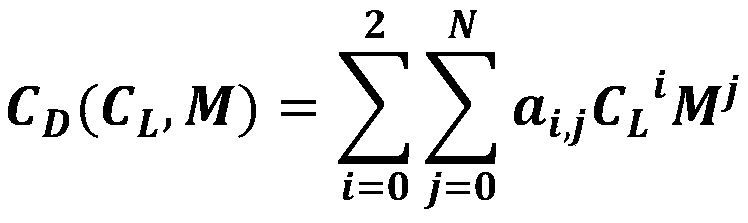Patents
Literature
49 results about "Climb" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
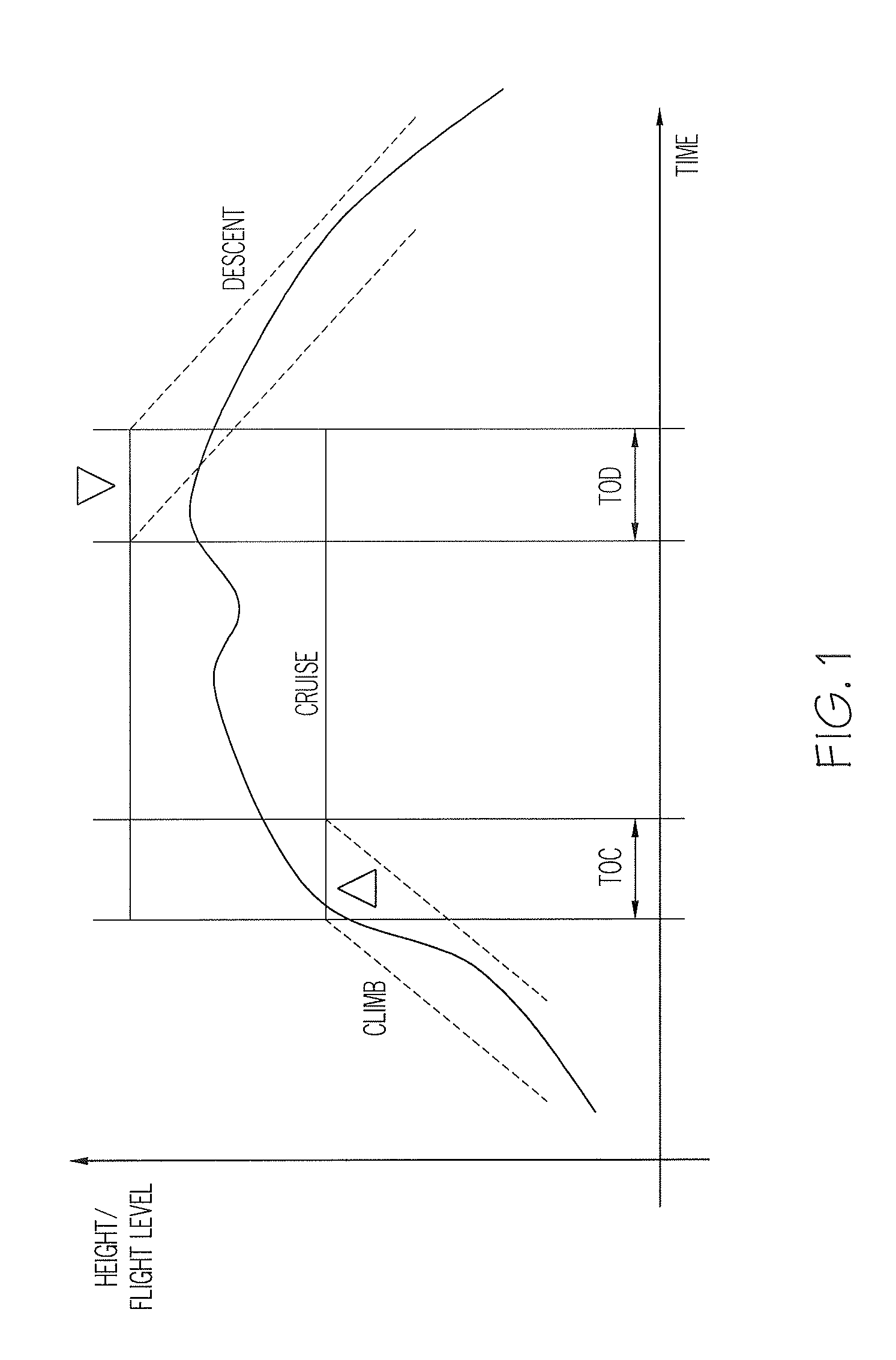
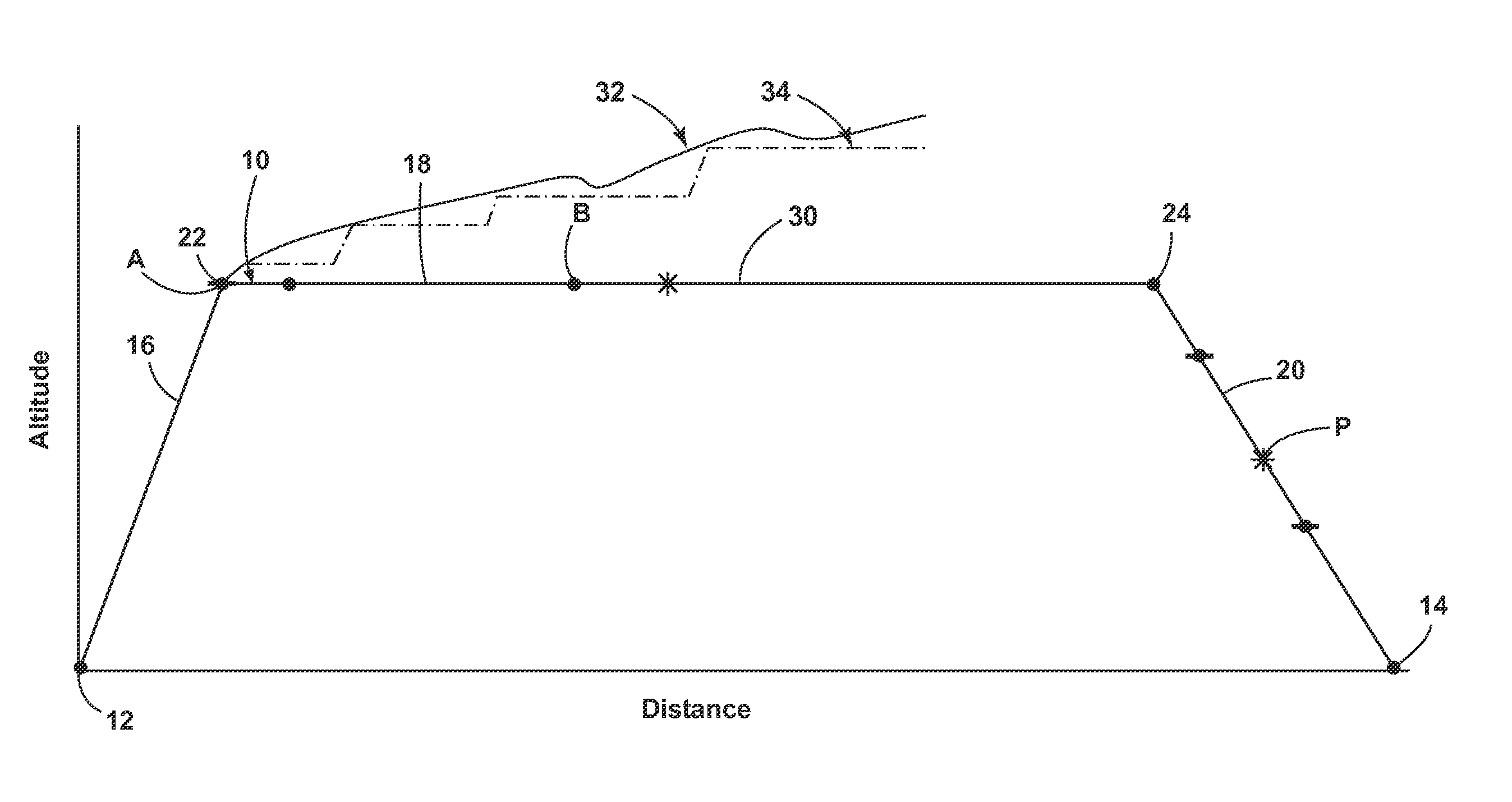
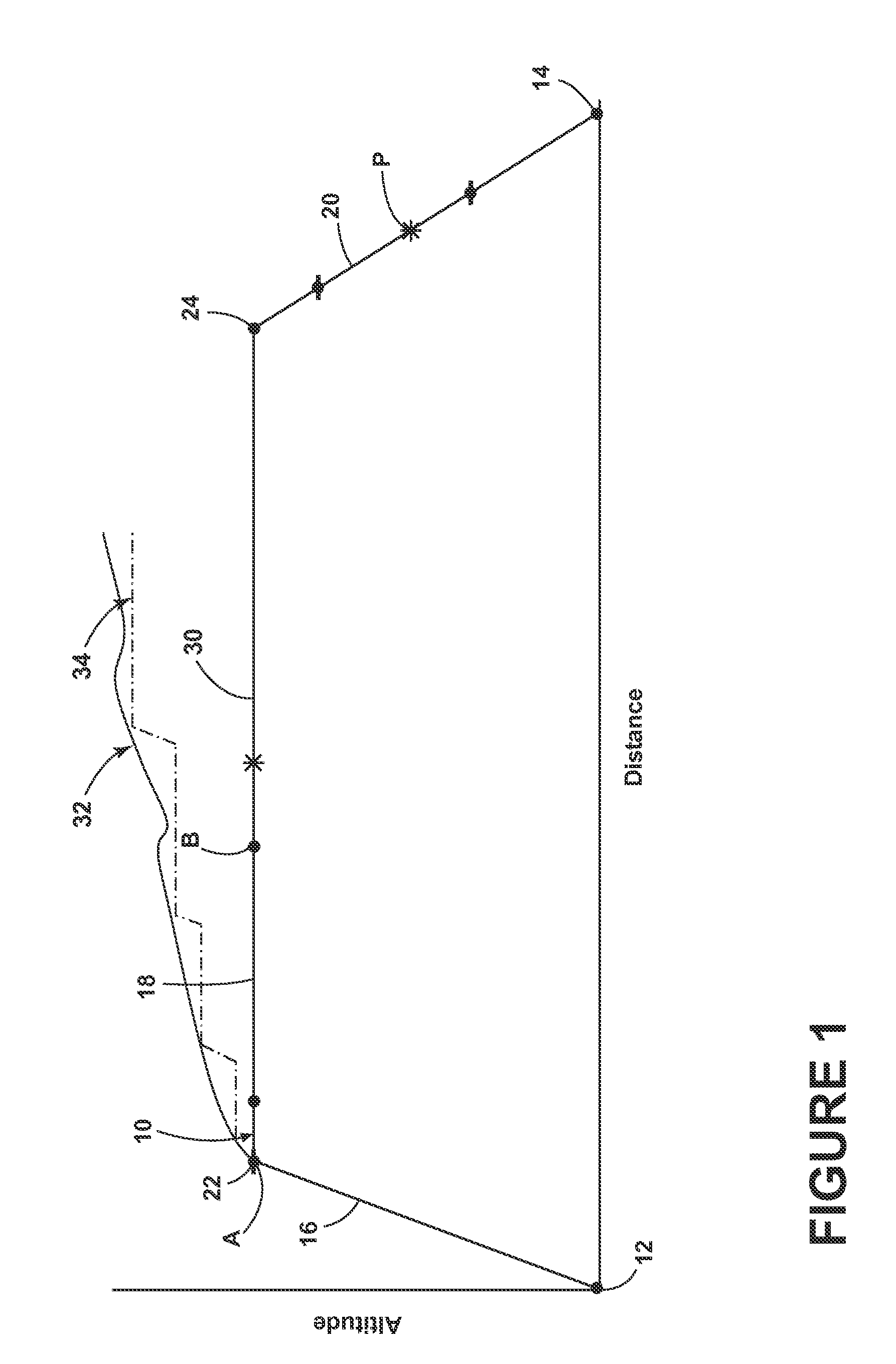
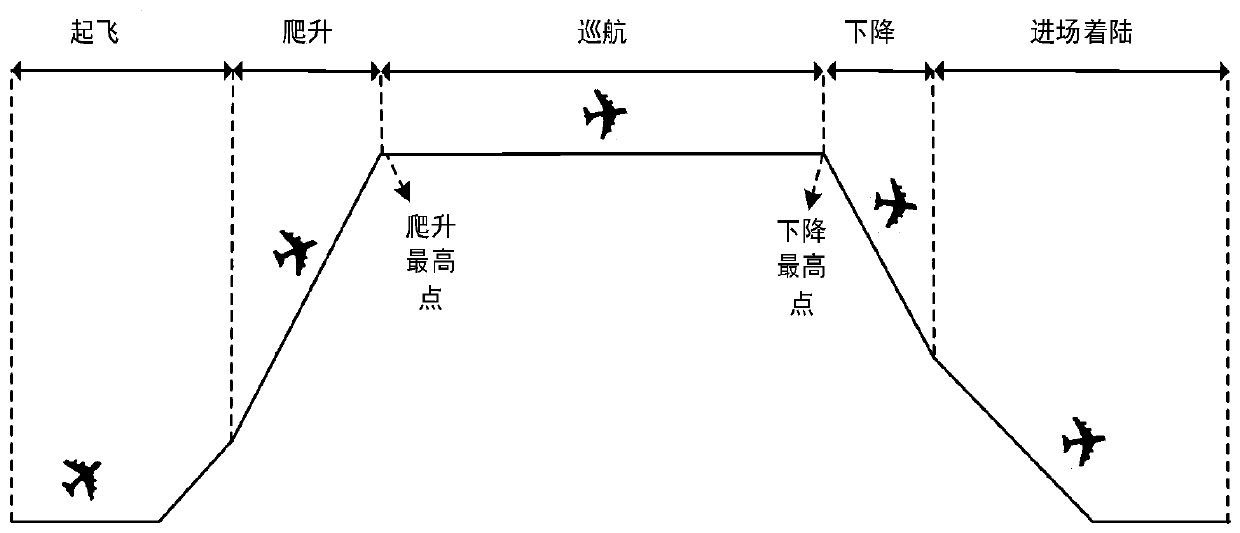
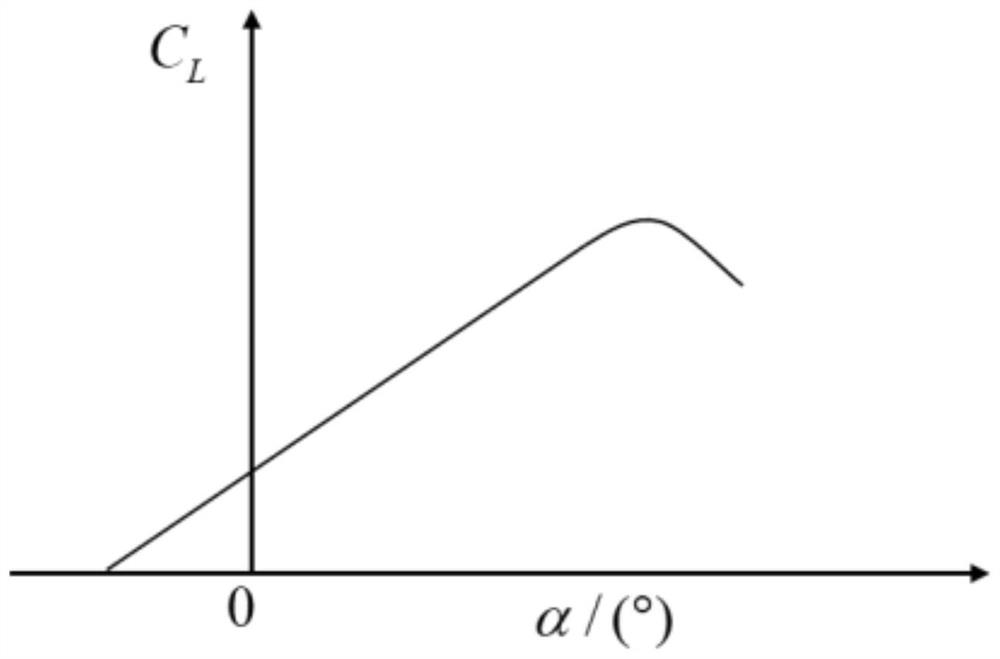
In aviation, a climb is the operation of increasing the altitude of an aircraft. It is also the logical phase of a typical flight (the climb phase or climbout) following takeoff and preceding the cruise. During the climb phase there is an increase in altitude to a predetermined level.
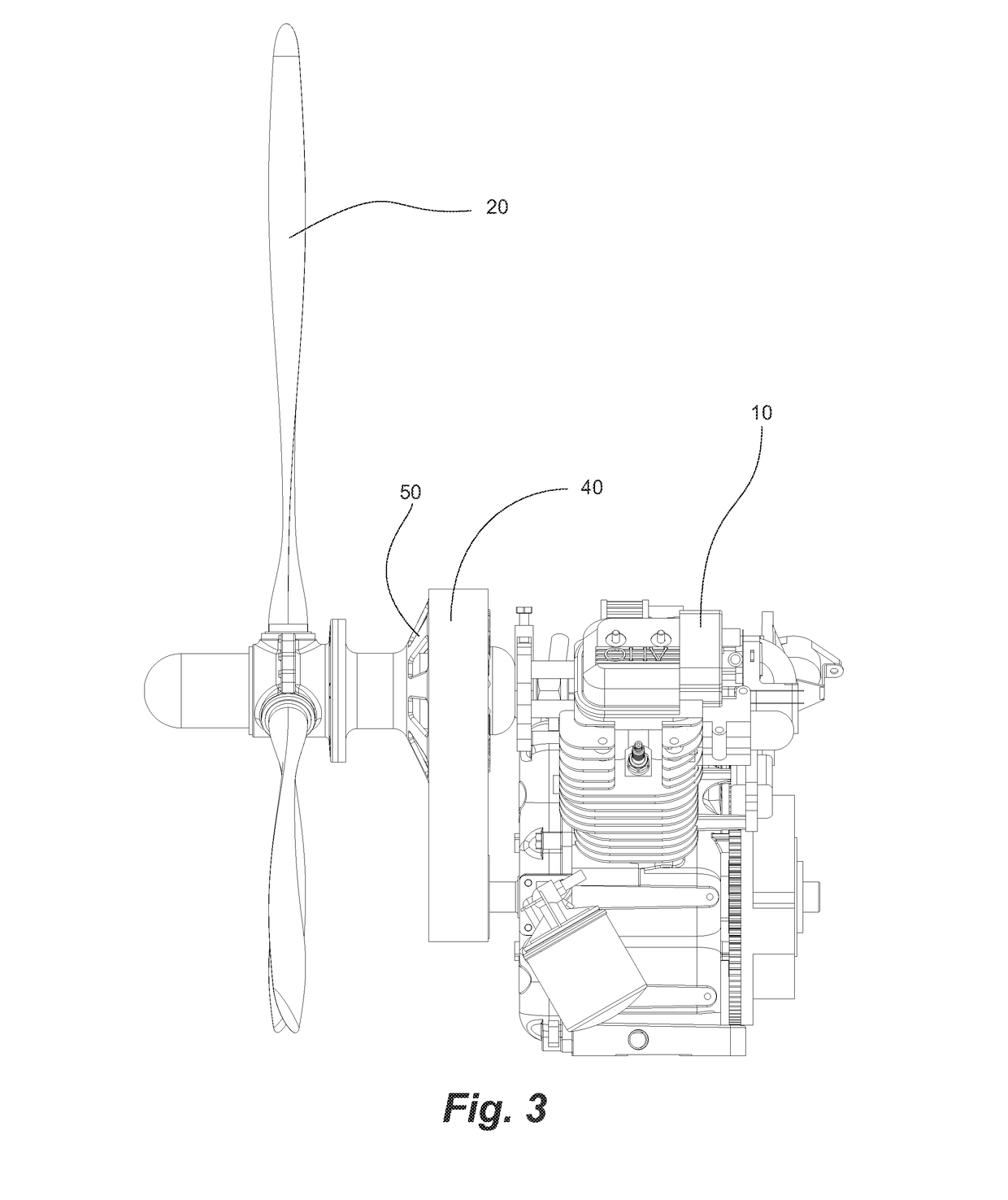
Lift Propulsion and Stabilizing System and Procedure For Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft
InactiveUS20130251525A1Inhibition effectLow costElectric power distributionPropellersLeading edgeTurbine
Lift propulsion and stabilizing system and procedure for vertical takeoff and landing aircraft that consists in applying simultaneously and combined as lifters during the initial portion of the climb and at the end of the descent of: a) some fans or electric turbines, EDF, and b) at least one rotor with external blades and / or rotary and / or c) the engine flow directed downwards and / or d) pressure air jets injected on leading edges control fins, and / or e) water jets and / or f) supplemented with aerodynamic lift produced during frontal advance of the aircraft, the stabilization is achieved by the gyroscopic stiffness of the rotor and two or more lifting fans oscillating fins and / or air jets located on two or stabilizers more peripheral points in a plane perpendicular to the vertical axis of the aircraft.
Owner:SAIZ MANUEL M
Hybrid Propulsion Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft
A hybrid propulsion aircraft is described having a distributed electric propulsion system. The distributed electric propulsion system includes a turbo shaft engine that drives one or more generators through a gearbox. The generator provides AC power to a plurality of ducted fans (each being driven by an electric motor). The ducted fans may be integrated with the hybrid propulsion aircraft's wings. The wings can be pivotally attached to the fuselage, thereby allowing for vertical take-off and landing. The design of the hybrid propulsion aircraft mitigates undesirable transient behavior traditionally encountered during a transition from vertical flight to horizontal flight. Moreover, the hybrid propulsion aircraft offers a fast, constant-altitude transition, without requiring a climb or dive to transition. It also offers increased efficiency in both hover and forward flight versus other VTOL aircraft and a higher forward max speed than traditional rotorcraft.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
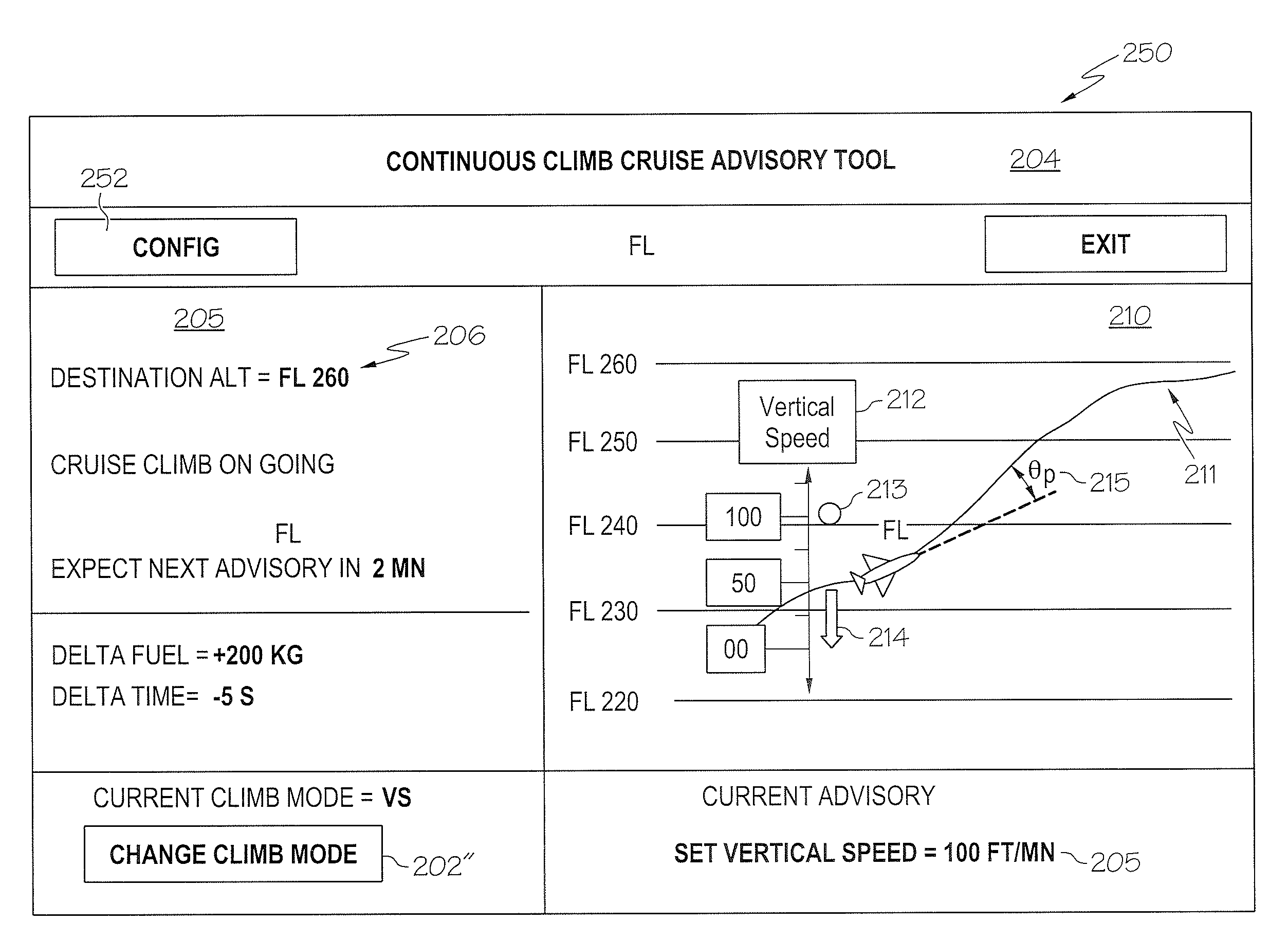
Display information to support climb optimization during cruise
InactiveUS20120078450A1Shorter delayEnergy saving arrangementsDigital data processing detailsFlight vehicleControl variable
Methods and systems are provided for executing a single continuous altitude change by an aircraft to cruise altitude using an electronic flight bag via a flight management system. The method comprises the determination of an altitude change in a flight plan during the cruise phase of the flight plan. Based on the altitude change and a mathematical model of the aircraft an optimum vertical trajectory profile or the aircraft is determined from which an angle of attack (AOA) and a thrust is derived to achieve the optimum vertical trajectory. From the AOA and the thrust, the required aircraft control variables are determined that may be applied to the engines and the control surface actuators of the aircraft.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Hybrid propulsion vertical take-off and landing aircraft
ActiveUS10926874B2Out of synchronizationAircraft power plant componentsRemote controlled aircraftControl theoryElectric generator
A hybrid propulsion aircraft is described having a distributed electric propulsion system. The distributed electric propulsion system includes a turbo shaft engine that drives one or more generators through a gearbox. The generator provides AC power to a plurality of ducted fans (each being driven by an electric motor). The ducted fans may be integrated with the hybrid propulsion aircraft's wings. The wings can be pivotally attached to the fuselage, thereby allowing for vertical take-off and landing. The design of the hybrid propulsion aircraft mitigates undesirable transient behavior traditionally encountered during a transition from vertical flight to horizontal flight. Moreover, the hybrid propulsion aircraft offers a fast, constant-altitude transition, without requiring a climb or dive to transition. It also offers increased efficiency in both hover and forward flight versus other VTOL aircraft and a higher forward max speed than traditional rotorcraft.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
Method for flying an aircraft along a flight path
A method of flying an aircraft, where the aircraft has an associated performance envelope, along a flight path based determining an altitude profile for a cruise-climb along the flight path based on the performance envelope of the aircraft and flying the aircraft along the flight path to approximate the altitude profile.
Owner:GE AVIATION SYST LLC
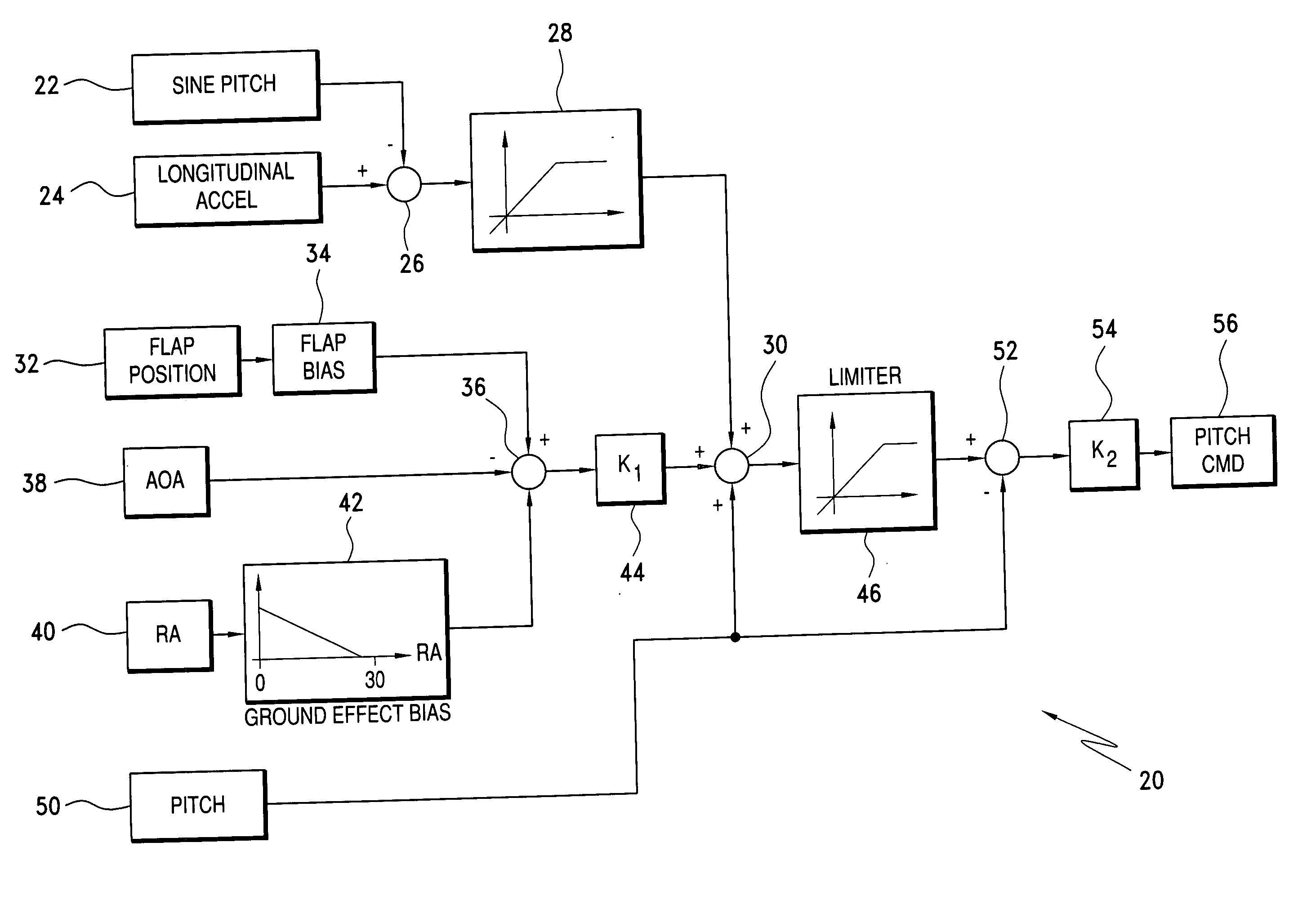
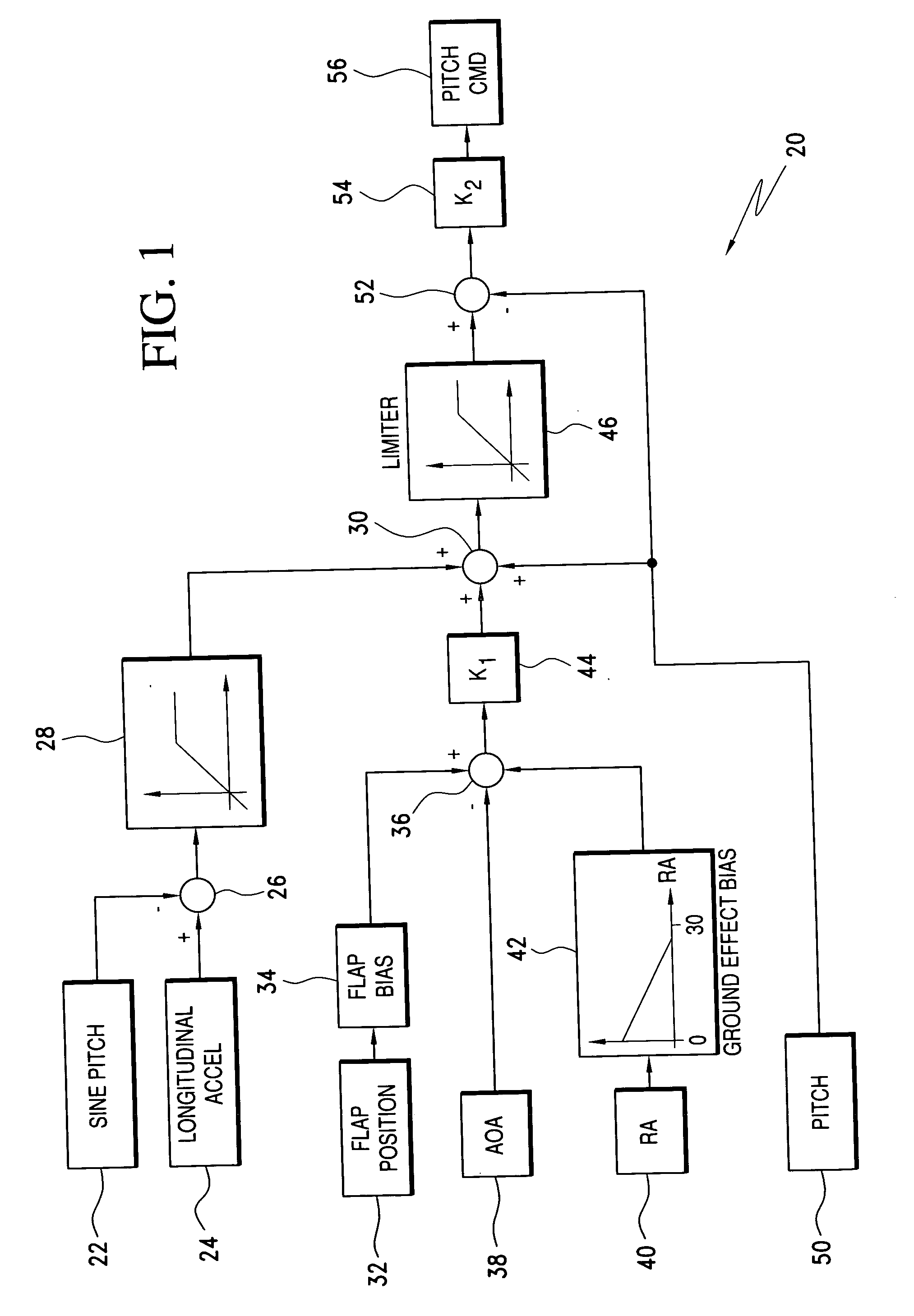
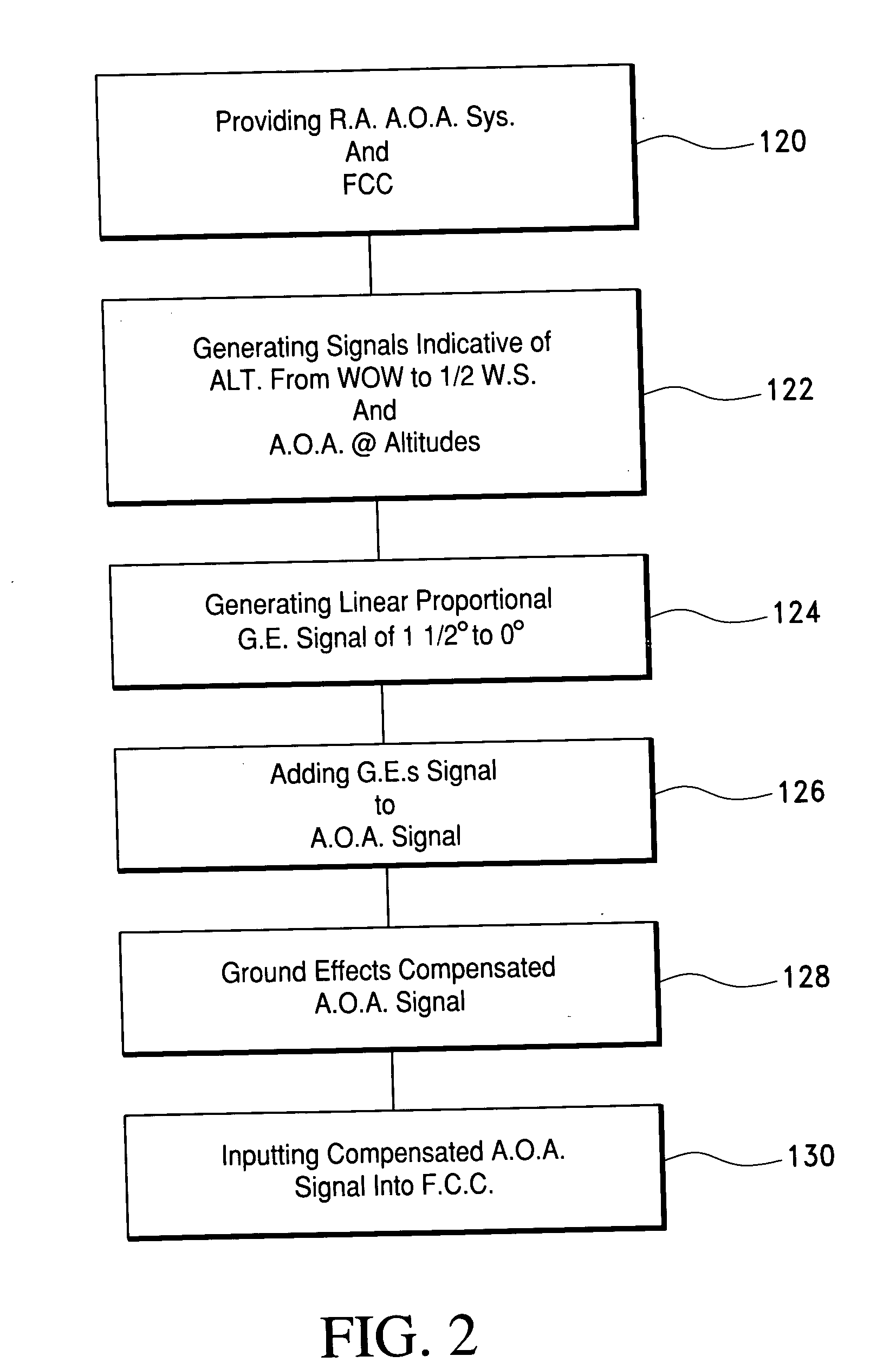
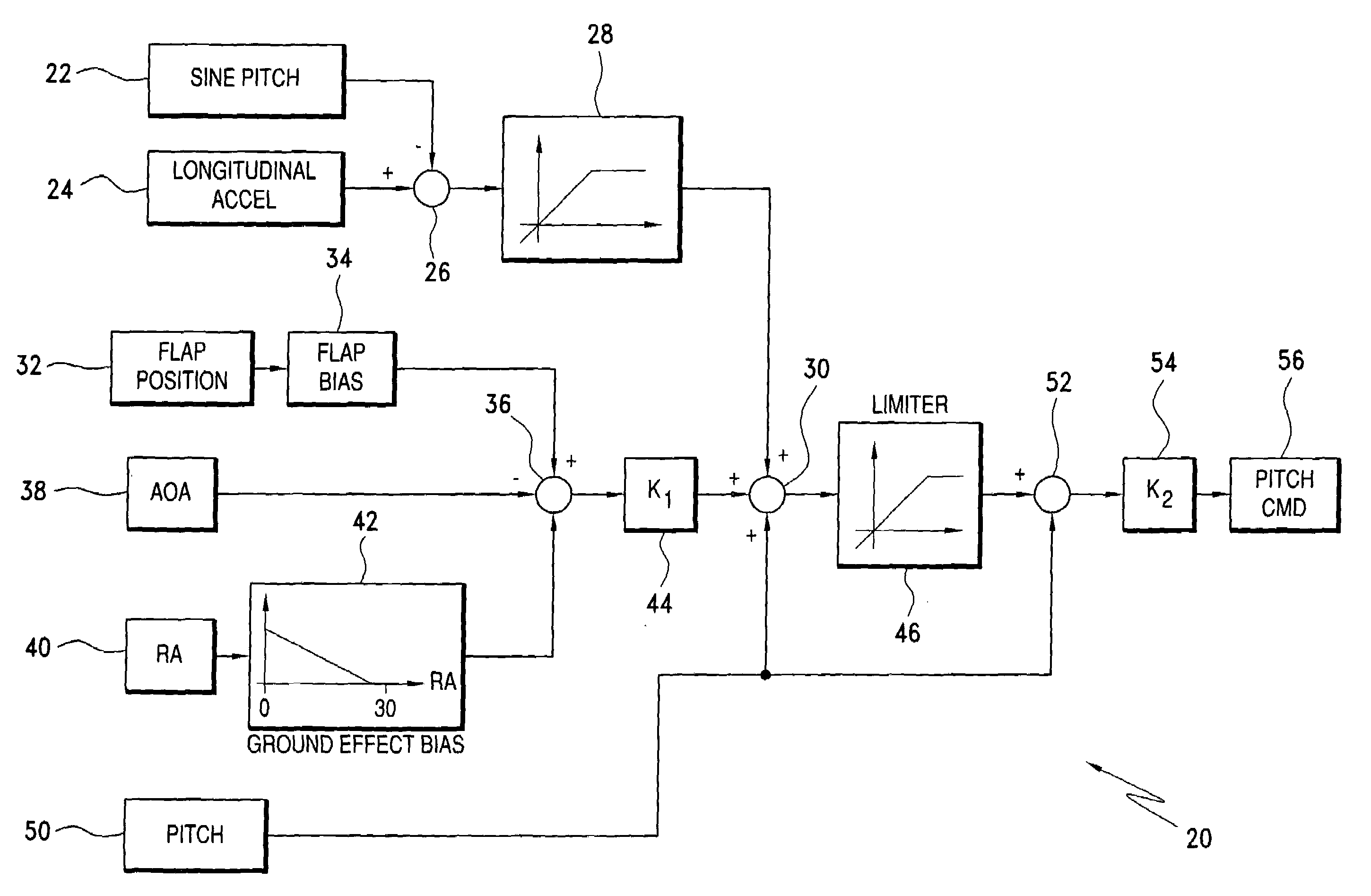
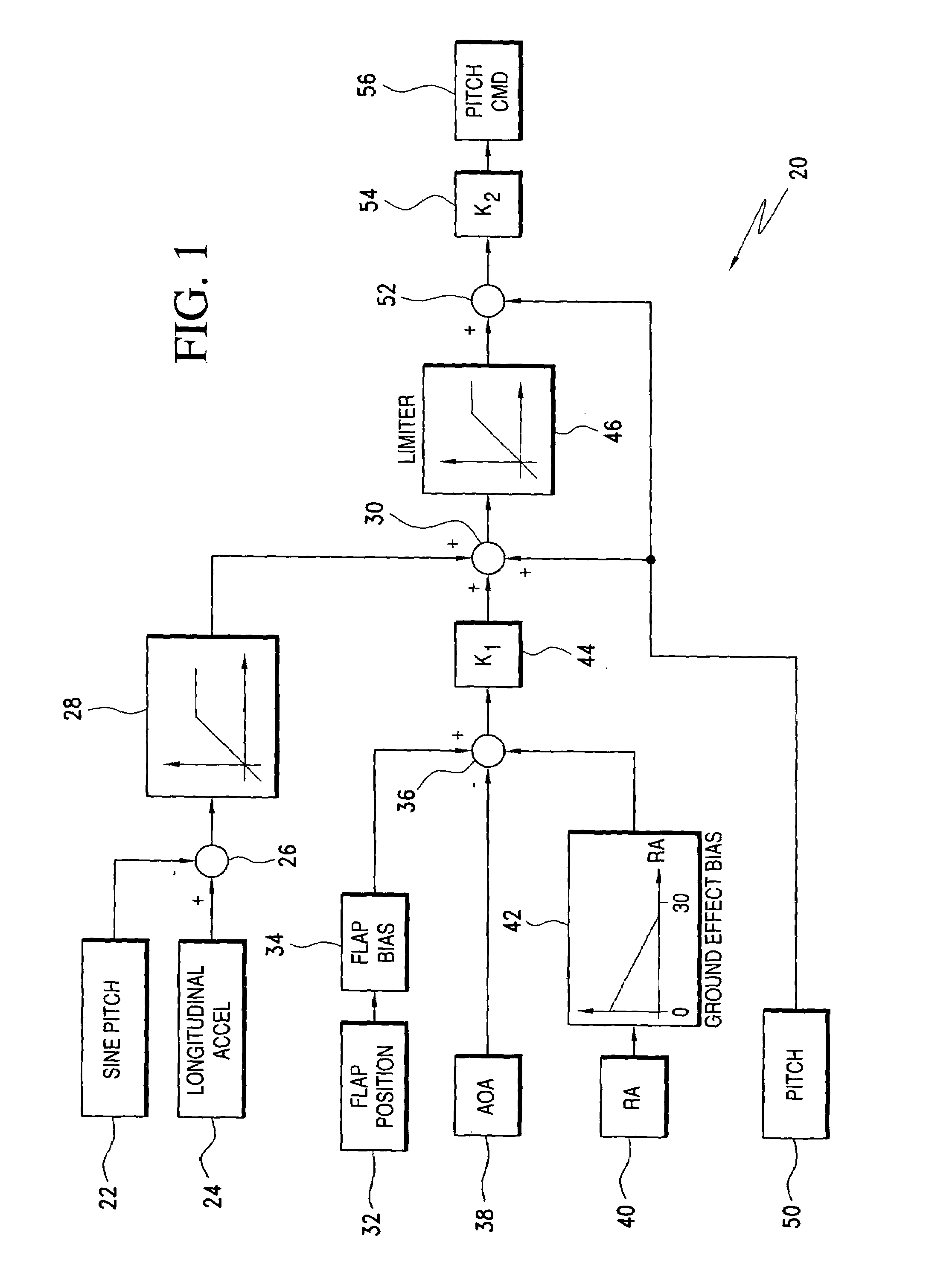
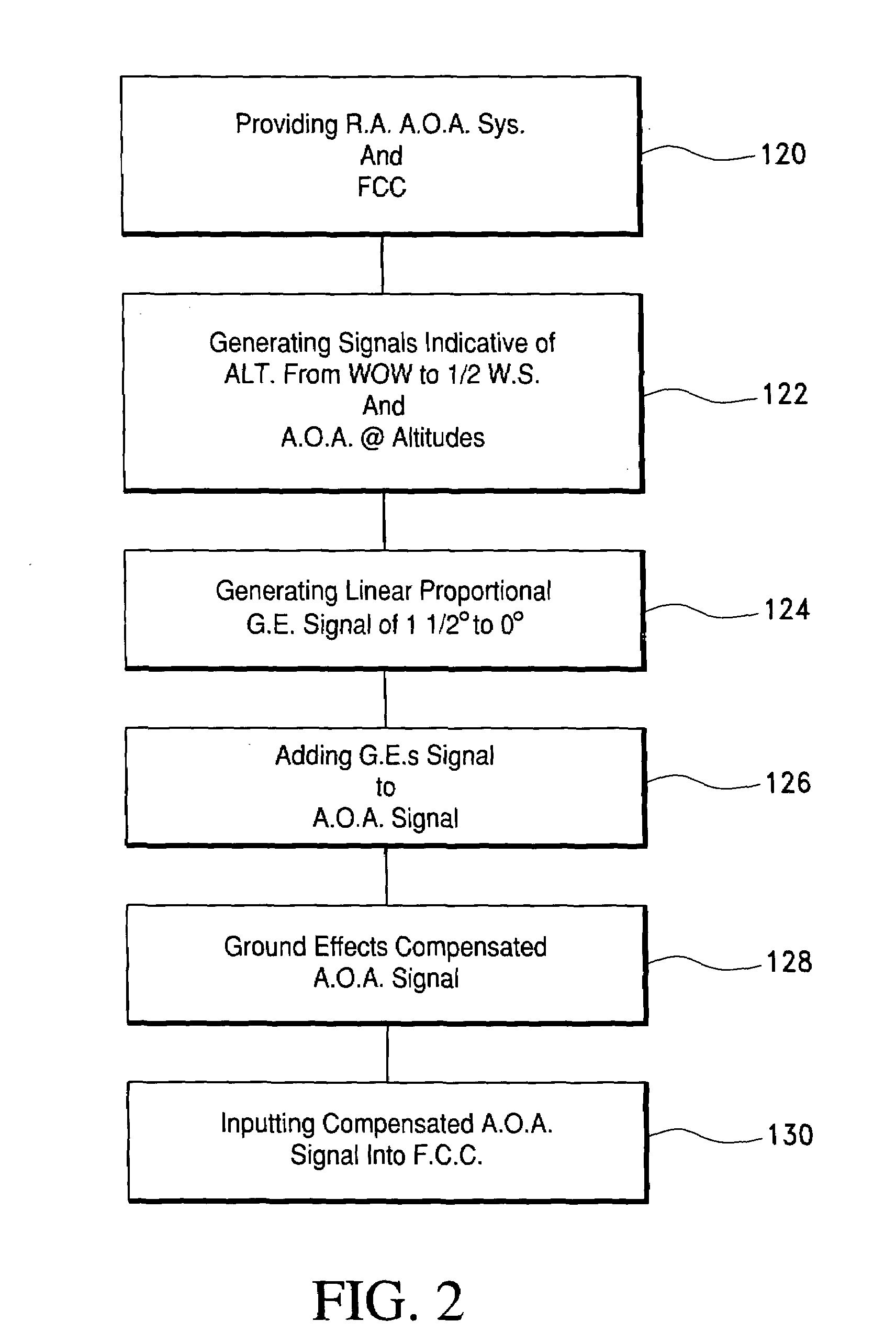
Ground effects compensated angle of attack command system and method
ActiveUS20060235582A1Digital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCommand systemDisplay device
A take off ground effects compensated angle of attack system includes a radio altimeter and / or timer, a pitch angle system and a flight control computer. The radio altimeter generates a signal which is indicative of the aircraft's altitude from 0 i.e., weight off wheels to an altitude of ½ the wing span of the aircraft. The angle of attack system simultaneously generates a signal which is indicative of the aircraft's angle of attack without compensation for ground effects. Therefore, a ground effects signal of from 1½° to 0° is generated and added to the angle of attack signal as the aircraft climbs from 0 ft. to an altitude which is equal to ½ the wing span of the aircraft. The ground effects signal is added to the angle of attack signal to provide a ground effects compensated angle of attacks signal which is then fed to the flight control computer or display.
Owner:SAFE FLIGHT INSTR LLC
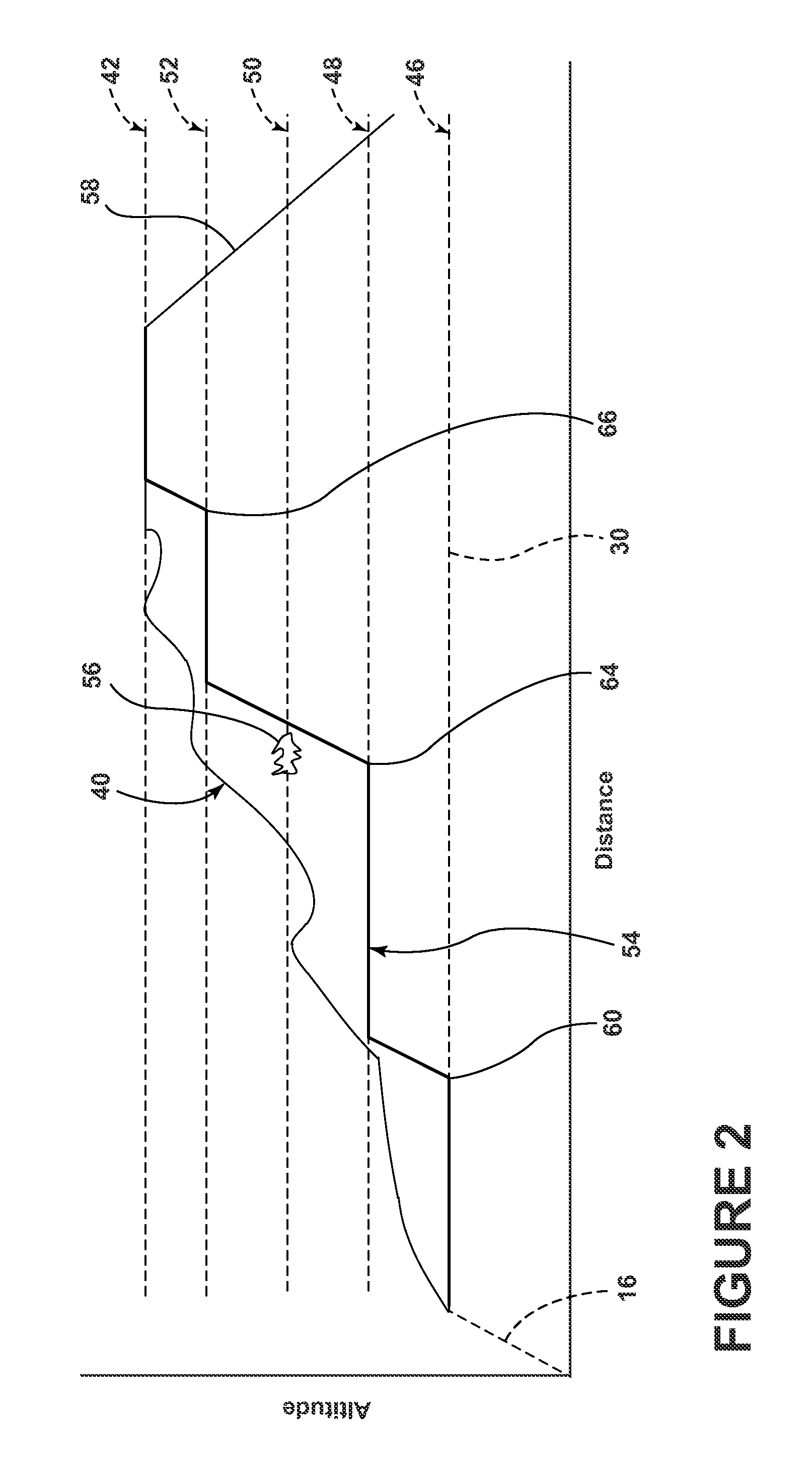
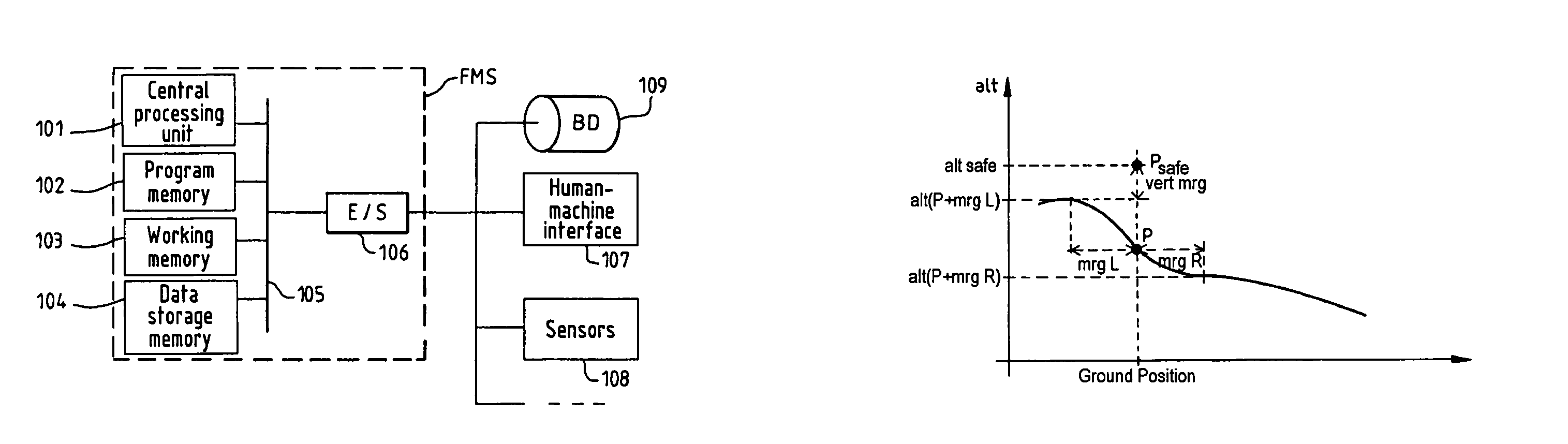
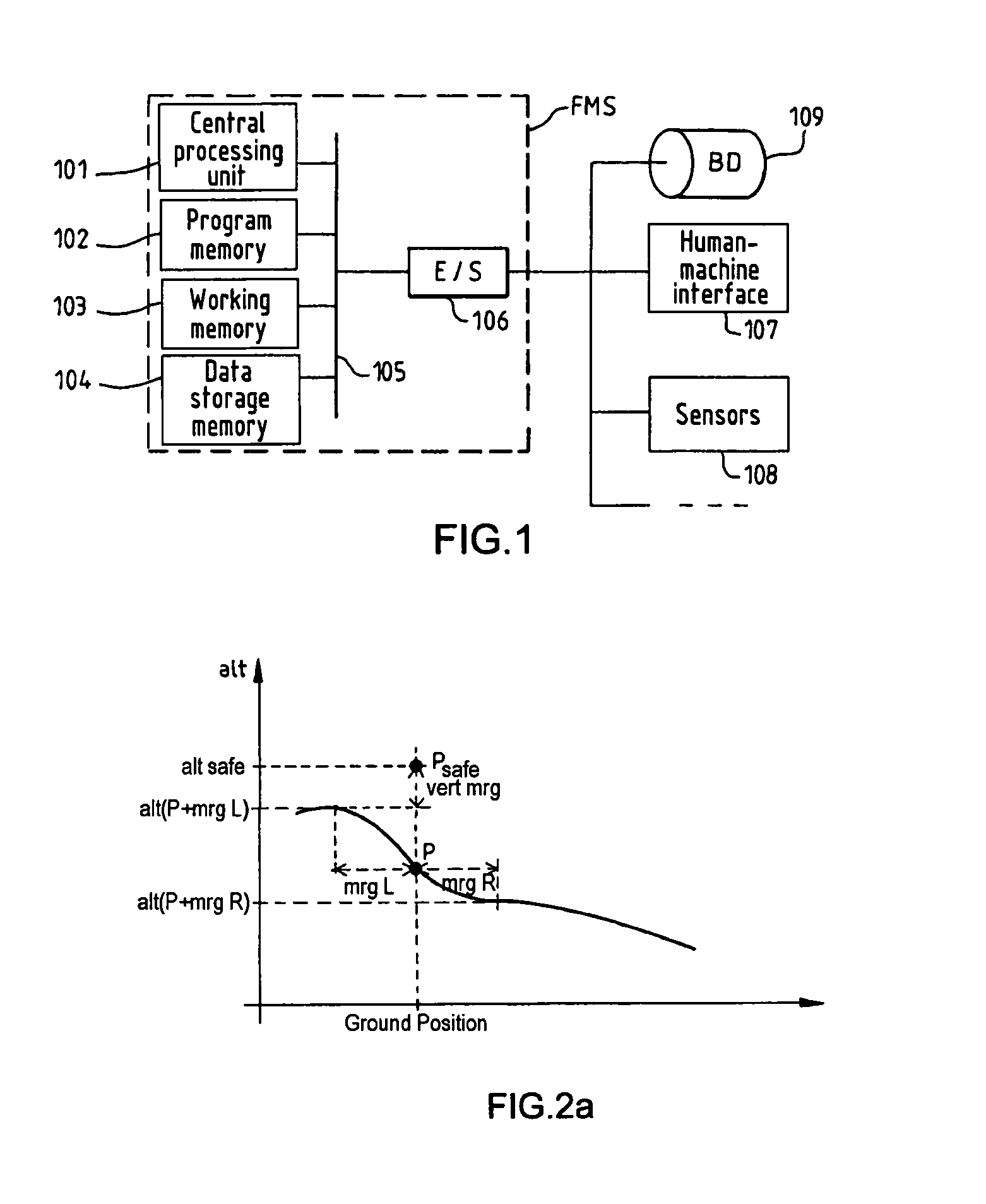
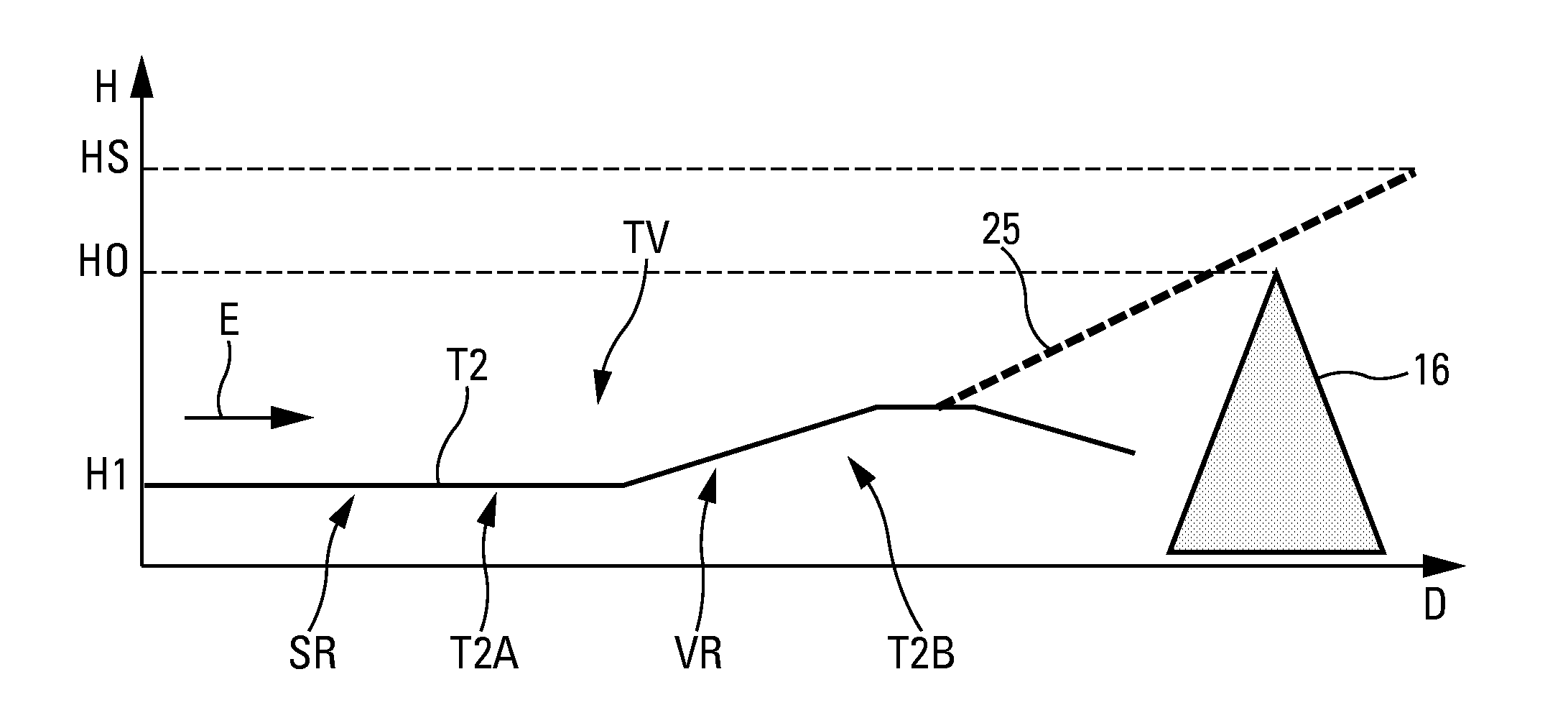
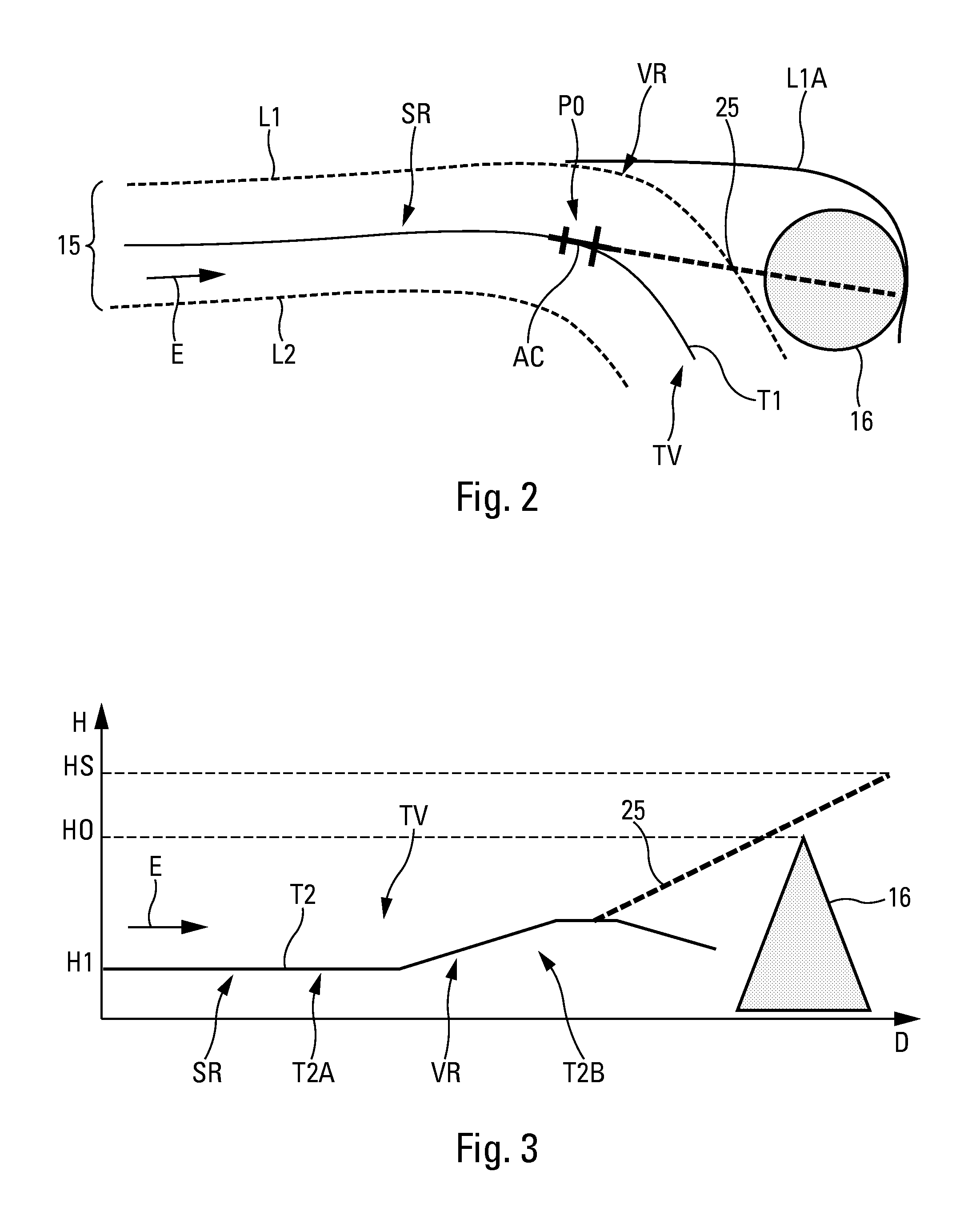
Method for assisting low altitude navigation of an aircraft
InactiveUS7584046B2Solve the excessive calculationMinimize timeAnalogue computers for vehiclesNavigational calculation instrumentsIntermediate pointLow altitude
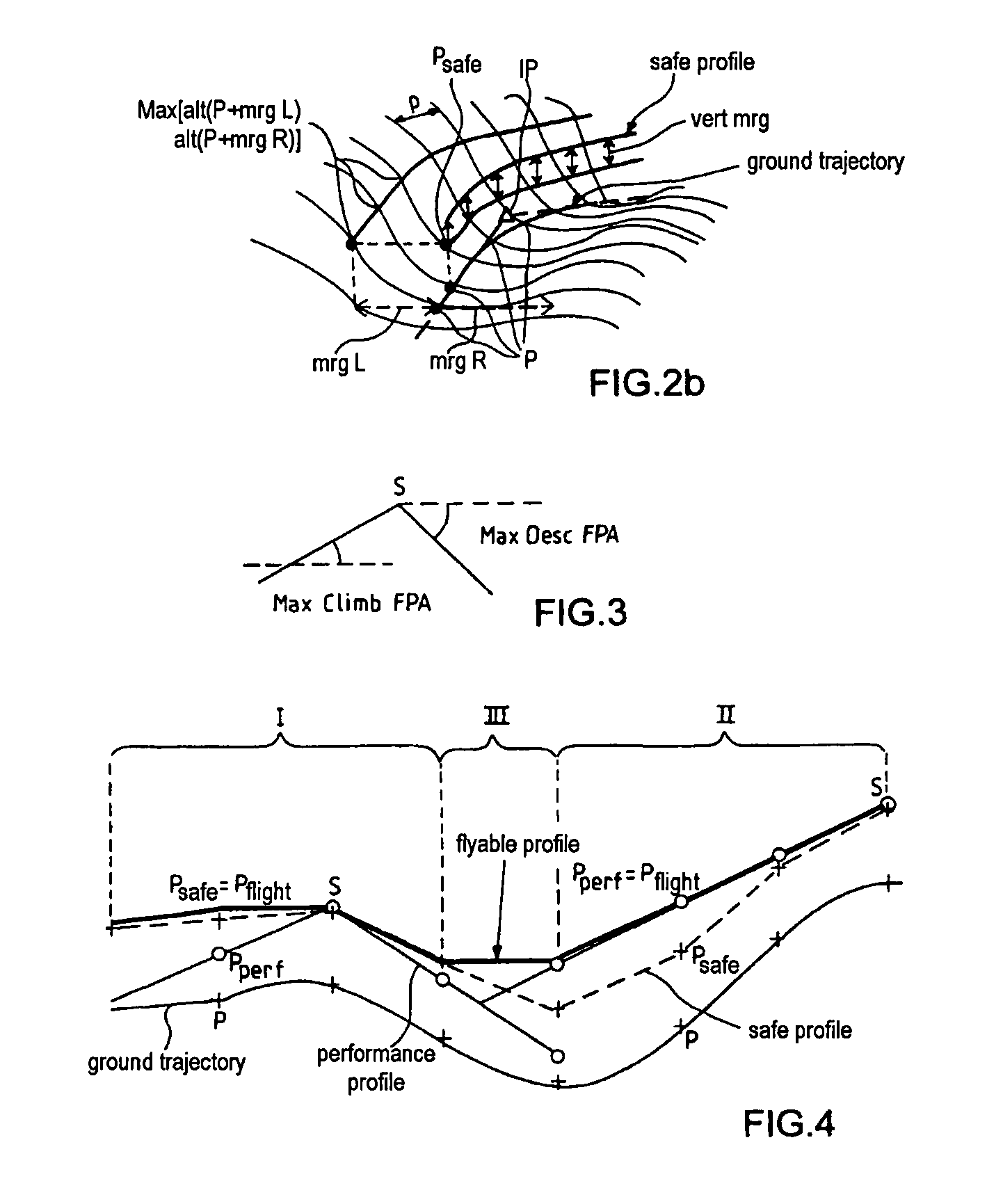
A method for assisting low-altitude navigation of an aircraft equipped with a system suited to determine a flight-plan ground trajectory based on intermediate points P at an altitude alt(P), and the aircraft's performance. The method includes the following steps: for each point P, calculating a safe altitude, to obtain a point Psafe, calculating a safe profile formed from segments joining the points Psafe, extracting summits S from among the points Psafe, determining the aircraft's weight at these points S, for each point S, determining the maximum climb slope MaxClimbFPA and the maximum descent slope MaxDescFPA, defining two performance segments which have slopes MaxClimbFPA and MaxDescFPA on either side of the point S and calculating a performance profile formed from performance segments.
Owner:THALES SA
Endurance performance optimization method integrating climb, cruise and descending
ActiveCN110794866AImprove performance indicatorsFunction increasePosition/course control in three dimensionsLevel flightClimb
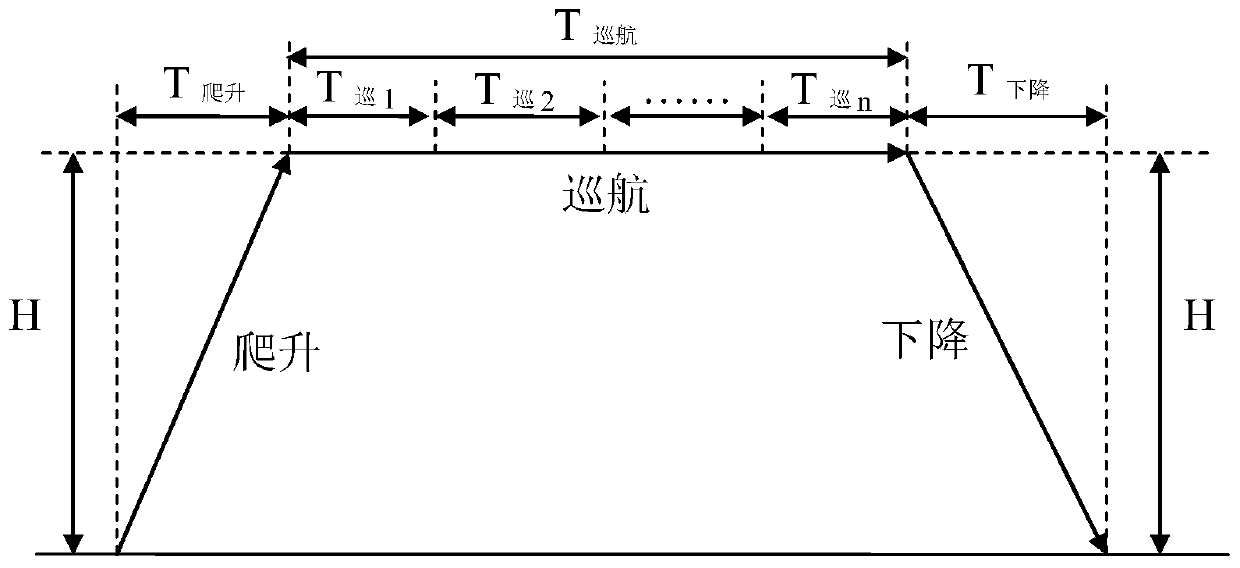
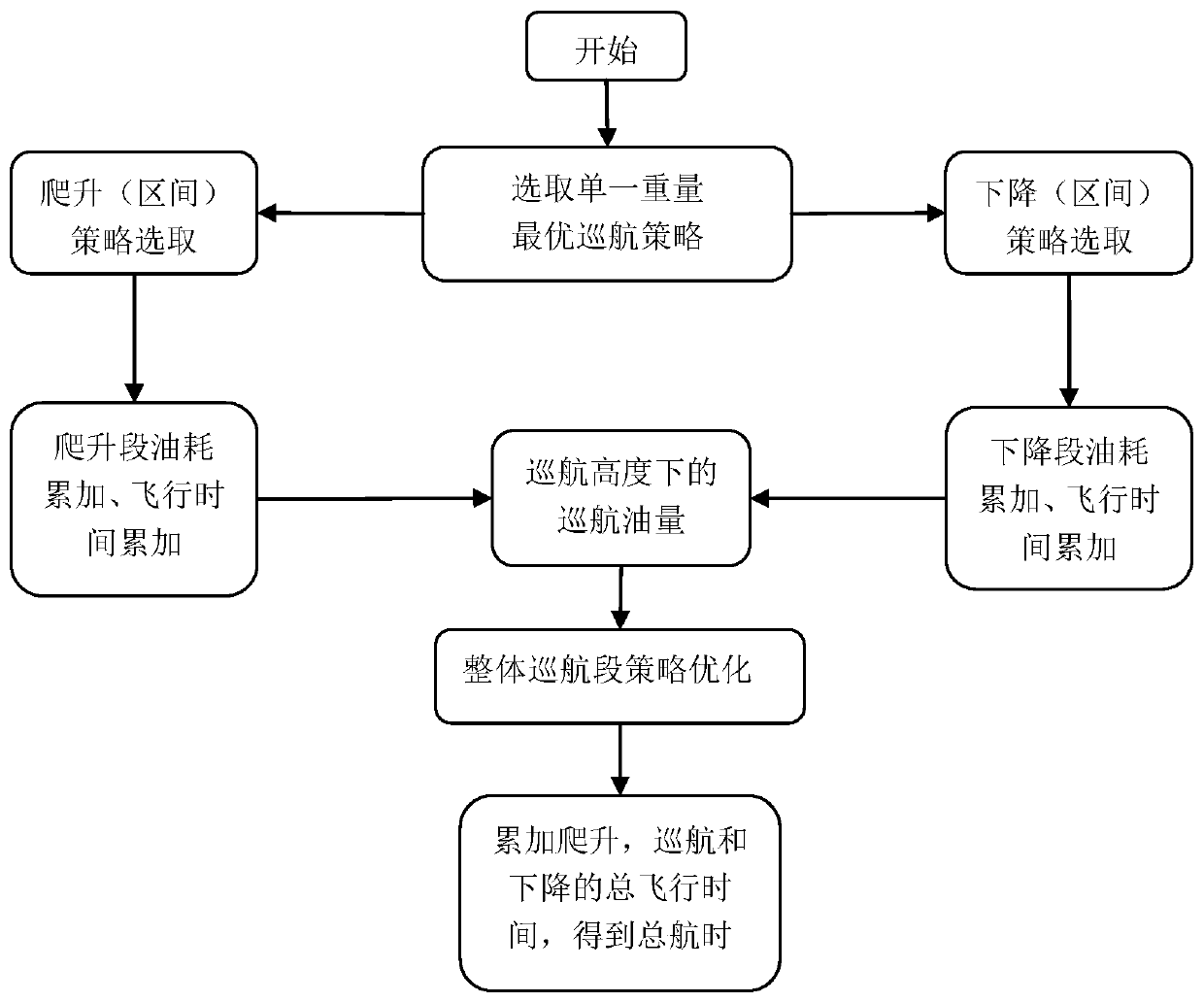
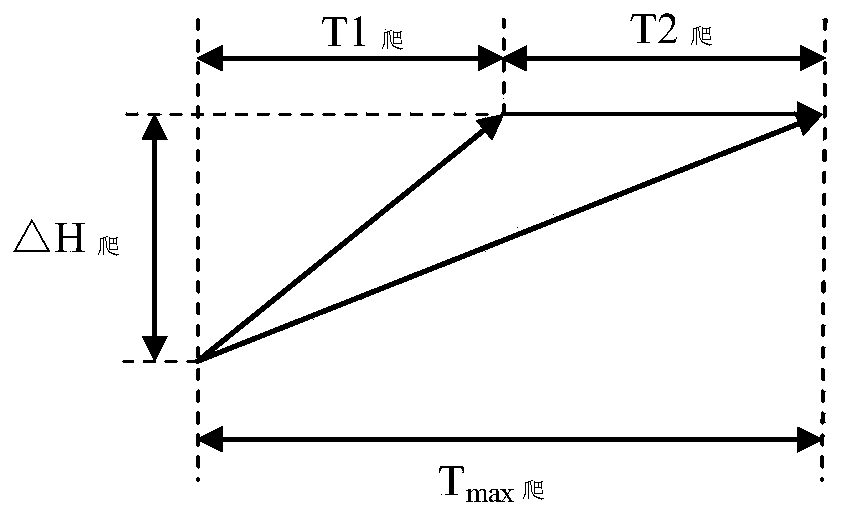
The present invention provides an endurance performance optimization method integrating climb, cruise and descending. The method comprises the following steps of selecting an optimal endurance cruisestrategy through cruise performance analysis under a single weight; integrally optimizing climb and level flight performance data of a climb interval in order to obtain an optimal endurance climb strategy; respectively accumulating oil consumption of the climb interval and a descending interval in order to obtain oil consumption of a climb section and a descending section, carrying out front-backsqueeze, computing the oil quantity of a cruise section, dividing different oil volume intervals, and carrying out endurance optimization of the whole cruise section in order to obtain endurance of the optimal cruise strategy; respectively accumulating the endurance of the climb interval and the descending interval in order to obtain the endurance of the whole climb section and the descending section; and piecewise accumulating the endurance of the climb section, the cruise section and the descending section in order to obtain the optimal endurance of the whole flight profile.
Owner:CHENGDU AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY GROUP
Optimizing a parametric model of aircraft performance
ActiveUS20200202725A1Instruments for road network navigationEnergy saving arrangementsFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
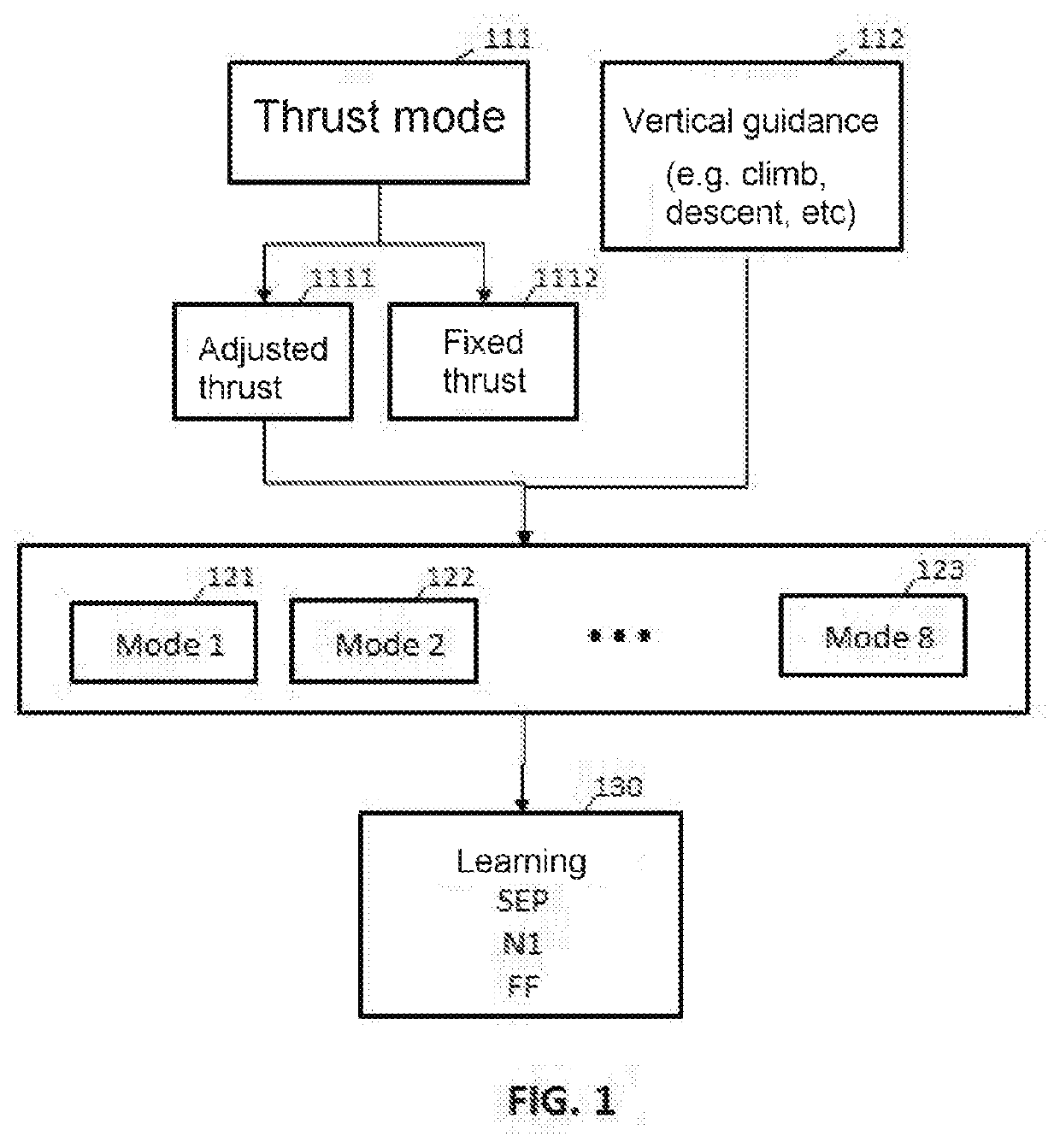
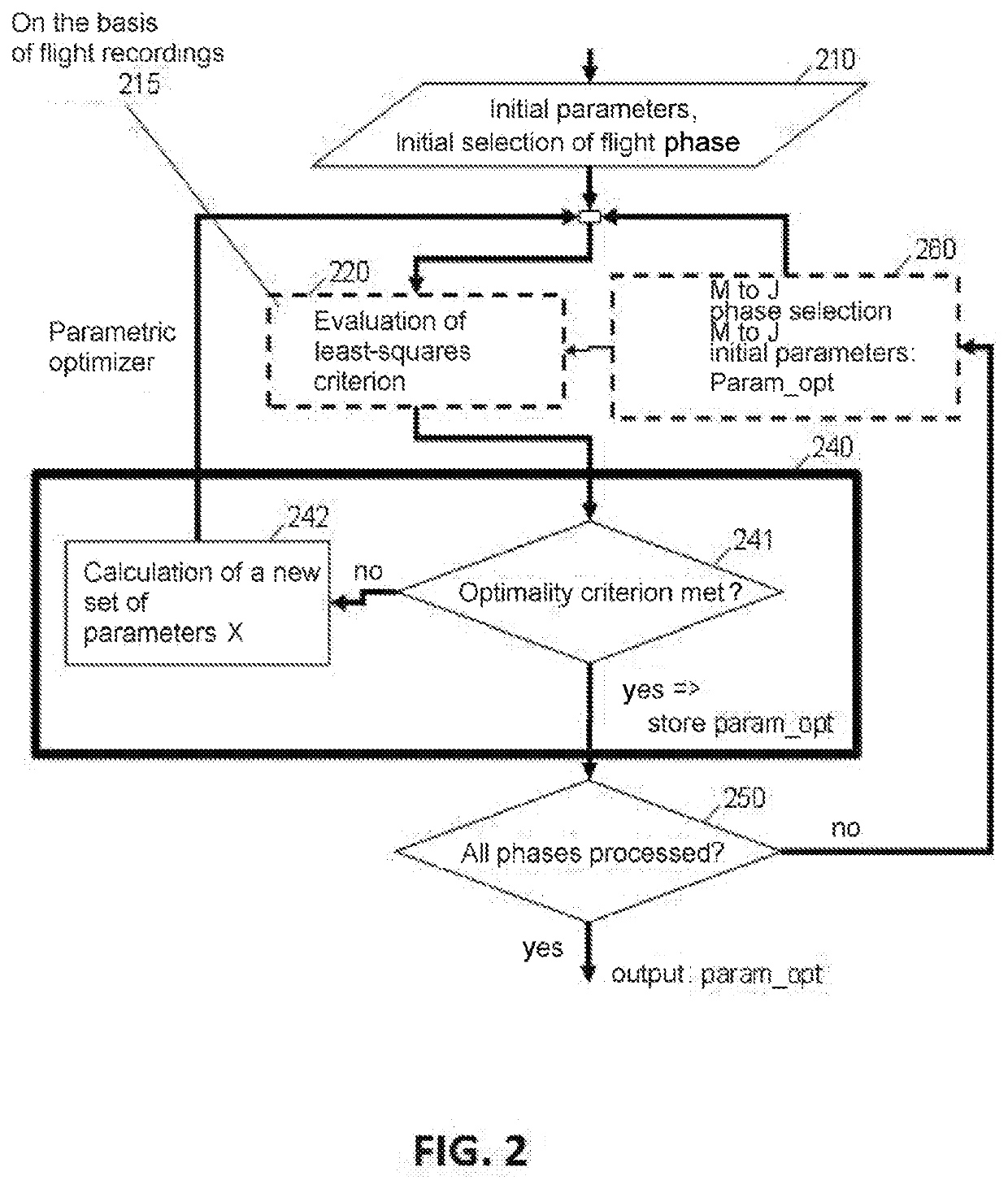
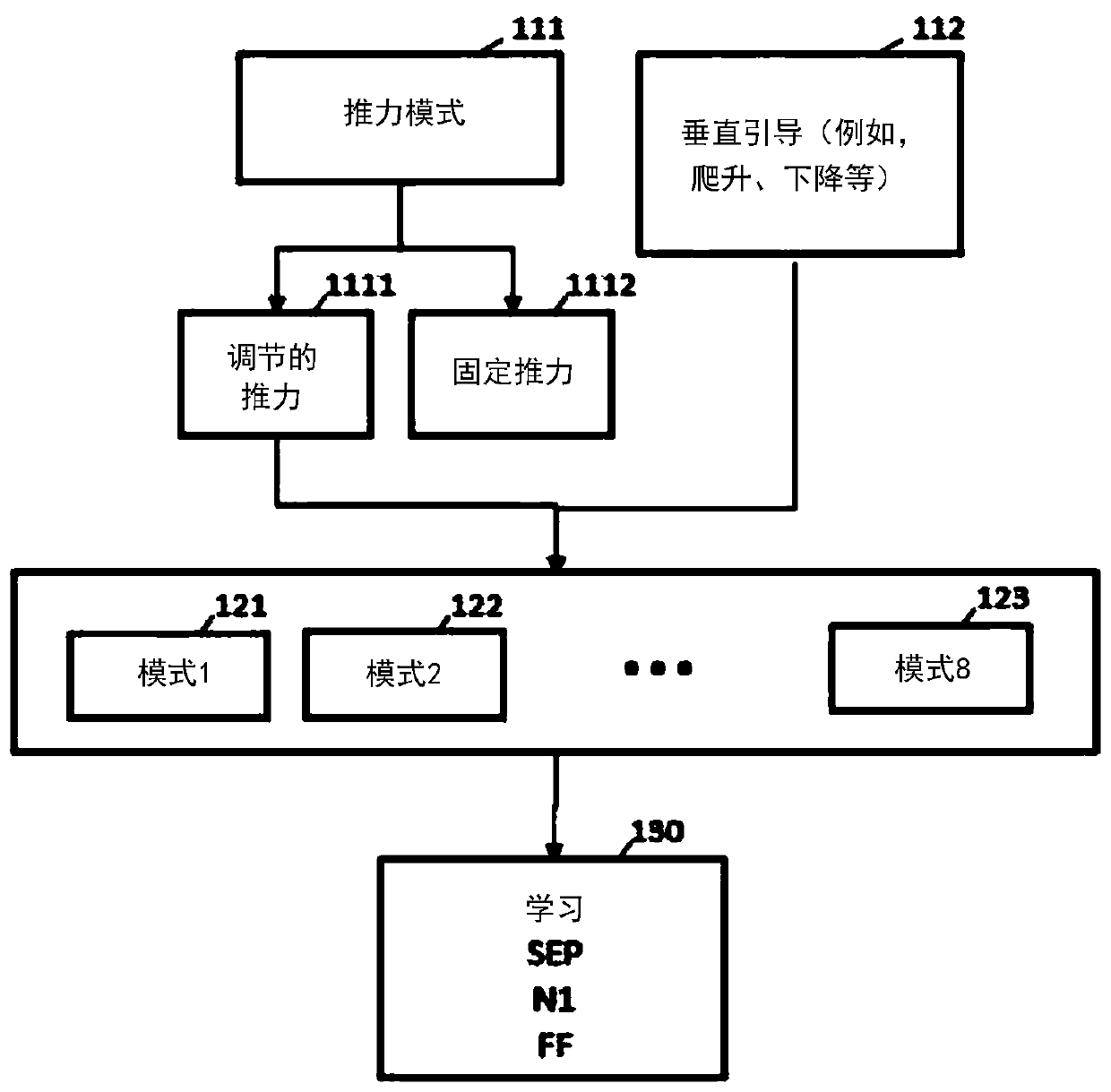
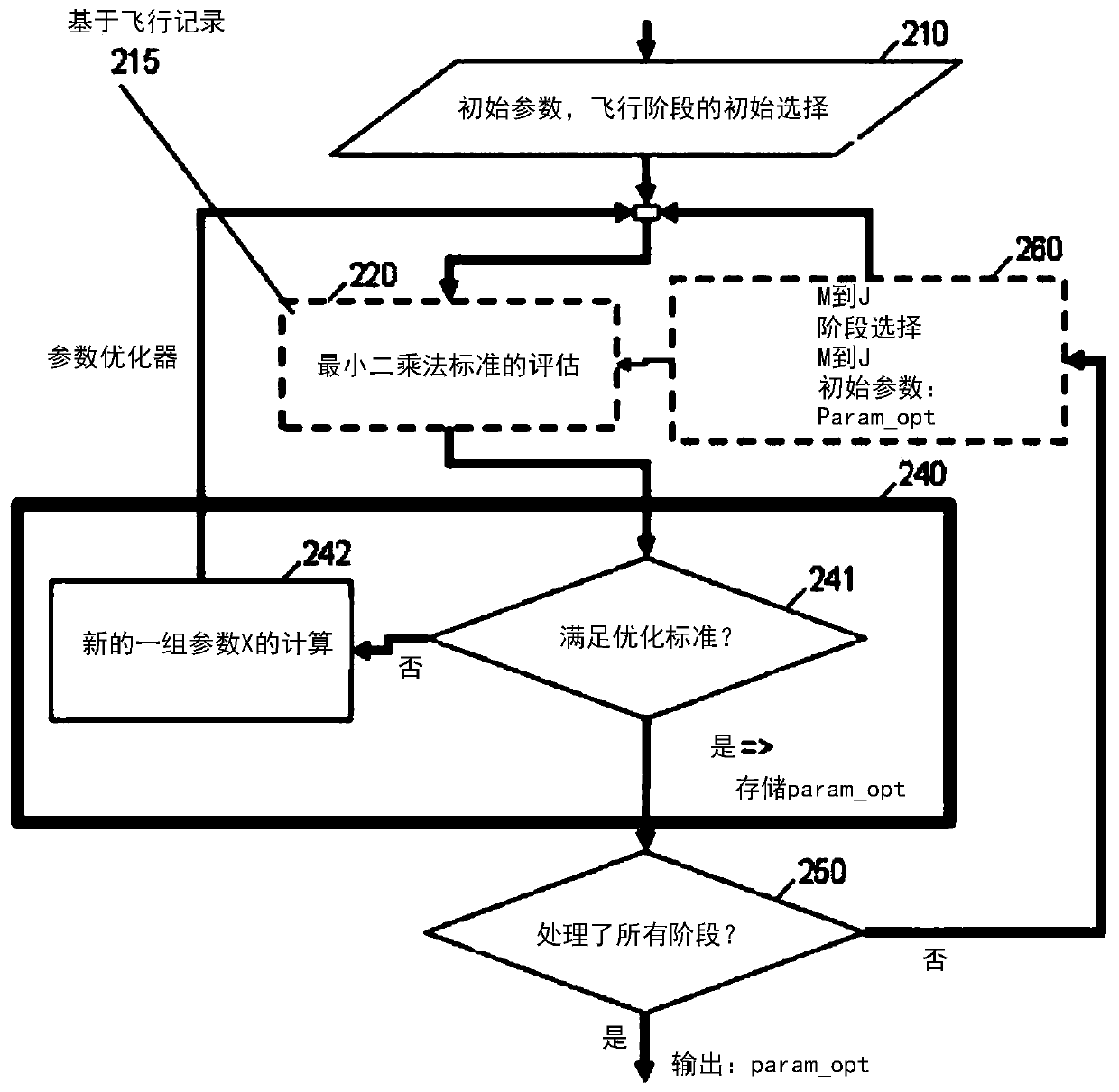
Methods and systems for optimizing the flight of an aircraft are disclosed. The trajectory is divided into segments, each of the segments being governed by distinct sets of equations, depending on engine thrust mode and on vertical guidance (climb, cruise or descent). By assuming two, aerodynamic and engine-speed, models, data from flight recordings are received and a number of parameters from a parameter-optimization engine is iteratively determined by applying a least-squares calculation until a predefined minimality criterion is satisfied. The parameter optimization engine is next used to predict the trajectory point following a given point. Software aspects and system (e.g. FMS and / or EFB) aspects are described.
Owner:THALES SA
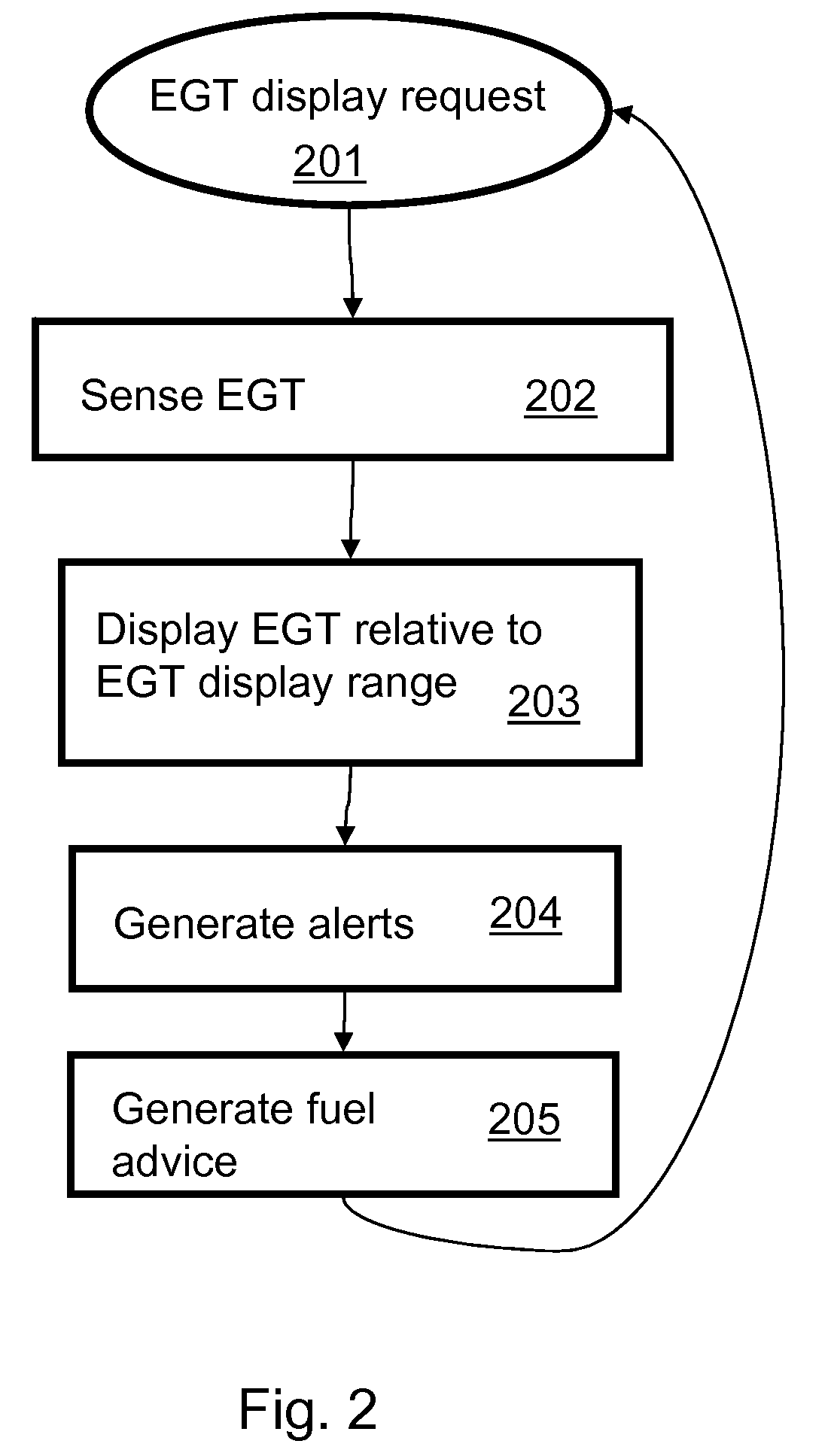
Aircraft Exhaust Gas Temperature Monitor
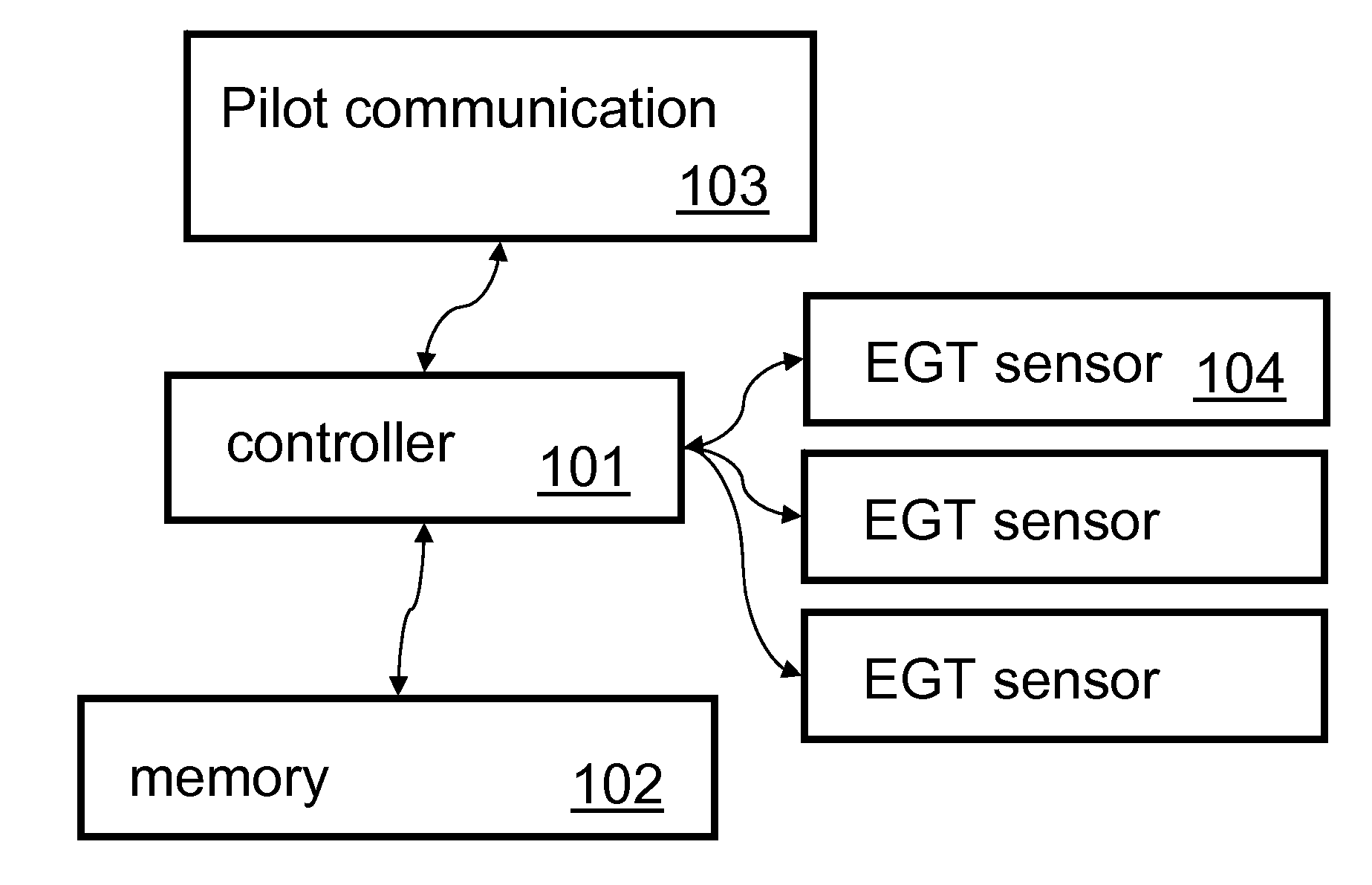
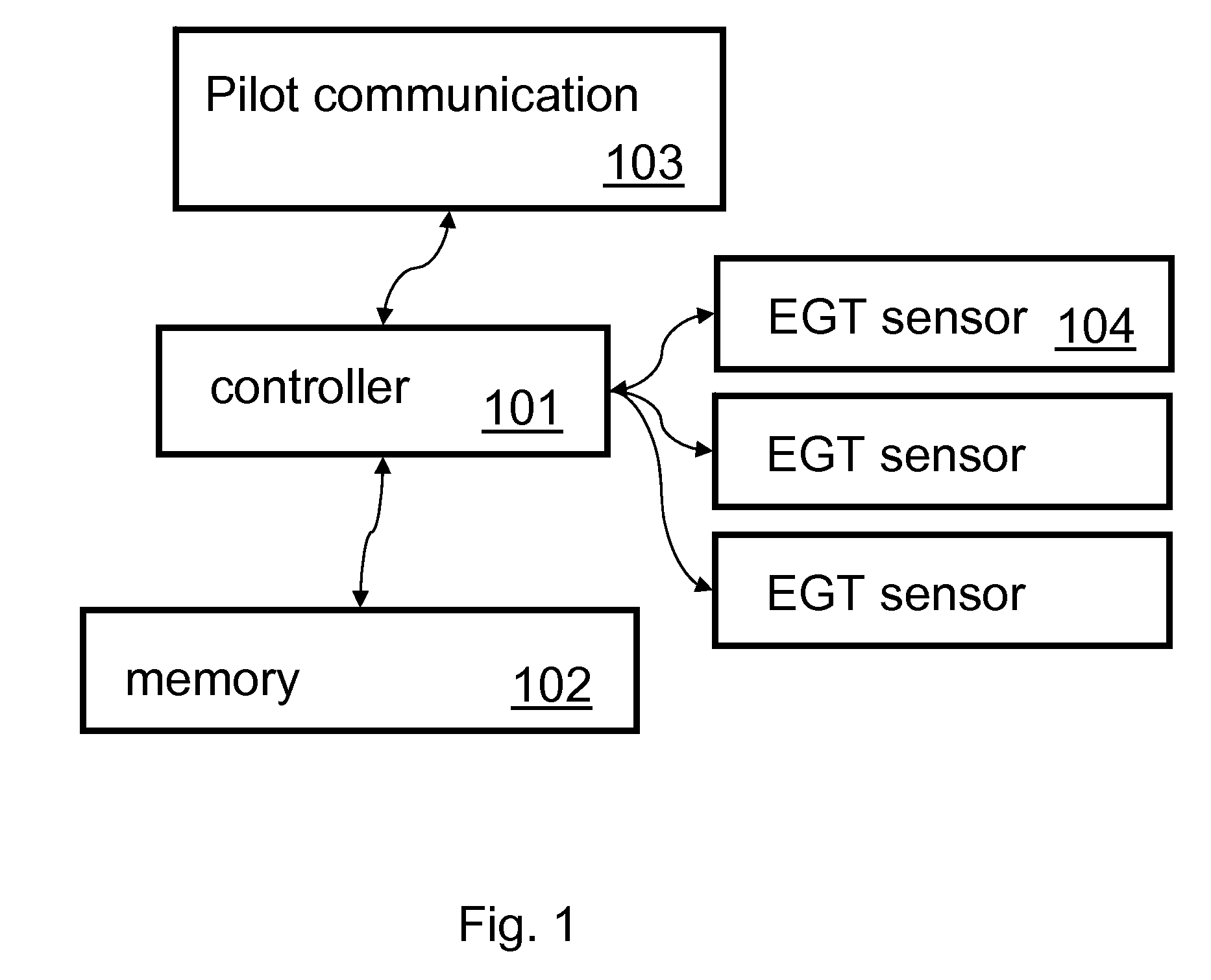
ActiveUS20090306837A1Reduce fuel consumptionReduce chanceElectrical controlControl initiation meansExhaust fumesAirplane
A computer-implemented function monitors and displays exhaust gas temperatures (EGT) in a plurality of cylinders in an engine. The invention provides an easy way to read exhaust gas temperature on a specific cylinder, and to provide a means for leaning the engine while in a climb. Efficient leaning in a climb reduces fuel consumption and reduces the chance of harmful conditions that can lead to engine failure.
Owner:ASTRONICS ADVANCED ELECTRONICS SYST
Method and device for guiding an aircraft during a low level flight
ActiveUS20150192927A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsLevel flightFlight vehicle
The guidance device of the aircraft includes a unit for constructing a flight trajectory of the aircraft, which adapts the height of the flight trajectory to a downstream relief so as to allow the aircraft to clear this downstream relief by implementing a rectilinear climb at maximum rate of climb of the aircraft, along a rectilinear lateral direction corresponding to the direction of the aircraft at the moment of the triggering of the maneuver.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
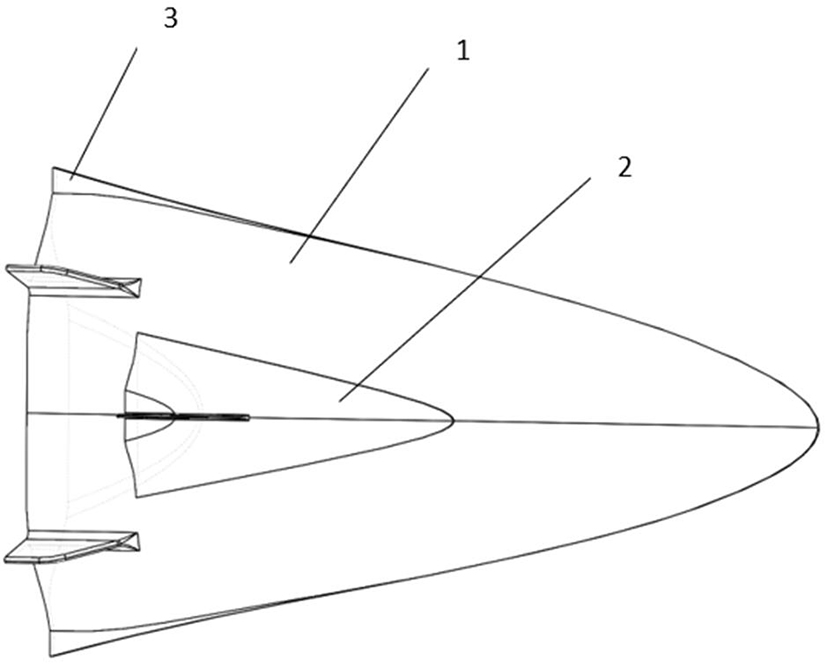
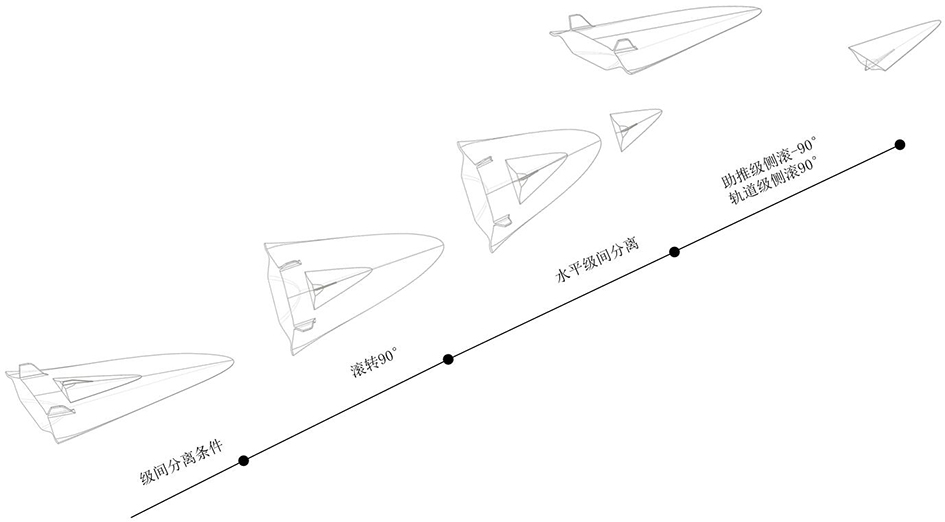
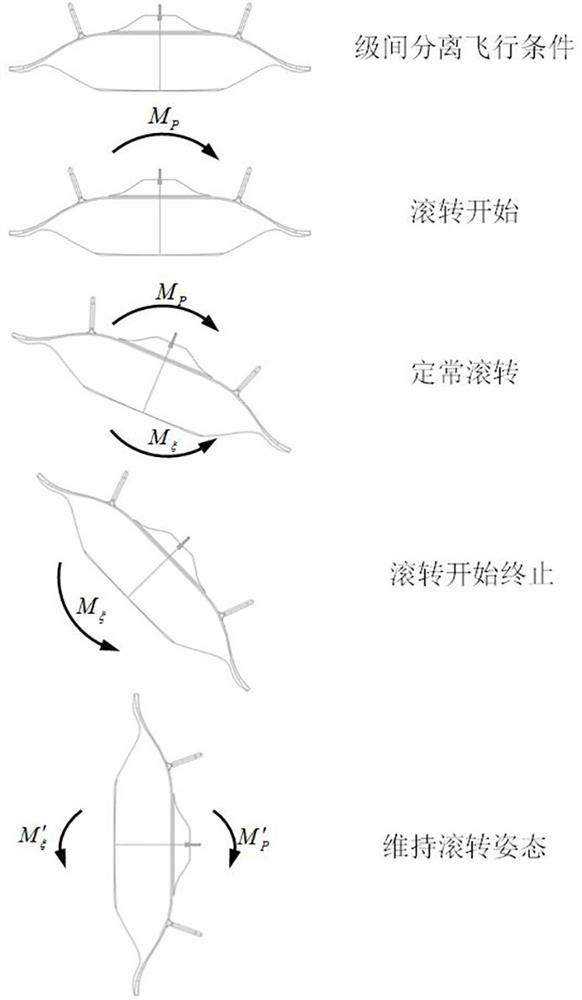
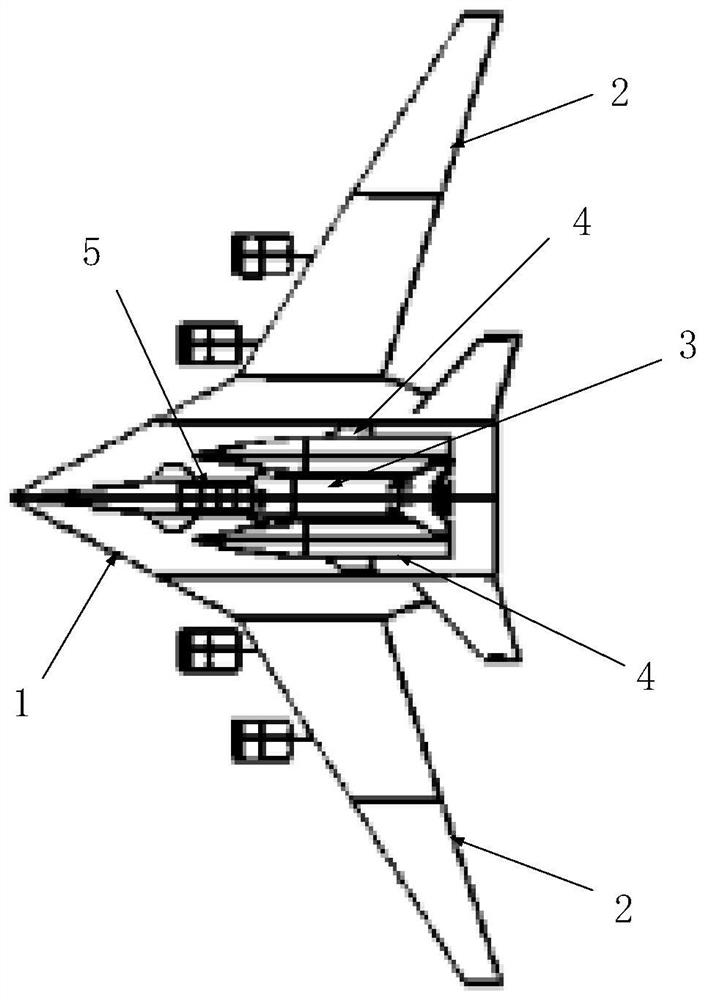
Parallel double-waverider two-stage injection aircraft horizontal stage separation design method
ActiveCN114261538AAvoid Shock Interference ProblemsAvoid unsteady aerodynamic loadsSpace shuttlesHeat flowFlight vehicle
The invention discloses a horizontal stage separation design method for a parallel double-waverider two-stage injection aircraft. The horizontal stage separation design method comprises the following steps: constructing a combined body structure of an orbit-stage waverider aircraft and a boosting-stage waverider aircraft; when the flight of the assembly structure reaches an interstage separation condition, the lift force borne by the two side wings of the boosting-stage waverider aircraft is unbalanced, and then the assembly structure rolls by 90 degrees in the lateral direction of the aircraft body; under the condition that the lateral rolling of the combined body structure is kept by 90 degrees, the track-level waverider aircraft is pushed by the power of the track-level waverider aircraft to perform horizontal separation action along the upper surface of the boosting-level waverider aircraft; after the orbit-level waverider aircraft is separated from the boosting-level waverider aircraft, the orbit-level waverider aircraft continues to laterally roll by 90 degrees and climbs to a target orbit, and the boosting-level waverider aircraft reversely rolls by 90 degrees to recover an initial flight state, so that horizontal-level separation of the orbit-level waverider aircraft and the boosting-level waverider aircraft is realized. According to the horizontal interstage separation method, the problems of high pressure, high heat flow and stability in the conventional separation process under the hypersonic speed condition are solved.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
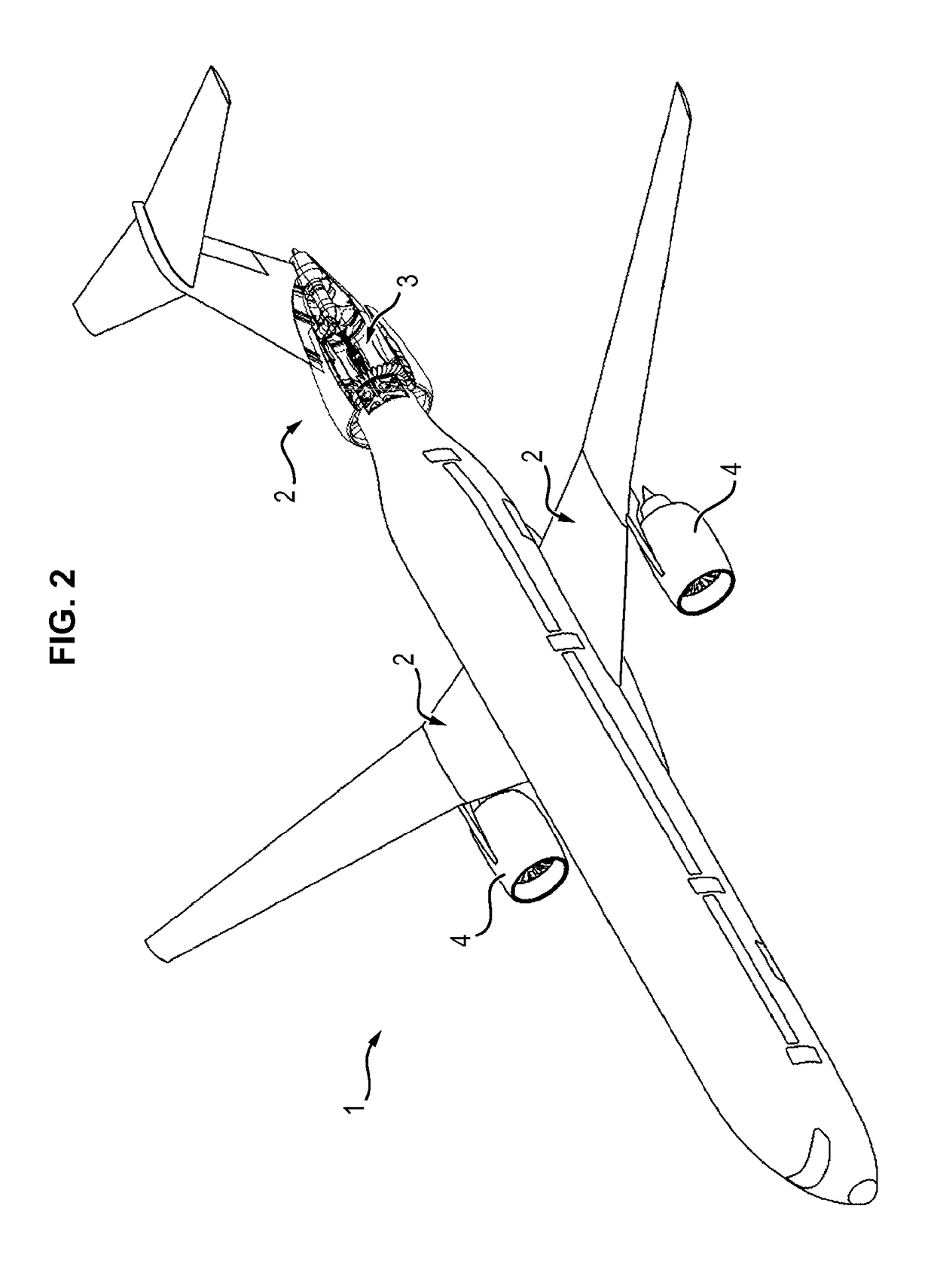
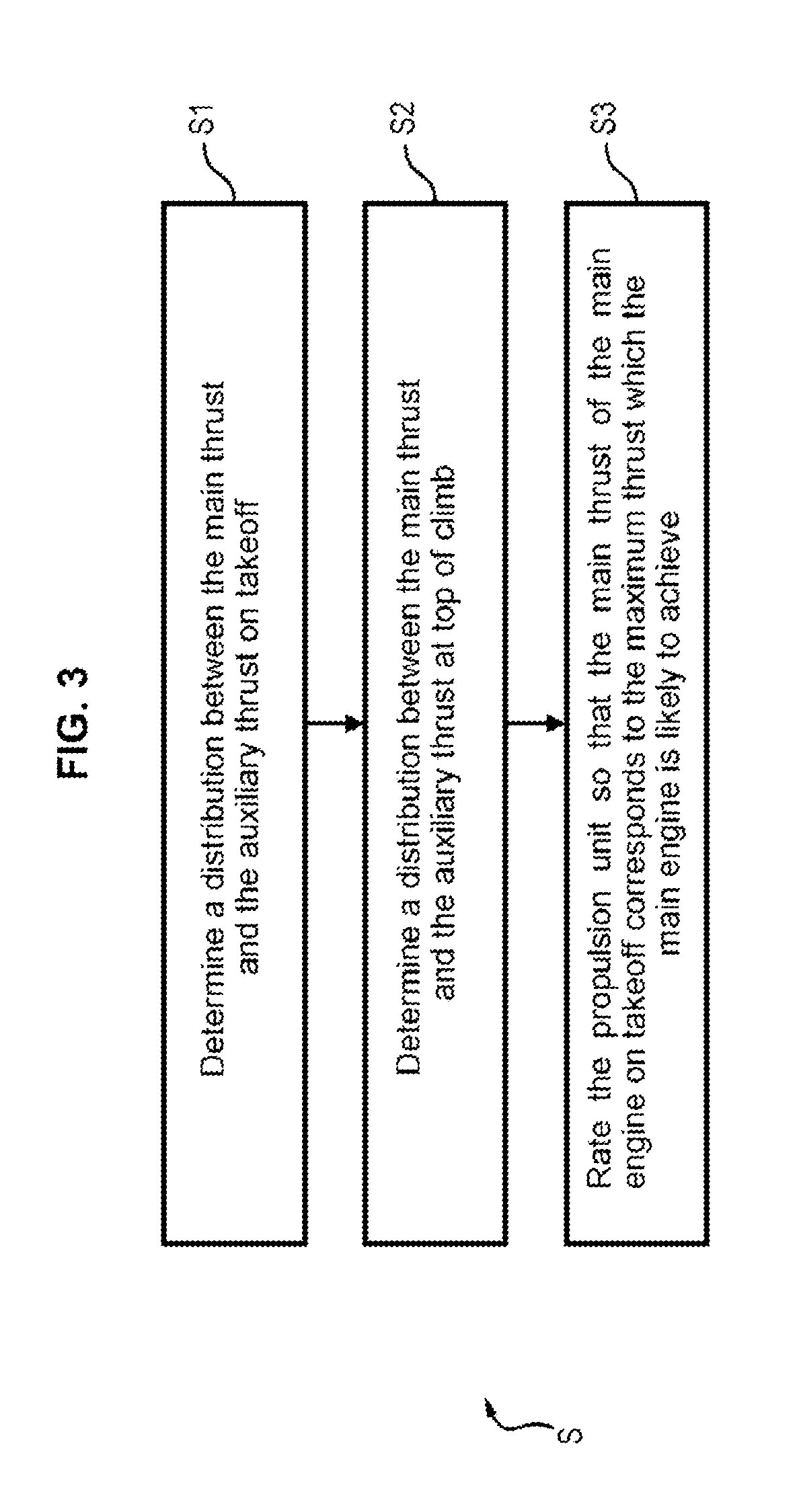
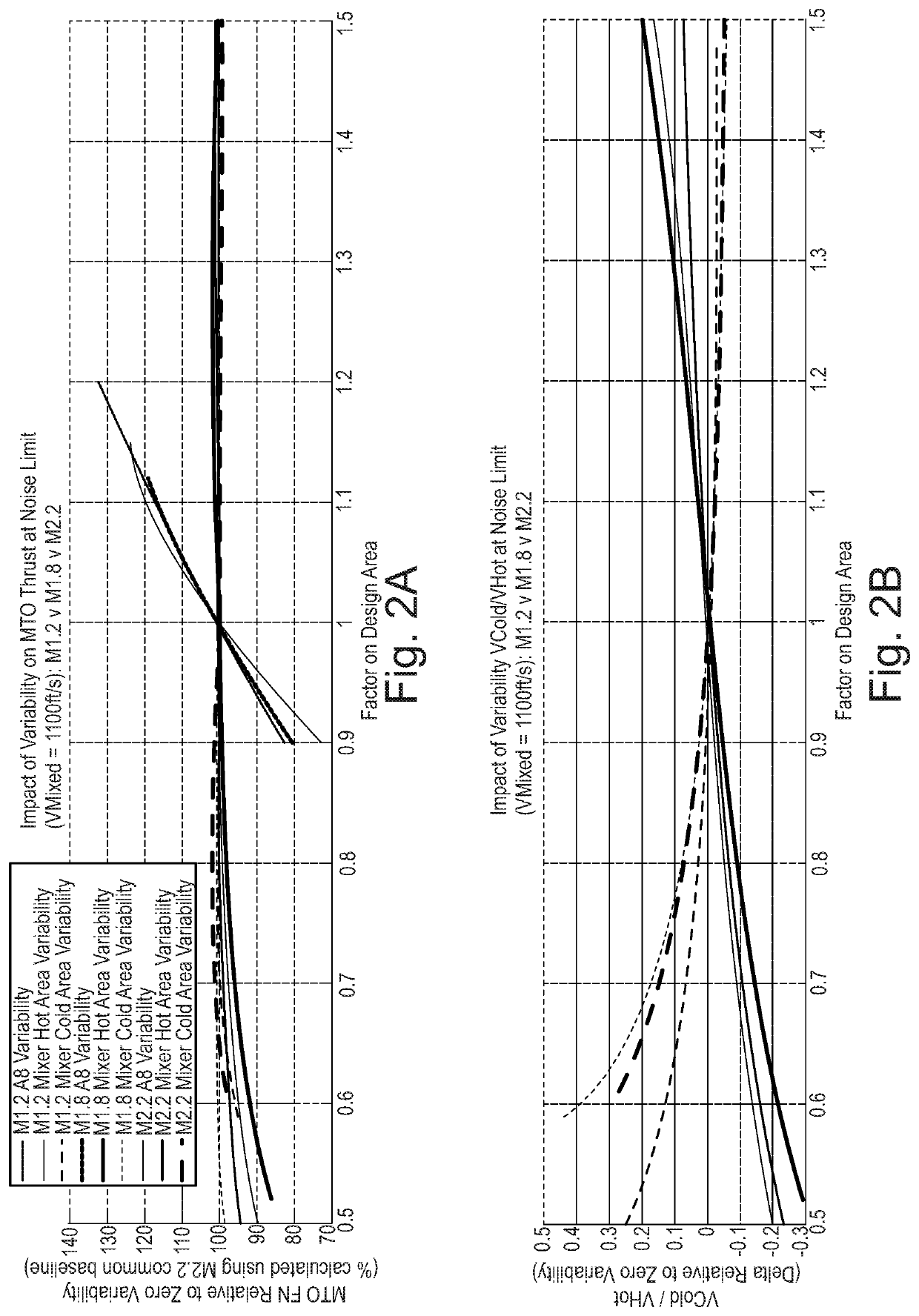
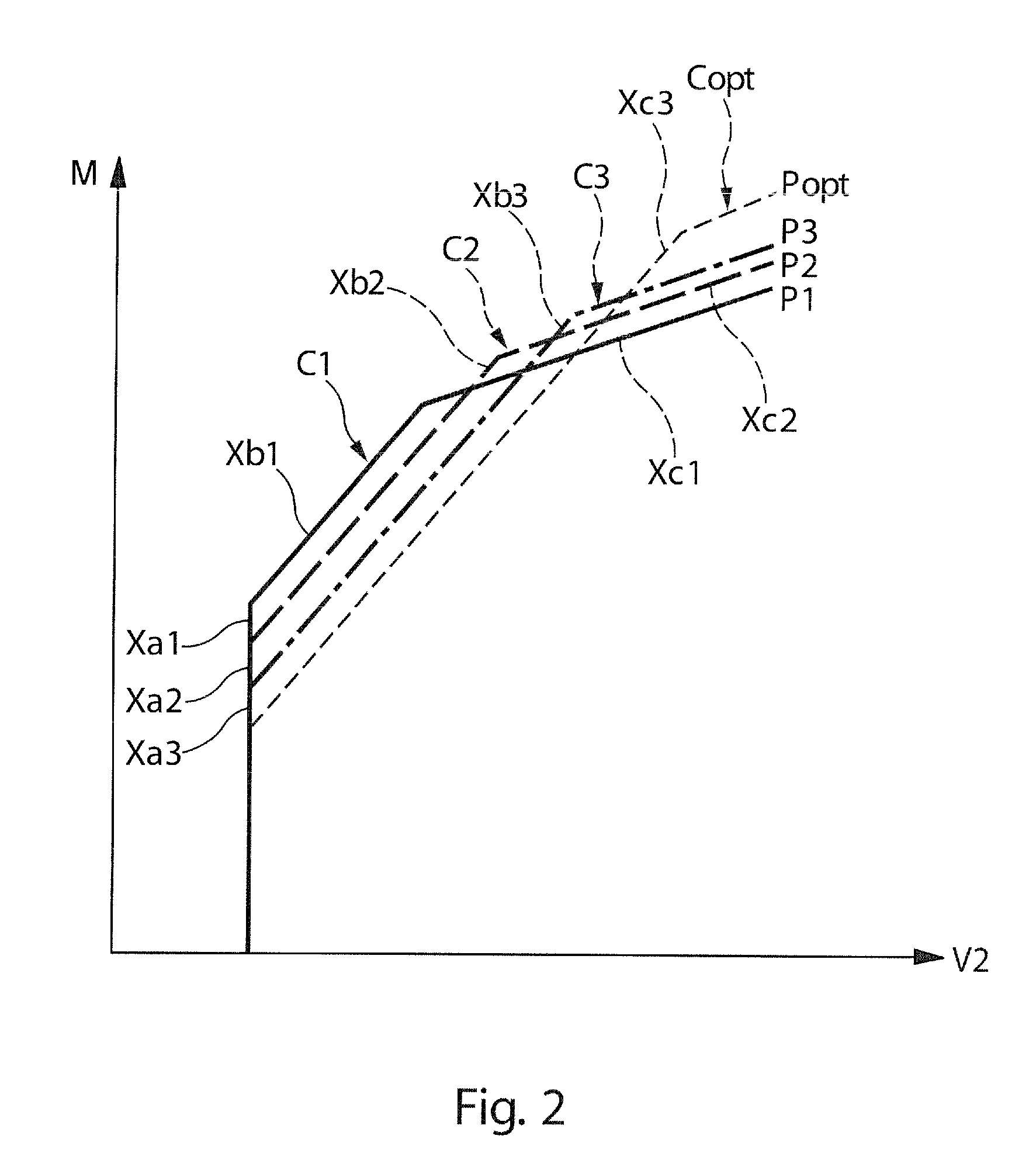
Method for rating a propulsion unit comprising a main engine and an auxiliary engine
The invention relates to the rating (S) of a propulsion unit (2) comprising a main engine (3) providing main thrust assisted by an auxiliary engine (4) providing auxiliary thrust, according to the following steps: (i) determining (S1) a distribution between the main thrust and the auxiliary thrust so as to obtain the takeoff thrust of the propulsion unit, the auxiliary thrust making a 5% to 65% contribution to the takeoff thrust, (ii) depending on the distribution determined for the takeoff condition, determining (S2) distribution between the main thrust and the auxiliary thrust so its to obtain the top of climb thrust of the propulsion unit, the auxiliary thrust making at most 70% contribution to the top of climb thrust, and (iii) rating (S3) the propulsion unit (2) in such a way that the main thrust of the main engine (3) determined fir the takeoff condition corresponds to the maximum thrust likely to be achieved by the main engine (3).
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Parallel hybrid-electric aircraft engine
ActiveUS20190047720A1Electric power distributionEfficient propulsion technologiesElectric aircraftExternal combustion engine
A parallel hybrid-electric aircraft engine that provides power for takeoff and climb by combining the output power of an electric motor with that an internal combustion engine and then converting the electric motor to a generator once the additional power of the electric motor is no longer neede
Owner:BOSMA MARINUS BERNARD
Electronic device and method for optimizing vertical profile for cruise phase of flight
The invention relates to electronic devices and methods for optimizing a vertical profile for the cruise phase of a flight. The electronic devices and methods are used for optimizing the vertical profile to be flown by an aircraft during the cruise phase of a flight. Based on continuously updated information about the aircraft's weight and the atmospheric wind and temperature, the method providesan optimal sequence of climbs and / or descents along the flight path during the cruise phase. Following the step climb / descent profile proposed by the method results in the most cost-optimal flight (ifa cost index was selected) or in the most fuel-efficient flight (if the long-range cruise mode was selected). The method may be implemented in the flight management computer or any other electronic data processing device that can access the required information to perform the calculations.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Air-based launched heavy reusable aerospace vehicle system
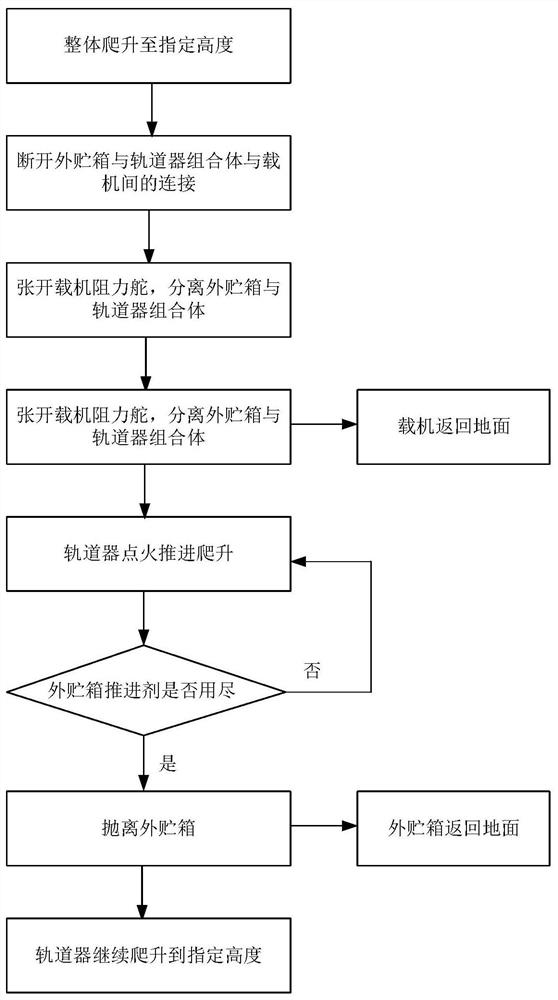
PendingCN111959824ALow costThe problem of increasing the ratio of the entry weight to the total take-off weightLaunch systemsCosmonautic partsFlight vehicleOrbiter
The invention discloses an air-based launched heavy reusable aerospace vehicle system. A transonic aircraft back-loaded aerospace vehicle is launched in the air by adopting a large-scale wing body fusion layout. The aerospace vehicle comprises an orbiter and two outer storage tanks. A carrier aircraft carries the orbiter, and the two outer storage tanks are symmetrically installed on the two sidesof the orbiter. When air-based launching is carried out, the aircraft firstly climbs to a specified height, and then a combined body of the outer storage tank and the orbiter is separated so that theorbiter climbs to the storage tank, a propellant is exhausted, and the outer storage tank is thrown away. And finally, the orbiter continuously accelerates and adjusts a posture to a specified heightto do circular motion around the earth. Cost of launching the heavy reusable aerospace vehicle is greatly reduced, and a proportion of injection weight to total take-off weight is greatly increased.
Owner:中国航空研究院
Ground effects compensated angle of attack command system and method
Owner:SAFE FLIGHT INSTR LLC
Amphibious multifunctional vertical take-off and landing vehicle
ActiveCN106004287BAchieving amphibious navigation capabilitySimple structureConvertible aircraftsVertical landing/take-off aircraftsBrushless motorsFlight vehicle
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
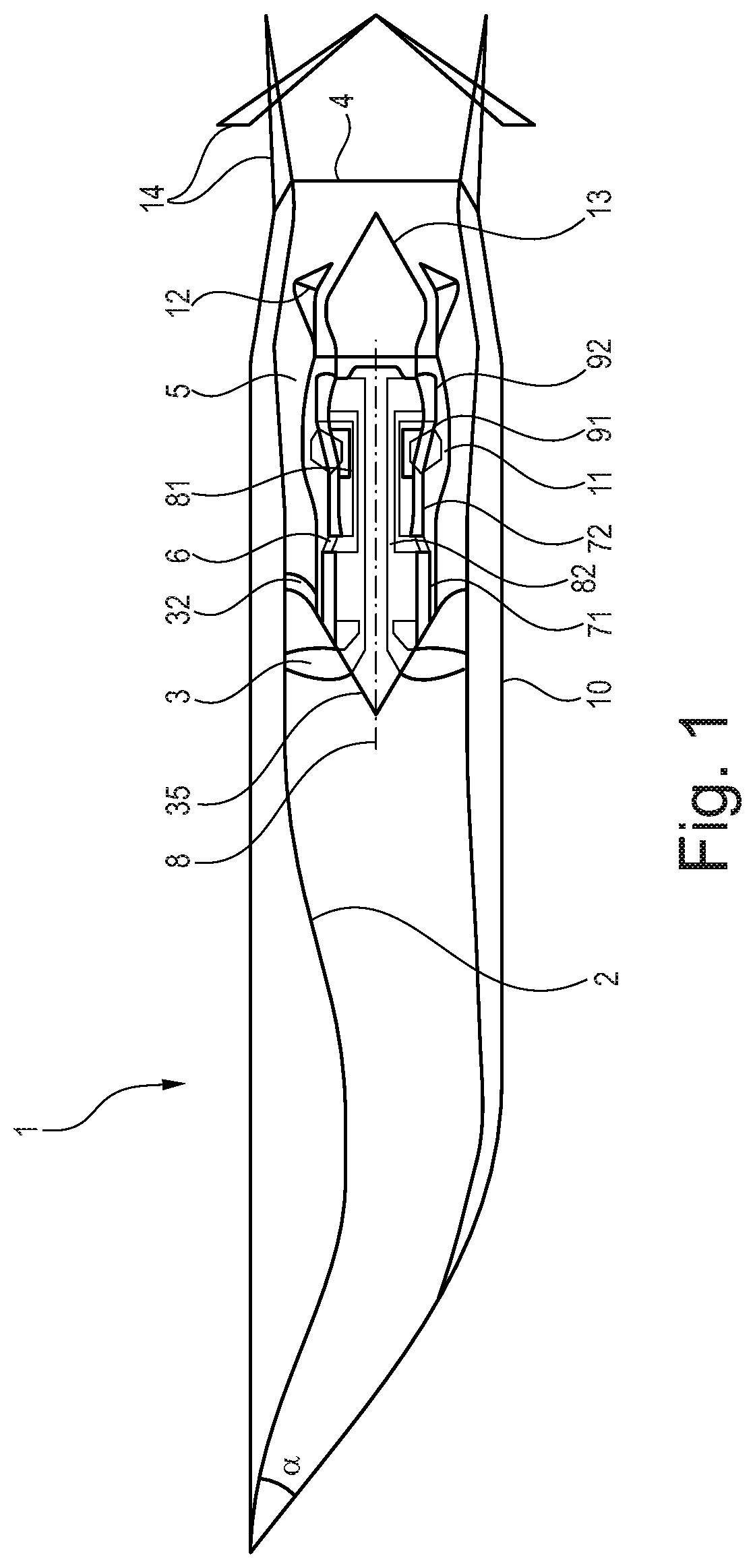
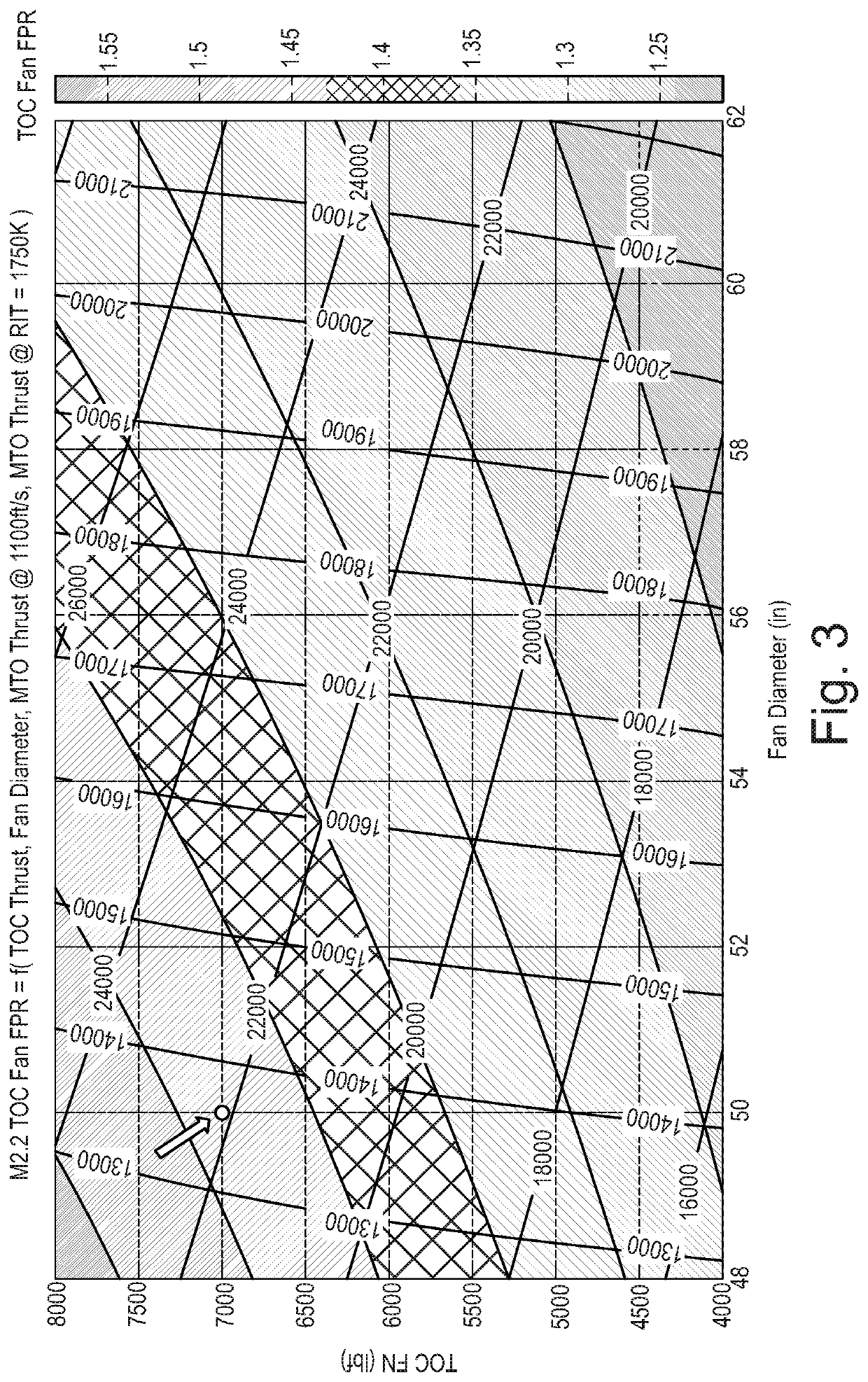
Supersonic aircraft turbofan
ActiveUS20200025109A1Reduce areaImprove the level ofPower plant exhaust arrangementsEngine fuctionsCombustorMixed flow
A turbofan engine has an engine core including in flow series a compressor, a combustor and a turbine. The engine further has a fan located upstream of the engine core, has a supersonic intake for slowing down incoming air to subsonic velocities at an inlet to the fan formed by the intake, has a bypass duct surrounding the engine core, wherein the fan generates a core airflow to the engine core and a bypass airflow through the bypass duct, and has a mixer for mixing an exhaust gas flow exiting the engine core and bypass airflow exiting bypass duct. The engine further has a thrust nozzle rearwards of the mixer for discharging mixed flows, the thrust nozzle having a variable area throat. The engine further has a controller controlling the thrust produced by the engine over a range of flight operations including on-the-ground subsonic take-off and subsequent off-the-ground subsonic climb.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
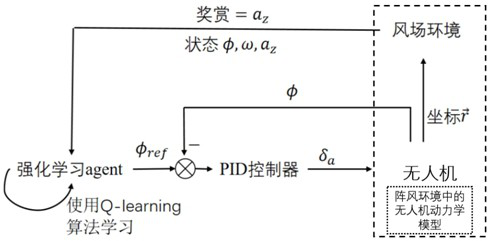
Unmanned aerial vehicle flight control strategy design method using gust environment
ActiveCN114578861ASimple designAvoid complicated debugging process and unsatisfactory resultsSustainable transportationPosition/course control in three dimensionsAir velocityUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle flight control strategy design method using a gust environment. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a flight dynamics model of an unmanned aerial vehicle in the gust environment; the roll angle of the unmanned aerial vehicle, the roll angle speed caused by the wind field gradient and the vertical wind speed change rate are selected as state quantities, iterative training is conducted on the state quantities through a reinforcement learning Q-learning algorithm, and an optimal control strategy is obtained; a flight control decision is made for the unmanned aerial vehicle in the gust environment according to the obtained optimal control strategy, and the real-time roll angle of the unmanned aerial vehicle is controlled through a PID controller to change the course of the unmanned aerial vehicle, so that the unmanned aerial vehicle finds up airflow and climbs by using the unmanned aerial vehicle; the method effectively overcomes the problems that a conventional common unmanned aerial vehicle flight control method using the gust environment needs a complicated debugging process and is not ideal in effect, can automatically adapt to different gust environments, and remarkably improves the all-weather safe flight capability of the unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
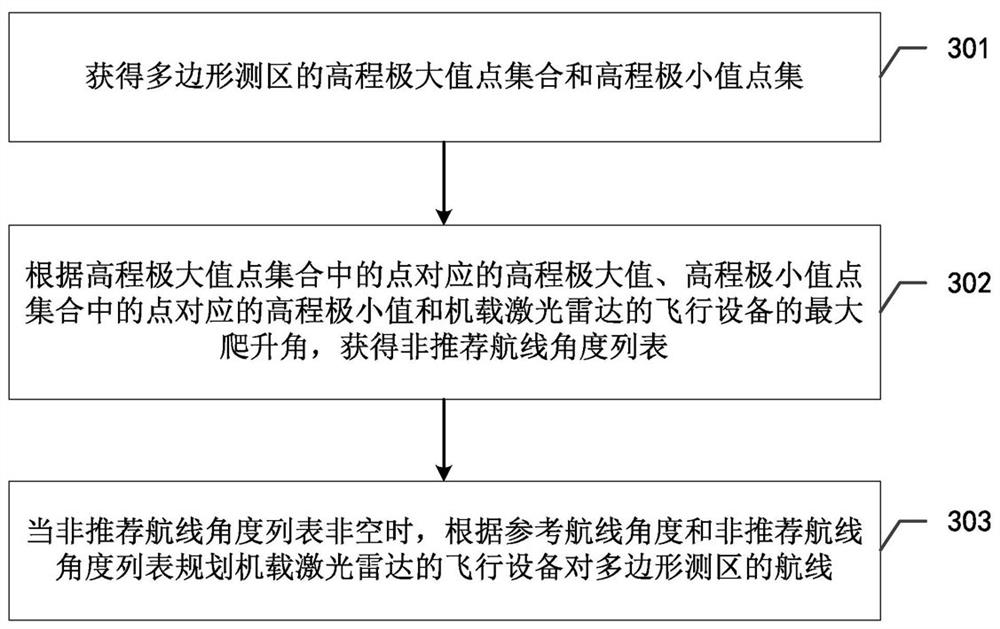
A route planning method, device, and flight equipment for airborne laser radar
ActiveCN113268085BGuarantee data qualityImprove securityPosition/course control in three dimensionsRadarClimb
Owner:成都纵横大鹏无人机科技有限公司 +1
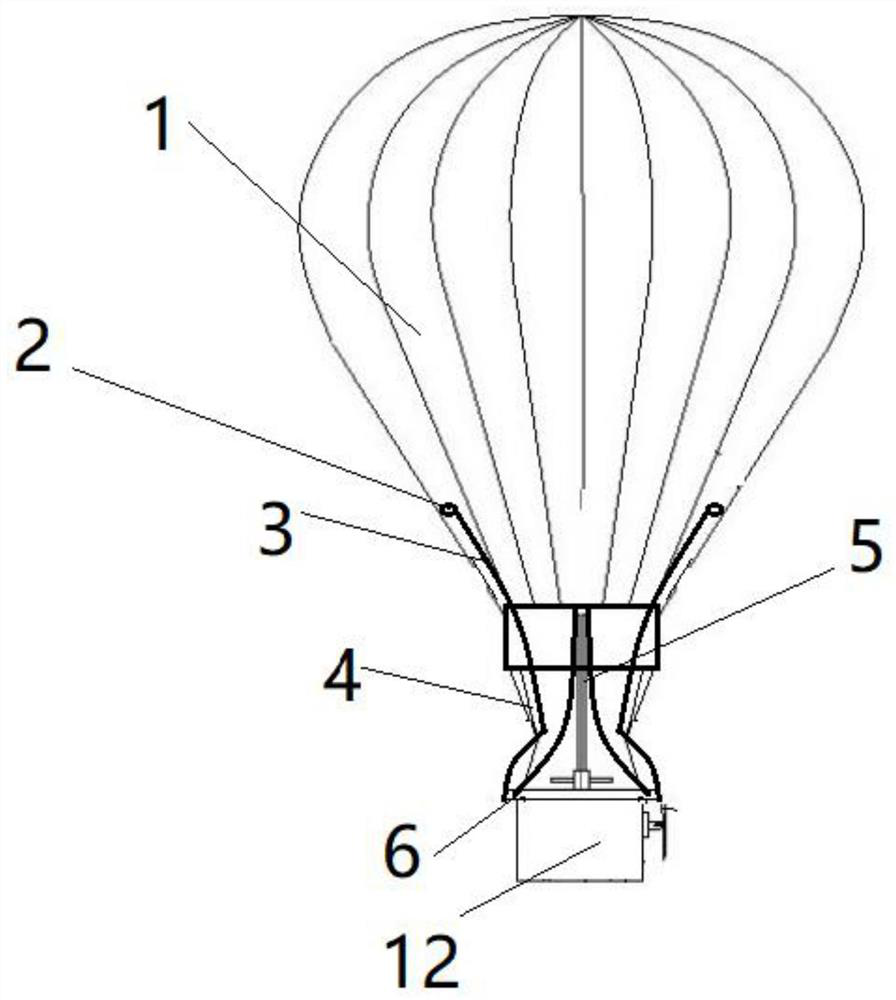
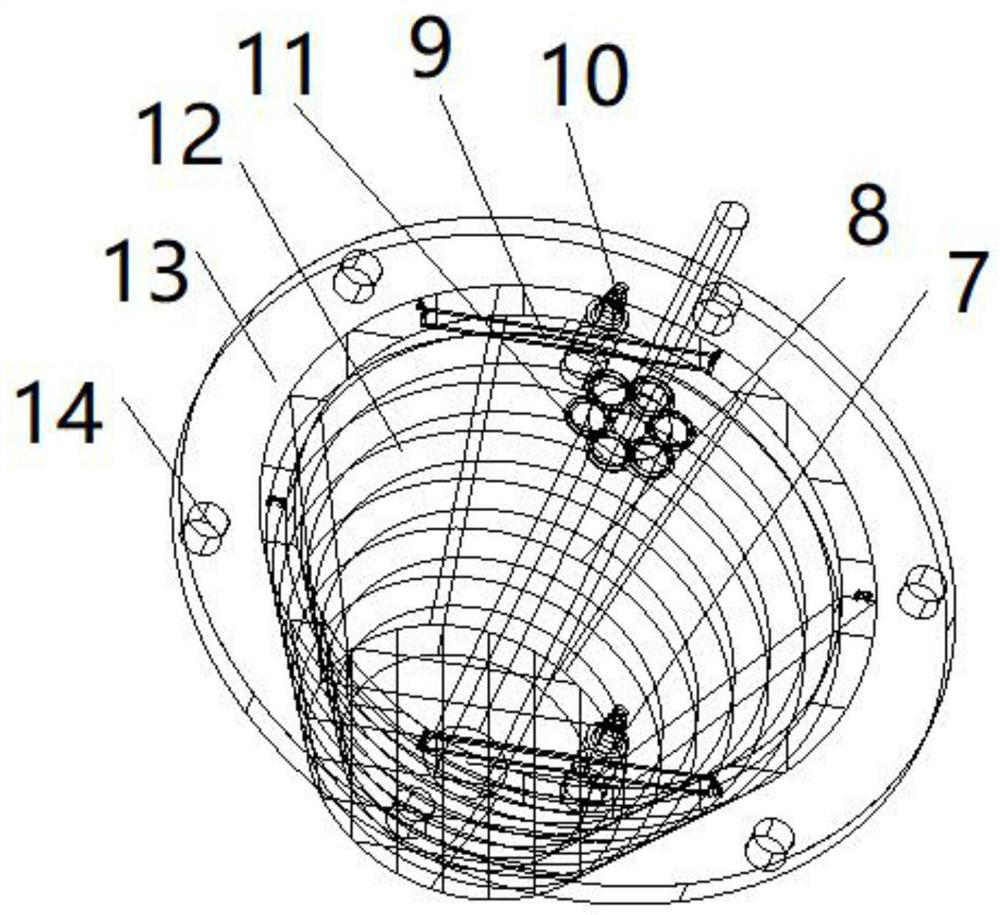
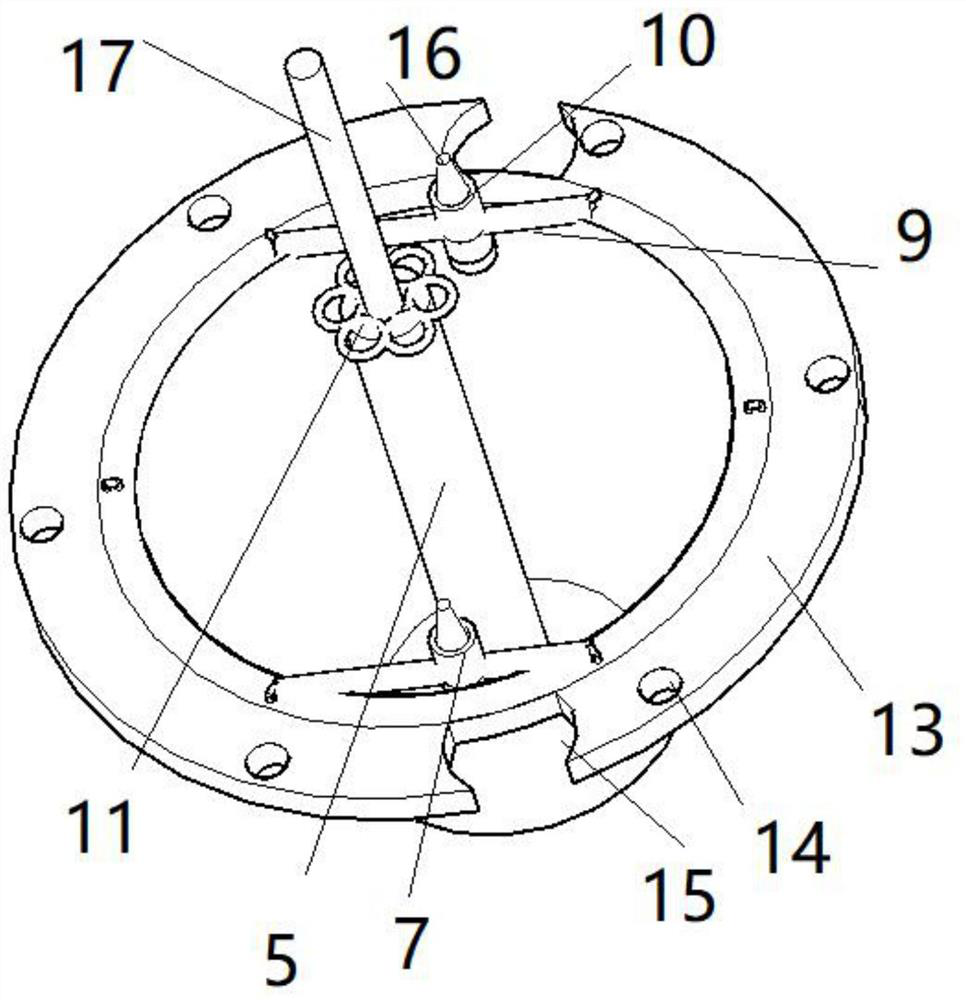
A multi-hull landing structure and method that can be turned to local climb for air force meteorological observation
The invention relates to the fields of air force and meteorological observation, in particular to a multi-hull safety landing structure and method capable of turning to local climb for air force meteorological observation. The lower part of the upper part of the hot air balloon is connected to the box (12) through an external fixing rope (4). The edge of the box (12) includes a circle of edge lifting and transfer holes (14), and the inner wall of the hot air balloon includes an inner fixing ring (2). , the middle part of the frame box (12) contains the middle hot air support (5), and the middle hot air support (5) contains a circle of upper rings (11), and the fixed rope (3) is pulled to the inner fixed ring (2), and the rope The middle part is the auxiliary stay rope (6), and the auxiliary stay rope (6) passes through the edge lifting transfer hole (14) and then connects to the upper ring (11); when the hot air balloon falls rapidly, tighten the rope, and the frame box (12) Moving up to the inside of the hot-air balloon; the whole body of the outer skin above the hot-air balloon can be used as a cushioning material to protect people in the box (12).
Owner:杭州翔毅科技有限公司
Optimizing a parametric model of aircraft performance
PendingCN111353209AGuaranteed convergenceOptimize flight operationsGeometric CADInstruments for road network navigationClassical mechanicsClimb
Methods and systems for optimizing the flight of an aircraft are disclosed. The trajectory is divided into segments, each of the segments being governed by distinct sets of equations, depending on engine thrust mode and on vertical guidance (climb, cruise or descent). By assuming two, aerodynamic and engine-speed, models, data from flight recordings are received and a number of parameters from a parameter-optimization engine is iteratively determined by applying a least-squares calculation until a predefined minimality criterion is satisfied. The parameter optimization engine is next used to predict the trajectory point following a given point. Software aspects and system (e.g. FMS and / or EFB) aspects are described.
Owner:THALES SA
Unreliable airspeed symbology based on pitch and power for primary flight display
A system for displaying pitch- and power-based guidance commands and flight path information to the pilot in various display modes (climb, cruise, descent, landing) in response to conditions in which measured airborne data cannot be relied upon. This information is presented on the primary flight display in an intuitive and convenient manner when and where it is needed. The displayed information changes dynamically in response to aircraft parameters.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
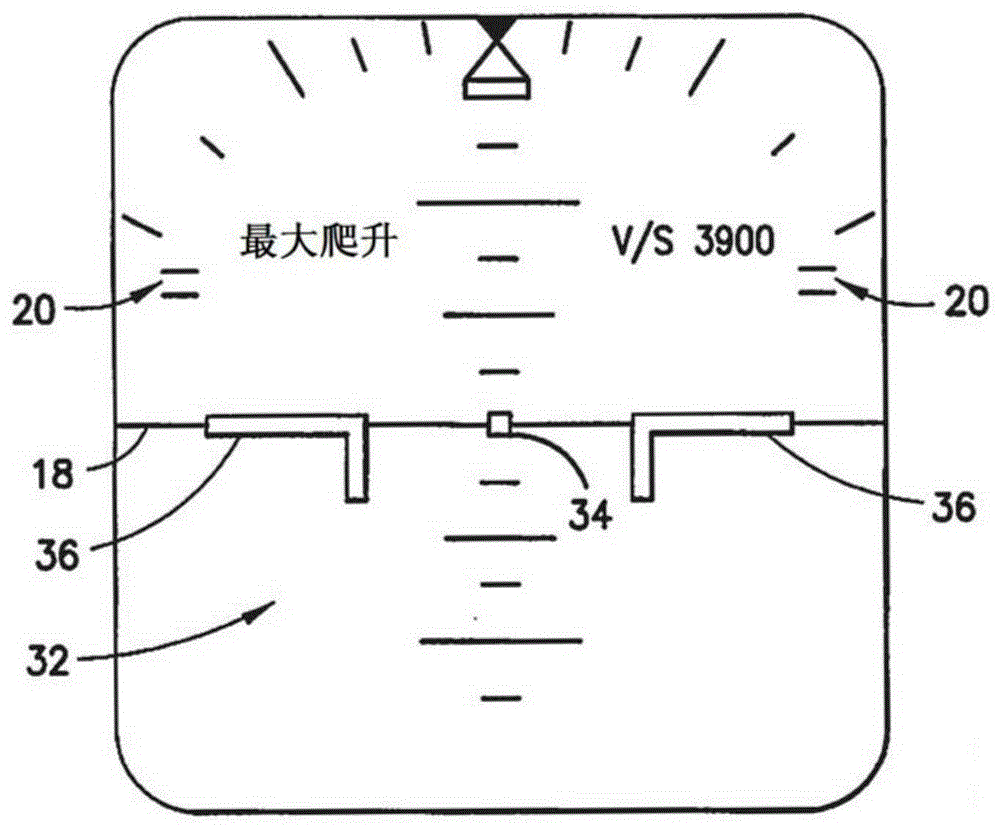
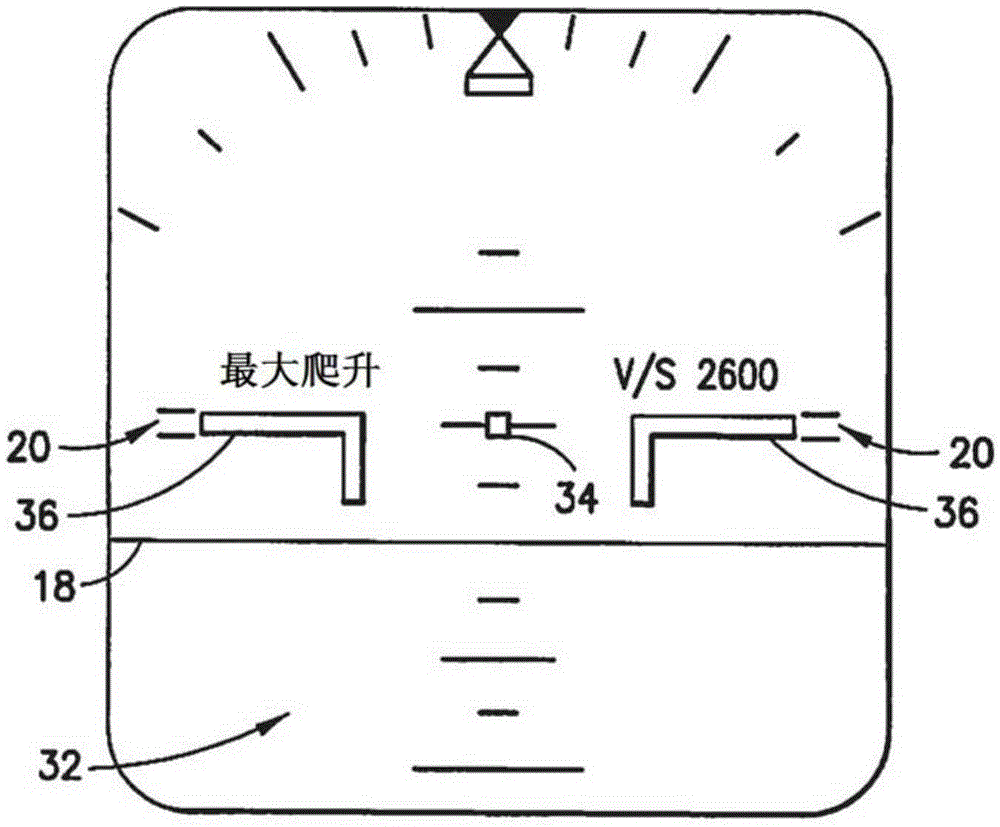
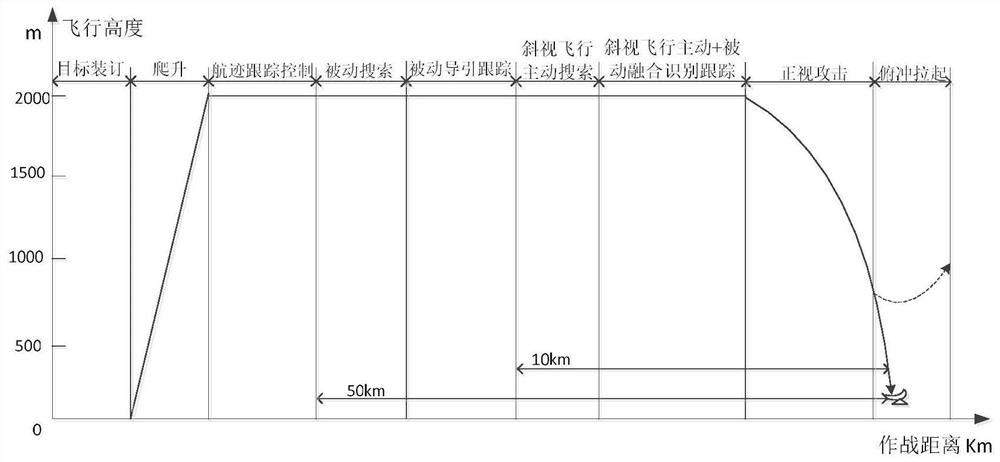
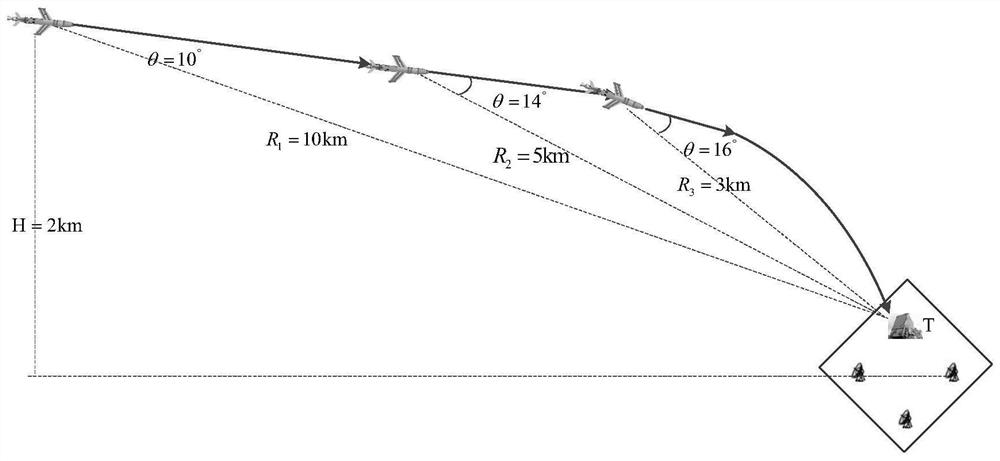
Unmanned aerial vehicle decoy-resistant flight path control method based on active and passive composite guidance
ActiveCN111736625AImprove the ability to resist baitMeet the needs of squint flightHigh level techniquesPosition/course control in three dimensionsPassive radarSimulation
The invention relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle decoy-resistant flight path control method based on active and passive composite guidance, and the method comprises the steps: entering a flight path tracking control stage when an unmanned aerial vehicle climbs to a specified flight height; performing distance estimation in a satellite navigation / inertial navigation / voyage calculation or integrated navigation mode, and when the distance is smaller than the detection and tracking action distance of the unmanned aerial vehicle passive guide device, entering a passive search stage; when an unmanned aerial vehicle passive radar seeker intercepts and tracks a target or bait, entering a passive guidance tracking stage; when the distance between the unmanned aerial vehicle and the center pointT of the target position is smaller than the range of the active radar recognition and tracking action distance of the unmanned aerial vehicle, enabling the unmanned aerial vehicle to enter a strabismus flight active search stage; and after the unmanned aerial vehicle recognizes that the target is a real target, enabling the unmanned aerial vehicle to enter a front-view attack stage, determining whether the unmanned aerial vehicle meets a diving attack condition or not according to the active and passive composite guide information, and if yes, enabling the unmanned aerial vehicle quickly to enter diving to strike the target.
Owner:XIAN AISHENG TECH GRP +1
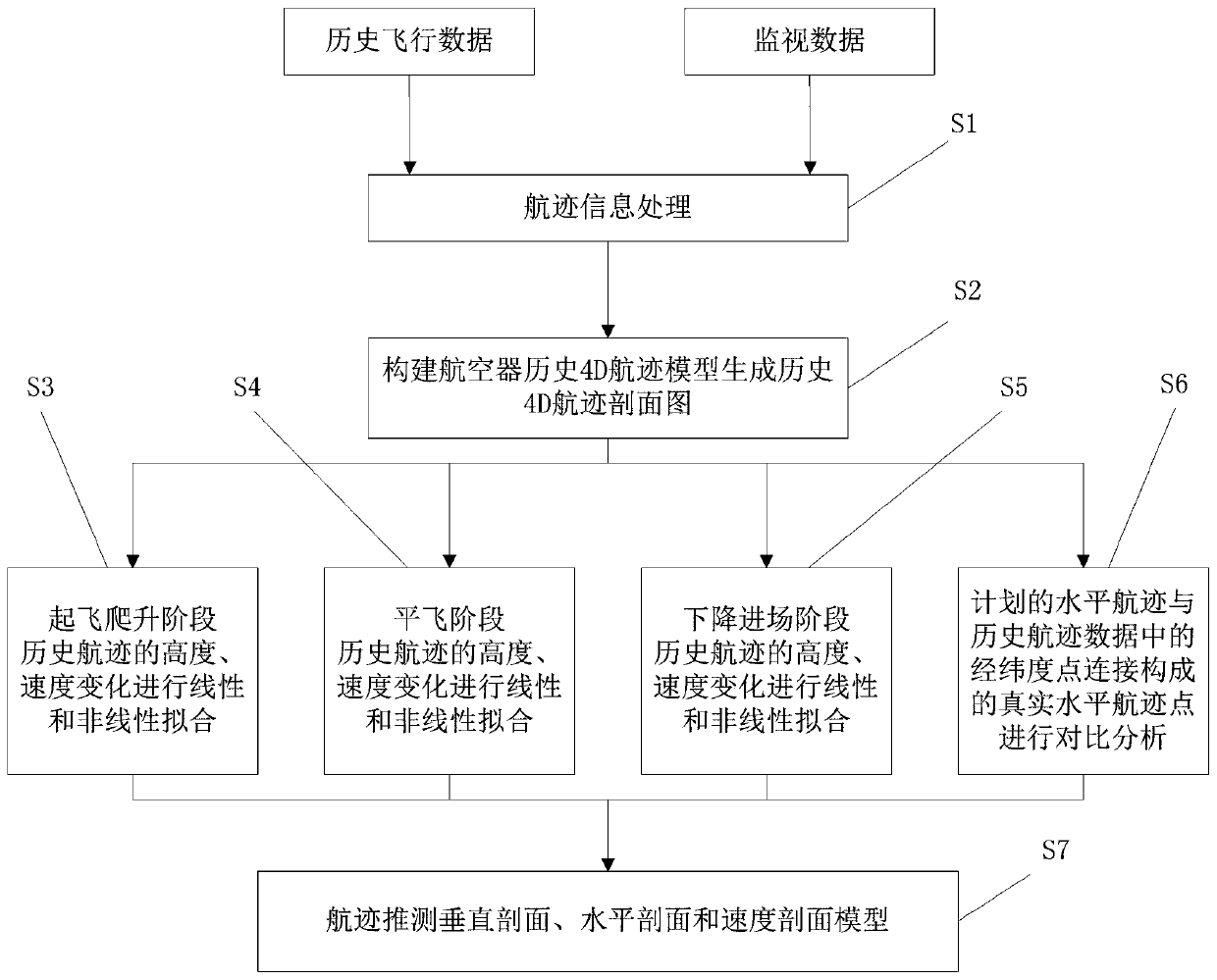
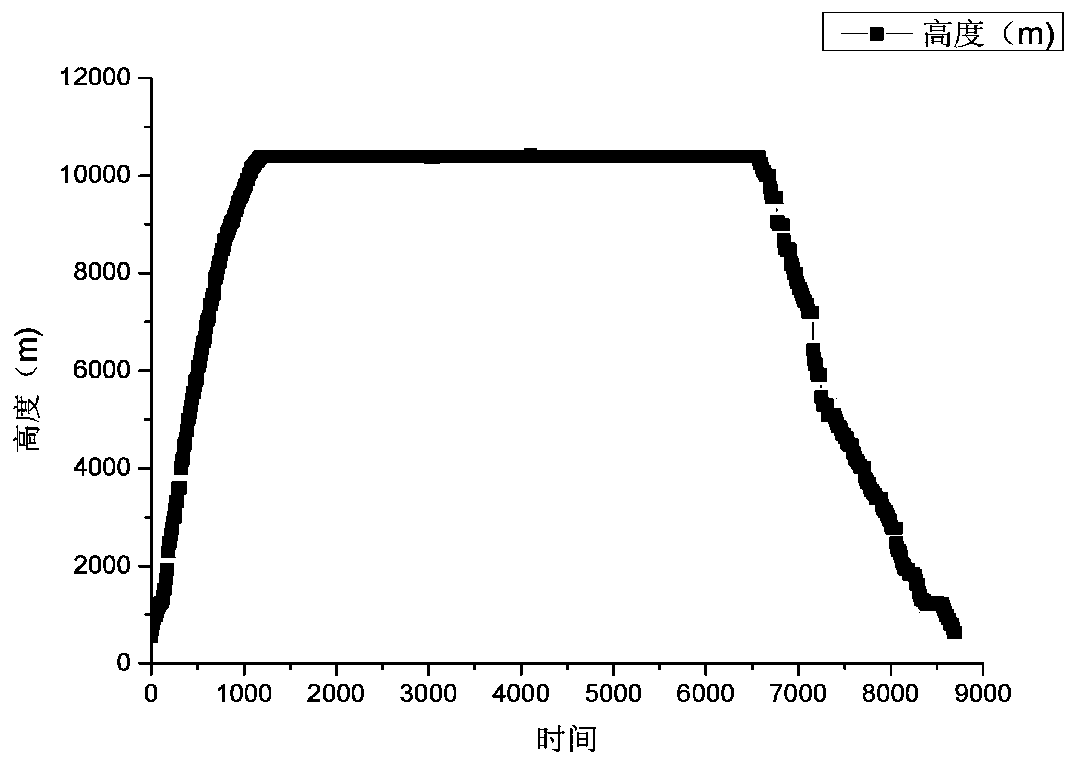
A 4D dead reckoning method based on historical track data mining
ActiveCN109493644BThe conclusion is true and credibleImprove accuracyGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsTracking modelTraffic flow
The invention discloses a four-dimensional track estimation method based on historical track data mining. The steps include: 1. Obtaining four-dimensional track information according to the association relationship between historical flight data and monitoring data; 2. Constructing a historical four-dimensional track model of an aircraft ; 3. Carry out linear and non-linear fitting to the altitude and speed of the aircraft in the take-off and climb phases, level flight phases, and descent phases; 4. Analyze the horizontal trajectory of the aircraft in each flight phase; 5. Based on the above analysis results, establish an aviation Trajectory extrapolated vertical profile, horizontal profile and velocity profile models. Compared with the four-dimensional track model commonly used in control systems, the method of the present invention is simpler and more practical, and the accuracy of track estimation is higher. Key technologies such as forecasting and formulation of traffic allocation measures provide basic guarantees.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
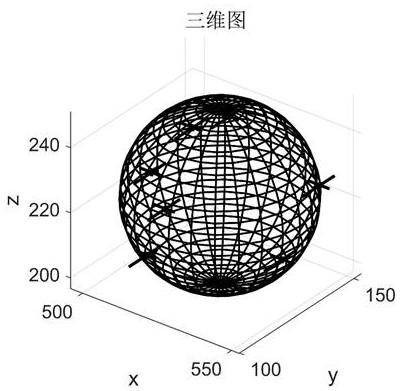
A security envelope construction method for UAV dense formation
ActiveCN113868780BComplexity close toUniversalGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationClassical mechanicsClimb
The present invention provides a method for constructing a security envelope of a dense formation of UAVs, the construction of which includes the following steps: S1: collecting all n The flight state parameters of the UAV, including the maximum length, width and height of the fuselage, and the maximum forward flight, backward flight, climb, descent, and lateral movement speed; S2: The spatial position points of all UAVs in the formation can be enveloped in the solution space The position and radius of the center of the minimum enveloping sphere S; S3: Calculate the maximum flight distance that the UAV formation can reach in all directions within a given safety response time; S4: According to the maximum length, width and height of the fuselage, the minimum The radius of the envelope sphere S and the maximum flight distance in each direction, solve the diagonal matrix M j ; S5: Construct the UAV safety envelope model. The method proposed in the present invention comprehensively considers the spatial position distribution, flight state and response speed of the UAVs in the formation, has low model complexity, and can be effectively used for low-altitude conflict prediction and obstacle avoidance planning of dense formations composed of multiple UAVs.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A hybrid propulsion unmanned aerial vehicle demand power prediction method
ActiveCN113110558BFix stability issuesFix security issuesAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsData setSimulation
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and system for improving the performance of an aircraft upon take off
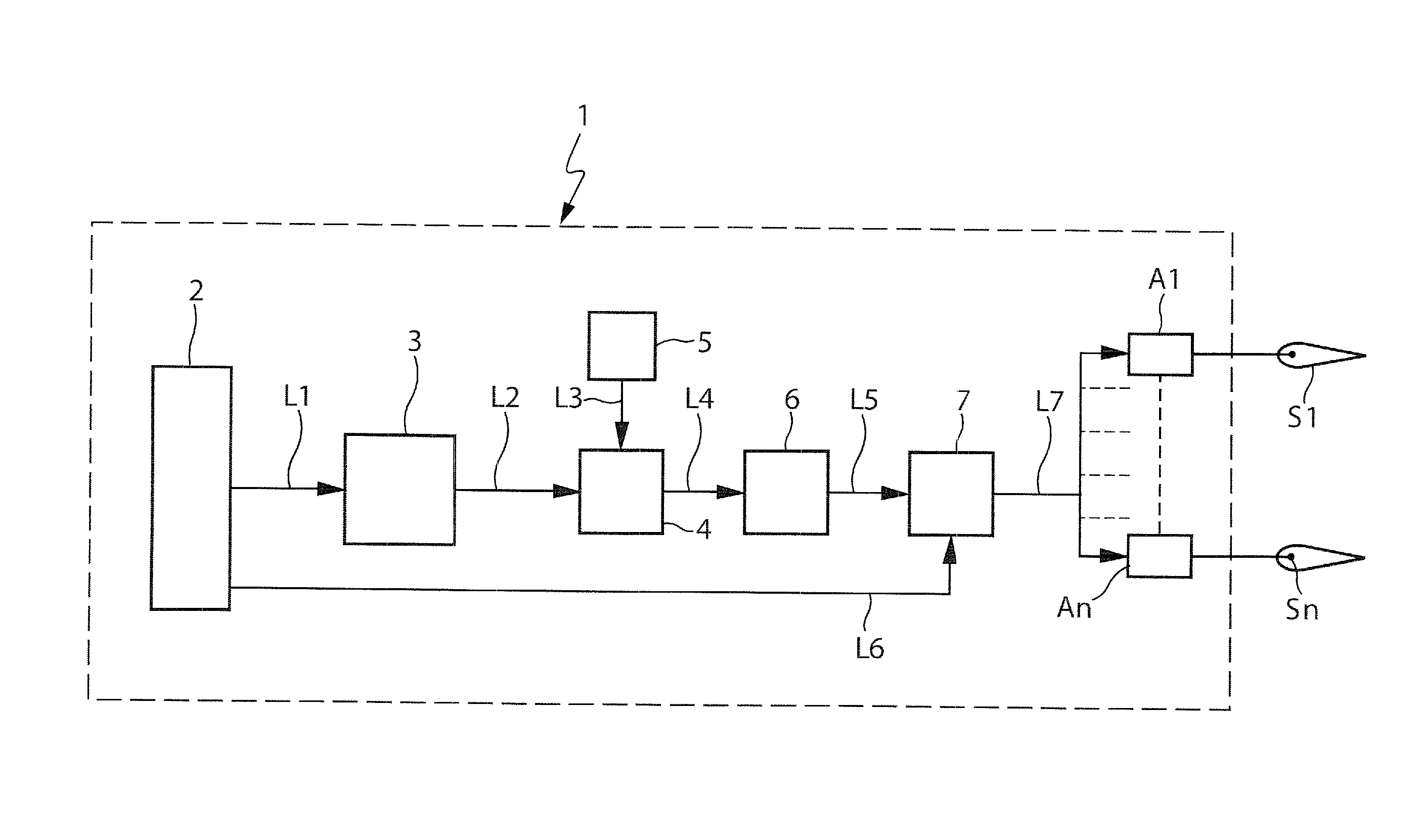
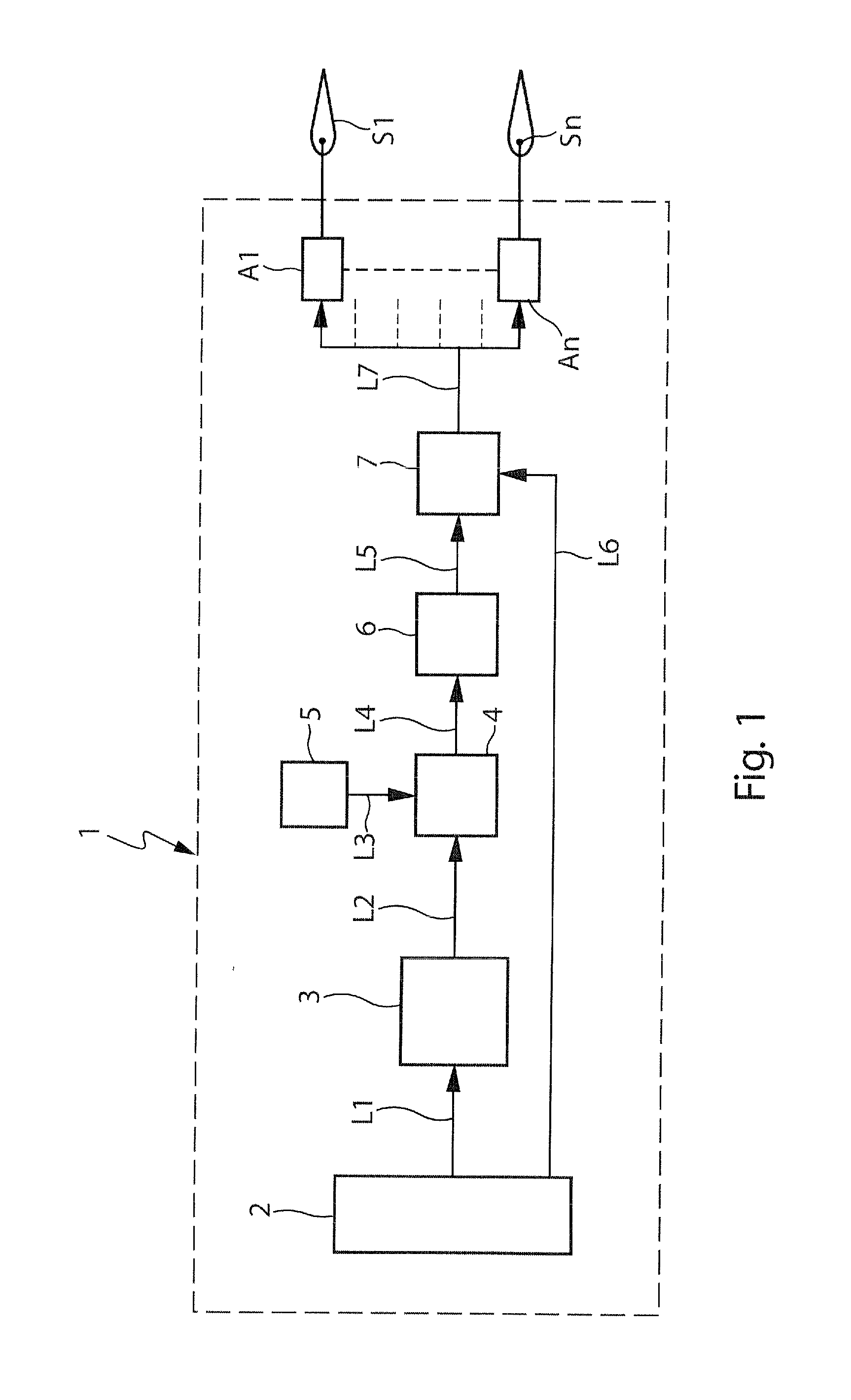
InactiveUS8437894B2Reducing control surfaceReduce biasAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficFlight vehicleClimb
A method and system for improving aircraft performances during take-off is described. The system (1) can include means (4, 6, 7) for determining an optimised take-off position of the control surfaces (S1-Sn) of the aircraft, in the case where a regulatory safety criterion relating to the minimum gradient of climb with a breakdown engine is predominant.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Non-cooperative low-thrust maneuvering target orbit determination method, device, equipment and medium
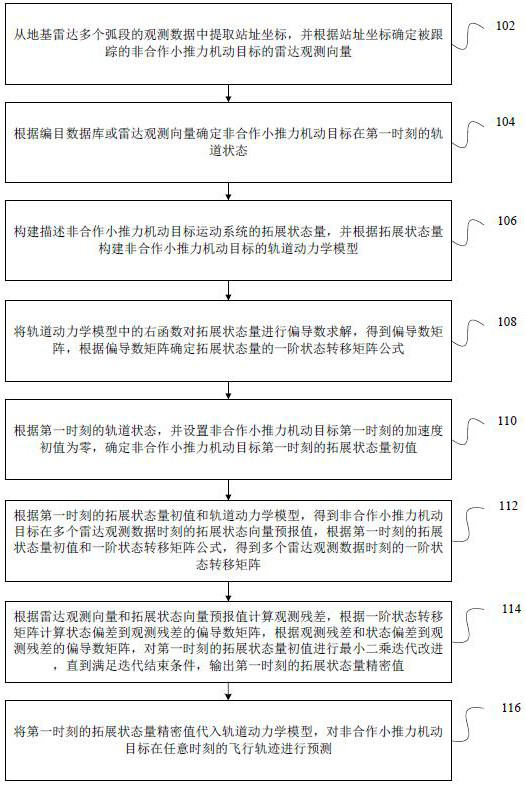
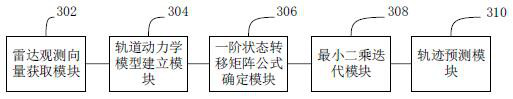
ActiveCN114462256BEfficient determinationCosmonautic vehiclesDesign optimisation/simulationRadar observationsTransition matrices
The present application relates to a non-cooperative low-thrust maneuvering target orbit determination method, device, computer equipment and storage medium. The method includes: proposing an orbit determination method for thrust acceleration modeling in the local orbit coordinate system of the tracked non-cooperative target, deriving the calculation equation of the extended state quantity transfer matrix including acceleration components under the high-precision perturbation orbit model, through Radar observation data and the least squares method are used to improve the orbit of non-cooperative small-thrust maneuvering targets, and finally the orbit prediction is carried out through the determined extended state quantity, which can effectively determine the orbit of non-cooperative targets with continuous low-thrust maneuvering, and can be used to solve non-cooperative Orbit determination for satellites performing continuous low-thrust maneuvers during climb or descend.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com