Patents
Literature
423 results about "Growth phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Growth phase. A phase in the life cycle of an industry when companies move beyond the startup phase into a phase of increased competition for market share.
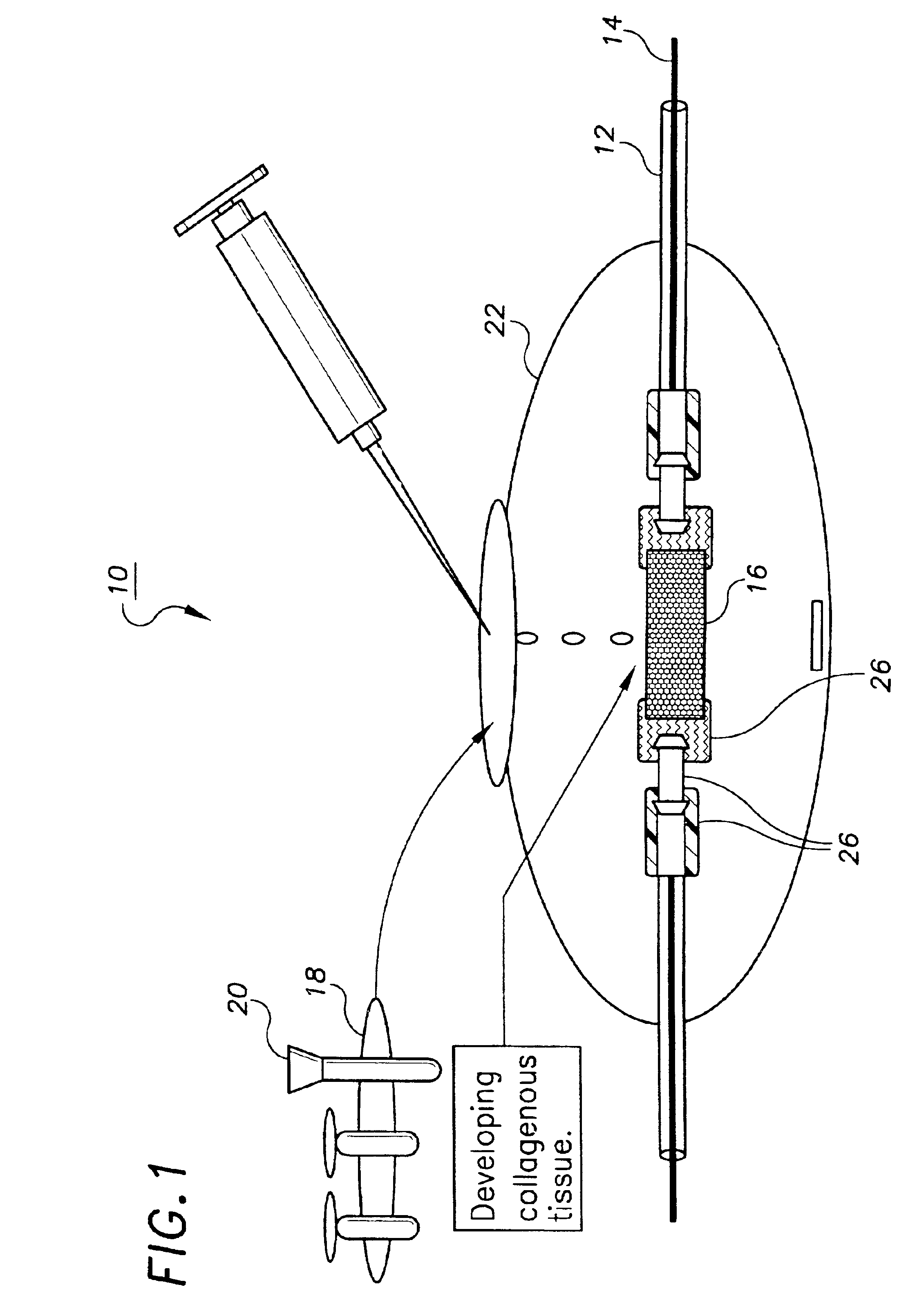
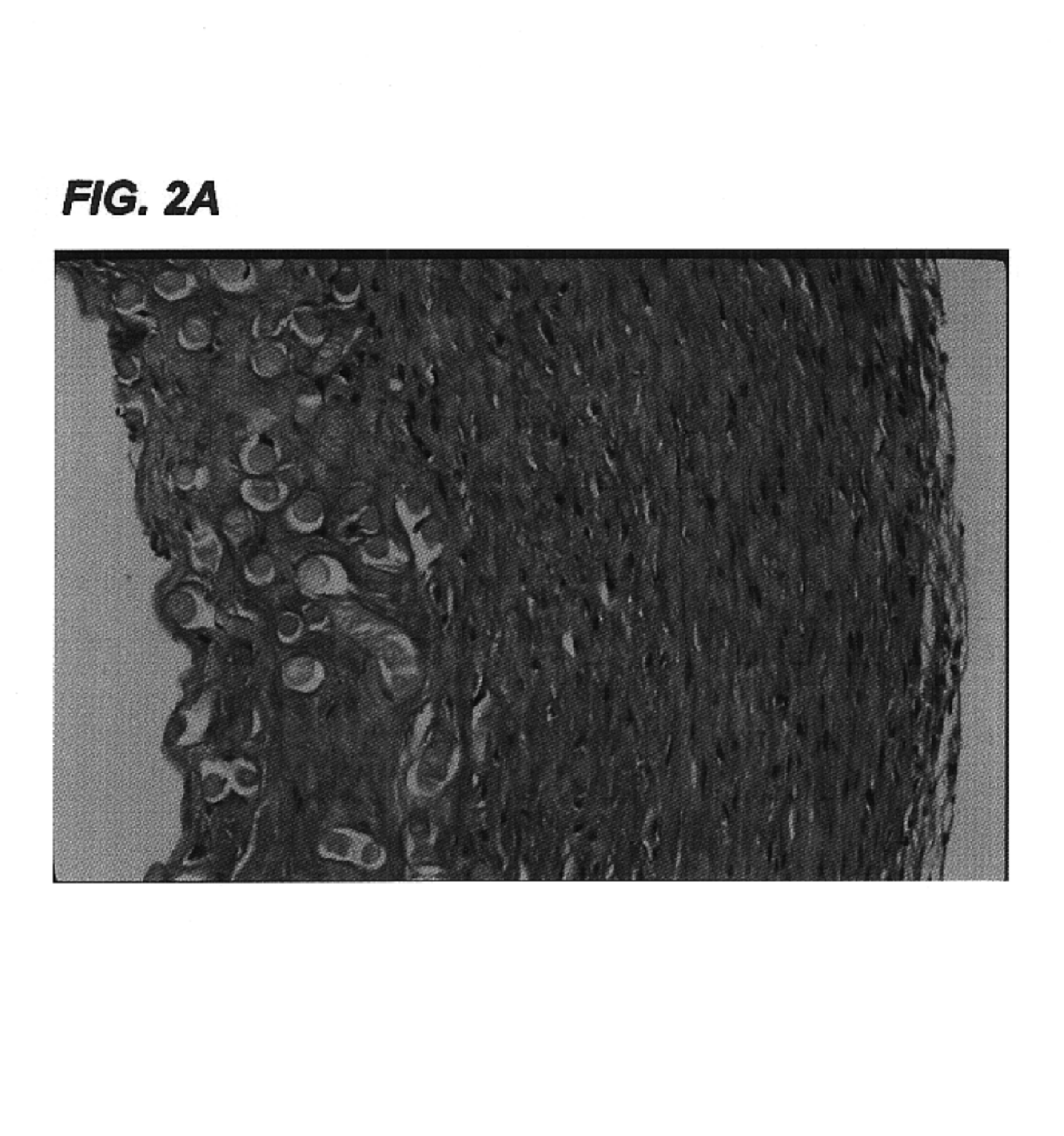
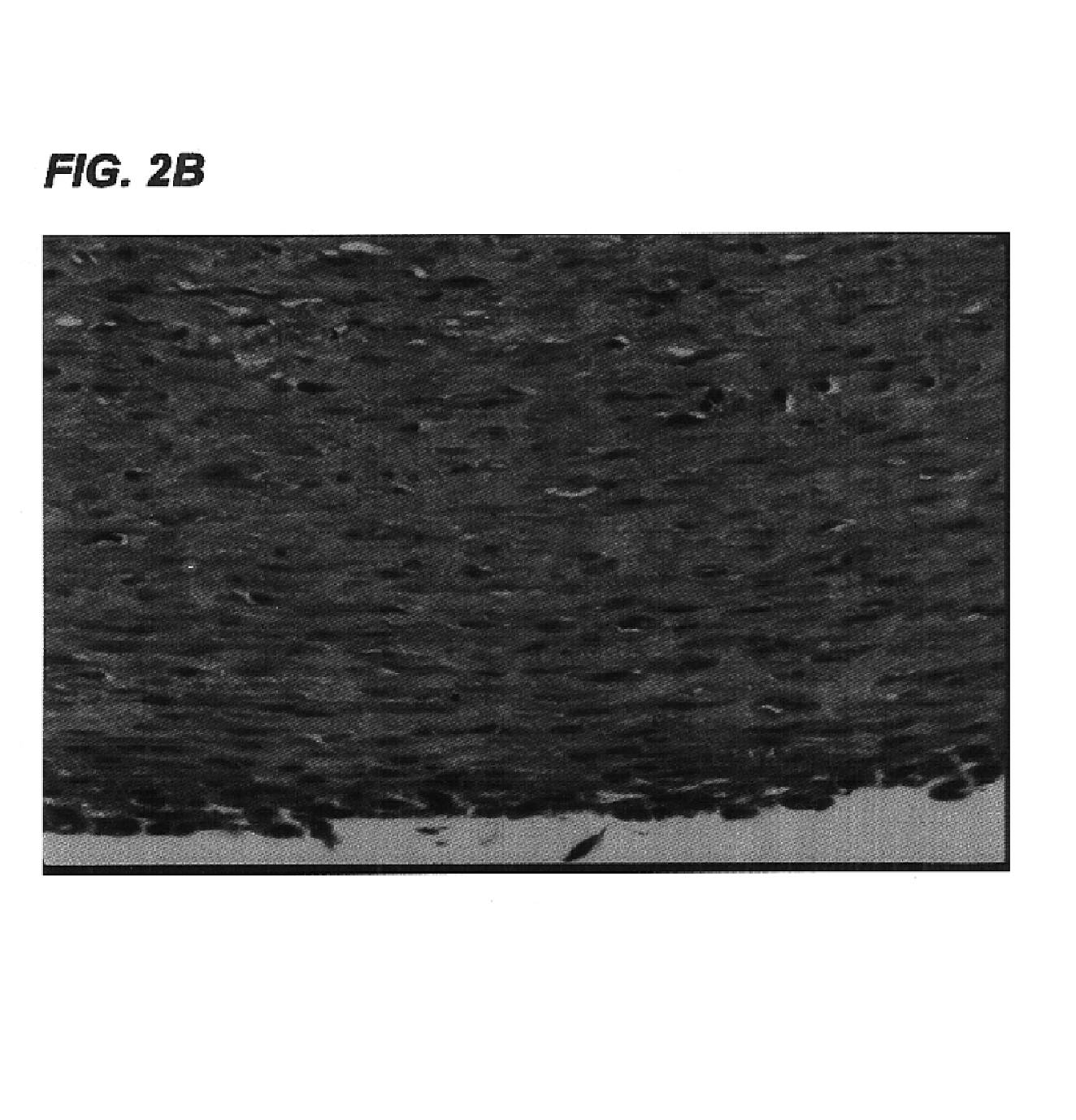
Decellularized tissue engineered constructs and tissues
InactiveUS6962814B2Low immunogenicityReduction in immuneBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth phaseCell-Extracellular Matrix
New methods for producing tissue engineered constructs and engineered native tissues are disclosed. The methods include producing a tissue engineered construct by growing cells in vitro on a substrate and then decellularizing the construct to produce a decellularized construct consisting largely of extracellular matrix components. The construct can be used immediately or stored until needed. The decellularized construct can be used for further tissue engineering, which may include seeding the construct with cells obtained from the intended recipient of the construct. During any of the growth phases required for production of the construct, the developing construct may be subjected to various tissue engineering steps such as application of mechanical stimuli including pulsatile forces. The methods also include producing an engineered native tissue by harvesting tissue from an animal or human, performing one or more tissue engineering steps on the tissue, and subjecting the tissue to decellularization. The decellularized, engineered native tissue may then be subjected to further tissue engineering steps.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
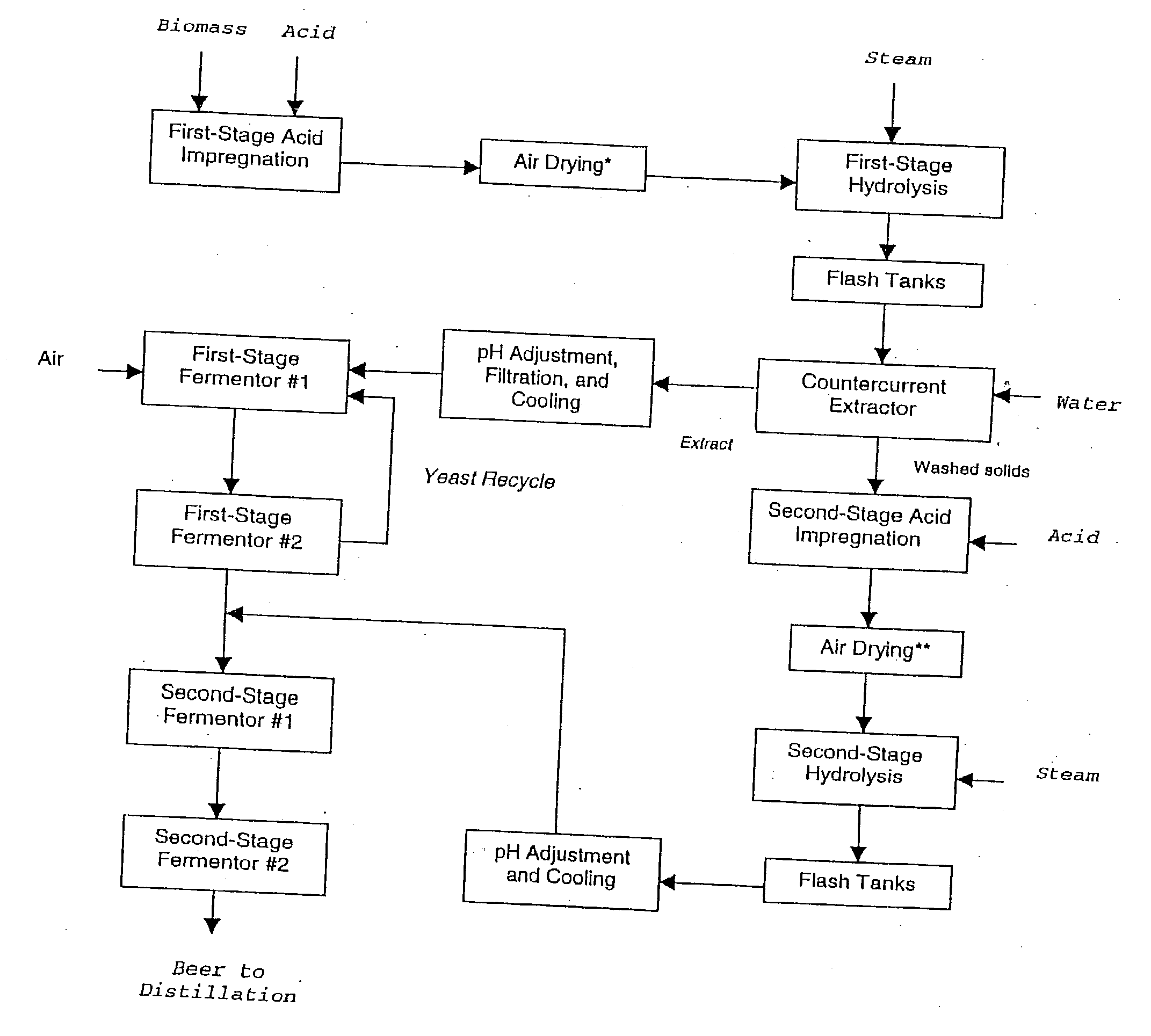
Ethanol production with dilute acid hydrolysis using partially dried lignocellulosics
InactiveUS20030199049A1Increase sugar yieldImprove digestibilityBiofuelsWaste based fuelCelluloseGrowth phase
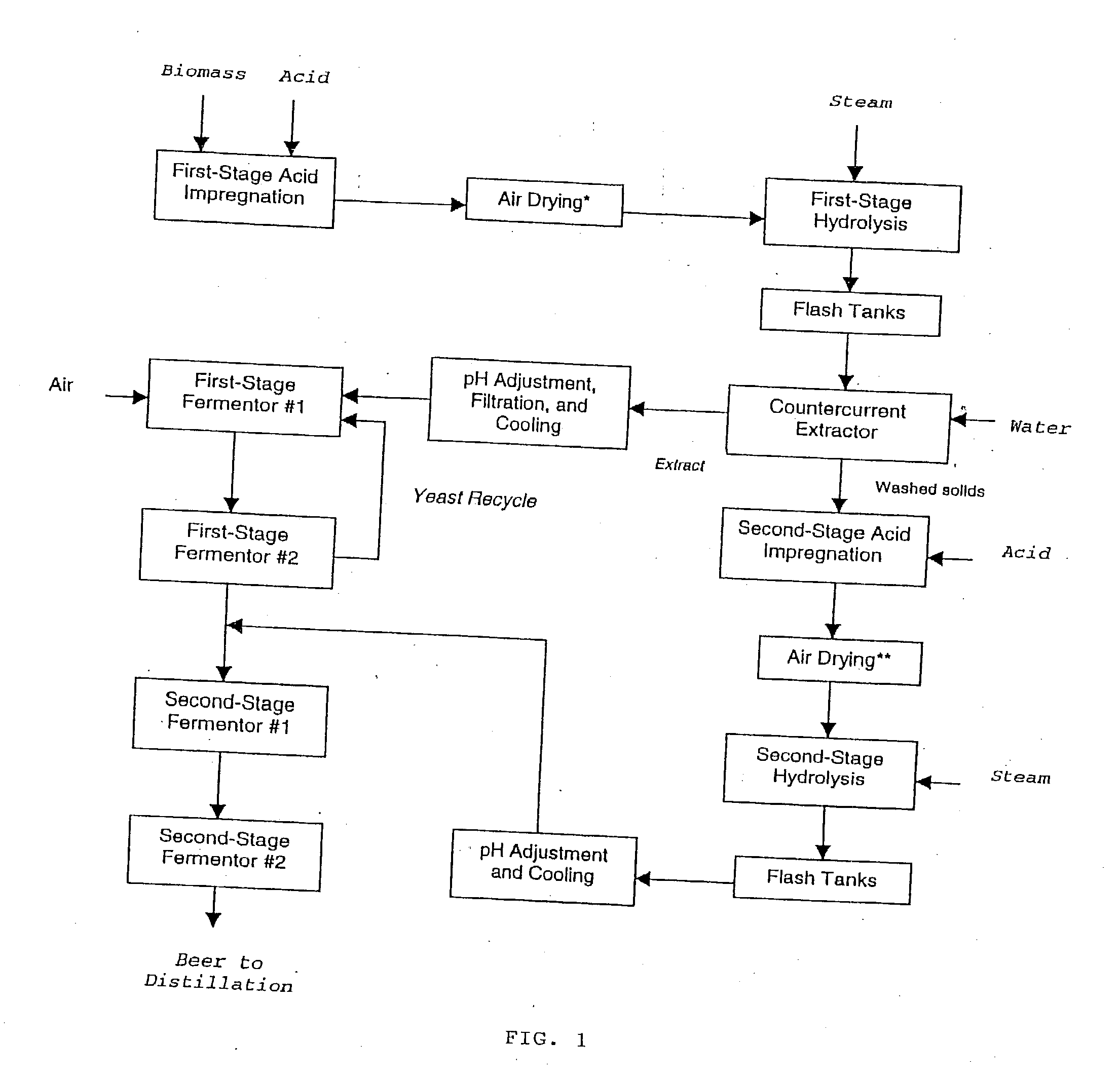
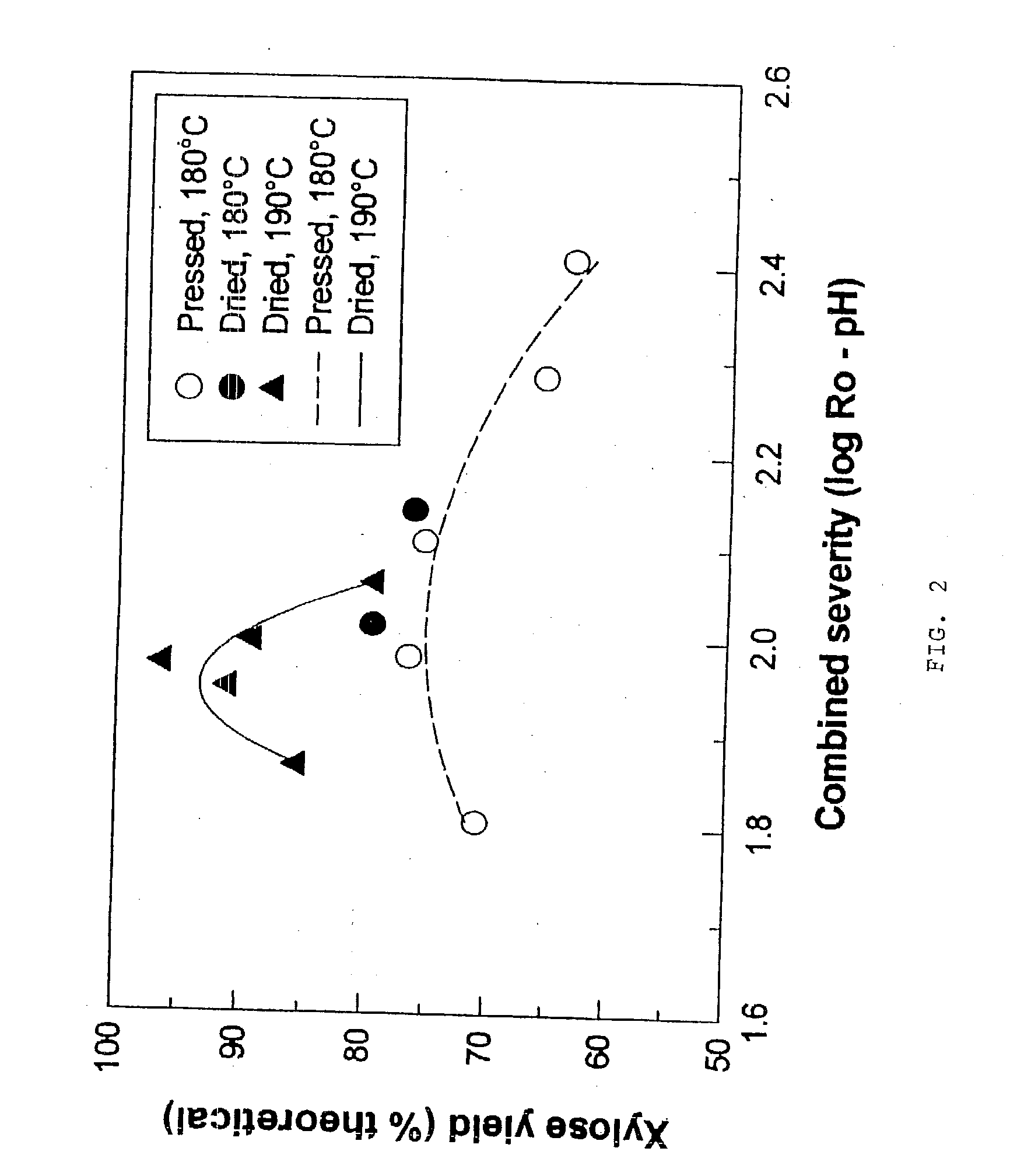
In a process for converting lingnocellulosic biomass to ethanol, the improvement of obtaining higher fermentable soluble sugar yields by drying acid impregnated biomass particles, comprising: a) feeding moist lignocellulosic biomass into an acid impregnator to render it acid-soaked and draining the acid-soaked biomass to about 30% to 35% by weight solids; b) dewatering the acid-soaked biomass by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of the biomass and arrive at about 40% to 60% by weight solids; c) subjecting the acid-impregnated biomass to a first-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature of from 130° C. to 220° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars, and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank-the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for a counter-current extractor; d) washing the hydrolysate, adjusting the pH of the sugar extract to about 5, and recovering more than 95% of the soluble sugars in the first-stage hydrolysate slurry by a counter-current extractor; e) subjecting remaining washed-first stage solids of pretreated biomass to a second-stage acid and metal salt impregnator and dewatering by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of biomass to arrive at 40% to 60% by weight solids; f) subjecting the acid and metal salt-impregnated biomass to a second-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature from 190° C. to 240° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank, at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank, the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for second-stage fementors; g) cooling pH-adjusted extract from the counter-current extractor, feeding the extract to a first-stage fermentor and air sparging the first-stage fermentor at a rate sufficient to promote enough yeast growth to compensate for loss through second-stage fermentors; h) pH adjusting second-stage hydrolysate slurry to 4.5, cooling the slurry and adding it into the top of the first fermentor of a two-fermentor train in the second stage fermentors, pumping broth from the bottom of the first stage fermentors to the second stage fermentors while the yeast is in the growth phase for a period sufficient to consume over 95% of fermentable sugars; and i) recovering ethanol.
Owner:MIDWEST RES INST
Apparatus for creating therapeutic charge transfer in tissue
InactiveUS7288062B2Avoid side effectsAvoid failureElectrotherapySurgeryGrowth phaseTherapeutic effect
An apparatus for creating therapeutic charge transfer in tissue includes a coil. The coil generates a changing magnetic field to induct an electric field in the tissue exceeding 10 mV / cm when the coil is 5 cm from the tissue. Preferably, the magnetic field has a growth phase and a decay phase and a duration of the growth phase is at least ten times a duration of the decay phase. The apparatus can include a control circuit to control a current fed to the coil. The control circuit includes two subcircuits and a switch for switching between a first of the subcircuits and a second of the subcircuits; preferably, a λ of the second subcircuit is at least ten times a λ of the first subcircuit. To generate the therapeutic effect, the coil should have a duty cycle of at least ten percent.
Owner:ADVATECH CORP
Direct expression of peptides into culture media
InactiveUS6103495AReduced viabilityImprove breathabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth phaseBiotechnology
Expression systems are disclosed for the direct expression of peptide products into the culture media where genetically engineered host cells are grown. High yield was achieved with novel vectors, a special selection of hosts, and / or fermentation processes which include careful control of cell growth rate, and use of an inducer during growth phase. Special vectors are provided which include control regions having multiple promoters linked operably with coding regions encoding a signal peptide upstream from a coding region encoding the peptide of interest. Multiple transcription cassettes are also used to increase yield. The production of amidated peptides using the expression systems is also disclosed.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
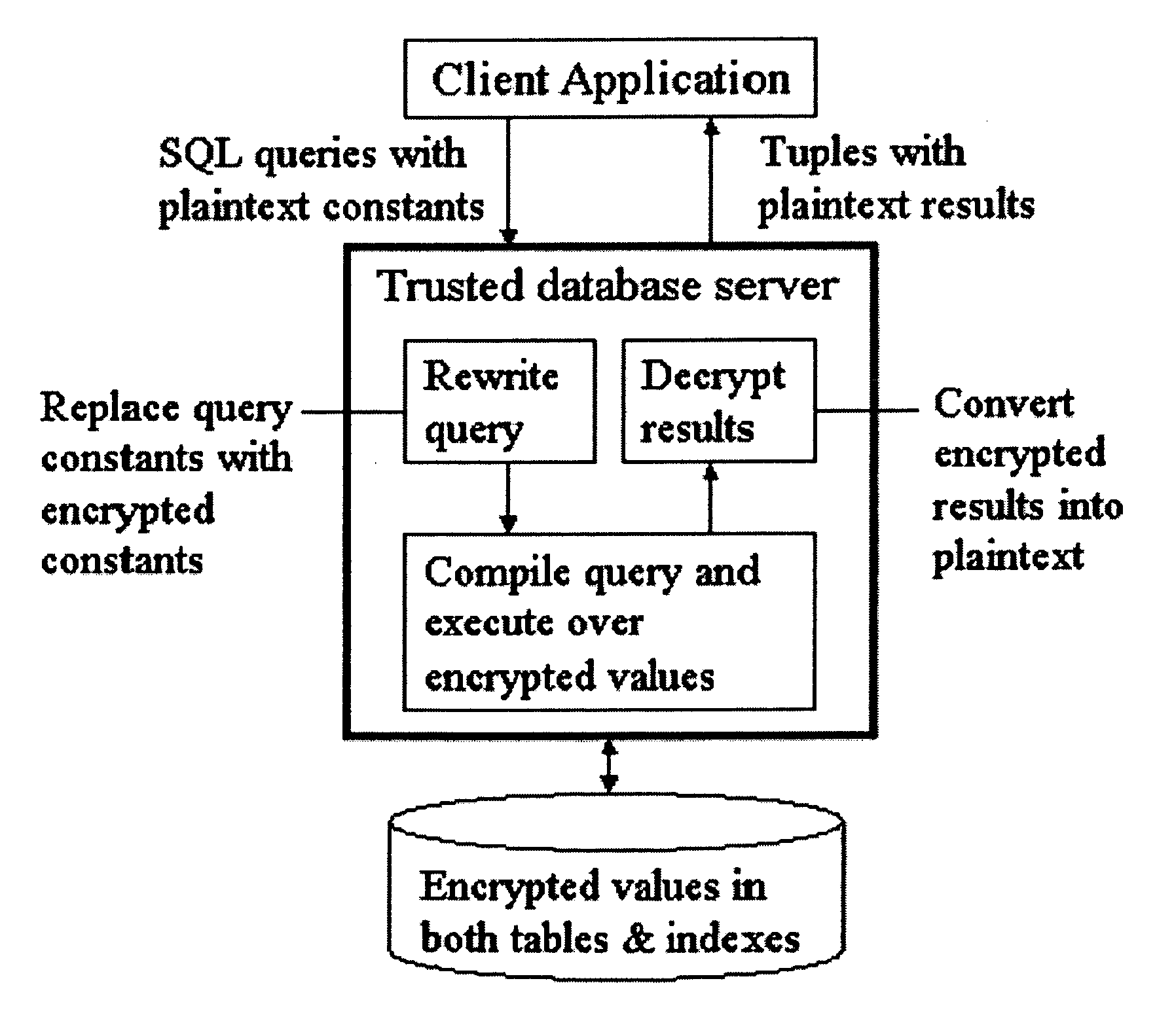
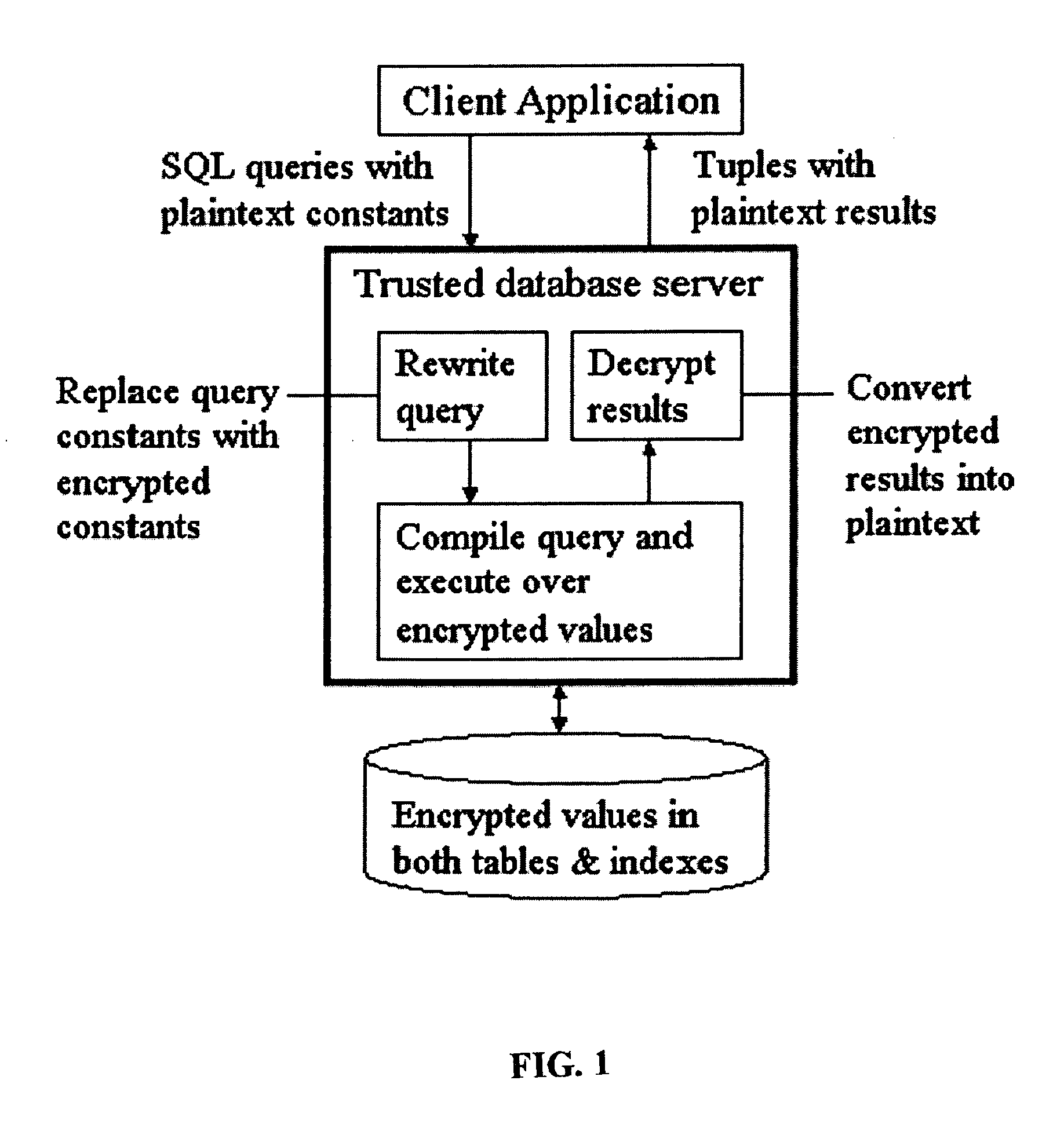
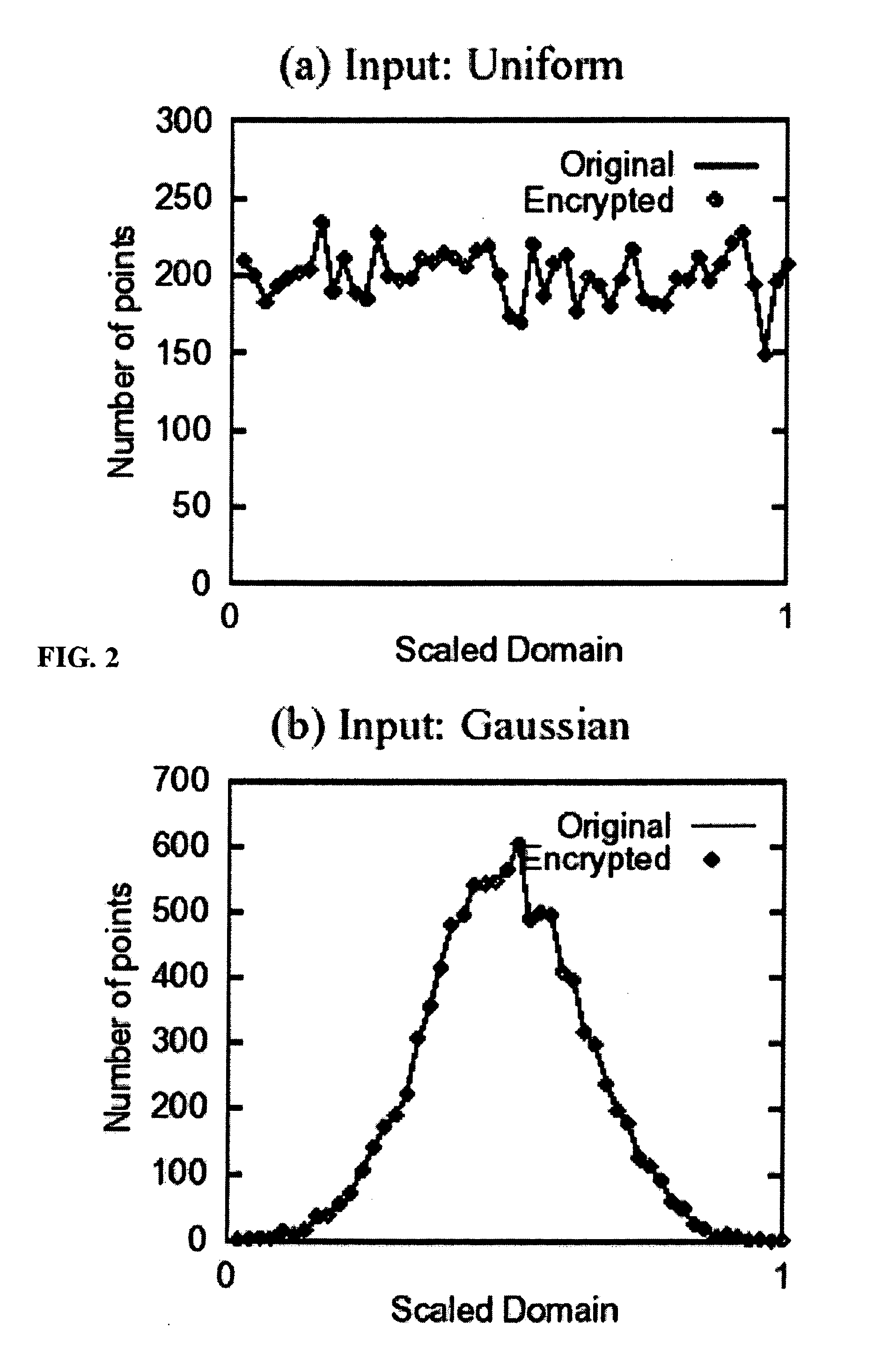
System and method for order-preserving encryption for numeric data
InactiveUS20050147240A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsGrowth phaseData set
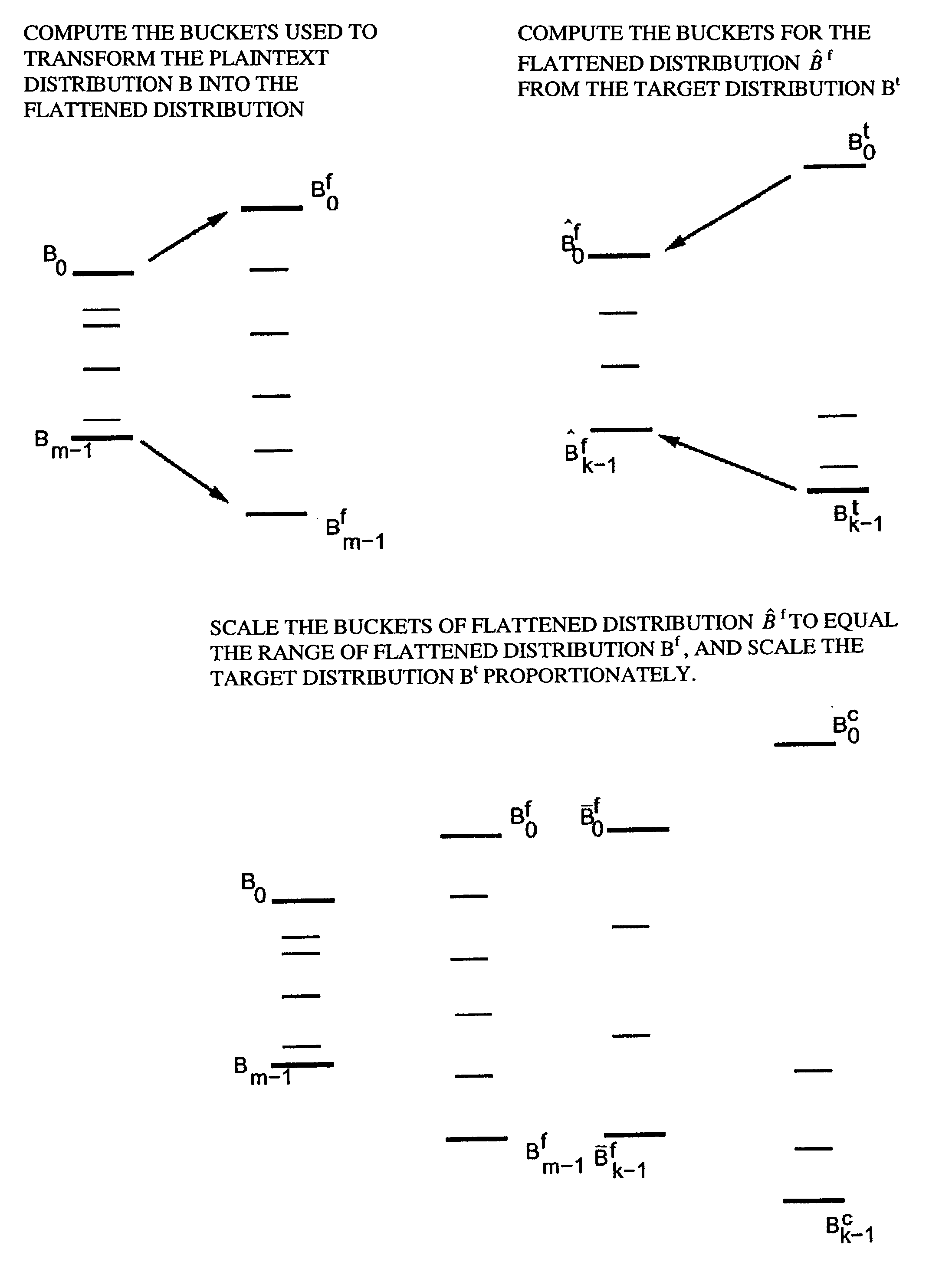
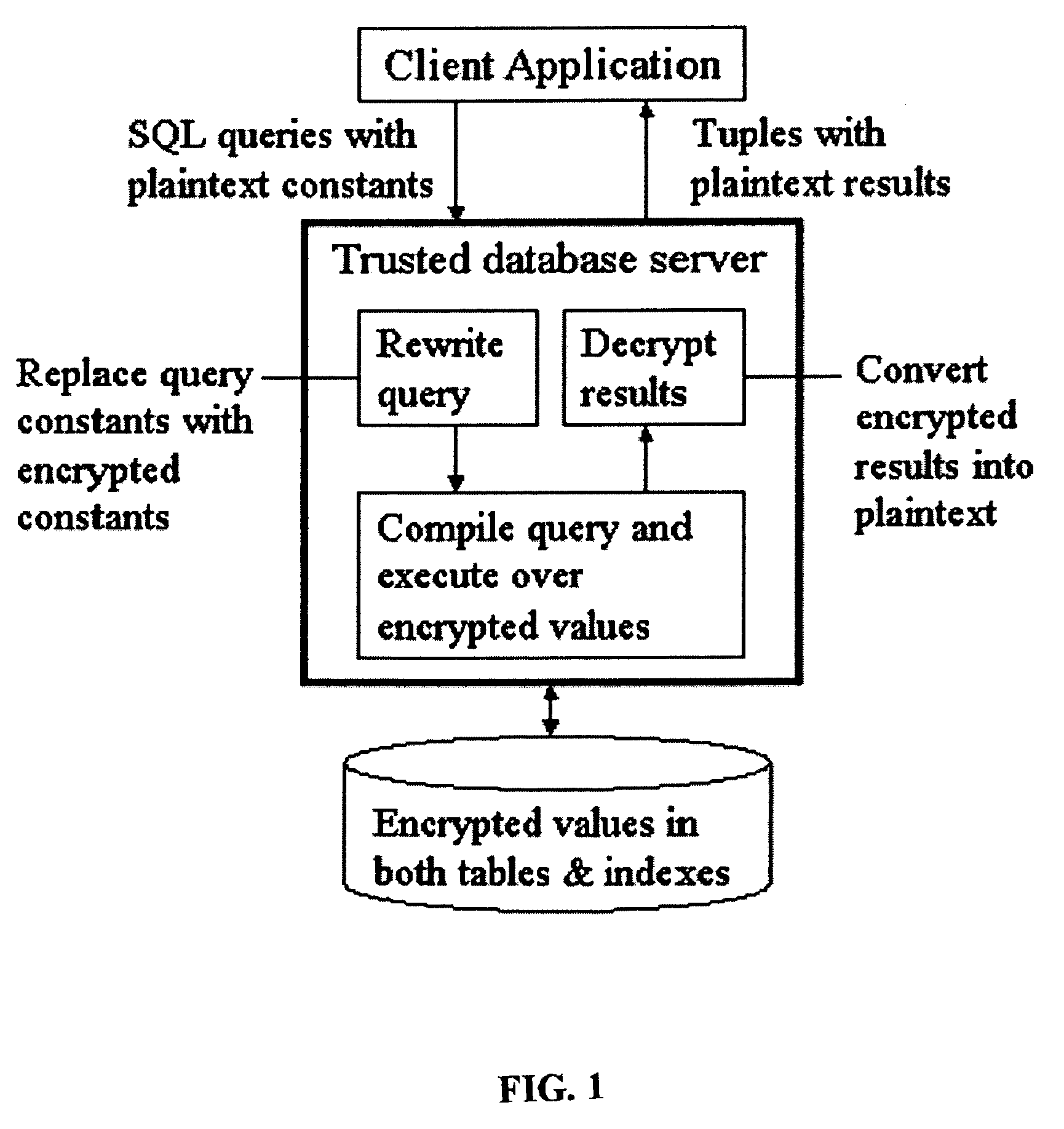
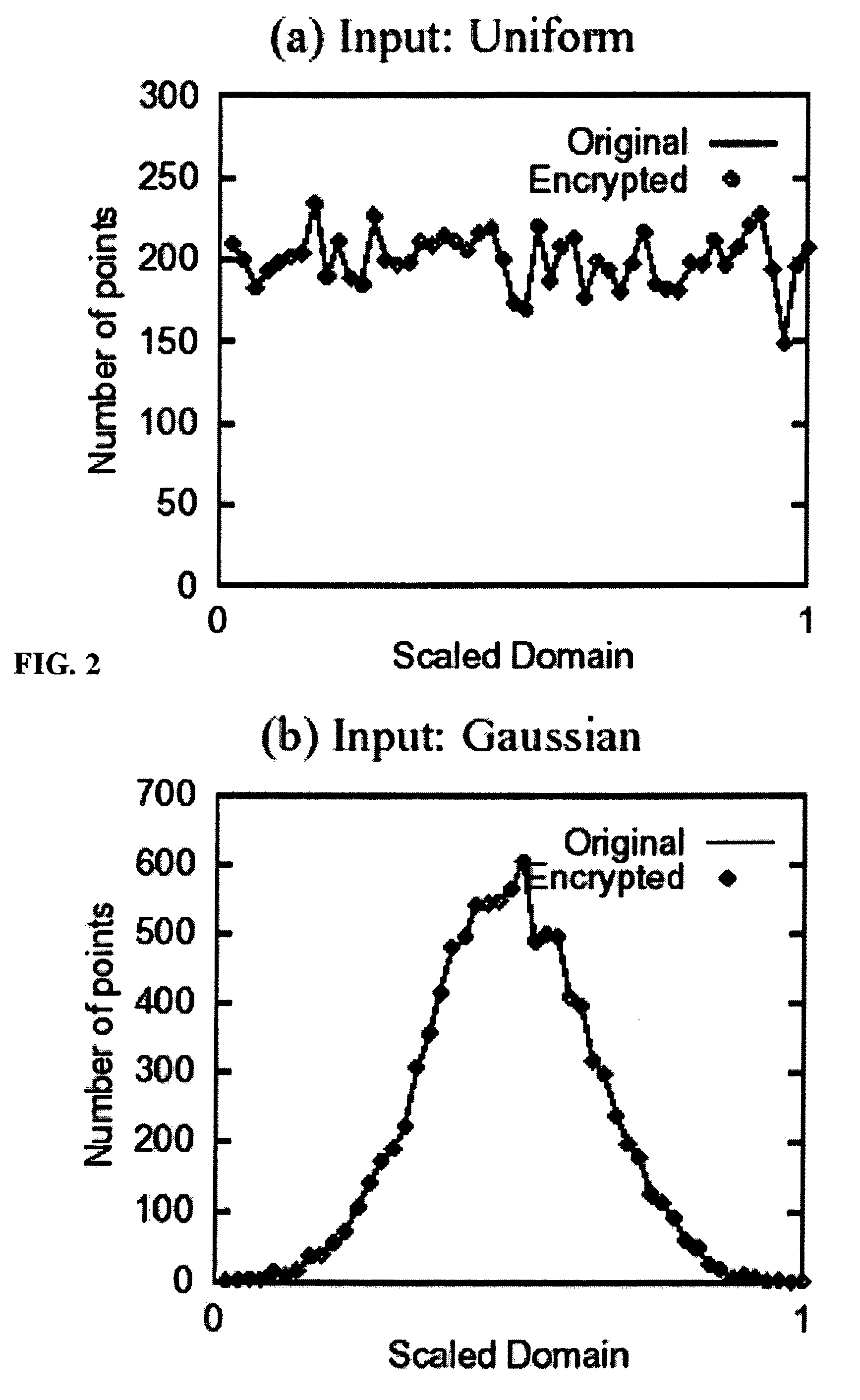
A system, method, and computer program product to automatically eliminate the distribution information available for reconstruction from a disguised dataset. The invention flattens input numerical values into a substantially uniformly distributed dataset, then maps the uniformly distributed dataset into equivalent data in a target distribution. The invention allows the incremental encryption of new values in an encrypted database while leaving existing encrypted values unchanged. The flattening comprises (1) partitioning, (2) mapping, and (3) saving auxiliary information about the data processing, which is encrypted and not updated. The partitioning is MDL based, and includes a growth phase for dividing a space into fine partitions and a prune phase for merging some partitions together.
Owner:IBM CORP
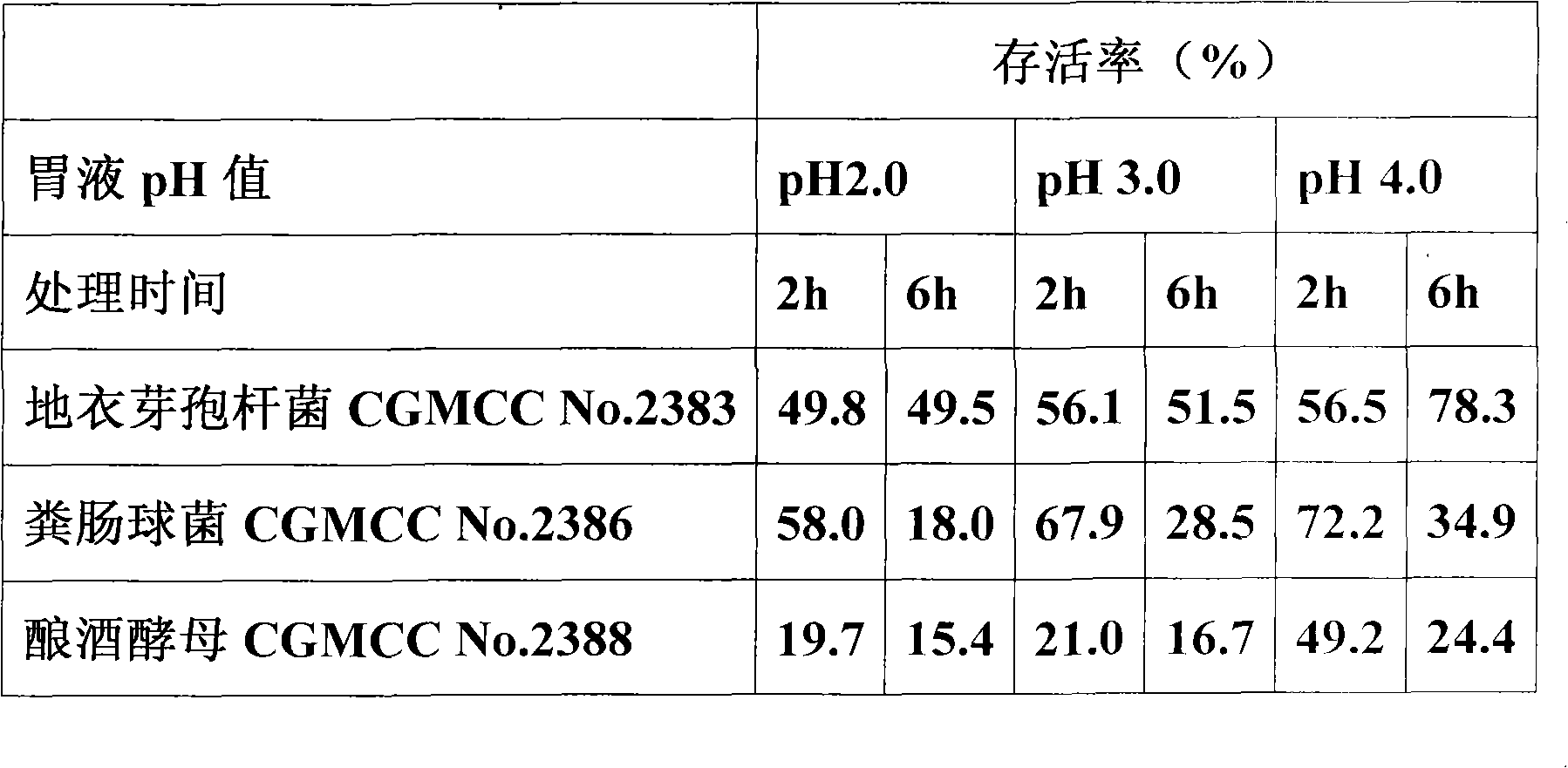
Micro-ecological preparation and application thereof
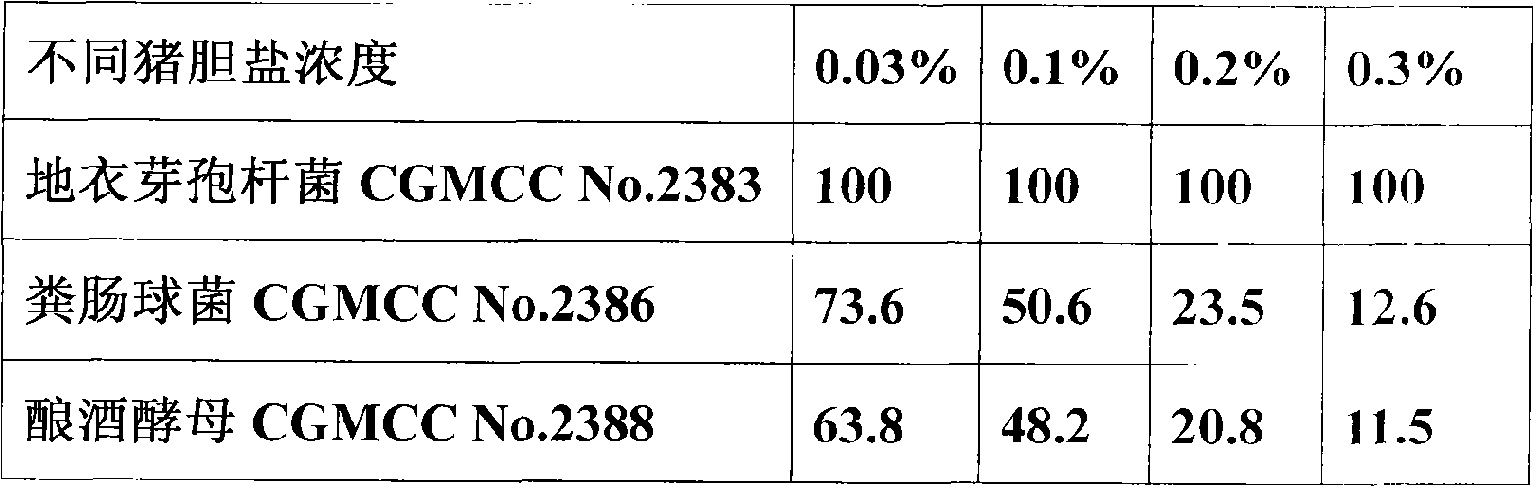
The invention relates to a micro-ecological preparation and the application thereof, in particular to a micro-ecological preparation containing a variety of probiotics and the application thereof. The micro-ecological preparation contains any three or four of the components including CGMCC No. 2383 bacillus licheniformis powder, bacillus subtilis powder, CGMCC No. 2386 enterococcus faecalis powder, lactobacillus acidophilus powder, and CGMCC No. 2388 saccharomyces cerevisiae. The micro-ecological preparation has content of live bacteria, has the adversity resistance such as gastric acid resistance, bile salt resistance, high-temperature resistance, common antibiotic resistance, and the like and the probiotic functions of producing acid and enzyme and resisting pathogenic bacteria. The variety and the proportion of the probiotics and carrier can be determined according to different kinds of animals and different animal growth phase. The micro-ecological preparation can improve the feed utilization efficiency, increase the yield of meat, eggs and milk, promote the growth of the animal, improve the immunity and the disease resistance of the animal, replace the antibiotic and improve the quality of the animal product.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Polypeptide production in animal cell culture
InactiveUS20050272124A1Promote cell growthHigh protein yieldGenetically modified cellsCulture processBiotechnologyGrowth phase
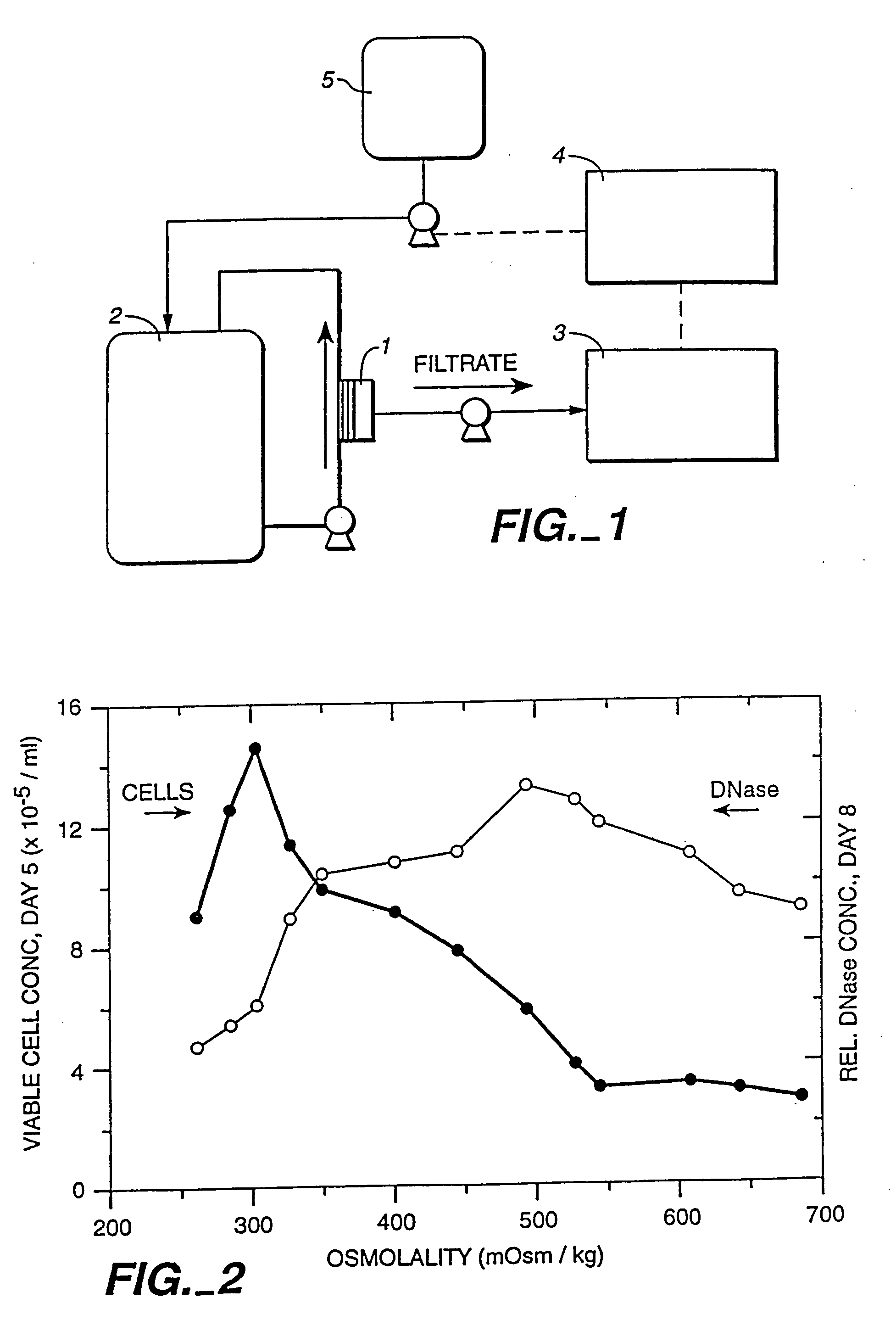
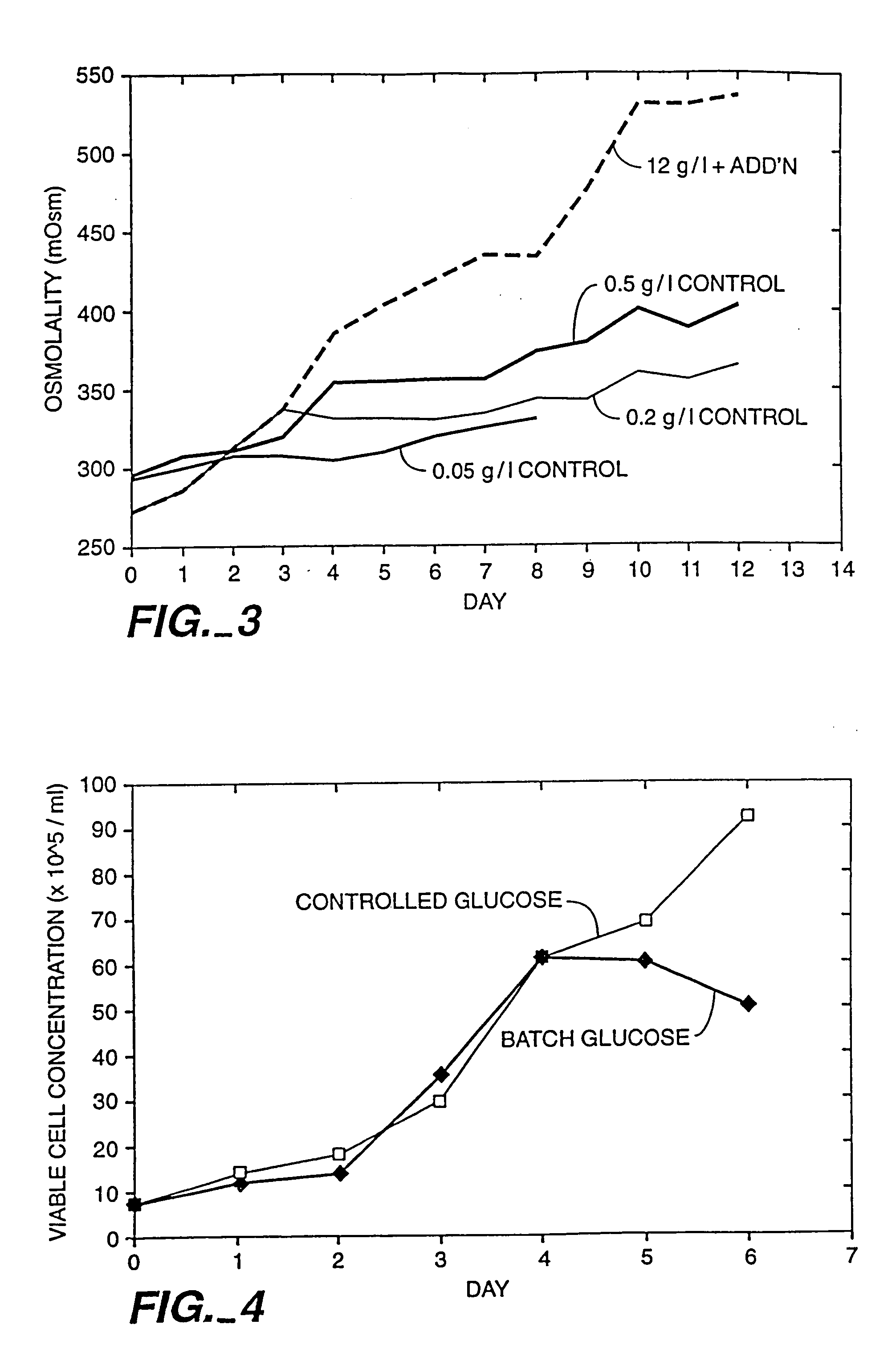
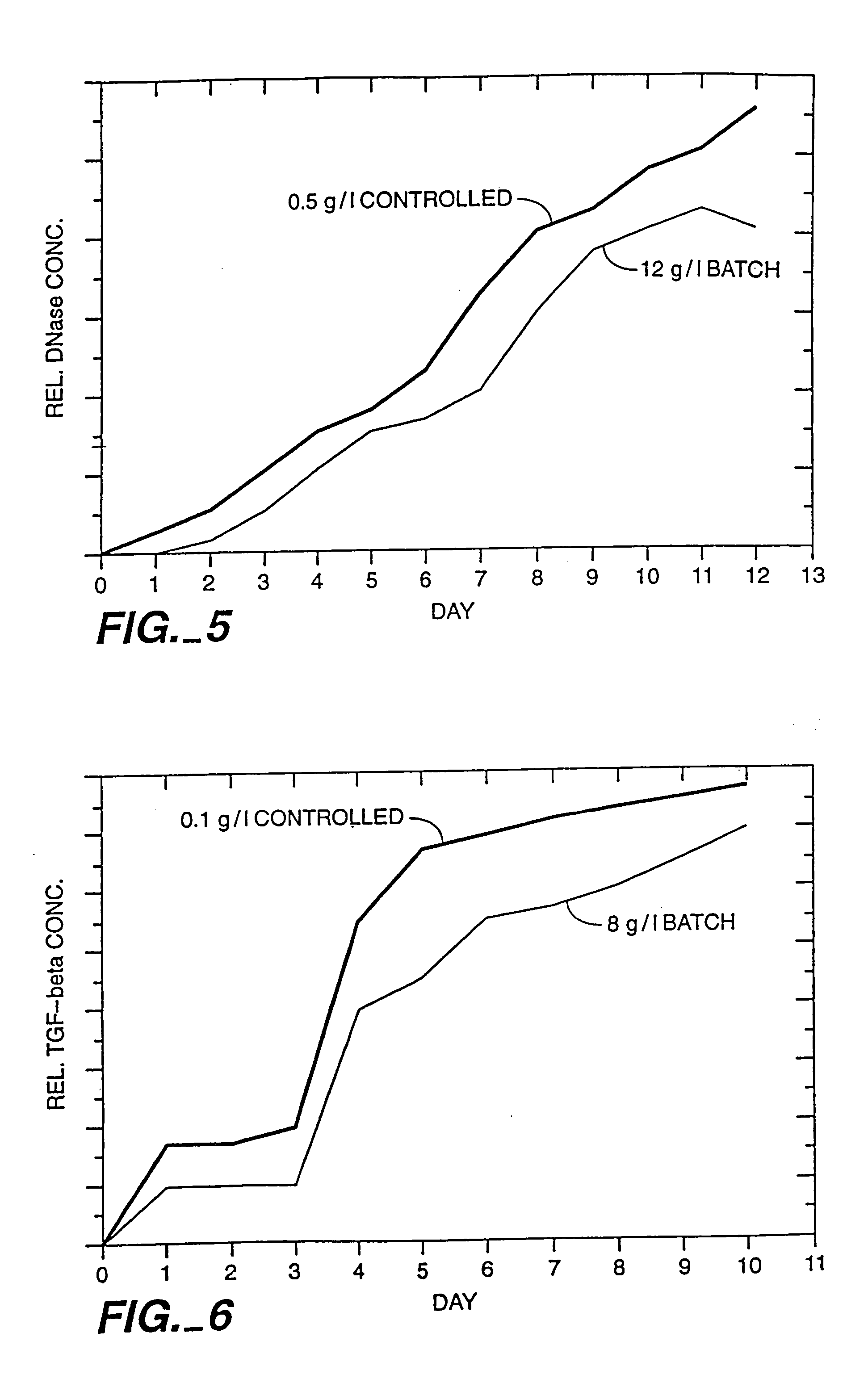
A method of producing a polypeptide in fed batch cell culture is provided which involves an initial cell growth phase and a distinct production phase. In the initial growth stage, animal cells having nucleic acid encoding the polypeptide are cultured at a starting osmolality of about 280-330 mOsm in the presence of a concentration of glucose controlled throughout the culturing to be within a range between about 0.01 and 1 g / L. This is followed by a production phase, where the cultured animal cells of the growth phase are inoculated at a cell seed density of at least 1.0×106 cells / mL and the cells are cultured at a starting osmolarity of about 400-600 mOsm in the presence of a concentration of glucose controlled throughout the culturing to be within a range between about 0.01 and 1 g / L. Preferably, the glutamine concentration in the cell culture medium is simultaneously controlled in order to curtail production of lactic acid and ammonia which result from unnecessarily high glutamine concentrations. During the growth phase, production of potentially detrimental metabolic waste products, such as lactic acid, is controlled thereby curtailing the increase of osmolality due to accumulation and neutralization of waste products. Thus, the cell growth can be improved. In the production phase, the cell culture conditions are modified in order to arrest or reduce cell growth and thereby direct nutrient utilization toward production, as opposed to cell growth. Overall, it is intended that the method results in an improvement in specific productivity, reduction in production run times and / or an increase in final product concentration.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Mammalian cell culture processes for protein production
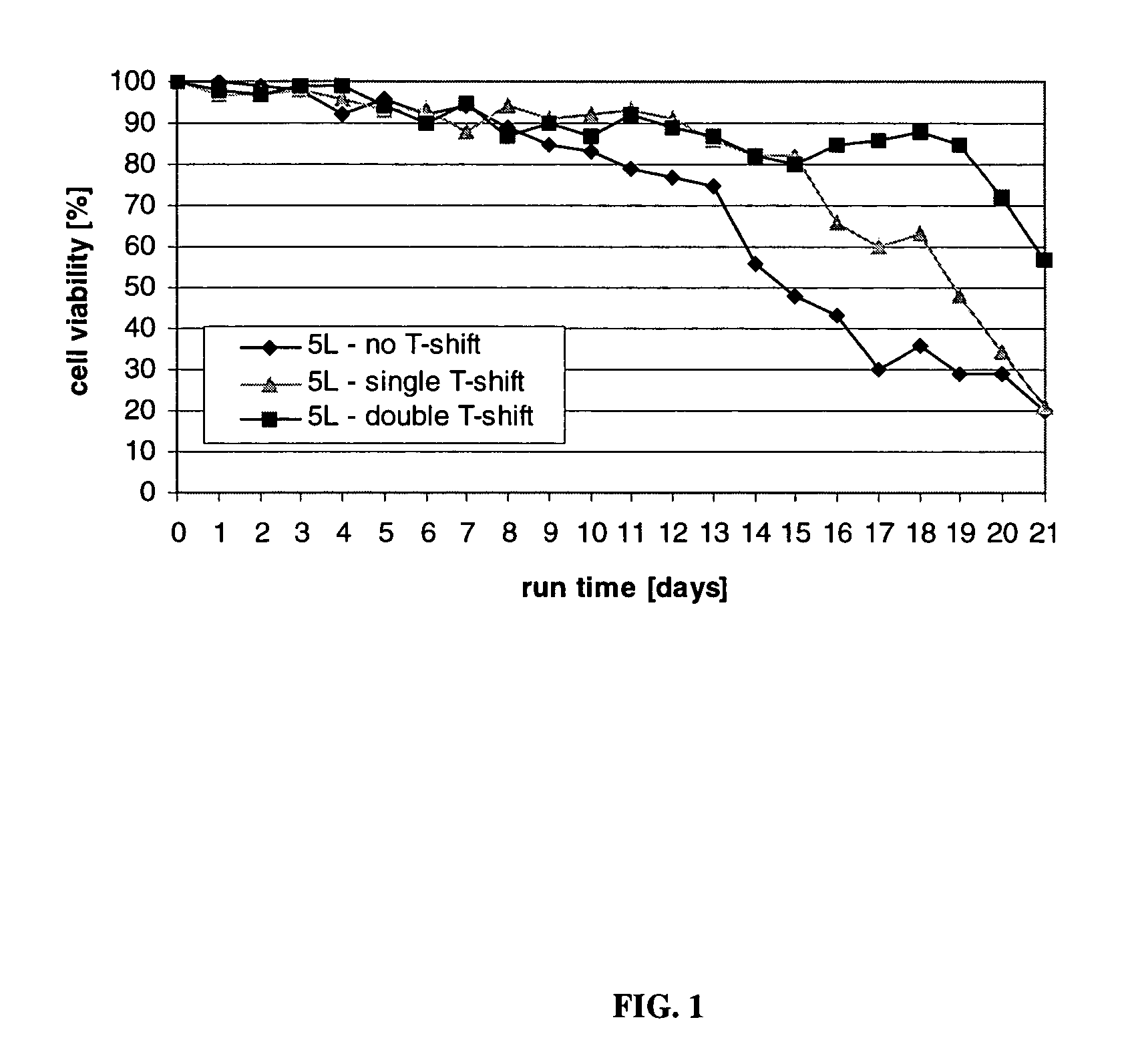
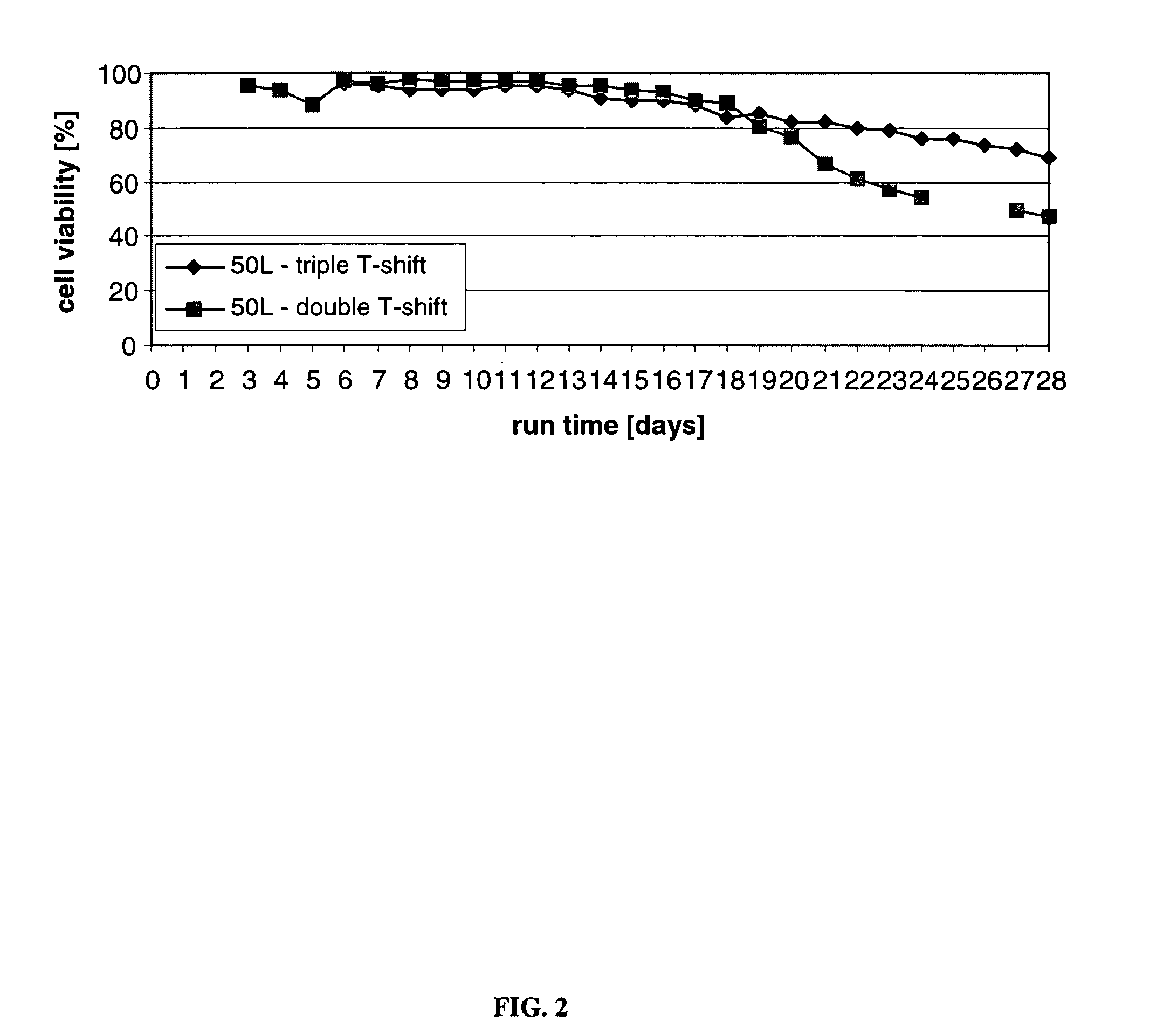
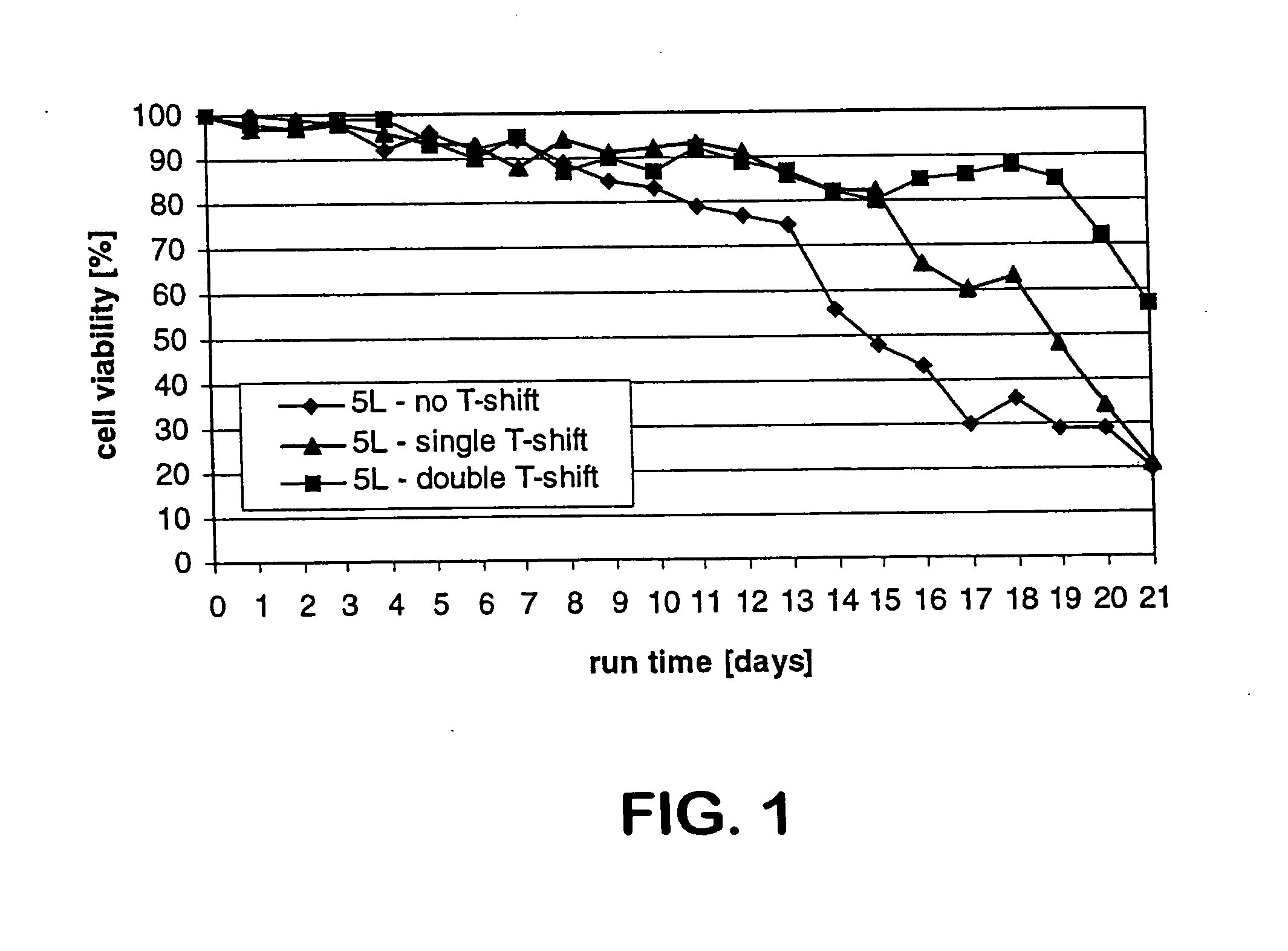
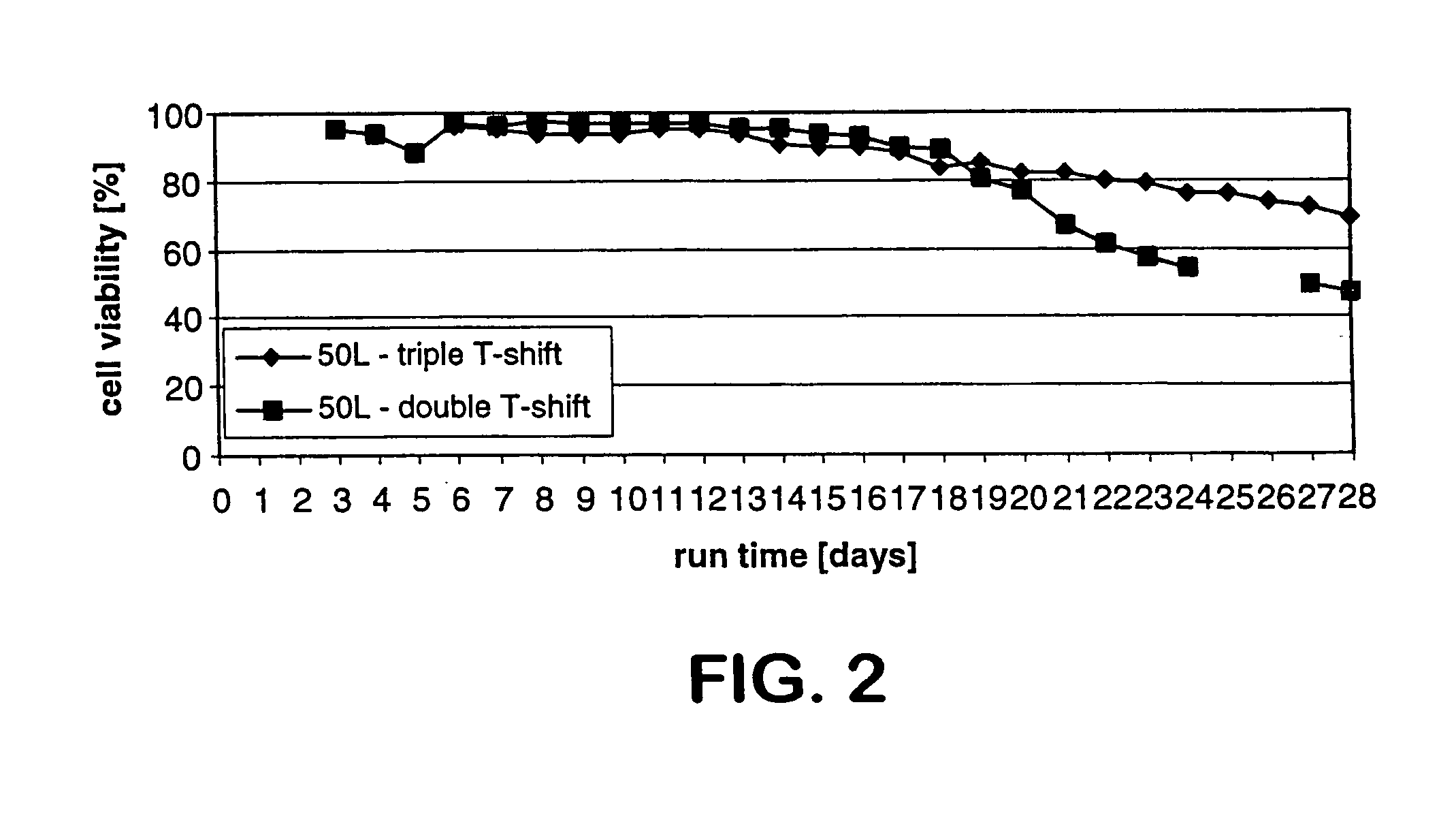
ActiveUS7541164B2Enhance cell viabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsGrowth phaseTwo temperature
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method and algorithm for quantifying polynucleotides
ActiveUS20060292619A1Microbiological testing/measurementAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsGrowth phaseRegression analysis
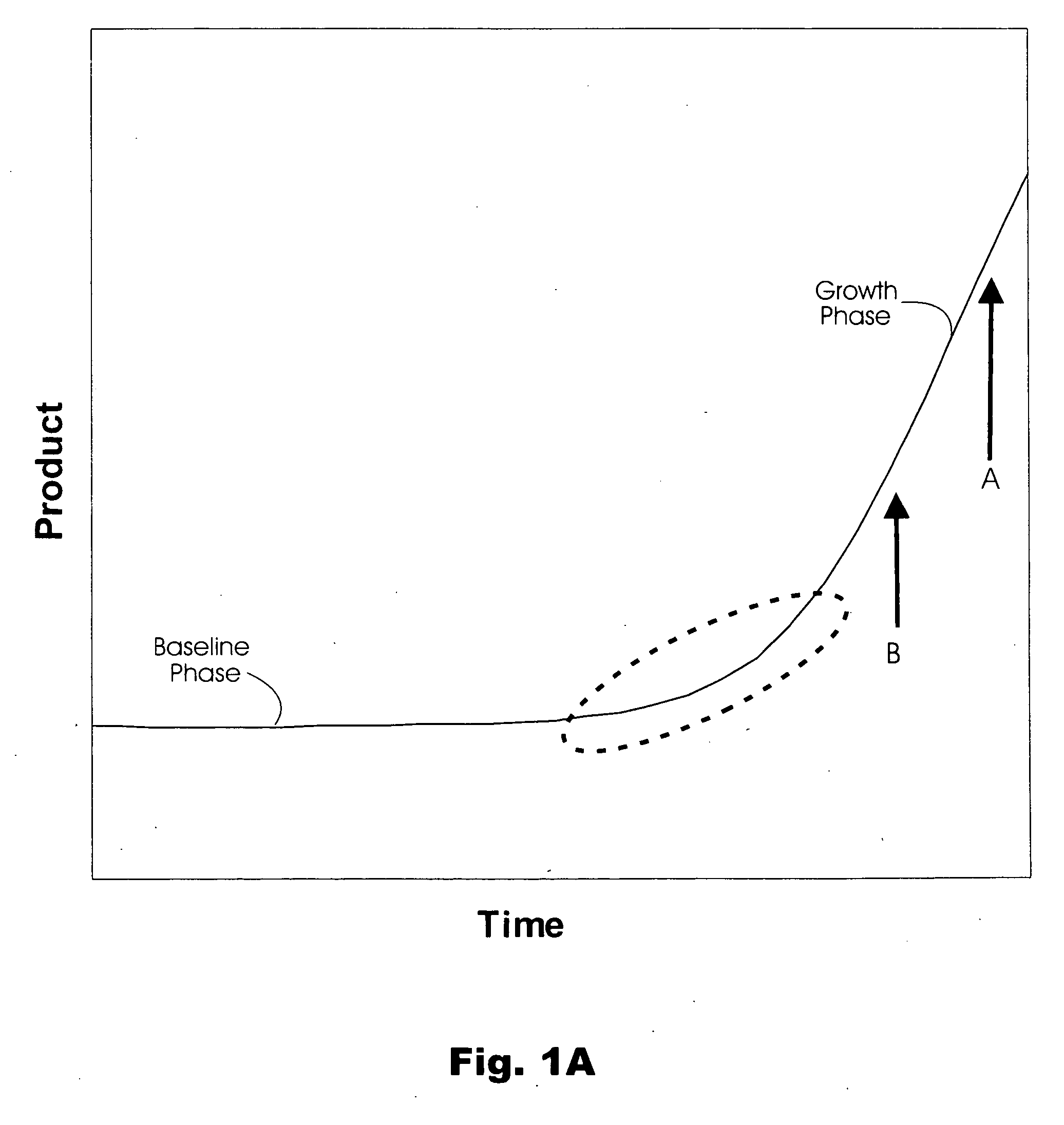
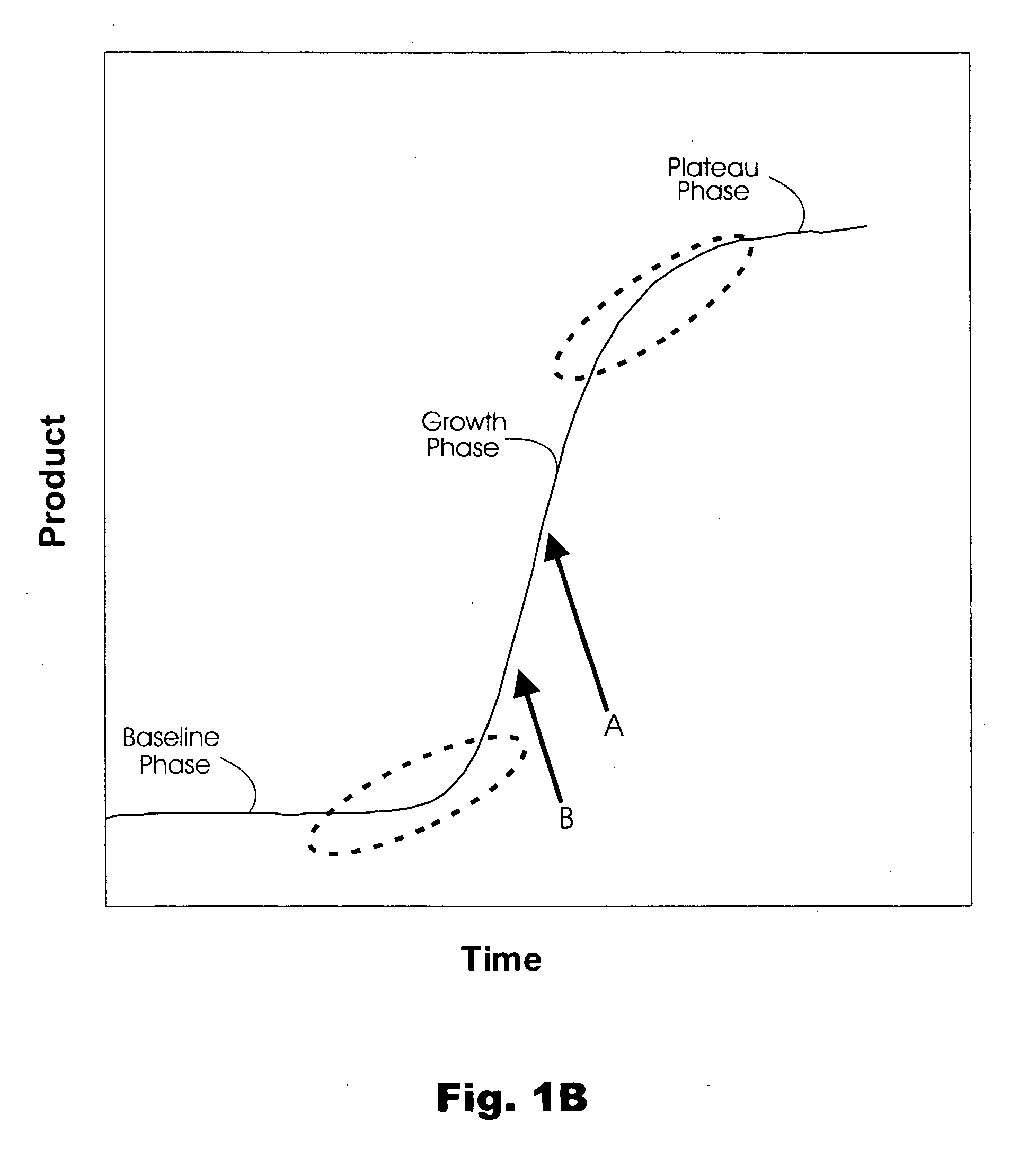
Machine executable method of analyzing growth curve data to identify the transition from a baseline phase into a growth phase. Applications of the method include analysis of results from time-dependent monitoring of amplicon synthesis in a nucleic acid amplification reaction to quantify a starting amount of a nucleic acid template in a test sample. The method advantageously simplifies the quantitation by circumventing the need to establish thresholds used for calculating initiation of the growth phase, to calculate derivatives, or to perform linear regression analysis.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Intensive pig farm weanling pig feed and feeding mode thereof
The invention discloses an intensive pig farm weanling pig feed and belongs to the field of feeds. The feed is composed of a milk replacer, a weanling feed and a piglet feed. According to the feed, a feed product suitable for different growth phases of a weanling pig are provided according to growth and development characteristics of the different growth phases of the weanling pig so as to promote the development of an intestinal system of the weanling pig and effectively solve the stress reaction appearing in a weaning process of the weanling pig; meanwhile, the utilization rate of the feed is high, the growth speed of the weanling pig can be accelerated, the immunity of the weanling pig can be enhanced and the foundation is laid for the rapid growth of a fattening period. Furthermore, the invention further provides a feeding mode of the feed, namely 6kg of the milk replacer is fed from the 7th day after the weanling pig is born to a 42-45-day age of the weanling pig; 20kg of the weanling feed is fed from the 42-45-day age to a 66-70-day age of the weanling pig; 40kg of the piglet feed is fed from the 66-70-day age to a 94-100-day age. The mode is scientific and reasonable, simple and efficient.
Owner:TWINS GRP
Mammallian cell culture process for protein production
InactiveUS20120015438A1Enhance cell viabilityEnhanced final titer and concentrationAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGrowth phaseSialic acid
The present invention describes methods and processes for the production of proteins, particularly glycoproteins, by animal cell or mammalian cell culture, preferably, but not limited to, fed-batch cell cultures. In one aspect, the methods comprise at least two temperature shifts performed during the culturing period, in which the temperature is lower at the end of the culturing period than at the time of initial cell culture. Throughout their duration, the culturing processes of the invention involving two or more downward shifts in temperature sustain a high viability of the cultured cells, and can yield an increased end titer of protein product, and a high quality of protein product, as determined, e.g., by sialic acid content of the produced protein. In another aspect, the methods comprise the delayed addition of polyanionic compound during the culturing period. The delayed addition of polyanionic compound sustains a high viability of the cultured cells, and can extend the growth phase, delay the onset of the death phase, and arrest the death phase.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Methods for enhanced protein production
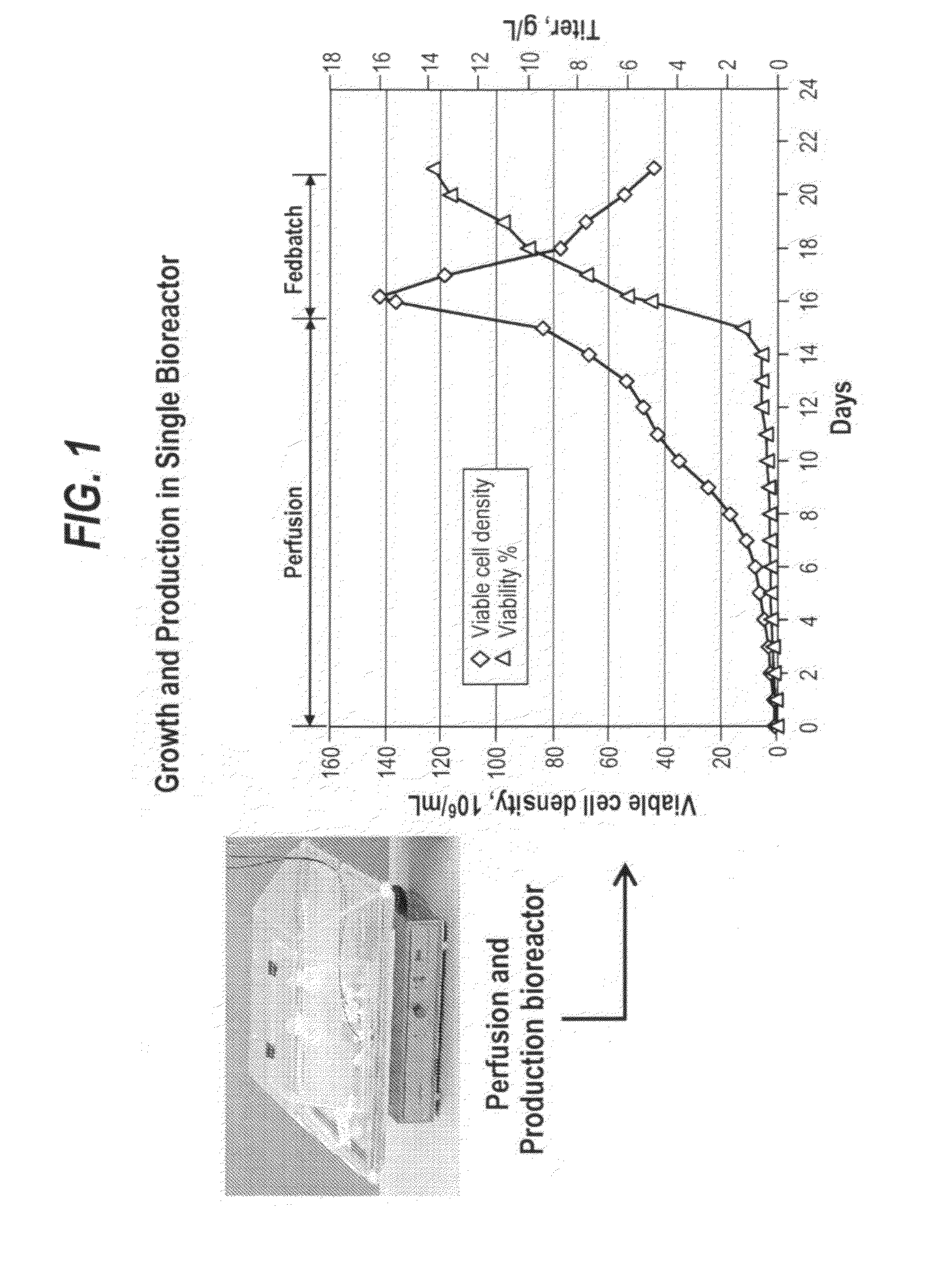
ActiveUS20130017577A1Increase cell densityA large amountAnimal cellsMicroorganism separationHigh cellLiquid layer
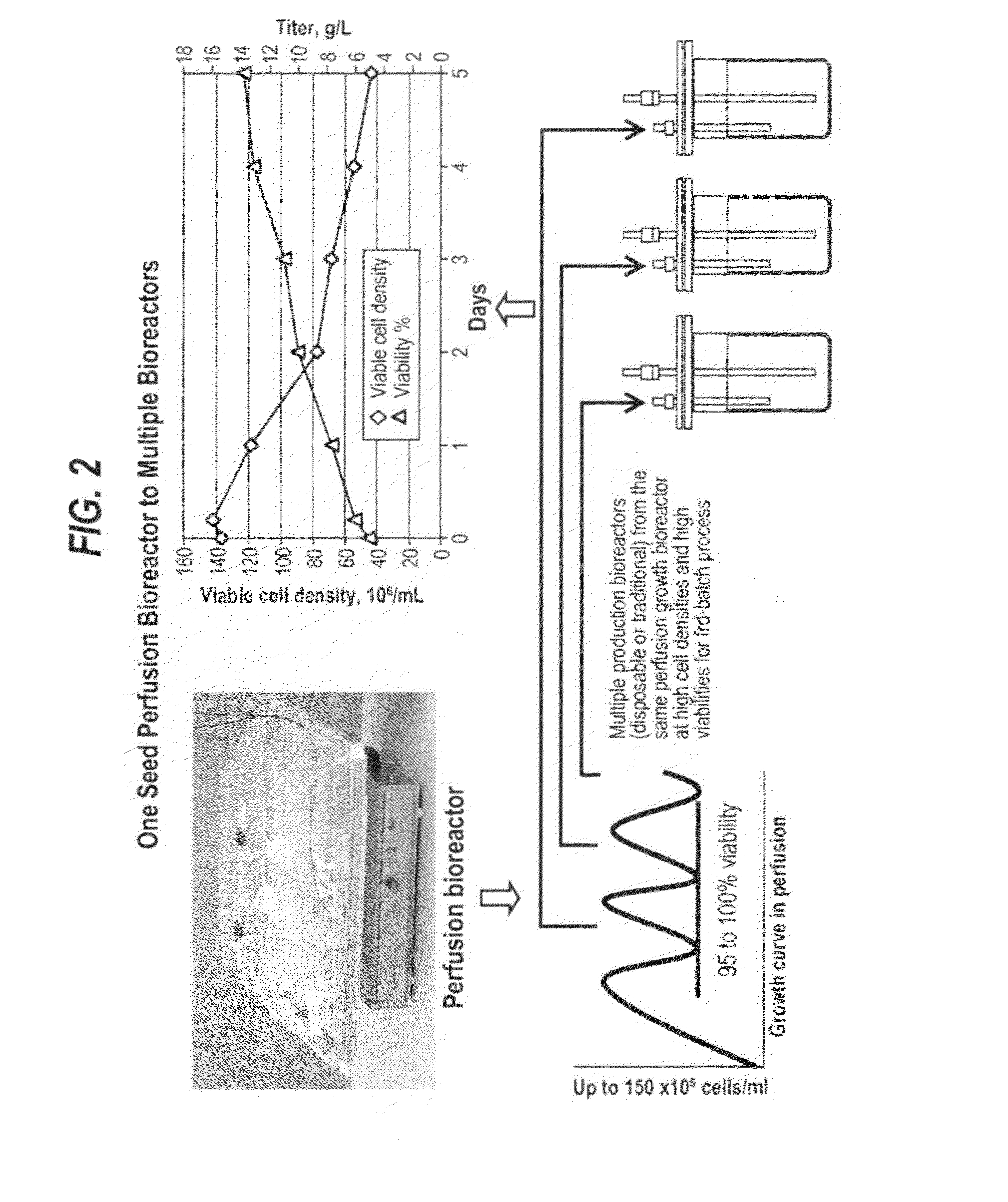
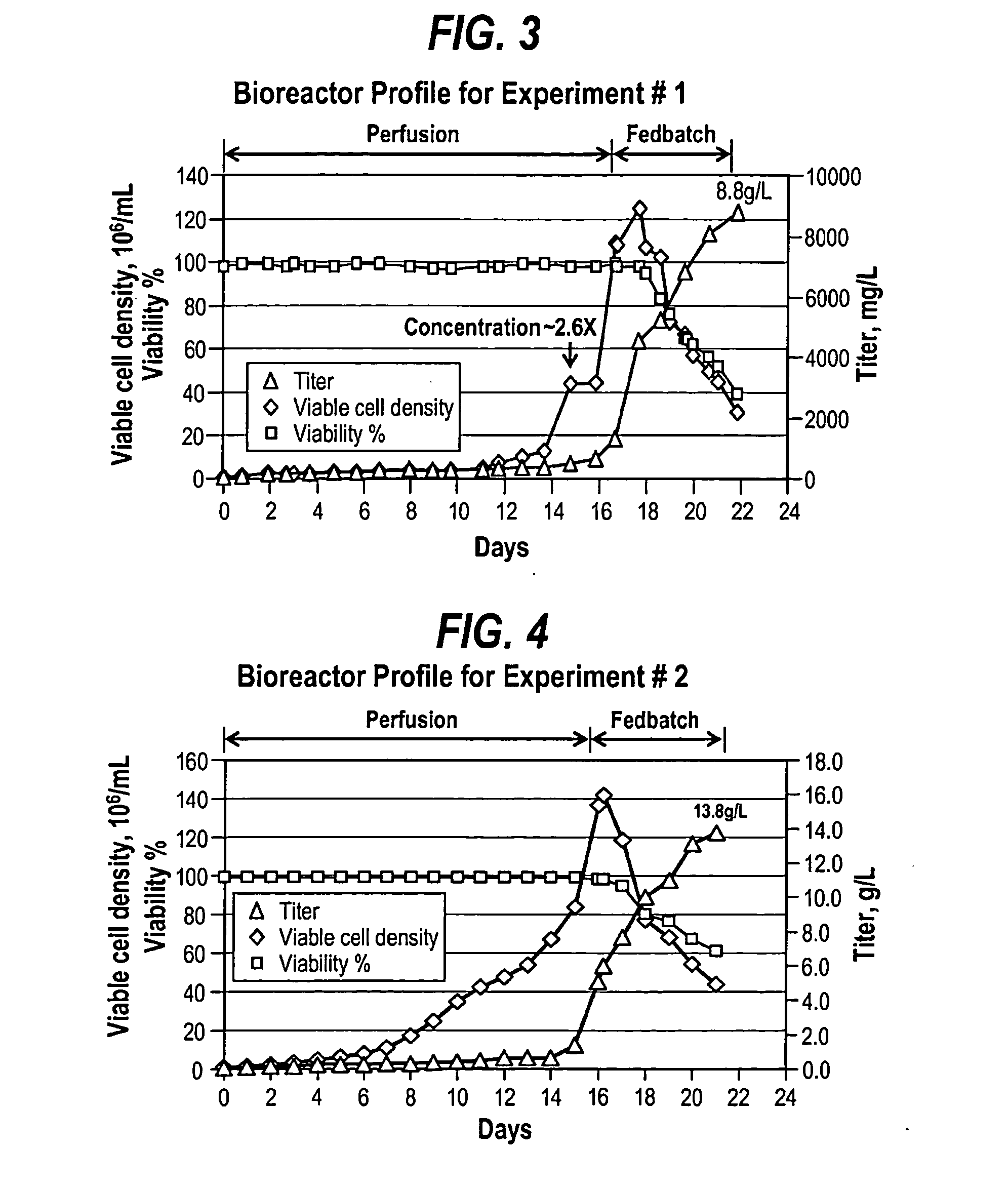
The present invention provides a method of increasing protein production in a cell culture by growing cells that produce the protein (e.g., the growth phase) in a perfusion cell culture to a high cell density (i.e., at least above about 40×106 cells / N mL) and then switching to a protein production phase, wherein the cells are cultured in a fed-batch cell culture. The present invention further provides a method for clarifying a protein from a cell culture by adjusting the pH of the cell culture to below neutral pH (i.e., below a pH of 7) and settling the cell culture, such that the cell culture separates to form a supernatant layer and a cell-bed layer, wherein the protein is in the supernatant layer.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Visual gas hydrate dynamic experimental device
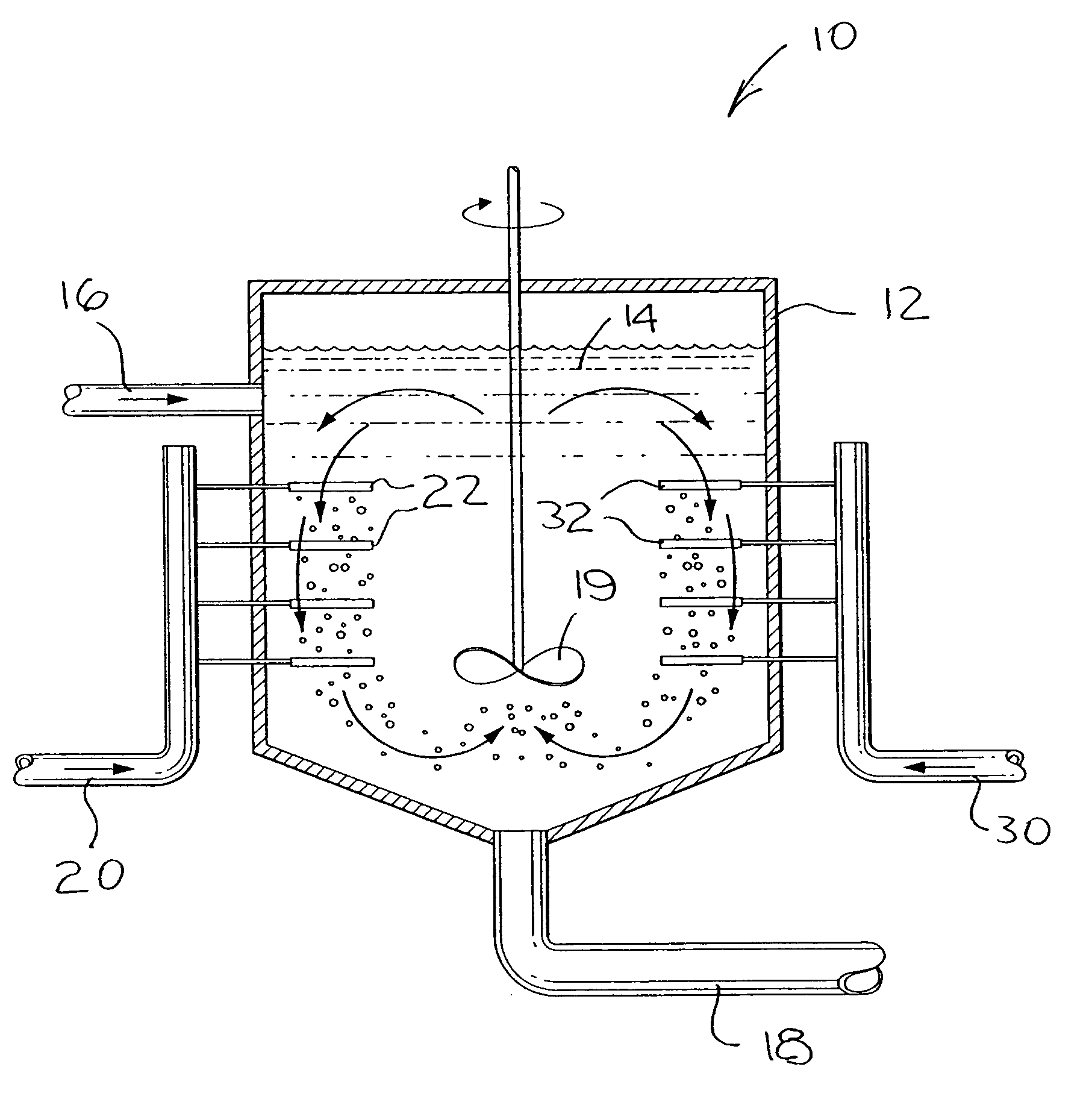
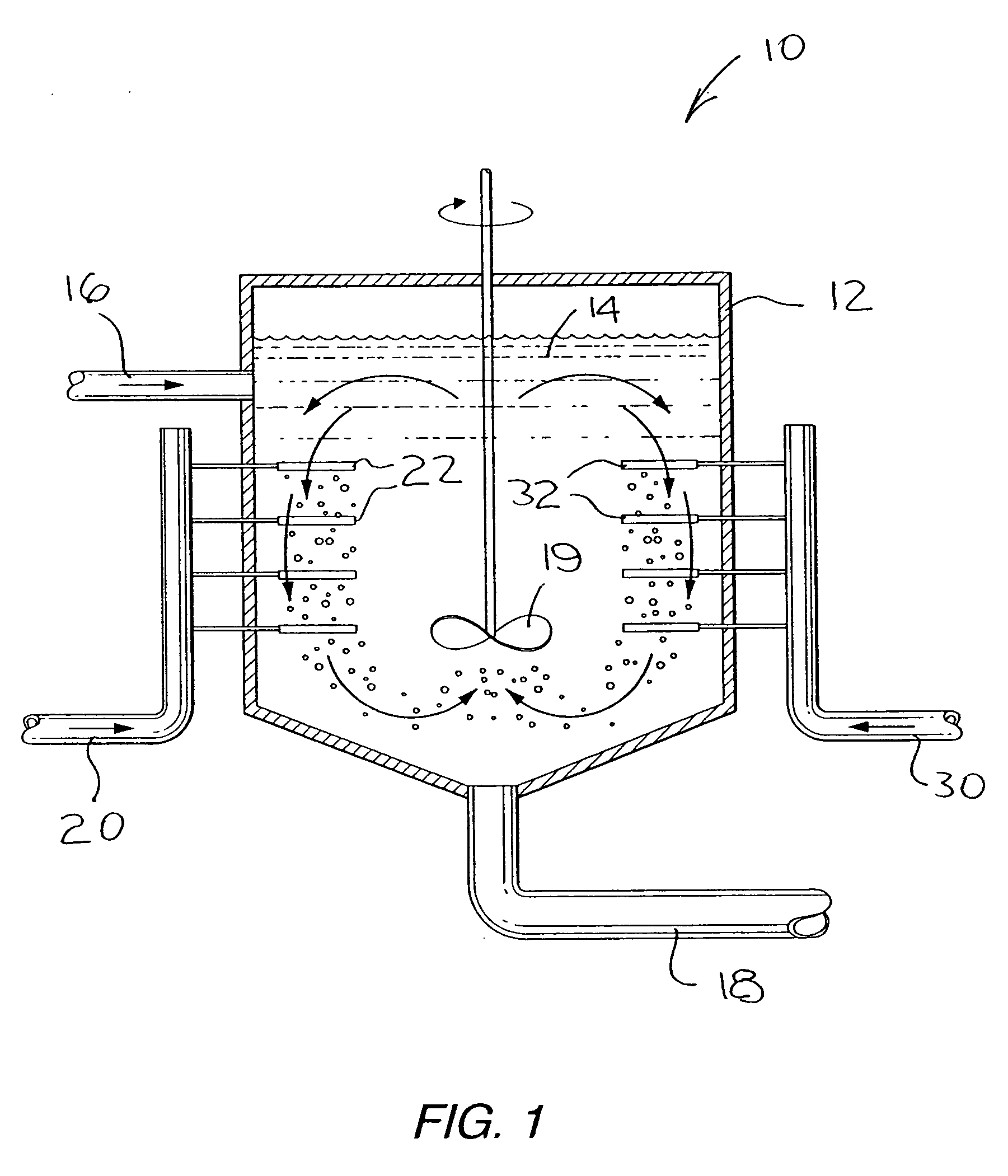
InactiveCN105301205AEasy dischargeEasy to operateChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsFeed devicesGrowth phaseTemperature control
The invention provides a visual gas hydrate dynamic experimental device. The visual gas hydrate dynamic experimental device comprises a visual electromagnetic stirring reaction still, a voltage stabilizing pre-cooling gas supplying unit, an gas exhaust unit, a liquid charging / discharging unit, a temperature control unit and a data collecting and processing unit, wherein the visual electromagnetic stirring reaction still is used for mixing experimental gas and experimental liquid in the reaction still for reaction to form and decompose hydrate; the voltage stabilizing pre-cooling gas supplying unit and the gas exhaust unit are used for supplying pre-cooling experimental gas for the visual electromagnetic stirring reaction still and discharging gas; the liquid charging / discharging unit is used for injecting the experimental liquid to the visual electromagnetic stirring reaction still or discharging the experimental liquid; the temperature control unit is used for controlling the temperature change of the visual electromagnetic stirring reaction still; the data collecting and processing unit is used for collecting, processing, saving and analyzing kinetic parameters during a hydrate formation and decomposition process. According to the visual gas hydrate dynamic experimental device, numerous defects of a common hydrate dynamic experimental device are overcome, the kinetic properties in a nucleation phase and a growth phase of gas hydrate can be accurately determined, and the experimental device is simple, economical and convenient to operate.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing low cholesterol egg without residual agricultural chemical
InactiveCN101213952AGood for healthImprove conversion rateAnthropod material medical ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyGrowth phase
The invention relates to a production method of a low cholesterol nondrug residue egg. The method is characterized in that the chicken is fed in cages in brooding period. The chicken is scattered and fed on the hilly country exposed to the sun and ventilated in finishing and egg production periods. The Chinese traditional medicine additives should be added at different growth phase of chicken. The invention can promote the viscera growth of chicken, and improve health condition of chicken without using medical medicine and hormone. The method can greatly reduce the content of the cholesterol in the egg, which is good for health.
Owner:JINAN KANGZHONG PHARMA TECH DEV
Wastewater treatment with alkanes
InactiveUS6669846B2Increasing communityExpand the populationWater treatment compoundsBiological water/sewage treatmentGrowth phaseAlkane
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Direct expression of peptides into culture media
InactiveUS6210925B1Reduced viabilityImprove breathabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth phaseBiotechnology
Expression systems are disclosed for the direct expression of peptide products into the culture media where genetically engineered host cells are grown. High yield was achieved with novel vectors, a special selection of hosts, and / or fermentation processes which include careful control of cell growth rate, and use of an inducer during growth phase. Special vectors are provided which include control regions having multiple promoters linked operably with coding regions encoding a signal peptide upstream from a coding region encoding the peptide of interest. Multiple transcription cassettes are also used to increase yield. The production of amidated peptides using the expression systems is also disclosed.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
Optimization of Algal Product Production through Uncoupling Cell Proliferation and Algal Product Production
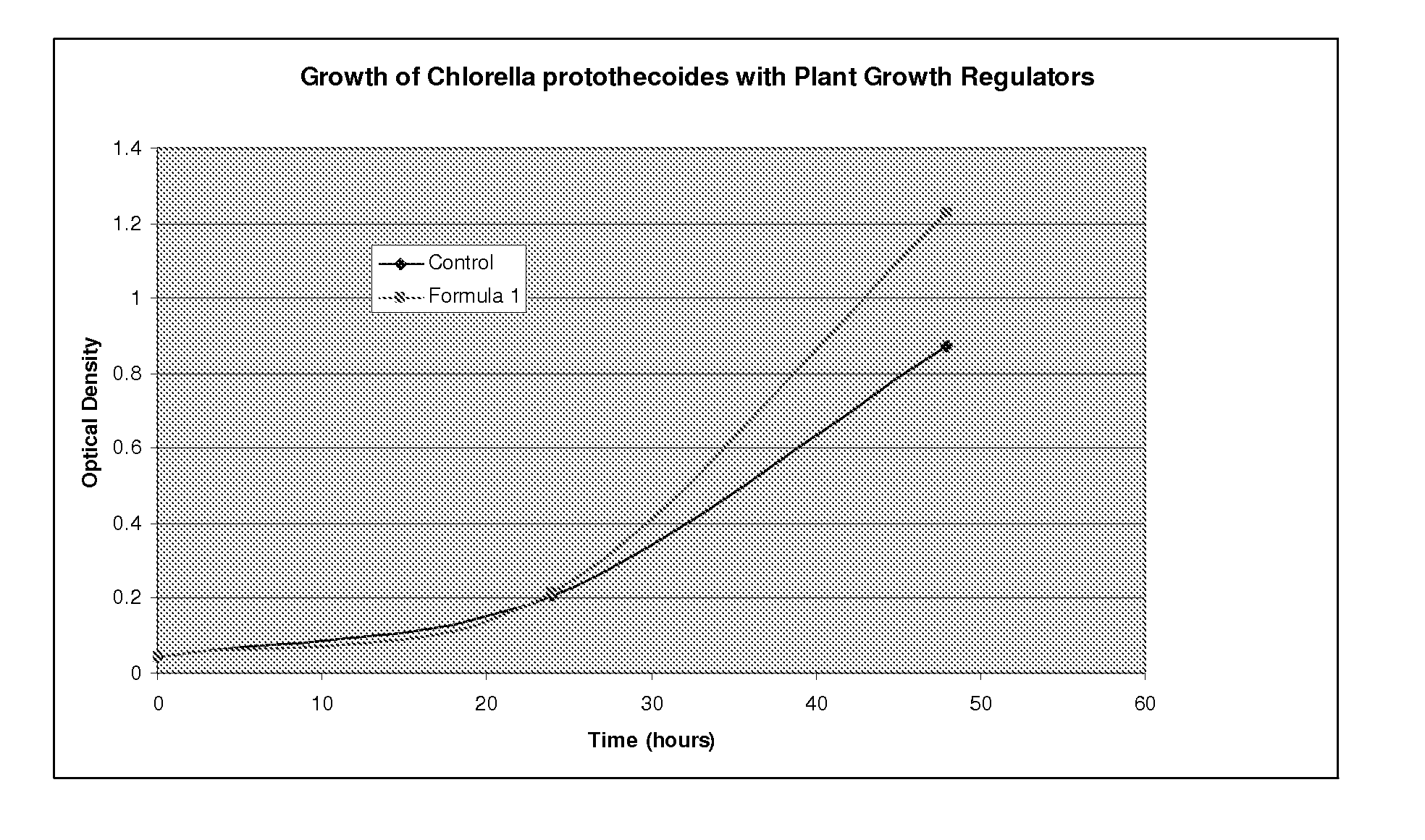
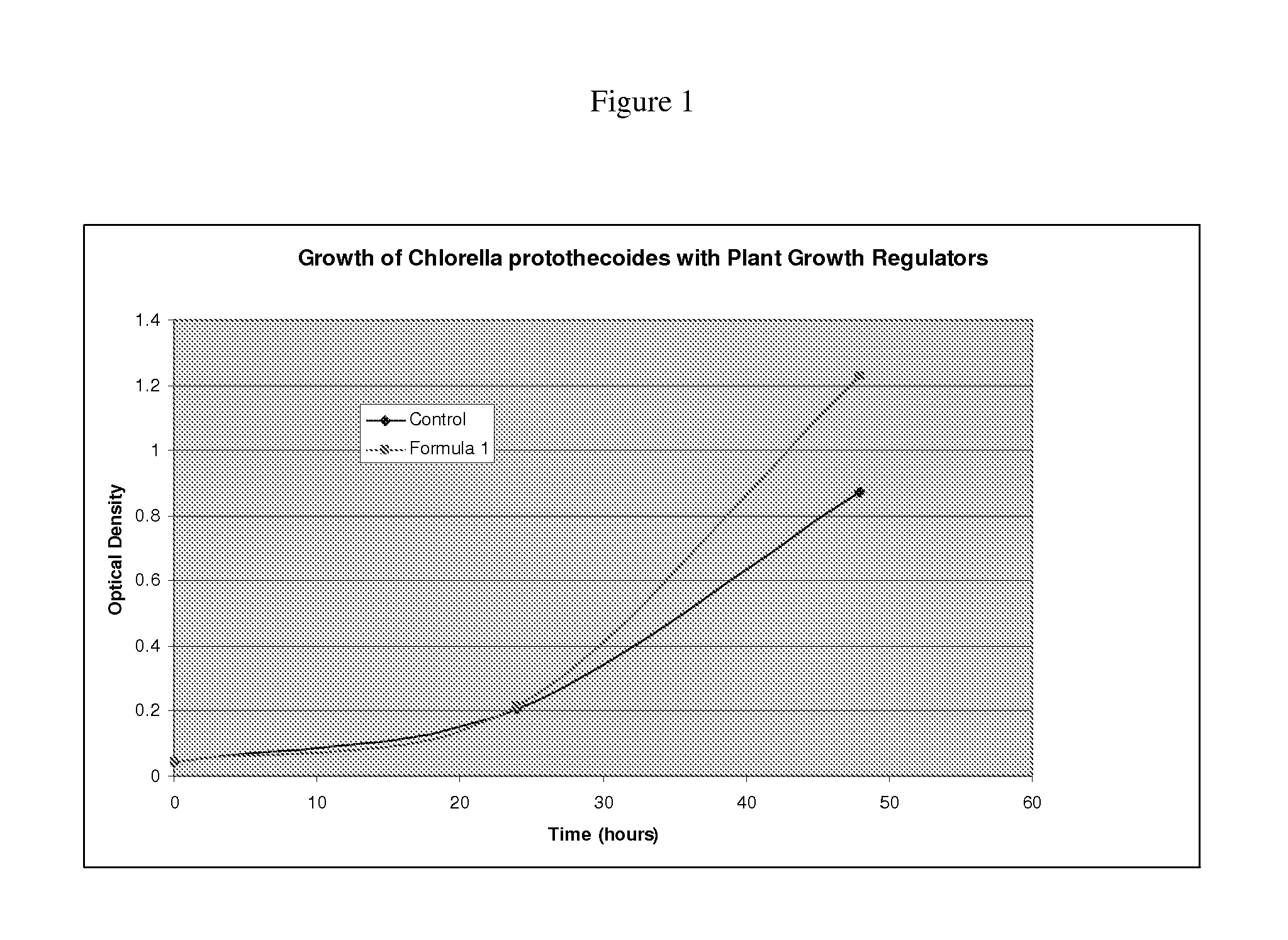
InactiveUS20100162620A1Increase productionIncrease typeAlgae productsUnicellular algaeLipid formationGrowth phase
In algae, the conditions for optimal production of biomass are different than the optimal conditions for oil / lipid production. Conventional processes require that both steps be optimized simultaneously which is necessarily sub optimal. The invention provides systems and processes for optimizing each type of production separately and independently, thereby improving overall production of oil, lipids and other useful products. This process is advantageous because it allows the optimization of the individual steps and growth phases in the production of oil from biomass. This allows the use of different feedstocks for various process steps.
Owner:MCCARTER & ENGLISH LLP
System and method for order-preserving encryption for numeric data
InactiveUS7426752B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsGrowth phaseData set
A system, method, and computer program product to automatically eliminate the distribution information available for reconstruction from a disguised dataset. The invention flattens input numerical values into a substantially uniformly distributed dataset, then maps the uniformly distributed dataset into equivalent data in a target distribution. The invention allows the incremental encryption of new values in an encrypted database while leaving existing encrypted values unchanged. The flattening comprises (1) partitioning, (2) mapping, and (3) saving auxiliary information about the data processing, which is encrypted and not updated. The partitioning is MDL based, and includes a growth phase for dividing a space into fine partitions and a prune phase for merging some partitions together.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Wastewater treatment with alkanes
InactiveUS20040050764A1Increasing communityExpand the populationWater treatment compoundsStationary filtering element filtersAlkaneGrowth phase
An apparatus is provided for treating wastewater with alkanes such as butane. An oxygen-containing gas may also be introduced into the wastewater. Butane, because of its relatively high solubility, rapidly dissolves in the wastewater, thereby significantly increasing the heterogeneous microbial community and heterotrophic microbial population. This enhanced microbial population may rapidly absorb and mineralize materials in the wastestream. After an initial growth phase, the organic matter available in the wastewater effluent may be rapidly decreased, thereby reducing the amount of BOD, TDS, sludge and other pollutants. In addition, the use of butane reduces noxious odors associated with municipal wastewater sludges and other types of wastewater.
Owner:PERRIELLO FELIX ANTHONY
Large-scale cultivation method and quality detection method of cordyceps militaris fruit bodies
InactiveCN102626036AQuality improvementIncrease productionComponent separationHorticultureGrowth phaseIncandescence
The invention discloses a large-scale cultivation method and a quality detection method of cordyceps militaris fruit bodies, comprising the steps of: (1) screening spawn; (2) preparing a rice solid culture medium (40-55 parts of rice and 45-60 parts of nutrient solution in every 100 parts by weight) and killing bacteria; (3) preparing liquid spawn: activating the spawn, inoculating the spawn into a liquid culture medium, conducting static culture for 24 hours and performing suspension culture on a shaking table; (4) culturing fruit bodies: inoculating the liquid spawn on the solid culture medium for dark culture for 6 days at the temperature of 20 DEG C until the surface of the medium is covered by mycelium; placing the well grown mycelium under incandescence with light intensity of 100 to 300 lux, wherein during a primordium growth phase, illumination is performed for 20-24 hours per day at the temperature of 20-24 DEG C; and during a fruit bodies growth phase, illumination is performed for 8-12 hours per day at the temperature of 18-20 DEG C and the fruit bodies are harvested 5 to 8 days after mature. The cordyceps militaris fruit bodies cultured by the method have the advantages of high yield and high content of active ingredients. Batches of cordyceps militaris fruit bodies have fingerprints with a similarity value greater than 0.950, indicating stable and controllable quality.
Owner:珠海市先康生物科技有限公司
Method and algorithm for quantifying polynucleotides
ActiveUS7739054B2Microbiological testing/measurementAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsGrowth phaseTest sample
Machine executable method of analyzing growth curve data to identify the transition from a baseline phase into a growth phase. Applications of the method include analysis of results from time-dependent monitoring of amplicon synthesis in a nucleic acid amplification reaction to quantify a starting amount of a nucleic acid template in a test sample. The method advantageously simplifies the quantitation by circumventing the need to establish thresholds used for calculating initiation of the growth phase, to calculate derivatives, or to perform linear regression analysis.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Remote sensing extraction method of agricultural disaster information based on vegetation index time-space statistical characteristics
The invention provides a remote sensing extraction method of agricultural disaster information based on vegetation index time-space statistical characteristics and belongs to the technical field of agricultural disaster information acquisition, aiming at solving the problems that existing agricultural disaster remote sensing monitoring cannot be used for monitoring and evaluating a large-scale region or a long time sequence in the region and a monitoring method has no universality. On the basis of considering that vegetation indexes of different phonological regions, crops and growth phases have difference, an NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) of each pixel in the phonological regions with known diseases and an average value NDVIm of the NDVI and a standard difference STD of the same crops are extracted; a relation between the parameters is analyzed by utilizing the statistical characteristics according to NDVI gradation histogram characteristics before and after the disasters and a disaster monitoring model is established; the agricultural disasters are extracted. According to the method provided by the invention, interference factors caused by the growth regions, different crops and growth phases are considered and the precision of a monitoring result is improved. The remote sensing extraction method provided by the invention is used for monitoring the agricultural disasters.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
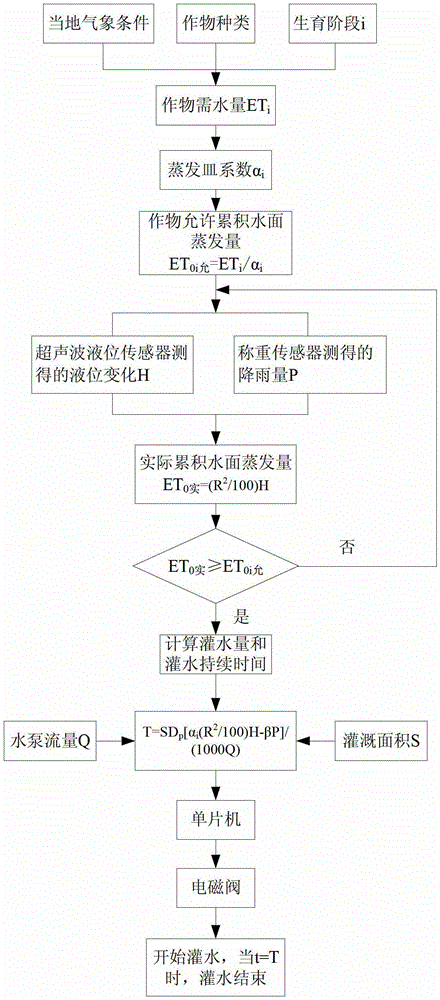
Control system and method for insufficient irrigation of crops
ActiveCN102870654AReduce productionIncrease profitClimate change adaptationWatering devicesGrowth phaseStart time
The invention relates to the technical field of forecast and control in insufficient irrigation of crops and discloses control system and method for insufficient irrigation of crops. A data base including data such as water requirement, pan coefficient and water deficit percentage allowed by insufficient irrigation is established for corps in different areas and different growth phases. Evaporation from water surface of evaporation pans and rainfall are acquired by an automatic data acquisition system. Start time and duration of irrigation are calculated according to a formula. Forecast and control in insufficient irrigation are achieved by a controller system. The control method is applicable to forecasting and controlling insufficient irrigation for field crops in arid and semi-arid areas, gardens and protected agriculture, and is applicable to various irrigation methods of spray irrigation, drip irrigation, basin irrigation and the like. The control system and method are widely applicable. The control method is simple and is low in cost. Precision is guaranteed, and automation level is high.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Organic-inorganic long-acting corn special-purpose compound fertilizer
InactiveCN101255082AMeet nutrient needsMaintain and improve structureAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersGrowth phasePhosphate
The invention relates to a fertilizer. A organic-inorganic slow-release compound fertilizer special for maize, contains grained inorganic nitrogen, phosphorus and potasium fertilizers, which is characterized in that: the grained inorganic nitrogen, phosphorus and potasium fertilizers are macroaggregate urea, slow-release coated urea, monoammonium phosphate and kalium sulphuricum; and the fertilizer is mixed with an organic grained fertilizer used animal manure, bean cake And straw as raw materials; where the fertilizer contains 18-20by weight of macroaggregate urea, 34-36by weight of slow-release coated urea, 15-17by weight of monoammonium phosphate, 14-16by weight of kalium sulphuricum and 14-15by weight of organic grained fertilizer. The invention can provides a long time nutrient based on the nutritional needs of each growth phase of the maize by once fertilization, can hold and improve soil structure and fertility, and solves the technical problems of convenient preparation, storage, transport and fertilization.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Apparatus for creating therapeutic charge transfer in tissue
InactiveUS20050065394A1Avoid high pressureConsume energyElectrotherapySurgeryGrowth phaseTherapeutic effect
An apparatus for creating therapeutic charge transfer in tissue includes a coil. The coil generates a changing magnetic field to induct an electric field in the tissue exceeding 10 mV / cm when the coil is 5 cm from the tissue. Preferably, the magnetic field has a growth phase and a decay phase and a duration of the growth phase is at least ten times a duration of the decay phase. The apparatus can include a control circuit to control a current fed to the coil. The control circuit includes two subcircuits and a switch for switching between a first of the subcircuits and a second of the subcircuits; preferably, a λ of the second subcircuit is at least ten times a λ of the first subcircuit. To generate the therapeutic effect, the coil should have a duty cycle of at least ten percent.
Owner:ADVATECH CORP
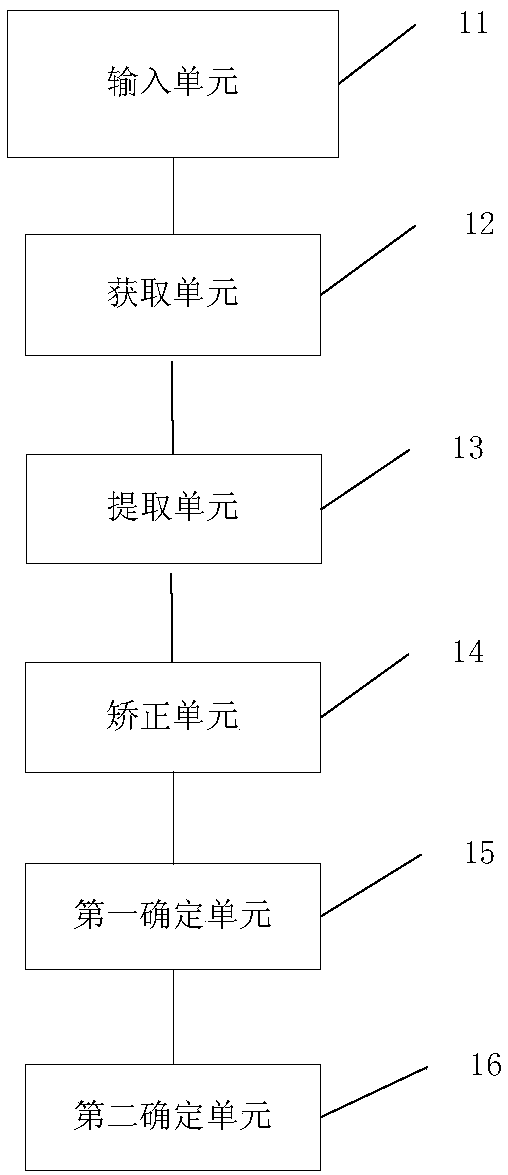
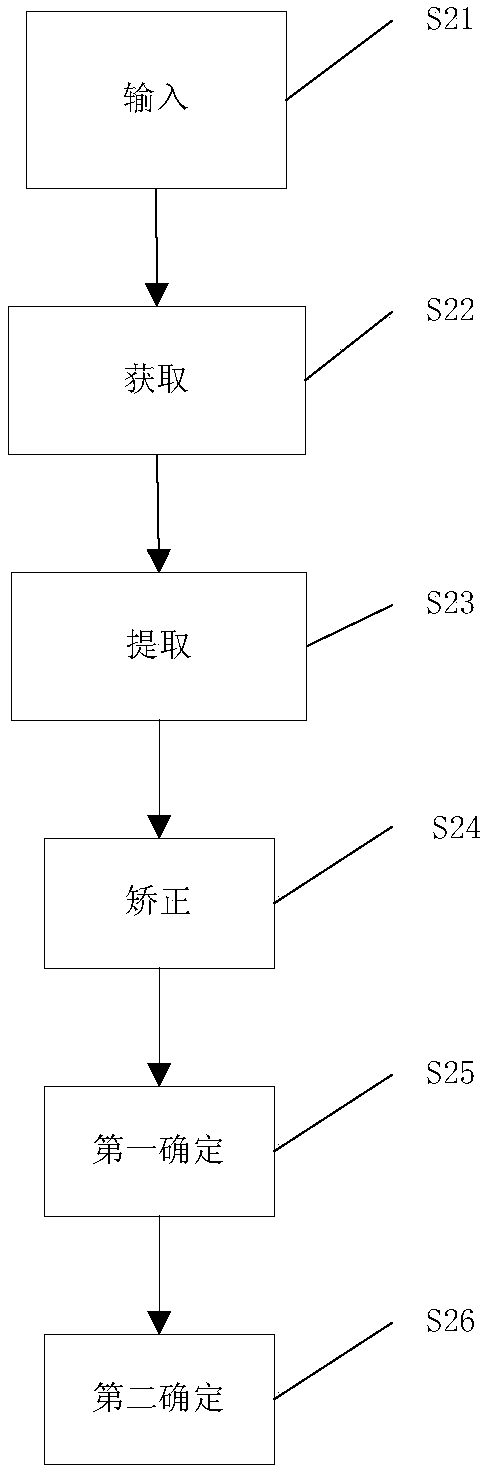
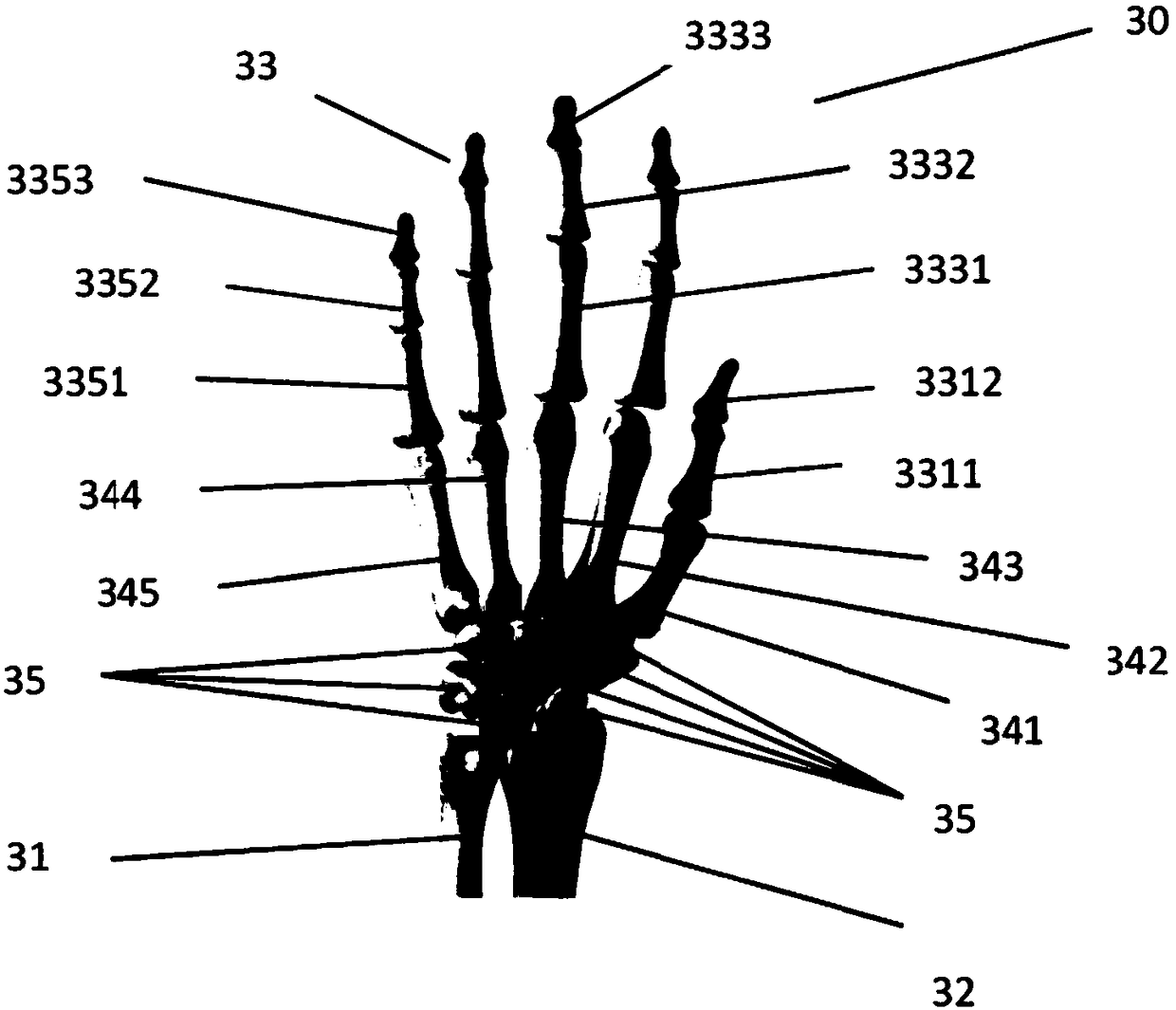
Skeletal age detecting method and device based on depth learning
The invention provides a skeletal age detecting method and device based on depth learning. The method comprises the steps of inputting, wherein X-ray pictures of hands of an examinee and the gender ofthe examinee are input; obtaining, wherein multiple key points corresponding to each skeleton on the hands are obtained from the X-ray pictures; extracting, wherein respective initial pictures of partial skeletons are extracted from the X-ray pictures; correcting, wherein the initial pictures of each skeleton in the partial skeletons are corrected to obtain respective correction pictures of the partial skeletons; primary determining, wherein growth phase information of each skeleton in the partial skeletons is determined, and on the condition that the skeletons do not include carpal bones, the growth phase information of the carpal bones is determined; secondary determining, wherein the skeletal age of the examinee is determined according to the growth phase information of each skeleton in the partial skeletons or the growth phase information of each skeleton in the partial skeletons and the growth phase information of the carpal bones.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Wastewater treatment with alkanes
InactiveUS20030136735A1Increasing communityExpand the populationMixing methodsBiological water/sewage treatmentAlkaneGrowth phase
An apparatus and method are provided for treating wastewater with alkanes such as butane. An oxygen-containing gas may also be introduced into the wastewater. Butane, because of its relatively high solubility, rapidly dissolves in the wastewater, thereby significantly increasing the heterogeneous microbial community and heterotrophic microbial population. This enhanced microbial population may rapidly absorb and mineralize materials in the wastestream. After an initial growth phase, the organic matter available in the wastewater effluent may be rapidly decreased, thereby reducing the amount of BOD, TDS, sludge and other pollutants. In addition, the use of butane reduces noxious odors associated with municipal wastewater sludges and other types of wastewater.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Fruit tree and Chinese medicinal herb interplanting method
InactiveCN103583204ADoes not affect medicinal propertiesYield is not affectedSeed and root treatmentClimate change adaptationGrowth phaseMedicinal herbs
The invention discloses a fruit tree and Chinese medicinal herb interplanting method. The method includes the steps of planting fruit tree seedlings according to the row spacing of 2-2.5m and plant spacing of 1-1.2m, and planting chrysanthemum, Anemarrhenae and bidentate achyranthes among the fruit tree seedlings; after two to three years, replacing the medicinal herbs planted among the fruit tree seedlings with Isatis tinctoria, honeysuckle and rehmannia; after five years, replacing the medicinal herbs planted among the fruit tree seedlings with pseudo-ginseng, ginseng and Ganoderma lucidum. The problems with interplanting of Chinese medicinal herbs and fruit trees are improved by various methods; different types of medicinal herbs are selected in the different growth phases of the fruit trees, different fertilizing methods and different fertilizers are selected for the different growth phases of the fruit trees, the seeds of Chinese medicinal herbs are specially treated, and the yield of both the fruit trees and the Chinese medicinal herbs is increased and income of fruit growers is increased.
Owner:香格里拉市三草生物资源开发有限公司
Fermentation method for accelerating ganoderic acids and ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide biological synthesis
InactiveCN101235393APromote growthIncrease contentMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyGrowth phase
The invention discloses a fermentation method for promoting mythic fungus acid or mythic fungus polysaccharide biology to synthesize. The invention investigates the condition which is needed in the growth phase of mythic fungus cell and product synthesis phase, which respectively investigates the influence of control strategies of pH two phases and oxygen dissolution two phases to mythic fungus acid or mythic fungus polysaccharide biology according to unconsistency of environmental conditions which are needed in the phases of mythic fungus cell growth and production synthesis, and the invention respectively investigates the influence to mythic fungus acid or mythic fungus polysaccharide biology synthesis after control strategies of pH two phases and oxygen dissolution two phases or the fed strategy are mutually coordinated together on the basis of combining with an intermediate fed strategy. The test result shows that mythic fungus cells are obviously prompted to grow no matter respectively adopting a pH value two phases control strategy, an oxygen dissolution concentration two phases control strategy, or coordinating the pH value two phases control strategy and the oxygen dissolution concentration two phases control strategy with the fed strategy together, and the content or yield of mythic fungus acid or mythic fungus polysaccharide are greatly improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Treatment of cyanophyta in eutrophic water by eichhornia crassipes
InactiveCN1406880AReduce pollutionBiological water/sewage treatmentGrowth phaseVolumetric Mass Density
An ecological technology for treating the nutrients-enriched water polluted by blue alga features that the water hyacinth is cultured in the water by a certain density and then periodically collectedin its growth phase. Its advantages are high effect and low cost.
Owner:林敏
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com