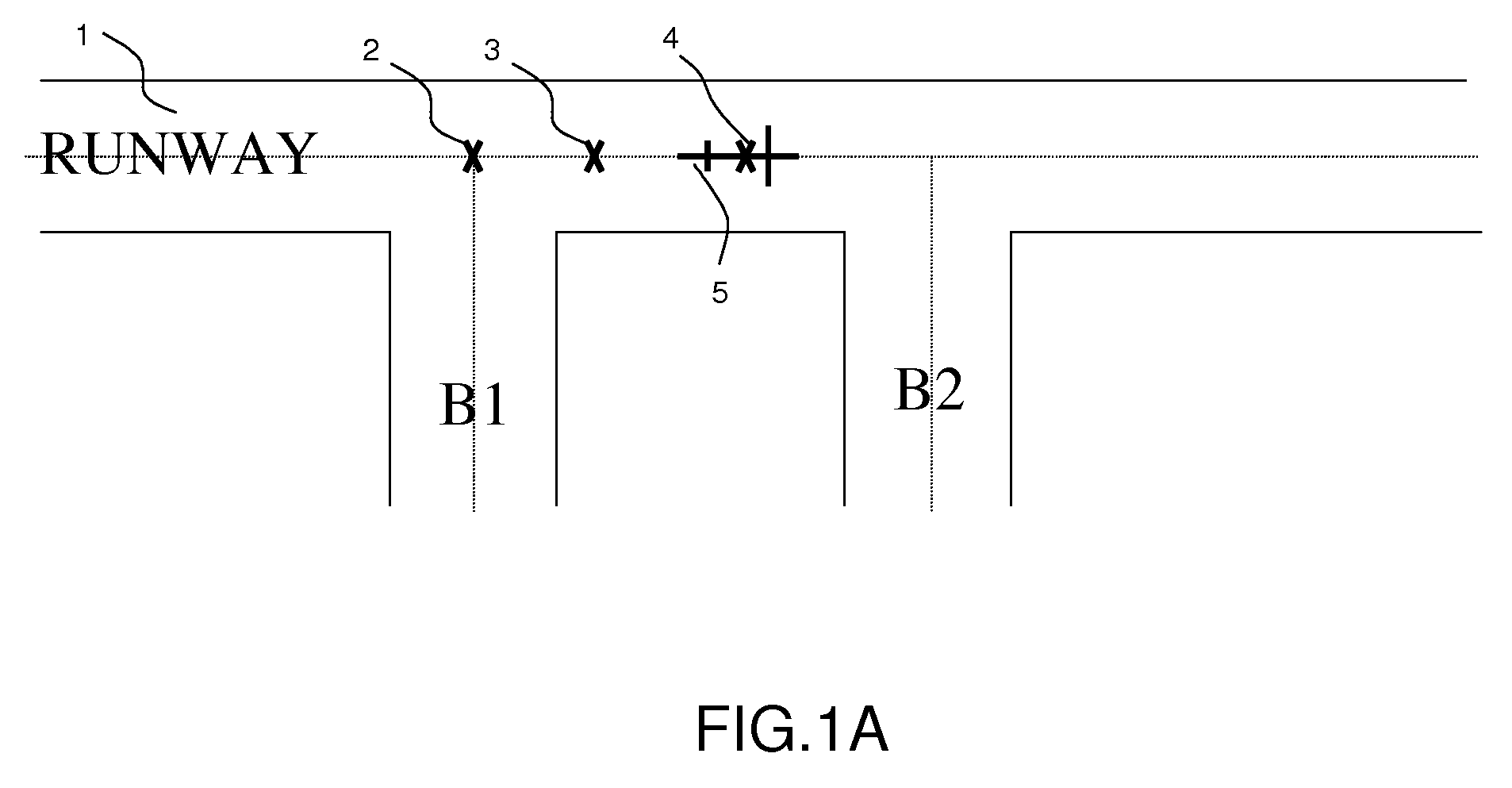
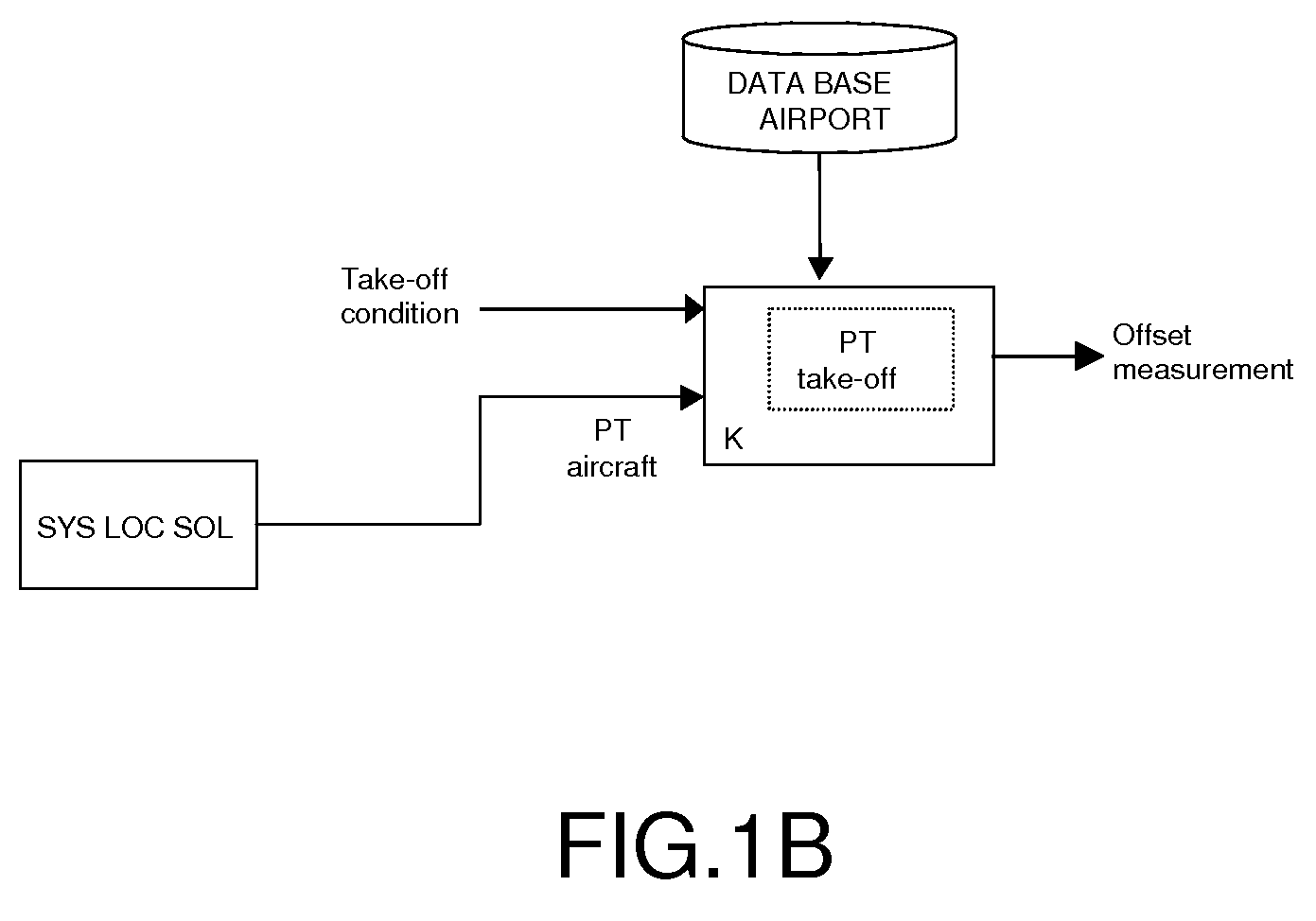
The present invention relates to the field of methods and systems for optimizing the locating of an aircraft in airports and, more particularly, in the take-off and landing phases, and notably in the air-ground and ground-air transition phases. The method of optimizing the locating of an aircraft during the take-off or landing phase comprising a transition step (21), the latter being defined between two events (A0, AS), the first event being a condition of contact between the aircraft and the runway and the second event being a threshold condition defining a stabilized flight phase, is wherein the transition step (21) comprises the determination of at least one “transition position” of the aircraft by a weighting between the “ground position” (LOC_SOL) determined by the ground locating system and the “flight position” (LOV_VOL) determined by the in-flight locating system.
Owner:THALES SA
Efficient drone for logistics distribution and with flight stability
InactiveCN109625284AStable flightEasy to transportAircraft stabilisationFreight handlingLogistics managementGravity center
The invention relates to an efficient drone for logistics distribution and with flight stability. The efficient drone comprises a main drone body, several conveying devices and several flight mechanisms, the conveying devices comprise adjusting mechanisms, adjusting plates and conveying mechanisms, the adjusting mechanisms comprise connecting rods, rotary plates, rotary assemblies and translationassemblies, and the translation assemblies comprise first motors, bearings, lead screws and translation blocks; the conveying mechanisms comprise detection assemblies, detection plates, lifting assemblies, lifting plates, air pumps and several fixing assemblies, and the fixing assemblies comprise air cylinders, pistons, vertical plates, bottom plates and fixing units. According to the efficient drone for logistics distribution and with flight stability, loading and unloading of goods are facilitated through the conveying mechanisms, the efficient drone conveniently carries multiple goods for conveying at a time, and the logistics distribution efficiency is improved; besides, by detecting the weight of the goods, the adjusting mechanisms control the positions of adjusting plates, thus the gravity center of the drone is adjusted to be located on the central axis of the main drone body, steady flight of the drone is facilitated, and the practicability of the drone is improved.
Owner:广州市妙伊莲科技有限公司
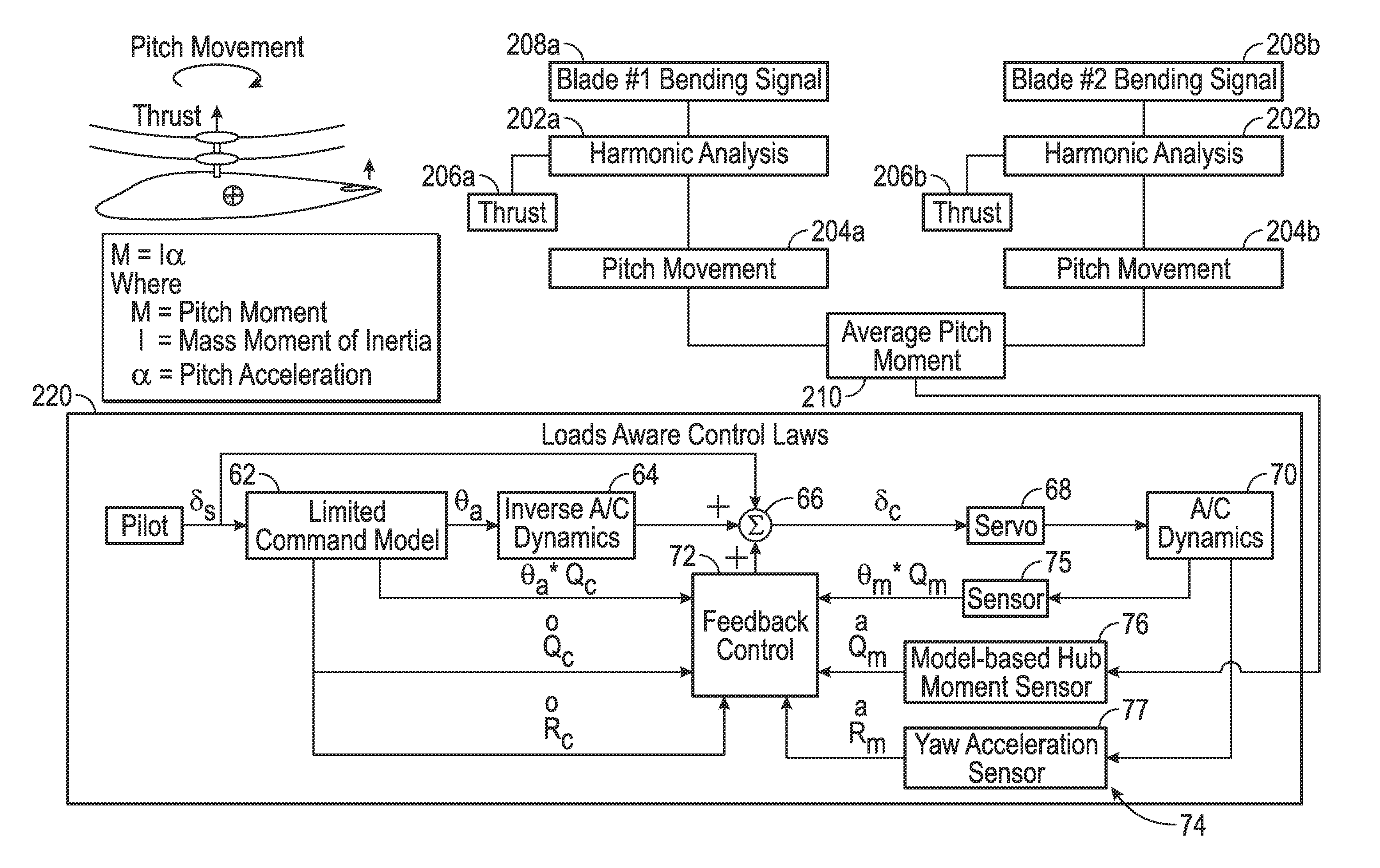
Rotor moment feedback for stability augmentation
Embodiments are directed to obtaining at least one measurement of blade bending associated with at least one blade of at least one rotor of an aircraft, processing, by a device comprising a processor, the at least one measurement to obtain moment data, obtaining data from an inertial measurement unit (IMU), and processing, by the device, the moment data and the data from the IMU to generate a command configured to stabilize the aircraft.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Estimation and self-healing control method for blade injury of multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle autopilot
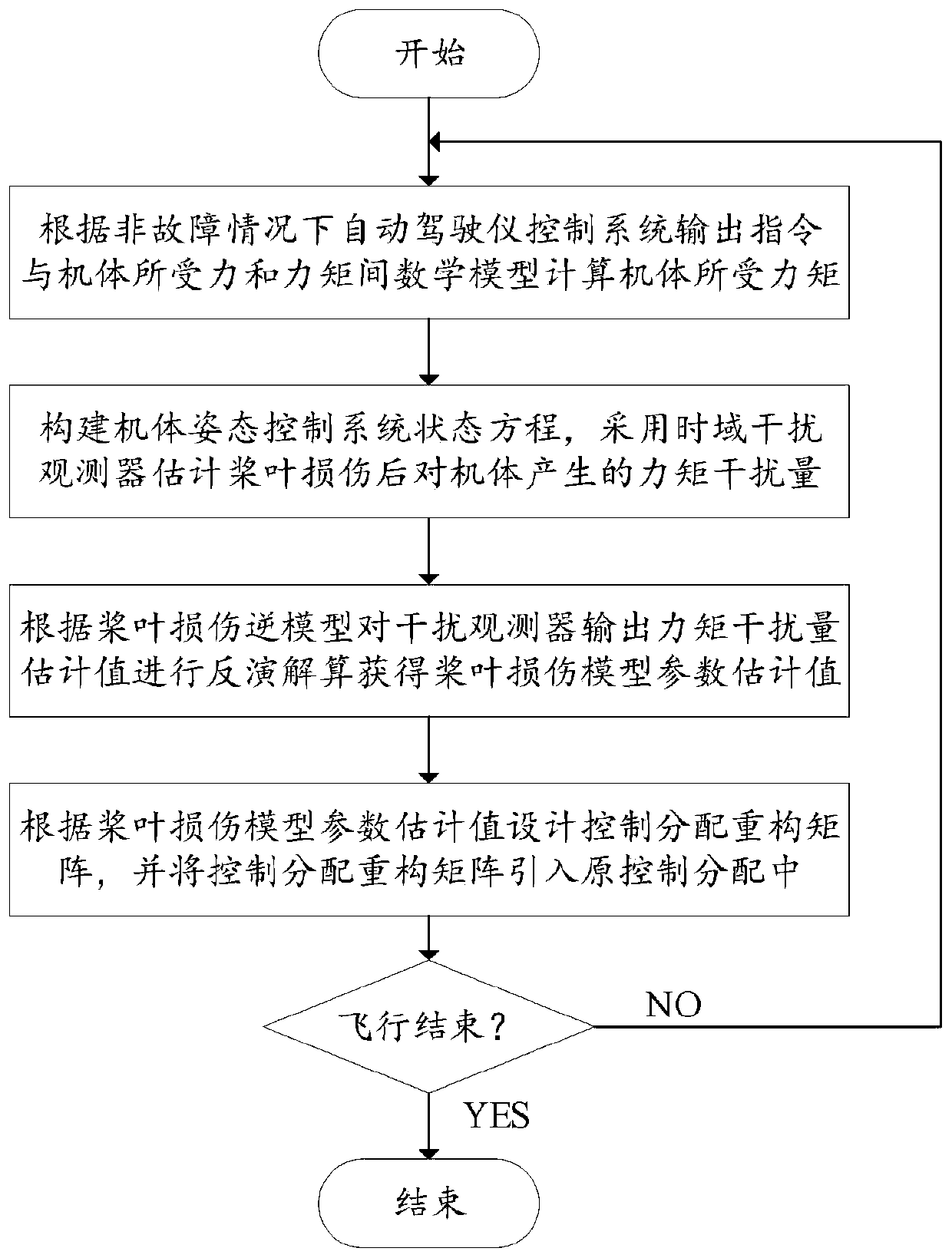
ActiveCN110531778AAccurate reconstructionResolve uncertaintyPosition/course control in three dimensionsSelf-healingTime domain
The invention relates to an estimation and self-healing control method for a blade injury of a multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle autopilot. The estimation and self-healing control method comprises the steps of: firstly, calculating a moment acted on a machine body by an instruction output by an autopilot control system under a non-fault condition and a mathematical model between a force and moment which are acted on the machine body; then constructing a machine body attitude control system state equation, and estimating a moment disturbance variable generated for the machine body after the blade injury by adopting a time domain disturbance observer; then inverting and resolving a parameter estimated value of a blade injury model according to an inverse model of the blade injury mathematical model; and finally, according to the parameter estimated value of the blade injury model, designing a control distribution reconstruction matrix to implement control distribution reconstruction ofthe autopilot. Compared with the prior art, the estimation and self-healing control method for the blade injury of the multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle autopilot, which is disclosed by the invention, has the following advantages that a blade injury degree can be estimated online; and by reconstructing a control object mathematical model online, control self-healing of the multi-rotor unmannedaerial vehicle autopilot under the blade injury is implemented, so as to ensure safe and stable flight of an unmanned aerial vehicle under the blade injury condition.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Flight simulation system and method and storage medium
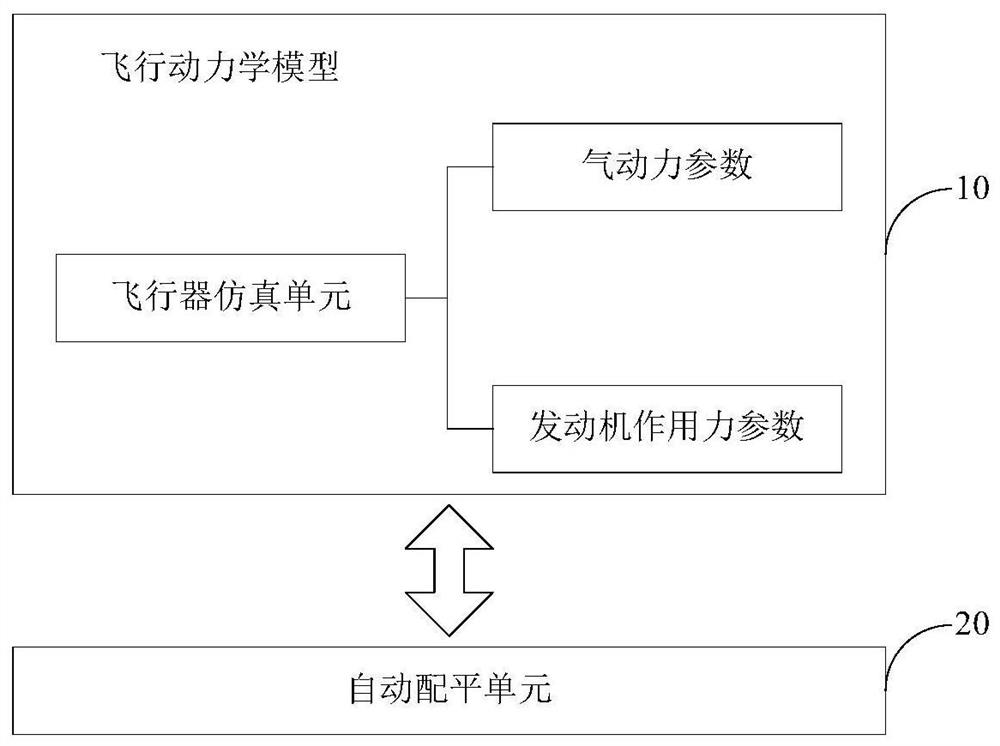
PendingCN112634704AStable postureSteady courseCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of flight simulation, in particular to a flight simulation system, a flight simulation method and a storage medium, which simulate the situation of moment imbalance caused by aerodynamic configuration and speed change in the flight process of an aircraft by simulating aerodynamic force and engine acting force received by the aircraft during flight. An automatic balancing unit is additionally arranged so that a balancing system in the real flight process is simulated, wherein flight balancing is conducted on the aircraft through the automatic balancing unit, in other words, an operation face (ailerons, elevators and rudders) is finely adjusted, unbalanced moment and rod force in the steady state are eliminated, and the purpose of stabilizing the posture and heading of the aircraft is achieved. Therefore, the whole system of the aircraft can be restored more truly, and the flight state of the aircraft can be completely simulated, so that the state and operation data of the aircraft in flight simulation training are more suitable for a real flight scene.
Owner:SHANGHAI KELIANG INFORMATION ENG
Architecture of a multiple-engine helicopter propulsion system, and corresponding helicopter
ActiveCN106458322AEconomic standby functionReach nominal operating modePower plant constructionEngine fuctionsAuxiliary power unitOn demand
The invention relates to an architecture of a multiple-engine helicopter propulsion system comprising turbine engines (1, 2) which are connected to a power transmission gearbox (3), comprising: a hybrid turbine engine (1) able to operate in at least one standby state during steady stabilized flight of the helicopter; a pack (5, 6) with a rapid restarting of said hybrid turbine engine (1) to cause it to exit said standby state and attain a nominal operating state; an auxiliary power unit (11) connected to said electro-technical restart pack (5, 6) via a first (10) AC / DC converter designed, on demand, to supply said restart pack (5, 6) with the power required to cause said hybrid turbine engine (1) to leave said standby state.
Owner:SAFRAN HELICOPTER ENGINES +1
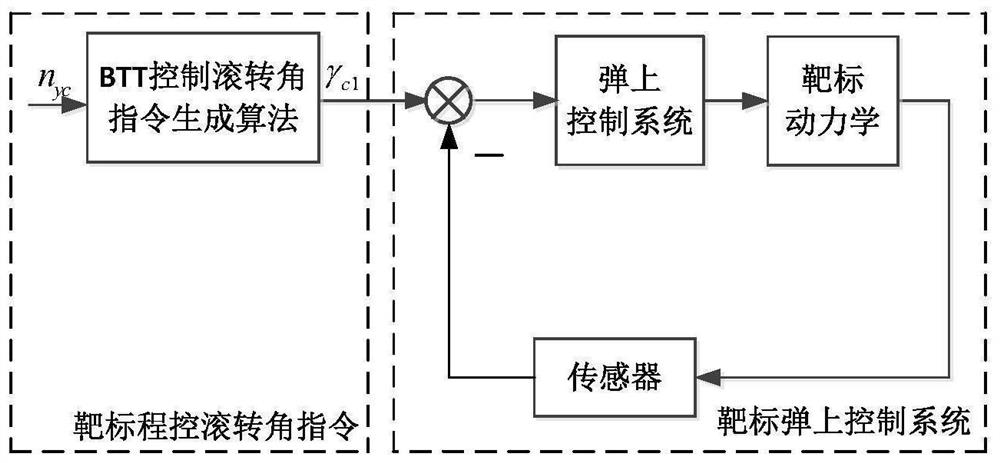
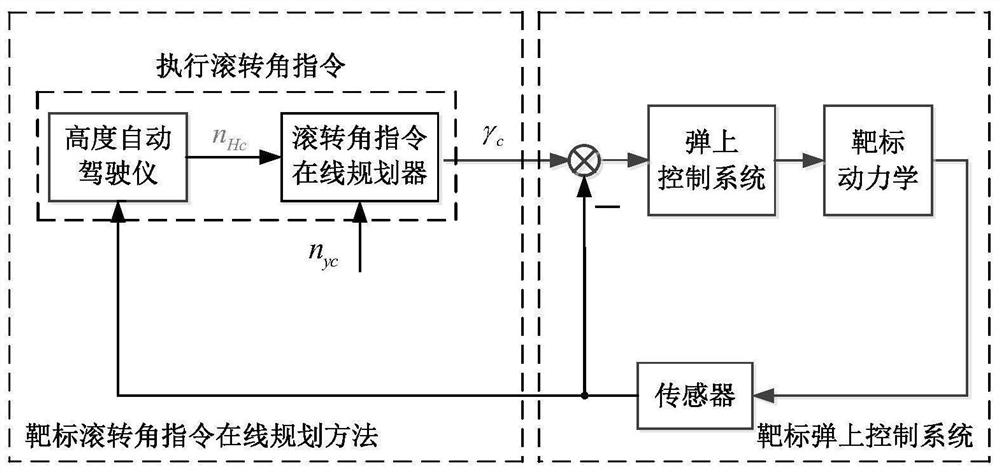
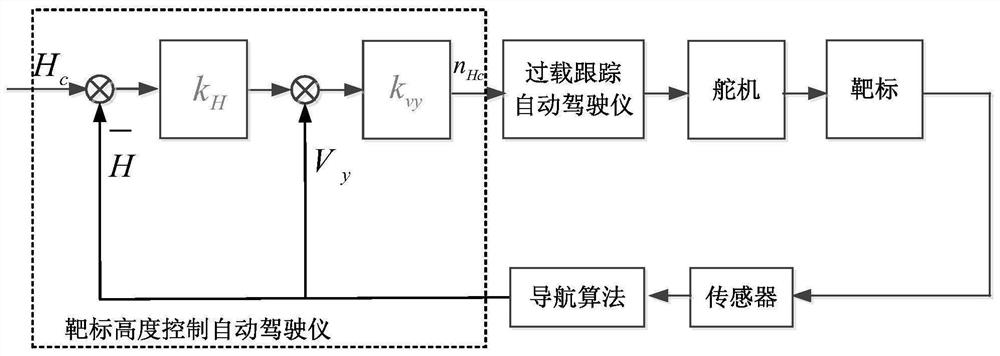
Supersonic speed large maneuvering target continuous large overload maneuvering height stability control method
ActiveCN114200826AImprove stability controlSimple and reliable working methodSustainable transportationAdaptive controlFlight testStabilization control
The invention provides a high-stability control method for continuous high-overload maneuver of a supersonic high-maneuver target, which is a high-stability control method for controlling the target of a pitching and rolling channel only by an elevator and an aileron in the process of continuous high-overload maneuver in a horizontal plane. According to the method, firstly, overload nHc in the y direction of a transmitting system required by target height stability control is analyzed, under the condition that a preset overload instruction nyc is non-adjustable, in order to ensure that the height is kept stable in the horizontal maneuvering process, an online roll angle instruction planning algorithm is designed, and according to the algorithm, a roll angle instruction is planned in real time, so that the target height stability is guaranteed. Therefore, the component of the predetermined overload instruction nyc in the y direction of the launch system is equal to the highly stable required overload nHc, and the highly stable target in the flying process of the horizontal maneuver process is ensured. Flight test results prove the effectiveness of the method.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
Low-altitude aircraft
InactiveCN105564647AEasy to operateTake off and land safelyConvertible aircraftsSeating arrangementsFlight vehicleSteady flight
The invention provides a low-altitude aircraft which can be used as an unmanned aerial vehicle and can also be used as a manned craft. The aircraft is mainly characterized in that the aircraft is a large or ultra-large air craft formed by a plurality of multi-axis aircraft bodies and is uniformly controlled by a controller. Each multi-axis aircraft body is an independent unit and can be used for normal flight, and the multi-axis aircraft bodies do not interfere with one another after being assembled to a main body rack; the main body rack is further provided with one or more balance rods which are used for maintaining steady flight; besides, a safety umbrella is installed above the main body rack and used for maintaining balance and safety of landing; foot stools are arranged below the main body rack and used for supporting an aircraft body and play a role of buffering when the aircraft descends and lands on the ground. The low-altitude aircraft is easy to install and operate and capable of taking off and landing safely and flying steadily and has better application prospect.
Owner:向东
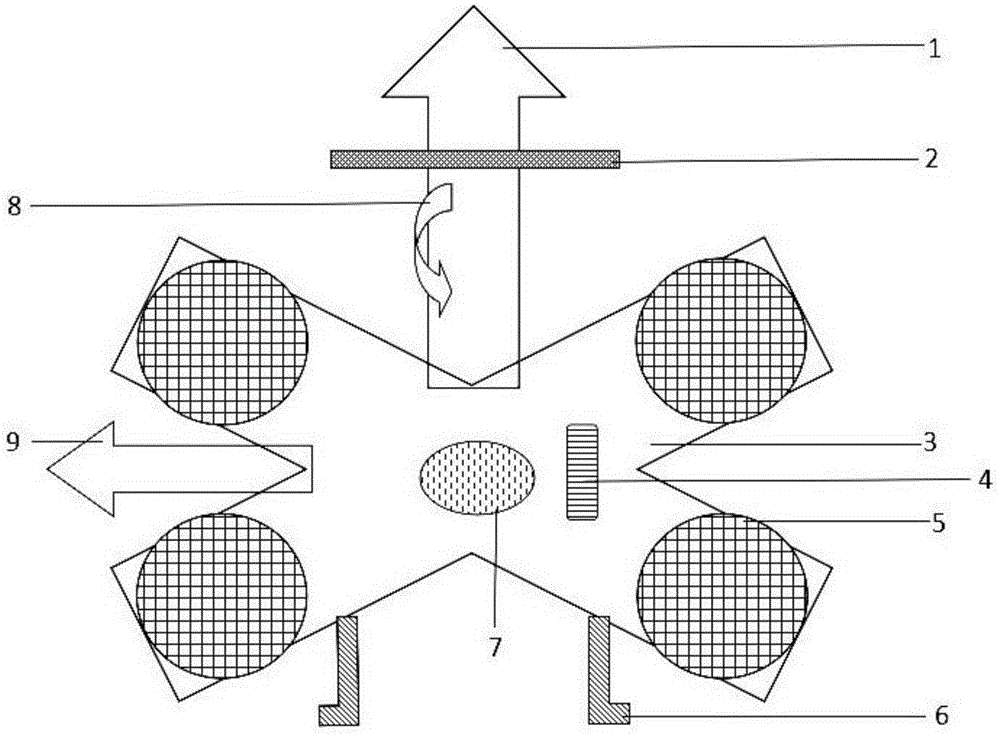
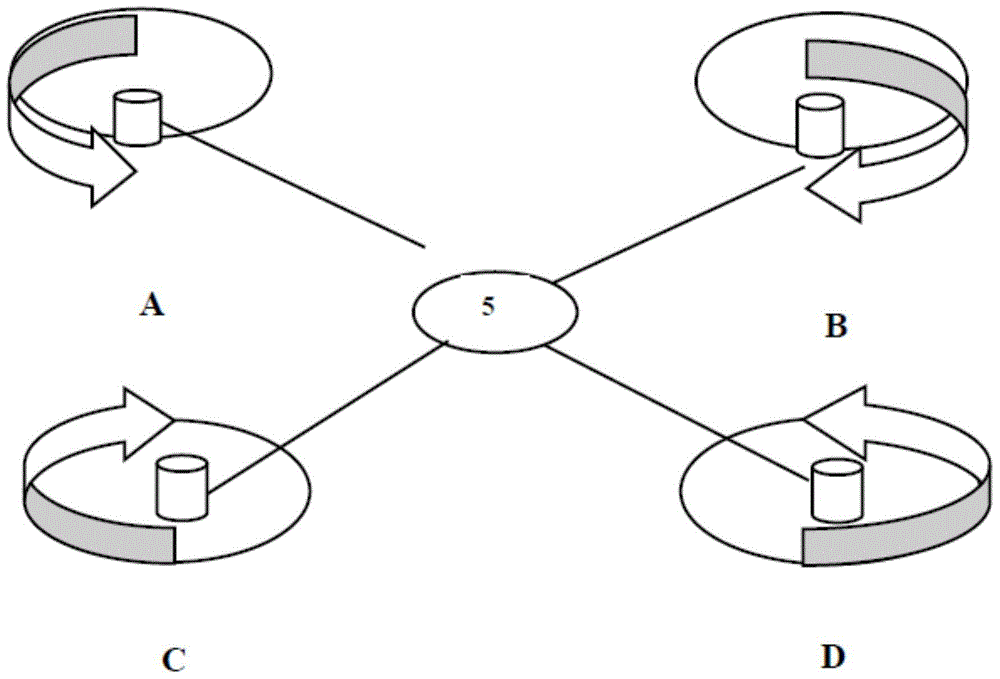
Intelligent control four-axis aircraft with multiple cameras
InactiveCN105323540AImprove effectivenessReduce monitoring blind spotsAircraft componentsTelevision system detailsGyroscopeSteady flight
The invention relates to an intelligent control four-axis aircraft with multiple cameras. The aircraft comprises a sensor 5 and the cameras A, B, C and D, and includes four propellers which are arranged in criss-cross intersection. A flight power system of independent research and development is integrated in the aircraft, the aircraft is configured with a professional radio remote control system, and the aircraft is capable autonomous navigation flight. Four rotors are mounted in four corners of the aircraft respectively, and driven by a motor, blades can rotate forwardly and backwardly, an inertial navigation module composed of gyroscopes of three directions and a three-axis acceleration sensor is mounted on the four-axis aircraft to maintain stable flight of the aircraft, and an electronic regulator is used to ensure rapid flight of the aircraft. The four cameras are respectively mounted on the four rotors, and connected with the sensor at the center of the aircraft to transmit information and monitor a moving object. According to the four-axis aircraft, monitoring is rapider and more comprehensive, and the monitoring efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING ZHUANCHUANG INTPROP SERVICES
Four-rotor aircraft fault tolerance control method based on switching adaptive algorithm
ActiveCN112114522AGuaranteed Progressive TrackingGuarantee the progressive tracking of the aircraft under the interference of energy bounded disturbanceComplex mathematical operationsAdaptive controlAviationFly control
The invention discloses a four-rotor aircraft fault tolerance control method based on a switching adaptive algorithm, belongs to the field of aircraft control, and is used for solving the problem thata high-maneuverability four-rotor aircraft cannot well track an expected signal under the conditions that an input fault exists and kinetic parameters are unknown. The method is technically characterized by comprising the following steps of constructing a four-rotor aircraft segmented ray-imitating linear system containing unknown input faults and unknown kinetic parameters, a reference system and a controller; obtaining an error system model according to the segmented radioactive system, the reference system and the controller; designing a residence time constraint-based switching signal according to the segmented radioactive system and the reference system; and obtaining an adaptive law of control parameters in the controller according to the error system model and the switching signal.The method can achieve the good tracking performance of the high-maneuverability four-rotor aircraft for an expected signal, and can be used for the flight control of the four-rotor aircraft so as toguarantee the stable flight of the four-rotor aircraft under the conditions that an input fault and a kinetic parameter are unknown.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
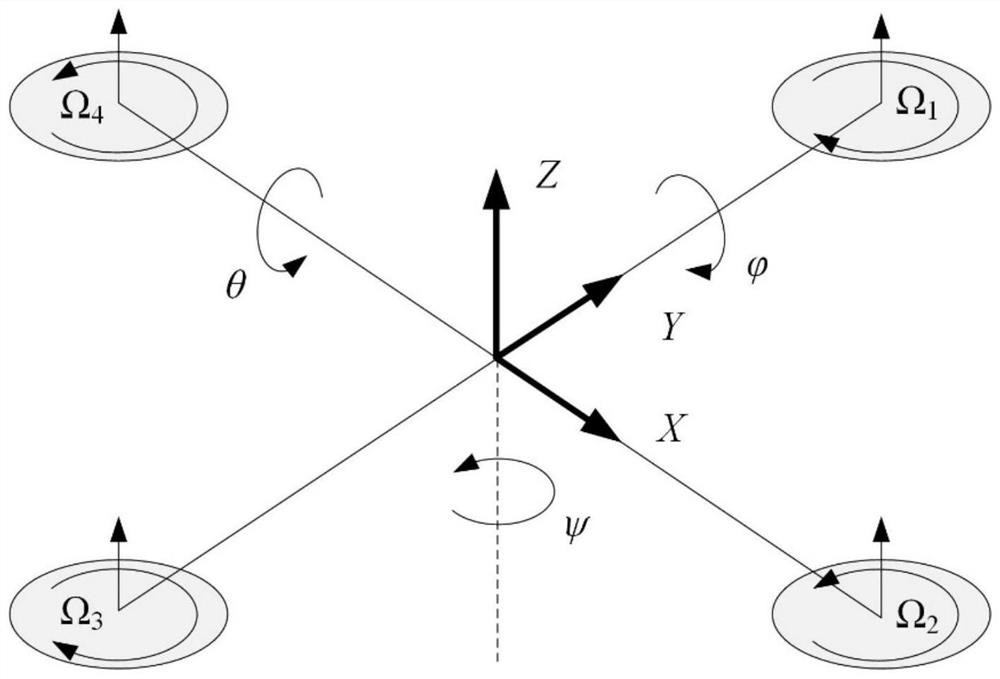
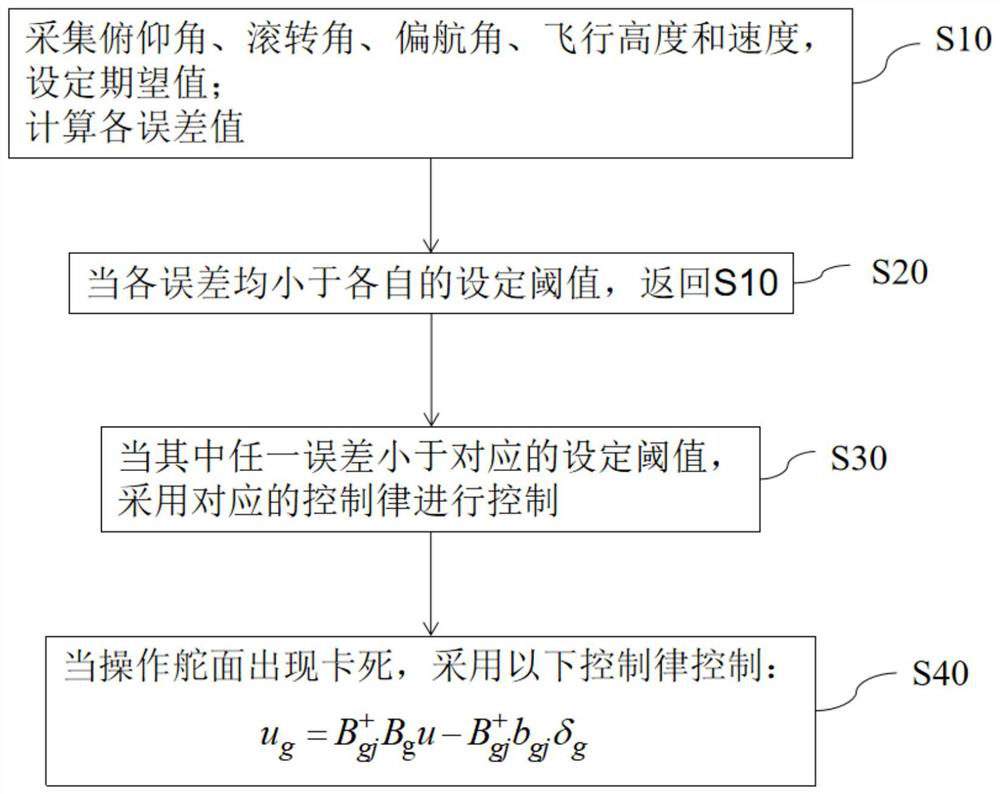
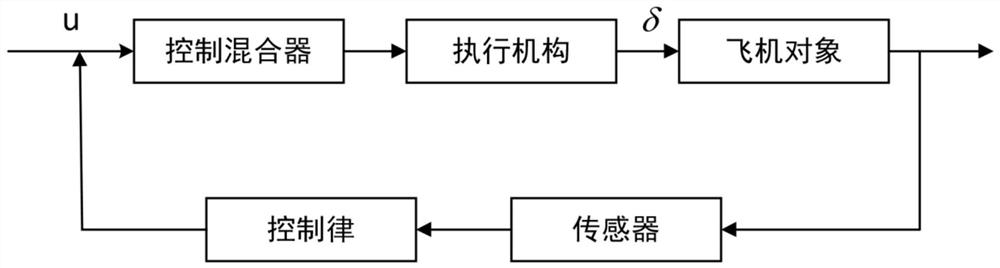
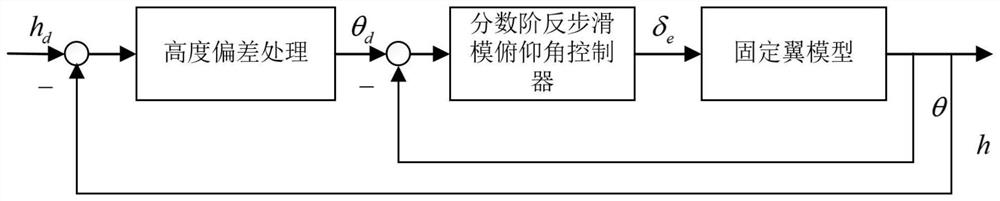
Fault-tolerant flight control method for fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle in control surface stuck state
ActiveCN114415515AFast convergenceEnsure stabilitySustainable transportationAdaptive controlFlight heightControl system
The invention is applicable to the technical field of fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicles, and provides a fault-tolerant flight control method for a fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle in a control surface stuck state, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring a pitch angle, a roll angle, a yaw angle, a flight height and a speed of the unmanned aerial vehicle, comparing the pitch angle, the roll angle, the yaw angle, the flight height and the speed with expected values to calculate errors; a corresponding control law is adopted to control a corresponding execution mechanism; on the basis of a normal control law, a control mixer is added for the stuck state of an operation control surface, and the output of the normal control law is used as the input of the control mixer to execute the following control laws: the control law under the control surface stuck fault does not change the structure of an originally designed fractional order backstepping sliding mode controller; the advantages of an original controller can be reserved, the whole control system can be kept stable under the two fault conditions of rudder jamming and aileron jamming, and the fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle can adapt to different jamming angles to stably fly.
Owner:LOW SPEED AERODYNAMIC INST OF CHINESE AERODYNAMIC RES & DEV CENT
Helicopter with adjustable empennage attitude
InactiveCN104015923AExtended service lifeAvoid rotation effectsAircraft controlRotocraftSufficient timeDrive motor
The invention discloses a helicopter with an adjustable empennage attitude, relates to the technical field of traffic tools, and aims to solve the problem of low landing and take-off safety of a conventional helicopter. An empennage of the helicopter with the adjustable empennage attitude comprises a first empennage part fixedly connected with a helicopter body and a second empennage part rotatably connected with the first empennage part; an attitude adjustment driving motor is used for driving the second empennage part to rotate, so that a main rotor wing and a tail rotor wing are positioned on the same horizontal plane, and influence, which is caused by high-speed rotation of the main rotor wing, on the tail rotor wing is avoided; a steady flight of the helicopter is guaranteed, and the service life of the helicopter is effectively prolonged; furthermore, a main engine is connected with the attitude adjustment driving motor through a generator and a processing conversion device; the processing conversion device is also connected with a storage battery; electric energy generated by the main engine can be stored in the storage battery; when the main engine has fault, the electric energy stored in the storage battery can be used for driving the second empennage part to adjust the attitude and stabilize the flying state, so that a pilot has enough time to escape.
Owner:杨雅茹
Foldable variable-structure unmanned aerial vehicle
PendingCN113895604ASimple structureOverall small sizeFuselage framesWeight reductionFlight vehicleUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses a foldable variable-structure unmanned aerial vehicle which comprises a fuselage, two pairs of wings rotatably mounted on the fuselage, a front propeller mounted at the head of the fuselage, an empennage mounted at the tail of the fuselage and ducted fans arranged on the wings. The wings can be driven to rotate to be approximately parallel to the fuselage to form a folded state or approximately perpendicular to the fuselage to form an unfolded state or obliquely intersect with the fuselage to form a semi-unfolded state. According to the unmanned aerial vehicle, the landing mode and the flight mode can be switched in a self-adaptive mode according to the terrain, the unmanned aerial vehicle can adapt to complex terrains, stable flight in various application scenes can be achieved, and operation is more flexible; when the wings of the structure are folded, the wings are horizontally stored to the two sides of the aircraft body, and the landing occupied area of the whole aircraft can be greatly reduced; the unmanned aerial vehicle with the structure is relatively simple in structure, lightweight design is favorably realized, energy consumption is reduced, the fuselage size of the unmanned aerial vehicle is favorably reduced, and a high space utilization rate is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
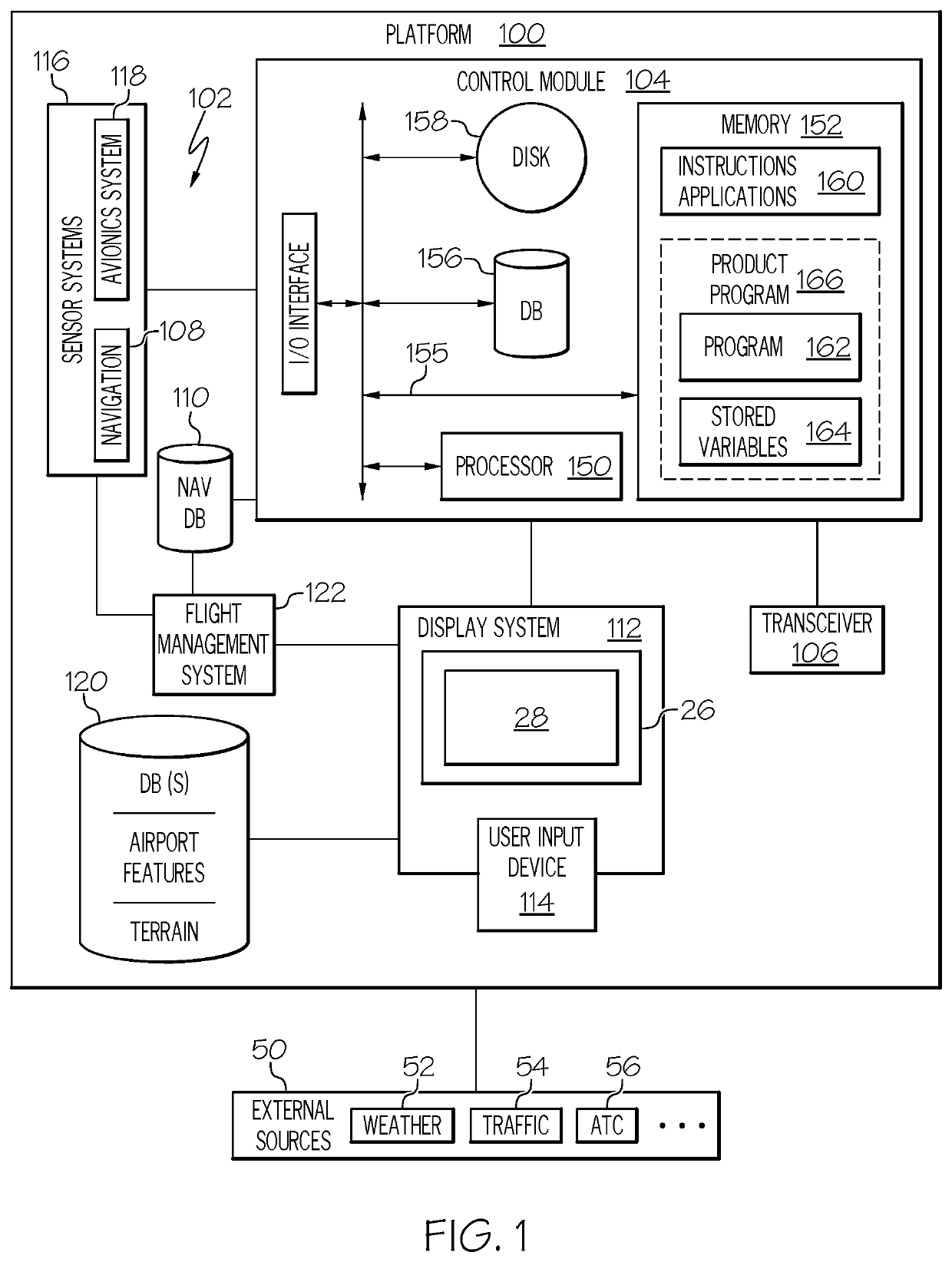
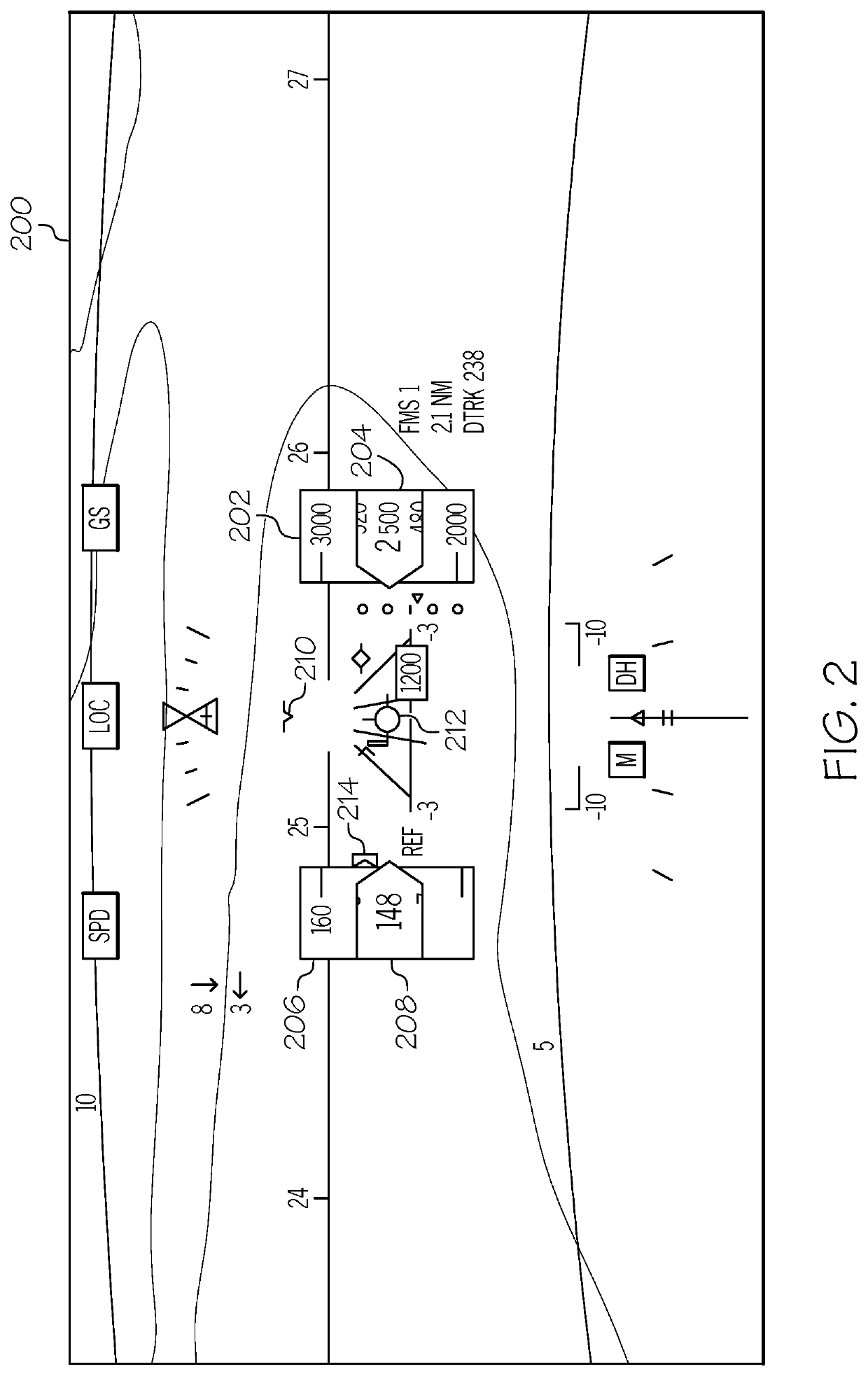
Systems and methods for dynamic readouts for primary flight displays
ActiveUS20200088542A1Simplified descriptionAircraft componentsNavigation instrumentsDisplay deviceClassical mechanics
Improved systems and methods for dynamic readouts on a primary flight display are provided. The system includes a computer system configured to receive and process aircraft status data and flight plan data to command a display system to overlay on the image, (i) an analog indicator of the airspeed, (ii) an analog indicator of altitude, (iii) a digital airspeed indicator, and (iv) a digital altitude indicator. The system continuously determines whether steady flight conditions are occurring. Steady flight conditions include one or both of: constant airspeed and constant rate of change of airspeed. When the steady flight conditions are occurring, (i) and (ii) are removed from the image. When the steady flight conditions are no longer occurring, (i) and (ii) again overlaid on the image.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
High-speed vtol aircraft
InactiveUS20150048200A1Aircraft navigation controlVertical landing/take-off aircraftsAirplanePayload
This invention can take-off like a helicopter and then roll forward as a single unit to fly faster and further than any conventional helicopter. Just like the seats in a Ferris wheel, the payload of passengers or freight can remain upright and comfortable as this aircraft rotates from take-off to fast forward and back to landing mode. Prior inventions claiming similar performance generate lift for take-off and landing by relative rotation of major aircraft components or by vectoring a thrust through large angles of deflection which produces inherently unstable flight characteristics. This invention requires neither rotation of major assemblies nor highly vectorable thrust, making it simpler and more reliable than the aircraft with major rotating assemblies and more stable and efficient than aircraft relying on vectored thrust for lift.
Owner:GREENE GEOFFREY BYRON
System for monitoring the health of a helicopter
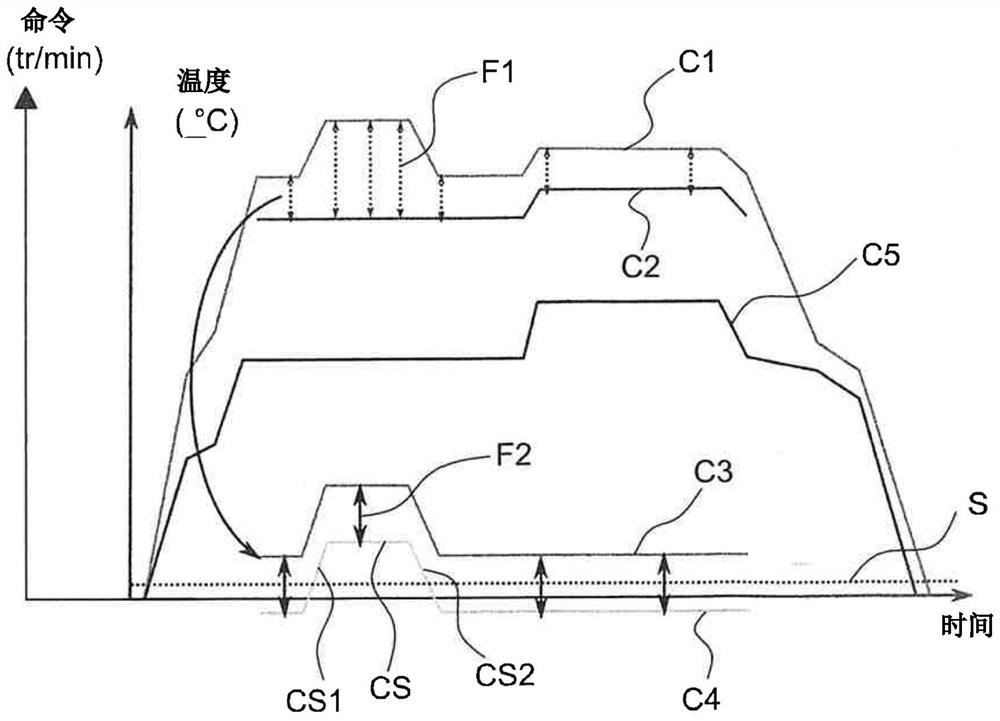
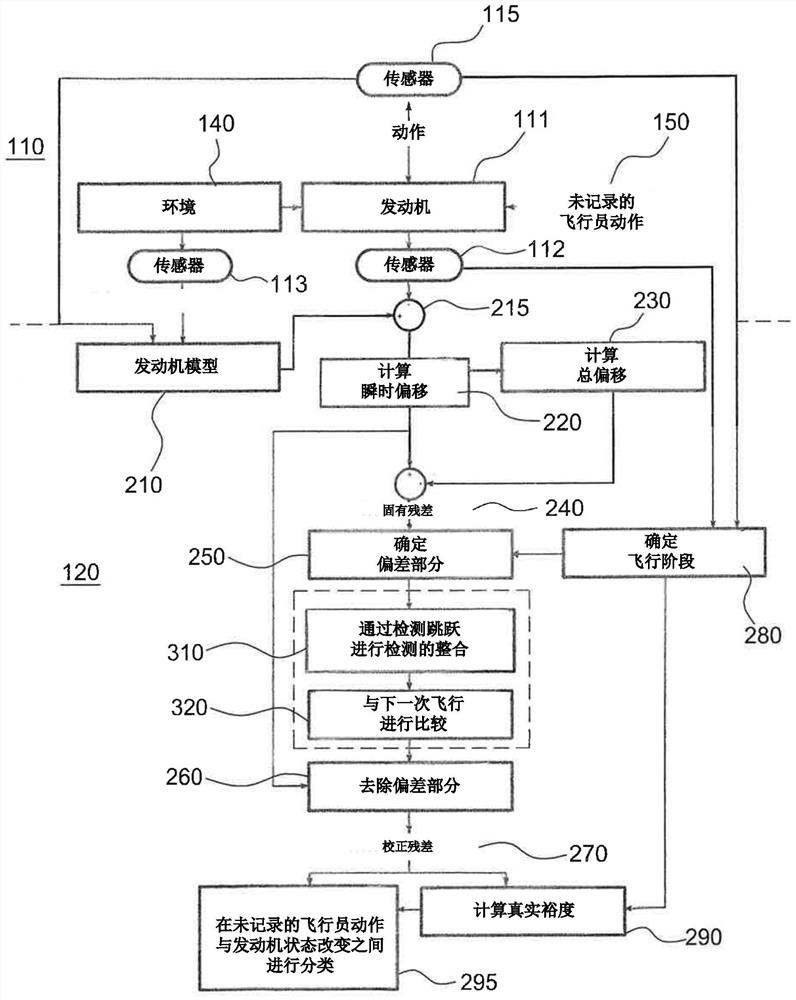
ActiveCN113727913AInternal-combustion engine testingGas-turbine engine testingReference modelSteady flight
The invention relates to a system for monitoring the health of a helicopter, comprising a helicopter and a device for determining a change in state of the engine that is configured to collect data measured by engine sensors and external conditions during a stable flight phase and to process said measured data in the following way: comparing said measured data with a reference model of the engine, determining, at each time interval, an instantaneous discrepancy between each item of data measured and each item of data estimated by the reference model of the engine, determining, throughout the stable flight phase, an overall discrepancy between the measured data and the data estimated by the reference model of the engine, determining, at each time interval of the stable flight phase, an intrinsic residual corresponding to a difference between the instantaneous discrepancy and the overall discrepancy, determining a deviating portion corresponding to the part of the intrinsic residual that does not satisfy a predetermined criterion, each deviating portion containing an item of information relating to a pilot action that is not recorded, and determining a corrected residual corresponding to the instantaneous discrepancy from which the deviating portion has been subtracted, the corrected residual being analysed in order to determine whether the state of the engine has changed.
Owner:SAFRAN +1
Aircraft and aircraft control method
The invention provides an aircraft and aircraft control method, and relates to the aircraft technical field. The aircraft includes at least four rotor arms; one end of each rotor arm is connected witheach other to form a connection point, and the multiple rotor arms are distributed along the circumferential direction of the connection point in a horizontal plane. Each rotor arm is provided with arotor. The rotor can rotate around the axis of the rotor arm in a vertical plane for adjustment of the working surface of the rotor. When the rotor on any one or more rotor arms fails, the rotor armon which a non-failure rotor is can rotate in the horizontal plane around the connection point, and is fixed at a position to ensure the aircraft can stably fly. In actual use, the aircraft adopting the air-changing technology can rapidly recover to a stable flight state through deformation when power failure causes instability, air crash and hazard to the ground can be avoided, and the safety ofthe aircraft can be improved.
Owner:刘红军
Fuzzy clustering-based envelope division and gain scheduling method for flying-wing unmanned aerial vehicle
PendingCN112487552AStabilized flight controlContinuous smooth outputGeometric CADCharacter and pattern recognitionControl engineeringUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses a fuzzy clustering-based envelope division and gain scheduling method for flying-wing unmanned aerial vehicle, and solves the problem that a conventional linear interpolation gain scheduling mechanism cannot deal with the nonlinear characteristic of a large envelope of an unmanned aerial vehicle. According to the method, a fuzzy clustering algorithm is adopted to obtain a typical flight state and a membership matrix of an unmanned aerial vehicle, and an optimal flight envelope division mechanism is determined; and the speed and the dynamic pressure are selected as scheduling variables, and a T-S fuzzy gain scheduling strategy is designed based on a Sigmoid type membership function. According to the method, continuous output and stable transition of unmanned aerial vehicle control gain are achieved, and stable flight control of the unmanned aerial vehicle in a full envelope range is ensured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Methods of optimizing the location of an aircraft on the ground and in the take-off and landing phases
ActiveUS8190310B2Easy to calculateAnalogue computers for vehiclesSatellite radio beaconingSteady flightPositioning system
The present invention relates to the field of methods and systems for optimizing the locating of an aircraft in airports and, more particularly, in the take-off and landing phases, and notably in the air-ground and ground-air transition phases. The method of optimizing the locating of an aircraft during the take-off or landing phase comprising a transition step (21), the latter being defined between two events (A0, AS), the first event being a condition of contact between the aircraft and the runway and the second event being a threshold condition defining a stabilized flight phase, is wherein the transition step (21) comprises the determination of at least one “transition position” of the aircraft by a weighting between the “ground position” (LOC_SOL) determined by the ground locating system and the “flight position” (LOV_VOL) determined by the in-flight locating system.
Owner:THALES SA
Model airplane PID algorithm control method based on gravity center dynamics
ActiveCN111781820AReduce the impactImprove stabilitySustainable transportationControllers with particular characteristicsPid control algorithmSimulation
The invention relates to a model airplane PID algorithm control method based on gravity center dynamics, and the method comprises the steps: firstly building a model airplane gravity center coordinatesystem and coordinate systems at all rotor wings, and solving a no-load rotor wing model airplane moment model and a loaded rotor wing model airplane moment model; calculating the gravity center momentum change rate of the model airplane through a gravity center kinetic model; and finally, dividing the resultant external force borne by the model airplane into acceleration calculation and inertiacalculation, and meanwhile, fusing gravity center dynamics and a PID control algorithm to realize the model airplane PID algorithm control method based on the gravity center dynamics, thereby reducingthe influence of gravity center shift on stable flight of the model airplane when the model airplane bears a load, and improving the flight stability of the model airplane.
Owner:深圳汇腾信息技术服务有限公司
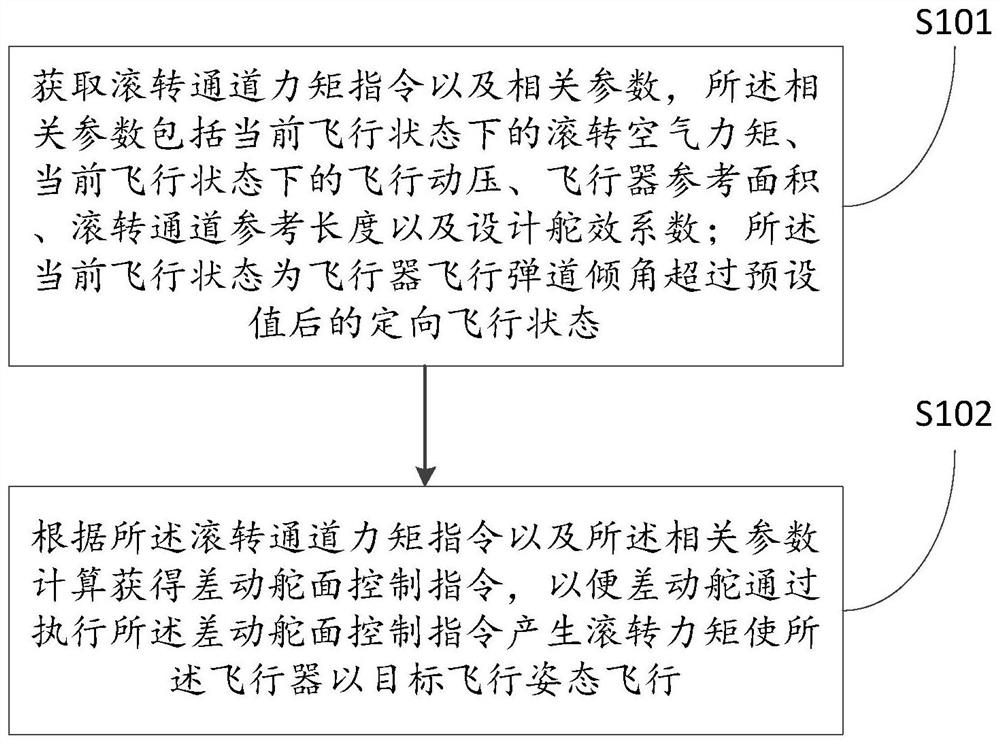
Near space vertical launching single-channel stability augmentation control method and system
The invention discloses a near space vertical launching single-channel stability augmentation control method and system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a rolling channel torque instruction and related parameters, wherein the related parameters comprise a rolling air torque, a flight pressure, an aircraft reference area, a rolling channel reference length and a design steering coefficient in a current flight state; and obtaining a differential control surface control instruction through calculation, and enabling the differential rudder to generate rolling torque by executing the differential control surface control instruction, and the aircraft flies in the target flight attitude. According to the embodiment of the invention, a pair of small differential control surfaces is added on the rolling channel of the aircraft, the stable flight effect of three channels of the aircraft is achieved only through rolling control, meanwhile, the influence of rapid change of atmospheric density in the process that the height is rapidly reduced after the aircraft is thrown in a near space is overcome, and the flight path can be adjusted in the preset flight vertical plane through a single channel, so that the requirement of a flight test for an airspace range is reduced, and the difficulty of searching and recovering an aircraft is also reduced.
Owner:广东空天科技研究院 +1
Four-wing flapping-wing air vehicle capable of adjusting attack angle
InactiveCN112319794AImprove flight efficiencyStable flightPower plant typeOrnithoptersFlapping wingFlight vehicle
The invention discloses a four-wing flapping-wing air vehicle capable of adjusting an attack angle. The four-wing flapping-wing air vehicle comprises a vehicle body, wing devices, a run-up device, a motor and a battery, the run-up device is mounted on the lower side of the body; the four sets of wing devices are installed on the two sides of the fuselage, the wing devices and the run-up device aredriven by motors, the multiple motors are powered by batteries, and an auxiliary lift device is arranged above the top of the fuselage. The wing device adopts a flapping wing form and simulates birdflight, the four groups of wings can effectively improve the flight stability and are combined with the rotor wings on the basis, the rotor wing blades are driven to rotate while the driving mechanismflaps, the rotation directions of the blades are the same during downward flapping and rising, continuous and stable lift force is provided, stable flight of the aircraft is guaranteed, and the flight efficiency is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUOSHIJIAN TECH DEV CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com