Patents
Literature
107 results about "Interphalangeal Joint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
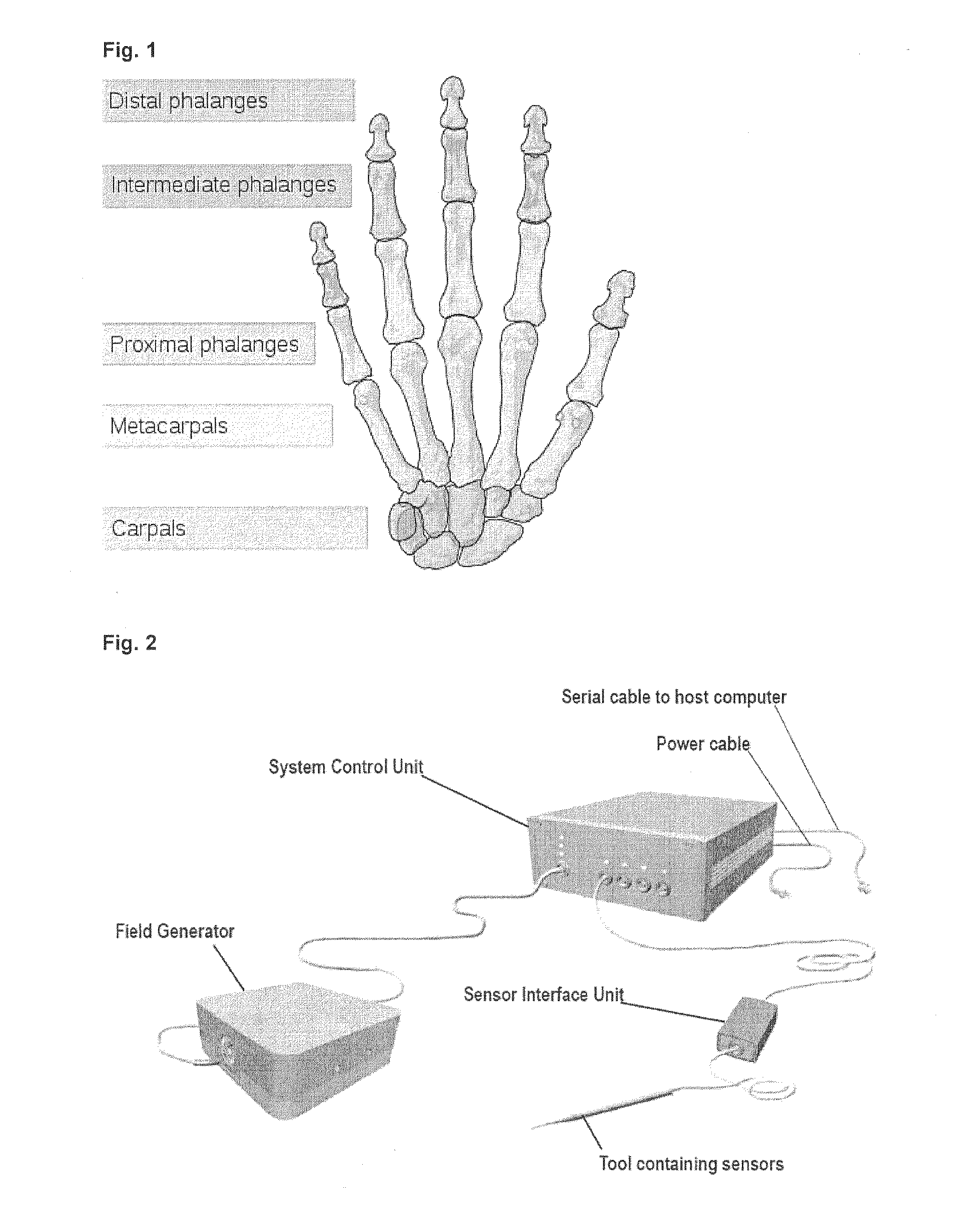
Hinge joints between the phalanges of the hand or foot.
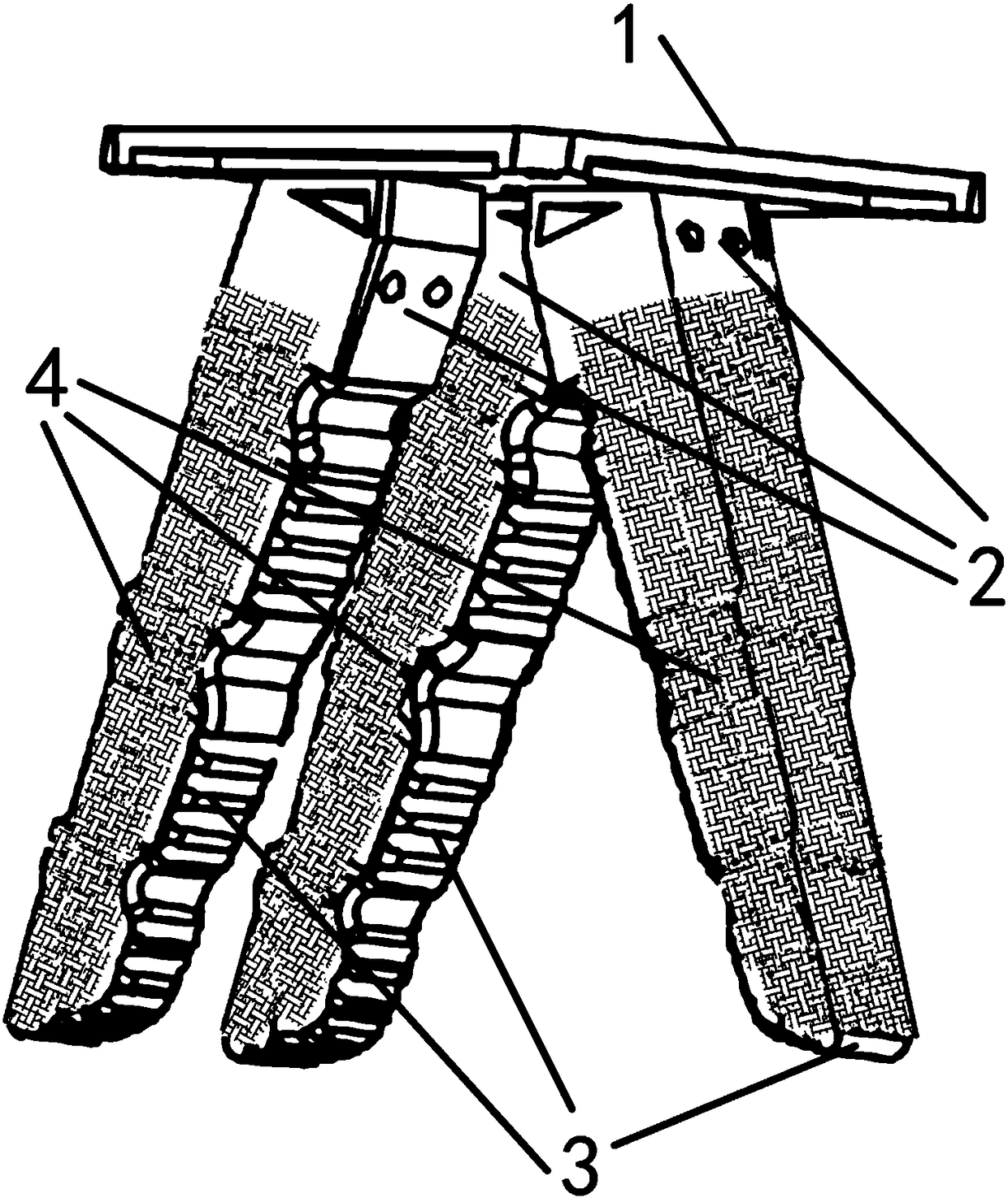
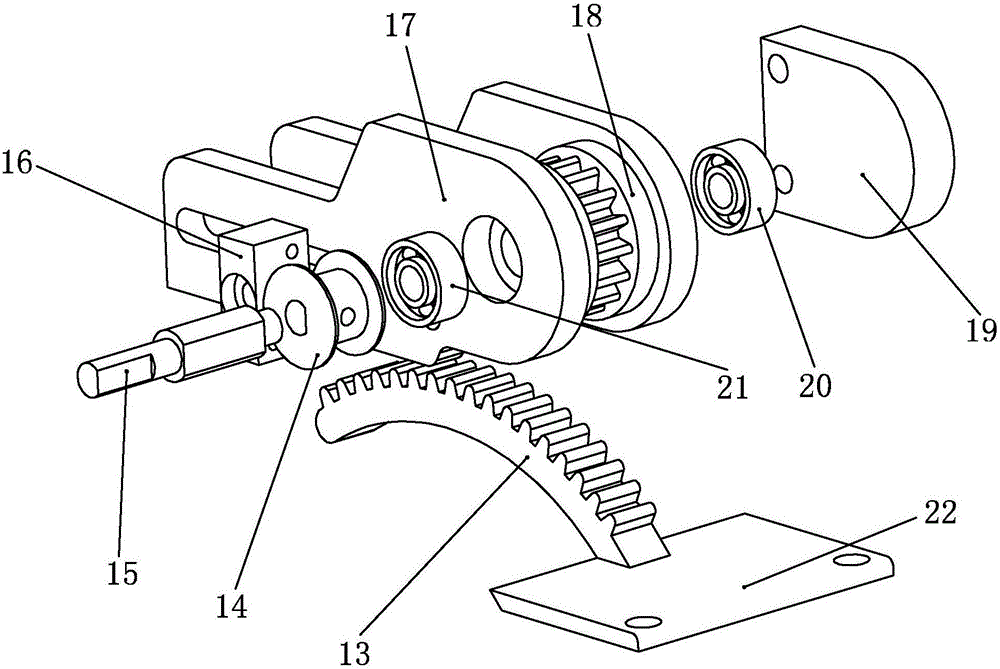
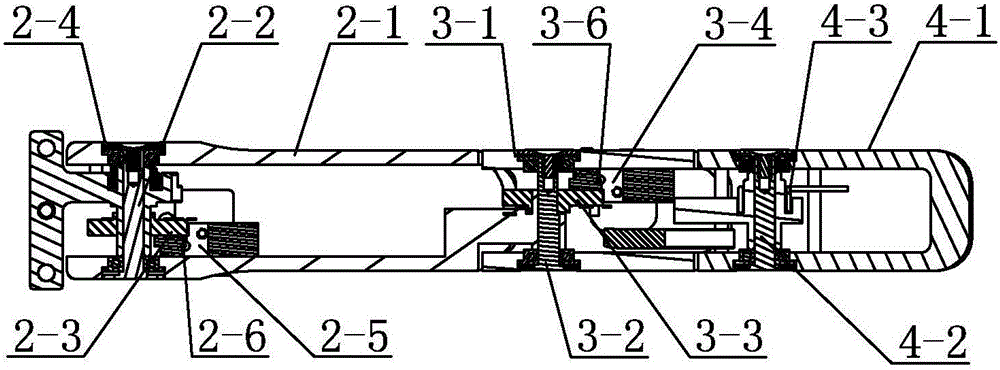
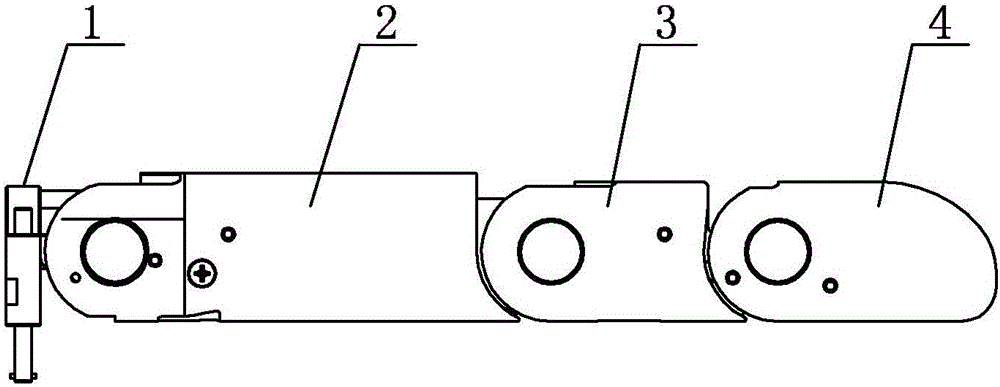
Intramedullary osteosynthesis implant
InactiveUS20050283159A1Stable osteosynthesisRegulate flexumSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisJoint arthrodesisDiaphysis
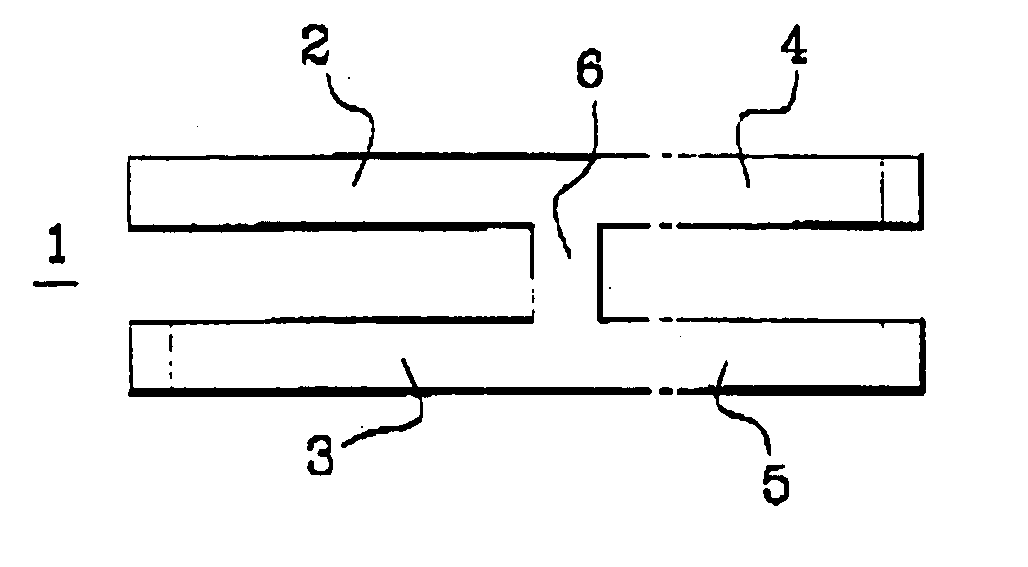
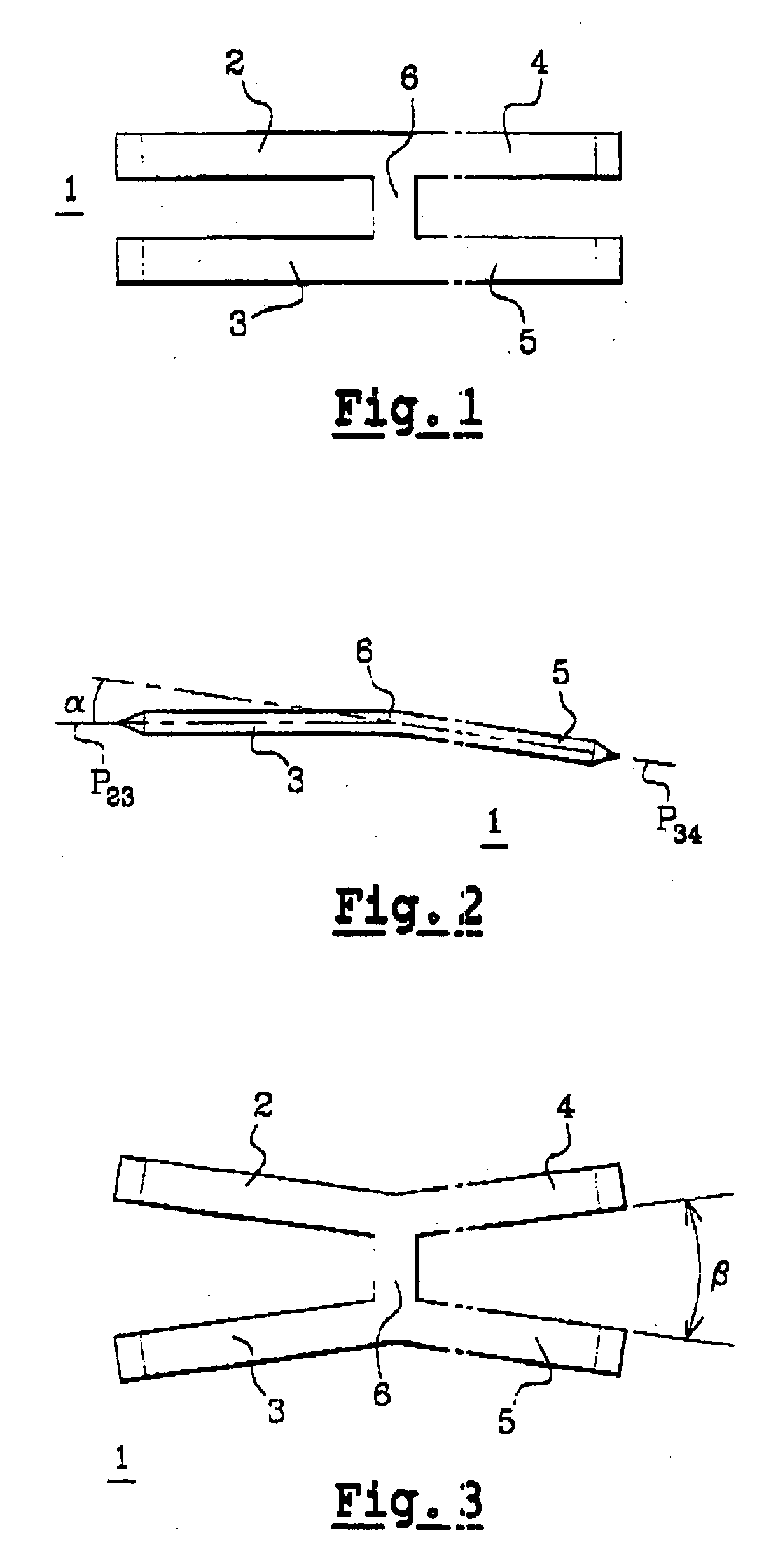
Intramedullary osteosynthesis implant, permitting in particular arthrodesis (1) of a joint, for example an interphalangeal joint, or diaphyseal osteosynthesis of the upper limb or of the lower limb, comprising two sets of at least two rods (2, 3, 4, 5) each extending on either side of a central zone (6), said rods (2, 3; 4, 5) being substantially parallel at ambient temperature within the same set, each set of rods being intended to be impacted in the medullary canal of a diaphysis, said implant being made from a shape-memory material so that, at body temperature, the rods (2, 3; 4, 5) of the same set spread apart so as to be able to immobilize themselves in said medullary canal.
Owner:AMADEX
Toe deformity repair using bioabsorbable pin
ActiveUS20080086139A1Overcome disadvantagesEliminate needInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsProximal phalanxDistal portion
Methods and apparatus for repair of toe deformities using a bioabsorbable pin. The apparatus is a kit of part comprising a bioabsorbable pin, a predrill, a bone tamp, a cutter and a forceps. One surgical method of repairing toe deformities includes resecting a proximal interphalangeal joint, drilling a hole in a proximal phalanx using a proximal portion of a pin, removing the pin from the proximal phalanx, drilling a tip of a toe through middle and distal phalanxes, driving the pin retrograde and traversing the distal, middle and proximal phalanxes until the pin stops advancing due to resistance at a proximal cortex, holding the pin and powering a pin driver to separate a distal portion of the pin, and suturing the wound.
Owner:ARTHREX
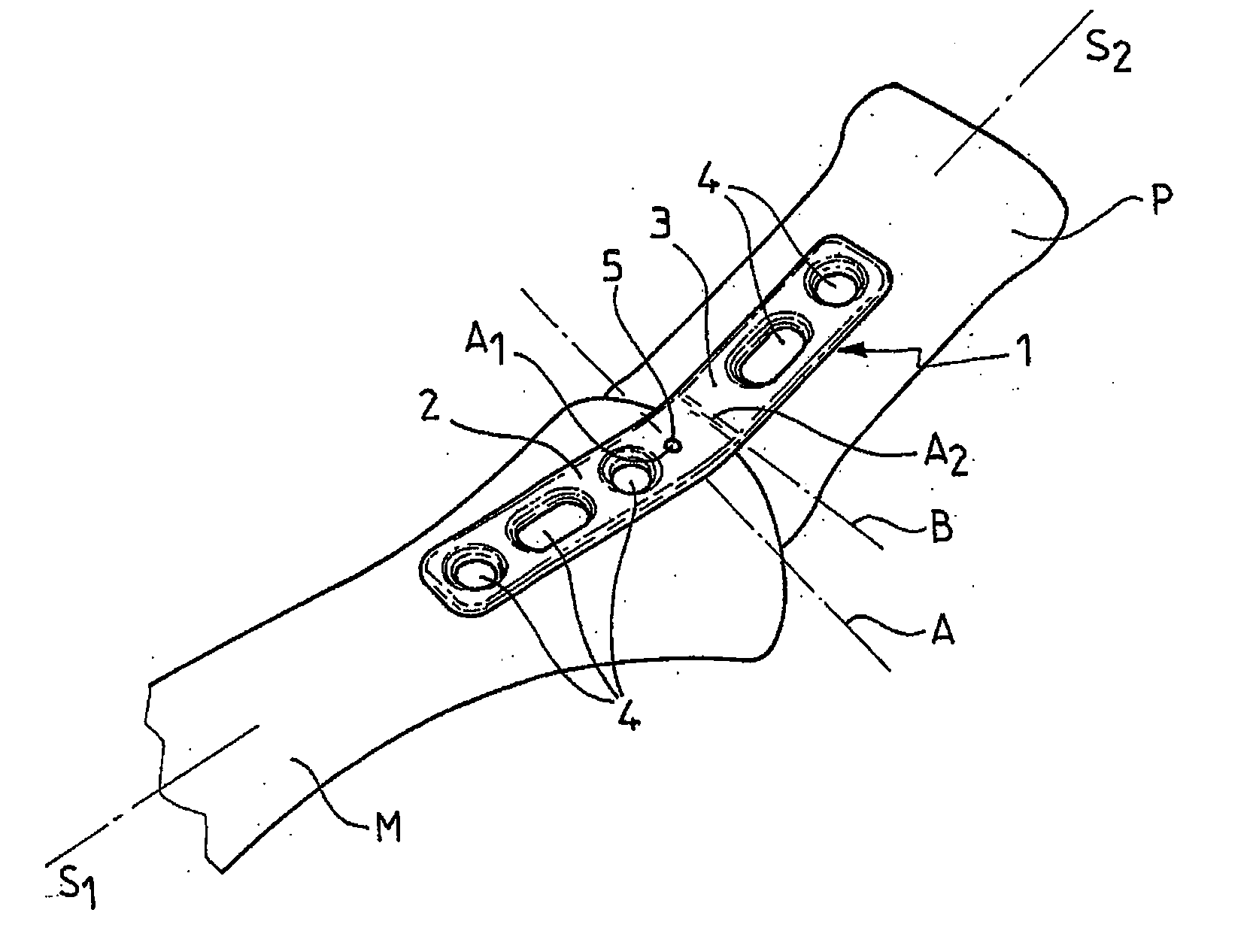
Plate for fixing the bones of a joint, in particular a metatarso-phalangeal joint
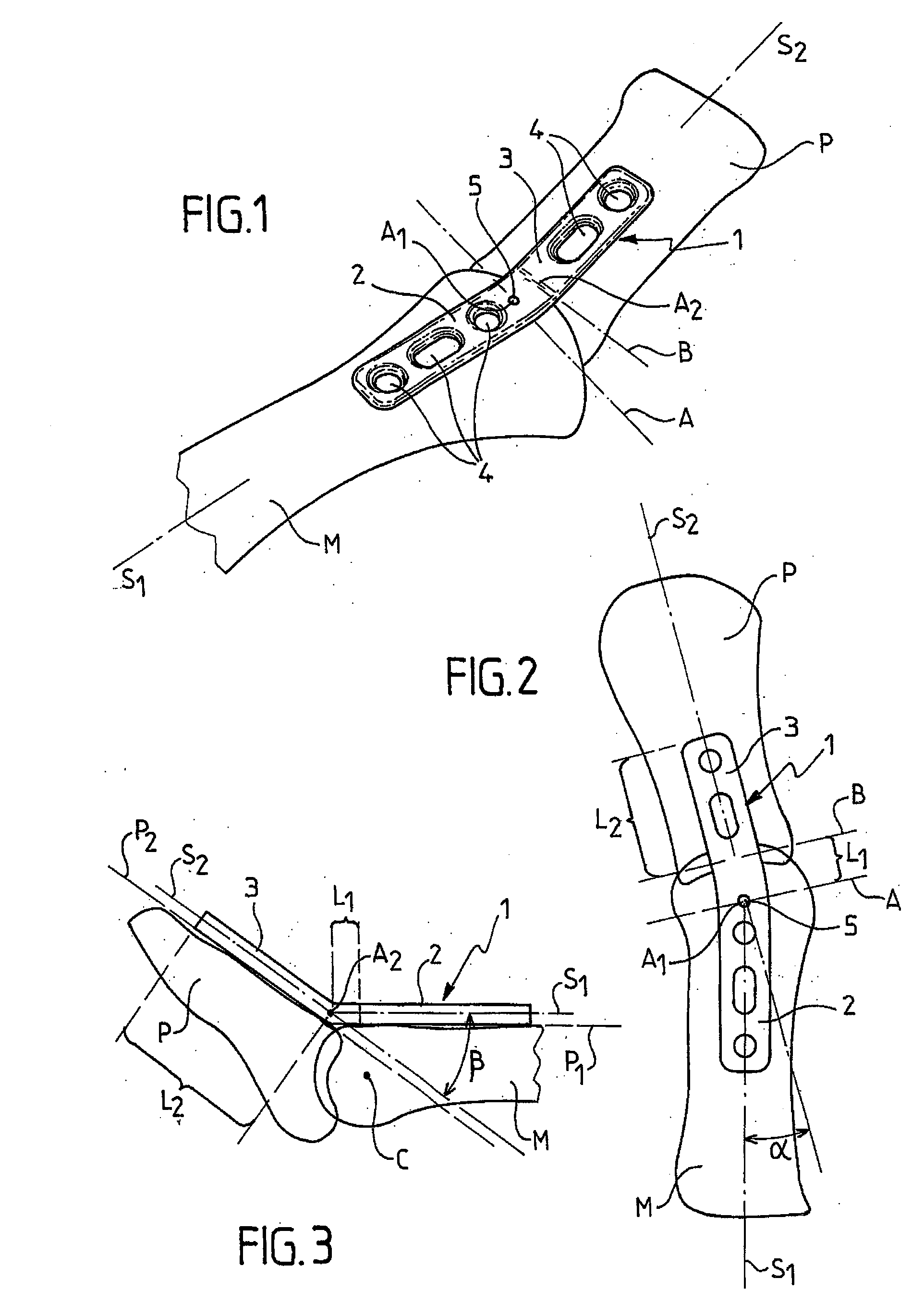
InactiveUS20030060827A1Improve accuracyEasy to placeJoint implantsBone platesJoint arthrodesisVertical plane
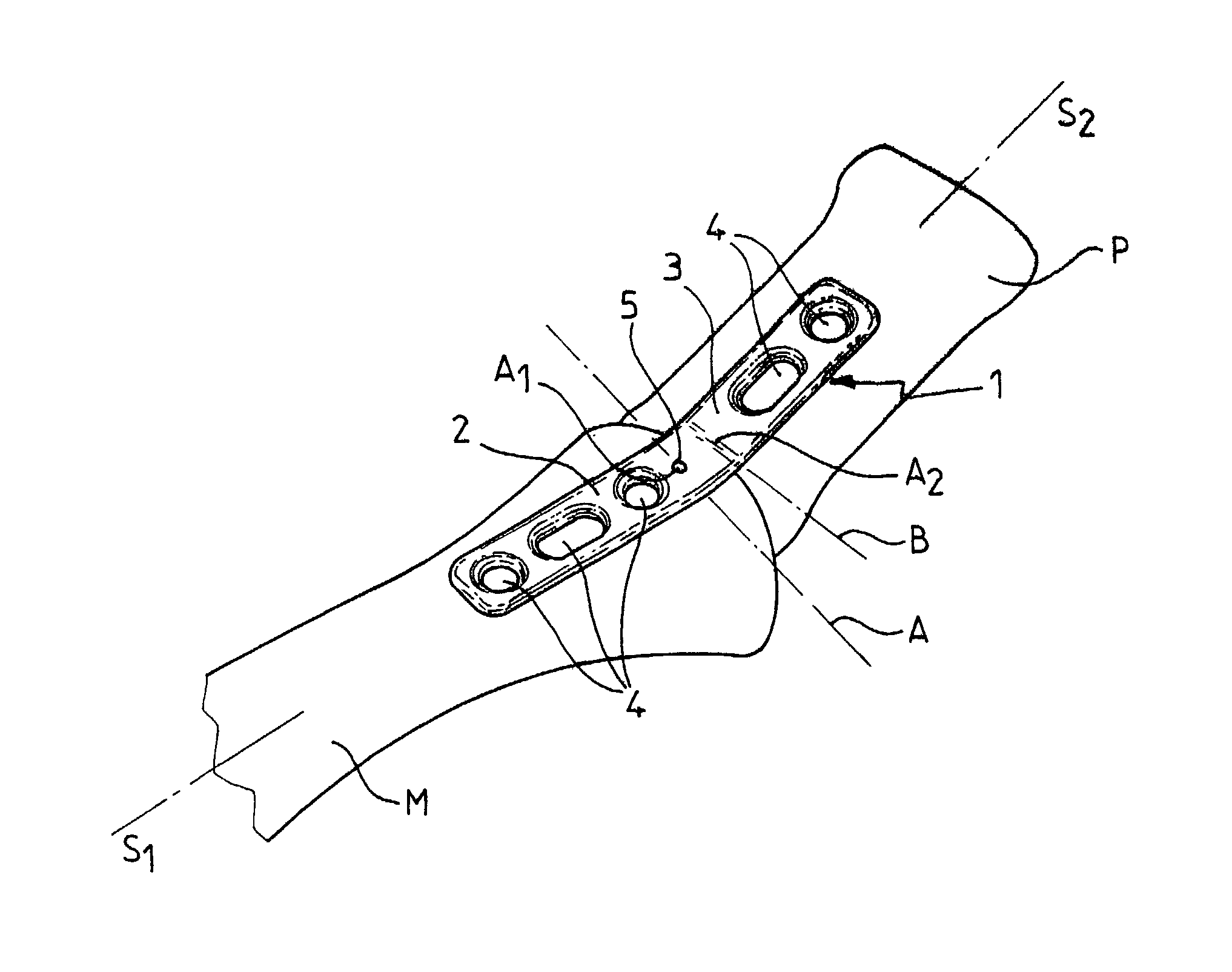
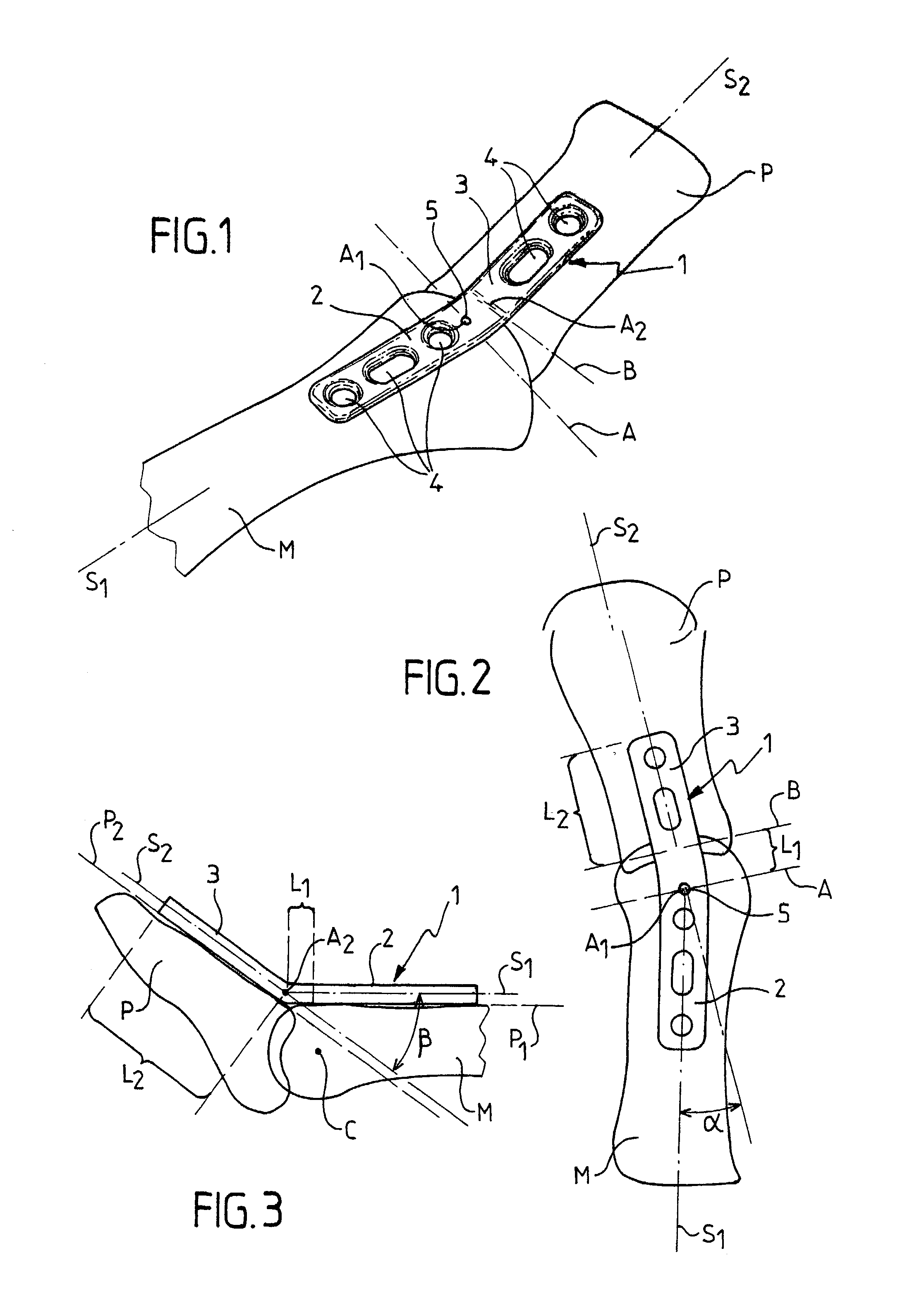
The invention relates to a plate for fixing the bones of a joint, in particular of a metatarso-phalanageal joint, for the purpose of performing arthrodesis, wherein: the plate comprises two sections, respectively a proximal section and a distal section, each section having a respective longitudinal axis of symmetry S1, S2 such that the projection onto a horizontal plane of tie axis of symmetry S2 of the distal section presents an angle of inclination relative to the projection of the axis of symmetry S1 of the proximal portion, the projections intersecting at a point A; and the projection onto a vertical plane of the axis of symmetry S2 presents an angle of inclination relative to the projection of the axis of symmetry S1, their intersection taking place at a point A2 which is distinct from the point A1
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
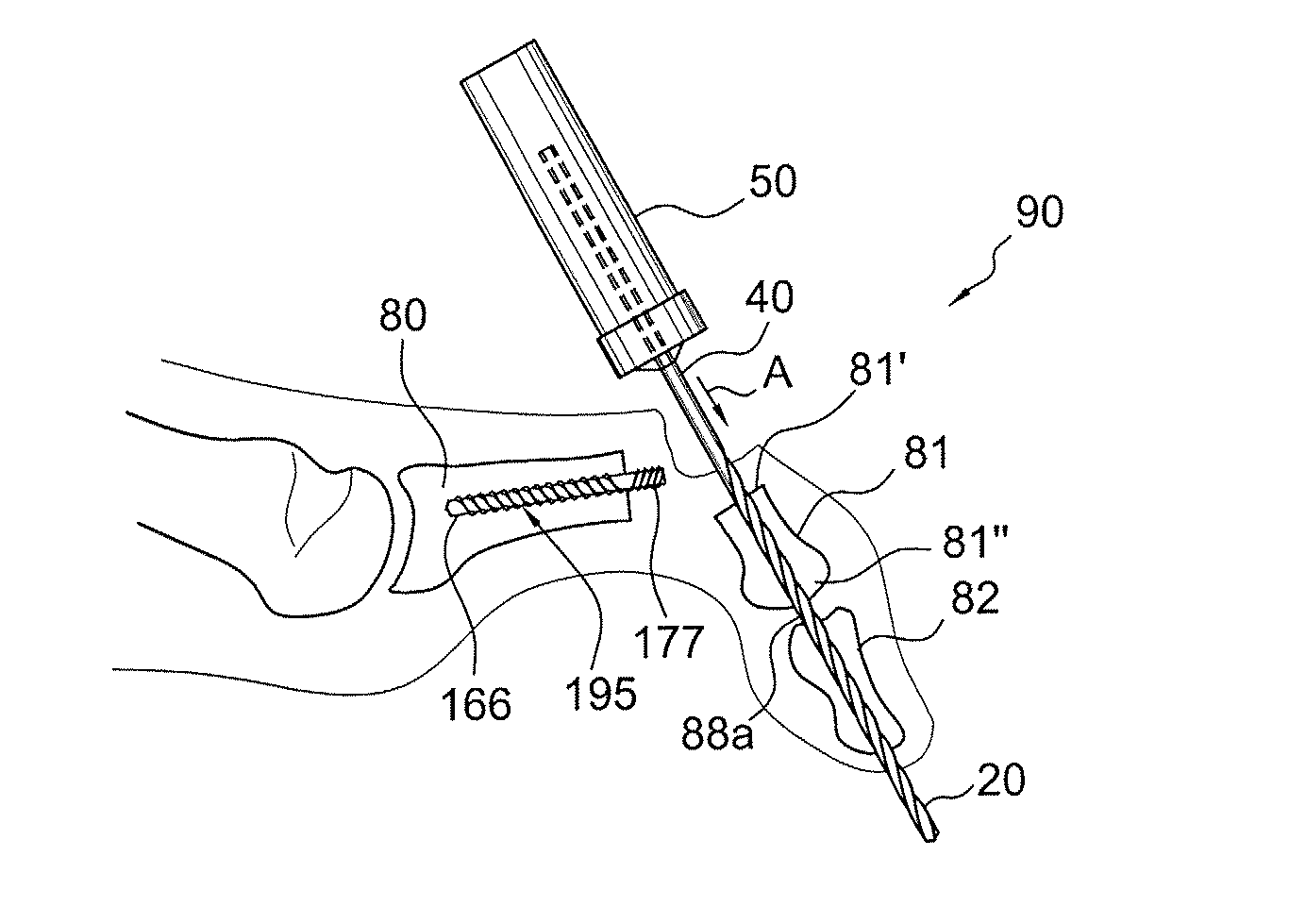
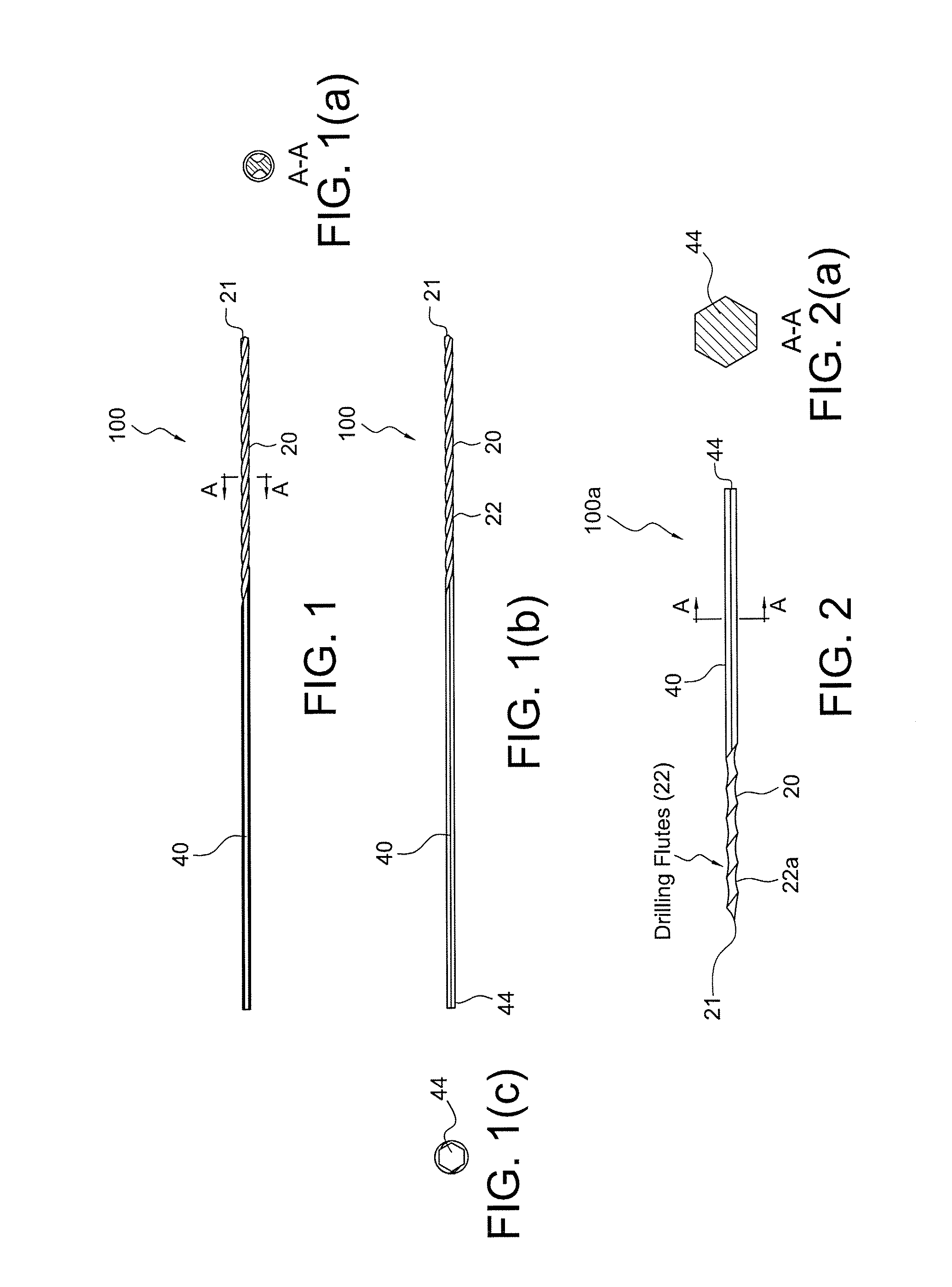
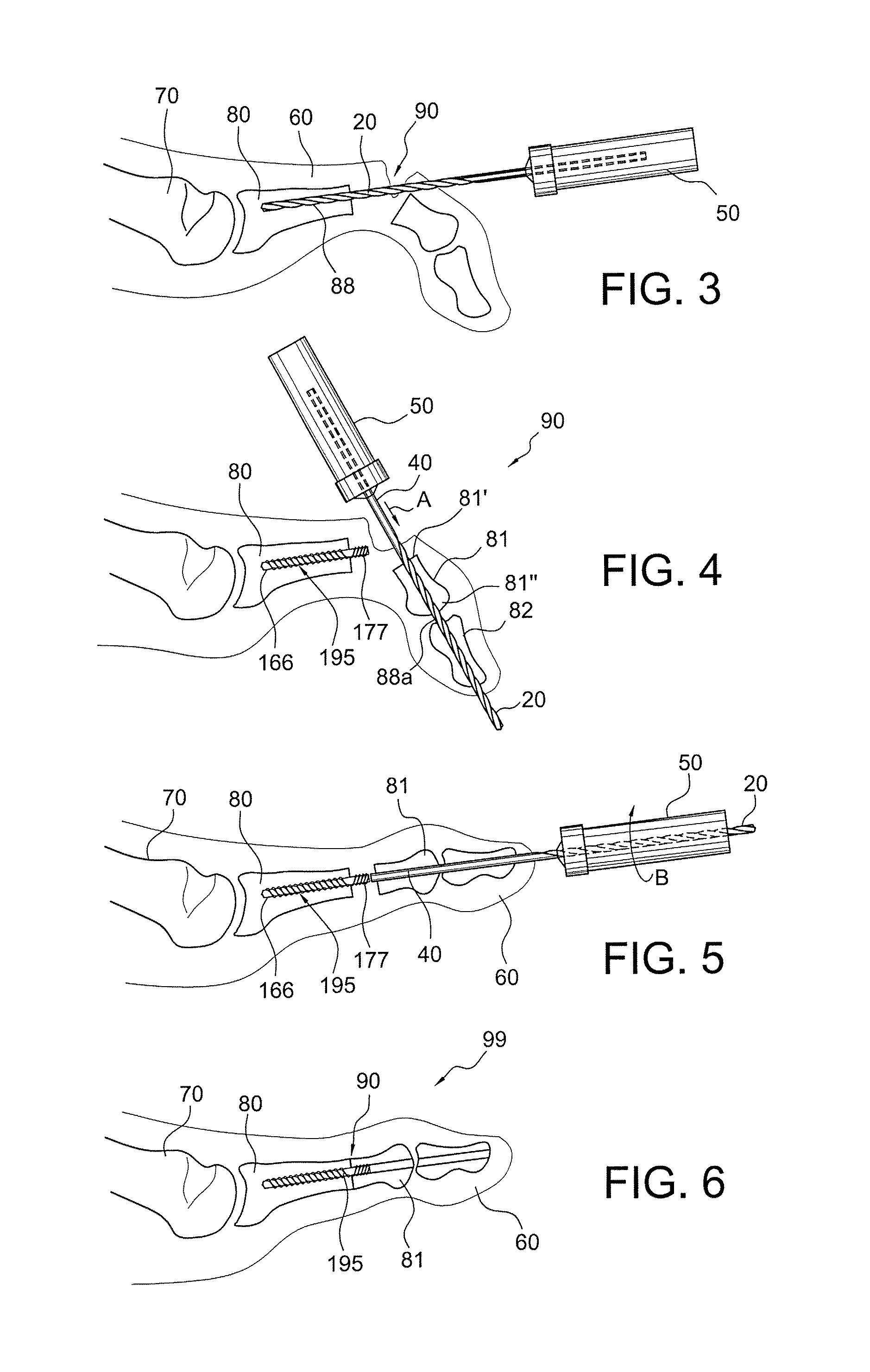
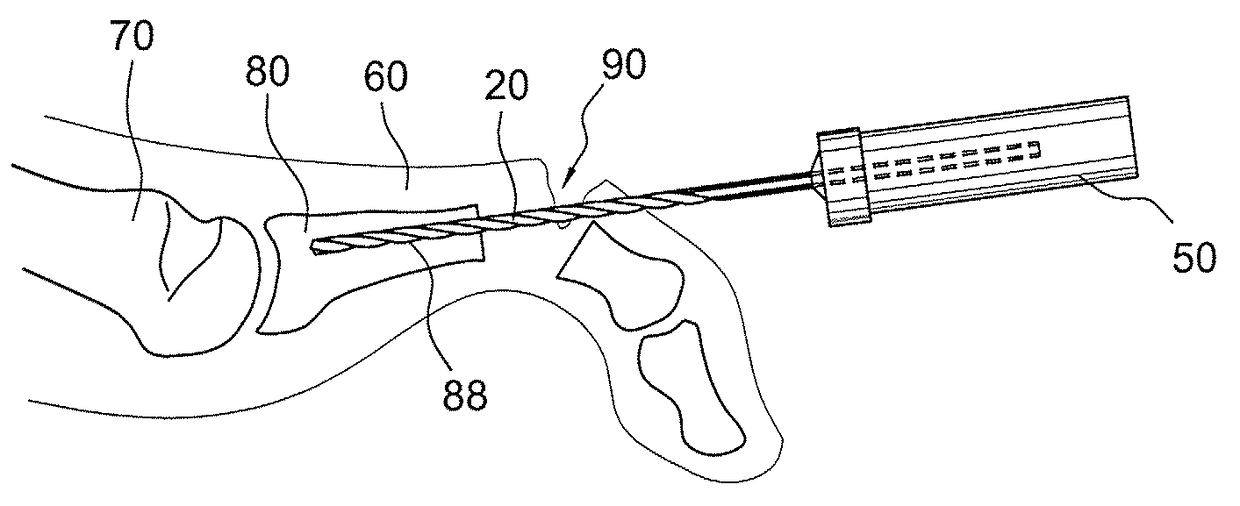
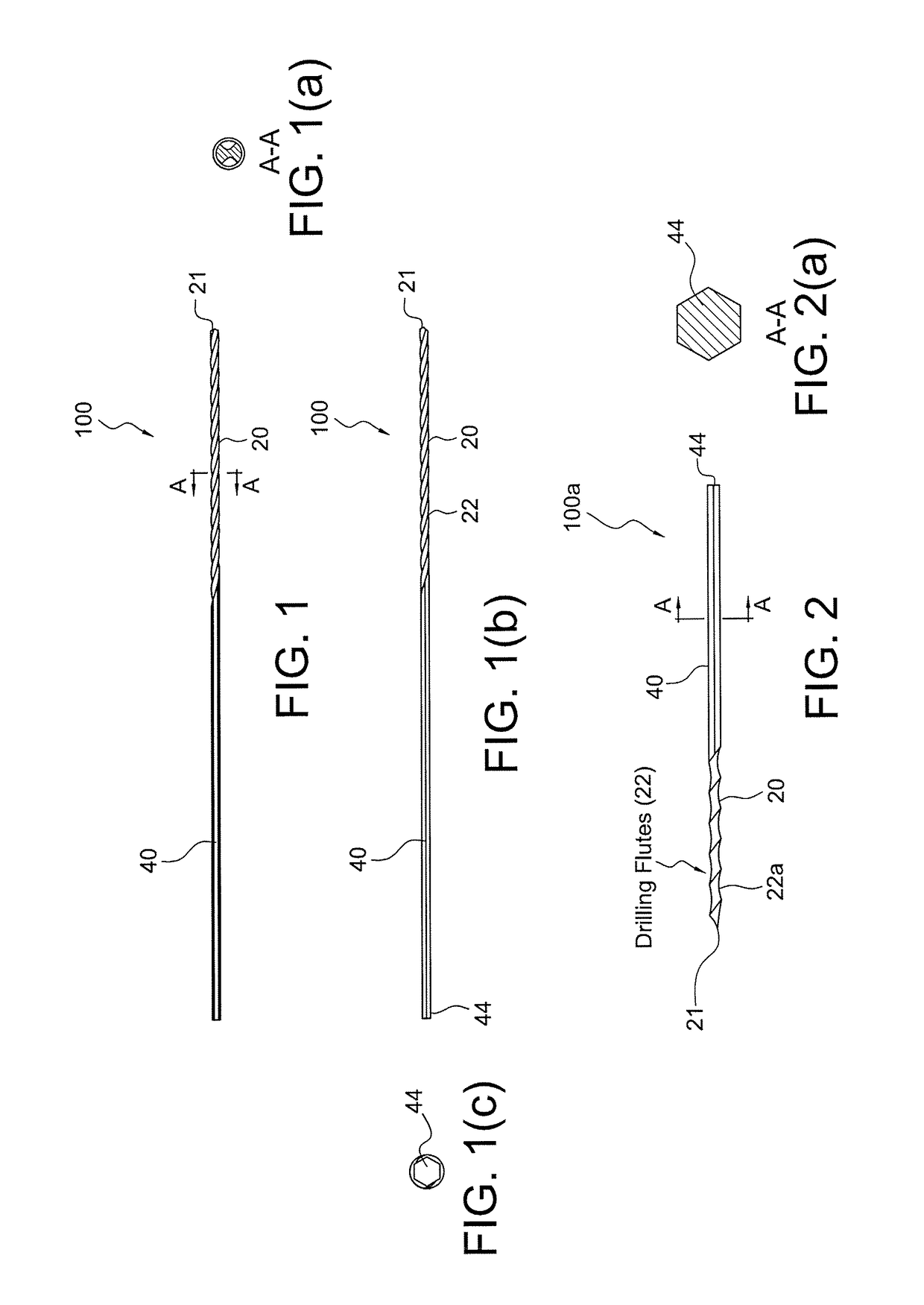
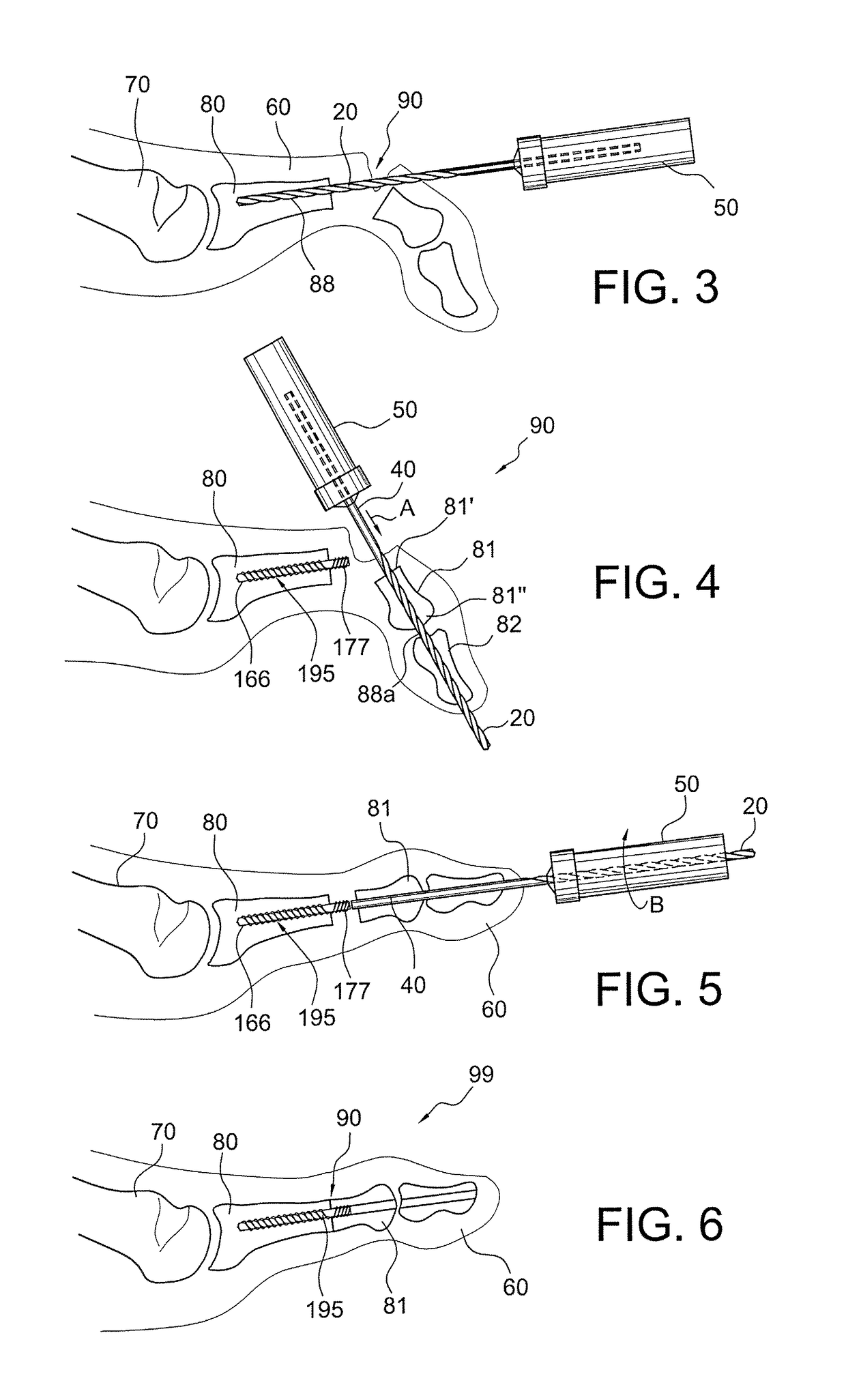
Drill/driver hybrid instrument for interphalangeal fusion
Surgical techniques, instruments and systems for bone fusions and repairs (for example, phalangeal fusion) which allow alignment of small bones (for example, phalanges) without the use of guidewire and cannulated instrumentation such as, for example, drills and drivers, and cannulated screws. A drill / driver hybrid instrument (a combined drill / driver device) may be used in fusion of two small bones (for example, in interphalangeal fusion). One end of the hybrid instrument is provided with a plurality of flutes so that the instrument can be used as a drill to remove bone. The other end is shaped to mate with a device to be inserted intraarticularly (for example, interphalangeally), acting as a driver for that device.
Owner:ARTHREX
Plate for fixing the bones of a joint, in particular a metatarso-phalangeal joint
InactiveUS20080091197A1Improve accuracyEasy to placeJoint implantsBone platesAxis of symmetryVertical plane
A plate for fixing the bones of a joint, in particular of a metatarso-phalangeal joint, for the purpose of performing arthodesis. The plate comprises two sections, respectively a proximal section and a distal section, each section having a respective longitudinal axis of symmetry S1, S2 such that the projection onto a horizontal plane of the axis of symmetry S2 of the distal section presents an angle of inclination relative to the projection of the axis of symmetry S1 of the proximal portion, the projections inserting at a point A. The projection onto a vertical plane of the axis of symmetry S2 presents an angle of inclination relative to the projection of the axis of symmetry S1, their intersection taking place at a point A2 which is distinct from the point A1.
Owner:NEWDEAL
Toe deformity repair using bioabsorbable pin
ActiveUS8021367B2Overcome disadvantagesEliminate needInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsProximal phalanxDistal portion
Methods and apparatus for repair of toe deformities using a bioabsorbable pin. The apparatus is a kit of part comprising a bioabsorbable pin, a predrill, a bone tamp, a cutter and a forceps. One surgical method of repairing toe deformities includes resecting a proximal interphalangeal joint, drilling a hole in a proximal phalanx using a proximal portion of a pin, removing the pin from the proximal phalanx, drilling a tip of a toe through middle and distal phalanxes, driving the pin retrograde and traversing the distal, middle and proximal phalanxes until the pin stops advancing due to resistance at a proximal cortex, holding the pin and powering a pin driver to separate a distal portion of the pin, and suturing the wound.
Owner:ARTHREX
Small joint hemiarthroplasty
Methods and apparatuses for digit joint arthroplasty. The present invention preferably allows for the treatment of disorders of digit joints generally and interphalageal joints more specifically. The present invention provides implants for the replacement of digit joint cartilage. The implants of the present invention preferably include a head and a shaft. The head may be shaped similarly to the cartilage that is being replaced. The shaft is adapted so as to be able to be fit into, for example, the phalanx. In certain preferred embodiments, the shaft is threaded so that it may gain purchase to the phalangeal cortex. The articulating portion of the implant preferably mimics the articular surface of the native phalanx and thereby places minimal motion restriction on the patient. The implants and methods of the present invention have particular utility with the DIP joint of the hand.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Identification authentication apparatus based on finger biologic characteristics
InactiveCN101408938AImprove anti-counterfeiting performanceImprove securityCharacter and pattern recognitionVeinInterphalangeal Joint
The invention discloses an identification and authentication device based on finger biometric. The device comprises a handle part, a fingerprint collection part, a light source, an image pickup part, a tact switch and a processing part. The processing part is respectively connected with the tact switch, the fingerprint collection part, the light source and the image pickup part. The device is usually in standby state, and a system starts to work when the tact switch is triggered: first, the light source is started to illuminate the position between the knuckle at a proximal interphalangeal joint of a finger and a distal interphalangeal joint of the finger, and the image pick-up part obtains a finger vein image; meanwhile, the fingerprint collection part collects a thumb fingerprint image, then the two images are subject to preprocessing and feature extraction respectively, and matched with the finger vein feature and the fingerprint feature stored in a database; finally, the judgment whether the authentication is successful is obtained by evaluating the similarity thereof. The invention fully utilizes two different biometrics at different cutaneous layers of the finger, can enhance the anti-counterfeiting property, the security and the accuracy of the system.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Humanoid electric hand
InactiveUS20130175816A1Easy maintenanceReduce weightGripping headsArtificial handsEngineeringSacroiliac joint
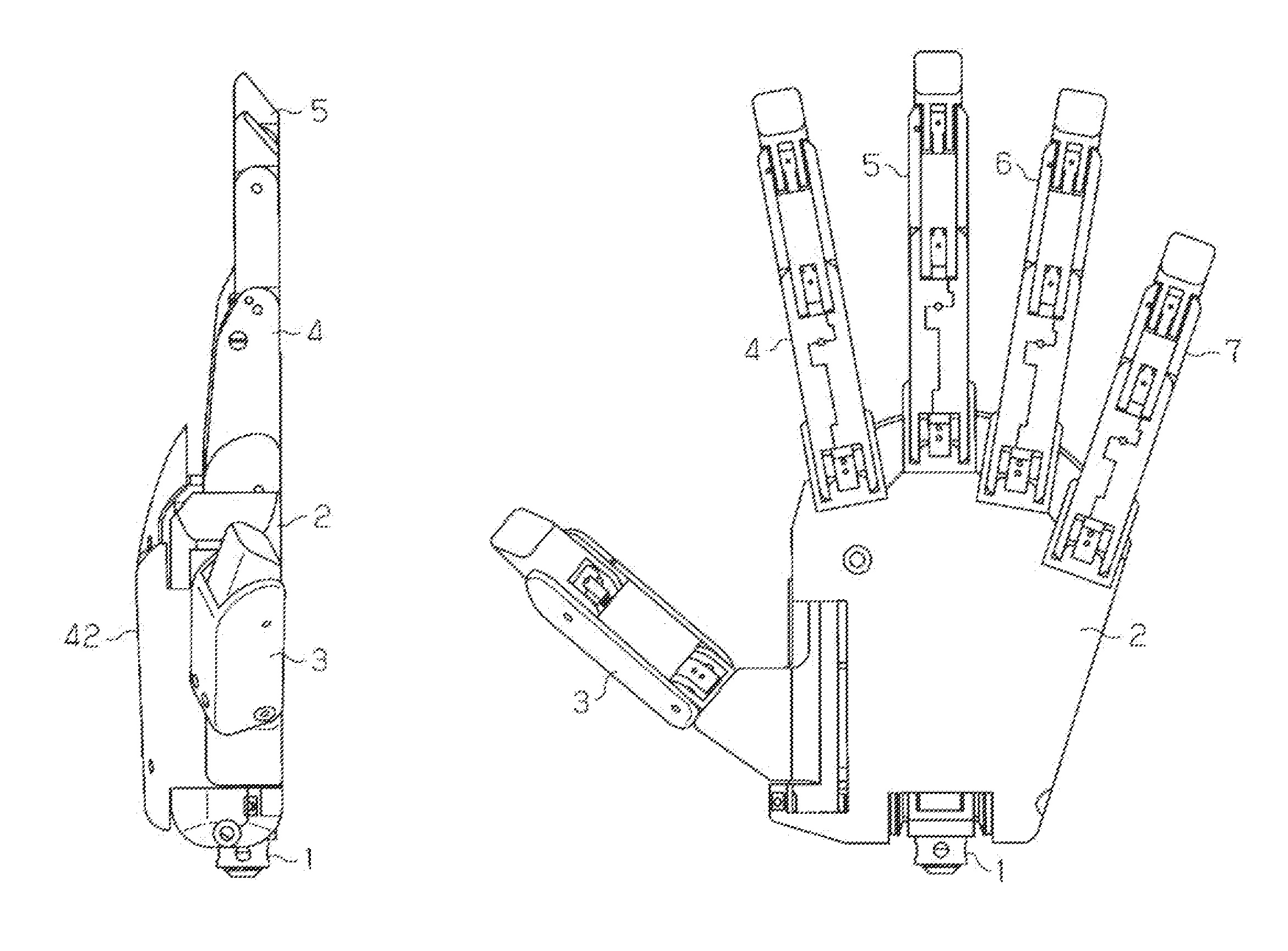
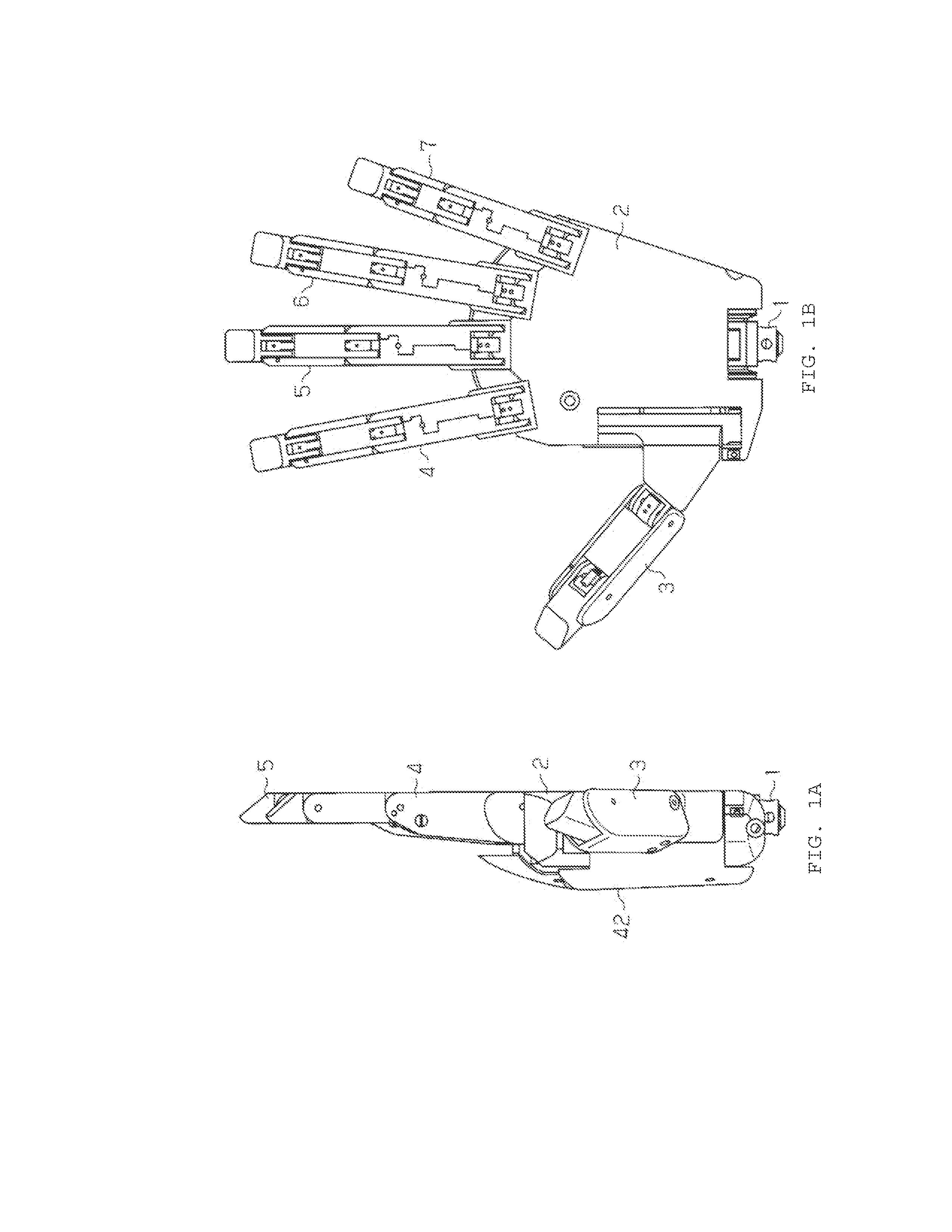
A humanoid electric hand includes a metacarpophalangeal joint and an interphalangeal joint. The interphalangeal joint bends or extends together with a bending or extending operation of the metacarpophalangeal joint, by linking a finger motor for driving a finger to a worm deceleration mechanism, an output gear of which moves rotationally to bend or extend the metacarpophalangeal joint, and by linking the metacarpophalangeal joint to the interphalangeal joint via a link mechanism.
Owner:GIFU UNIVERSITY +1
Humanoid electric hand
InactiveUS8747486B2Reduce weightEasy maintenanceGripping headsArtificial handsEngineeringSacroiliac joint
Owner:GIFU UNIVERSITY +1
Drill/driver hybrid instrument for interphalangeal fusion
Surgical techniques, instruments and systems for bone fusions and repairs (for example, phalangeal fusion) which allow alignment of small bones (for example, phalanges) without the use of guidewire and cannulated instrumentation such as, for example, drills and drivers, and cannulated screws. A drill / driver hybrid instrument (a combined drill / driver device) may be used in fusion of two small bones (for example, in interphalangeal fusion). One end of the hybrid instrument is provided with a plurality of flutes so that the instrument can be used as a drill to remove bone. The other end is shaped to mate with a device to be inserted intraarticularly (for example, interphalangeally), acting as a driver for that device.
Owner:ARTHREX
Method and device for measuring biological information
InactiveUS20050209514A1Accurately determineDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiological bodyEponychium
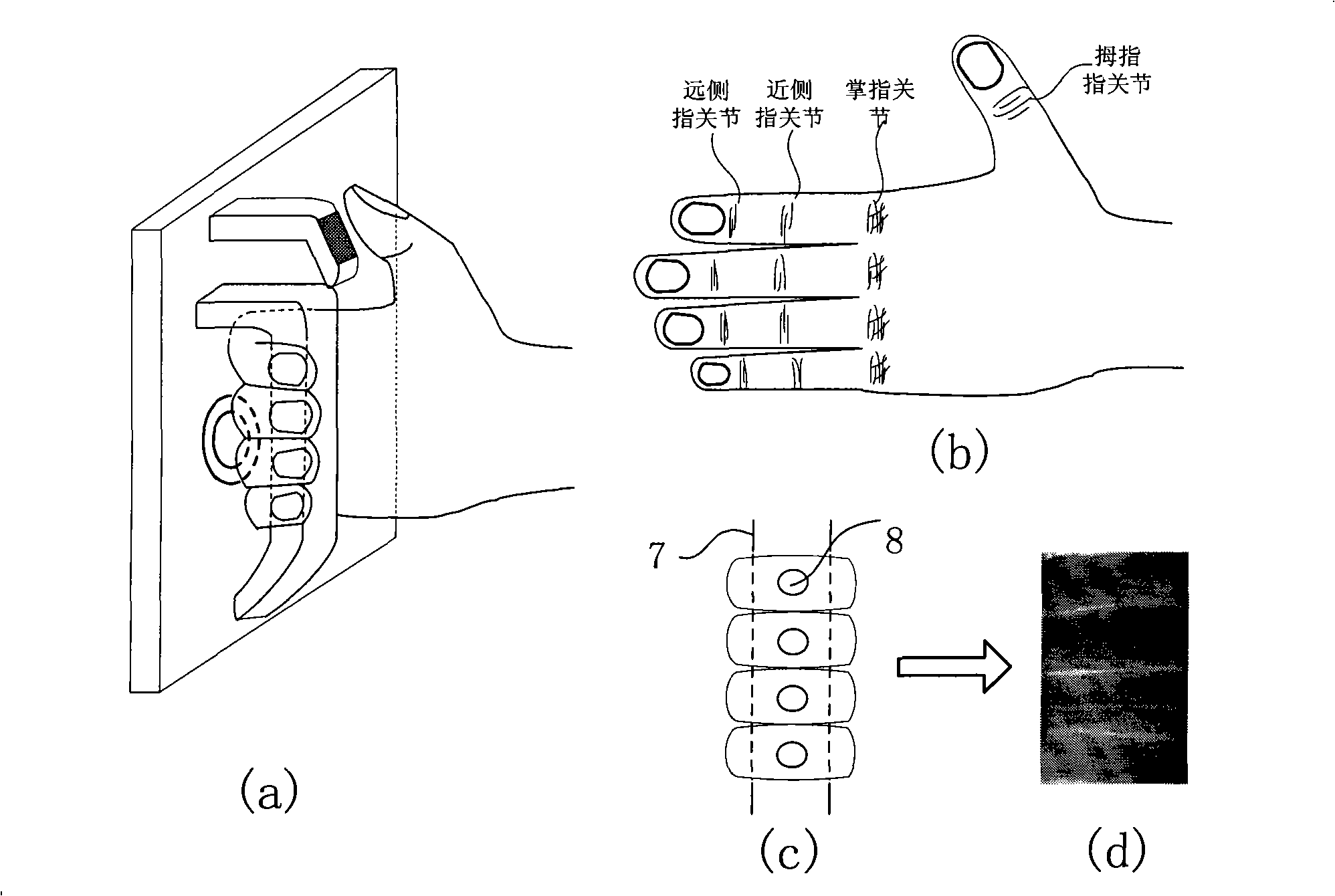
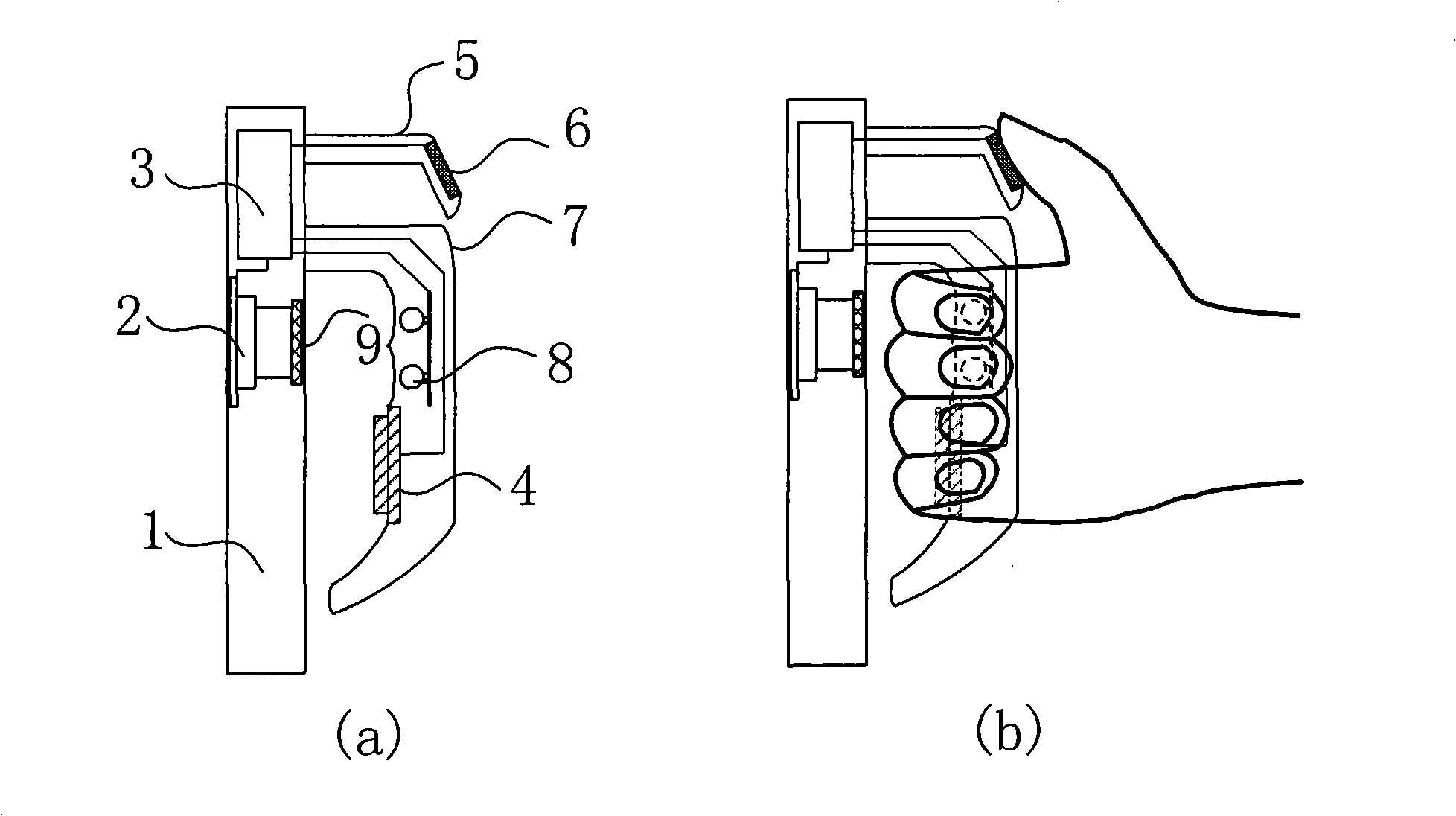
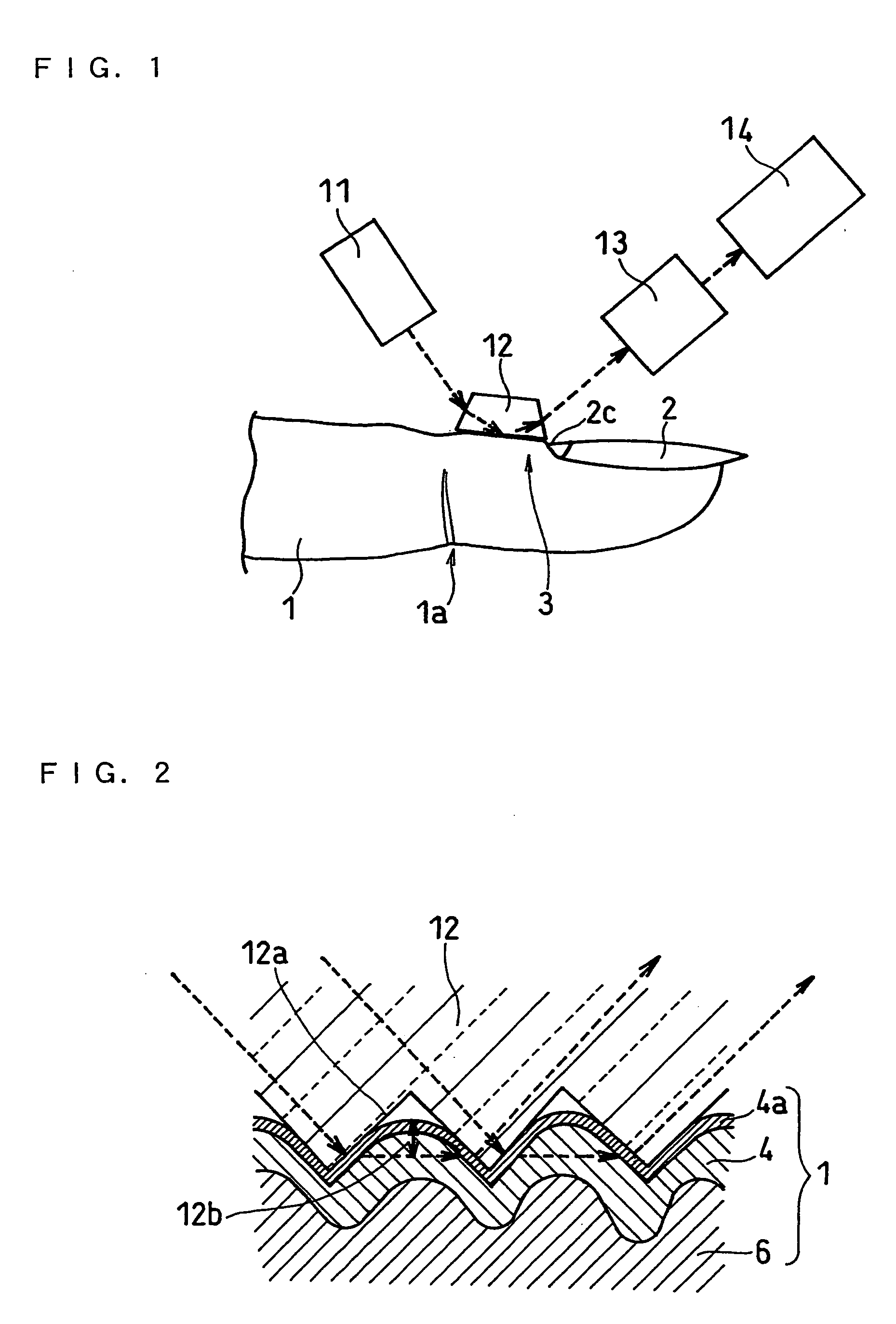
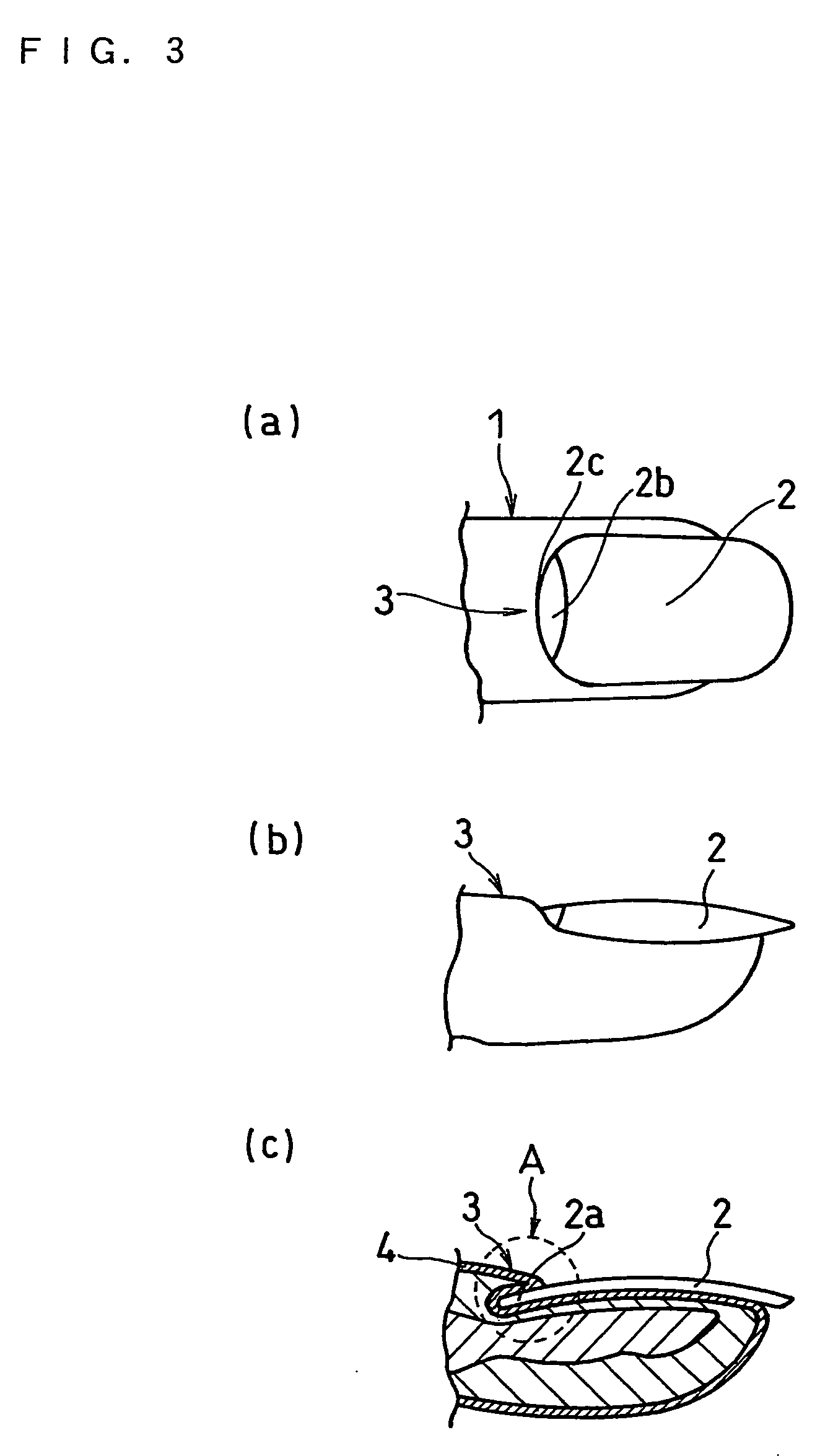
In order to precisely determine a stable measuring region appropriate for a measurement of biological information, and to measure a concentration of a specific component, i.e. biological information, without inconsistency, a biological information measuring device is provided with, a measuring region determining means for determining a measuring region in between an eponychium and a distal interphalangeal joint; an information detector for applying a light to measuring region; a light source for entering a light to information detector; a light detector for detecting a light which exits from the information detector; and a processor for measuring specific component based on information obtained from light detector.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Data Glove
ActiveUS20170215495A1Accurate detectionInput/output for user-computer interactionGlovesEngineeringFifth fingers
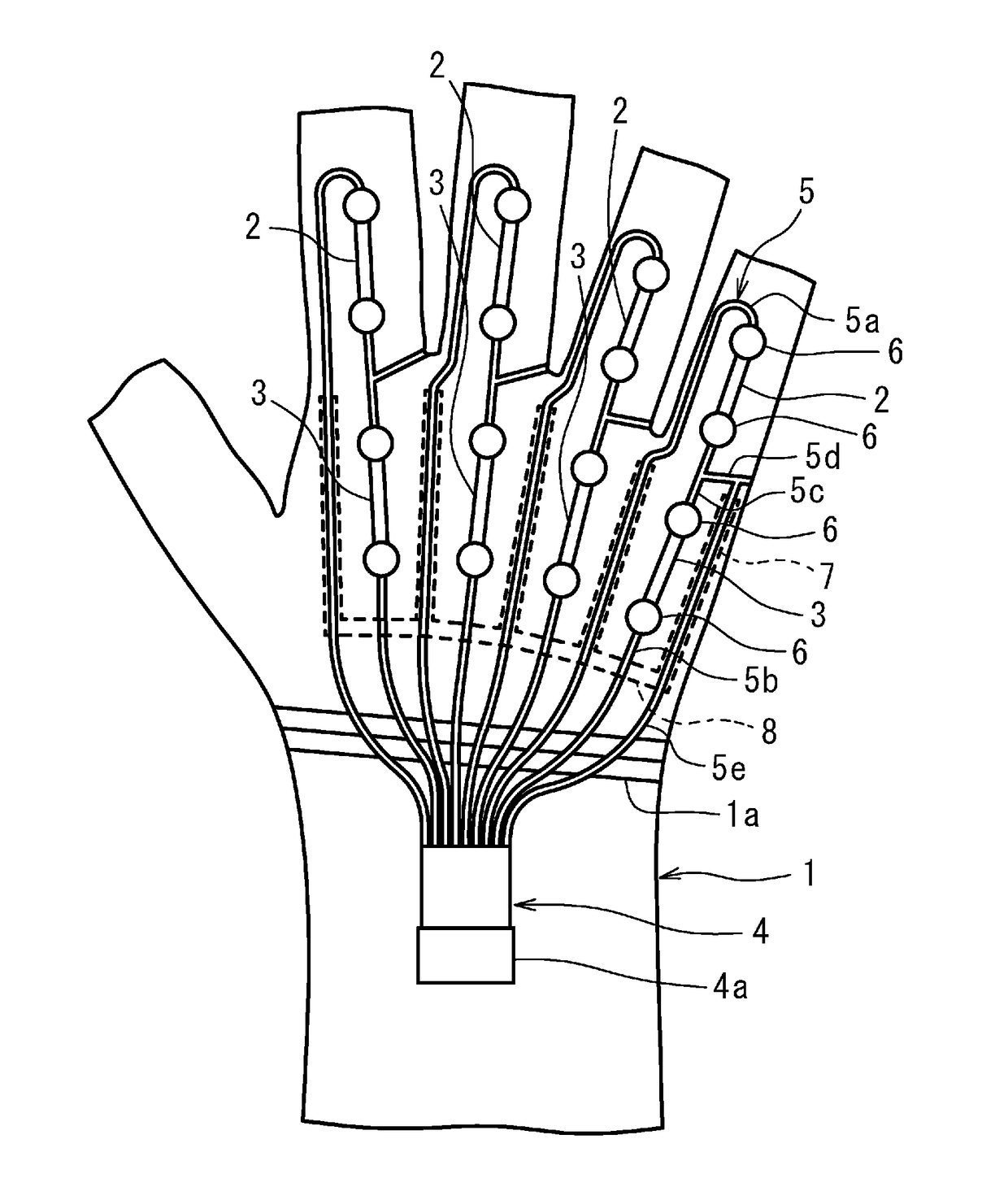
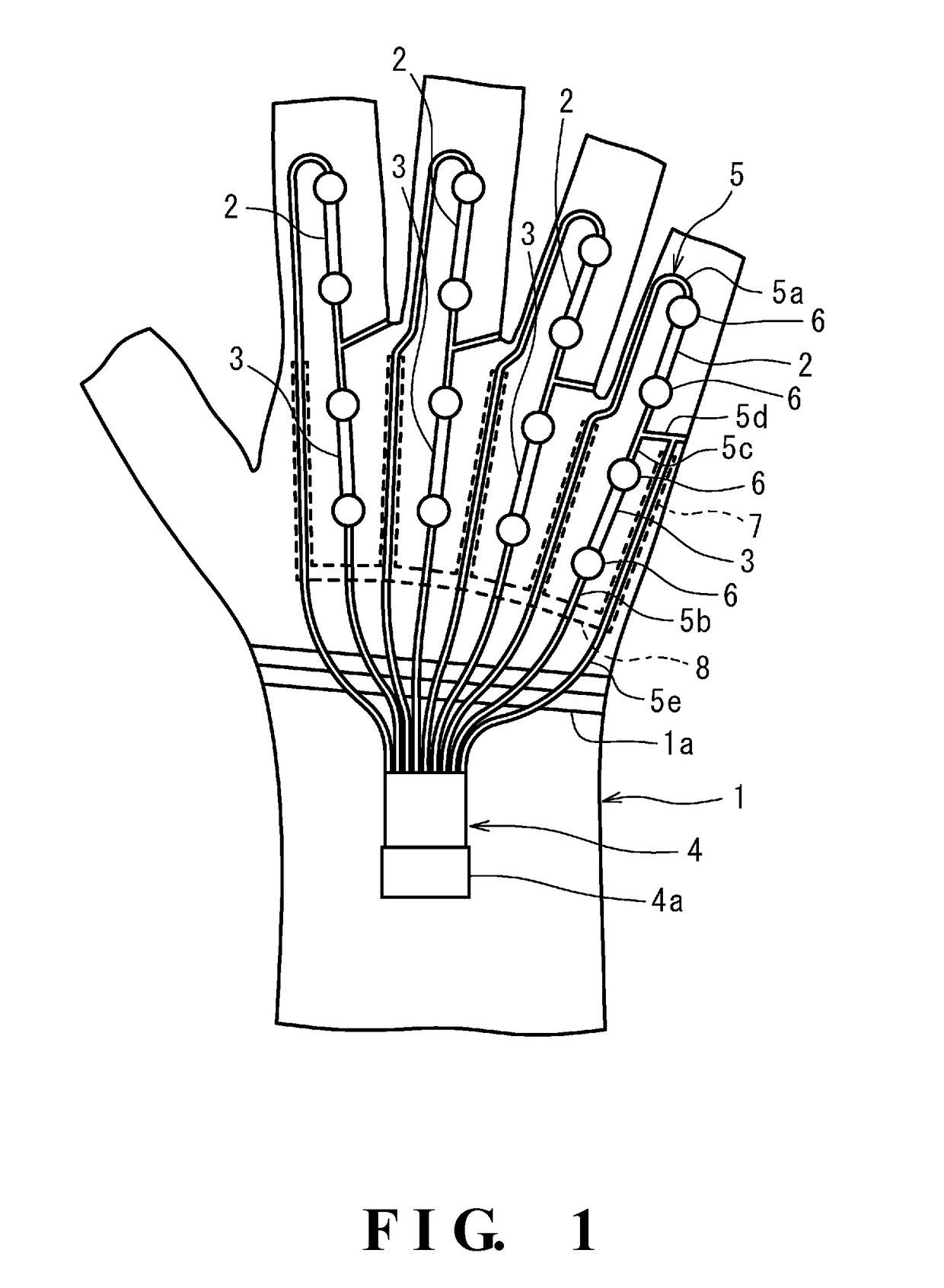
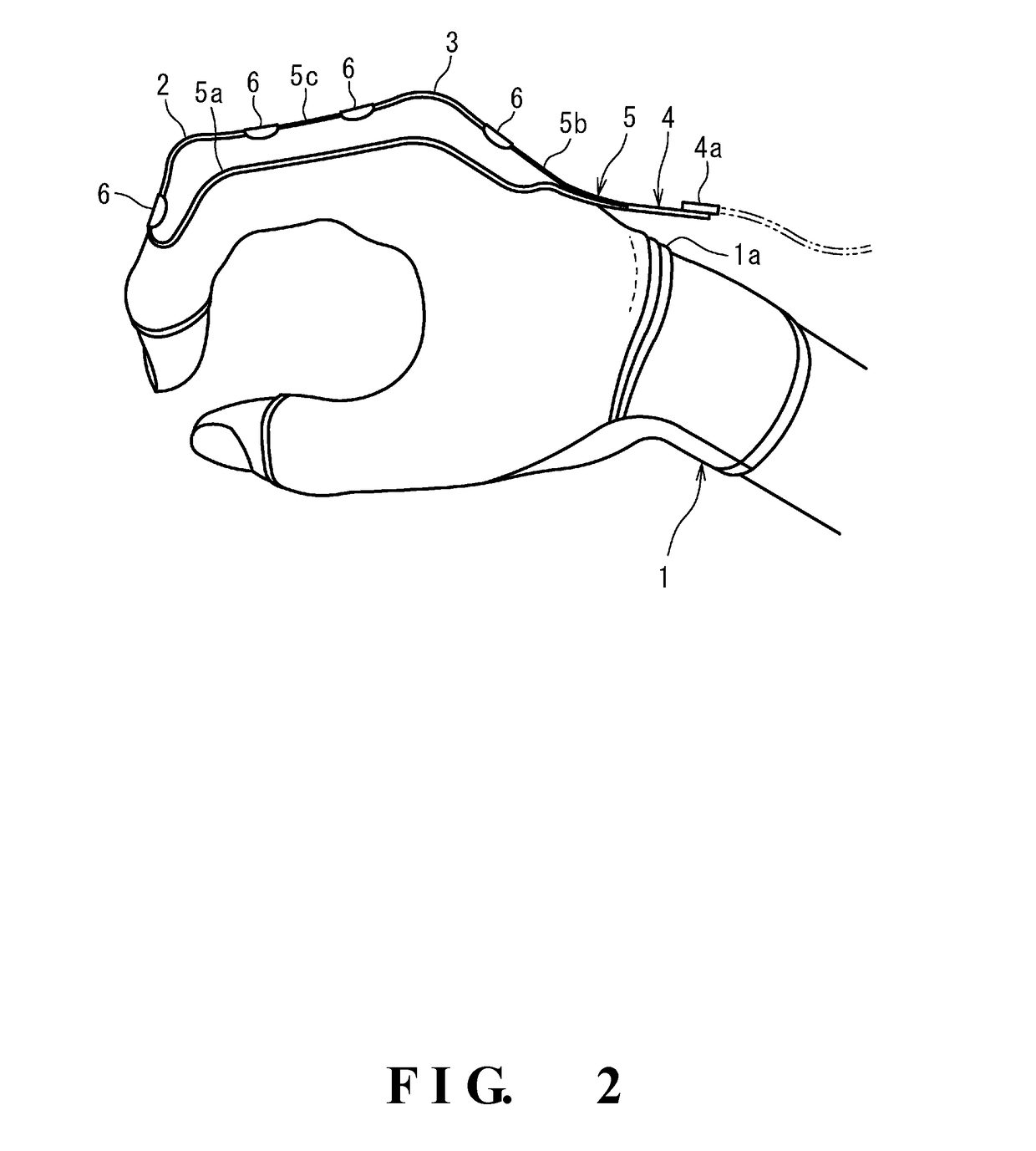
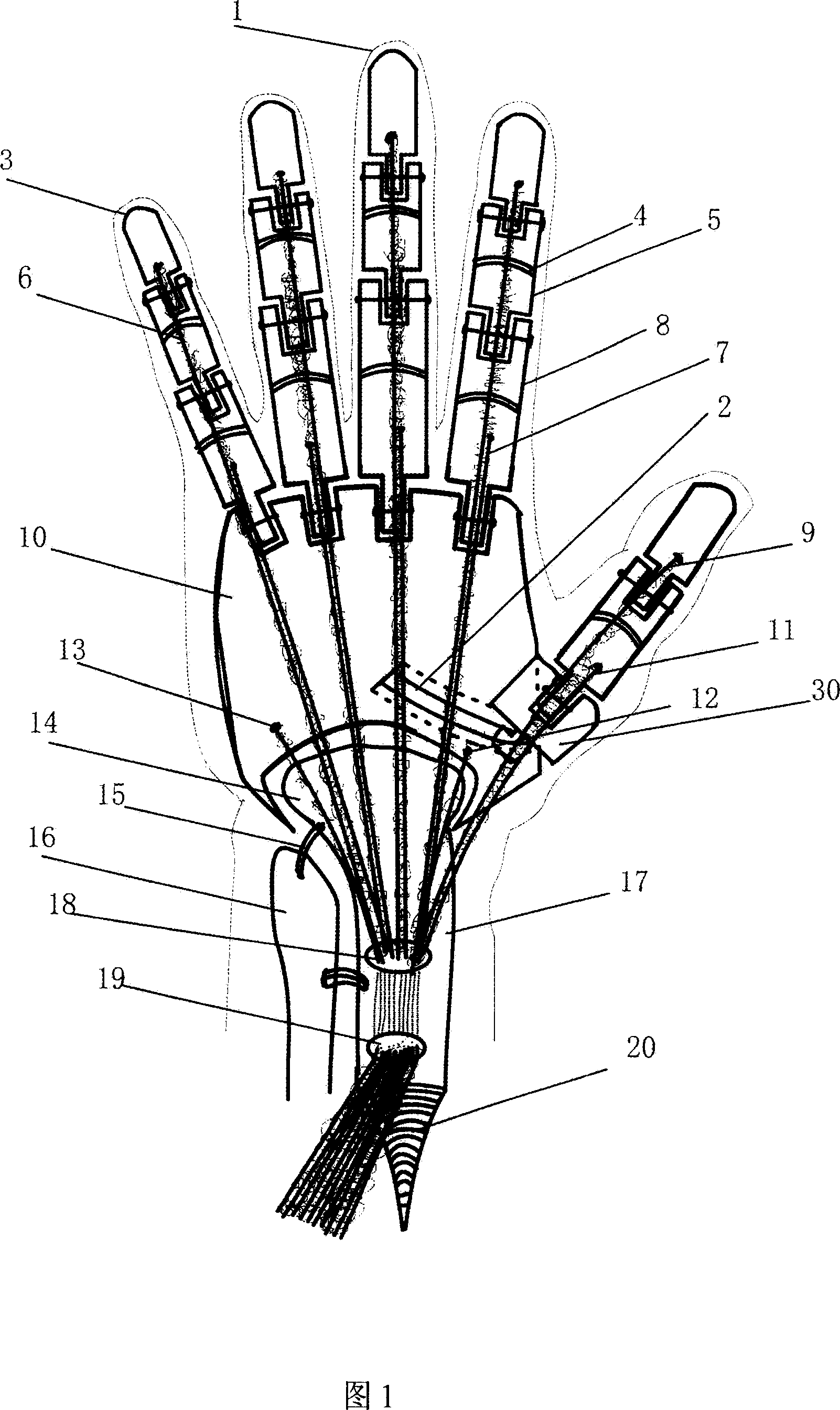
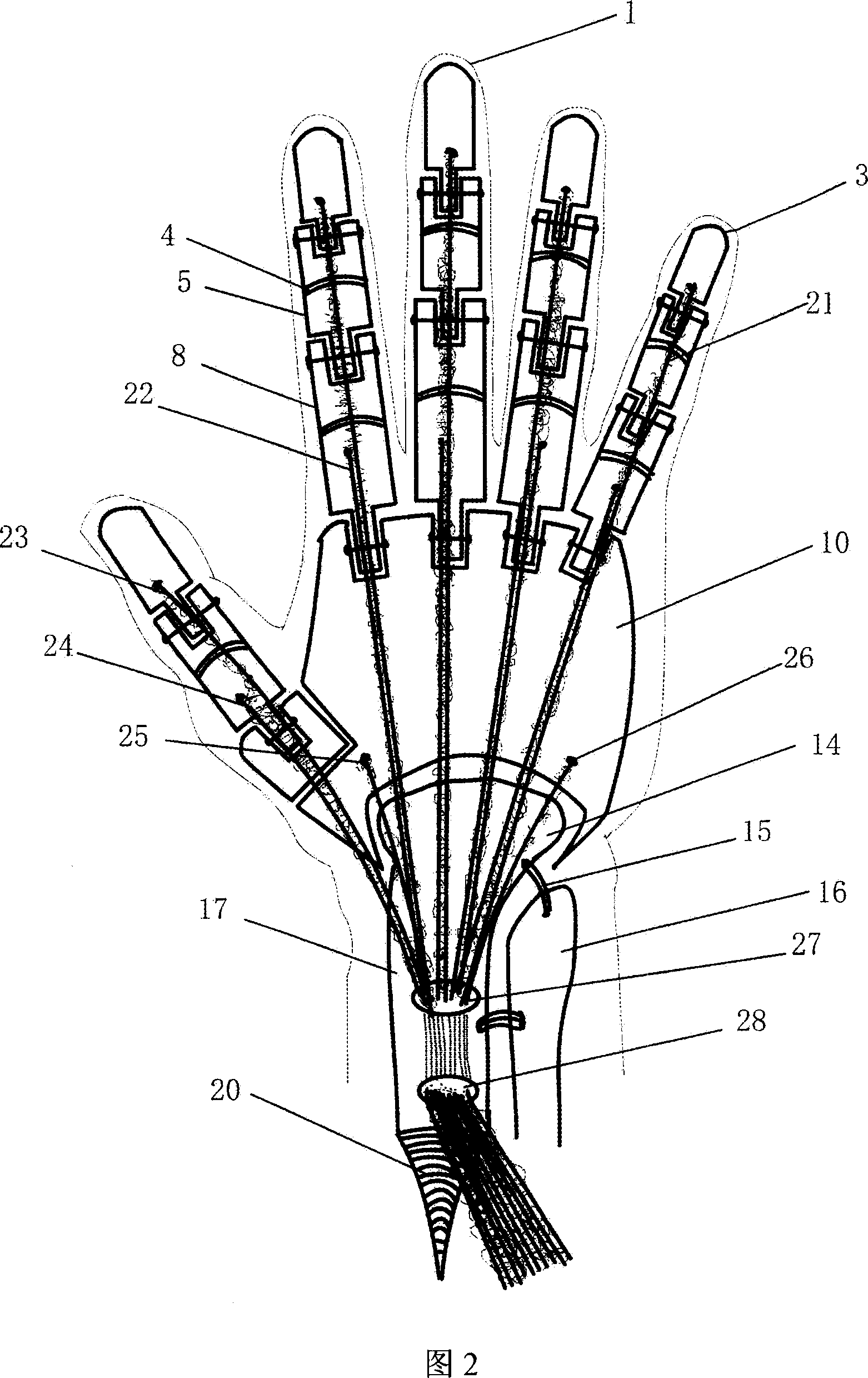
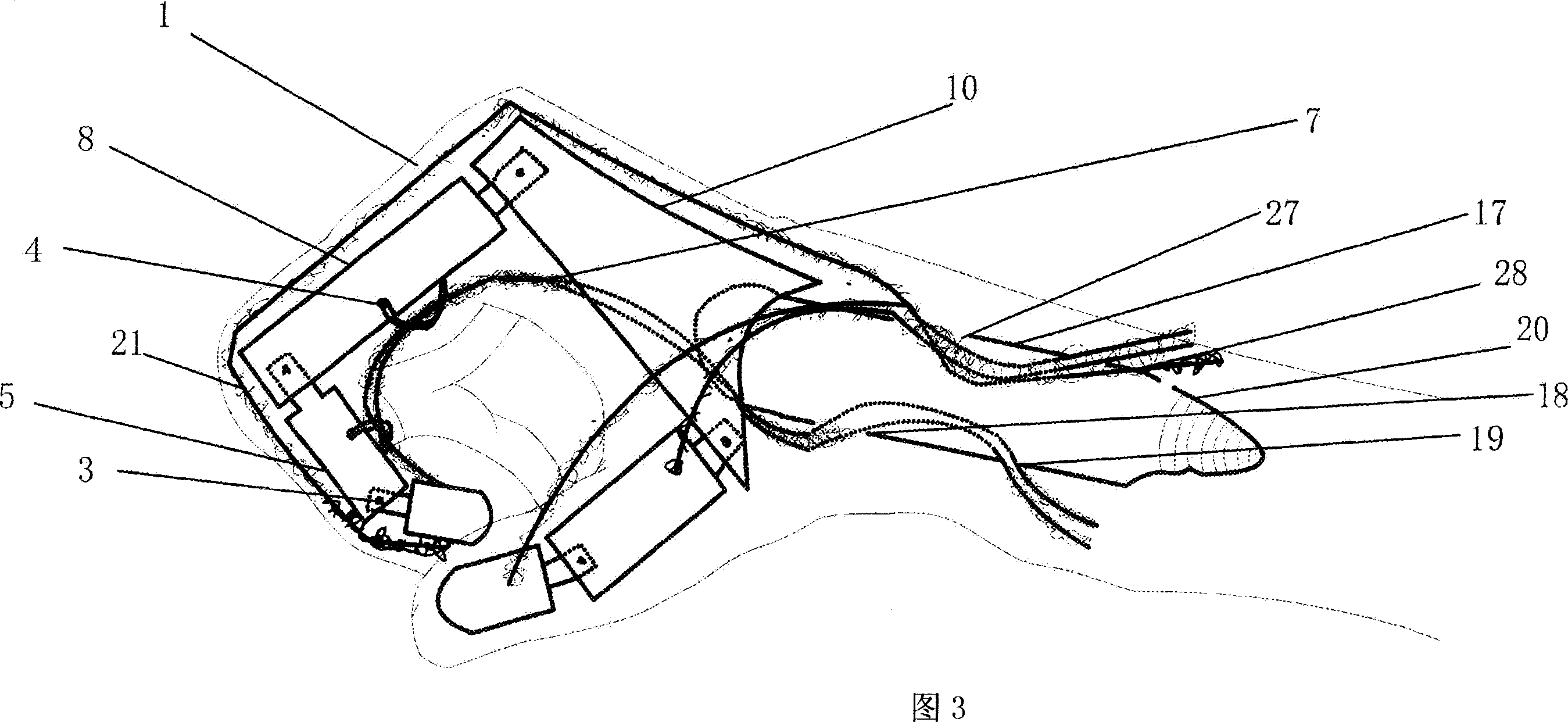
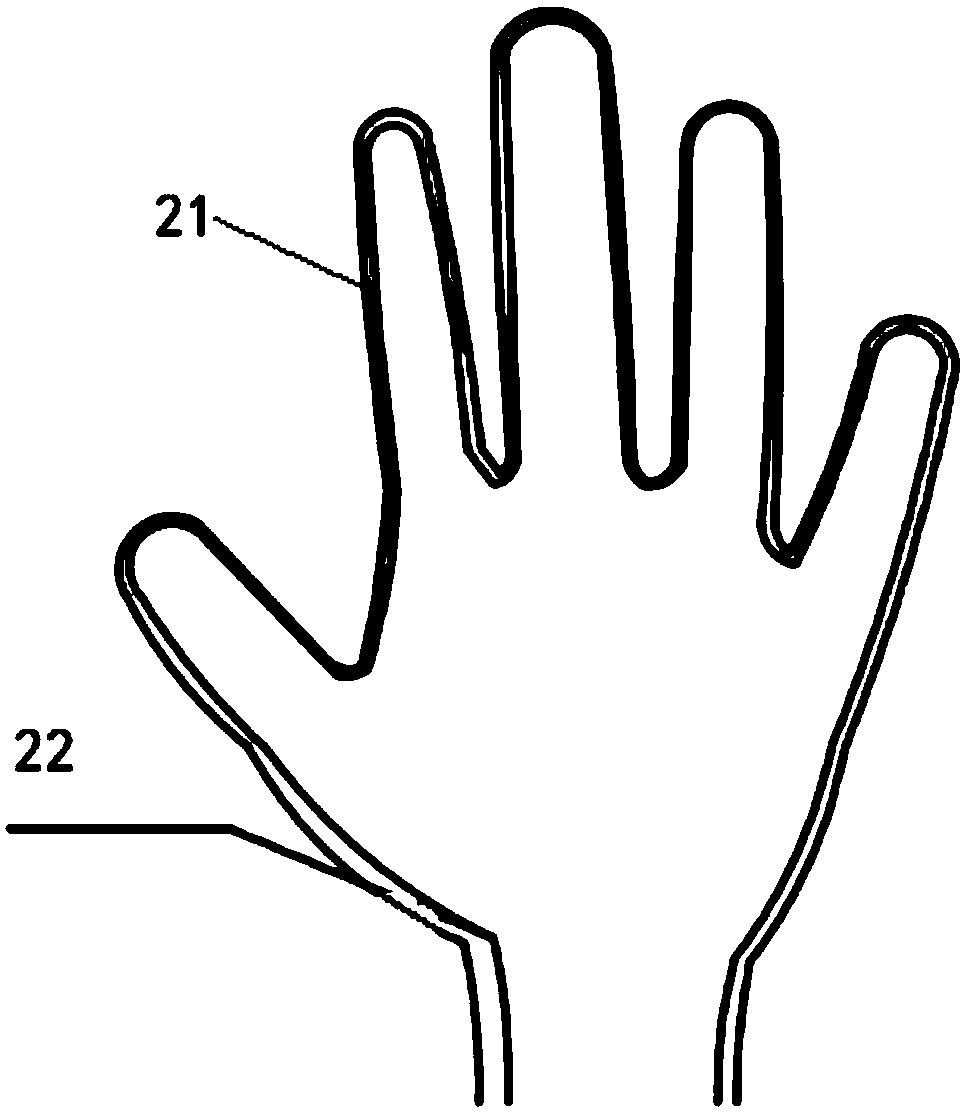
Provided is a data glove which imparts little discomfort when worn, and is capable of accurately detecting movement of a hand, comprising: a glove main body; and a plurality of strain sensors which are disposed on the dorsal side of the glove main body in regions corresponding to at least one finger, and which detect stretch and contraction of the glove main body. The strain sensors preferably include a first strain sensor and a second strain sensor which are disposed on the dorsal side of the glove main body to correspond respectively to a proximal interphalangeal joint and a metacarpophalangeal joint of at least one finger of the second through fifth fingers, and which detect stretch and contraction of the glove main body in a proximal-distal direction. The data glove preferably further comprises a plurality of stretch prevention parts which limit the elongation of the glove main body.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Wearable exoskeleton device for hand rehabilitation
ActiveUS20150223959A1Assisting the flexion/extension of the joints of a handChiropractic devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesProximal phalanxDistal phalange
An exoskeleton device for assisting the movement of a metacarpal-phalangeal joint of a hand in a flexion / extension plane Γ of the joint, including a metacarpal support arranged integrally with a metacarpal portion of the hand, a phalangeal support having means for fastening to a proximal phalanx, a kinematical chain between the metacarpal support and the phalangeal support arranged to provide and carry out a rotation of the phalangeal support with respect to the metacarpal support.
Owner:SCUOLA SUPERIORE S ANNA
Exoskeletal thumb moving function rehabilitation robot
InactiveCN102319162ASolve the problem of bad wearingSuitable for wearingGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesDrive shaftEngineering
The invention relates to an exoskeletal thumb moving function rehabilitation robot. The robot comprises an execution part, a transmission part and a drive part, wherein the execution part is divided into an interphalangeal joint module, a metacarpophalangeal joint module and a carpometacarpal joint module; in the carpometacarpal joint module, a metacarpal seat is fixed on the palm and wrist of a patient; the metacarpal seat and a metacarpal seat connector form a dip angle of 30 degrees, and the metacarpal seat connector has an angle of 45 degrees; an angle sensor is fixedly connected to a joint horizontal rotor, and is fixedly connected with an abduction / adduction coil; an adjustable bearing block is fixedly connected with a size adjusting jack; one end of a palm driven rod and the adjusting bearing block form a rotating pair, and the other end of the palm driven rod and a palm drive rod form a rotating pair; and the palm drive rod is fixed on a palm drive shaft, and the drive shaft and a palm drive bearing block form a rotating pair. According to the exoskeletal thumb moving function rehabilitation robot, four degrees of freedom active and passive rehabilitation of the thumb can be realized, and the problem that the robot is difficult to wear due to the difference between the physiological structure of the thumb and the other four fingers can be solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Humanoid finger inflatable soft three-finger gripper
The invention discloses a humanoid finger inflatable soft three-finger gripper, and relates to a three-finger gripper. The problem that existing soft grippers are low in load capacity is solved. Eachsoft finger module is installed on one end face of a bottom plate through a module base, a soft finger module body is internally provided with a first air cavity and a second air cavity in sequence, the first air cavity communicates with one end of a first interphalangeal joint air pipe, and the second air cavity communicates with one end of a second interphalangeal joint air pipe. The finger backof each soft finger module body is provided with at least two phalangeal joint clearance grooves through machining in the length direction of the finger back, the positions, except the finger prominence side, of the soft finger module body is wrapped with an elastic bandage, the finger prominence of the soft finger module body is provided with an elastic body, and a limiting layer is arranged between the finger prominence and the elastic body of the soft finger module body and made of a material which is easy to bend and cannot be stretched. The humanoid finger inflatable soft three-finger gripper is applied to manufacturing of a soft gripper, a robot hand, an artificial limb, a rehabilitation hand and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
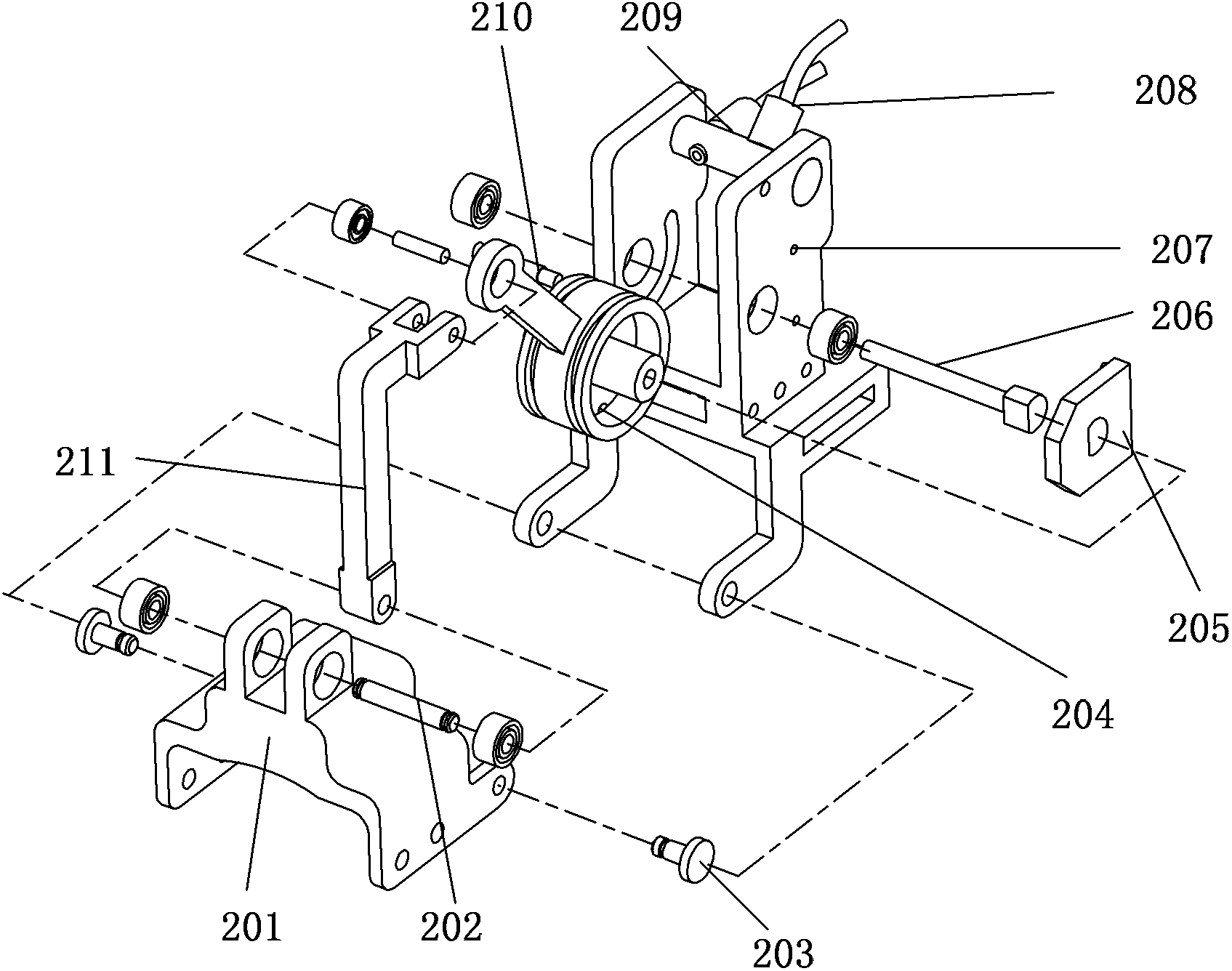
Exoskeleton type wounded finger rehabilitation robot
The invention relates to a finger rehabilitation robot, in particular to an exoskeleton type wounded finger rehabilitation robot. The exoskeleton type wounded finger rehabilitation robot can solve the problems that an existing exoskeleton type wounded finger rehabilitation robot is large in labor intensity and long in rehabilitation time and cannot directly feed a rehabilitation effect back. A metacarpophalangeal joint unit of an index finger exoskeleton is fixed to a first spur gear at the front end of a drive module through a screw; a metacarpophalangeal joint unit of a middle finger exoskeleton is fixed to a second spur gear at the front end of the drive module through a screw; a metacarpophalangeal joint unit of a ring finger exoskeleton is fixed to a third spur gear at the front end of the drive module through a screw; a metacarpophalangeal joint unit of a little finger exoskeleton is fixed to a fourth spur gear at the front end of the drive module through a screw, three steel wires are respectively led out of a pulley block of an artificial muscle drive module, and the led-out ends of the three steel wires are sequentially connected with the a first pulley of a distal interphalangeal joint unit, a second pulley of a proximal interphalangeal joint unit and a third pulley of the metacarpophalangeal joint unit. The exoskeleton type wounded finger rehabilitation robot is applied to exoskeleton type wounded finger rehabilitation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
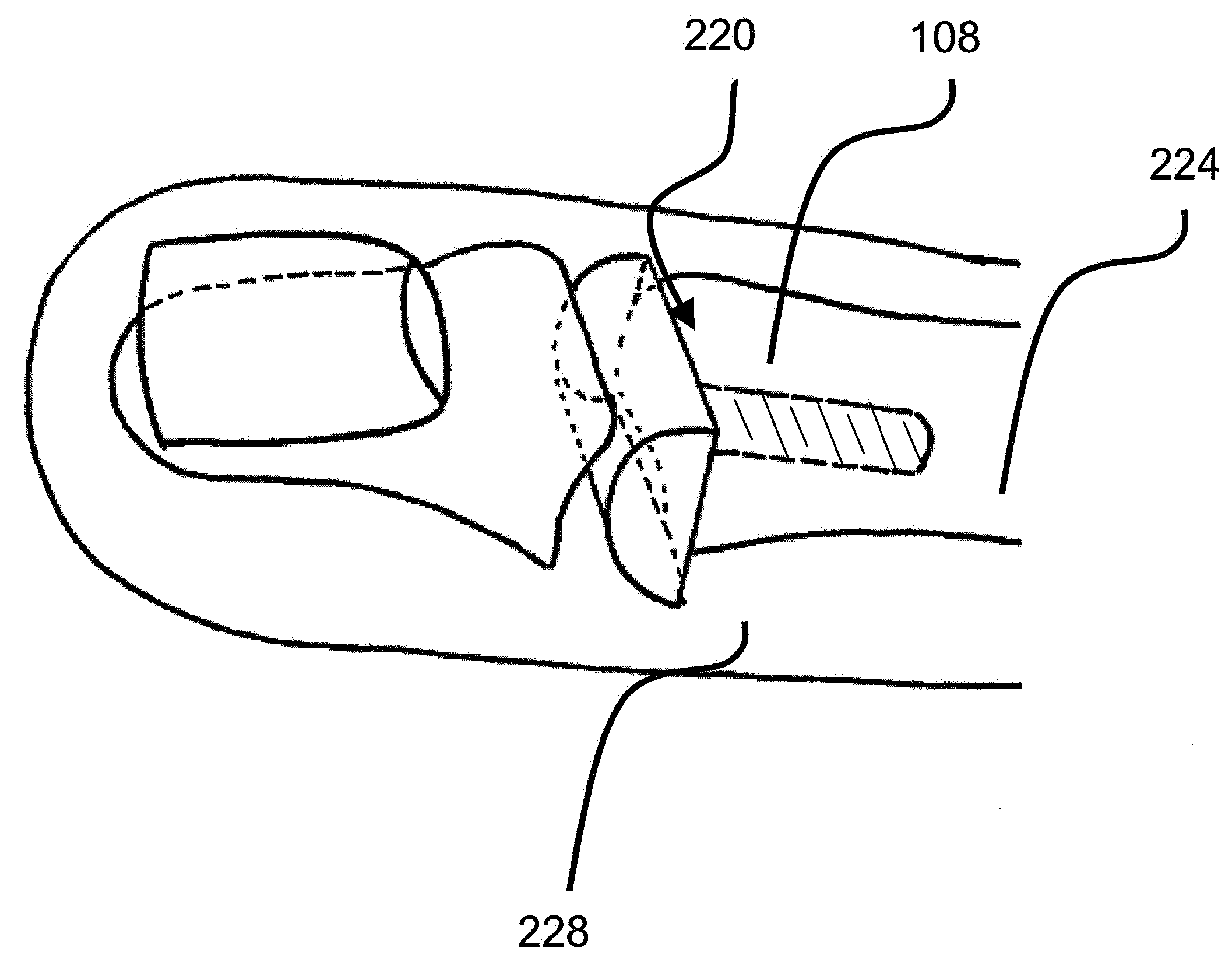
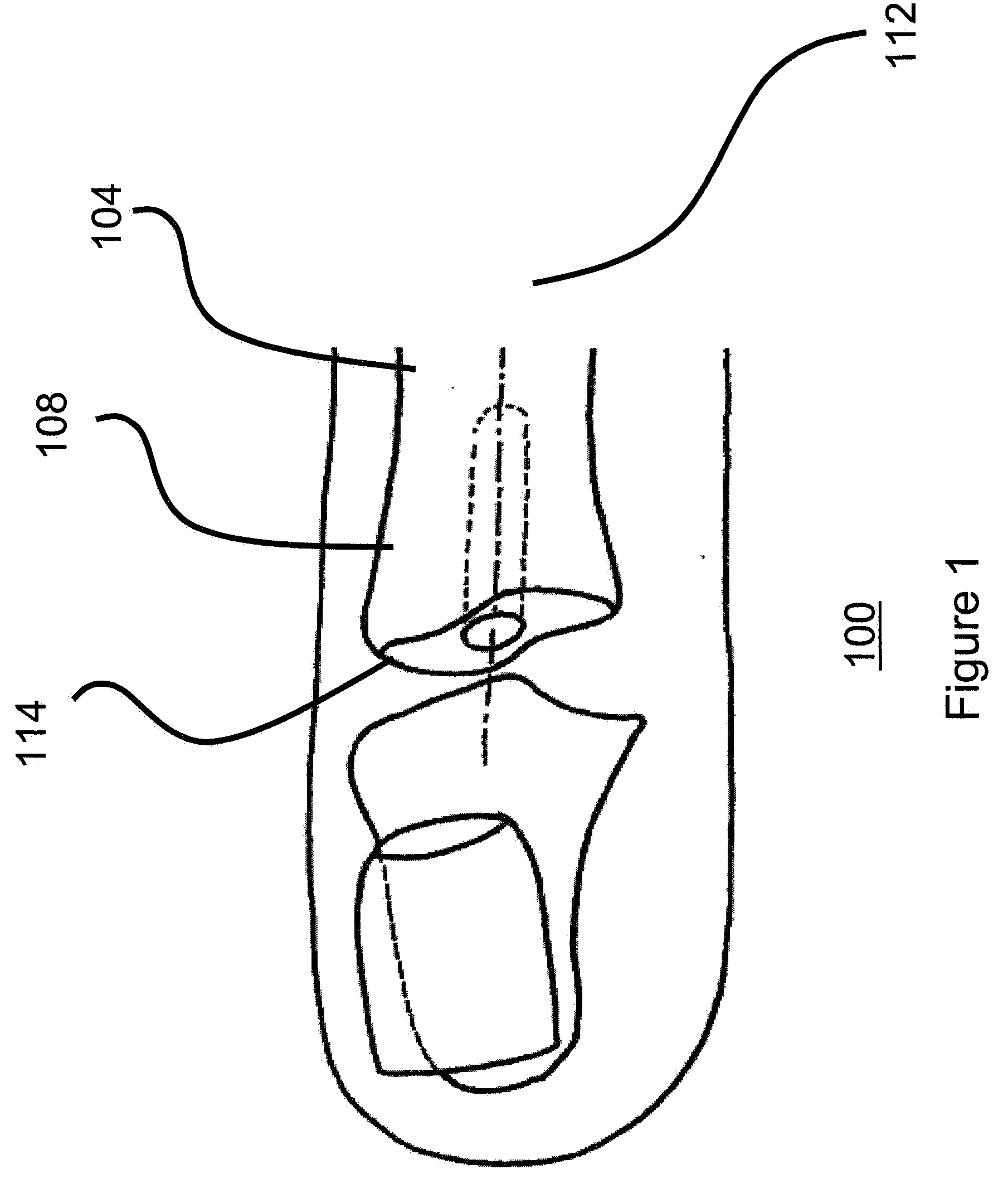
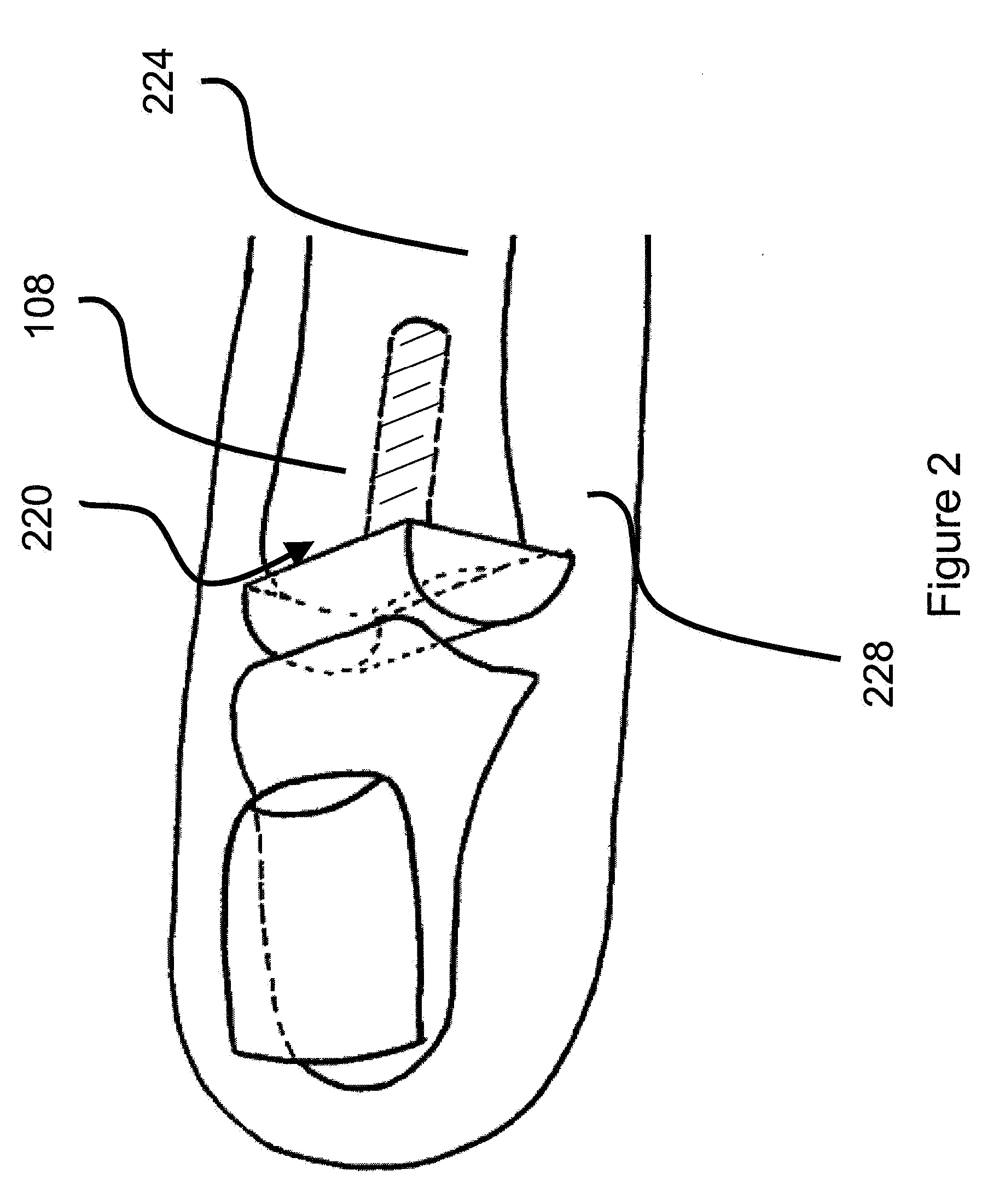
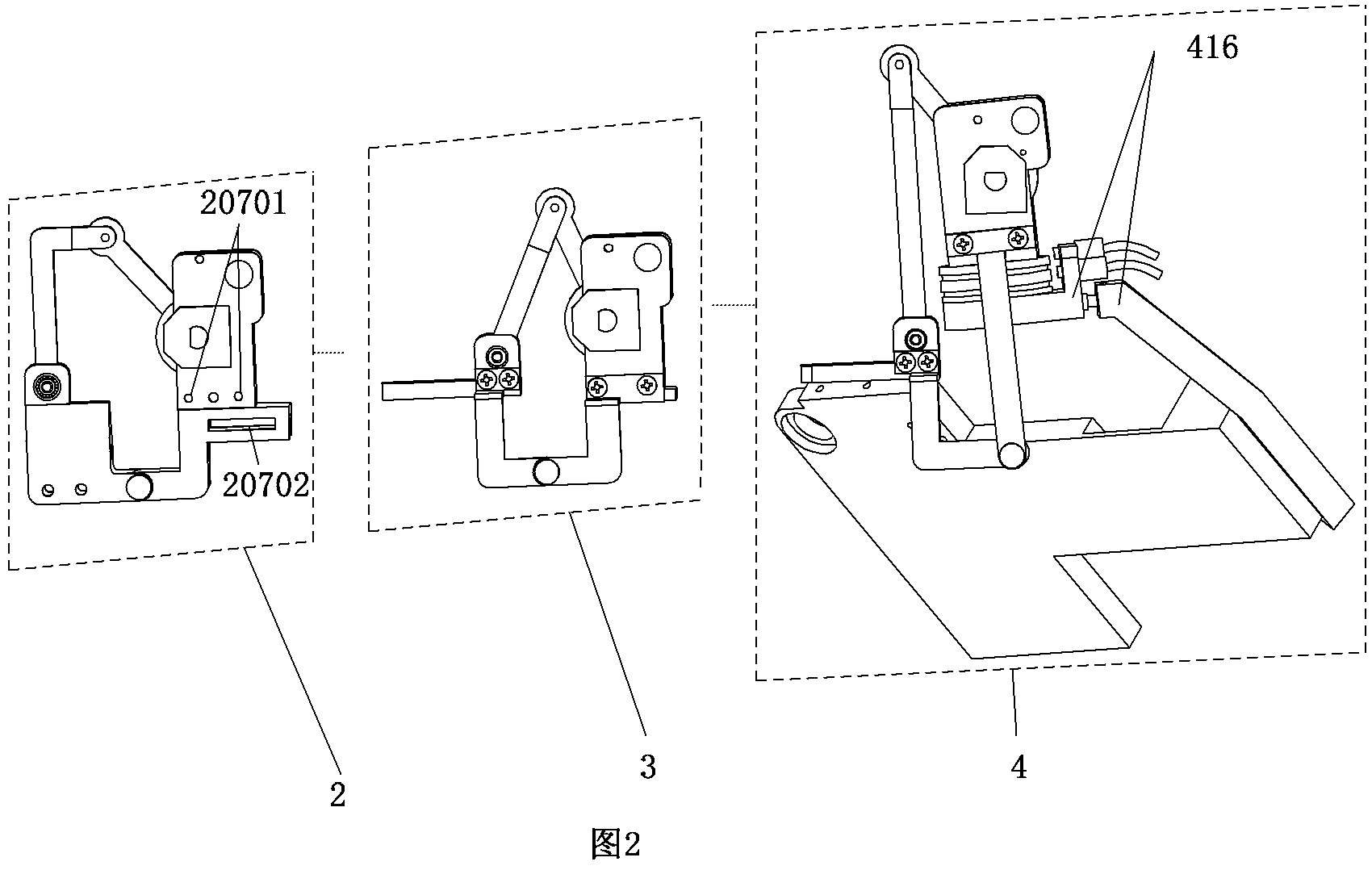
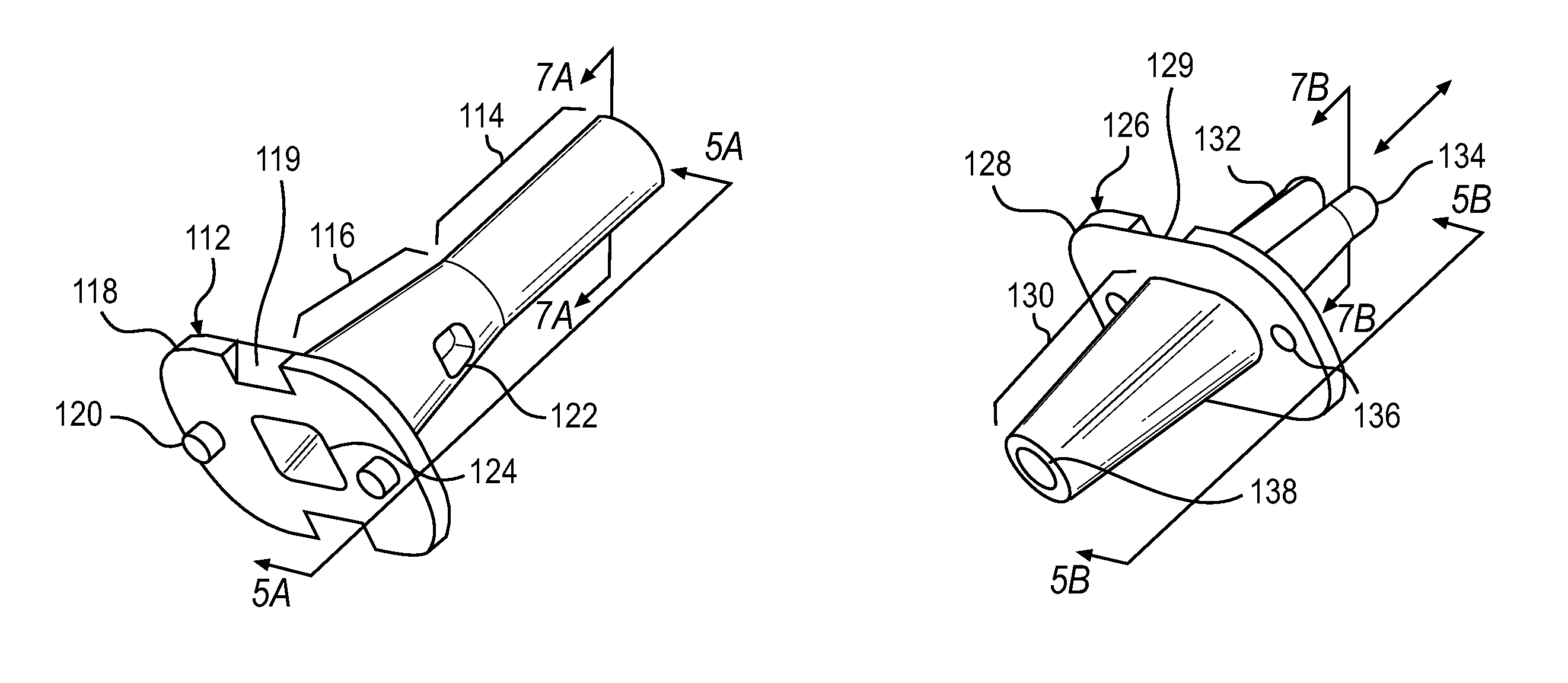
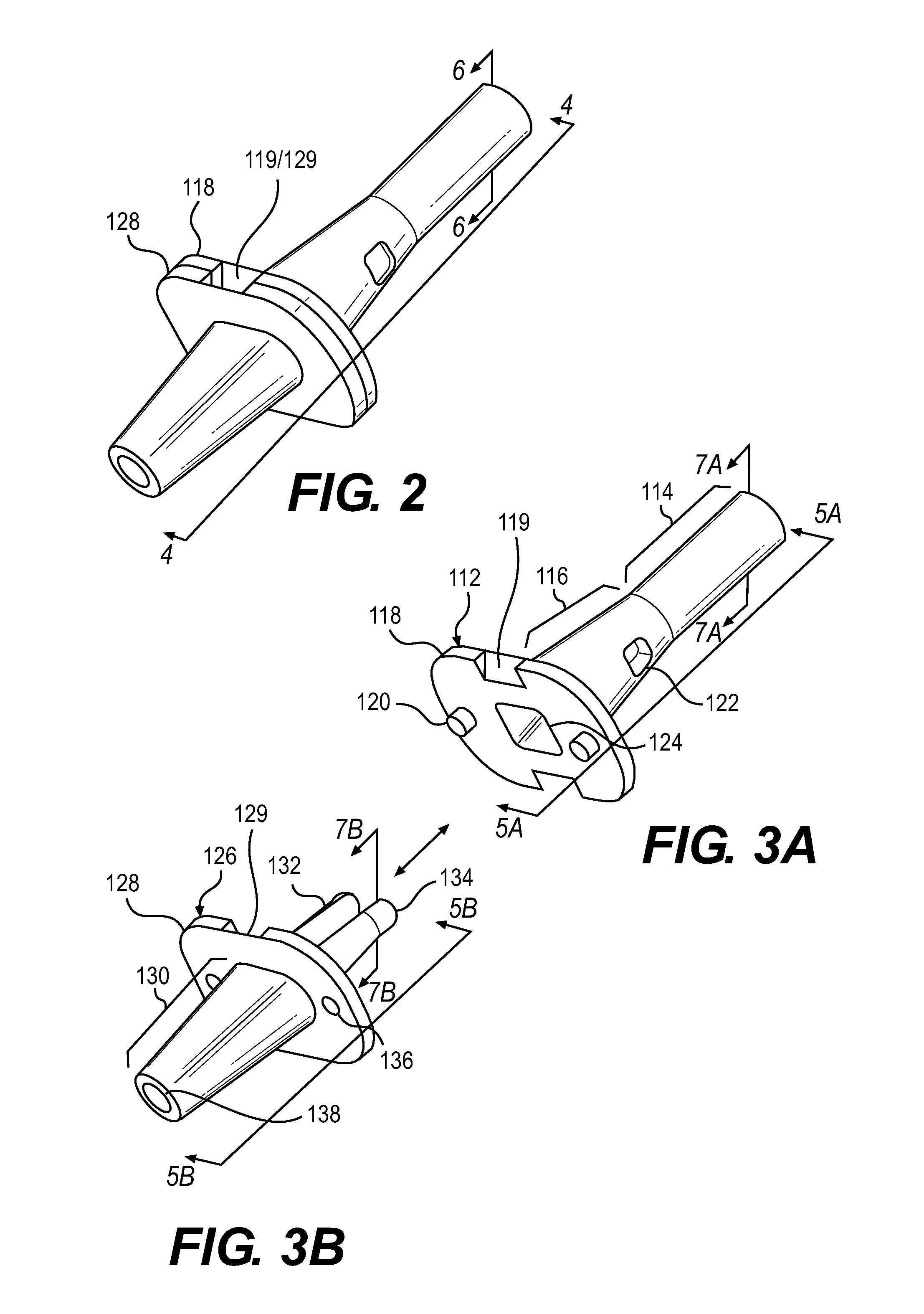
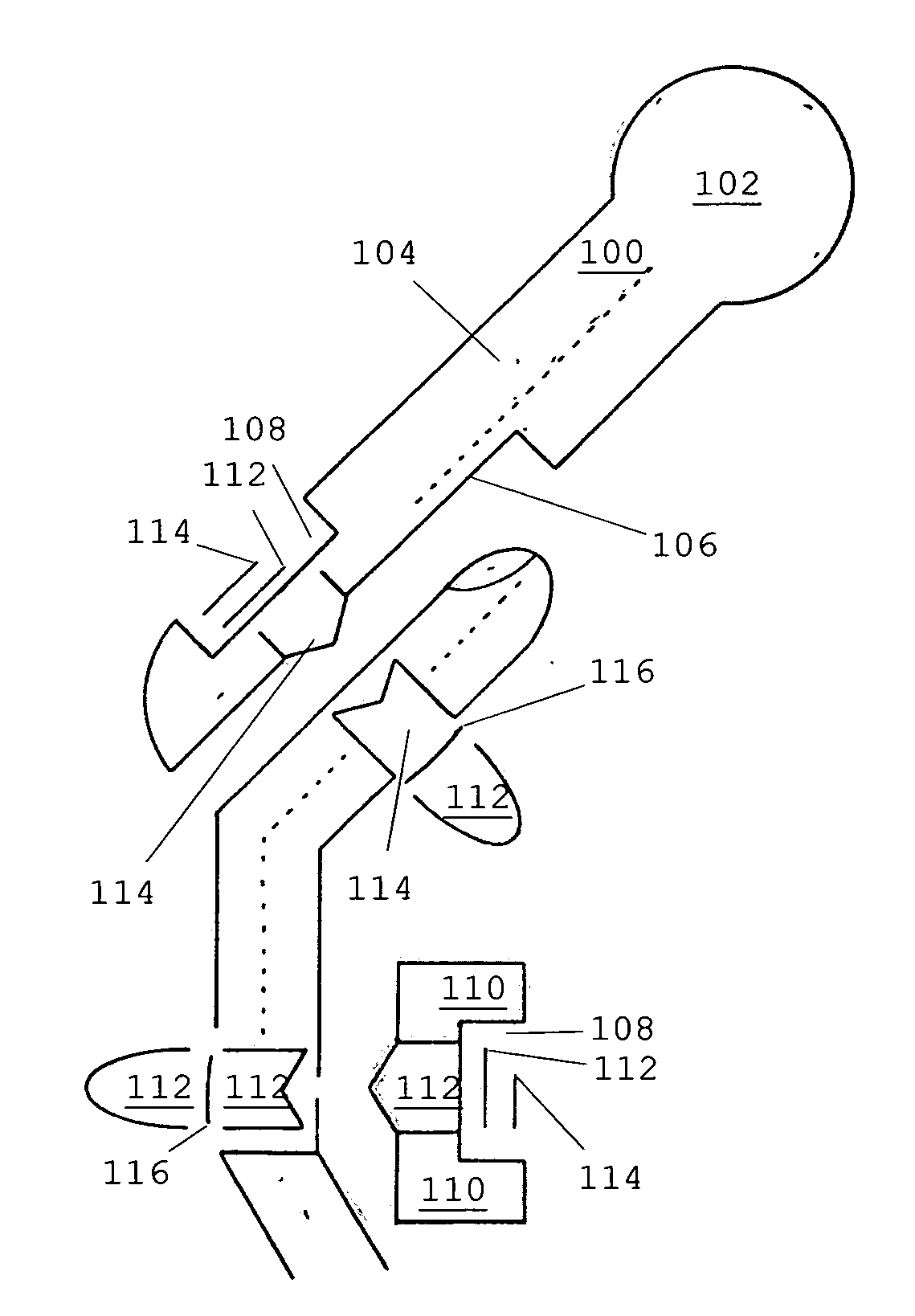
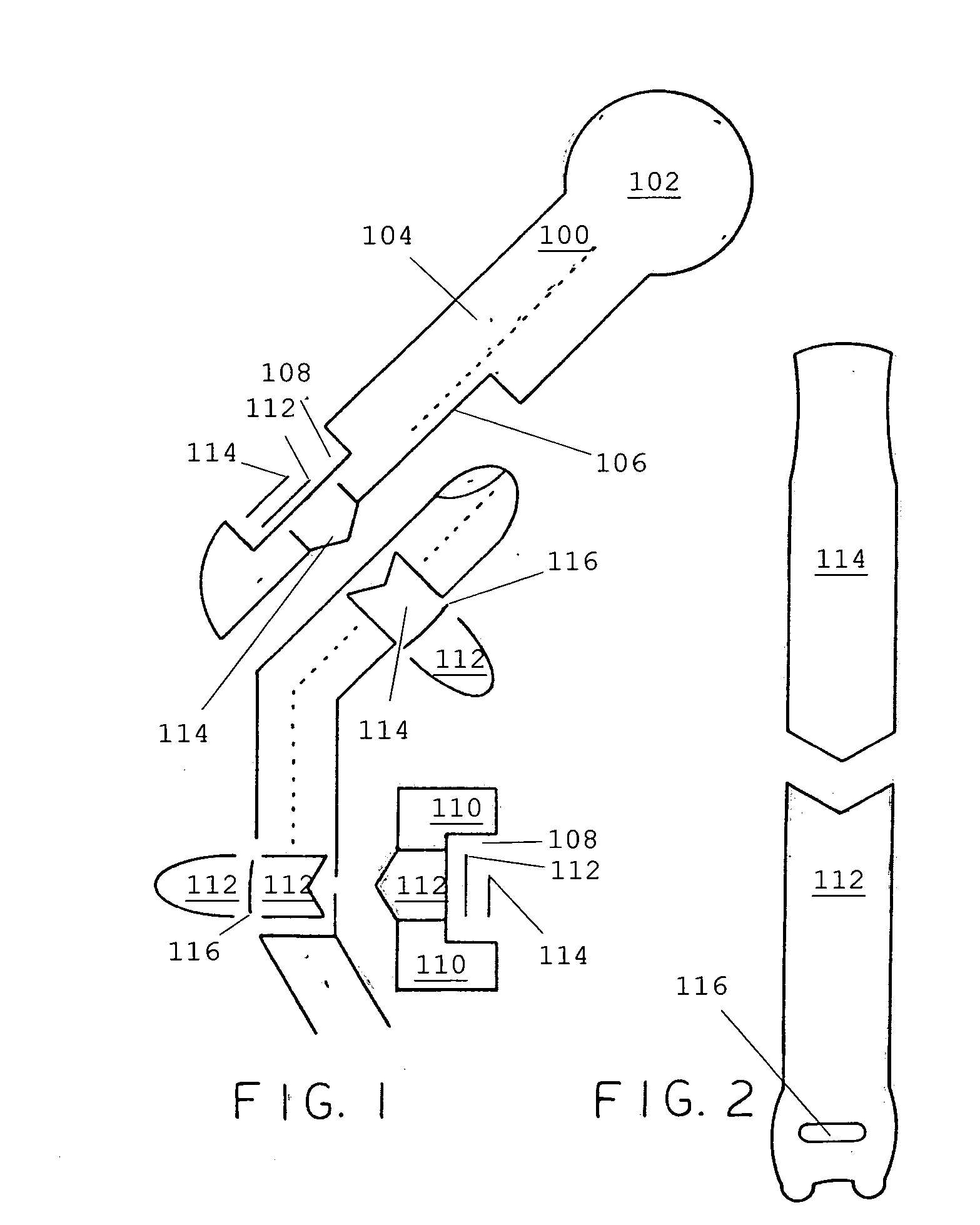
Interphalangeal joint implant methods and apparatus
ActiveUS8764842B2Decreasing eliminating incidenceSimple procedureFinger jointsInternal osteosythesisProximal phalanxDetent
A method and apparatus for correcting malformed joints, in particular the “hammer toe” contraction of the proximal interphalangeal joint. The disclosure comprises a two-component implant: a proximal phalanx component and a middle phalanx component. An endosseous stem on each component is inserted axially into the end of a respective host bone and, after insertion, the components are attached. The attached components are held together in various ways, for example a detent arm / aperture mechanism. Each component can be cannulated to allow for the passage of a kirschner wire, if necessary, to stabilize adjacent joints such as the proximal interphalangeal joint. The bones of the treated joint can be set to form a desired angle by adjusting the angle formed by the corresponding endosseous stems.
Owner:GRAHAM MICHAEL
Artificial simulation arm
InactiveCN100998527AMeet the requirements of mechanical transmissionFunctional Movement FlexibilityArtificial handsHuman bodyTendon sheath
An artificial hand with multiple functions, no error operation and no complication is composed of such artificial units as finger bones, metacarpal bones, ulna, radius, muscle tendons, tendon sheaths, slide mechanism, muscles and skin. It can be connected to the crippled end of human radius by screw and its artificial muscle tendons can be linked with relative ones of human body by stitch.
Owner:张为众
Modelling of hand and arm position and orientation
InactiveUS20130158946A1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsEngineeringDegrees of freedom
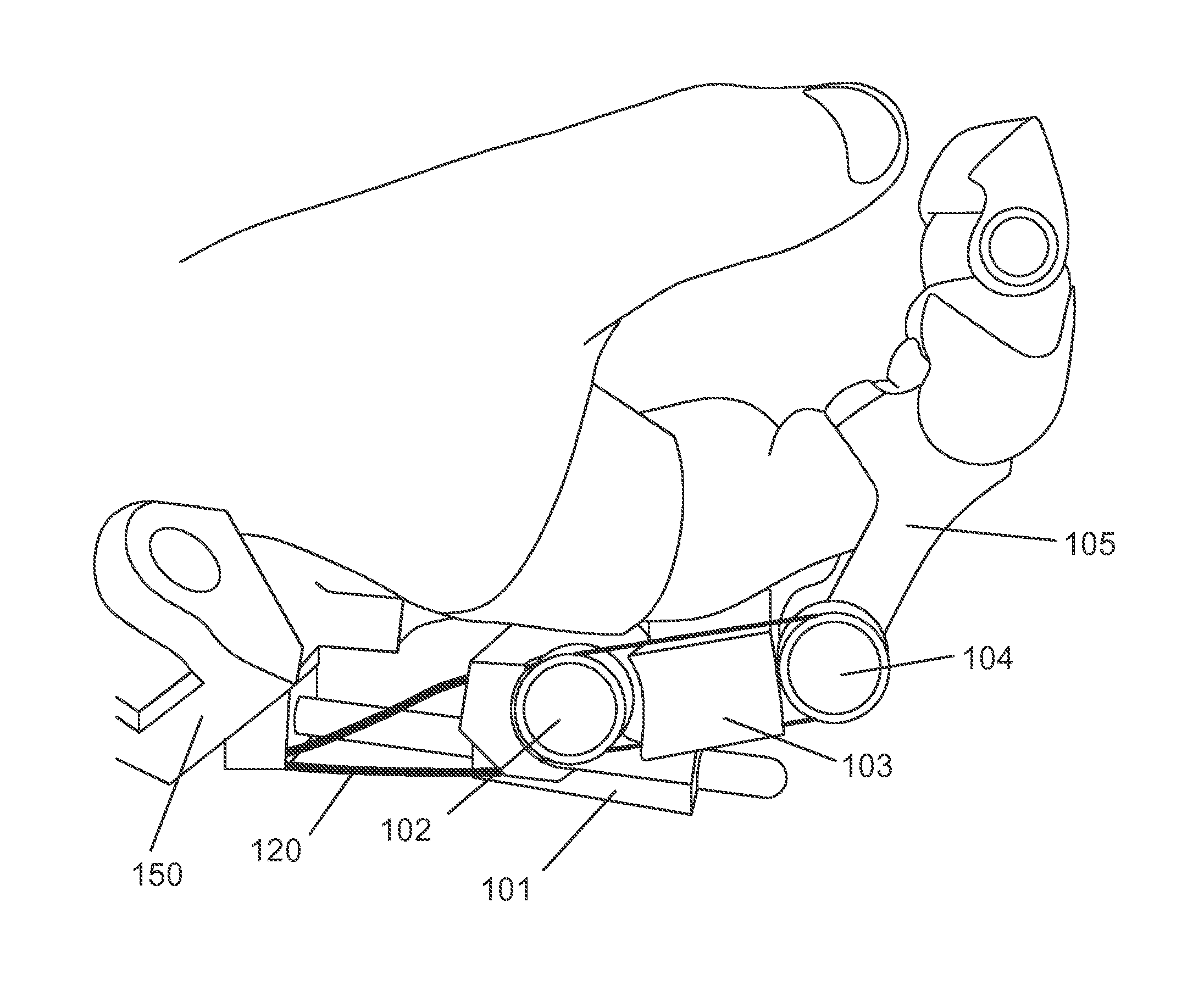
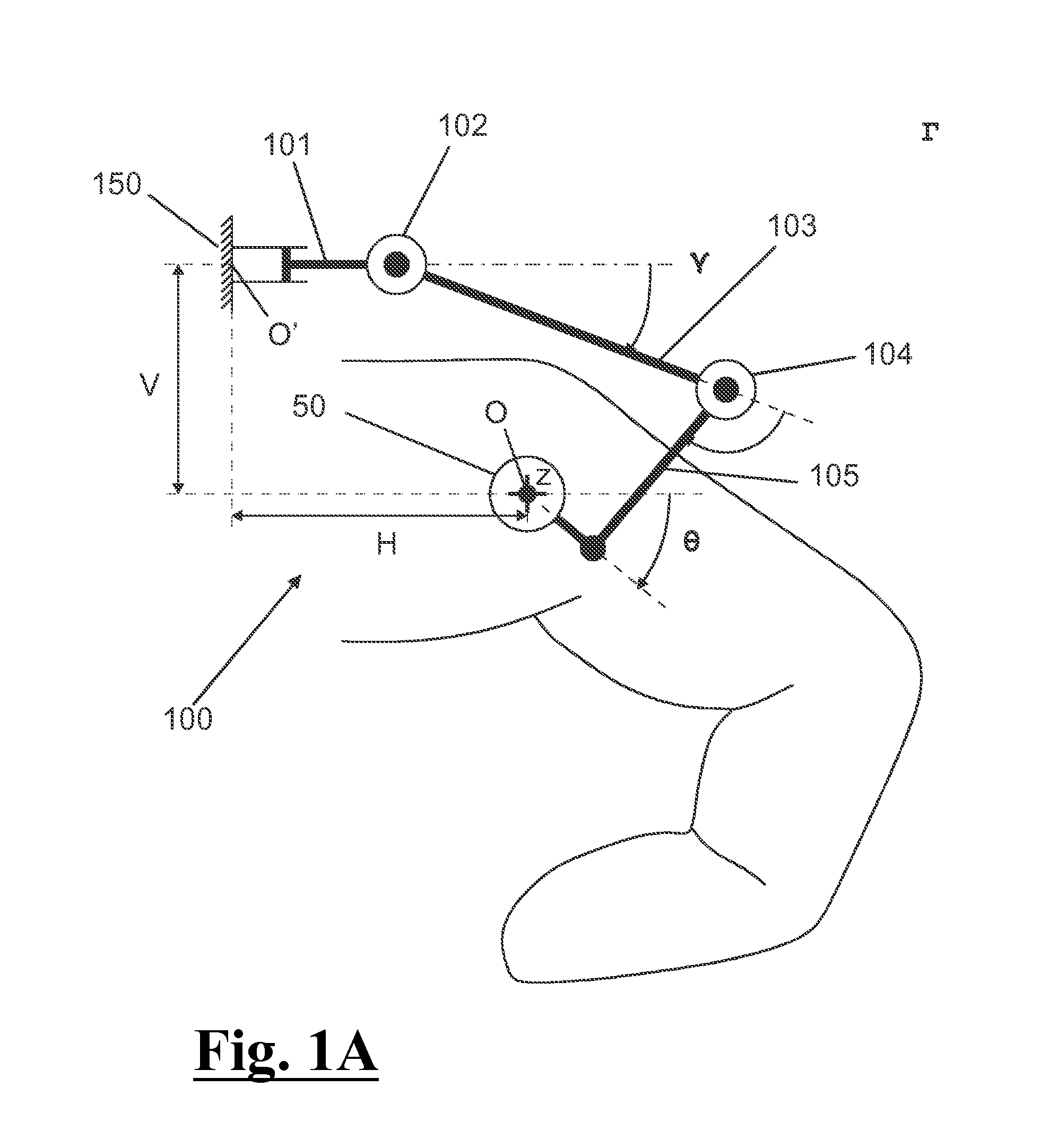
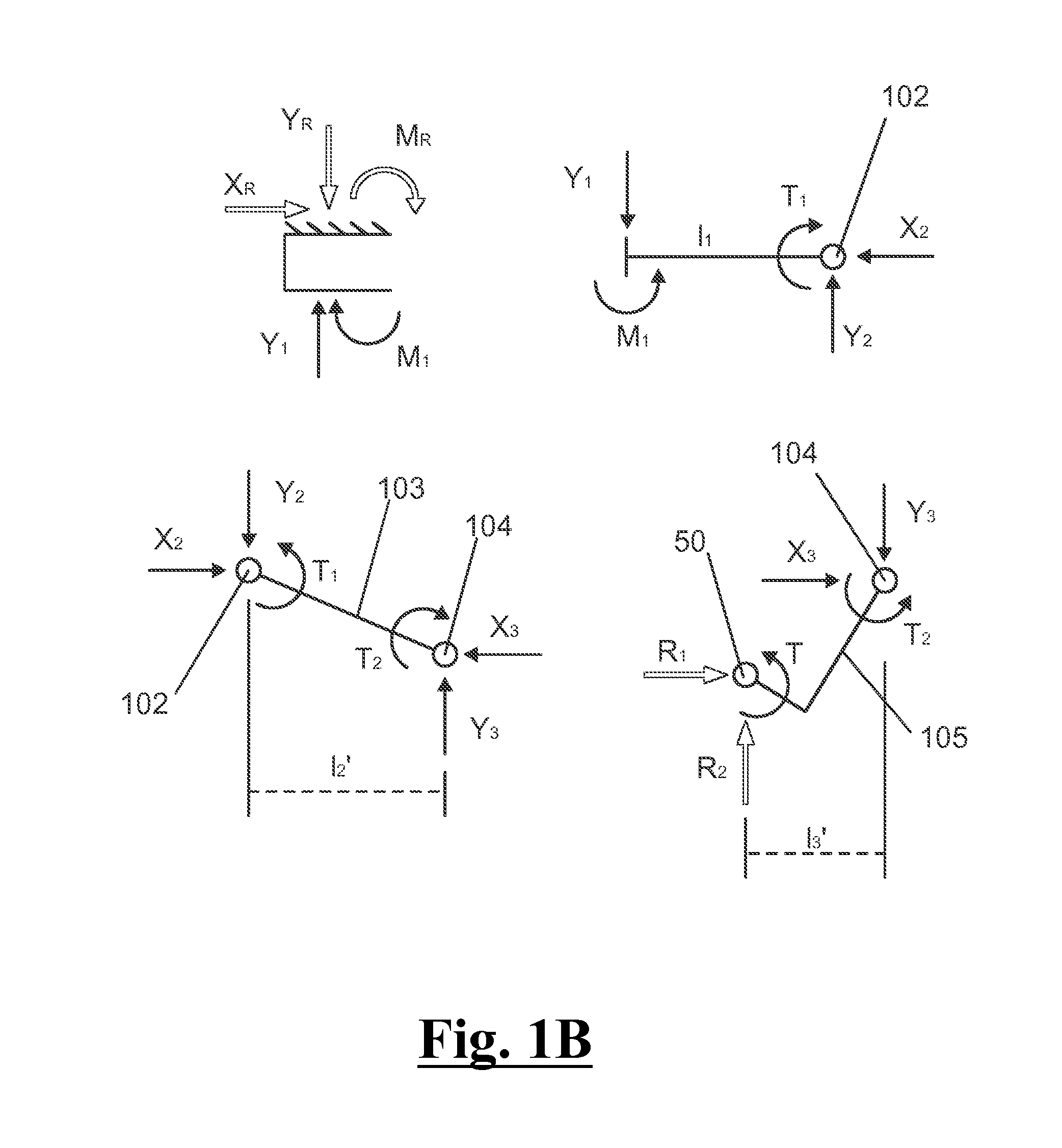
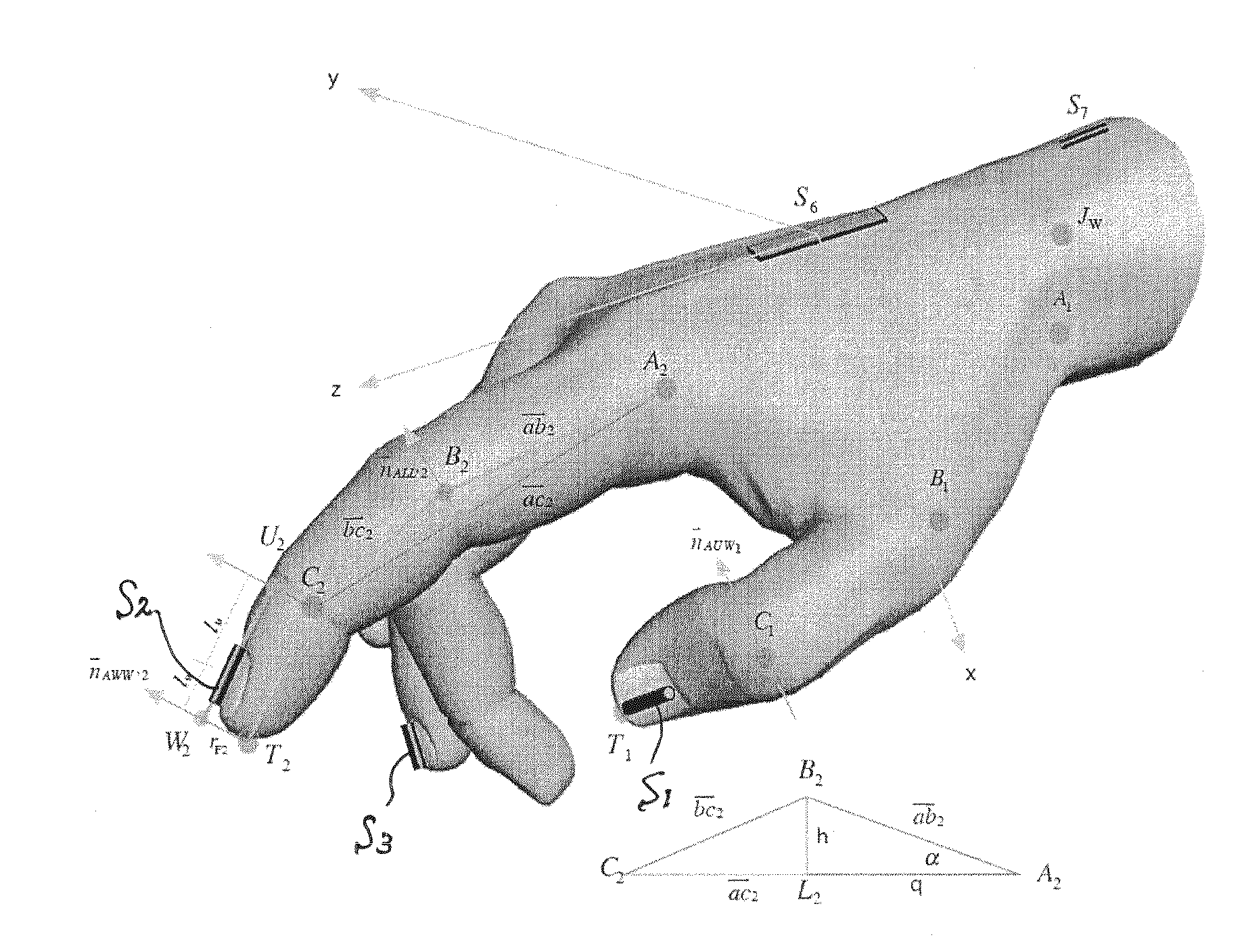
The present invention provides a method for modelling a position and orientation of a hand with as small a number of sensors as possible. A first sensor is attached on a phalanx distalis of a finger. The first sensor is adapted to provide information on at least five degrees of freedom that correspond to three translations, yaw and pitch. A second sensor is placed at a fixed position relative to a dorsum or palm of the hand. The second sensor is adapted to provide information on at least six degrees of freedom that correspond to three translations, yaw, pitch and roll with respect to a point of the dorsum or palm of the hand. A position and orientation of each of the first and second sensors is detected. A first distance between said point and a metacarpal-phalangeal joint of the finger, a second distance between the metacarpal-phalangeal joint and a proximal interphalangeal joint, a third distance between the proximal interphalangeal joint and a distal interphalangeal joint, and a fourth distance between the distal interphalangeal joint and the first sensor are measured. A position and orientation of each of the three joints is calculated on the basis of the measured first to fourth distances, the detected position and orientation of the first sensor, and the detected position and orientation of the second sensor.
Owner:DEUT PRIMATENZENT GMBH LEIBNIZ INST FUR PRIMATENFORSCHUNG
Full-joint measurement type data glove
InactiveCN107825393AAvoid squeezingAvoid data distortionInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingSacroiliac jointInterphalangeal Joint
The invention discloses a full-joint measurement type data glove. The data glove is connected with a manipulator or a computer end and comprises a glove body with two layer structures and a pluralityof bending degree sensors and a plurality of strain sensors, wherein the bending degree sensors and the strain sensors are located between the two layer structures. The bending degree sensors are arranged at metacarpophalangeal joints and interphalangeal joints at the glove body. The strain sensors are arranged at the metacarpophalangeal joints of the glove body. The bending degree sensors and thestrain sensors are used for obtaining the movement information of the fingers perpendicular to the palm and the fingers parallel to the palm. By means of the full-joint measurement type data glove, the longitudinal and transverse movement information of the fingers of an operator can be obtained, and the movement information is transmitted to the manipulator or the computer end; and in addition,the inner layer structure of the glove body is made of nitrile or rubber, the outer layer structure is made of cotton, and the full-joint measurement type data glove further has the advantages of being simple in wearing mode and low in maintenance difficulty.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of conductive thermoplastic starch polymer and polymer-based humanoid soft finger with folding paper structure
The invention relates to a preparation method of a conductive thermoplastic starch polymer and a polymer-based humanoid soft finger with a folding paper structure, belongs to the technical field of humanoid fingers, and aims to solve the problems that in an existing humanoid soft finger with the variable rigidity realized by utilizing a thermal phase change material, the variable rigidity responsespeed is low due to long response time of conversion from a glass state to a high-elasticity state, and the joint motion flexibility and the rigidity of the humanoid soft finger cannot be realized atthe same time. The polymer-based humanoid soft finger comprises a finger root, a metacarpophalangeal joint, a proximal phalanx, an interphalangeal joint, a middle phalanx, a finger tip joint, a distal phalanx, a strain restraint layer, a variable rigidity layer, a cooling layer and a contact layer, wherein each joint is provided with a U-shaped groove, and the outer side of each joint is wrappedwith Yoshimura line type folding paper; and three self-made conductive thermoplastic starch polymer plates are arranged at the bottom of the finger. The humanoid soft finger not only can realize rapidand active control of the rigidity of the phalanxes, but also can realize synchronous and passive adjustment of joint flexible motion and joint rigidity, and has the advantages of fast variable rigidity, high adaptability and flexibility in motion.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
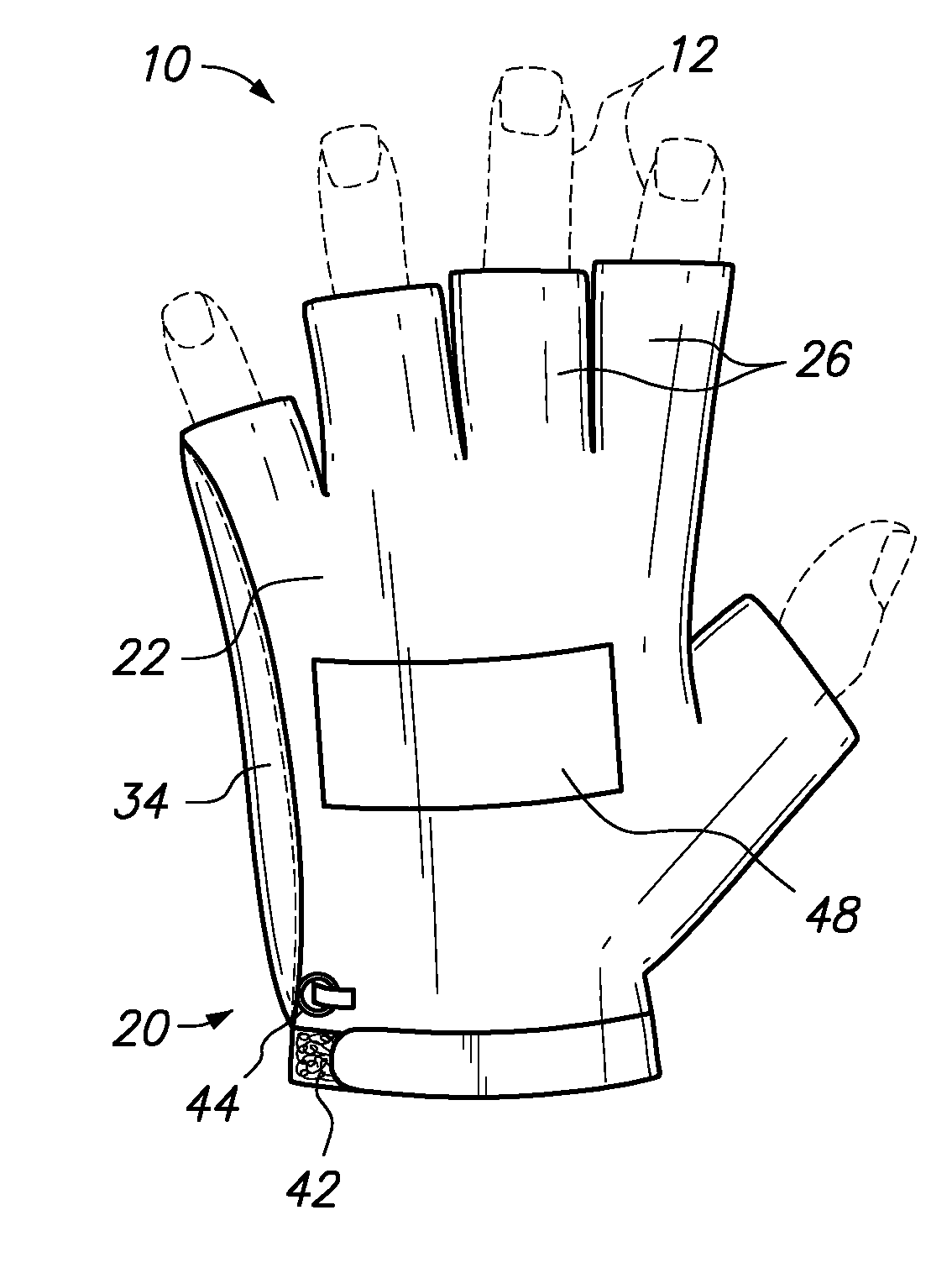
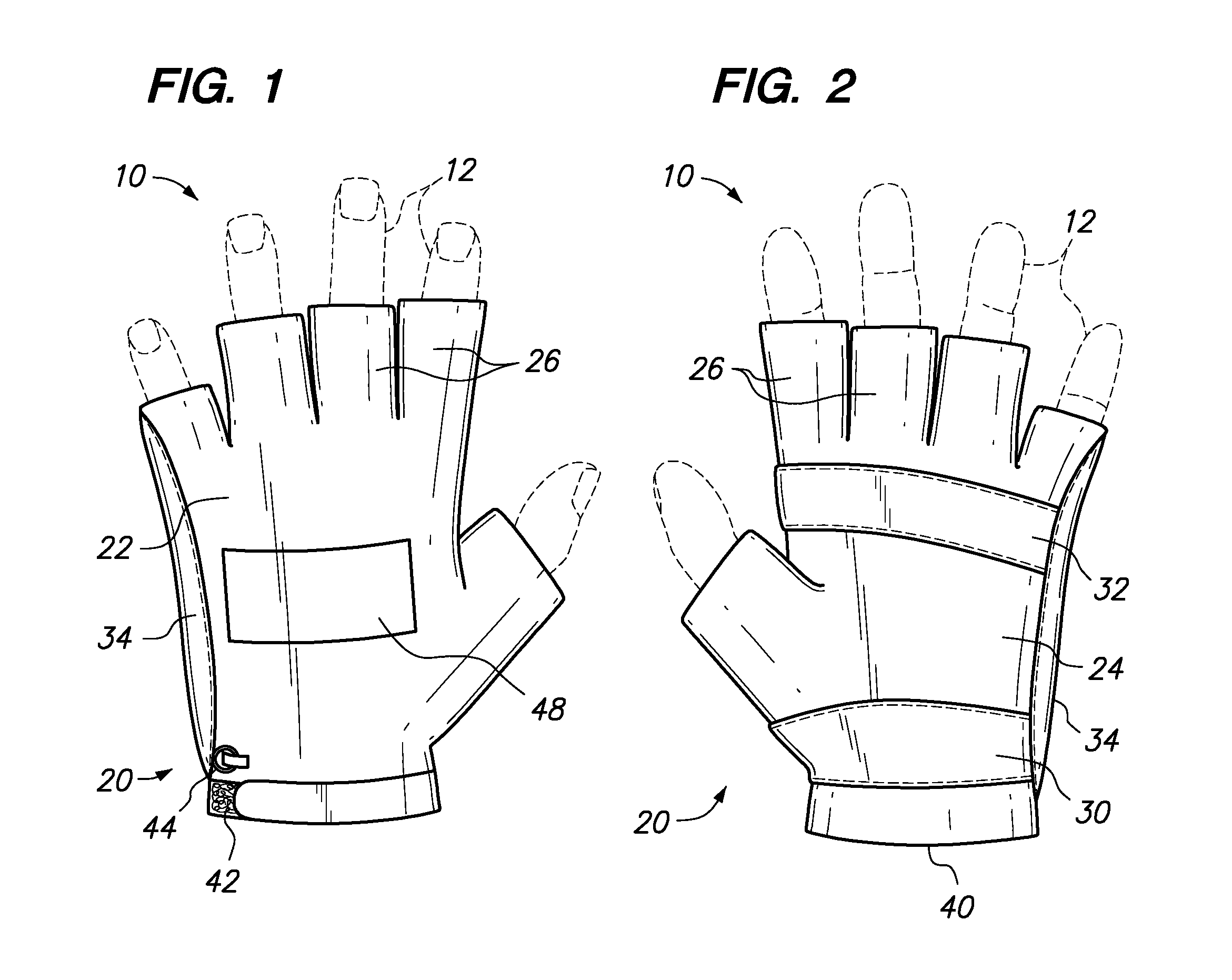
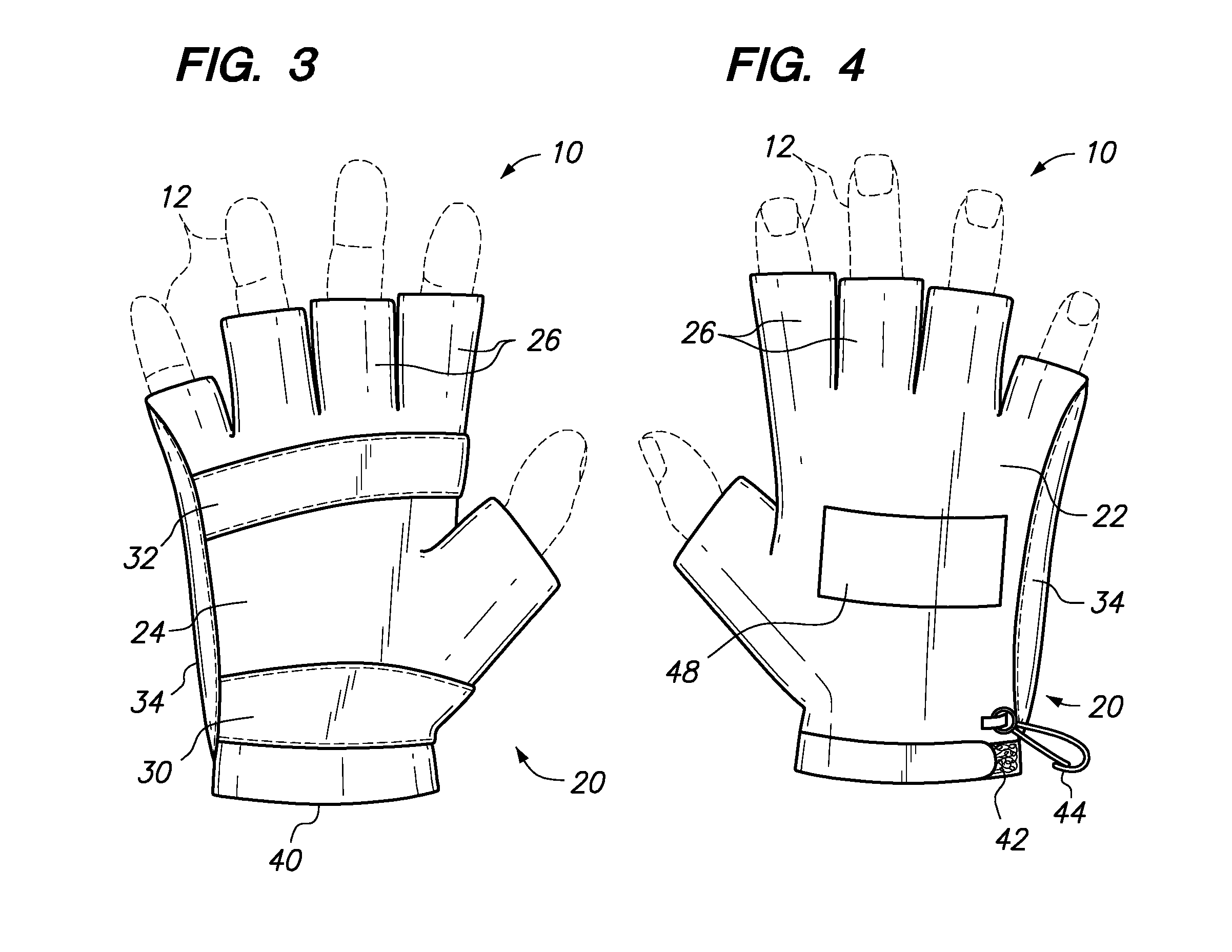
Playground Glove
InactiveUS20110099687A1Provide protectionGripping protection to the fingersGlovesSport apparatusEngineeringInterphalangeal Joint
The invention provides a glove having connected back and palmar portions for overlaying and protecting respective back and palm regions of a human hand, the back and palmar portions having distal and proximal ends with a plurality of digital segments projecting from the distal ends, where the digital segments overlay the proximal interphalangeal joints of the fingers of the hand and are open over the distal interphalangeal joints of the fingers, where the palmar portion comprises a padded region overlaying the base of the metacarpal bones of the hand, and where the glove comprises a padded region overlaying the length of the fifth metacarpal of the hand.
Owner:SKROCKI SUSAN MARIE
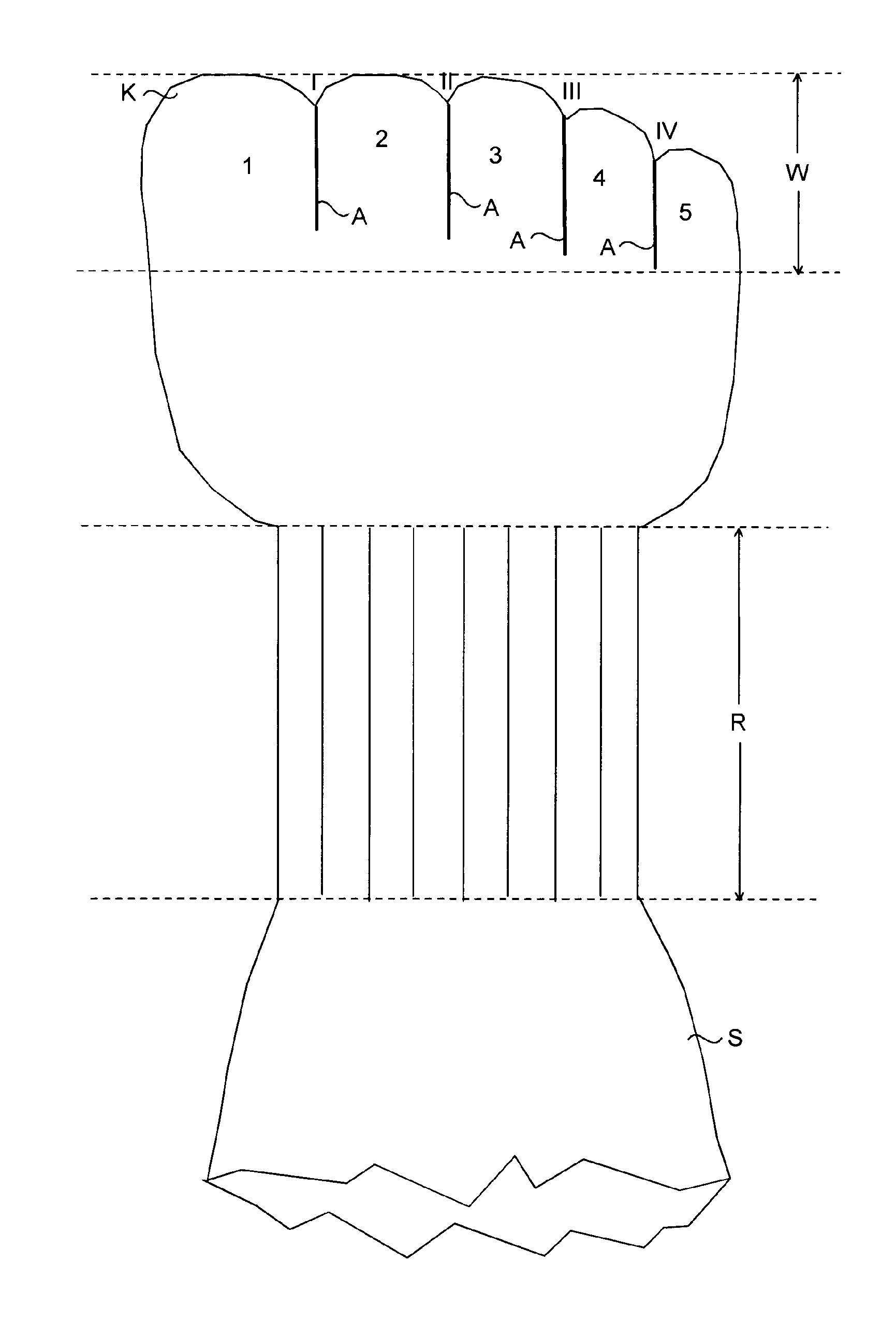
Orthotic toe sock
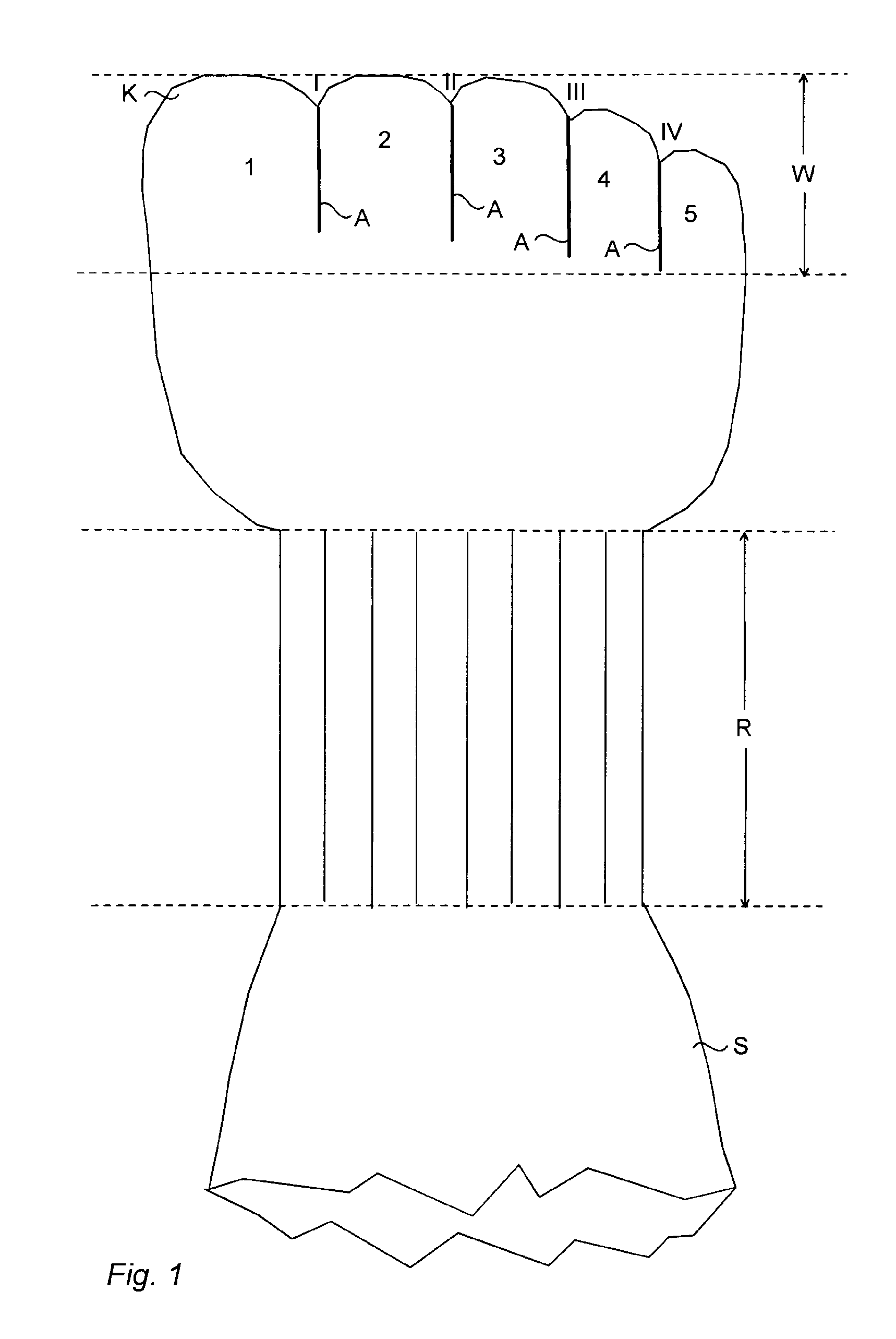
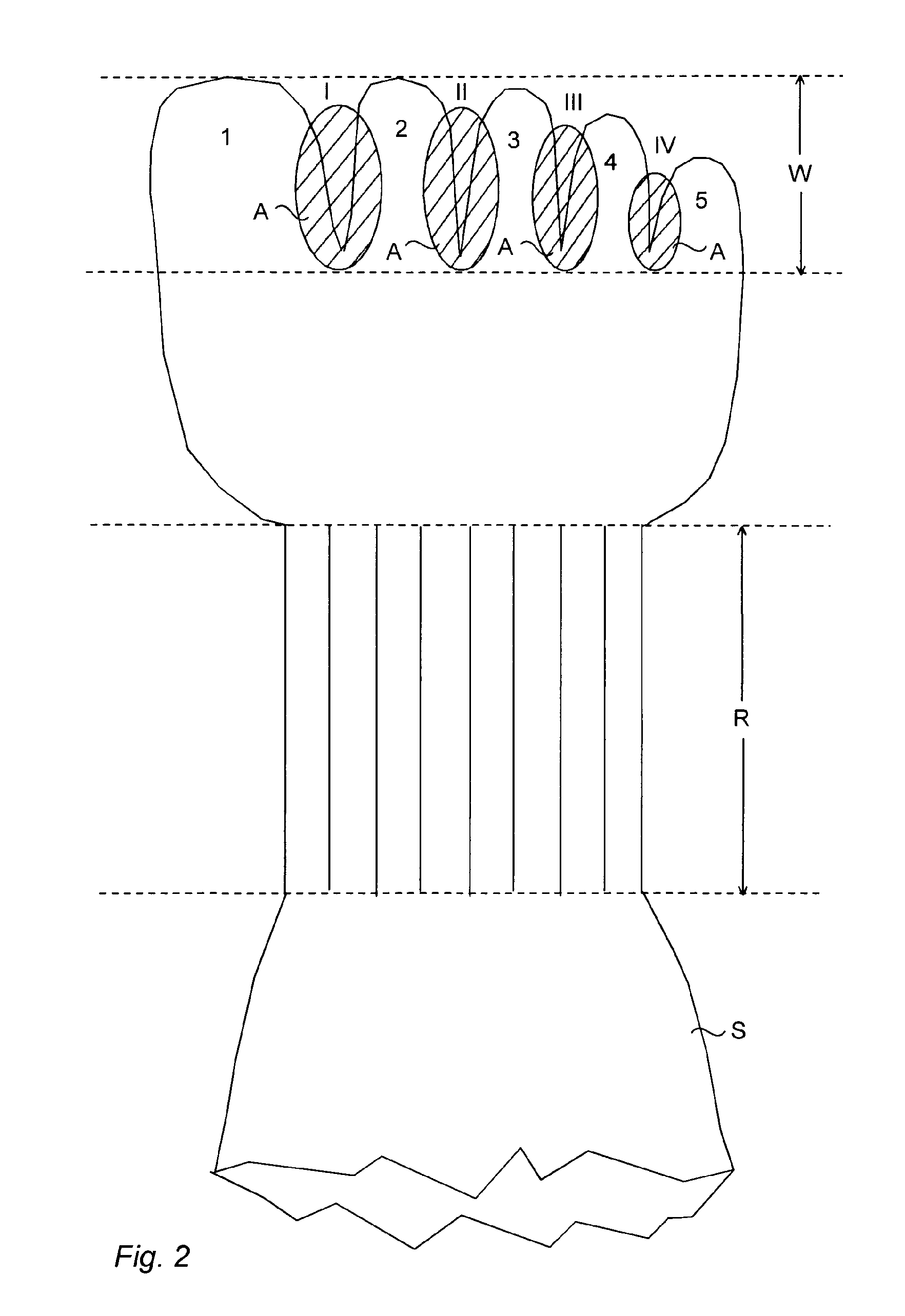
The present invention is based on providing, in order to correct or prevent a toe deformity, an orthotic toe sock (S) wherein a toe part (W) of the sock (S) comprises at least two toe-specific toe elements (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) arranged to receive adjacent toes. The adjacent toe elements are, in a corresponding space (I, II, Ill, IV) in between the toes, attached to one another over an area (A) extending, when the sock is being worn, from a base or from above the base, e.g. from a proximal interphalangeal joint region, of the toe in question, e.g. the second, third, fourth or fifth toe, to a tip of the toe or almost to the tip of the toe.
Owner:KOTKAMAA ROBERT +2
Flexible manipulator based on sensing of bionic strain sensor array
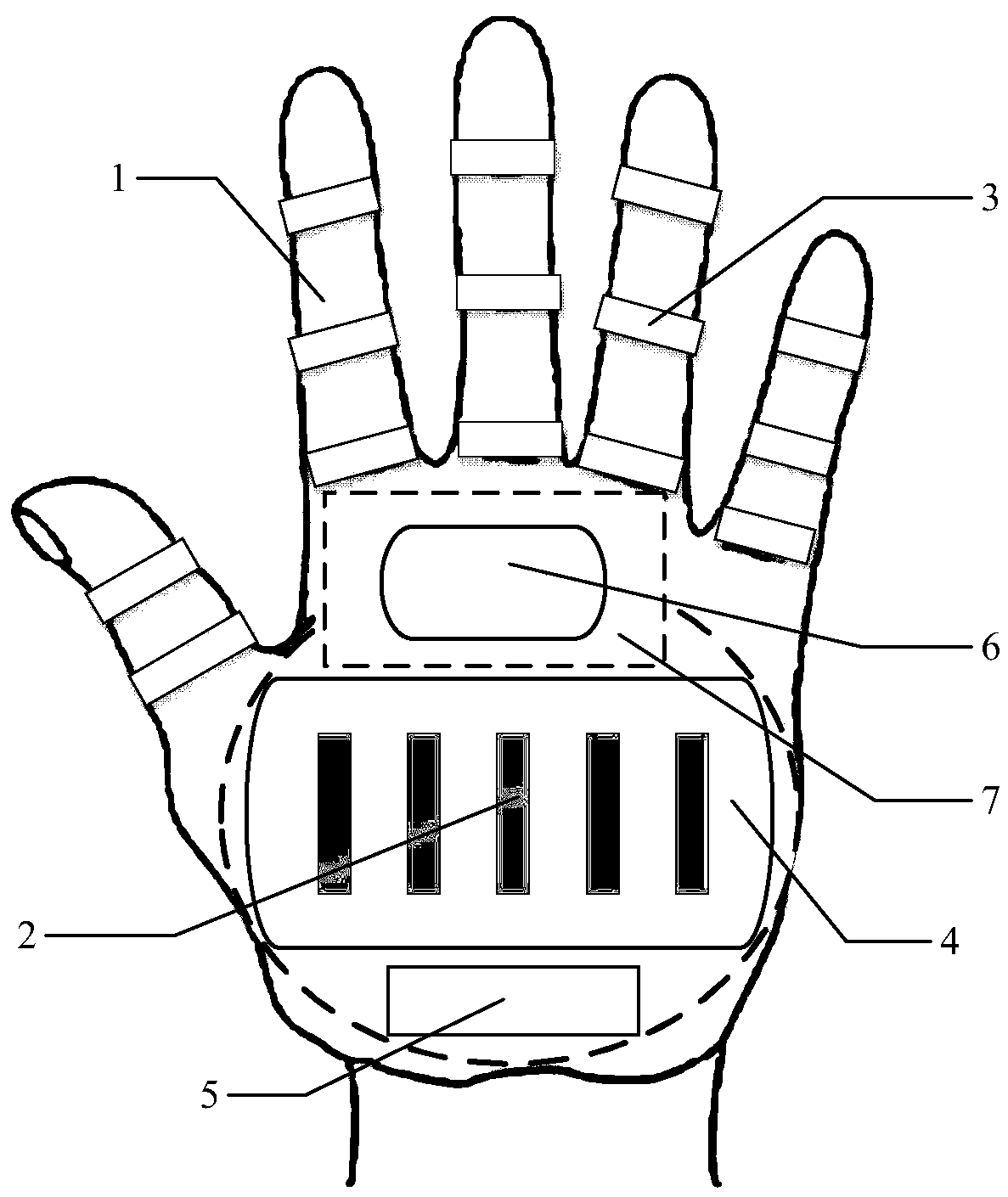
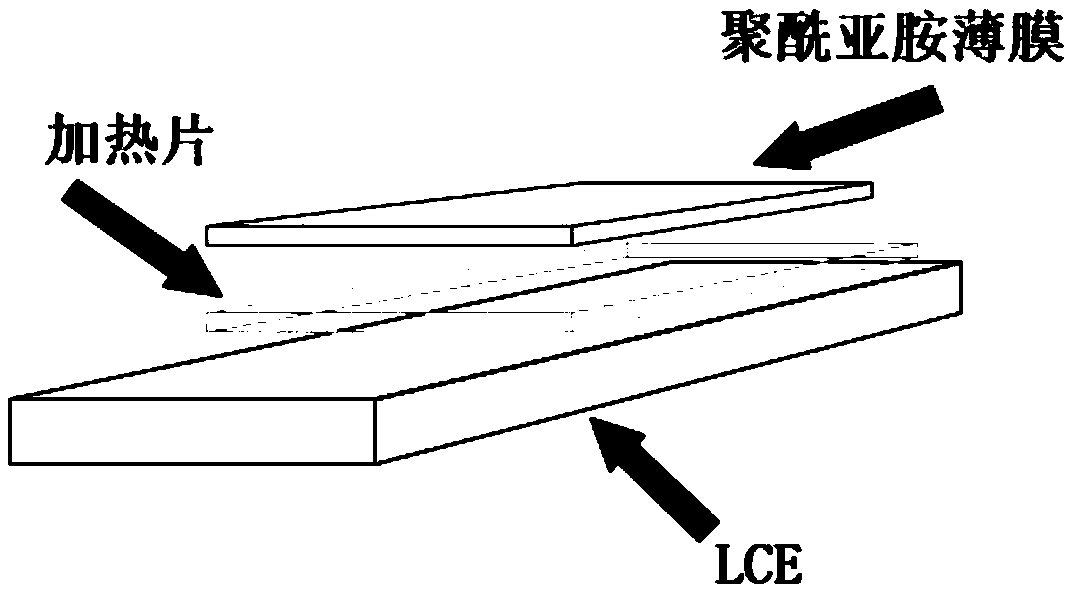
The invention relates to a flexible manipulator based on sensing of a bionic strain sensor array. A liquid crystal elastic body (1) has a hand-shaped structure, and an elastic insulating bottom plate(4) is positioned at the position of a palm, is embedded in the liquid crystal elastic body (1) and can deform when pressure is applied to the elastic insulating bottom plate (4); an array formed by bionic strain sensors (2) adheres to the elastic insulating bottom plate (4); the bionic strain sensors (2) are connected with power supply portions (5), the power supply portions (5) are Wheatstone electric brides, and the inside of each electric bridge is connected with the corresponding bionic strain sensor (2); each power supply portion (5) is connected with a control module (7) through an amplifying circuit module (6); flexible circuit polyimide films are separately embedded at positions of first interphalangeal joints, second interphalangeal joints and metacarpophalangeal joints of all fingers of the liquid crystal elastic body (1), and can bent along with bending of the liquid crystal elastic body (1); and each polyimide film heater (3) is connected with the corresponding control module (7). The flexible manipulator based on sensing of the bionic strain sensor array is suitable for objects which are small in mass, small in size and difficult to grab comparatively.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for extracting region of interest of finger vein based on fusion of finger contour and gradient distribution
InactiveCN108830158AIncrease contrastImage quality variesSubcutaneous biometric featuresBlood vessel patternsVeinImaging processing
The invention, which belongs to the field of image processing, proposes a method for extracting a region of interest of a finger vein, thereby providing the reliability guarantee for follow-up fingervein feature extraction and recognition. To be specific, the invention provides a method for extracting a region of interest of a finger vein based on fusion of finger contour and gradient distribution. On the basis of the imaging principle of the finger vein and the characteristic of low absorption coefficient of the near-infrared light by the interphalangeal joint, the finger rotation and gradient distribution are corrected based on the finger contour and the interphalangeal joint position is located; and thus the region of interest having the vein information is extracted automatically. Themethod is mainly applied to the image processing occasion.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Distal phalangergonic finger device
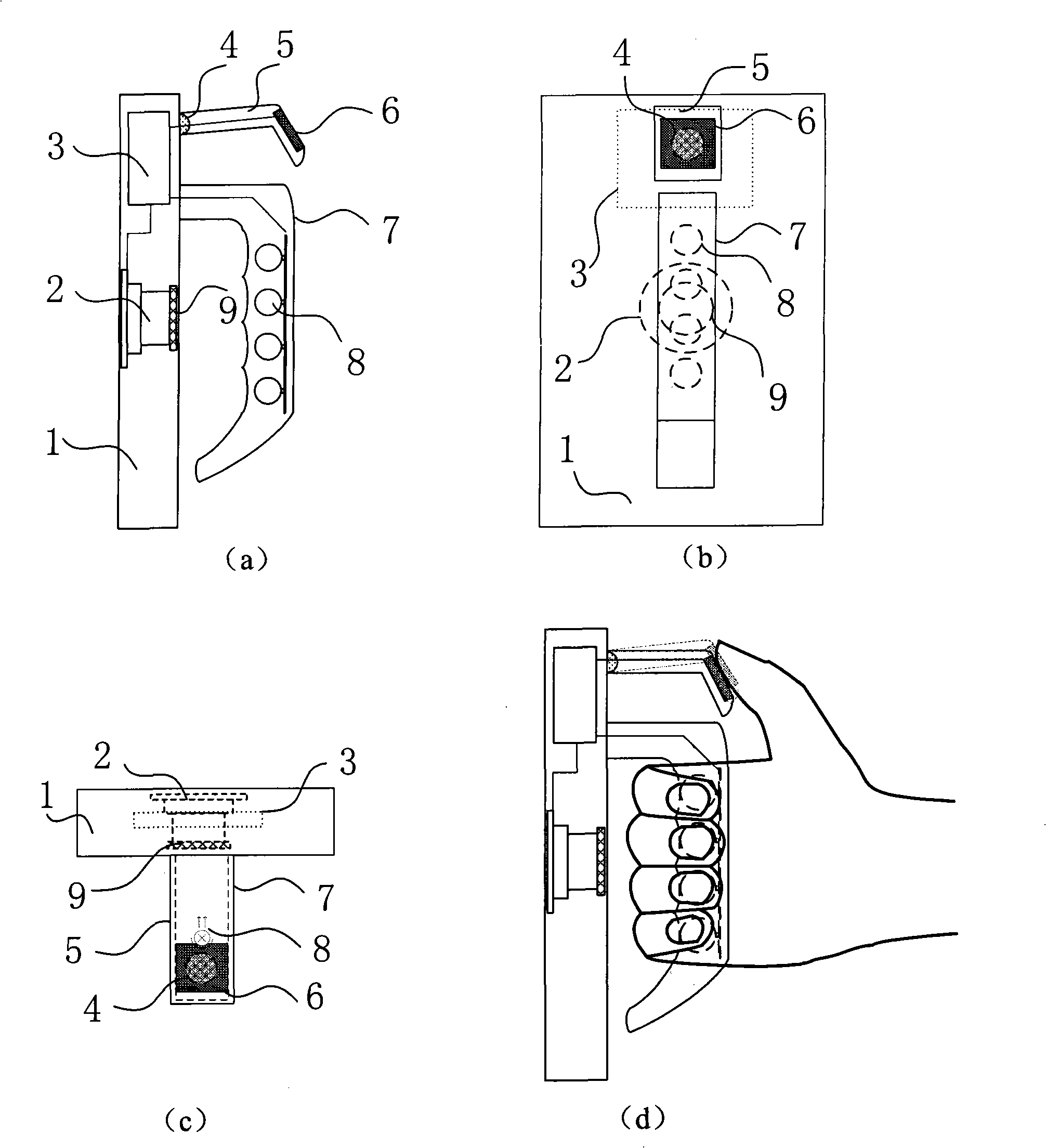
InactiveUS20140357453A1Movement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesPalmar surfaceInterphalangeal Joint
A finger weight that is functional. A normal sized, weighted sphere is attached to an end of a cylinder-shaped body. The weighted sphere and body has a hard particulate material to provide a resistance transfer through the body. A flattened surface and groove are provided in both the implement and the assistive implement. The flattened surface of the implement of the body half distant from the sphere is cinctured in the groove by an adhesive resinous strip to the non-palmar surface of the distal finger digit. The flattened surface along the entire length of the assistive implement is cinctured in the groove by an adhesive resinous strip to the proximal interphalangeal joint. The operation of the finger weight is extending and flexing the distal finger digit while restricting the extending and flexing of the proximal interphalangeal joint.
Owner:TAMANAHA DWIGHT MASAICHI
Hand exoskeleton
InactiveCN104768714AProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesProximal phalanxIndex finger
A hand exoskeleton device is provided having at least three robotic units. One is for attachment to the thumb and has two elements for attachment to the distal and proximal phalanges. The other two each have three elements, for attachment to the distal, middle and proximal phalanges of the index and middle fingers. The elements of each robotic unit are interconnected by suitable hardware to provide for relative angular movement of the elements about an axis of rotation that corresponds substantially to the axis of rotation of a user's interphalangeal joint movement. An actuator is associated with the interconnecting hardware to enable adjustment of the two elements in each of two opposite directions. A sensor senses the angular position or force of one element relative to the other element of each pair. A computerized controller controls movement of the elements of each pair by means of the associated actuator.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN
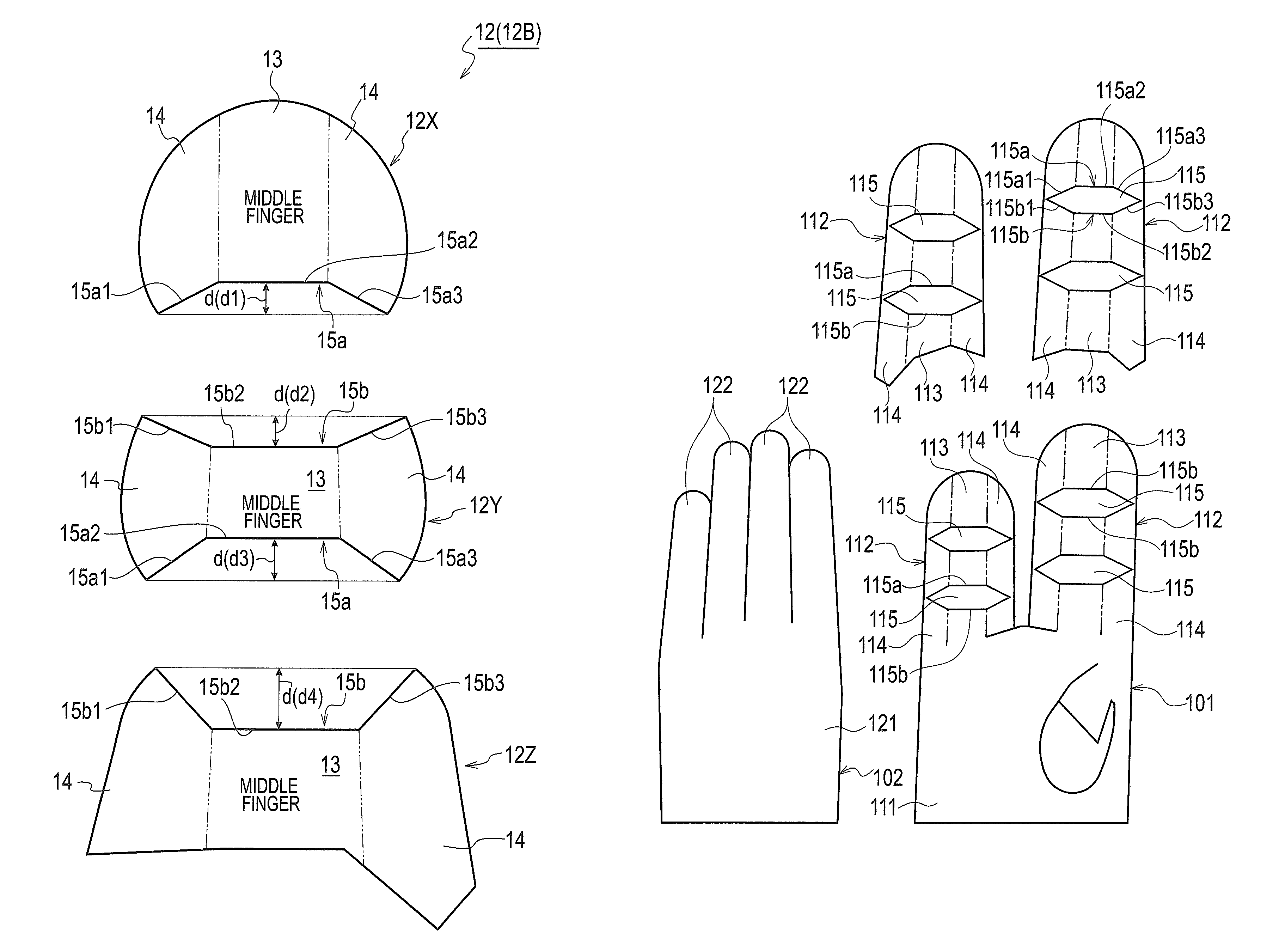
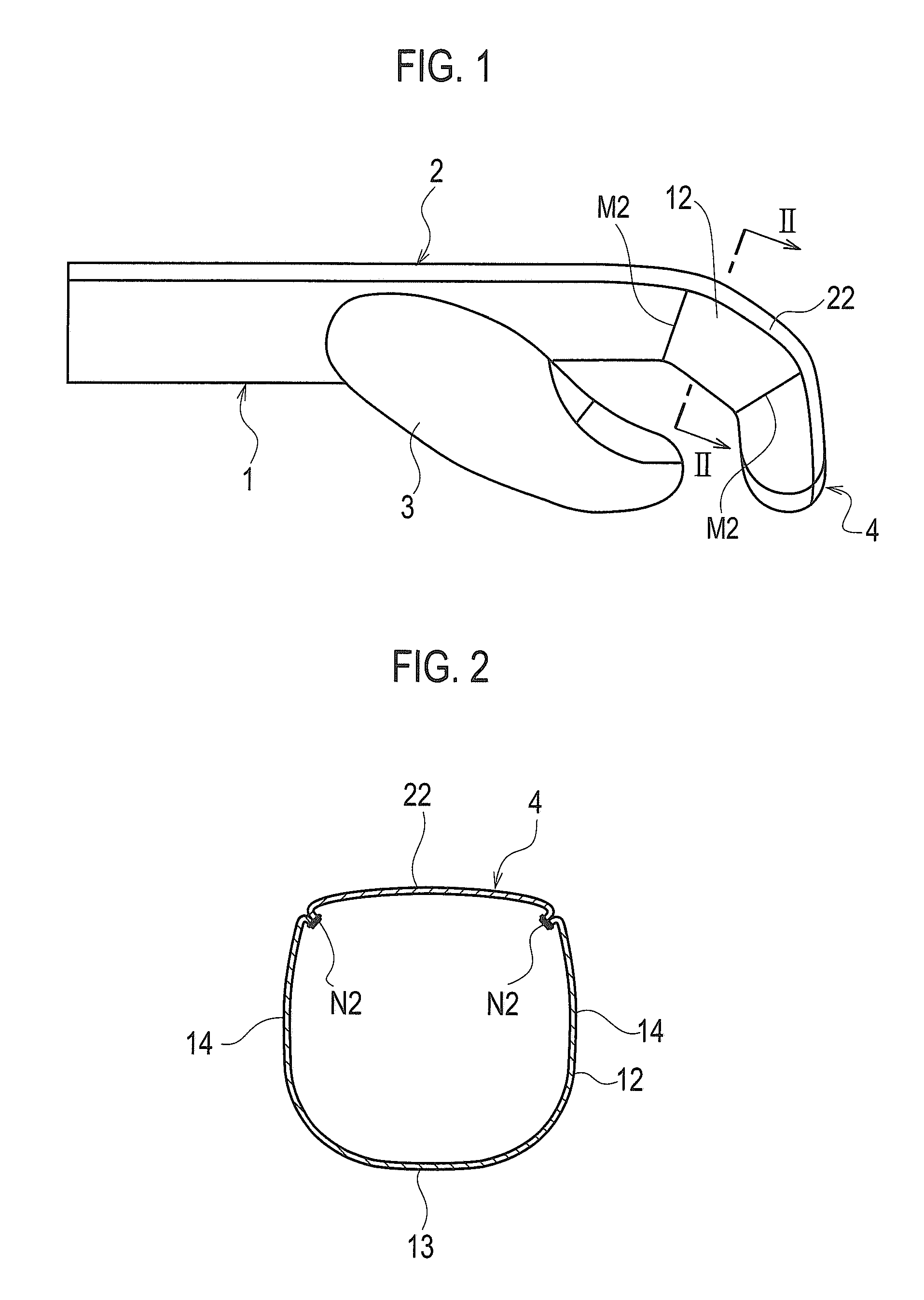
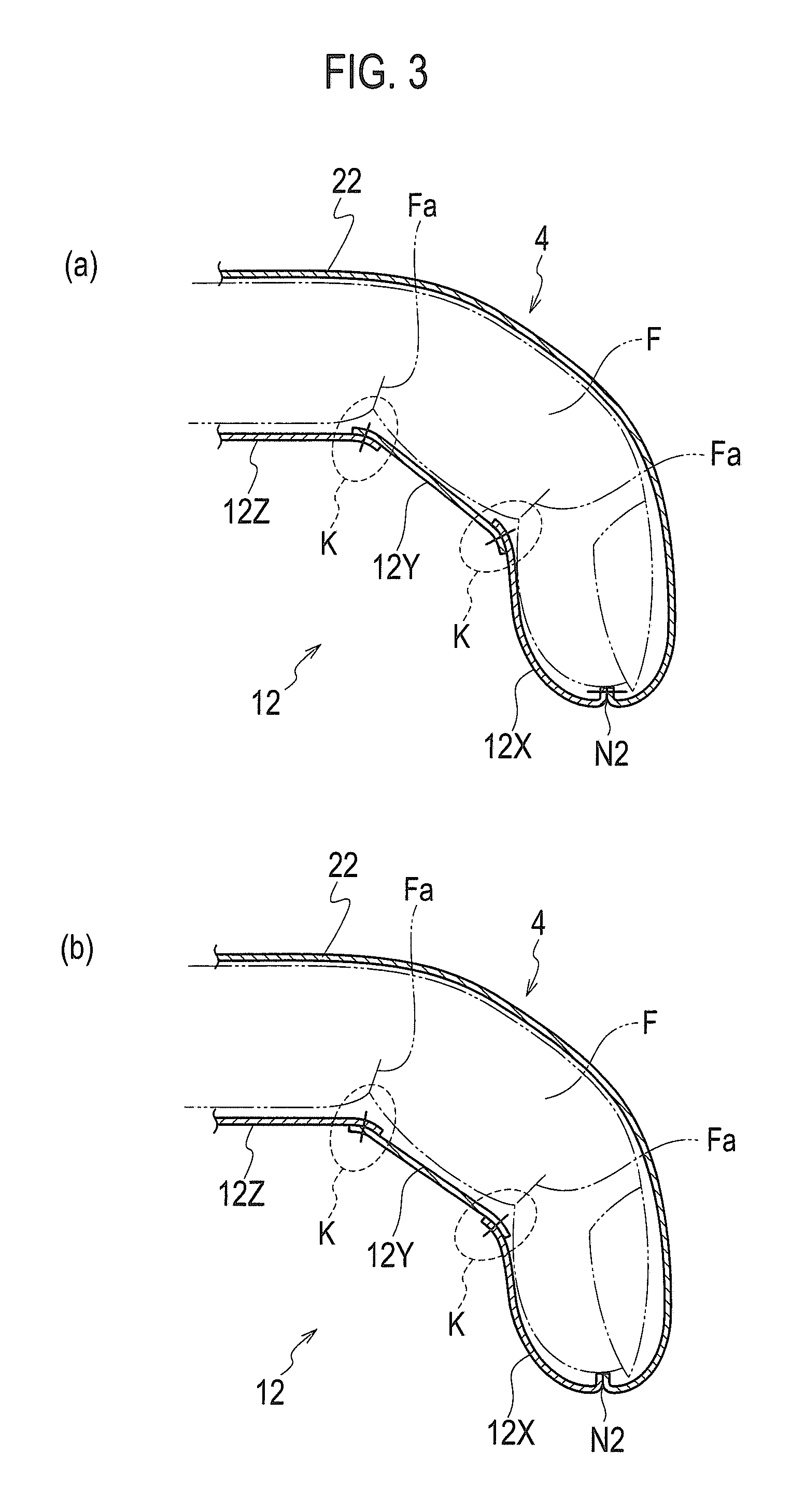
Sewn glove
Owner:MATSUOKA GLOVE
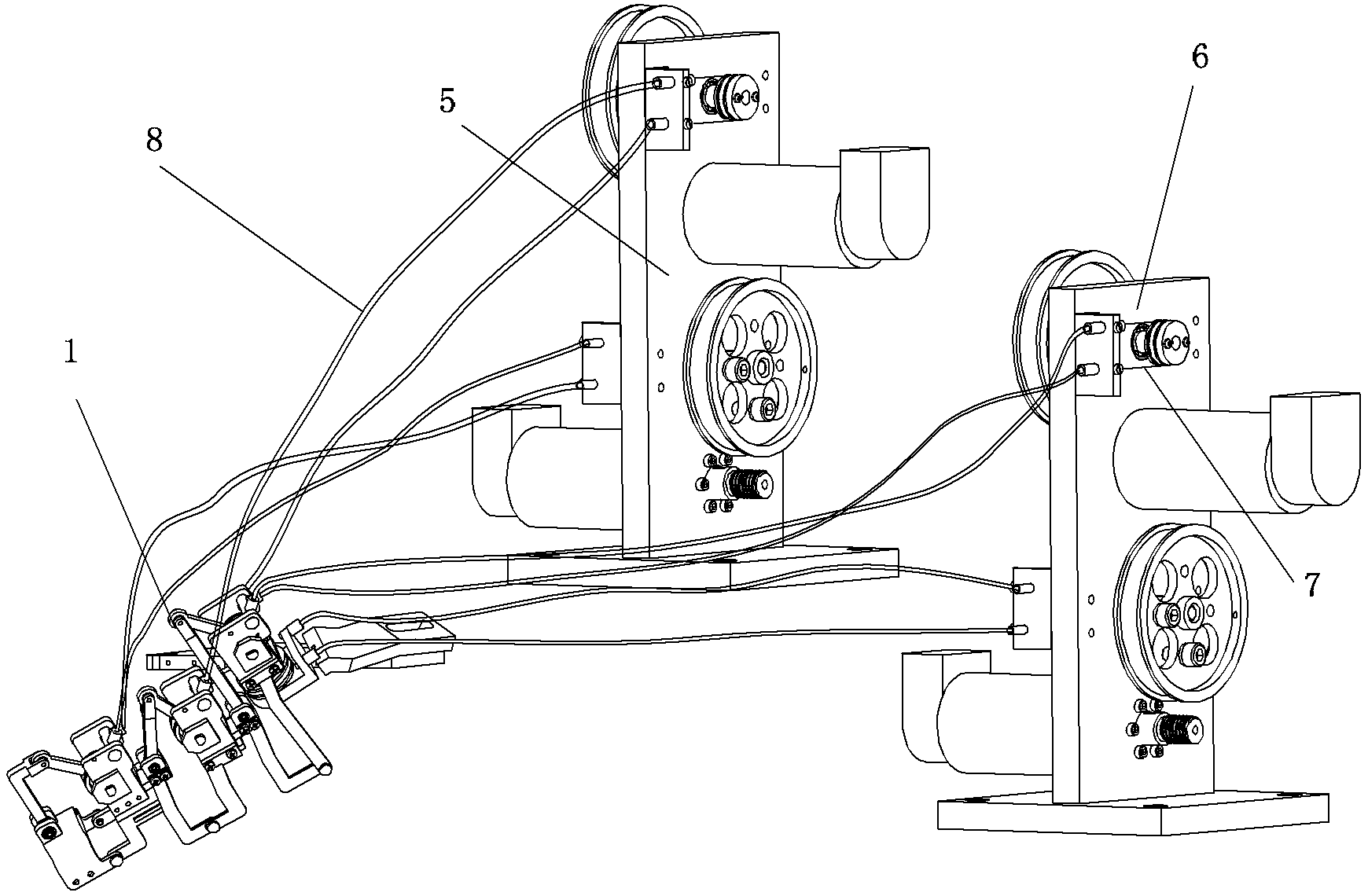
Human-simulated finger with base joint and interphalangeal joint respectively and independently driven
ActiveCN105751232AReduce rotationHigh dexterityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsIndependent motionEngineering
The invention relates to a human-simulated finger, in particular to a human-simulated finger with a base joint and an interphalangeal joint respectively and independently driven.A near joint and a far joint in an existing human-simulated finger cannot respectively and independently move, finger action implementation has limitation, and the flexicity of the human hand cannot completely reproduced.A first pulley of a near knuckle in the human-simulated finger is fixedly arranged in a shell for the near knuckle, one end of a first steel wire is fixedly connected to a palm part, and the other end of the first steel wire goes around the base joint to be fixedly connected to the first pulley.A middle knuckle comprises a shell for the middle knuckle, the interphalangeal joint, an interphalangeal joint potentiometer, a second pulley, a steel wire sleeve and a second steel wire.A far knuckle is arranged at the end, away from the near knuckle, of the middle knuckle.The second pulley is fixedly installed in the shell for the middle knuckle, one end of the second steel wire is arranged on the palm part, the other end of the second steel wire penetrates through the steel wire sleeve to be fixedly connected to the second pulley, and the far knuckle is connected with the shell for the near knuckle in the near knuckle through a four-bar mechanism.The human-simulated finger is used for a robot.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com