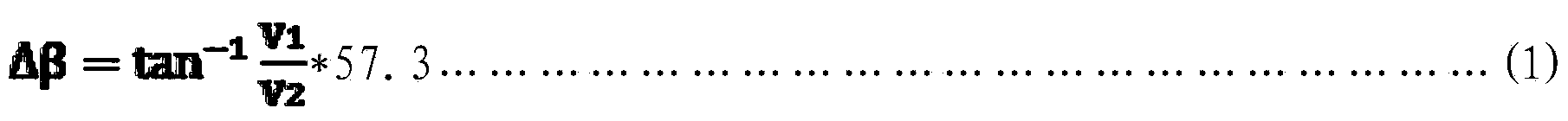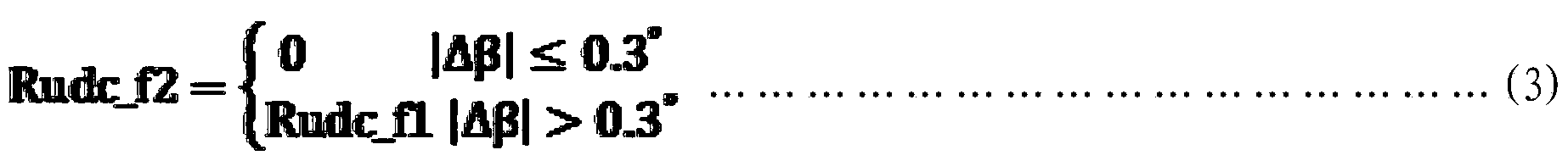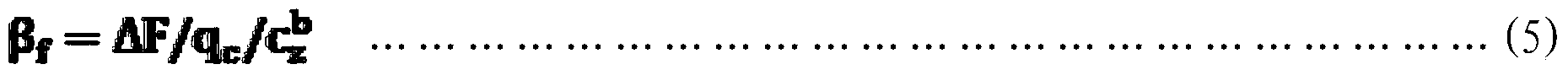Patents
Literature
203 results about "Wind gust" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
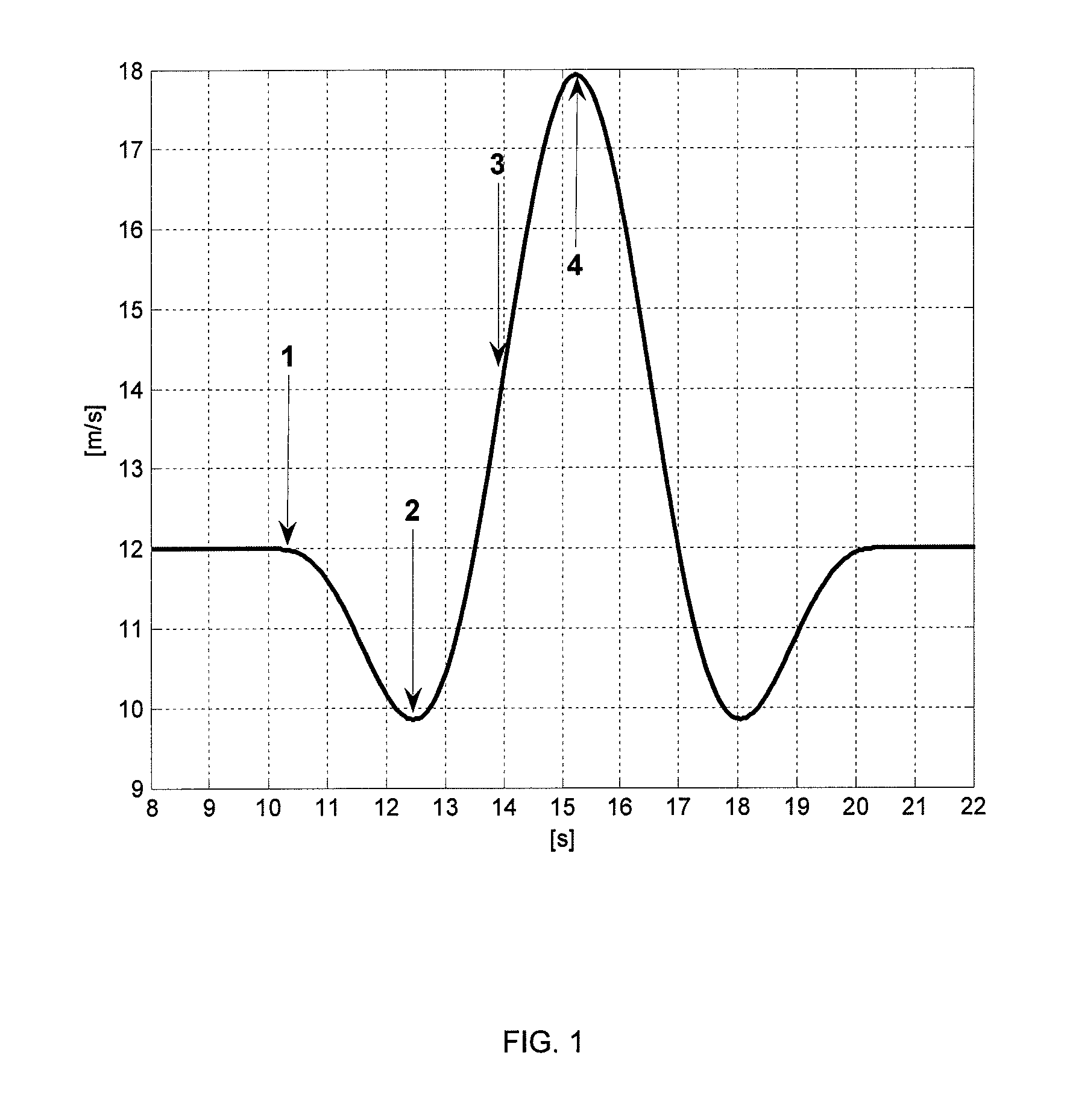
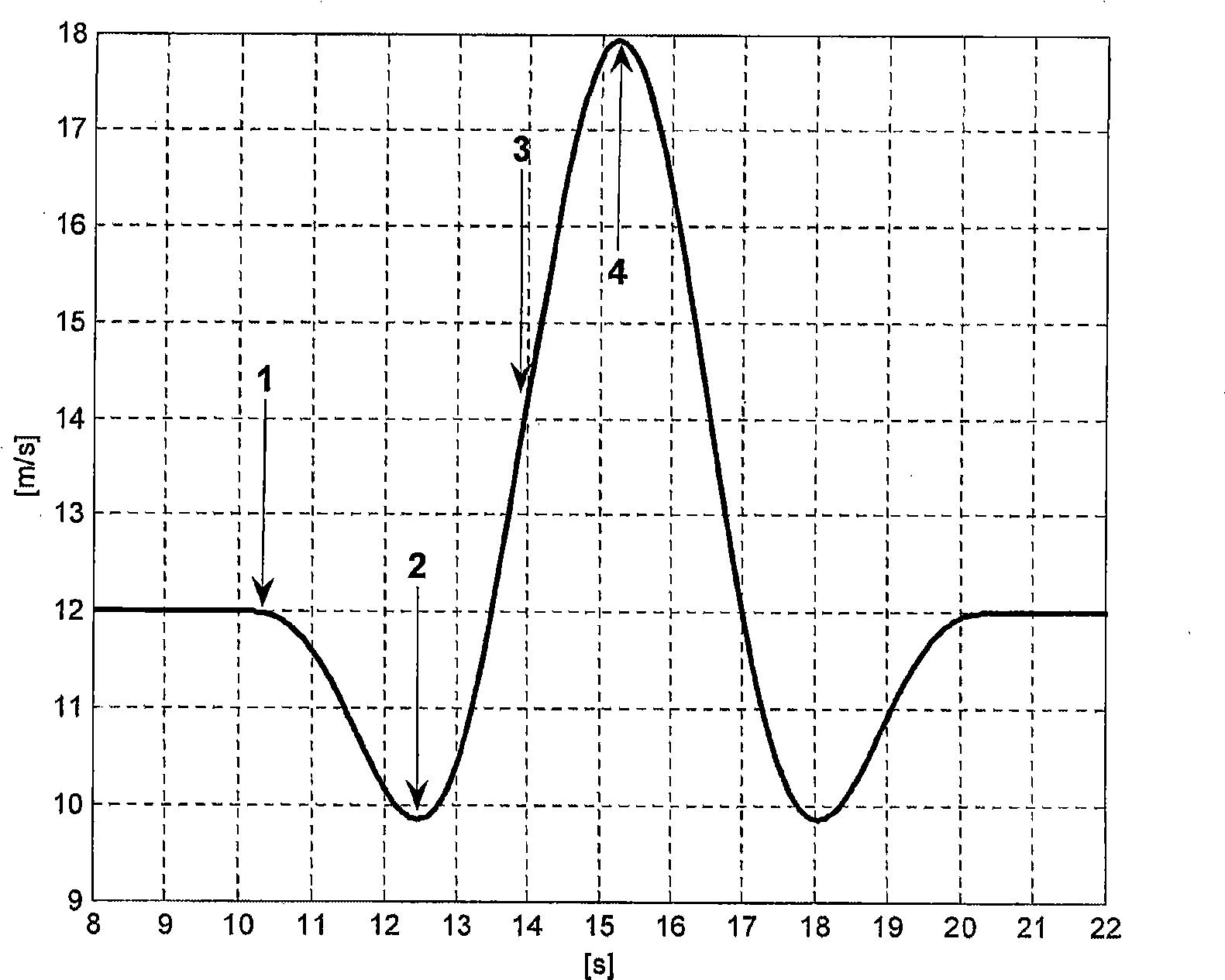
A wind gust is a sudden, brief increase in the speed of the wind followed by a lull. According to National Weather Service observing practice, gusts are reported when the peak wind speed reaches at least 18 mph and the variation in wind speed between the peaks and lulls is at least about 10 mph.
PV wind performance enhancing methods and apparatus
InactiveUS20050126621A1Uniform pressurePressure equalization can be enhancedPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyAerodynamic dragAir volume
Pressure equalization between upper and lower surfaces of PV modules of an array of PV modules can be enhanced in several ways. Air gaps opening into the air volume, defined between the PV modules and the support surface, should be provided between adjacent PV modules and along the periphery of the array. The ratio of this air volume to the total area of the air gaps should be minimized. Peripheral wind deflectors should be used to minimize aerodynamic drag forces on the PV modules. The time to equalize pressure between the upper and lower surfaces of the PV modules should be maintained below, for example, 10-20 milliseconds. The displacement created by wind gusts should be limited to, for example, 2-5 millimeters or less. For inclined PV modules, rear air deflectors are advised for each PV module and side air deflectors are advised for the periphery of the array.
Owner:SUNPOWER CORPORATION
Method of reducing wind gust loads acting on an aircraft
InactiveUS6161801AReduce wing load of wingReduce loadEnergy saving arrangementsActuated automaticallyWing configurationRolling moment
A method of reducing the bending moment effect of wind gust loads acting on the wing of an aircraft involves adjusting the aerodynamic configuration of the wing so as to alter the distribution of lift generated by the wing during phases of flight in which critical wind gusts are expected to occur. Particularly, during climb and descent phases of flight below cruise altitude, the lift generated by outboard portions of the wings is reduced while the lift generated by inboard portions of the wings is increased. Thereby, the 1 g basis load acting on the outboard portions of the wings is reduced, and consequently the total load applied to the outboard portions of the wings, resulting from the 1 g basis load plus the additional wind gust load, is correspondingly reduced. This leads to a reduction of the bending moments effective on the wings, and of any rolling moment effective on the aircraft. The required adjustment of the lift distribution is preferably achieved by deflecting the ailerons of both wings symmetrically upward and / or deflecting the flaps of both wings symmetrically downward during climb and descent. The adjustment of the wing configuration is carried out dependent only on flight parameters such as the altitude, speed and gross weight, and does not require rapid sensing of the occurrence of a wind gust and rapid actuation of control surfaces to try to instantaneously counteract a wind gust as it occurs.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER AEROSPACE AIRBUS
Method of modeling dynamic characteristics of a flight vehicle
InactiveUS20100318336A1Increased complexitySatisfactory level of complexityGeometric CADSimulator controlAviationModel dynamics
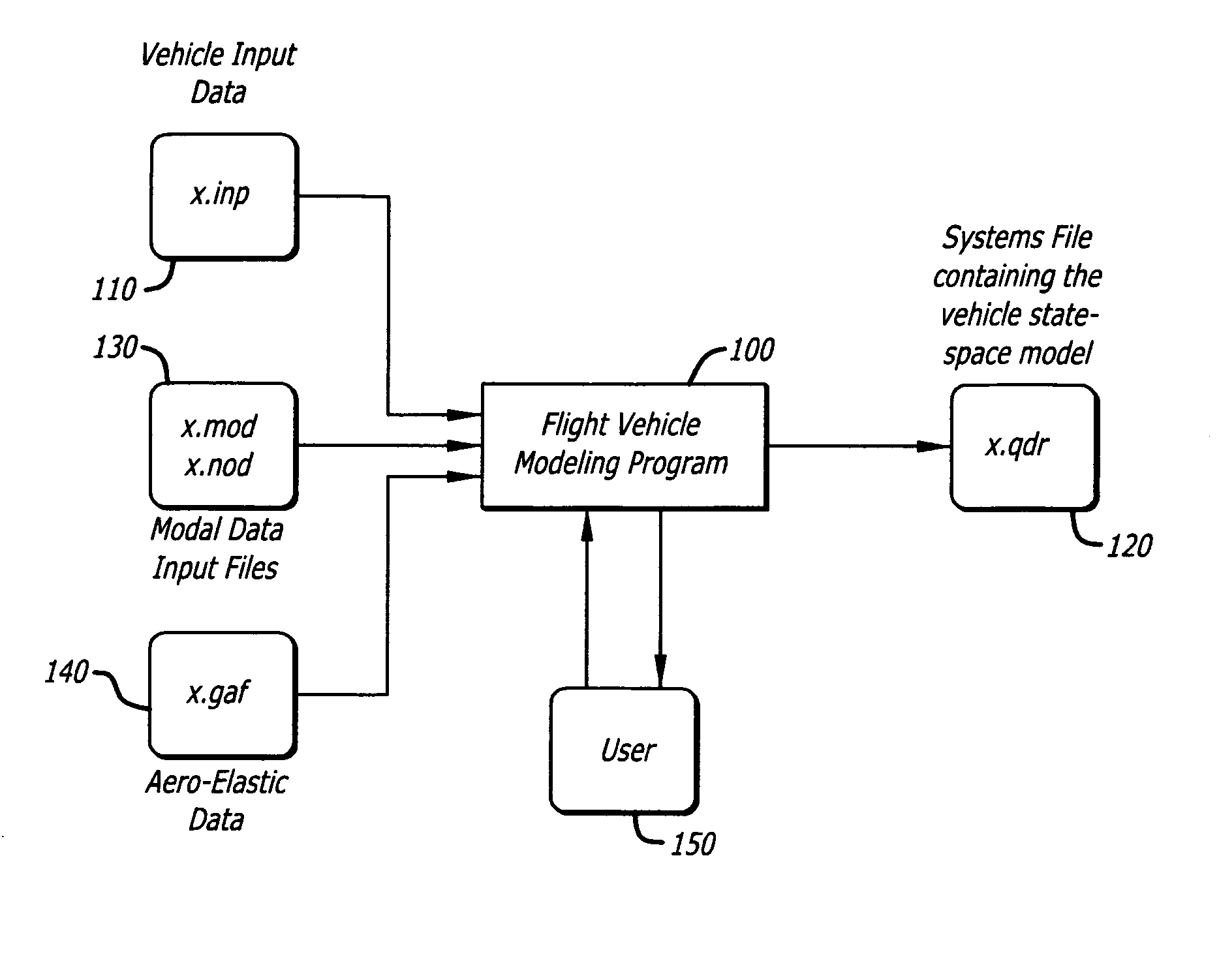
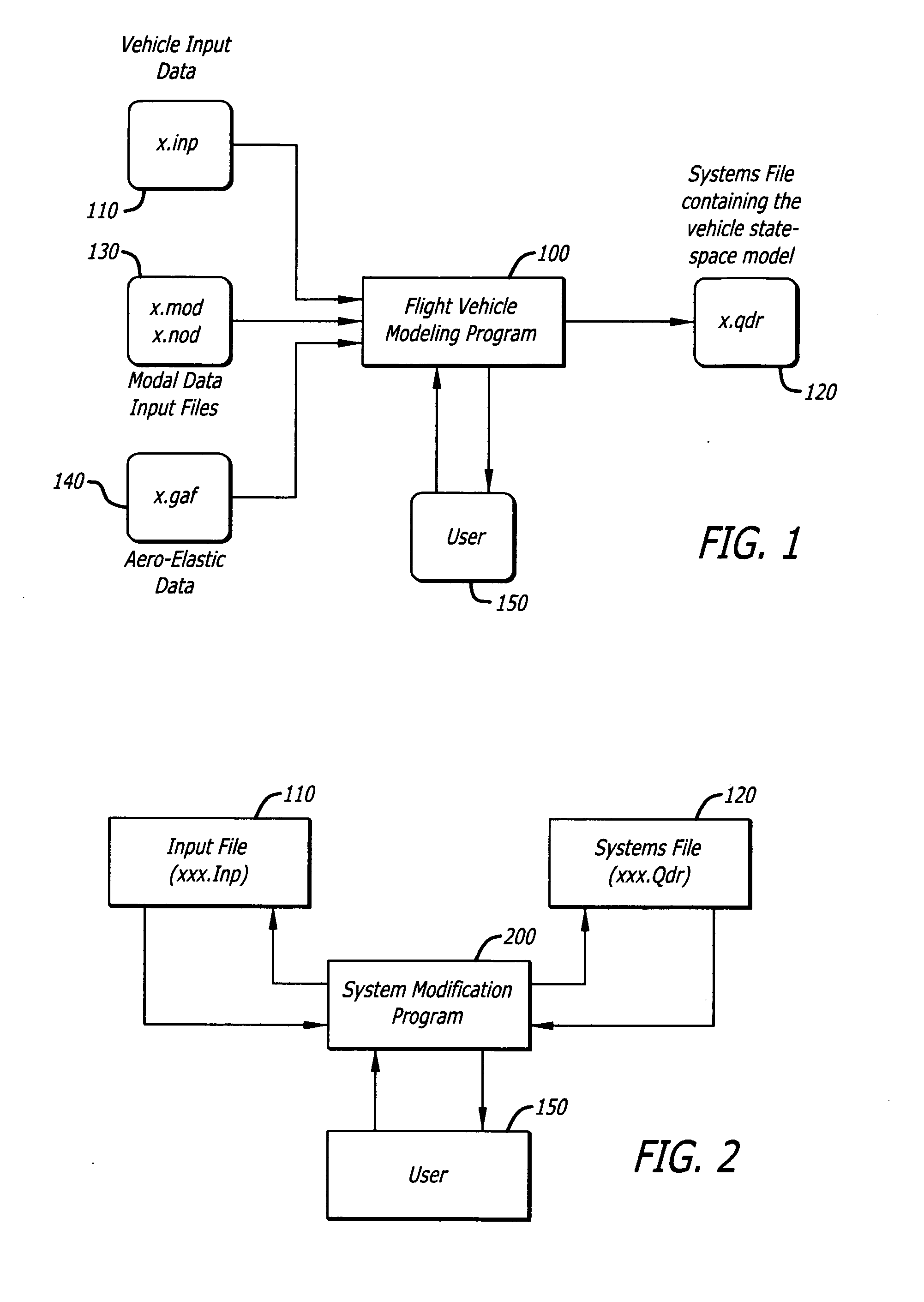
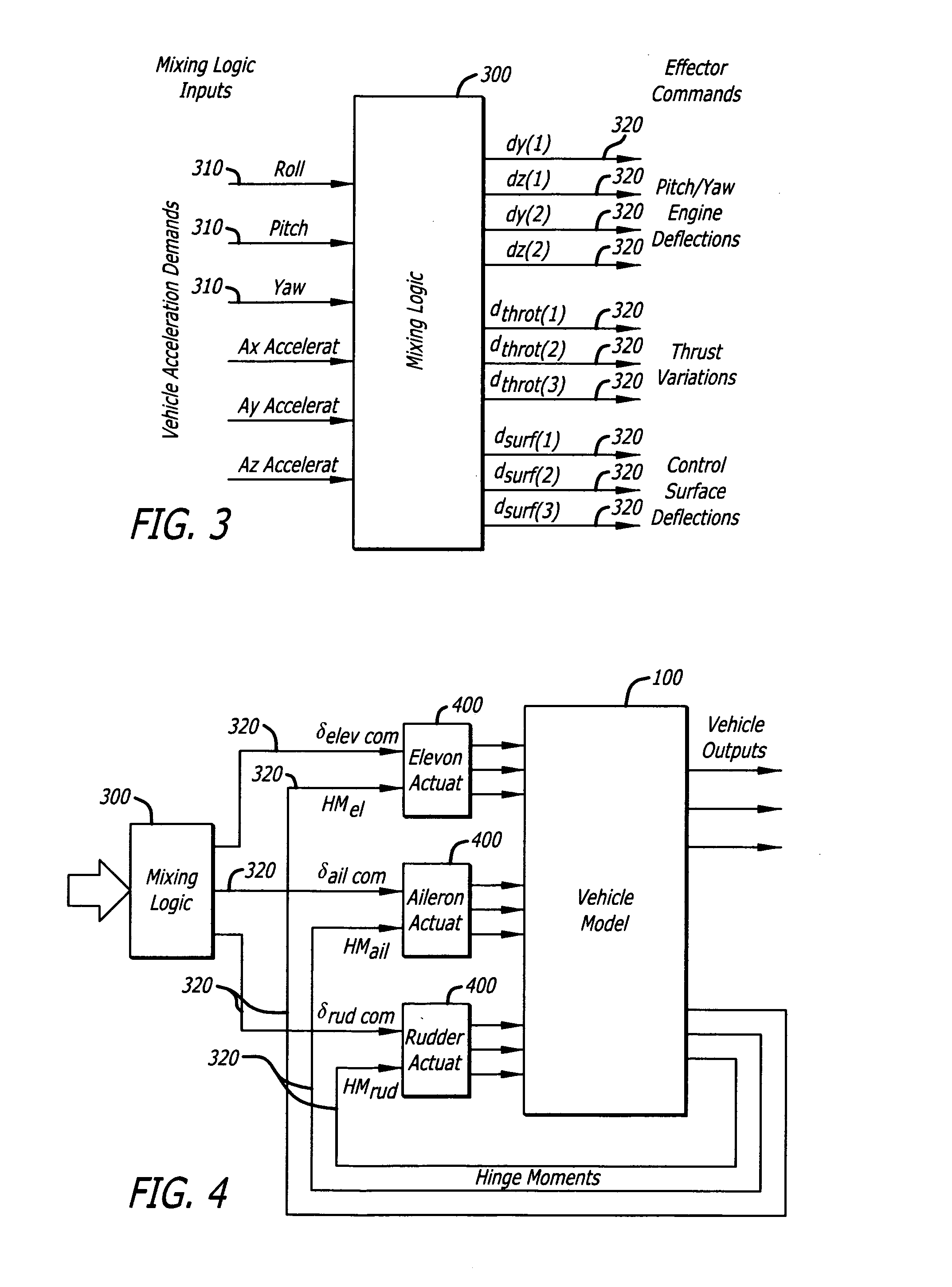
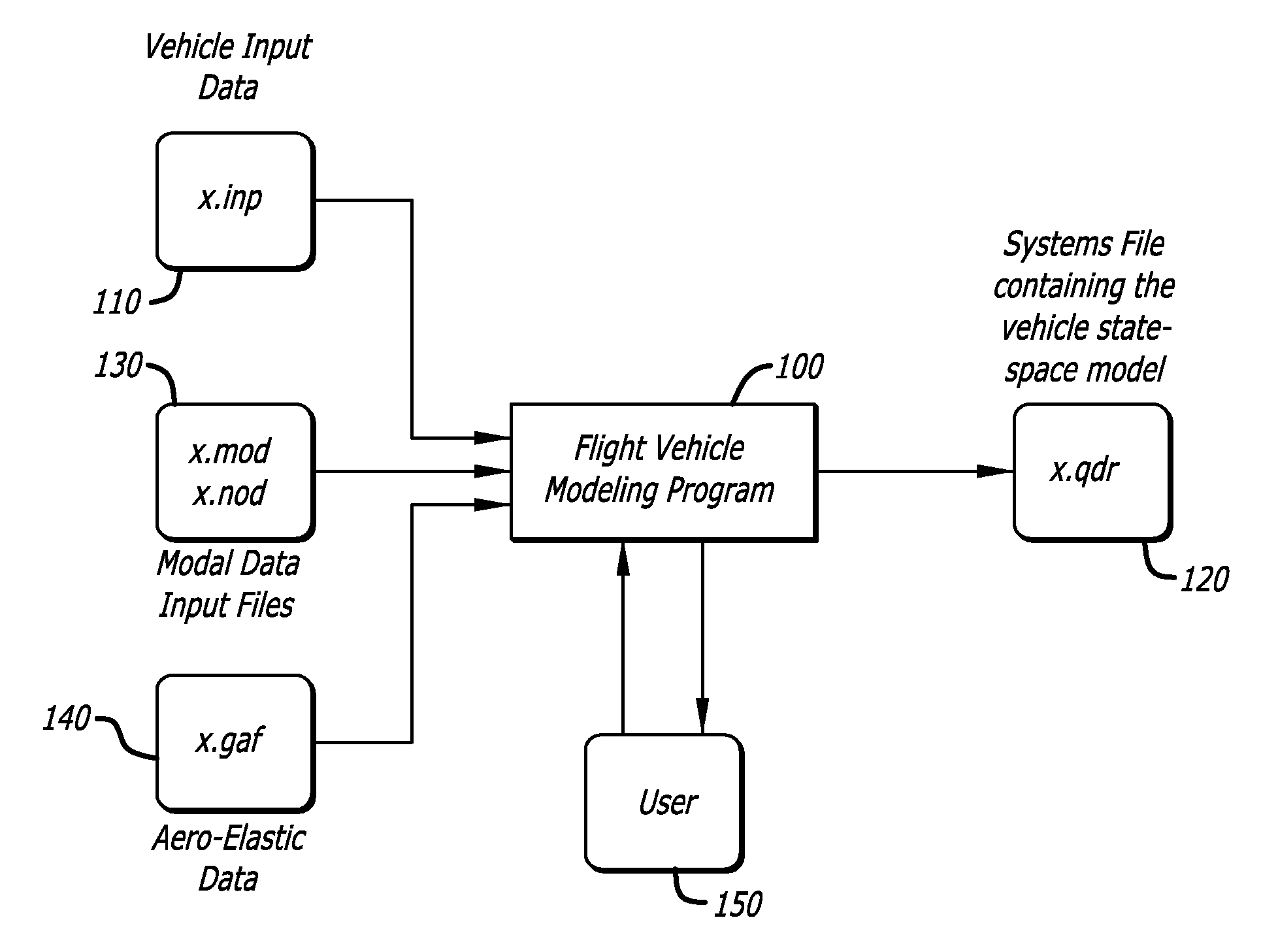
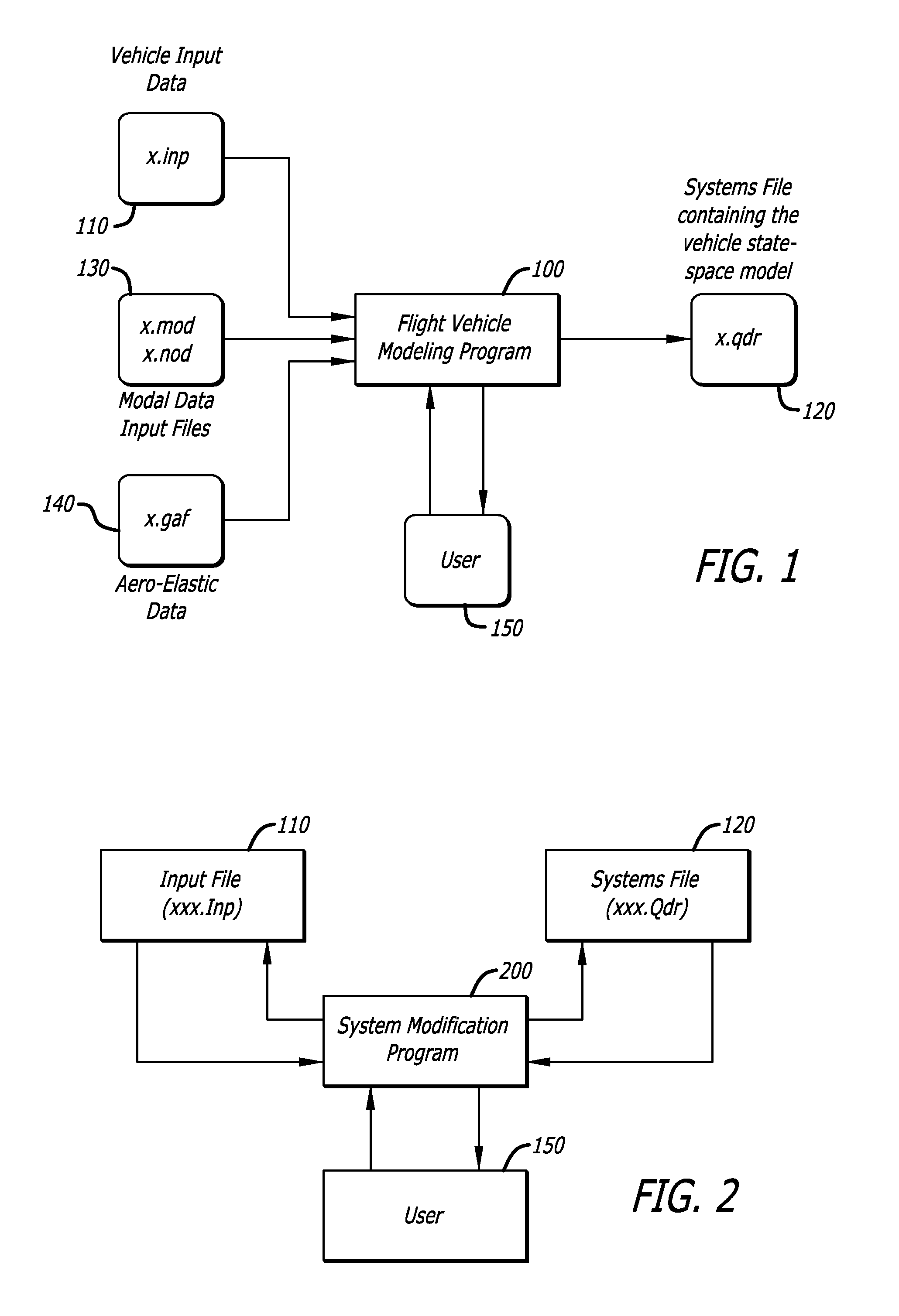
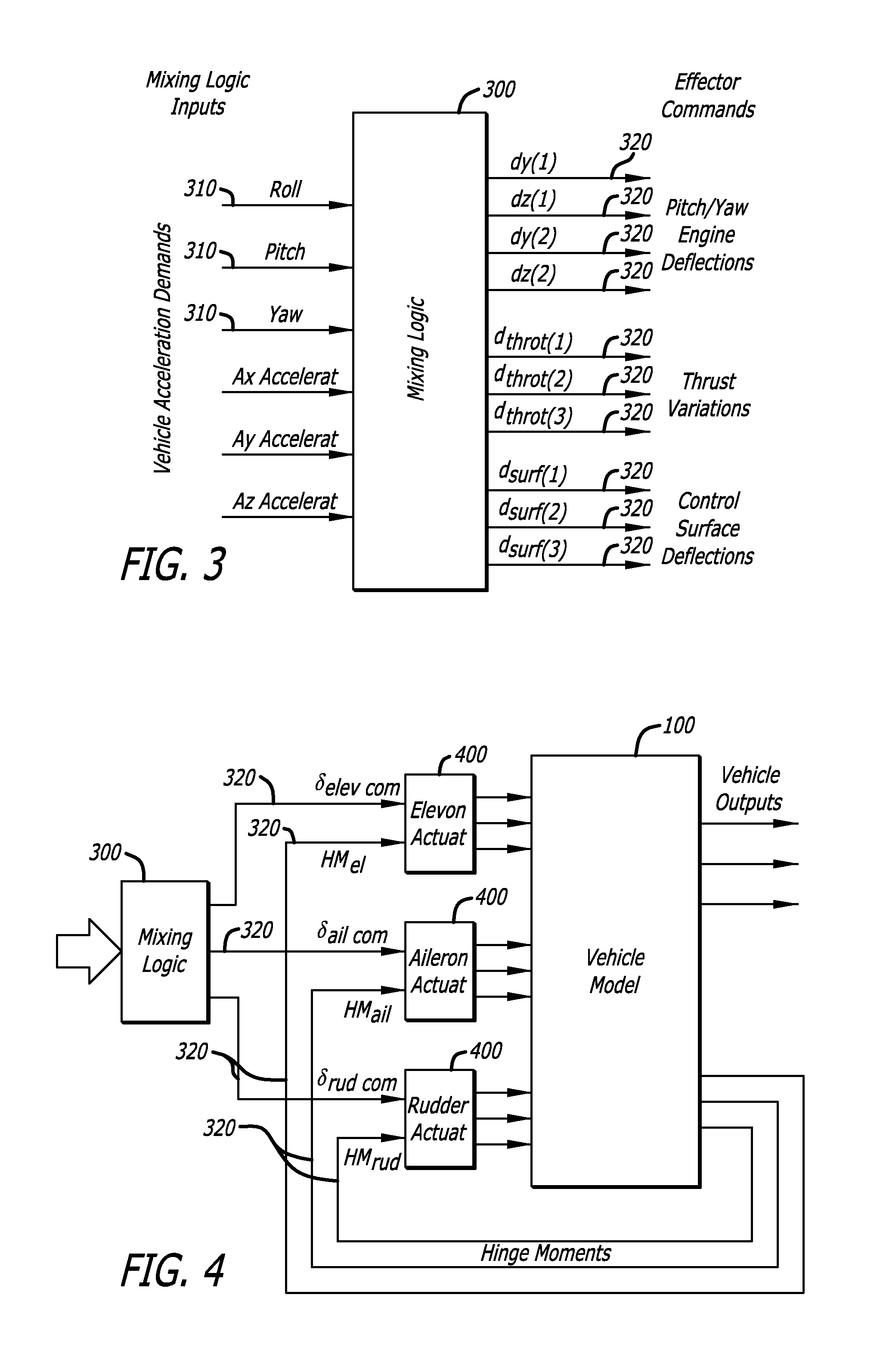
The present invention models dynamic behavior of flight vehicles for simulation, analysis, and design. The present invention allows a user to define the complexity of a flight vehicle model, and such models may be simple rigid body models, models of medium complexity, or very complex models including high order dynamics comprising hundreds of structural flexibility modes and variables related to aero-elasticity, fuel sloshing, various types of effectors, tail-wags-dog dynamics, complex actuator models, load-torque feedback, wind gusts, and other parameters impacting flight vehicles. The present invention accommodates and analyzes multiple vehicle and actuator concepts and configurations as defined in flight vehicle input data, which specifies flight vehicle parameters at a steady-state condition for modeling flight vehicle response to dynamic forces and flight control commands with respect to steady state operation.
Owner:FALANGAS ERIC T
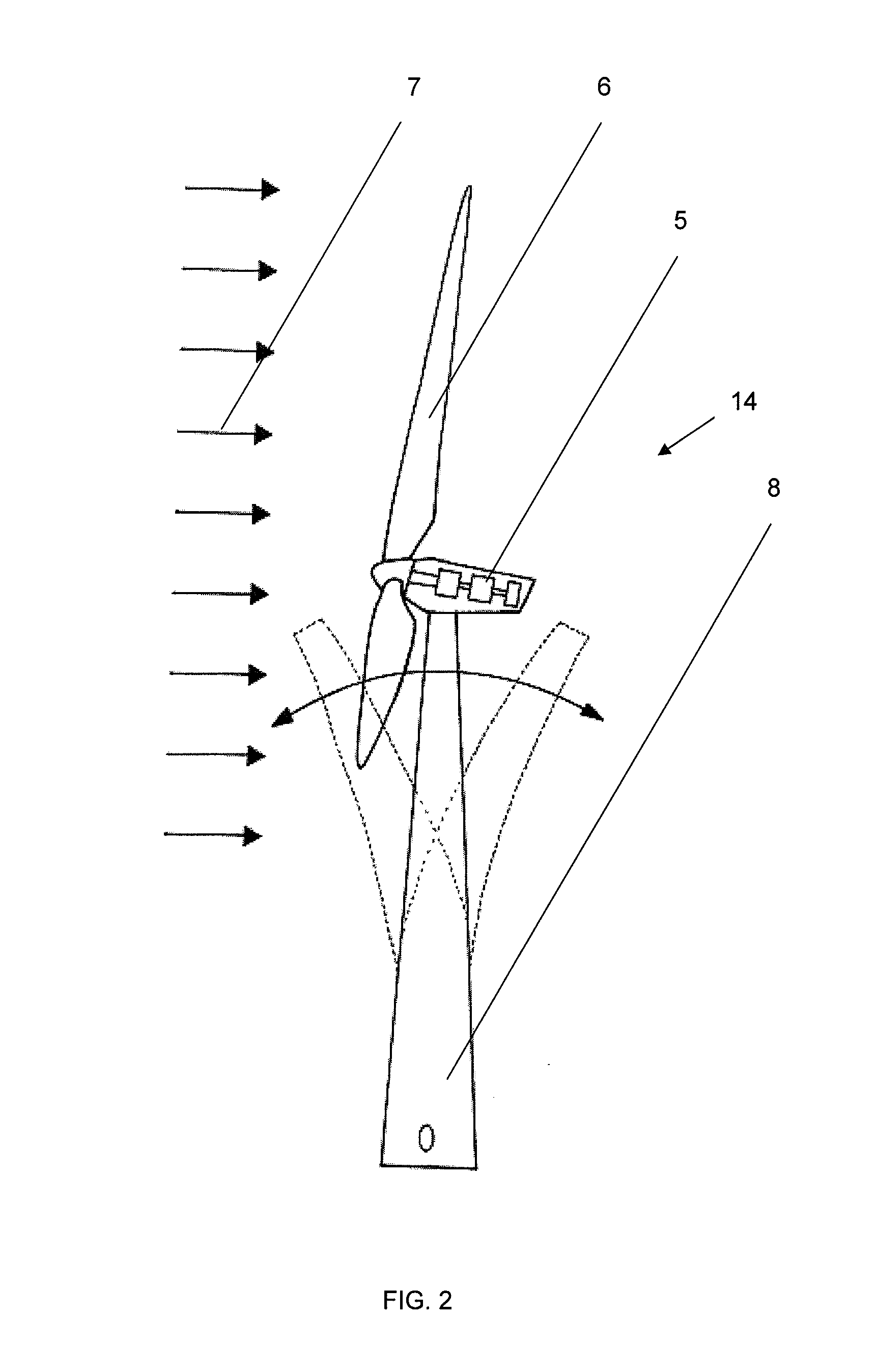
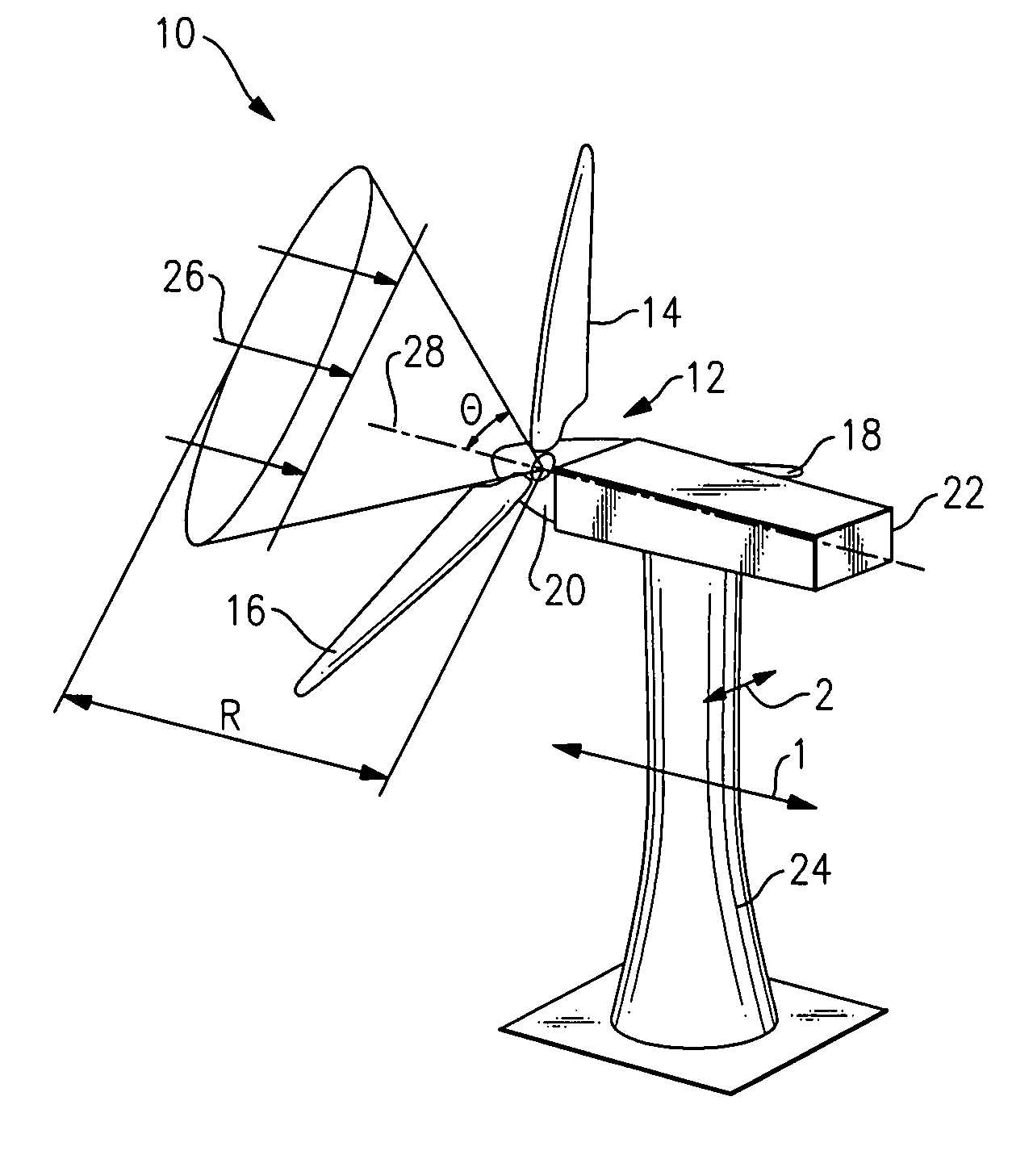
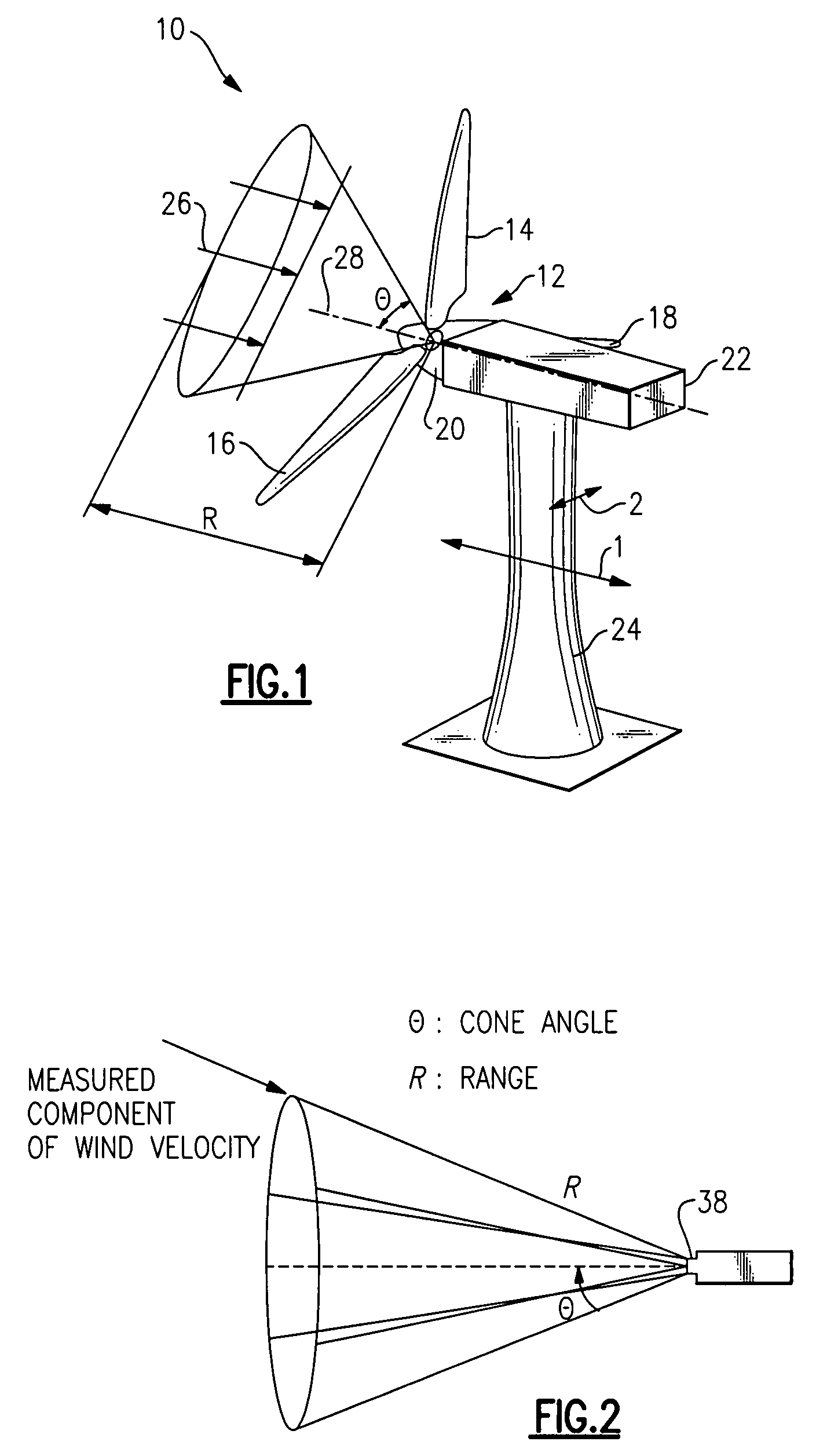
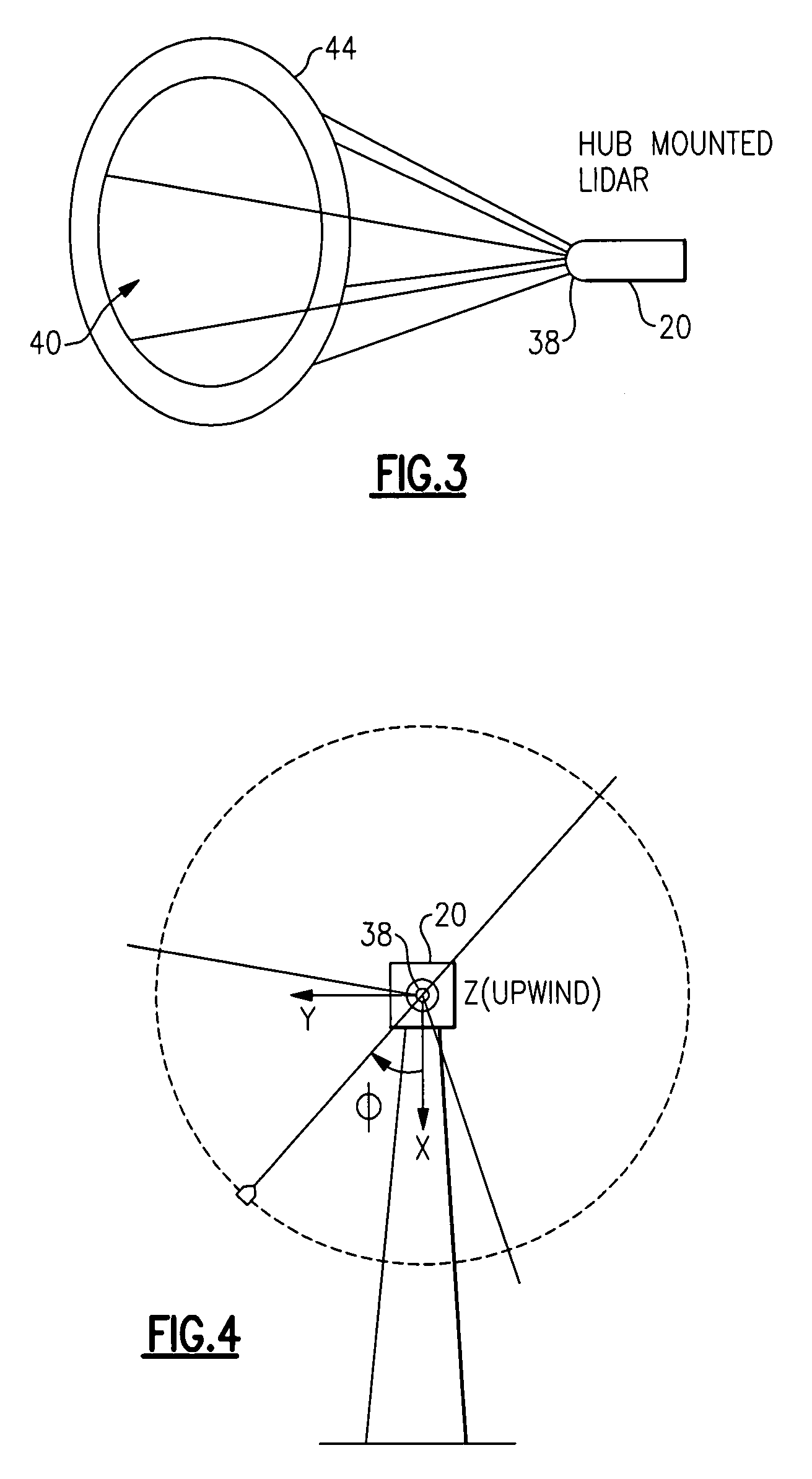
System and method for loads reduction in a horizontal-axis wind turbine using upwind information
A system and method provide a proactive mechanism to control pitching of the blades of a wind turbine to compensate for rotor imbalance during normal operation by pitching the blades individually or asymmetrically, based on turbulent wind gust measurements in front of the rotor, determined before it reaches the rotor blades.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
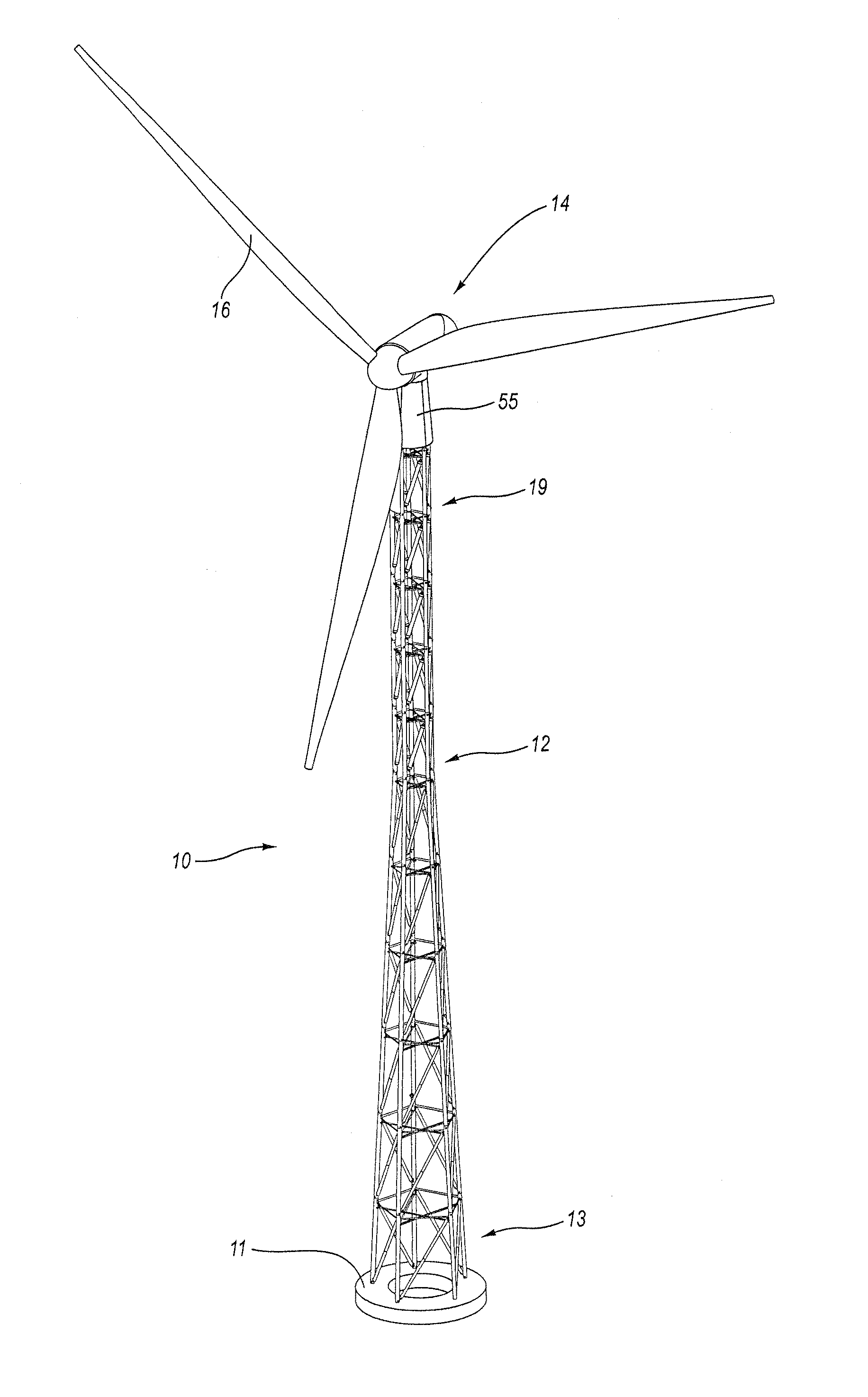
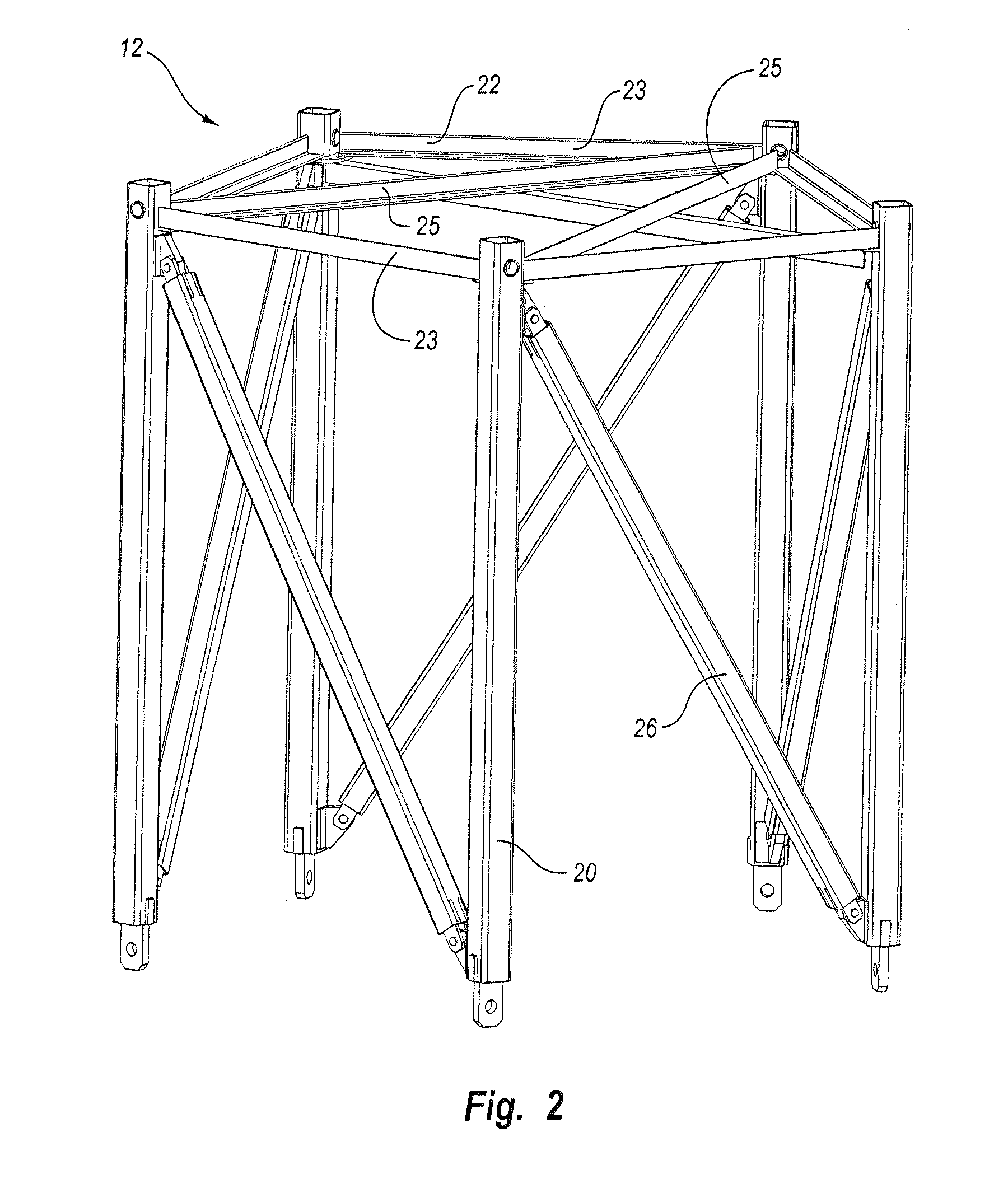
Structural tower
InactiveUS20060277843A1Reduce energy costsGenerate efficientlyCollapsable antennas meansEngine manufactureHigh elevationDiagonal
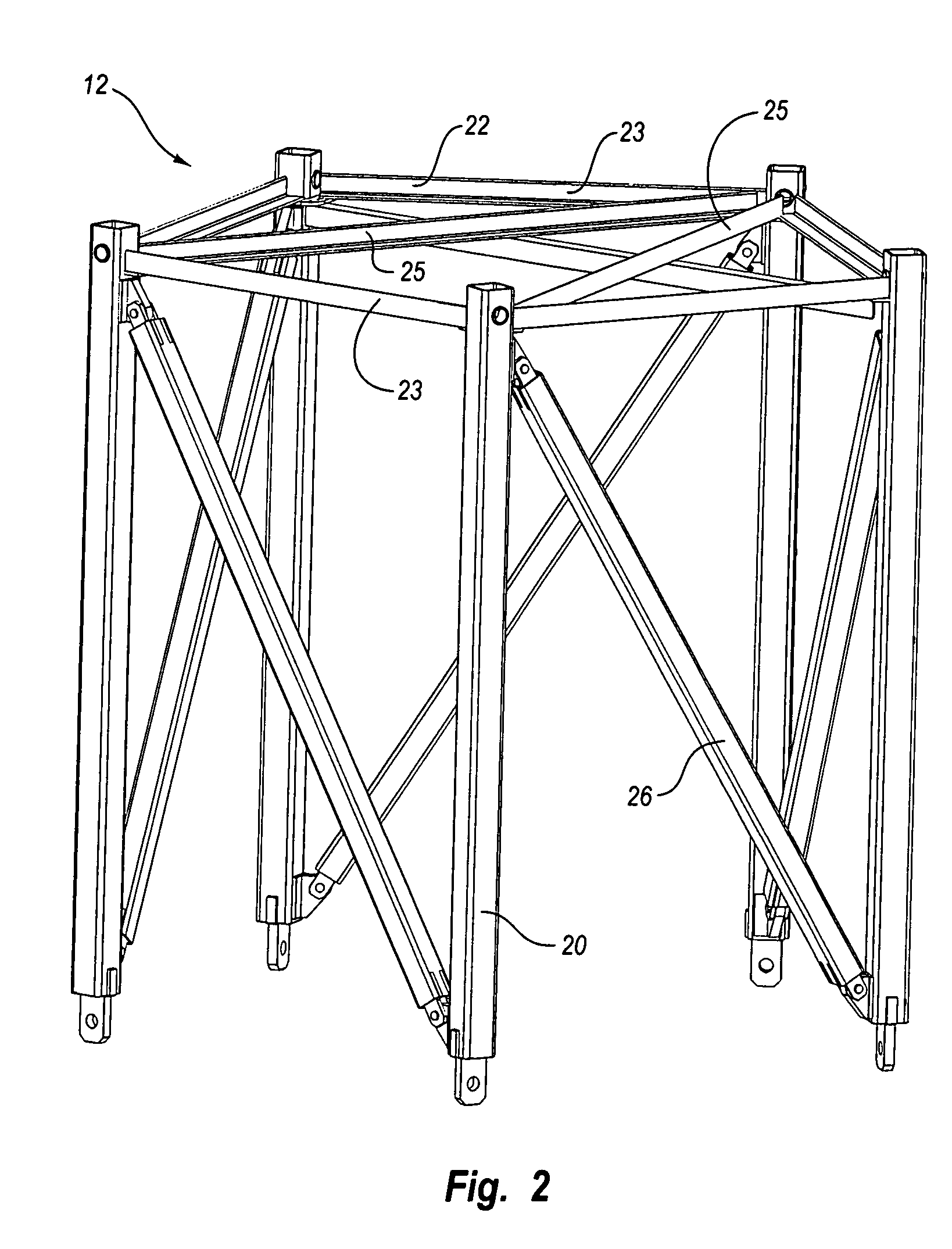
A structural tower having a space frame construction for high elevation and heavy load applications is disclosed, with particular application directed to wind turbines. The structural tower includes damping or non-damping struts in the longitudinal, diagonal or horizontal members of the space frame. One or more damping struts in the structural tower damp resonant vibrations or vibrations generated by non-periodic wind gusts or sustained high wind speeds. The various longitudinal and diagonal members of the structural tower may be secured by pins, bolts, flanges or welds at corresponding longitudinal or diagonal joints of the space frame.
Owner:LIVINGSTON TRACY +1
Method of modeling dynamic characteristics of a flight vehicle
InactiveUS20130124177A1Shorten the timeGood indicationGeometric CADSimulator controlAviationModel dynamics
The present invention models dynamic behavior of flight vehicles for simulation, analysis, and design. The present invention allows a user to define the complexity of a flight vehicle model, and such models may be simple rigid body models, models of medium complexity, or very complex models including high order dynamics comprising hundreds of structural flexibility modes and variables related to aero-elasticity, fuel sloshing, various types of effectors, tail-wags-dog dynamics, complex actuator models, load-torque feedback, wind gusts, and other parameters impacting flight vehicles. The present invention accommodates and analyzes multiple vehicle and actuator concepts and configurations as defined in flight vehicle input data, which specifies flight vehicle parameters at a steady-state condition for modeling flight vehicle response to dynamic forces and flight control commands with respect to steady state operation.
Owner:FALANGAS ERIC T
Wind blade assembly and method for damping load or strain
The transducers are incorporated in or laminated to wind blades and electrically connected to a self-powered electrical circuit. The transducers in combination with the self-powered electrical circuit improve the wind blades' response to changing wind conditions by reducing loads, at least until the turbines pitch axis system can alter the lie of the blades. Thus, when there is a change in wind conditions, the resultant twisting or bending of the wind blade during the impact of the wind (gust) on the wind blade is used to extract energy from the transducers. This energy is then transferred to the electrical circuit which in turn sends a signal back to the transducers to actuate them so as to resist the imposed load.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine with gust compensating air deflector
ActiveUS20090284016A1Extended very quicklyReduce loadPropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeWind gust
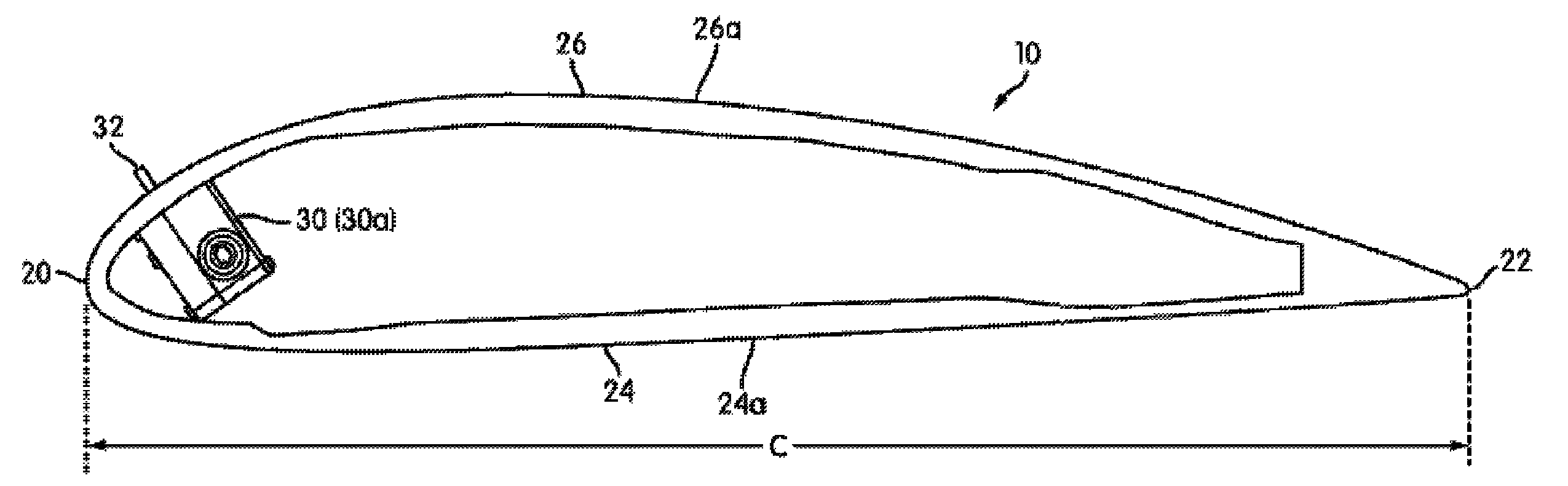
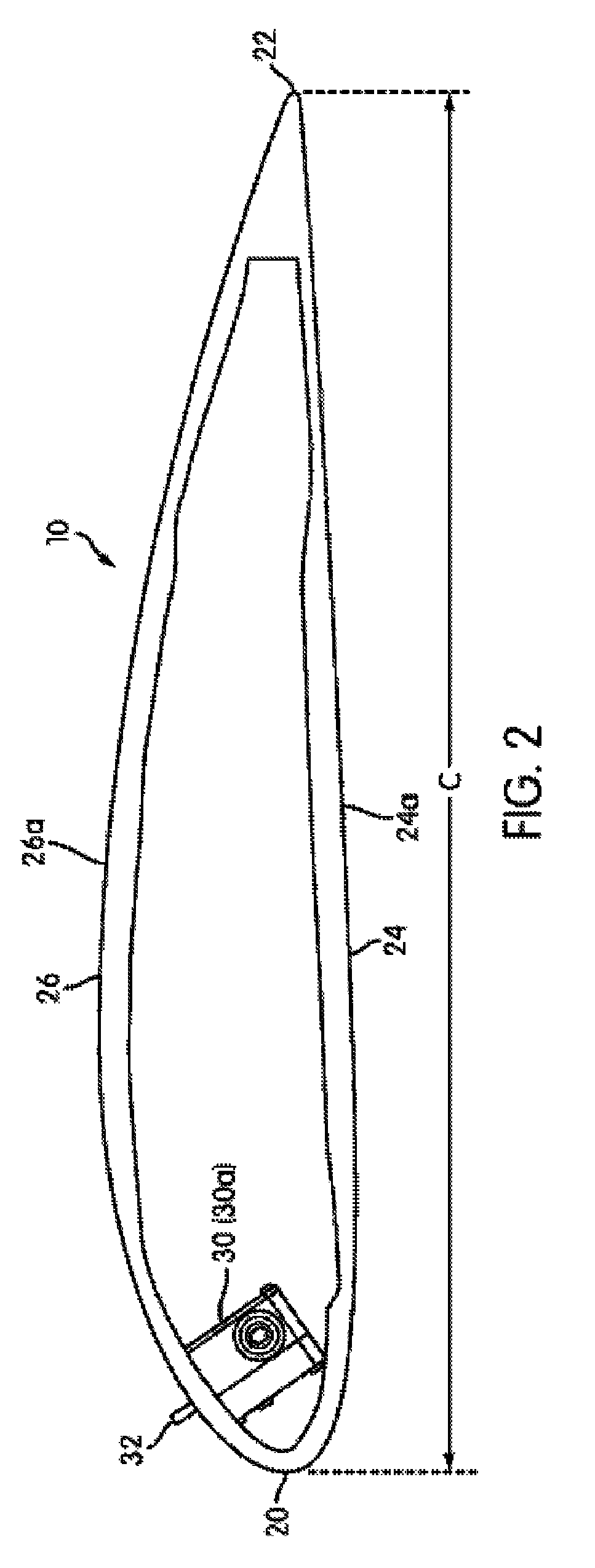
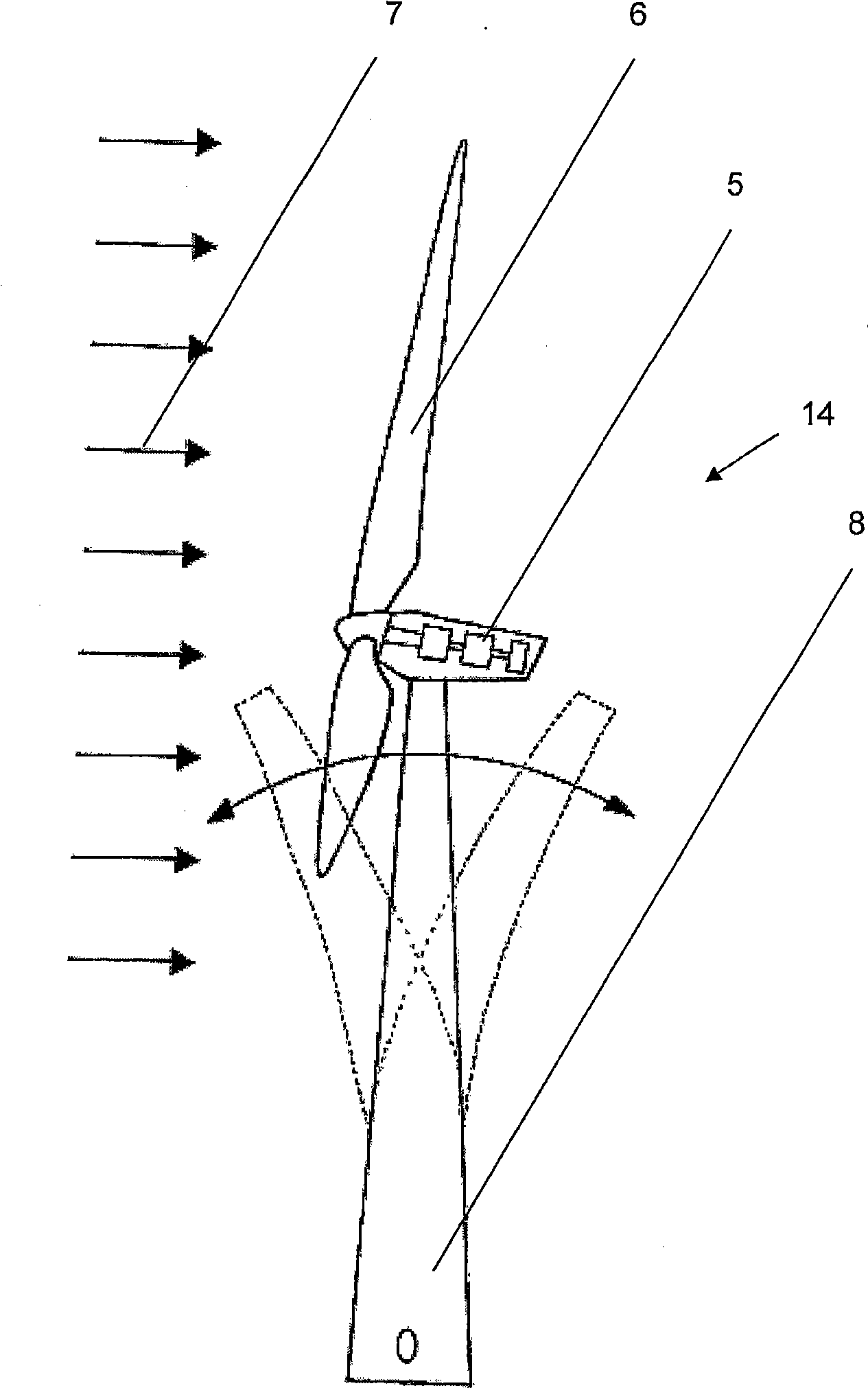
An apparatus and system for counteracting wind gusts and other high load situations in a wind turbine includes the use of one or more gust counteracting devices configured to extend an air deflector outwardly from a surface of a turbine rotor blade. The air deflector may subsequently be retracted into the rotor blade once the wind gust has subsided or once the load falls below a certain threshold. Mechanisms for extending and retracting the air deflector may include pneumatic or hydraulic systems and / or electromechanical devices. Air deflectors are generally configured to normalize air flow around the rotor blade so that the risk of potential damage to components of the wind turbine is minimized. In one arrangement, the gust counteracting device may be located at a leading section of the turbine blade. Additionally or alternatively, the device may be modular in nature to facilitate the removal and replacement of the device.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Method for reducing loads in a wind turbine
InactiveUS20120139240A1Protect the loadMore speedWind motor controlWind motor combinationsControl systemTurbine blade
Loads reduction method in a wind turbine for power-grid disconnection during a wind gust, which uses a control system made up of three loops used to correct the speed at which the wind turbine blades are moved to the feathered position throughout a controlled emergency stop, with a non-linear law that takes into account blade position, tower vibrations and generator rotation speed limits.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
System and method for loads reduction in a horizontal-axis wind turbine using upwind information
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Wind turbine with gust compensating air deflector
ActiveUS8267654B2Extended very quicklyReduce loadPropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeWind force
An apparatus and system for counteracting wind gusts and other high load situations in a wind turbine includes the use of one or more gust counteracting devices configured to extend an air deflector outwardly from a surface of a turbine rotor blade. The air deflector may subsequently be retracted into the rotor blade once the wind gust has subsided or once the load falls below a certain threshold. Mechanisms for extending and retracting the air deflector may include pneumatic or hydraulic systems and / or electromechanical devices. Air deflectors are generally configured to normalize air flow around the rotor blade so that the risk of potential damage to components of the wind turbine is minimized. In one arrangement, the gust counteracting device may be located at a leading section of the turbine blade. Additionally or alternatively, the device may be modular in nature to facilitate the removal and replacement of the device.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
PV Wind Performance Enhancing Methods
InactiveUS20100179678A1Amplified equalizationUniform pressurePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyAir volumeAerodynamic drag
Pressure equalization between upper and lower surfaces of PV modules of an array of PV modules can be enhanced in several ways. Air gaps opening into the air volume, defined between the PV modules and the support surface, should be provided between adjacent PV modules and along the periphery of the array. The ratio of this air volume to the total area of the air gaps should be minimized. Peripheral wind deflectors should be used to minimize aerodynamic drag forces on the PV modules. The time to equalize pressure between the upper and lower surfaces of the PV modules should be maintained below, for example, 10-20 milliseconds. The displacement created by wind gusts should be limited to, for example, 2-5 millimeters or less. For inclined PV modules, rear air deflectors are advised for each PV module and side air deflectors are advised for the periphery of the array.
Owner:SUNPOWER CORPORATION
Docking and locking system for solar panel cleaning system
ActiveUS9080791B1Easy constructionEasy to operateSolar heating energyCarpet cleanersSelf lockingEngineering
Solar panels row cleaning system that can dock and lock itself at a docking extension attached to the solar row. The self-docking and self-locking is optimally used when the cleaning system is not working. Movement of a cleaning apparatus of the cleaning system is controlled to cause an anchoring element on the cleaning apparatus to engage with an anchoring element on the docking extension when in the docking position and thereby lock the cleaning apparatus preventing its movement in horizontal and downward directions. This is particularly useful when strong wind gusts are present.
Owner:ECOPPIA SCI
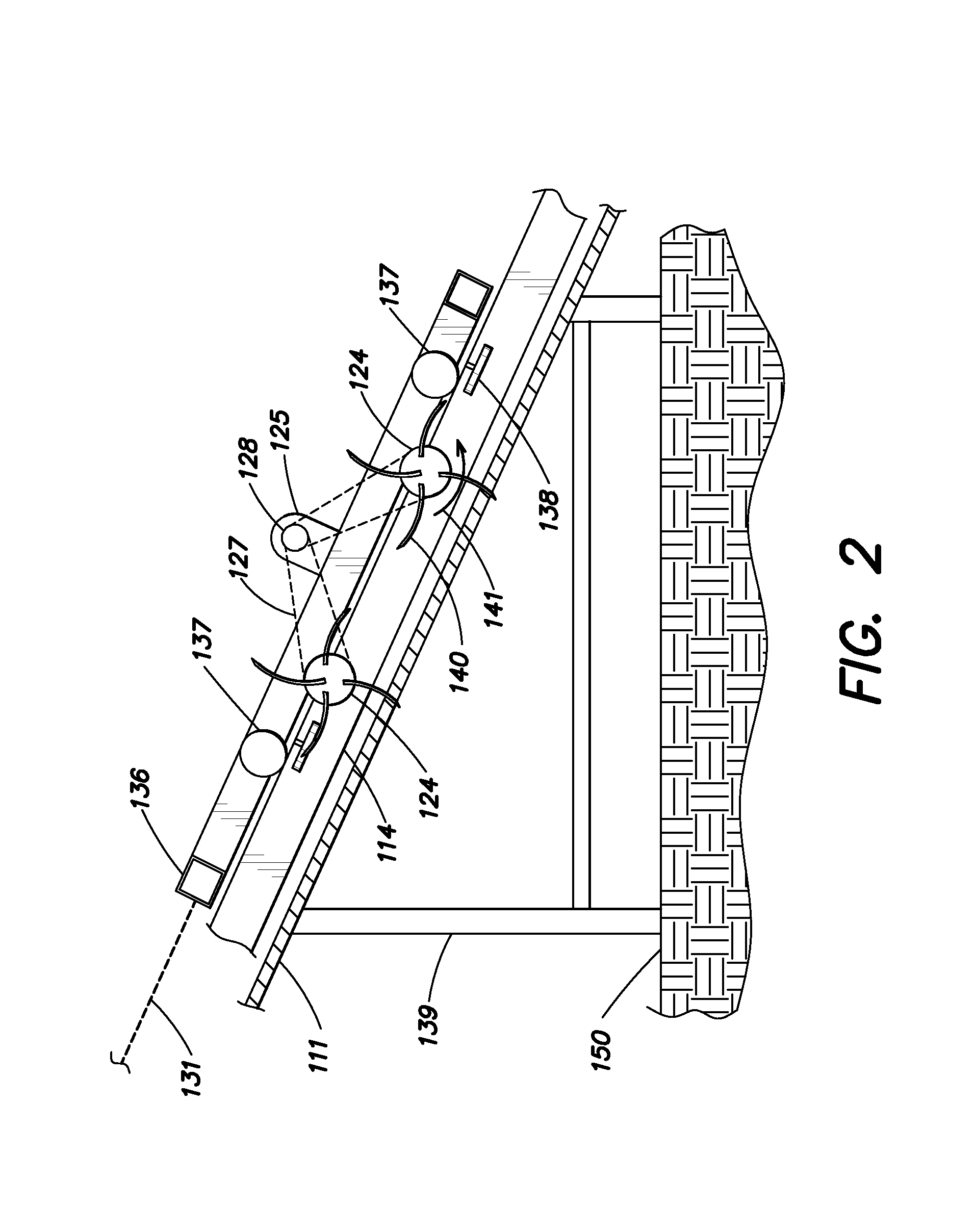
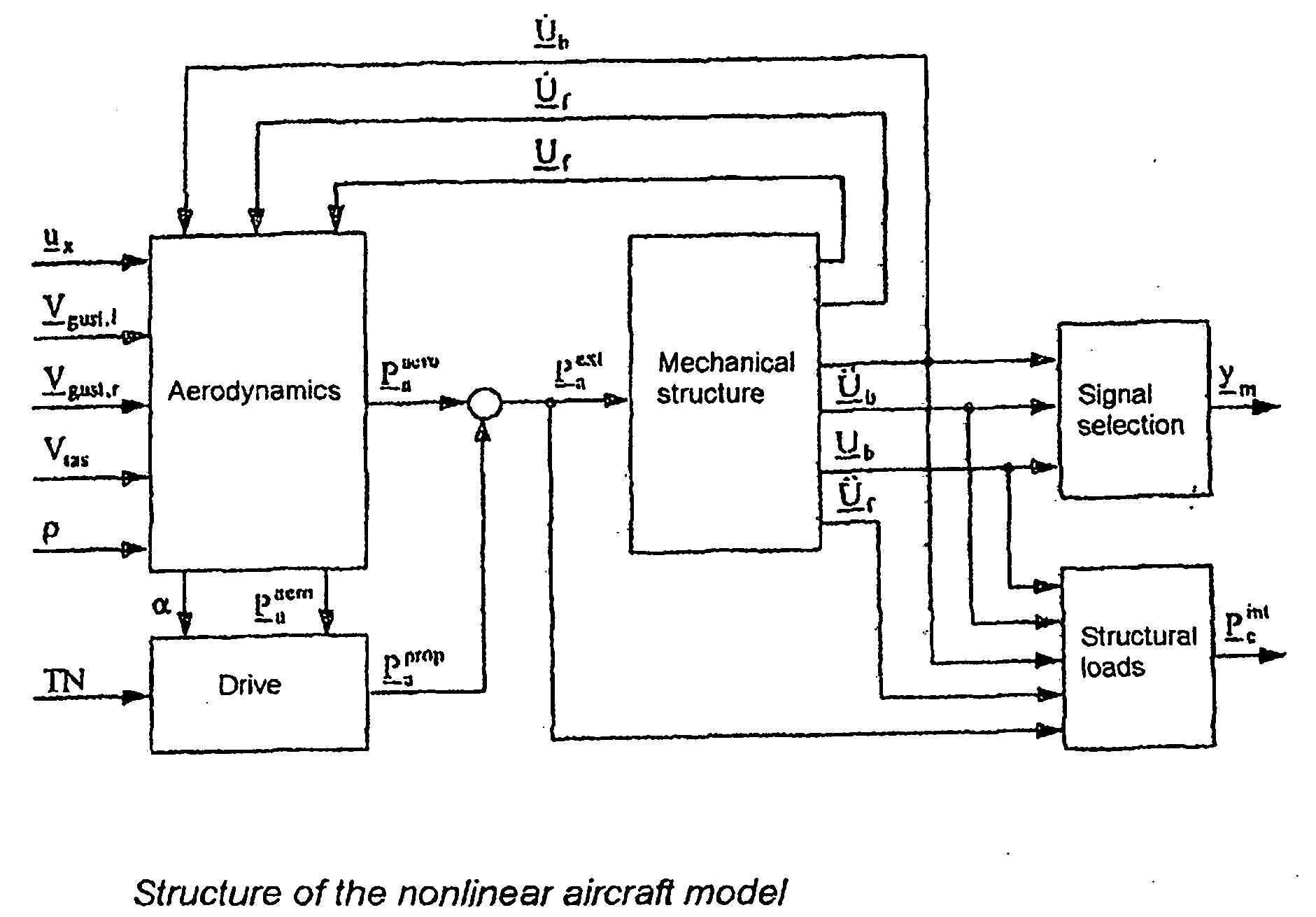
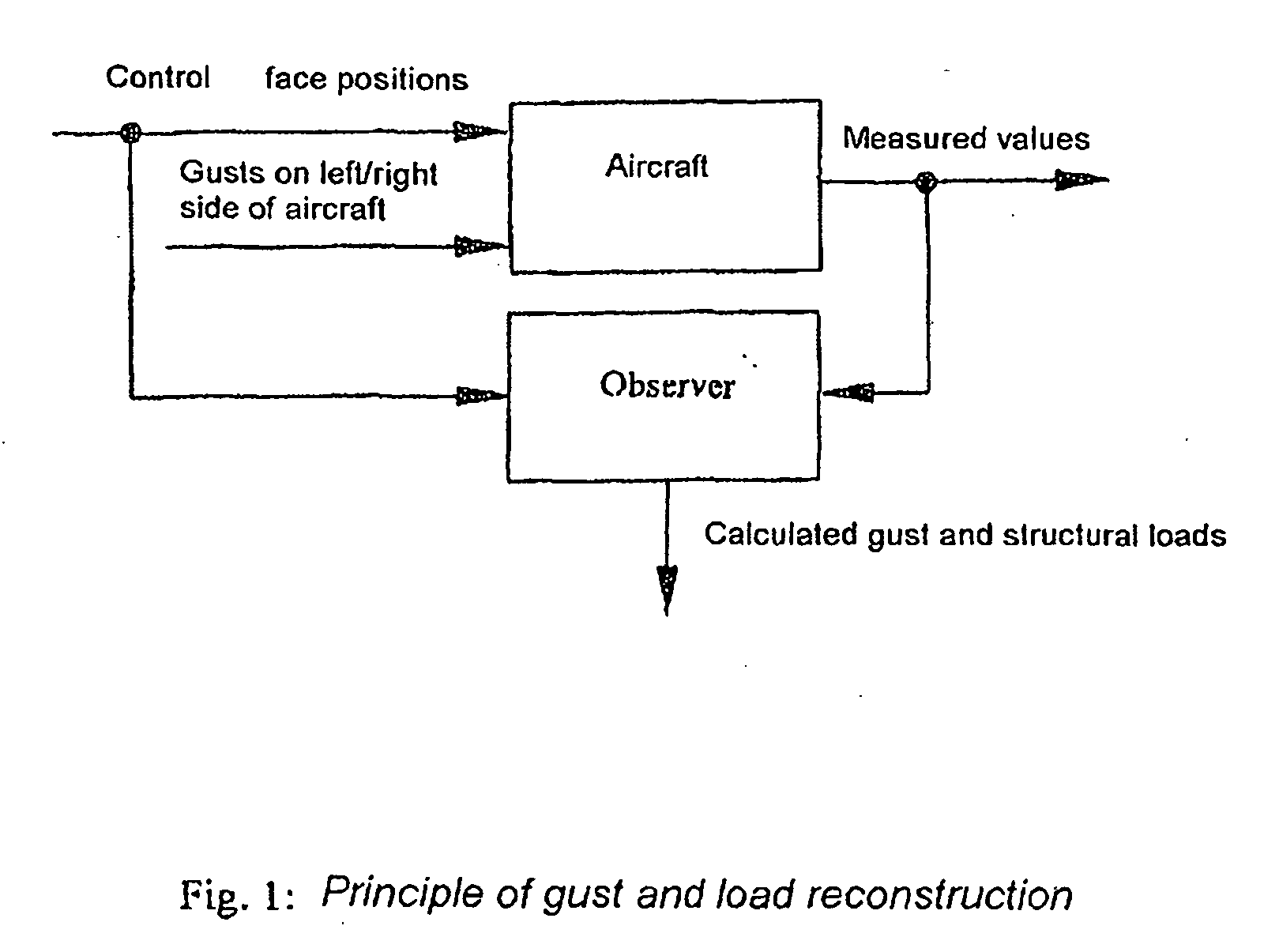
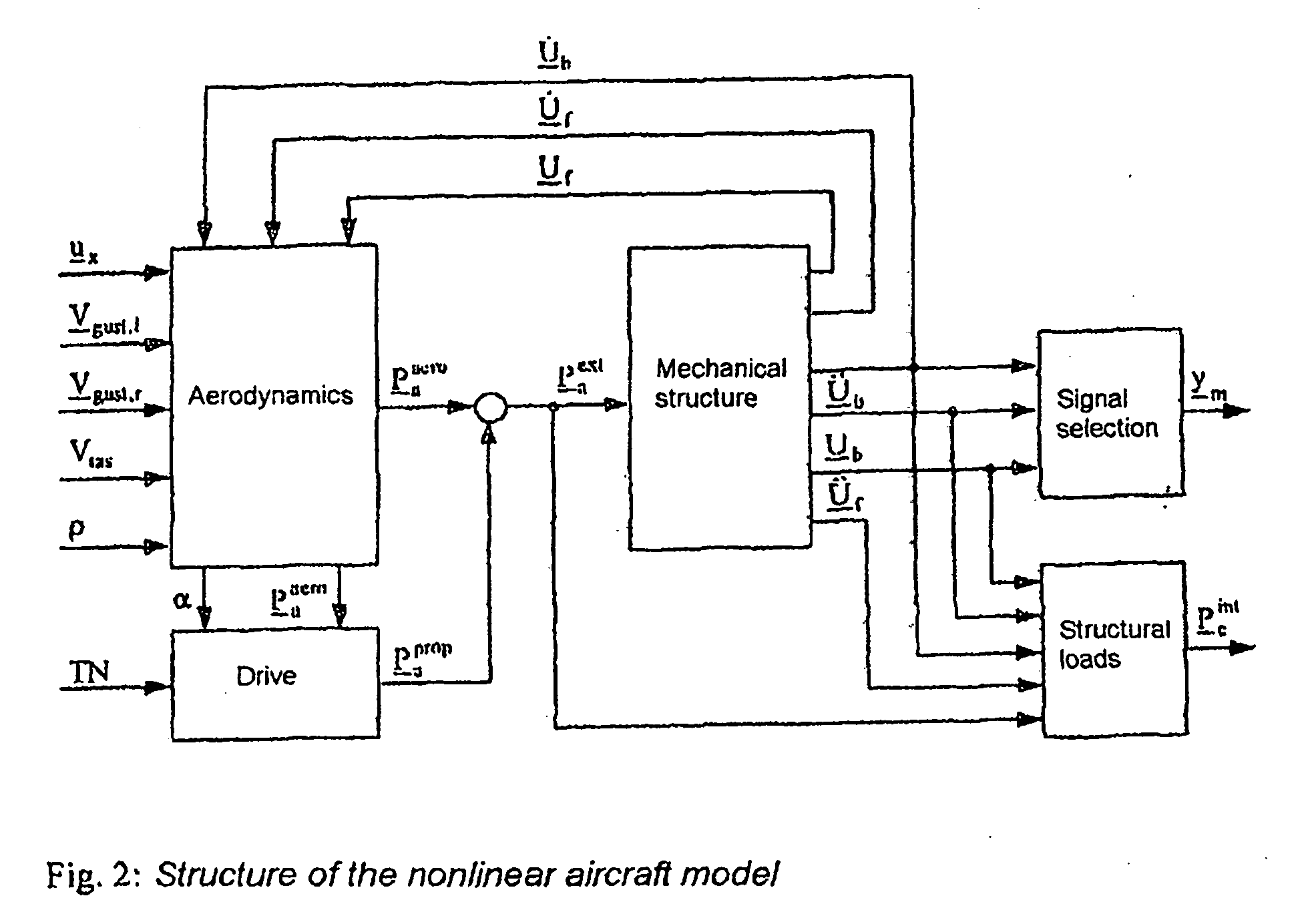
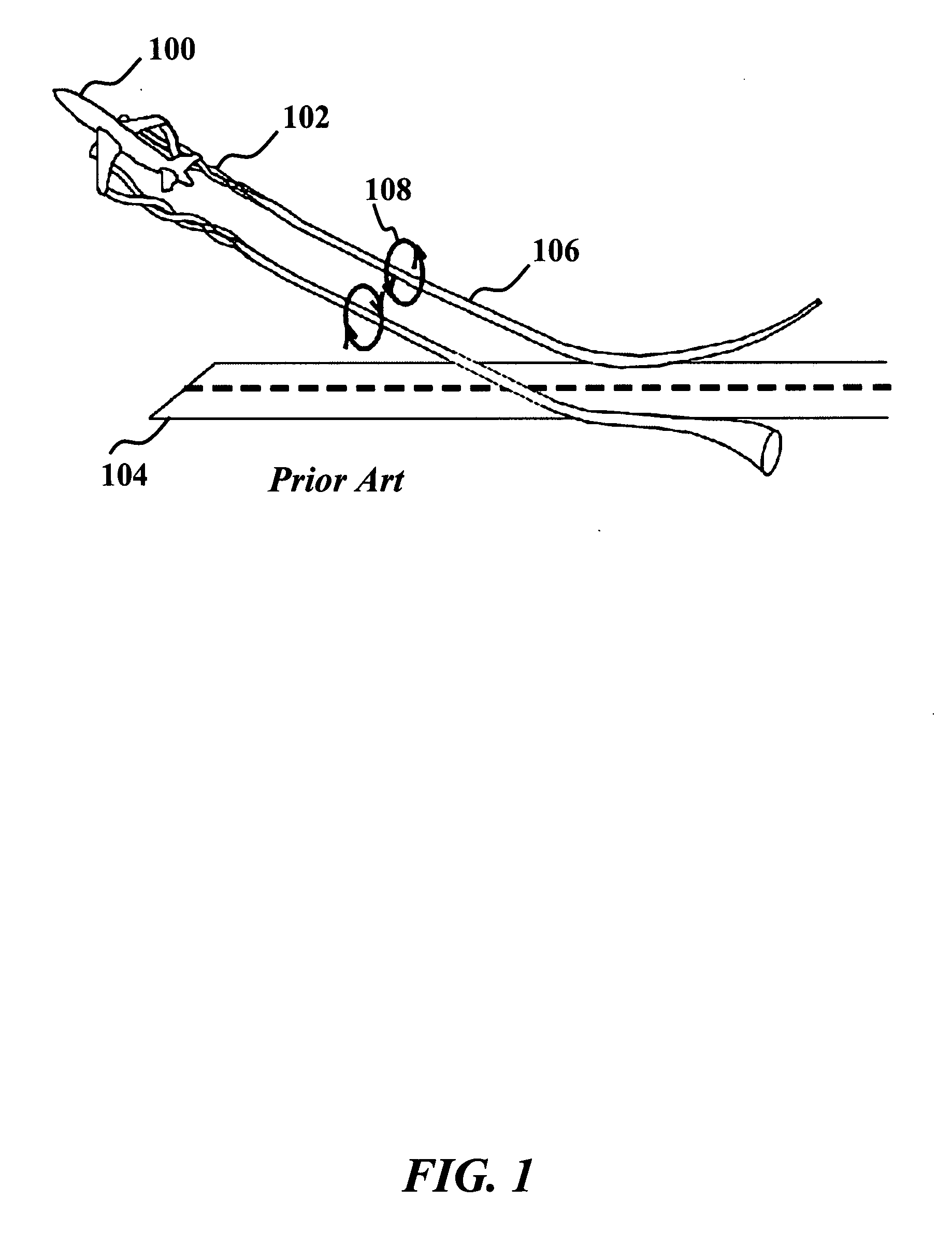
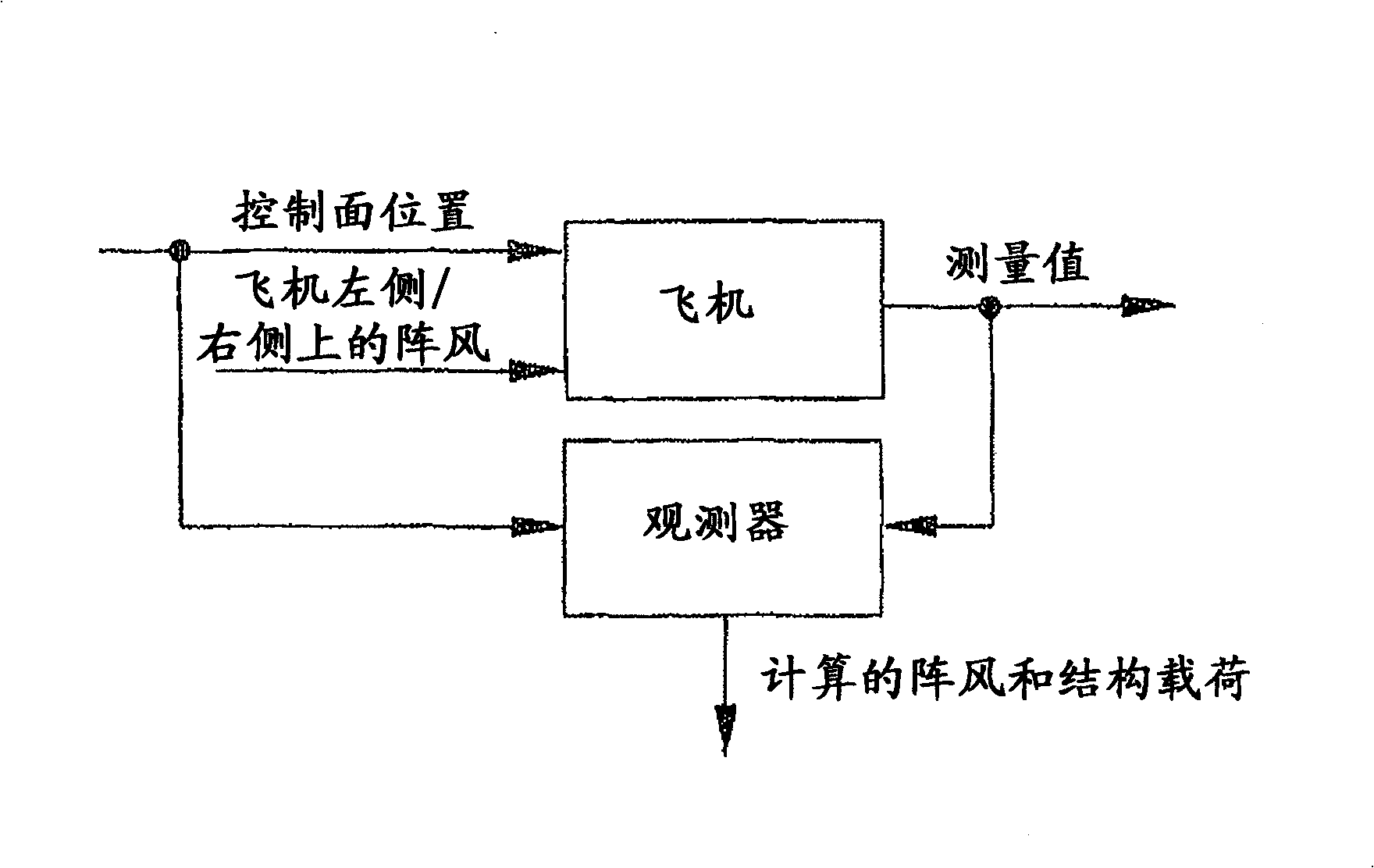
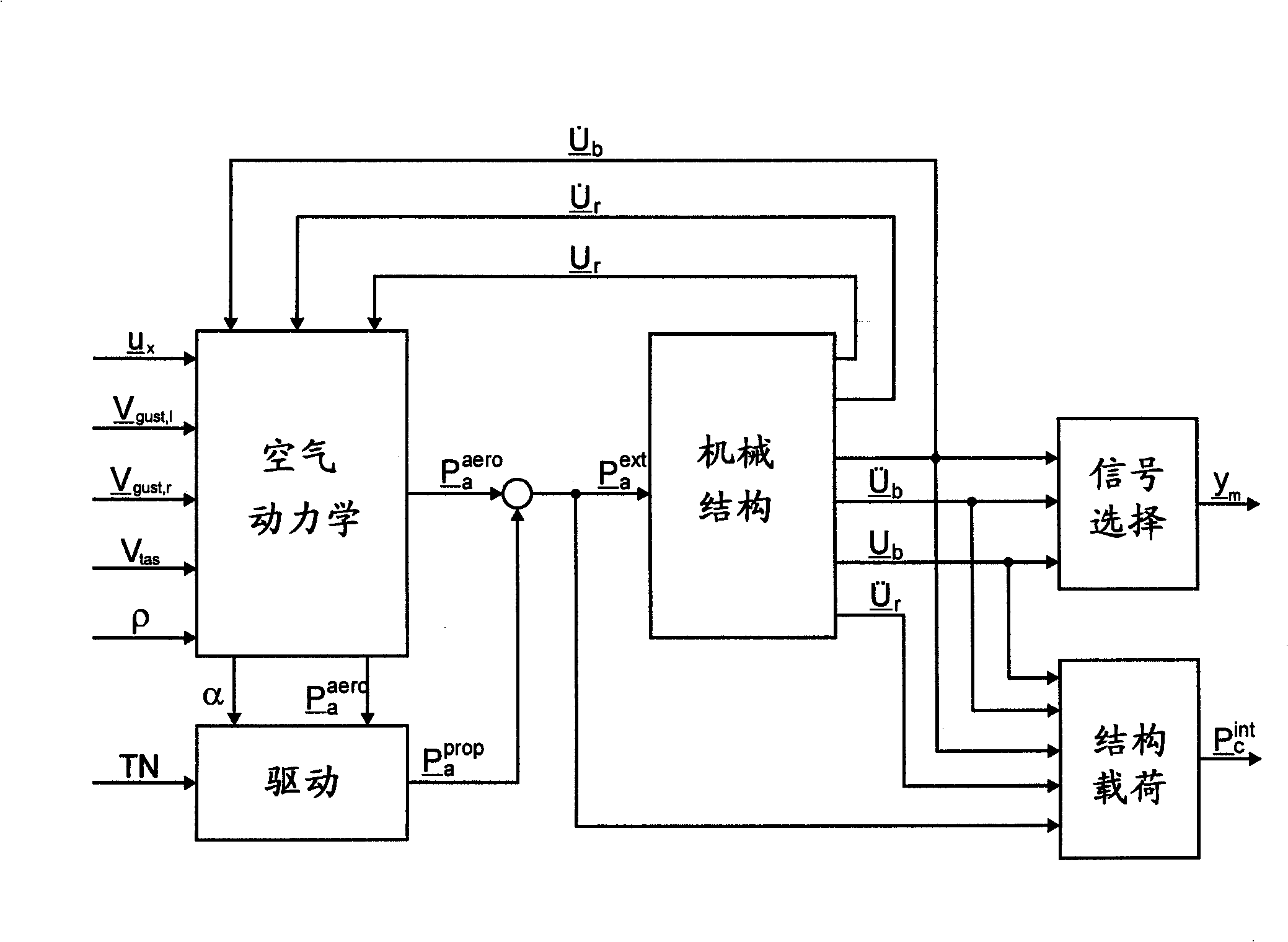
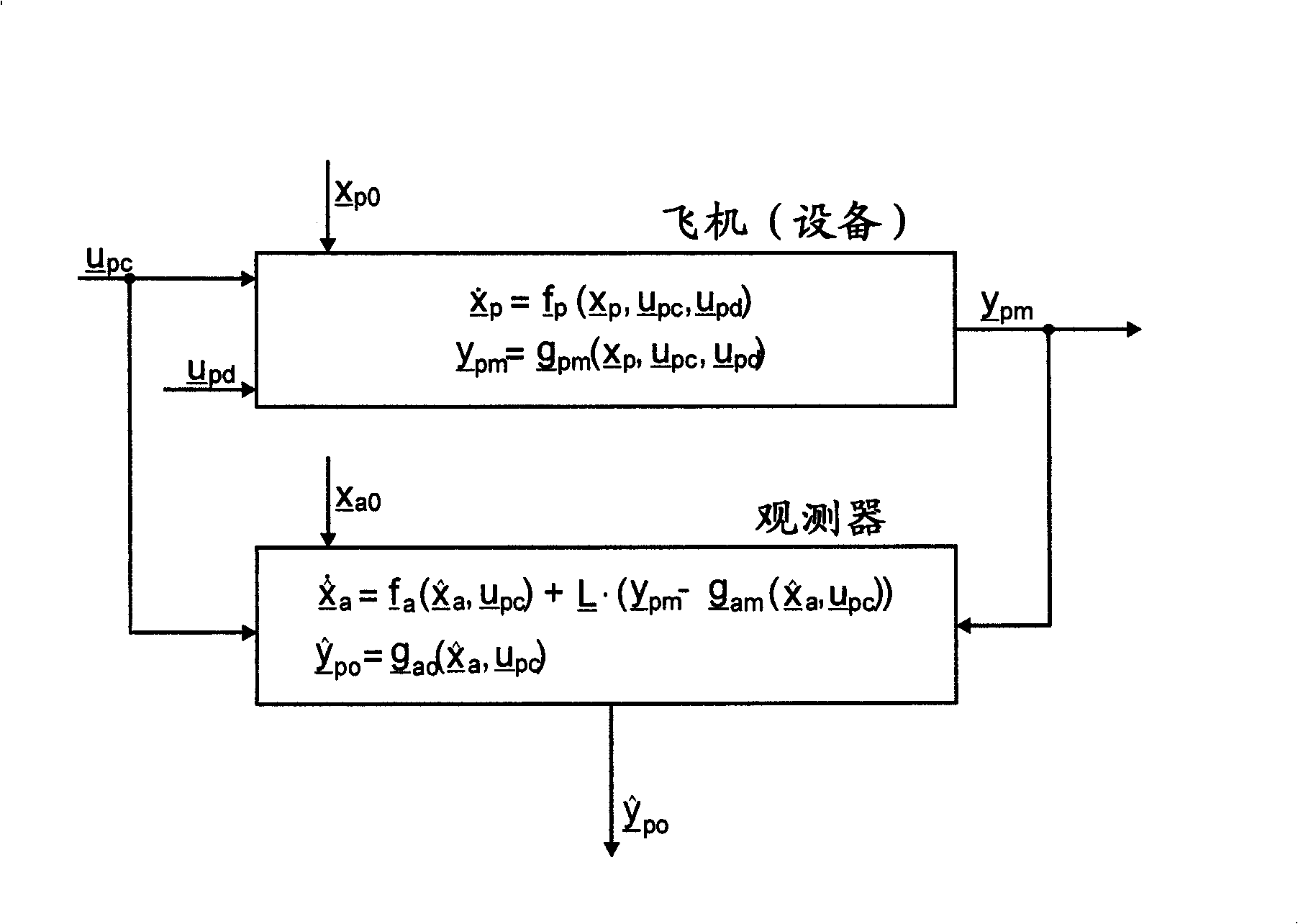
Method for Reconstructing Gusts and Structural Loads at Aircraft, in Particular Passenger Aircraft
InactiveUS20090171634A1Minimises ground timeReduce operating costsSimulator controlComputation using non-denominational number representationJet aeroplaneFlight vehicle
A method for reconstructing gusts and / or structural loads at aircraft, in particular passenger aircraft. The method includes generating an observer on the basis of a nonlinear model of the aircraft which describes the movement of the aircraft in all six degrees of freedom (DoF) and the elastic motion of the aircraft structure; continuously supplying all the data and measurements substantial for the description of the state of the aircraft to the observer; and calculating the gust velocities and structural loads (manoeuvre and gust loads) by the observer from the supplied data and measurements.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Structural tower
InactiveUS20100226785A1Reduce energy costsGenerate efficientlyEngine manufactureEngine fuctionsHigh elevationDiagonal
Owner:GE WIND ENERGY
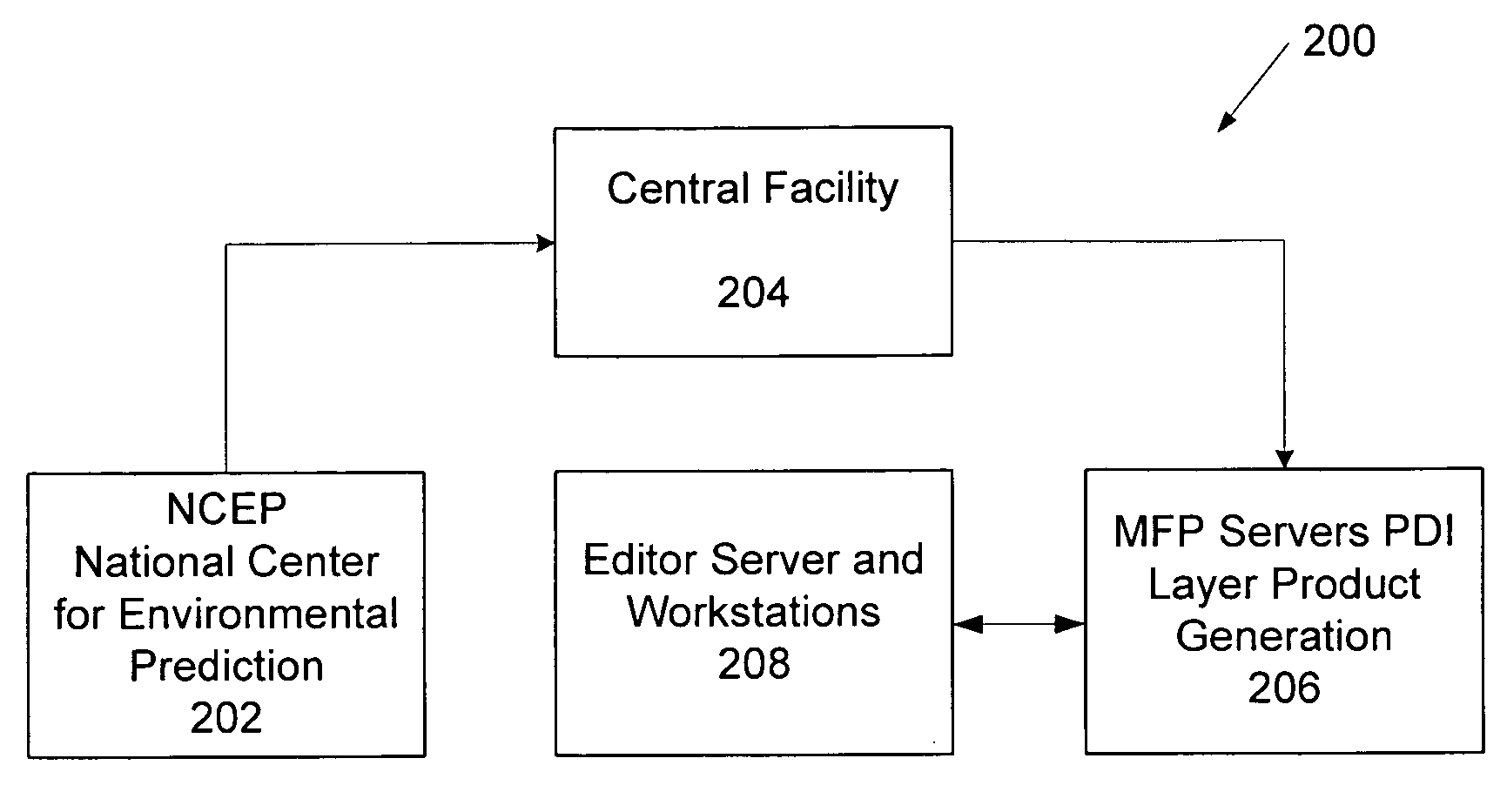
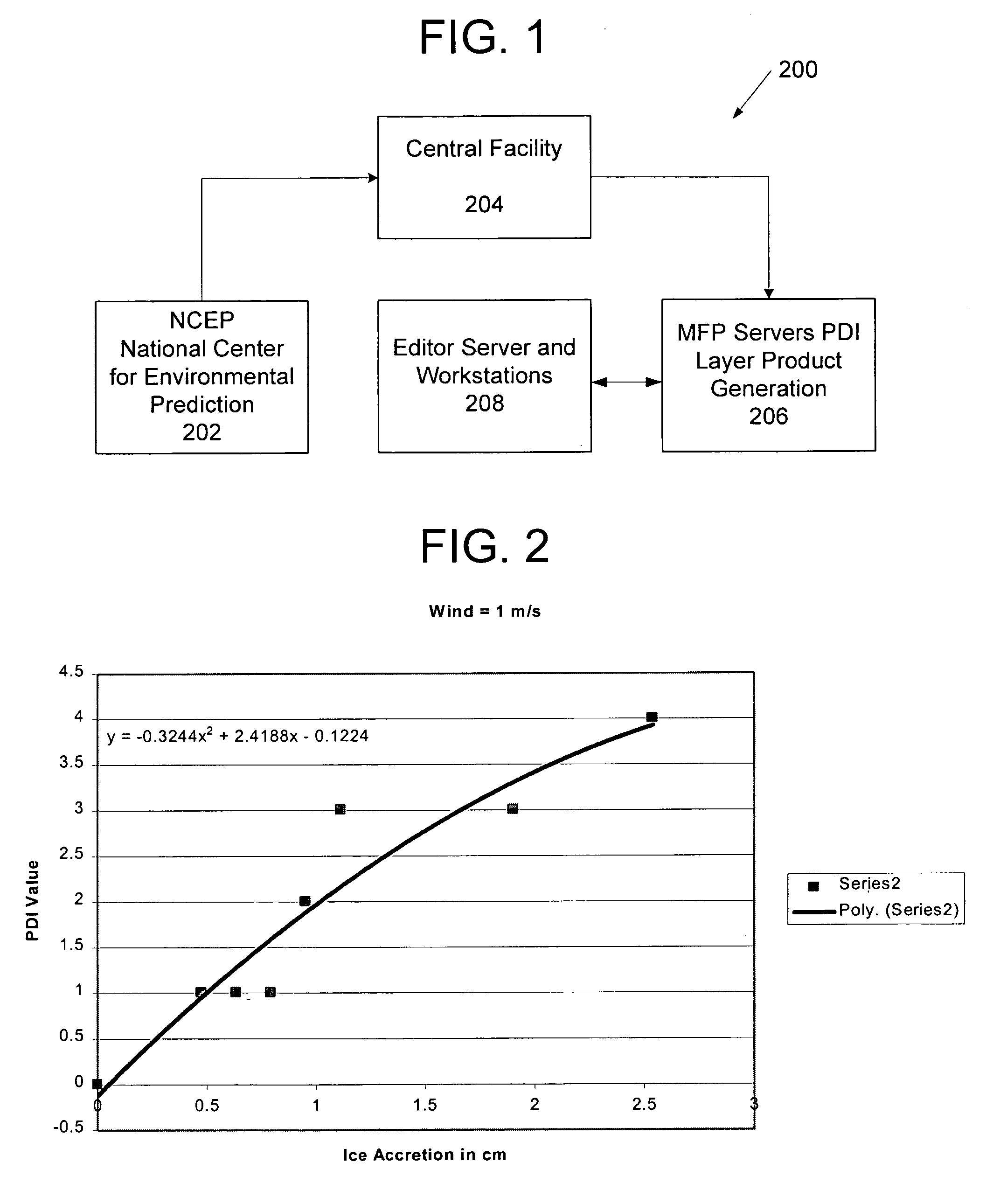
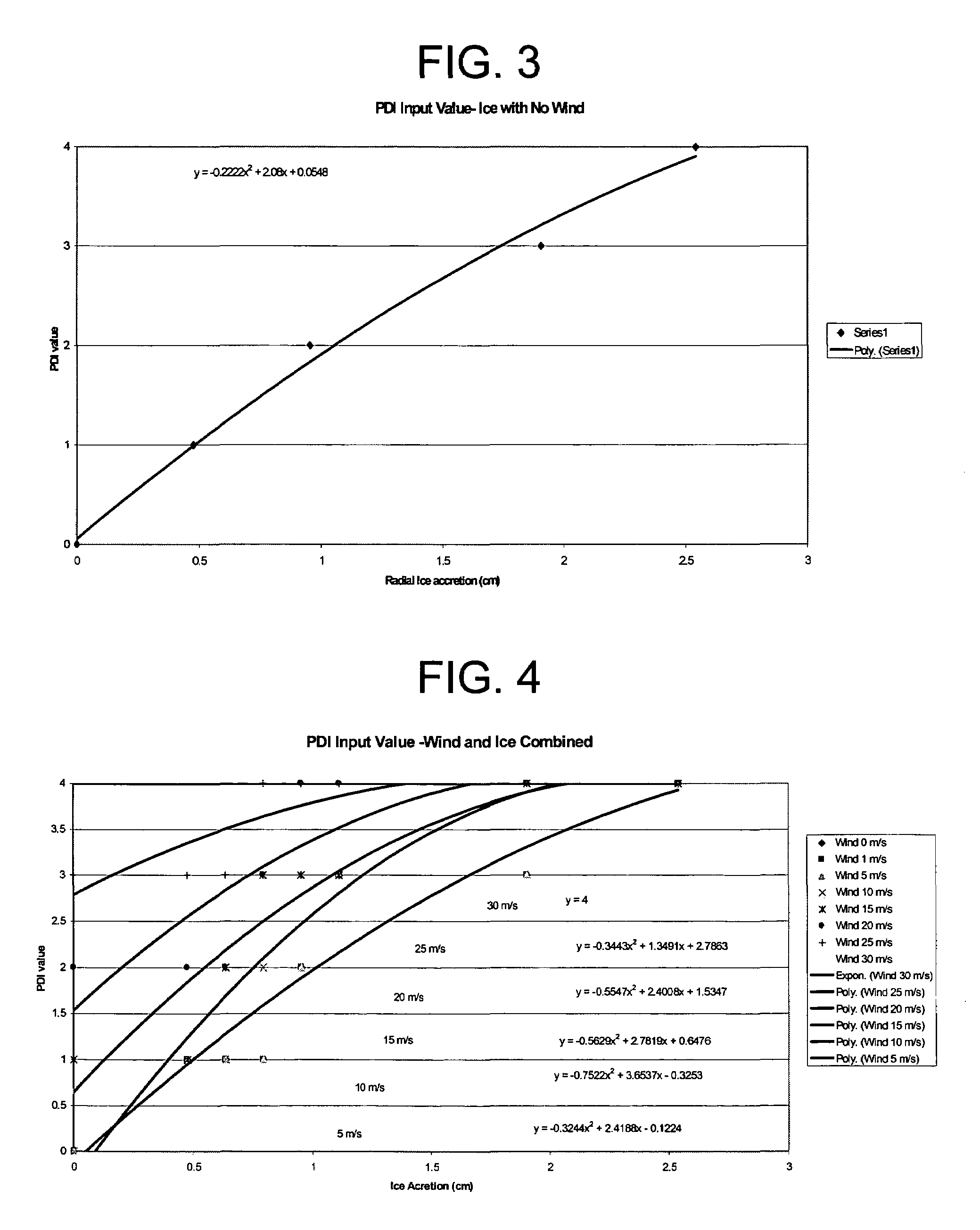
Power disruption index
Systems and methods for determining a power disruption index indicative that provides subscribers with a forecast of weather conditions that are likely to cause interruptions to power distributions systems within their specific areas of service. The Power Disruption Index (PDI), is a calculation of a number of forecast weather parameters including severe thunderstorm probabilities and intensities, wind speeds, wind gusts, and snowfall and ice accretion. The index combines each of these input parameters with a specific weighting based on the forecast intensity of each of the parameters, along with alert threshold criteria provided by each client utility. The output PDI is a forecast of local weather conditions for a specific local service area or power distribution network.
Owner:DTN LLC
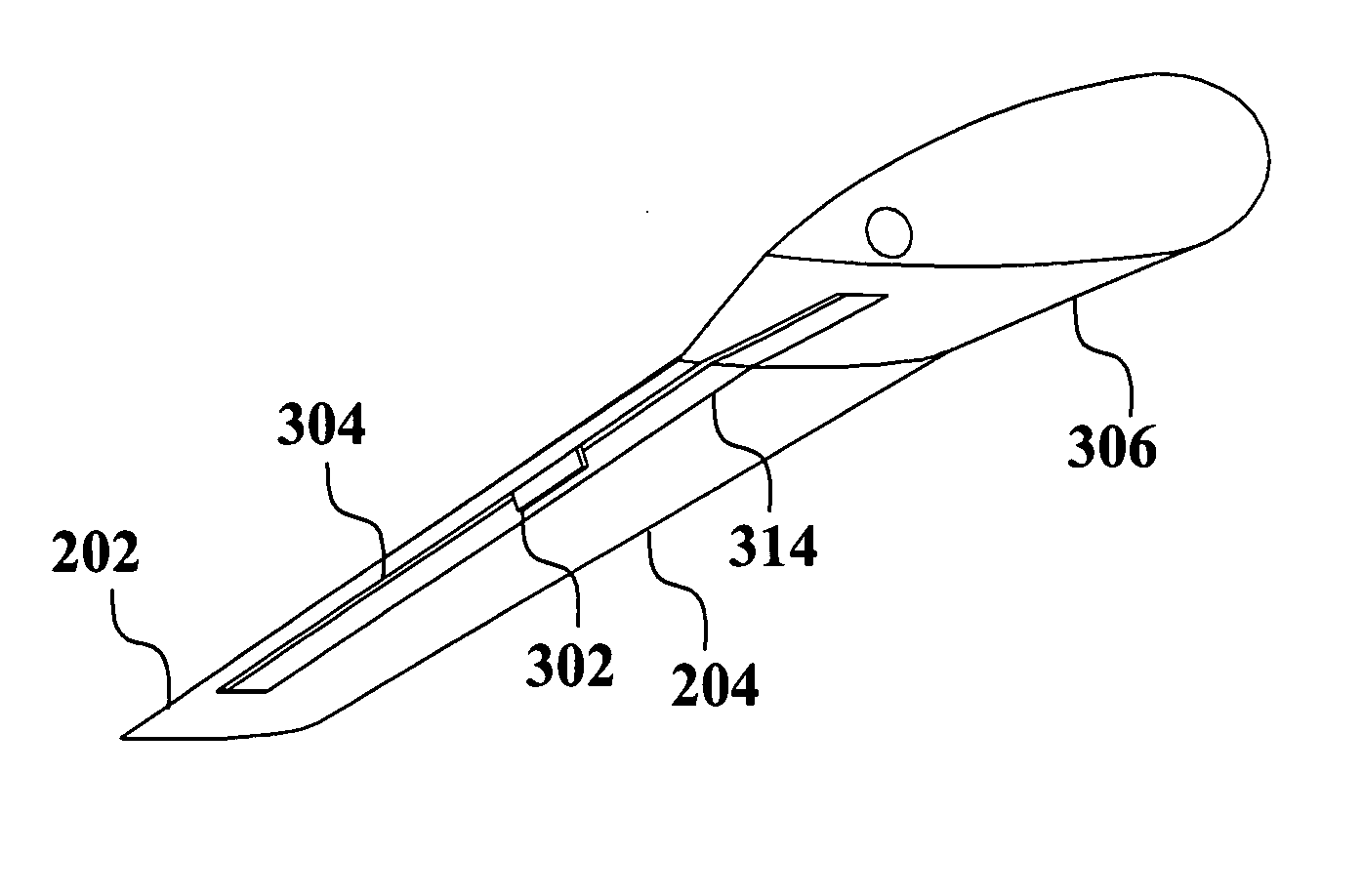
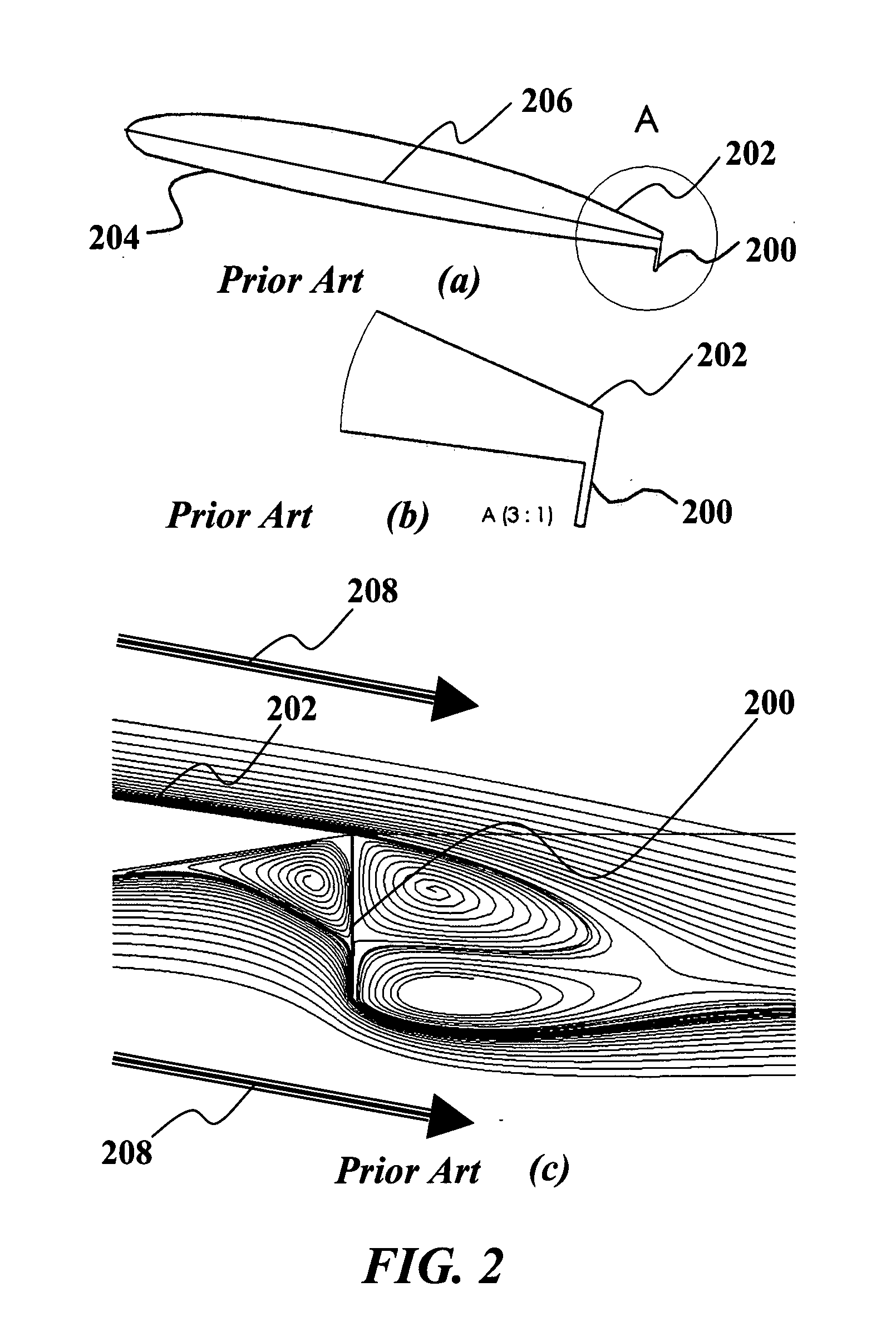
Translating active Gurney flap to alleviate aircraft wake vortex hazard
InactiveUS7740206B2Quick changeMinimizing wake vortex hazardsInfluencers by generating vorticesWing adjustmentsActuatorTrailing edge
A wake vortex alleviator is provided. The wake vortex alleviator produces rapid variations in the position of vortices emanating from aerodynamic surfaces by using an active flap that moves span-wise back and forth along the outboard section of the surface. Rapidly moving the flap back and forth in a slot at an appropriate frequency will cause the vortex to oscillate, resulting in interaction between other vortices and subsequent destruction much earlier than it would occur naturally. The slot is positioned near the aerodynamic surface trailing edge and generally transverse to a chord line of the aerodynamic surface. The flap can be moved using a variety of actuators to position, translate and stow the flap. The oscillation frequency and position are guided by information feedback according variations in lift in the aerodynamic surface, such as wind gusts. The flaps can control yaw, roll and pitch of the aerodynamic surface.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Wind turbine operational method
ActiveUS20090224542A1Avoid large generator accelerationsLevel controlWind motor controlTurbine bladeVariable speed wind turbine
Operation method for a variable speed wind turbine which comprises control methods for blade pitch in cases of extreme gusts of wind, characterised by the fact that it is comprised of the following steps: a) detection of the presence of an extreme gust of wind; b) performance of a sudden increase in pitch within the range of 6 to 14 degrees at the maximum speed permitted by the wind turbine blade pitch control mechanisms. The method also includes an additional step; c) vary the generator speed to avoid an increased acceleration of the generator which could make a subsequent step b) necessary.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Large aircraft lateral gust moderating method
ActiveCN103625637AImprove comfortActuated automaticallyAttitude controlDifferential pressureOptimal control
The invention belongs to flight control technology, and relates to improvement on a large aircraft lateral gust mitigating method, which is characterized by comprising the steps of calculating a sideslip angle Delta Beta generated by front gusts, calculating a rudder compensation instruction Rudc_f1, calculating a rudder correction instruction Rudc_f2, calculating a gust advanced restrain rudder instruction Rudc_f, calculating a gust advanced restrain aileron instruction Ailc_f, calculating a differential pressure sideslip angle Beta f, calculating a corrected sideslip angle Beta fc, calculating a high-frequency sideslip angle, calculating a low-frequency sideslip angle, calculating a final sideslip angle Beta c, calculating an optimal control rudder instruction Rudc_p, calculating an optimal control aileron instruction Ailc_p, determining a rudder comprehensive instruction Rudc1, determining a rudder input instruction Rudc, calculating an aileron comprehensive instruction Ailc1 and calculating aileron input instruction Ailc. The improved large aircraft lateral gust moderating method, disclosed by the invention, enhances the effect of gust moderating and improves comfort for passengers.
Owner:中国航空工业集团有限公司
Wind turbine with compensated motor torque
ActiveUS20120133148A1Smooth motionImprove running stabilityRotational speed controlWind motor controlLow speedNacelle
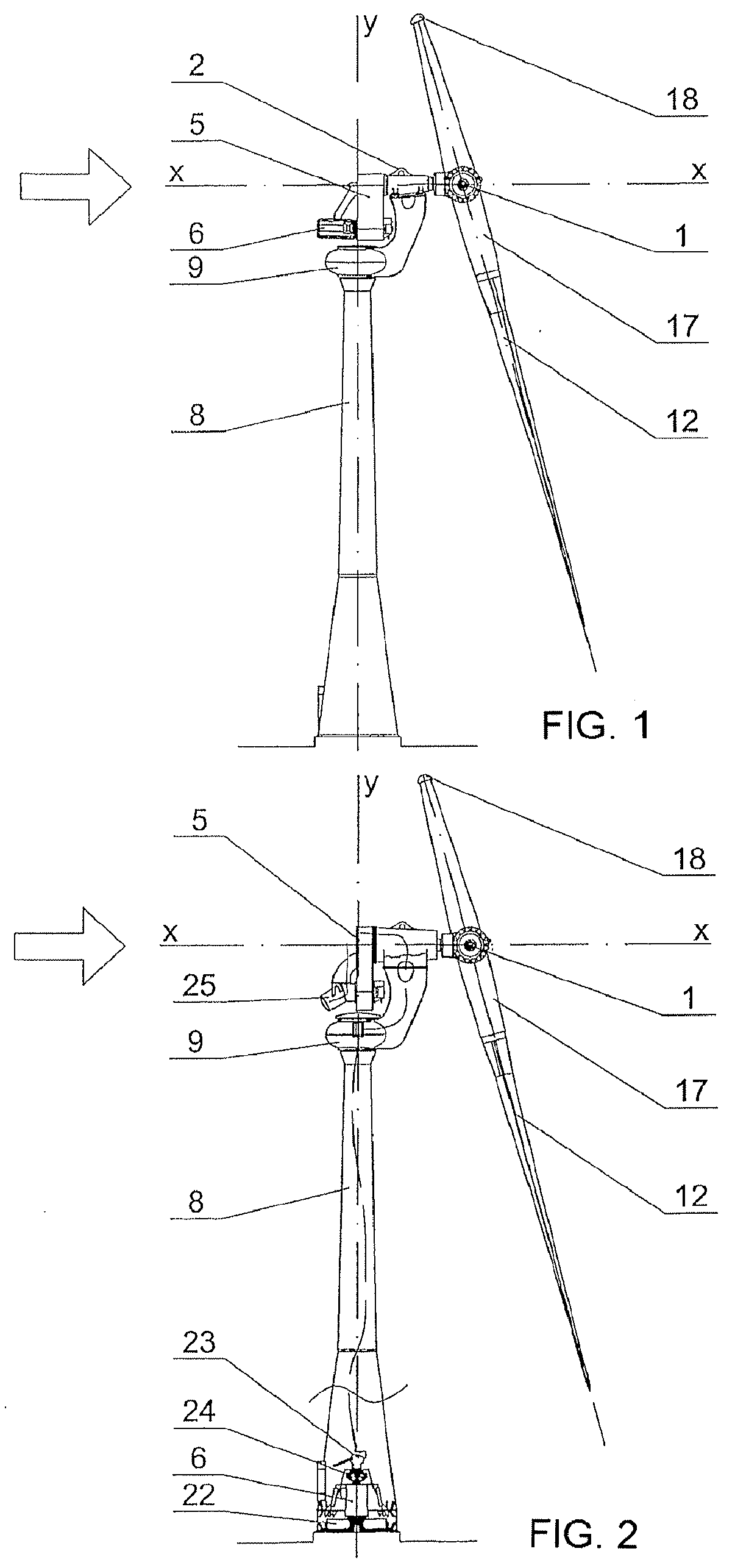
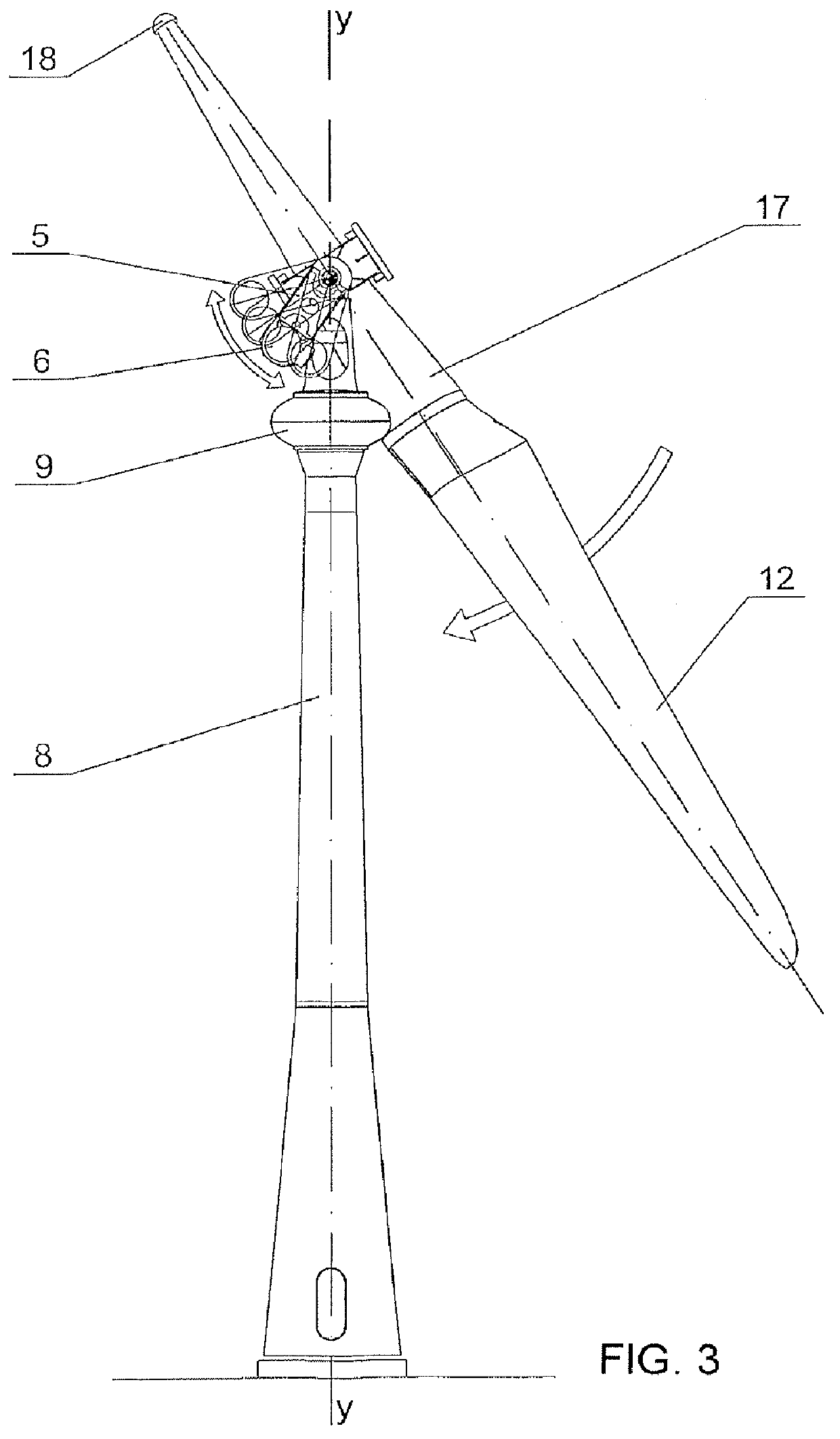
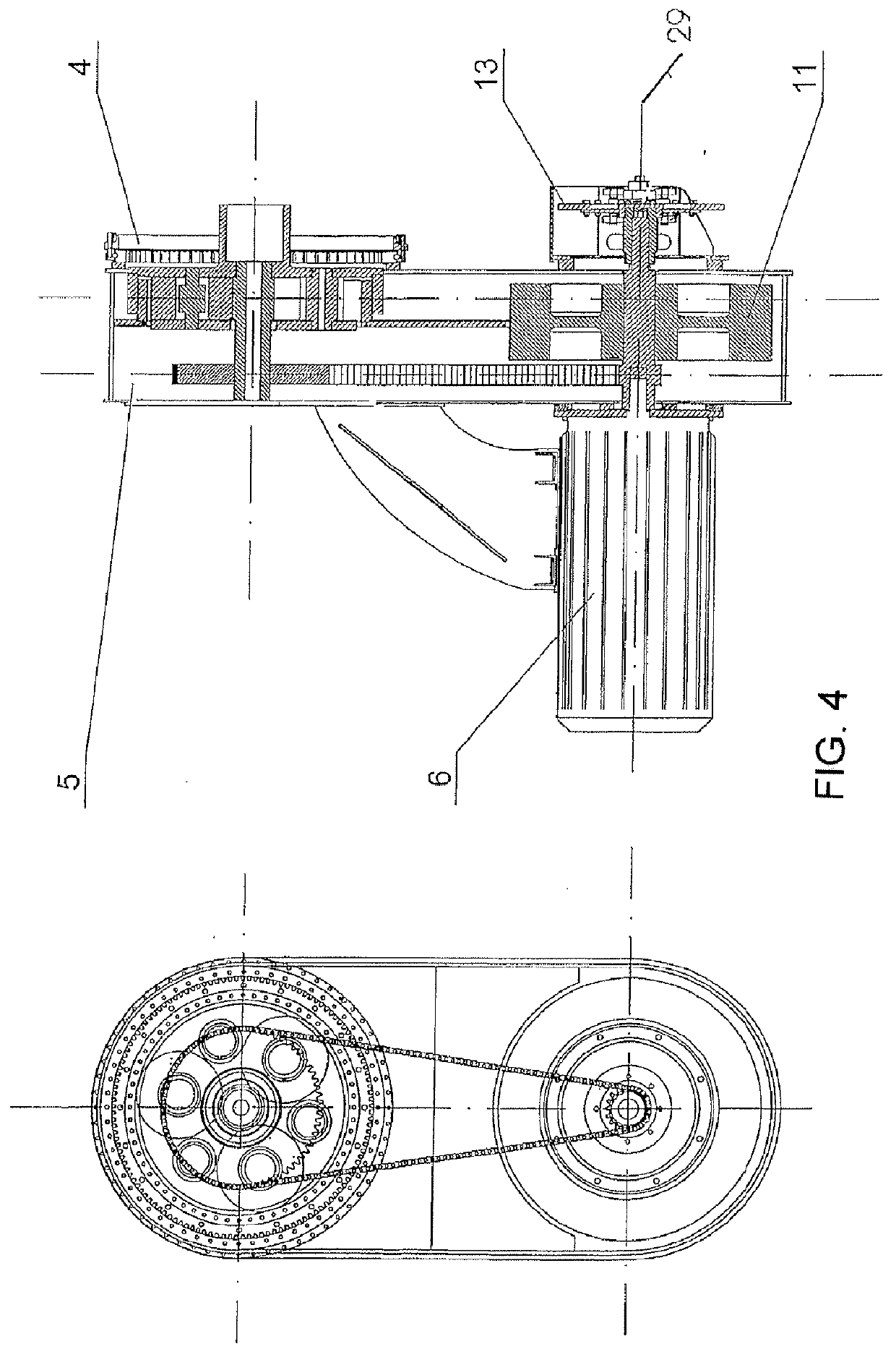
COMPENSATED MOTOR TORQUE WIND TURBINE, constituted by a single blade (12) rotor (1) attached to a low speed shaft (3) with spindle (2) sustained in a nacelle (9), on gear bearing (7), at the end of the tower (8), being the power train elements: multiplier (5), generator (6) and brake (13) suspended from the nacelle (9) through a first bearing (4) aligned with the low speed shaft (3), forming a pendulum set (28) that allows them to rotate, compensating in its angular motion the rotor (1) torque, said pendulum set (28) accumulates potential energy when rising in its angular motion and releases it when the gust stops by descending and turning in the opposite direction of the rotation of the turbine's rotor (1) restituting turns to the generator's (6) rotor, being this effect a power regulator.
Owner:TEMPERO 2000
Method for reducing loads in an aerogenerator
The invention relates to a method for reducing loads in an aerogenerator when disconnected from the power grid during a wind gust, employing a three-loop control system which can be used to correct the speed at which the blades are moved to the feathered position during a controlled emergency shutdown, using a non-linear law taking account of the position of the blades, the vibration of the tower and the generator rotation speed limits.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
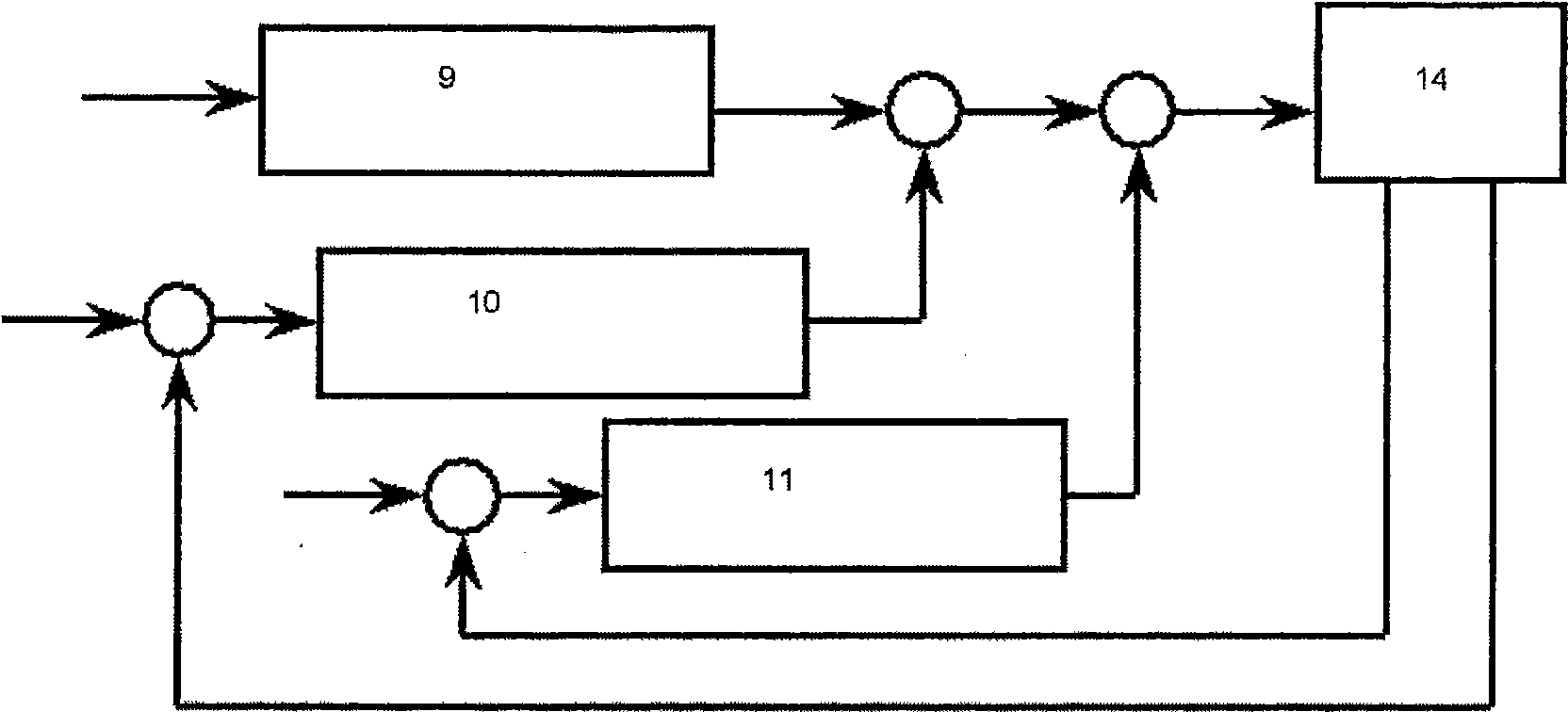
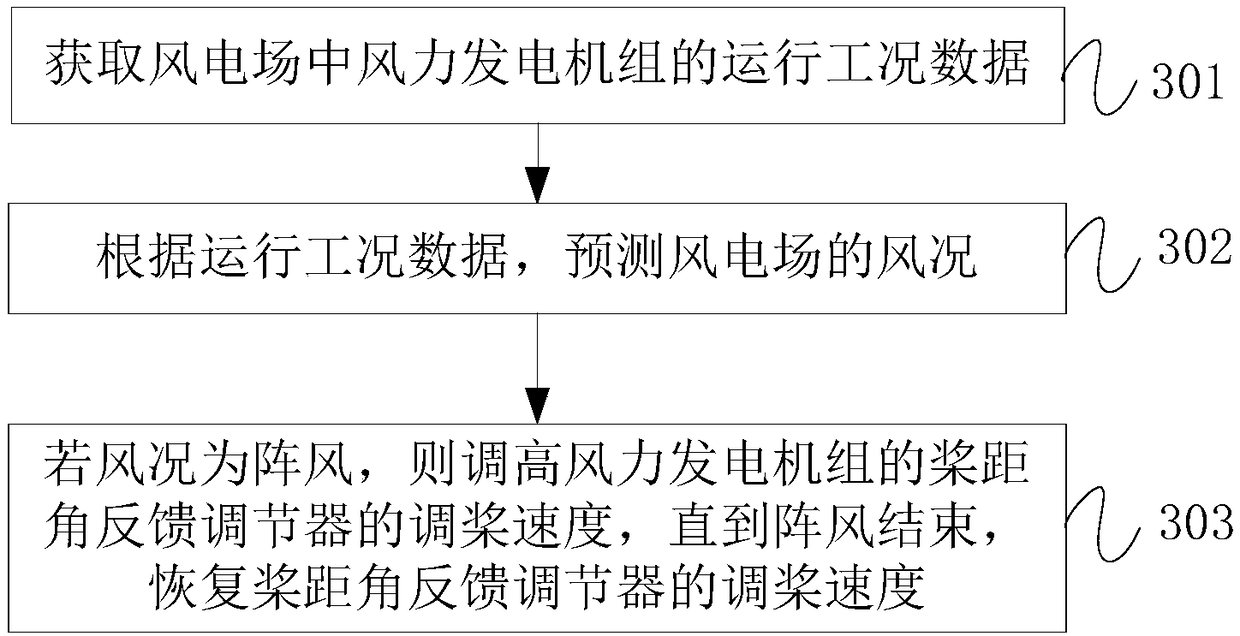
Tuning propeller control method and device, and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN108894918AExecute propeller adjustment operation in timeAffect safe operationWind motor controlMachines/enginesPropellerEngineering
The invention discloses a tuning propeller control method and device, and computer readable storage medium. The tuning propeller control method includes: acquiring operating condition data of a wind generating set in a wind farm; predicting wind conditions of the wind farm according to the operating condition data; and if the wind condition is gust, increasing the tuning propeller speed of the pitch angle feedback regulator of the wind generating set until the end of the gust, and restoring the tuning propeller speed of the pitch angle feedback regulator. By adopting the technical scheme, thegust wind condition can be effectively predicted, and the tuning propeller can be cut into the wind generating set in time based on the gust wind condition.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDWIND SCI & CREATION WINDPOWER EQUIP CO LTD
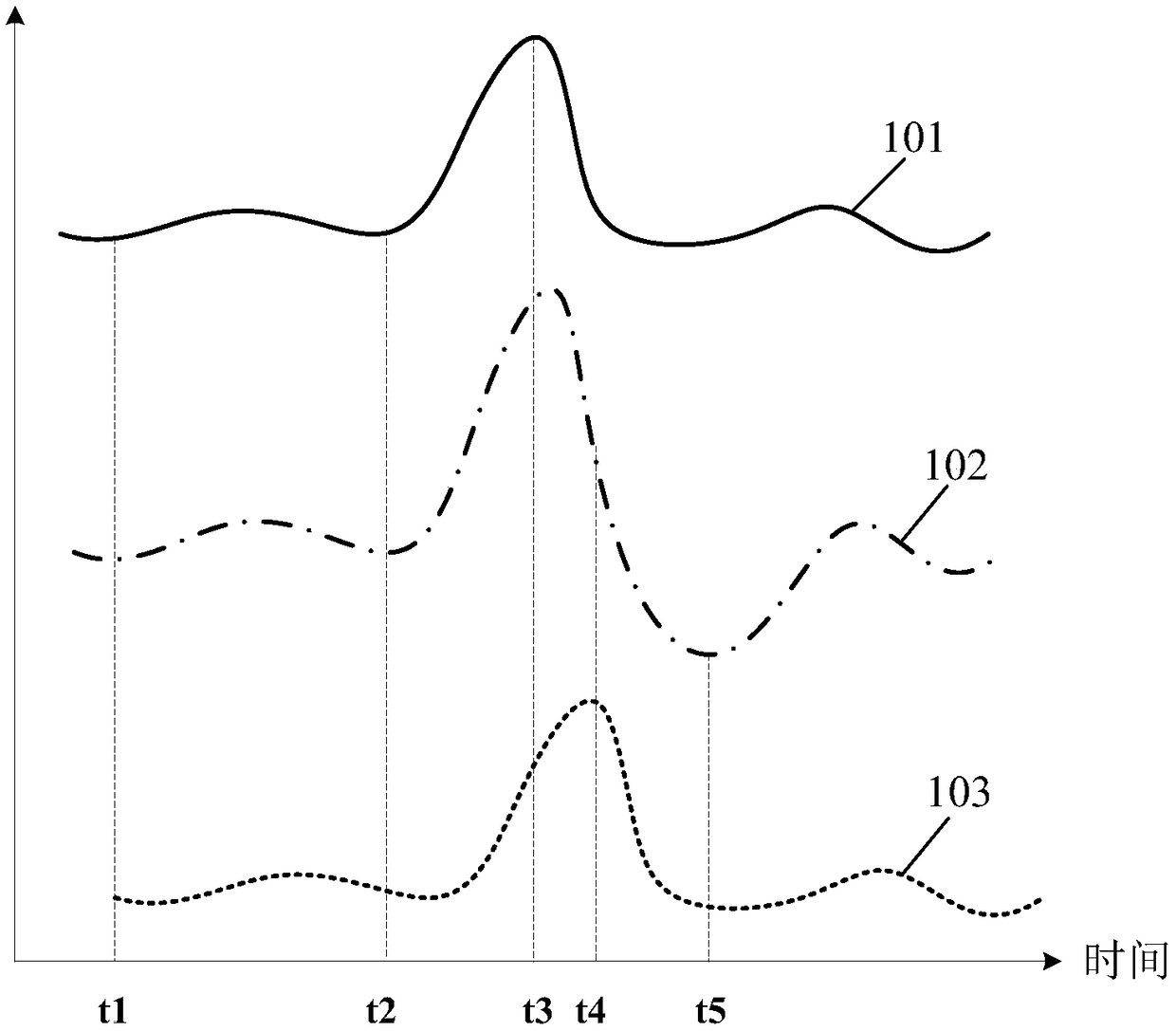
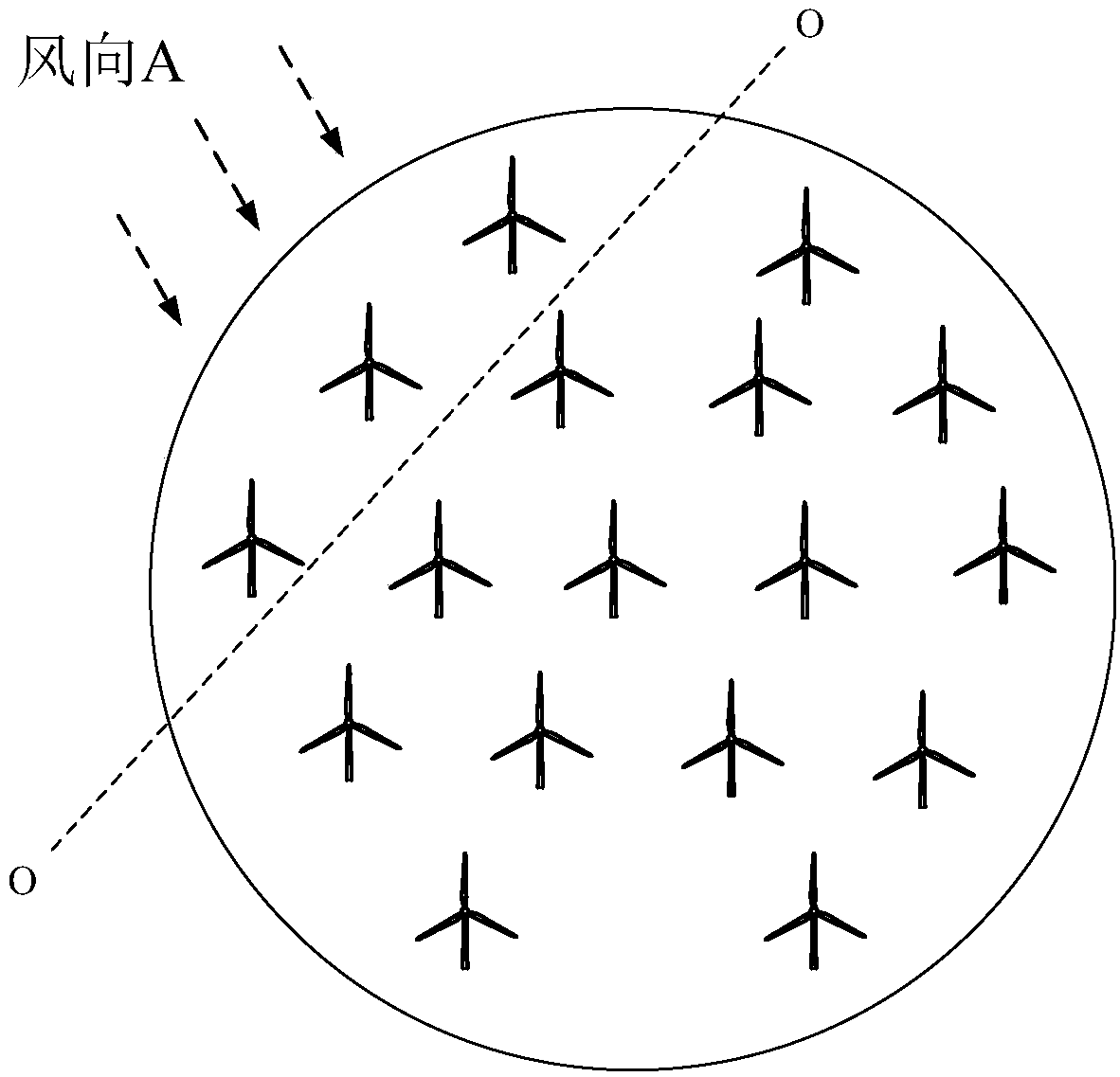
Wind power field gust prediction method and system
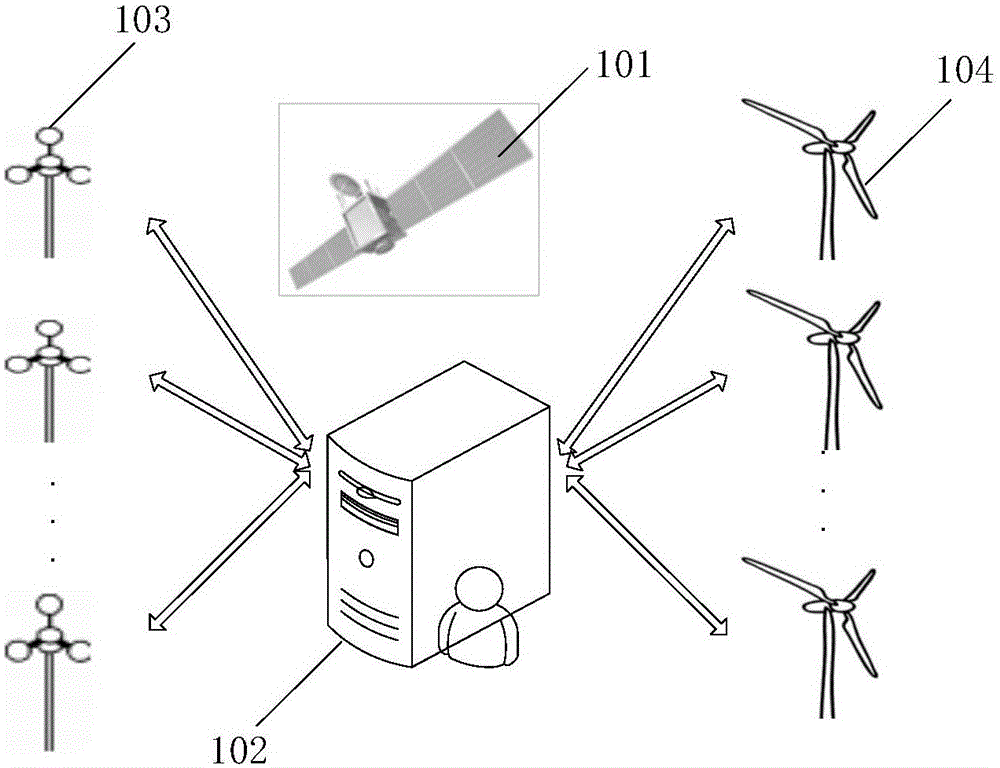
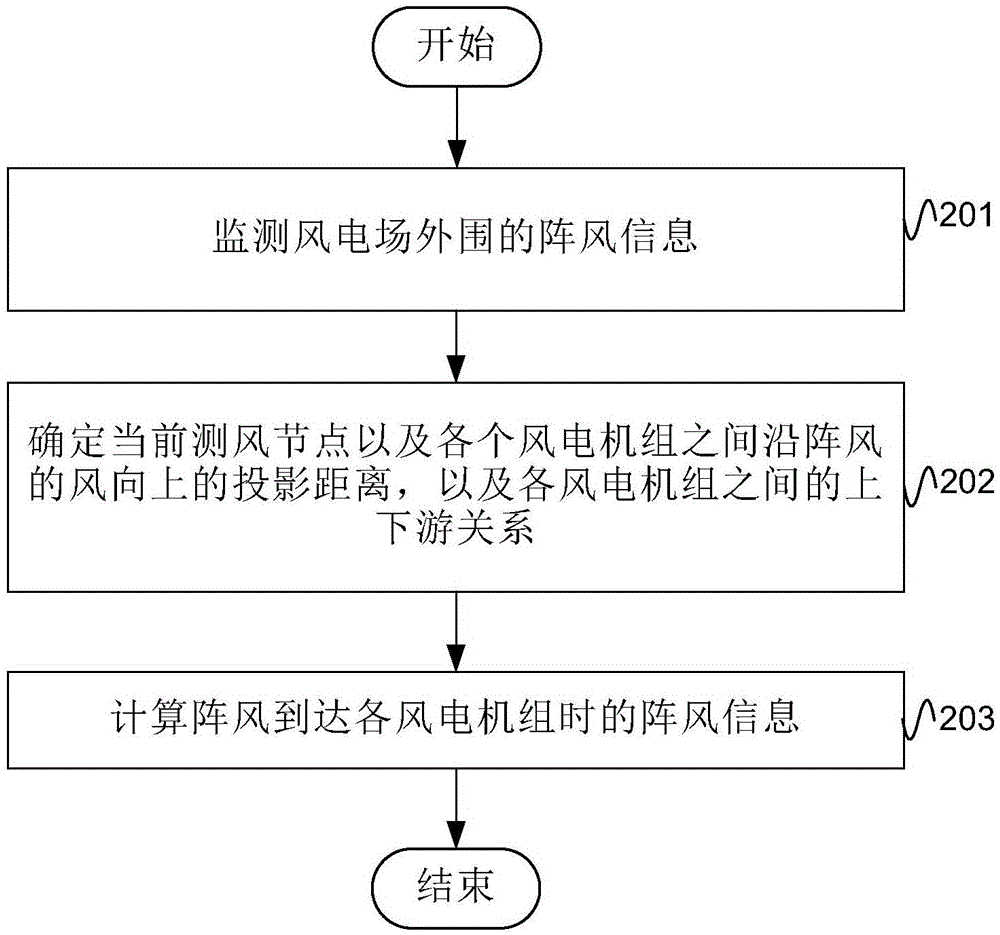
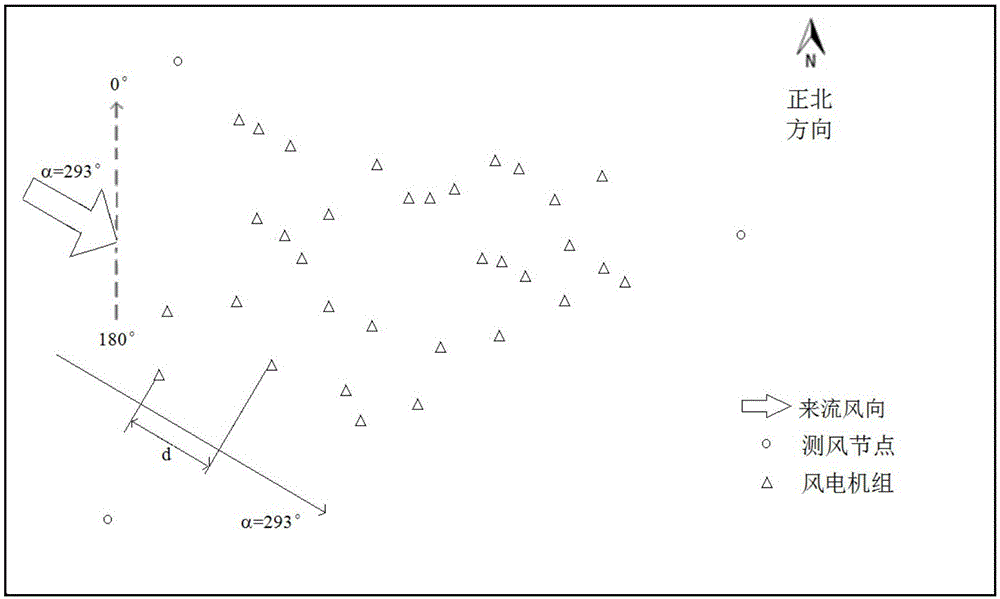
Embodiments of the invention provide a wind power field gust prediction method and system. The method comprises the following steps: 1) monitoring gust information of wind measurement nodes located at the periphery of a wind power field; 2) marking the wind measurement node, which firstly monitors gust, as a current wind measurement node, projecting the current wind measurement node and various wind power machine sets on a wind direction of the gust, obtaining projection distances of the current wind measurement node and the various wind power machine sets on the wind direction of the gust, and determining an upstream and downstream relationship between the various wind power machine sets; and 3) according to the gust information of the current wind measurement node, the projection distances of the current wind measurement node and the various wind power machine sets on the wind direction of the gust, and the upstream and downstream relationship between the various wind power machine sets, calculating gust information when the gust at the current wind measurement node arrives at the various wind power machine sets. According to the technical scheme of the invention, prediction of the gust in the wind power field is achieved, and then a foundation is laid for improvements of power generation efficiency and safety of the wind power machine sets.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDWIND SCI & CREATION WINDPOWER EQUIP CO LTD
Translating active Gurney flap to alleviate aircraft wake vortex hazard
InactiveUS20090321582A1Minimizing wake vortex hazardReducing large longitudinal spacingInfluencers by generating vorticesWing adjustmentsActuatorTrailing edge
A wake vortex alleviator is provided. The wake vortex alleviator produces rapid variations in the position of vortices emanating from aerodynamic surfaces by using an active flap that moves span-wise back and forth along the outboard section of the surface. Rapidly moving the flap back and forth in a slot at an appropriate frequency will cause the vortex to oscillate, resulting in interaction between other vortices and subsequent destruction much earlier than it would occur naturally. The slot is positioned near the aerodynamic surface trailing edge and generally transverse to a chord line of the aerodynamic surface. The flap can be moved using a variety of actuators to position, translate and stow the flap. The oscillation frequency and position are guided by information feedback according variations in lift in the aerodynamic surface, such as wind gusts. The flaps can control yaw, roll and pitch of the aerodynamic surface.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for reconstructing gusts and structural loads at aircraft, in particular passenger aircraft
InactiveCN101321667AIncrease profitHigh safety standardsSimulator controlGround installationsFlight vehicleNonlinear model
A method for reconstructing gusts and / or structural loads at aircraft, in particular passenger aircraft, characterised by the process steps: a) generating an observer on the basis of a nonlinear model of the aircraft which describes the movement of the aircraft in all six degrees of freedom (DoF) and the elastic motion of the aircraft structure; b) continuously supplying all the data and measurements substantial for the description of the state of the aircraft to the observer; c) calculating the gust velocities and structural loads (manoeuvre and gust loads) by the observer from the supplied data and measurements.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
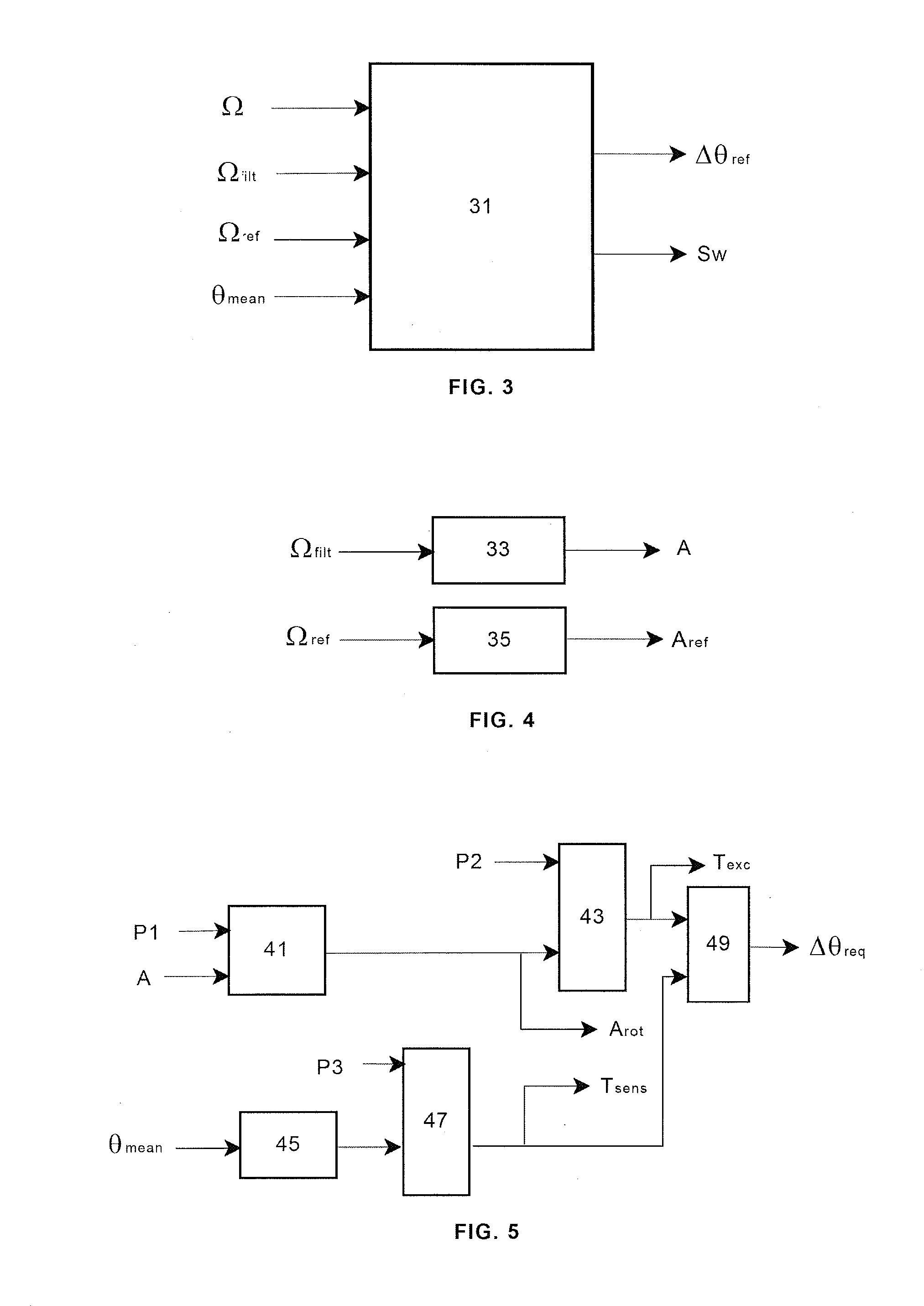
Wind turbine control methods and systems
ActiveUS20120193918A1Control speedRapid responseRotational speed controlWind motor controlAerodynamic torqueControl system
Improved wind turbine control methods and systems. The invention relates to a method for the operation of a variable speed wind turbine having pitch and torque control means that include additional steps for providing to the pitch control means in case of a wind gust a pitch angle reference increment Dθref in the amount needed for avoiding that the aerodynamic torque added by the wind gust exceeds a predetermined limit. The present invention also relates to a wind turbine comprising a control system arranged for performing an additional regulation in case of wind gust
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Signal processing method of wireless anemobiagraph
The invention discloses a signal processing method of a wireless anemobiagraph, which comprises the steps of: analyzing signals in a certain time interval according to a wind speed and a wind direction in the signals subjected to A / D (Analog-to-Digital) conversion by the wireless anemobiagraph, calculating a horizontal average wind speed, a horizontal average wind direction, a vertical average wind speed, a vertical average wind direction as well as turbulence intensities, gust factors, turbulence integral scales and fluctuating wind power spectrums in a down wind direction, a horizontal wind direction and a vertical wind direction; fitting the fluctuating wind power spectrums in the horizontal wind direction and the vertical wind direction by adopting a Kaimal spectrum and a Panofsky spectrum to obtain a coefficient of a power spectrum density function; and storing a calculating result to a data storage of the wireless anemobiagraph, and compiling all relevant embedded calculating programs. According to the invention, demands of signal characteristics and wind load analysis of the wireless anemobiagraph are fully considered, automatic calculation of wind filed characteristic parameters is realized in the wireless anemobiagraph, and data transmission quantity of the wireless anemobiagraph and later stage analysis workload of the wind load data are greatly reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
All weather wind turbines
InactiveUS20040042899A1Reduce rotationContinuous operationPropellersPump componentsTurbineWind force
The technology of all weather wind turbine is disclosed by applying it to a savonius design wind turbine although it can be applied to all kinds of windmills based on rotational mechanism in general and specifically in the field of wind turbines. In this current embodiment the art is used to a savonius design rotor. A Savonius rotor assembly includes two blades. Each of the blades has an outer edge and an inner edge with the outer edges of the blades lying on a circle which define the diameter of the rotor. Each of the blades has a linear portion adjacent to the inner edge and a first curved portion which is substantially an arc of a circle tangent to the linear portion and tangent to the circle defining the rotor diameter. A second curved portion is substantially coincident to the circle defining the rotor diameter. In some applications multiple blades or multiple units are mounted in layers for more torque. The major modifications however from savonius type turbine are as follows: First feature of this preferred embodiment is the free sliding movement of rotor blades / air foils cushioned by elastics / springs and balanced by counter weights. Secondly a smart self regulating system, enabling the assembly not only to survive the windy storms but also provide steadier RPMs by shutting the wind inlet gates, corresponding to the increase in RPMs caused by the gusty winds. The central shaft between the air foils can be eliminated if so desired to give free passage to the air to improve efficiency however the basic emphasis is on the principle of automatic governor mechanism rather than the rotor blade shape or angle of curve.
Owner:KHAN GHAZI
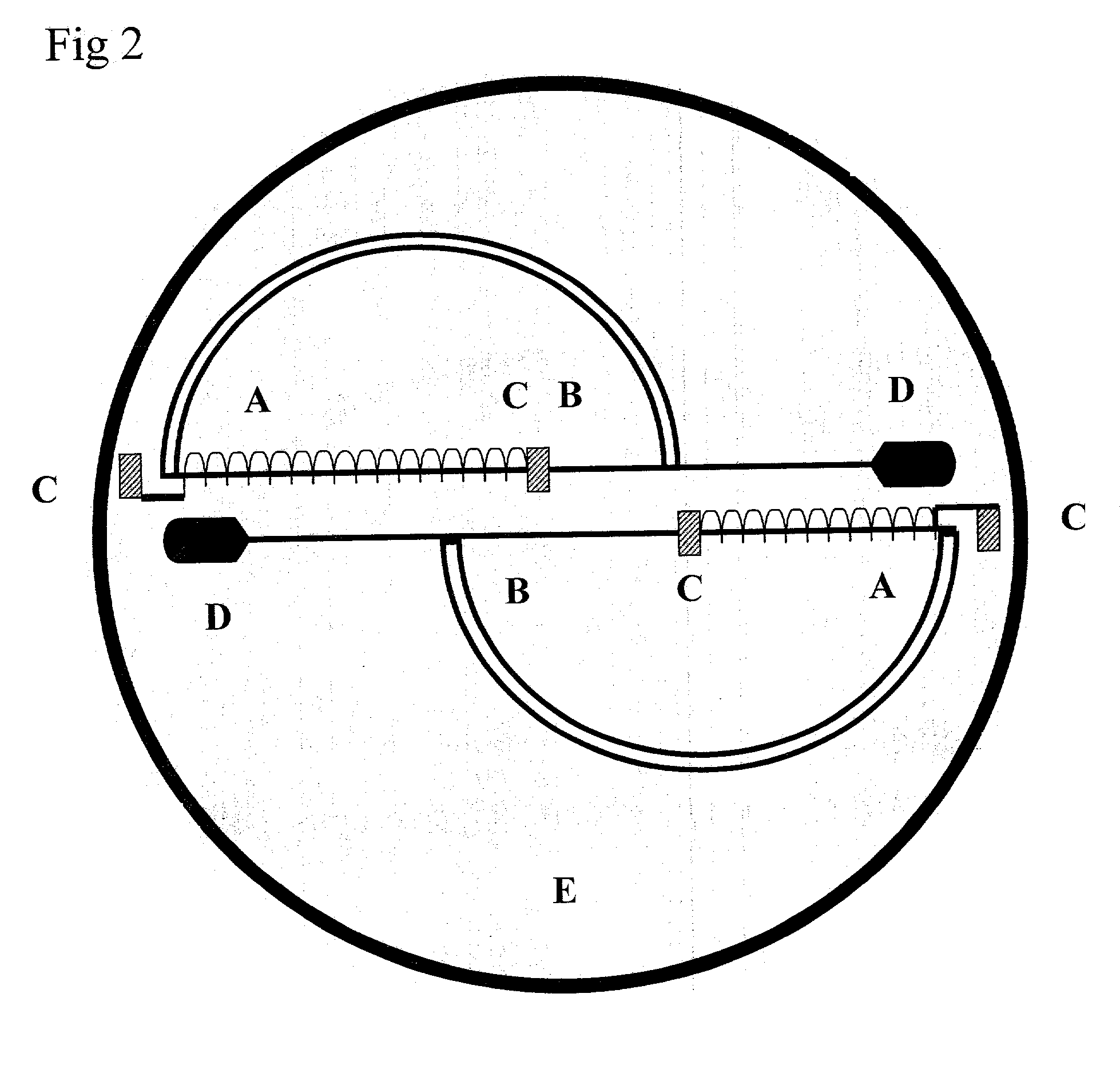
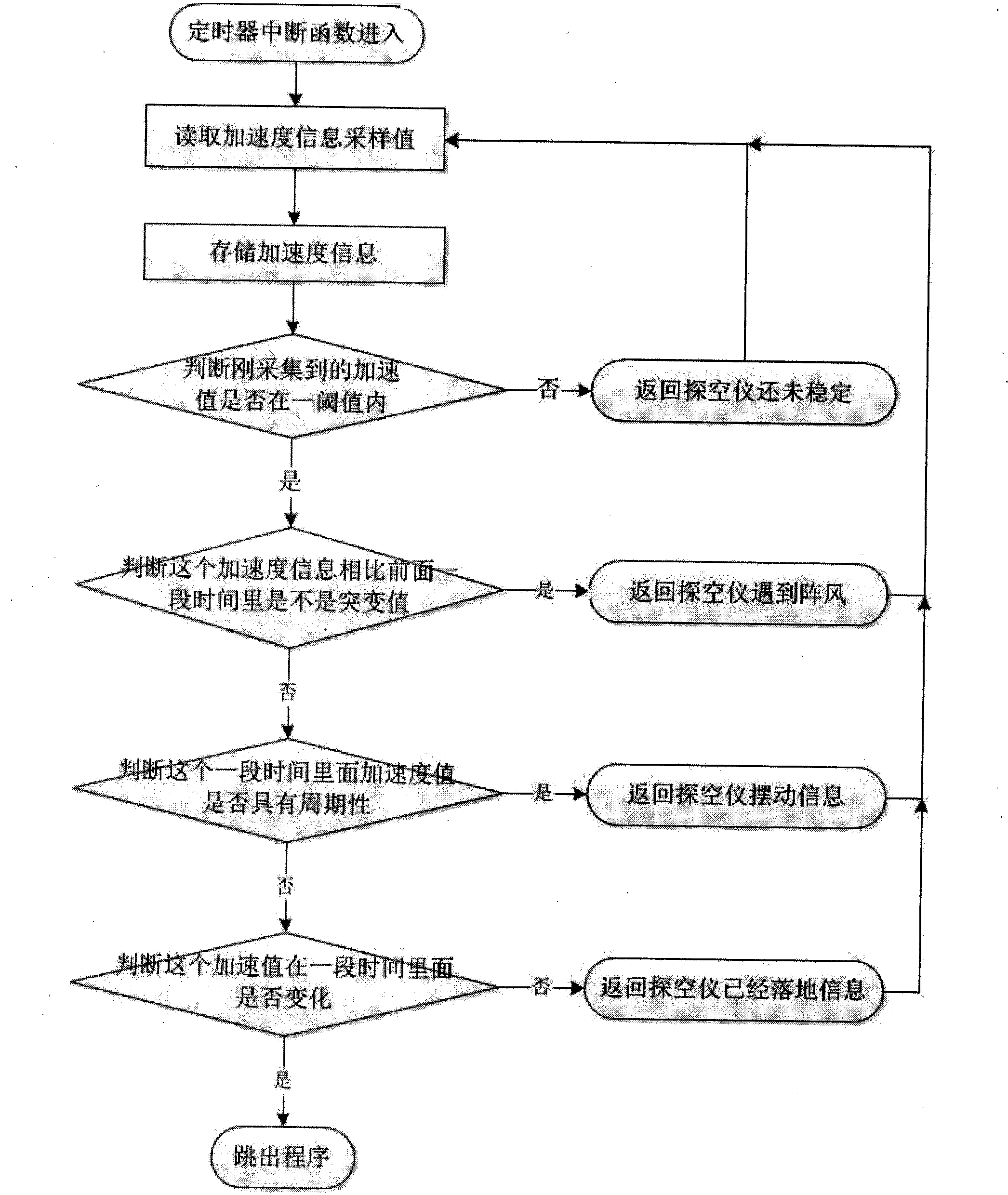
Method for detecting initial posture and motion states of weather detecting sonde based on three-dimensional acceleration sensor
The invention provides a method for detecting an initial posture and motion states of a cannon projectile weather detecting sonde based on a triaxial accelerometer sensor. The posture of delivering from godown of the cannon projectile weather detecting sonde is uncertain, and is greatly interfered by wind in the working process. To solve the problems, the triaxial accelerometer sensor is additionally arranged in the sonde and is used for detecting the initial posture of the sonde, whether the sonde encounters gust or not and whether the sonde falls to the ground or not are detected, and the reliability of the data detected by the sonde is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
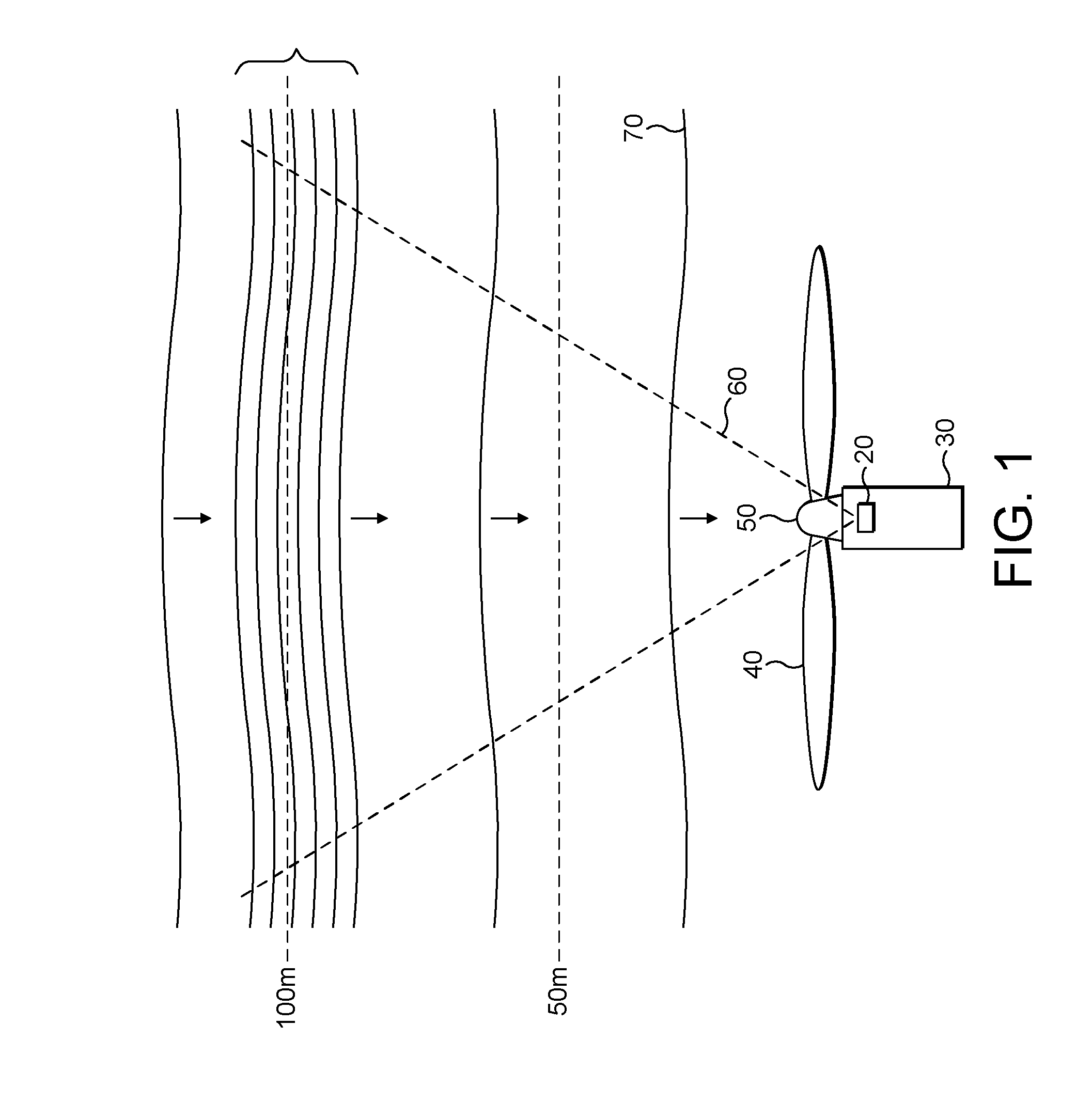
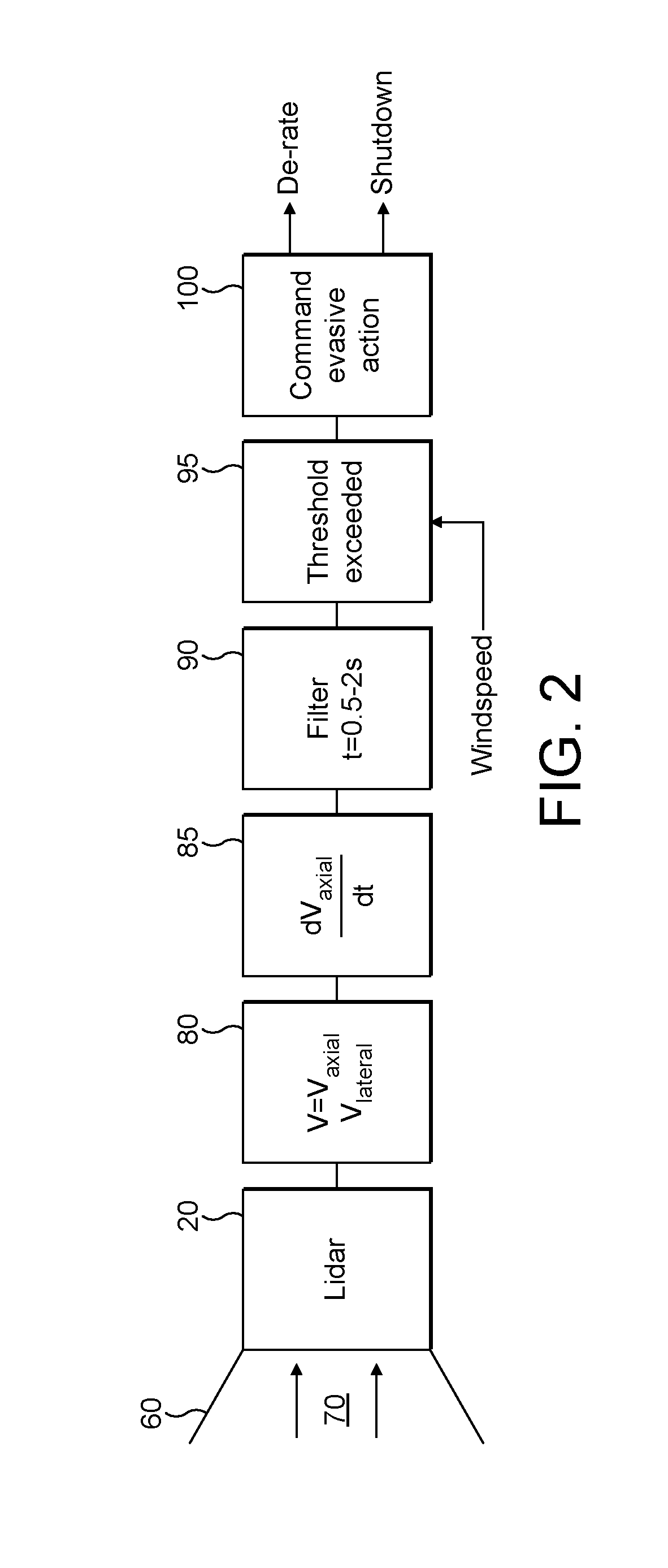
Method and apparatus for protecting wind turbines from extreme events
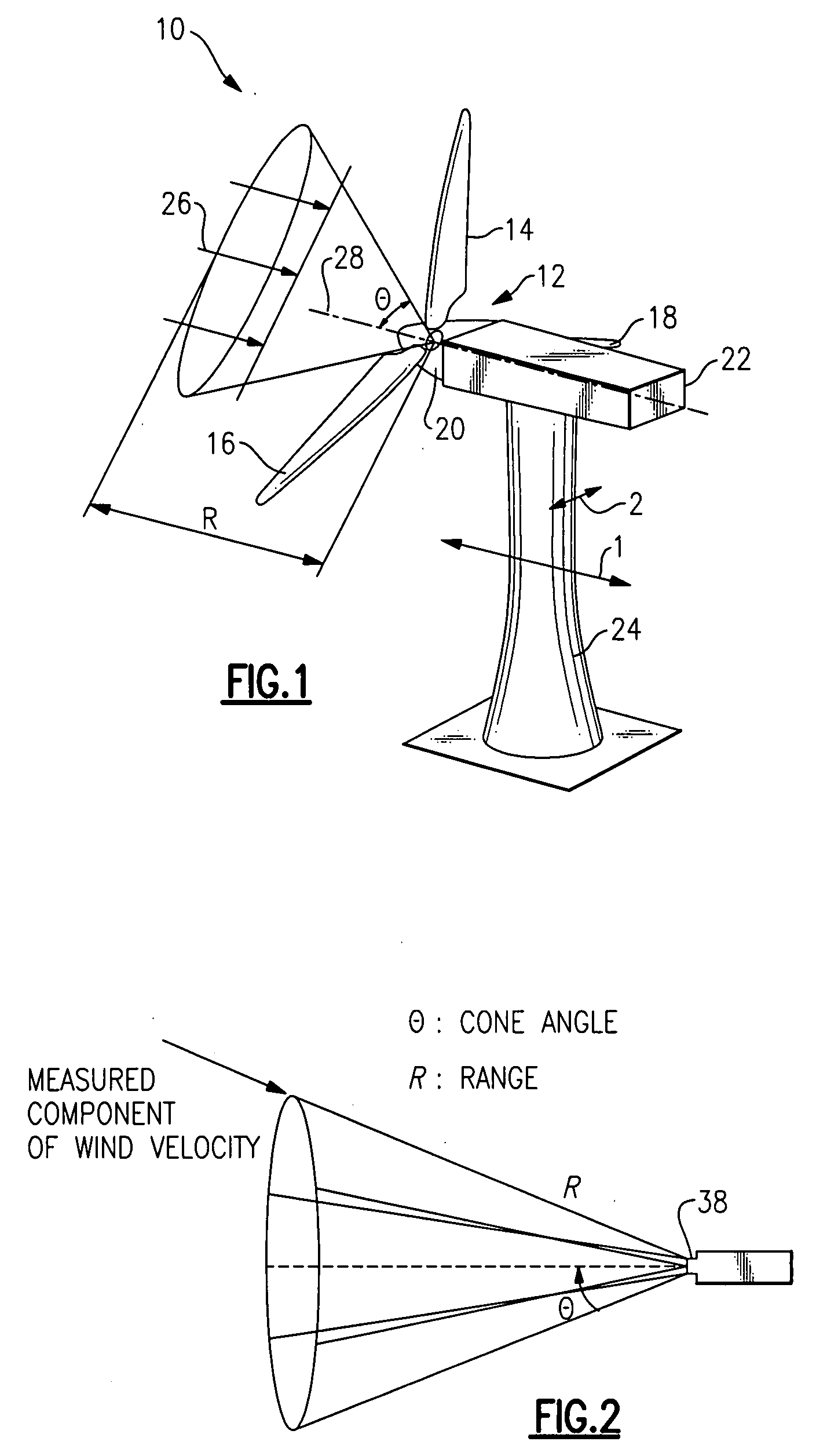
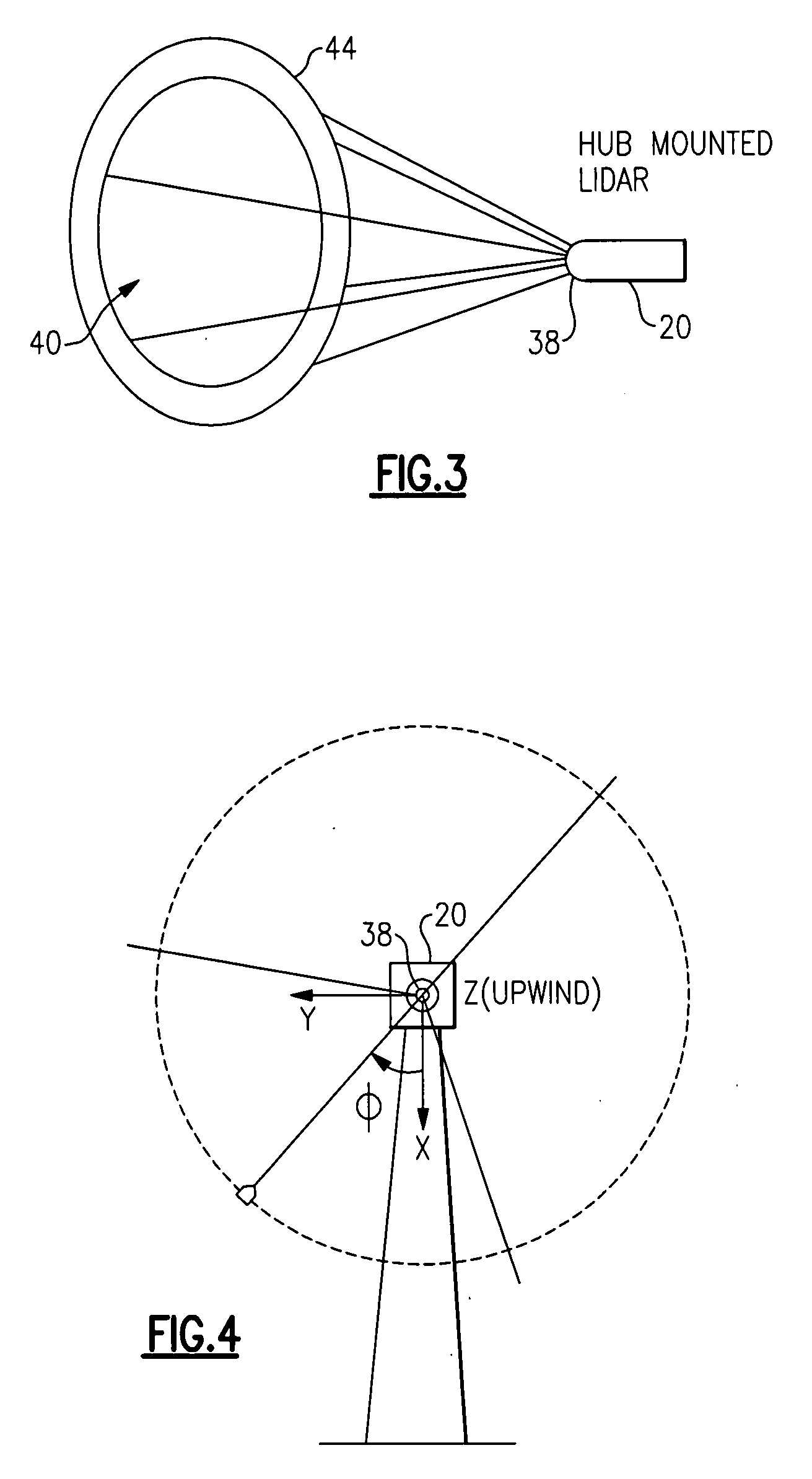
A wind turbine has a Lidar device to sense wind conditions upstream of the wind turbine. Wind speed signals from the wind turbine are processed to detect an extreme operating gust. The detection is performed by differentiating the axial wind velocity and filtering for a period of time. On detection of extreme operating gust the system controller takes necessary evasive action which may include shutting down the turbine or varying the blade pitch angle.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com