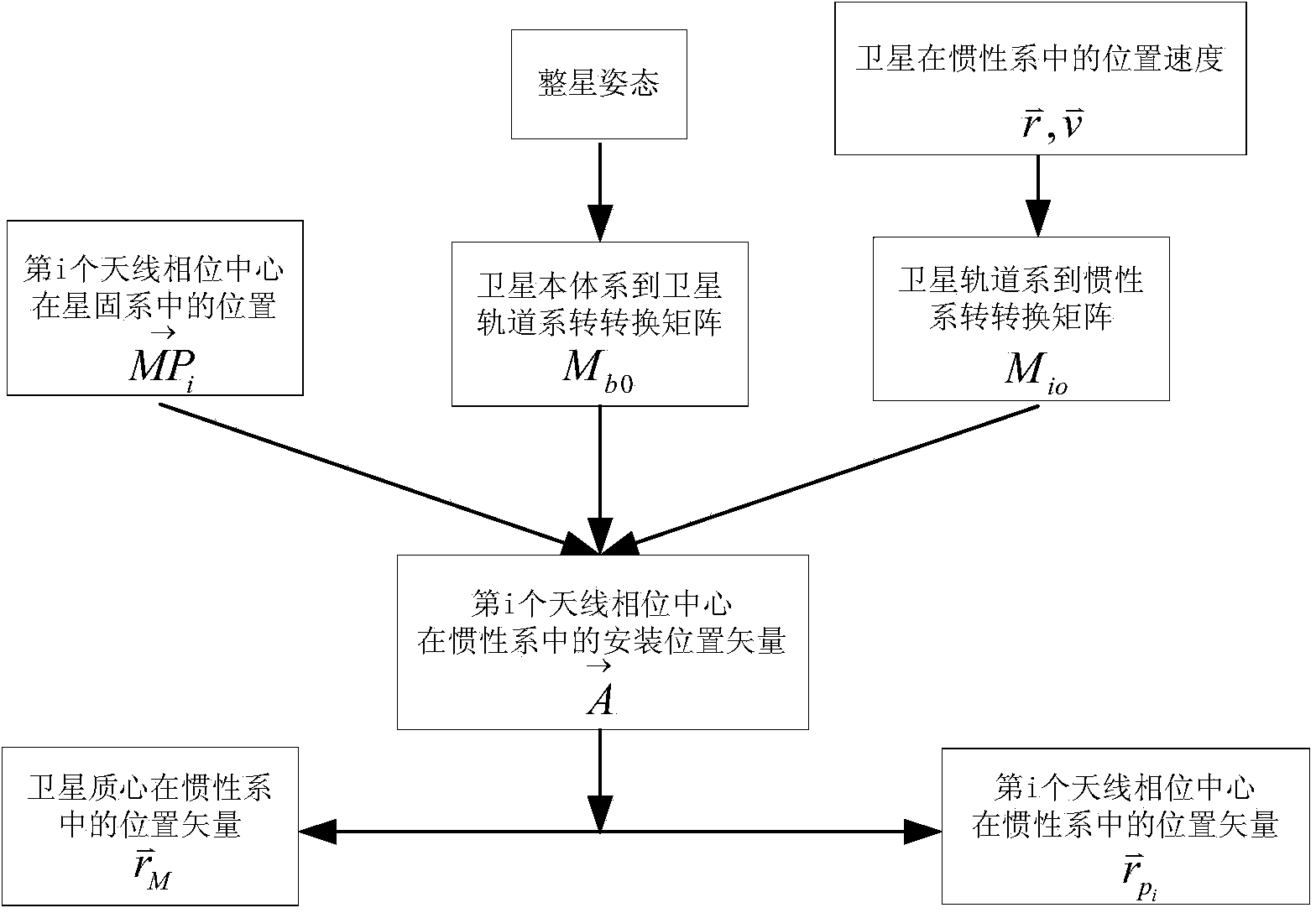
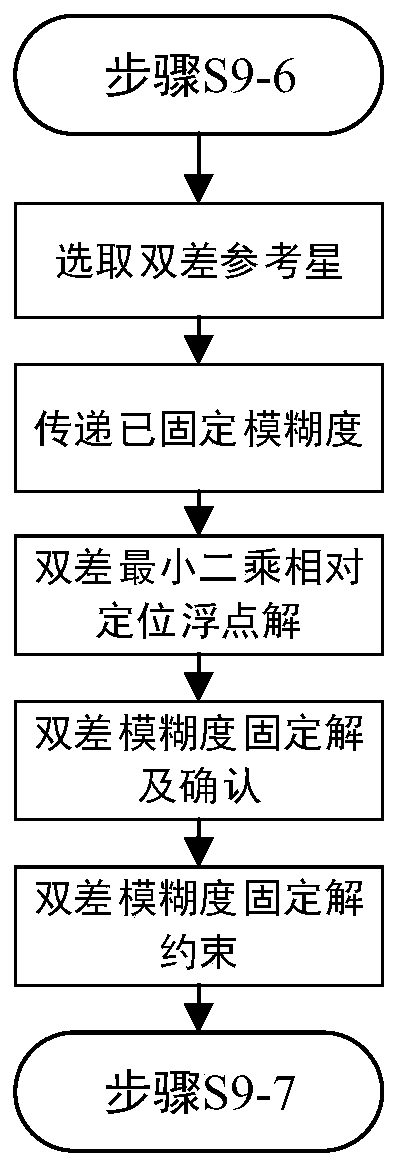
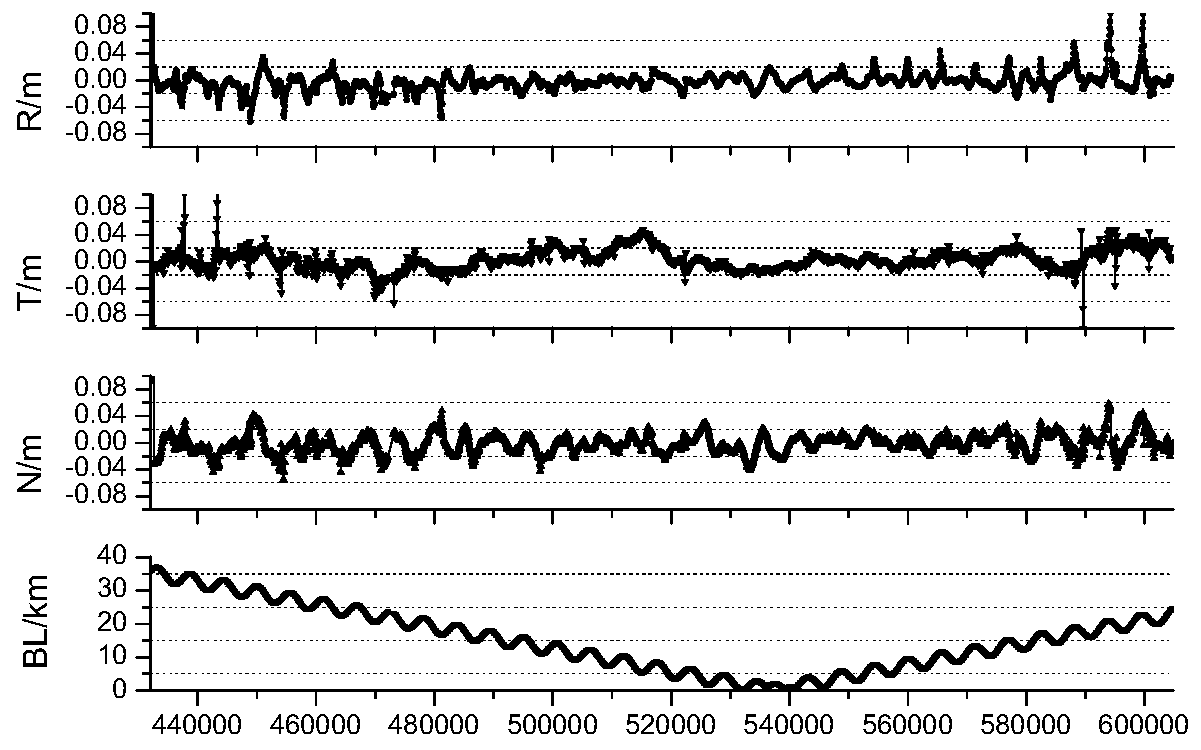
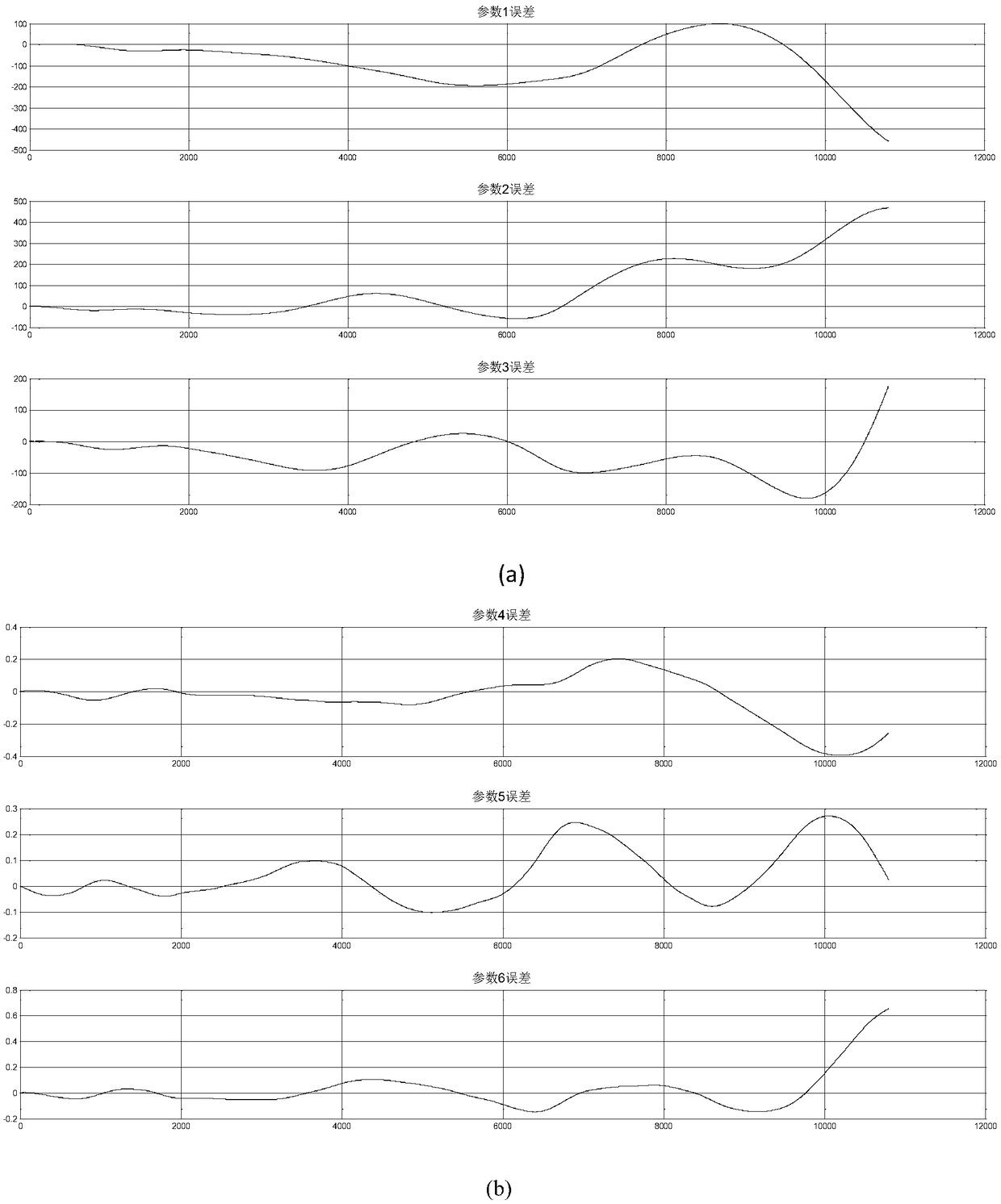
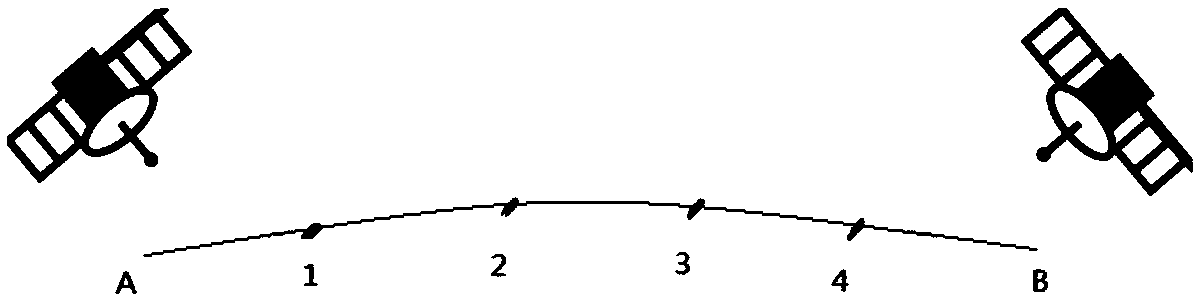
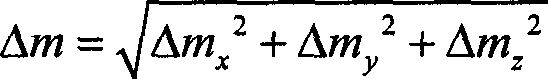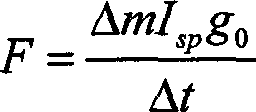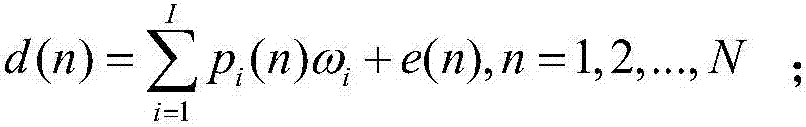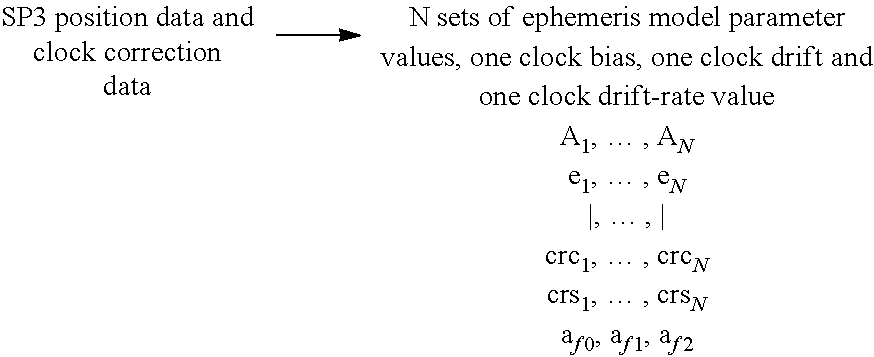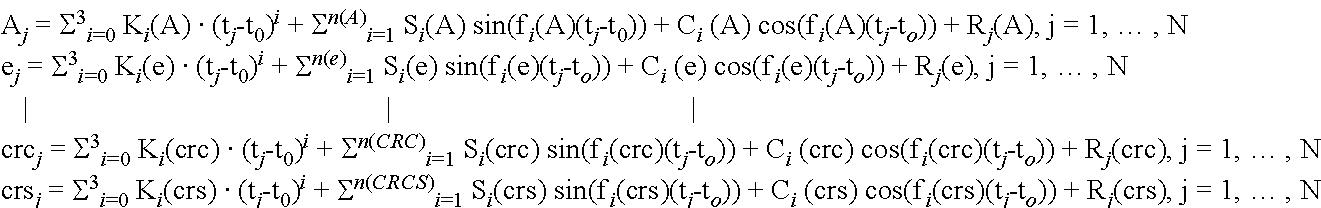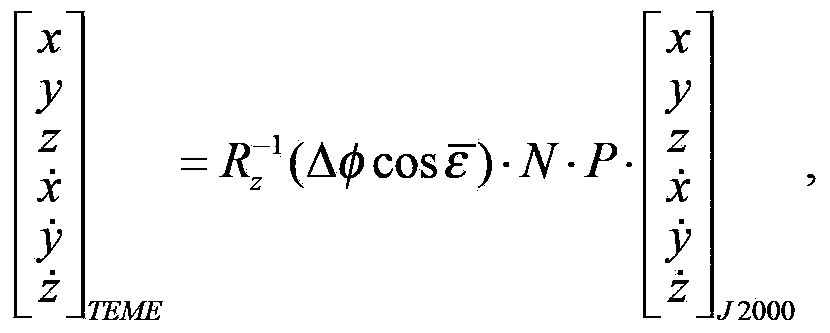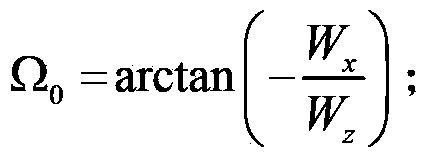Patents
Literature
94 results about "Orbit prediction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
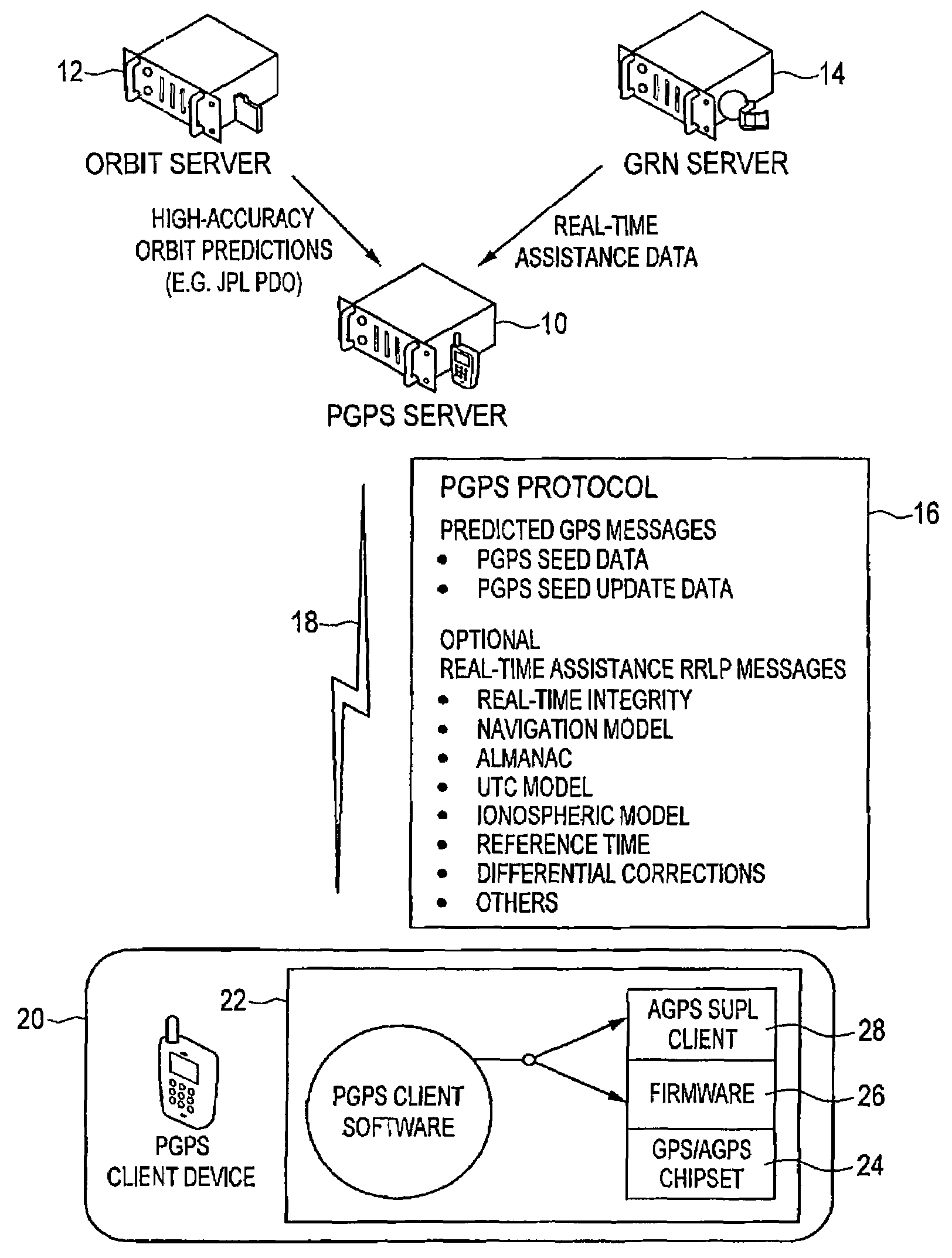
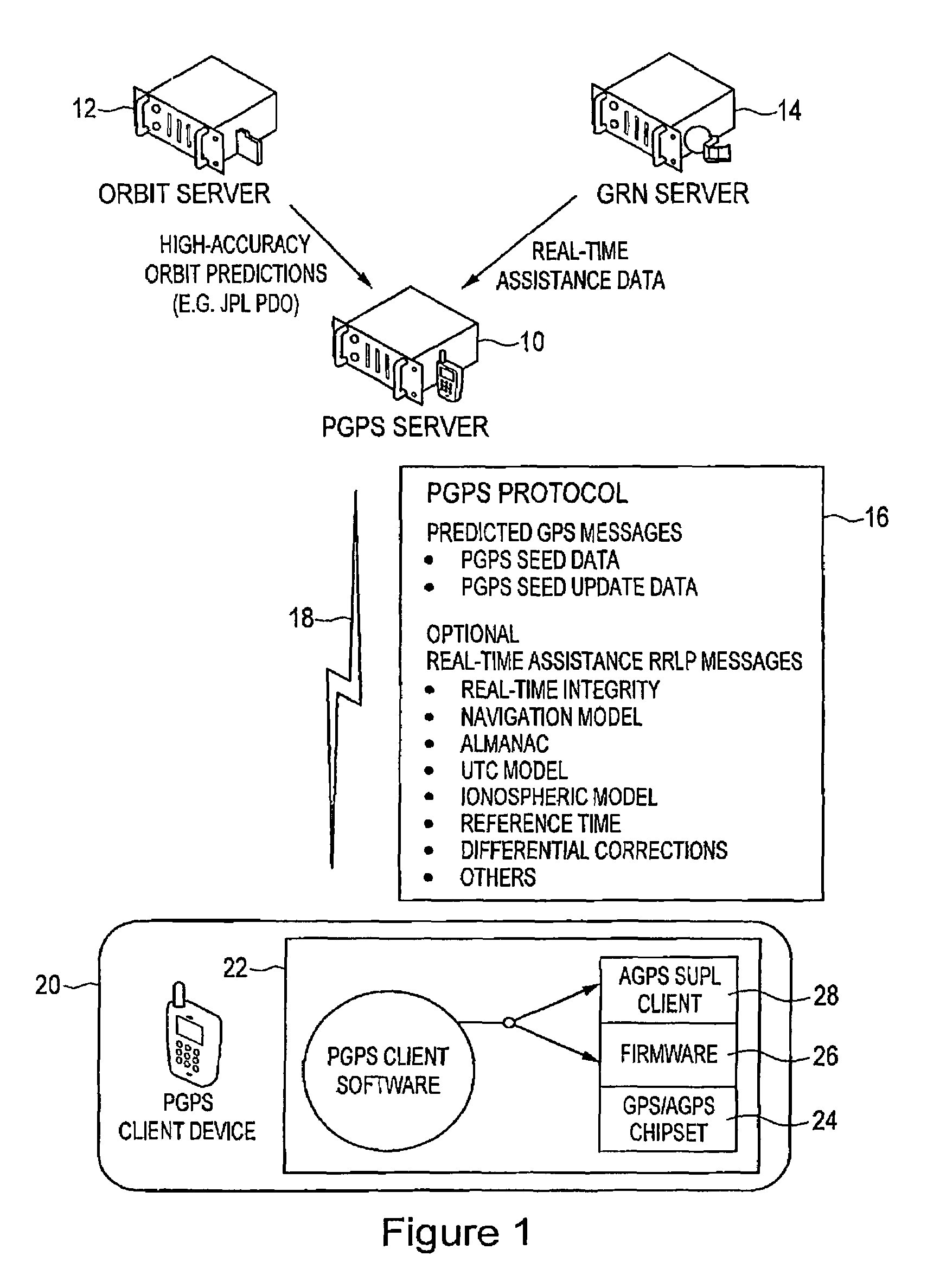
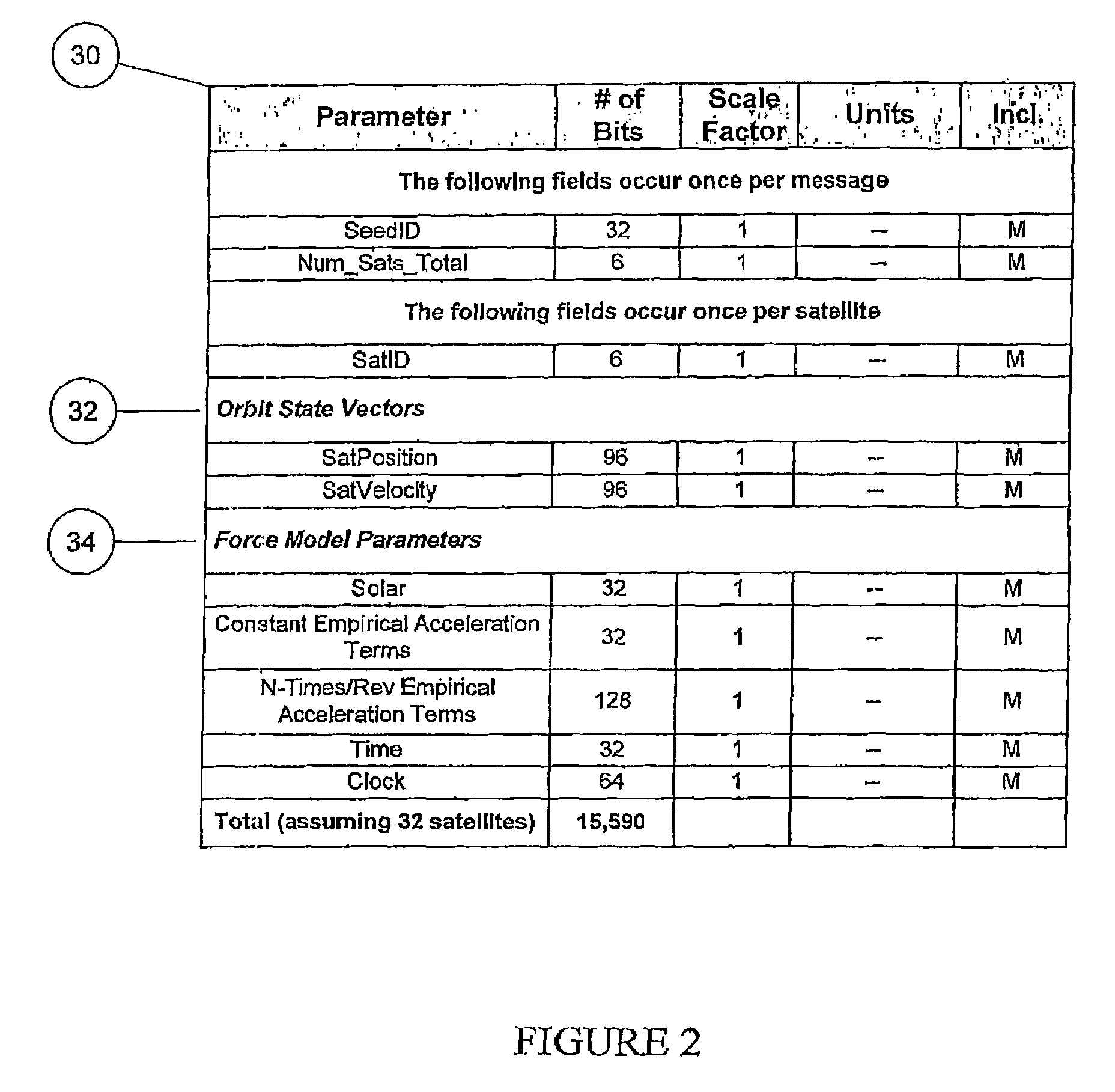
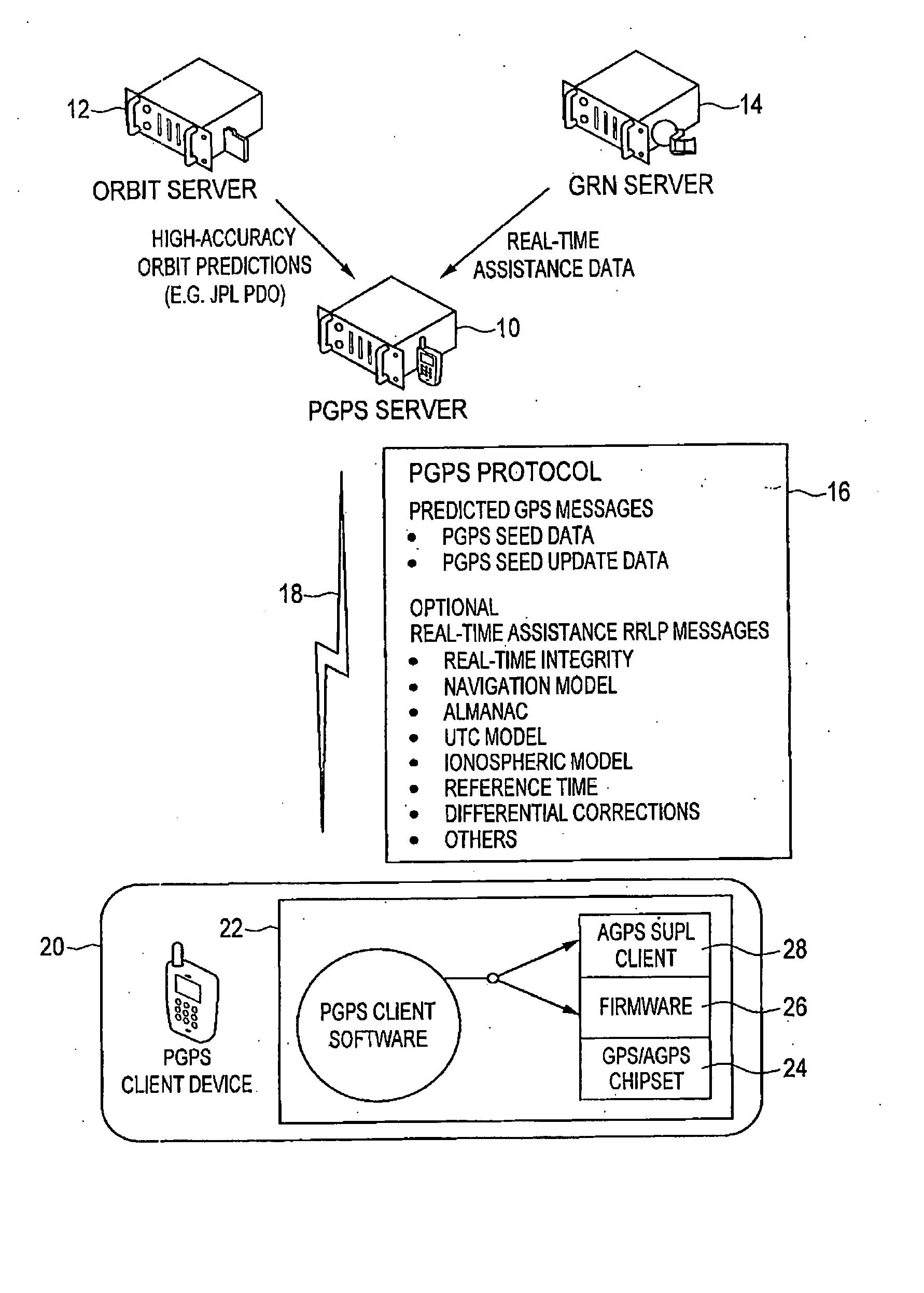
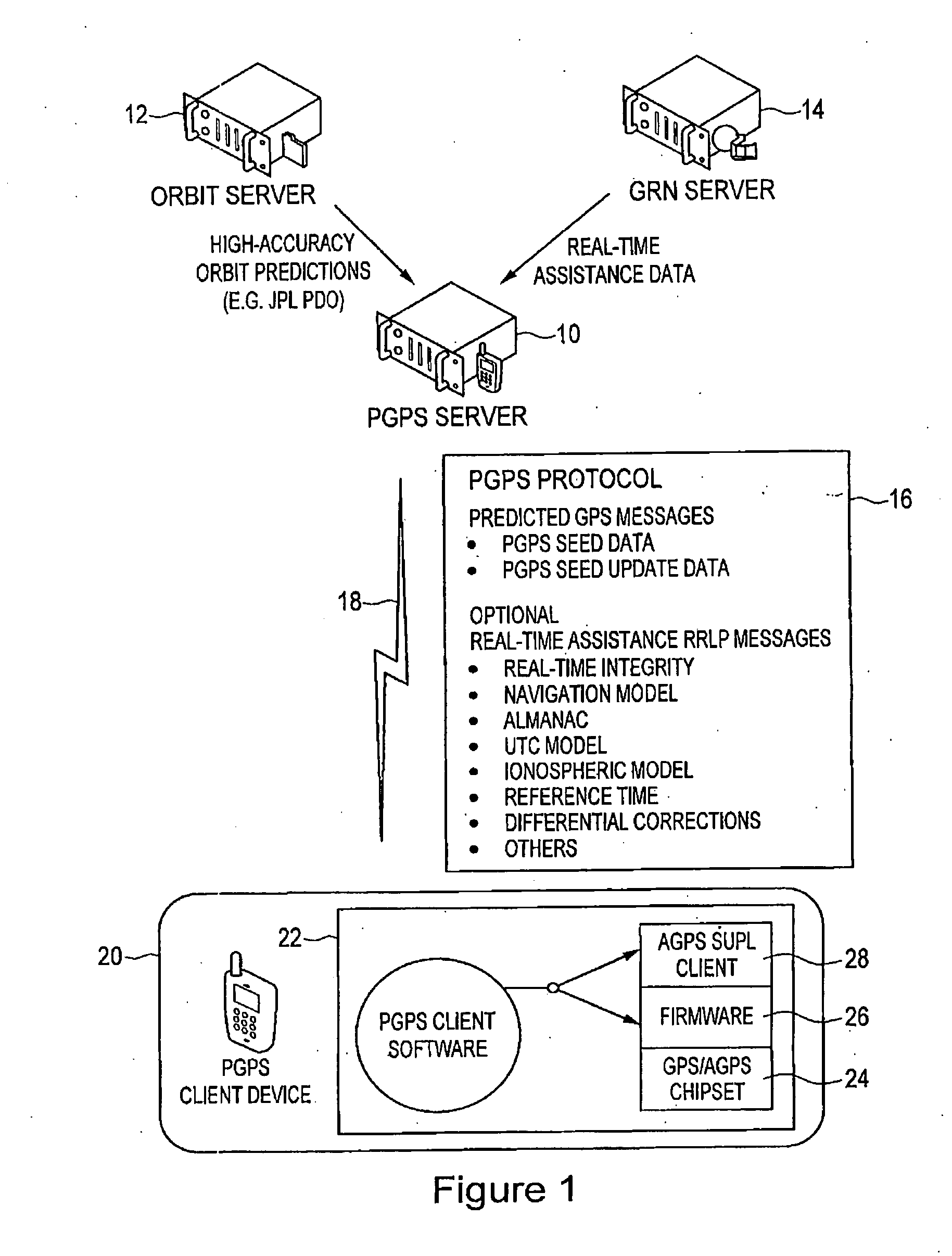
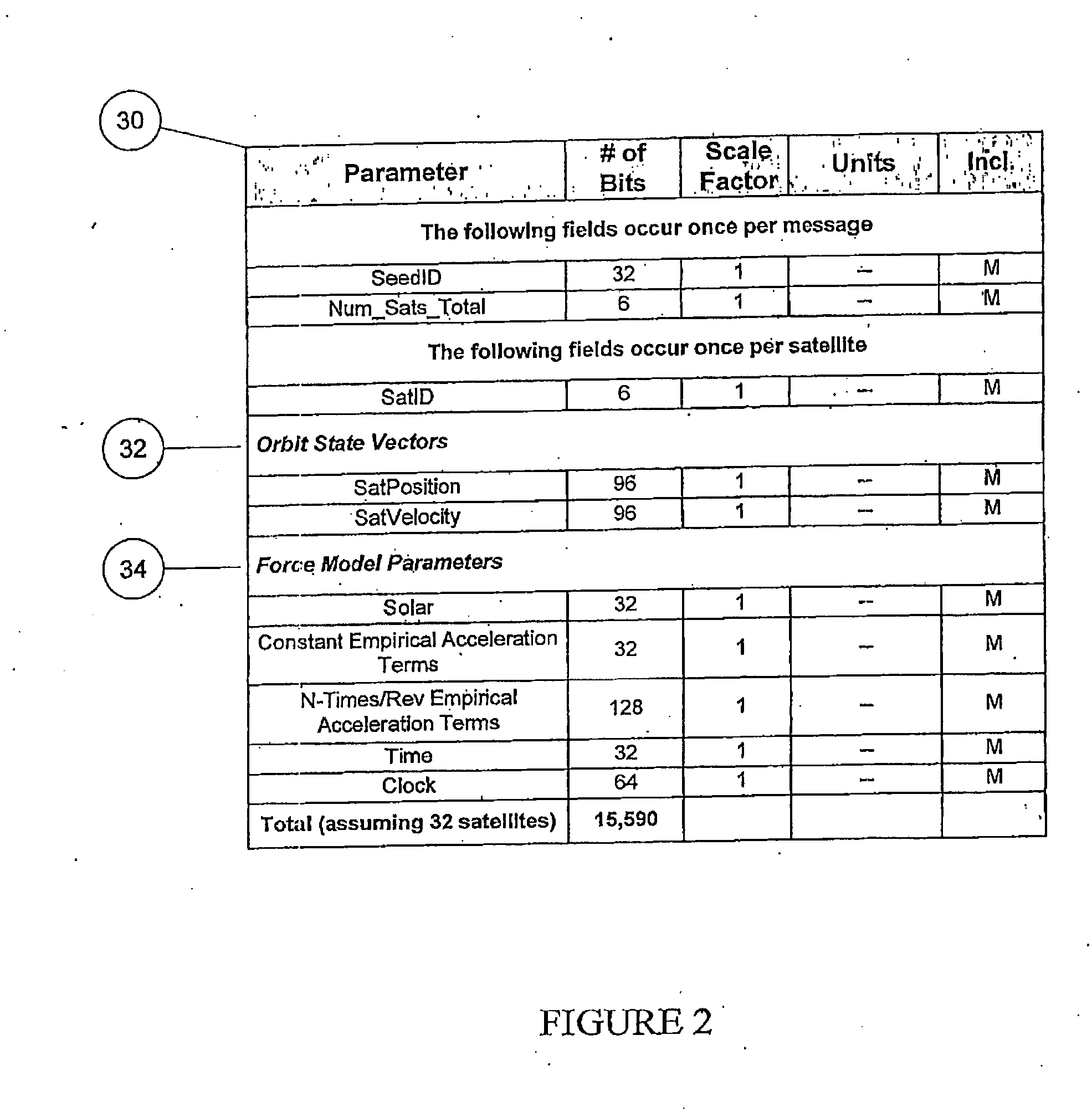
Distributed orbit modeling and propagation method for a predicted and real-time assisted GPS system
ActiveUS7612712B2Easy to integrateNavigational calculation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingData setTime to first fix
A distributed orbit and propagation method for use in a predicted GPS or GNSS system, which includes a predicted GPS server (PGPS Server), a source of high accuracy orbit predictions (Orbit Server), a global reference network (GRN Server) providing real-time GPS or GNSS assistance data to the PGPS Server, a predicted GPS client (PGPS Client) running on a device equipped with a GPS or AGPS chipset. In response to requests from the PGPS Client, the PGPS Server produces and disseminates an initial seed dataset consisting of current satellite orbit state vectors and orbit propagation model coefficients. This seed dataset enables the PGPS Client to locally predict and propagate satellite orbits to a desired future time. This predictive assistance in turn helps accelerate Time To First Fix (TTFF), optimize position solution calculations and improve the sensitivity of the GPS chip present on, or coupled with, the device. In contrast with other conventional predicted GPS systems that forward large volumes of predicted orbits, synthetic ephemeris or synthetic almanac data, this method optimally reduces data transfer requirements to the client, and enables the client to locally synthesize its own predicted assistance data as needed. This method also supports seamless notification of real-time satellite integrity events and seamless integration of predicted assistance data with industry standard real-time assistance data.
Owner:RX NETWORKS INC
Distributed orbit modeling and propagation method for a predicted and real-time assisted GPS system
ActiveUS20080018527A1Easy to integrateNavigational calculation instrumentsRadio transmissionData setTime to first fix
A distributed orbit and propagation method for use in a predicted GPS or GNSS system, which includes a predicted GPS server (PGPS Server), a source of high accuracy orbit predictions (Orbit Server), a global reference network (GRN Server) providing real-time GPS or GNSS assistance data to the PGPS Server, a predicted GPS client (PGPS Client) running on a device equipped with a GPS or AGPS chipset. In response to requests from the PGPS Client, the PGPS Server produces and disseminates an initial seed dataset consisting of current satellite orbit state vectors and orbit propagation model coefficients. This seed dataset enables the PGPS Client to locally predict and propagate satellite orbits to a desired future time. This predictive assistance in turn helps accelerate Time To First Fix (TTFF), optimize position solution calculations and improve the sensitivity of the GPS chip present on, or coupled with, the device. In contrast with other conventional predicted GPS systems that forward large volumes of predicted orbits, synthetic ephemeris or synthetic almanac data, this method optimally reduces data transfer requirements to the client, and enables the client to locally synthesize its own predicted assistance data as needed. This method also supports seamless notification of real-time satellite integrity events and seamless integration of predicted assistance data with industry standard real-time assistance data.
Owner:RX NETWORKS INC
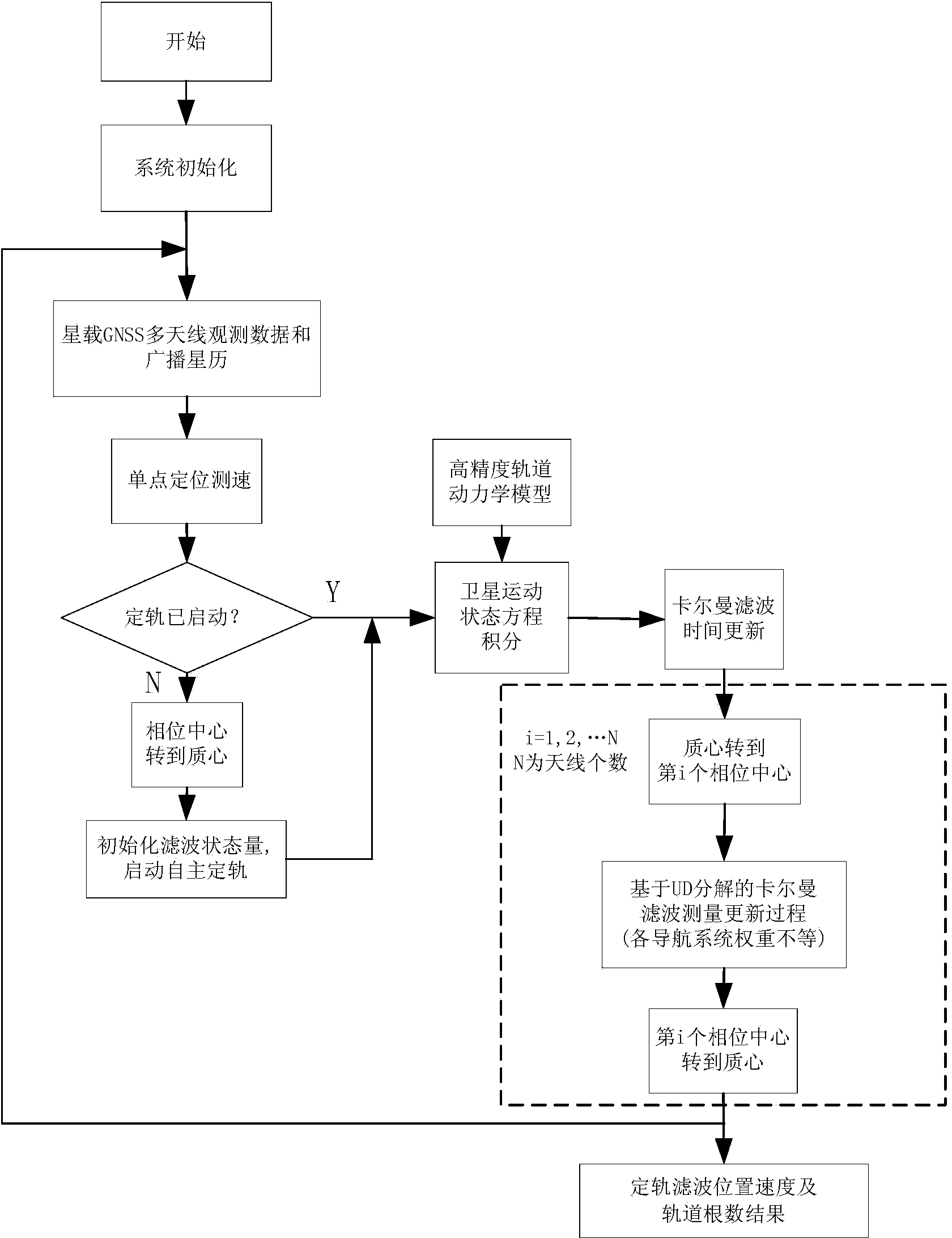
Satellite autonomous orbit determination method based on satellite-borne GNSS multiple antennas
ActiveCN103675861AExcellent data fusion resultsImprove the accuracy of orbit determinationInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteKaiman filter
A satellite autonomous orbit determination method based on satellite-borne GNSS multiple antennas. According to the method, a Kalman filter is extended; multiple GNSS antennas measured pseudorange observation values are made full use of to carry out real-time filtering correction of an orbit prediction value using a high precision mechanical model; and high precision satellite orbit information is obtained. According to the invention, the problems of the high precision orbit determination in a complex posture maneuver can be solved. In the invention, the orbit determination result is high in precision, good in stability, and highly real-time, can meet the orbit determination demand of the low orbit satellite and high precision satellite, can be widely applied to the high precision orbit determination of the space station, high resolution earth observation satellite and other space missions, and has a wide promotion and application prospect.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
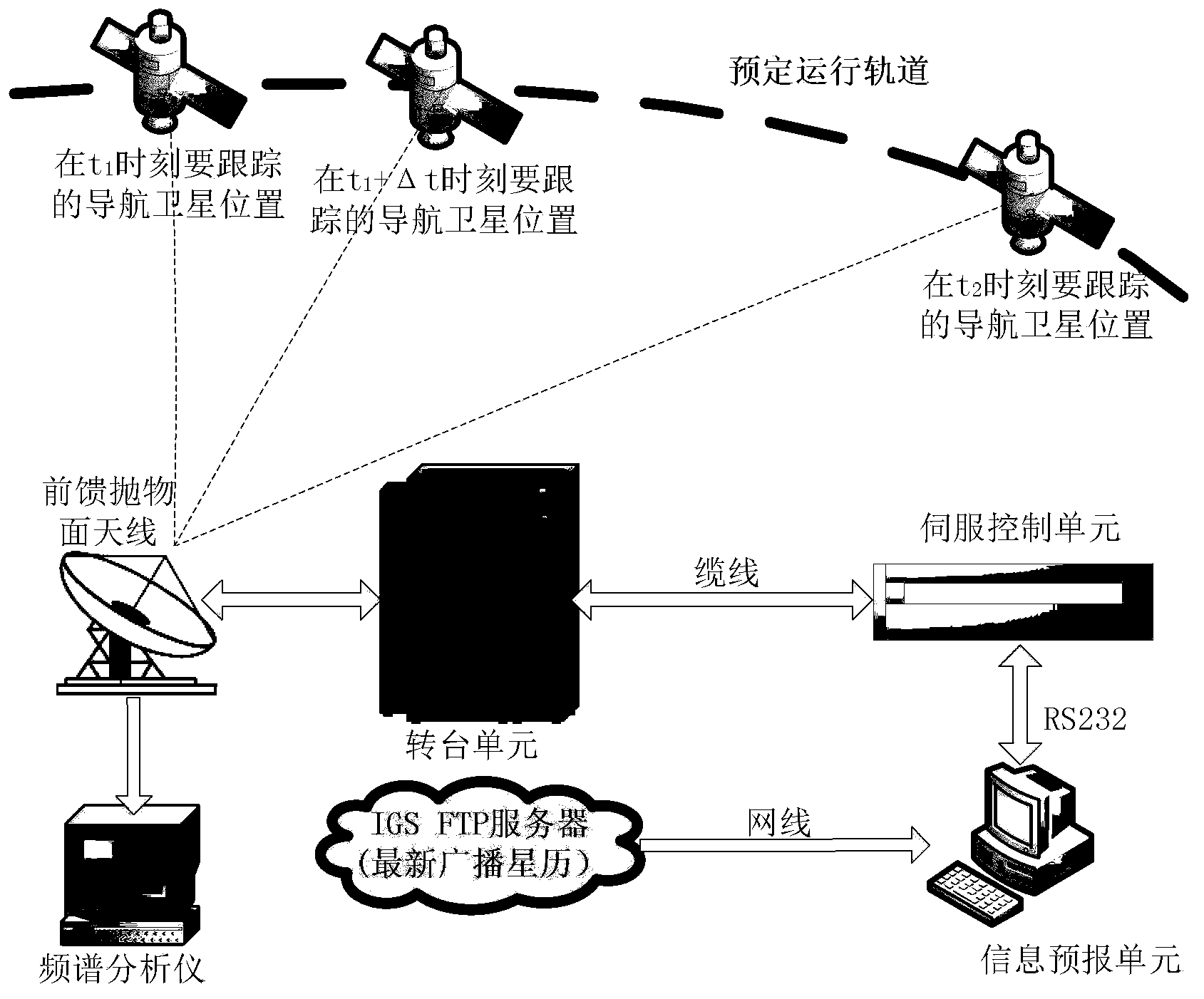
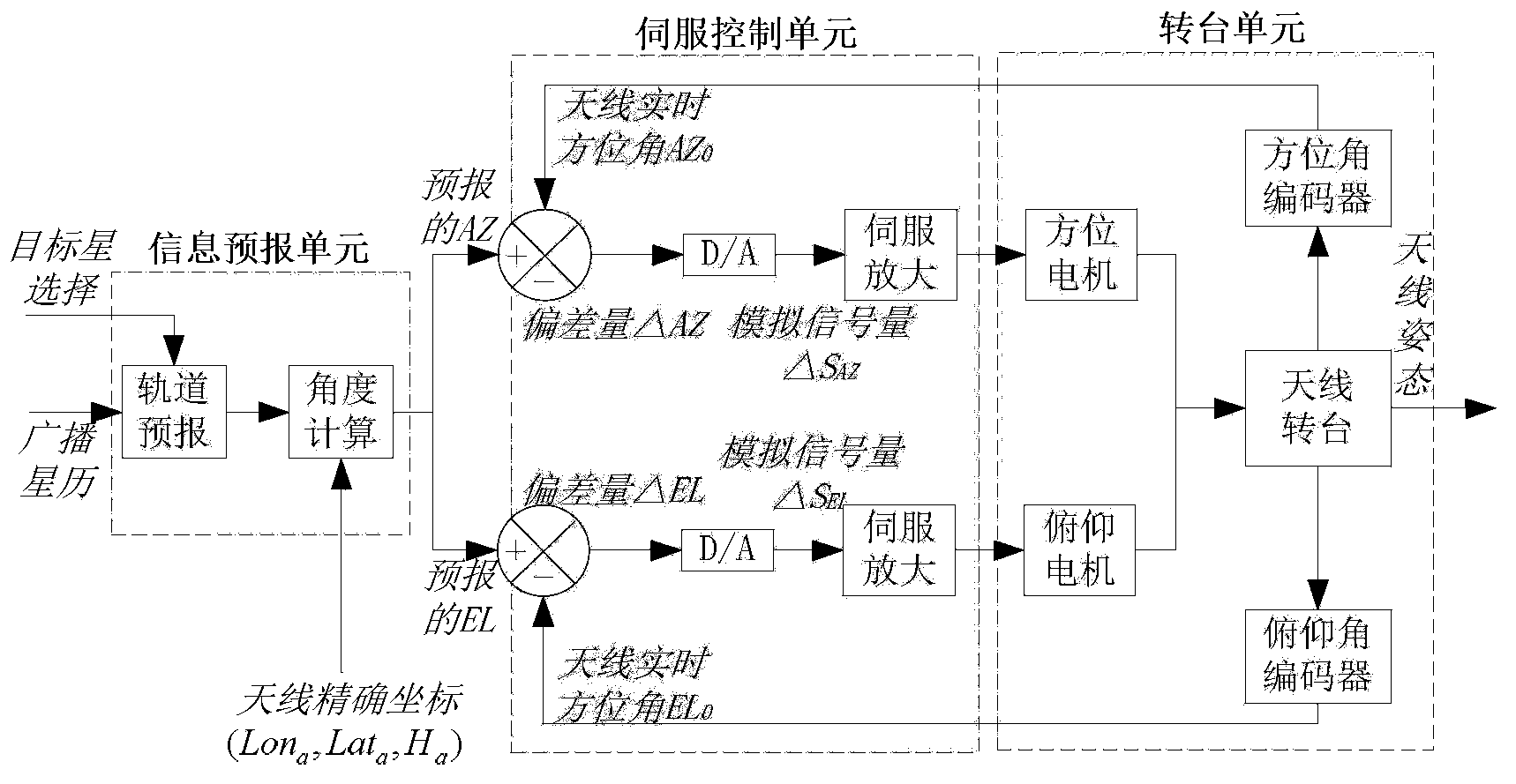
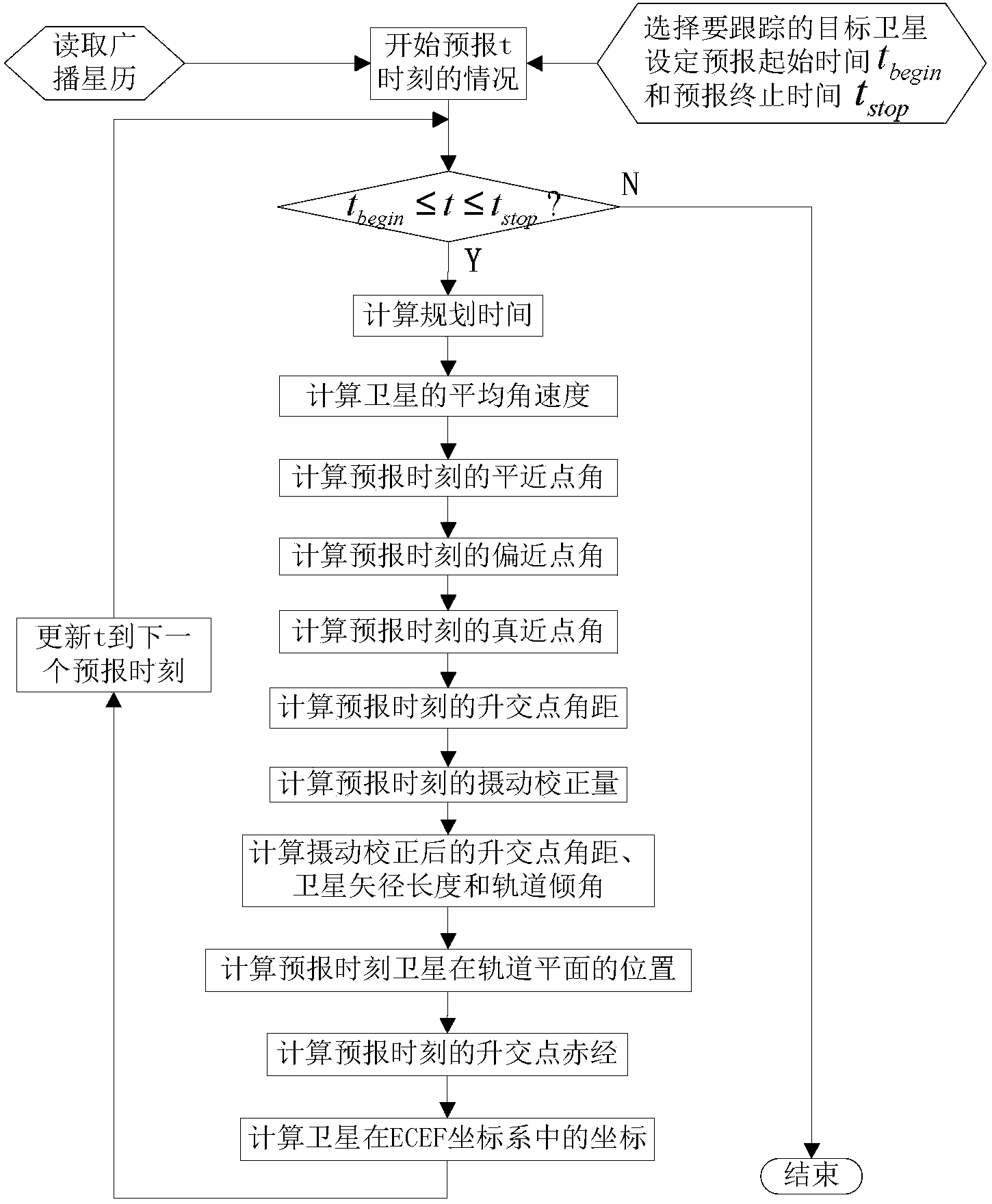
Method and system for automatically tracking medium earth orbit navigational satellite through servo antenna
ActiveCN103364805AAccurate trackingAccurate pointing trackingSatellite radio beaconingSignal qualityFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a method and system for automatically tracking a medium earth orbit navigational satellite through a servo antenna, and belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation signal quality monitoring. The system comprises an information prediction unit, a servo control unit, a rotary table unit, the feed-forward large-diameter parabolic antenna and a spectrum analyzer. The information prediction unit is used for the operation of orbit prediction and angle calculation, the servo control unit is used for adjusting antenna postures in a closed loop feedback mode, the rotary table unit is used for driving an antenna rotary table to rotate in the azimuth axial direction and in the pitch axial direction, the feed-forward large-diameter parabolic antenna is used for receiving target satellite signals, and the spectrum analyzer is used for observing quality of received signals. The method and system for automatically tracking the medium earth orbit navigational satellite can achieve an ideal tracking effect in the state of being divorced from manual monitoring.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
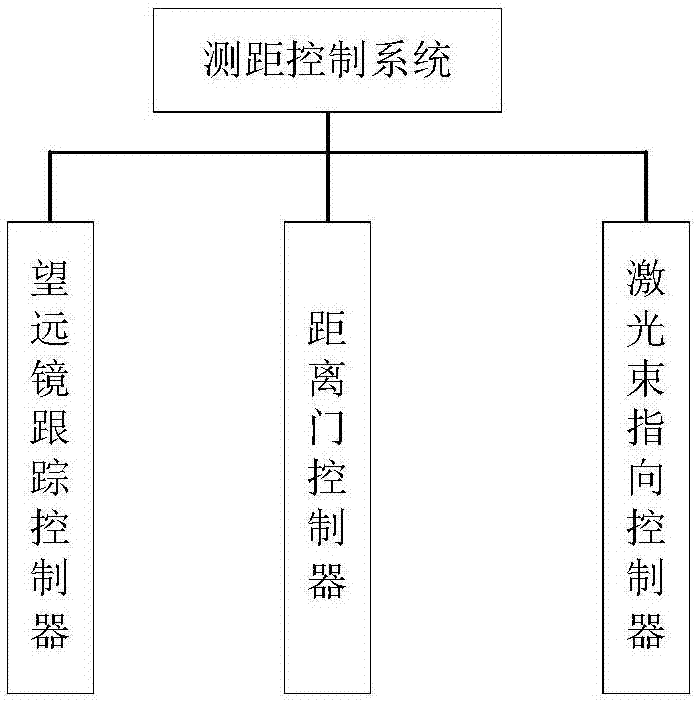
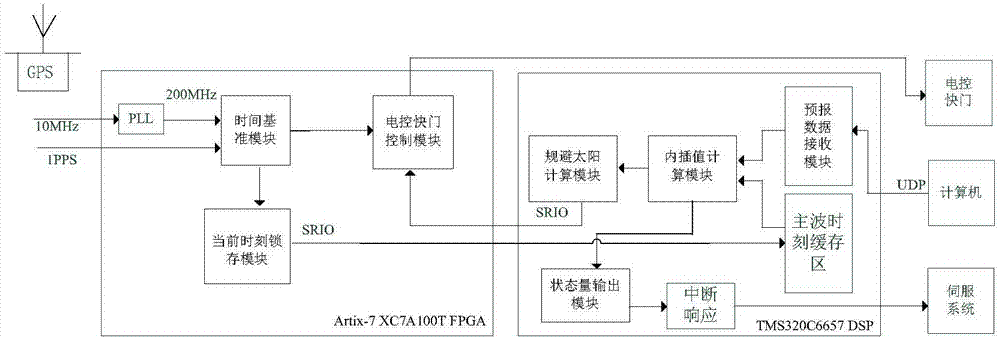
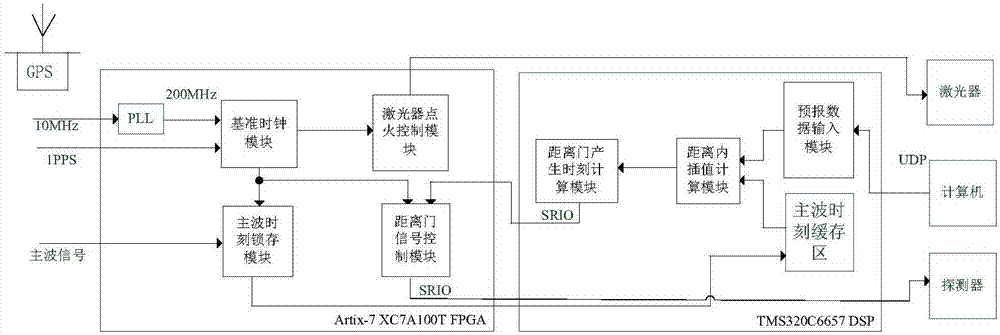
Embedded satellite laser ranging control system
ActiveCN107015234AIncrease flexibilityEasy to handleElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingOrbit prediction
The invention relates to an embedded satellite laser ranging control system, and solves problems that the satellite laser ranging control technology implemented through a main control computer is complex in ranging method, is low response speed and causes the data loss. A telescope tracking controller reads a current observation moment, calculates the azimuth and height position at the current moment through orbit prediction interpolating of an observation station, and outputs the azimuth and height position to a servo system of a motor. A distance gate controller outputs an igniting signal of a laser according to a distance measuring frequency, locks a main wave signal, and calculates the moment when a distance gate signal corresponding to a main wave is generated. A gate control signal is outputted through the distance gate controller. A laser beam direction controller recognizes a light beam image, obtains a light peak position, calculates the deviation between the light peak point and the center of a receiving visual field, and corrects the direction deviation of a laser beam through a control algorithm. The system can meet the demands of higher-repetition-frequency laser ranging through employing an FPGA+DSP heterogeneous processor configuration, and facilitates the upgrading of the whole ranging system.
Owner:中国科学院国家天文台长春人造卫星观测站
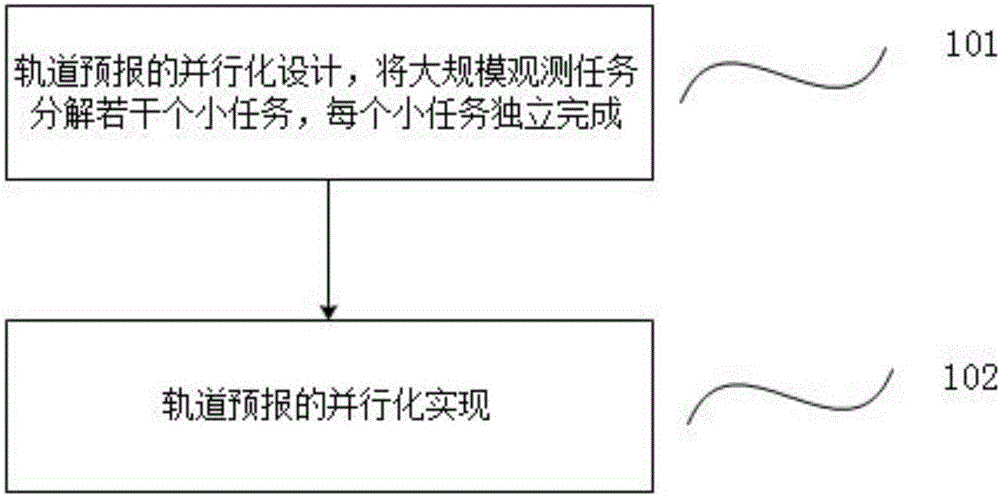
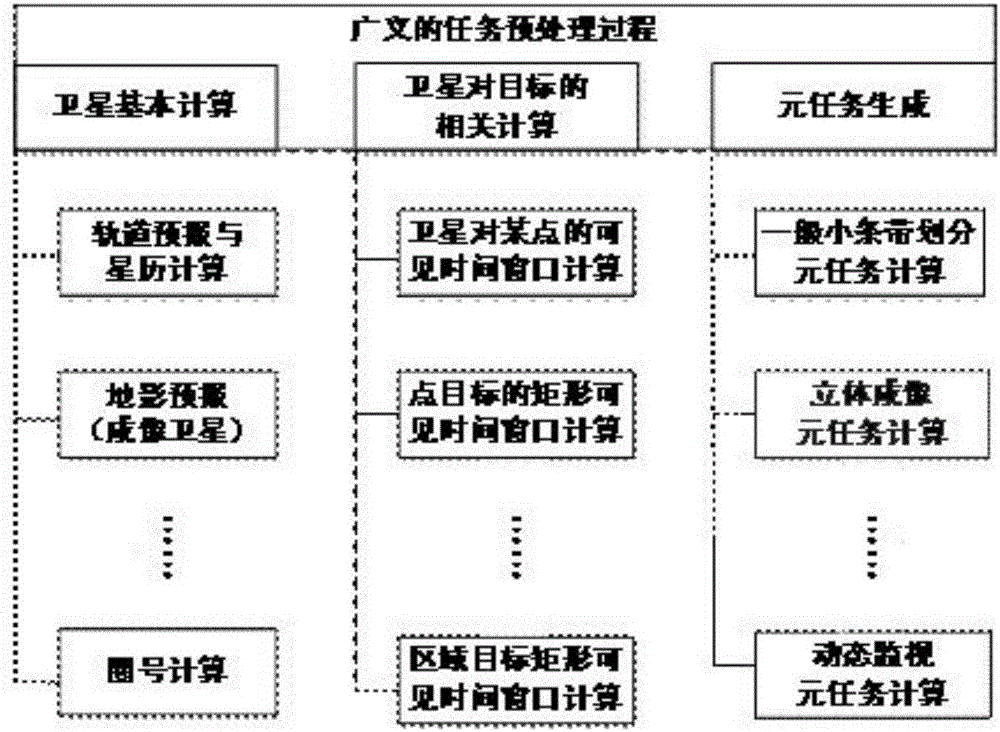
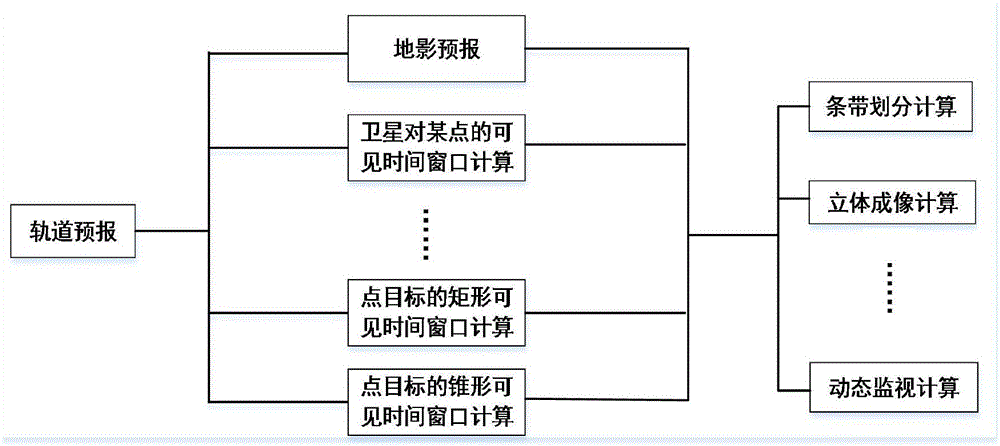
Method for parallelizing preprocessing of tasks of imaging satellites on basis of Spark
ActiveCN106681807AReduce computing timeImprove computing efficiencyProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationOrbit predictionSingle task
The invention discloses a method for parallelizing preprocessing of tasks of imaging satellites on the basis of Spark. The method includes steps of A, parallelly designing orbit prediction, decomposing each large-scale observation task into a plurality of small tasks and independently fulfilling each small task; B, parallelly implementing orbit prediction. The satellites are independent from one another, or task preprocessing of each satellite on the optional single task is independent for solving problems in the aspect of preprocessing of the large-scale observation tasks of the satellites, and the problems can be decomposed by means of distributed parallel computation. The method has the advantages that the integral computation time for preprocessing the tasks can be saved, and the computation efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
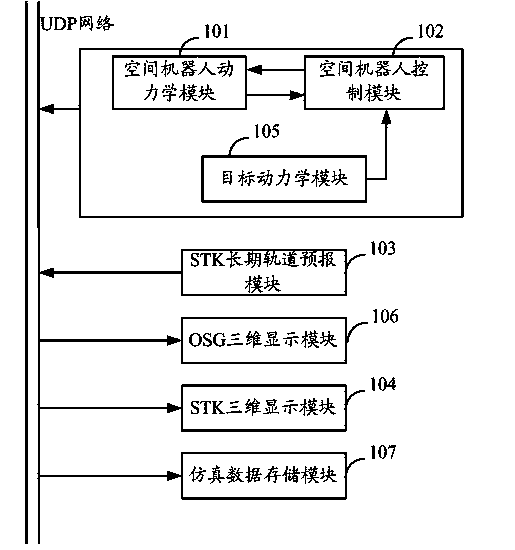
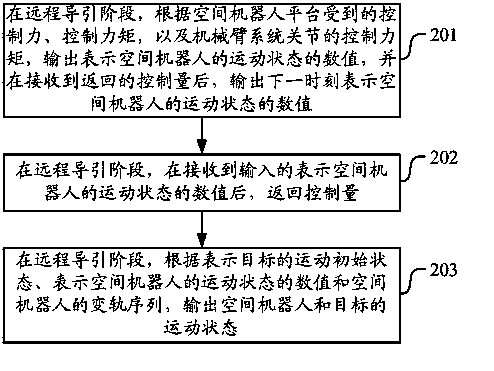
System and method for dynamics simulation of space robot
The invention discloses a system and method for dynamics simulation of a space robot. The method for dynamics simulation of the space robot comprises the steps that a space robot dynamics module outputs a value representing the motion state of the space robot in the remote guiding stage according to the control force and the control moment which are received by a space robot platform and the control moment of a mechanical arm system joint and after the returned control amount is received, a value representing the motion state of the space robot at the next moment is output; after a space robot control module receives the value which is input by the space robot dynamics module and represents the motion state of the space robot in the remote guiding stage, the control amount is returned to the space robot dynamics module by the space robot control module; an STK long-term orbit prediction module outputs the motion state of the space robot and the motion state of a target in the remote guiding stage according to a value representing the motion initial state of the target, the value representing the motion state of the space robot and the orbital transfer sequence of the space robot. According to the system and method for dynamics simulation of the space robot, complete simulation of the whole task stage of the space robot can be provided.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG DEV LTD
Mid-term orbit prediction method and device of low-orbit spacecraft and storage medium
ActiveCN108820260ASolve technical problems with low accuracyHigh precisionCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic component separationOrbit predictionEngineering
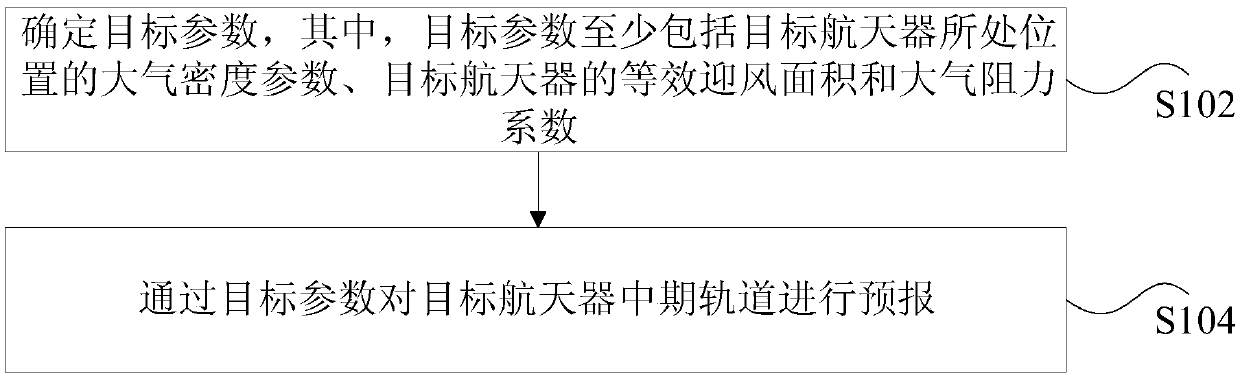
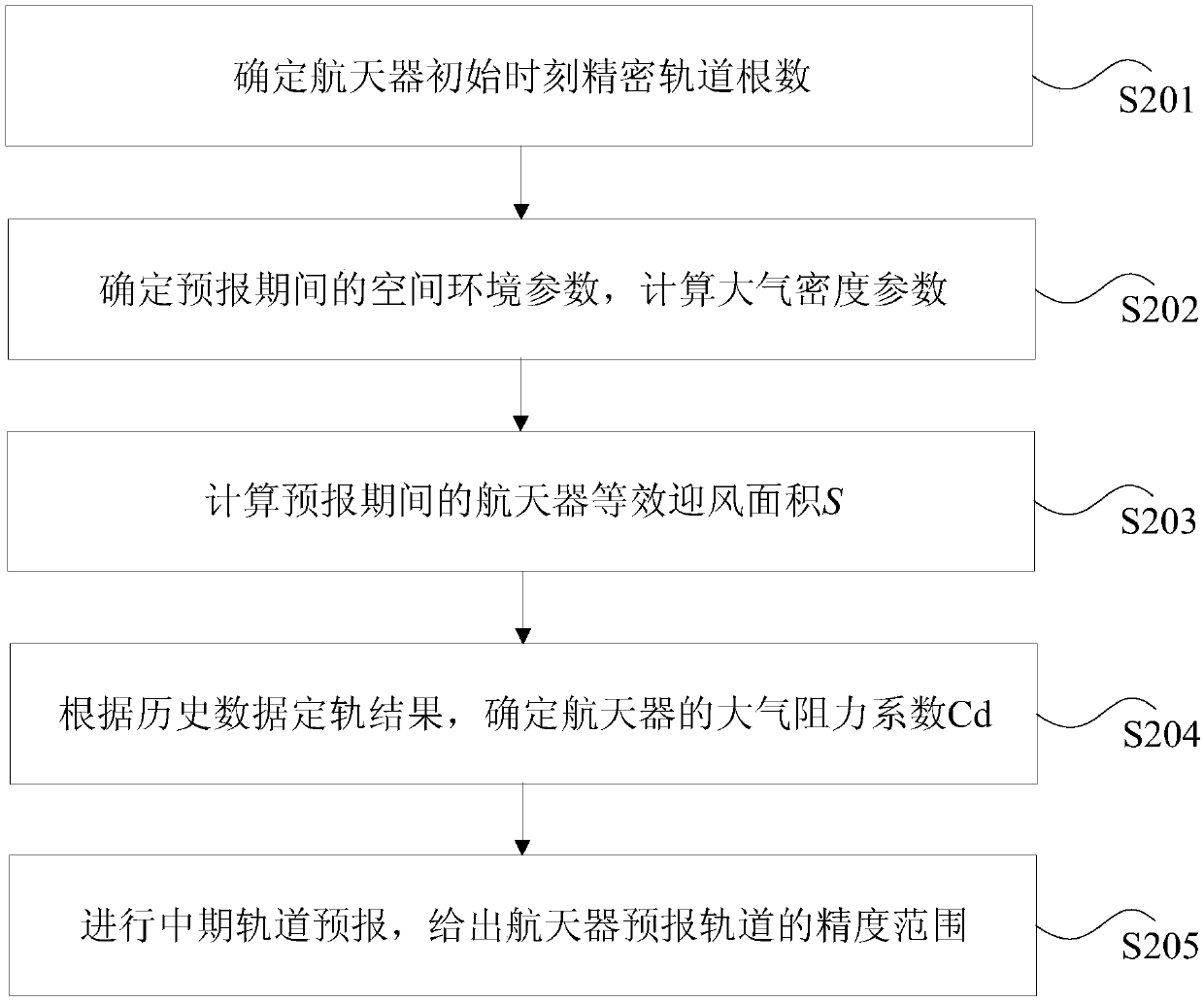
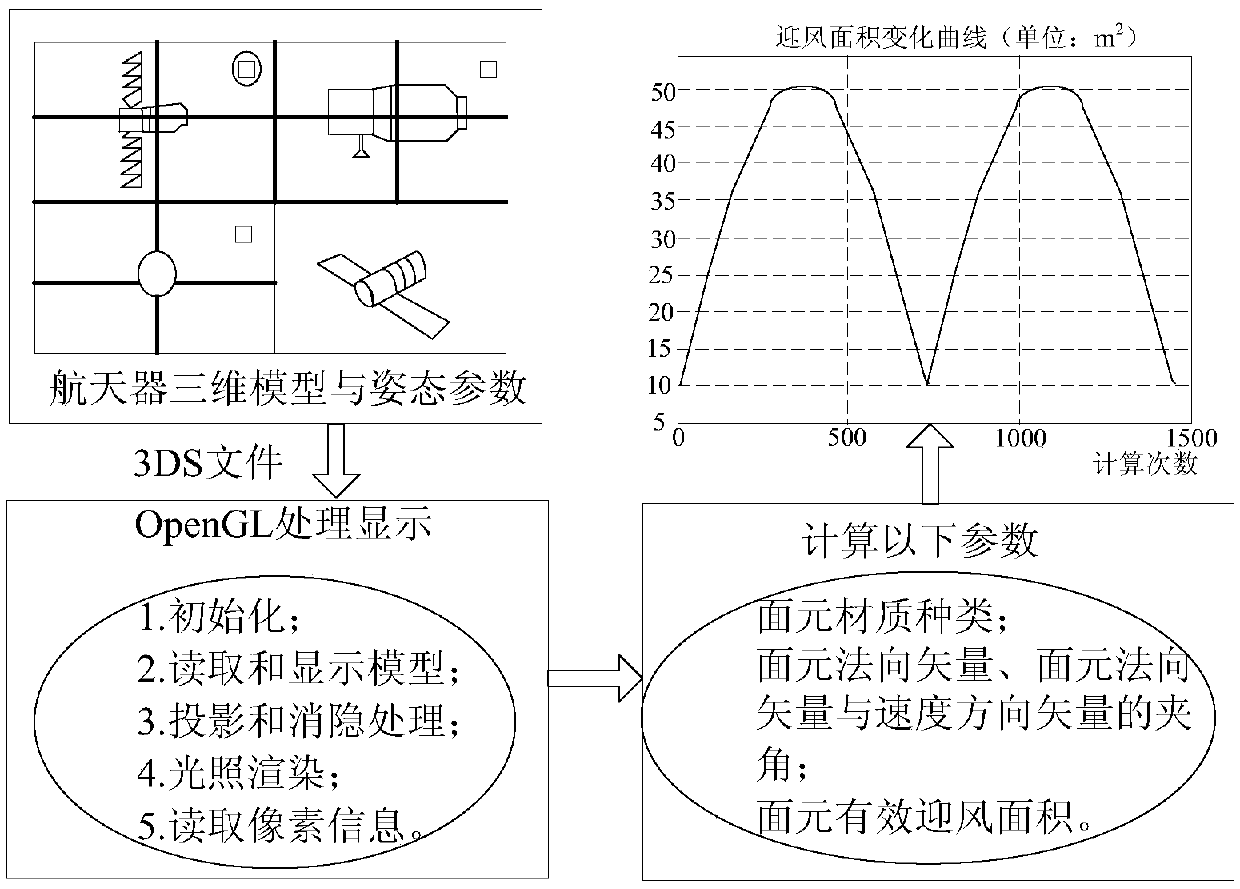
The invention discloses a mid-term orbit prediction method and device of a low-orbit spacecraft and a storage medium. The method includes the steps that target parameters are determined, wherein the target parameters at least comprise the atmospheric density parameter of the position where the target spacecraft is located, and the equivalent windward area and the atmospheric drag coefficient of the target spacecraft; and the mid-term orbit of the target spacecraft is predicted through the target parameters. The effect that the mid-term orbit prediction accuracy of the low-orbit spacecraft is improved is achieved through the method and device.
Owner:中国人民解放军63920部队
Unattended satellite ground station tracking control system
InactiveCN110838864AAccurate forecastStrong tracking abilityRadio transmissionAutomatic controlControl system
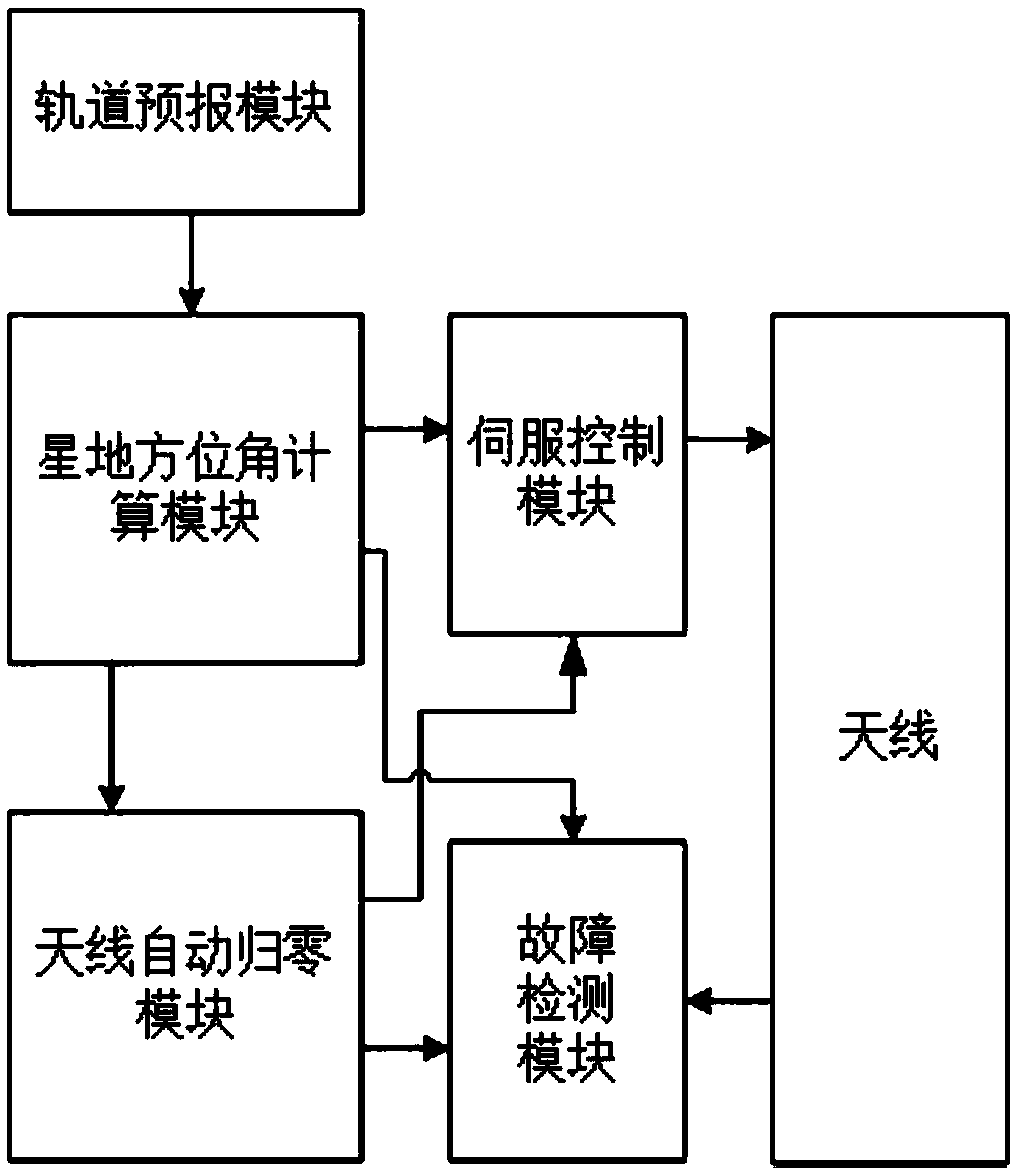
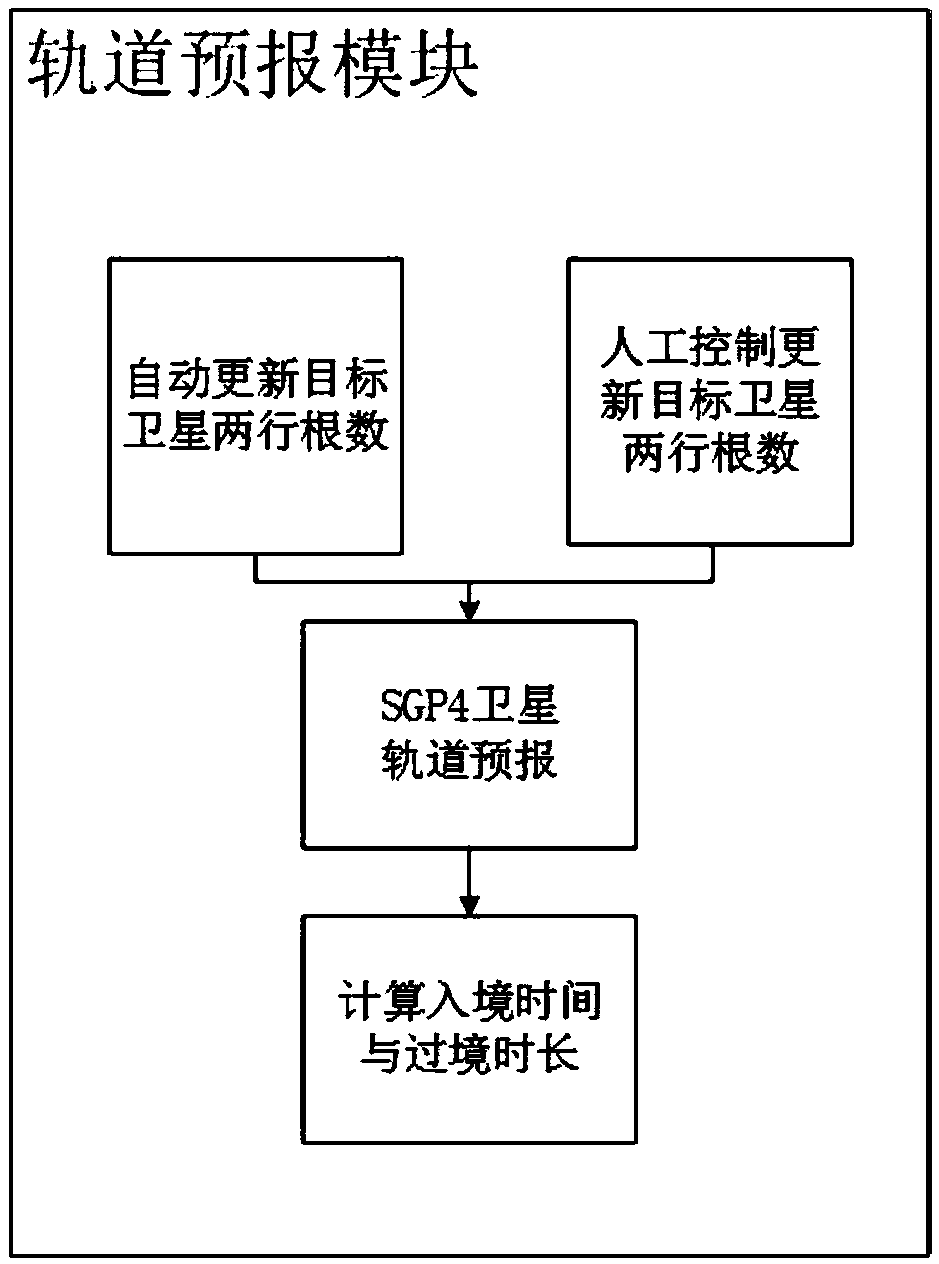
The invention discloses an unattended satellite ground station tracking control system. The system is suitable for task execution of satellite constellation satellite-ground communication, and specifically comprises an orbit prediction module, a satellite-ground azimuth angle calculation module, a servo control module, an antenna automatic zeroing module and a fault detection module. The orbit data of a satellite in the target constellation can be automatically updated and forecasted in real time, the antenna pointing is automatically controlled to realize the optimal satellite-ground communication gain, the antenna pointing can be automatically returned to zero after the task is finished, and the real-time antenna pointing monitoring can be performed during the task proceeding period. According to the invention, the traditional working mode of manually operating the ground station is changed, the communication effect is optimal, and the reliability is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application-oriented heterogeneous constellation space-ground integrated task planning method and device
ActiveCN111912412AReduce computational complexityInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingObservation dataGreedy algorithm
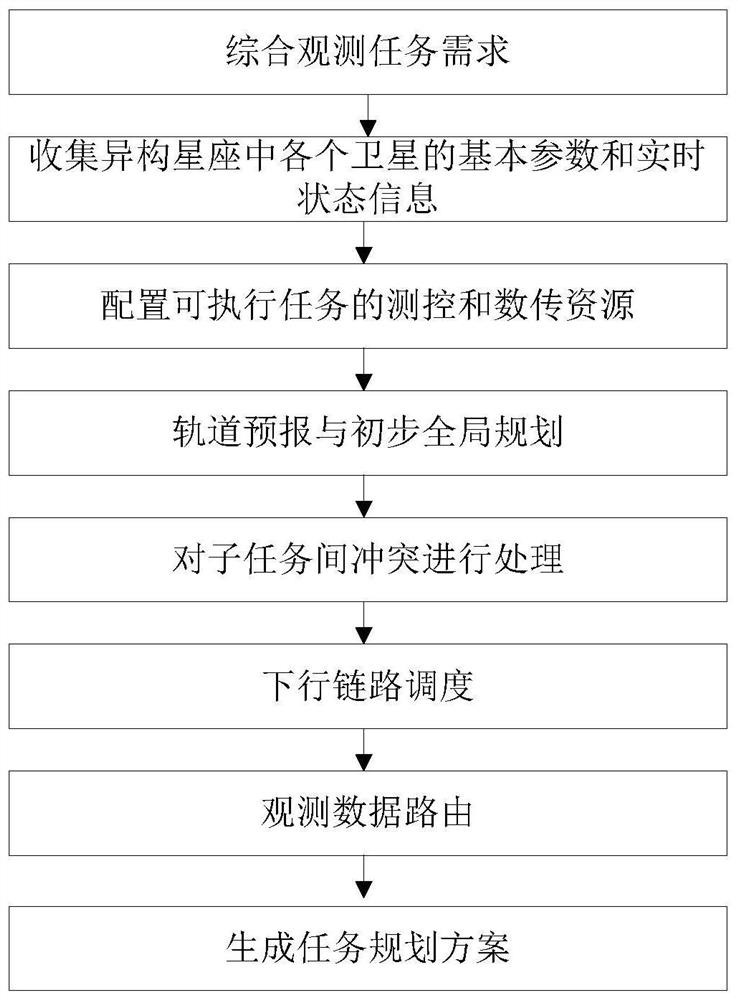
The embodiment of the invention provides an application-oriented heterogeneous constellation space-ground integrated task planning method and device, wherein the method comprises the steps of synthesizing an observation task demand; collecting the basic parameters and real-time state information of each satellite in the heterogeneous constellation; configuring the measurement and control and datatransmission resources of executable tasks; giving a time function of each satellite orbit position by utilizing accurate orbit prediction; sorting all the sub-tasks, processing conflicts among the sub-tasks, and judging whether a conflict relationship between the current to-be-added observation sub-task and each observation sub-task in the current observation sub-task set meets constraints or not; carrying out downlink scheduling; scheduling an observation data route by adopting a greedy algorithm; and generating a task planning scheme, estimating the duration of each observation and data transmission activity, the conversion time of satellite attitudes and the change of satellite related state parameters, and generating a task arrangement scheme containing the observation activities andthe data transmission activities.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
High-precision satellite-borne orbit prediction method based on numerical fitting
ActiveCN110132261AImprove forecast accuracyNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by astronomical meansSpace environmentNumerical fitting
The invention discloses a high-precision satellite-borne orbit prediction method based on numerical fitting. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining atmospheric environment parameters including the latest solar radiation flow and a geomagnetic index, satellite star parameters and the latest precise orbital elements of the satellite, combining the star and space environment parameters, carrying out orbit prediction by utilizing a ground high-precision numerical method so as to obtain a set of satellite instantaneous orbital elements in a prediction arc section, then, converting into an average element to perform numerical fitting so as to obtain a change item coefficient of each orbital element, arranging multiple sets of primary orbits to carry out segmented extrapolation according to an satellite-borne predication requirement, carrying out orbit prediction according to the arranged initial orbital element and the change item coefficient to obtain the average element of the satellite at the prediction moment, if the prediction precision requirement is high, arranging a plurality of sets of initial values for staged prediction, converting the average element ofthe satellite at the prediction moment into the instantaneous element, so that the instantaneous position of the satellite is obtained. According to the method in the invention, the problem that the precision of satellite-borne orbit prediction is poor in the prior art is solved.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
A method and apparatus for correcting three-axis antenna pointing
ActiveCN110377929ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHorizonSimulation
The invention provides a method and a device for correcting the orientation of a three-axis antenna, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an approximate value of an orientation angle set by an antenna under an equipment horizon system and an antenna guide angle under an equipment measurement system according to a target position, provided by orbit prediction, under the equipment horizon system through coordinate transformation; obtaining a corresponding pointing angle of the approximate value of the antenna guide angle under the equipment horizon system through correction calculation;and obtaining an accurate value of the antenna guiding angle set by the antenna under the equipment horizon system under the equipment measurement system through recursive calculation and by utilizing the corresponding pointing angle of the approximate value of the antenna guiding angle under the equipment horizon system. By utilizing the method, digital tracking or program tracking can be completed in real time and with high precision under the working condition of the high frequency band of the three-axis antenna.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA +1
Satellite accurate orbit prediction method
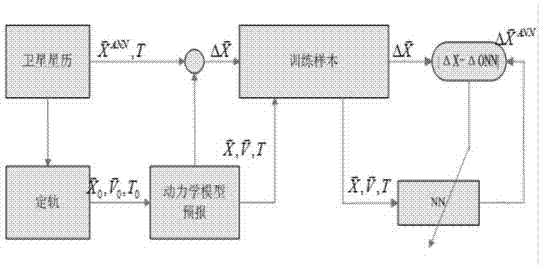
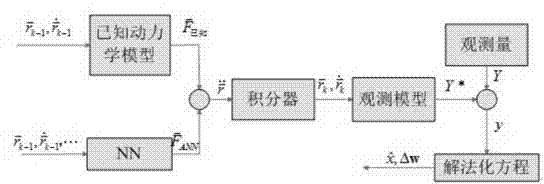
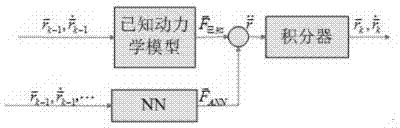
InactiveCN103886368AHigh precisionEasy to controlBiological neural network modelsOrbit predictionEphemeris
The invention relates to a satellite accurate orbit prediction method. Deep neural network automatic learning training is carried out according to comparison results of a prediction ephemeris calculated through a satellite ephemeris and kinetic models and a real ephemeris to obtain a deep neural network compensator, and then the prediction of satellite accurate obits is obtained by adding the error compensation obtained through the deep neural network compensator and prediction orbit results obtained through the kinetic models. According to the satellite accurate orbit prediction method, the kinetic prediction models and deep neural networks are two independent parts, the structure is simple, the method is easy to achieve, compared with pure kinetic models or other neural network algorithms, prediction accuracy and control over prediction errors in long-term prediction are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
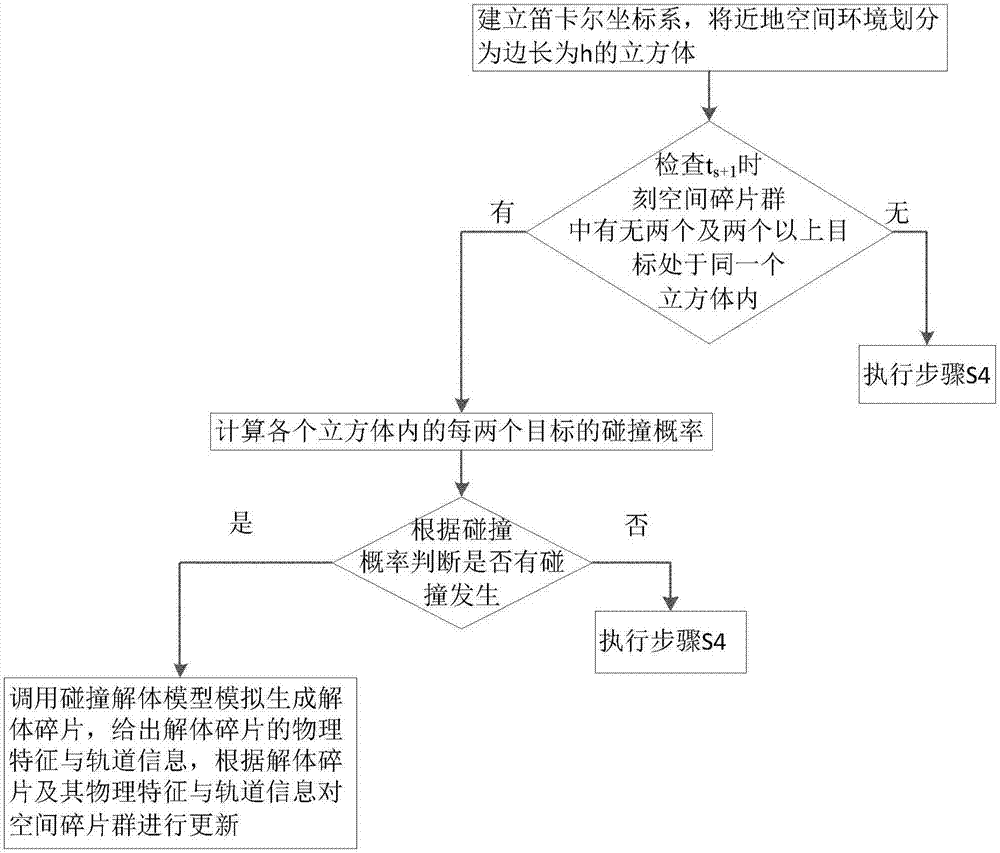
Multiple-constraint multi-spacecraft flight interval indicating and collision avoidance method
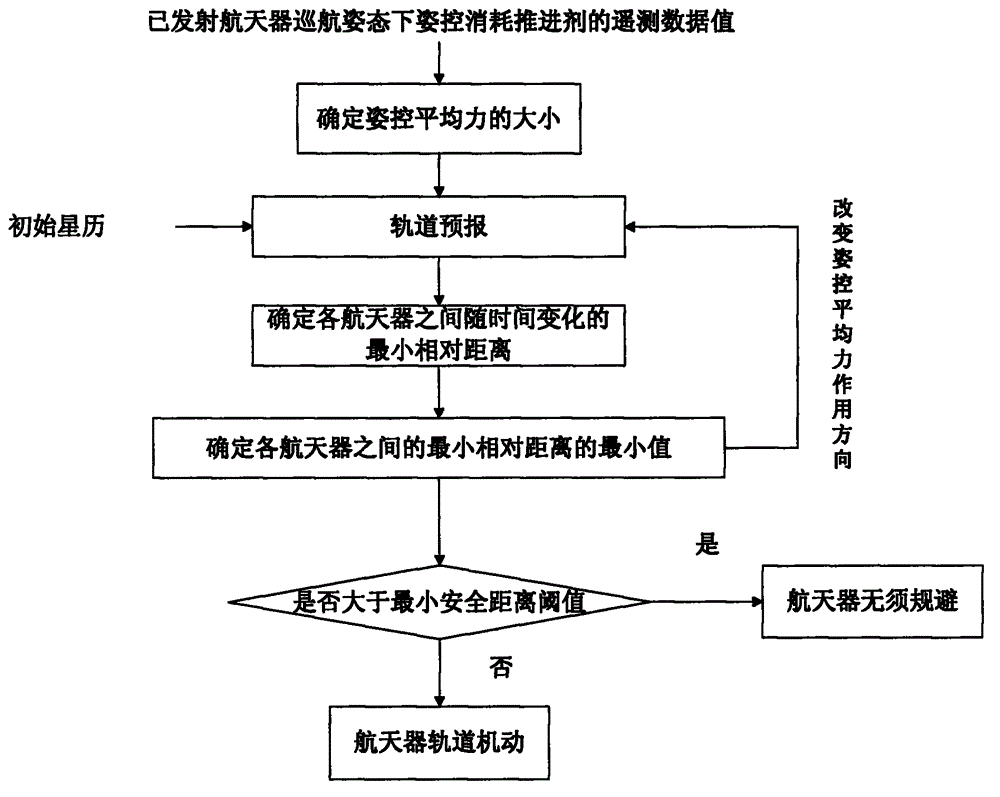
ActiveCN103064423AGuaranteed validityEnsure safetyPosition/course control in three dimensionsAttitude controlEngineering
A multiple-constraint multi-spacecraft flight interval indicating and collision avoidance method includes the following steps: (1) confirming magnitude of attitude control average force according to telemeasuring data value of propellant consumed by attitude control of launched spacecrafts on an orbit under the cruising attitude, (2) conducting high-accuracy orbit prediction according to initial ephemeris information of each spacecraft and the attitude control average force confirmed in the step one, calculating ephemeris of each spacecraft in an inertial frame at any time and relative distance between each spacecraft at any time, and confirming the minimum relative distance between the spacecrafts, (3) changing the direction of the attitude control average force, repeating the step one and the step two, calculating the minimum value of the minimum relative distance between each spacecraft, namely, the direction of the attitude control average force corresponding to the minimum value is the worst situation, (4) comparing the minimum value confirmed in the step three with the minimum safe distance, when the minimum value is greater than the minimum safe distance, the spacecrafts has no risk of collision, otherwise, within a first circle observation and controlling track segmental arc, one spacecraft which is selected conducts orbital maneuver, and thereby the distance between the spacecrafts is widened and the collision risk of the spacecrafts is avoided.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
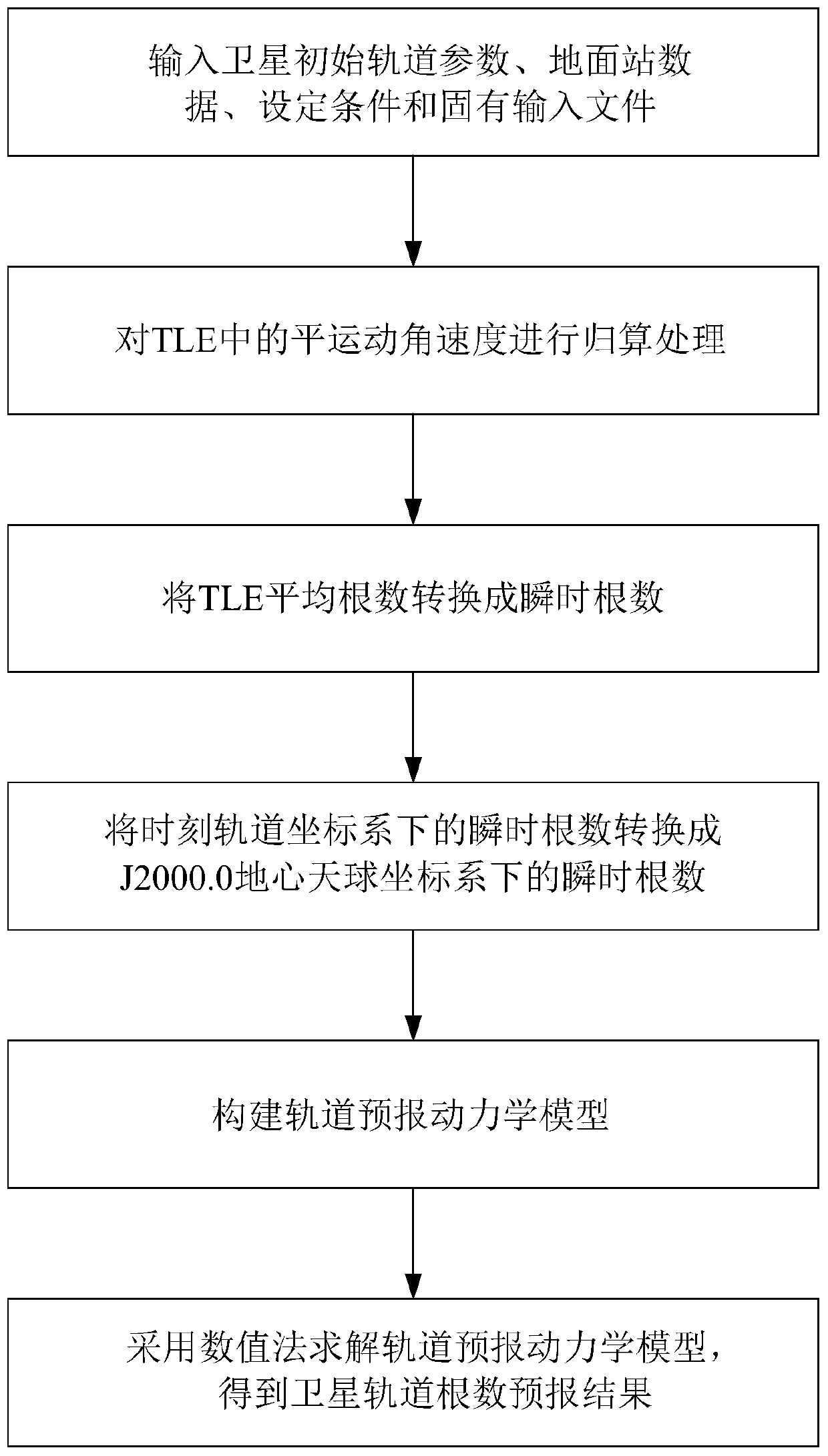
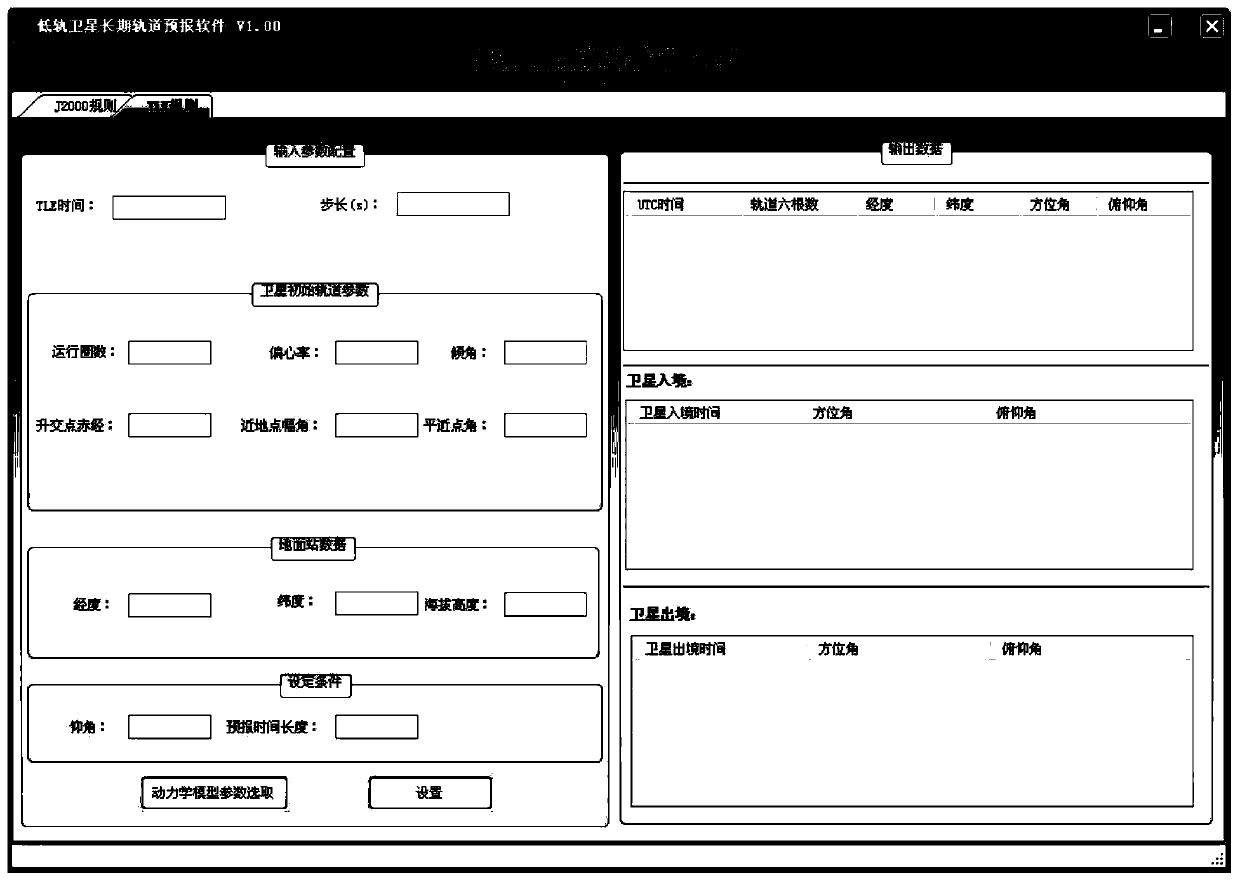
Low-earth-orbit satellite long-term orbit prediction method based on two line element
PendingCN110595485AHigh solution accuracyReduce computationInstruments for comonautical navigationSustainable transportationAngular velocityOrbit prediction
The invention relates to a low-earth-orbit satellite long-term orbit prediction method based on a two line element. The method comprises the following steps: performing related processing on a two line element in an orbital coordiante system at a moment t, thus obtaining a satellite orbital element initial value applicable to an orbit prediction dynamical model in a J2000.0 geocentric celestial coordinate system; and solving the orbit prediction dynamical model by adopting a numerical method, thus obtaining a satellite orbital element prediction result, wherein the related processing comprisesreduction processing performed on angular velocity of peace movement in the two line element, conversion of a mean element into an instant element in the orbital coordinate system at the moment t andconversion of the instant element in the orbital coordinate system at the moment t into an instant element in the J2000.0 geocentric celestial coordinate system. The low-earth-orbit satellite long-term orbit prediction method based on the two line element is high in prediction precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
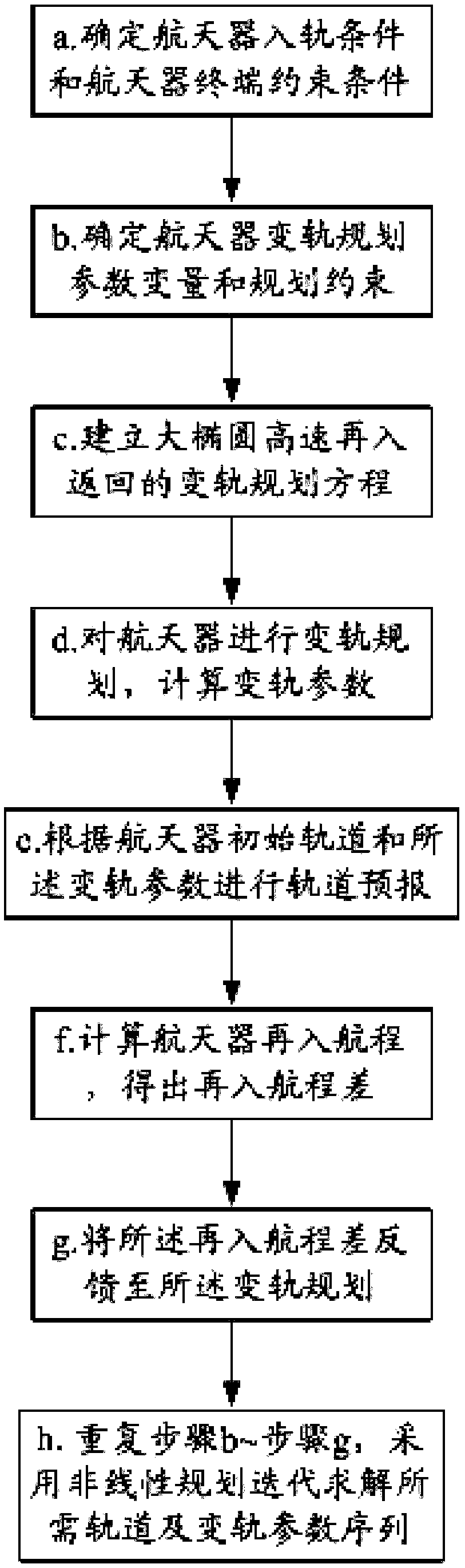
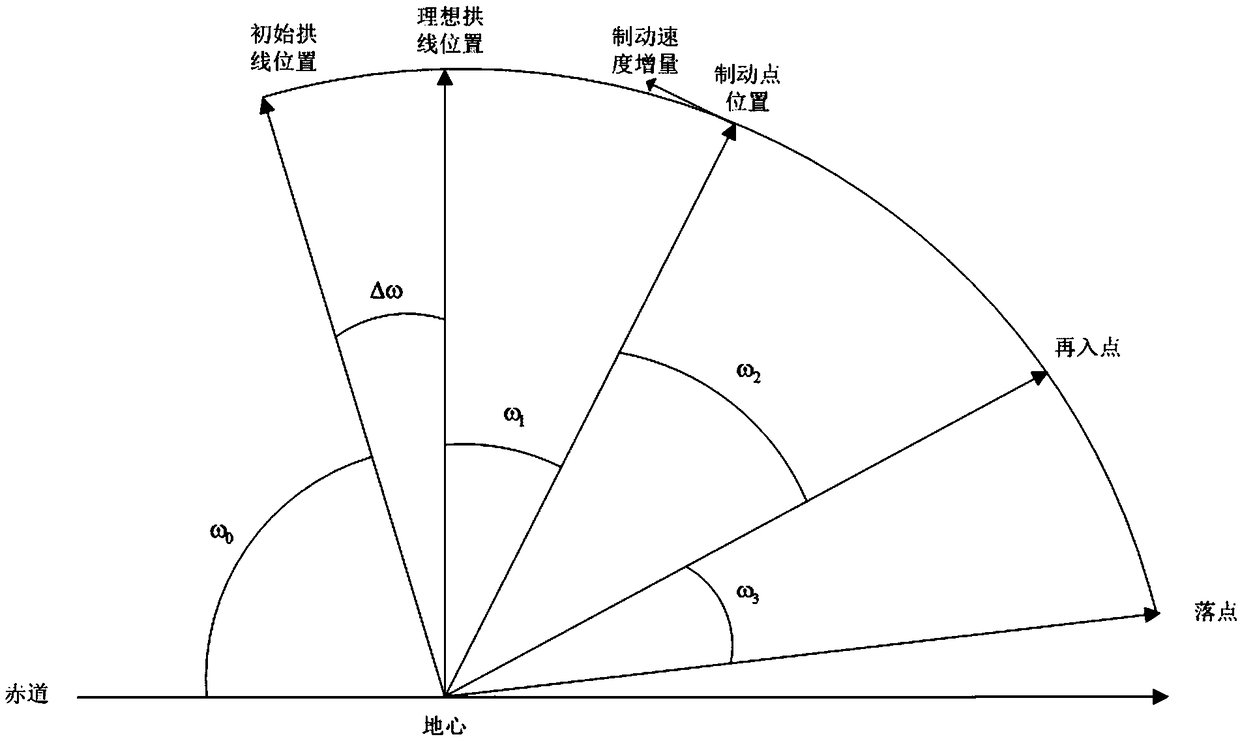
A large elliptical orbit transfer planning method for spacecraft returning to a predetermined landing point
ActiveCN109080854AFast convergenceEasy to implementCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusRe entryEllipse
The invention relates to a large elliptical orbit transfer planning method for a spacecraft returning to a predetermined landing point, comprising the following steps: a. Determining a spacecraft orbit entry condition and a spacecraft terminal constraint condition; (b) determine parameter variable and planning constraints of spacecraft orbit transfer planning; C. Setting up the orbit-changing programming equation of high-speed reentry of large ellipse; D. planning Orbit transfer of the spacecraft and calculating orbit transfer parameters; E. Orbiting prediction based on the initial orbit of the spacecraft and the orbit transfer parameters; F. Calculating the re-entry distance of the spacecraft to obtain the re-entry distance difference; (g) feeding back the reentry range difference to theorbit transfer planning, and adopting nonlinear programming iteration to calculate the required orbit and the orbit transfer parameted sequence. The large elliptical orbit transfer planning method ofthe spacecraft returning to the predetermined landing point can solve the orbit transfer planning problem of a near-earth spacecraft returning to a large elliptical orbit at a high speed.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
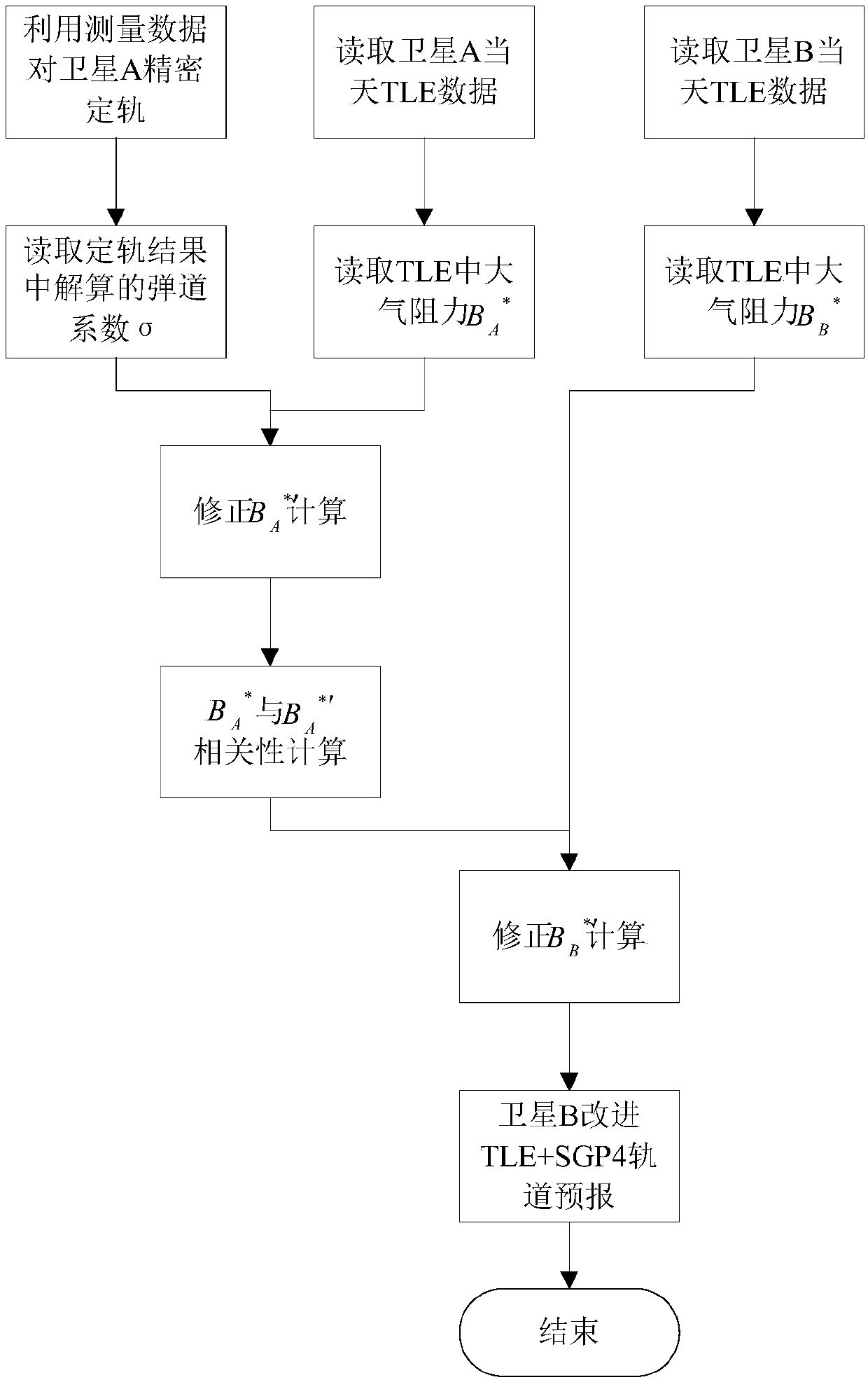
Resistance coefficient adaptive modulation method based on precise ephemeris
ActiveCN108508457ASolve the problem of adaptive modulationImplement Adaptive ModulationSatellite radio beaconingOrbit predictionEphemeris
The present invention provides a resistance coefficient adaptive modulation method based on precise ephemeris. Measurement data of a measurement station and a high-precision dynamical model are combined to optimize and correct a resistance modulation coefficient of TLE data, correlation of equal-height satellite correction is analyzed in a space environmental change condition, correlation of the TLE data of the equal-height satellite in the same day and the precise ephemeris is employed to design an orbit prediction algorithm for correction of a TLE+SGP4 model when the satellite is difficult to obtain enough outer measurement data and improve the TLE short-term prediction precision in a space environmental dramatic change period. The resistance coefficient adaptive modulation method basedon precise ephemeris can achieve adaptive modulation of abnormal satellite resistance coefficients, is high in adaptability and improves the prediction precision.
Owner:中国人民解放军63789部队
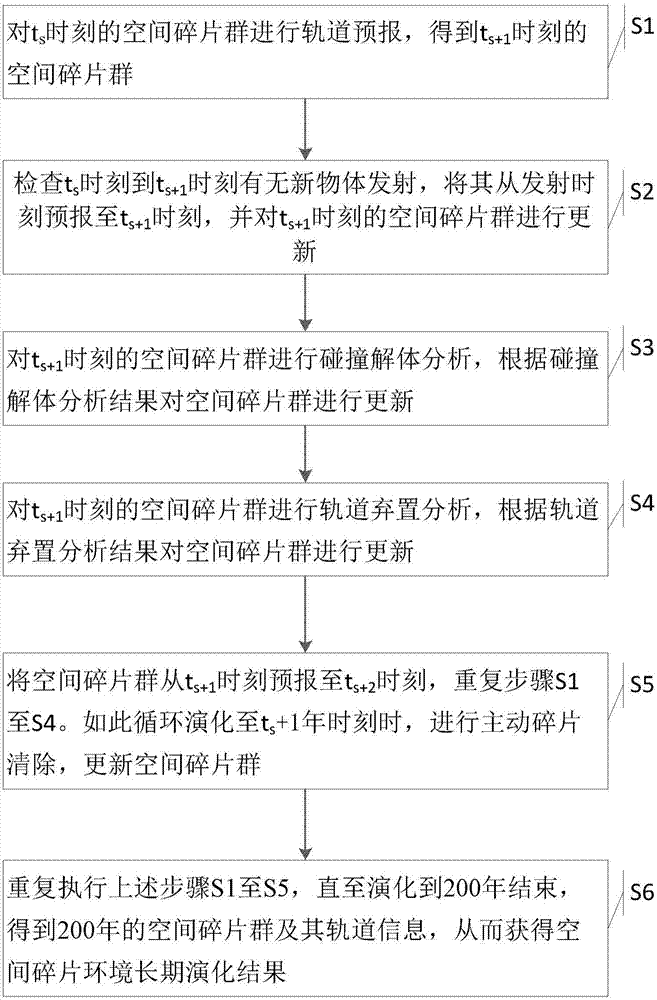
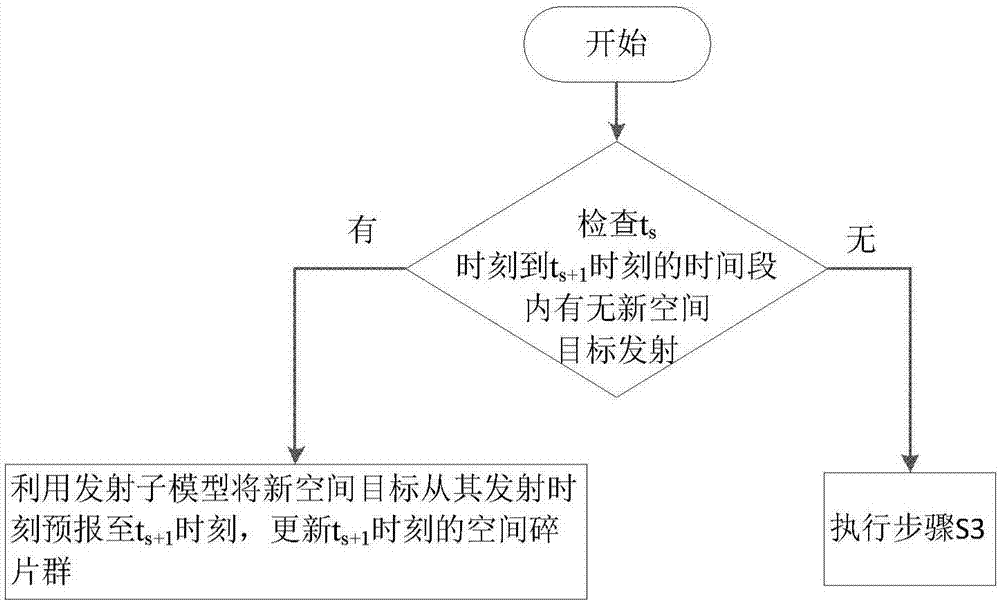
Modeling method of space debris environment long-term evolution model
ActiveCN107451319ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsModel methodOrbit prediction
The invention provides a modeling method of a space debris environment long-term evolution model. The current space debris group is used as initial input; the current space debris group is subjected to orbit prediction by a simplified semi-analysis method; and further space object emission, on-orbit object collision disassembly analysis, orbit discarding analysis and active debris clearing are considered, so that the space debris environment long-term evolution result is obtained. The evolution model can describe the space debris environment evolution condition at a random moment in next two hundred years at different emission levels by using different debris retarding and clearing measures, so that strategy analysis and model support can be provided for China for active debris clearing in further.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
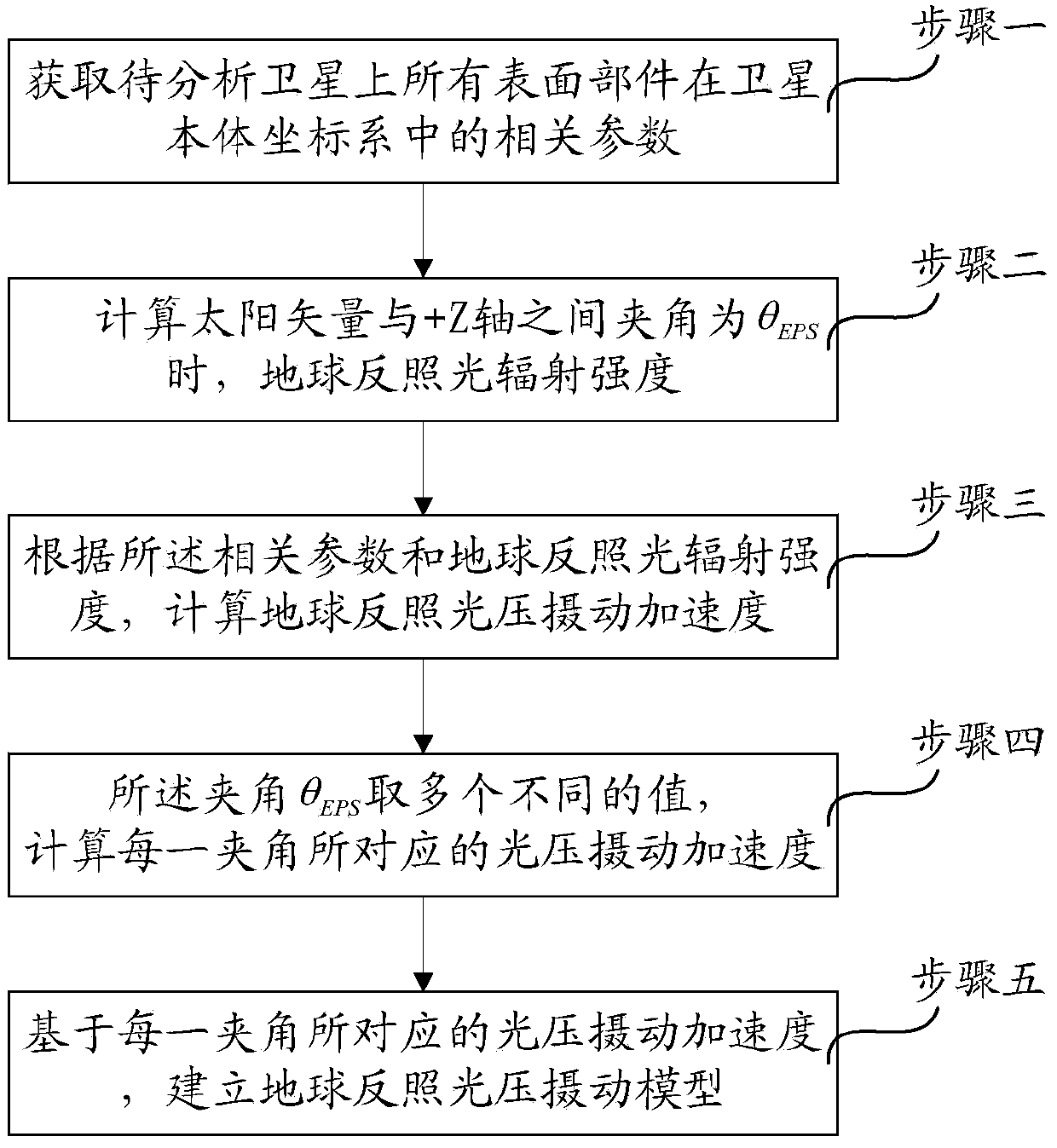
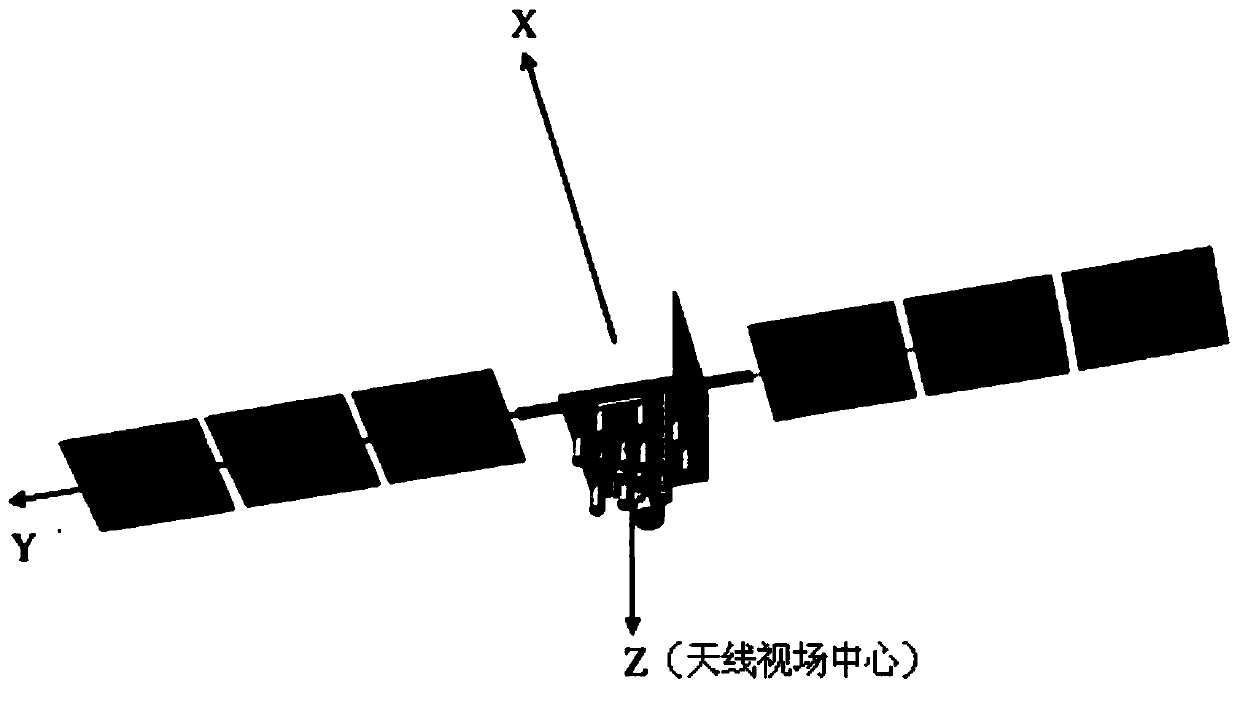
Earthlight light pressure perturbation modeling method for navigational satellite complicated model
ActiveCN104021241AComplete and improve the kinetic modelImprove precision orbit determinationSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemOptical radiationOrbit prediction
The invention provides an earthlight light pressure perturbation modeling method for a navigational satellite complicated model. The method particularly includes the first step of obtaining related parameters of all surface components on a satellite to be analyzed in a satellite body coordinate system, the second step of calculating the optical radiation intensity of earthlight when the included angle between a sun vector and the positive Z-axis in the satellite body coordinate system is theta EPS, the third step of establishing light path tracking of the earthlight according to the related parameters and the optical radiation intensity of the earthlight and calculating the light pressure perturbation accelerated speed a of the earthlight, the fourth step of allowing the included angle theta EPS to be different values and calculating the light pressure perturbation accelerated speed a corresponding to each included angle theta EPS, and the fifth step of establishing an earthlight light pressure perturbation model f (theta EPS) on the basis of the light pressure perturbation accelerated speed corresponding to each included angle theta EPS with the included angle theta EPS as an independent variable. Trough the method, a high-precision satellite dynamical model can be improved, and the accuracy of precise orbit determination and orbit prediction can be further improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Simulation method of signal acquisition process of inter-satellite link based on orbit prediction
ActiveCN109543292ASimulation results are accurateAdjust capture strategyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAcquisition timeOrbit prediction
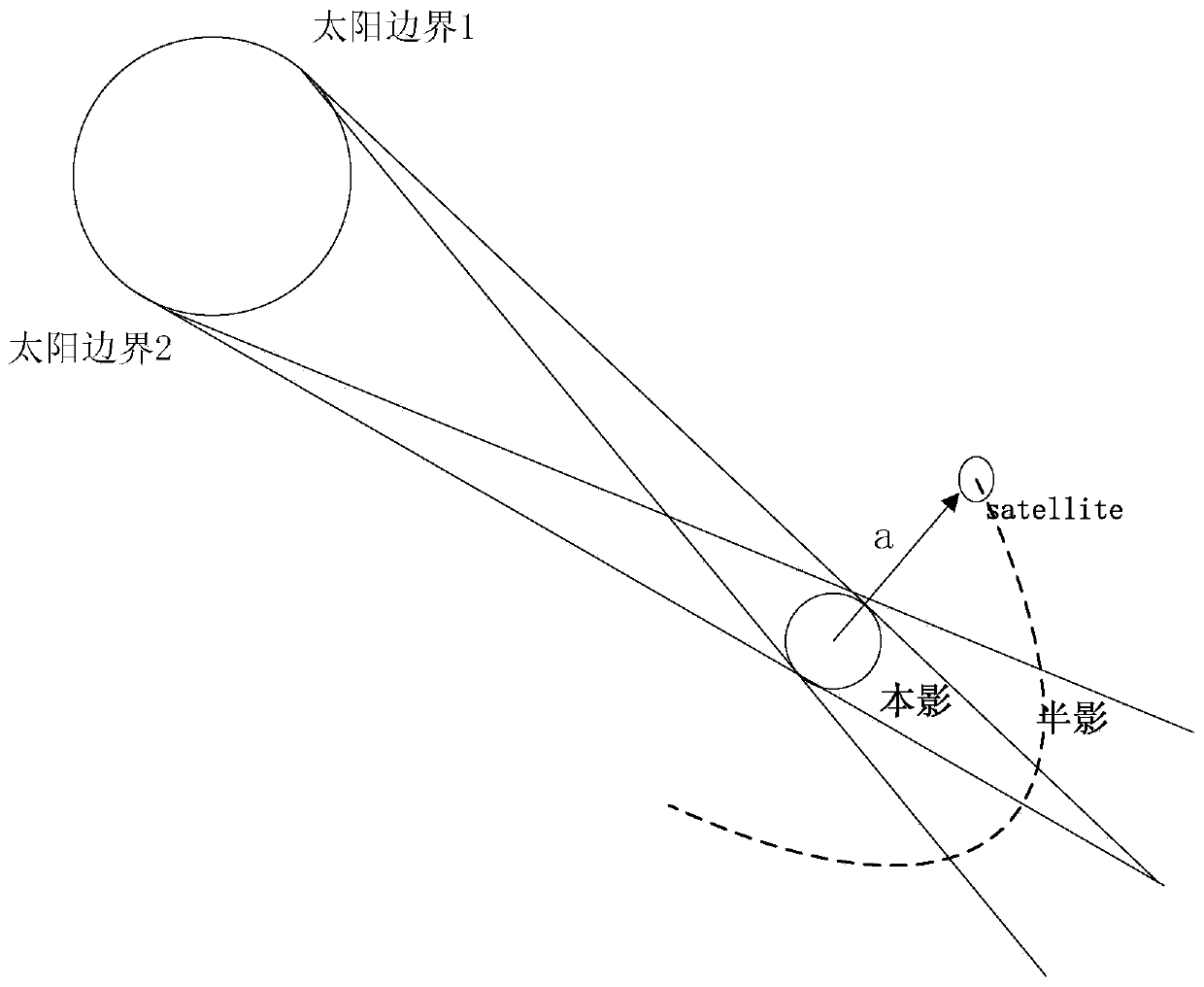
The simulation method of signal acquisition process of inter-satellite link based on orbit prediction is used in the field of satellite communication technology. The invention solves the problem thatthe signal acquisition process of the inter-satellite link between the medium-low orbit satellites cannot be accurately described by the traditional simulation method. The invention considers the influence of the motion trajectory of the user satellite, Therefore, the simulation result obtained based on the invention can be more accurate, and the significance of the invention also lies in that after accurately obtaining the acquisition time and the acquisition probability of the medium and low orbit targets, the acquisition strategy used in the satellite acquisition process can be adjusted, and the simulation result has strong practical reference value. The invention can be applied to the field of satellite communication technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Mars probe onboard autonomous orbit calculation method
InactiveCN107451656AMeet limited resourcesConstrained limited resourcesNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNerve networkDynamic models
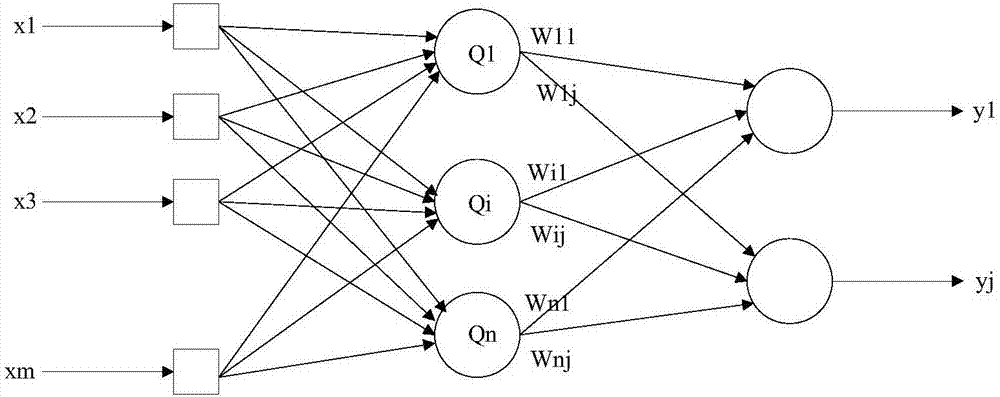
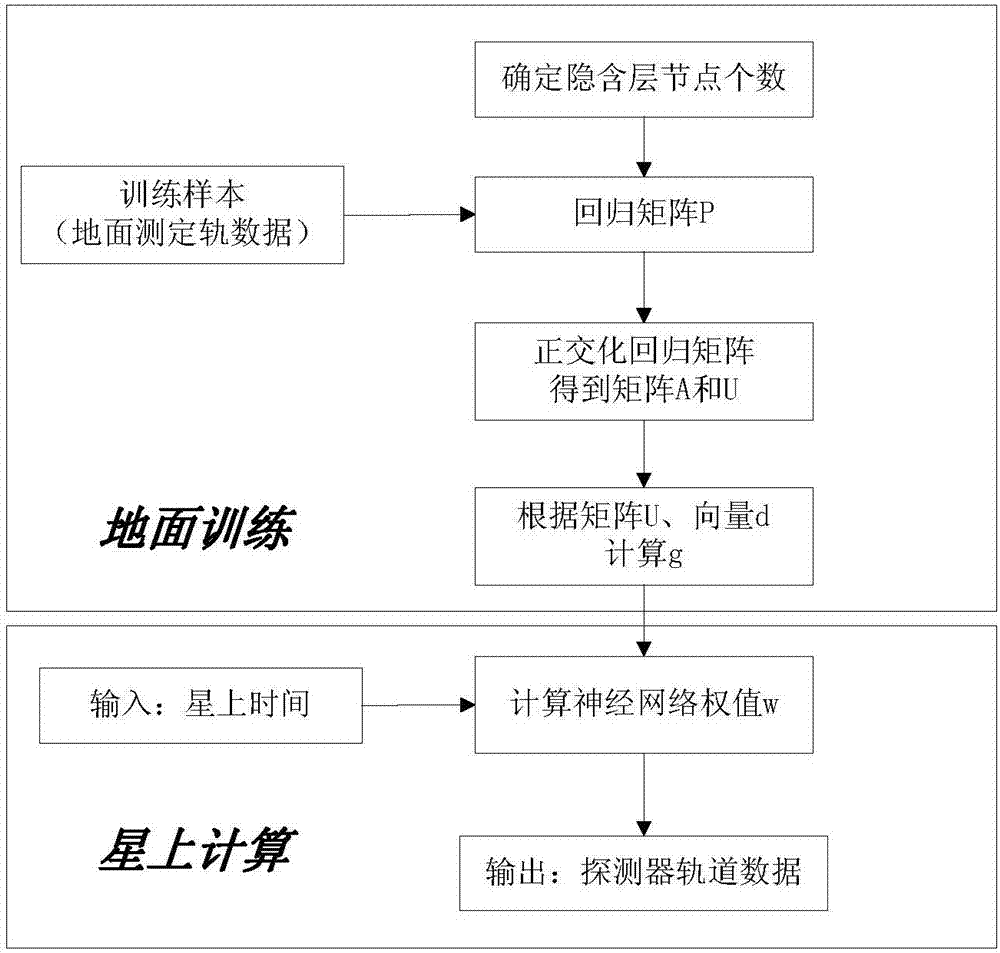
The invention discloses a mars probe onboard autonomous orbit calculation method, which is a calculation method based on radial basis function neural network curve fitting. The method includes the following steps: building a three-layer radial basis function network model; getting orbit prediction data of a mars probe within a period of time according to ground orbit determination, and training the radial basis function network model by taking the data as a training sample; and finally, uploading the trained radial basis function neural network model as an onboard orbit prediction model to the mars probe. There is neither need for establishment of a complex dynamic model on a satellite nor need for ephemeris calculation. The prediction precision is almost equal to the ground orbit prediction precision. The method is also suitable for engineering implementation. The method not only can satisfy the engineering precision constraints of the recursion result, but also can satisfy the constraints of limited resources of onboard computers.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Formation satellite relative orbit determination method facilitating satellite-borne on-orbit real-time processing
ActiveCN110764127AContinuously output high-precision navigation resultsLower requirementSatellite radio beaconingRelative orbitObservation data
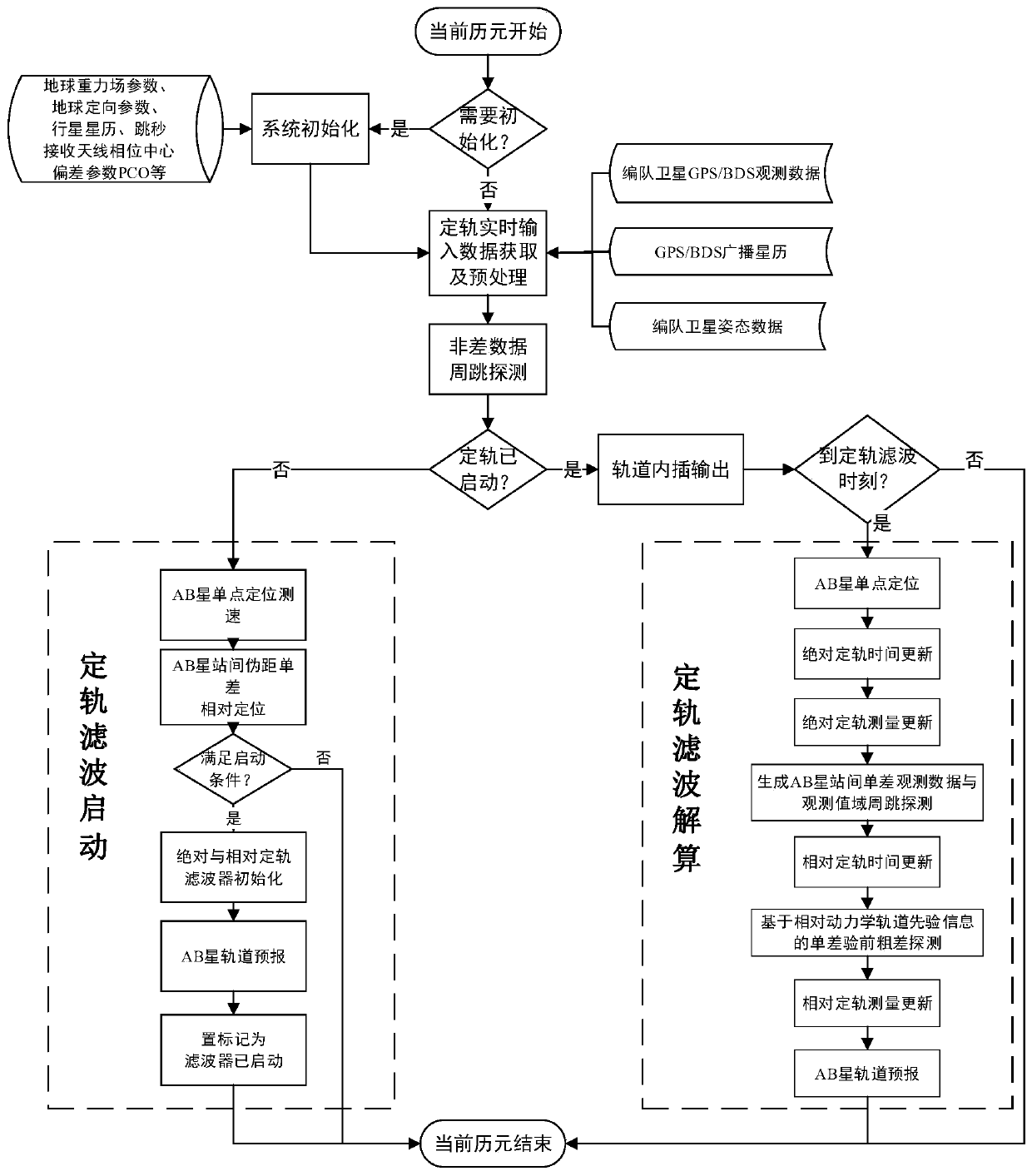
The invention discloses a formation satellite relative orbit determination method facilitating satellite-borne on-orbit real-time processing and belongs to the field of satellite formation relative navigation. According to the method, a GPS / BDS broadcast ephemeris and a simplified relative kinetic model are used, the in-orbit real-time processing is carried out on GPS / BDS double-frequency observation data of formation satellites, in consideration of limited computing resources of a satellite-borne processor, an operation mode of dynamic orbit prediction matched with orbit interpolation is designed, a core complex data processing process is realized in multiple steps in a time-sharing manner to reduce the computing time consumption of a single epoch, and high-precision absolute and relativeorbit results of the formation satellites with adjustable frequencies can be output. The method is suitable for inter-satellite formation with a large inter-satellite distance range, a smooth navigation result meeting certain precision requirements still can be continuously output under the condition that GPS / BDS signals are interrupted, and the method has the advantages of high orbit determination precision, good stability, low requirement for the performance of the satellite-borne processor, easy engineering achievement and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
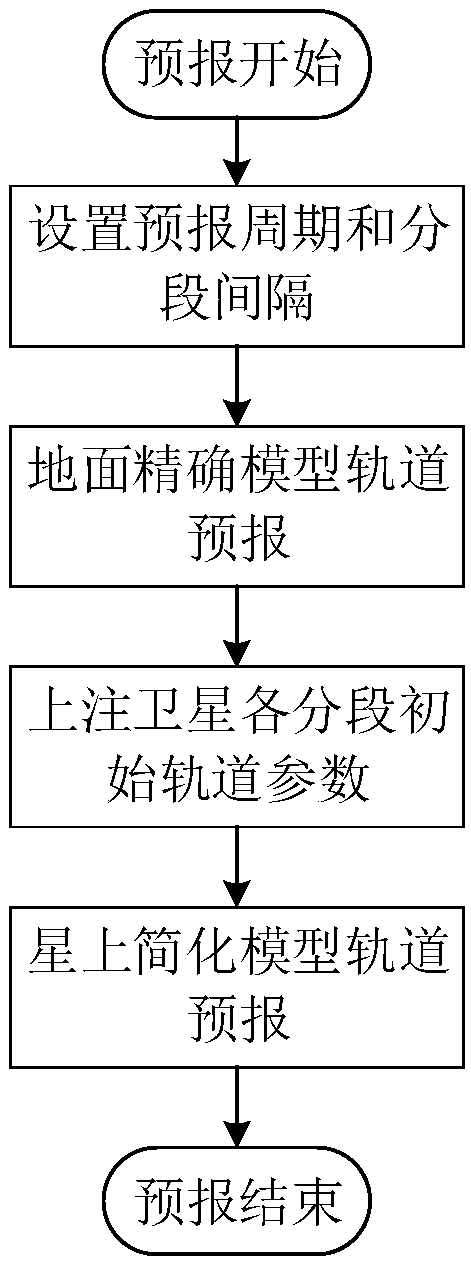
On-satellite autonomous satellite orbit prediction method
ActiveCN109059937AEffective use of high computing powerEffective use of computing powerInstruments for comonautical navigationPrediction algorithmsControl system
The invention discloses an on-satellite autonomous satellite orbit prediction method. Firstly, a user comprehensively considers prediction precision of an orbit and the acceptable running time of an actual project and presets an orbit prediction period and segment time intervals, and a ground control system performs precise prediction on orbit prediction requirements proposed by the user to generate all segment initial orbital parameters in the orbit prediction period; secondly, the ground control system inputs the generated segment initial orbital parameters into an on-satellite control system sequentially in accordance with the preset segment time intervals as the input of the on-satellite control system autonomous satellite orbit prediction; and finally, the on-satellite control systemperforms on-satellite autonomous orbit prediction of based on the segment initial orbital parameters. Based on satellite-ground cooperation, the high computing power of the ground is effectively exerted. The operation time of an on-satellite autonomous satellite orbit prediction algorithm is reduced. Engineering practice precision of orbit prediction is balanced.
Owner:中科天智运控(深圳)科技有限公司
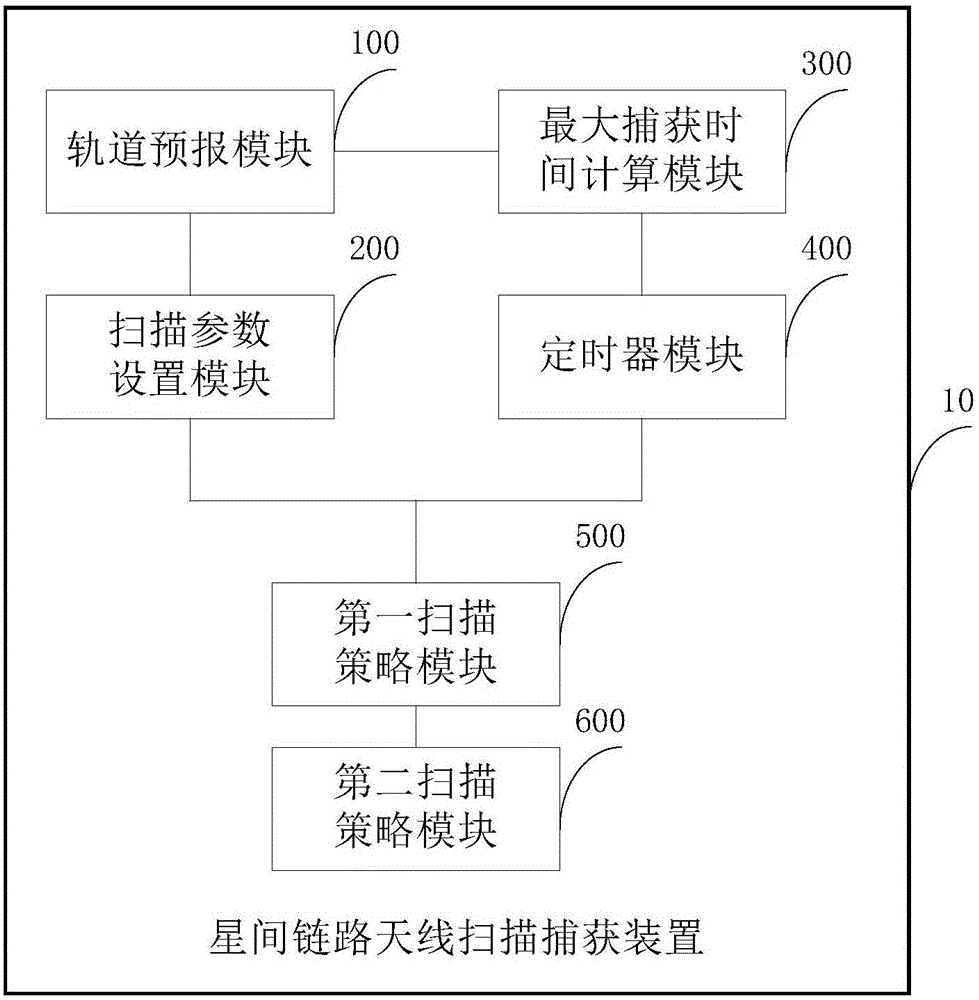
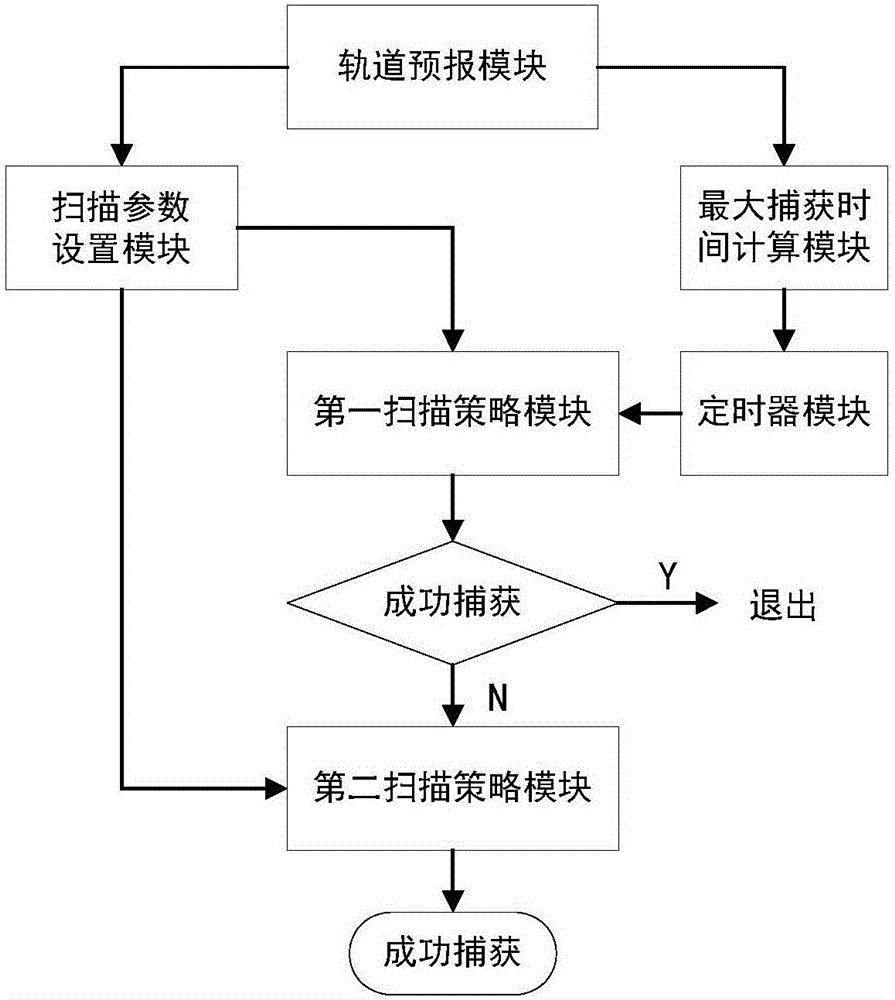
Inter-satellite link antenna scanning acquisition device and method
ActiveCN107181521AShorten capture timeImprove capture success rateRadio transmissionSatellite antennasConstant linear velocity
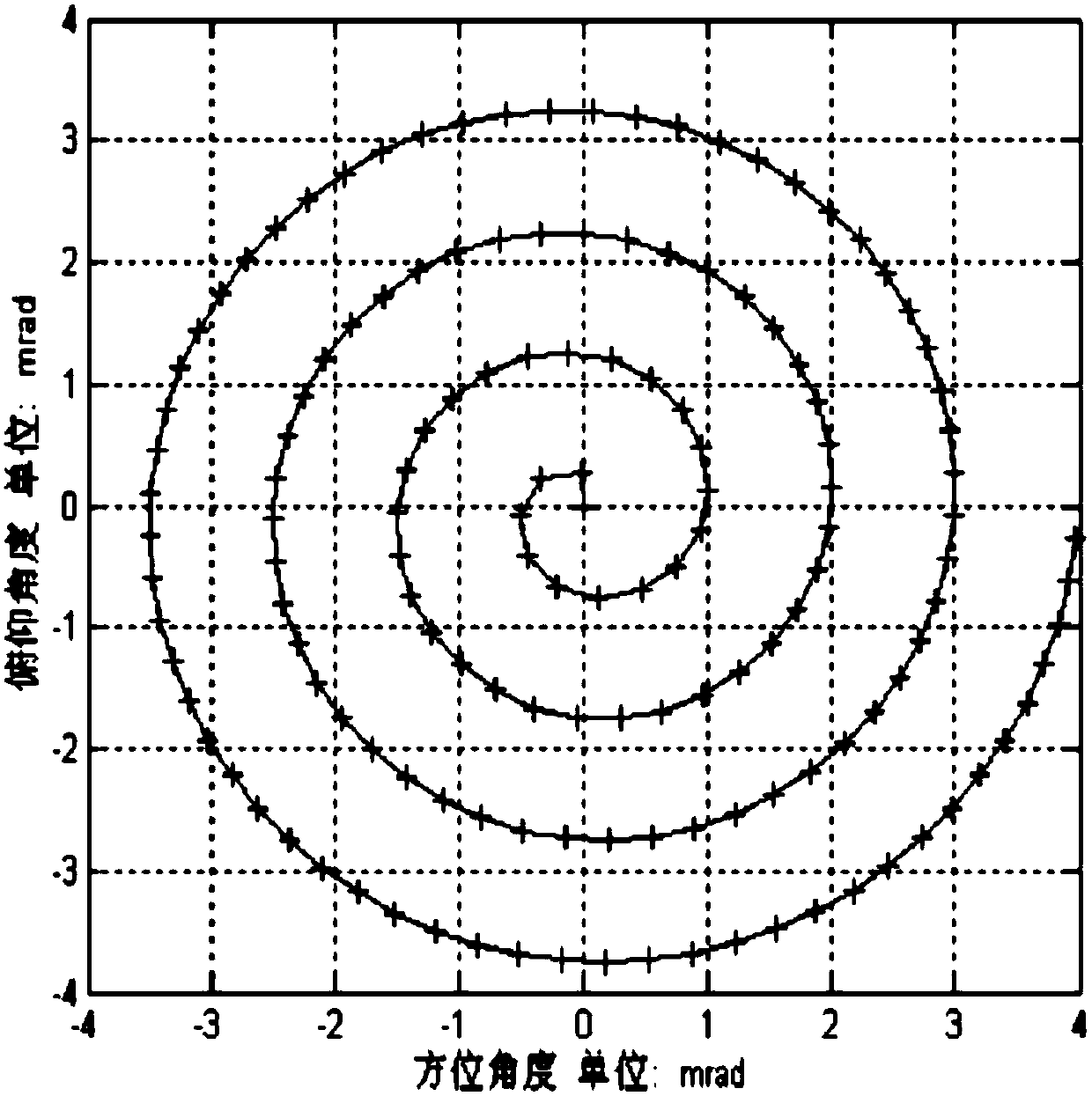
The present invention discloses an inter-satellite link antenna scanning acquisition device and method. The device comprises: an orbit prediction module configured to predicate antenna parameters; a scanning parameter setting module configured to obtain scanning parameters; a maximum capture time calculation module configured to obtain the required time of scanning the whole determinate region according to the antenna parameters when two satellite antennas are rotated at opposite directions; a timer module configured to limit the scanning time of the two satellite antennas being rotated; a first scanning strategy module configured to perform scanning of the rotation of the two satellite antennas at the opposite directions and determine whether the acquisition is successful or not; and a second scanning strategy module configured to allow the two satellite antennas to return back to the direction of the opposite antenna through orbit prediction at a constant linear velocity and perform scanning in a mode of only one satellite antenna rotation when the two satellite antennas cannot be subjected to successful acquisition in a maximum acquisition time, and determine whether the acquisition can be successful or not. The device can effectively reduce the acquisition time and improve the probability of successful acquisition in a short time.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods for Encoding and Recovering GNSS Ephemeris For Over-The-Air Transmission
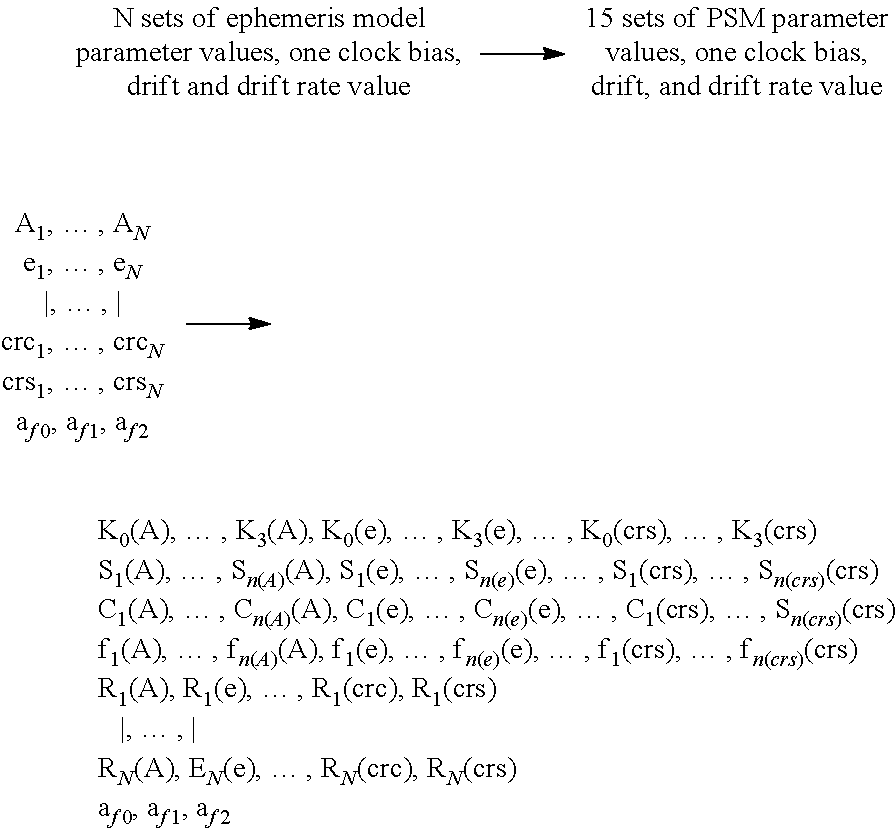
InactiveUS20140125519A1Improve accuracyRadio transmissionSatellite radio beaconingCurve fittingOrbit prediction
A method and apparatus for processing and transmitting precise orbit predictions of satellites in a Global Navigation Satellite System such as Navstar-GPS which employs curve fitting techniques and a polynomial and sinusoidal model to encode ephemerides, and particularly ephemerides of durations 6 hours or longer, in order to minimize bandwidth requirements over-the-air and NVRAM storage requirements. The methods also apply to GNSS constellations such as Galileo or GLONASS. Also, methods are disclosed for recovering the ephemeris on a GNSS receiver device in the constellation's native format.
Owner:SORCE4
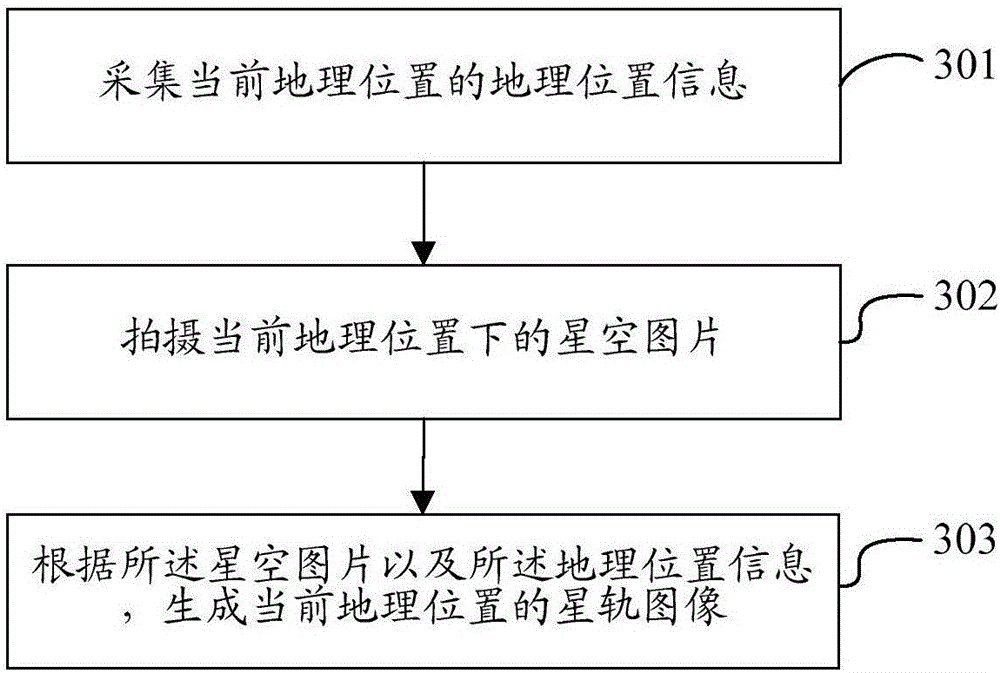
Star orbit prediction method and device
The invention discloses a star orbit prediction method and device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring geographic position information of a current geographic position; taking a starry sky picture at the current geographic position; and generating a star orbit image of the current geographic position according to the starry sky picture and the geographic position information. Through adoption of the star orbit prediction method and device, the starry sky picture under a current shooting condition can be predicted through a mobile terminal, so that a user can pre-judge the starry orbit picture formed under the current shooting condition conveniently.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
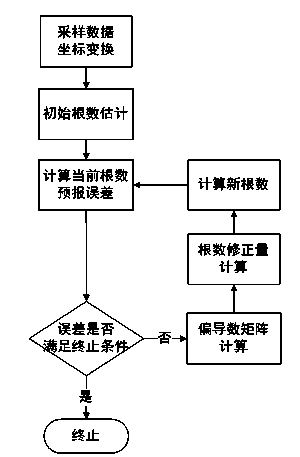
Two-line element generation method based on model error compensation
ActiveCN103514362ARelatively small errorSpecial data processing applicationsSampling instantAlgorithm
The invention discloses a two-line element generation method based on model error compensation. According to the method, first, observed position and speed vectors are converted to a true equator mean equinox coordinate system through a geocentric equatorial inertial coordinate system, then corresponding instant orbital elements are computed and are used as the initial estimated values of two-line element iterative computation; the position and speed vectors at the corresponding sampling instant are respectively predicted according to the initial estimated values, the difference values between the position and speed vectors and the position and speed vectors at the practical observing sampling instant are computed, whether a termination condition is met is judged; through a numerical differentiation method, a partial derivative matrix about the two-line elements of a simplified pervasive perturbation orbit prediction function at the sampling instant is computed; by solving a compensation least square problem, the correction of the two-line elements is obtained; new two-line elements are computed, and repeated iterative operation is carried out until the accuracy requirement is met. According to the method, the situations of single-point fitting and sampling fitting can be processed, and average errors are small when the two-line elements obtained by fitting are used for orbit prediction.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Method for thermal radiation force modeling of navigation satellite complex model
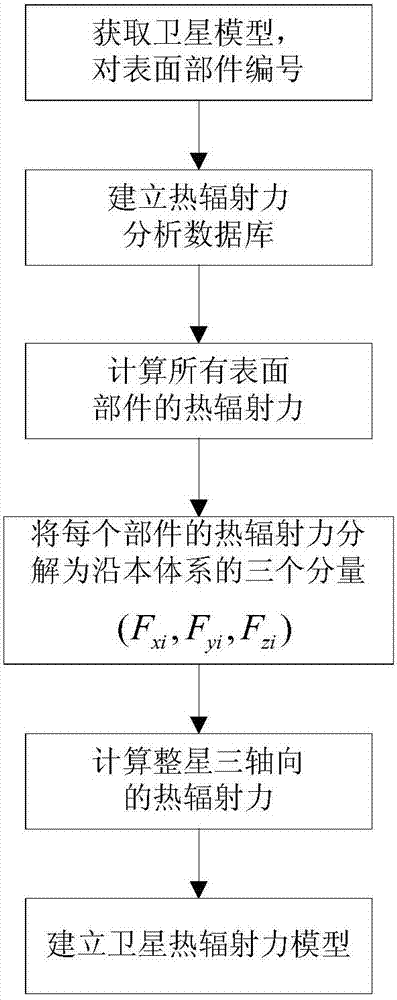
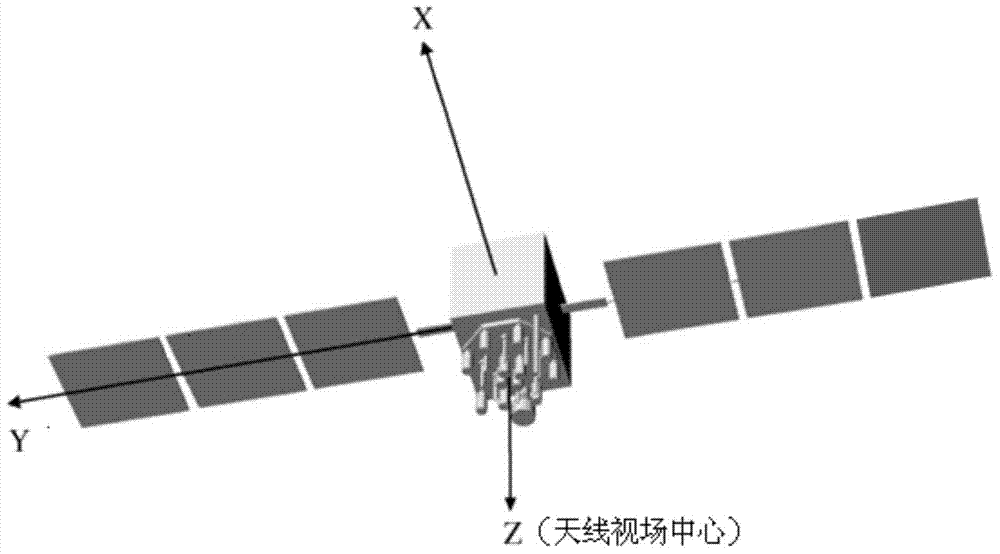
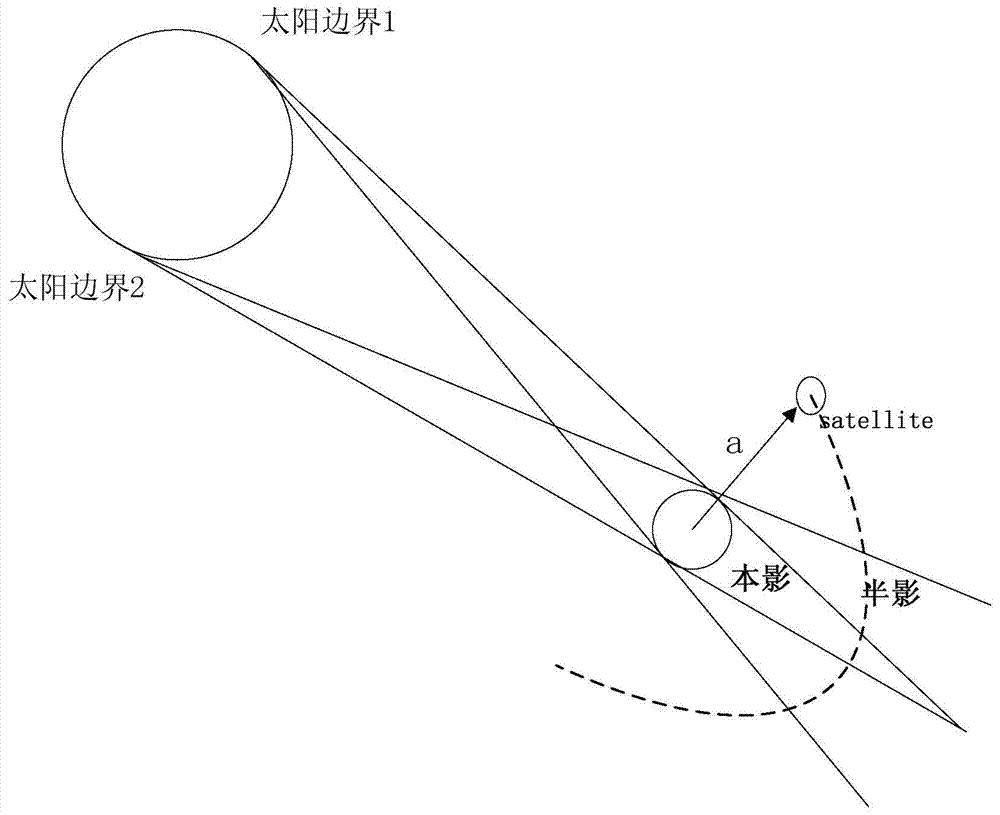
ActiveCN103488833AHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationSpecial data processing applicationsInformation repositoryMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for thermal radiation force modeling of a navigation satellite complex model. The method comprises the steps of establishing a data information base of surface components generating thermal radiation force by obtaining a surface three-dimensional model of a to-be-analyzed satellite; analyzing thermal radiation force of the working conditions of the components under a body coordinate system, and calculating the thermal radiation force and thermal radiation force acceleration by vector synthesis of the thermal radiation force of the surface components so as to establish a mathematical model of the thermal radiation force and the thermal radiation force acceleration. The high-precision thermal radiation force model can be established through the modeling method, and the thermal radiation force serving as non-conservative force can improve a kinetic model of the high-precision satellite and further improve orbit determination precision and orbit prediction precision.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Satellite measurement and control station antenna automatic control method based on cloud service
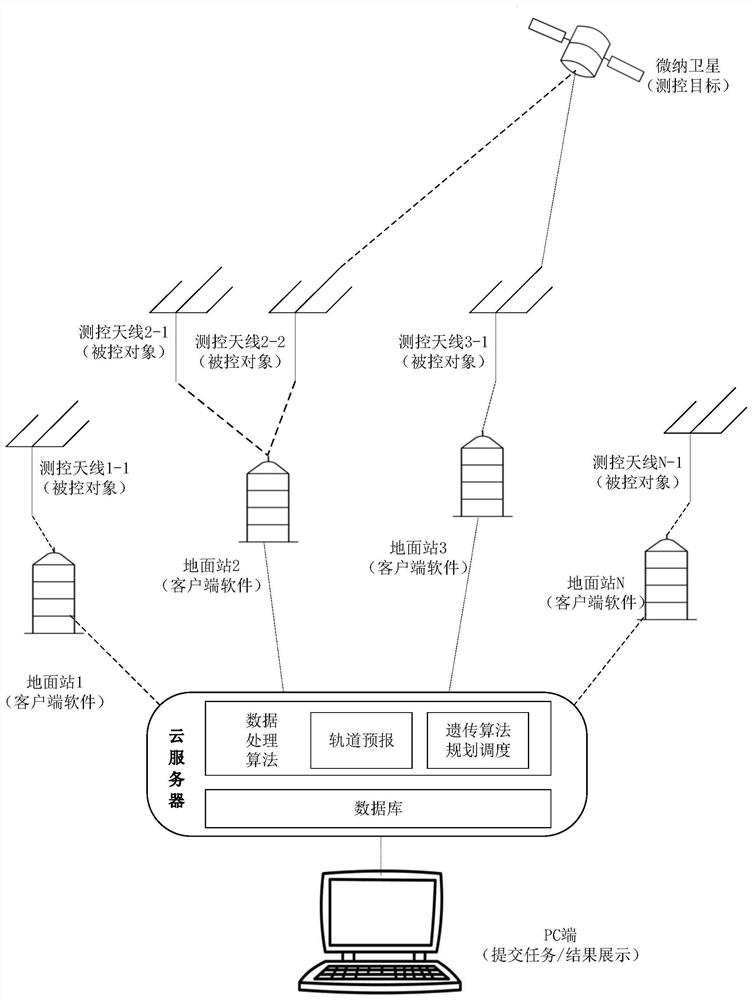
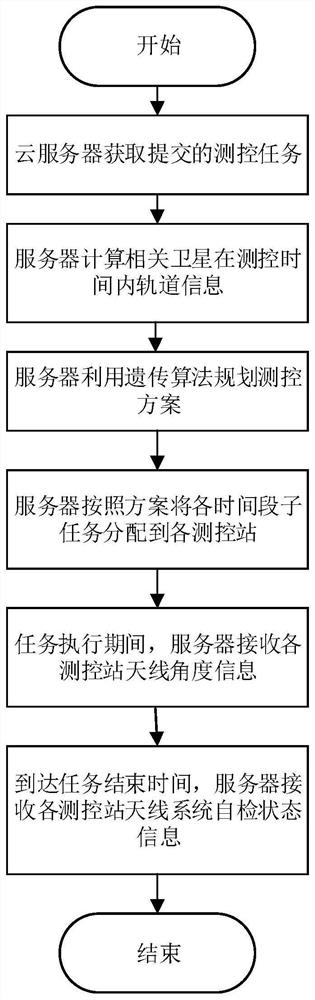
ActiveCN112381344AHigh degree of automationReduce labor costsForecastingResourcesAutomatic controlTelecommunications
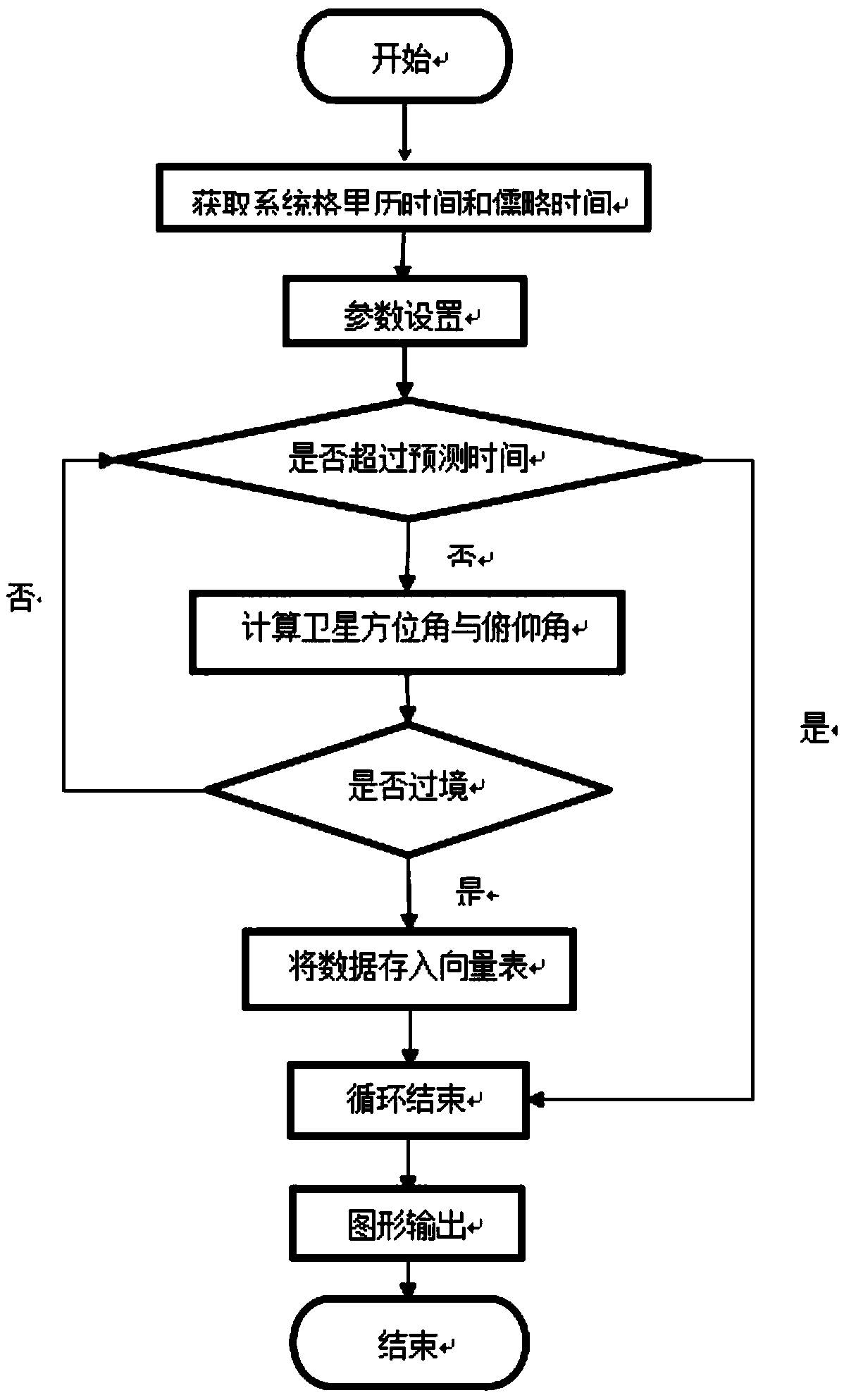
The invention discloses a satellite measurement and control station antenna automatic control method based on cloud service, and the method comprises the steps that a cloud server generates an orbit prediction and time window set for related satellites according to a measurement and control task specified by a user through an SGP4 algorithm; and then the server performs task planning on the antenna resources of each measurement and control station by using a genetic algorithm based on the generated time window set to generate an optimal scheduling scheme meeting requirements. The server allocates tasks to the measurement and control stations in various places according to the scheme, the measurement and control stations in various places read the tasks and then automatically control the antennas of the stations to track, capture and release related satellites, and the task execution conditions are fed back to the server. The invention has the advantages that automatic control over themeasurement and control antenna is achieved, meanwhile, the utilization rate of measurement and control resources is increased through algorithm planning and optimization, and the overall measurementand control efficiency of the system is also improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Moon-tracking segment ultraviolet sensor earth and moon photography time predication method
ActiveCN101236090ASuccessfully photographed the earth in orbitSolve the problems of the moonInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansTime rangeUltraviolet
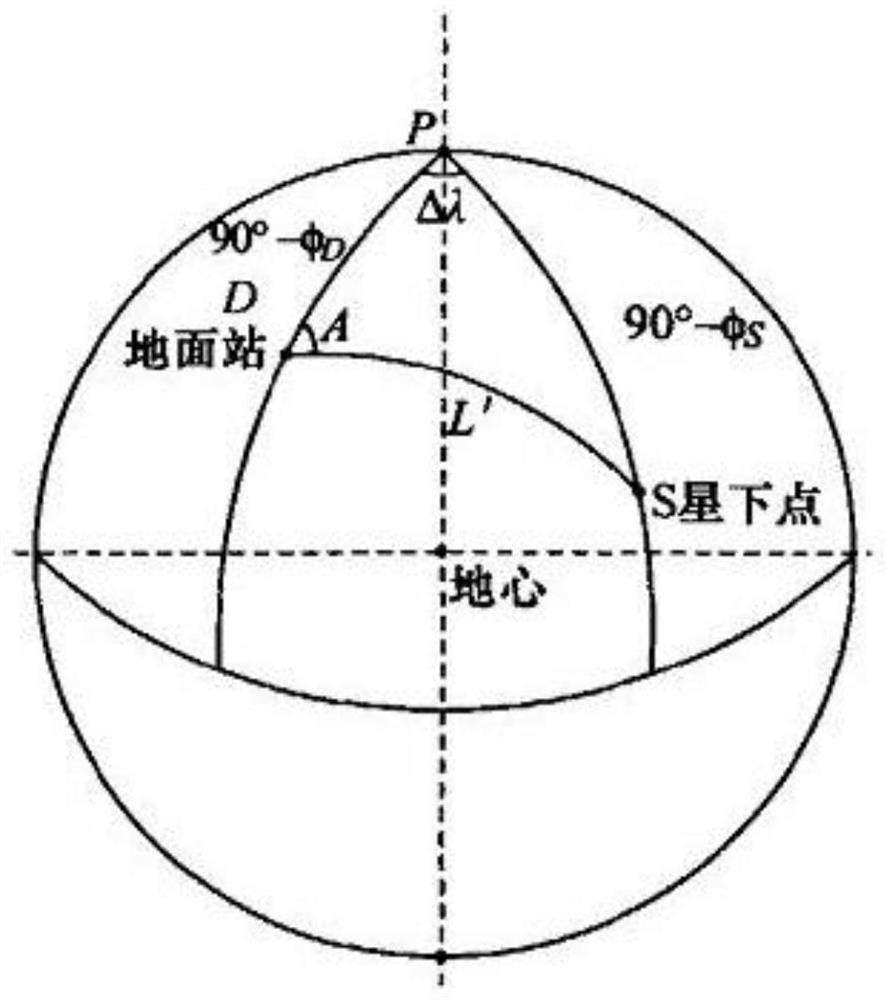
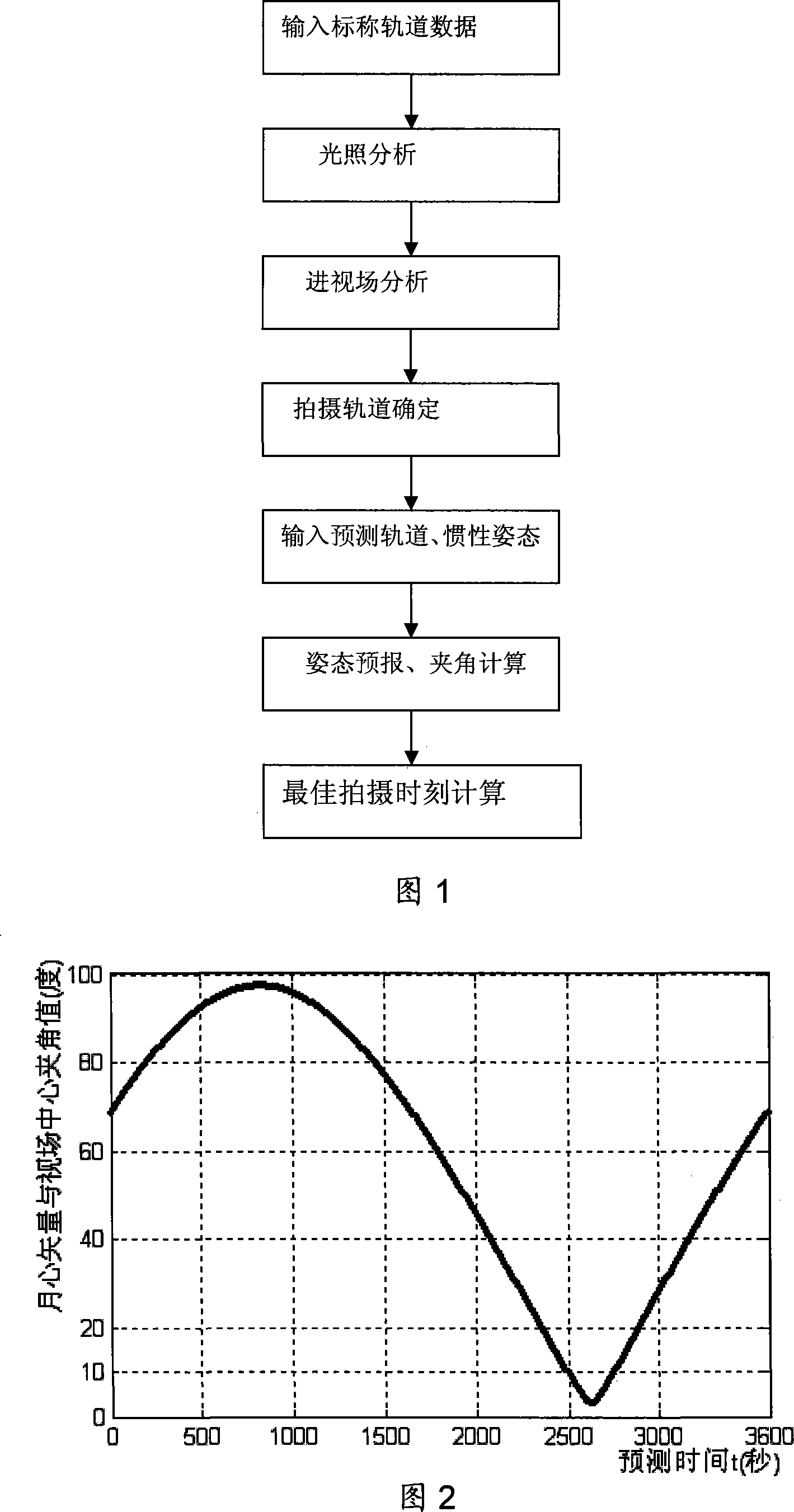
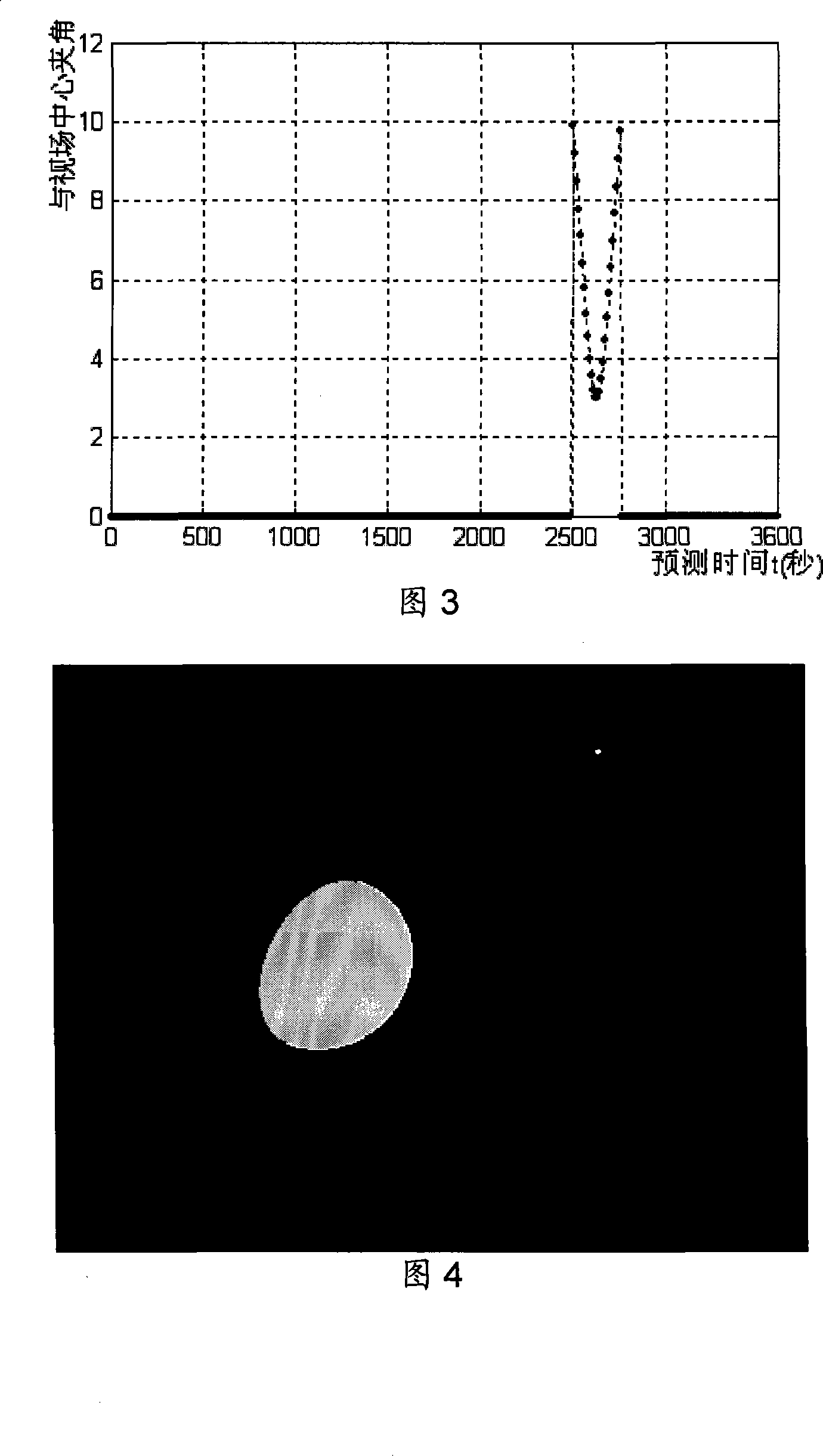
The invention discloses a time prediction method for earth-moon picture shooting by an ultraviolet sensor at cislunar fight, which comprises steps of (1) selecting an orbit arc meeting the light condition for earth-moon shooting, (2) selecting an orbit arc, in which earth-moon appears, within viewing field area of the ultraviolet sensor, (3) taking the orbit position simultaneously meeting the step (1) and the step (2) as a selectable orbit for shooting, inputting an orbit prediction position corresponding to the selectable orbit, attitude matrix at a certain time before the selectable orbit, sun-moon-earth ephemeredes and a satellite attitude motion model after launching the satellite and before the coming of the selectable orbit, calculating the attitude matrix and a selenocentric / geocentric vector within the prediction time period and making a curve, changing along the time, of an included angle of the selenocentric / geocentric vector and a viewing field central vector, then obtaining continuous visible time range(t1-t2) of earth / moon by the curve and the size of the viewing field of the ultraviolet sensor and calculating the best time according to the obtained continuous visible time range.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com