Patents
Literature
600 results about "Smart material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
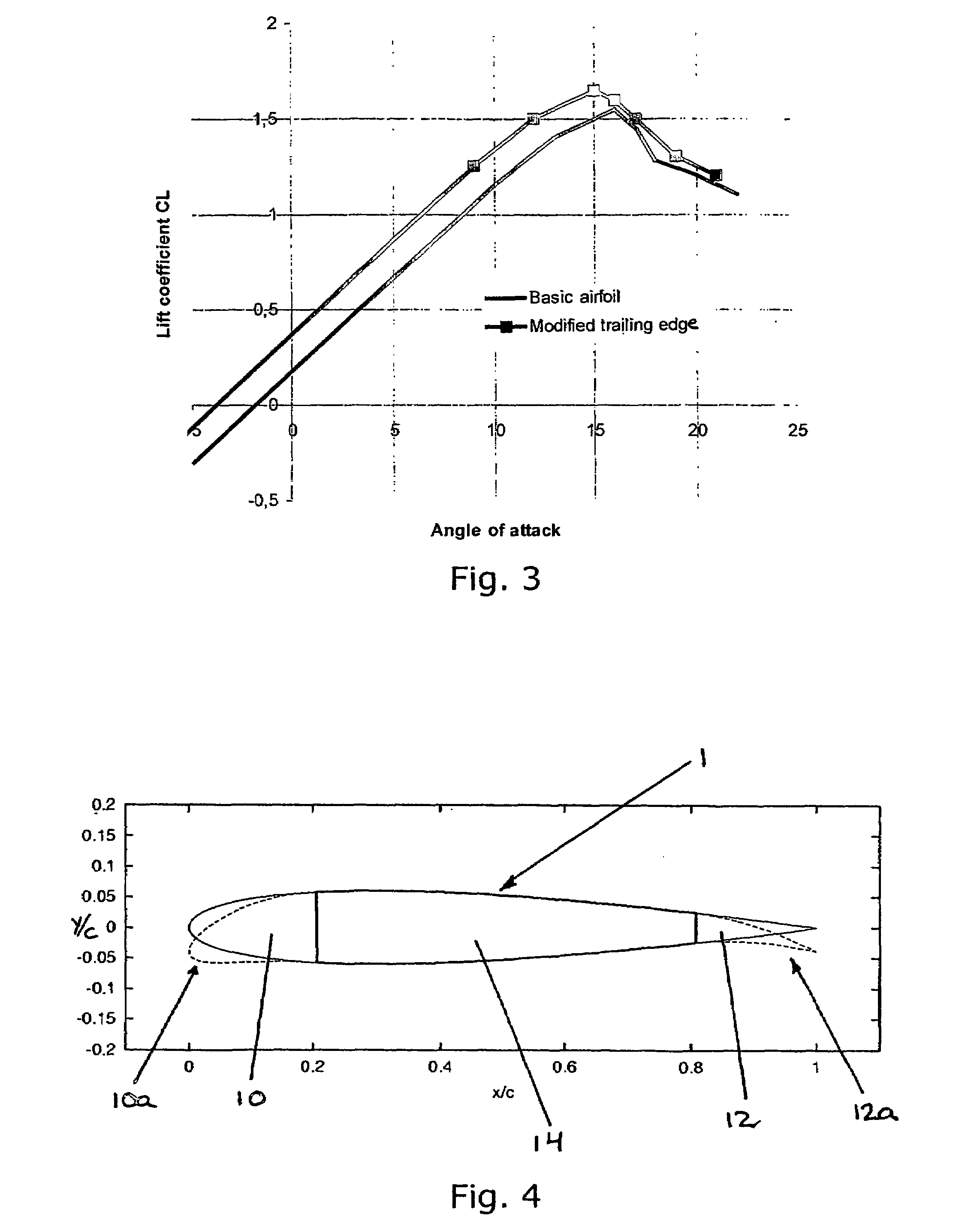
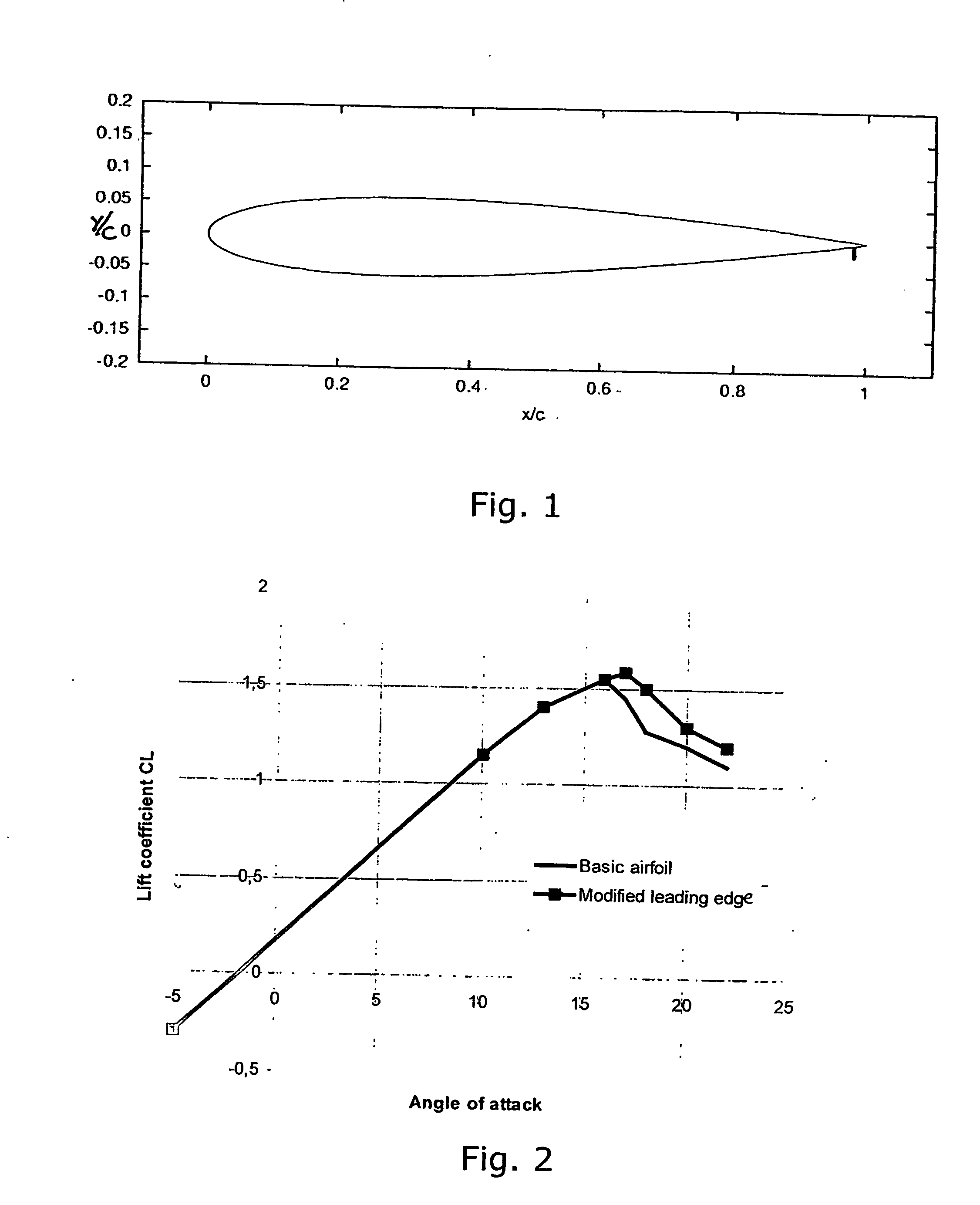
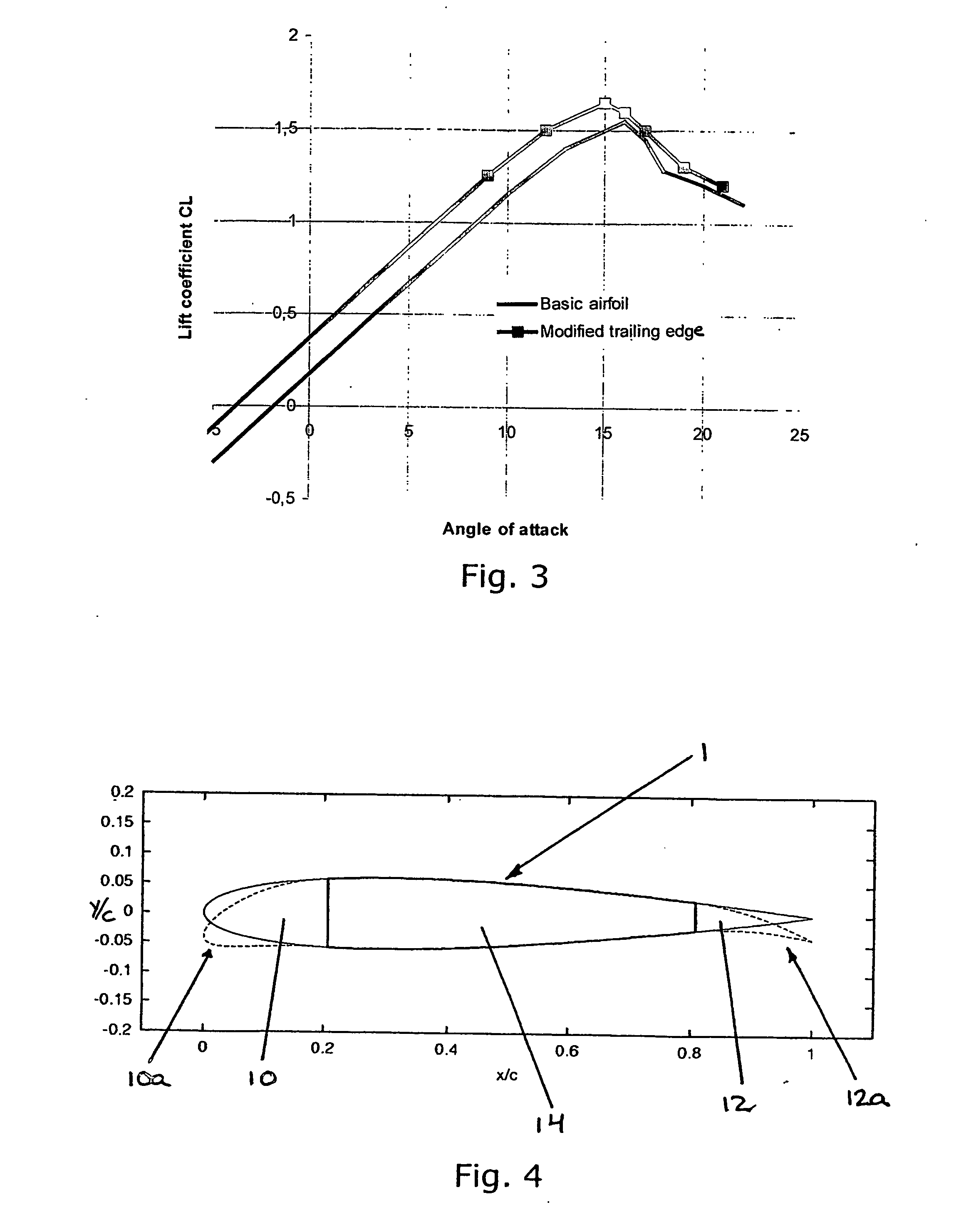
Smart materials, called also intelligent or responsive materials, are designed materials that have one or more properties that can be significantly changed in a controlled fashion by external stimuli, such as stress, moisture, electric or magnetic fields, light, temperature, pH, or chemical compounds. Smart materials are the basis of many applications, including sensors and actuators, or artificial muscles, particularly as electroactive polymers (EAPs).,,
Single-molecule selection methods and compositions therefrom
InactiveUS20020034757A1Highly specific controlImprove complianceNanotechSugar derivativesNucleotideAdhesive
Single-molecule selection methods are provided for identifying target-binding molecules from diverse sequence and shape libraries. Complexes and imprints of selected target-binding molecules are also provided. The subject selection methods are used to identify oligonucleotide and nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties for use in pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, drug delivery, diagnostics, medical devices, cosmetics, agriculture, environmental remediation, smart materials, packaging, microelectronics and nanofabrication. Single oligonucleotide molecules with desirable binding properties are selected from diverse sequence libraries and identified by amplification and sequencing. Alternatively, selected oligonucleotide molecules are identified by sequencing without amplification. Nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties are identified by single-molecule selection from libraries of conjugated molecules or nucleotide-encoded nonnucleotide molecules. Alternatively, target-specific nonnucleotide molecules are prepared by imprinting selected oligonucleotide molecules into nonnucleotide molecular media. Complexes and imprints of molecules identified by single-molecule selection are shown to have broad utility as drugs, prodrugs, drug delivery systems, willfully reversible cosmetics, diagnostic reagents, sensors, transducers, actuators, adhesives, adherents and novel multimolecular devices.
Owner:MOLECULAR MACHINES
Image making medium
InactiveUS8921473B1Improve aestheticsEnhance and enable bondingDuplicating/marking methodsSpecial tyresEngineeringSmart material
The invention relates to an image support medium for creation of an aesthetic image that is a work or object for display. This support medium is made from a smart or intelligent material so that the medium provides or enables formation of an image having at least one aesthetic element that can be responsive, interactive, controlled, changed, programmed, and / or modulated. The support medium can further comprise stimuli, triggers or influences that cause the smart or intelligent material to respond to change shape, size, volume, density, light properties, color, appearance, and / or another physical property of the aesthetic element. In a preferred embodiment, the smart or intelligent material is reversibly responsive to the stimuli, triggers or influences.
Owner:HYMAN SYDNEY
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
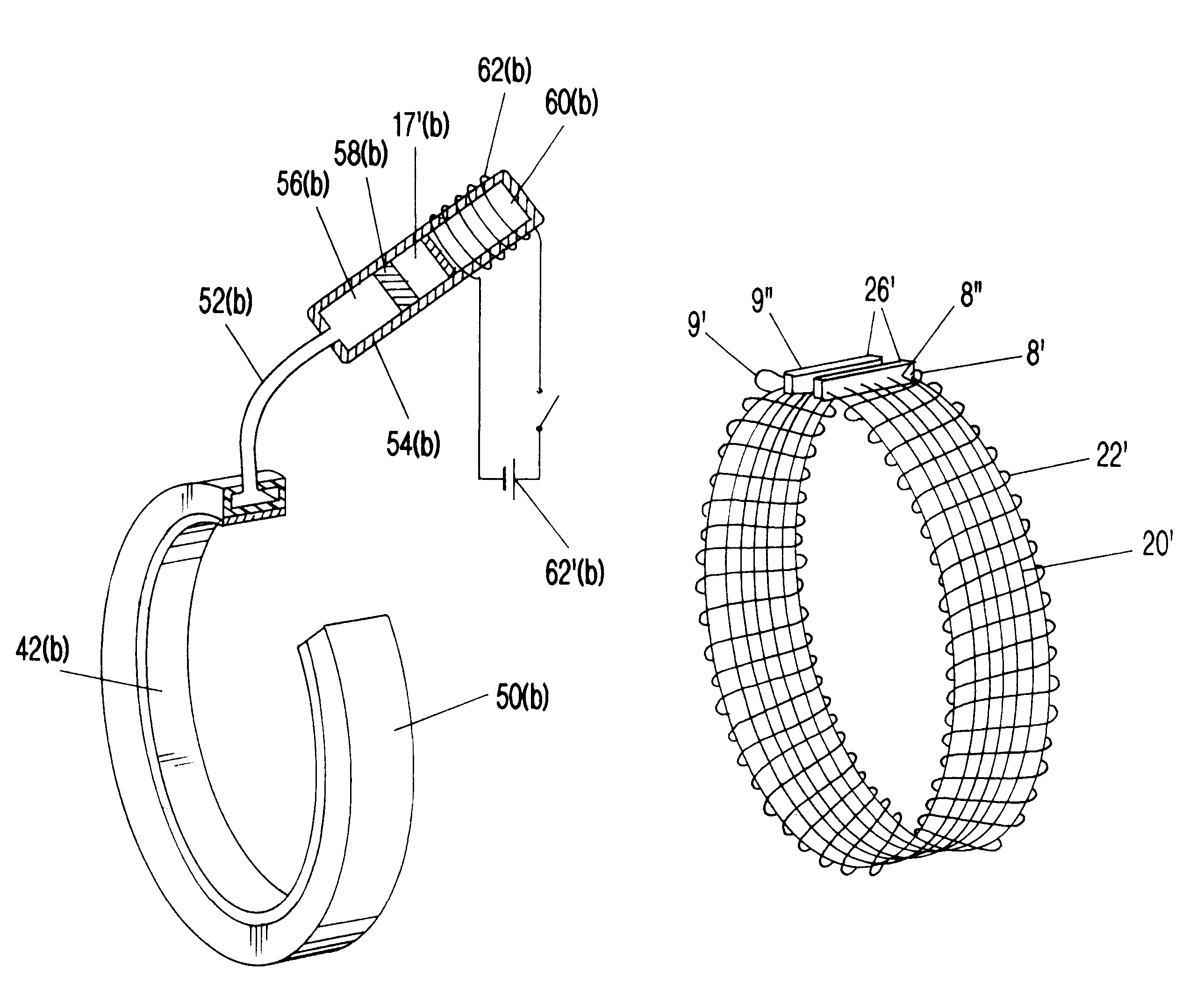
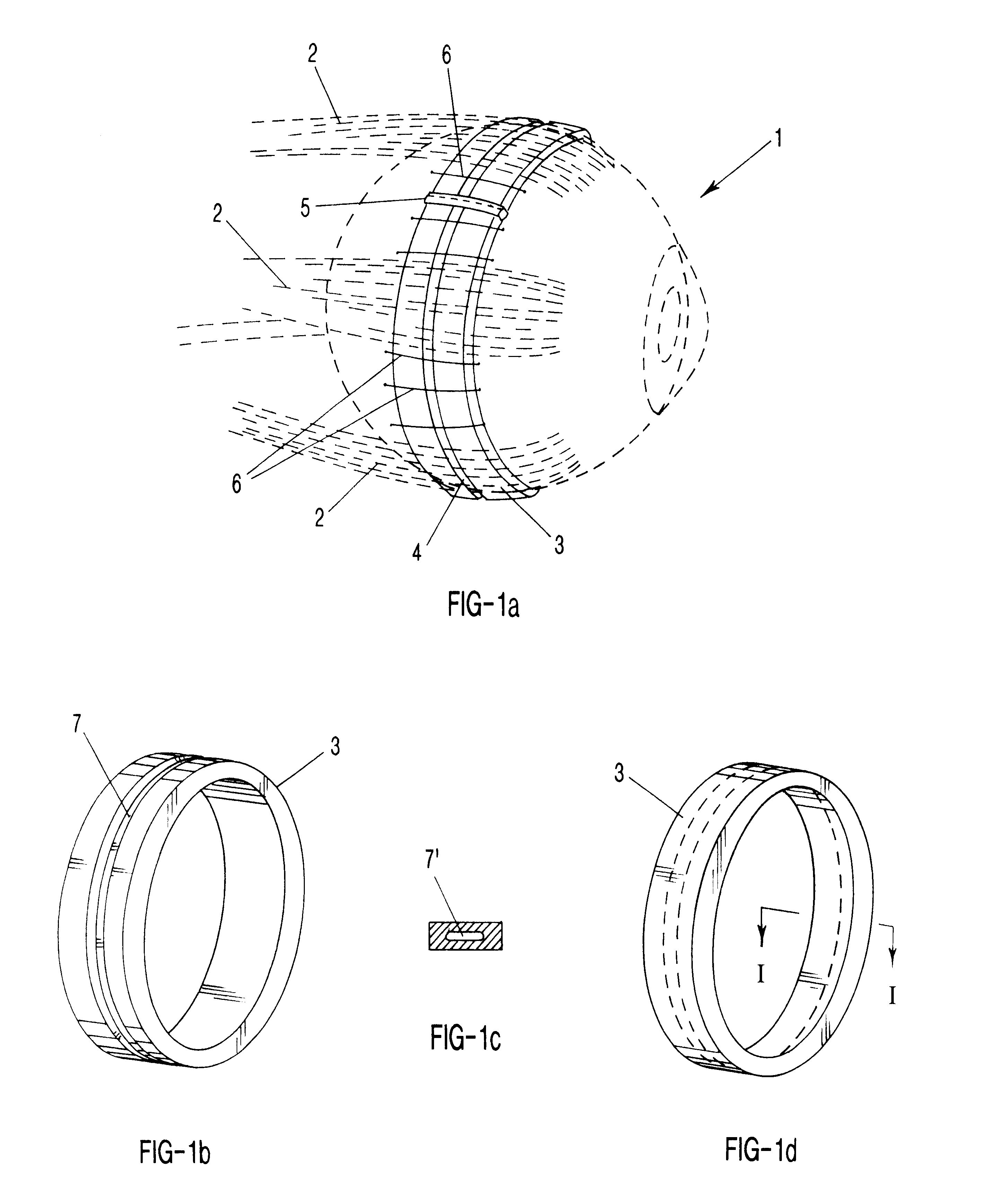
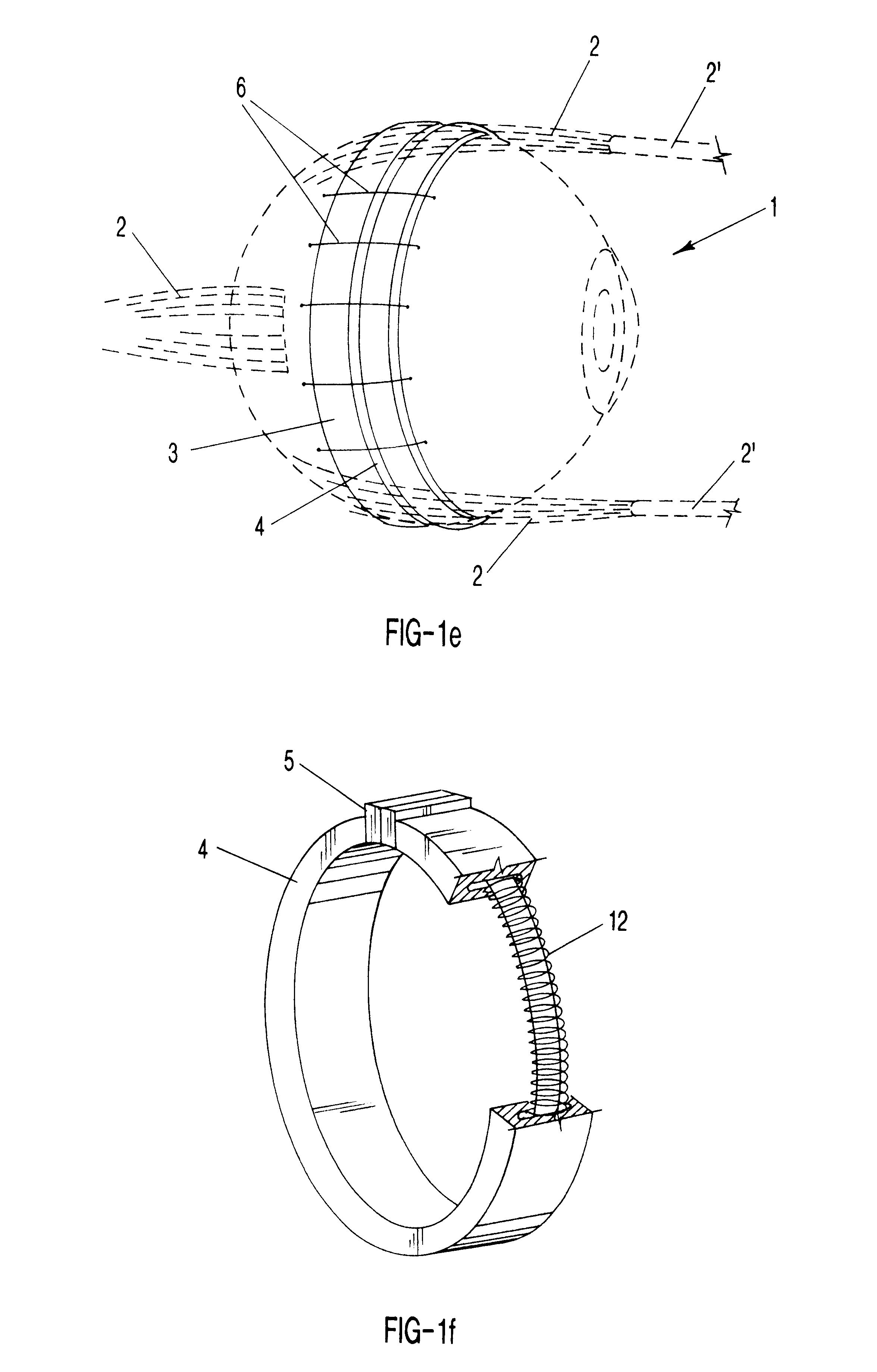
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
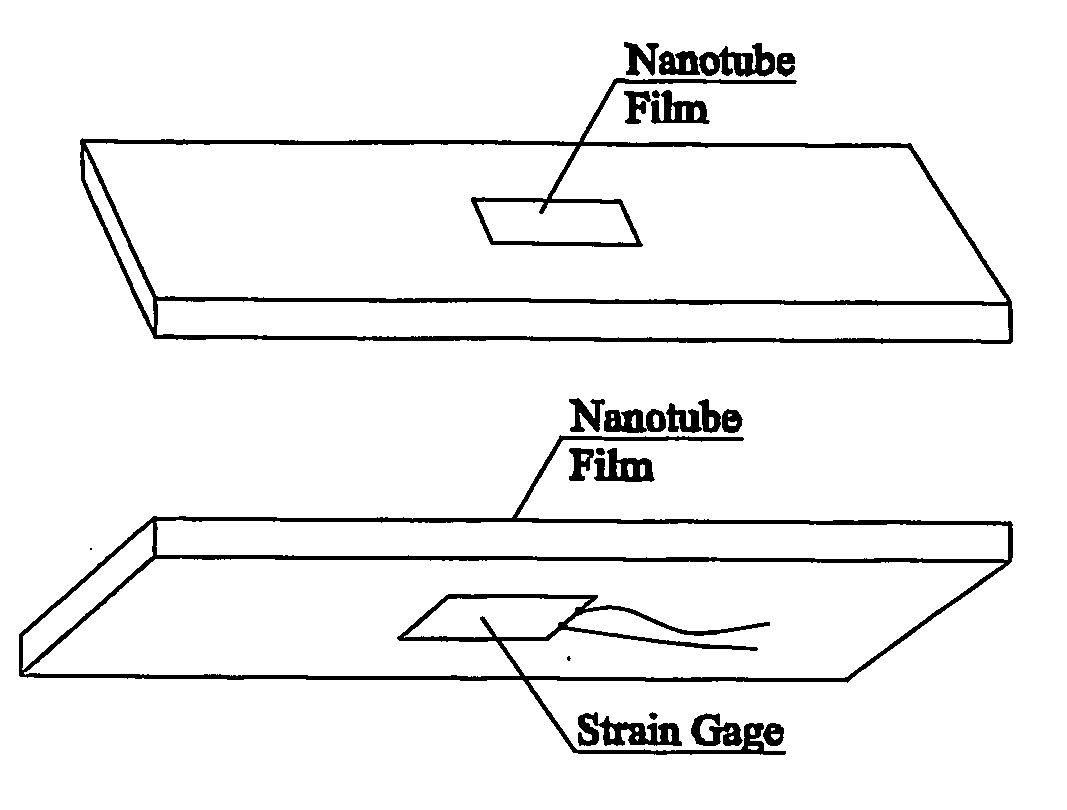
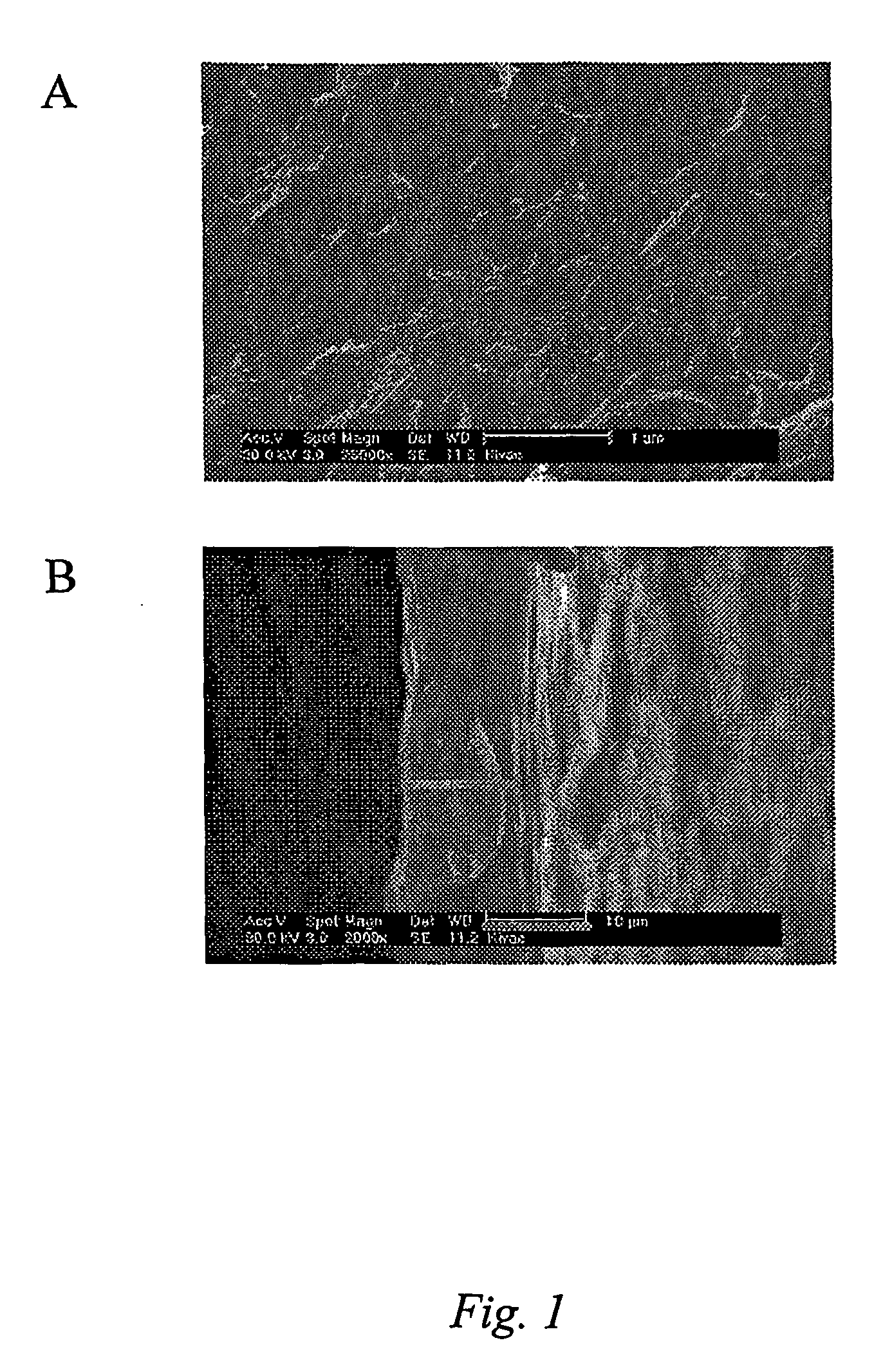
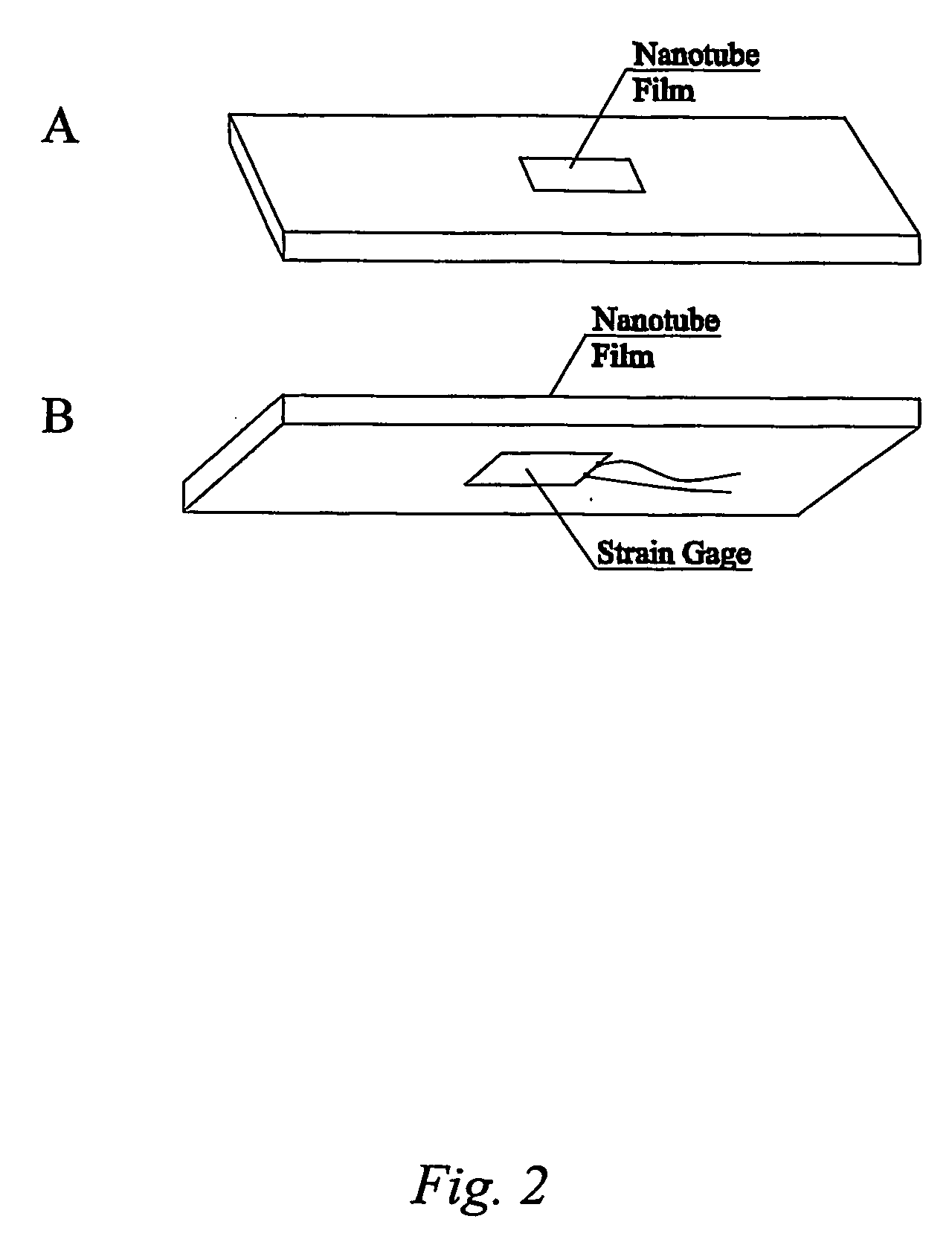
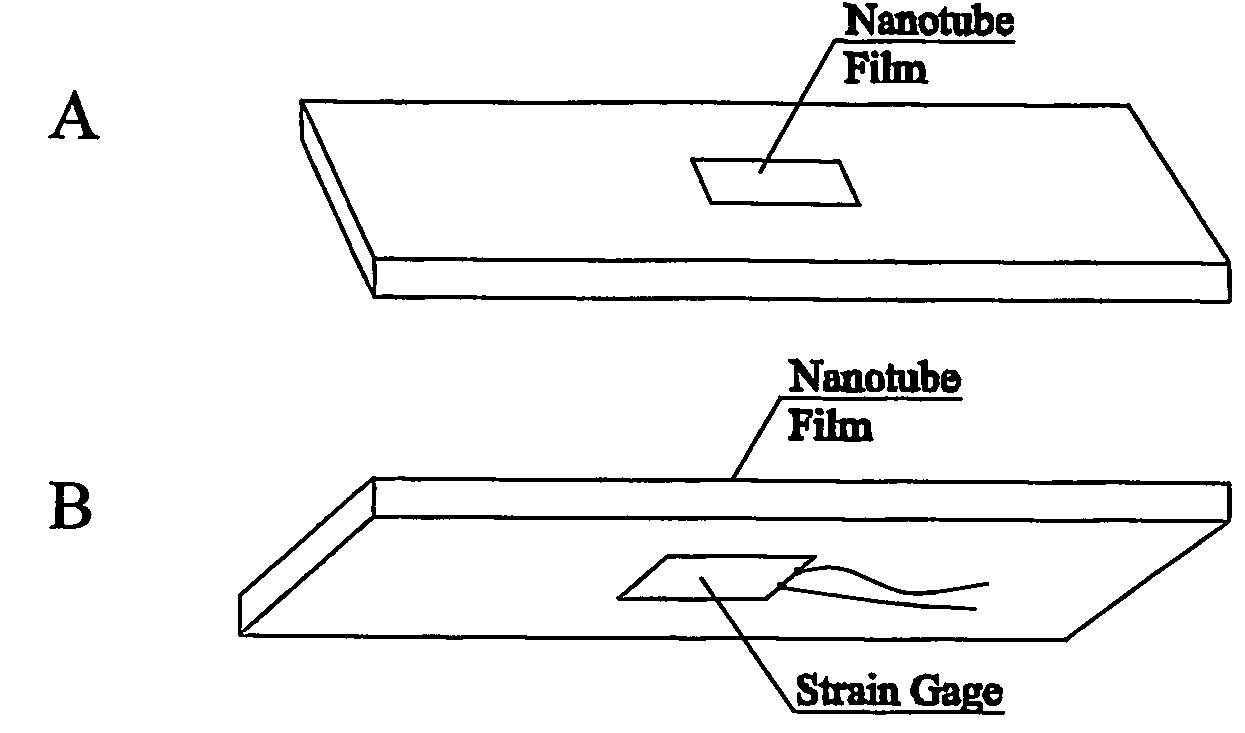
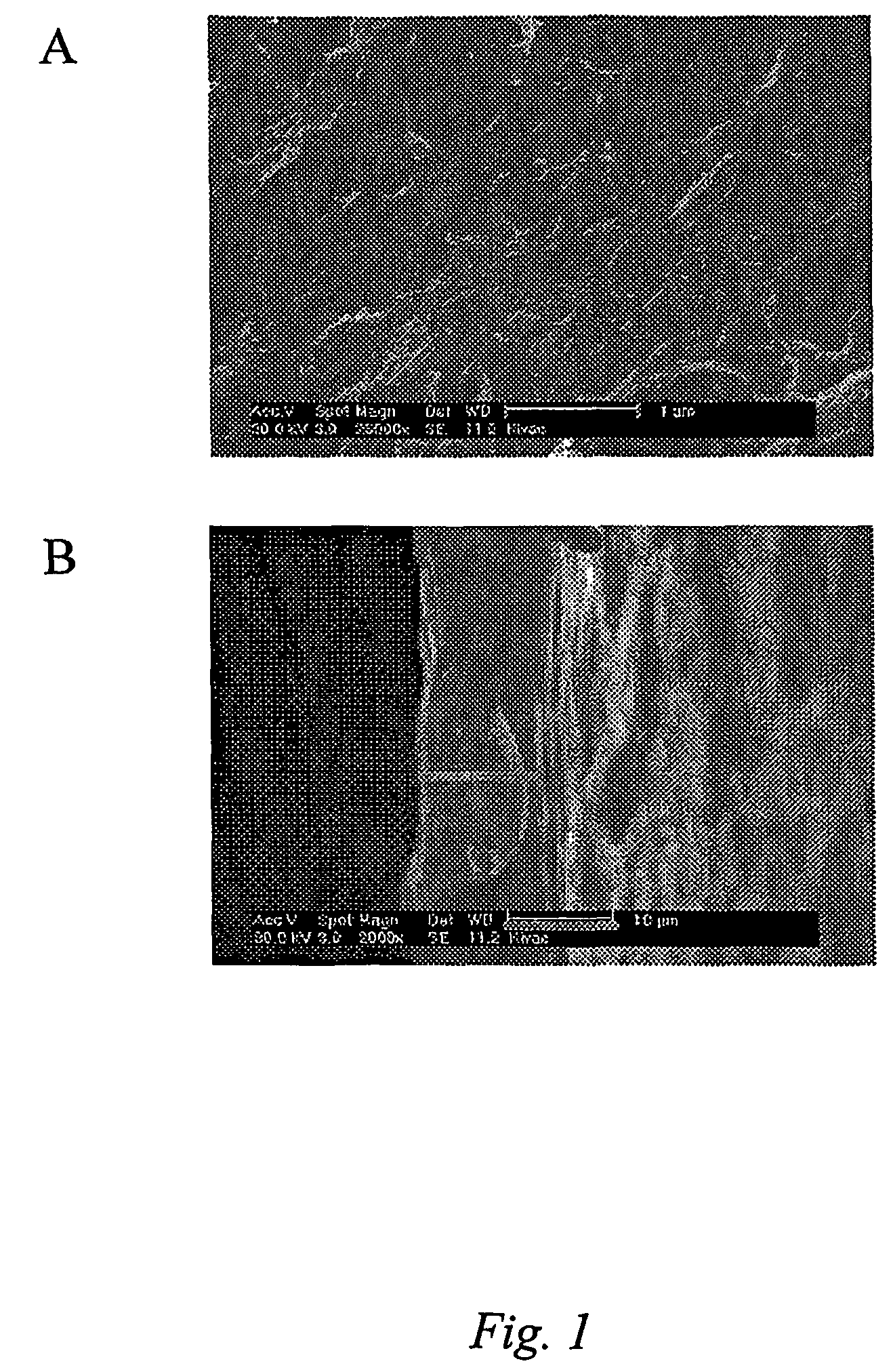
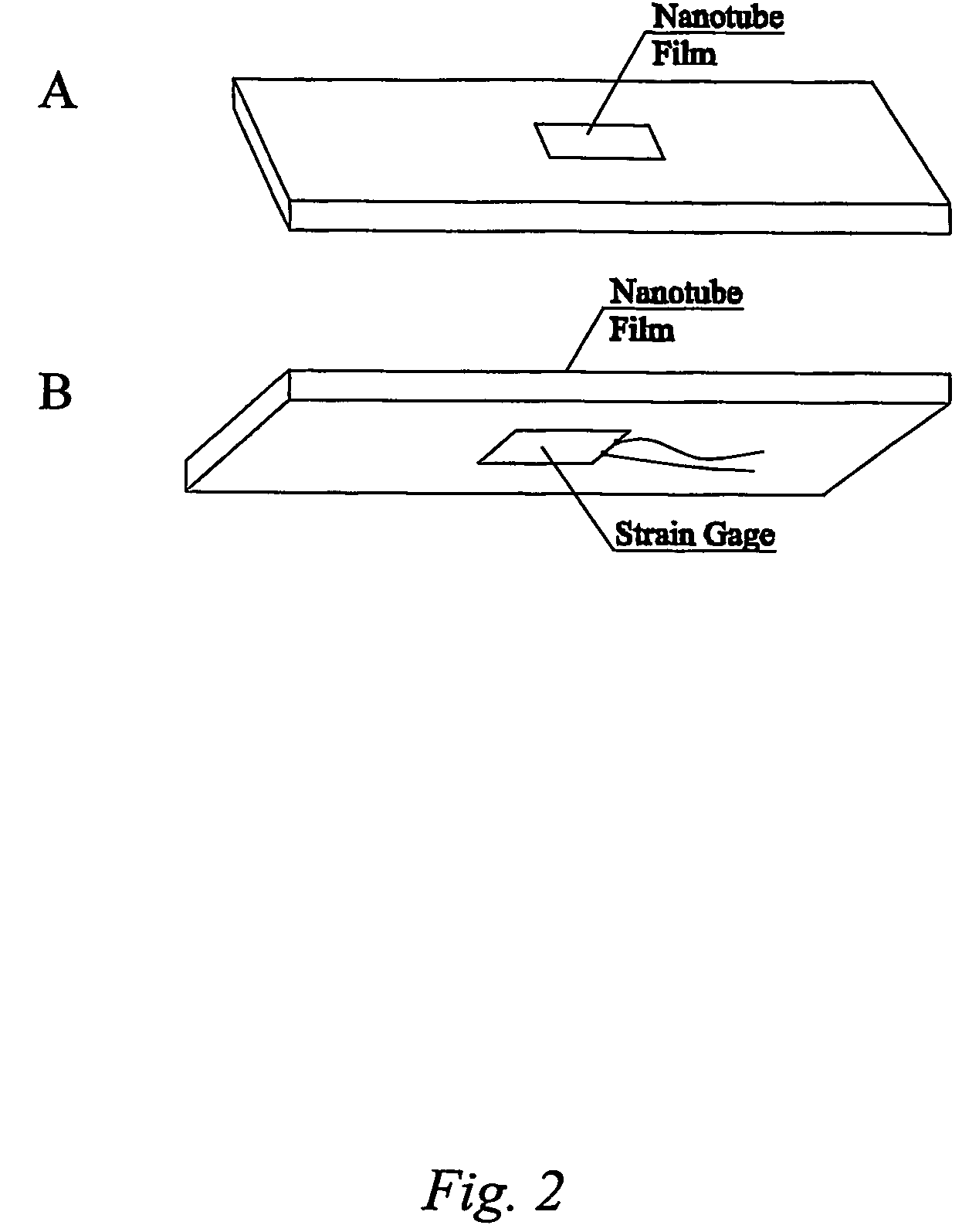
Smart materials: strain sensing and stress determination by means of nanotube sensing systems, composites, and devices
InactiveUS20060253942A1High strengthImproved thermal managementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by observing immersed bodiesThermal conductivitySmart material
The present invention is directed toward devices comprising carbon nanotubes that are capable of detecting displacement, impact, stress, and / or strain in materials, methods of making such devices, methods for sensing / detecting / monitoring displacement, impact, stress, and / or strain via carbon nanotubes, and various applications for such methods and devices. The devices and methods of the present invention all rely on mechanically-induced electronic perturbations within the carbon nanotubes to detect and quantify such stress / strain. Such detection and quantification can rely on techniques which include, but are not limited to, electrical conductivity / conductance and / or resistivity / resistance detection / measurements, thermal conductivity detection / measurements, electroluminescence detection / measurements, photoluminescence detection / measurements, and combinations thereof. All such techniques rely on an understanding of how such properties change in response to mechanical stress and / or strain.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Single-molecule selection methods and compositions therefrom
InactiveUS6762025B2Highly specific controlImprove complianceNanotechSugar derivativesNucleotideOligonucleotide
Single-molecule selection methods are provided for identifying target-binding molecules from diverse sequence and shape libraries. Complexes and imprints of selected target-binding molecules are also provided. The subject selection methods are used to identify oligonucleotide and nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties for use in pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, drug delivery, diagnostics, medical devices, cosmetics, agriculture, environmental remediation, smart materials, packaging, microelectronics and nanofabrication. Single oligonucleotide molecules with desirable binding properties are selected from diverse sequence libraries and identified by amplification and sequencing. Alternatively, selected oligonucleotide molecules are identified by sequencing without amplification. Nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties are identified by single-molecule selection from libraries of conjugated molecules or nucleotide-encoded nonnucleotide molecules. Alternatively, target-specific nonnucleotide molecules are prepared by imprinting selected oligonucleotide molecules into nonnucleotide molecular media. Complexes and imprints of molecules identified by single-molecule selection are shown to have broad utility as drugs, prodrugs, drug delivery systems, willfully reversible cosmetics, diagnostic reagents, sensors, transducers, actuators, adhesives, adherents and novel multimolecular devices.
Owner:MOLECULAR MACHINES
Control of power, loads and/or stability of a horizontal axis wind turbine by use of variable blade geometry control
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Control of power, loads and/or stability of a horizontal axis wind turbine by use of variable blade geometry control
The present invention relates to a design concept by which the power, loads and / or stability of a wind turbine may be controlled by typically fast variation of the geometry of the blades using active geometry control (e.g. smart materials or by embedded mechanical actuators), or using passive geometry control (e.g. changes arising from loading and / or deformation of the blade) or by a combination of the two methods. The invention relates in particular to a wind turbine blade, a wind turbine and a method of controlling a wind turbine.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
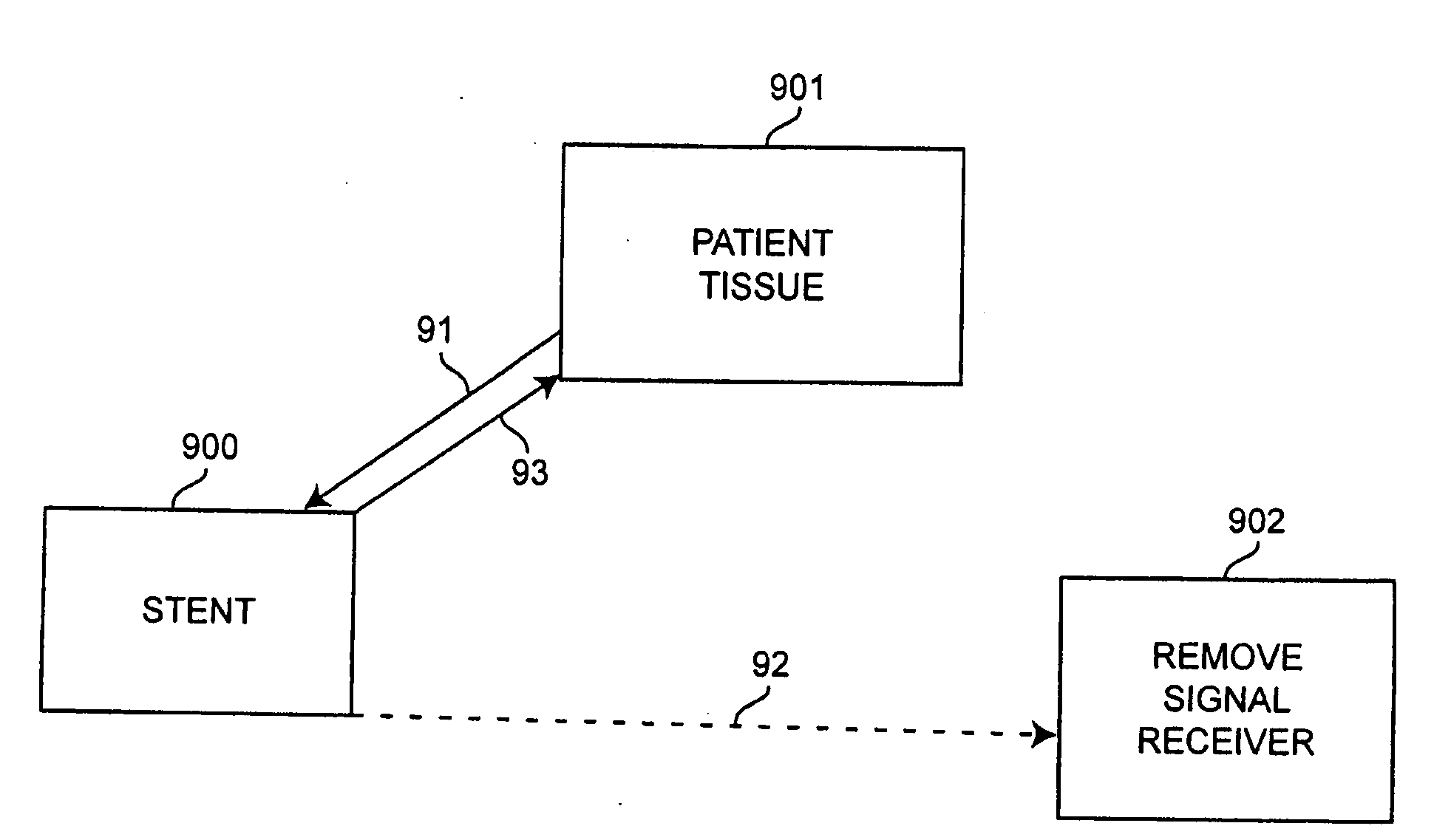
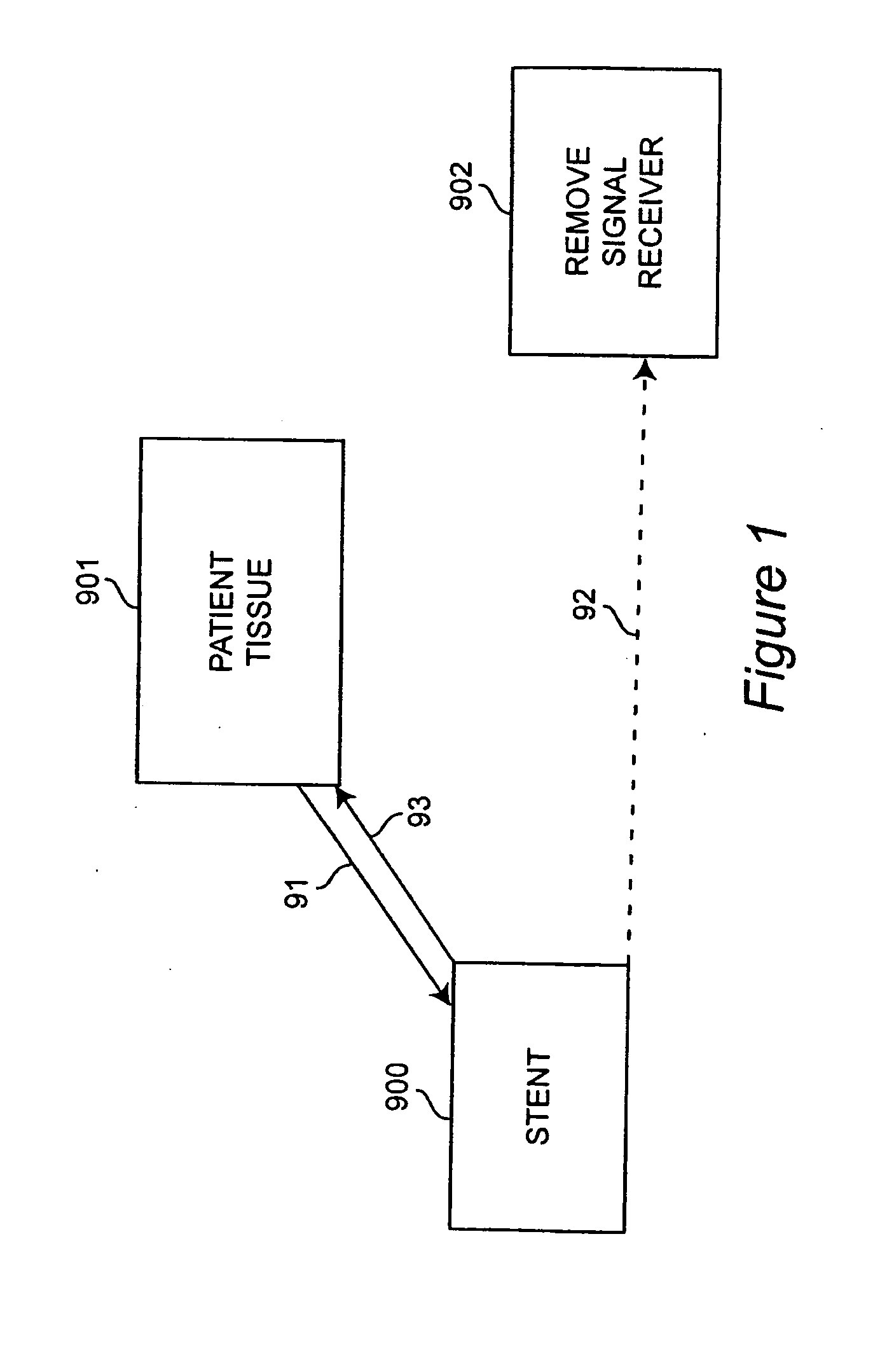
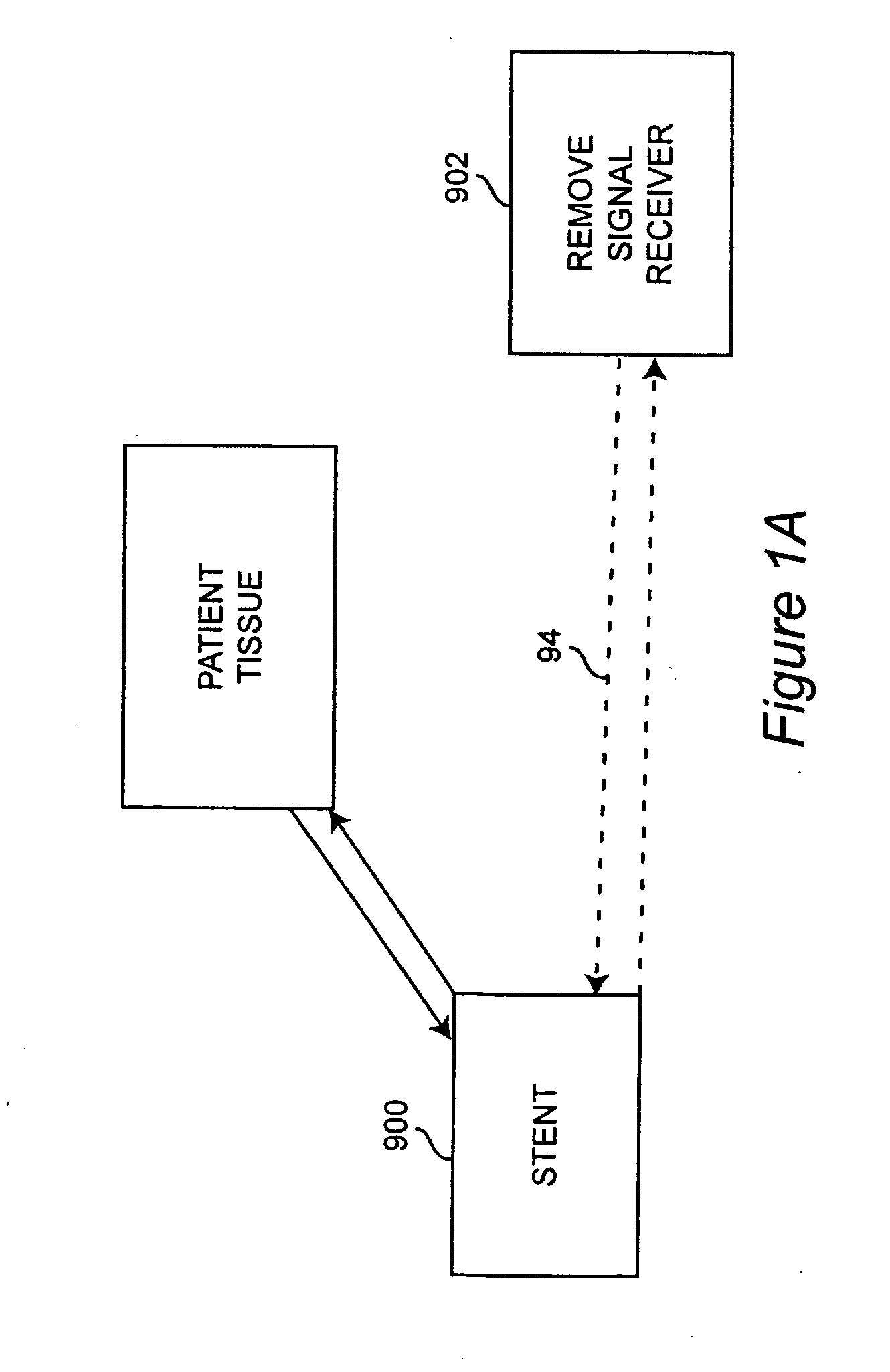
Self-sensing stents, smart materials-based stents, drug delivery systems, other medical devices, and medical uses for piezo-electric materials
InactiveUS20090036975A1Advanced technologyProvide solutionStentsElectrotherapyTreatment effectSelf sensing
A medically implantable stent comprising at least one piezo-electric material may be active, such as by one or more of: delivering an anti-coagulant or other therapeutic effect to a patient in which it is implanted; powering itself; and / or sending an outbound electronic signal to a remote device. When a stent can send such an outbound signal, a physician may non-invasively ascertain the condition of the tissue near the stent.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
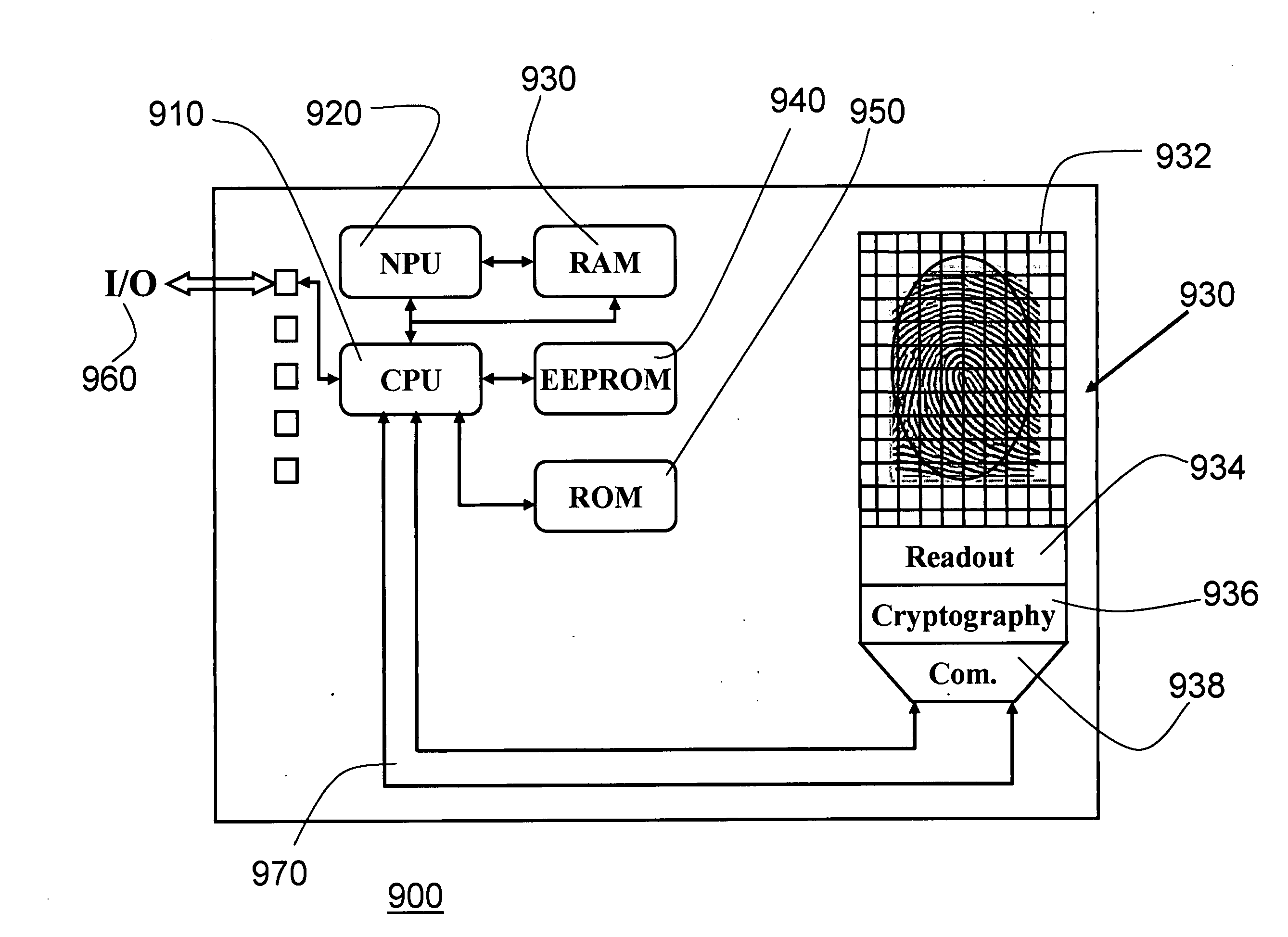
System and method for self-authenticating token
InactiveUS20090199004A1Facilitates secure transactionUser identity/authority verificationRecord carriers used with machinesPasswordSmart card
A secure token, possibly in the form of a smartcard, has a smart window with smart materials such as an electrophoretic or an electrochromic layer or assembly. When authenticated, such as by using biometrics or a password, the smart window layer is electronically pulsed, thereby transforming the once opaque layer to transparent and revealing information printed under, on or over the layer, or vice versa, transforming once transparent laminate to opaque and obfuscating printed information. In another embodiment, when the smart window layer is electronically pulsed to transform the once opaque laminate to transparent, a timer is started. At the end of a certain amount of time, the smart window layer is pulsed a second time, thereby transforming the layer back from transparent to opaque.
Owner:KRAWCZEWICZ MARK STANLEY +2
Handheld Computer Interface with Haptic Feedback
InactiveUS20110121953A1Input/output for user-computer interactionIndication apparatusHand Held ComputerEngineering
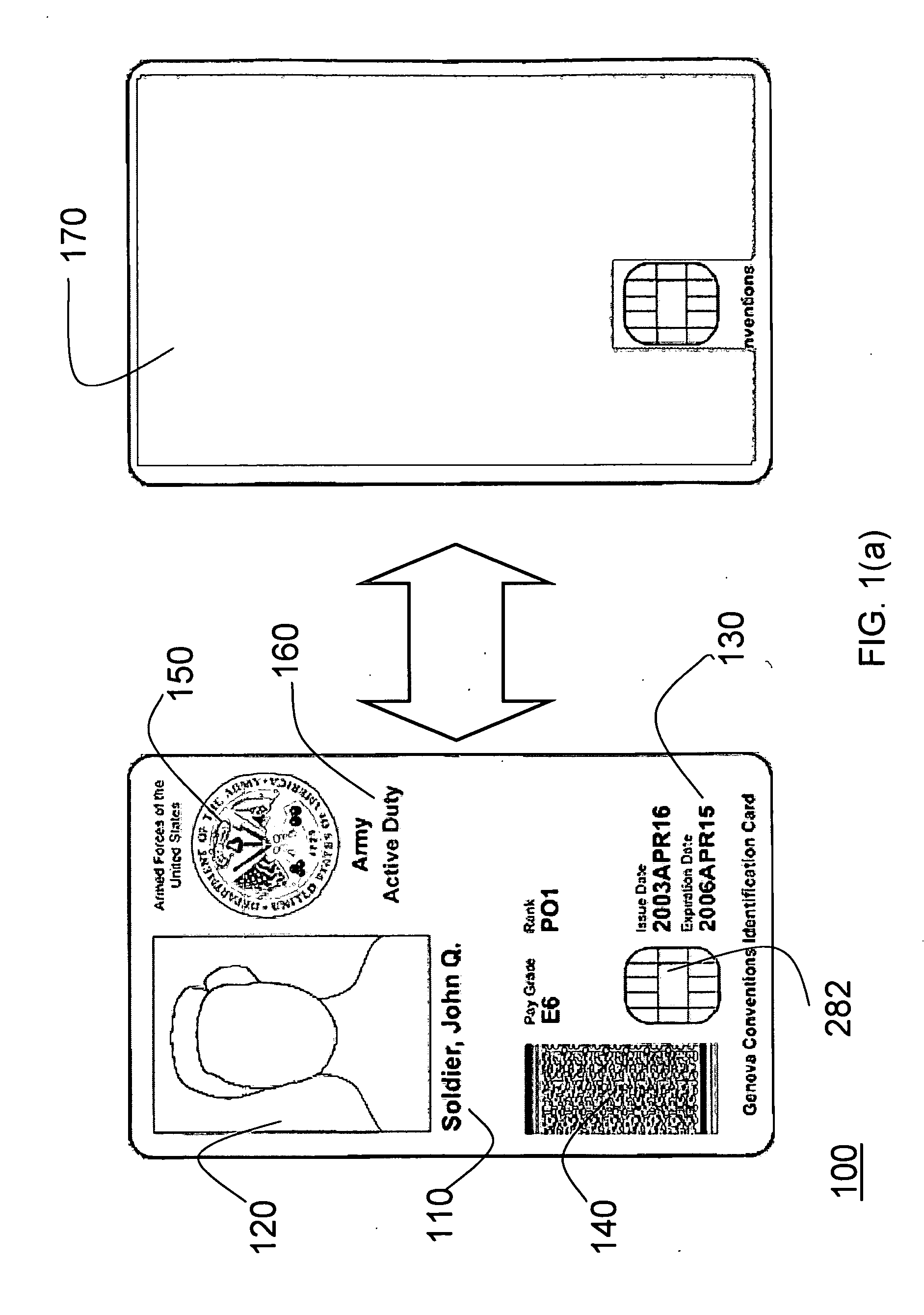
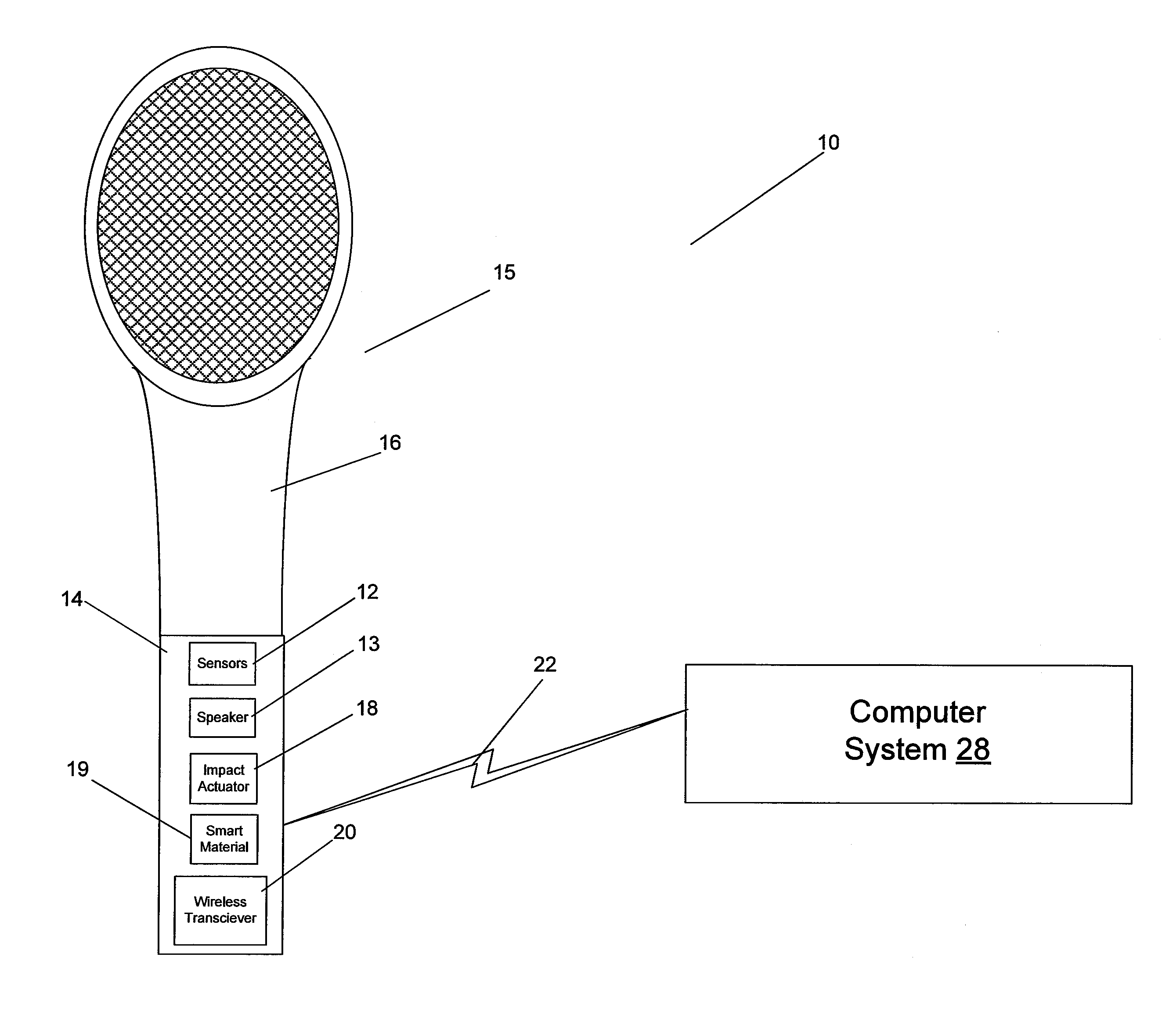
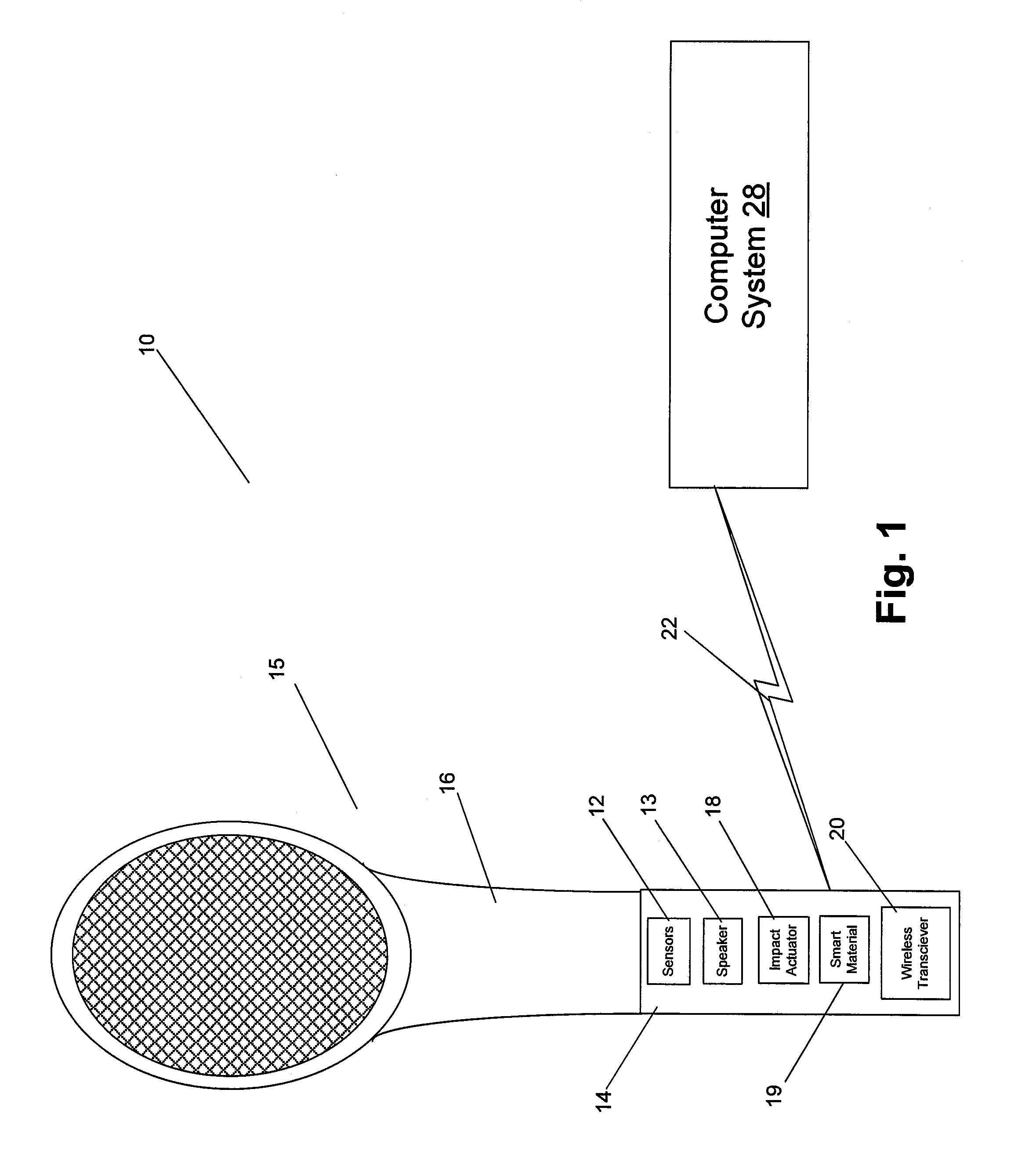
Various systems, devices, and methods are provided for generating an impact and / or surface haptic effect for a handheld computer interface such as a video game controller. For example, the handheld computer interface may include a handle coupled to an impact actuator. The impact actuator includes a movable mass and an end stop. The impact actuator may receive a haptic effect signal and in response cause the mass to contact the end stop to generate a haptic effect. A smart material that outputs a surface haptic effect may be coupled to a surface of the handle such that the surface haptic effect is output substantially from the smart material rather than the handle. The handle may be coupled to an end piece having a shape that simulates an object such as a tennis racket, golf club, or other object.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
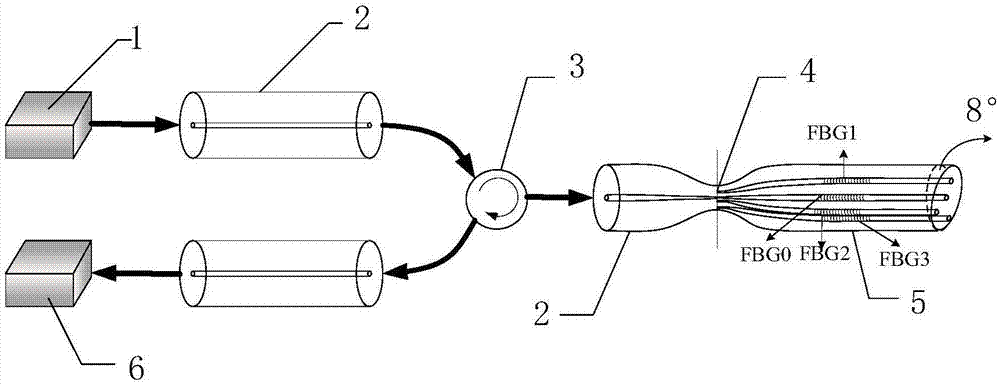
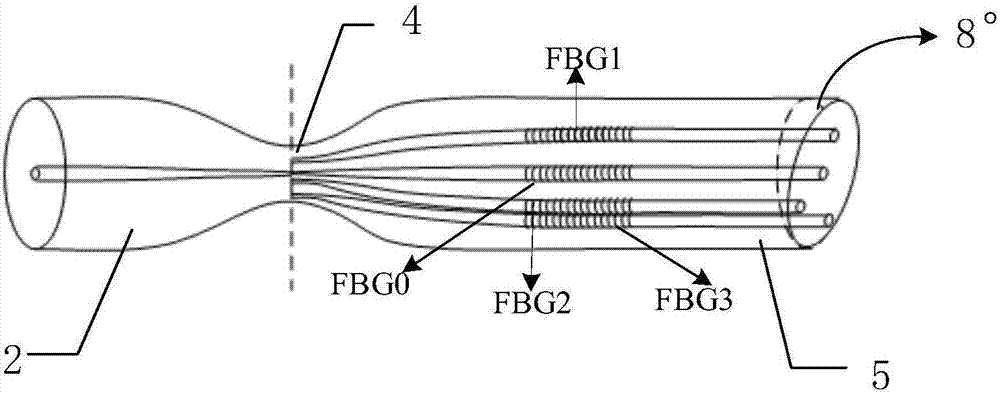
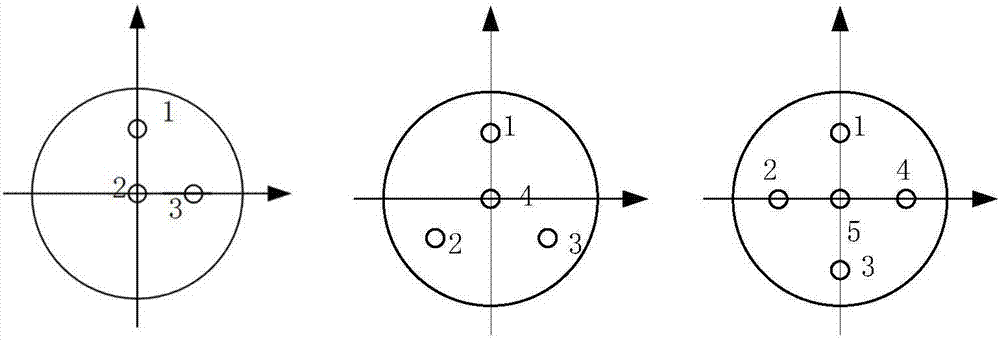
Multi-core fiber bragg grating (FBG) universal bending sensor
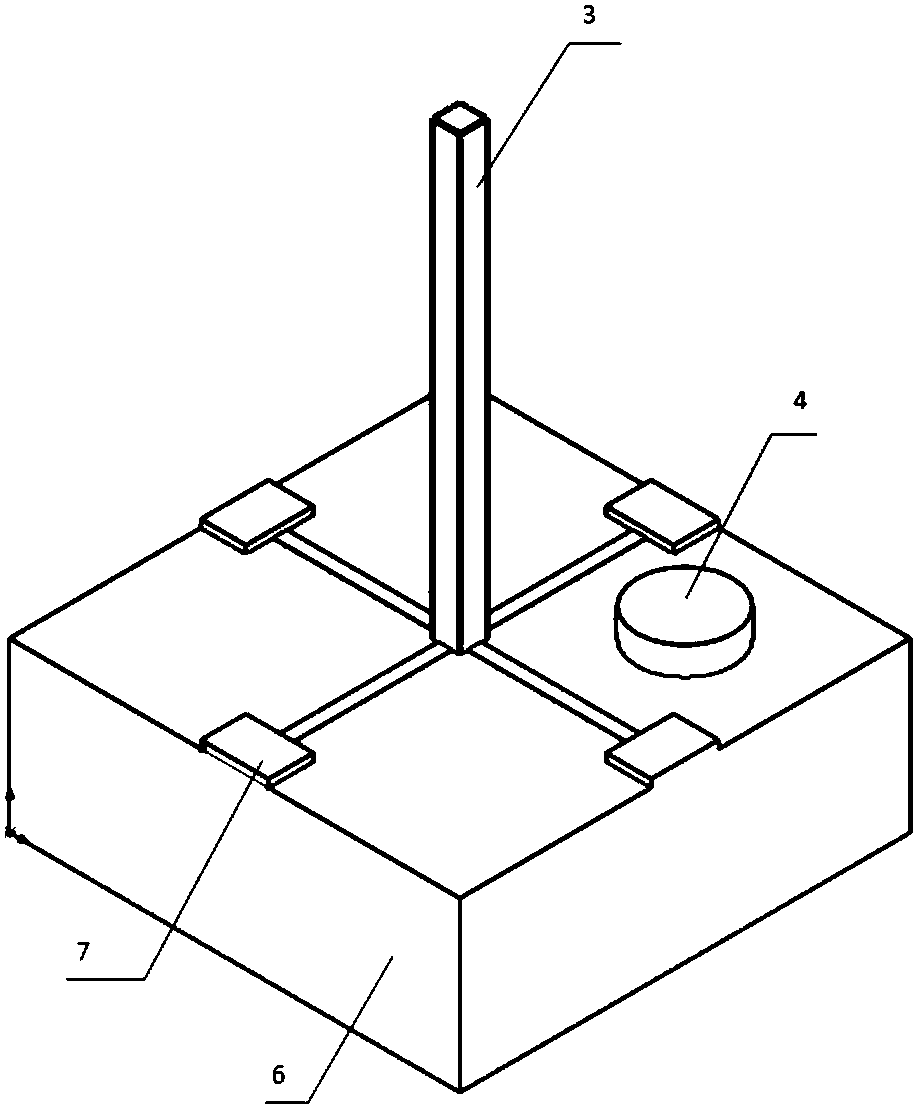
The invention belongs to the fiber sensing technical field, and specifically relates to a multi-core fiber bragg grating (FBG) universal bending sensor; the multi-core fiber bragg grating (FBG) universal bending sensor is suitable for smart material and structure on-line detection and analysis, can control and monitor space structure space three dimensional positions and attitudes, and is formed by using the multi-core fiber bragg grating (FBG) as the basic sensing unit; the multi-core fiber bragg grating (FBG) universal bending sensor comprises multi-core fibers including one center fiber core, and the resting fiber cores are arranged around the center fiber core in quadrature distribution or symmetrical distribution; each fiber core in the same transverse position of the multi-core fiber uses the same phase mask slice to simultaneously expose the FBG; the central wavelengths of various Bragg gratings on the multi-core fiber are different; the multi-core fiber bragg grating (FBG) universal bending sensor can monitor various reflection wavelength changes of the multi-core FBG, thus measuring the bending amplitude and direction angles.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
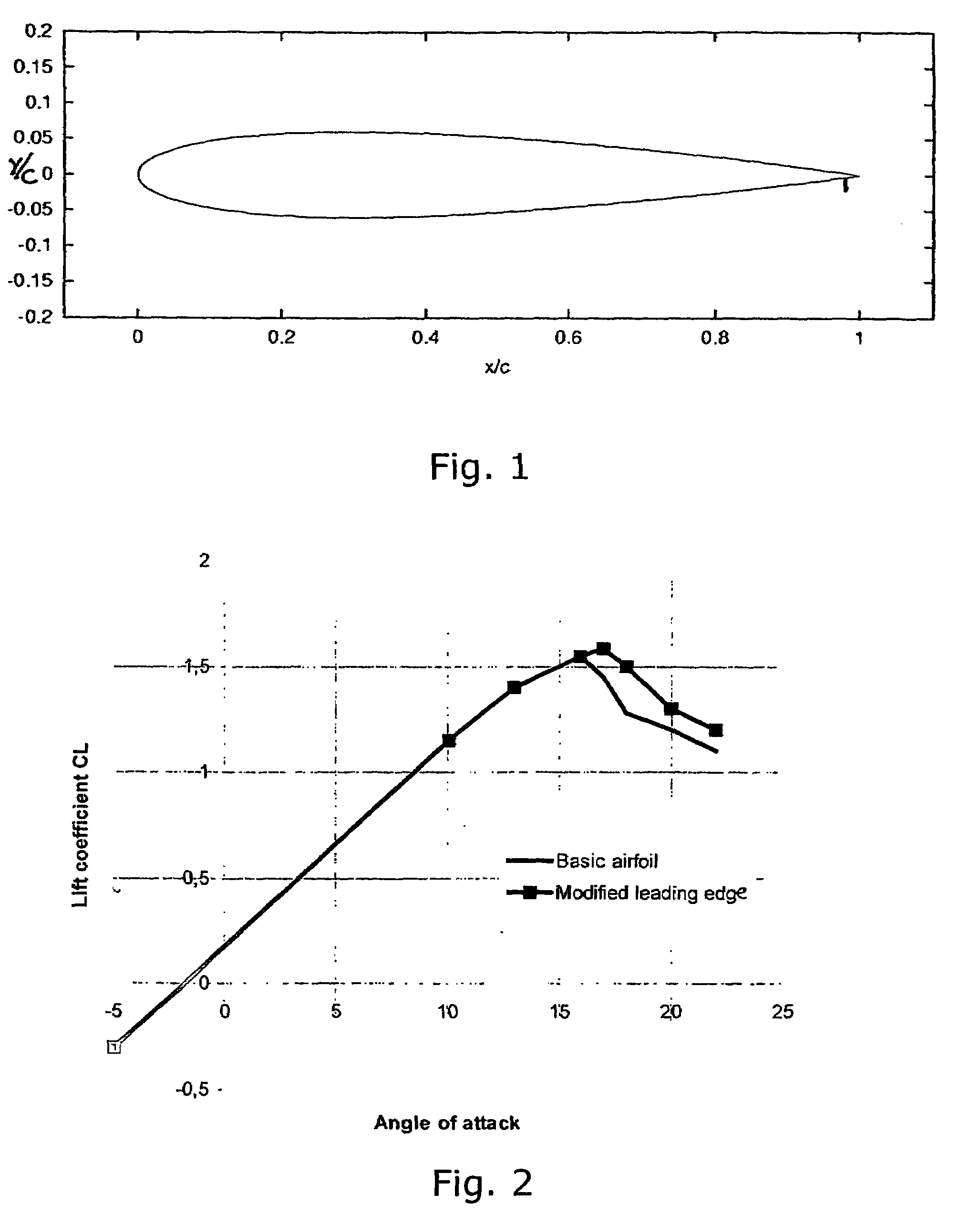
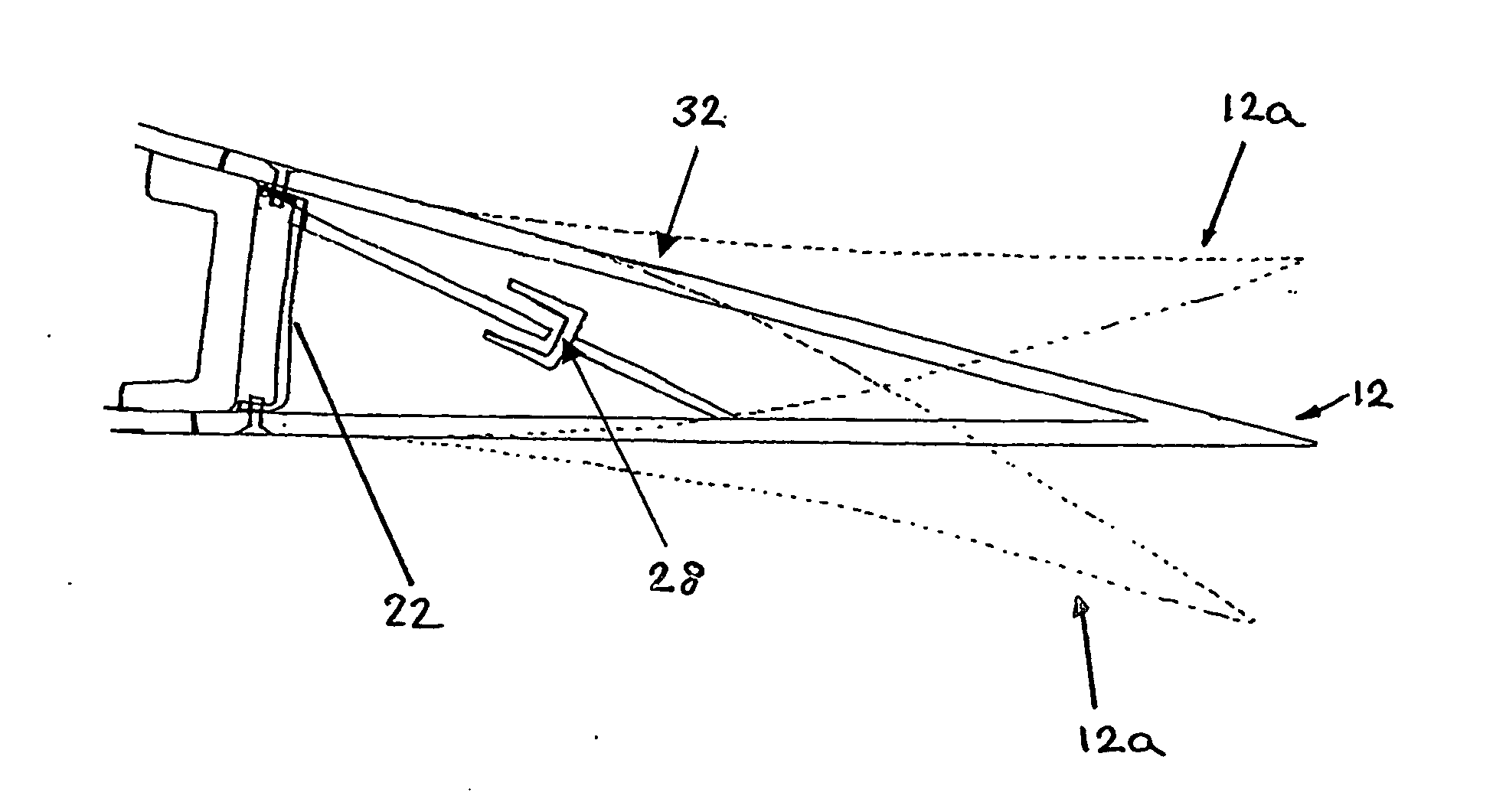
Self-adapting morphing trailing edge based on SMA
InactiveCN101693467ARealize continuous deformationImprove aerodynamicsHeat reducing structuresMorphing wingPower flow
The invention relates to a self-adapting morphing trailing edge based on SMA, belonging to a self-adapting morphing wing which combines intellectual materials and structures. The wing is divided into 2-5 trailing edge segments, the adjacent trailing edge segments are connected by joints (5, 6 and 7) arranged at wing ribs, a deflection driving mechanism is arranged between the adjacent trailing edge segments, and the deflection of the entire trailing edge is realized by accumulative effects of the trailing edge segments. The self-adapting morphing wing is characterized in that the deflection driving mechanism comprises an upper SMA wire (10), a lower SMA wire (11) and a current excitation unit (15) which are respectively connected with the adjacent trailing edge segments. The self-adapting morphing trailing edge has the advantages of simple structure and easy control and achieves the goal of quick, stable and accurate pre-deformation of the trailing edge.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
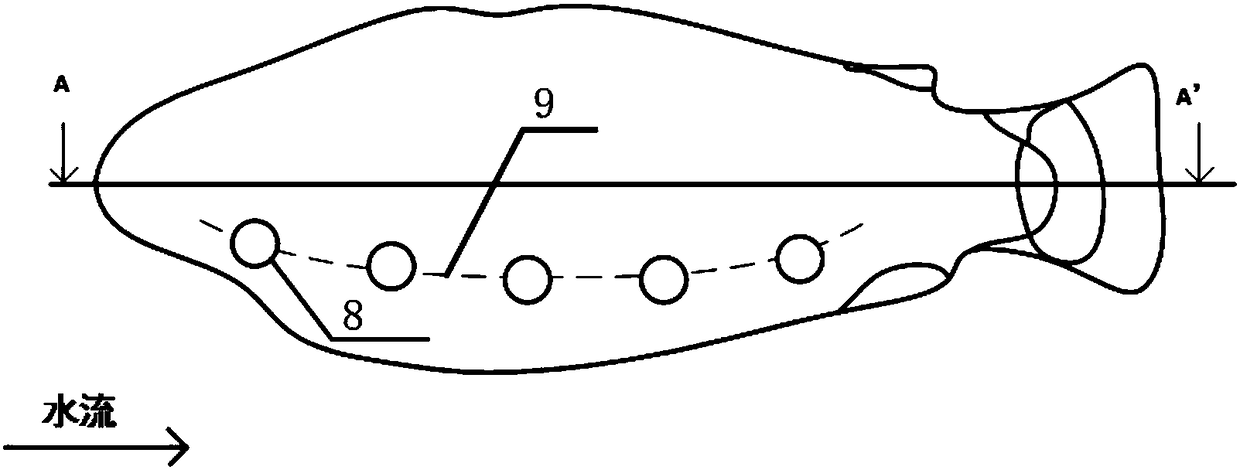
Underwater bionic lateral line sensing array
ActiveCN108362334AAvoid being affected by the surrounding large flow field environmentAccurate measurementHydrodynamic testingTransducerWater flow
An underwater bionic lateral line sensing array includes a bionic lateral line array structural body, runner water holes, an inner channel and a plurality of water current and water pressure compositesensors, wherein each water pressure composite sensor includes cilia made of electric reactive polymer smart material, a pressure transducer, electrodes and a pedestal. The bionic lateral line arraystructural body is therein provided with the inner channel in the length direction. The water current and water pressure composite sensors are arranged in the inner channel. The runner water holes communicating with the inner channel are arranged in one side of the bionic lateral line array structural body. The pedestals are arranged in the inner channel. Four electrodes are arranged on each pedestal. Each pedestal is provided with the cilia made of electric reactive polymer smart material and the pressure transducer is arranged on the pedestal. The underwater bionic lateral line sensing arrayhas a fish lateral line simulating system and senses water current and water pressure change at the same time, is high in anti-interference capability, high in sensibility and precision, and can provide measurement basis for accurate sensing of water environment change in the surrounding of a lateral line system.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing composite microspheres with surface functional group and controllable function
InactiveCN101053811ASimple methodImprove efficiencyMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationPolyelectrolyteMicrosphere
The invention relates to a preparation method of microsphere with surface functional group and controllable functionality, and to the field of nano-technology. The invention firstly uses the microsphere with the surface having ionic functional group as a starting shuttering to coat layer of layer the nano-particle with certain functionality or polyelectrolyte by the power of static electrification to obtain the composite microsphere with surface functional group and controllable functionality. The microsphere with surface functional group and controllable functionality prepared by the invention, of which the size is controllable, has single functionality or multiple functionality, can respond to the circumstance of magnetism, light and pH value, and the response intensity is controllable. Furthermore, the surface can have different functional groups. The invention can get an extensive use in the fields of biology medical carrier, bioanalysis and intelligent material, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation of shape memory micro-nano composite material and application of shape memory micro-nano composite material in 4D (four-dimensional) printing
The invention discloses preparation of a shape memory micro-nano composite material and application of the shape memory micro-nano composite material in 4D (four-dimensional) printing. The invention relates to the field of the 4D printing of intelligent materials, in particular to the field that the shape memory micro-nano composite material can be applied to a 4D printing technology. The invention aims to solve the technical problem of difficulty in realizing the 4D printing of the shape memory micro-nano composite material. The shape memory micro-nano composite material disclosed by the invention is formed by means of mixing a hydrogen-abstracting type photoinitiator, functional micro-nano particles, a substance containing active hydrogen in a molecular chain and an organic solvent with a low boiling point and high volatility according to a certain mass, and performing ultrasonic treatment. The composite material is applied to the 4D printing technology by means of controlling a motion direction, a motion speed and an applied pressure of a three-dimensional movement platform on an X-axis, a Y-axis and a Z-axis through software, applying pressure force on a high-pressure dispensing needle cylinder equipped with a micro-needle head through an air pump, and constructing a required three-dimensional structure by means of casting according to a constructed model. The shape memory micro-nano composite material disclosed by the invention is applied to the 4D printing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Printable semiconductor structures and related methods of making and assembling
ActiveCN101632156APrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSpatial OrientationsSemiconductor structure
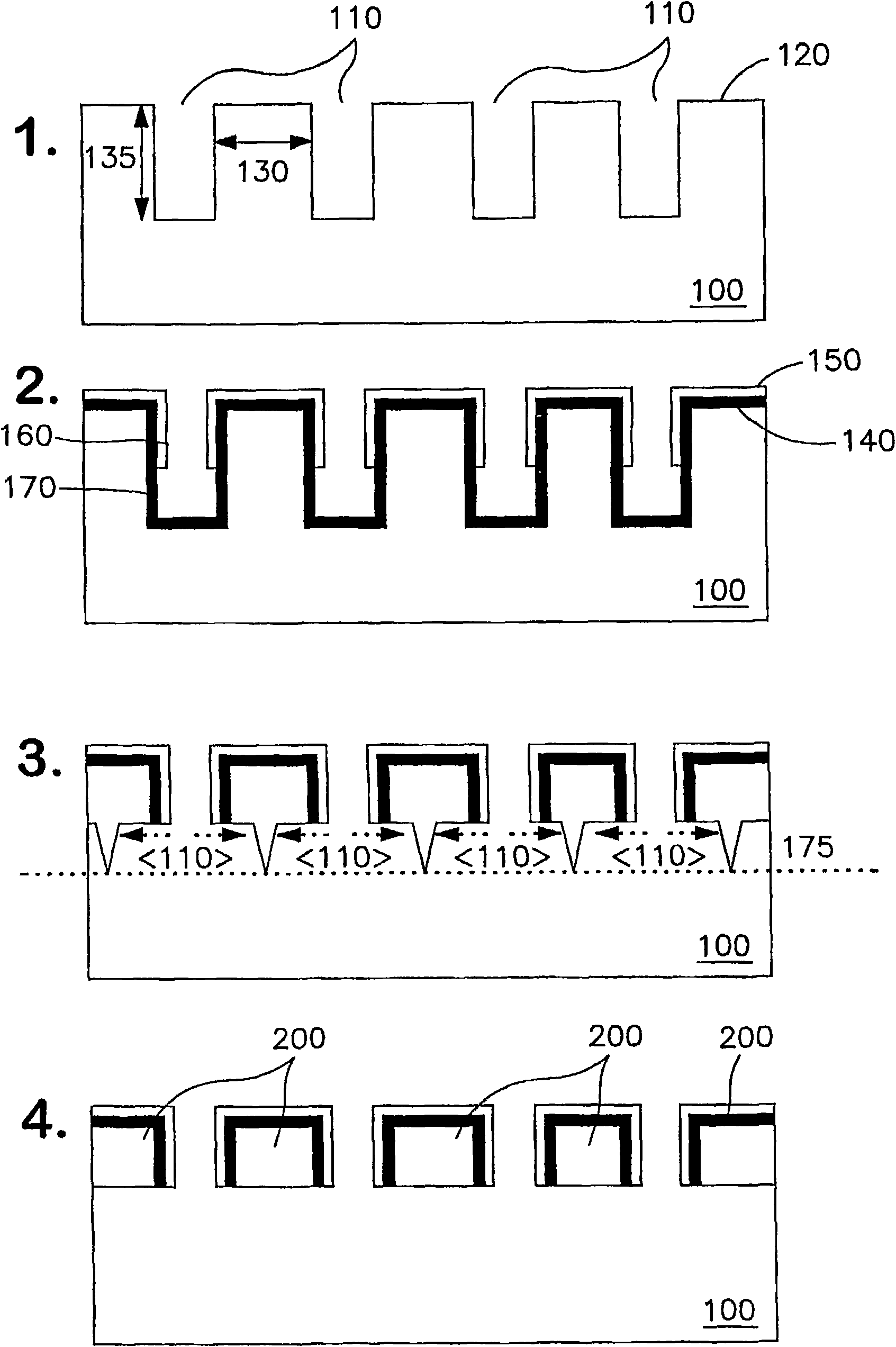
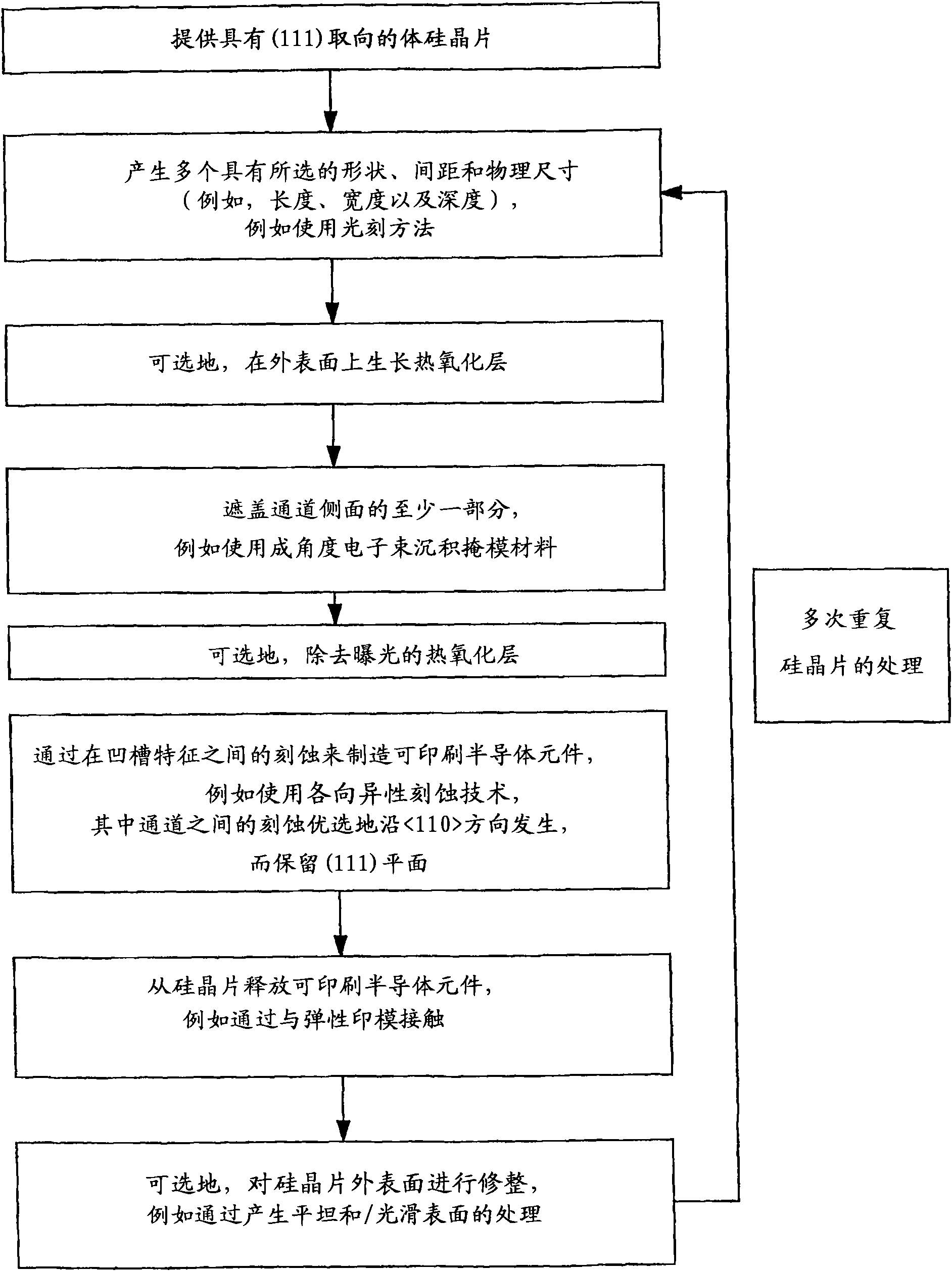
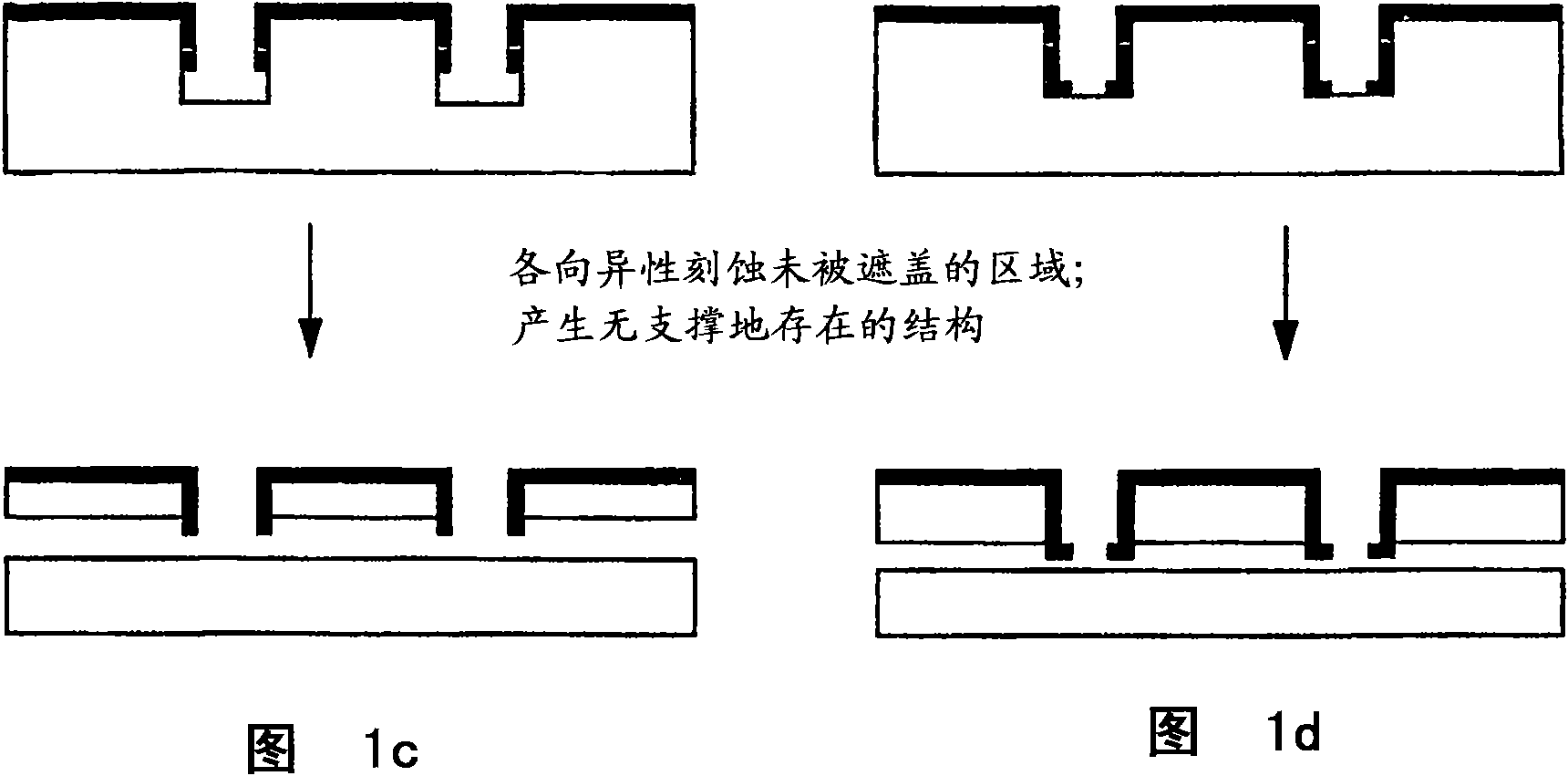
The present invention provides a high yield pathway for the fabrication, transfer and assembly of high quality printable semiconductor elements having selected physical dimensions, shapes, compositions and spatial orientations. The compositions and methods of the present invention provide high precision registered transfer and integration of arrays of microsized and / or nanosized semiconductor structures onto substrates, including large area substrates and / or flexible substrates. In addition, the present invention provides methods of making printable semiconductor elements from low cost bulk materials, such as bulk silicon wafers, and smart-materials processing strategies that enable a versatile and commercially attractive printing-based fabrication platform for making a broad range of functional semiconductor devices.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Preparation method of reversible photoinduced deformation liquid crystal high polymer and carbon nano tube composite thin film
InactiveCN102615885AImprove performanceImprove conductivityGlass/slag layered productsNon-linear opticsUltraviolet lightsThin membrane
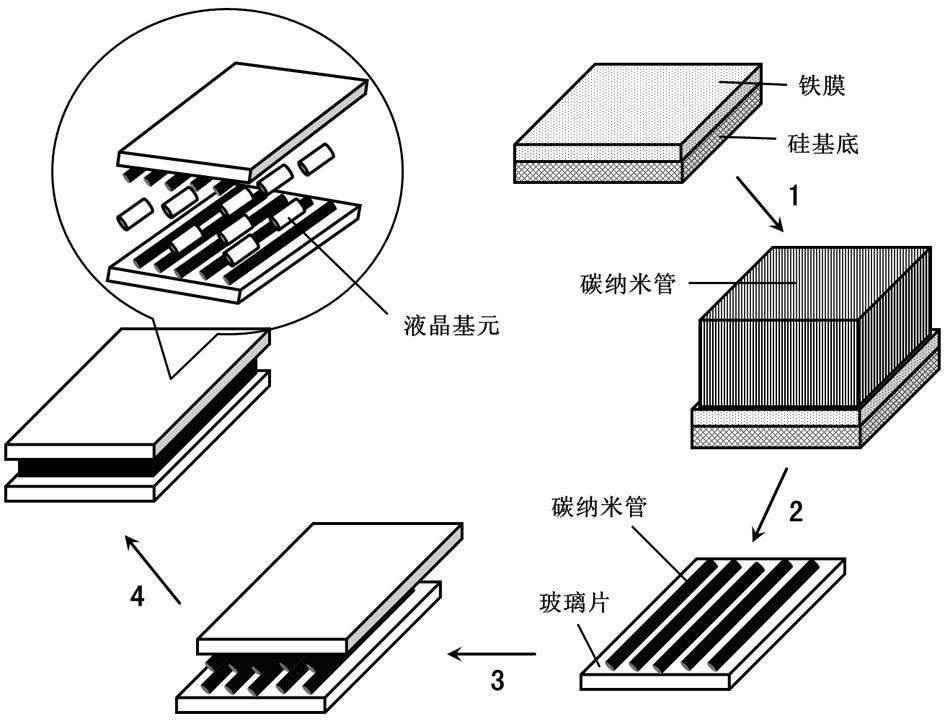
The invention belongs to the technical field of an intelligent material and particularly relates to a reversible photoinduced deformation liquid crystal high polymer and carbon nano tube composite thin film and a preparation method thereof. A liquid crystal high polymer in the composite thin film is a cross-linked type liquid crystal elastic body containing a photosensitive azobenzene liquid crystal element; and a carbon nano tube is a highly and sequentially oriented carbon nano tube thin film. In the composite thin film, a carbon nano tube orienting structure induces the liquid crystal element to be oriented along the axial direction of the carbon nano tube; and other orienting layers are not needed. When the prepared composite thin film is in ultraviolet illumination, the composite thin film is bent towards lights and can be recovered to the original state when the composite thin film is irradiated by visible lights. Reversible deformation generated by alternatively illuminating the composite thin film by ultraviolet lights and visible lights can be repeated for hundreds of times and has no obvious attenuation and fatigue. Moreover, the introduction of the carbon nano tube greatly enhances the mechanical performance of the material, and the material has excellent electric performance.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Control of power, loads and/or stability of a horizontal axis wind turbine by use of variable blade geometry control
InactiveCN1780983AReduce loadReduce aerodynamic noiseWind motor controlEngine fuctionsTurbine bladeHorizontal axis
The present invention relates to a design concept according to which, by using active geometry control (for example, smart materials or embedded mechanical actuators), or using passive geometry control (for example caused by the loading and / or deformation of the blade) changes), or a combination of these two methods, allows rapid changes in the blade geometry to control the power, load and / or stability of the wind turbine. In particular the invention relates to a wind turbine blade, a wind turbine and a method of controlling a wind turbine.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
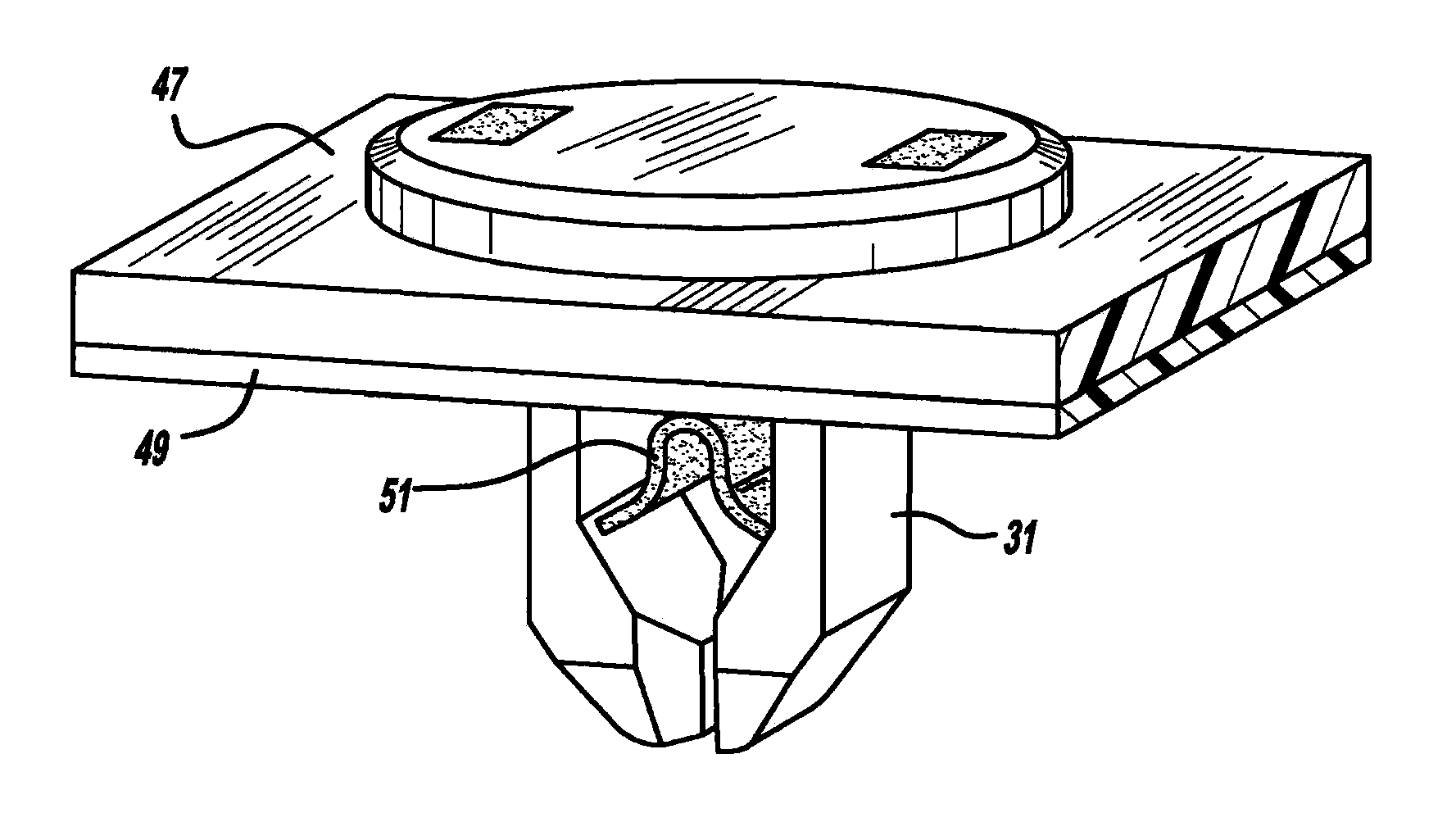
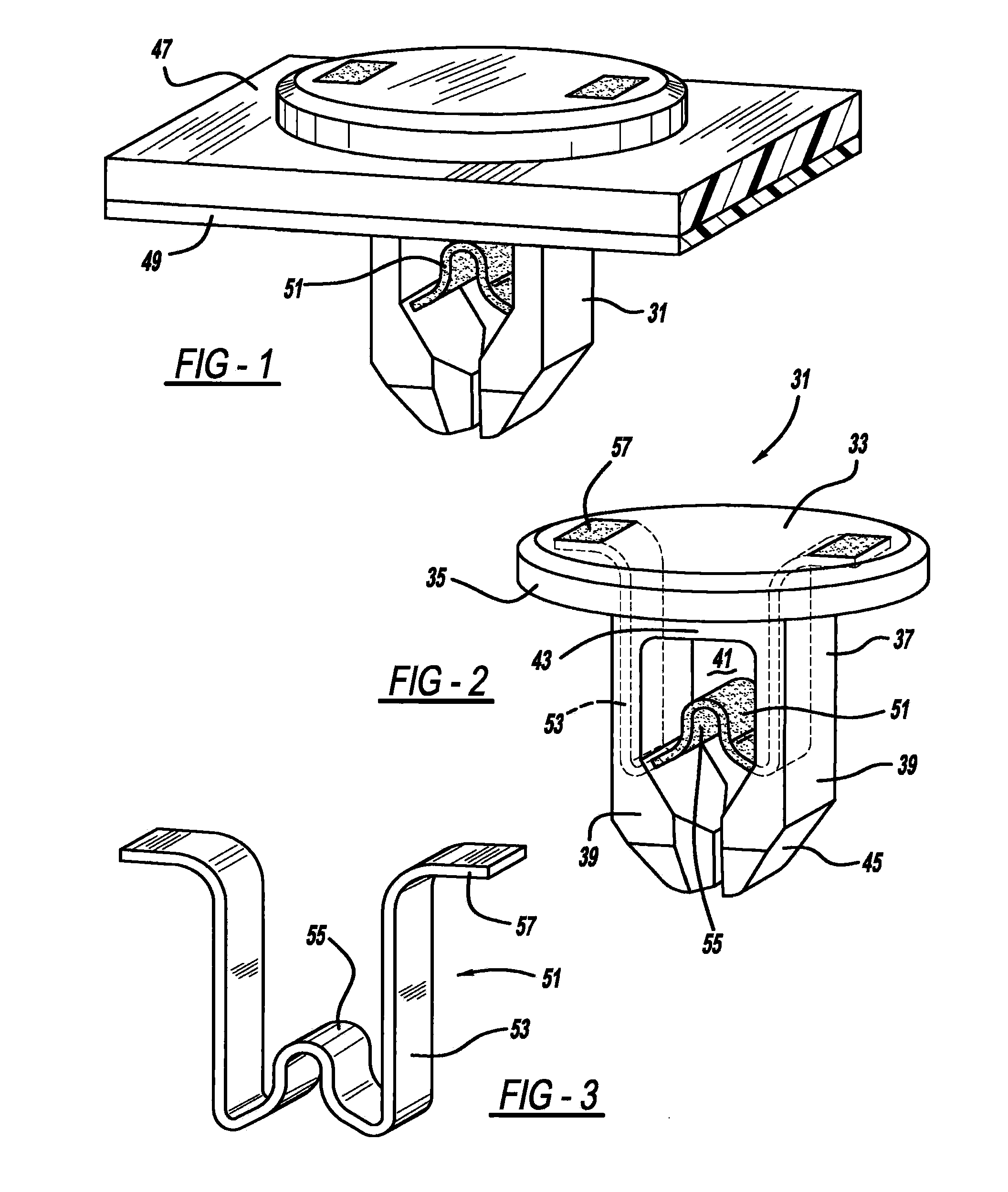
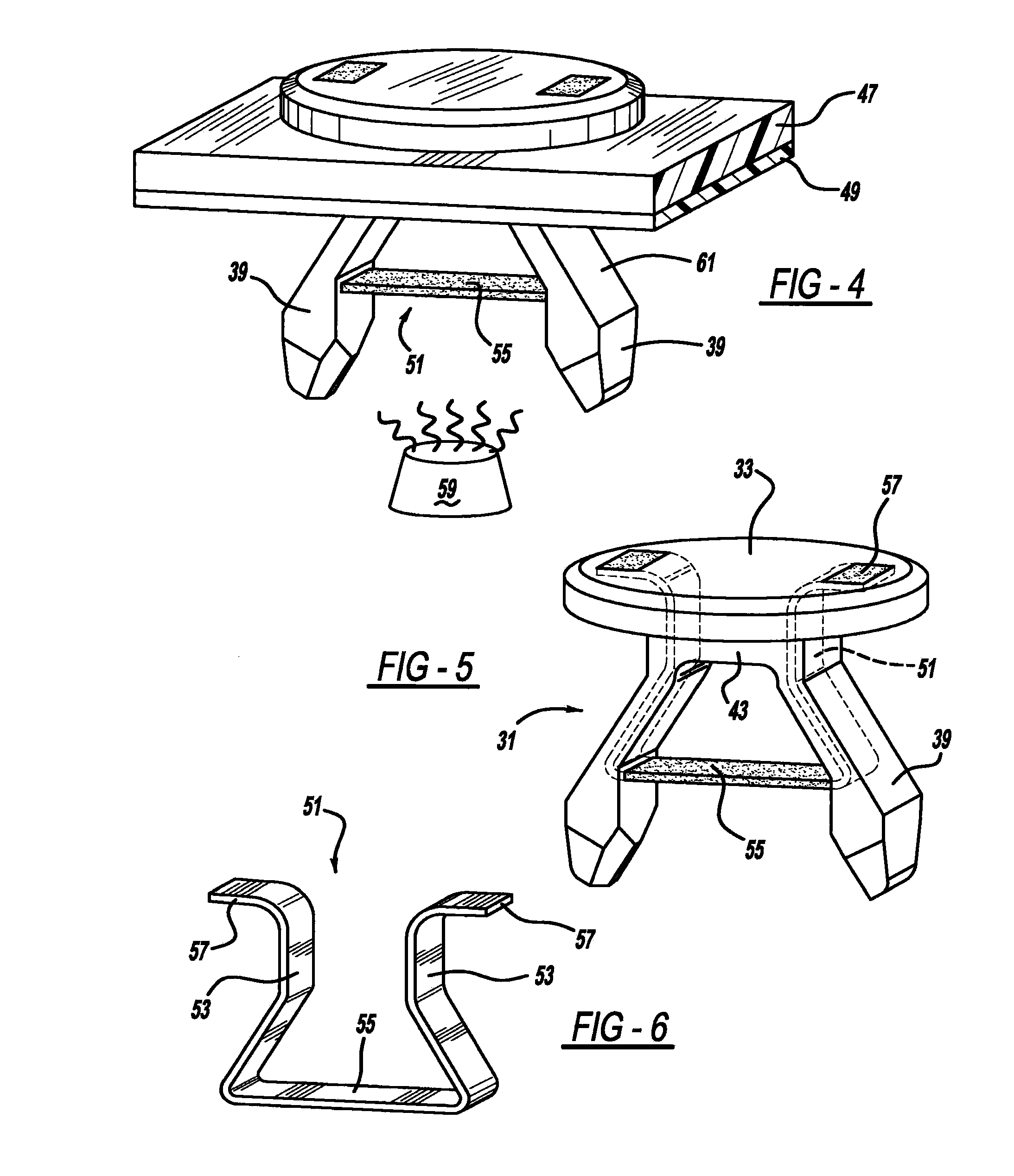
Smart material actuated fasteners
A smart material actuated fastener is provided. In another aspect, a fastener includes a shape memory material and a non-shape memory material with the shape memory material being a minority of the total fastener materials. A further aspect provides a fastener having workpiece-engaging surfaces made of an inactive and non-shape memory material.
Owner:A RAYMOND & CO
Preparation method of response-temperature-adjustable temperature sensitive hydrogel
ActiveCN103408693APrecise control of response temperatureWide variety of sourcesCross-linkMechanical property
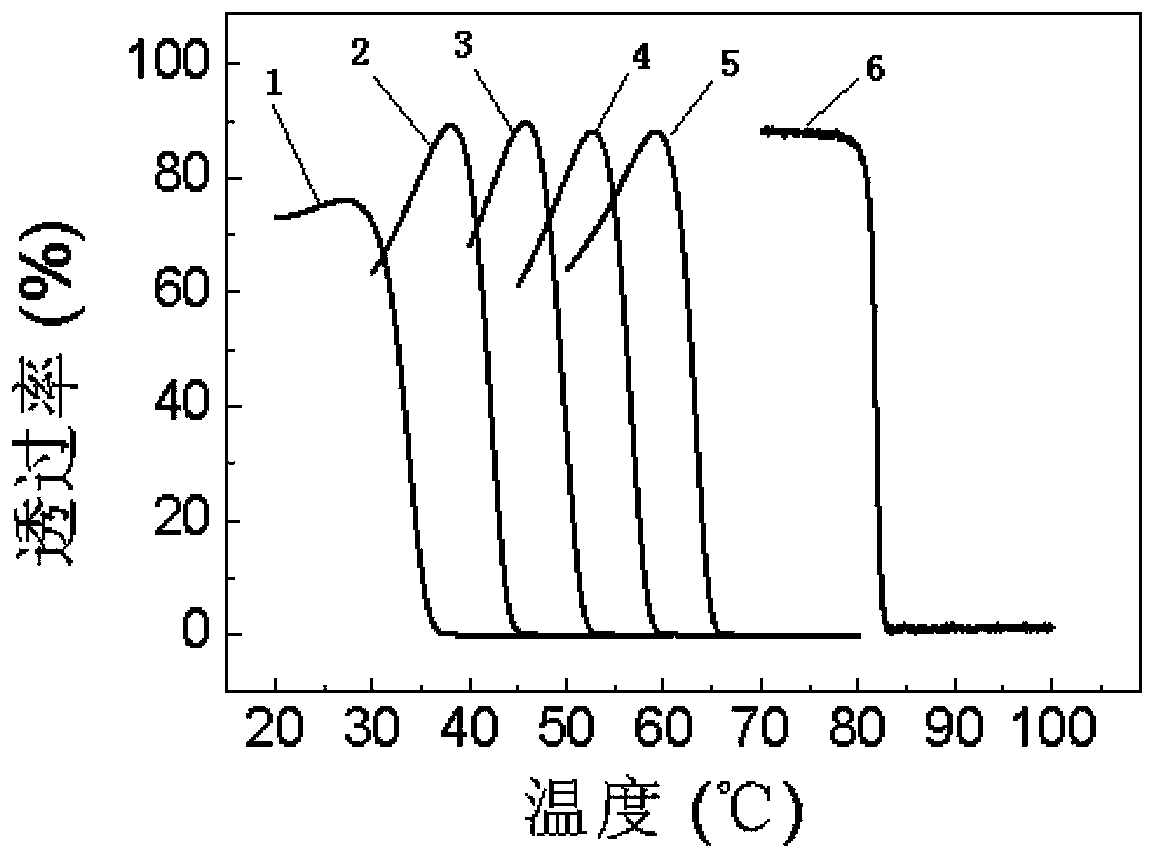
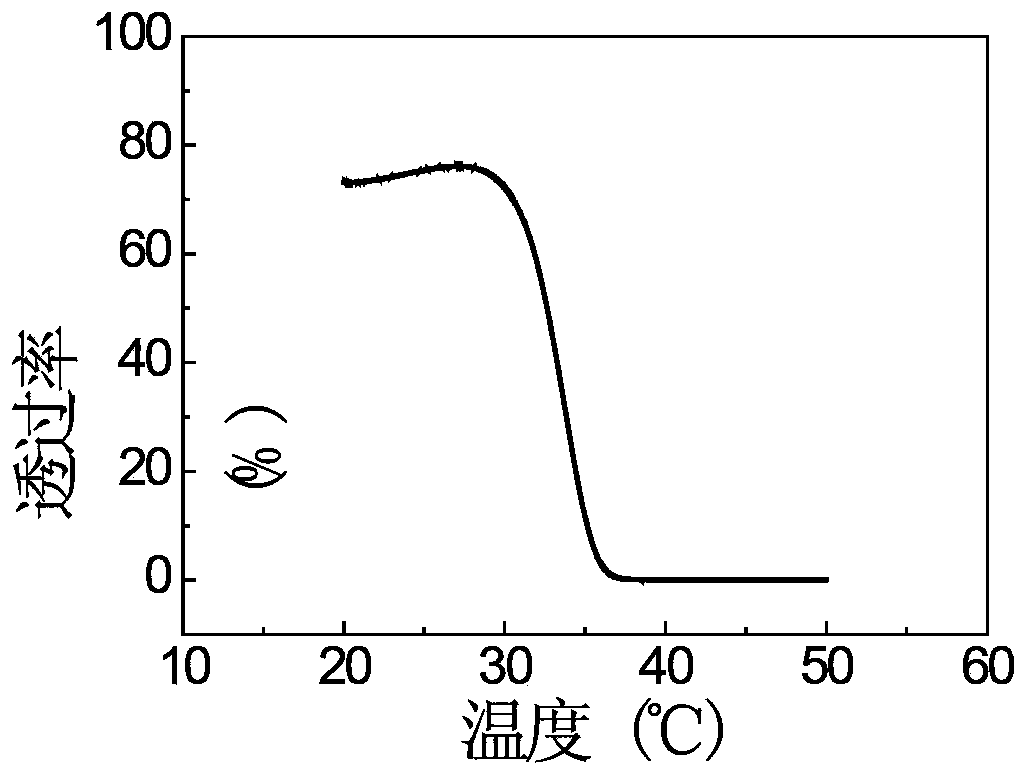
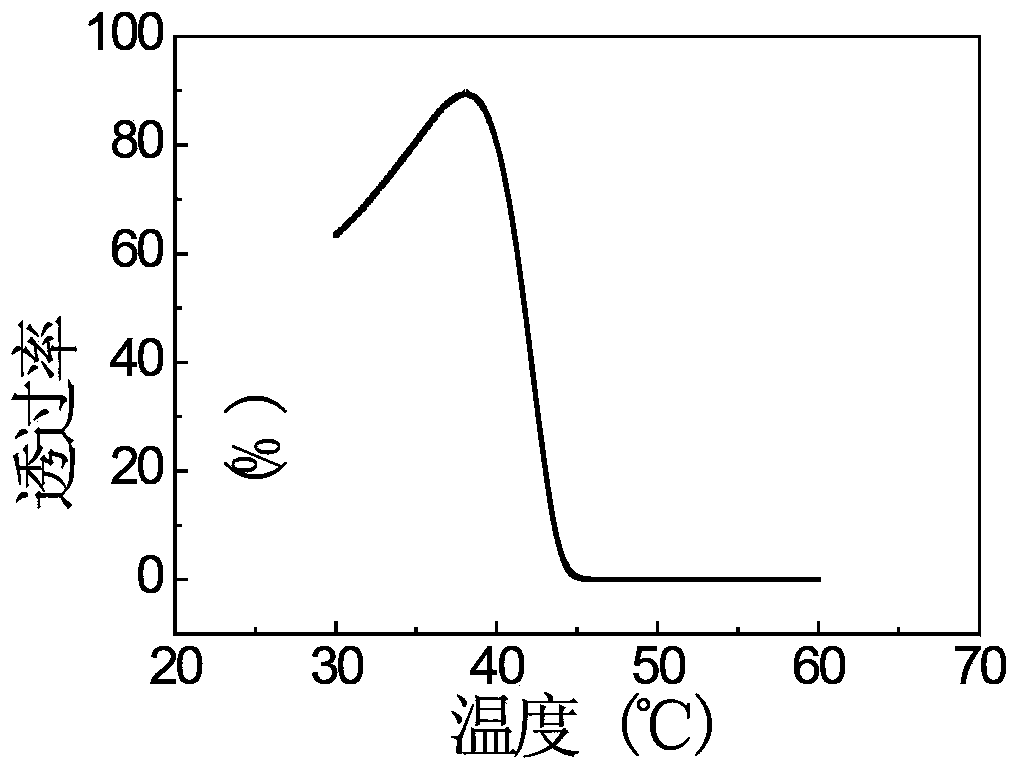
The invention relates to a preparation method of a response-temperature-adjustable temperature sensitive hydrogel. The method comprises a step that a hydrogel prepolymerization liquid is polymerized at 0-50DEG C for 1-48h, and the hydrogel prepolymerization liquid comprises a copolymerization monomer, a cross-linking agent, an initiator, a catalyst and deionized water. The method has the advantages of simplicity, low cost, large raw material selection range; and the prepared temperature sensitive hydrogel has the advantages of uniform three-dimensional net structure, excellent mechanical properties, and realization of accurate regulation of the response temperature in a range of 25-90DEG C, and can be widely applied in the intellectual material field.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of stress-discoloring photonic crystal fibers
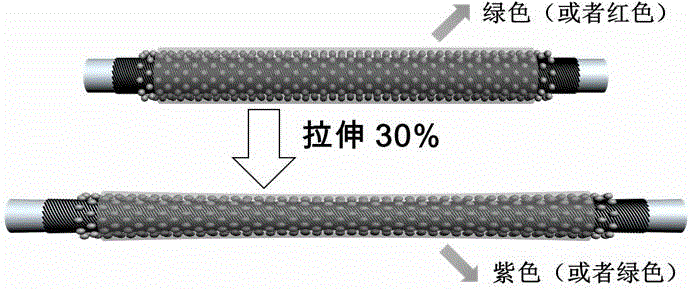
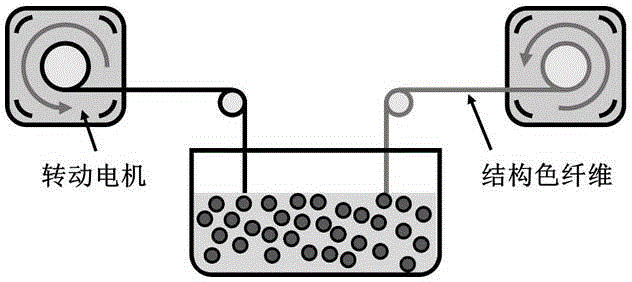
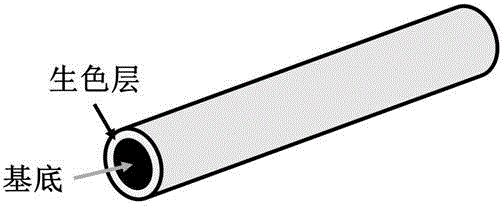
InactiveCN104592971AFast and reversible structural color changeColor changes quickly and steadilyTenebresent compositionsElastomerMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the technical field of intelligent materials, and in particular relates to carbon nanotube based stress-discoloring photonic crystal fibers and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: winding a height-oriented carbon nanotube as a conducting layer outside stretchable elastic polymer fibers serving as a substrate; depositing polymer microspheres by using an electrophoretic deposition method to form a photonic crystal with a periodic structure; then packaging the photonic crystal in a transparent elastomer; and finally, swelling the transparent elastomer to prepare the stress-discoloring photonic crystal fibers. The structural color of the photonic crystal fibers can be regulated and controlled by virtue of the particle size of the polymer microspheres and the sphere center distances among the microspheres. During stretching and restoring, the structural color of the photonic crystal fibers changes quickly and reversibly and comprises red, green and blue, and the color still changes quickly and stably even though the fibers are stretched for one thousand times. The photonic crystal fibers not only can be woven into many fabrics to show various patterns but also can be used as a sensor.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Intelligent experimental bench for driver performance test
InactiveCN101319967ATroubleshoot performance testing challengesSolve the problem of installing load cells at the same timeStructural/machines measurementElectricityFree state
The invention belongs to the technology for testing the performances of intelligent materials and relates to a research on the performance testing method of an intelligent driver. The performance test-bed of the intelligent driver mainly consists of three systems of a skeleton system (comprising a pedestal, a left guide rail, a right guide rail, the bottom board of a displacement sensor, the bottom board of a screw rod, etc), a force application system ( comprising a handle, a trapezium screw rod seat, a trapezium screw rod, a ball joint boot, the bottom board of a ball joint seat, a piezoelectric force actuator, a force measuring bridge, the bottom board of the bridge, a linear bearing, a buttery spring seat, a battery spring, a spoke type force sensor, etc) and a micro-displacement testing system (comprising a displacement sensor sleeve, a displacement sensor sleeve cover, a displacement sensor, etc); wherein, the skeleton system is the basic supporting part of the test-bed and is used for supporting the force application system, the micro-displacement testing system and the tested intelligent driver; the force application system can apply various forces for the detected force intelligent driver for detecting the load characteristics of the tested intelligent driver; the micro-displacement testing system is used for testing the output displacement (under a free state or a load state) of the tested intelligent driver. As the intelligent driver (mainly including a piezoelectric ceramics driver, a giant magnetostriction driver, a shape memorizing alloy, etc) has small displacement, high precision and high frequency response, the common test-bed can not meet the demands for the performance testing of the intelligent driver, the test-bed for performance testing of the intelligent driver is developed so as to meet the demands for the performance testing of various intelligent drivers.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for preparing multi-wall carbon nano-tube composite material
The invention discloses a method for preparing multi-wall carbon nanotube / polymeric type ionic liquid composite material with controllable hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. The method comprises: an ionic liquid containing a metacrylic acid ester functional group has polymerization reaction on the surface of a carbon nanotube to form the carbon nanotube coated with polyelectrolyte; hydrophilic and hydrophobic anions are utilized to modulate the dispersibility of the carbon nanotube / polymeric type ionic liquid composite material in an organic solvent and water, thereby realizing the reversible change of the hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. The preparation process and the preparation method are simple and feasible. The carbon nanotube / polymeric type ionic liquid composite material with the controllable hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties can be applied in the field of catalysis, electrochemistry, novel sensors and intelligent materials.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Smart materials: strain sensing and stress determination by means of nanotube sensing systems, composites, and devices
InactiveUS7730547B2High strengthMaterial is facilitatedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by observing immersed bodiesElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention is directed toward devices comprising carbon nanotubes that are capable of detecting displacement, impact, stress, and / or strain in materials, methods of making such devices, methods for sensing / detecting / monitoring displacement, impact, stress, and / or strain via carbon nanotubes, and various applications for such methods and devices. The devices and methods of the present invention all rely on mechanically-induced electronic perturbations within the carbon nanotubes to detect and quantify such stress / strain. Such detection and quantification can rely on techniques which include, but are not limited to, electrical conductivity / conductance and / or resistivity / resistance detection / measurements, thermal conductivity detection / measurements, electroluminescence detection / measurements, photoluminescence detection / measurements, and combinations thereof. All such techniques rely on an understanding of how such properties change in response to mechanical stress and / or strain.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Magnetorheological continuously variable transmission
The present invention relates to a magnetorheological stepless speed changer, and is characterized by that it includes inner rotor fixedly connected with input shaft, excitation coil fixed in the interior, outer rotor supported on the input shaft by means of two end bearings and working medium magnetorheological fluid filled in the V-shaped working gap between inner rotor and outer rotor, in which the input torque and rotating speed can be passed through input shaft and inner rotor and can utilize the magnetorheological effect produced by means of magnetorheological fluid working medium under the action of coil field to produce force moment transferring action so as to implement stepless changed load torque and rotating speed output by outer rotor.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and apparatus for conversion of movement to electrical energy
InactiveUS20060255663A1Economical and efficientPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method for converting useful movement into electrical energy includes moving a structure against a surface thereby generating a force against a material integrated into the structure, deforming the material in response to the force to thereby generate electrical energy from the material, and harvesting the electrical energy. An apparatus for converting useful movement into electrical energy includes a smart material adapted to produce electrical energy when a force against the smart material is applied, and a plurality of coils in contact with the smart material for harvesting the electrical energy.
Owner:GLYCON TECH
Luminescent material having aggregation-induced emission, method of making and application thereof
ActiveCN104877666AHas aggregation-induced luminescent propertiesImprove the possibility of applicationOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesAggregation-induced emissionLength wave
The invention discloses a luminescent material having aggregation-induced emission, a method of making and an application thereof. The luminescent material herein has properties of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) / aggregation-enhanced emission (AEE) with the maximum absorption wavelength red shift to a visible area so that this type of luminescent material has the potential applications in the field of biology and photoelectricity. The luminescent material herein also has excellent optical waveguide property with an optical loss lower to 0.100dB / [mu]m, and is applicable to produce optical waveguide materials and also applicable to organic light emitting diodes. The luminescent material herein also has the characteristic of mechanochromism and reversible mechanochromism, thus having potential application in the aspect of smart materials.
Owner:HKUST SHENZHEN RES INST +1
Material with schemochrome and capable of being induced to change color through stress and preparation method of material
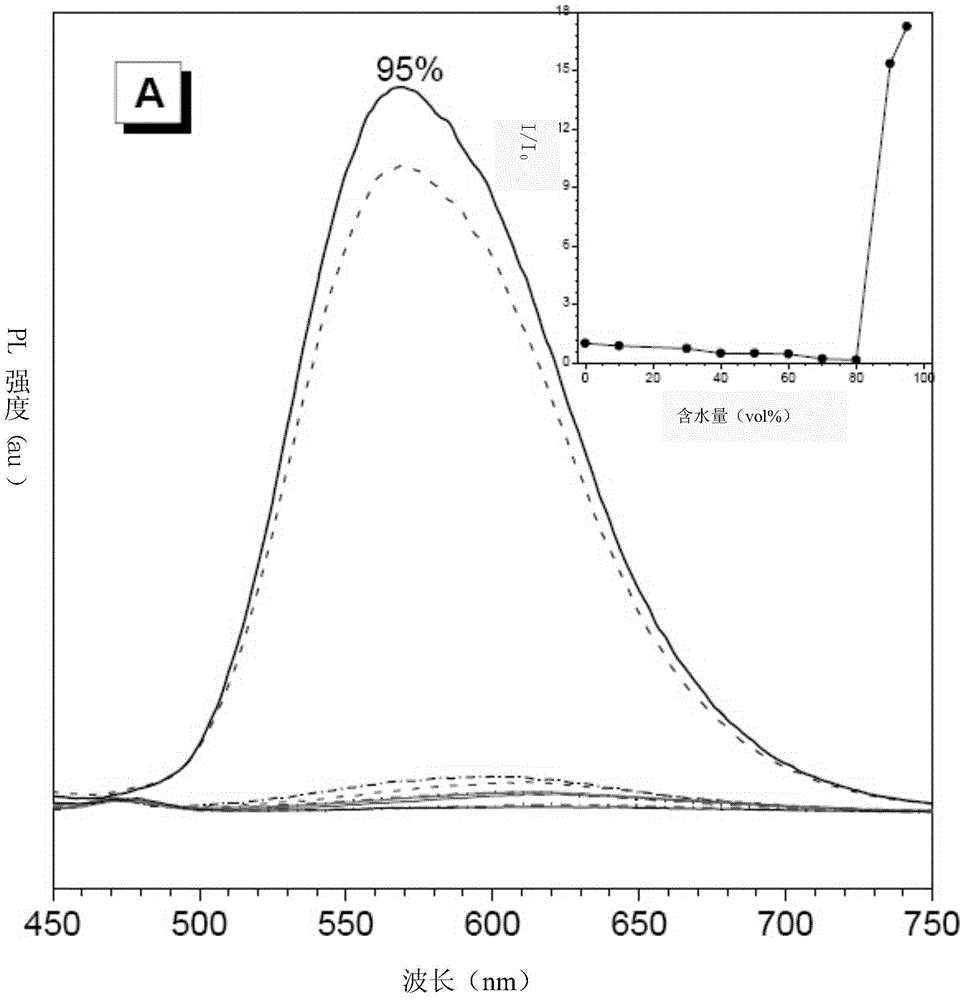
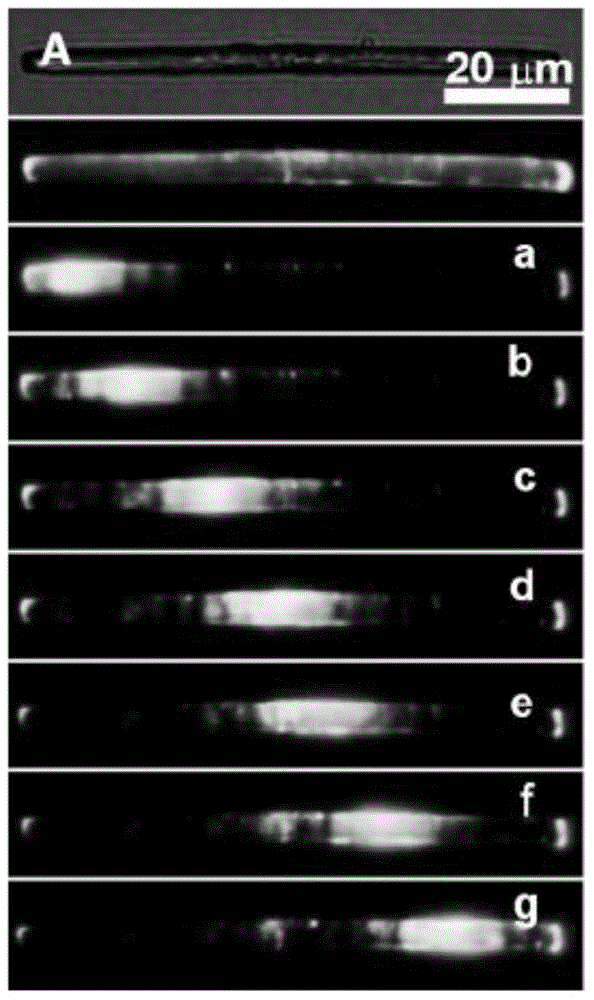
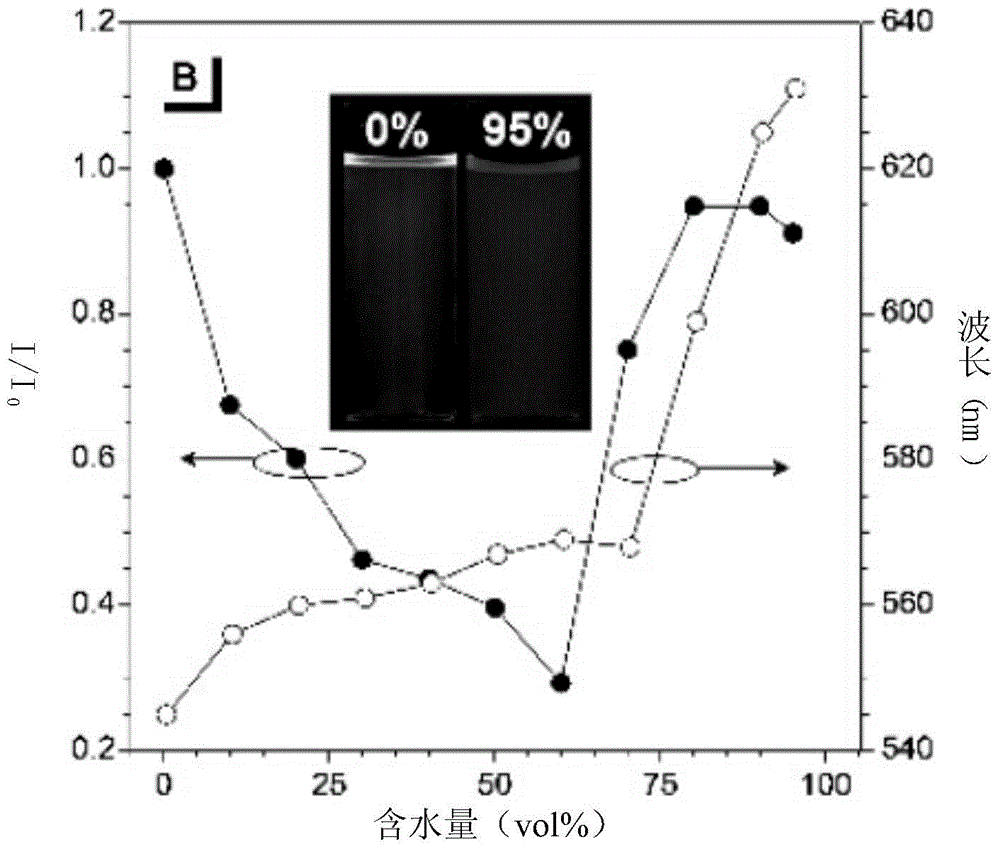
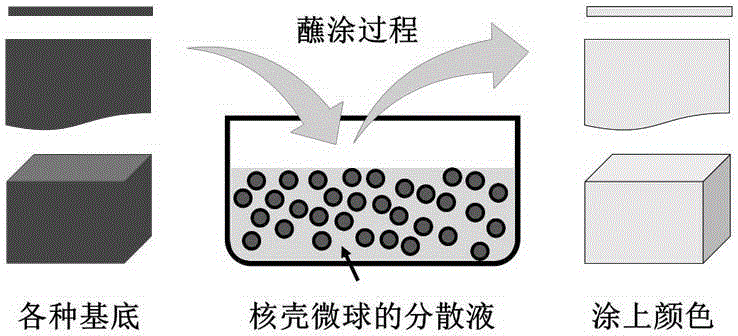
The invention belongs to the technical field of intelligent materials and particularly provides a material with schemochrome and capable of being induced to change color through stress and a preparation method of the material. According to the method, dispersion liquid of a polymeric microsphere of a core-shell structure provided with a hard inner core and a soft outer shell serves as treating liquid, objects of various shapes and materials serve as substrates, the surfaces of the objects are coated with the dispersion liquid of the polymeric microsphere in a dipping mode, the objects with the schemochrome are obtained, and the color can be changed according to the external environment, such as the stress change. The color change is fast and reversible, the whole visible light region, even the ultraviolet and infrared spectral region can be included. The material with the schemochrome and capable of being prepared simply, fast and in batches can be used in the field of displays, sensitive materials and textile industries, for example, photonic crystal fibers prepared with elastic fibers as substrates can be woven into fabric bright in color, and by means of the fabric, color change in the movement process can be achieved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
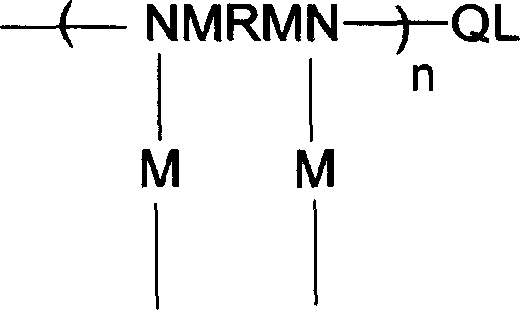
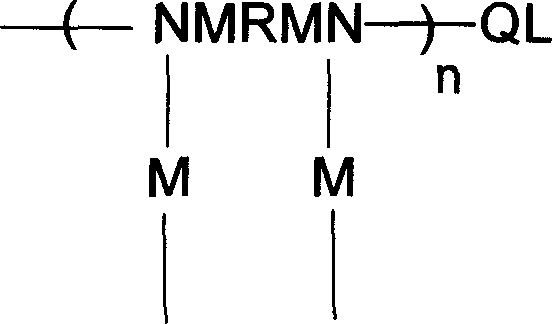
Energy storage material of solid - solid phase change in opal / polyurethane type, and preparation method
InactiveCN1958711ALarge specific surface areaHigh phase change enthalpyHeat-exchange elementsPolyethylene glycolGlycol synthesis
This invention relates to a method for preparing opal / polyurethane solid-solid phase transition energy-storage material. The molecular structure of the material is shown in formula I, where, poly (ethylene glycol) is the soft segment, while aliphatic and aromatic isocyanate, and trihydroxyl substance are the hard segments. The method comprises: (1) preparing prepolymer of poly (ethylene glycol) with terminal groups activated by isocyanate groups; (2) preparing opal / polyurethane solid-solid phase transition energy-storage material. The method has such advantages as low raw material cost, no toxicity of the product, and simple process. The addition of natural nanomaterial (opal) can increase the phase transition enthalpy value and heat response rate of the material, and can reduce the cost. The opal / polyurethane solid-solid phase transition energy-storage material can effectively save energy, and has potential applications in such fields as agriculture, energy resources, textile, construction and electronics.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
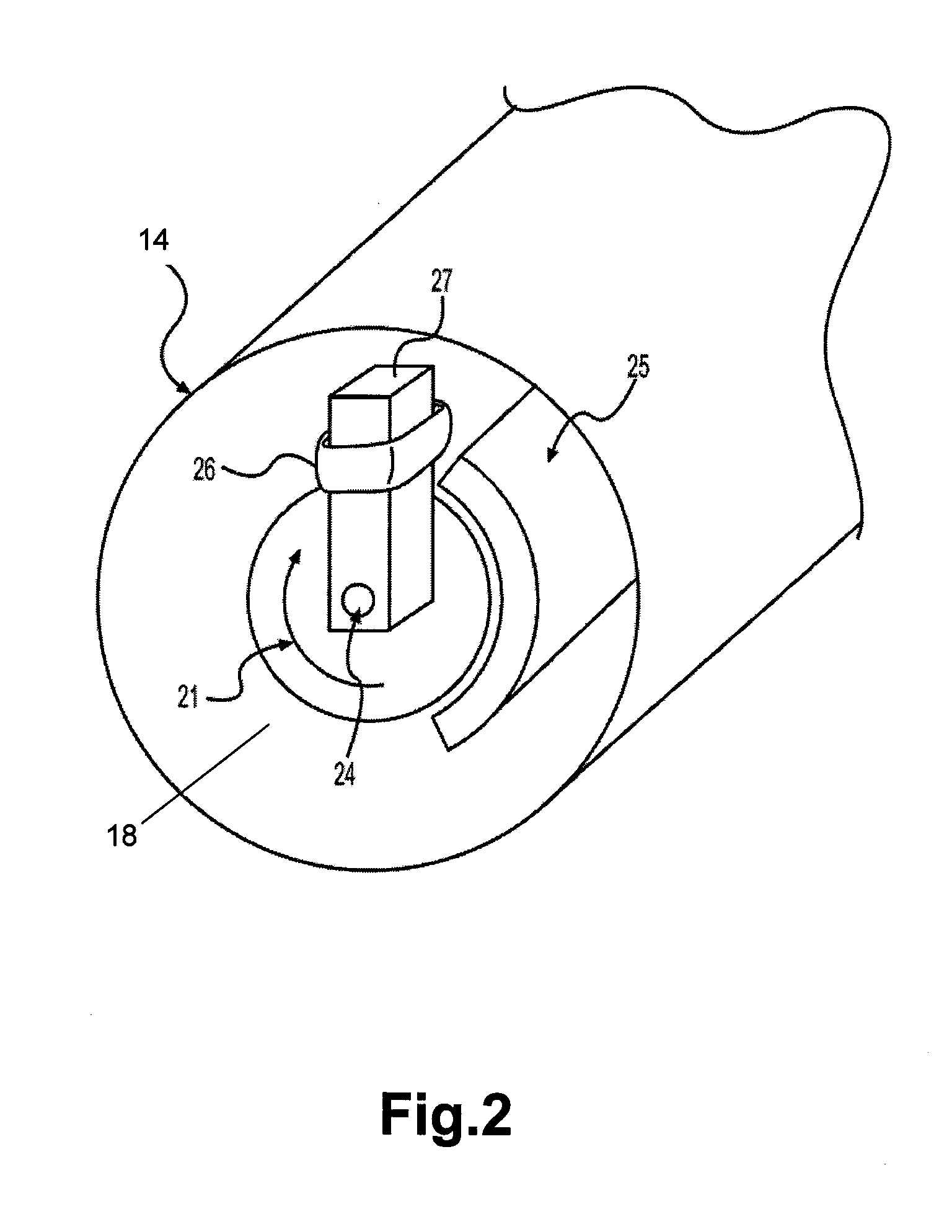
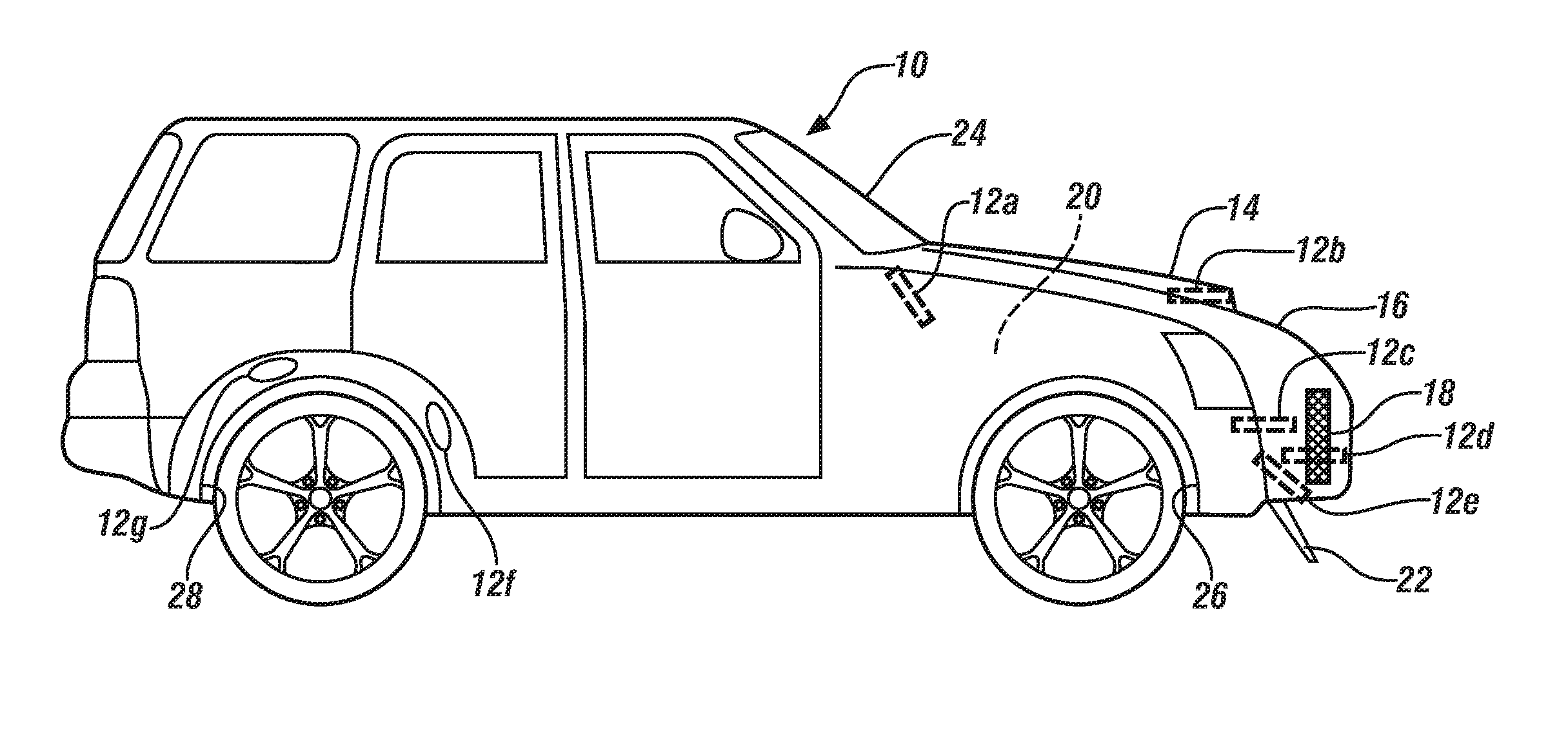
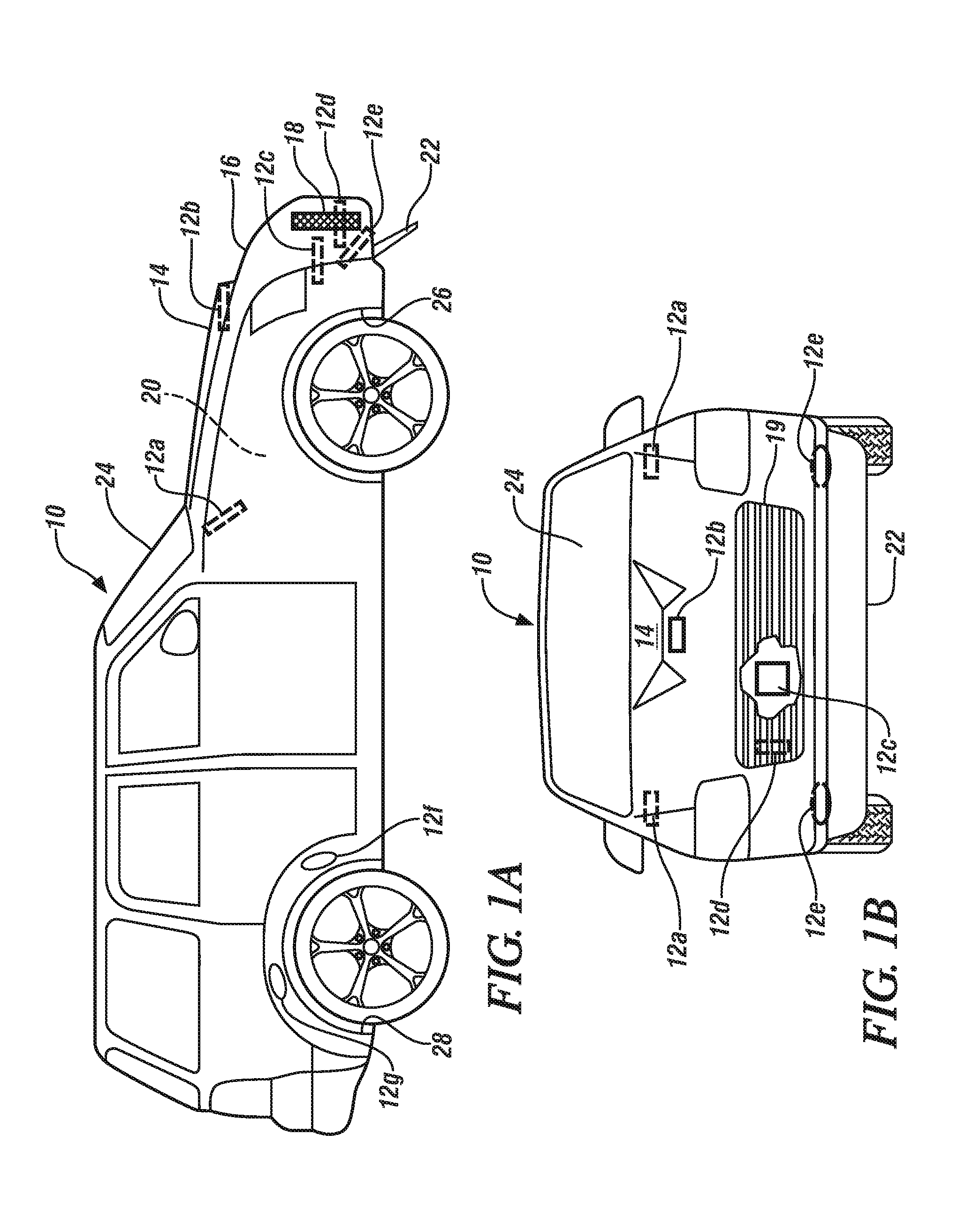
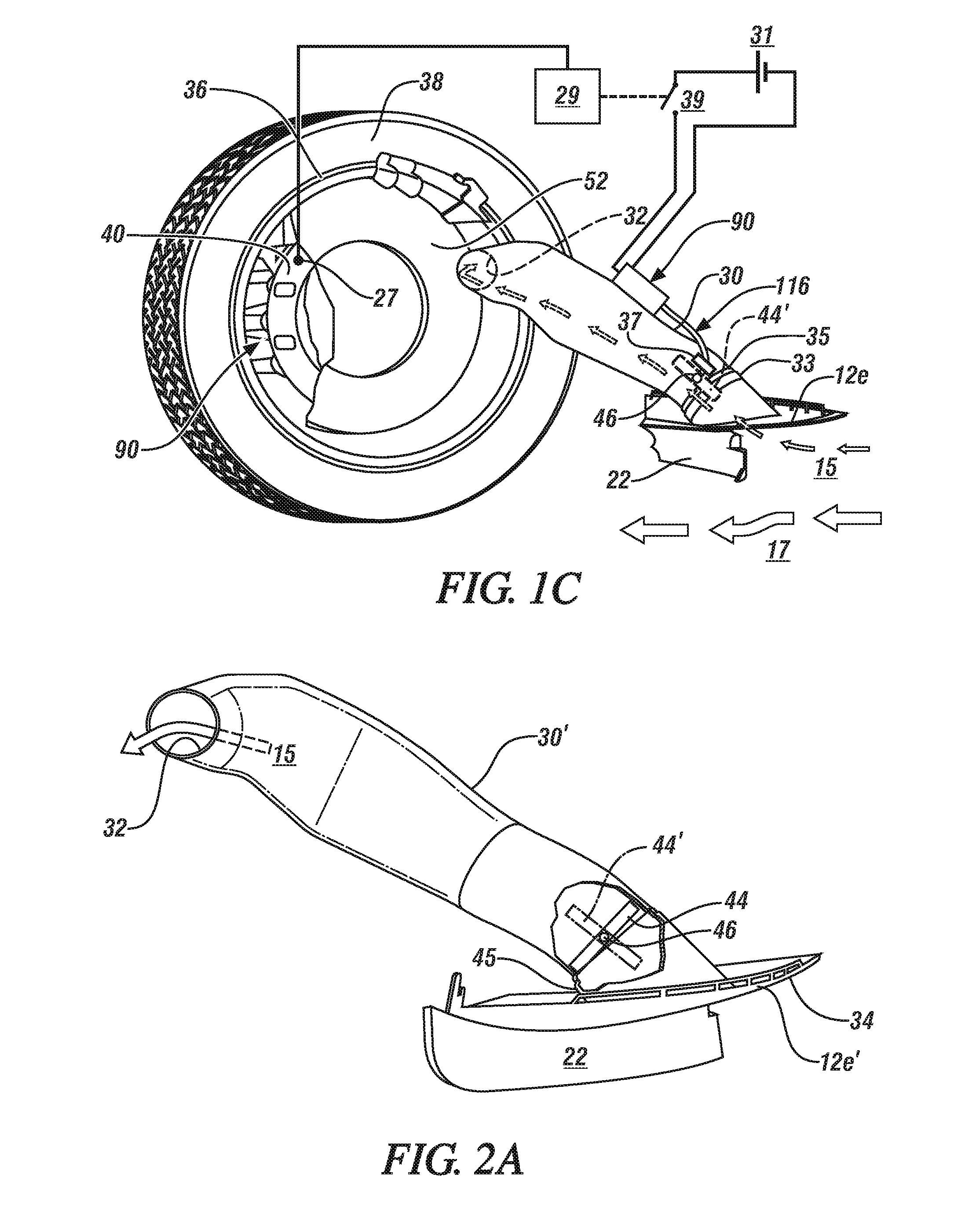
Powered vehicle brake cooling system
InactiveUS20140262644A1Easy to moveFacilitate reverse transformationFluid actuated brakesBraking discsMobile vehicleActuator
An inlet, positioned to access the flow of air passing around and under a moving vehicle, may draw in air which is conveyed through a duct and discharged to cool a brake on a vehicle. The inlet has a closure. The closure is opened and closed on demand by a temperature-operated actuator incorporating an active or smart material under the direction of a controller. In embodiments, a sensor, suitably positioned to sense a temperature representative of the brake temperature, communicates the sensed brake temperature to the controller. The controller may respond to the sensed brake temperature, by triggering operation of the actuator. Typically the closure is opened to allow passage of cooling air to the brake when the sensed brake temperature exceeds, or is anticipated to exceed, a predetermined temperature.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com