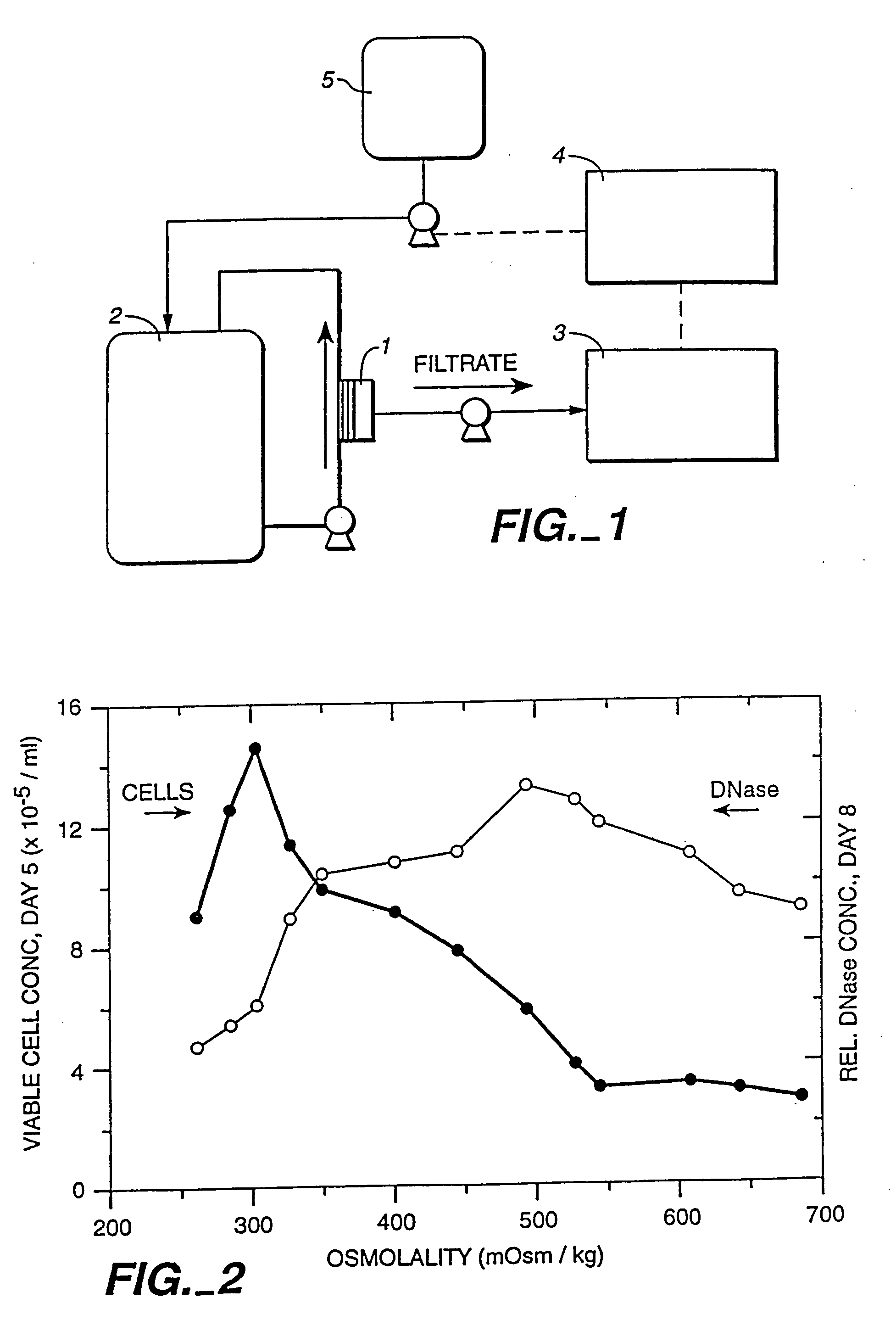
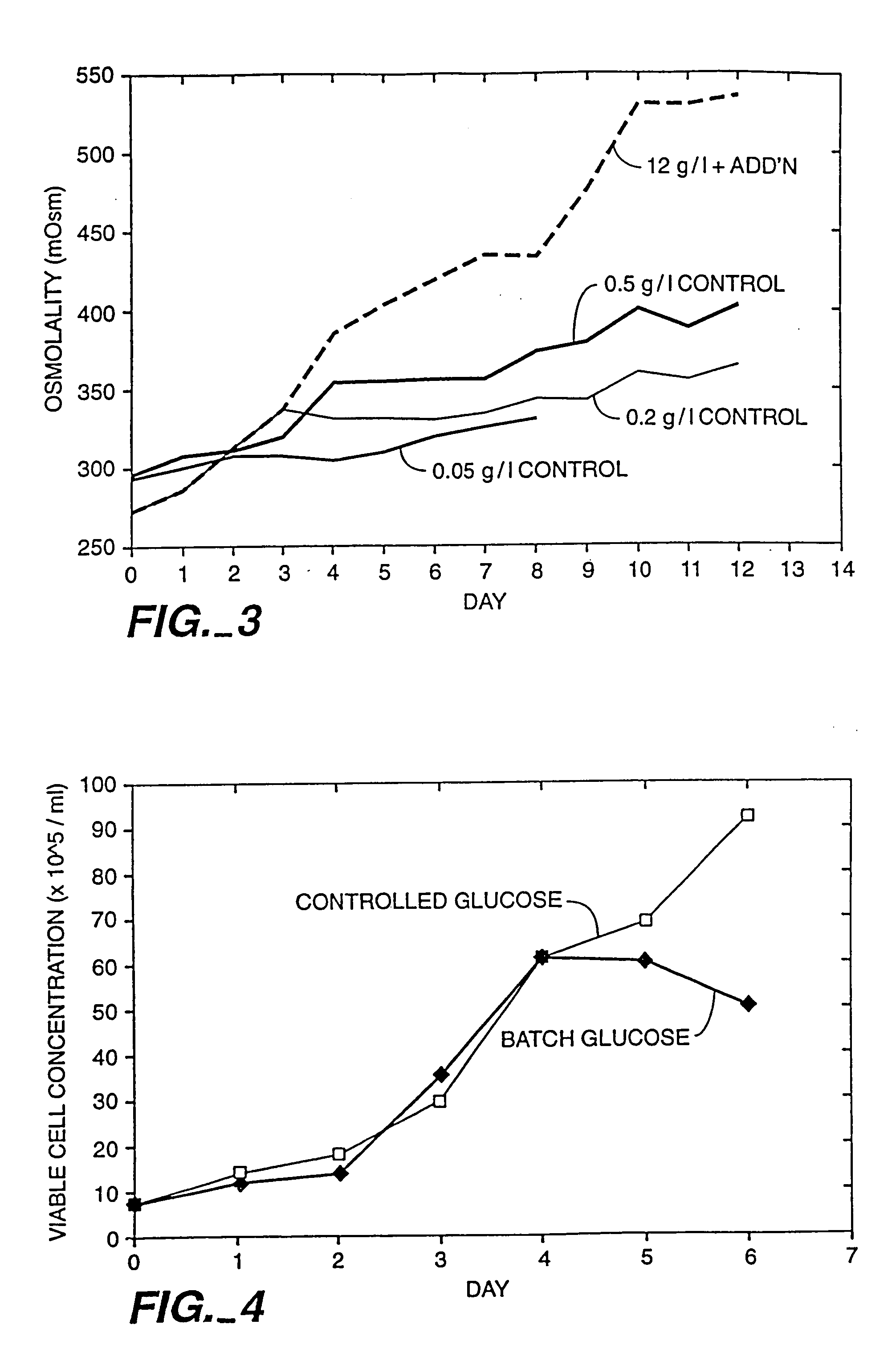
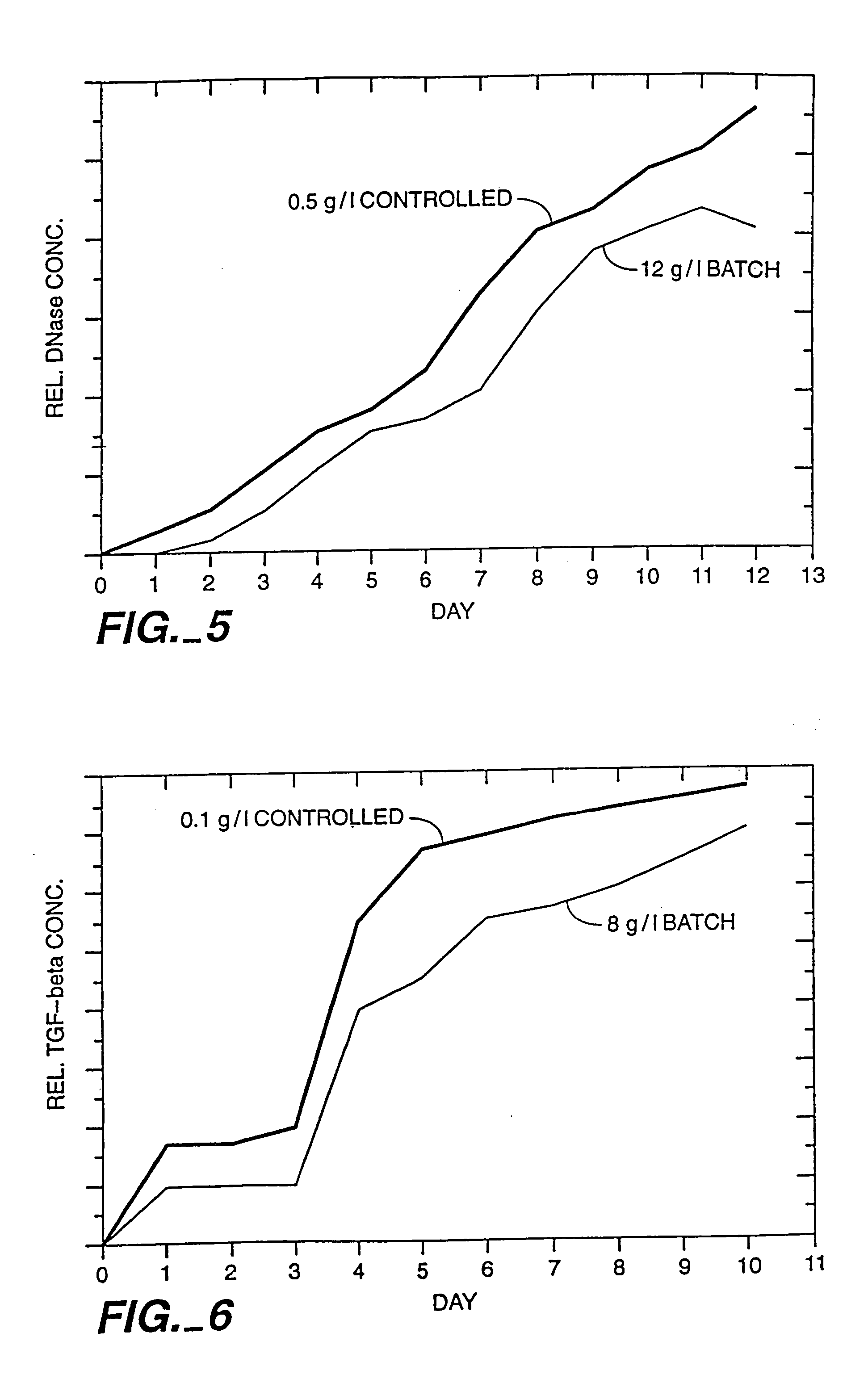
Polypeptide production in animal cell culture
a cell culture and polypeptide technology, applied in the field of improving the production of polypeptides in animal cell culture, can solve the problems of not being able to disclose a method of controlling the osmolality of the cell culture medium, the concept of controlling the glucose in fed-batch cell culture in order to control the osmolality within a desired range has not been proposed by these researchers, and the time required for optimal production of polypeptides is reduced. , to achieve the effect o
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cell Growth and Productivity vs Osmolality
[0091] The impact of osmolality on cell growth and productivity was determined in petri dish culture. CHO cells were transformed with nucleic acid encoding recombinant human deoxyribonuclease (rhDNase) using the techniques disclosed by Shak et al., PNAS, 87: 9188-9192 (1990), expressly incorporated by reference herein. These recombinant CHO cells were grown in petri dish culture in medium consisting essentially of the Super medium referred to in U.S. Pat. No. 5,122,469 (except that NaCl was added to the Super medium at various concentrations in order to achieve an osmolality in the range from about 260-680 mOsm). The glucose concentration was 4.5 g / L. The osmolality was measured using an OSMETTE™ osmometer. The pH of the culture medium was 7.2 and cells were cultured in a 37° C. humidified CO2 incubator. The results are depicted in FIG. 2; the closed circles represent the CHO cell density (expressed as 105 cells / ml) after 5 days and the ope...
example 2
Osmolality Chance vs Glucose Concentration
[0092] The osmolality change during cultivation at various controlled glucose concentrations versus high (batch) glucose concentration was quantified. CHO cells transformed with rhDNase cells (see Shak et al., supra) were cultured in a pH controlled Applikon (Foster City, Calif.) bioreactor at a 2.5 liter working volume. The Super cell culture medium of U.S. Pat. No. 5,122,469 (with adjusted NaCl and glucose concentrations) was used and the CHO cells were stirred at 150 rpm agitation. The initial osmolality was adjusted to about 270-300 mOsm via the amount of NaCl added. The cell seed density was 1×106 cells / ml. The other cell culture medium and culturing conditions were: pH=7.2, dO2=60% and culturing temperature=37° C. Glucose was added either in batch (at a concentration of 12 g / L) at the start of the culturing or was controlled throughout the culturing to be at a concentration of 0.05 g / L, 0.2 g / L or 0.5 g / L, respectively. Glucose contro...
example 3
Cell Growth vs Glucose Concentration
[0093] The effects of glucose concentration and glucose control on growth of CHO cells transformed with TBFβ were investigated. CHO cells were transformed with TGFβ using the techniques disclosed in Brunner et al., Mol. Endocrinol., 6(10): 1691-1700 (1992). The results are depicted in FIG. 4; the symbols represent the experiment wherein on line glucose control (OLGC) at 0.1 g / L using FIA was performed throughout the culturing, the ♦ symbols represent the experiment wherein the glucose was added initially in batch (8 g / L). In the experiments, CHO cells were cultured in an Applikon bioreactor at a 2.5 liter working volume. Super cell culture medium (with adjusted NaCl and glucose concentrations) was used and the CHO cells were stirred at 150 rpm agitation. The initial osmolality was adjusted to 280 mOsm via the addition of NaCl. The osmolality of the medium was measured using an OSMETTE™ osmometer. The cell seed density was 8×105 cells / ml. The oth...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com