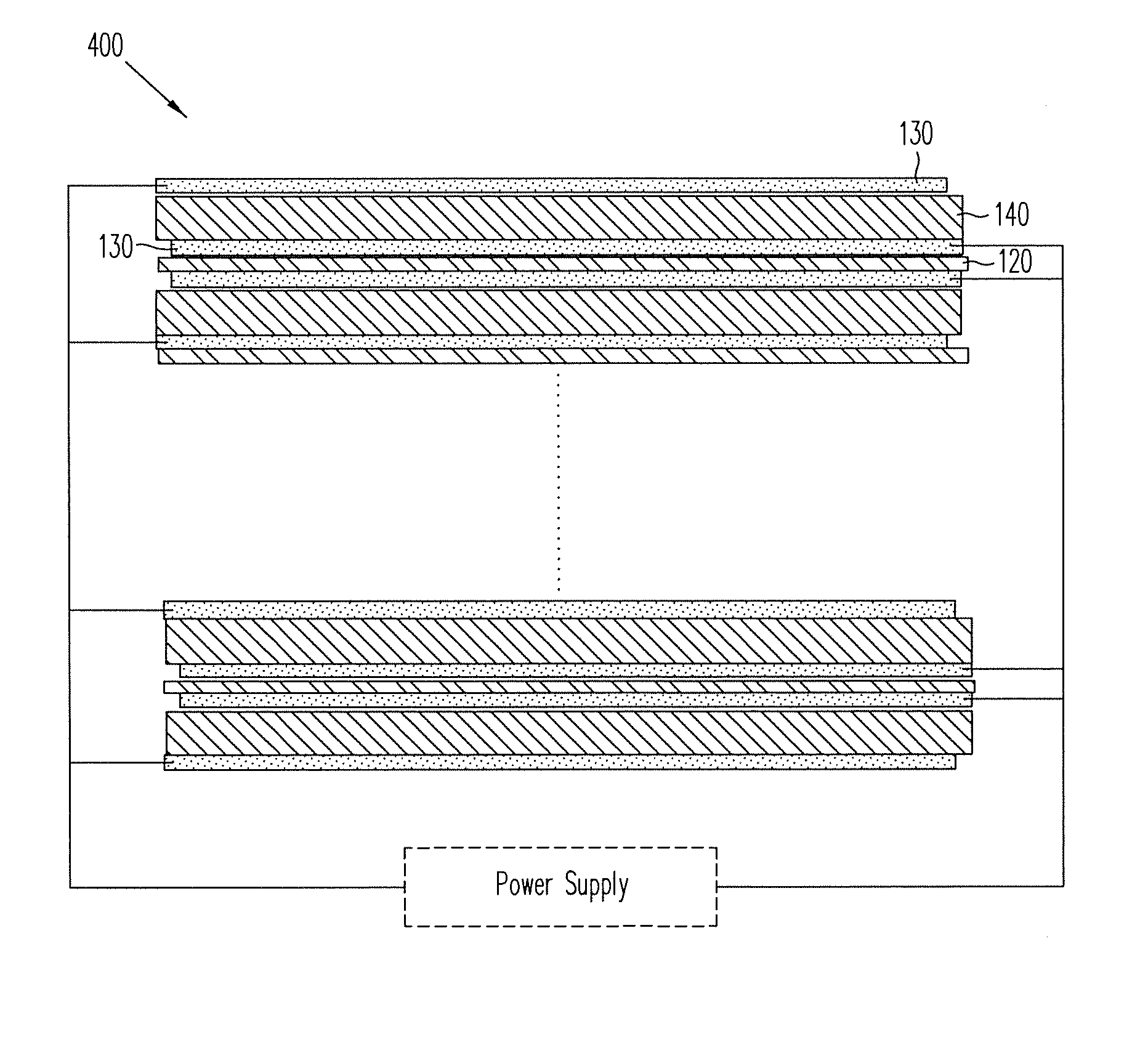
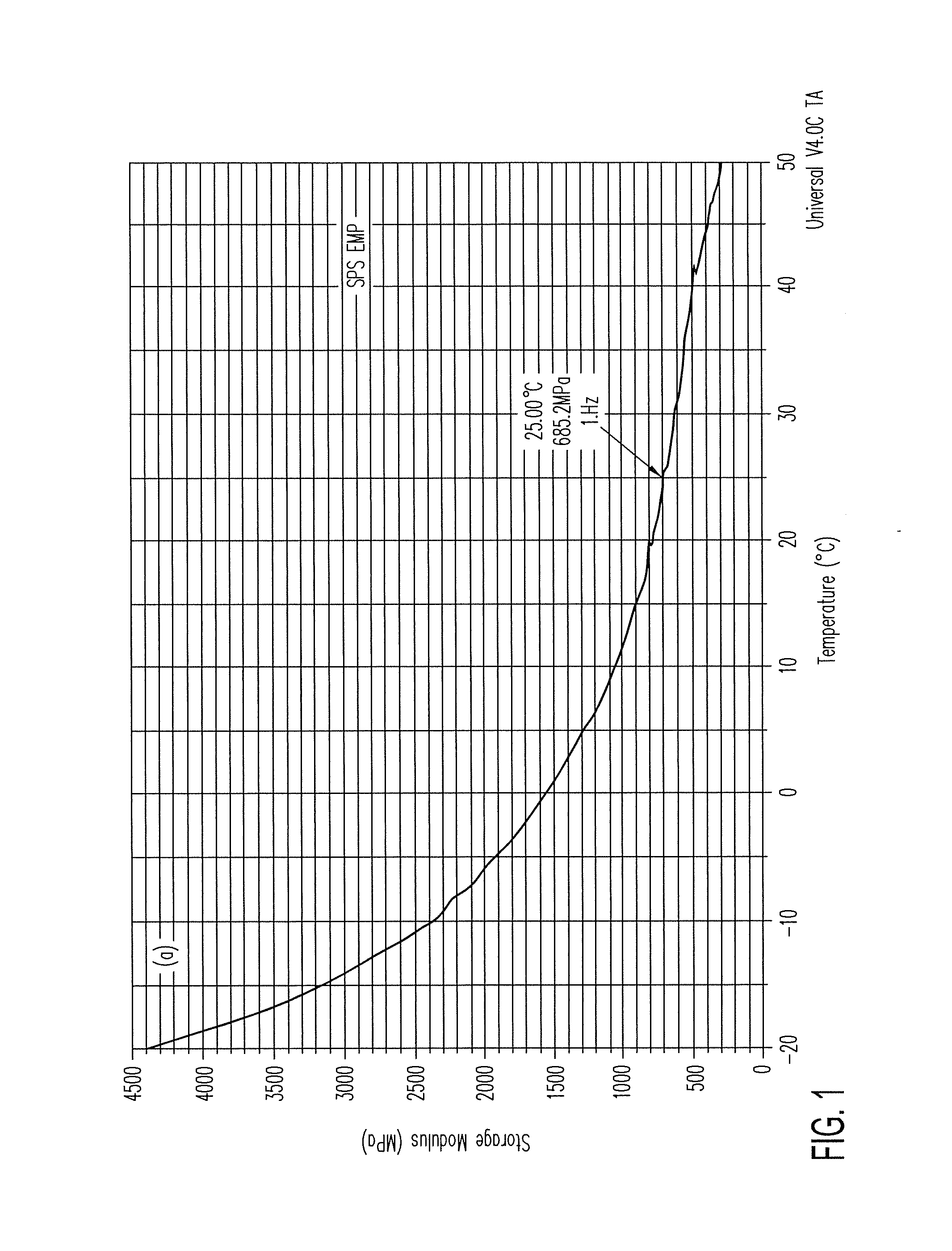
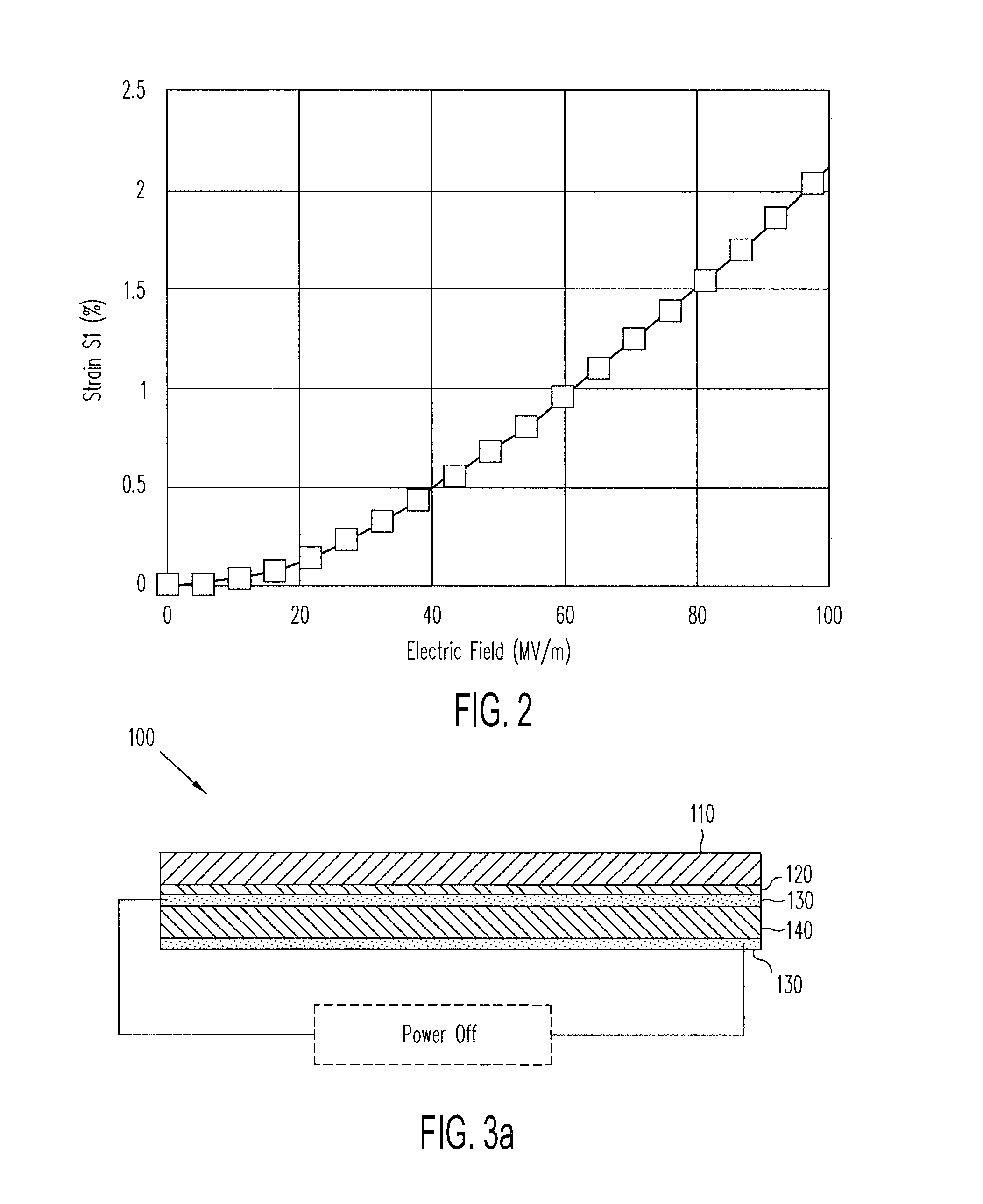
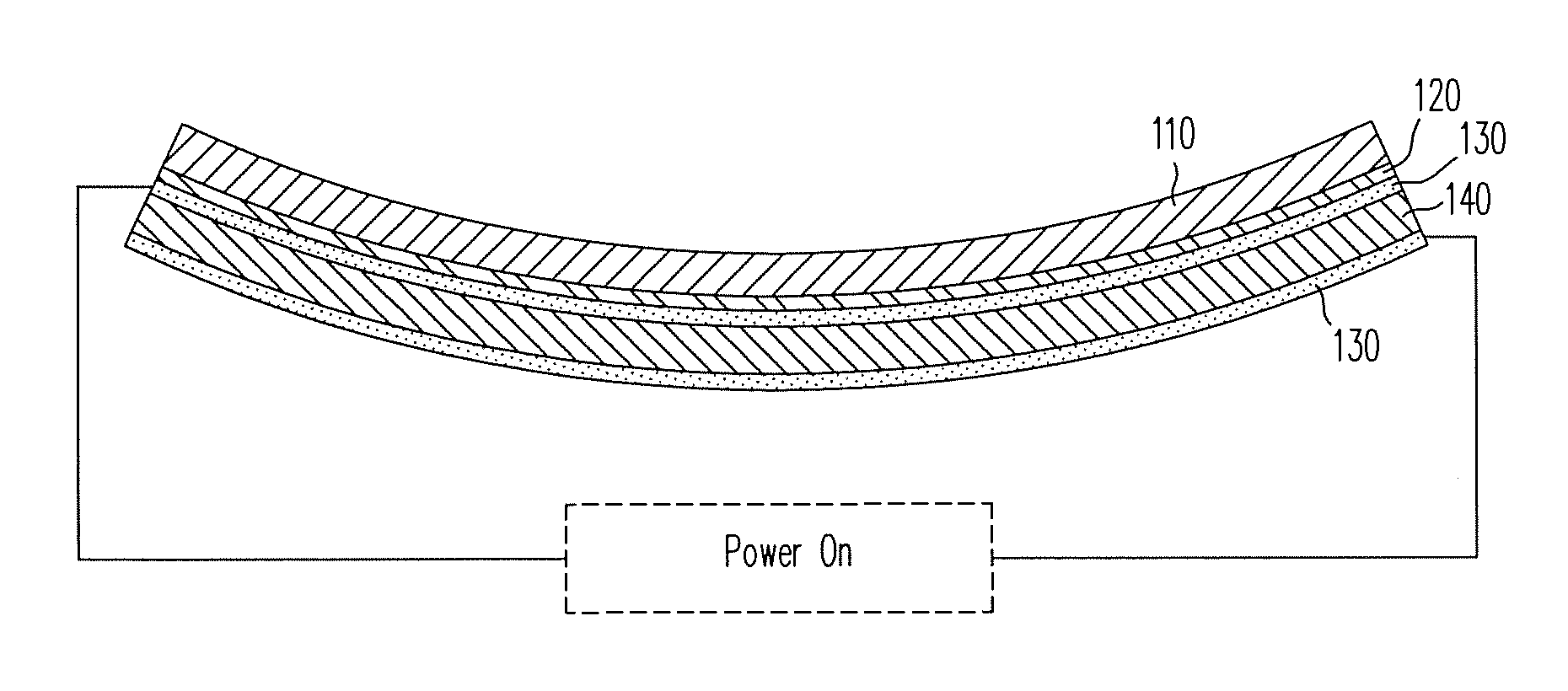
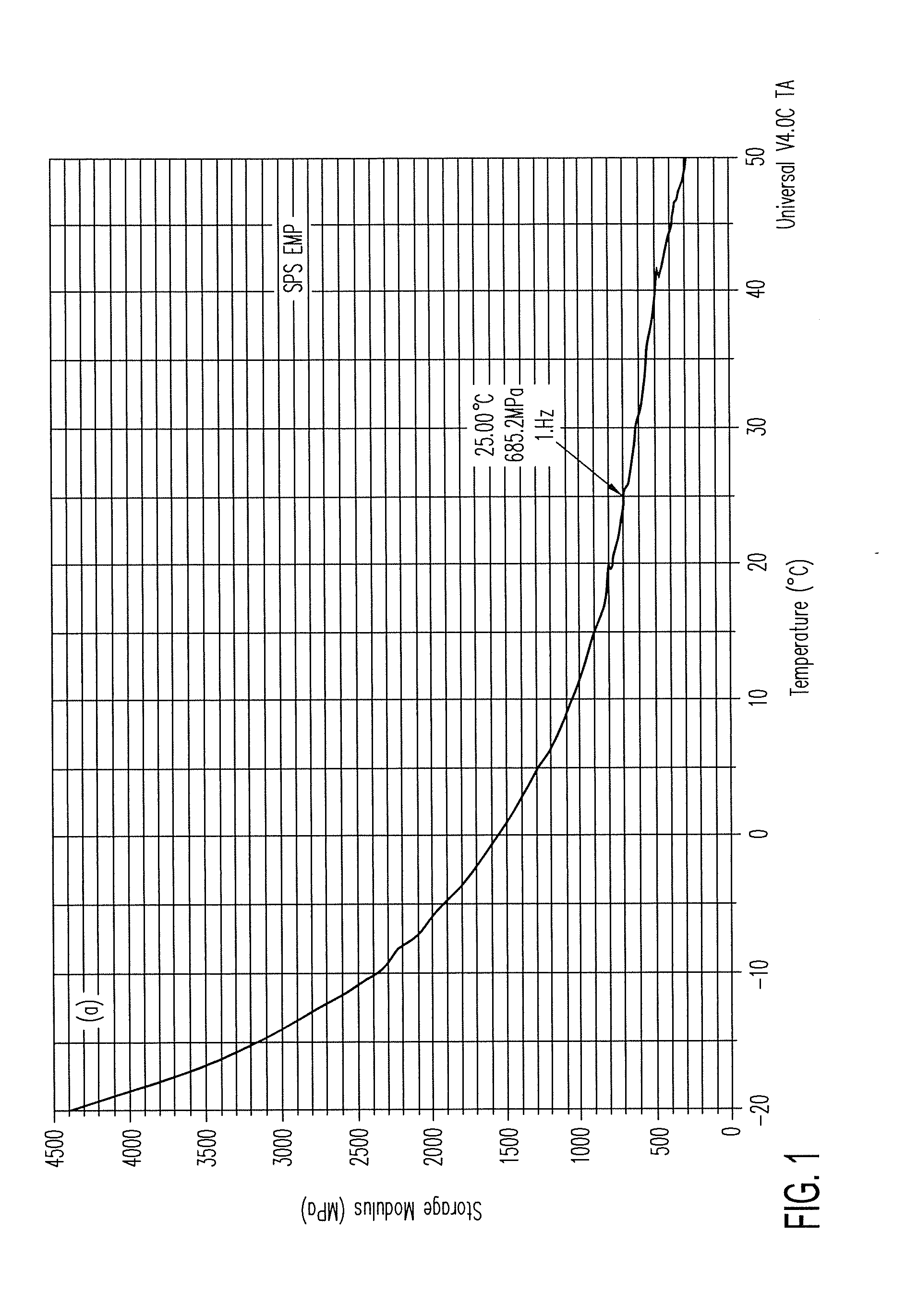
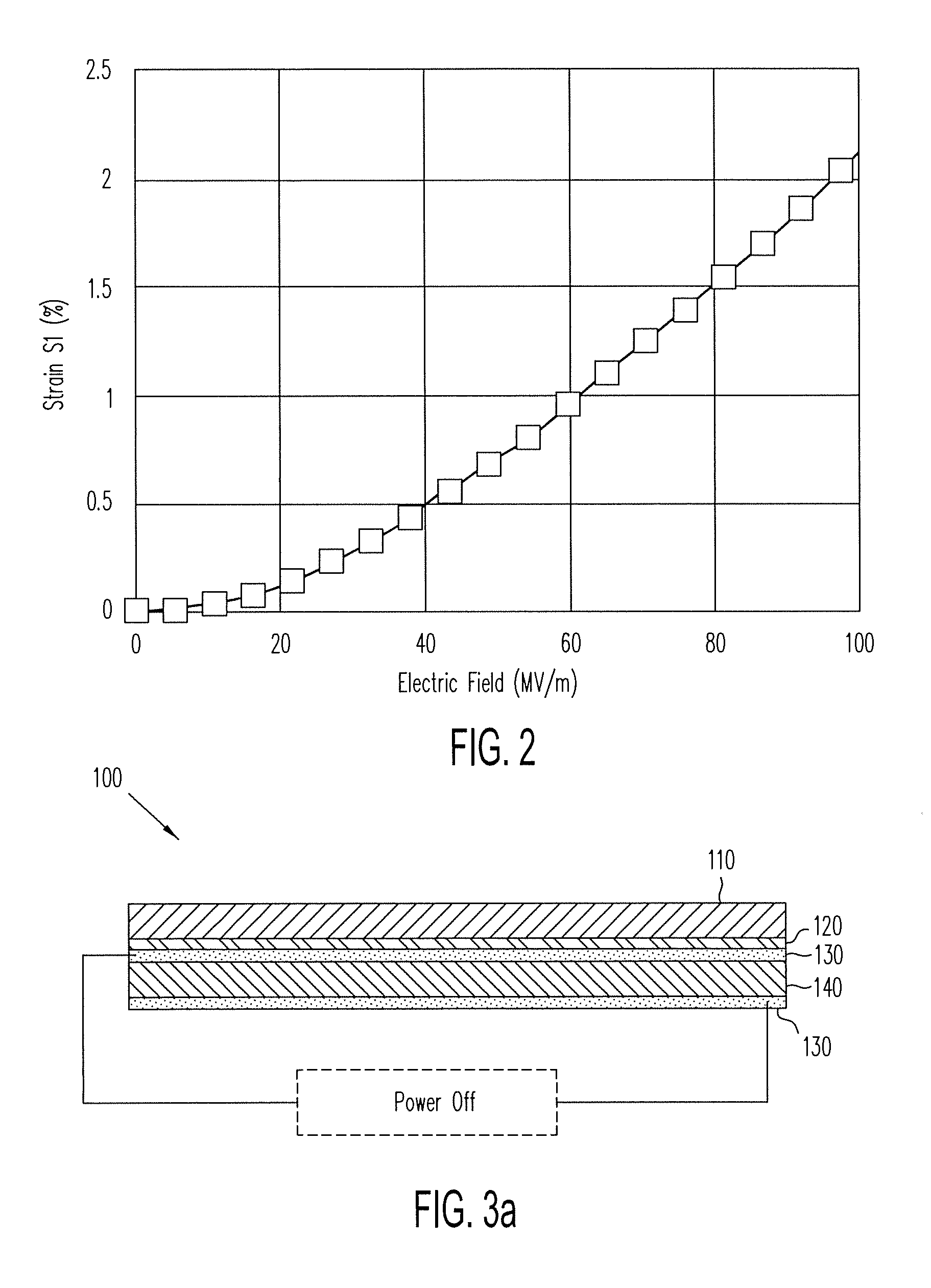
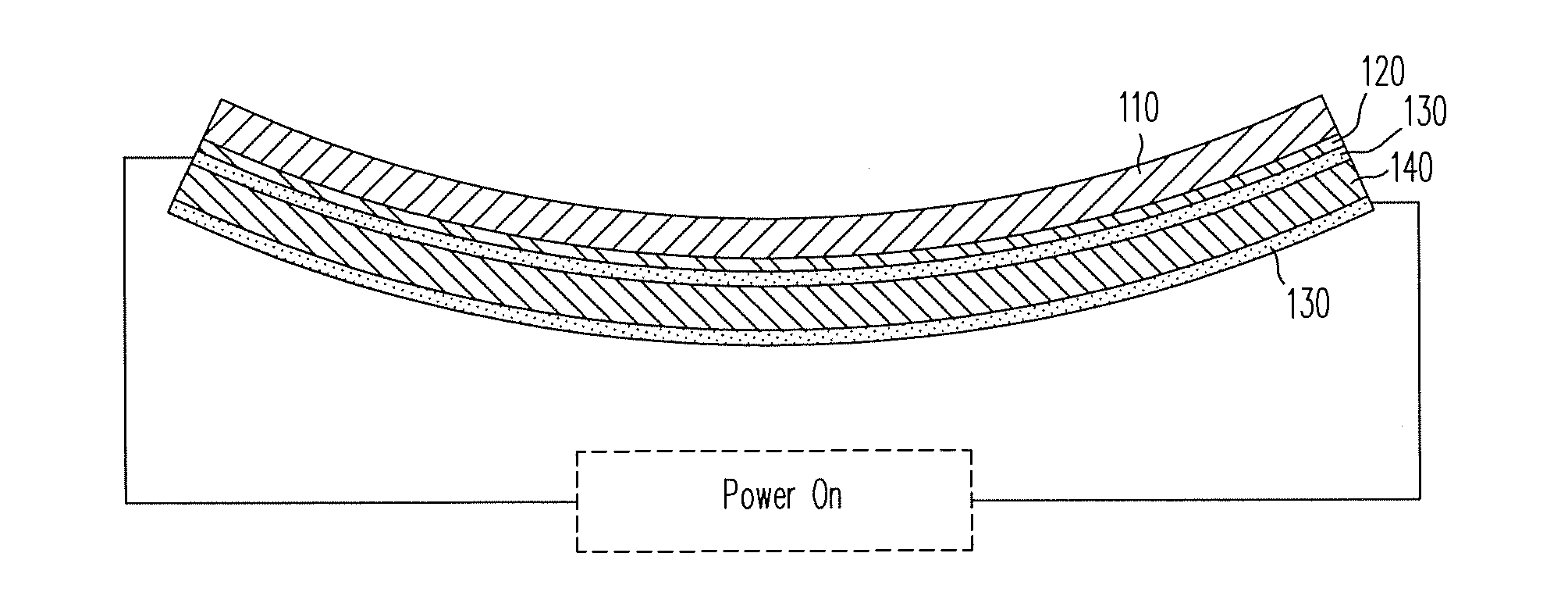
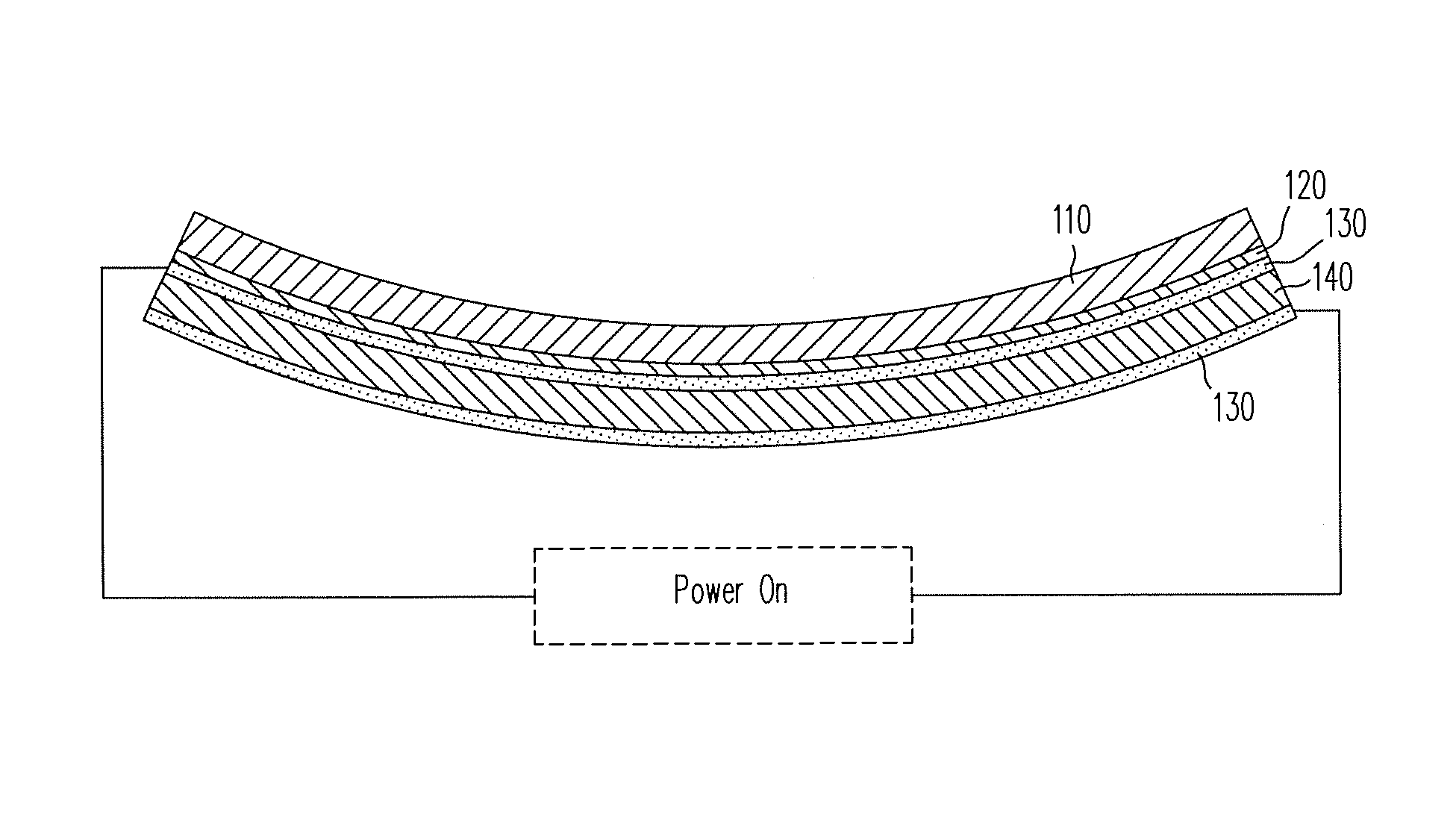
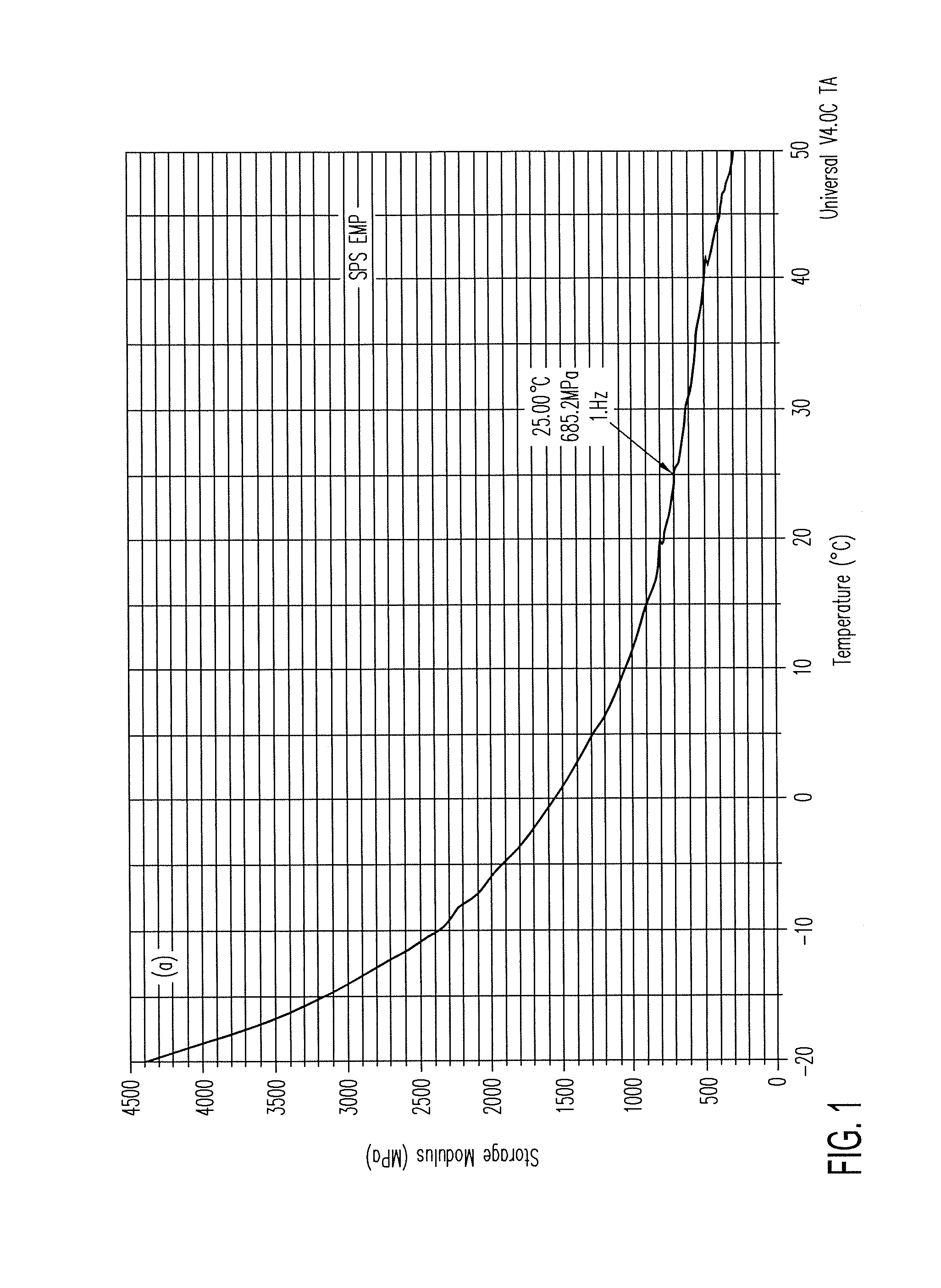
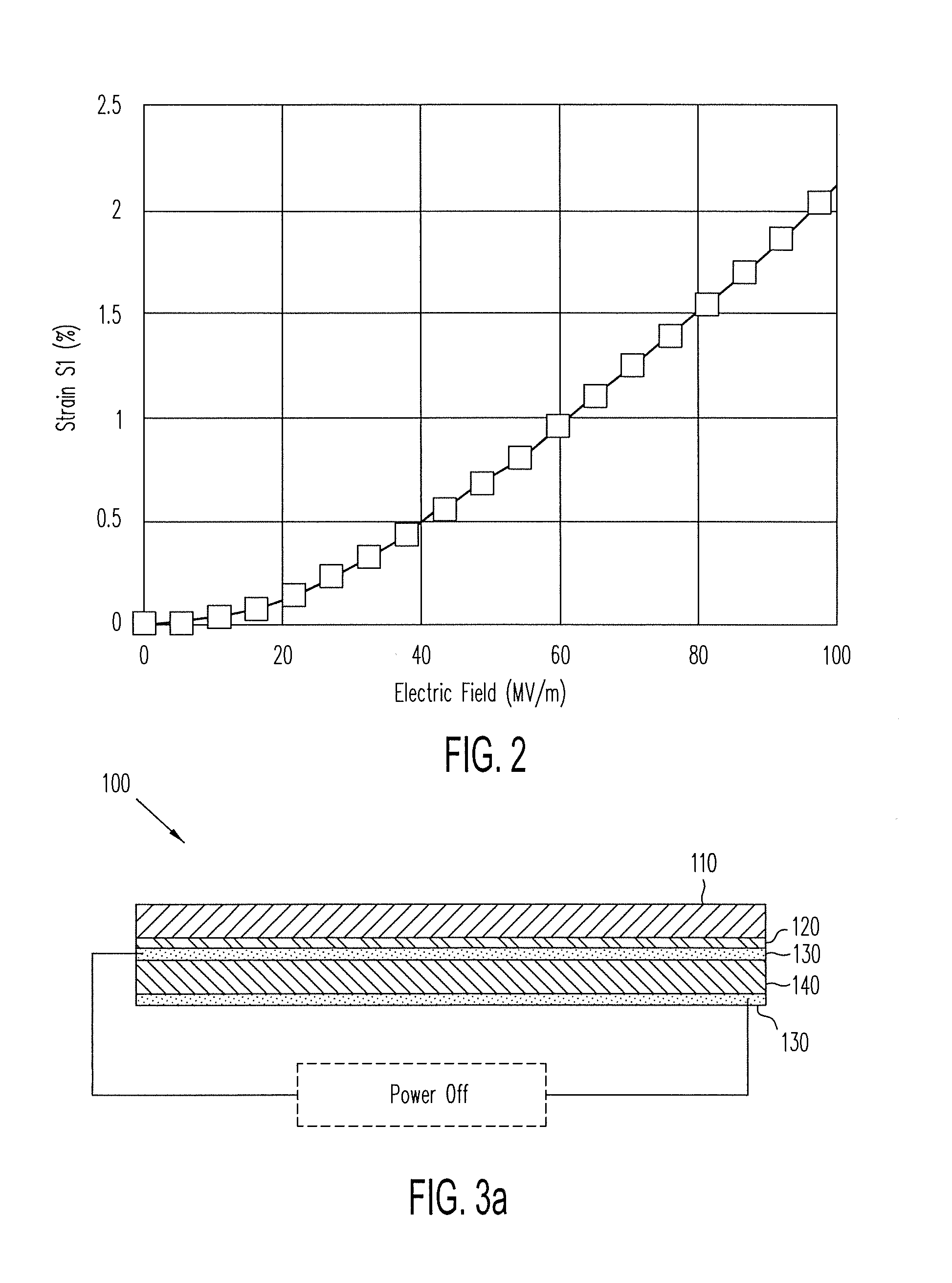
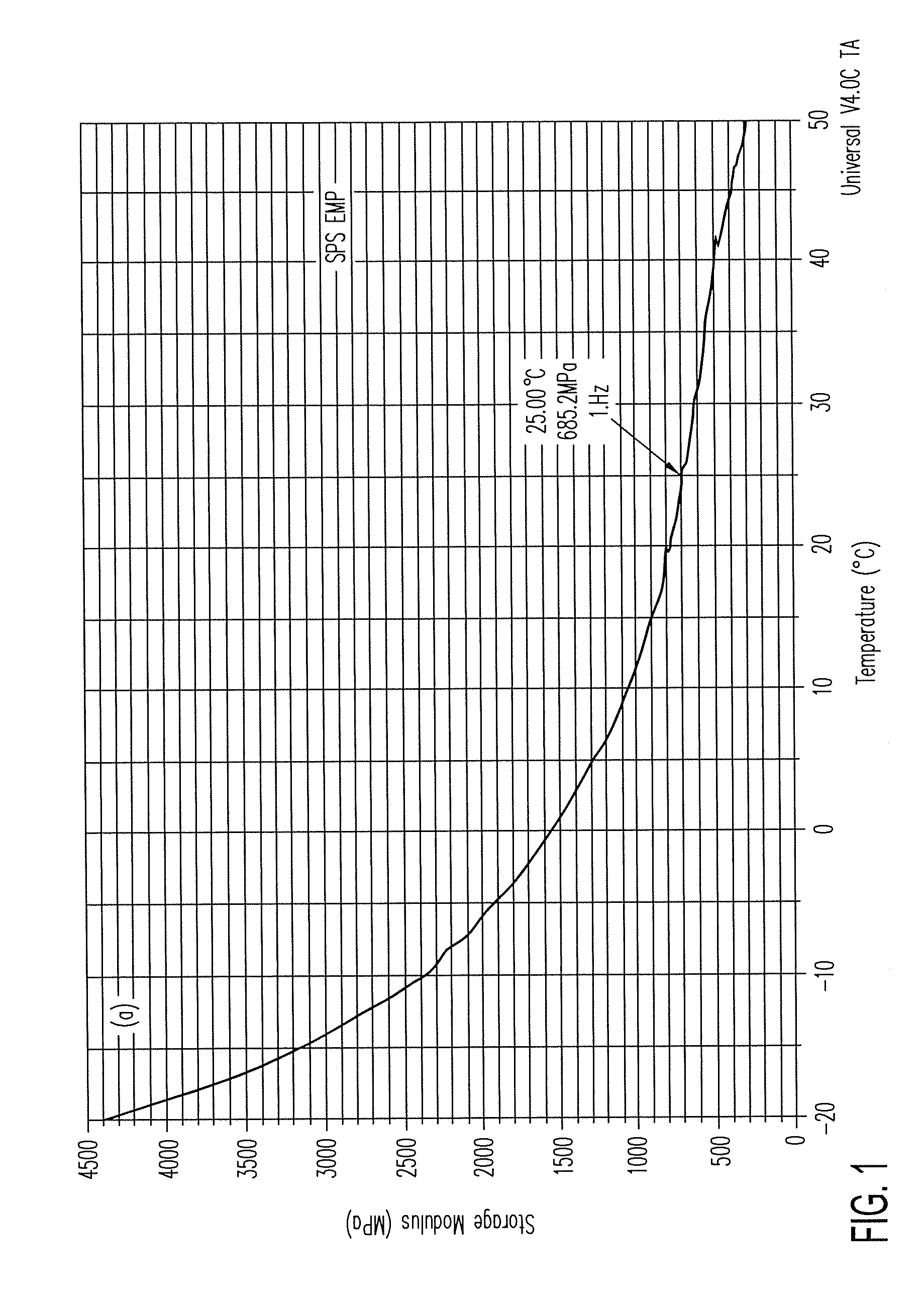
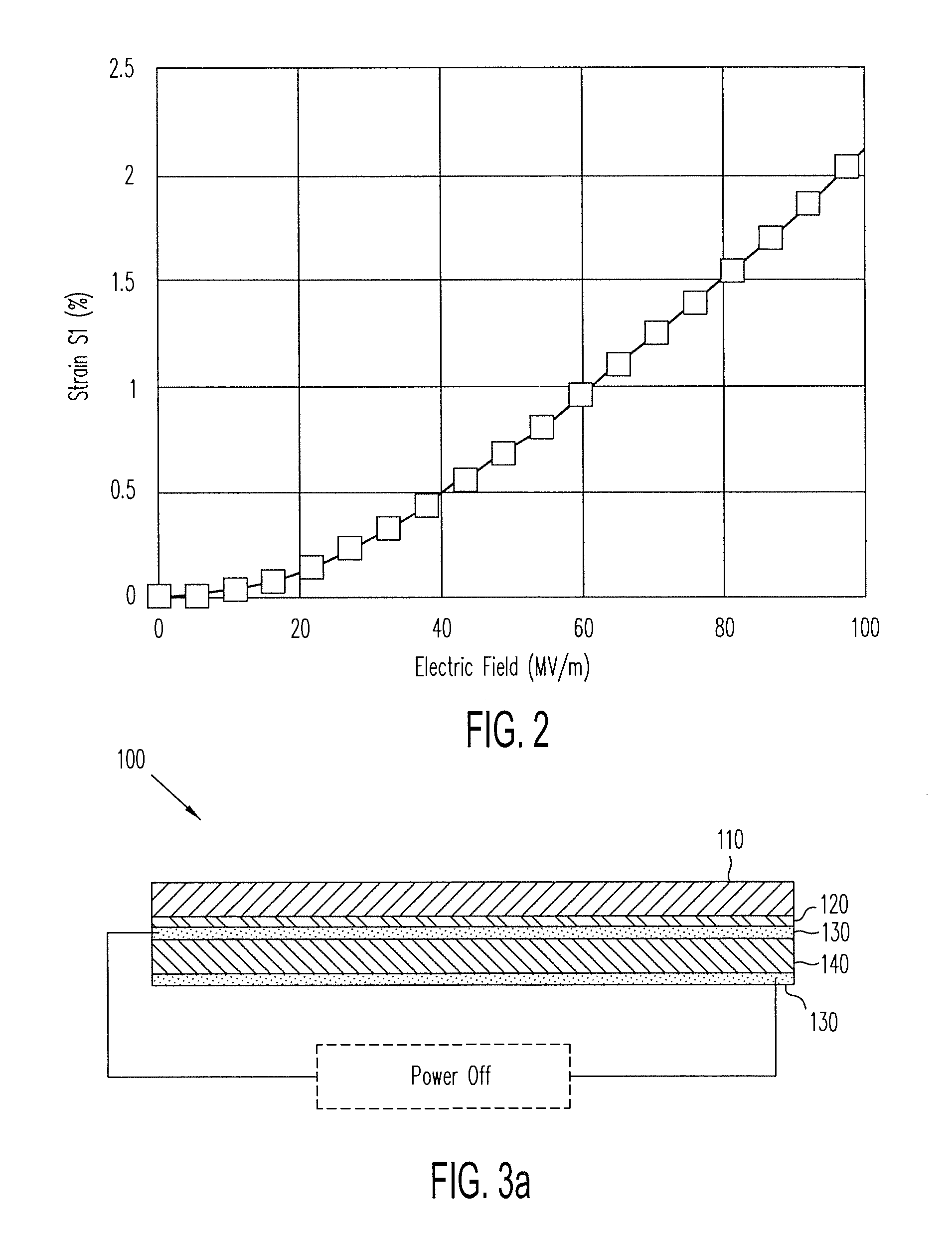
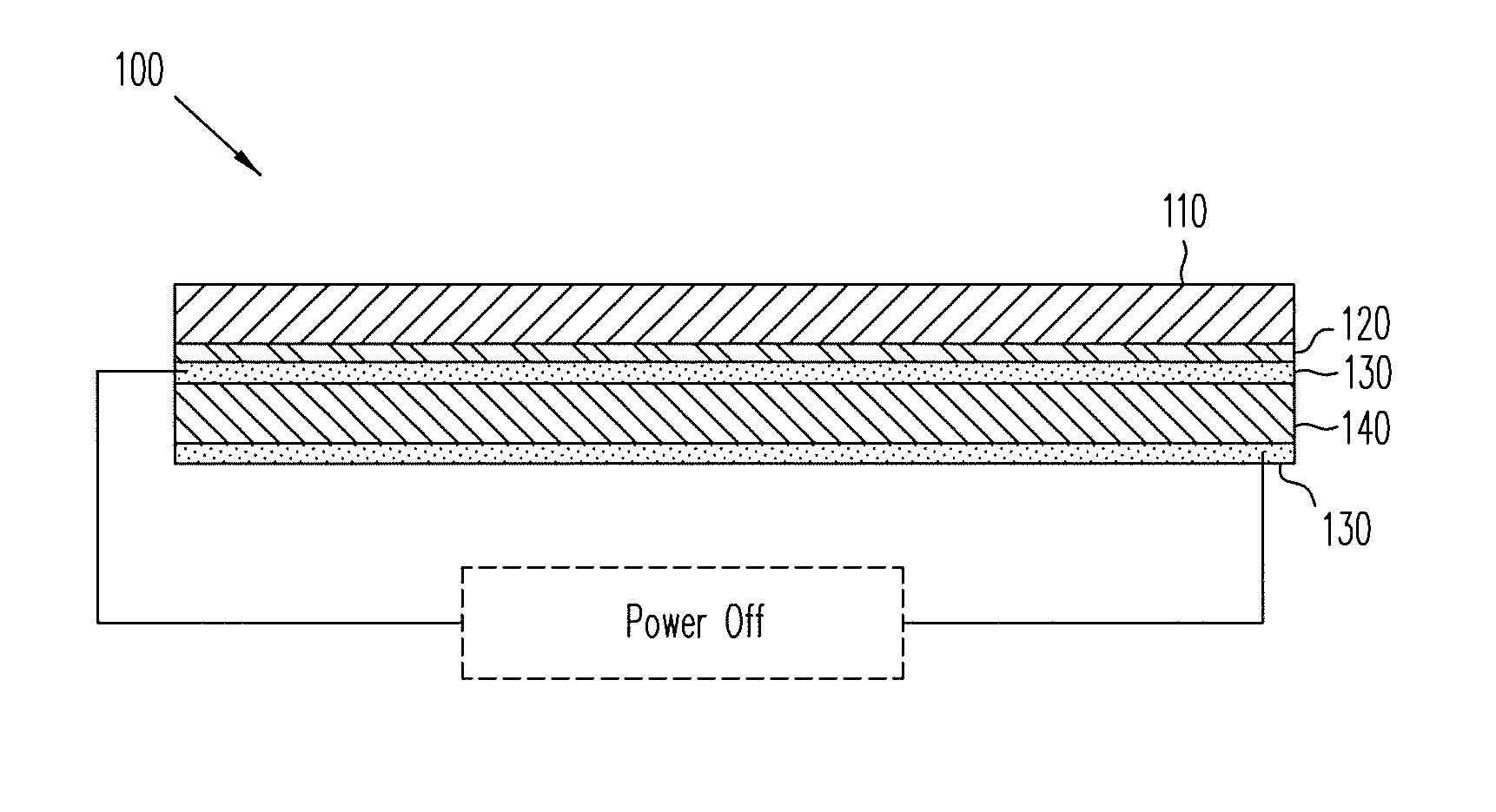
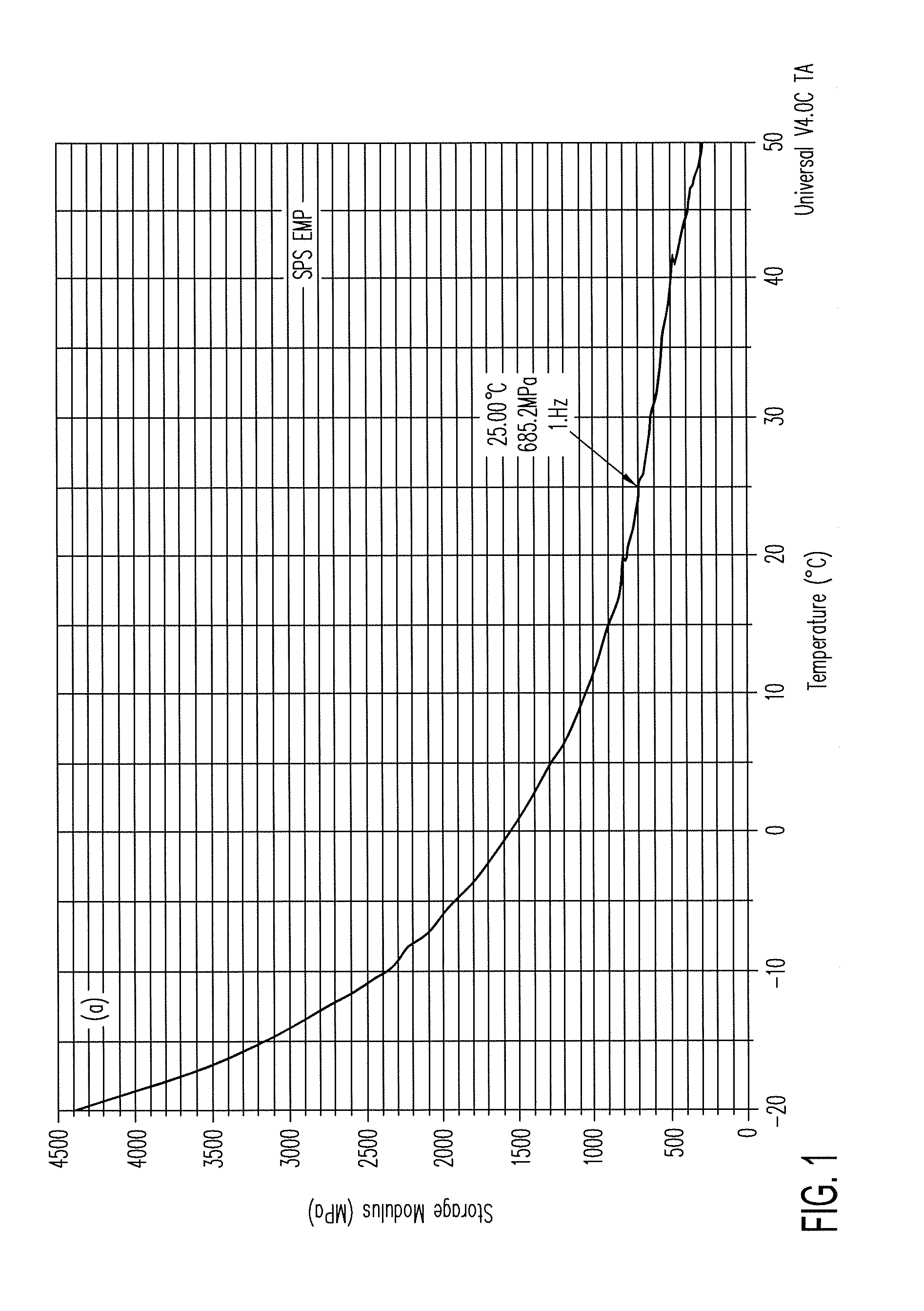
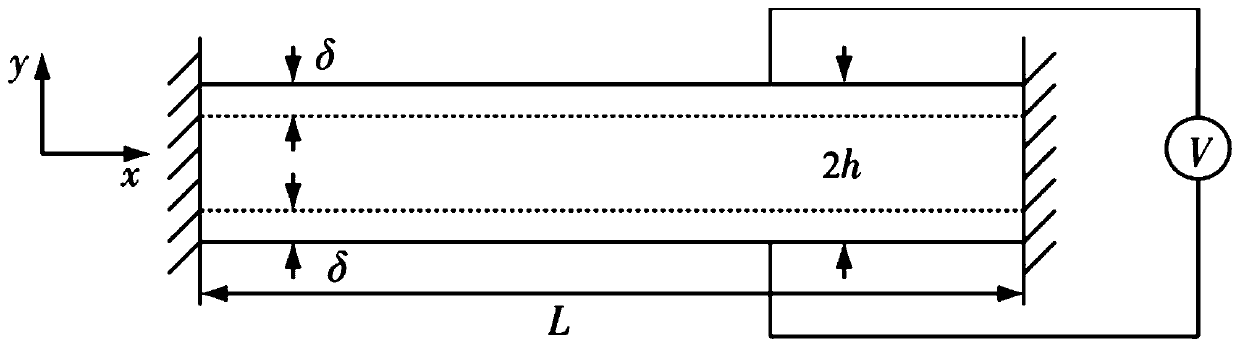
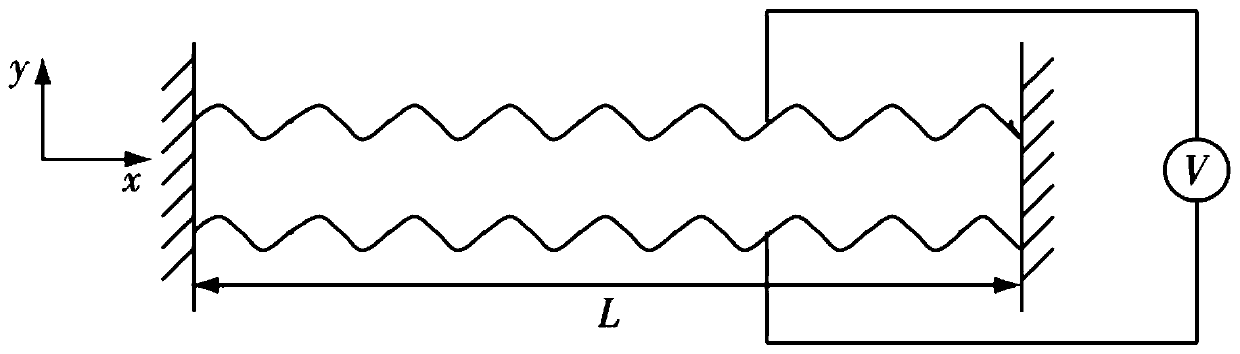
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Electrostrictive polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
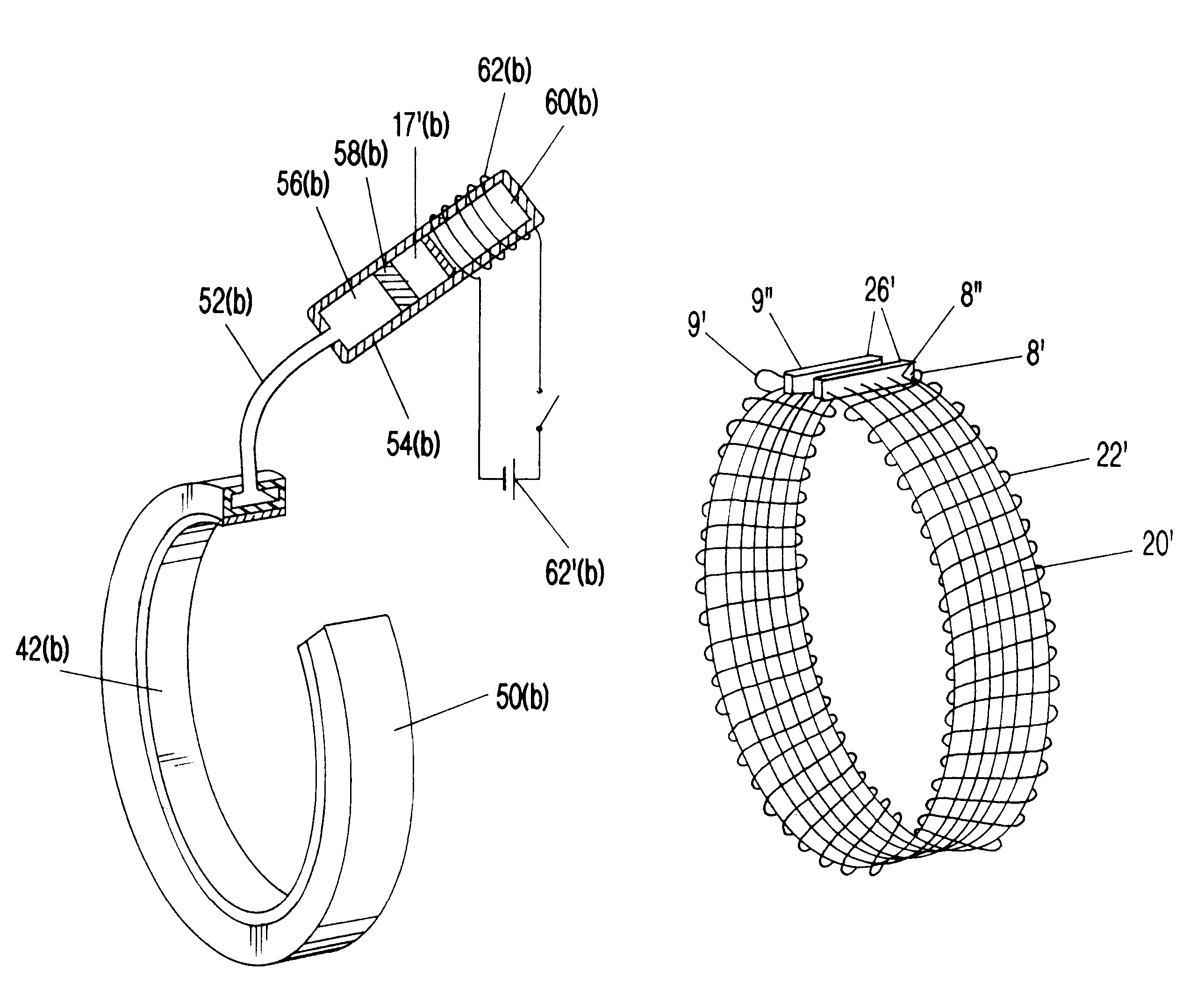
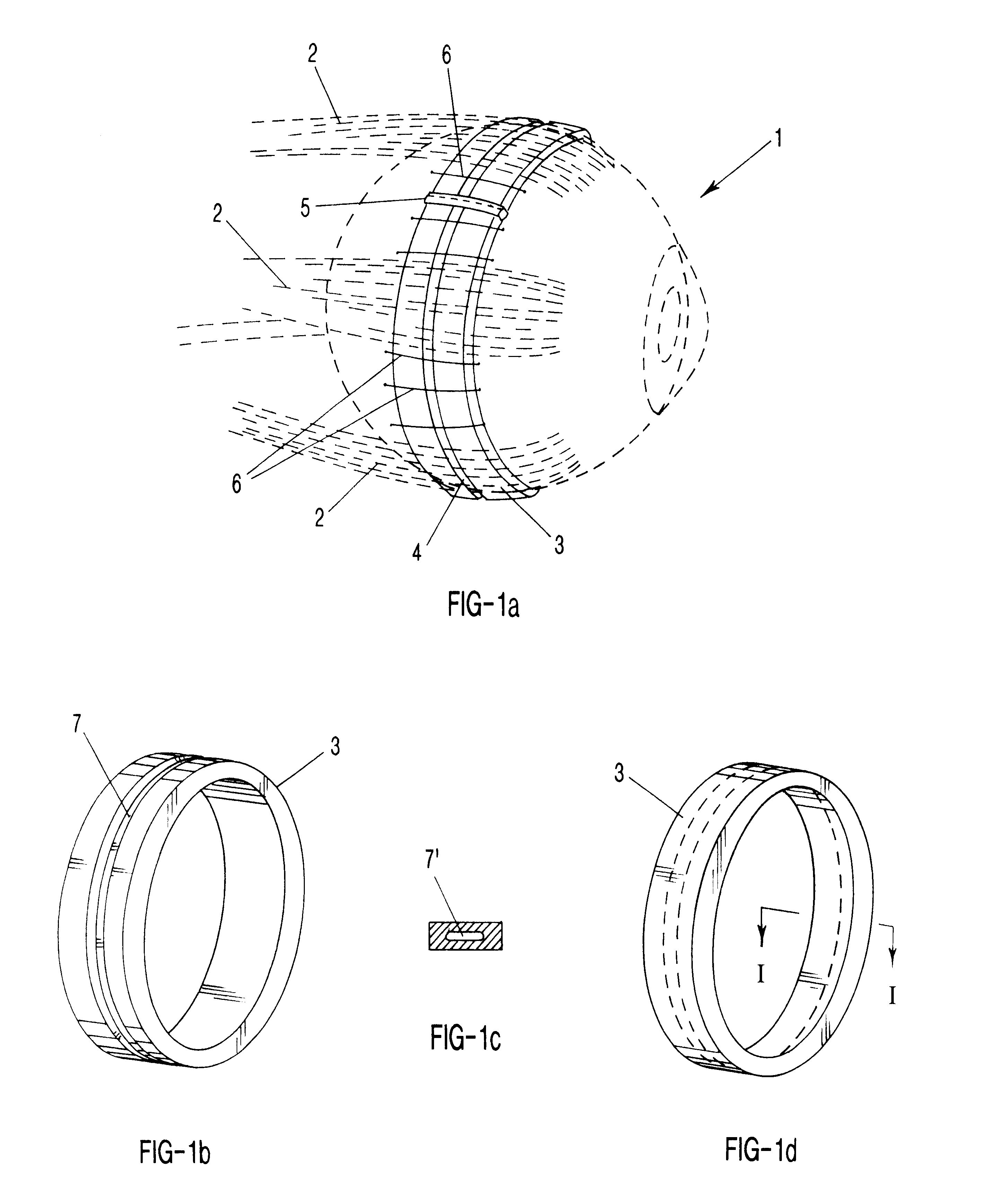
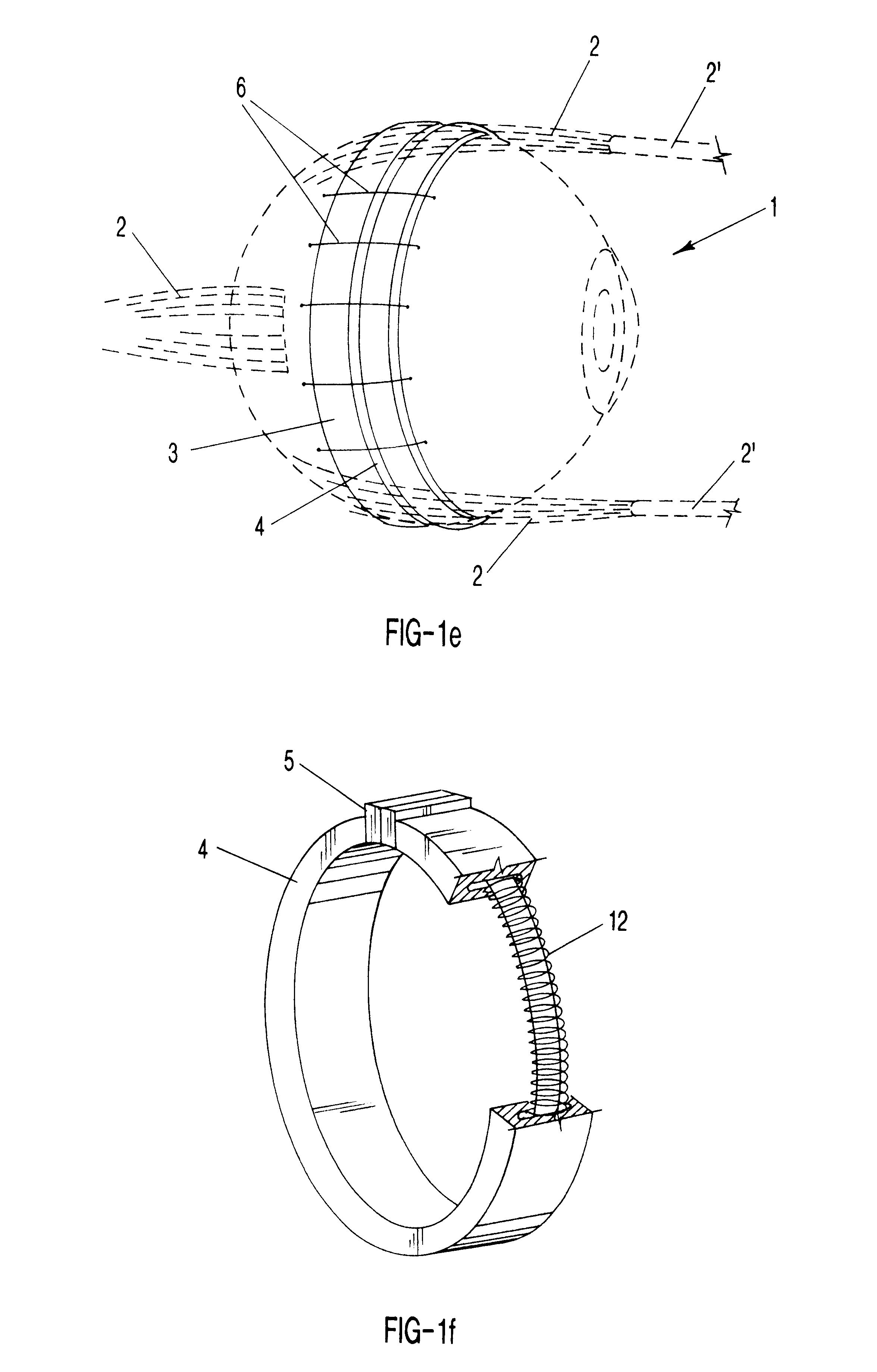
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
Electrostrictive polymer as a combined haptic-seal actuator
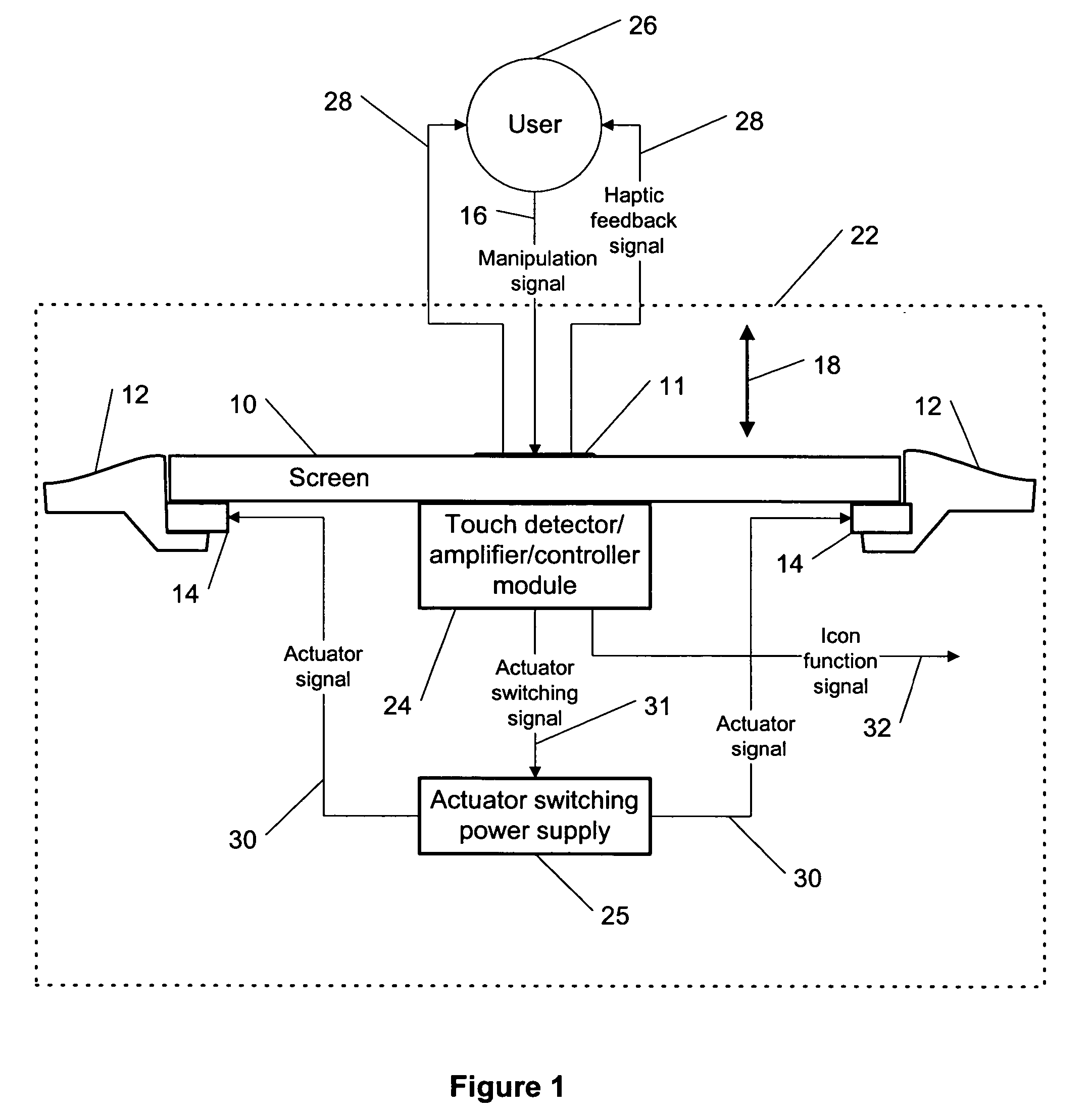
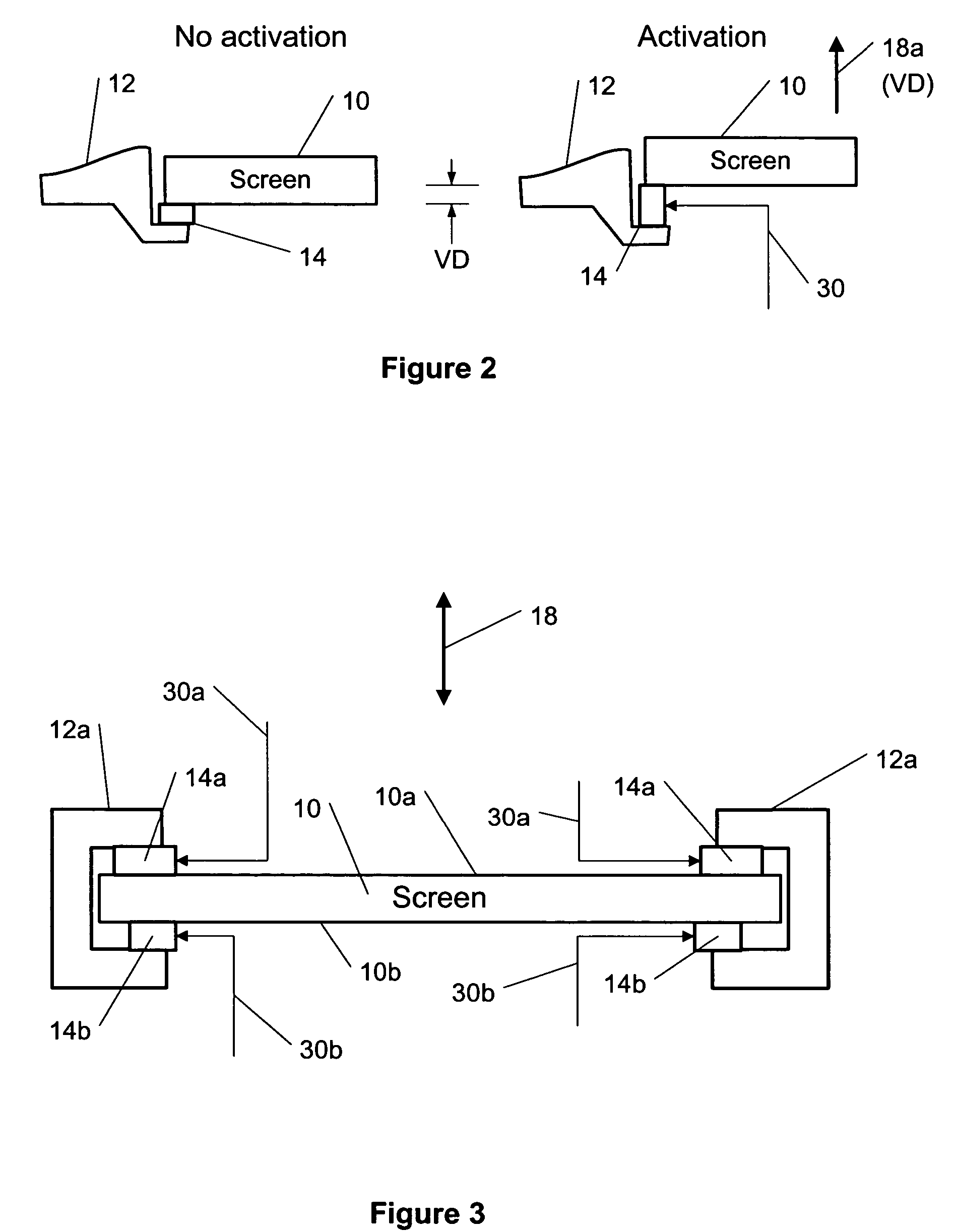
ActiveUS7342573B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringActuator
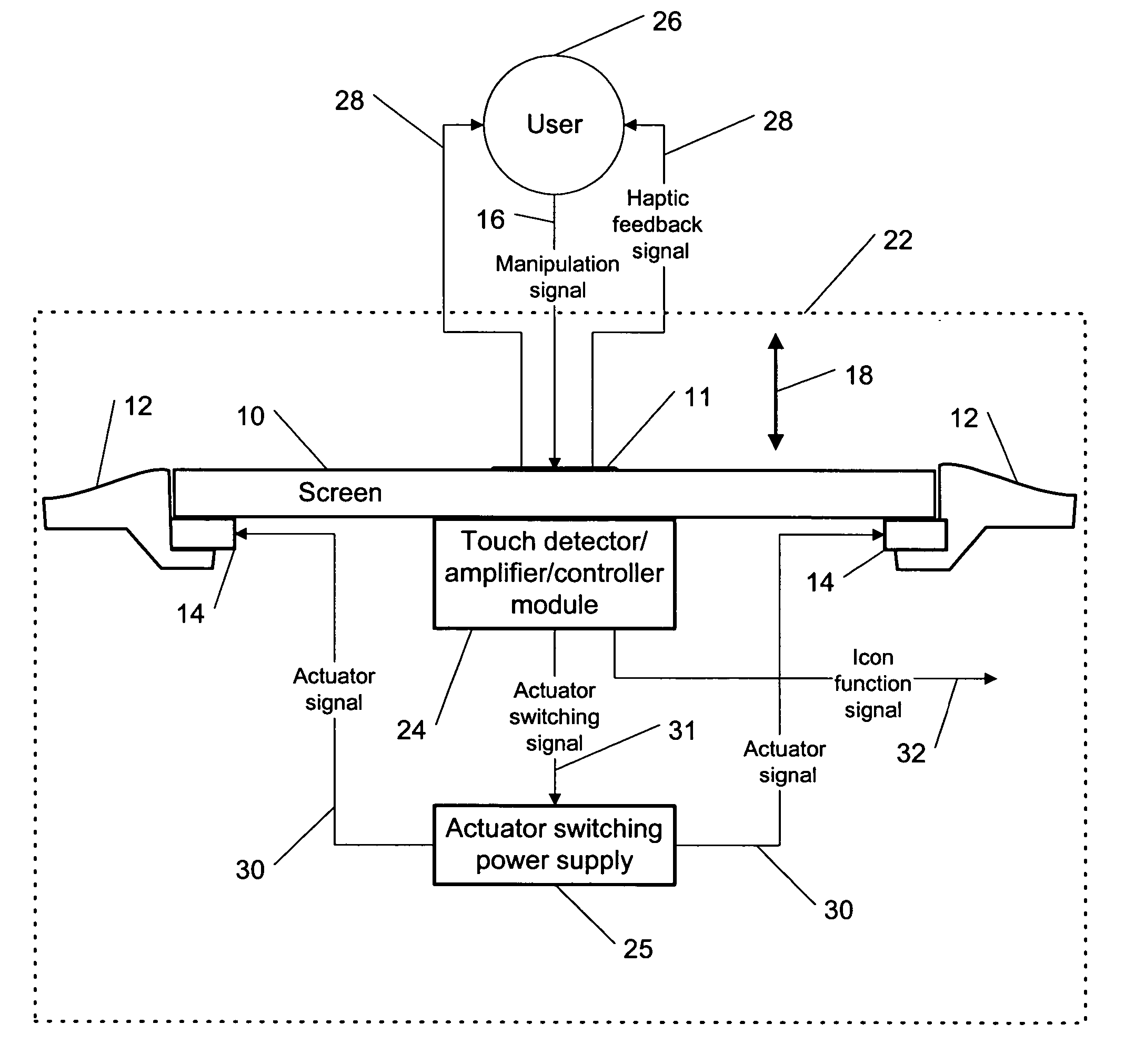
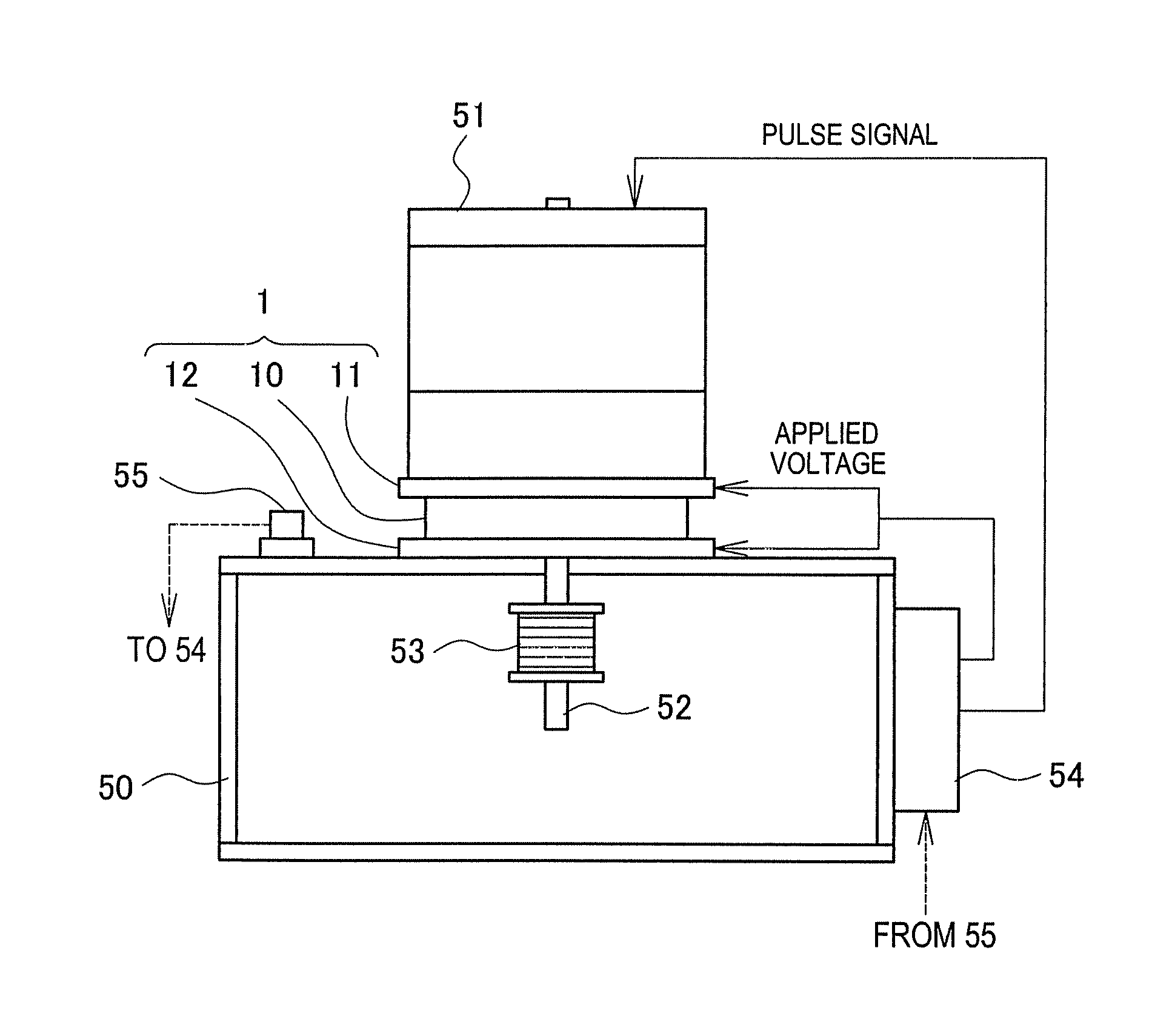
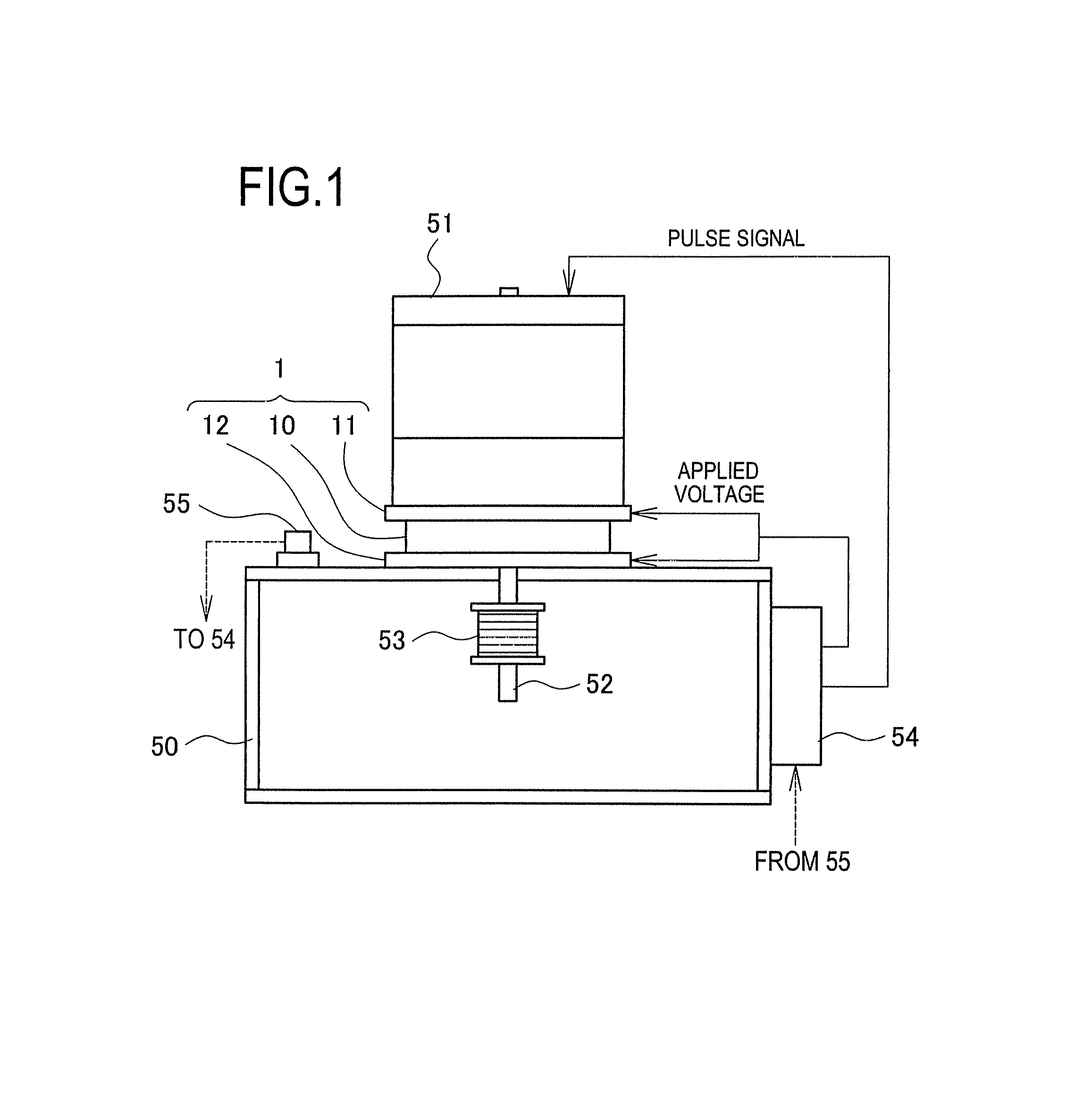
This invention describes a method for a haptic (tactile) feedback to a user of an electronic device having a touch display (screen) by utilizing an electrostrictive polymer as a combined haptic-seal actuator attached to the touch screen. In addition, the combined seal-actuator also makes a shock absorber. The electrostrictive polymer is a suitable material for haptic-seal-shock absorbing actuator because of its robustness and large stroke.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
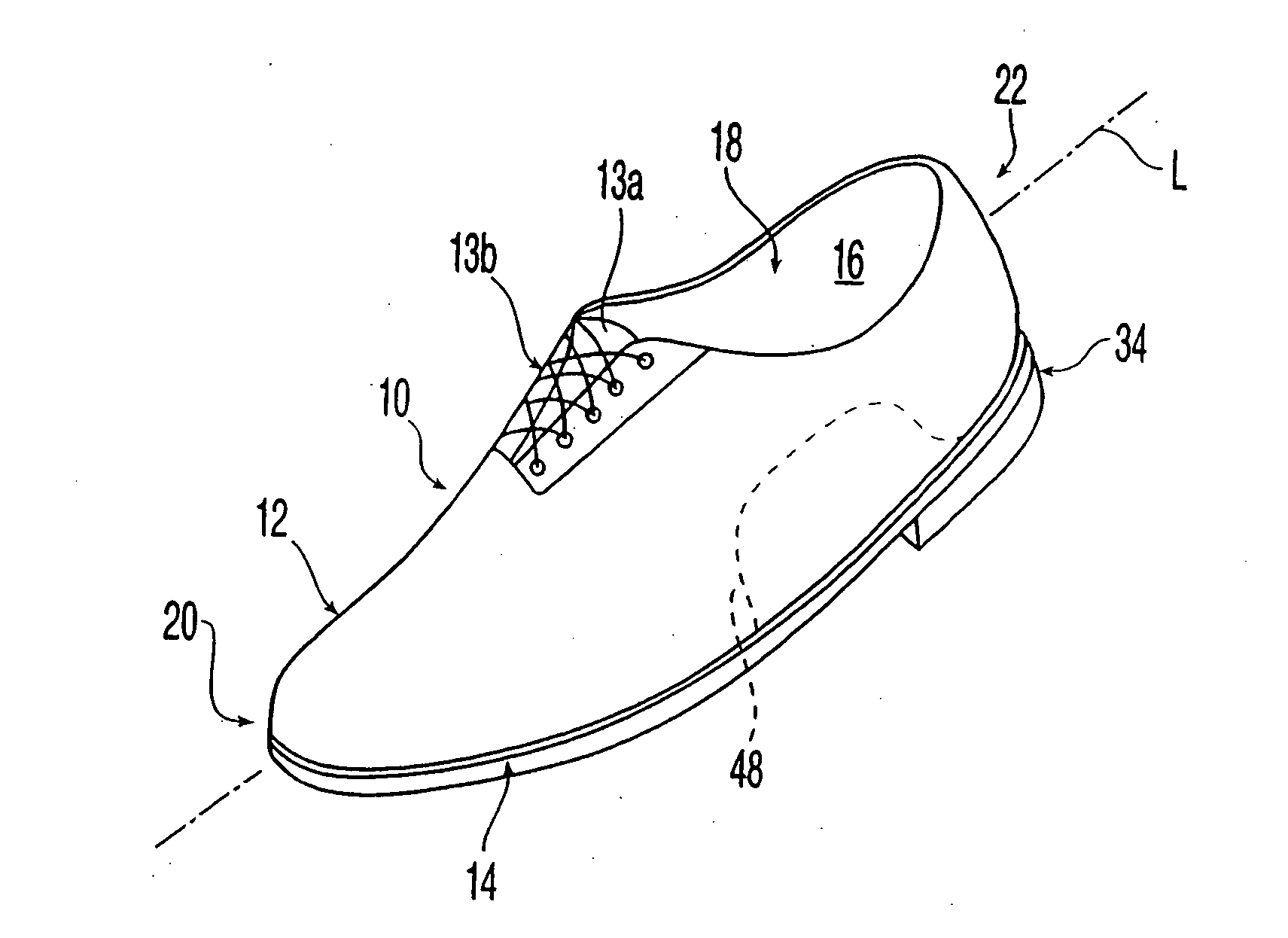
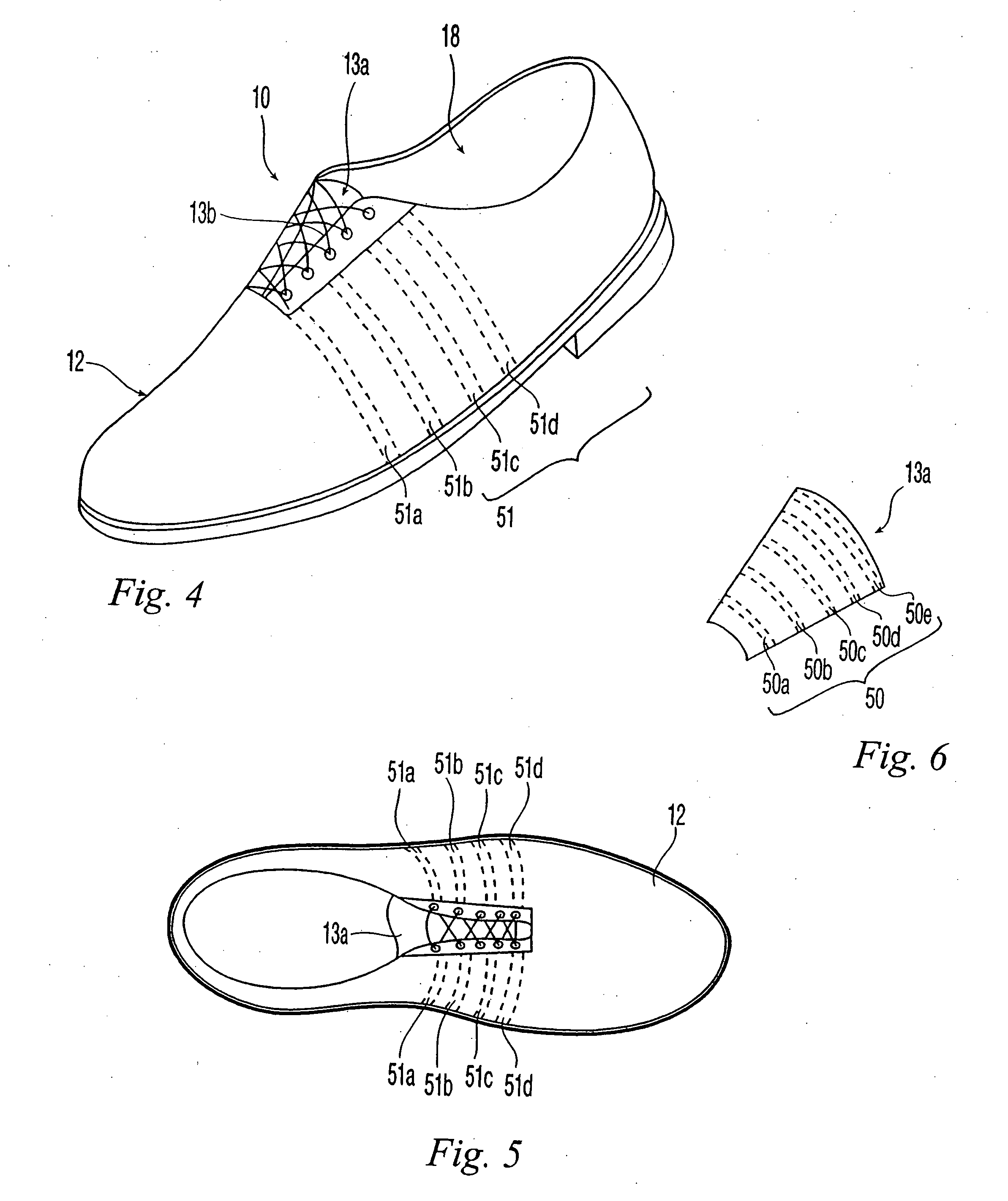
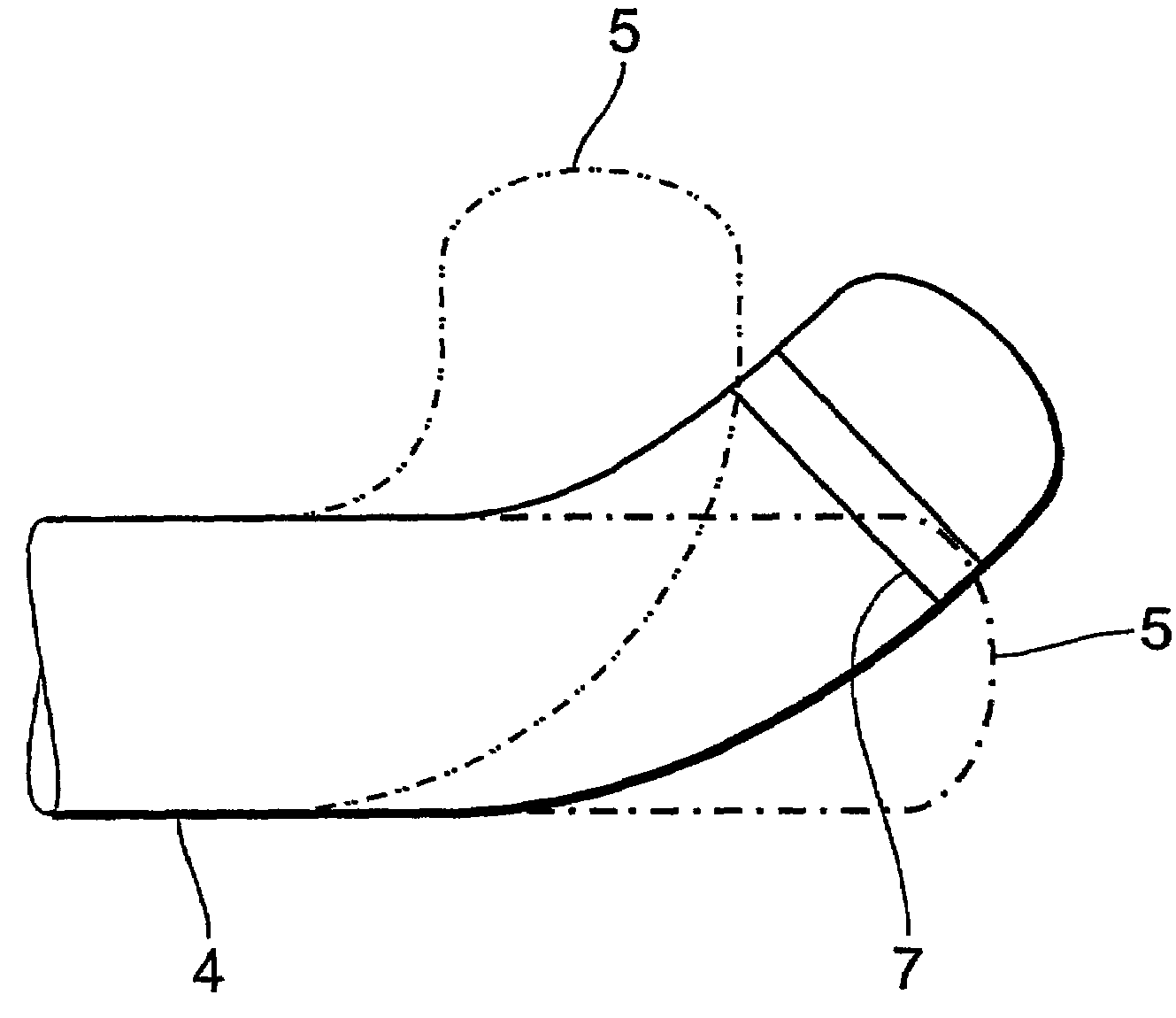
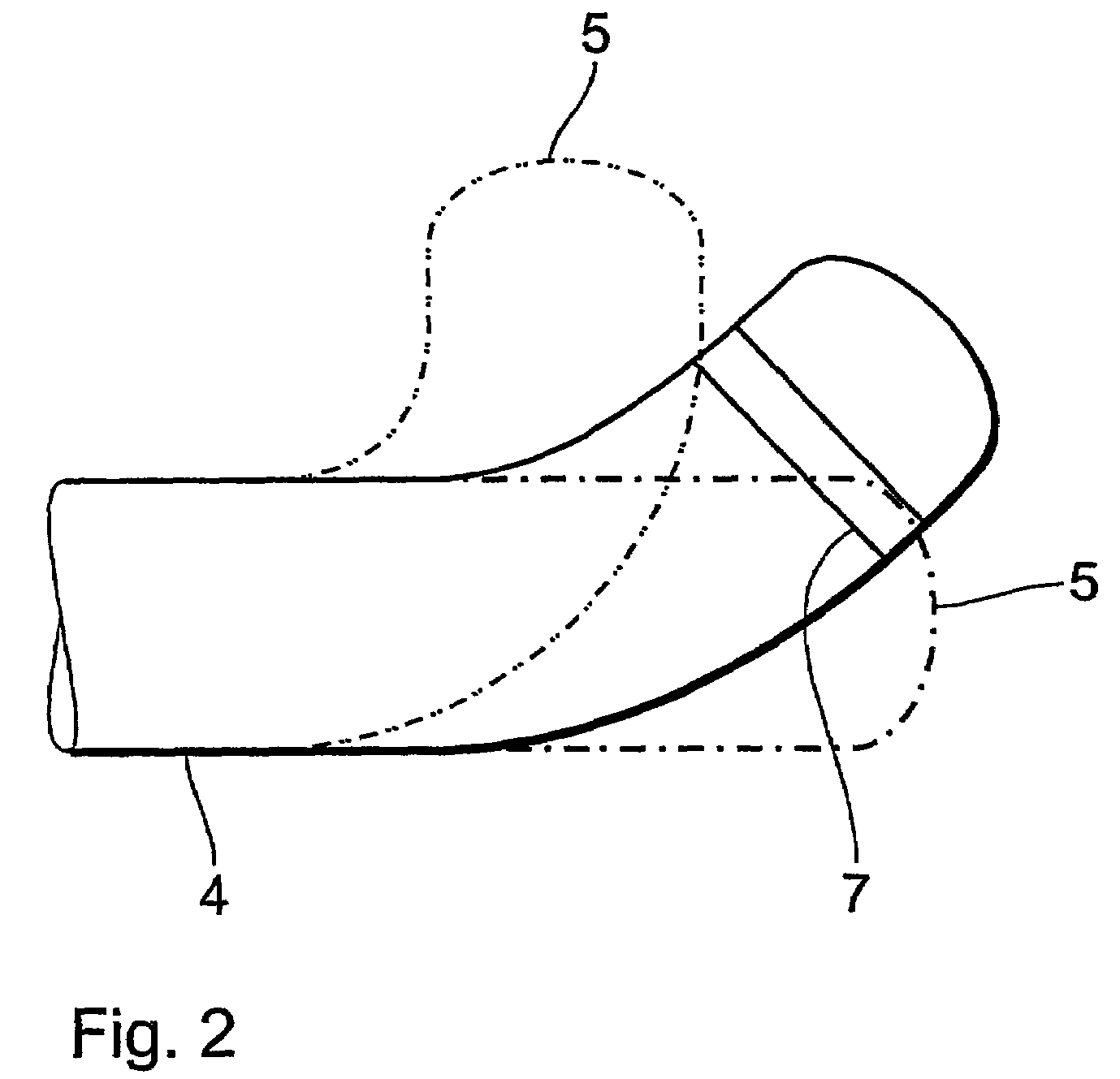
Shoe with sensors, controller and active-response elements and method for use thereof
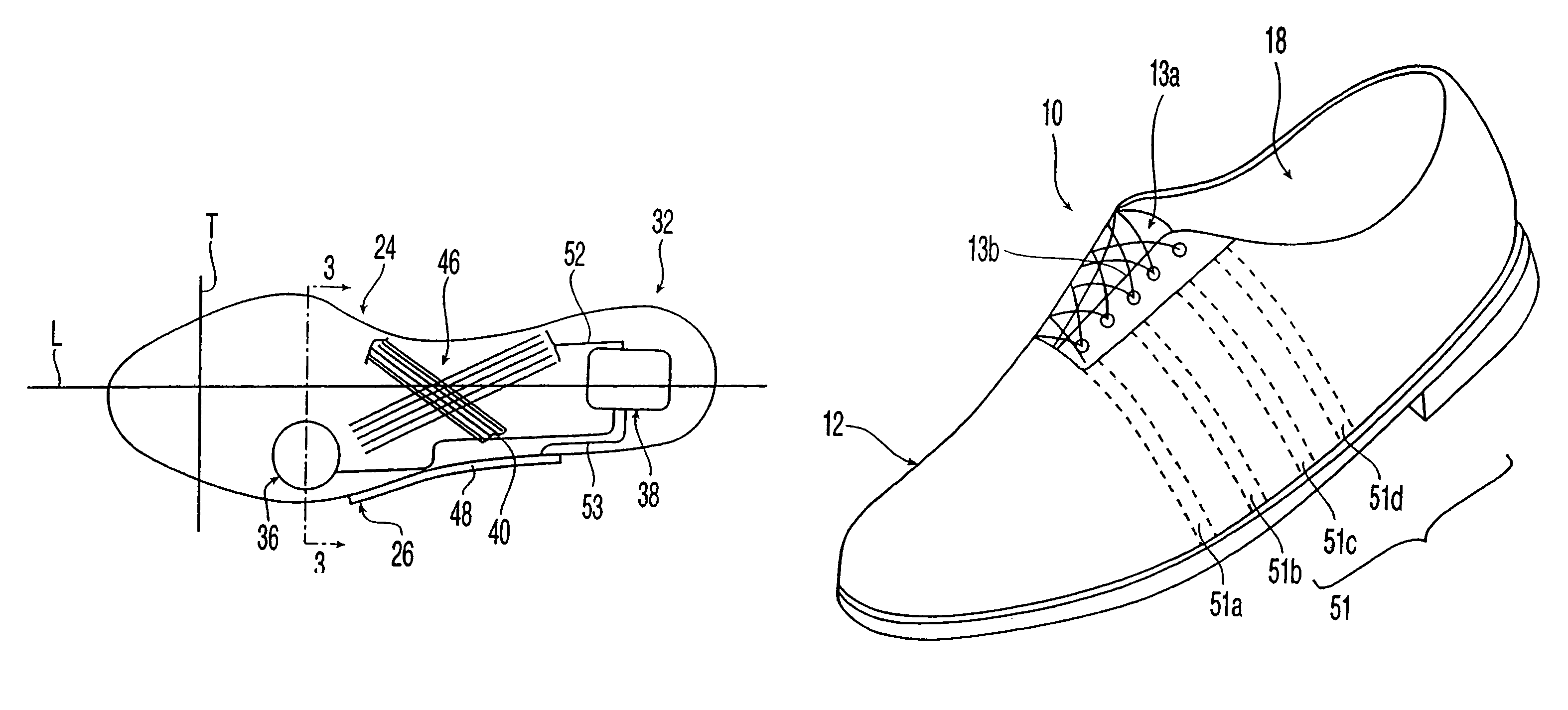
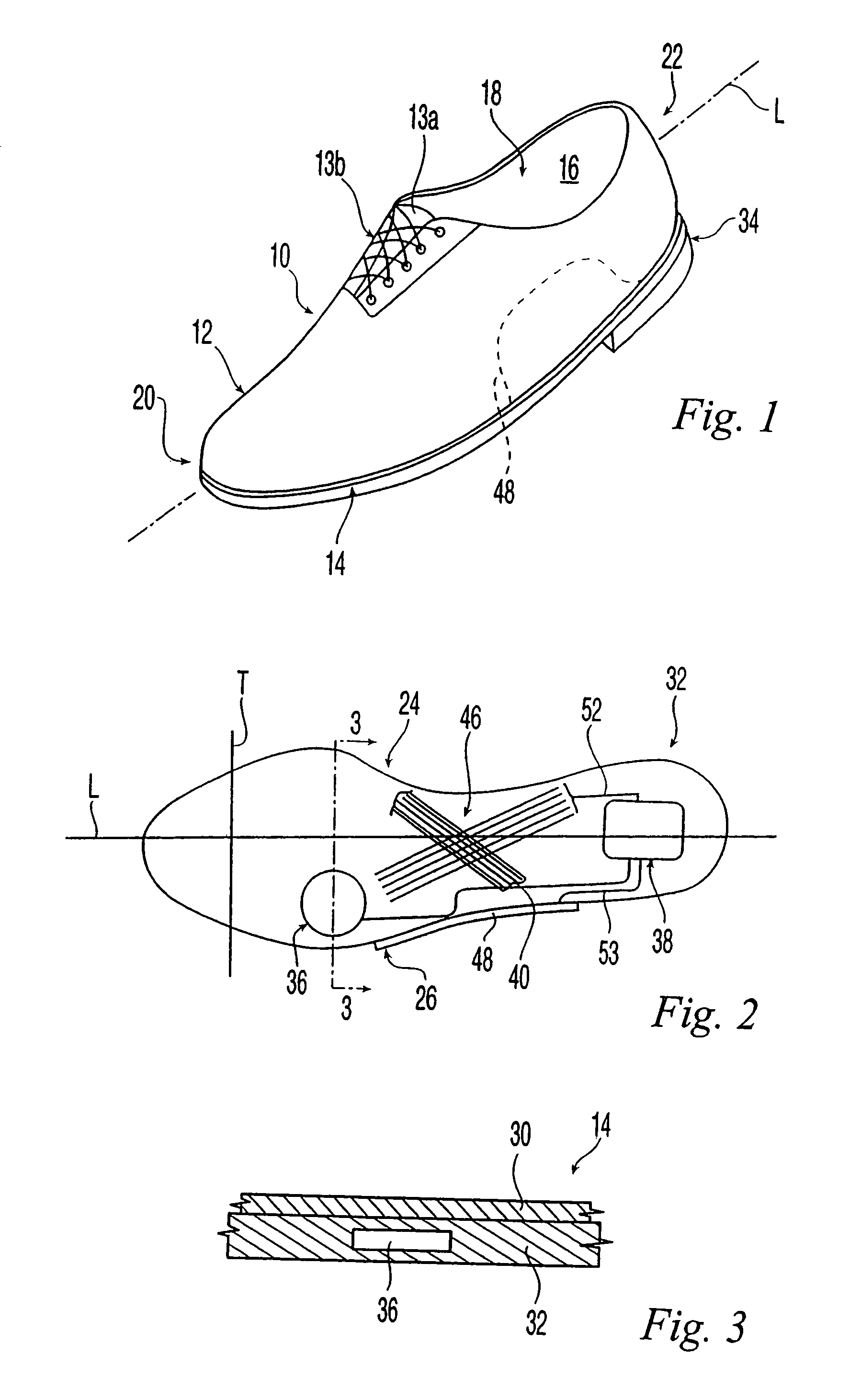
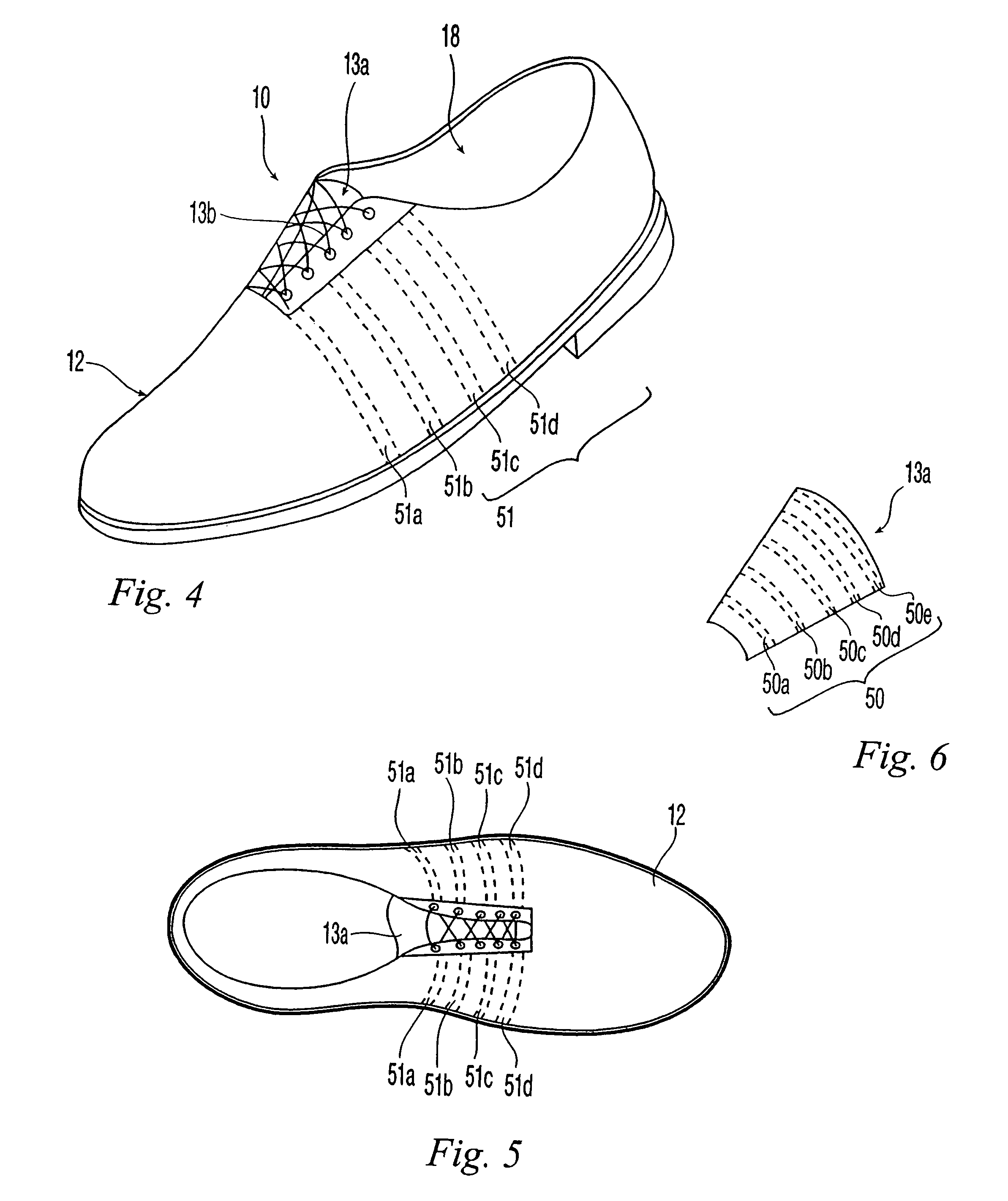
Active-response golf shoes are disclosed. The golf shoes include a plurality of sensors, a controller, and at least one active-response element. The sensor and controller operate to rapidly determine if a golfer is walking or swinging a golf club. Once this determination is made the controller and active-response element rapidly change the shoe's characteristics. If the controller determines that the golfer is walking, the shoe provides a soft and flexible walking platform. If the controller determines that the golfer is swinging, the shoe morphs or changes automatically to provide a stable hitting platform. The controller senses various predetermined conditions such as pressure of the user's foot to determine whether the golfer is walking or swinging. The active-response element is a lateral adjuster having an upper bracket located in the laces area and a lower bracket affixed to the side of the sole, brackets supporting a plurality of electrostrictive polymer bands;
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
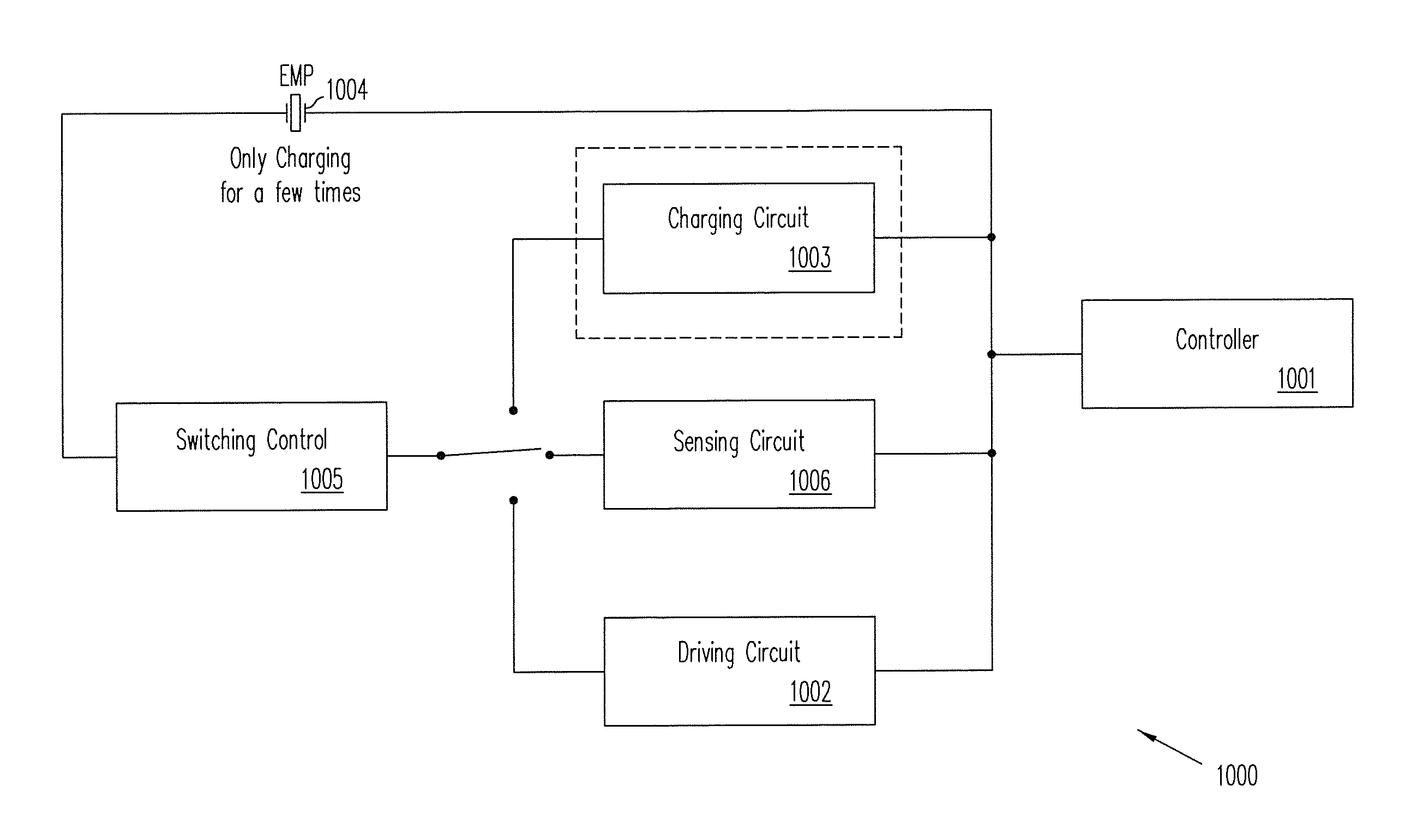
EMP Actuators for Deformable Surface and Keyboard Application
ActiveUS20140139436A1Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureInput/output for user-computer interactionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerDisplay device
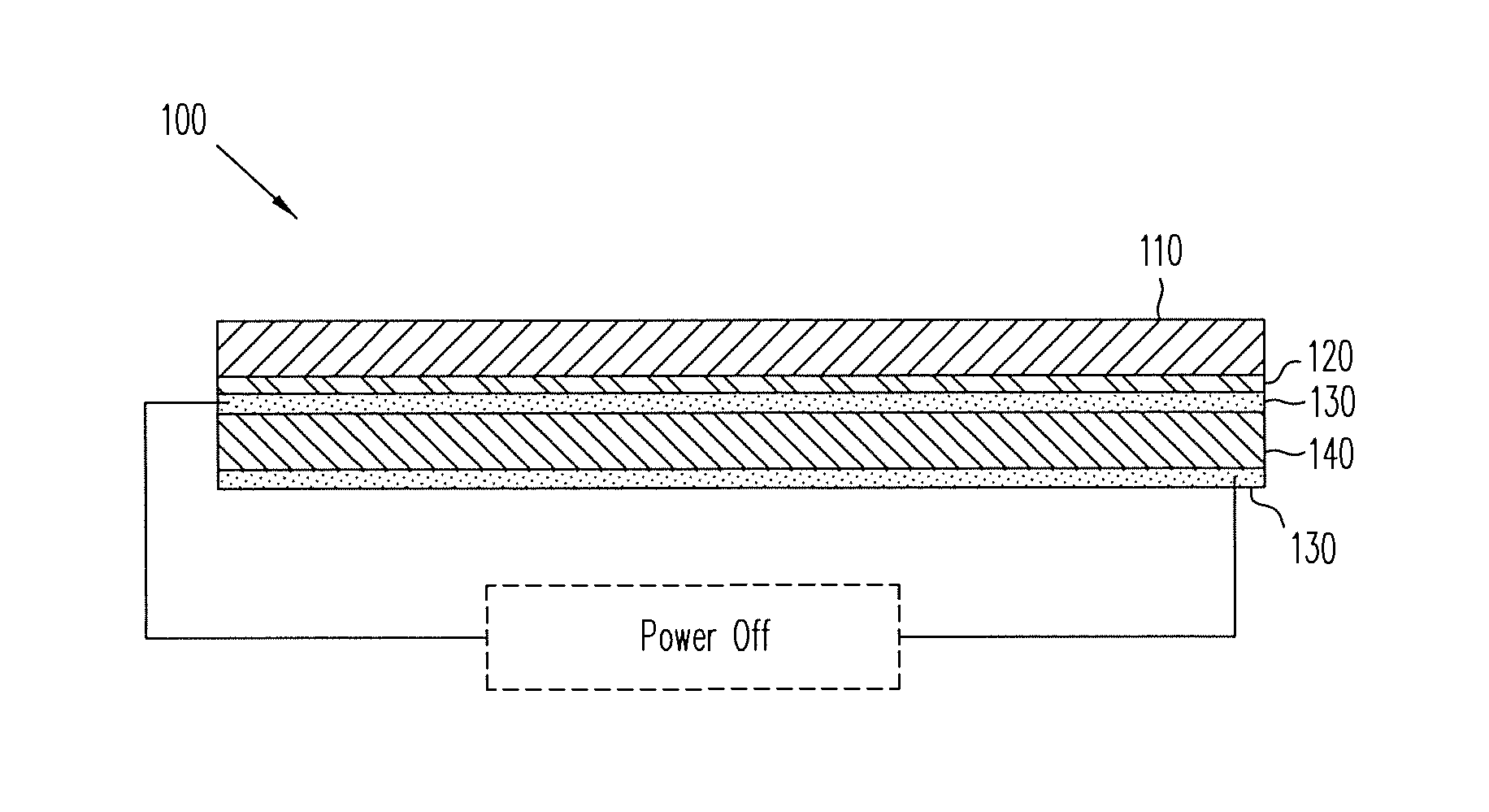
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology, keyboard, braille display, and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
System of Audio Speakers Implemented Using EMP Actuators
ActiveUS20140140551A1Maximize displacementReduce entropyMicrophonesTransducers for sound channels pluralityTransducerEngineering
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Systems including electromechanical polymer sensors and actuators
ActiveUS20140139329A1Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureRepeater circuitsTactile signalling systemsTransducerEngineering
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Haptic system with localized response
ActiveUS20140139328A1Maximize displacementReduce entropyRepeater circuitsTactile signalling systemsLoudspeakerElectrostrictive polymer
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
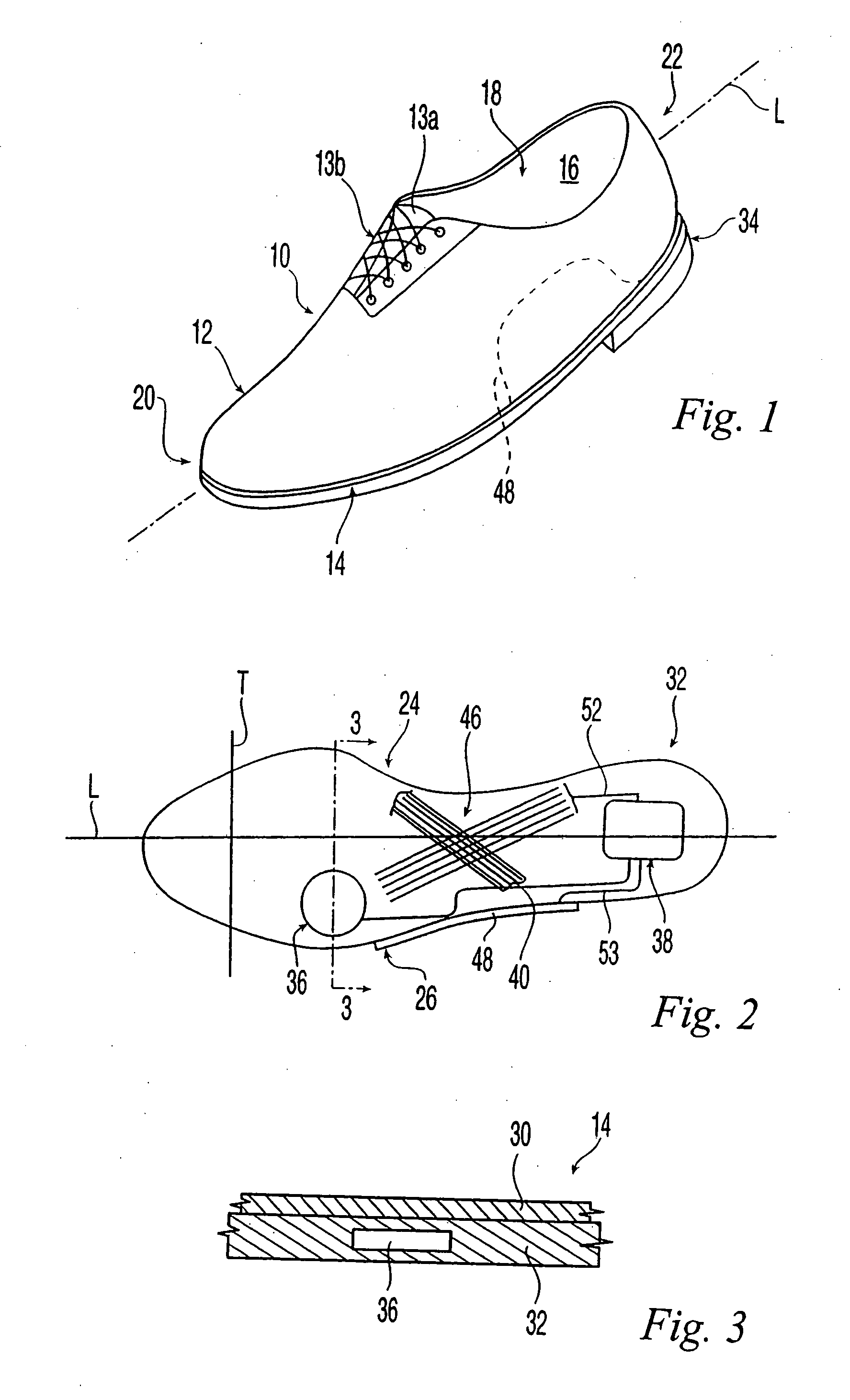
Shoe with sensors, controller and active-response elements and method for use thereof
Active-response golf shoes are disclosed. The golf shoes include a plurality of sensors, a controller, and at least one active-response element. The sensor and controller operate to rapidly determine if a golfer is walking or swinging a golf club. Once this determination is made the controller and active-response element rapidly change the shoe's characteristics. If the controller determines that the golfer is walking, the shoe provides a soft and flexible walking platform. If the controller determines that the golfer is swinging, the shoe morphs or changes automatically to provide a stable hitting platform. The controller senses various predetermined conditions such as pressure of the user's foot to determine whether the golfer is walking or swinging. The active-response element is a lateral adjuster having an upper bracket located in the laces area and a lower bracket affixed to the side of the sole, brackets supporting a plurality of electrostrictive polymer bands.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Haptic system with localized response
ActiveUS9164586B2Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureInput/output for user-computer interactionTactile signalling systemsTransducerEngineering
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
High strain electrostrictive polymer
InactiveUS7078101B1Less cumbersomeHigher electrostrictiveSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingPolymer scienceHalogen
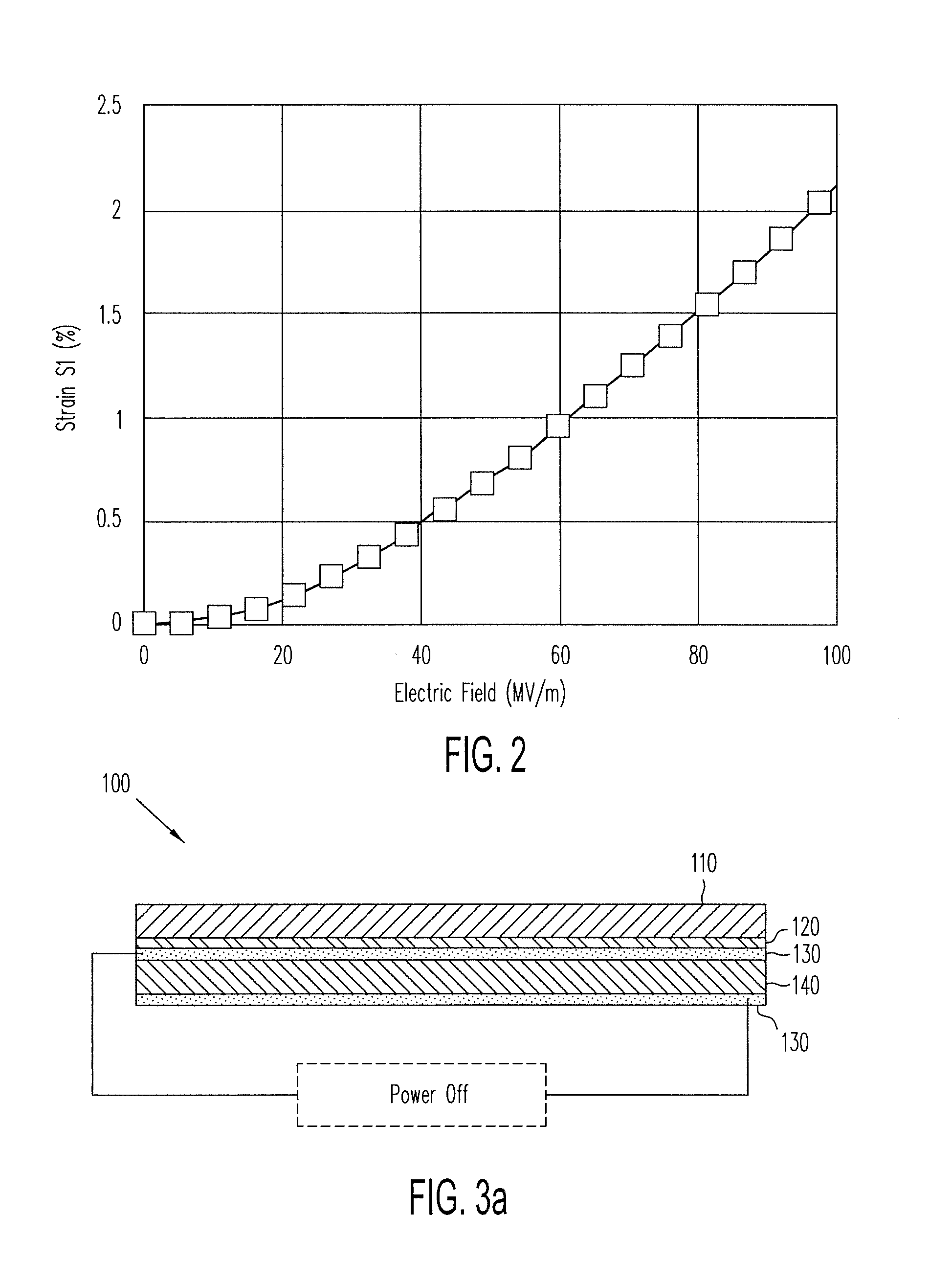
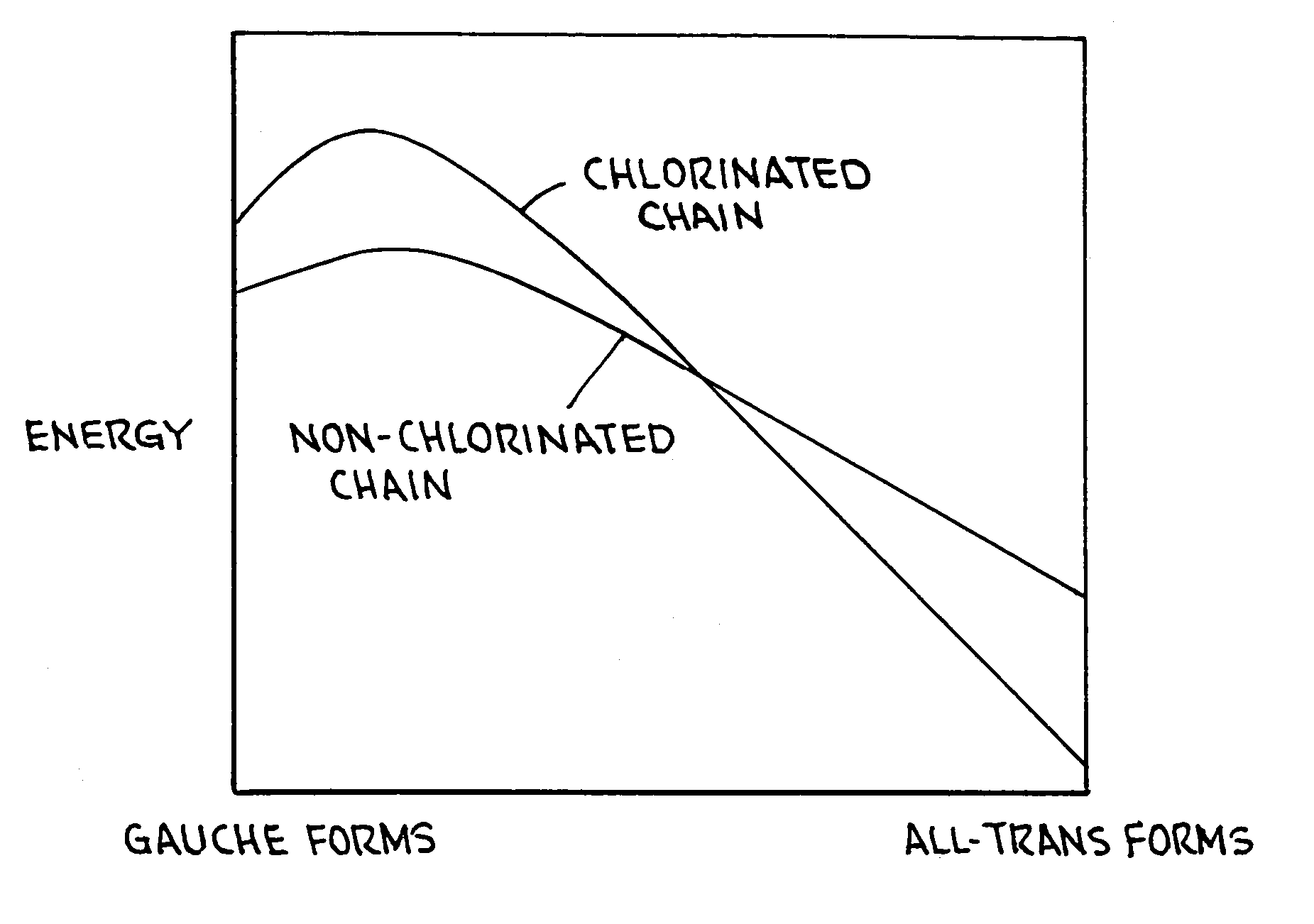
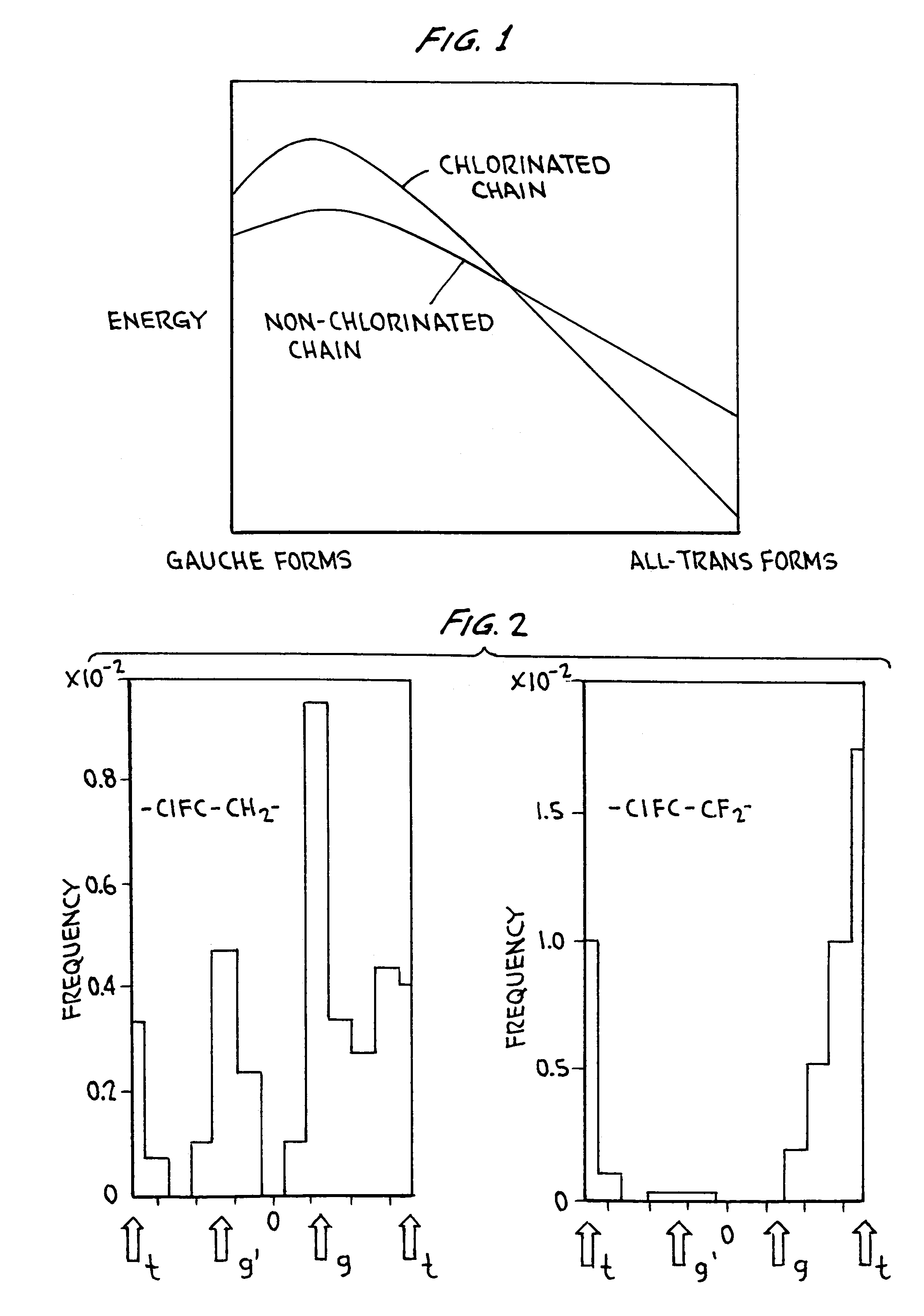
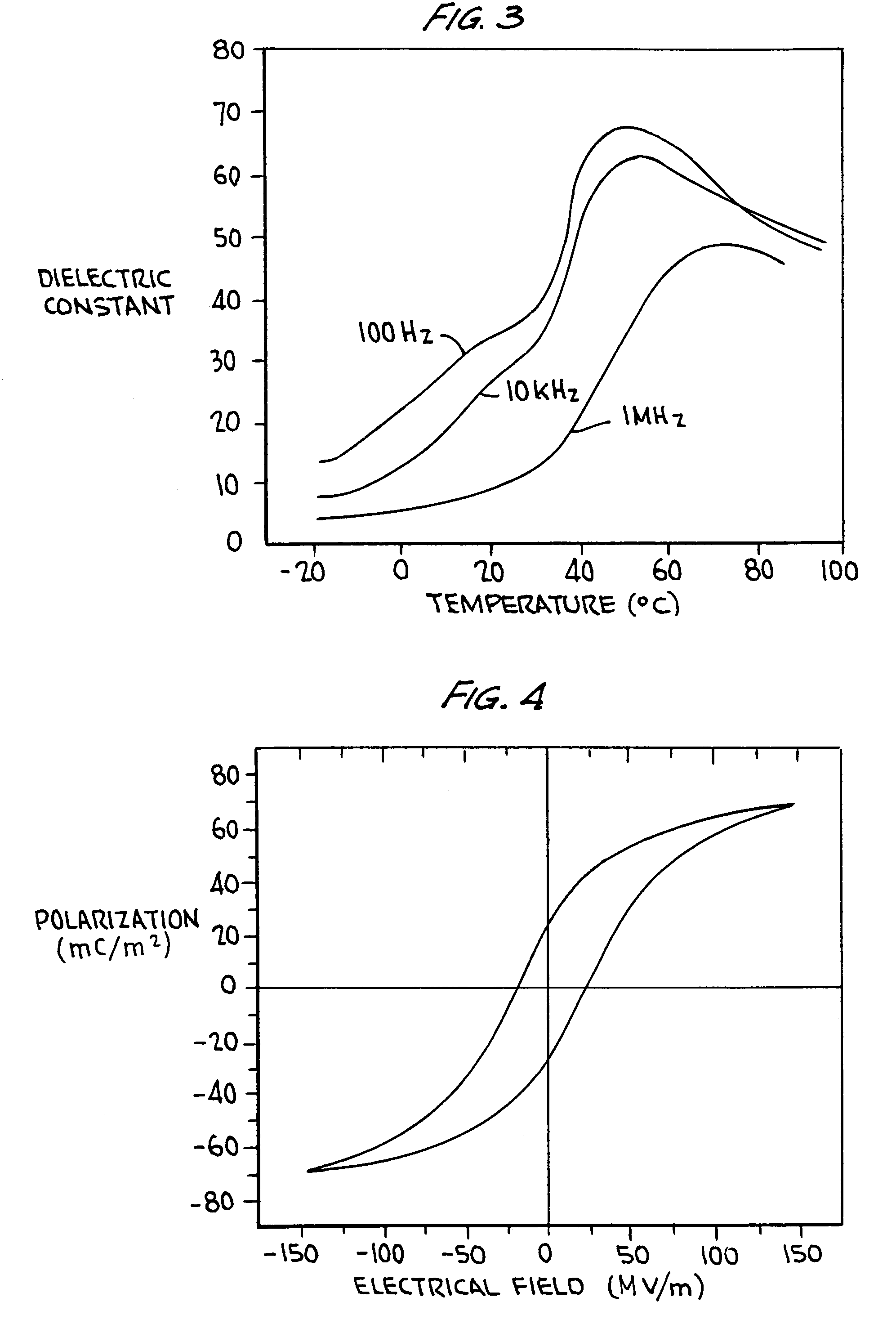
The present invention is a new class of terpolymers for use as high strain electrostrictive polymer films. More particularly, the invention is a class of electrostrictive terpolymers comprising vinylidene fluoride (VDF), trifluoroethylene (TrFE) and at least one monomer having at least one halogen atom side group. The monomer is preferably an ethylene-based monomer and preferably selected to favor gauche-type linkage along the polymer backbone. The halogen atom side group is preferably large enough to move or cause adjacent polymer chains to be farther apart from or away from each other than in the absence of such side group, but not so large that it would inhibit polymer crystallites from forming. The monomer is preferably a chloro-monomer such as chlorofluoroethylene (CFE). The chlorofluoroethylene (CFE) is preferably 1-chloro-2-fluoroethylene or 1-chloro-1-fluoroethylene. The chlorofluoroethylene (CFE) favors gauche-type linkage which favors high electrostrictive strains.
Owner:BOARD OF GOVERNORS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION STATE OF R I +2
Membrane tension control
InactiveUS6867533B1Small massLow densityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionMembrane tensionMembrane surface
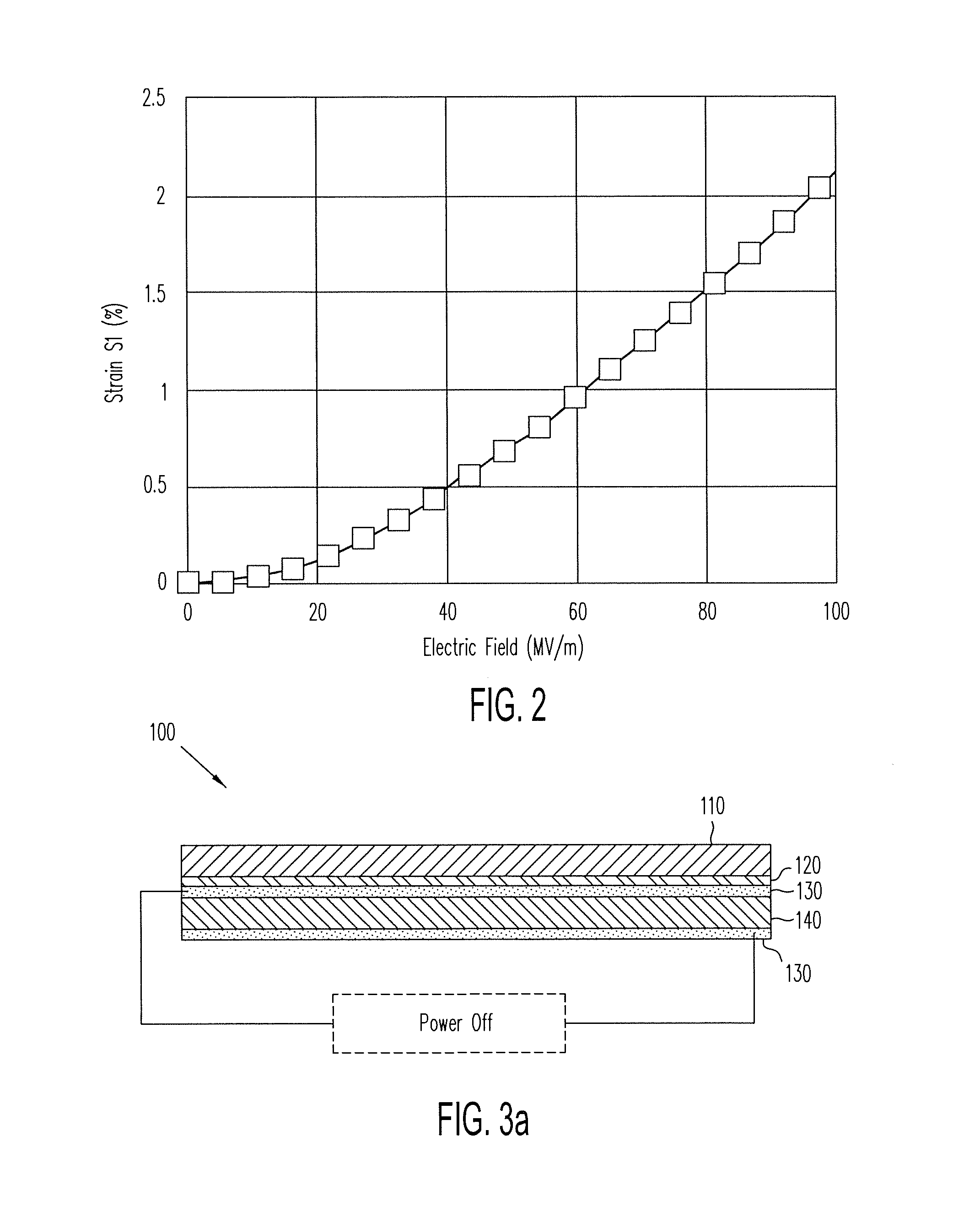
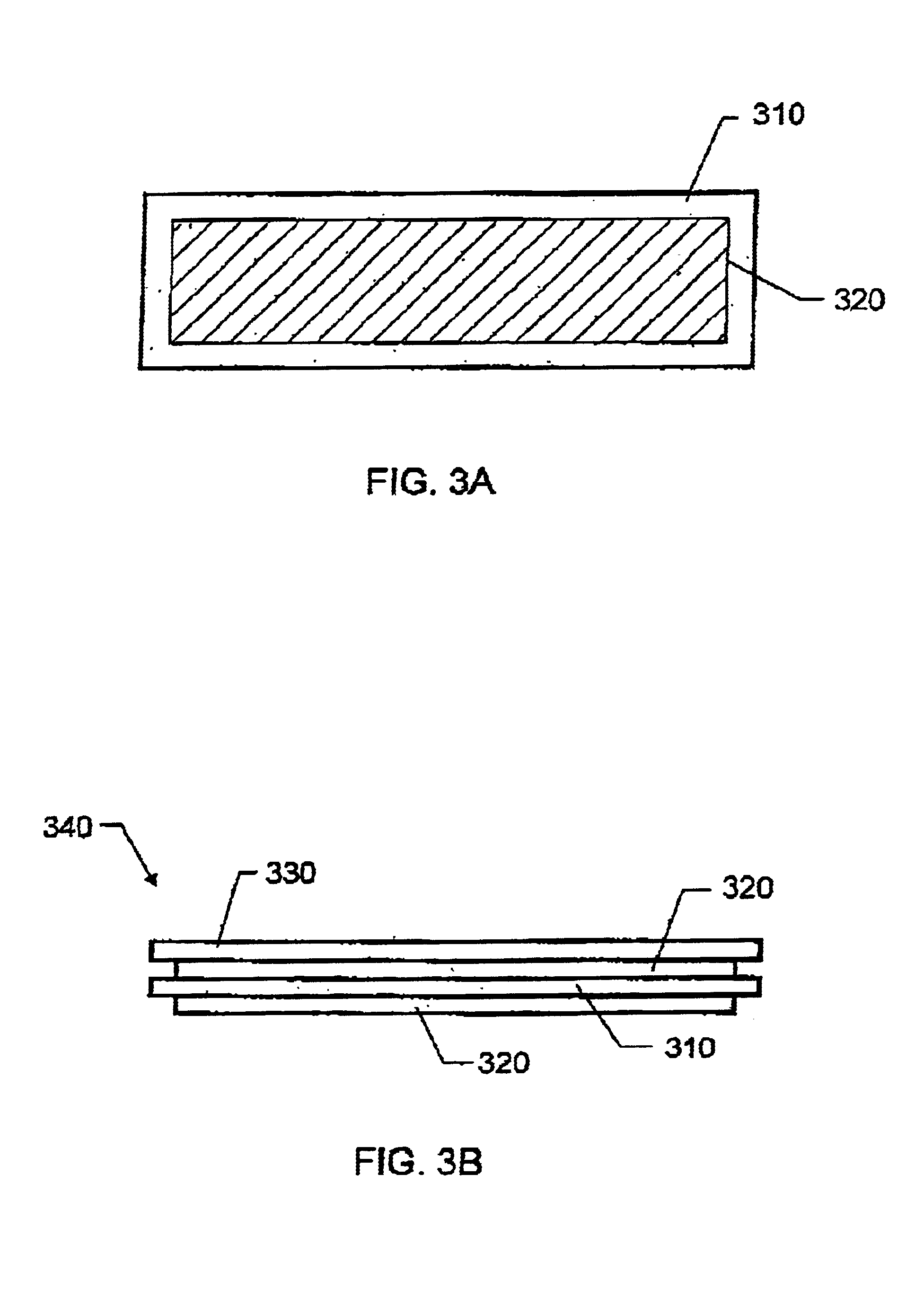
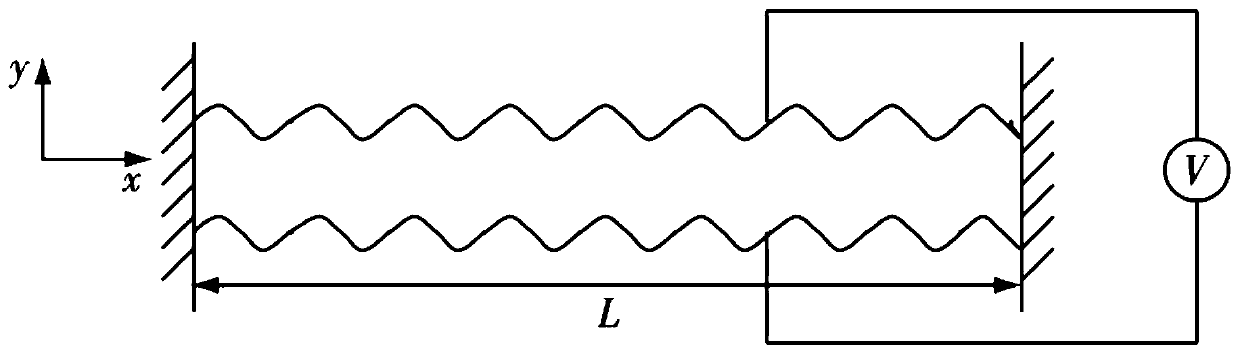
An electrostrictive polymer actuator comprises an electrostrictive polymer with a tailorable Poisson's ratio. The electrostrictive polymer is electroded on its upper and lower surfaces and bonded to an upper material layer. The assembly is rolled tightly and capped at its ends. In a membrane structure having a membrane, a supporting frame and a plurality of threads connecting the membrane to the frame, an actuator can be integrated into one or more of the plurality of threads. The electrostrictive polymer actuator displaces along its longitudinal axis, thereby affecting movement of the membrane surface.
Owner:NASA
Aperture construction for a mobile camera
ActiveUS20070216803A1Reduce complexitySmall sizePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesActive material electrodesMobile cameraElectricity
The invention relates in general to the field of digital cameras, especially small digital cameras. In particularly the invention relates for adjusting an aperture for mobile cameras. The adjustable aperture construction of the invention comprises two electrodes, and an electrical circuit for applying a voltage to the electrodes in order to create an electric field between the electrodes. In addition the construction comprises between the electrodes a center unit with a hole in the middle of it, the center unit being made of an electroactive material, such as dielectric material or electrostrictive polymer. The aperture can be adjusted by deforming the shape of the center unit. The shape of the center unit is advantageously deformed by the electric field created between said electrodes by said electrical circuit.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Systems including electromechanical polymer sensors and actuators
ActiveUS9053617B2Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureTactile signalling systemsInput/output processes for data processingTransducerEngineering
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
EMP actuators for deformable surface and keyboard application
ActiveUS9170650B2Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureInput/output for user-computer interactionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionTouch SensesDisplay device
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology, keyboard, braille display, and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Localized multimodal electromechanical polymer transducers
ActiveUS9183710B2Reduce entropyReduce the temperaturePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectronic switchingTransducerEngineering
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
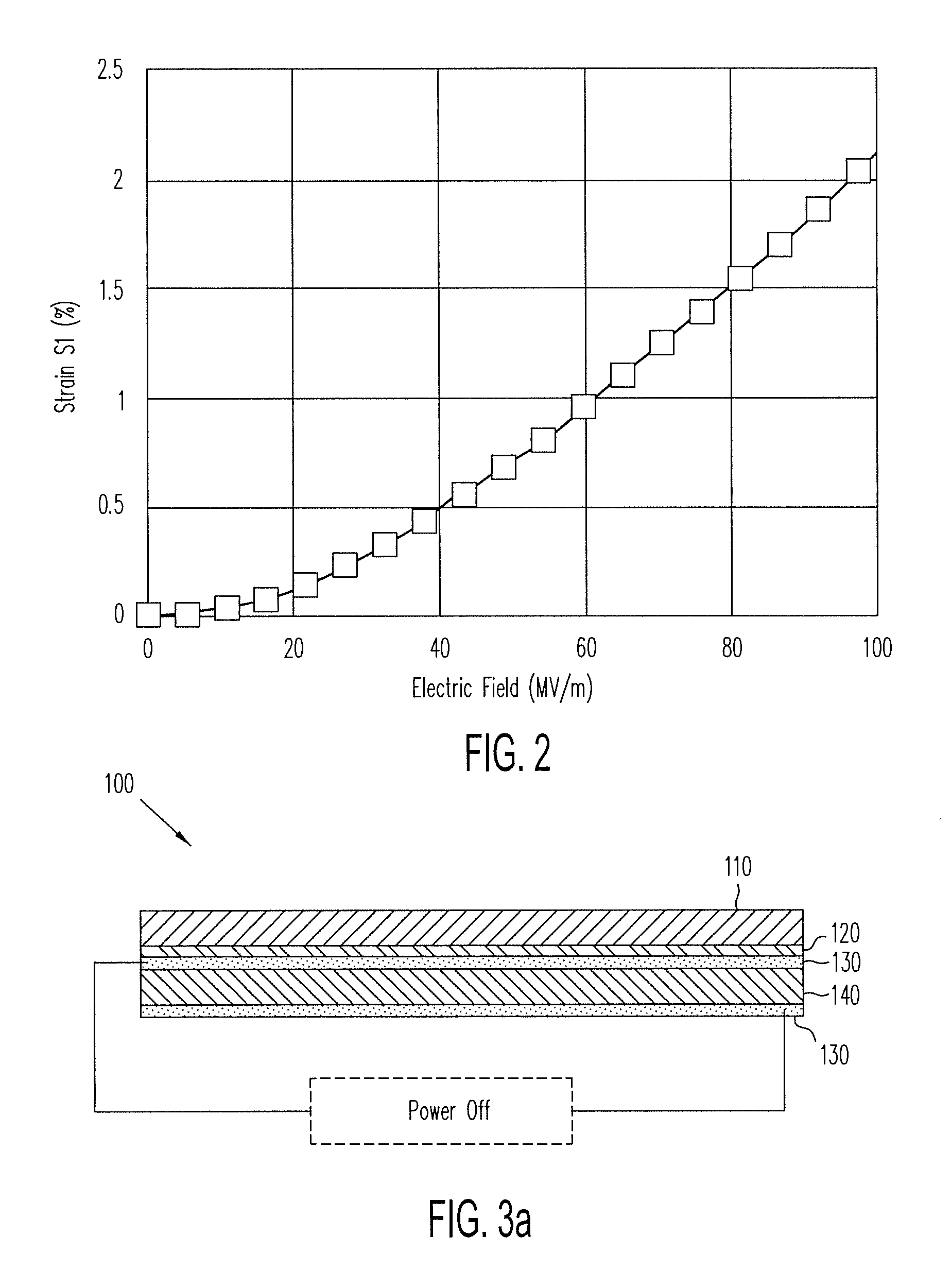
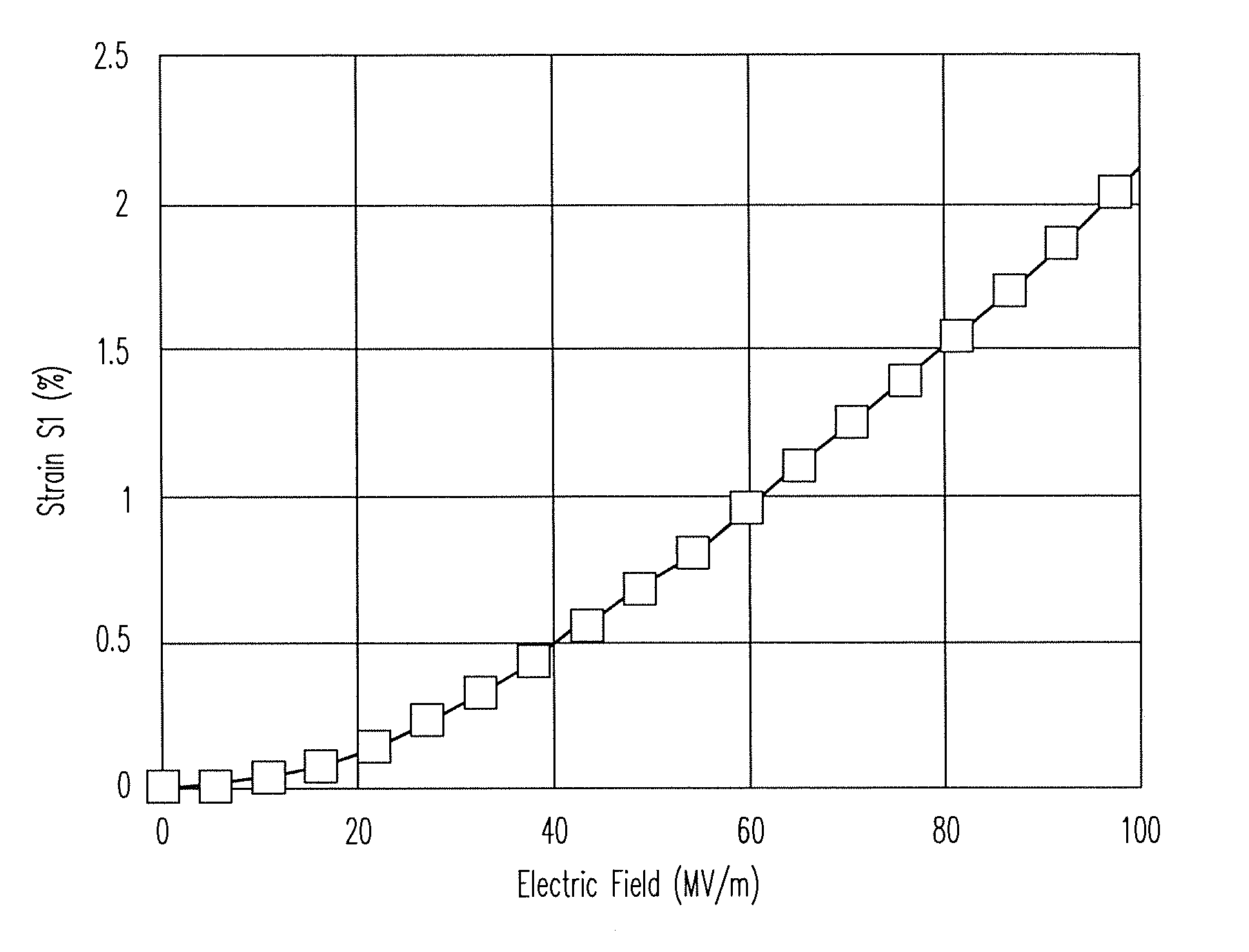
Electrostriction polymer laminar nano composite material and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101077930AImprove electric drive performanceImprove mechanical propertiesLigamentsMusclesElectricityFilm plane
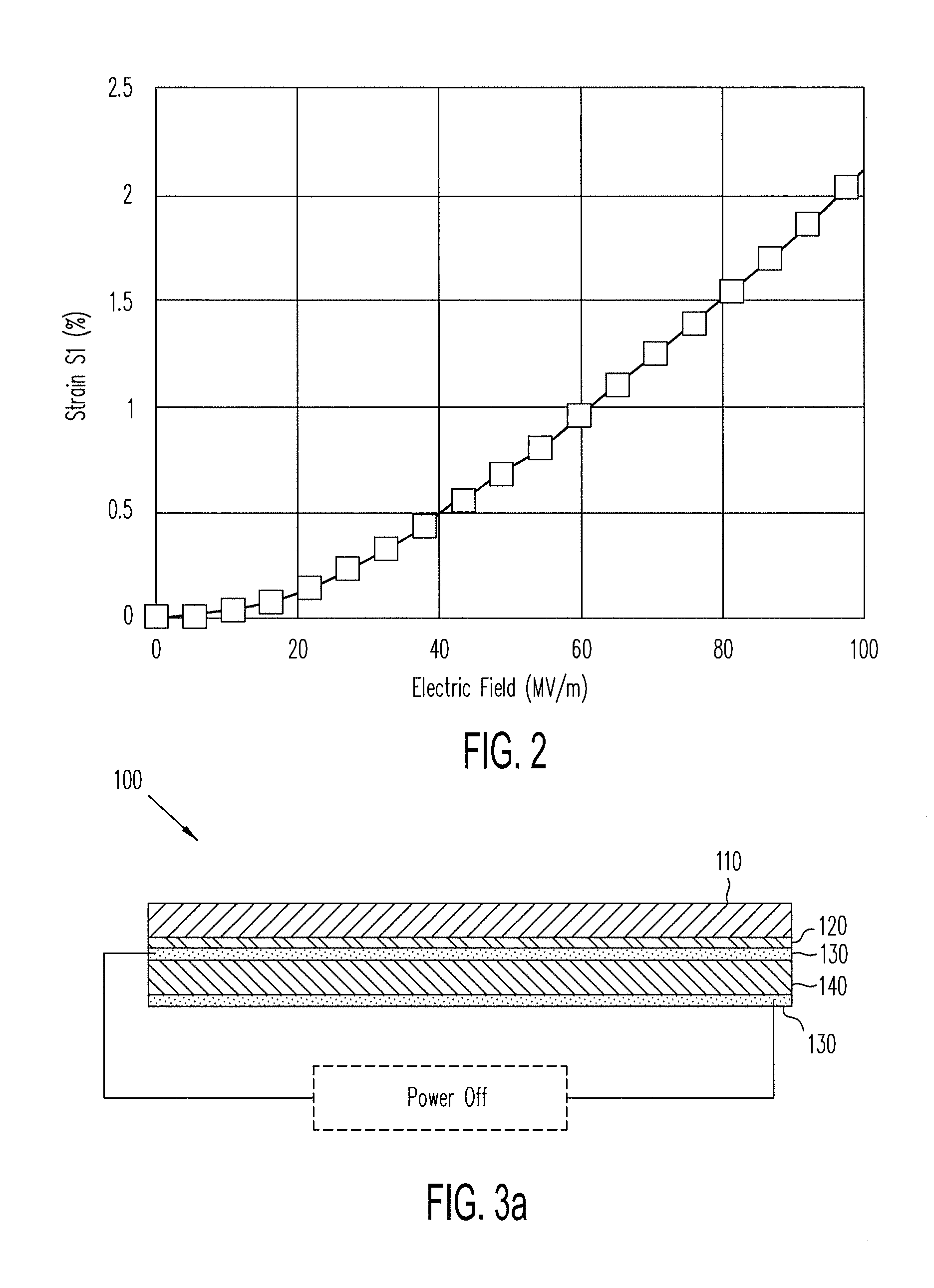
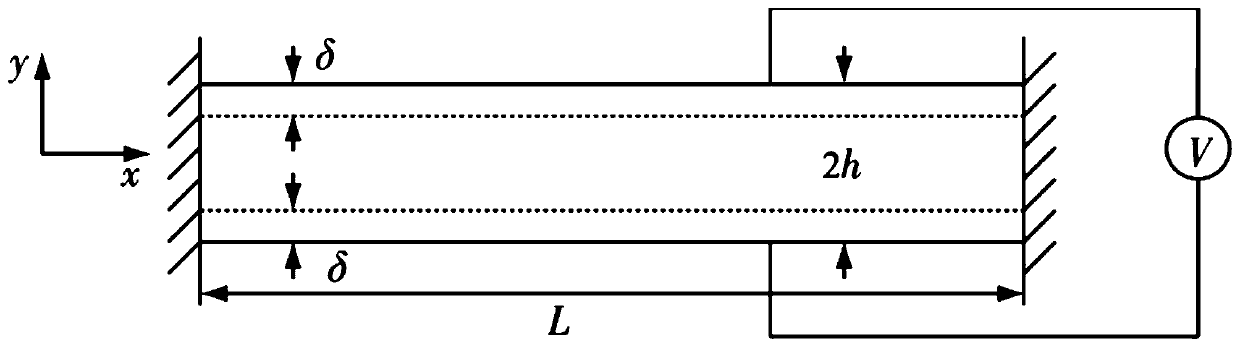
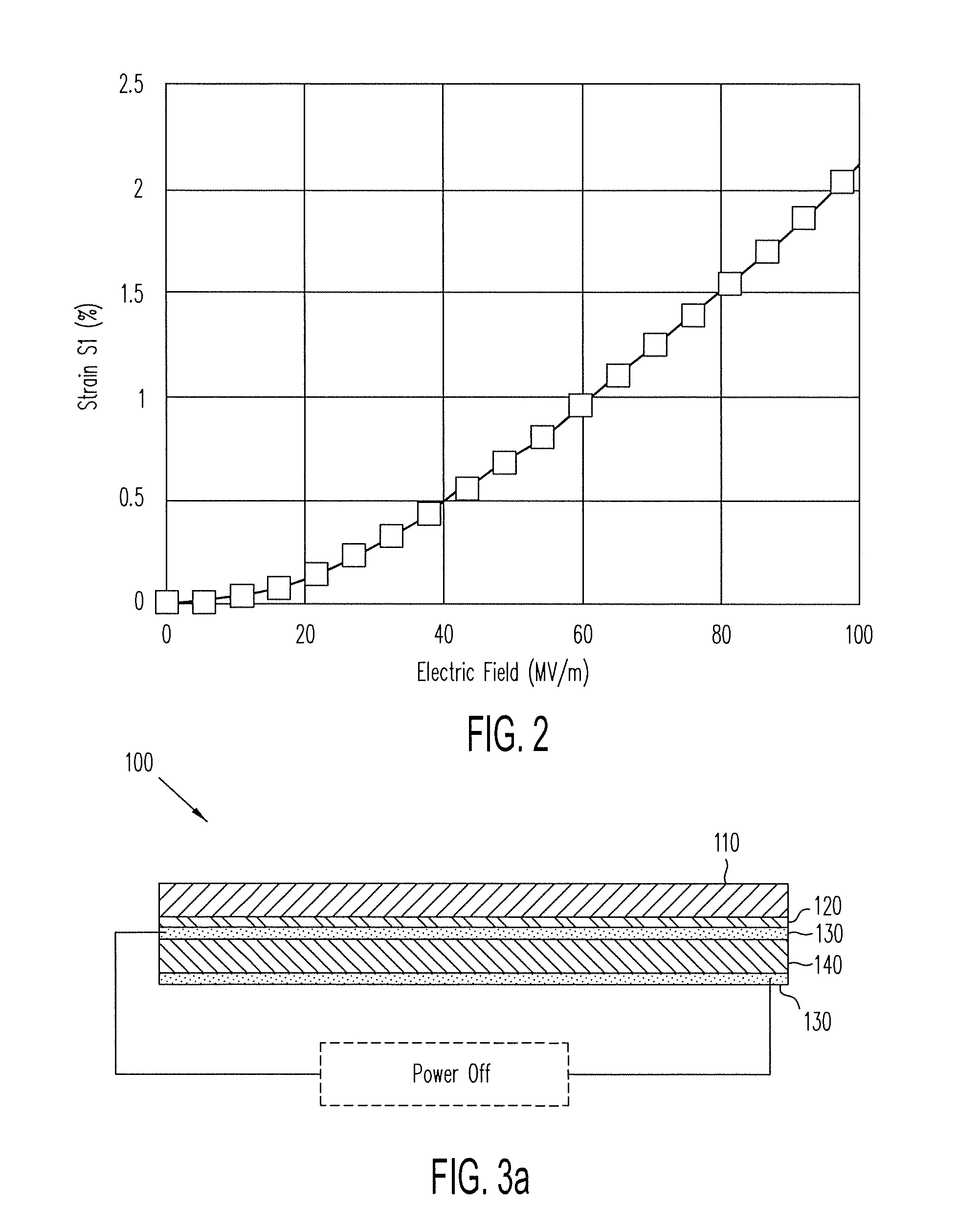
The present invention relates to one kind of electrostrictive layered nanometer composite polymer material, which is prepared with electrostrictive polymer, layered nanometer inorganic material, organic intercalative agent, cross-linking agent, catalyst and protonating agent, and through curing at 40-120 deg.c to form 10-1000 micron thick film and the subsequent drawing orientation. When 10-100 V / micron electric field is applied in the direction perpendicular to the film plane, one strain in 1-100 % may generate in the direction perpendicular to the electric field direction and the drawing direction, with the deformation being eliminated fast after the electric field is eliminated. The electrostrictive composite polymer material may be applied in electric driver, pump and sensor related to artificial muscle, and compared with available technology, the present invention has the advantages of simple preparation and lower driving voltage.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Ultrasonic treatment device
InactiveCN101277652ASimple structureMiniaturizationTurning machine accessoriesSurgical instrument detailsEngineeringActuator
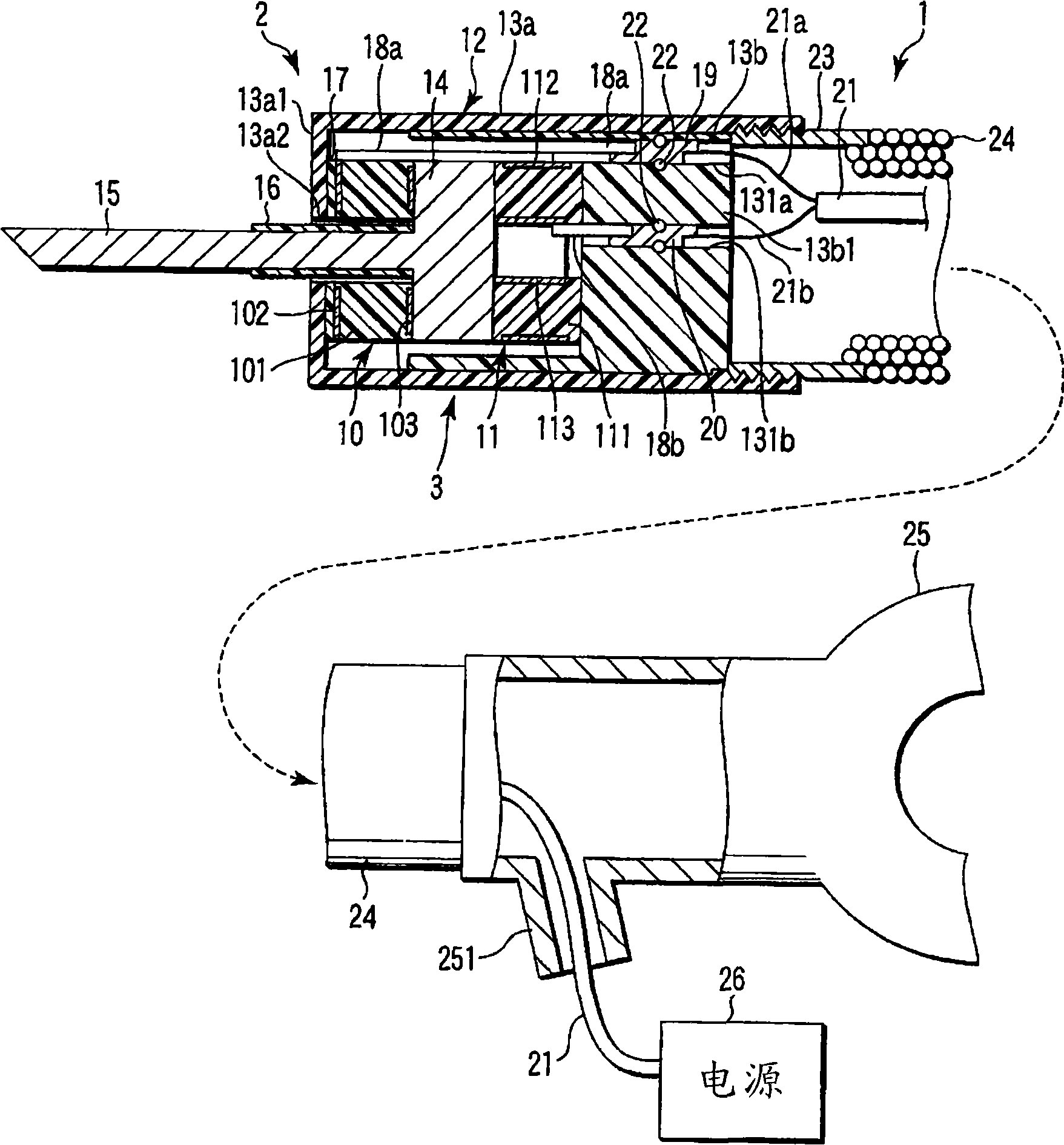
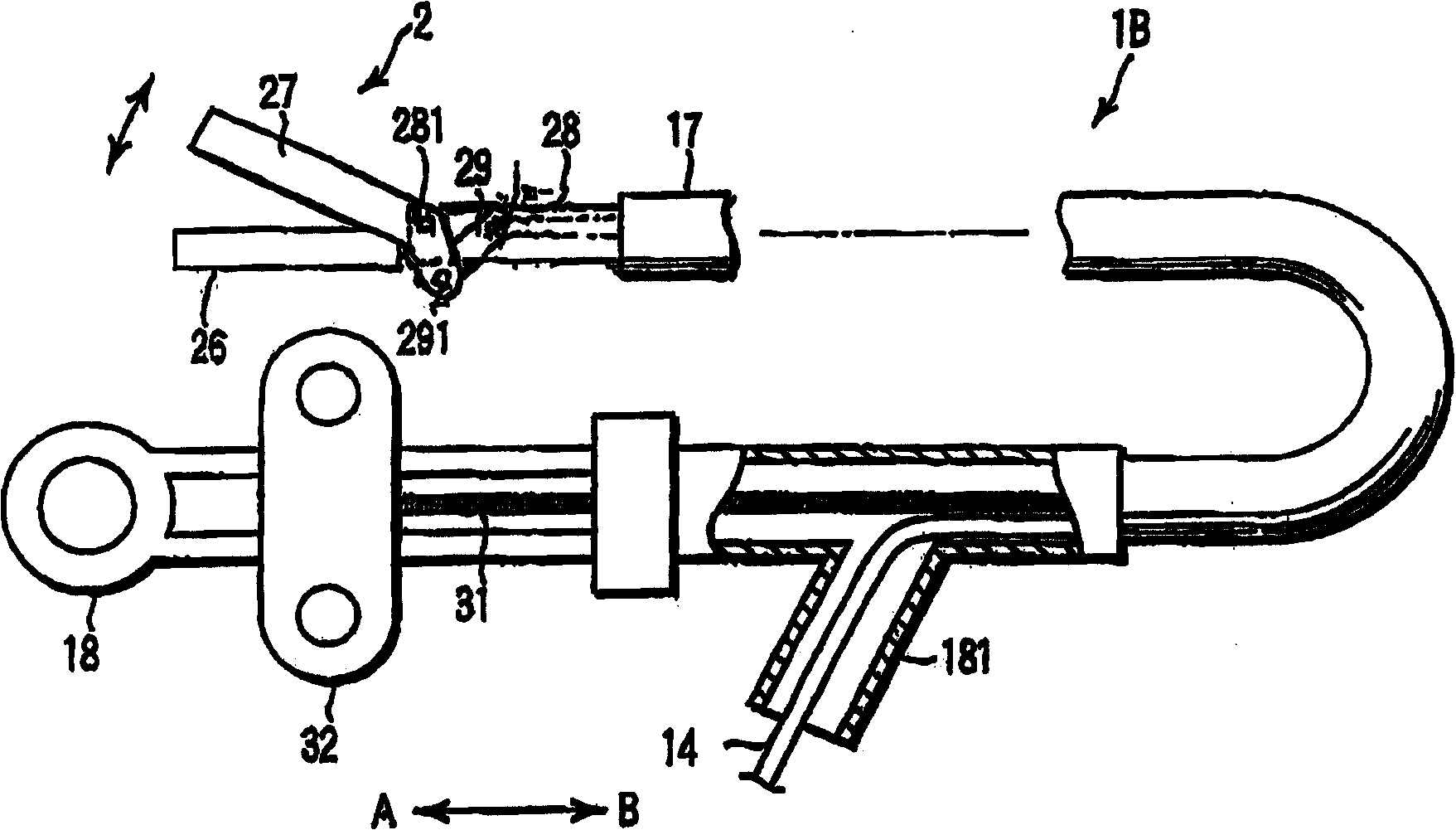
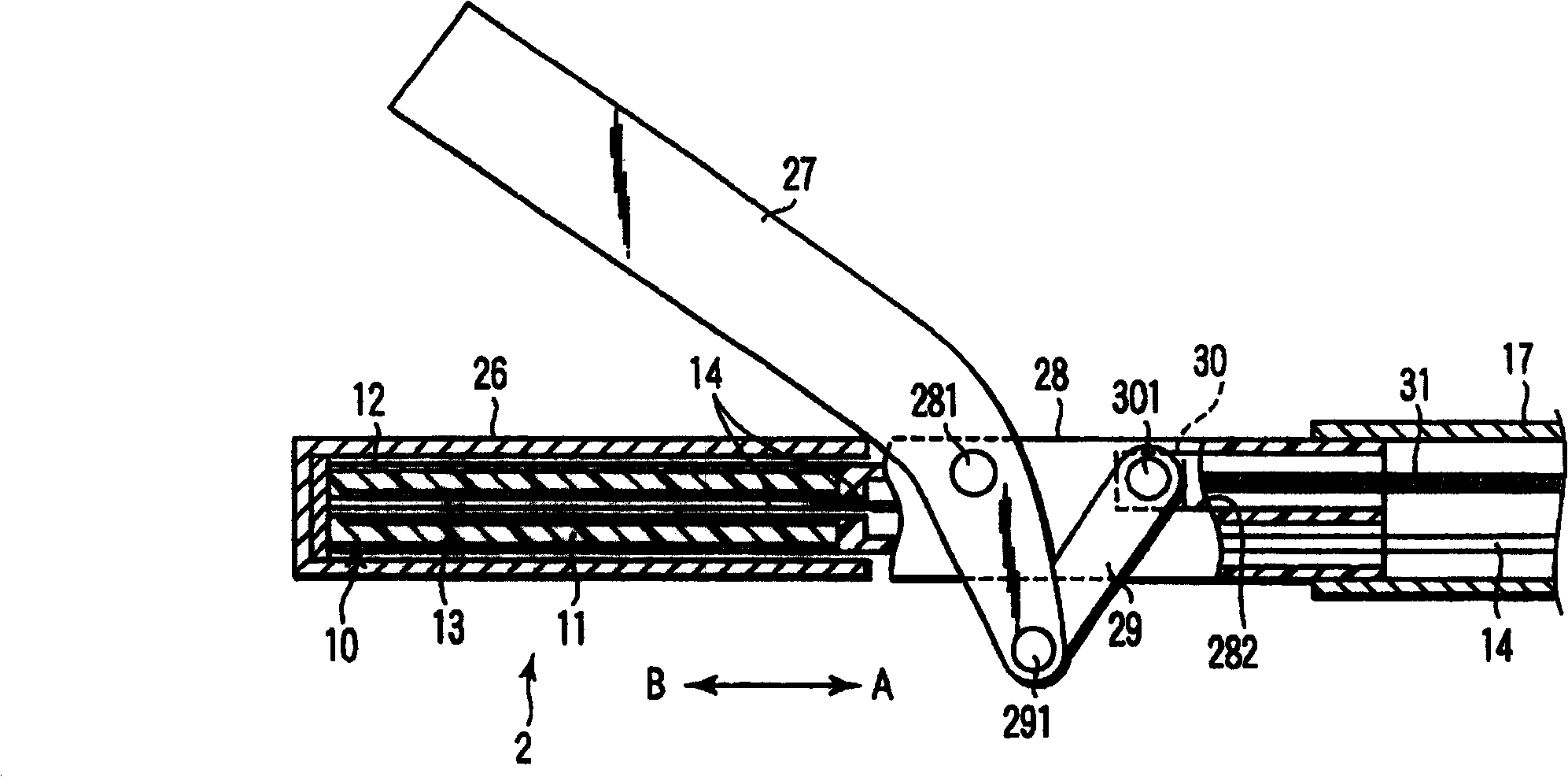
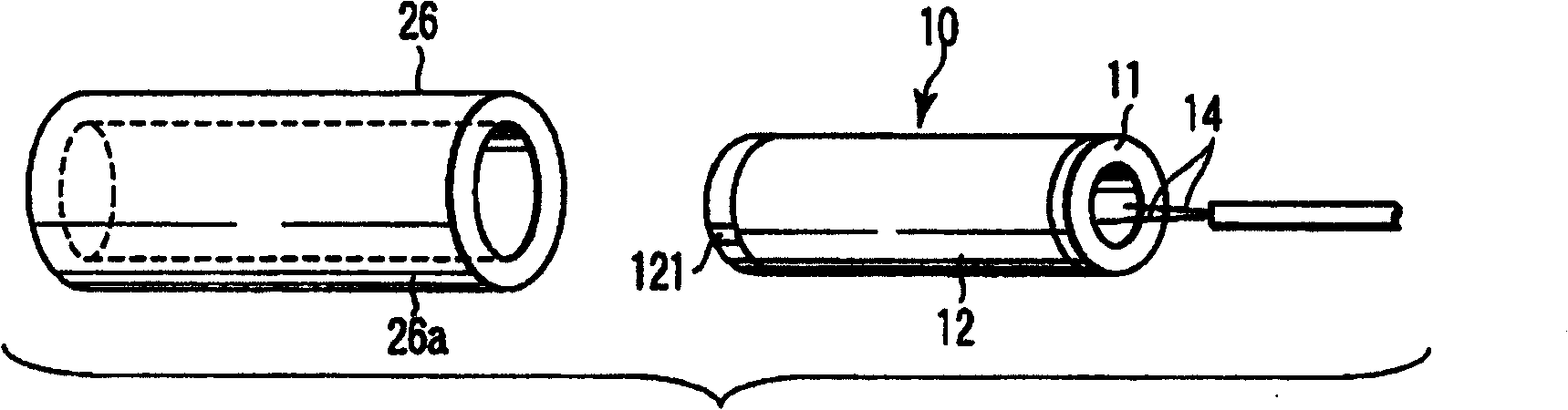
First and second actuators (10, 11) where plus electrodes (102, 112) and minus electrodes (103, 113) are arranged on tubular electrostrictive polymers (101, 111), are arranged oppositely via a fixing member (14). The fixing member (14) is provided with a blade (15) for inserting the first actuator (10) and then the first and second actuators (10, 11) are driven simultaneously such that one actuator contracts while the other actuator extends, thereby vibrating the blade (15) ultrasonically through the fixing member (14).
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Terminal and screen display control method applied to terminal
ActiveCN110187822AAchieve precise controlEasy to operate and controlInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringFlexible display
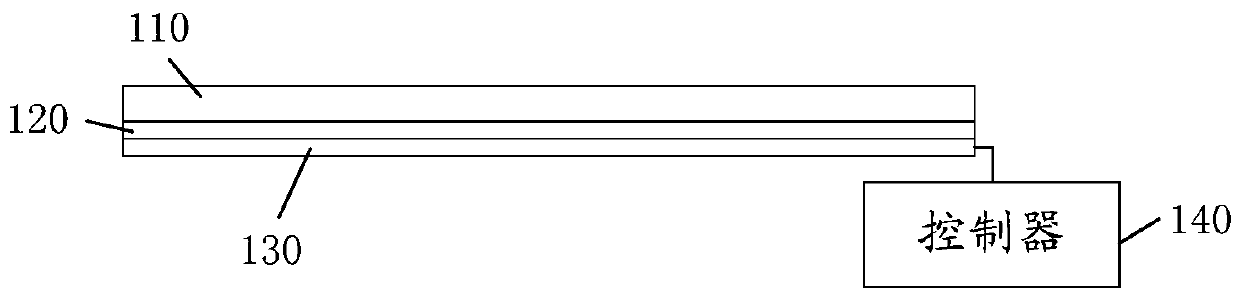
The invention provides a terminal and a screen display control method applied to the terminal, and relates to the technical field of terminals. The terminal comprises a flexible display screen, a flexible electrostrictive polymer film which is arranged on the first surface of the flexible display screen, an electrode assembly which is attached to the flexible electrostrictive polymer film, and a controller which is connected with the electrode assembly and is used for providing control voltage for the electrode assembly, wherein the first surface is a surface close to a circuit board of the terminal; and a target thin film area of the flexible electrostrictive polymer thin film is deformed through the control voltage, and a target screen area, corresponding to the target thin film area, onthe flexible display screen is driven to deform. According to the scheme, the flexible electrostrictive polymer film is arranged in the terminal to assist the terminal in deformation of the flexibledisplay screen, so that the user is assisted in controlling sliding operation well, and accurate control over the terminal is achieved.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
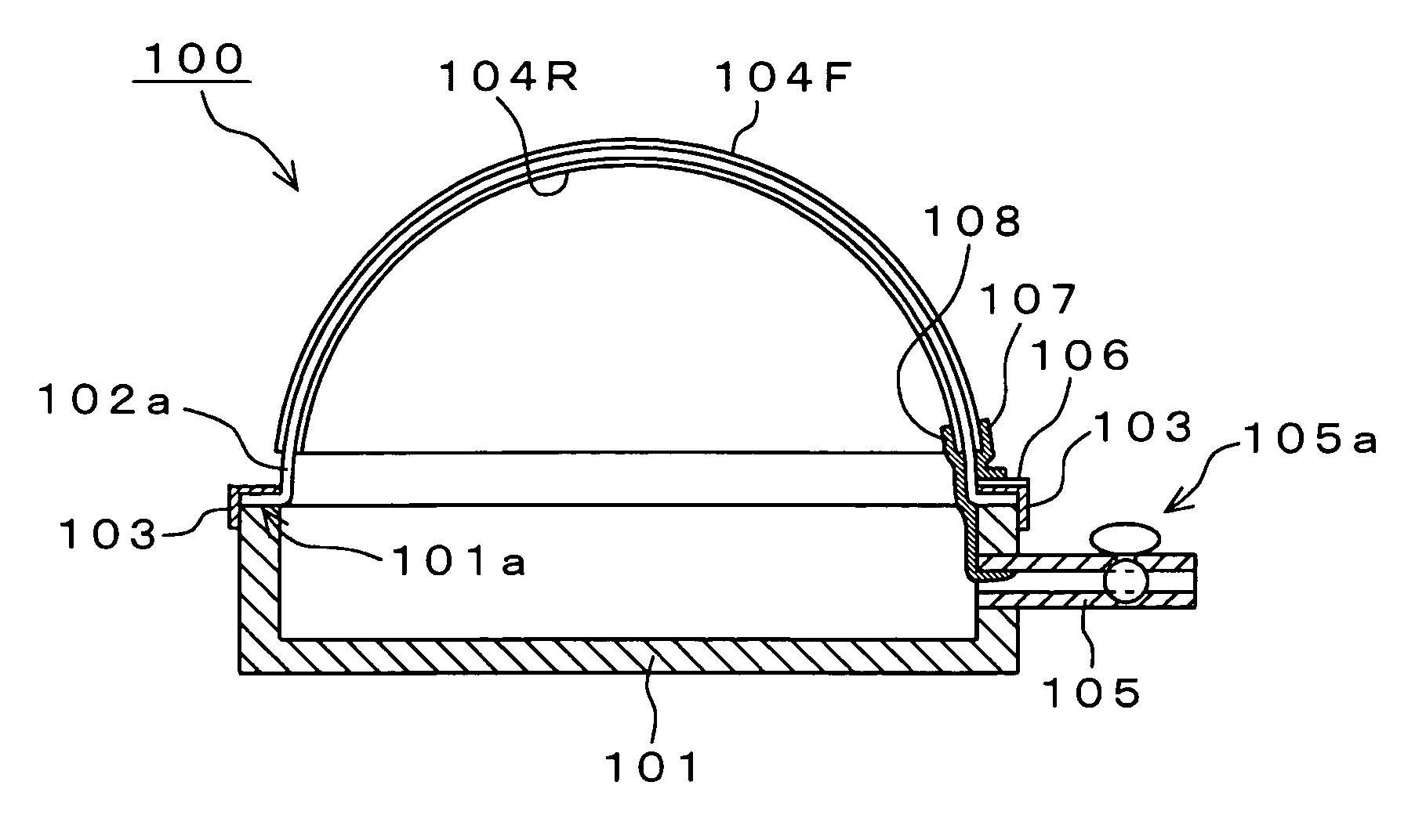
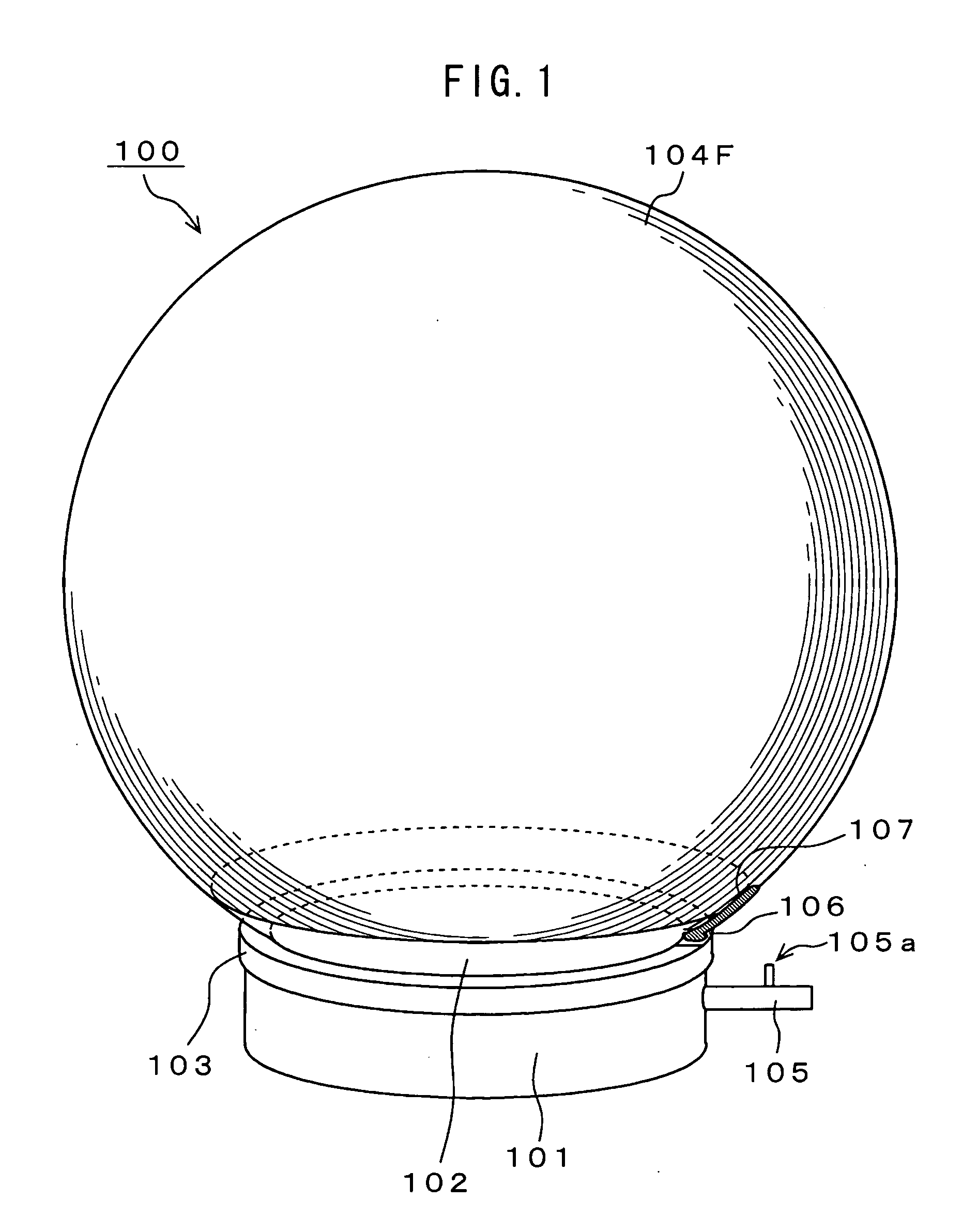
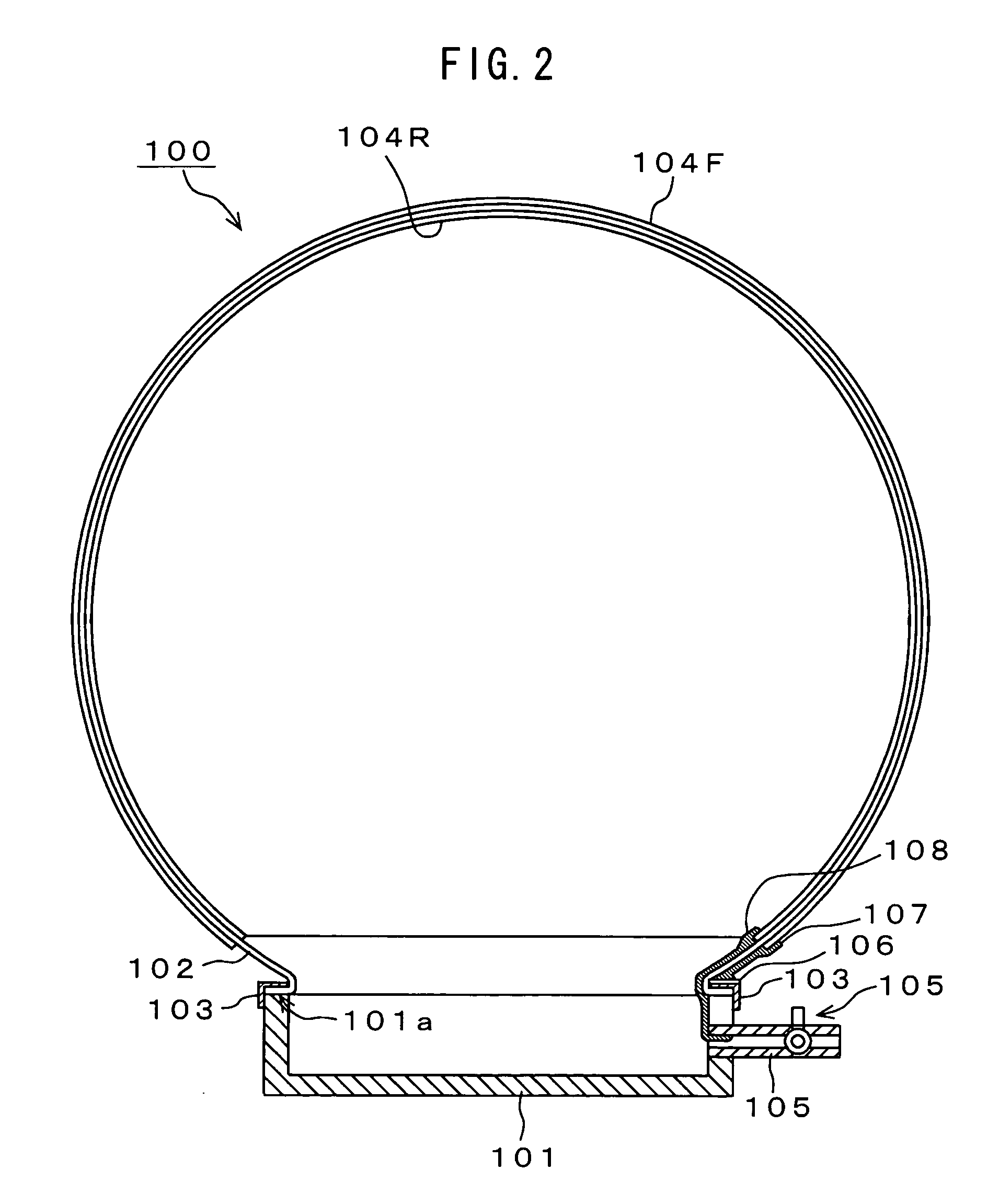
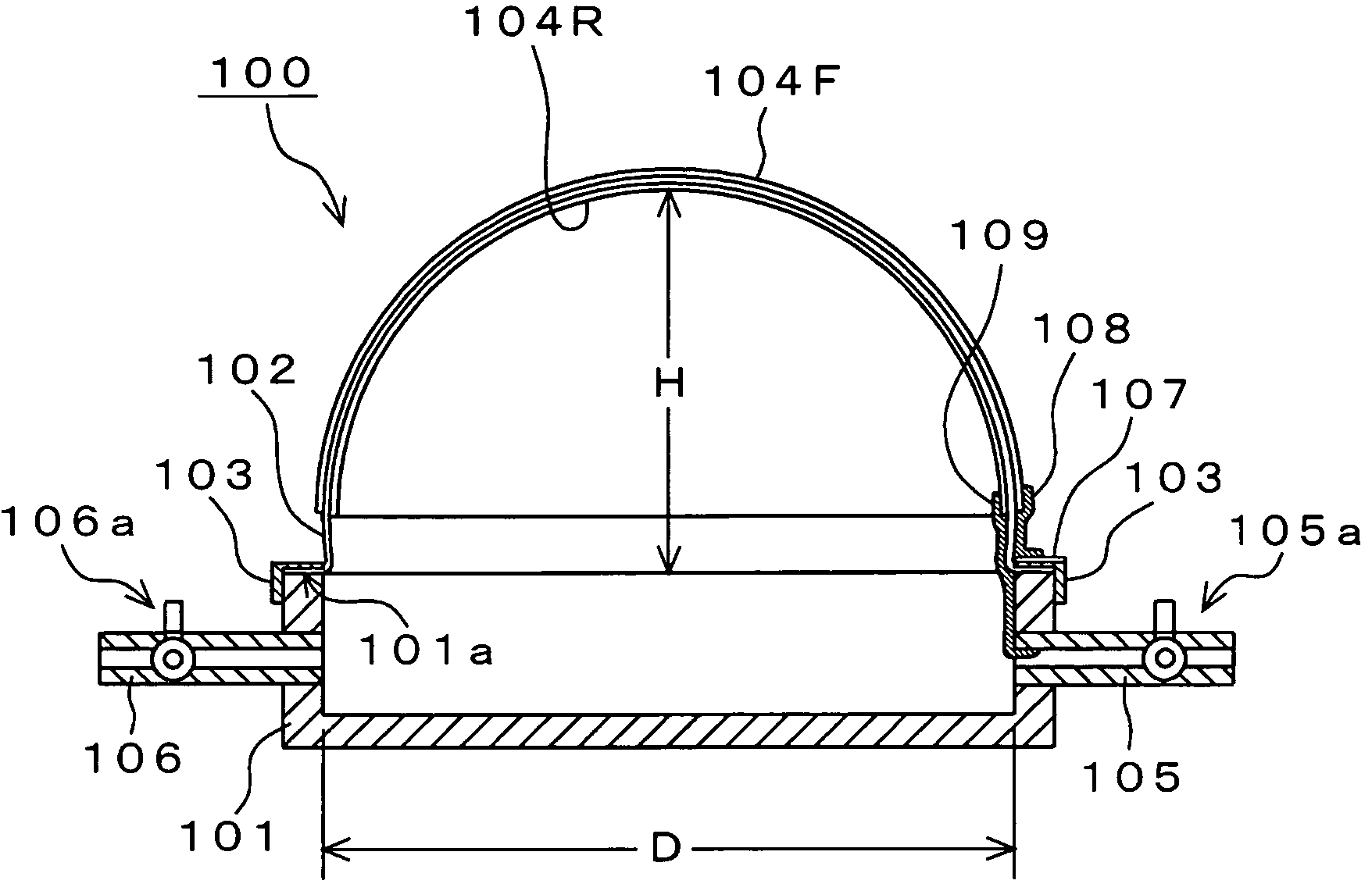
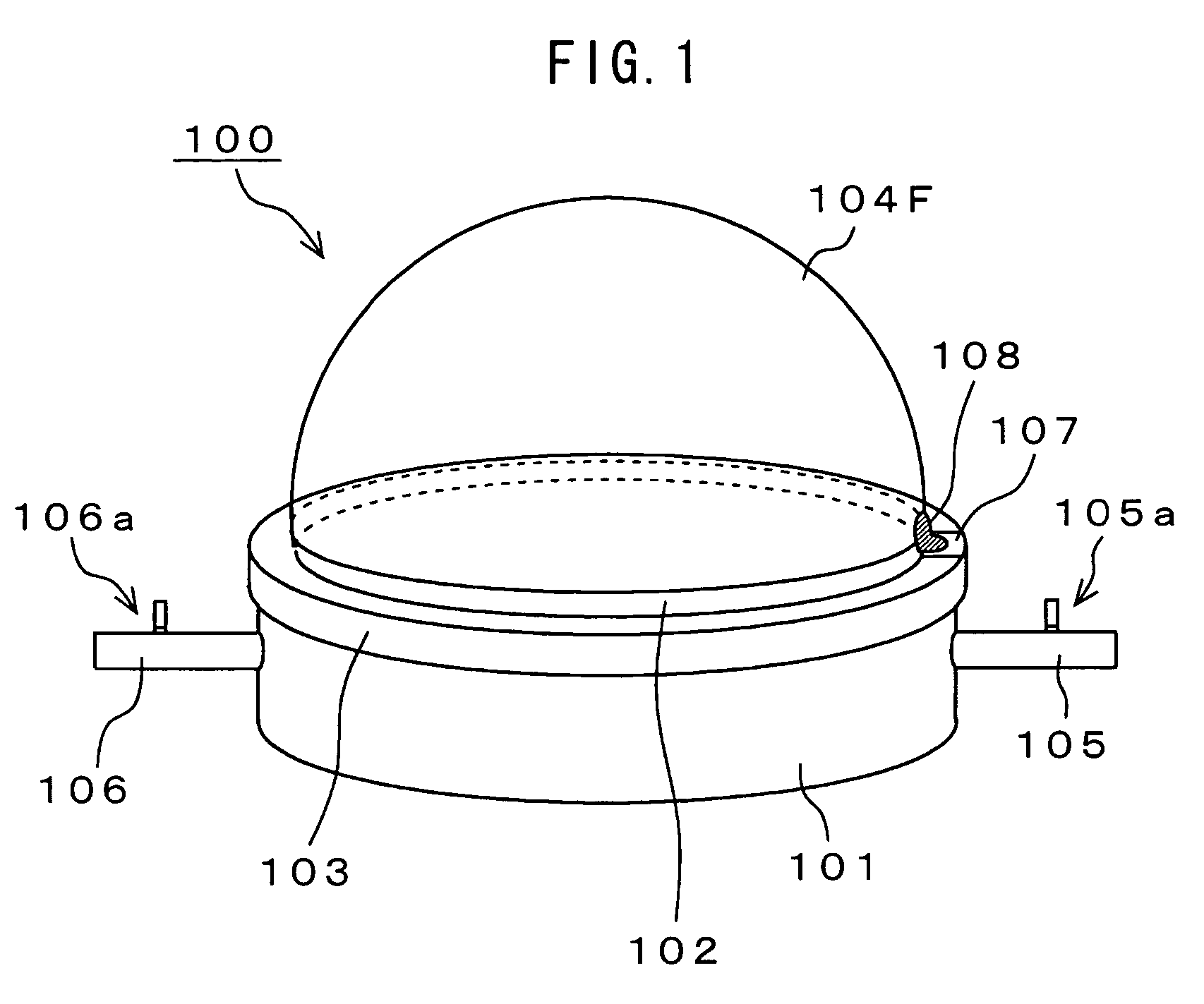
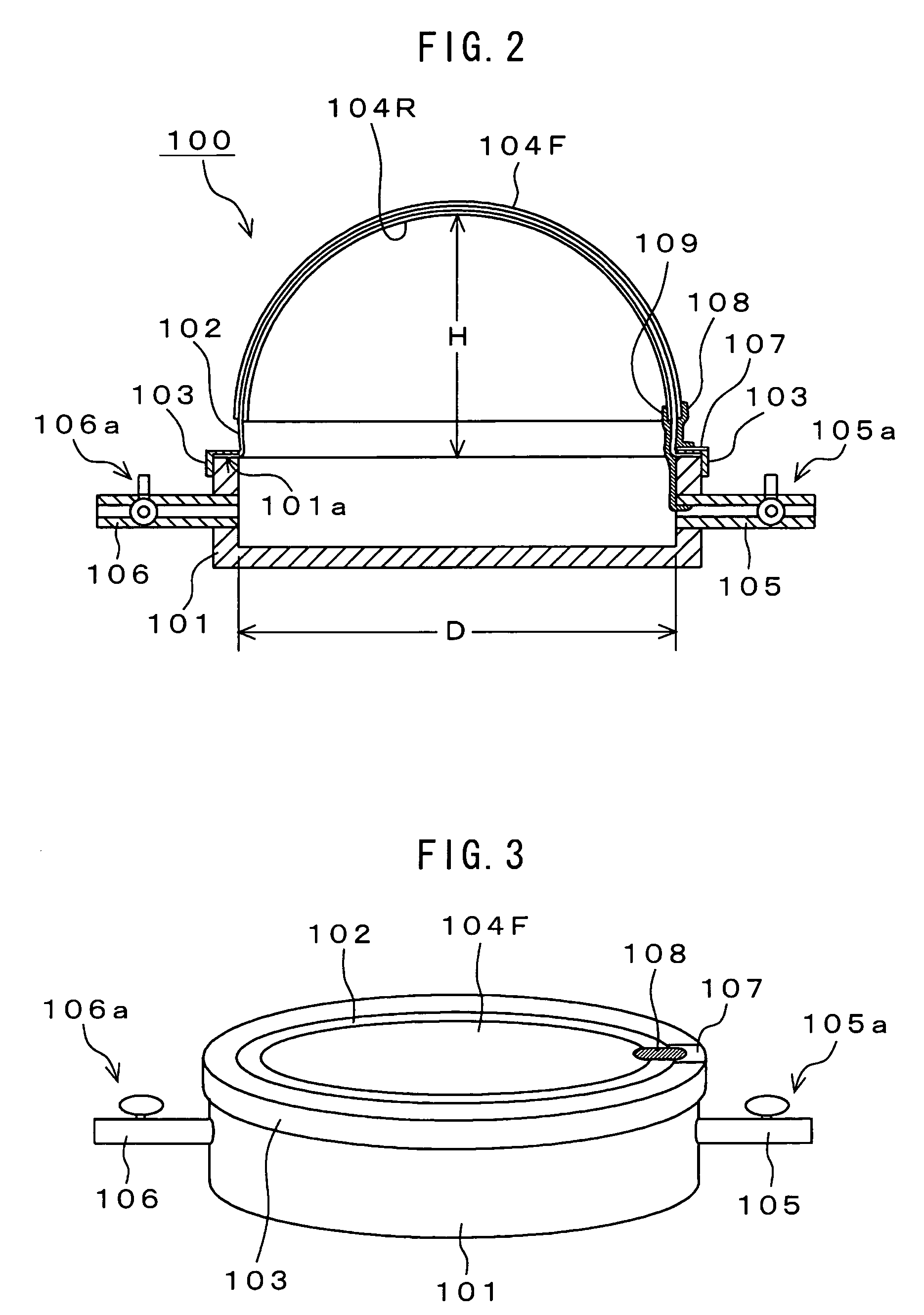
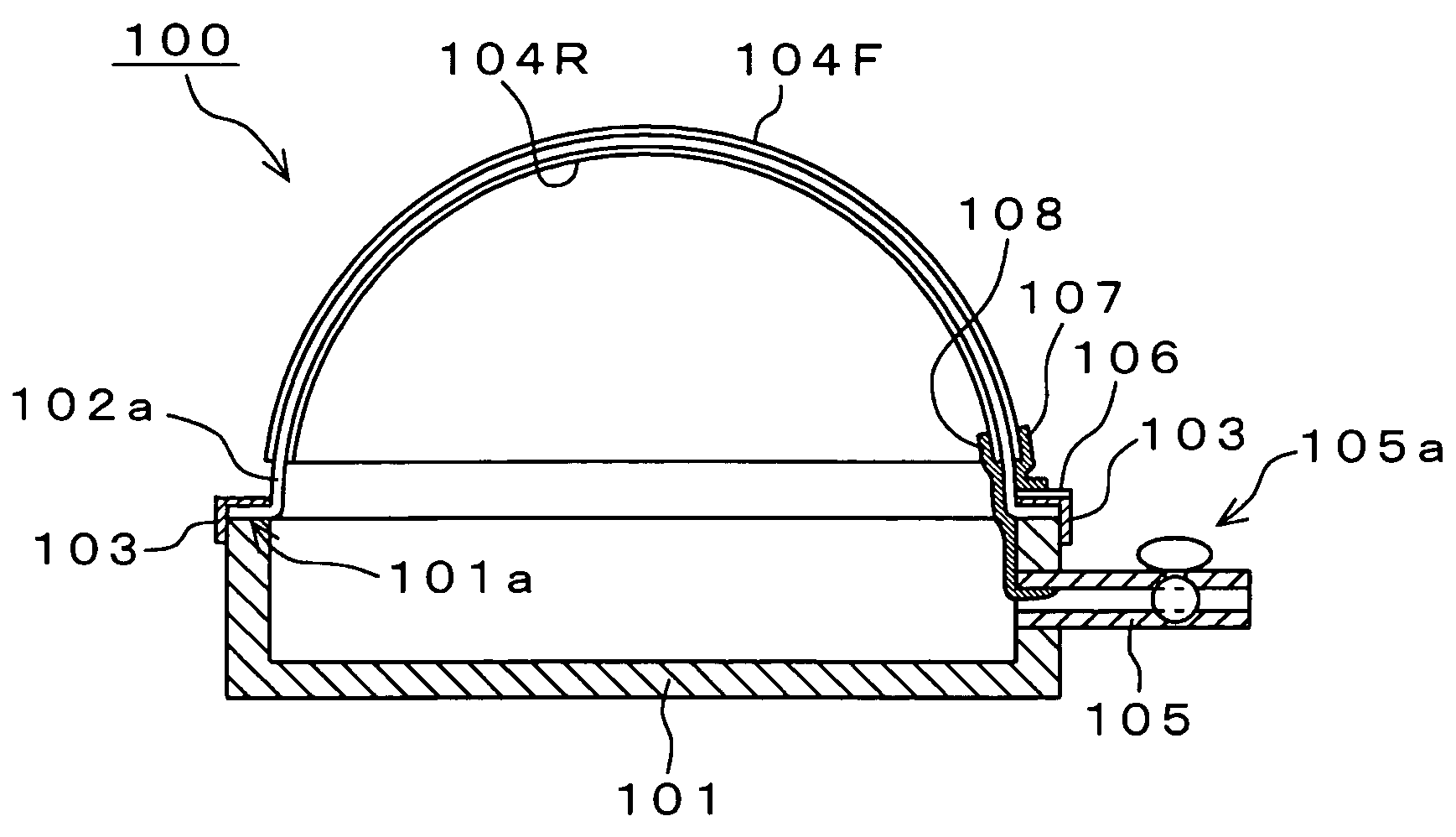
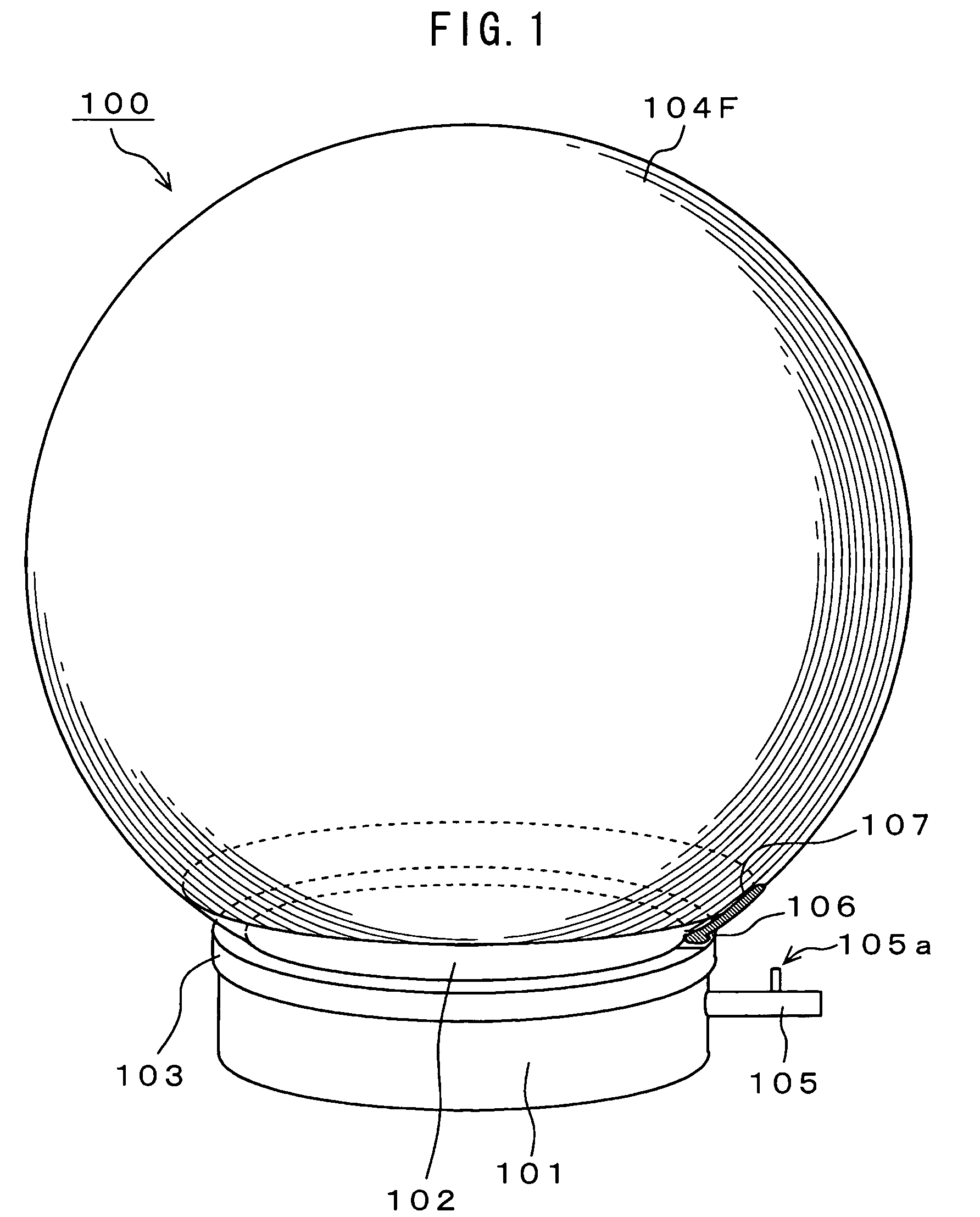
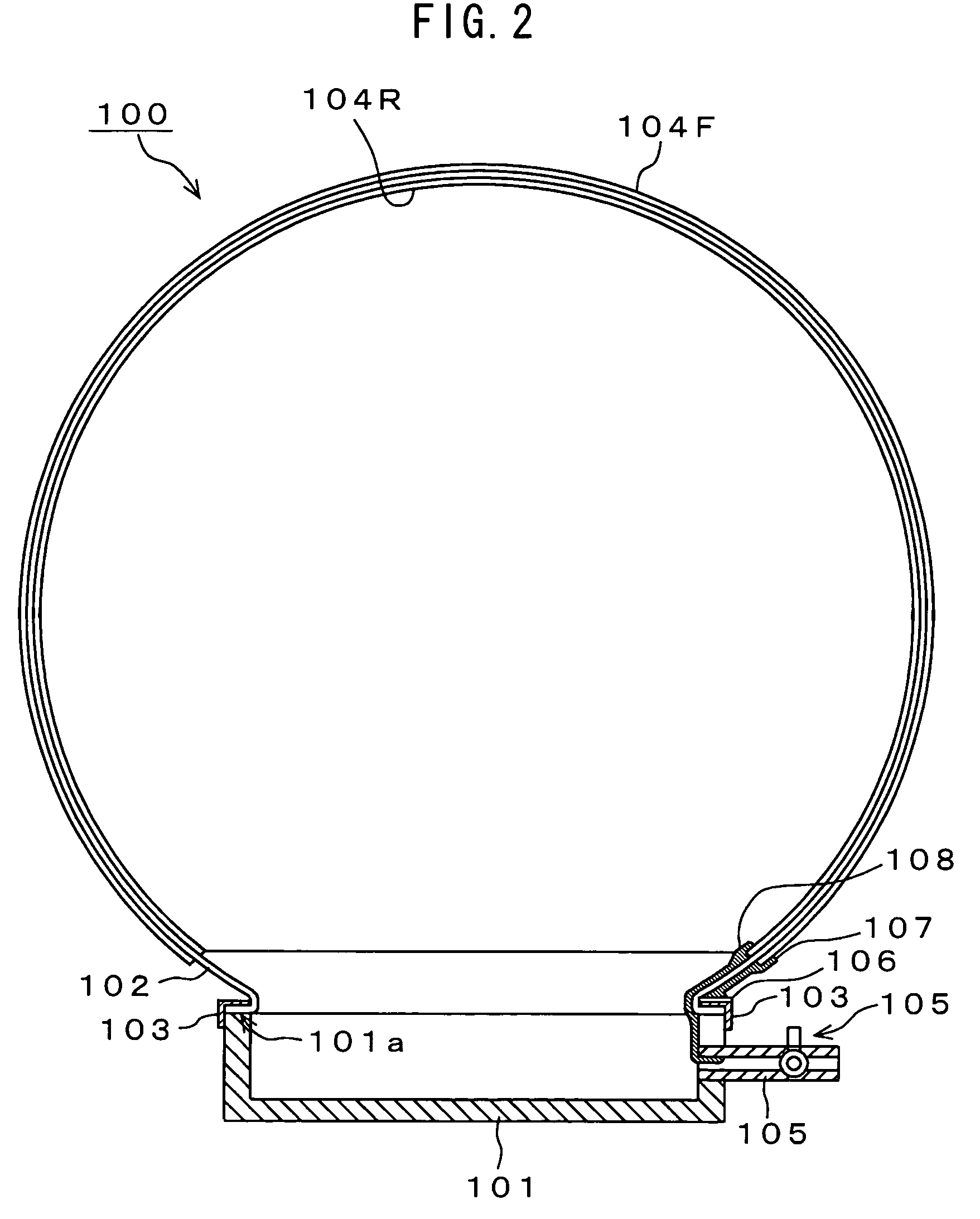
Electroacoustic transducer using diaphragm and method for producing diaphragm
InactiveUS20070019830A1Audio signal efficientlyEfficient emissionsTransducer detailsDeaf-aid setsTransducerAtmospheric pressure
An electroacoustic transducer has a cup chamber and a diaphragm made of deformable electrostrictive polymer, which is attached to an opening of the chamber. The electroacoustic transducer also has first and second adaptive electrode layers formed on a front surface and a rear surface of the diaphragm, across which audio signal voltage biased by a direct-current biased voltage is applied. The first and second adaptive electrode layers have shapes that are adjustable according to a change in a shape of the diaphragm. To form the diaphragm, the electrostrictive polymer that has been previously formed to have a concave or convex shape is further formed to have a concave or convex shape, thereby generating a difference in air pressure between the front surface and the rear surface of the previously formed electrostrictive polymer.
Owner:SONY CORP
Electroacoustic transducer using diaphragm and method for producing diaphragm
InactiveUS7822216B2Efficient emissionsAudio signal efficientlyTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsDeaf-aid setsTransducerEngineering
An electroacoustic transducer has an cup chamber and a diaphragm made of deformable electrostrictive polymer, which is attached to an opening of the chamber. The electroacoustic transducer also has first and second adaptive electrode layers formed on a front surface and a rear surface of the diaphragm, across which audio signal voltage biased by a direct-current biased voltage is applied. The first and second adaptive electrode layers have shapes that are adjustable according to a change in a shape of the diaphragm. The diaphragm is formed to make maximum a difference in air pressure of the front surface and the rear surface of the diaphragm, thereby forming any one of concave and convex shapes thereof.
Owner:SONY CORP
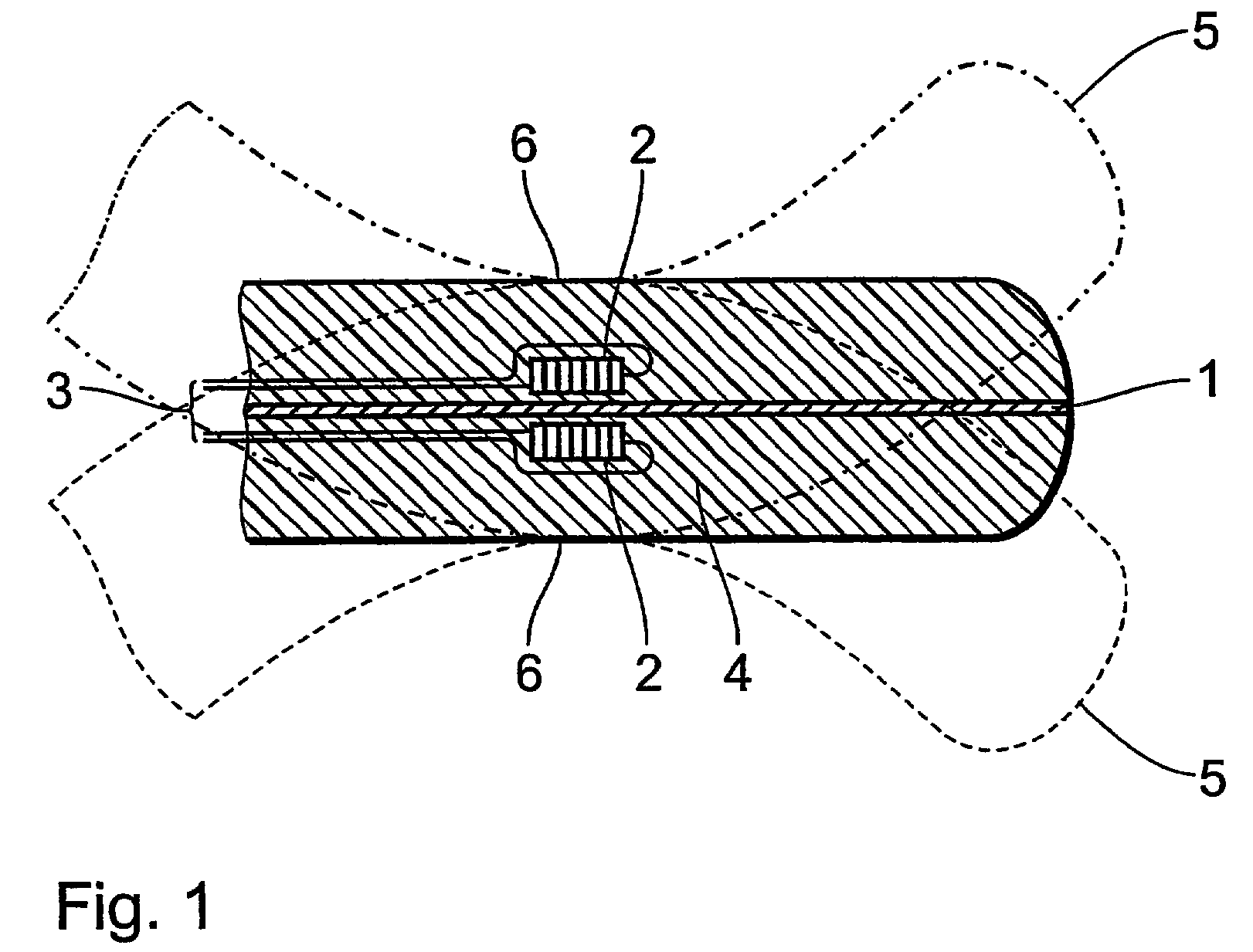
Electrode line
InactiveUS7167759B2Easy to operateSmall diameterTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityHeart chamber
An electrode line, in particular for an implantable electrostimulation device, which is adapted for insertion into body vessels such as heart chambers or blood vessels, comprising electrodes for the stimulation of body tissue, a longitudinal axis and a distal end, wherein there is provided at least one structural element (2) in the region of the distal end, which has an electrostrictive polymer and which can be connected to a voltage source by way of at least one electrical feed line (3) and which is adapted to change its shape when an electrical voltage is applied.
Owner:BIOTRONIK MESS UND THERAPIEGERAETE GMBH & CO
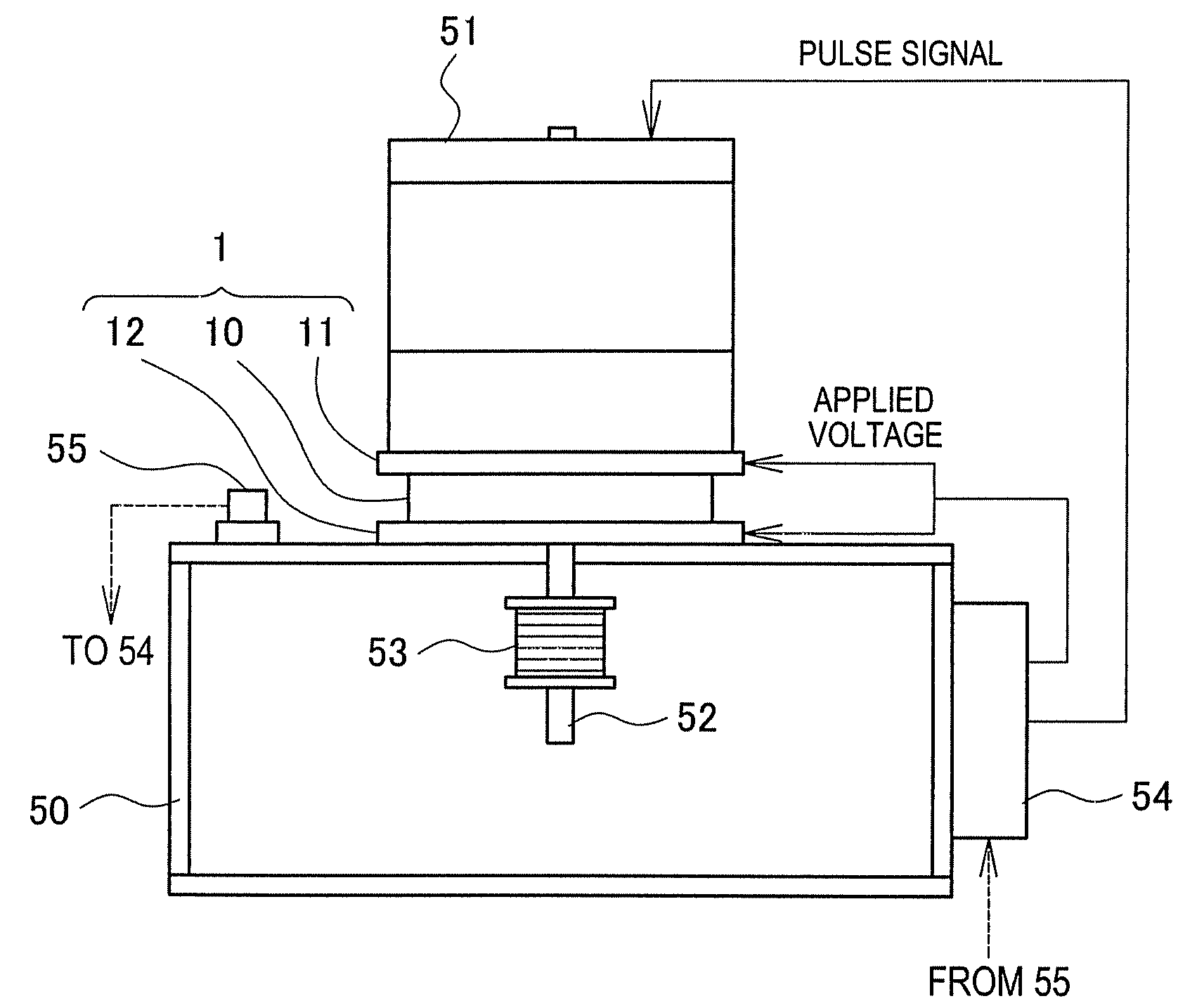
Mount damper and image forming apparatus using the mount damper
InactiveUS20090301828A1Reliably and constantly preventing resonanceReliably and constantly preventing and absorbing vibrationPortable framesStands/trestlesEngineeringPolymer
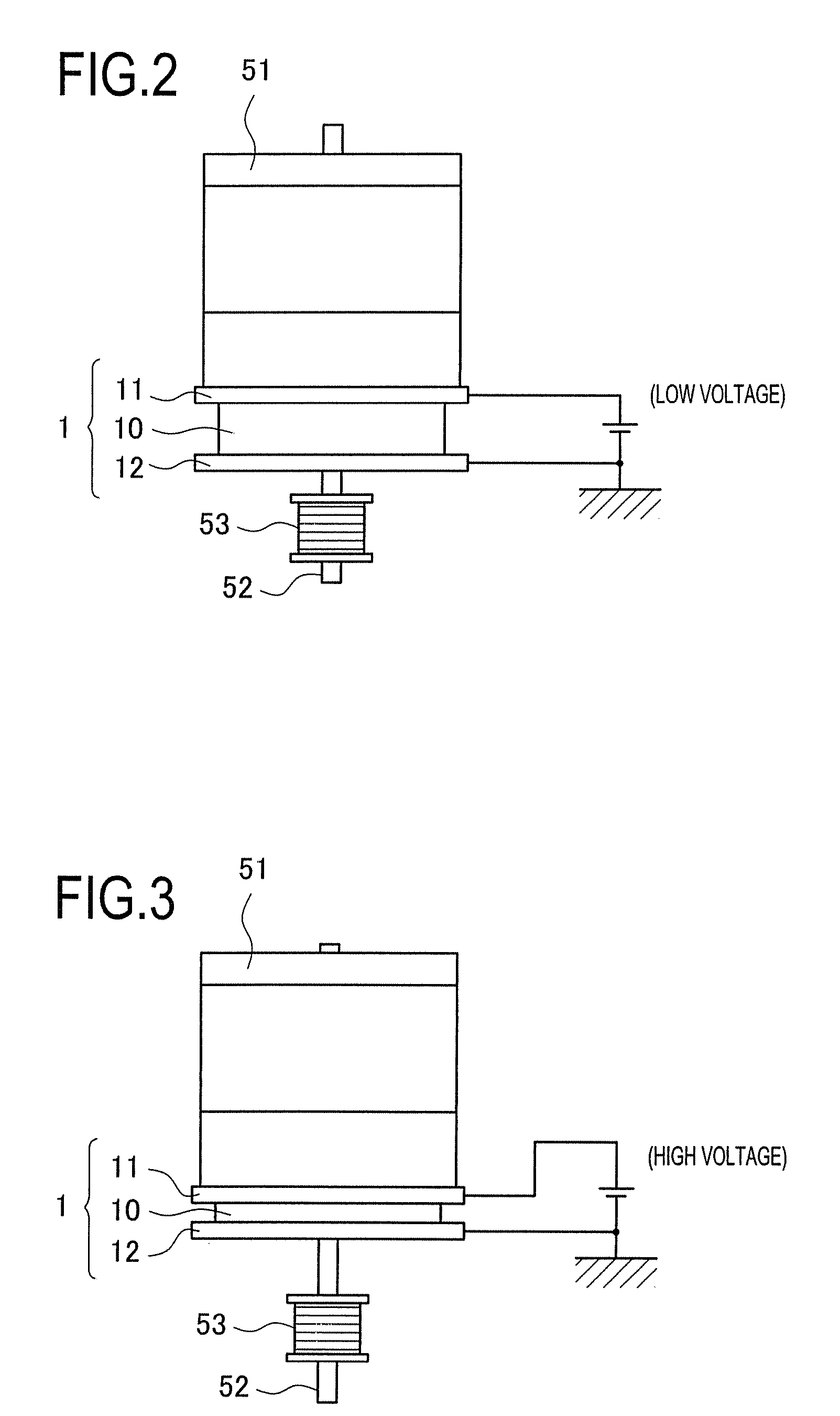
A mount damper comprises electrode plates placed on a motor side and a support body side respectively, a control unit for adjusting voltage between the electrode plates, and an electrostrictive polymer member for changing a distance between the electrode plates by the voltage therebetween. The electrostrictive polymer member is also an elastic body sandwiched between the electrode plates and has a hardness changeable with a change in the interelectrode distance. A motor is mounted through this mount damper. The control unit adjusts voltage applied between the electrode plates to a value different from a value causing resonance of the motor and the electrostrictive polymer member, thereby absorbing vibration of the motor during rotation thereof, irrespective of a rotation speed. Thus, the mount damper and the image forming apparatus using it can reliably prevent resonance and absorb vibration constantly even if a device selectively uses plural levels of the rotation speed.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Terminal and screen control method applied to terminal
ActiveCN110166601APrevent slippingProne to slippingTelephone set constructionsComputer terminalEngineering
The invention provides a terminal and a screen control method applied to the terminal, and relates to the technical field of terminals. The terminal comprises a flexible display screen; a flexible electrostrictive polymer film arranged on the first surface of the flexible display screen, and the first surface being close to one surface of the terminal circuit board; an electrode assembly attachedto the flexible electrostrictive polymer film; and a controller connected with the electrode assembly and used for providing control voltage for the electrode assembly, so that a target thin film areaof the flexible electrostrictive polymer thin film is deformed through the control voltage, and a target screen area, corresponding to the target thin film area, on the flexible display screen is driven to deform. According to the scheme, the flexible electrostrictive polymer film is arranged in the terminal, the terminal is assisted in deformation of the flexible display screen, and the problemthat a user holds the terminal by hand and the terminal is prone to sliding off can be avoided.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Electrostriction polymer laminar nano composite material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN100509960CEasy to manufactureReduce the driving voltageLigamentsMusclesArtificial muscleMaterials science
The present invention relates to one kind of electrostrictive layered nanometer composite polymer material, which is prepared with electrostrictive polymer, layered nanometer inorganic material, organic intercalative agent, cross-linking agent, catalyst and protonating agent, and through curing at 40-120 deg.c to form 10-1000 micron thick film and the subsequent drawing orientation. When 10-100 V / micron electric field is applied in the direction perpendicular to the film plane, one strain in 1-100 % may generate in the direction perpendicular to the electric field direction and the drawing direction, with the deformation being eliminated fast after the electric field is eliminated. The electrostrictive composite polymer material may be applied in electric driver, pump and sensor related to artificial muscle, and compared with available technology, the present invention has the advantages of simple preparation and lower driving voltage.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Mount damper and image forming apparatus using the mount damper
InactiveUS8496097B2Reliably and constantly preventing resonance and absorbing vibrationPortable framesStands/trestlesElectricityResonance
A mount damper comprises electrode plates placed on a motor side and a support body side respectively, a control unit for adjusting voltage between the electrode plates, and an electrostrictive polymer member for changing a distance between the electrode plates by the voltage therebetween. The electrostrictive polymer member is also an elastic body sandwiched between the electrode plates and has a hardness changeable with a change in the interelectrode distance. A motor is mounted through this mount damper. The control unit adjusts voltage applied between the electrode plates to a value different from a value causing resonance of the motor and the electrostrictive polymer member, thereby absorbing vibration of the motor during rotation thereof, irrespective of a rotation speed. Thus, the mount damper and the image forming apparatus using it can reliably prevent resonance and absorb vibration constantly even if a device selectively uses plural levels of the rotation speed.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
A terminal and screen control method applied to the terminal
ActiveCN110166601BPrevent slippingProne to slippingTelephone set constructionsPolymer thin filmsFlexible display
The present invention provides a terminal and a screen control method applied to the terminal, and relates to the technical field of terminals. The terminal includes: a flexible display screen; a flexible electrostrictive polymer film arranged on the first surface of the flexible display screen, the first surface being the side close to the terminal circuit board; pasted on the flexible electrostrictive polymer film An electrode assembly on a stretchable polymer film; a controller connected to the electrode assembly, the controller is used to provide a control voltage to the electrode assembly, and through the control voltage, the flexible electrostrictive polymer film The target film area deforms, and drives the target screen area corresponding to the target film area on the flexible display screen to deform. In the above solution, by arranging a flexible electrostrictive polymer film in the terminal to assist the terminal in deforming the flexible display screen, the problem of the terminal slipping easily caused by the user holding the terminal can be avoided.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Refolding method for protein in electrostrictive polymer
InactiveCN100586956CSimple and effective experimental meansAchieve the purpose of isolationPeptide preparation methodsElectricityInclusion bodies
The invention relates to an analysis method of protein refolding in electrical contraction polymer. The invention utilizes the crosslink network of electrical contraction polymer to insulate modifiedprotein molecule and removes modifier and contracts polymer at electric field, to loosen the polymer packing modified protein, therefore, modifier protein can fold without interfered and coiled by other proteins, and without the generation of inclusion body. The inventive analysis method builds a model of external molecule mate, for protein folding dynamic research.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
System of audio speakers implemented using EMP actuators
ActiveUS9357312B2Reduce entropyReduce the temperaturePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesTransducerEngineering
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Ultrasonic treatment device
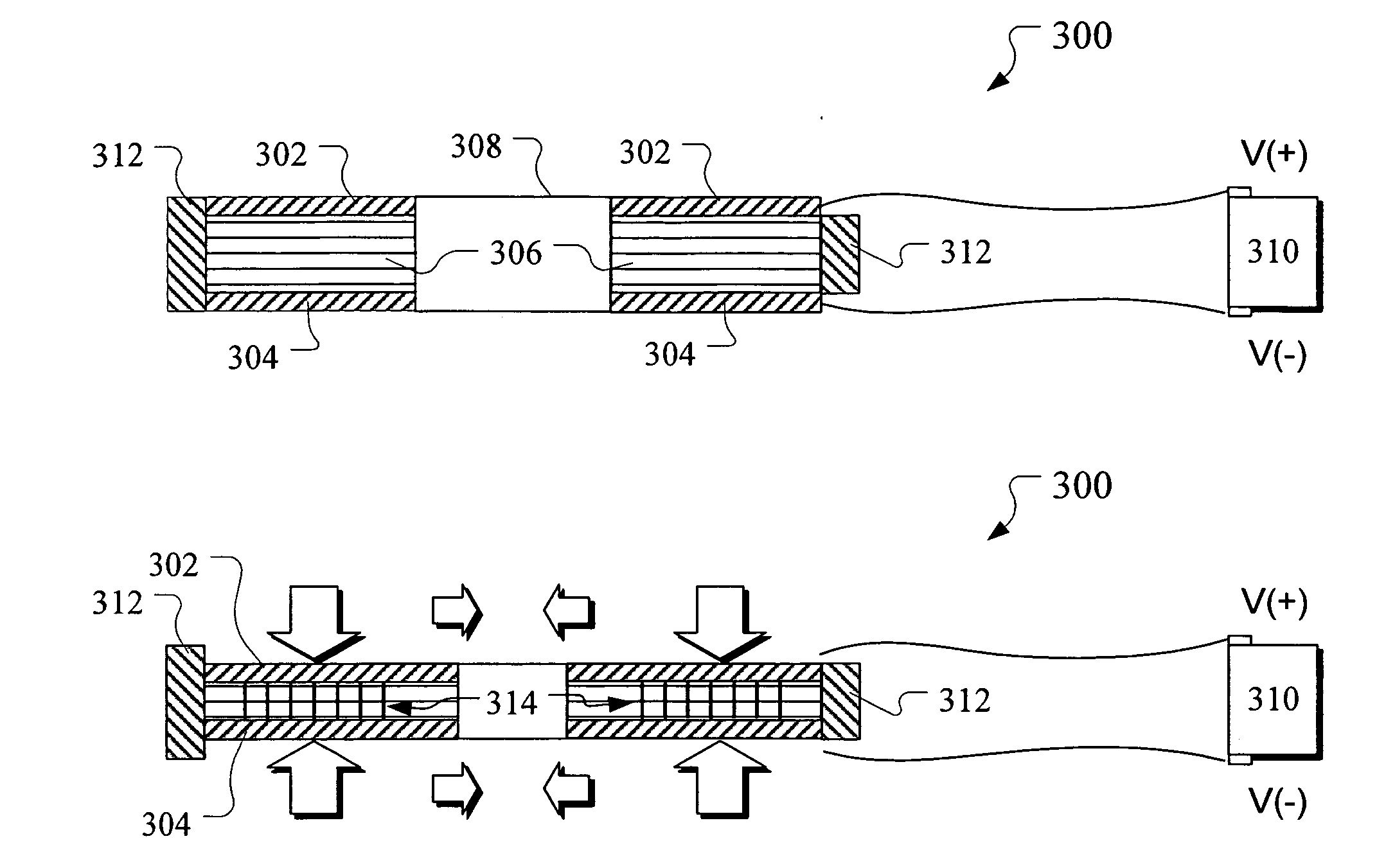
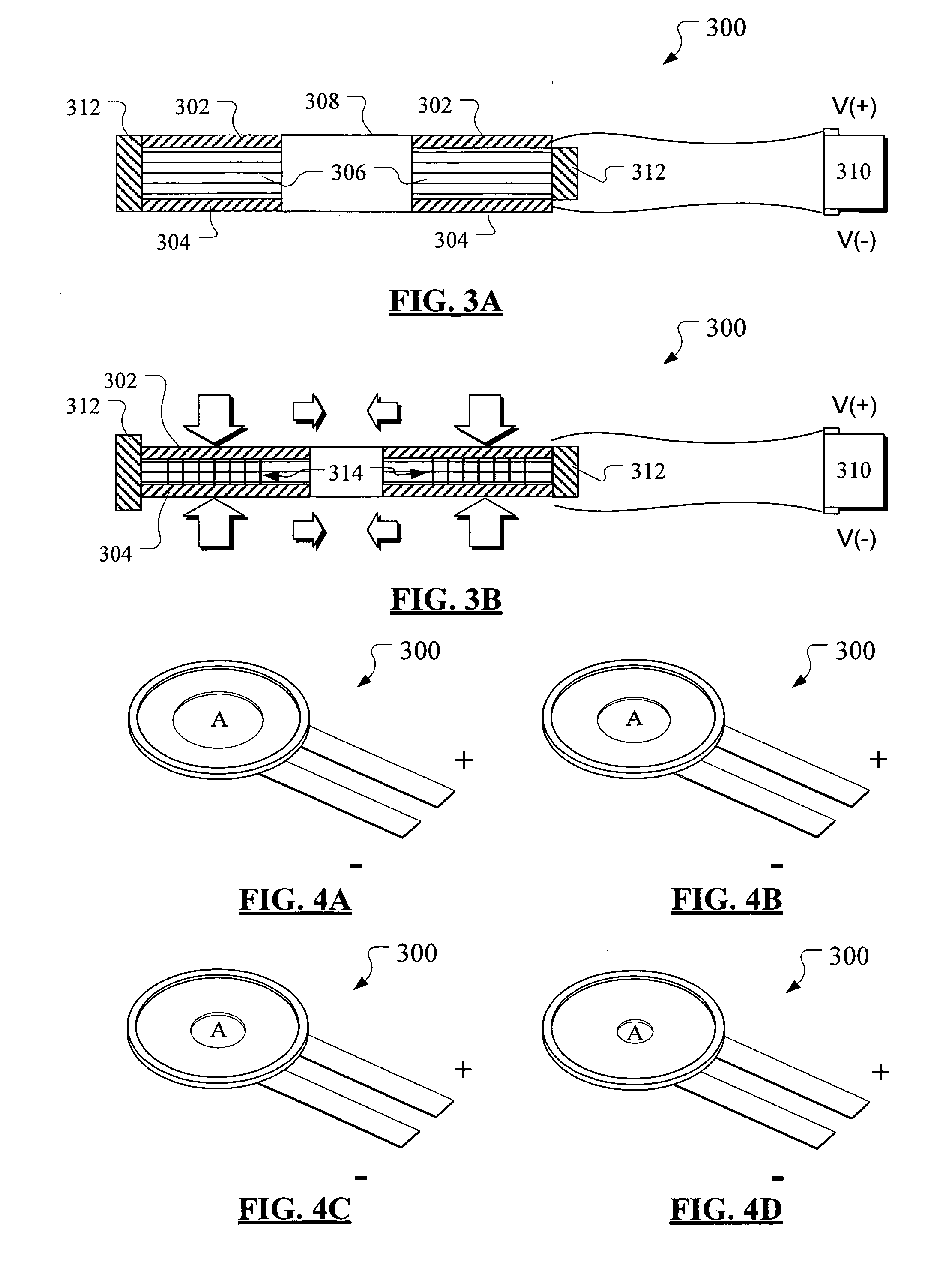
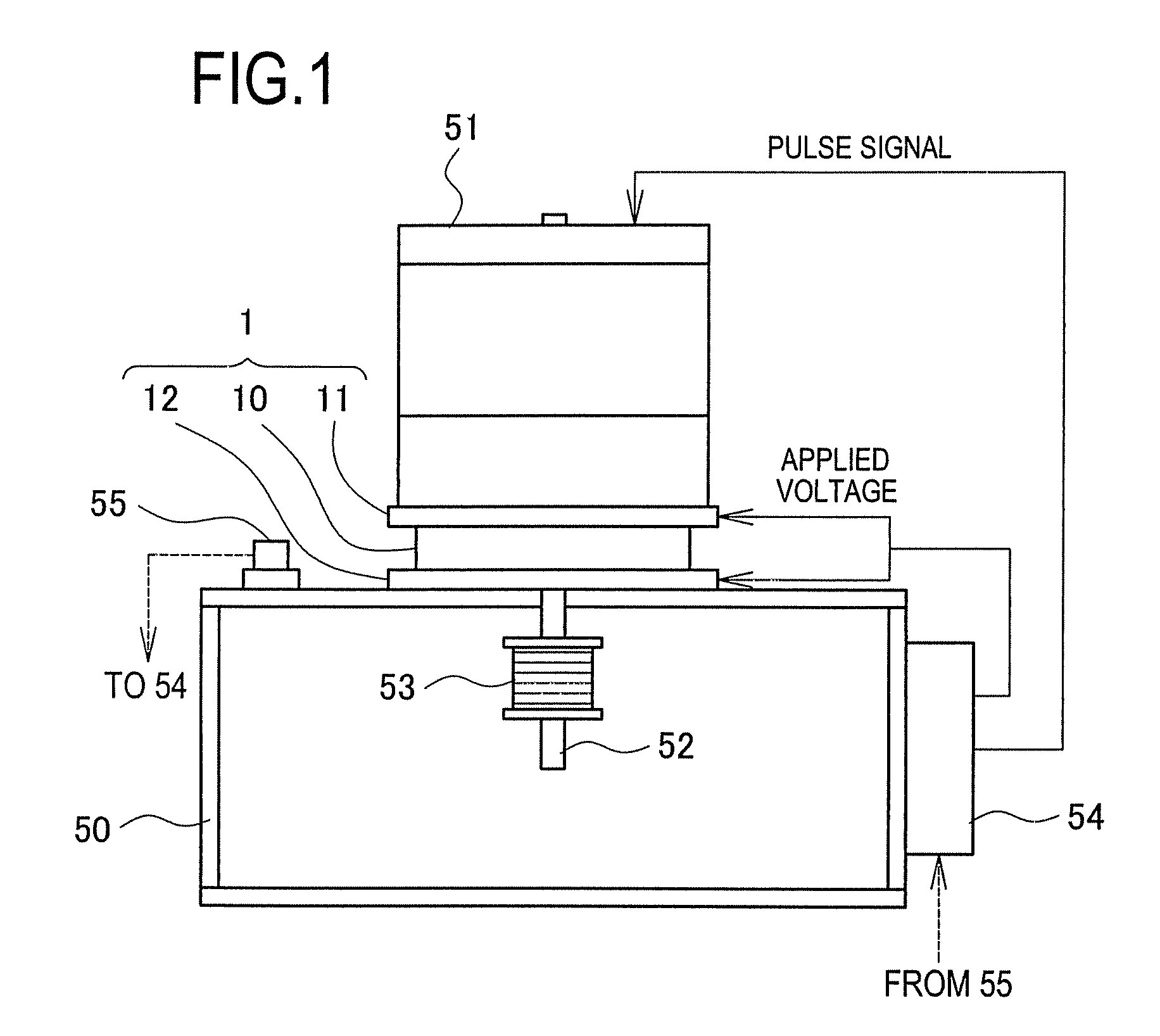
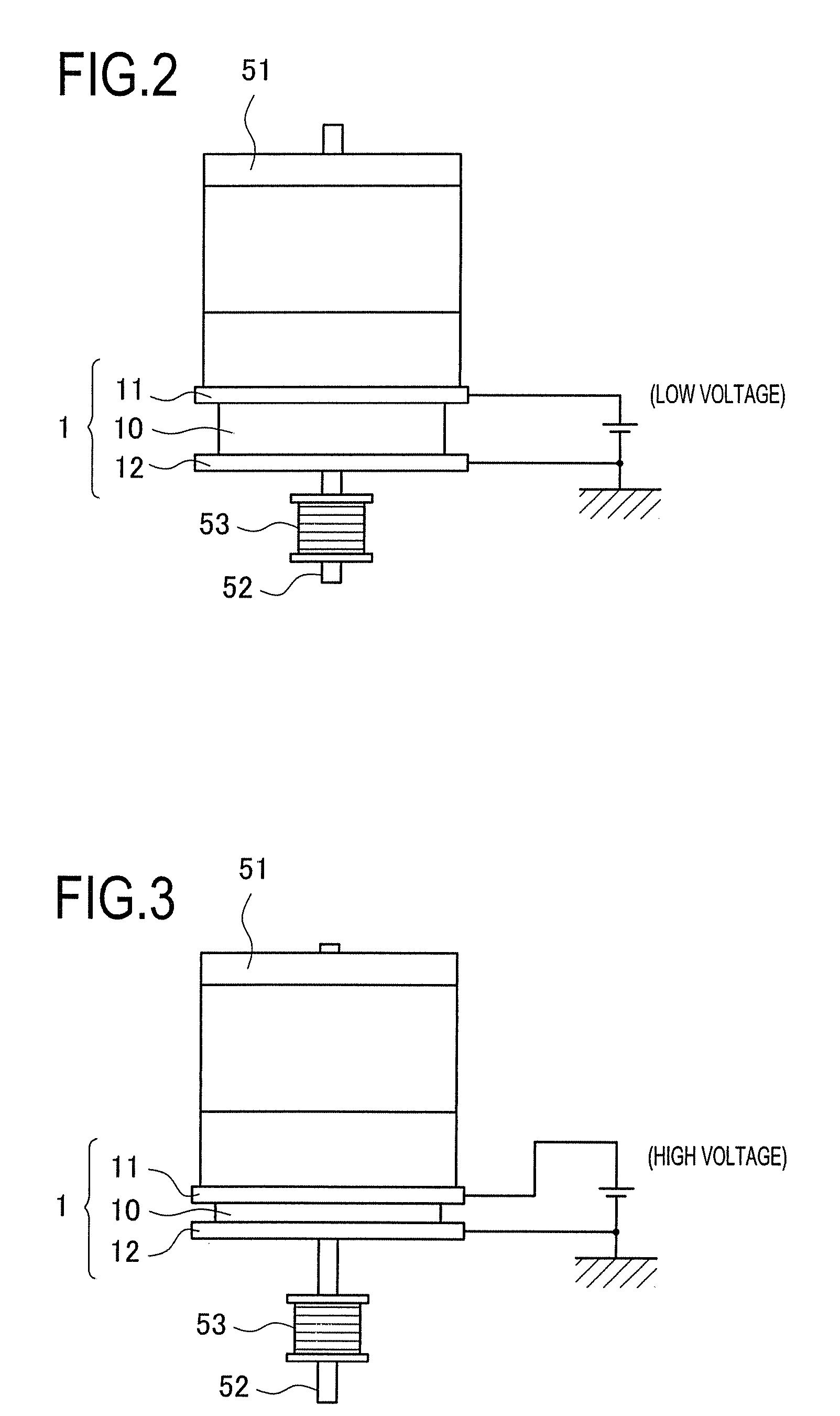
An ultrasonic treatment device comprises an actuator (10) where a plus electrode (12) and a minus electrode (13) are arranged on a tubular electrostrictive polymer (11) which is driven to expand and contract when a voltage is applied between the electrodes (12, 13). A voltage is supplied in a predetermined period to the plus electrode (12) and the minus electrode (13) of the actuator (10) and theelectrostrictive polymer (11) is driven to expand and contract, thereby vibrating the blade (16) ultrasonically.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Electroacoustic transducer using diaphragm and method for producing diaphragm
InactiveUS7835539B2Audio signal efficientlyEfficient emissionsTransducer detailsTransducer diaphragmsTransducerAtmospheric pressure
An electroacoustic transducer has a cup chamber and a diaphragm made of deformable electrostrictive polymer, which is attached to an opening of the chamber. The electroacoustic transducer also has first and second adaptive electrode layers formed on a front surface and a rear surface of the diaphragm, across which audio signal voltage biased by a direct-current biased voltage is applied. The first and second adaptive electrode layers have shapes that are adjustable according to a change in a shape of the diaphragm. To form the diaphragm, the electrostrictive polymer that has been previously formed to have a concave or convex shape is further formed to have a concave or convex shape, thereby generating a difference in air pressure between the front surface and the rear surface of the previously formed electrostrictive polymer.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com