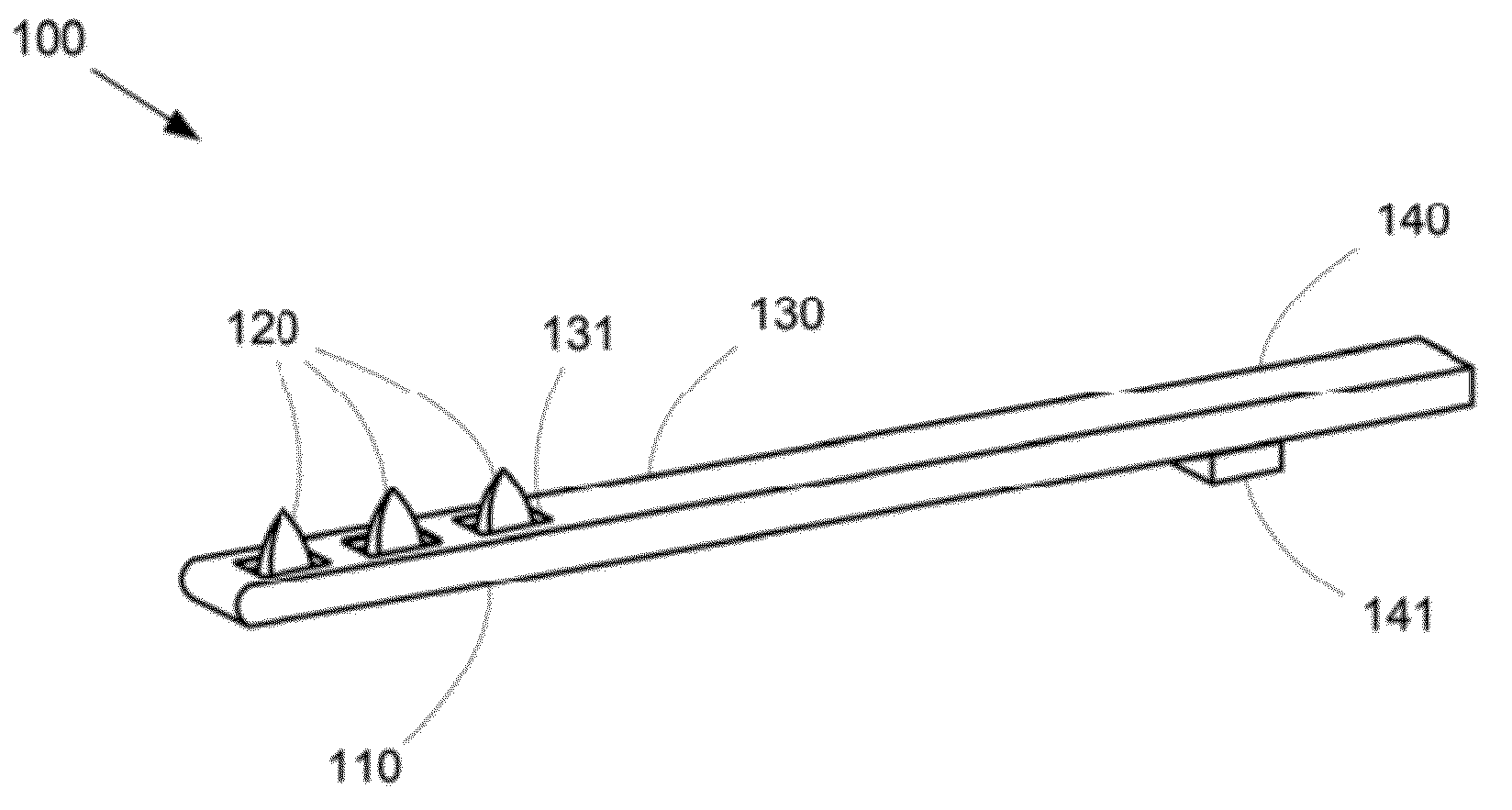
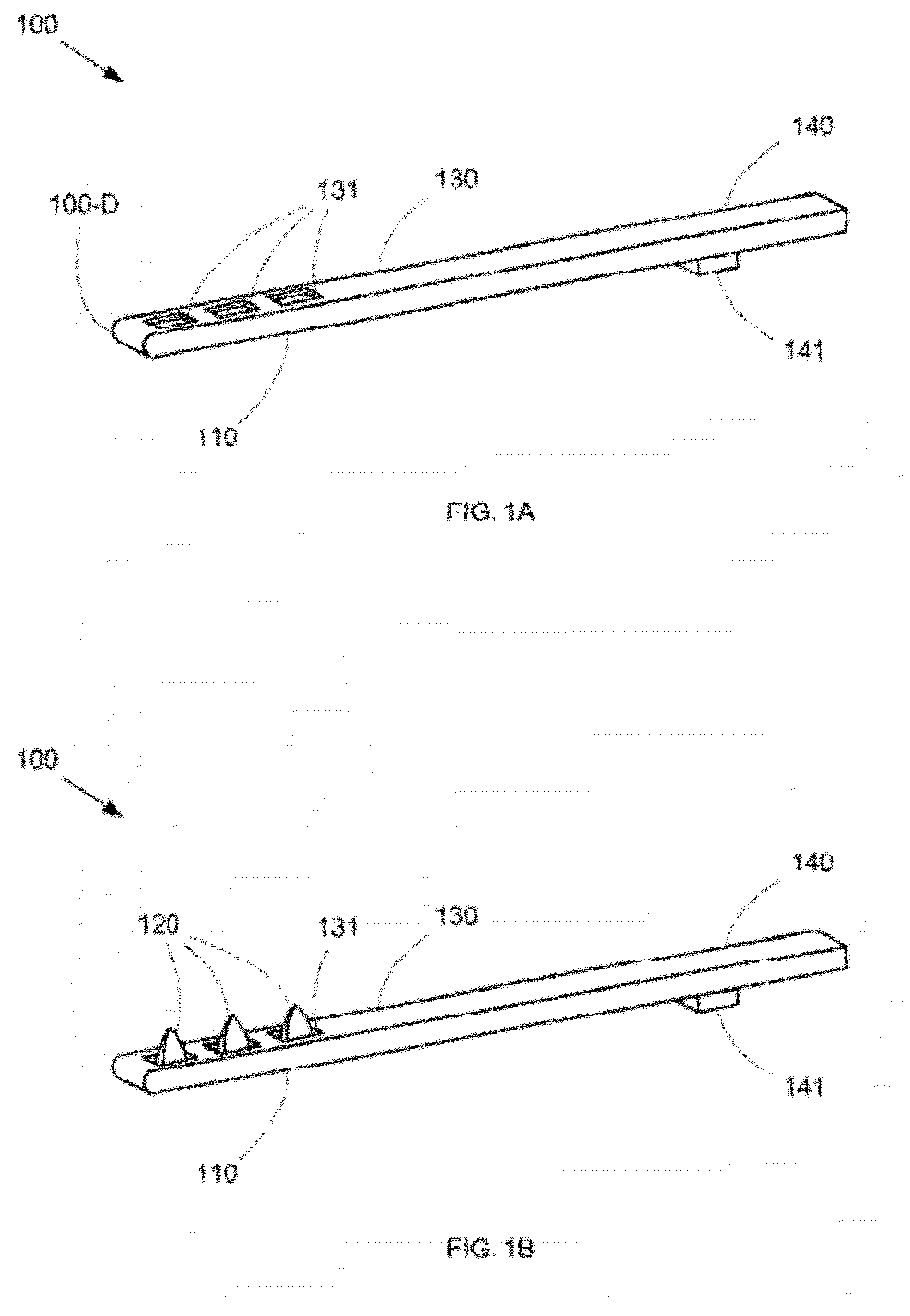
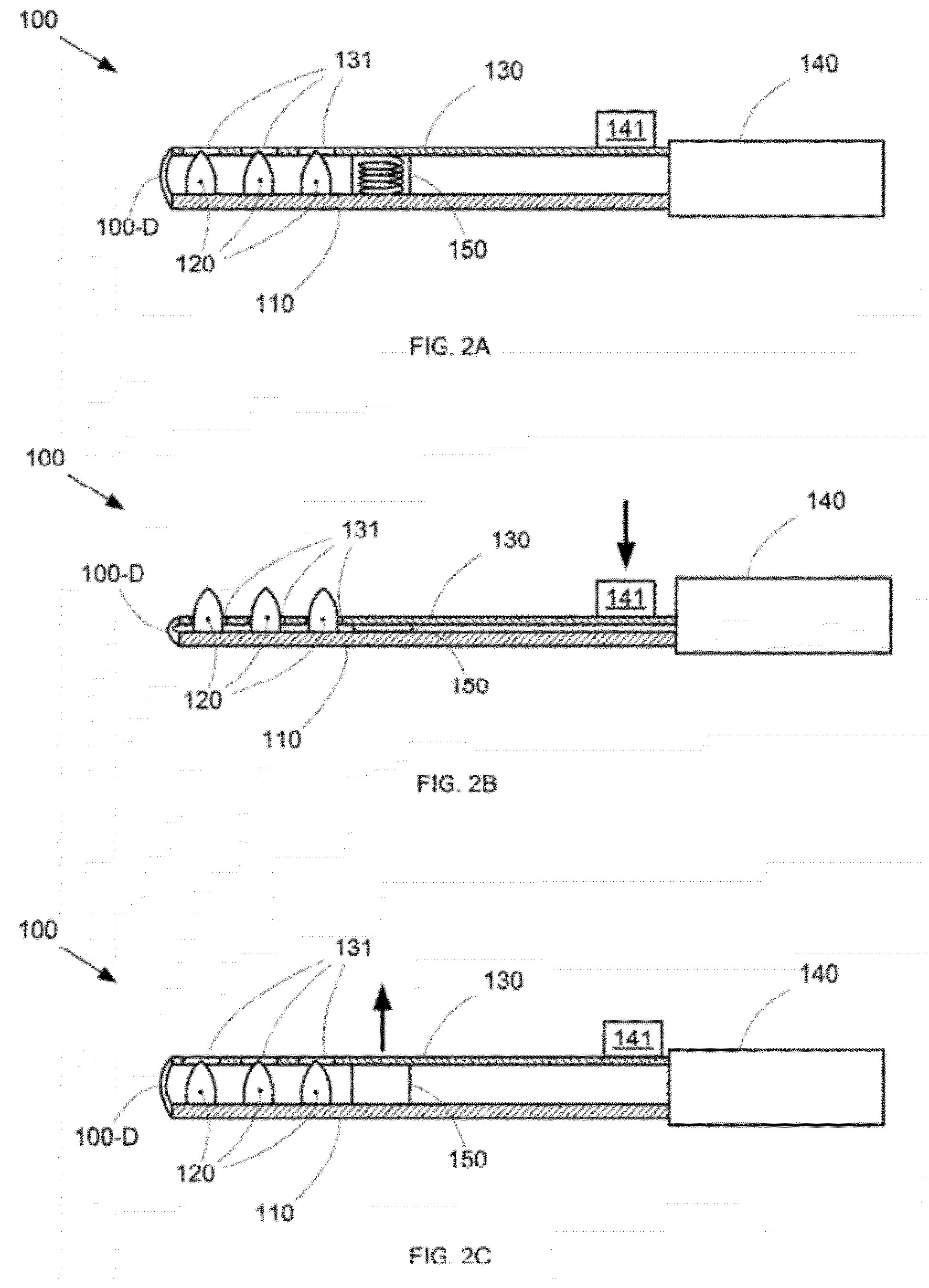
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Carpal bones" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
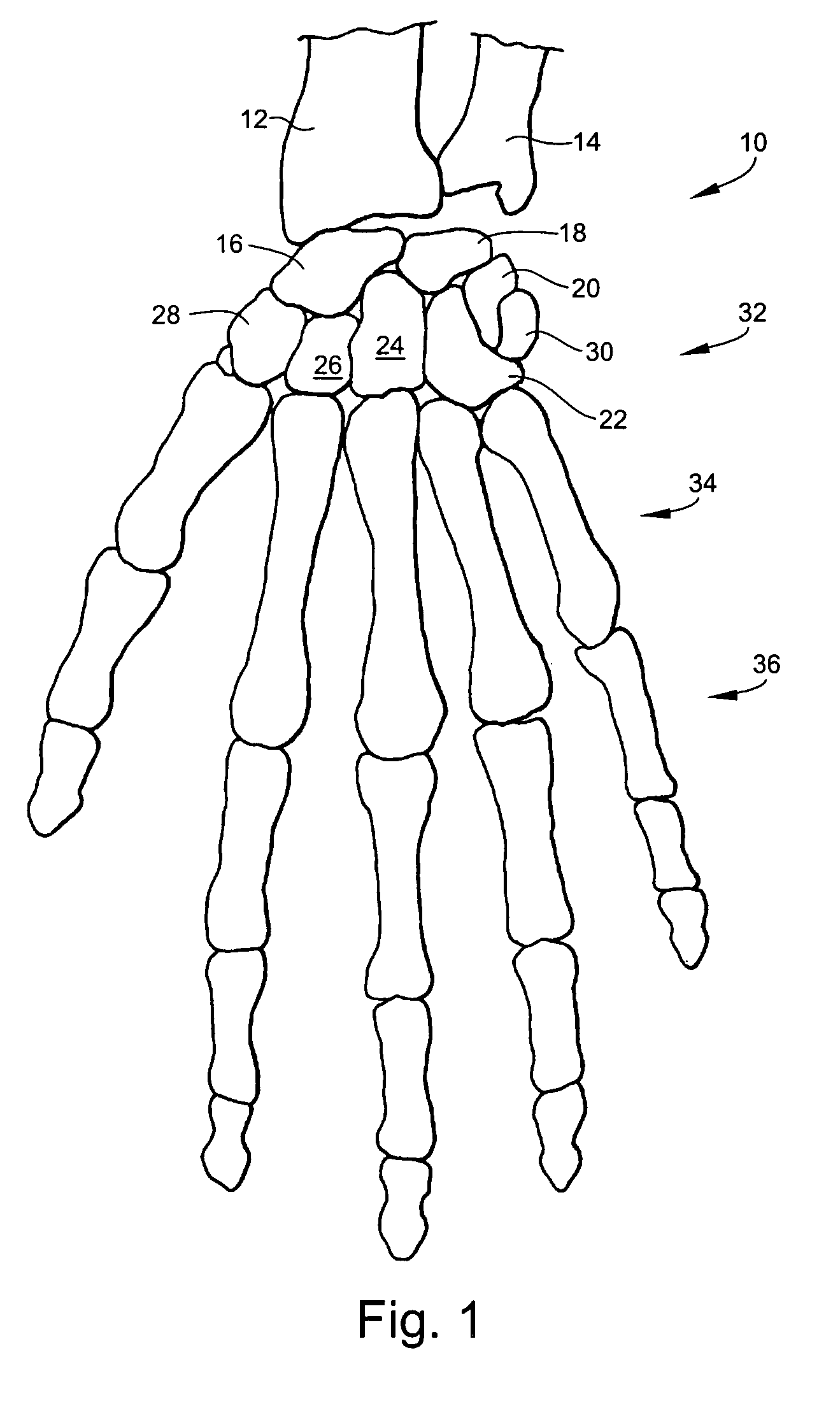
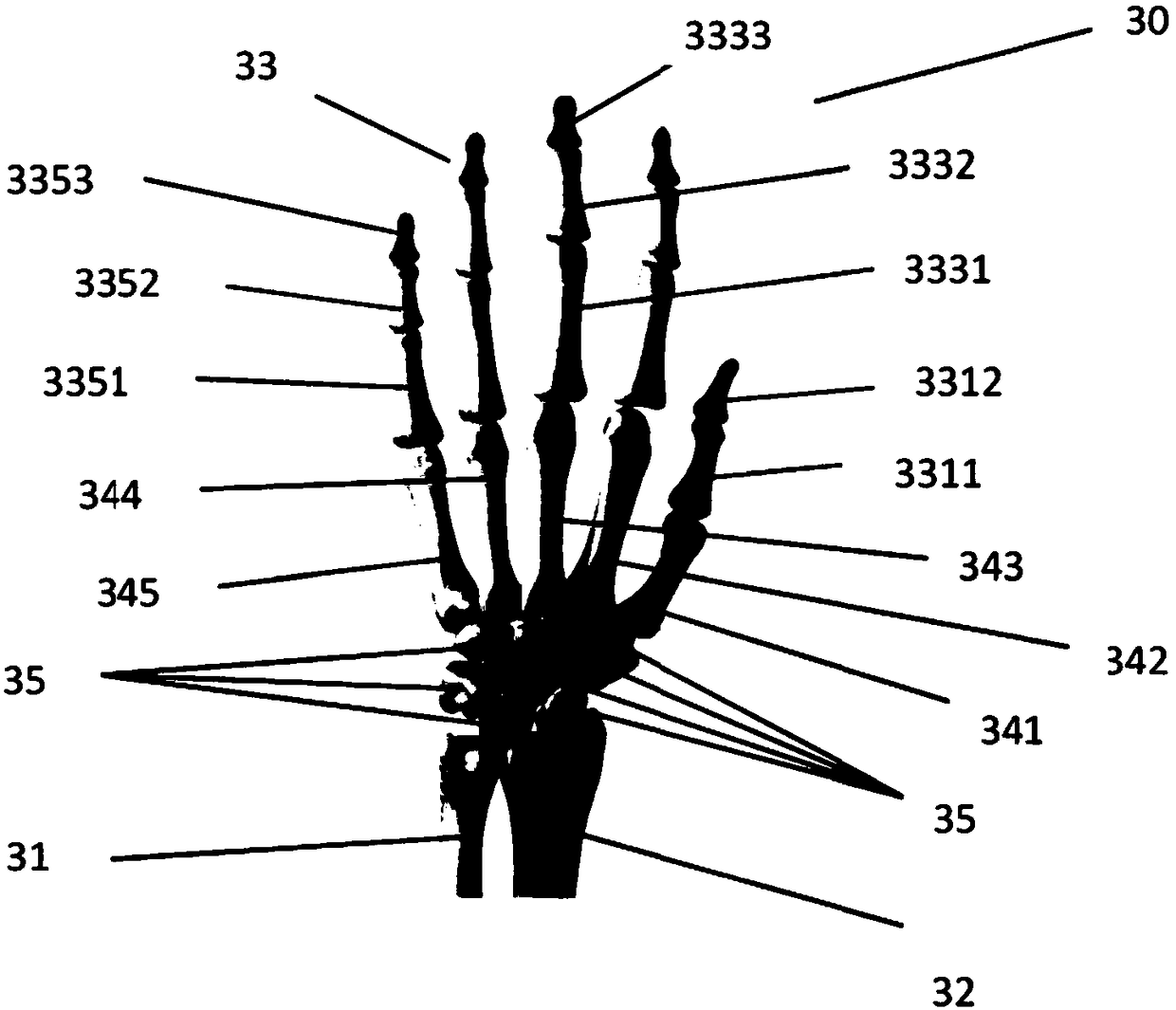
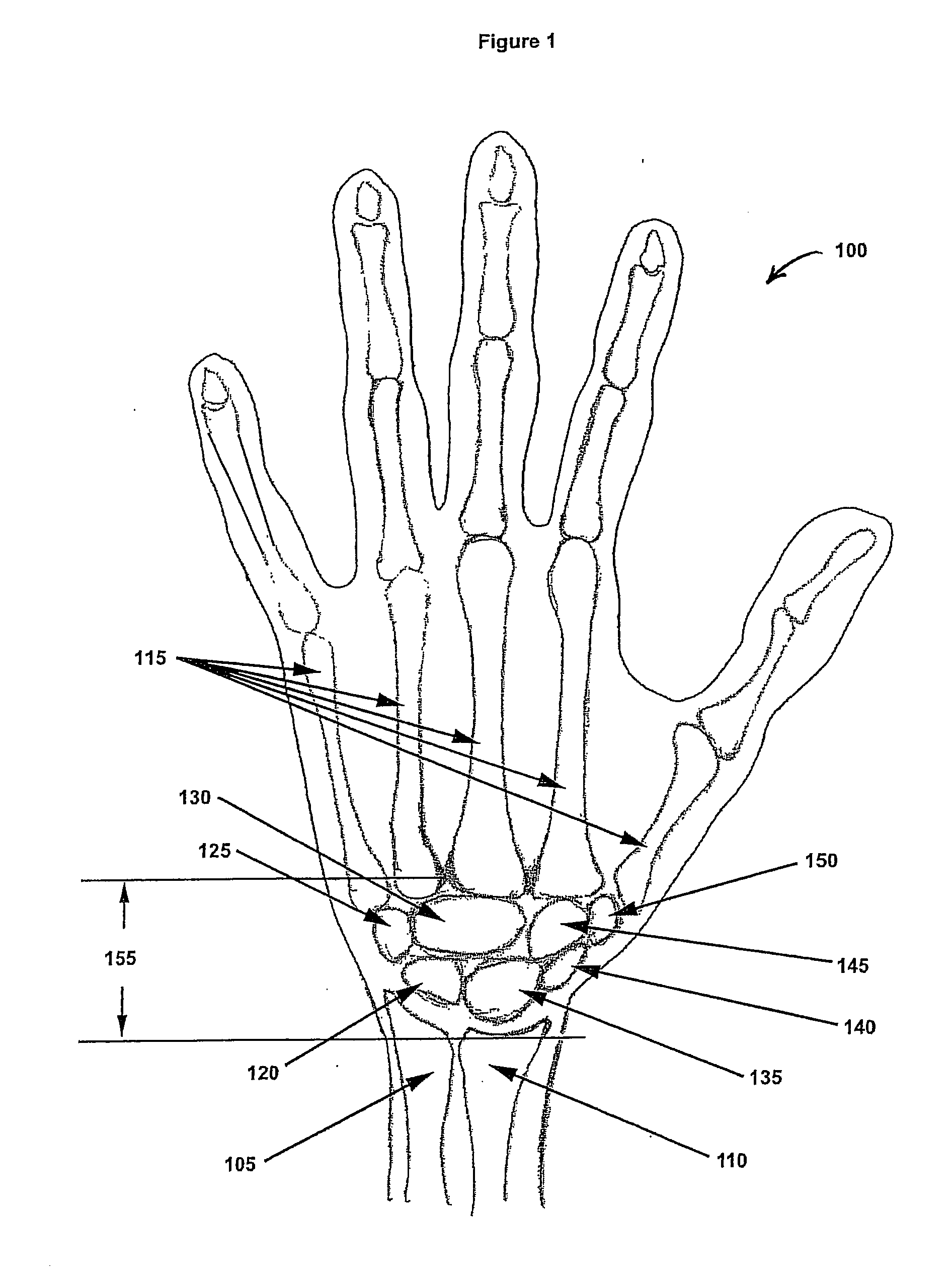
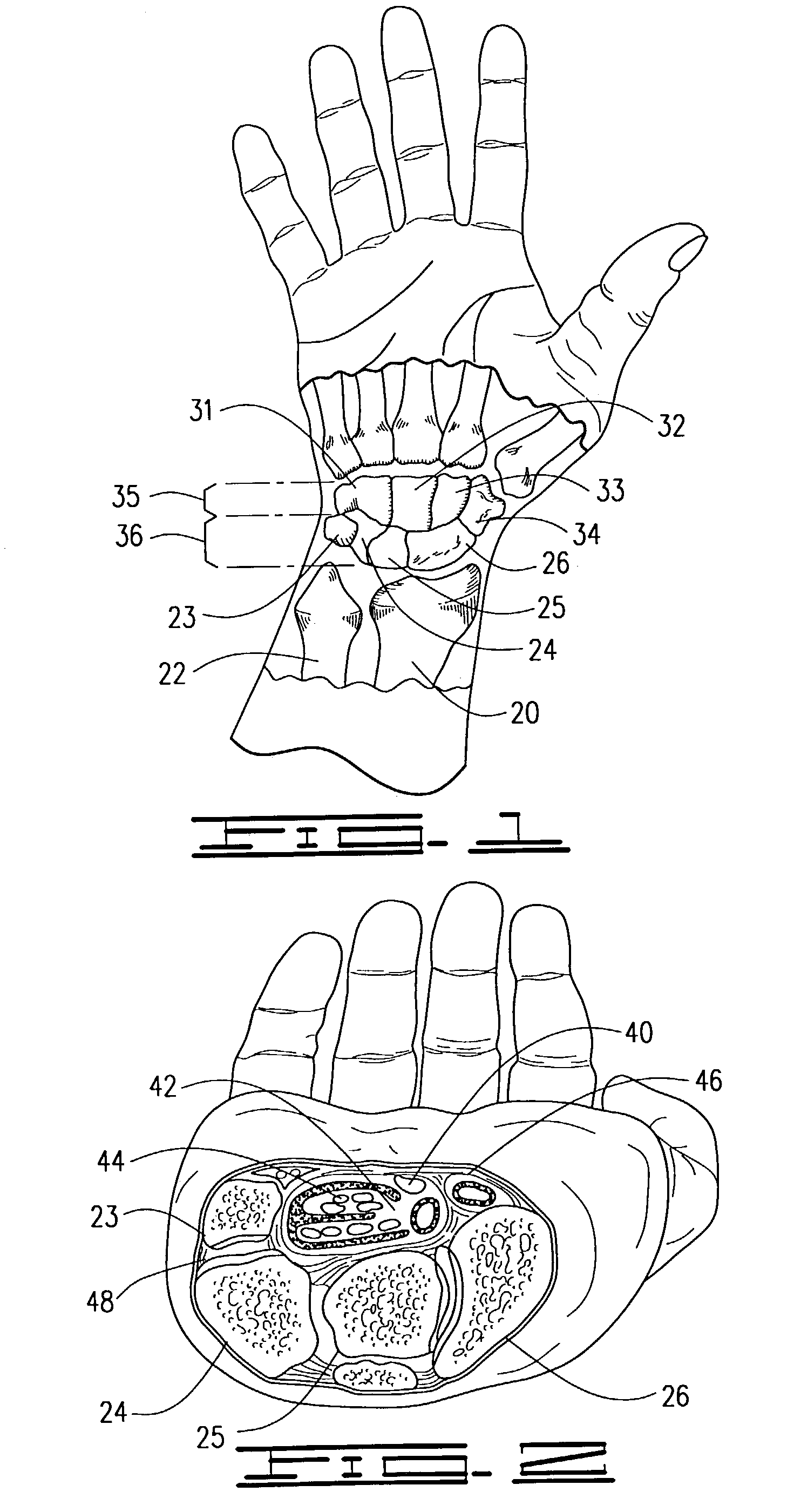
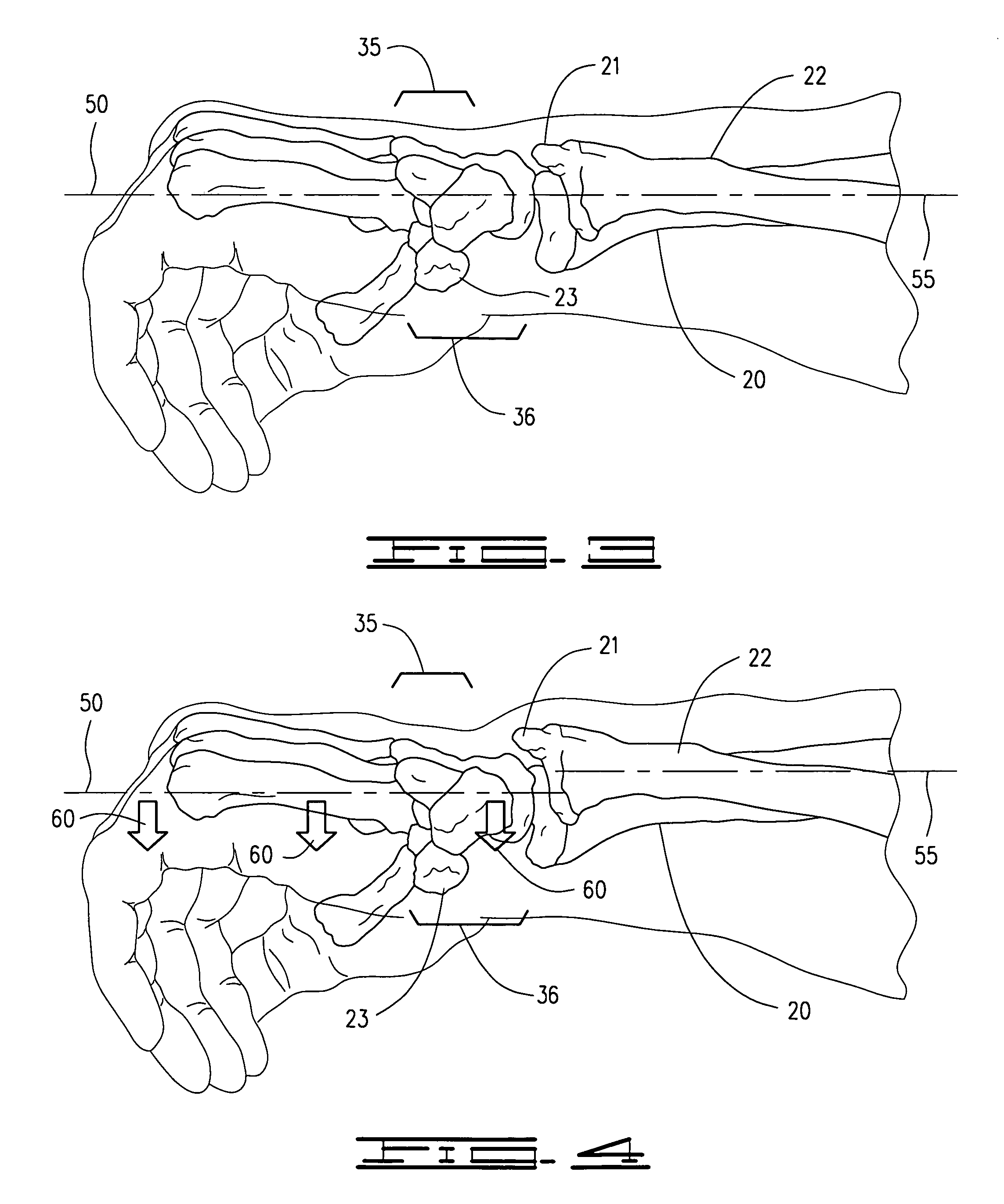
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the wrist is to facilitate effective positioning of the hand and powerful use of the extensors and flexors of the forearm, and the mobility of individual carpal bones increase the freedom of movements at the wrist.
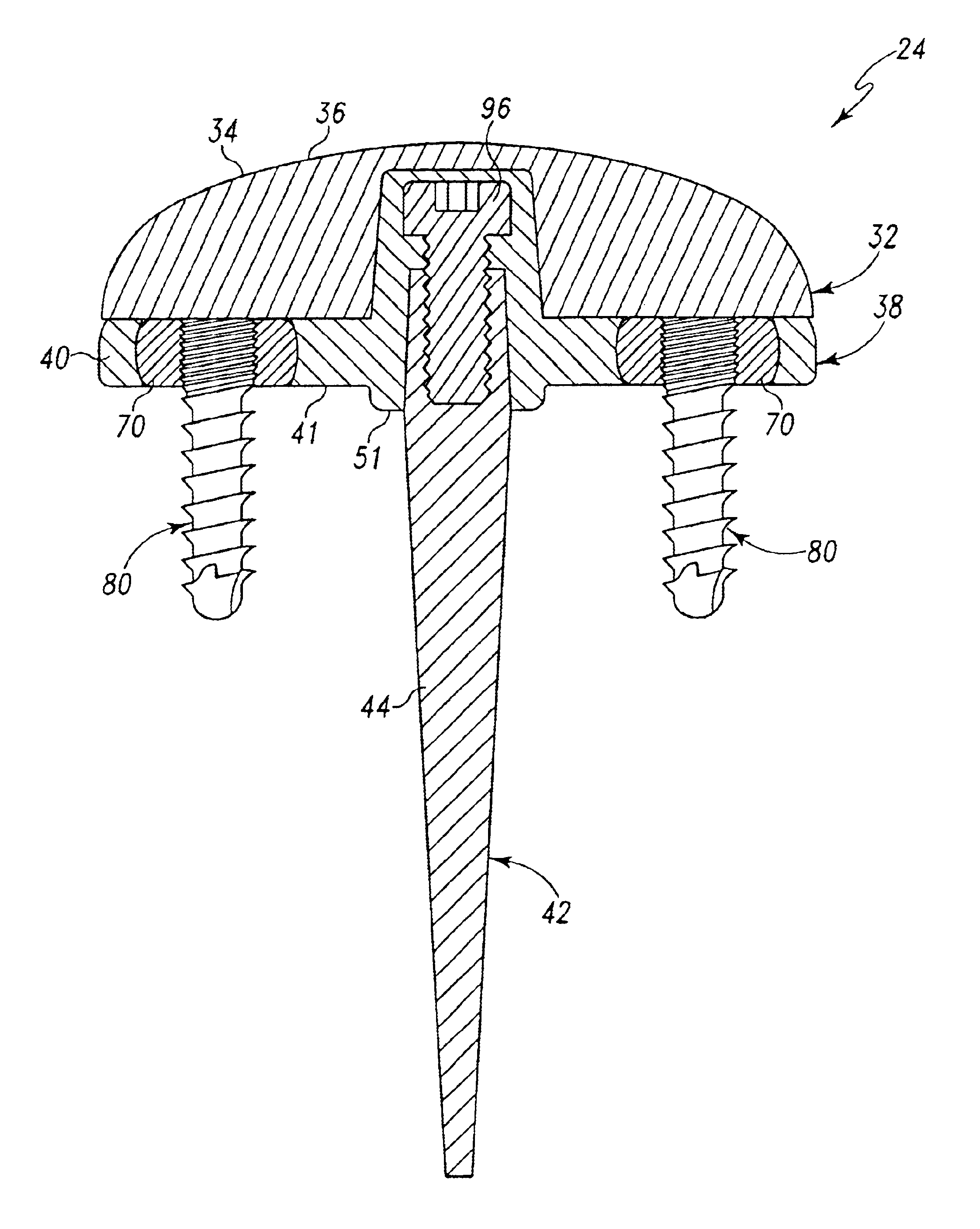
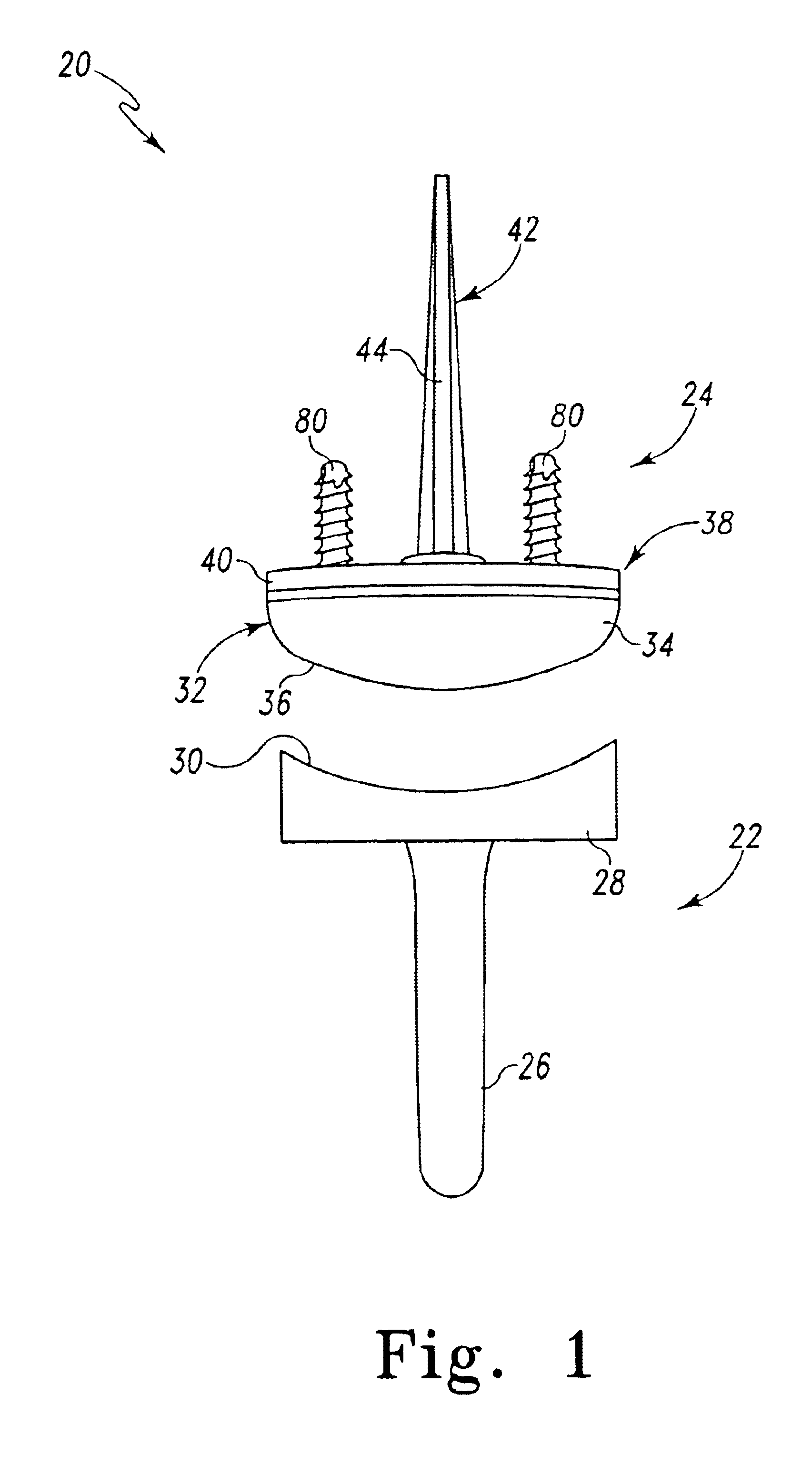
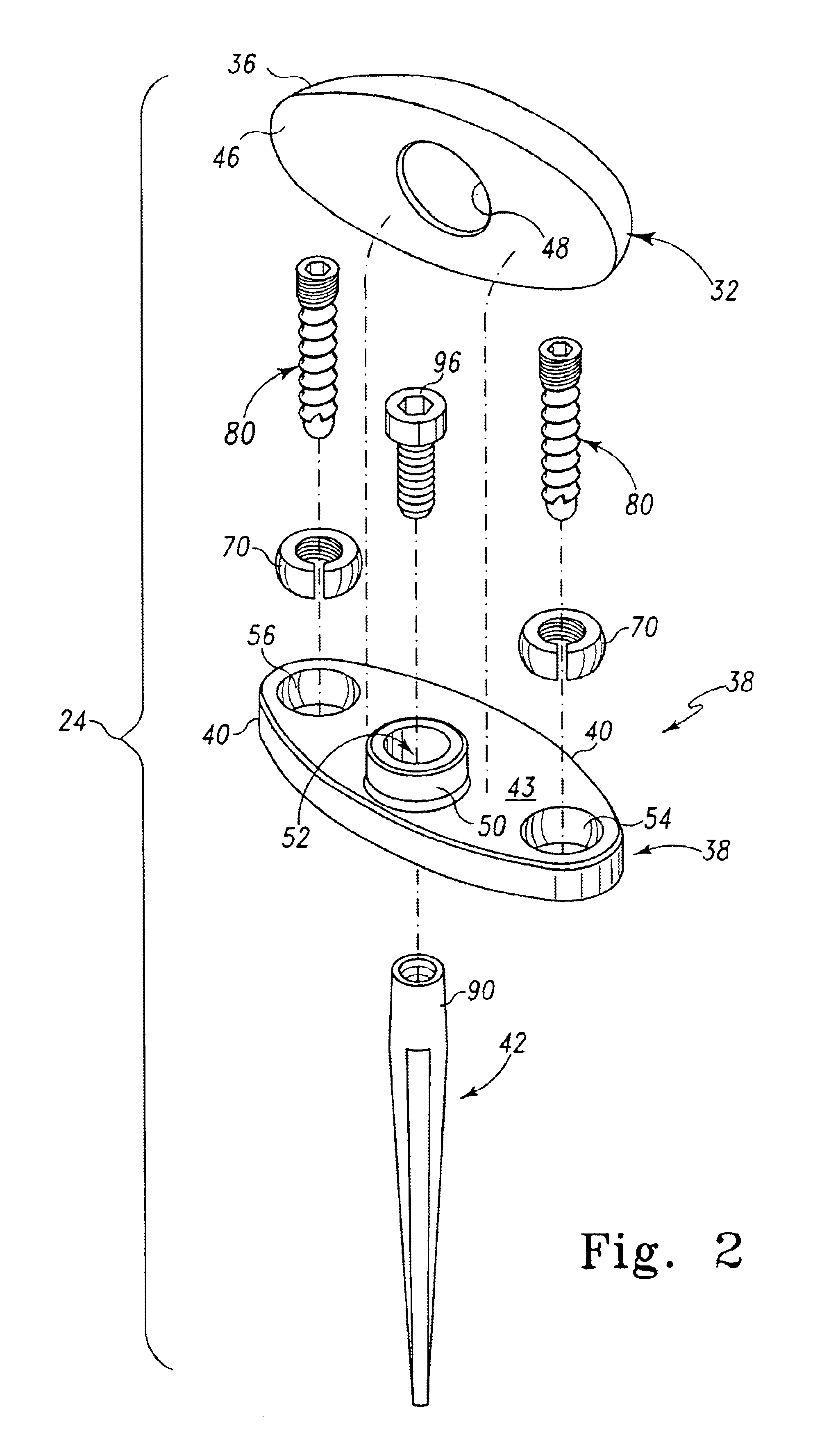
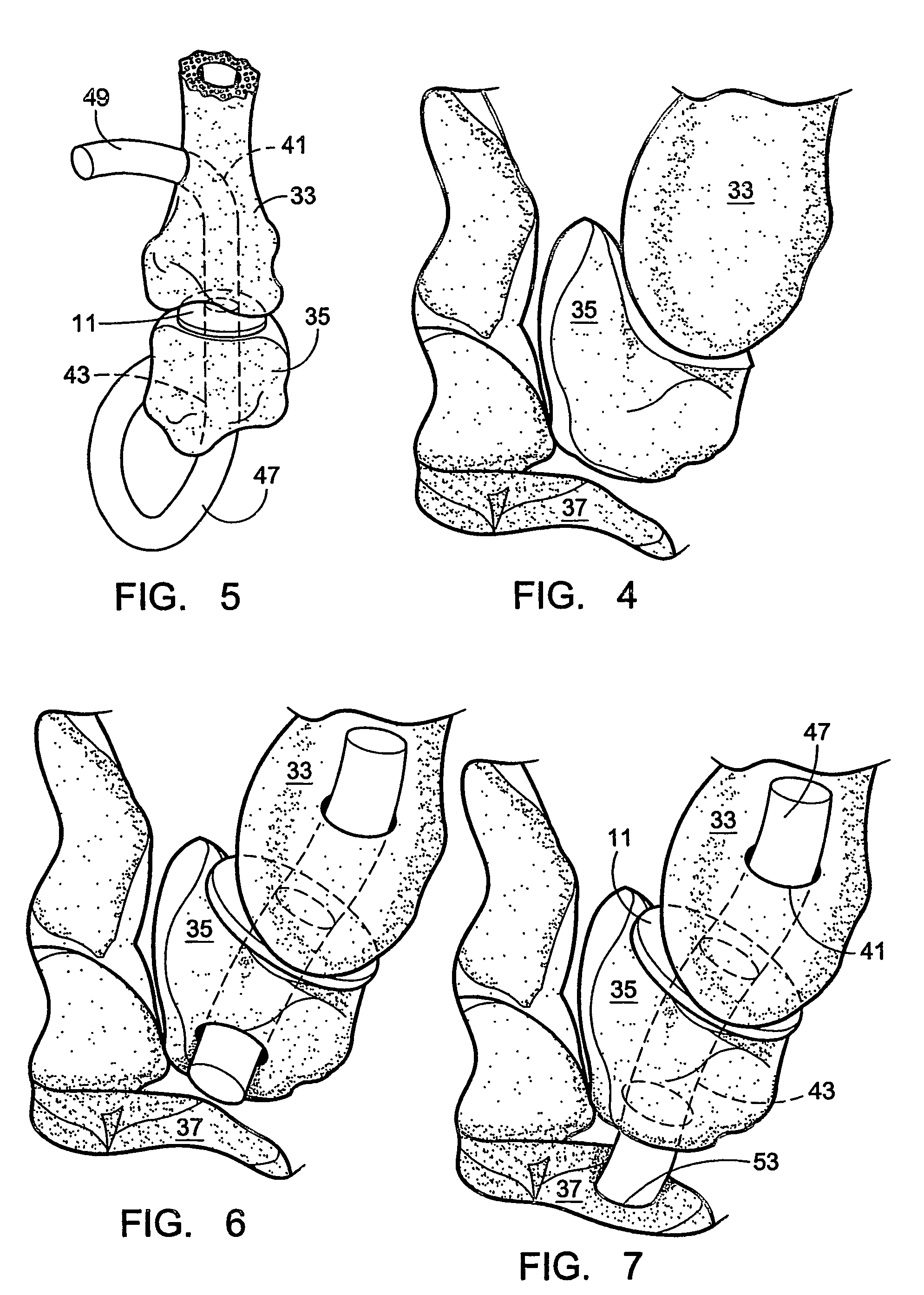
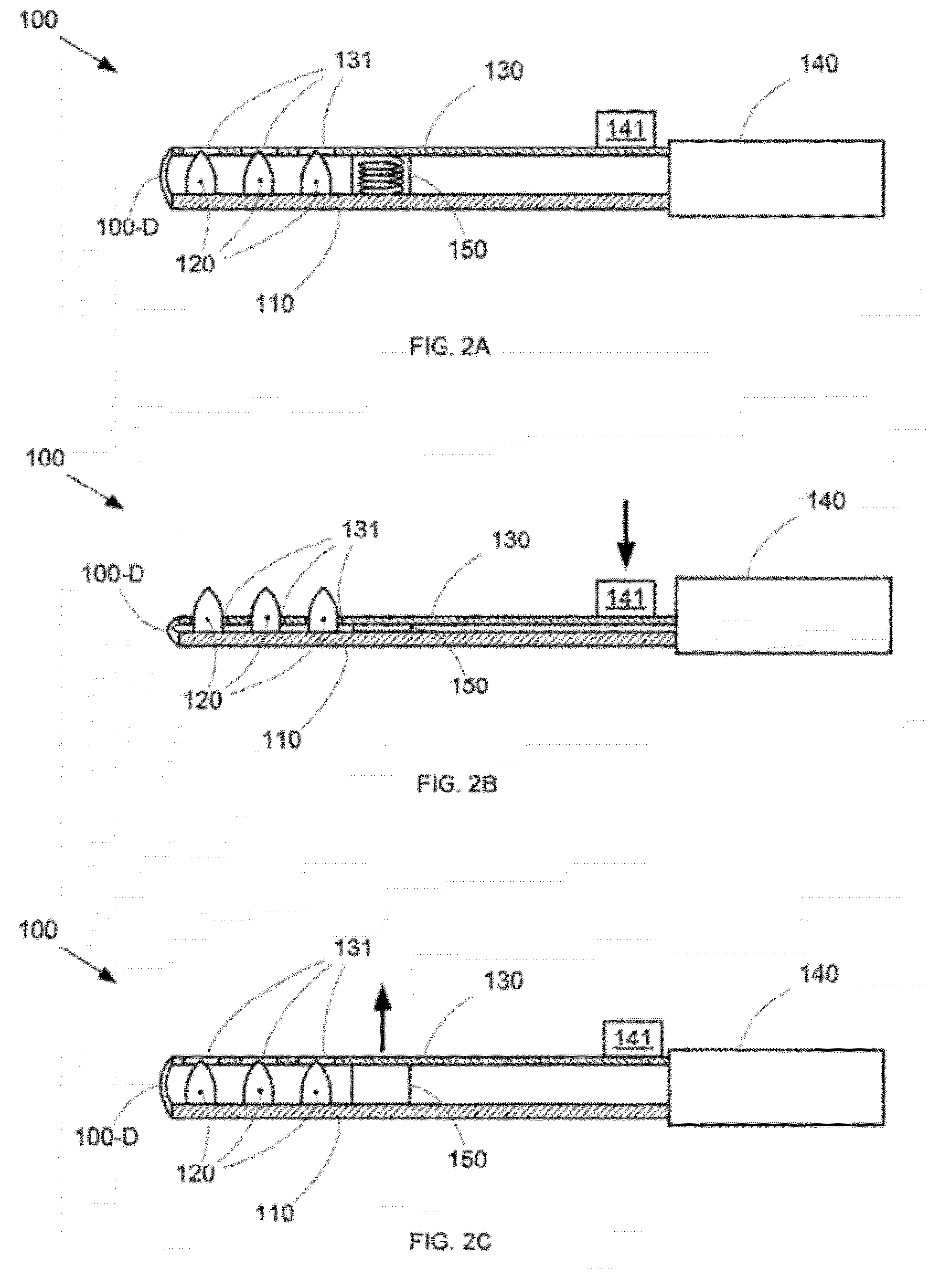
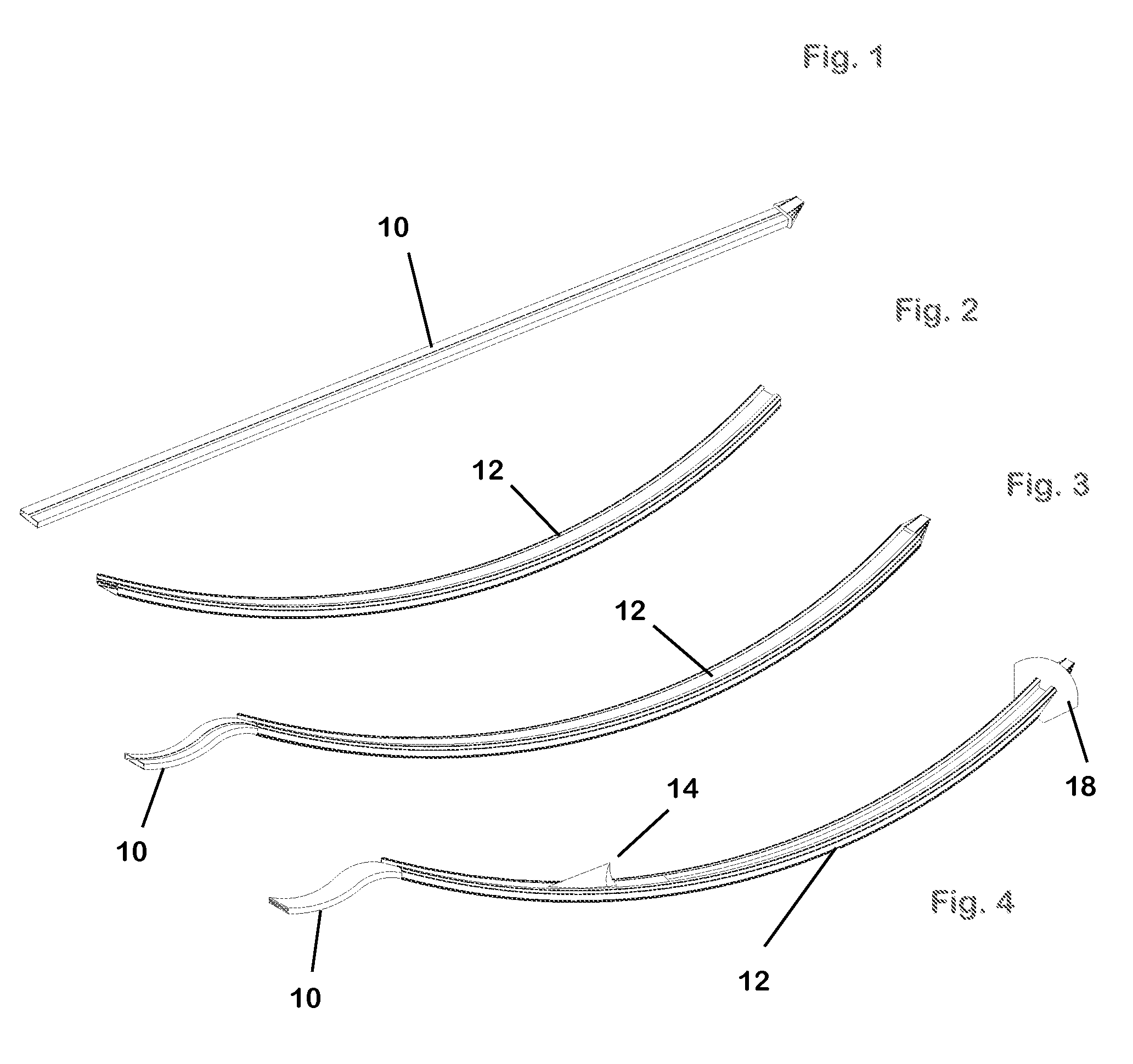
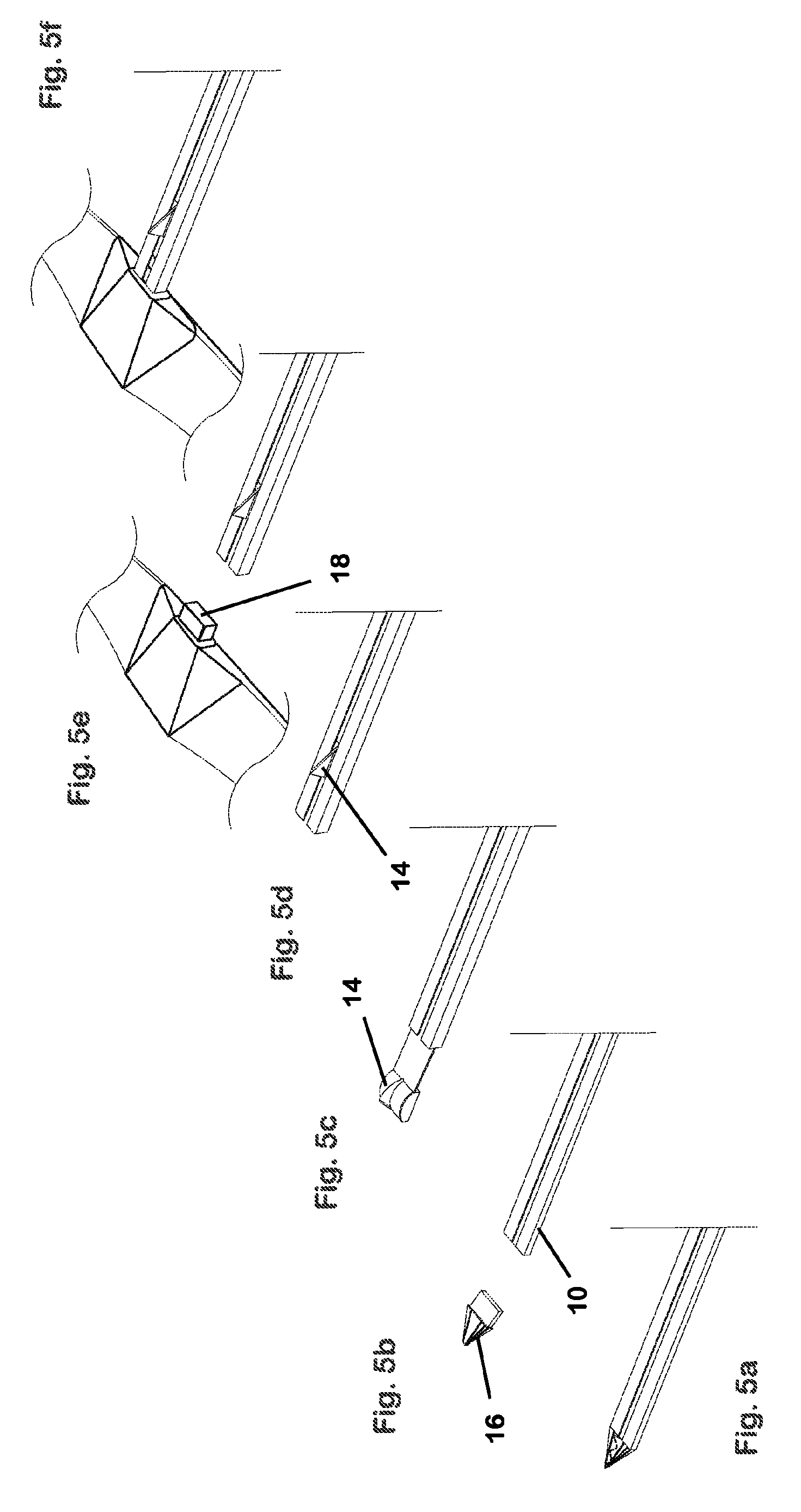
Distal component for wrist prosthesis
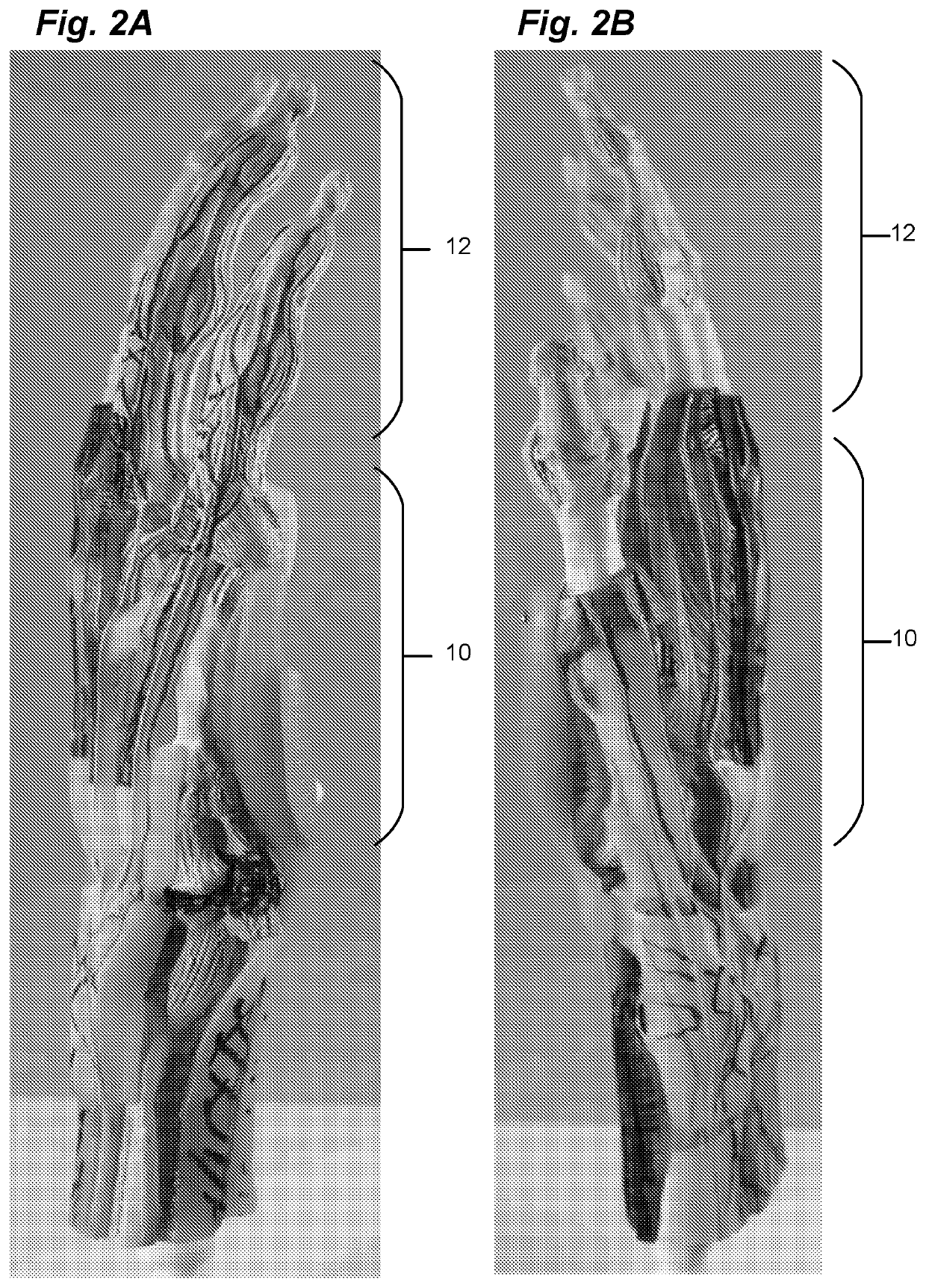
InactiveUS6890358B2Precise processingFirmer engagementWrist jointsAnkle jointsModularityCarpal bones
A distal component for a wrist prosthesis that utilizes fixation within the carpus complex, incorporates features that improve the probability of intercarpal fusion and allows modularity of articulating components. In one form, the subject invention includes an ovoid fixation plate having three holes and a boss. The three holes allow attachment of stems and / or screws distally for fixation in the carpus. The boss projects proximally from the plate, and serves as an attachment point for the articulating head. Modularity of the fixation and articulating components allow a surgeon many options for optimizing fixation distally, and articulation proximally. The proximal head of the distal component is designed to articulate with existing radial components. Since the proximal head of the distal component is modular, however, the head can be redesigned to accommodate later design changes in proximal components.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
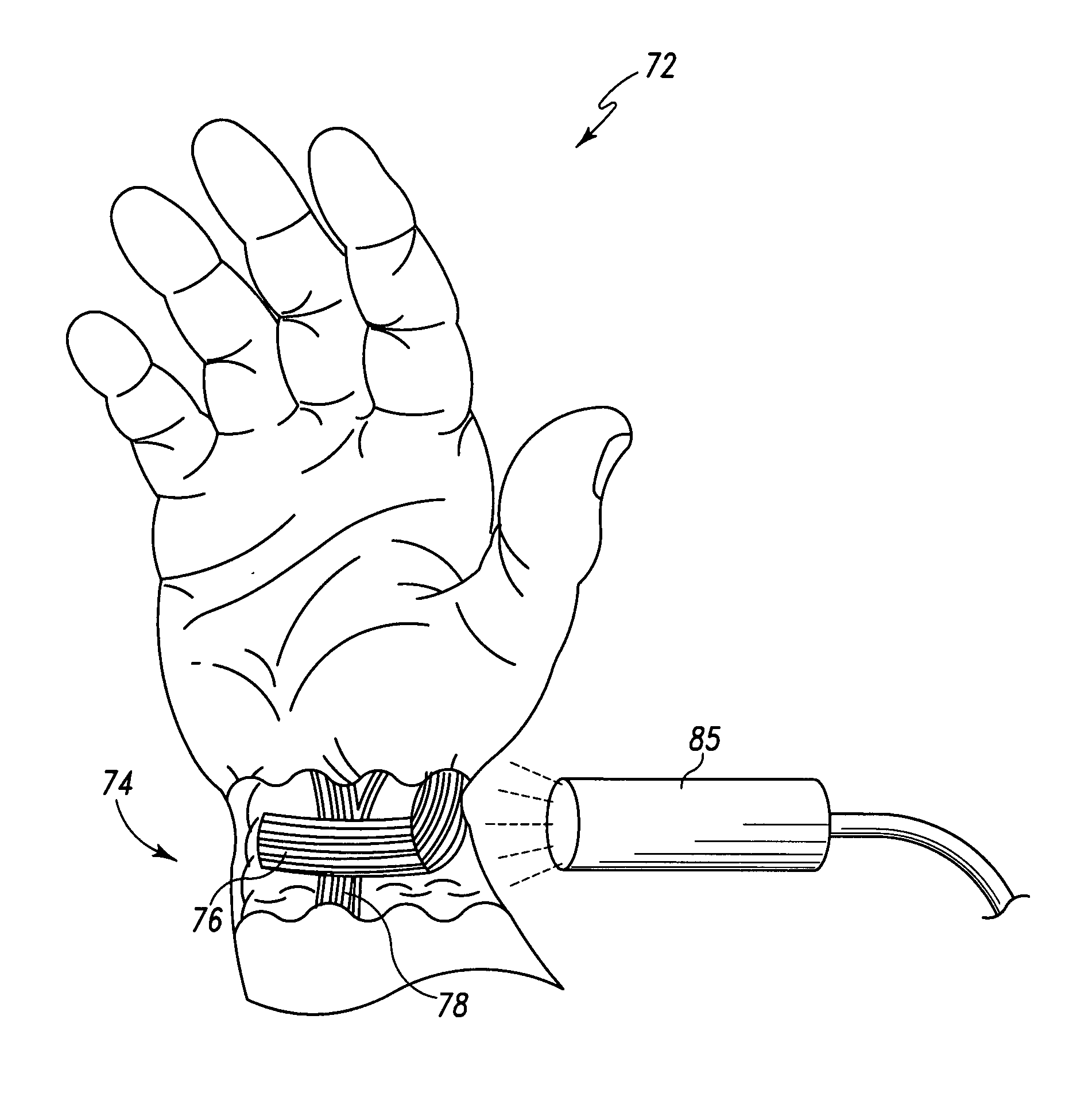
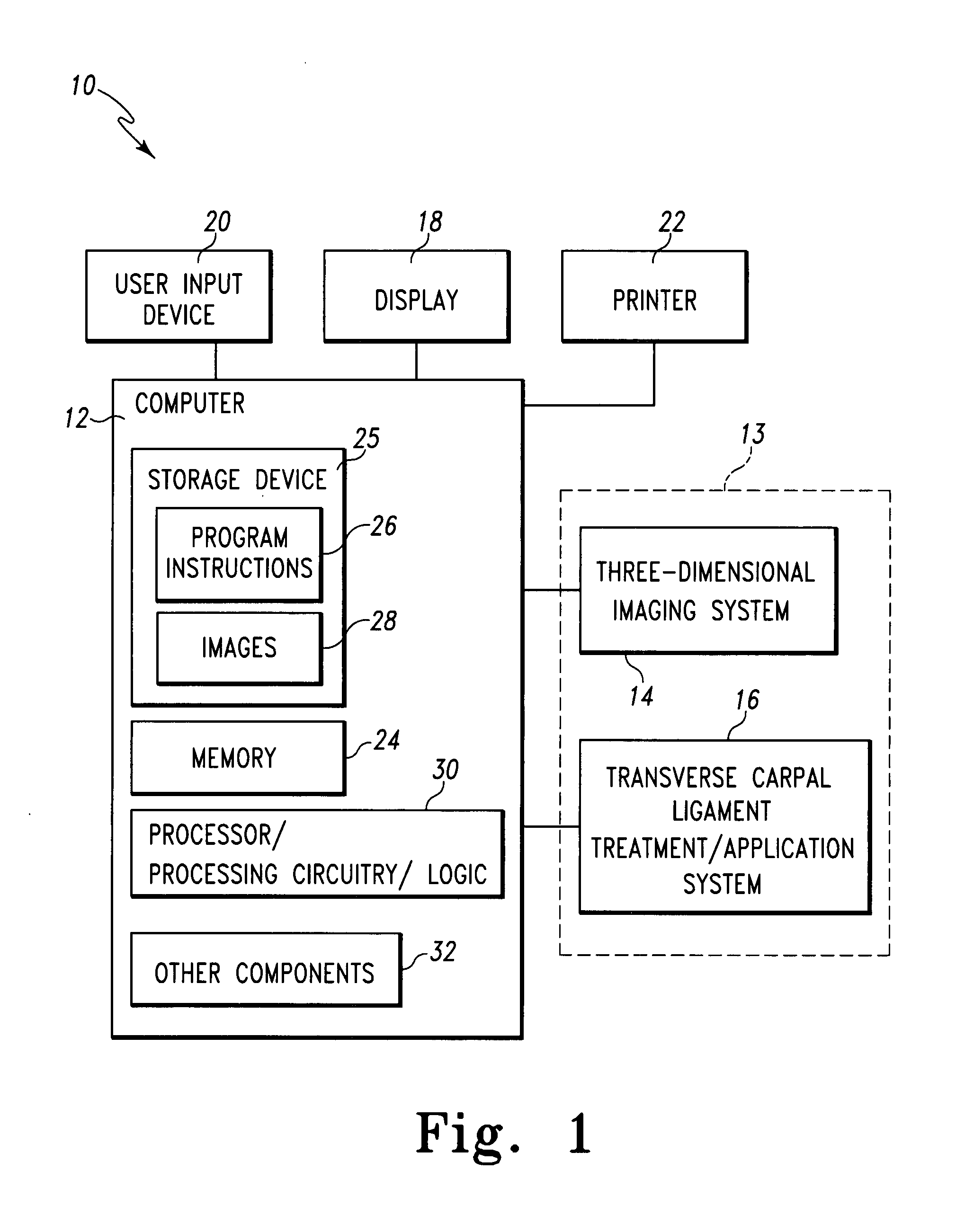
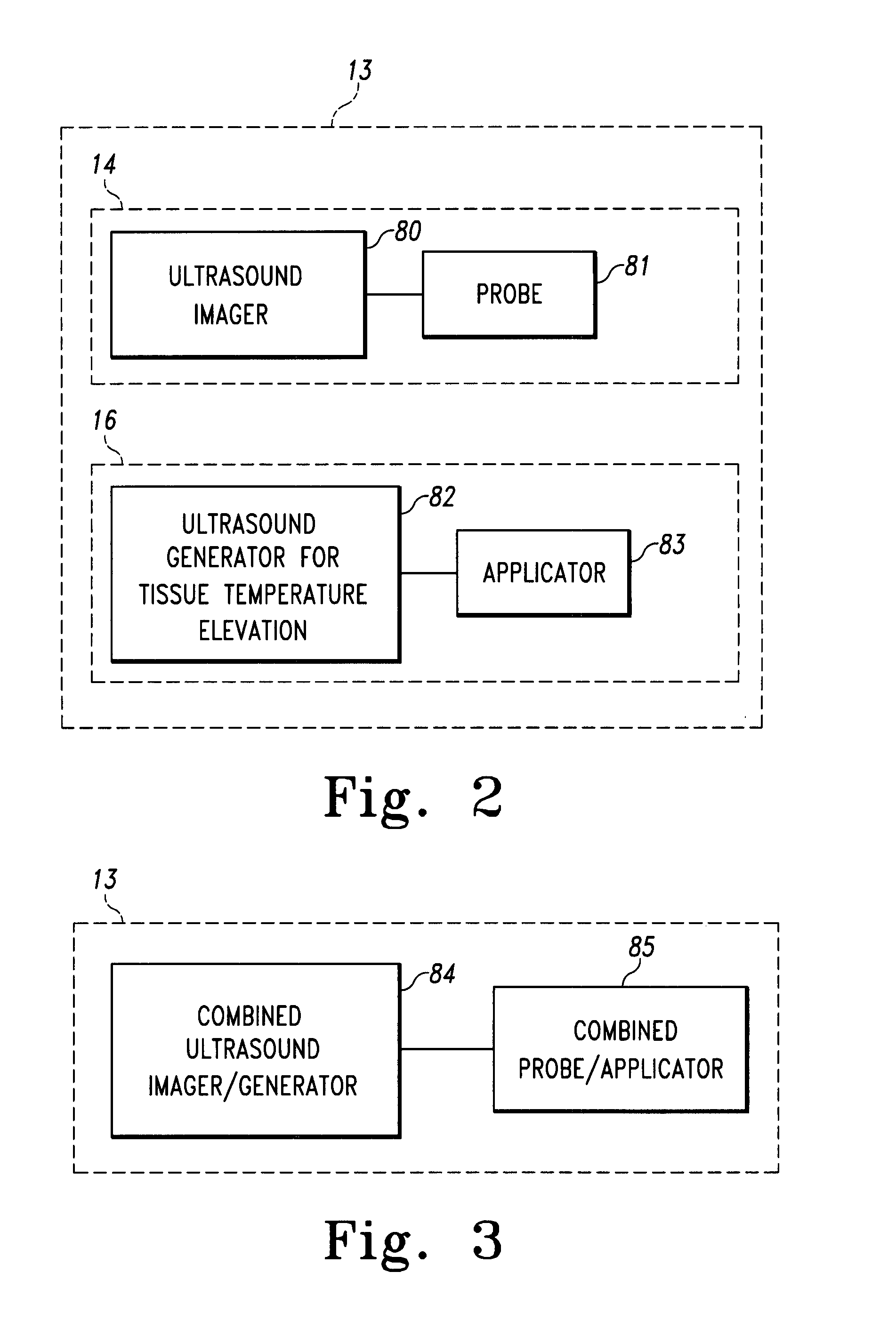
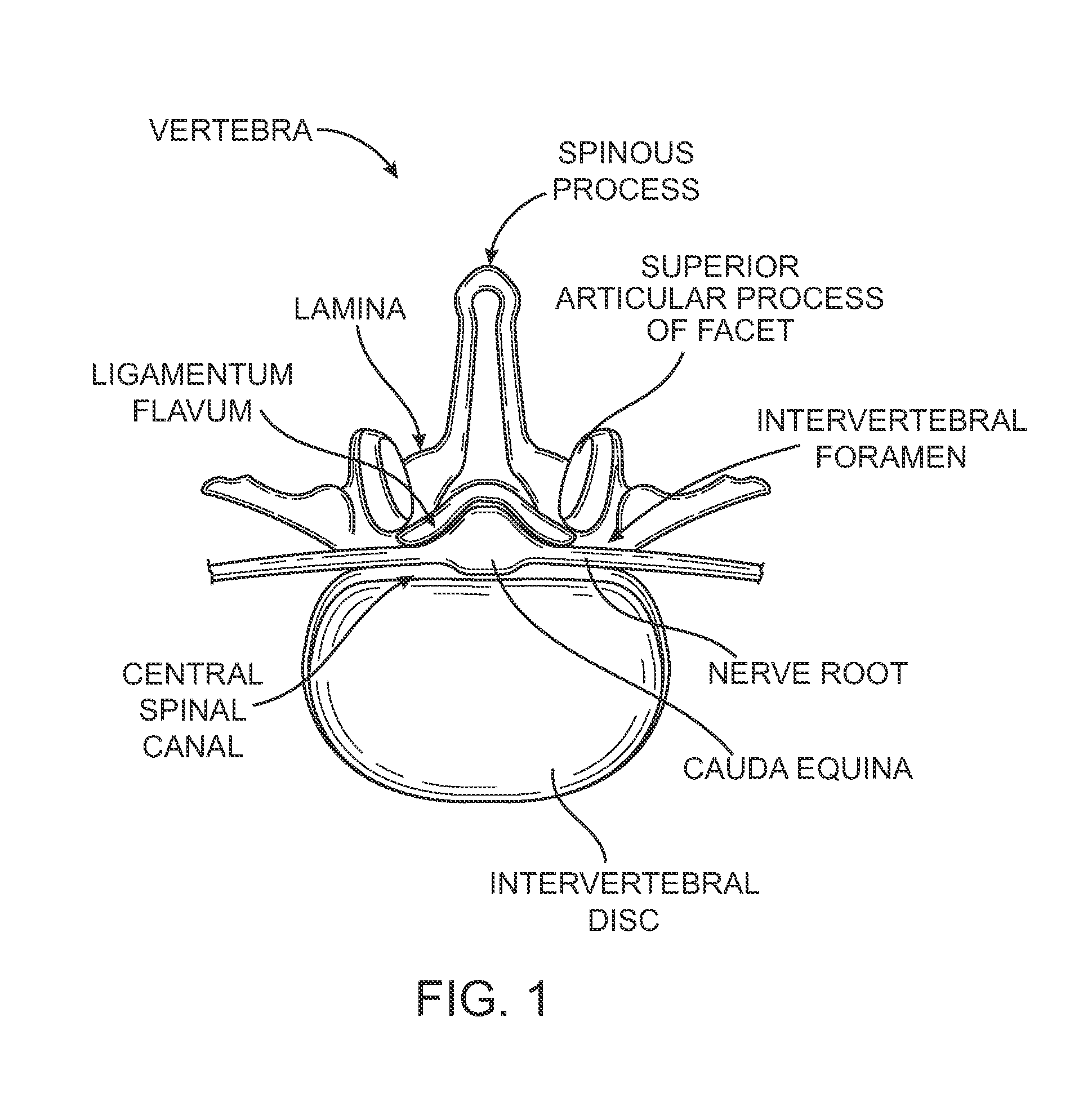
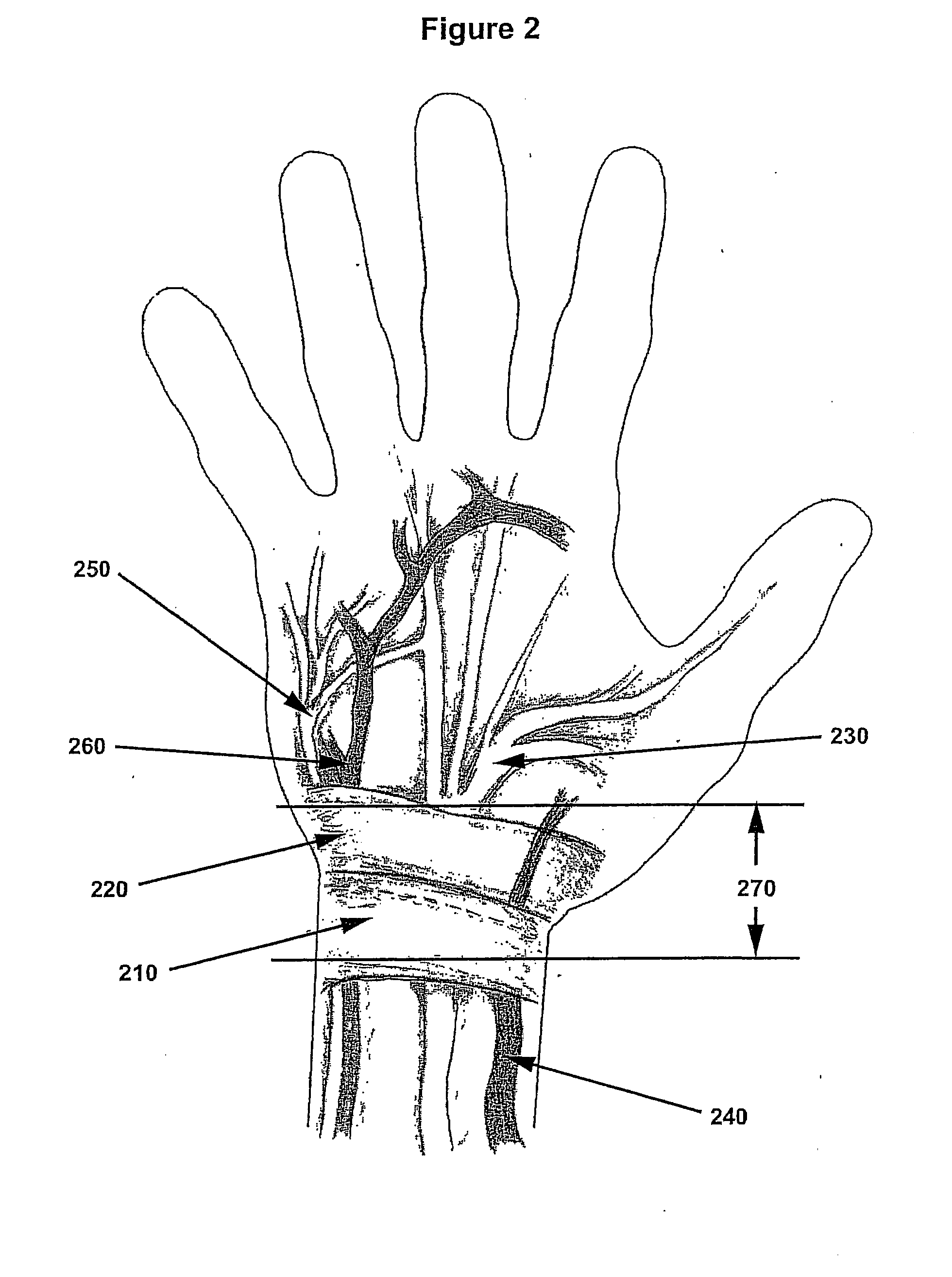
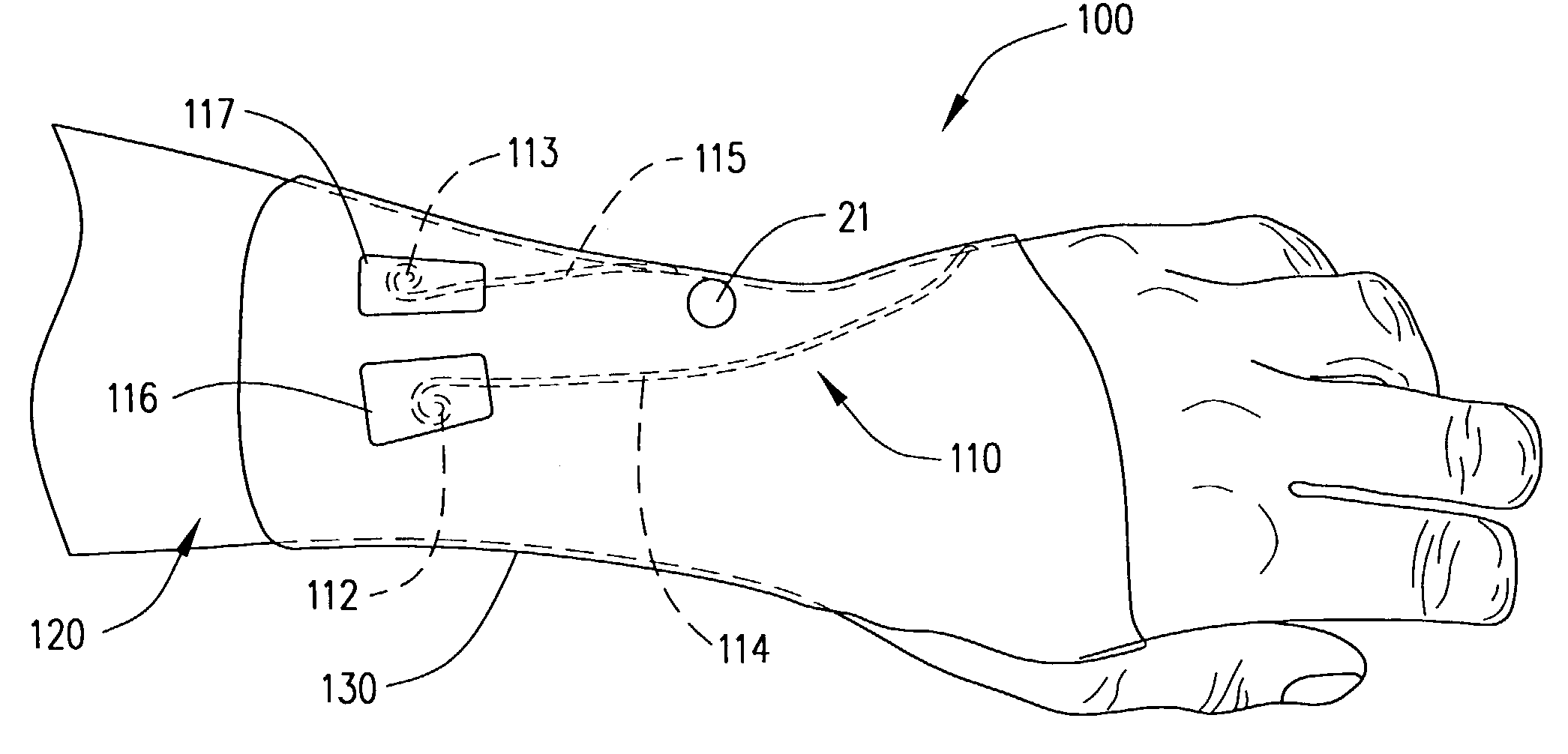
Imaging and therapeutic procedure for carpal tunnel syndrome
InactiveUS7303555B2Accurate identificationPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCarpal tunnel releaseCavitation
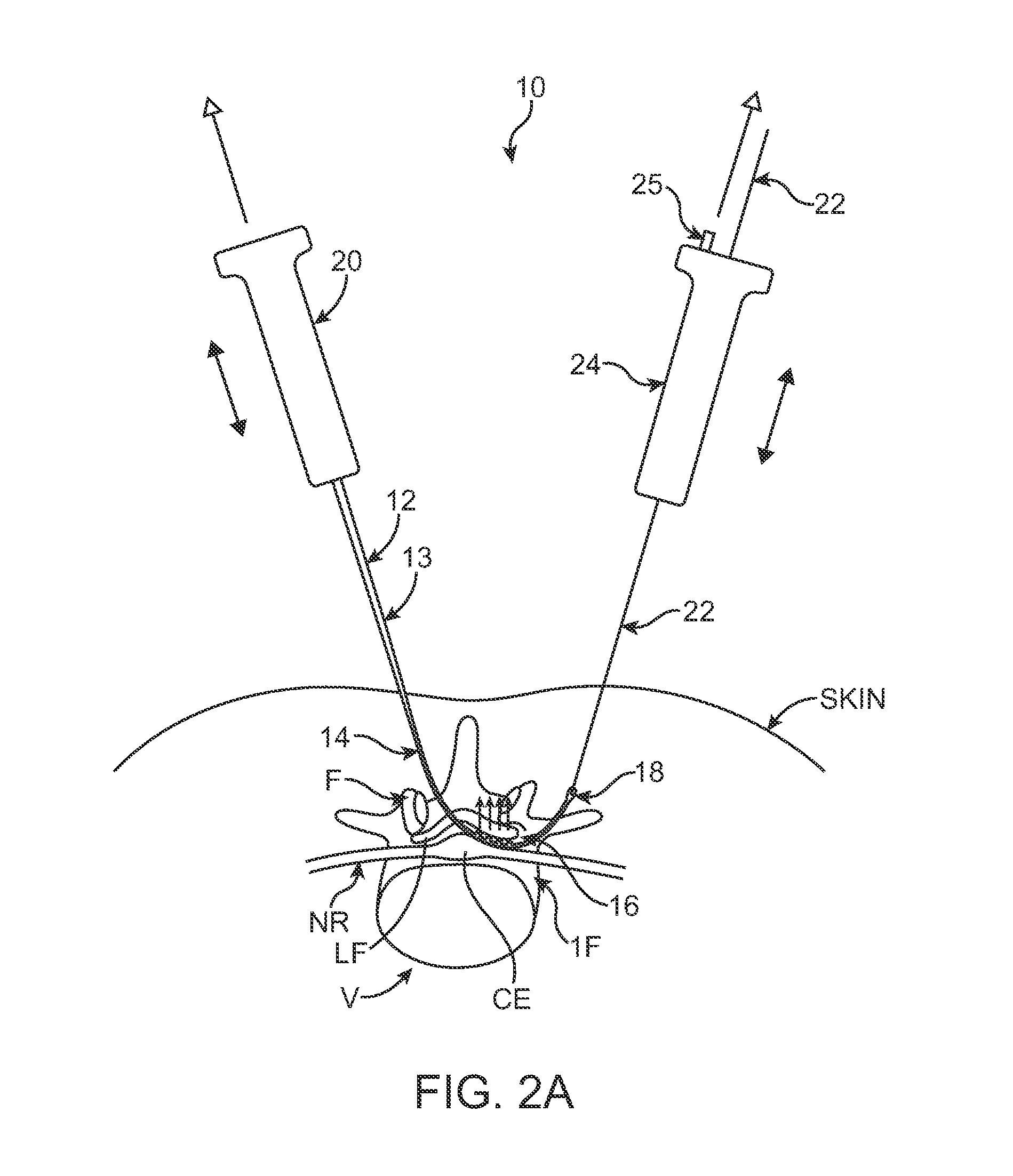
A system, method and / or apparatus is provided for visualization or imaging of the transverse carpal ligament and surrounding structures / features of a hand of a patient, and treatment of the transverse carpal ligament, particularly, but not necessarily, for performing non-invasive carpal tunnel release. The subject invention utilizes ultrasound waves preferably, but not necessarily, in the high frequency range and cavitations to image the transverse carpal ligament (TCL), record its location in three-dimensional space, and perform precision treatment on the transverse carpal ligament. Treatment may range from stretching or lengthening the TCL to complete tissue ablation or dissection of a portion or portions of the TCL (as is performed in a standard carpal tunnel release procedure) in order to release pressure within the carpal tunnel. Particularly, high temperature conditions are generated at target tissue of the TCL resulting in elongation or necrosis / dissection. The subject system, apparatus and / or method provides the surgeon to relieve a patient of carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms in a bloodless, efficient, and accurate manner.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
System and method for trapezium bone replacement
ActiveUS20090254190A1Efficiently distribute forceEffective forceSuture equipmentsFinger jointsTrapezium BoneProsthesis
A carpometacarpal joint replacement system for replacing the trapezium bone in the hand is provided. The system includes a trapezial implant for the carpometacarpal joint resulting in replacement of the carpal trapezium bone with a prosthesis having the same anatomical configuration as the trapezium bone. The implant device comprises a plurality of concave surfaces, with the plurality of concave surfaces articulating with the carpal and metacarpal bones.
Owner:EXTREMITY MEDICAL
Methods, systems and devices for carpal tunnel release
Described herein are methods, systems, and devices for performing a minimally invasive carpal tunnel release procedure to cut a target transverse carpal ligament. In some embodiments, the method may include the steps of advancing a probe percutaneously though a patient's skin from a first location, advancing a tissue modification device from the first location and between the target ligament and non-target tissue so that a proximal handle on the tissue modification device extends from the patient at the first location, attaching a distal handle in communication with the distal end of the tissue modification device. In some embodiments, a system may include a probe configured to be advanced percutaneously though a patient's skin from a first location, a tissue modification device comprising a proximal handle and a flexible distal region having uni-directional blades, and a distal handle configured to connect to the distal end of the tissue modification device.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC +1
Wrist implant apparatus and method
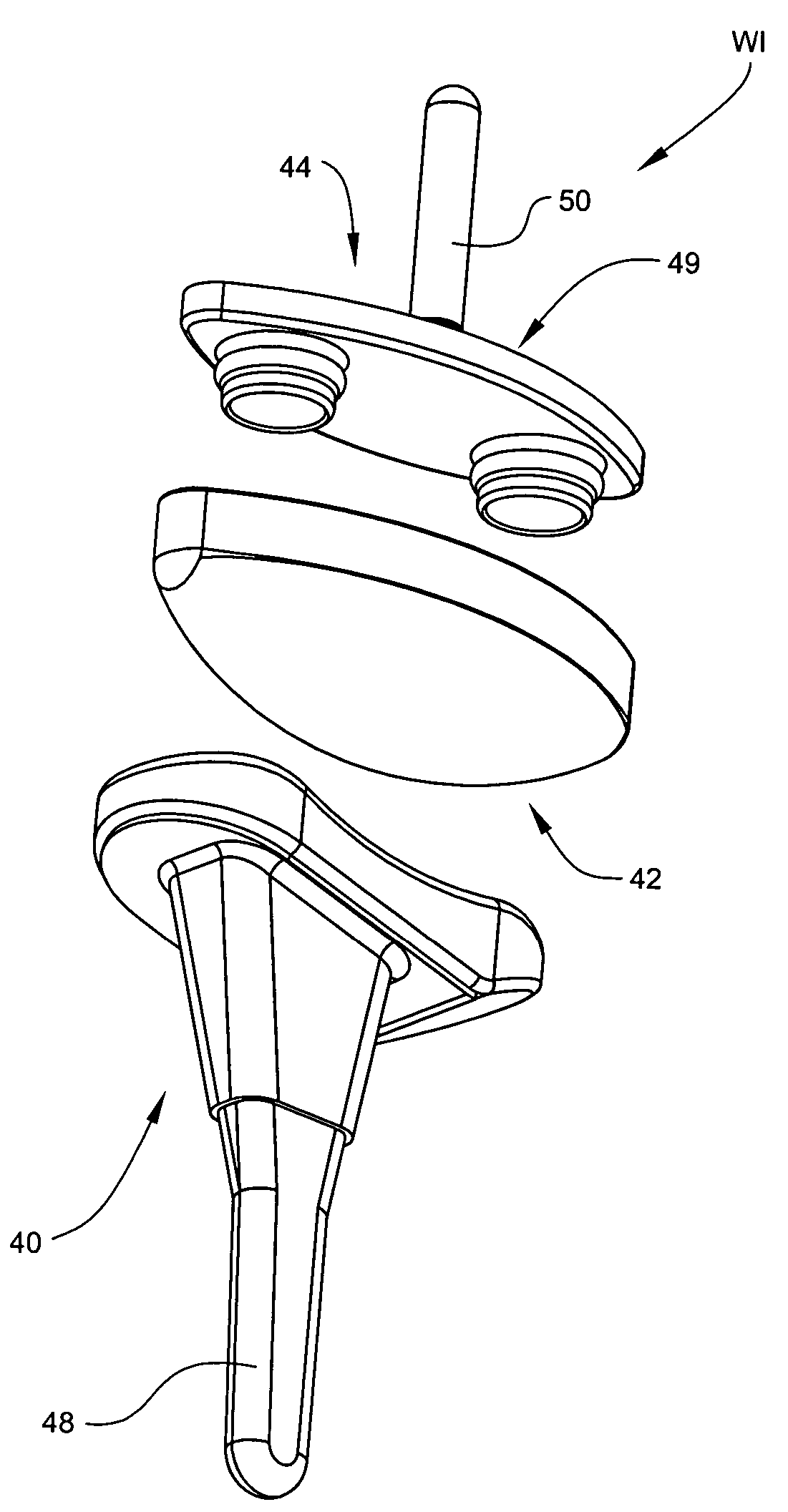
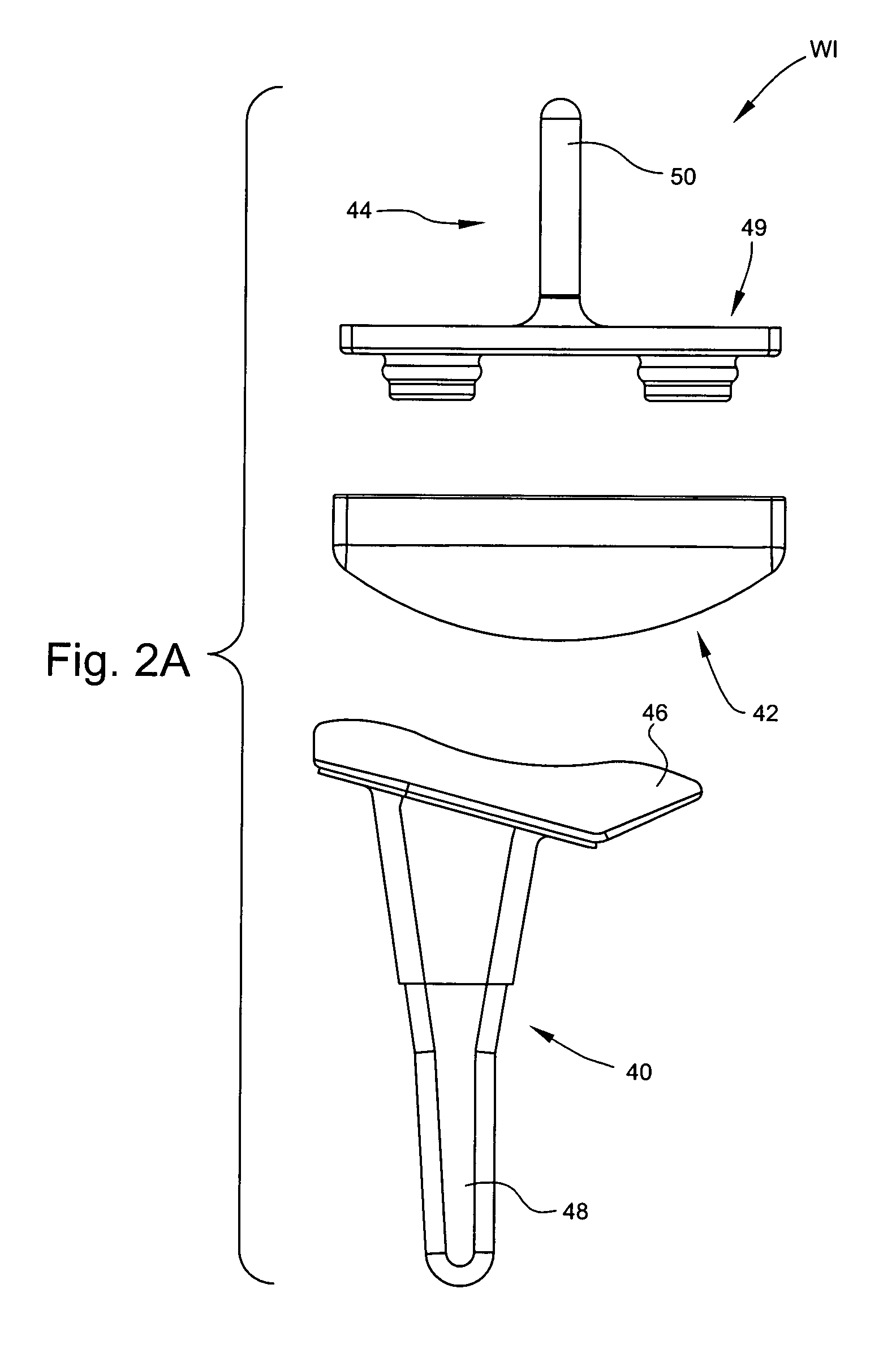
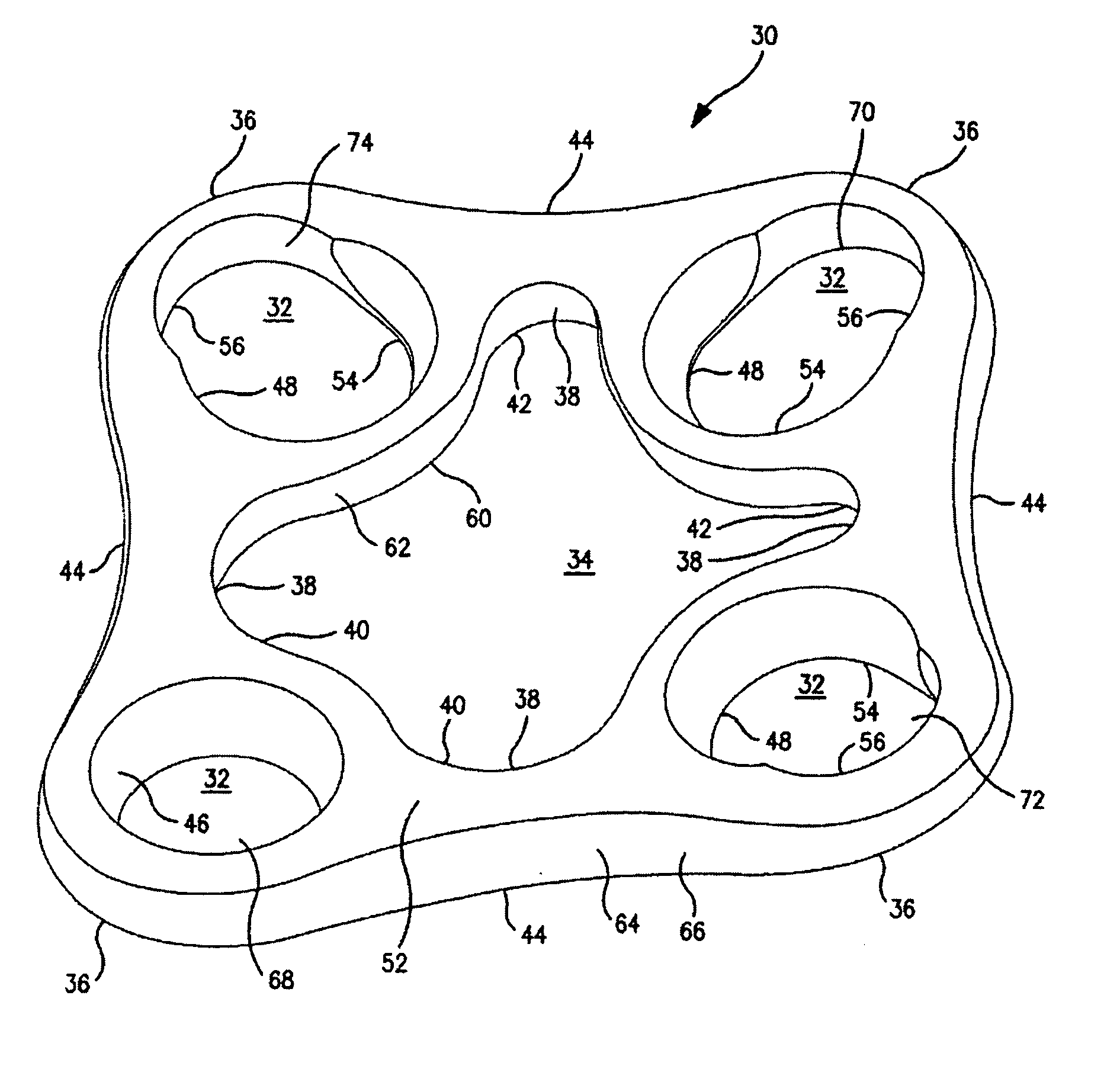
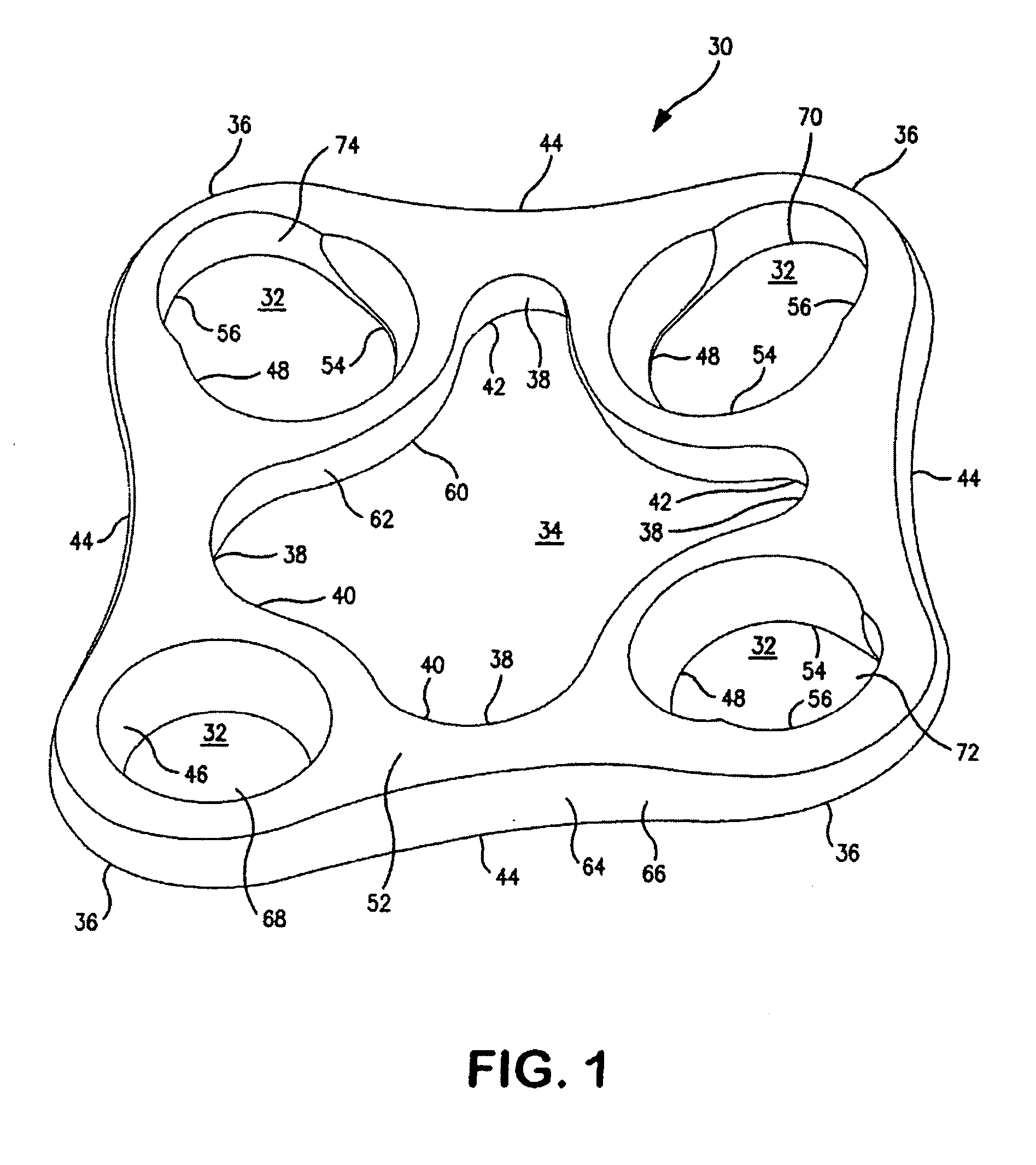
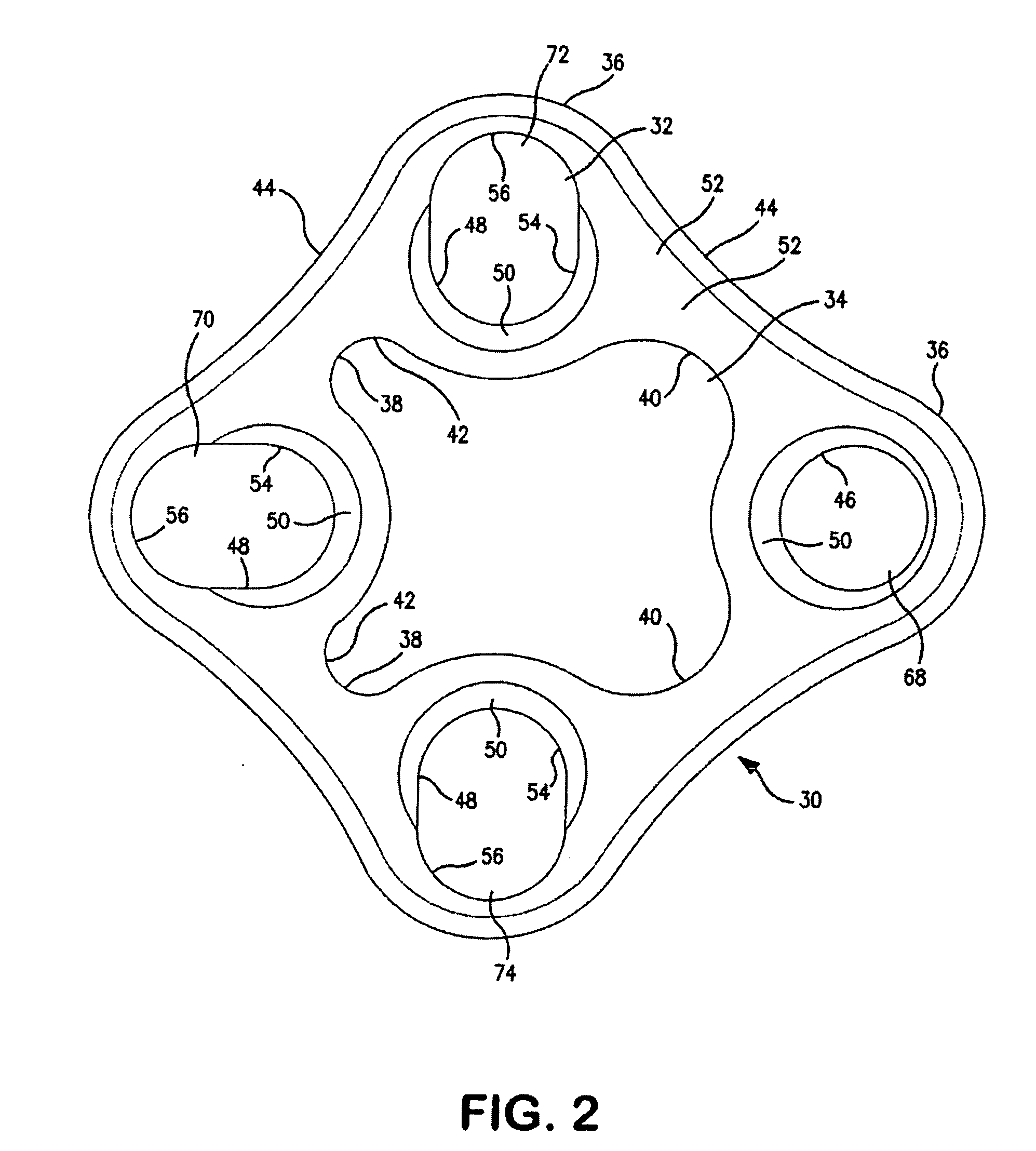
ActiveUS7531003B2Large range of motionAcceptable flexionWrist jointsAnkle jointsProsthesisCarpal bones
Prosthetic wrist implants and methods are provided. The prosthetic wrist implant includes a radial component including a base member having an upper bearing surface and a lower surface having an elongated radial stem for fixation to a radius bone. The elongated radial stem can be in an off-center position in relation to a center of the lower surface. A carpal component is also provided including a substantially planar base member having an upper surface and a lower surface with at least one socket protrusion extending therefrom, and may further included an elongated carpal post member for fixation to one or more carpal bones. An articulating bearing component for placement between the radial and carpal components is provided and includes an upper surface defining at least one socket recess and a lower bearing surface for cooperative engagement with the upper bearing surface of the radial component. The socket protrusion of the carpal component is adapted to linearly engage the socket recess of the bearing component to desirably limit rotational and translational movement of the carpal component relative to the bearing component.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
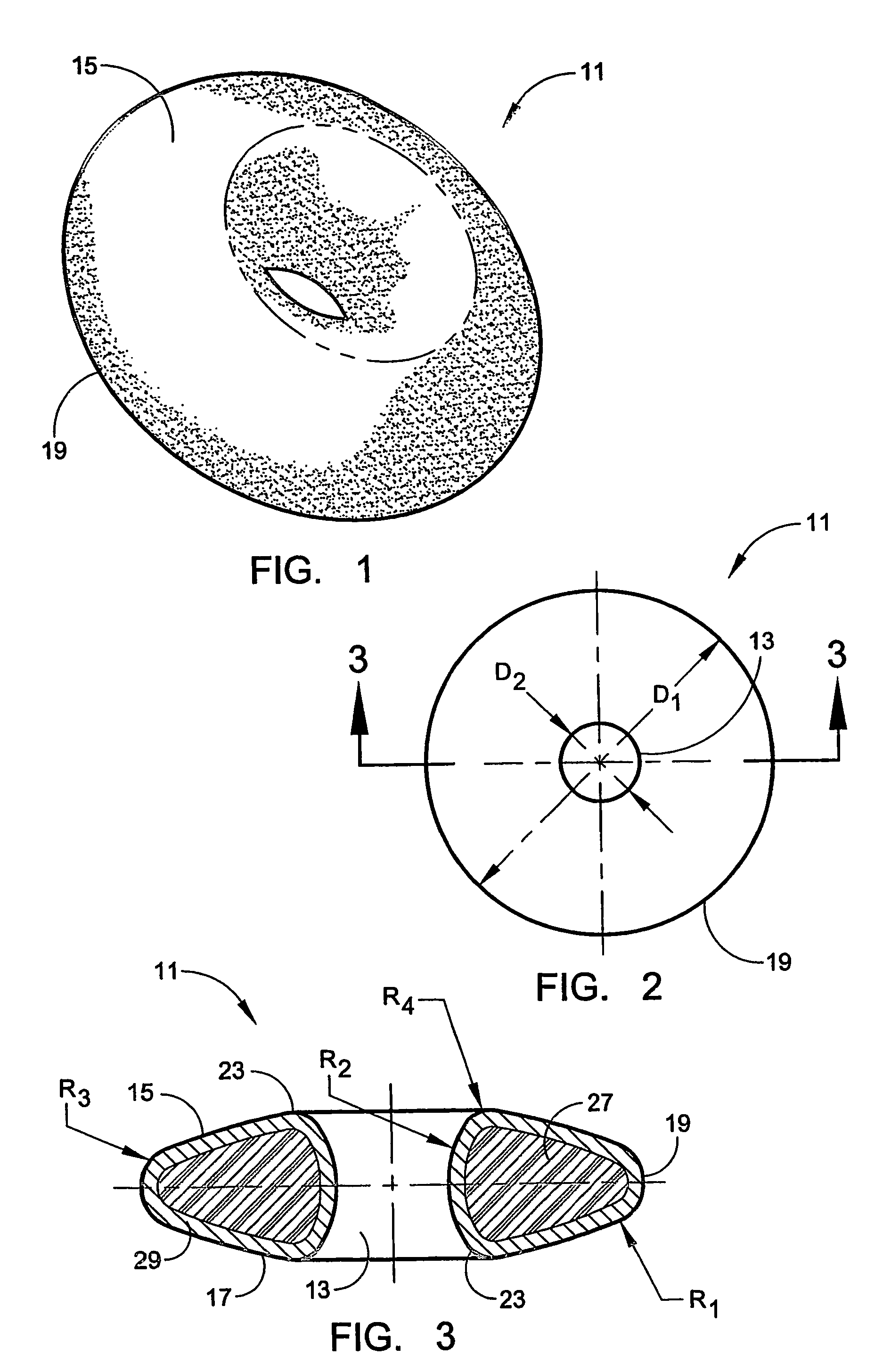
Interpositional biarticular disk implant
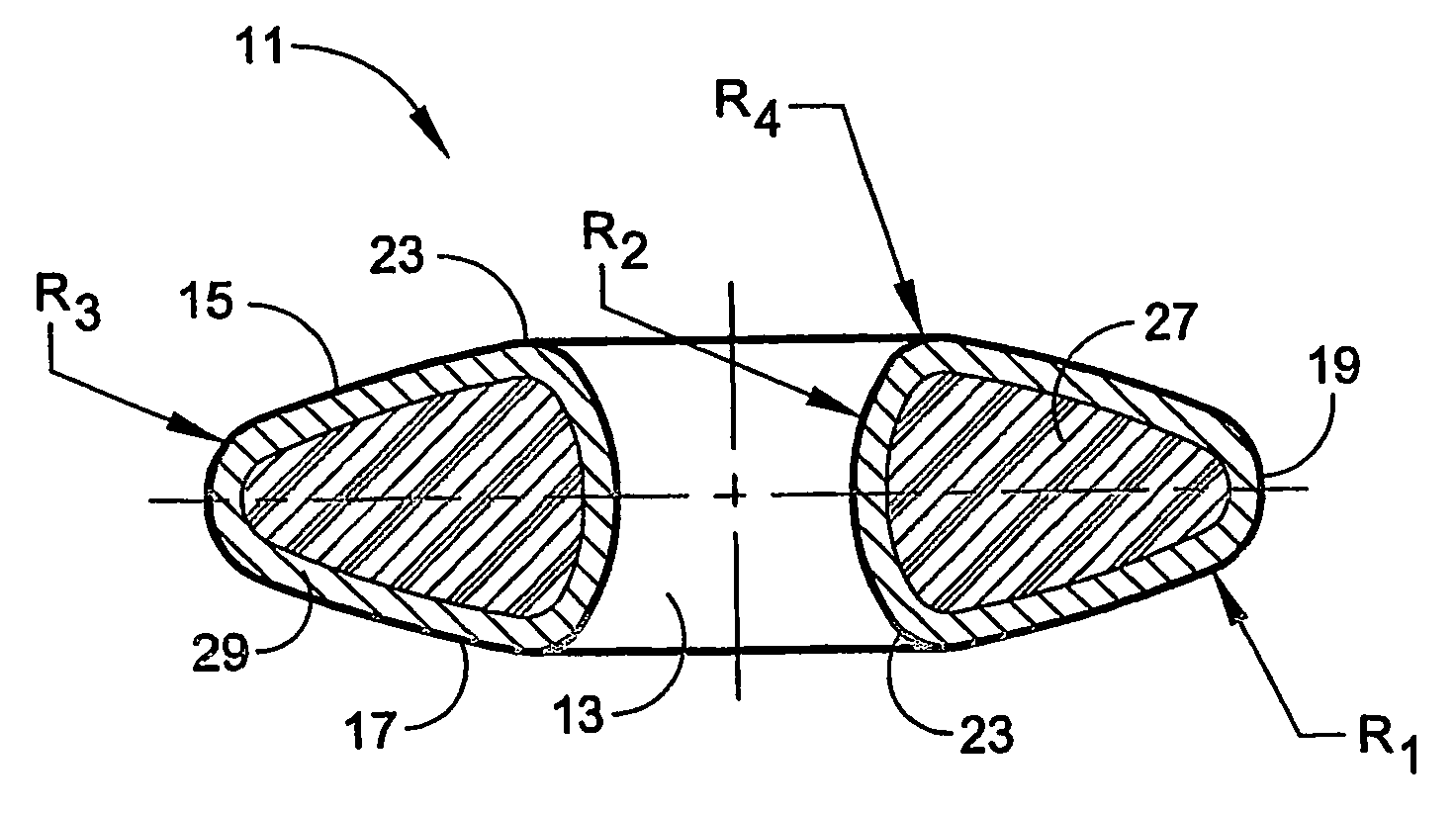
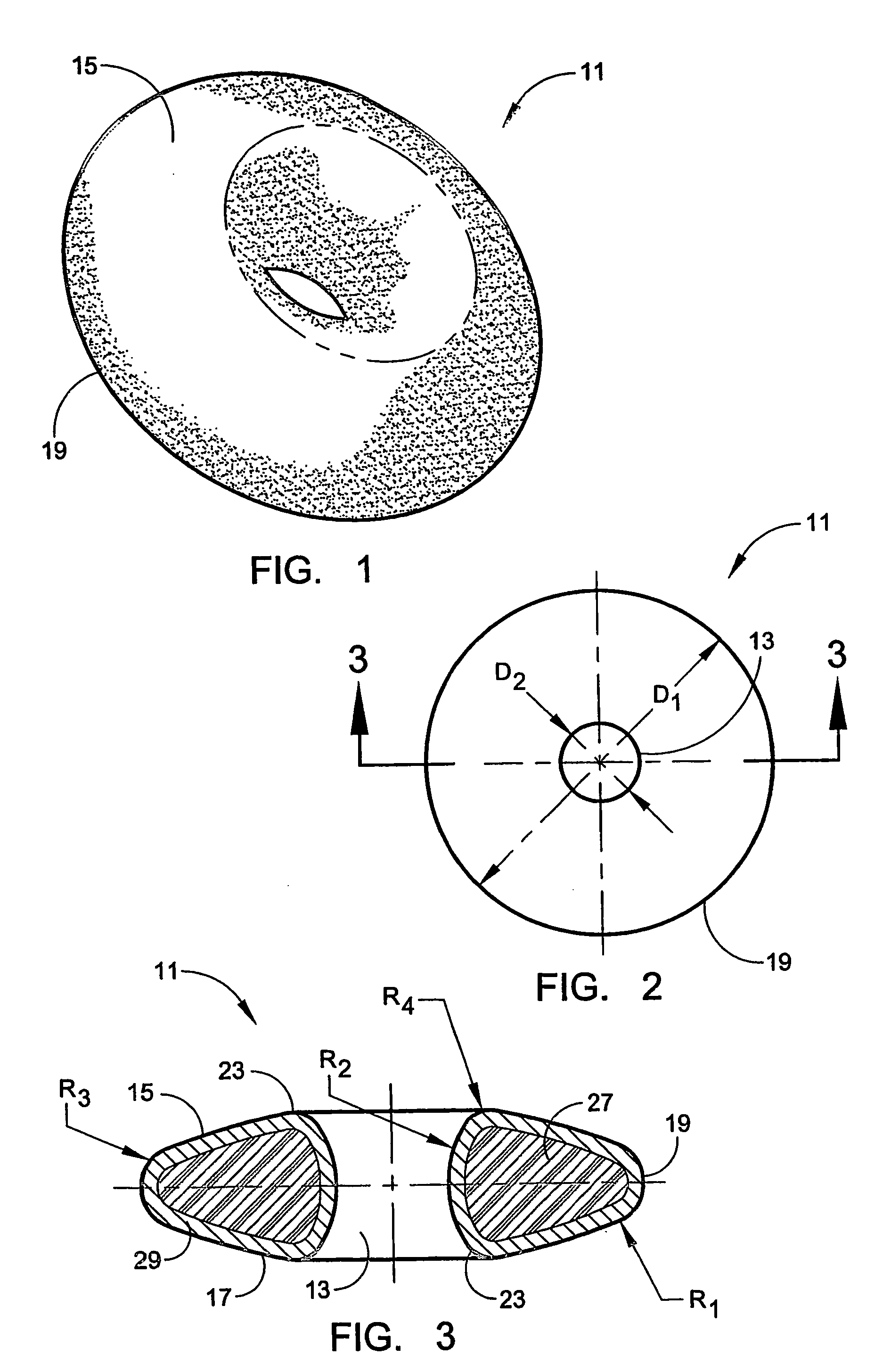
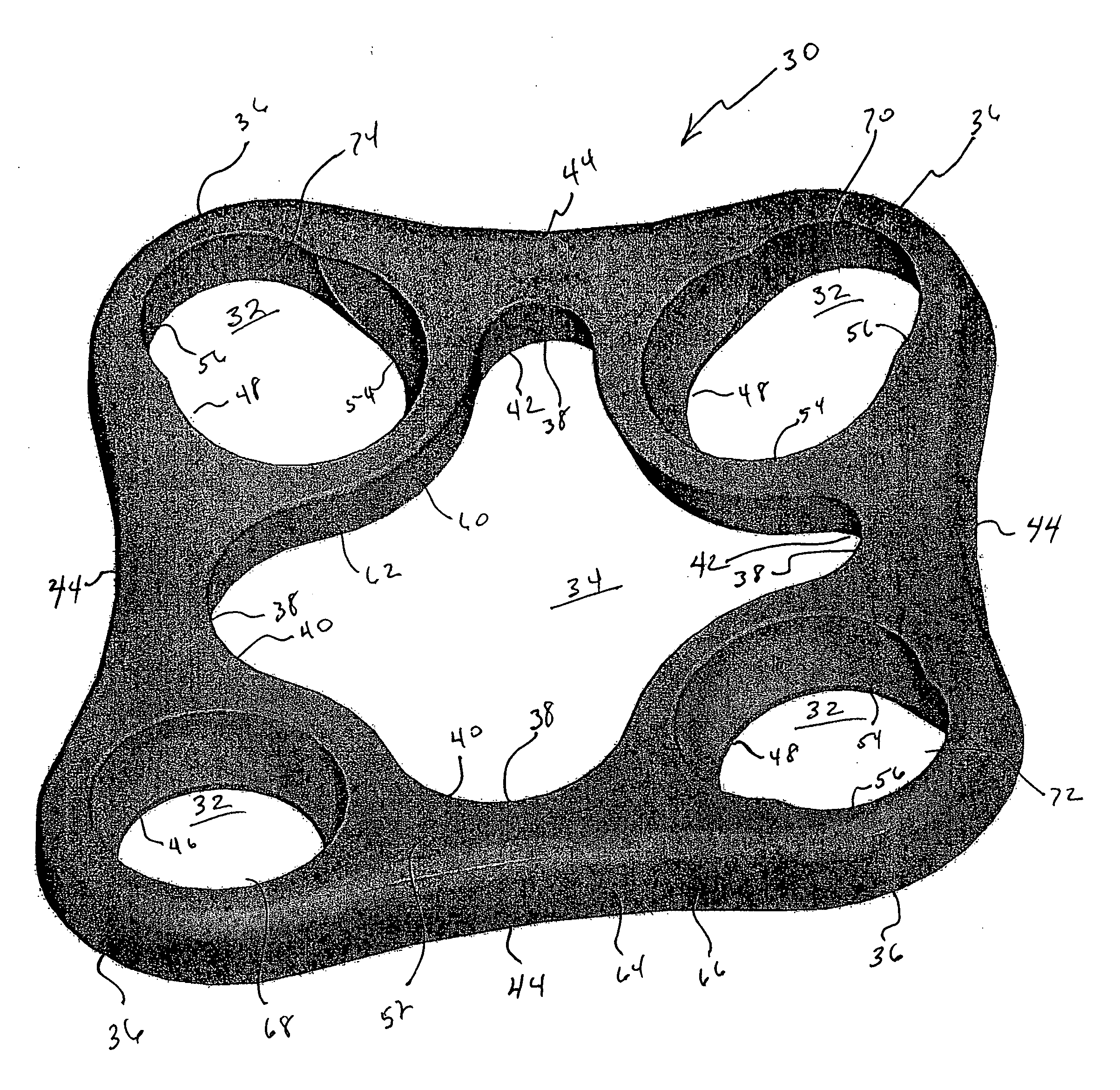
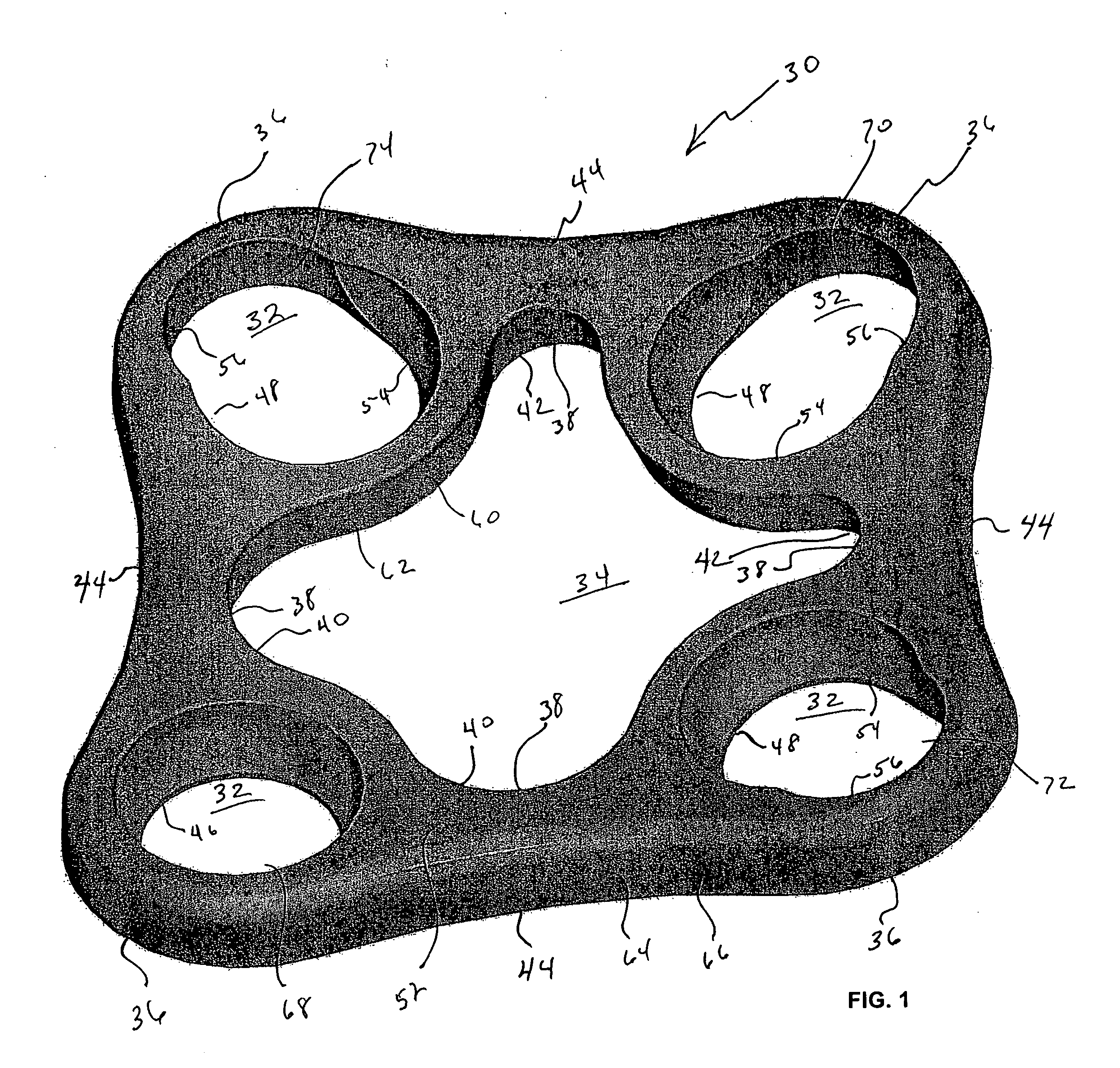
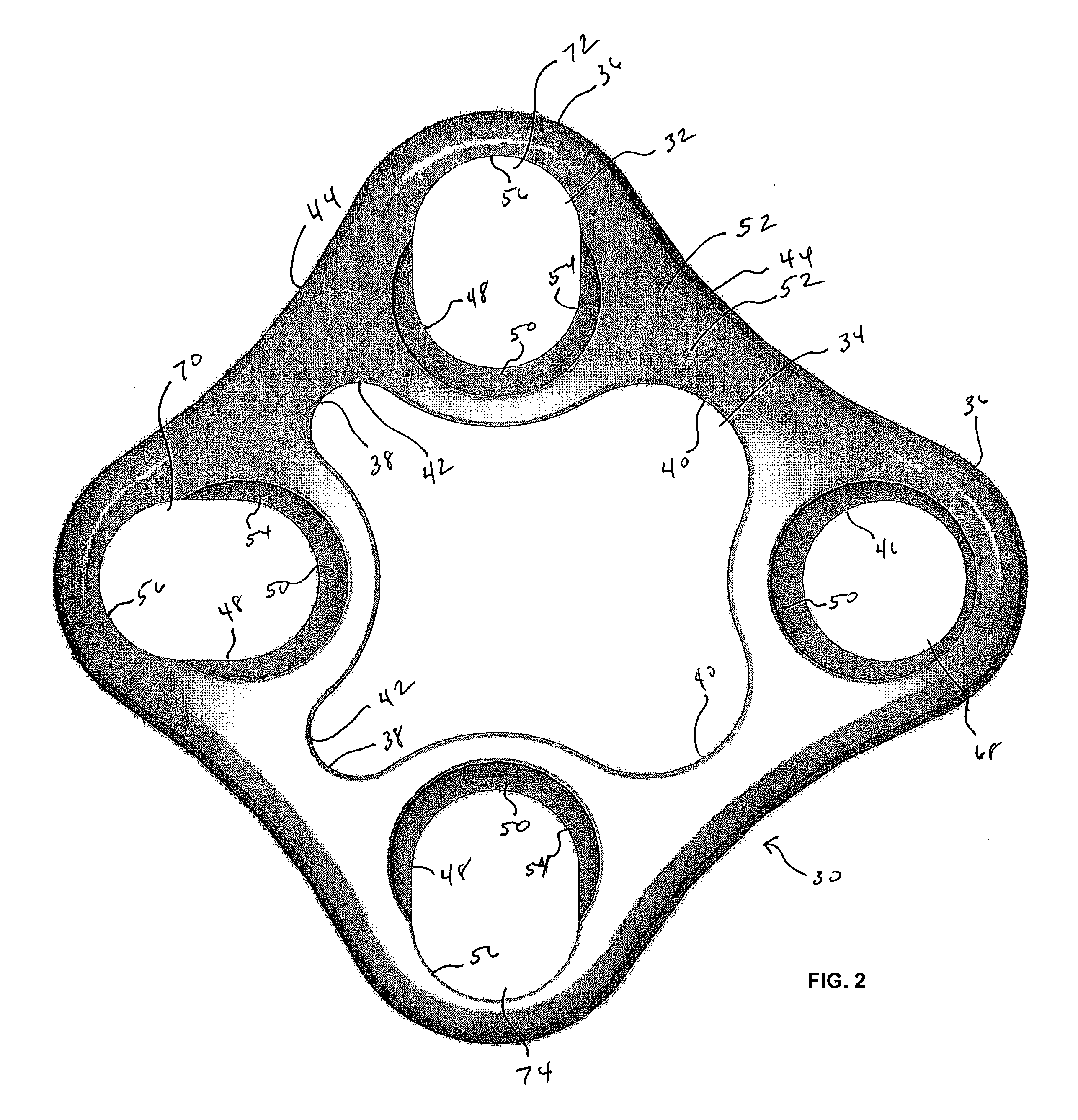
ActiveUS20060241778A1Process stabilityImplant stabilityFinger jointsAnkle jointsCarpal bonesMetacarpal bones
An interpositional biarticular disk implant (11) having a circular peripheral rim, a generally toroidal axial center opening (13) and convex upper and lower surfaces (15, 17) is implanted between resected concave surfaces of the metacarpal base and the trapezium or other carpal bone in a CMC joint replacement. The disk (11) is anchored in operative position through the use of a flexable cond, such as a harvested tendon that passes through the center opening (13) and through osseous passageways created in the two facing bones.
Owner:ASCENSION ORTHOPEDICS
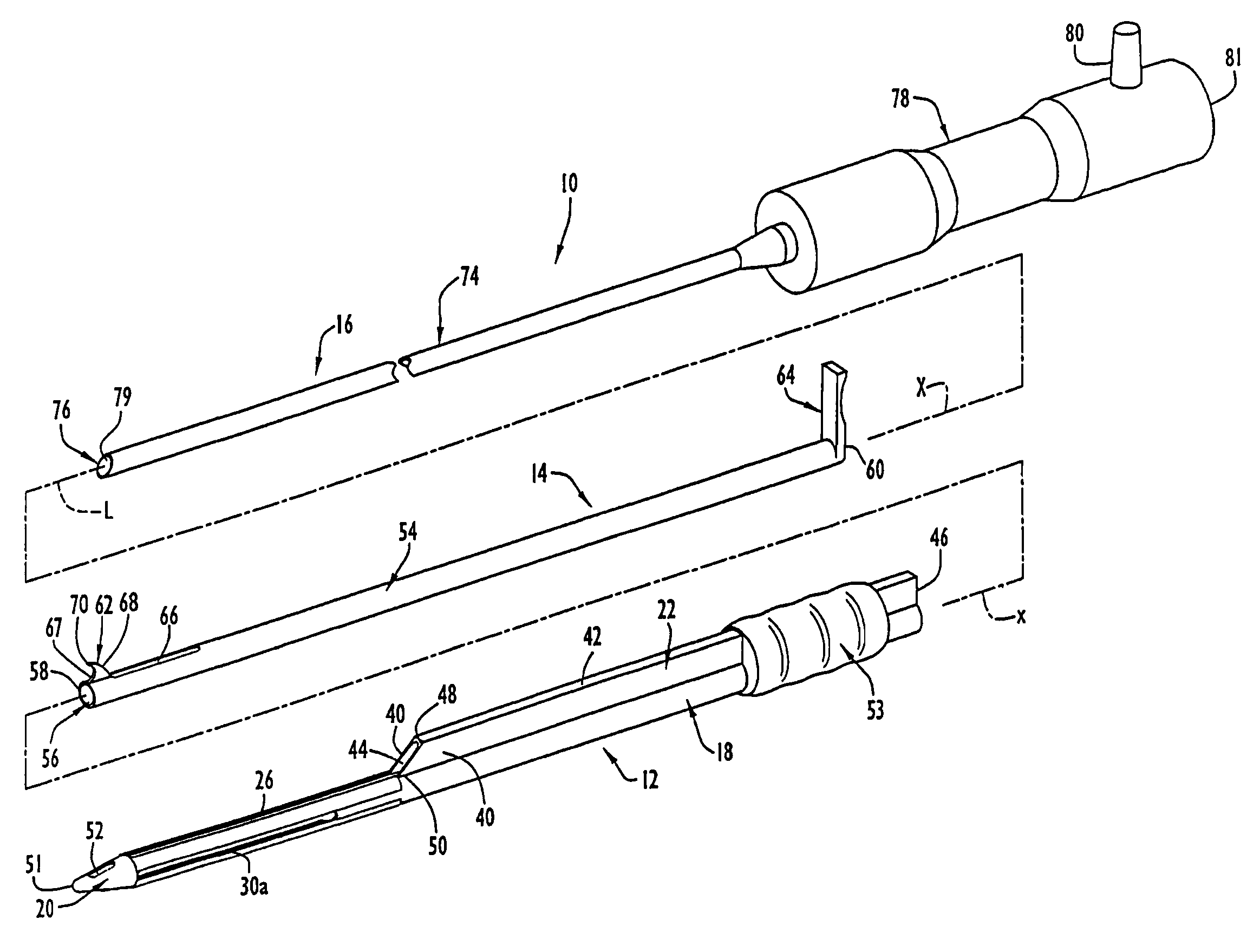
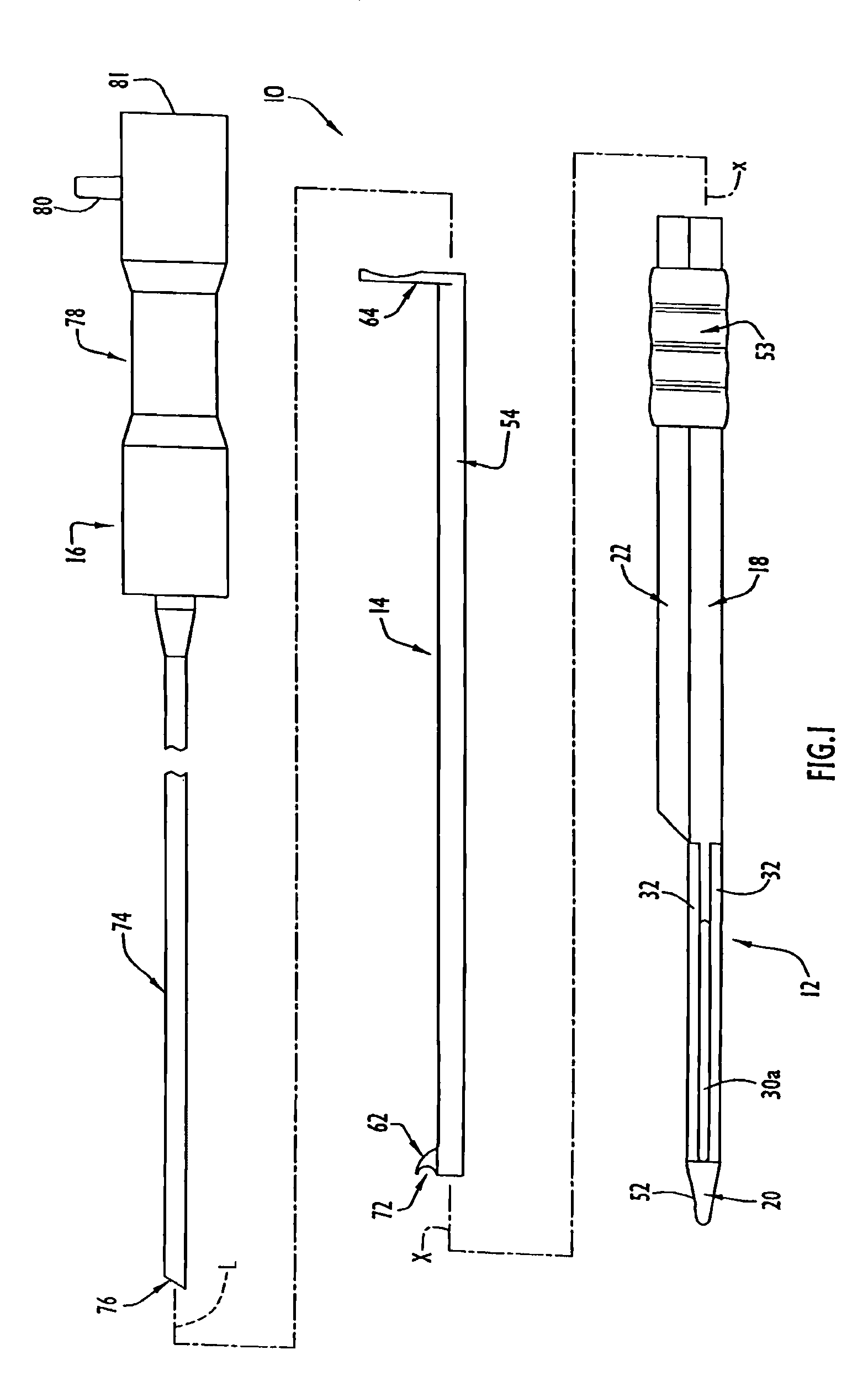
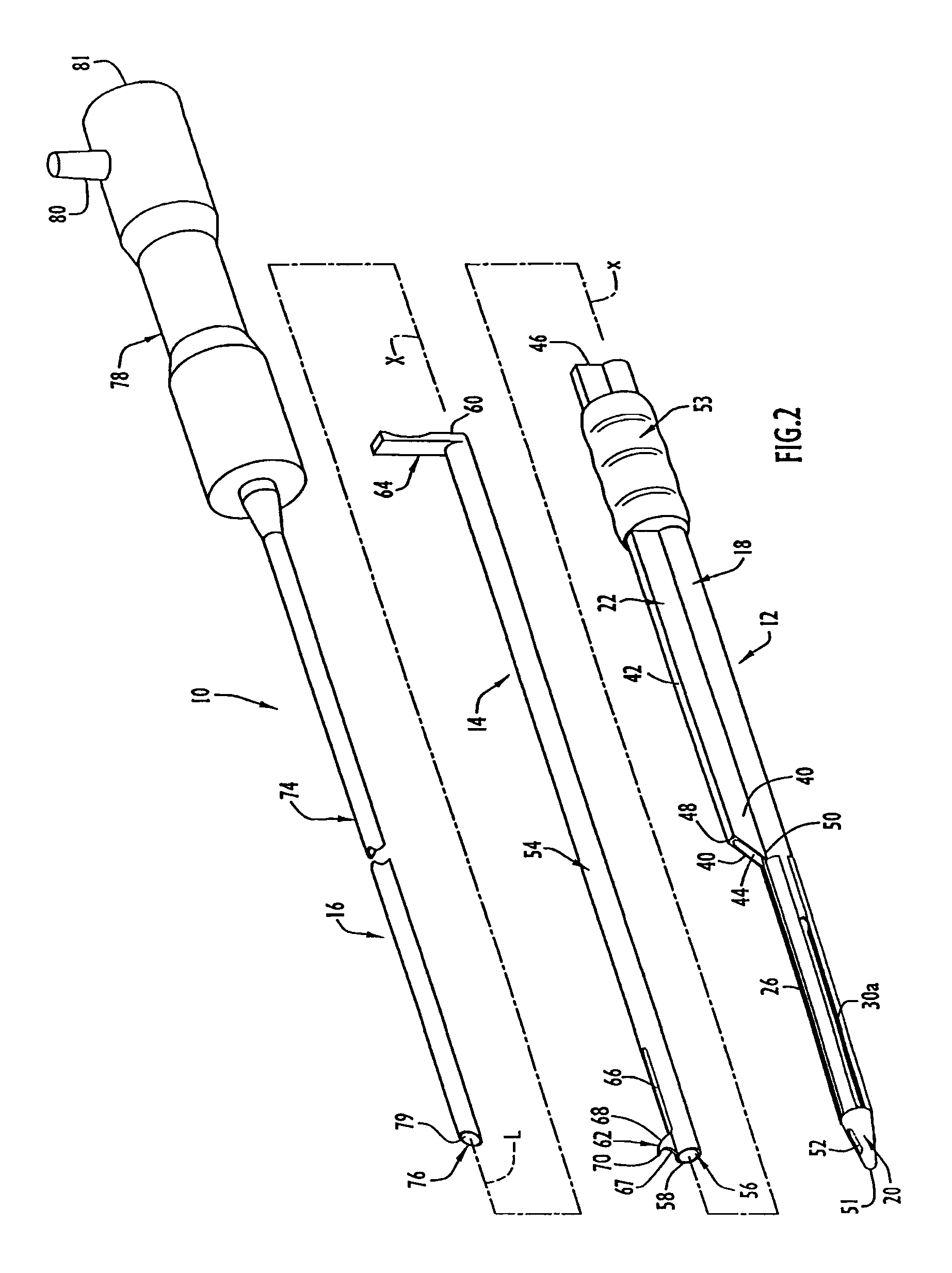
Instruments and method for minimally invasive carpal tunnel release
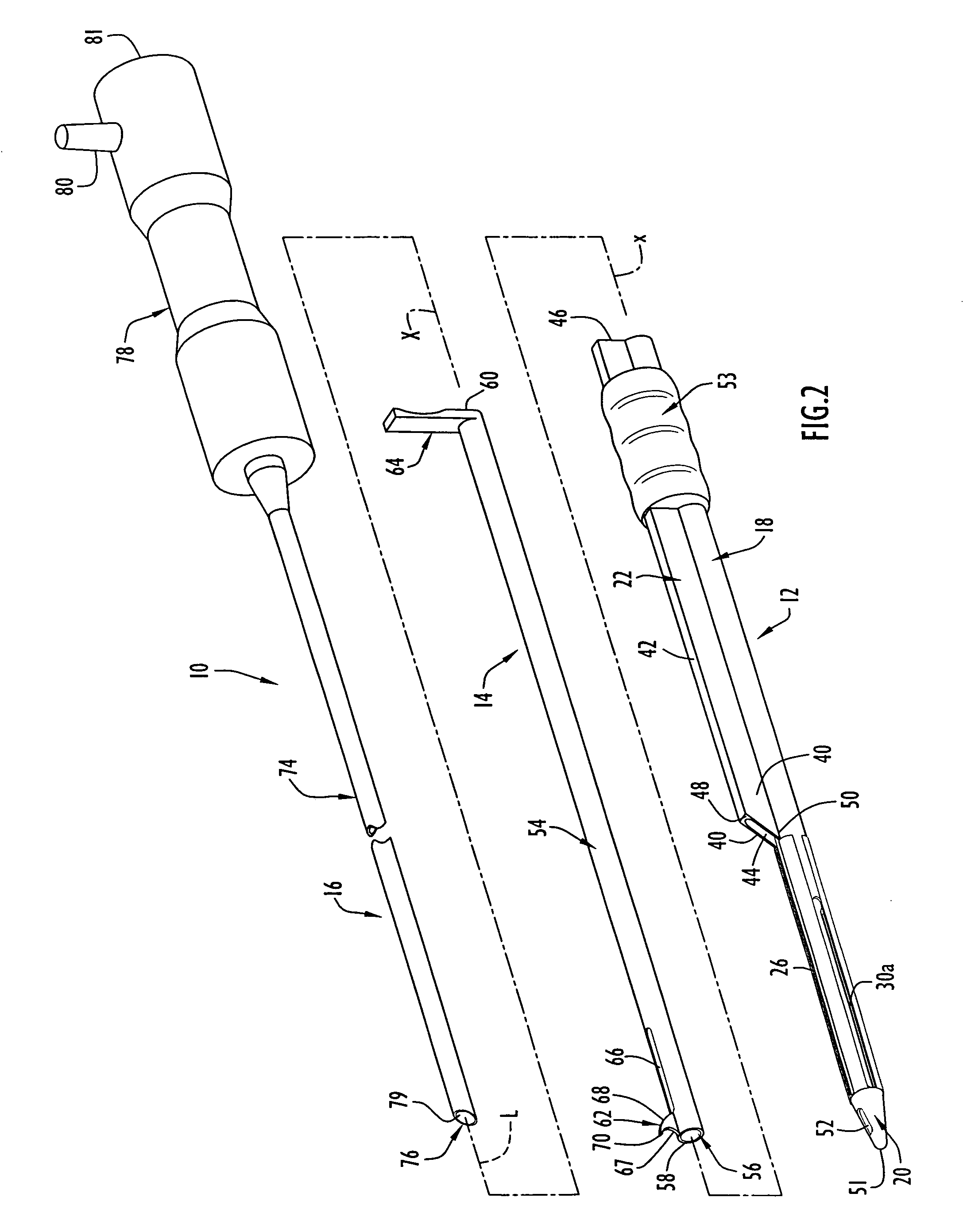
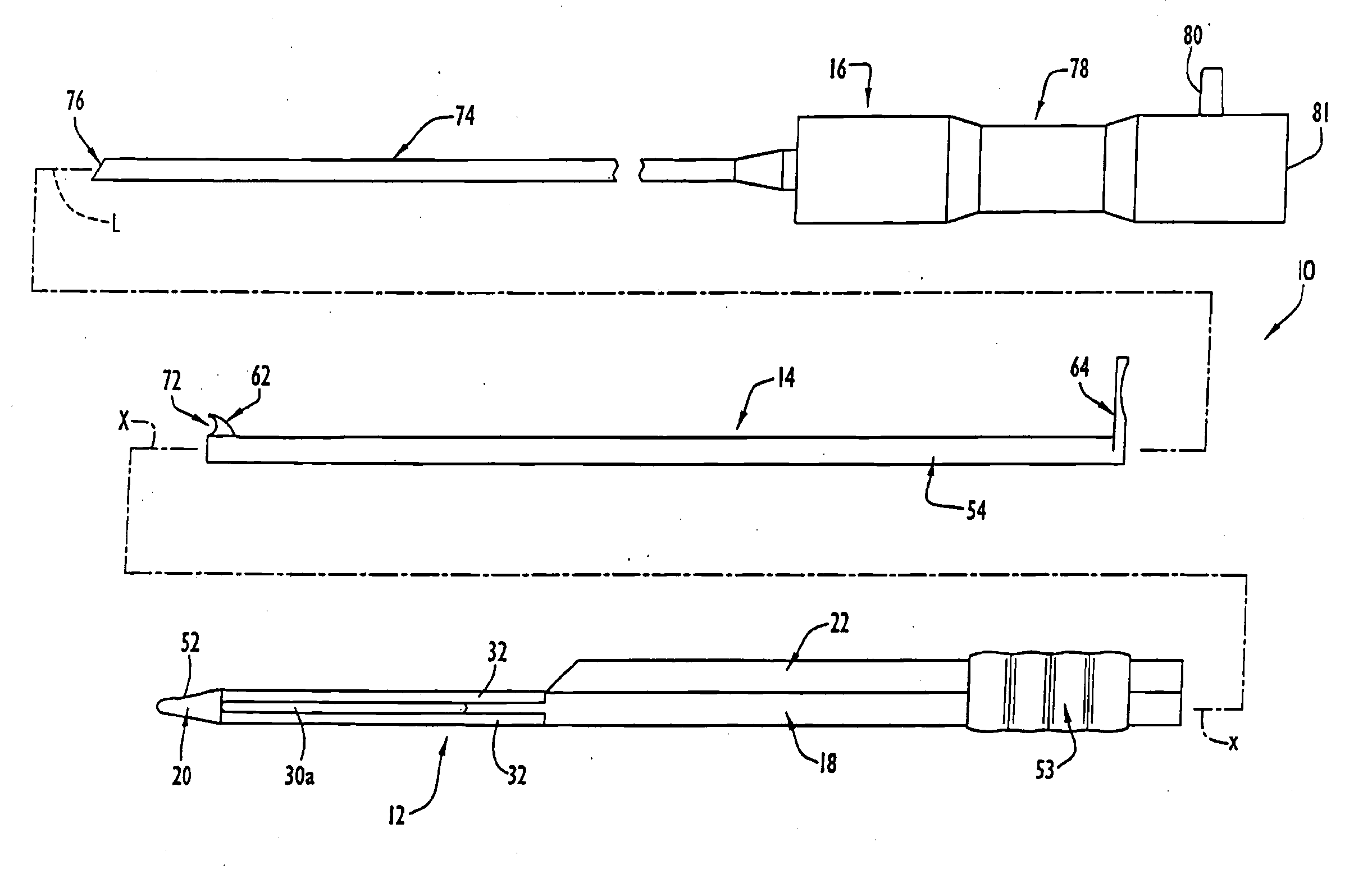
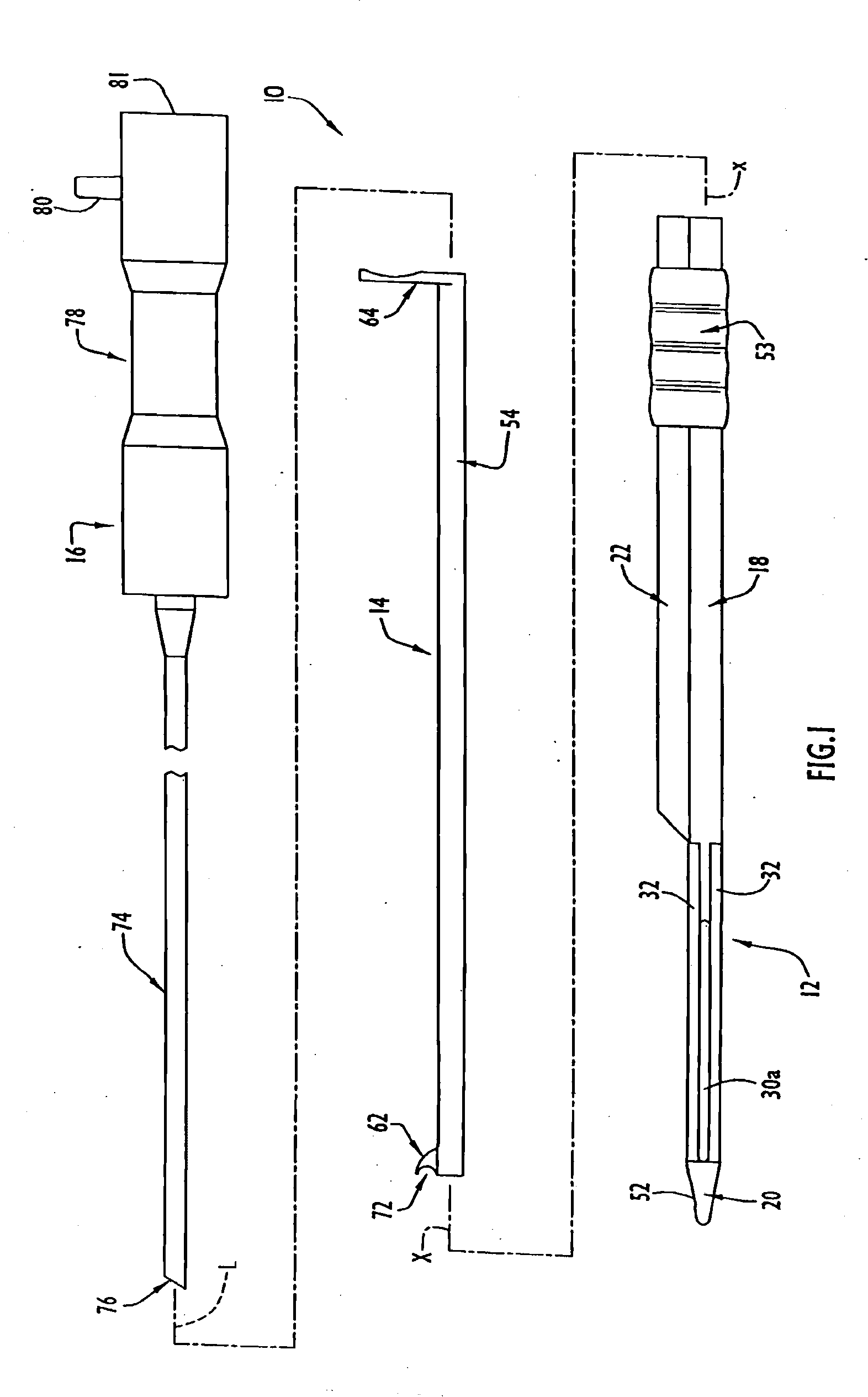
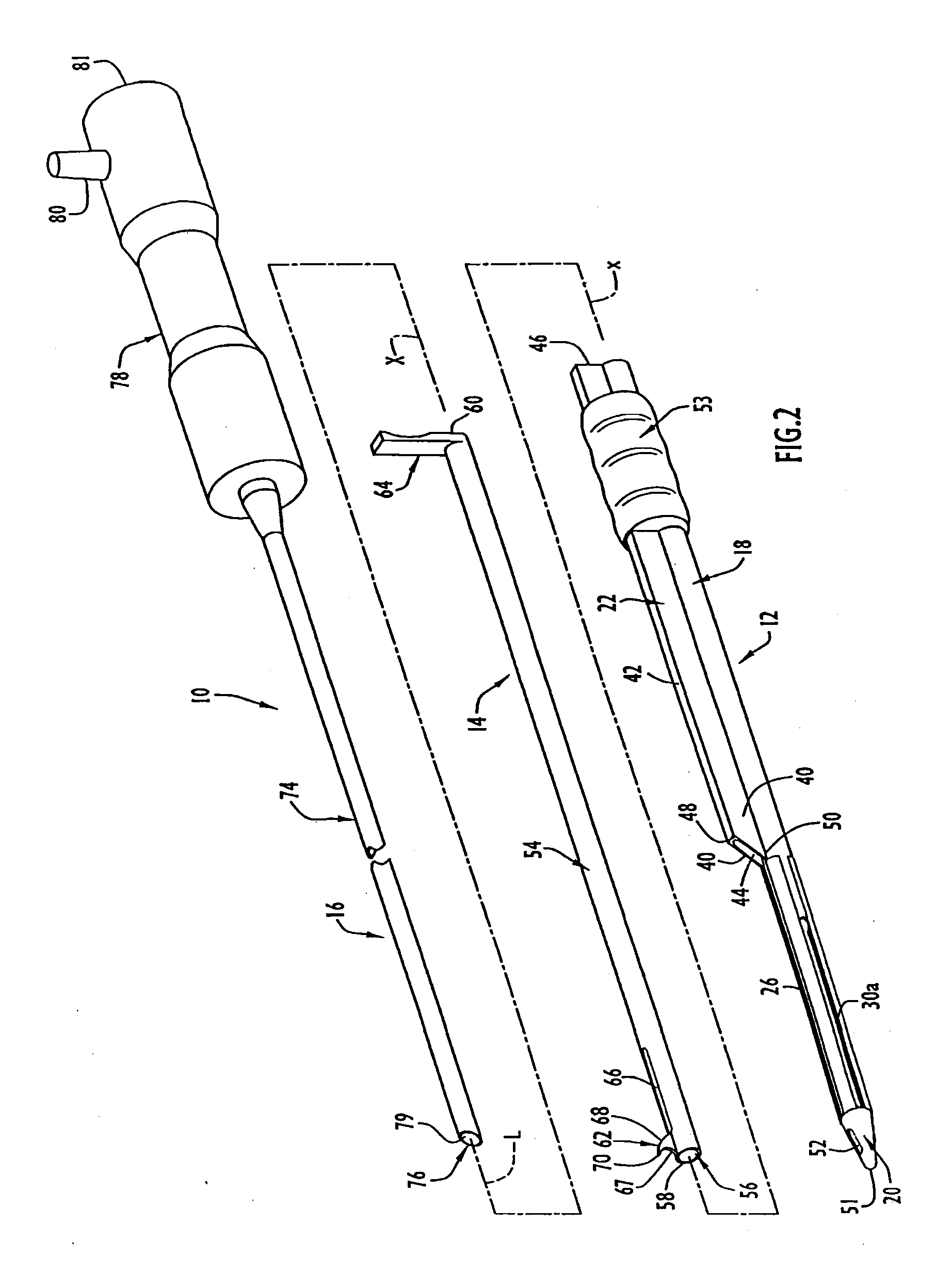
InactiveUS7780690B2Increase widthEasy to insertSurgeryLaproscopesCarpal tunnel releaseCarpal ligament
Instruments for use in minimally invasive carpal tunnel release include a cannula and a cutting member movable longitudinally within the cannula to advance a cutting blade of the cutting member along a longitudinal slot in the cannula to sever a transverse carpal ligament disposed over the slot. A dilating member is provided for creating a subligamentous space to accommodate the cannula and / or for removing adhered synovium from a lower surface of the ligament. A method for minimally invasive carpal tunnel release involves establishing a subcutaneous pathway to the carpal tunnel from an incision in the forearm, introducing the cannula in the carpal tunnel via the pathway, and severing the transverse carpal ligament with the cutting blade of the cutting member, all of which steps are performed under direct endoscopic visualization.
Owner:RECON SURGICAL
Instruments and Methods for Minimally Invasive Carpal Tunnel Release
InactiveUS20110046652A1Increase widthEasy to insertSurgeryLaproscopesCarpal ligamentEndoscopic carpal tunnel release
Instruments for use in minimally invasive carpal tunnel release include a cannula and a cutting member movable longitudinally within the cannula to advance a cutting blade of the cutting member along a longitudinal slot in the cannula to sever a transverse carpal ligament disposed over the slot. A dilating member is provided for creating a subligamentous space to accommodate the cannula and / or for removing adhered synovium from a lower surface of the ligament. A method for minimally invasive carpal tunnel release involves establishing a proximal entry into the carpal tunnel from an incision in the volar aspect of the forearm, introducing the cannula in the carpal tunnel via the incision, and severing the transverse carpal ligament from proximal to distal with the cutting blade of the cuffing member under direct endoscopic visualization.
Owner:RECON SURGICAL
Bone fusion plate
InactiveUS20060025772A1High retention rateEfficient compressionSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsBones fusionEngineering
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Interpositional biarticular disk implant
Owner:ASCENSION ORTHOPEDICS
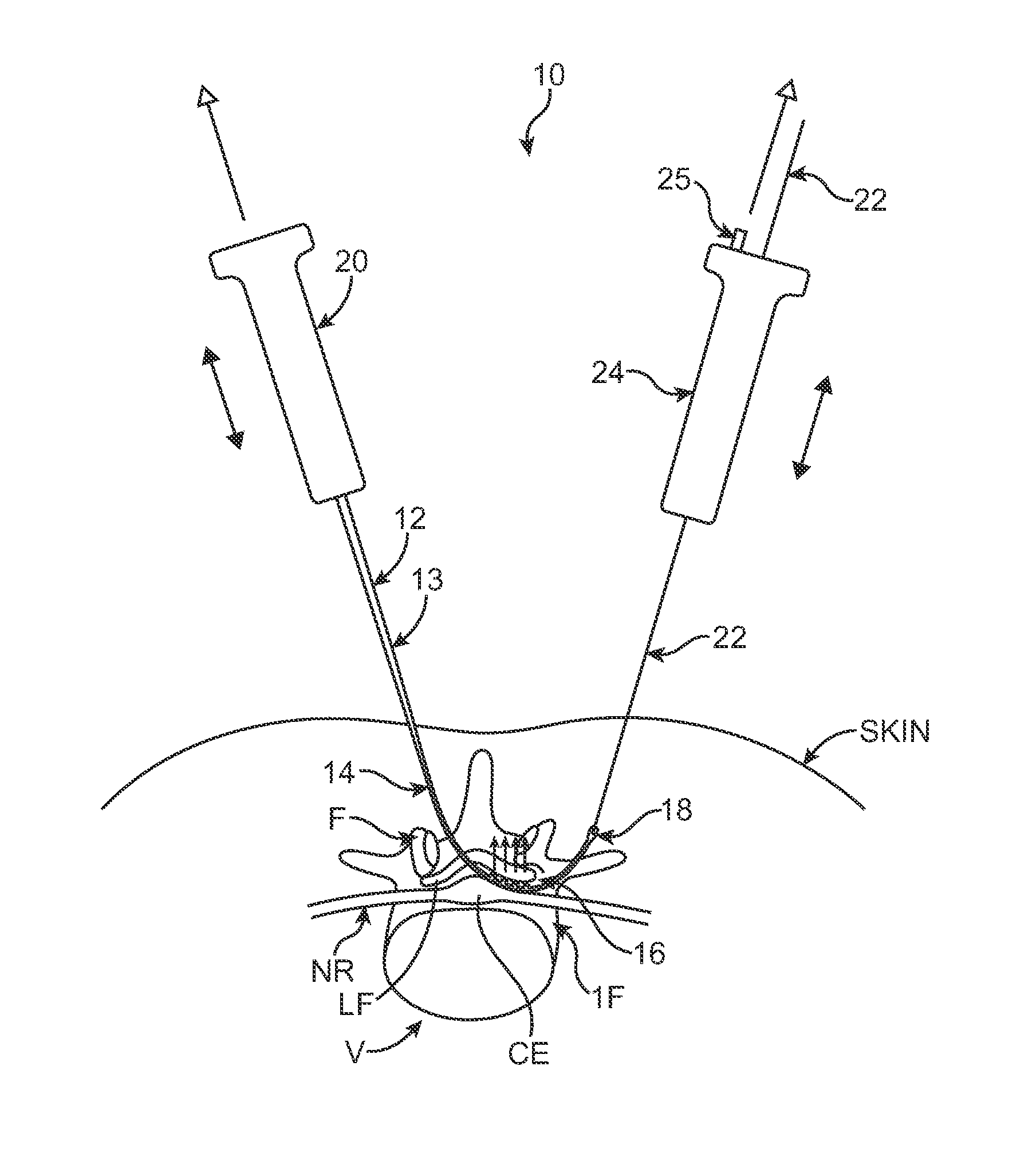
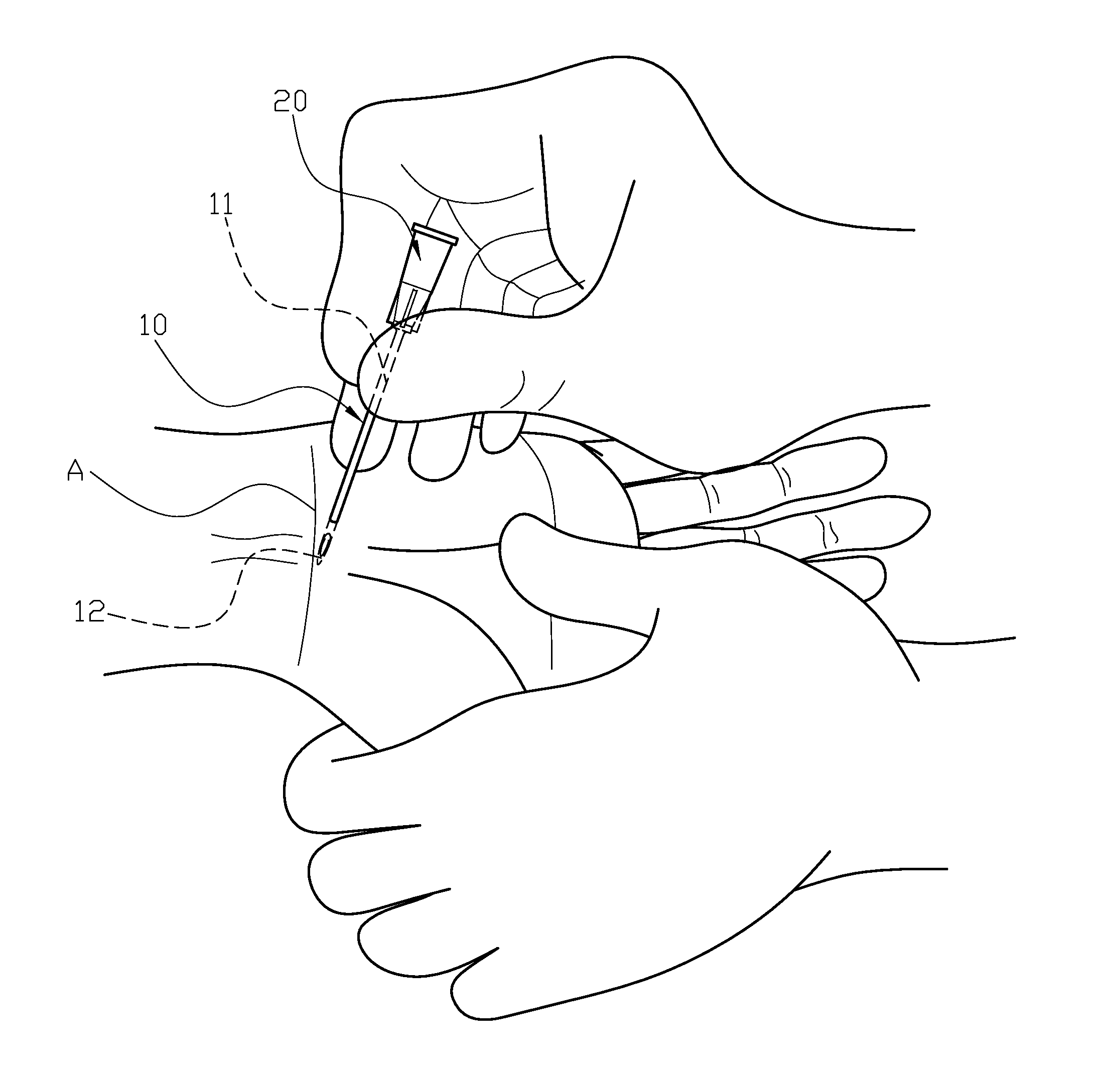
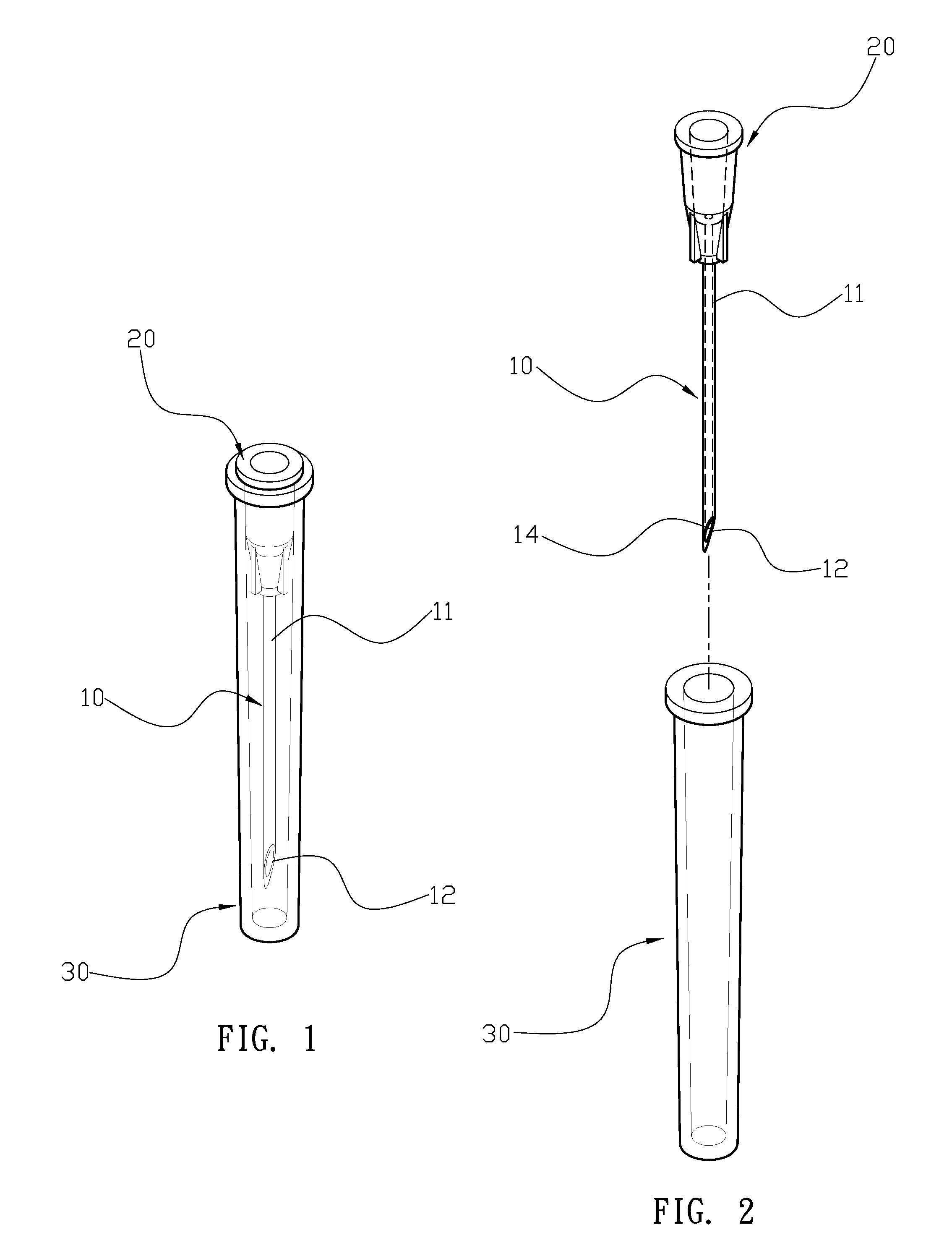
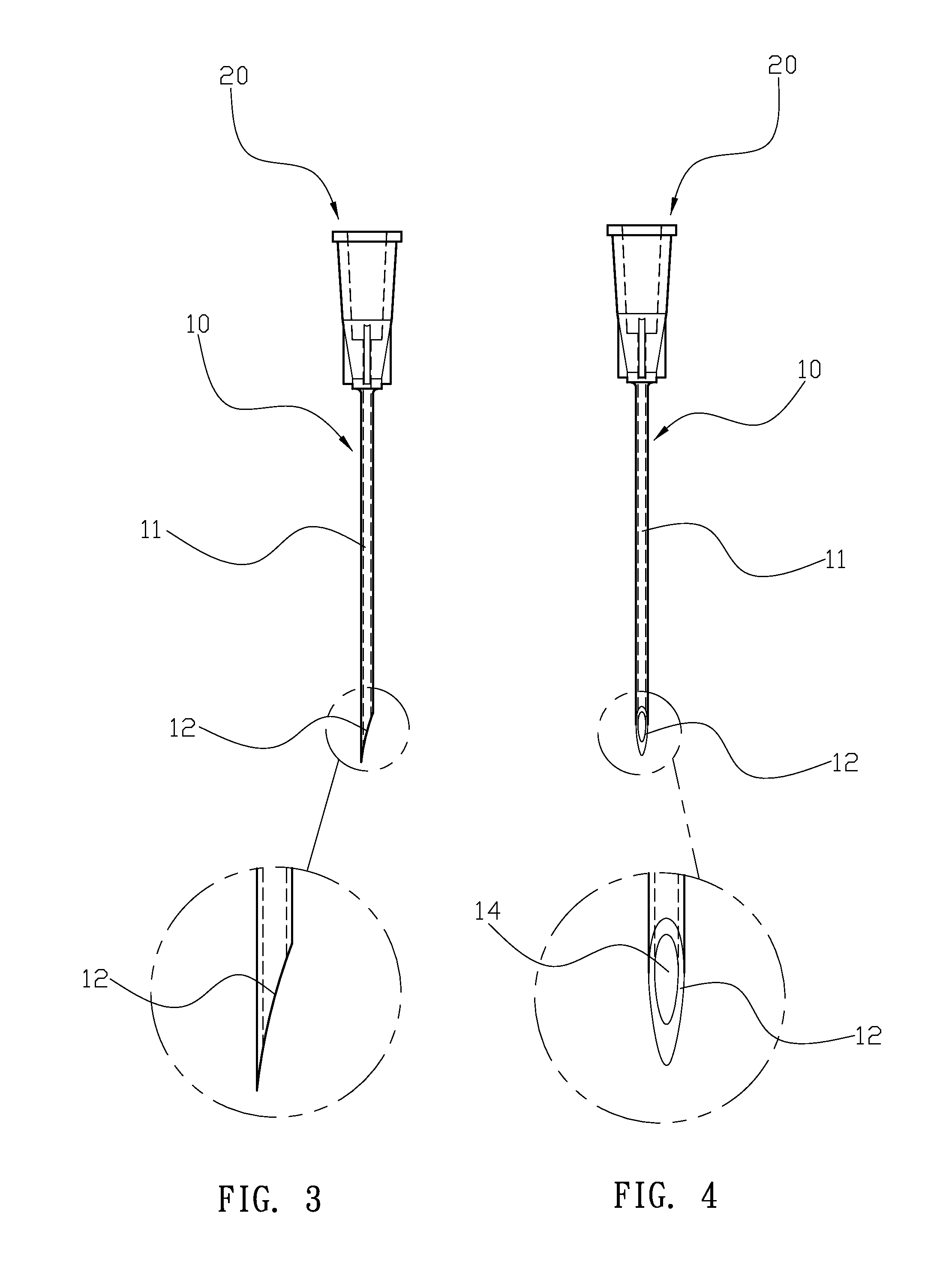
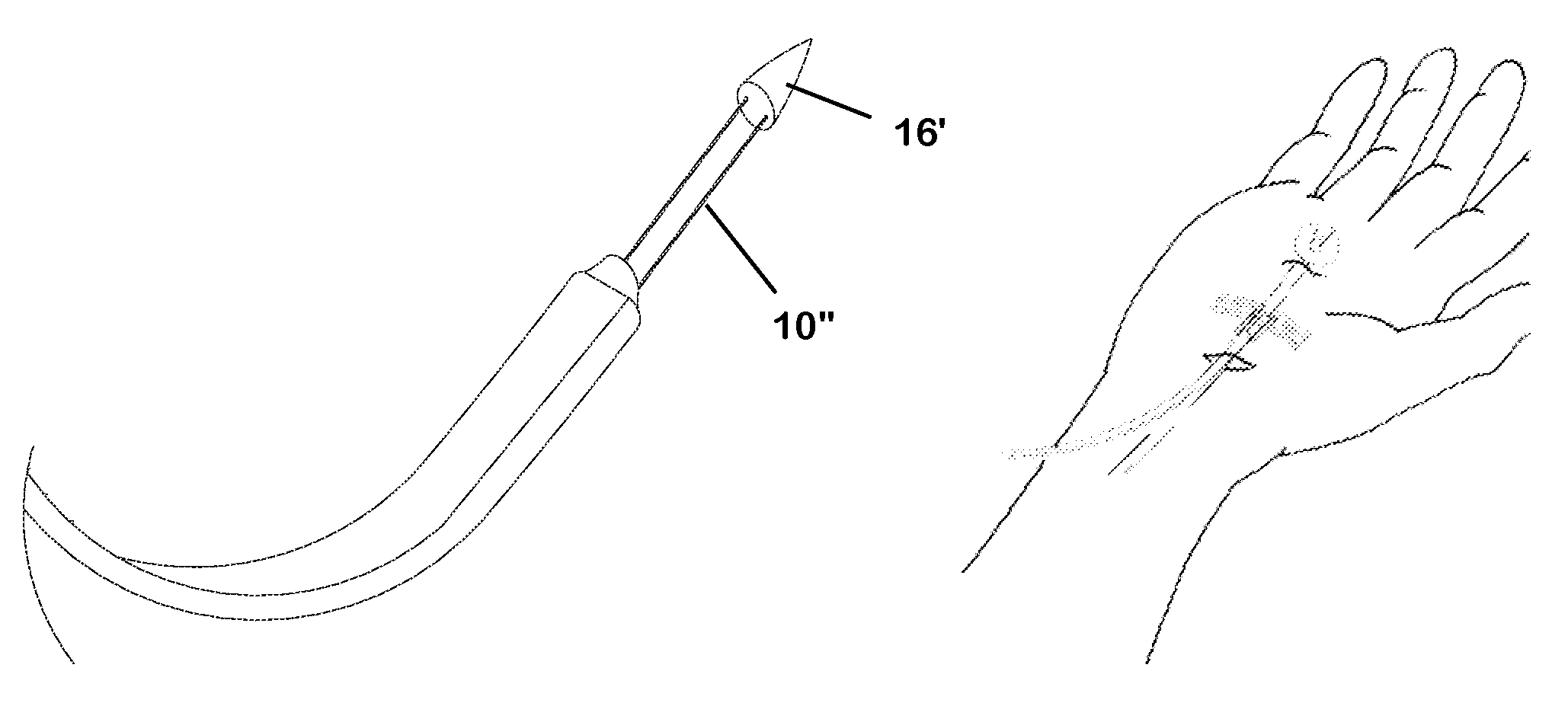
Flexible Wire Transection of the Transverse Carpal Ligament
InactiveUS20060271080A1Easy to passIncrease the cross-sectional areaSurgical needlesBlunt dissectorsCross cutCarpal ligament
A flexible cutting filament or wire is led through the carpal tunnel, beneath the transverse carpal ligament, by a passer. Thereafter, the opposite ends of the wire are secured in an instrument which tightens the wire and may be used to move the wire as a cutting tool to transect the overlying ligament, while preserving surrounding tissues. The small wire diameter enables minimally invasive techniques to limit post-operative pain and speed recovery.
Owner:SUDDABY LOUBERT
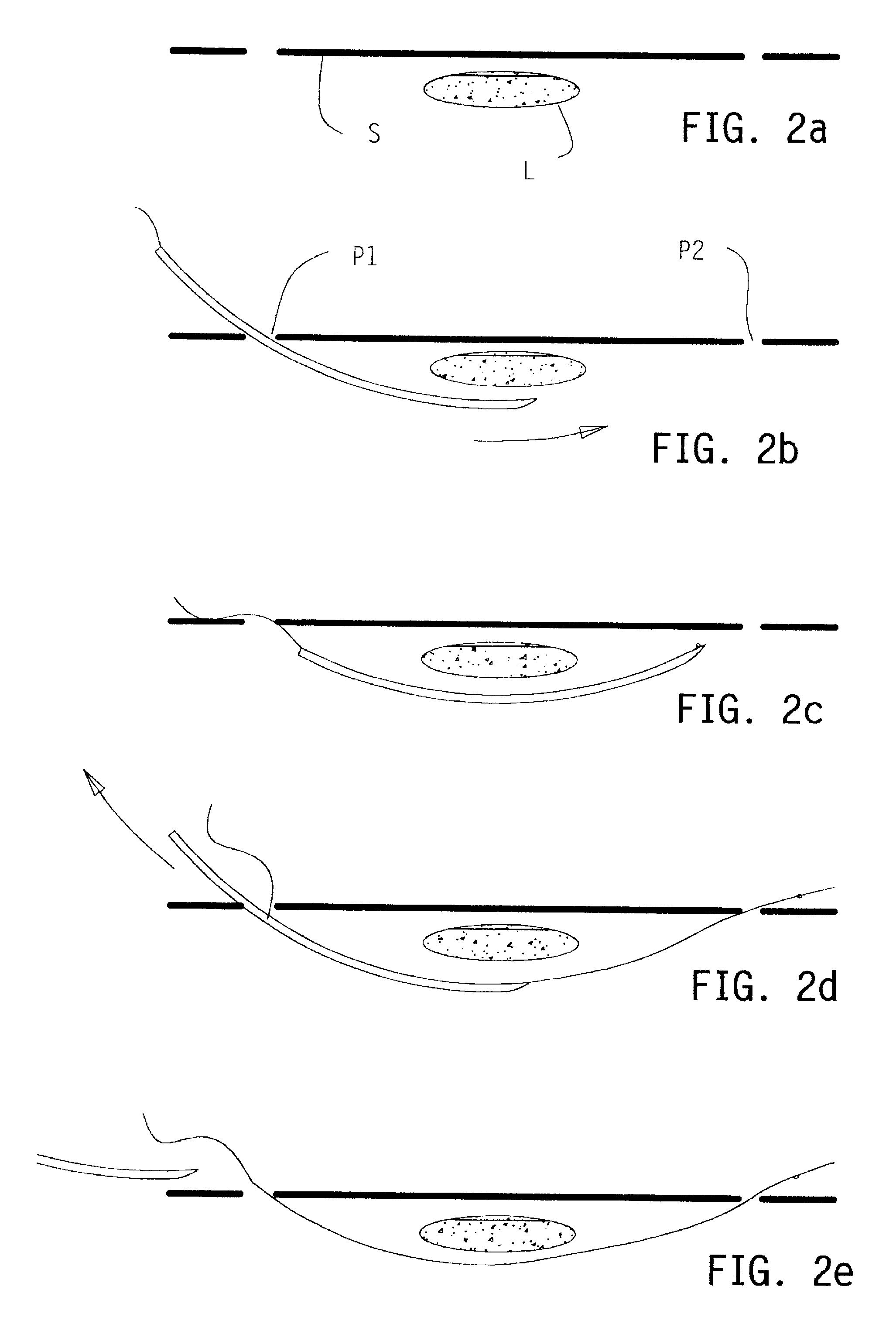
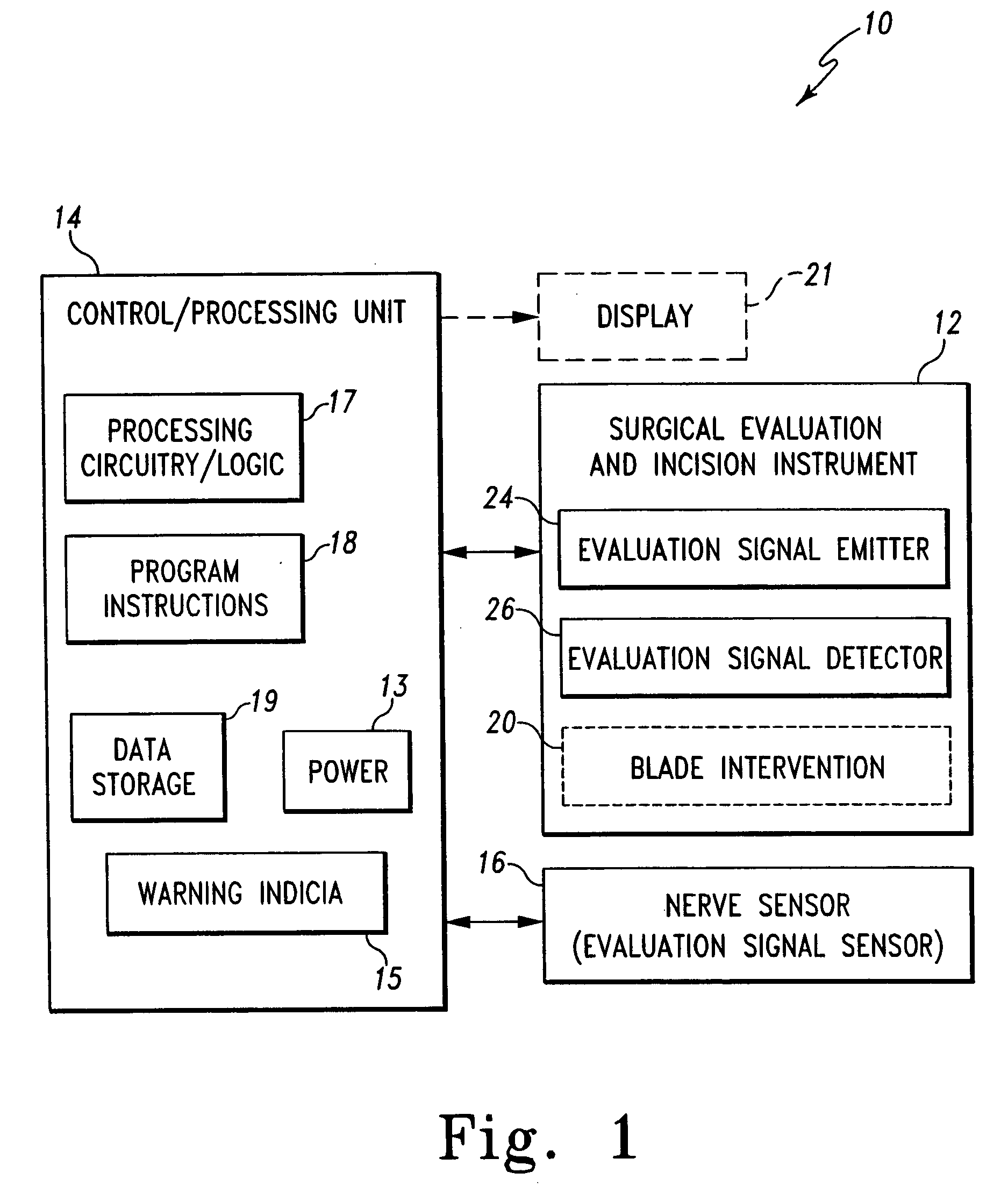
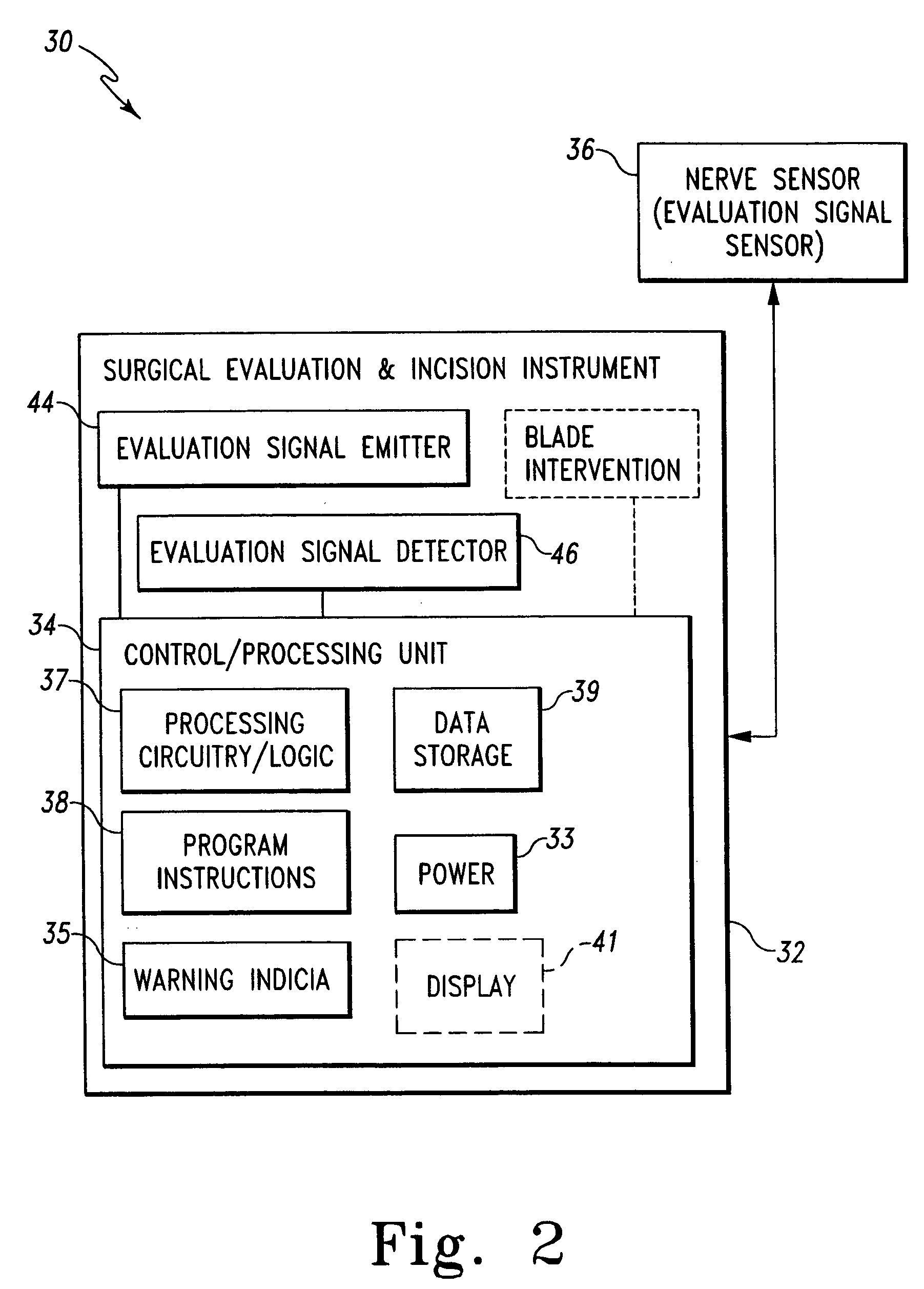
Surgical scalpel and system particularly for use in a transverse carpal ligament surgical procedure
The subject invention is a surgical scalpel, scalpel instrument and / or scalpel system (collectively, scalpel), particularly designed for use in a transverse carpal ligament surgical procedure, that evaluates an incision path with respect to a nerve in the incision path, and is used to perform the incision if appropriate. The scalpel emits an evaluation signal through a potential incision path through tissue captured by the scalpel. The scalpel utilizes the emitted evaluation signal to determine the presence of a nerve in the incision path. The dissection and evaluation (surgical) instrument includes a blade that is retractable relative to a target tissue capture area thereof. Evaluation may include determining the presence of a nerve before incision and / or the evaluating whether the target tissue has been appropriately captured. A warning is provided when the evaluation determines that a nerve is in the incision path and / or when the captured target tissue is determined to be inappropriate. Alternatively, the surgical instrument may disable extension of the blade when the evaluation determines that a nerve is in the dissection path and / or when the captured target tissue is determined to be inappropriate.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Bone Fusion Plate
InactiveUS20080091198A1Accurate placementGreater bone purchaseSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsBones fusionEngineering
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
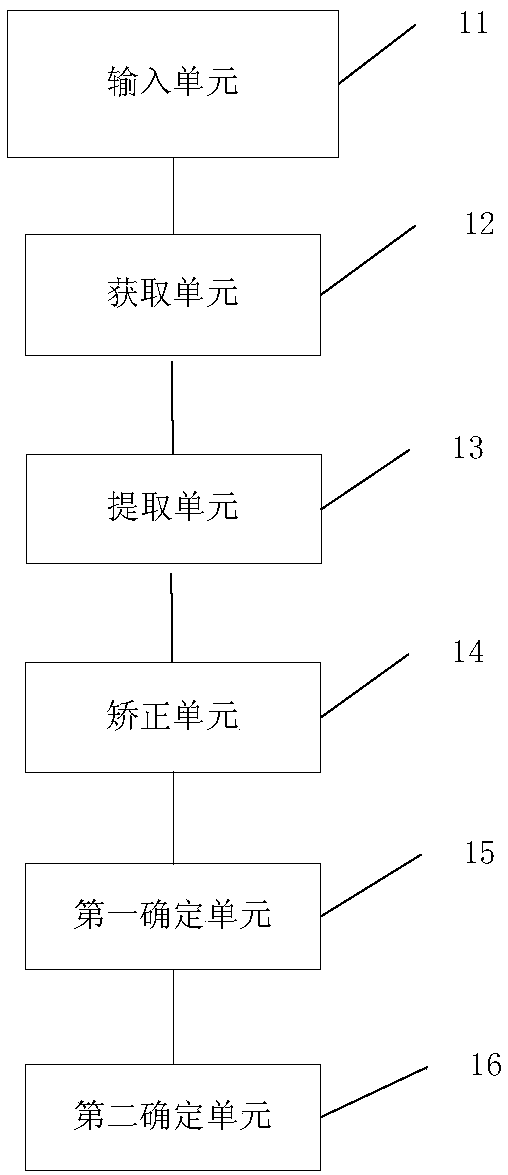
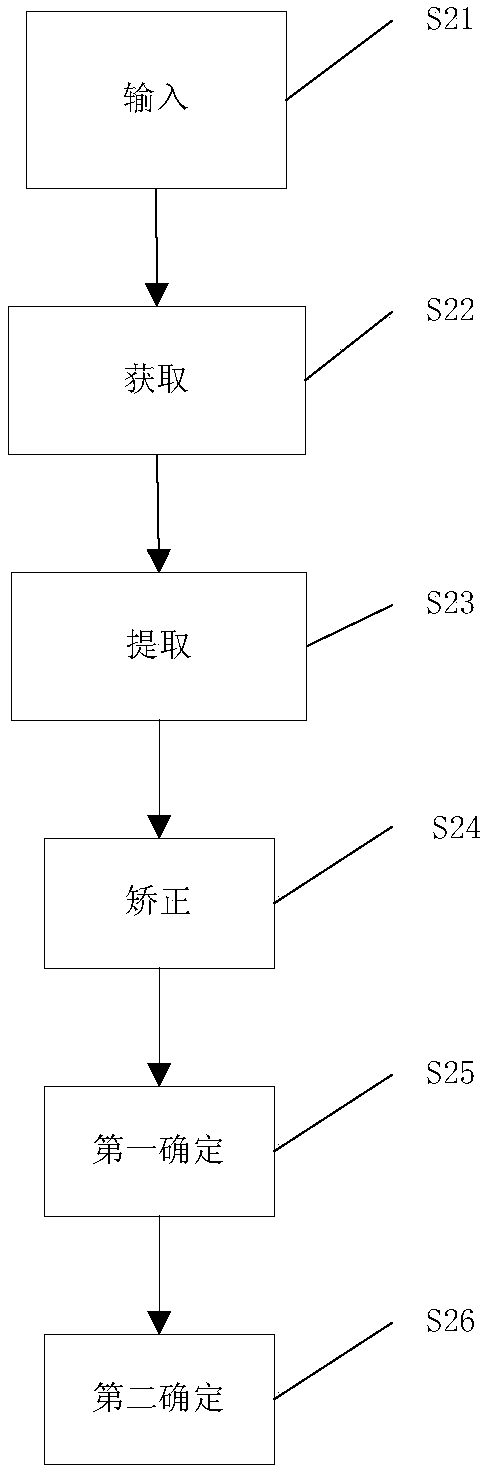
Skeletal age detecting method and device based on depth learning
The invention provides a skeletal age detecting method and device based on depth learning. The method comprises the steps of inputting, wherein X-ray pictures of hands of an examinee and the gender ofthe examinee are input; obtaining, wherein multiple key points corresponding to each skeleton on the hands are obtained from the X-ray pictures; extracting, wherein respective initial pictures of partial skeletons are extracted from the X-ray pictures; correcting, wherein the initial pictures of each skeleton in the partial skeletons are corrected to obtain respective correction pictures of the partial skeletons; primary determining, wherein growth phase information of each skeleton in the partial skeletons is determined, and on the condition that the skeletons do not include carpal bones, the growth phase information of the carpal bones is determined; secondary determining, wherein the skeletal age of the examinee is determined according to the growth phase information of each skeleton in the partial skeletons or the growth phase information of each skeleton in the partial skeletons and the growth phase information of the carpal bones.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Methods, systems and devices for carpal tunnel release
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC +1
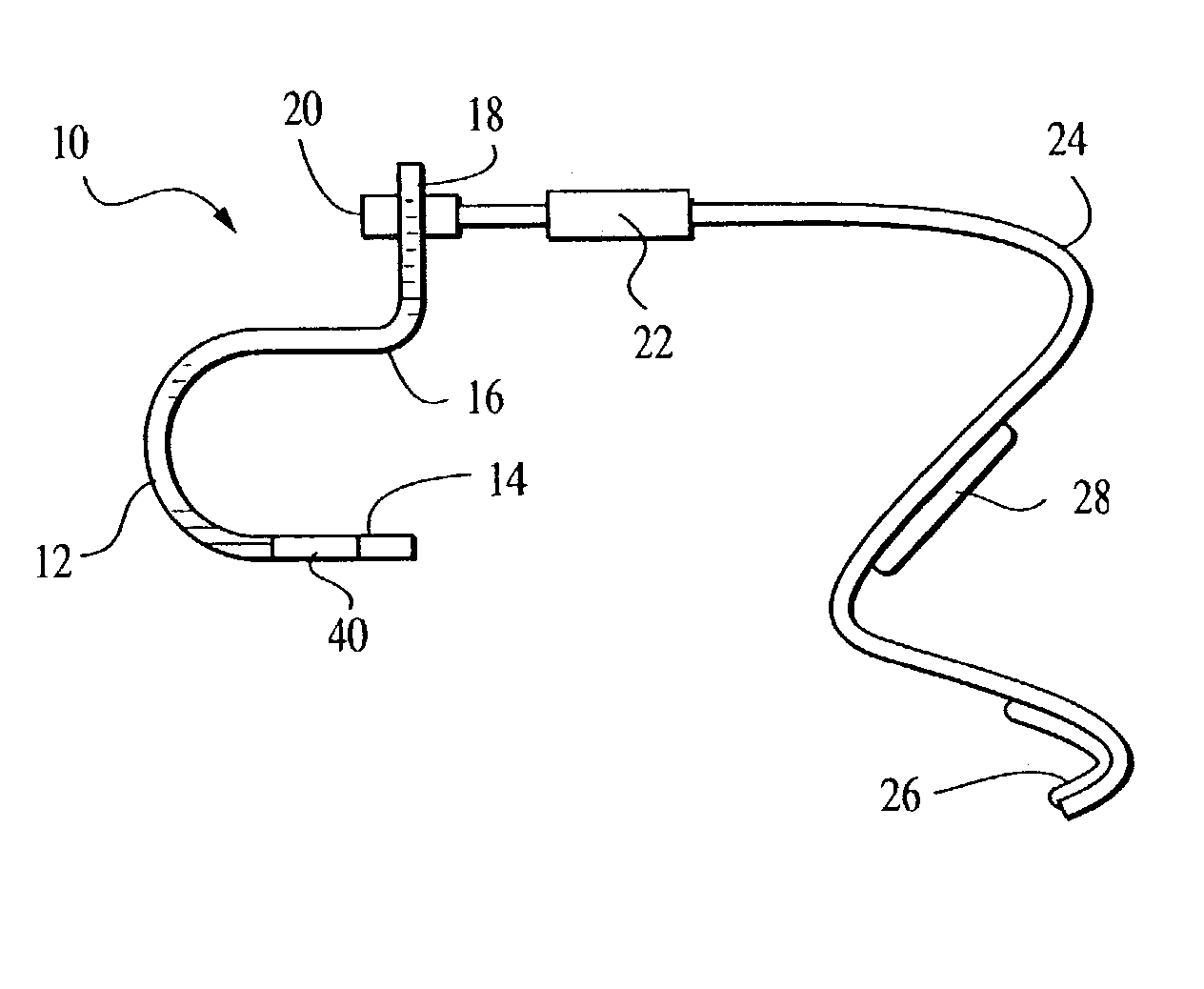
Adaptable apparatus and method for treating carpal tunnel syndrome
InactiveUS7182741B2Easy to useSimple and inexpensive to manufactureDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsCTS - Carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal ligament
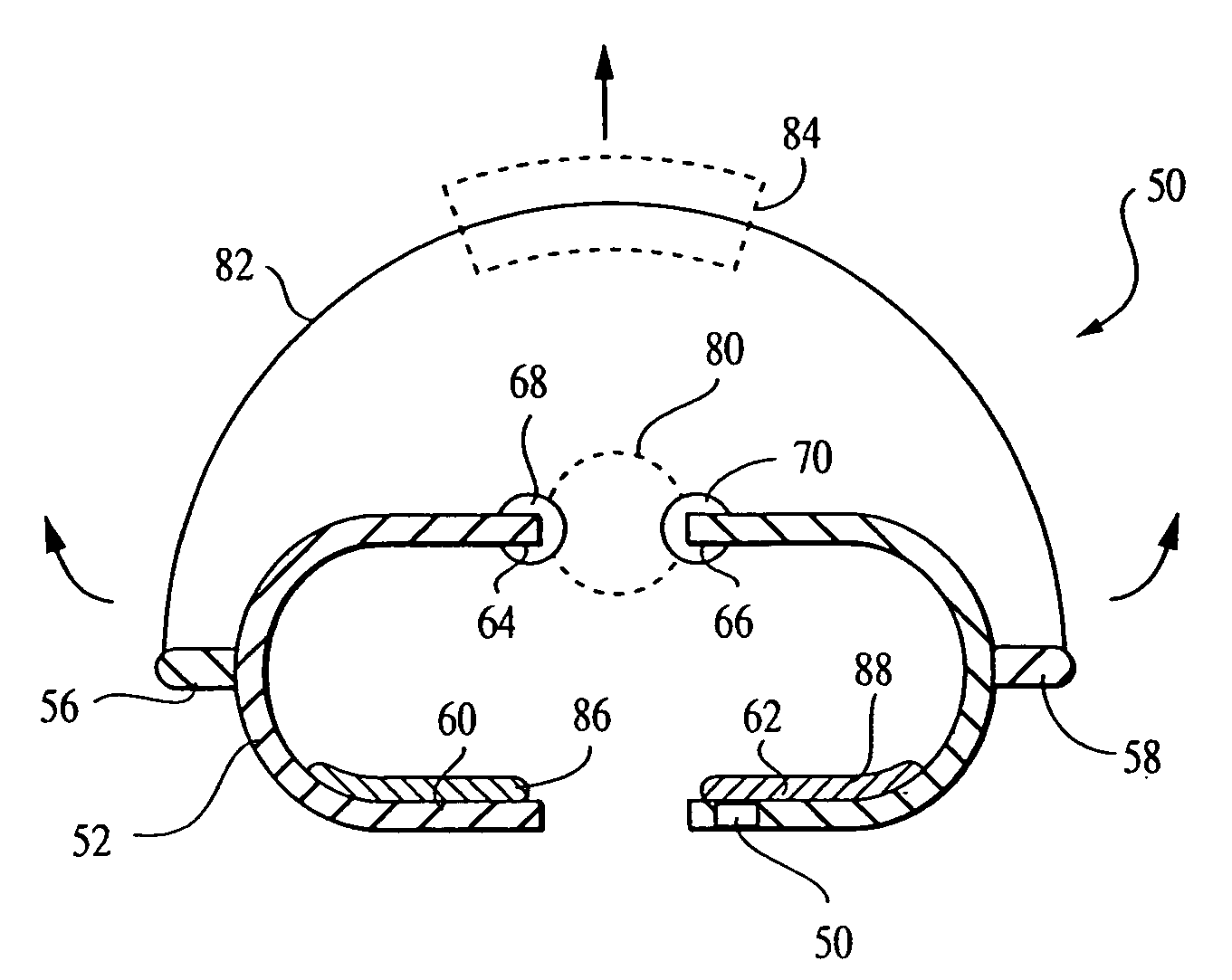
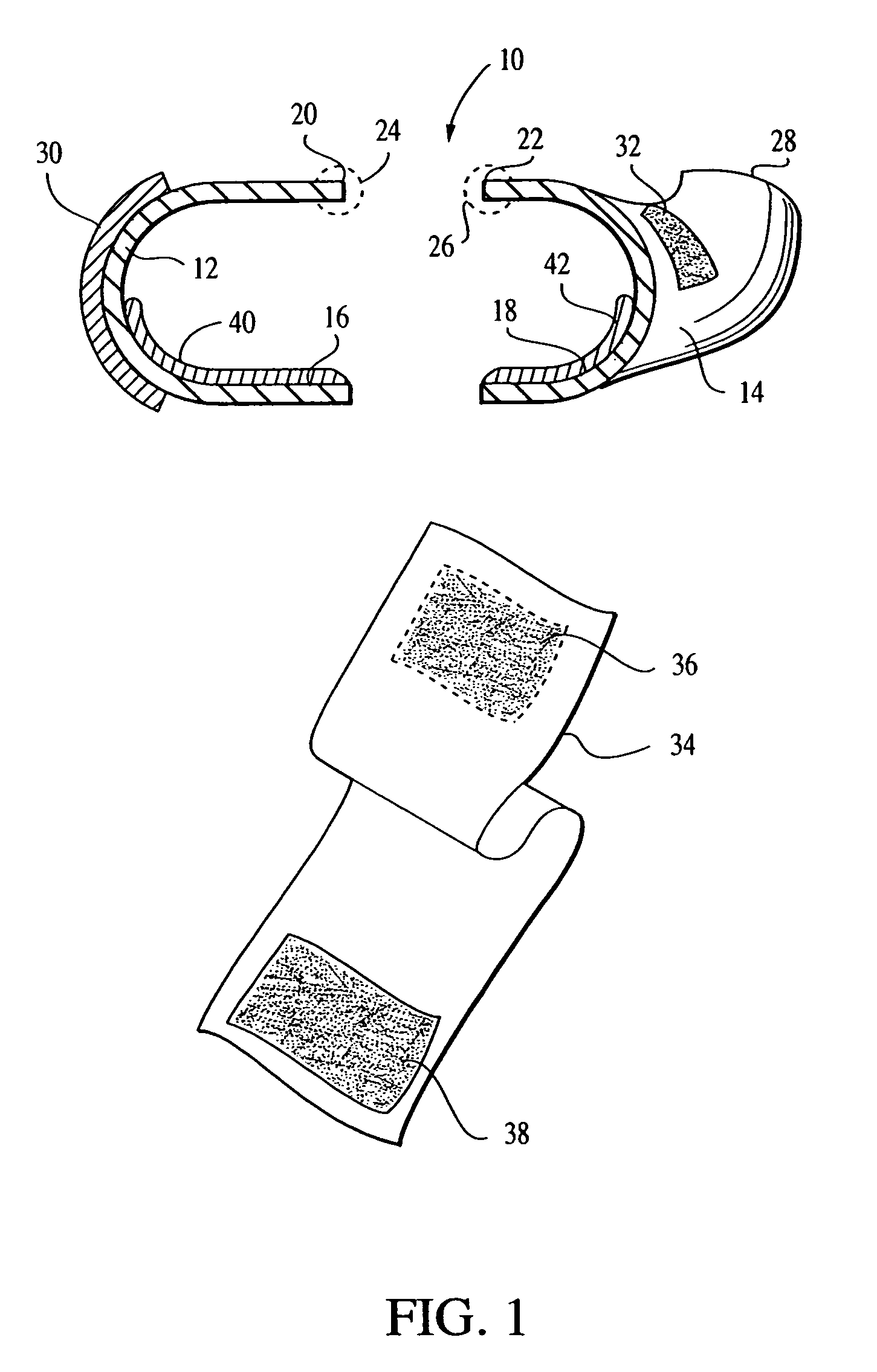
The apparatus of the present invention stretches the carpal ligament and the flexor retinaculum, as well as the superficial structures and muscles of the hand, in a safe manner under precise control of the patient or a healthcare professional. The preferred embodiment of the inventive apparatus includes a first housing with an open side portion adapted and configured to contact and retain the hypothenar region of the patient's hand, with a first edge of the first housing extending along a central longitudinal dorsal portion of the hand, and a second housing with an open side portion adapted and configured to contact and retain the thenar region of the patient's hand, with a second edge of the second housing also extending along a central longitudinal dorsal portion of the hand. A flexible resilient strap is secured to the first housing, and then wrapped around the second housing encompassing the thenar portion of the hand (i.e. around the thumb area), in such a manner as to pull the second housing (and thus the thenar portion of the hand) upward with the first and the second edges of the respective first and second housings serving as a fulcrum around which the hypothenar and thenar portions of the hand are bent. The strap is then secured to itself or to the first and / or the second housing to keep the hypothenar and thenar portions pulled apart during the course of treatment.
Owner:PORRATA GROUP
Instruments and methods for minimally invasive carpal tunnel release
InactiveUS8523892B2Increase widthEasy to insertSurgeryLaproscopesCarpal tunnel releaseCarpal ligament
Instruments for use in minimally invasive carpal tunnel release include a cannula and a cutting member movable longitudinally within the cannula to advance a cutting blade of the cutting member along a longitudinal slot in the cannula to sever a transverse carpal ligament disposed over the slot. A dilating member is provided for creating a subligamentous space to accommodate the cannula and / or for removing adhered synovium from a lower surface of the ligament. A method for minimally invasive carpal tunnel release involves establishing a proximal entry into the carpal tunnel from an incision in the volar aspect of the forearm, introducing the cannula in the carpal tunnel via the incision, and severing the transverse carpal ligament from proximal to distal with the cutting blade of the cuffing member under direct endoscopic visualization.
Owner:RECON SURGICAL
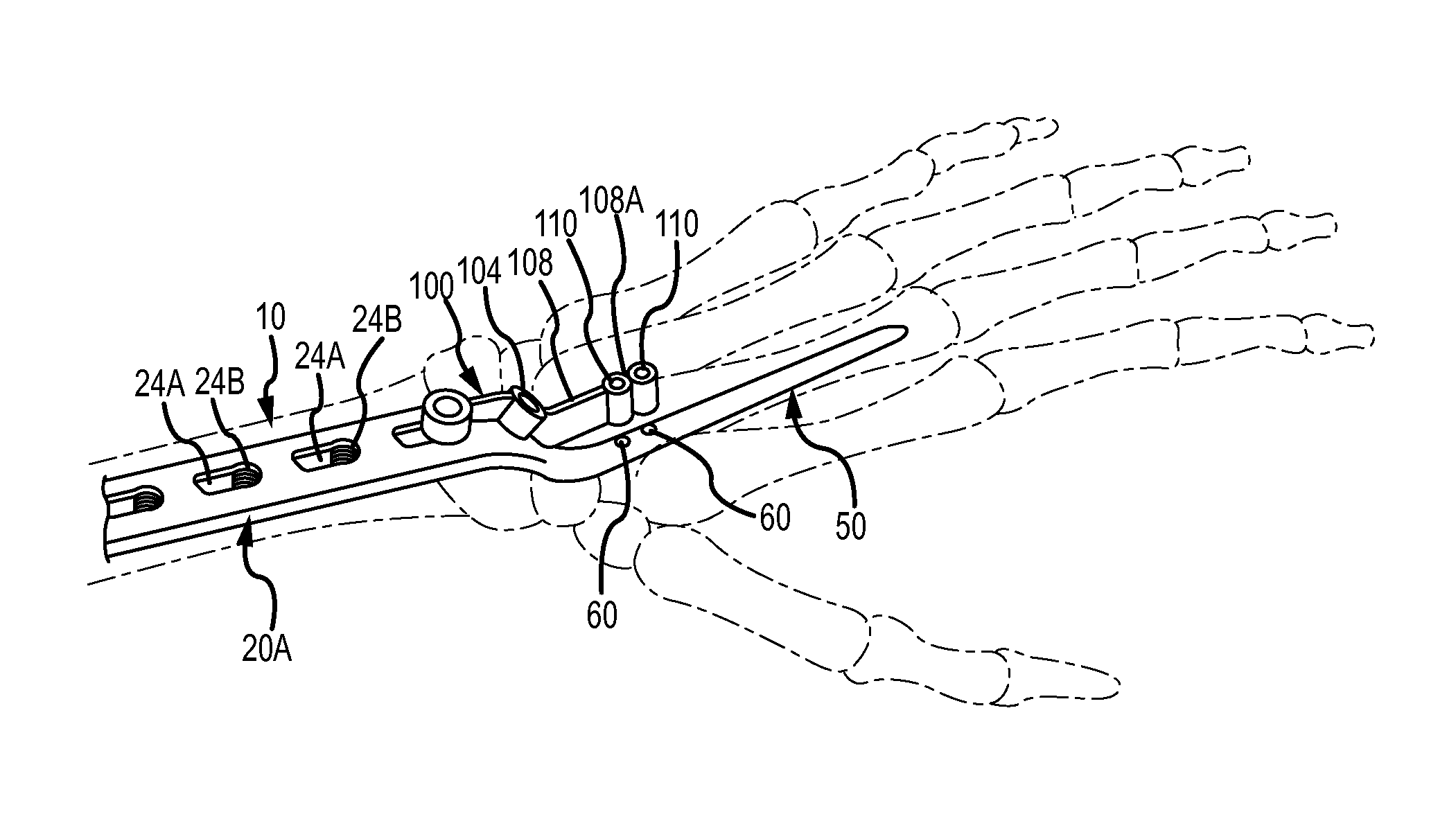
Full wrist fusion device
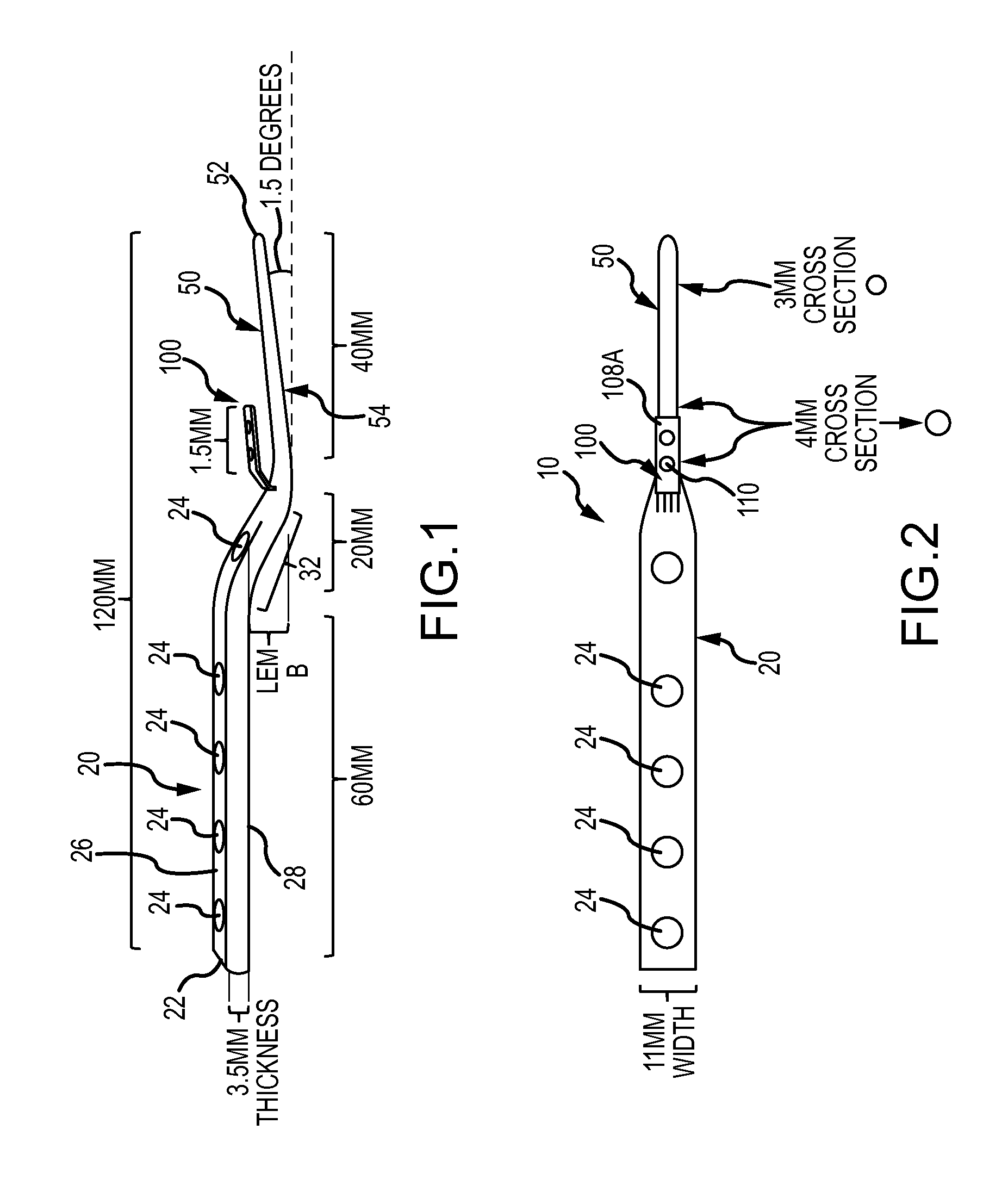
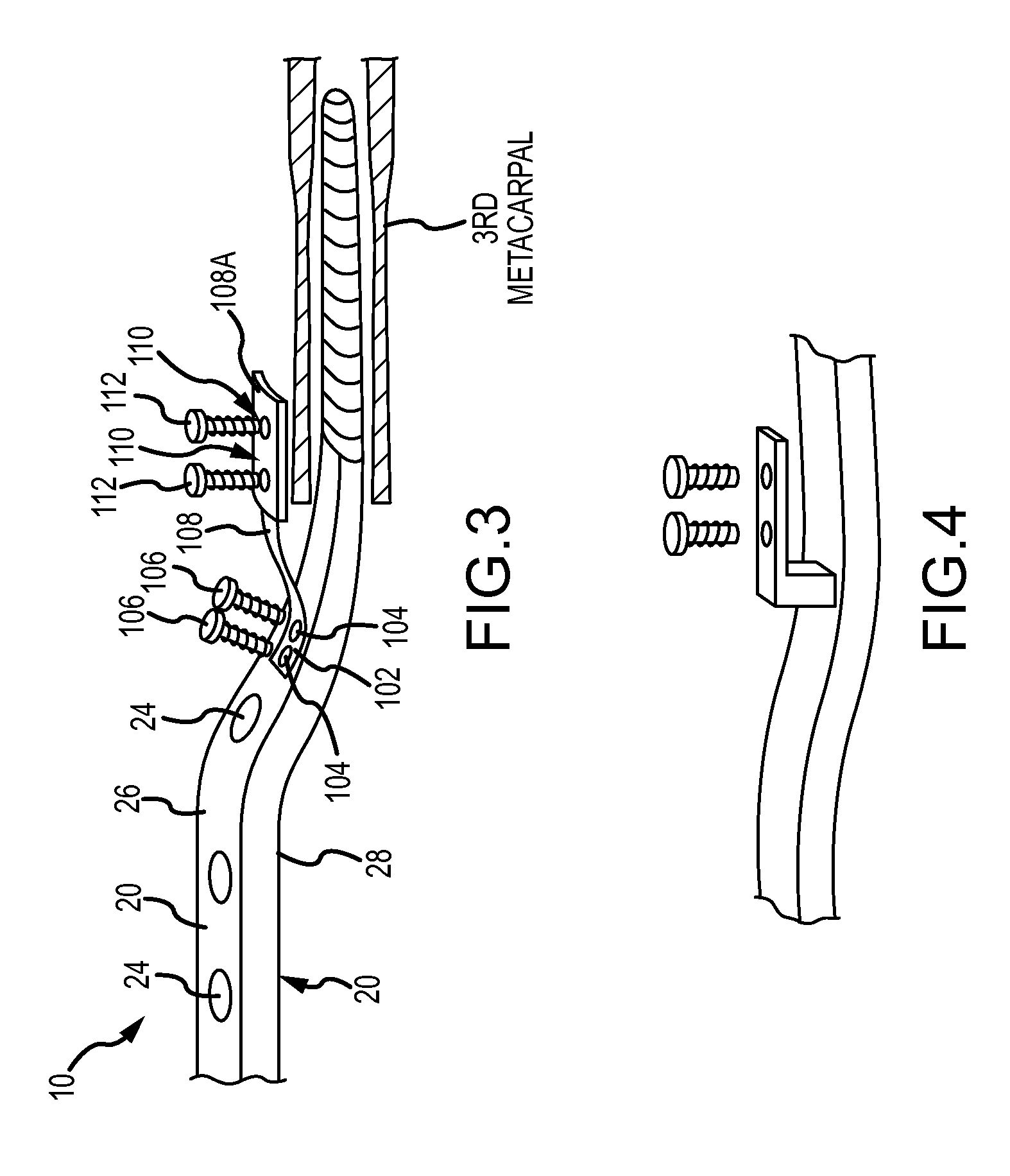
ActiveUS20150094722A1Additional anti-rotational stabilityImprove stabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCarpal JointCarpal bones
Disclosed is a device for total wrist fusion that includes (a) a first section, which is preferably a plate, that is positioned under the skin on top of the forearm, wrist and potentially part of the hand and connected to one or more of the radius or carpal bones, (b) a second section, which is preferably in the shape of an awl and is received in the cannula of the third metacarpal bone. Optionally, an anti-rotational third section may be included, which can connect to the top of the third metacarpal bone.
Owner:EXSOMED CORP
Tissue structure perforation system and method
ActiveUS8257379B2Relieve stressReduce lossesIncision instrumentsSurgical needlesCTS - Carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal ligament
A surgical treatment can involve creating a pattern of perforations in a tissue structure to allow lengthening of that tissue structure. For example, a pattern of perforations can be created in the transverse carpal ligament of a patient suffering from carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) that allows the carpal ligament to lengthen slightly. This lengthening can relieve pressure on the median nerve, thereby reducing the symptoms of CTS while maintaining the structural integrity of the wrist. A surgical instrument for use in perforating a tissue structure (such as the transverse ligament) can be an elongate structure with one or more retractable blades. Such a tool can be used in either an open or minimally invasive procedure to create a desired pattern of perforations in the tissue structure.
Owner:KYPHON
Micro-scalpel used to treat carpal tunnel syndrome
InactiveUS20120029542A1Reduce the number of cutsShorten the timeIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsCTS - Carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal tunnel surgery
A micro-scalpel used to treat carpal tunnel syndrome has an elongated columnar blade, one end of the blade obliquely cut to form a tip, the obliquely-cut surface of the tip sufficiently sharp to pierce and cut skin of a patient. The other end of the blade is connected to a hollow sleeve connector, and the hollow sleeve connector is combined with a handle. The micro-scalpel is oriented perpendicular to a transverse carpal ligament, and swings from its proximal end toward its distal end to cut the transverse carpal ligament, thereby reducing the number of cuts of the blade and saving time for completing the carpal tunnel surgery.
Owner:HUANG CHI YUEN
Tissue structure perforation system and method
ActiveUS20120029543A1Relieve stressReduce lossesIncision instrumentsCTS - Carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal ligament
A surgical treatment can involve creating a pattern of perforations in a tissue structure to allow lengthening of that tissue structure. For example, a pattern of perforations can be created in the transverse carpal ligament of a patient suffering from carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) that allows the carpal ligament to lengthen slightly. This lengthening can relieve pressure on the median nerve, thereby reducing the symptoms of CTS while maintaining the structural integrity of the wrist. A surgical instrument for use in perforating a tissue structure (such as the transverse ligament) can be an elongate structure with one or more retractable blades. Such a tool can be used in either an open or minimally invasive procedure to create a desired pattern of perforations in the tissue structure.
Owner:KYPHON
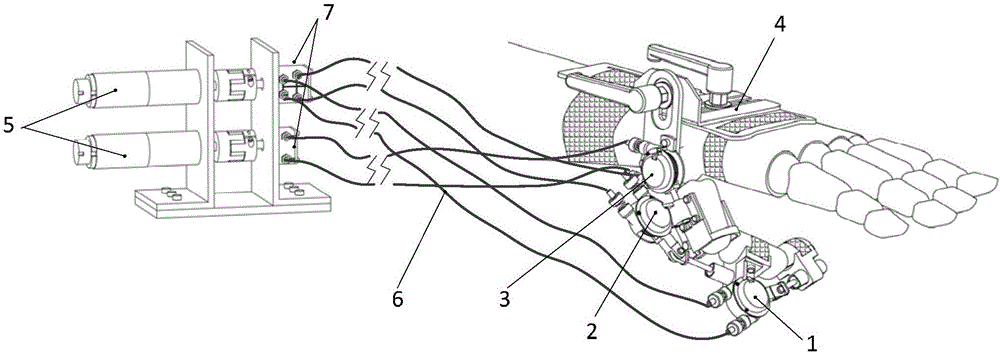
Thumb function rehabilitation exoskeleton robot
ActiveCN107432816AReduce the burden onNo pulling effectAdditive manufacturing apparatusChiropractic devicesExoskeleton robotFinger joint
A thumb function rehabilitation exoskeleton robot relates to exoskeleton robots. The thumb function rehabilitation exoskeleton robot solves the problem that existing rehabilitation mechanical arm cannot thoroughly simulate natural motions of finger joints, is poor in rehabilitation treatment effects and lacks a sensing function. According to the thumb function rehabilitation exoskeleton robot, an interphalangeal joint unit and a metacarpophalangeal joint unit drive thumb joints and metacarpophalangeal joints to bend or stretch through flat guide rod mechanisms; a thumb carpal joint unit is centered to the carpal joint of a thumb directly through a metacarpal adjustment mechanism to achieve contracting or extending motions of the carpal joint; a transmission driving mechanism is powered by a direct current motor; a cable reel module transfers the moment output by the direct current motor to the interphalangeal joint unit, the metacarpophalangeal unit and the carpal joint unit through Bowden cables. The thumb function rehabilitation exoskeleton robot is applicable thumb function rehabilitation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
System and method for simultaneously applying a plurality of therapeutic modalities to treat carpal tunnel syndrome
InactiveUS20070293793A1Improve efficiencyIncrease the number ofChiropractic devicesEye exercisersDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCTS - Carpal tunnel syndrome
Embodiments of the present invention provide a system and method for delivering a plurality of modalities for the treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Light therapy is applied to the carpal tunnel region of the hand during alternating periods of automated carpal bone structure extensions, whereby said light therapy penetrates beyond the bone structures to the carpal (volar and transverse) ligament structures, median nerve, and muscles. The light therapy is applied both above and below these structures. Simultaneously applied electrical stimulation may occurs between electrodes located both above and below various positions about the carpal tunnel region. Both light therapy and electrical stimulation are positioned optimally to affect the carpal tunnel via automated structures that provide continuous feedback to a control system. The automated structures also stimulate the flow of blood and movement of fluids associated with pressure inducing edema through the carpal tunnel region.
Owner:AXIOM WORLDWIDE
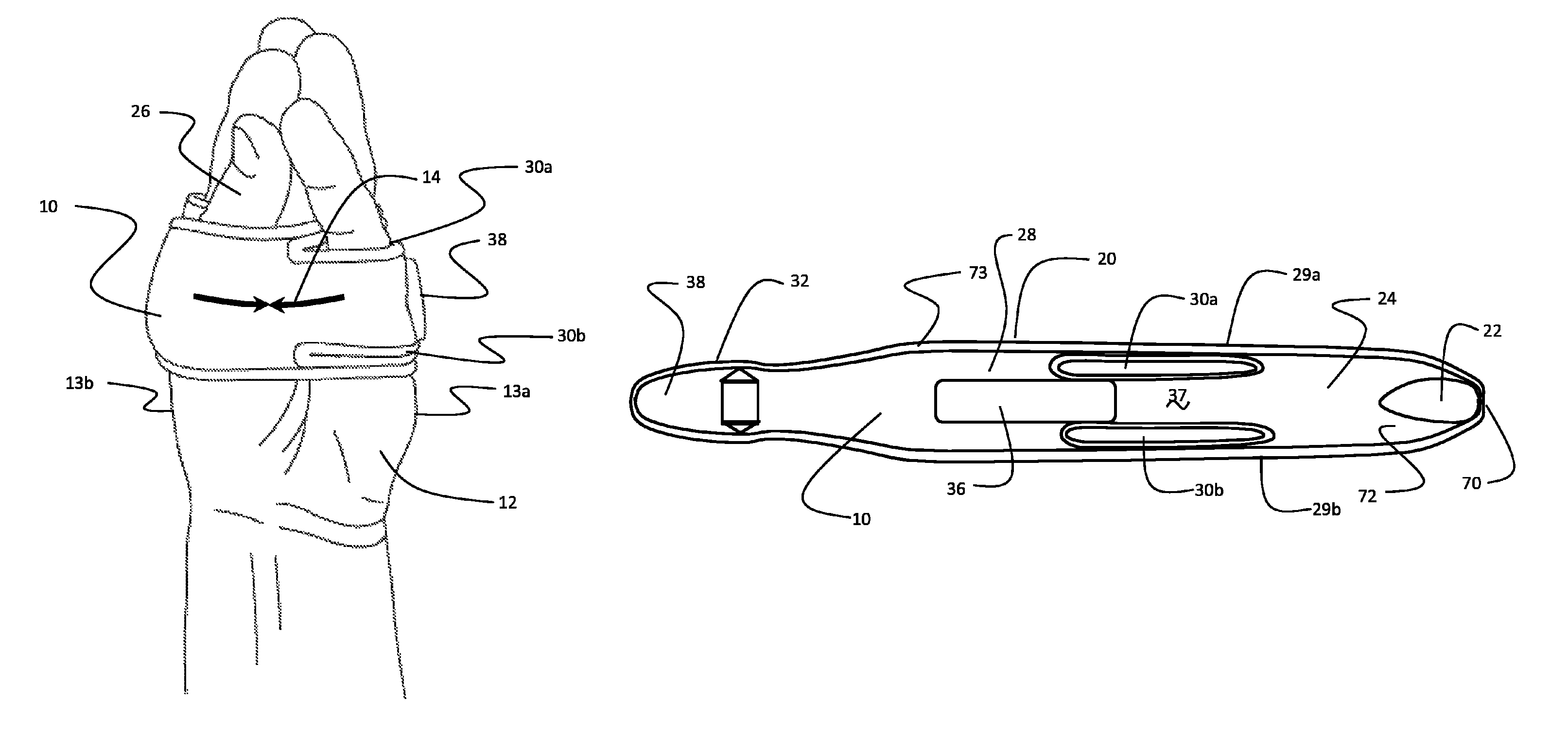
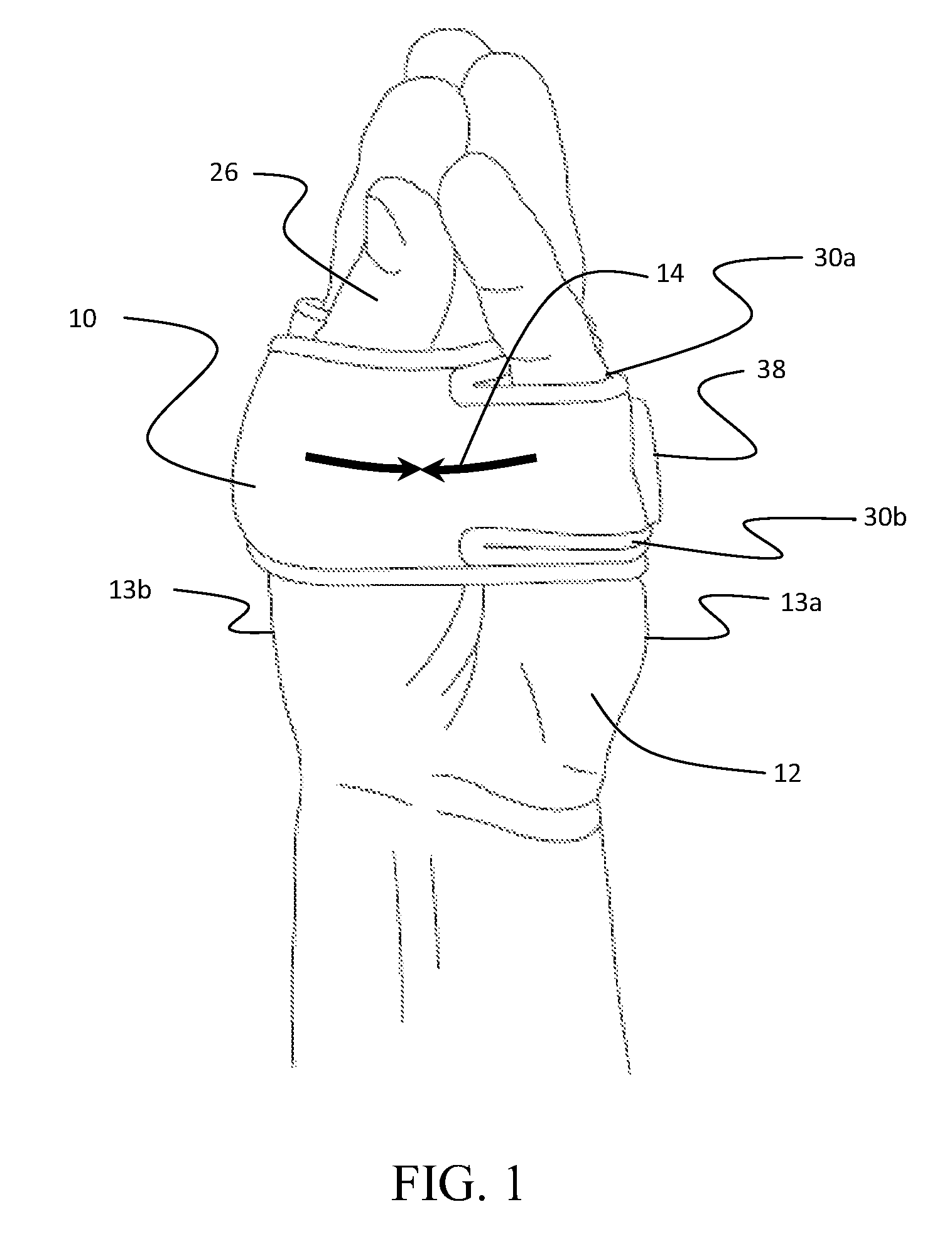
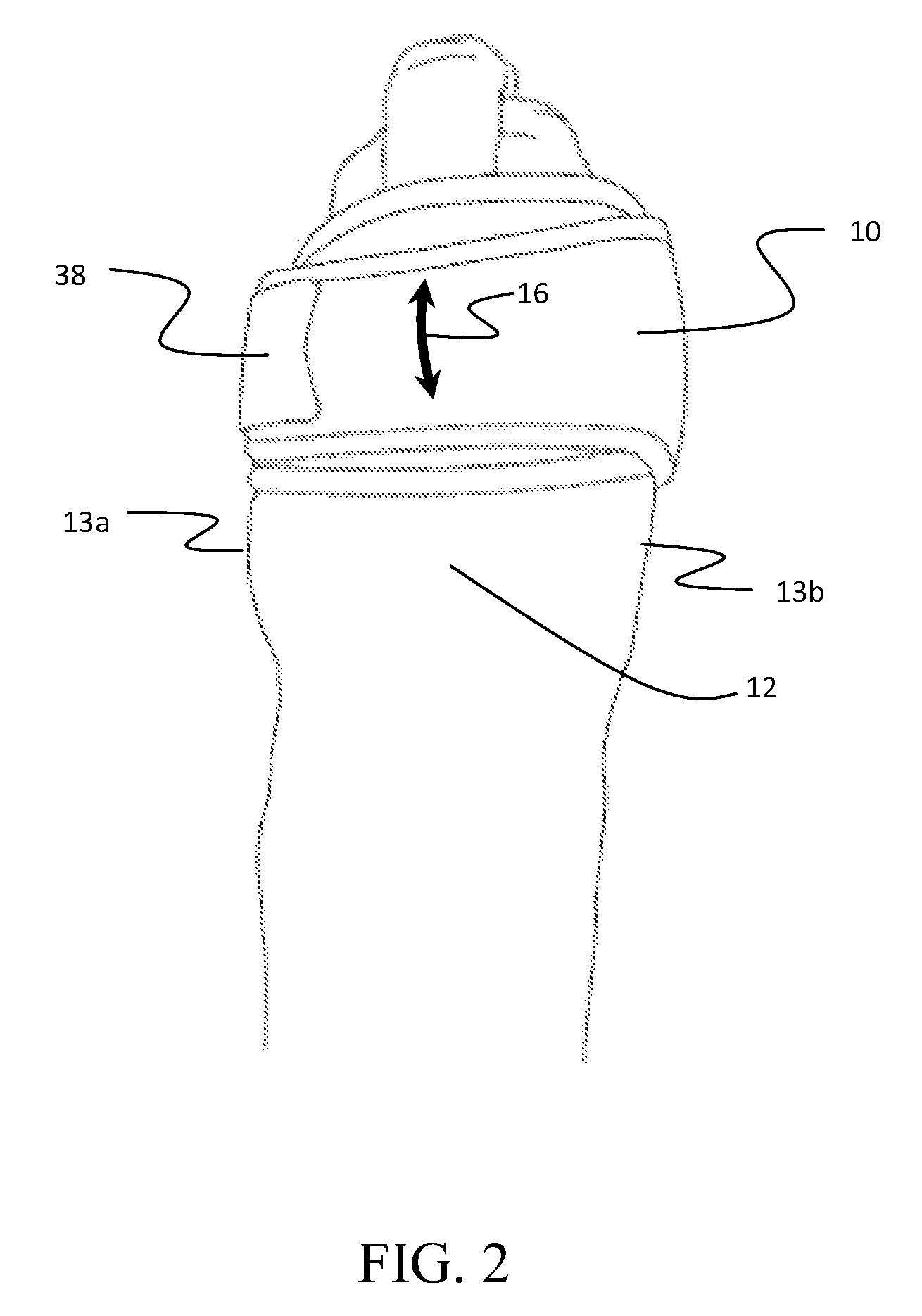
Co-dynamic adjustable orthotic appliance for carpal tunnel syndrome
The present invention provides an orthotic appliance for the carpus of a human hand for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome using co-dynamic, rather than traditional static or dynamic, techniques. The appliance may apply a 2 pound dorsally directed force about the region of the pisiform bone in the neutral carpal position of a human hand upon co-contraction of the hand and up to 8 pounds dorsally directed during arc of motion in carpal flexion, as the wrist and hand is encouraged to actively move in all planes of motion without negatively affecting the normal activities of daily living. The appliance may comprise a biasing structure for applying the dorsally directed force and a base structure for maintaining the biasing structure in its proper configuration during normal hand motion.
Owner:WILLLIAMS GEORGE ROGER
Carpal tunnel brace
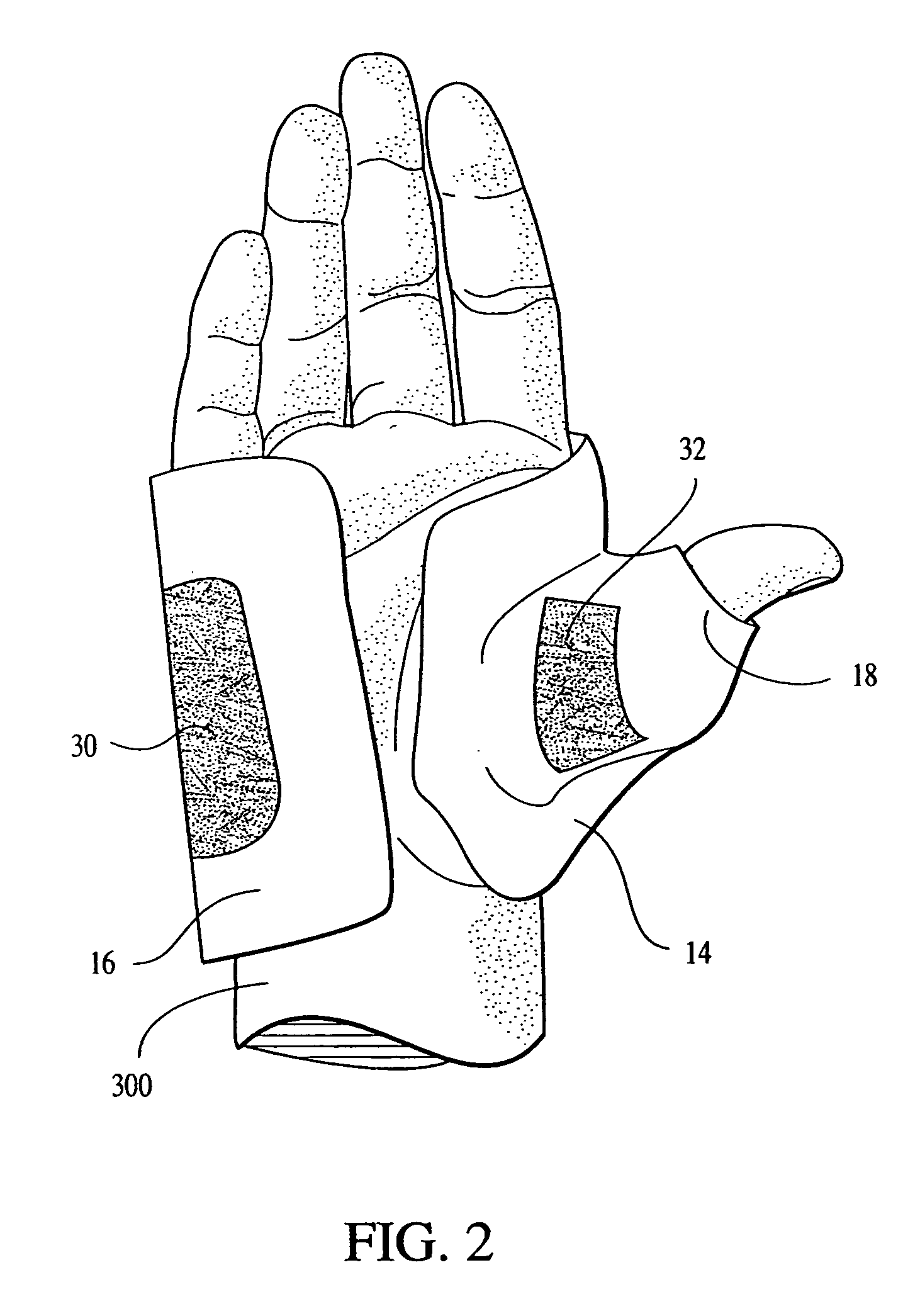
A brace for relief of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome employs a strap element having a thumb aperture proximate a first end and a slot adjacent a peripheral edge of the strap element to receive a fifth finger. The strap element extends from the thumb aperture to be received in a central portion across a dorsal portion of a hand. The strap element then extends around the ulnar border and across the palm of the hand past the radial border with a tail portion of the strap element overlapping the central portion. A fastener moiety is provided on the tail portion of the strap element and a mating moiety on an outer surface of the strap element to engages the fastener moiety. The strap element tensioned around the hand produces approximation of carpals and metacarpals in the hand.
Owner:KEOSHIAN CRAIG +1
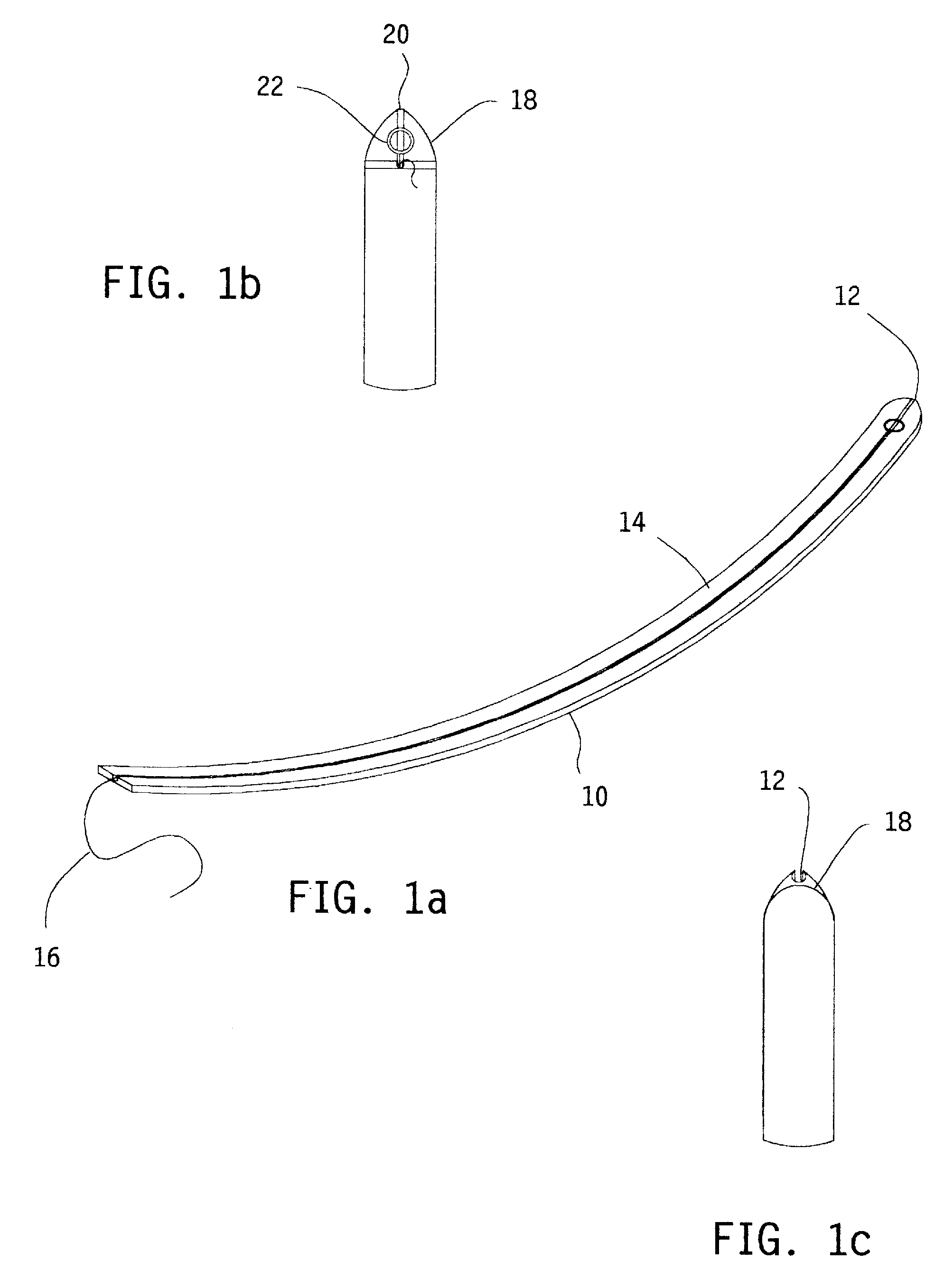
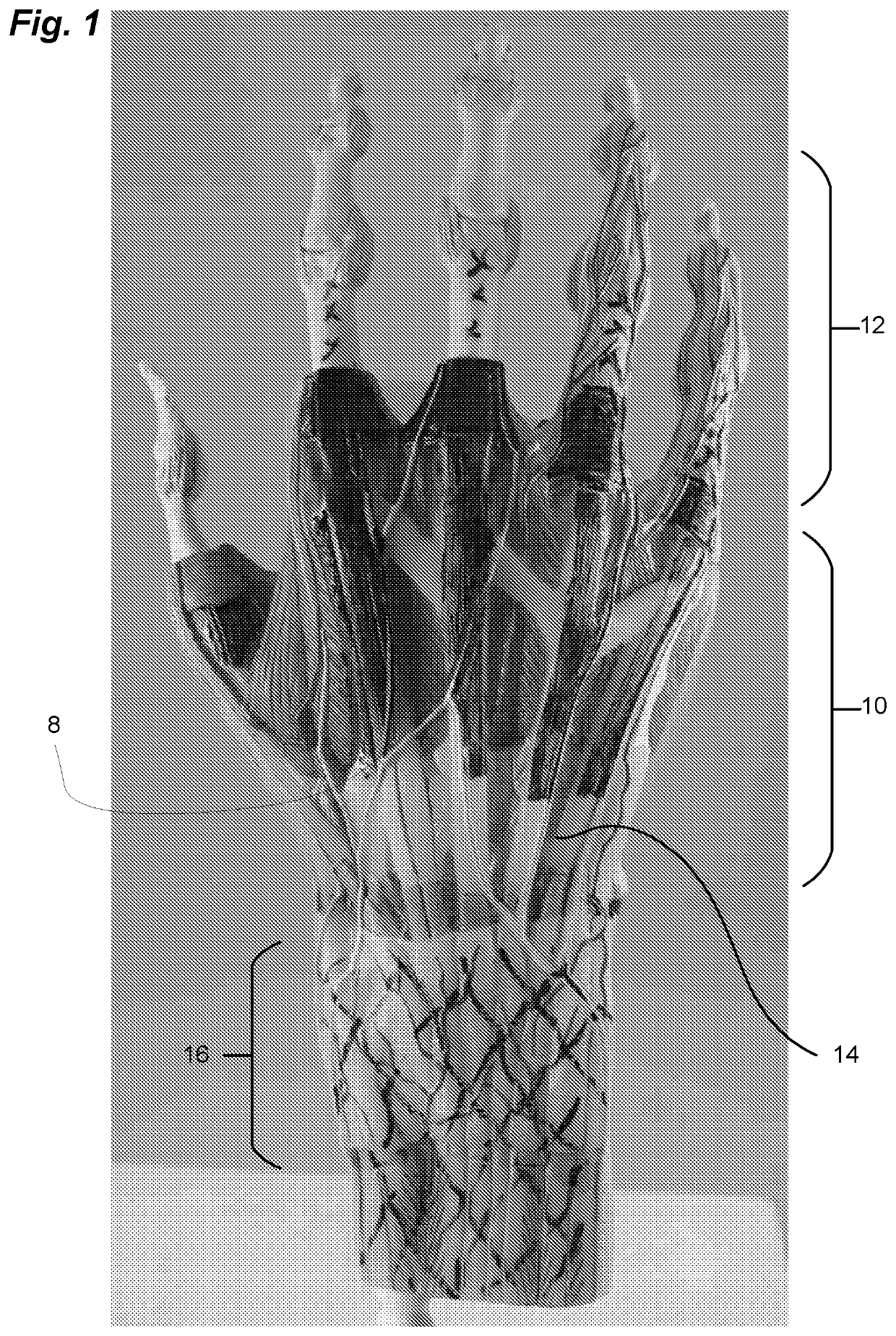
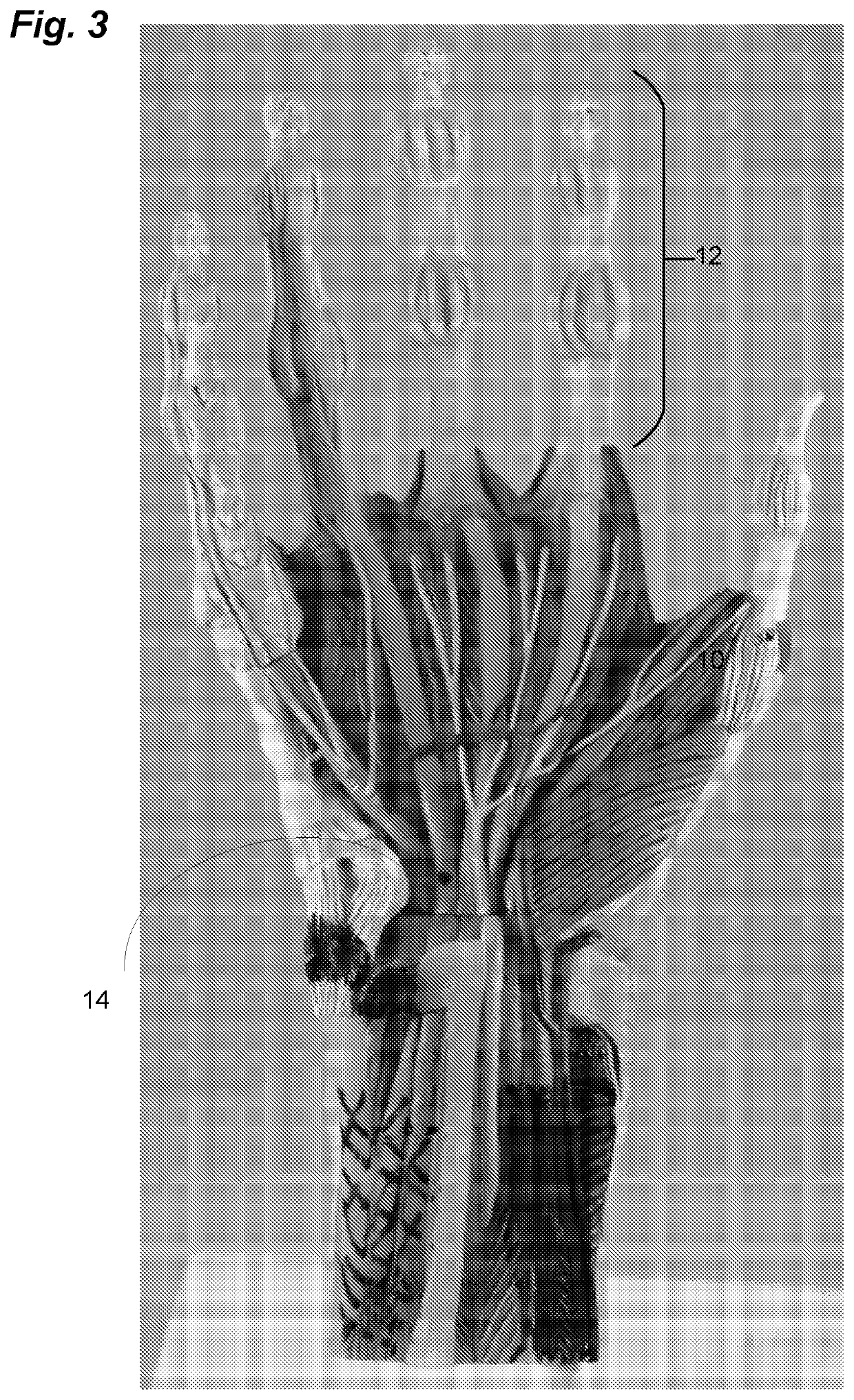
Sling blade transection of the transverse carpal ligament
A sling blade apparatus allows percutaneous transaction of fascia or ligaments and in particular for use in transaction of the human transverse carpal ligament. A flexible sling guide is deployed percutaneously beneath the transverse carpal ligament and when drawn taut interfaces intimately with the transverse carpal ligament. The sling in turn serves as a guide along which cutting instruments can be passed to transect the ligament while simultaneously serving as a protective shield for the adjacent median nerve.
Owner:SUDDABY LOUBERT
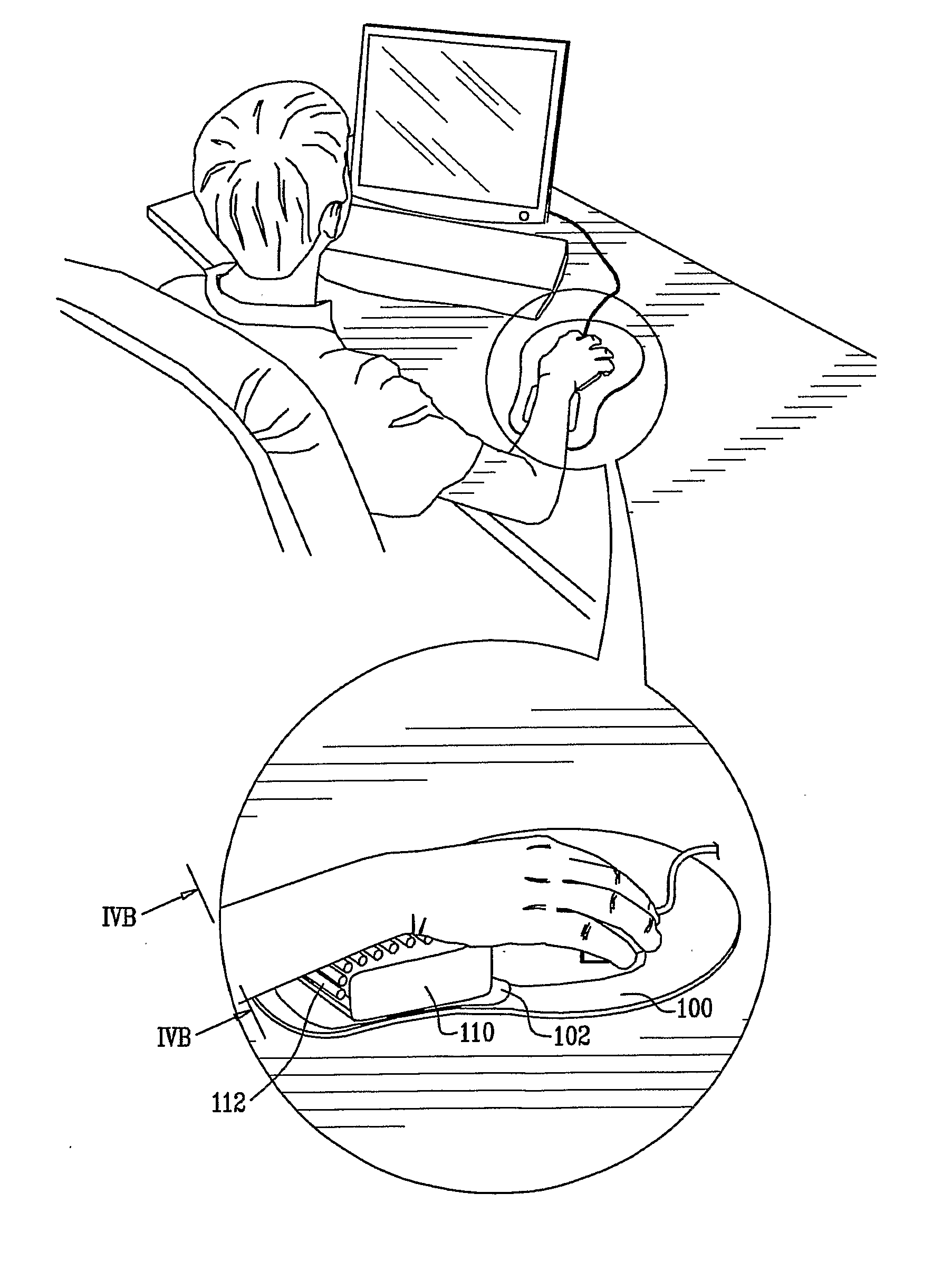
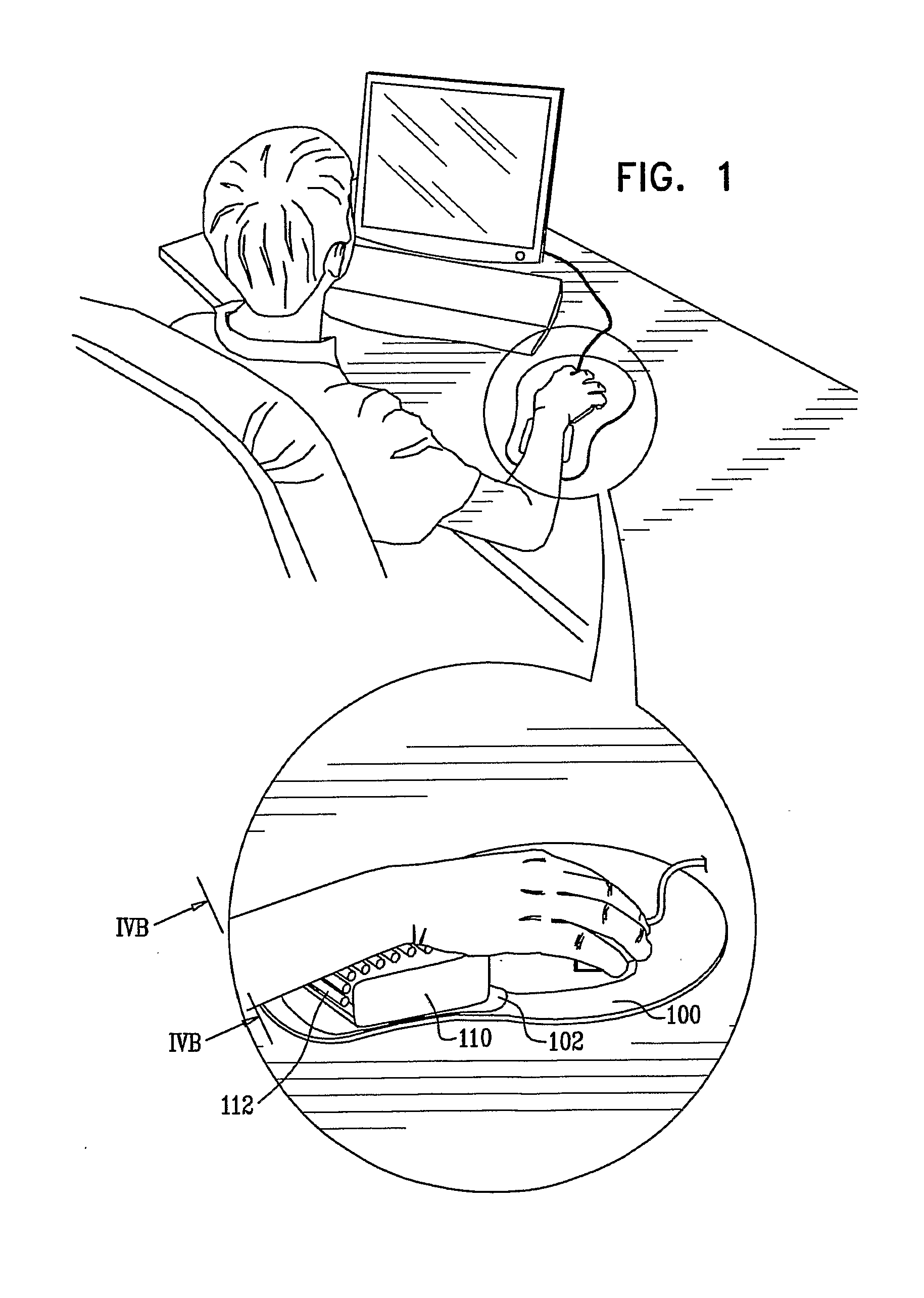
Carpal active protection systems (CAPS)
InactiveUS20110230805A1Enhancement in venous outflowEnhancing venous sufficiencyRoller massageSuction-kneading massageDiseaseComputer users
A specially designed support is disclosed aimed at supporting the proximal and / or distal forearm and wrist areas while actively transferring a limited and directed pressure to the volar aspect of the distal forearm and wrist. The action is not coupled to movement performed by the user. This force, in turn, allows for enhancing venous return from the area, and thus acts to prevent ailments caused by use of computer input devices (e.g. computer mouse, keyboard). The support further comprises a motor exerting said repetitive pressure or possibly other means for forming such movement as described. The support utilizes continuous movement to alter and better the physiology of computer users, lessening chances of occurrence of pathology specifically known as carpal tunnel syndrome and possibly alleviating this condition altogether The support may be used in a mouse pad, keyboard rest or arm rest. This design may be augmented by other modifications and additions which may be utilized in conjunction with the current invention or as inventions or modifications in their own right.
Owner:ORON AMIR
System and method for trapezium bone replacement
A carpometacarpal joint replacement system for replacing the trapezium bone in the hand is provided. The system includes a trapezial implant for the carpometacarpal joint resulting in replacement of the carpal trapezium bone with a prosthesis having the same anatomical configuration as the trapezium bone. The implant device comprises a plurality of concave surfaces, with the plurality of concave surfaces articulating with the carpal and metacarpal bones.
Owner:EXTREMITY MEDICAL
High impact-resistive protective glove
A glove for hand protection during sports, conforming to hands, fingers, and thumb, extending from carpal bones to cover proximal phalanges up to the proximal interphaiangeal joint comprising impact-absorbing materials: an outer glove conforming to hand, fingers, and thumb extending from carpal bones to cover distal phalanges, comprising abrasion-resistant materials.
Owner:MCPP INC
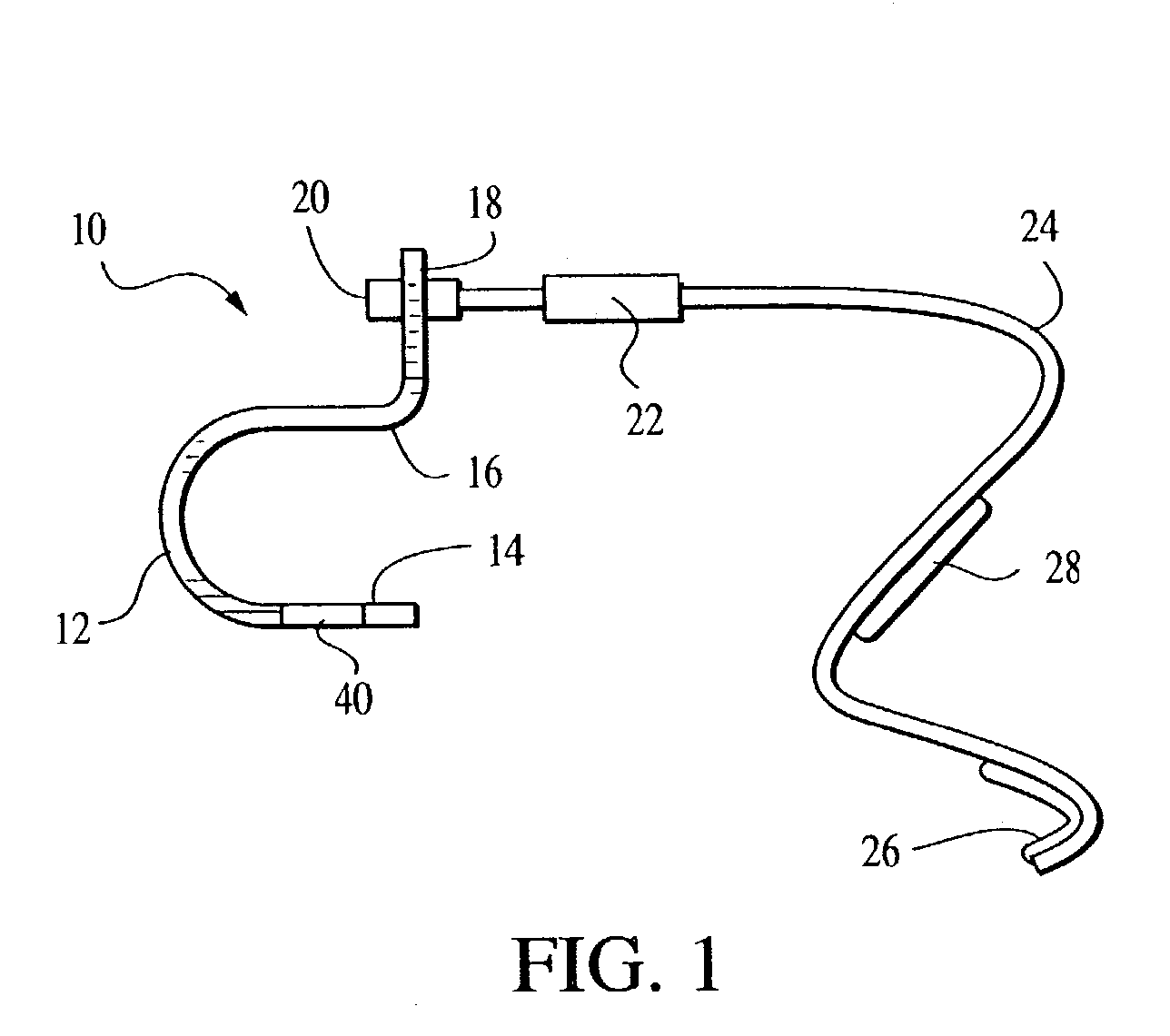
Adjustable apparatus and method for treating carpal tunnel syndrome
InactiveUS7344511B2Easy to useSimple and inexpensive to manufactureDiagnosticsRestraining devicesCTS - Carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal ligament
The apparatus of the present invention stretches the carpal ligament and the flexor retinaculum, as well as the superficial structures and muscles of the hand, in a safe manner under precise control of the patient or a healthcare professional. Various embodiments of the inventive apparatus commonly include a housing for receiving the hypothenar portion of the patient's hand with an open side portion adapted and configured to contact and retain the hypothenar region of the patient's hand, with an edge of the housing extending along a central longitudinal dorsal portion of the hand, while a flexible resilient strap is wrapped around the thenar portion of the hand (i.e. around the thumb area) in such a manner as to pull the thenar portion of the hand upward with the edge of the housing serving as a fulcrum around which the thenar and hypothenar portions of the hand are bent. The strap is then secured to itself or to the housing to keep the thenar and hypothenar portions pulled apart during the course of treatment. The bending of the thenar and hypothenar regions of the hand around the fulcrum cause the carpal ligament and the flexor retinaculum to stretch expanding the carpal tunnel and relieving pressure on the median nerve.
Owner:PORRATA GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com