Patents
Literature
51 results about "Microcalcification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
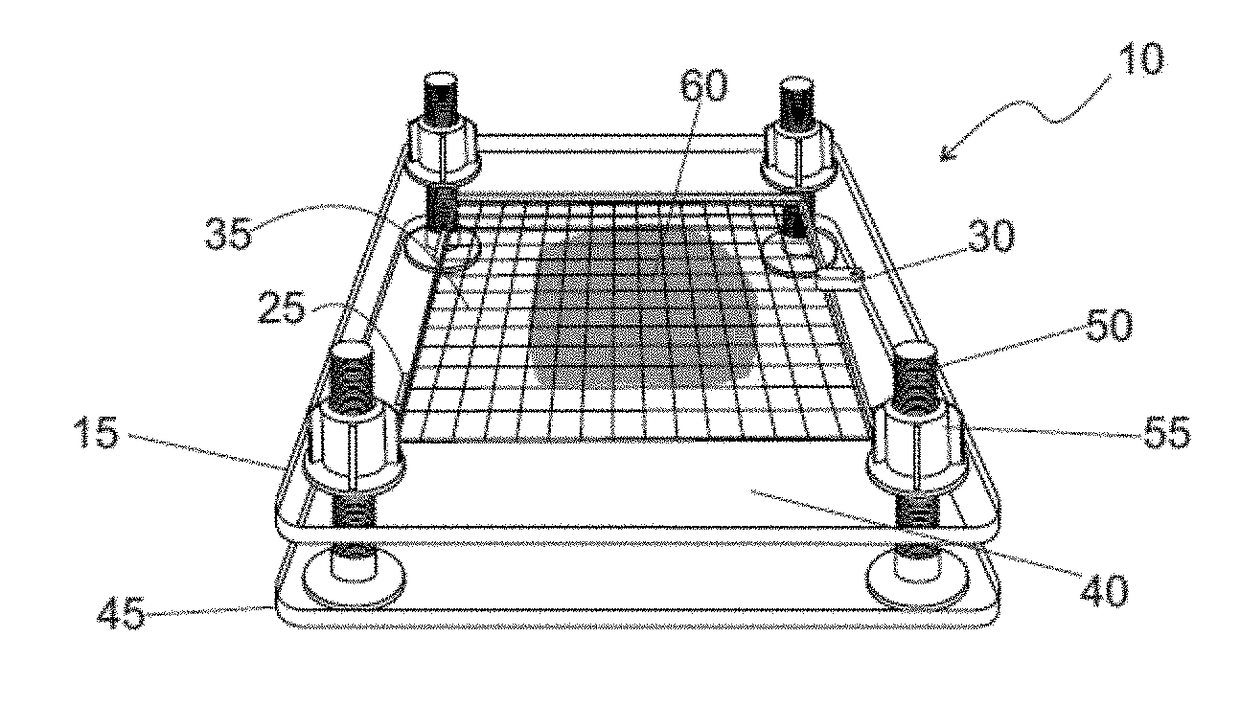
Microcalcifications are tiny deposits of calcium salts that are too small to be felt but can be detected by imaging. They can be scattered throughout the mammary gland, or occur in clusters. Microcalcifications can be an early sign of breast cancer. Based on morphology, it is possible to classify by radiography how likely microcalcifications are to indicate cancer.
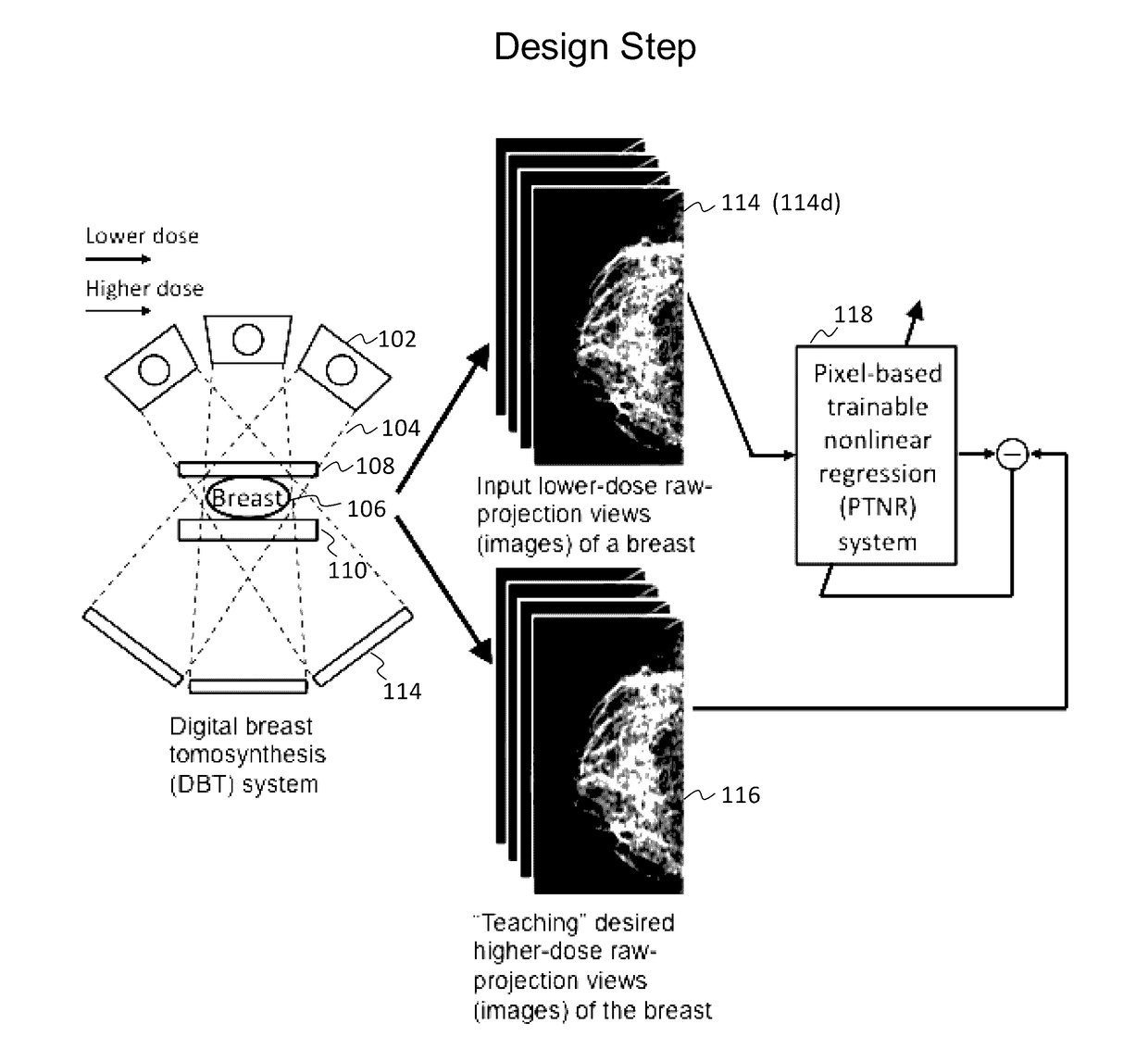
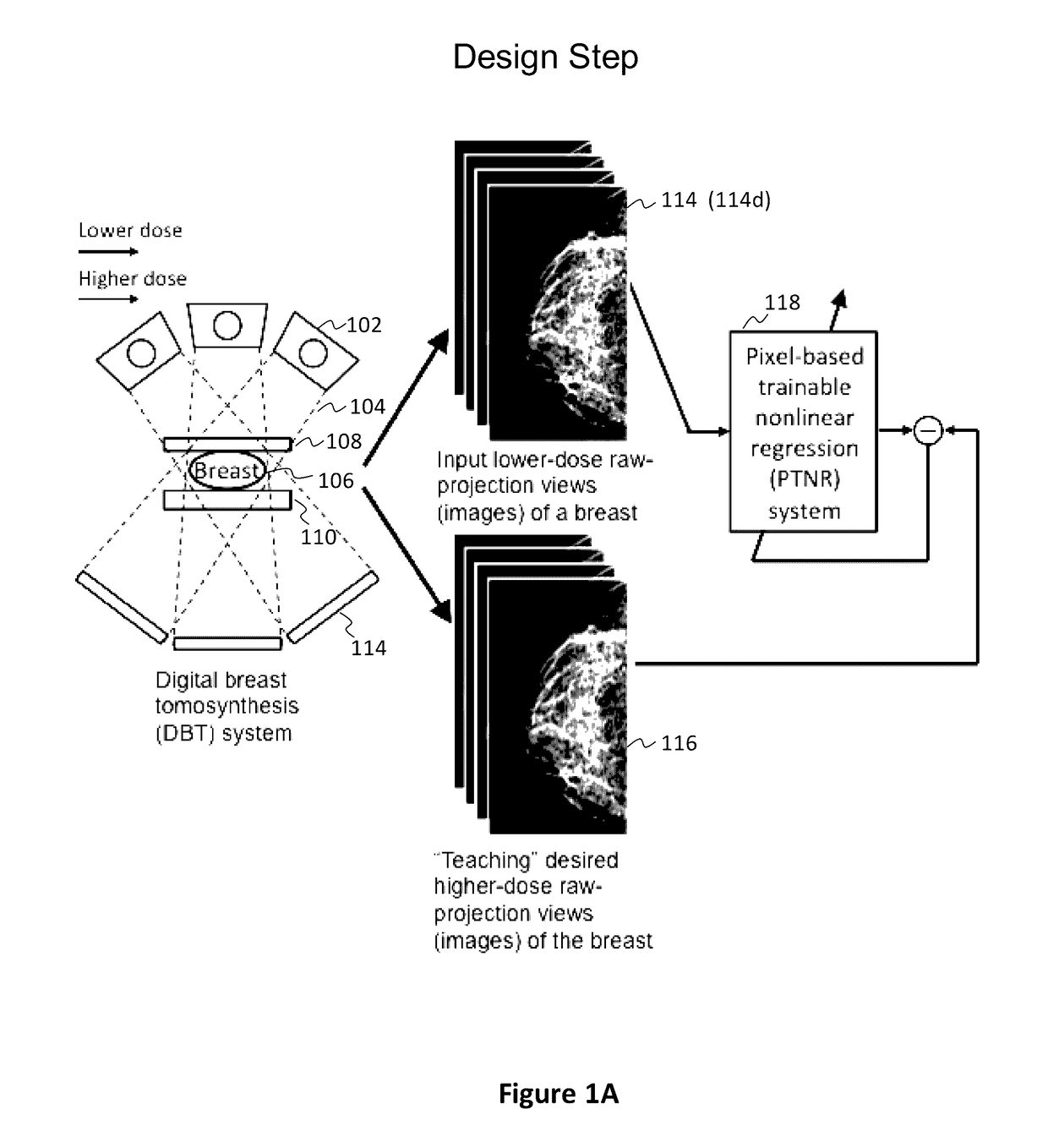
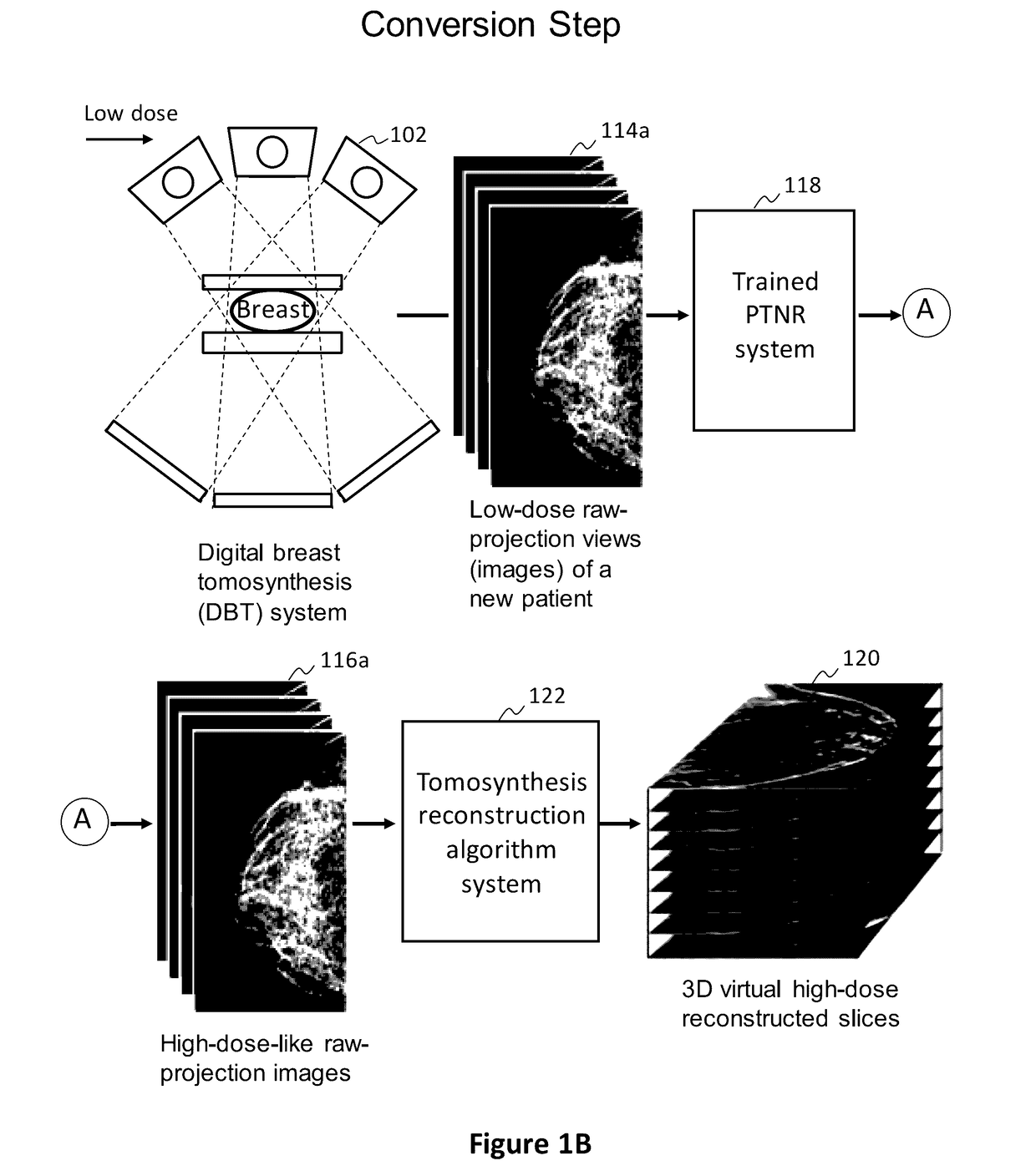
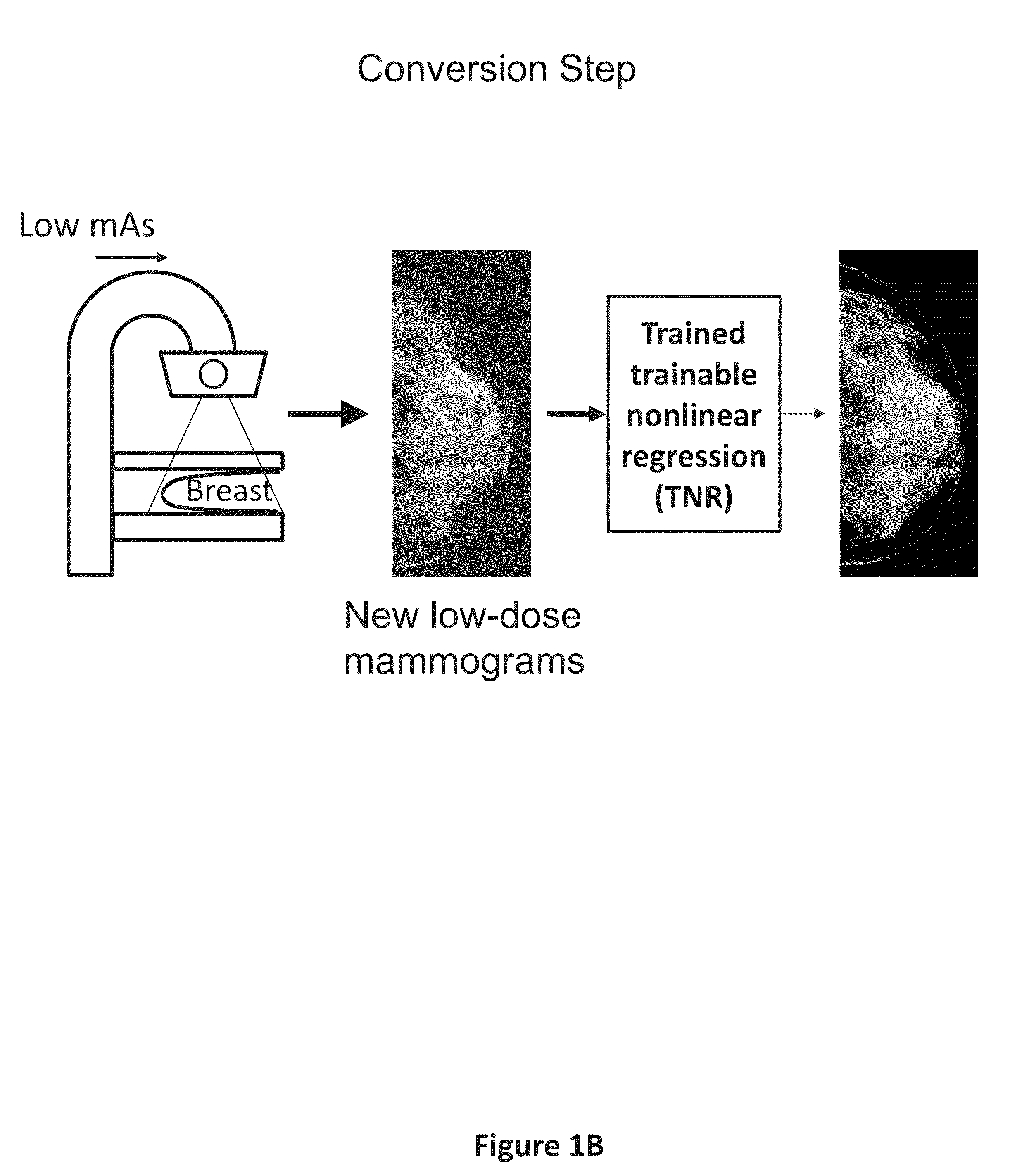
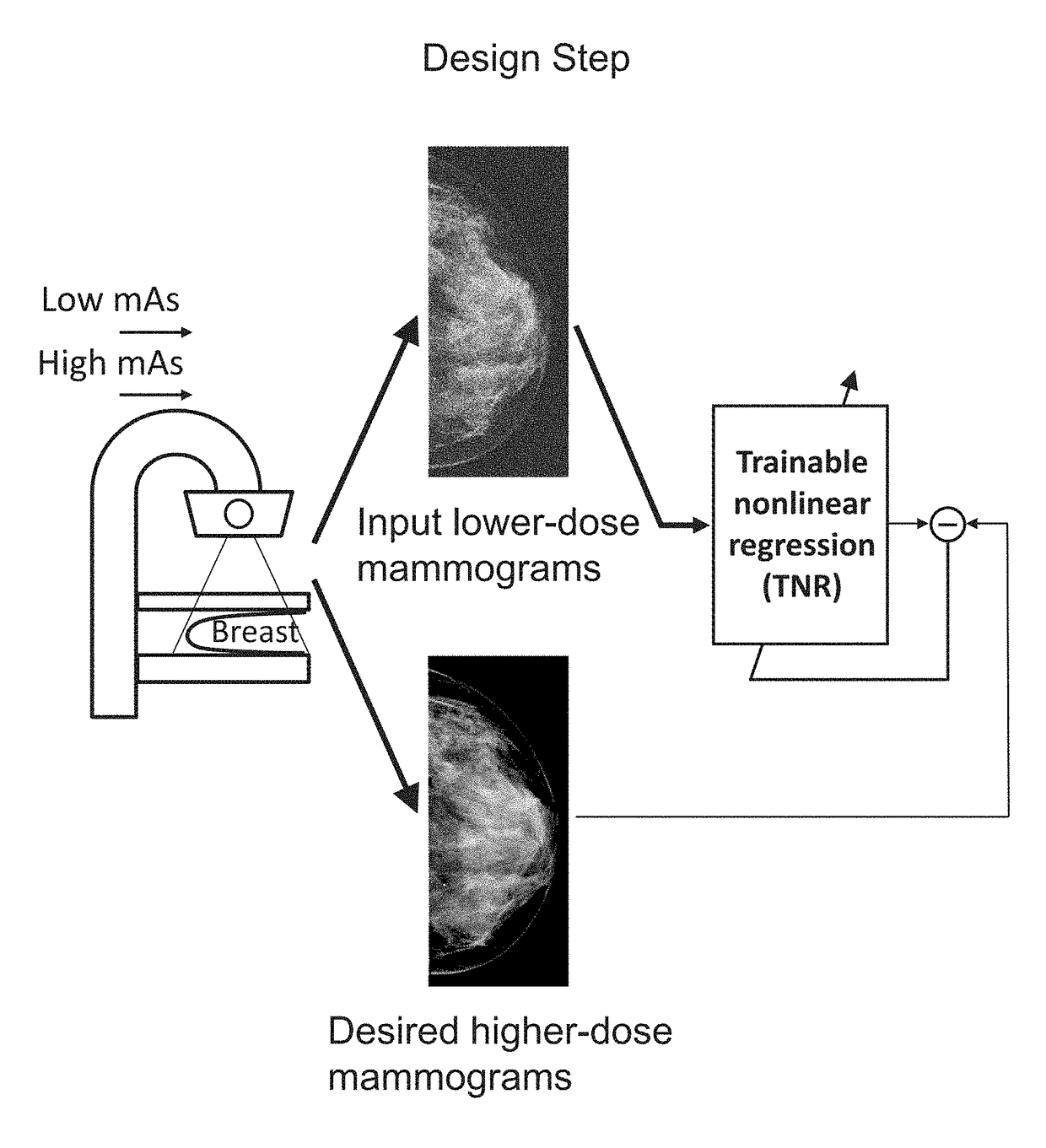
Converting low-dose to higher dose 3D tomosynthesis images through machine-learning processes
ActiveUS20170071562A1Quality improvementReduce noiseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisImaging quality
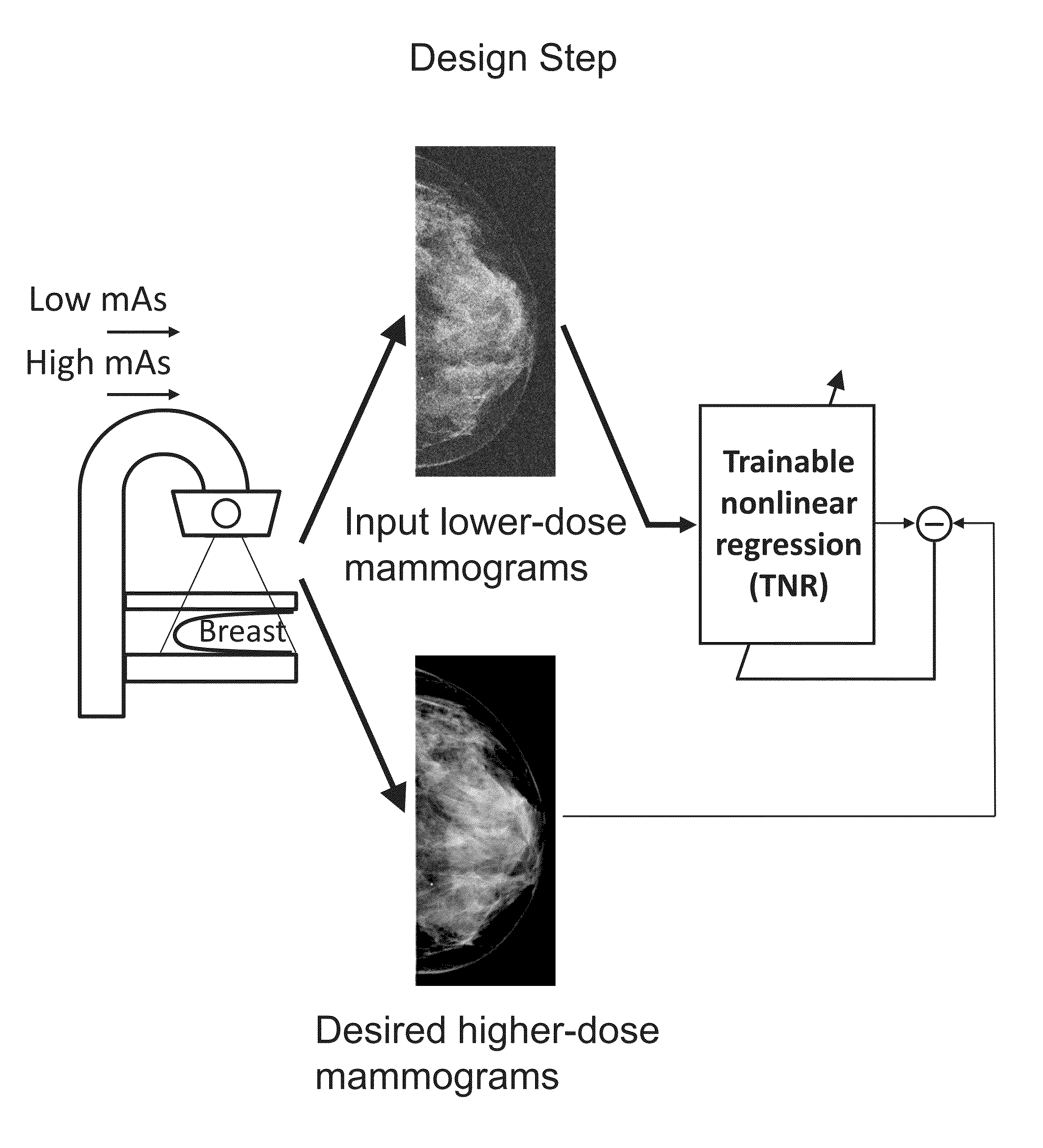
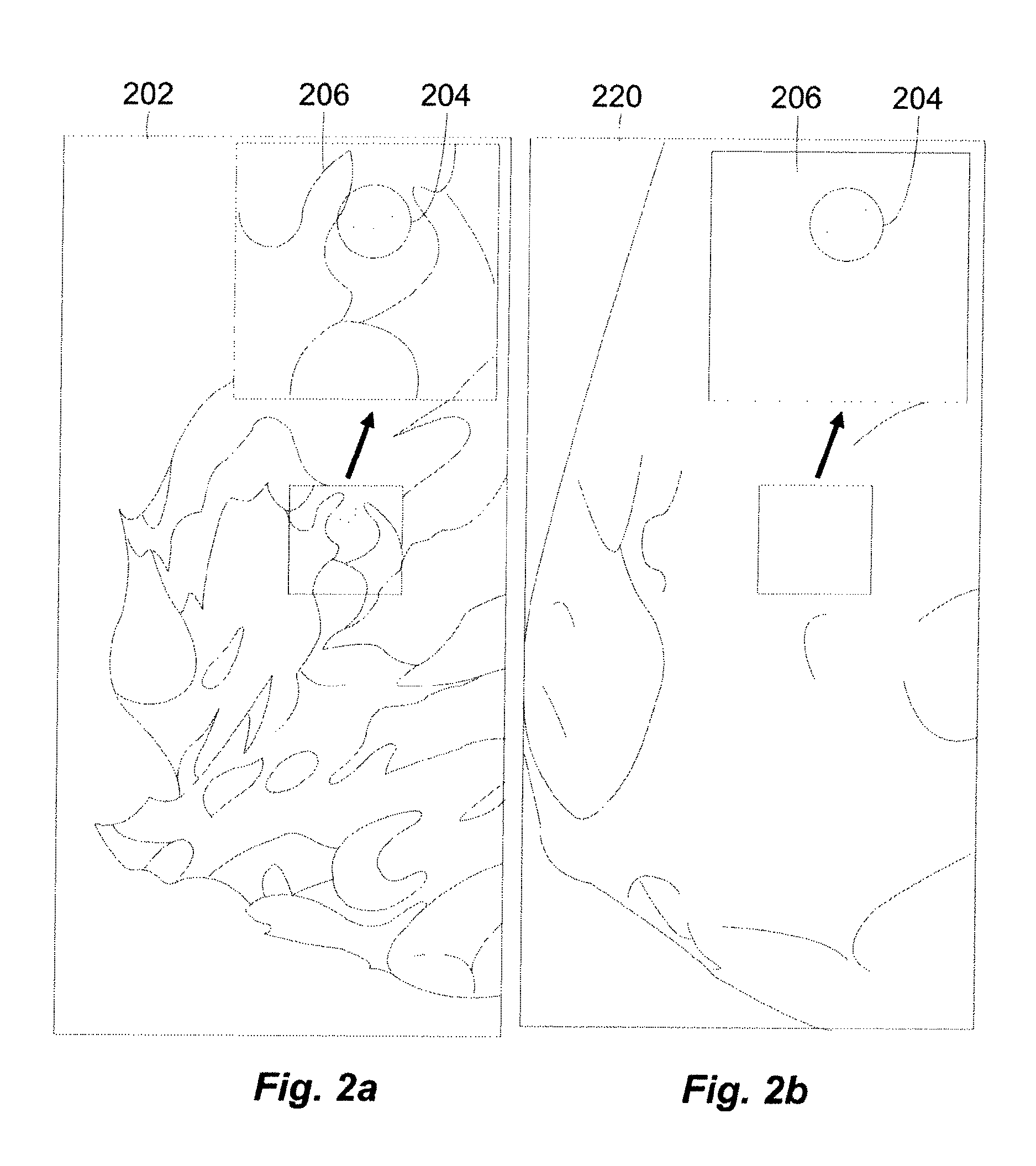
A method and system for converting low-dose tomosynthesis projection images or reconstructed slices images with noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like tomosynthesis reconstructed slices, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme called a pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input raw projection views (images) of a breast acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of raw projection views (images together with corresponding desired x-ray radiation dose raw projection views (images) (higher-dose). Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose raw projection images to high-dose-like raw projection images. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose raw projection images anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) raw projection images is entered, the trained PTNR outputs a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it outputs high-dose-like raw projection images where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. Then, from the “high-dose-like” projection views (images), “high-dose-like” 3D tomosynthesis slices are reconstructed by using a tomosynthesis reconstruction algorithm. With the “virtual high-dose” tomosynthesis reconstruction slices, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
X-ray image processing
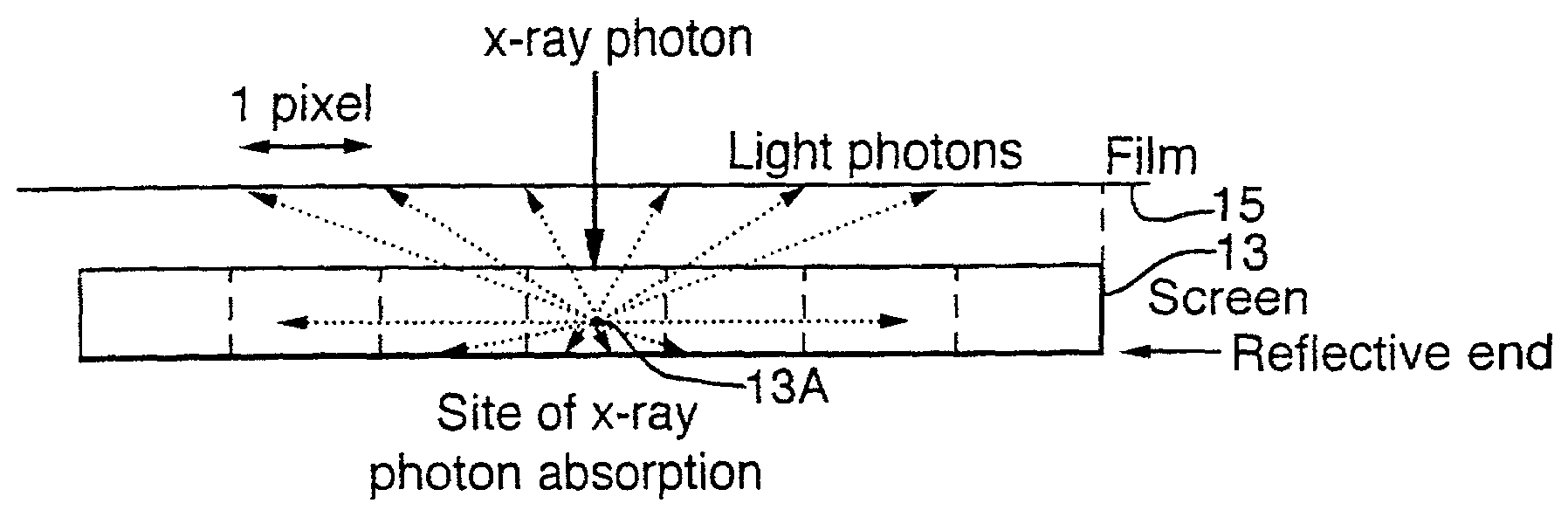
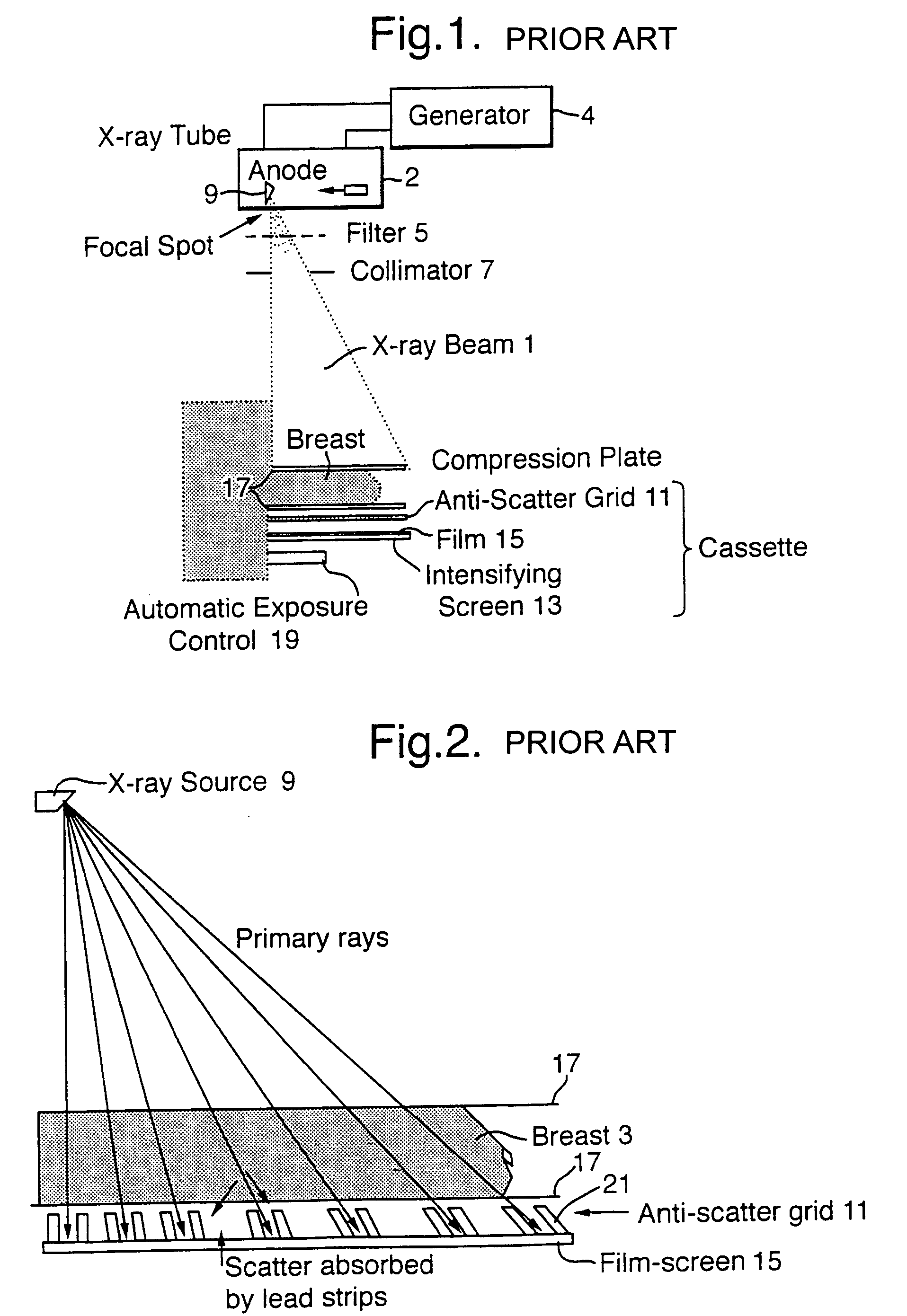
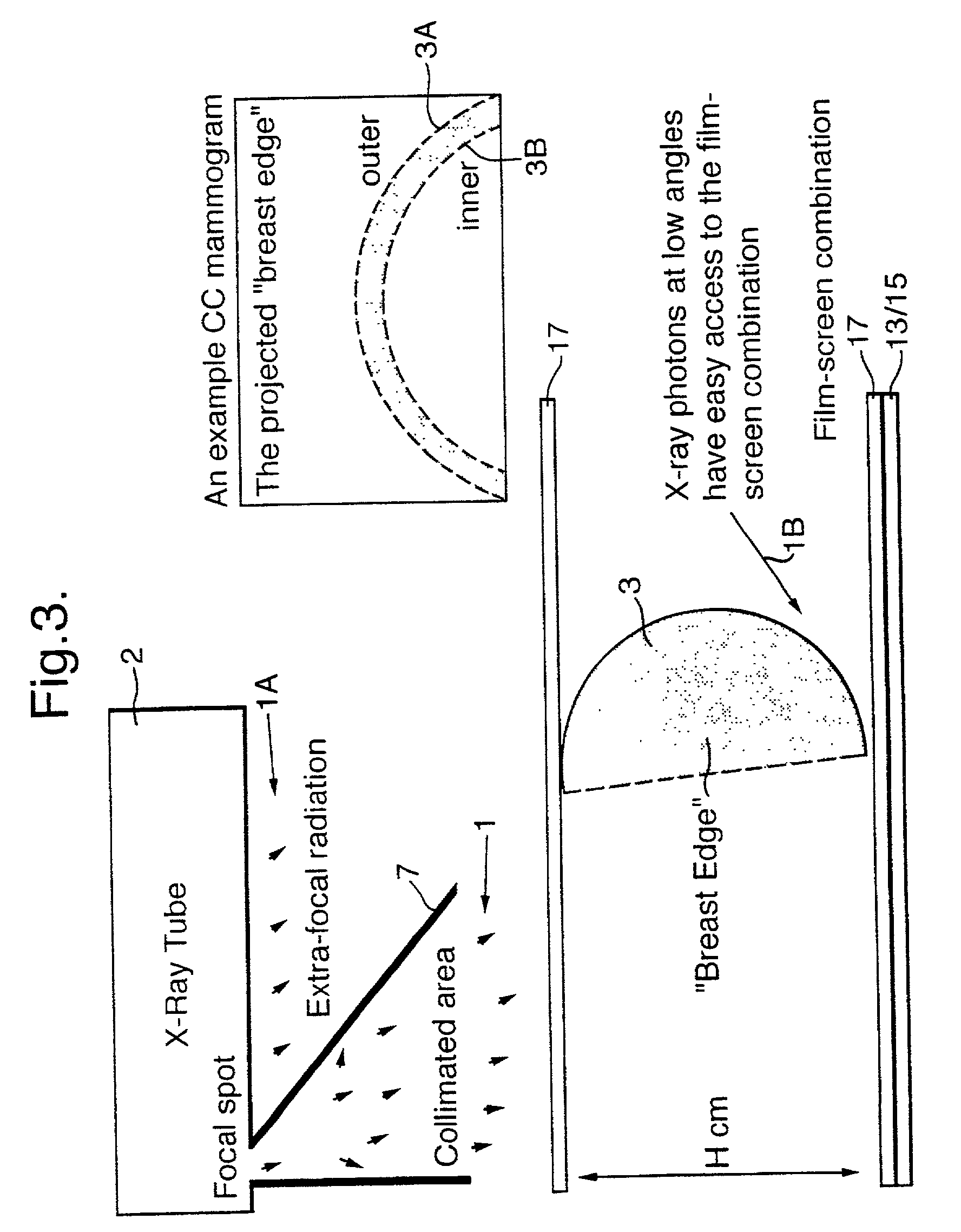
A method of enhancing and normalizing x-ray images, particularly mammograms, by correcting the image for digitizer blur, glare from the intensifying screen and the anode-heel effect. The method also allows the calculation of the compressed thickness of the imaged breast and calculation of the contribution to the mammograms of the extra focal radiation. The correction of the image for glare from the intensifying screen allows the detection of noise, such as film shot noise, in the image, and in particular the differentiation between such noise and microcalcifications.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
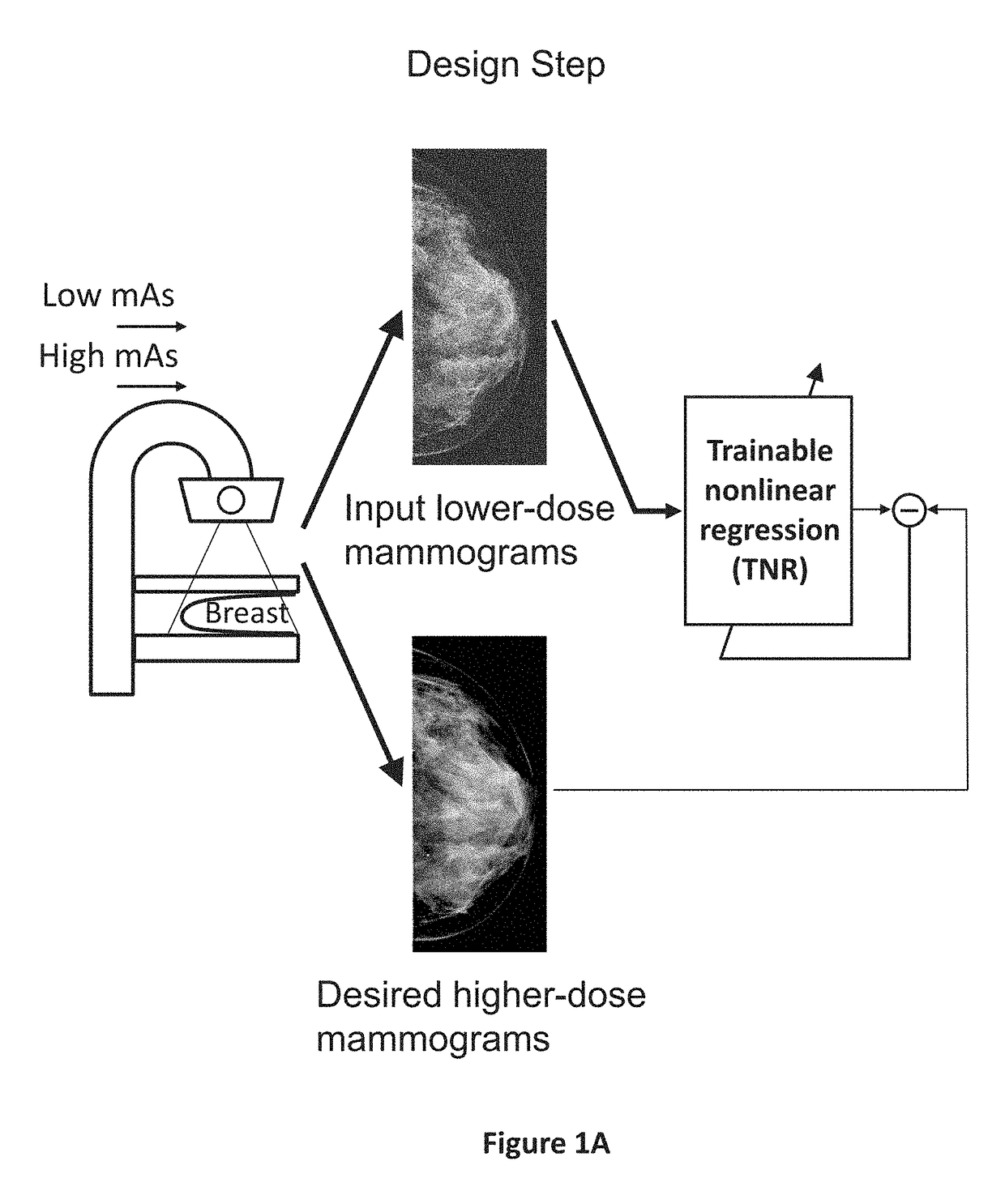
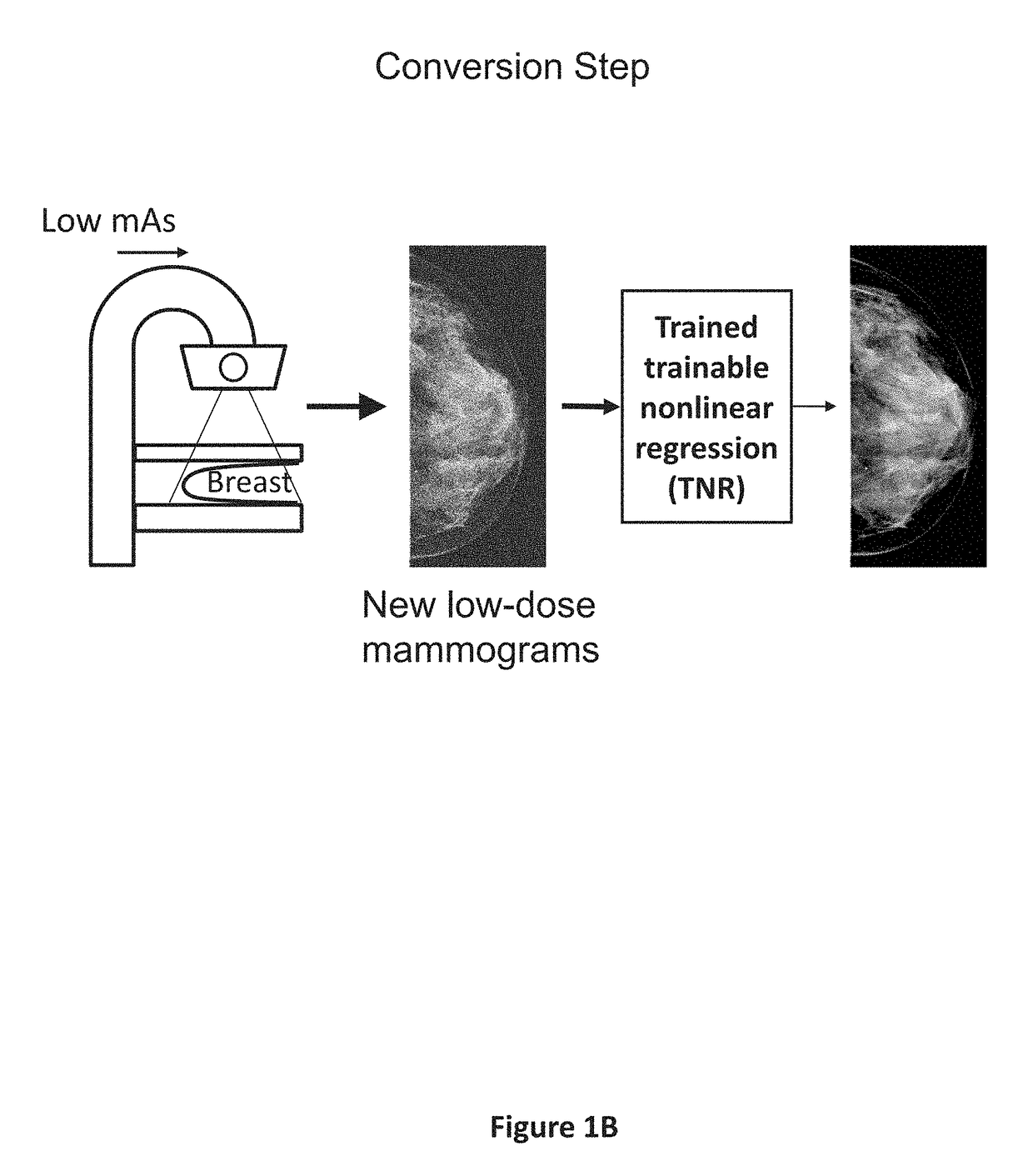
Converting low-dose to higher dose mammographic images through machine-learning processes
ActiveUS20150196265A1Improve image qualityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityX-ray
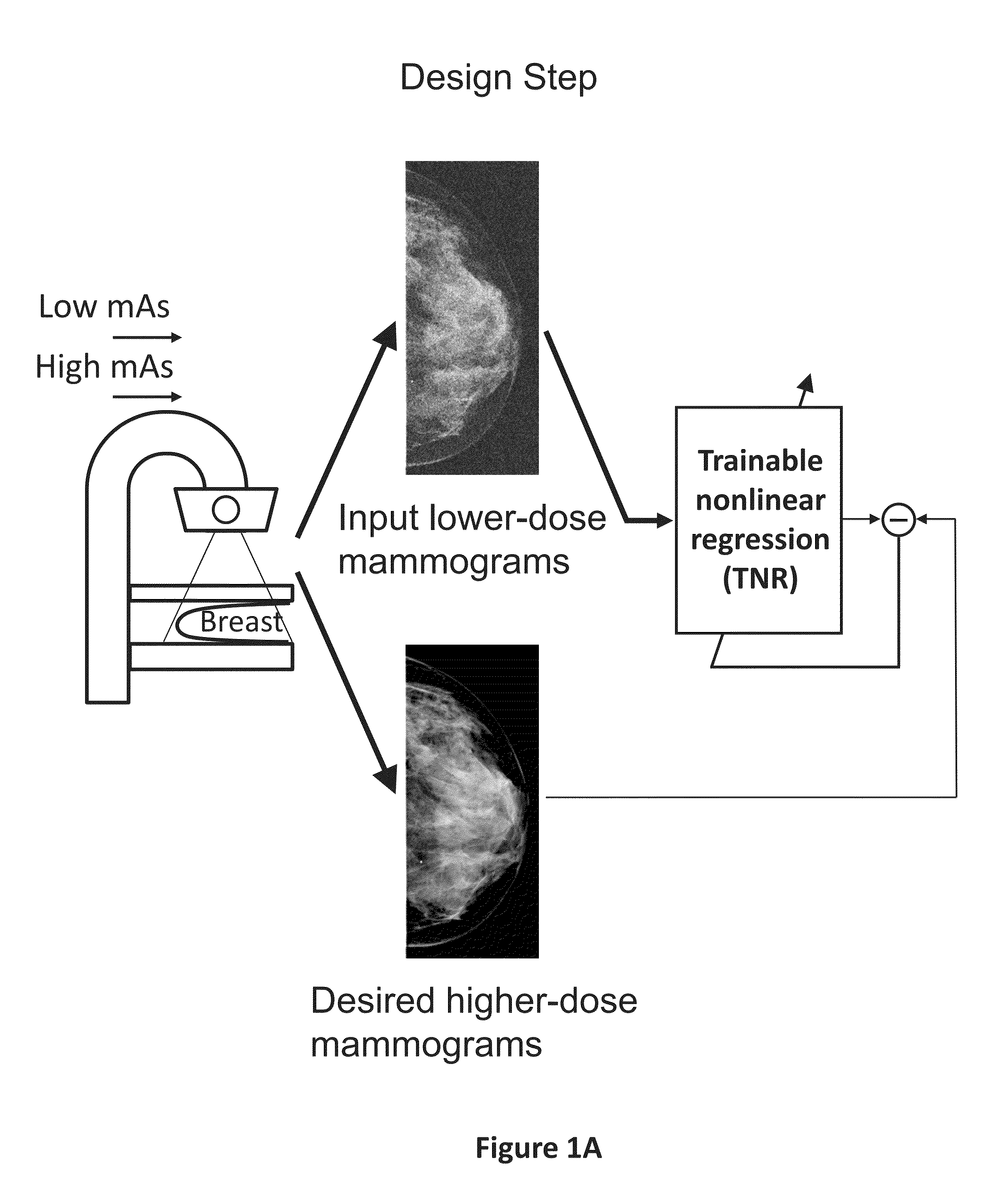
A method and system for converting low-dose mammographic images with much noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like mammographic images, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme, which can be called a call pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input mammogram acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of mammograms, inputting low-dose mammograms together with corresponding desired standard x-ray radiation dose mammograms (higher-dose), which are ideal images for the output images. Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose mammograms to high-dose-like mammograms. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose mammograms anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) mammogram is entered, the trained PTNR would output a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it would output high-dose-like mammograms or “virtual high-dose” mammograms where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. With the “virtual high-dose” mammograms, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
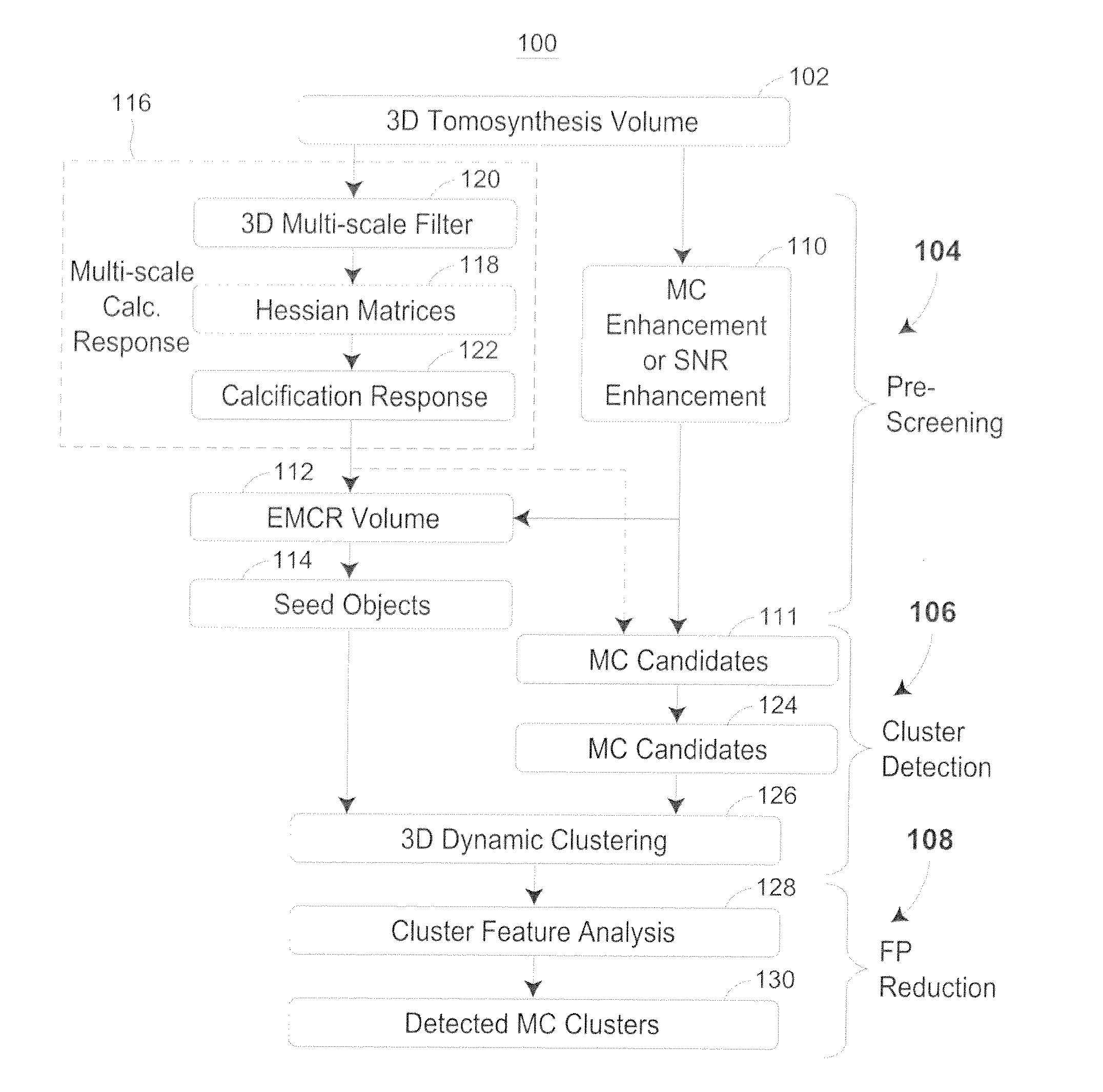
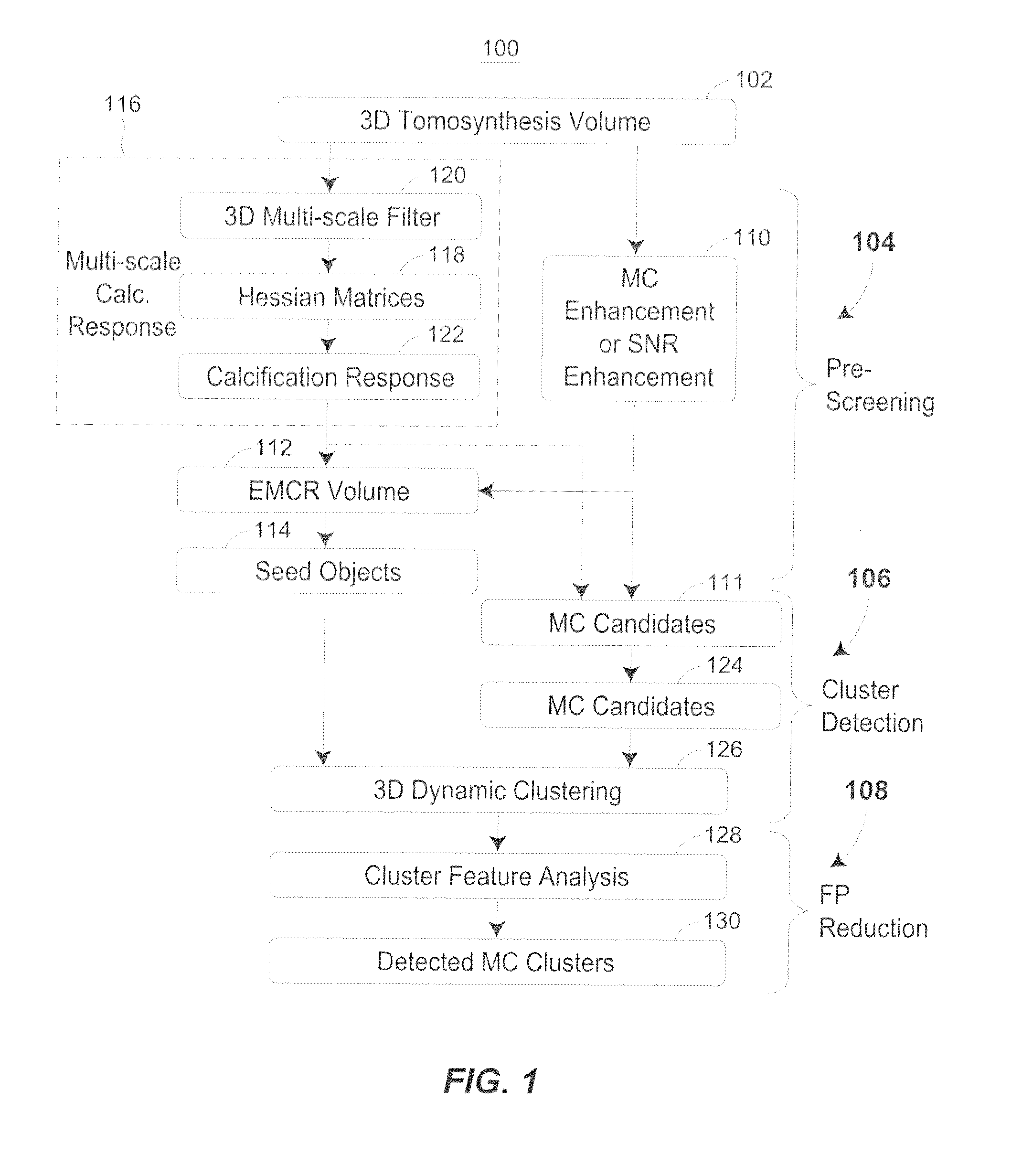
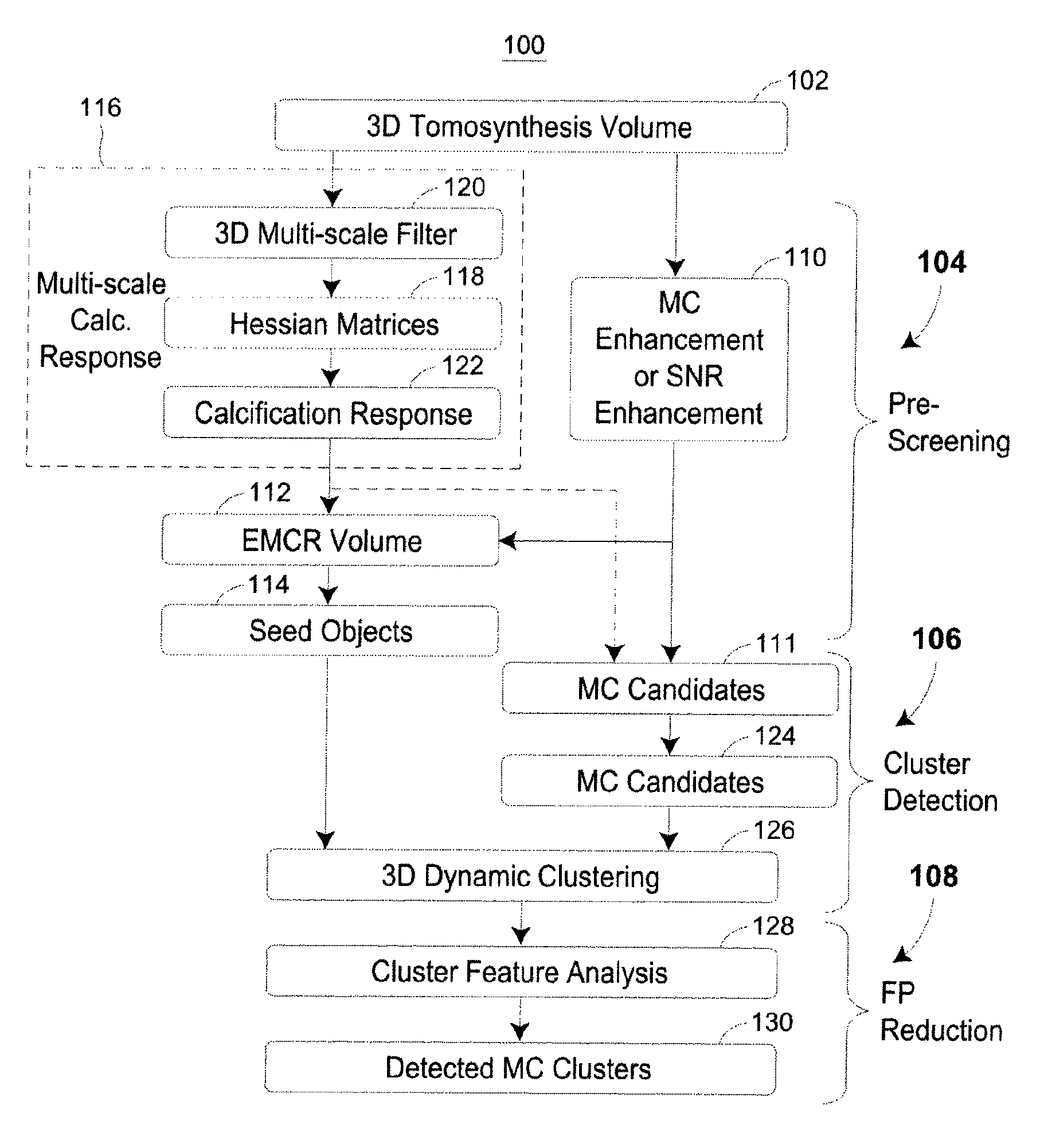
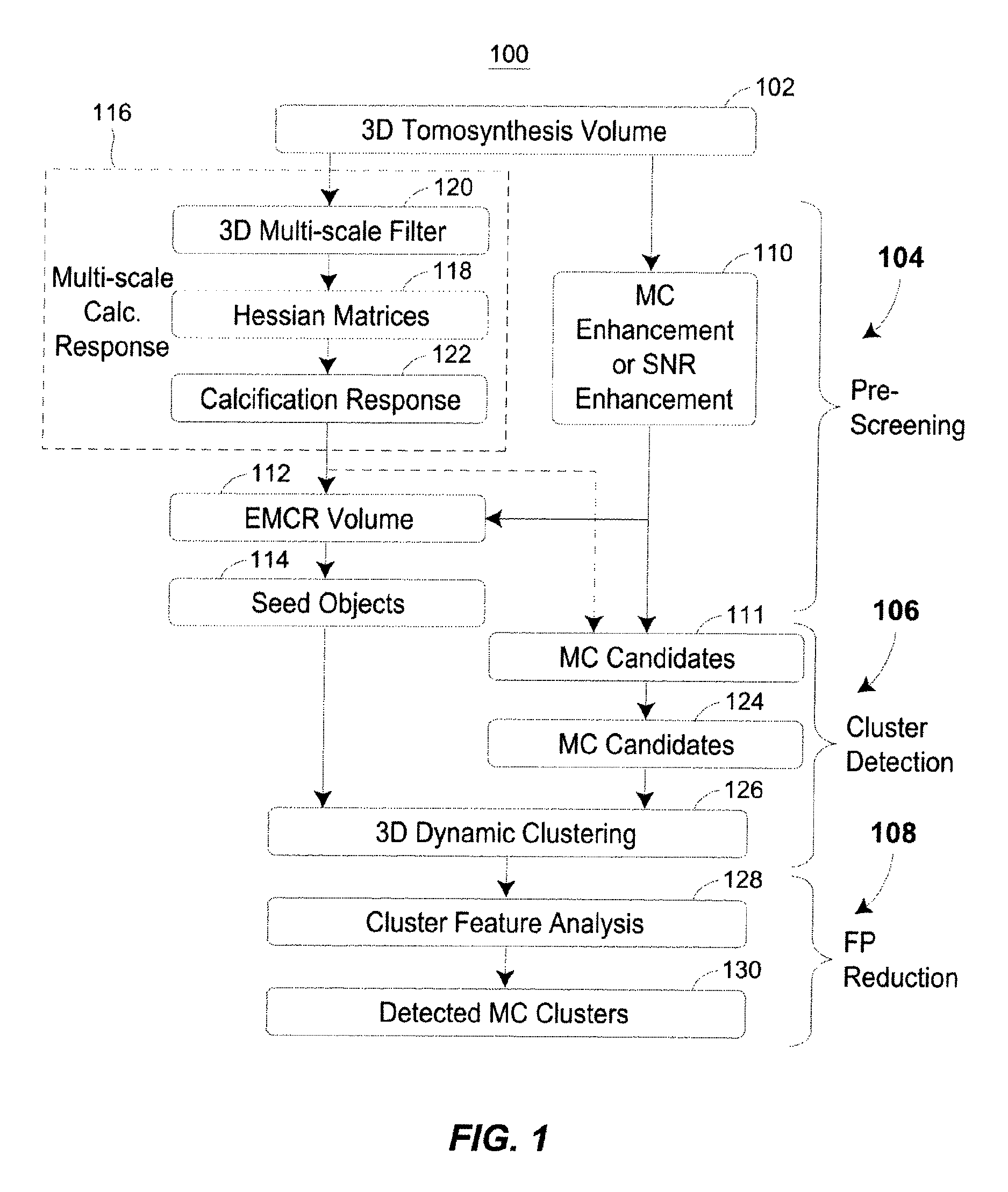
Methods for Microalification Detection of Breast Cancer on Digital Tomosynthesis Mammograms
ActiveUS20120294502A1Reduce in quantityImprove visibilityImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisVoxel
A computer-aided detection system to detect clustered microcalcifications in digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is disclosed. The system performs detection in 2D images and a reconstructed 3D volume. The system may include an initial prescreening of potential microcalcifications by using one or more 3D calcification response function (CRF) values modulated by an enhancement method to identify high response locations in the DBT volume as potential signals. Microcalcifications may be enhanced using a Multi-Channel Enhancement method. Locations detected using these methods can be identified and the potential microcalcifications may be extracted. The system may include object segmentation that uses region growing guided by the enhancement-modulated CRF values, gray level voxel values relative to a local background level, or the original DBT voxel values. False positives may be reduced by descriptors of characteristics of microcalcifications. Detected locations of clusters and a cluster significance rating of each cluster may be output and displayed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Computer aided detection method for microcalcification in mammograms
InactiveCN101853376AAccurate detectionReduce workloadImage enhancementImage analysisSupport vector machineMissed diagnosis
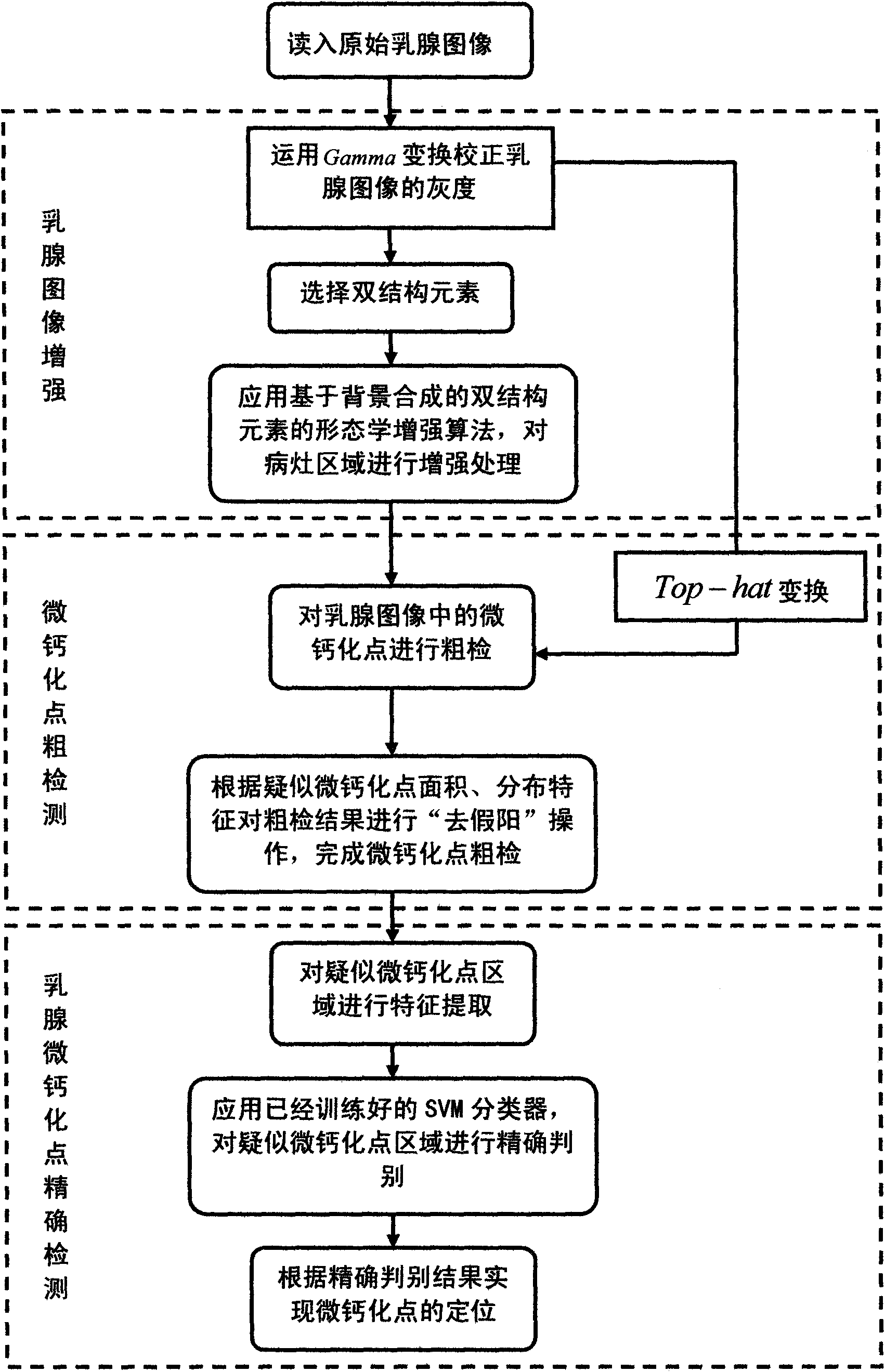
The invention discloses a computer aided detection method for microcalcification in mammograms, which comprises the following steps of: performing grayscale correction and transformation on a mammogram image to obtain an image after grayscale correction; acquiring microcalcification enhanced mammogram image by adopting dual-structure element-based background superposition method, and simultaneously acquiring another background suppressed mammogram image by adopting a Top-hat transformation method in morphology; segmenting the two images by adopting double thresholds to acquire a preliminary microcalcification image, and performing postprocessing to form a coarse microcalcification detection image; and extracting characteristics from coarsely detected microcalcification destination area, classifying by using a support vector machine, removing false microcalcification destination areas, marking the rest microcalcification into the mammogram image for the reading of doctors. The method can free the doctors from trivial mammogram reading and classifying work, and assists the doctors in better understanding and judging the images so as to reduce error diagnosis and missed diagnosis and fulfill the aim of improving diagnostic accuracy.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method of locating the position of a microcalcification in a human breast
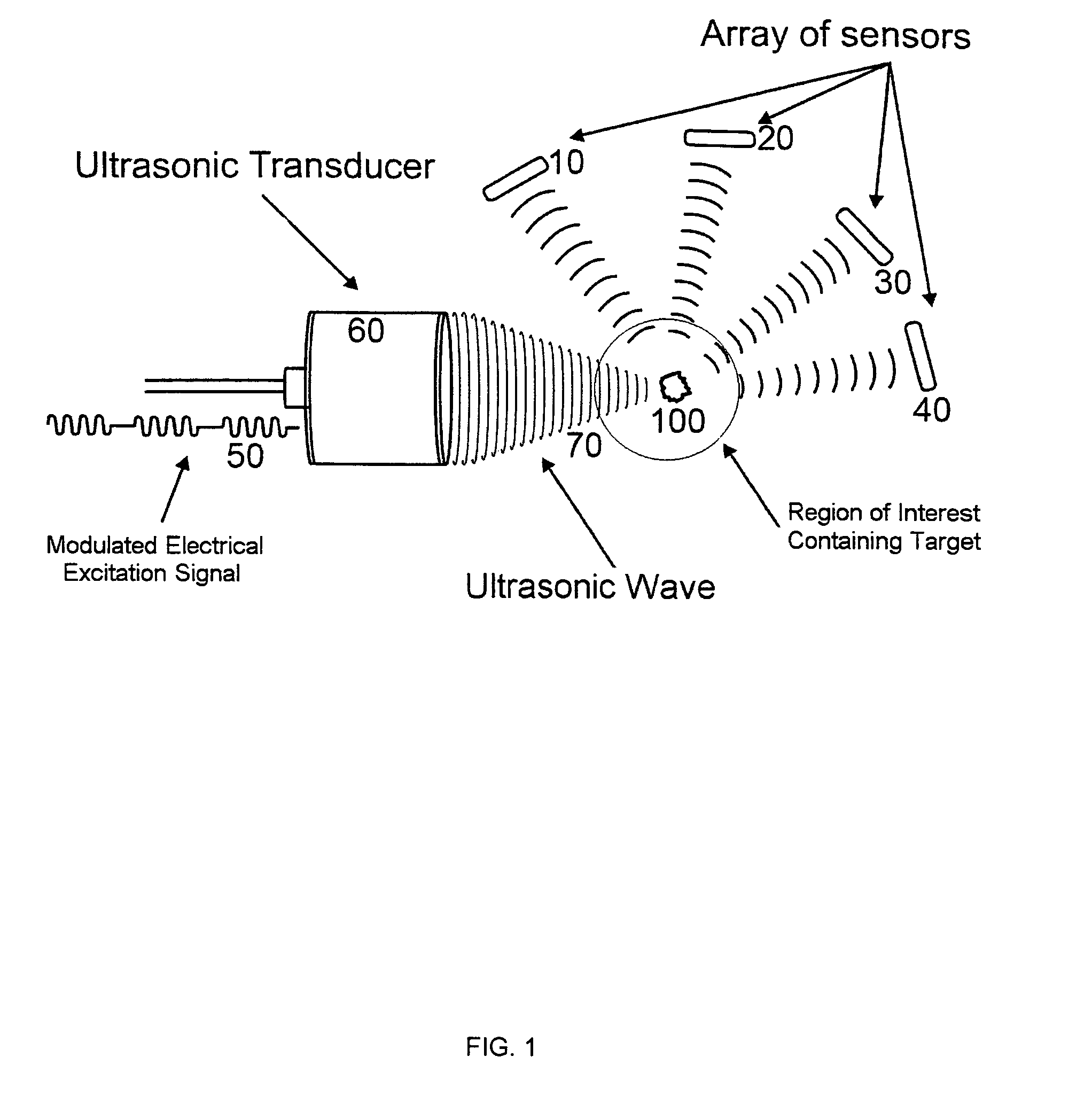
InactiveUS8622909B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasonographySonification
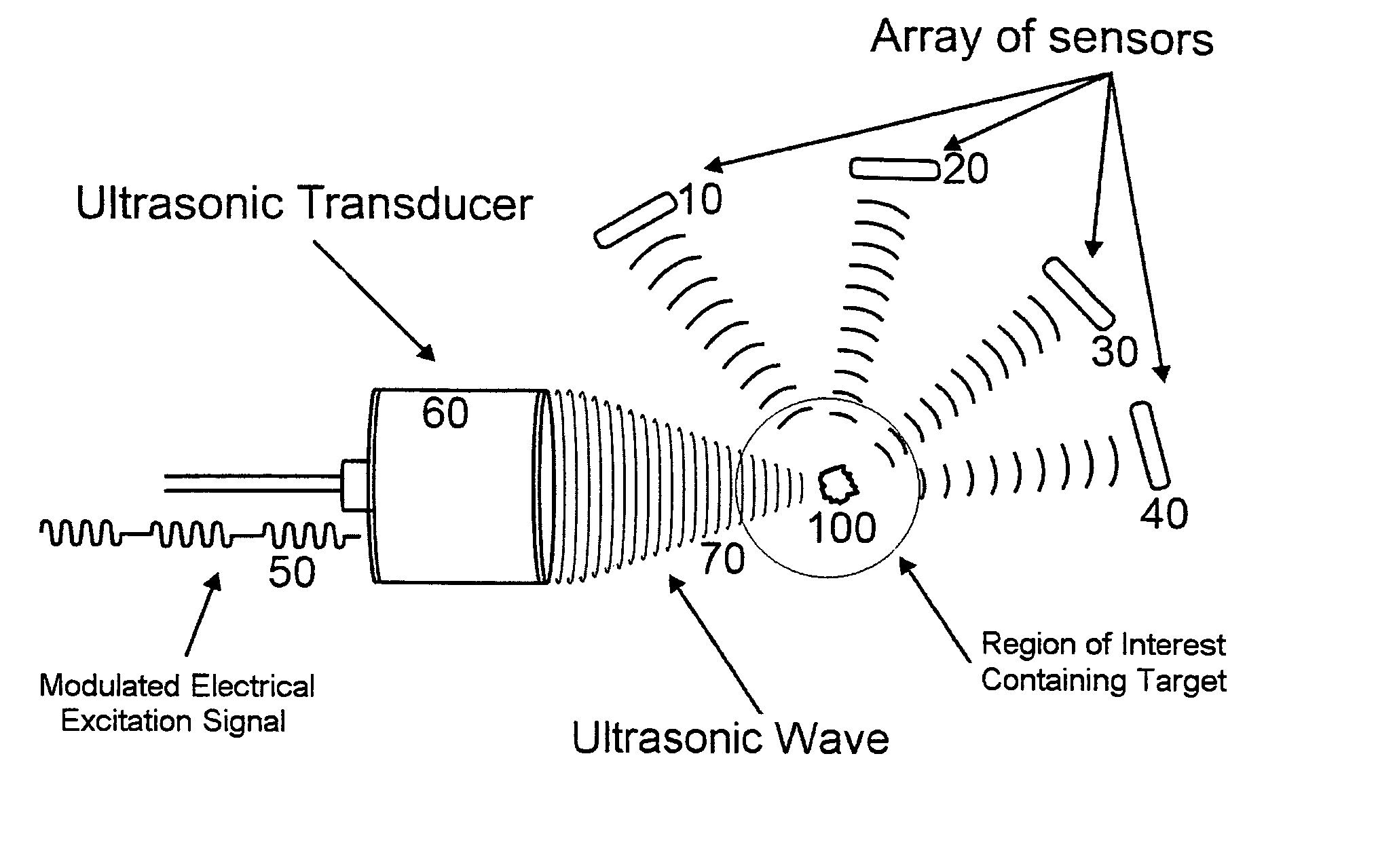
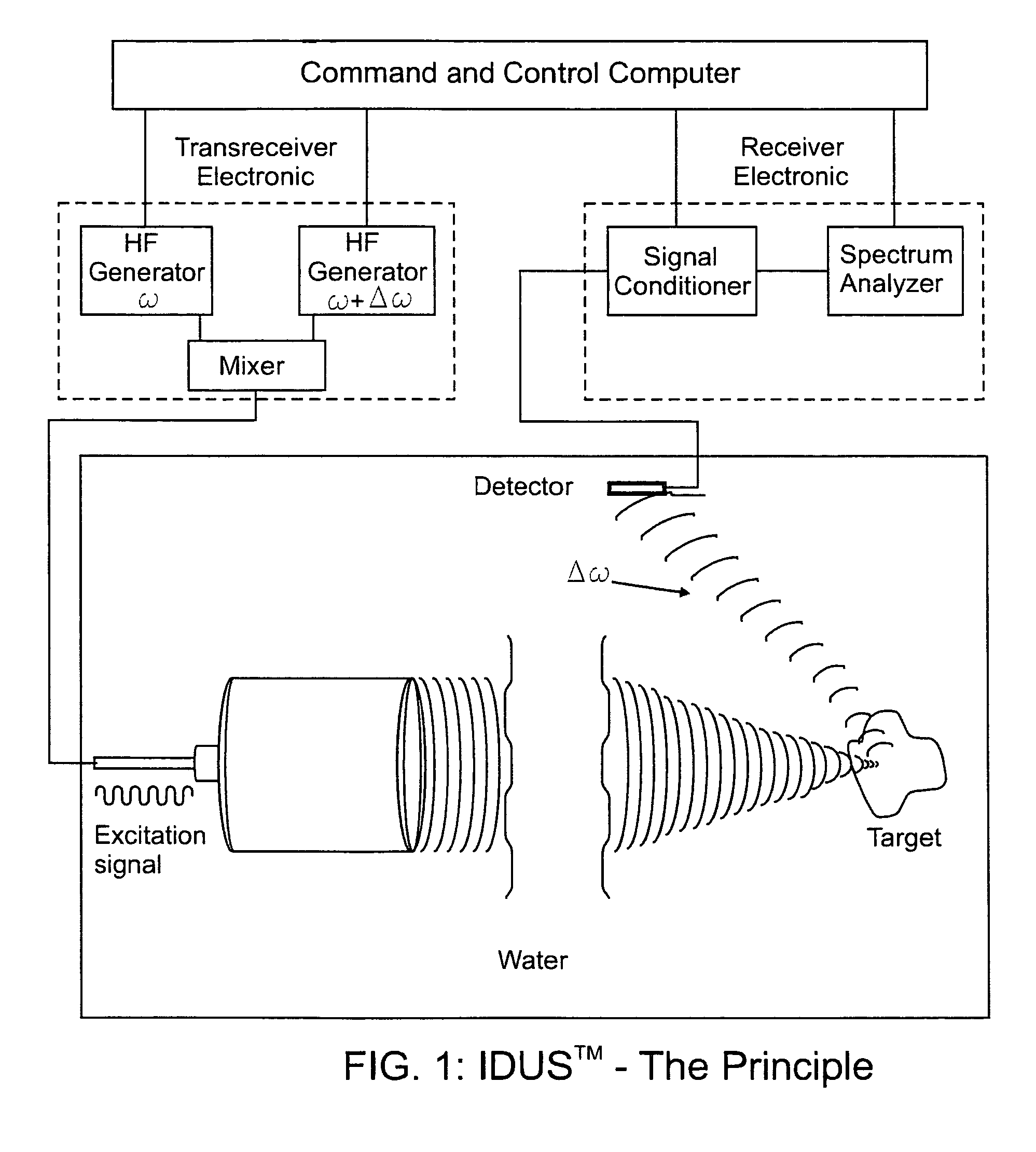
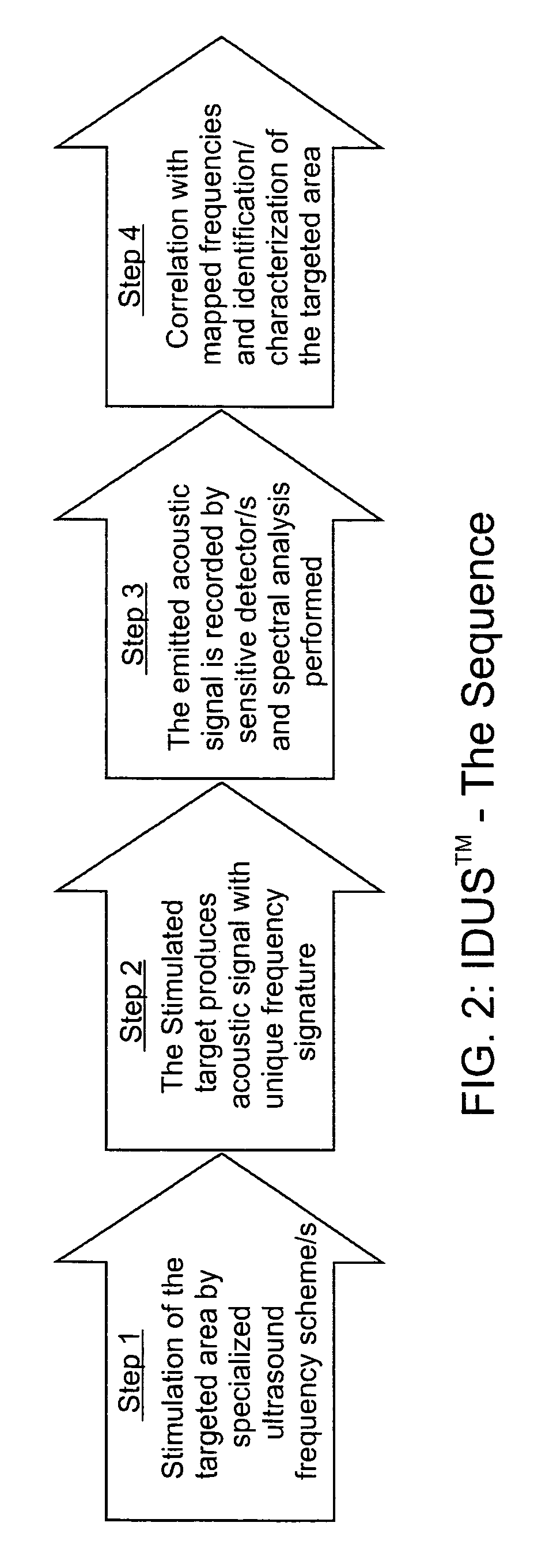
This invention relates to diagnostic and screening medical ultrasound in general and to ultrasound-stimulated detection and location, Image-based Dynamic Ultrasound Spectrography, Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging, and similar modalities in particular. In this invention, an ultrasound signal is emitted into tissue and the resulting radiation force induces localized lower frequency oscillations, which are then received by various acoustic sensors and analyzed to determine certain features or characteristics of the interrogated region. The sensors can be arranged in the form of a ring, in any random arrangements, or positioned in specifically chosen locations. An ultrasonic imaging and excitation transducer generates certain stimulating signals which are received by the breast tissues and which, if they contact a microcalcification, other target, or any region with sharply different mechanical and visco-elastic properties, will result in reflected, demodulated, or re-radiated signals. These signals will propagate away from the targets and detected by the various receiving sensors.
Owner:QUANTASON
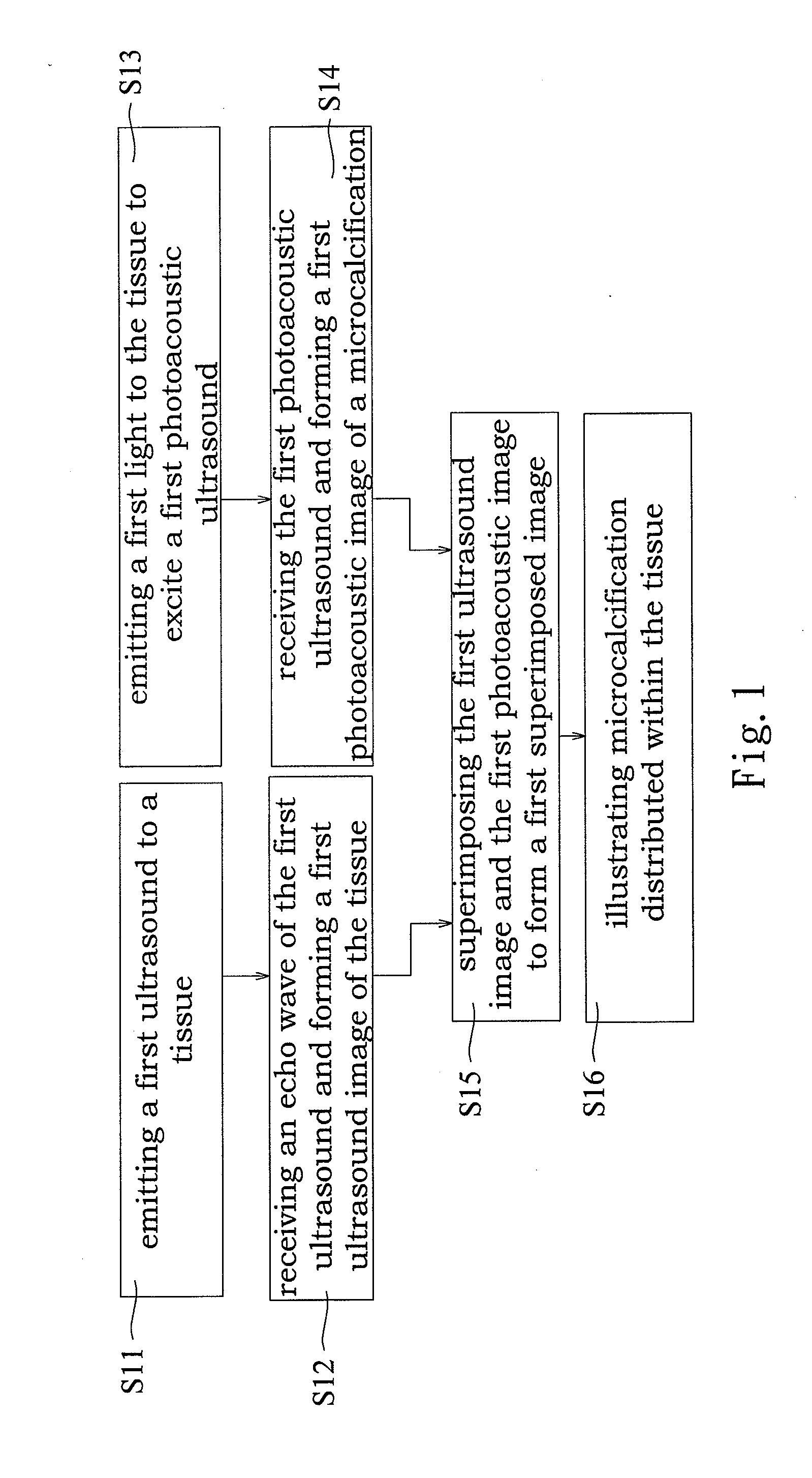
Imaging method for microcalcification in tissue and imaging method for diagnosing breast cancer
InactiveUS20110144496A1High optical contrastHigh resolutionBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsImage resolutionEarly breast cancer
An imaging method for microcalcification displays microcalcification distribution by acquiring and overlapping a photoacoustic image of microcalcification and an ultrasonic image of tissue. The image acquired by the present invention, in comparison to images acquired by ultrasonic and X-ray mammography, has advantages in no speckle noises, higher optical contrast, higher ultrasonic resolution, and so on. The present invention also has advantage in safety by adopting a light source having no ionizing radiation. An imaging method for diagnosing breast cancer is also herein disclosed.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
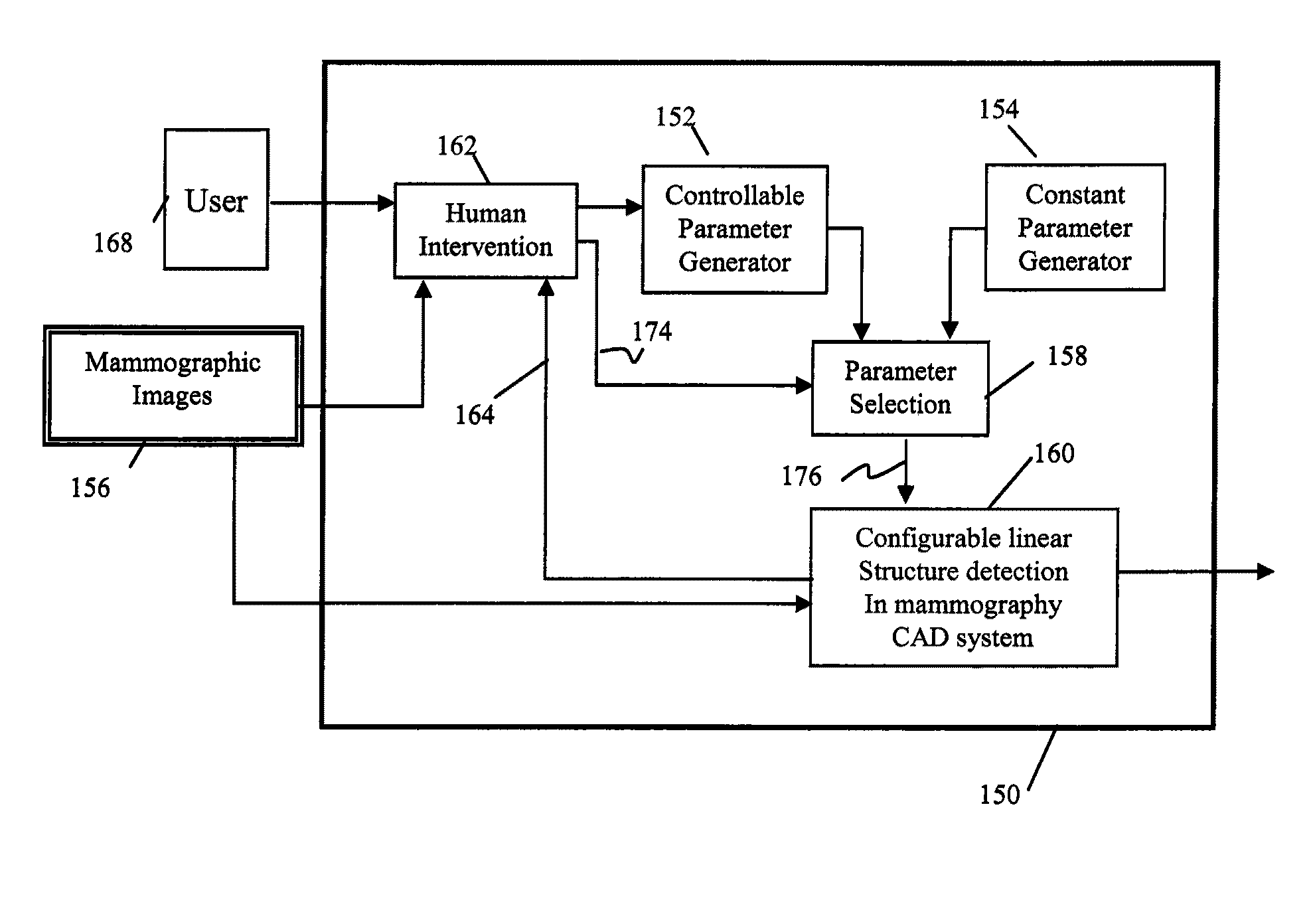
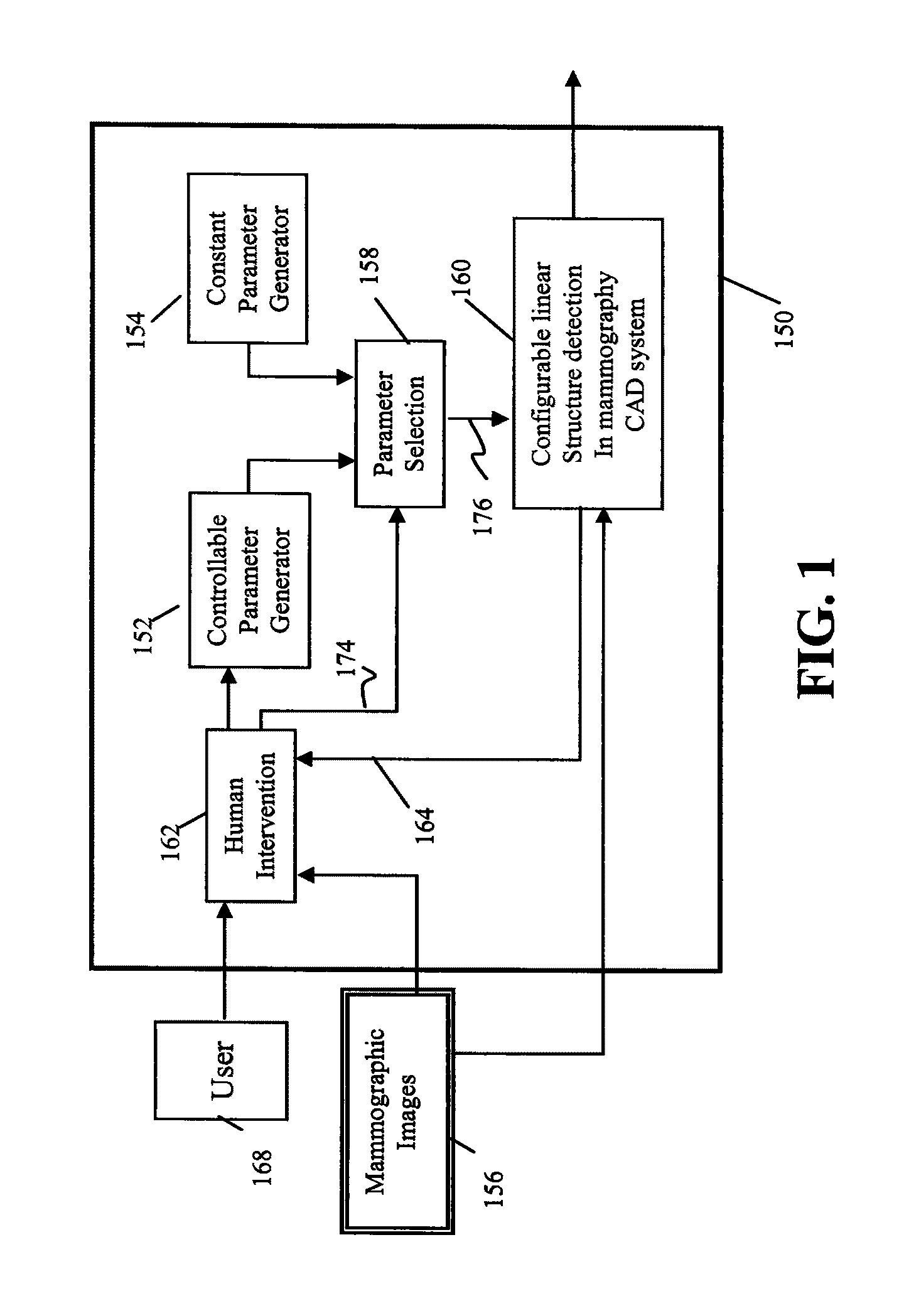
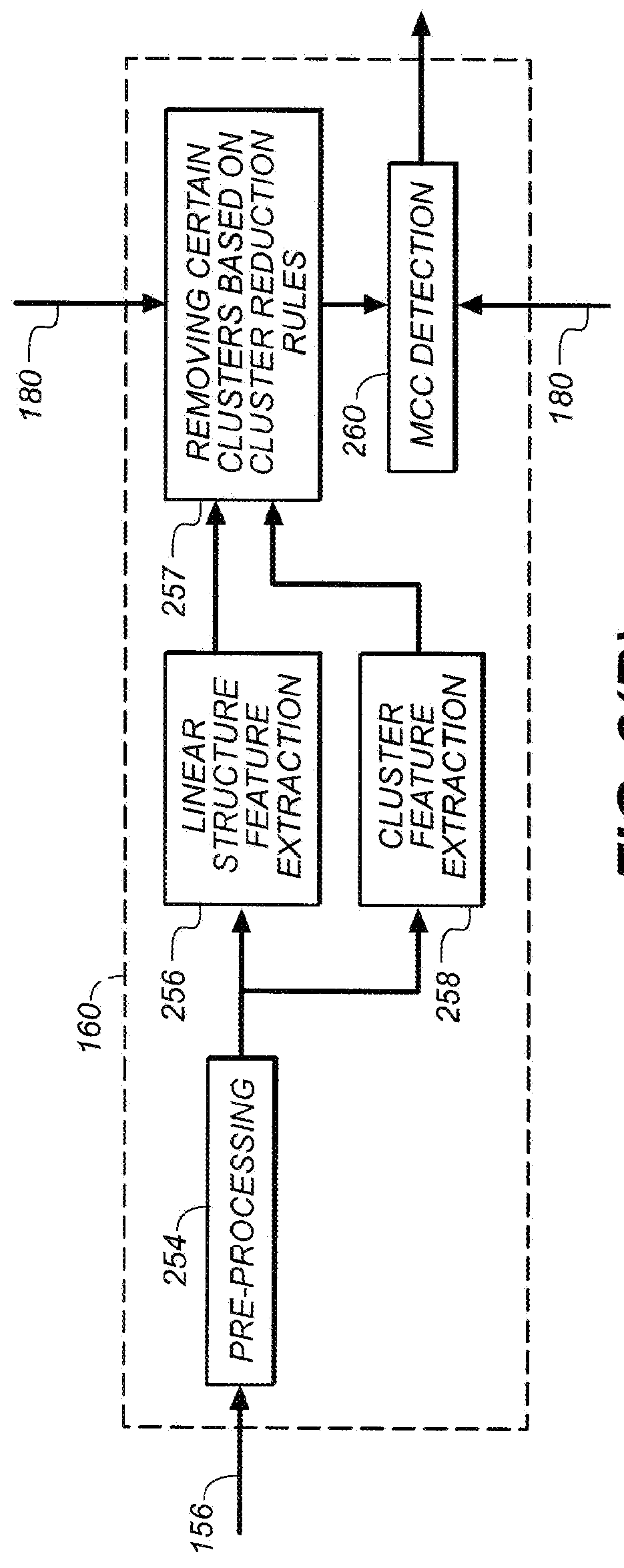
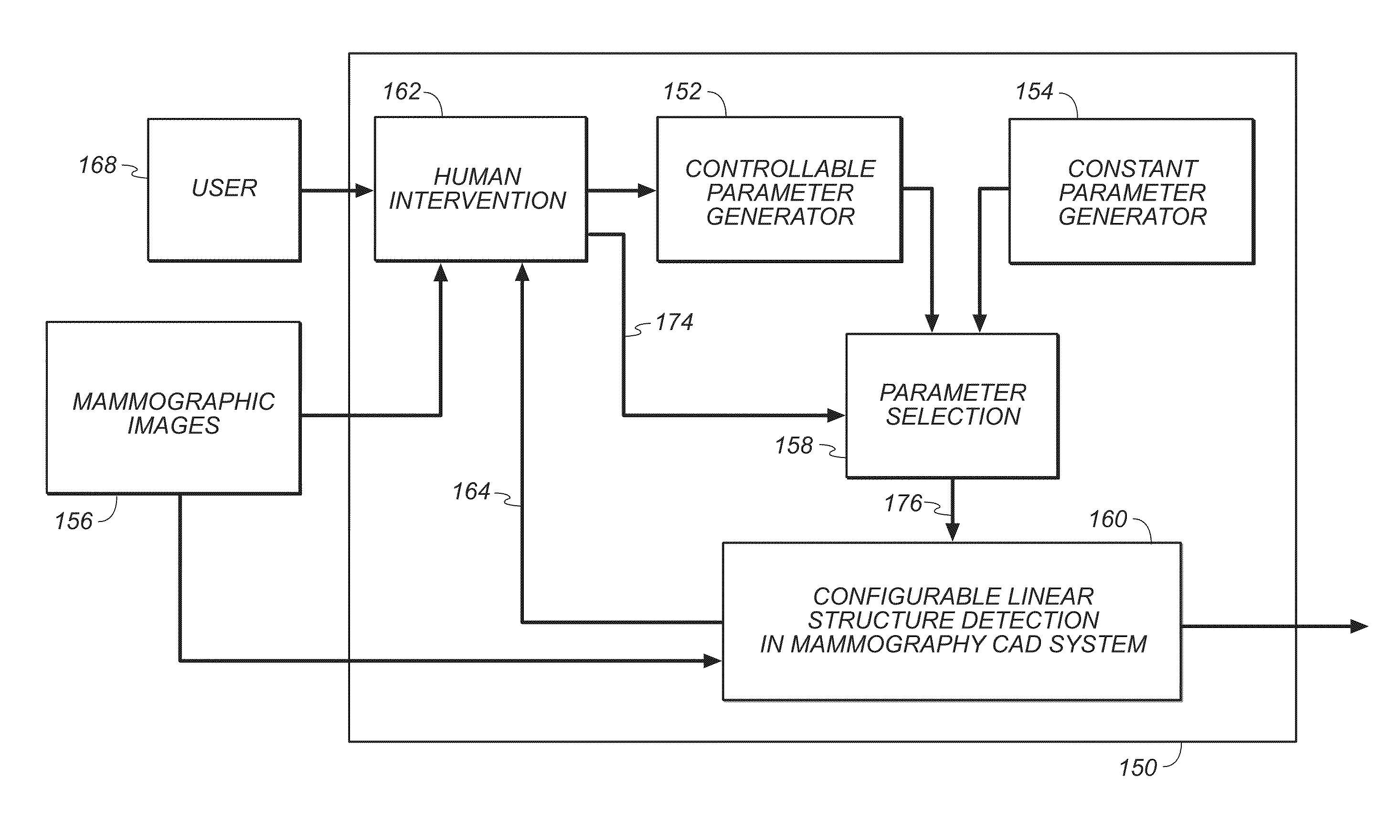
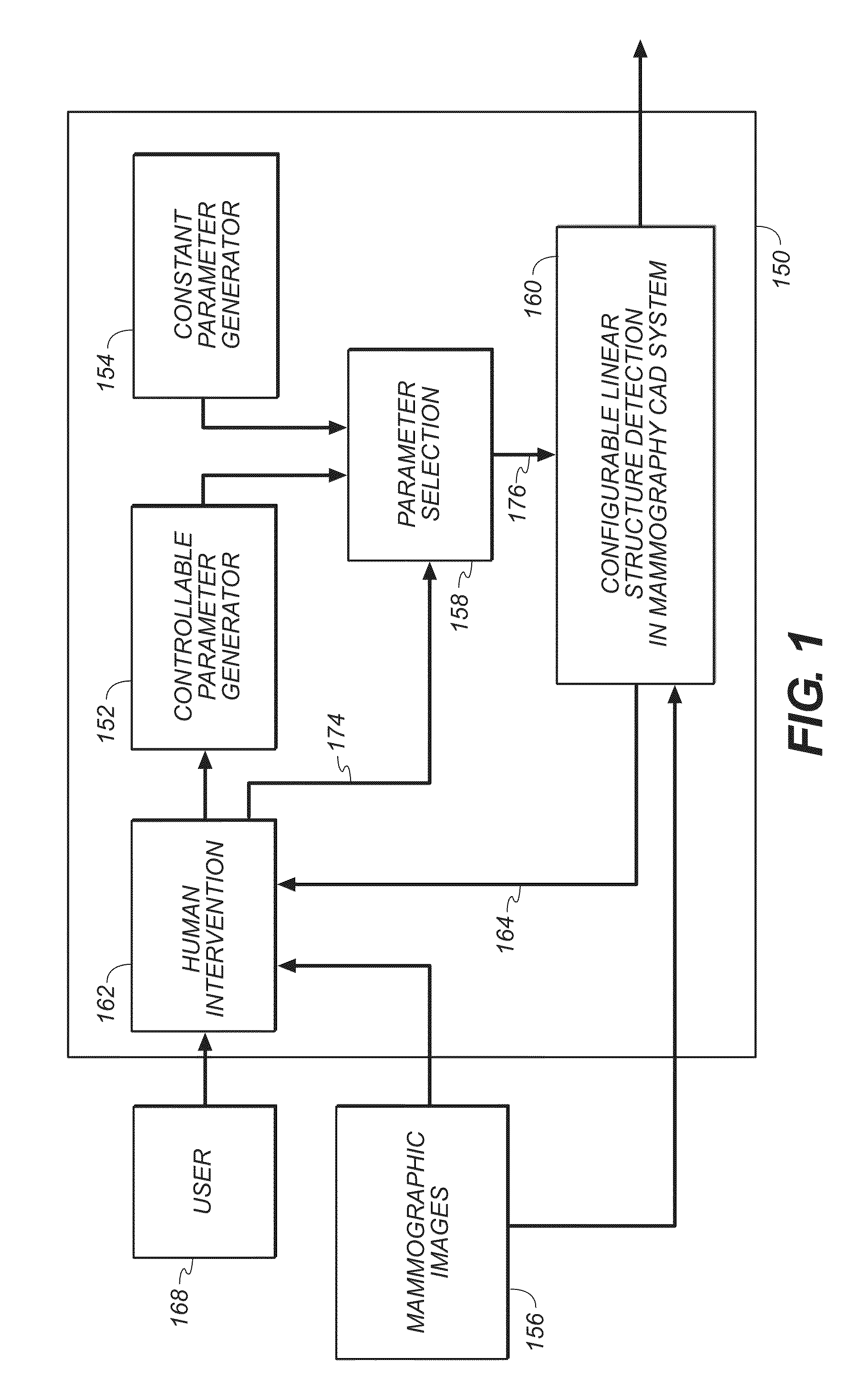
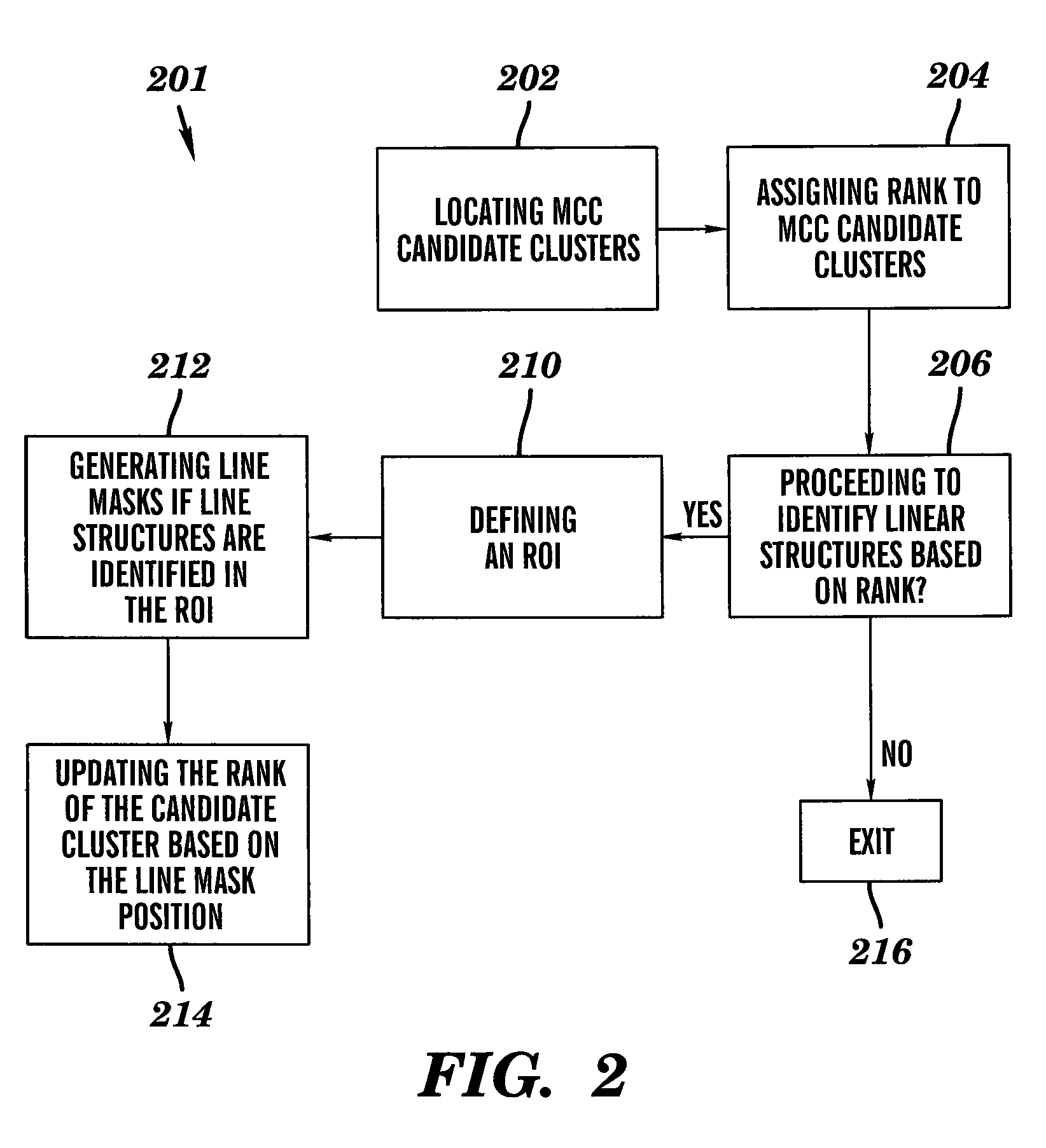
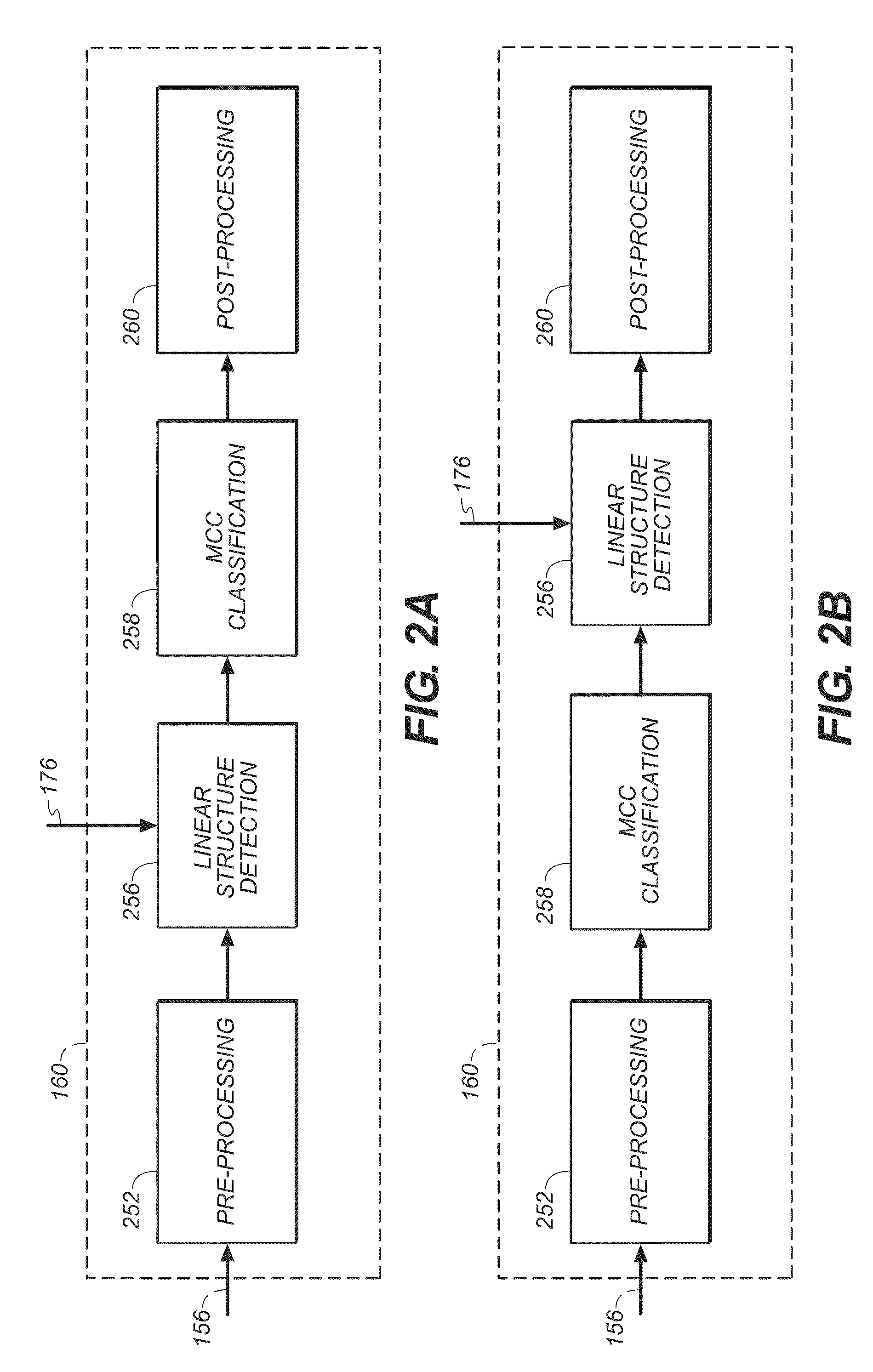
Method for detection of linear structures and microcalcifications in mammographic images
InactiveUS20100104155A1Reducing MCC FPsImage enhancementImage analysisGeometric propertyPattern recognition
A method for linear structure detection in mammographic images, comprising: locating a plurality of microcalcification candidate clusters in digital mammographic images; extracting a region of interest that encloses each of the candidate clusters; processing the region of interest to generate feature points that reveal geometric properties in the region; applying a line detection algorithm to the feature points to produce a line model; and analyzing the line model to determine whether a true linear structure is present in the first region of interest.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
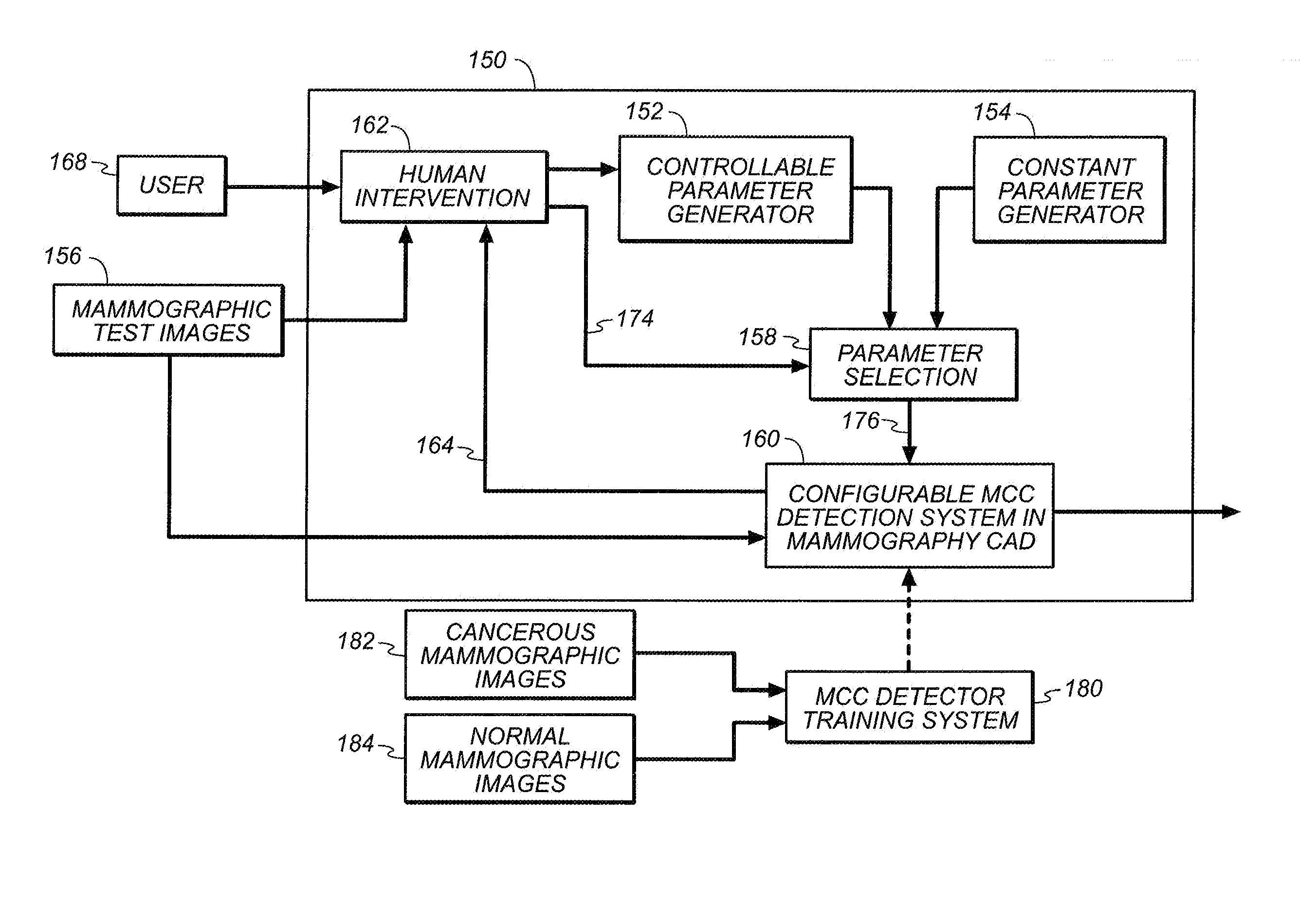
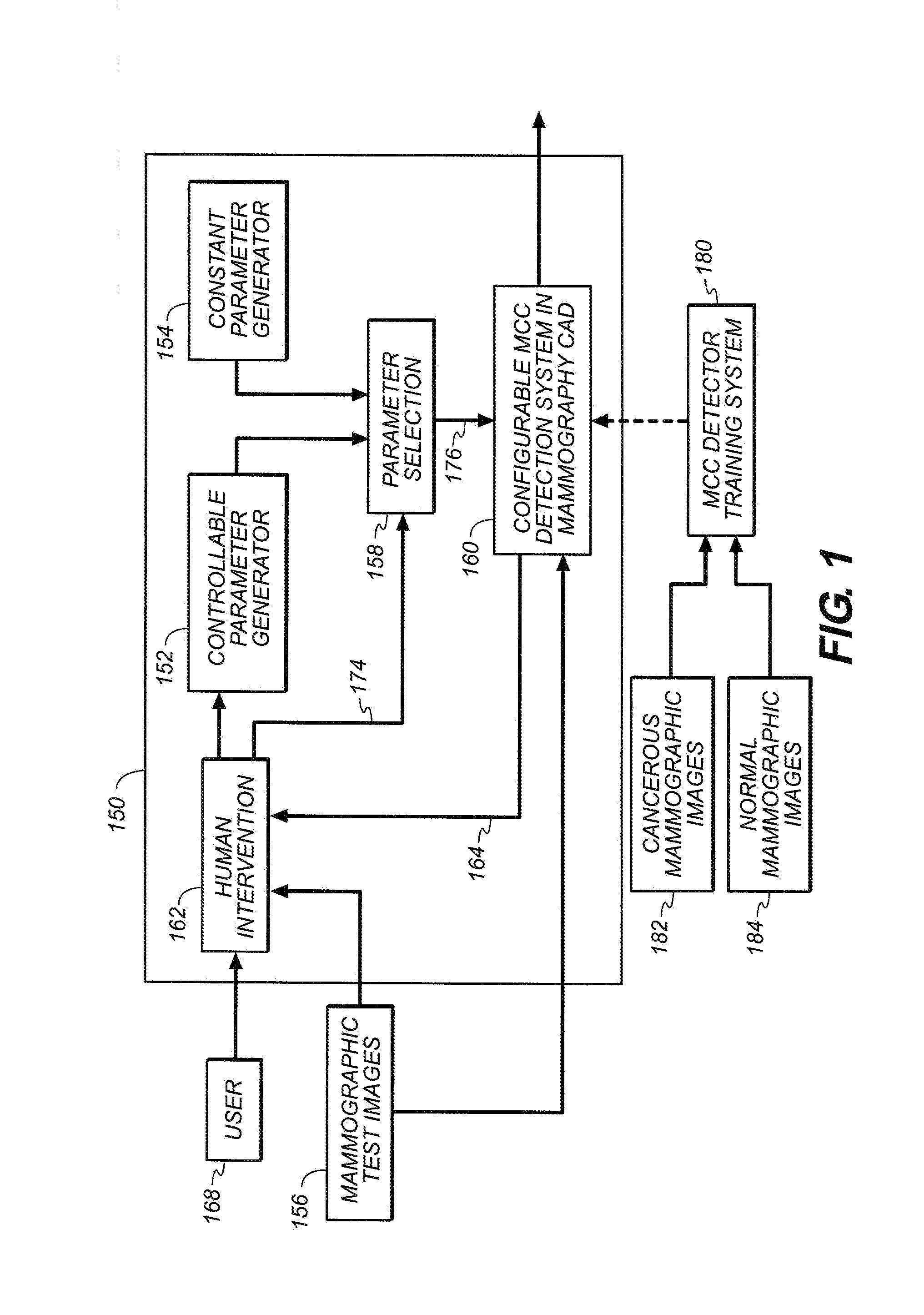
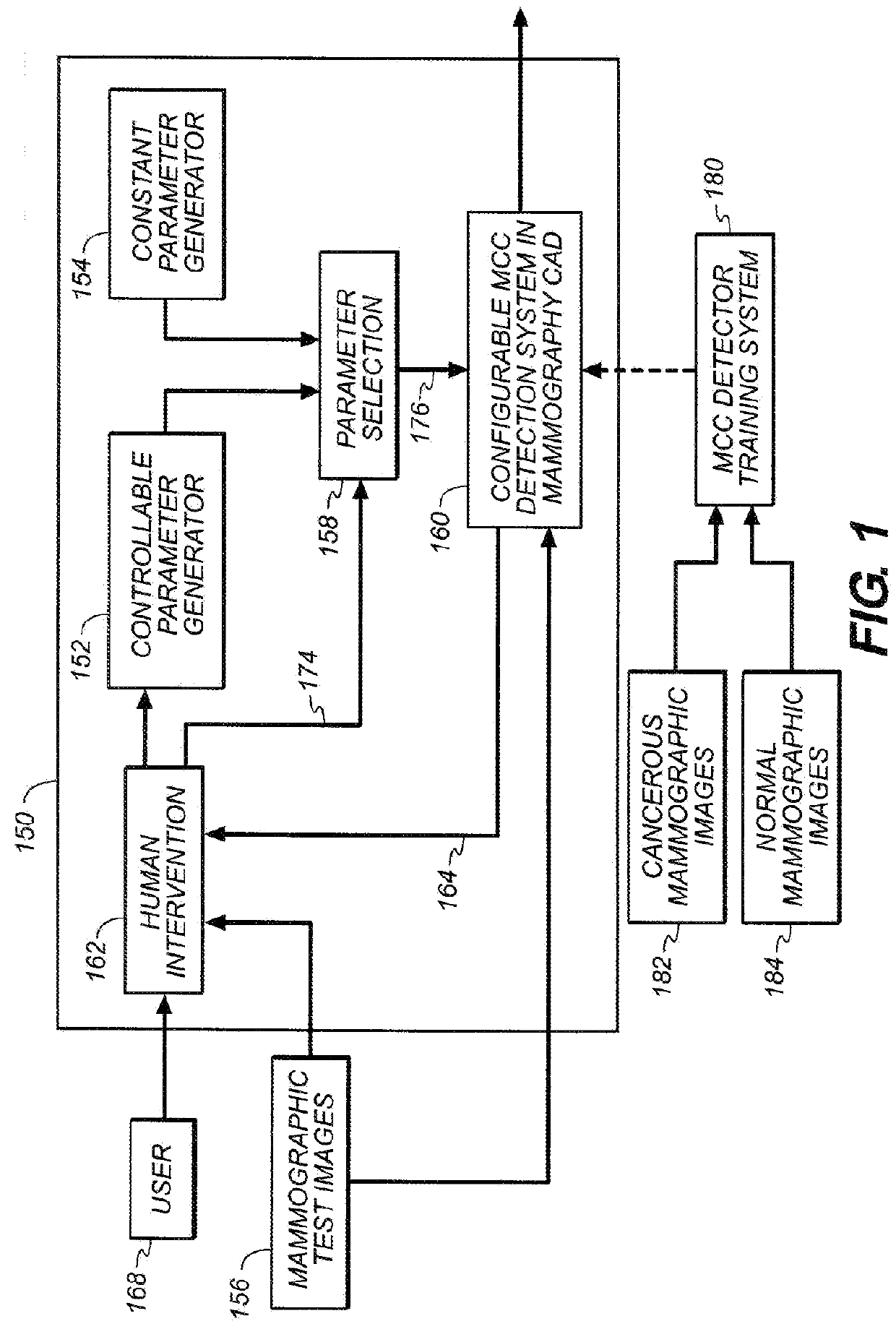
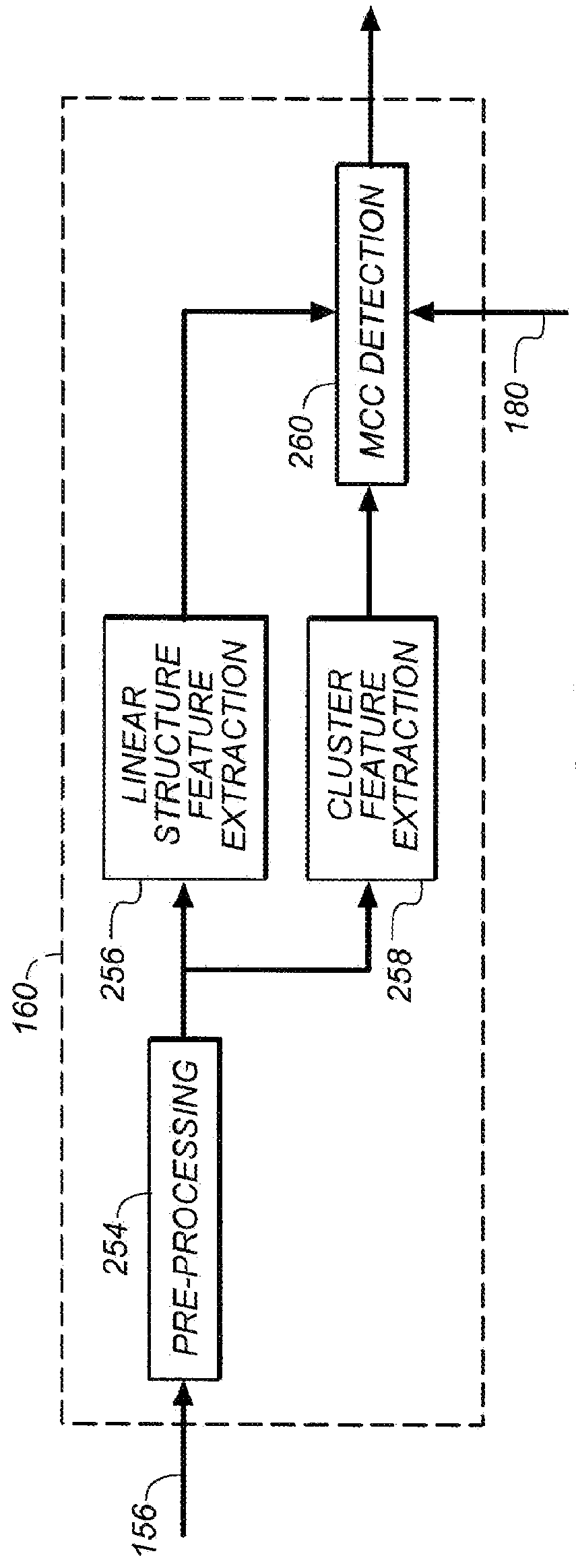
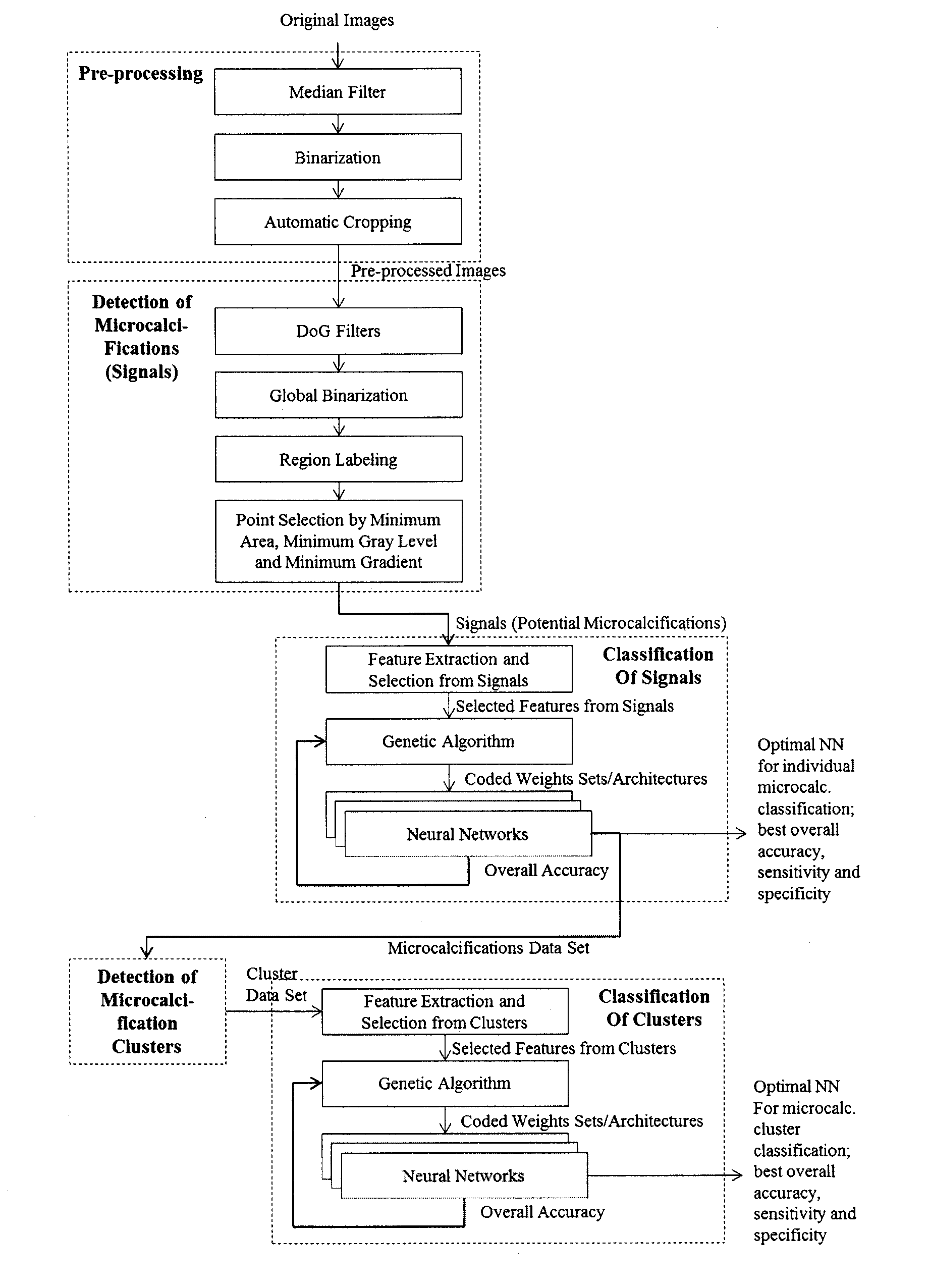
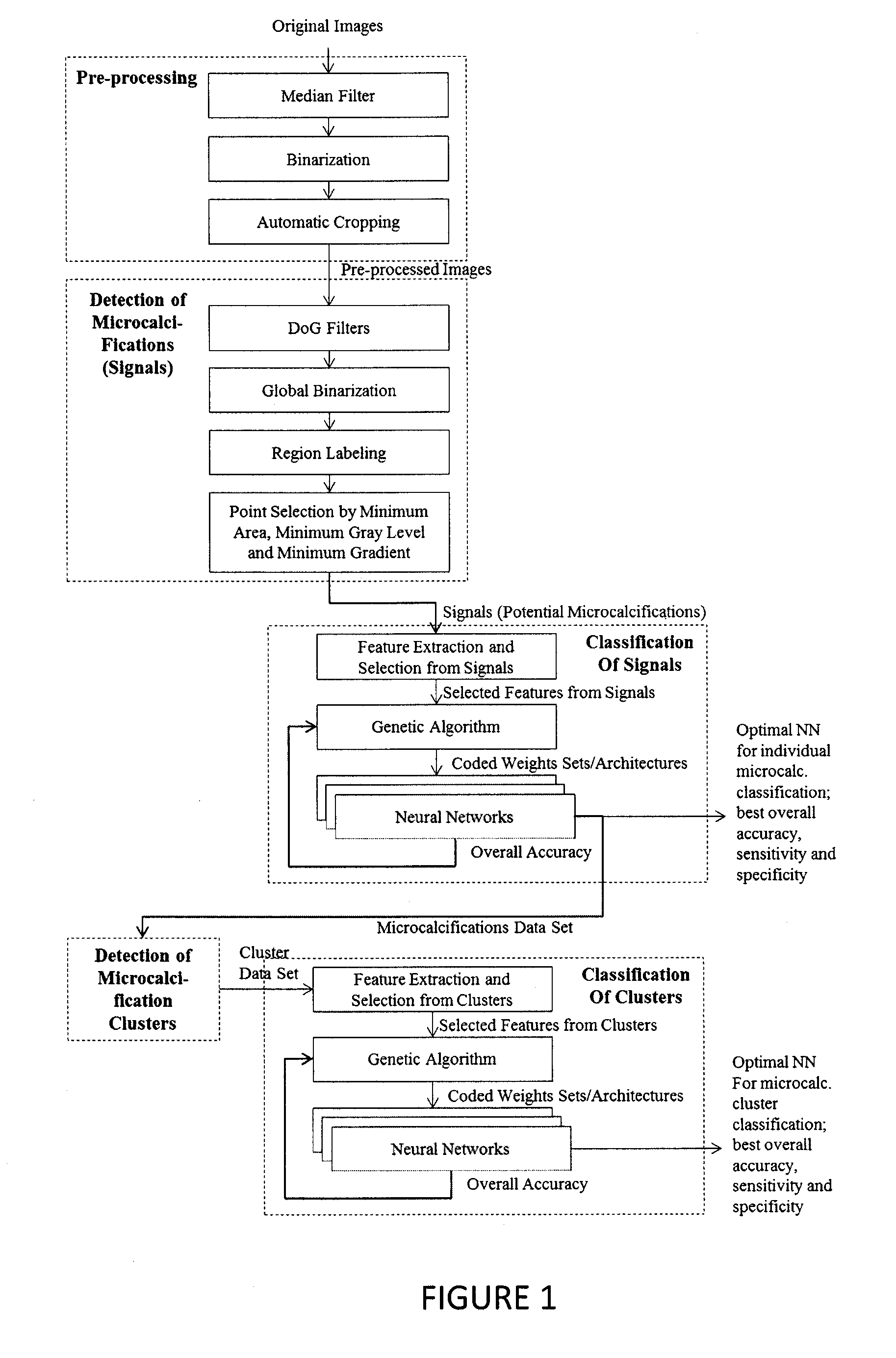
Microcalcification detection in mammography cad using a classifier
A system is disclosed that is configured for microcalcifications (mcc) detecting by forming a plurality of true mcc clusters and a plurality of normal clusters, gathering spot and cluster features from said clusters, extracting linear structure features, and using said spot, cluster and linear structure features in mcc detector algorithm training.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
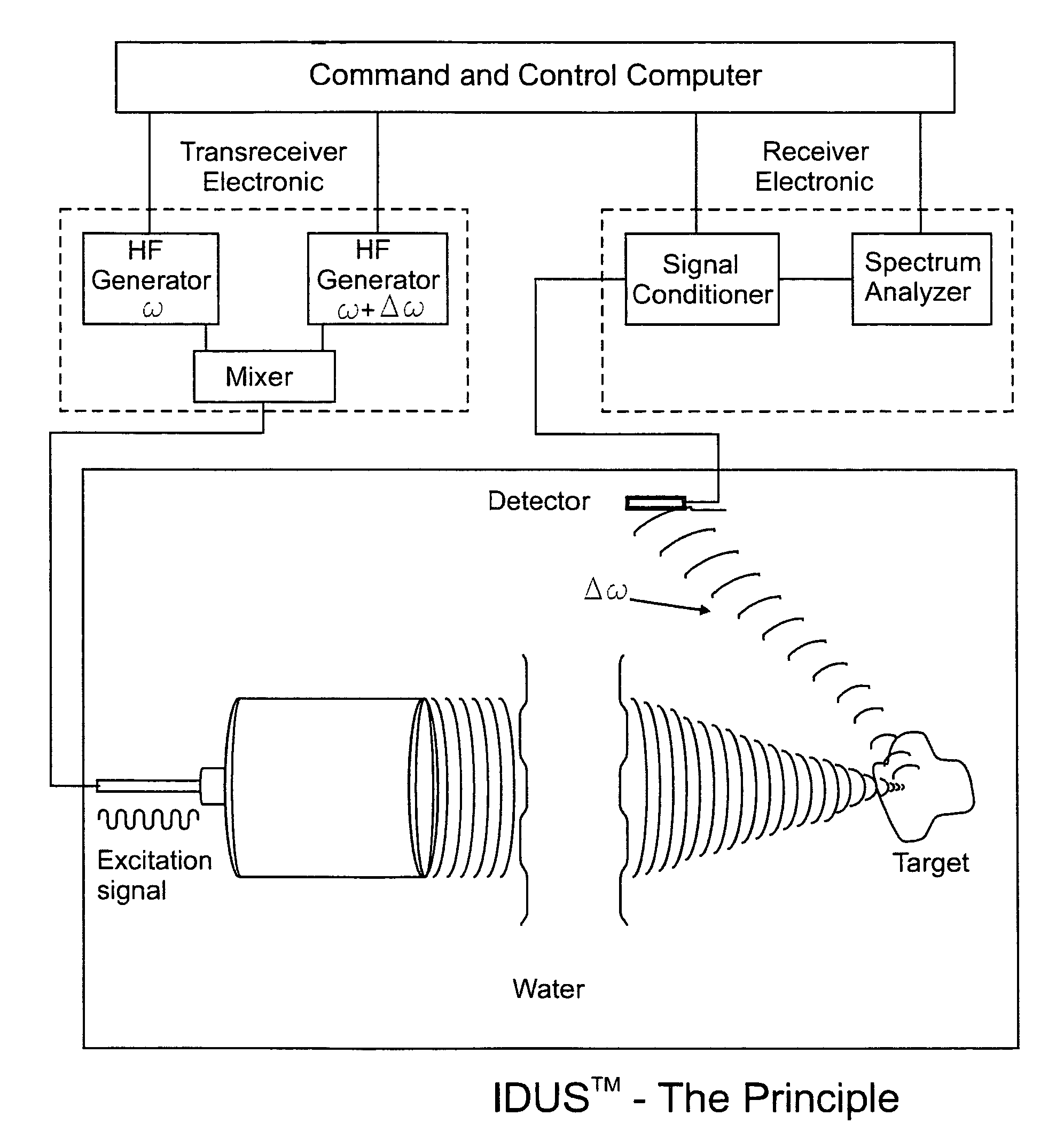
Application of image-based dynamic ultrasound spectrography (IDUS) in detection and localization of breast microcalcifcation
InactiveUS8376947B2Accurate locationCost-effectiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency waveBi modal
Owner:BIOQUANTETICS
Method and system for detecting microcalcifications in mammogram
InactiveCN102663410AImprove recognition accuracyImprove recognition efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorAdaptive optimization
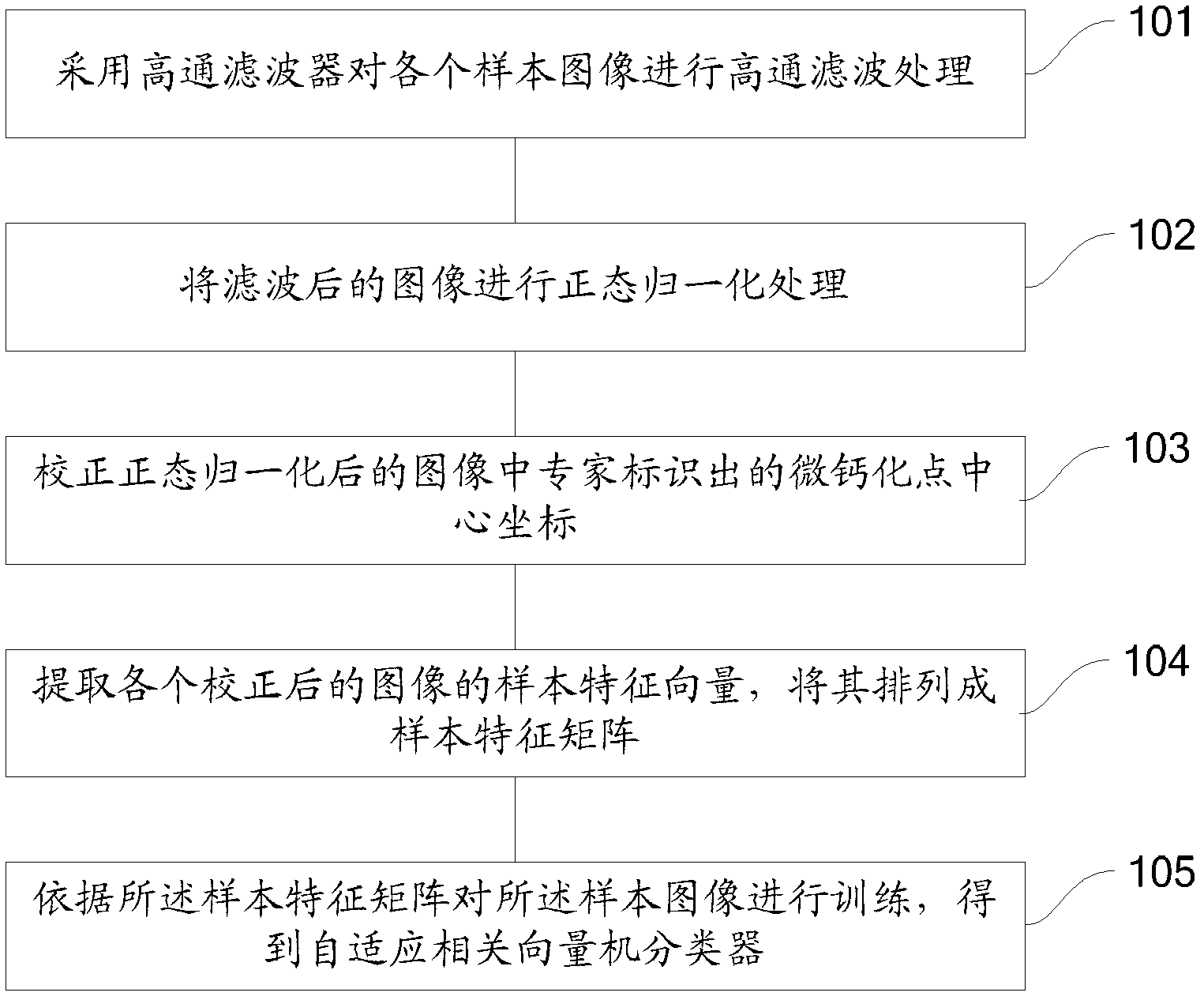
The invention discloses a method and a system for detecting microcalcifications in a mammogram, wherein the system comprises carrying out a processing of high-pass filtering on a mammogram to be identified by adopting a high-pass filter; carrying out a normalized processing on the filtered mammogram; extracting a feature vector of the normalized mammogram, and inputting the feature vector into an adaptive relevance vector machine classifier; and identifying microcalcifications in the mammogram according to the feature vector by using the adaptive relevance vector machine classifier. The method and the system of the invention apply an adaptive relevance vector machine classifier to the detection of microcalcifications in a mammogram. An optimization of incremental amount of model parameters is carried out directly by using parameter adaptive optimization ability of the adaptive relevance vector machine classifier, and identification accuracy and efficiency are improved.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Microcalcification detection in mammography CAD using a classifier
A system is disclosed that is configured for microcalcifications (mcc) detecting by forming a plurality of true mcc clusters and a plurality of normal clusters, gathering spot and cluster features from said clusters, extracting linear structure features, and using said spot, cluster and linear structure features in mcc detector algorithm training.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
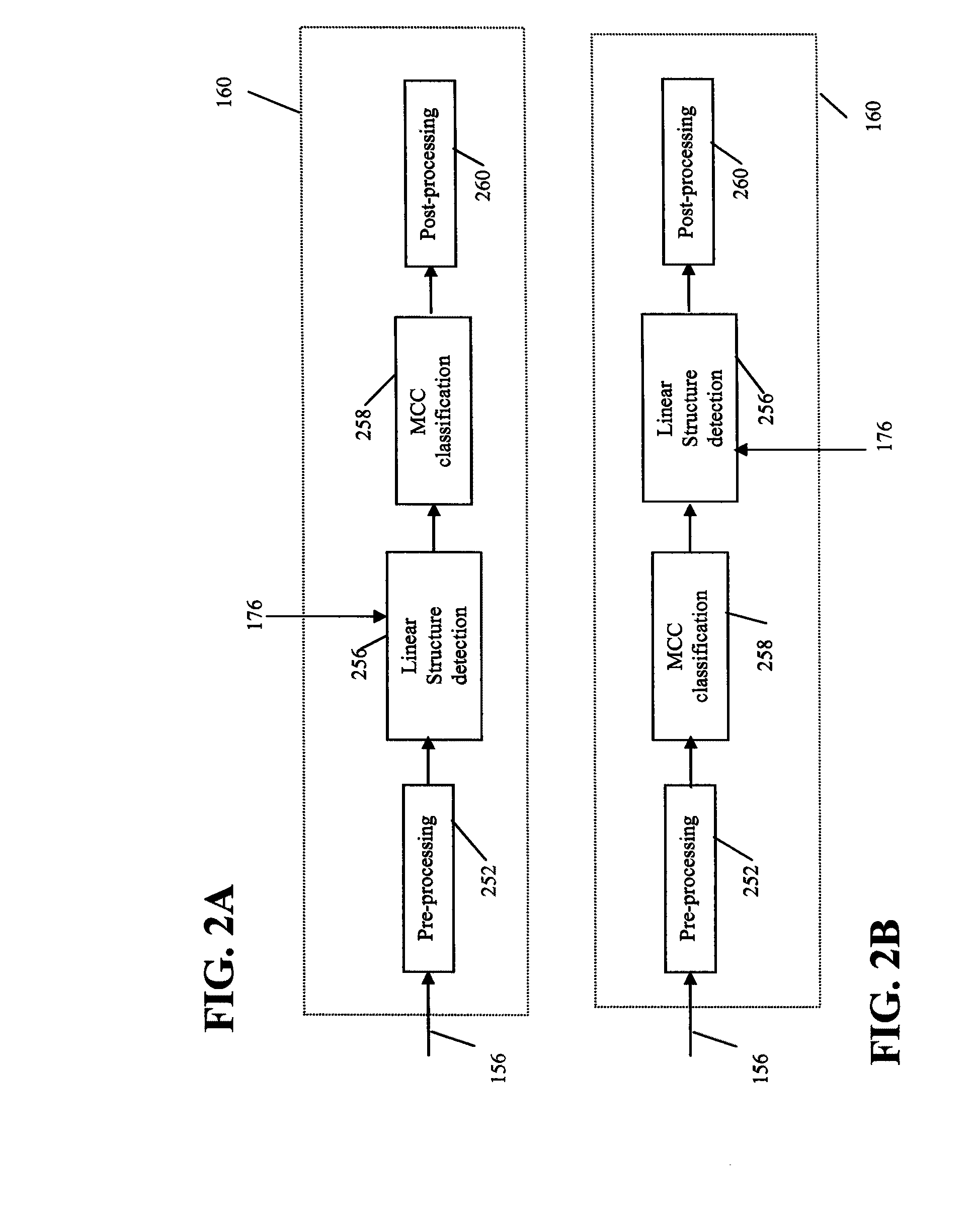
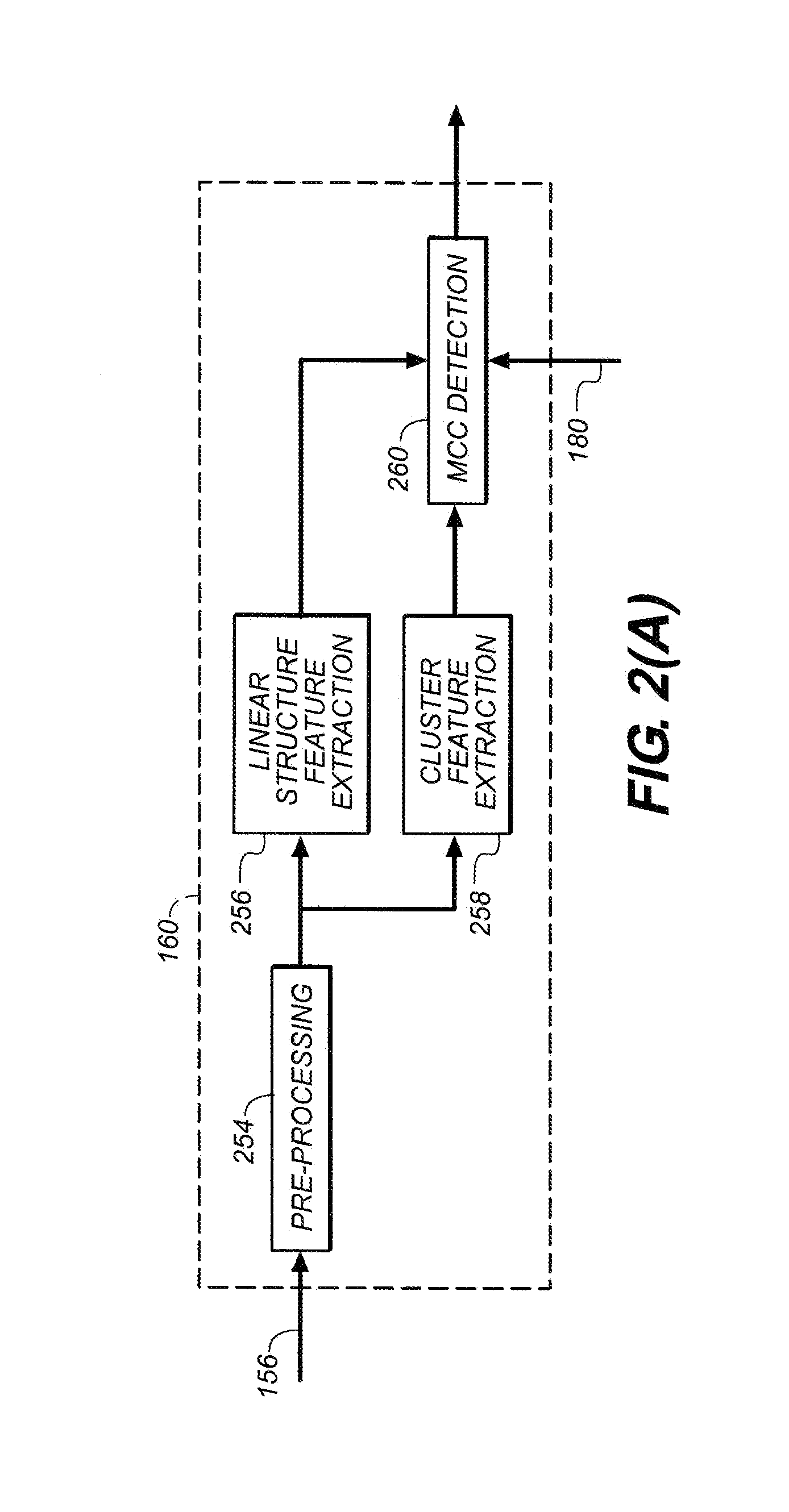
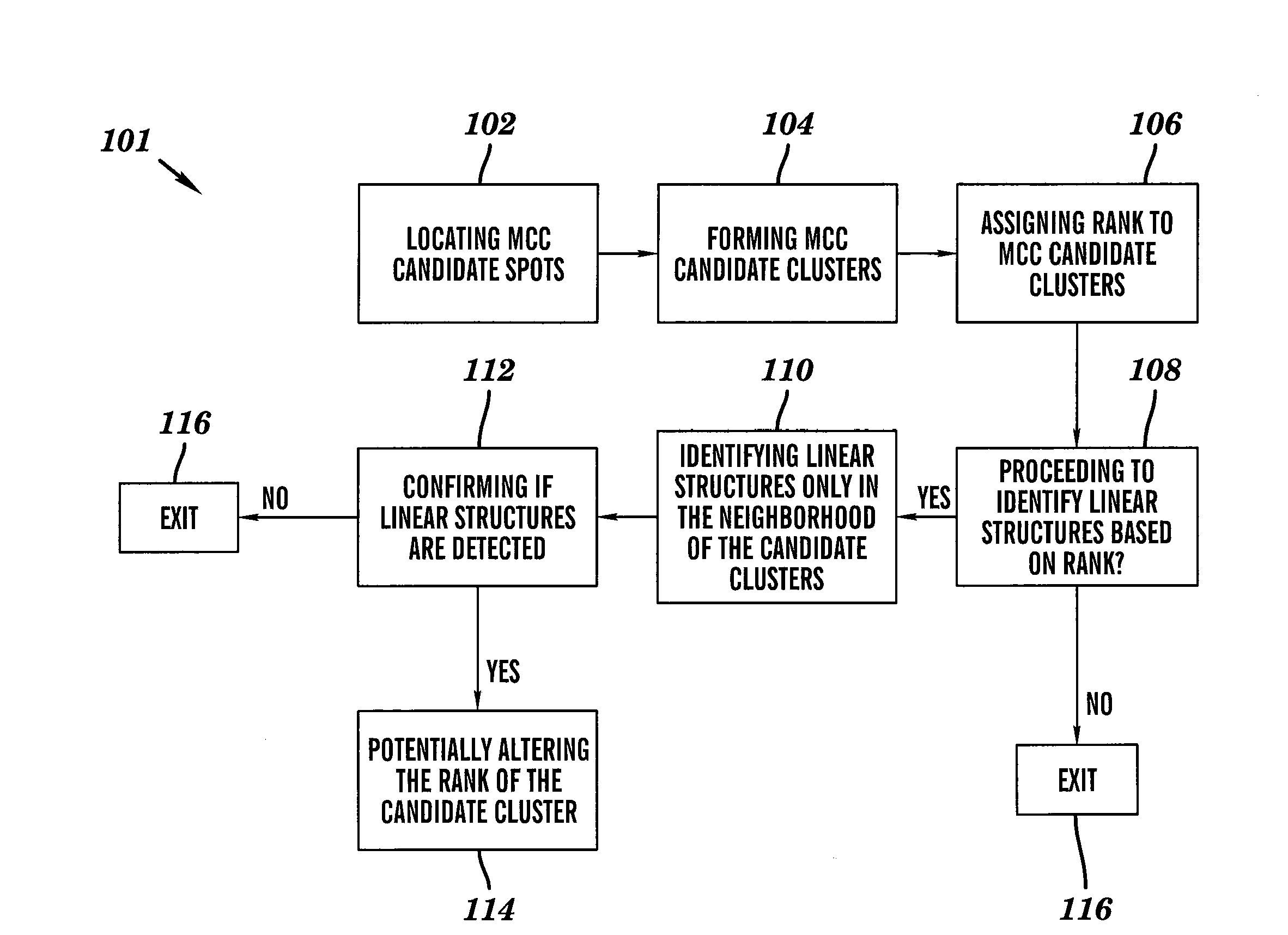
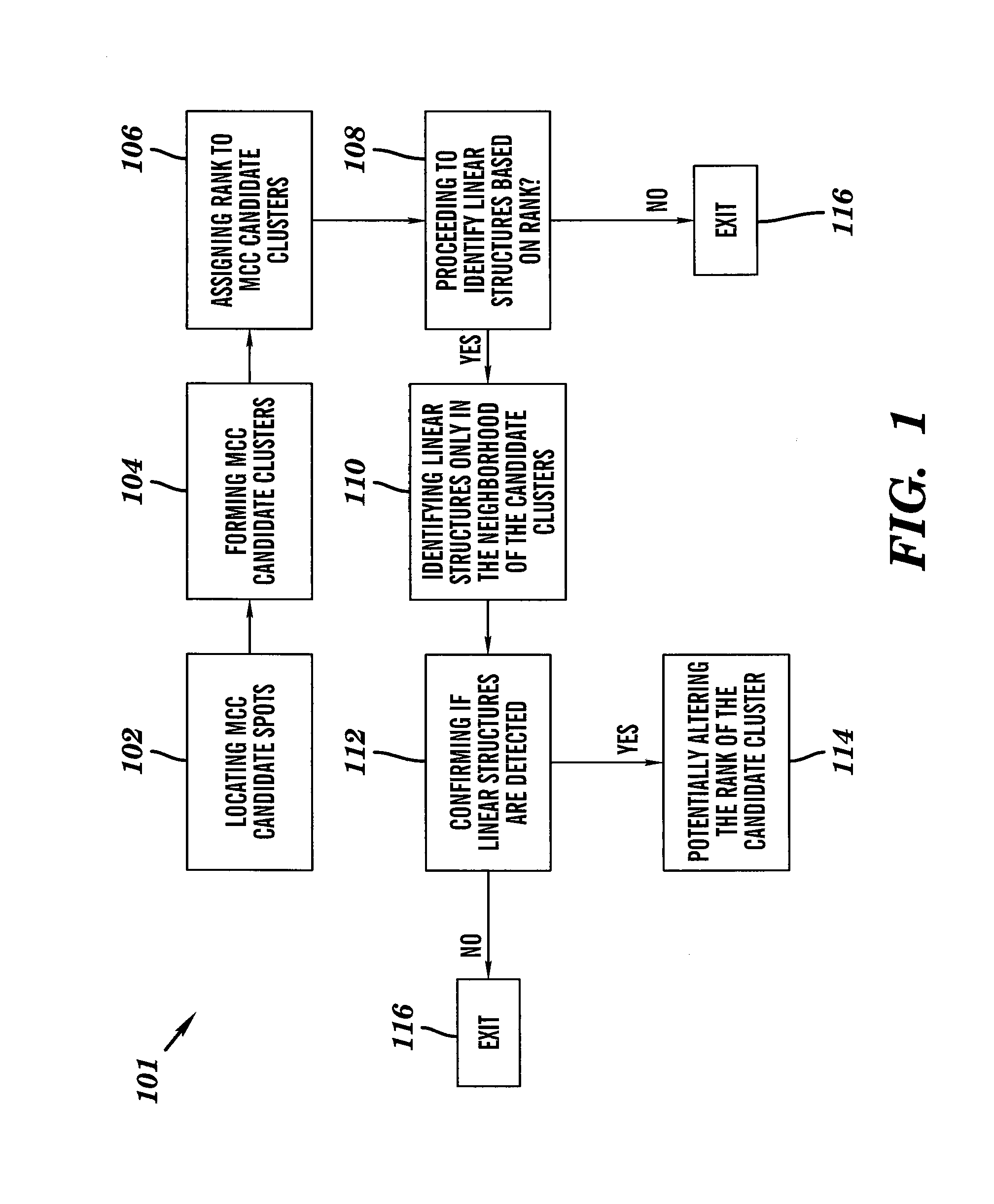
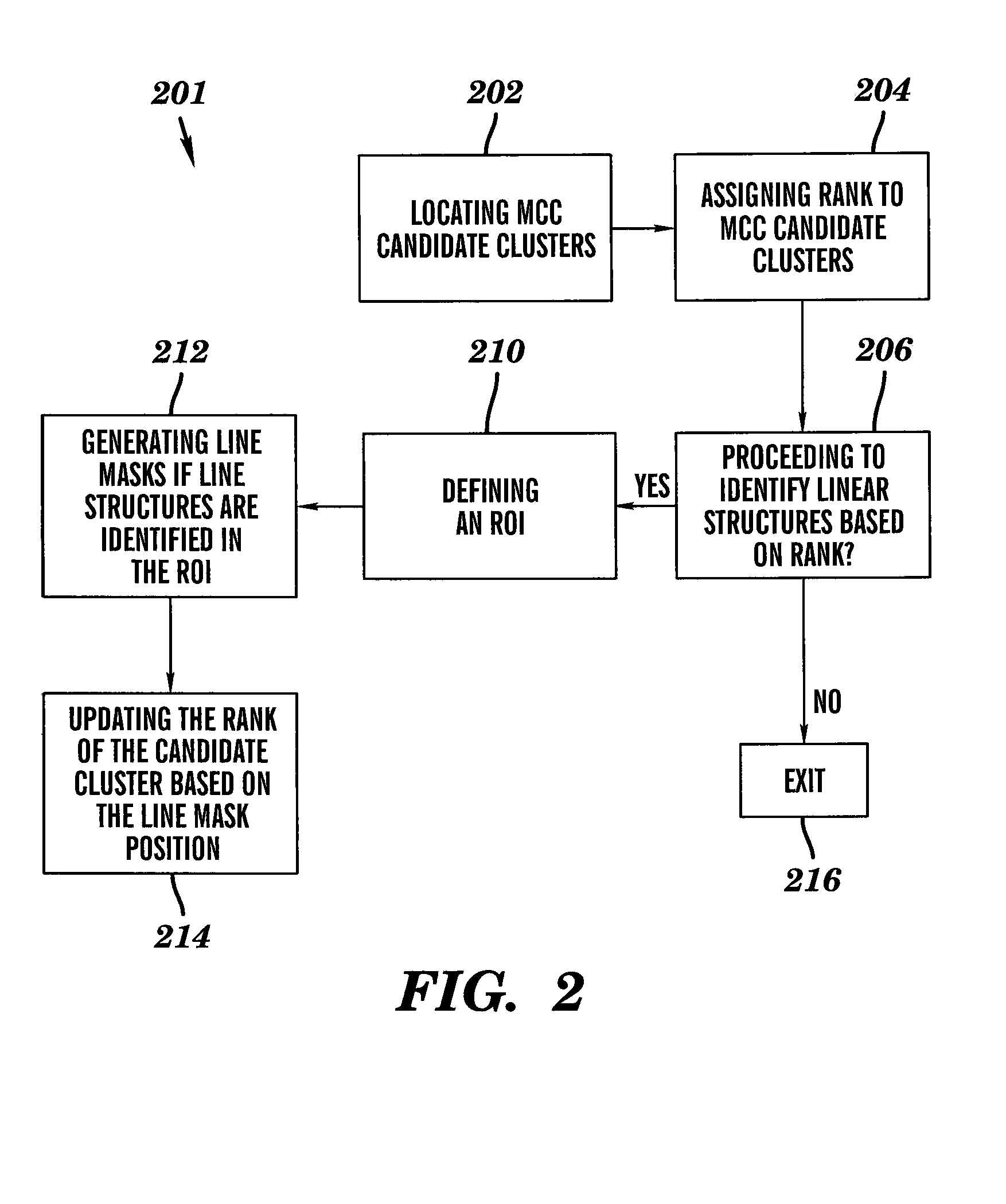
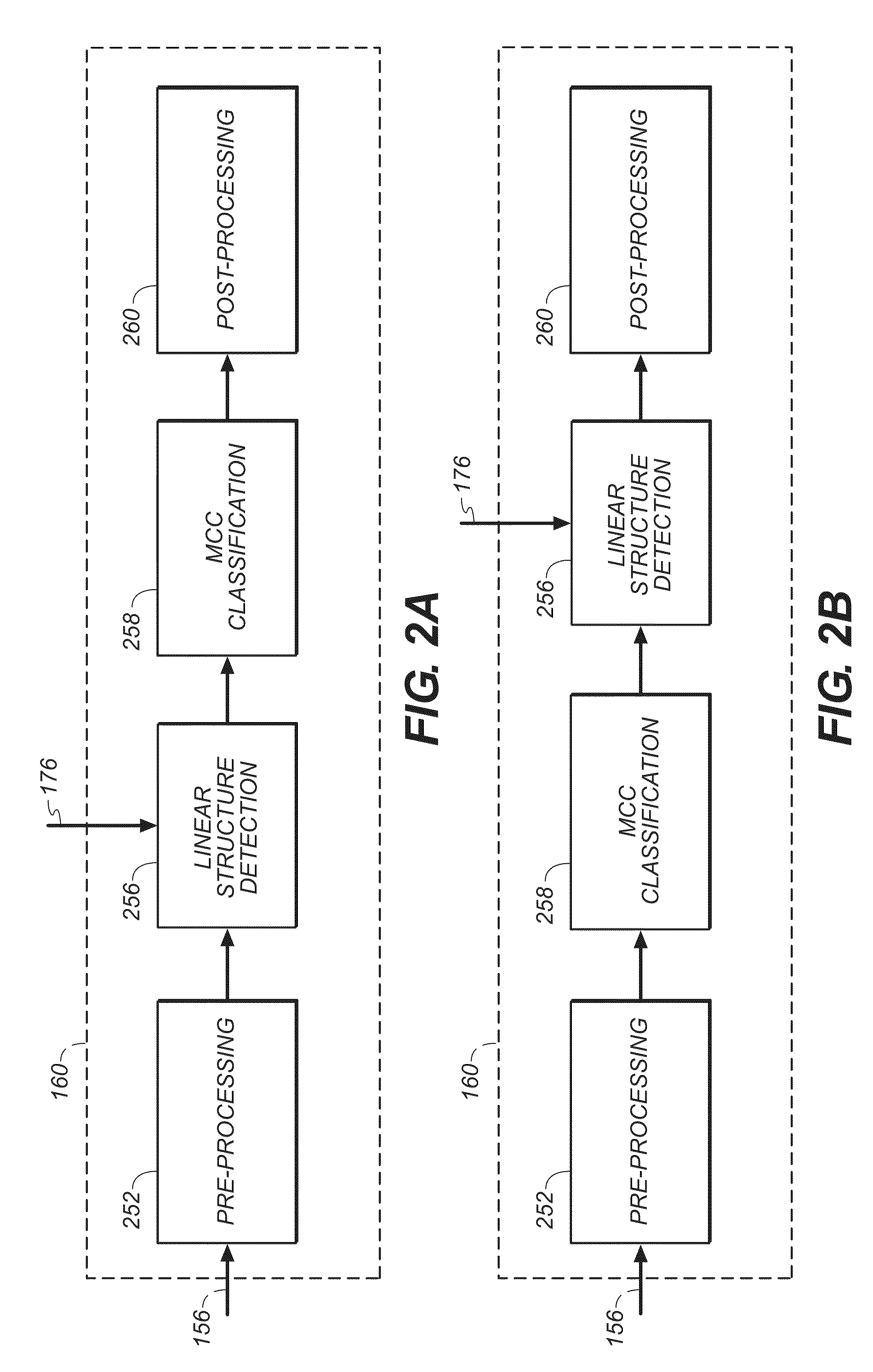
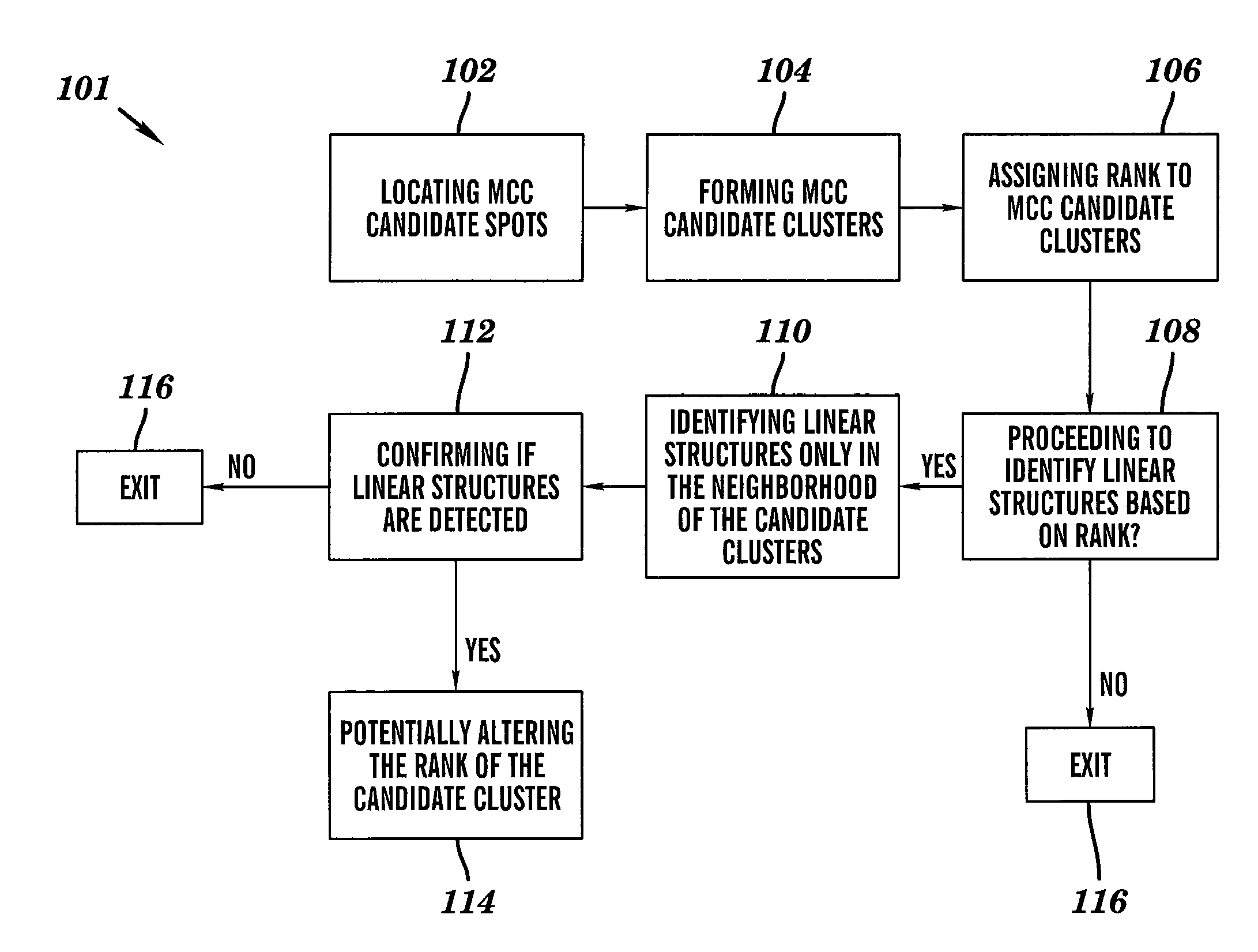
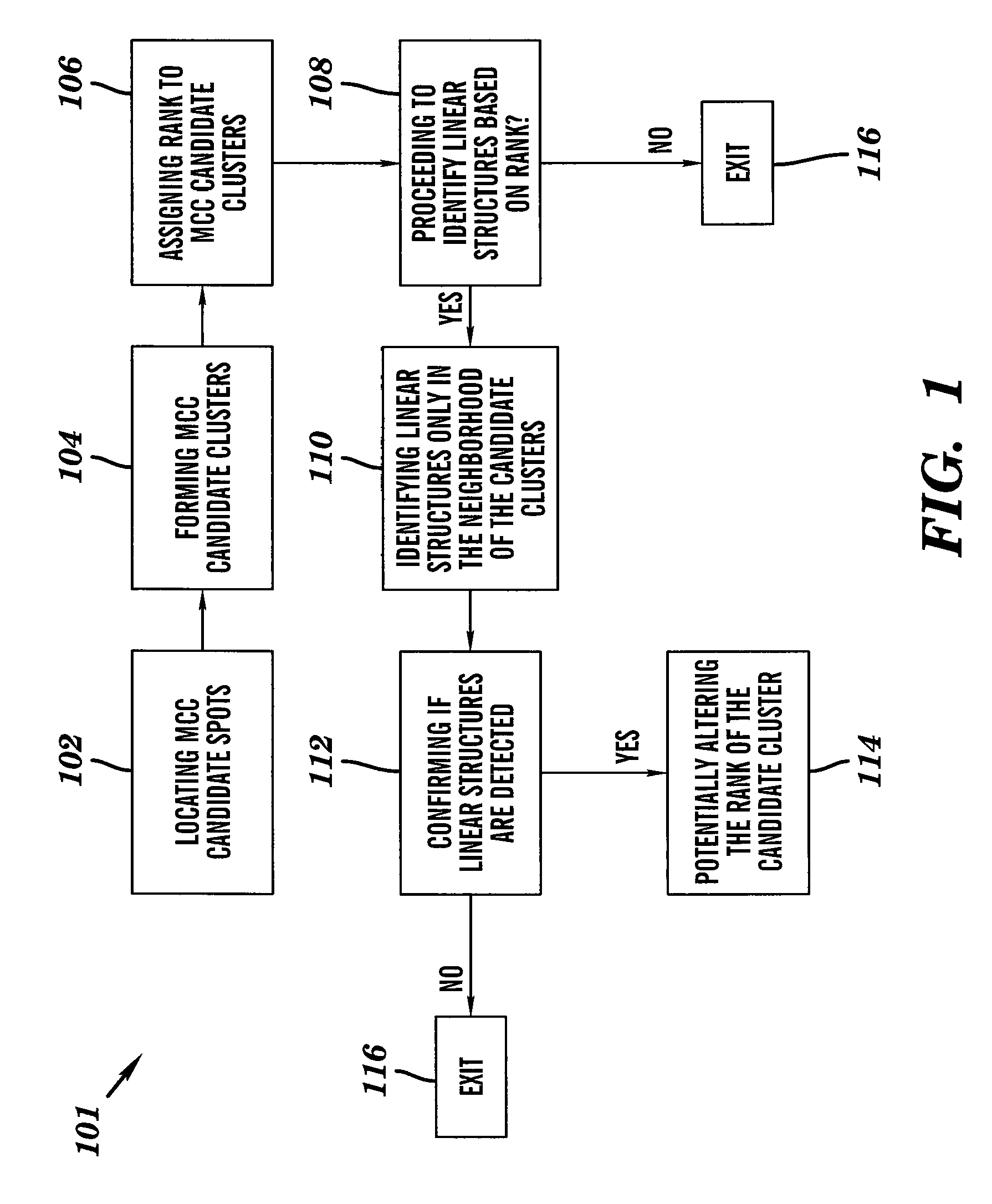
Line structure detection and analysis for mammography cad
A method for image linear structure detection in medical imaging. The method includes locating microcalcification (mcc) candidate spots in a mammographic image; forming candidate clusters; assigning ranks to the candidate clusters; identifying linear structures in the neighborhood where the candidate clusters reside; and altering the ranks of the candidate clusters for which linear structures have been identified in the neighborhood.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
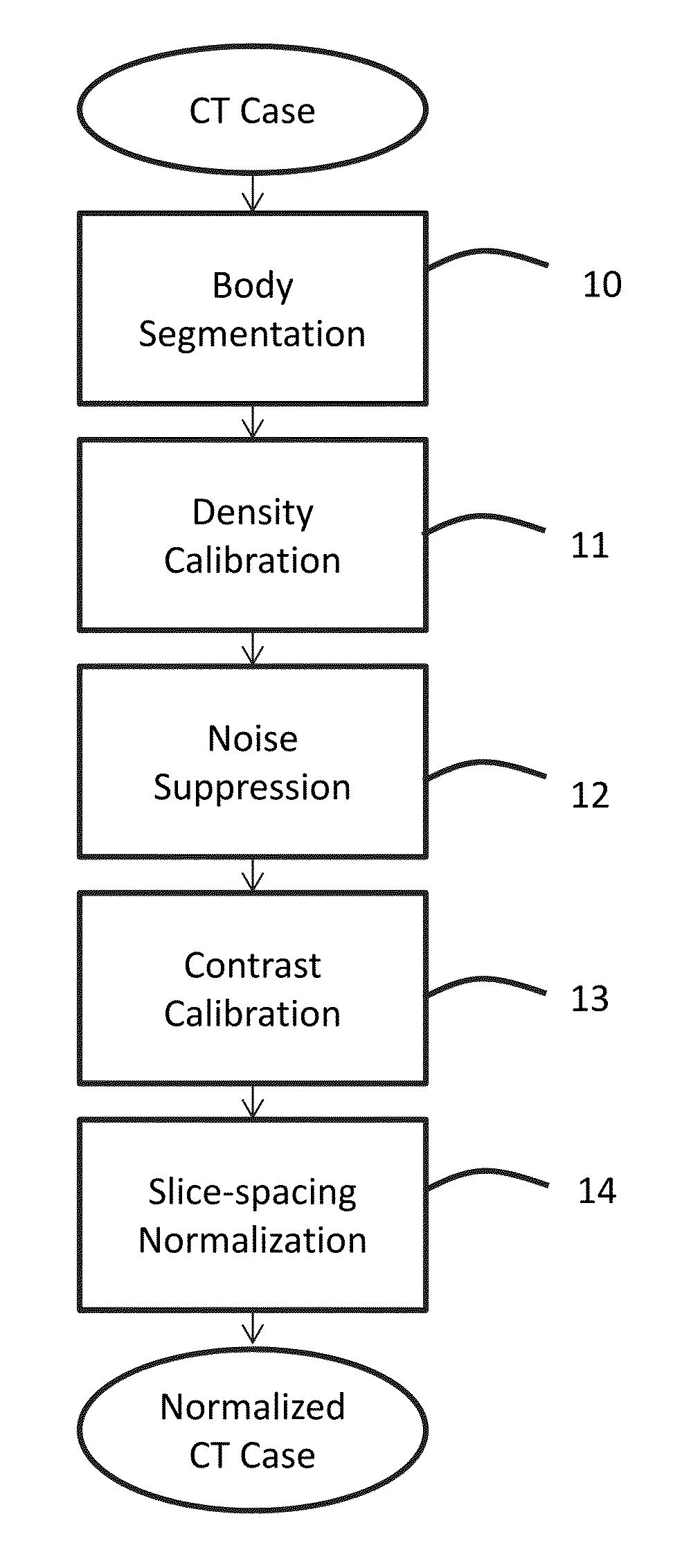
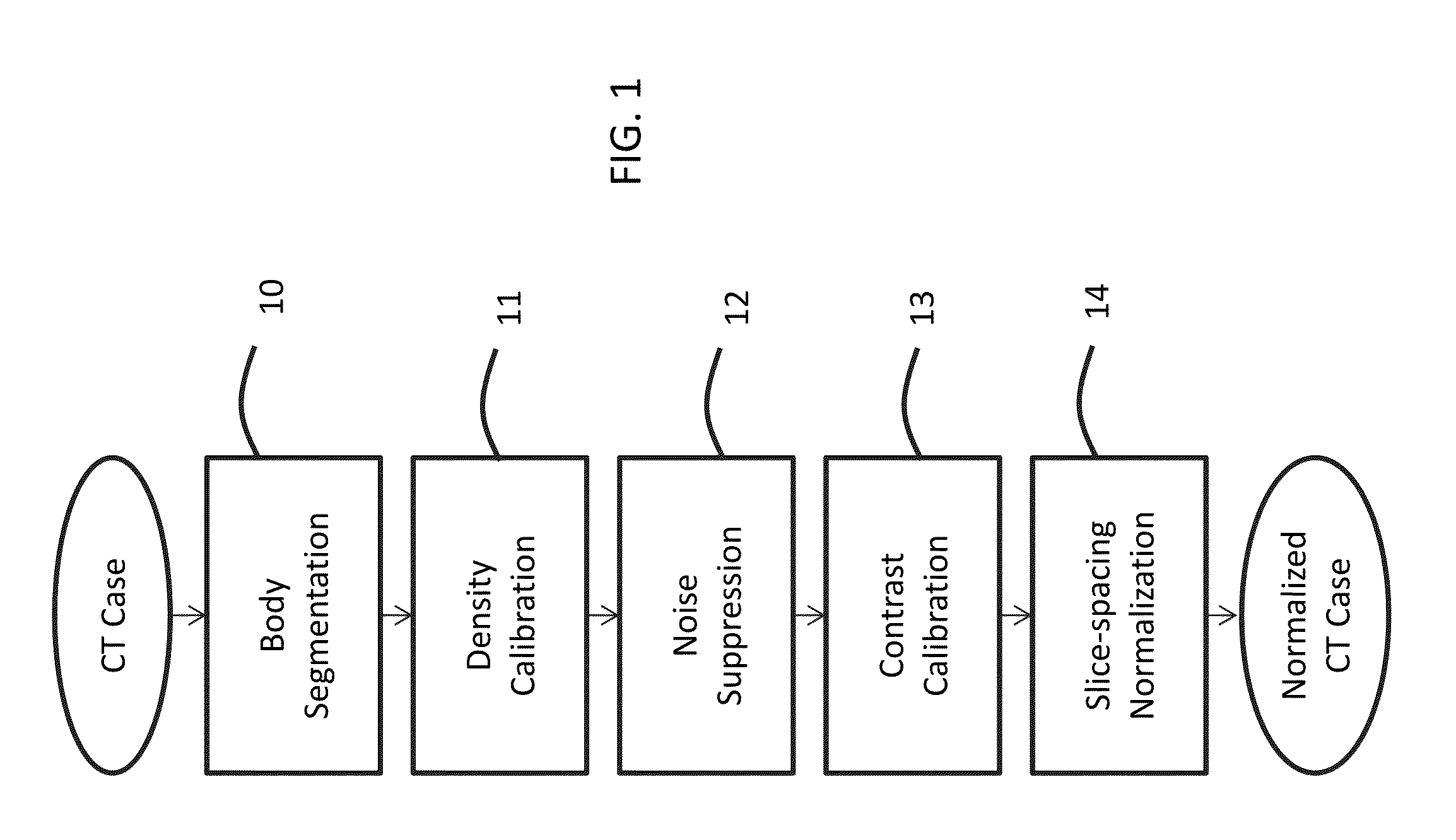
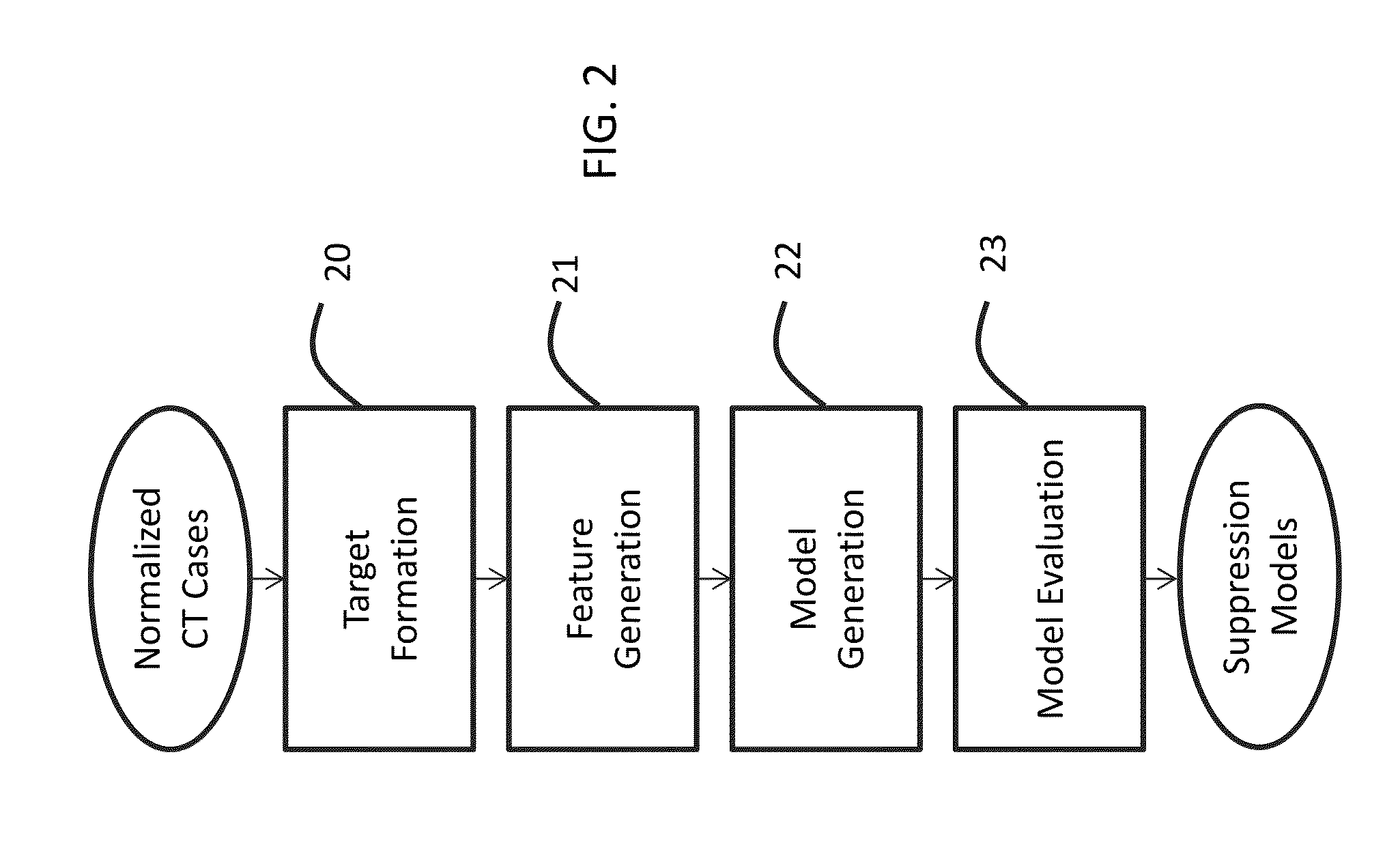
Suppression of vascular structures in images
ActiveUS20150279034A1Easy to detectSuppressing selected non-nodule structuresImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionAnatomical structuresVoxel
Image processing techniques may include a methodology for normalizing medical image and / or voxel data captured under different acquisition protocols and a methodology for suppressing selected anatomical structures from medical image and / or voxel data, which may result in improved detection and / or improved rendering of other anatomical structures. The technology presented here may be used, e.g., for improved nodule detection within computed tomography (CT) scans. While presented here in the context of nodules within the lungs, these techniques may be applicable in other contexts with little modification, for example, the detection of masses and / or microcalcifications in full field mammography or breast tomosynthesis based on the suppression of glandular structures, parenchymal and vascular structures in the breast.
Owner:RIVERAIN TECH
Microcalcification enhancement from digital mammograms
InactiveUS20110222752A1Enhance microcalcificationsImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisComputer-aided
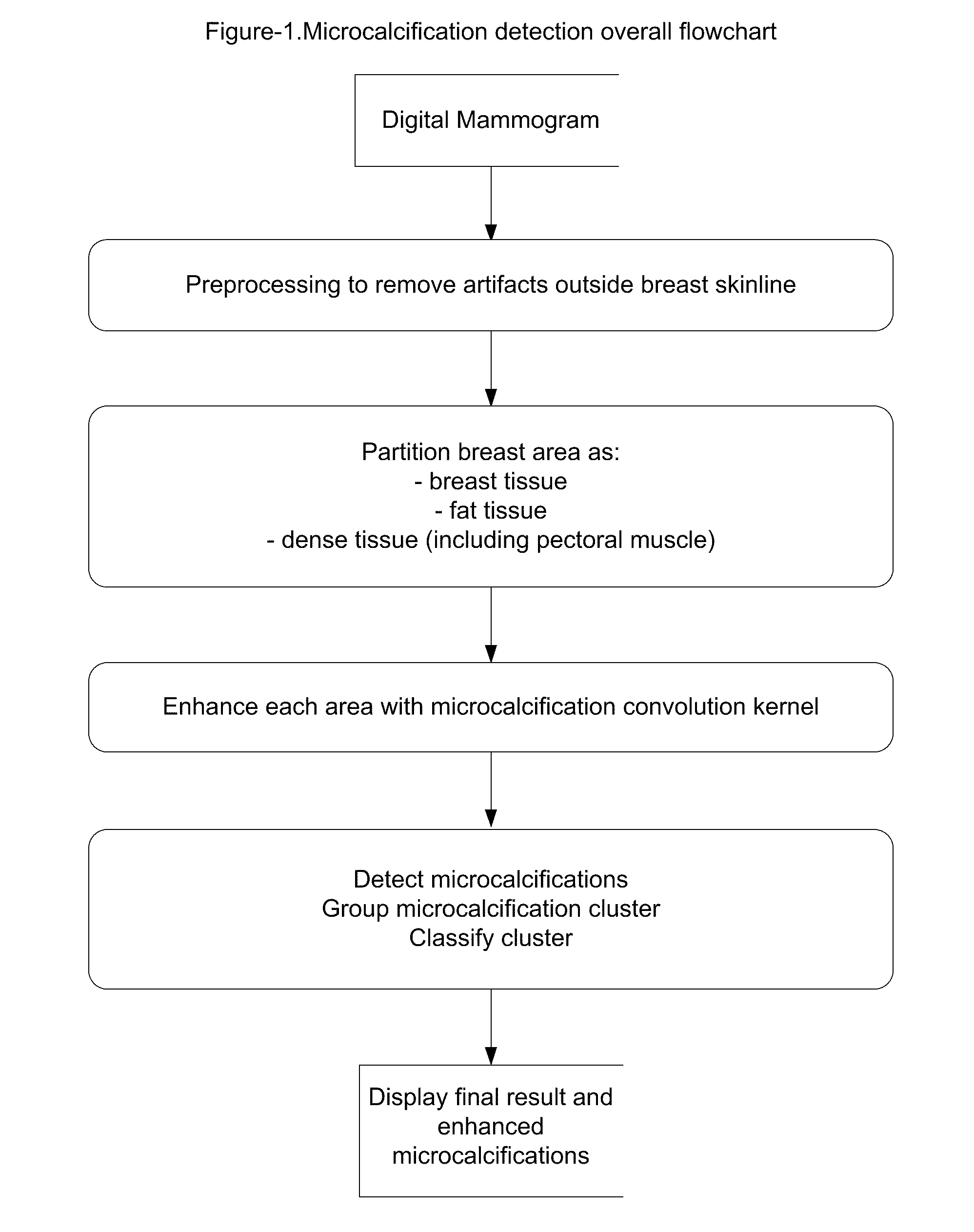
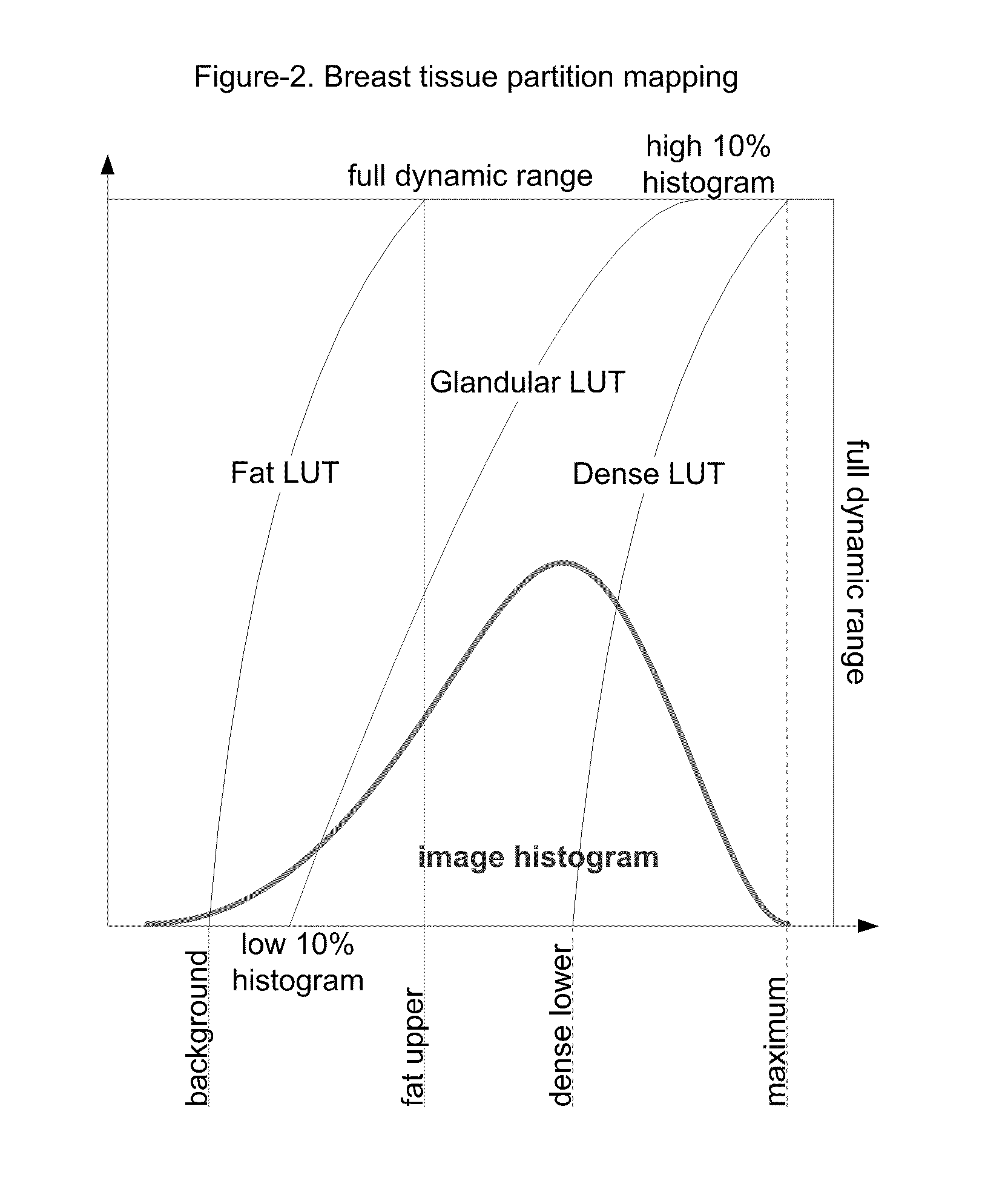
The present invention provides a method for enhancing microcalcifications for computer-aided lesion detection, review and diagnosis. The method includes two steps: partitioning of the breast tissue area and filtering with a convolution kernel. The partitioning process delineates: breast glandular tissue area; fat tissue sub-area and dense tissue sub-area. The 2D or 3D convolution kernels are designed to highlight small spot regions of rapid intensity changes on 2D mammograms or 3D tomosynthesis mammography images. The size of such a kernel is calculated based on the resolution of the mammographic images that are produced from each manufacturer's digital radiography device.
Owner:THREE PALM SOFTWARE
Method for the detection and classification of microcalcification clusters in digital mammograms
InactiveUS20120121159A1Character and pattern recognitionImage analysisPattern recognitionDigital mammogram
A method for the detection and classification of microcalcification clusters in digital mammograms which comprises the following steps: obtaining one or more digital mammograms; pre-processing the one or more digital mammograms by eliminating the noise from each one or more digital mammograms; detecting the points that are potential microcalcifications represented by their centroids, in the one or more pre-processed digital mammograms; identifying each mass center of potential microcalcifications as a microcalcification or non-microcalcification; identifying microcalcification clusters, using an algorithm for locating microcalcification cluster; and classifying each cluster into the classes benign or malignant.
Owner:CAPIO TECH S A DE
Method for detection of linear structures and microcalcifications in mammographic images
A method for detecting a linear structure in a digital mammographic image, using a processor or computer at least in part, locates at least one microcalcification candidate cluster in the image data and extracts a first region of interest that encloses the at least one microcalcification candidate cluster. The first region of interest is processed to identify feature points that correspond to geometric structures in the first region of interest. A linear detection algorithm is applied by a repeated process that selects a line model from a predefined set of line models and analyzes the line model to determine whether a linear structure is present in the first region of interest.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
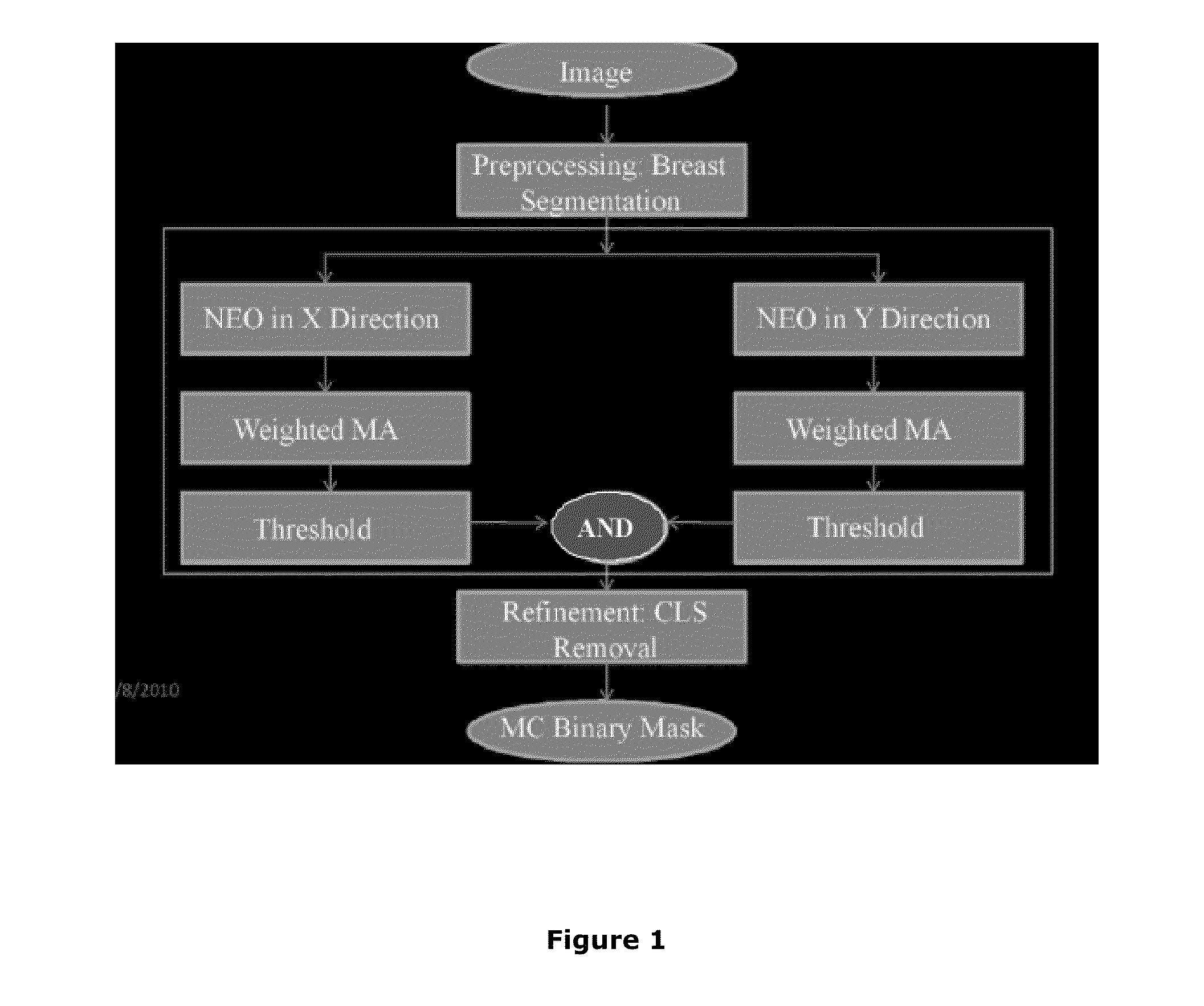
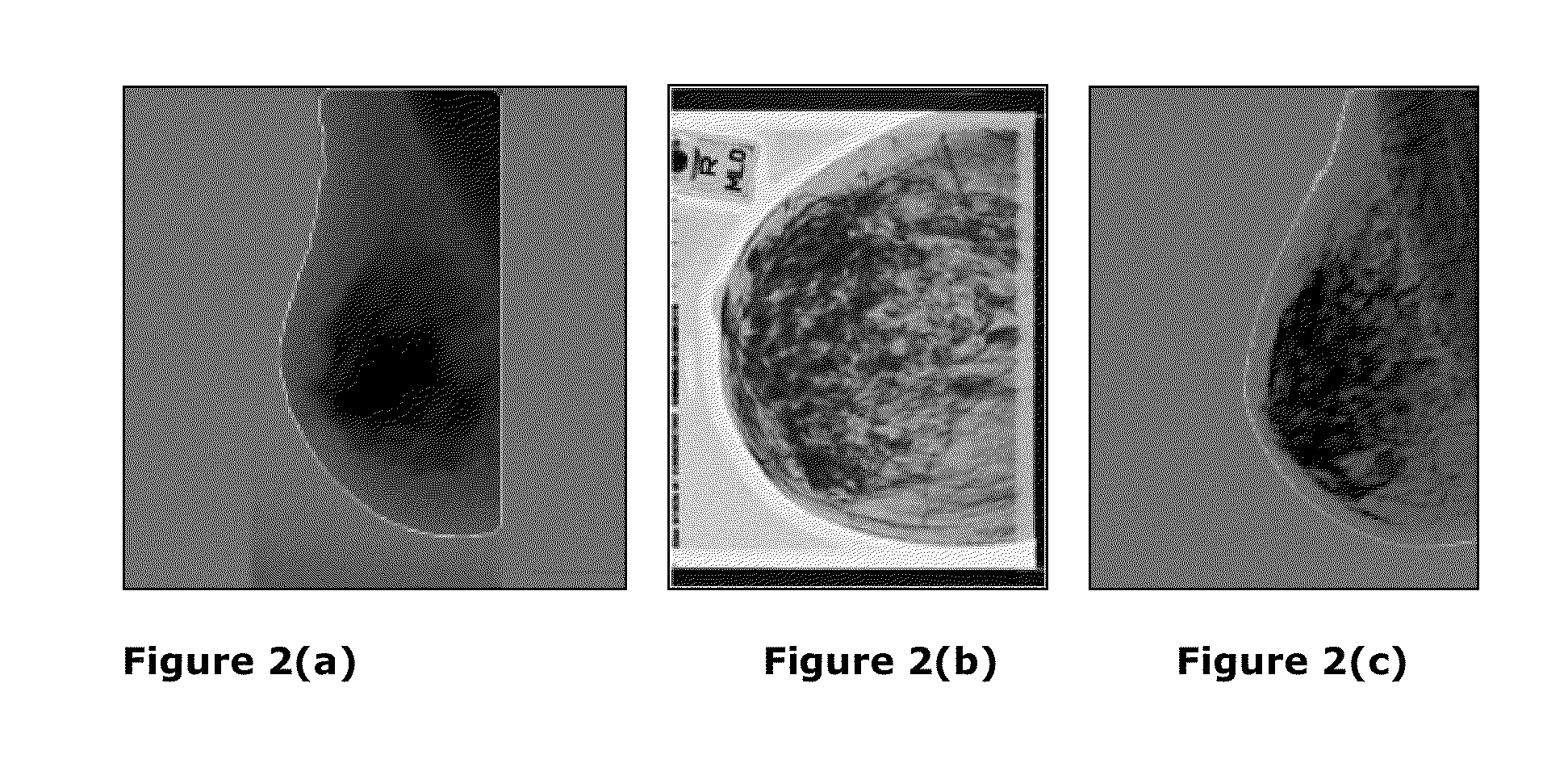
Method and system to detect the microcalcifications in X-ray images using nonlinear energy operator
InactiveUS9305204B2Low costAccurate and reliable detectionImage enhancementImage analysisBreast compositionData set
A method and system to detect the microcalcifications (MC) in different type of images viz. X-ray images / mammograms / computer tomography with varied densities using nonlinear energy operator (NEO) is disclosed to favor precise detection of early breast cancer. Such Microcalcifications are associated with both high intensity and high frequency content. The same NEO output is useful to detect and remove the irrelevant curvilinear structures (CLS) thereby helps in reducing the false alarms in micro calcification detection technique. This is effective on different dataset (scanned film, mammograms with large spatial resolution such as CR and DR) of varied breast composition (viz. dense, fatty glandular, fatty), demonstrated quantitatively by Free-response receiver operating characteristic (FROC). Importantly, the method and apparatus of the invention can be used in conjunction with machine learning techniques viz. SVM to favor detection of incipient or small microcalcifications, thus benefiting radiologists in confirming detection of micro-calcifications in X-rays images / mammograms and reducing death rates.
Owner:INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYKHARAGPUR
Methods for microcalcification detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
ActiveUS8977019B2Reduce in quantityImprove visibilityImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisVoxel
A computer-aided detection system to detect clustered microcalcifications in digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is disclosed. The system performs detection in 2D images and a reconstructed 3D volume. The system may include an initial prescreening of potential microcalcifications by using one or more 3D calcification response function (CRF) values modulated by an enhancement method to identify high response locations in the DBT volume as potential signals. Microcalcifications may be enhanced using a Multi-Channel Enhancement method. Locations detected using these methods can be identified and the potential microcalcifications may be extracted. The system may include object segmentation that uses region growing guided by the enhancement-modulated CRF values, gray level voxel values relative to a local background level, or the original DBT voxel values. False positives may be reduced by descriptors of characteristics of microcalcifications. Detected locations of clusters and a cluster significance rating of each cluster may be output and displayed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Converting low-dose to higher dose mammographic images through machine-learning processes
A method and system for converting low-dose mammographic images with much noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like mammographic images, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme, which can be called a call pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input mammogram acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of mammograms, inputting low-dose mammograms together with corresponding desired standard x-ray radiation dose mammograms (higher-dose), which are ideal images for the output images. Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose mammograms to high-dose-like mammograms. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose mammograms anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) mammogram is entered, the trained PTNR would output a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it would output high-dose-like mammograms or “virtual high-dose” mammograms where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. With the “virtual high-dose” mammograms, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
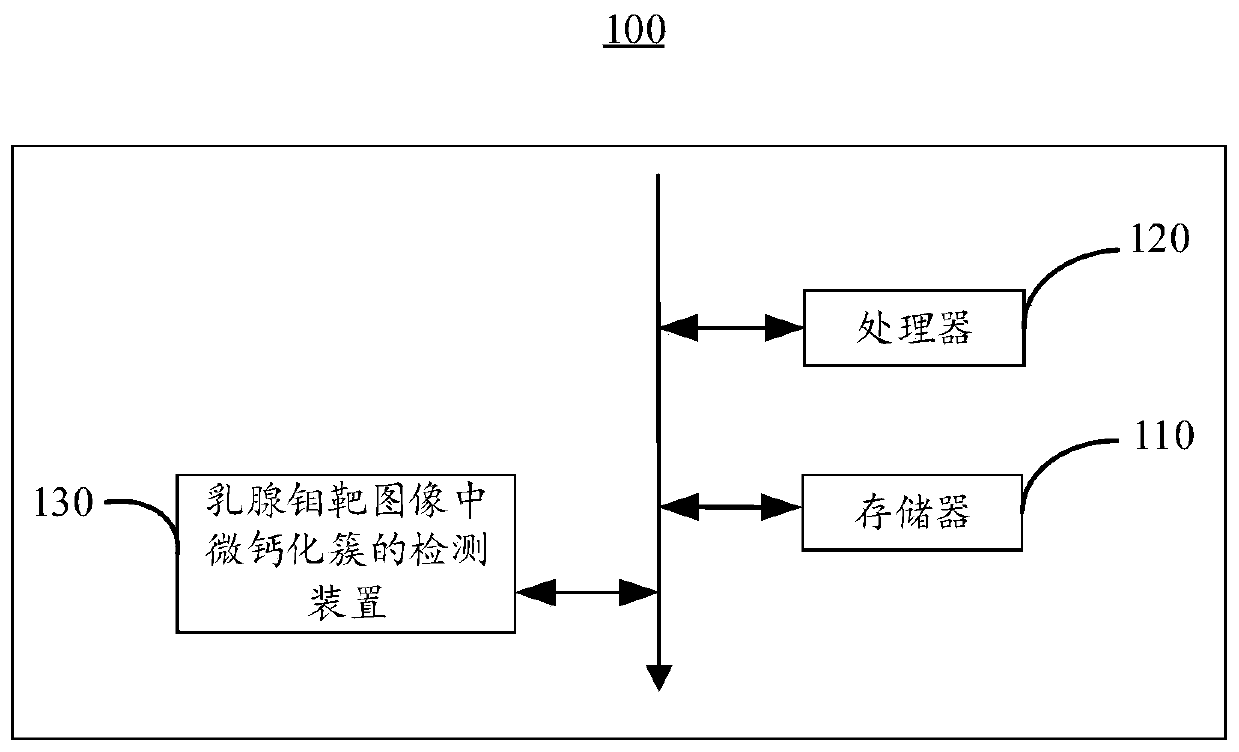
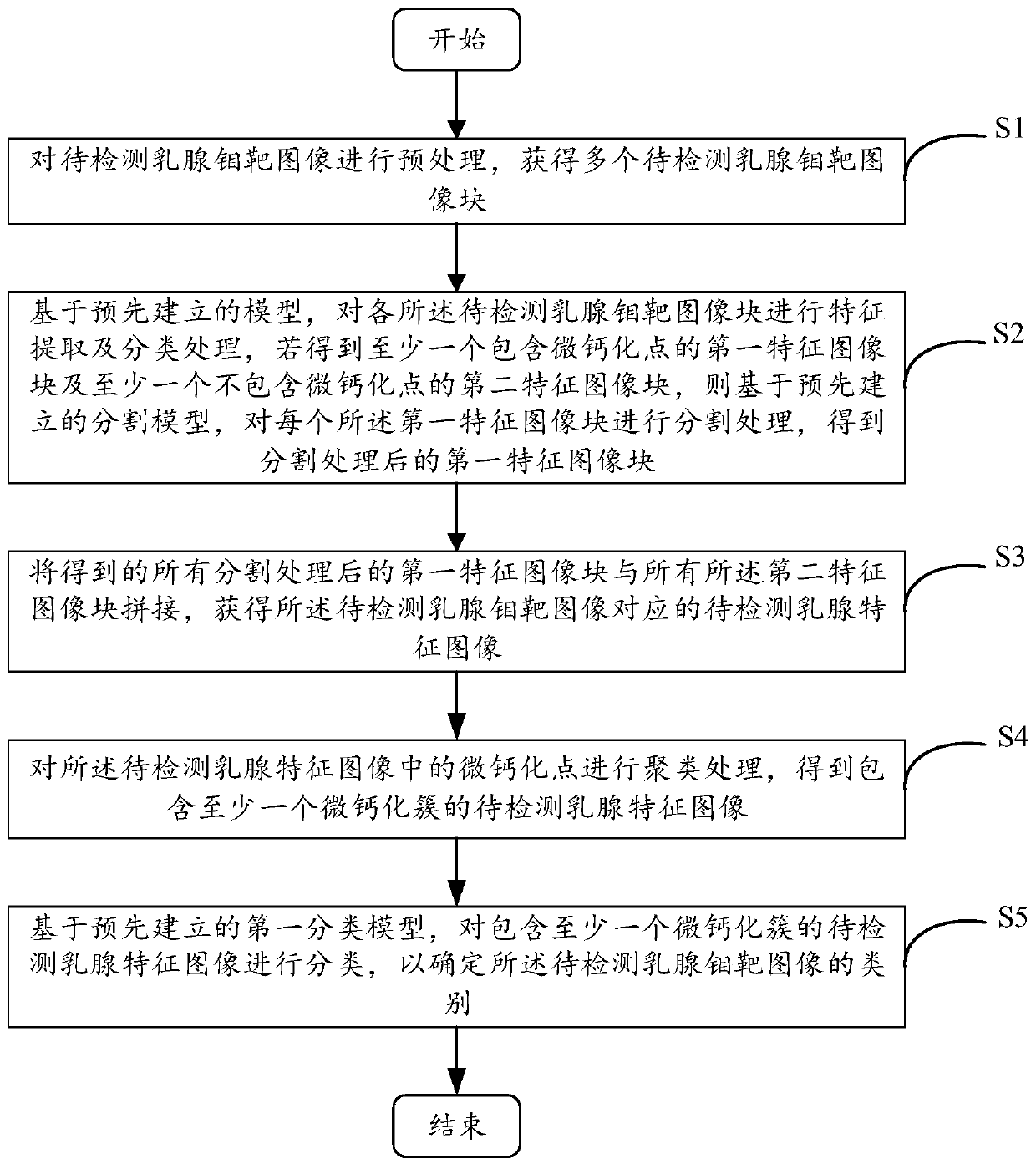
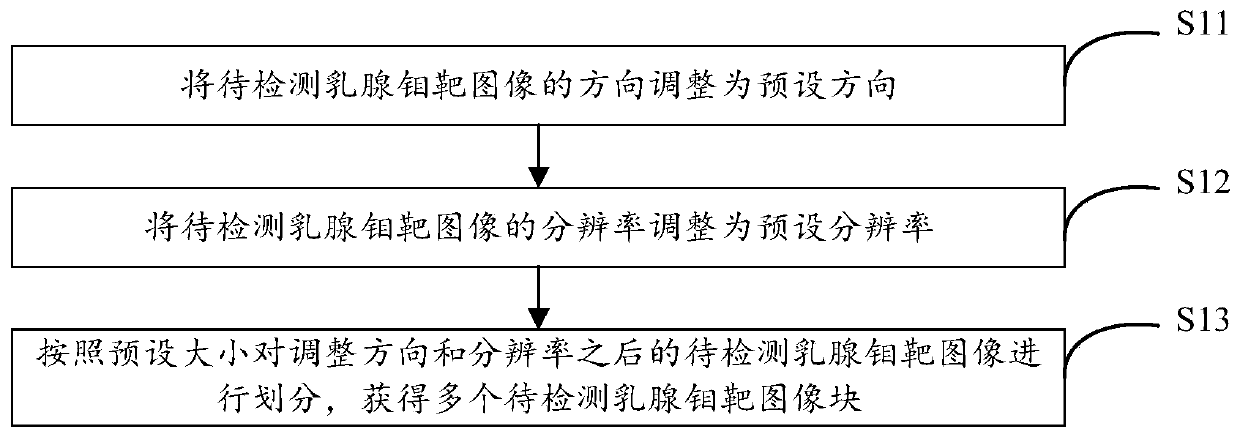
Method and device for detecting micro-calcification clusters in mammary gland molybdenum target image and electronic equipment
PendingCN111325266AIncrease the proportionReduce difficultyGeometric image transformationRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsFeature extractionCalcification cluster
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and device for detecting a micro-calcification cluster in a mammary gland molybdenum target image and electronic equipment, and relates to the technical field of medical images. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, partitioning a to-be-detected mammary gland molybdenum target image; after a plurality of to-be-detected mammary gland molybdenum target image blocks are obtained, feature extraction is carried out on the to-be-detected mammary gland molybdenum target image blocks; carrying out segmentation processing on the first feature image blocks containing the micro-calcification points; splicing the segmented first feature image blocks and the second feature image blocks which do not contain the micro-calcification points into a complete image; and finally, carrying out clustering processing on the micro-calcification points. According to the method, the micro-calcification clusters are obtained, and the to-be-detected mammary gland feature image containing at least one micro-calcification cluster is classified based on the pre-established classification model to determine the category of the to-be-detected mammary gland molybdenum target image, so that the image proportion of micro-calcification is improved, the difficulty of micro-calcification point segmentation is reduced, and the accuracy of subsequent analysis is improved.
Owner:HUIYING MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Line structure detection and analysis for mammography CAD
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Method for detection of linear structures and microcalcifications in mammographic images
InactiveUS20110142323A1Reducing MCC FPsImage enhancementImage analysisMicrocalcificationImaging data
A method for detecting a linear structure in a digital mammographic image, using a processor or computer at least in part, locates at least one microcalcification candidate cluster in the image data and extracts a first region of interest that encloses the at least one microcalcification candidate cluster. The first region of interest is processed to identify feature points that correspond to geometric structures in the first region of interest. A linear detection algorithm is applied by a repeated process that selects a line model from a predefined set of line models and analyzes the line model to determine whether a linear structure is present in the first region of interest.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
System and method for in vivo imaging of blood vessel walls to detect microcalcifications
InactiveUS20080091105A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using spectroscopyImage resolutionMicrometer
A system includes an in vivo imaging device for imaging a blood vessel with a resolution level of at least fifty micrometers. The in vivo imaging device is capable of detecting a microcalcification in a fibrous cap of an atheroma. The system also includes a processor for receiving an image of the blood vessel from the in vivo imaging device. The processor uses the image to determine whether the blood vessel contains at least one microcalcification within the fibrous cap. In some embodiments, the processor is configured and arranged to predict a risk of rupture of the fibrous cap based, at least in part, on the presence of the at least one microcalcification. In some embodiments, treatment of a patient is based on the determination from the imaging whether the blood vessel includes at least one microcalcification within the fibrous cap of the atheroma.
Owner:COLUMBIA UNIV (US) +1
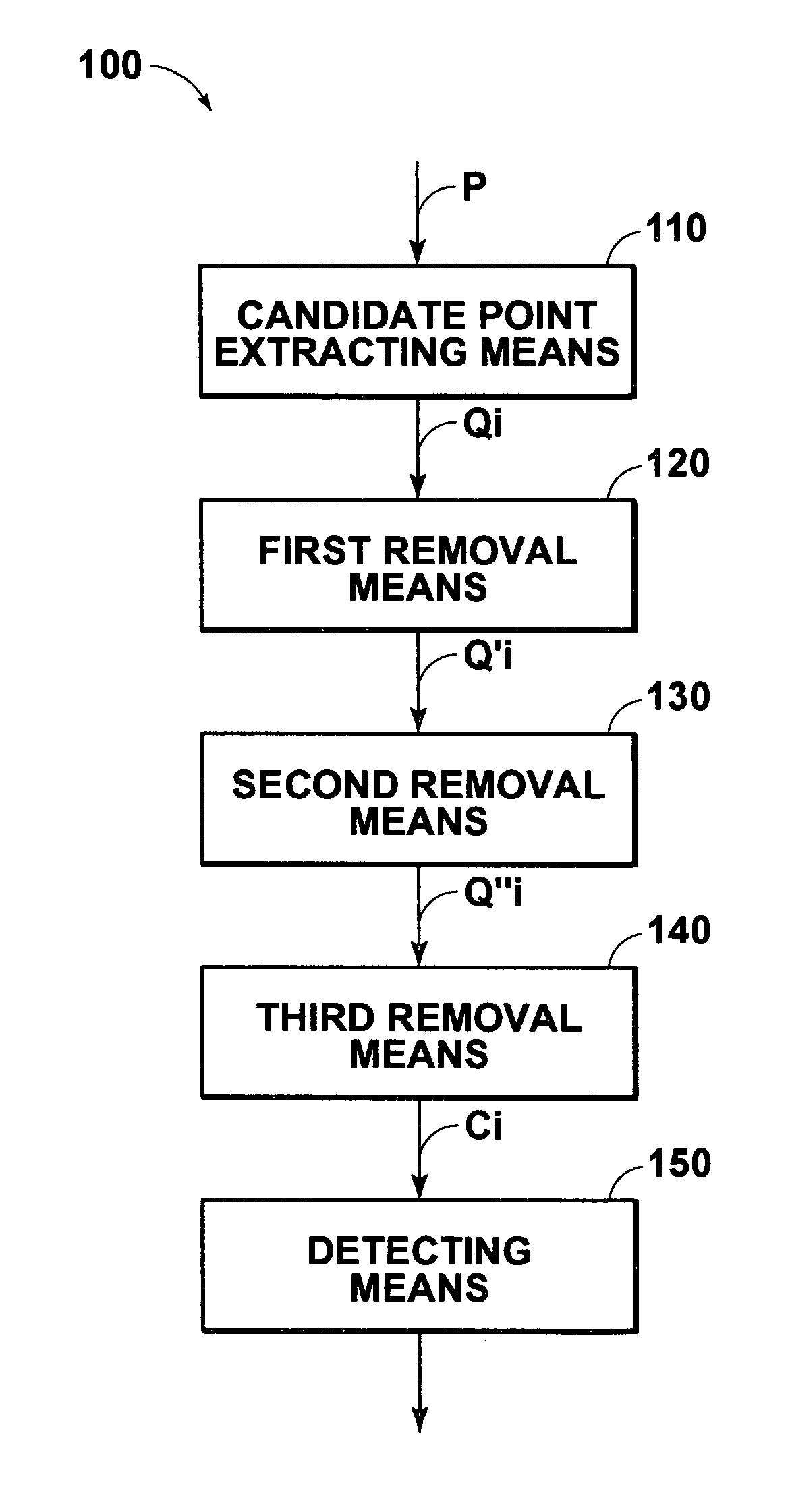
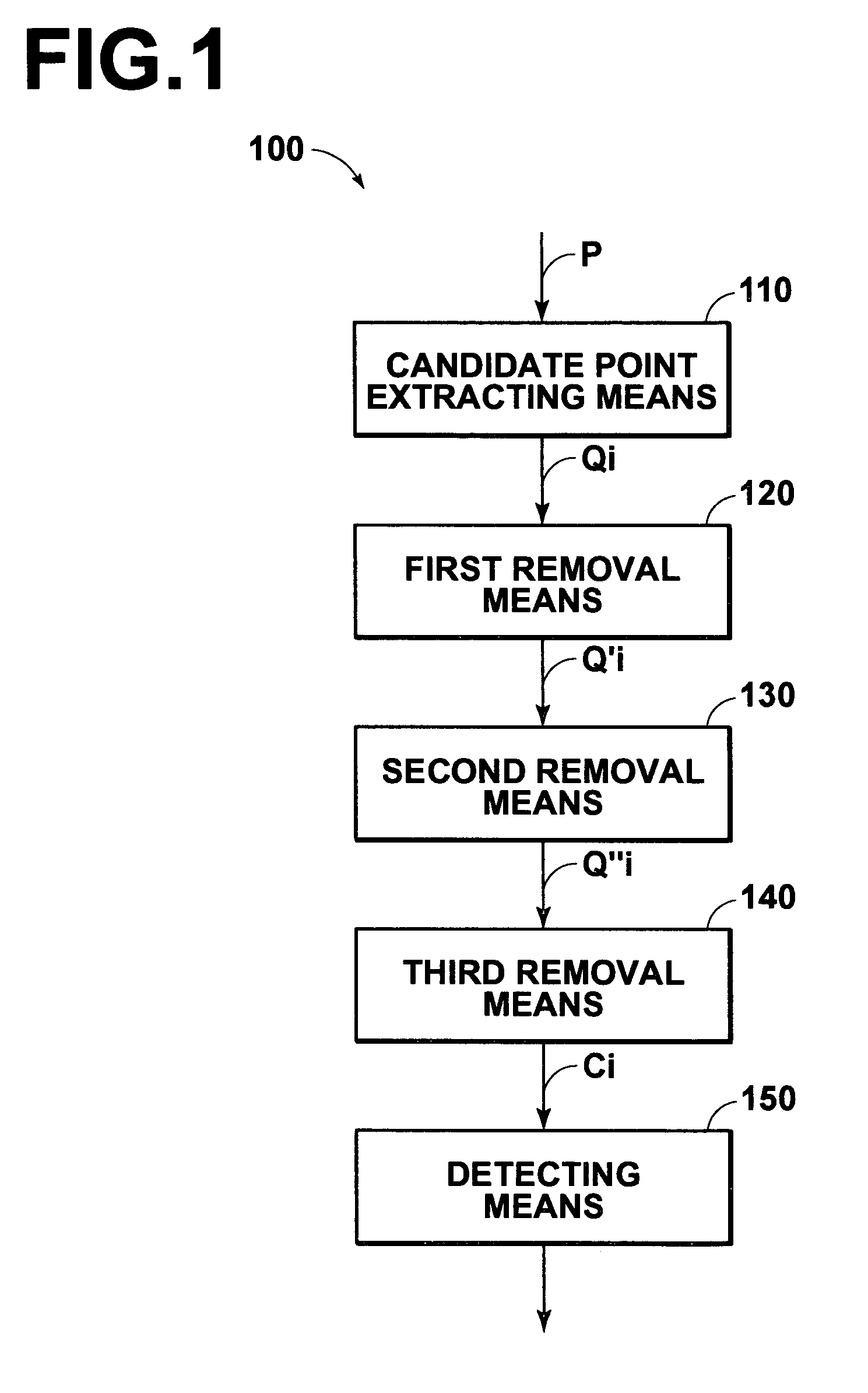
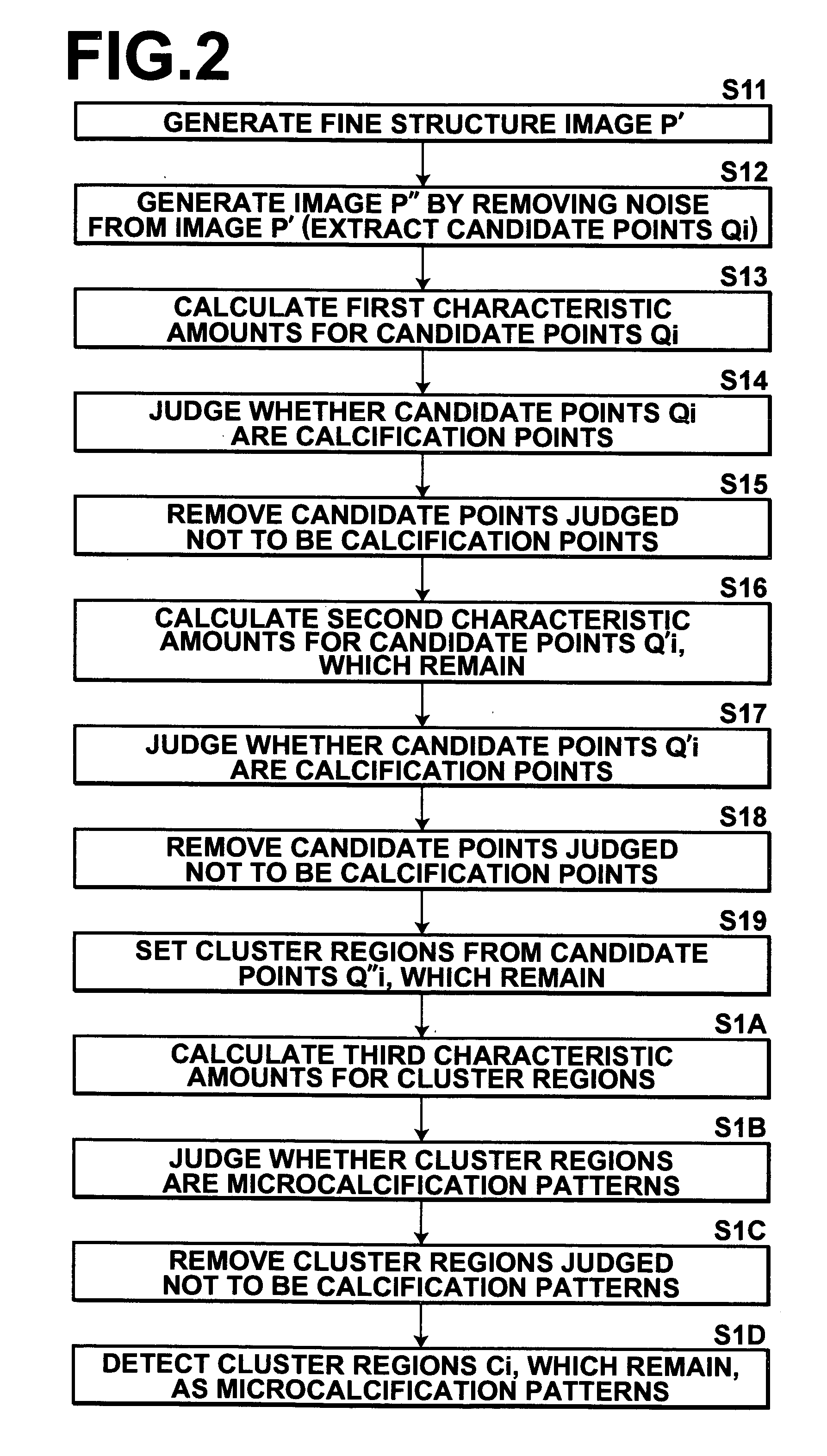
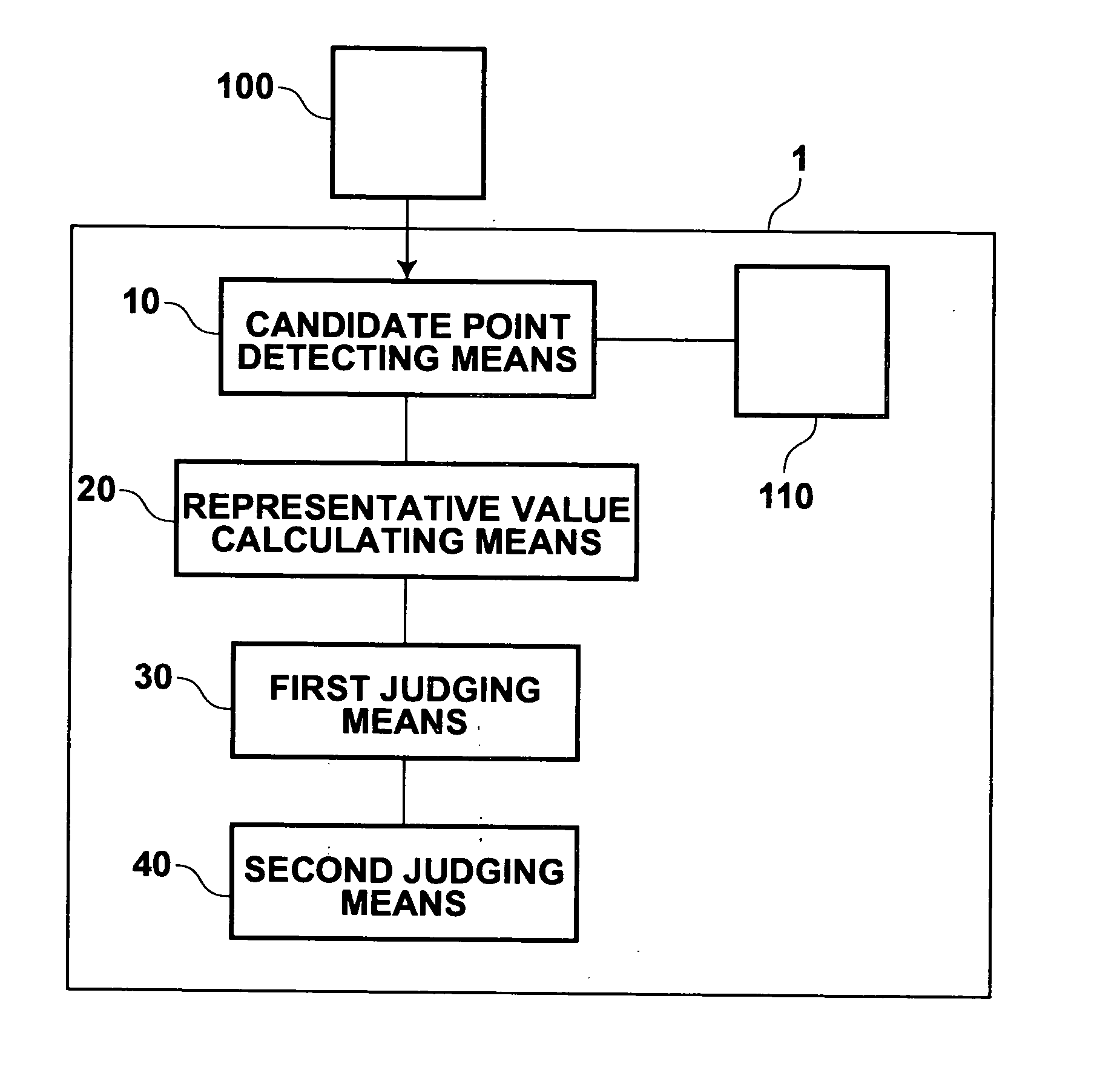
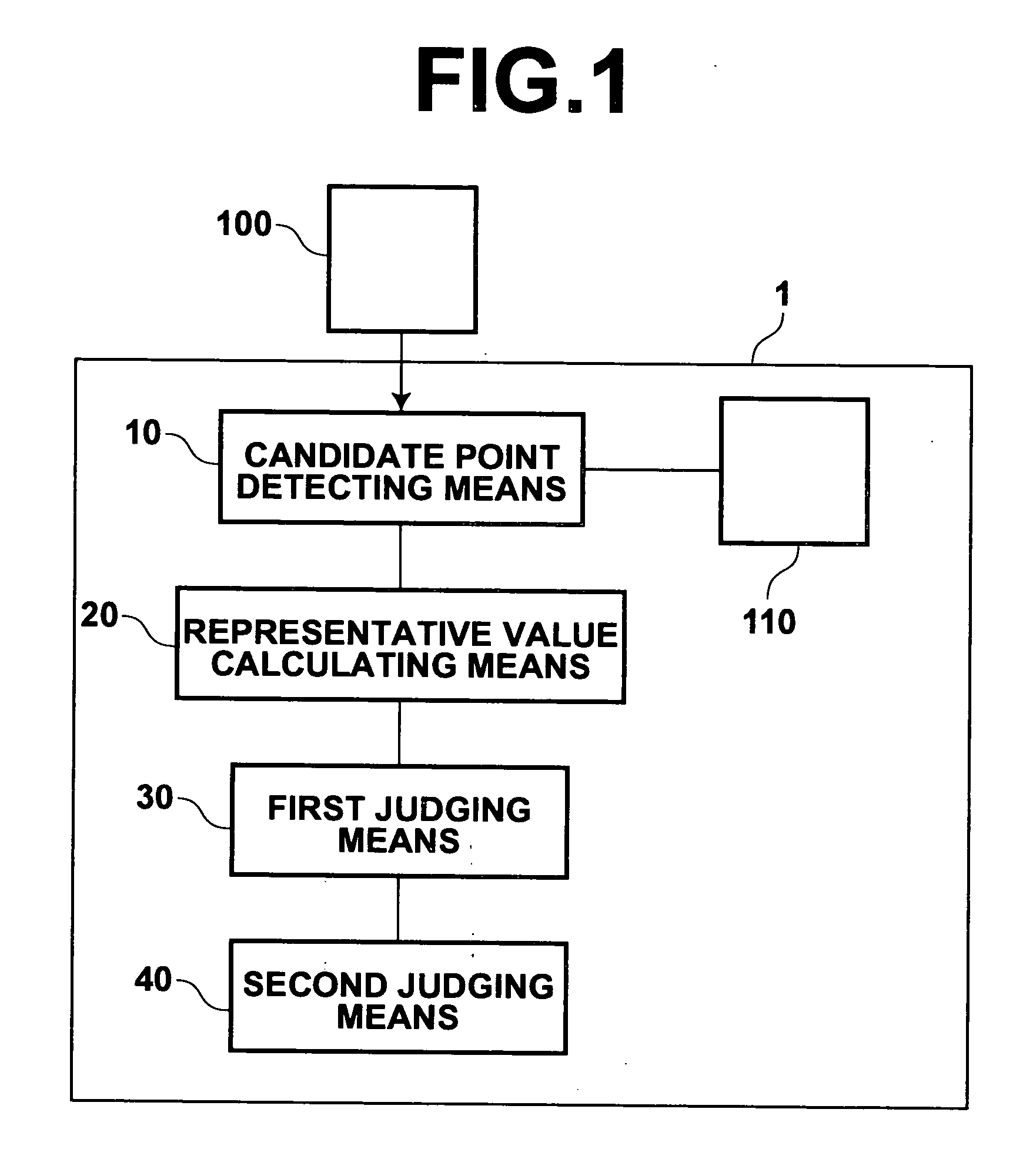
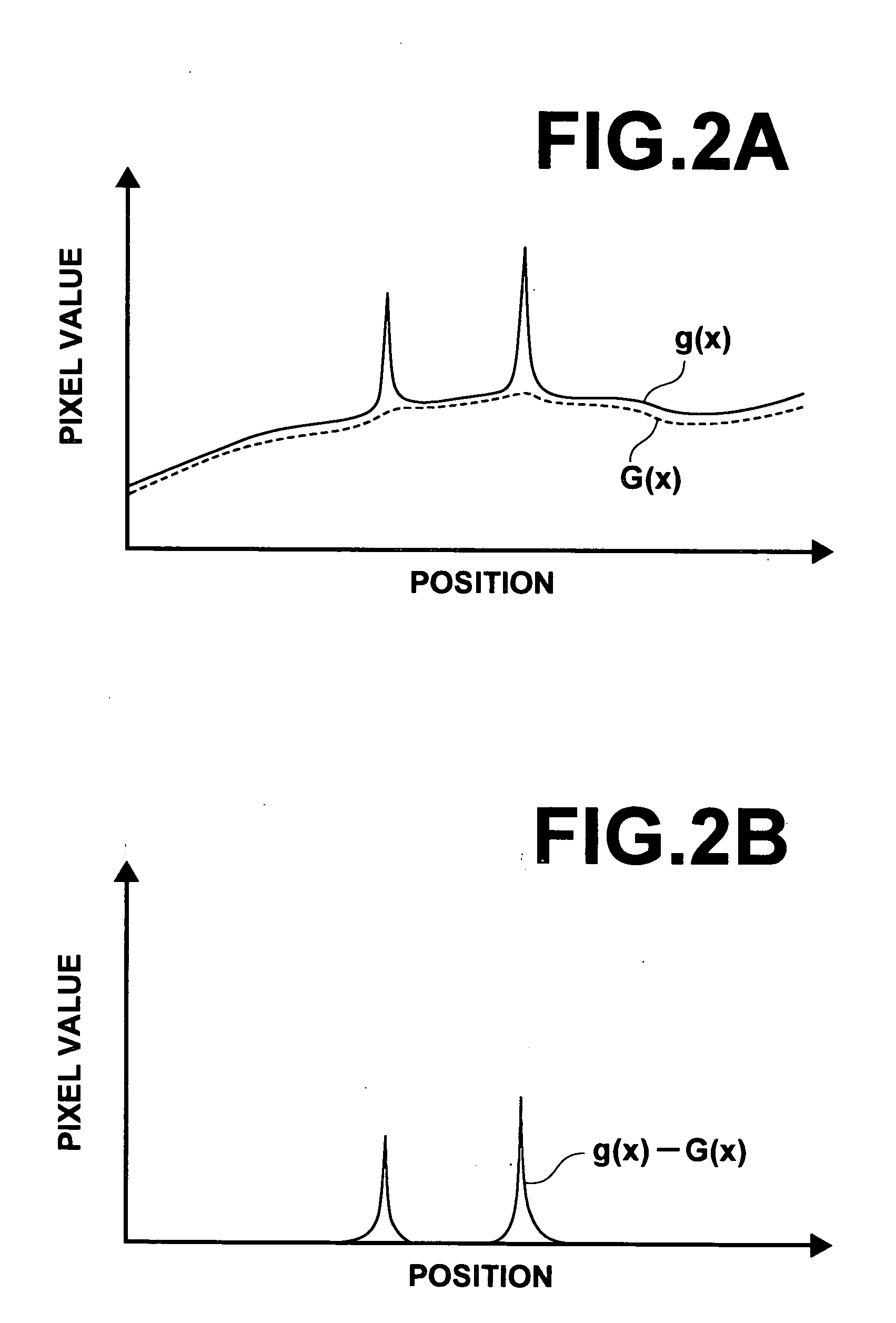
Method, apparatus, and program for detecting abnormal patterns
InactiveUS20050036669A1Improve accuracyEfficient removalImage enhancementImage analysisCalcificationMicrocalcification
Microcalcification patterns within images are more accurately detected. A candidate point extracting means extracts candidate points for calcification points from an image. A first removal means performs judgment regarding whether the candidate points are calcification points or noise, based on first characteristic amounts that focus on the calcification points themselves, and based on second characteristic amounts that focus on the vicinities of calcification points. Candidate points which are judged to be noise components are removed. A second removal means performs judgment regarding whether the candidate points, which remain after the removal process by the first removal means, are calcification points or noise, based on third characteristic amounts that focus on cluster regions of calcification points. Cluster regions formed of noise components are removed, and a detecting means 240 detects the remaining cluster regions as microcalcification patterns.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +2
Method and System for Enhancing Contrast of Spatially-Localized Phenomena in Mammography Image
ActiveUS20110123089A1Increase contrastContrastImage enhancementImage analysisMultiscale decompositionComputer vision
In a method to enhance the contrast of spatially-localized phenomena in an image such as microcalcifications in a mammogram, a multi-scale decomposition is applied to a digital signal representation of the image thereby generating a number of detail images at different scales, the detail signals pertaining to the spatially-localized phenomena having a common polarity (either negative or positive) being modified at at least one scale.
Owner:AGFA NV
Method for the detection and classification of microcalcification clusters in digital mammograms
InactiveUS9122897B2Character and pattern recognitionImage analysisPattern recognitionDigital mammogram
A method for the detection and classification of microcalcification clusters in digital mammograms which comprises the following steps: obtaining one or more digital mammograms; pre-processing the one or more digital mammograms by eliminating the noise from each one or more digital mammograms; detecting the points that are potential microcalcifications represented by their centroids, in the one or more pre-processed digital mammograms; identifying each mass center of potential microcalcifications as a microcalcification or non-microcalcification; identifying microcalcification clusters, using an algorithm for locating microcalcification cluster; and classifying each cluster into the classes benign or malignant.
Owner:CAPIO TECH S A DE
Auxiliary device for locating, mapping and microscopically measuring neoplasias
InactiveUS20180067096A1Preparing sample for investigationMicroscopesSurgery.breastMicrocalcification
The present invention refers to an auxiliary device for locating, mapping and microscopically measuring neoplasias, in particular microcalcifications in breast surgery specimens, linked to a radiological procedure.
Owner:FUNDACAO ANTONIO PRUDENTE
Method, apparatus, and program for discriminating calcification patterns
InactiveUS20050141758A1Reduce detectionAccurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionPattern detection
Detection of pseudo calcification patterns is reduced, to improve detection accuracy of microcalcification patterns. Candidate points for microcalcification patterns are detected from a medical image. Mean pixel values are obtained for pixels along a plurality of lines that pass through the candidate points in a plurality of directions. Whether the candidate points are points within linear structural elements that appear along a line, along which the mean pixel value is greatest (maximum line), is judged based on the difference between the maximum mean pixel value and the minimum mean pixel value.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
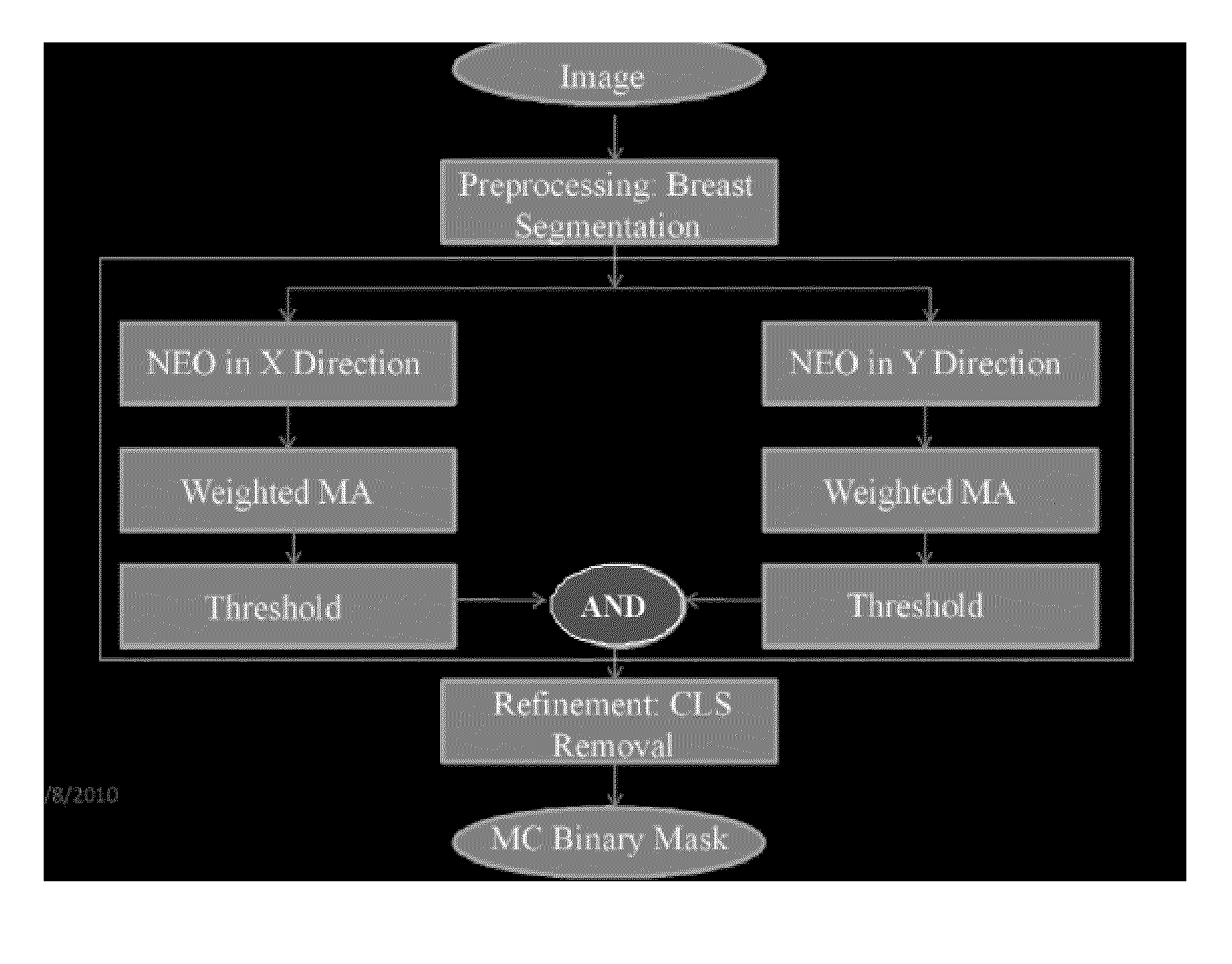
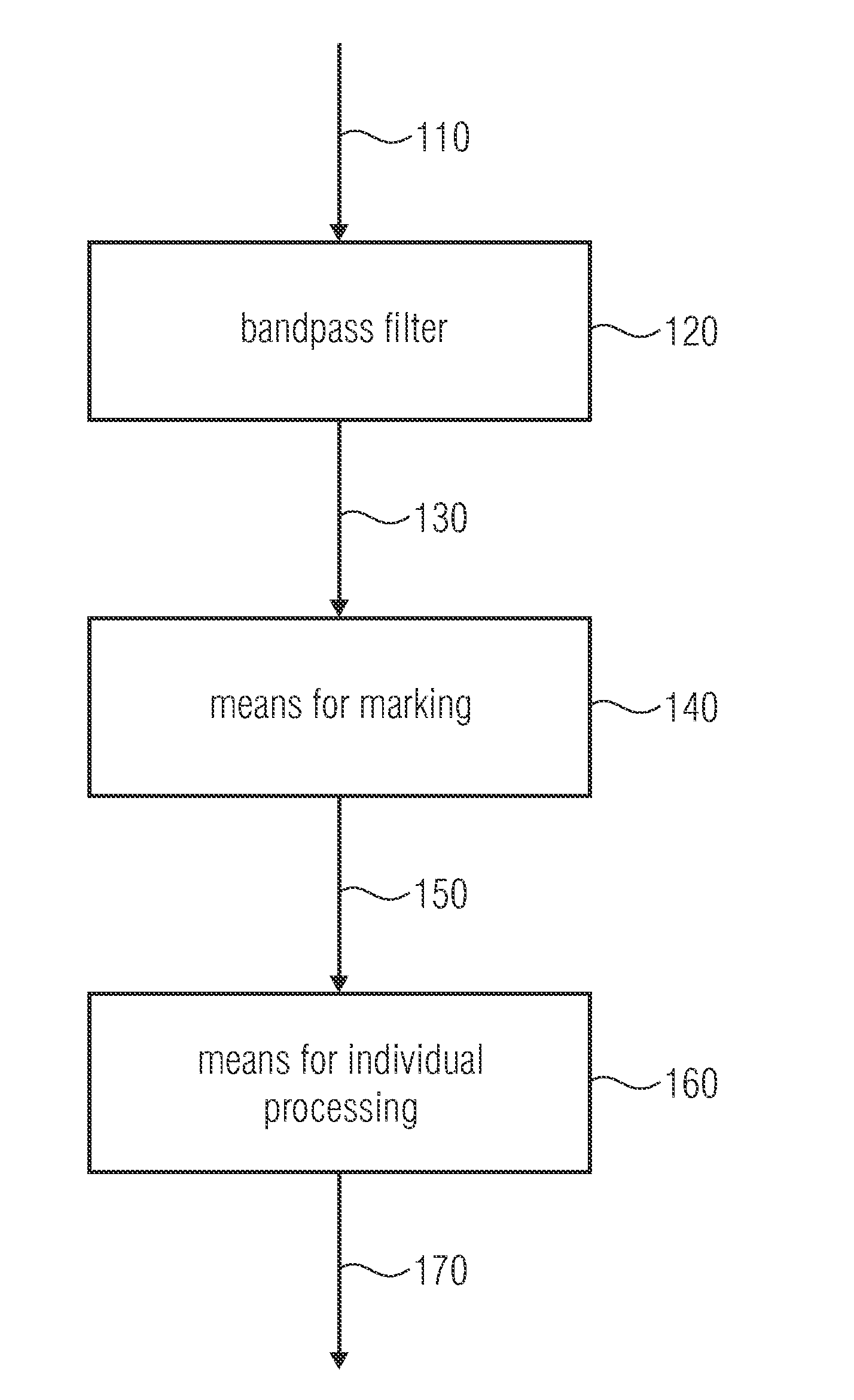
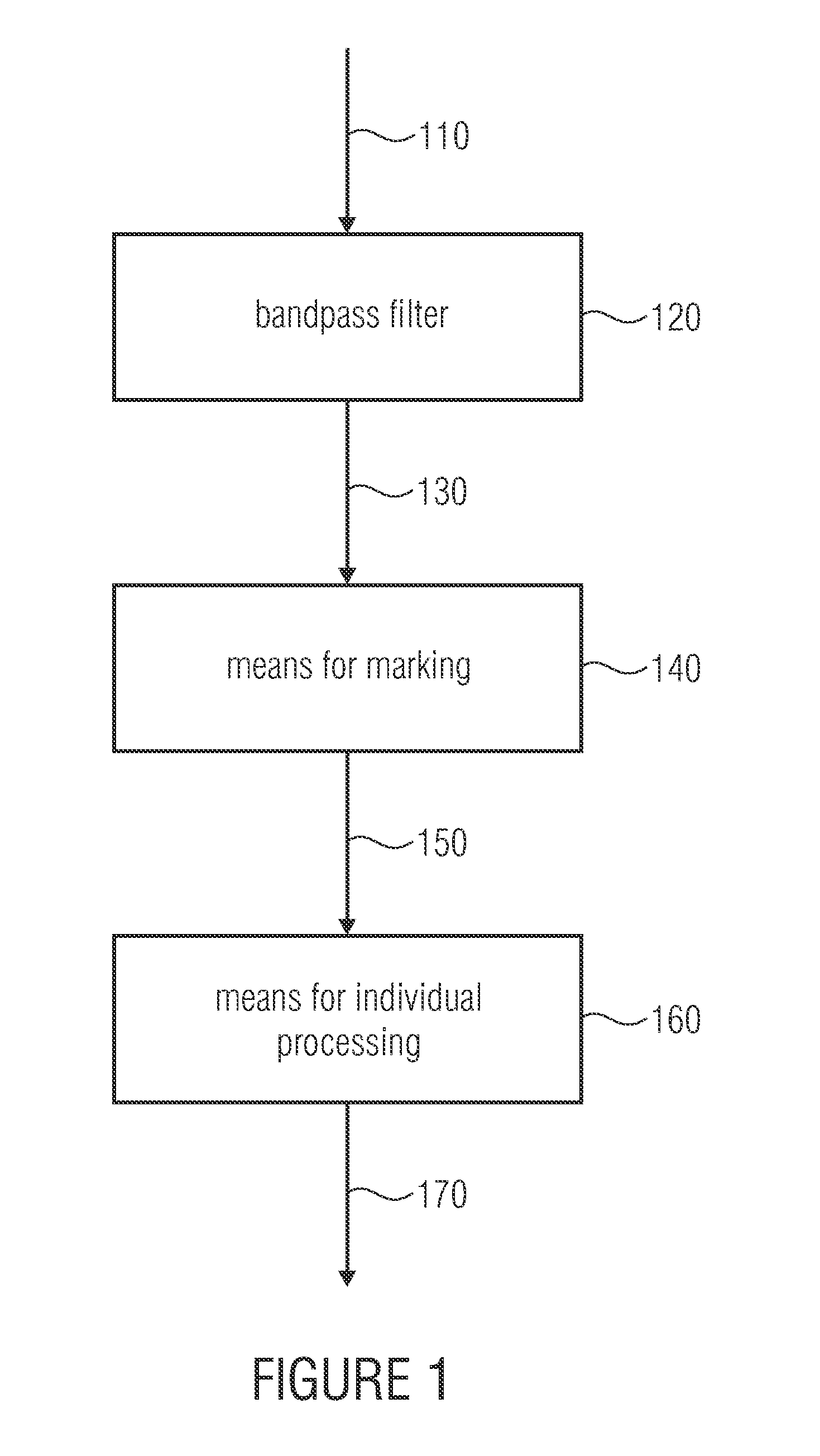
Segmentation of microcalcifications in a mammographic image
InactiveUS20100284586A1Increase of extracted formIncrease of distribution featureImage enhancementImage analysisBandpass filteringComputer vision
Apparatus for segmenting microcalcifications in a mammographic image having a bandpass filter for bandpass filtering the mammographic image obtaining the filtered mammographic image, a marker and a processor for individual processing. The marker marks image points in the filtered mammographic image as potential regions of microcalcifications when a they exceed or fall below a predetermined threshold. The processor for individual processing processes one of the regions of adjacent marked image points for changing an extension of the one region for illustrating a segmentation of microcalcifications.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com