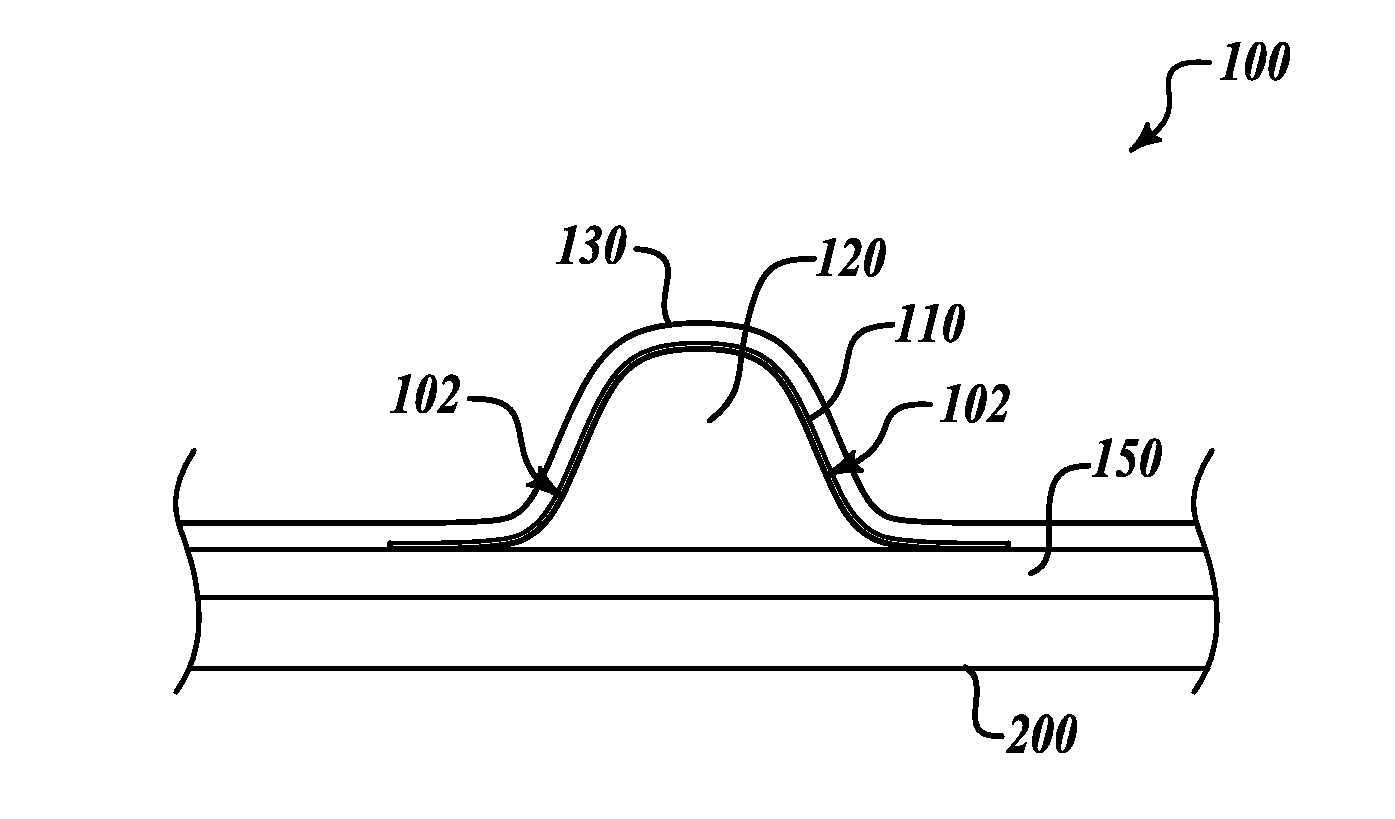
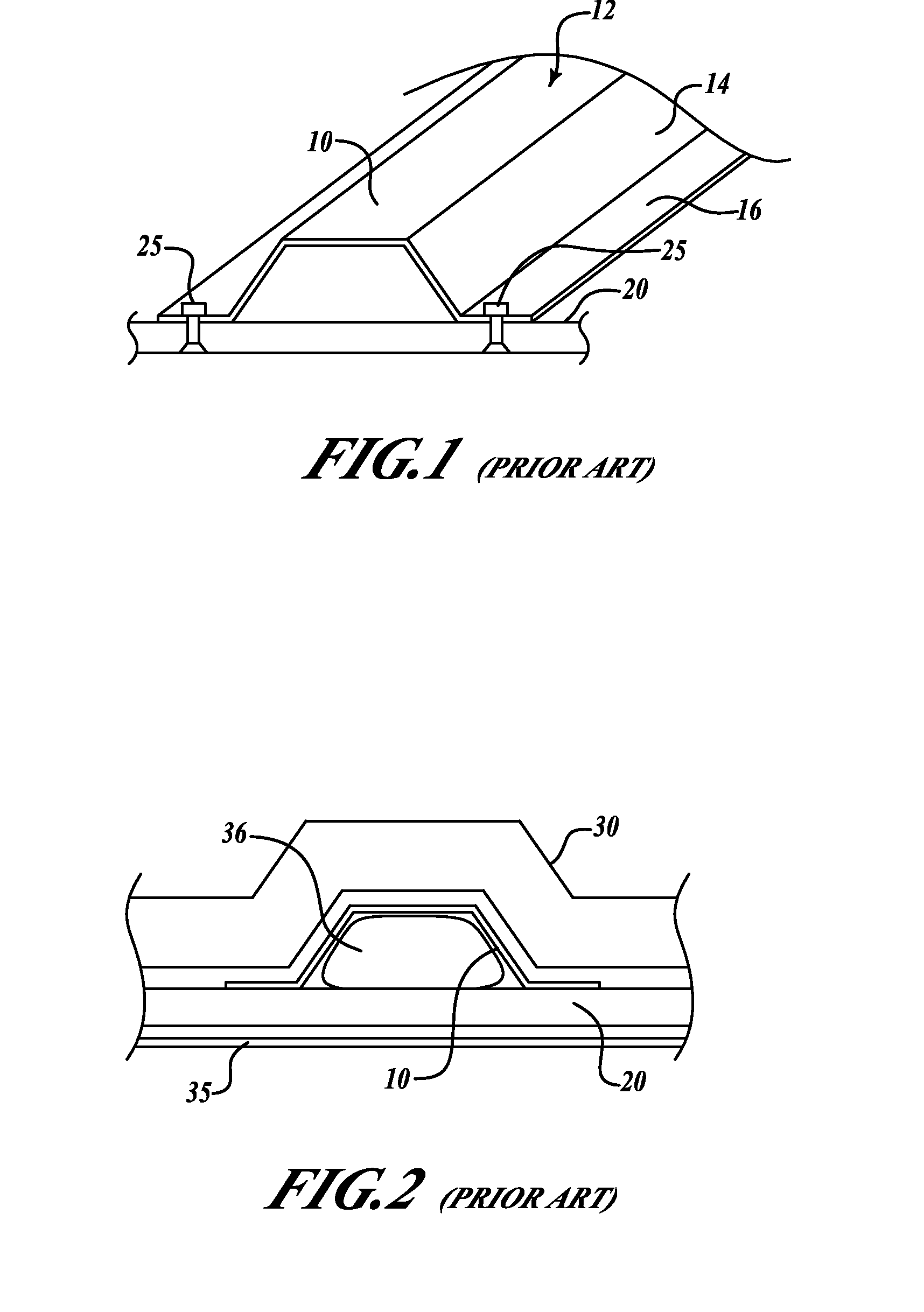
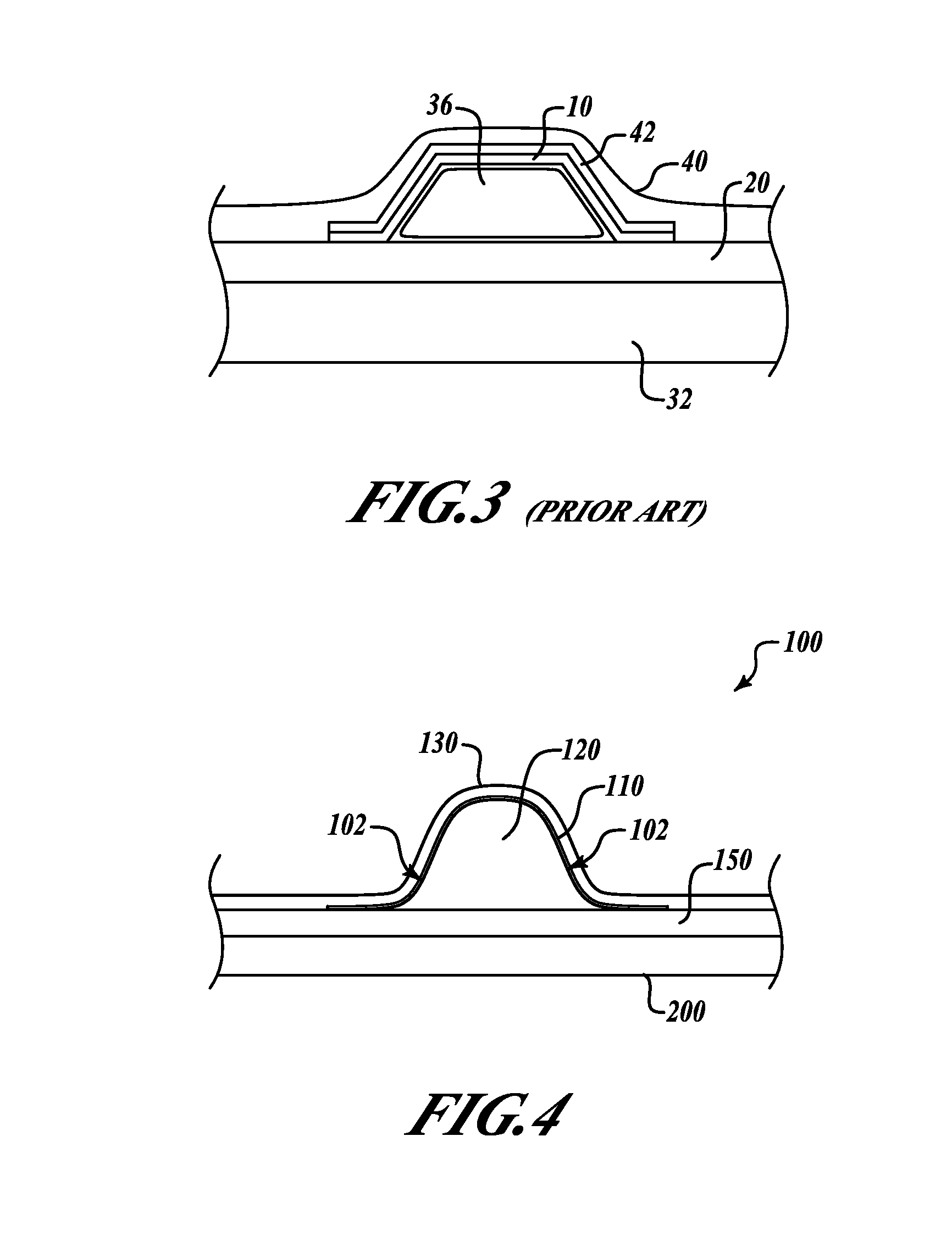
Patents
Literature
6810results about "Weight reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
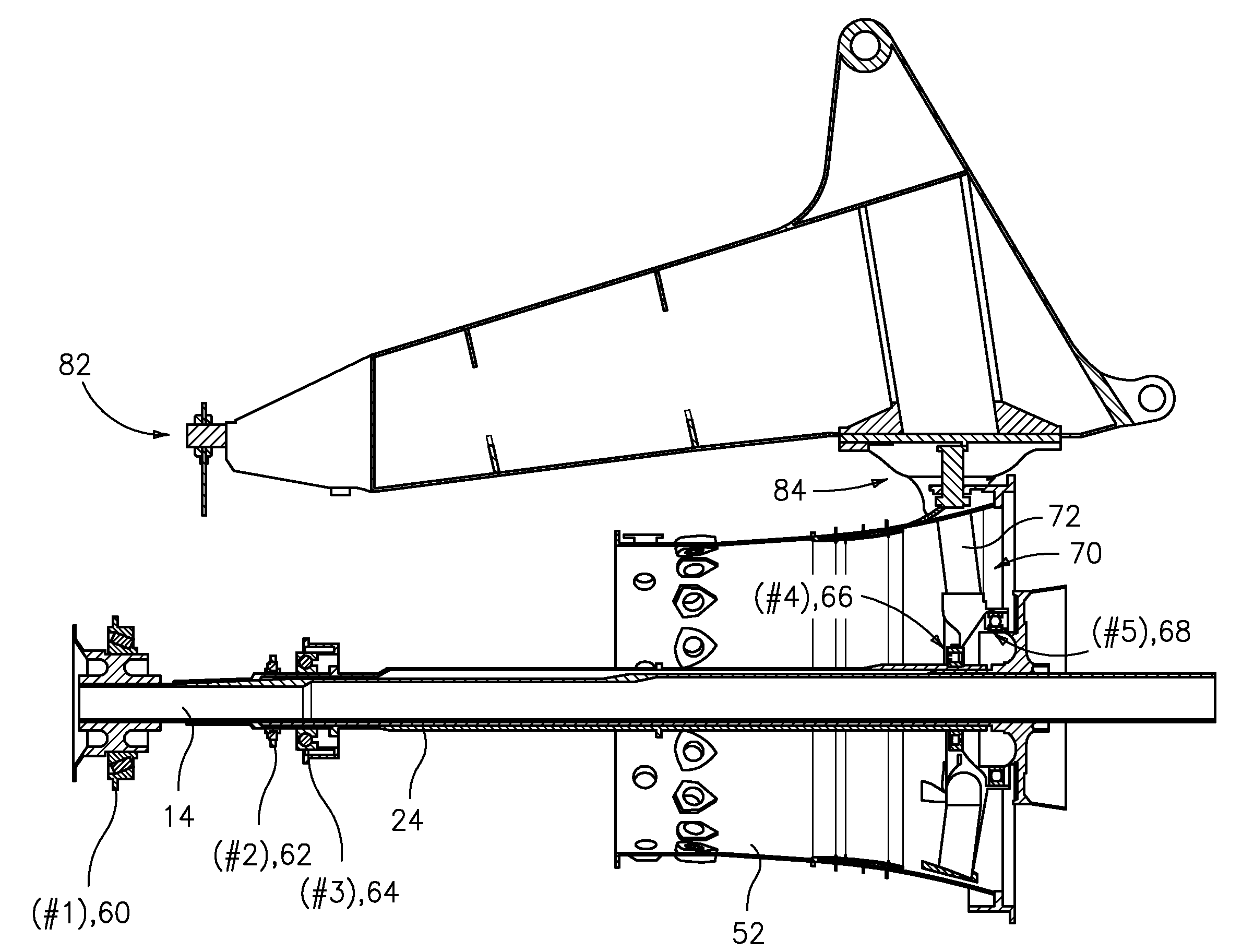
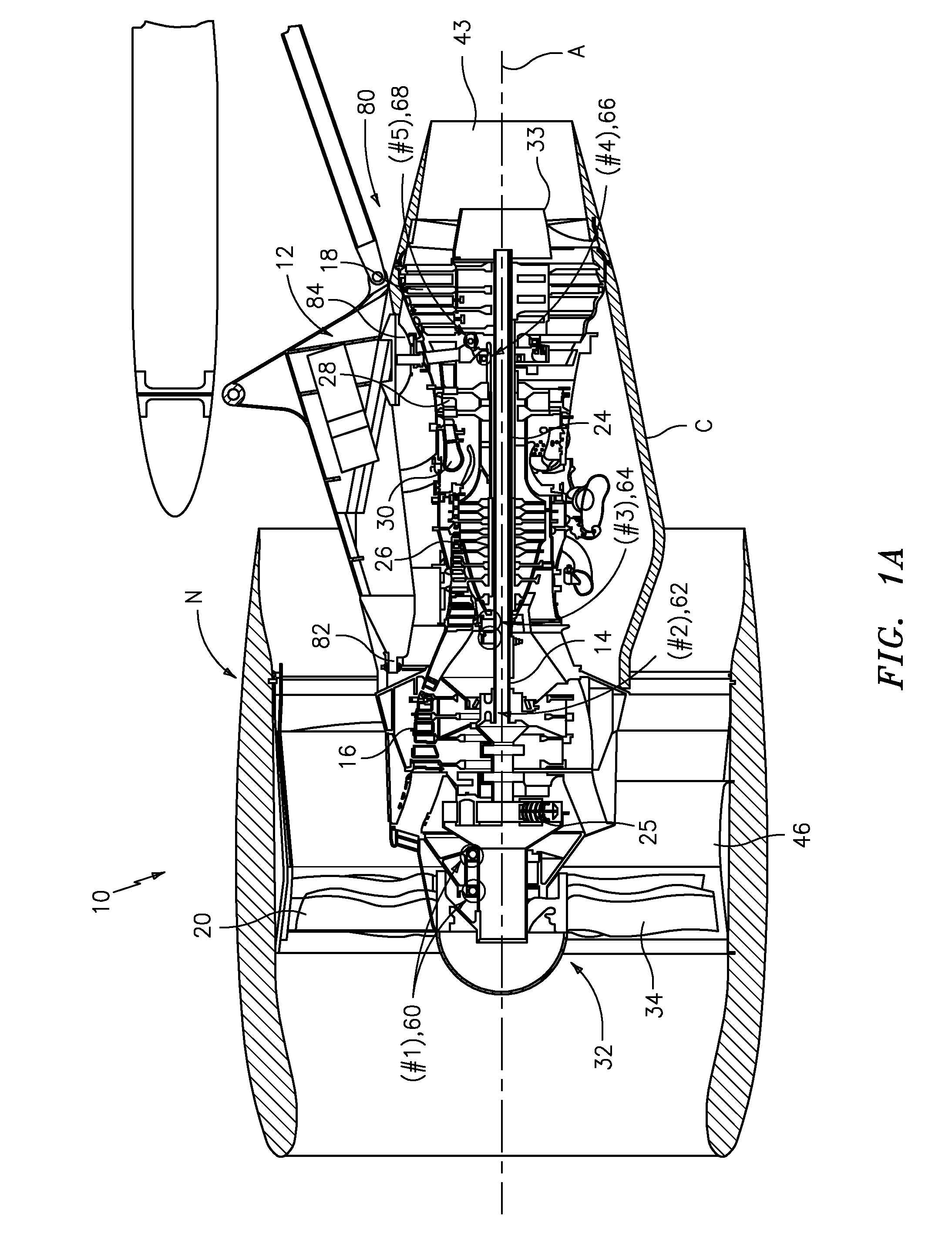
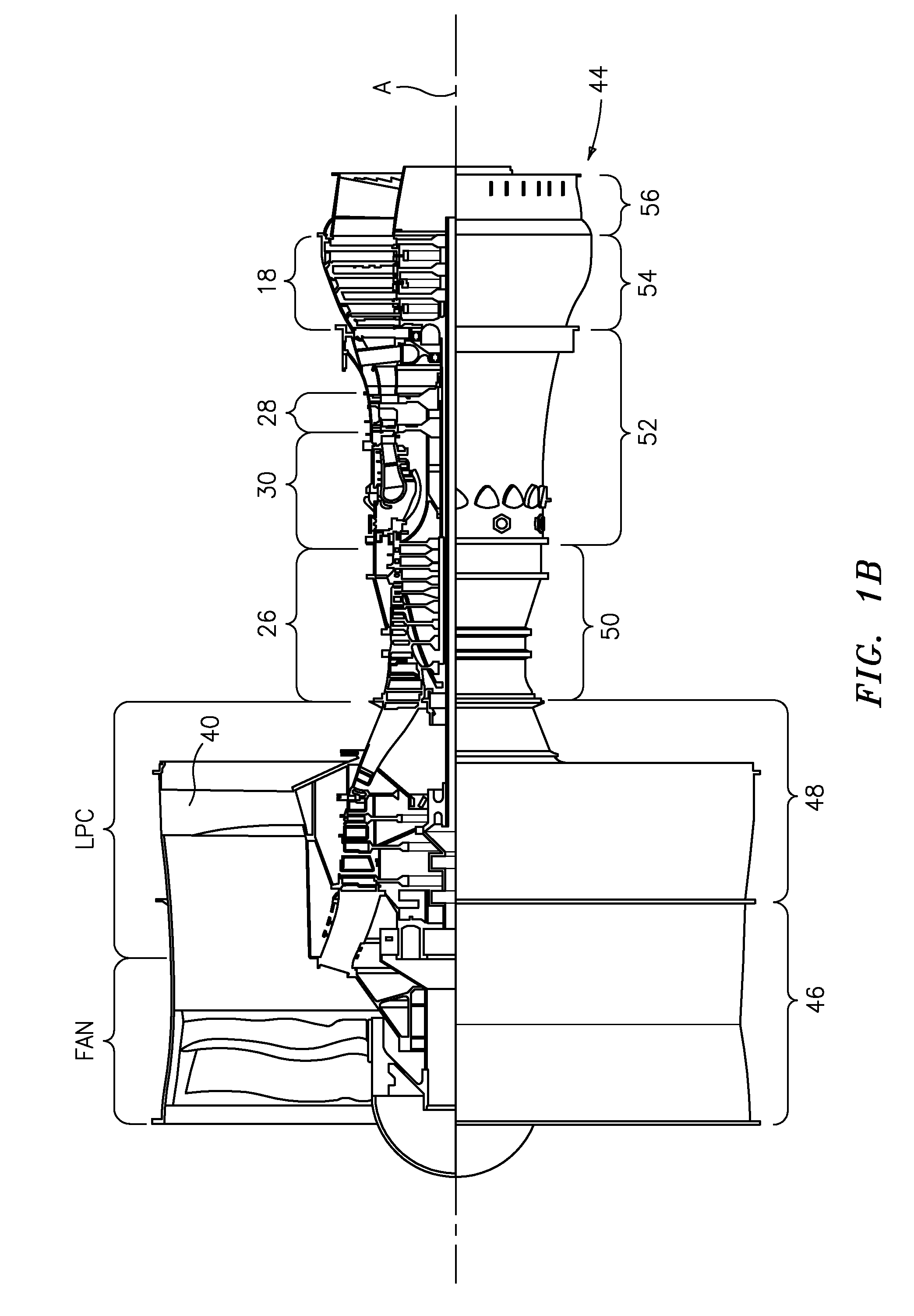
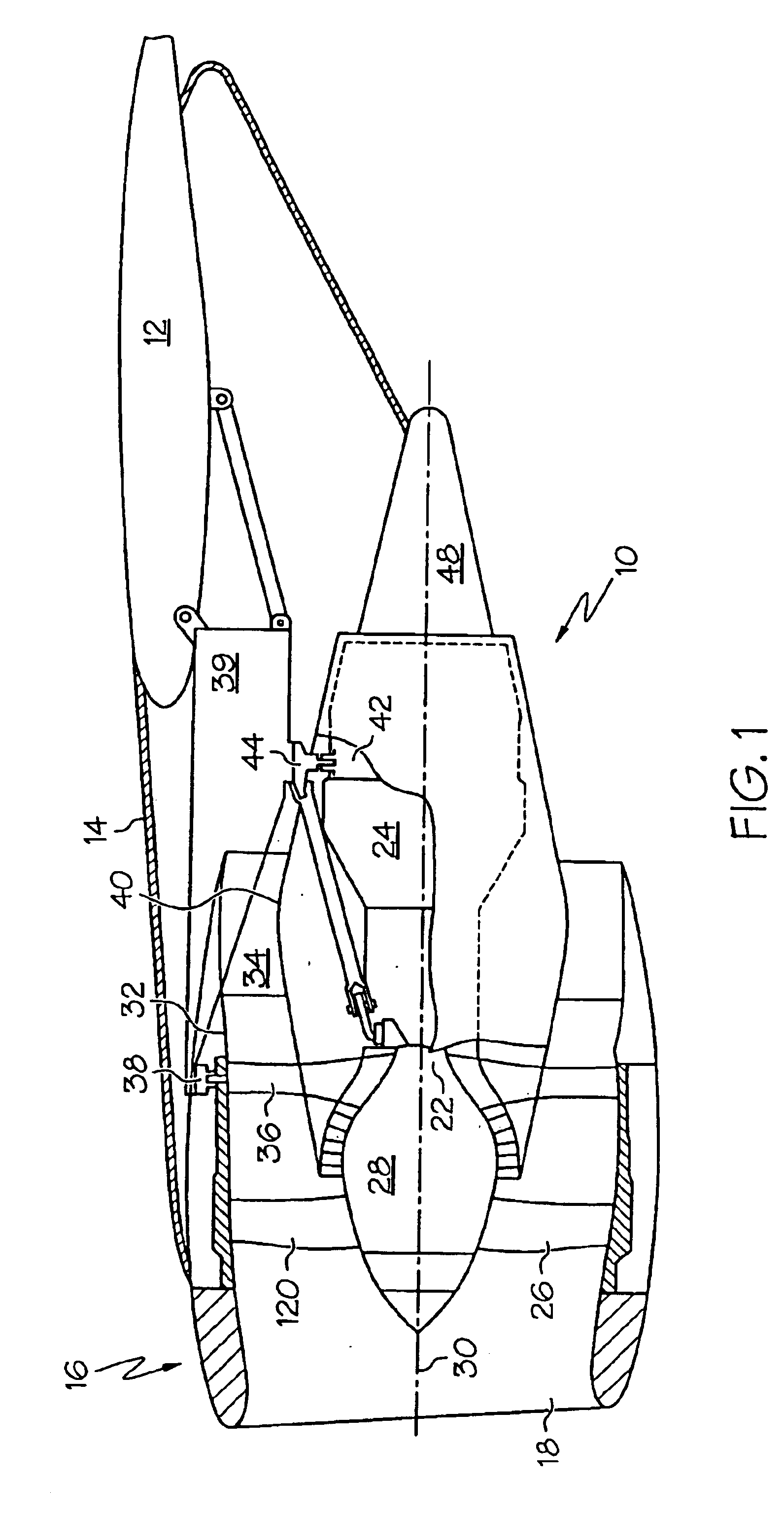
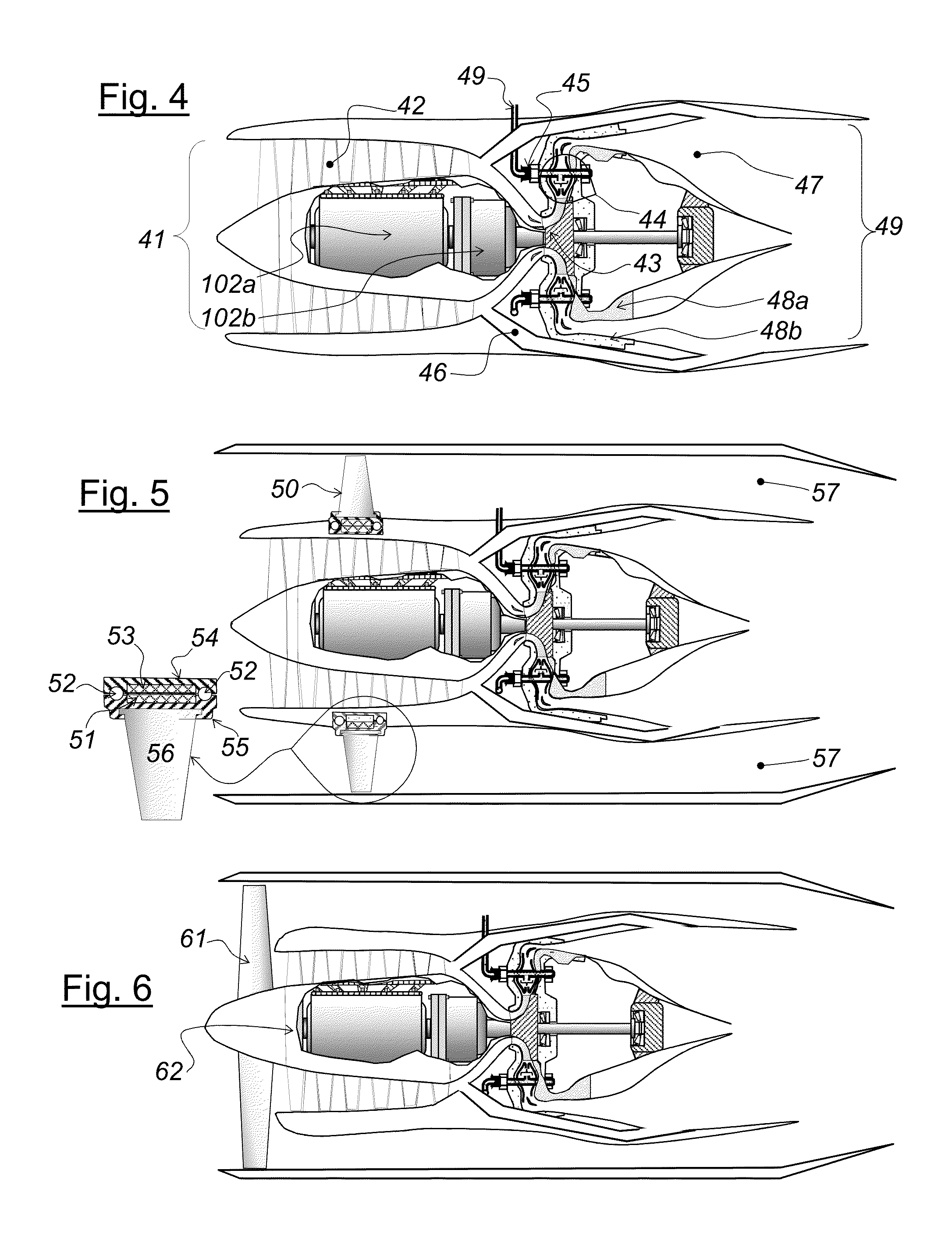
Engine mounting configuration for a turbofan gas turbine engine
ActiveUS20090056343A1Minimizes backbone bendingMinimizes engine case distortionPower plant constructionJet type power plantsNacelleEngine mount
An engine mounting configuration reacts engine thrust at an aft mount. The engine mounting configuration reduces backbone bending of the engine, intermediate case distortion and frees-up space within the core nacelle.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Monolithic composite wing manufacturing process
InactiveUS6190484B1Aircraft stabilisationPaper/cardboard wound articlesLeading edgeIncreased torsion
A method of manufacturing a monolithic composite wing without using mechanical fasteners is described. The process begins with the formation of a center wing box in combination with a pair of spars, riblets and a pair of skin-molds including the wrapping and binding of the box by means of resin impregnated composite tapes. Next, additional cells are adjoined contiguously on either side of the current framework and an overlap wrapping and bonding process is continued around the current framework. The overlap wrapping and binding procedure provides increased torsion stiffness and reduced structural weight. All cells up to the leading and trailing edges will be included in the assembly process. Conduits to convey fuel, hydraulic fluid and electrical wiring will also be installed in designated cells. Finally, the completed wing will be cured in an autoclave under uniform pressure and temperature.
Owner:APPA KARI
Multi-receiver communication system with distributed aperture antenna
InactiveUS20070176840A1Reduce distanceEqually distributedNear-field transmissionWeight reductionCommunications systemEngineering
A multi-user wireless communication system for use in an enclosed space includes a distributed aperture antenna having multiple apertures distributed along an outer shield of the antenna. The apertures allow radiated energy to leak from the antenna and form low-power, localized electric fields that can couple receivers to the antenna. The multiple electric fields ensure that the electric field strength is distributed evenly throughout the communication system. The low-power electric fields also reduce the likelihood of electric field leakage that may cause interference with other communication systems outside the enclosed space.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
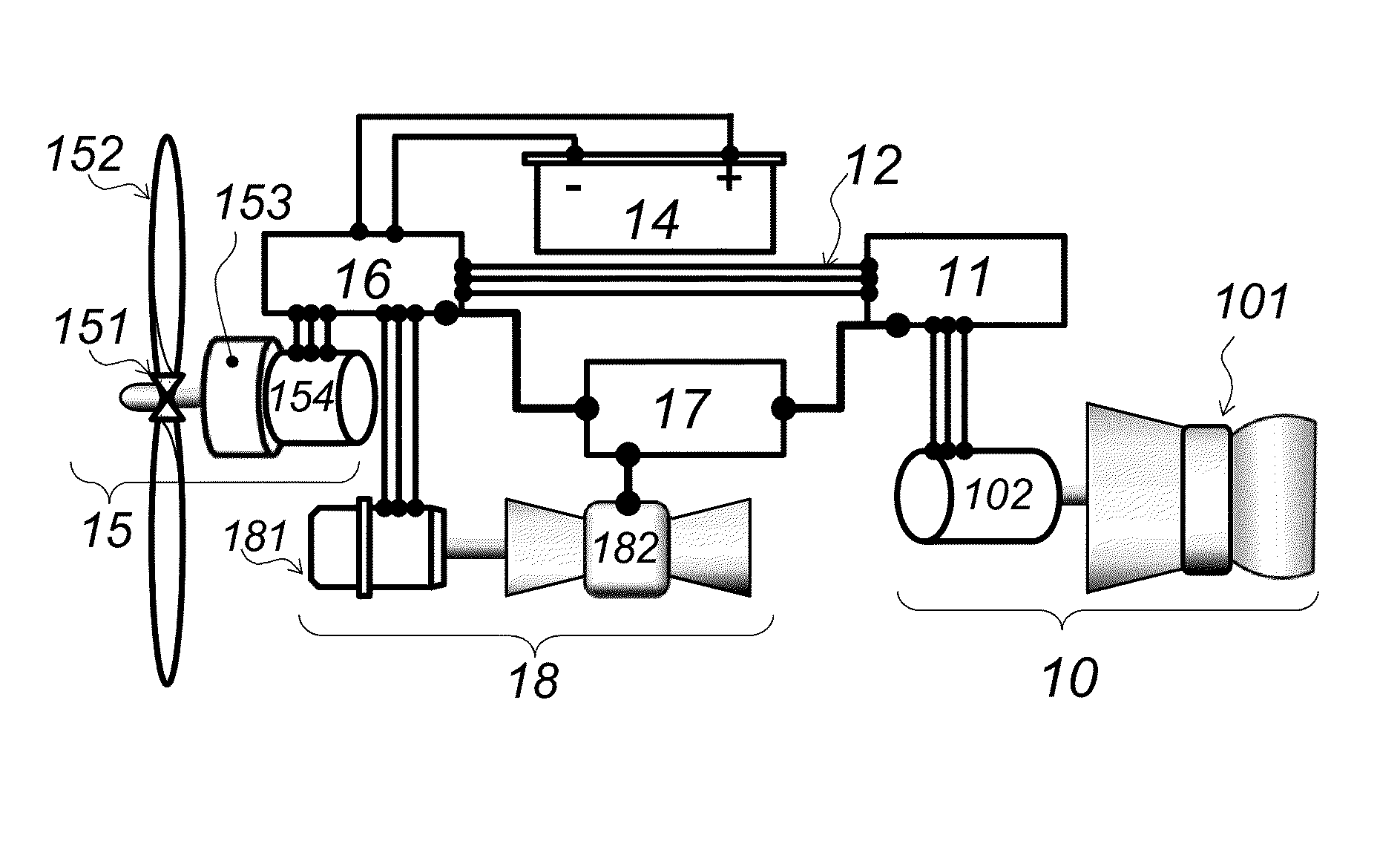
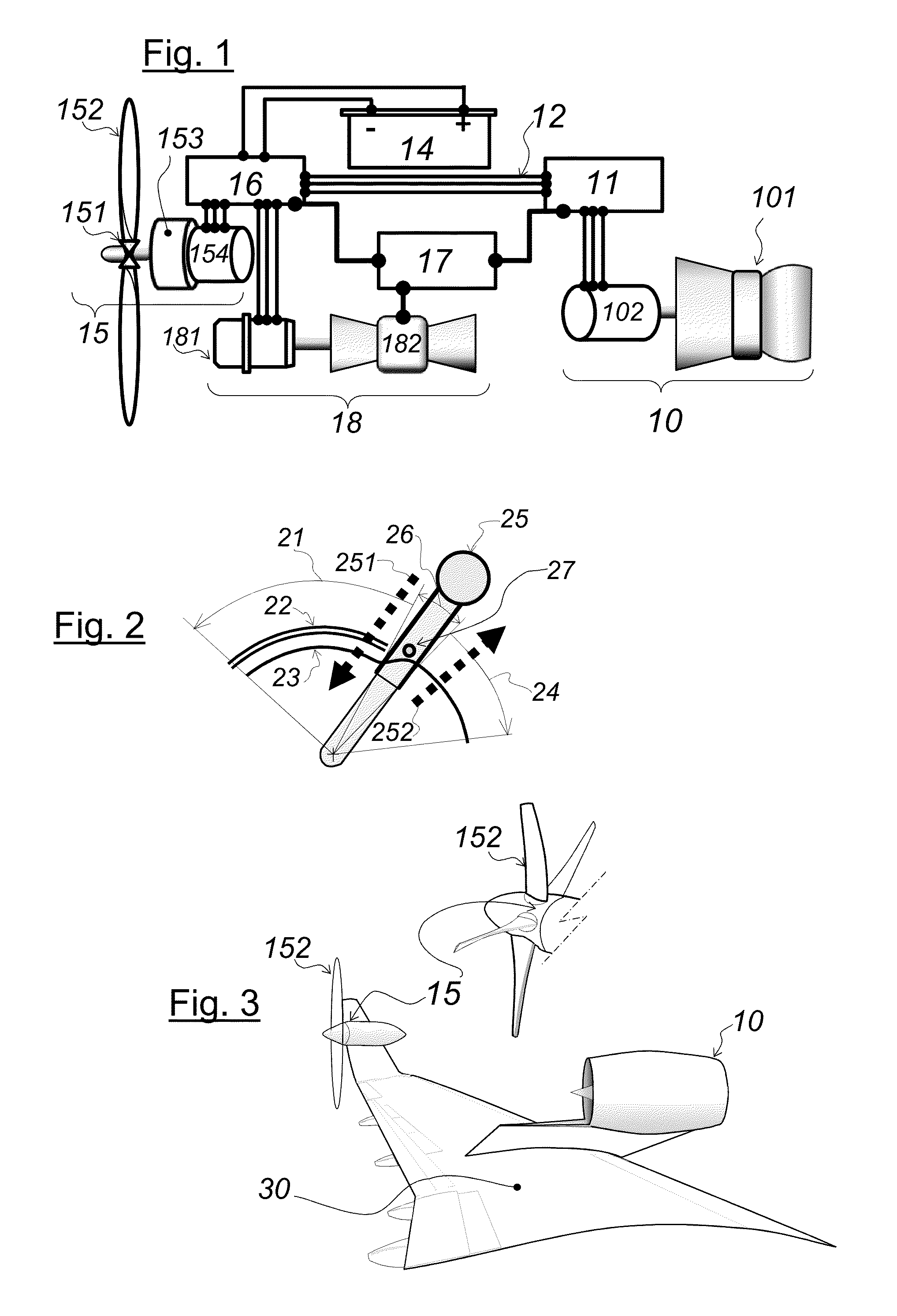
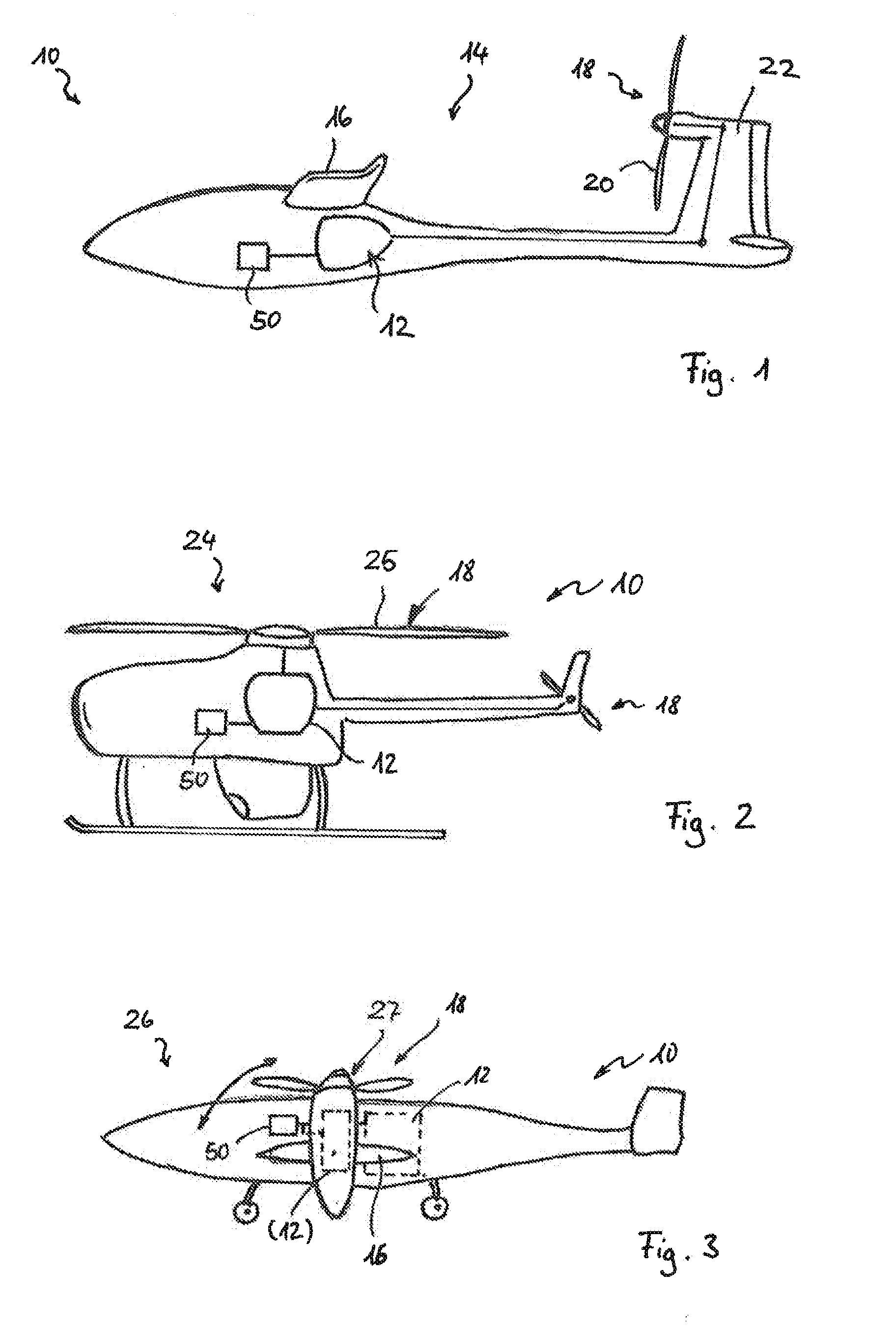
Aircraft using turbo-electric hybrid propulsion system
InactiveUS20090145998A1Reduce usageAnalogue computers for vehiclesGas turbine type power plantsFlight vehicleCoupling
An air vehicle incorporating a hybrid propulsion system. The system includes a gas turbine engine as a first motive power source, and one or more battery packs as a second motive power source. Through selective coupling to a DC electric motor that can in turn be connected to a bladed rotor or other lift-producing device, the motive sources provide differing ways in which an aircraft can operate. In one example, the gas turbine engine can provide operation for a majority of the flight envelope of the aircraft, while the battery packs can provide operation during such times when gas turbine-based motive power is unavailable or particularly disadvantageous. In another example, both sources of motive power may be decoupled from the bladed rotor such that the vehicle can operate as an autogyro.
Owner:SALYER IVAL O
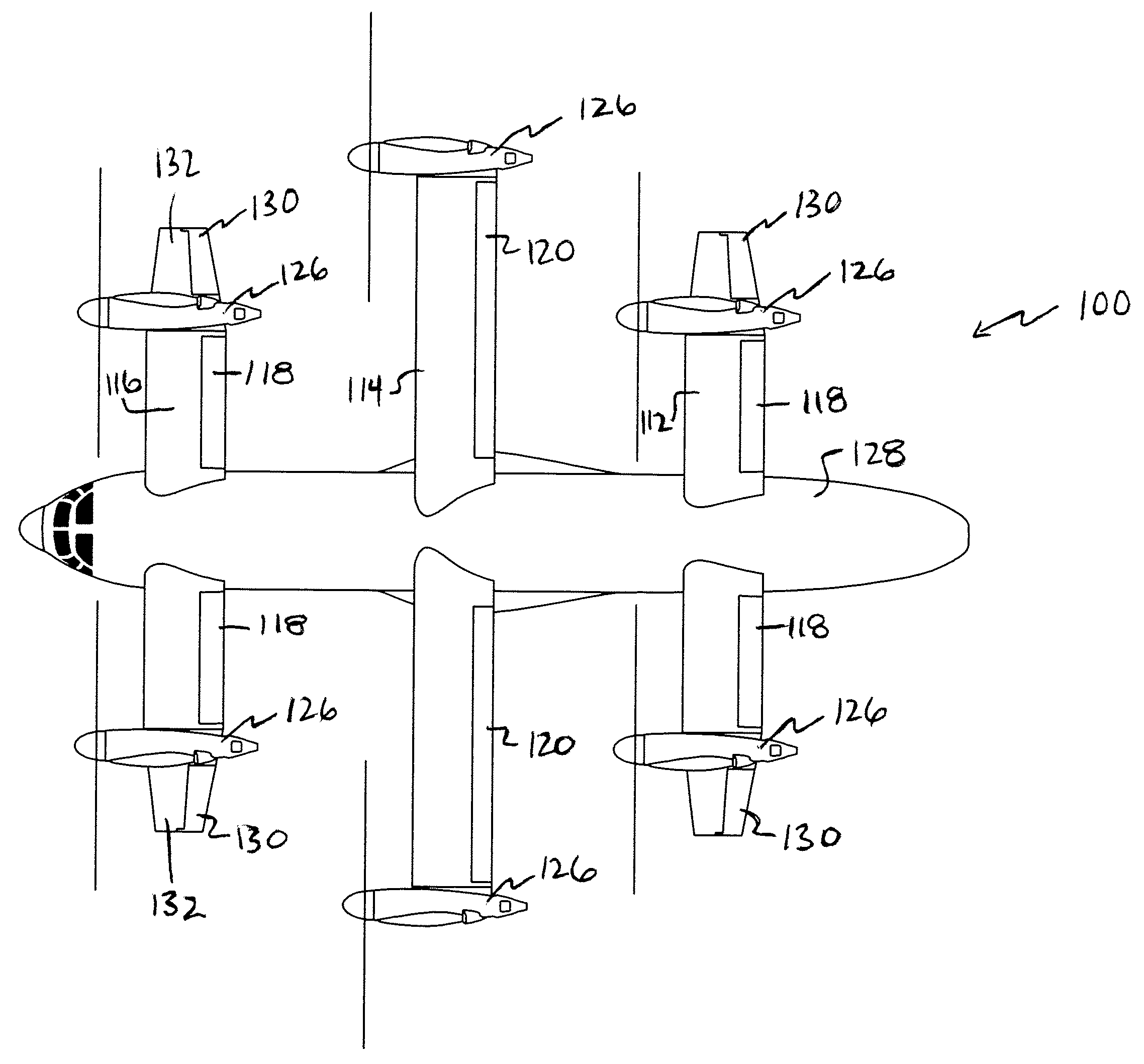
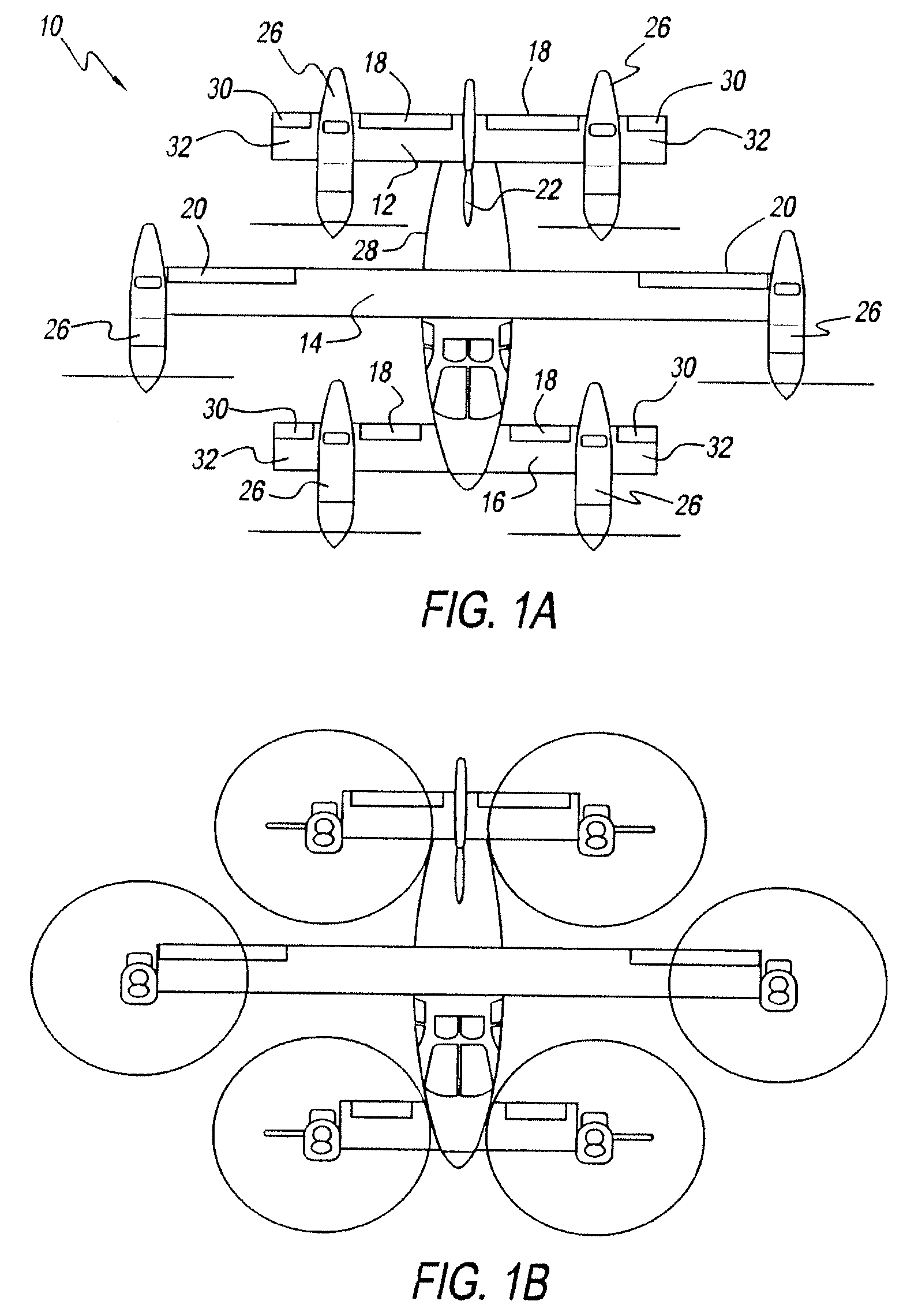
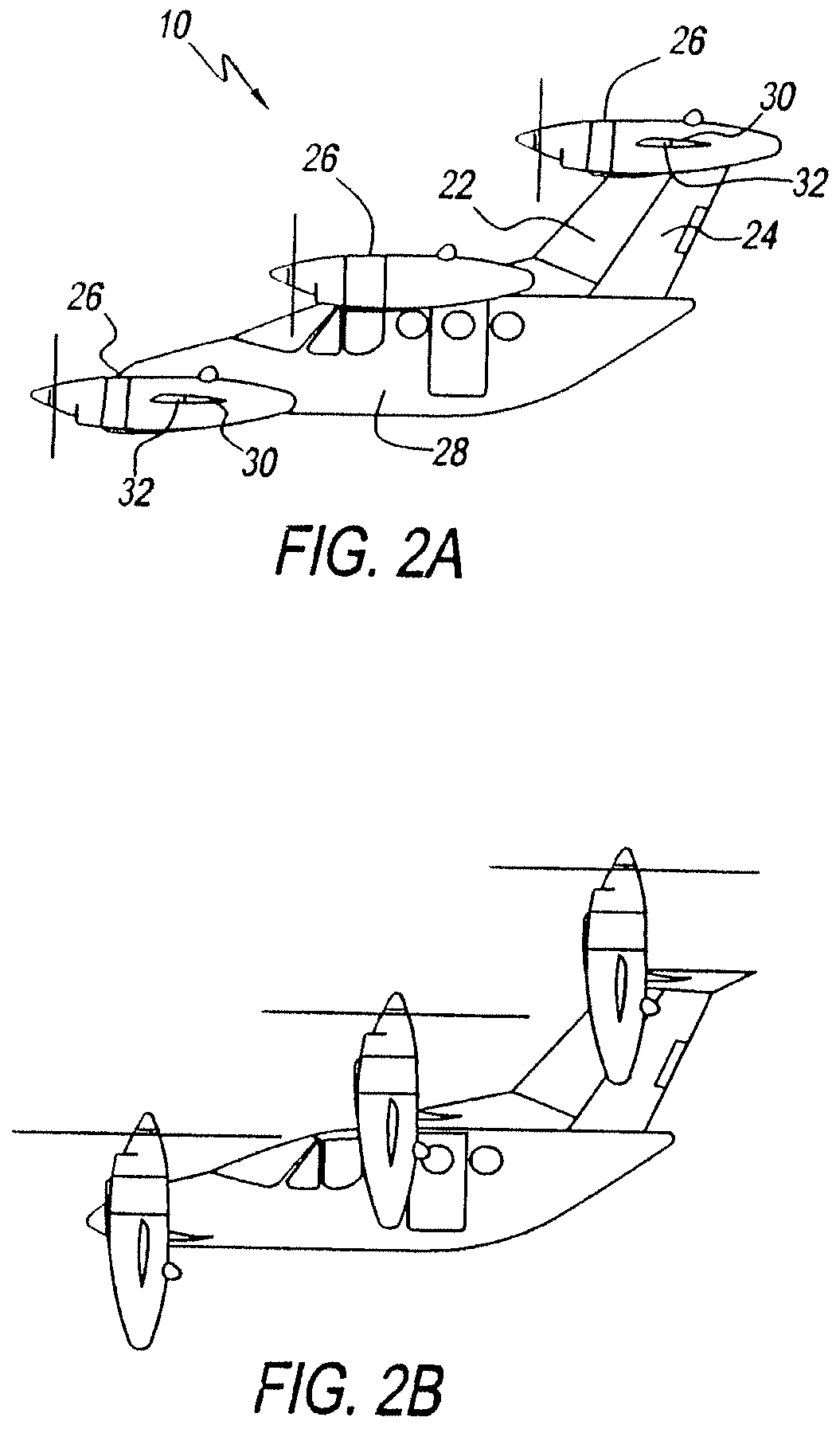
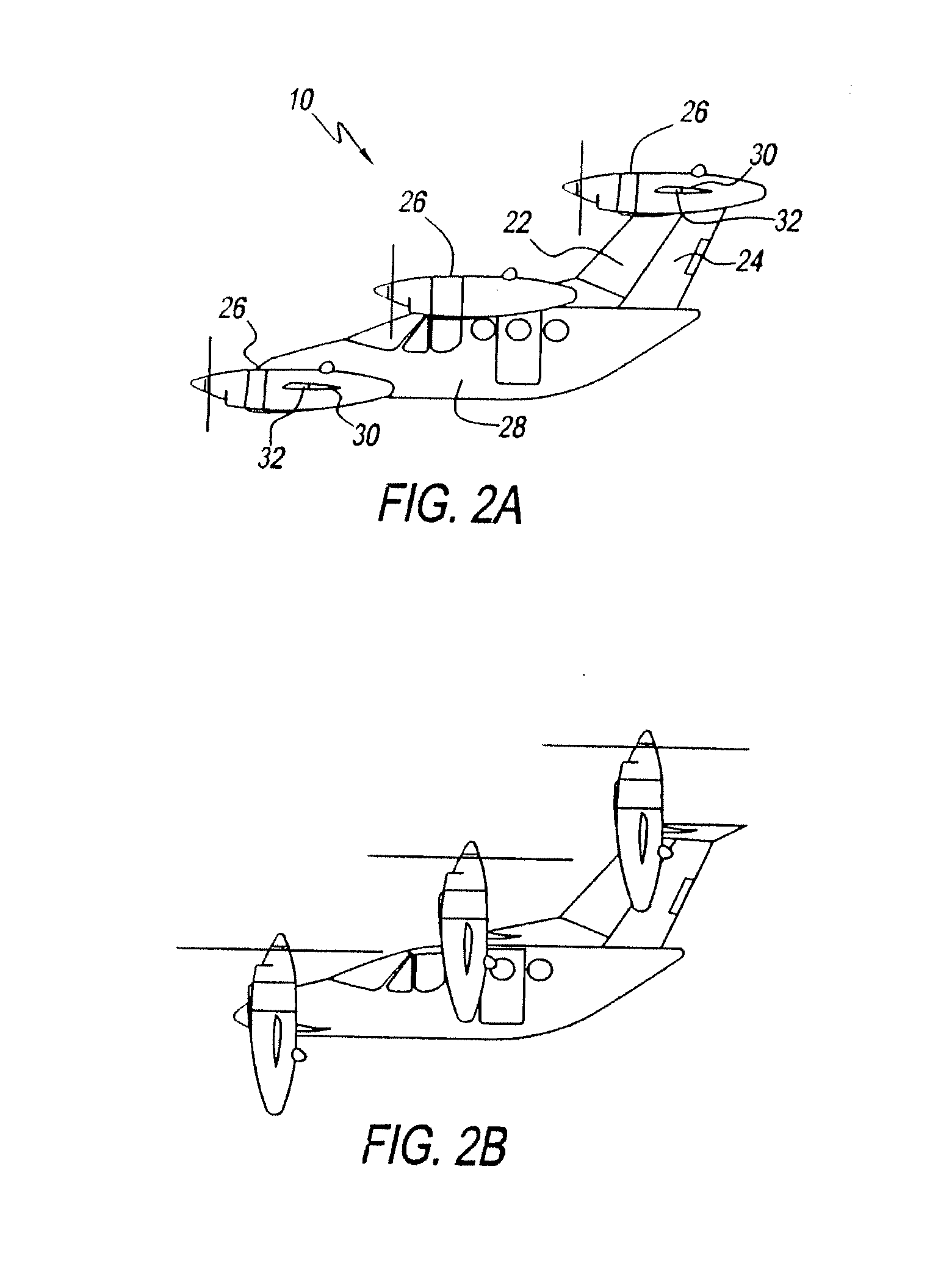
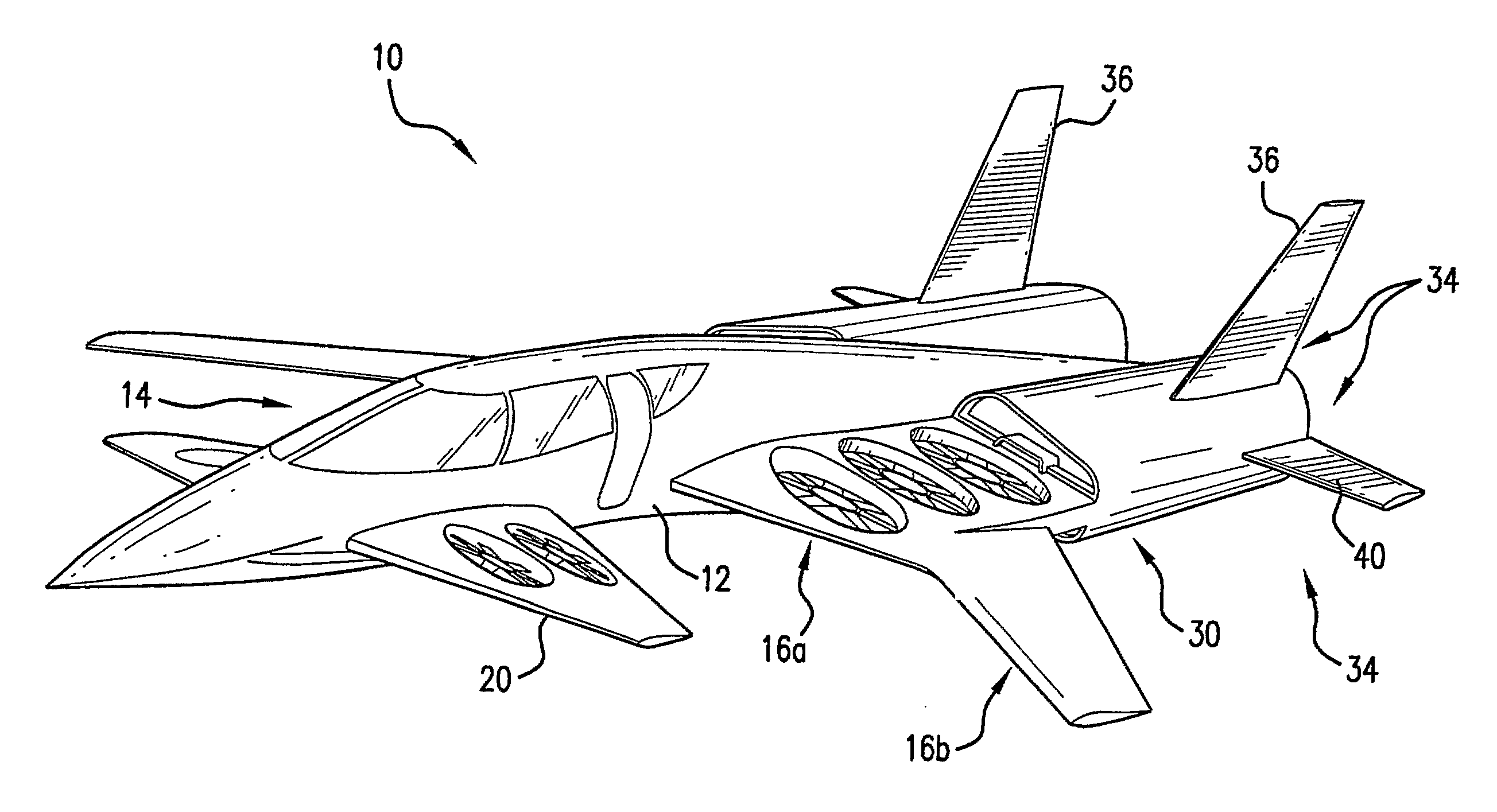
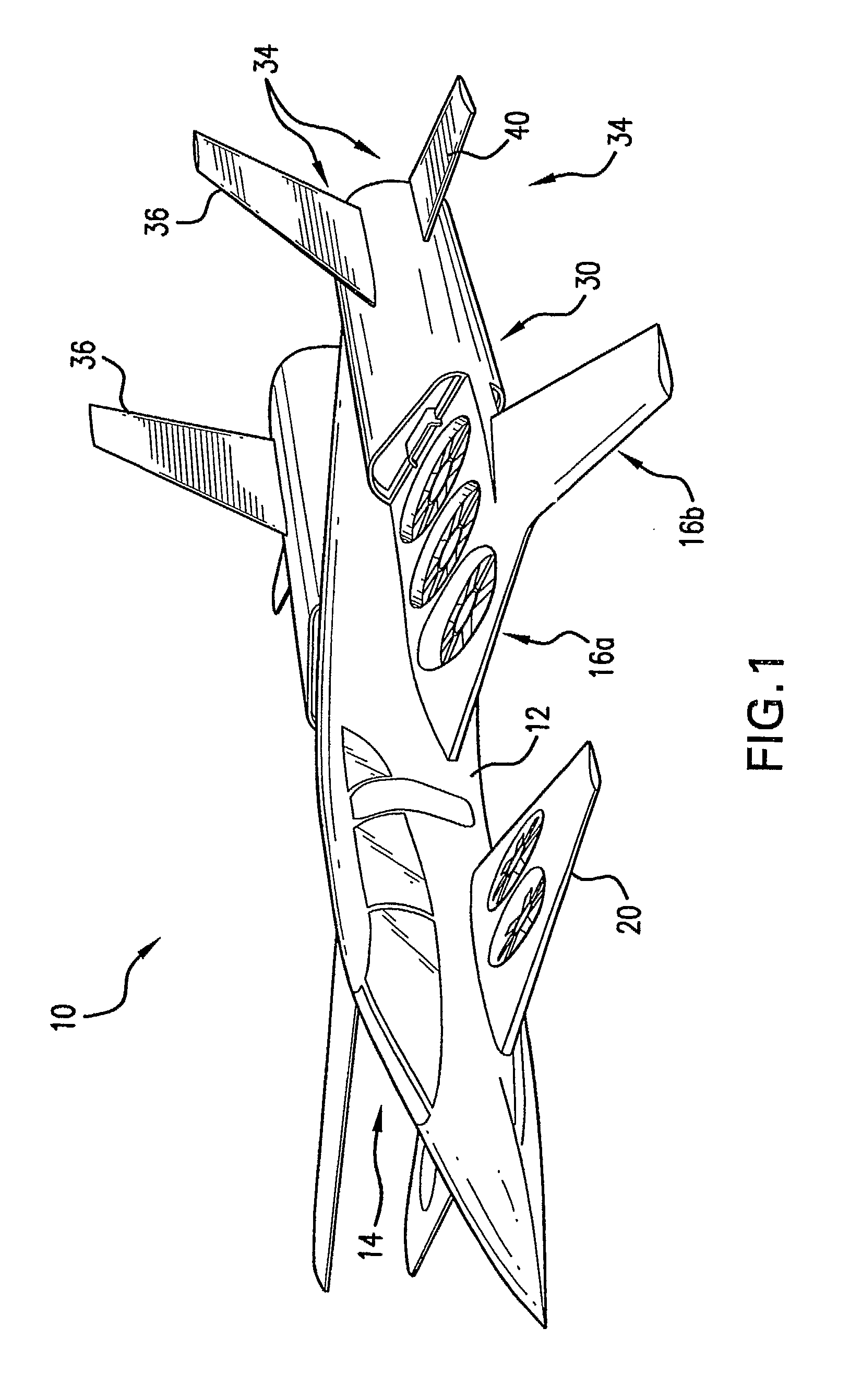
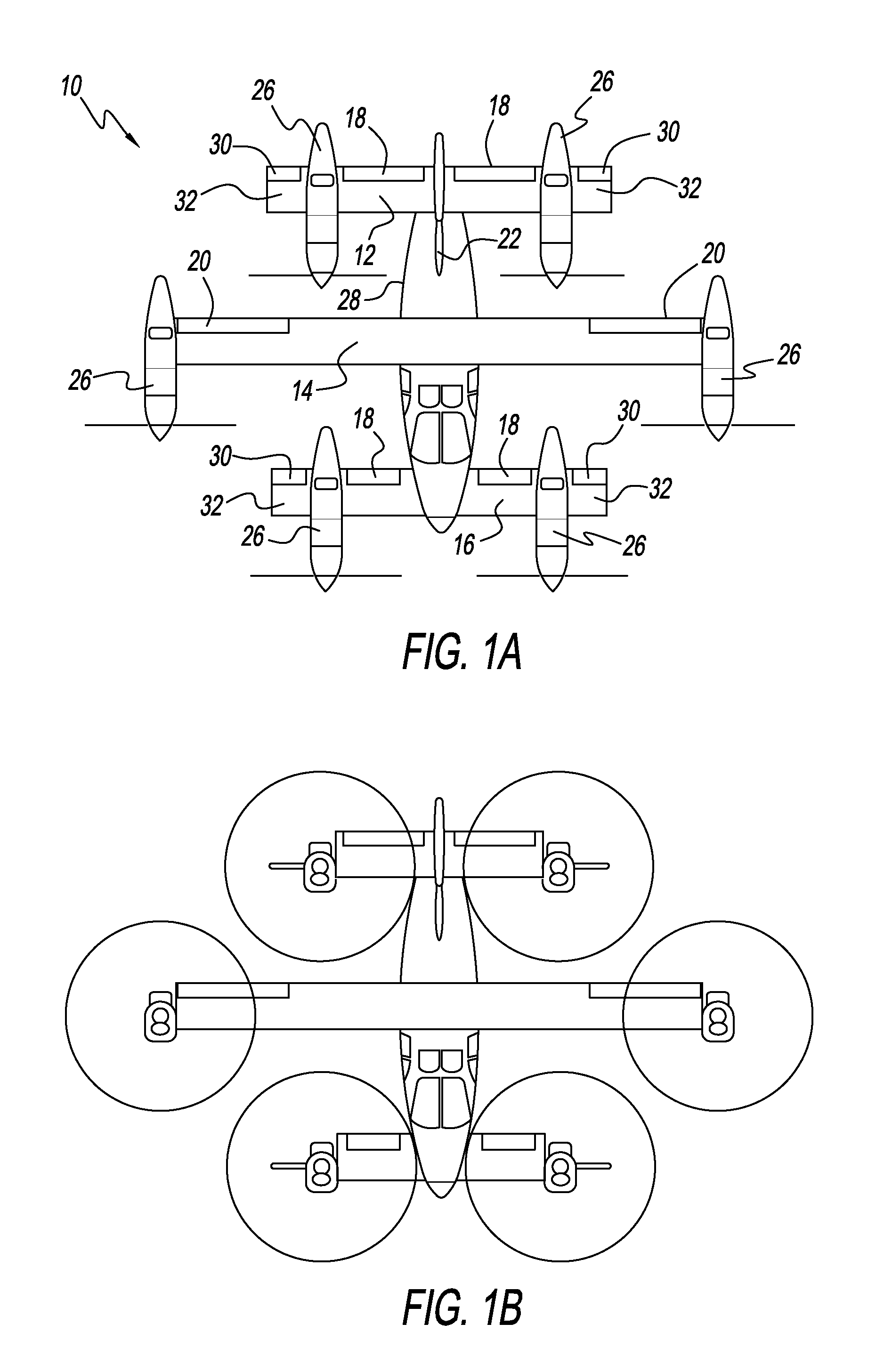
Three wing, six-tilt propulsion unit, VTOL aircraft
Owner:OLIVER VTOL
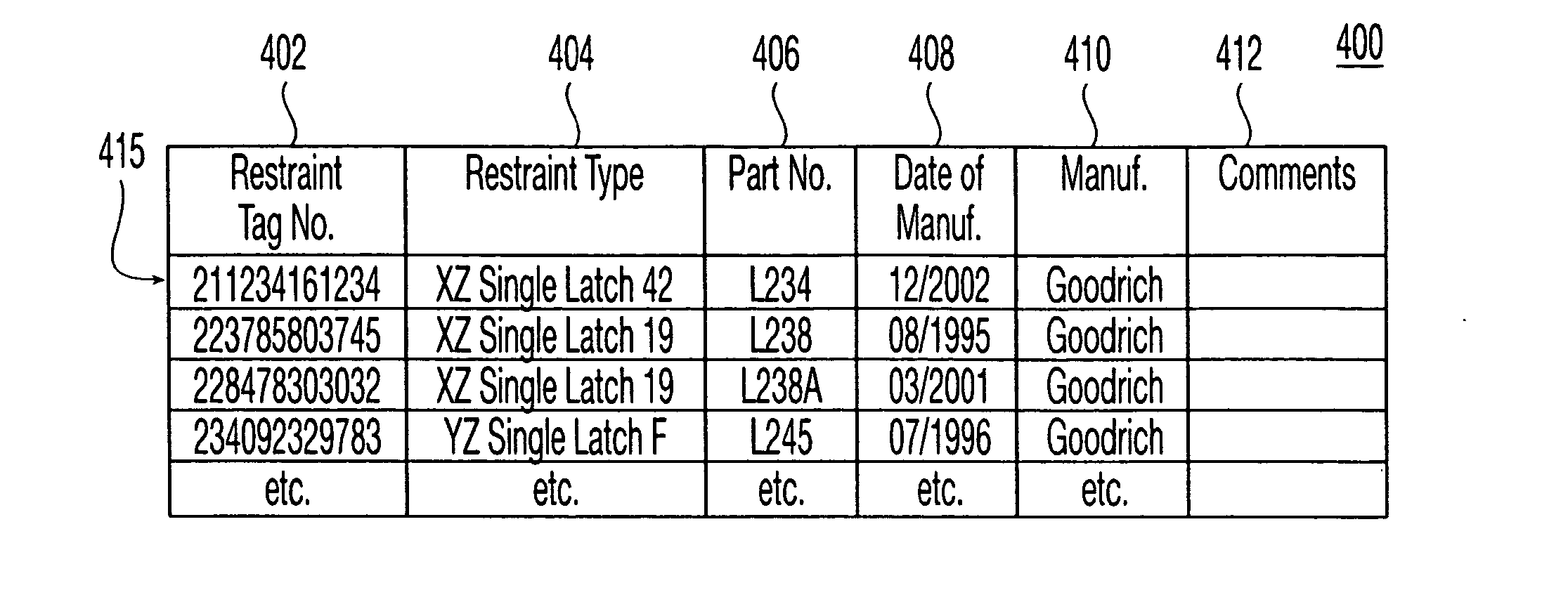
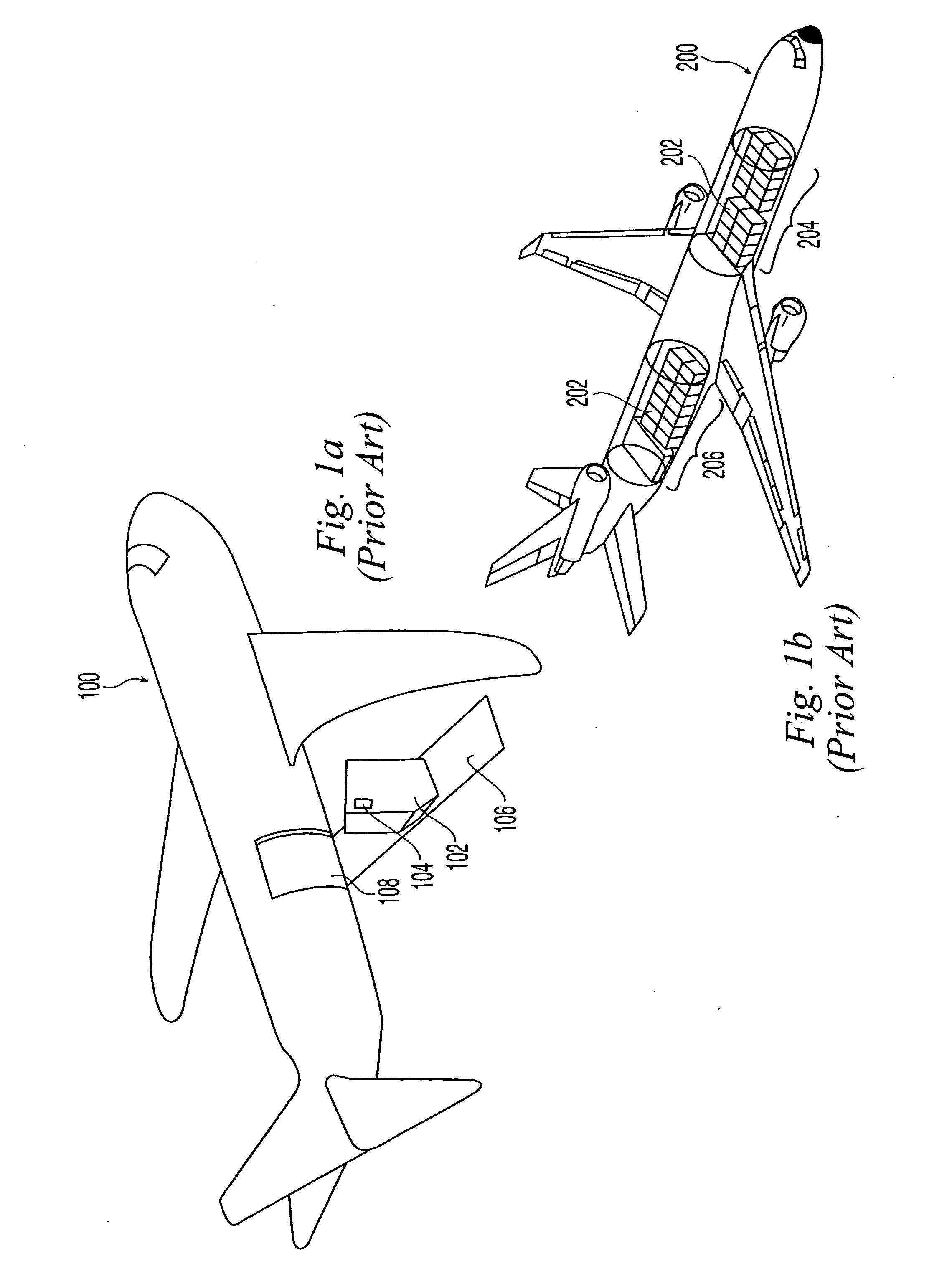
Aircraft cargo loading logistics system
A cargo loading logistics system for verifying cargo loaded on an aircraft receives a desired restraint configuration from a database and determines an actual restraint configuration on the aircraft by receiving data from a plurality of machine readable identifiers corresponding to a plurality of install points and data from a plurality of machine readable identifiers corresponding to a plurality of restraints. The cargo loading logistics system then compares the desired restraint configuration with the actual restraint configuration and determines if the aircraft is properly configured to be loaded for an upcoming flight.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
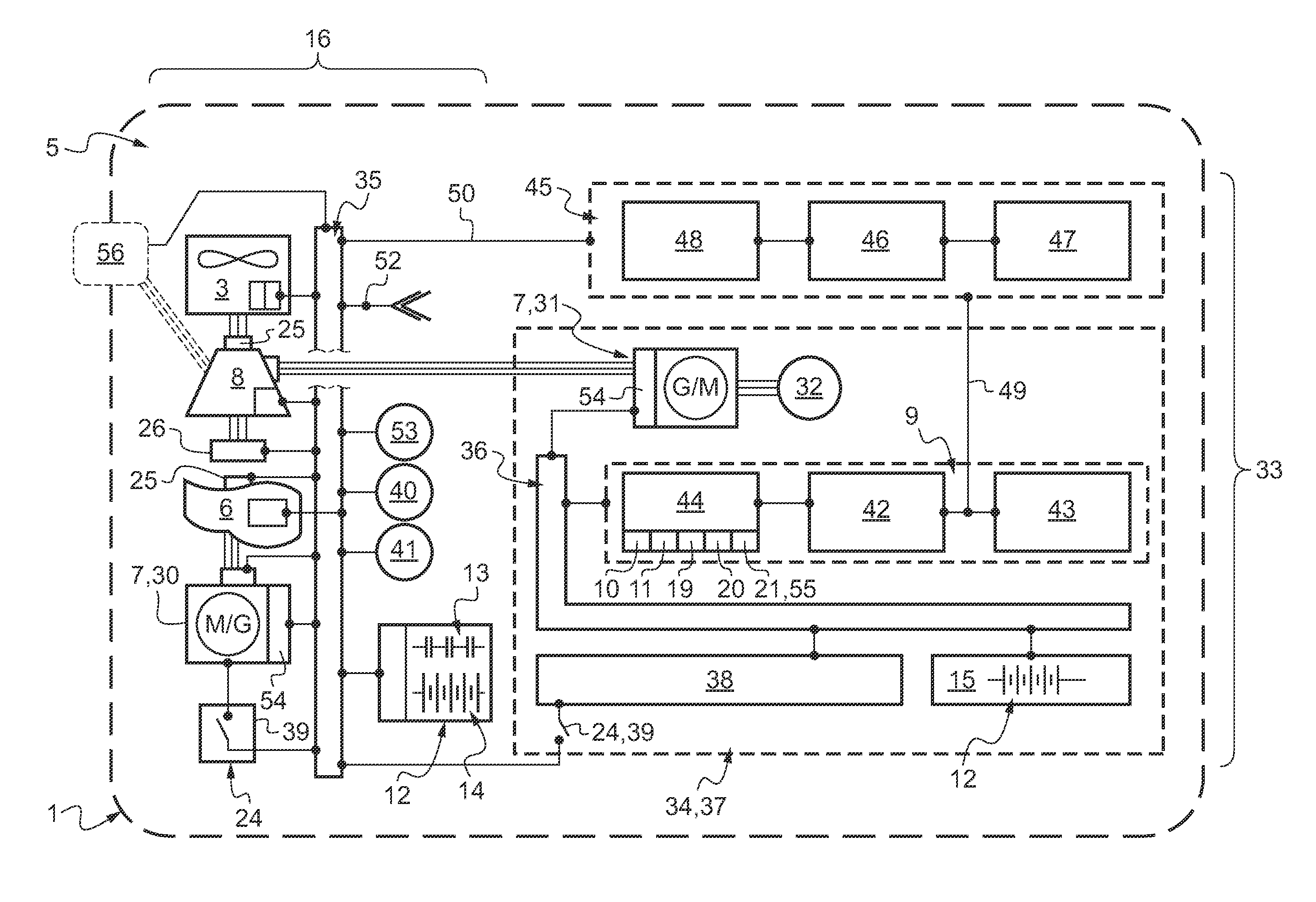
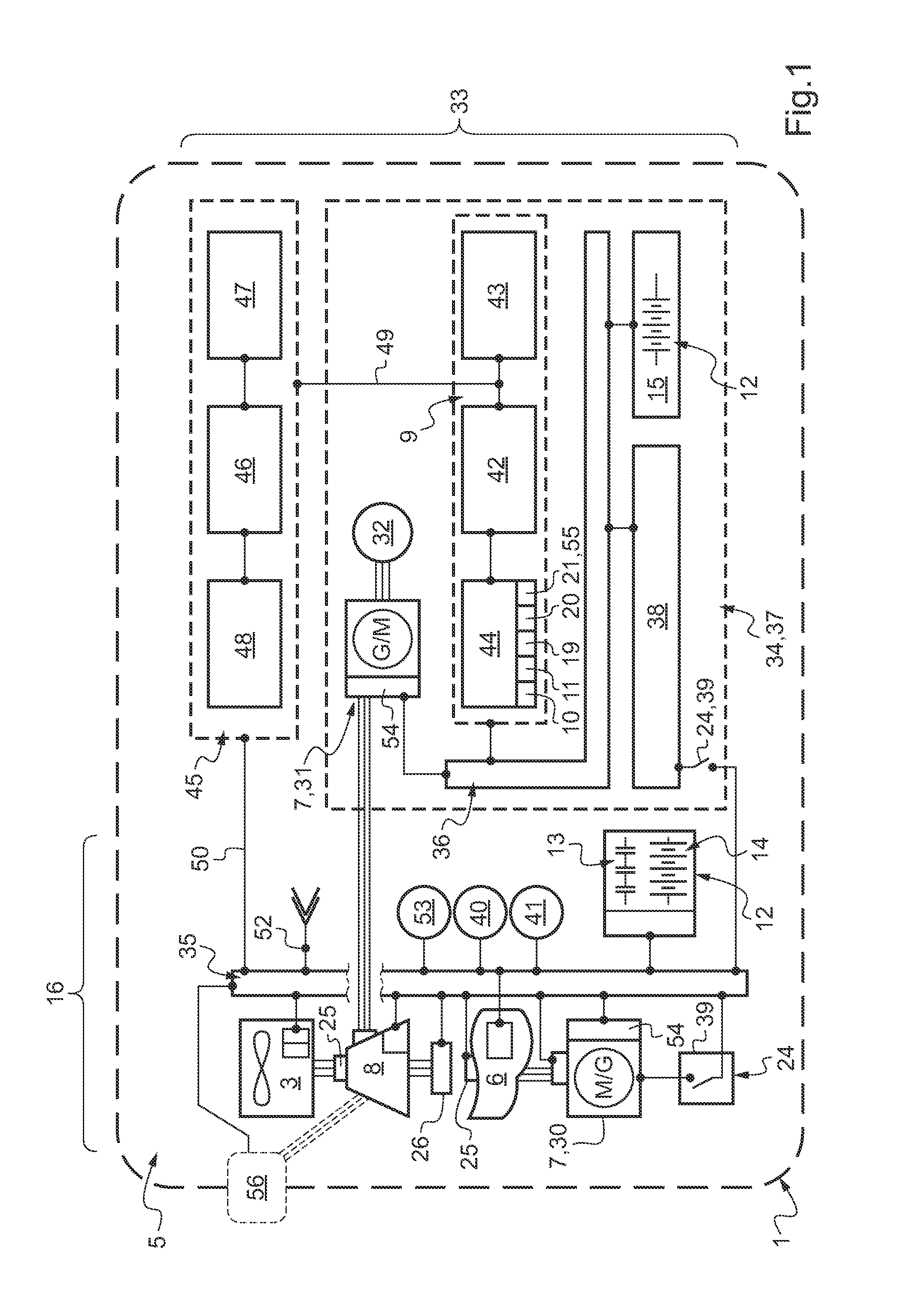
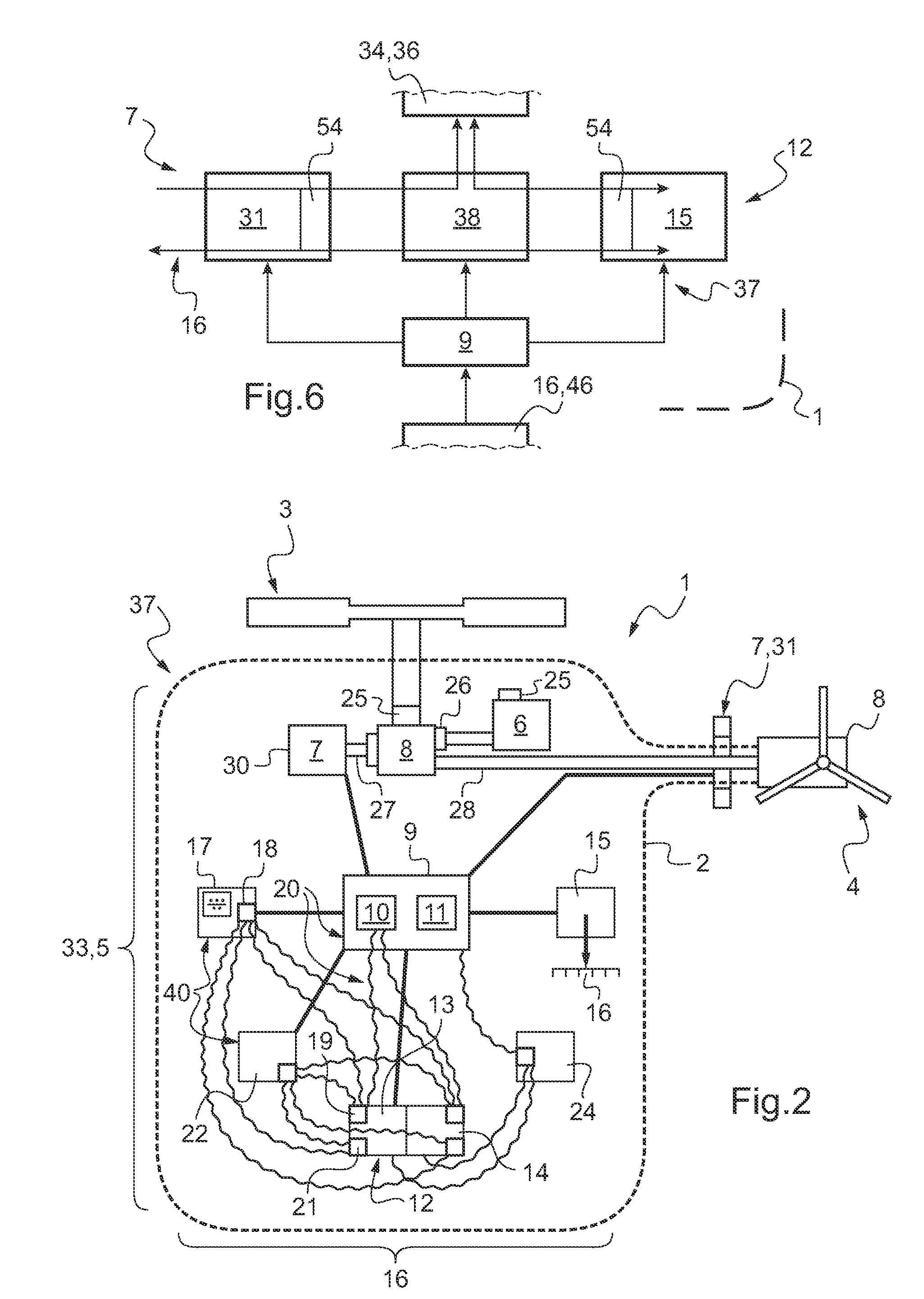
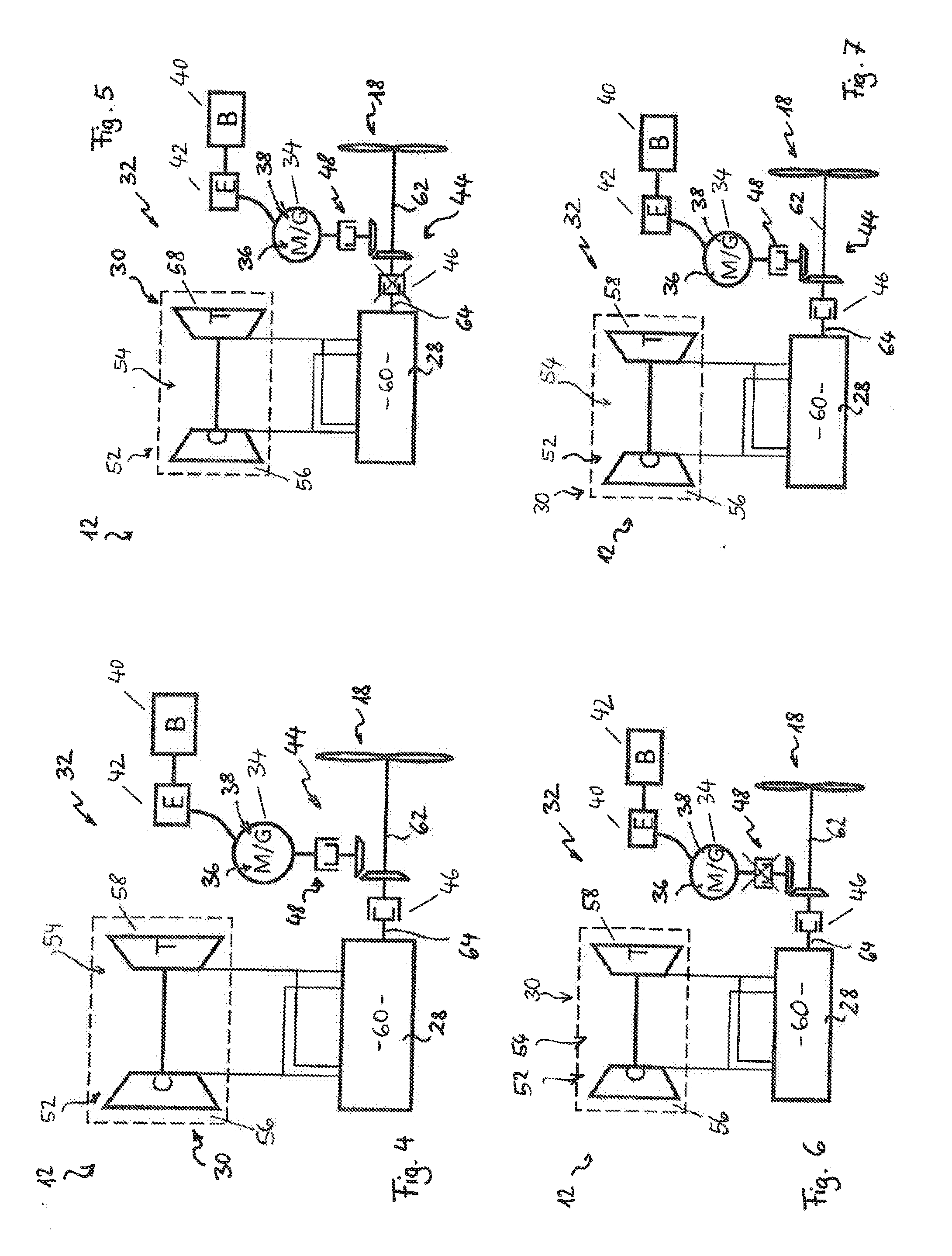
Electrical architecture for a rotary wing aircraft with a hybrid power plant
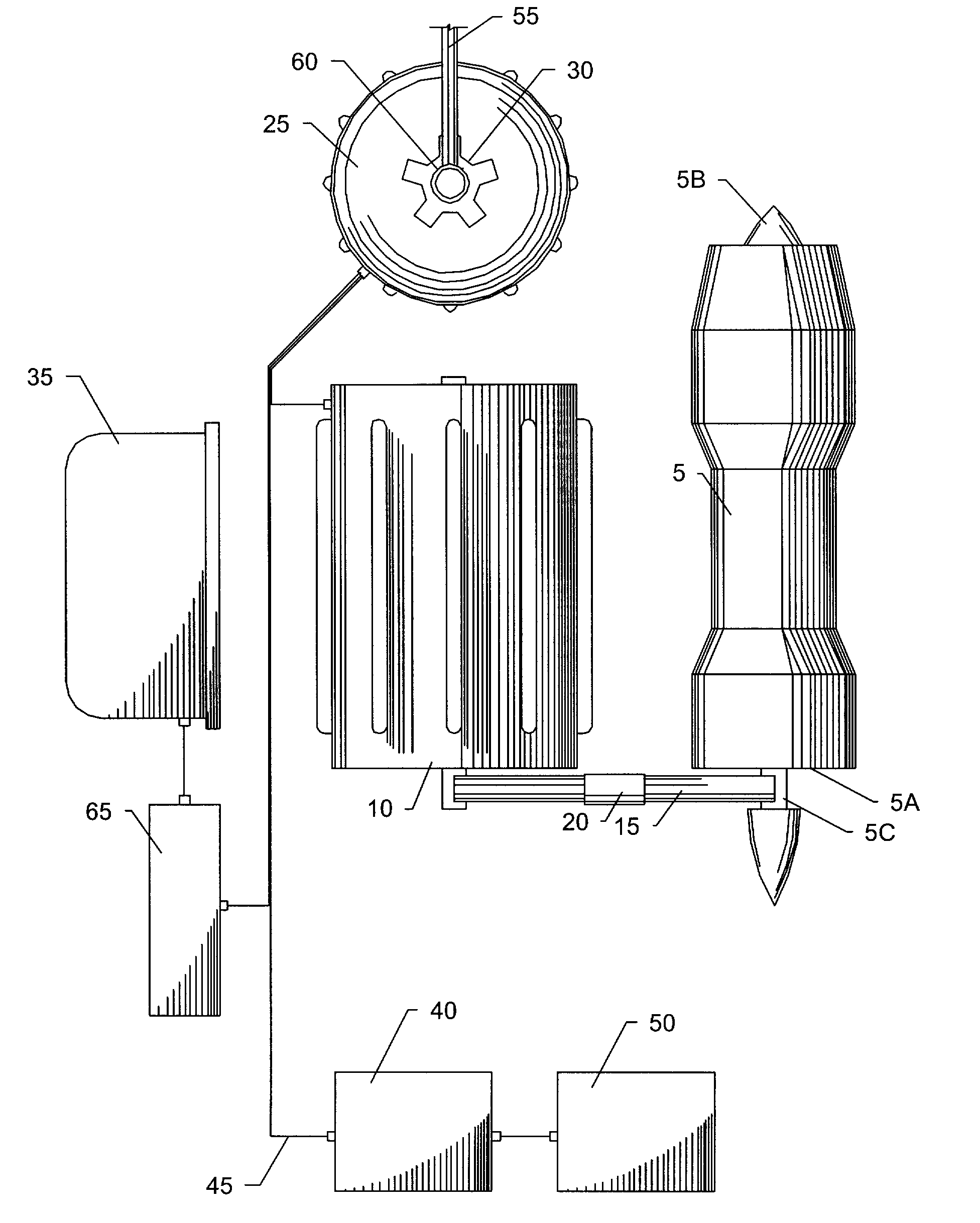
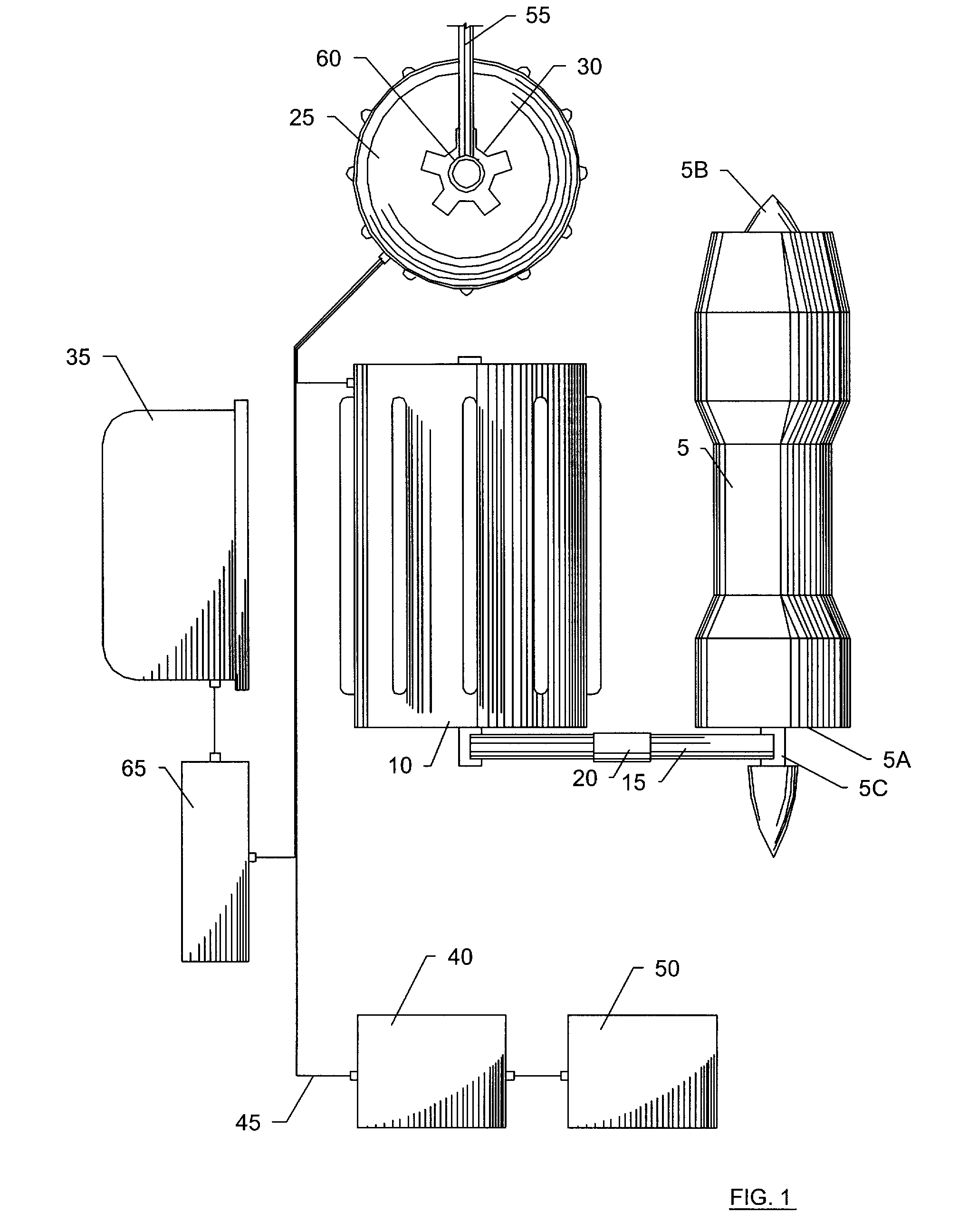
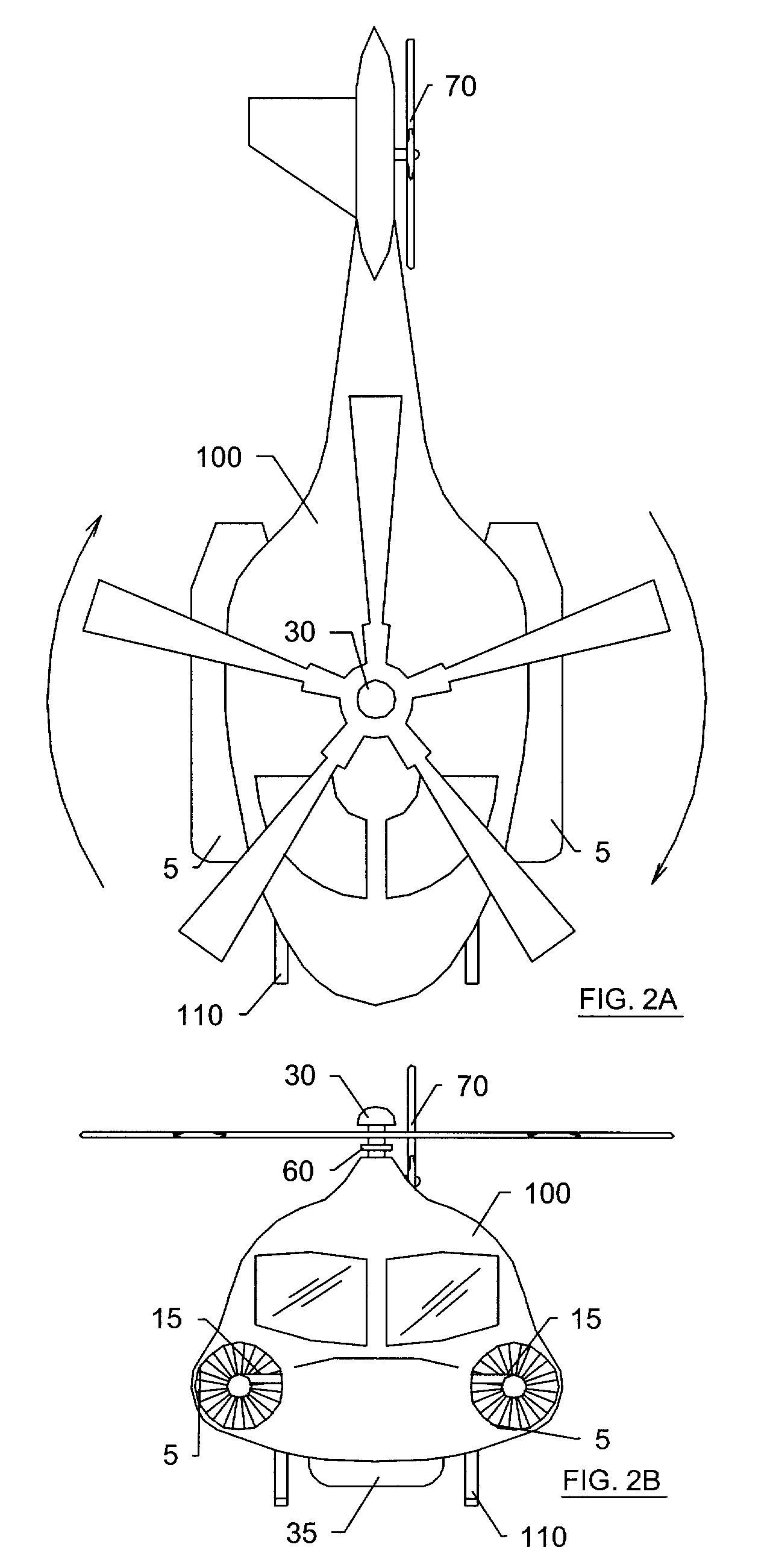
ActiveUS20120025032A1Reduce loadSave energy consumptionAircraft power plant componentsPropulsion by batteries/cellsOn boardEngineering
A hybrid power plant (5) for an aircraft (1) comprises at least: a hybrid drive system (37) having a main on-board electricity network (16) and an auxiliary electricity network (34); and a selective adaptation interface (38) arranged to enable electrical energy to be exchanged selectively between the main and auxiliary electricity networks (16; 34). At least one engine and a hybrid drive auxiliary electrical machine (7, 31) are mechanically connected to a transmission (8); said machine (7) being electrically connected to at least one auxiliary electrical bus (36) in parallel with at least one auxiliary device for delivering electric charge.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
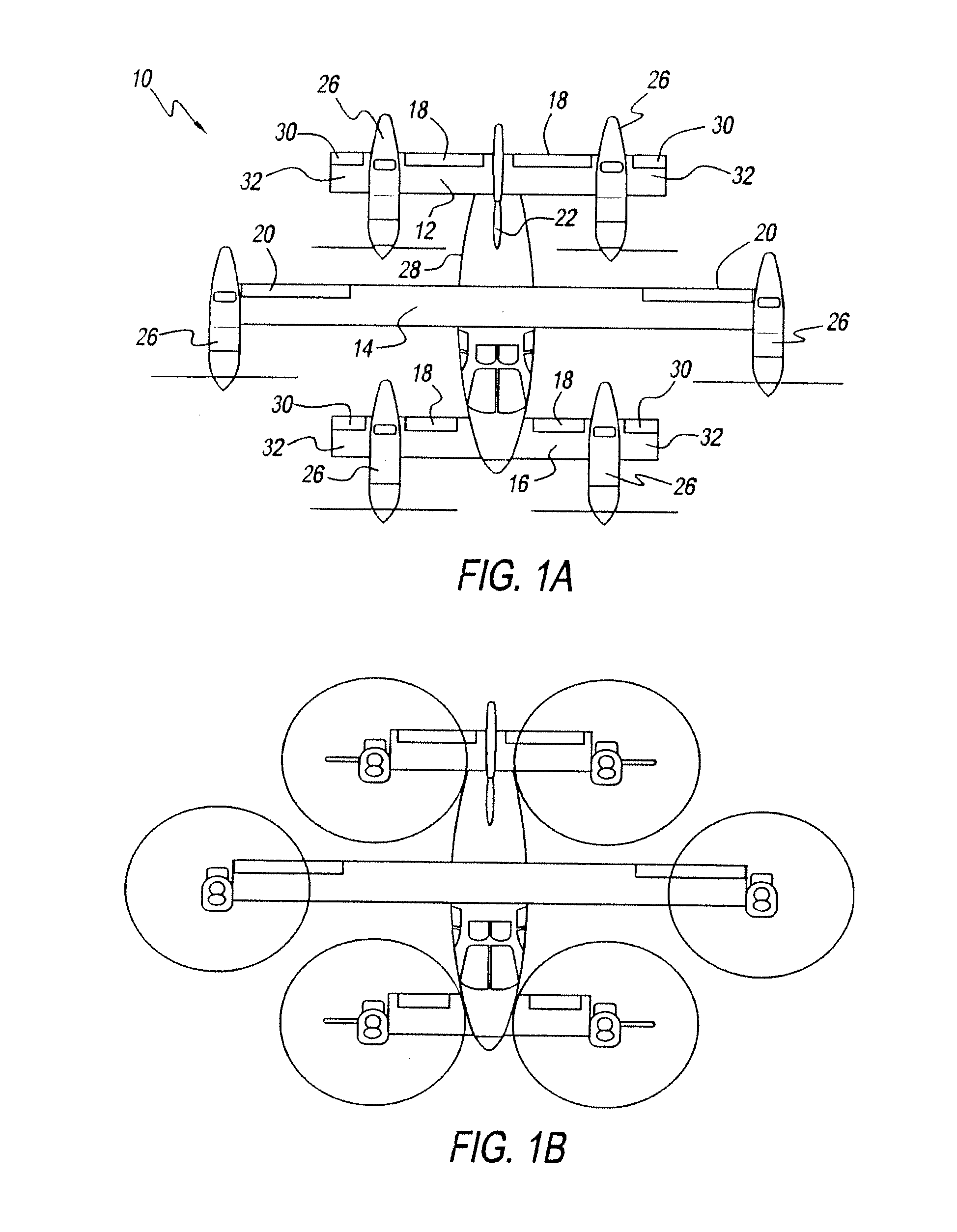
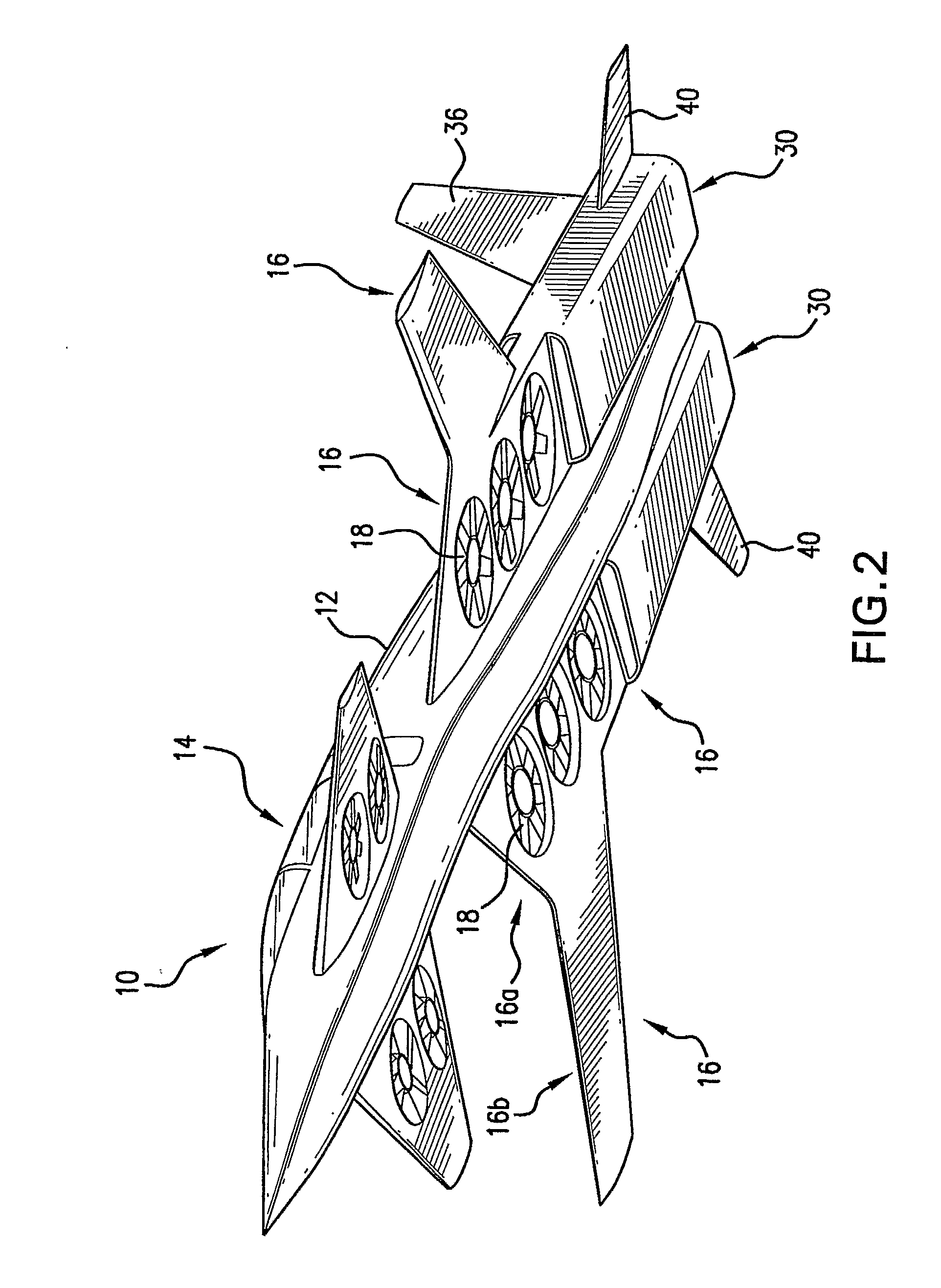
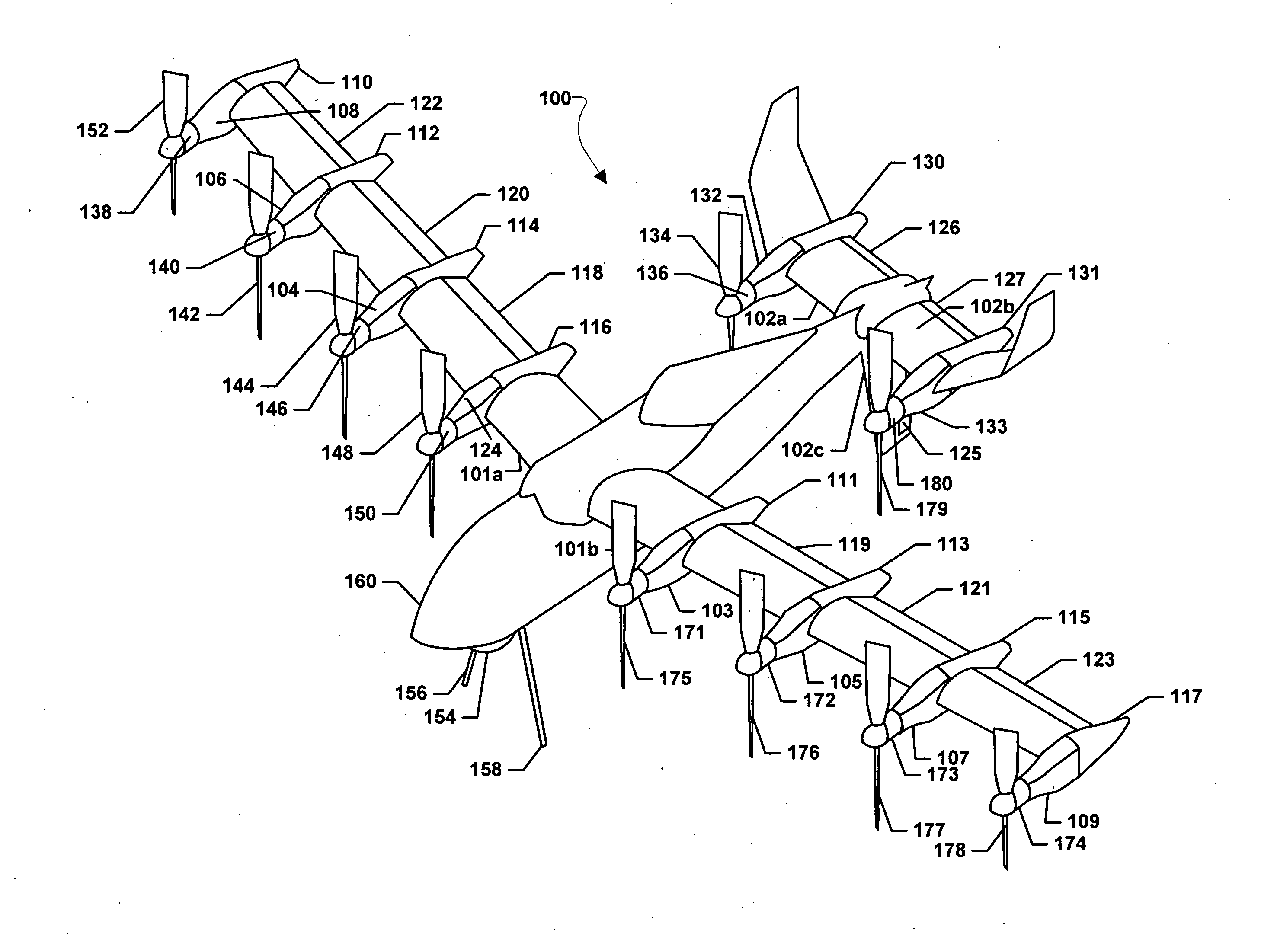
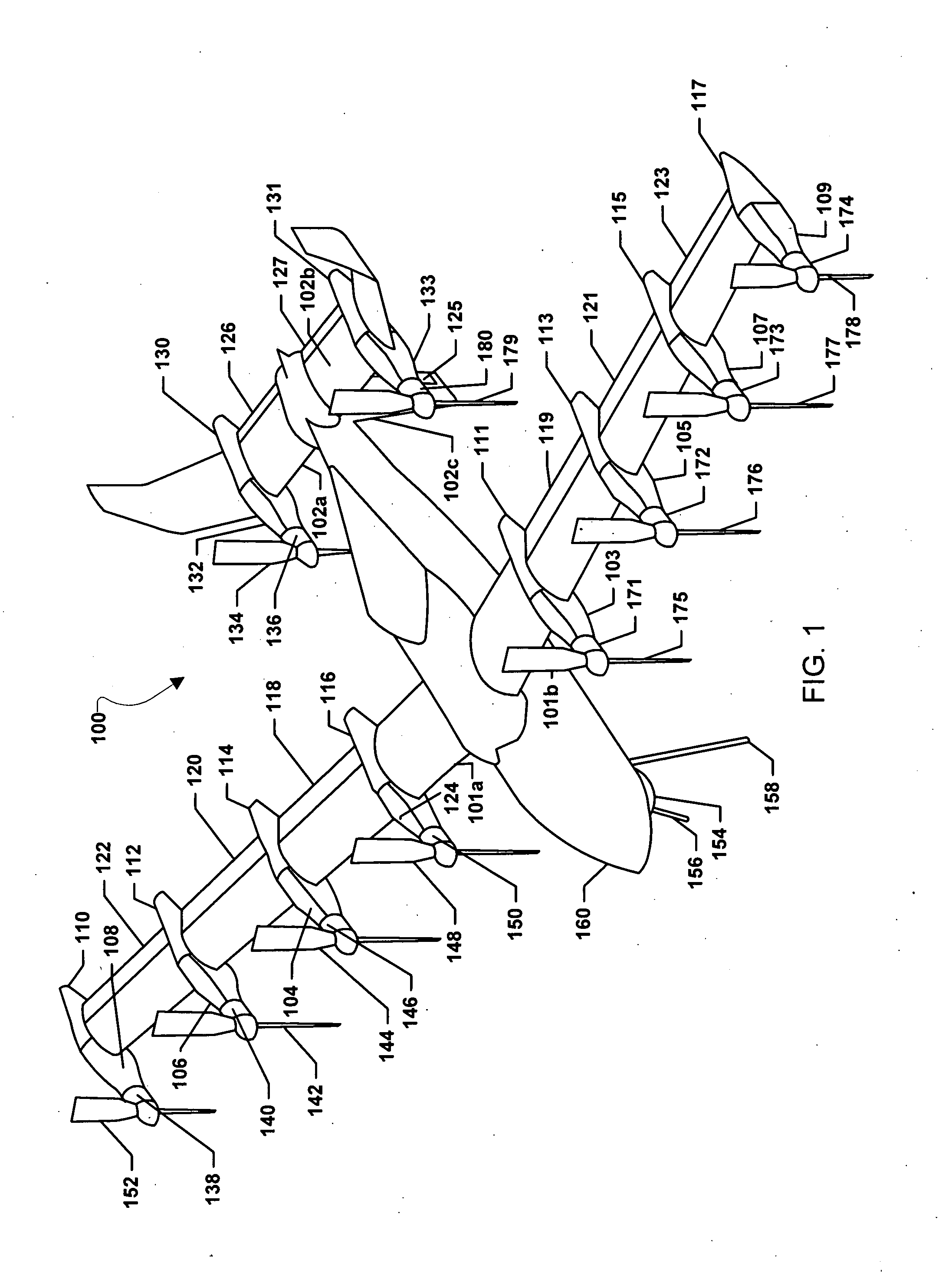
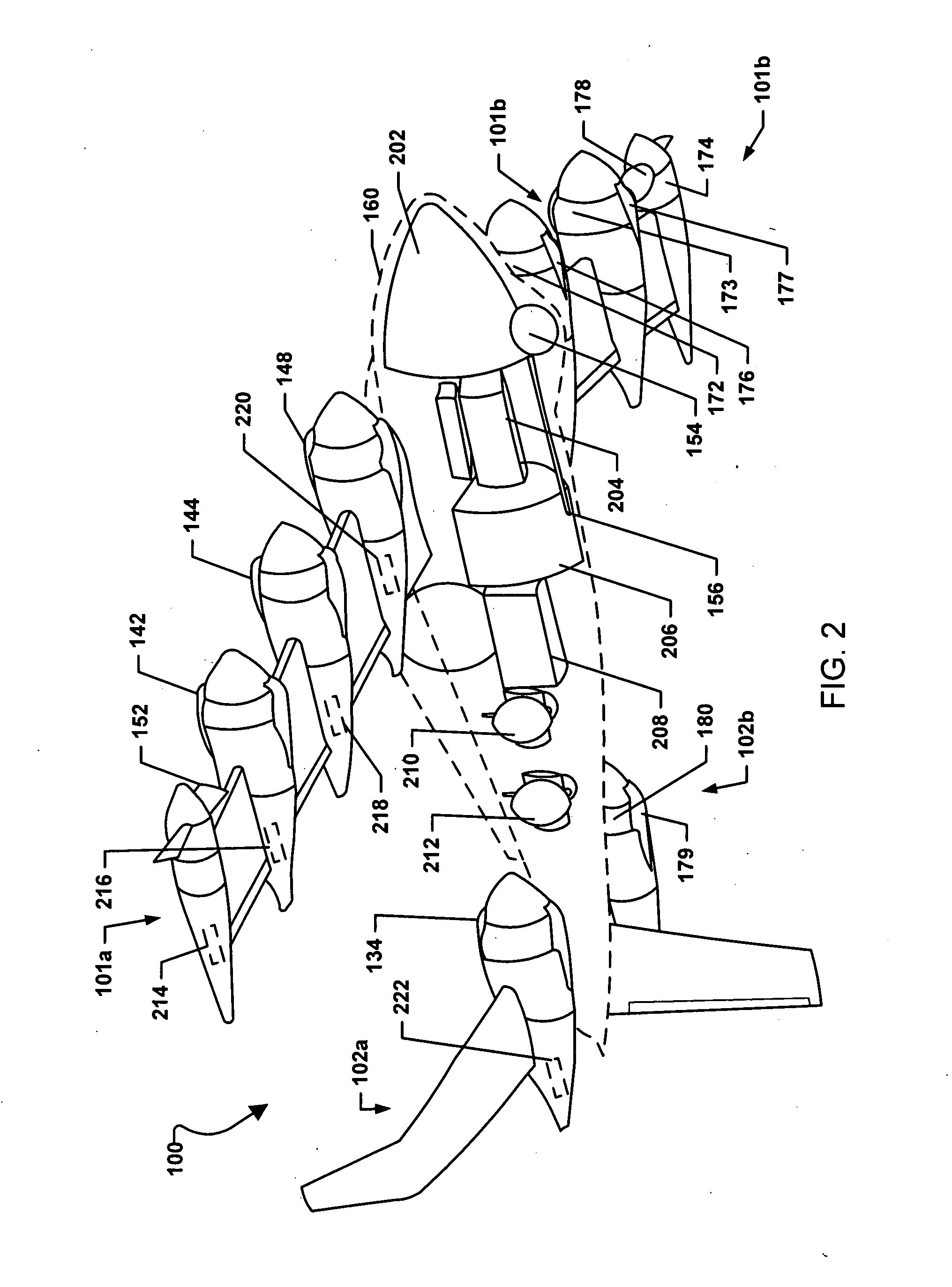
Three wing, six-tilt propulsion unit, vtol aircraft
A vertical takeoff and landing aircraft having at least three wings and at least six propulsion units, each of which are located radially from two adjacent propulsion units, by equal or substantially equal angles. The at least six propulsion units together being located symmetrically, or at substantially symmetric positions, about the approximate center of gravity of the aircraft, when viewed from above. A vertical stabilizer may or may not be employed. If no vertical stabilizer is employed, yaw control during horizontal flight may be achieved through differential thrust using the at least six propulsion units. Yaw control during vertical flight may be provided by a plurality of yaw control panels. Absent yaw control panels, yaw control during vertical flight may be provided using differential propulsion unit tilt angles.
Owner:OLIVER VTOL
Method and apparatus for forming structural members
A method and associated apparatus for forming a composite structural member from a charge are provided. The charge can be disposed on a first die of the apparatus and formed to a desired configuration defined by a recess of the die by inserting a second die or a tool into the recess. In some cases, the first die can include two portions that are adjustable in a transverse direction so that the recess can be opened by the insertion of the second die or tool. The second die or tool can be a substantially rigid member or an inflatable bladder. In either case, the charge can be disposed on the first die, formed, and then further processed on the first die, thereby facilitating indexing of the charge for each operation.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
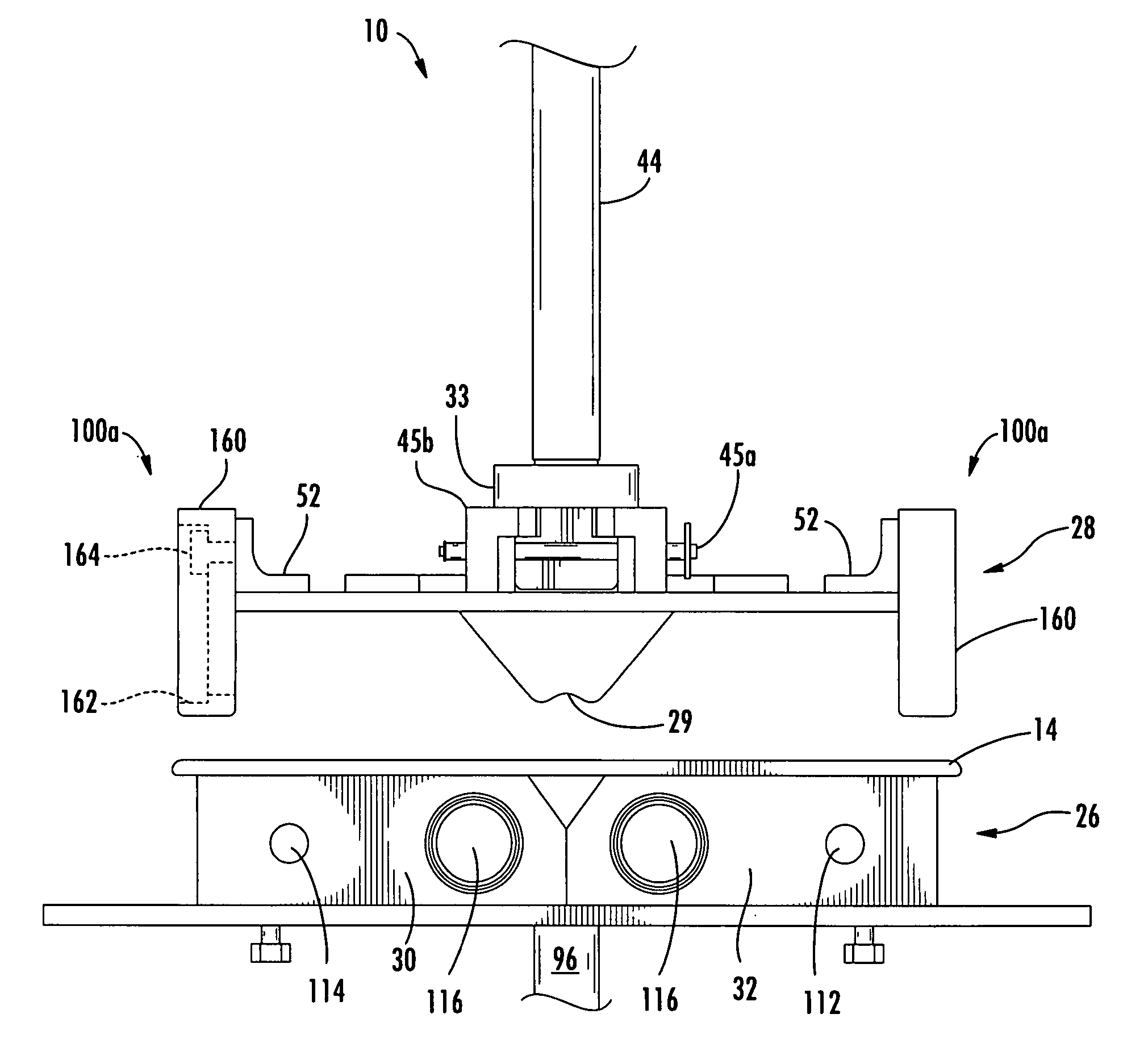
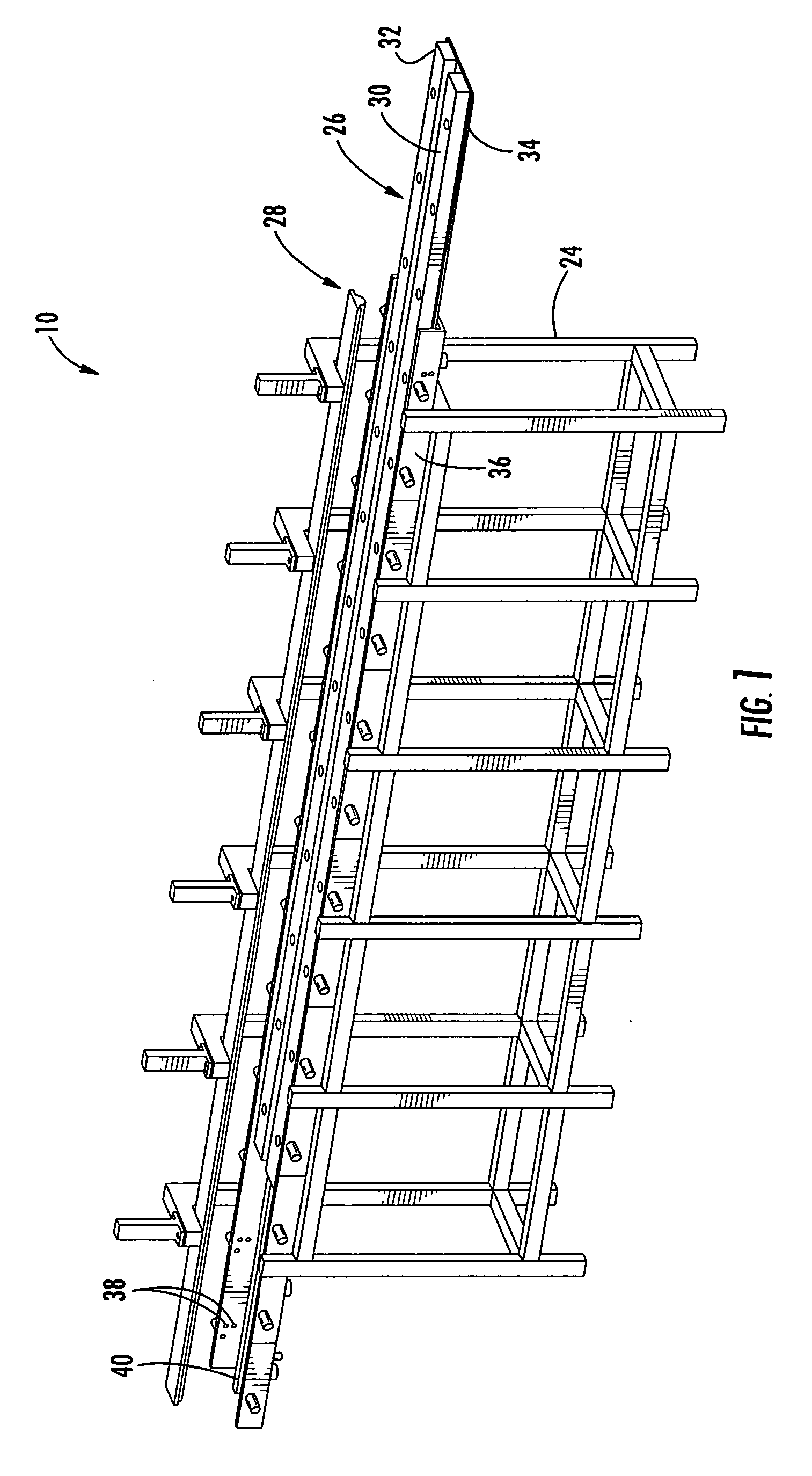
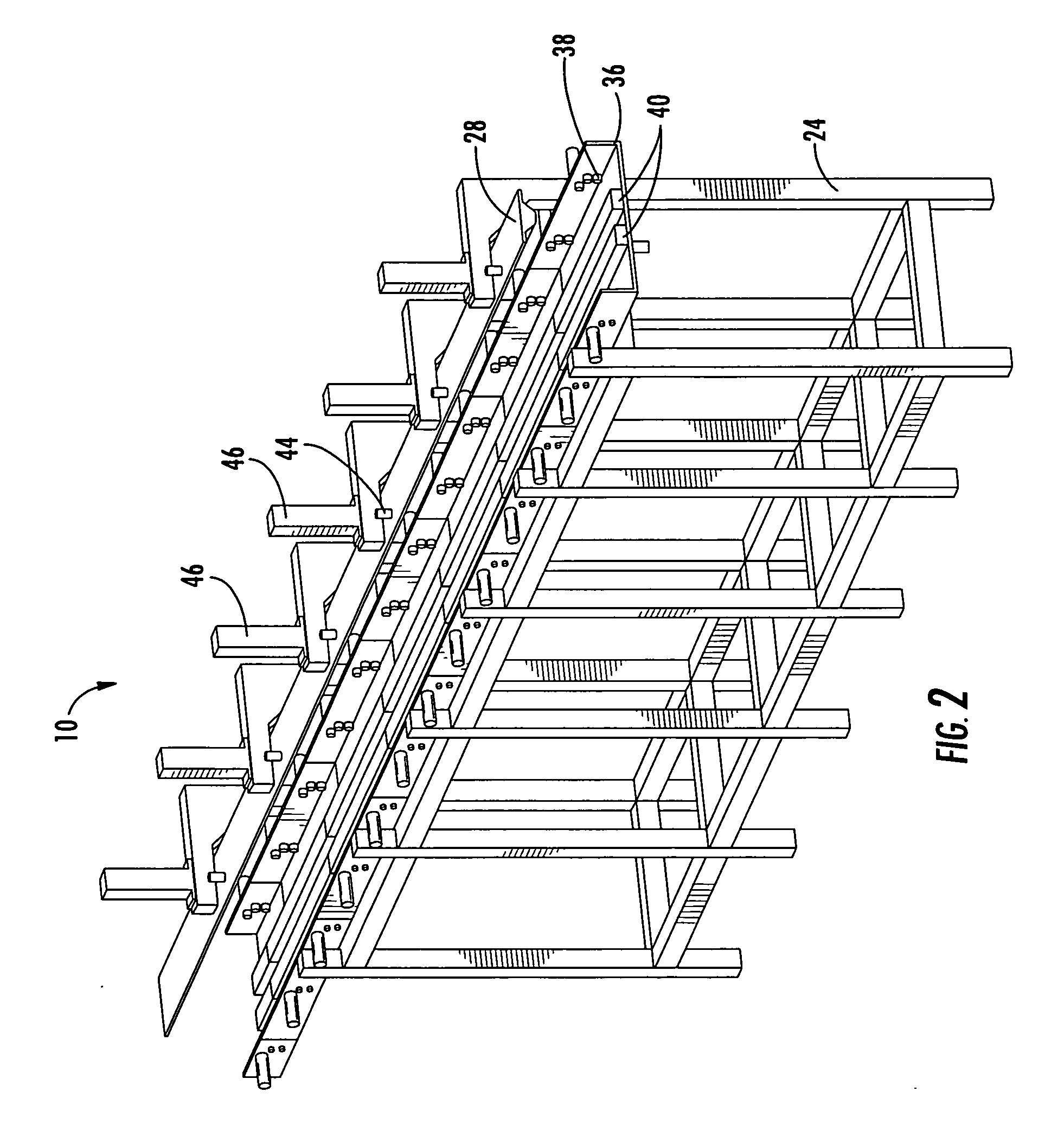
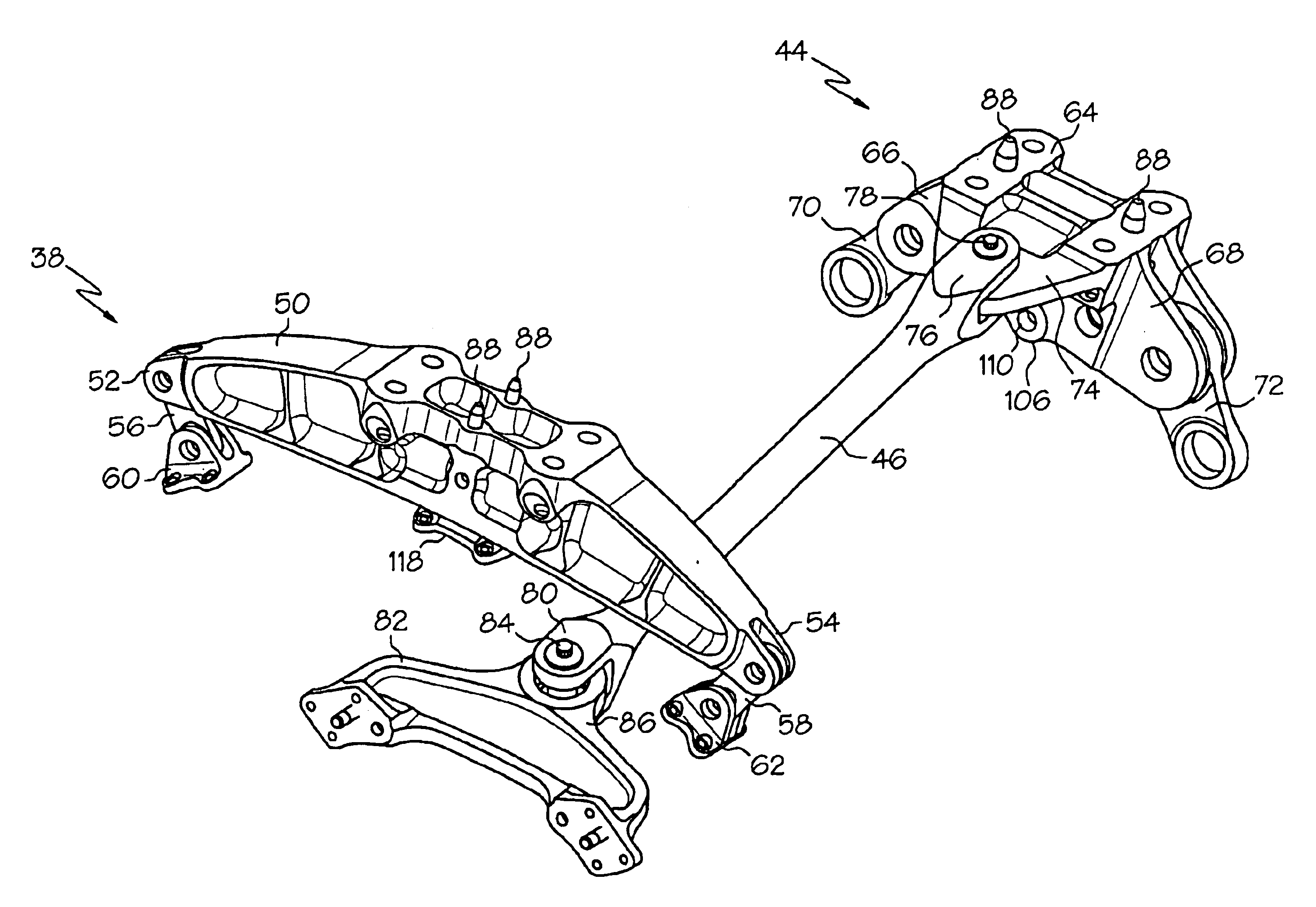
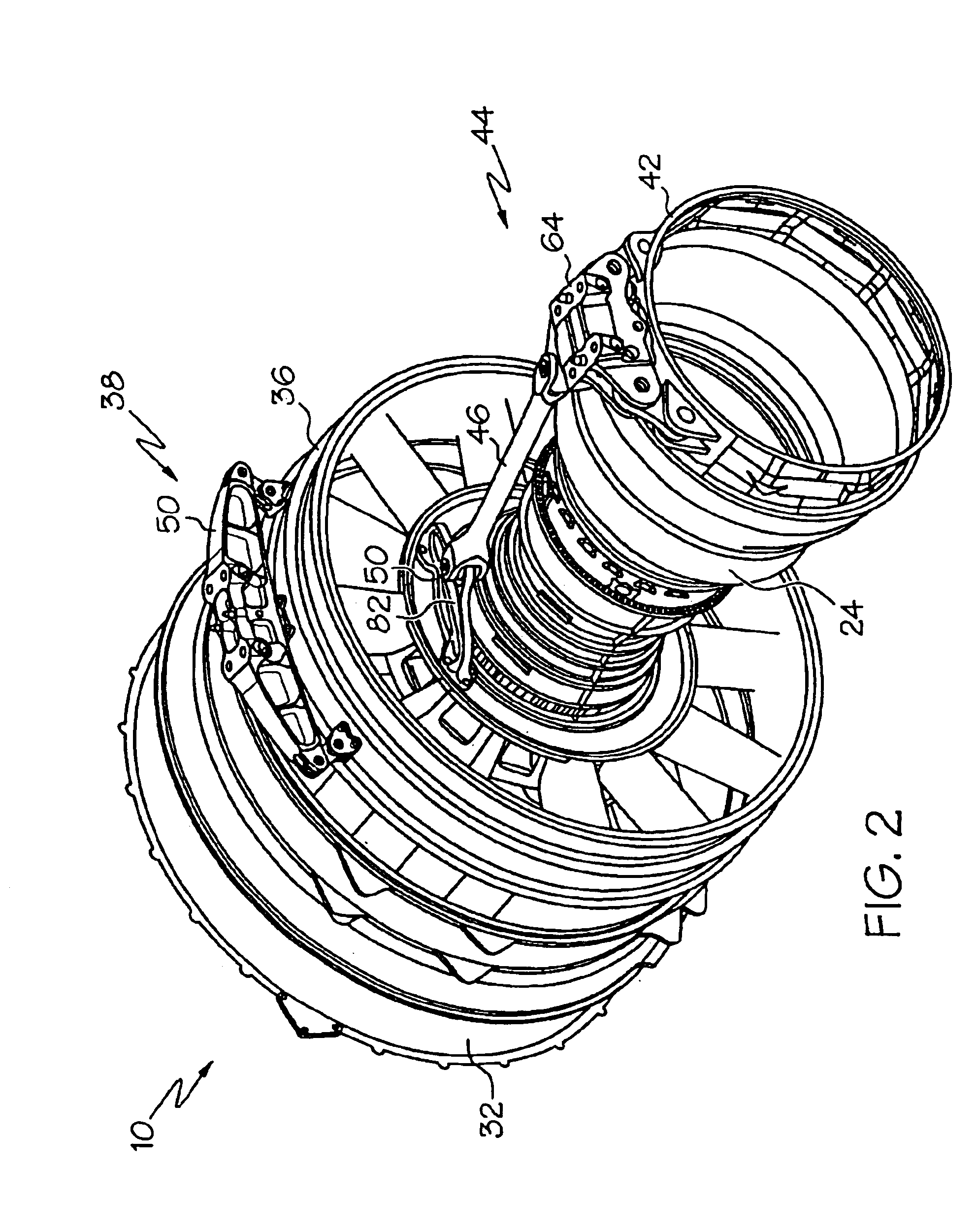
Fail-safe aircraft engine mounting system
A fail-safe lug is carried by an engine frame member and receives a clevis carried by an engine mount member. The mount member includes side links that transmit transverse loads between the engines and the airframe and a thrust link that transmits axial, engine thrust loads between the engine and the airframe. A fail-safe pin is carried by the clevis and has an outer diameter that is smaller than an aperture in the lug and through which the pin passes, so that no loads are imposed on the fail-safe pin in normal operation. When one or more of the links are no longer capable of transmitting loads, the fail-safe arrangement becomes operative to accommodate the loads transmitted between the engine and the airframe.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Composite material-stiffened panel and manufacturing method thereof
A composite material-stiffened panel has a skin obtained by molding a fiber-reinforced resin composite material into a flat skin, stiffeners arranged in rows on one surface of the skin, and a fiber-reinforced resin-composite material stitched on the skin covering the stiffeners. The composite material-stiffened panel can be manufactured as follows: A first fabric material is placed on a tool having a panel-shaped surface. Stiffeners are placed on the first fabric materials. A second fabric material is placed on the stiffeners to cover at least some of the stiffeners. The second fabric materials are reformed to match the shape of the stiffeners. The reformed second fabric material is stitched on the first fabric material along edges of the stiffeners. All the materials are covered with a bagging film for vacuum. Resin is infiltrated into the fabric materials by a RTM or a RFI method. The infiltrated resin is heated to be hardened.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
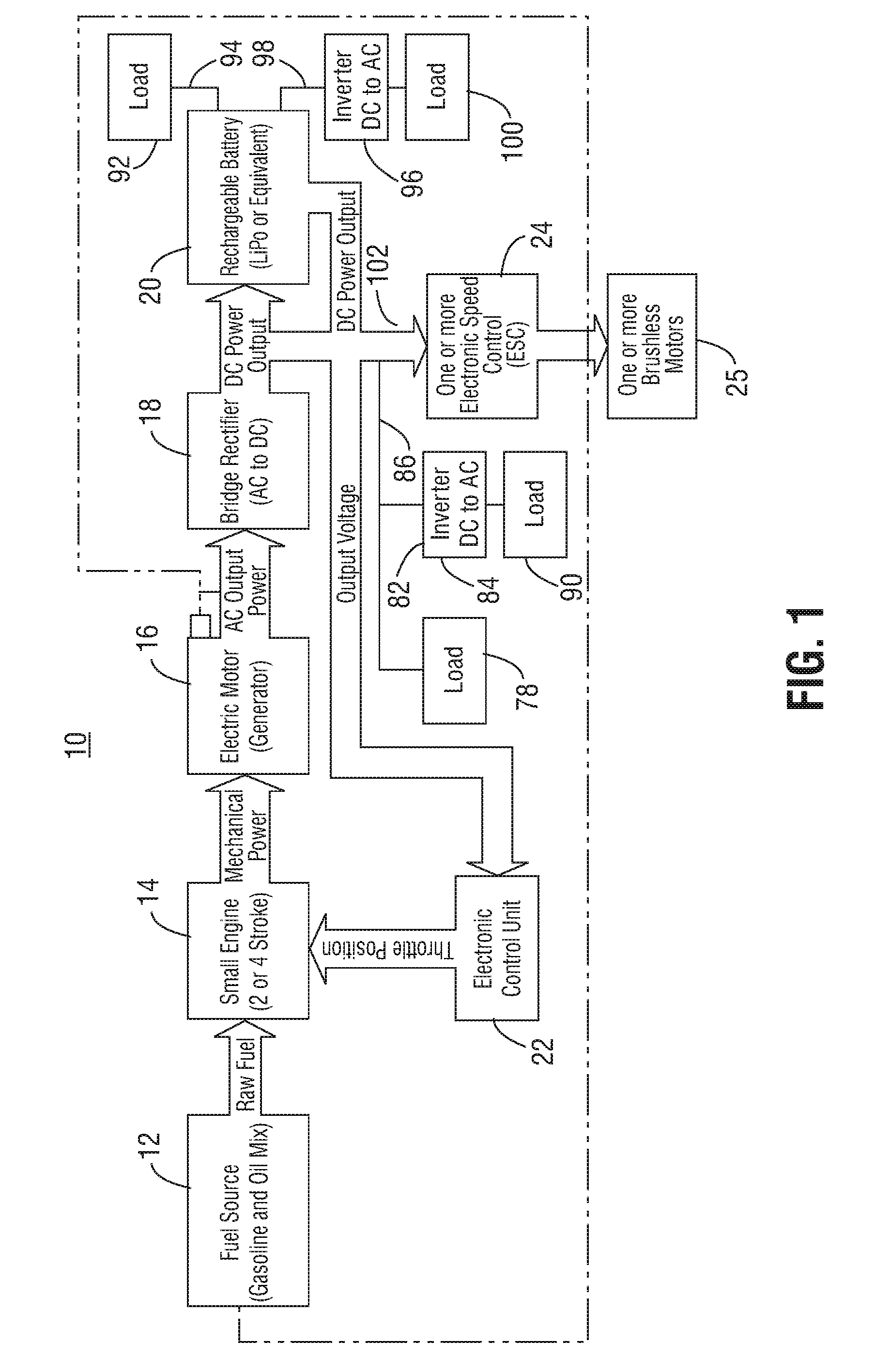
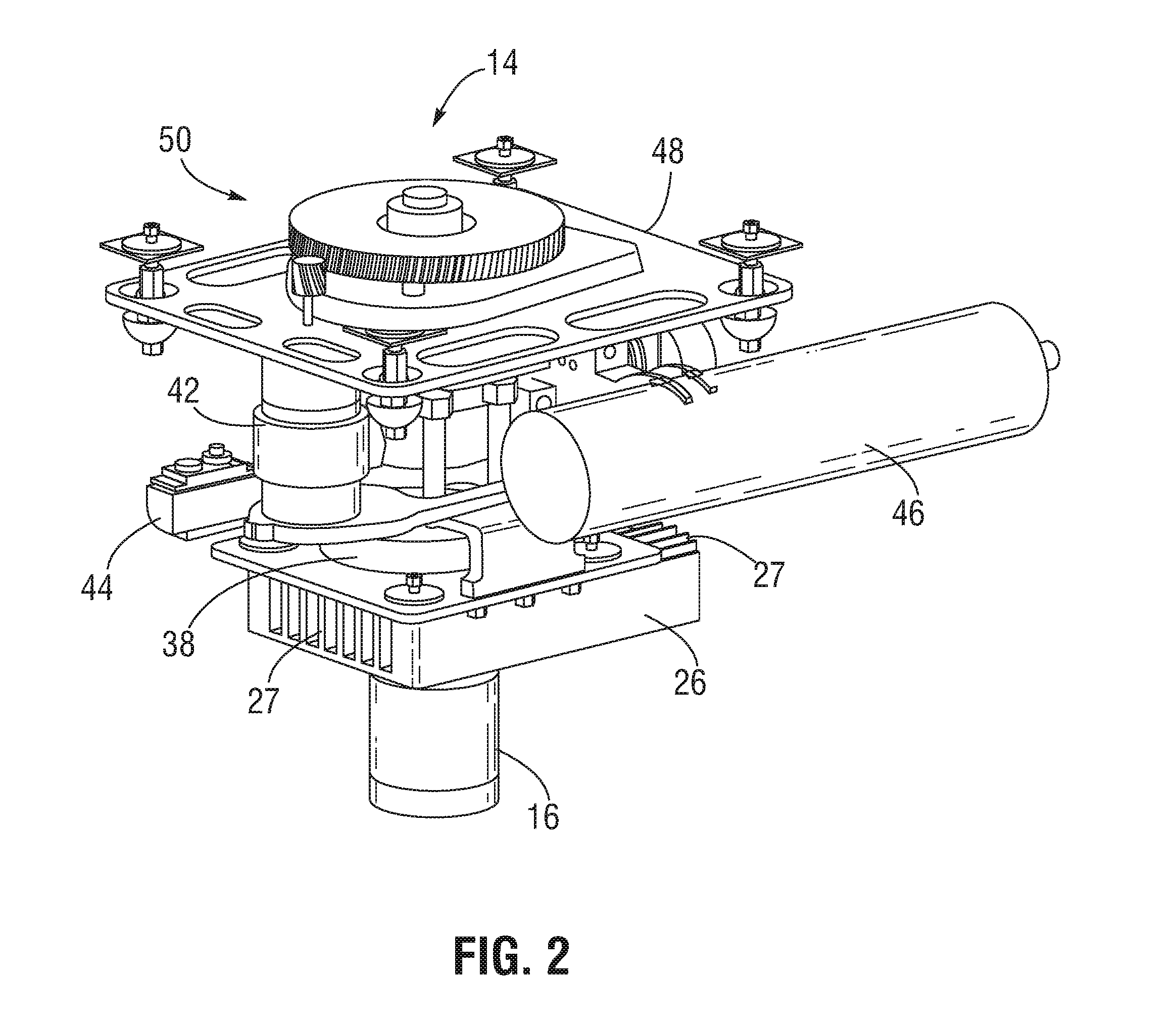
Micro hybrid generator system drone
ActiveUS20160137304A1Power plant cooling arrangmentsElectric power distributionElectrical batteryAC power
An unmanned aerial vehicle comprising at least one rotor motor. The rotor motor is powered by a micro hybrid generation system. The micro hybrid generator system comprises a rechargeable battery configured to provide power to the at least one rotor motor, a small engine configured to generate mechanical power, a generator motor coupled to the small engine and configured to generate AC power using the mechanical power generated by the small engine, a bridge rectifier configured to convert the AC power generated by the generator motor to DC power and provide the DC power to either or both the rechargeable battery and the at least one rotor motor, and an electronic control unit configured to control a throttle of the small engine based, at least in part, on a power demand of at least one load, the at least one load including the at least one rotor motor.
Owner:ISTARI
Hybrid jet/electric vtol aircraft
ActiveUS20130062455A1Improve efficiencyLess thrust capacityAircraft navigation controlEfficient propulsion technologiesJet aeroplaneElectricity
A fixed-wing VTOL aircraft features an array of electric lift fans distributed over the surface of the aircraft. A generator is (selectively) coupled to the gas turbine engine of the aircraft. During VTOL operation of the aircraft, the engine drives the generator to generate electricity to power the lifting fans. Power to the lifting fans is reduced as the aircraft gains forward speed and is increasingly supported by the wings.
Owner:SONIC BLUE AEROSPACE
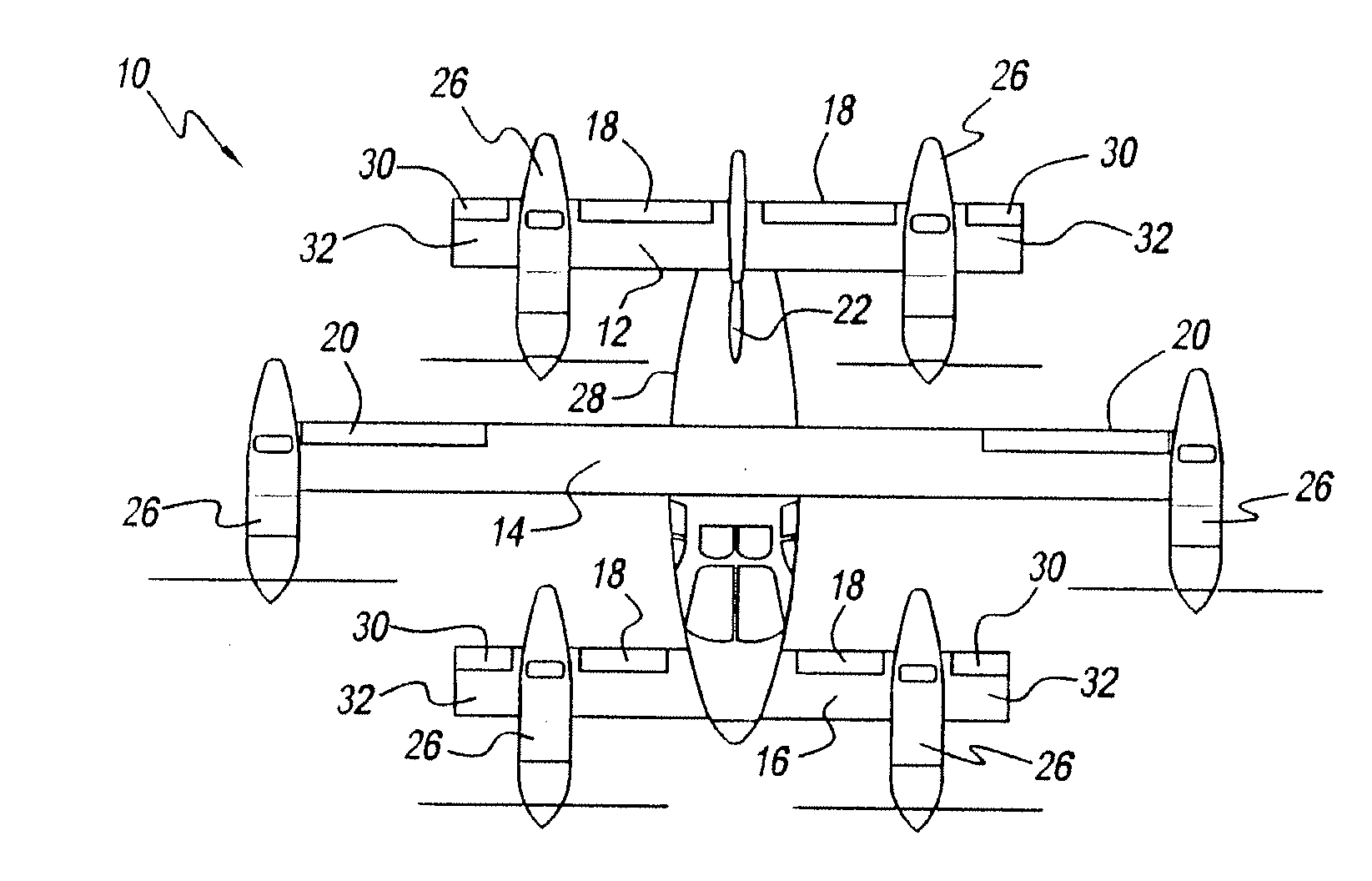
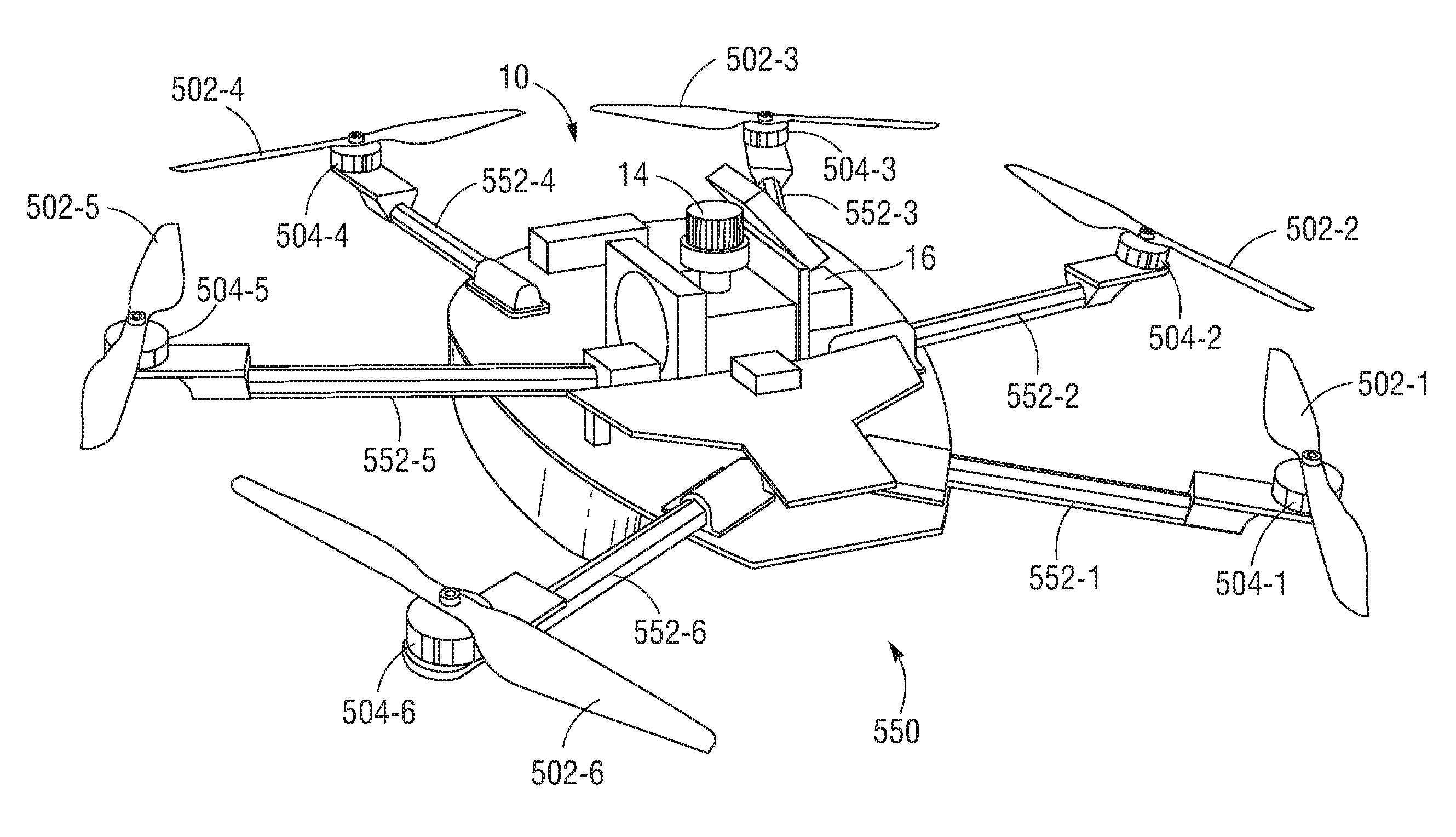
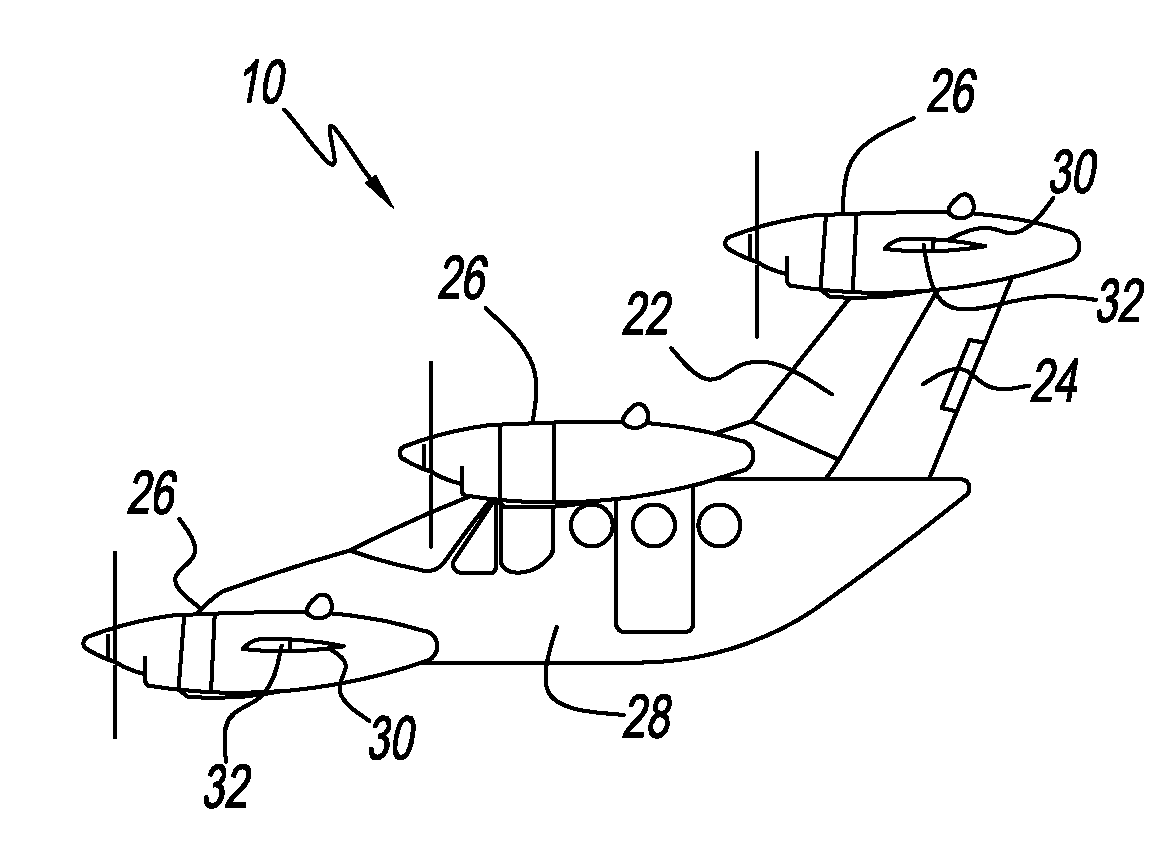
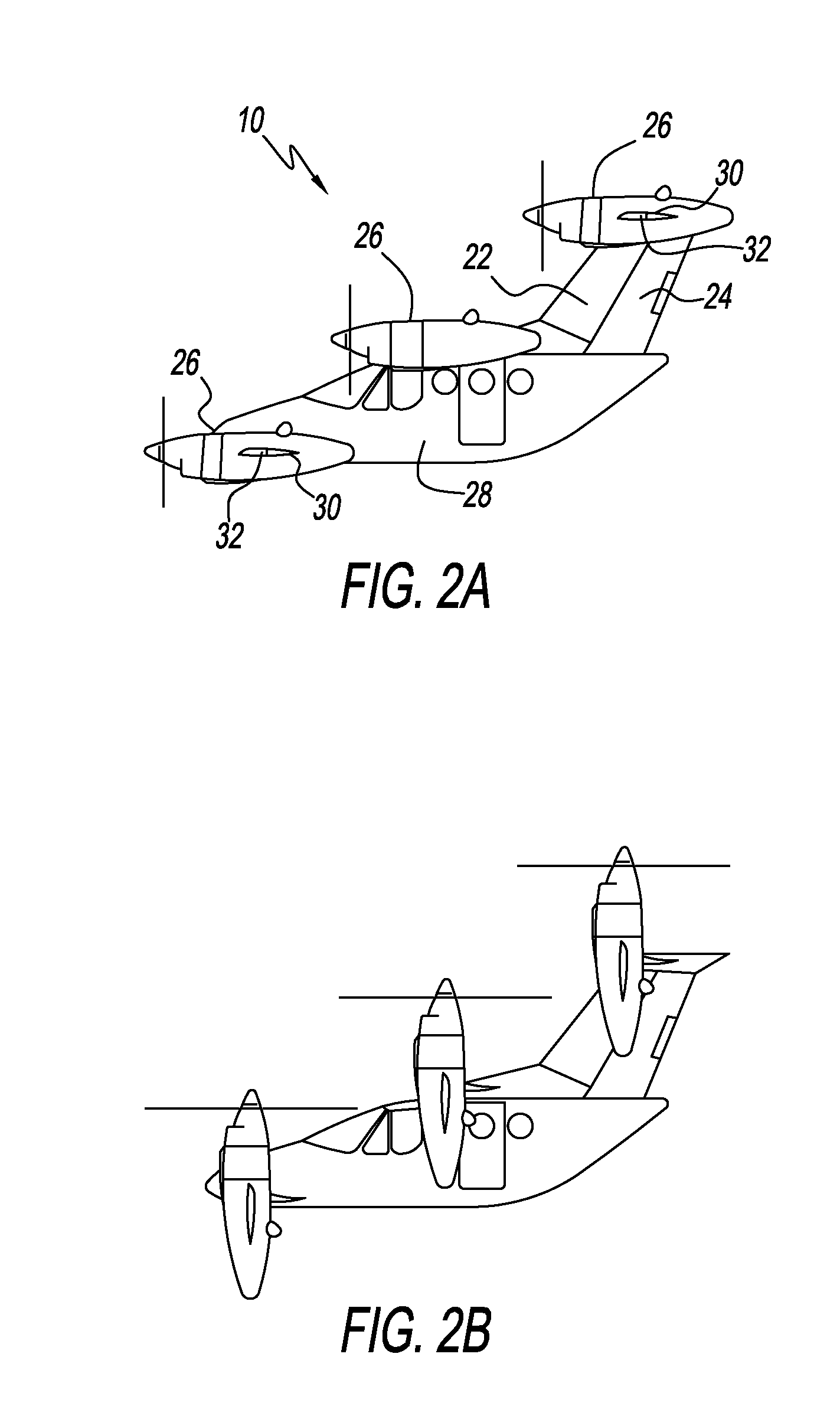
Three Wing, Six Tilt-Propulsion Units, VTOL Aircraft
ActiveUS20110168835A1Aircraft navigation controlGas turbine type power plantsFlapping wingFlight vehicle
A vertical takeoff and landing aircraft having a fuselage with three wings and six synchronously tilt-able propulsion units, each one mounted above, below, or on each half of the aforementioned three wings. The propulsion units are vertical for vertical flight, and horizontal for forward flight. The aircraft wings are placed such that the rear wing is above the middle wing which is placed above the front wing. The placement of each of the propulsion units relative to the center of gravity of the aircraft about the vertical axis inherently assures continued stability in vertical flight mode, following the loss of thrust from any one propulsion unit. The placement of the propulsion units, viewing the aircraft from the front, is such that each propulsion units' thrust wake does not materially disturb the propulsion unit to its rear. When engine driven propellers or rotors are utilized, flapped wing panels are attached outboard of the forward and / or rearward propulsion units to provide yaw control during vertical flight.
Owner:OLIVER VTOL
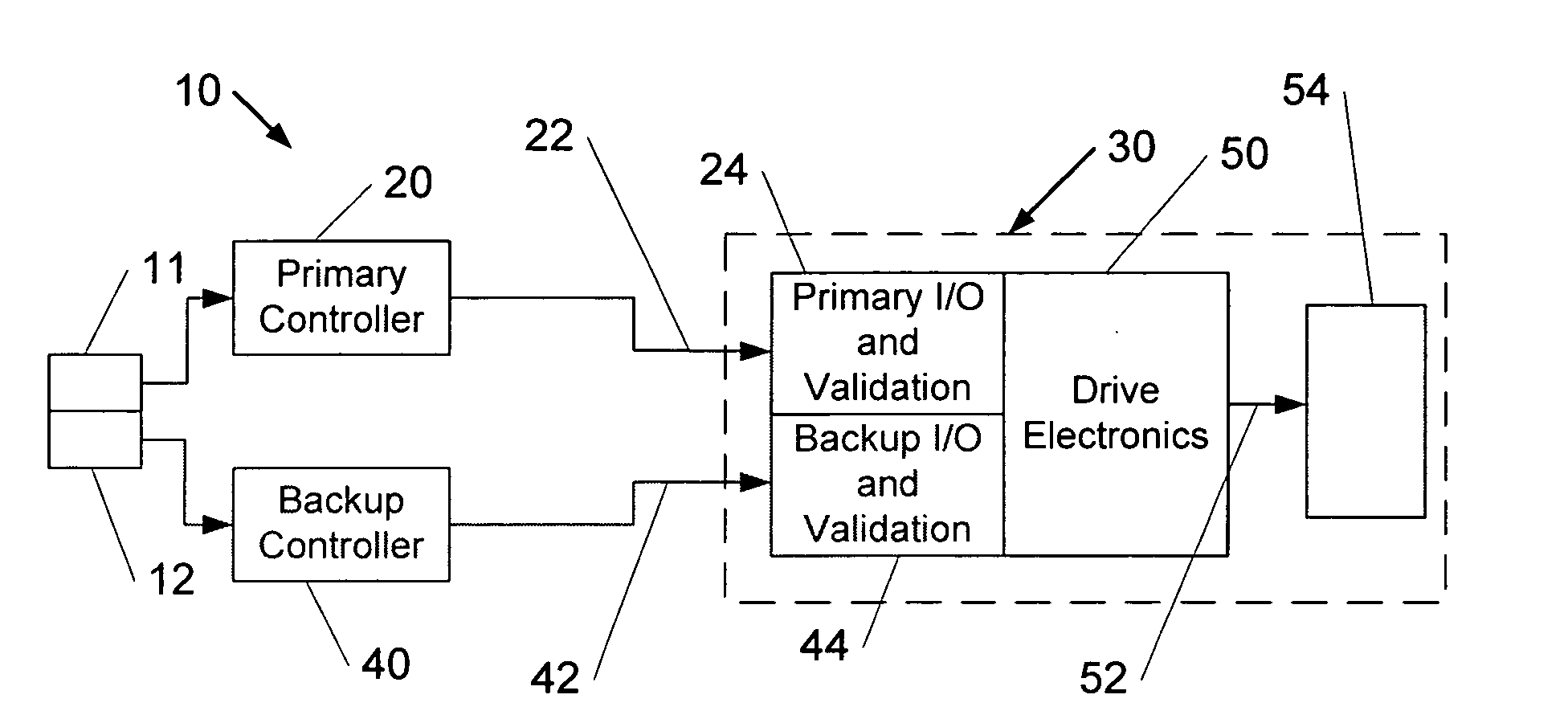
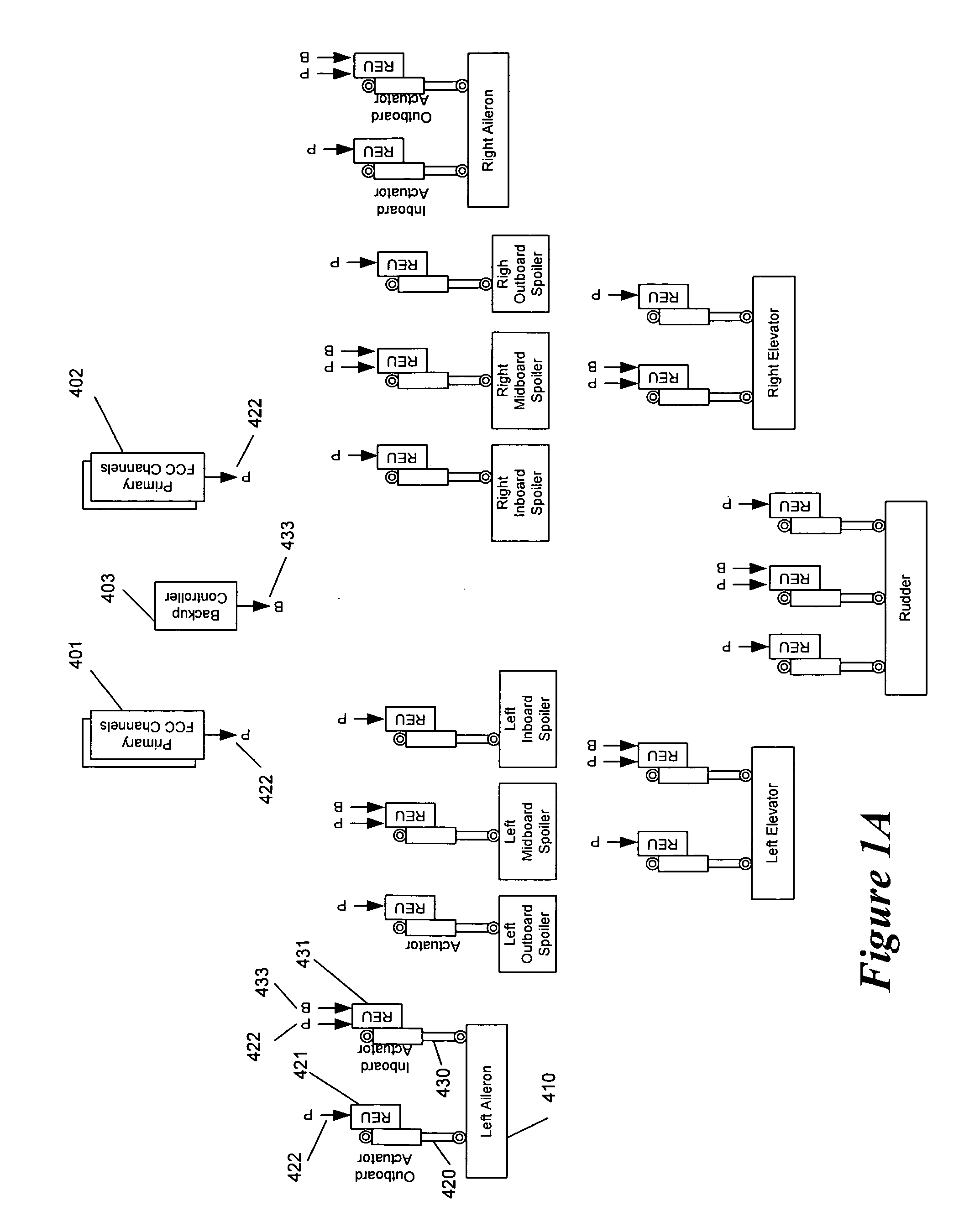
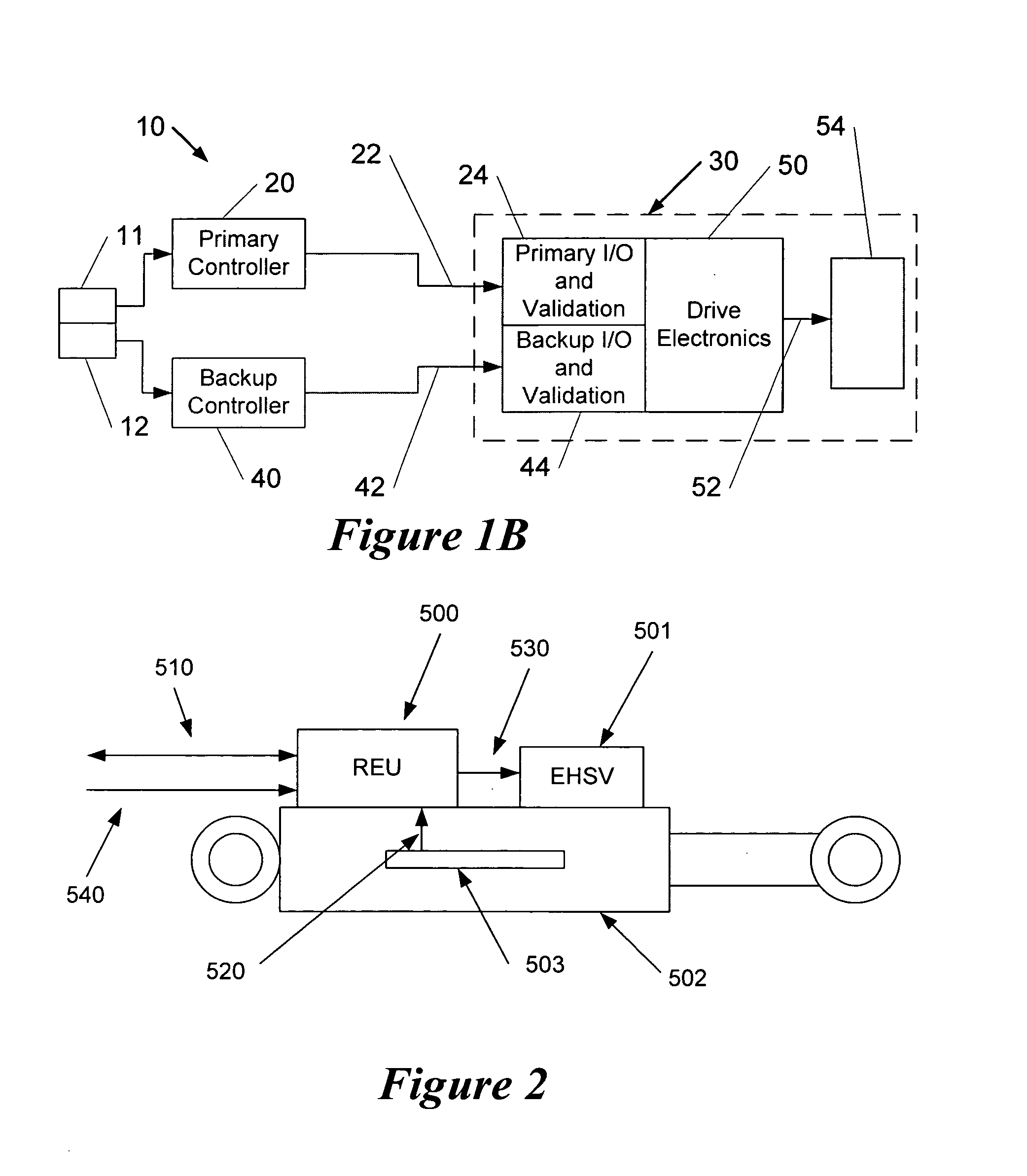
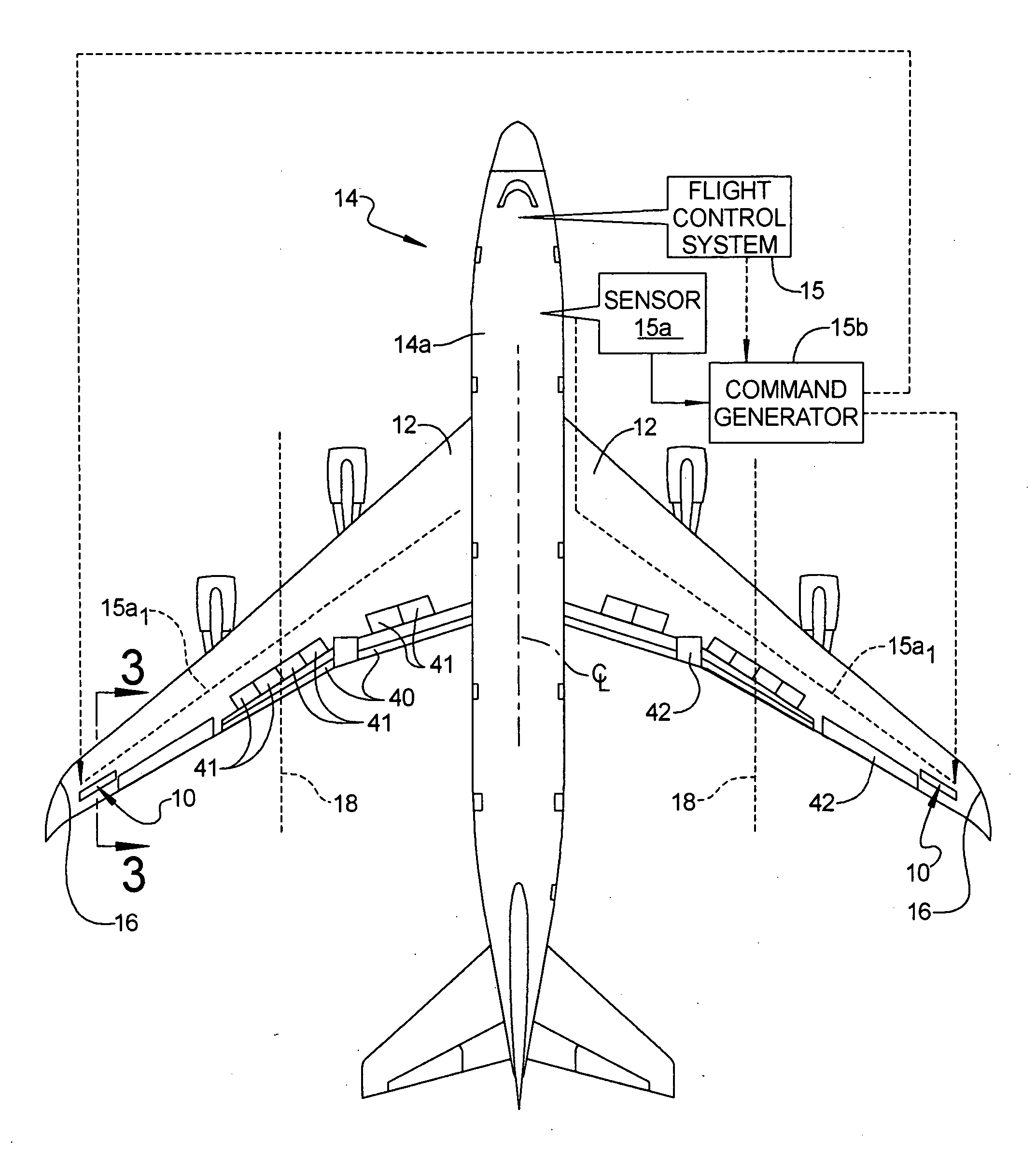
Apparatus and method for backup control in a distributed flight control system
ActiveUS20070164166A1Without compromisingWith power amplificationActuated automaticallyControl signalMaster controller
Embodiments of the invention relate to a flight control system for controlling an aircraft during flight. The flight control system may include a primary controller configured to receive an input from a pilot and to output a primary control signal and a primary transmission path connected to the primary controller and configured to relay the primary control signal. The flight control system may also include a backup controller configured to receive the input from the pilot and to output a backup control signal and a backup transmission path connected to the backup controller and configured to relay the backup control signal. Additionally, the flight control system may include an actuator having a remote electronics unit configured to receive the primary control signal and the backup control signal and to determine if the primary control signal is available and valid. The remote electronics unit may be configured to output an actuator command based on the primary control signal if the primary control signal is available and valid and to output the actuator command based on the backup control signal if the primary control signal is unavailable or invalid.
Owner:GULFSTREAM AEROSPACE CORP
Hybrid Gas Turbine Propulsion System
ActiveUS20150013306A1Reduce fuel consumptionImprove responsivenessGas turbine type power plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesAir compressionDual-thrust
A hybrid aerodynamic thrust system as a prime mover for aircraft or other high-speed vehicles. An arrangement of dual thrust resources to alternately accommodate low and high airspeed regimes. Electromotive force is used in lieu of hot section power turbines to achieve engine air compression or alternately perform thrust work at low velocities.
Owner:SHELLEY RUDOLPH ALLEN
Shaped composite stringers and methods of making
A stiffened skin panel of an aircraft that includes an aircraft skin panel of composite material and a composite stringer consolidated with the aircraft skin panel. The stringer has a pair of stringer sides, each extending from a stringer top to a stringer leg. The stringer sides may each extend through a wide radius, smooth continuous curve to a stringer leg. The wide radius, smooth continuous curve may be proximate the base of the stringer side in a region where the stringer side transitions to the stringer leg.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Unmanned Aircraft and Operation Method for the Same
InactiveUS20150285165A1Low powerIncrease powerPower installationsUnmanned aerial vehiclesJet aeroplaneExternal combustion engine
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
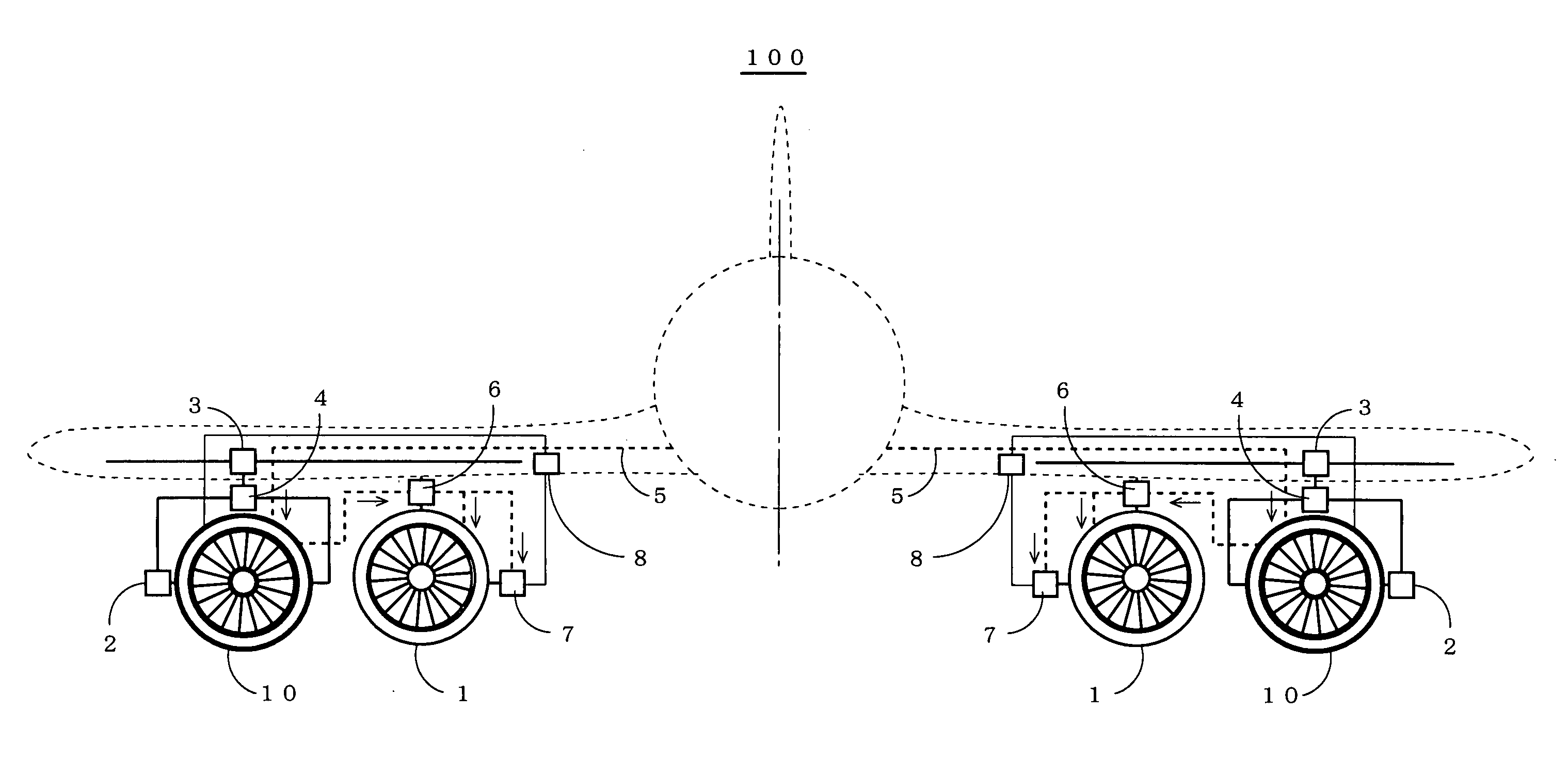
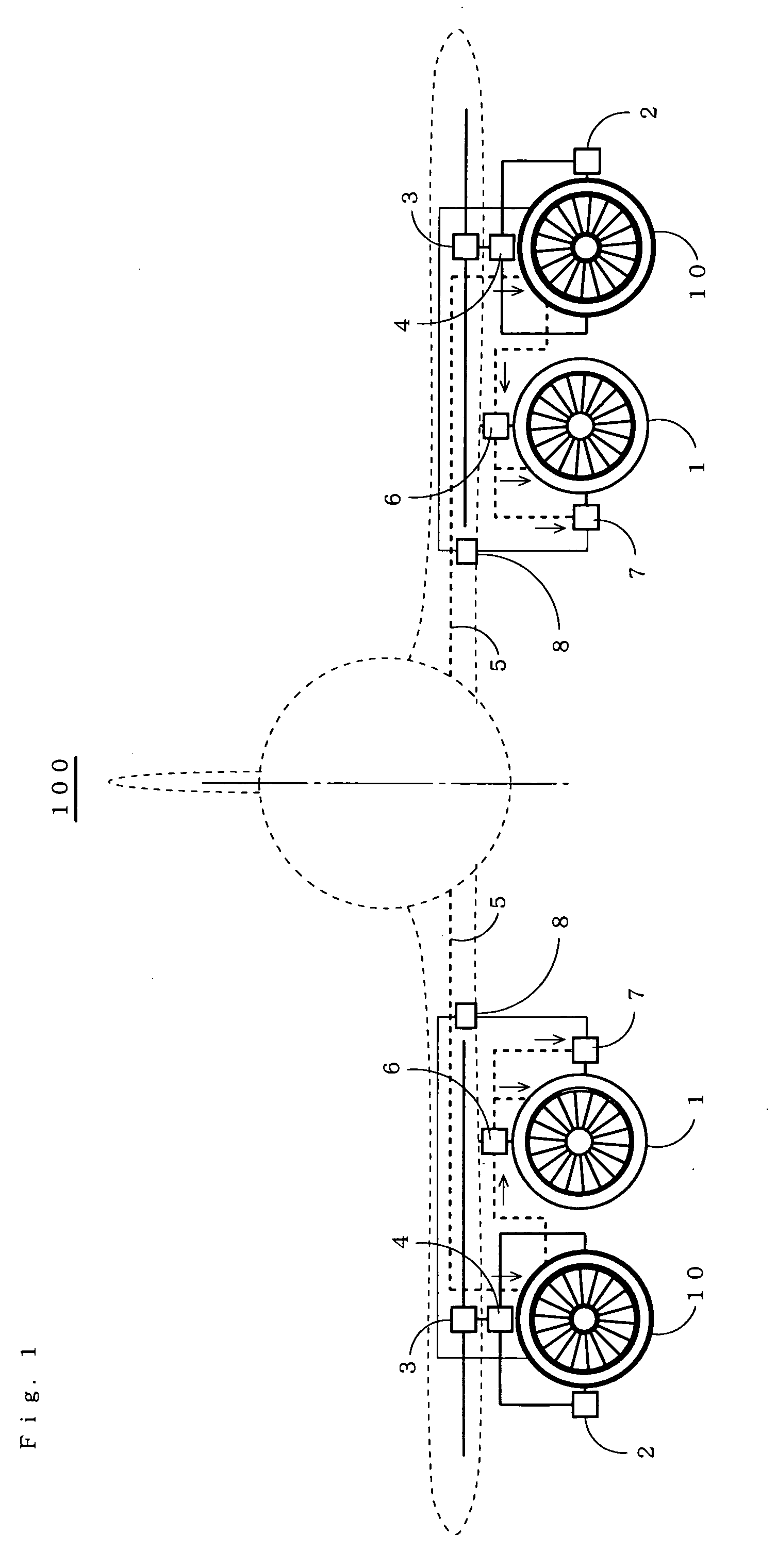
Aircraft propulsion system
InactiveUS20060254255A1Highly compatible with environmentSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuitCombustion chamberLiquid hydrogen
To provide an aircraft propulsion system which can secure the optimum thrust and thrust vector for flight conditions, as well as the optimum sectional area for the engine, and which is highly compatible with the environment. An electrical generator is coupled to a turbofan engine, the electrical generator is driven by output power of the turbofan engine to output electric power, and an electromagnetic driving fan is driven by the electric power. On the other hand, after bringing each of coils in the electromagnetic driving fan to a superconductive state, liquid hydrogen is introduced to a heat exchanger, collects the energy of exhaust as heat, is then vaporized, and thereafter supplied to a combustor and to a fuel cell. Further, the electromagnetic driving fan is changed in its rotational phase by a rotating mechanism portion, is made movable in a width direction of a wing and a wing chord direction by a slide mechanism portion, and can be stored inside or outside the wing by a storage mechanism portion.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY +1
System and method for enhancing the payload capacity, carriage efficiency, and adaptive flexibility of external stores mounted on an aerial vehicle
InactiveUS20050204910A1Enhanced volumetric efficiency storeIncreased payload capacityRocket launchersPower plant fuel tanksFuel tankSelf adaptive
A system and method for the conversion of fuel tanks, detachably mountable on the exterior of an aerial vehicle, into high volume, high capacity, diverse functionality and aerodynamically efficient airborne stores is disclosed. A conventional external fuel drop tank is modified such that the exterior shape of the tank is substantially retained while the interior of the tank is suitable restructured to allow for the introduction of diverse airborne stores, associated airborne store mounting means, control and monitoring means and support means therein, which replace the fuel store. The airborne store is suitably interfaced to the stores control and management system of the aerial vehicle. The airborne store is integrated into a new external stores configuration The enhanced airborne store will have aerodynamic characteristics substantially similar to the original external fuel tank while its payload capacity is substantially improved.
Owner:PADAN NIR
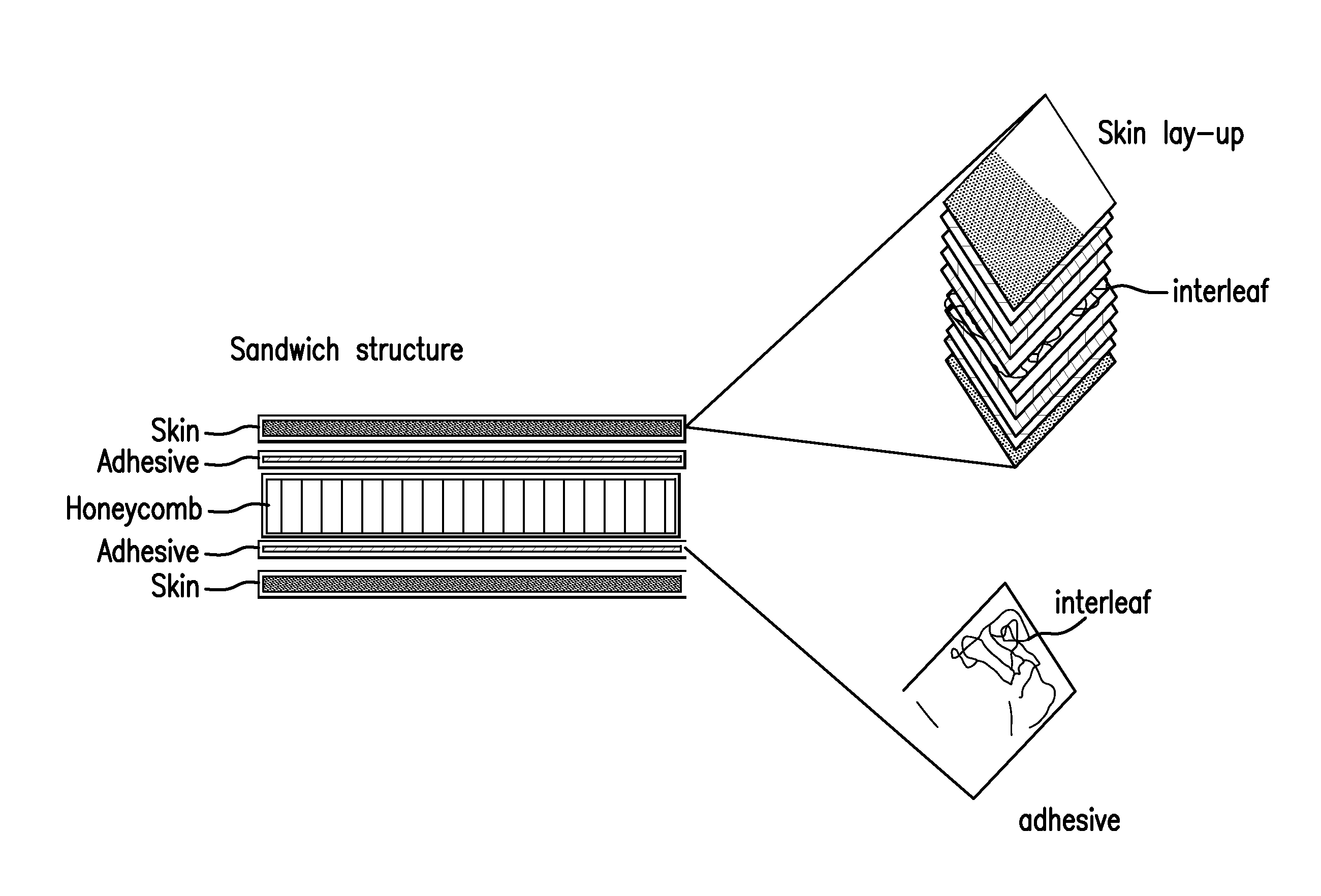
Structural composite material with improved acoustic and vibrational damping properties
A composite material comprises a nonwoven layer having a viscoelastic interleaf, which may be positioned mid-ply therein.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Aircraft using turbo-electric hybrid propulsion system for multi-mode operation
InactiveUS20140346283A1Easy to adaptImprove mobilityHybrid vehiclesConvertible aircraftsWater basedOperation mode
A vehicle incorporating a hybrid propulsion system. In one form, the vehicle may be an aircraft such that the system includes gas turbine engines as a first motive power source, and one or more battery packs as a second motive power source. Through selective coupling to an electric motor that can in turn be connected to a bladed rotor or other lift-producing device, the motive sources provide differing ways in which an aircraft can operate. In one example, the gas turbine engines can provide operation for a majority of the flight envelope of the aircraft, while the battery packs can provide operation during such times when gas turbine-based motive power is unavailable or particularly disadvantageous. In another example, both sources of motive power may be decoupled from the bladed rotor such that the vehicle can operate as an autogyro. In another mode of operation, the movement of a bladed rotor can be both decoupled from the sources of propulsion as well as fixed relative to the aircraft such that the aerodynamic surfaces formed on the bladed rotors can act as a fixed wing. In another particular form, the vehicle may be ground-based or water-based.
Owner:SALYER IVAL O
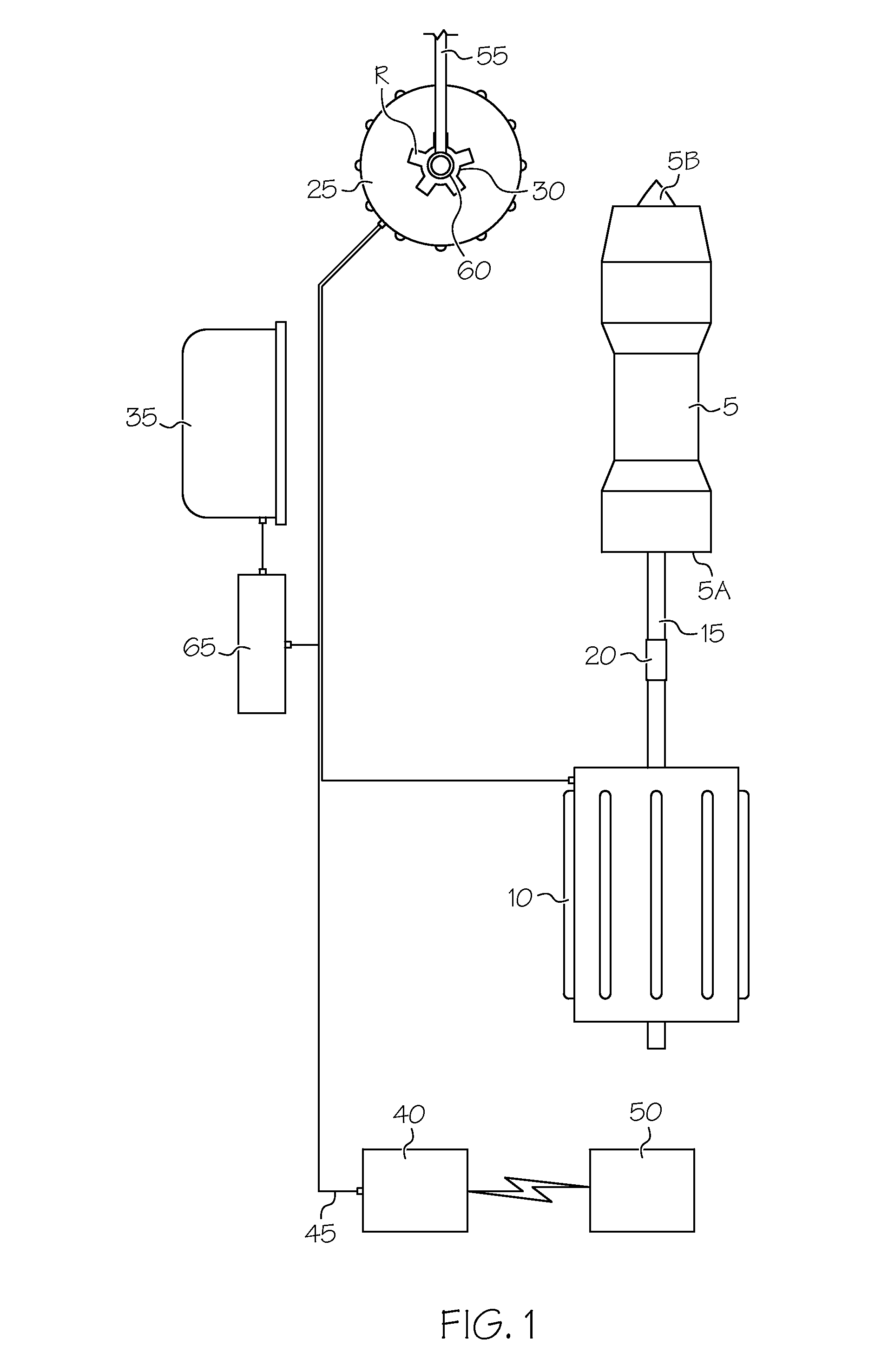
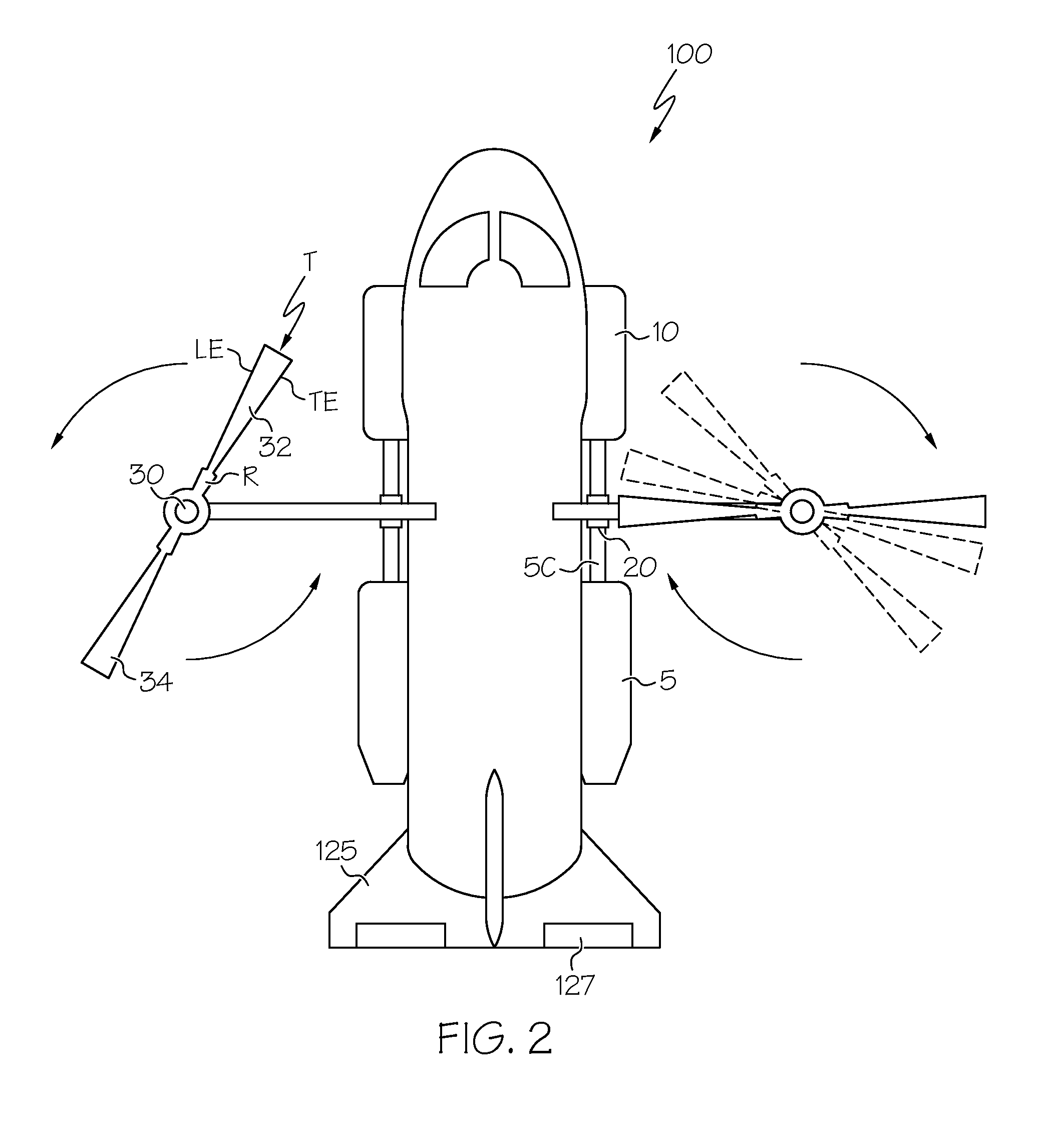
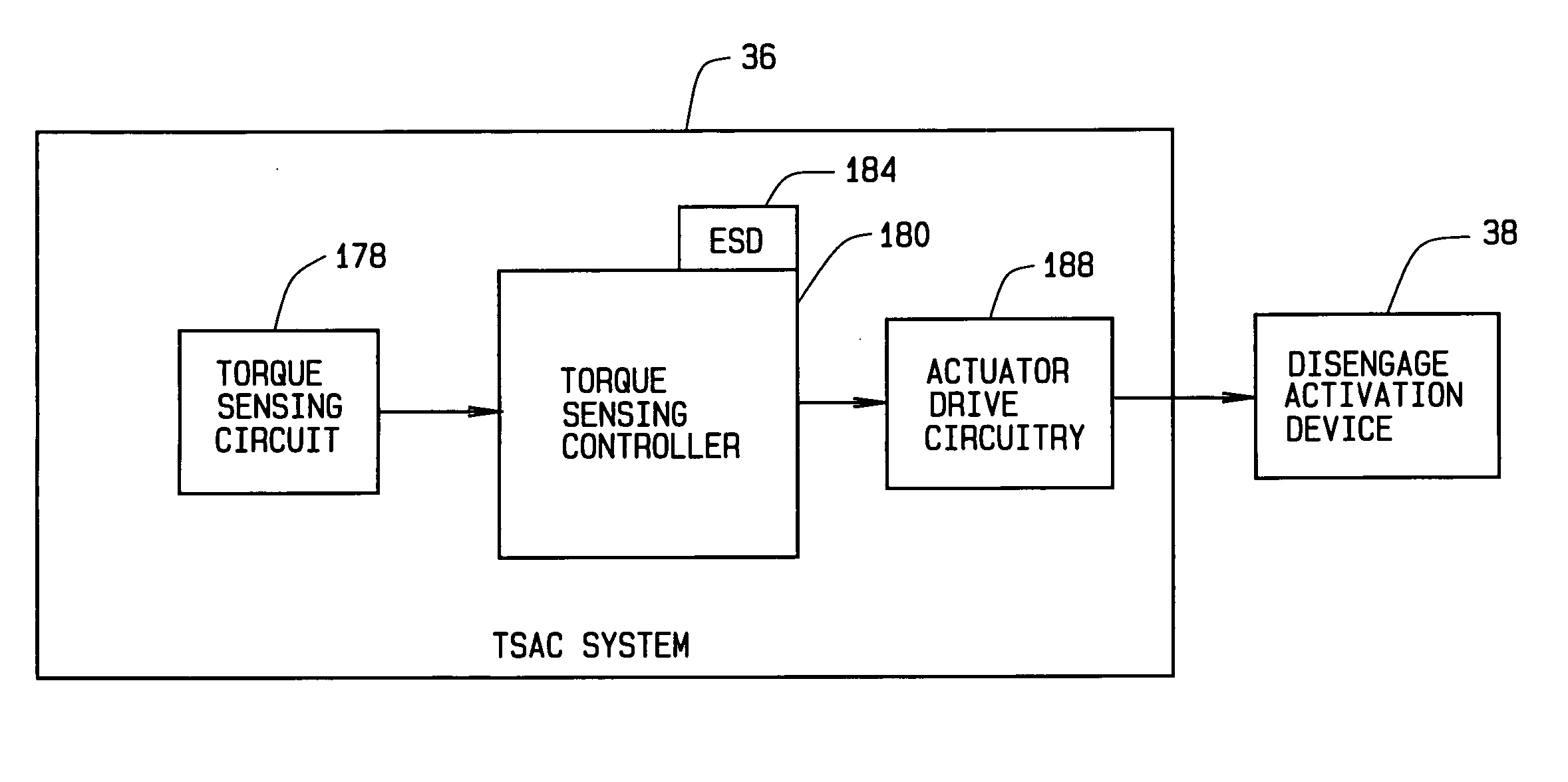
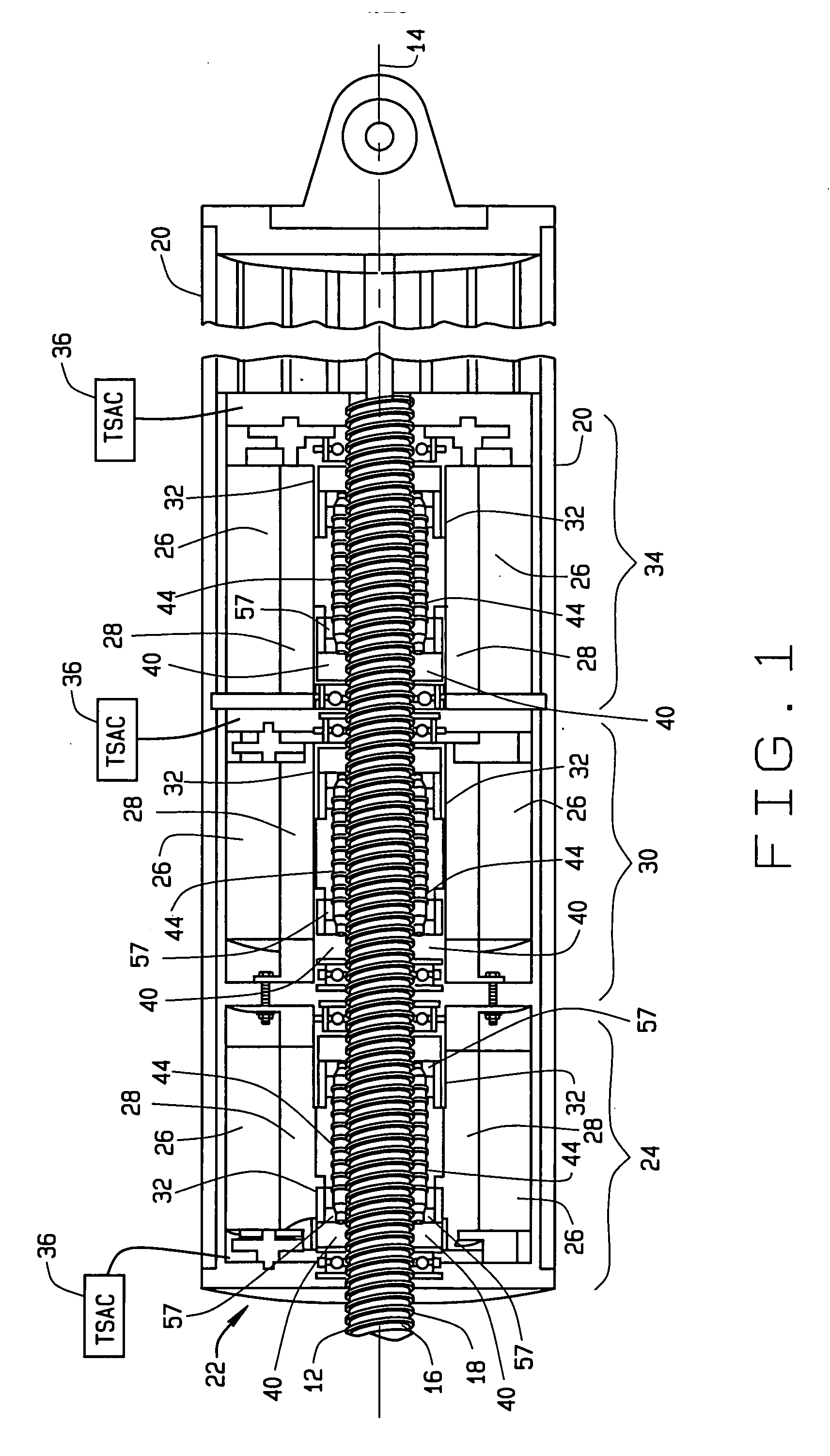
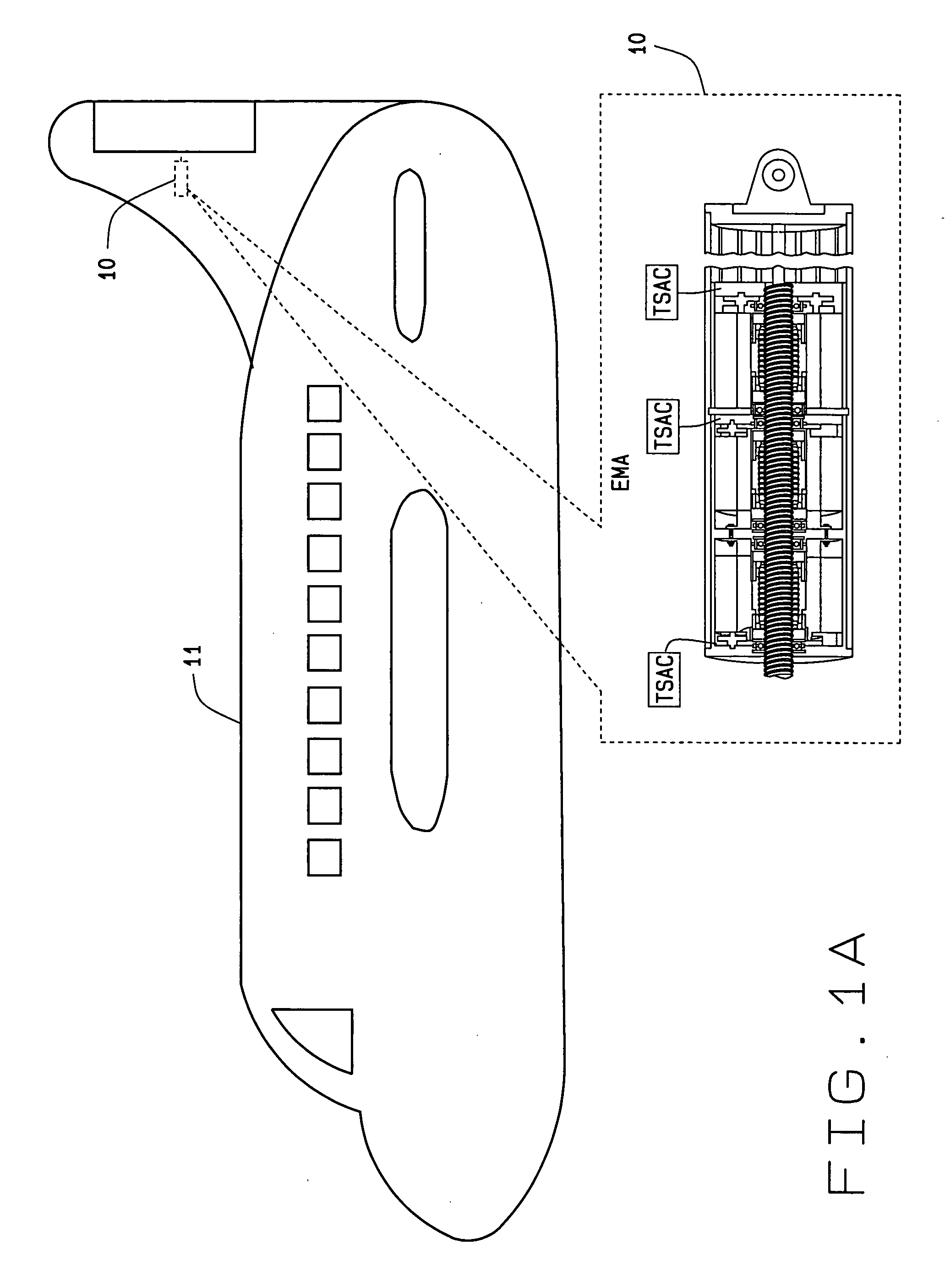
Fault-tolerant electromechanical actuator having a torque sensing control system
ActiveUS20060113933A1Low costEffectively prevent failureSynchronous generatorsDC motor speed/torque controlMechanical componentsControl system
An electromechanical actuator (EMA) is provided. The EMA includes a threaded output ram connectable to a mechanical component and at least one motor module engageable with the output ram for controllably translating the output ram along a linear axis of the output ram. The actuator further includes a torque sensing adaptive control (TSAC) system for monitoring torque within the motor module. The TSAC generates a disengagement command signal when the TSAC system determines torque within the motor module is outside an allowable motor module torque range. The disengagement command signal initiates disengagement of the motor module from the output ram.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Vertical take-off and landing vehicle with increased cruise efficiency
Systems, methods, and devices are provided that combine an advance vehicle configuration, such as an advanced aircraft configuration, with the infusion of electric propulsion, thereby enabling a four times increase in range and endurance while maintaining a full vertical takeoff and landing (“VTOL”) and hover capability for the vehicle. Embodiments may provide vehicles with both VTOL and cruise efficient capabilities without the use of ground infrastructure. An embodiment vehicle may comprise a wing configured to tilt through a range of motion, a first series of electric motors coupled to the wing and each configured to drive an associated wing propeller, a tail configured to tilt through the range of motion, a second series of electric motors coupled to the tail and each configured to drive an associated tail propeller, and an electric propulsion system connected to the first series of electric motors and the second series of electric motors.
Owner:NASA
Hybrid Propulsion Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft
A hybrid propulsion aircraft is described having a distributed electric propulsion system. The distributed electric propulsion system includes a turbo shaft engine that drives one or more generators through a gearbox. The generator provides AC power to a plurality of ducted fans (each being driven by an electric motor). The ducted fans may be integrated with the hybrid propulsion aircraft's wings. The wings can be pivotally attached to the fuselage, thereby allowing for vertical take-off and landing. The design of the hybrid propulsion aircraft mitigates undesirable transient behavior traditionally encountered during a transition from vertical flight to horizontal flight. Moreover, the hybrid propulsion aircraft offers a fast, constant-altitude transition, without requiring a climb or dive to transition. It also offers increased efficiency in both hover and forward flight versus other VTOL aircraft and a higher forward max speed than traditional rotorcraft.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
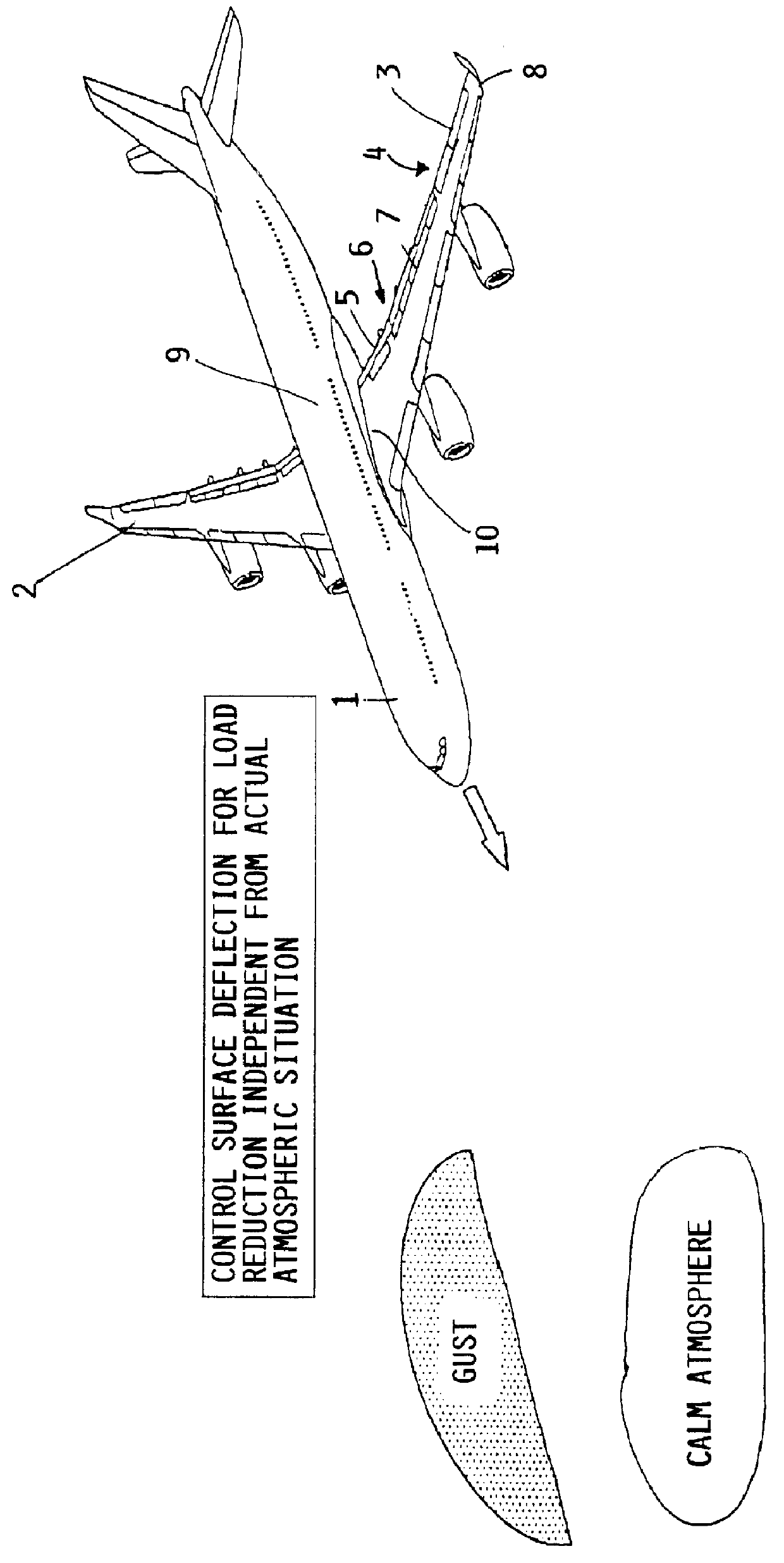
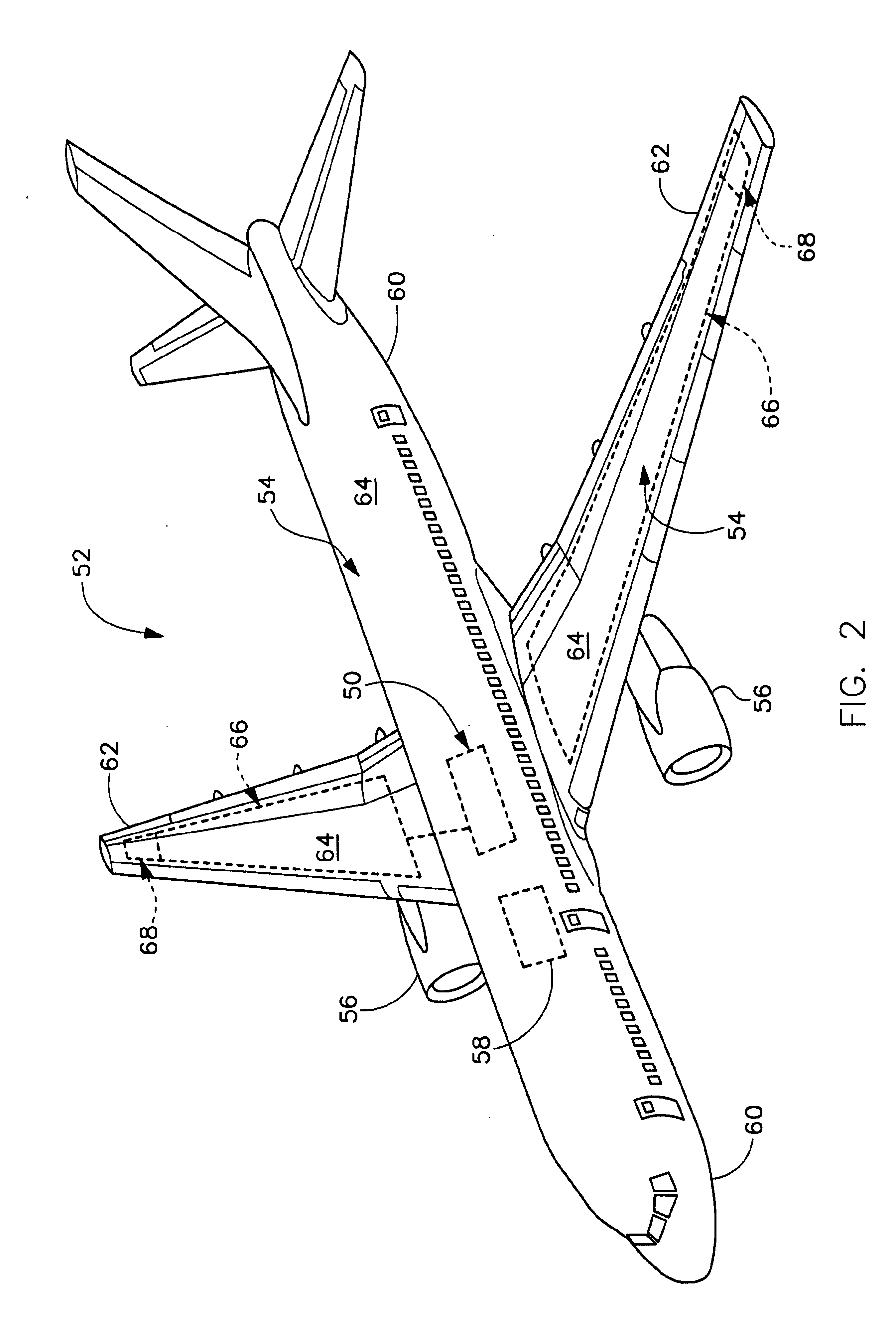
Method of reducing wind gust loads acting on an aircraft
InactiveUS6161801AReduce wing load of wingReduce loadEnergy saving arrangementsActuated automaticallyWing configurationRolling moment
A method of reducing the bending moment effect of wind gust loads acting on the wing of an aircraft involves adjusting the aerodynamic configuration of the wing so as to alter the distribution of lift generated by the wing during phases of flight in which critical wind gusts are expected to occur. Particularly, during climb and descent phases of flight below cruise altitude, the lift generated by outboard portions of the wings is reduced while the lift generated by inboard portions of the wings is increased. Thereby, the 1 g basis load acting on the outboard portions of the wings is reduced, and consequently the total load applied to the outboard portions of the wings, resulting from the 1 g basis load plus the additional wind gust load, is correspondingly reduced. This leads to a reduction of the bending moments effective on the wings, and of any rolling moment effective on the aircraft. The required adjustment of the lift distribution is preferably achieved by deflecting the ailerons of both wings symmetrically upward and / or deflecting the flaps of both wings symmetrically downward during climb and descent. The adjustment of the wing configuration is carried out dependent only on flight parameters such as the altitude, speed and gross weight, and does not require rapid sensing of the occurrence of a wind gust and rapid actuation of control surfaces to try to instantaneously counteract a wind gust as it occurs.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER AEROSPACE AIRBUS
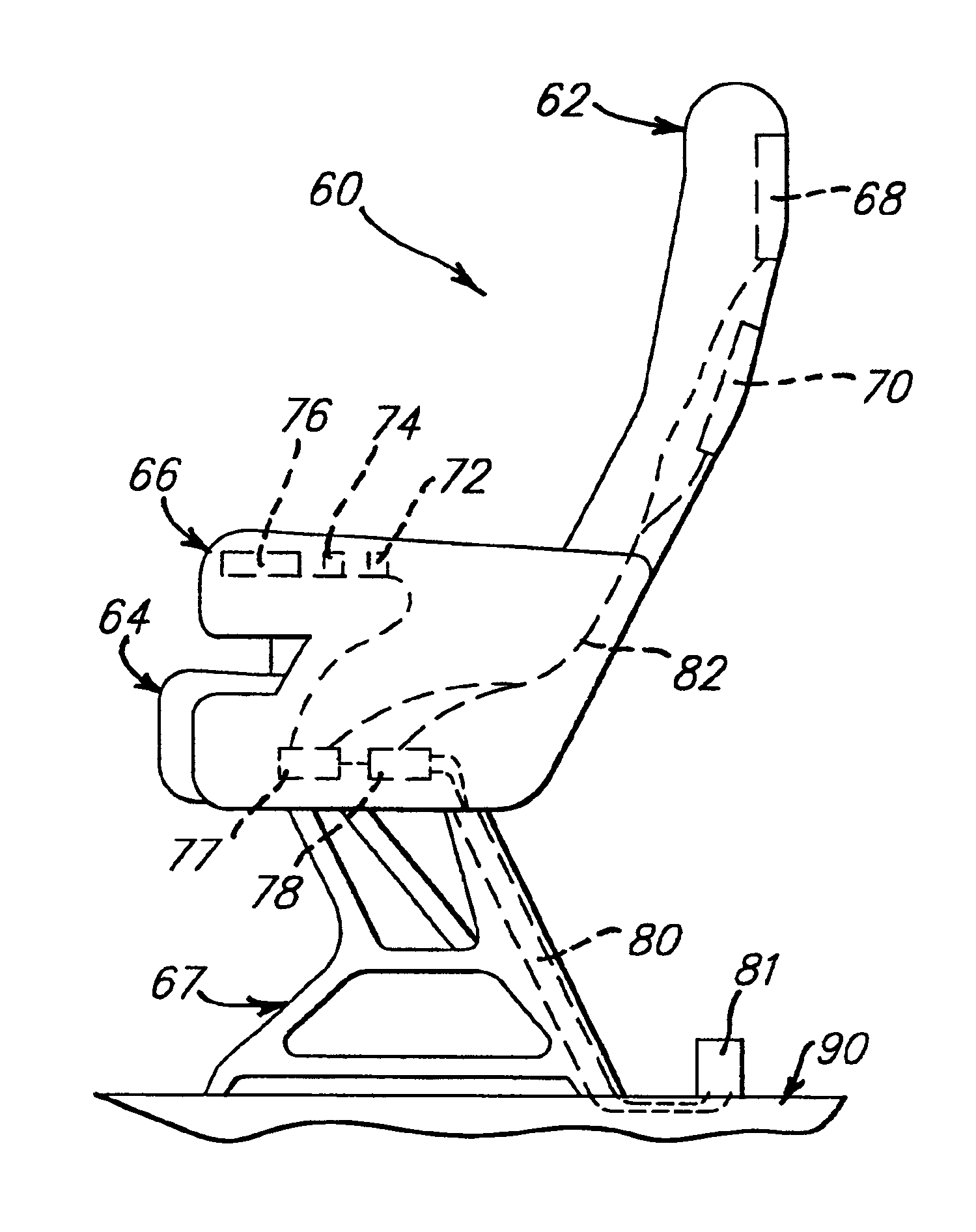
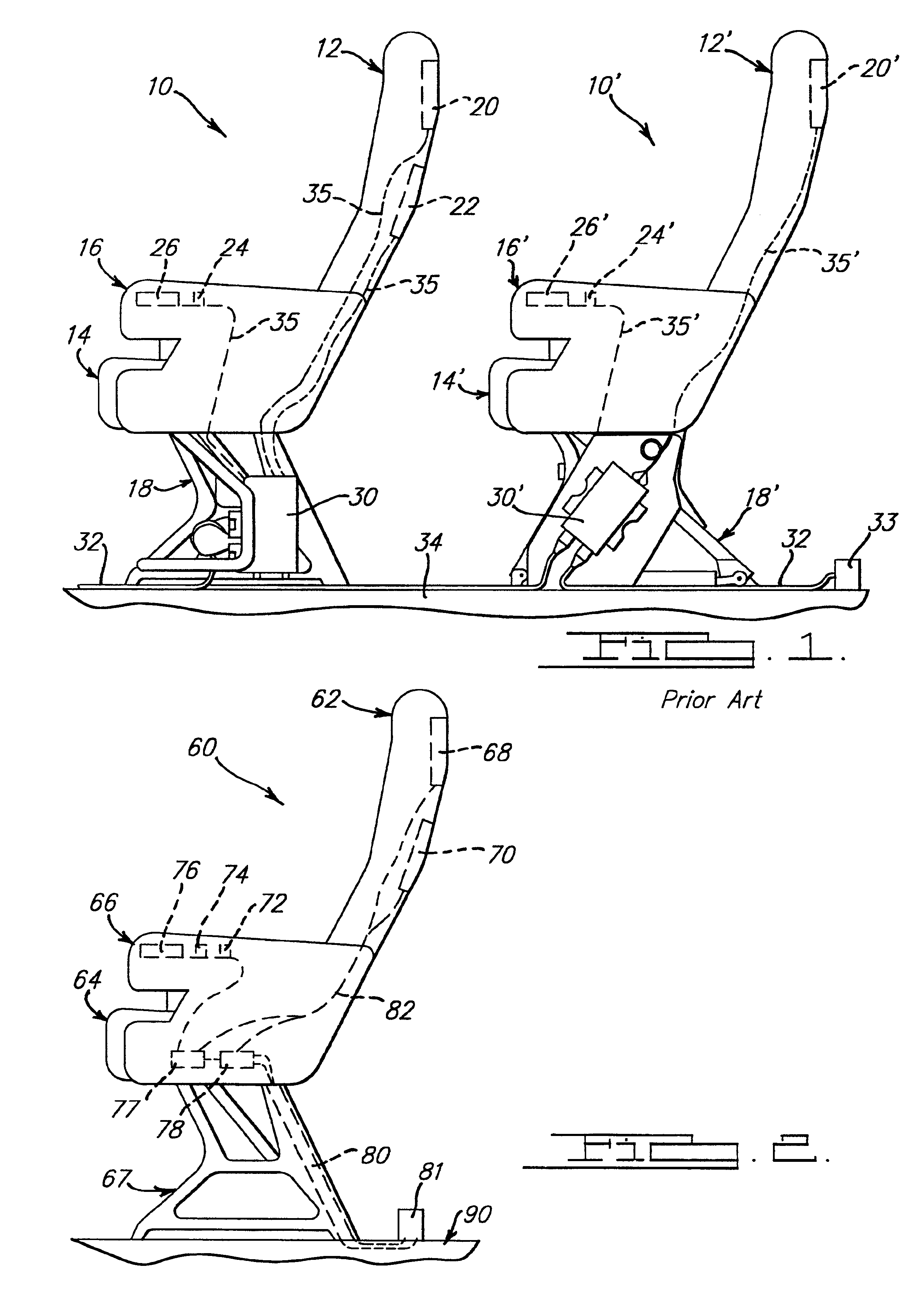
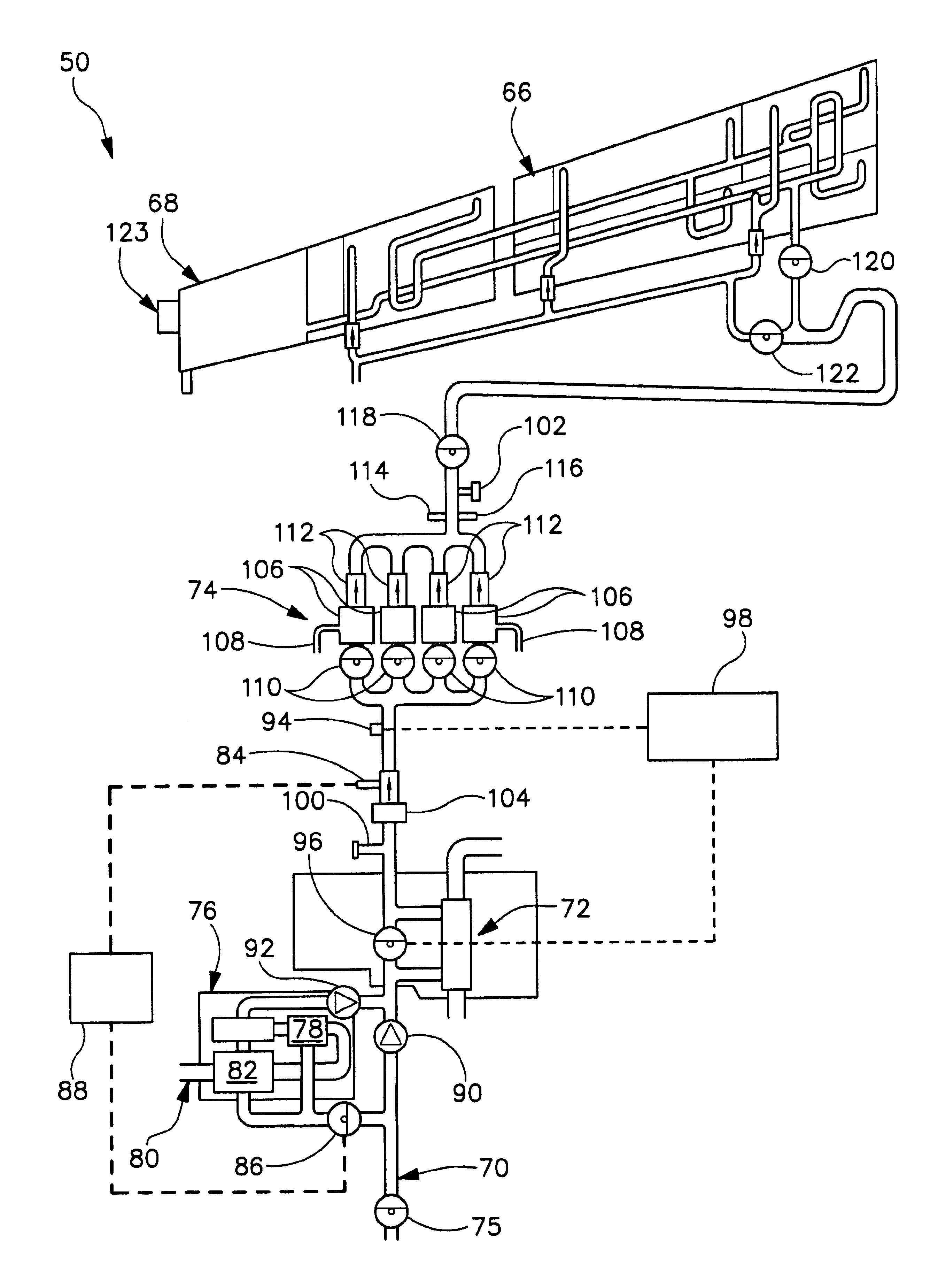
Aircraft passenger seat and in-flight entertainment integrated electronics
InactiveUS6899390B2Multiple and redundant and weightVehicle seatsSeating arrangementsSignal routingIntegrated electronics
An aircraft seat assembly including at least one electronic component usable by a passenger and a single integrated electronics system which provides signal decoding, signal routing, data management, built in test, and power conversion for each user accessible electronic component which is installed in the seat assembly. The integrated electronics system provides power conversion, signal routing, data management and other electronic requirements for each of the electronic components. The integrated electronics system not only integrates power conversion and signal management responsibilities into one system, but also is integrated into the seat assembly.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method and apparatus for generating an inert gas on a vehicle
An inert gas generating system for generating inert gas on a vehicle having a fuel tank and a fuel tank vent. The system includes an inlet for receiving a flow of gas having a nitrogen component and an oxygen component from a gas source, a heat exchanger downstream from the inlet and in fluid communication with the inlet for cooling gas received from the inlet, and a gas separation module downstream from the heat exchanger and in fluid communication with the heat exchanger for separating gas received from the heat exchanger into a nitrogen-enriched gas flow and an oxygen-enriched gas flow. The gas separation module is adapted to deliver nitrogen-enriched gas from the nitrogen-enriched gas flow to the fuel tank without delivering the nitrogen-enriched gas through the fuel tank vent. The gas separation module is also adapted to deliver nitrogen-enriched gas from the nitrogen-enriched gas flow to the fuel tank vent.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
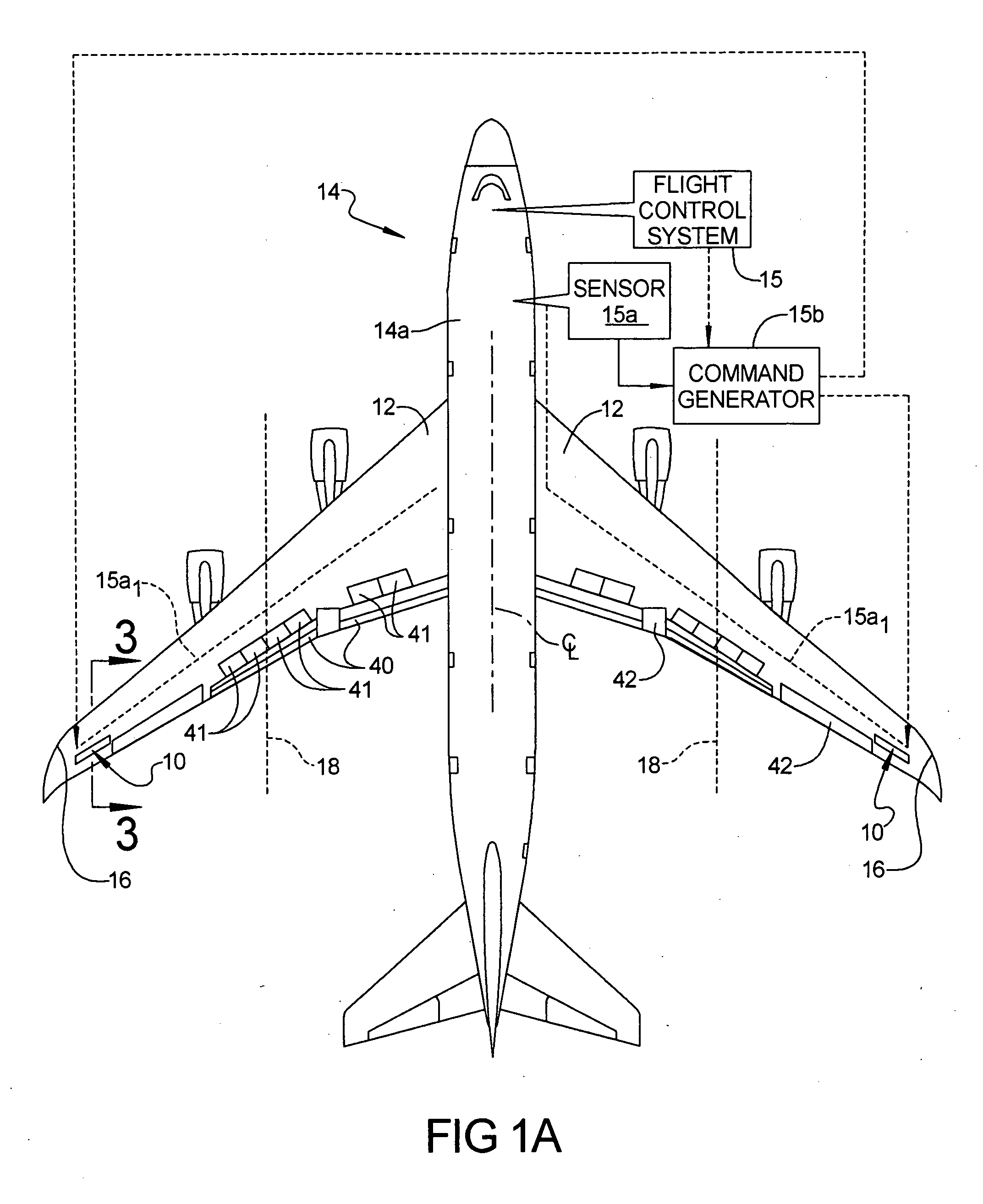
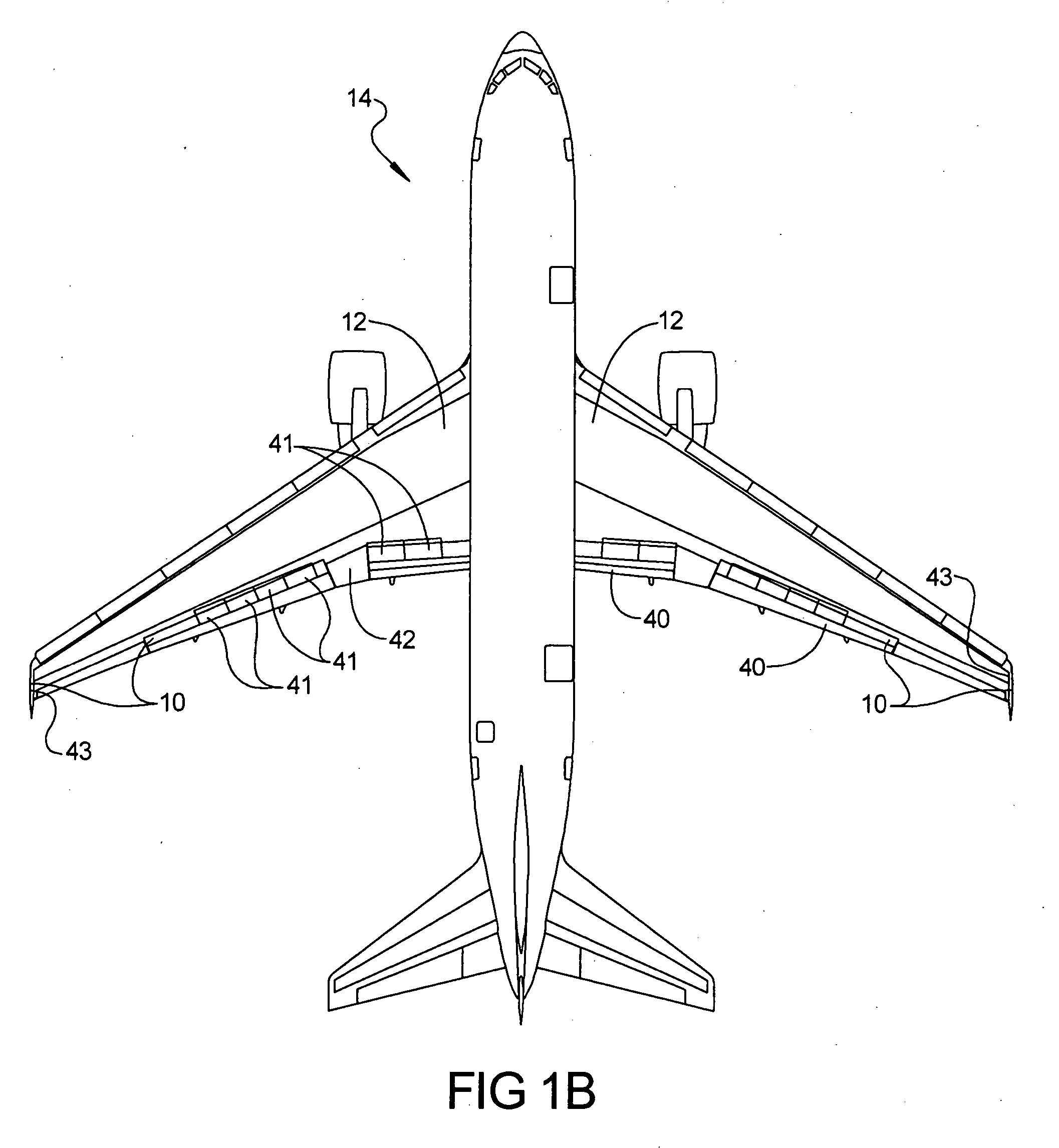
Wing load alleviation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070114327A1Reduces local aerodynamic loadEffective movementAircraft stabilisationActuated automaticallyTrailing edgeActuator
A wing load alleviation system and method for alleviating the lift-inducing structural-bending force (i.e., moment) experienced by each of the wings of an aircraft. The apparatus includes a deployable panel and an actuator mounted in each wing. The actuators are responsive to a command generator. The actuator is mounted inside the wing and the panel is mounted flush with an outer surface of its respective wing. Each panel can be moved between a retracted position, where it has no affect on airflow moving over the wing, to a deployed position in which it deflects air off of the wing. Each panel is preferably located at a span-wise location at least about halfway along the length of the wing toward the wing tip, and more preferably at least in part outboardly of the outboard-most trailing edge device in the wing. The apparatus effectively shifts the lift-inducing structural-bending forces experienced by the wing more inboard towards the fuselage.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Tubular members integrated to form a structure
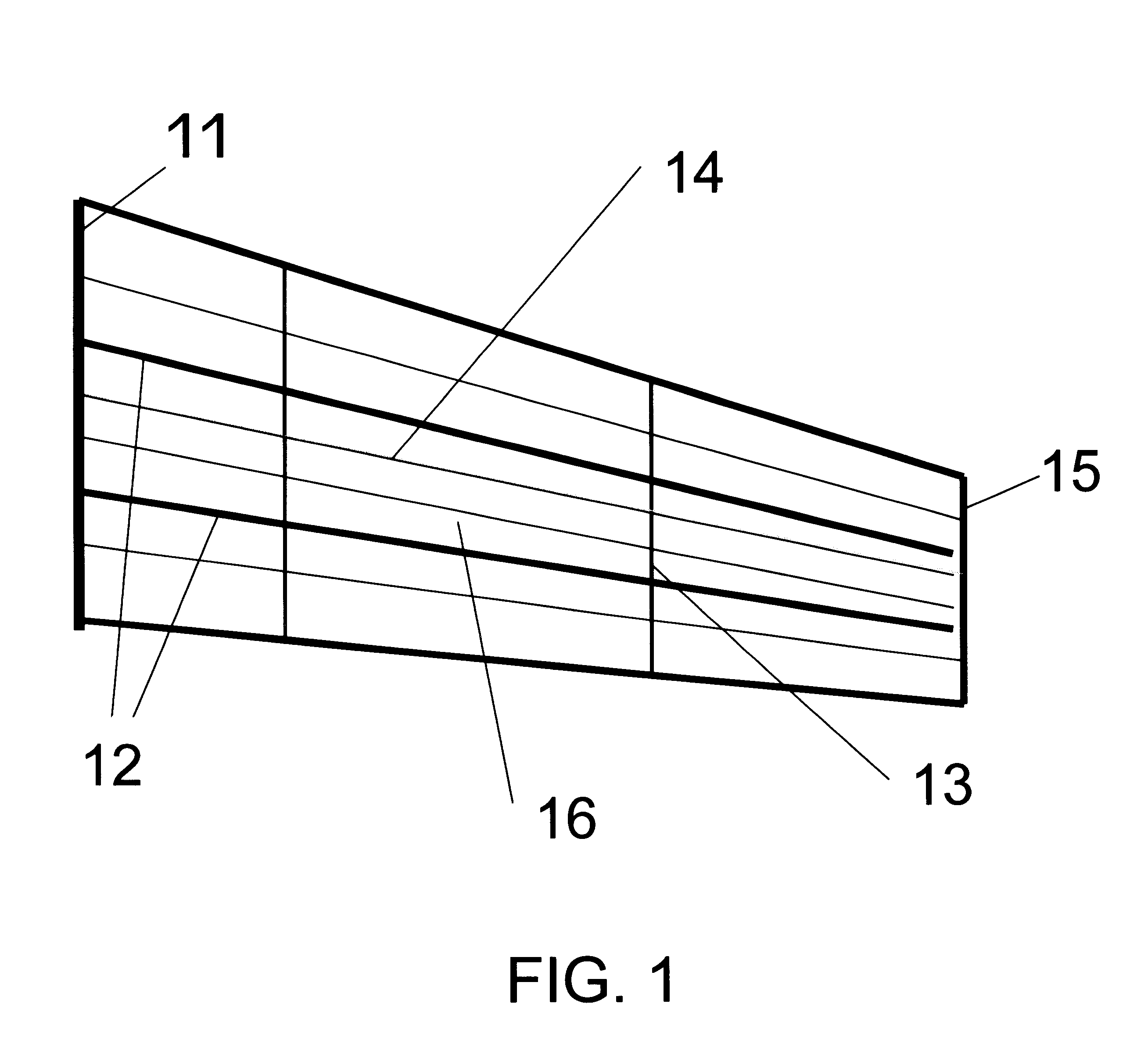
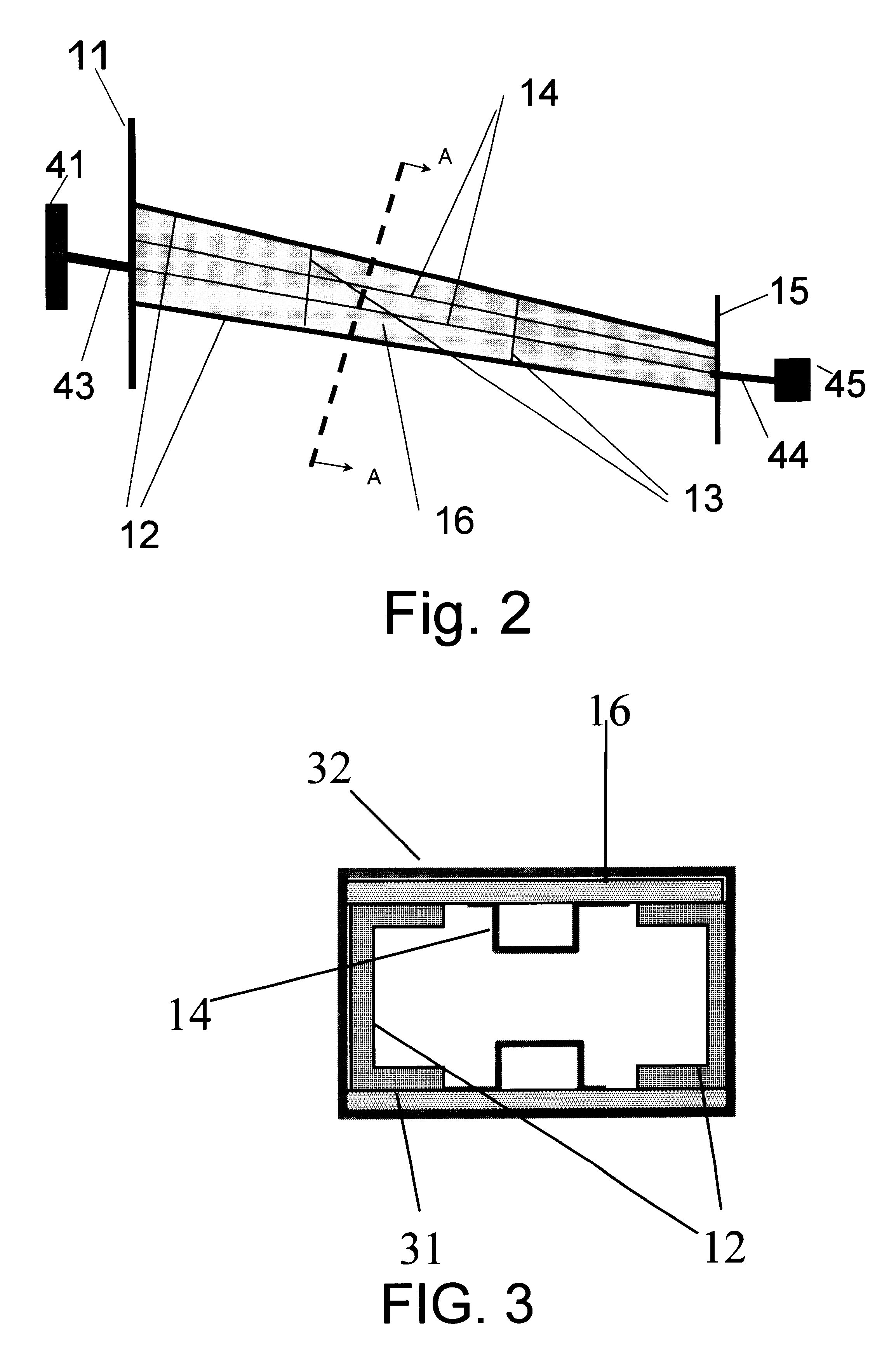
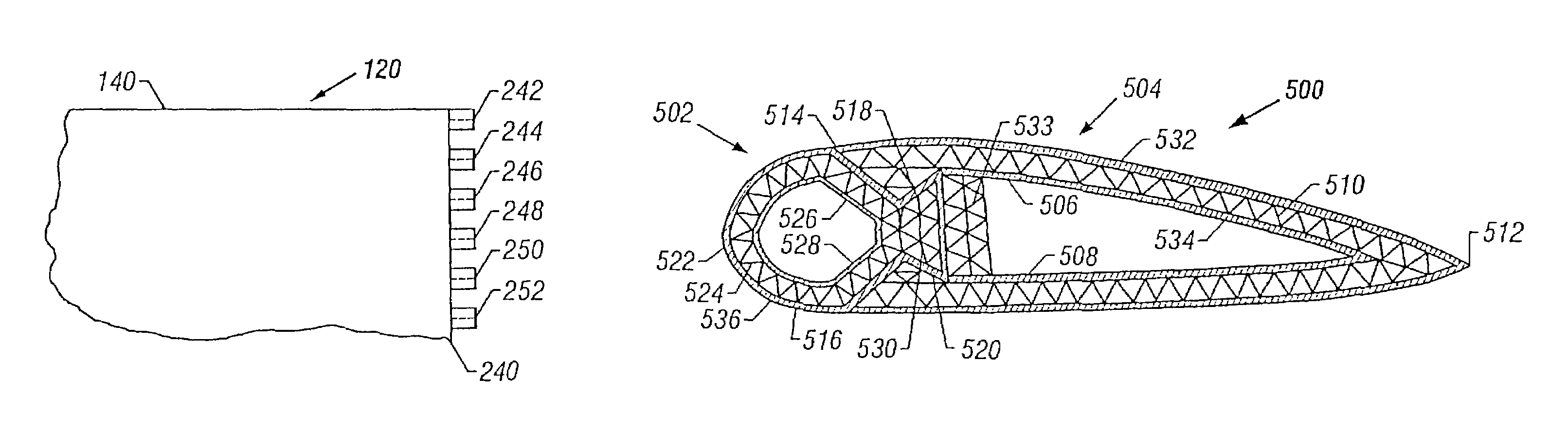
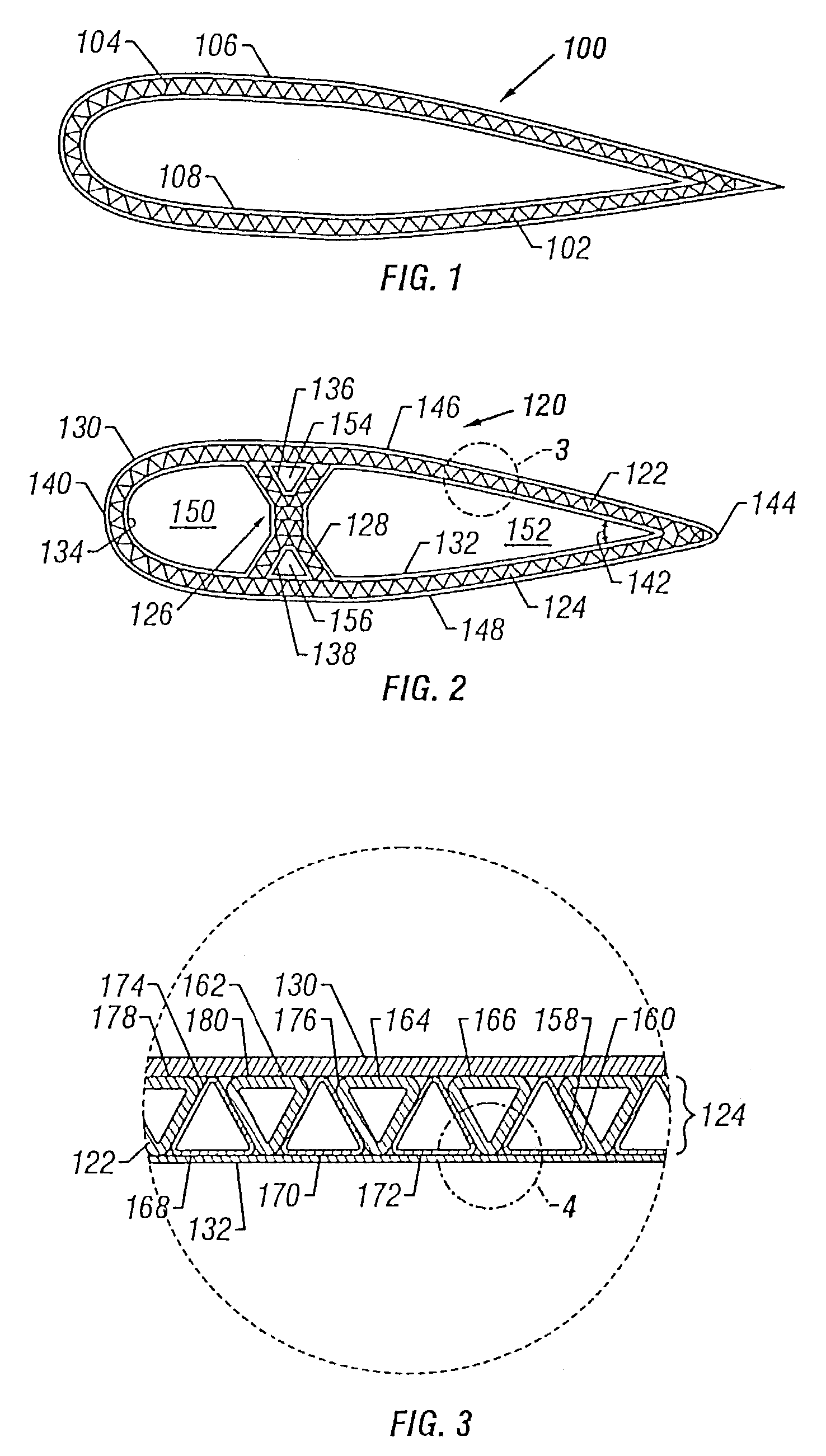
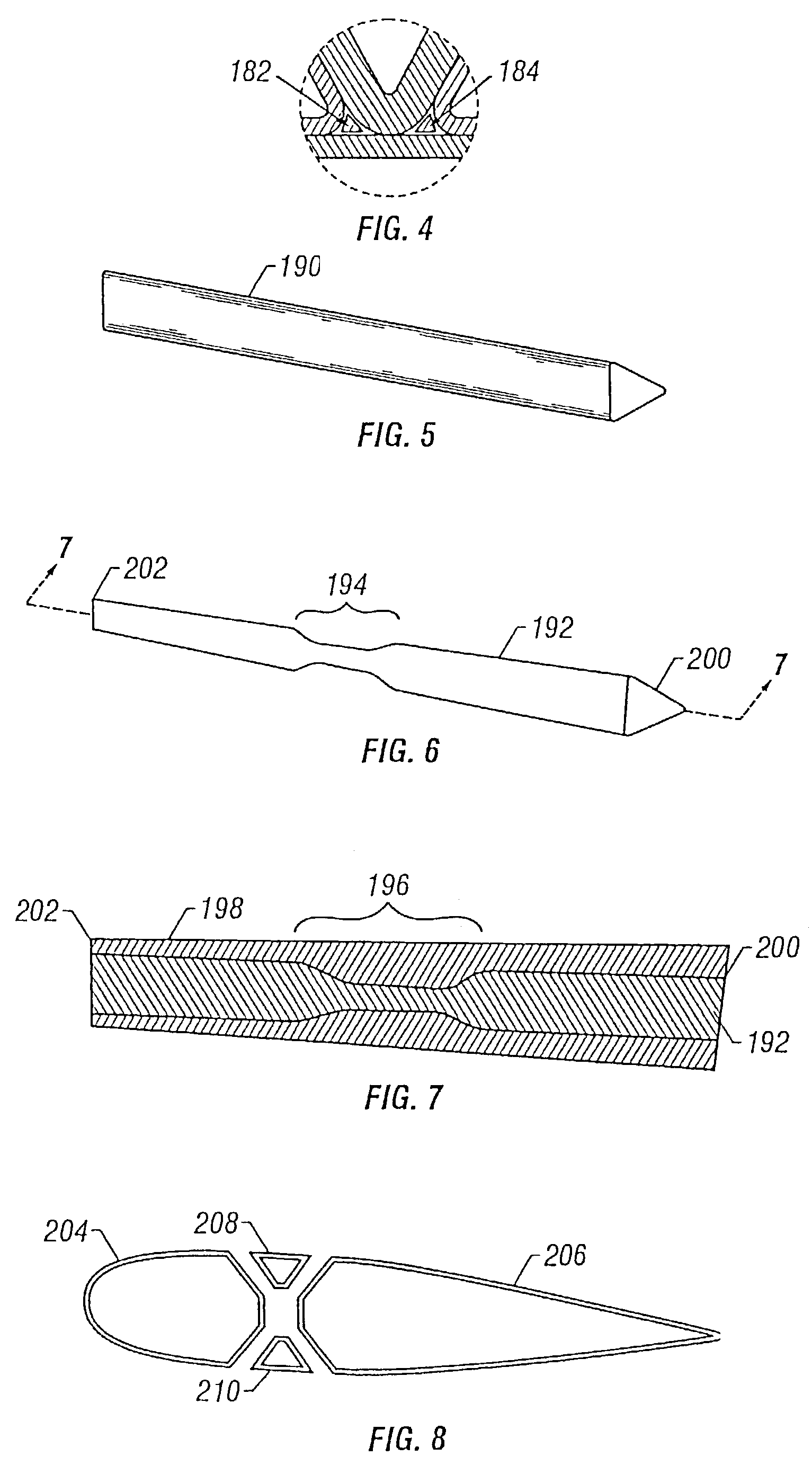
InactiveUS7063763B2Eliminate needEffective carryFuselage framesAircraft stabilisationMechanical engineeringFilament winding
Integrally stiffened and formed, load carrying structures comprising a plurality of elongated thin-walled tubes placed co-extensively in a complementary side-by-side fashion which together form a hollow structure having a desired external contour. Integral skins forming the external and internal surfaces of the structure cooperatively therewith. The structure can be formed with an underlying internal support member spanning the interior of the load carrying structure, thereby connecting opposite sides of the structure together. Also, each of the tubes are wound with fibers in controlled orientations generally paralleling the direction of the loads applied to the tubes to optimize the strength to weight ratio of the tubes.
Owner:CHAPMAN JR W CULLEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com