Patents
Literature
467 results about "Artificial muscle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Artificial muscles are actuators, materials or devices that mimic natural muscle and can reversibly contract, expand, or rotate within one component due to an external stimulus (such as voltage, current, pressure or temperature). The three basic actuation responses– contraction, expansion, and rotation can be combined together within a single component to produce other types of motions (e.g. bending, by contracting one side of the material while expanding the other side). Conventional motors and pneumatic linear or rotary actuators do not qualify as artificial muscles, because there is more than one component involved in the actuation.
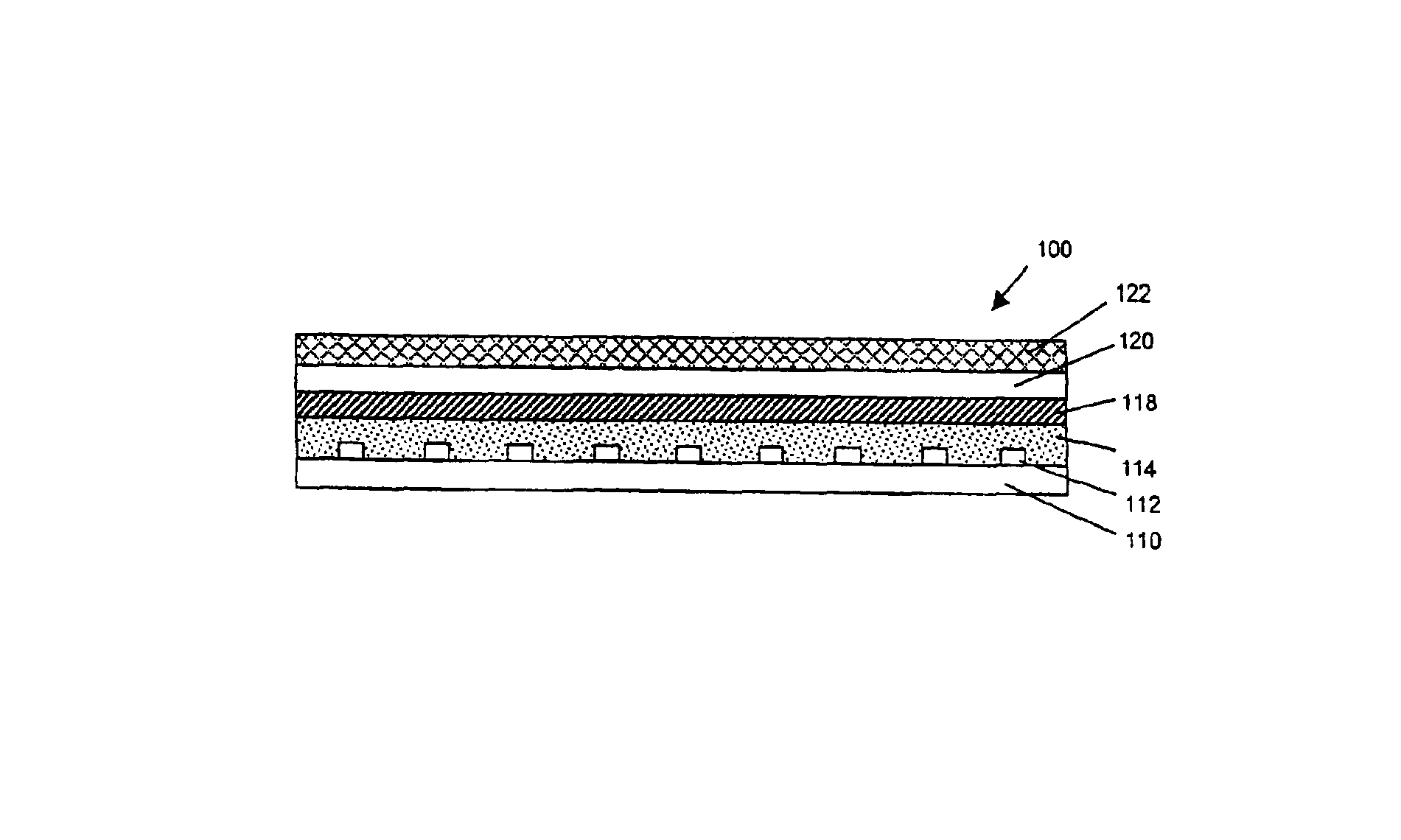
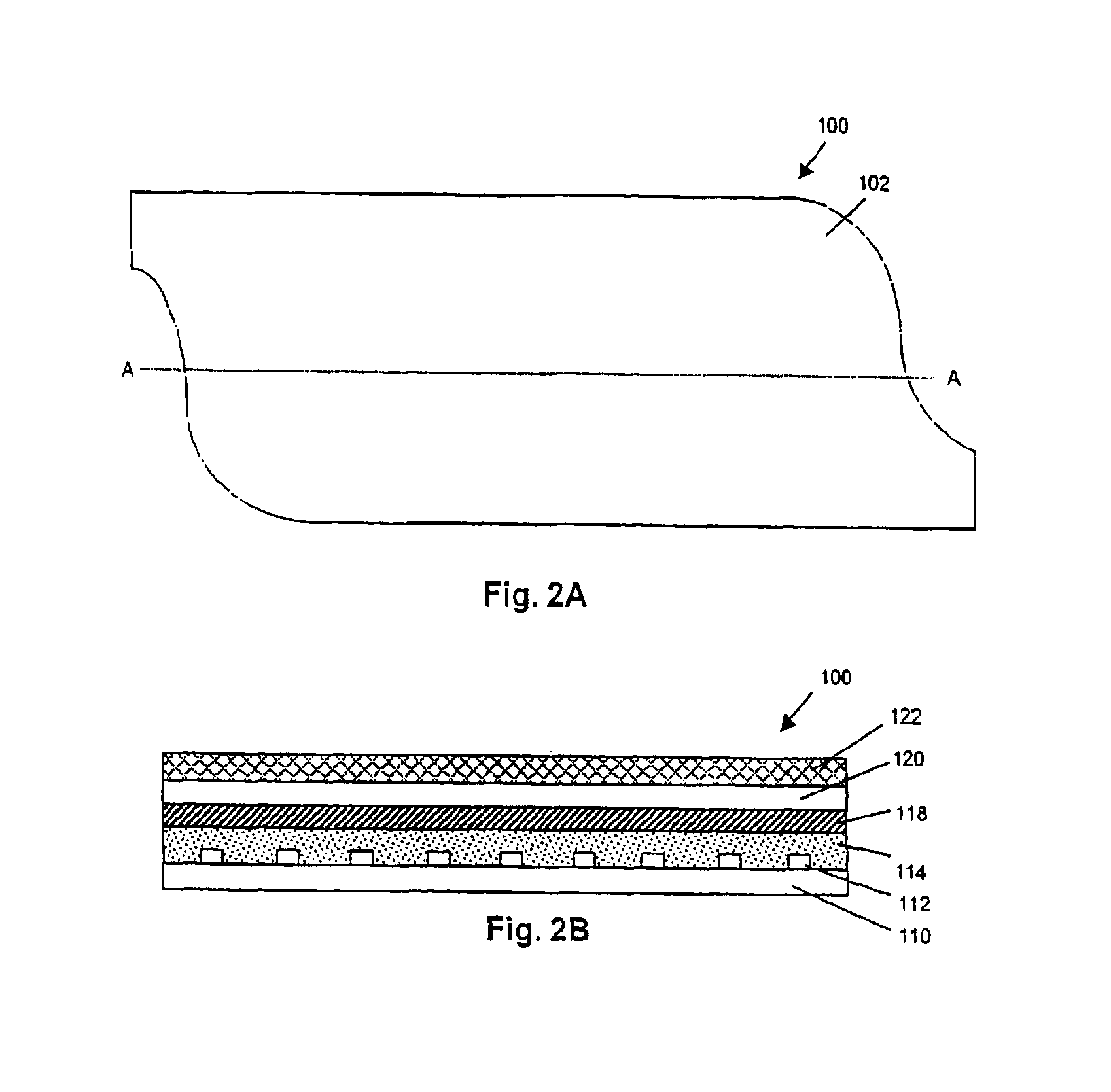
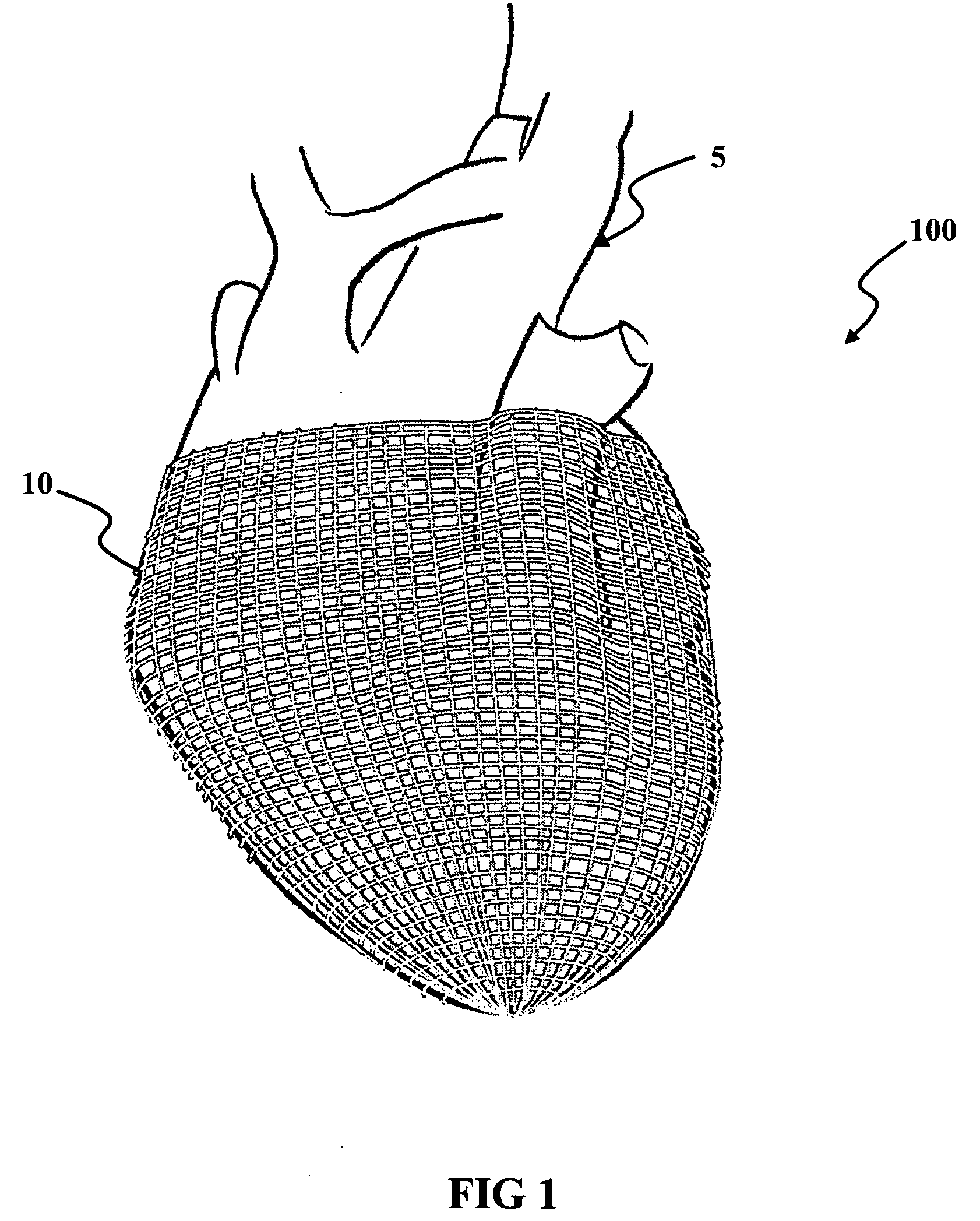
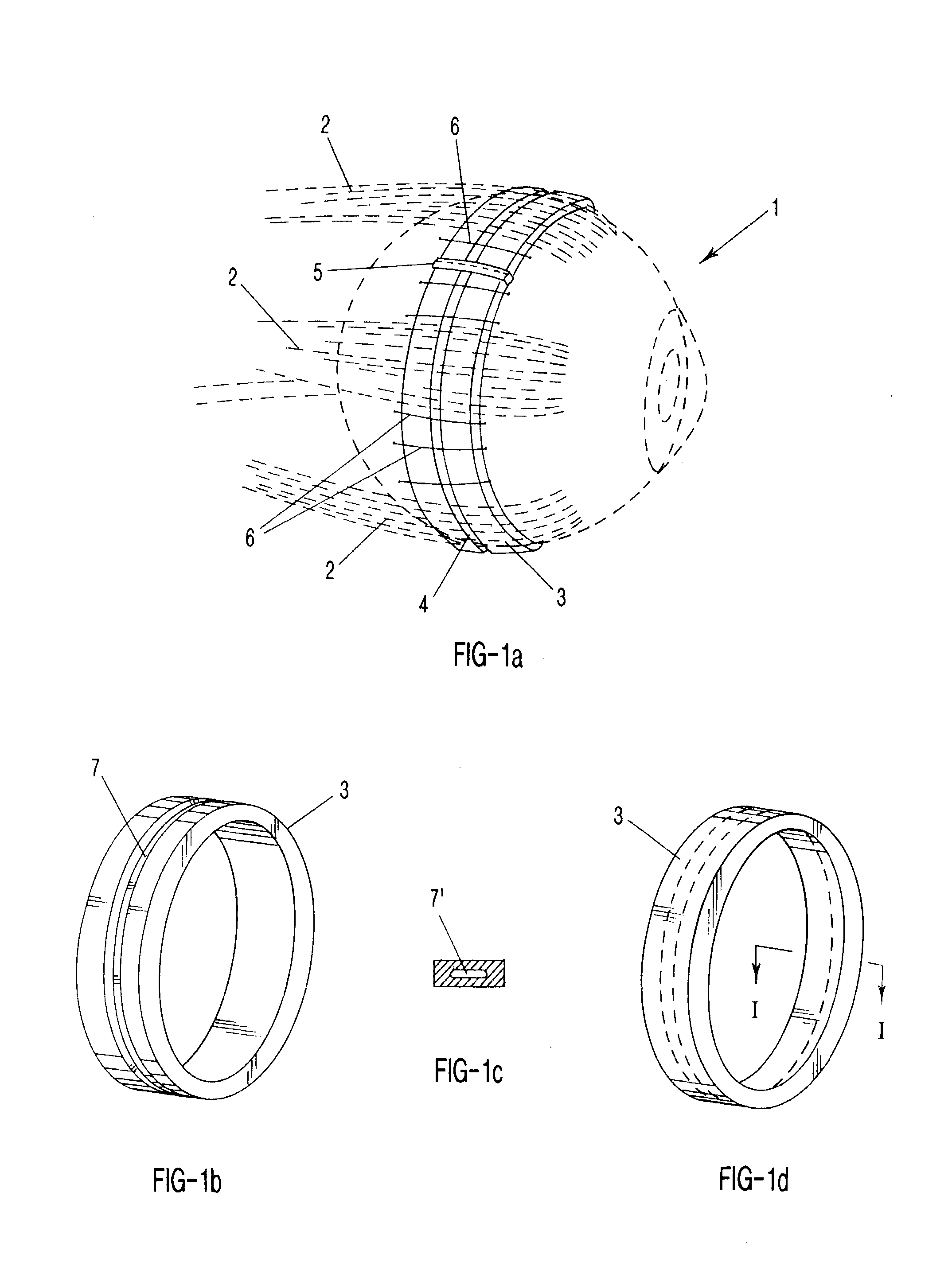
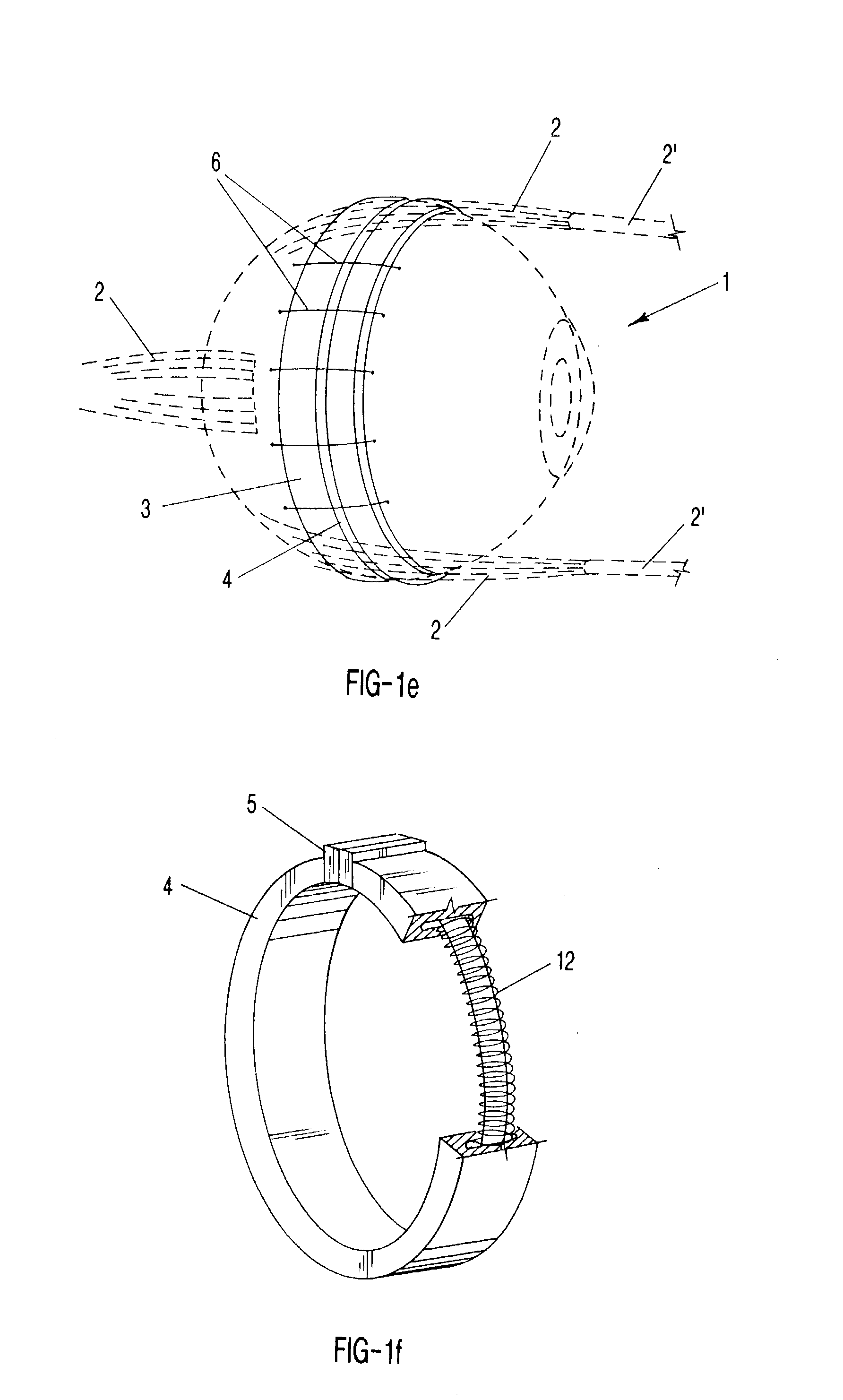
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
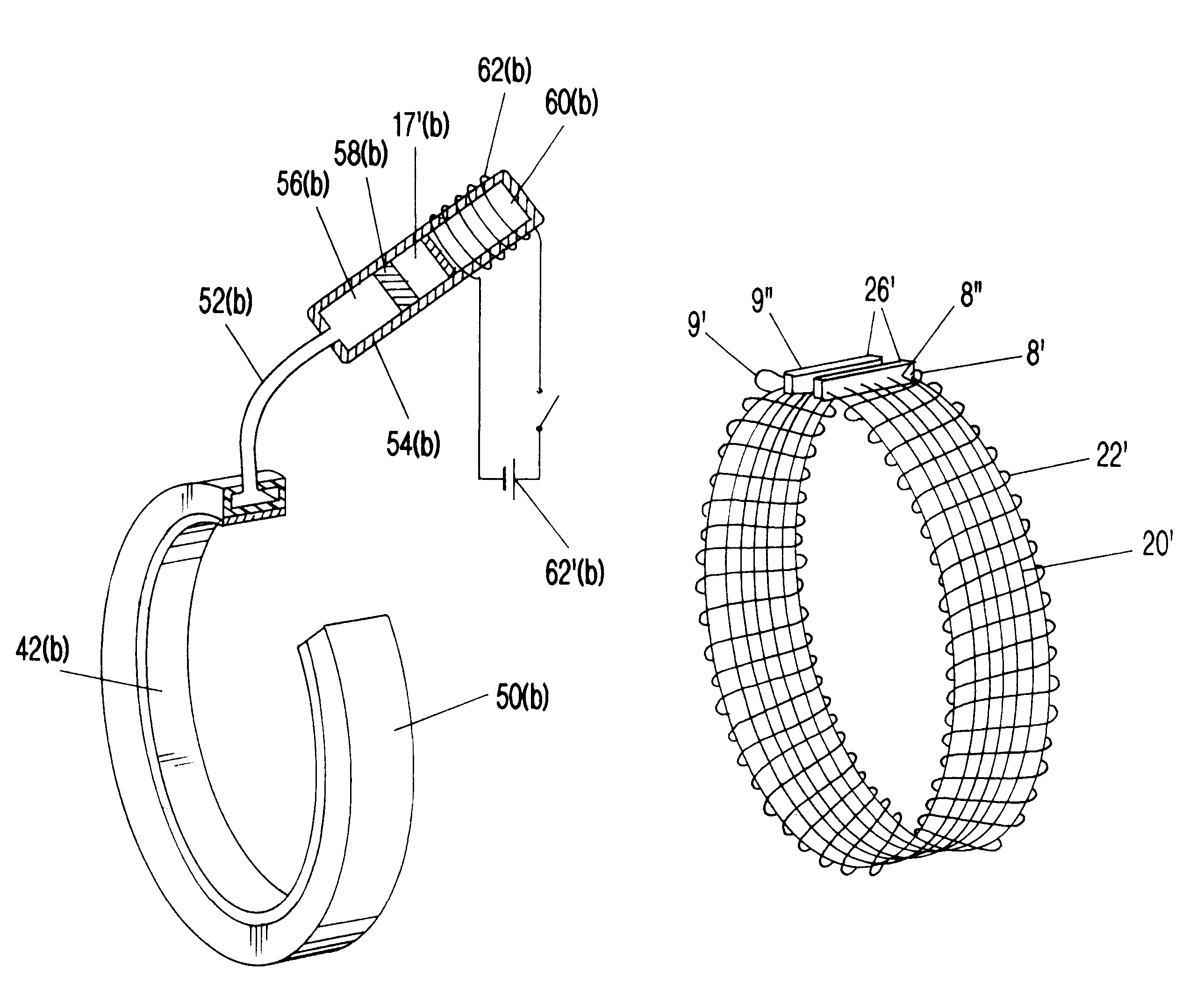
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
Dielectric elastomer fiber transducers
ActiveUS20090085444A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesTransducerPolymer chemistry
Disclosed are electroactive polymer fibers, processes of preparing electroactive polymer fibers, and devices containing electroactive polymer fibers. Devices can be used as actuators and sensors, generators and transducers. Applications include inter alia artificial muscles, prosthetics and robotics.
Owner:WOODCOCK WASHBURN +1
Artificial muscle actuator assembly
InactiveUS6223648B1Substantially flexibleAvoid formingFlexible wall reciprocating enginesFluid-pressure actuatorsDistal portionEngineering
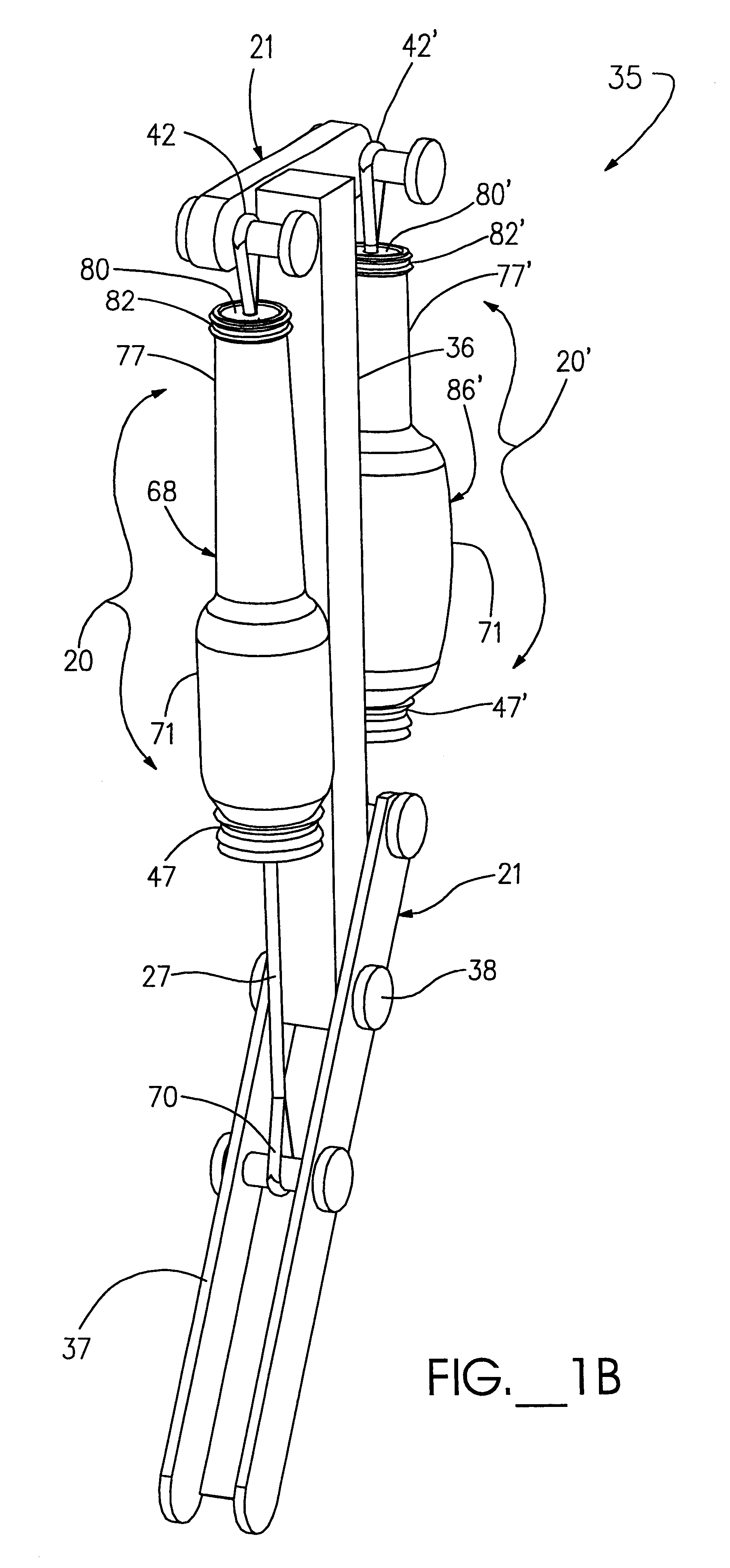
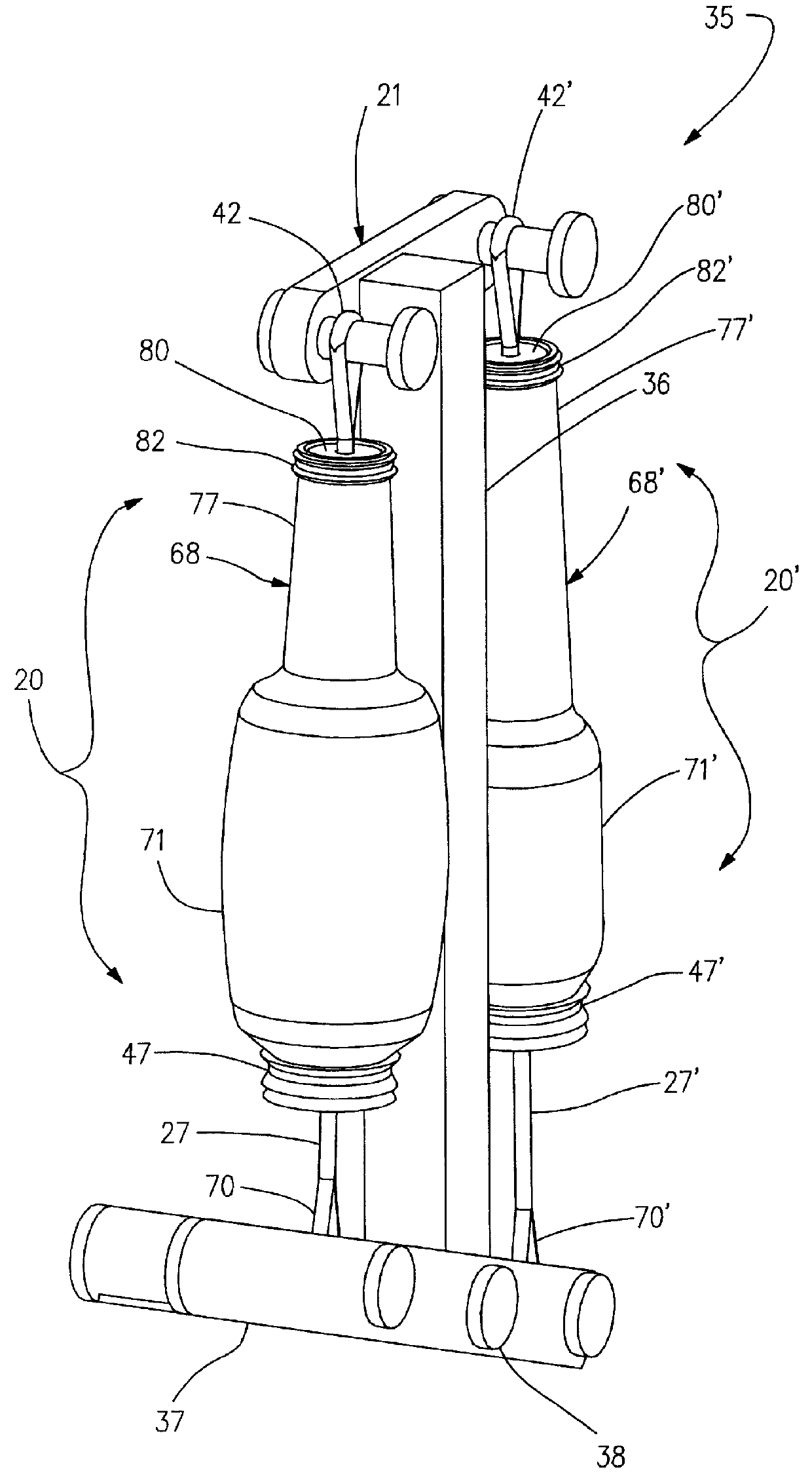
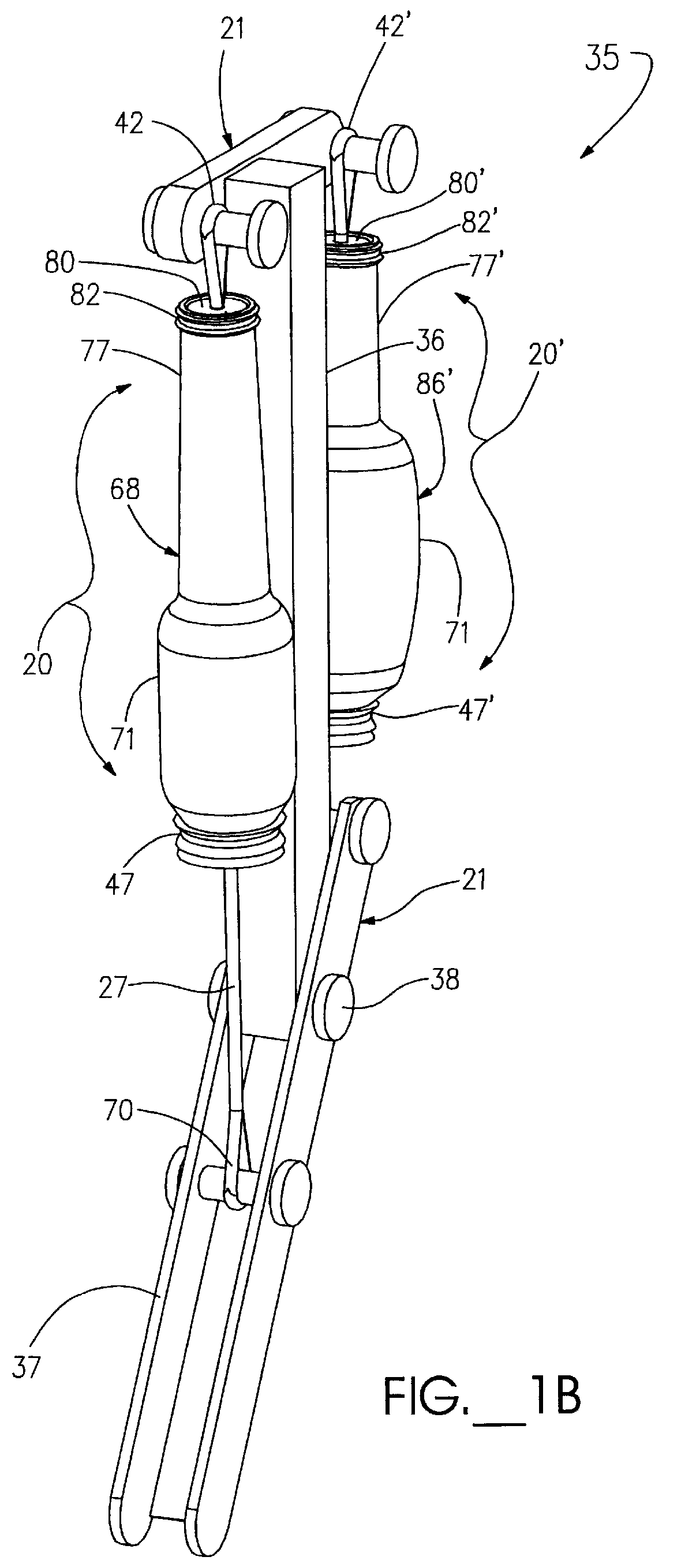
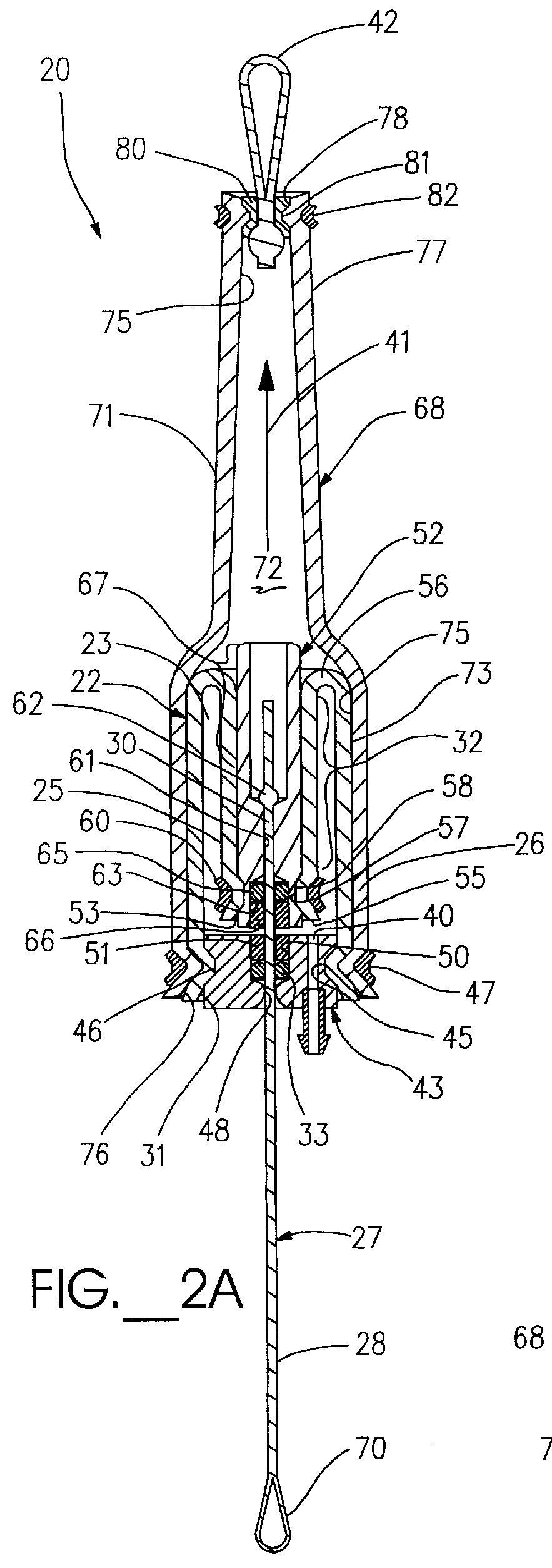
A flexible actuator assembly (20) including a flexible bladder device (22) having an expandable sealed chamber (23) adapted to substantially directionally displace between a deflated condition and an inflated condition, displacing a proximal portion (25) of the bladder device (22) away from a distal portion (26) thereof. An elongated tendon member (27) includes a distal portion (28) oriented outside the chamber (23), while an anchor portion (30) extends into the chamber (23) through a distal opening (31) in the bladder device (22). The tendon anchor portion (30) is further coupled proximate to the bladder proximal portion (25) in a manner adapted to: selectively invert displaceable portions (32) of the bladder device (22) when urged toward the deflated condition to position the anchor portion (30) and the bladder proximal portion (25) relatively closer to the bladder distal portion (26); and selectively evert the inverted displaceable portions (32) of the bladder device (22) when displaced toward the inflated condition which positions the anchor portion (30) and the bladder proximal portion (25) relatively farther away from the bladder distal portion (26) for selective movement of the tendon distal portion (28) between an extended condition and a retracted condition, respectively.
Owner:ERICKSON JOEL R
Artificial muscle actuator assembly
InactiveUS6067892ASubstantially flexibleAvoid formingFlexible wall reciprocating enginesFluid-pressure actuatorsDistal portionEngineering
A flexible actuator assembly (20) including a flexible bladder device (22) having an expandable sealed chamber (23) adapted to substantially directionally displace between a deflated condition and an inflated condition, displacing a proximal portion (25) of the bladder device (22) away from a distal portion (26) thereof. An elongated tendon member (27) includes a distal portion (28) oriented outside the chamber (23), while an anchor portion (30) extends into the chamber (23) through a distal opening (31) in the bladder device (22). The tendon anchor portion (30) is further coupled proximate to the bladder proximal portion (25) in a manner adapted to: selectively invert displaceable portions (32) of the bladder device (22) when urged toward the deflated condition to position the anchor portion (30) and the bladder proximal portion (25) relatively closer to the bladder distal portion (26); and selectively evert the inverted displaceable portions (32) of the bladder device (22) when displaced toward the inflated condition which positions the anchor portion (30) and the bladder proximal portion (25) relatively farther away from the bladder distal portion (26) for selective movement of the tendon distal portion (28) between an extended condition and a retracted condition, respectively.
Owner:ERICKSON JOEL R
Electroactive polymer based artificial sphincters and artificial muscle patches
InactiveUS6921360B2Lower esophageal sphincter dysfunctionAnti-incontinence devicesSurgeryLower esophagusElectroactive polymer actuators
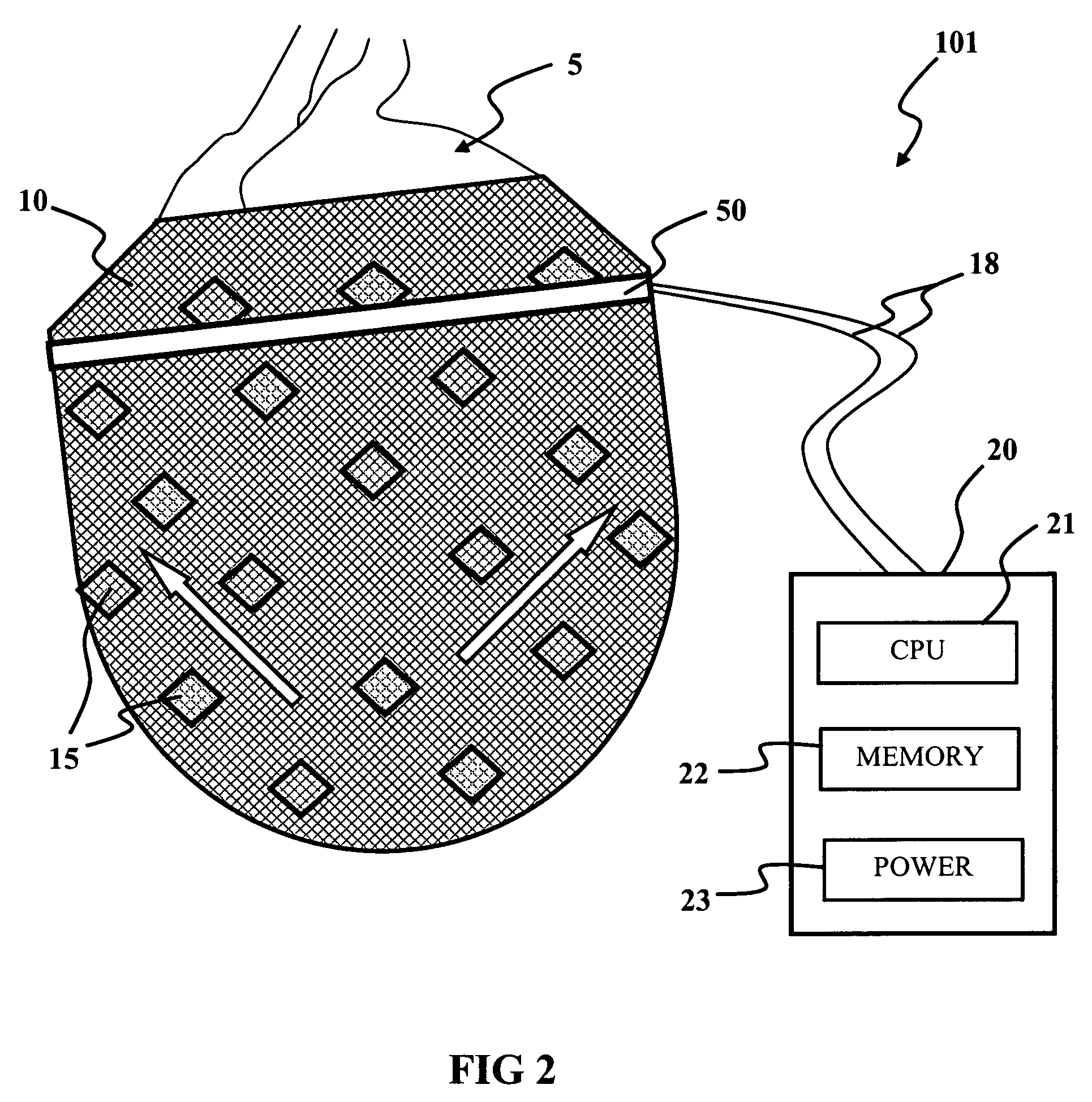
Provided are artificial muscle patches, which are adapted to be implanted adjacent a patient's heart, and artificial sphincter cuffs, which are adapted to be implanted around a body lumen, such as the urethra, the anal canal, or the lower esophagus. The devices of the present invention comprise: (a) one or more electroactive polymer actuators; and (b) a control unit for electrically controlling the one or more electroactive polymer actuators to expand or contract the devices.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Electromechanical machine-based artificial muscles, bio-valves and related devices
InactiveUS20060041183A1Easy to understandAnti-incontinence devicesHeart valvesSphincterFailing heart
A biological function assist apparatus composed an electromechanically-based system wrapped in protective coating and controlled by a controller, which also provides power to the electromechanically-based system. The electromechanically-based system can be formed as a mesh using MEMS or a larger electromechanically grid and wrapped around a failing heart, or the electromechanical system can be formed in a circle forming an artificial valve (e.g., sphincter). The electromechanically-based system can operate as a bone-muscle interface, thereby functioning in place of tendons.
Owner:ORSEN
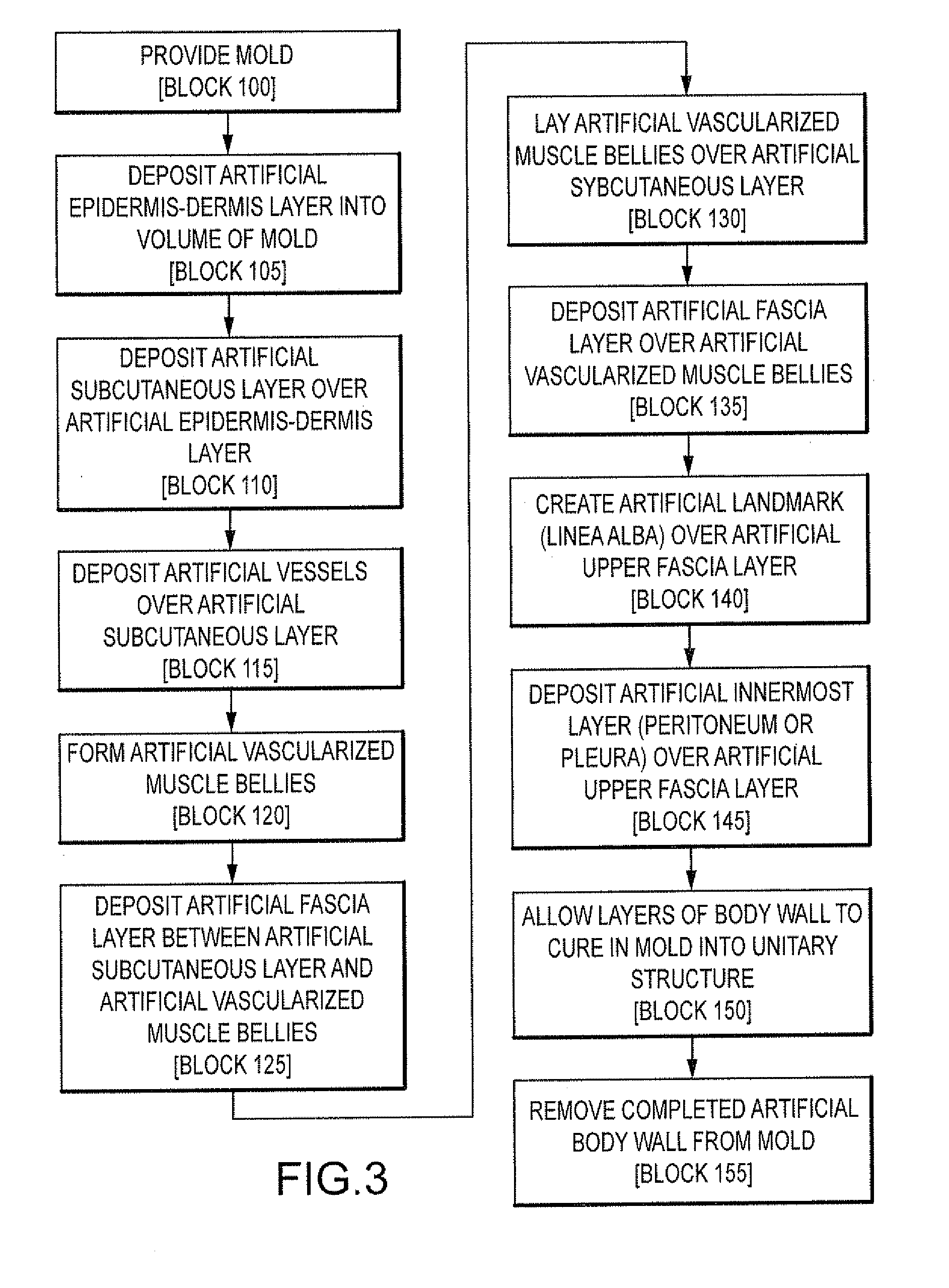
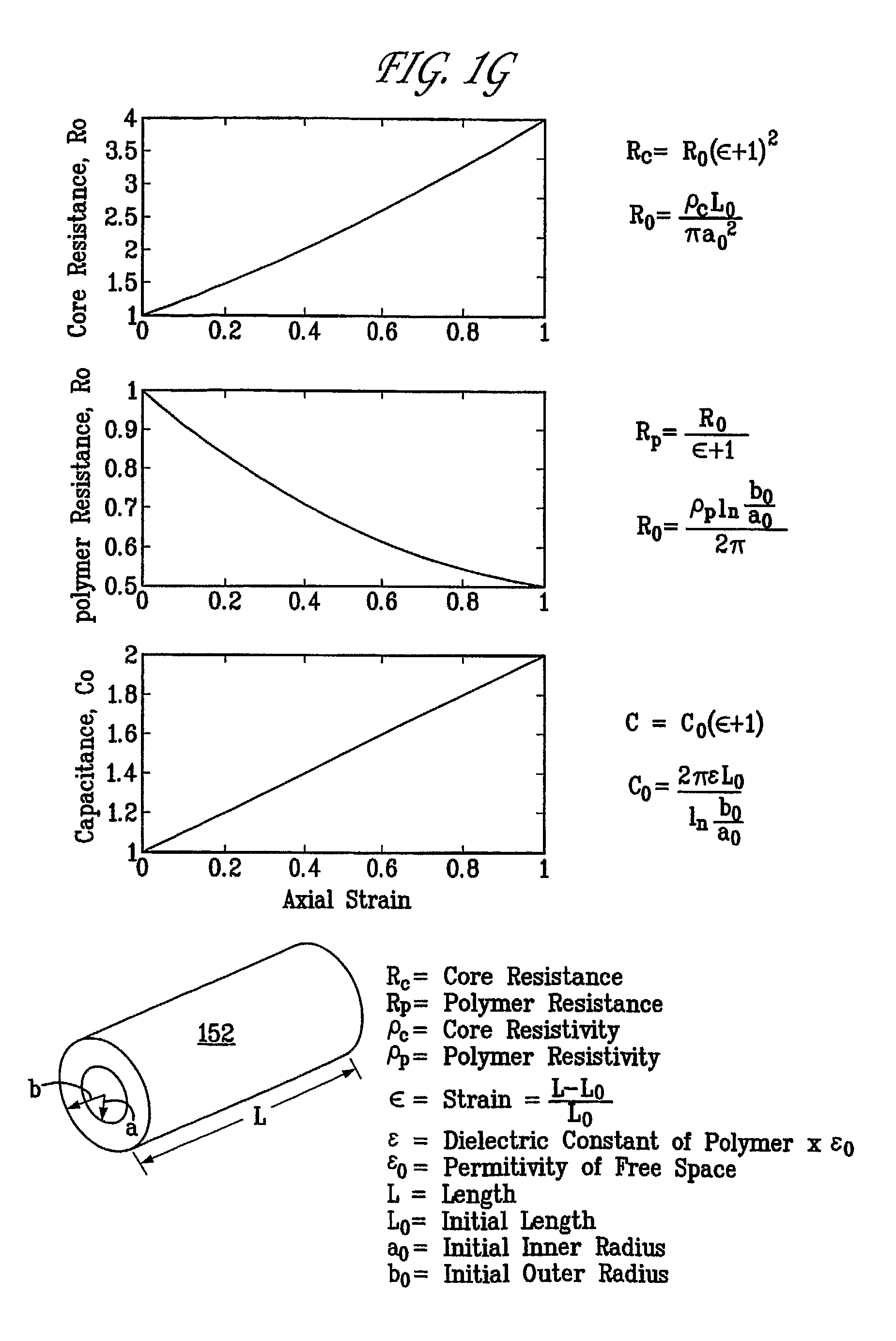
Simulated tissue, body lumens and body wall and methods of making same
An artificial body wall is disclosed herein. The artificial body wall may include a first layer and a second layer. The first layer is substantially formed of a silicone rubber and includes at least one of an artificial epidermis-dermis layer or an artificial subcutaneous layer. The second layer extends along and below the first layer and is substantially formed of a silicone rubber. The second layer includes at least one of an artificial fascia layer or an artificial muscle layer. At least one of the first layer or second layer may be vascularized.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Multiple network compound aquogel material with high mechanical intensity and electrochemical activity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101602876AImprove mechanical propertiesElectrochemically activeElectricityNetwork structure
The invention relates to a multiple network compound aquogel material with high mechanical intensity and electrochemical activity and a preparation method thereof; artificially-synthesized aquogel material and natural aquogel material are used as a first network or a second network, electric-conducting macromolecule aquogel material is used as a second and a third network, so as to prepare the compound aquogel material with a multiple network structure. The networks at different levels are provided with different mechanical performances which are mutually acted on, so as to lead the compound aquogel material to have high mechanical intensity; the electric-conducting macromolecule aquogel material is used as a constituent of the compound aquogel, so as to lead the compound aquogel material to have electrochemical activity. The multiple network compound aquogel material with high mechanical intensity and electrochemical activity can be applied to the field of electrochemical sensors, supercapacitors, electrochemical exciters, artificial muscles and the like. The invention also discloses a preparation method thereof.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Dielectric elastomer fiber transducers
ActiveUS7834527B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsTransducerArtificial muscle
Disclosed are electroactive polymer fibers, processes of preparing electroactive polymer fibers, and devices containing electroactive polymer fibers. Devices can be used as actuators and sensors, generators and transducers. Applications include inter alia artificial muscles, prosthetics and robotics.
Owner:WOODCOCK WASHBURN +1
Trunk-simulating mechanical arm unit device
InactiveCN103895012AImprove mobilityImprove flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorArmsUnit deviceEngineering
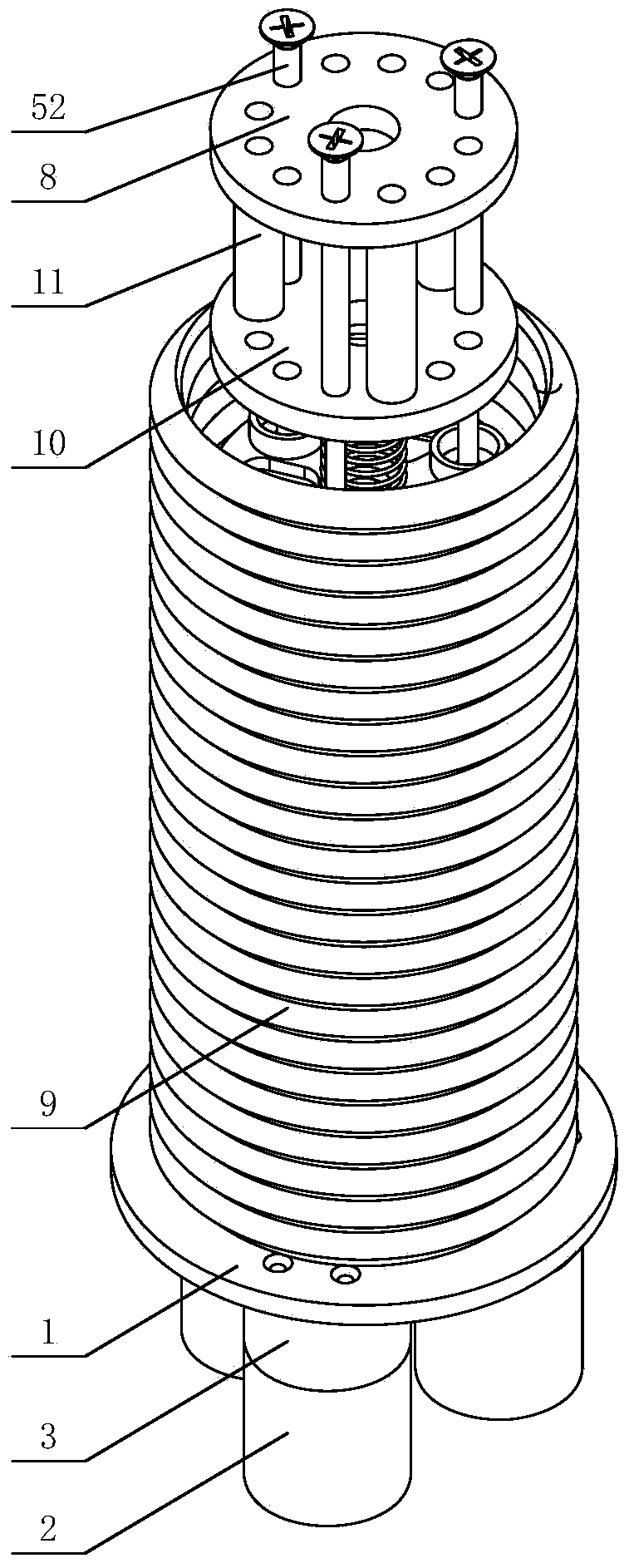
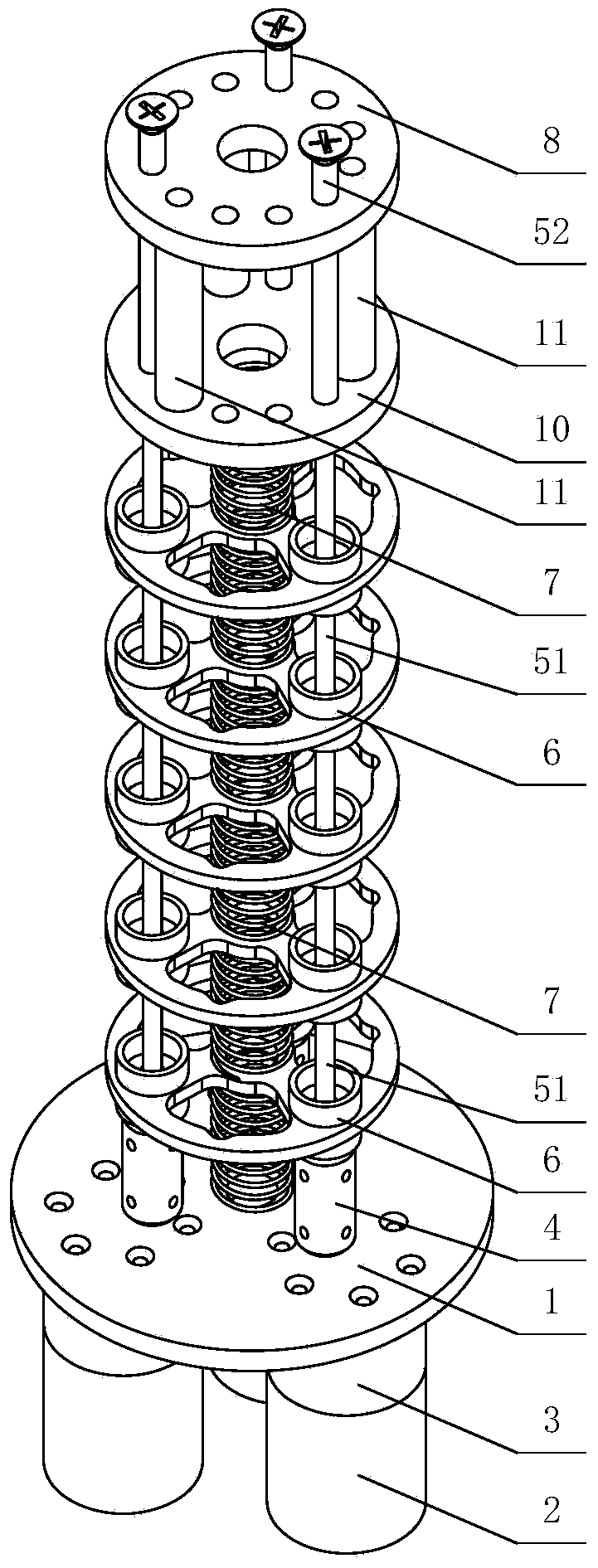
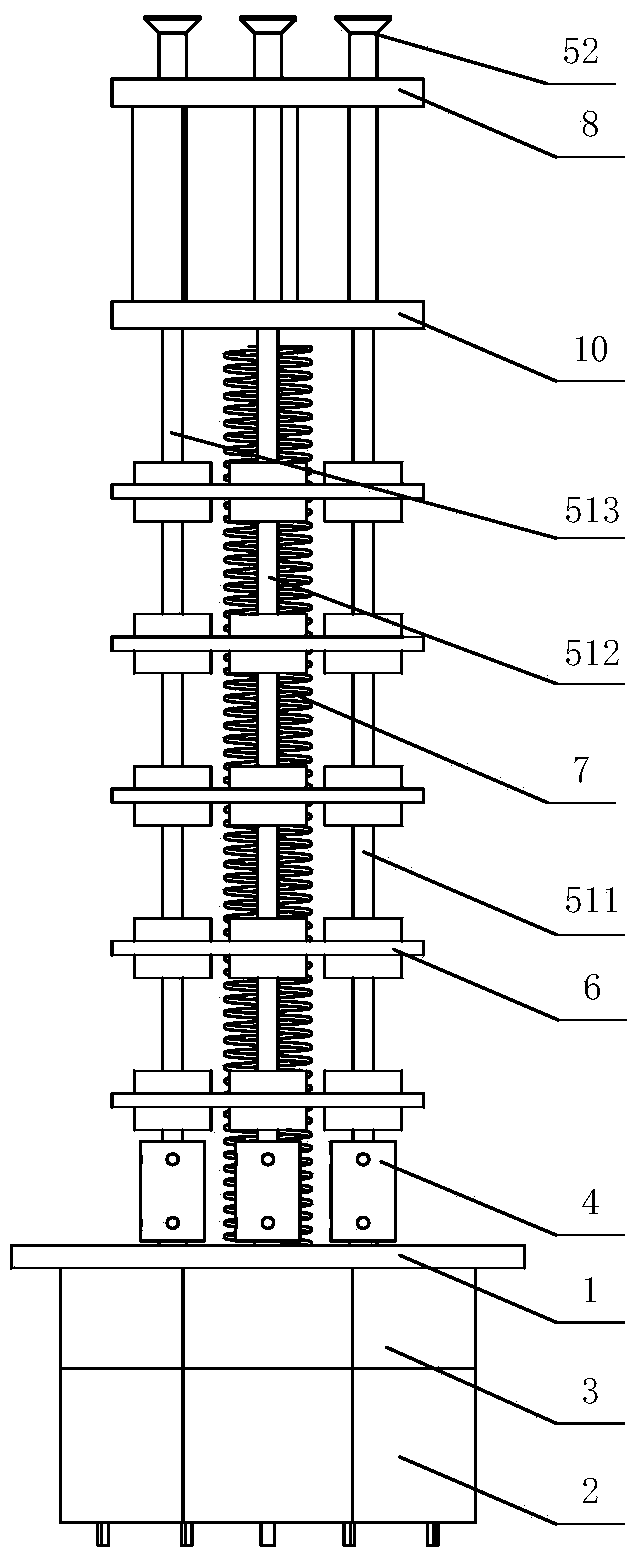
The invention discloses a trunk-simulating mechanical arm unit device and belongs to the technical field of robots. The trunk-simulating mechanical arm unit device comprises a base, a plurality of artificial muscle assemblies, a plurality of middle parts, a plurality of springs, an end part and a flexible cover, wherein each artificial muscle assembly comprises a driver, a transmission mechanism and a flexible screw rod assembly. The trunk-simulating mechanical arm unit device has multiple degrees of freedom, can bend, stretch out and draw back in multiple directions, can form various bending spatial shapes, enables a tool connected with the tail end of the trunk-simulating mechanical arm unit device to reach any spatial position, is good in maneuverability, is good in flexibility, is high in safety in the interaction process with people, and meanwhile is light in self-weight, small in size, compact in structure and low in cost. The trunk-simulating mechanical arm unit device can be widely applied to various automatic systems needing mechanical arms.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
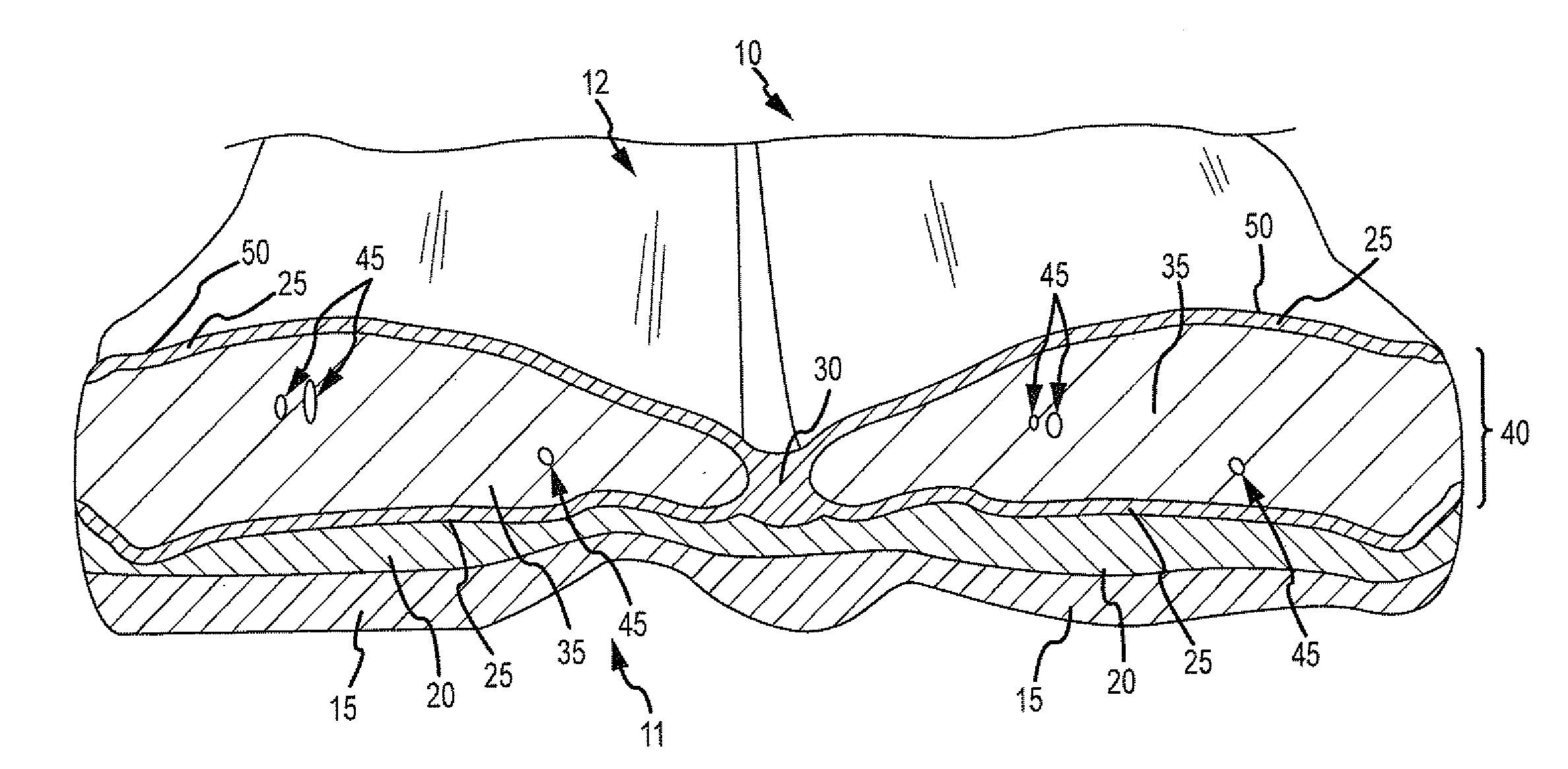
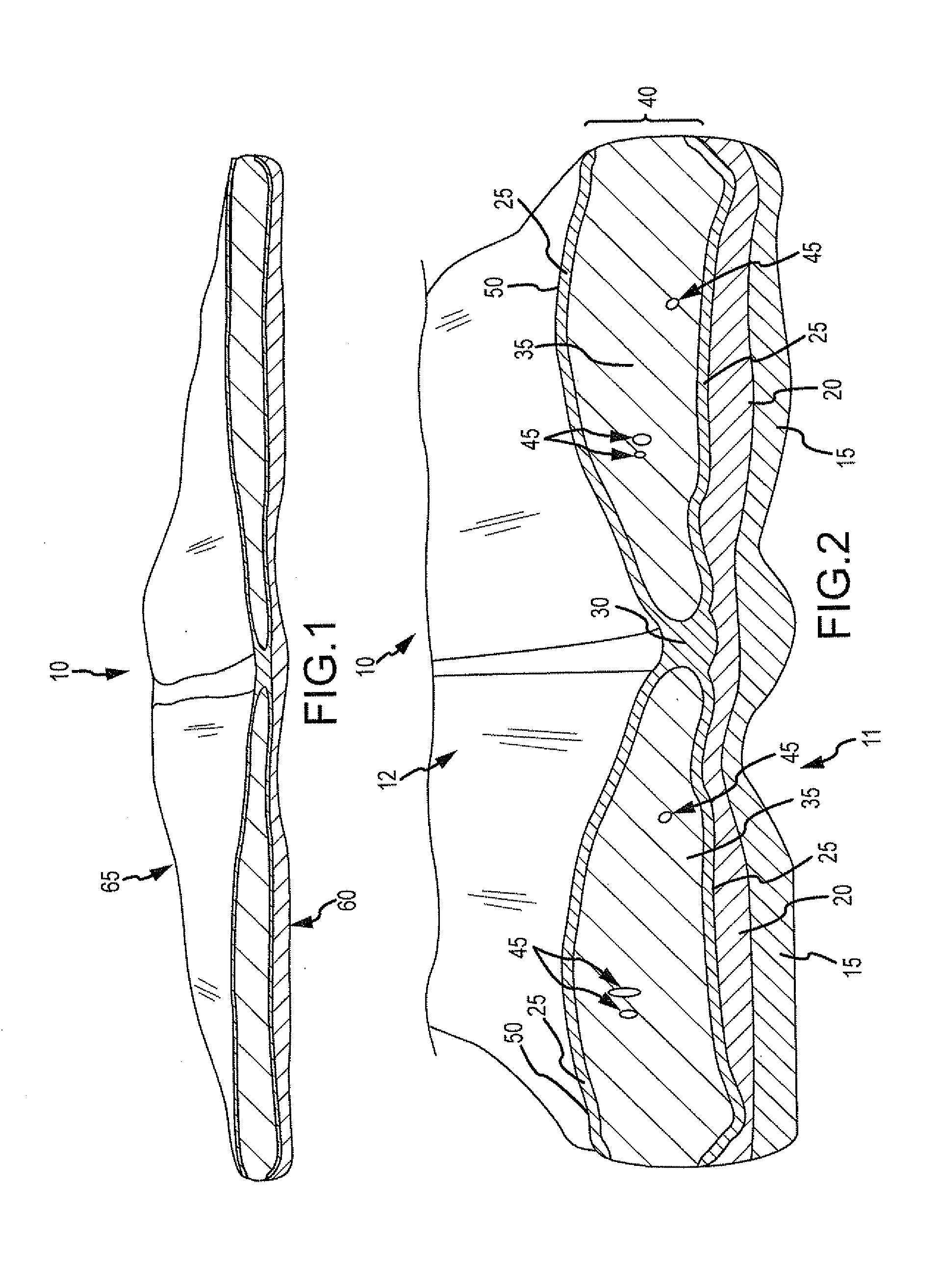
Correction of eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and astigmatism by using either pre-tensioned or transcutaneously energized artificial muscle implants to change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe by bringing the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants are scleral constrictor bands, segments or ribs for inducing accommodation of a few diopters, to correct the refractive errors on demand or automatically. The implant comprises an active sphinctering band encircling the sclera, implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing(decreasing) the length and curvature of the globe. Multiple and specially designed constrictor bands enable surgeons to correct astigmatism. The artificial muscles comprise materials such as composite magnetic shape memory (MSM), heat shrink, shape memory alloy-silicone rubber, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscles or electrochemically contractile ionic polymers bands.
Owner:OPHTHALMOTRONICS
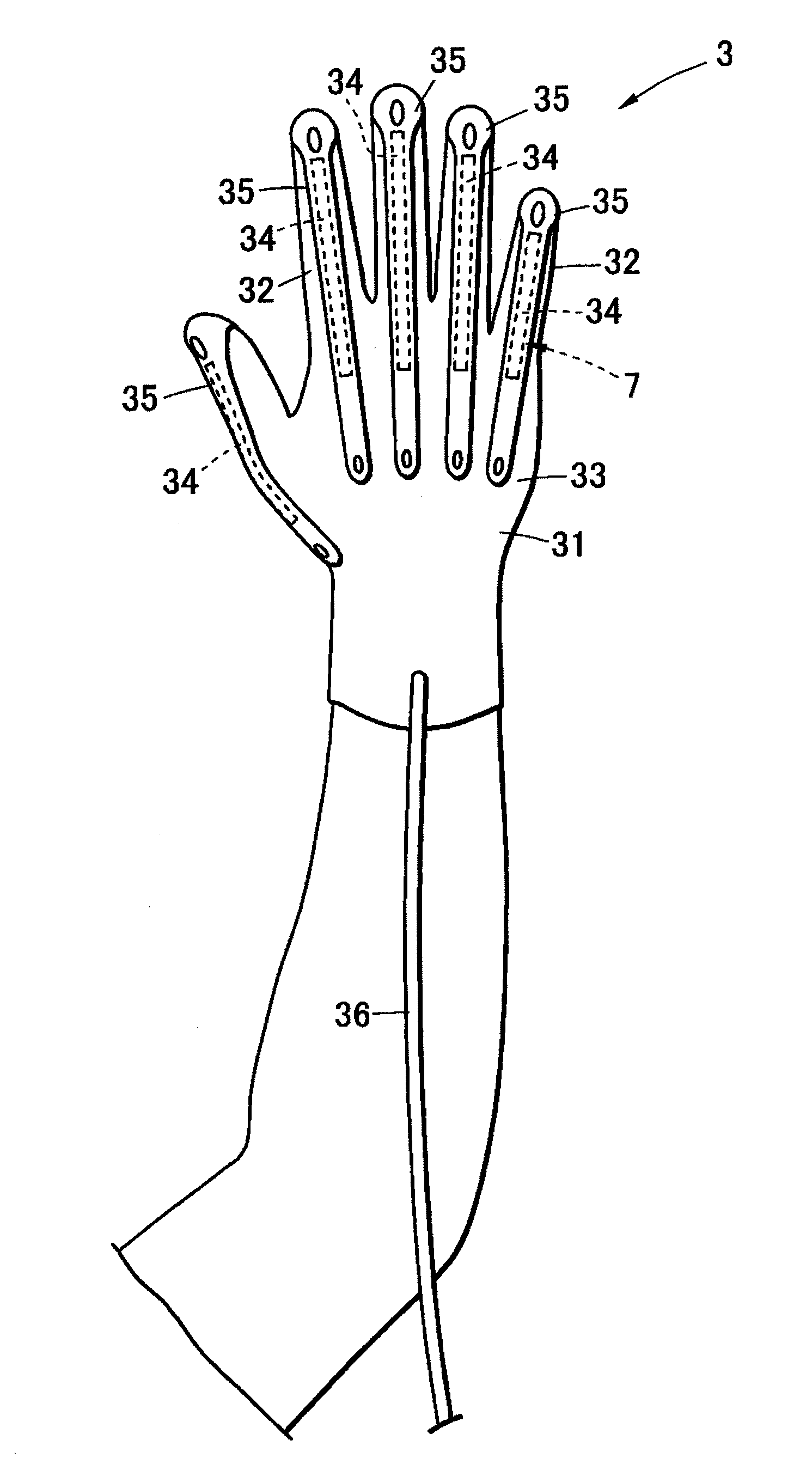
Motion assist apparatus
InactiveUS20100249675A1Avoid damageEasily damagedProgramme-controlled manipulatorGymnastic exercisingEngineeringSacroiliac joint
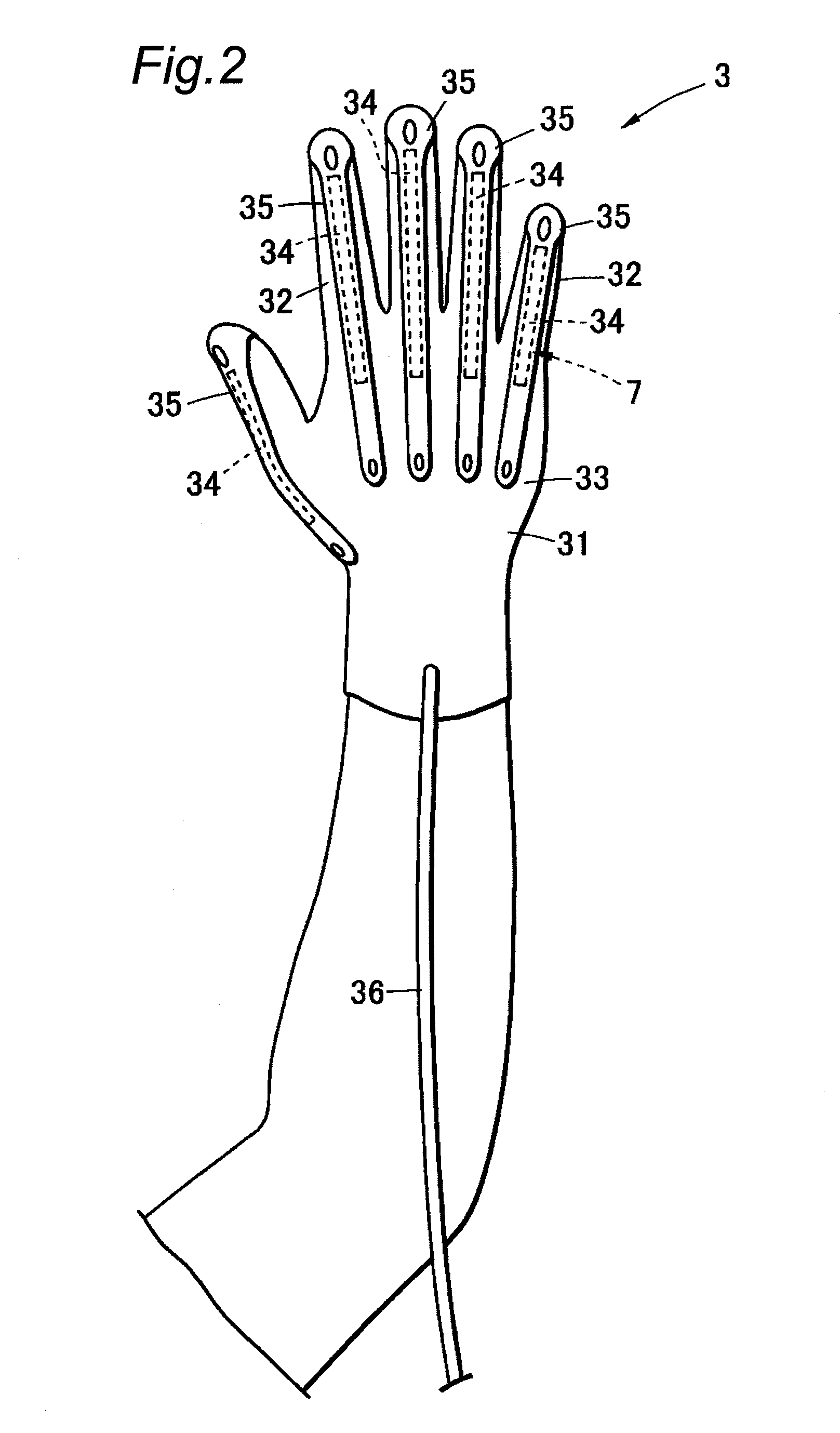
A motion assist apparatus is provided with an attaching member that has a glove shape with finger portions and a middle hand portion that is attachable to one of hands of a user, a back-side actuator that is freely expanded and contracted, and bridged between a tip of each of the finger portions and the middle hand portion on the back side of the attaching member, and a palm-side actuator that is freely expanded and contracted, and bridged between the tip of each of the finger portions and the middle hand portion on the palm side of the attaching member, and in this structure, the palm-side actuator is provided with a wire unit formed of two wires that are disposed on each of the finger portions on the palm side from the tip of each of the finger portions on the back side to the middle hand portion along the finger portion, passing through two side portions of the finger portion, so that intervals therebetween are made different at respective positions corresponding to joints of the finger portion, and rubber artificial muscle is coupled to the wire unit and is formed on the middle hand portion.
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
Biologically inspired gripping device
ActiveUS20060004395A1Clean plumbingPliable materialCannulasSurgical veterinaryBiological activationBiomedical engineering
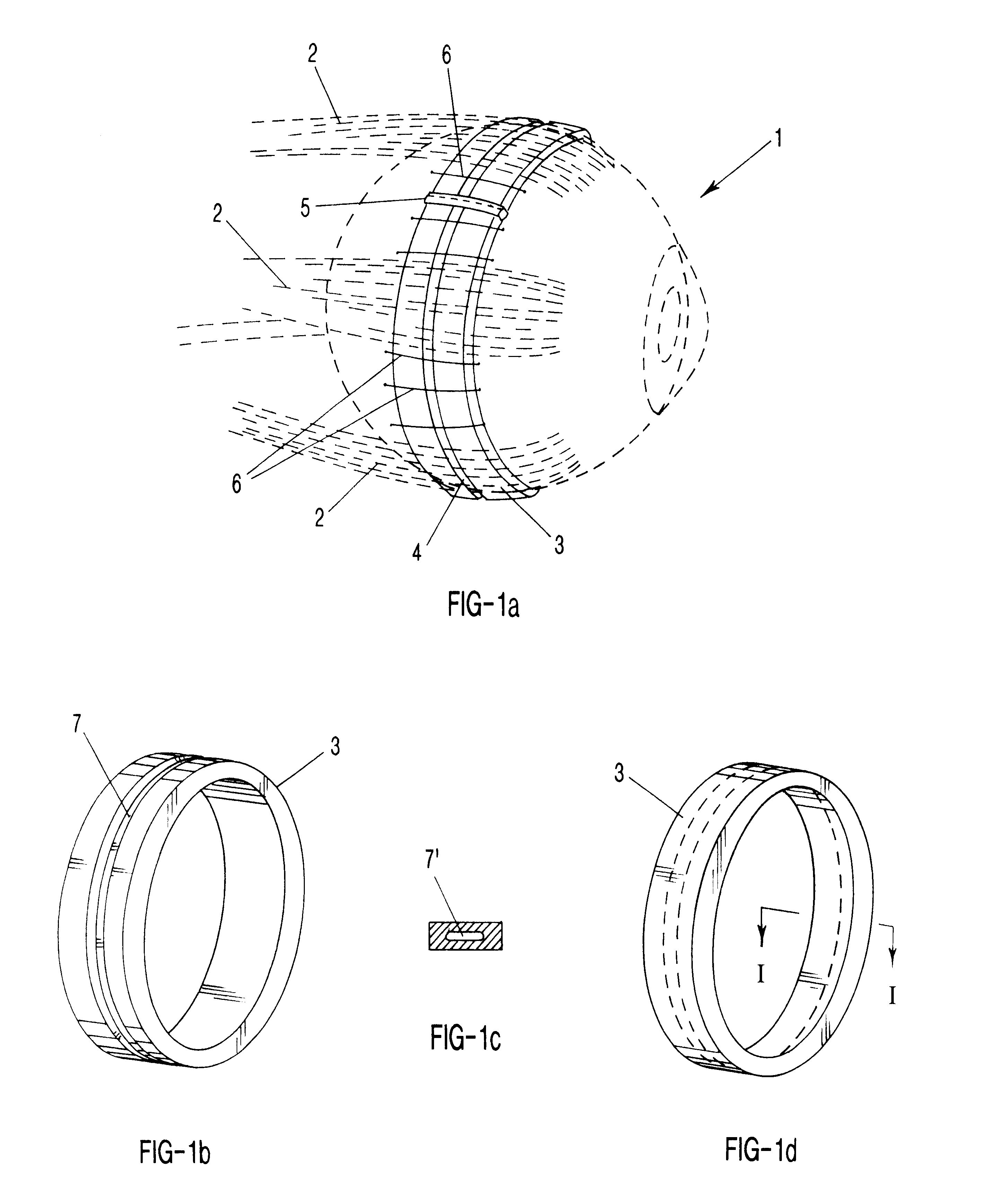
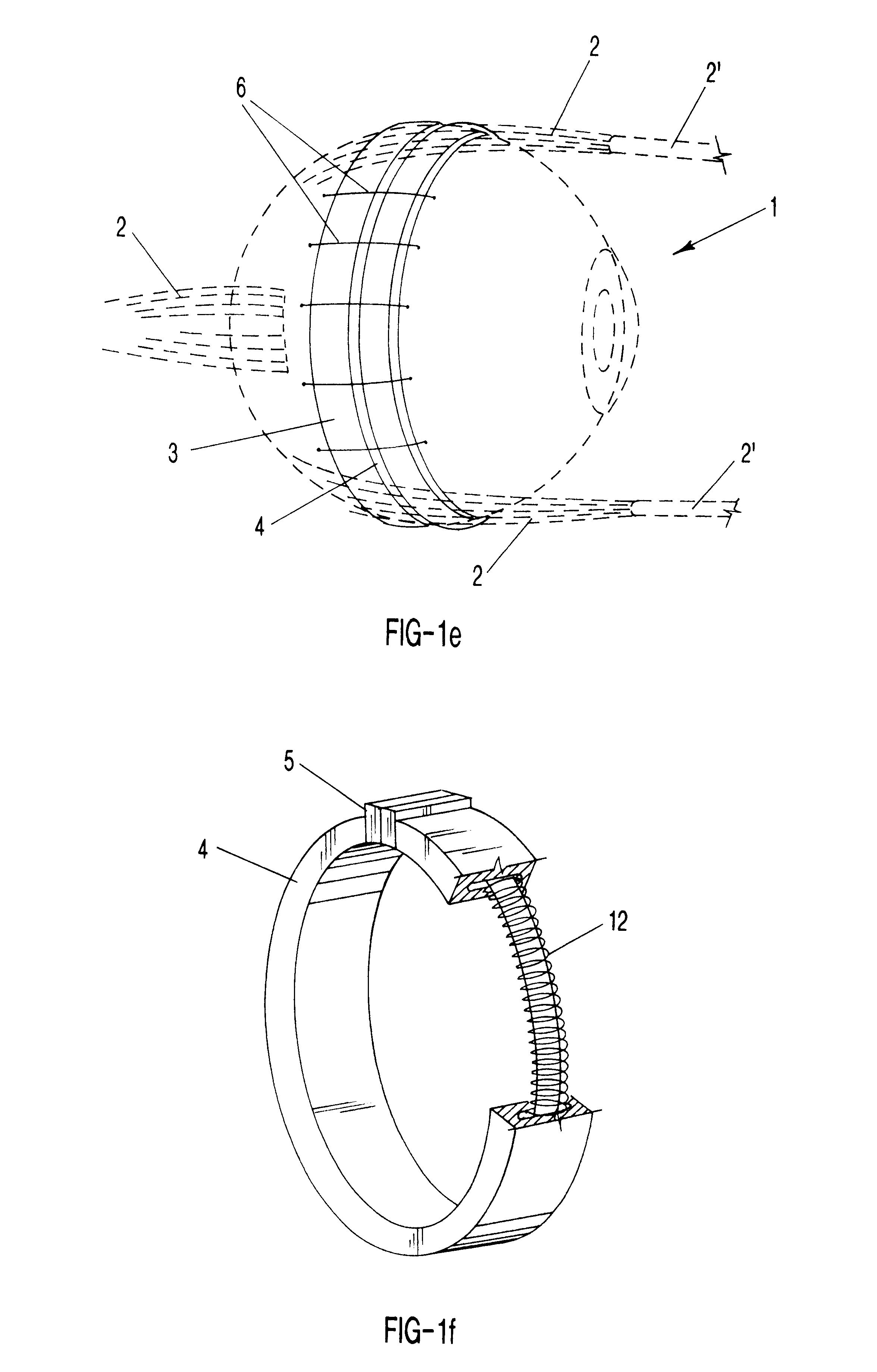
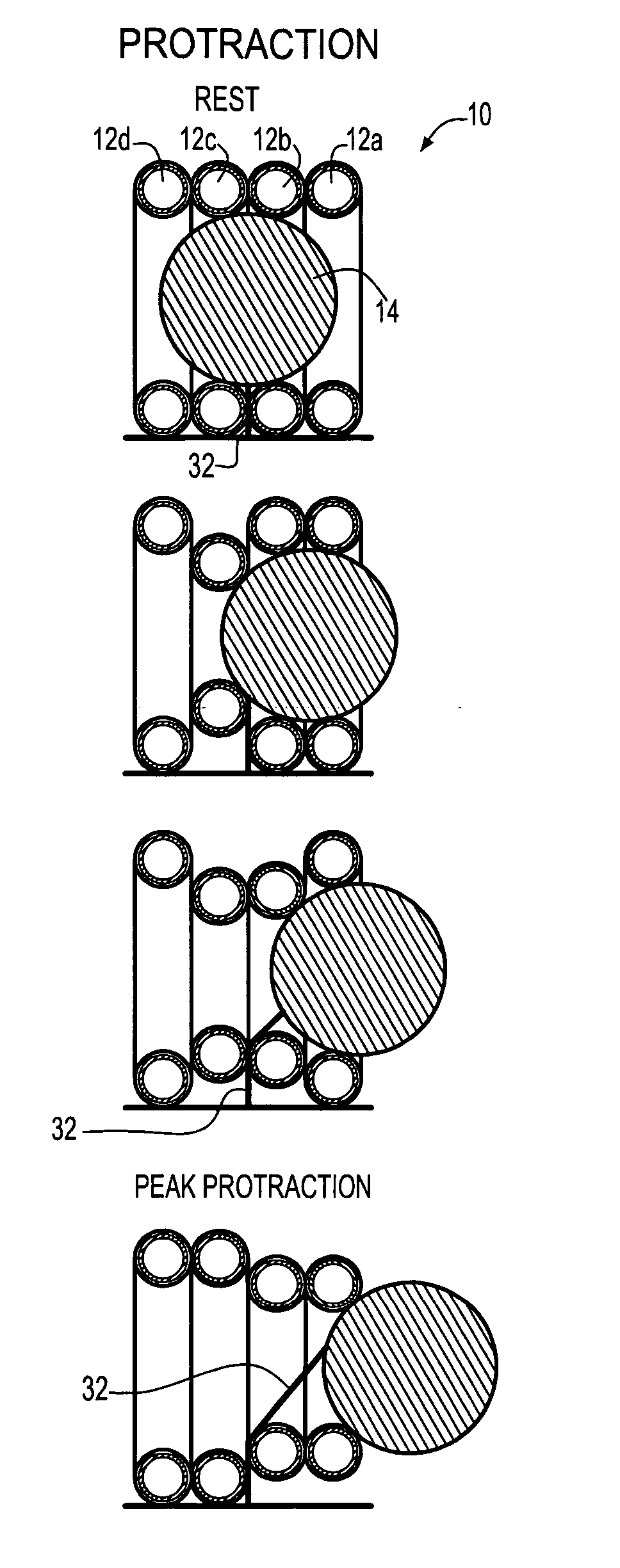
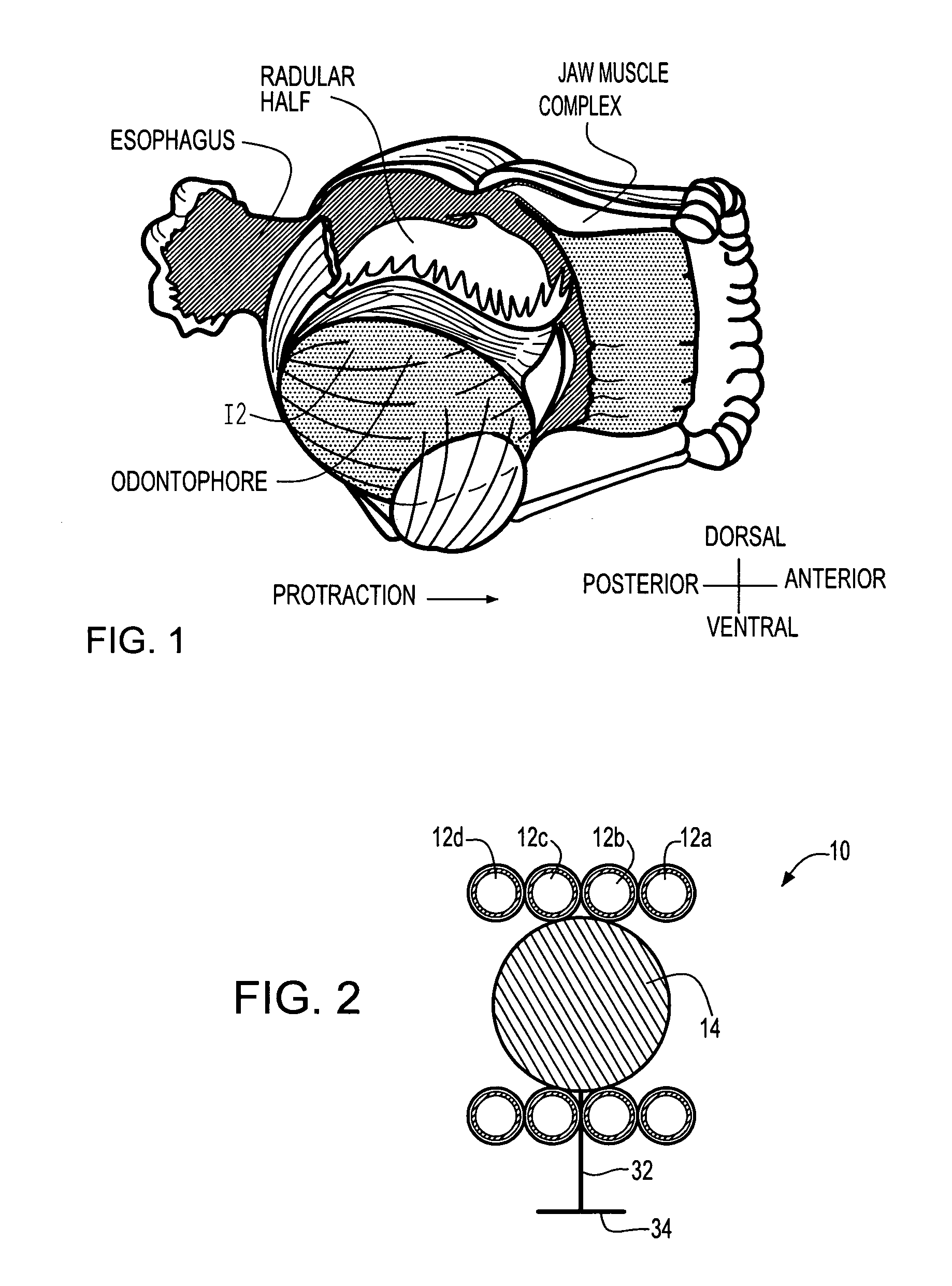
The present invention relates to a gripping device that consists of four artificial muscle rings arranged in parallel. A grasper is placed in the middle of the rings. Sequential activation of the rings produces a peristaltic motion that moves the grasper back and forth within the rings. By activating the grasper appropriately, it can grab, ingest, and move soft and irregular material from one side of the lumen formed by the rings to the other side.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
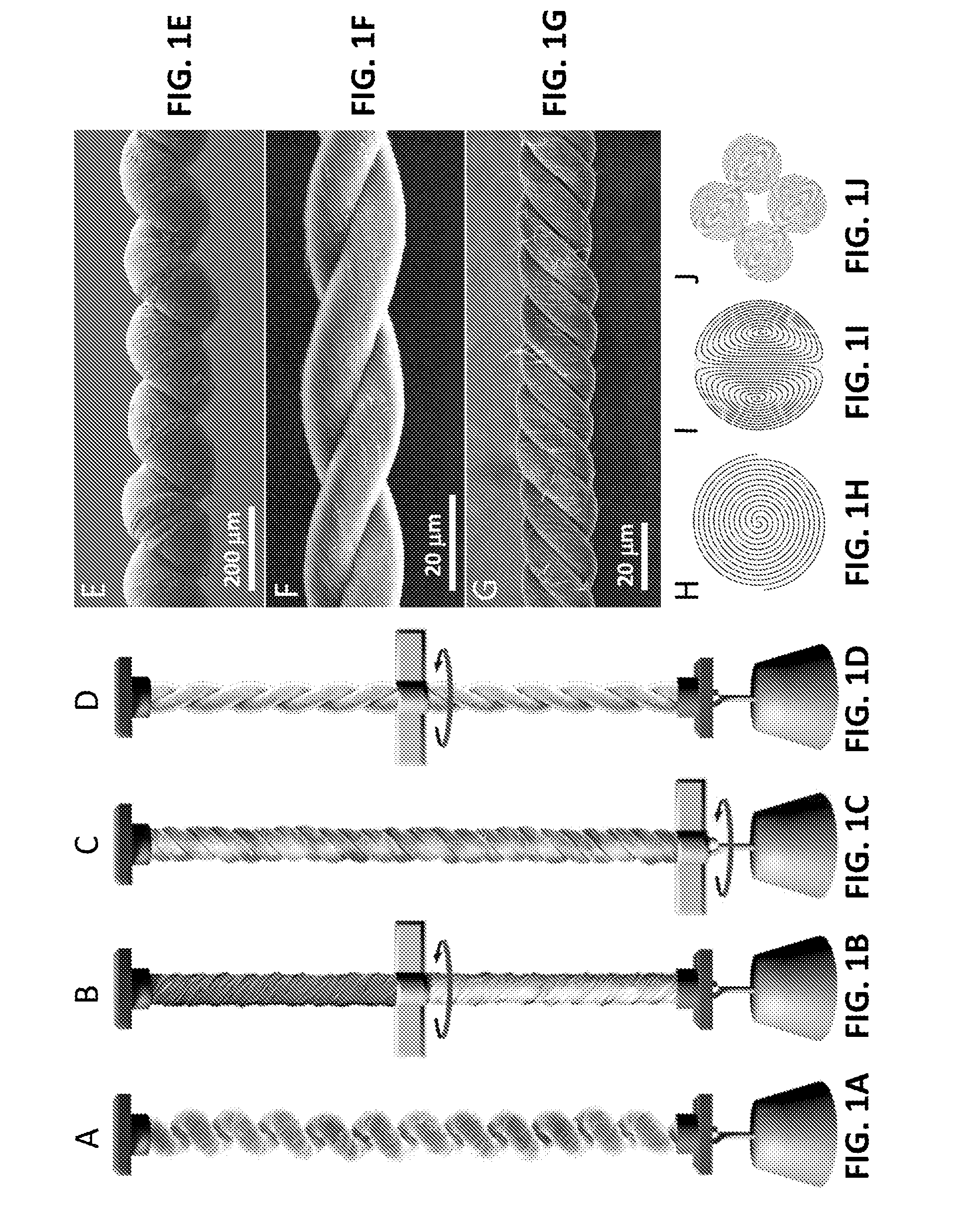
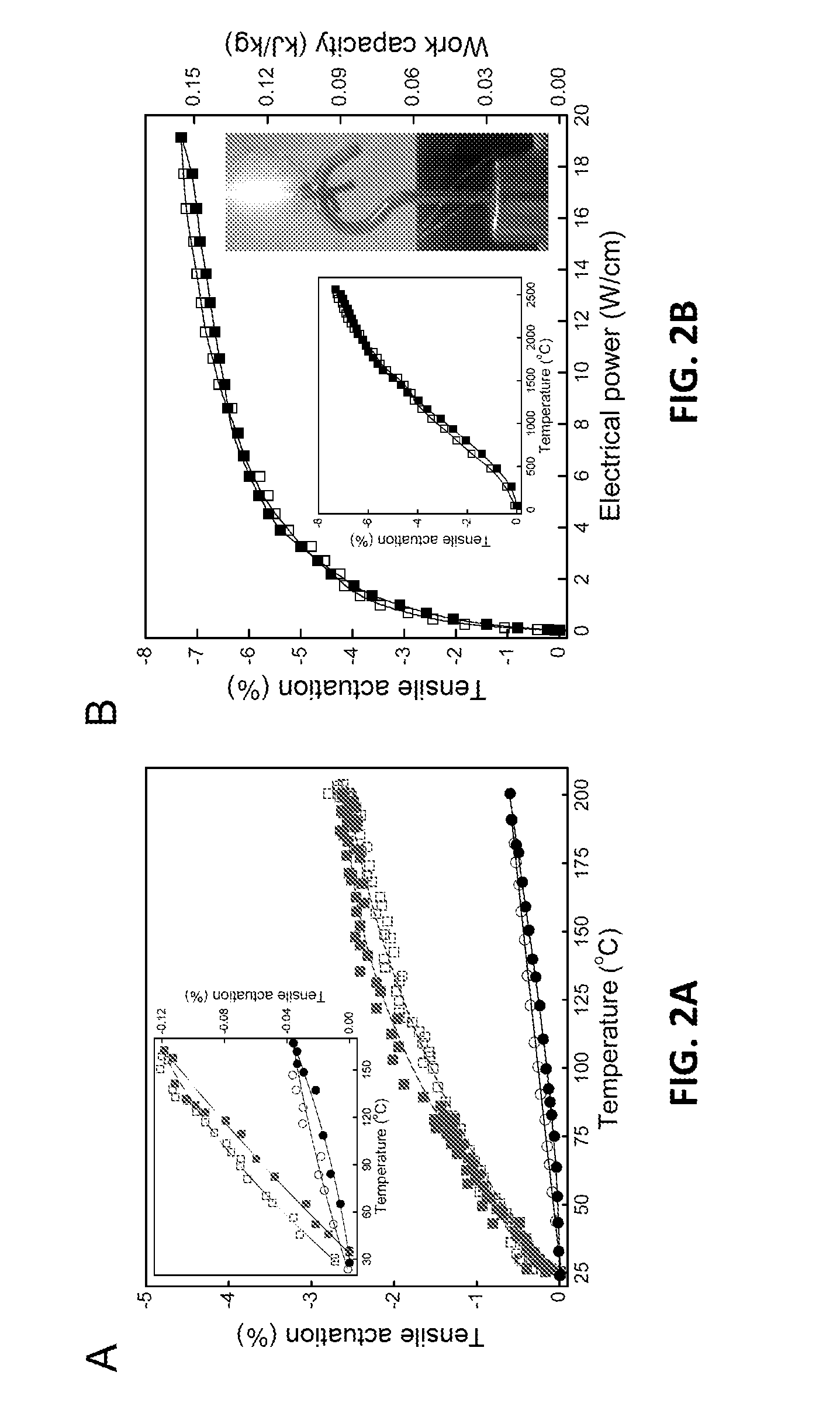
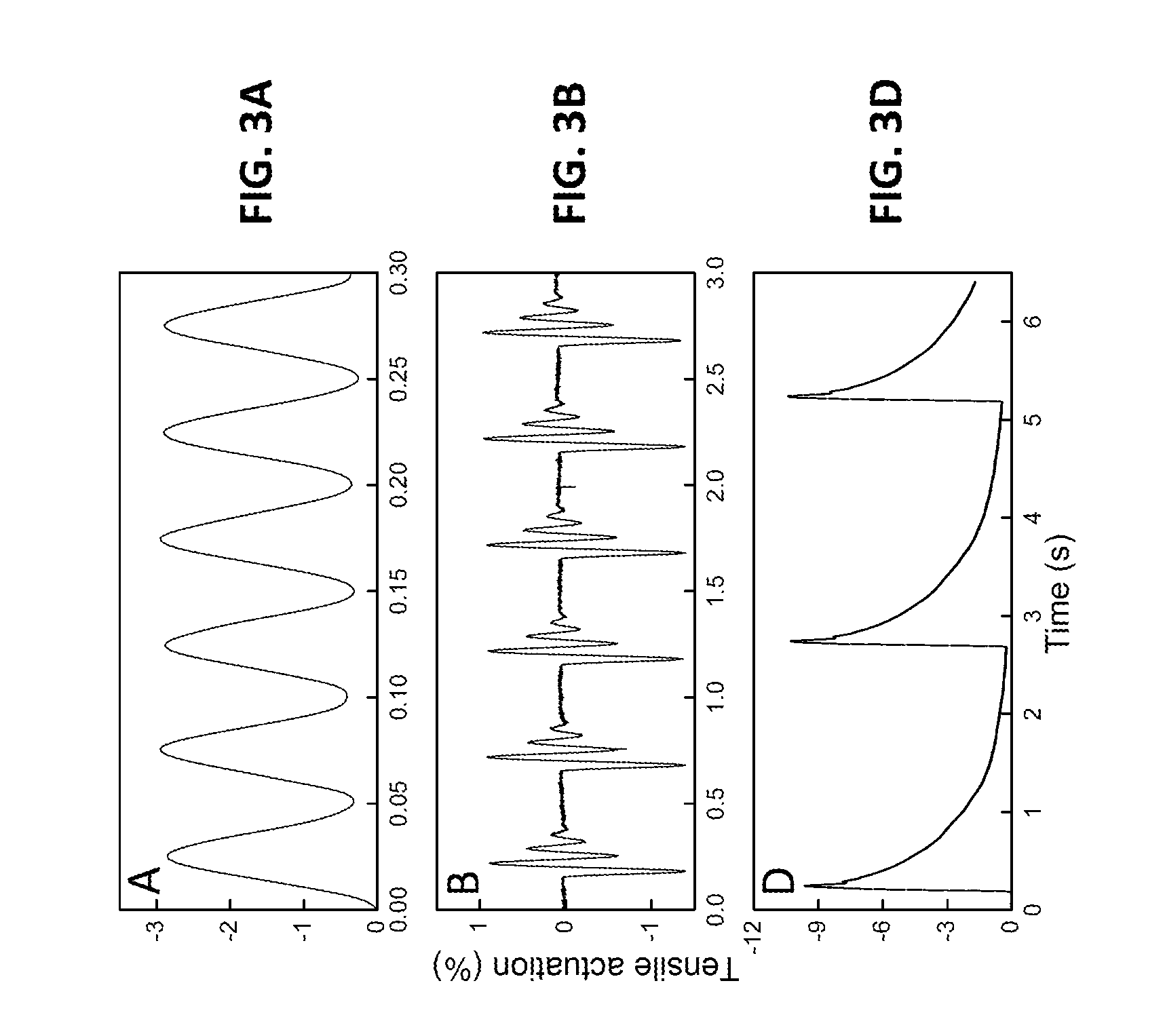
Coiled and non-coiled twisted nanofiber yarn torsional and tensile actuators
Actuators (artificial muscles) comprising twist-spun nanofiber yarn or twist-inserted polymer fibers generate torsional and / or tensile actuation when powered electrically, photonically, chemically, thermally, by absorption, or by other means. These artificial muscles utilize non-coiled or coiled yarns and can be either neat or comprising a guest. Devices comprising these artificial muscles are also described.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Combined muscular multi-directional bending flexible joint
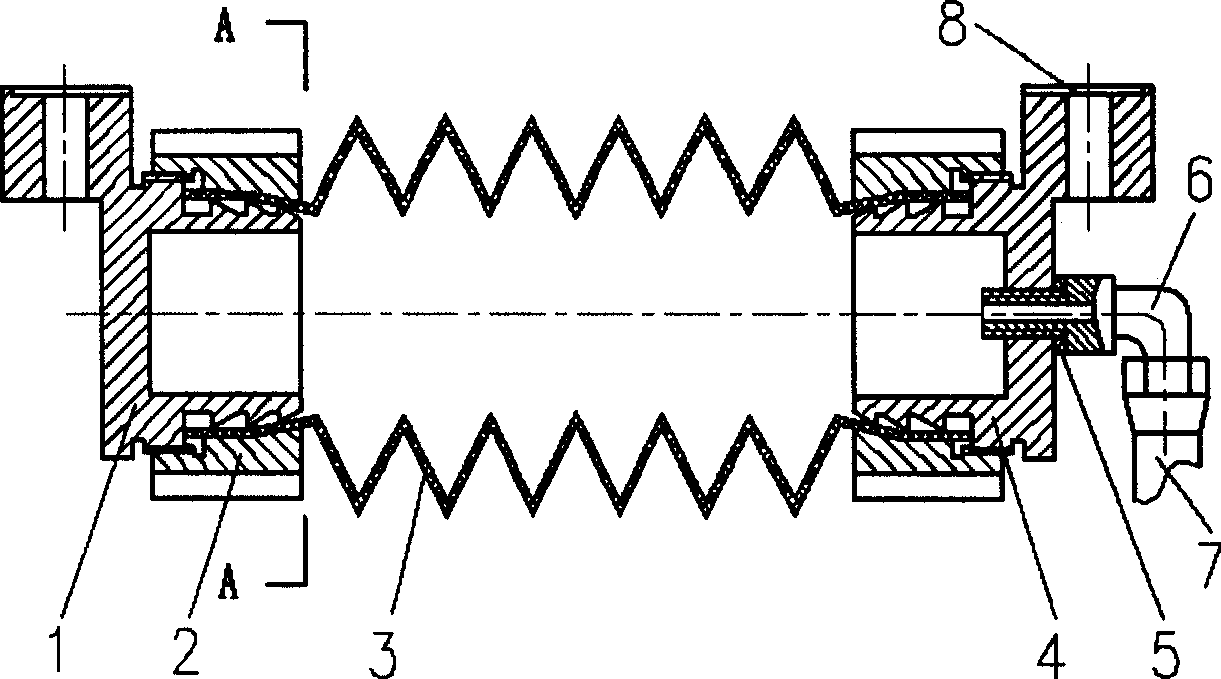
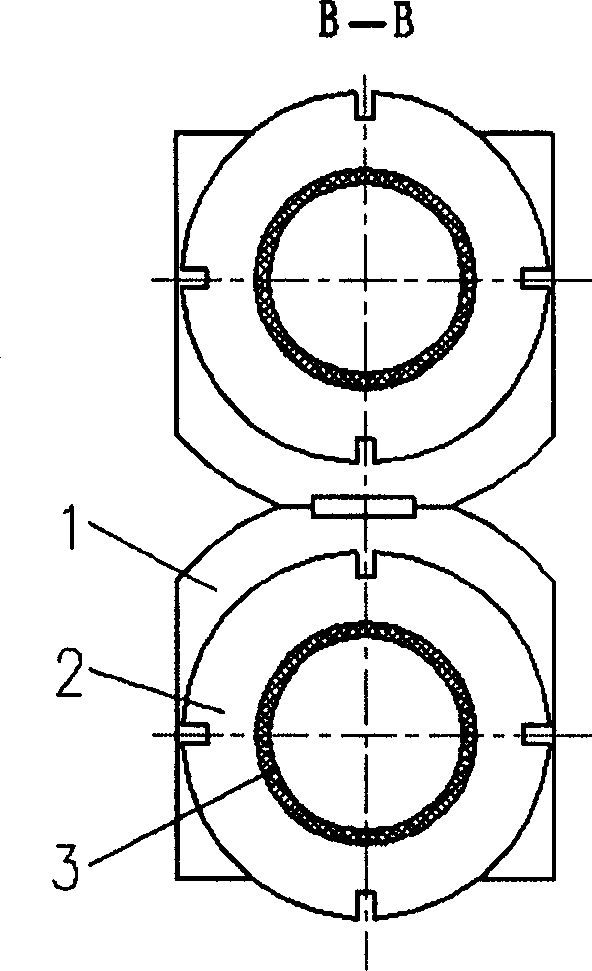
The present invention relates to a combinatory muscle type flexible joint capable of bending toward several directions. It can be used as various joints of robot and artificial limb. Said flexible joint adopts the axial expasion of elastic corrugated pipe after which is forced by fluid pressure as muscle power, several artificial muscle components are formed into said flexible joint. It adopts plate spring or plate hinge as flexible joint skeleton capable of bending toward two directions, and adopts bar spring and ball universal joint or cross universal joint as flexible joint sekelton capable of bending toward several directions.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Three-dimensional composite flexible joint
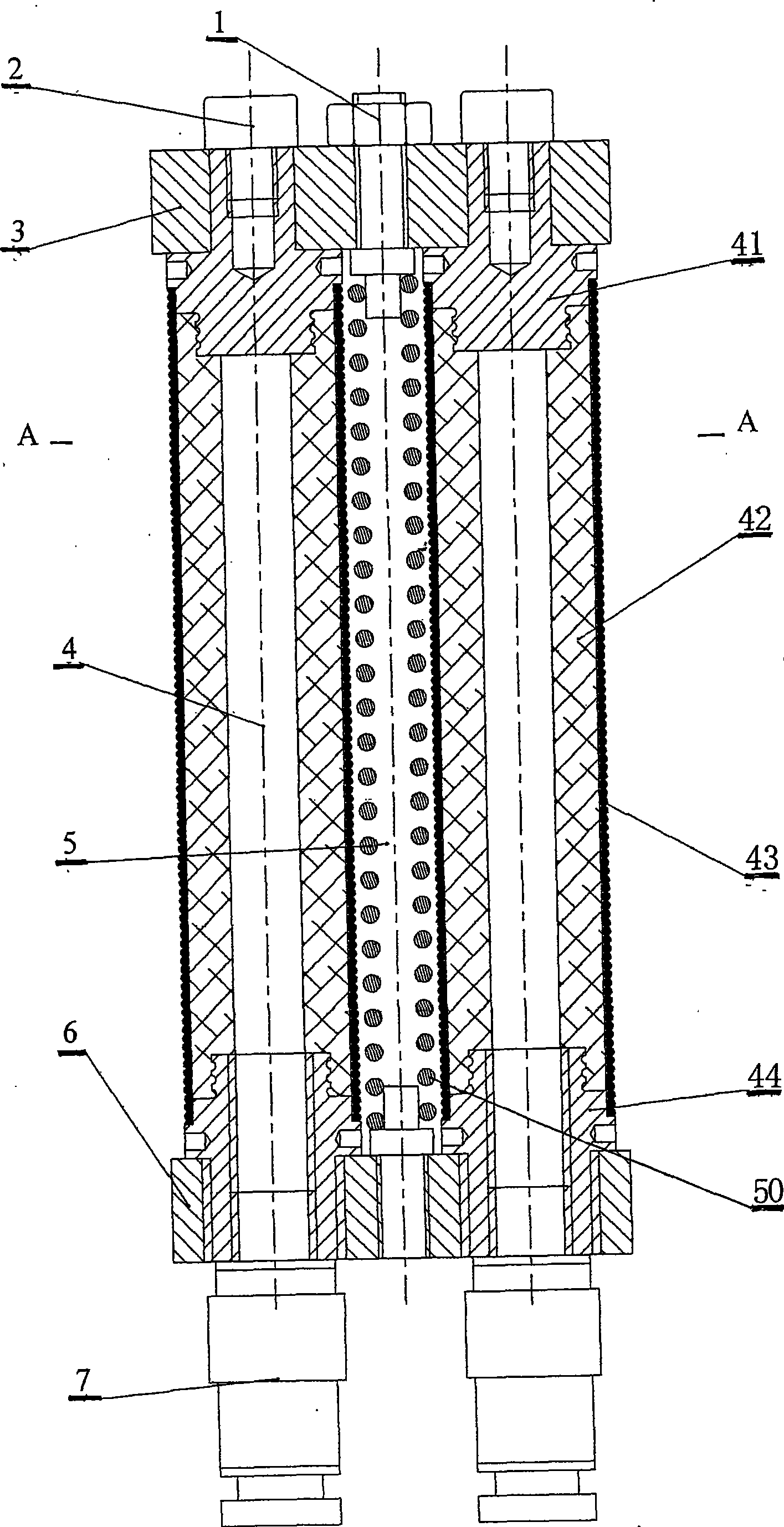
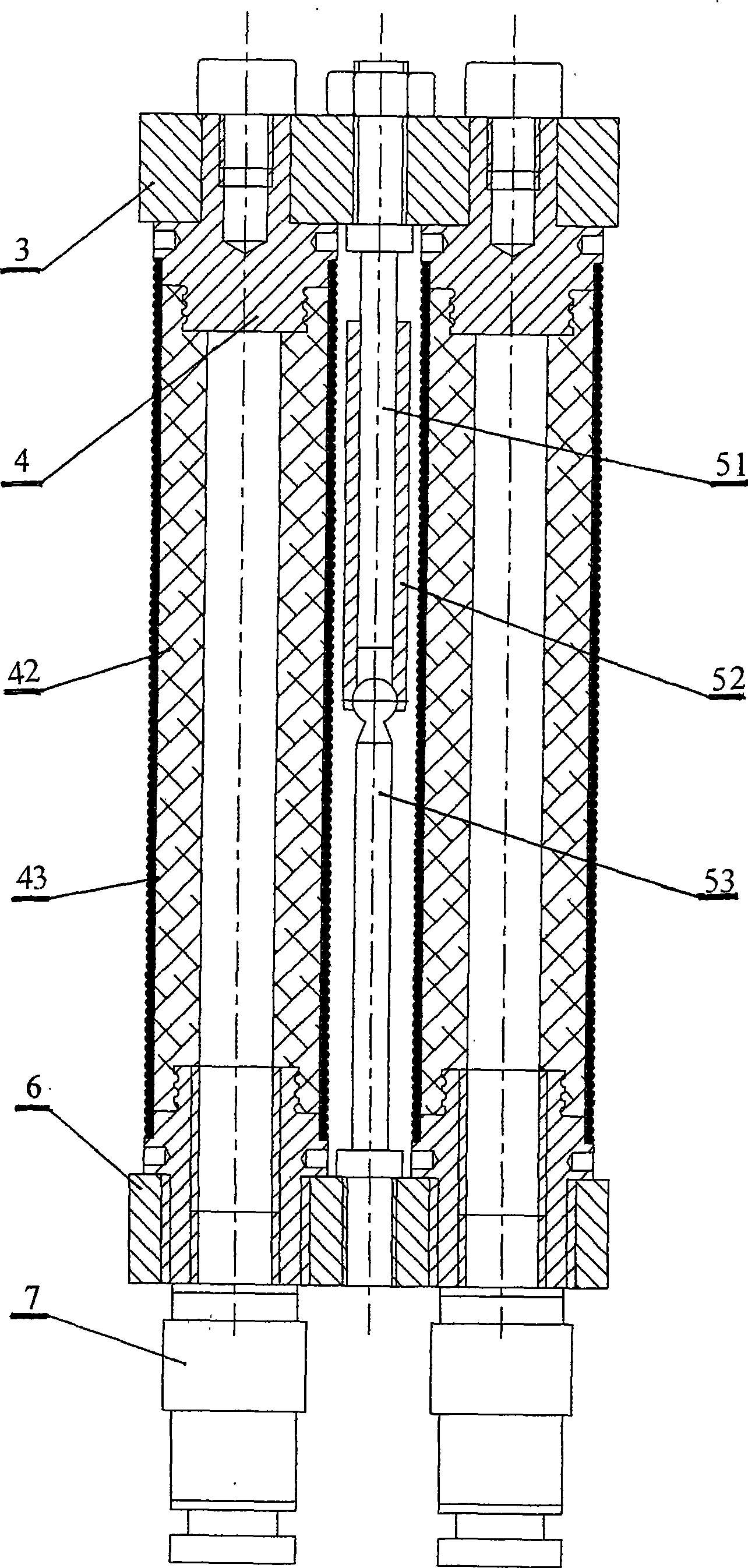
The invention discloses a joint used for a robot limb and relates to a three-dimensional composite flexible joint which is characterized in that several groups of extended artificial muscles are arranged between an upper flange and a lower flange; a framework is arranged in a cavity formed by the several groups of extended artificial muscles; the extended artificial muscle is as follows: a spring is arranged between an upper end cover and a lower end cover, a capsule is arranged in a tubular cavity formed by the spring, and the lower end cover is provided with a fluid inlet; the framework is made of a tubular spring and also can be a component formed by a movable pair and a spherical pair in series; and two ends of the framework are fixed on the upper flange and the lower flange of the joint. The three-dimensional composite flexible joint has the advantages that the three-dimensional composite flexible joint has small size and good flexibility; a drive set of the joint is combined with the joint as a whole; the three-dimensional composite flexible joint can realize axial elongation and curvature of space, can realize the complex action of a bionic artificial joint, act stably and is fit for capturing or conveying objects with irregular shapes; and the three-dimensional composite flexible joint has popularization and application values in the field of bionic and specific robot and has very good market prospect.
Owner:BEIHUA UNIV
Wake absorber
InactiveUS6935263B1Decrease wakeLess pronouncedPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesRotary propellersBending forceArtificial muscle
A wake absorber, wherein an aquatic vehicle with a propulsor mounted on the vehicle and operative to propel the vehicle through a water medium, has a wake absorber mounted on the vehicle aft of the propulsor. The wake absorber includes an artificial muscle surface adapted to be impinged upon by a wake created by the propulsor. The wake absorber further includes electrodes mounted on the artificial muscle surface. Pressure of the wake upon the muscle surface exercises a bending force on the surface, which creates energy that is recovered by the electrodes as electrical power that can be digitized. Energy removed from the muscle surface by the electrodes weakens the wake and renders the wake less pronounced visually and acoustically.
Owner:NAVY US SECREATY OF THE
Biomimetic benthon fishing robot
ActiveCN103029818ADoes not damage the ecological environmentImprove survival rateUnderwater equipmentOcean bottomFishing
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Novel metal hydride artificial muscles
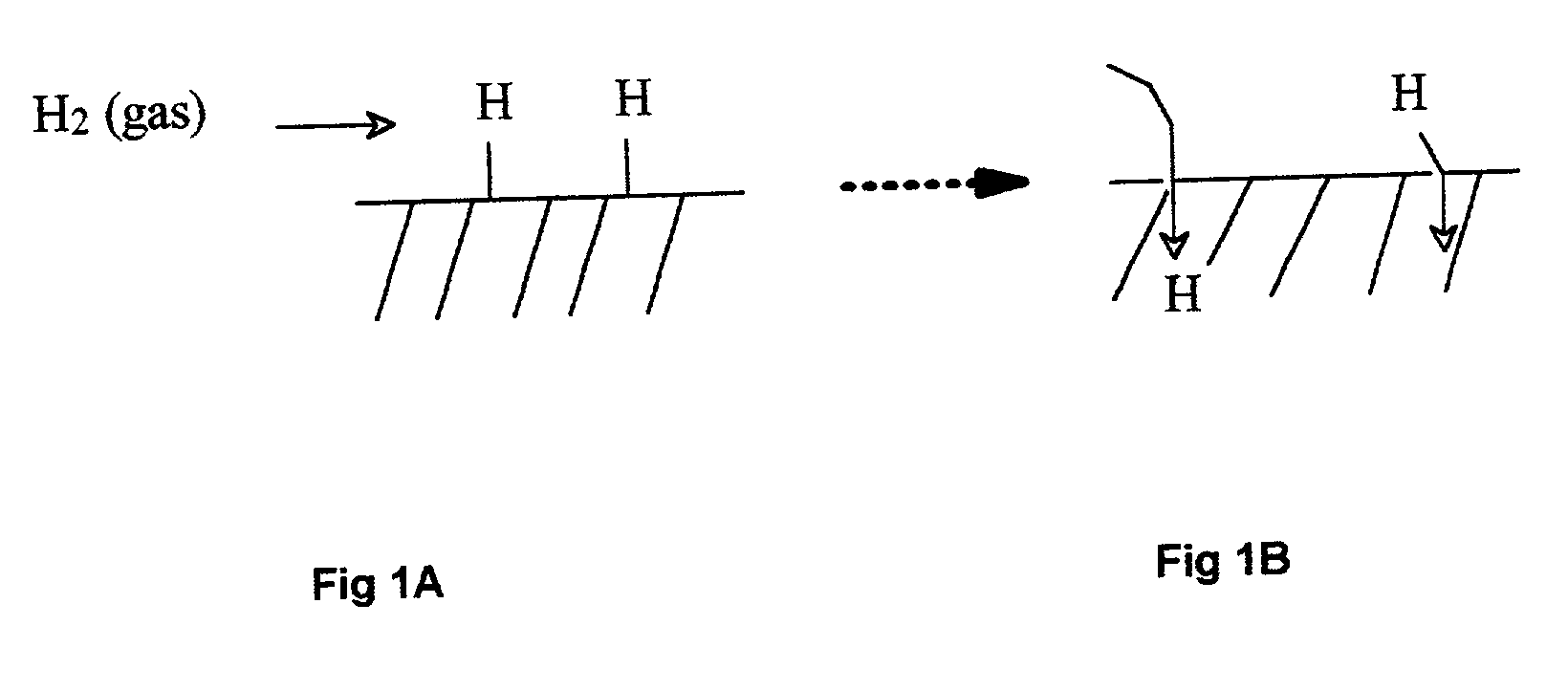
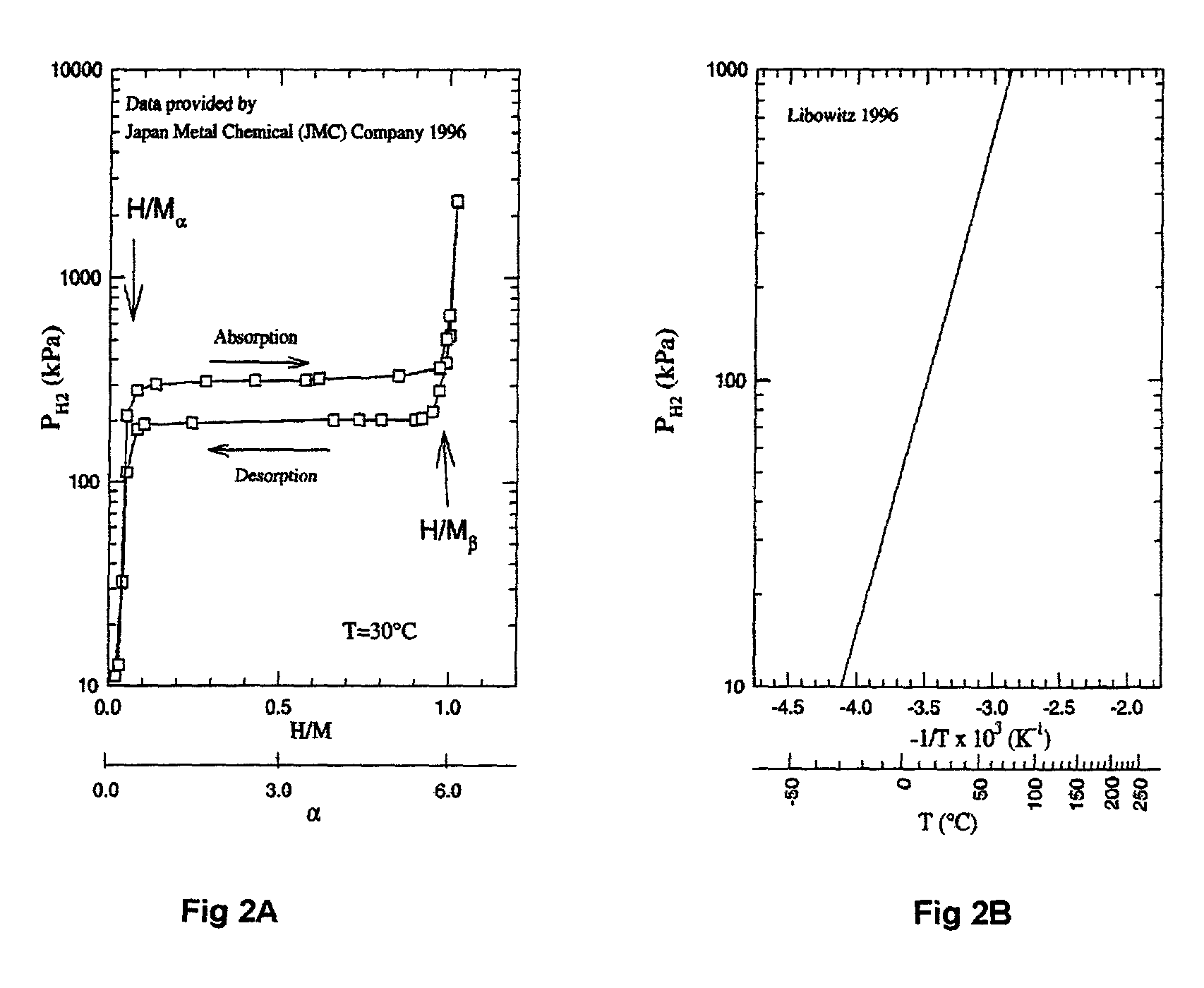
InactiveUS20020026794A1Guaranteed uptimeLong stroke capabilities of actuationProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpace suitsEngineeringArtificial muscle
New artificial muscles and actuators, that are operated by hydrogen gas as working fluid stored interstitially in metal hydrides as a hydrogen sponge. These artificial muscles and actuators are operated both electrically and thermally. The artificial muscles and actuators have fast response, are compact / light-weight, are noiseless, and produce high-power density. They can be used for biomedical, space, defense, micro-machines, and industrial applications.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
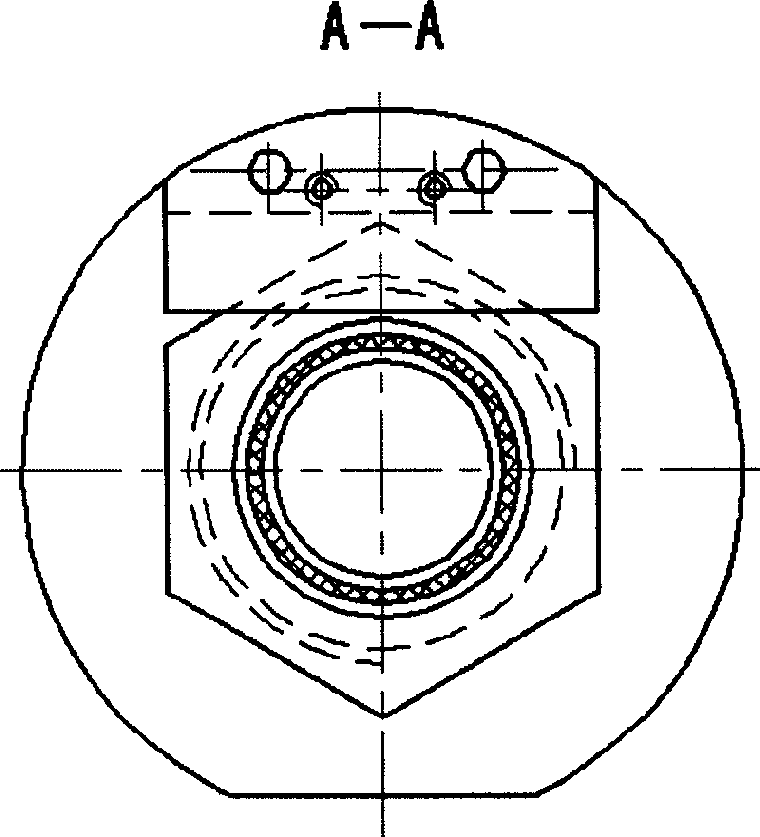
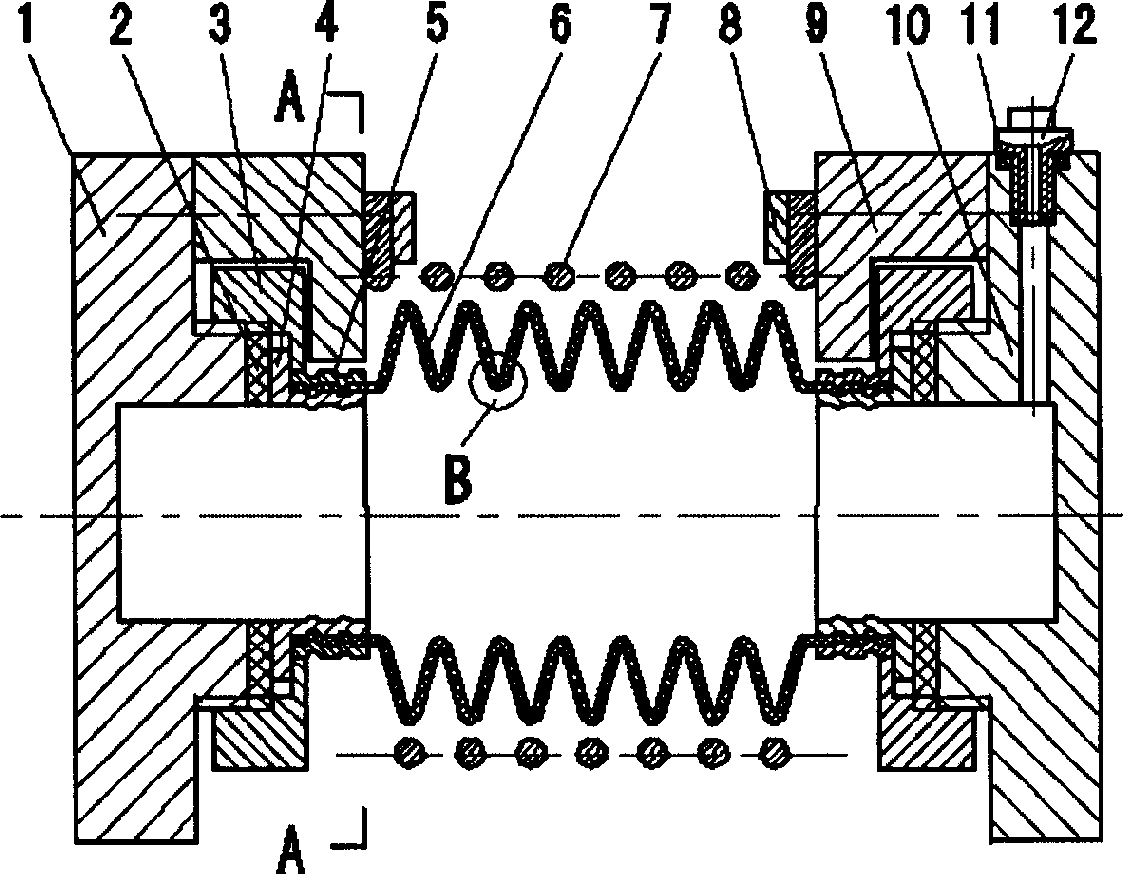
Flexible joint of helical spring type artificial muscle
The invention relates to a helical spring type flexible joint of artificial muscle as executing agency of automated equipment, belonging to application technology of mechanical arm. Said flexible joint is similar to one-way flexible joint of finger, elbow, and knee, can be used as ankle that need keeping balance and having better, and the multiple-directional flexible joint of shoulder. The elastomeric bellow pressed by fluid expand axially to supple power of muscle; the flexible joint consist of one artificial muscle component or more; plate butt and sphere universal joint are utilized as the skeleton of flexible joint; the joints that bended stretch again by the rebound of helical spring. The helical spring and closed squeezable elastomeric bellow have perfect function of buffer; the longitudinal and latitudinal threads are held in the tube wall of elastomeric bellow whose deformation is sensitive to the pressure change of fluid, therefore demanding small quantity of flow and little dissipating energy for flexible action of joint.
Owner:广西爱玛车业有限公司
Coiled and non-coiled twisted polymer fiber torsional and tensile actuators
Actuators (artificial muscles) comprising twist-spun nanofiber yarn or twist-inserted polymer fibers generate torsional and / or tensile actuation when powered electrically, photonically, chemically, thermally, by absorption, or by other means. These artificial muscles utilize non-coiled or coiled yarns and can be either neat or comprising a guest. Devices comprising these artificial muscles are also described.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Human-simulated mechanical arm based on hybrid driving of various artificial muscles
ActiveCN104842345ASimple structureHigh power density ratioProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsShape-memory alloyEngineering
The invention discloses a human-simulated mechanical arm based on hybrid driving of various artificial muscles, which comprises a motor driving cradle head, a pneumatic muscle (PAM) bionic elbow joint, a shape memory alloy (SMA) bionic wrist joint and an IPMC bionic hand, wherein a shoulder joint has two rotational degrees of freedom; the elbow joint has three rotational degrees of freedom; the wrist joint has two rotational degrees of freedom; and the bionic hand has four fingers and eleven degrees of freedom, so that the mechanical arm has eighteen degrees of freedom. The cradle head is connected with the elbow joint through a shaft, the elbow joint is fixedly connected with the wrist joint through three bolts, and the wrist joint is fixedly connected with the bionic hand through a screw thread. Compared with a motor driving mechanical arm with the same specifications, the mechanical arm disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, high power-density ratio, good safety, high flexibility and the like, and the mechanical arm is enabled to have better flexibility and bionics characteristics through simulating a bone-muscle system of an upper limb of the human body. The human-simulated mechanical arm disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to the fields of home services, rehabilitation therapy, risk elimination and rescue, material handling and the like.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Multi-degree-of-freedom hybrid drive artificial muscle
ActiveCN106956254AGreat bending freedomAchieving telescoping freedomProgramme-controlled manipulatorFiberAxial displacement
The invention discloses a multi-degree-of-freedom hybrid drive artificial muscle. A polyethylene terephthalate (PET) woven mesh is mounted outside an elastic rubber hose, two ends of the elastic rubber hose are sealed by the aid of outer clamps and inner plugs, a front-end fixing frame and a pneumatic joint are mounted on the inner plug at the front end, a back-end fixing frame is mounted on the inner plug at the back end, three guide frames are longitudinally arranged between the two fixing frames at equal distances, and four shape memory alloy-nylon fishing line muscle fibers are evenly distributed between the two fixing frames in the circumferential direction. The initial weaving angle of the woven mesh on the outer side of the elastic rubber hose is set to be larger than 54 degrees, and the axial displacement and the axial push force are produced when the inside of the rubber hose is pressurized by air. The shape memory alloy-nylon fishing line muscle fibers are heated by pulse current, and thus bending deformation of the hybrid artificial muscle is realized. The artificial muscle has the positive effects that the drive characteristics of an elongation type pneumatic muscle are improved, the degree of freedom of the elongation type pneumatic muscle is increased, and the artificial muscle can be applied in the field of bionic robots requiring high-precision compliant drive.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
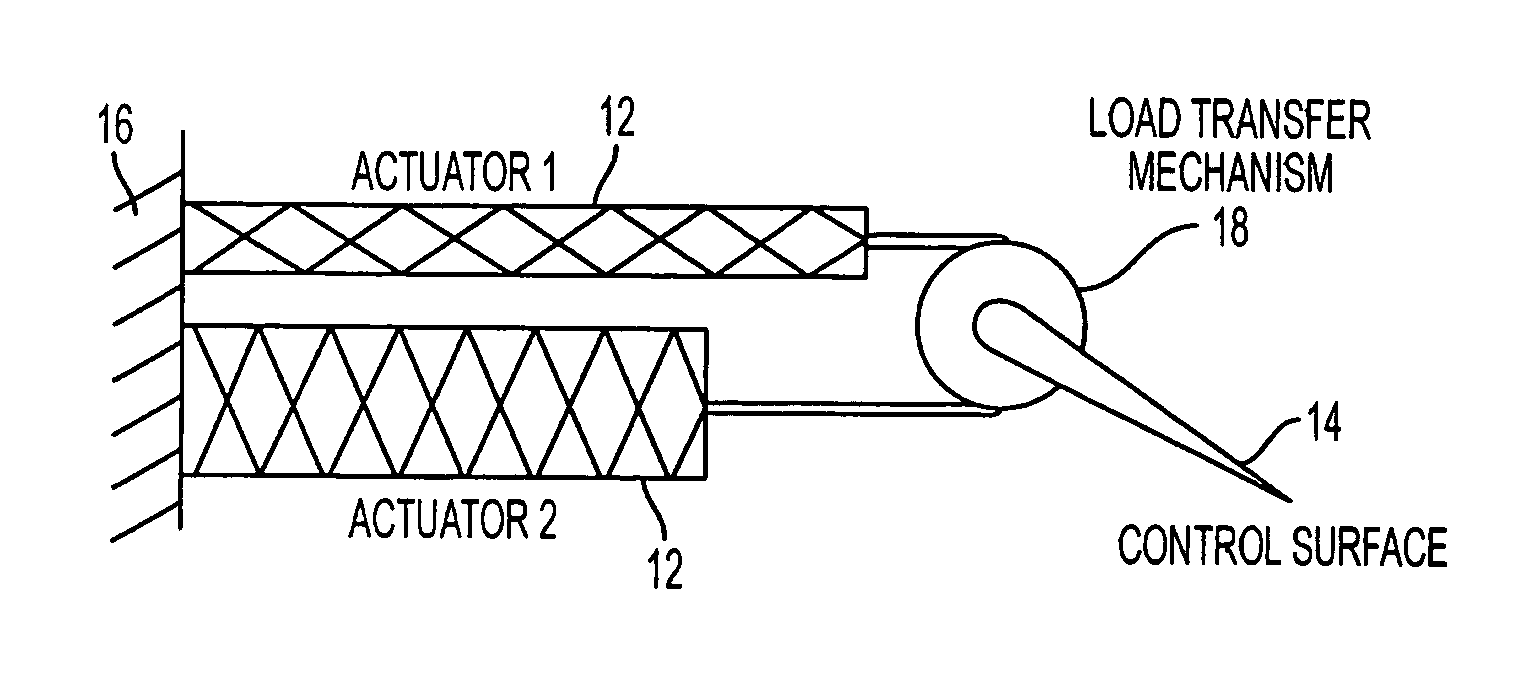
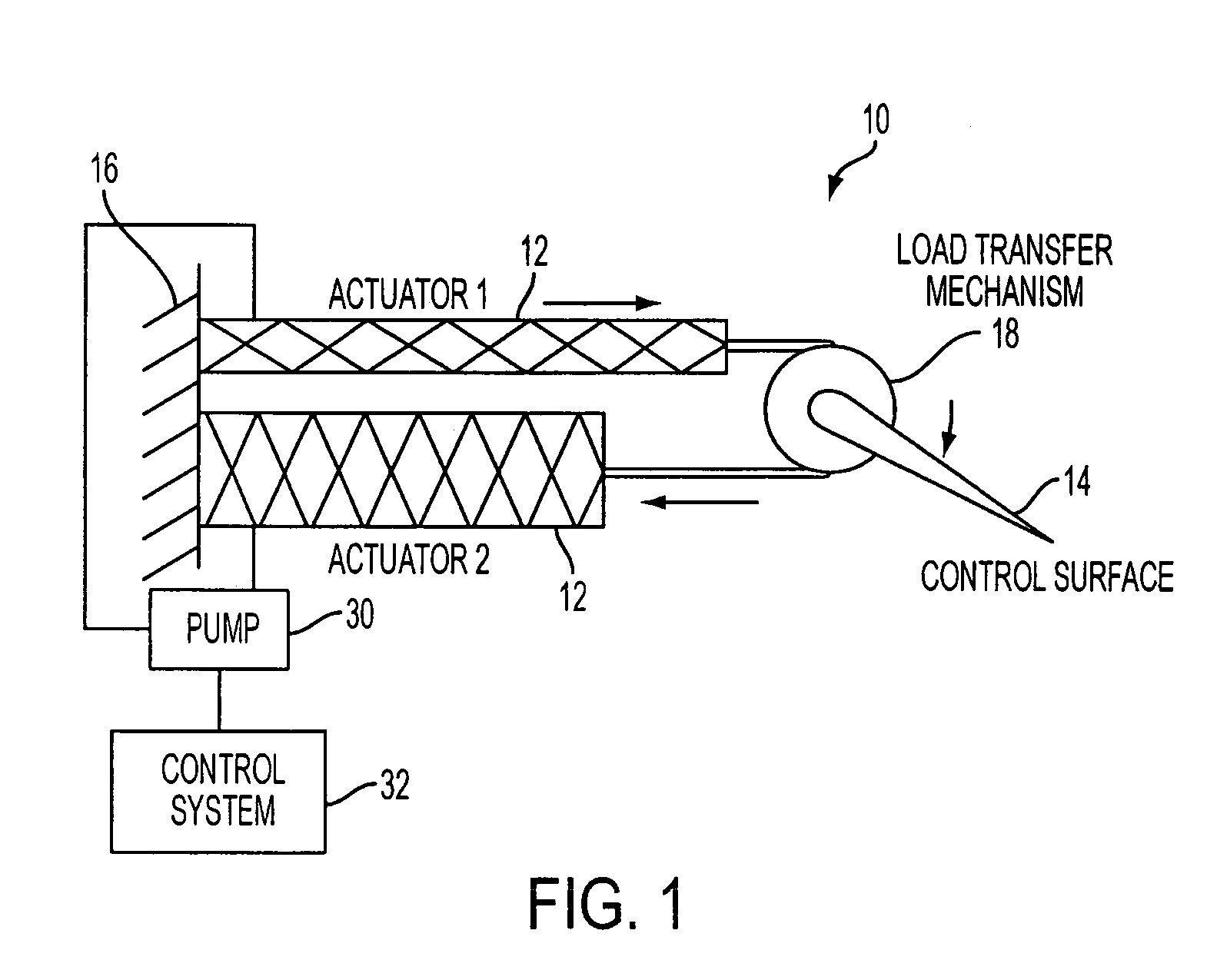
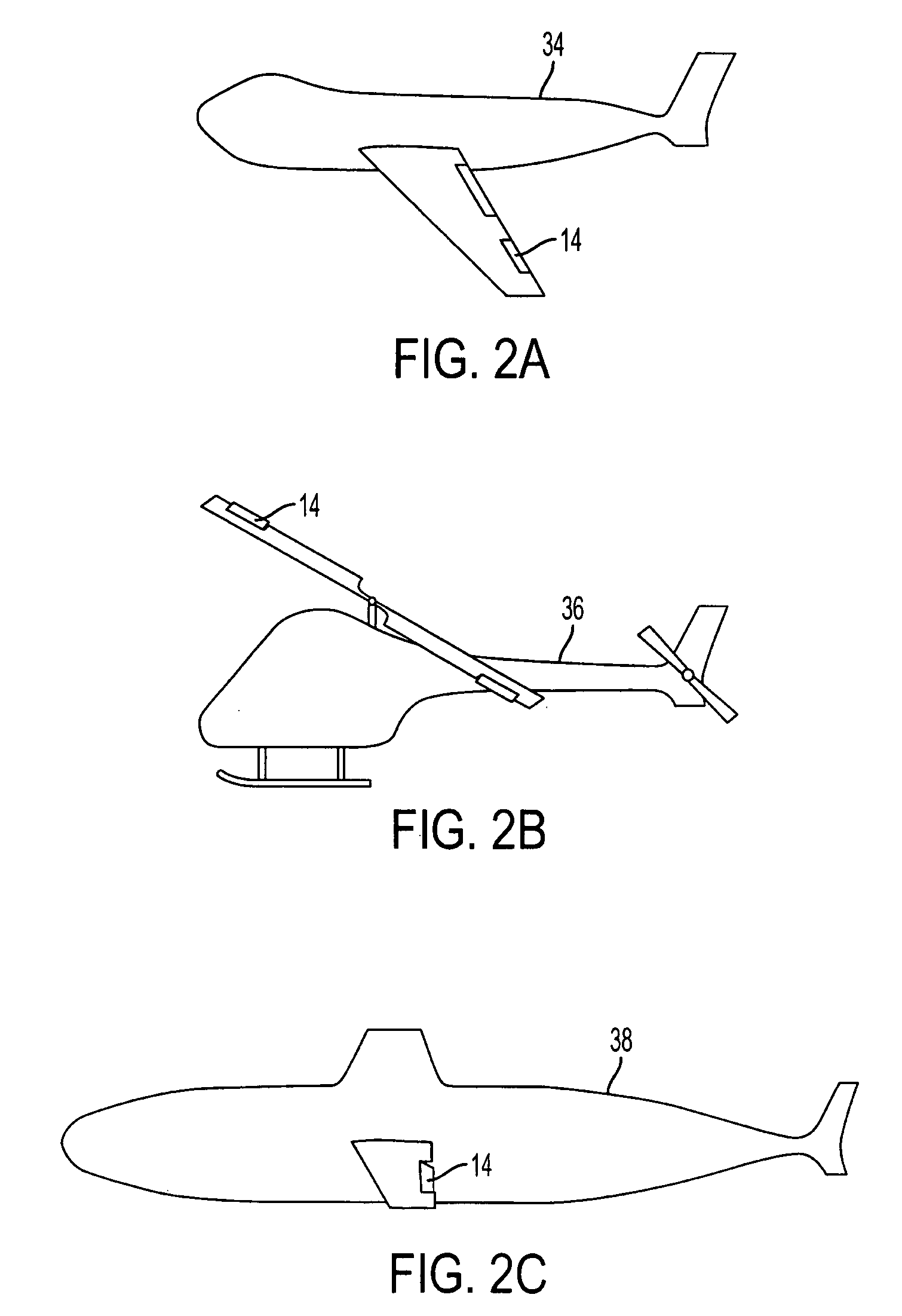
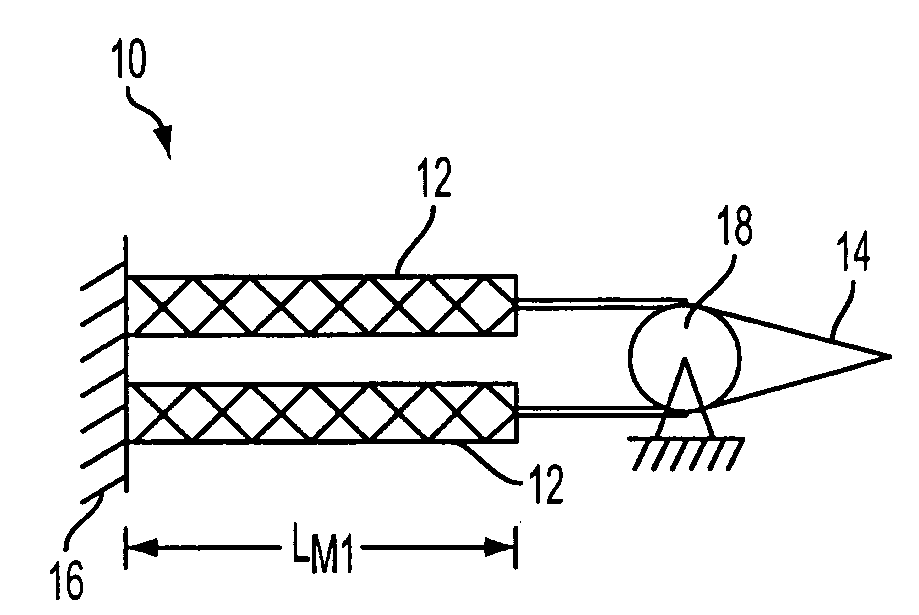
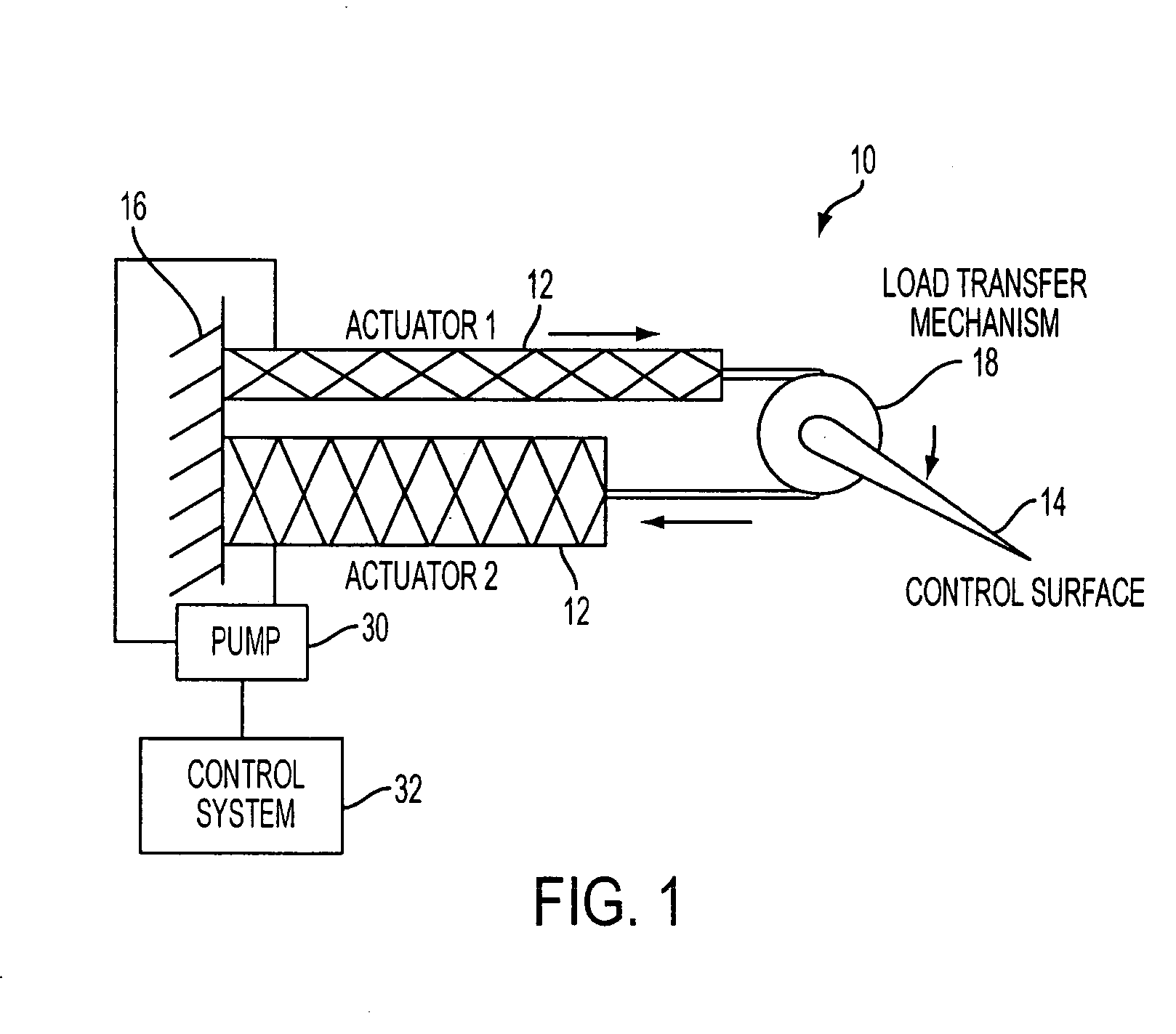
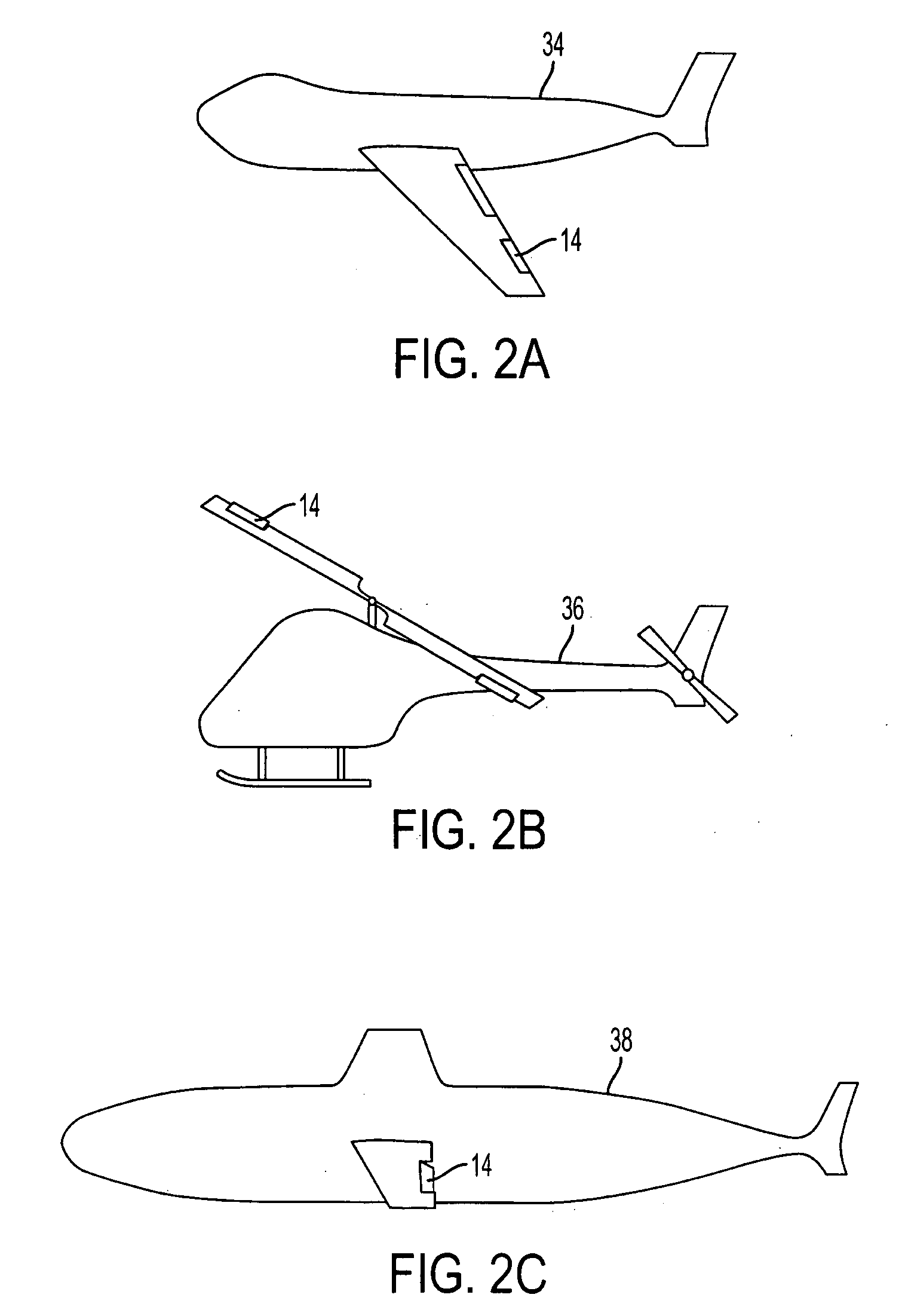
Fluid-driven artificial muscles as mechanisms for controlled actuation
InactiveUS7837144B2AdaptableEasily interchangeableFlexible wall reciprocating enginesAircraft stabilisationBiomedical engineeringArtificial muscle
A fluid contact surface actuation system for a vehicle, including a first fluid contact surface constructed and arranged to act against a first fluid passing over the first fluid contact surface; and a first fluid actuator coupled to the first fluid contact surface to move the first fluid contact surface between a first position and a second position to enable control of the vehicle in a predetermined manner, the first fluid actuator having a first resilient bladder that receives a second fluid such that pressure of the second fluid moves the first bladder between a contracted configuration and an expanded configuration.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +2
Fluid-driven artificial muscles as mechanisms for controlled actuation
InactiveUS20080035798A1AdaptableEasily interchangeableFlexible wall reciprocating enginesAircraft stabilisationBiomedical engineeringArtificial muscle
A fluid contact surface actuation system for a vehicle, including a first fluid contact surface constructed and arranged to act against a first fluid passing over the first fluid contact surface; and a first fluid actuator coupled to the first fluid contact surface to move the first fluid contact surface between a first position and a second position to enable control of the vehicle in a predetermined manner, the first fluid actuator having a first resilient bladder that receives a second fluid such that pressure of the second fluid moves the first bladder between a contracted configuration and an expanded configuration.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +2
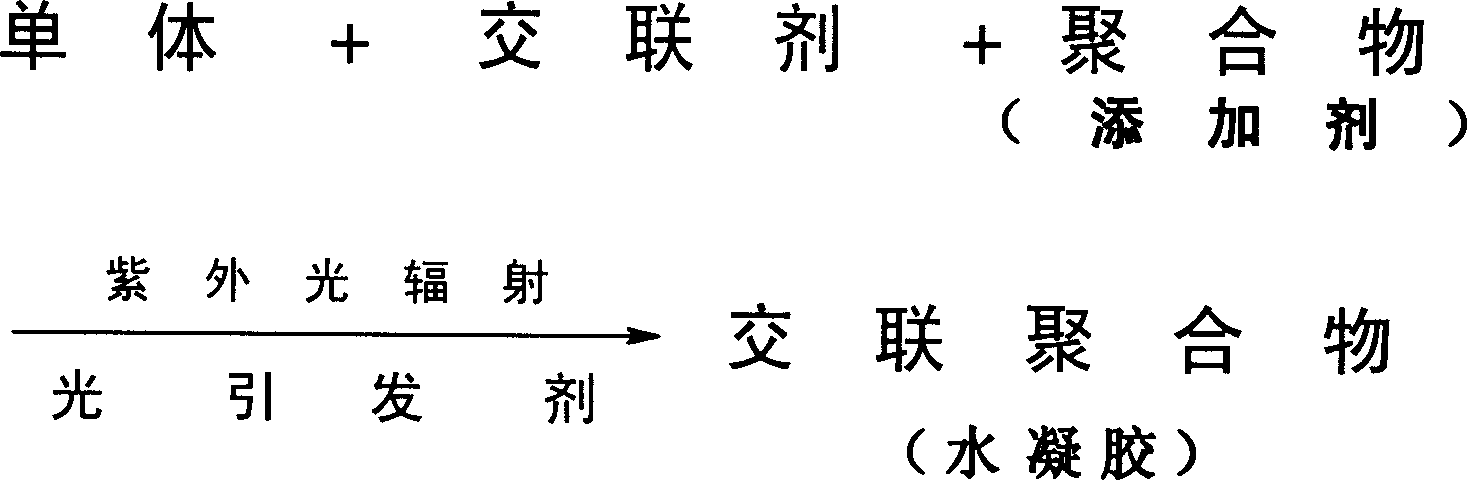
Direct synthesis of temperate sensitive aquogel by ultraviolet radiant polymerization
Synthesis of warm sensitive aquagel from ultraviolet light radiation polymerization is carried out by adding reacting raw materials into deionized water to prepare preformed solution, laying aside under ultraviolet light radiation, exposing, polymerizing directly to prepare cross-linking polymer, putting the polymer into sorbitic extractor, extracting from boiled deionized water for 24hrs, taking it out, and drying in vacuum drier to obtain warm sensitive aquagel. Its low critical temperature varies between 30-40 Deg C. with raw material formula. It can be used for various aquagels, medicine control-releasing system, memory element switch, artificial muscle and chemical industrial separation. It achieves low cost, simple process, high efficiency and normal-temperature operation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Photo-induced deformation liquid crystal macromolecular material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101041779AAchieving directional bending deformationLiquid crystal compositionsChemical structureBenzene
The invention discloses a new photo-induced deforming liquid crystal macromolecular material in liquid crystal macromolecular material technical domain, which is characterized by the following: choosing ethoxyl group as main chain and azo-benzene derivant as lateral chain with part crosslinking; choosing azo-benzene derivant of monocyclic oxygen group and bicycle oxygen group as monomer; mixing finite quantity light trigger and trigger of positive ion; putting into reactor; choosing proper reacting temperature; copolymerizing the light trigger positive ion under the function of wavelength light; getting the product. This material is a controlled photo-inducer flexural deformation material, which can be used to study driver and artificial muscle.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Display apparatus
InactiveUS20160195902A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital processing power distributionFlexible displayComputer science
A display apparatus includes a flexible display panel; an image processing board configured to output a video signal to the display panel; and a support member provided between the display panel and the image processing board and configured to support the display panel, the support member including: at least two plates arranged along one side of the display panel; and at least one artificial muscle connecting the at least two plates and configured to be deformed to change a shape of the support member in accordance with a voltage applied thereto.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Exoskeleton-type hand function rehabilitation robot
ActiveCN103750977APromote functional recoveryEffective recovery from exerciseChiropractic devicesLittle fingerAfter treatment
The invention provides an exoskeleton-type hand function rehabilitation robot, relates to medical instruments applied in injured finger rehabilitation, and aims to solve the problems that according to an existing hand function optimizing and recovering manner, hand rehabilitation is difficult, the rehabilitation period after treatment is long and hand functions are influenced. The exoskeleton-type hand function rehabilitation robot comprises an exoskeleton finger drive mechanism, a self-adaptive dorsal metacarpal adjusting platform and a rear artificial muscle module. The exoskeleton finger drive mechanism comprises an exoskeleton thumb, an exoskeleton index finger, an exoskeleton middle finger, an exoskeleton ring finger and an exoskeleton little finger. Proximal interphalangeal exoskeleton joints are arranged between metacarpophalangeal exoskeleton joints and distal interphalangeal exoskeleton joints, and the proximal interphalangeal exoskeleton, the metacarpophalangeal exoskeleton joints and the distal interphalangeal exoskeleton joints are in slidable connections detachably. The self-adaptive dorsal metacarpal adjusting platform covers the upper surface of the exoskeleton finger drive mechanism, and the self-adaptive dorsal metacarpal adjusting platform and the exoskeleton finger drive mechanism are in slidable connections detachably. The exoskeleton-type hand function rehabilitation robot is applied in injured finger rehabilitation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Shape memory alloy (SMA) actuators and devices including bio-inspired shape memory alloy composite (bismac) actuators
InactiveUS20120174571A1Extended range of motionMechanical power devicesClosed-cycle gas positive displacement engine plantBiological motionShape-memory alloy
An actuator comprising a flexible spring affixed at a separation distance from a shape memory alloy or artificial muscle element amplifies strain developed by the shape memory alloy or artificial muscle element while maintaining a substantial fraction of the force developed during activation of the shape memory alloy or artificial memory element. A plurality of such actuators positioned relative to each other by encapsulation or attachment to a body of material such as a terminal hub can emulate a wide variety of biological movements such as for providing gripping in the manner of an opposed human thumb or propulsion in the manner of a jellyfish.
Owner:VIRGINIA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE AND STATE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com