Patents
Literature
43 results about "Surgical correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bunion correction surgery is done to improve the position and alignment of the big toe. A bunion occurs when the big toe turns toward the smaller toes, which creates a bump and can cause pain. Bunion correction surgery is an operation to improve the position and alignment of the big toe.
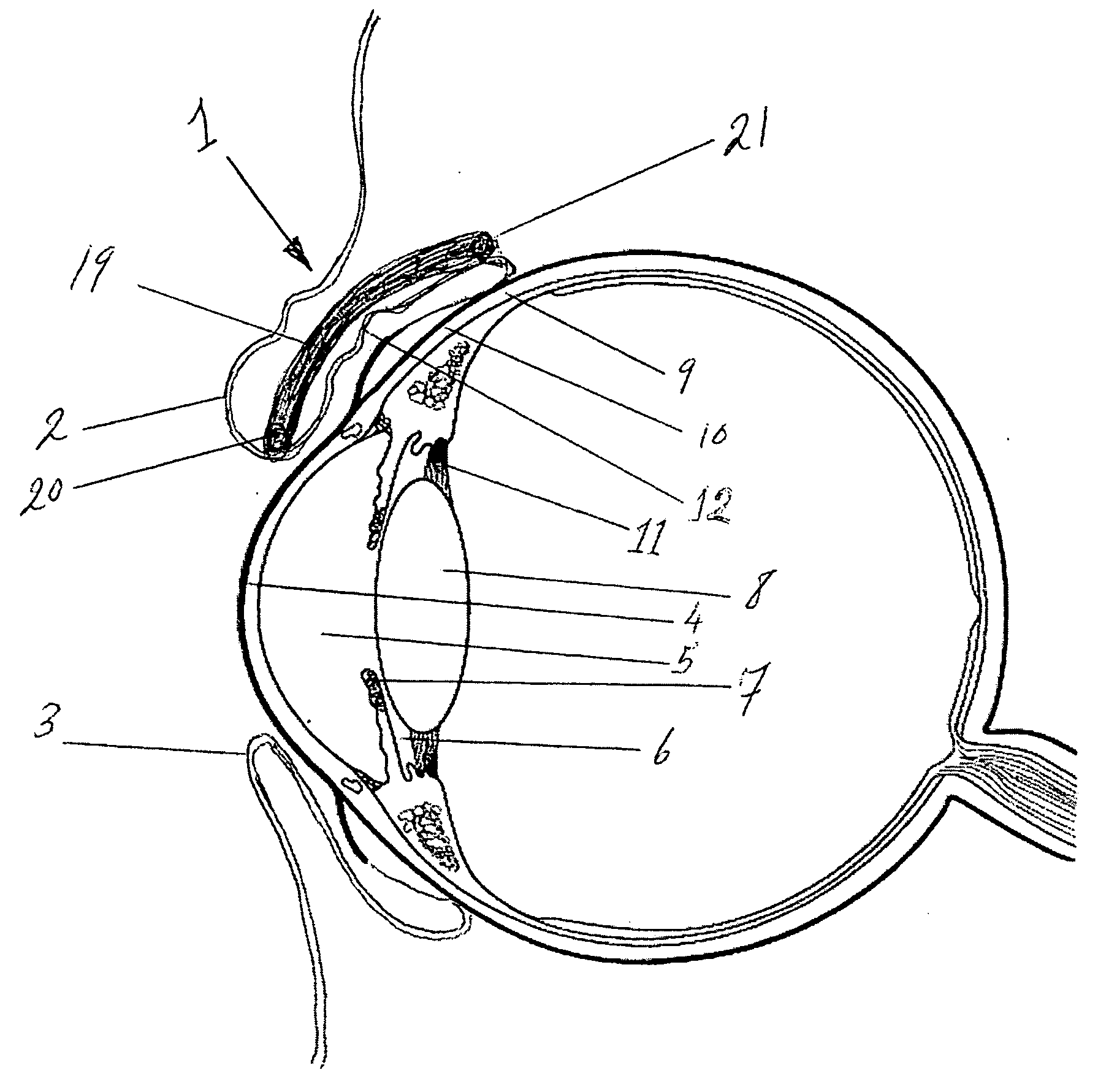
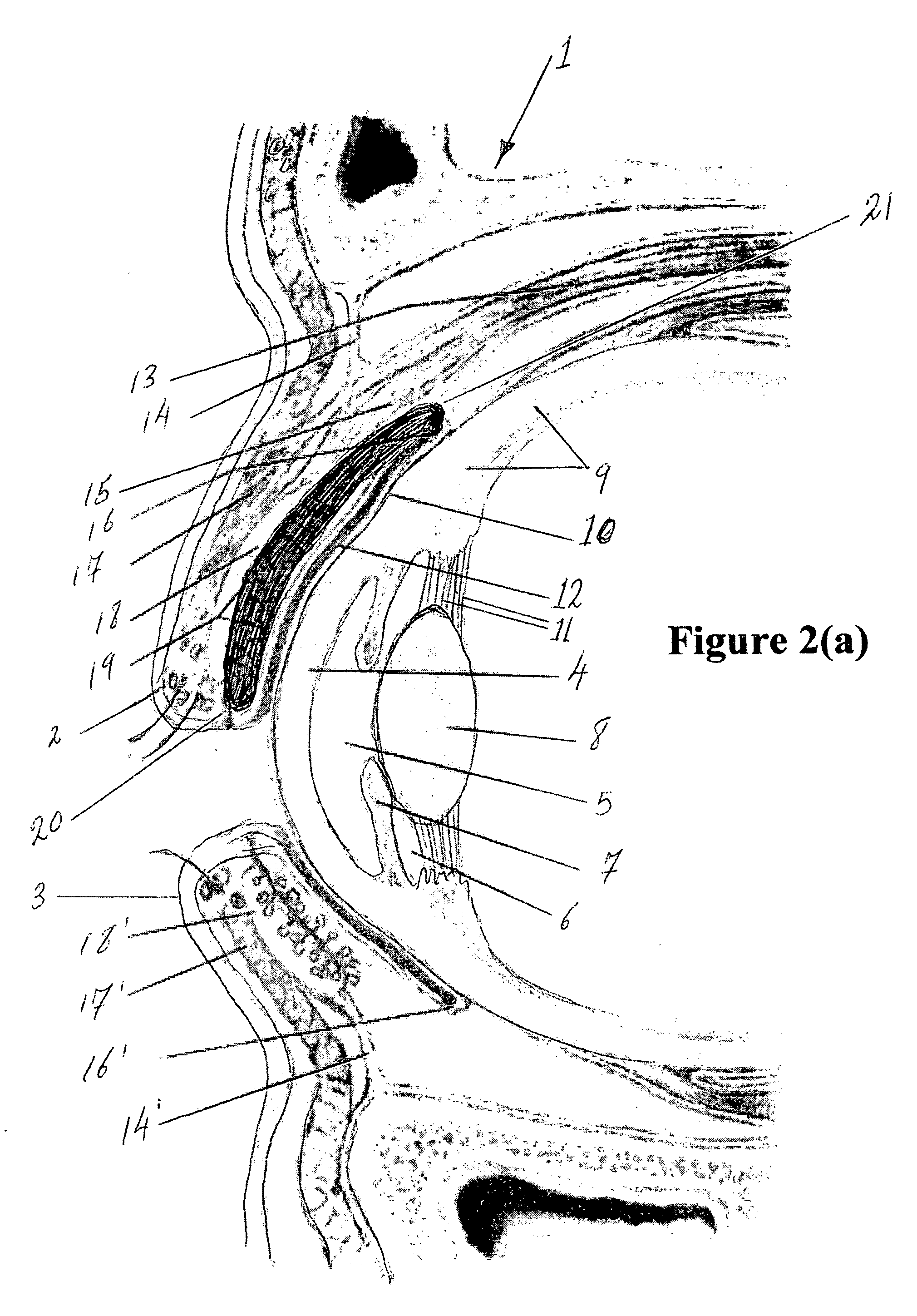
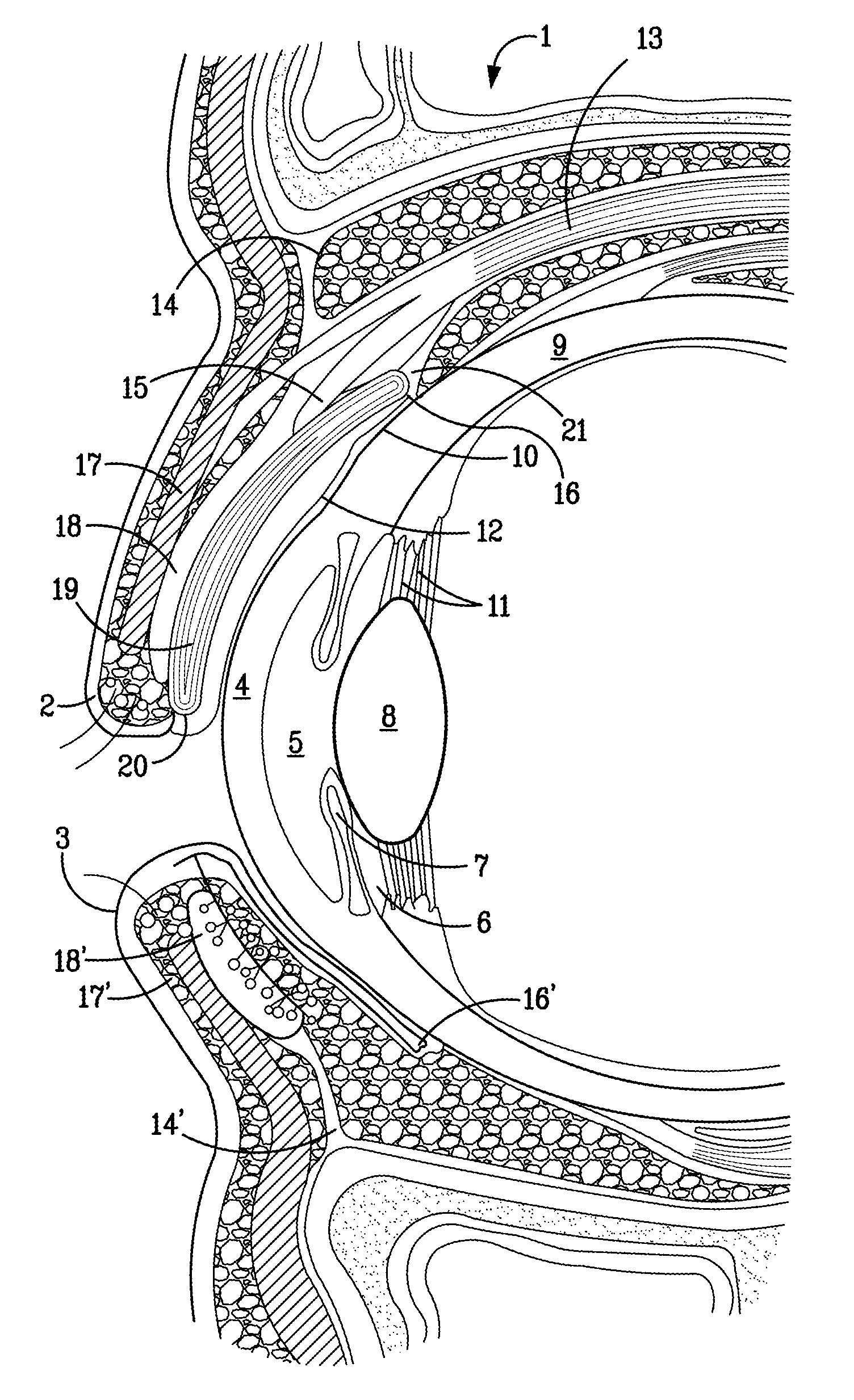
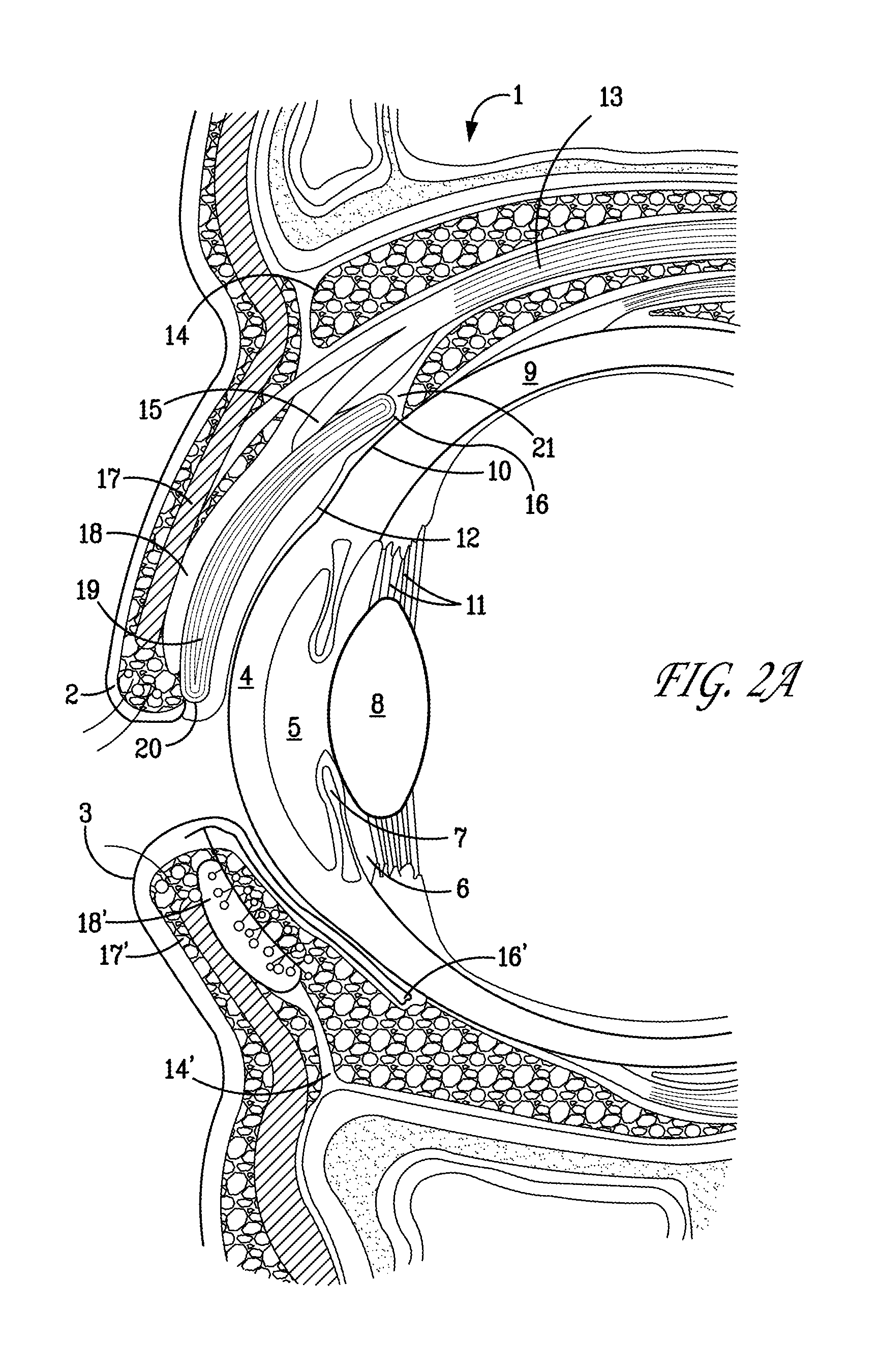
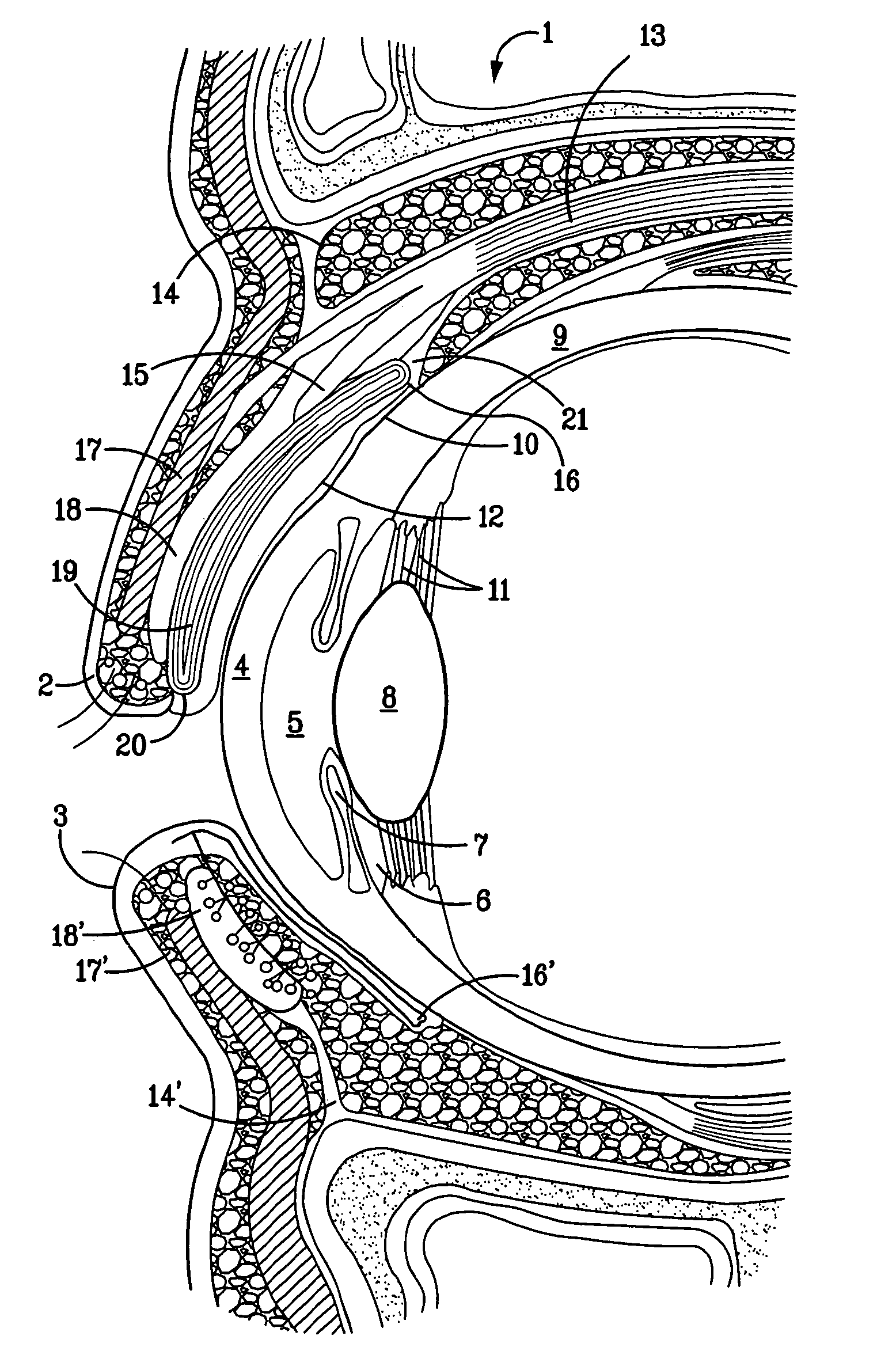
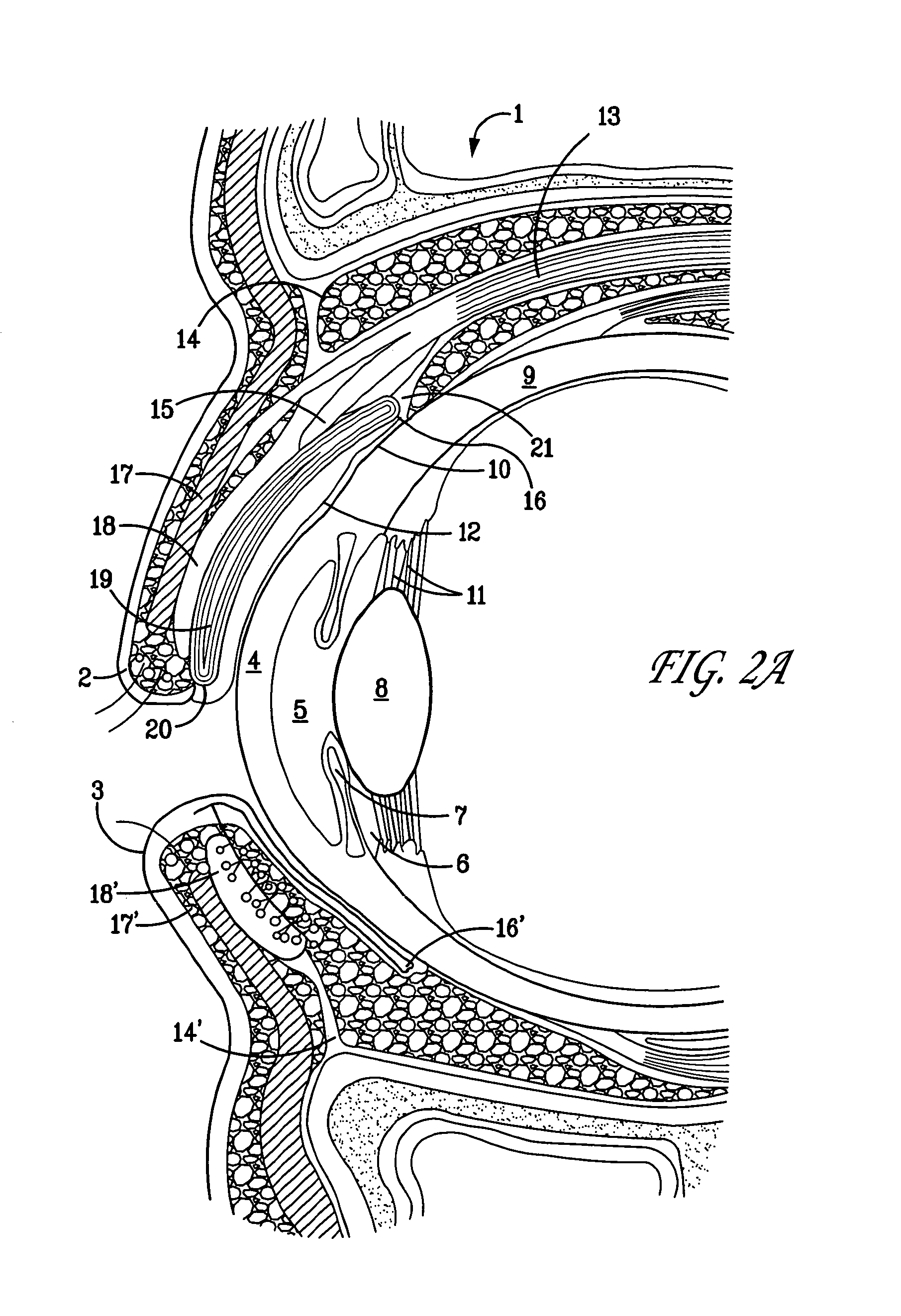
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
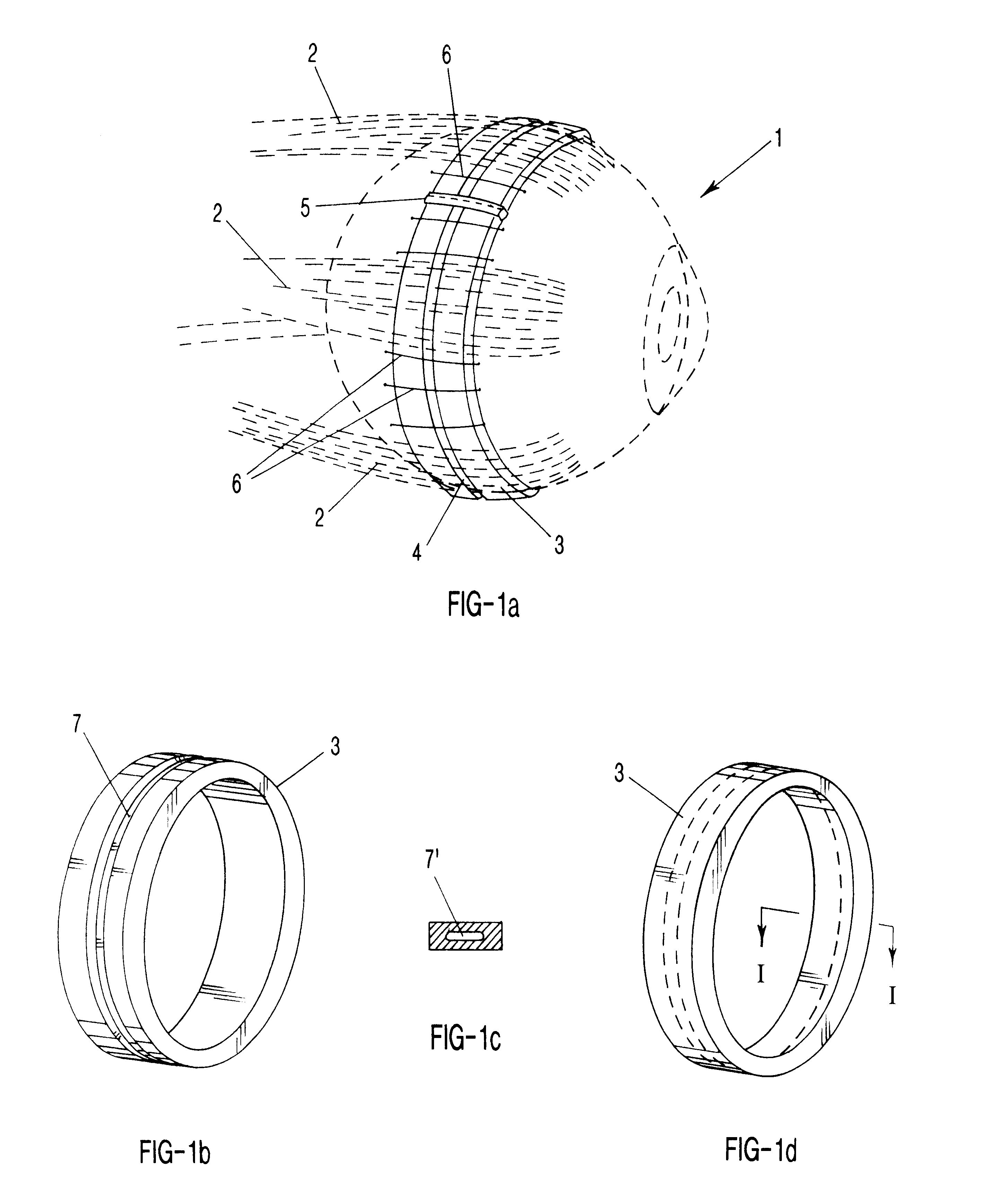
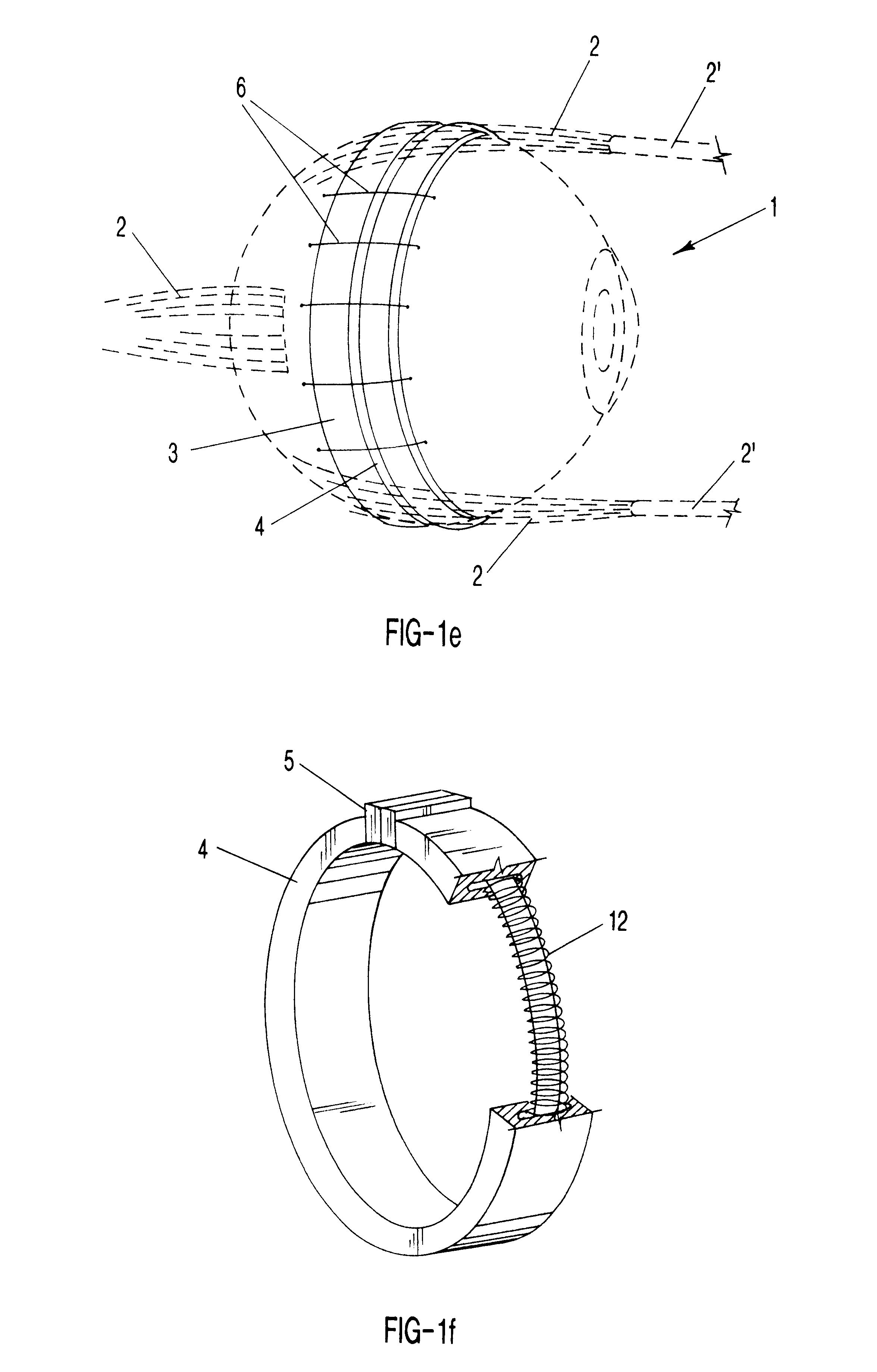
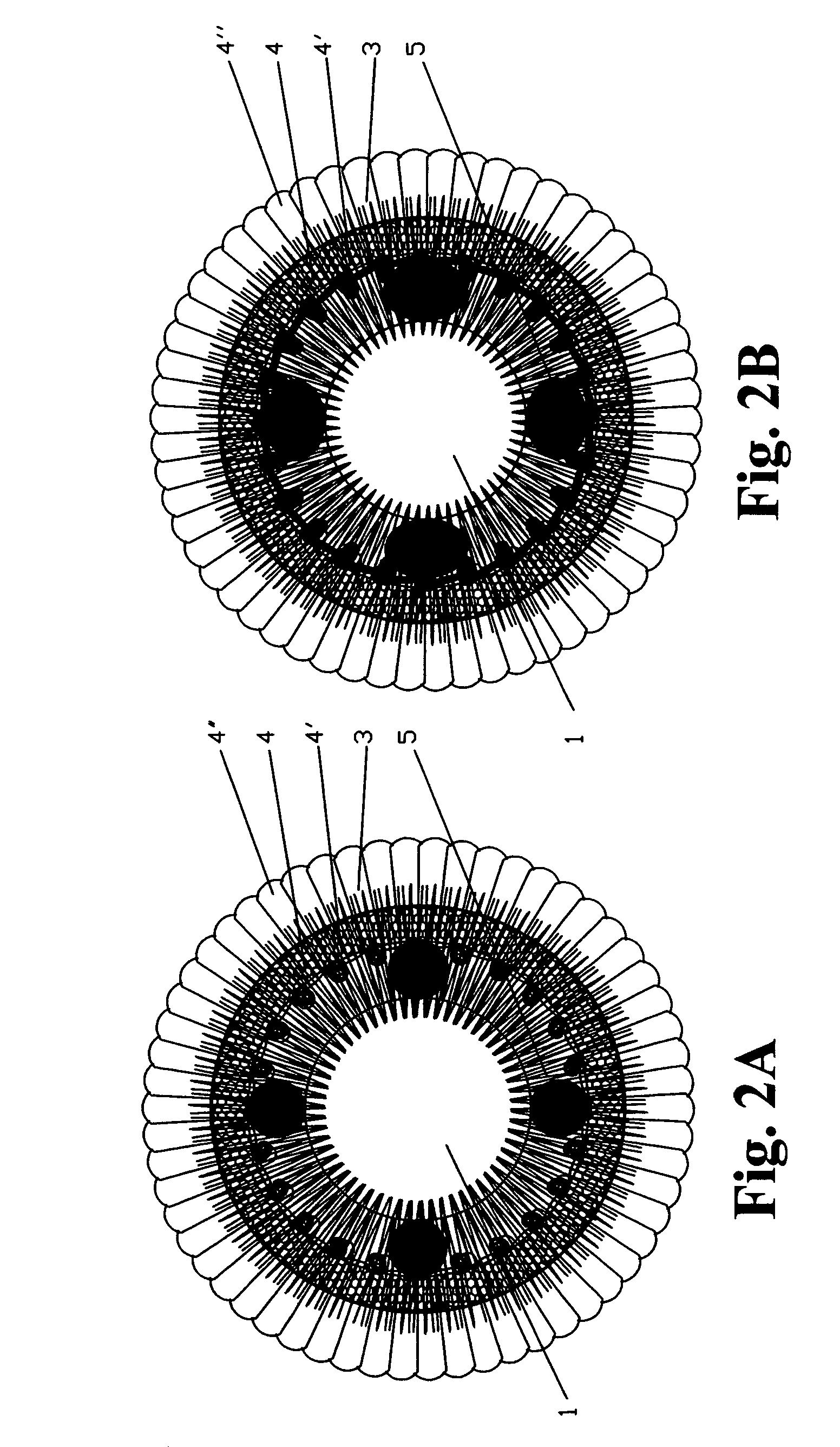
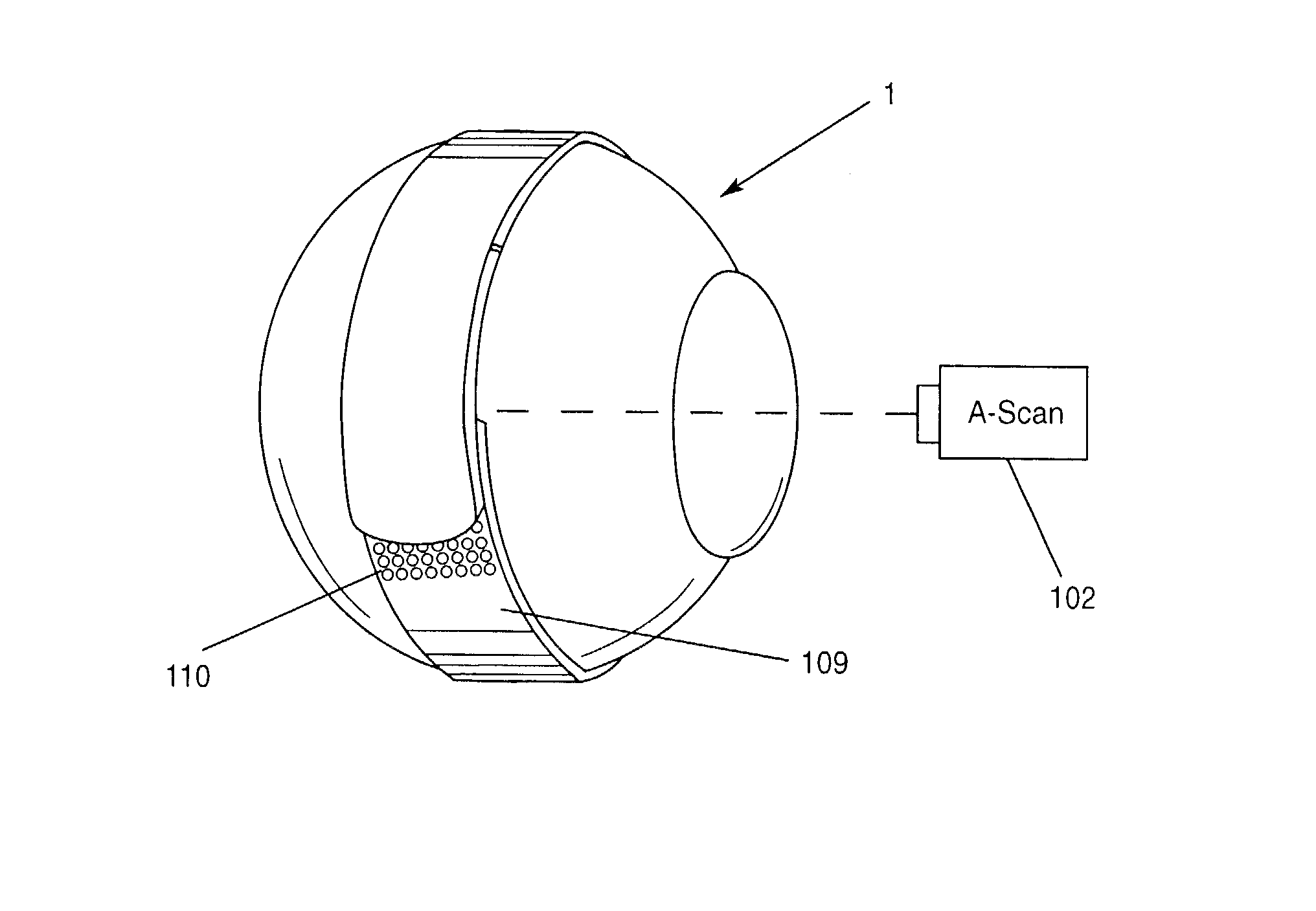
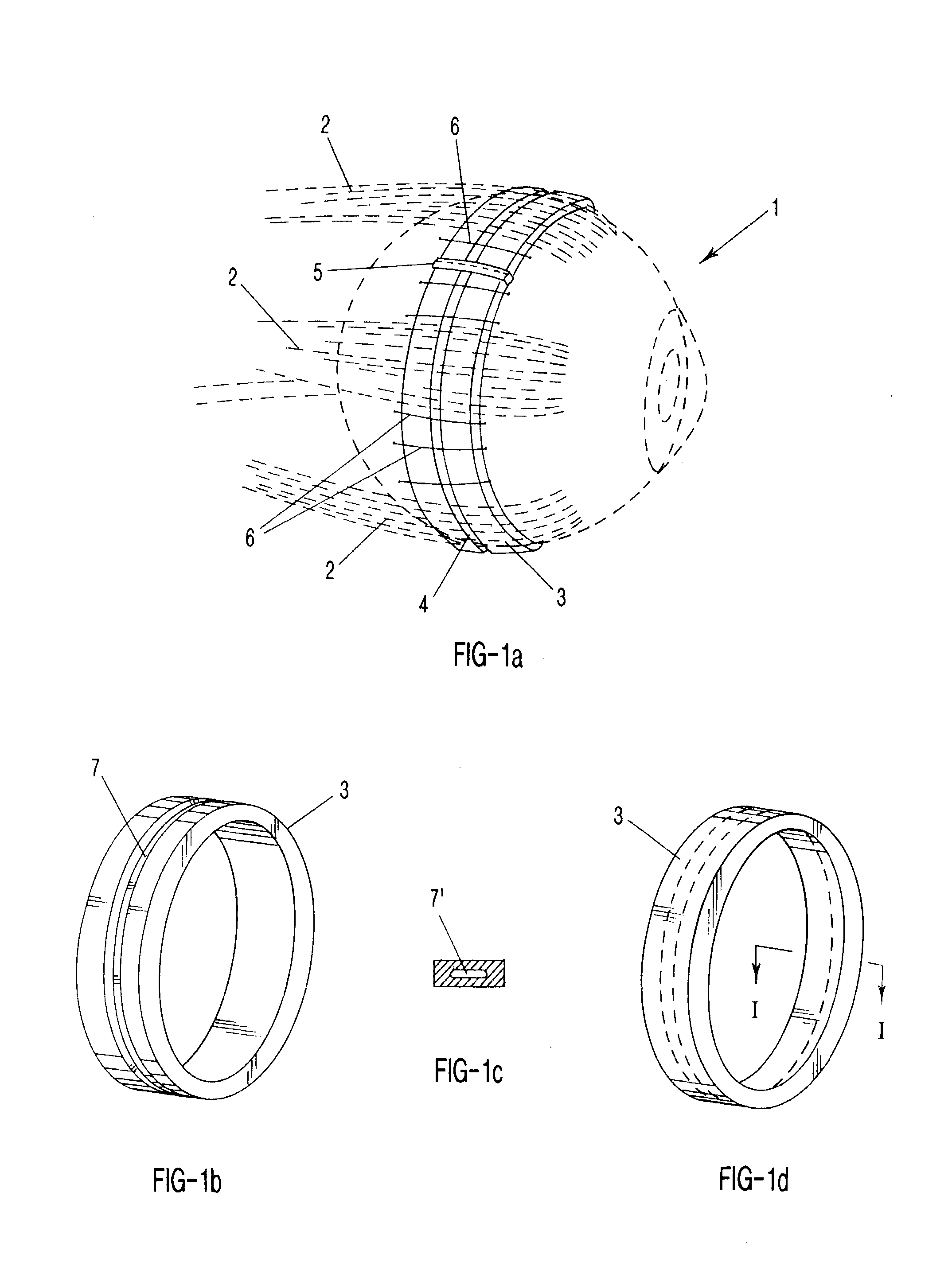
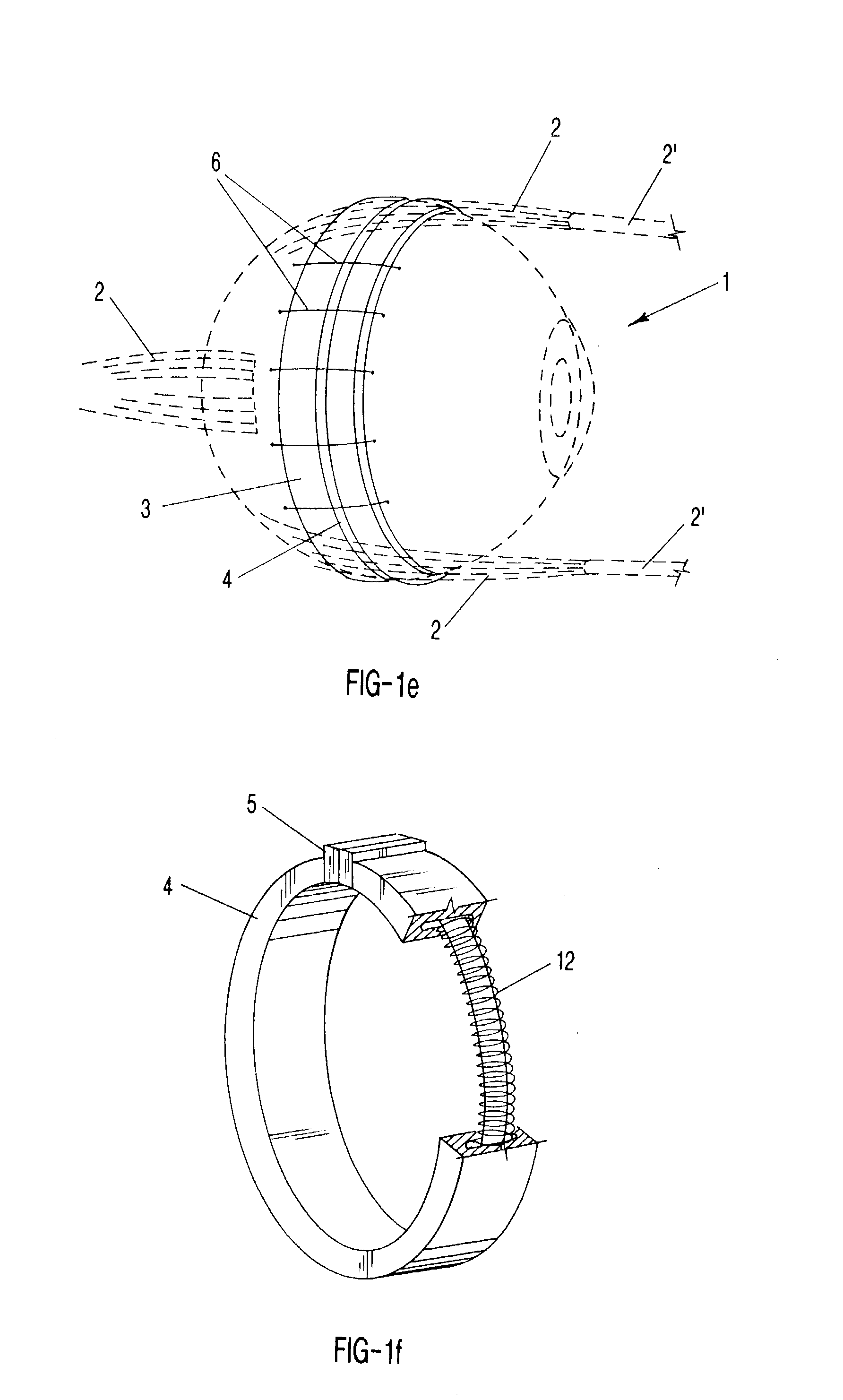
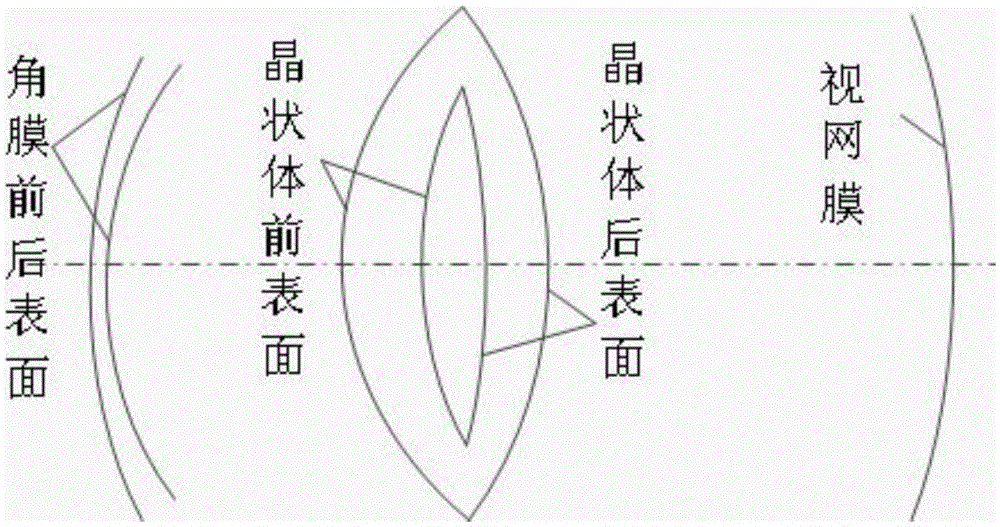
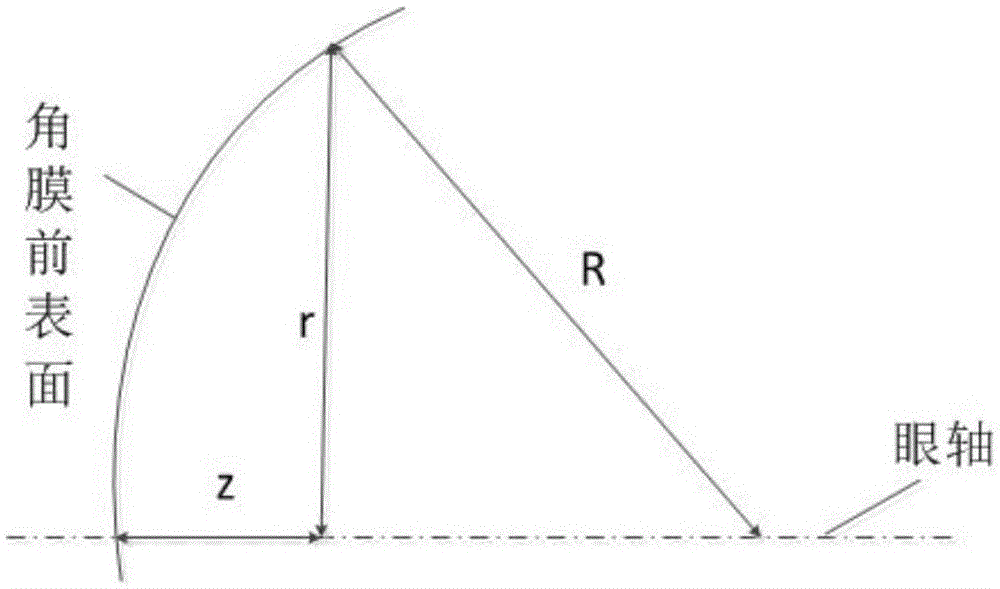
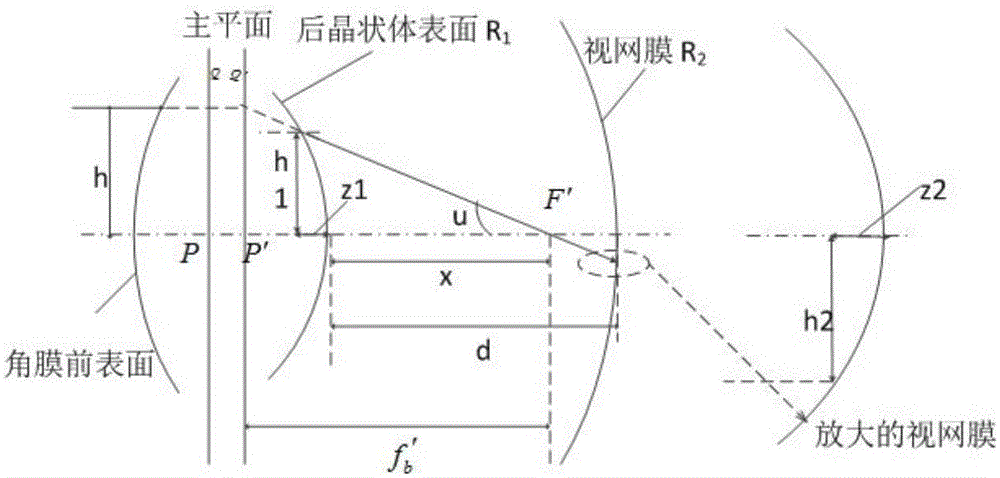
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
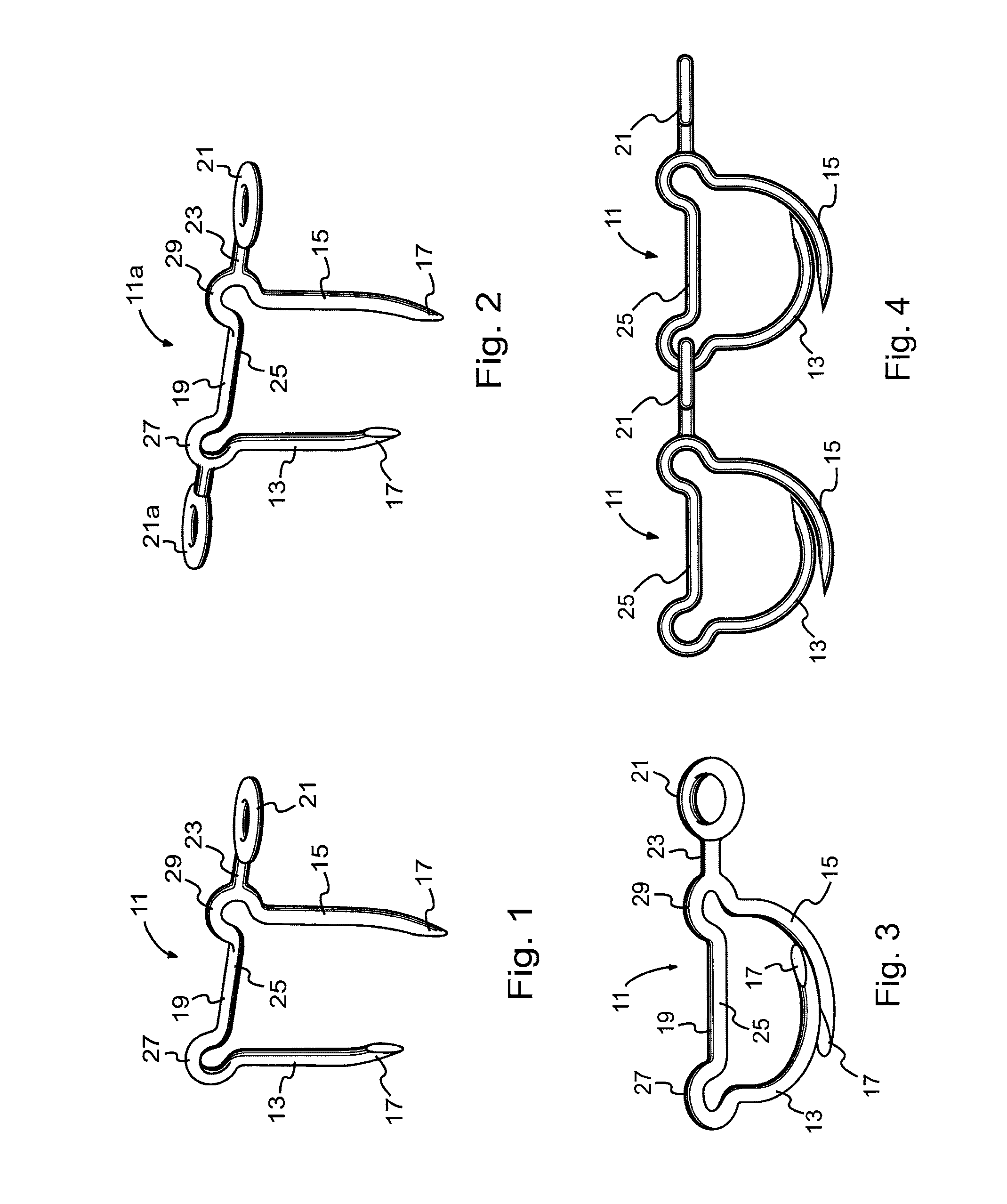
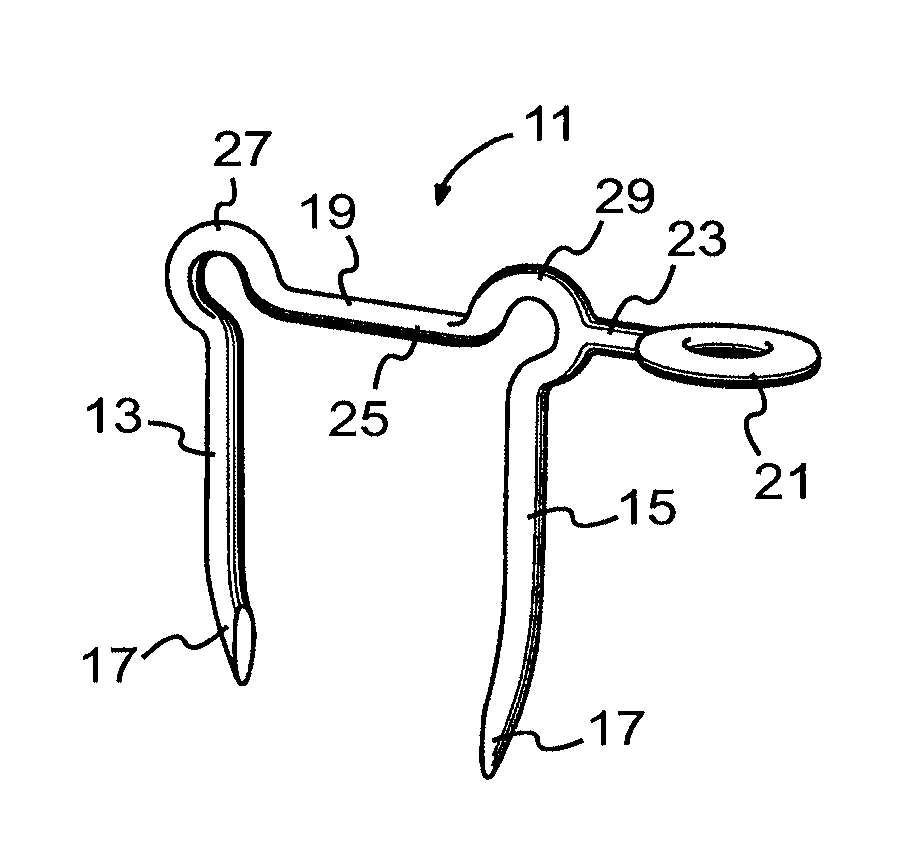
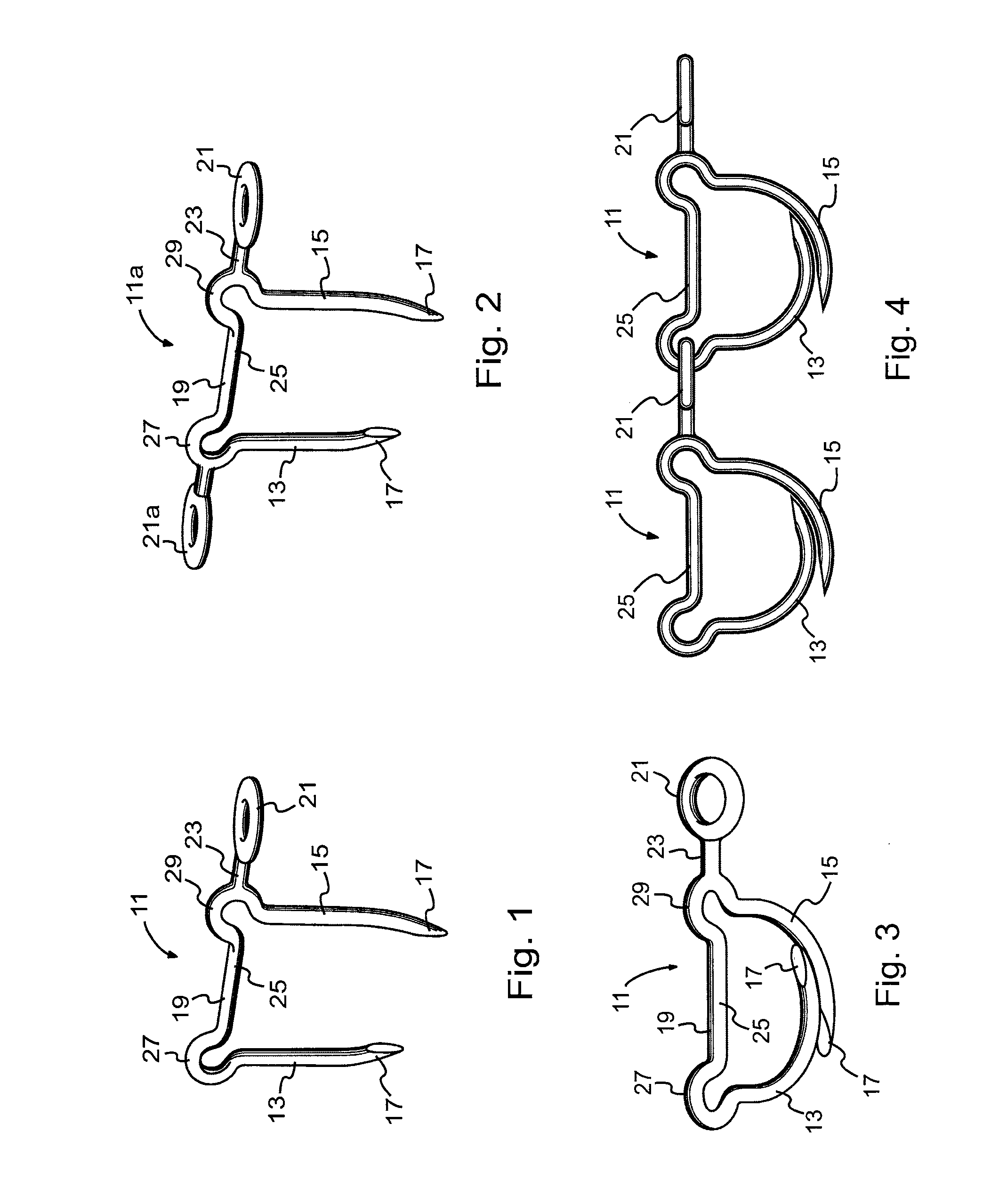
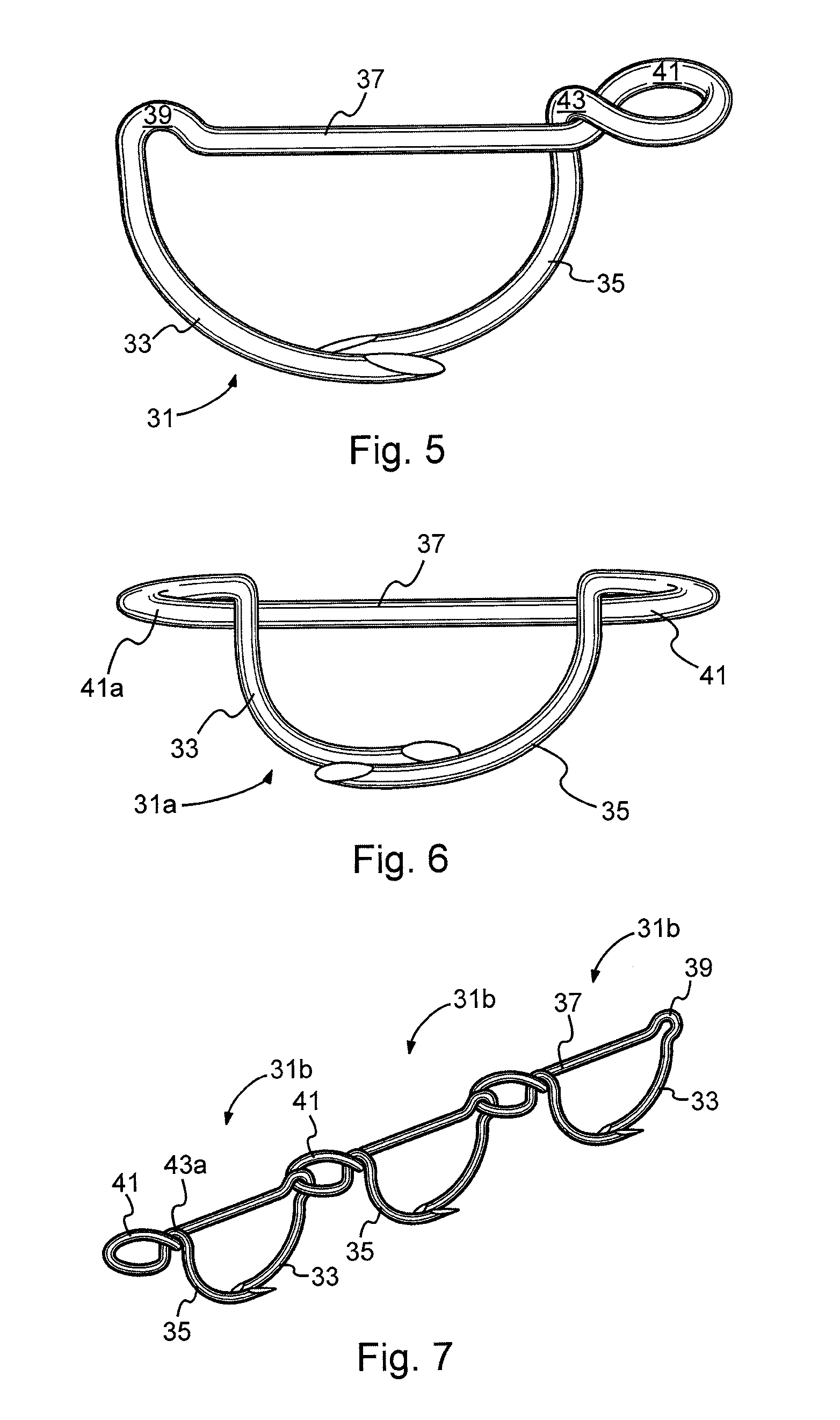
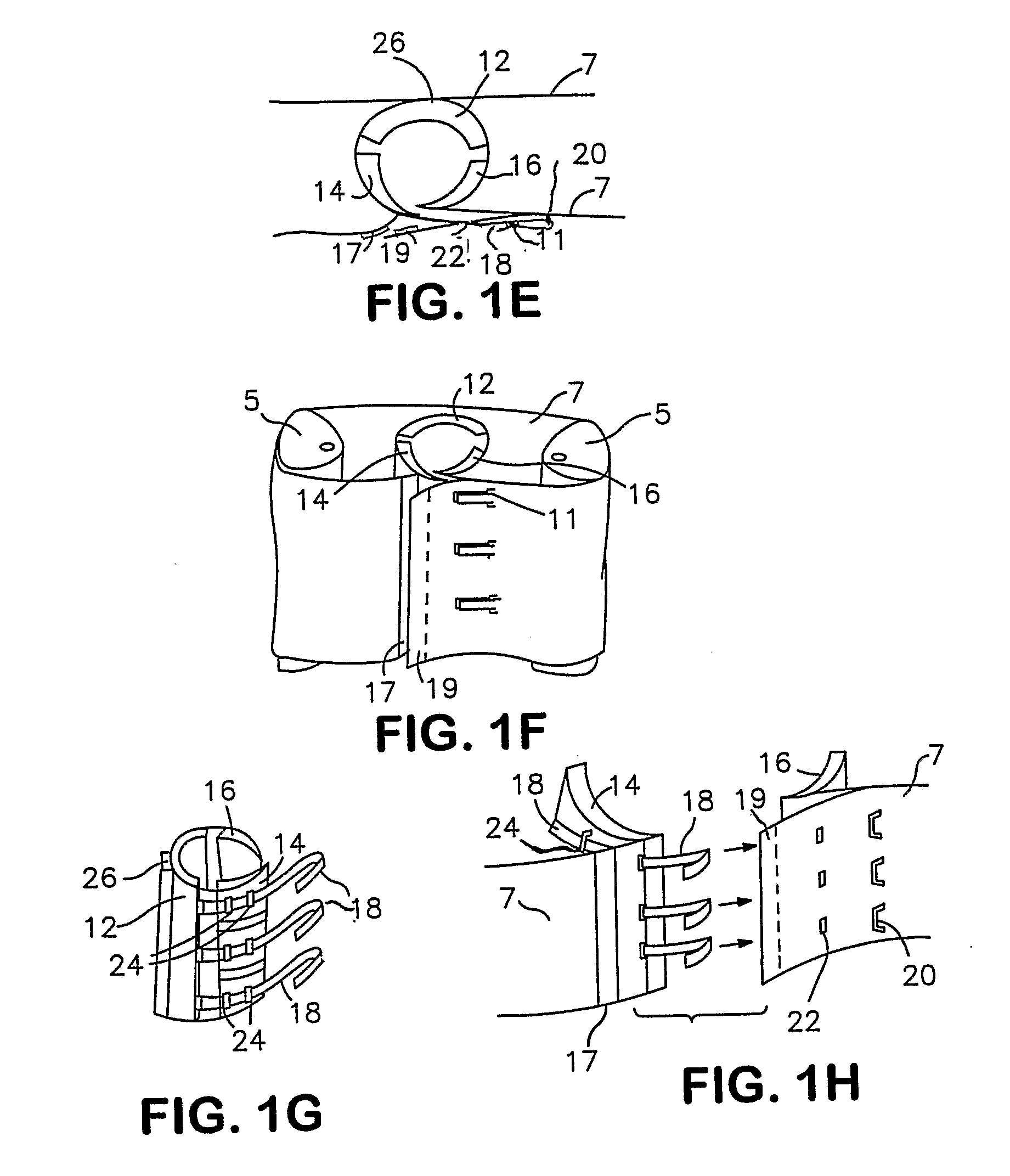
Surgical stapling systems
ActiveUS8475491B2Efficient and effectiveAnnuloplasty ringsSurgical veterinarySurgical stapleSurgical correction
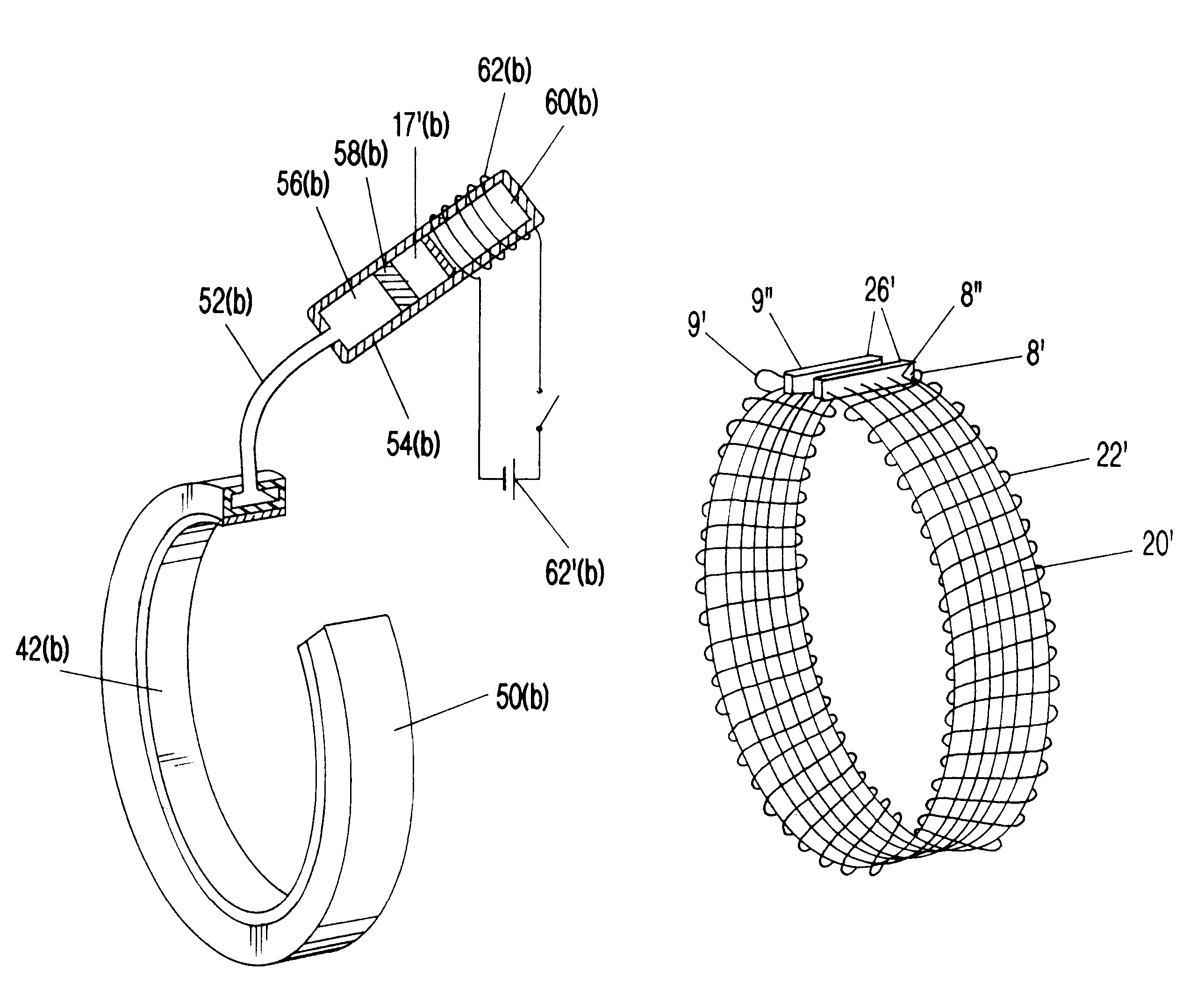
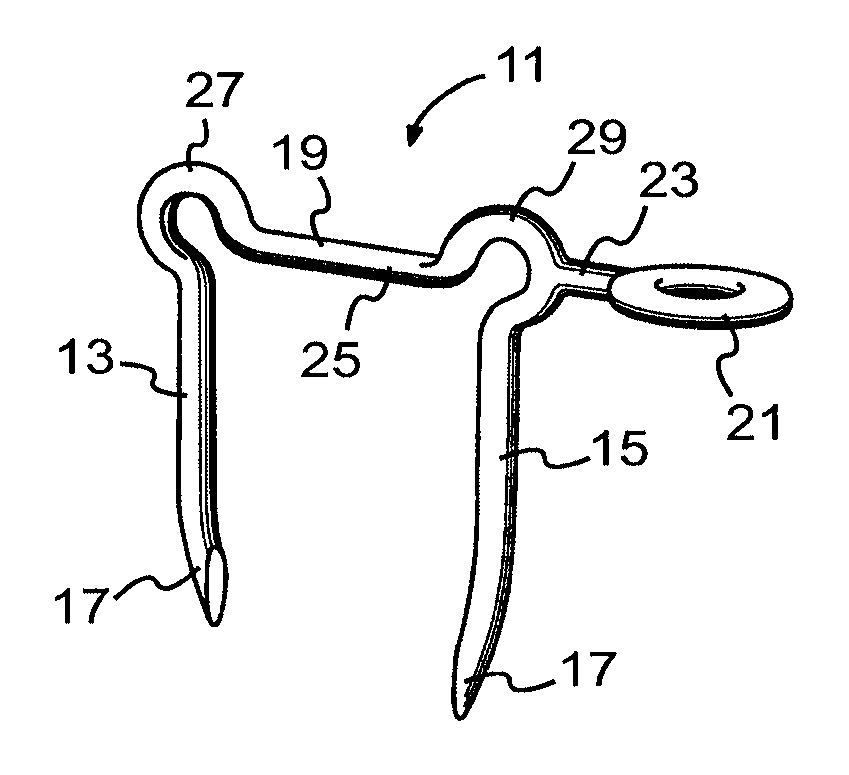
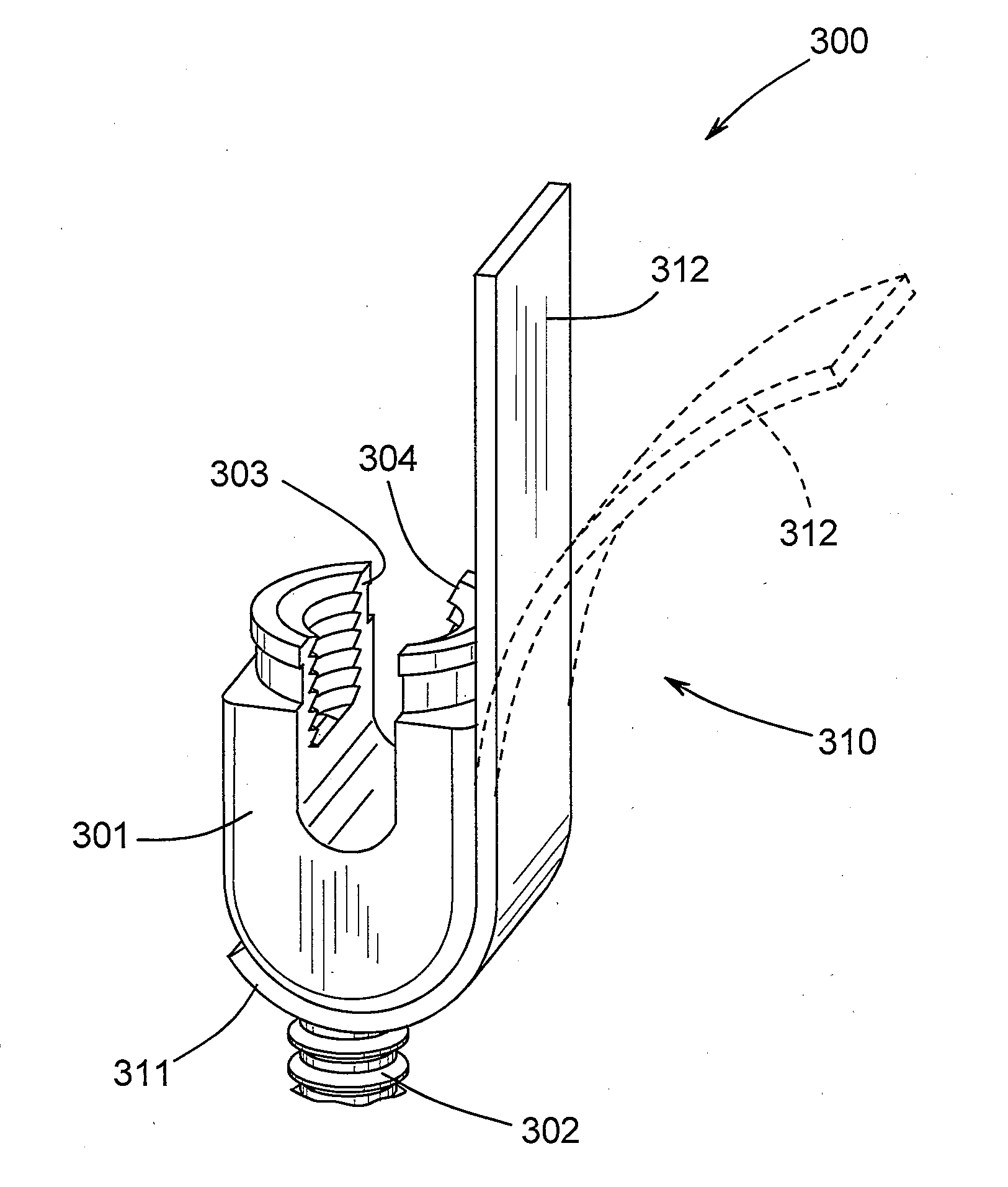
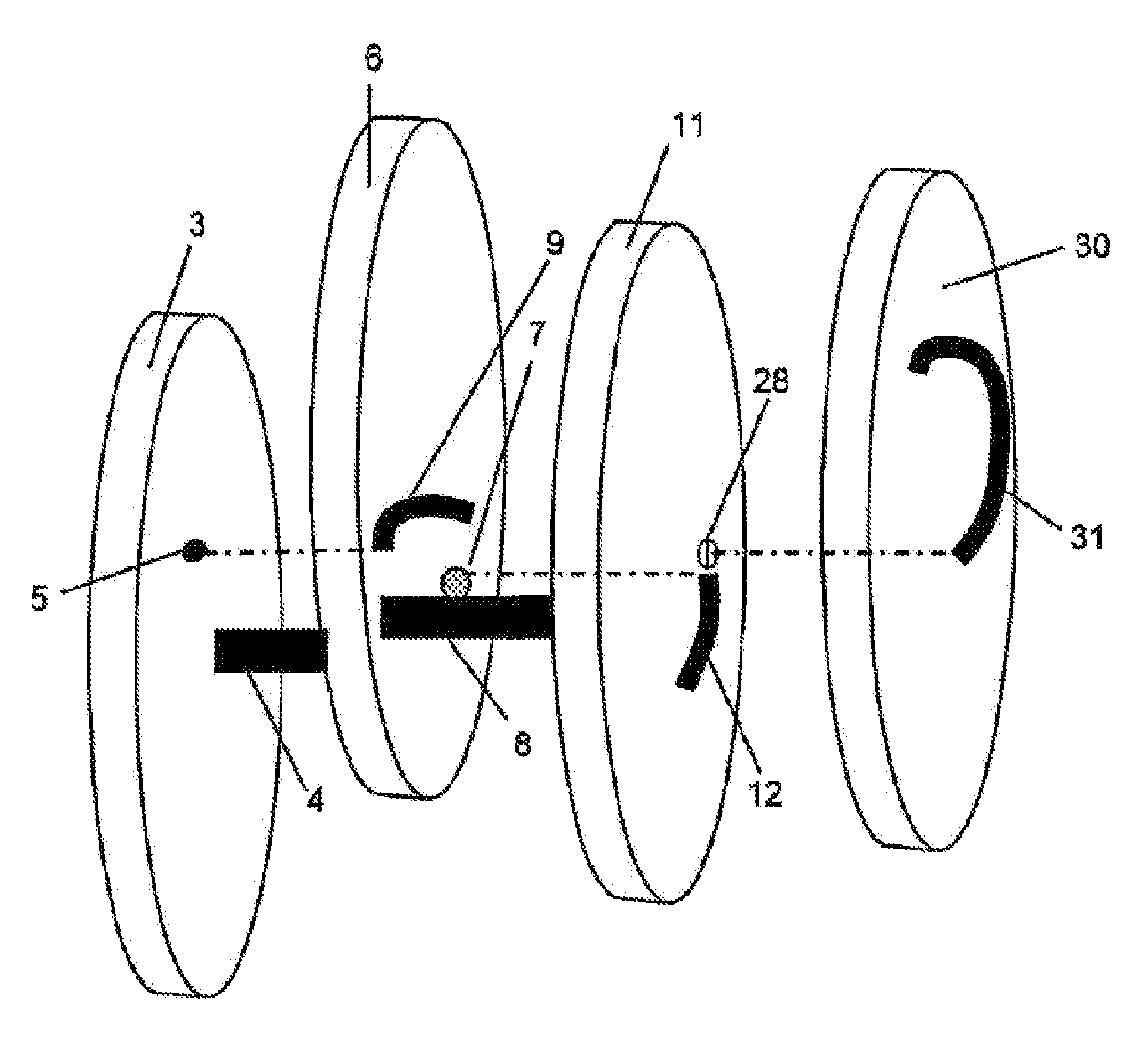
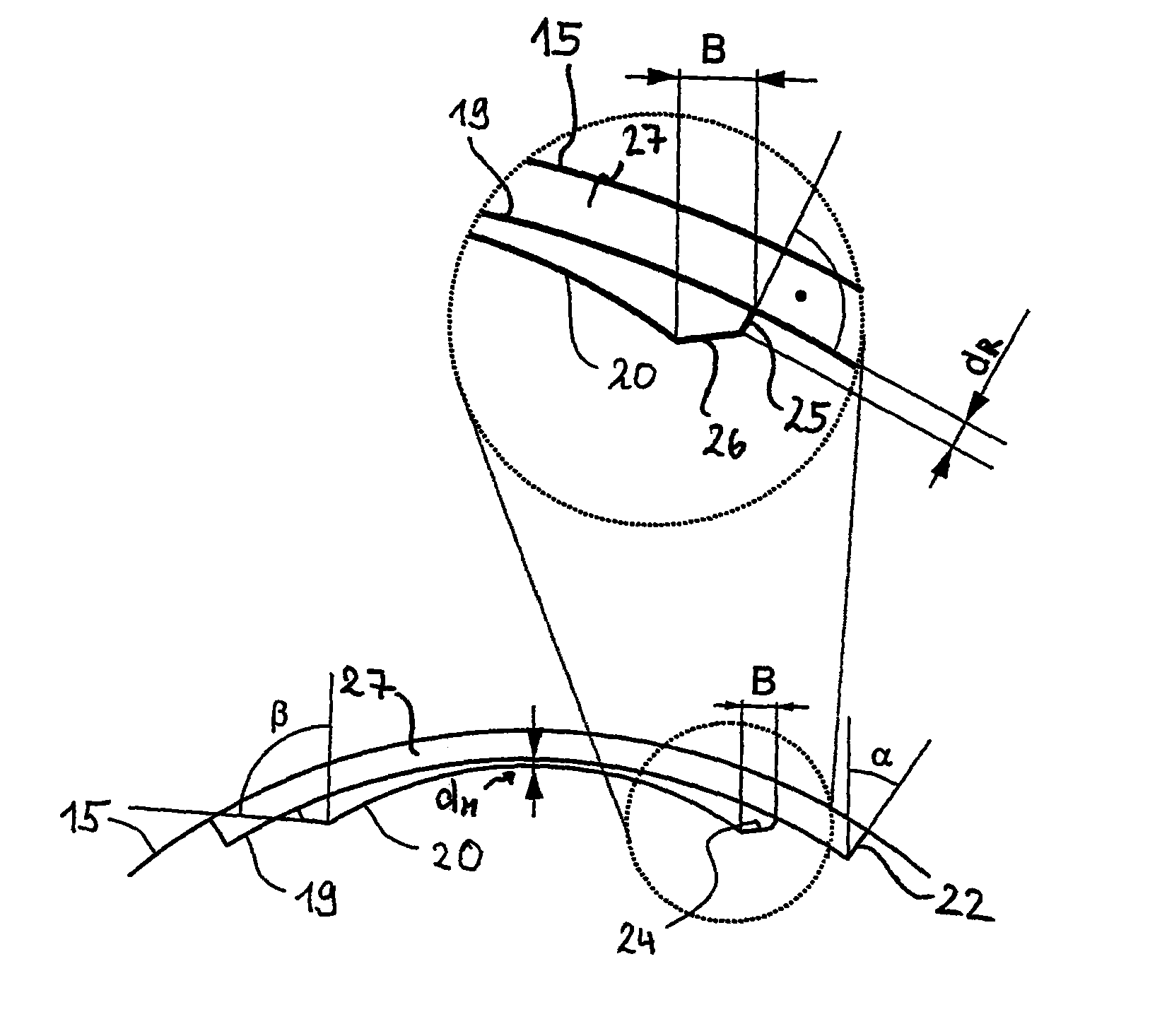
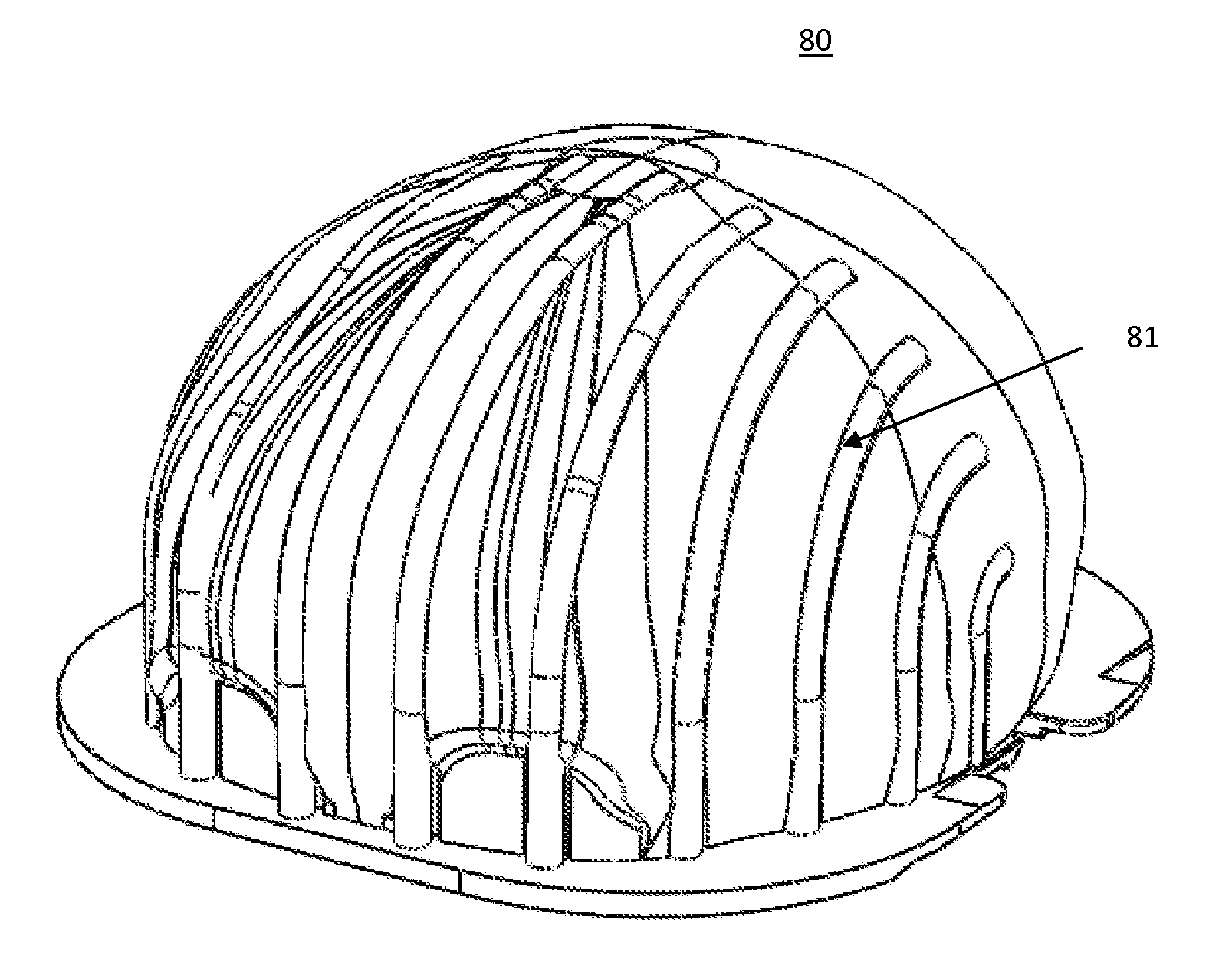
Interengaging surgical staples (11, 31, 51, 71) are provided that are useful in systems for the surgical correction of defects in cardiac valves and / or supporting weaknesses in abdominal regions. The staples are constructed with at least one ring (21, 41, 61, 81) extending laterally from the upper end of one staple leg (15, 35, 55, 75), which once implanted provides for interengagement with the next staple by passage of the other leg (13, 33, 53, 73) of it therethrough. Either shape-memory staple design or an implantation tool causes the two staple legs to curve respectively toward each other once having penetrated the tissue, thus gathering and constricting the tissue in a region below the surface thereof. Elastic sections (67, 83) may be provided in the crown connectors to allow flex in the plane thereof.
Owner:QUICKRING MEDICAL TECH LTD
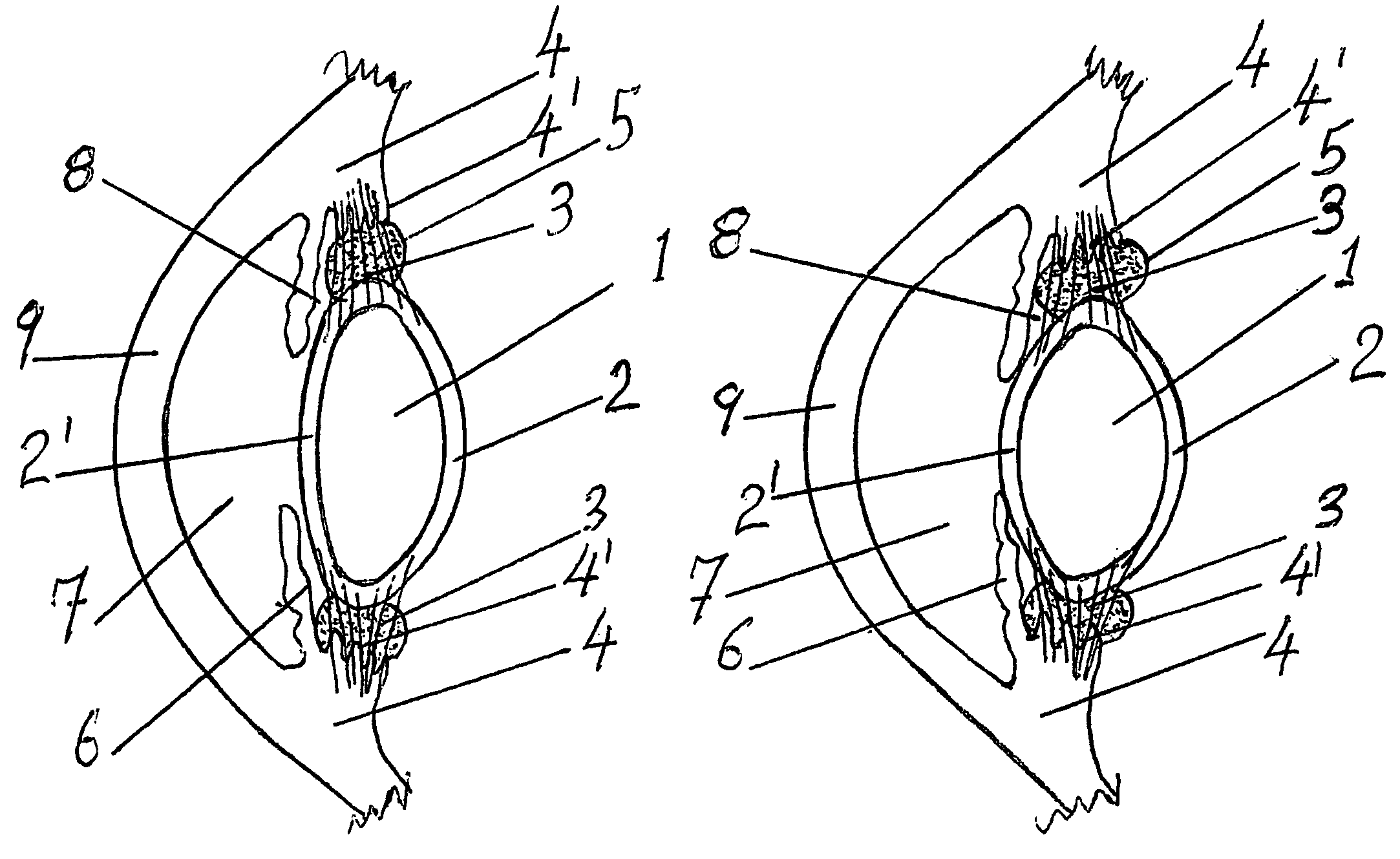
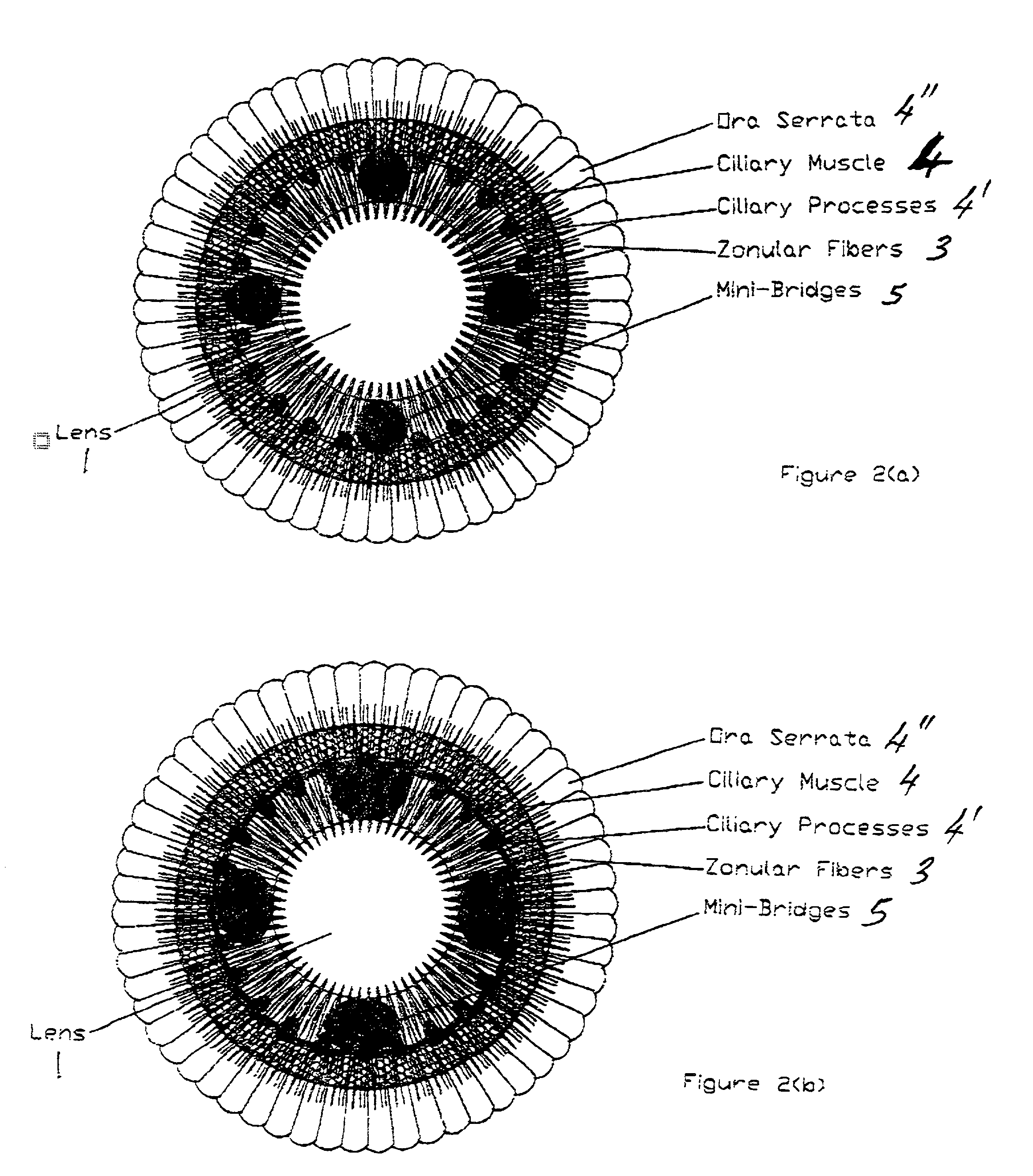
Accommodating zonular mini-bridge implants
InactiveUS7060094B2Simplify surgical proceduresEye surgeryLigamentsSurgical correctionSurgical department
Surgical correction of presbyopia and hyperopia by a circularly distributed assembly of mini-bridges implanted between the interior surfaces of the ciliary muscle and the exterior surface of the lens capsule, for augmenting the transmission of the contraction force of the ciliary muscle / zonule assembly to the lens capsule. The lens is symmetrically squeezed by mini-bridges acting in concert with the ciliary muscle thus changing the curvature of the lens. The mini-bridges are composite synthetic muscles comprising either passive biocompatible mini-bridges made with polymeric gels, silicone polymers or a composite, electromagnetically or mechanically deployable mini-bridges, inflatable balloons or synthetic muscles. The surgical procedure comprises using a ciliary muscle relaxant to stretch the lens / zonules / ciliary muscle assembly. An ultrasonic biomicroscope (UBM) is then used to enable the surgeon to see the area for implantation and the mini-bridges and thus perform endoscopic or incisional surgery to implant the mini-bridges in and around zonular cavities.
Owner:OPHTHALMOTRONICS
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
Correction of eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and astigmatism by using either pre-tensioned or transcutaneously energized artificial muscle implants to change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe by bringing the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants are scleral constrictor bands, segments or ribs for inducing accommodation of a few diopters, to correct the refractive errors on demand or automatically. The implant comprises an active sphinctering band encircling the sclera, implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing(decreasing) the length and curvature of the globe. Multiple and specially designed constrictor bands enable surgeons to correct astigmatism. The artificial muscles comprise materials such as composite magnetic shape memory (MSM), heat shrink, shape memory alloy-silicone rubber, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscles or electrochemically contractile ionic polymers bands.
Owner:OPHTHALMOTRONICS
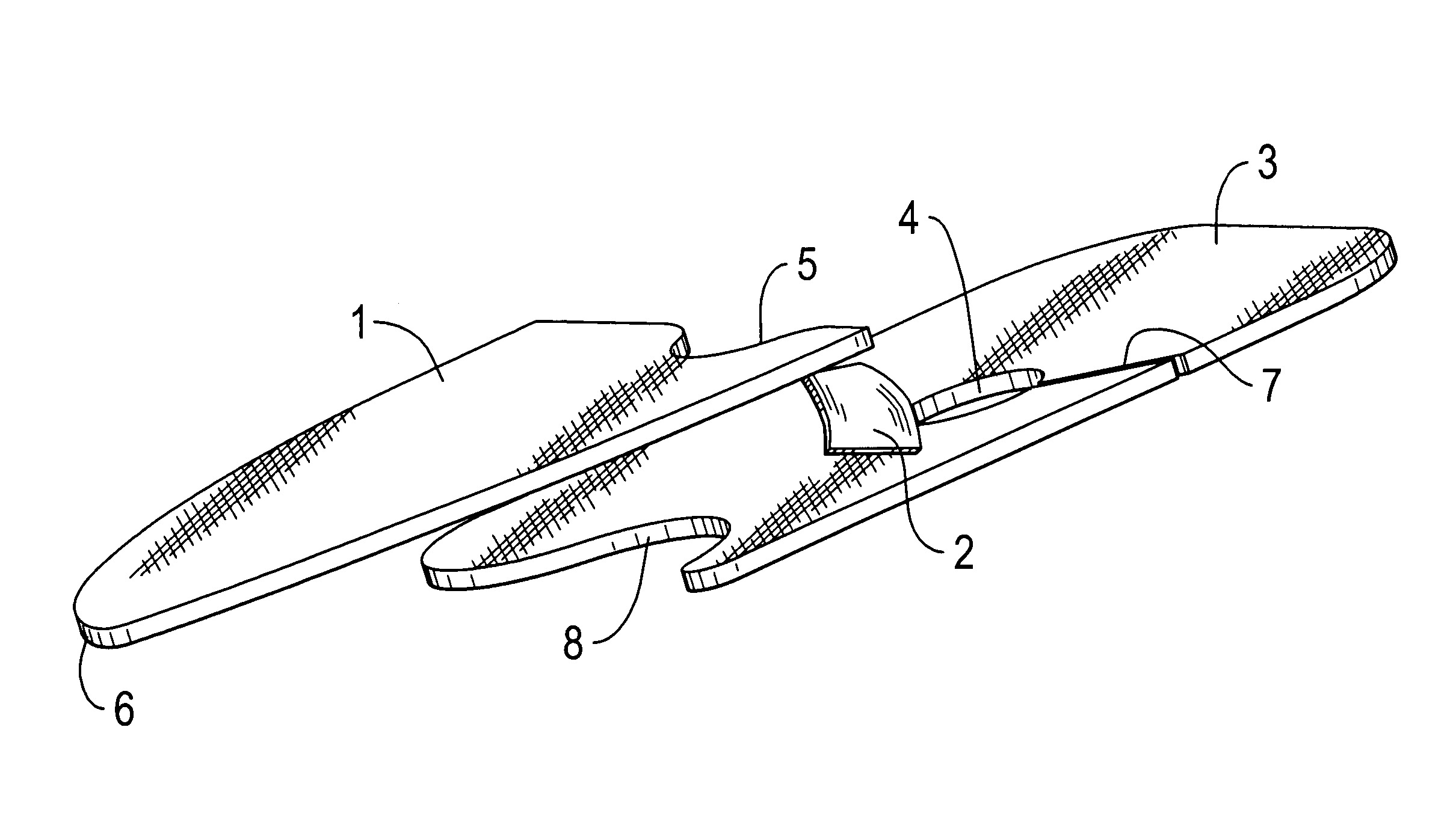
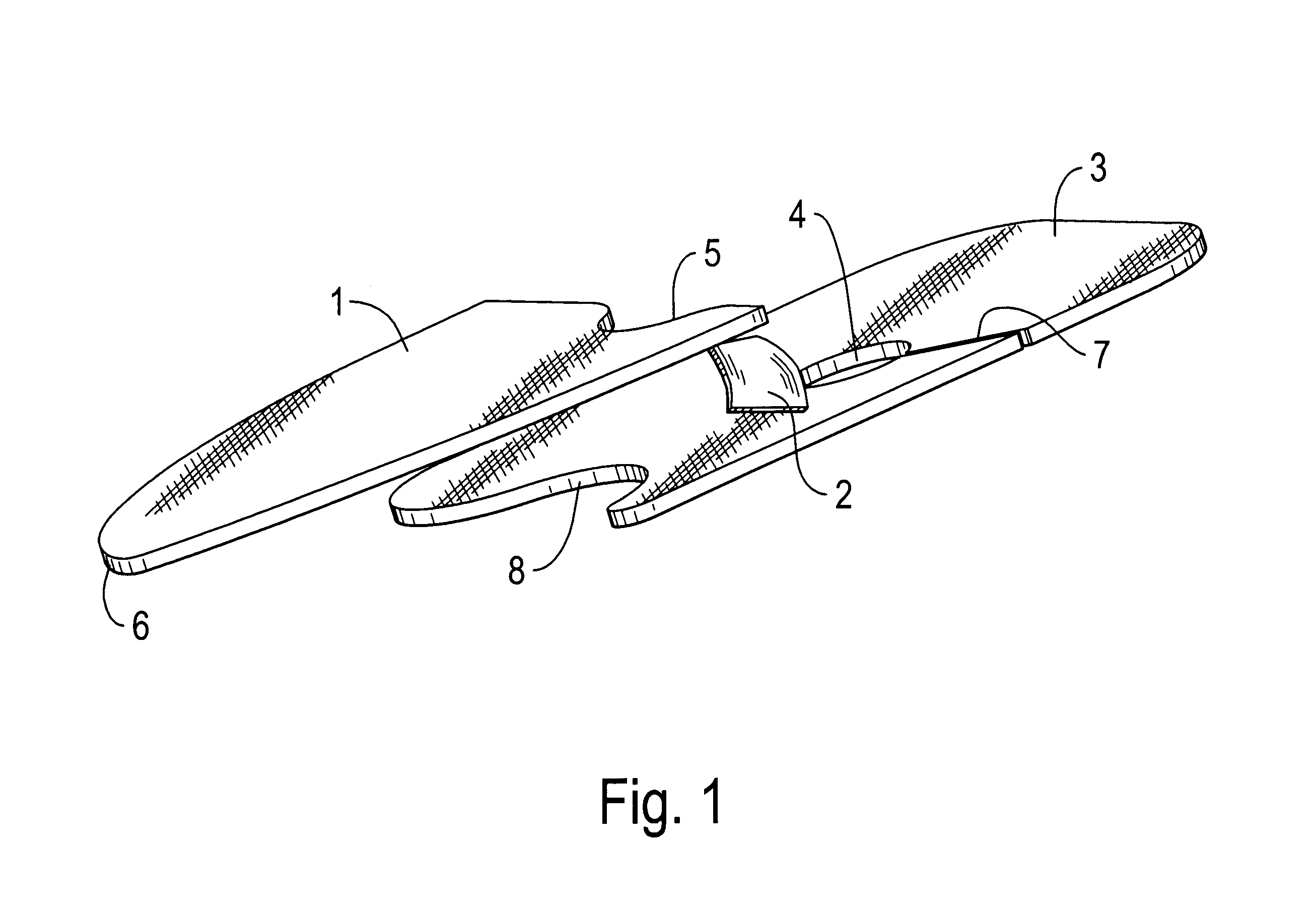
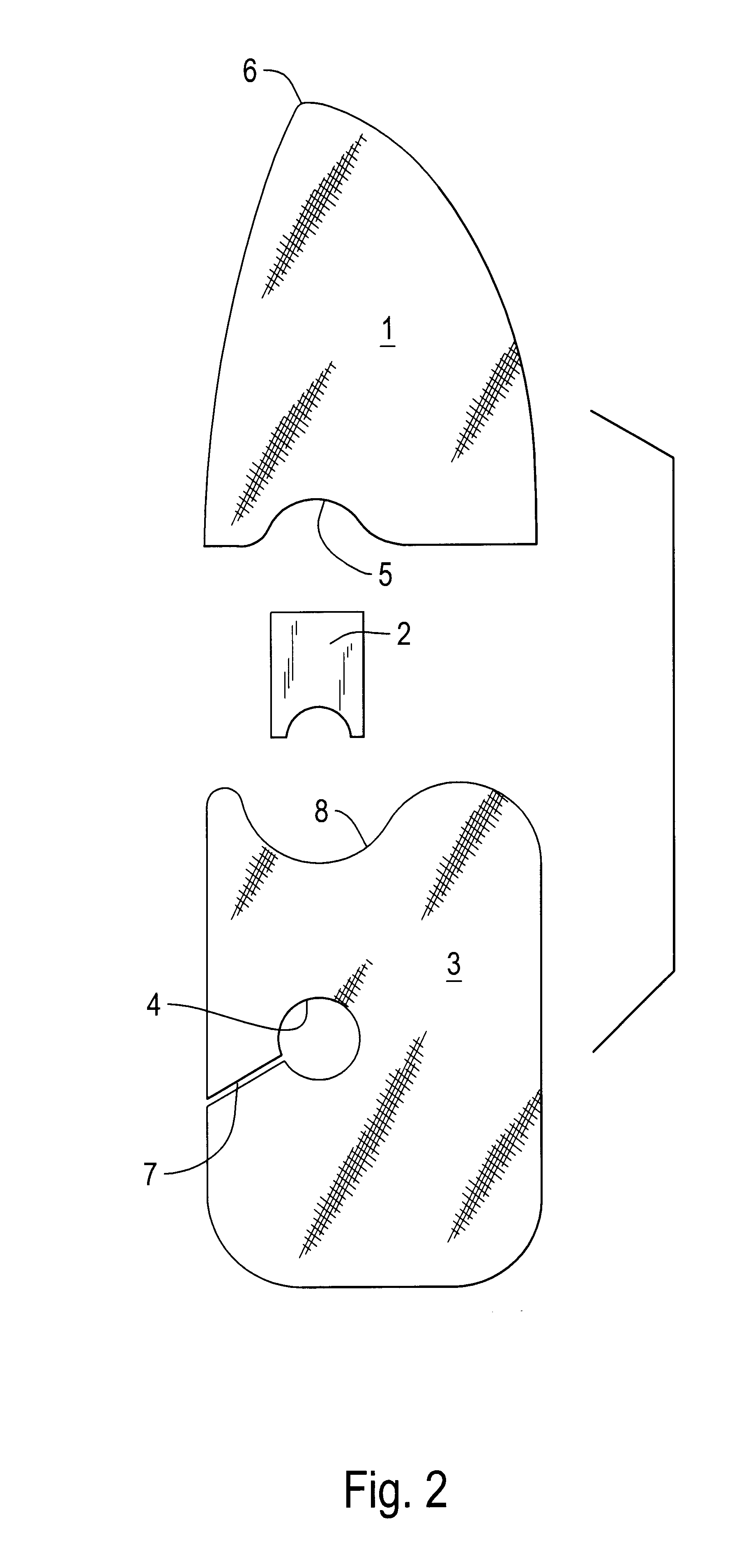
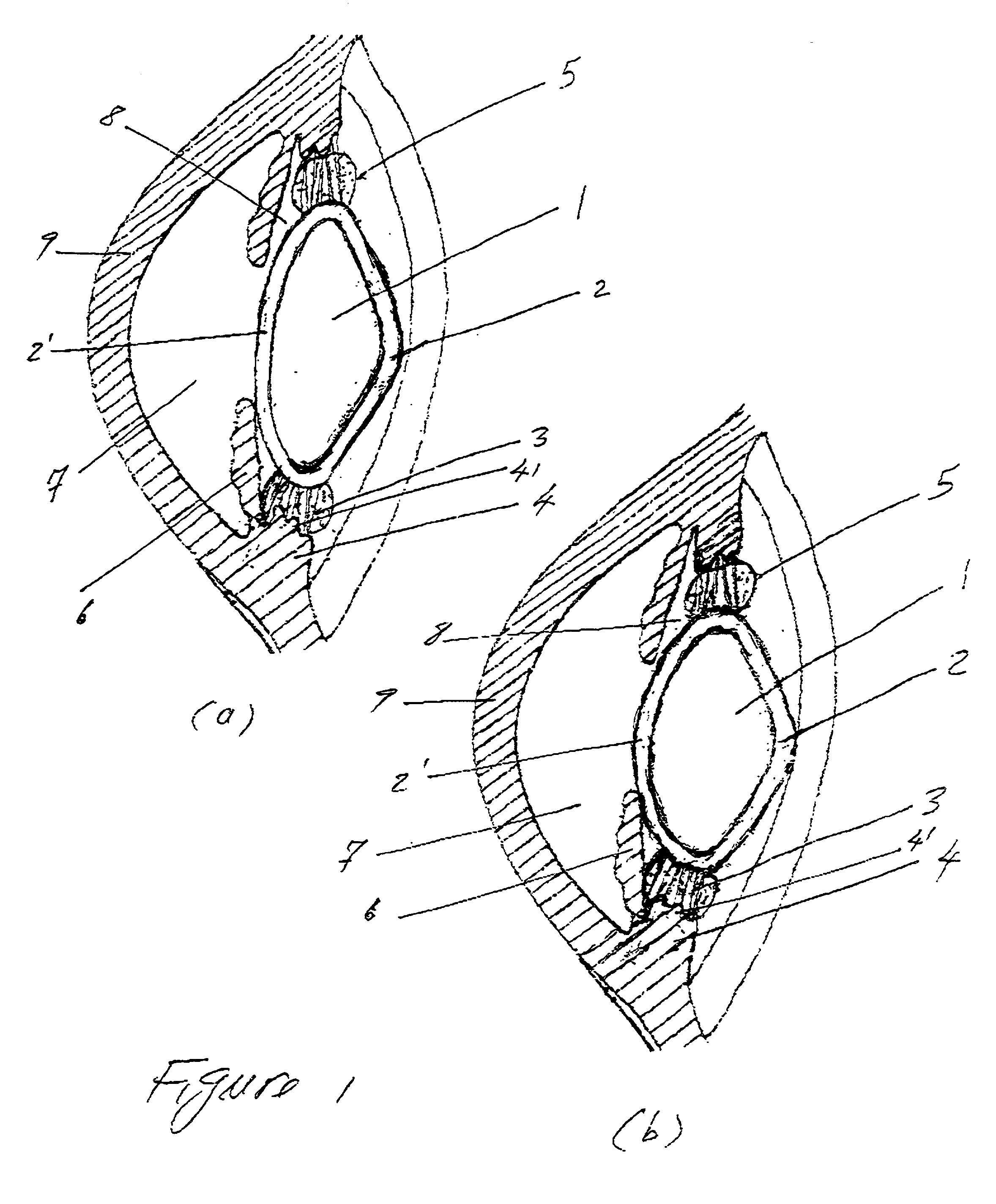
Multilayer prosthesis to surgically correct inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernia correcting prosthesis having an upper layer and a lower layer connected to each other by a flexible band, the flexible band having a first end fixed to the upper layer next to a recess provided on an edge of the upper layer, and a second end fixed next to a hole provided in the lower layer and connected by a cut to an external edge of the lower layer, the hole being axially aligned with the band and the recess.
Owner:SOFRADIM PROD SAS
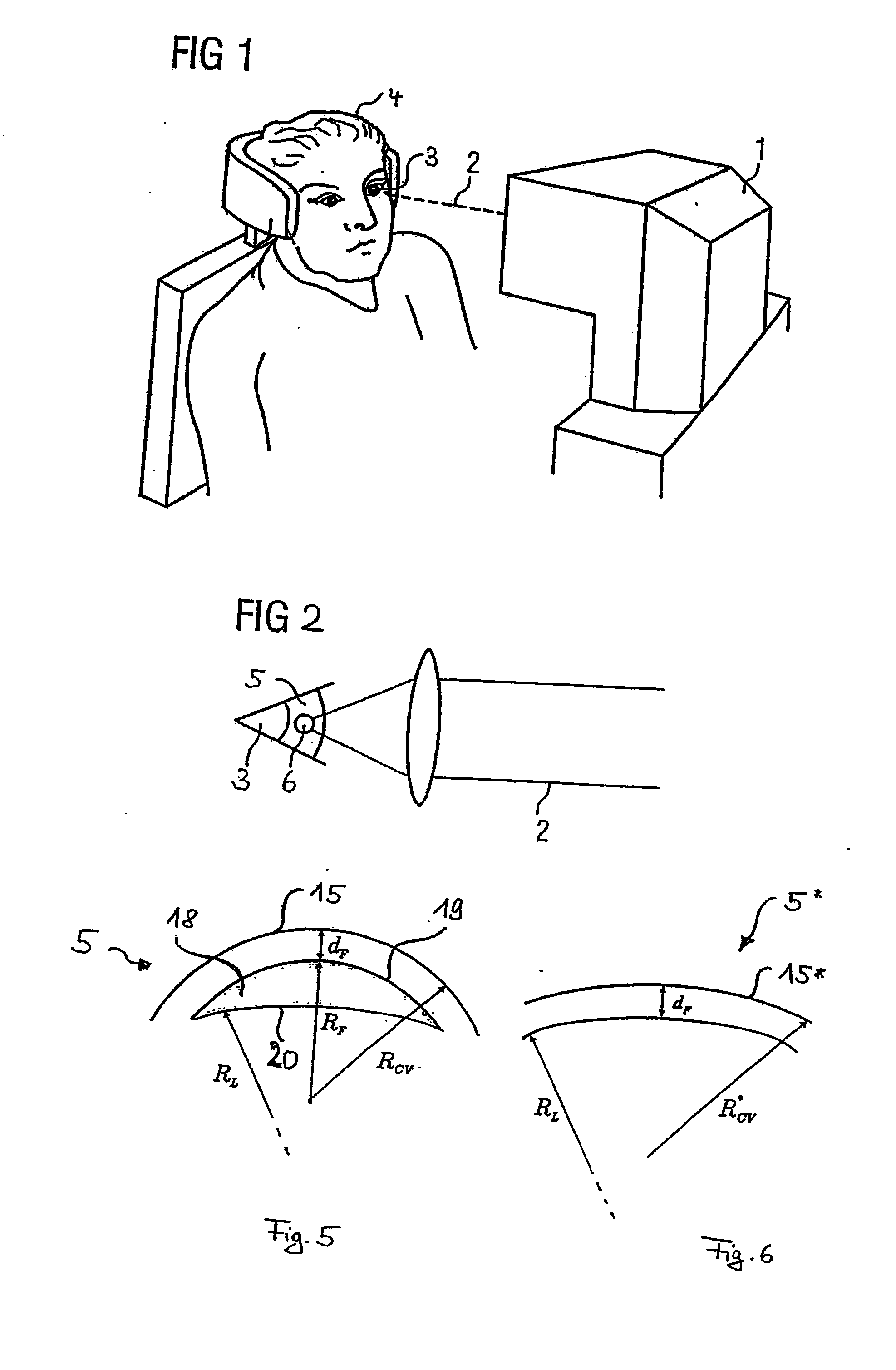
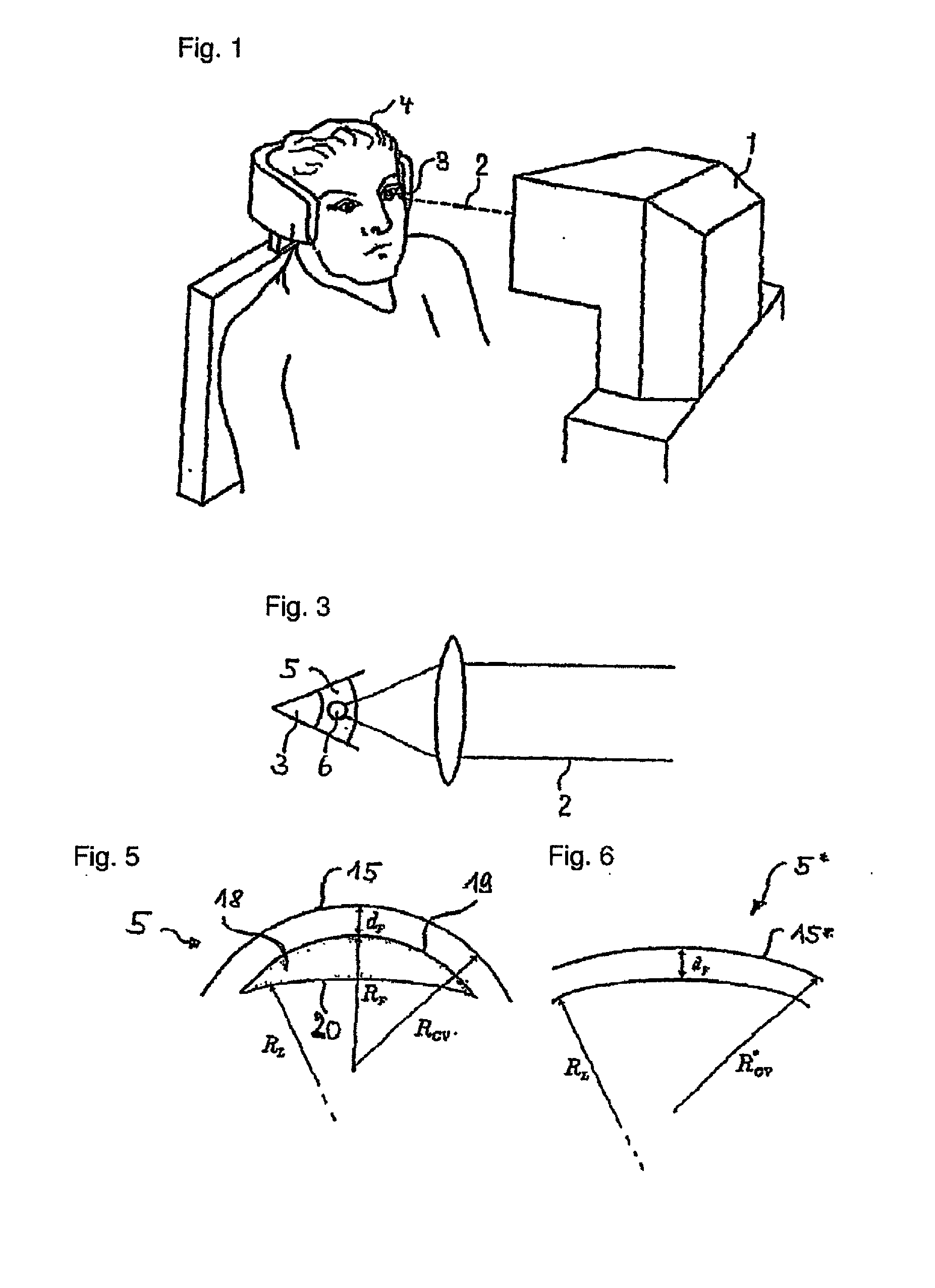
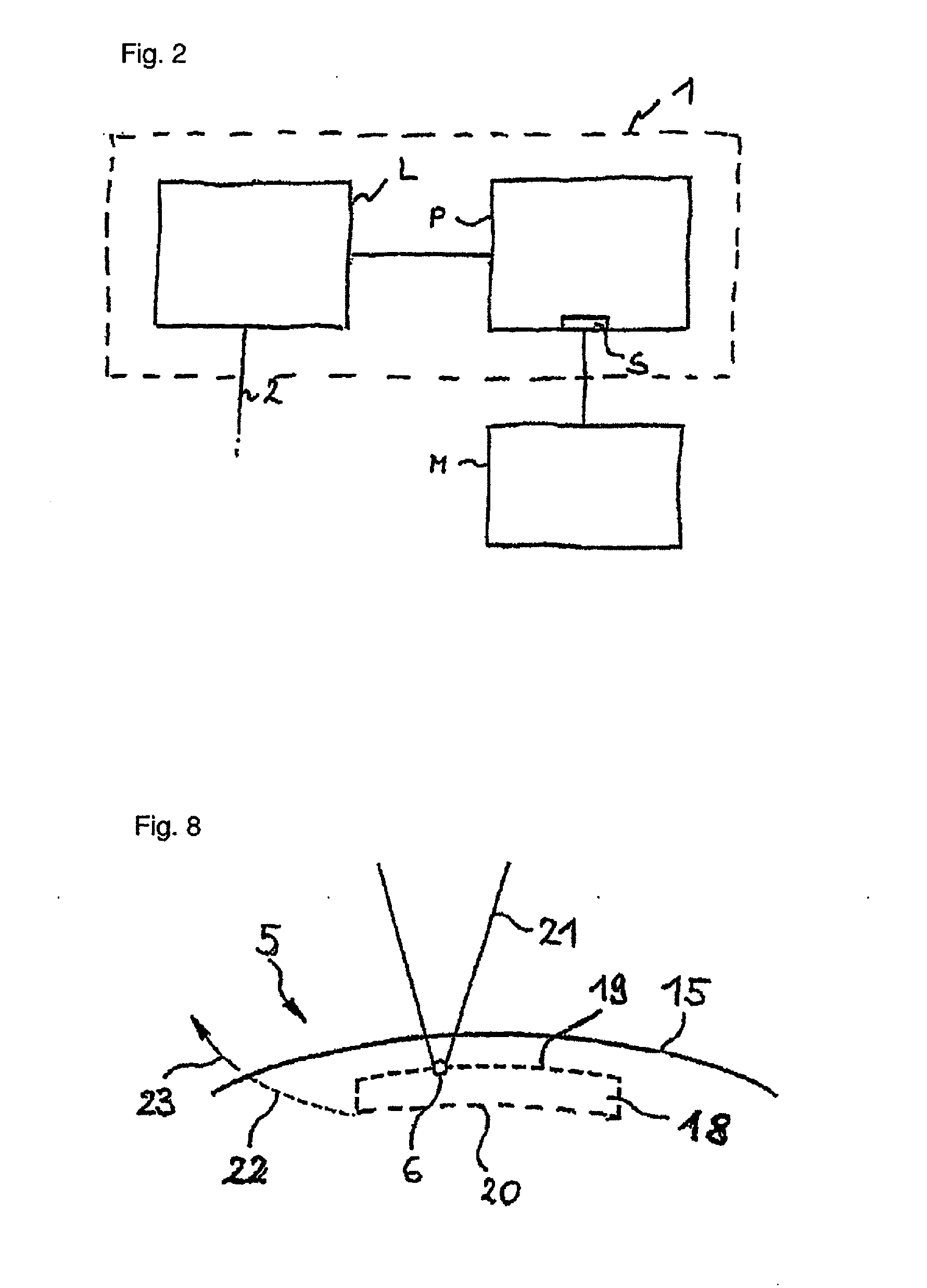
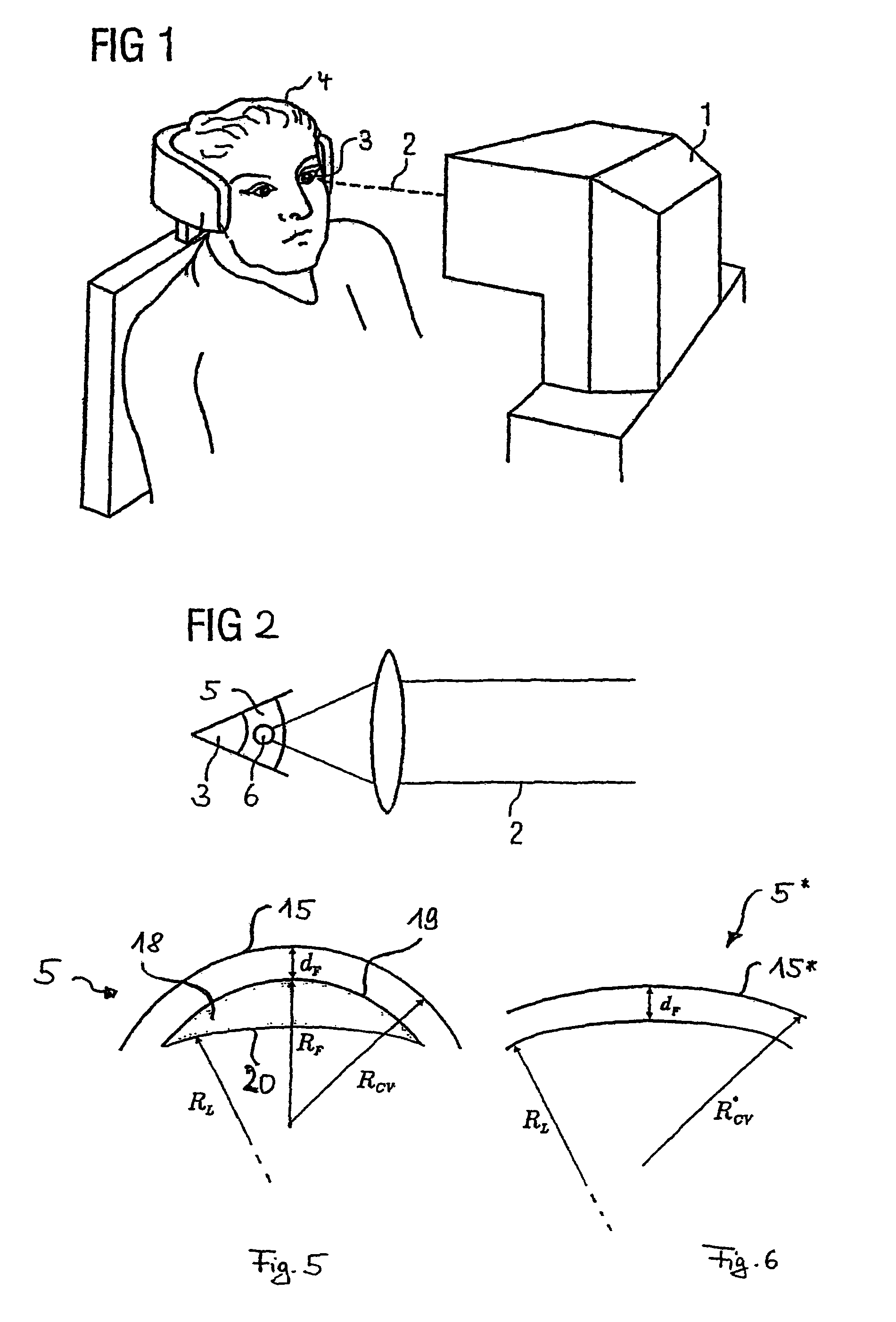
Treatment device for surgically correcting ametropia of an eye and method for creating control data therefore
ActiveUS20100331830A1Decreased regressionEfficient removalLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorFar-sightedness
A treatment device for the surgical correction of hyperopia in the eye comprising a laser device controlled by a control device. The laser device separating corneal tissue by applying laser radiation. The control device controls the laser device for emitting the laser radiation into the cornea such that a lenticule-shaped volume is isolated. Removal thereof effects the desired correction. The control device (12) predefines the volume such that a posterior surface and an anterior surface are connected via an edge surface that has a width in projection along the visual axis that is wider than the one which a straight line in the same projection, that is perpendicular at the edge of the posterior or the anterior surface would have relative to the associated surface and connects the anterior surface to the posterior surface or to the perceived extension thereof.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
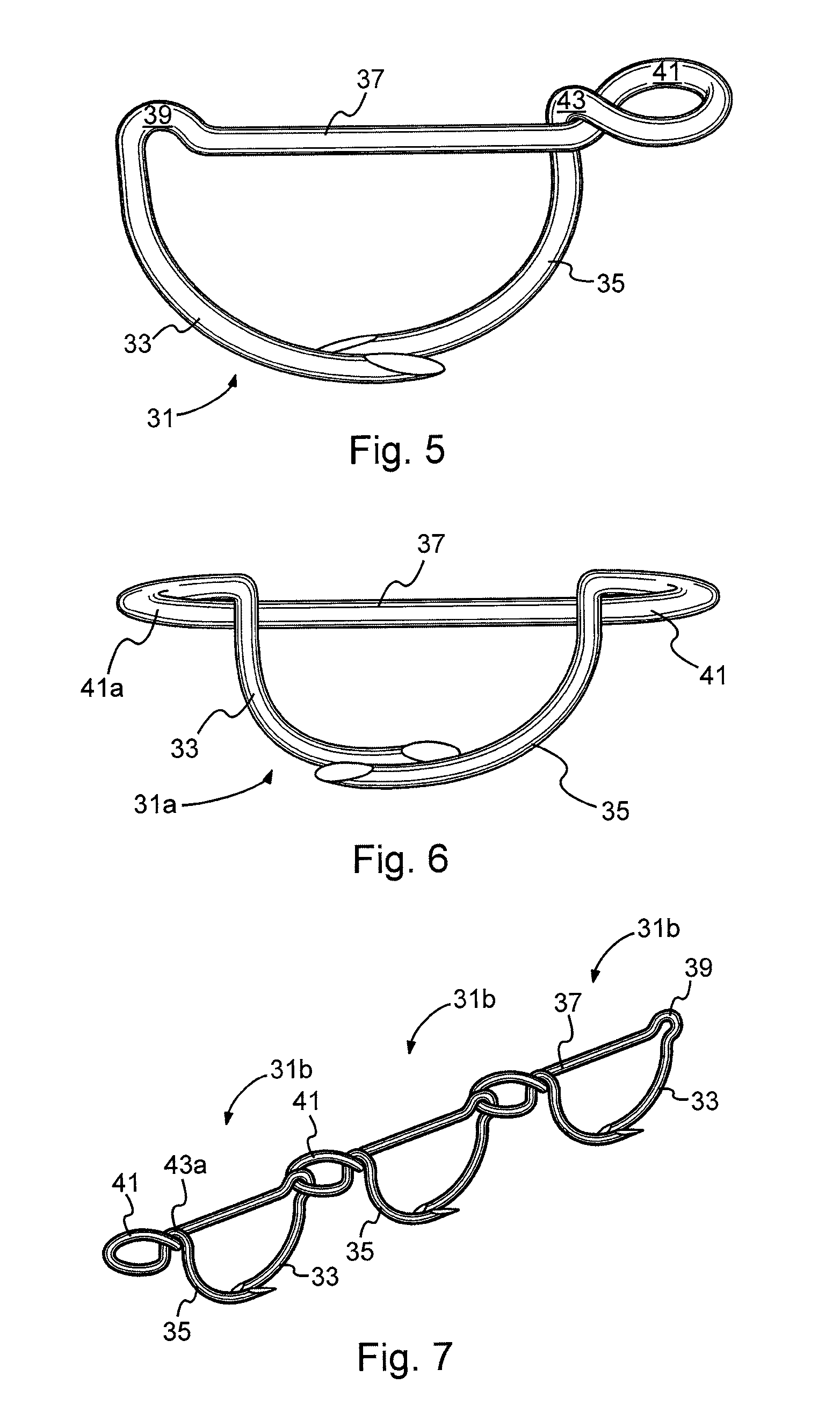
Surgical stapling systems
ActiveUS20110034953A1Efficient and effectiveInhibit refluxAnnuloplasty ringsStaplesSurgical stapleWeakness
Interengaging surgical staples (11, 31, 51, 71) are provided that are useful in systems for the surgical correction of defects in cardiac valves and / or supporting weaknesses in abdominal regions. The staples are constructed with at least one ring (21, 41, 61, 81) extending laterally from the upper end of one staple leg (15, 35, 55, 75), which once implanted provides for interengagement with the next staple by passage of the other leg (13, 33, 53, 73) of it therethrough. Either shape-memory staple design or an implantation tool causes the two staple legs to curve respectively toward each other once having penetrated the tissue, thus gathering and constricting the tissue in a region below the surface thereof. Elastic sections (67, 83) may be provided in the crown connectors to allow flex in the plane thereof.
Owner:QUICKRING MEDICAL TECH LTD
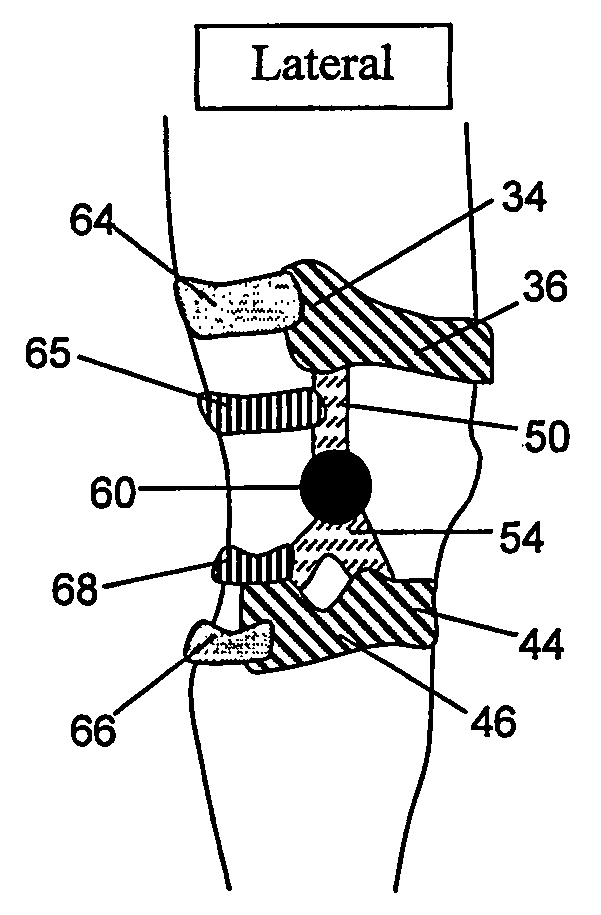
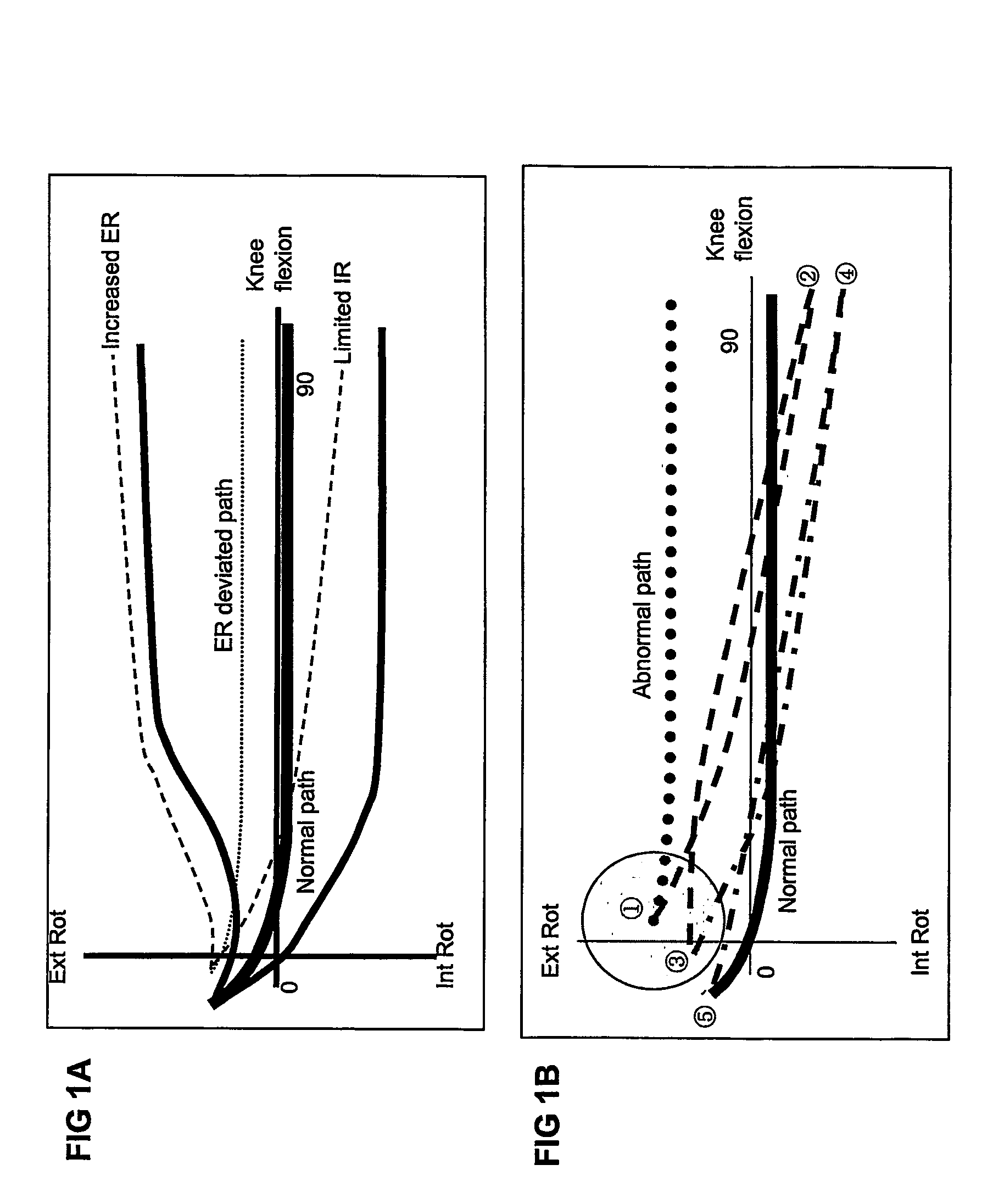
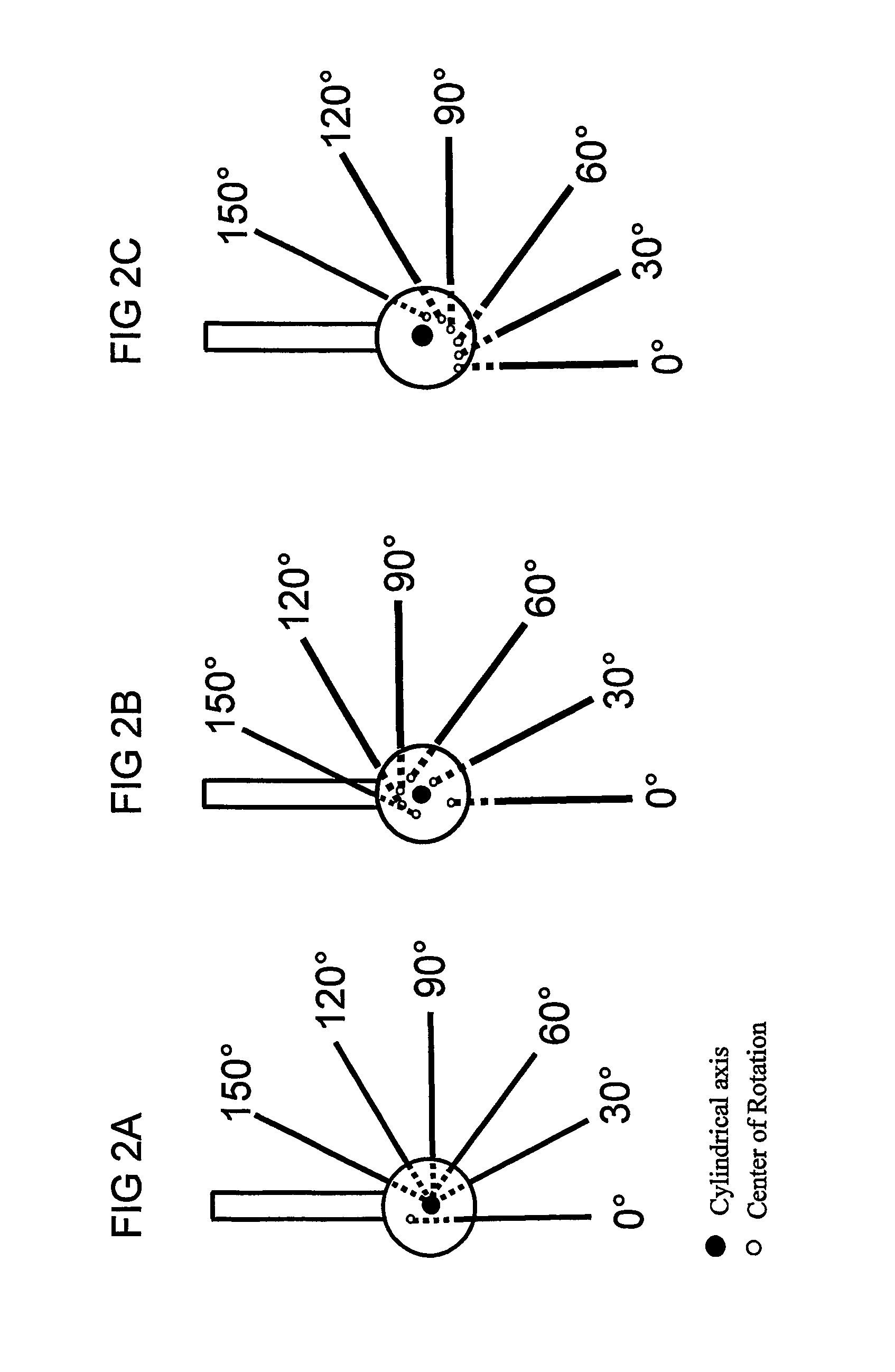
Non-surgical correcting abnormal knee loading
InactiveUS20070100265A1Reduce impactReduce alignmentNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee loadingPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention provides hinges for use in knee braces to correct and prevent knee pathology. Further provided are knee braces comprising the hinges of the present invention to correct and prevent knee pathology including osteoarthritis. Also provided are methods of treating knee pathology by using the hinges and braces of the present invention to apply a corrective rotational force and an off-loading force to the affected knee compartment.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
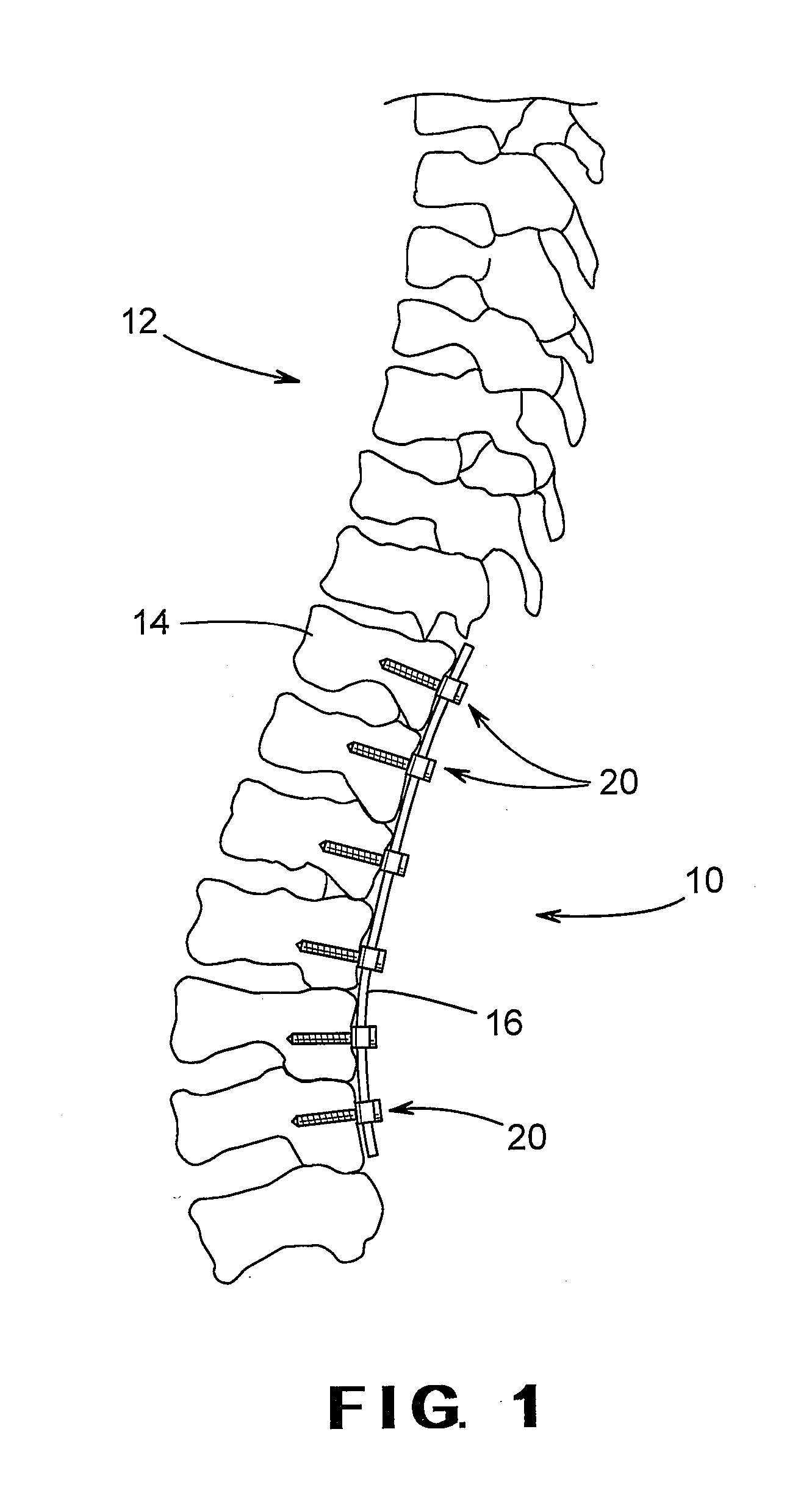
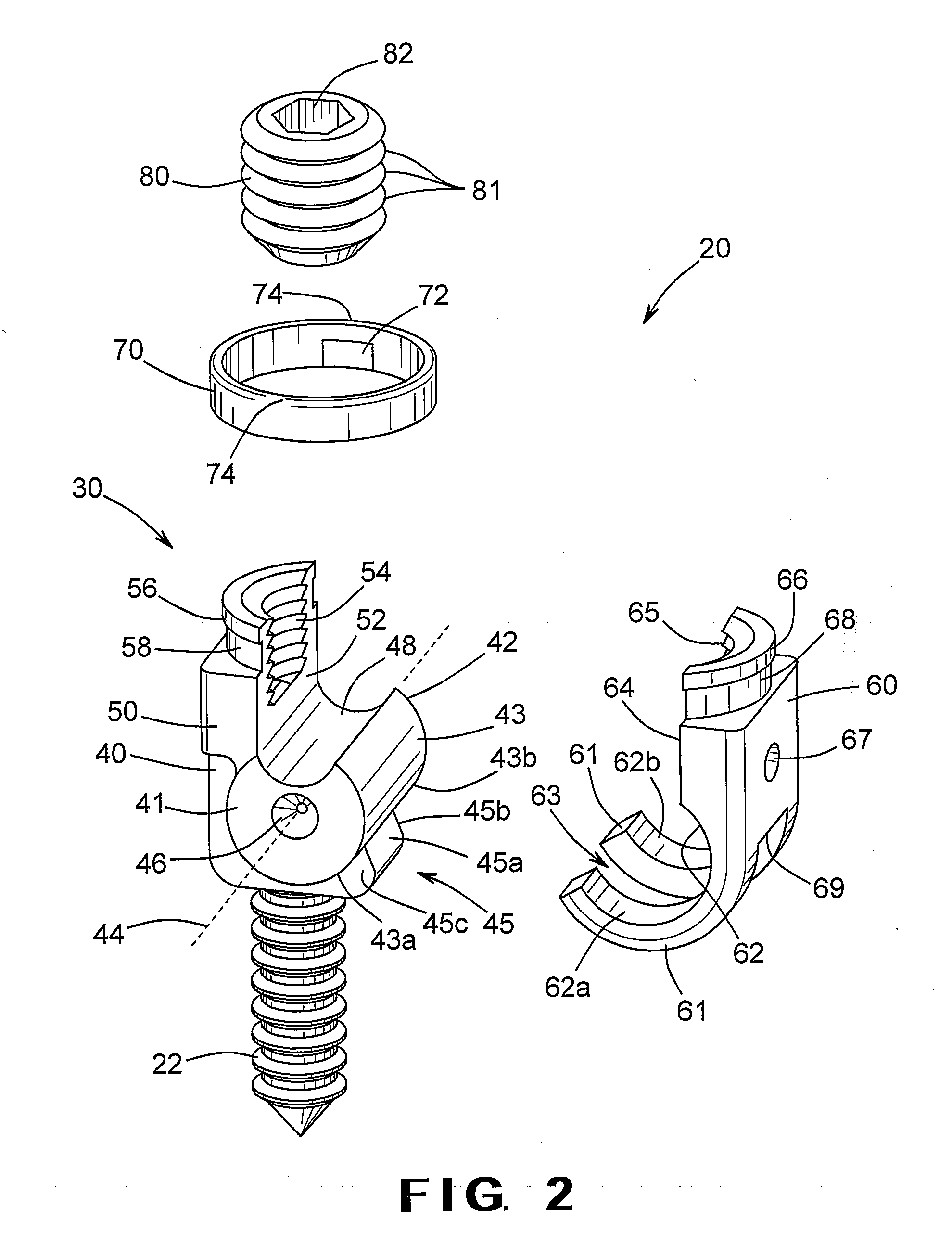
Pedicle screw including stationary and movable members for facilitating the surgical correction of spinal deformities
InactiveUS20100241172A1Precise alignmentSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnEngineering
A pedicle screw for use in the treatment of a spinal deformity includes a head assembly and a fastener portion extending from the head assembly. The pedicle screw includes a head assembly and a fastener portion that extends from the head assembly. The fastener portion extends from the head assembly and is adapted to be secured to a vertebra of a spinal column. The head assembly includes a stationary member and a movable member. The movable member is supported on the stationary member for movement (such as pivoting movement) relative thereto between an opened position and a closed position. When the movable member is in the opened position, the head assembly is adapted to receive a longitudinal member therein for treatment of a spinal deformity. Thereafter, the movable member can be moved to the closed position to properly align the pedicle screw with the longitudinal member. A locking member and a retention member can then be used to maintain the movable member in the closed position.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Non-surgical correcting abnormal knee loading
InactiveUS7435234B2Reduce impactReduce alignmentNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationKnee loading
The invention provides hinges for use in knee braces to correct and prevent knee pathology. Further provided are knee braces comprising the hinges of the present invention to correct and prevent knee pathology including osteoarthritis. Also provided are methods of treating knee pathology by using the hinges and braces of the present invention to apply a corrective rotational force and an off-loading force to the affected knee compartment.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
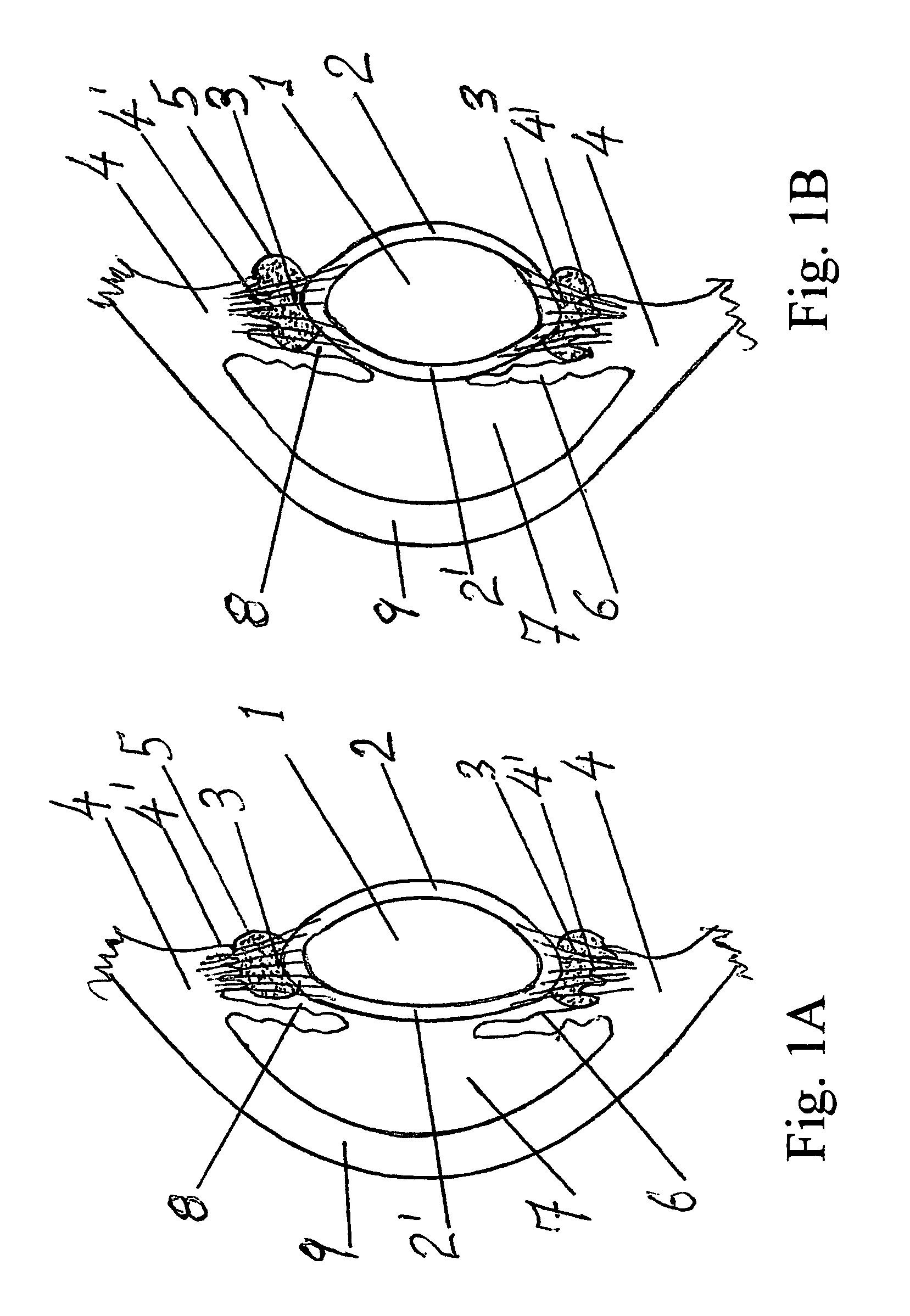
Accommodating zonular mini-bridge implants
Owner:OPHTHALMOTRONICS
Device and method for producing control data for the surgical correction of defective eye vision
ActiveUS20120016351A1Simple definitionEasy to set upLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsControl dataRefractive index
A device for producing control data for a laser device for the surgical correction of defective vision. The device produces the control data such that the laser emits the laser radiation such that a volume in the cornea is isolated. The device calculates a radius of curvature RCV* to determine the control data, the cornea reduced by the volume having the radius of curvature RCV* and the radius of curvature being site-specific and satisfying the following equation: RCV*(r,φ)=1 / ((1 / RCV(r,φ))+BCOR(r,φ) / (nc−1))+F, wherein RCV(r,φ) is the local radius of curvature of the cornea before the volume is removed, nc is the refractive index of the material of the cornea, F is a coefficient, and BCOR(r,φ) is the local change in refractive force required for the desired correction of defective vision in a plane lying in the vertex of the cornea, and at least two radii r1 and r2 satisfy the equation BCOR(r=r1,φ)≠BCOR(r=r2,φ).
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
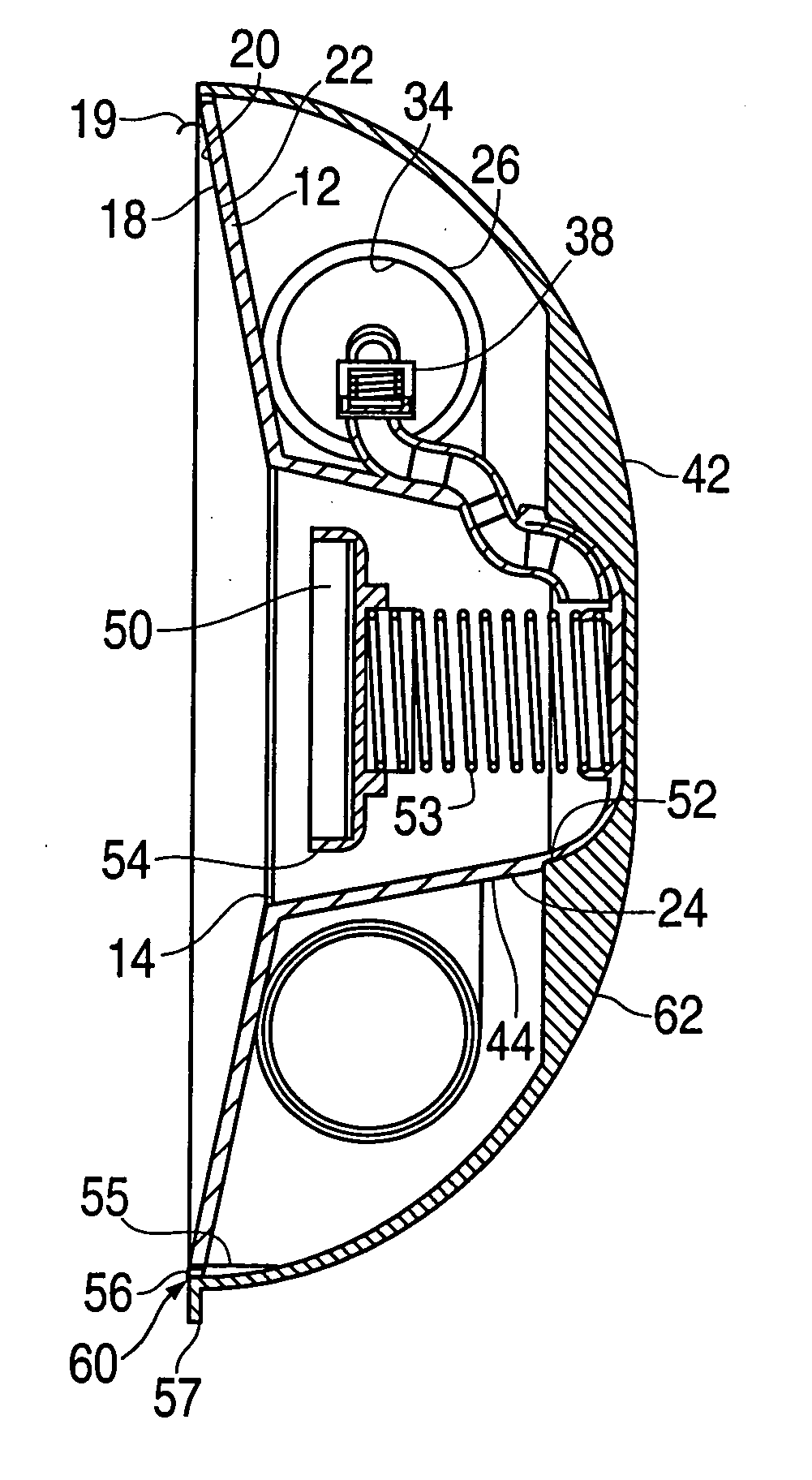
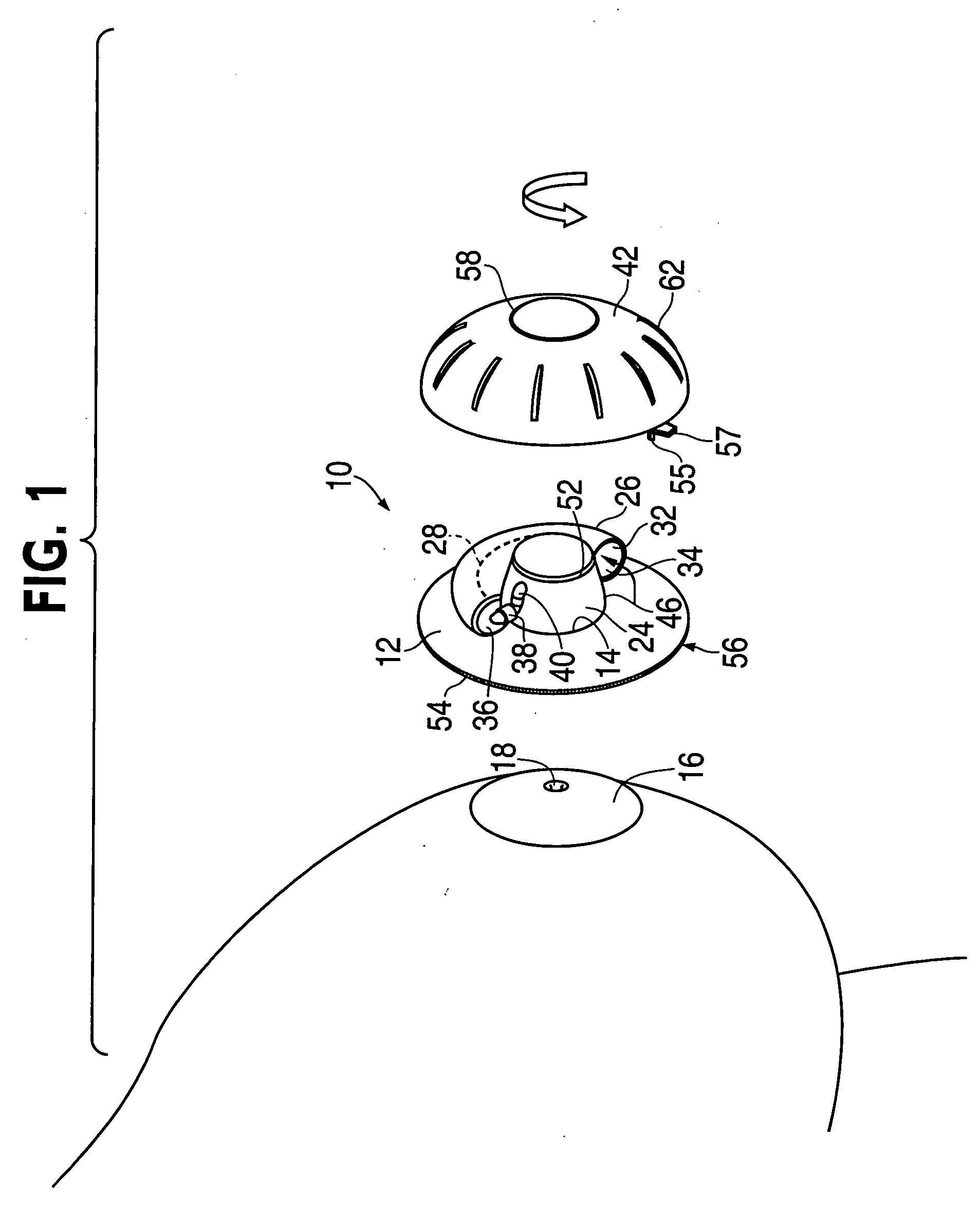
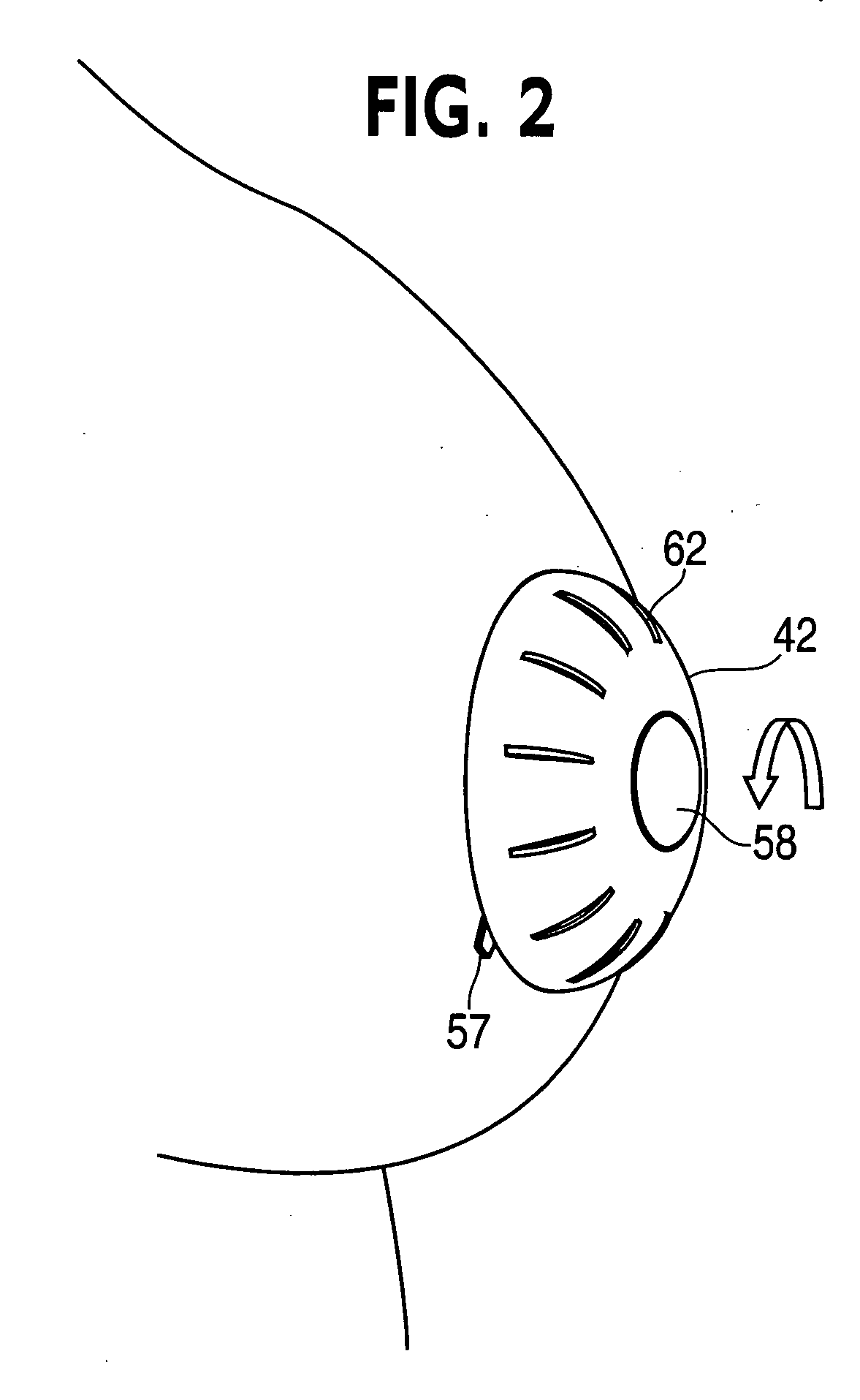
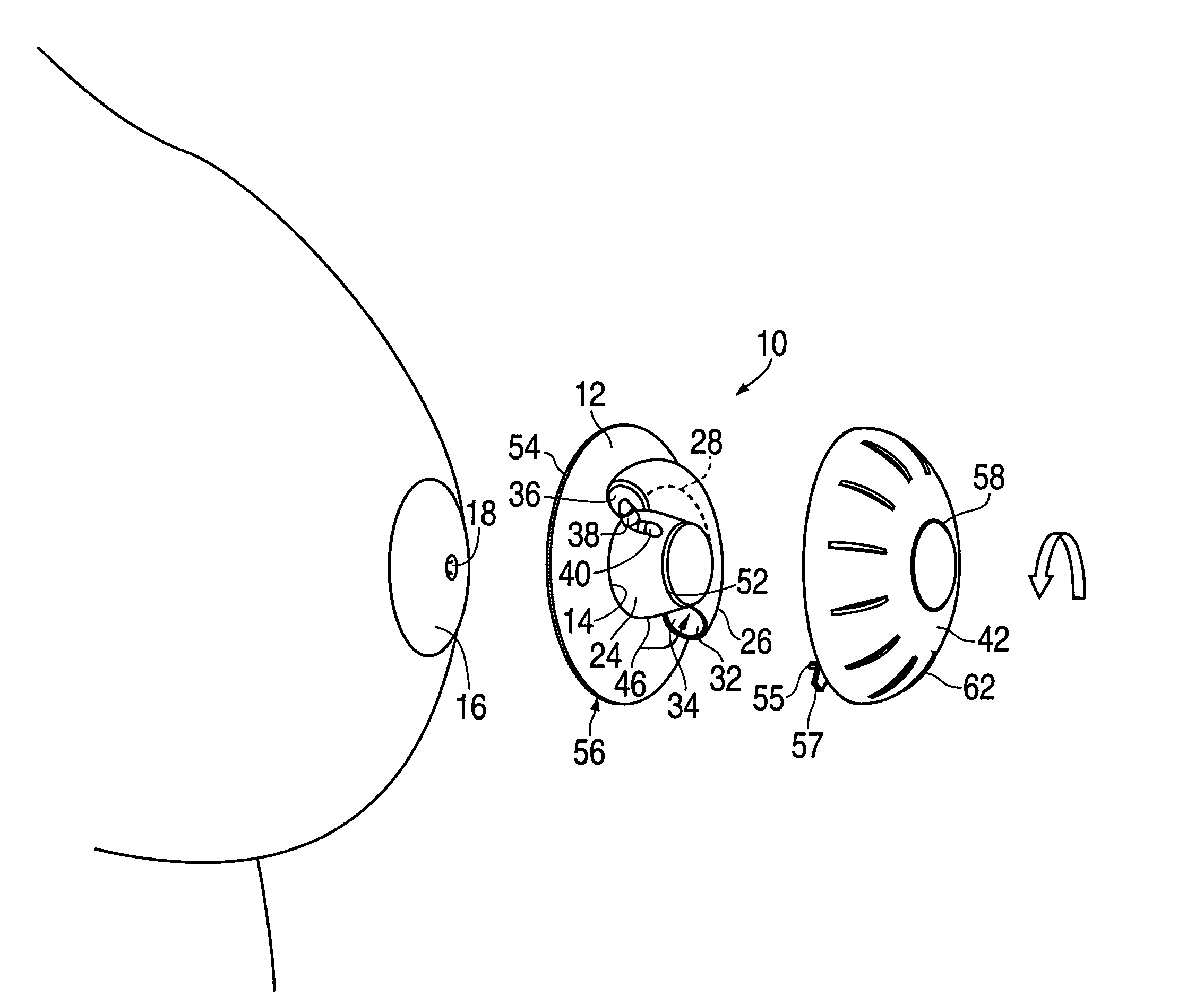
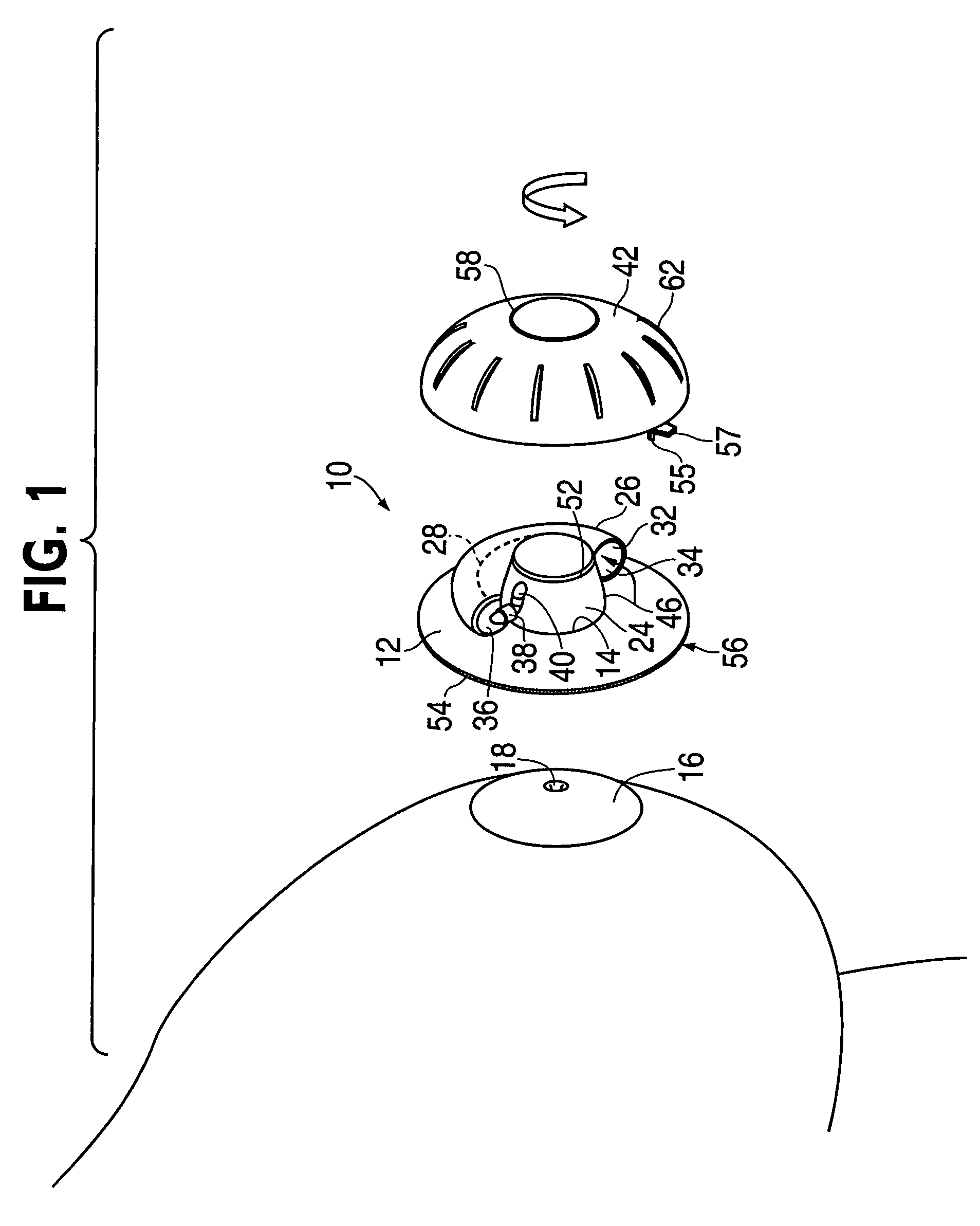
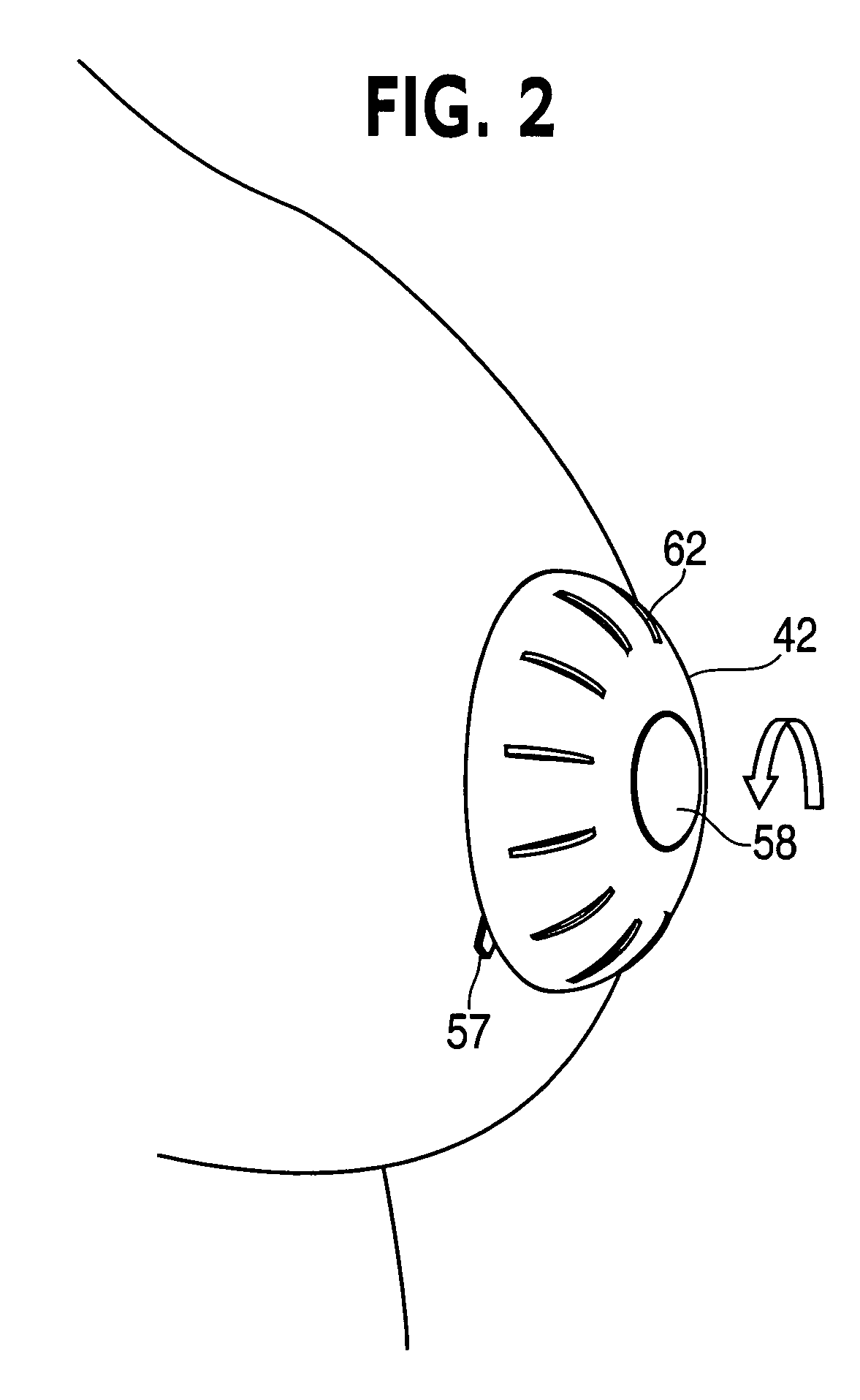
Device for non-surgical correction of congenital inverted nipples and/or collection of nipple aspirate fluid
InactiveUS20060178601A1Increase partial vacuumEasy to collectPneumatic massageMilking pumpEngineeringAreola
The invention is an apparatus (10) for treating inverted nipples and / or the collection of NAF. The invention includes an assembly which creates an airtight seal upon attachment to at least an areola (16) of an inverted nipple (18) and by rotation of a part thereof draws a partial vacuum to apply an outward force to the nipple; and a syringe (26) including a curved longitudinal axis (28), the syringe being carried by the assembly and being in fluid communication with a chamber (24) of the assembly upon attachment of the assembly to at least an areola of an inverted nipple, the syringe including a plunger (30) which is sealed against an inner surface (34) of the syringe and is rotatable to move along the longitudinal axis relative to the chamber which moves the plunger within a syringe body to expel air from the syringe body away from the chamber upon rotation of the plunger in a first direction and to aspirate air from the chamber upon attachment of the apparatus to the breast surrounding the nipple upon rotation in a second direction opposite to the first direction to create a partial vacuum within the chamber to evert the nipple.
Owner:WANG PAUL C +1
Device for non-surgical correction of congenital inverted nipples and/or collection of nipple aspirate fluid
Owner:WANG PAUL C +1
Non-Surgically Correcting Abnormal Knee Loading: Treatment and Training Equipment
InactiveUS20080051684A1Restore muscle strengthSolve the lack of resistanceChiropractic devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention provides a device and a method for exercising a user's leg whose lower leg tibial portion can be rotatably controlled during exercise. The device includes user-controlled rotatable drums connected to a sheet that surrounds a lower leg cuff for rotating and providing corrective forces on a user's knee joint during leg exercise. The device can be used with weight training equipment commonly found in commercial gyms, as well as in a user's home, or in clinics, to assist in rehabilitating malaligned knee joints.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF COLORADO THE BODY
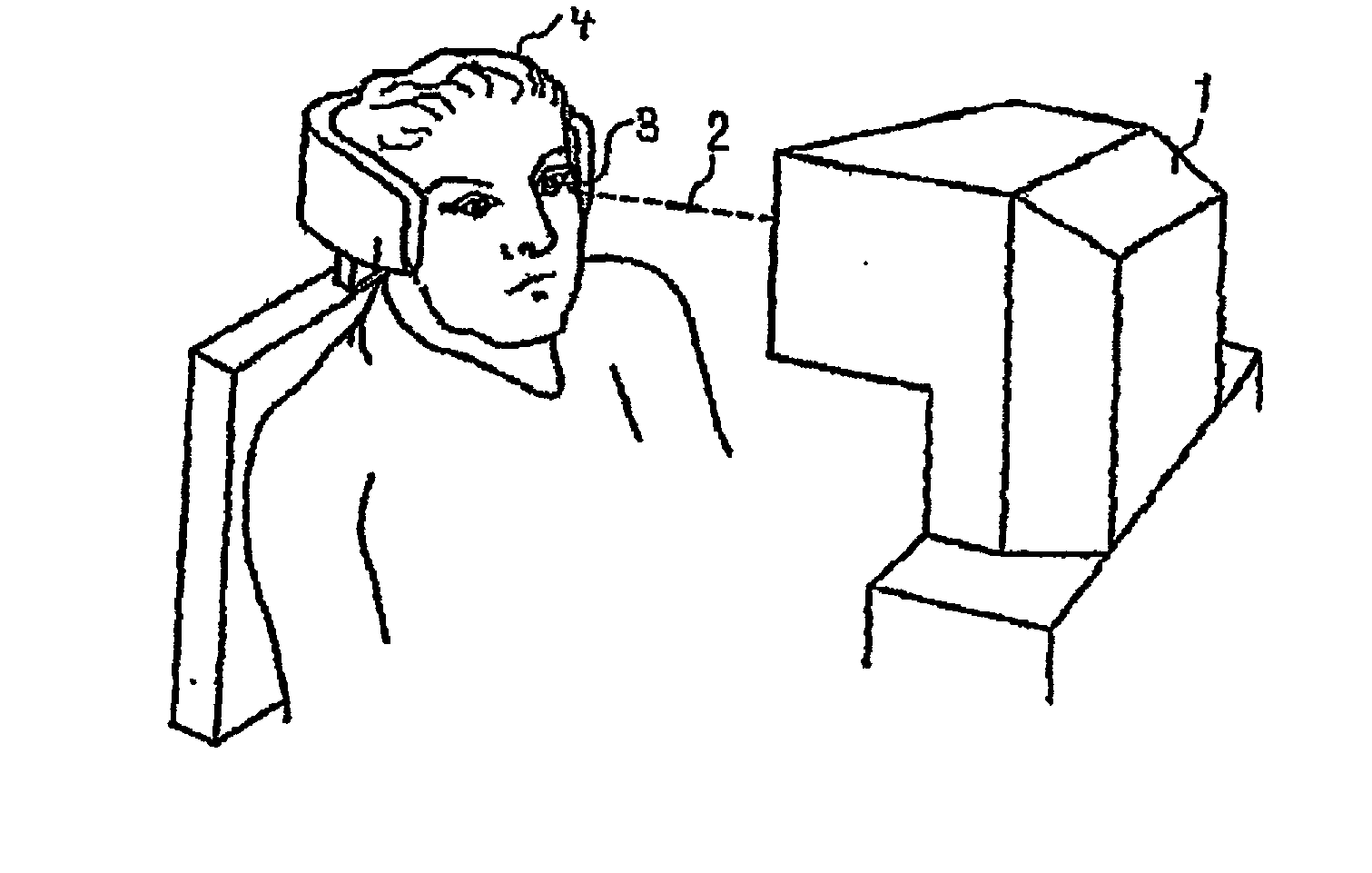
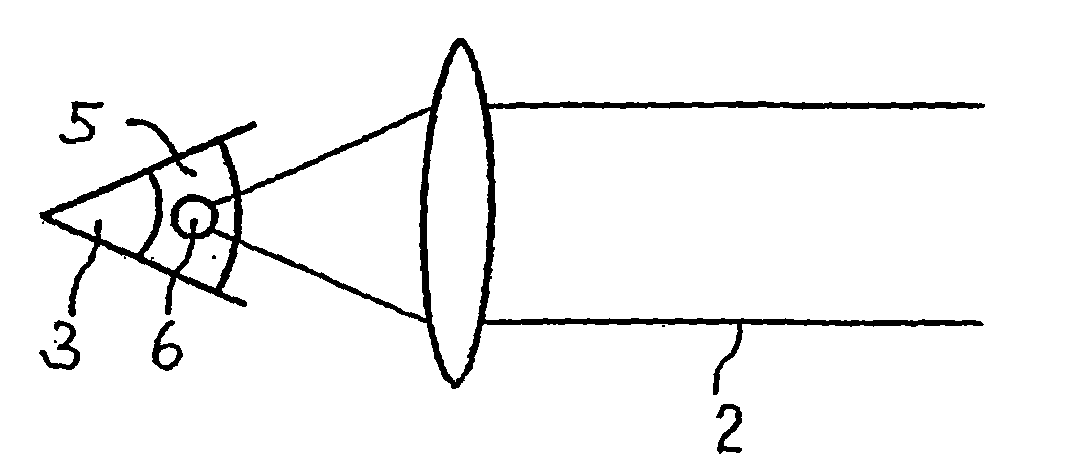
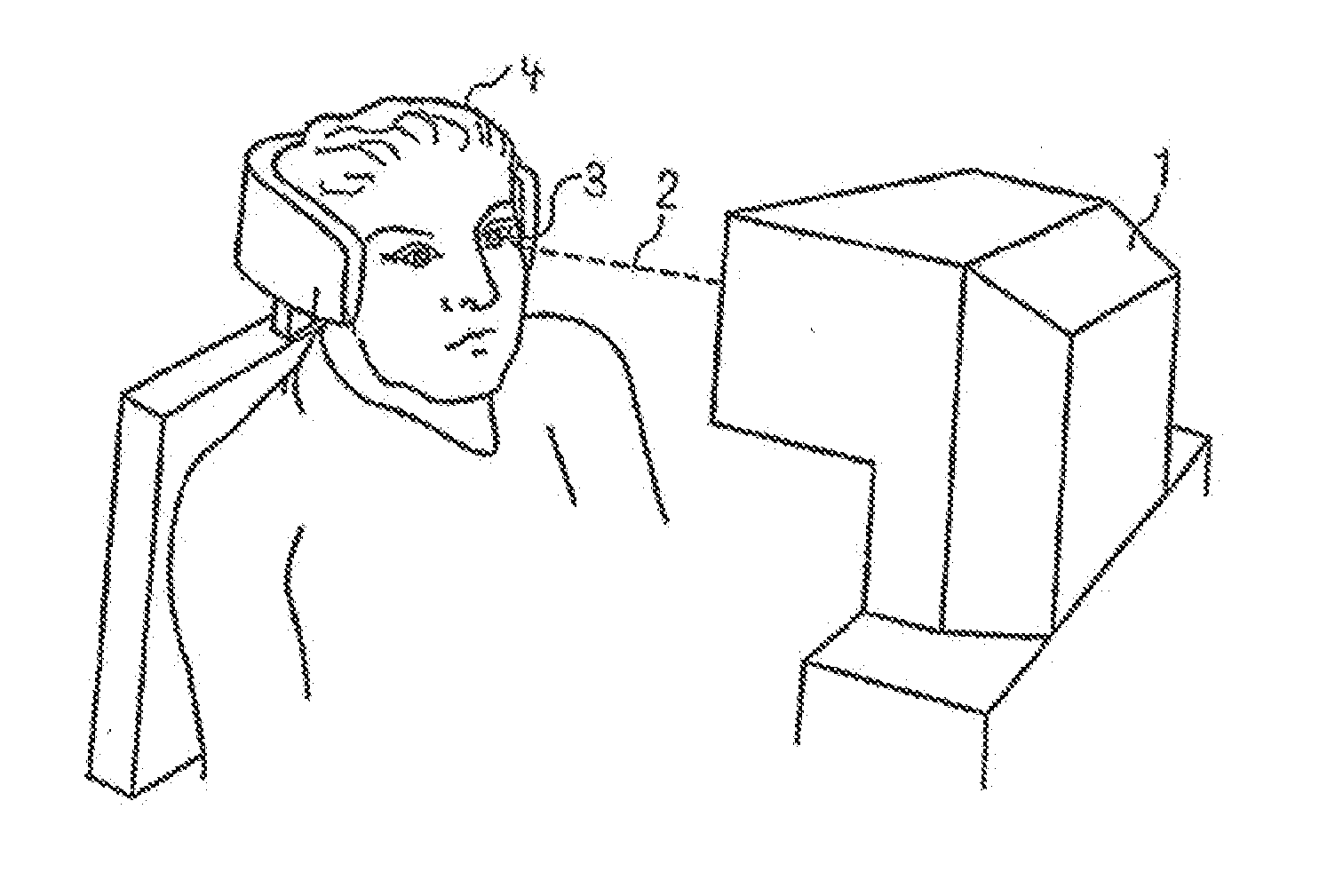
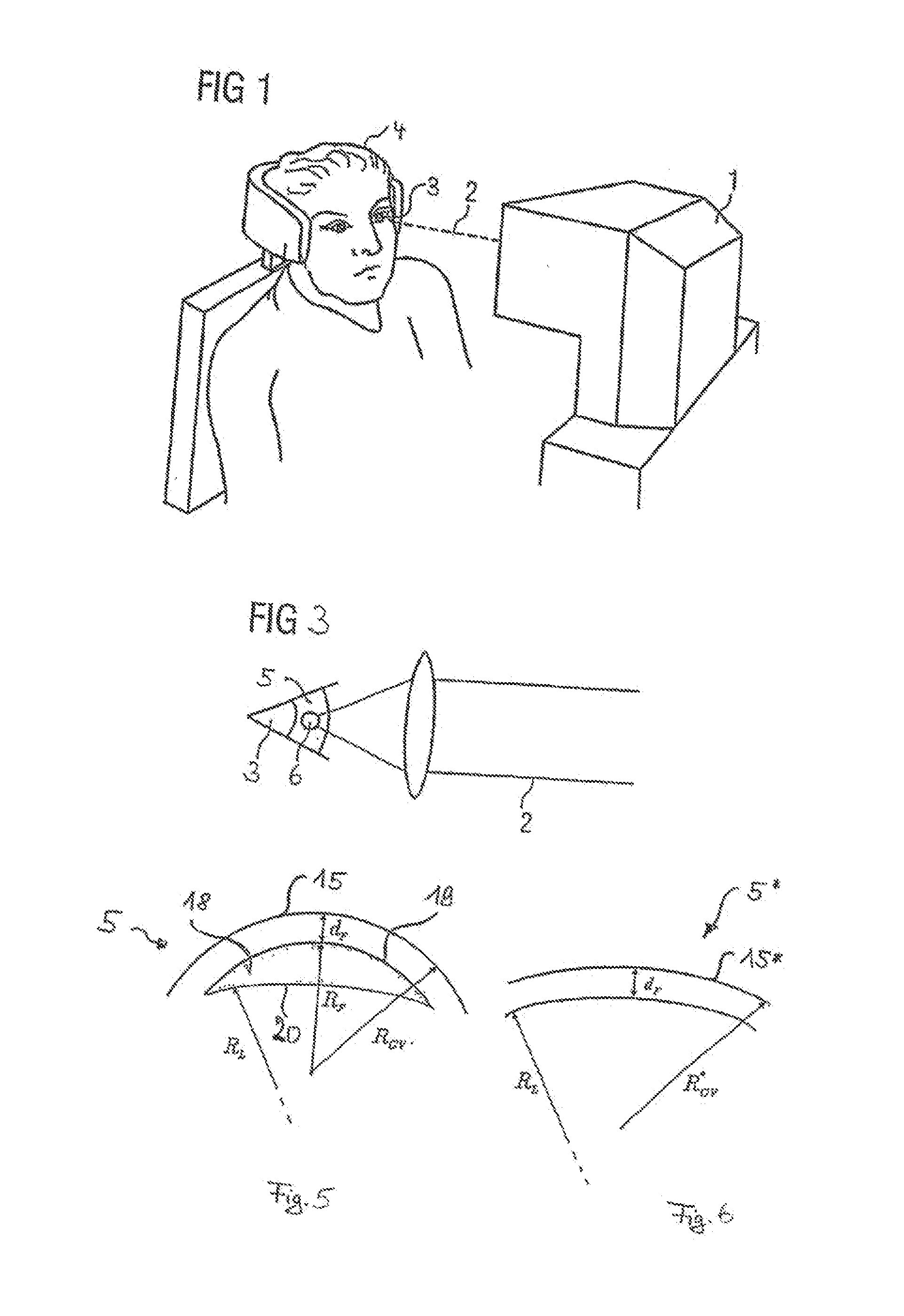
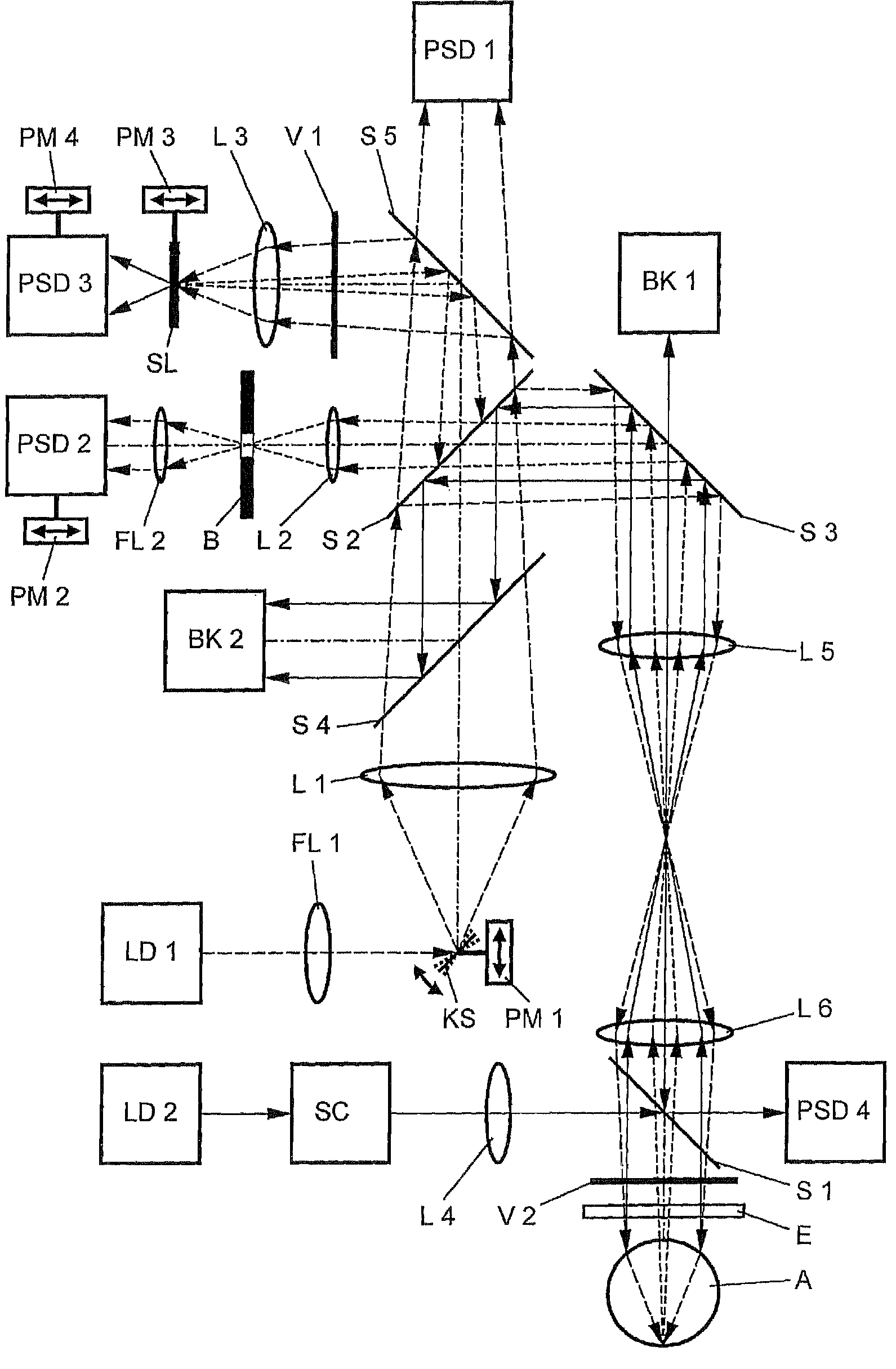
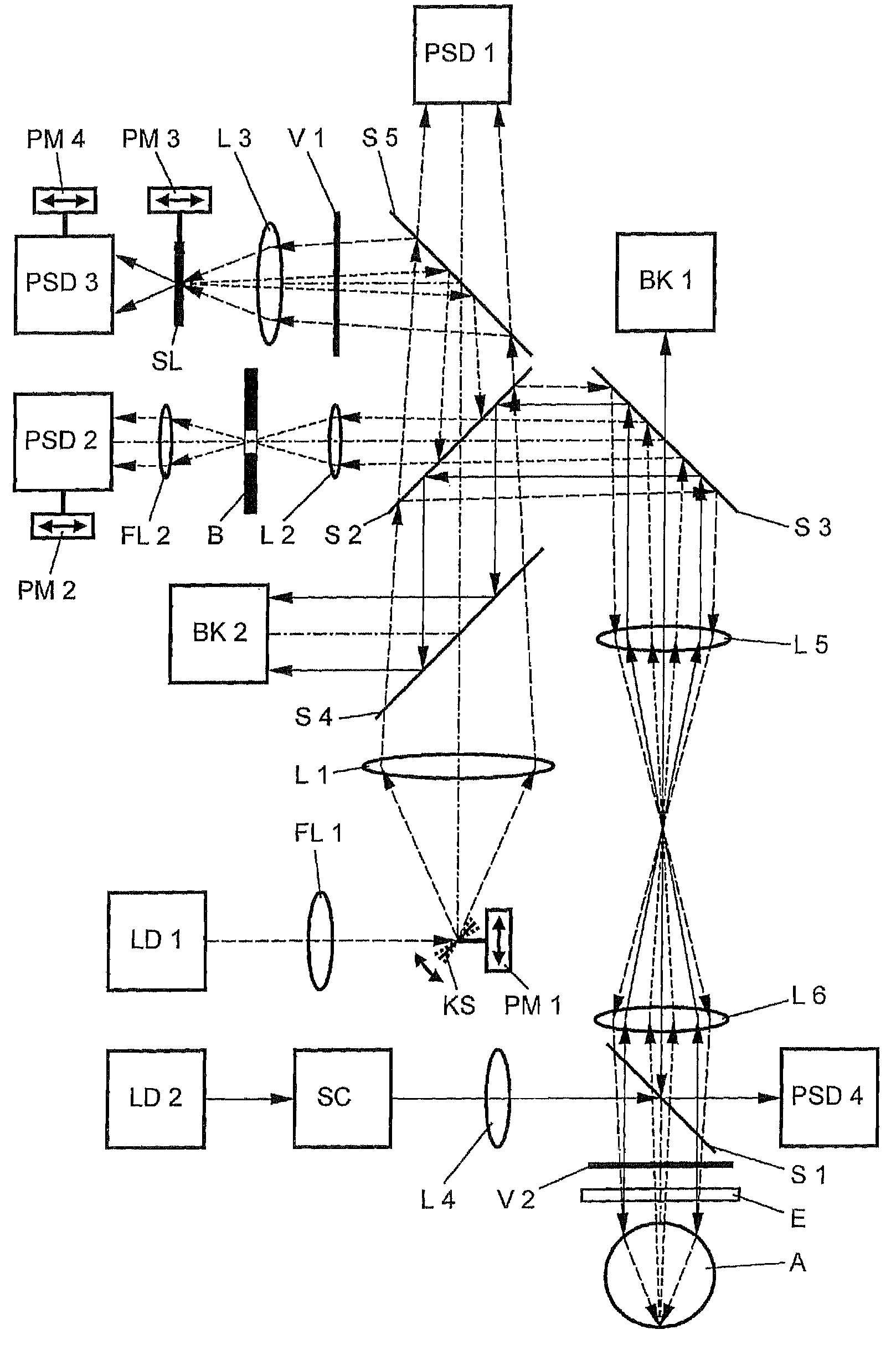
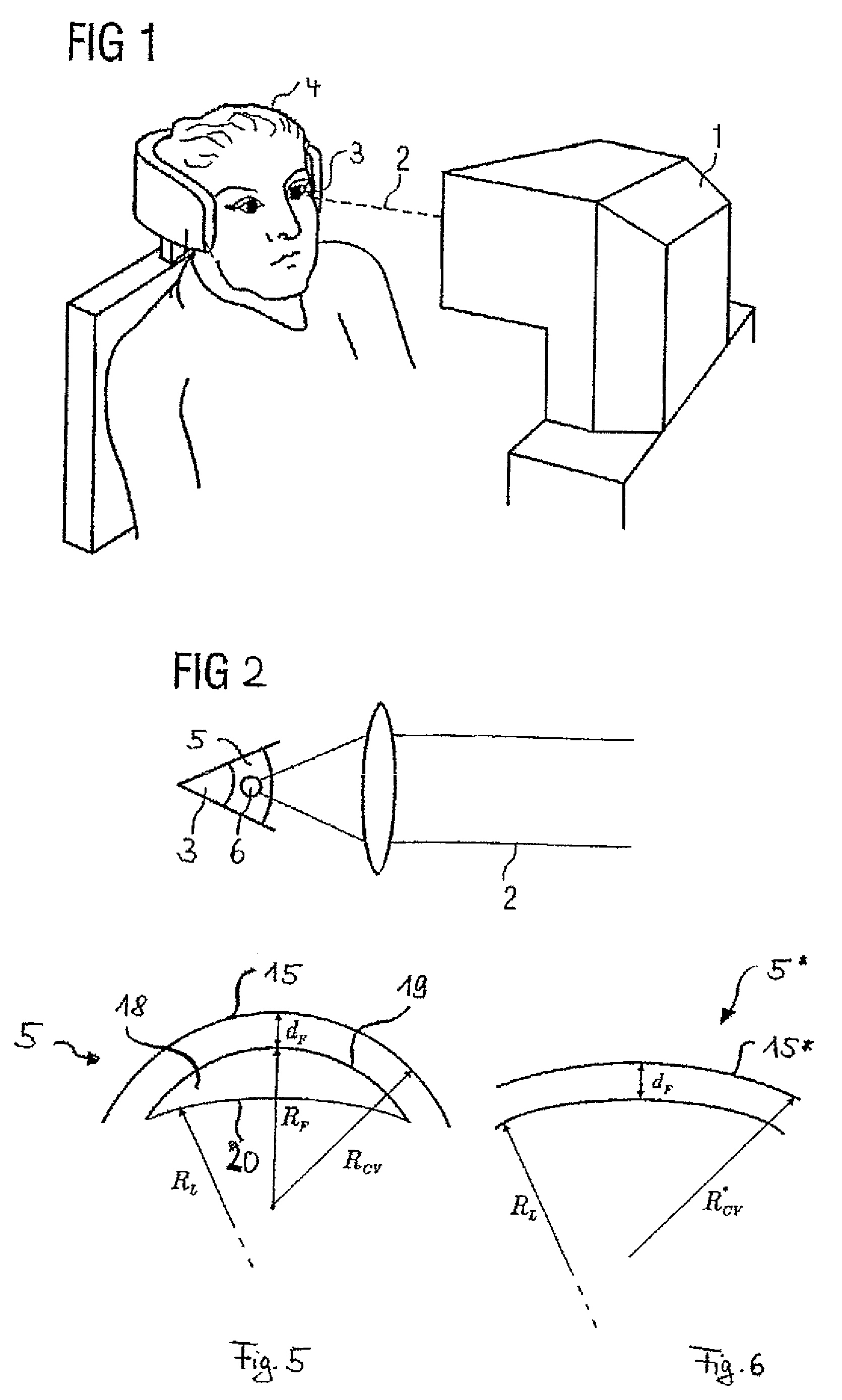
Device for measuring and surgical correction imaging errors in the human eye
InactiveUS7686450B2Improve spatial resolutionLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsMeasurement deviceMeasurement precision
The invention relates to a device for measuring imaging errors in the human eye, wherein substantial scanning of the lens of the eye with a light beam or laser diode determines the measuring accuracy of local refractive power. Measuring accuracy of locally dependent refractive power is achieved by a two-dimensionally refractable tilting mirror which is embodied in the form of a microscanner mirror with the aid of a piezomotor for positioning and by electrically controllable liquid lenses. As a result, it is possible to manufacture the measuring device as small as possible, enabling it to be integrated in to a processing laser in order to monitor the result of treatment with a laser during individual adaptation of contact lenses, intraocular lenses or surgical correction of the retina in situ and to calculate data of a required correction.
Owner:EYESIGHT & VISION
Treatment device for the surgical correction of defective vision of an eye, method for producing control data therefor, and method for the surgical correction of defective vision of an eye
ActiveUS20140288538A1Avoid poor resultsEasy to implementLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsControl dataSurgical correction
A treatment device for the surgical correction of defective vision in an eye. The device includes a laser apparatus controlled by a controller. The controller determines a desired correction of defective vision from measurement data of the eye to produce control data for the laser, and to control the laser to emit radiation according to the control data, such that a lenticule-shaped volume is isolated in the cornea. The controller computes a lenticule-shaped intended volume, the removal of which from the cornea leads to an actual correction of defective vision in an optical zone in the eye which differs from the desired correction more at the edge of the optical zone than at the center of the optical zone. The thickness of the lenticule-shaped intended volume is less than the thickness of a lenticule-shaped comparison volume, the removal of which would bring about the desired correction of defective vision.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Treatment apparatus for surgical correction of defective eyesight, method of generating control data therefore, and method for surgical correction of defective eyesight
ActiveUS8685006B2Highly focusedReduce datasetLaser surgeryDiagnosticsControl dataSurgical correction
A treatment method and apparatus for surgical correction of defective-eyesight in an eye of a patient, wherein a laser device is controlled by a control device, said laser device separating corneal tissue by irradiation of laser radiation to isolate a volume located within a cornea, wherein the control device controls the laser device to focus the laser radiation, by providing target points located within the cornea, into the cornea, wherein the control device, when providing the target points, allows for focus position errors which lead to a deviation between the predetermined position and the actual position of the target points when focusing the laser radiation, by pre-offsets depending on the positions of the respective target points to compensate for said focus position errors.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
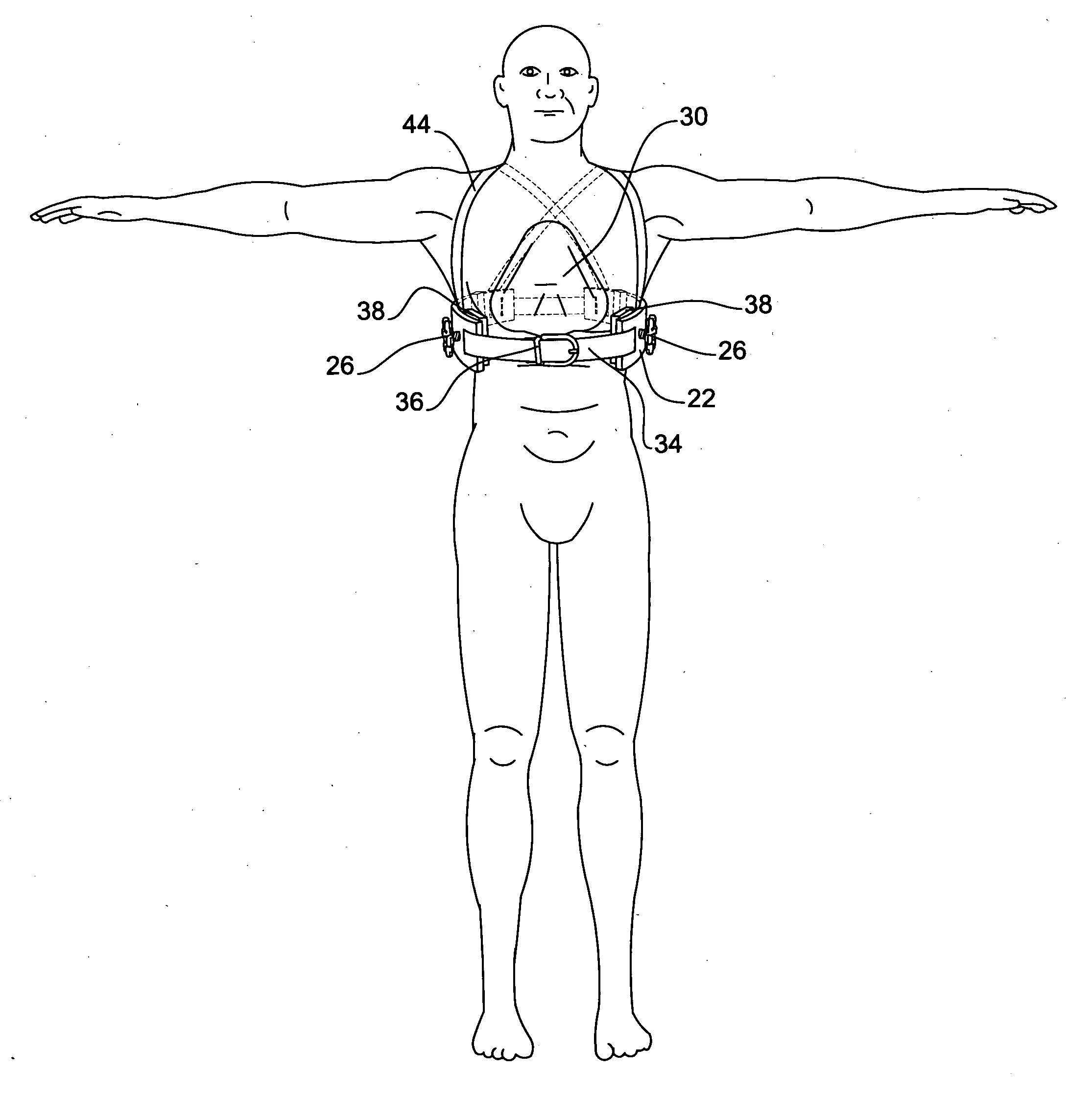
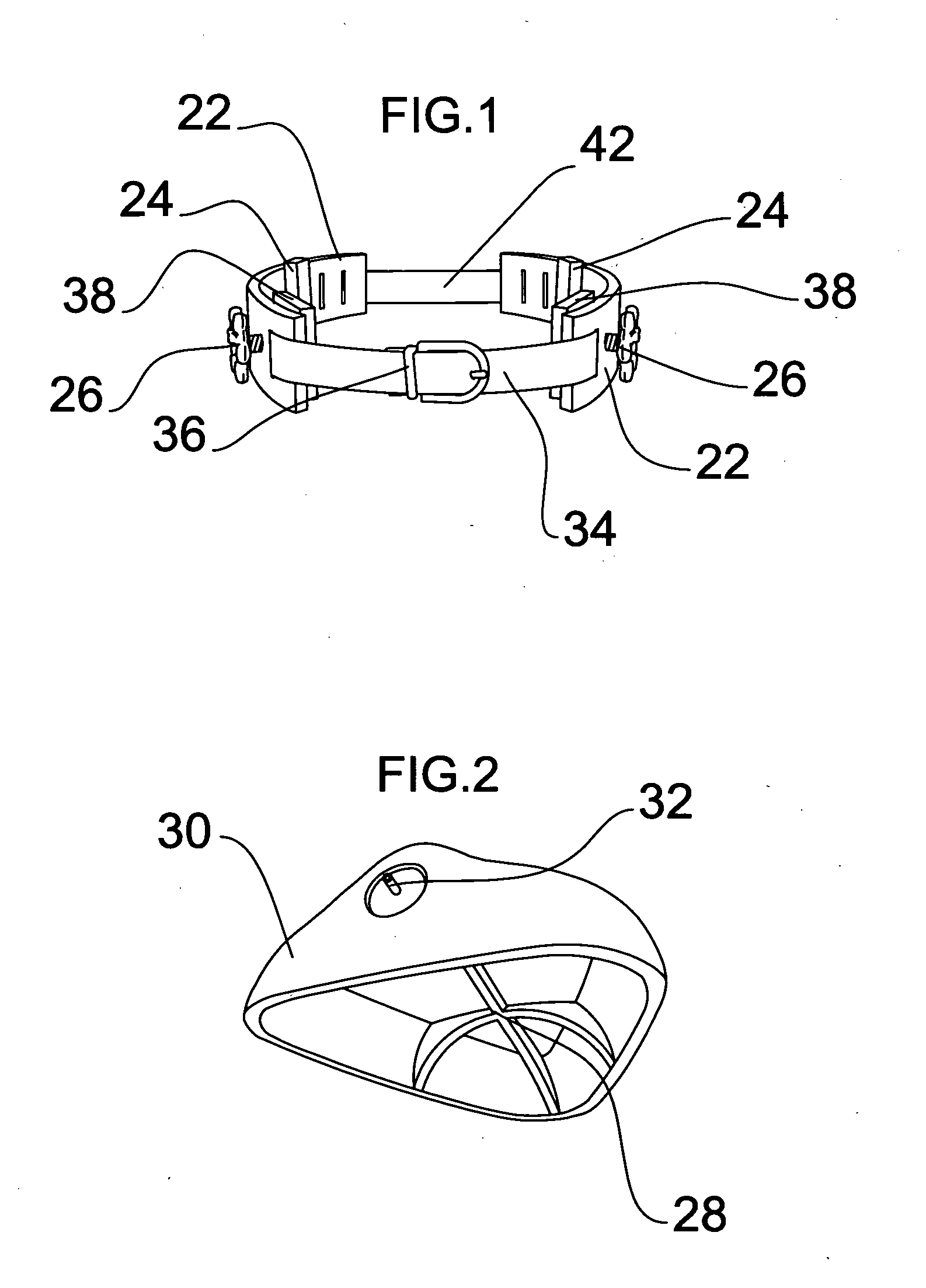
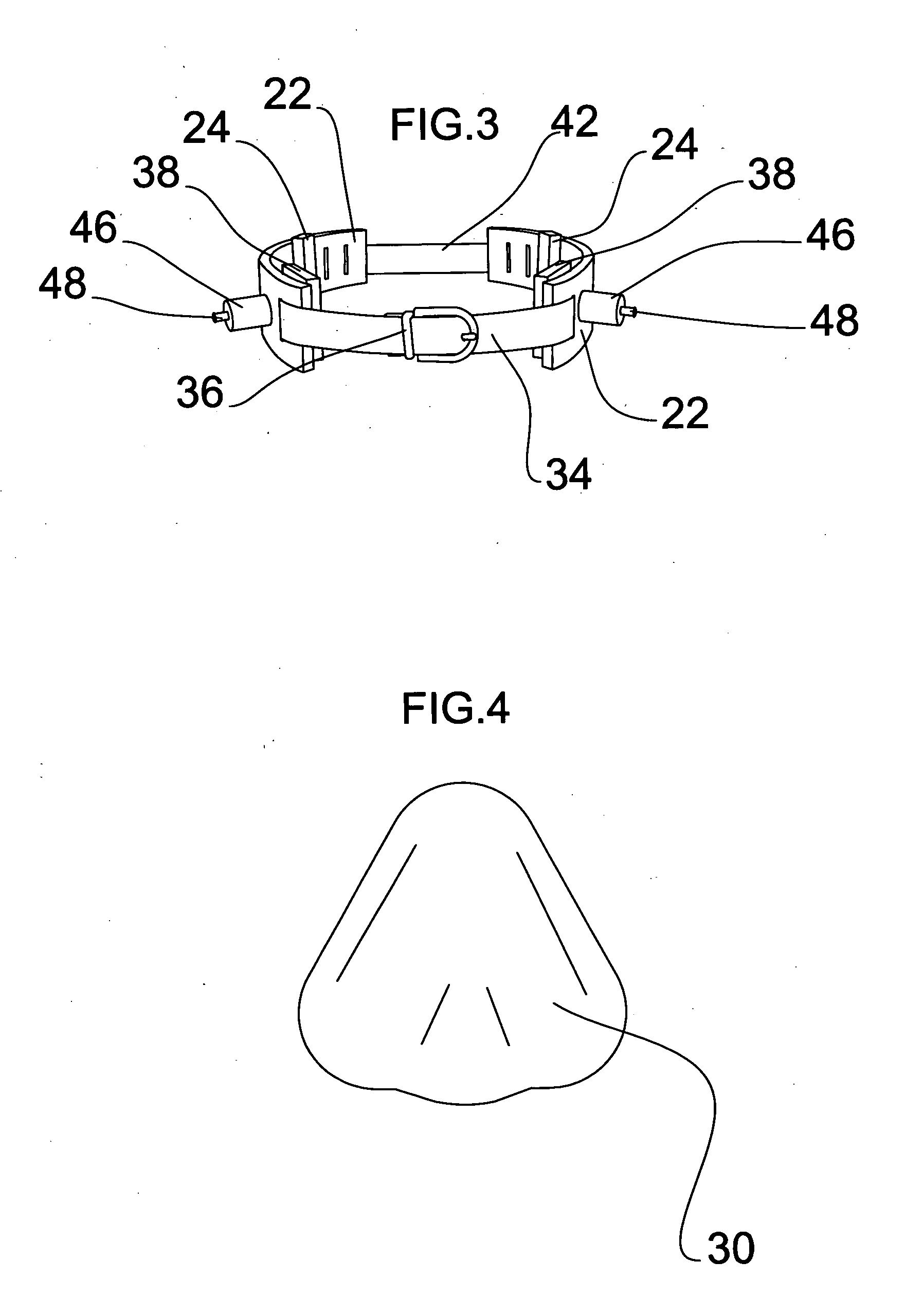
Method and apparatus for nonsurgical correction of chest wall deformities
One embodiment of a method and apparatus for the correction of pectus excavatum, having two arch shaped braces (22), made of a rigid durable material, and connected by a flexible belt (42 and 34), each half having a means of applying positive pressure (26) to the flared ribs caused by the condition. Positive pressure is to be applied to the ribs while a suction cup or other device simultaneously pulls or pushes the sternum to a natural position. Other embodiments are described and shown.
Owner:GALLO WILLIAM
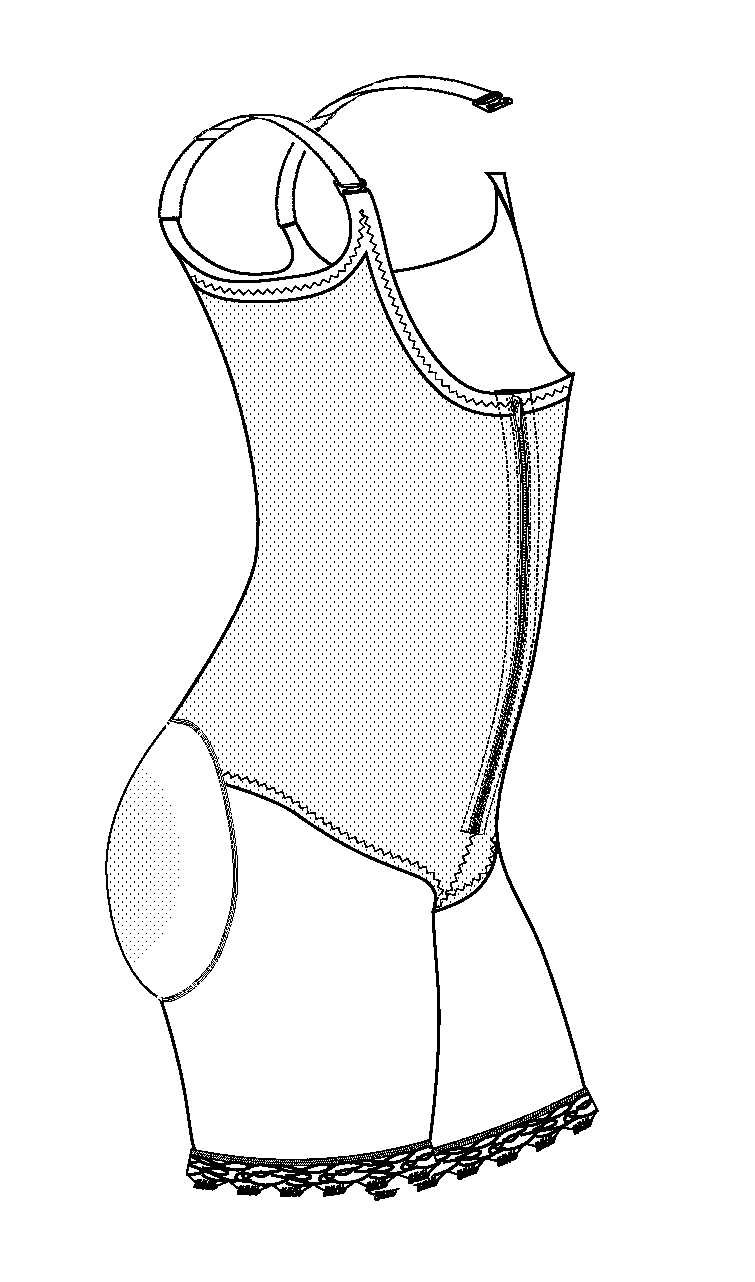
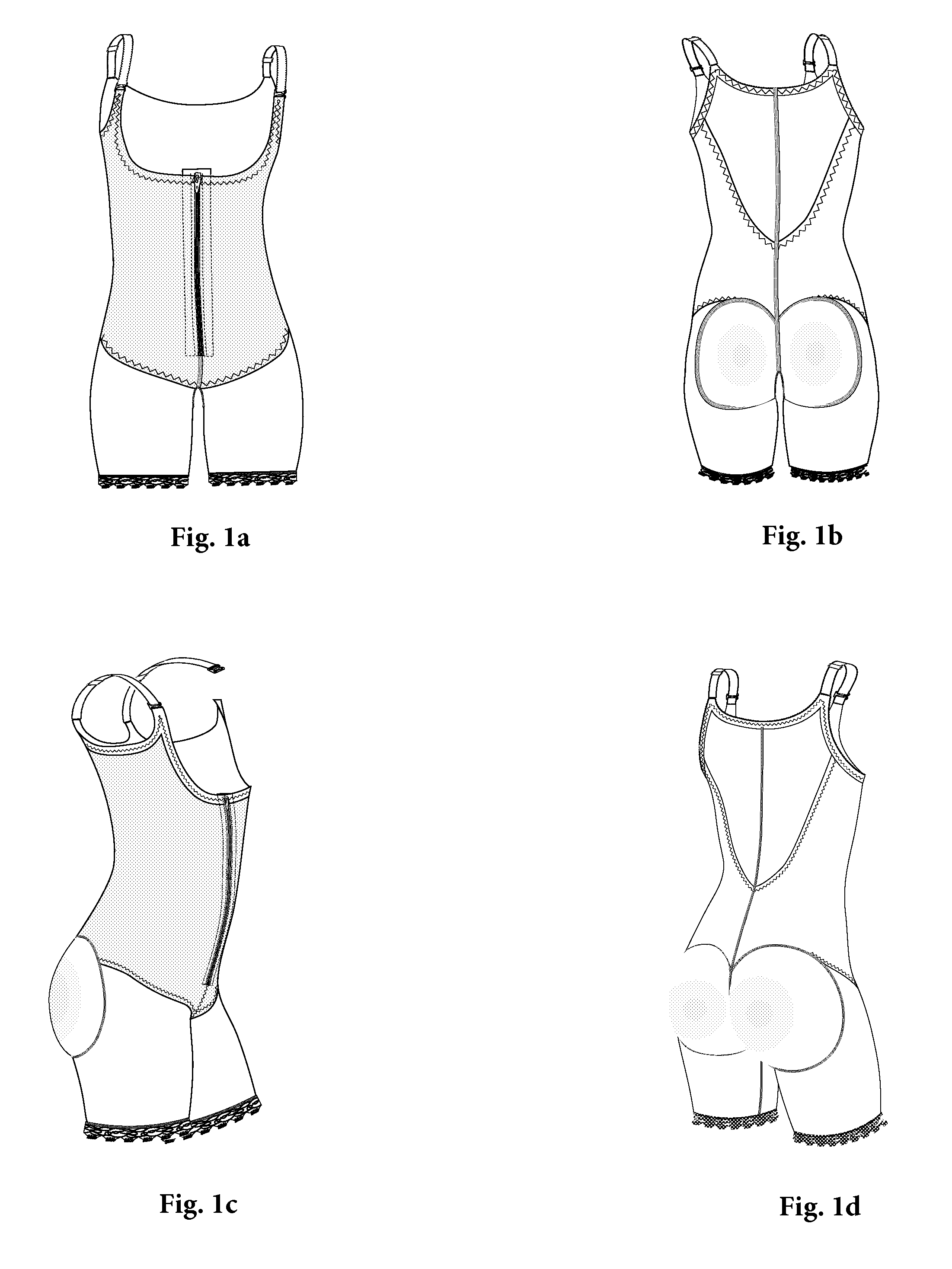
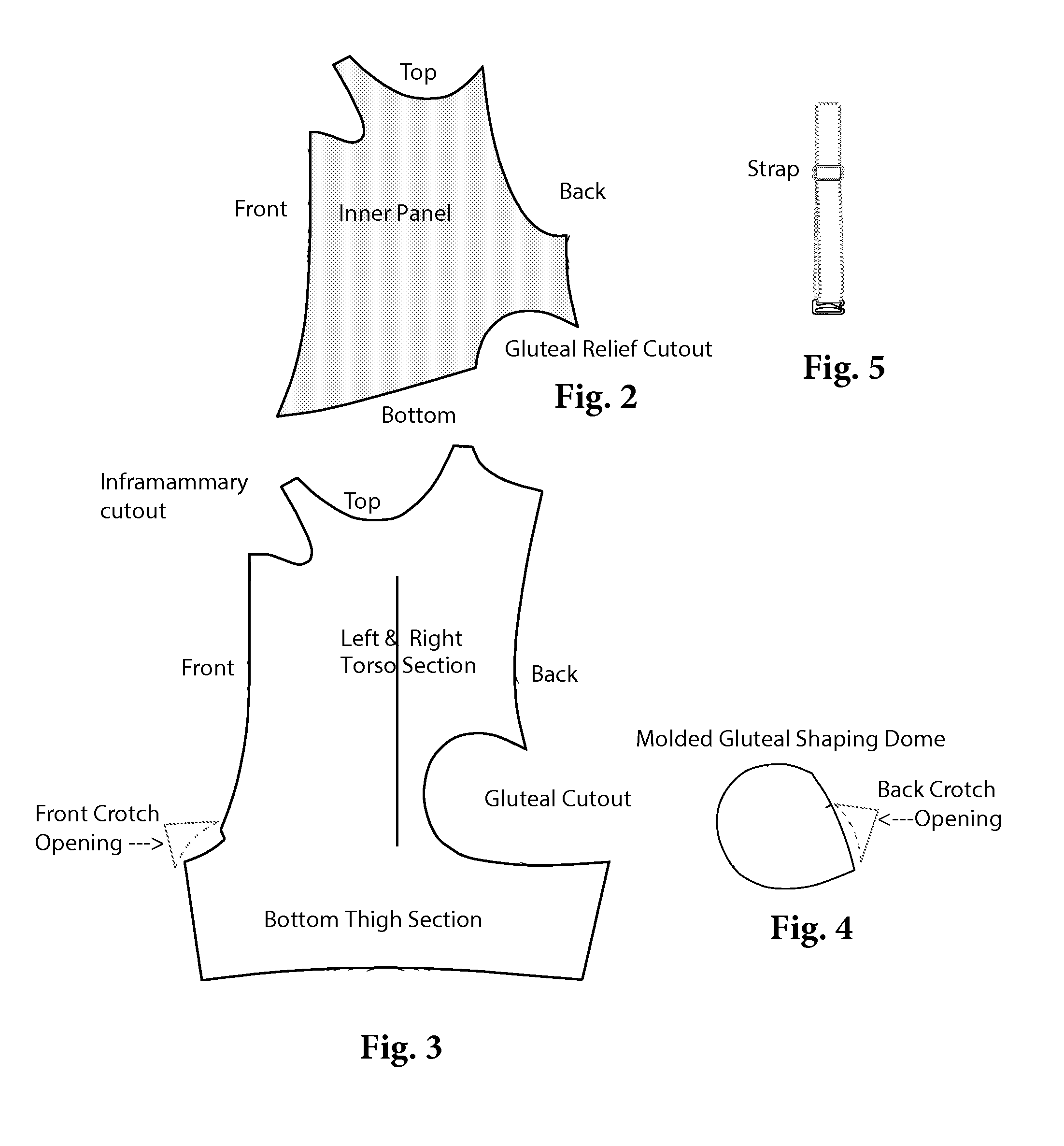
High-back gluteal shaping compression garment
A post-surgery, high-back, compression garment is described for post-operatively immobilizing surgically corrected tissues to ensure proper healing and provide molded gluteal-shaping power-net domes that preserve desired anatomic curvature enhancements and corrections in the gluteal regions of the human body during convalescence following contouring gluteoplasty procedures.
Owner:SMITH VERONICA C
Method, system and algorithm related to treatment planning for vision correction
The present invention relates to systems and methods for automatically determining various possible treatment plans for correcting a patient's vision through photoablative refractive surgery. Embodiments of the present invention rely on various selected diagnostic inputs about the patient's eye to classify the eye as particularly suitable for processing by several different processing algorithms. The invention further relates to the simultaneous representation of various treatment plans based on selected input data and available treatment algorithms that can be evaluated, modified and finally selected by the surgeon for application to the patient's eye. A system embodiment according to the invention comprises means for receiving diagnostic input data about a patient's vision, for analyzing said input data and deciding on potentially applicable processing algorithms, and for processing said potential available treatment algorithms; and means for displaying a multi-level graphical user interface that facilitates evaluation, modification, and selection of possible treatment plans for correcting the patient's vision. The system is further operatively associated with a storage medium for storing the calculated and selected treatment plan for applying the selected treatment plan to the patient's eye, wherein the treatment plan includes light ablation for the system Executable instructions for the laser component.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Surgical spinal correction
A method is provided for planning, performing, and assessing of surgical correction to the spine during a spinal surgical procedure. This method is implemented by a control unit through a GUI to digitize screw locations, digitize anatomical reference points, accept one or more correction inputs, and generate one or more rod solution outputs shaped to engage the screws at locations distinct from the originally digitized locations.
Owner:纽文思公司
Cornea ablation method for customized vision correction
InactiveCN104997588APrecise cutting contourGood surgical correctionEye surgeryMedicineSurgical correction
The invention discloses a cornea ablation method for customized vision correction. According to the invention, the shape of the front surface of a cornea is constructed through a backlight tracing manner, and the data of the cornea front surface before and after the design can be converted into the depth for the customized cornea ablation. By employing the method, the cornea ablation contour in eye refractive surgery can be more accurate, and better surgical correction effects can be achieved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Treatment device for surgically correcting ametropia of an eye and method for creating control data therefore
ActiveUS9084666B2Decreased regressionEfficient removalLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFar-sightednessRefractive error
A treatment device for the surgical correction of hyperopia in the eye comprising a laser device controlled by a control device. The laser device separating corneal tissue by applying laser radiation. The control device controls the laser device for emitting the laser radiation into the cornea such that a lenticule-shaped volume is isolated. Removal thereof effects the desired correction. The control device (12) predefines the volume such that a posterior surface and an anterior surface are connected via an edge surface that has a width in projection along the visual axis that is wider than the one which a straight line in the same projection, that is perpendicular at the edge of the posterior or the anterior surface would have relative to the associated surface and connects the anterior surface to the posterior surface or to the perceived extension thereof.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Surgical correction of ptosis polymeric artificial muscles
InactiveUS20070150058A1Easy surgical implantationGuaranteed uptimeSkin implantsEye implantsEyelid droopEyelid surgery
A surgical procedure is described for the restoration of eyelid function in individuals suffering from ptosis or upper eyelid droop syndrome that makes a patient unable to voluntarily fully raise an eyelid. The surgical procedure includes implantation and suturing of eye drop (pH) activated and actuated fibrous contractile and expansive artificial muscles such as pH active hydrogels of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) artificial muscles that are surgically implanted and sutured under the superior palpebral conjunctiva in a serpentine parallel configuration with respect to the tarsal (meibomian) glands of the upper eyelid and anchored to the tissues of superior fornix.
Owner:SHAHINPOOR MOHSEN +1
Planning systems and methods for surgical correction of abnormal bones
ActiveCN105228548AImprove reliabilityMedical simulationMedical automated diagnosisNormal boneSurgical correction
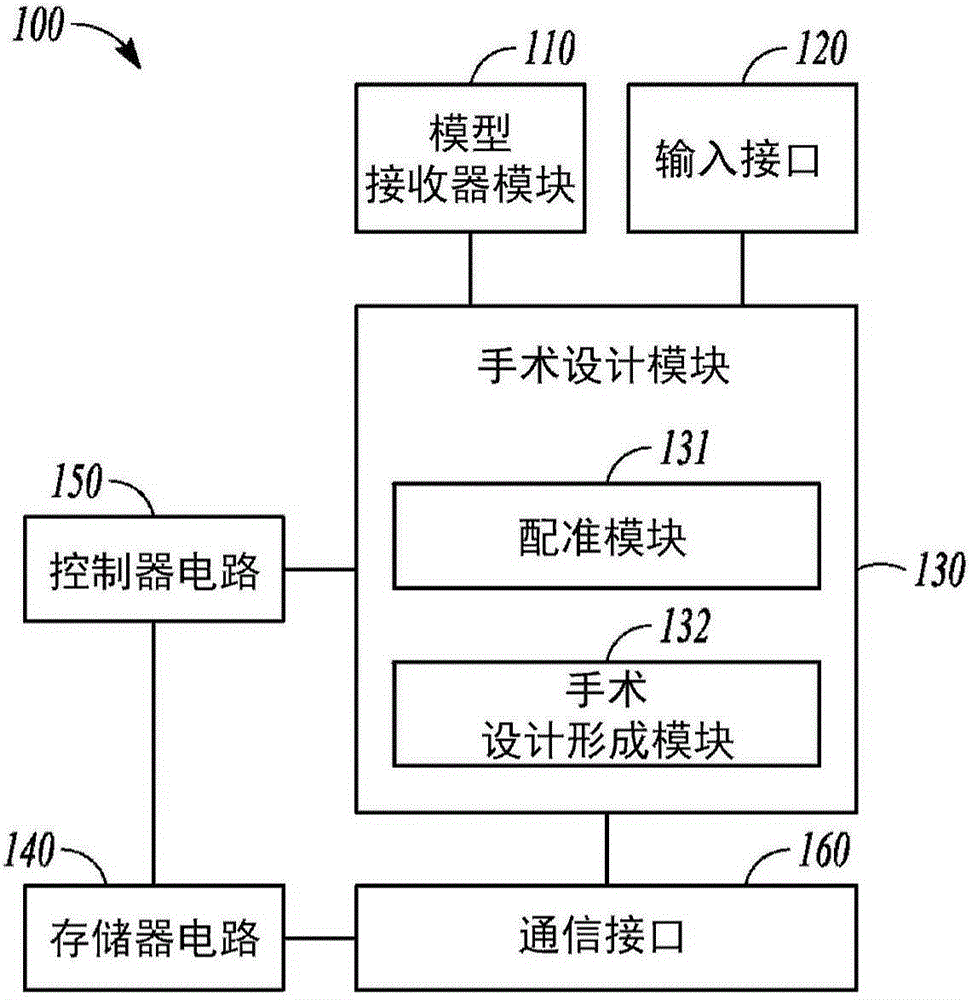
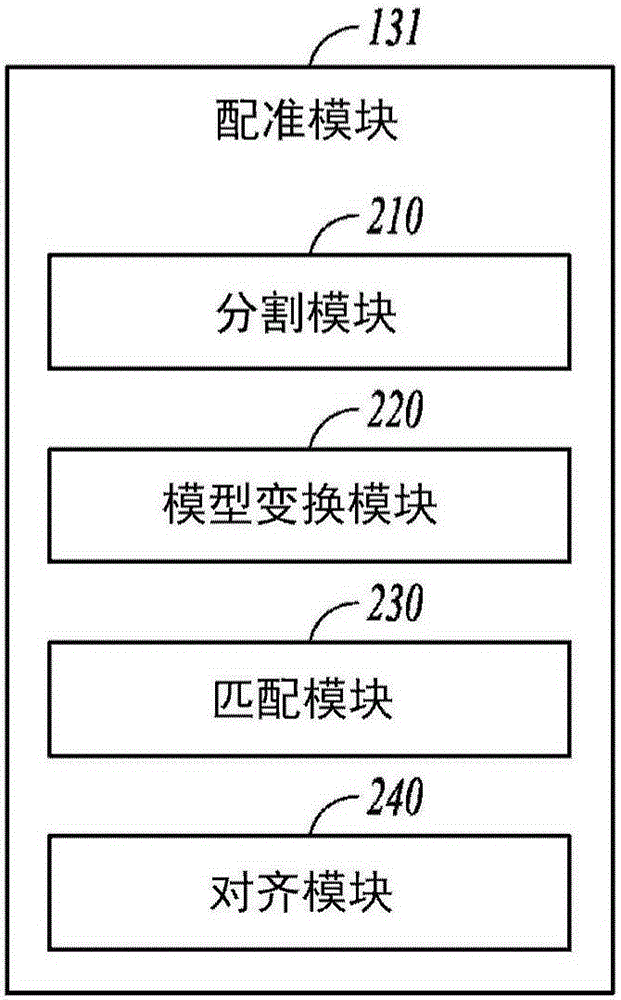
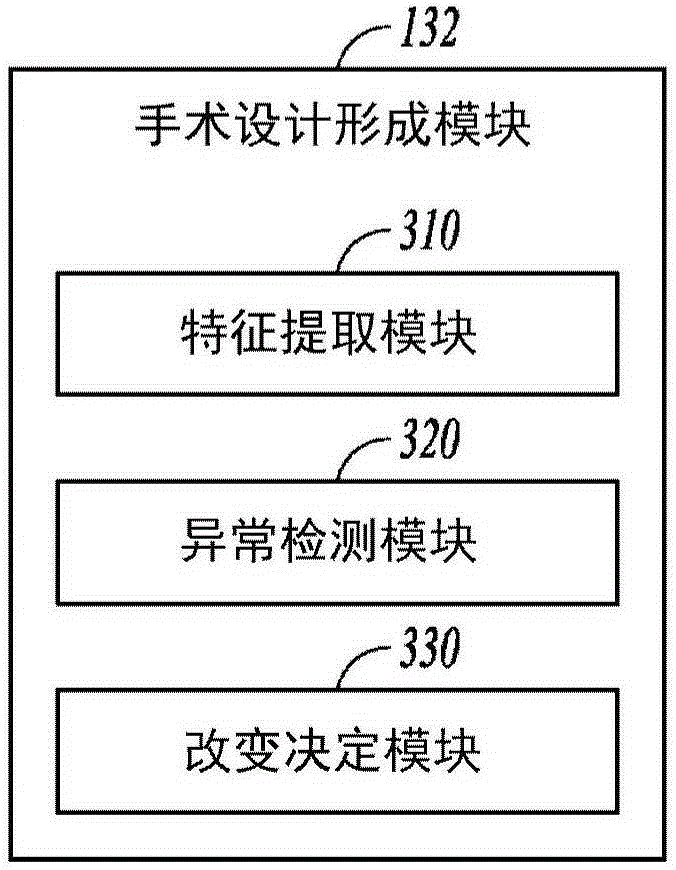
Systems and methods for generating a surgical plan for altering an abnormal bone using a generic normal bone model are discussed. For example, a system for planning a surgery on an abnormal bone can include a model receiver module (110) configured to receive a generic normal bone model (440). The generic normal bone model (440) can include a data set representing a normal bone having an anatomical origin comparable to the abnormal bone. An input interface (120) can receive an abnormal bone representation (430) including a data set representing the abnormal bone. A surgical planning module (130) can include a registration module (131) configured to register the generic normal bone model to the abnormal bone representation by creating a registered generic model. A surgical plan formation module (132) can be configured to identify one or more abnormal regions (452) of the abnormal bone (430) using the registered generic model.
Owner:蔚蓝纽带科技公司
Surgical correction of ptosis by polymeric artificial muscles
ActiveUS8454691B2Easy surgical implantationGuaranteed uptimeEye implantsSurgical needlesEyelid droopSurgical correction
A surgical procedure is described for the restoration of eyelid function in individuals suffering from ptosis or upper eyelid droop syndrome that makes a patient unable to voluntarily fully raise an eyelid. The surgical procedure includes implantation and suturing of eye drop (pH) activated and actuated fibrous contractile and expansive artificial muscles such as pH active hydrogels of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) artificial muscles that are surgically implanted and sutured under the superior palpebral conjunctiva in a serpentine parallel configuration with respect to the tarsal (meibomian) glands of the upper eyelid and anchored to the tissues of superior fornix.
Owner:SHAHINPOOR MOHSEN +1
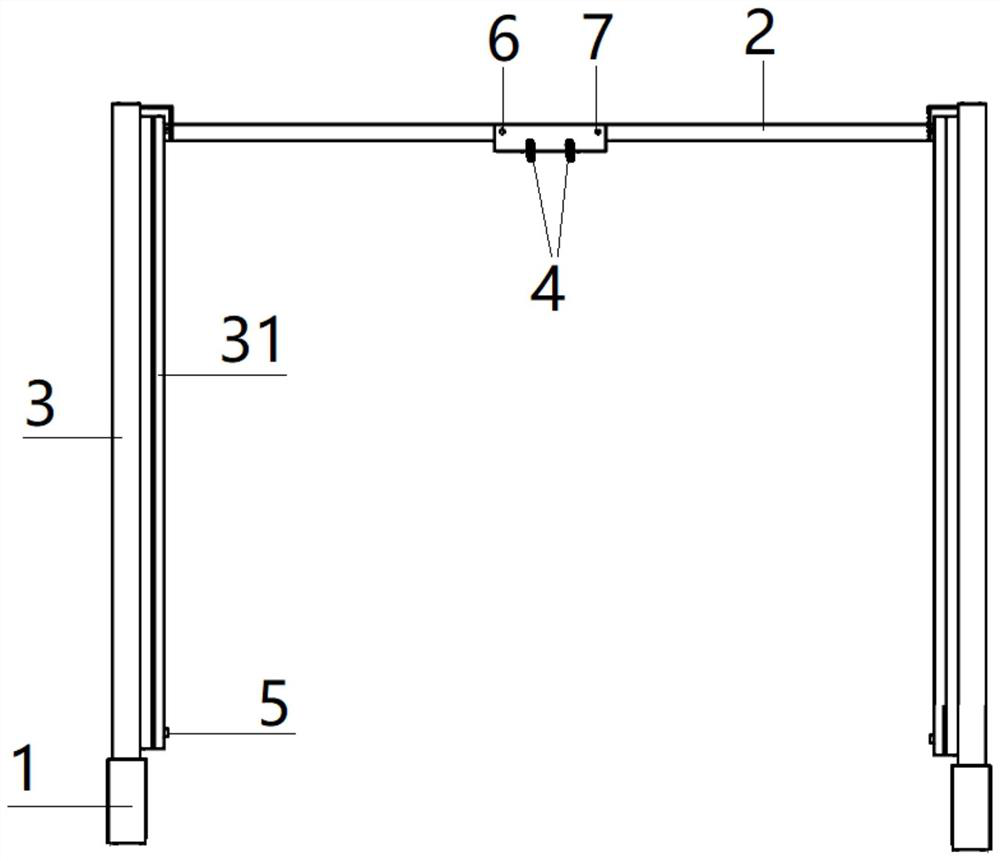
Intraoperative correction device for scoliosis
PendingCN111803198AAccurate locationAchieve orthopedic purposeInternal osteosythesisInstruments for stereotaxic surgerySpinal columnScoliosis
The invention relates to an intraoperative correction device for scoliosis. The intraoperative correction device comprises two cross bars arranged at two ends and parallel to each other and longitudinal connecting bars with adjustable length and located above the cross bars. The cross bars are perpendicular to the longitudinal connecting bars. When surgical correction is performed, a current position of a spine can be accurately determined, when a linear light spot coincides with the position of the spine, the purpose of correction is achieved, and the effects of equal height of postoperativeshoulders and balanced spine sagittal position are achieved.
Owner:沈建雄
Surgical correction of ptosis by polymeric artificial muscles
InactiveUS7625404B2Easy surgical implantationGuaranteed uptimeSkin implantsEye implantsMedicineEyelid droop
Owner:SHAHINPOOR MOHSEN +1
System for reshaping skull
InactiveUS20150265448A1Avoid distortionReduce usageNon-surgical orthopedic devicesOsteosynthesis devicesCranial vaultCraniosynostosis
The present invention relates to a system intended to aid in the surgical correction of malformed regions of the skull by reshaping bone pieces, particularly in remodeling a skull. The present invention provides a system intended to aid in the surgical correction of a skull, particularly of craniosynostosis, wherein the system shall be based around a set of disposable three-dimensional skull templates, but it is also within the scope of the invention to use skull templates, which are sterilisable and can be re-used. A skull template corresponding to the size and desired head form of the patient is used as a template to remodel the cranial vault.
Owner:IBB TECH ENTWICKLUNGS FONDS GMBH & CO KG TEF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com