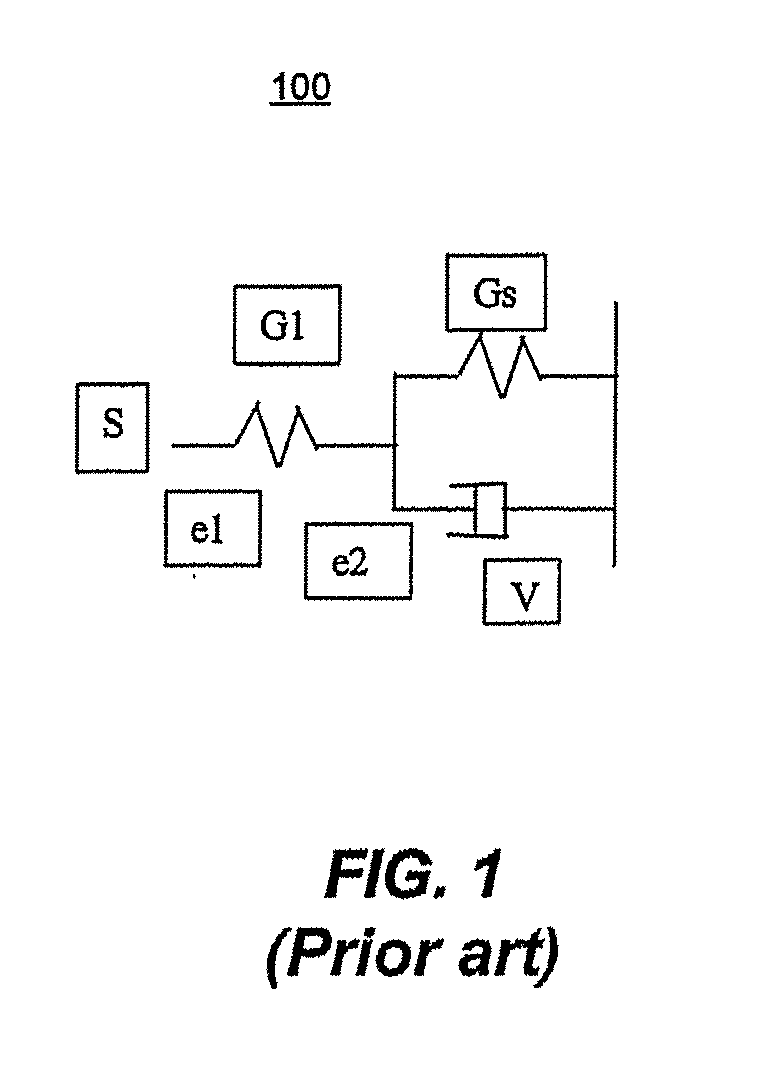
Patents
Literature
147 results about "Radiation force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
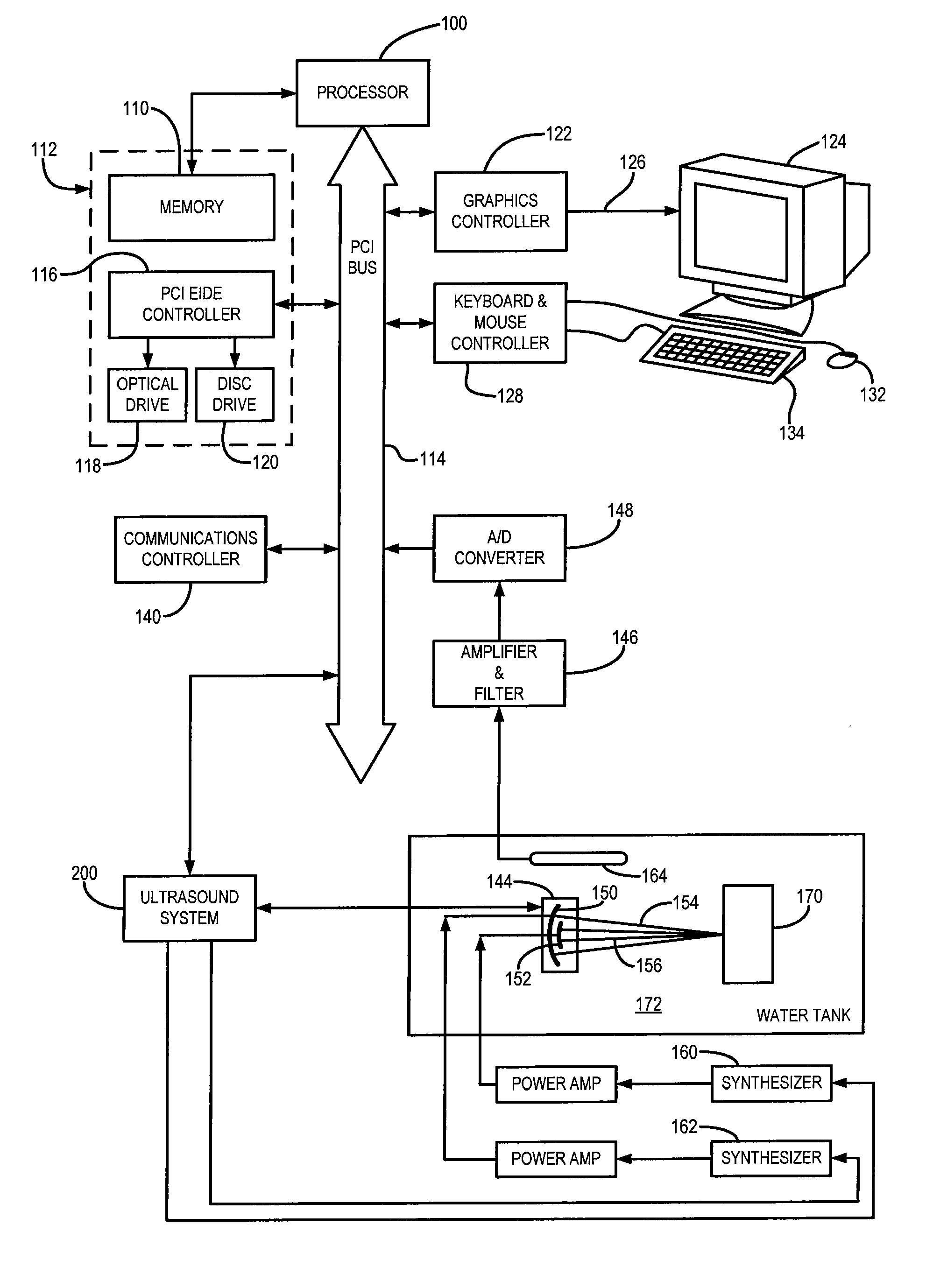
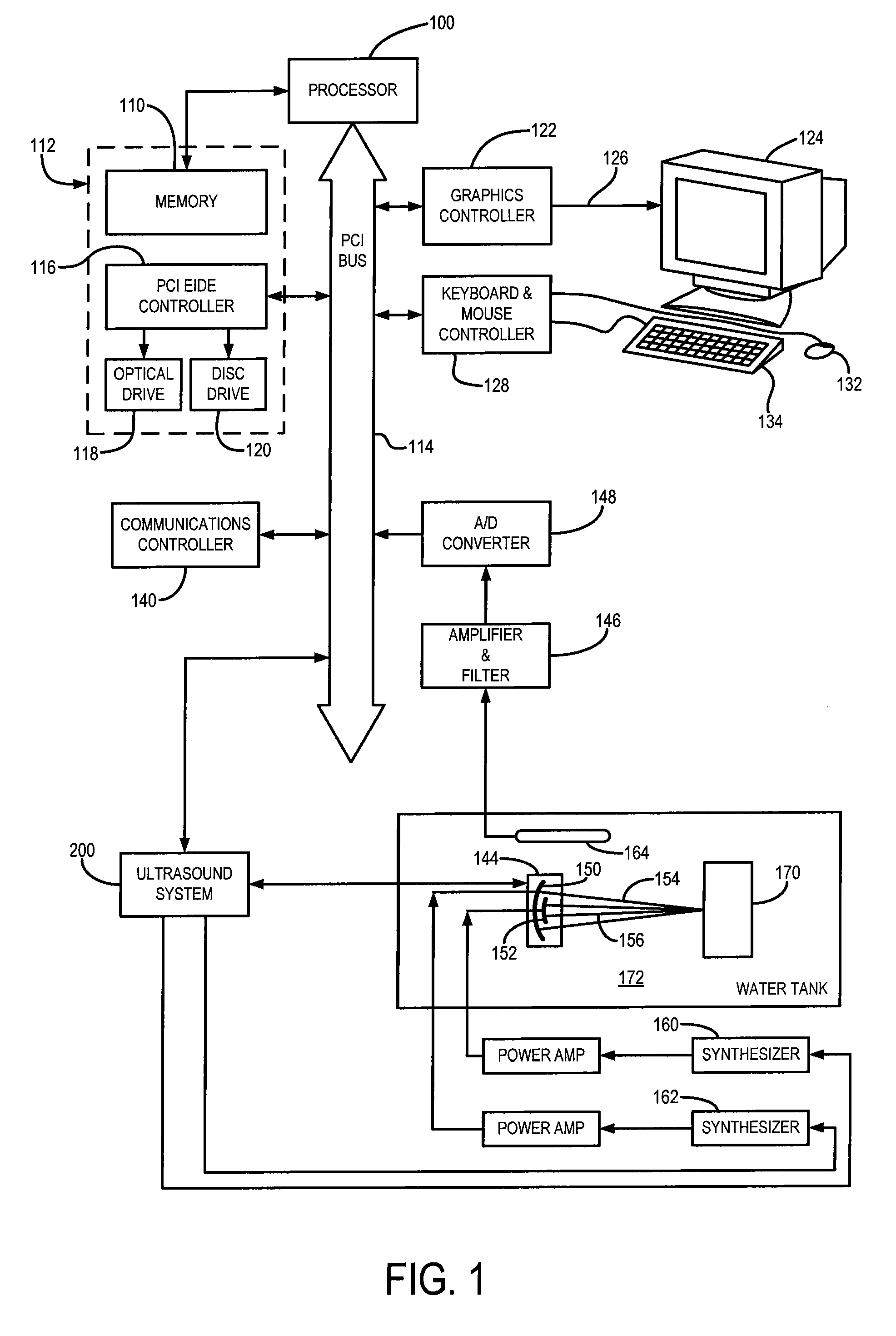
Radiation force. a small, steady force that is produced when a sound beam strikes a reflecting or absorbing surface. It is proportional to the acoustic power.
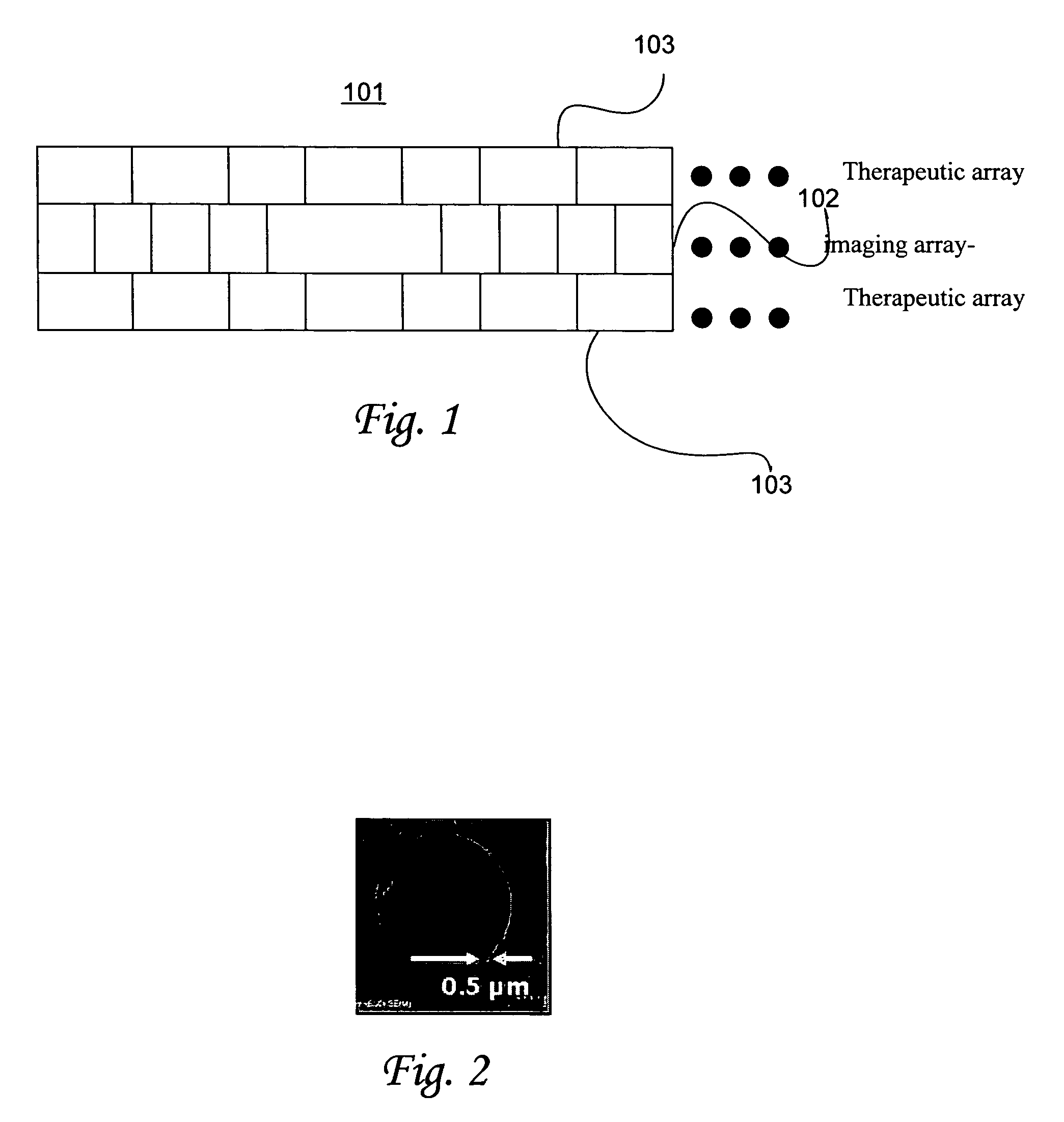
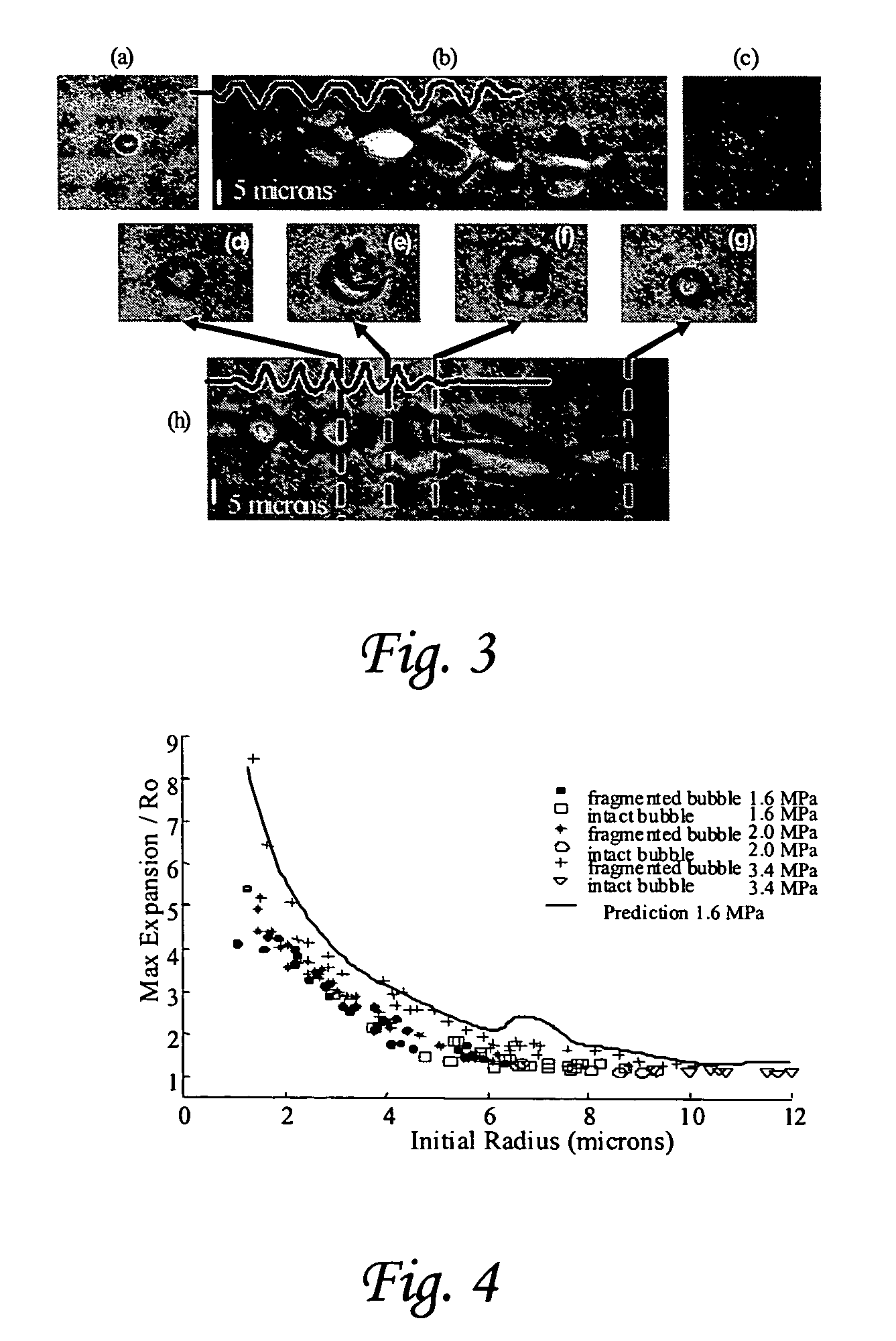
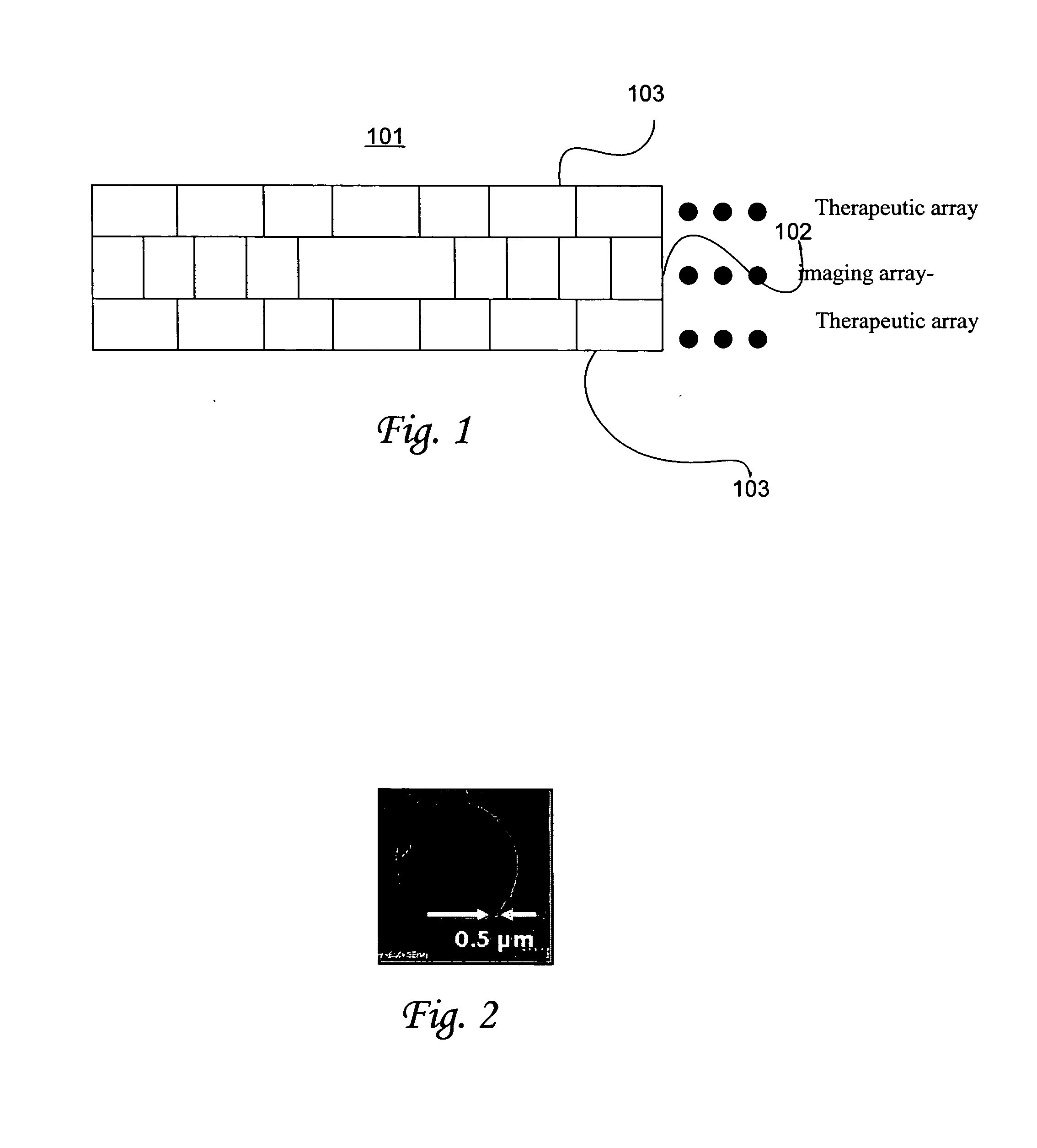
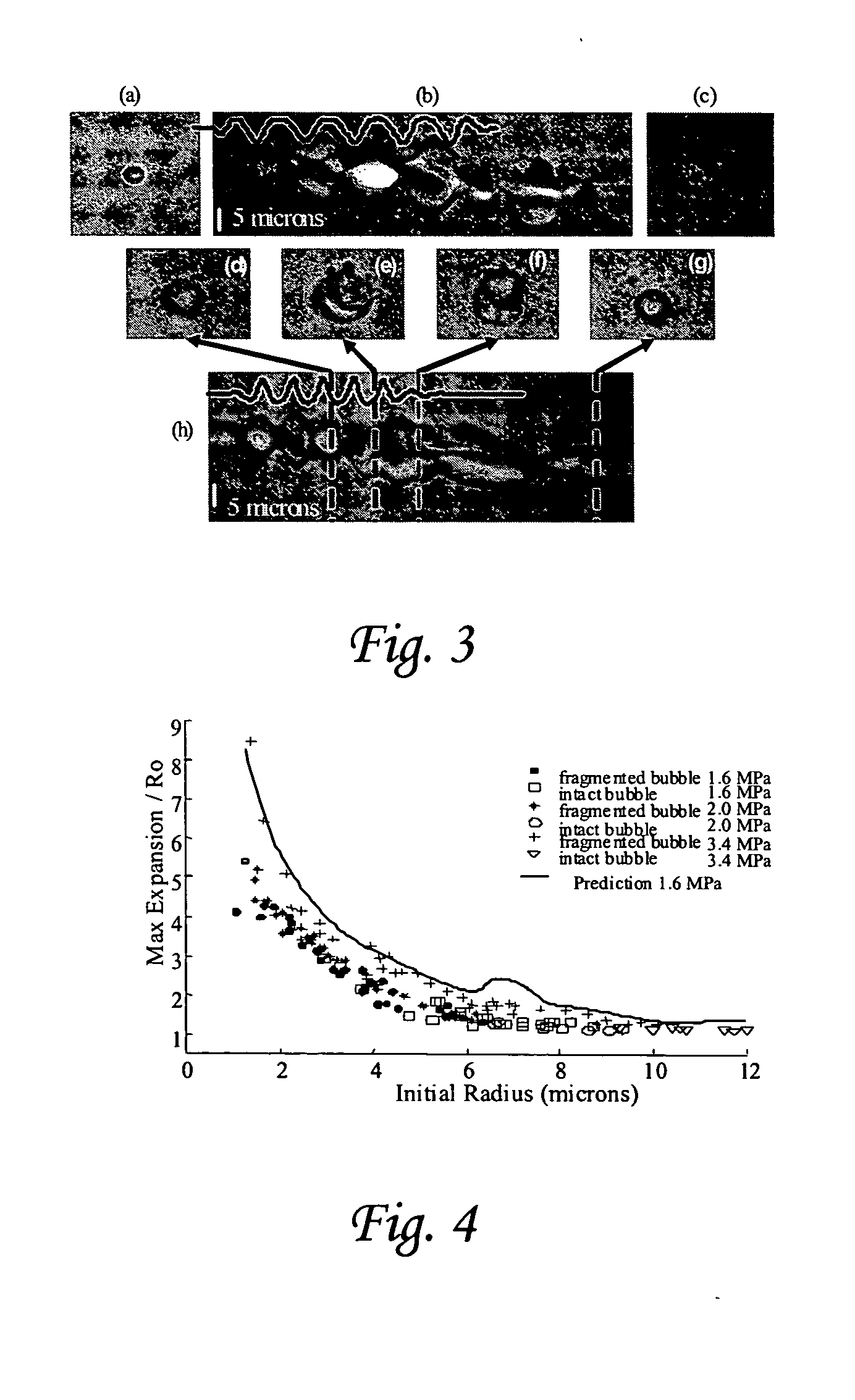
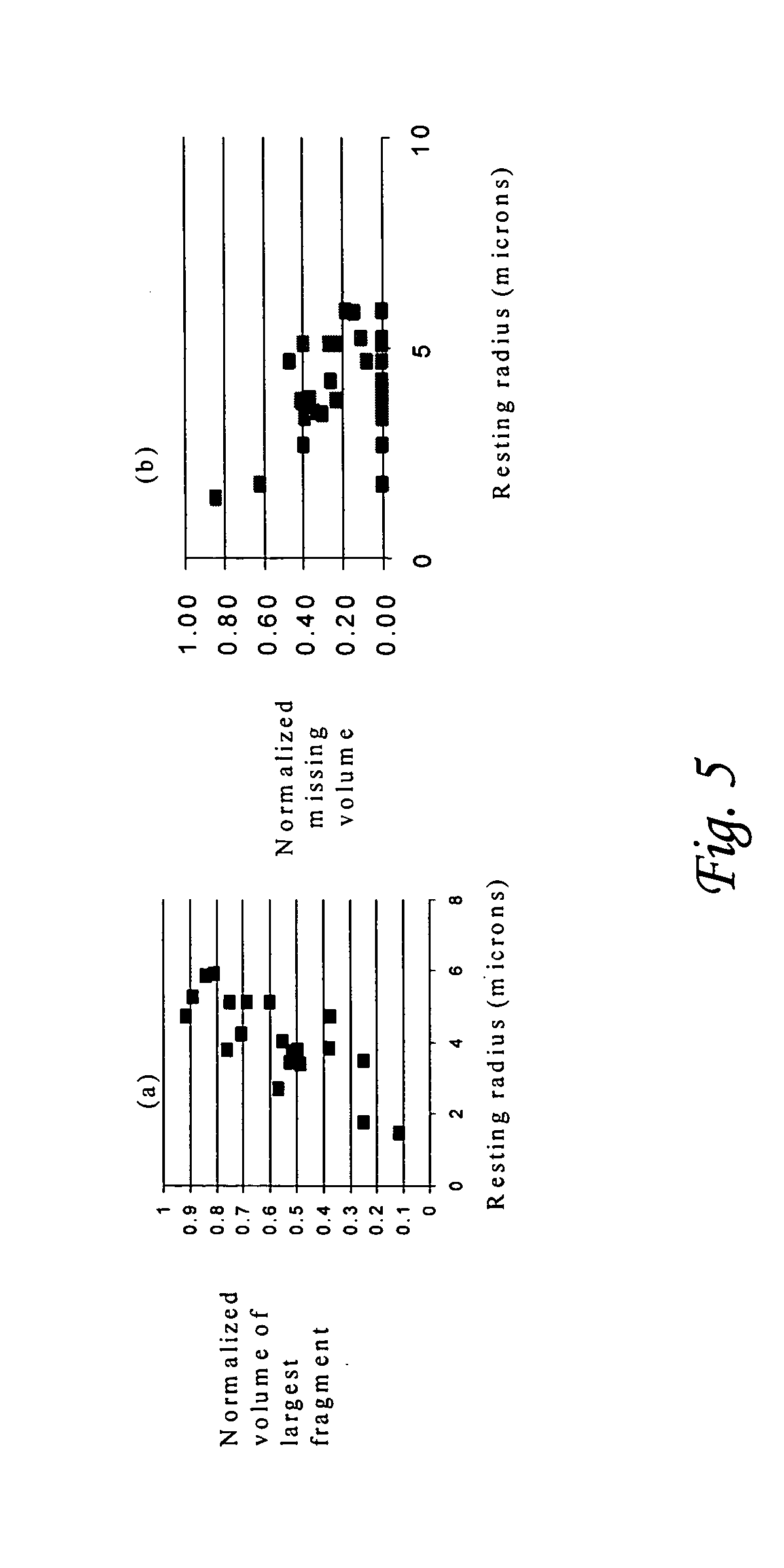
Ultrasonic concentration of drug delivery capsules
ActiveUS7358226B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsUltrasound RadiationTreating Site
Methods, compositions and apparatus for localized delivery of compounds are provided. In certain embodiments, radiation force is used to direct carriers to a target site, and additional radiation is used to fragment the localized carriers, releasing associate compounds. Ultrasound radiation is preferred as the source for radiation force and for fragmentation. Also encompassed are embodiments in which targeting and fragmentations are combined with imaging of the treatment site. Alternate embodiments are disclosed in which compounds are locally delivered without use of carriers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Ultrasonic concentration of drug delivery capsules
ActiveUS20050084538A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryUltrasonic radiationCompound (substance)
Methods, compositions and apparatus for localized delivery of compounds are provided. In certain embodiments, radiation force is used to direct carriers to a target site, and additional radiation is used to fragment the localized carriers, releasing associate compounds. Ultrasound radiation is preferred as the source for radiation force and for fragmentation. Also encompassed are embodiments in which targeting and fragmentations are combined with imaging of the treatment site. Alternate embodiments are disclosed in which compounds are locally delivered without use of carriers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
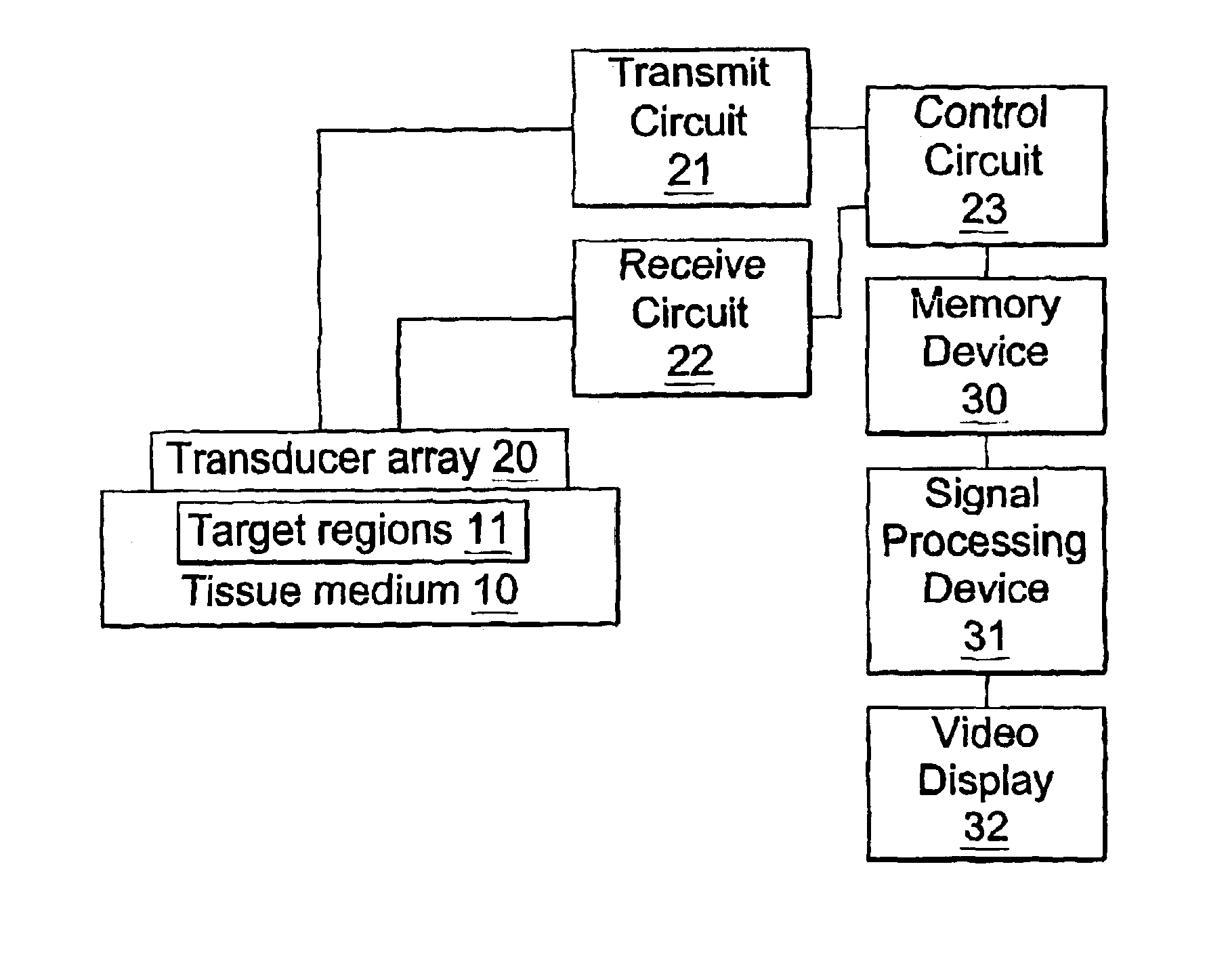
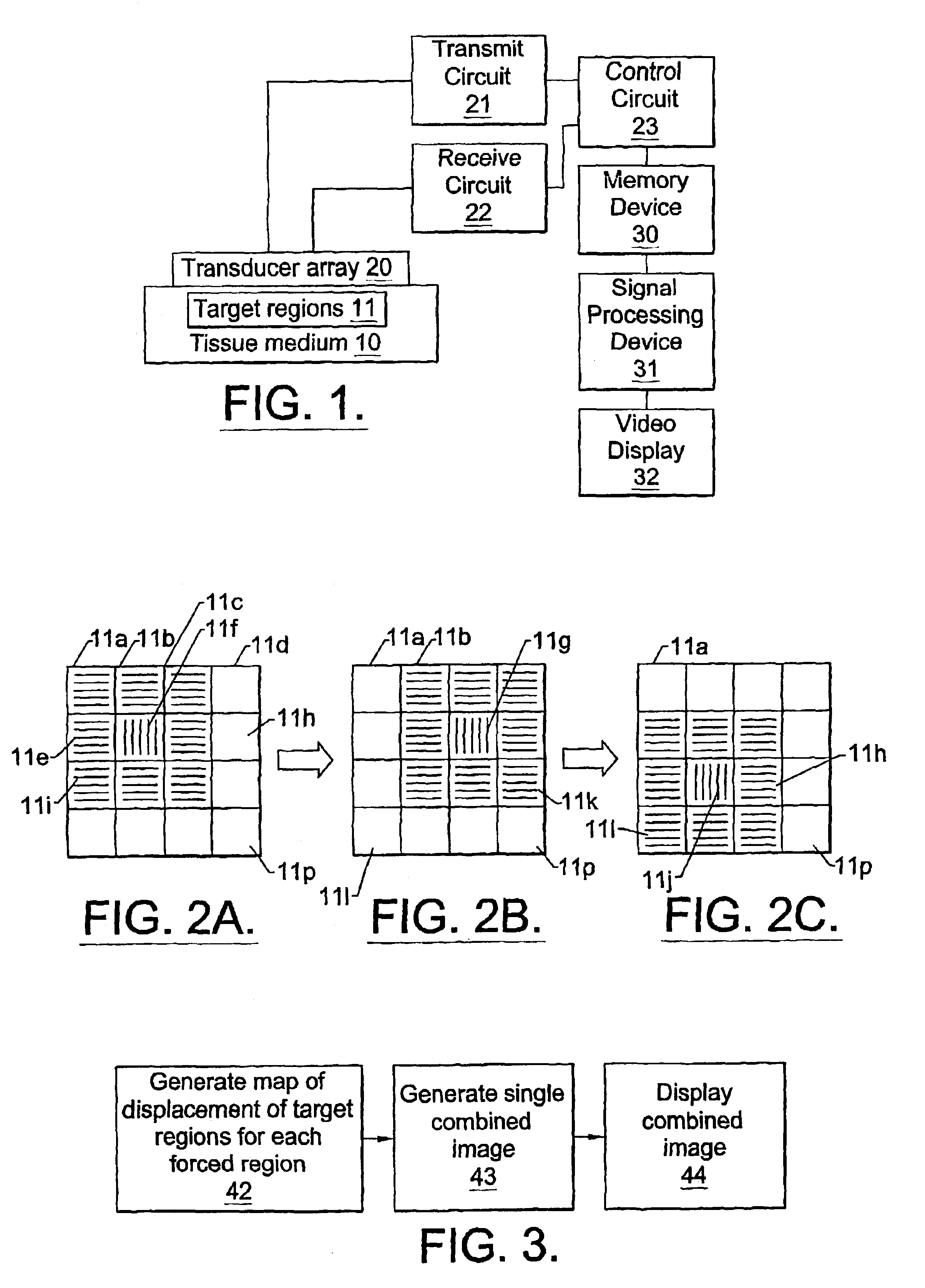
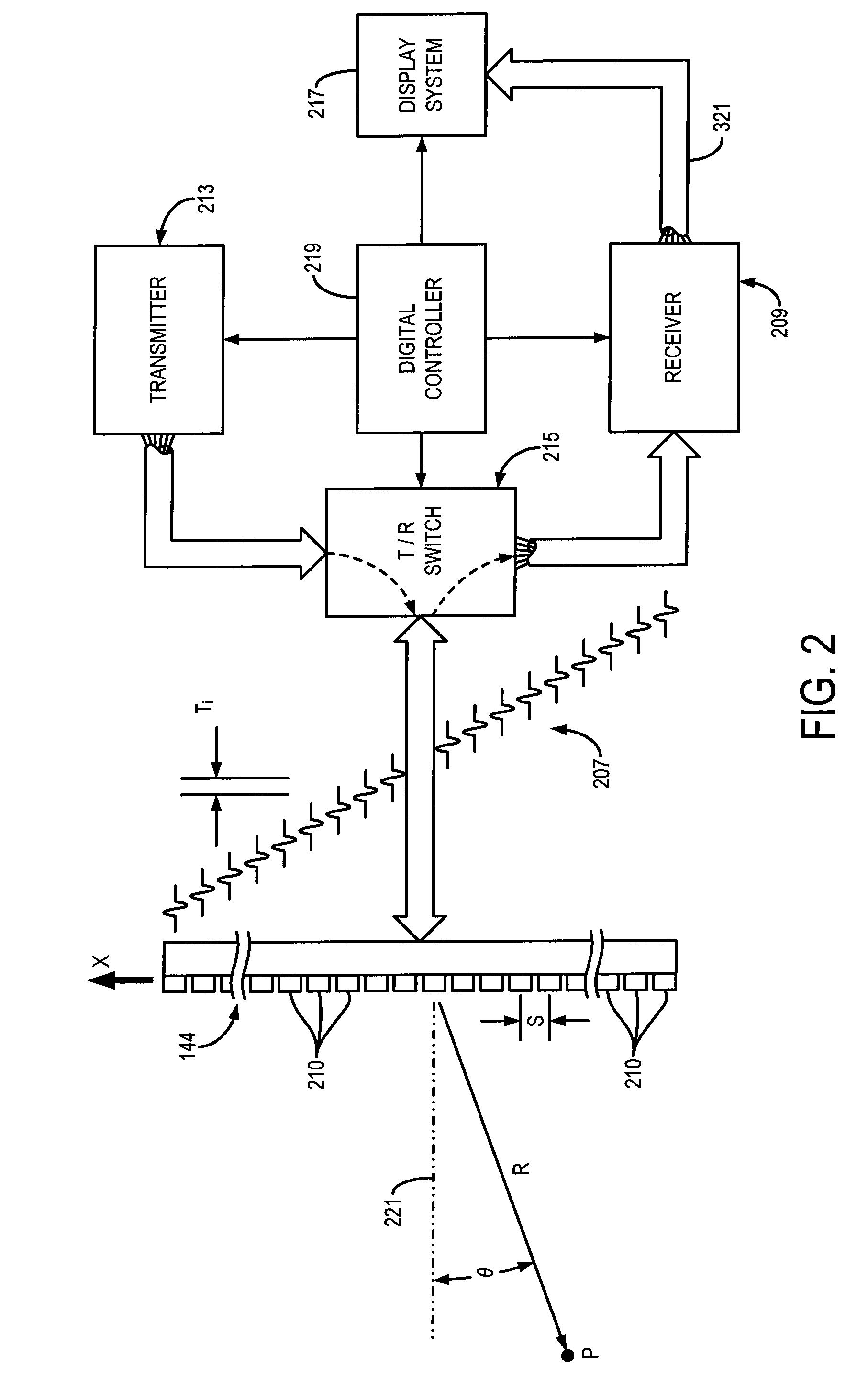
Method and apparatus for the identification and characterization of regions of altered stiffness
InactiveUS6951544B2Facilitate real-timeEasy to implementBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionPalpationTarget tissue
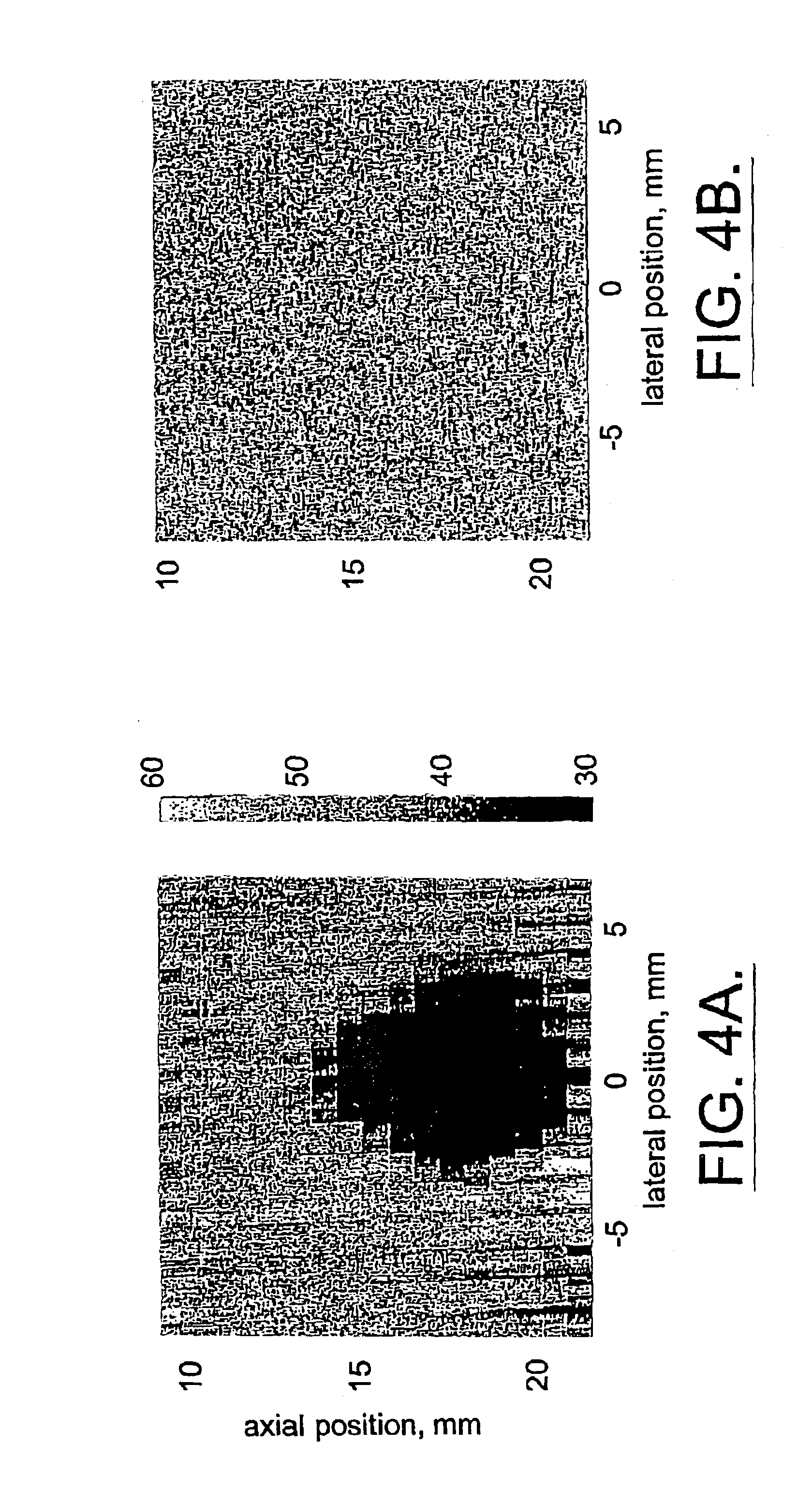
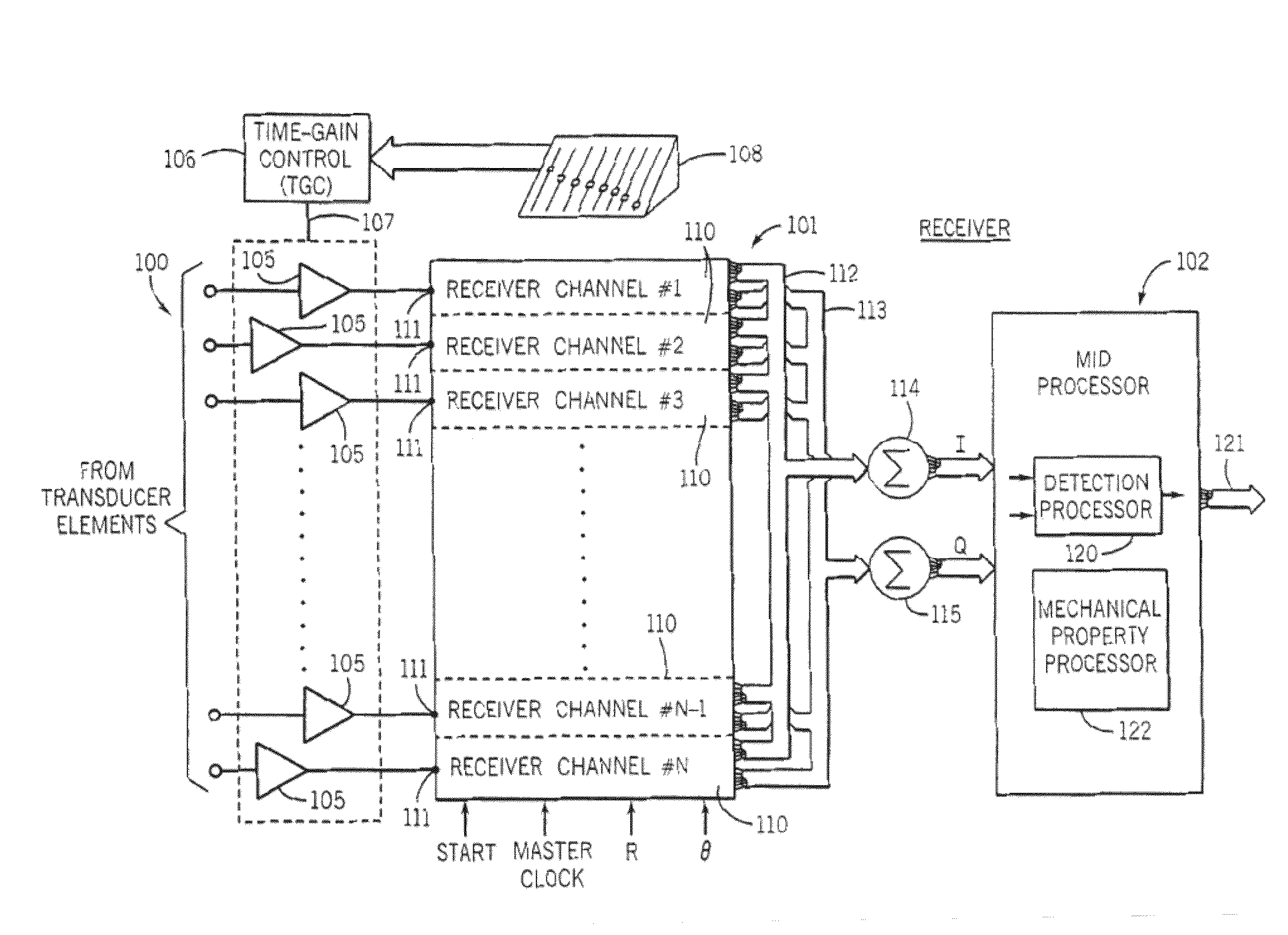
A remote palpation technique in breast imaging involves the use of multiple applications of radiation force in rapid succession throughout a two-dimensional plane in the target tissue medium (10), and combination of the small, two-dimensional displacement maps from each force location into a single, larger remote palpation image (block 43). Apparatus for carrying out the foregoing method is also disclosed.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Method and apparatus for shear property characterization from resonance induced by oscillatory radiation force
ActiveUS20050004463A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurgeryFrequency spectrumResonance
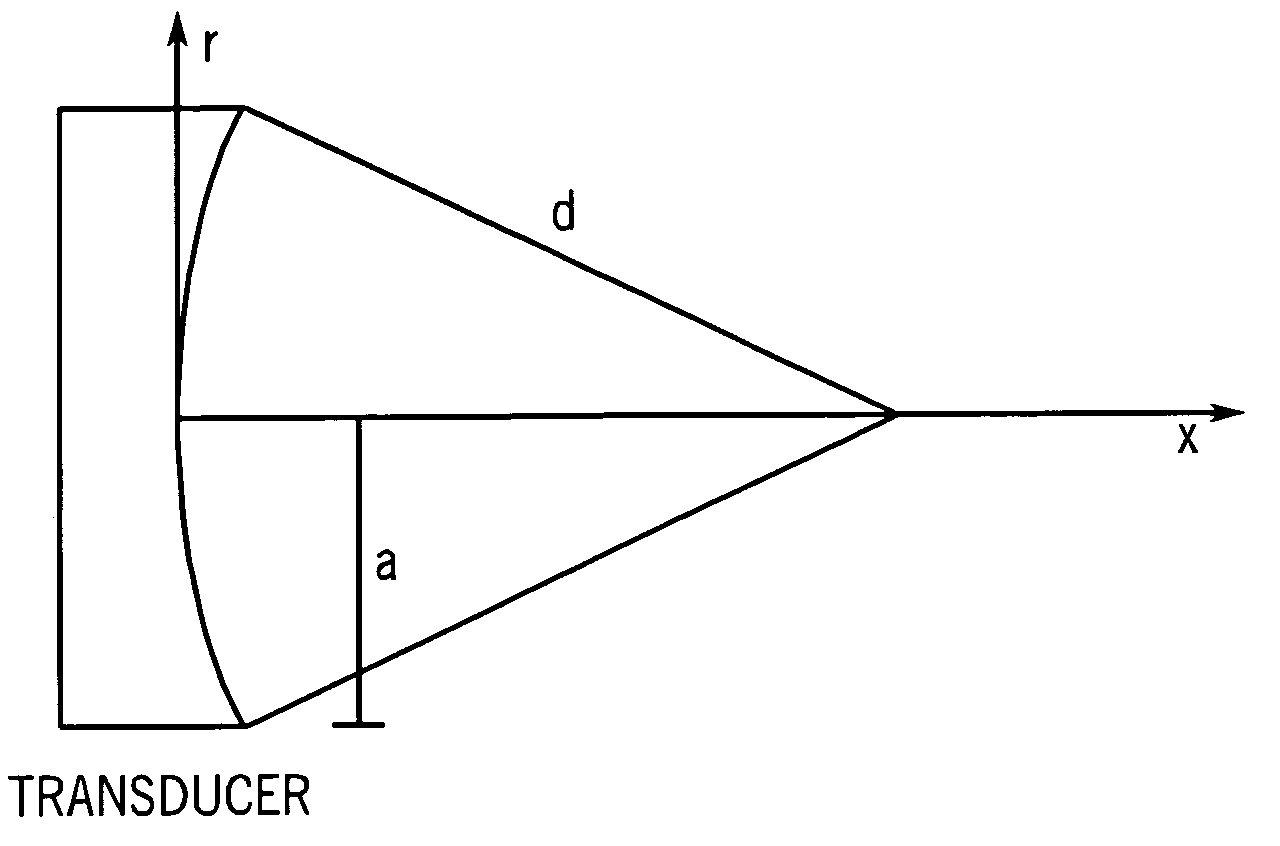
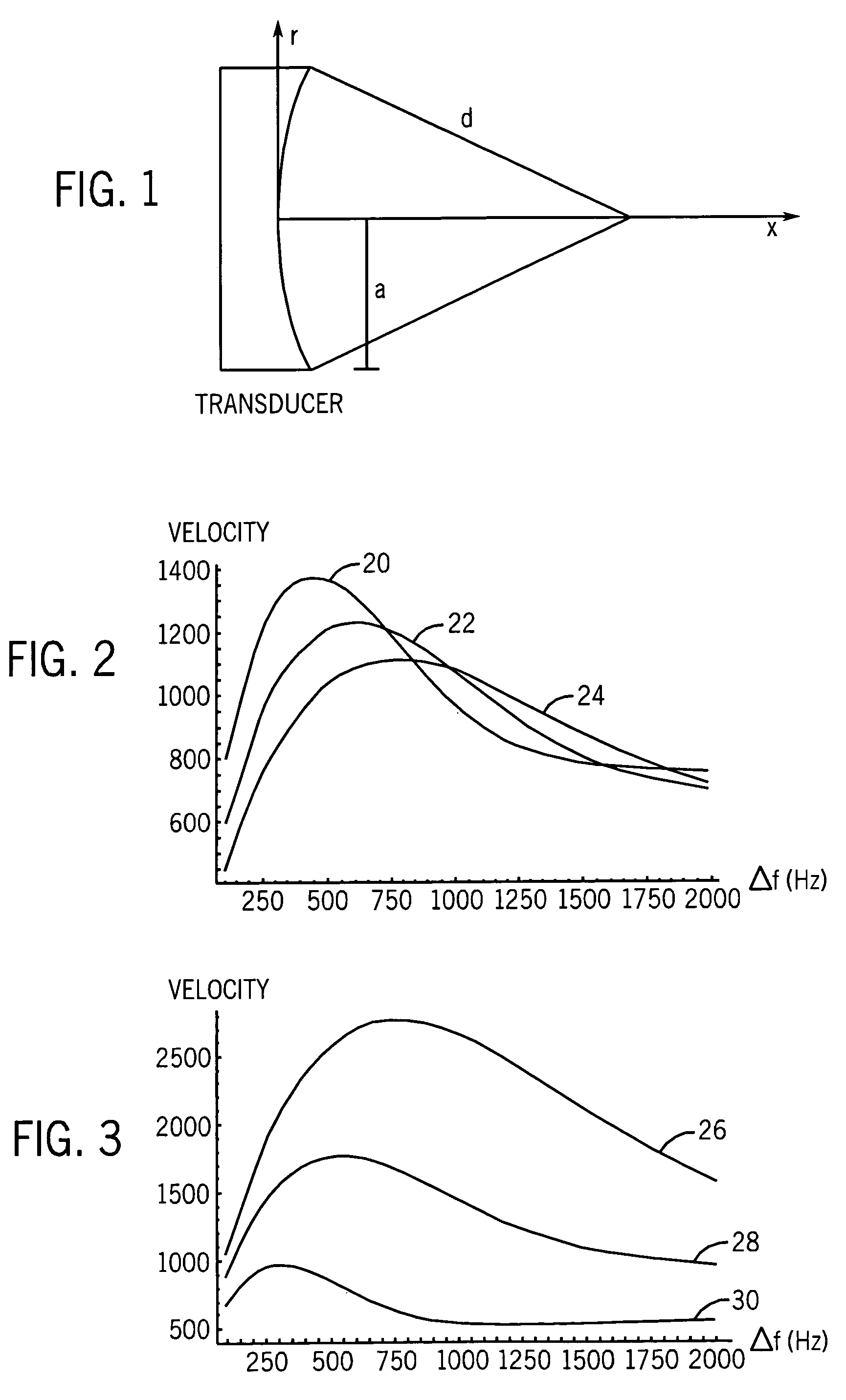
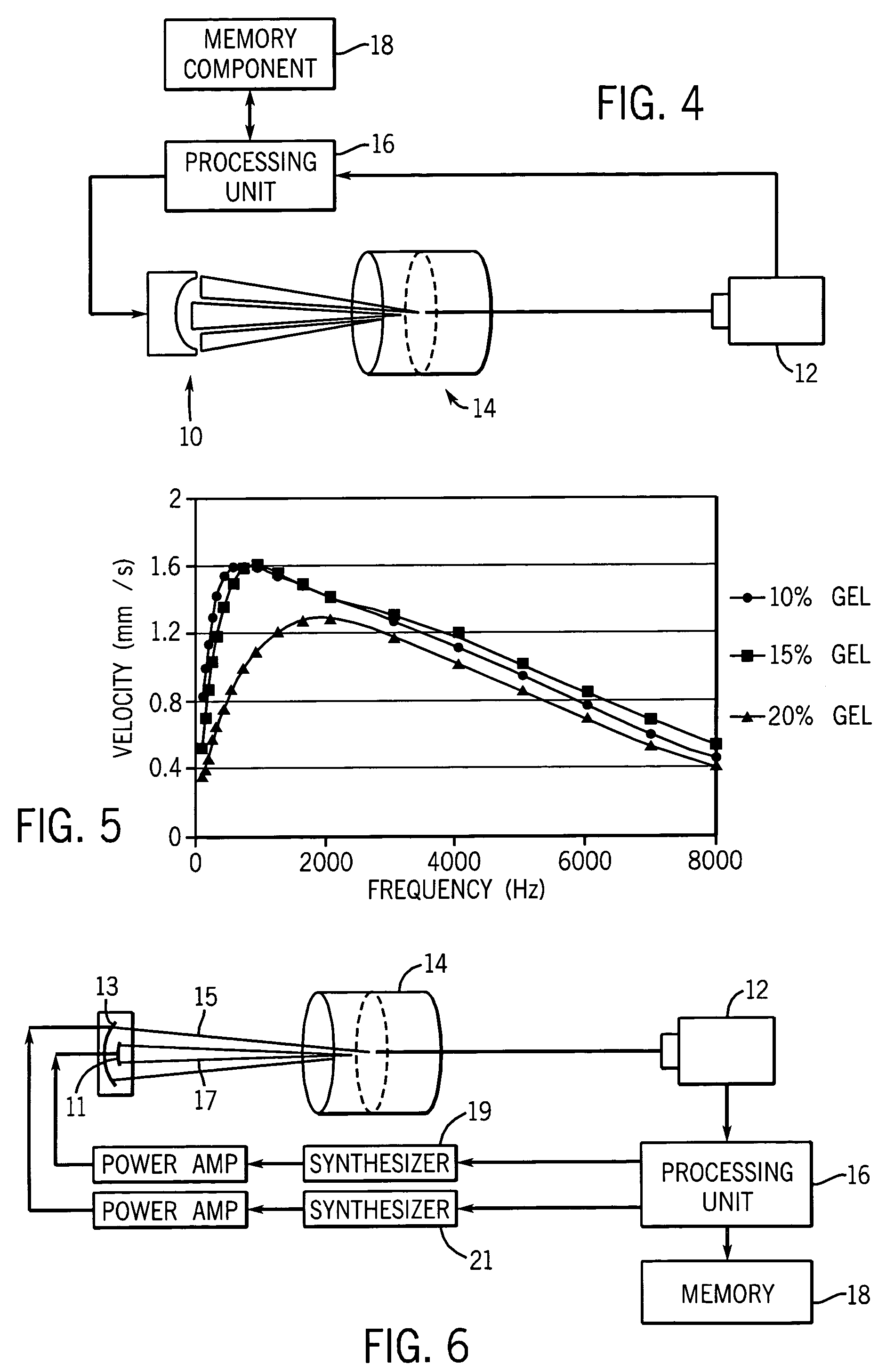
A method for determining a shear elasticity and shear viscosity of a material based on resonance characteristics. A focused ultrasound wave is directed at the material to induce oscillations in the material, and a velocity of the material is measured. A spectrum of frequency of oscillation versus velocity is developed, and the resonance characteristics exhibited by the spectrum are used to estimate the shear elasticity and viscosity of the material.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Methods And Systems For Spatially Modulated Ultrasound Radiation Force Imaging
ActiveUS20110184287A1Easy to detectAvoid noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsShear modulusAcoustic radiation force
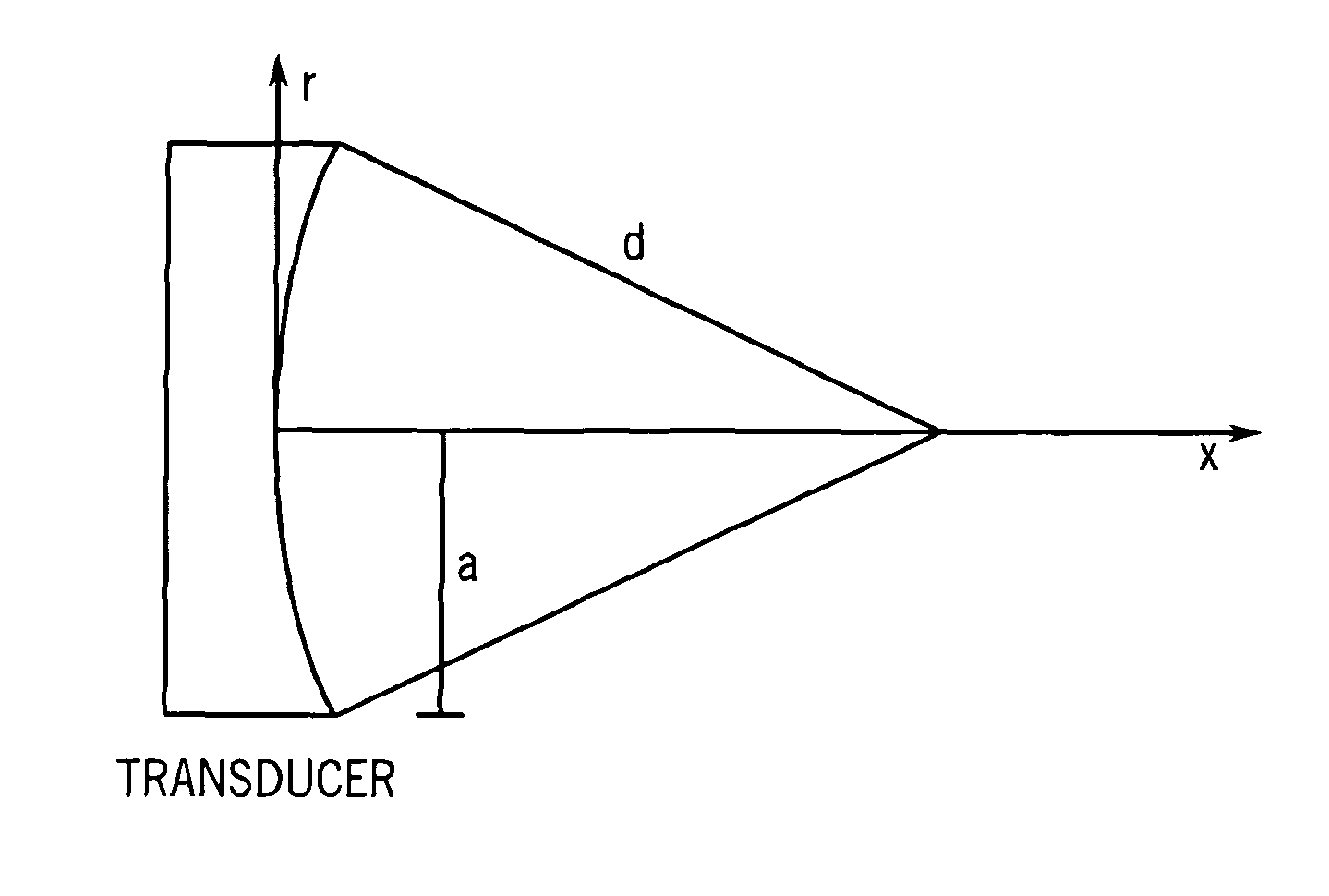
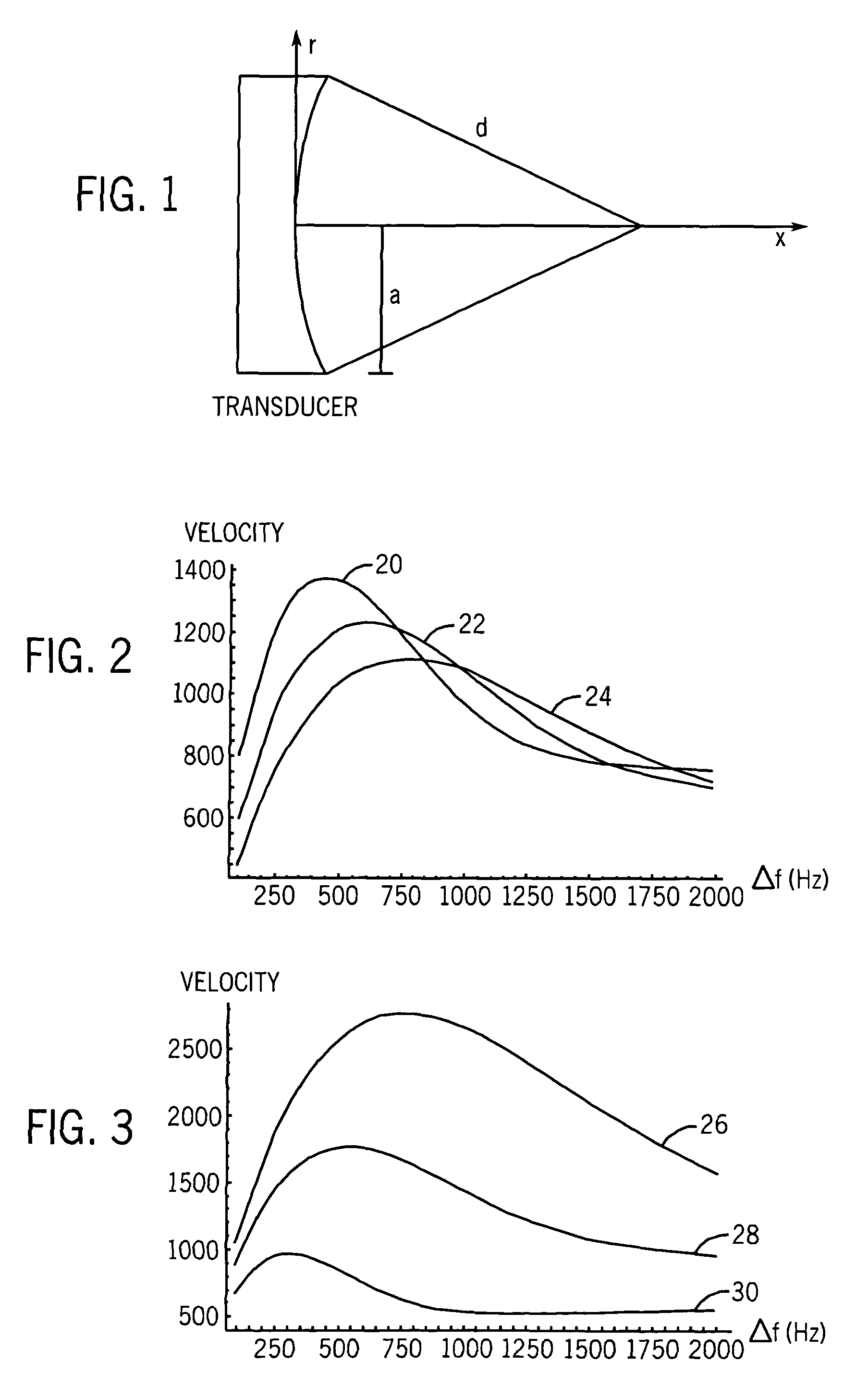
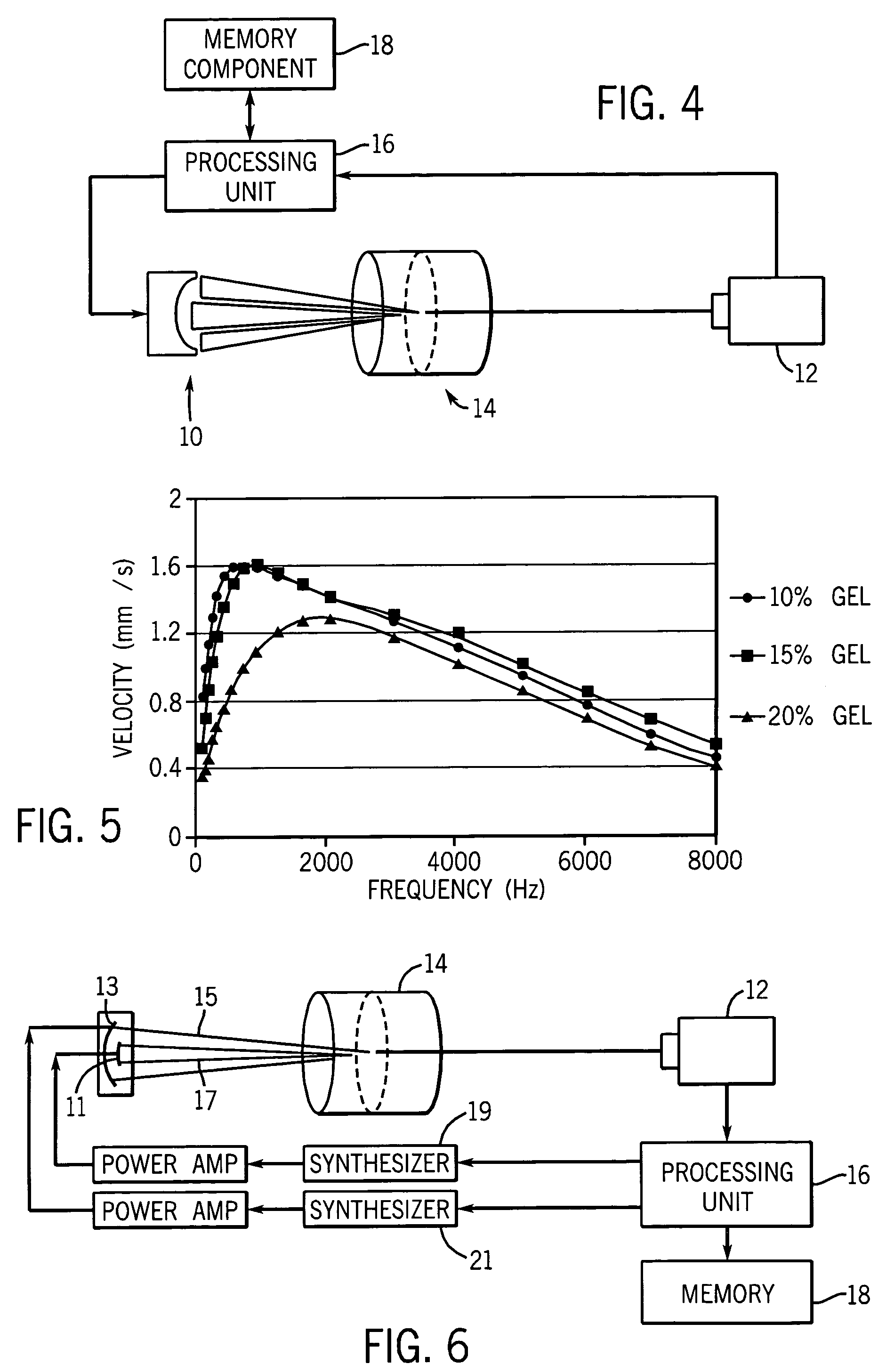
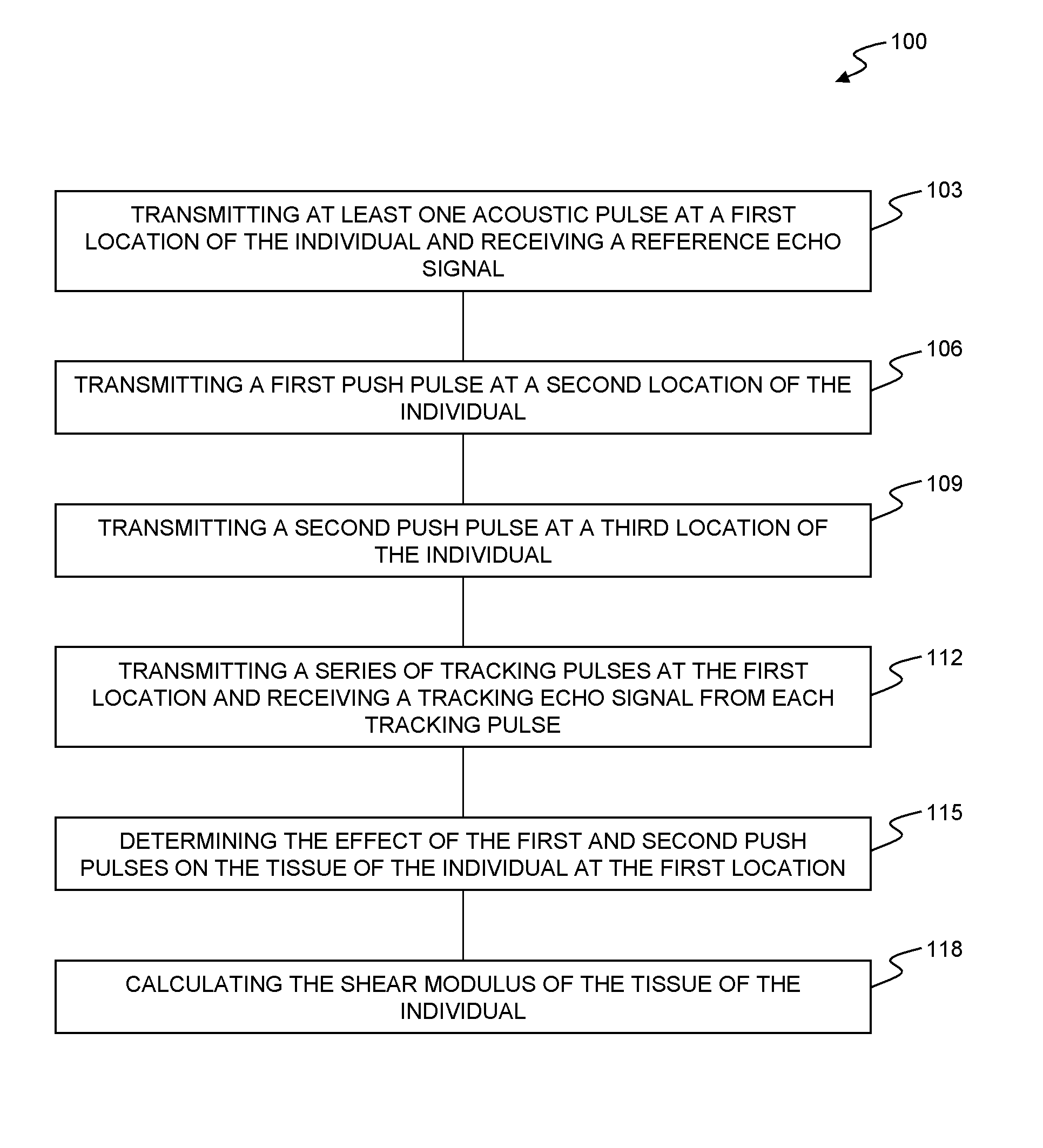
Methods for determining the shear modulus of a tissue of an individual are disclosed. In one embodiment, an acoustic pulse is transmitted and a reference echo signal is received. A first push pulse is transmitted at a second location of the individual. A second push pulse is transmitted at a third location of the individual. A series of tracking pulses are transmitted at the first location and a tracking echo signal is received from each tracking pulse. The effect of the first and second push pulses on the tissue is determined through analysis of the tracking echo signals. The shear modulus of the tissue is calculated based on the effect of the push pulses on the tissue. A system for imaging a region of tissue is presented.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
System And Method For Localized Measurement And Imaging Of Viscosity Of Tissues
InactiveUS20070276242A1Simpler transducer designSimple designOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsPhase shiftedClassical mechanics
A system and method for imaging the localized viscoelastic properties of tissue is disclosed. An oscillatory radiation force is applied to tissue in order to induce a localized oscillatory motion of the tissue. The phase and amplitude of the induced localized oscillatory motion of the tissue is also detected while the oscillatory radiation force is being applied. The viscous properties of the tissue are determined by a calculation of a phase shift between the applied oscillatory radiation force and the induced localized oscillatory motion of the tissue. The oscillatory force force inducing local oscillatory motion may be a single amplitude modulated ultrasound beam.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
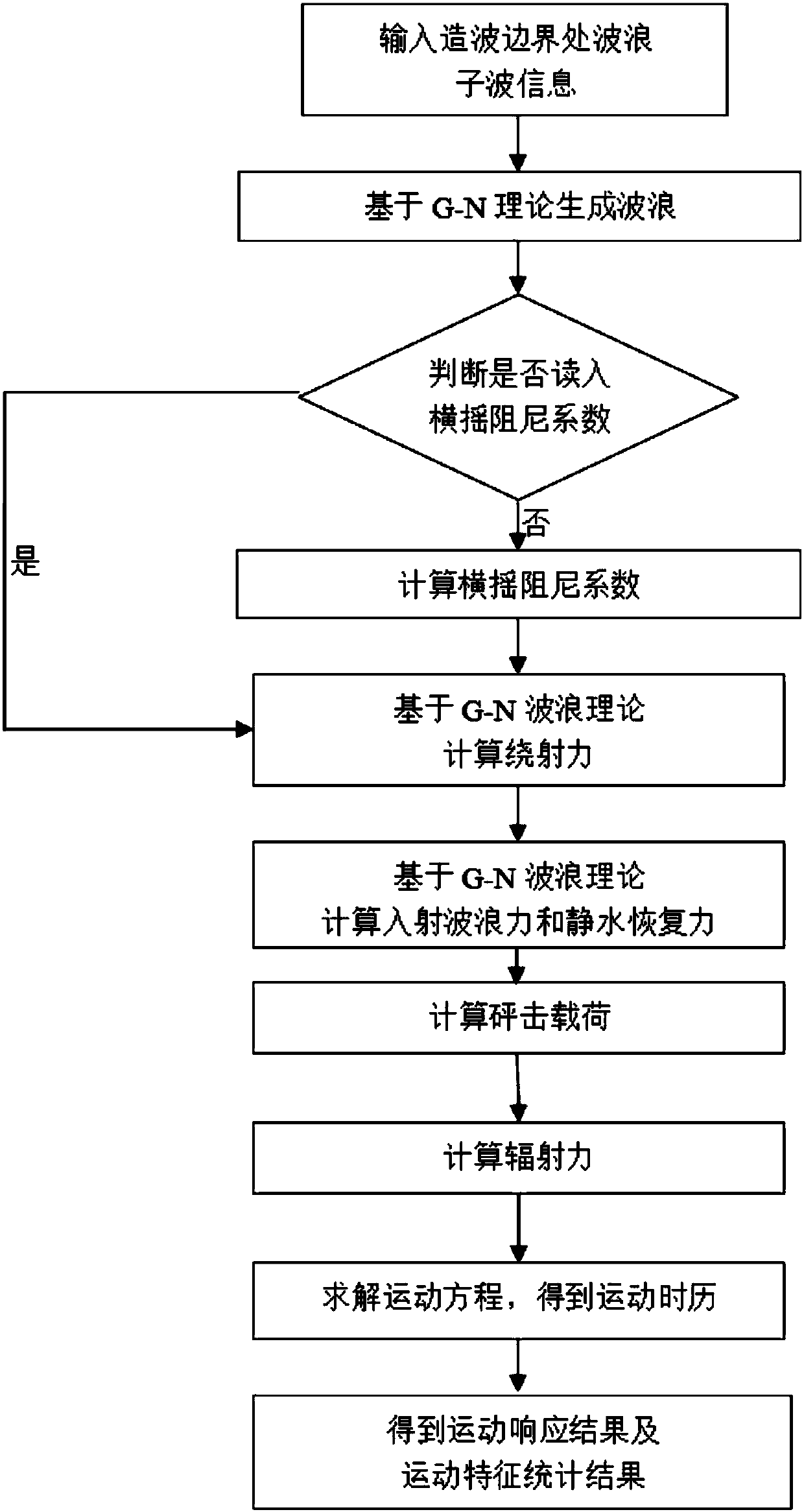
G-N wave model-based forecast method for large-amplitude motion of ship in severe sea condition
The invention discloses a G-N wave model-based forecast method for a large-amplitude motion of a ship in a severe sea condition, and belongs to the technical field of ship motion forecast. Through nonlinear simulation of the motion of the ship in waves, a nonlinear effect of an incident wave force and a hydrostatic restoring force of a ship body is considered, and an incident wave pressure on thewet surface of the ship body is calculated. A fluid pressure is solved based on a G-N wave theory, so that the incident wave force and a hydrostatic pressure are obtained; a radiation force and a diffraction force are solved by adopting an impulse response function method, wherein the wave surface of the diffraction force is obtained by a G-N wave model; and consistency correction can be performedin calculation. The large-amplitude motion of the ship is forecast by adopting a weak nonlinear motion equation based on coupling of three freedom degrees including heaving, pitching and rolling; RAOis calculated for analyzing motion characteristics of the ship; a simulated motion response time history significant valve, a motion extremum value and oscillation statistics are analyzed by utilizing a wave-by-wave analysis theory; and the motion of the ship body can be forecast more accurately.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method of making a stratified paper
The present invention provides a method making stratified paper by redistributing the pulp suspension inside the headbox nozzle using acoustic radiation waves. Acoustic radiation forces fractionate fibers based on fiber radius. The acoustic radiation waves separate the fibers by pushing the coarse and longer fibers to the inner area while fines and smaller fibers remain in the outer area. This has a similar effect of multi-layer stratification headbox, and provides paper with a smoother surface.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
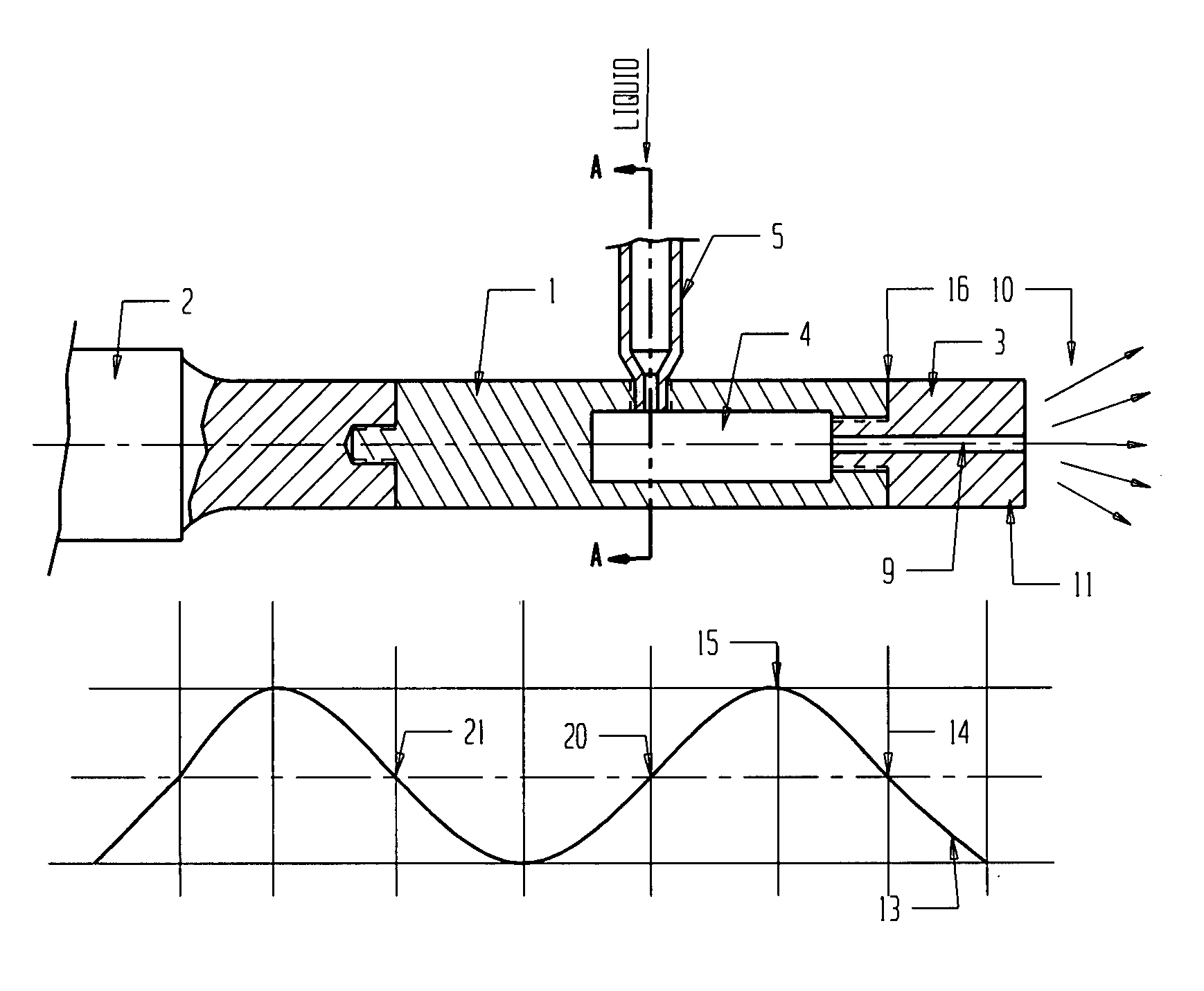
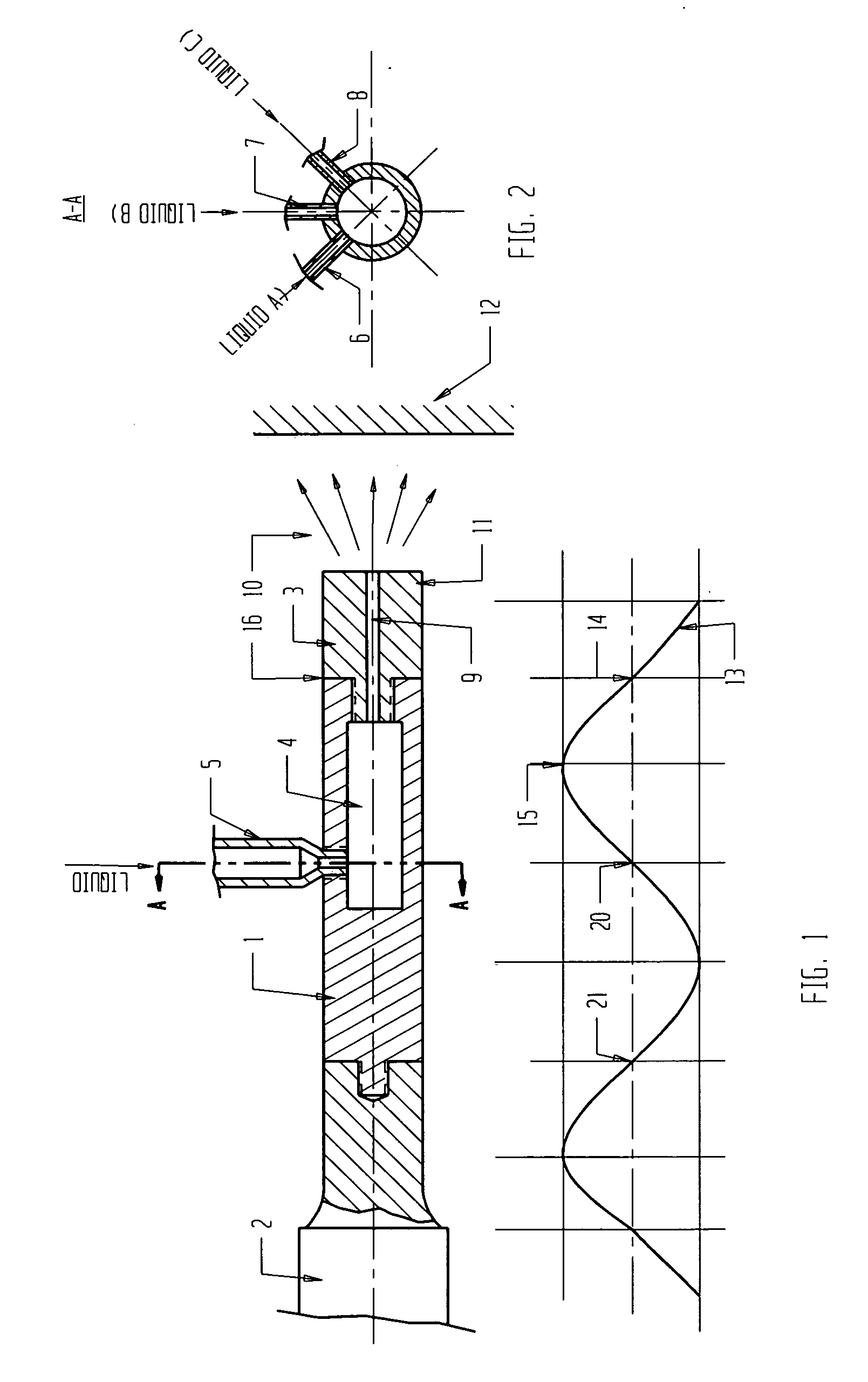
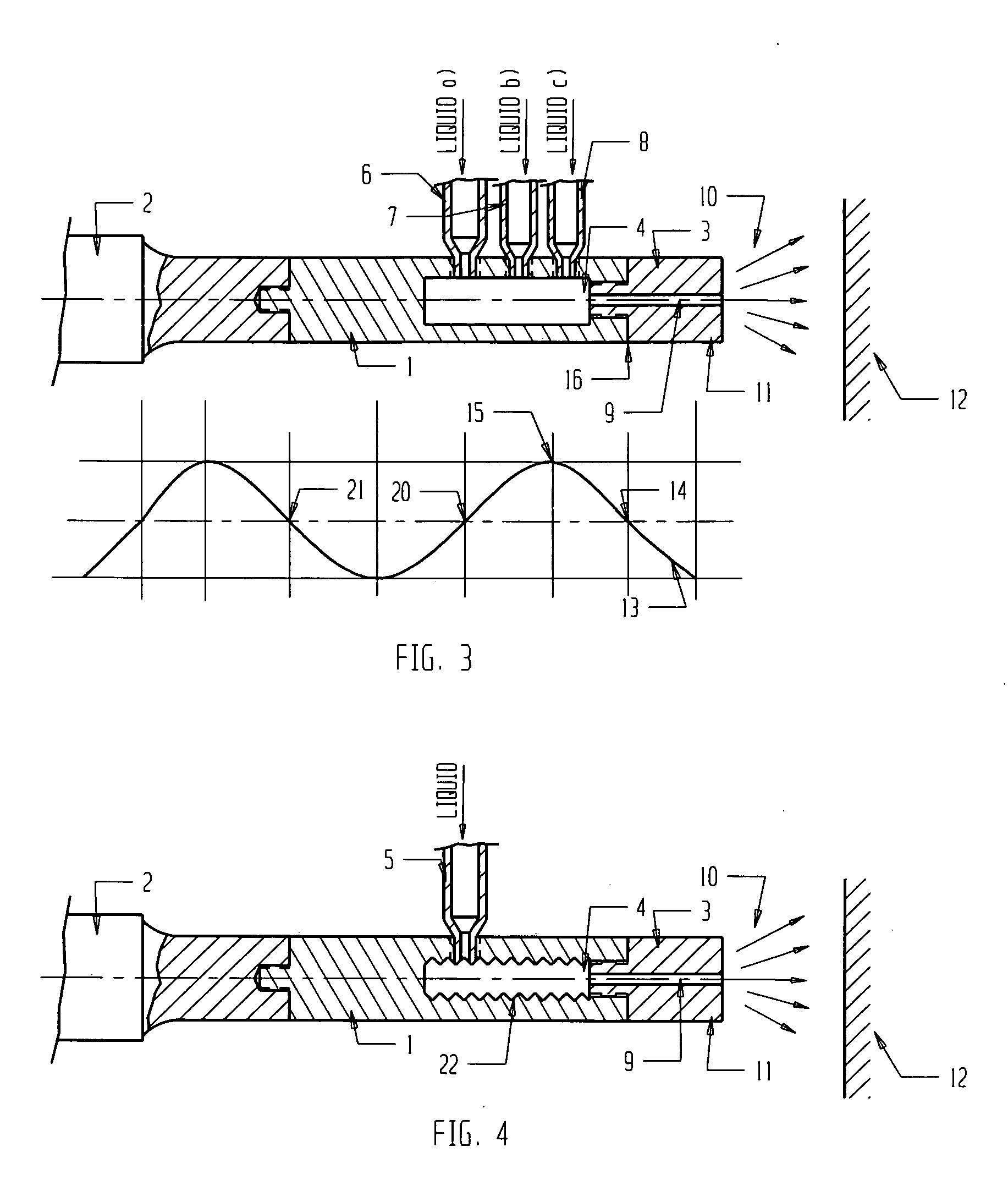
Ultrasound apparatus and methods for mixing liquids and coating stents
InactiveUS20070051307A1Improve propertiesStentsLiquid surface applicatorsUltrasonic sensorUltrasound cavitation
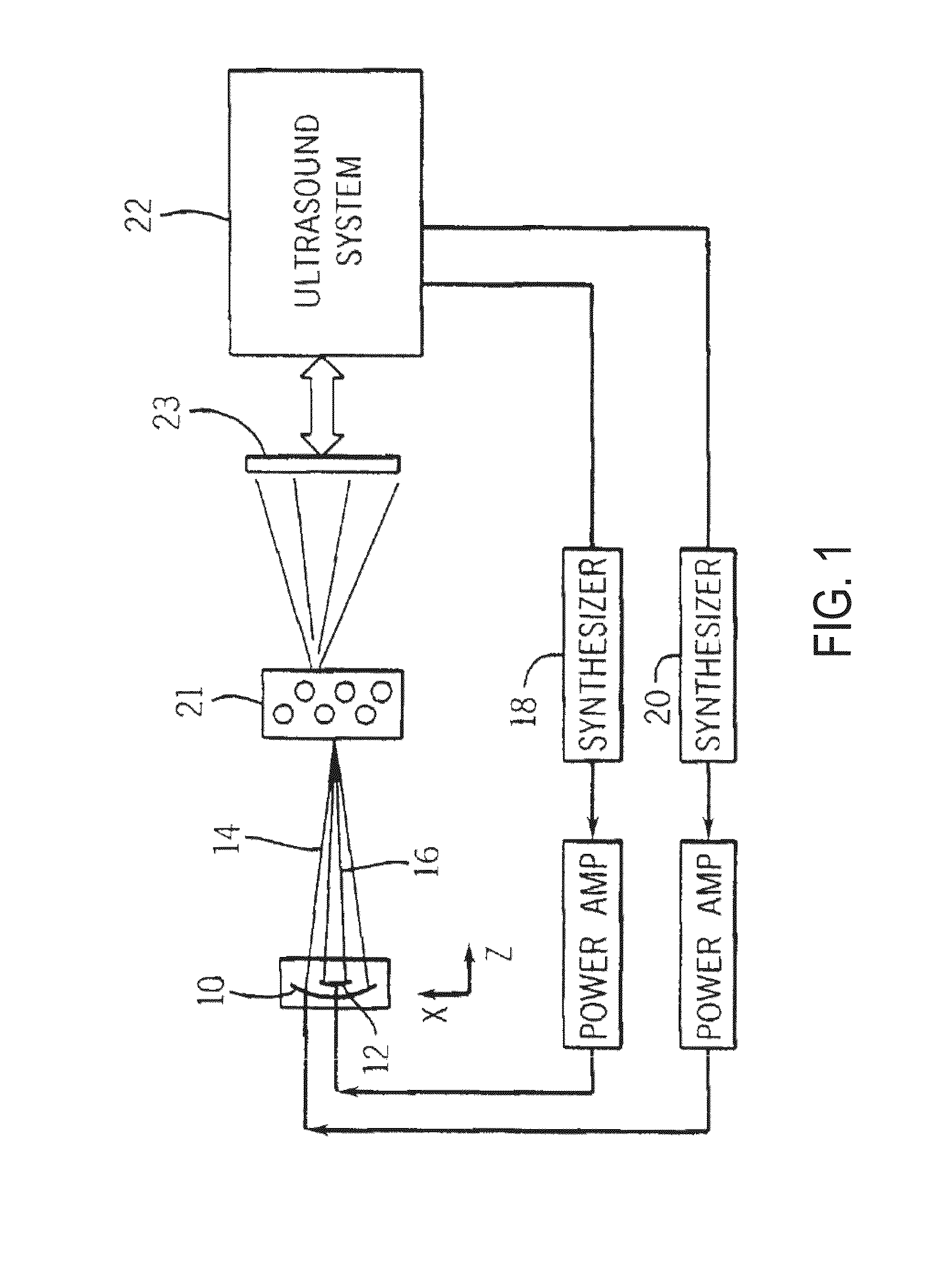
Ultrasound methods and apparatus for mixing two or more different liquids are disclosed. The ultrasound methods and apparatus may mix varied components including drugs, polymers, and coatings for application to a variety of medical apparatus surfaces. The apparatus and technique can generate a proper mixture which is uninterruptedly / continuously delivered to the surface of the medical apparatus. The apparatus may include specific ultrasound transducer / tip configurations which may allow for the mixing of different liquids in a mixing camera located inside of the vibrating tip. The apparatus and methods of the present invention may mix different drugs, applying them to stent surface using different effects like ultrasound cavitation and radiation forces. Furthermore, the disclosed methods and apparatus may generate a mixture and may deliver a targeted, gentle, highly controllable dispensation of continuous liquid spray which can reduce the loss of expensive pharmaceuticals.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
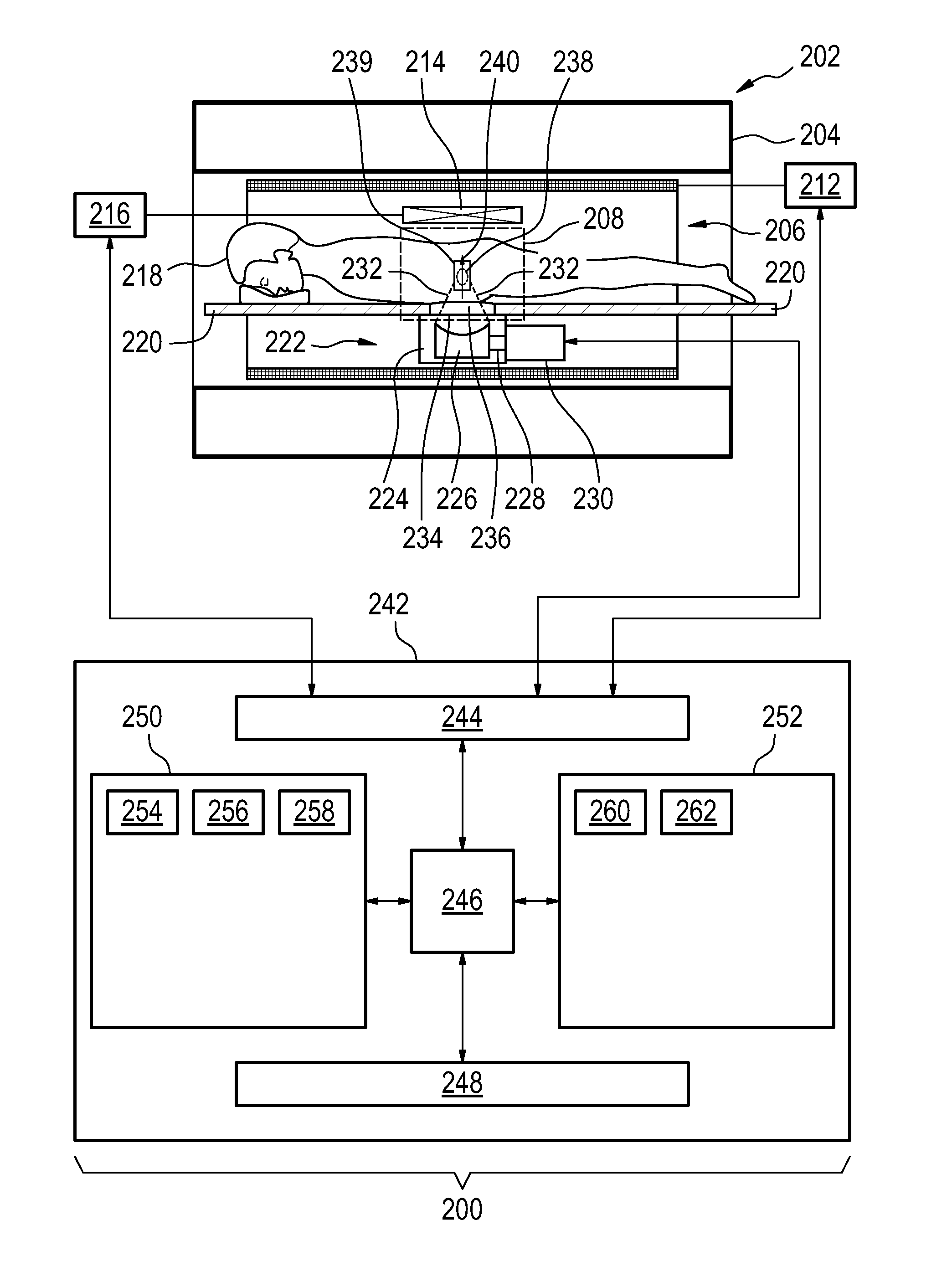
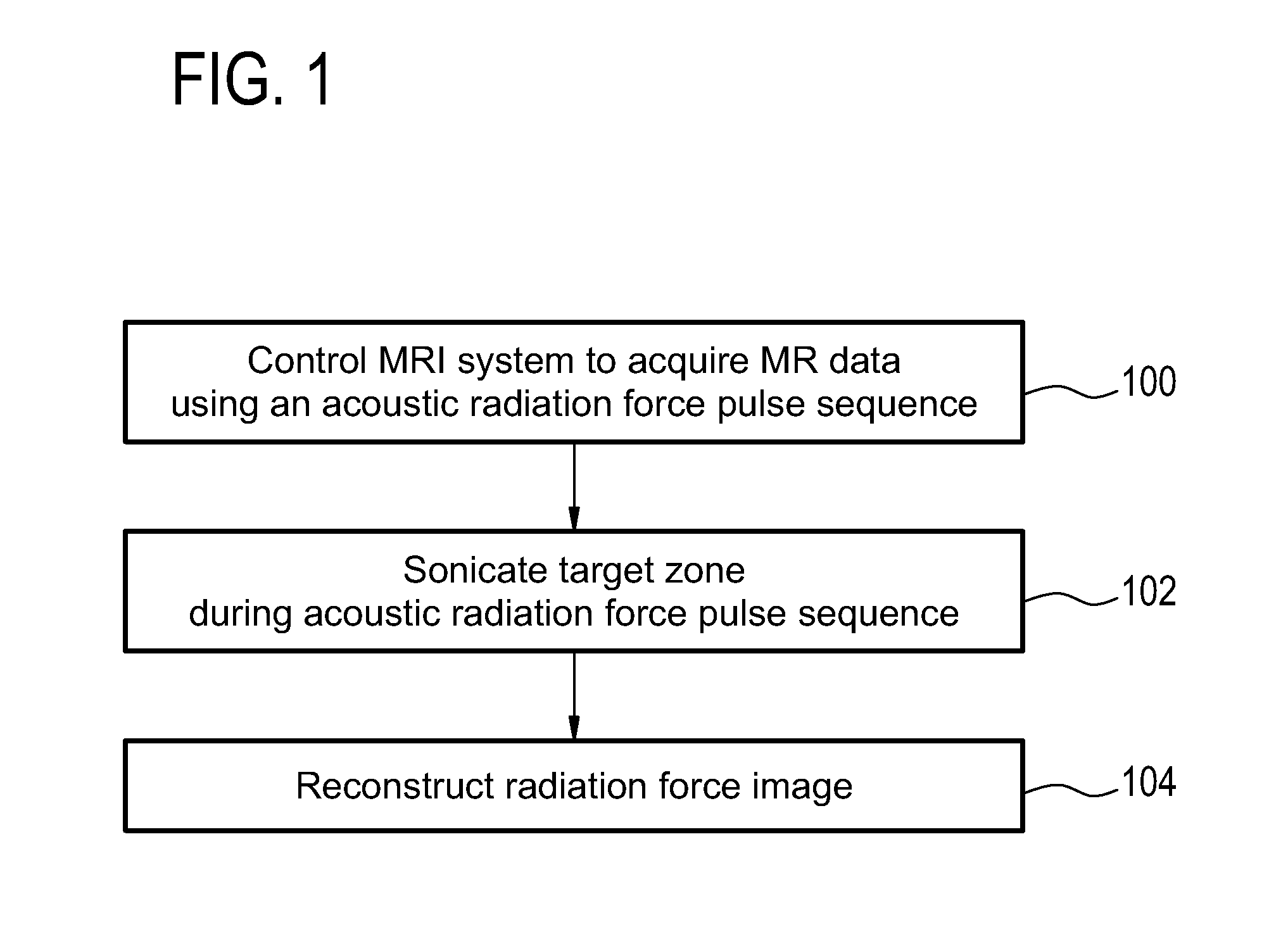
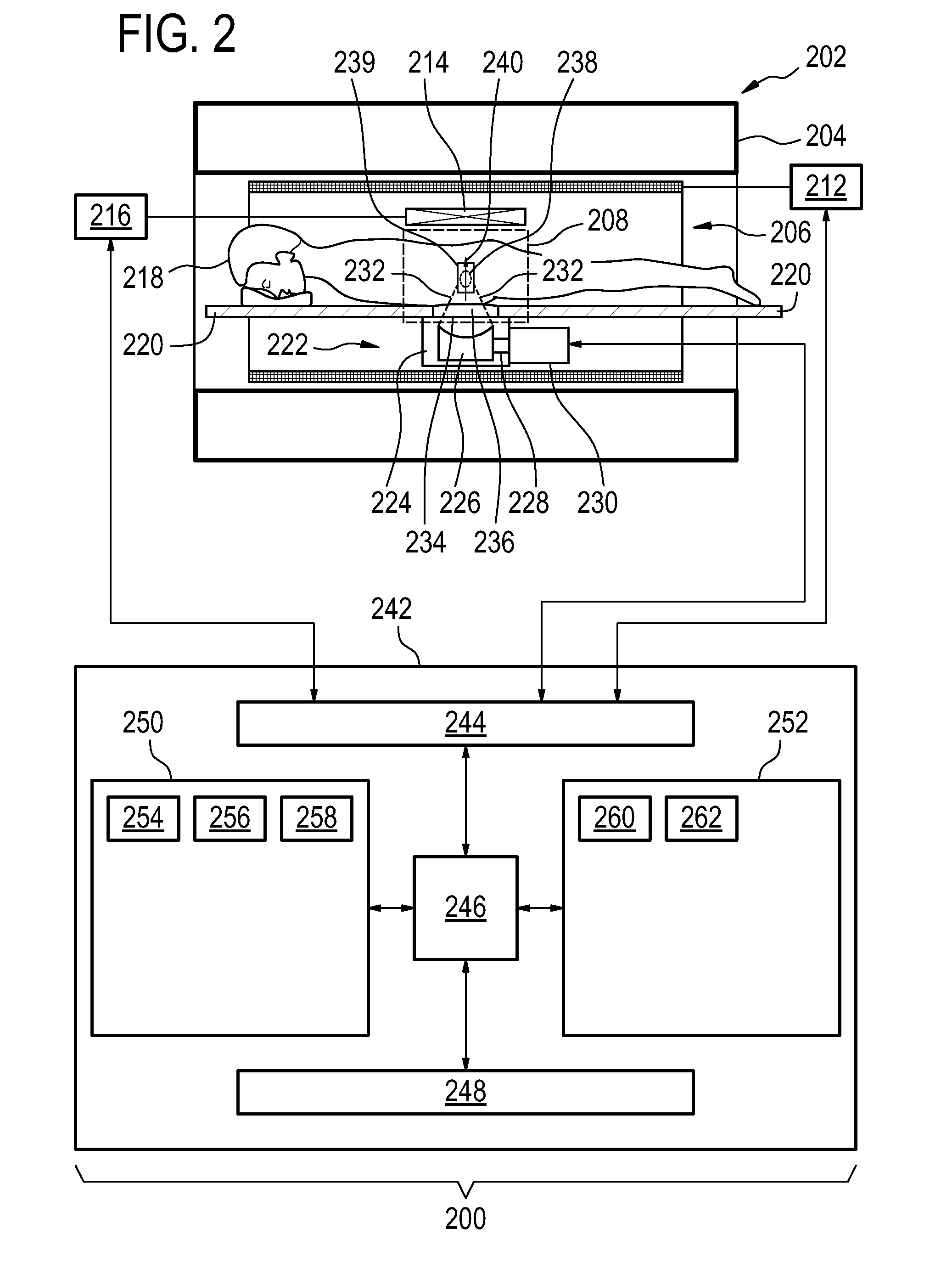
Acoustic radiation force magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20150190659A1Accurate valueSpeeding acquisitionUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsSonificationPulse sequence
The invention provides for medical instrument (200, 400) comprising a magnetic resonance imaging system (202) and a high intensity focused ultrasound system (222). A processor (246) controls the medical instrument. Instructions cause the processor to control (100) the magnetic resonance imaging system to acquire the magnetic resonance data using a pulse sequence (254). The pulse sequence comprises an acoustic radiation force imaging pulse sequence (500, 600). The acoustic radiation force imaging pulse sequence comprises an excitation pulse (512) and a multi-dimensional gradient pulse (514) applied during the radio frequency excitation pulse for selectively exciting a region of interest (239) encompassing a target zone and at least a portion of the beam axis. The instructions cause the processor to control (102) the high intensity focused ultrasound system to sonicate the target zone during the acoustic radiation force imaging pulse sequence and reconstruct (104) a radiation force image (258) using the magnetic resonance data.
Owner:PROFOUND MEDICAL
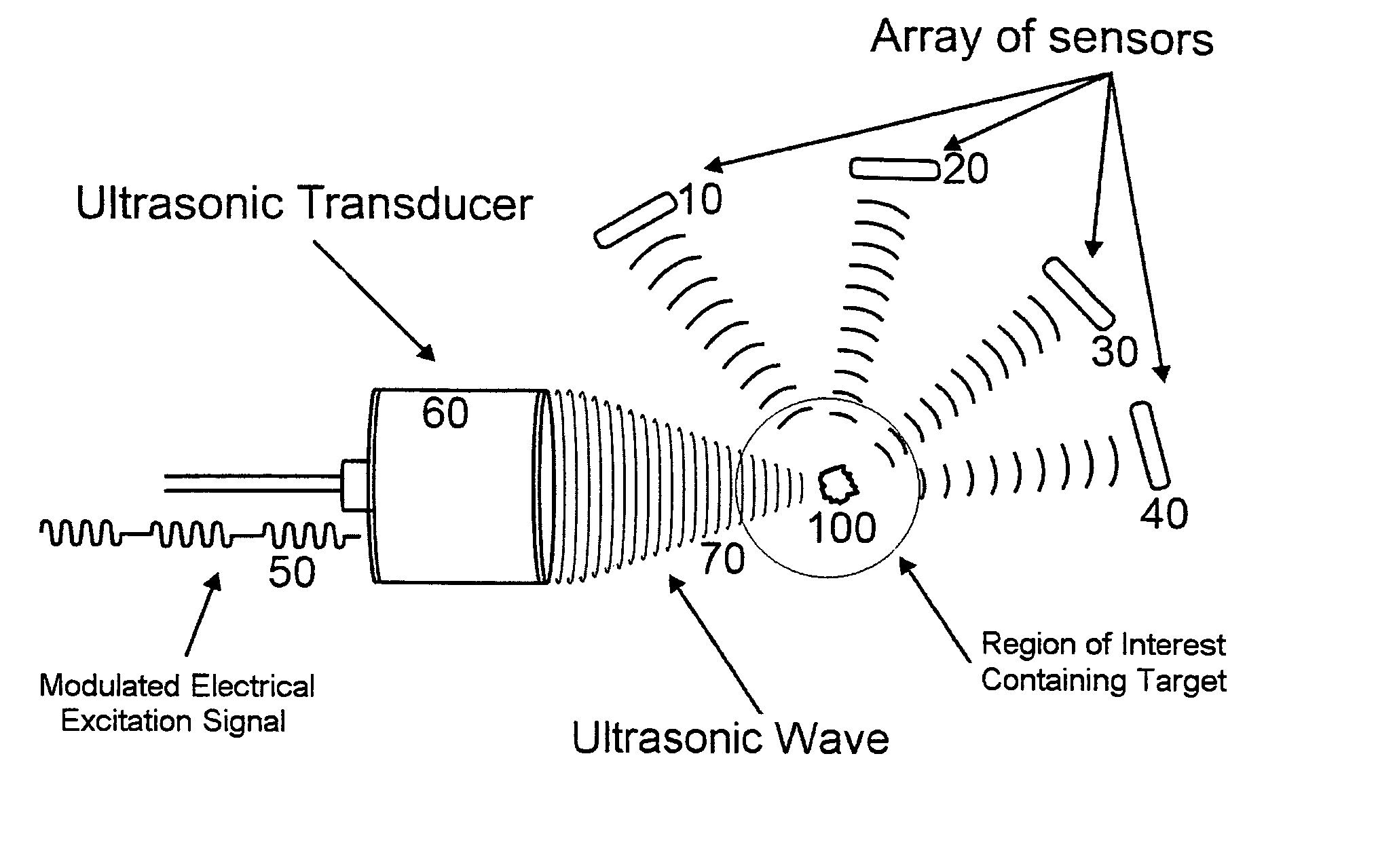
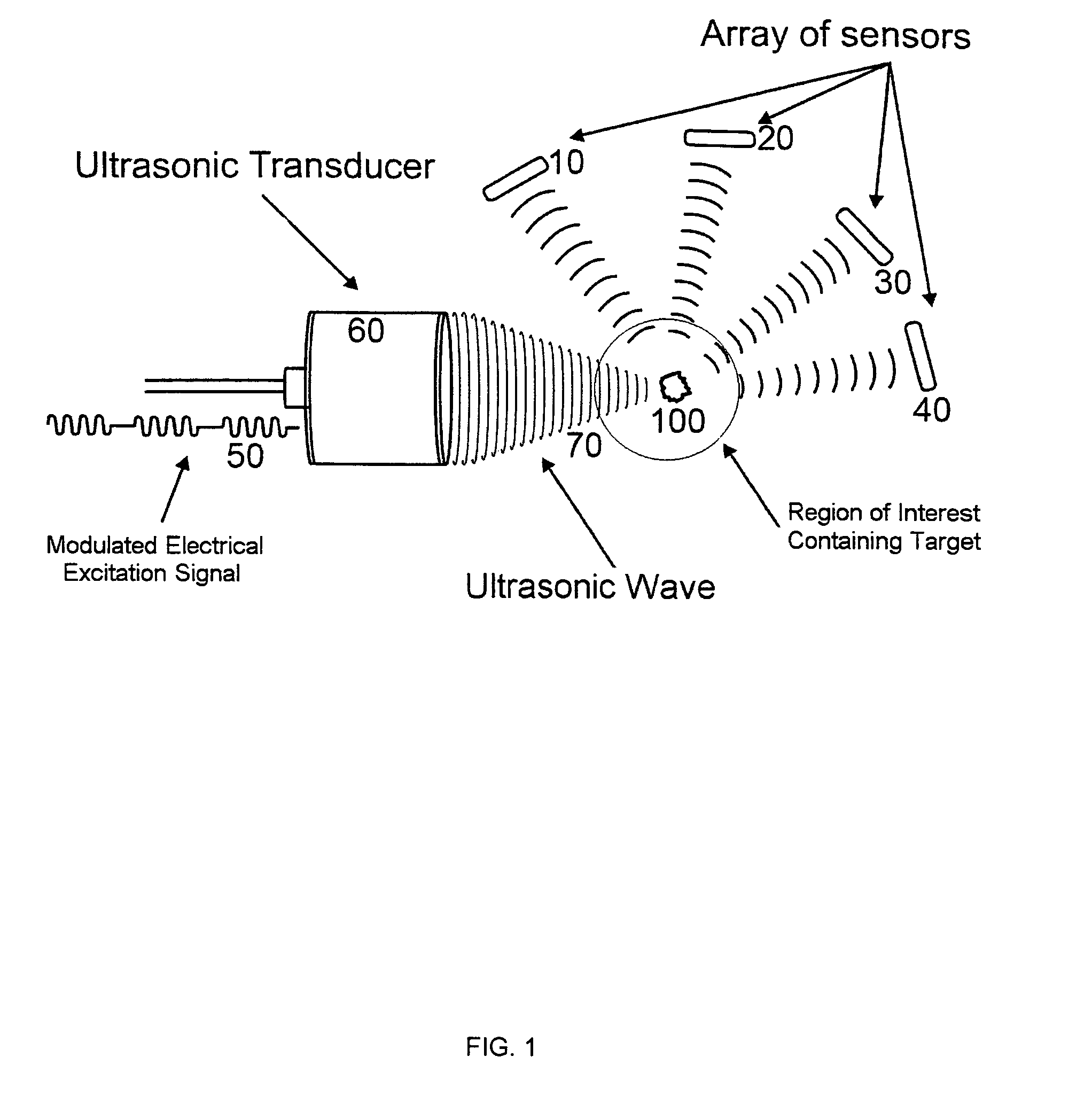
Method of locating the position of a microcalcification in a human breast
InactiveUS8622909B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasonographySonification
This invention relates to diagnostic and screening medical ultrasound in general and to ultrasound-stimulated detection and location, Image-based Dynamic Ultrasound Spectrography, Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging, and similar modalities in particular. In this invention, an ultrasound signal is emitted into tissue and the resulting radiation force induces localized lower frequency oscillations, which are then received by various acoustic sensors and analyzed to determine certain features or characteristics of the interrogated region. The sensors can be arranged in the form of a ring, in any random arrangements, or positioned in specifically chosen locations. An ultrasonic imaging and excitation transducer generates certain stimulating signals which are received by the breast tissues and which, if they contact a microcalcification, other target, or any region with sharply different mechanical and visco-elastic properties, will result in reflected, demodulated, or re-radiated signals. These signals will propagate away from the targets and detected by the various receiving sensors.
Owner:QUANTASON
Method for imaging surface roughness using acoustic emissions induced by ultrasound
ActiveUS20090114019A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce frequencyVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveSonification
A method for measuring variations of the surface of an object using acoustic energy in the audio range is provided. Imaging fine surface roughness on the order of few microns is achievable by using a vibroacoustography technique. This technique provides a method for imaging surface roughness on the basis of an ultrasound radiation force that stimulates acoustic emissions at an ultrasound standing wave field. The present invention may be employed as a tool for the nondestructive inspection and imaging of the surface variations of an object.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
System and method for non-invasive determination of tissue wall viscoelasticity using ultrasound vibrometry
ActiveUS20140296709A1Non-invasively determinesNo painHealth-index calculationOrgan movement/changes detectionRadiologyNon invasive
System and method for determining viscoelasticity of curved tissue walls using ultrasound bladder vibrometry (UBV). The UBV is a non-invasive technique utilizing, in a specific case, a focused ultrasound radiation force to excite Lamb waves in a curved bladder wall and pulse-echo techniques to track the tissue deformation propagating through such curved wall. Cross-spectral analysis is used to calculate the wave velocity, which is directly related to the elastic properties of the bladder wall.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Biological tissue multi-characteristic imaging method based on acoustoelectric effect and acoustic radiation force
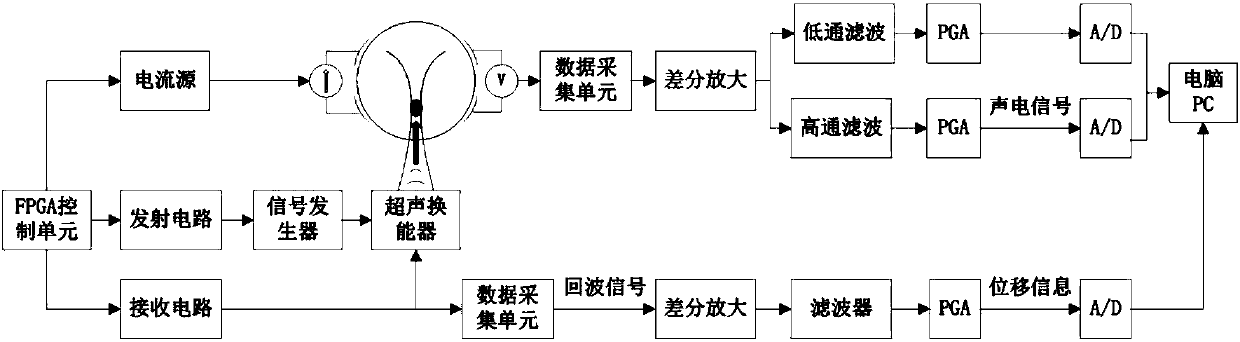
ActiveCN107550458AAdd measurement informationHigh-resolutionOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationVoltage vector
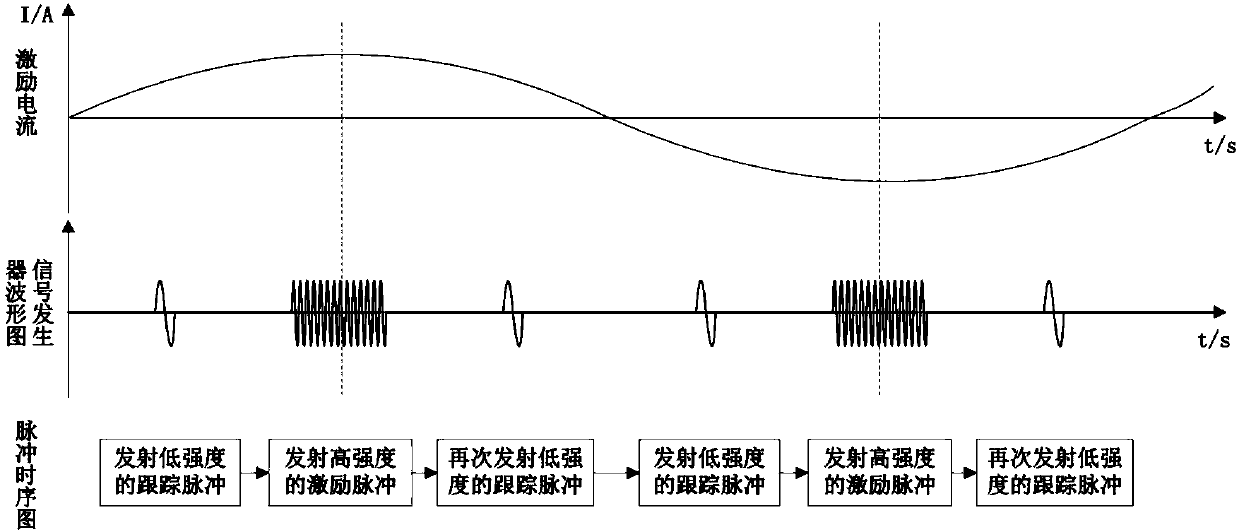
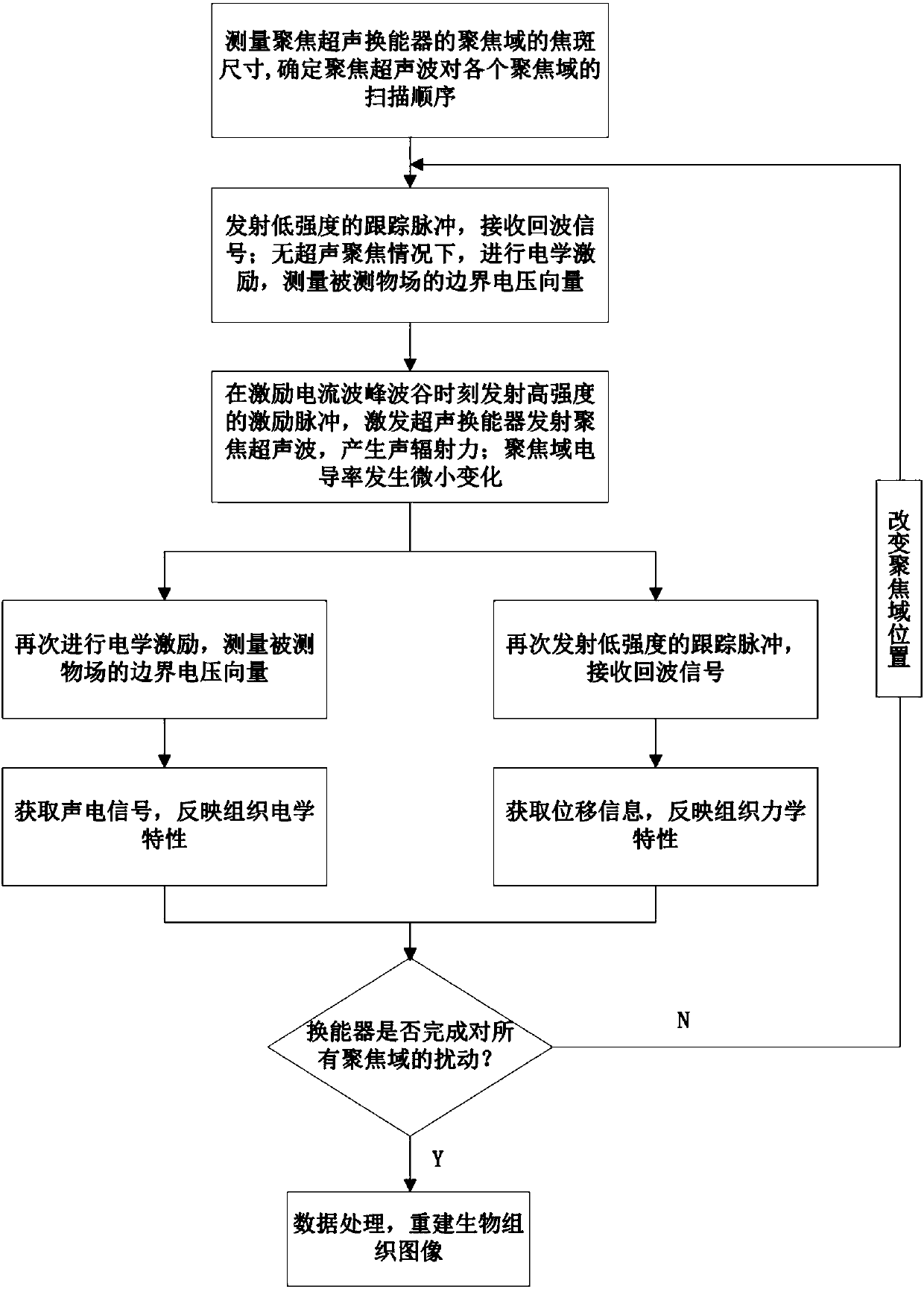
The invention relates to a biological tissue multi-characteristic imaging method based on the acoustoelectric effect and acoustic radiation force. The method comprises the steps that the size of the focal spot of each focusing domain of an ultrasonic transducer under a focusing ultrasonic disturbance mode is measured, and the sequence that the focusing domains are scanned by focusing ultrasonic waves is determined; a low-intensity tracking pulse is emitted to the ultrasonic transducer, and under the condition that ultrasonic focusing is ignored, a boundary measurement voltage vector phi and anecho signal of the tracking pulse are obtained; when an excitation current reaches the wave peak or the wave trough moment, a high-intensity excitation pulse is emitted to the ultrasonic transducer,so that an emission and scanning mechanism of the ultrasonic transducer works in a focused ultrasonic disturbance mode, and the focusing ultrasonic waves disturb the nth focusing domain; during focusing ultrasonic disturbance, the boundary measurement voltage vector phi n obtained after disturbance is measured, a low-intensity tracking pulse is emitted to the ultrasonic transducer again, and an echo signal is received; an acoustoelectric signal and corresponding displacement information of the nth focusing domain are obtained; the obtained data is processed, and a biological tissue image is reconstructed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
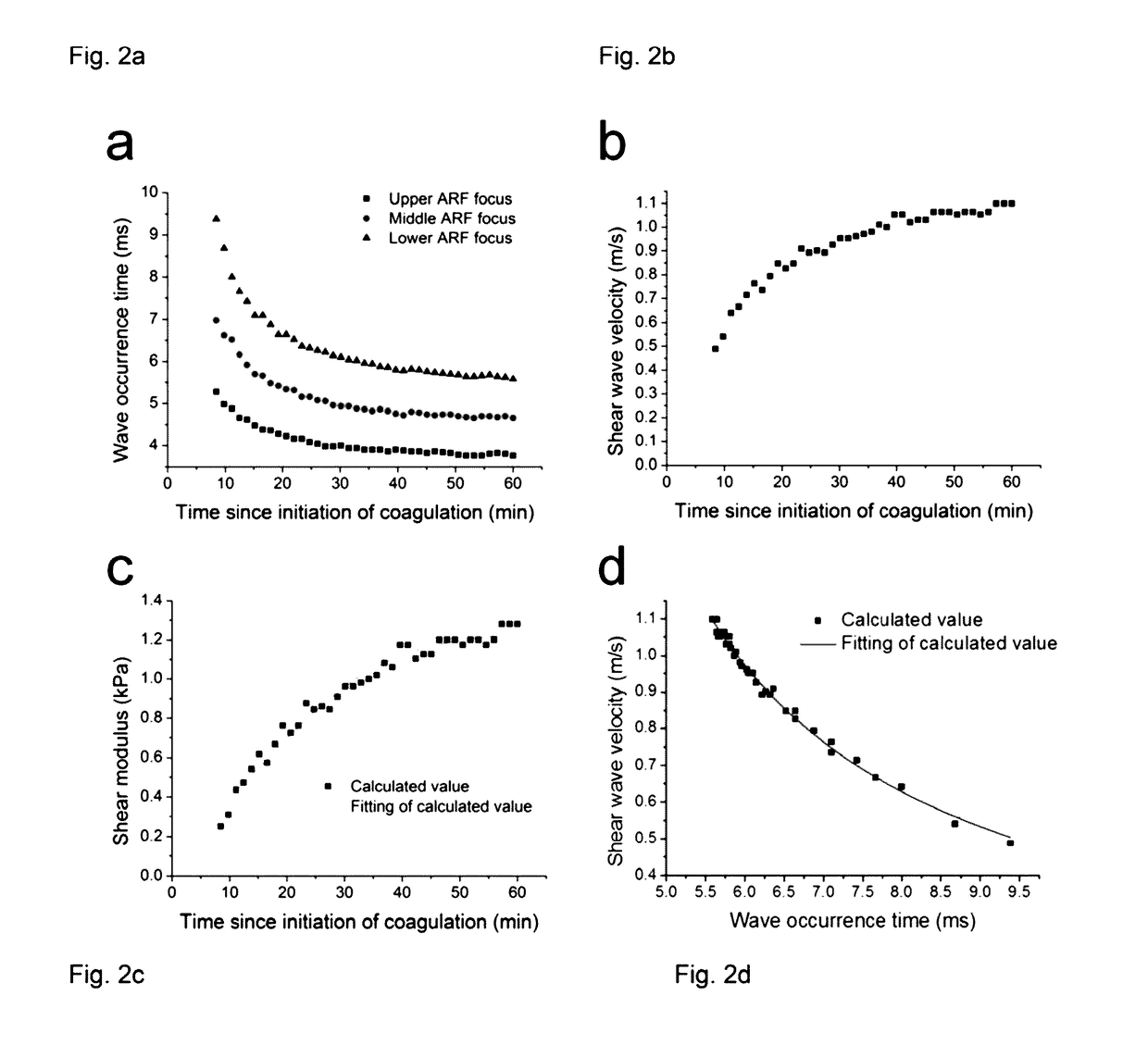
Assessment Of Blood Coagulation Using An Acoustic Radiation Force Based Optical Coherence Elastography (ARF-OCE)
ActiveUS20170107558A1Increased fibrinogen concentrationIncreased coagulabilityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMicrobiological testing/measurementAcoustic radiation forceLight beam
An apparatus and method of using an optical coherence elastography (OCE) under acoustic radiation force (ARF) excitation includes the steps of inducing an excitation wave in a blood sample by use of an ultrasound beam from an ultrasonic transducer; measuring an elastic property of the blood sample by use of an optical coherence tomography (OCT) beam transverse to the ultrasound beam to dynamically measure the elastic property of the blood sample during coagulation and assessing the clot formation / dissolution kinetics and strength.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Particle capturing and releasing device based on bulk acoustic wave excitation and moving bubbles
ActiveCN107583696AThe output energy density is smallDirectional movement controllableFlexible member pumpsLaboratory glasswaresPiezoelectric actuatorsAcoustic radiation force
The invention discloses a particle capturing and releasing device based on bulk acoustic wave excitation and moving bubbles. The particle capturing and releasing device based on bulk acoustic wave excitation and moving bubbles can be used in fields such as life engineering, medical science, micro assembly, and chemical analysis, and comprises a micro-fluidic upper chip, a PDMS membrane, a piezoelectric actuator, a glass substrate, and a magnet exciting coil; the micro-fluidic upper chip is provided with a liquid inlet, a main runner, a side runner, and a liquid outlet; when particles are captured by bubbles successively, the particles are stored in the side runner, and are released back into the main runner based on requirements. The particle capturing and releasing device is prepared viamicro machining, bulk acoustic wave generated by the piezoelectric actuator is capable of exciting bubbles in the runners to perform radial vibration, and radial vibration of the bubbles is capable ofacoustic radiation force on nearby particles, so that particle capturing is realized. Expansion of the volume of paraffin is capable of providing the PDMS membrane with force so as to realize deformation of the PDMS membrane, the pressure in the side runner is changed, the positions of the bubbles carrying the particles in the side runner are controlled, and particle moving is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for imaging surface roughness using acoustic emissions induced by ultrasound
ActiveUS8286467B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveAcoustic emission
A method for measuring variations of the surface of an object using acoustic energy in the audio range is provided. Imaging fine surface roughness on the order of few microns is achievable by using a vibroacoustography technique. This technique provides a method for imaging surface roughness on the basis of an ultrasound radiation force that stimulates acoustic emissions at an ultrasound standing wave field. The present invention may be employed as a tool for the nondestructive inspection and imaging of the surface variations of an object.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
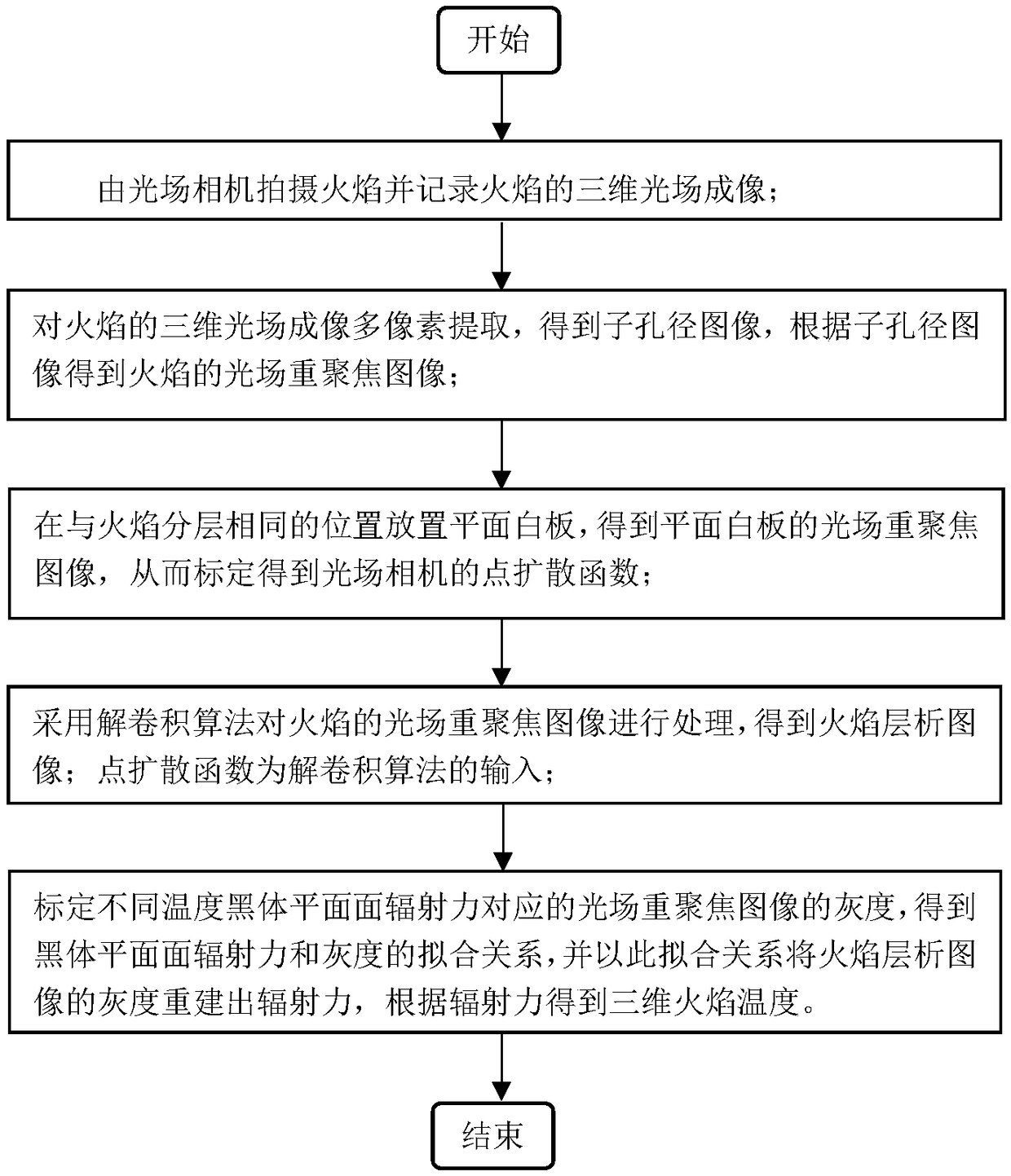
Three-dimensional temperature reconstruction combination method based on flame light field refocus image
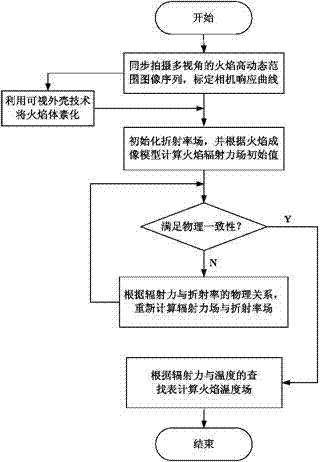
ActiveCN109115348AHigh precisionImprove accuracySensing radiation from gases/flamesPyrometry using electric radation detectorsImaging processingPoint spread function
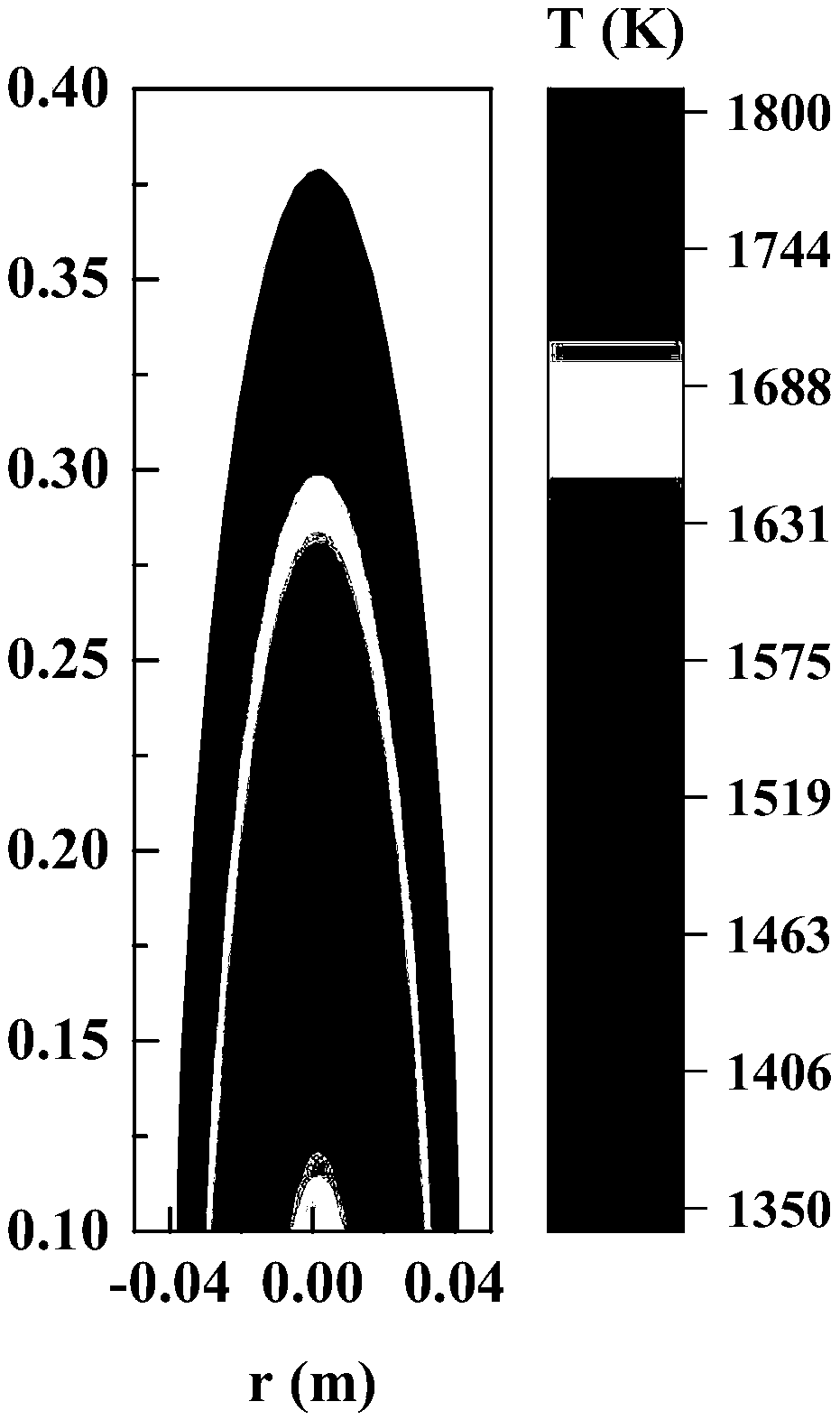
A three-dimensional temperature reconstruction combination method based on a flame light field refocus image is disclosed. The invention relates to the three-dimensional temperature reconstruction combination method based on the flame light field refocusing image. By using an existing nearest neighbor method, the physical reconstruction precision of the outermost layer and secondary outer layer offlames is low, and when a Lucy-Richardson deconvolution method is used in intermediate layer flame physical reconstruction, the precision is low. In the invention, the above problems are solved. Themethod has the following steps of 1, using a light field camera to shoot the flame and record the three-dimensional light field image of the flame; 2, acquiring the light field refocusing image of theflame; 3, acquiring the point spread function of the light field camera; 4, acquiring a flame chromatography image; and 5, acquiring a fitting relationship between a black body plane surface radiation force and a gray scale, and reconstructing the radiation force for the gray scale of the flame chromatography image based on the fitting relationship, and according to the radiation force, acquiringa three-dimensional flame temperature. The method is used for the flame image processing field during a high temperature flame temperature reconstruction process.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Instrument and method for ultrasound mediated drug delivery
InactiveUS20140135681A1Prevention and therapyIncreases mechanical indexUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic radiationMechanical index
A method and instrumentation for ultrasound mediated delivery of drugs to diseased tissue use ultrasound beams with frequency and focusing that provides an ultrasound radiation force acting on the drug and surrounding fluid, which produces a convection of drugs and compensates for the lack of a pressure gradient. To manipulate drug encapsulations and also stimulate transport of drugs across biological membranes, like the cell membrane or the blood brain barrier, the method and instrumentation use low frequency beams with high mechanical index. The method and instrumentation additionally uses ultrasound heating of the tissue to increase blood flow and manipulate thermally sensitive particles.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
Illumination sources and customizable spectral profiles
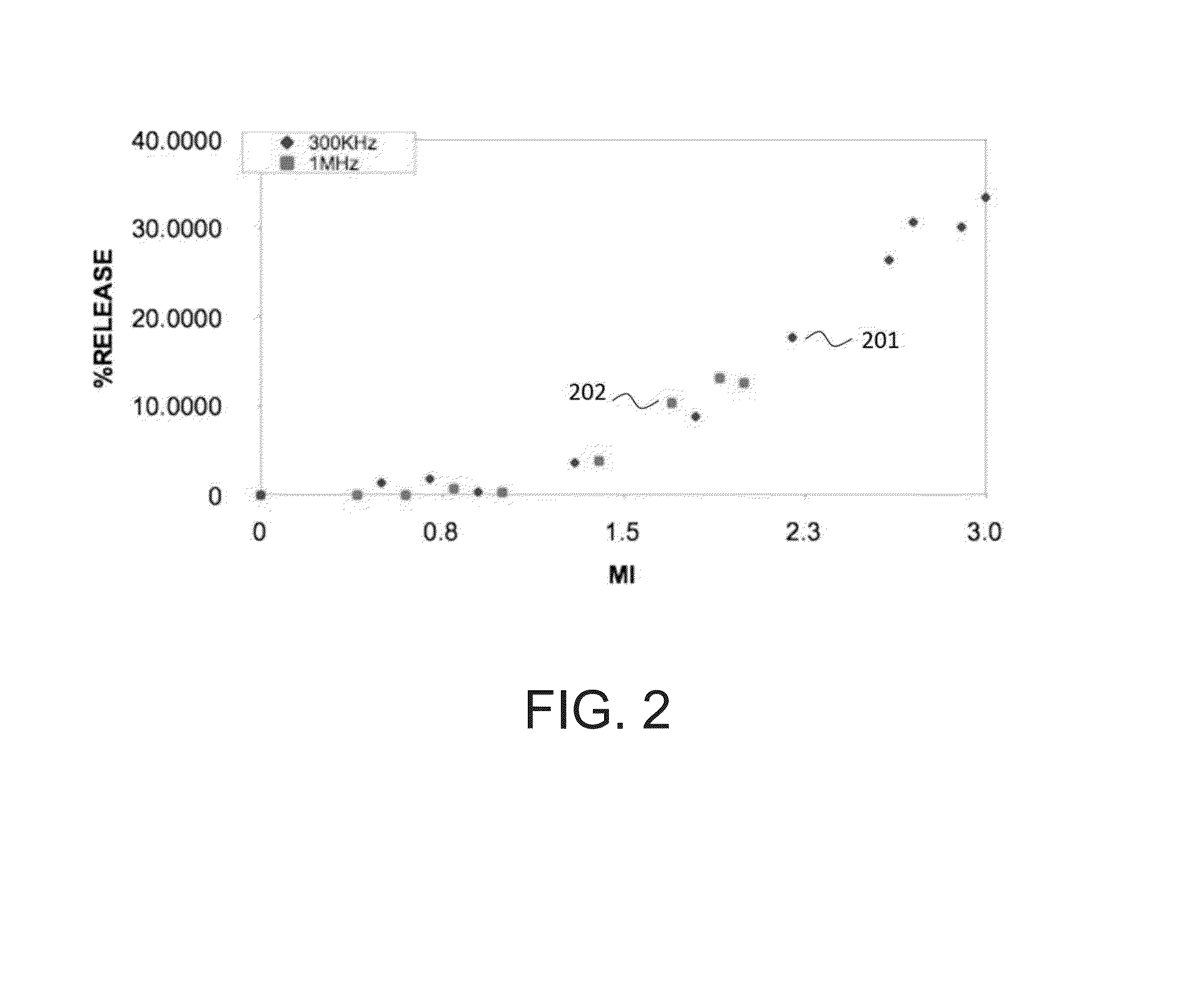
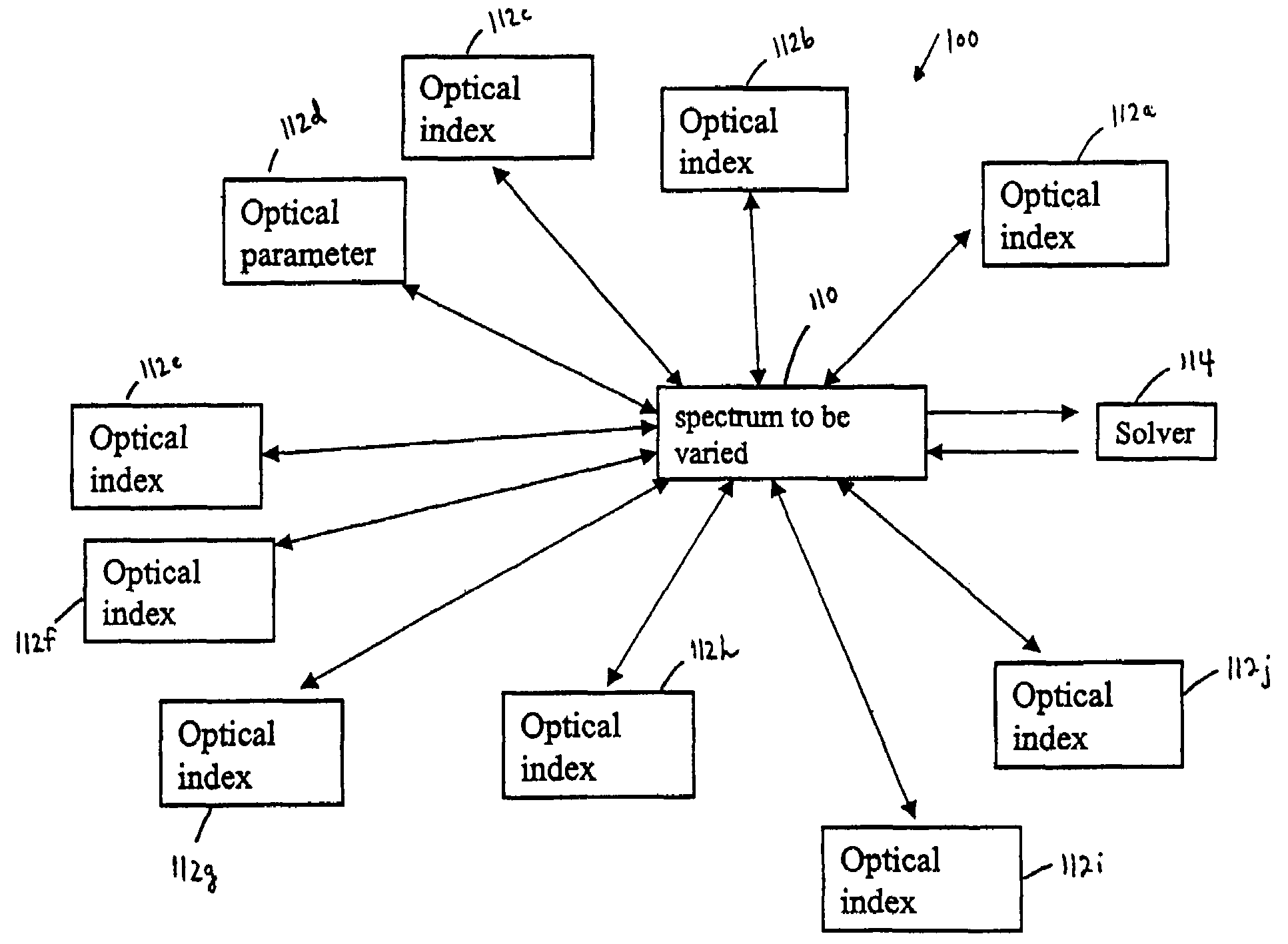
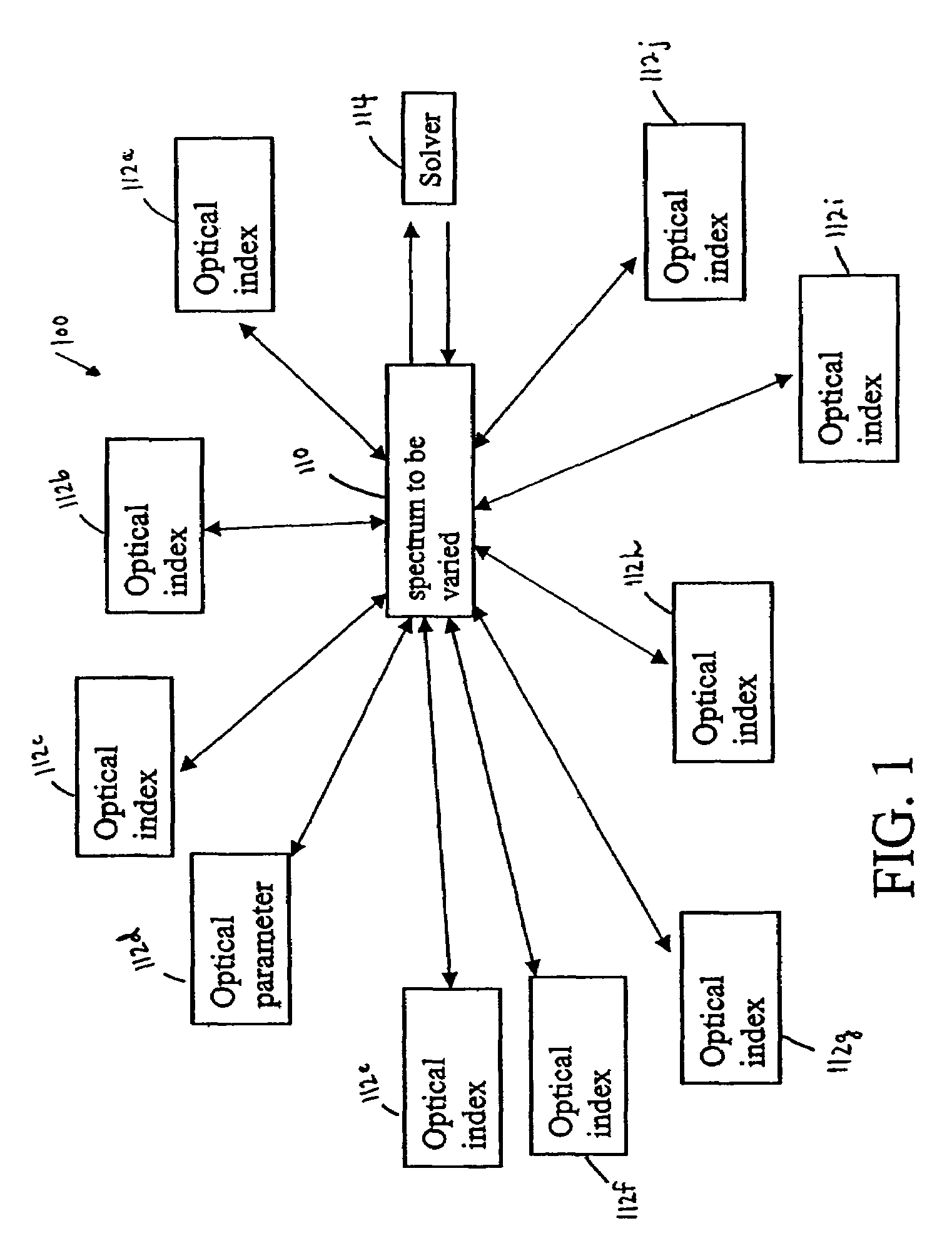
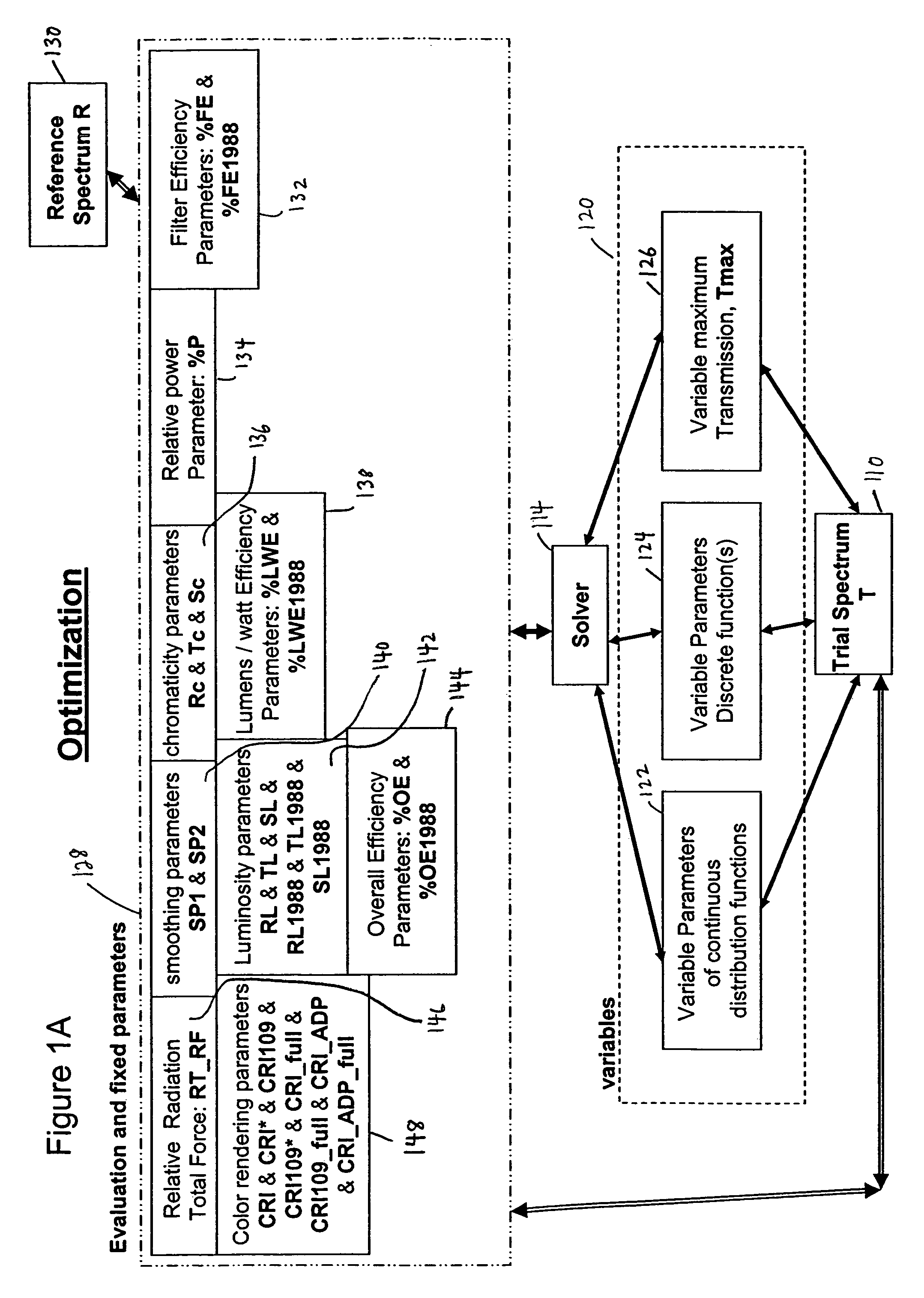
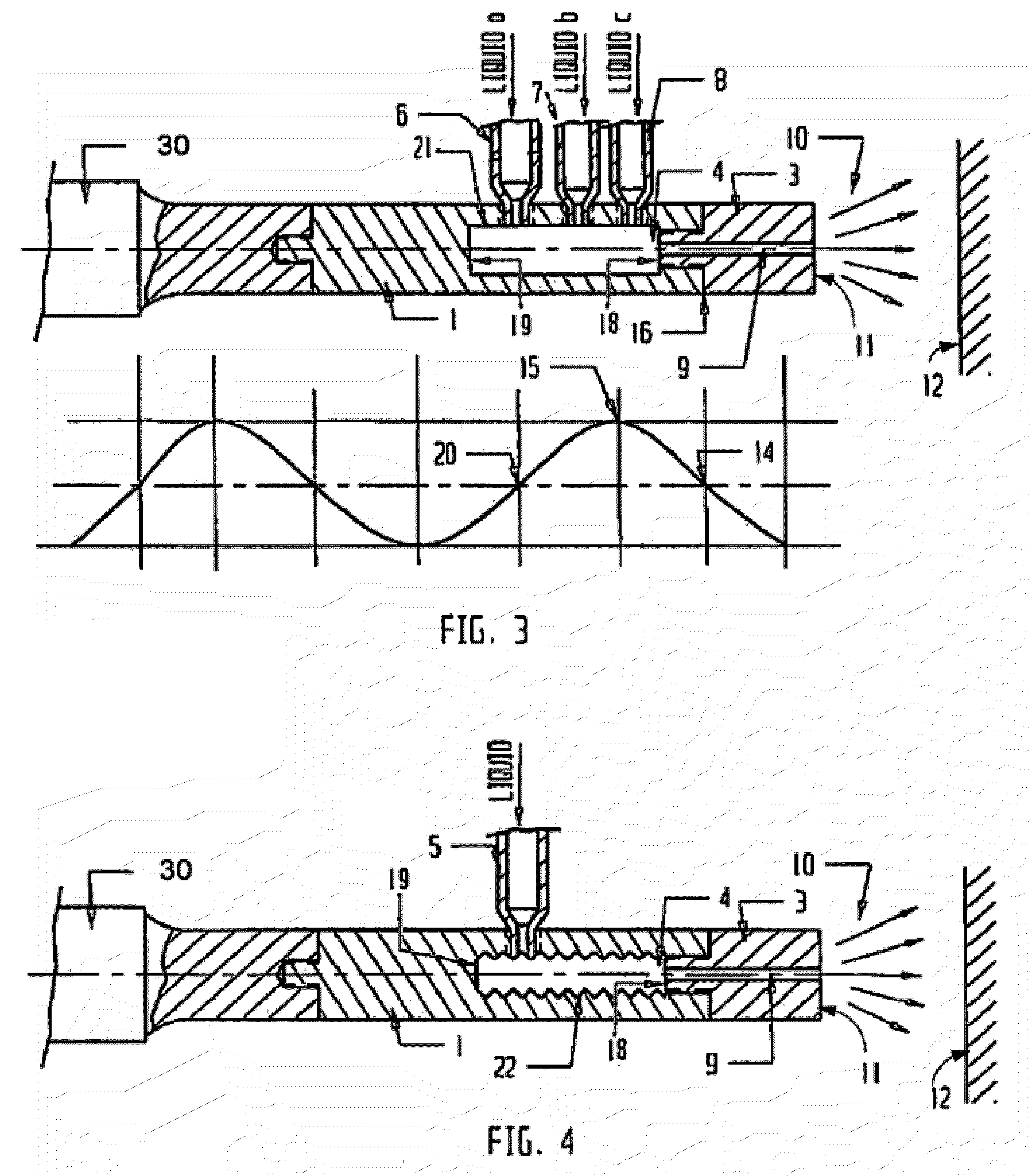
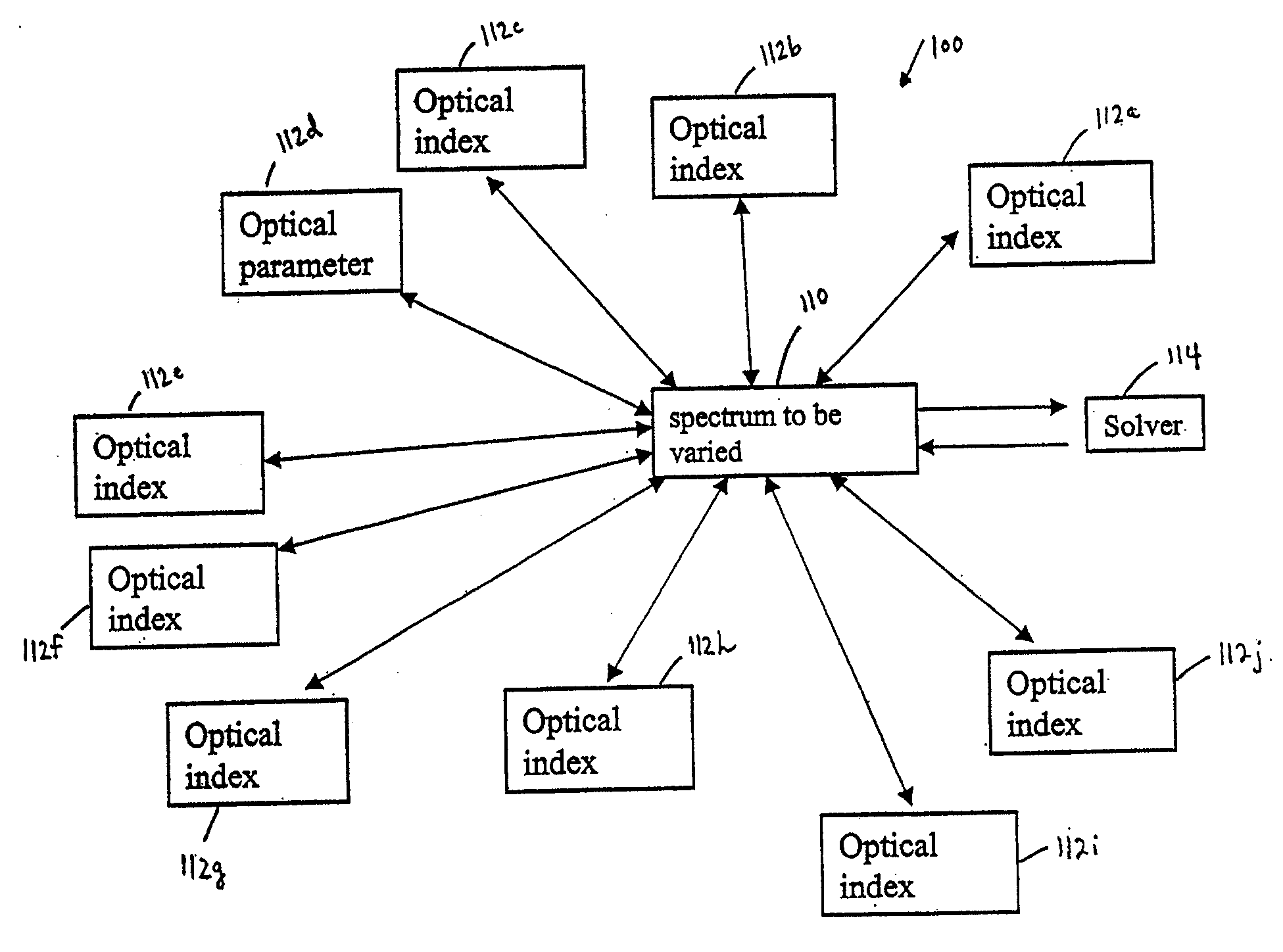
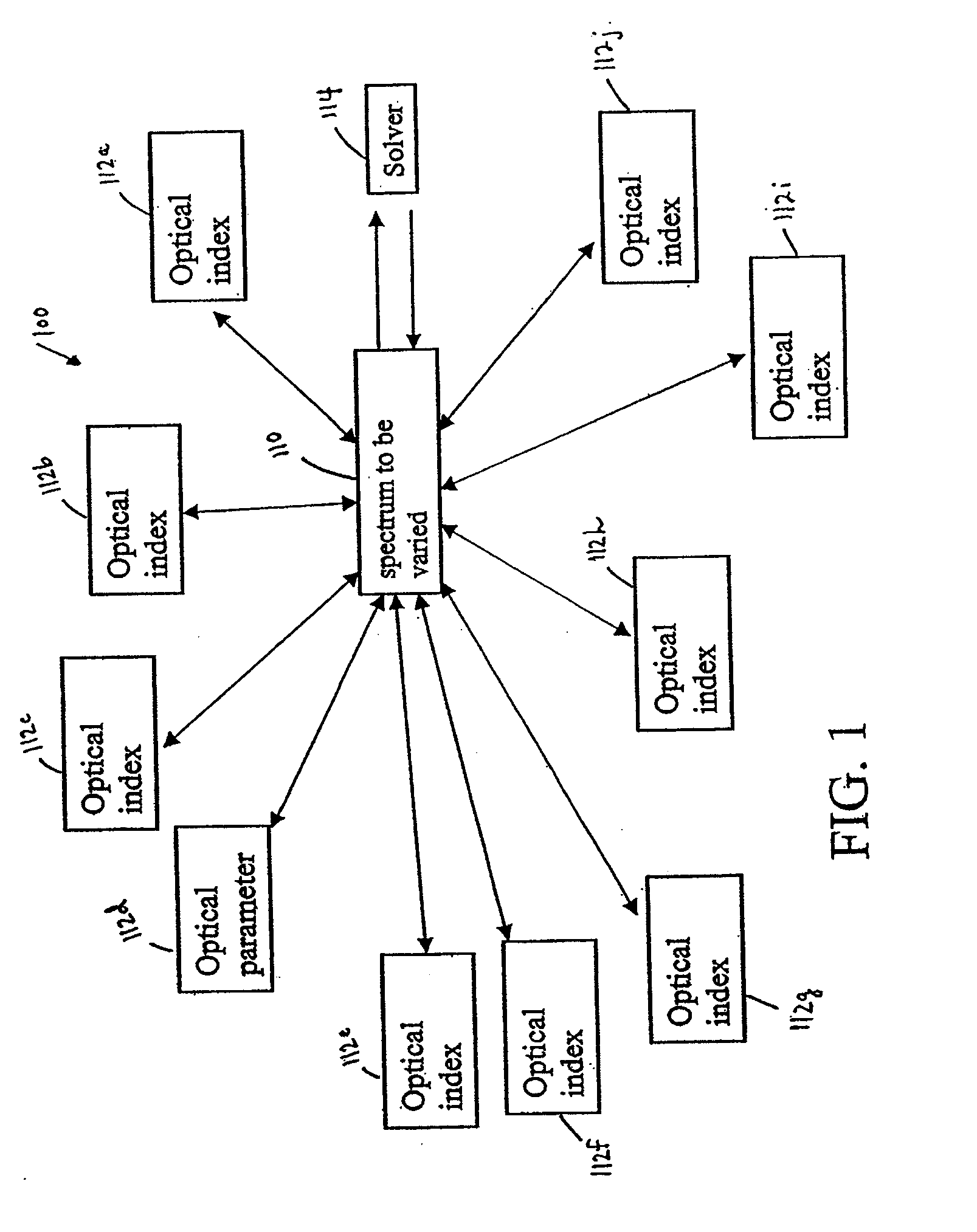
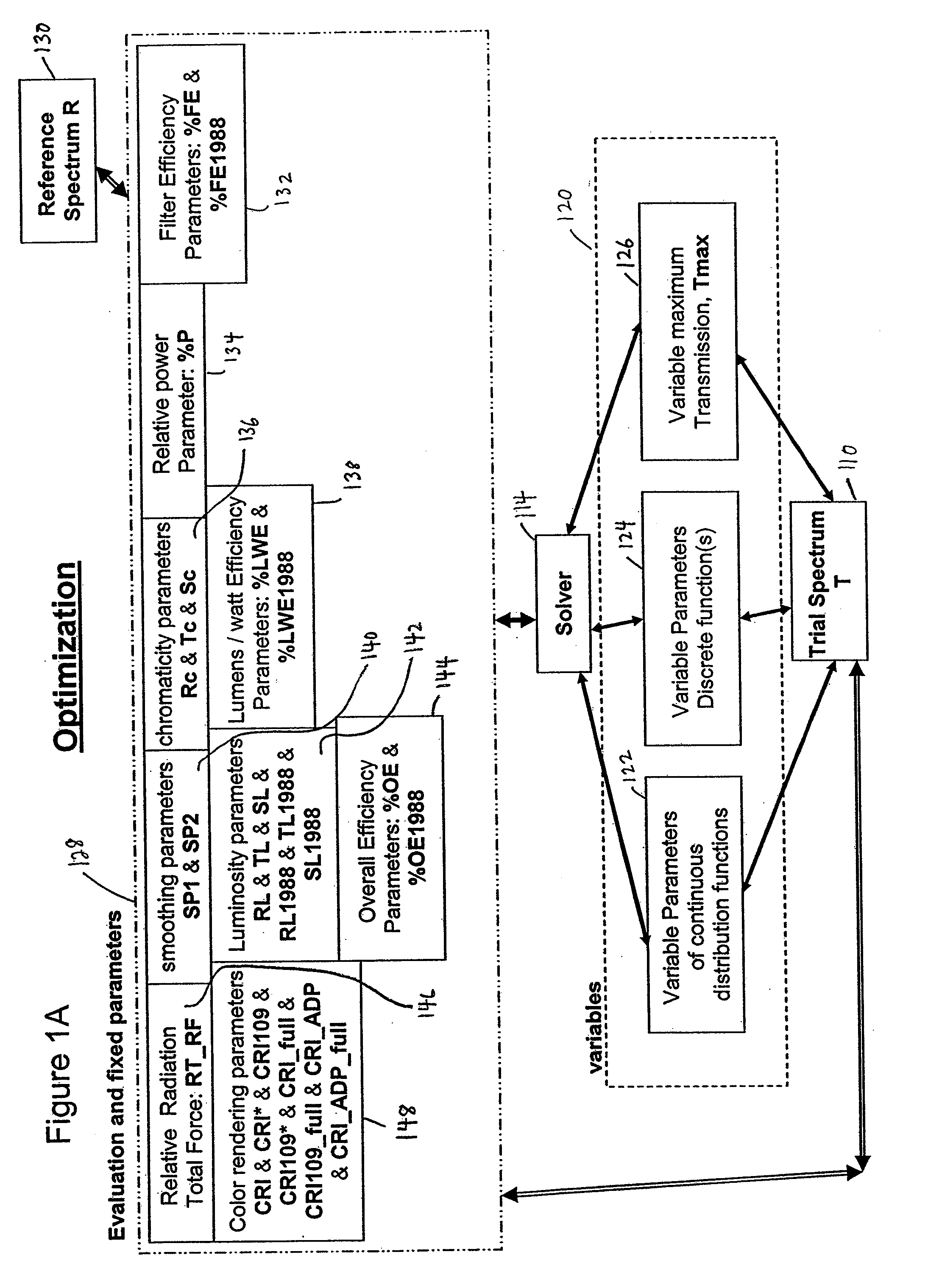
InactiveUS7626693B1Optimize to spectral distributionMore robustnessSpectral/fourier analysisRadiation pyrometrySource spectrumRadiation force
Methods for generating a customized spectral profile, which can be used to generate a corresponding filter, lamp or other type of illuminant. A trial spectrum is generated. A reference spectrum is determined or otherwise obtained. A SOURCE spectrum is determined or otherwise obtained. One or more optical indices are calculated using the trial spectrum and one or more of the optical indices are optimized by varying the trial spectrum to generate the customized spectral profile. A radiation force parameter can be used to minimize unsafe build-up of light in spectral regions. Adaptations of color rendering parameters can be used in the optimization process. Smoothing parameters can be used to enable easier design of filter structures. A reflectance camera can be used to measure reflectance data at one or more pixels of a digital representation of an object to be illuminated.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Laser micro control device and method for transportation and orientation of movable corpuscle and cell
InactiveCN101206308ARealize transportationEnable mobilityRadiation/particle handlingMaterial analysisOptical axisLight beam
The present invention relates to a laser micro-control device and method for the transportation and directional movement of particles and cells. In the device, a light source system and a two-dimensional moving loading platform are arranged in the same plane. The light source system is a laser, a light beam converting system and a focusing system which are orderly placed. The laser, the light beam converting system and the focusing system are arranged on the same optical axis. The present invention utilizes the characteristic that laser beam has gradient force and radiation force to restrict particles and cells needing transportation and directional movement in a light beam focusing area, and can carry out the transportation of particles and cells through a single laser beam as well as the directional movement of particles and cells through two intersecting laser beams, so as to realize the method of controlling particles and cells. The present invention can utilize laser micro-control technology to realize the direct transportation and directional movement of particles and cells, and can be applied to micro-fluidic chemistry or biological analysis systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
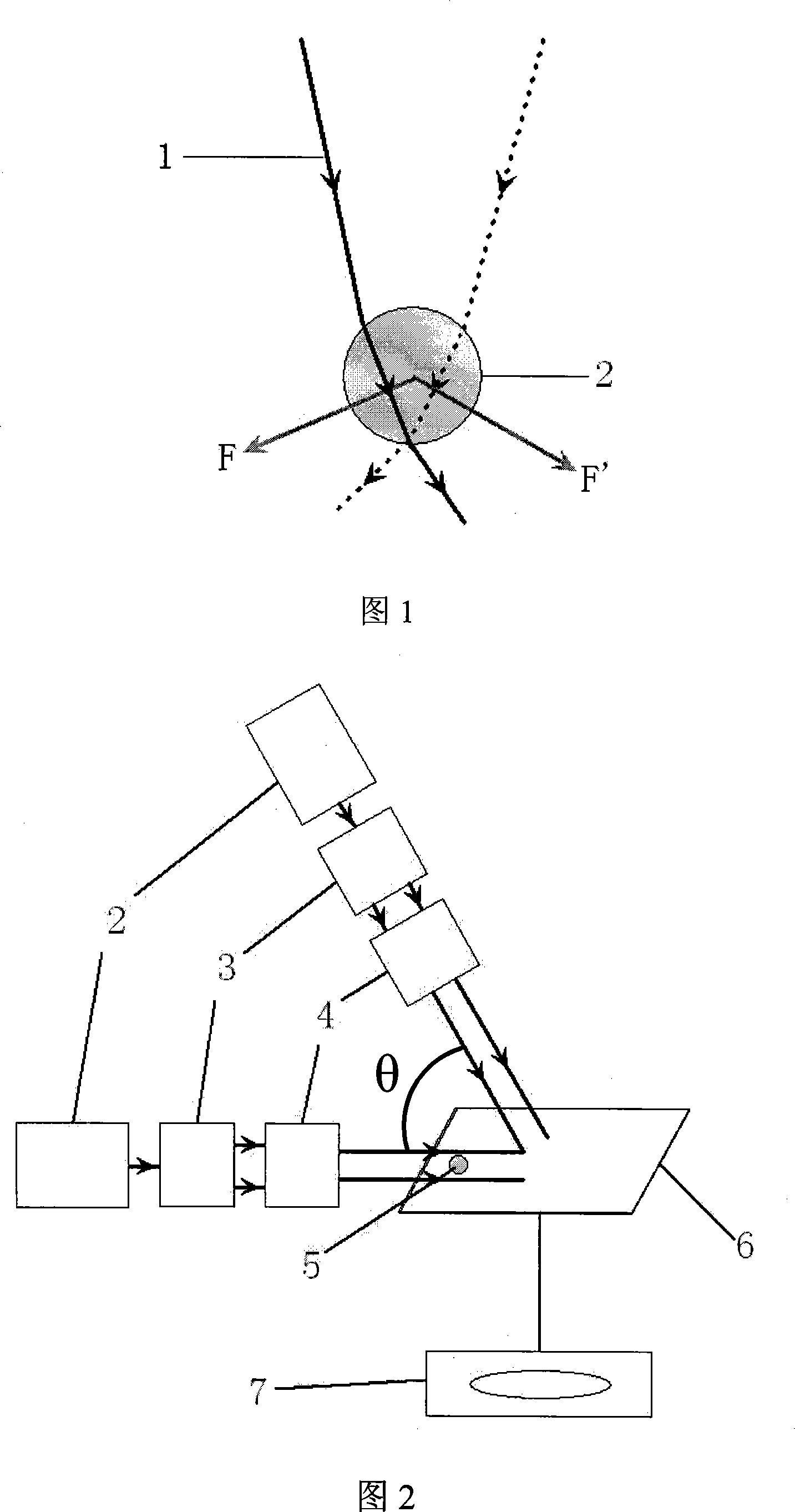
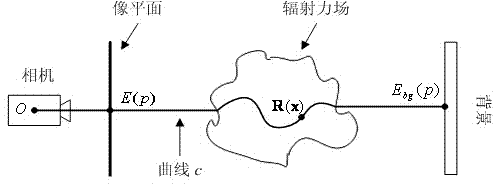
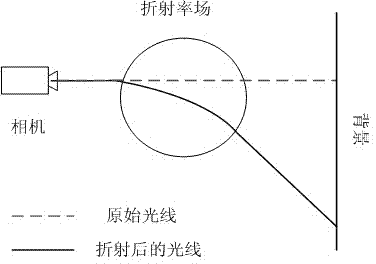
Flame temperature field rebuilding method based on physical parameter consistency
A flame temperature field rebuilding method based on physical parameter consistency comprises the following steps of a, synchronously shooting an image sequence of a combustion flame from a plurality of angles of view and voxelizing the flame through a visual hull technology; b, calibrating a response curve of a camera; c, initiating a flame refractive index field and computing an initial radiation force field of the flame according to an imaging model of the flame; d, computing the radiation force field and the refractive index field in an iterative mode until the radiation force field and the refractive index field meet physical consistency in numerical value; e, computing a final flame temperature field according to a lookup table between a radiation force and a temperature. The flame temperature field rebuilding method based on the physical parameter consistency is based on the fact of the consistency of the two physical parameters of the flame radiation force field and the refractive index field, an algorithm for computing the flame temperature field in an iterative is provided, and the flame temperature field rebuilding method fully takes refraction on light rays due to uneven distribution of the flame refractive index field into consideration, so that the accuracy of temperature rebuilding is greatly improved. The flame temperature field rebuilding method based on the physical parameter consistency can be applied to field of commercial measurement, thermal power plant monitoring, virtual reality and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method and apparatus for shear property characterization from resonance induced by oscillatory radiation force
ActiveUS7713201B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurgeryFrequency spectrumResonance
A method for determining a shear elasticity and shear viscosity of a material based on resonance characteristics. A focused ultrasound wave is directed at the material to induce oscillations in the material, and a velocity of the material is measured. A spectrum of frequency of oscillation versus velocity is developed, and the resonance characteristics exhibited by the spectrum are used to estimate the shear elasticity and viscosity of the material.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Methods and systems for spatially modulated ultrasound radiation force imaging
ActiveUS8753277B2Avoid noiseHigh resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsShear modulusSonification
Methods for determining the shear modulus of a tissue of an individual are disclosed. In one embodiment, an acoustic pulse is transmitted and a reference echo signal is received. A first push pulse is transmitted at a second location of the individual. A second push pulse is transmitted at a third location of the individual. A series of tracking pulses are transmitted at the first location and a tracking echo signal is received from each tracking pulse. The effect of the first and second push pulses on the tissue is determined through analysis of the tracking echo signals. The shear modulus of the tissue is calculated based on the effect of the push pulses on the tissue. A system for imaging a region of tissue is presented.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Ultrasound apparatus and methods for mixing liquids and coating stents
ActiveUS7896539B2Improve propertiesStentsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersUltrasonic sensorUltrasound cavitation
Ultrasound methods and apparatus for mixing two or more different liquids are disclosed. The ultrasound methods and apparatus may mix varied components including drugs, polymers, and coatings for application to a variety of medical apparatus surfaces. The apparatus and technique can generate a proper mixture which is uninterruptedly / continuously delivered to the surface of the medical apparatus. The apparatus may include specific ultrasound transducer / tip configurations which may allow for the mixing of different liquids in a mixing camera located inside of the vibrating tip. The apparatus and methods of the present invention may mix different drugs, applying them to stent surface using different effects like ultrasound cavitation and radiation forces. Furthermore, the disclosed methods and apparatus may generate a mixture and may deliver a targeted, gentle, highly controllable dispensation of continuous liquid spray which can reduce the loss of expensive pharmaceuticals.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
Illumination Sources and Customizable Spectral Profiles
InactiveUS20100085563A1Reduce the required powerOptimize distributionRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesSource spectrumRadiation force
Methods for generating a customized spectral profile, which can be used to generate a corresponding filter, lamp or other type of illuminant. A trial spectrum can be generated. A reference spectrum can be determined or otherwise obtained. A SOURCE spectrum can be determined or otherwise obtained. One or more optical indices can be calculated using the trial spectrum and one or more of the optical indices are optimized by varying the trial spectrum to generate the customized spectral profile. A radiation force parameter can be used to minimize unsafe build-up of light in spectral regions. Adaptations of color rendering parameters can be used in the optimization process. Smoothing parameters can be used to enable easier design of filter structures. A reflectance camera can be used to measure reflectance data at one or more pixels of a digital representation of an object to be illuminated.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
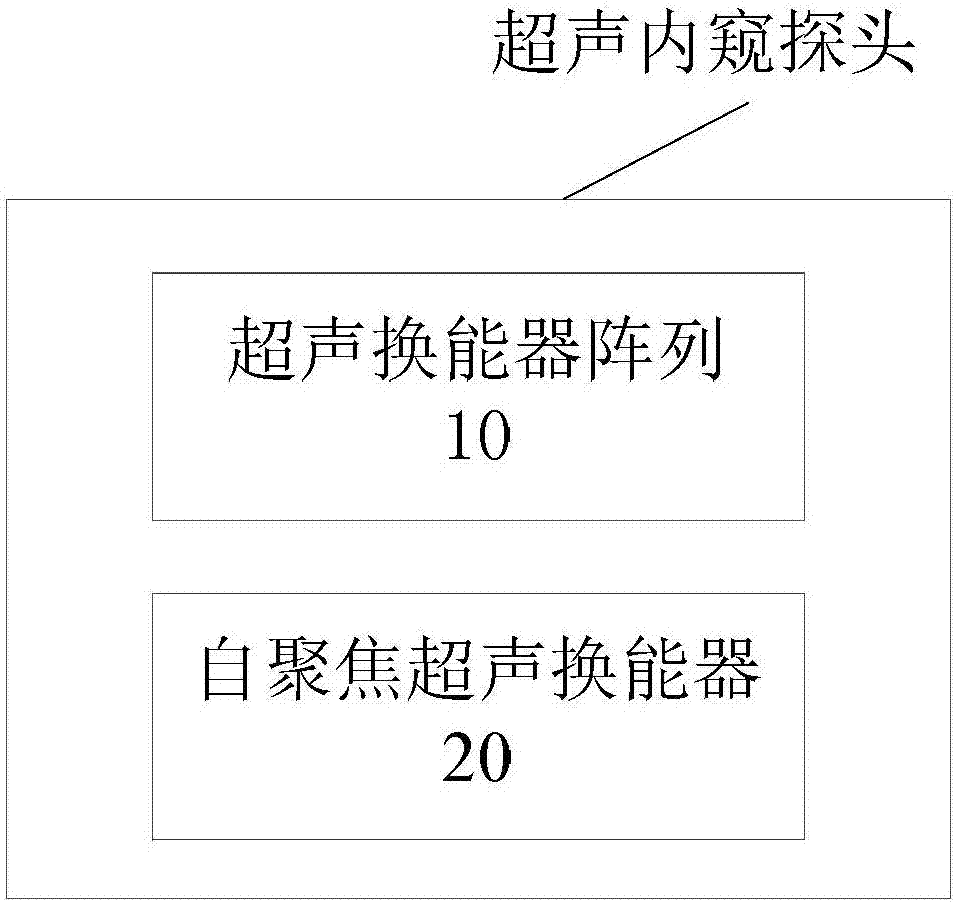
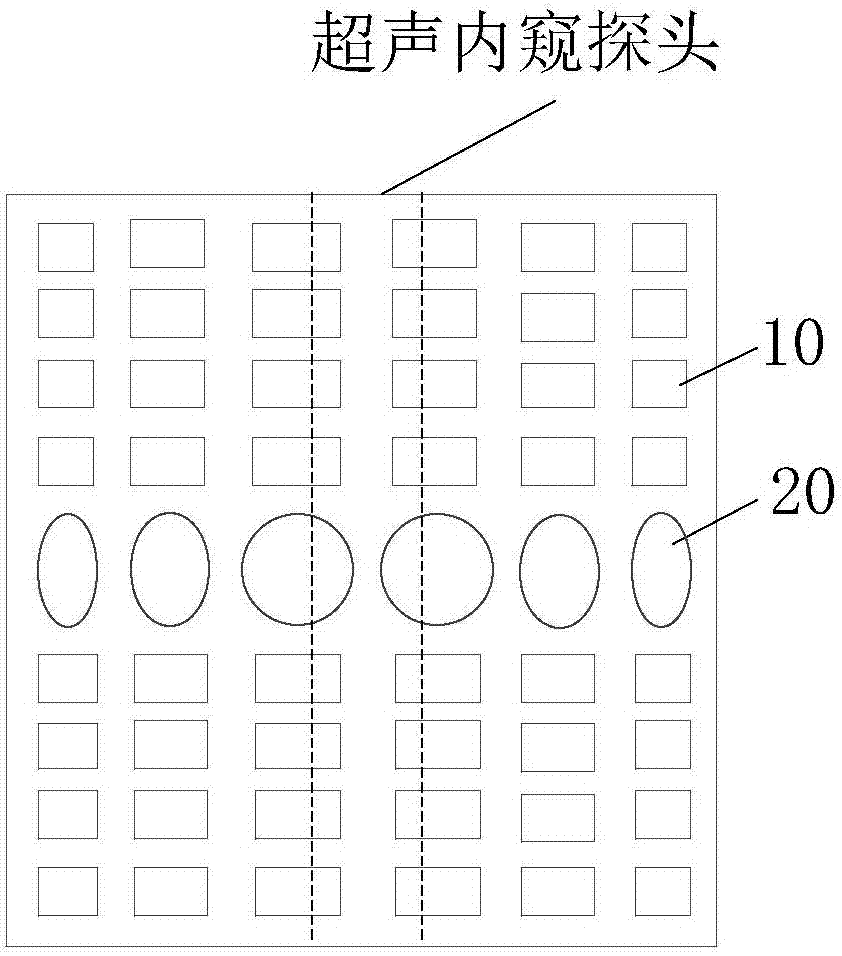
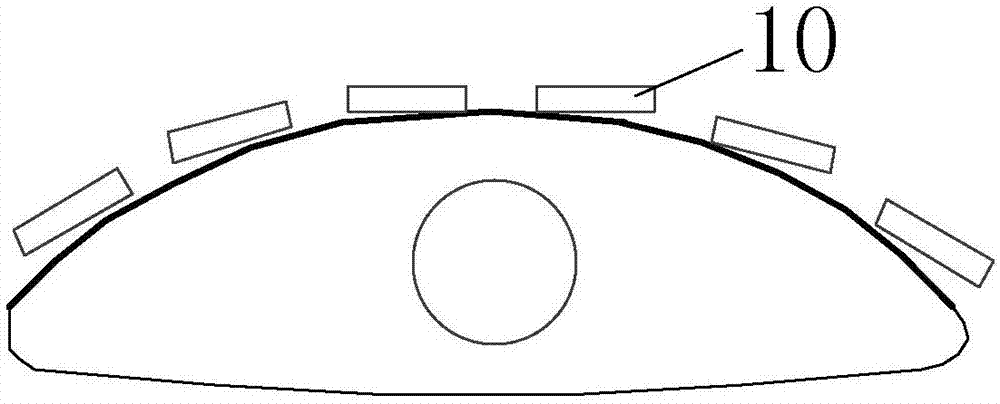
Ultrasonic peeping probe and elastic imaging system and method
PendingCN107260216ARelieve painSimple and fast operationOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryEngineeringMechanical engineering
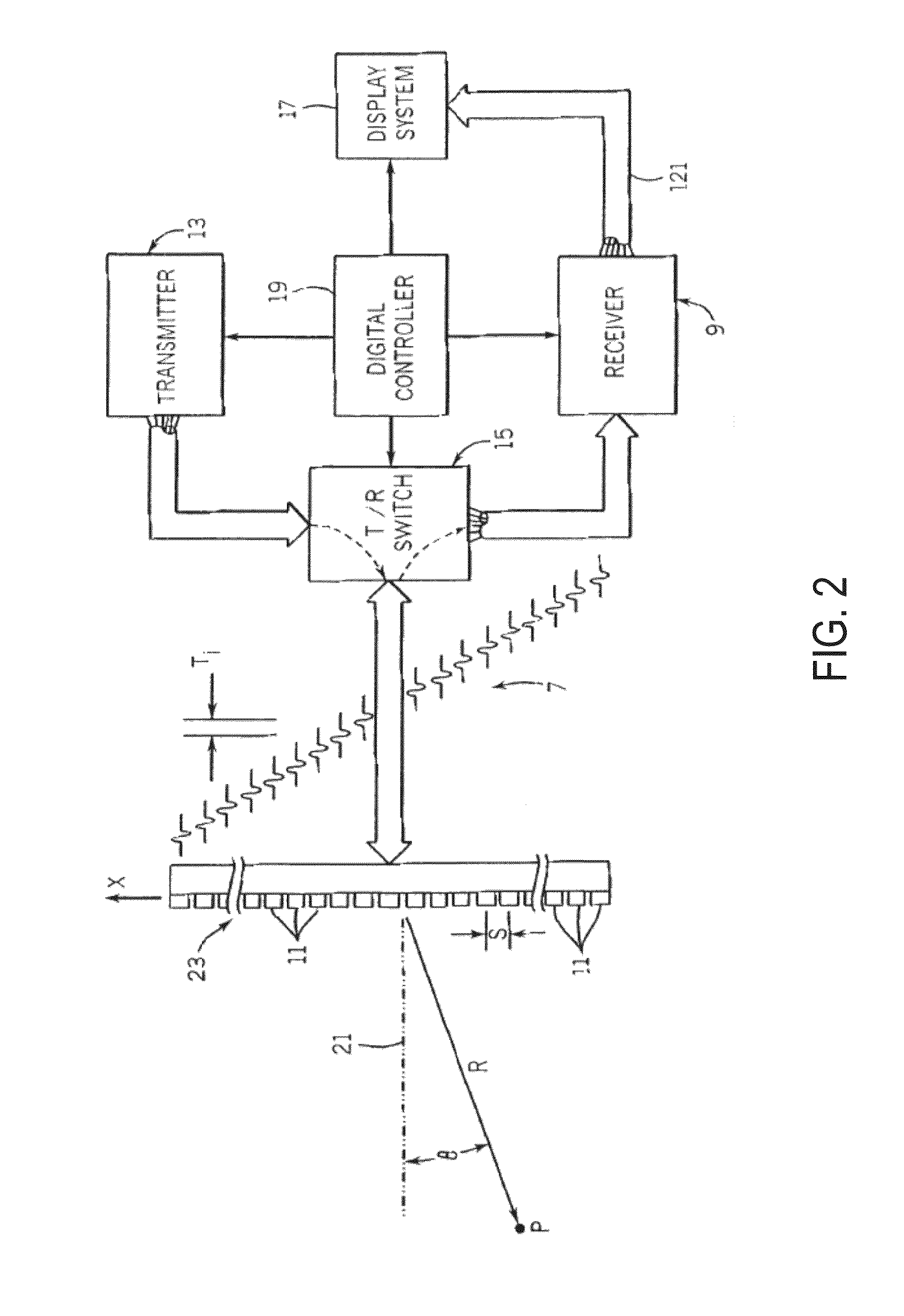
The invention discloses an ultrasonic peeping probe and an elastic imaging system and method. The ultrasonic peeping probe comprises an ultrasonic transducer array including multiple ultrasonic transducers for transmitting ultrasonic waves and receiving ultrasonic echoes, reflected by the biological tissue to be detected of ultrasonic waves, and a self-focused ultrasonic transducer for producing focused ultrasonic wave beams, wherein the focused ultrasonic wave beams produce an acoustic radiation force acting on the biological tissue to be detected. The ultrasonic peeping probe produces the focused ultrasonic wave beams through the self-focused ultrasonic transducer, acts on the biological tissue to be detected through the acoustic radiation force of the focused ultrasonic wave beams and accordingly makes the biological tissue to be detected deform. Accordingly, the ultrasonic echo signals of the biological tissue before and after compression are obtained by adopting the ultrasonic peeping probe without the external force exerted by an operator, the operating process is simple and convenient without external mechanical devices, and the system cost is reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOKE ULTRA MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Cell adhesion force measuring instrument and cell adhesion force measuring method based on acoustic surface waves
ActiveCN107238556ALess distracting factorsAvoid destructionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVisual servoing systemCell adhesion
The invention discloses a cell adhesion force measuring instrument and measuring method based on acoustic surface waves. The cell adhesion force measuring instrument comprises a lithium niobate crystal plate, a silver interdigitatal electrode annular array, a PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) micro-channel and a micro-vision servo system, the micro-vision servo system comprises an upper computer system based on a PXI (peripheral component interconnect) bus, a multi-path signal generating system and a micro-vision monitoring system, the silver interdigitatal electrode annular array is arranged on the upper periphery of the lithium niobate crystal plate, the lithium niobate crystal plate and the silver interdigitatal electrode annular array form an interdigital transducer, and the silver interdigitatal electrode annular array is connected with the multi-path signal generating system. According to the measuring instrument, an expected sound field is synthesized in a PDMS micro-channel cavity by the aid of the interdigital transducer and the micro-vision servo system, cells are operated by the aid of radiation force of the acoustic surface waves, cell adhesion force is measured, and the measuring instrument has the advantages of simplicity and easiness in operation, fewer interference factors and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Novel acoustic tweezers based on artificial structure flat plate
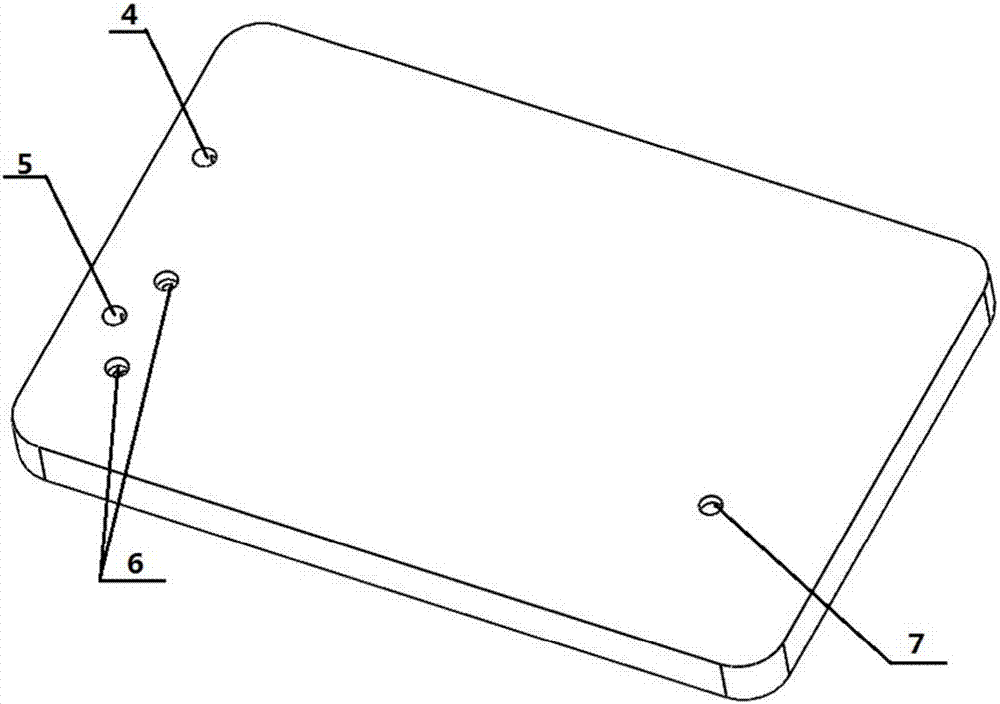
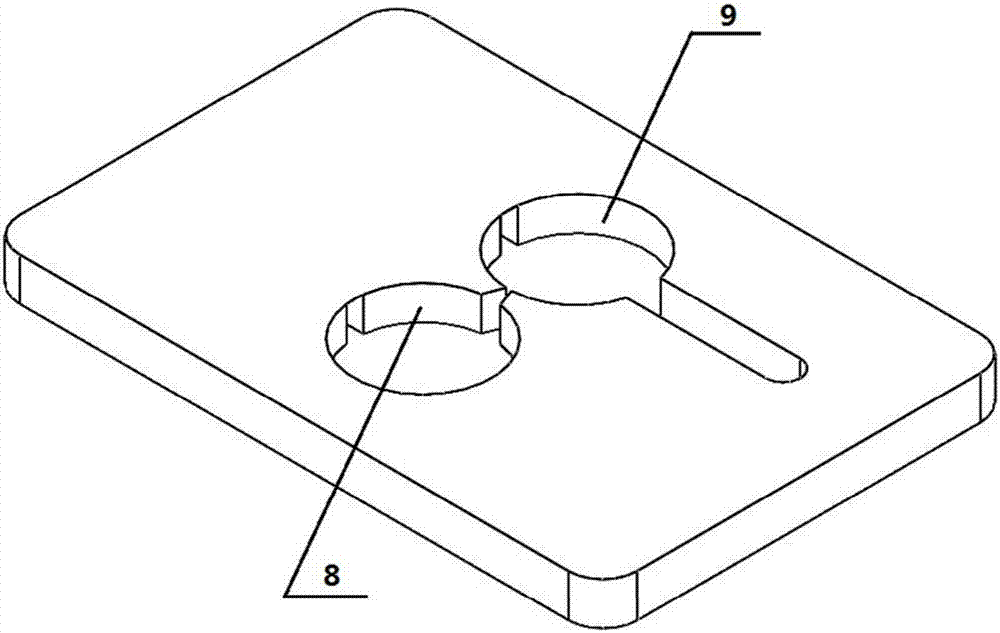
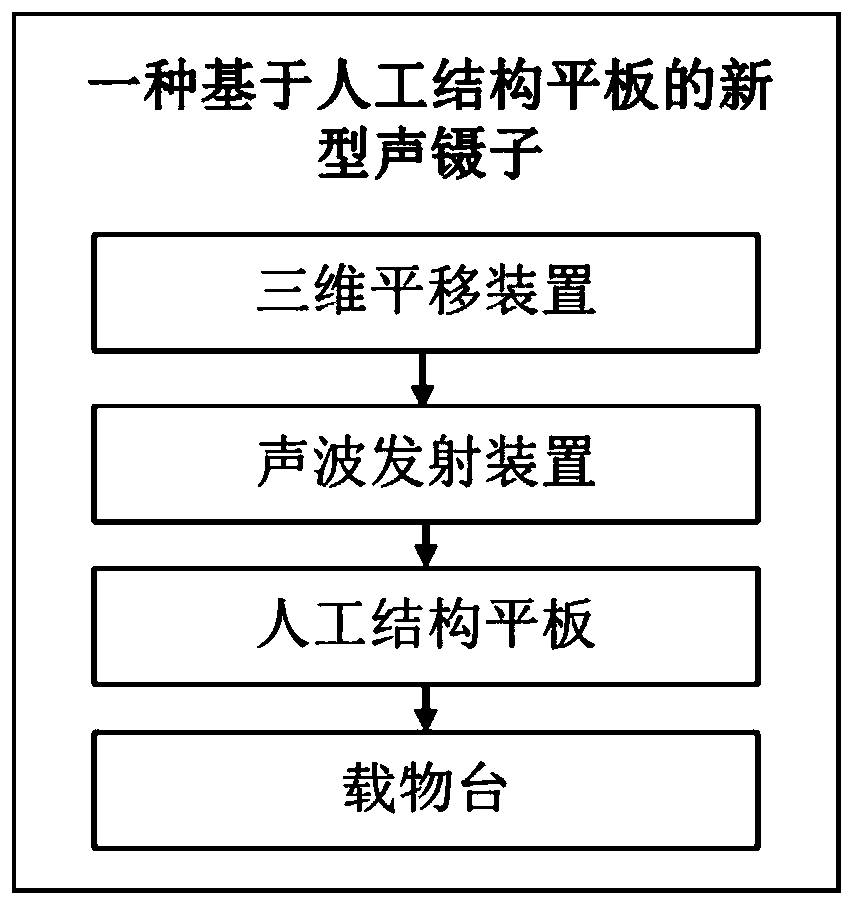
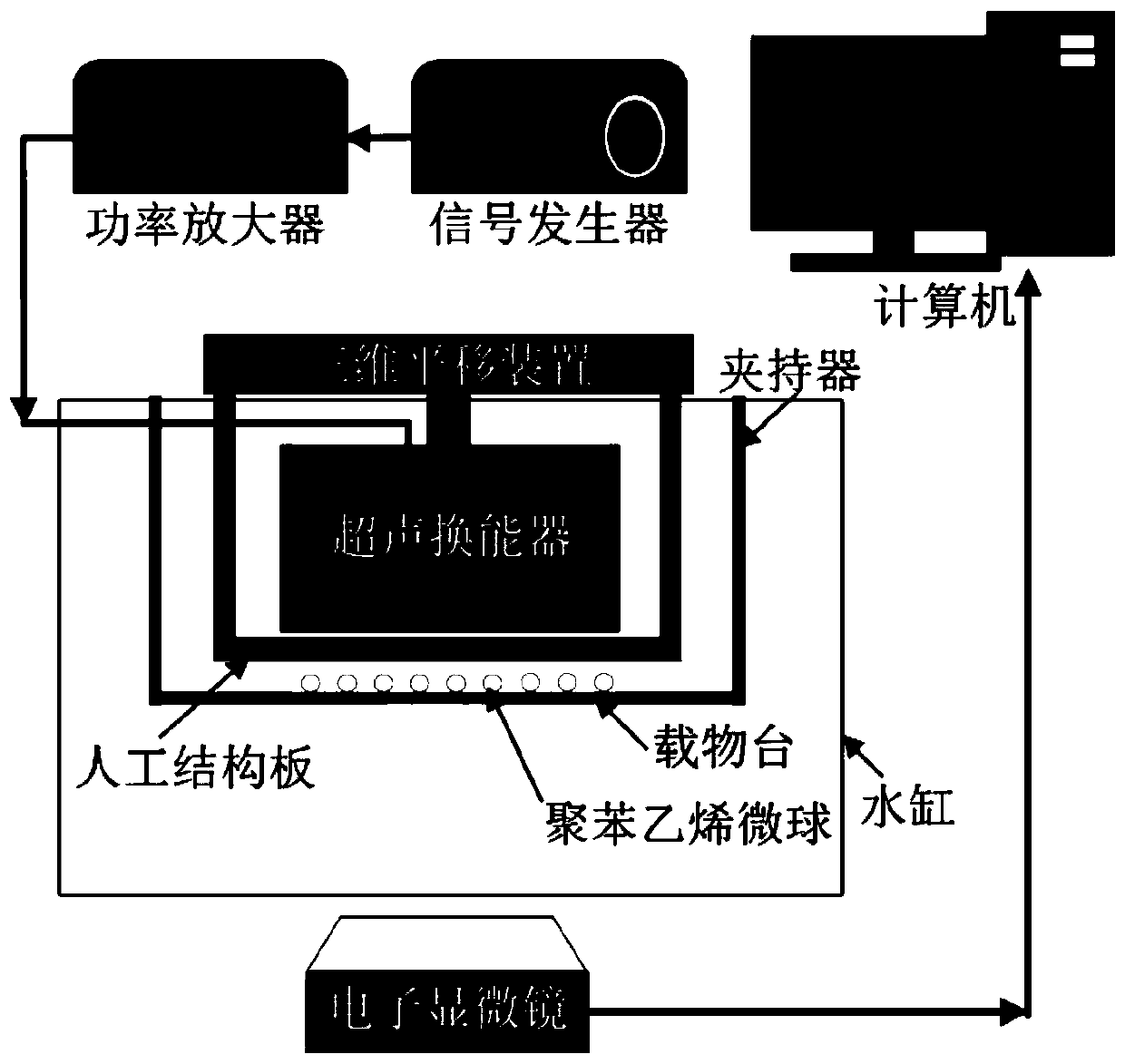
ActiveCN111530513AEasy to controlEasy to operateLaboratory glasswaresFluid controllersAcoustic radiation forceTechnology dependent
The invention discloses novel acoustic tweezers based on an artificial structure flat plate. The technology-dependent operating system comprises a three-dimensional translation device, an ultrasonic transmitting device for radiating ultrasonic waves, an artificial structure flat plate and an objective table, the objective table is used for placing particles to be controlled, the artificial structure flat plate has a special geometric design and is used for modulating a sound field to form focused petal sound beams with various special configurations and capturing particles with different sizes, and the three-dimensional translation device is used for moving the focused petal sound beams generated by the artificial structure flat plate, so that free transmission and transportation of the particles are realized. According to the novel acoustic tweezers, the artificial structure flat plate is mainly used for modulating a sound field to generate various focusing petal acoustic beams, particles with different sizes are captured in the central area of an acoustic beam by using the acoustic radiation force characteristic of the acoustic beam, and the transmission and transportation of theparticles are realized by moving the focusing petal acoustic beam, so that the technology has important research value in the practical application aspects of material preparation, cell separation, drug transportation, bioengineering and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Acoustic tweezers device
ActiveCN109939913AEasy to processRealize quantitative productionMechanical vibrations separationMicron scaleSonification
The invention discloses an acoustic tweezers device. The acoustic tweezers device comprises an ultrasonic emitting mechanism, and a waveguide structure arranged on the ultrasonic emitting mechanism; the ultrasonic emitting mechanism is used for emitting ultrasonic waves; and the waveguide structure is used for conducting the ultrasonic waves. The acoustic tweezers device further comprises a resonant unit body arranged on the waveguide structure; the ultrasonic waves excite the resonant unit body for resonance; and a local area field for capturing particles is generated on the surface of the resonant unit body. The used ultrasonic frequency is lower, and the precise phase modulation is not needed, so that a transducer is easily machined and manufactured, and no complicated electronic systemis needed; a low-frequency sound field emitting mode is modulated only through the designed resonant unit body; and the local area field is generated on the surface of the resonant unit body to realize such operations as capturing of micron-scale particles. When the ultrasonic emitting mechanism is turned off, due to loss of the sound radiation force, the captured particles on the surface of theresonant unit body can be released. The acoustic tweezers device is simple in manufacturing process and low in cost, and can achieve mass production.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com