Patents
Literature
2071 results about "Micron scale" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
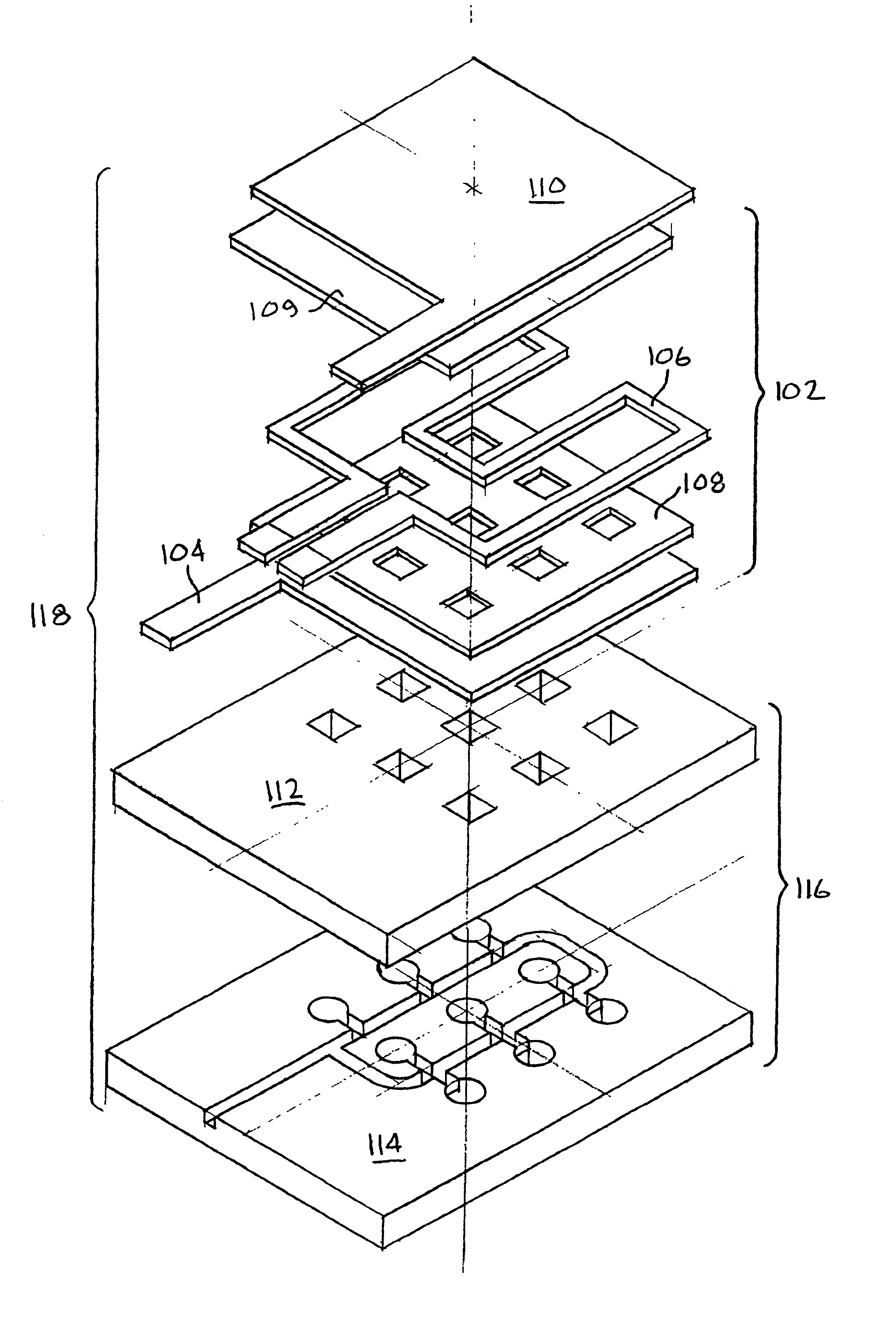
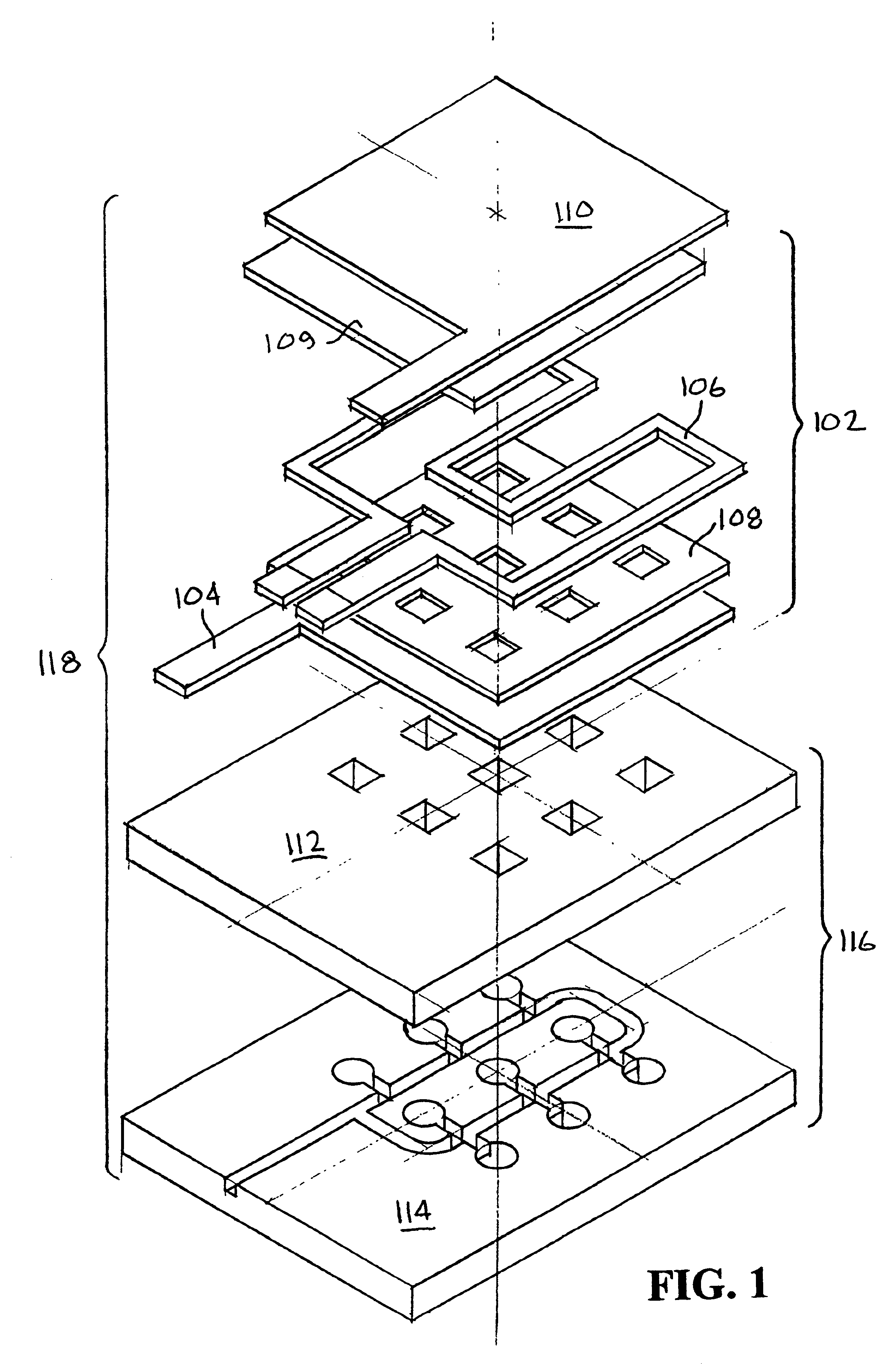
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
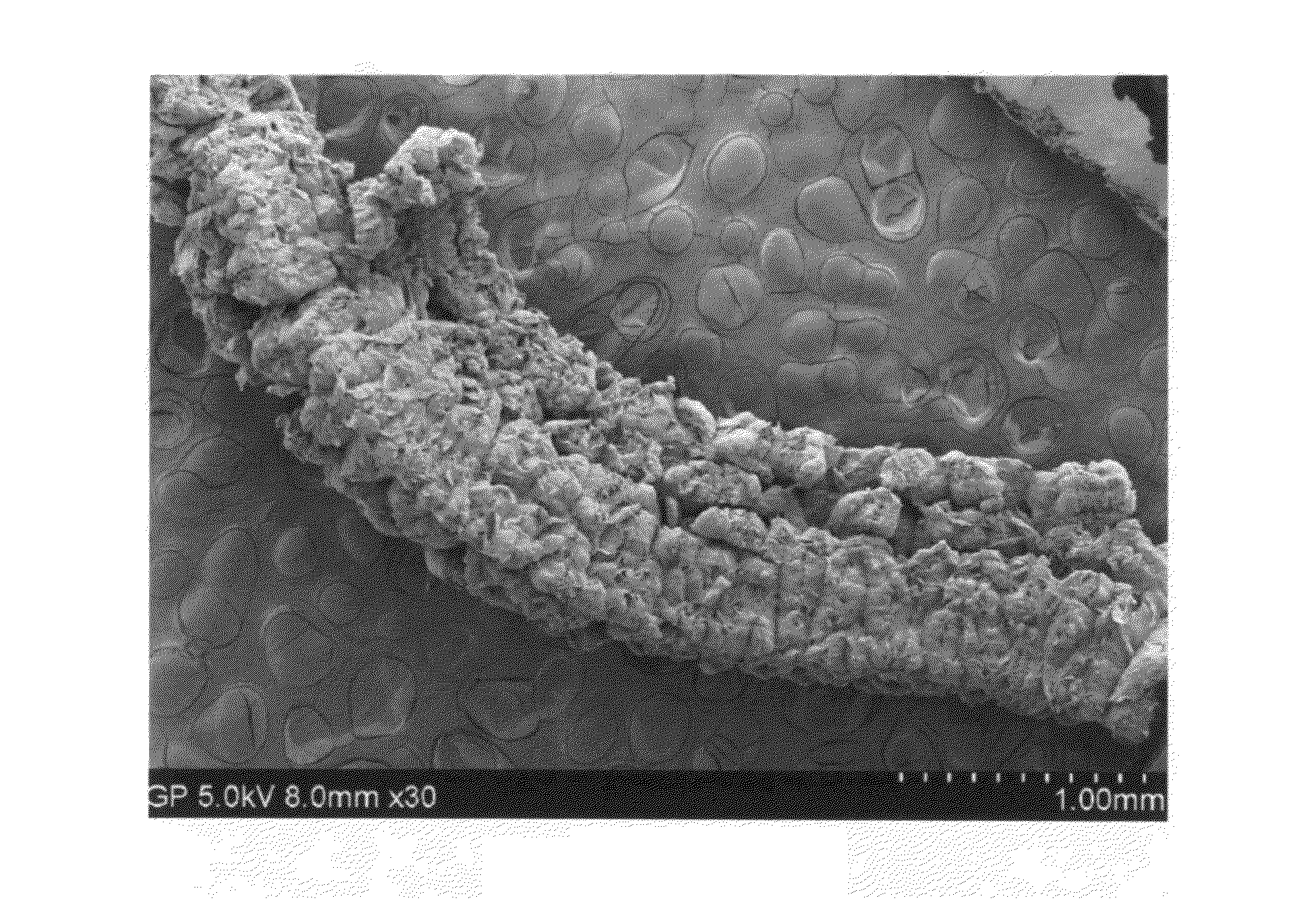
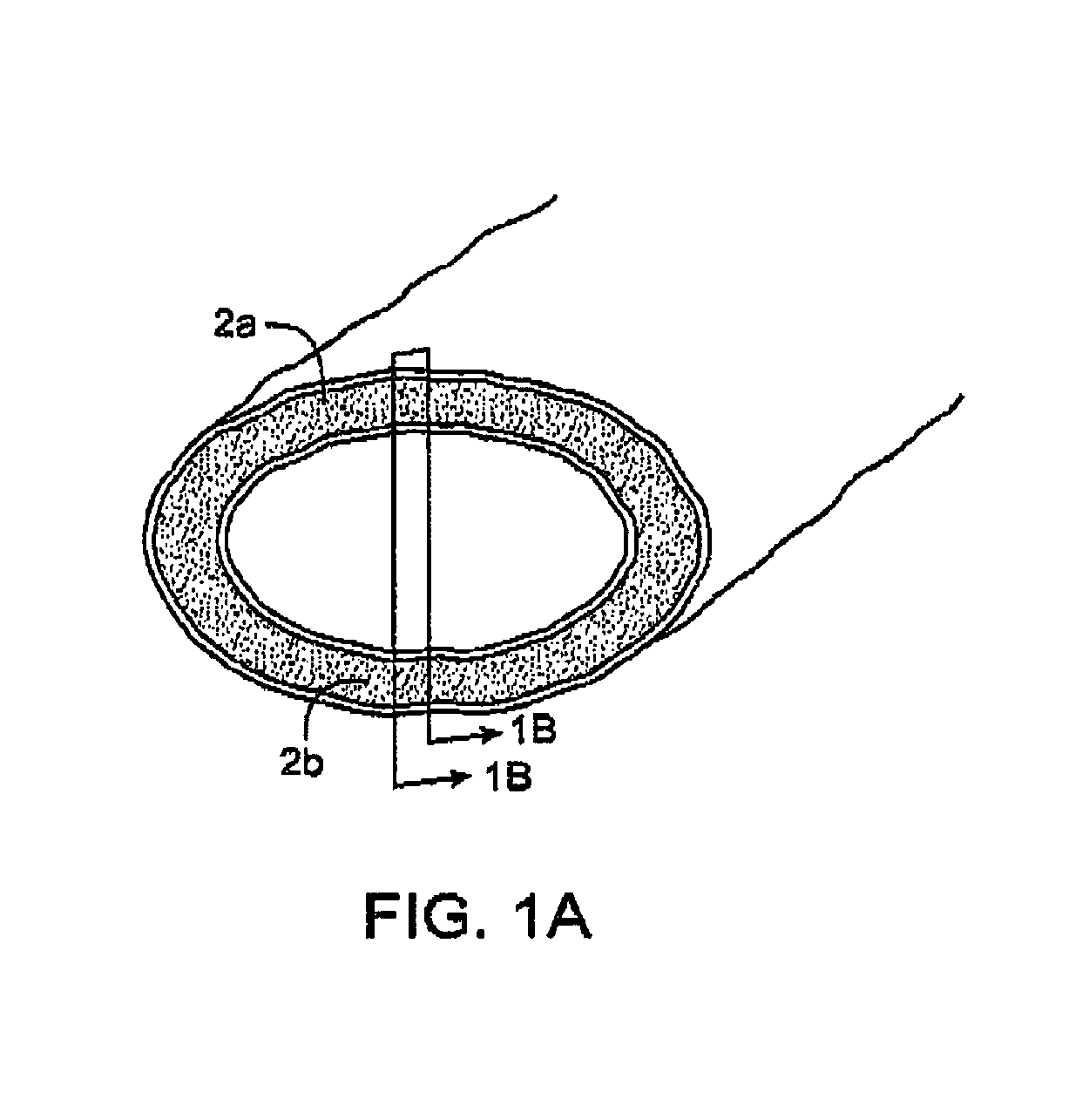
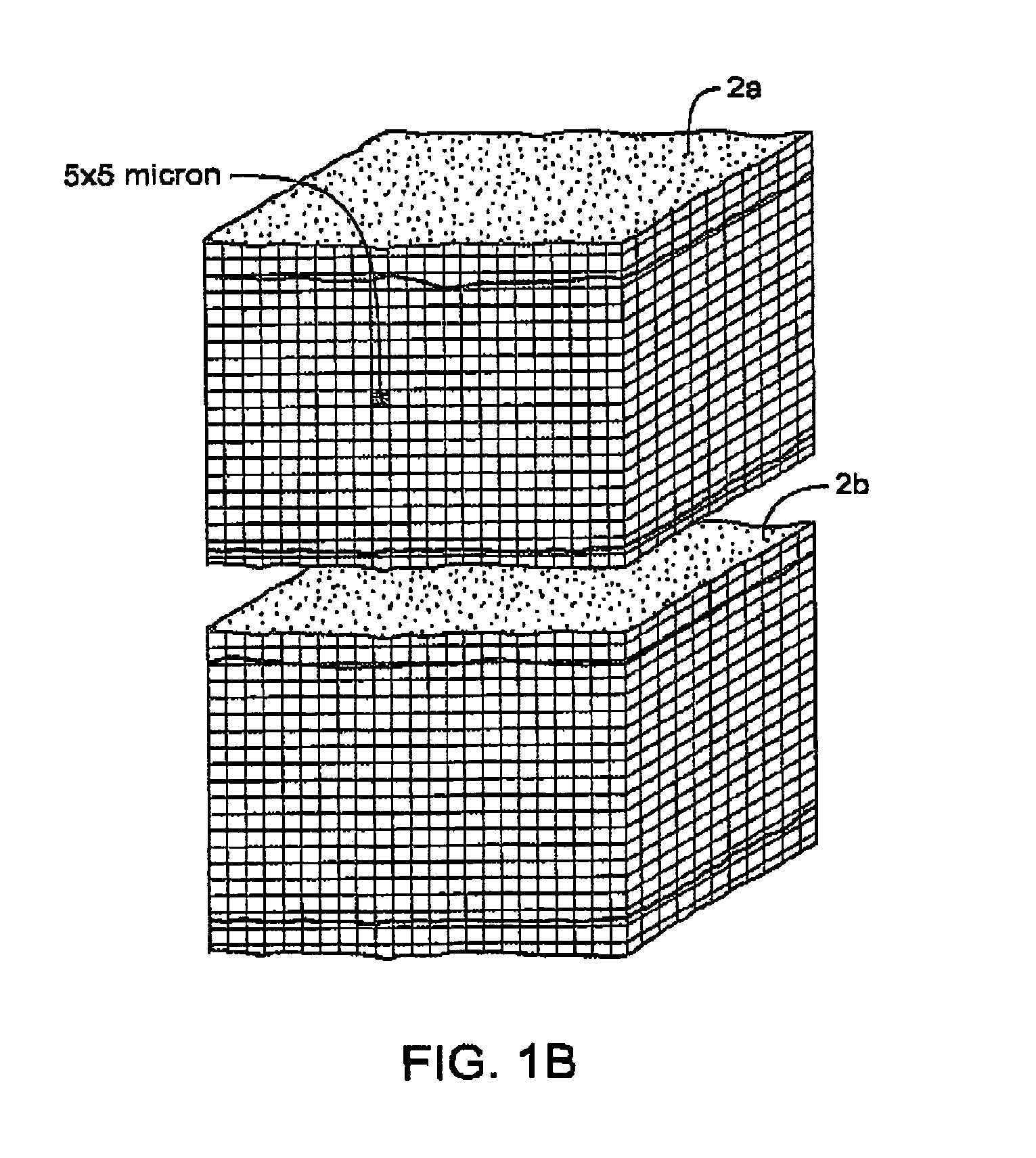
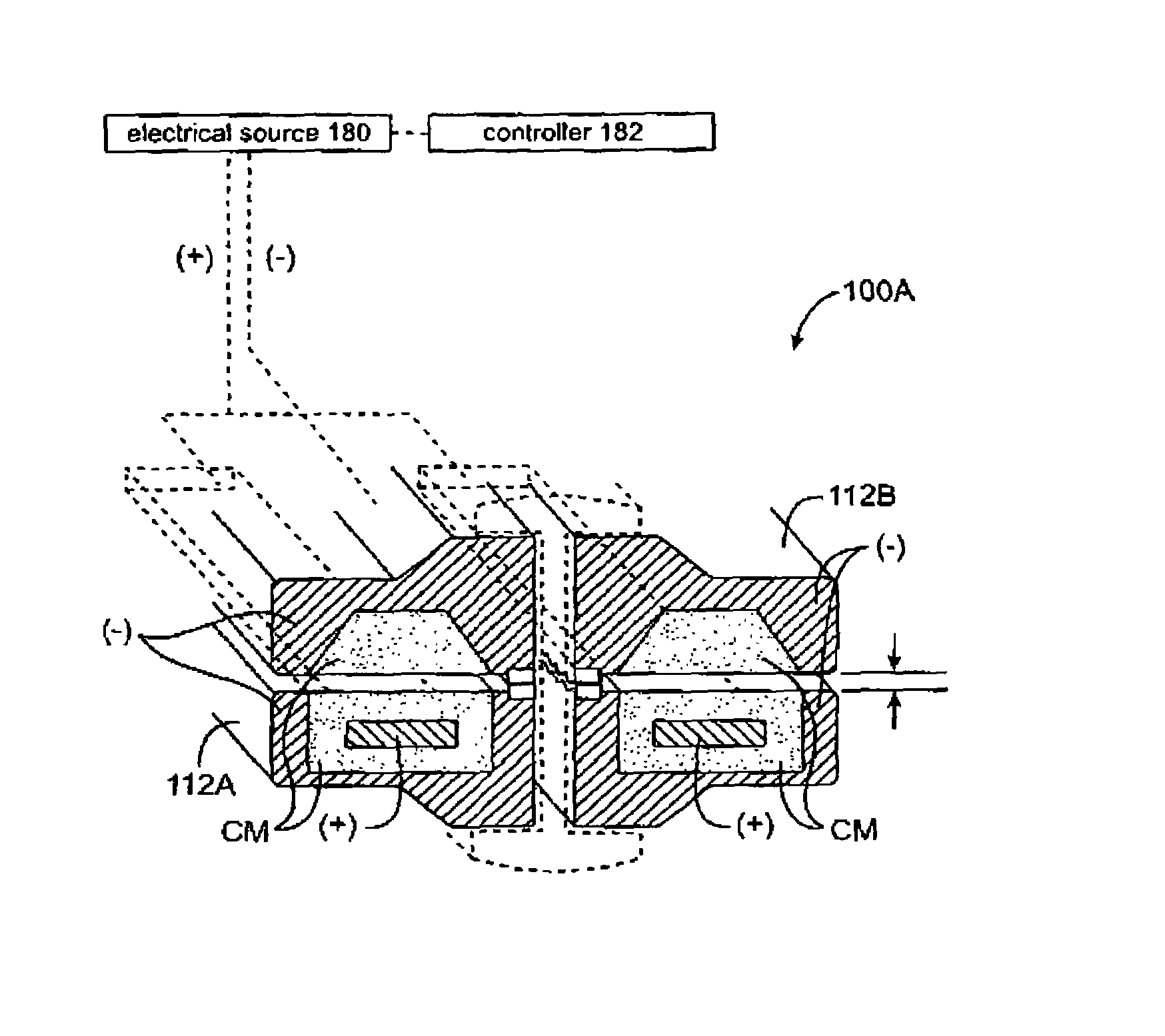
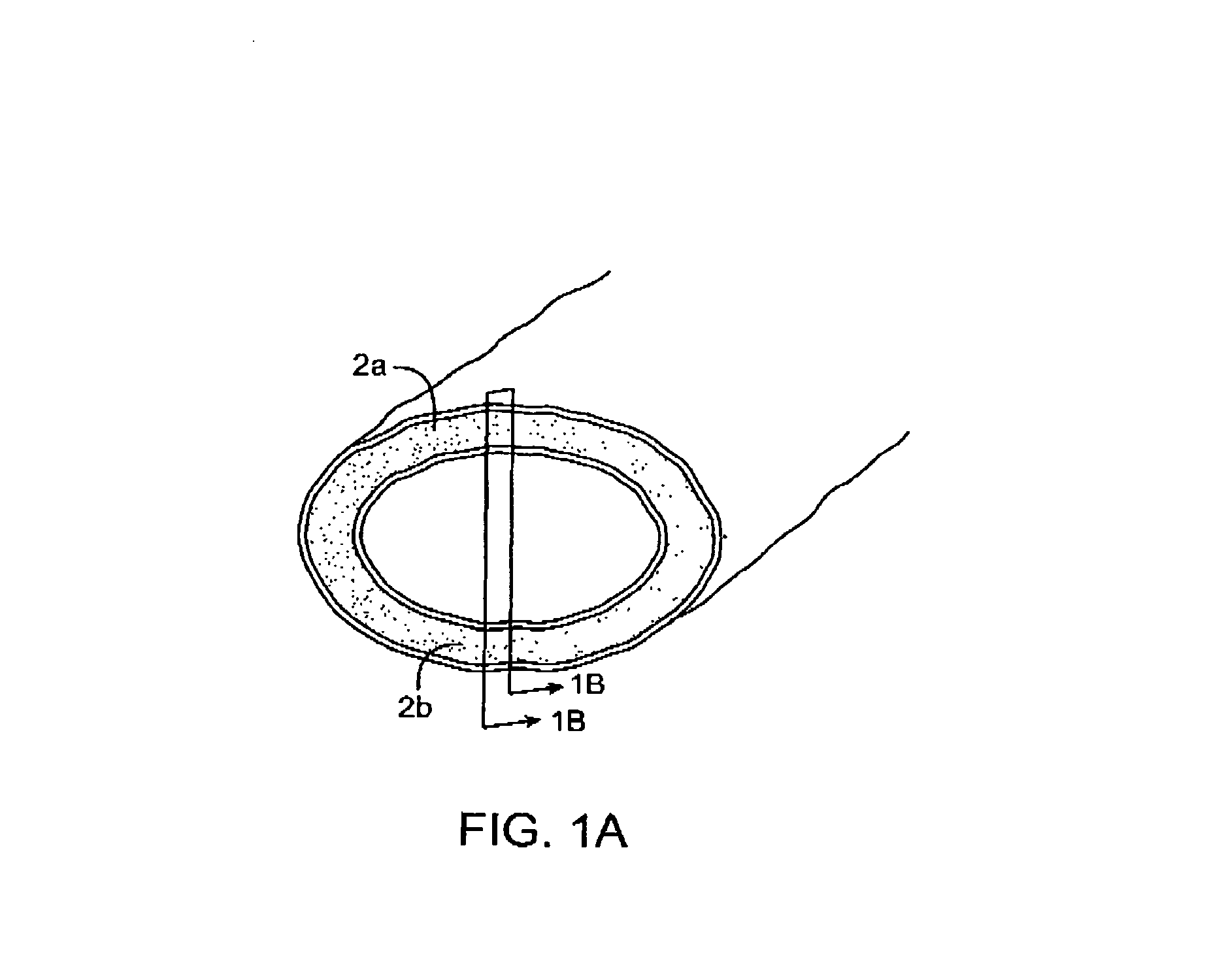
InactiveUS7083619B2Reduce conductancePrevent any substantial dehydrationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicron scaleElastomer
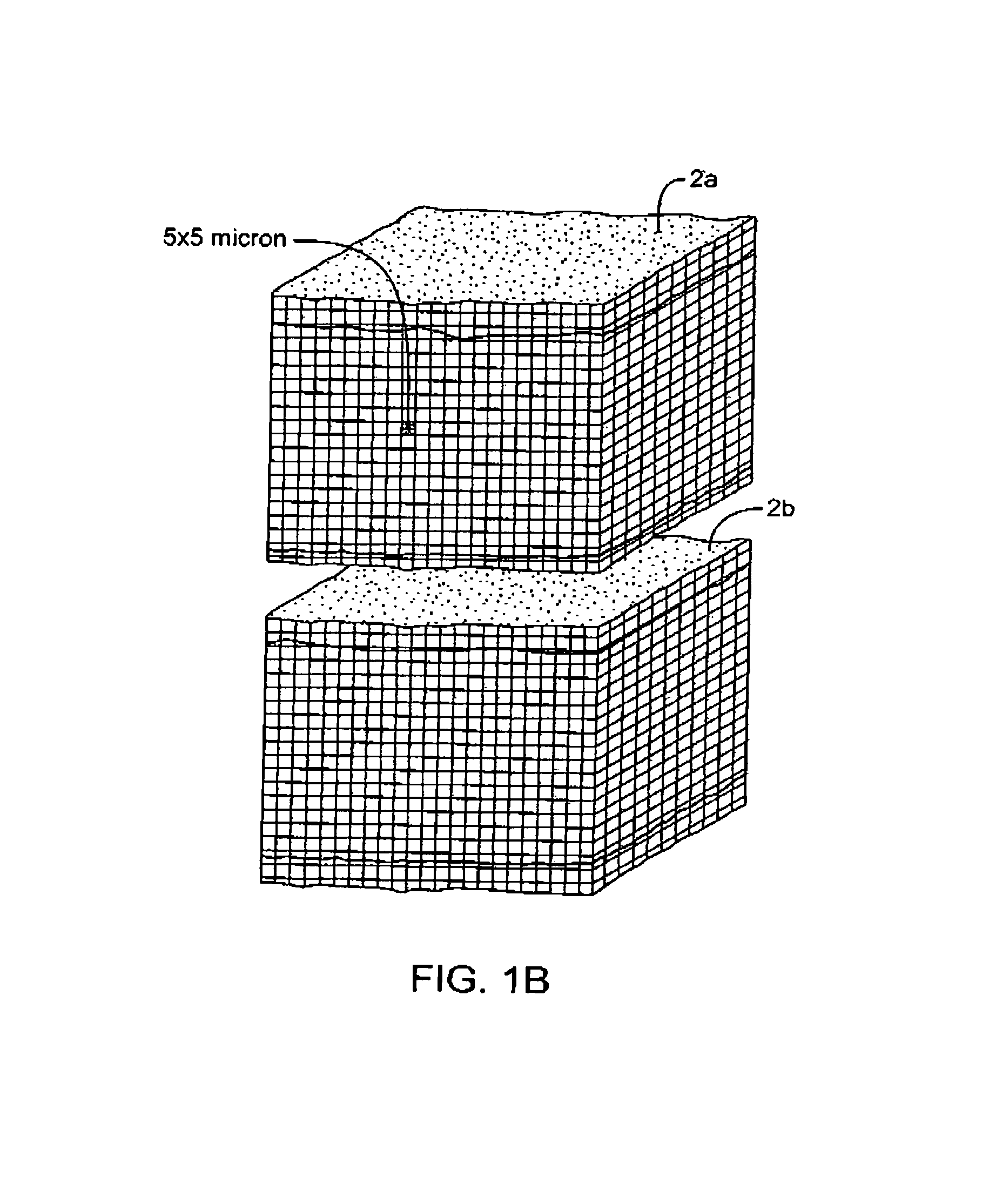
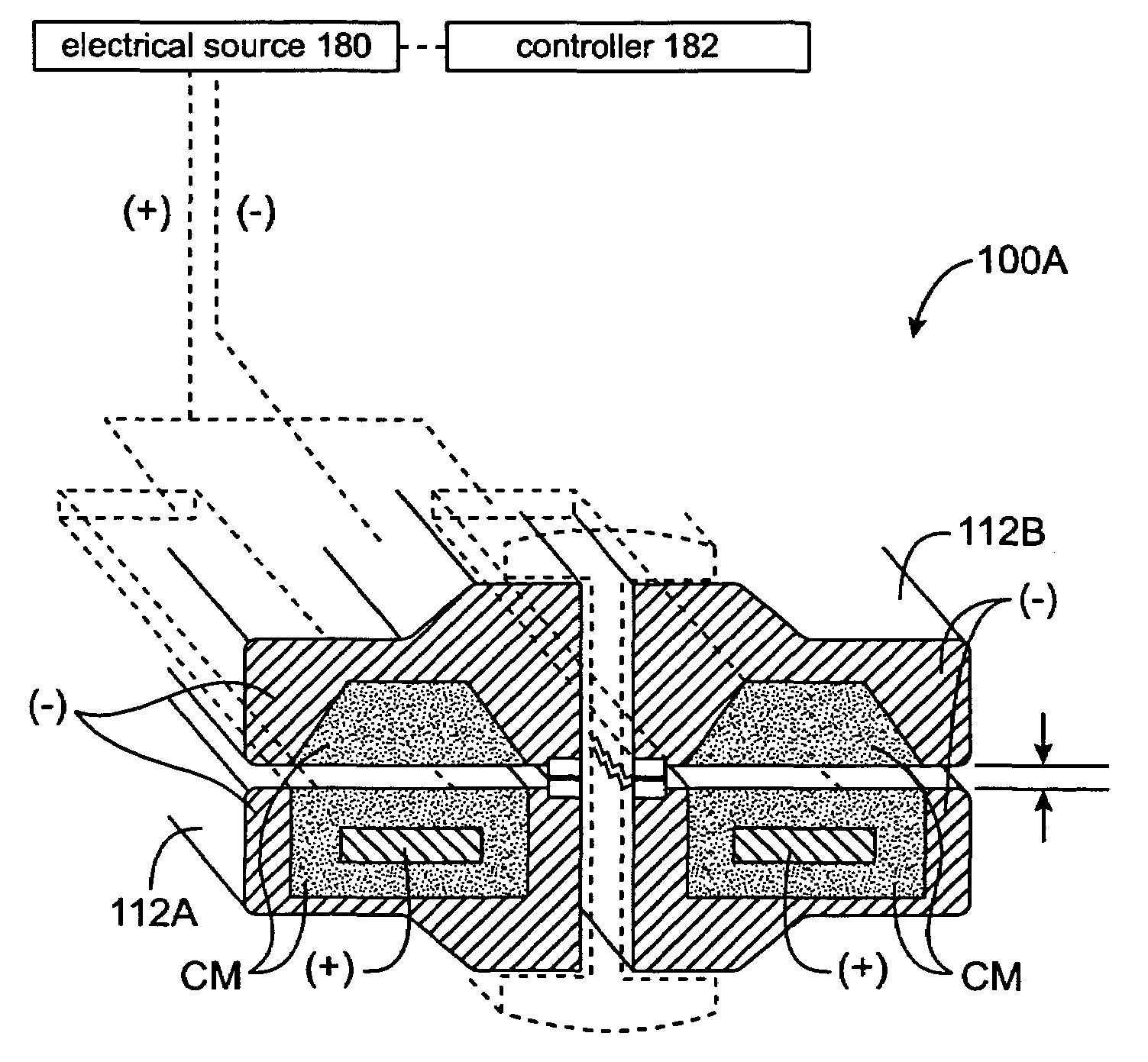
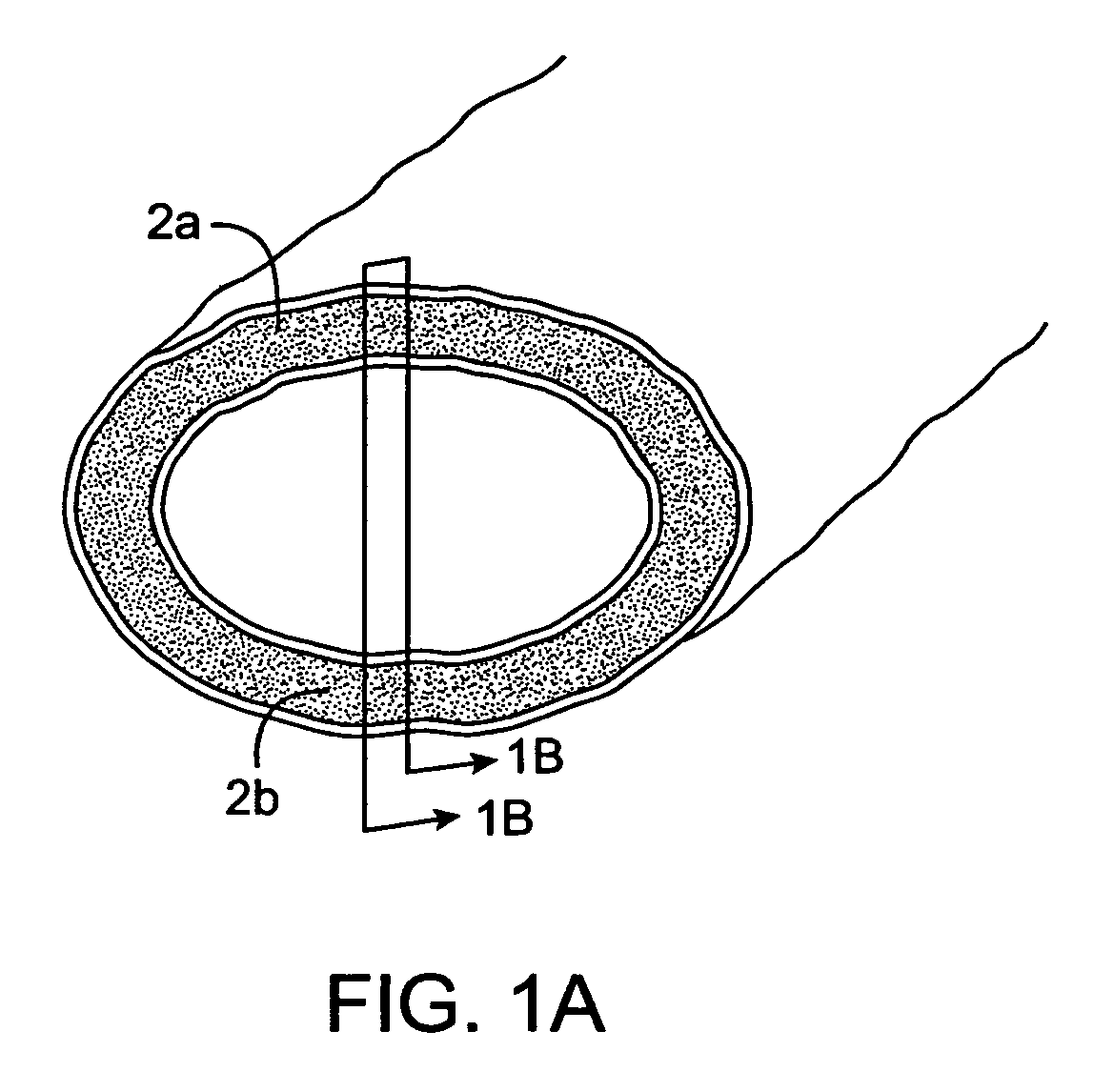
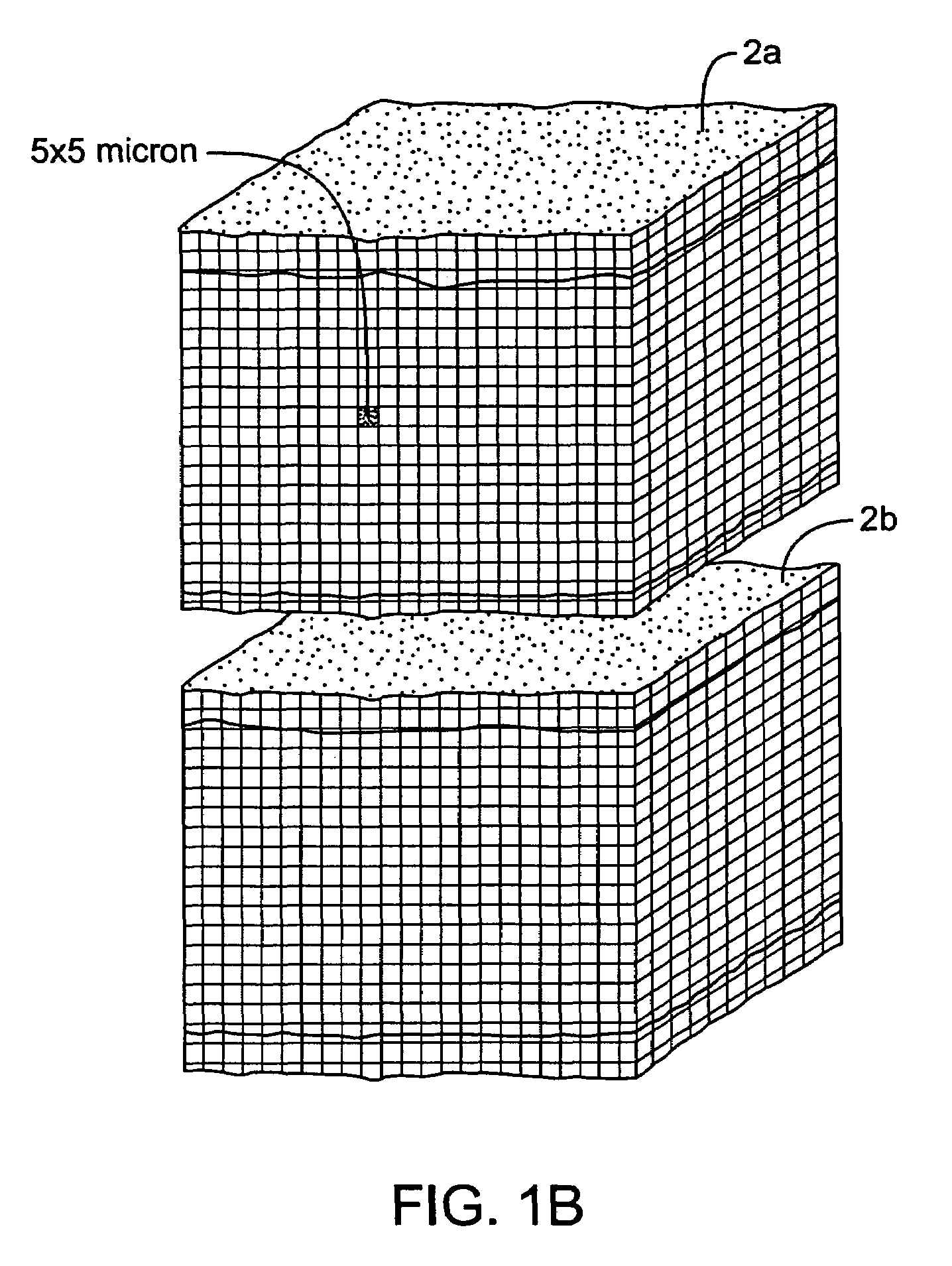
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue. In one embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying a conductive-resistive matrix of a conductively-doped non-conductive elastomer. The engagement surface portions thus can be described as a positive temperature coefficient material that has a unique selected decreased electrical conductance at each selected increased temperature thereof over a targeted treatment range. The conductive-resistive matrix can be engineered to bracket a targeted thermal treatment range, for example about 60° C. to 80° C., at which tissue welding can be accomplished. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane will automatically modulate and spatially localize ohmic heating within the engaged tissue from Rf energy application—across micron-scale portions of the engagement surface.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
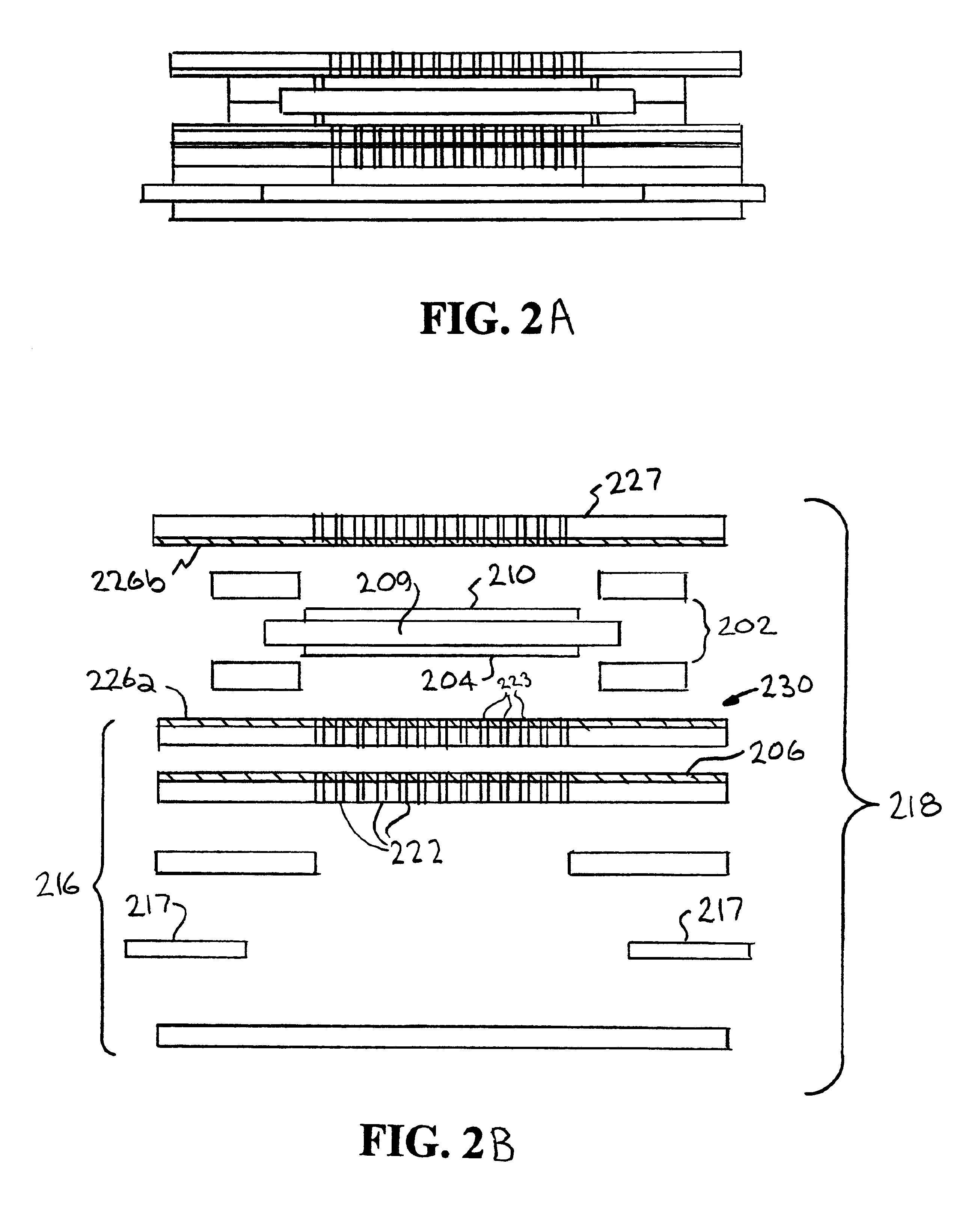
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS7311709B2Reduce conductancePrevent any substantial dehydrationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicron scaleSpatial positioning
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue. In one embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying a variable resistive body of a positive temperature coefficient material that has a selected decreased electrical conductance at each selected increased temperature thereof over a targeted treatment range. The variable resistive body can be engineered to bracket a targeted thermal treatment range, for example about 60° C. to 80° C., at which tissue welding can be accomplished. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane will automatically modulate and spatially localize ohmic heating within the engaged tissue from Rf energy application across micron-scale portions of the engagement surface. In another mode of operation, a variable resistive body will focus conductive heating in a selected portion of the engagement surface.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS7112201B2Reduce conductancePrevent any substantial dehydrationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicron scaleElastomer
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue. In one embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying a conductive-resistive matrix of a conductively-doped non-conductive elastomer. The engagement surface portions thus can be described as a positive temperature coefficient material that has a unique selected decreased electrical conductance at each selected increased temperature thereof over a targeted treatment range. The conductive-resistive matrix can be engineered to bracket a targeted thermal treatment range, for example about 60° C. to 80° C., at which tissue welding can be accomplished. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane will automatically modulate and spatially localize ohmic heating within the engaged tissue from Rf energy application—across micron-scale portions of the engagement surface. In another mode of operation, a conductive-resistive matrix can induce a “wave” of Rf energy density to sweep across the tissue to thereby weld tissue.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Wound healing device
ActiveUS20080275409A1Promote growthPromote woundWound drainsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsMicron scaleVacuum pressure
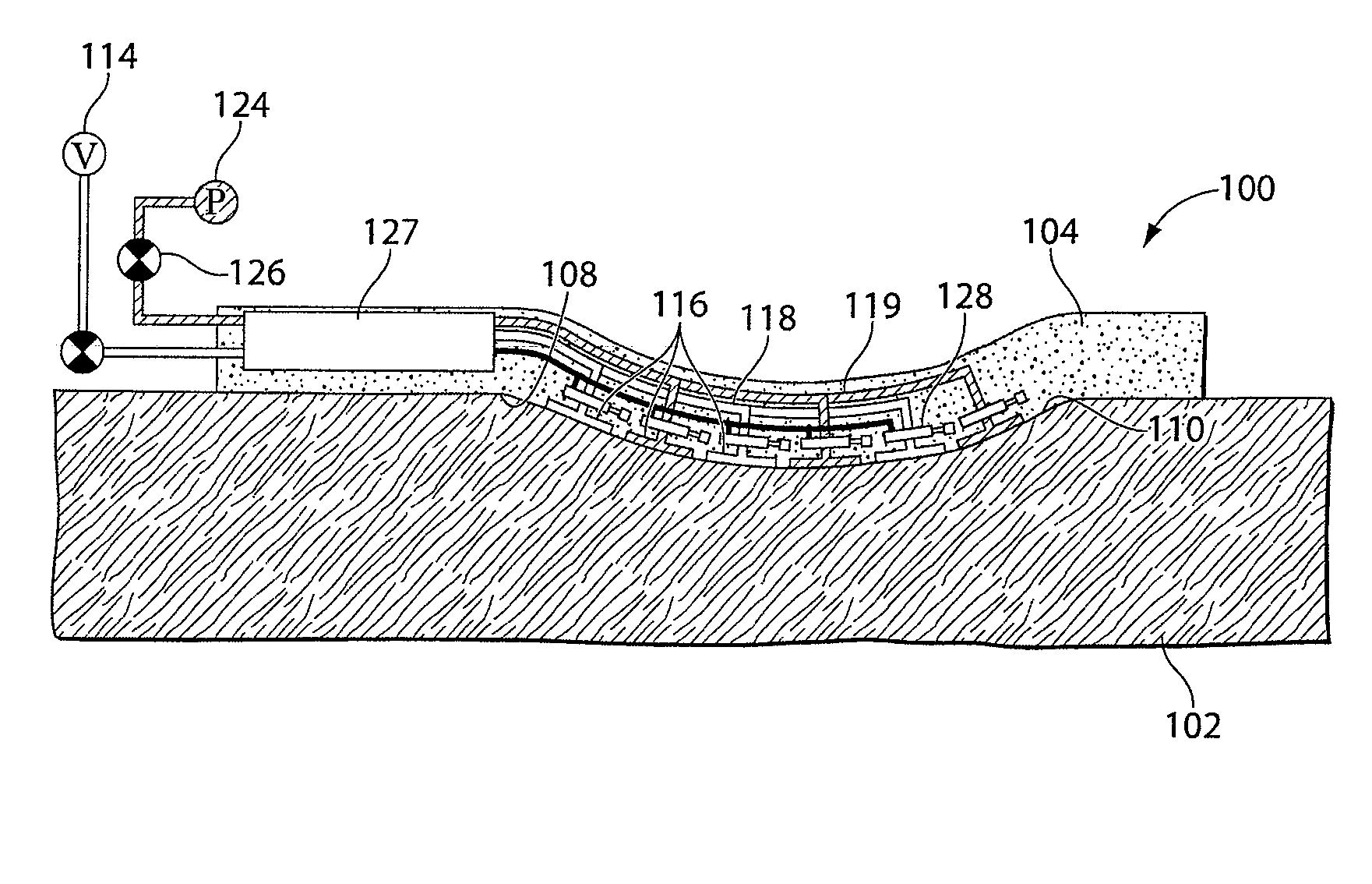
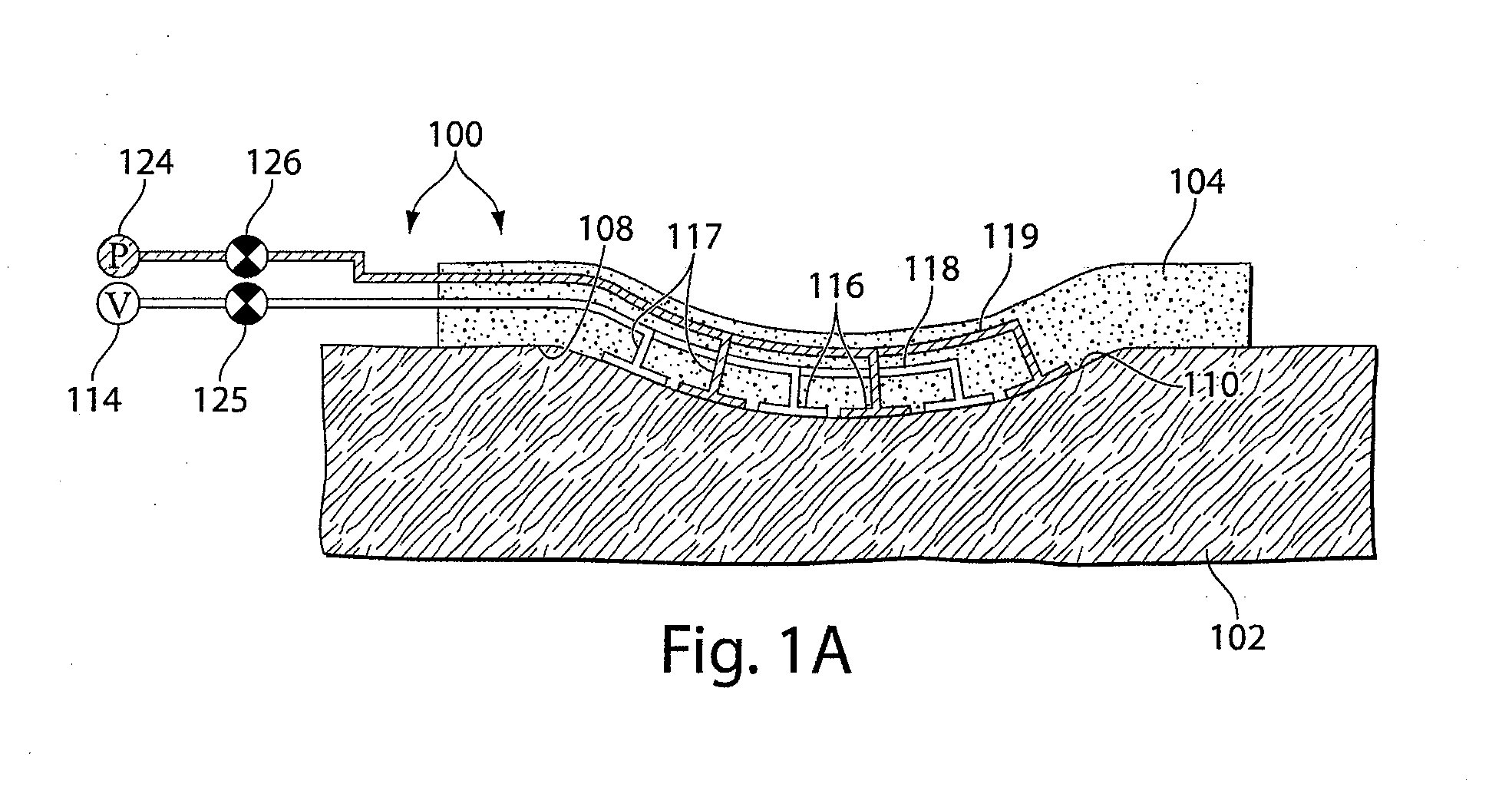
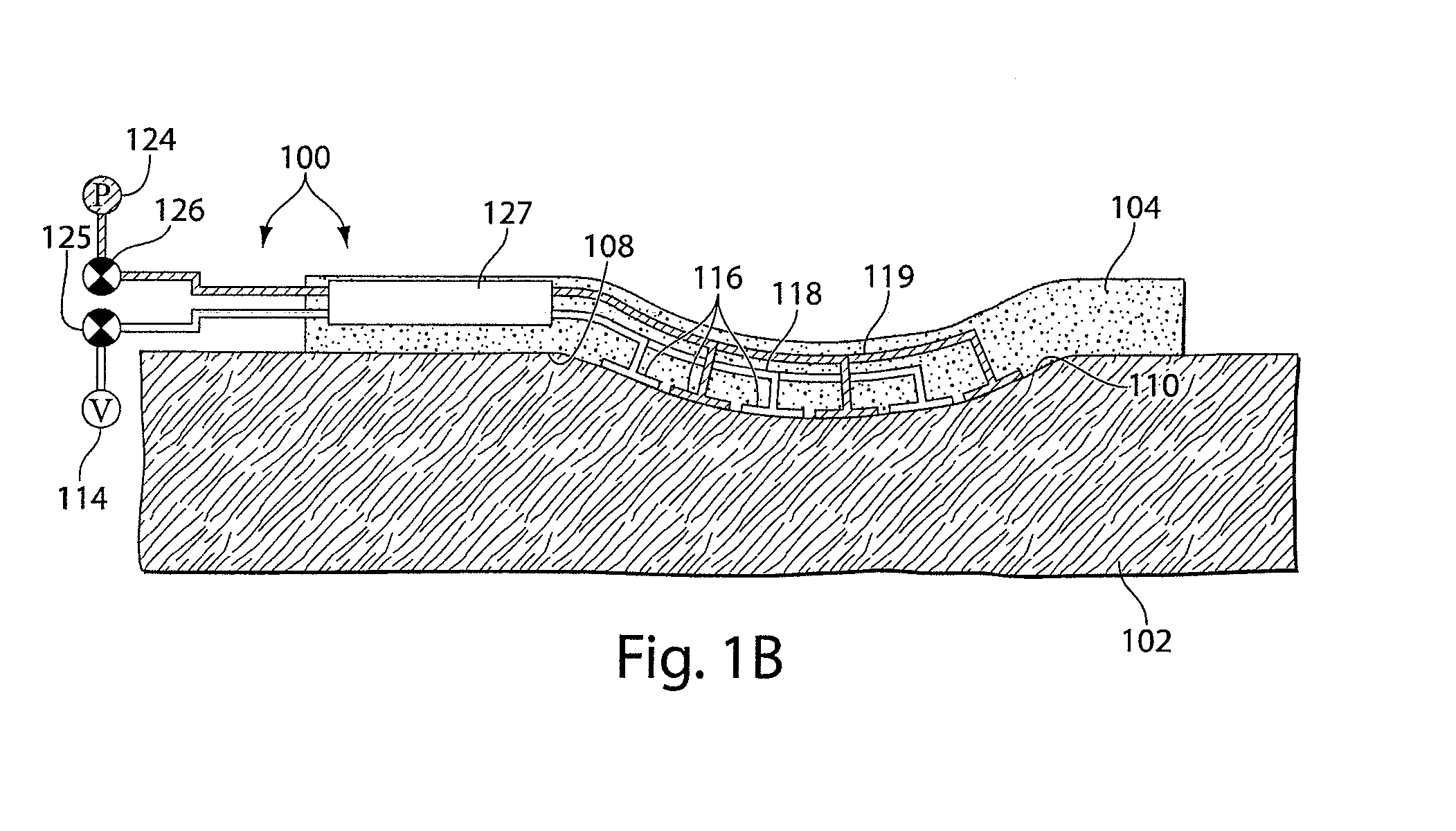
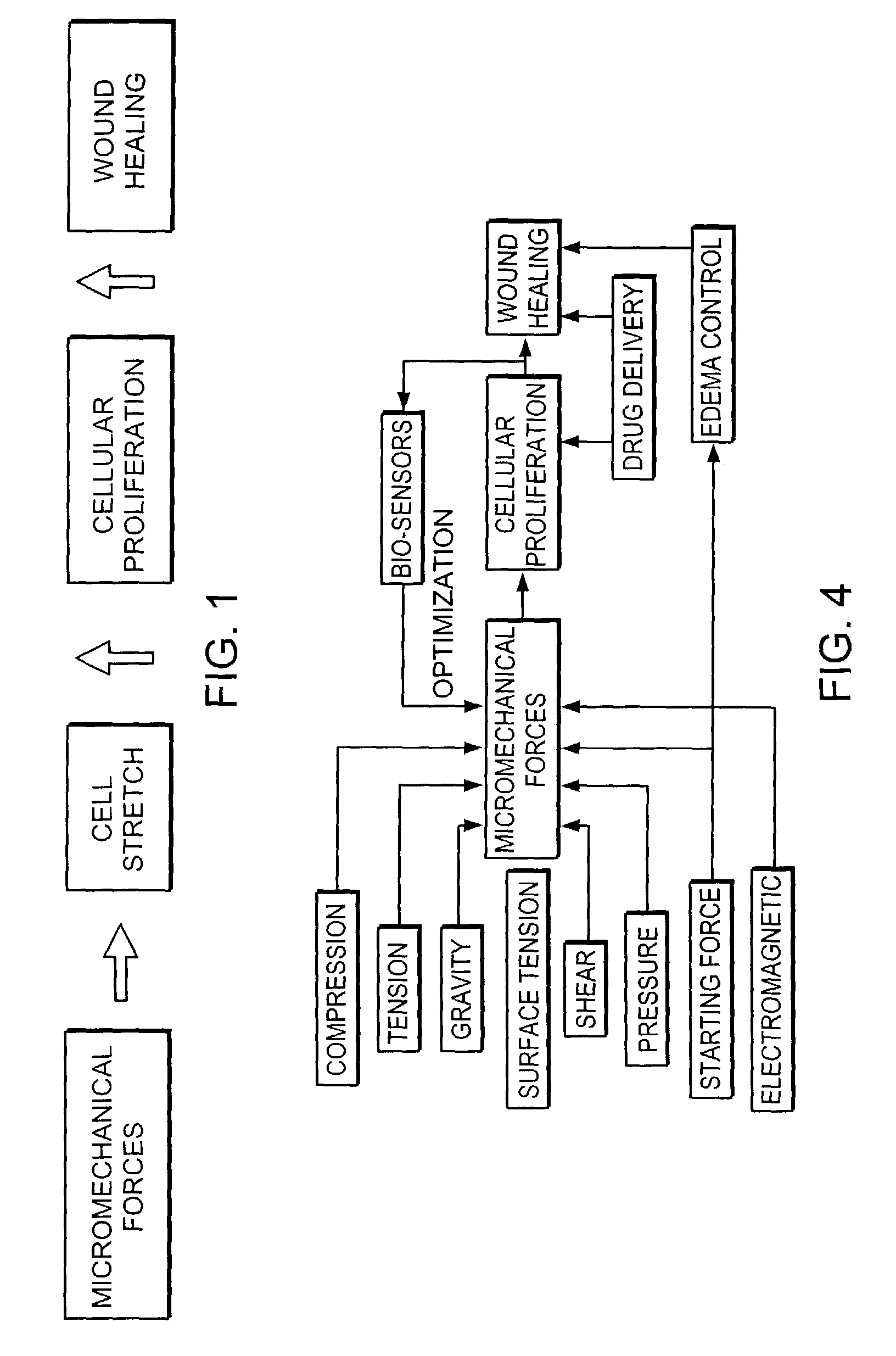
Methods and devices transmit micromechanical forces locally on the millimeter to micron scale for promoting wound healing. Micromechanical forces can selectively be applied directly to tissue, in some embodiments, by using microchambers fluidically connected to microchannels. Each chamber, or in some cases, group of chambers, may be associated with a valve to control vacuum pressure, positive pressure, liquid delivery, and / or liquid removal from each chamber or group of chambers. Application of embodiments of the invention may shorten wound-healing time, reduce costs of therapy, enable restoration of functional tissue, and reduce the need for more invasive therapies, including surgery.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Methods and apparatus for application of micro-mechanical forces to tissues
InactiveUS7494482B2Accelerate tissue ingrowthEnhancing tissue repairNon-adhesive dressingsBone implantMicron scaleCell-Extracellular Matrix
Methods and devices for transmitting micromechanical forces locally to induce surface convolutions into tissues on the millimeter to micron scale for promoting wound healing are presented. These convolutions induce a moderate stretching of individual cells, stimulating cellular proliferation and elaboration of natural growth factors without increasing the size of the wound. Micromechanical forces can be applied directly to tissue, through biomolecules or the extracellular matrix. This invention can be used with biosensors, biodegradable materials and drug delivery systems. This invention will also be useful in pre-conditioned tissue-engineering constructs in vitro. Application of this invention will shorten healing times for wounds and reduce the need for invasive surgery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +2
Optical identification element using separate or partially overlapped diffraction gratings
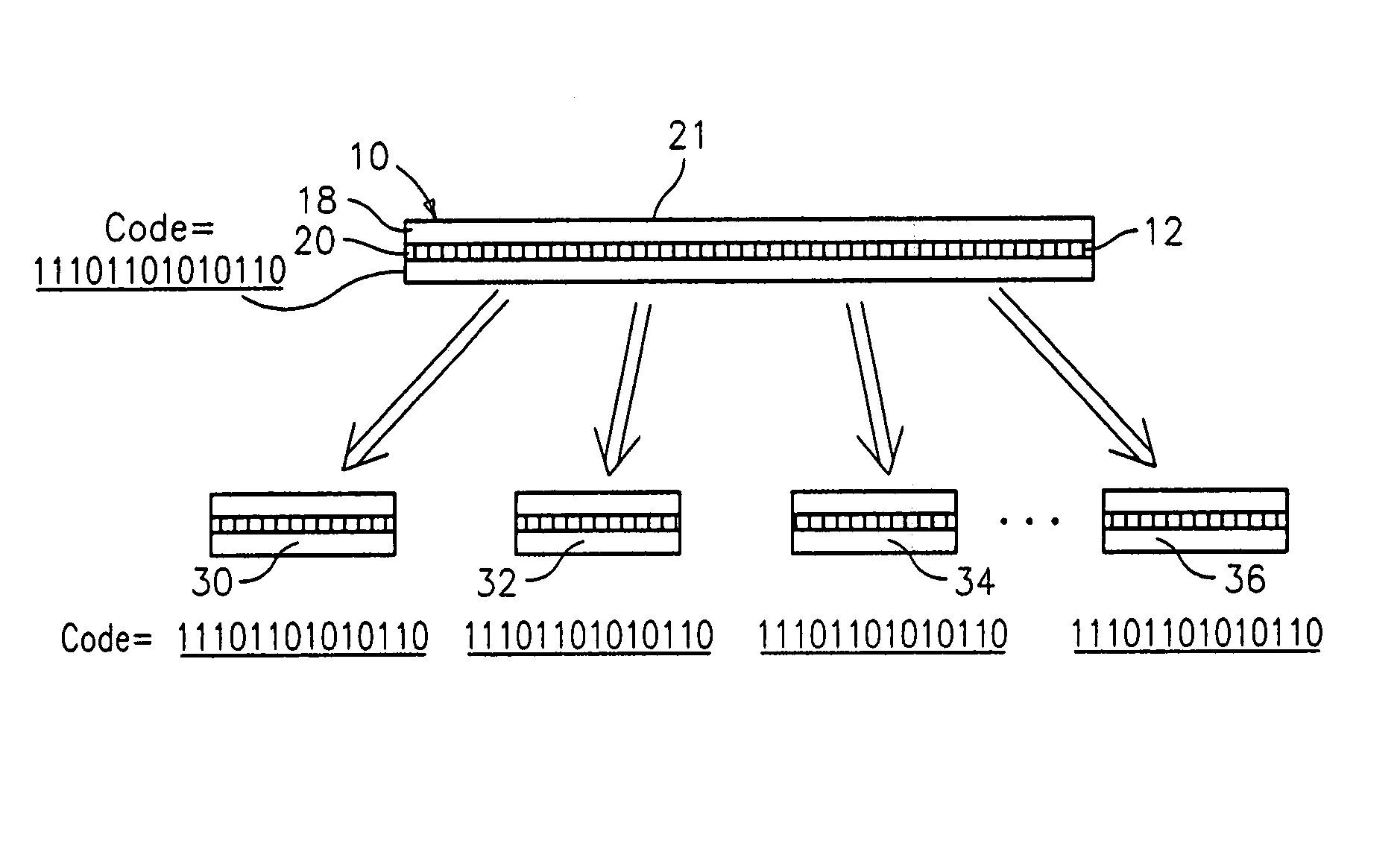
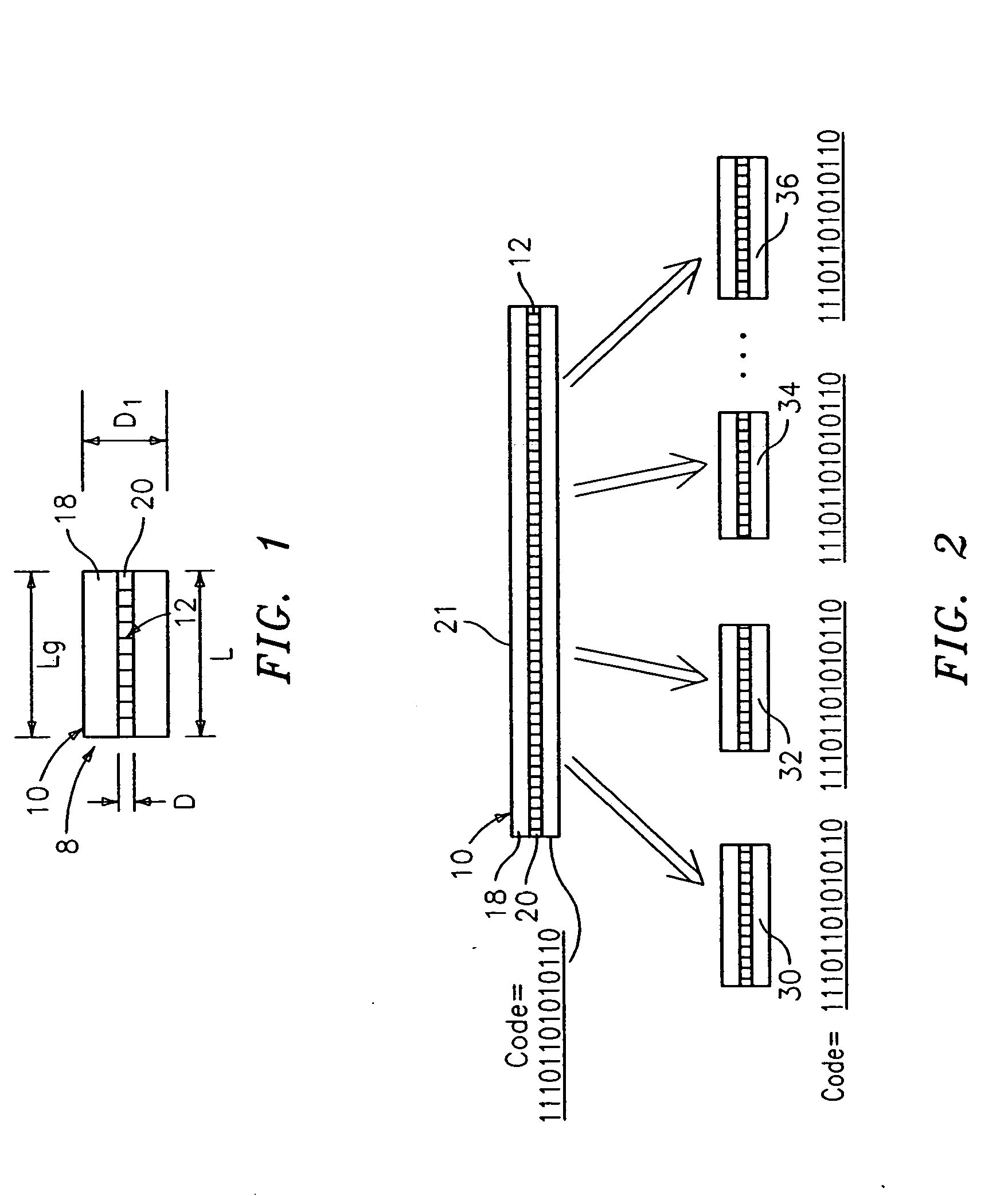
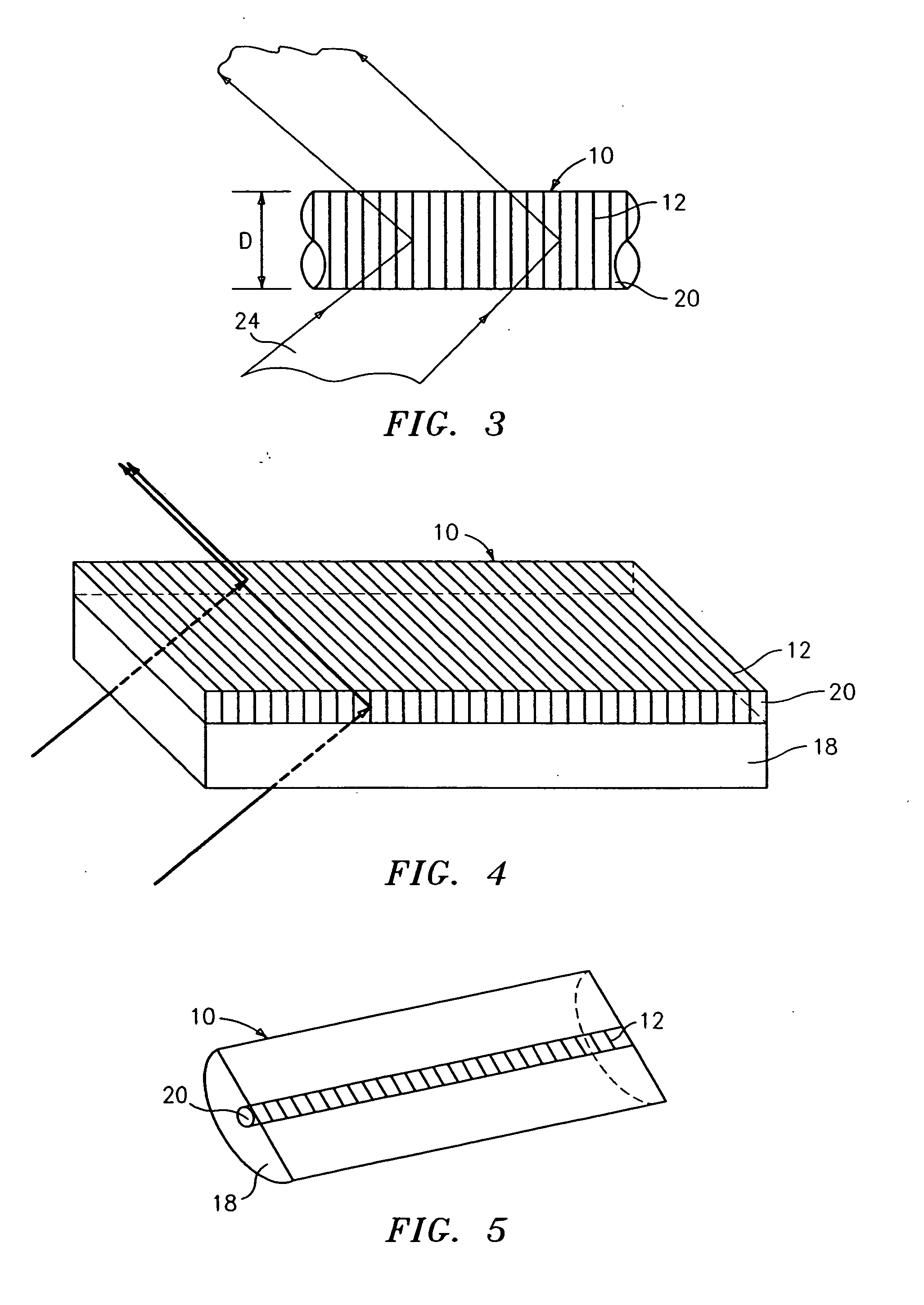
An optical identification element 8 includes an optical substrate 10 having at least one diffraction grating 12 disposed therein. The grating 12 has a one or more of collocated pitches Λ which represent a unique identification N bit digital code that is detected when illuminated by incident light 24. The incident light 24 may be directed transversely onto the side or onto an end of the substrate 10 with a narrow band (single wavelength) or multiple wavelength source, in which case the code is represented by a spatial distribution of light or a wavelength spectrum, respectively. The element 8 can provide a large number of unique codes, e.g., greater than 67 million codes, and can withstand harsh environments. The element 8 can be used in any application that requires sorting, tagging, tracking or identification, and can be made on a micron scale “microbeads” if desired, or larger “macro-elements” for larger applications. The code may be digital binary or may be other numerical bases.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
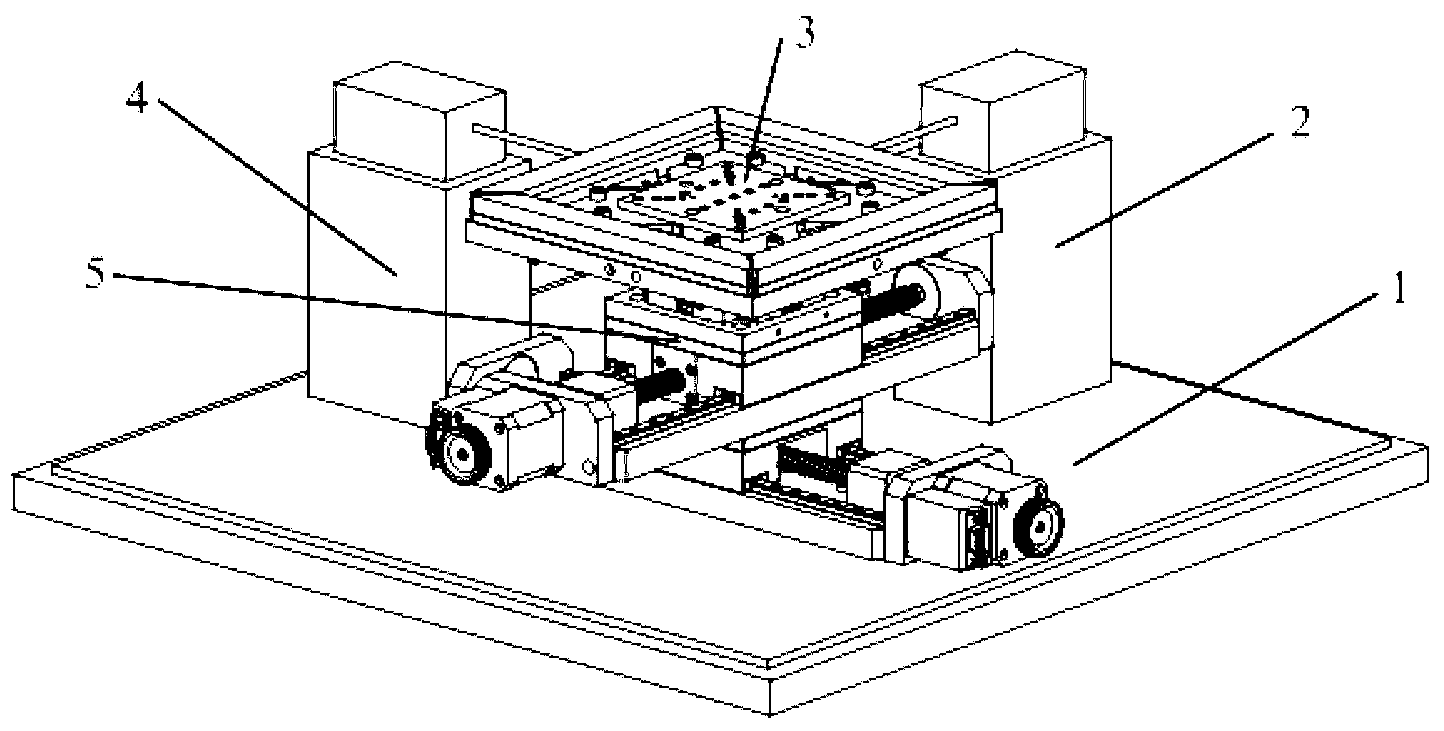
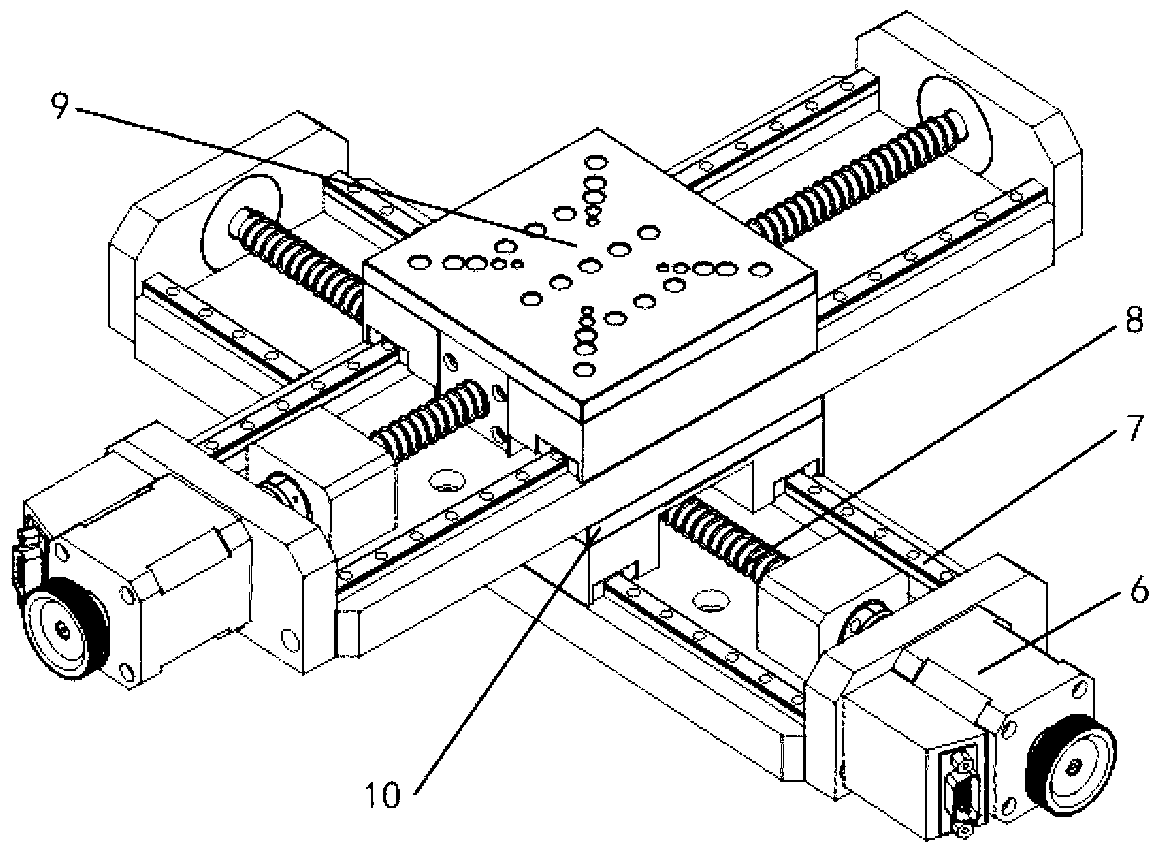
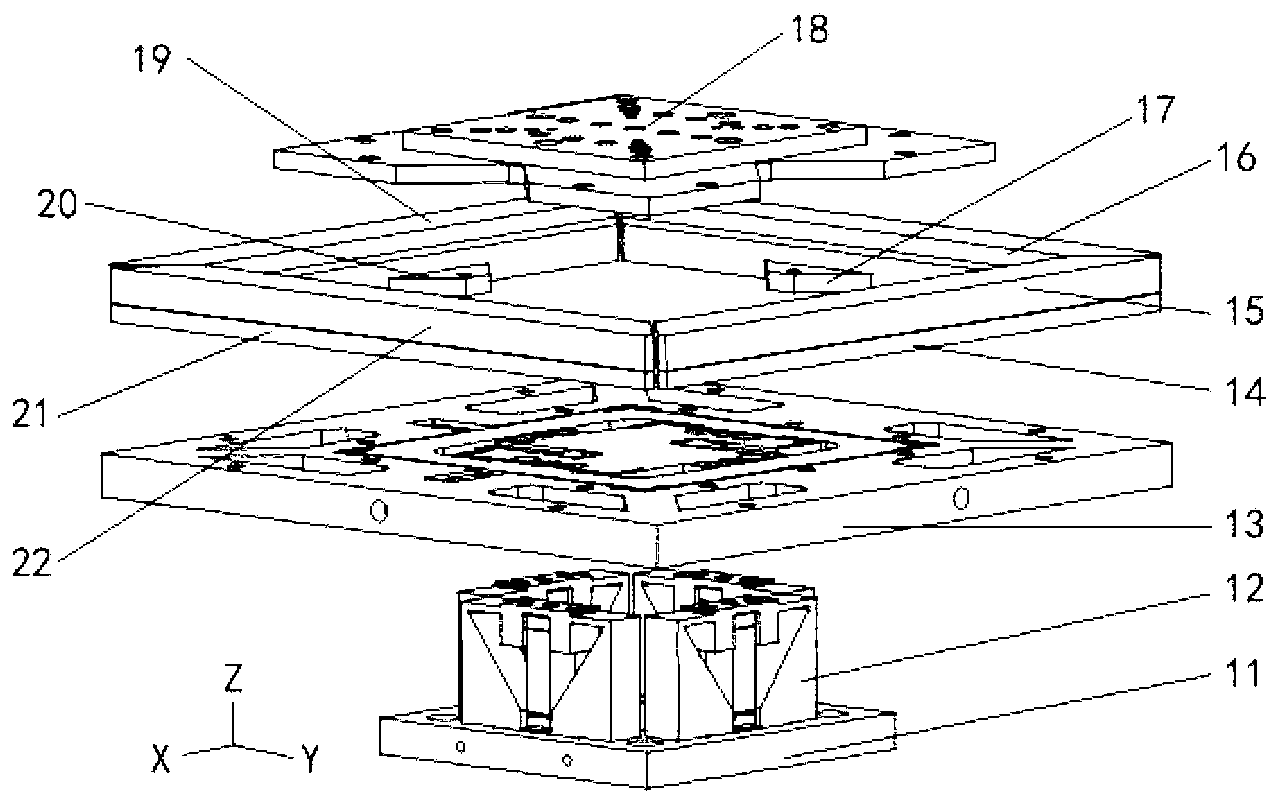
Long-stroke two-dimensional nano worktable system with angle compensation function
The invention discloses a long-stroke two-dimensional nano worktable system with an angle compensation function. A six-degree-of-freedom micro table designed on the basis of a piezoelectric ceramic actuator and a soft hinge chain carries out comprehensive compensation of linear positioning and angle errors on a long-stroke two-dimensional nano worktable. A driving mode that a stepping motor and a ball screw are combined is adopted, so a long-stroke two-dimensional nano worktable has a large pitching angle, a deflection angle and roll angle errors, and positioning precision is of micron size. The six-degree-of-freedom micro table has nanoscale linear positioning precision and millisecond-level angle positioning precision. The long-stroke two-dimensional nano worktable and the six-degree-of-freedom micro table are combined to form the long-stroke two-dimensional nano worktable system. Under control of a closed-loop control system, the six-degree-of-freedom micro table carries out the comprehensive compensation of the linear positioning errors and the angle errors on the long-stroke two-dimensional nano worktable, so two-dimensional long-stroke nano positioning is achieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
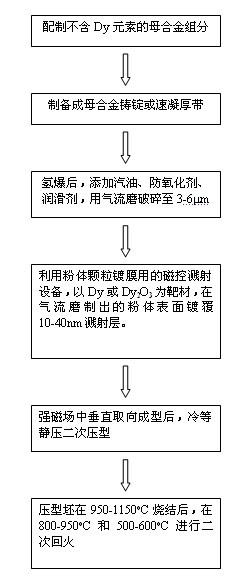
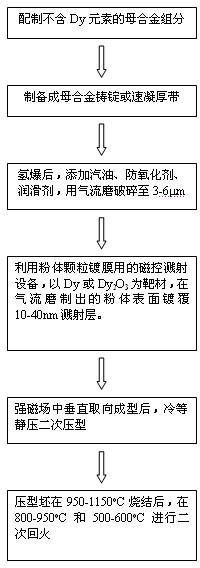
A preparation method of high-performance sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content
The invention discloses a method for preparing sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium (Dy) content and high performance; the method comprises the following steps of: sputtering and plating the Dy element on the surface of jet mill powder by using the powder plate technology based on magnetron sputtering on the basis of preparing NdFeB powder, and then sufficiently dispersing the Dy element to micron-sized NdFeB crystal particles by dispersing the Dy element at high temperature in the sintering and tempering process, thereby achieving the effect of improving magnetic performance of the sintered NdFeB. Compared with the introduction of the Dy element in the proportioning process of the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages: the low dysprosium content and high performance is limited in the nano-size by adopting the physical gas-phase deposition, the consumption quantity of the Dy element during the production process is controlled effectively and the preparationof sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content and high performance is realized. Compared with the sintered NdFeB of the same components prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, both the intrinsic coercivity and the maximum magnetic energy product of the sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnetic material obtained according to the invention are improved obviously; compared with the sintered NdFeB with the same performance prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, the dosage of the dysprosium element is reduced remarkably. The method can be widely applicable to producing and manufacturing sintered NdFeB with high performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Composite fibre membrane with unidirectional water permeable performance and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a composite fibre membrane with an unidirectional water permeable performance and a preparation method of the composite fibre membrane, belonging to the field of functional micron / nano composite fibre materials; the composite fibre membrane is composed of a two-layer structure; a hydrophile layer is a nano-scale fibre membrane composed of hydrophile polymers such as polyvinyl alcohol, cellulose acetate, polyacrylate and the like; fibre diameter is 100-800nm; thickness is 25-35 microns; a lyophobic layer is the micron-scale fibre membrane composed of lyophobic polymers such as polyurethane, polystyrene, polymethylmethacrylate or polycaprolactone and the like; thickness is 5-10 microns; and fibre diameter is1.0-3.0 microns. The composite fibre membrane can be controlled by regulating technical parameters and has hydrophile / lyophobic differences and an excellent directional water permeable performance; and the preparation method is characterized by simple operation, low energy consumption, high efficiency and is widely used for fields of perspiring-type waterproof dress materials, fuel cell electrolyte membranes, unidirectional liquid transmission and separation and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
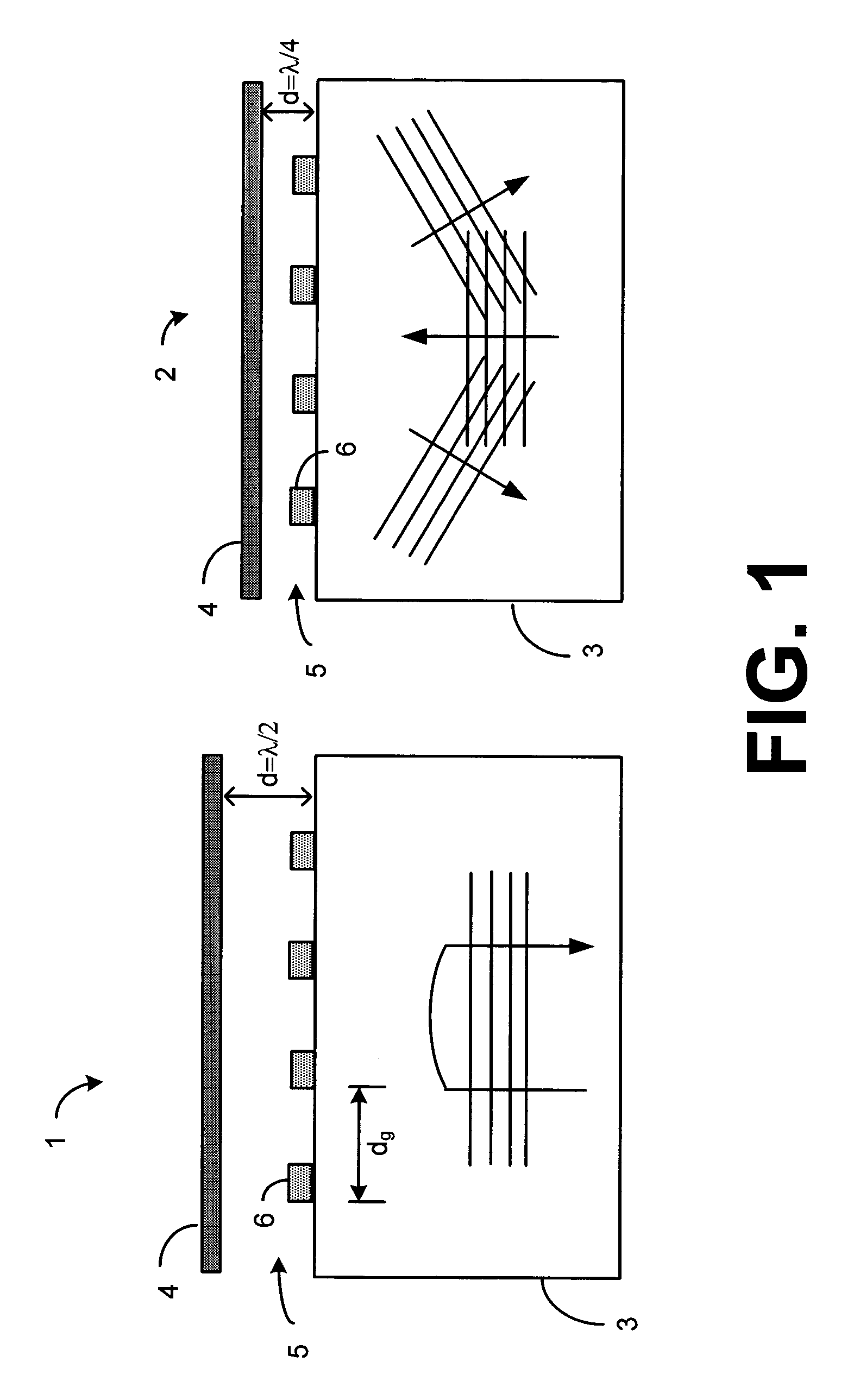
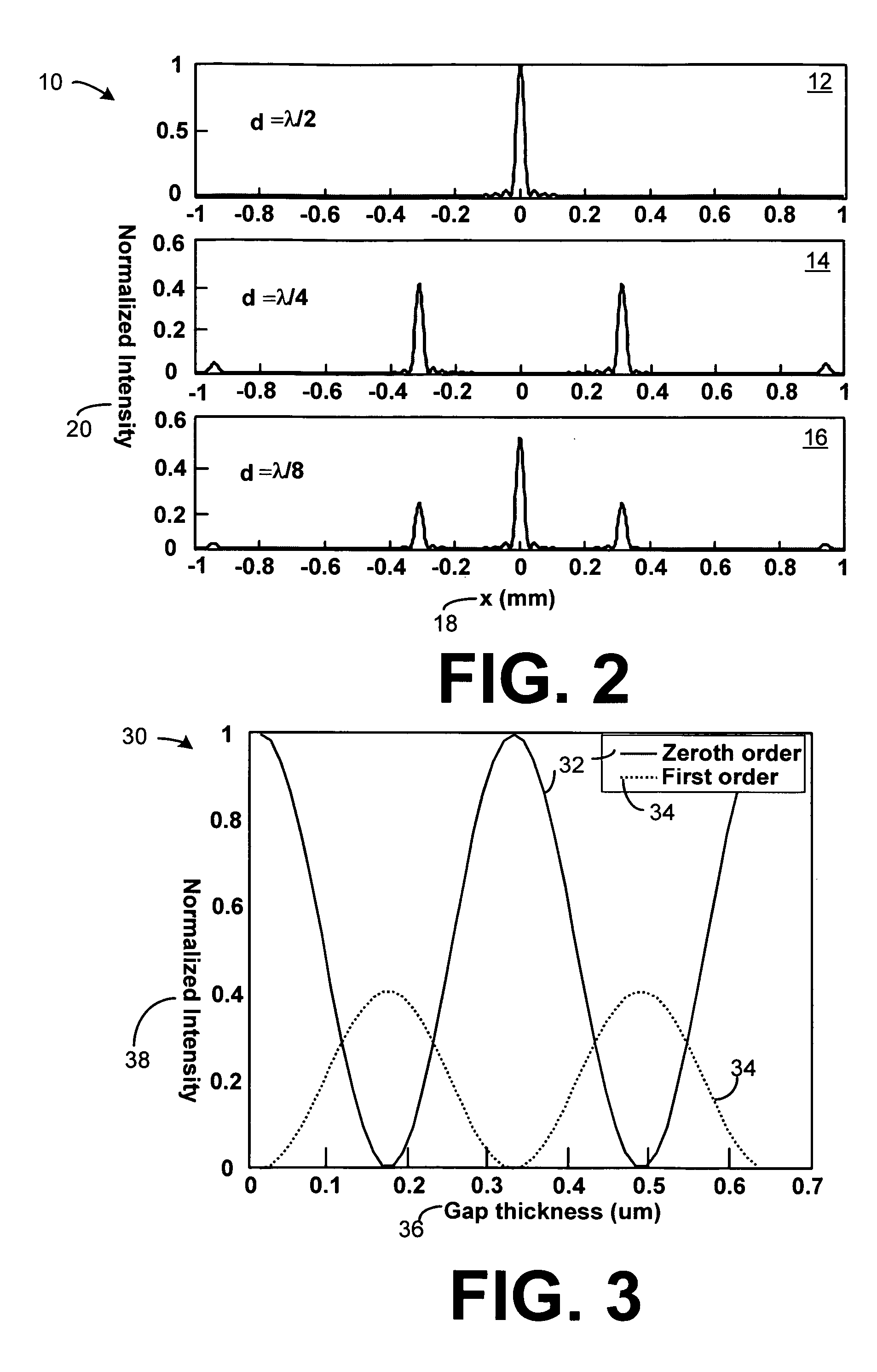
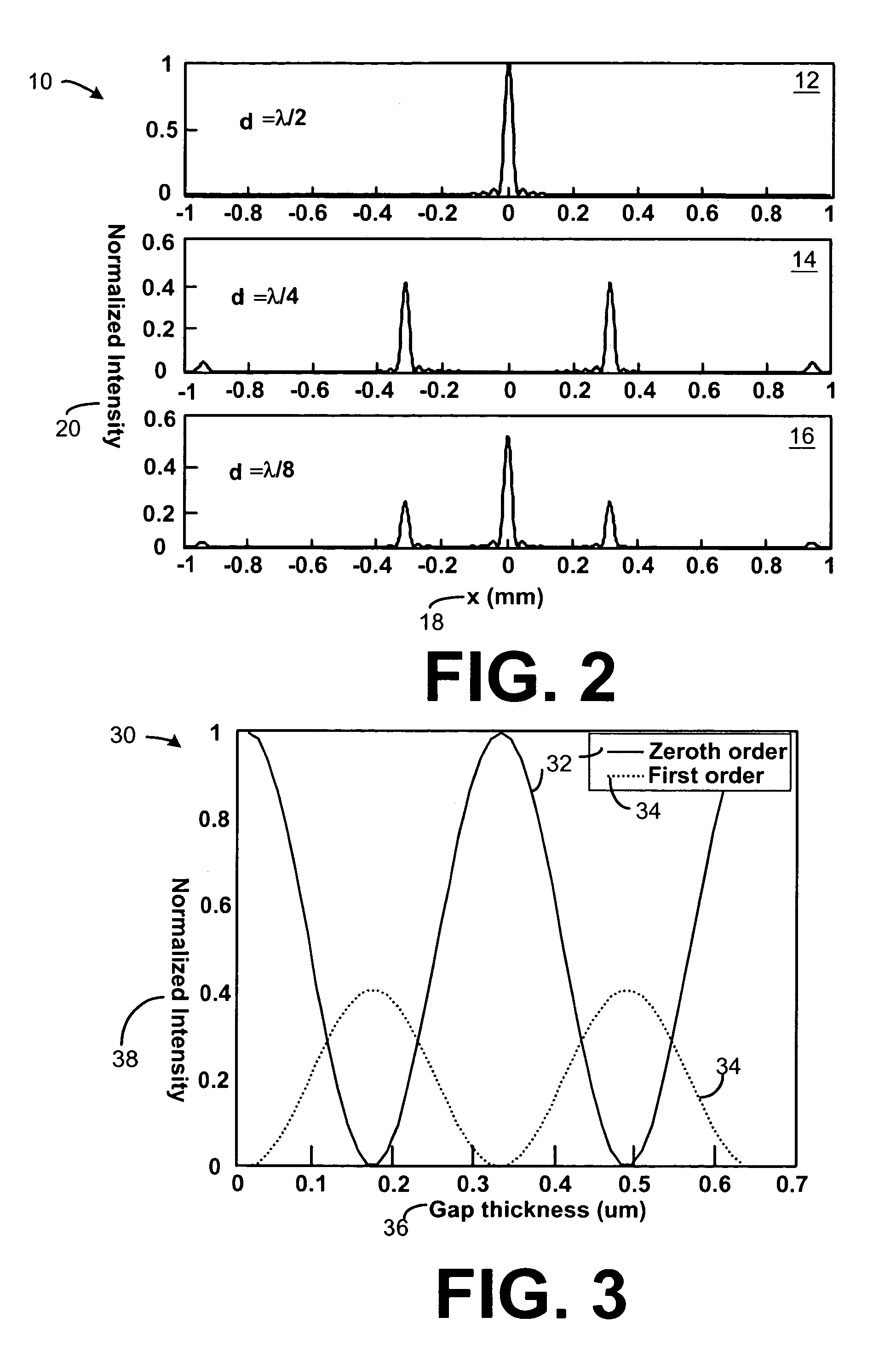
Highly-sensitive displacement-measuring optical device
Micron-scale displacement measurement devices having enhanced performance characteristics are disclosed. One embodiment of a micron-scale displacement measurement device includes a phase-sensitive reflective diffraction grating for reflecting a first portion of an incident light and transmitting a second portion of the incident light such that the second portion of the incident light is diffracted. The device can further include a mechanical structure having a first region and a second region, the mechanical structure positioned a distance d above the diffraction grating and forming a wall of a cavity, the second portion of the incident light is reflected off of the first region of the structure such that an interference pattern is formed by the reflected first portion and the reflected second portion of the incident light. The device can further include an orifice formed in the cavity to provide for the passage of air between the inside and outside of the cavity.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
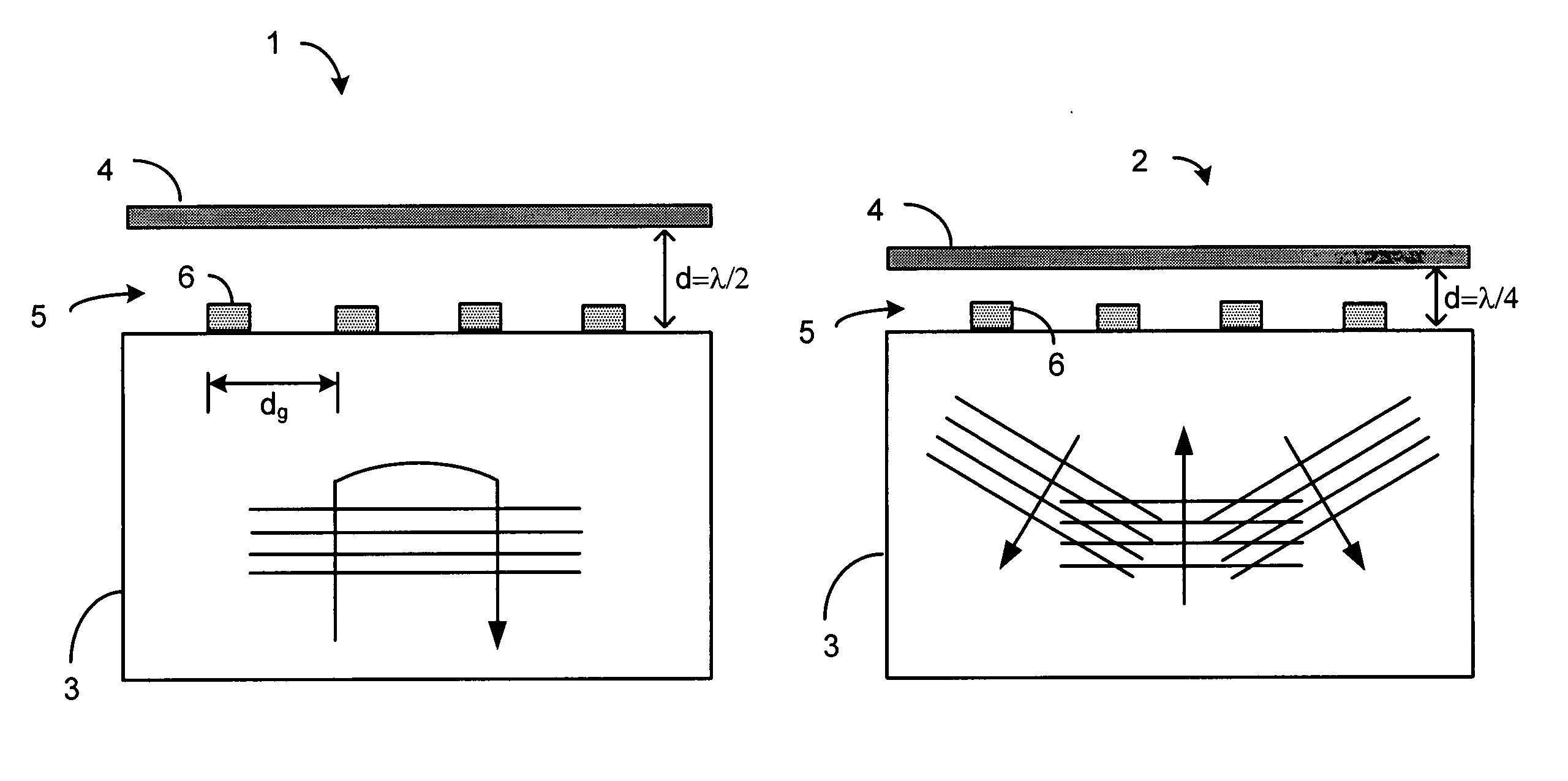
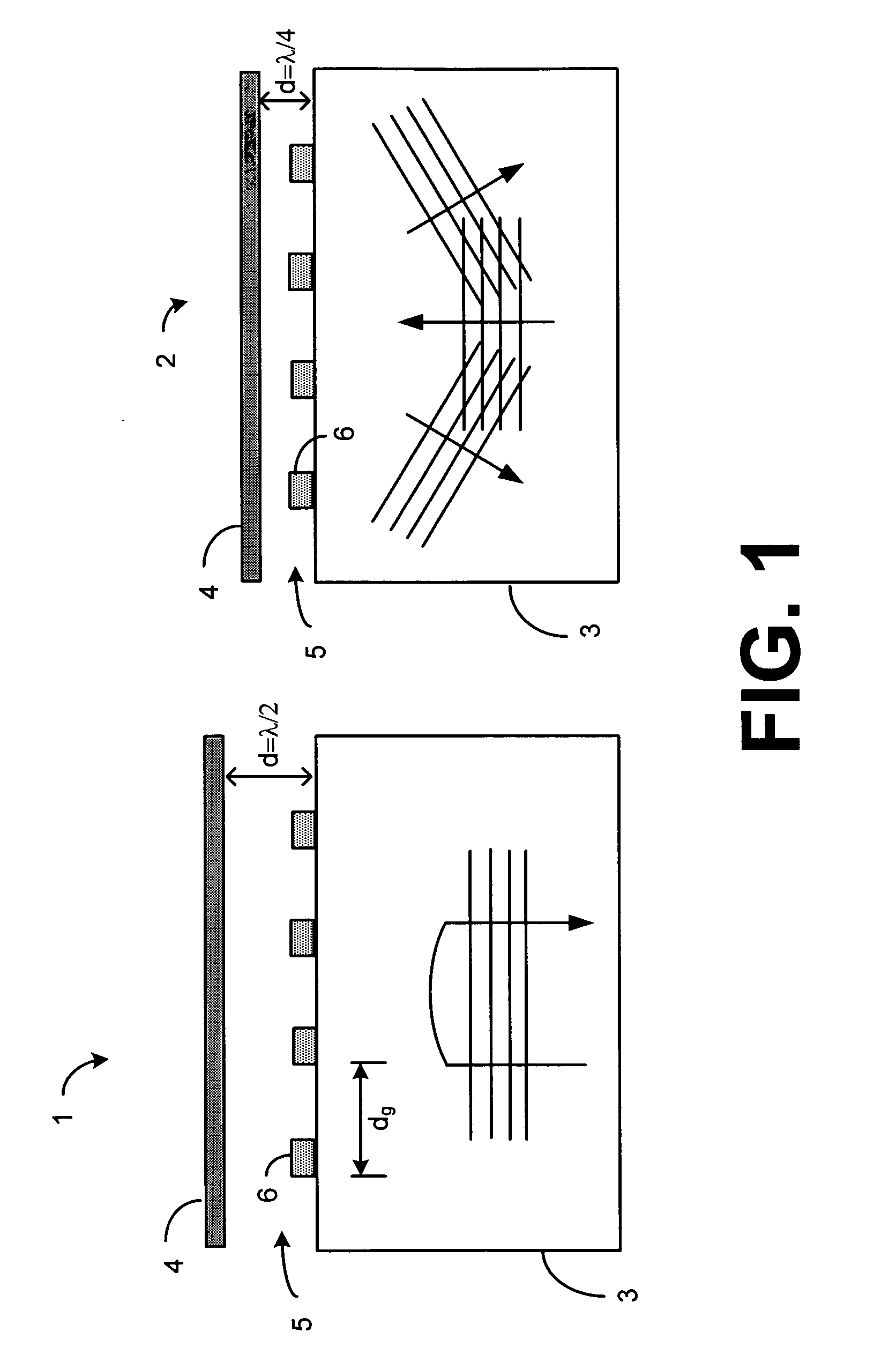
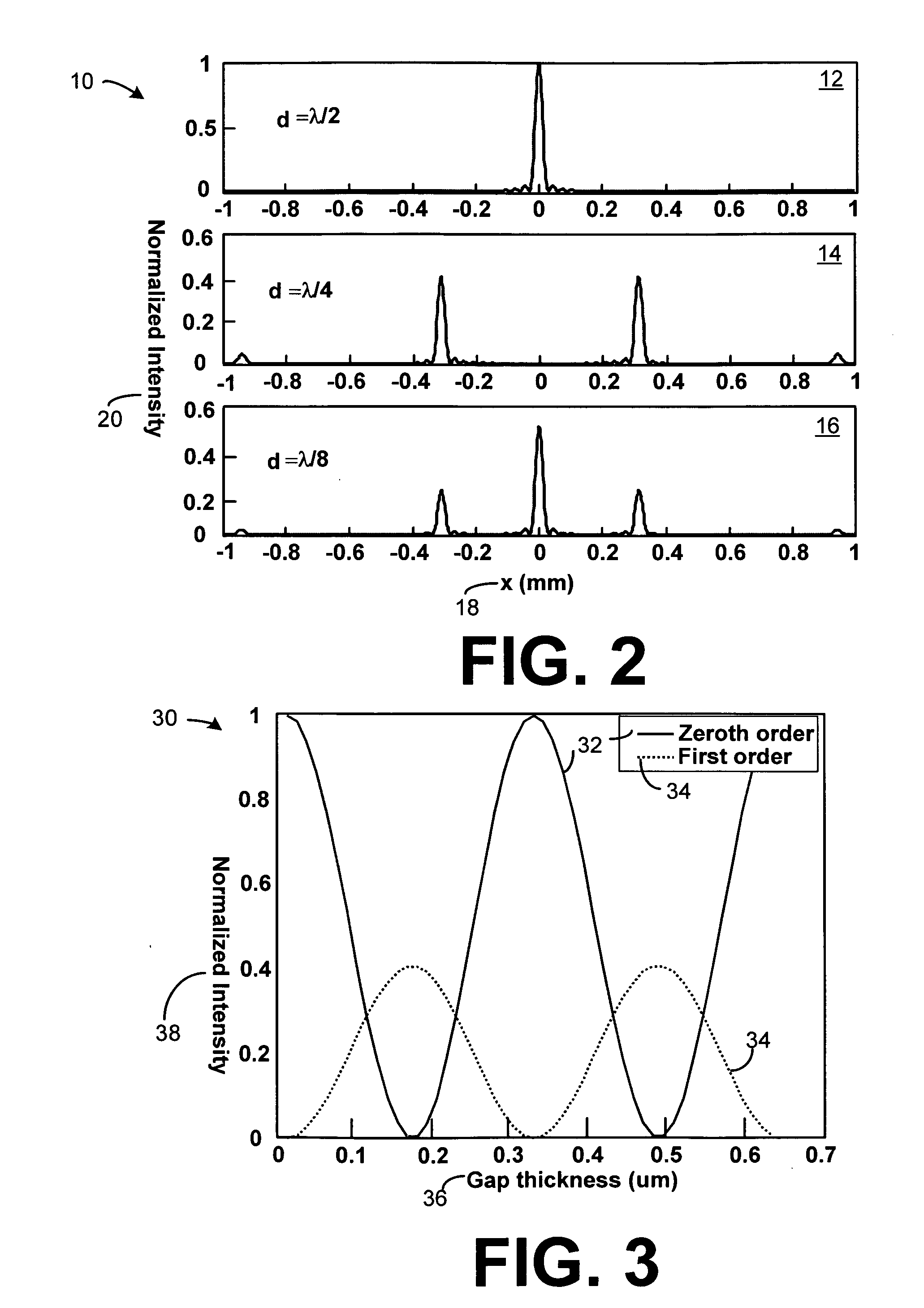
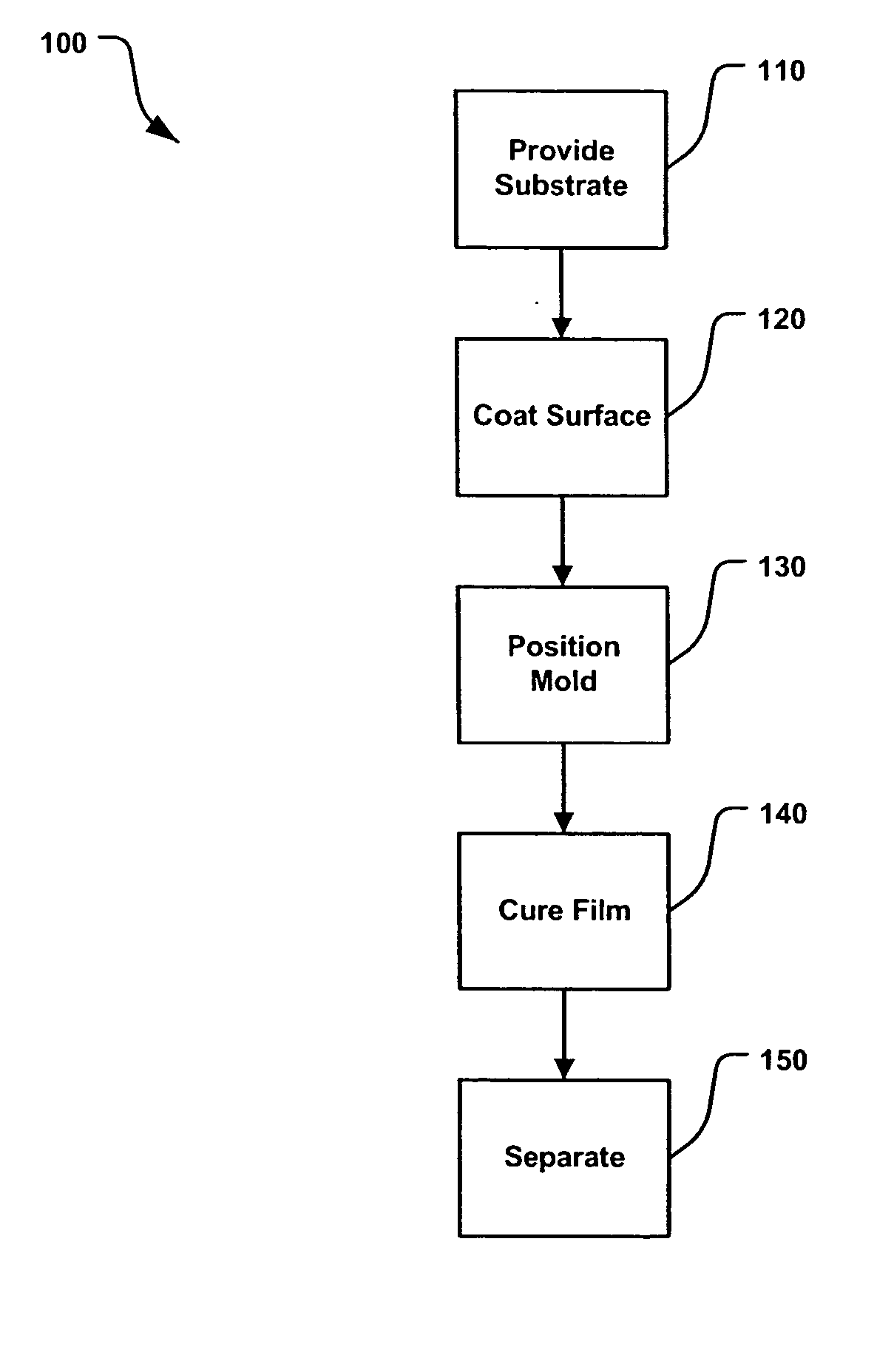
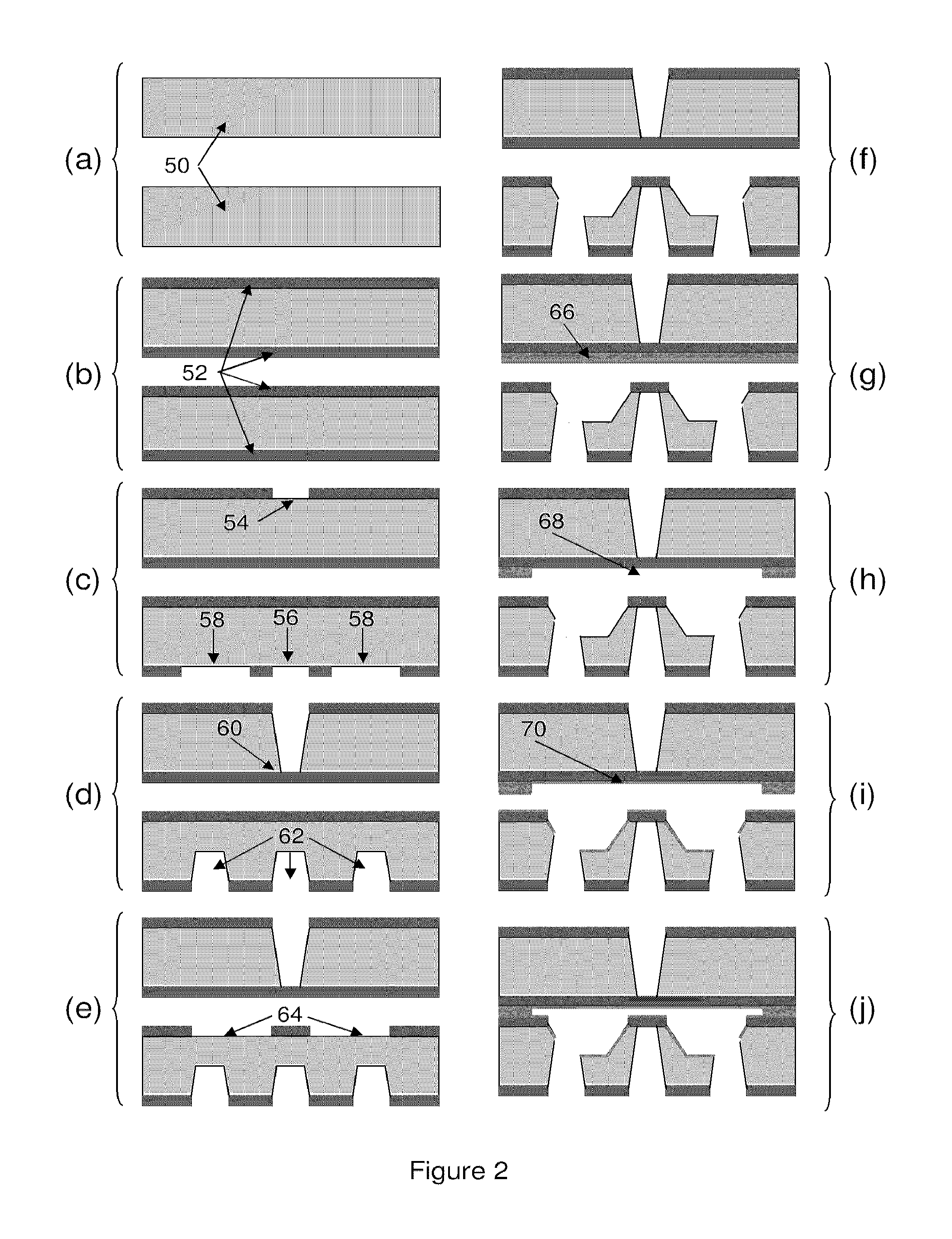
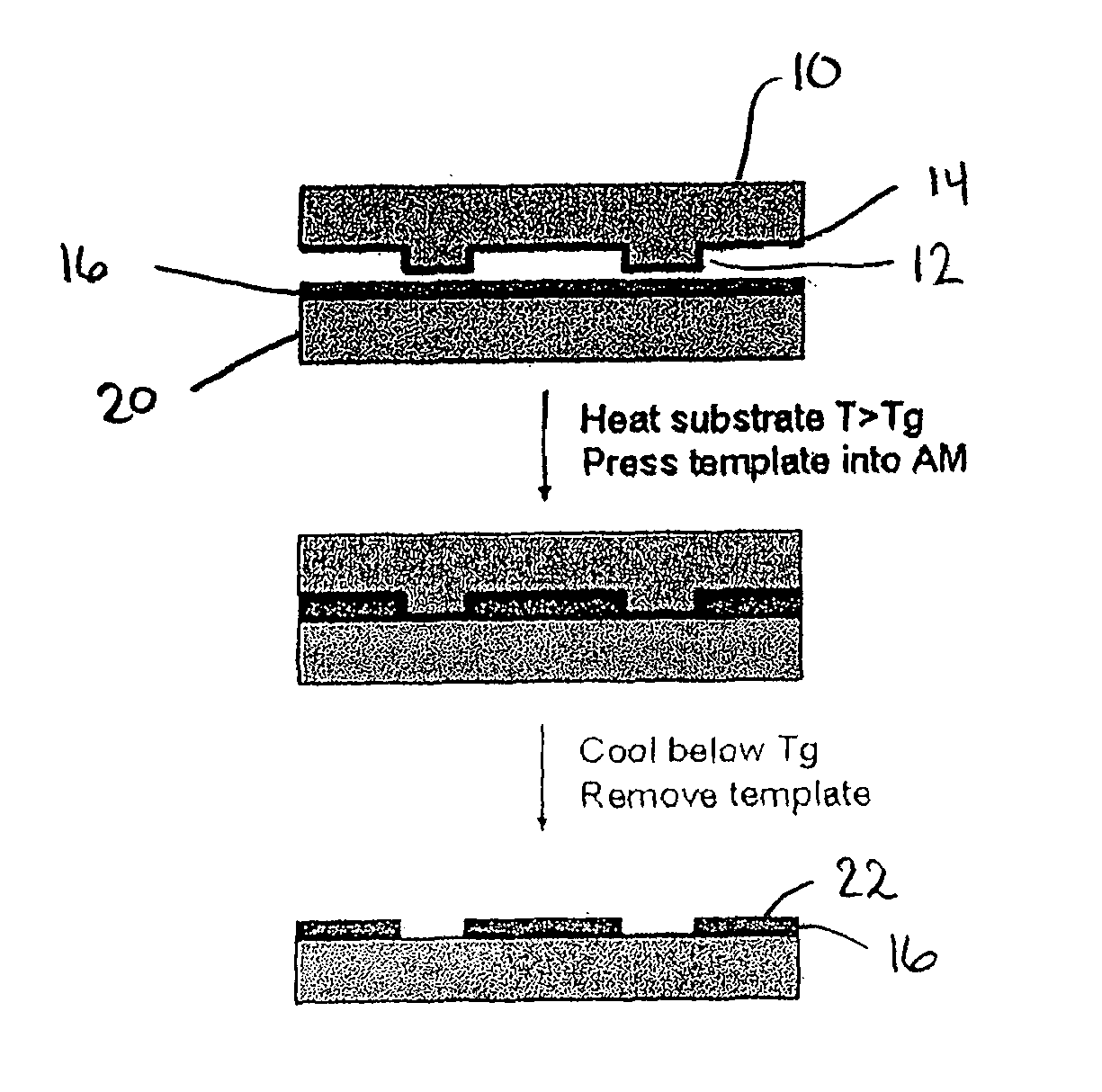
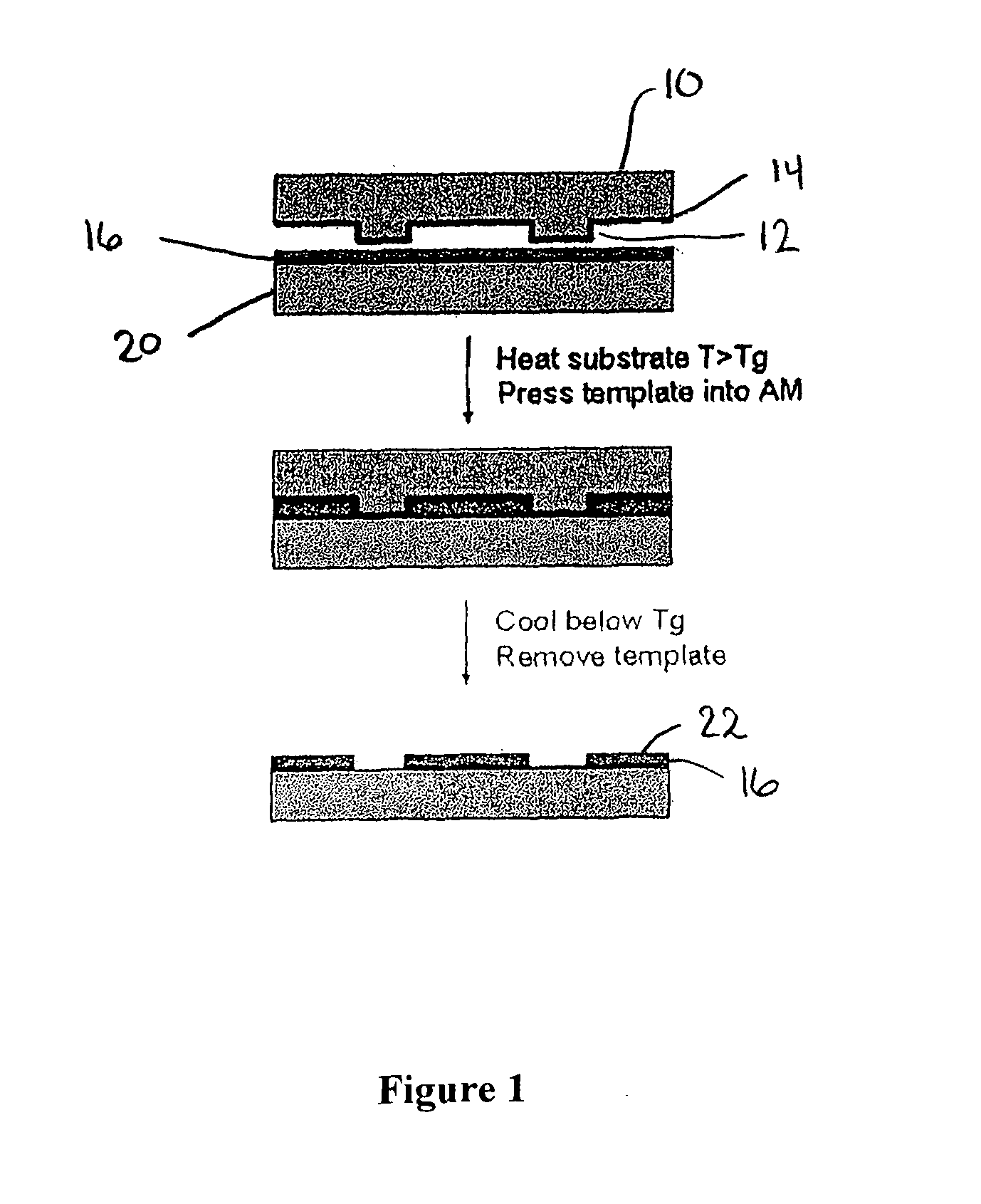
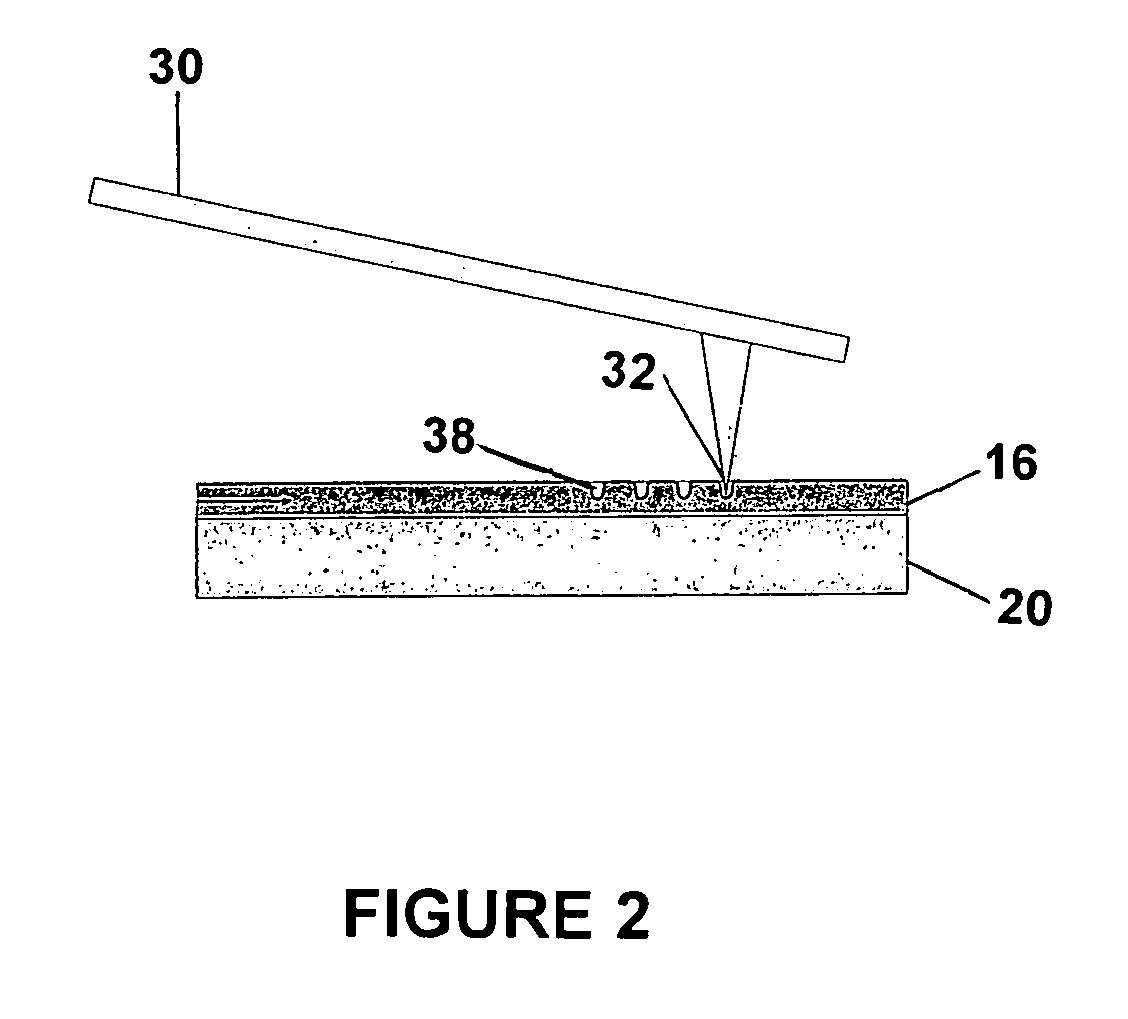
Sub-micron-scale patterning method and system
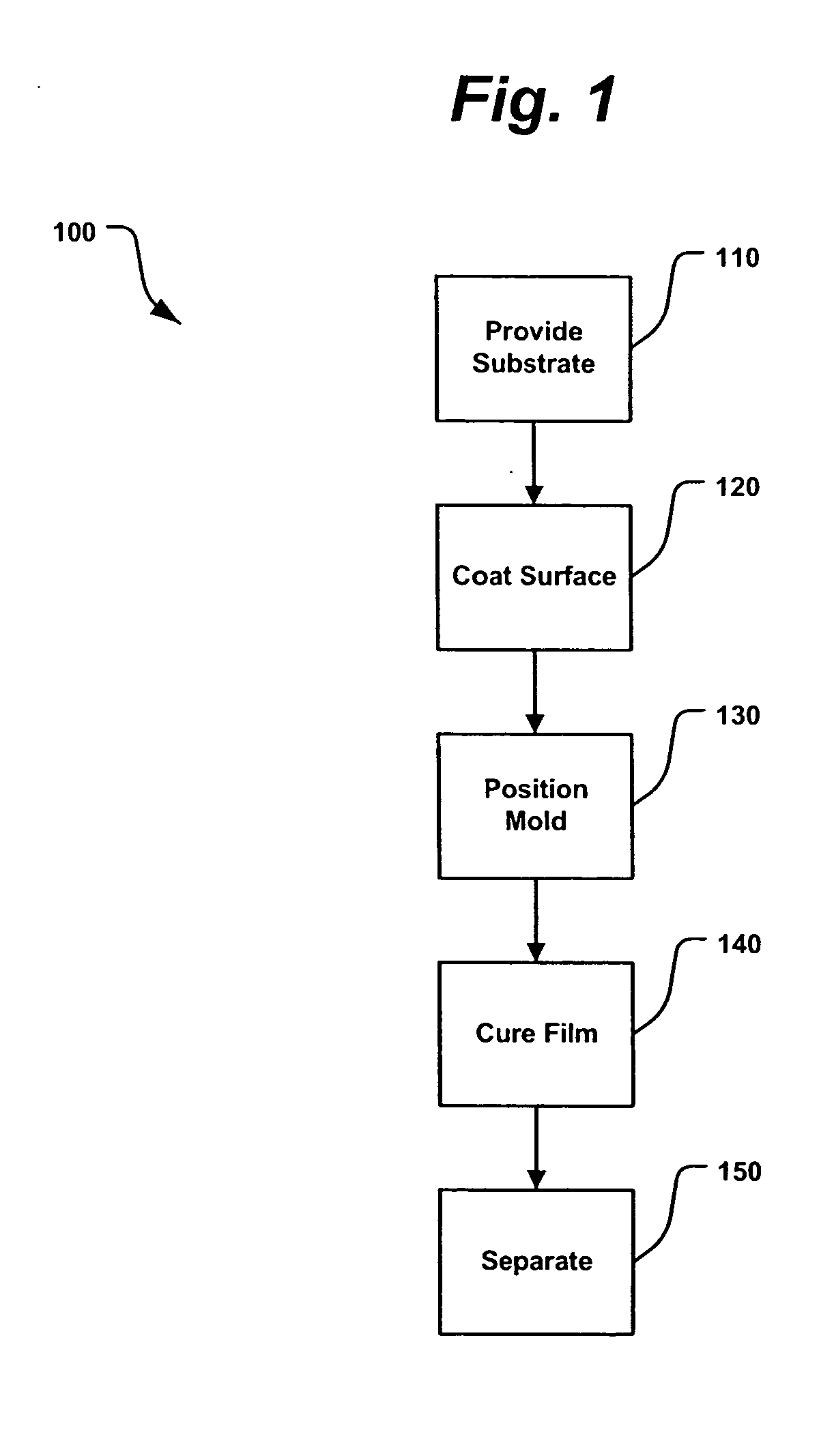
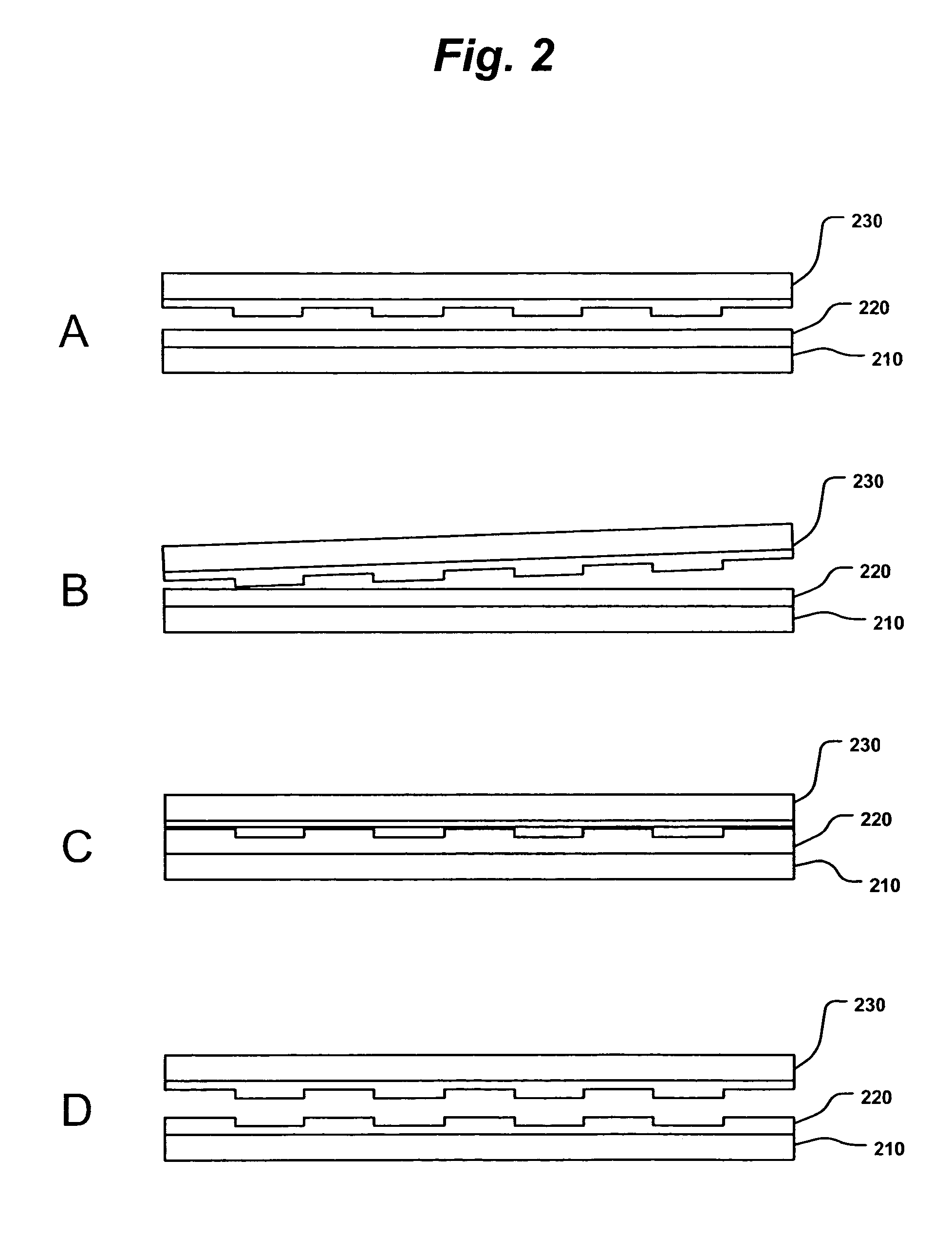
InactiveUS20050084613A1Control thicknessGood film uniformityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesLiquid layerMicron scale
A method for replicating a nanopattern is disclosed. This method includes identifying a substrate; coating a surface of the substrate with a liquid layer; positioning a mold having a plurality of recesses defining a negative of the nanopattern in sufficient proximity with the coated liquid layer to cause the liquid layer to self-fill at least a portion of the plurality of recesses of the mold; and, chemically transforming the liquid layer to enable the transformed film to substantially retain the nanopattern.
Owner:WANG JIAN +2
Structured targets for x-ray generation
InactiveUS20150092924A1Improve cooling effectHeat generationX-ray tube laminated targetsX-ray tube anode coolingMicron scaleHigh energy
We disclose targets for generating x-rays using electron beams, along with their method of fabrication. The targets comprise a number of microstructures fabricated from an x-ray target material arranged in close thermal contact with a substrate such that the heat is more efficiently drawn out of the x-ray target material. This in turn allows irradiation of the x-ray generating substance with higher electron density or higher energy electrons, which leads to greater x-ray brightness, without inducing damage or melting.The microstructures may comprise conventional x-ray target materials (such as tungsten) that are patterned at micron-scale dimensions on a thermally conducting substrate, such as diamond. The microstructures may have any number of geometric shapes to best generate x-rays of high brightness and efficiently disperse heat.In some embodiments, the target comprising microstructures may be incorporated into a rotating anode geometry, to enhance x-ray generation in such systems.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Method for preparing micro-nano composite texturing cutting tool by using femtosecond laser
The invention relates to the technical field of micro-structural surface preparation and laser micro-processing, and in particular provides a method for preparing a micro-nano composite texturing cutting tool by using femtosecond laser. In the method, micro-nano texturing and micro / nano composite texturing preparation is performed on the cutting tool surface by utilizing the unique interaction property between femtosecond laser and materials, the operation is simple, and the accuracy can be controlled. The preparation of micro / nano composite texture can be performed on a coated cutting tool by adopting a coated surface direct texturing method or a two-step composite texturing method. The method overcomes the defect of singleness of texturing only in micron scale in the conventional cutting tool texturing technology, and can further improve the abrasion resistance of the cutting tool, and prolong the service life of the cutting tool.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Superhydrophobic and self-cleaning powders and fabrication method thereof
The invention discloses nano / micron binary structured powders for superhydrophobic, self-cleaning applications. The powders are featured by micron-scale diameter and nano-scale surface roughness. In one embodiment, the average diameter is about 1-25 μm, and the average roughness Ra is about 3-100 nm. The nano / micron binary structured powders may be made of silica, metal oxide, or combinations thereof.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Emulsion deep profile/displacement control agent and preparation method of emulsion deep profile/displacement control agent containing gel microspheres of core shell structure
The invention relates to a preparation method of an emulsion deep profile / displacement control agent containing gel microspheres of a core shell structure. According to the method, materials are fed many times to carryout inverse emulsion low-temperature oxidation and reduction to initiate free radical polymerization so that water-solubility monomers (including acrylamide, ionic monomer I, the ionic monomer II and the third monomer) react with a cross-linking agent to generate the emulsion deep profile / displacement control agent containing gel microspheres of a core shell structure. The invention also relates to the emulsion deep profile / displacement control agent containing gel microspheres of a core shell structure, which is prepared by using the method. The profile / displacement control agent is a water-solubility microgel oil displacement material containing gel microspheres from nano scale to micron scale; with small initial grain size, the profile / displacement control agent can enter into the deep part of stratum; in addition, the profile / displacement control agent has high emulsion active component content and good flowability, can have volume expansion and mutual cementation under the actions of formation water and temperature according to the condition whether charges carried by the ionic monomers at a core layer and a shell layer are same or not; therefore the profile / displacement control requirements of different geological oil deposits of oil fields can be met.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Controlling peel strength of micron-scale structures
InactiveUS20060078725A1Facilitate and resist peelingLayered productsFilm/foil adhesivesMicron scaleEngineering
A fabricated microstructure includes a base and one or more nano-structures disposed on one or more portions of the base to adhere to a contact surface. The one or more portions of the base with the one or more nano-structures are located on the base such that, when the one or more nano-structures adhere to the contact surface and an external force is applied to peel the base from the contact surface, the one or more nano-structures in the one or more portions of the base facilitate or resist peeling of the nano-structures from the contact surface.
Owner:LEWIS & CLARK COLLEGE +1
Microporous filter membrane, method of making microporous filter membrane and separator employing microporous filter membranes
InactiveUS20050263452A1High porosityLittle precisionPaper/cardboard articlesDispersed particle filtrationMicron scaleFiltration membrane
A filter membrane, methods of making such filter membrane and apparatus employing such filter membrane are disclosed, in which the filter membrane is a monolithic polymeric membrane that includes a polymeric filter layer including a micron-scale precision-shaped pores and a polymeric support layer that has a precision-shaped porous support structure for the filter layer. Several methods are disclosed for making such a membrane using micromachining techniques, including lithographic, laser ablation and x-ray treatment techniques. Several filter apparatus employing such a membrane are also disclosed.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
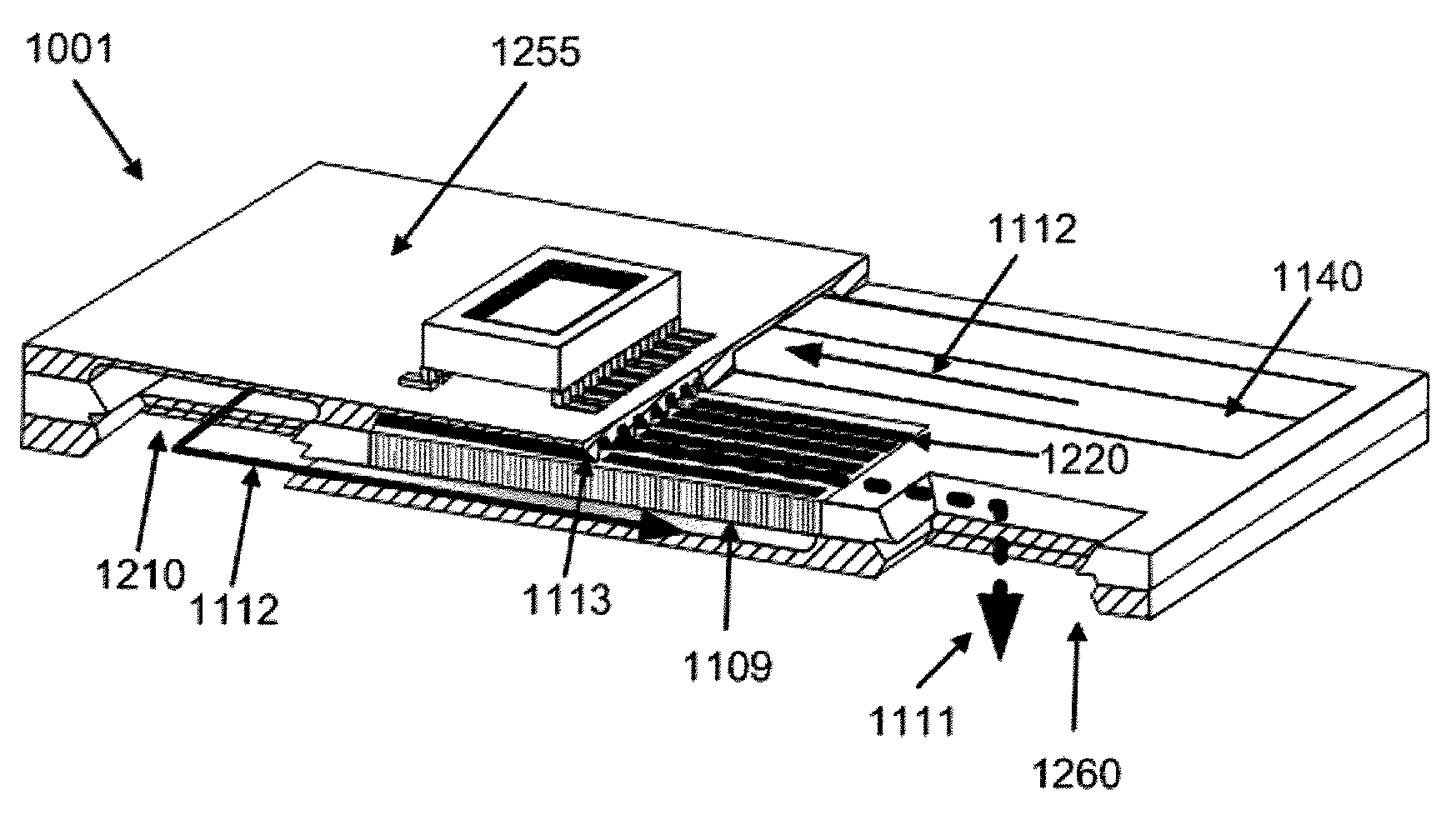
Silicon MEMS based two-phase heat transfer device
InactiveUS20070095507A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMicron scaleVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention is a MEMS-based two-phase LHP (loop heat pipe) and CPL (capillary pumped loop) using semiconductor grade silicon and microlithographic / anisotrophic etching techniques to achieve a planar configuration. The principal working material is silicon (and compatible borosilicate glass where necessary), particularly compatible with the cooling needs for electronic and computer chips and package cooling. The microloop heat pipes (μLHP™) utilize cutting edge microfabrication techniques. The device has no pump or moving parts, and is capable of moving heat at high power densities, using revolutionary coherent porous silicon (CPS) wicks. The CPS wicks minimize packaging thermal mismatch stress and improves strength-to-weight ratio. Also burst-through pressures can be controlled as the diameter of the coherent pores can be controlled on a sub-micron scale. The two phase planar operation provides extremely low specific thermal resistance (20-60W / cm2). The operation is dependent upon a unique micropatterened CPS wick which contains up to millions per square centimeter of stacked uniform micro-through-capillaries in semiconductor-grade silicon, which serve as the capillary “engine,” as opposed to the stochastic distribution of pores in the typical heat pipe wick. As with all heat pipes, cooling occurs by virtue of the extraction of heat by the latent heat of phase change of the operating fluid into vapor. In the cooling of a laptop computer processor the device could be attached to the processor during laptop assembly. Consistent with efforts to miniaturize electronics components, the current invention can be directly integrated with a unpackaged chip. For applications requiring larger cooling surface areas, the planar evaporators can be spread out in a matrix and integrally connected through properly sized manifold systems.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
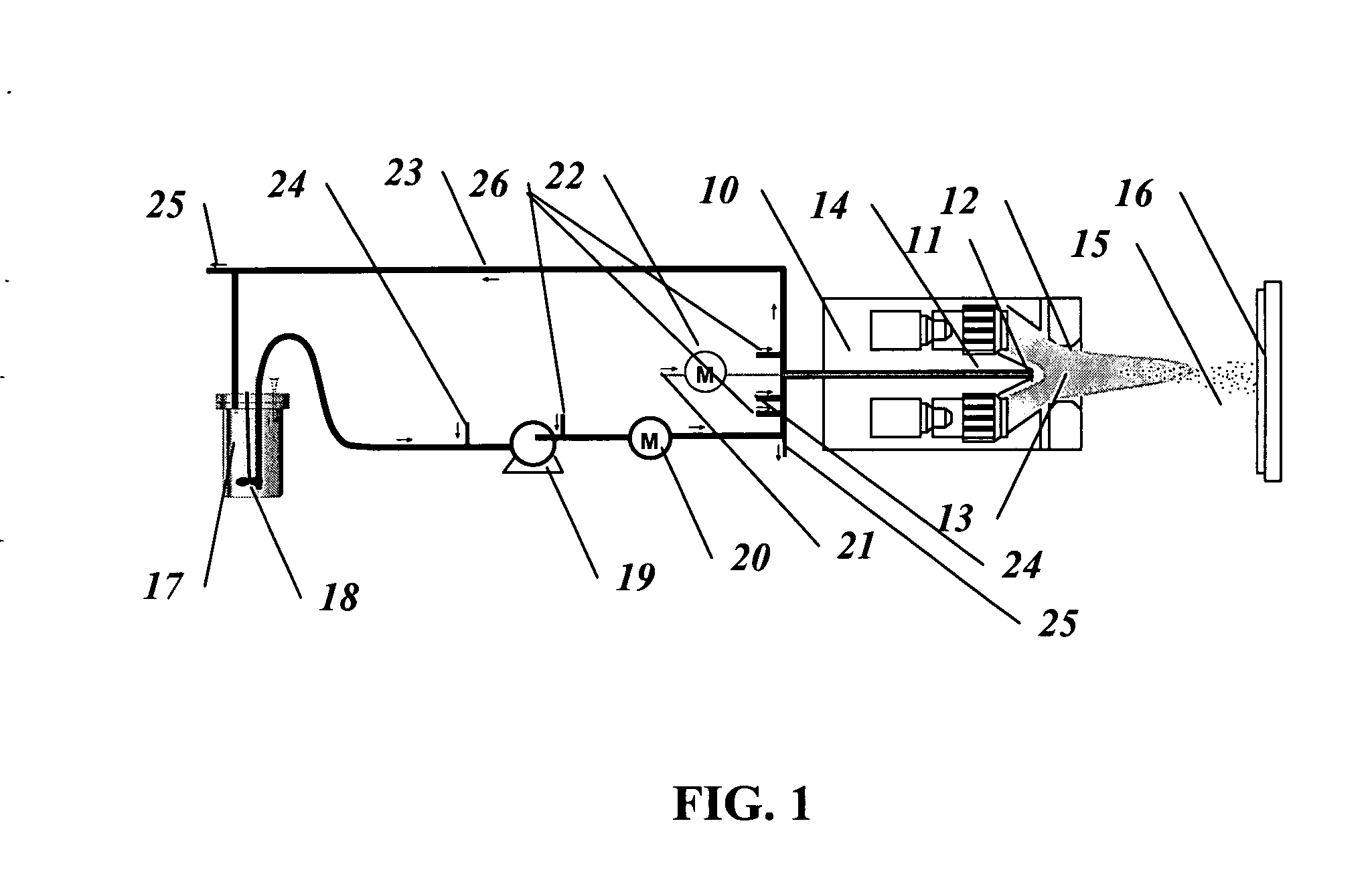
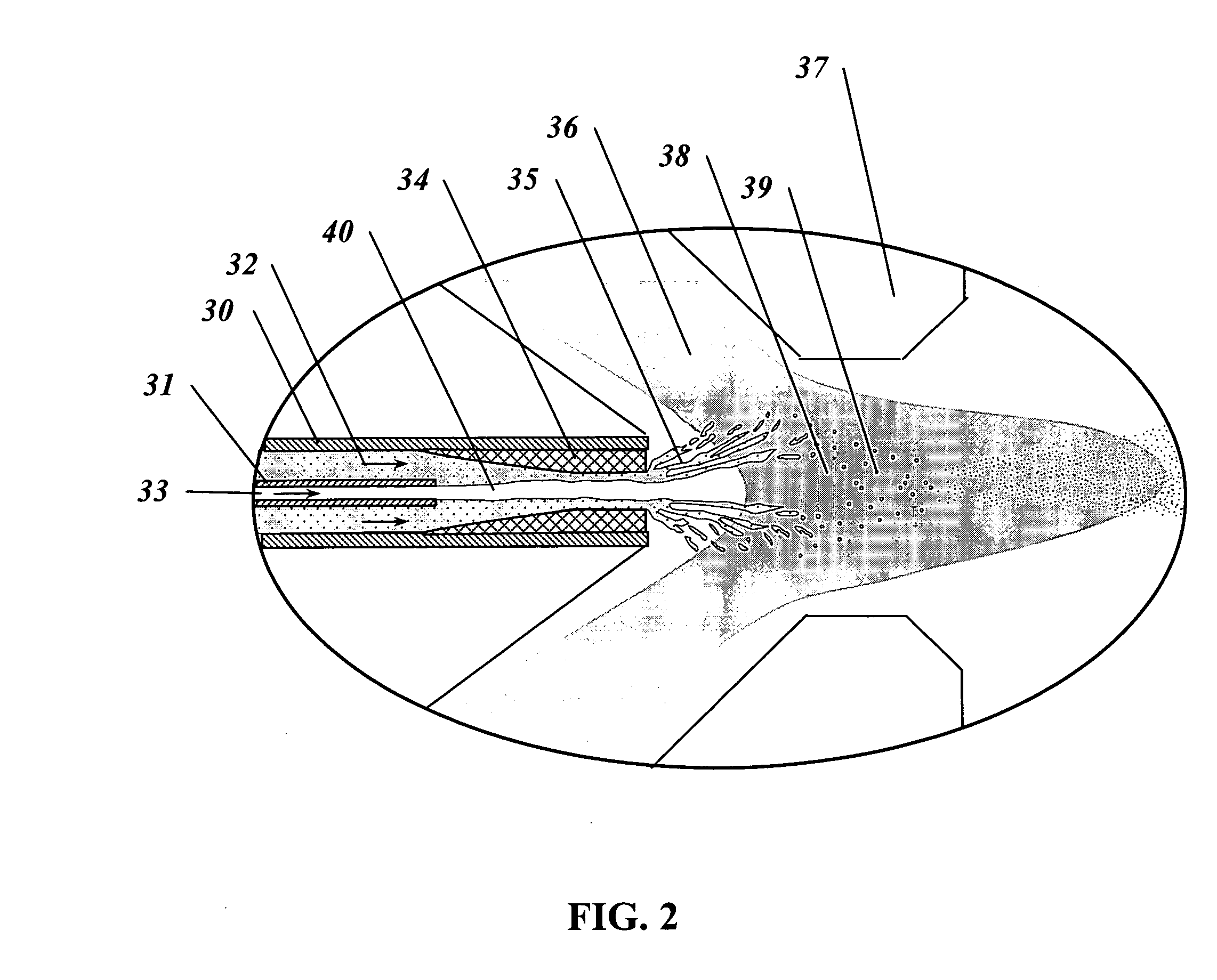
Method and apparatus for fine particle liquid suspension feed for thermal spray system and coatings formed therefrom
ActiveUS20060289405A1Efficient use ofImprove protectionMolten spray coatingCell electrodesThermal sprayingEngineering
This invention relates to a method by which liquid feedstock suspensions containing fine particles, micron- and nano-sized, are injected, with sufficient droplet velocity, preferably axially, into a thermal spray apparatus for the production of high-quality nanostructured coatings. The method allows complete entrainment of the droplets in a high temperature gas stream, while the injection orifice remains potentially blockage-free for long periods of operation.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Preparation method of pre-dispersed carbon nano-tube rubber masterbatches
ActiveCN104513410AHigh tear strengthWear volume reductionSpecial tyresMicron scaleHigh concentration
The invention belongs to the field of materials and specifically relates to a preparation method of pre-dispersed carbon nano-tube rubber masterbatches. The method is characterized in that the rubber masterbatches comprise the following ingredients, by weight, 5-100 parts of carbon nano-tube, 5-100 parts of rubber, 5-100 parts of wax, 0.5-50 parts of a dispersing aid, 0.5-5 parts of an anti-aging agent and 0.1-10 parts of an activator. The preparation method of the rubber masterbatches comprises the following specific steps: carrying out high-speed shearing on the above ingredients, mixing, carrying out in situ activated modification on carbon nano-tube such that carbon nano-tube is uniformly dispersed and has no micron-scale aggregate, and pelleting so as to obtain the pre-dispersed high-concentration carbon nano-tube rubber masterbatches. By the use of the pre-dispersed carbon nano-tube rubber masterbatches prepared by the above formula and method, tear strength of tire tread rubber can be raised by about 5-10% and even more, wear volume of Akron is reduced by about 30% and even more, volume resistivity is minimized by two orders of magnitudes, and mechanical properties such as tensile strength, elongation at break and the like are basically unchanged or increased a little.
Owner:SHANDONG DAZHAN NANO MATERIALS
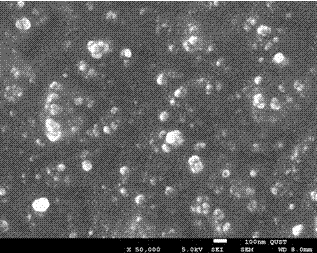
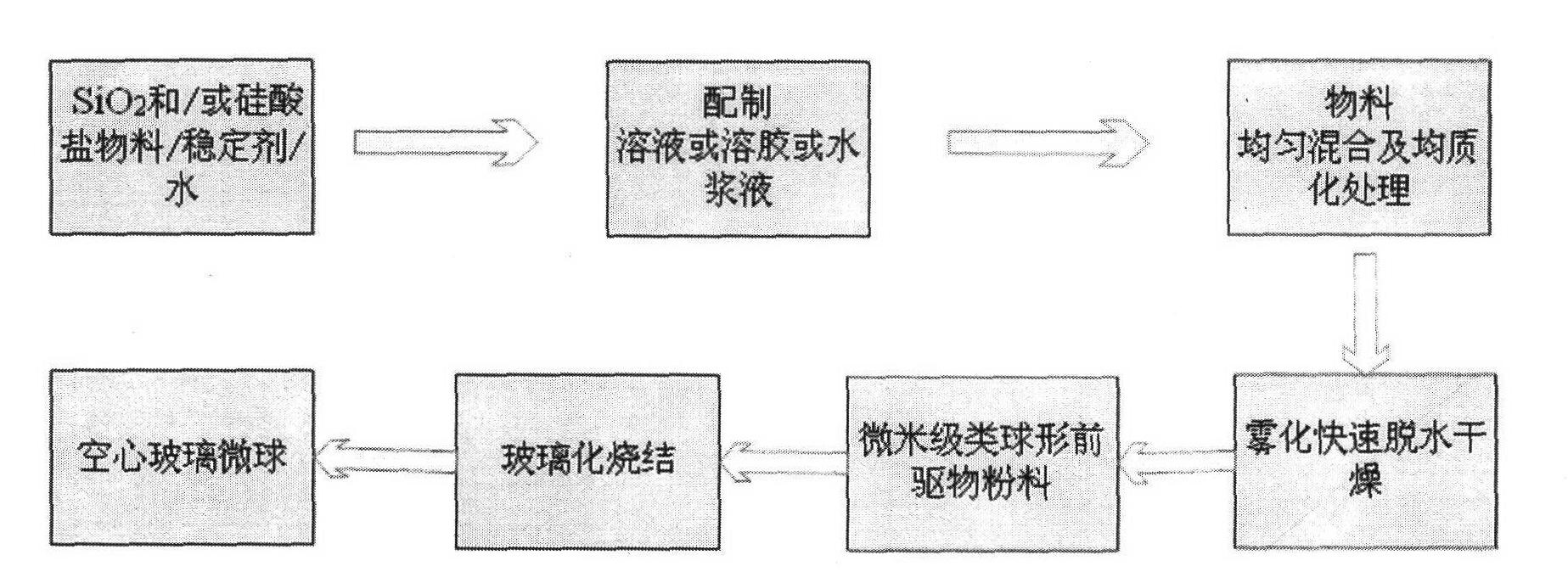
Soft chemical preparation method for hollow glass micro-balloon, prepared hollow glass micro-balloon and application thereof
ActiveCN102583973AHigh strengthHigh compressive strengthGlass shaping apparatusMicron scalePolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of a soft chemical method. According to the invention, the method is used for overcoming the defects that the traditional solid-phase glass powder method for preparing a hollow glass micro-balloon is high in energy consumption, long in technical process and difficult in controlling grain size distribution and the hollow glass micro-balloon prepared according to a liquid-phase atomizing method is high in alkalinity, easy to absorb water, high in strength and easy to break, and the like. A liquid material system is compounded through a chemical reaction; after the system is homogenized, the system is quickly atomized, dewatered and dried, thereby obtaining approximate spherical precursor powder with required grain size and corresponding distribution; and the powder is treated under high temperature at 600-1100 DEG C, thereby obtaining a micron-scale hollow glass micro-balloon with the volume floating rate being above 90%, the SiO2 content (weight) being 55-88%, the true density being 0.1-0.7g / cm<3> and the compression strength being 1-50MPa. The method is low in energy consumption, free from fusion and sintering, and high in yield. The prepared hollow glass micro-balloon is high in compression strength, light in weight, low-alkali, waterproof, excellent in fluidity and dispersibility, and suitable for various high-performance light compound materials.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photonic crystals and method for producing same
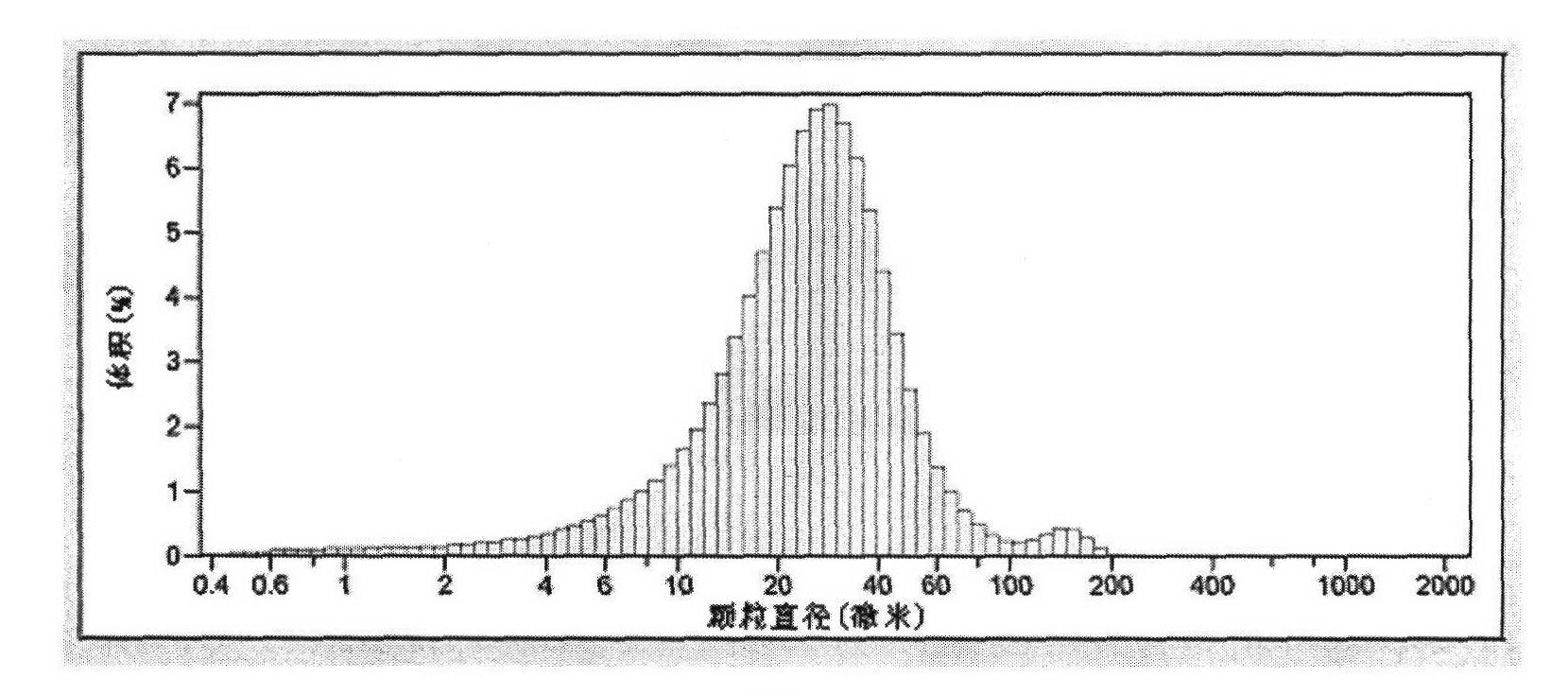
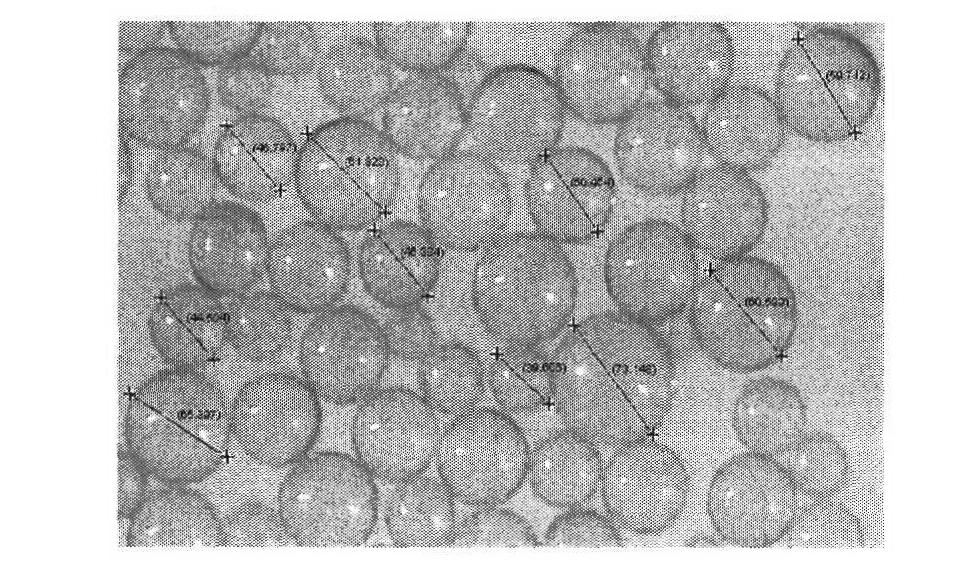
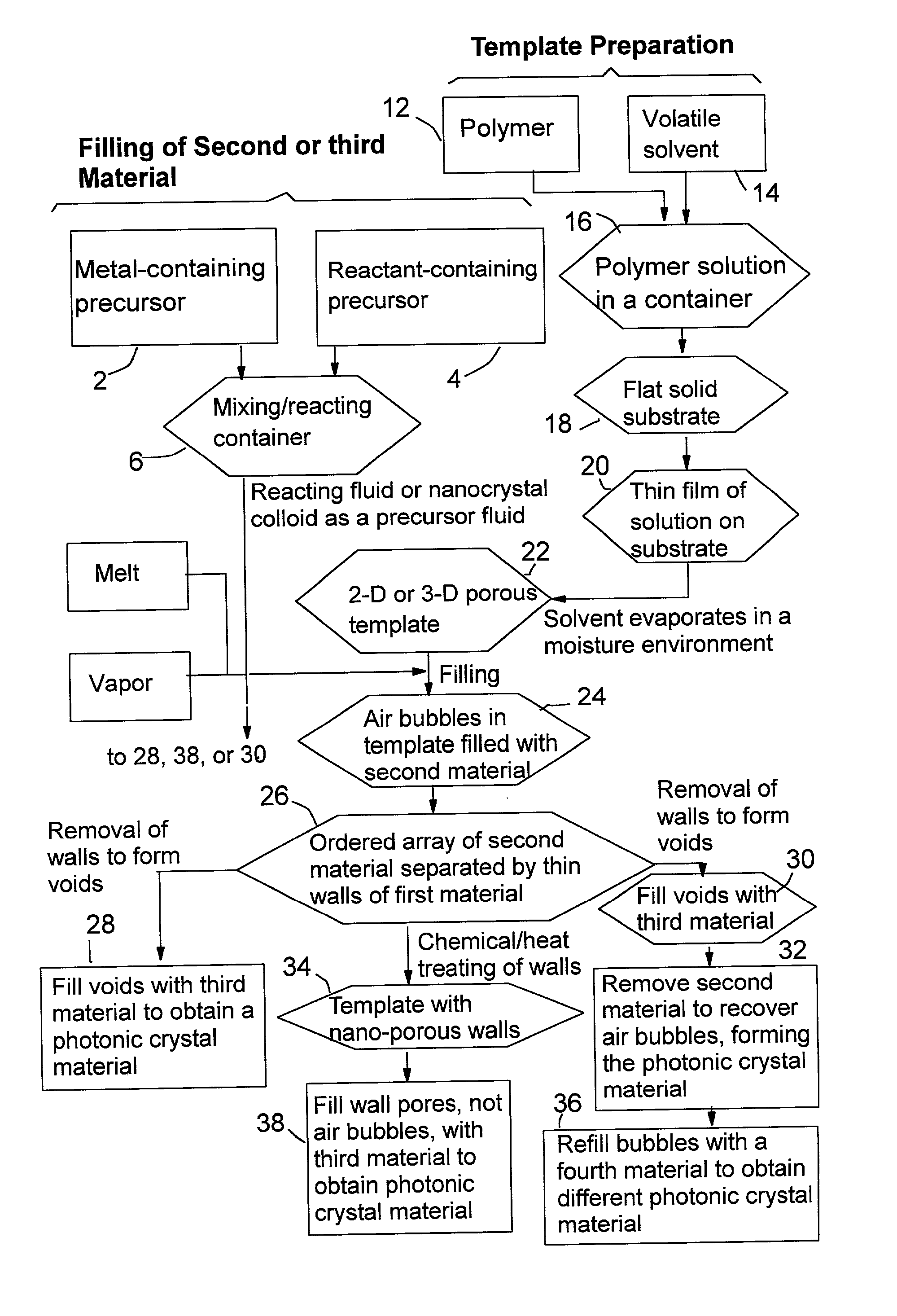
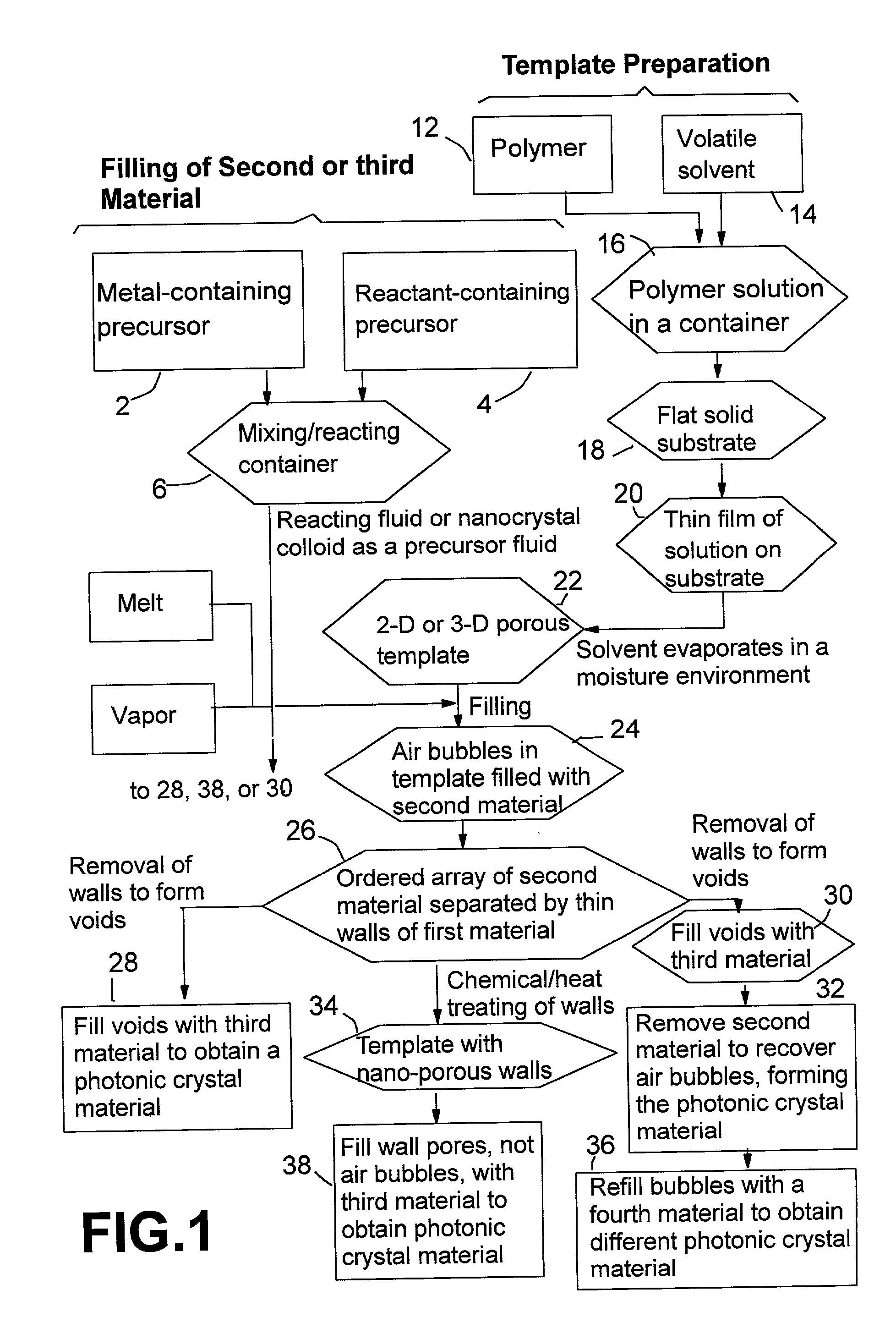
InactiveUS20030106487A1Simple and fastSimple procedureFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthChemistryMicrometer
A photonic crystal material and a method for producing such a material according to a predetermined, two-dimensional or three-dimensional porous template. The method include the steps of: (A) preparing a porous template, wherein the preparation step includes the sub-steps of (i) dissolving a first material in a volatile solvent to form an evaporative solution, (ii) depositing a thin film of the solution onto a substrate, and (iii) exposing the solution film to a moisture environment while allowing the solvent in the solution to evaporate for forming the template that is constituted of an ordered array of micrometer- or nanometer-scaled air bubbles, which are surrounded with walls and are dispersed in a film of the first material; (B) filling the air bubbles with a second material; (C) at least partially removing the walls to create a plurality of voids; (D) refilling the voids with a third material; and (E) removing the second material from the air bubbles to obtain the photonic crystal material in the form of an array of air bubbles with walls made of the third material.
Owner:HUANG WEN CHIANG
Hollow foam material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108069725AConducive to quality transferEasy to passCeramicwarePolymer resinNetwork structure
The invention relates to the field of porous materials, in particular to a hollow foam material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The hollow foam material is formed by three-dimensional connective support framework networks from the macroscopic angle, the support frameworks are microchannels with hollow structures in three-dimensional connection, the walls of the microchannels are compact or contain nano-scale pores and / or micro-scale pores. The hollow foam material with three-dimensional connective networks is prepared from a polymer resin foam material with three-dimensional connective networks with the structure design and the preparation method. The hollow foam material has three types of pores with adjustable sizes: macroscopic three-dimensional connective open meshes, three-dimensional connective hollow microchannels and nano-scale pores and / or micro-scale pores in microchannel wall bodies. The innovative structure characteristic of the three-dimensionalconnective hollow microchannels of the hollow foam material lays a foundation for application of the hollow foam material.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nanofluidic cell
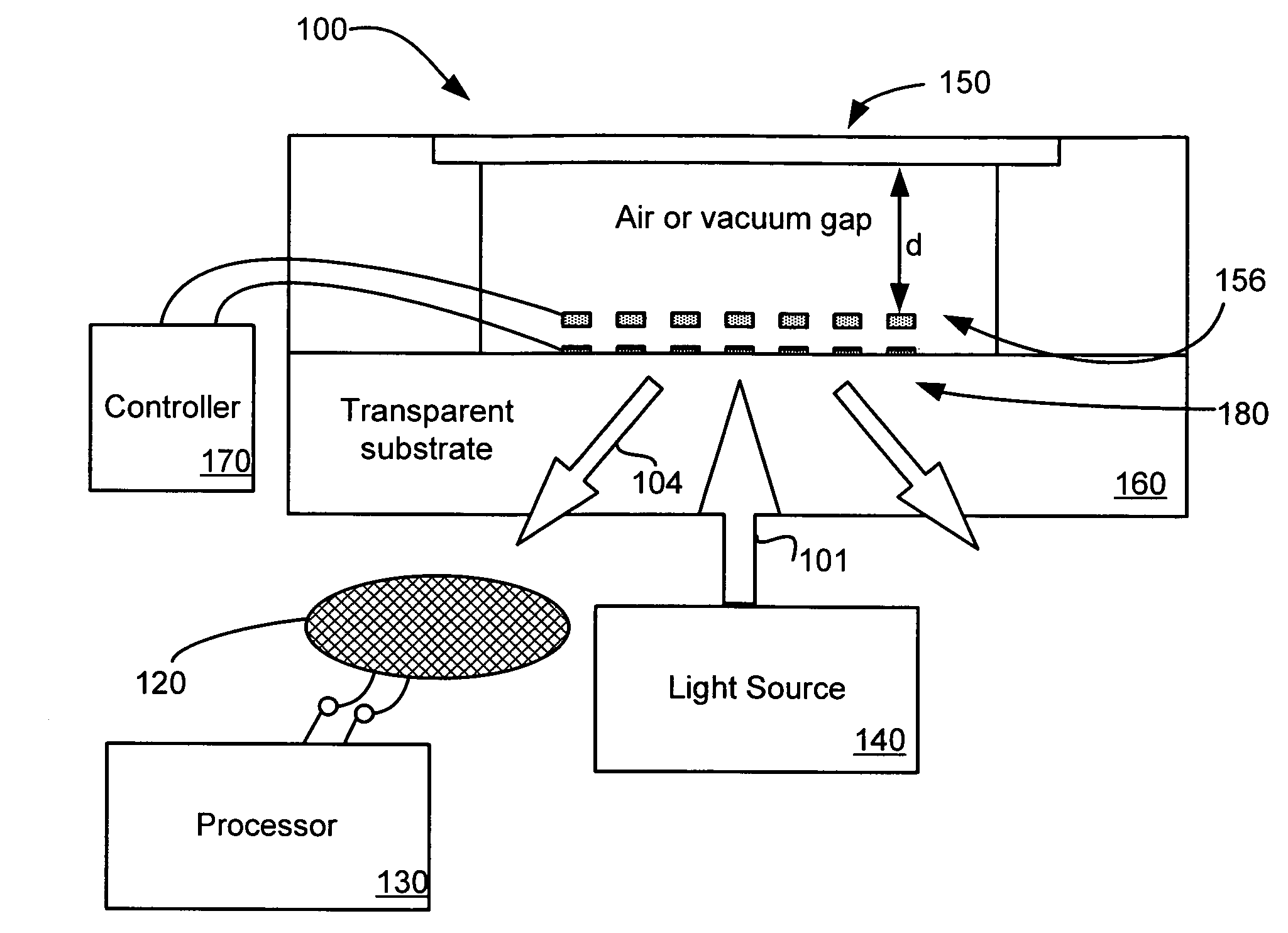
InactiveUS20120182548A1Reduced fluidic resistanceReduce resistanceMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMicron scaleActive feedback
A flow cell is provided for the analysis and / or microscopy of liquid or gas samples on the nanometer to micron scale. The flow cell preferably includes a thin membrane that is transparent to electrons and / or photons, thereby enabling the penetration of electrons or photons into a liquid flowing through the cell. Trenches are provided on either side of the membrane, which advantageously minimize fluidic resistance outside of the window area of the cell and also enable a faster response time in response to changes in external fluidic pressure. This feature enables active feedback using pathlength sensitive probes to stabilize the fluid flow to thin streams from nanometer to micron scale thicknesses with nanometer precision.
Owner:INSIGHT NANOFLUIDICS
Highly-sensitive displacement-measuring optical device
InactiveUS20060181712A1Slow imagingHigh precisionOptical signal transducersUsing optical meansMicron scaleMeasurement device
Micron-scale displacement measurement devices having enhanced performance characteristics are disclosed. One embodiment of a micron-scale displacement measurement device includes a phase-sensitive reflective diffraction grating for reflecting a first portion of an incident light and transmitting a second portion of the incident light such that the second portion of the incident light is diffracted. The device further includes a mechanical structure having a first region and a second region, the mechanical structure positioned a distance d above the diffraction grating, the second portion of the incident light is reflected off of the first region of the structure such that an interference pattern is formed by the reflected first portion and the reflected second portion of the incident light. The device can further include an electrode extending toward, but spaced a distance away from, the second region of the mechanical structure.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Microfluidic fuel cell systems with embedded materials and structures and method thereof
Described herein is a process for fabricating microfluidic systems with embedded components in which micron-scale features are molded into the polymeric material polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Micromachining is used to create a mold master and the liquid precursors for PDMS are poured over the mold and allowed to cure. The PDMS is then removed form the mold and bonded to another material such as PDMS, glass, or silicon after a simple surface preparation step to form sealed microchannels.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Method for Imprinting and Erasing Amorphous Metal Alloys
ActiveUS20100098967A1Surface roughnessLayered productsMechanical recordingMicron scaleNano manufacturing
The present invention relates to materials, methods and apparatuses for performing imprint lithography using amorphous metallic materials. The amorphous metallic materials can be employed as imprint media and thermoplastic forming processes are applied during the pattern transfer procedure to produce micron scale and nanoscale patterns in the amorphous metallic layer. The pattern transfer is in the form of direct mask embossing or through a serial nano-indentation process. A rewriting process is also disclosed, which involves an erasing mechanism that is accomplished by means of a second thermoplastic forming process. The amorphous metallic materials may also be used directly as an embossing mold in imprint lithography to allow high volume imprint nano-manufacturing. This invention also comprises of a method of smoothening surfaces under the action of the surface tension alone.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Highly-sensitive displacement-measuring optical device
InactiveUS7116430B2Accurate measurementOptical signal transducersInterferometersMicron scaleMeasurement device
The present invention relates to micron-scale displacement measurement devices. A first embodiment is a device that includes a substrate and a rigid structure suspended above the substrate to form a backside cavity. Formed in the rigid structure is a reflective diffraction grating positioned to reflect a first portion of an incident light and transmit a second portion of the incident light such that the second portion of the incident light is diffracted. The device also includes a membrane positioned a distance d above the reflective diffraction grating and at least a first photo-detector for receiving interference patterns produced from the first portion of the incident light reflected from the diffraction grating and the second portion of the incident light reflected from the membrane.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
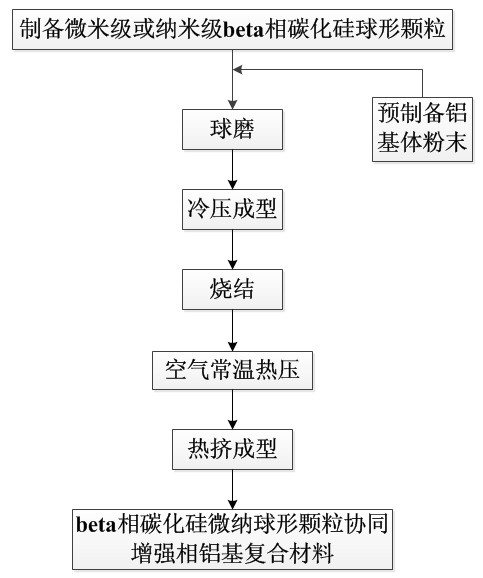
Silicon carbide reinforced aluminum-based composite material and its preparation method
The invention relates to a silicon carbide reinforced aluminum-based composite material and its preparation method. The composite material is characterized by being composited by micron-scale and nano-scale beta-phase silicon carbide spherical particles and an aluminum substrate, with the beta-phase silicon carbide spherical particles distributed in the aluminum substrate to form a synergistic reinforced phase. The preparation method is summarized to be mainly composed of: pre-preparing beta-phase silicon carbide spherical particles, adding aluminum substrate powder and the beta-phase silicon carbide spherical particles accounting for 0-25wt% of the composite material into a ball mill for ball milling treatment, and conducting cold press molding, sintering, as well as air hot pressing sequentially, and finally carrying out hot extrusion molding to obtain a molded product of the composite material. Specifically, the particle size of the aluminum substrate powder is 1micrometer to 100micrometers. The technical scheme of the invention innovatively uses spherical particulate beta-phase silicon carbide and makes use of the synergistic reinforcement effect of the micron and nano-silicon carbide particles, substantially improves the strength, toughness, abrasion resistance and others of the aluminum-based composite material. The preparation process is simple, and the cost input is effectively reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI +1
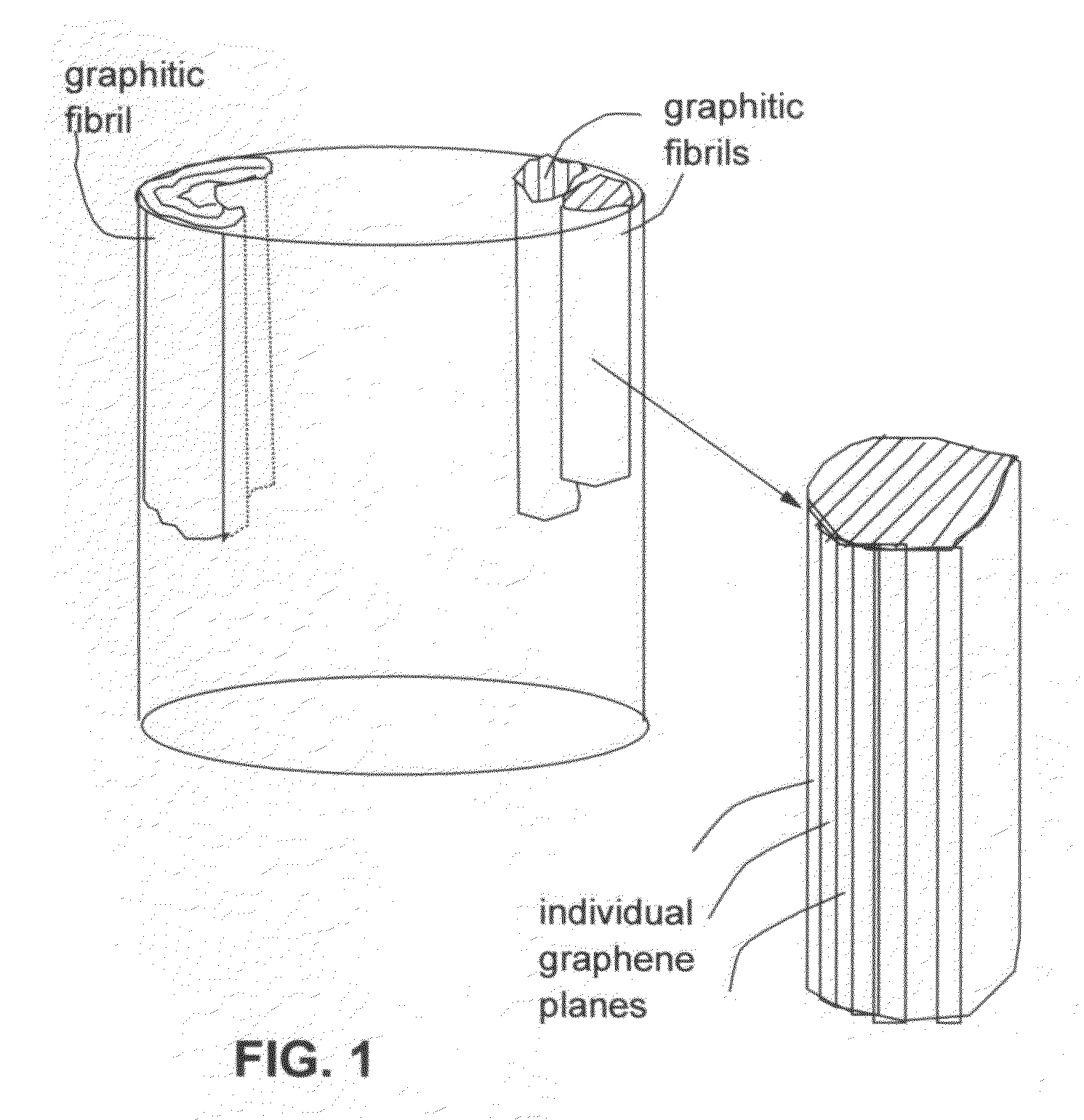
Chemically functionalized submicron graphitic fibrils, methods for producing same and compositions containing same
ActiveUS20110133132A1Different propertyGood hardening effectMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsMicron scaleFiber
The present invention provides a chemically functionalized submicron graphitic fibril having a diameter or thickness less than 1 μm, wherein the fibril is free of continuous thermal carbon overcoat, free of continuous hollow core, and free of catalyst. The fibril is obtained by splitting a micron-scaled carbon fiber or graphite fiber along the fiber axis direction. These functionalized graphitic fibrils exhibit exceptionally high electrical conductivity, high thermal conductivity, high elastic modulus, high strength and good interfacial bonding with a matrix resin in a composite. The present invention also provides several products that contain submicron graphitic fibrils: (a) paper, thin-film, mat, and web products; (b) rubber or tire products; (c) energy conversion or storage devices, such as fuel cells, lithium-ion batteries, and supercapacitors; (d) adhesives, inks, coatings, paints, lubricants, and grease products; (e) heavy metal ion scavenger; (f) absorbent (e.g., to recover spill oil); (g) sensors; (h) friction and brake components; (i) radiation-shield components; (j) catalyst carrier; and (k) composite materials.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com