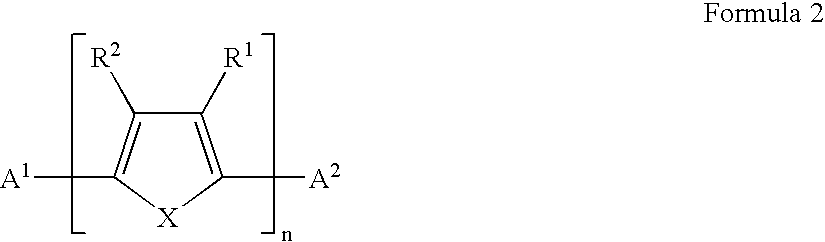Patents
Literature
1465 results about "Liquid layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
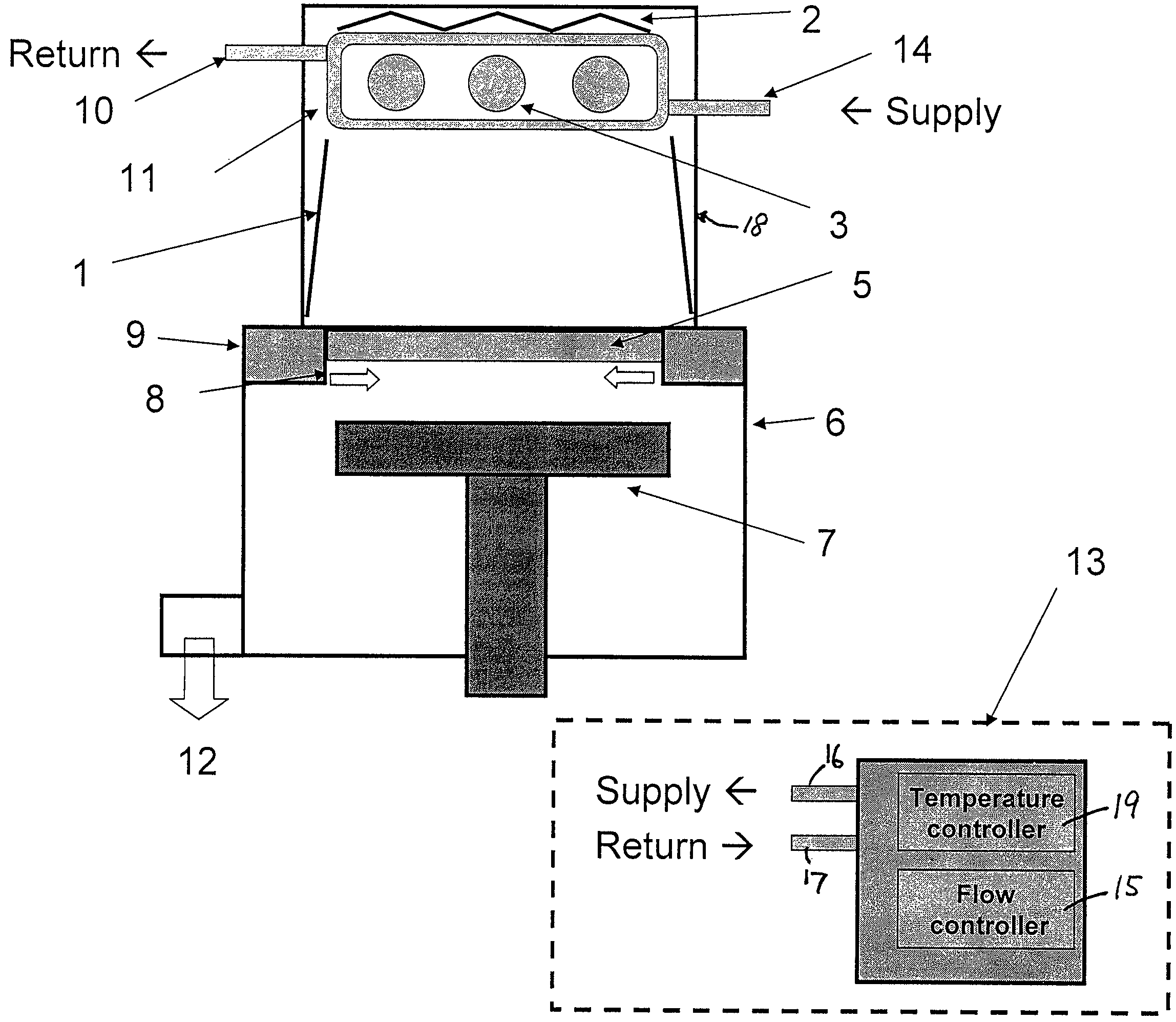
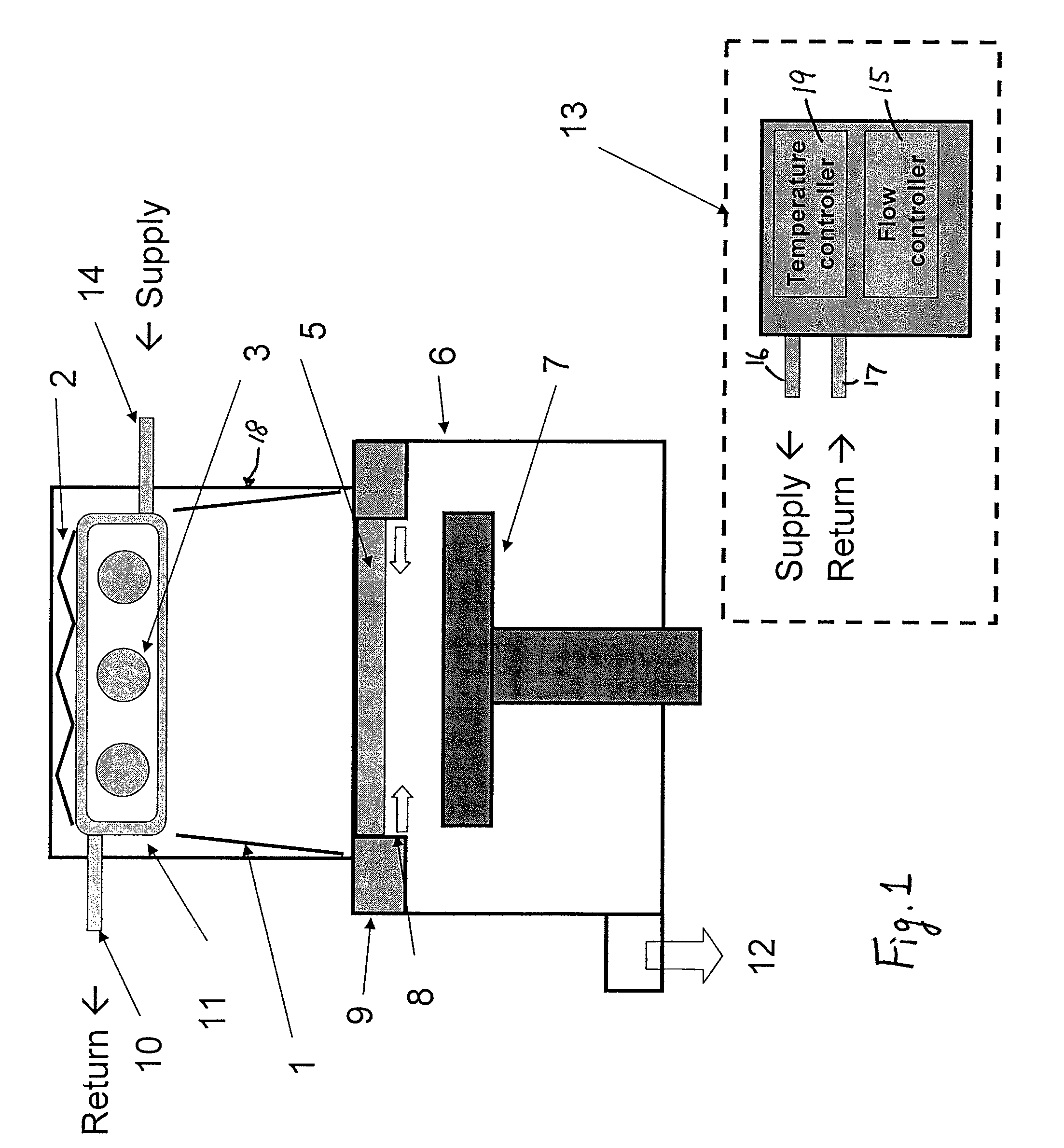
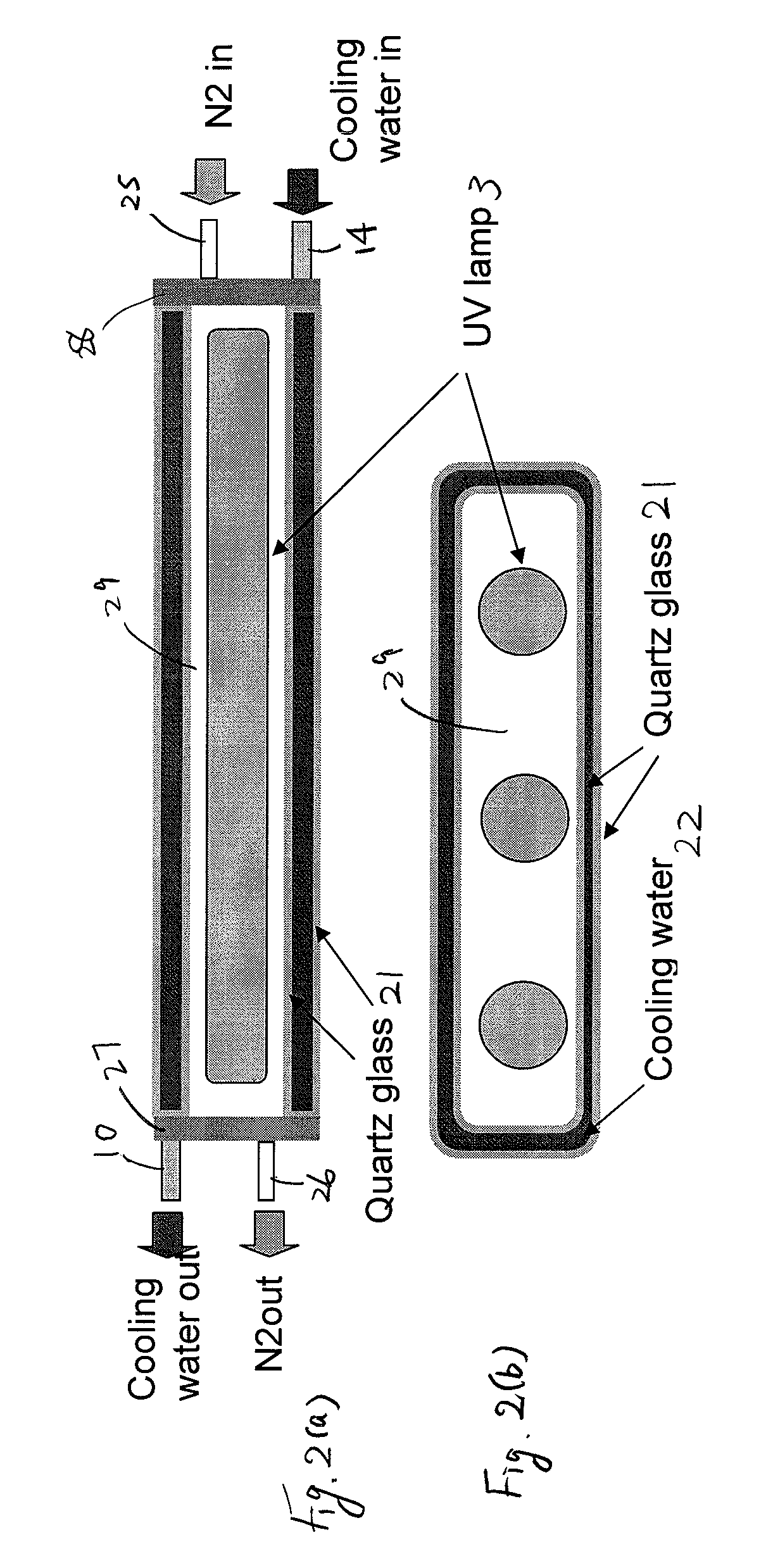
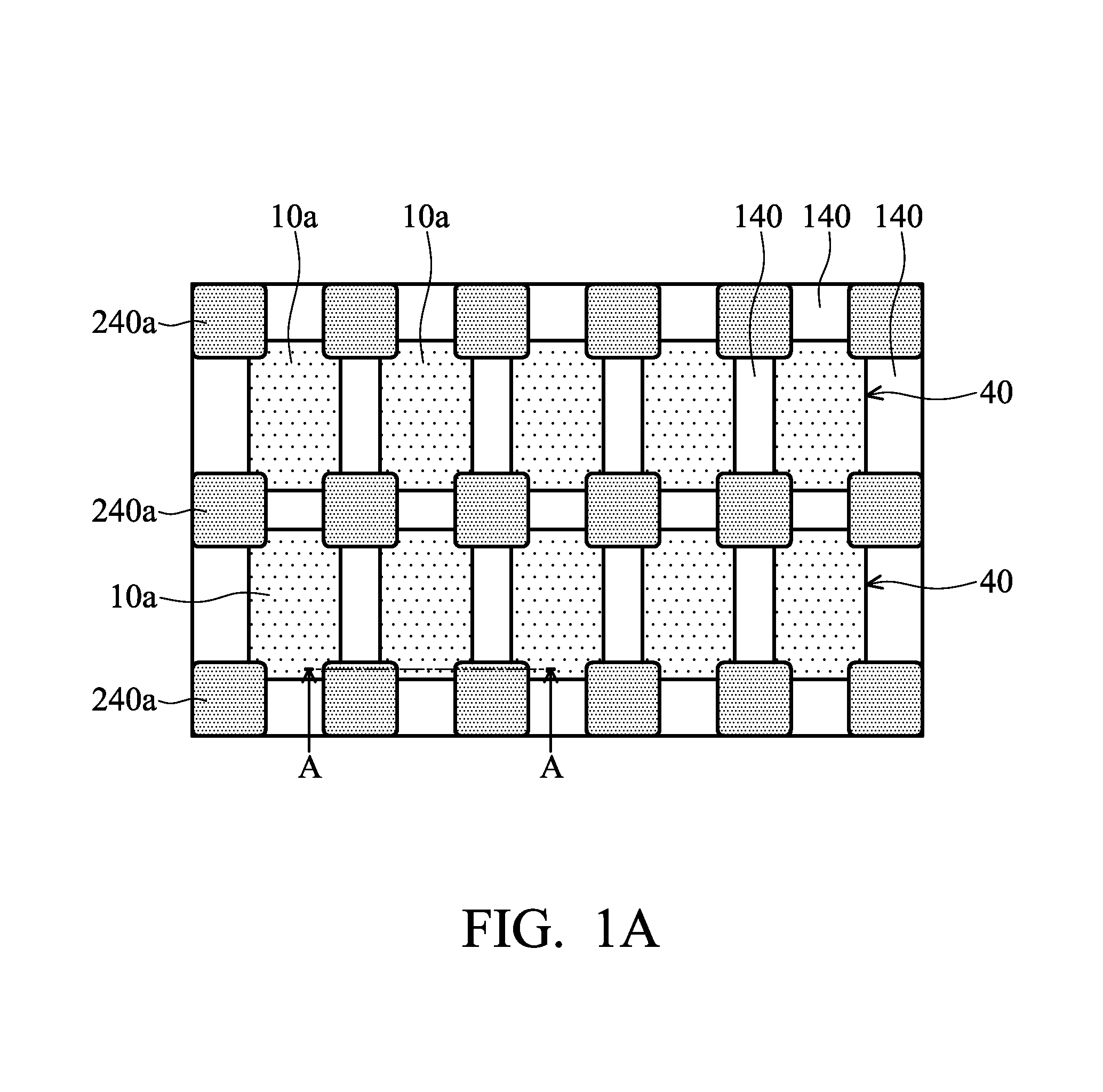
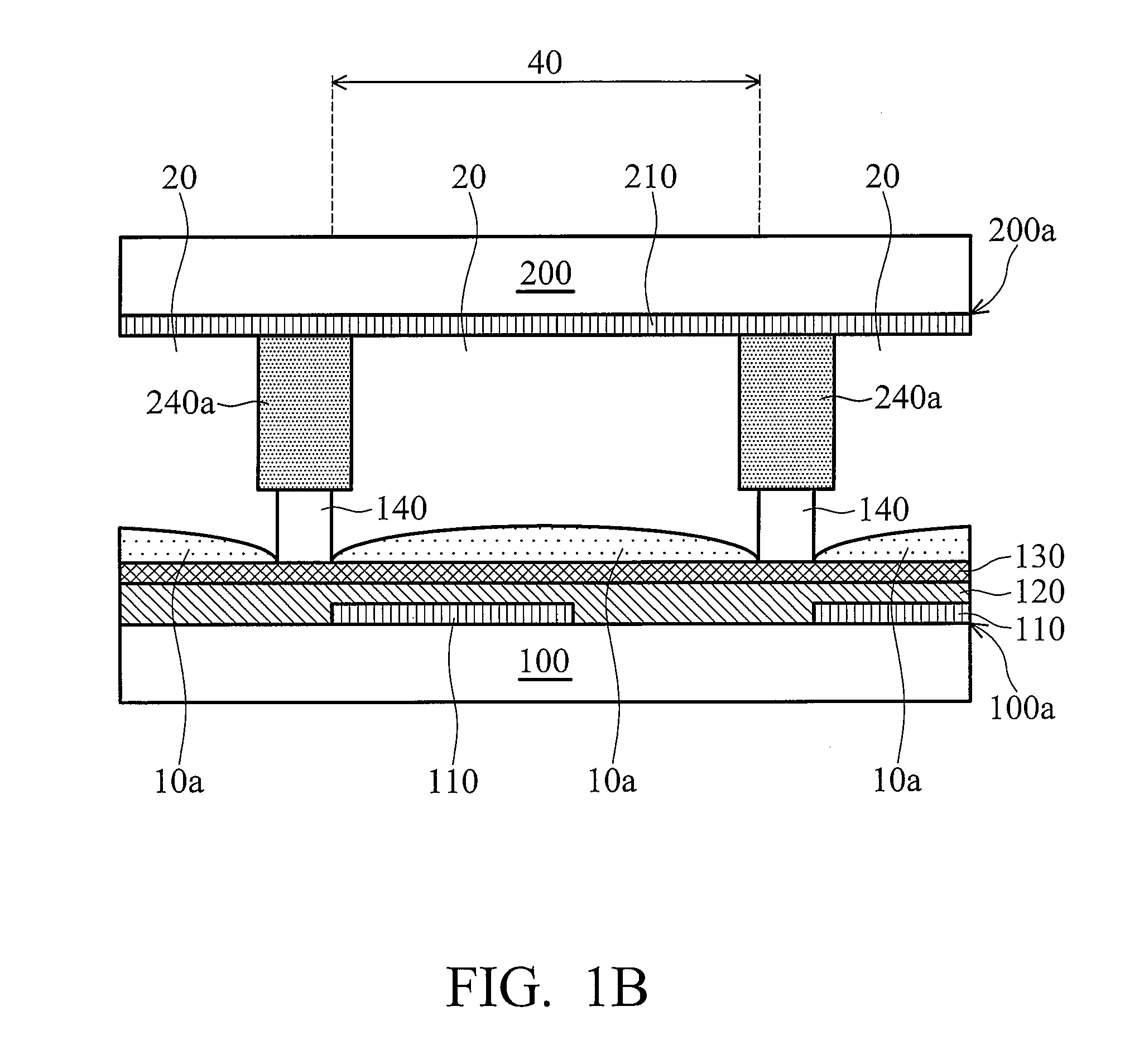
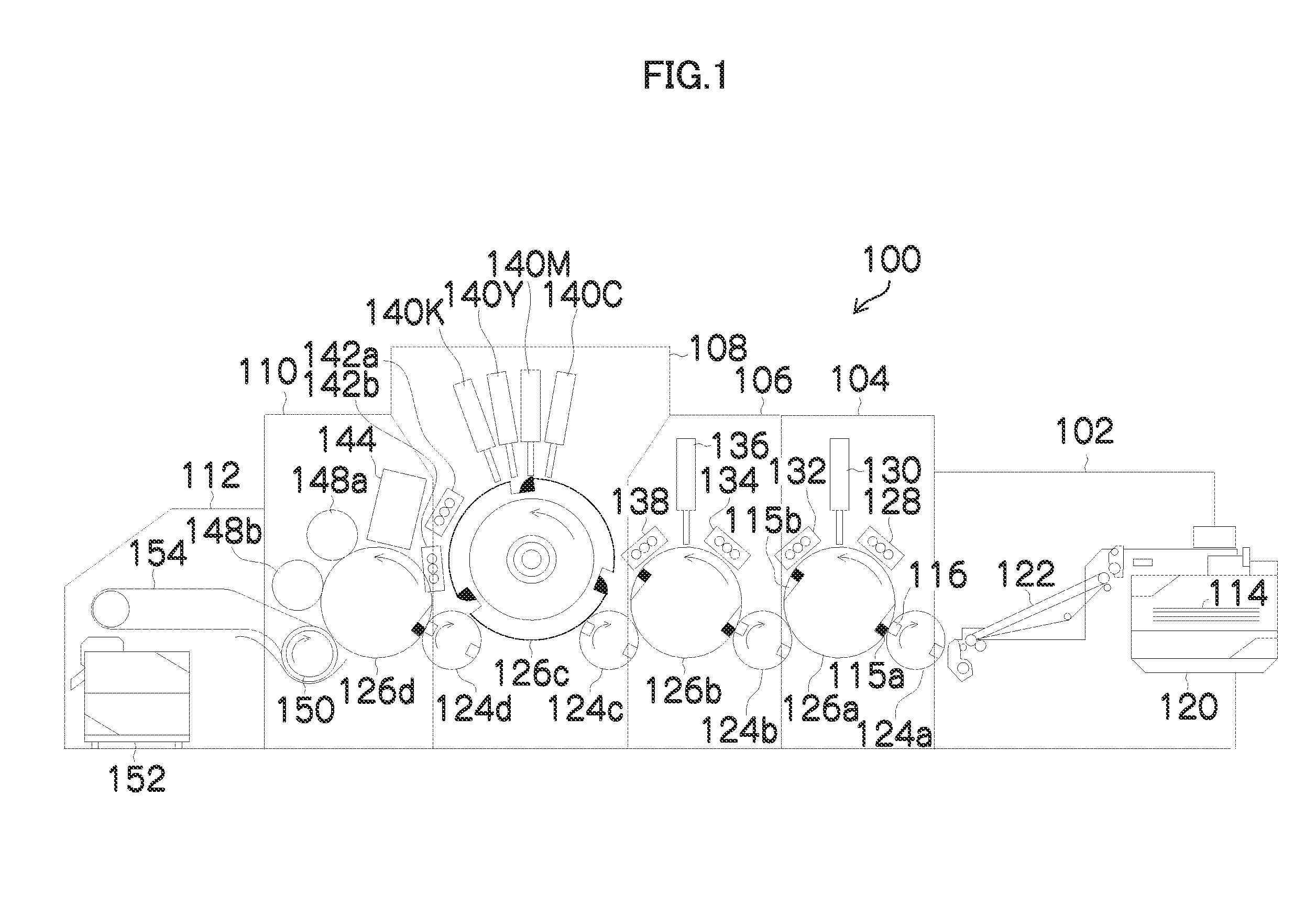
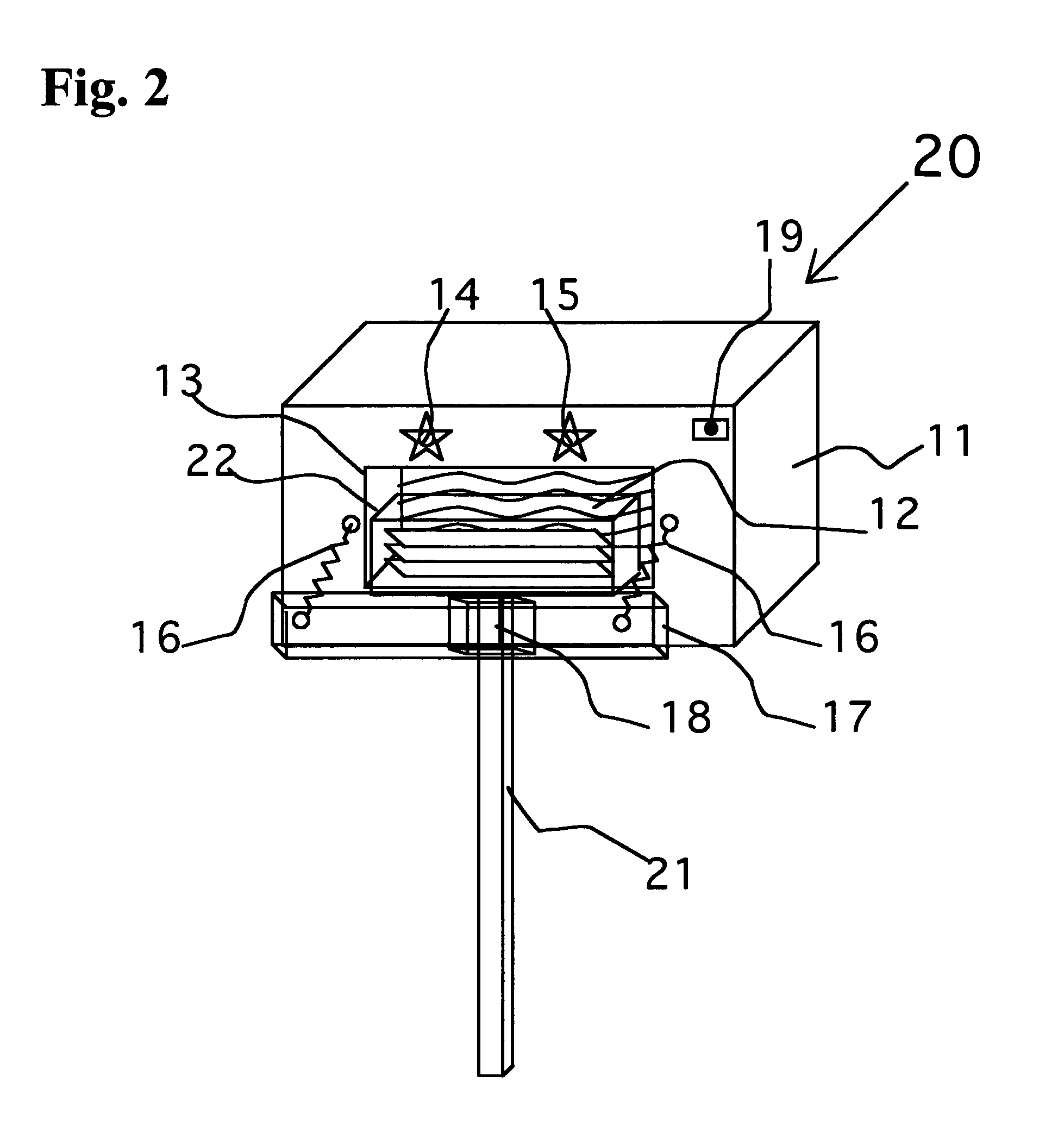
UV light irradiating apparatus with liquid filter
ActiveUS7763869B2High mechanical strengthHigh energyMirrorsOptical filtersLiquid layerLight irradiation
A UV light irradiating apparatus for irradiating a semiconductor substrate with UV light includes: a reactor in which a substrate-supporting table is provided; a UV light irradiation unit connected to the reactor for irradiating a semiconductor substrate placed on the substrate-supporting table with UV light through a light transmission window; and a liquid layer forming channel disposed between the light transmission window and at least one UV lamp for forming a liquid layer through which the UV light is transmitted. The liquid layer is formed by a liquid flowing through the liquid layer forming channel.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Field effect transistors and materials and methods for their manufacture
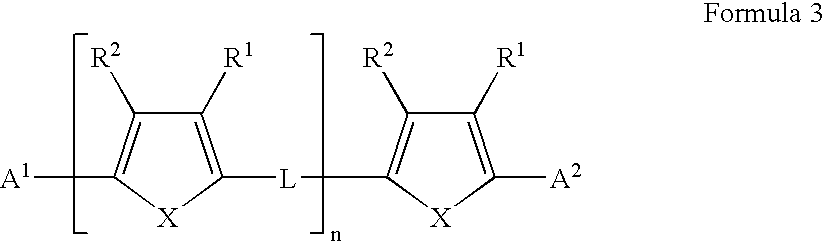
A field effect transistor in which a continuous semiconductor layer comprises:a) an organic semiconductor; and,b) an organic binder which has an inherent conductivity of less than 10−6Scm−1 and a permittivity at 1,000 Hz of less than 3.3and a process for its production comprising:coating a substrate with a liquid layer which comprises the organic semiconductor and a material capable of reacting to form the binder; and,converting the liquid layer to a solid layer comprising the semiconductor and the binder by reacting the material to form the binder.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
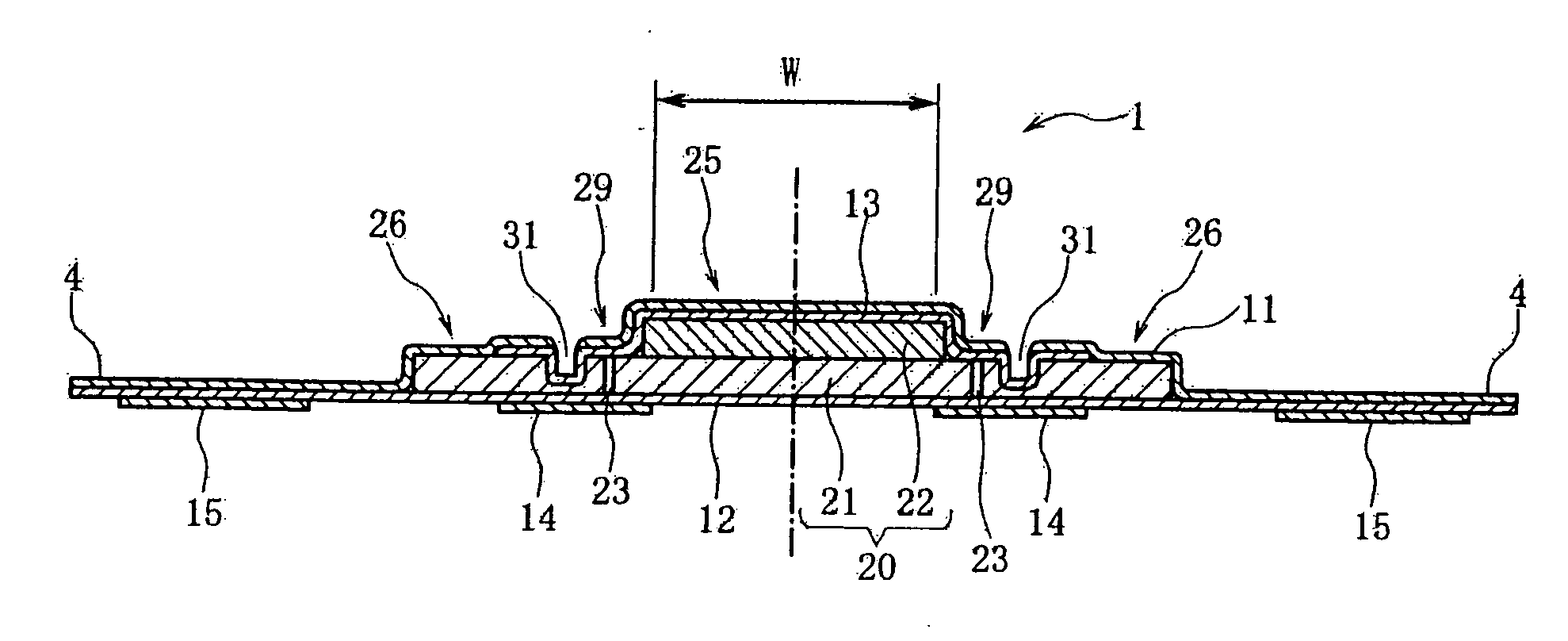
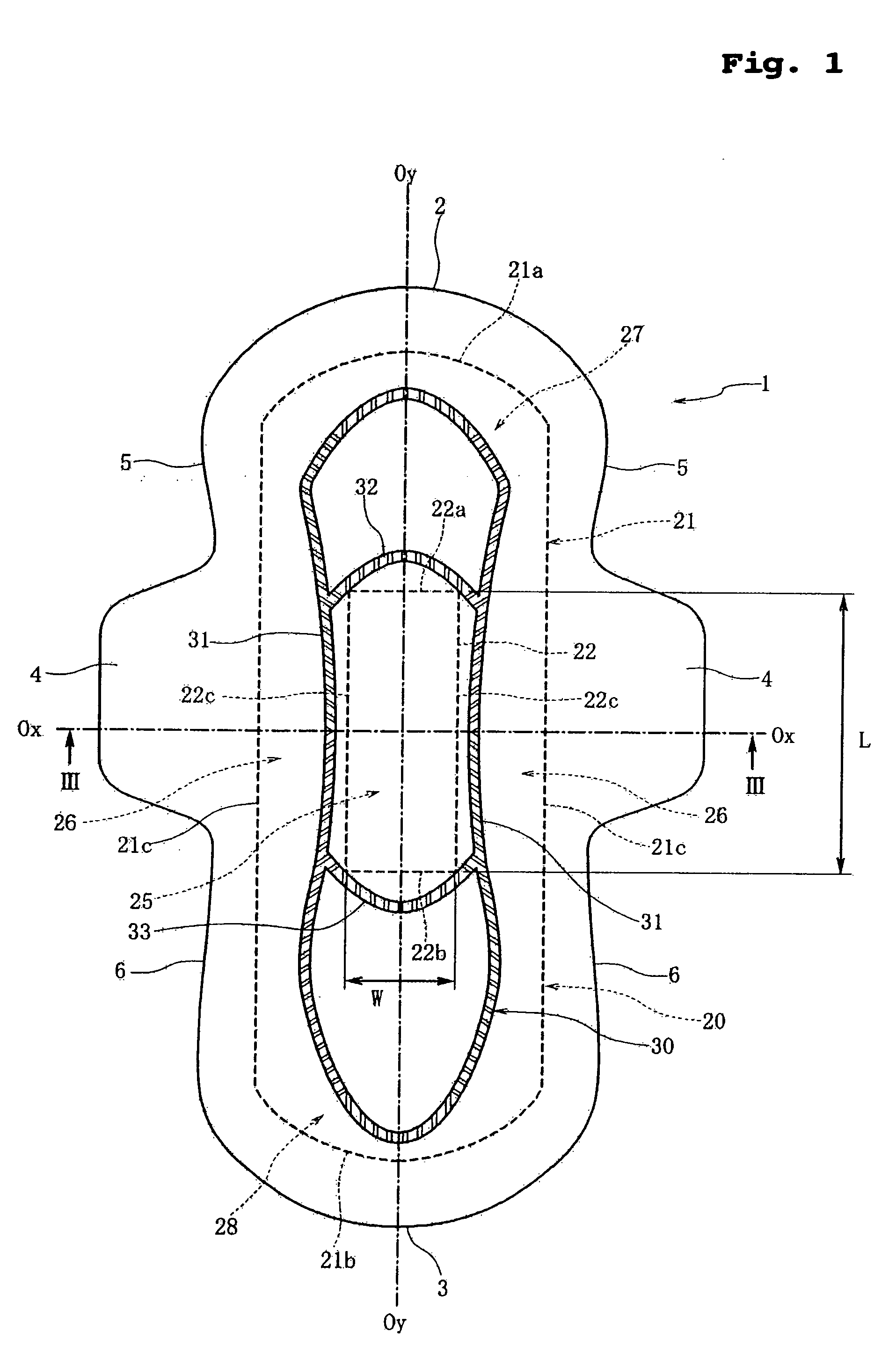
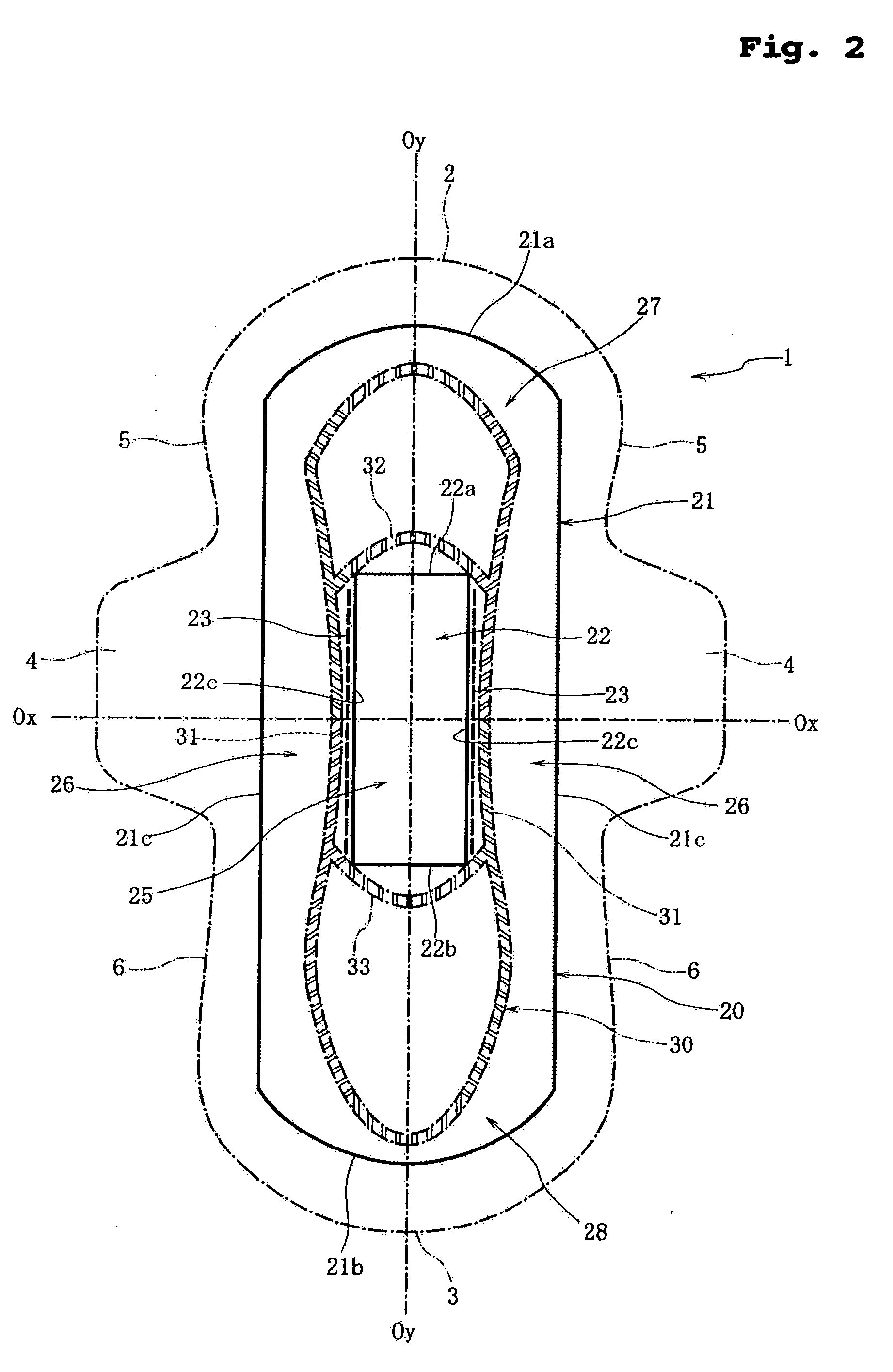
Sanitary napkin
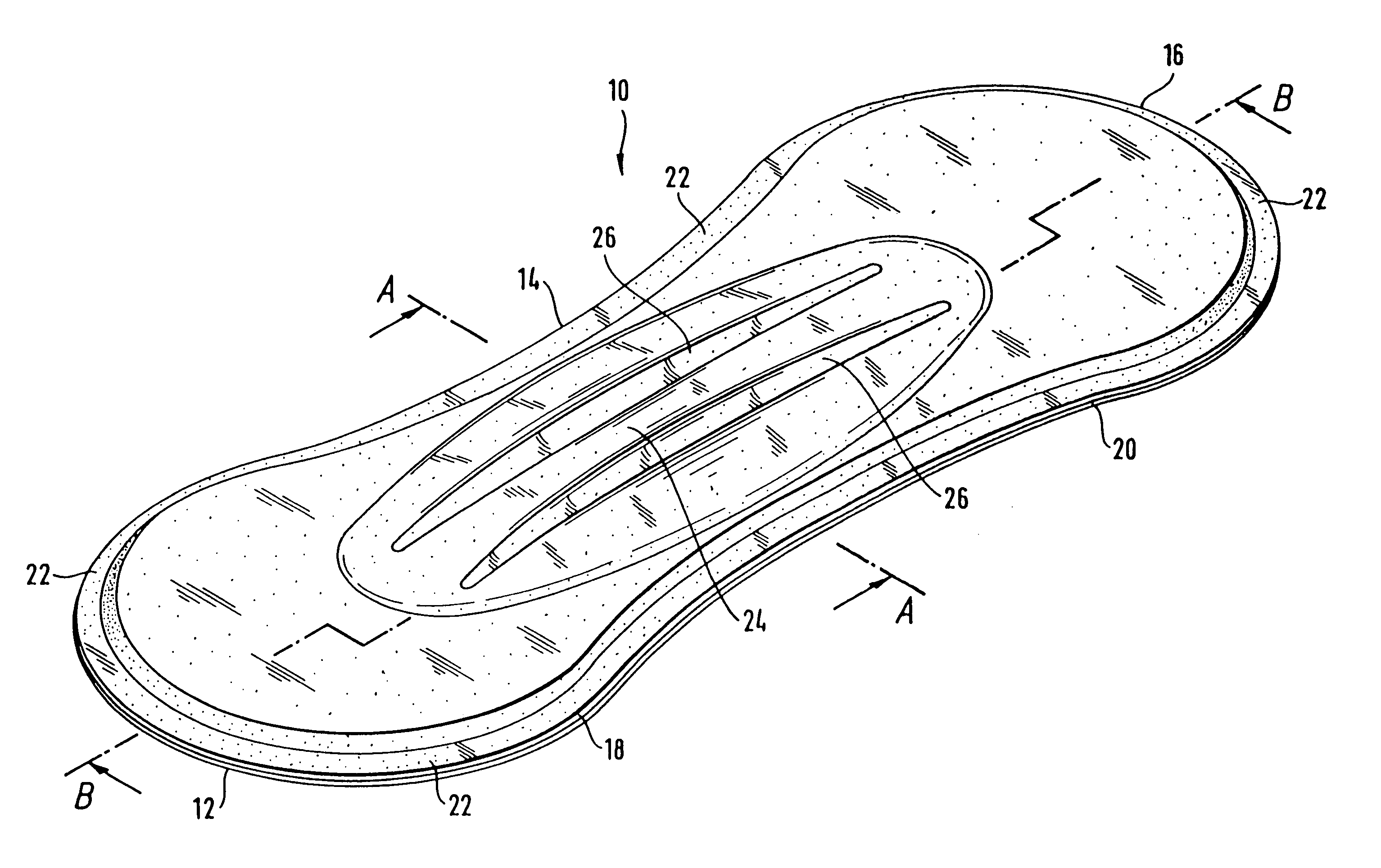
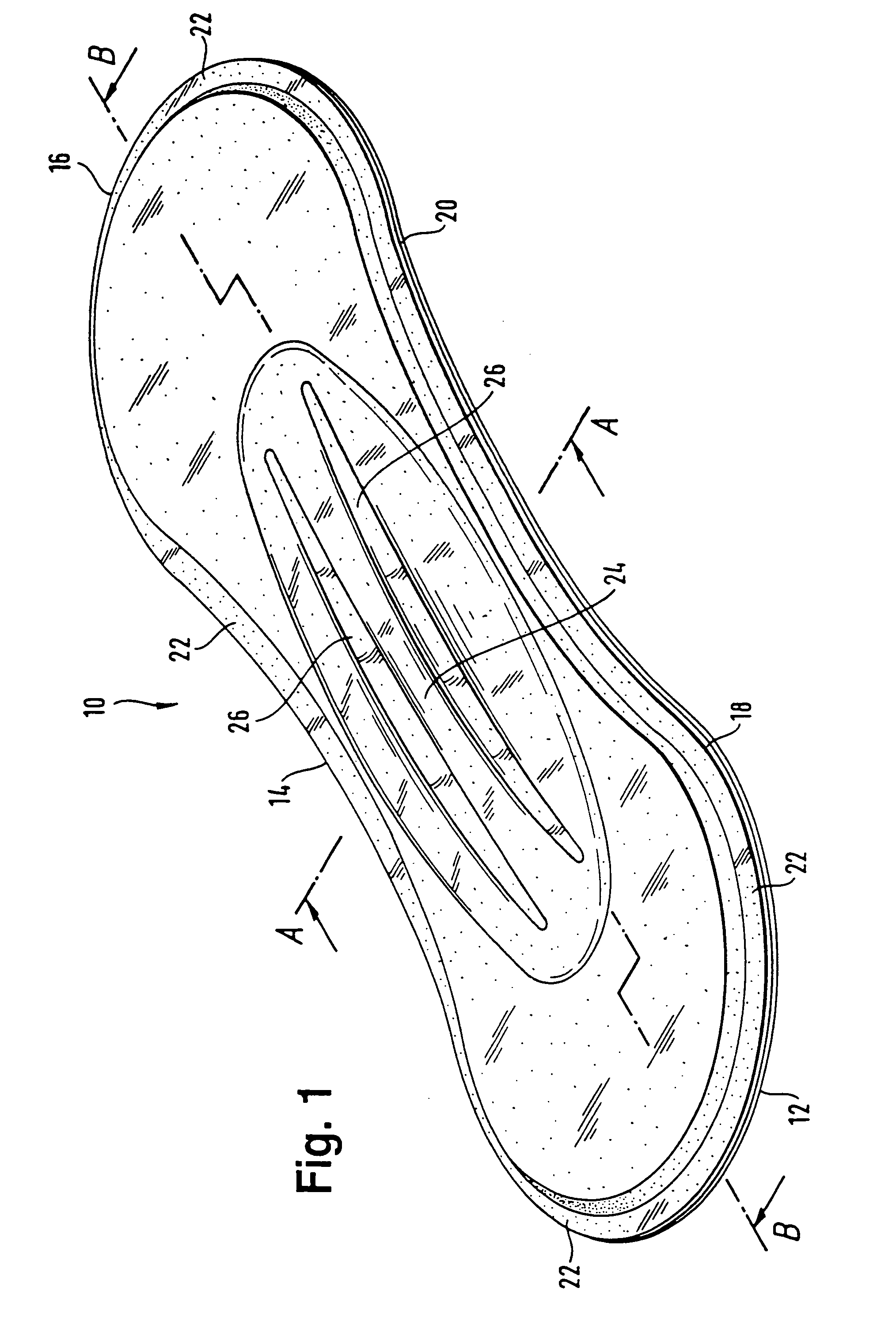
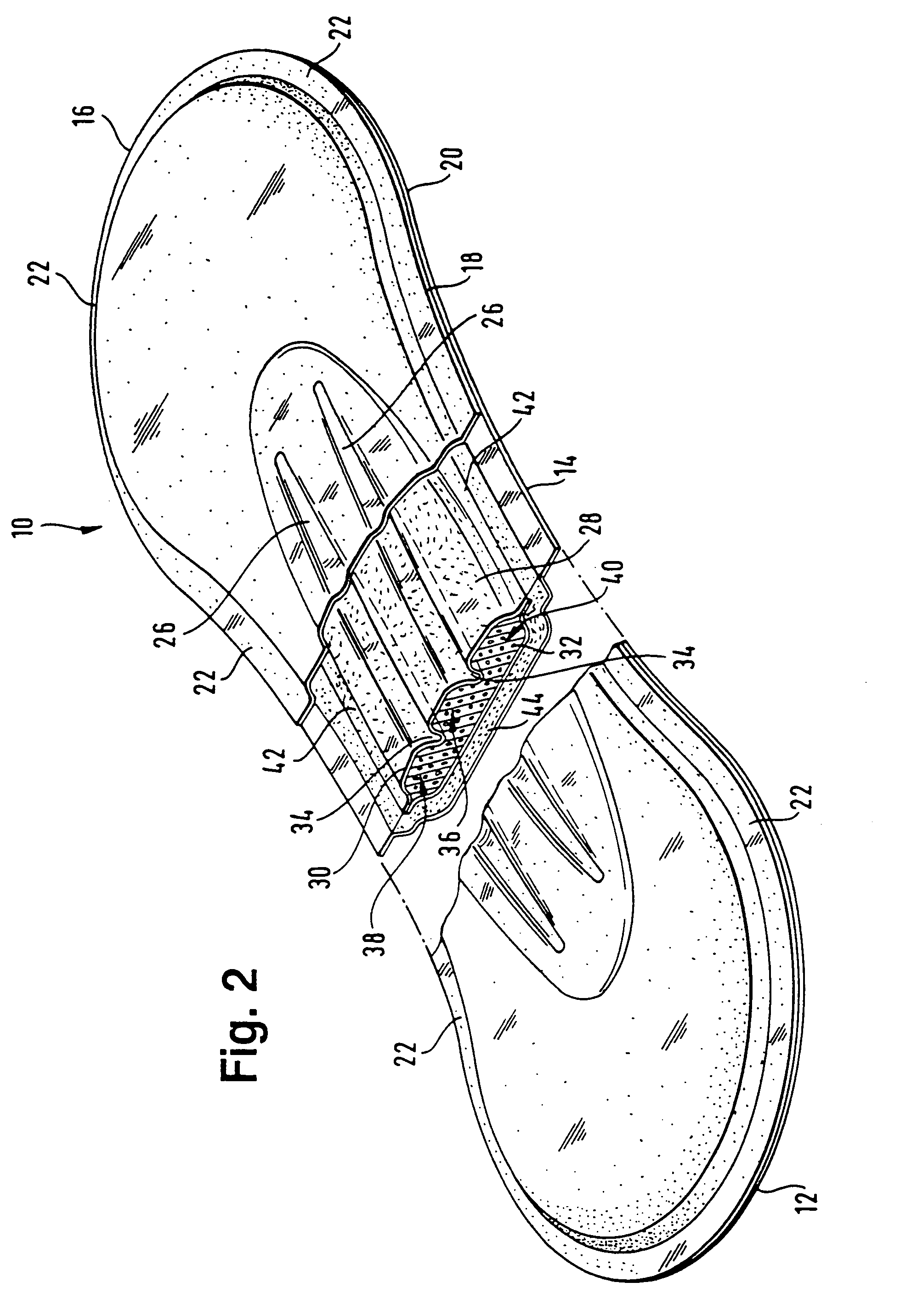
ActiveUS20060189954A1Easy to foldIncreased bending stiffnessSanitary towelsBaby linensLiquid layerEngineering
A sanitary napkin includes a liquid-permeable topsheet, a backsheet, and a liquid-absorbent layer disposed between the topsheet and the backsheet. The liquid-absorbent layer has a vagina-facing region on a longitudinal centerline of the sanitary napkin and side regions on both sides of the vagina-facing region. The liquid-absorbent layer has a greater thickness and a greater bending stiffness in the vagina-facing region than in the side regions to provide hinge lines along boundaries between the vagina-facing region and the side regions.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
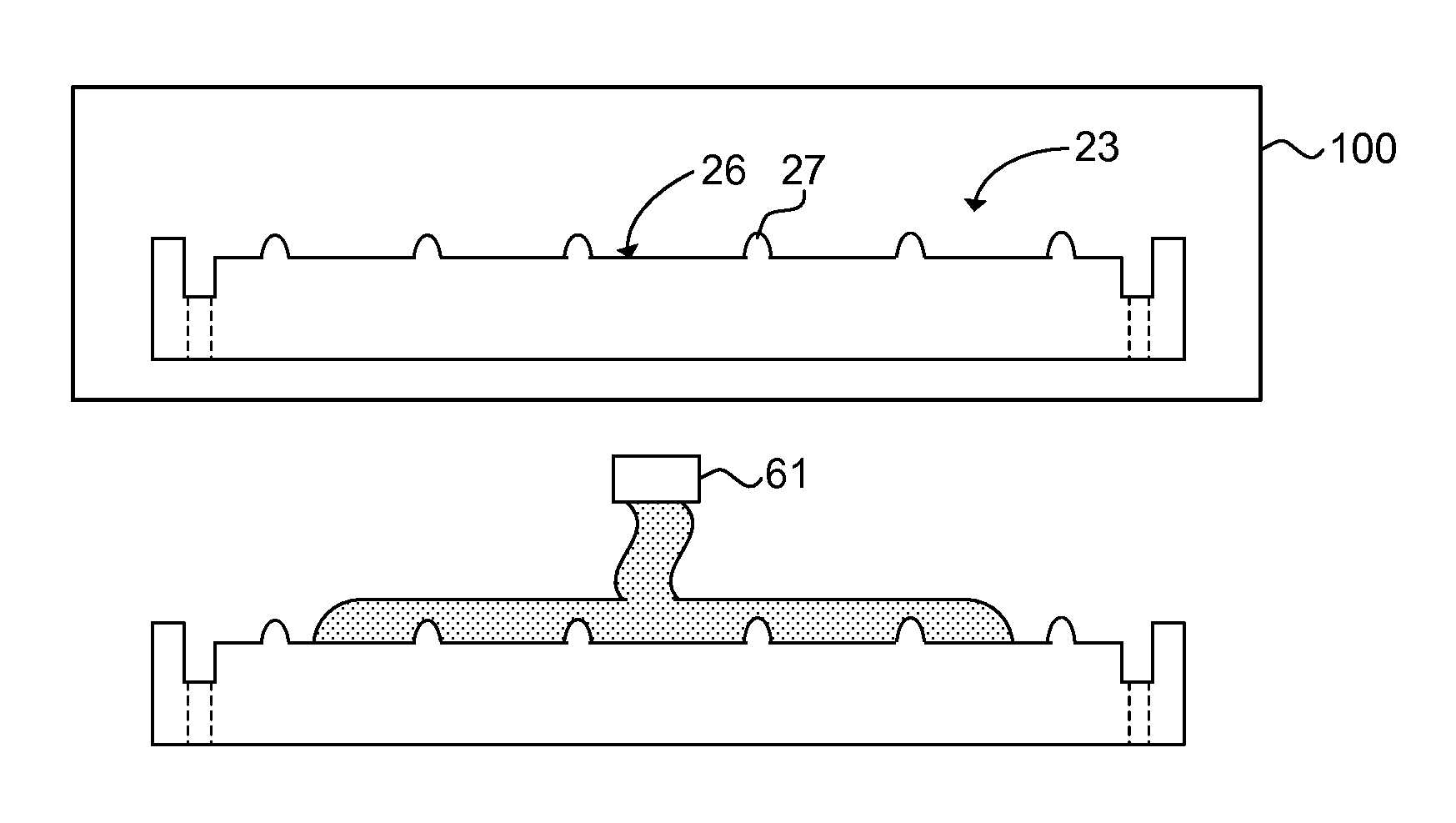
Method of clamping a substrate and clamp preparation unit using capillary clamping force
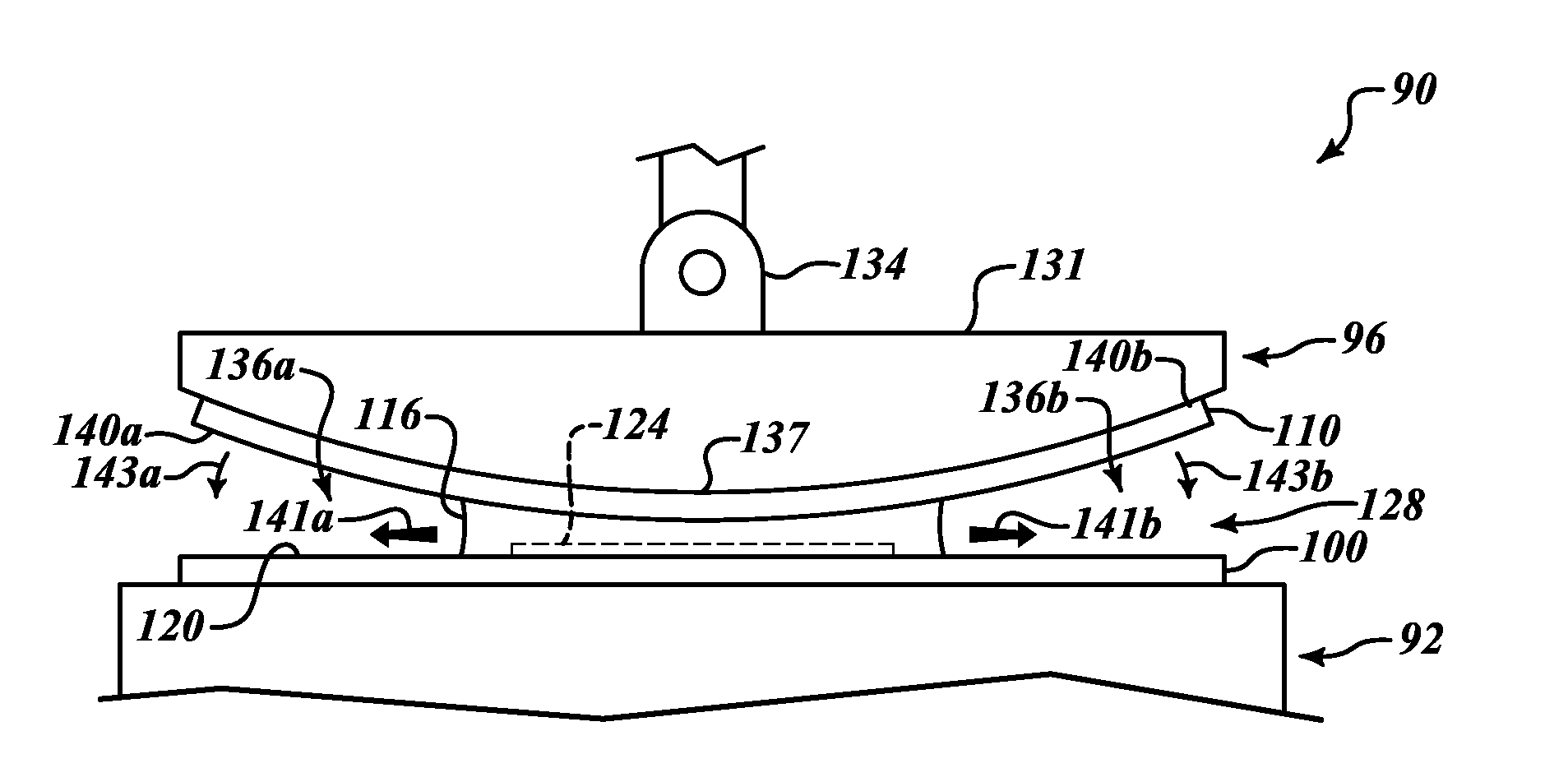
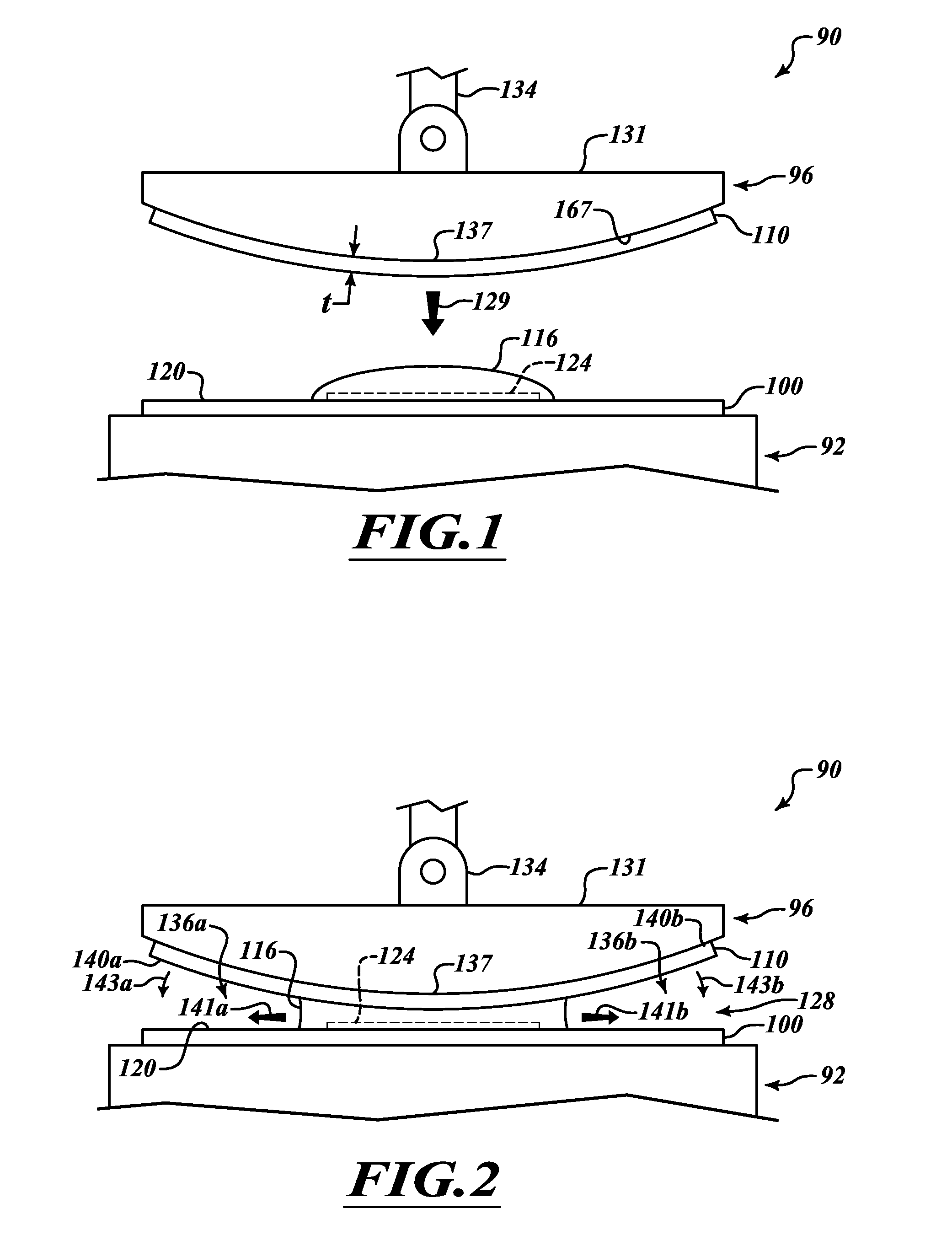
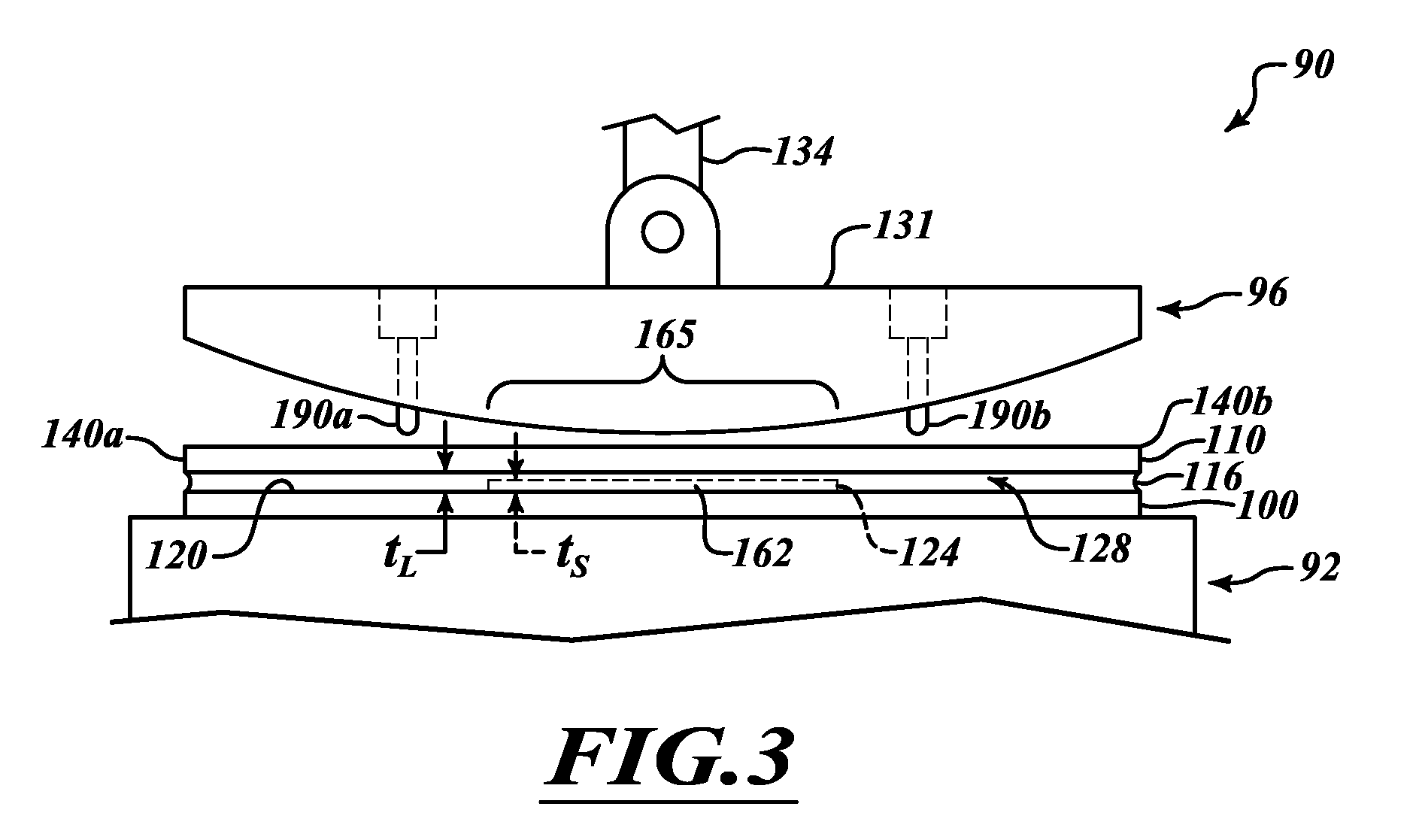
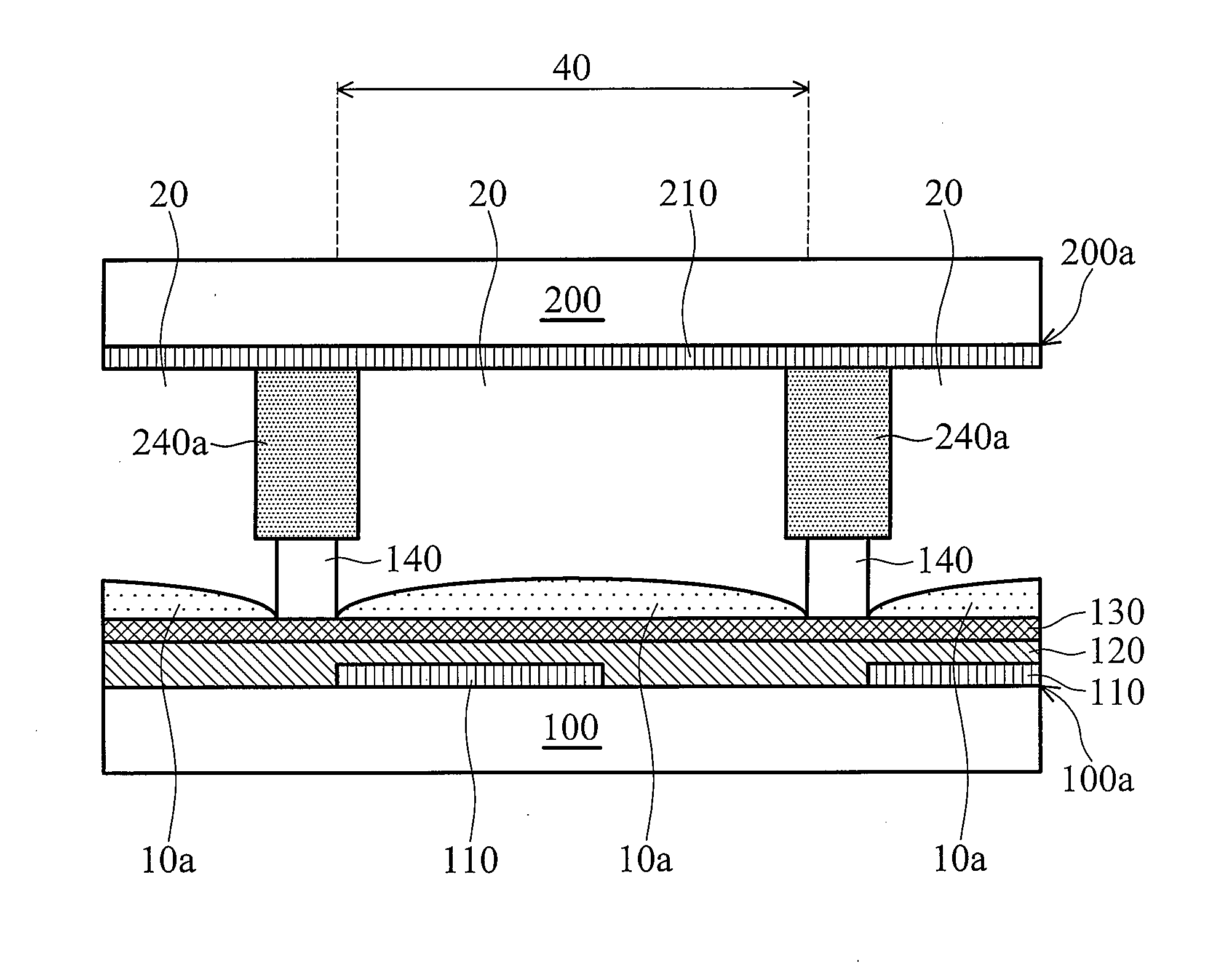
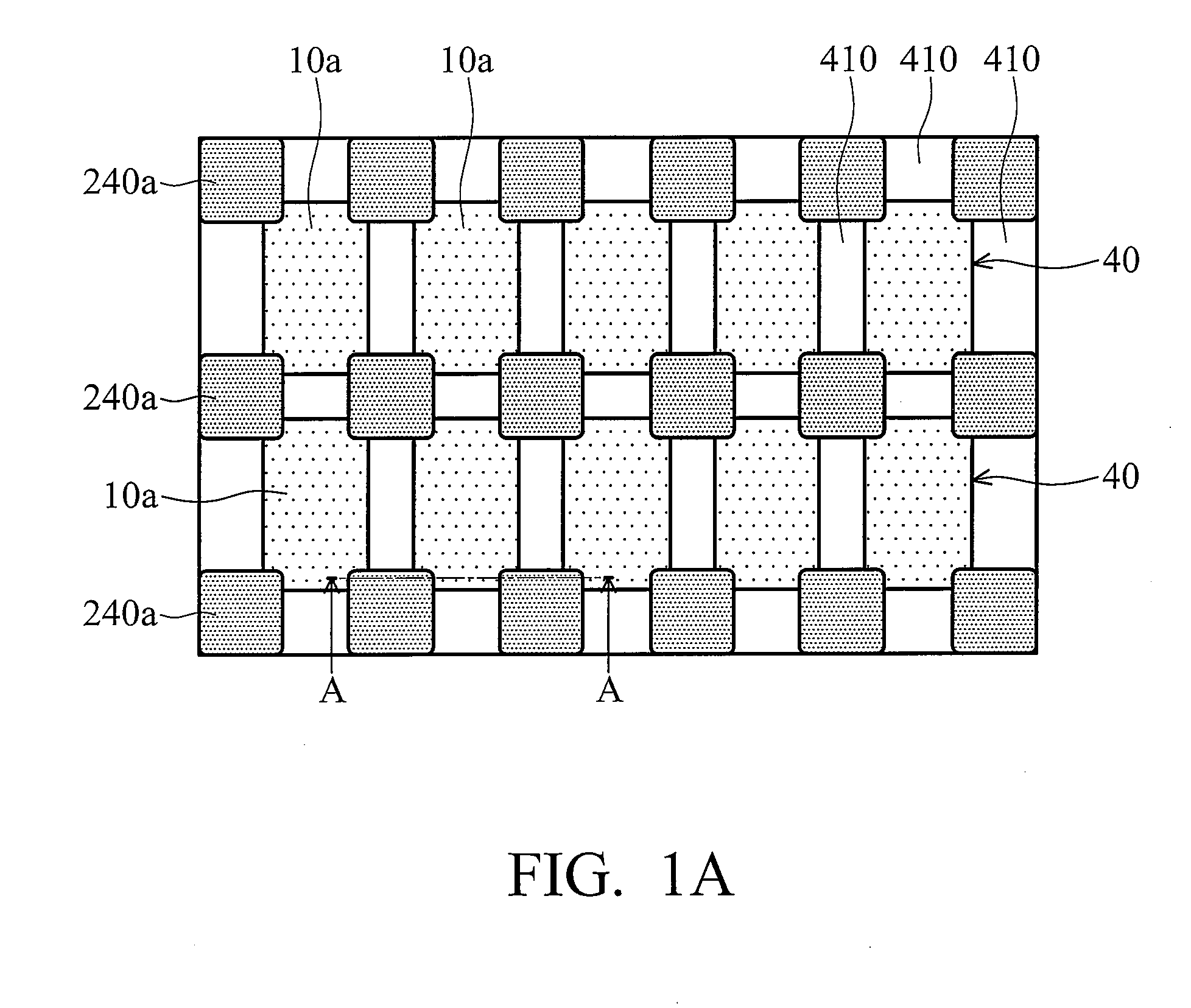
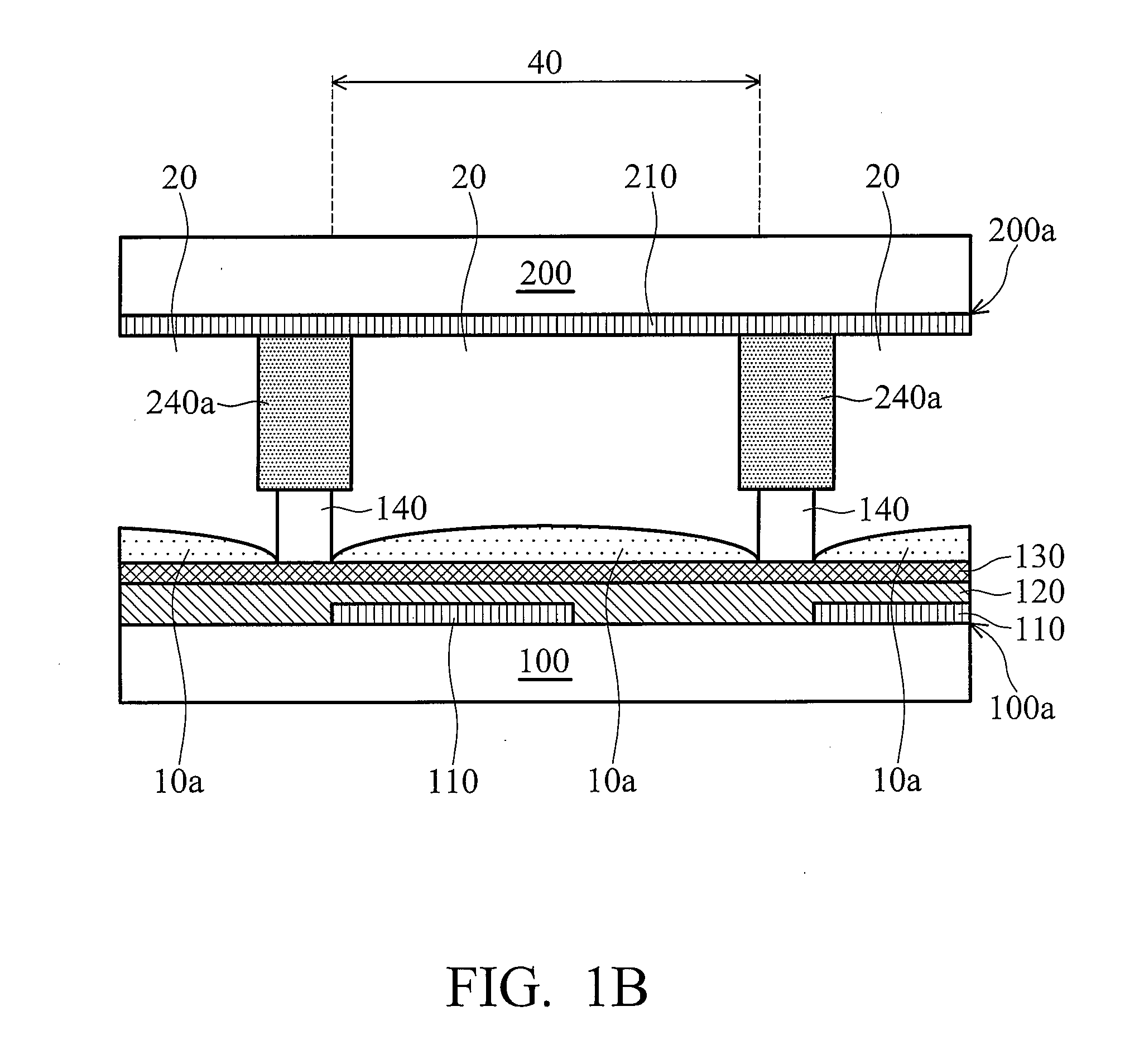
ActiveUS9460954B2Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLiquid layerEngineering
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Absorbent article
InactiveUS6965058B1Easy to adaptPrevent skinSanitary towelsBaby linensLiquid layerAbsorbent material
Described is an absorbent article comprising a liquid-permeable layer (18) disposed towards the wearer's body when the said article is in use; a liquid-impermeable layer (20) disposed away from the wearer's body when the said article is in use; as well as an absorbent body arranged between the liquid-permeable layer (18) and the liquid-impermeable layer (20). The absorbent body comprises an absorbent material (32) which remains able to flow even after contact with a liquid. In addition, the invention discloses an absorbent article which comprises a liquid-impermeable layer disposed away from the wearer's body when the article is in use, as well as an absorbent body covered by a liquid-permeable layer; with the said absorbent body containing an absorbent material which remains able to flow even after contact with a liquid. In this, the absorbent body is connected to the liquid-impermeable layer in a central area of the said absorbent body.
Owner:HAKLE KIMBERLY DEUTLAND
Sub-micron-scale patterning method and system
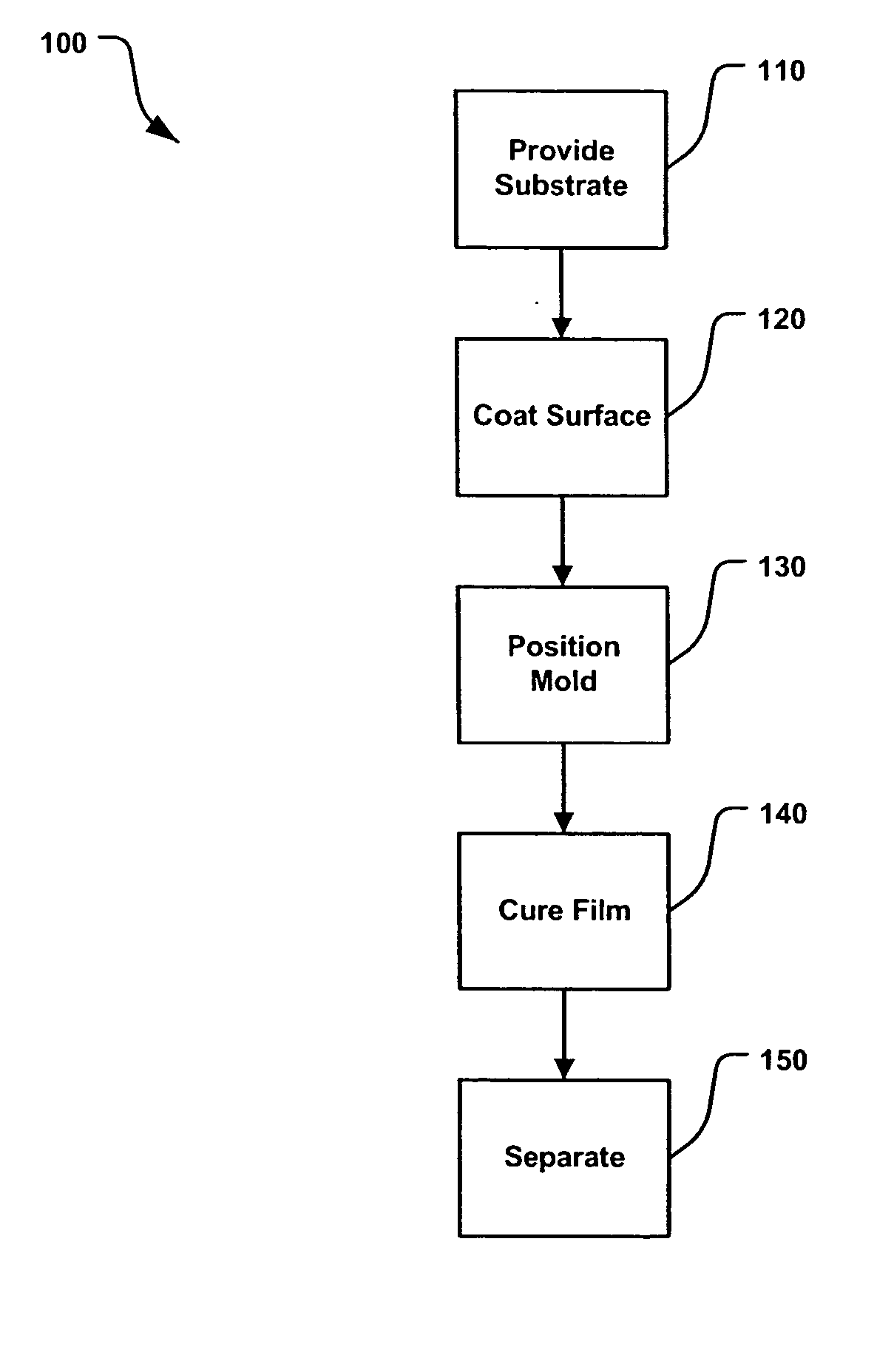
InactiveUS20050084613A1Control thicknessGood film uniformityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesLiquid layerMicron scale
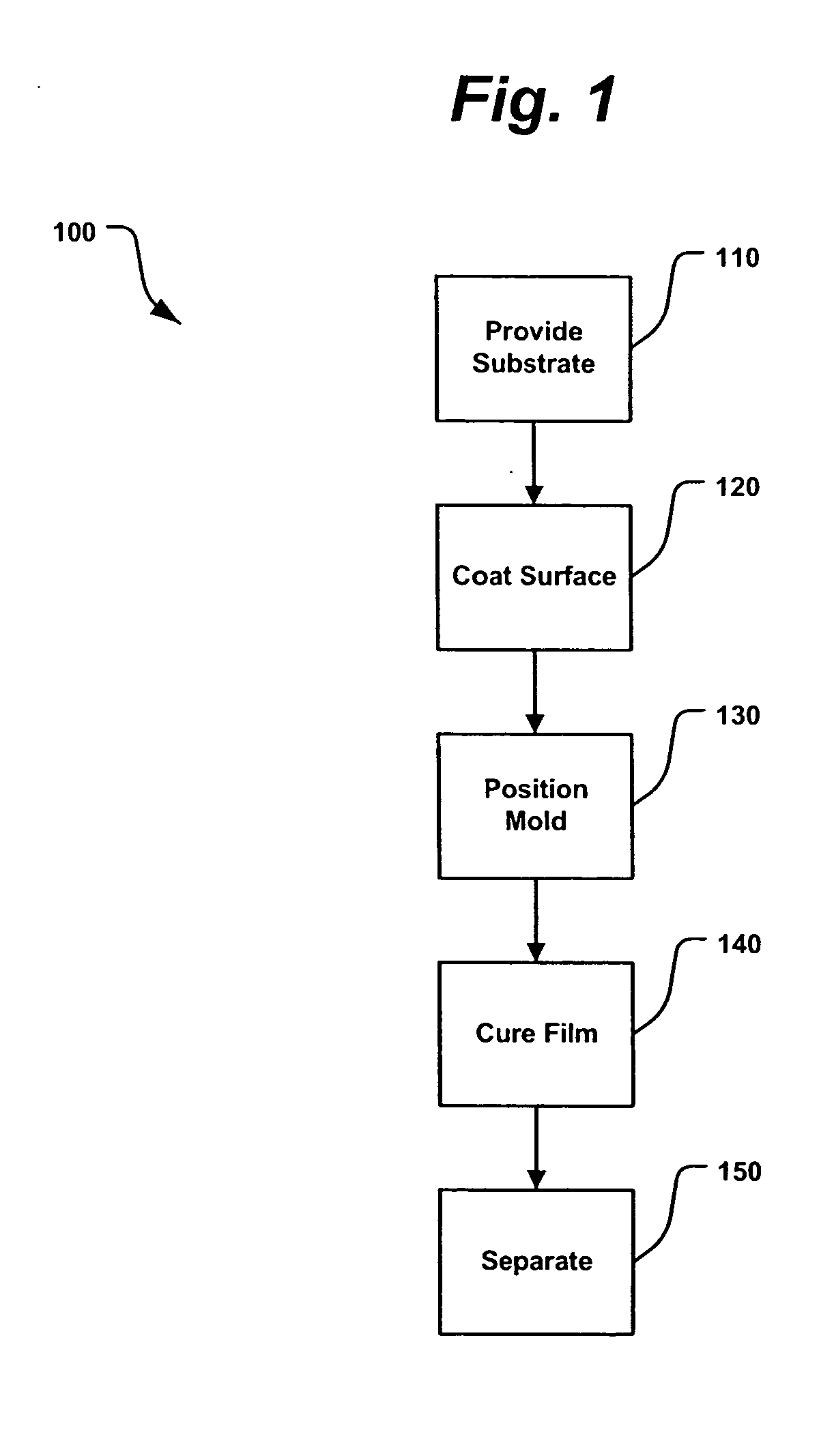
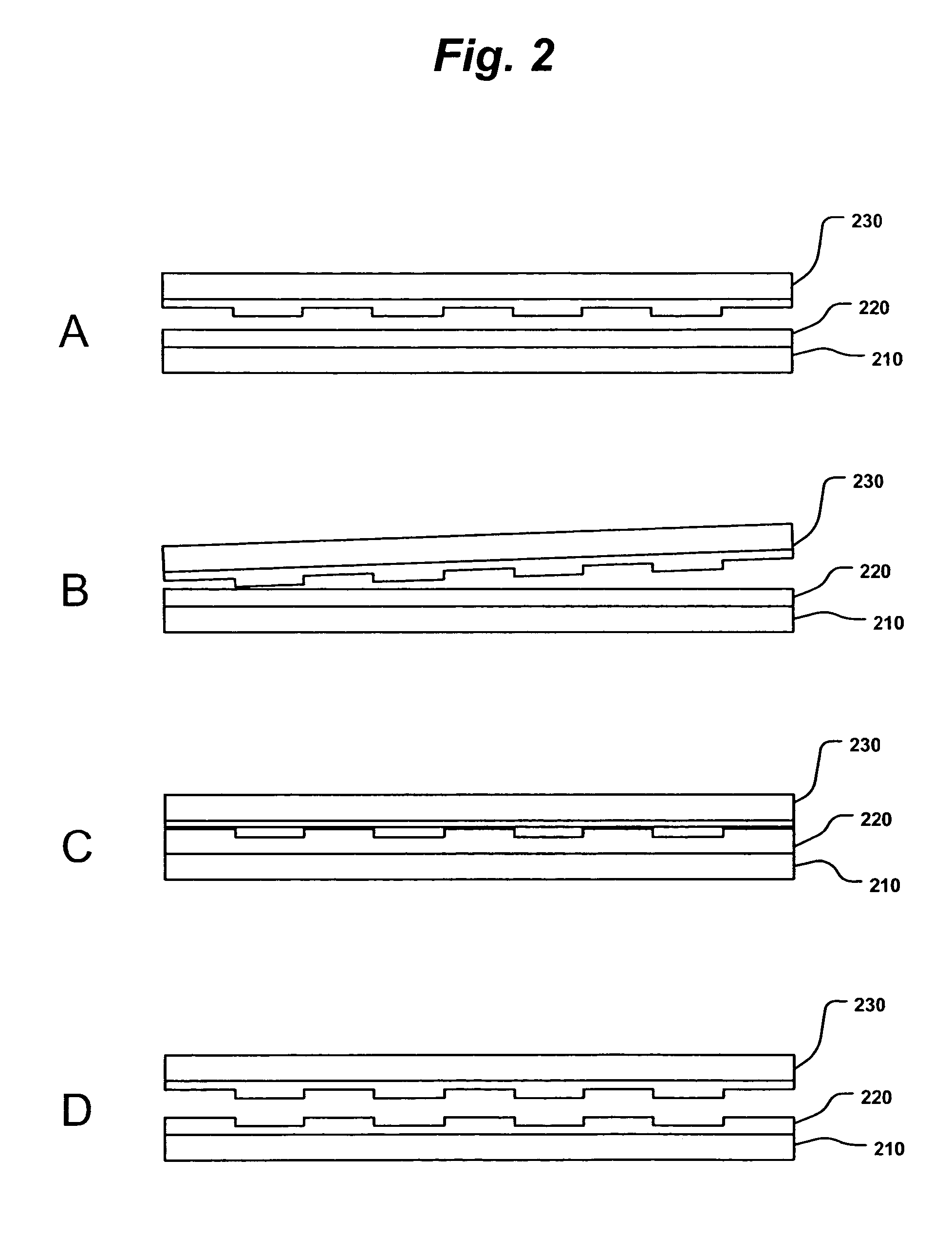
A method for replicating a nanopattern is disclosed. This method includes identifying a substrate; coating a surface of the substrate with a liquid layer; positioning a mold having a plurality of recesses defining a negative of the nanopattern in sufficient proximity with the coated liquid layer to cause the liquid layer to self-fill at least a portion of the plurality of recesses of the mold; and, chemically transforming the liquid layer to enable the transformed film to substantially retain the nanopattern.
Owner:WANG JIAN +2
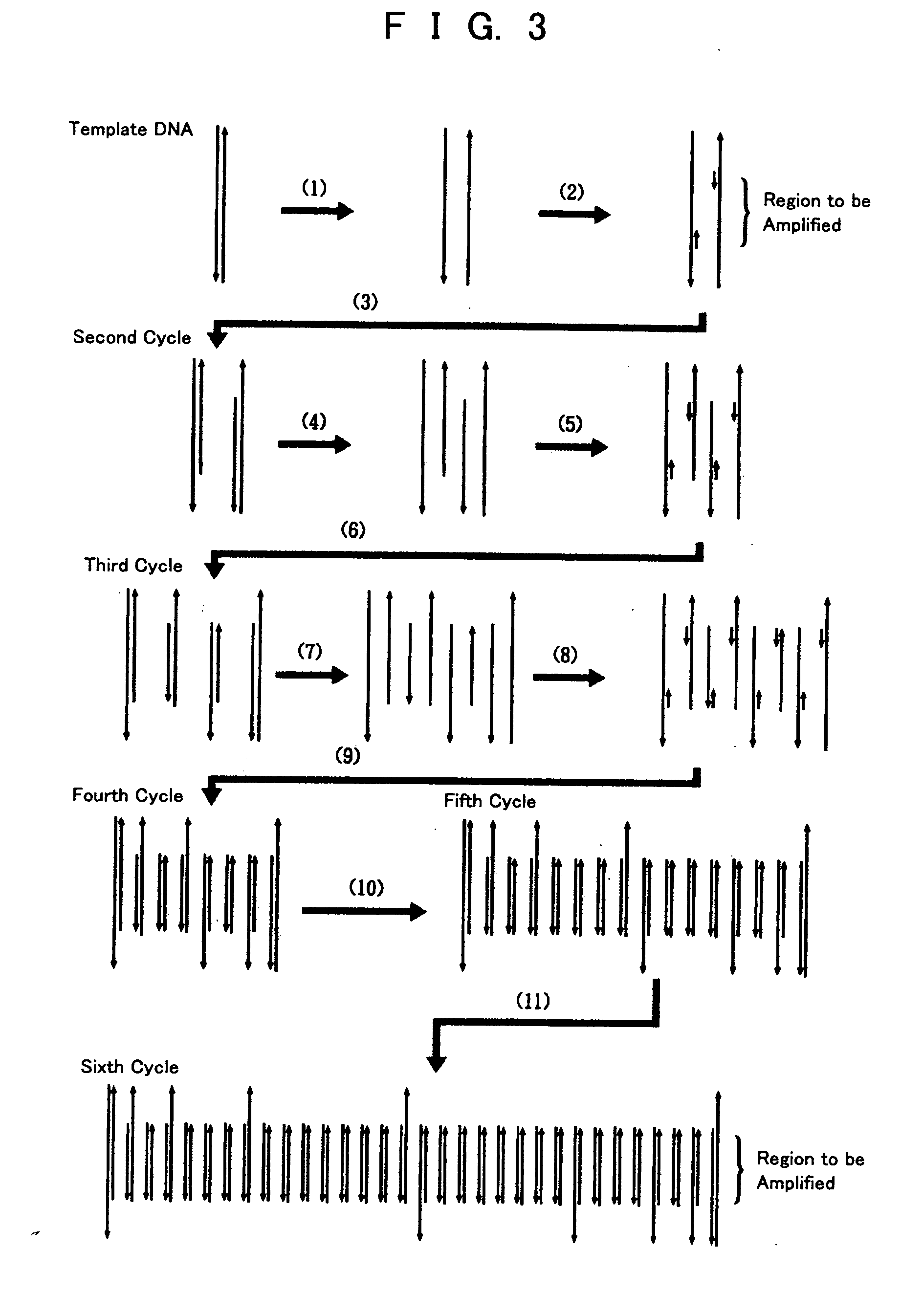
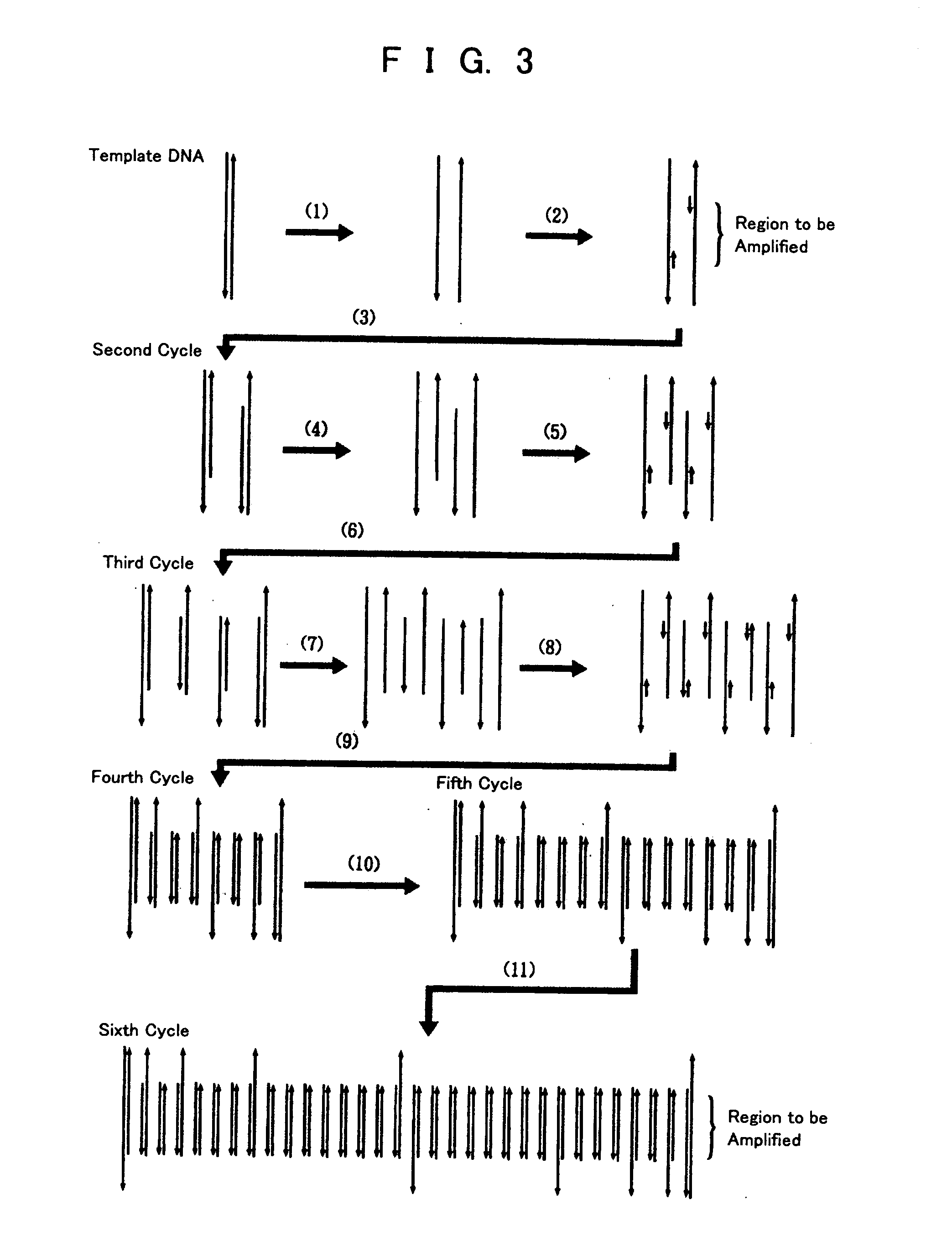
Pcr method by electrostatic transportation, hybridization method for electrostatic transportation and devices therefor
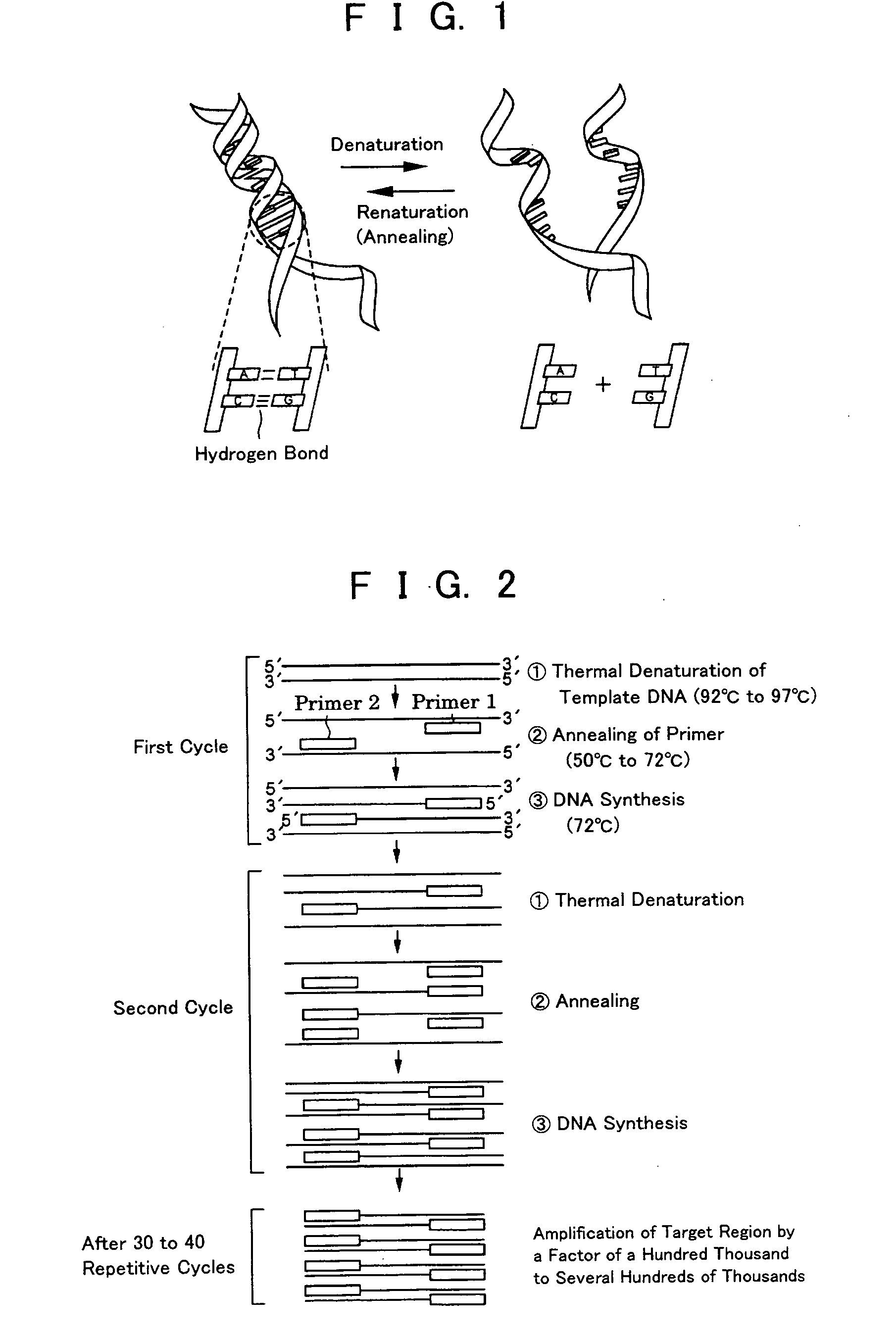
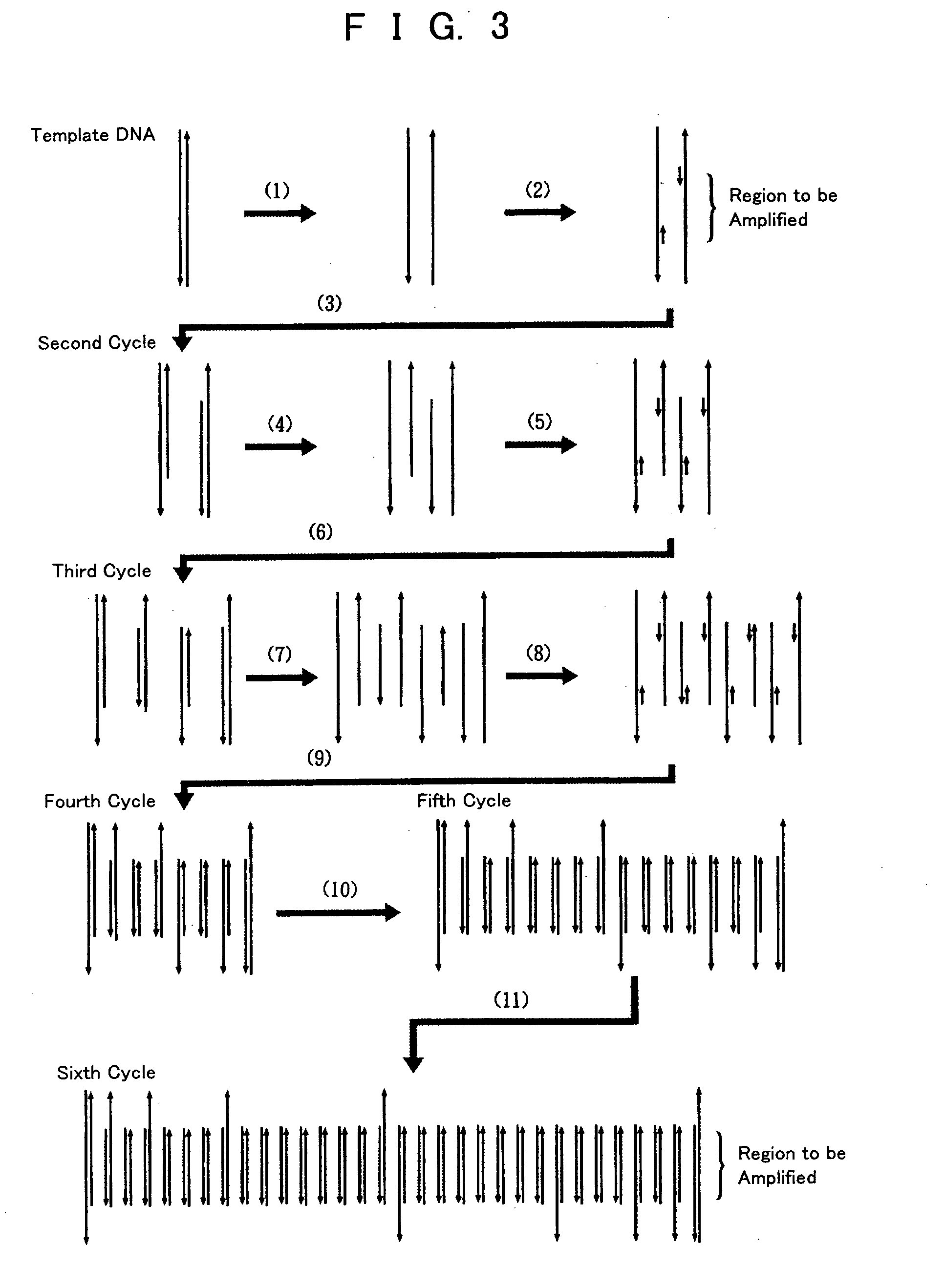
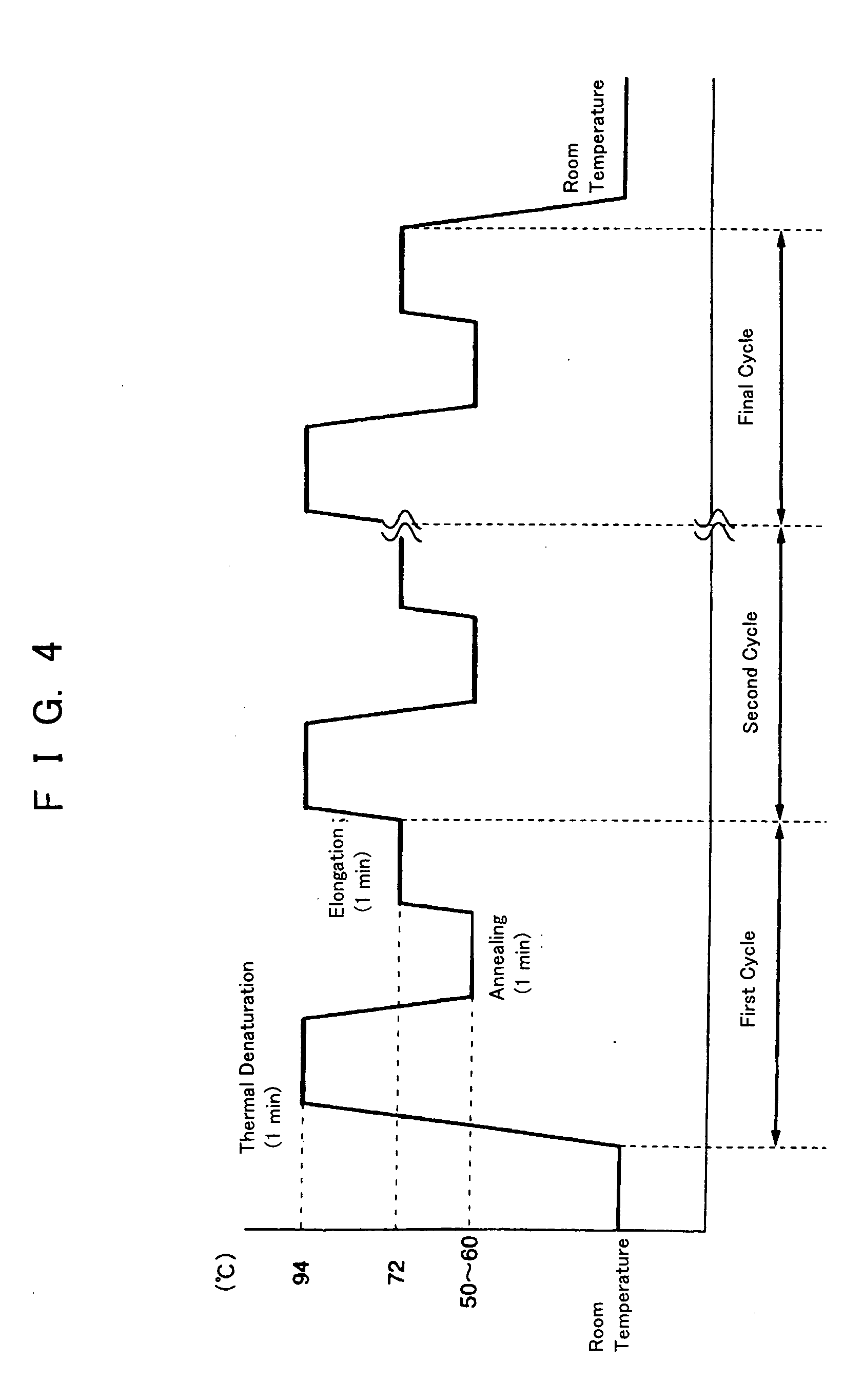
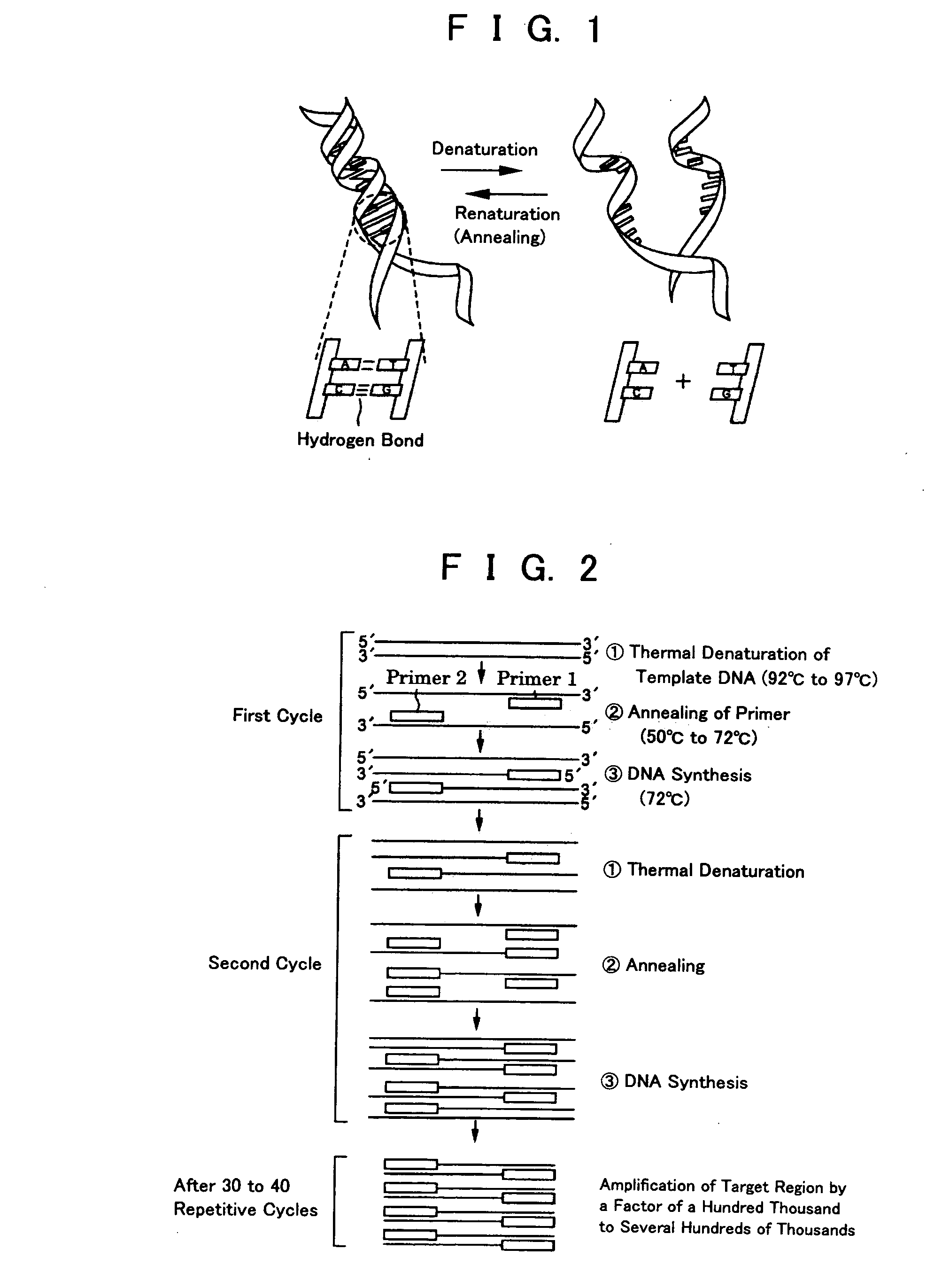
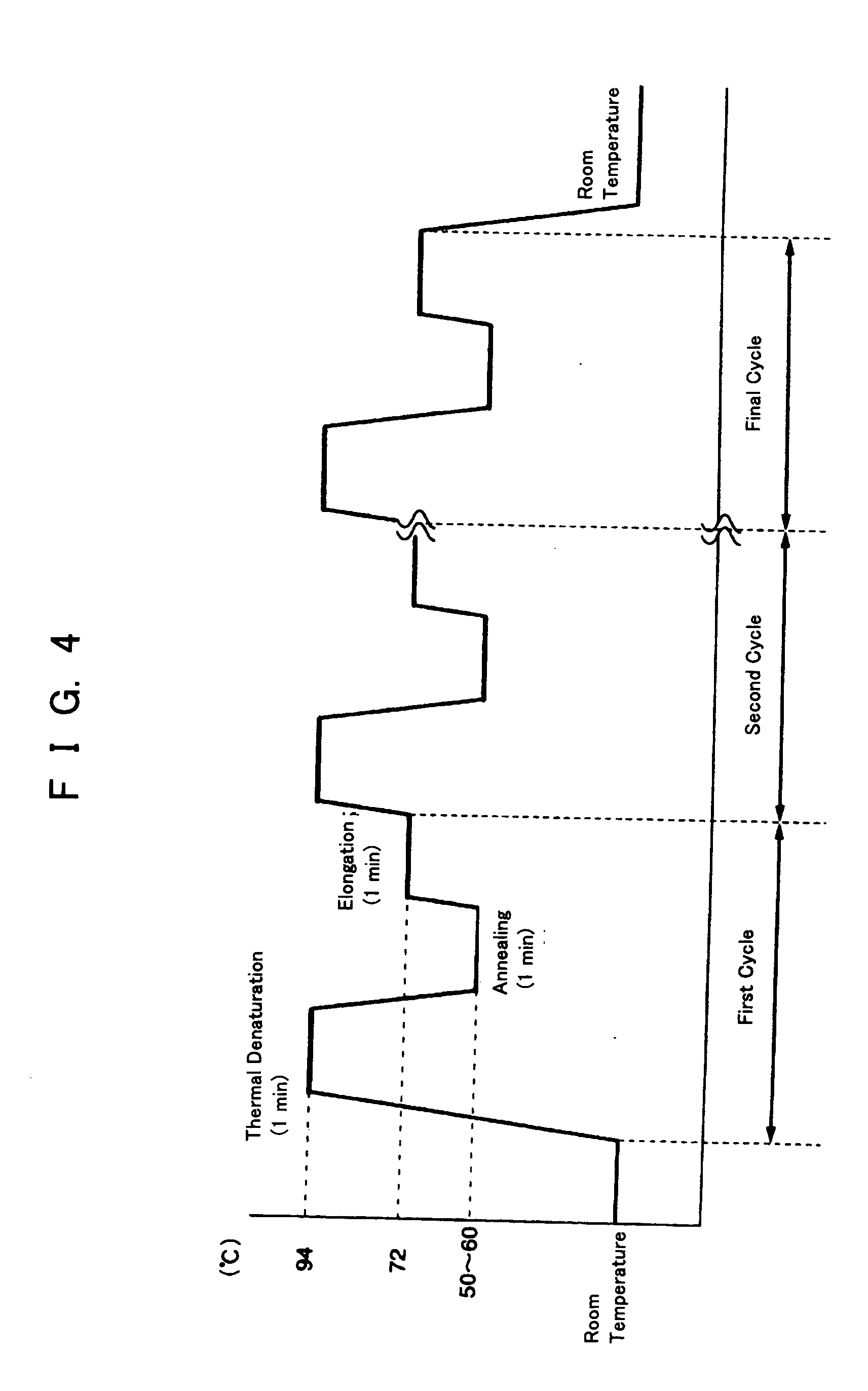
InactiveUS20050064423A1Quick checkSimple and easyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid layerPcr method
To provide a PCR method utilizing electrostatic transportation which allows separate control of individual DNA-containing droplets by accurately transporting the droplets, suitably controlling the temperature thereof and allowing a primer to react therewith; a hybridization method utilizing electrostatic transportation which allows rapid and easy detection of hybridization; and devices therefor. A biological sample (droplets containing DNA and primer) (9) is prepared in a chemically inert liquid layer (8), is electrostatically transported by the action of an electrostatic transportation plate (1) with electrostatic transportation electrodes (2) and is heated at a predetermined position of the electrostatic transportation plate (1), thus carrying out PCR.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Floatable opposables for applying fluids to process biological samples
InactiveUS20110305842A1Minimize and avoid over-fillingMinimize and avoid and under-fillingSamplingPretreated surfacesLiquid layerBiomedical engineering
A slide processing apparatus is used to apply substances for processing specimens. The slide processing apparatus can deliver a substance to a mounting surface of a slide carrying the specimen. The substance can be contacted with an opposable held by an opposable holder device. The opposable is pulled towards the slide by the substance. The substance can spread along the mounting surface as the opposable is flattened. If the substance is a liquid, the opposable can float on the liquid to form a thin liquid layer.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Display and fabricating method thereof
ActiveUS20090169806A1Prevent overflowLamination ancillary operationsStatic indicating devicesLiquid layerDisplay device
A display and fabricating method thereof is provided. The display includes a first substrate, a second substrate, a hydrophobic layer, a nonpolar liquid layer, a hydrophilic separator, a polar liquid layer, and a protruding spacer. The first and second substrates respectively include an opposing surface, and are disposed in a way that the opposing surfaces are face-to-face opposing to each other. The hydrophobic layer overlies the opposing surface of the second substrate. The nonpolar liquid layer overlies the hydrophobic layer. The hydrophilic separator overlies the hydrophobic layer and surrounds the nonpolar liquid layer. The polar liquid layer overlies the nonpolar liquid layer. The protruding spacer is disposed between the hydrophilic separator and the first substrate.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
PCR and hybridization methods utilizing electrostatic transportation and devices therefor
InactiveUS20060166262A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusLiquid layerPcr method
To provide a PCR method utilizing electrostatic transportation which allows separate control of individual DNA-containing droplets by accurately transporting the droplets, suitably controlling the temperature thereof and allowing a primer to react therewith; a hybridization method utilizing electrostatic transportation which allows rapid and easy detection of hybridization; and devices therefor. A biological sample (droplets containing DNA and primer) (9) is prepared in a chemically inert liquid layer (8), is electrostatically transported by the action of an electrostatic transportation plate (1) with electrostatic transportation electrodes (2) and is heated at a predetermined position of the electrostatic transportation plate (1), thus carrying out PCR.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
PCR and hybridization methods utilizing electrostatic transportation and devices therefor
InactiveUS20060166261A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusLiquid layerPcr method
To provide a PCR method utilizing electrostatic transportation which allows separate control of individual DNA-containing droplets by accurately transporting the droplets, suitably controlling the temperature thereof and allowing a primer to react therewith; a hybridization method utilizing electrostatic transportation which allows rapid and easy detection of hybridization; and devices therefor. A biological sample (droplets containing DNA and primer) (9) is prepared in a chemically inert liquid layer (8), is electrostatically transported by the action of an electrostatic transportation plate. (1) with electrostatic transportation electrodes (2) and is heated at a predetermined position of the electrostatic transportation plate (1), thus carrying out PCR.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Thermoplastic light-duty composite plate and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a thermoplastic light compound plate and the manufacturing method, characterized in that it comprises acupuncture fiber carpet dipped in double faced foam of thermoplastic glue liquid and thermoplastic glue liquid layer coated on the surface, the density of compound plate is 0.35-0.90g / cm3, the weight of fiber scattered in bunchiness is 15-45% of acupuncture fiber carpet. The merit of invention is very remarkable. Special super long fiber and bunchiness fiber with certain proportion are maintained in the material so that the mechanical performance of material can be improved. In addition, the material is provided with foam structure, very good effect of heat and sound insulation. The invention is also provided with environmental protection and recovery.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
Optical films and process for making them
InactiveUS20060068128A1Good dimensional stabilityLow in-planeLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid layerSolvent
A method of film fabrication is taught that uses a coating and drying apparatus to fabricate resin films suitable for optical applications. In particular, resin films are prepared by simultaneous application of multiple liquid layers to a moving carrier substrate having low surface energy. After solvent removal, the resin films are peeled from the sacrificial carrier substrate. Films prepared by the current invention exhibit good dimensional stability and low out-of-plane retardation.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Methods for removing photoresist
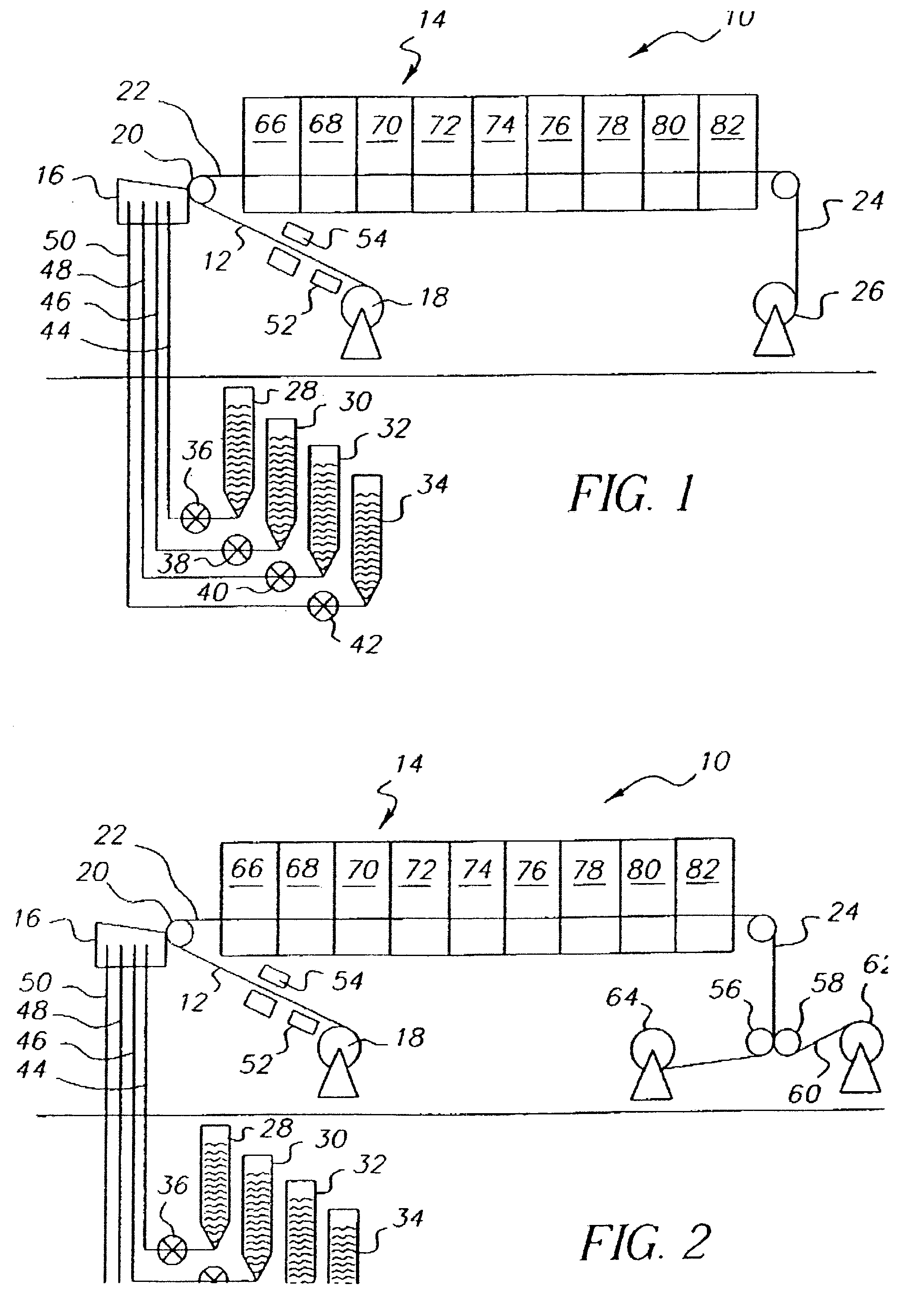
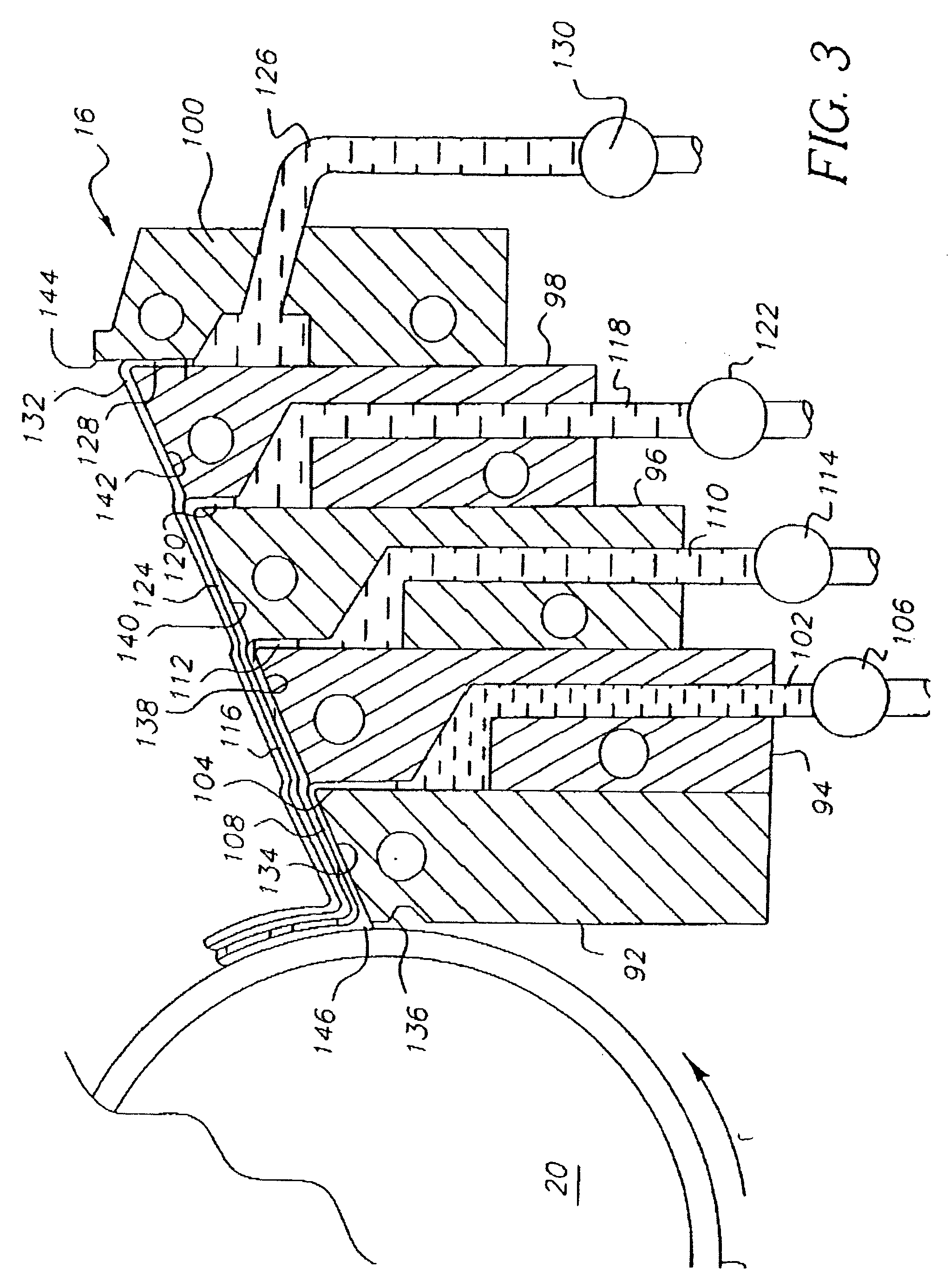
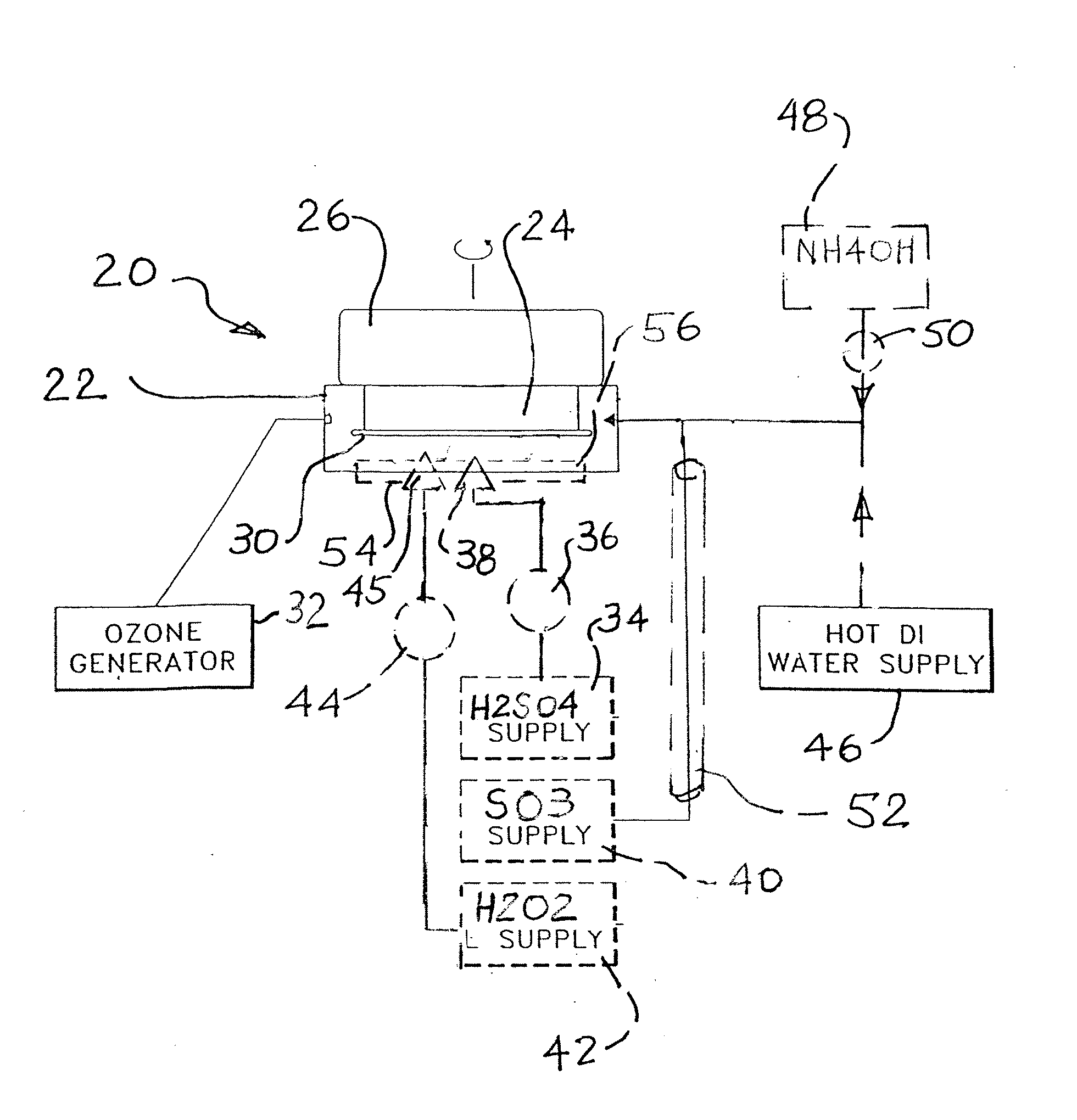
InactiveUS20070227556A1Affect strip performancePromote resultsPhotomechanical apparatusCleaning using liquidsLiquid layerOrganic film
In a method for removing an organic film such as photoresist from a wafer, the wafer is placed into a chamber. A liquid including an acid, such as sulfuric acid is applied to the surface of the wafer. Sulfur trioxide is supplied into the chamber. Alternatively, fuming sulfuric acid may be used. The wafer may optionally be spinning in the chamber. The liquid forms a liquid layer on the surface of the workpiece. The chemical reaction of the acid and the SO3 removes the organic film. Further improved results may be achieved in removing many organic films by heating the wafer, or the liquid, or both. Providing ozone gas into the chamber may also be helpful in some applications. In a related method, an organic film is removed from a wafer by applying an acid film or layer on to the surface of the wafer. The acid, is heated. An oxidizer is then delivered to the heated acid film. The combined action of the acid and the oxidizer removes the organic film, typically without leaving any residues. The acid may be sulfuric acid and the oxidizer may be hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:SEMITOOL INC
Fabrication of 3d photopolymeric devices
InactiveUS20060066006A1Easy to customizeHigh resolutionMouldsNanoinformaticsLiquid layerMechanical engineering
A process and apparatus for making polymeric layers. A layer of liquid (20) including a photopolymerizable precursor is formed between a substrate (17) and a photomask (12). A reaction chamber is formed by a base (15), side walls (16) and photomask (12) polymerizes one or more regions of the liquid layer (20) to form a polymeric layer.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
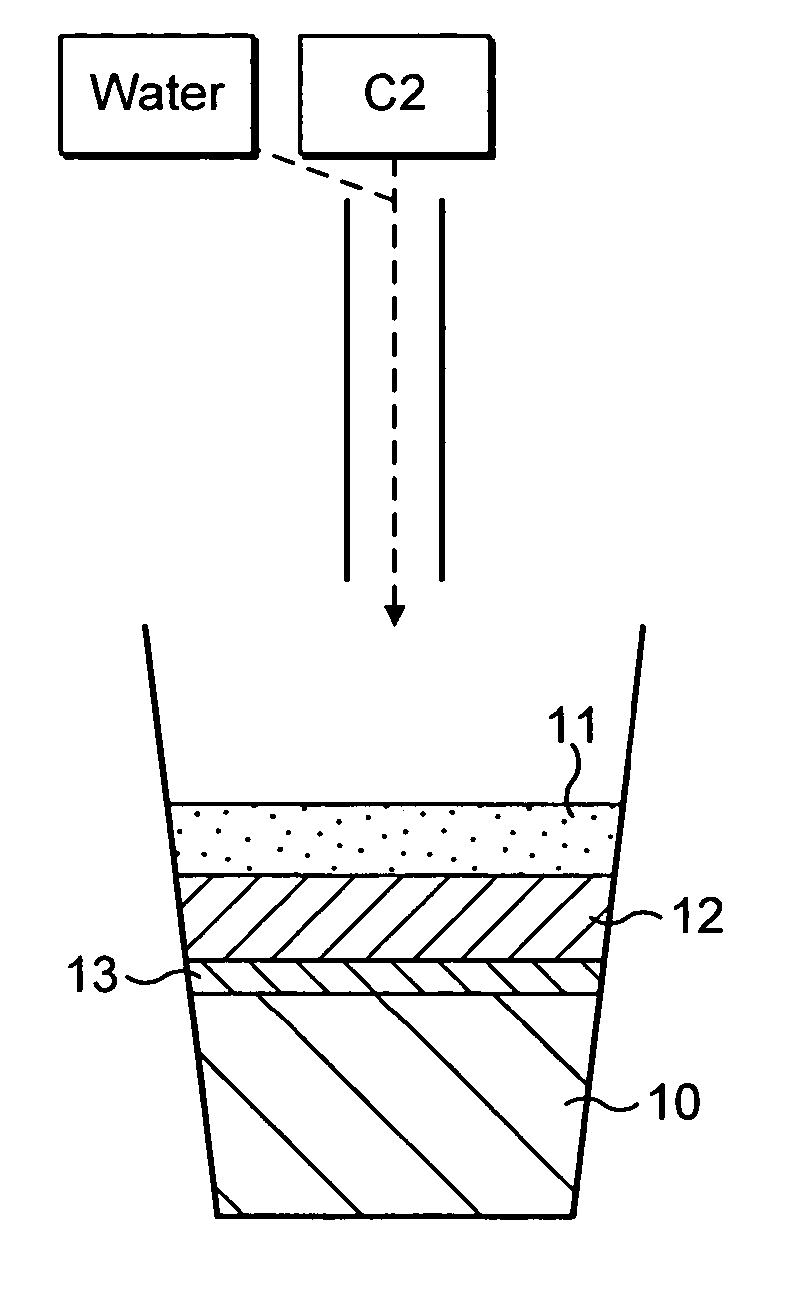
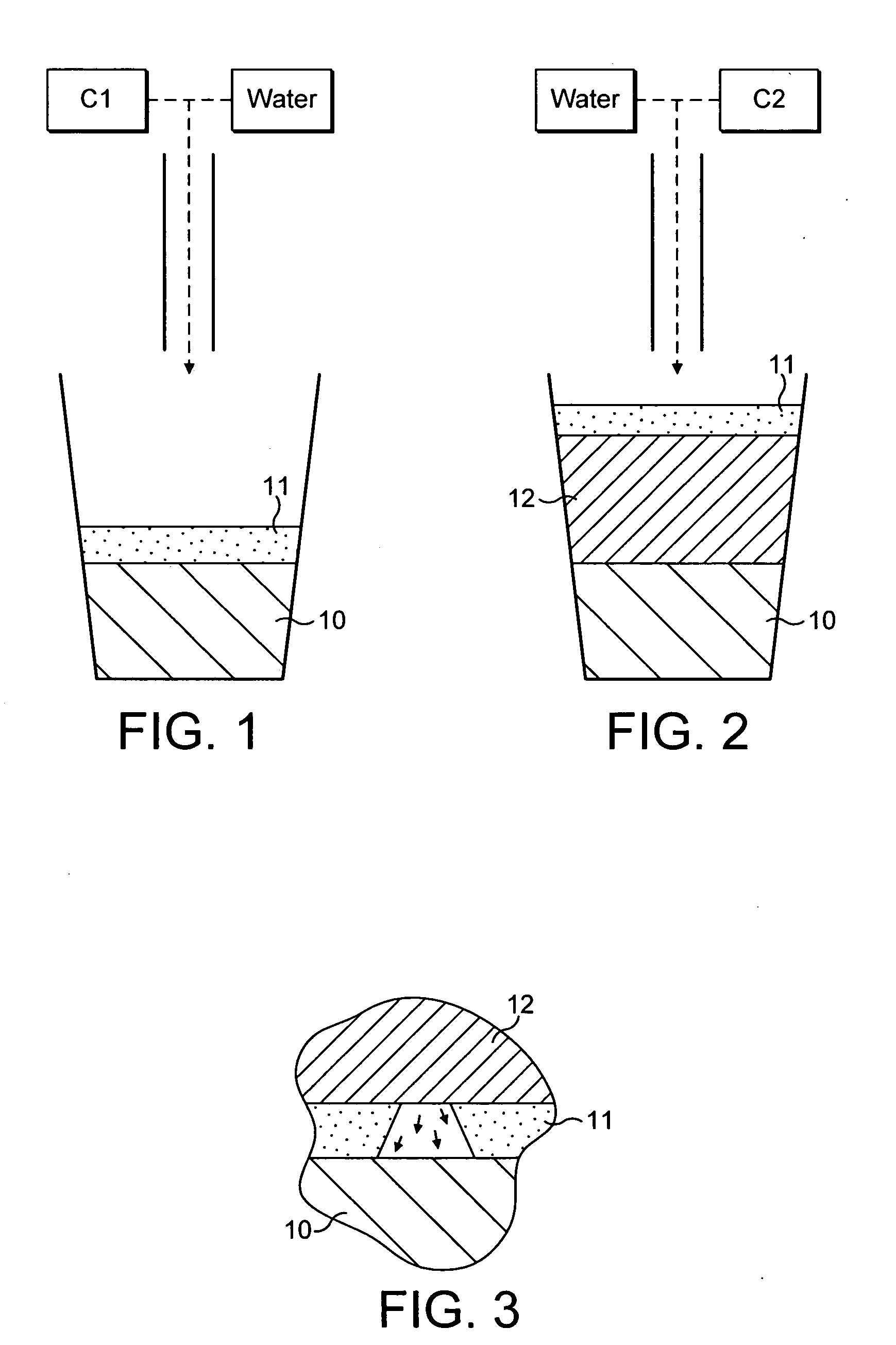
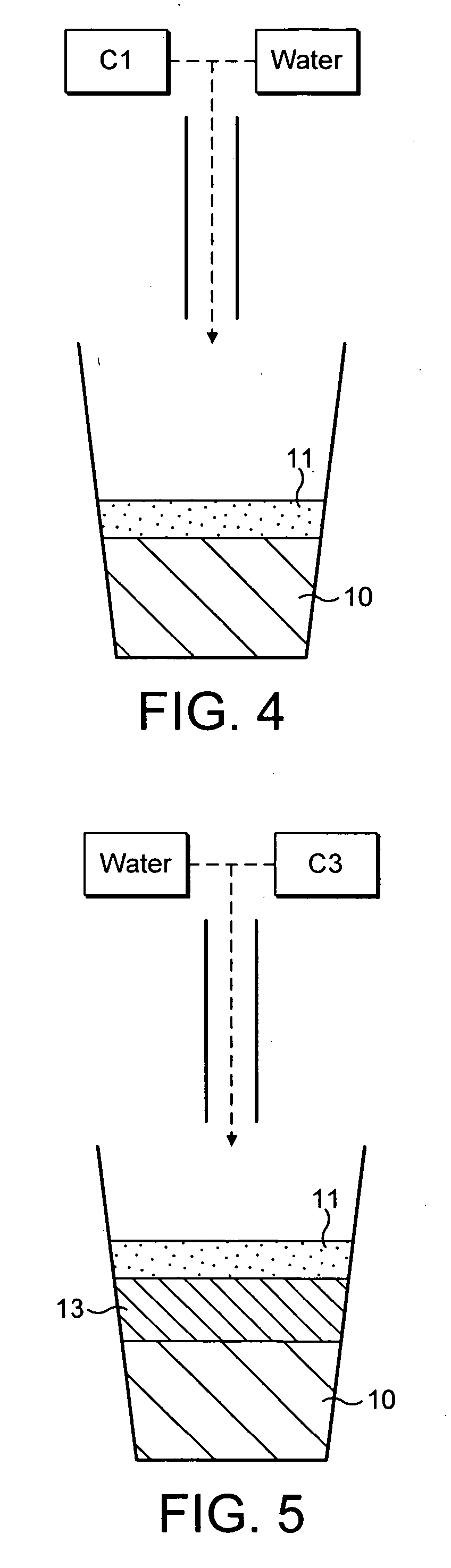
Method and device for dispensing from liquid concentrates beverages having multi-layer visual appearance
ActiveUS20050095341A1High densityMiniaturization exerciseLiquid fillingLiquid transferring devicesLiquid layerLow density
The invention relates to a method for dispensing a beverage with the visual appearance of multi-layers obtained from dilution of concentrates in proper dilution ratios. A first liquid layer is first delivered with a controlled density. A second liquid layer is diluted to a density that is lower than the density of the first liquid layer so that the first and second layers form a stable layered arrangement with the second liquid layer of lower density remaining spatially above the first liquid layer to provide a visually distinct layer as compared to the first liquid layer in the container. The invention also relates to a dispensing device and to a machine readable program enabling the device to deliver the multi-layer appearance beverage according to the method of the invention.
Owner:NESTEC SA
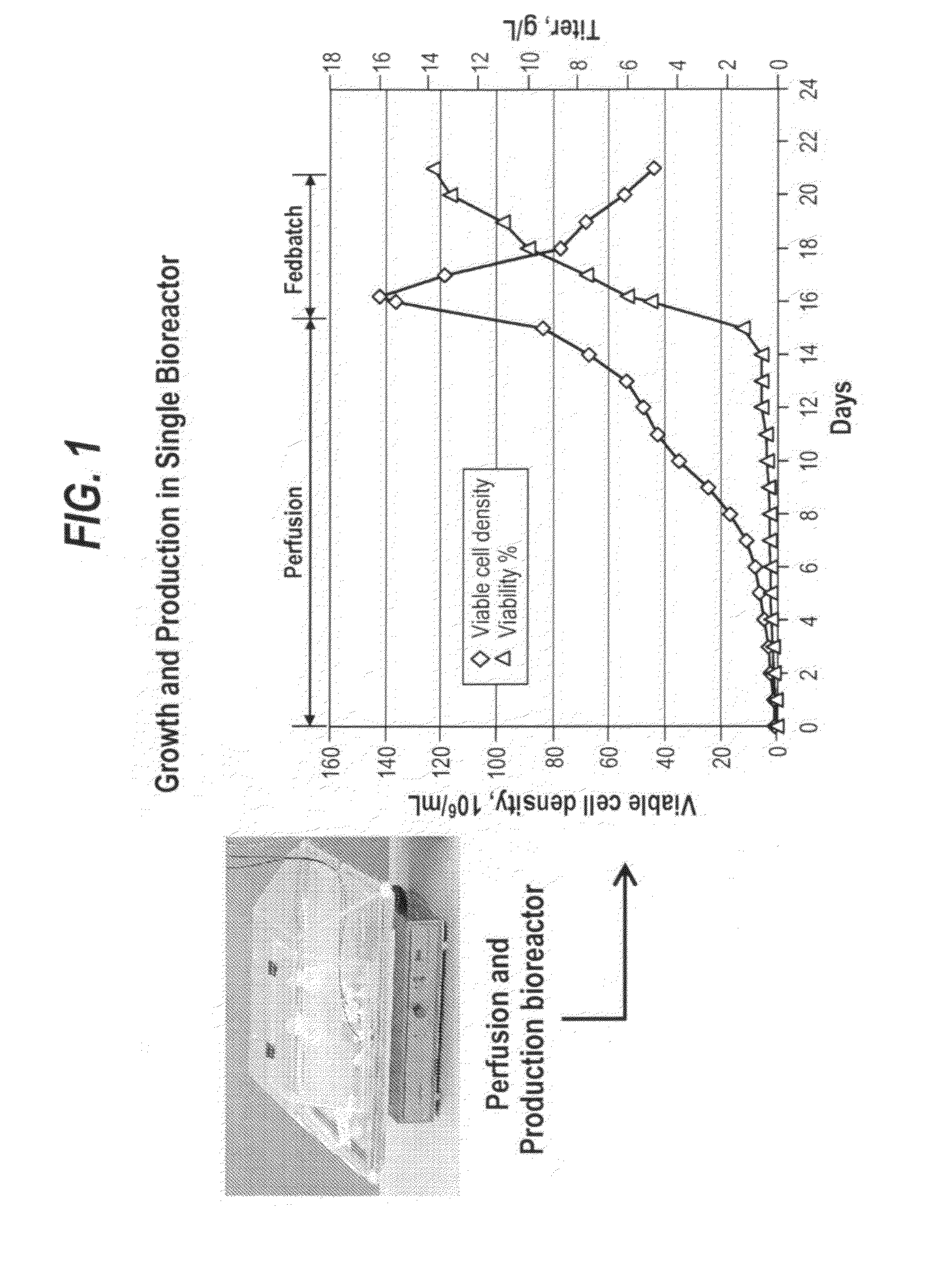
Methods for enhanced protein production
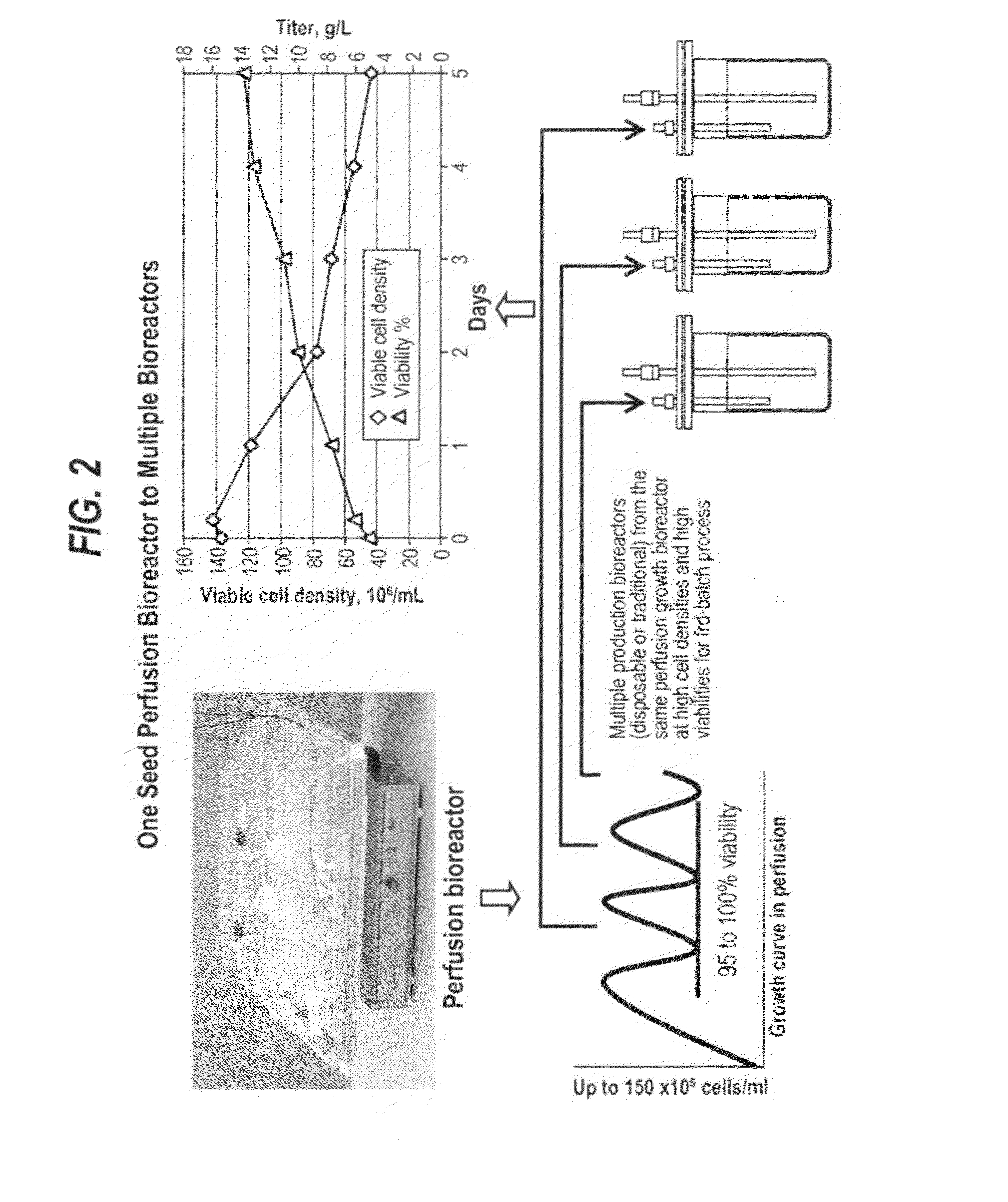
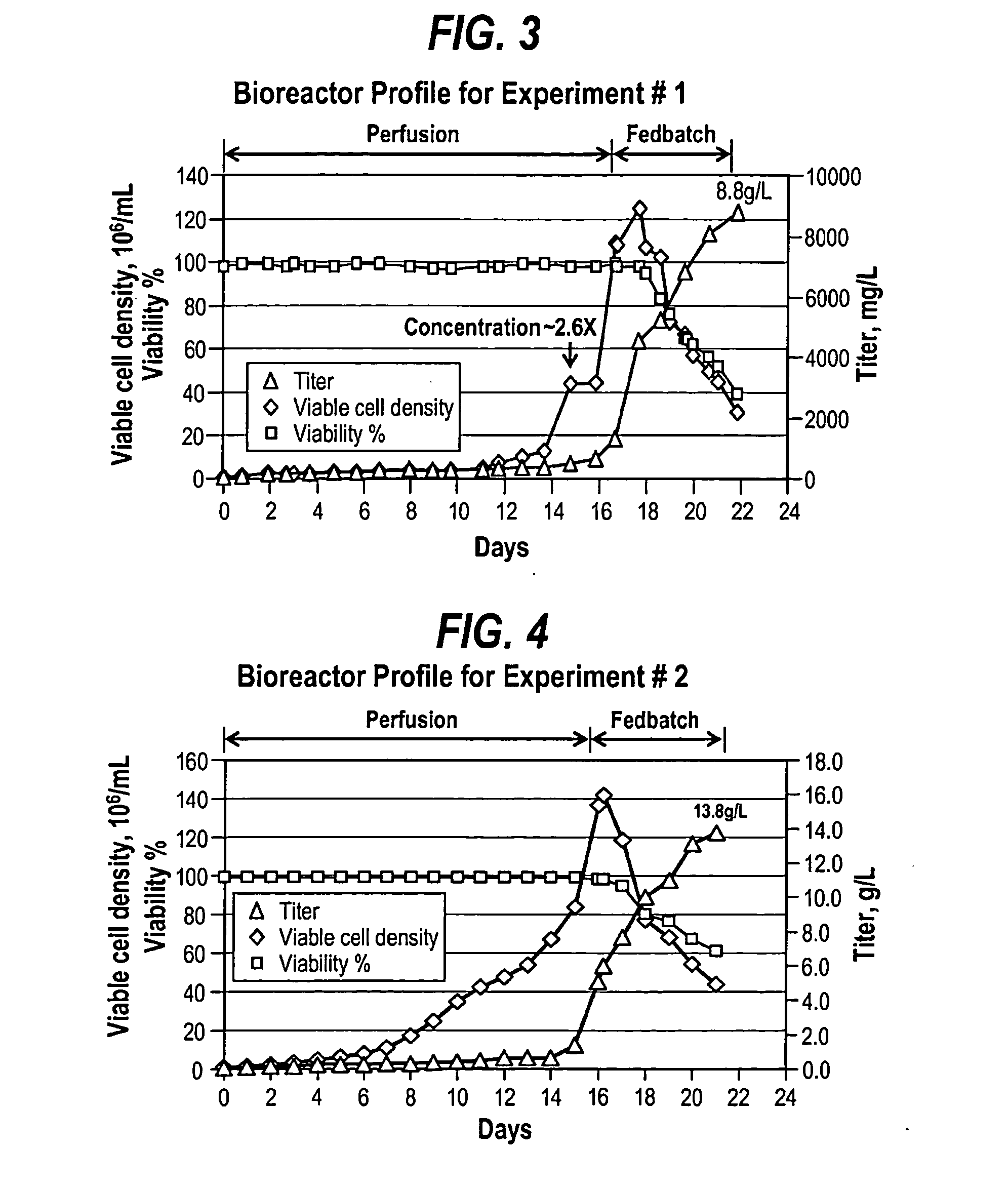
ActiveUS20130017577A1Increase cell densityA large amountAnimal cellsMicroorganism separationHigh cellLiquid layer
The present invention provides a method of increasing protein production in a cell culture by growing cells that produce the protein (e.g., the growth phase) in a perfusion cell culture to a high cell density (i.e., at least above about 40×106 cells / N mL) and then switching to a protein production phase, wherein the cells are cultured in a fed-batch cell culture. The present invention further provides a method for clarifying a protein from a cell culture by adjusting the pH of the cell culture to below neutral pH (i.e., below a pH of 7) and settling the cell culture, such that the cell culture separates to form a supernatant layer and a cell-bed layer, wherein the protein is in the supernatant layer.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Textured surface coating for gloves and method of making
ActiveUS20050035493A1Improve comfortImprove wet grippingGarment special featuresGlovesLiquid layerDiscrete particle
There is provided, in accordance with the principles of the present invention, a glove having a textured surface or textured foam coating produced by embedding a layer of discrete particles, such as a salt, into a previously formed liquid layer, gelling or curing the layer and dissolving the discrete particles to leave a textured or textured foamed surface.
Owner:ANSELL HEALTHCARE PRODS
Cleaning with electrically charged aerosols
InactiveUS20060118132A1Easy to cleanEasy maintenanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic cleaningLiquid layerAerosol droplet
In a method for cleaning a wafer, the wafer is placed a processing chamber. A layer or film of liquid is provided on the wafer. Electrically charged aerosol droplets of a liquid are formed and directed to the workpiece. The charged aerosol particles accumulate on the workpiece. This creates an electrical charge on the workpiece. Contaminant particles on the workpiece are released and / or repelled by the electrical charge and are carried away in the liquid layer. The liquid layer is optionally continuously replenished with fresh liquid. The liquid layer may be thinned out in a localized aerosol impingement area, via a jet of gas, to allow the electrical charge of the aerosol to better collect on or near the surface of the workpiece.
Owner:SEMITOOL INC
Apparatus and method for edge bevel removal of copper from silicon wafers
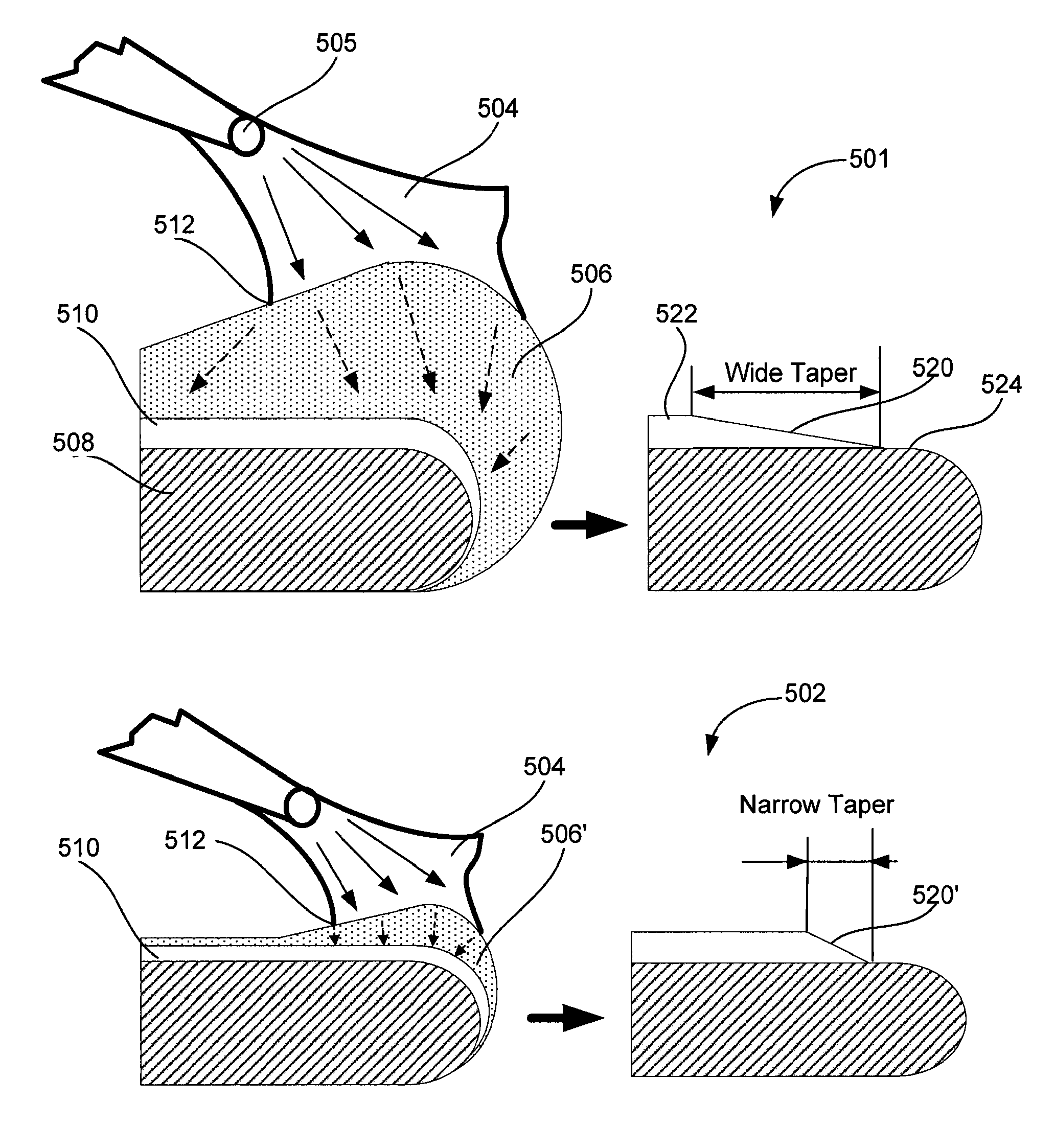
ActiveUS20100055924A1Facilitated DiffusionIncrease etch rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid layerThin layer
Chemical etching methods and associated modules for performing the removal of metal from the edge bevel region of a semiconductor wafer are described. The methods and systems provide the thin layer of pre-rinsing liquid before applying etchant at the edge bevel region of the wafer. The etchant is less diluted and diffuses faster through a thinned layer of rinsing liquid. An edge bevel removal embodiment involving that is particularly effective at reducing process time, narrowing the metal taper and allowing for subsequent chemical mechanical polishing, is disclosed.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Display and fabricating method thereof
ActiveUS7813030B2Prevent overflowLamination ancillary operationsStatic indicating devicesLiquid layerDisplay device
A display and fabricating method thereof is provided. The display includes a first substrate, a second substrate, a hydrophobic layer, a nonpolar liquid layer, a hydrophilic separator, a polar liquid layer, and a protruding spacer. The first and second substrates respectively include an opposing surface, and are disposed in a way that the opposing surfaces are face-to-face opposing to each other. The hydrophobic layer overlies the opposing surface of the second substrate. The nonpolar liquid layer overlies the hydrophobic layer. The hydrophilic separator overlies the hydrophobic layer and surrounds the nonpolar liquid layer. The polar liquid layer overlies the nonpolar liquid layer. The protruding spacer is disposed between the hydrophilic separator and the first substrate.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Ink jet recording method, ink jet recording apparatus, and ink jet recorded matter
ActiveUS20120242768A1Good effectQuality improvementDuplicating/marking methodsInksLiquid layerDistribution pattern
An ink jet recording method including: applying at least two energy beam curable liquids different from each other in surface tension on a recording medium to form an energy beam curable liquid layer having a distribution pattern of different surface tensions; ejecting an energy beam curable ink on the energy beam curable liquid layer formed on the recording medium; and irradiating the energy beam curable liquid layer and the energy beam curable ink with energy beams to cure the energy beam curable liquid layer and the energy beam curable ink to form an image.
Owner:RICOH KK
Liquid zoom lens
A liquid zoom lens mounted on a portable terminal is provided. In the liquid zoom lens, a cylindrical body has upper and lower openings to which one pair of lenses is coupled. An auto-focus lens part includes a first insulating liquid layer, a first electrolyte layer, and a first lens. The first insulating layer and the first electrolyte layer are disposed to form an interface at a lower portion of the body. The first lens is disposed on the first electrolyte layer and has a periphery closely attached to a lower portion of an inner periphery of the body. An optical zoom lens part includes a second insulating liquid layer, a second electrolyte layer, and a second lens. The second insulating liquid layer and the second electrolyte layer are disposed to form an interface on the first lens. The second lens is fixed to be movable within the second insulating liquid layer, such that a periphery is closely attached to the inner periphery of the body. Accordingly, the auto-focus function and the optical zoom function can be simultaneously achieved through a single liquid lens whose curvature is varied by the difference of the inherent refractive index between the electrolyte and the insulating liquid.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Printing of radiation curable inks into a radiation curable liquid layer
InactiveUS20060092254A1Limited to printing imageHigh and uniform glossPattern printingOther printing apparatusLiquid layerImage resolution
A printing process is disclosed for ink-jet printing a radiation curable image on a substrate (14). First a radiation curable liquid layer (12) is provided on at least a portion of the substrate (14). Radiation curable ink-jet ink droplets (10) are jetted into the radiation curable liquid layer (12) and the radiation curable liquid layer (12) containing the radiation curable ink-jet ink droplets (13) is then cured. The resolution of the radiation curable image is controlled by uniformly adjusting the thickness of the liquid layer (12) for the dotsize of the radiation curable ink-jet ink jetted onto the cured layer.
Owner:AGFA NV
Eyewear lens production by multi-layer additive techniques
ActiveUS20150276987A1Limit angleColor becomes smallerAdditive manufacturing apparatusVacuum evaporation coatingLiquid layerOptical property
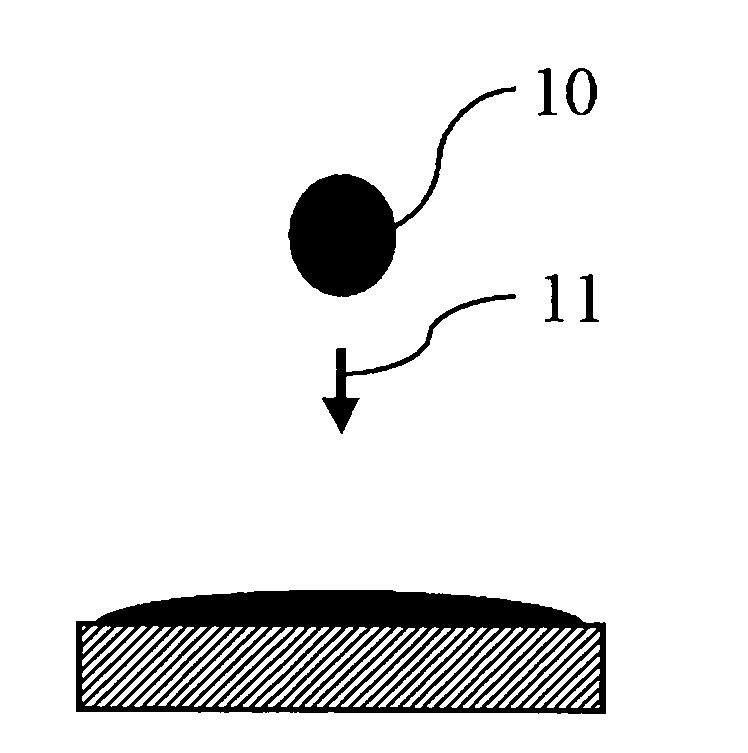
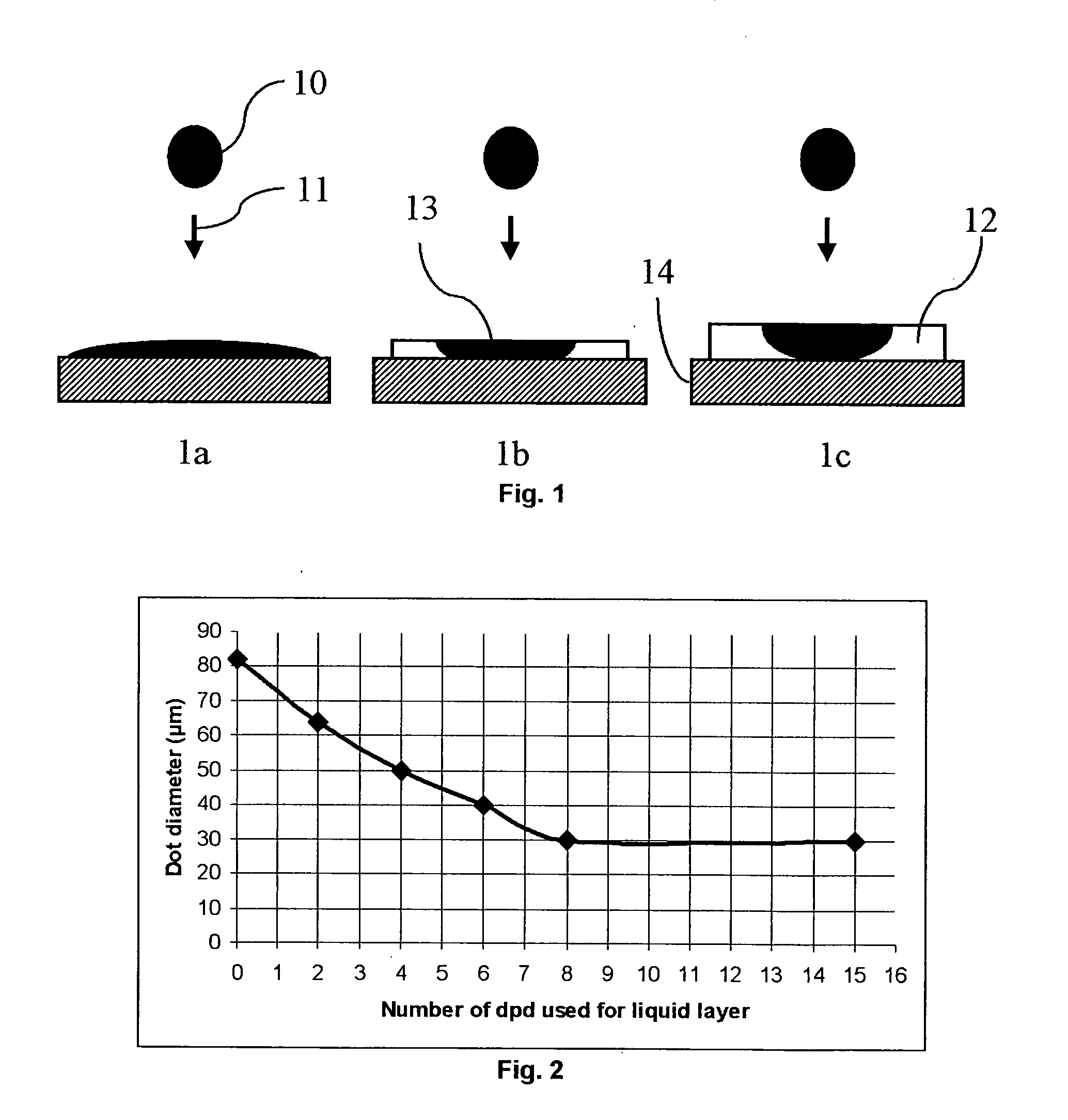
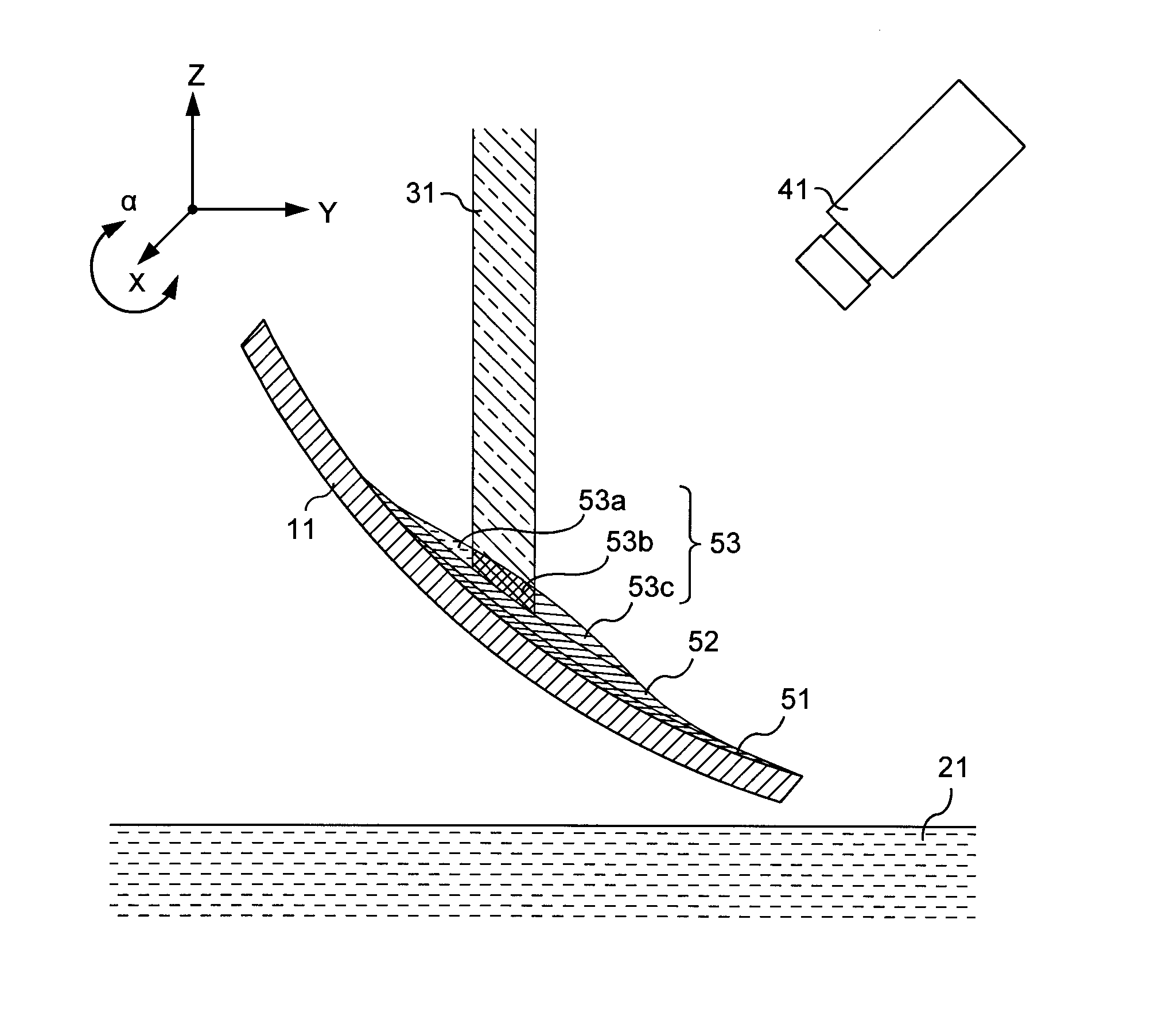
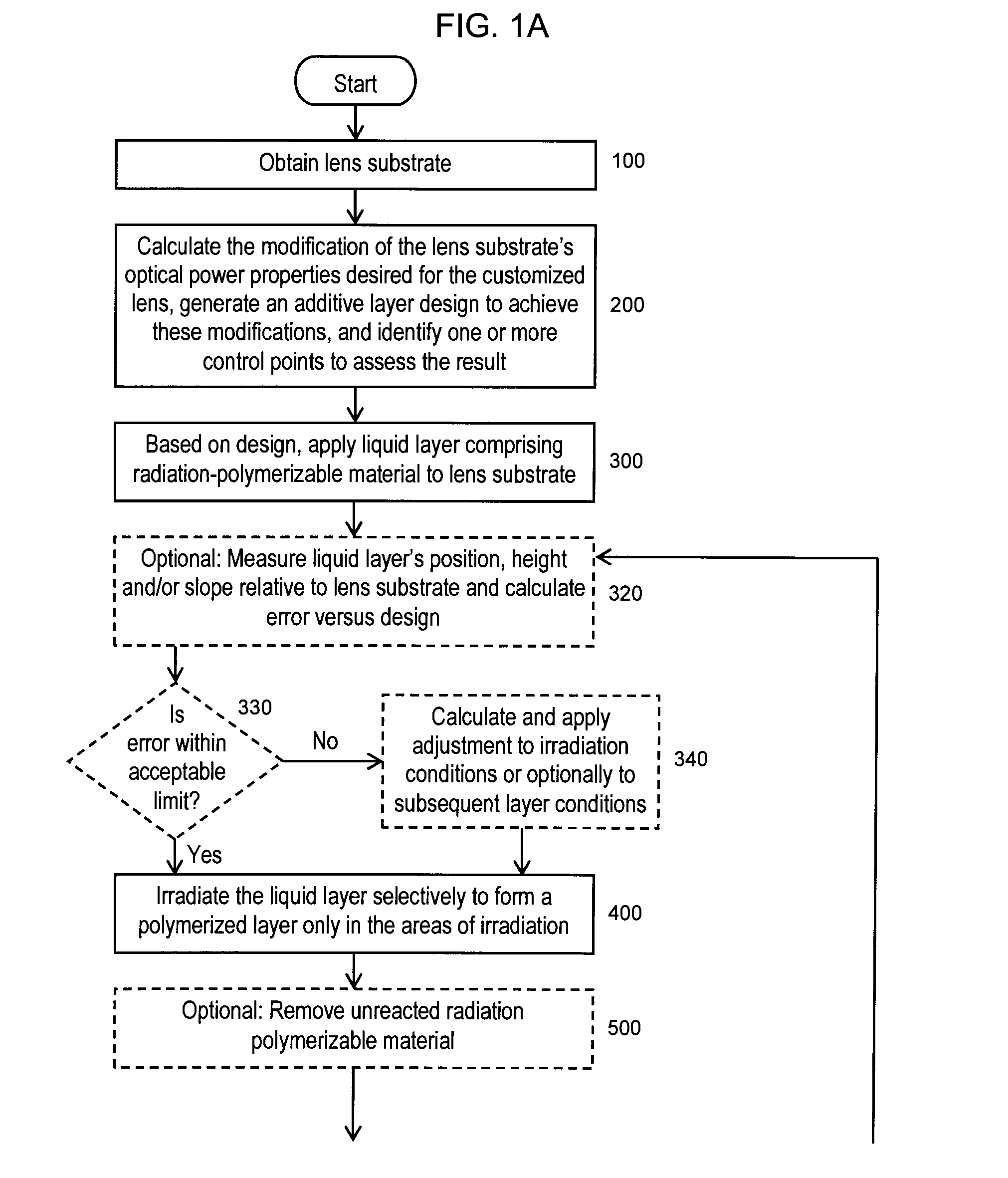
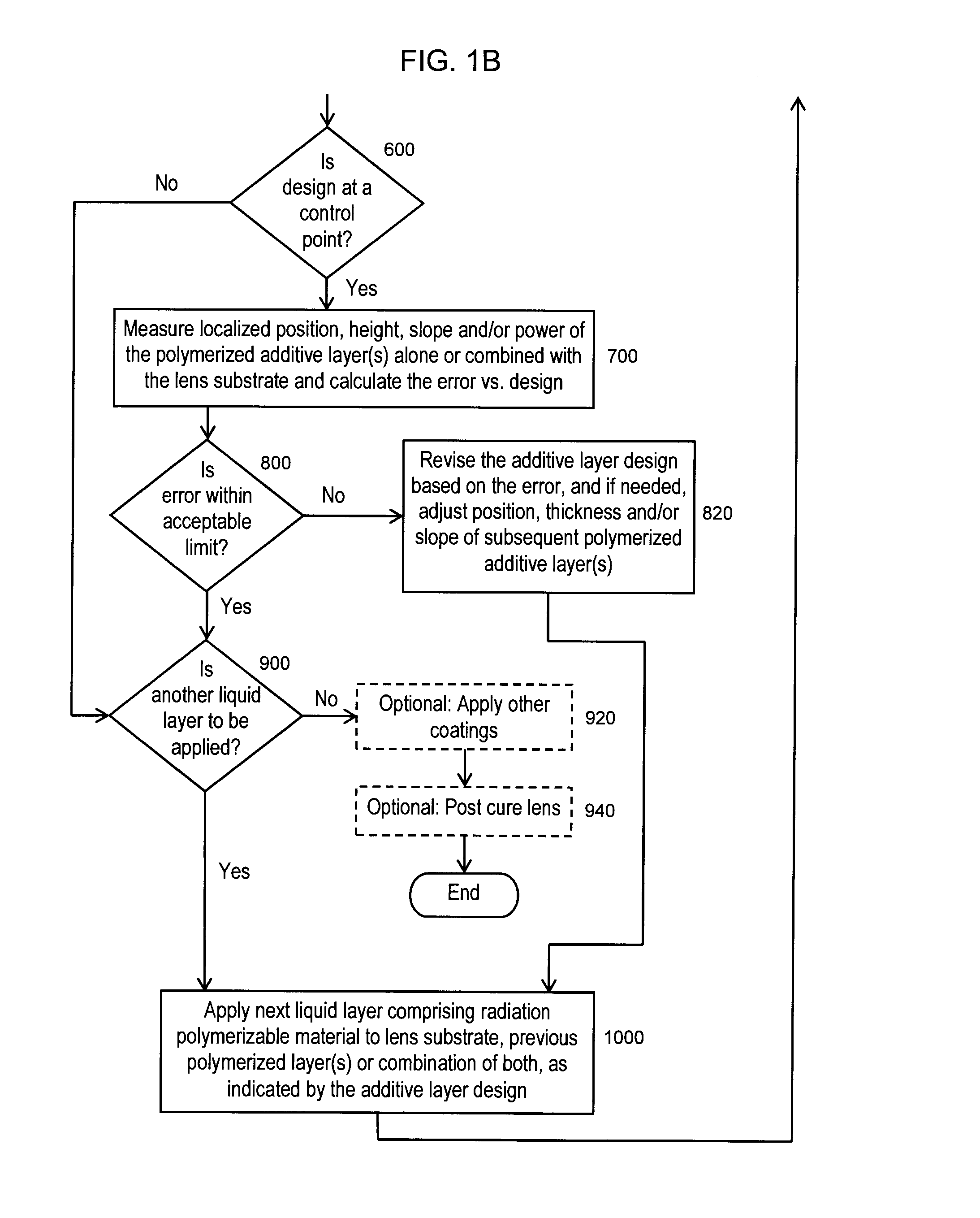
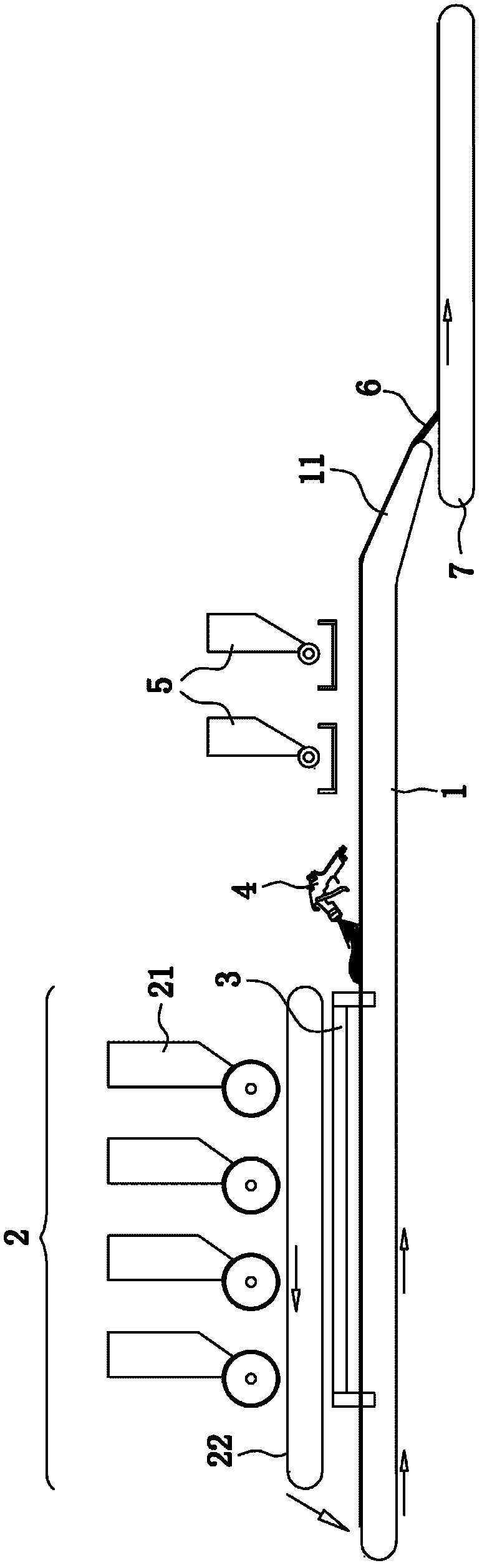
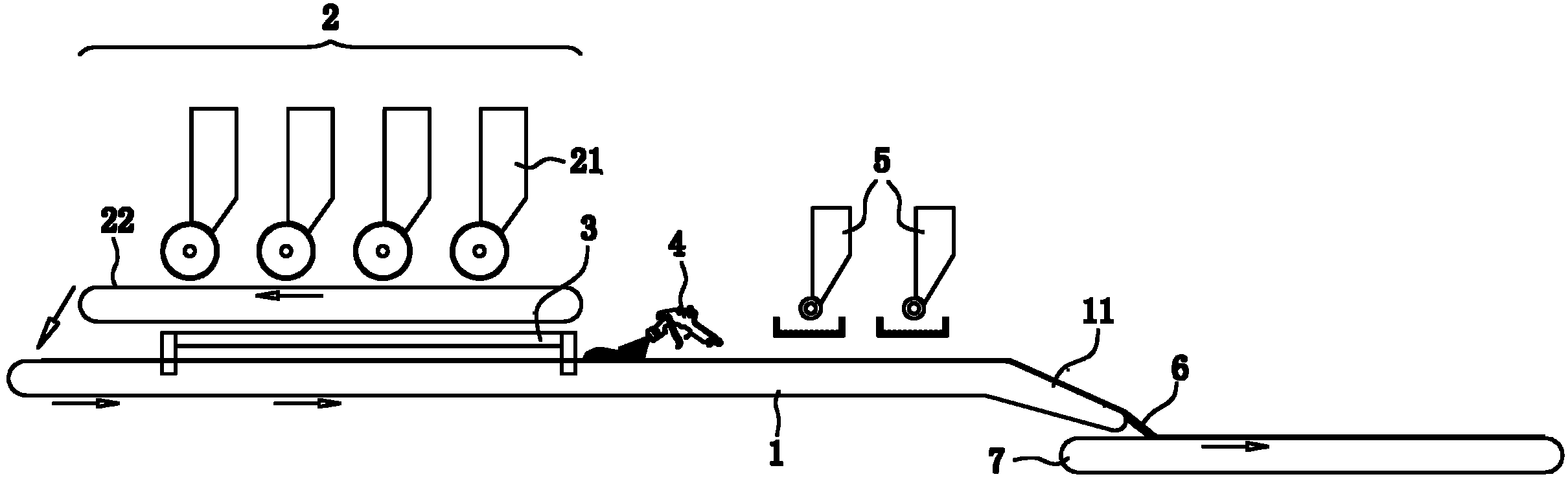
An additive processing method is used to produce a customized eyewear lens by selectively building layers of radiation-polymerized material onto a lens substrate that has optical power properties discernibly different from the optical properties of the customized eyewear lens. The method involves obtaining the lens substrate, calculating the modifications needed to convert the lens substrate's properties to the desired set of properties of the customized lens, generating an additive layer design to achieve the calculated modifications, and identifying at least one control point for confirmation or revision of the additive layer design. The method further involves applying liquid layers of radiation-polymerizable material to the lens substrate and irradiating the liquid layers in selected areas with controlled radiation such that the material is only polymerized and the additive layer is only formed in the select areas irradiated, according to the additive layer design.
Owner:INDIZEN OPTICAL TECH
Material distribution method and device for production of ceramic tile
InactiveCN102303357AHigh degree of simulationHigh degree of clusteringFeeding arrangmentsShaping conveyorsLiquid layerBrick
The invention discloses a material distribution method and device for the production of a ceramic tile, wherein the method comprises the steps of: 1, distributing a surface material on a first feeding belt; 2, shaping the surface material by a shaping machine; 3, coating a coloring liquid layer, which forms irregular textured patterns, on the surface of the surface material; 4, randomly distributing a ceramic material on the surface of the liquid layer; and 5, transferring the distributed ceramic material to a second feeding platform and piling up the ceramic material on the second feeding platform to complete material distribution, wherein the first feeding belt has the speed higher than that of a second feeding belt. By adopting the technical proposal, a pattern which is both delicate and raw and which is extremely close to natural texture can be formed, thus the simulation for surface texture of the finished ceramic tile product is improved.
Owner:佛山市新海舟科技有限公司
Cleaning apparatus and liquid ejection apparatus and cleaning method
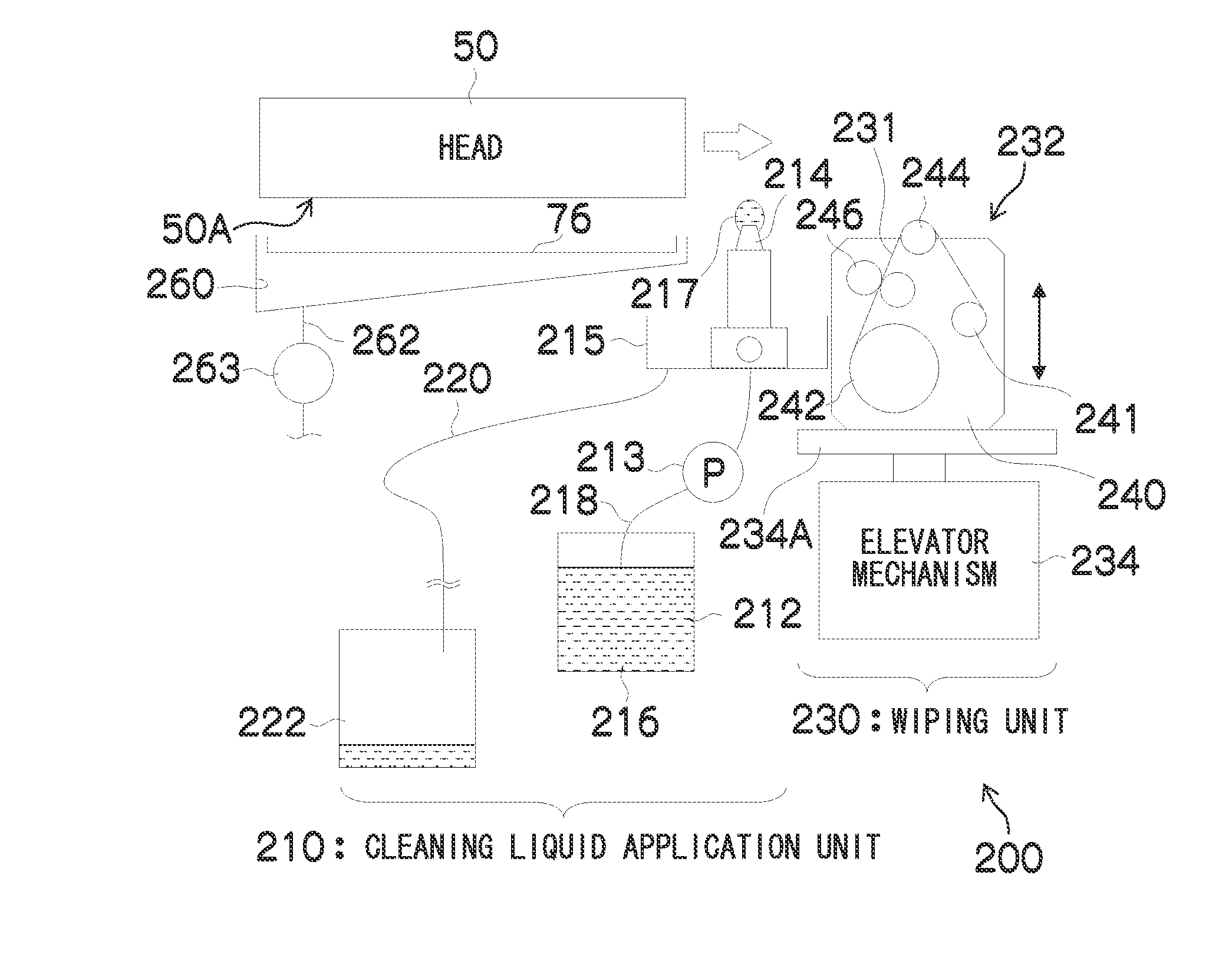
InactiveUS20100214355A1Improvement in ejection reliabilityEasy to cleanInking apparatusLiquid jetLiquid layer
The cleaning apparatus cleans a nozzle surface of a liquid ejection head. The cleaning apparatus includes: a cleaning liquid supply device which supplies cleaning liquid to the nozzle surface while being not in contact with the nozzle surface; a liquid layer formation control device which causes the cleaning liquid supply device to supply a prescribed amount of the cleaning liquid to form a layer of the cleaning liquid that fills in a space between the cleaning liquid supply device and the nozzle surface; and a movement control device which controls a movement device so as to move the cleaning liquid supply device and the liquid ejection head relatively to each other at a relative speed in which a meniscus is not broken down, the meniscus being of the layer of the cleaning liquid in a portion of the layer of the cleaning liquid that makes contact with the nozzle surface.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Razor blade sharpener
An automatic razor blade sharpener simultaneously sharpens multiple edges of a spring-loaded disposable razor blade cartridge by gently contacting the blade edges with a moving rubber or polymeric compliant belt that is motor driven. The disposable razor blade handle is set in a cradle aperture, which is spring loaded against the moving belt. A timer terminates the blade sharpening operation, indicated by a green LED. A liquid is dispersed on the moving belt forming a thin liquid layer on the belt surface, illuminated by transversely located light illumination and the reflected light is received by a transversely located sensor. When the blade contacts the thin liquid layer, deep grooves in the blade cutting edge reduce this reflection indicating that the blade is too worn to be sharpened and a red LED light is indicated. Absence of reflection indicates that the thin liquid film has evaporated or spilled out.
Owner:PAPETTI JULIA GRACE
Method of clamping a substrate and clamp preparation unit
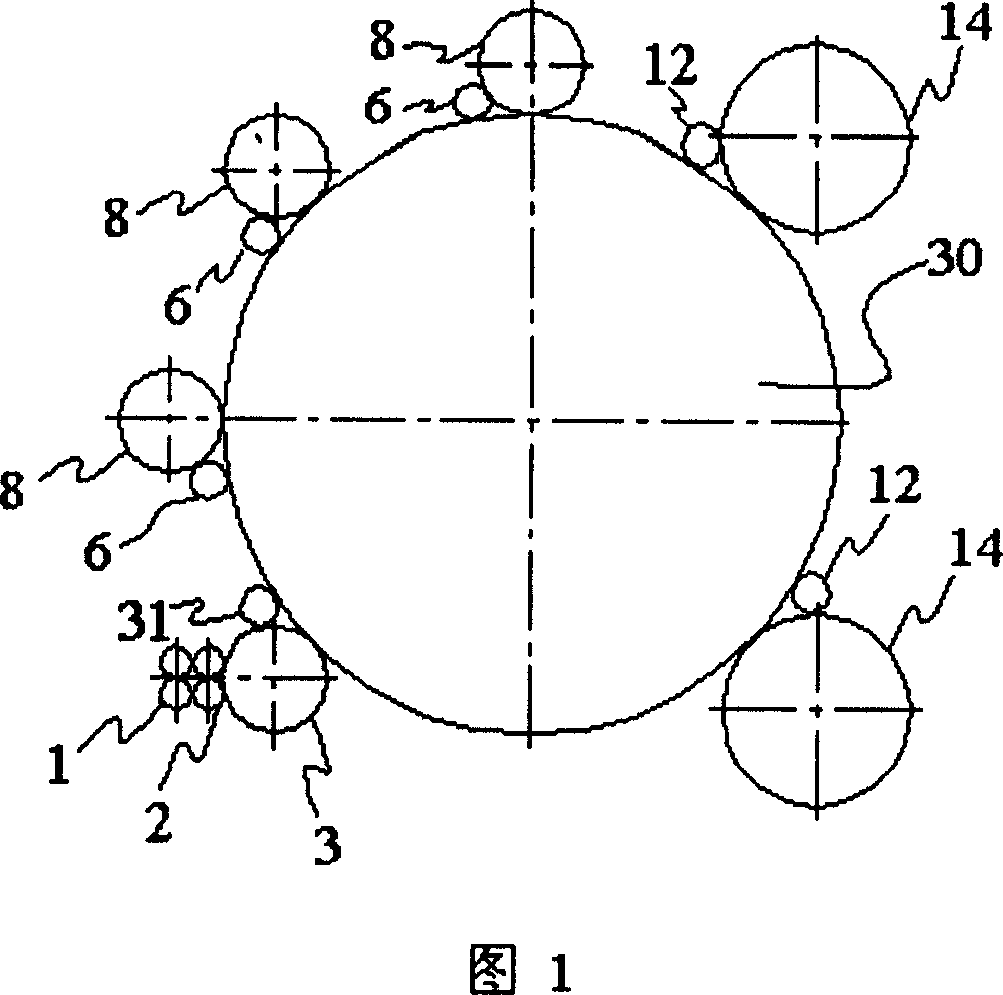
ActiveUS20100265486A1Improve performancePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid layerEngineering
The invention relates to a method of clamping a substrate on a surface of a substrate support structure. First, a liquid is applied on a surface of the substrate support structure. The surface is provided with a plurality of contact elements. The liquid is applied such that the contact elements are fully covered by a liquid layer. Then the substrate is provided and placed onto the liquid layer. Finally, liquid underneath the substrate is removed such that the substrate rests on the plurality of contact elements and is clamped by means of a capillary clamping force exerted by a capillary layer of the liquid between the substrate and the surface of the substrate support structure.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
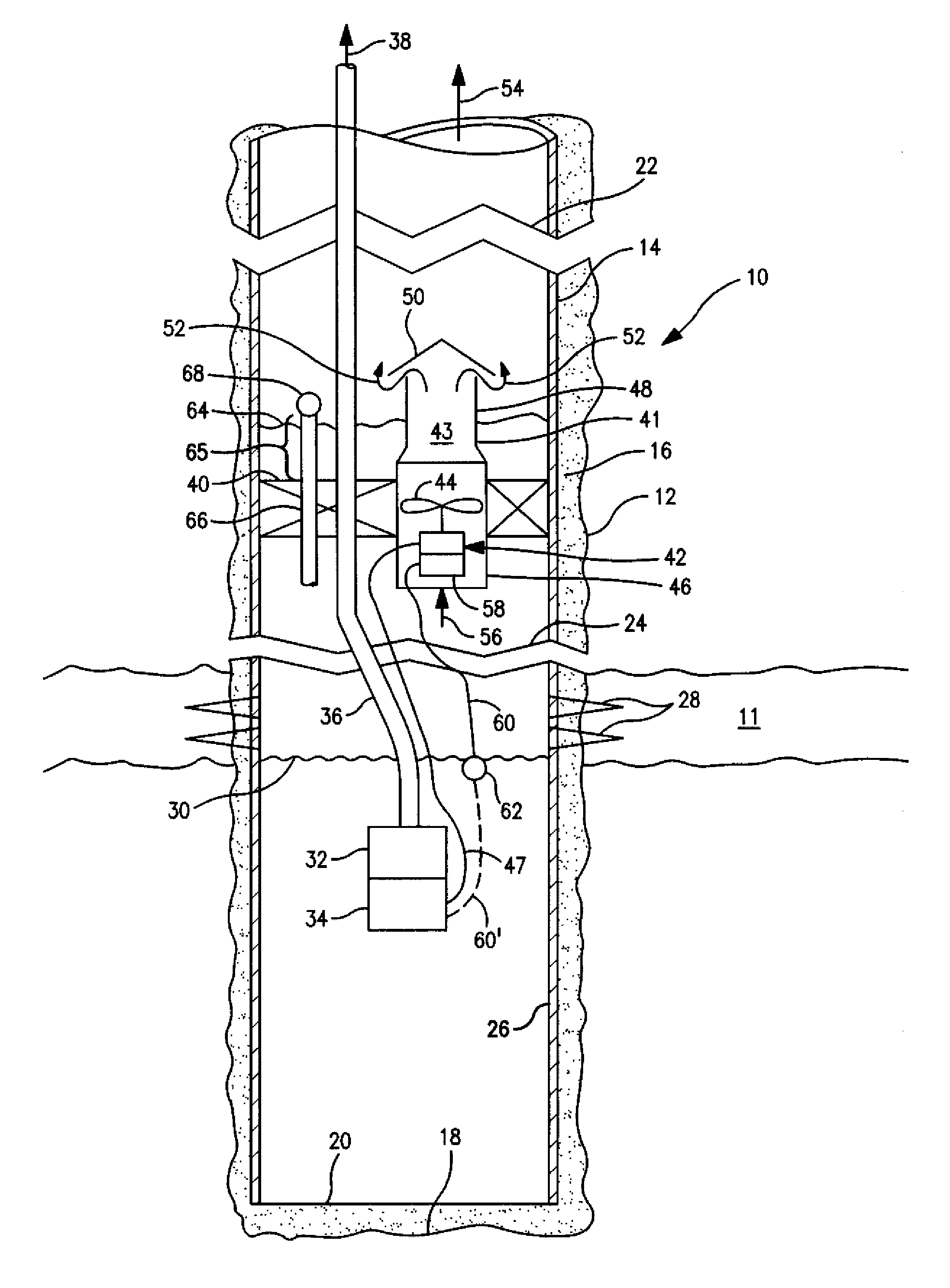
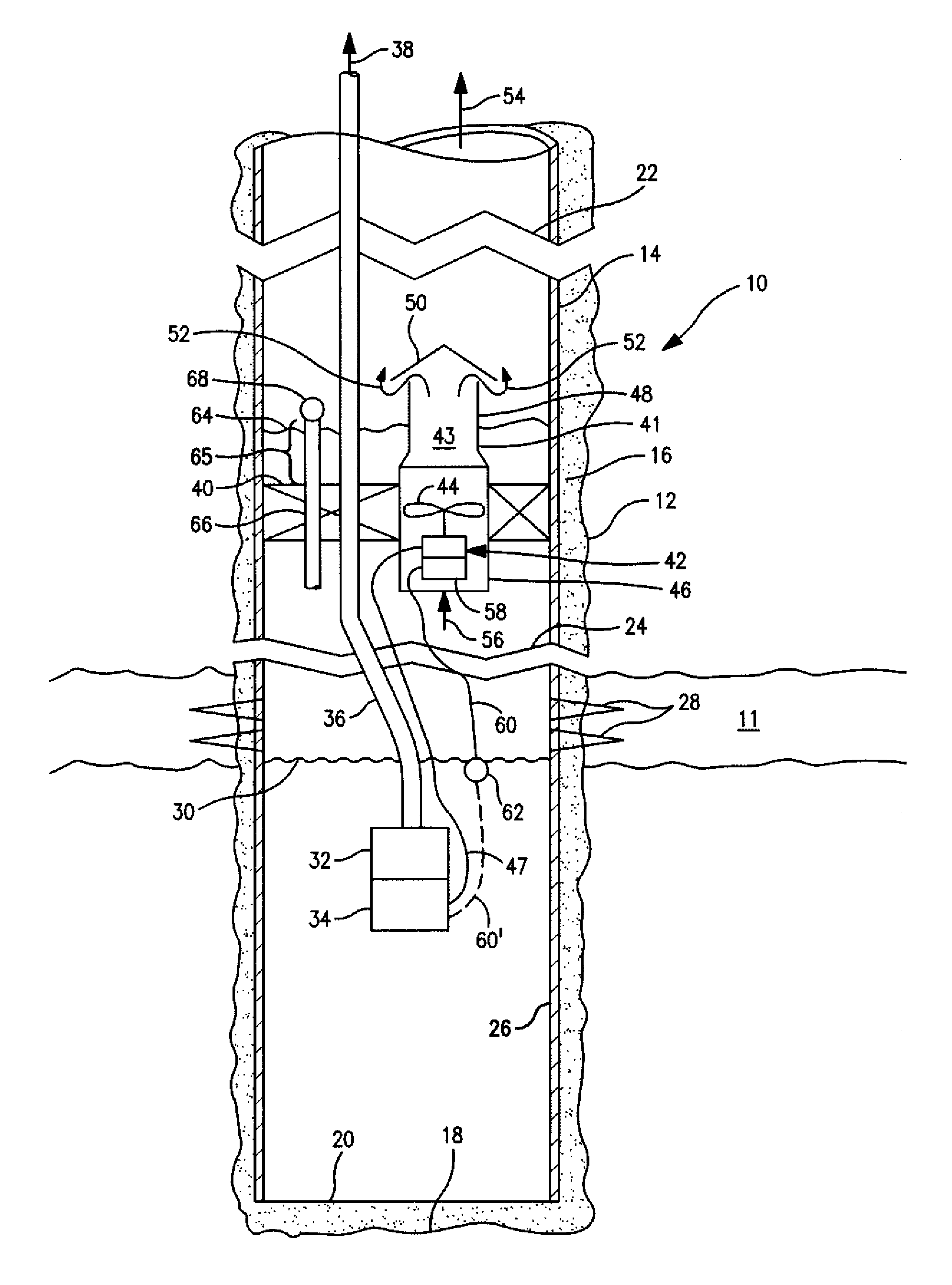
Downhole gas flow powered deliquefaction pump
The present invention relates to a method and system for removing water from gas wells. The water is removed by positioning a pump in a liquid layer below the perforations through which gas enters a gas well and powering a water pump with electrical power generated by an energy recovery system which produces electricity from a gas flow through the energy recovery system to an earth surface.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com