Patents
Literature
71results about How to "Reduce entropy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for compressing dictionary data
InactiveUS7181388B2Efficient compressionEasy to compressCode conversionSpeech recognitionStatistical algorithmData processing
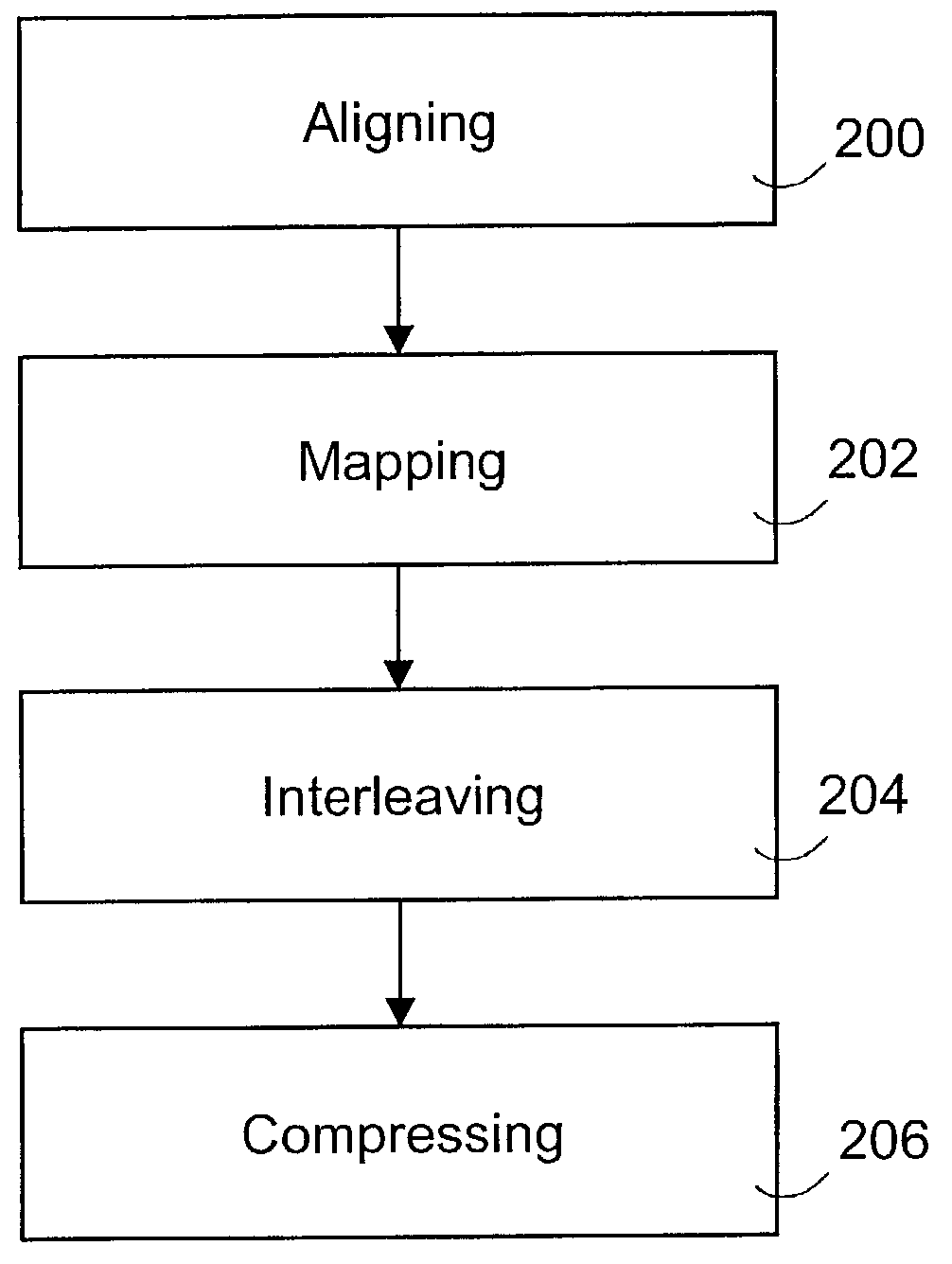
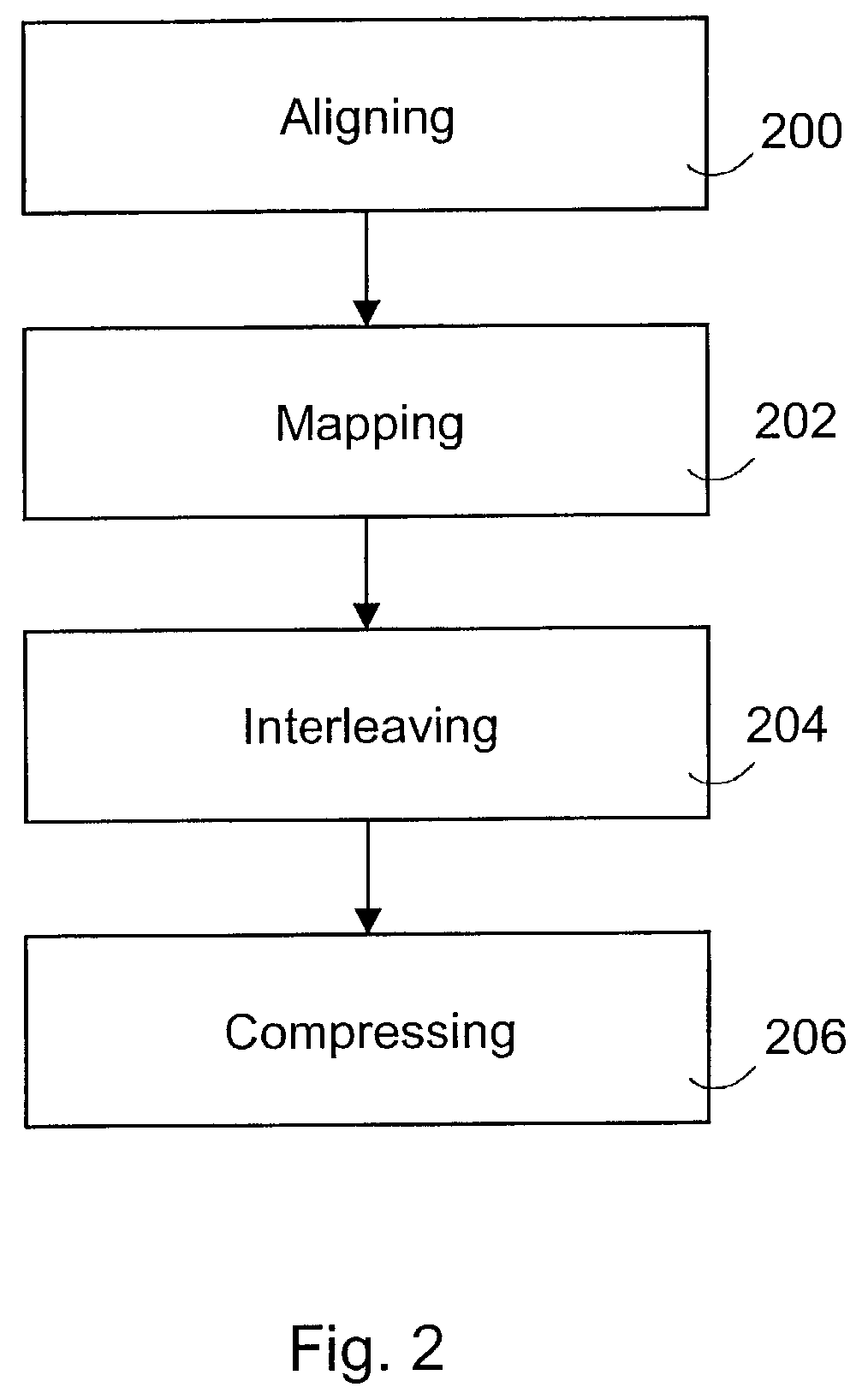
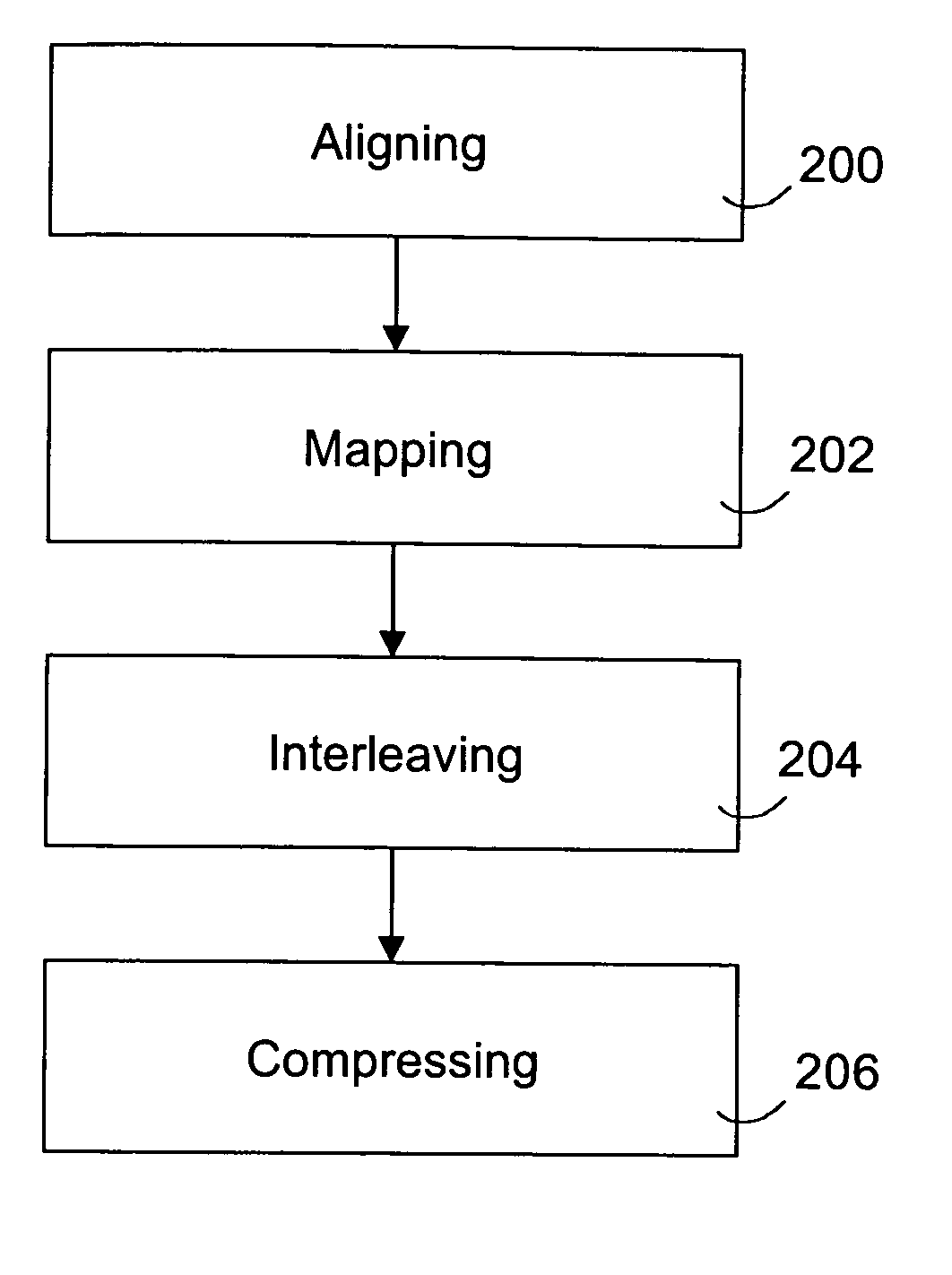
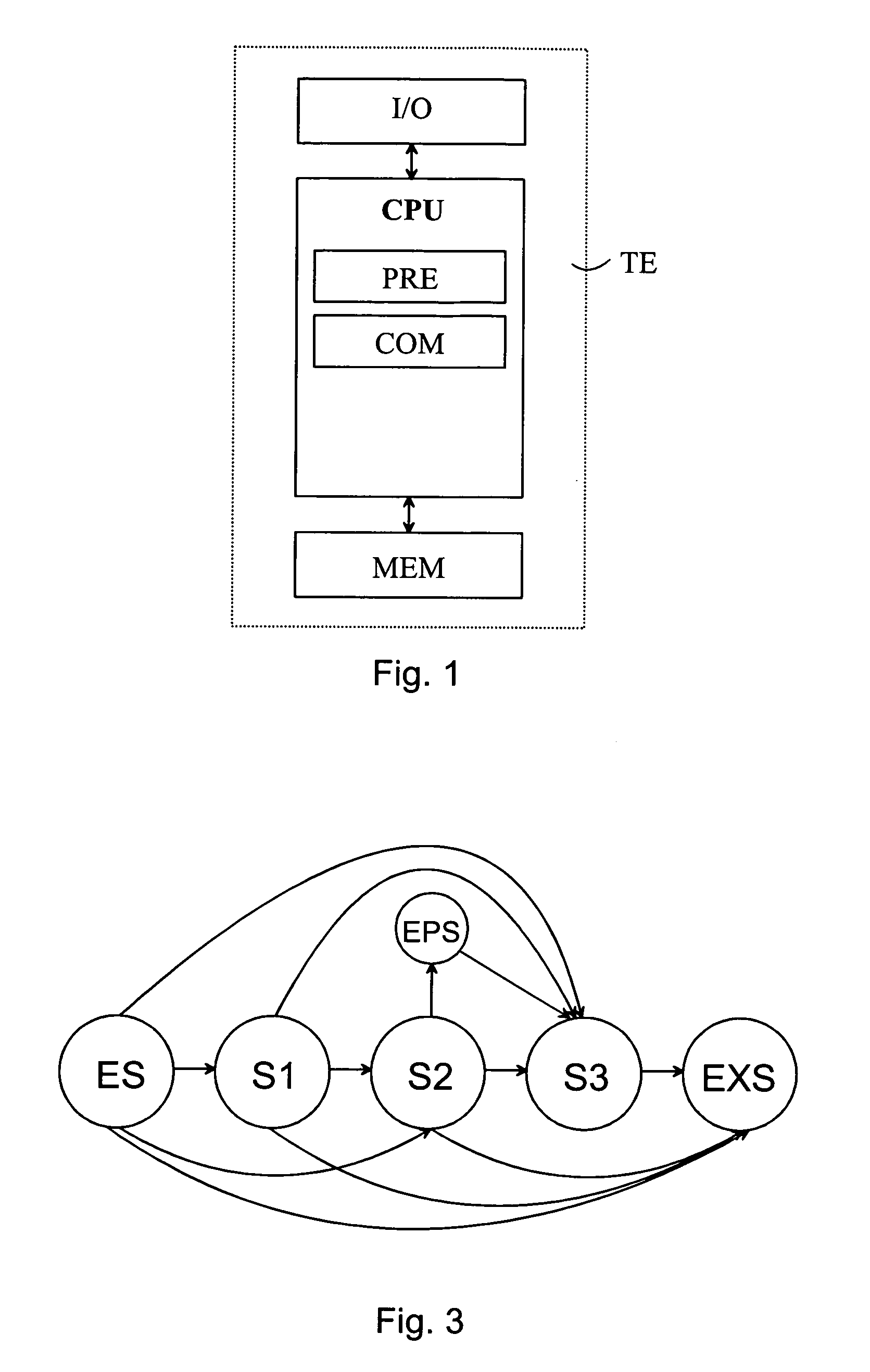
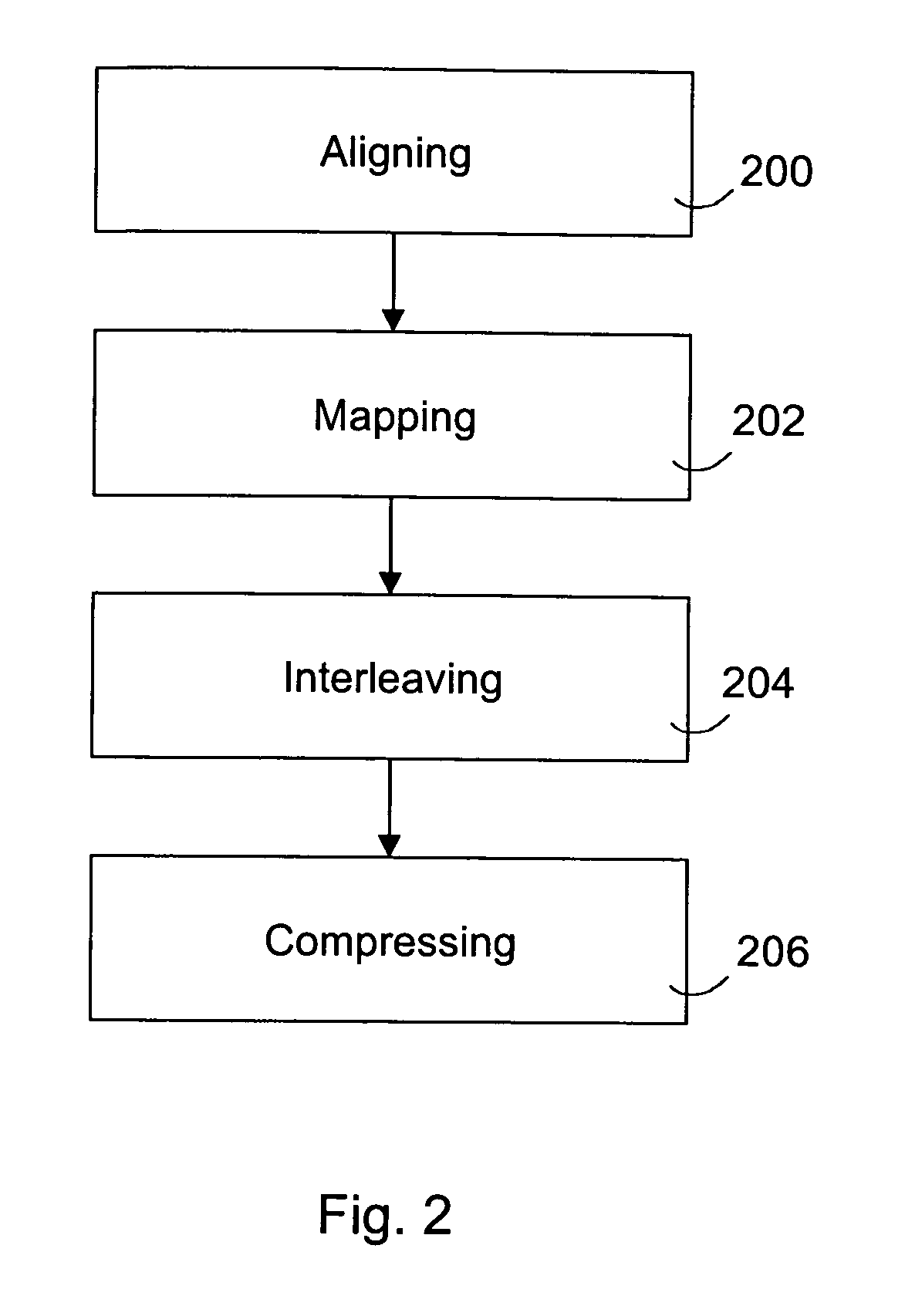
The invention relates to pre-processing of a pronunciation dictionary for compression in a data processing device, the pronunciation dictionary comprising at least one entry, the entry comprising a sequence of character units and a sequence of phoneme units. According to one aspect of the invention the sequence of character units and the sequence of phoneme units are aligned using a statistical algorithm. The aligned sequence of character units and aligned sequence of phoneme units are interleaved by inserting each phoneme unit at a predetermined location relative to the corresponding character unit.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method for compressing dictionary data
InactiveUS20070073541A1Pronunciation simple and fastSimple and fast to recognitionCode conversionSpeech recognitionNatural language processingEngineering
The invention relates to pre-processing of a pronunciation dictionary for compression in a data processing device, the pronunciation dictionary comprising at least one entry, the entry comprising a sequence of character units and a sequence of phoneme units. According to one aspect of the invention the sequence of character units and the sequence of phoneme units are aligned using a statistical algorithm. The aligned sequence of character units and aligned sequence of phoneme units are interleaved by inserting each phoneme unit at a predetermined location relative to the corresponding character unit.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Data Compression For Video
ActiveUS20120044990A1Reduce in quantityWeakening rangeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData compressionAffect perception
The present invention provides a technique for performing one or more aspects of video coding such as quantization, intra prediction coding or inter prediction coding in dependence on a perceptual model taking into account human sensitivity to data in the video signal. The perceptual model may relate to spatial frequency, temporal frequency, contrast sensitivity, colour sensitivity, a structural metric, and / or one or more parameters affecting perception such as motion in the video, the distance of a recipient user from the screen, and the size, aspect ratio or resolution of the screen of the recipient terminal.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
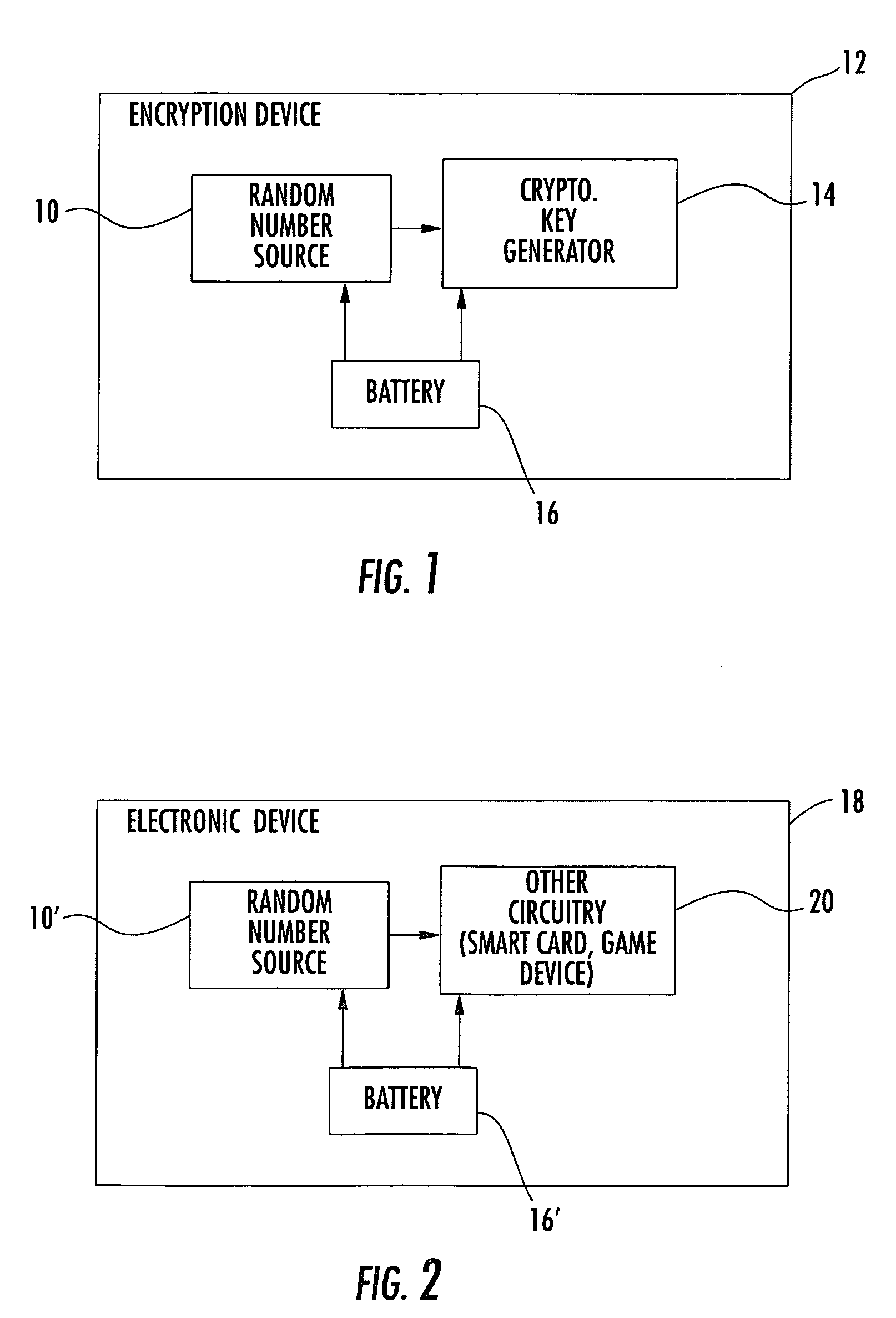
Random number slip and swap generators
InactiveUS7206797B2Increase unpredictabilityIncrease randomnessRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsAlgorithmElectronic equipment
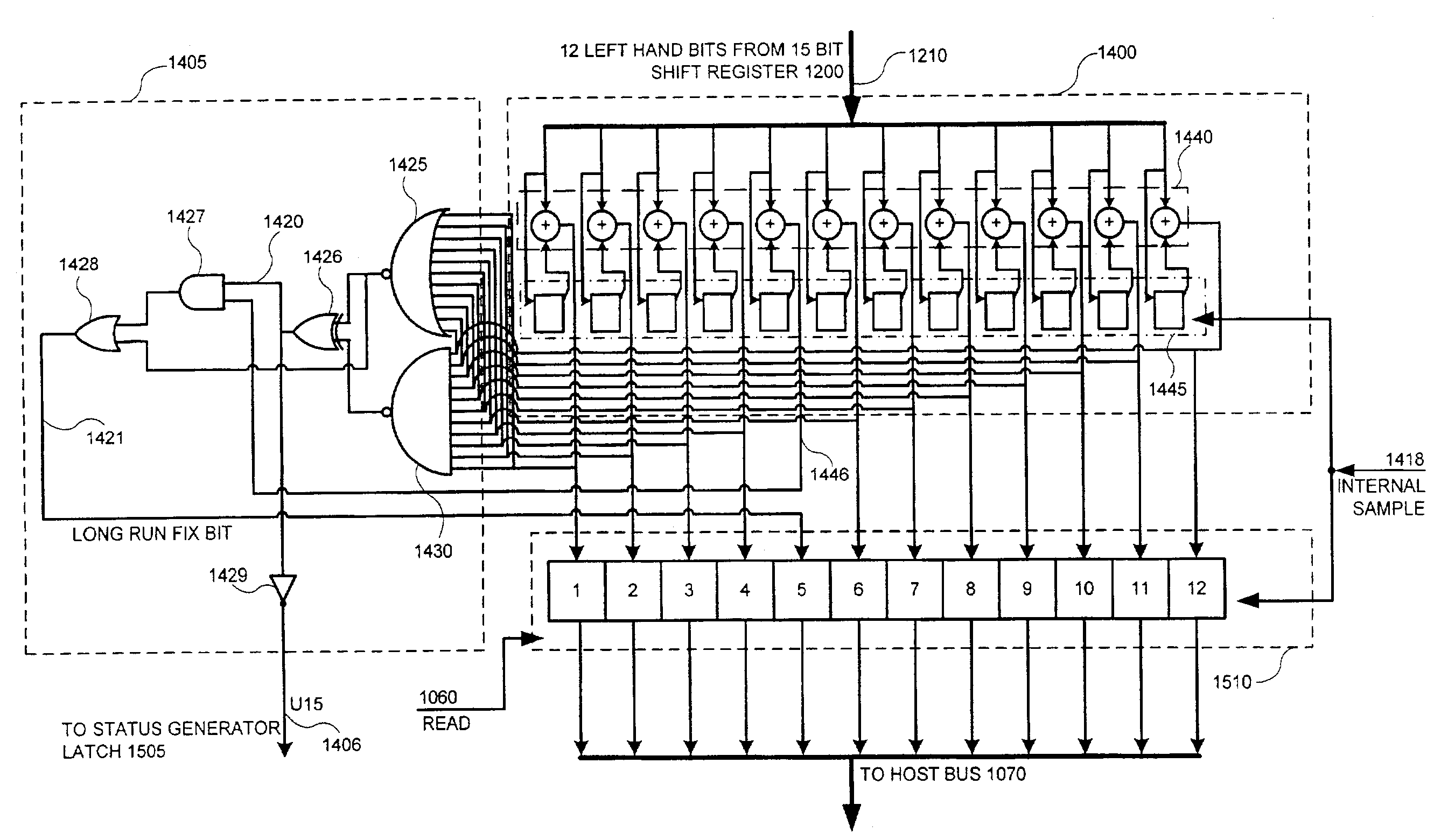
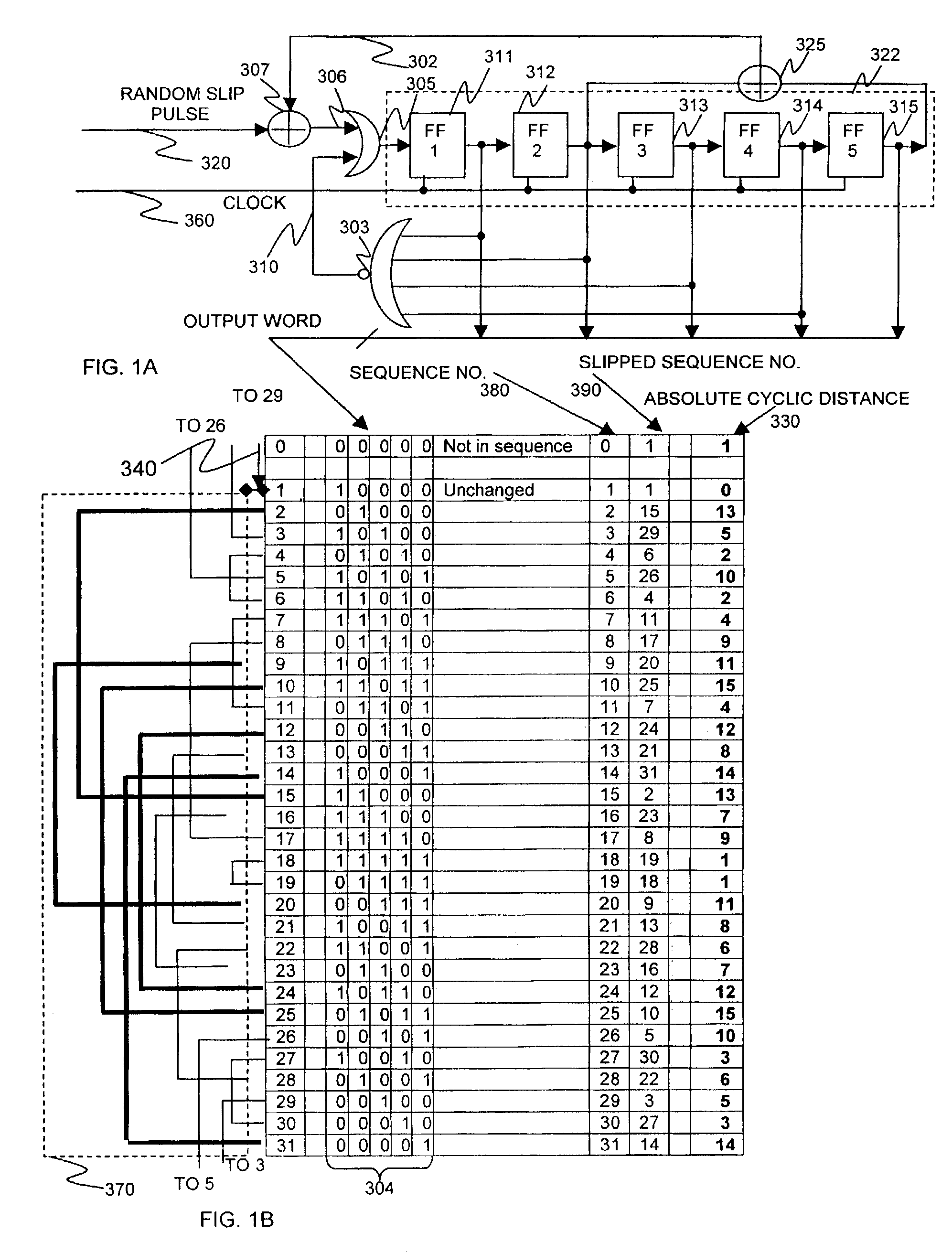
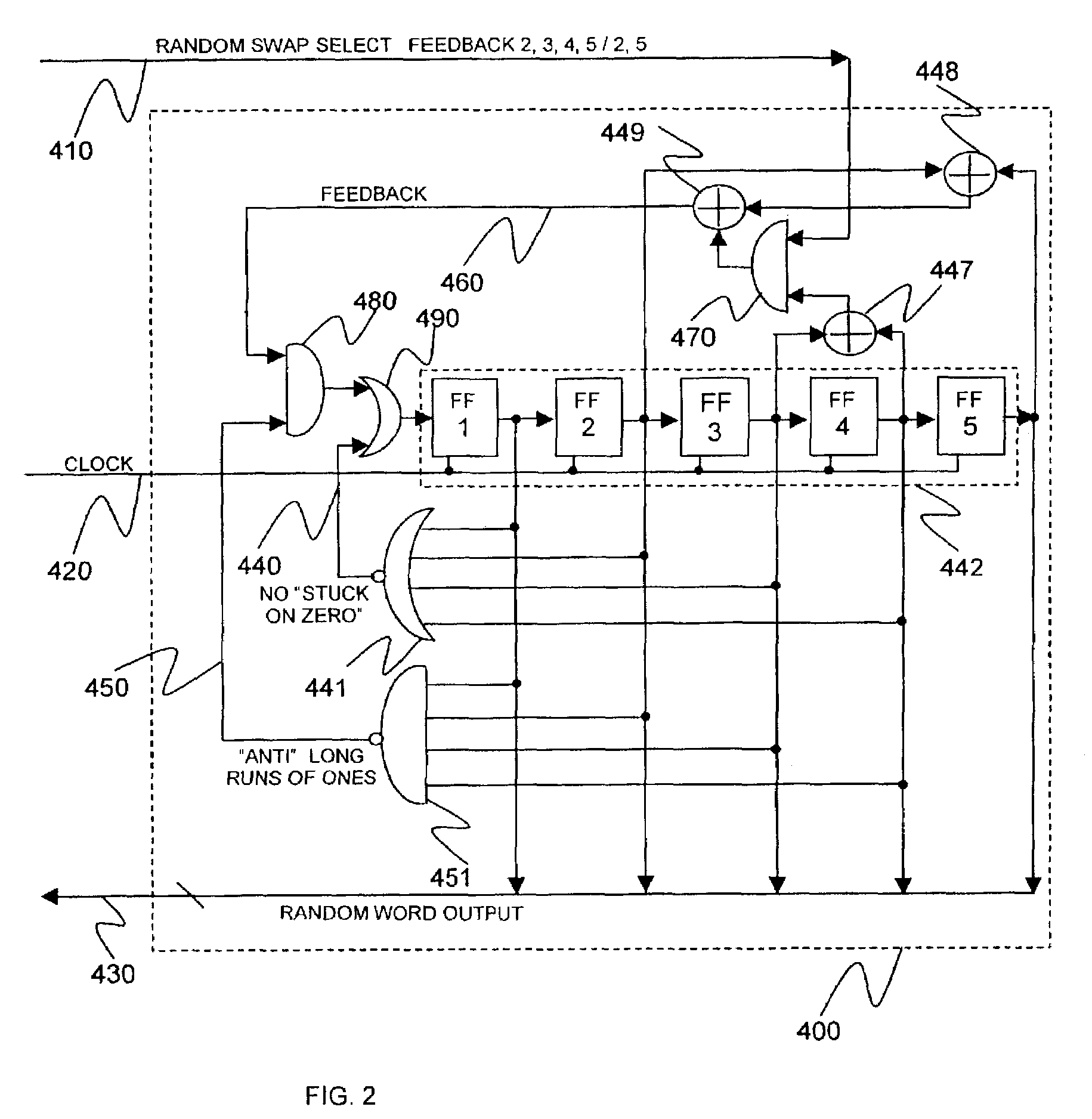
A microelectronic apparatus and method for generating random binary words including at least one clocked pseudorandom binary number sequence generator normally operative to generate a cyclic output sequence of binary numbers, each number including a string of binary symbols, the cyclic output sequence including a basic sequence which is generated repeatedly, at least one bit stream generator generating a clocked bit stream including a stream of binary symbols of a first type occasionally interrupted by a binary symbol of a second type, wherein a first varying time interval between the occasional interruptions is intractably correlated to the output sequence of the number sequence generator, wherein each occurrence of an interruption of the stream of binary symbols of the first type by a binary symbol of the second type causes a pseudorandom modification of the cyclic output sequence of the number sequence generator and a sampling device operative to sample the cyclic output sequence of binary numbers thereby to generate a sampled output sequence including at least one sampled binary word.
Owner:SANDISK IL
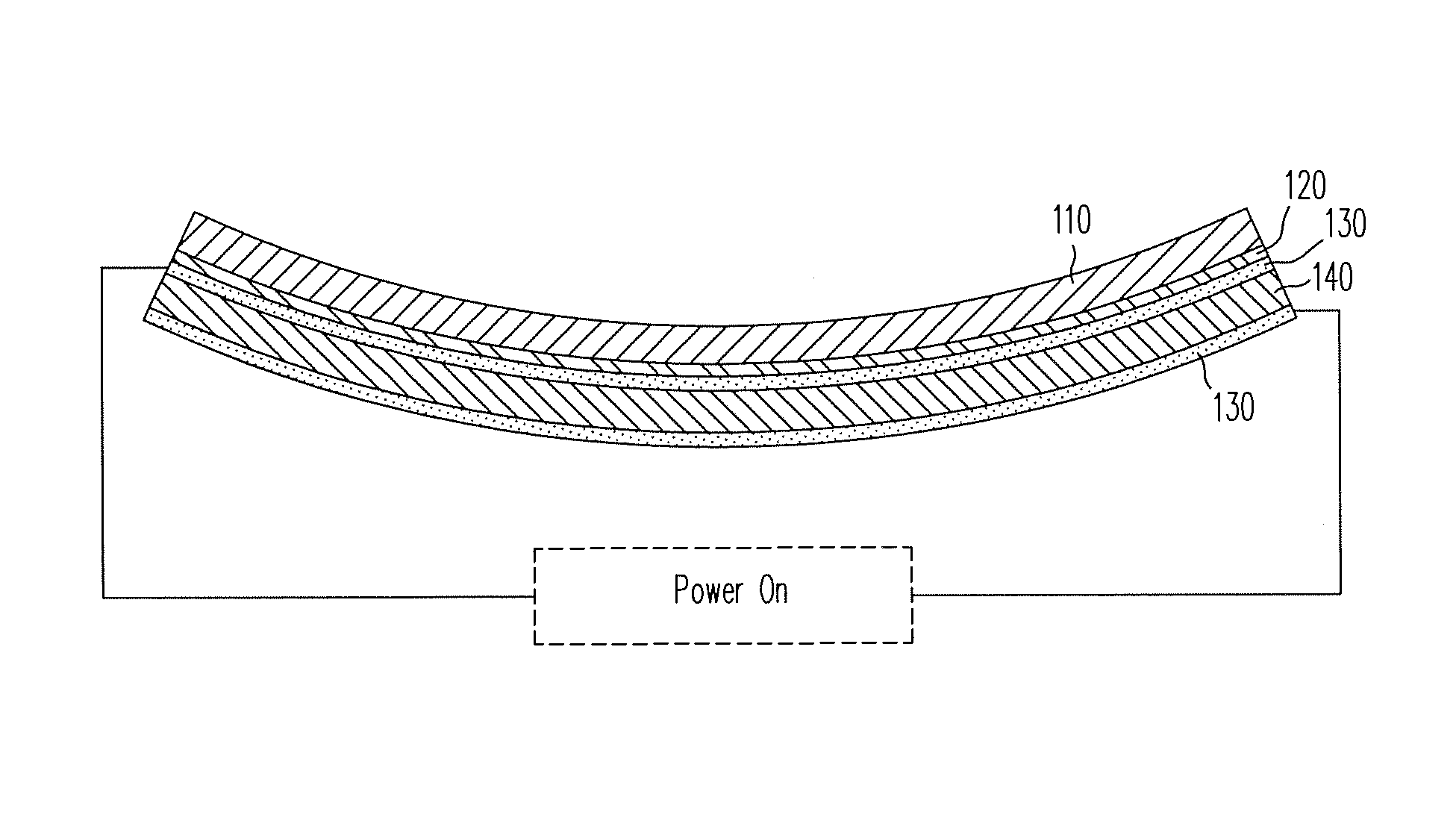
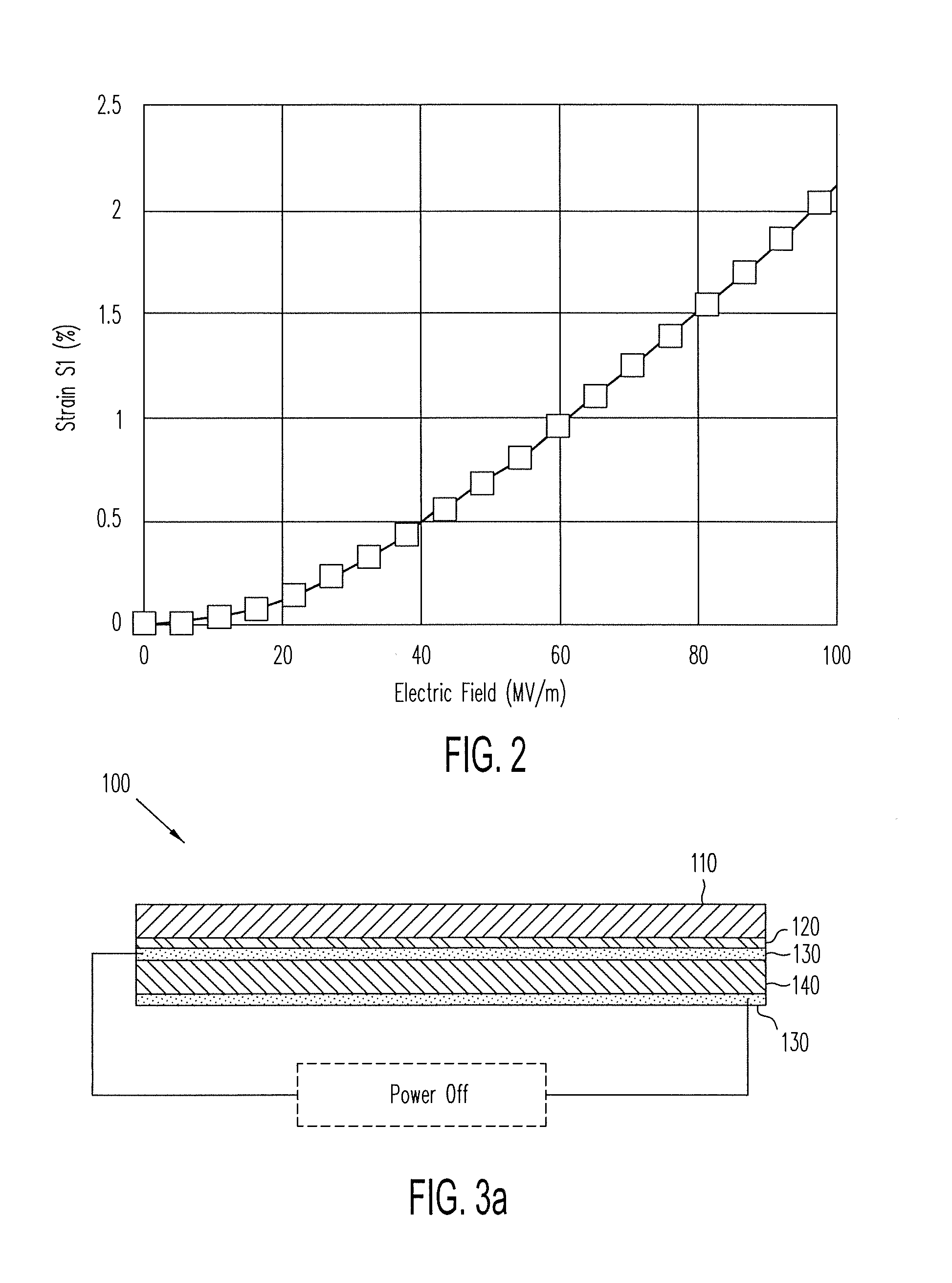
EMP Actuators for Deformable Surface and Keyboard Application
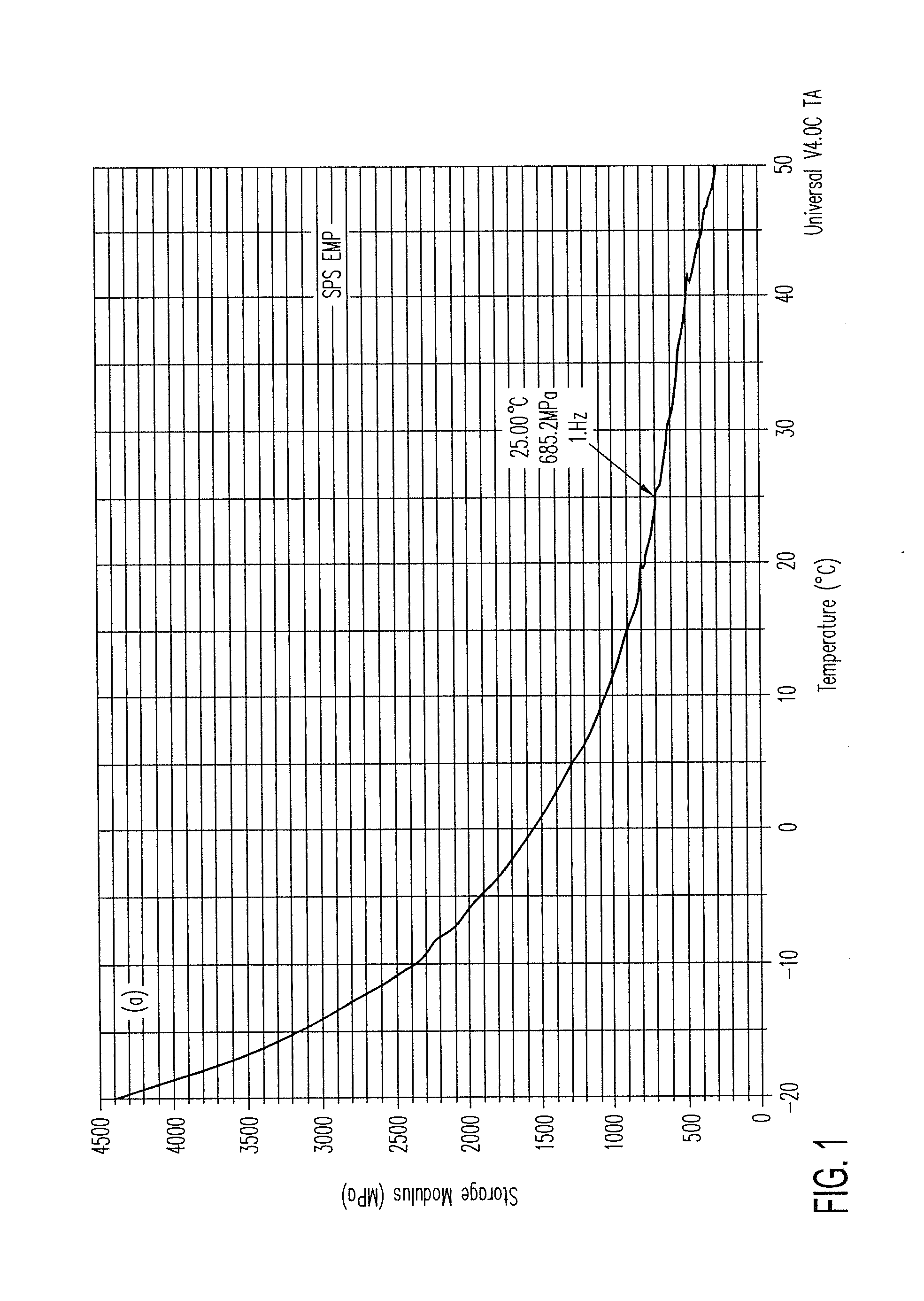
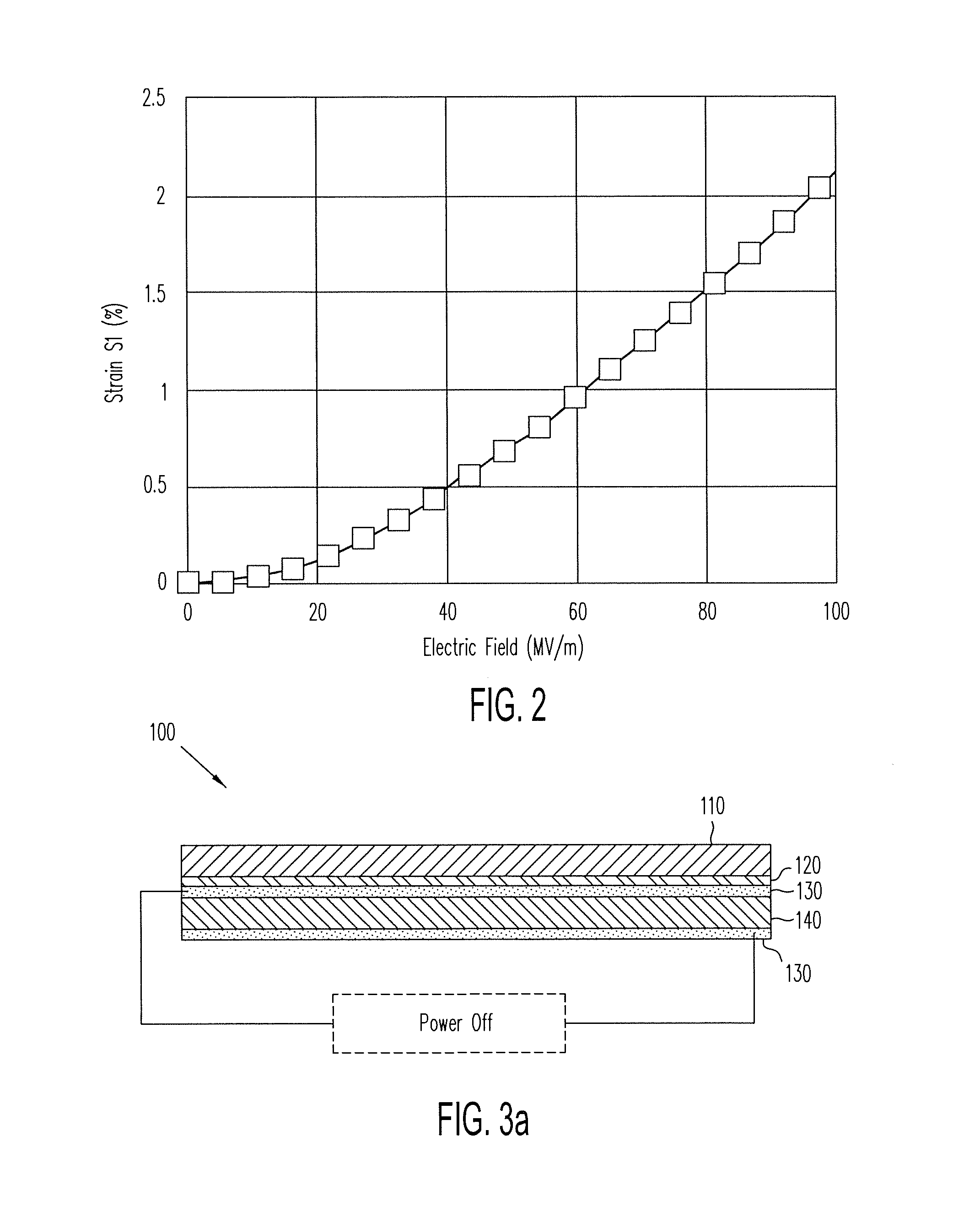
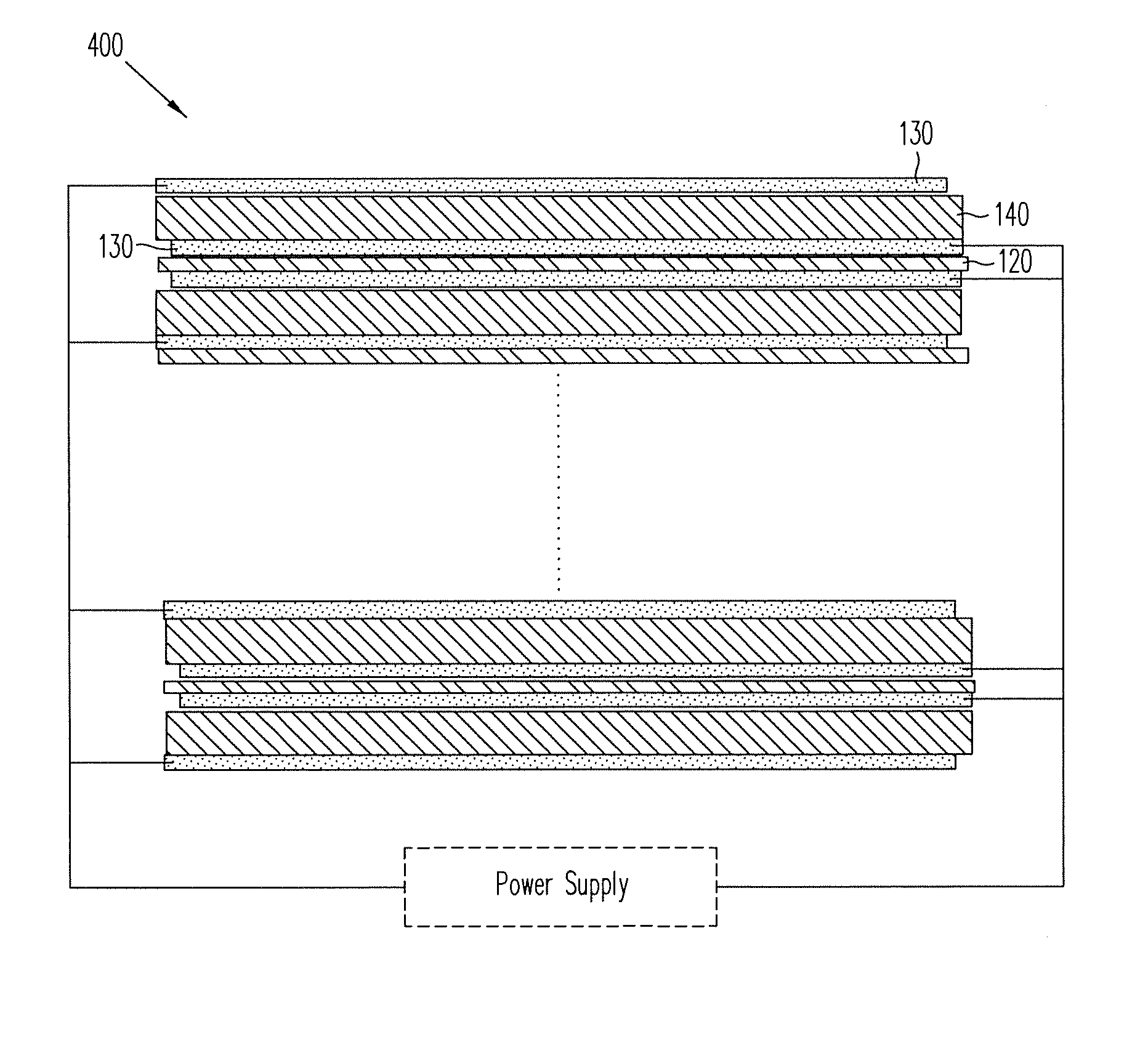
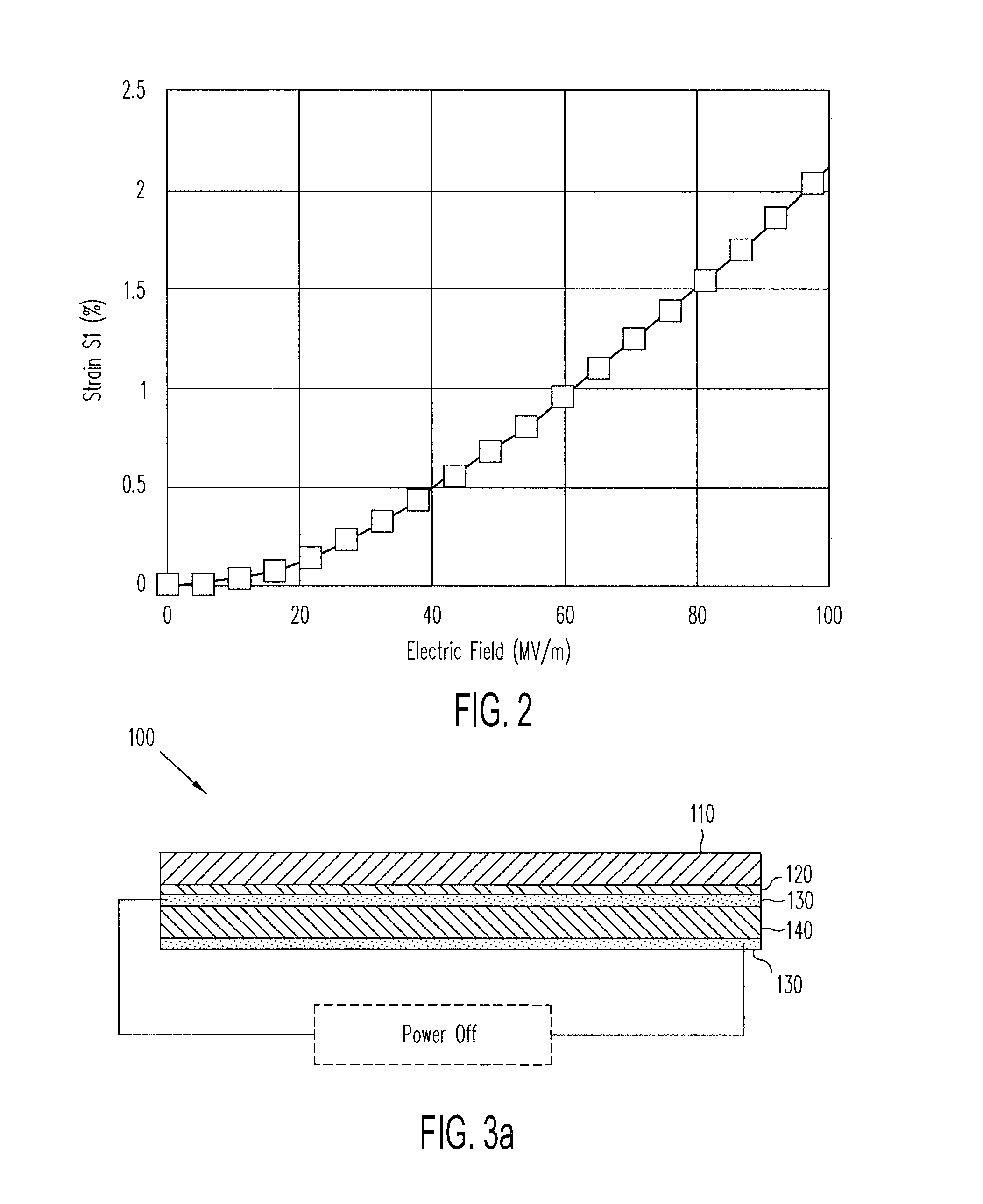
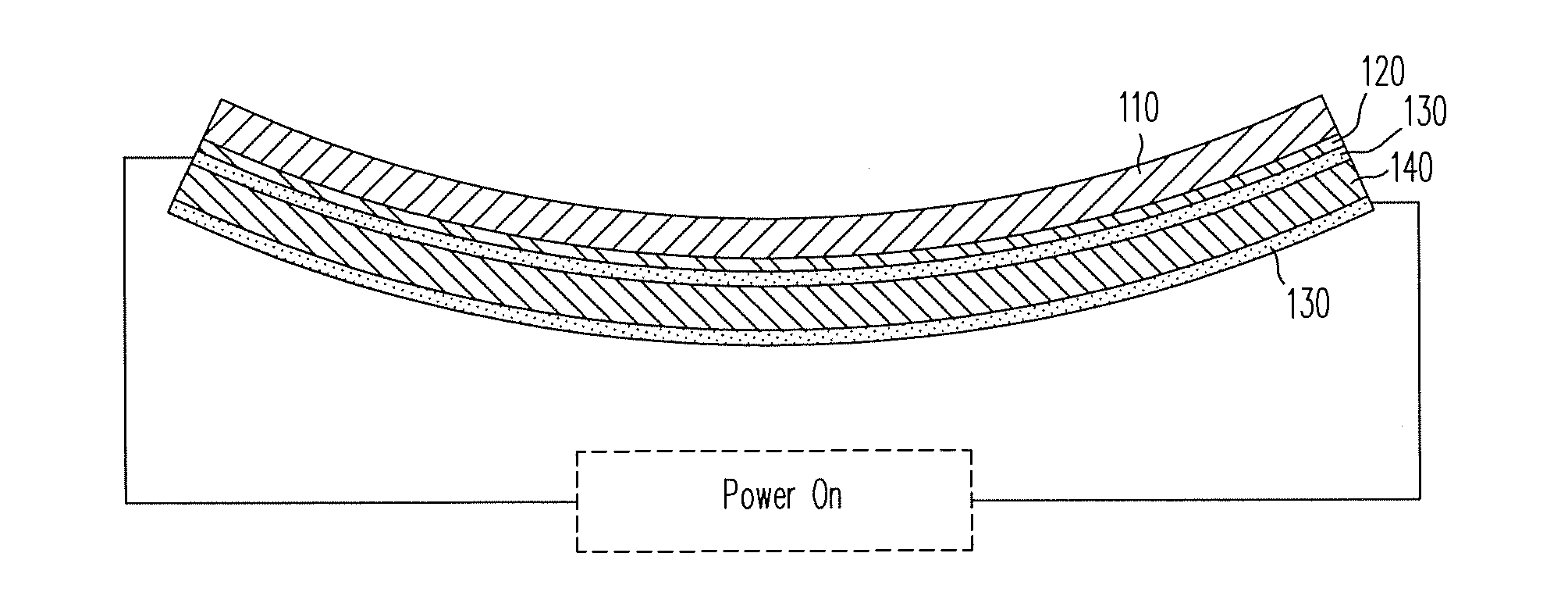
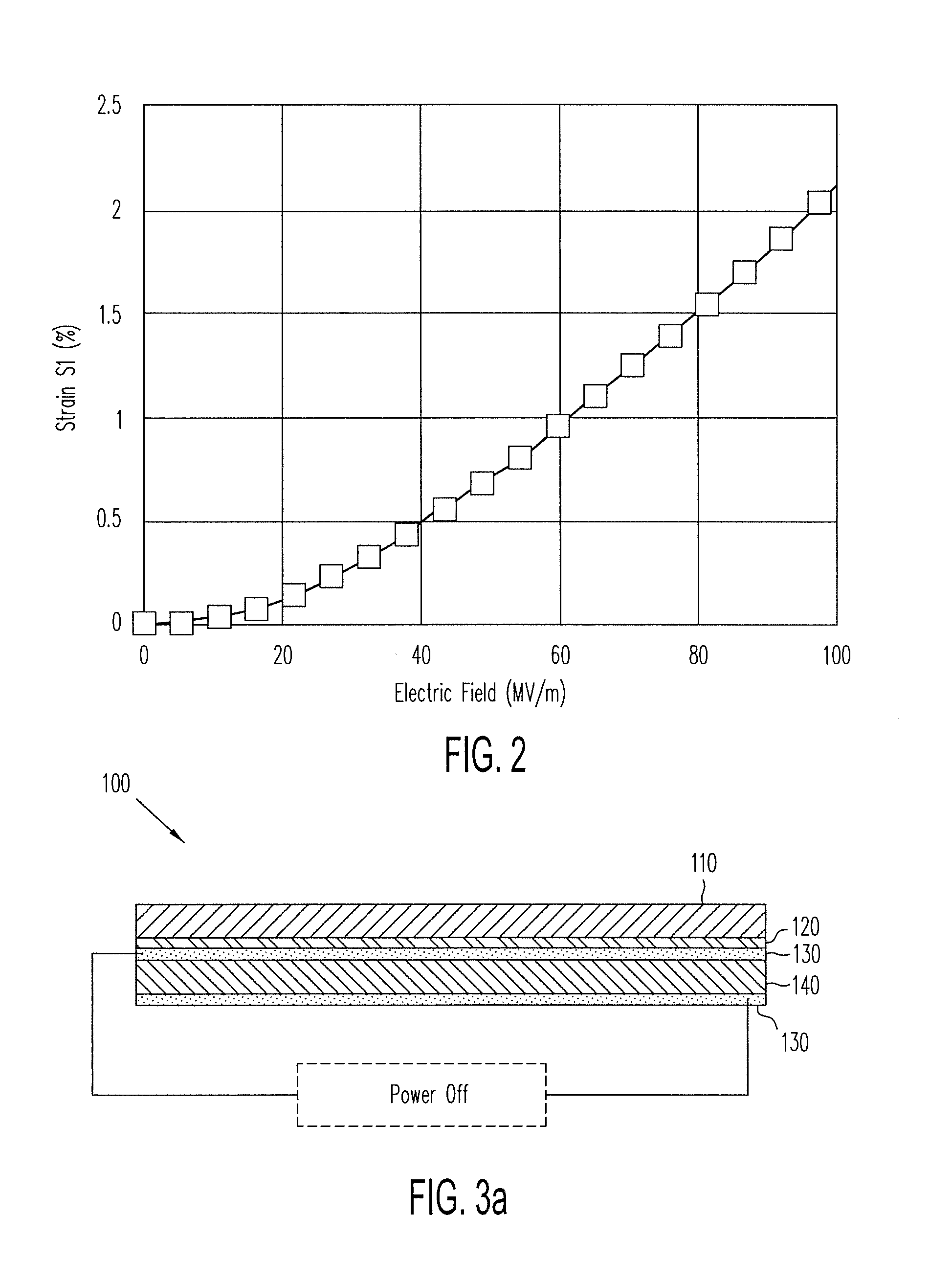
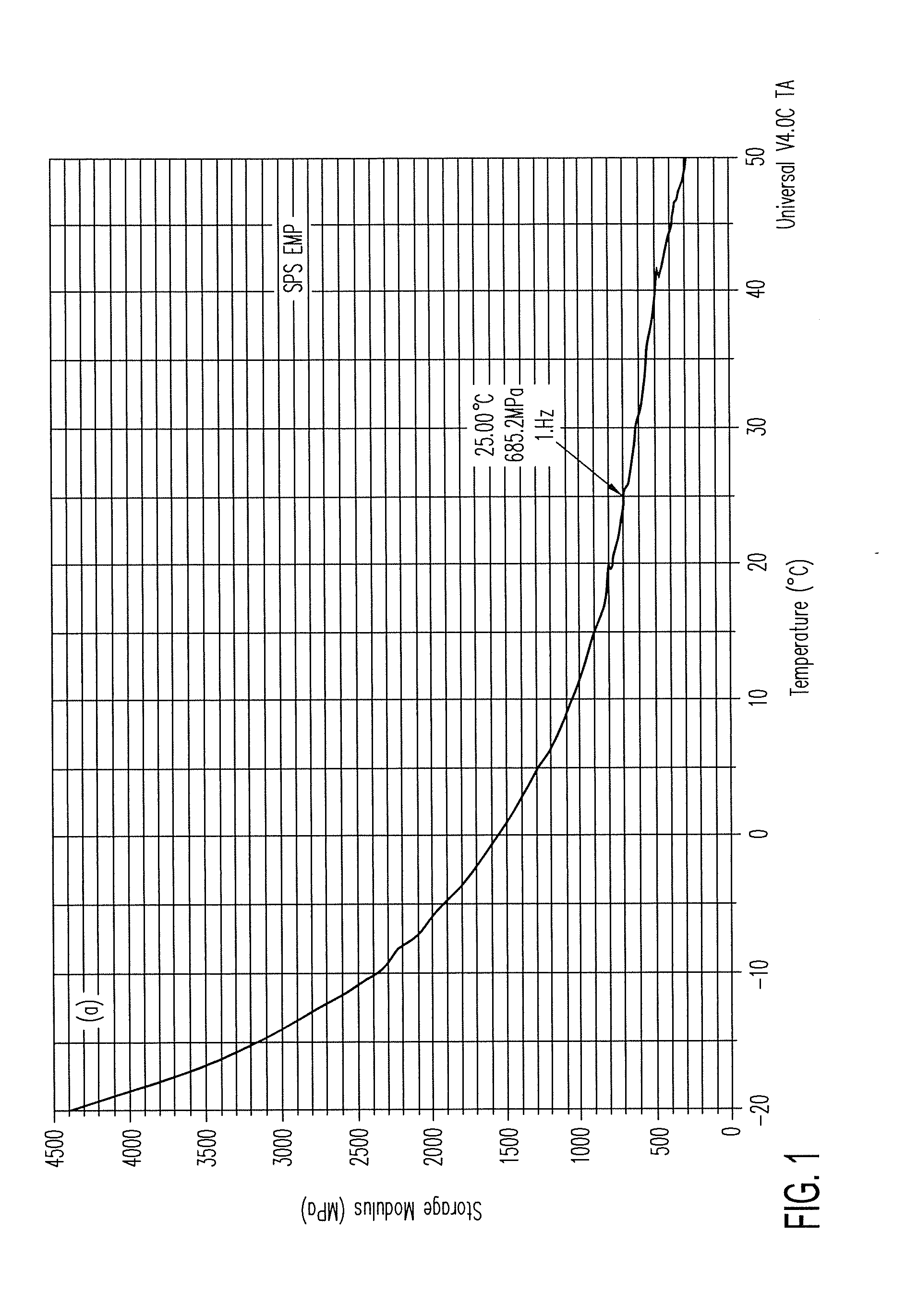
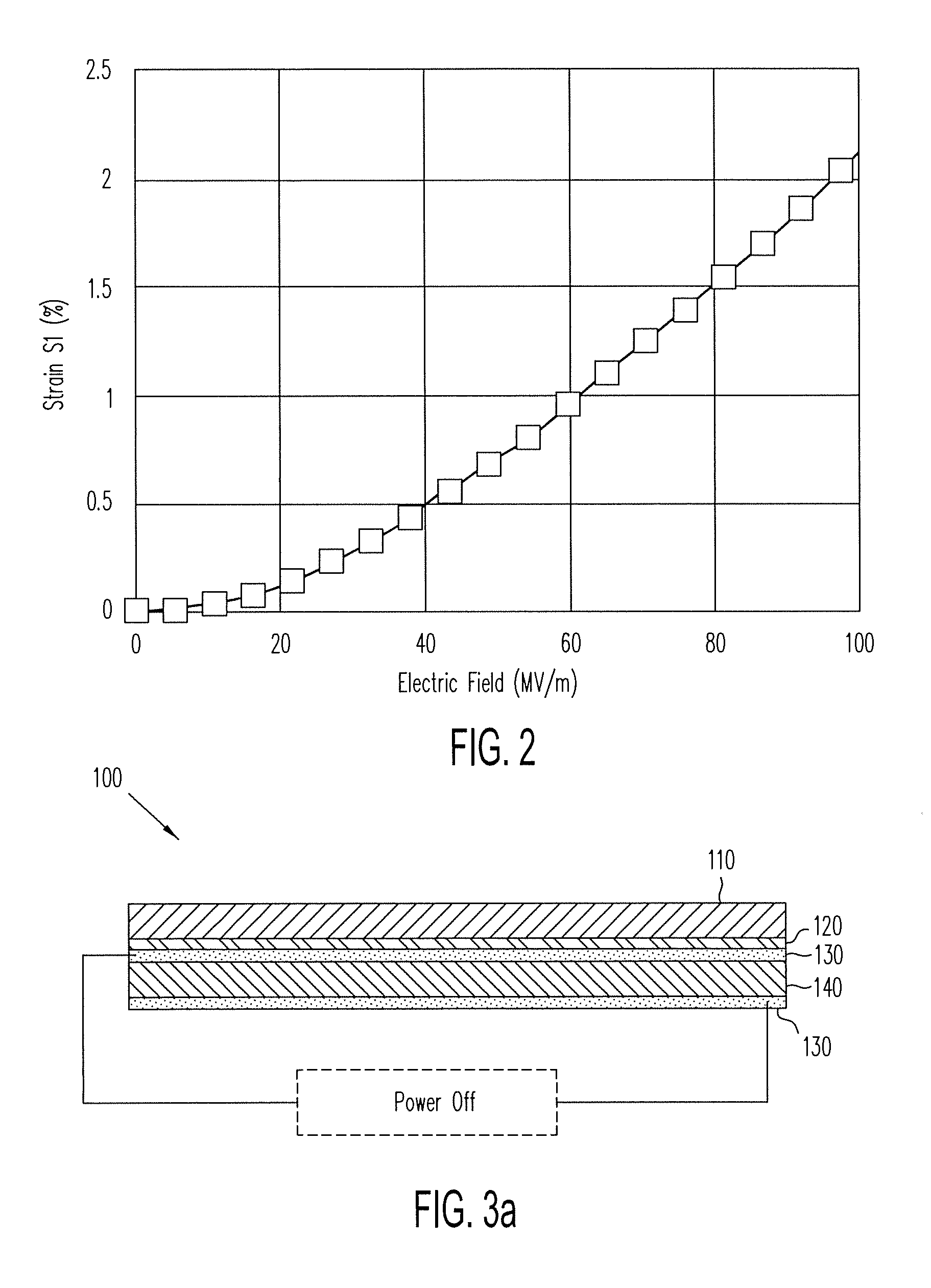
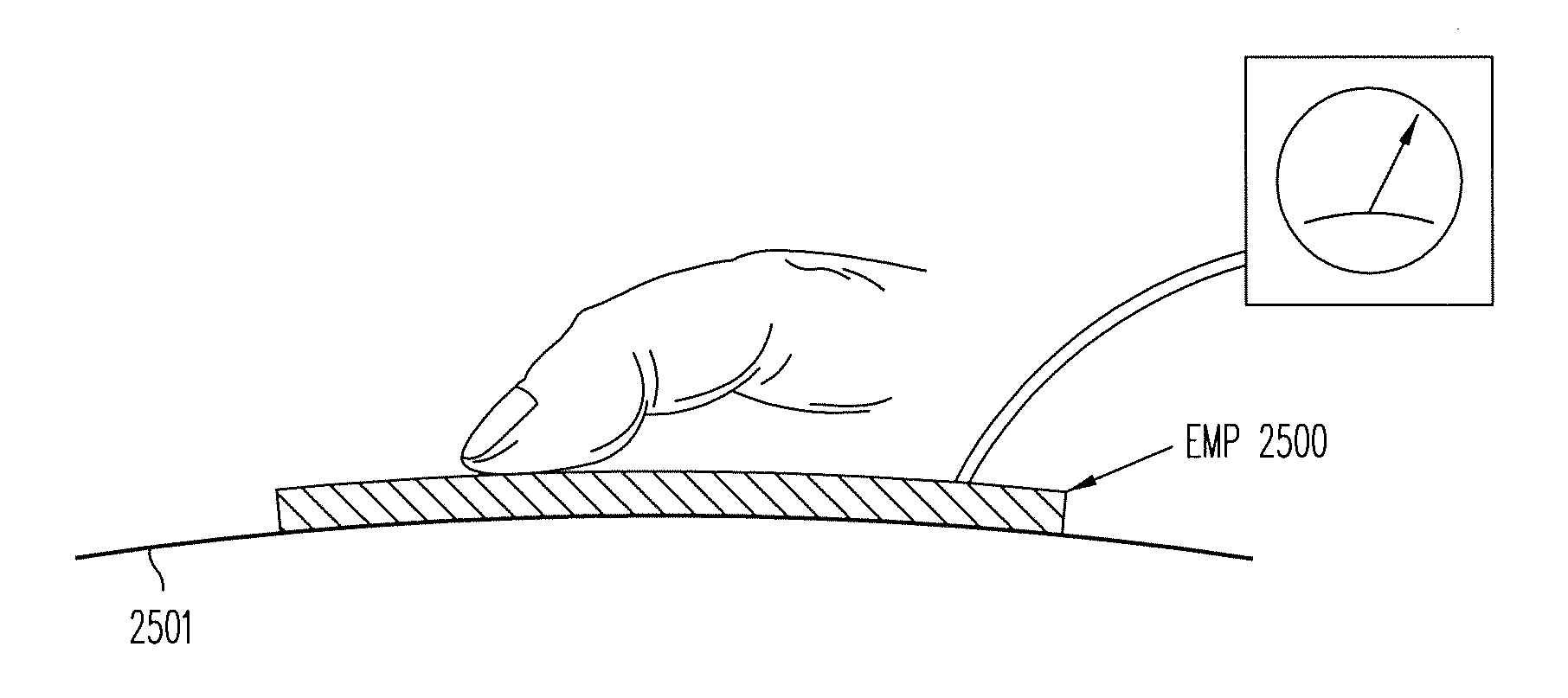
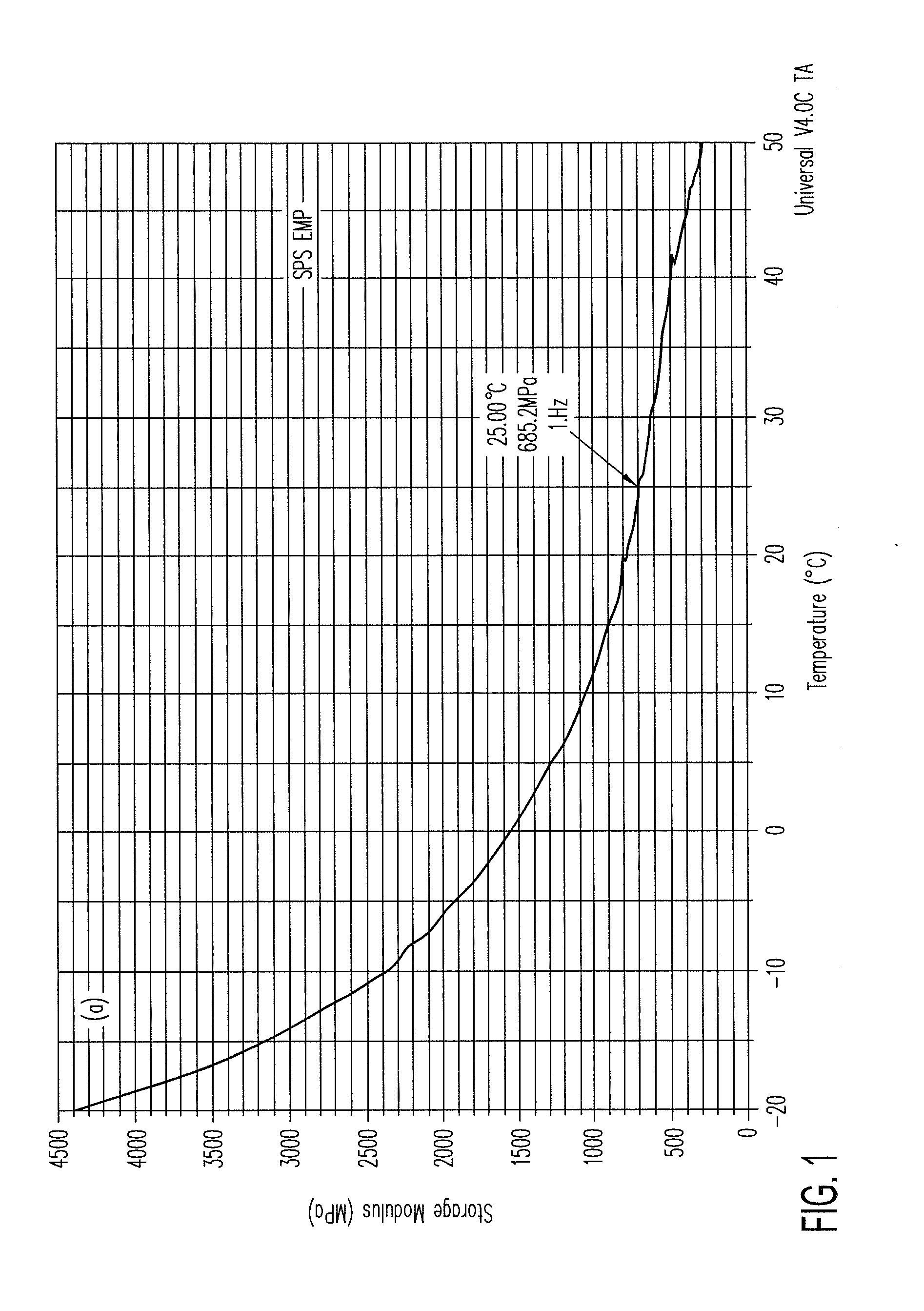
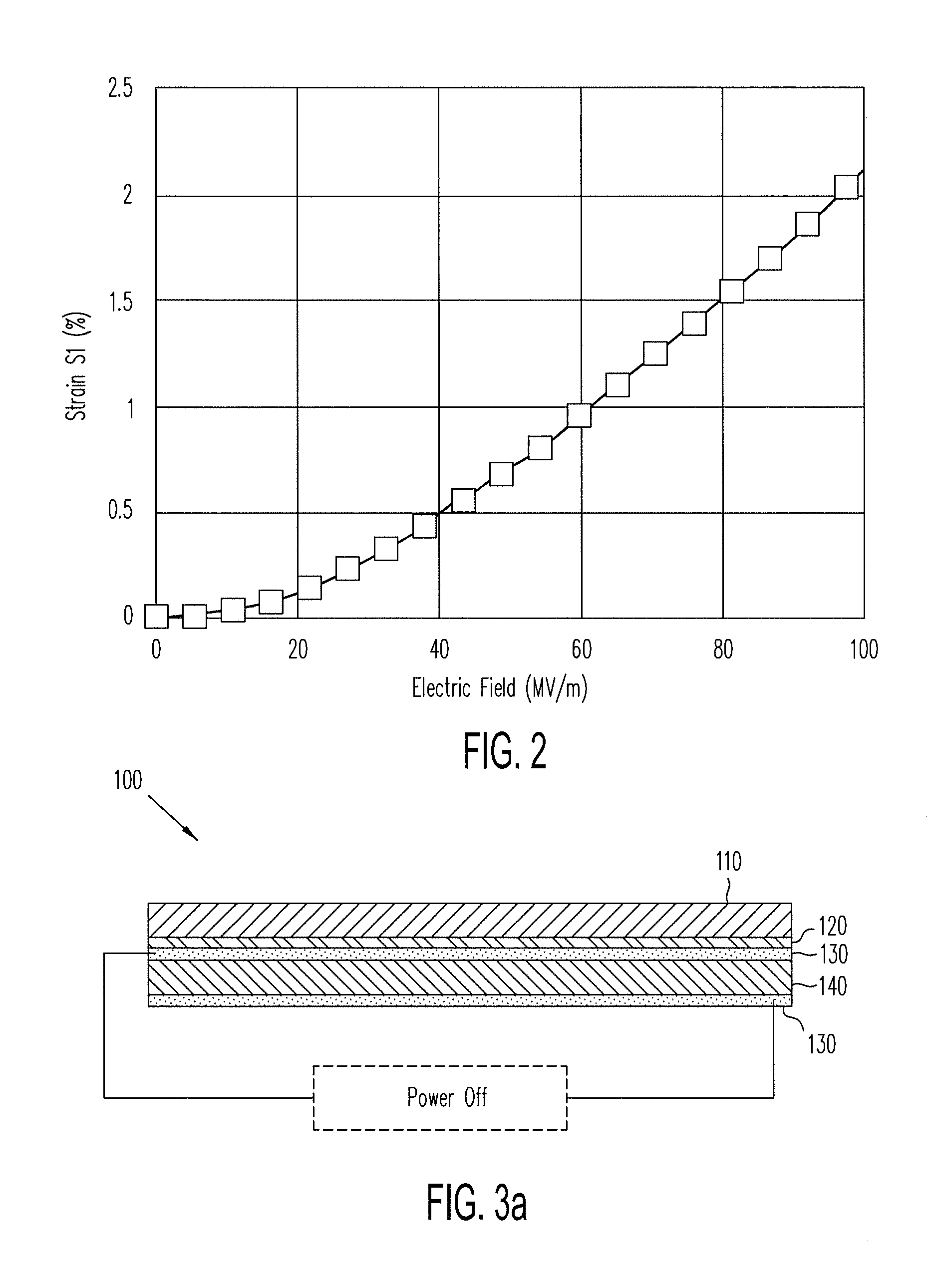
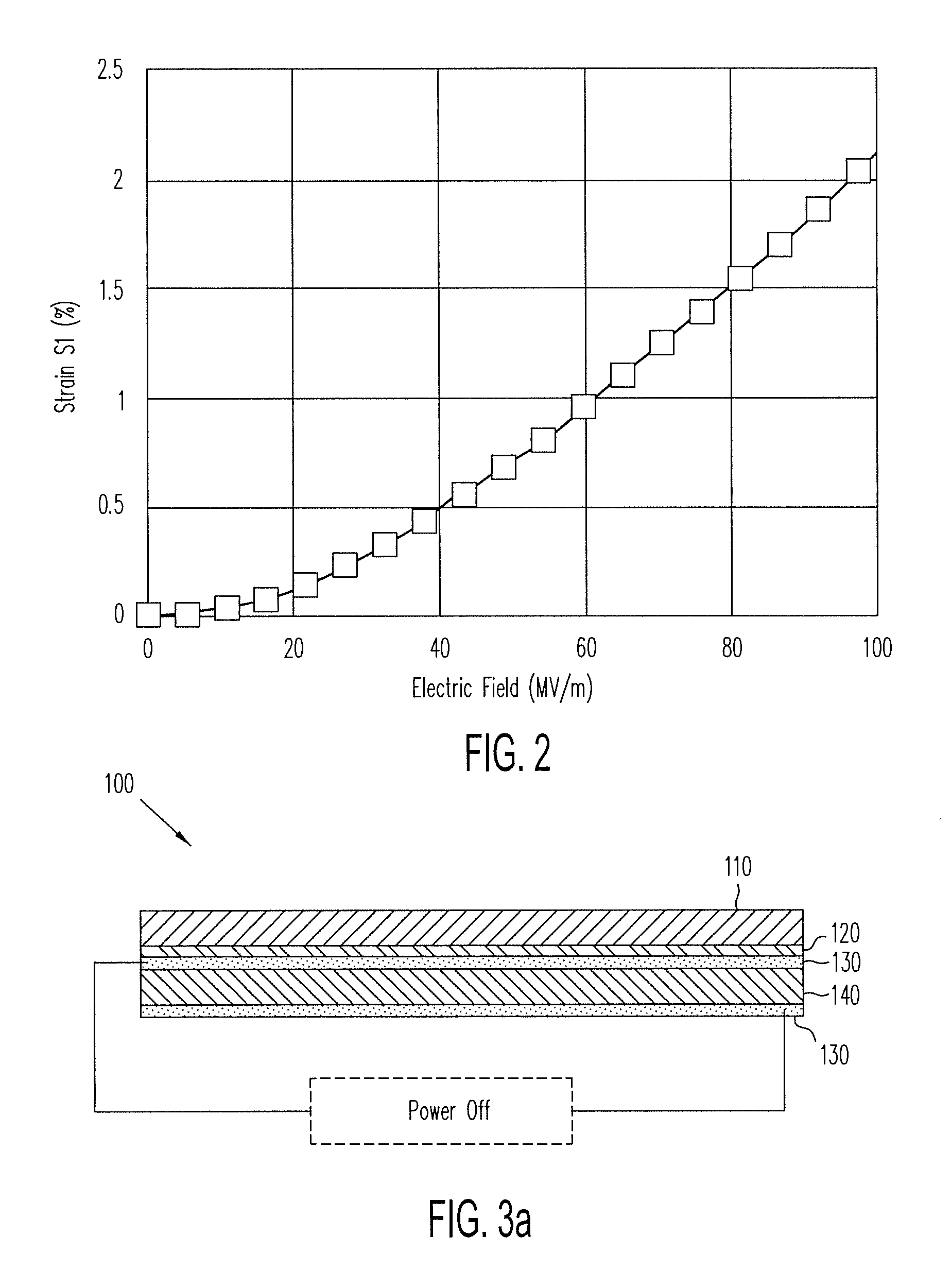
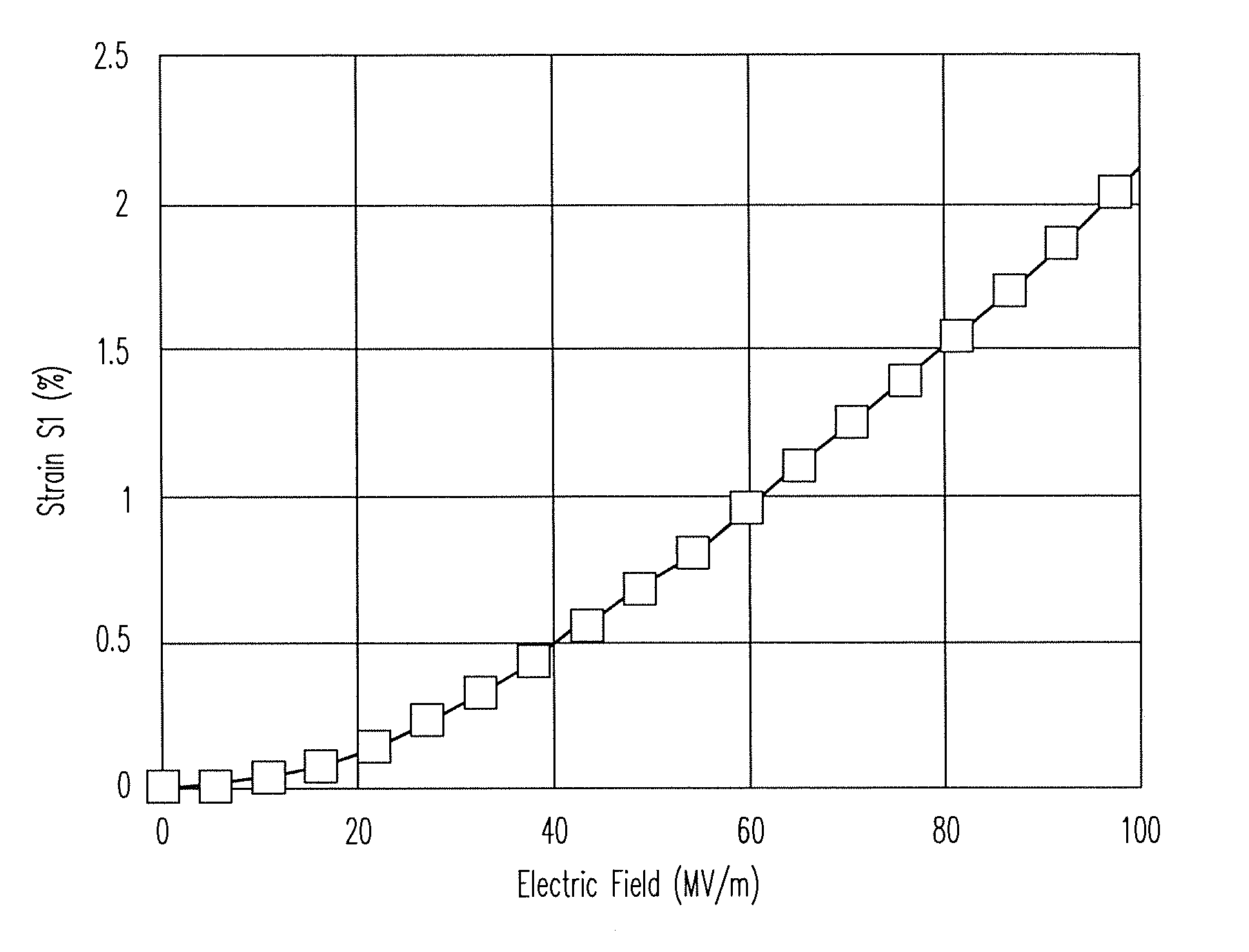
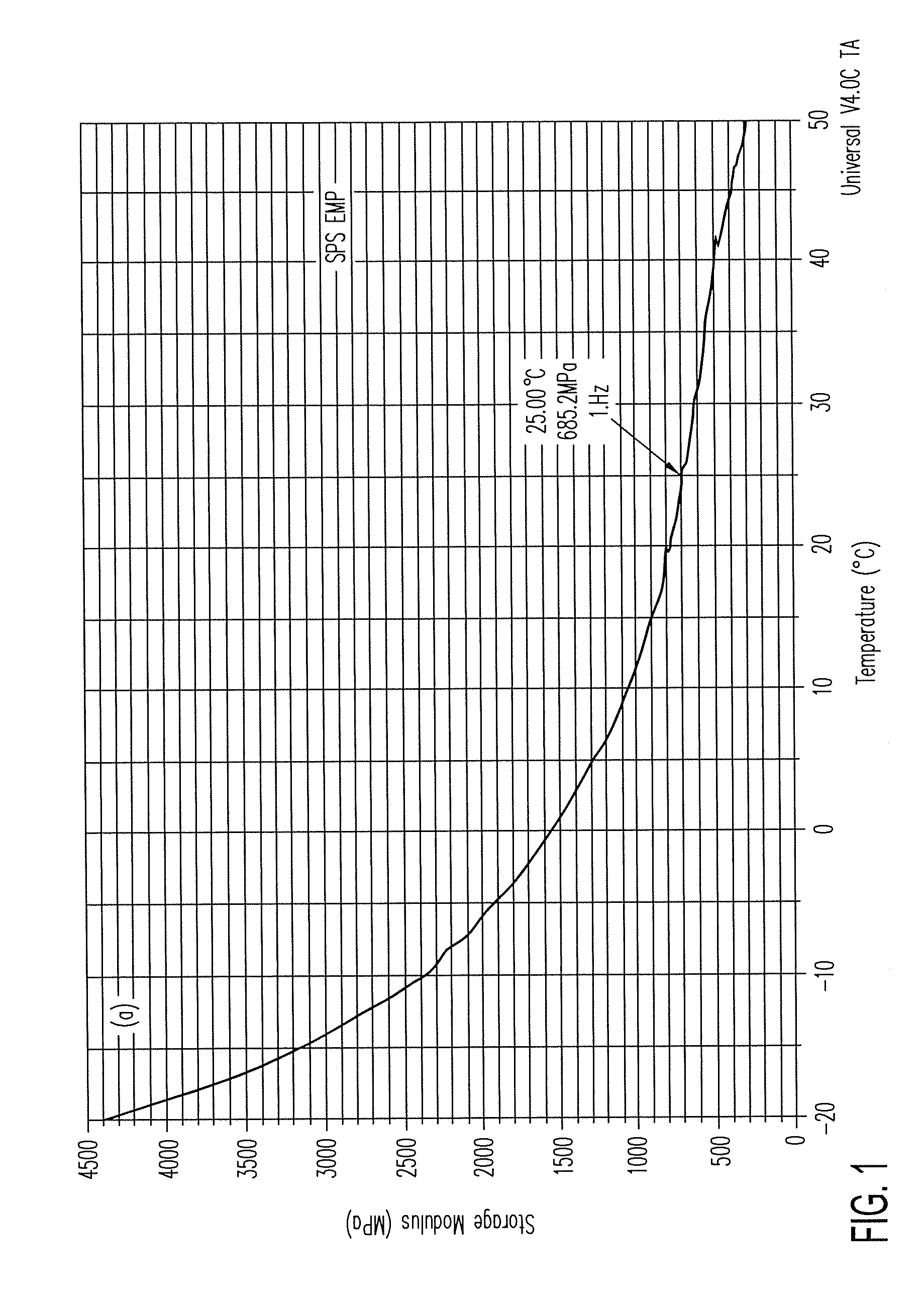
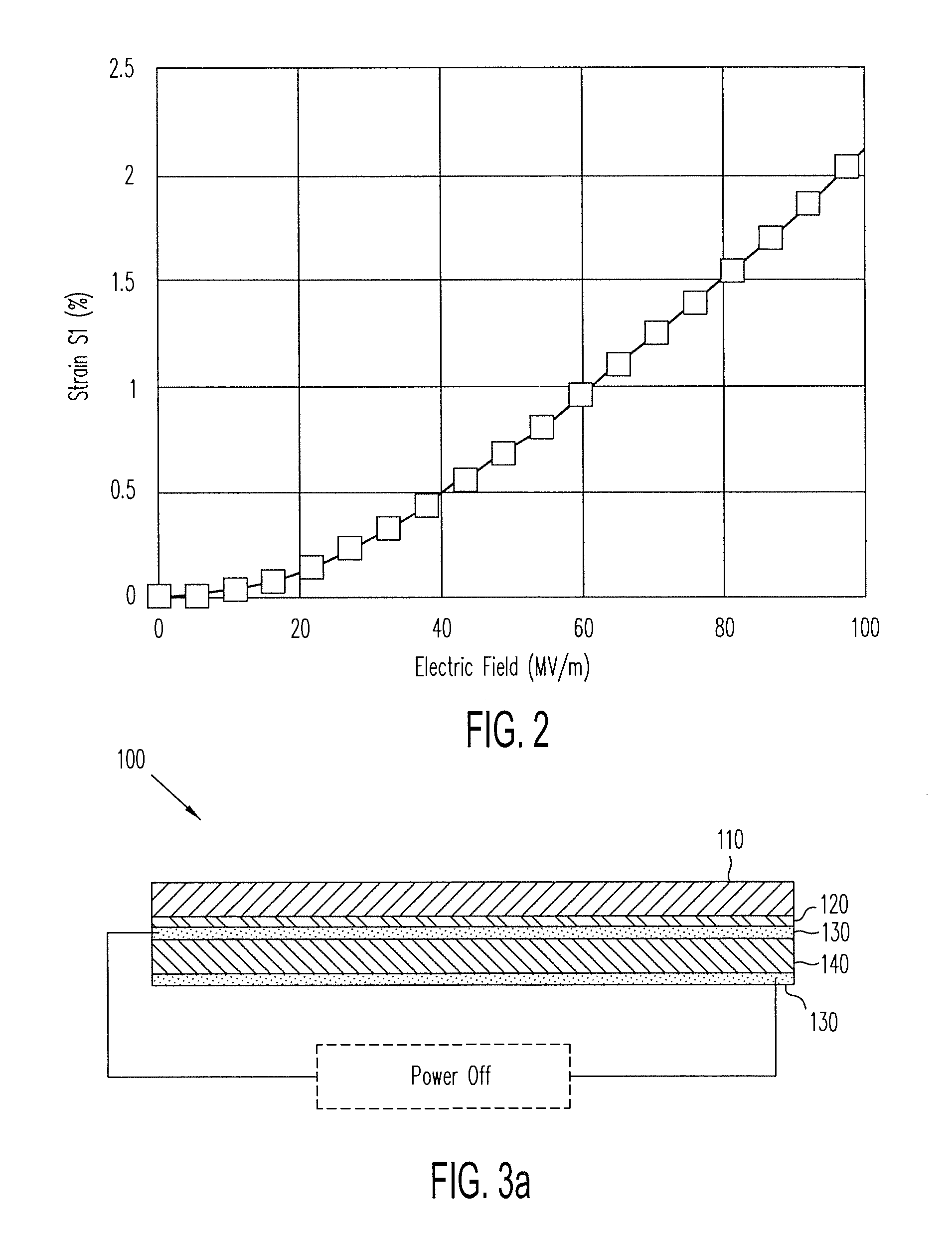
ActiveUS20140139436A1Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureInput/output for user-computer interactionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerDisplay device
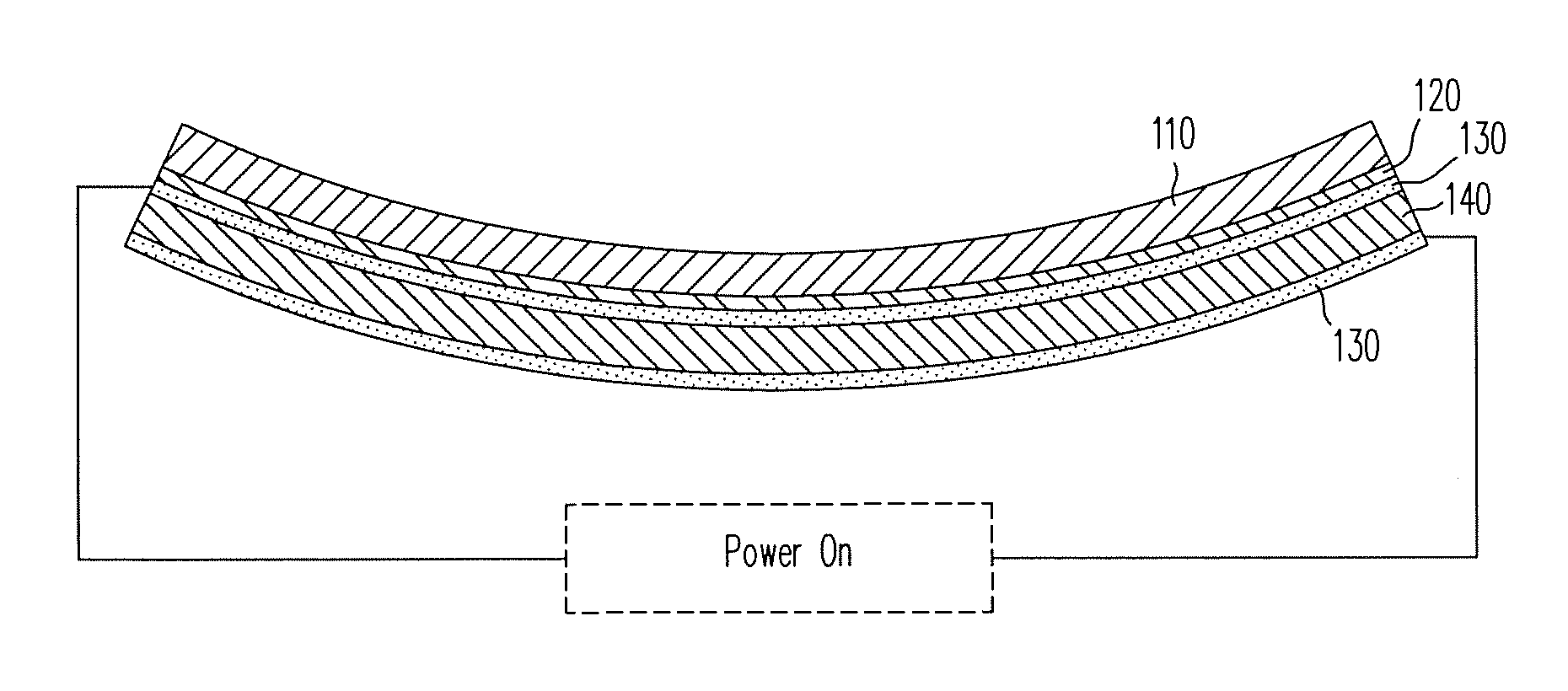
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology, keyboard, braille display, and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
System of Audio Speakers Implemented Using EMP Actuators
ActiveUS20140140551A1Maximize displacementReduce entropyMicrophonesTransducers for sound channels pluralityTransducerEngineering
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Haptic system with localized response
ActiveUS20140139328A1Maximize displacementReduce entropyRepeater circuitsTactile signalling systemsLoudspeakerElectrostrictive polymer
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Generating shares of secret data
ActiveUS20170228547A1Wide rangeIncrease the number ofDigital data protectionCommunication with homomorphic encryptionData setComputer science
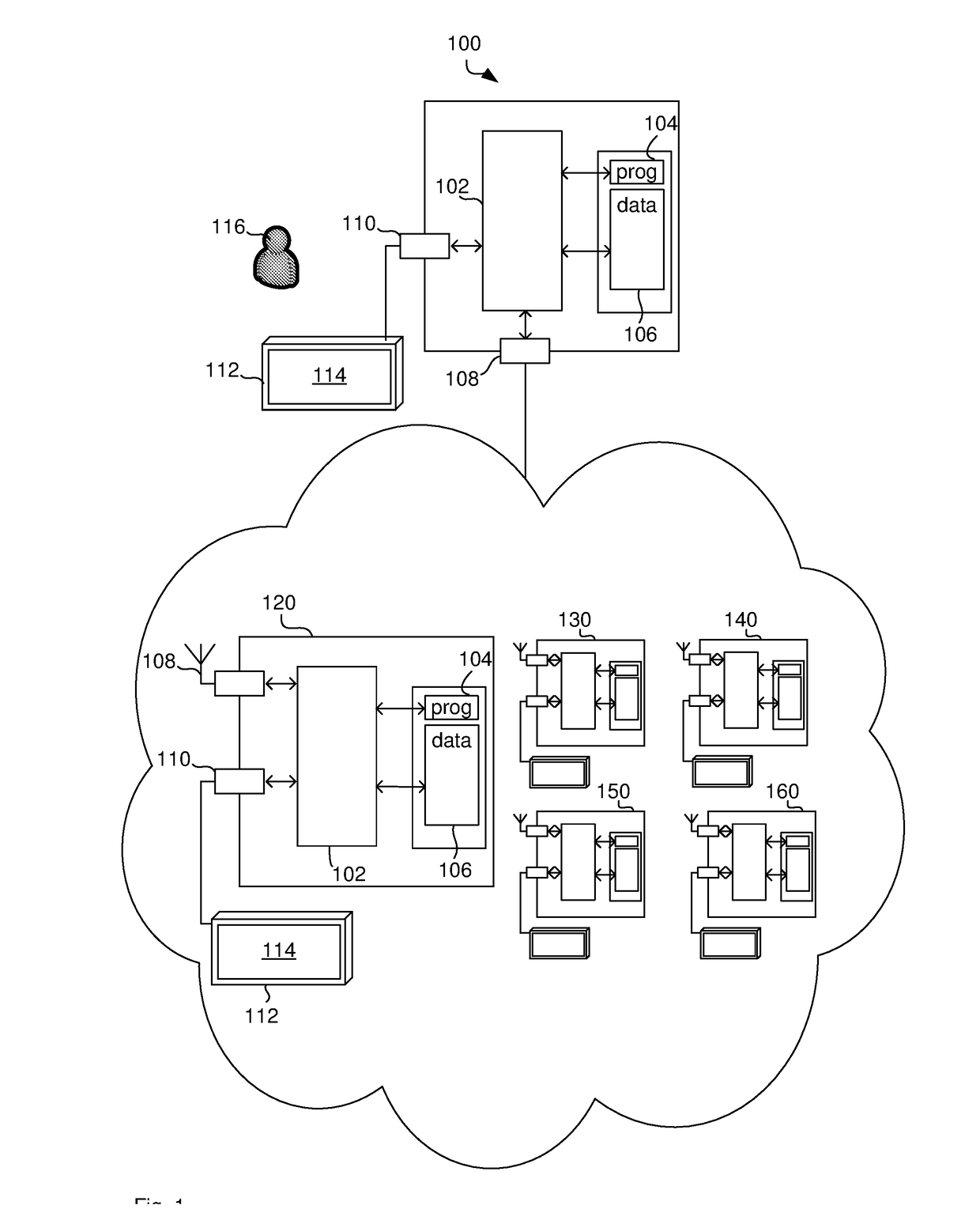
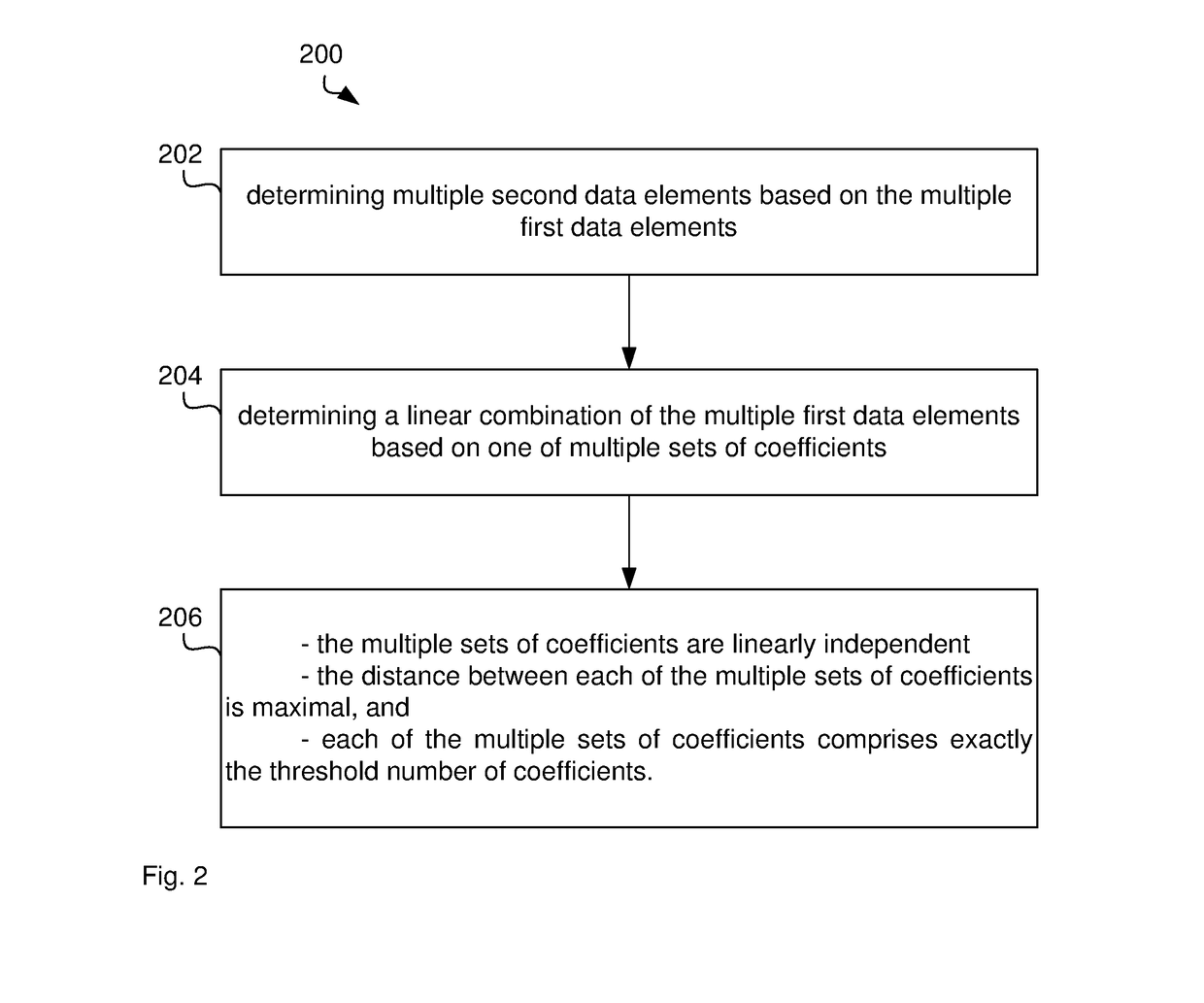
This disclosure relates to generating shares of secret data represented by secret data elements based on a first threshold for the number of shares that allow determining the secret data. The shares are determined based on the secret data, one or more random data elements added to the secret data and coefficients of a systematic maximum distance separable (MDS) code. The MDS code has a number of input data elements that is equal to the first threshold and that is also equal to the number of secret data elements plus the number of the one or more random data elements. The method of determining shares can be used for different data sets and multiple pairs of the shares can be generated to allow performing an operation between the first secret data with the second secret data based on distributed processing of each of the multiple pairs.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
Systems including electromechanical polymer sensors and actuators
ActiveUS20140139329A1Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureRepeater circuitsTactile signalling systemsTransducerEngineering
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
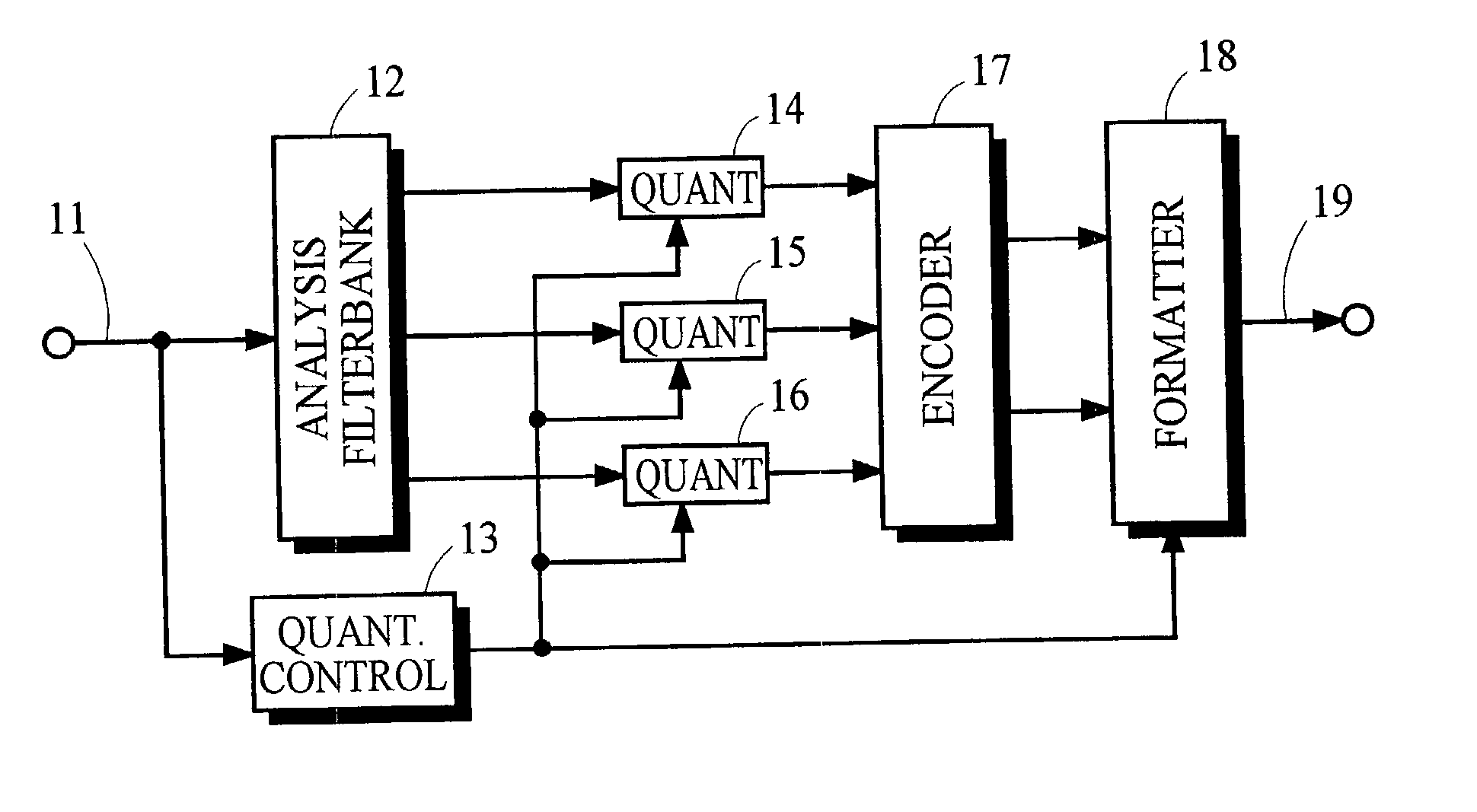
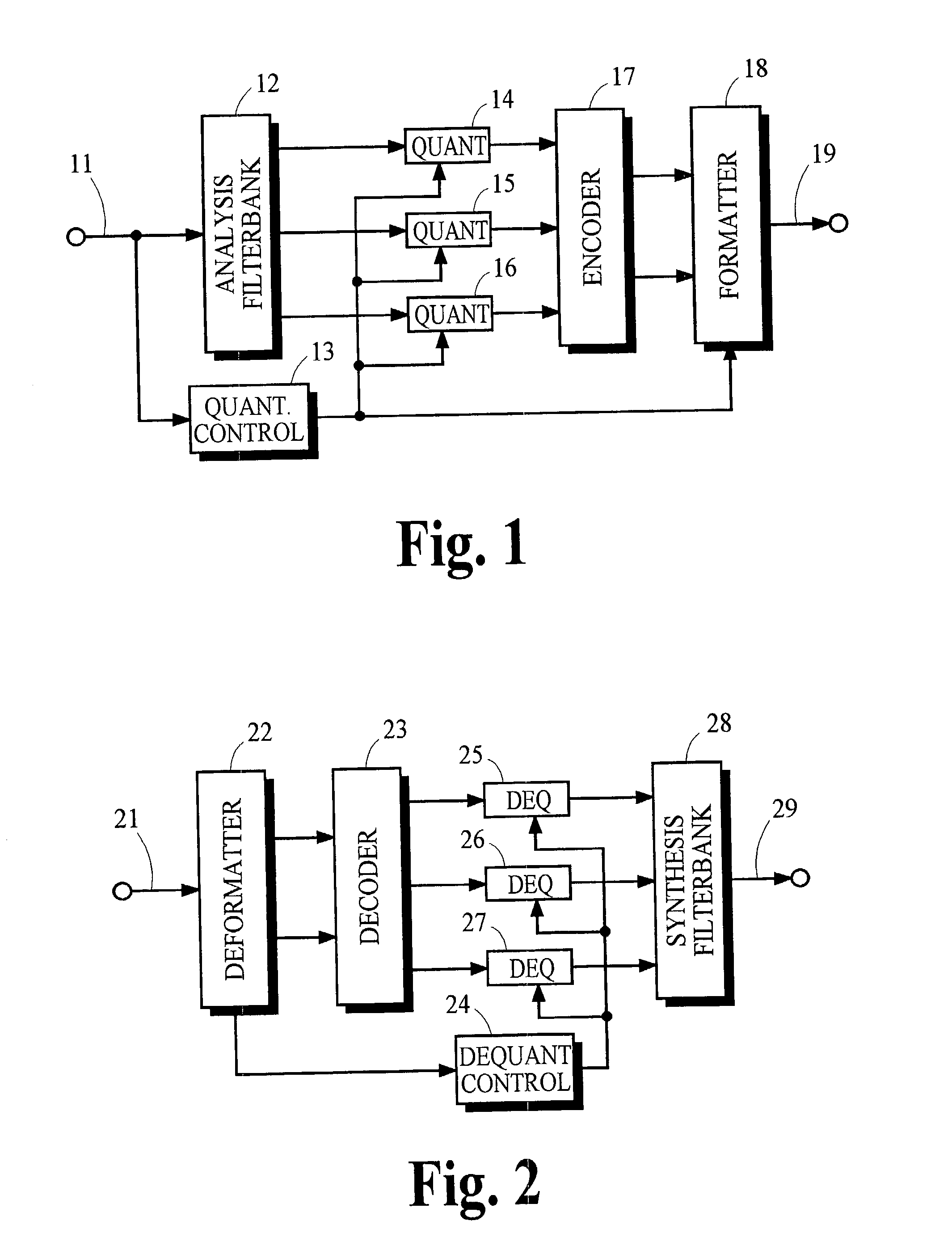
Signal processing and tiered signal encoding
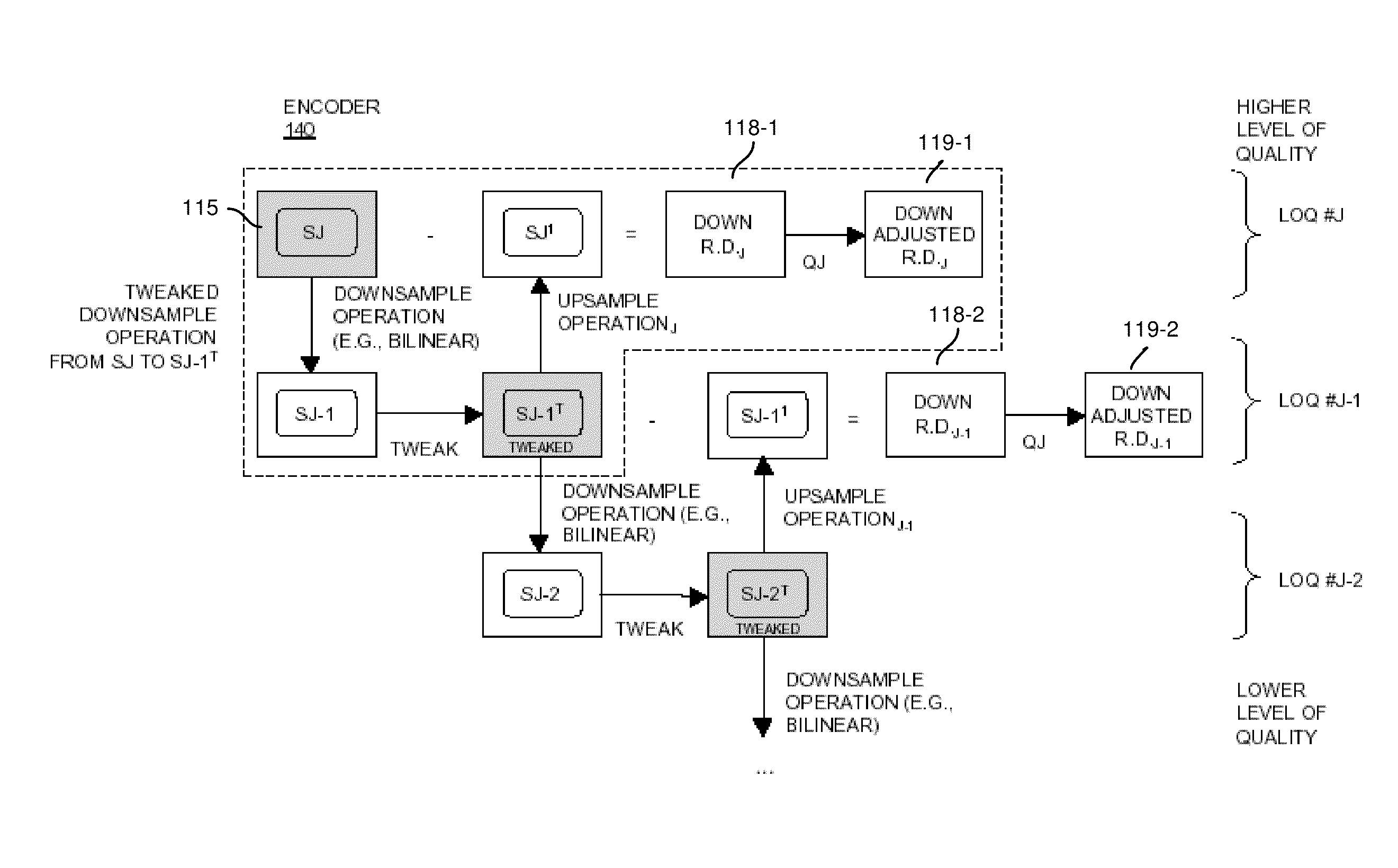
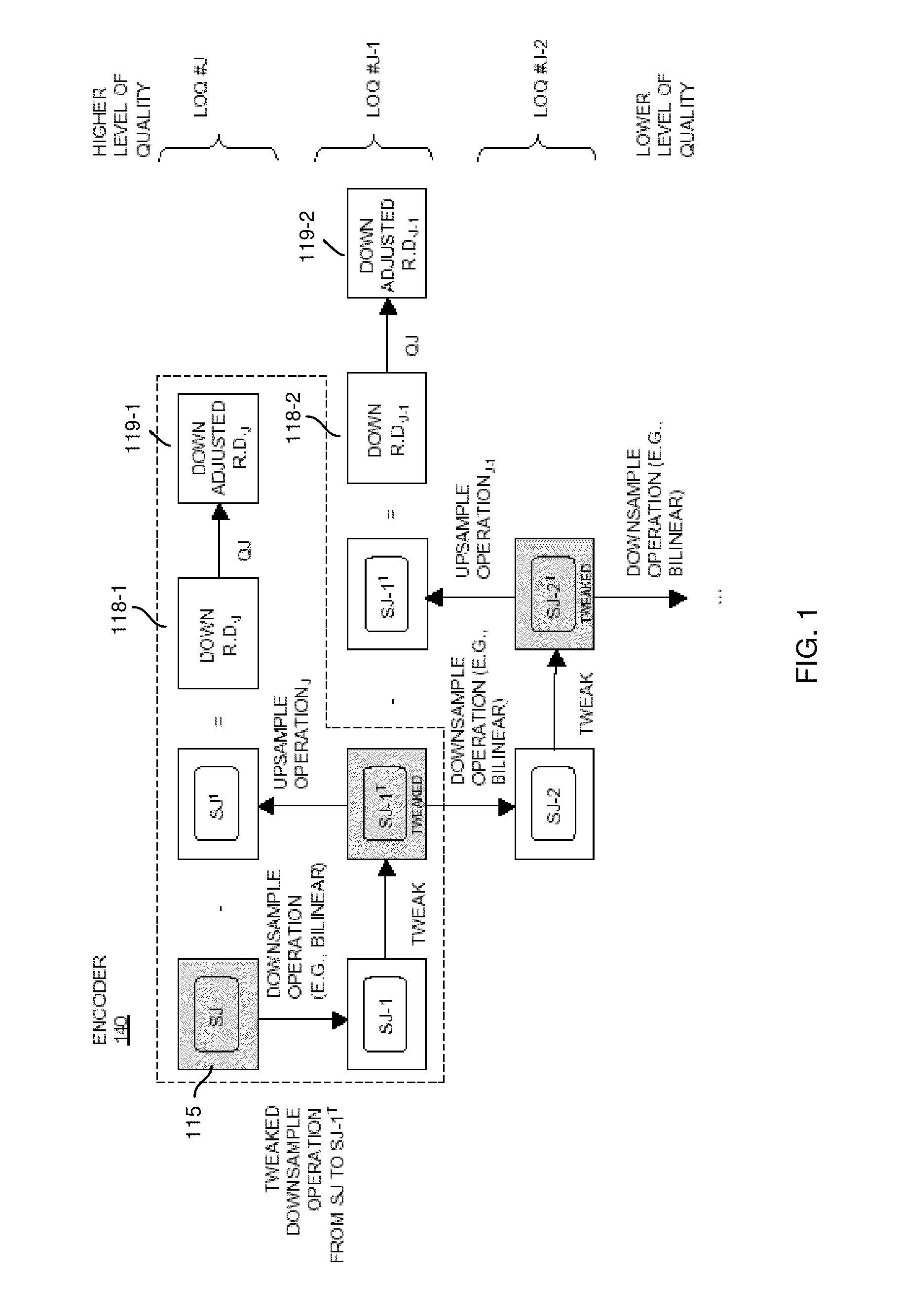
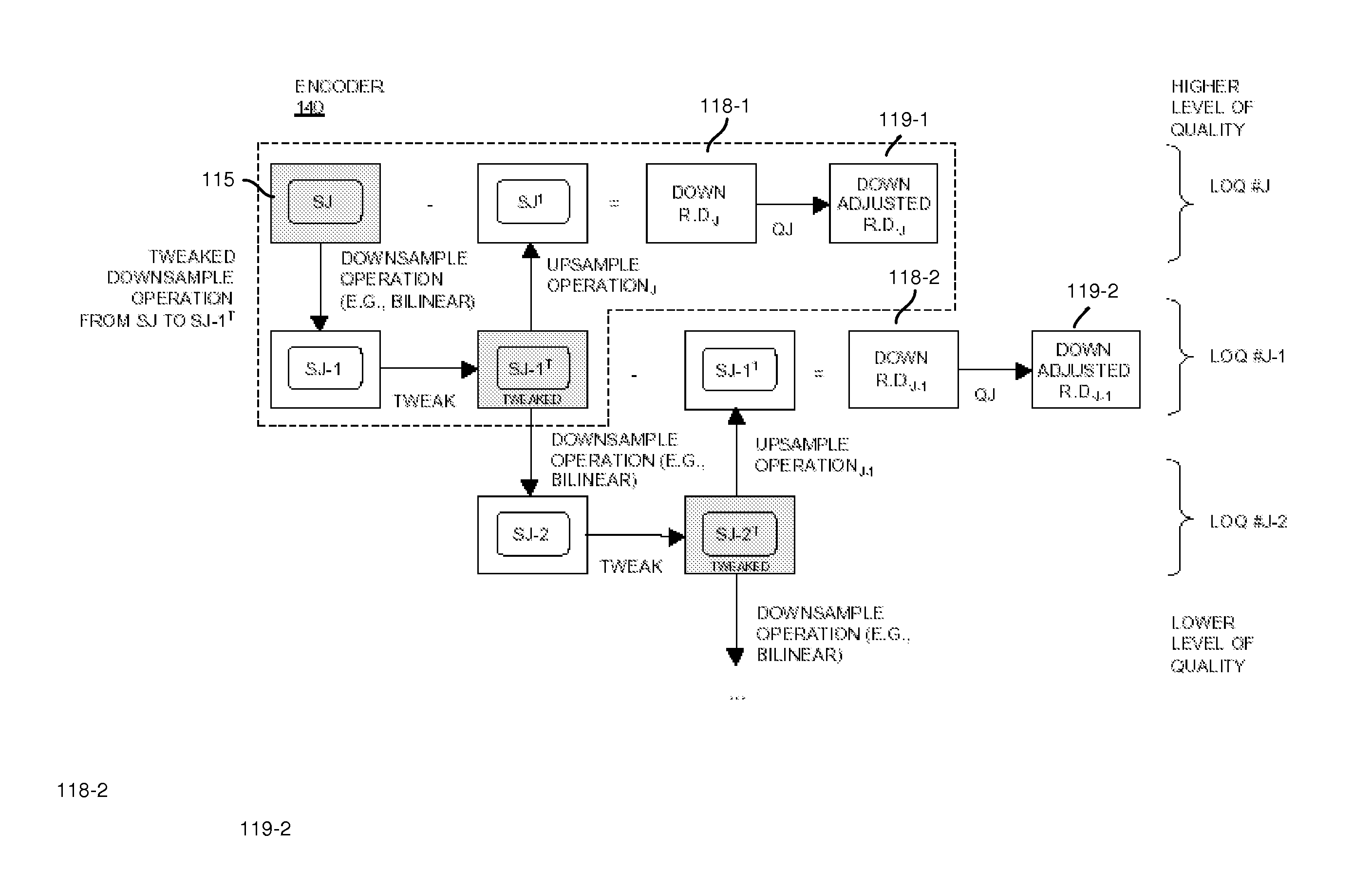
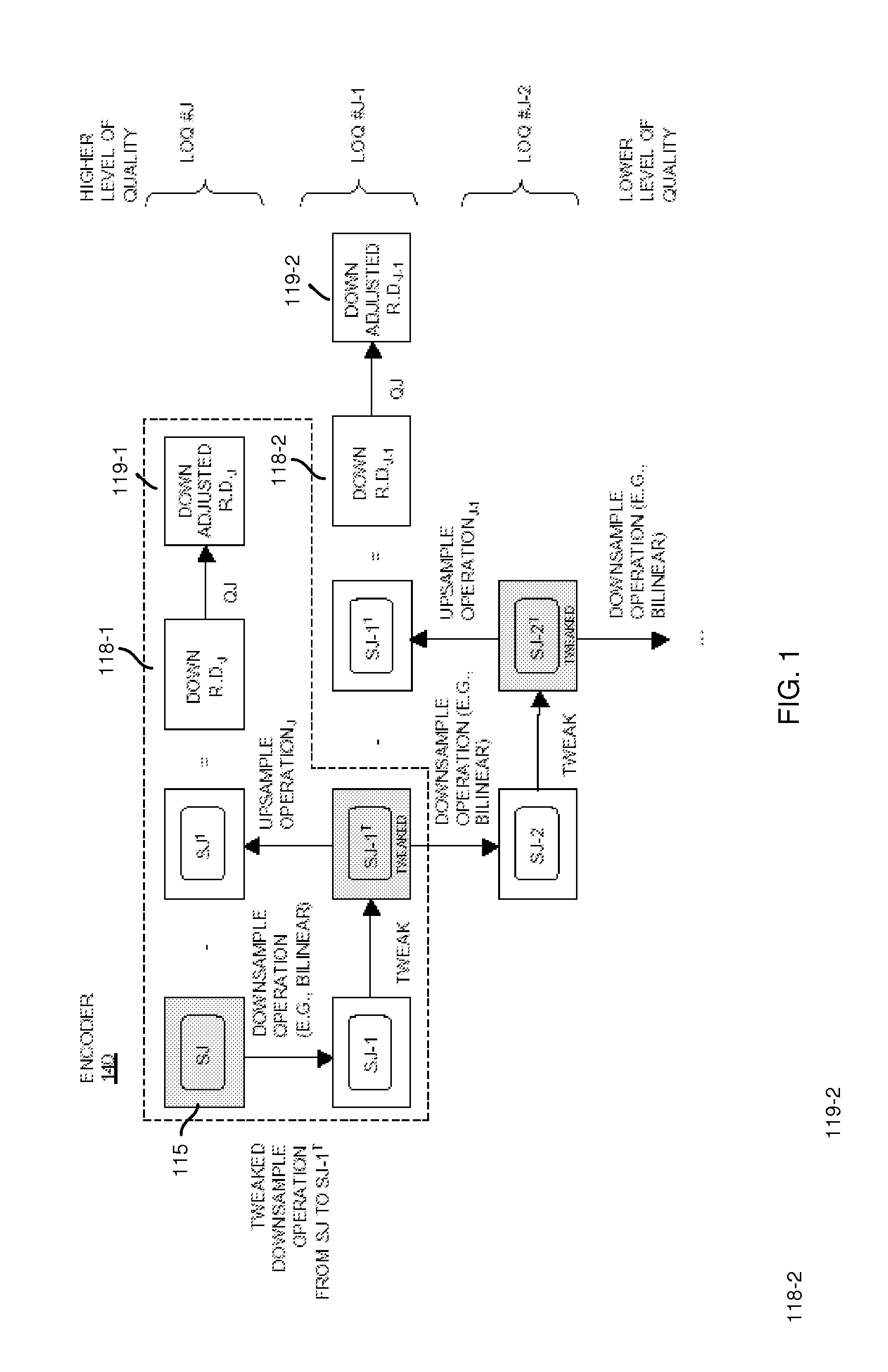
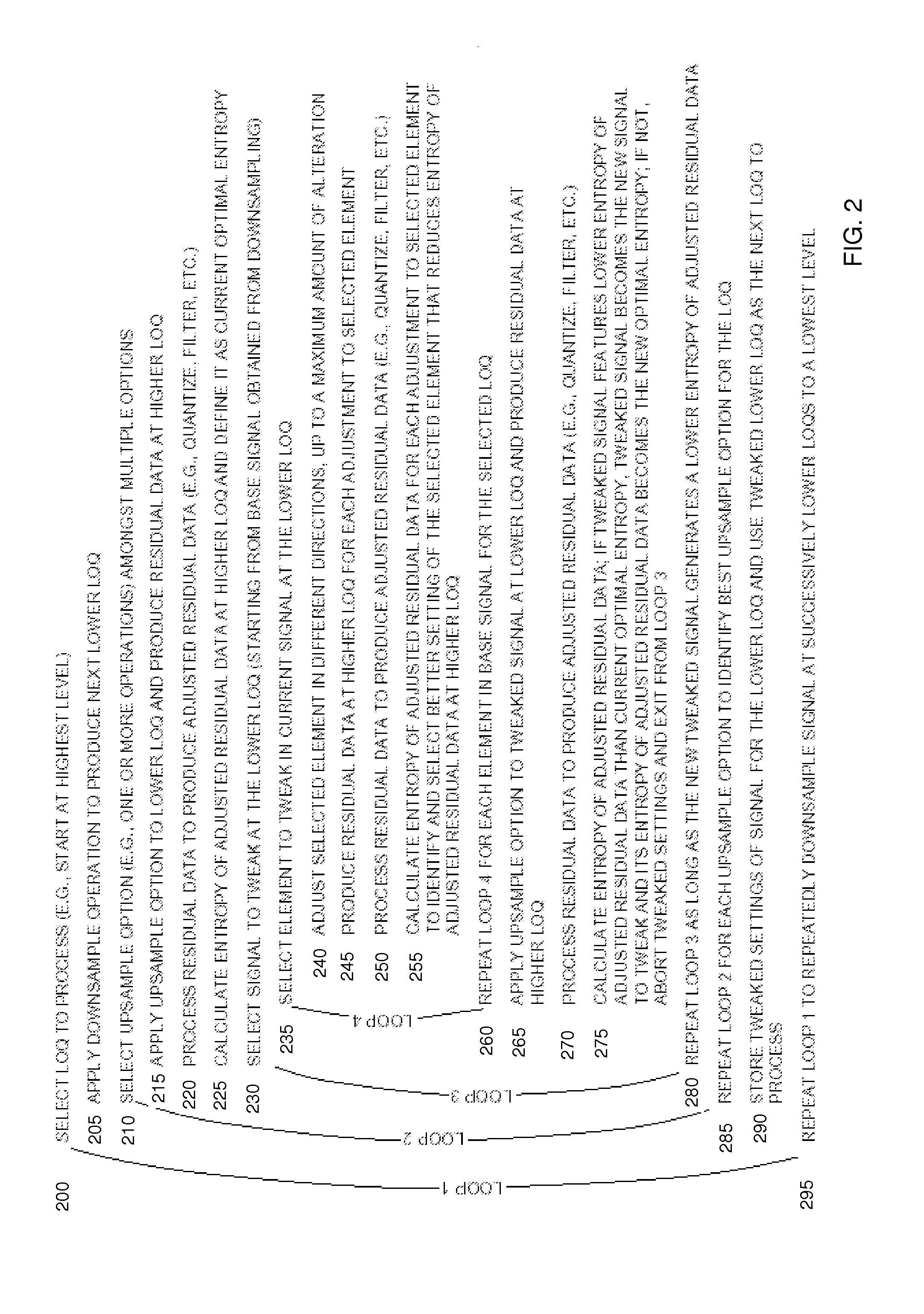
ActiveUS8711943B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce entropyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionQuality levelSignal encoding
An encoder receives a signal. The encoder utilizes one or more downsample operations to produce downsampled renditions of the signal at successively lower levels of quality in the hierarchy. In a reverse direction, the encoder applies the one or more upsample operations to a downsampled rendition of the signal at a first level of quality to produce an upsampled rendition of the signal at a second level of quality in the hierarchy. The second level of quality is higher than the first level of quality. The one or more upsample operations and one or more downsample operations can be asymmetrical with respect to each other. That is, the function applied during downsampling can differ from the function applied when upsampling. The encoder produces residual data indicating a difference between the downsampled rendition of the signal at the second level of quality and the upsampled rendition of the signal at the second level of quality.
Owner:V NOVA INT LTD
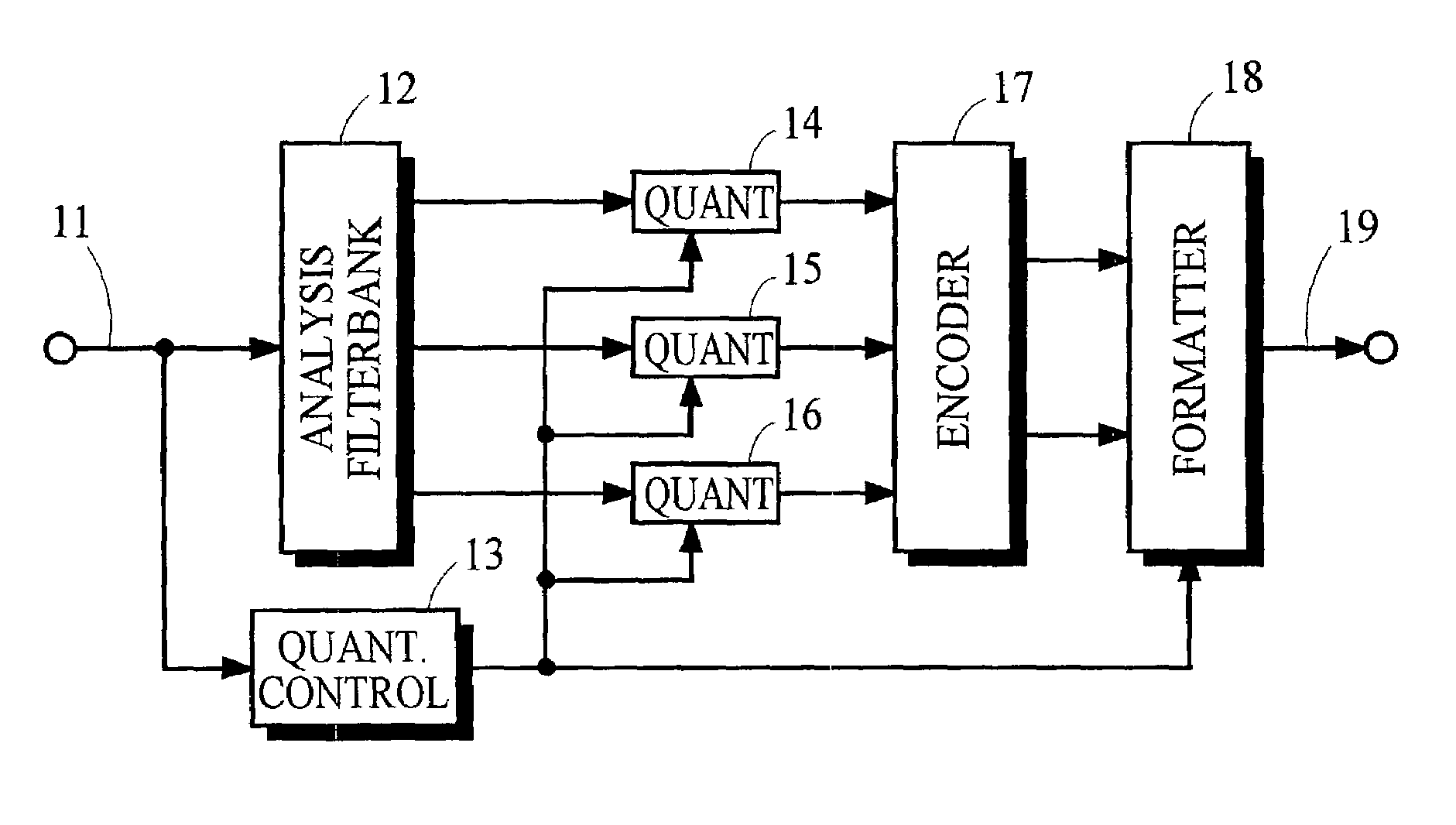
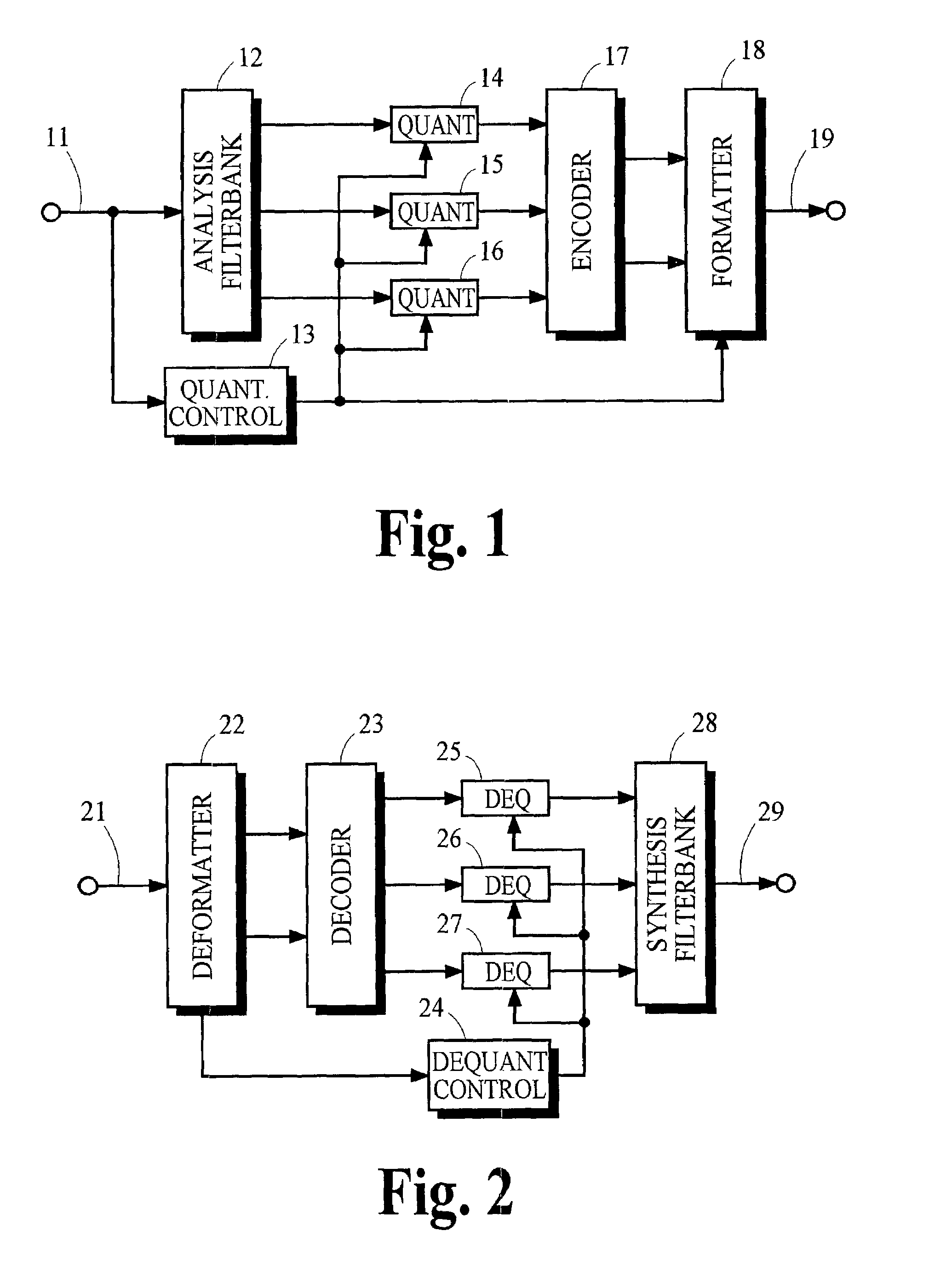
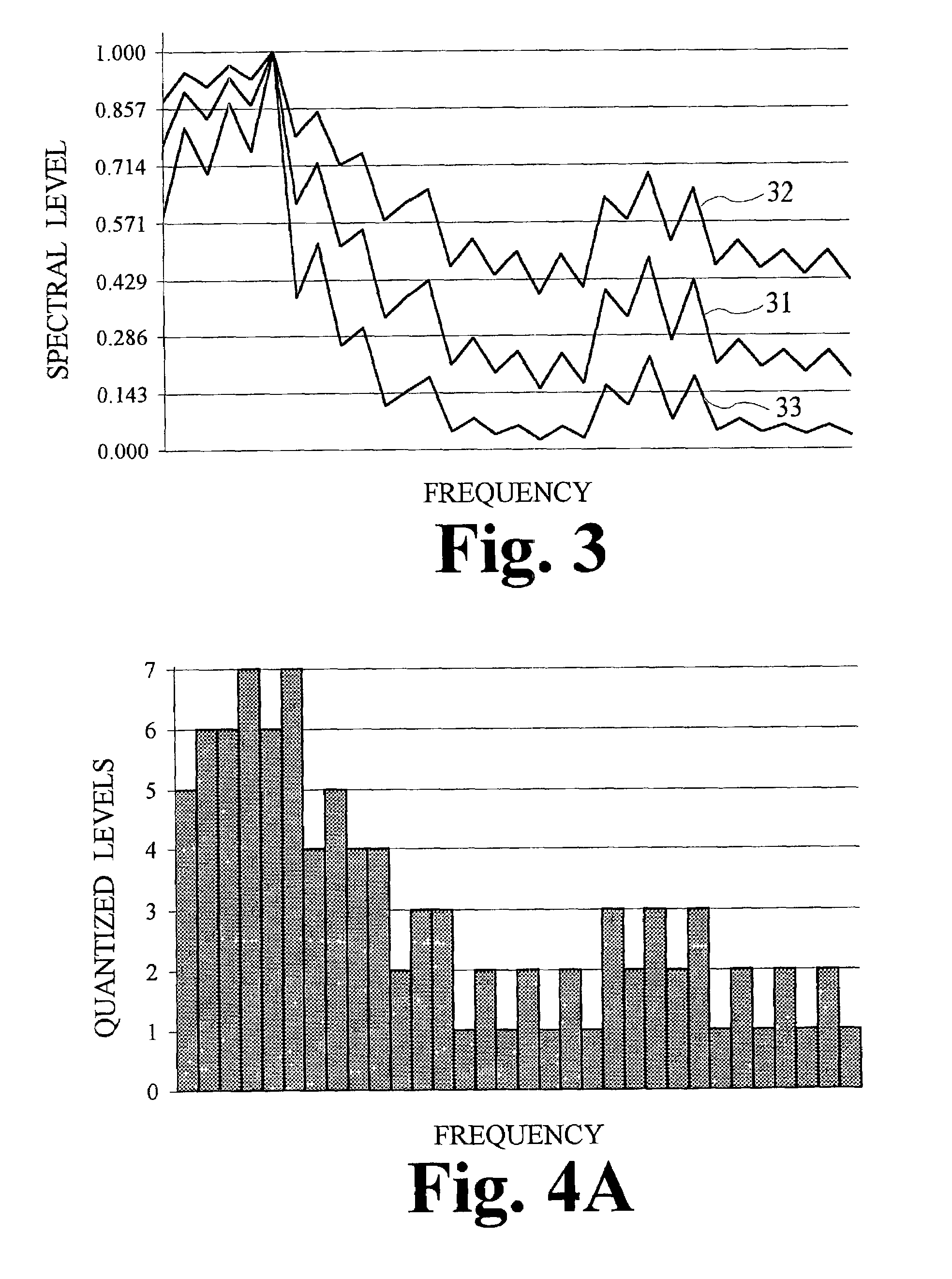
Low bit-rate audio coding systems and methods that use expanding quantizers with arithmetic coding
InactiveUS7043423B2Overcome disadvantagesReduce entropySpeech analysisCode conversionArithmetic codingComputer science
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Localized multimodal electromechanical polymer transducers
ActiveUS20140035735A1Maximize displacementReduce entropyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesRepeater circuitsLoudspeakerElectrostrictive polymer
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS
Signal processing and tiered signal encoding
ActiveUS20130294523A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce entropyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionQuality levelComputer science
An encoder receives a signal. The encoder utilizes one or more downsample operations to produce downsampled renditions of the signal at successively lower levels of quality in the hierarchy. In a reverse direction, the encoder applies the one or more upsample operations to a downsampled rendition of the signal at a first level of quality to produce an upsampled rendition of the signal at a second level of quality in the hierarchy. The second level of quality is higher than the first level of quality. The one or more upsample operations and one or more downsample operations can be asymmetrical with respect to each other. That is, the function applied during downsampling can differ from the function applied when upsampling. The encoder produces residual data indicating a difference between the downsampled rendition of the signal at the second level of quality and the upsampled rendition of the signal at the second level of quality.
Owner:V NOVA INT LTD
Hardware module-based authentication in intra-vehicle networks
ActiveUS20190104149A1Minimal latencyImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesElectronic control unitVehicle networks
A secure hardware-based module or Security Electronic Control Unit (SECU) for a Controller Area Network (CAN) prevents an attacker from sending malicious messages through the CAN bus to take over control of a vehicle. The SECU shares a unique key and counter with each ECU on the CAN bus. When a legitimate ECU sends a message, it first compresses the message and then generates a MAC of the counter and a secret key. The counter is increased by one for each transmitted message. The ECU then fits the compressed message and the MAC into one CAN frame and sends it onto the CAN bus. The SECU performs the message verification on behalf of the intended receiver(s) of the message. If the verification passes, the receiver(s) simply decompress the message and use it as a normal CAN message. If the verification fails, the SECU will corrupt the CAN frame before it is fully received by the intended receiver(s). The corrupted CAN frame will be ignored by the intended receiver(s) as if it was never received. Therefore, a malicious message generated by an attacker will inflict no damage on the system.
Owner:GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
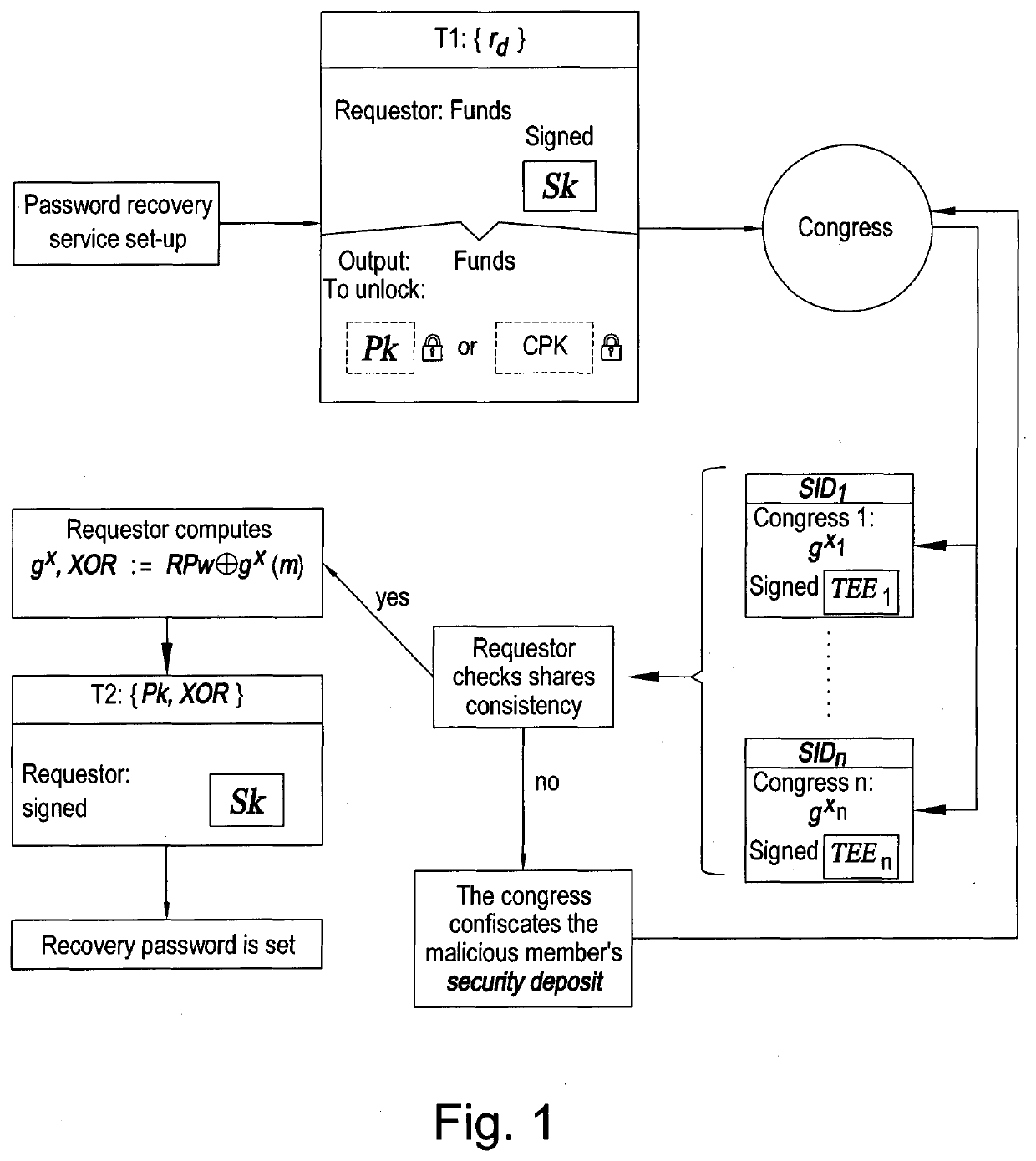
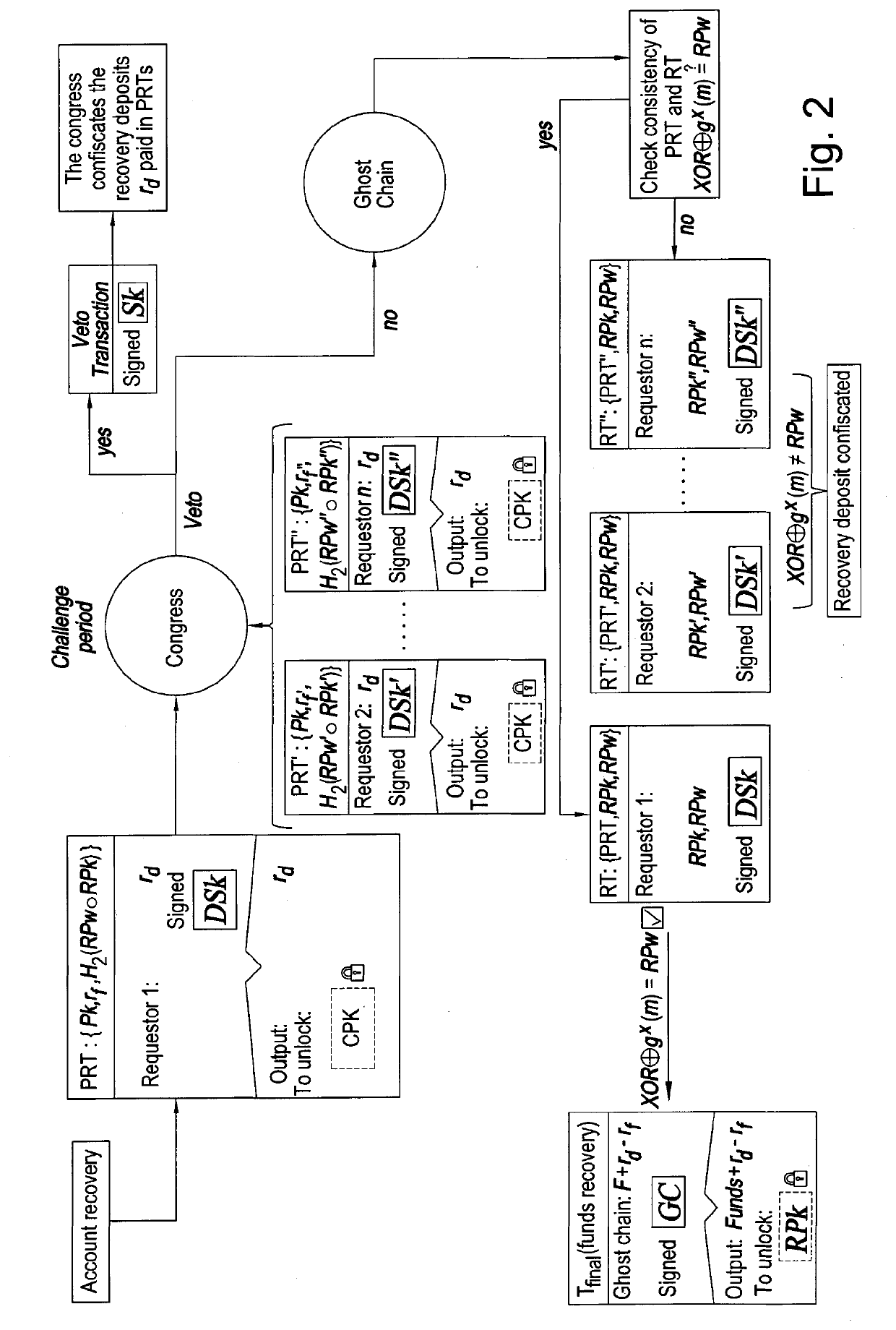
Computer-implemented system and method providing a decentralised protocol for the recovery of cryptographic assets
ActiveUS20200127835A1Improve securityAvoid problemsKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPasswordEngineering
A computer-implemented method is described for enabling recovery of one or more digital assets held on a blockchain by a user under a public key Pk after a corresponding private key Sk for accessing the one or more digital assets is lost. The computer implemented method comprises setting access for the one or more digital assets held on the blockchain under the public key Pk and accessible using the corresponding private key Sk of the user such that the one or more digital assets are also accessible using a private key x shared by a congress on the blockchain network, the congress comprising a group of users on the blockchain network, each member of the congress having a private key share xi, the private key share xi to be used in a threshold signature scheme in which at least a threshold of private key shares must be used to generate a valid signature through the combination of partial signatures of the congress to access the one or more digital assets on behalf of the user. If the private key Sk is lost then the congress can be notified to access the one or more digital assets on behalf of the user, the user proving their identity to the congress by providing a recovery password.
Owner:NCHAIN LICENSING AG
Haptic system with localized response
ActiveUS9164586B2Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureInput/output for user-computer interactionTactile signalling systemsTransducerEngineering
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Low bit-rate audio coding systems and methods that use expanding quantizers with arithmetic coding
InactiveUS20040015349A1Overcome disadvantagesReduce entropySpeech analysisCode conversionArithmetic codingComputer science
The perceived quality of an audio signals obtained from very low bit-rate audio coding system is improved by using expanding quantizers and arithmetic coding in a transmitter and using complementary compression and arithmetic decoding in a receiver. An expanding quantizer is used to control the number of signal components that are quantized to zero and arithmetic coding is used to efficiently code the quantized-to-zero coefficients. This allows a wider bandwidth and more accurately quantized baseband signal to be conveyed to the receiver, which regenerates an output signal by synthesizing the missing components.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Adaptive lossless data compression method for compression of color image data
InactiveUS20090226084A1Reduce entropyIncrease the compression ratioCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionColor image
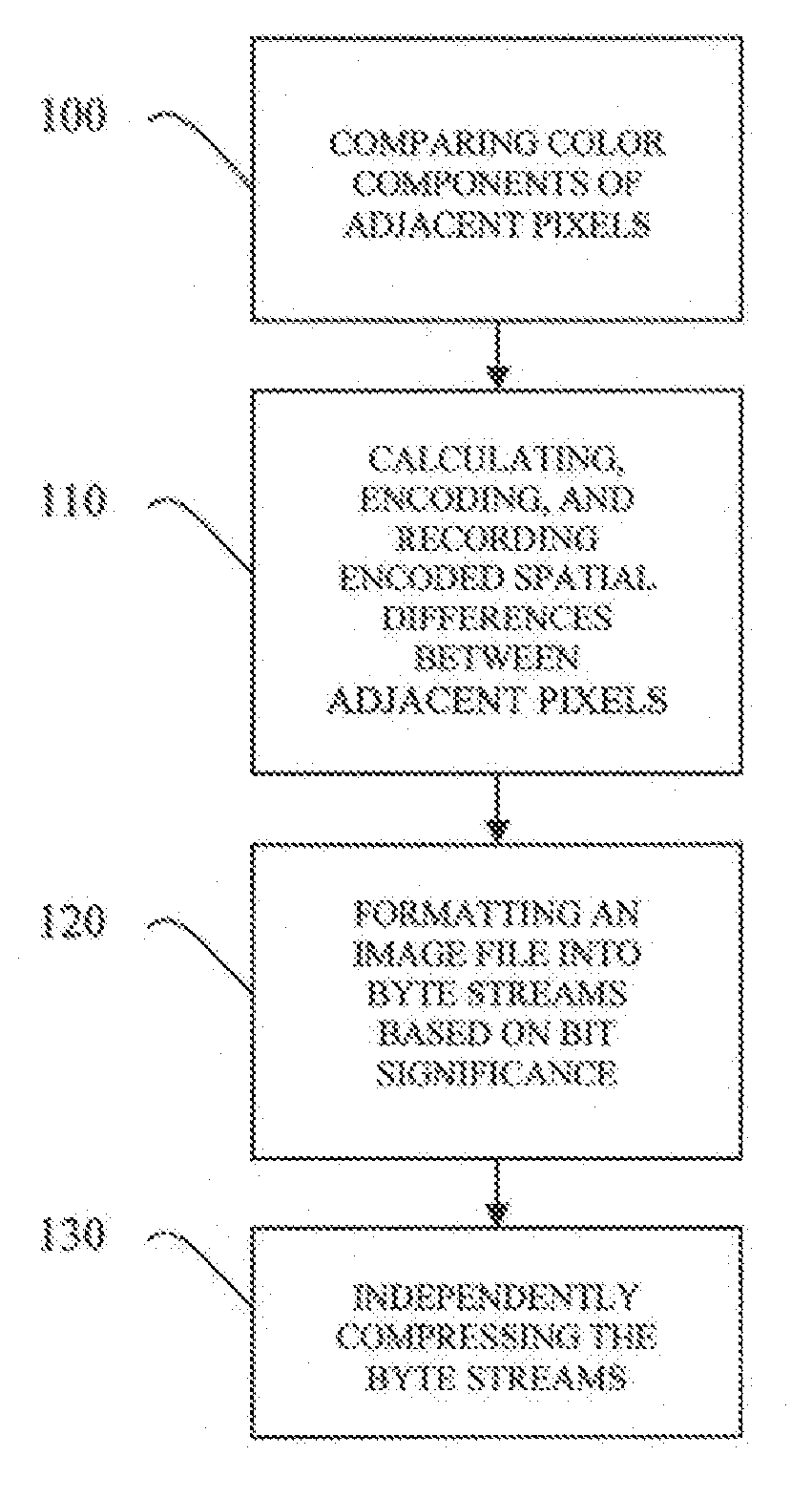
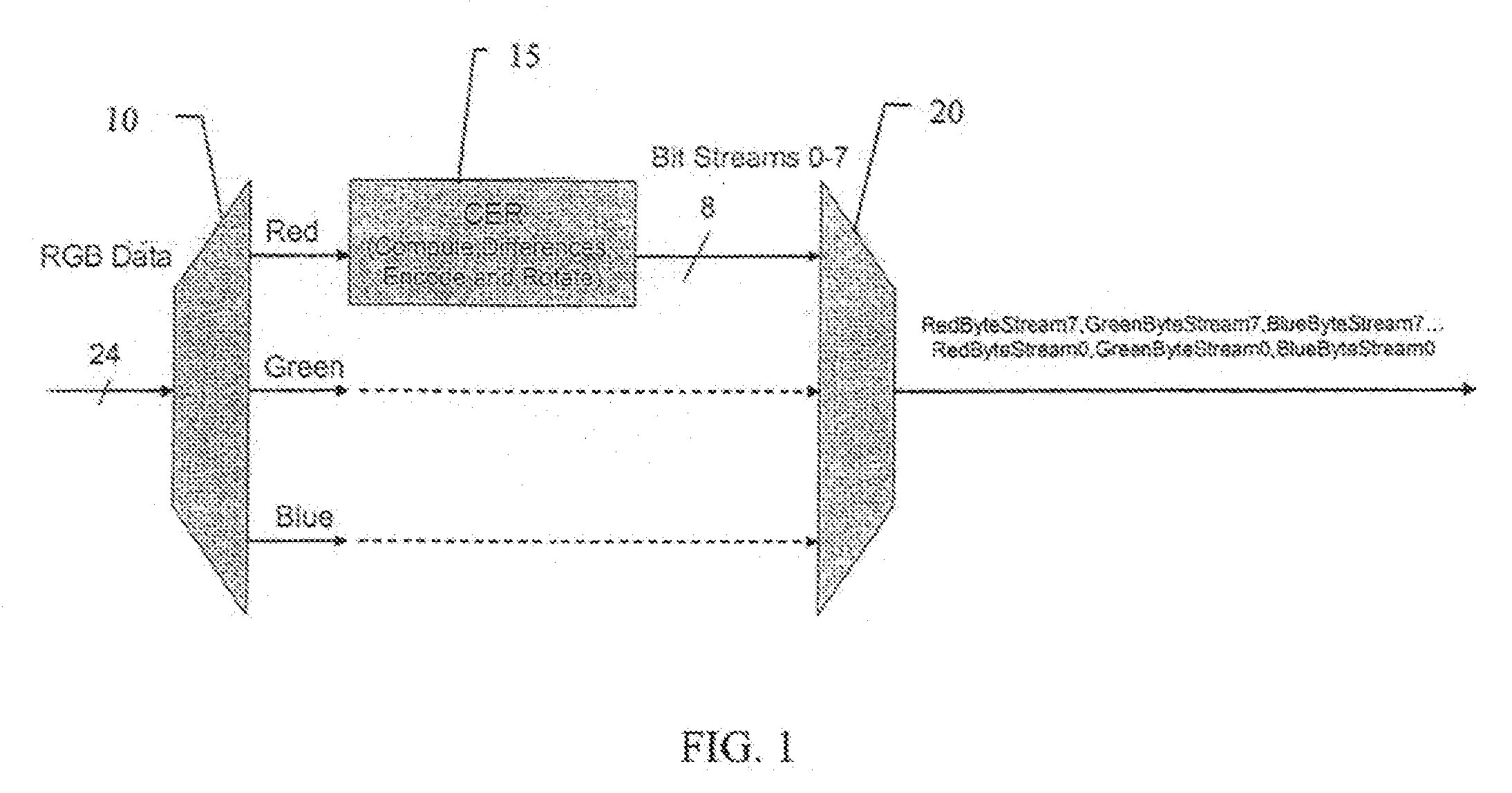
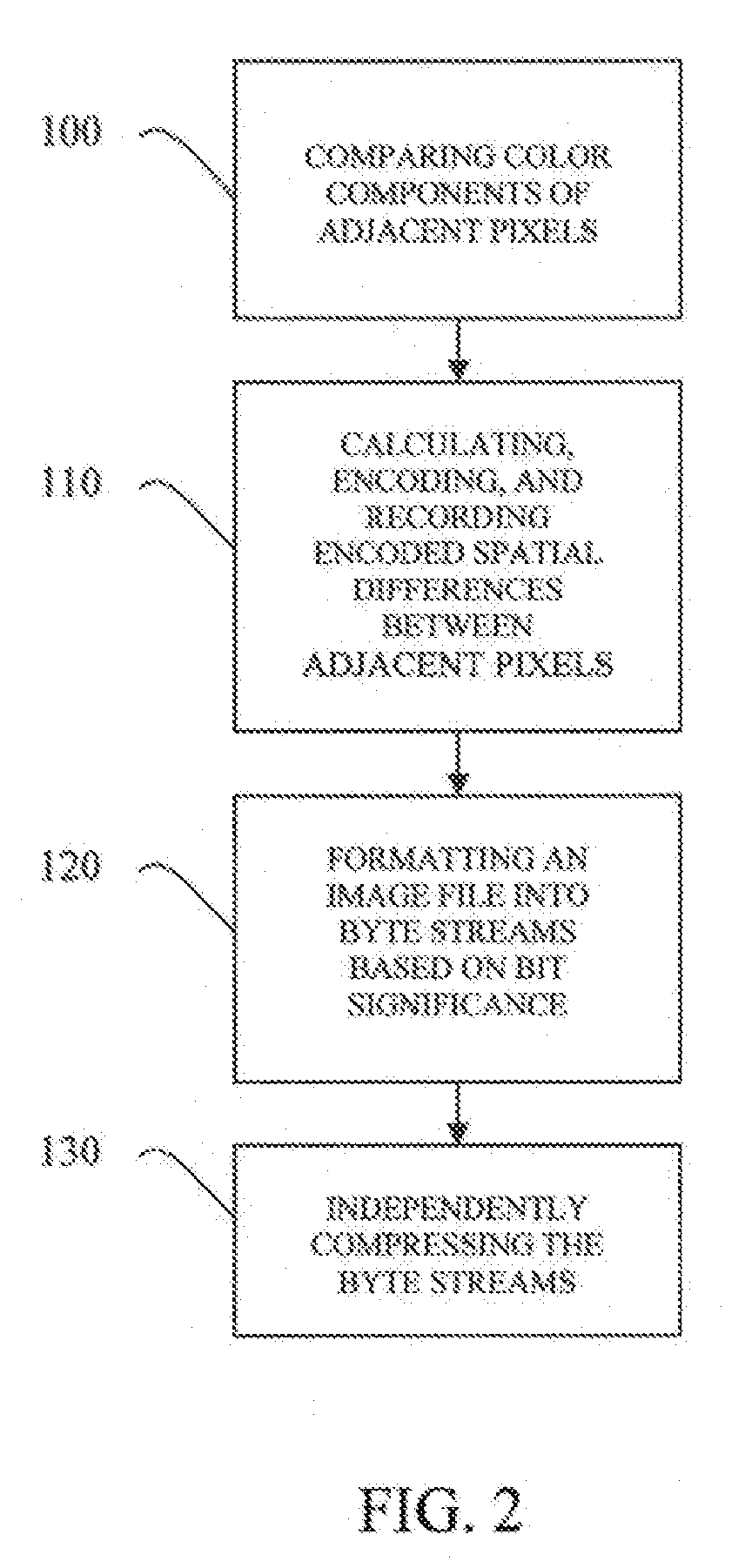
An adaptive lossless data compression method for compression of color image data in a data processing system. The method includes comparing a plurality of components of a plurality of adjacent pixels in a digital image, calculating spatial differences between the plurality of adjacent pixels, encoding the spatial differences and recording the encoded spatial differences, formatting an image file representing the digital image into byte streams based on bit significance, and compressing, independently, the byte streams associated with each bit significance of the encoded spatial differences.
Owner:IBM CORP
Length-dependent recoil separation of long molecules
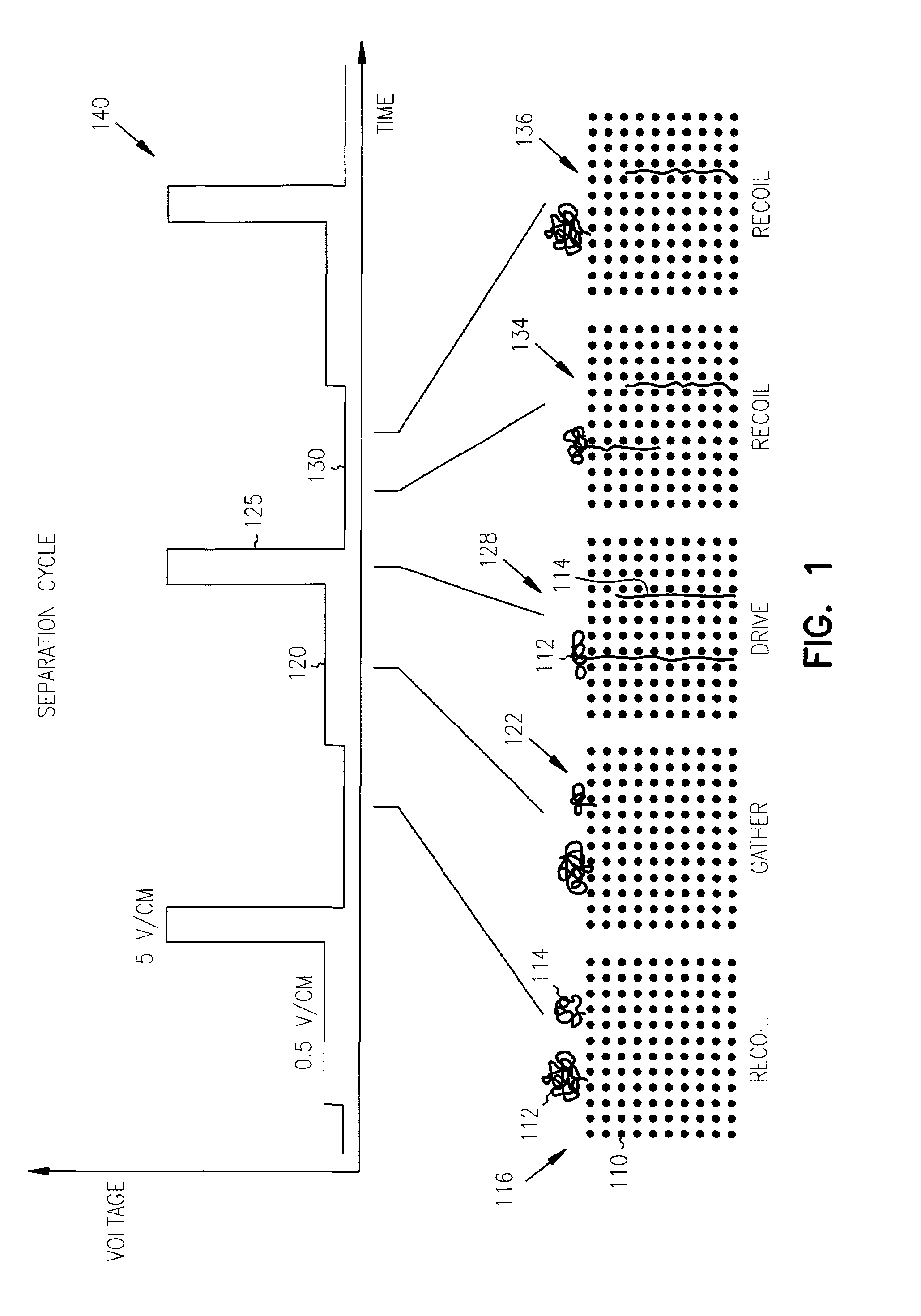
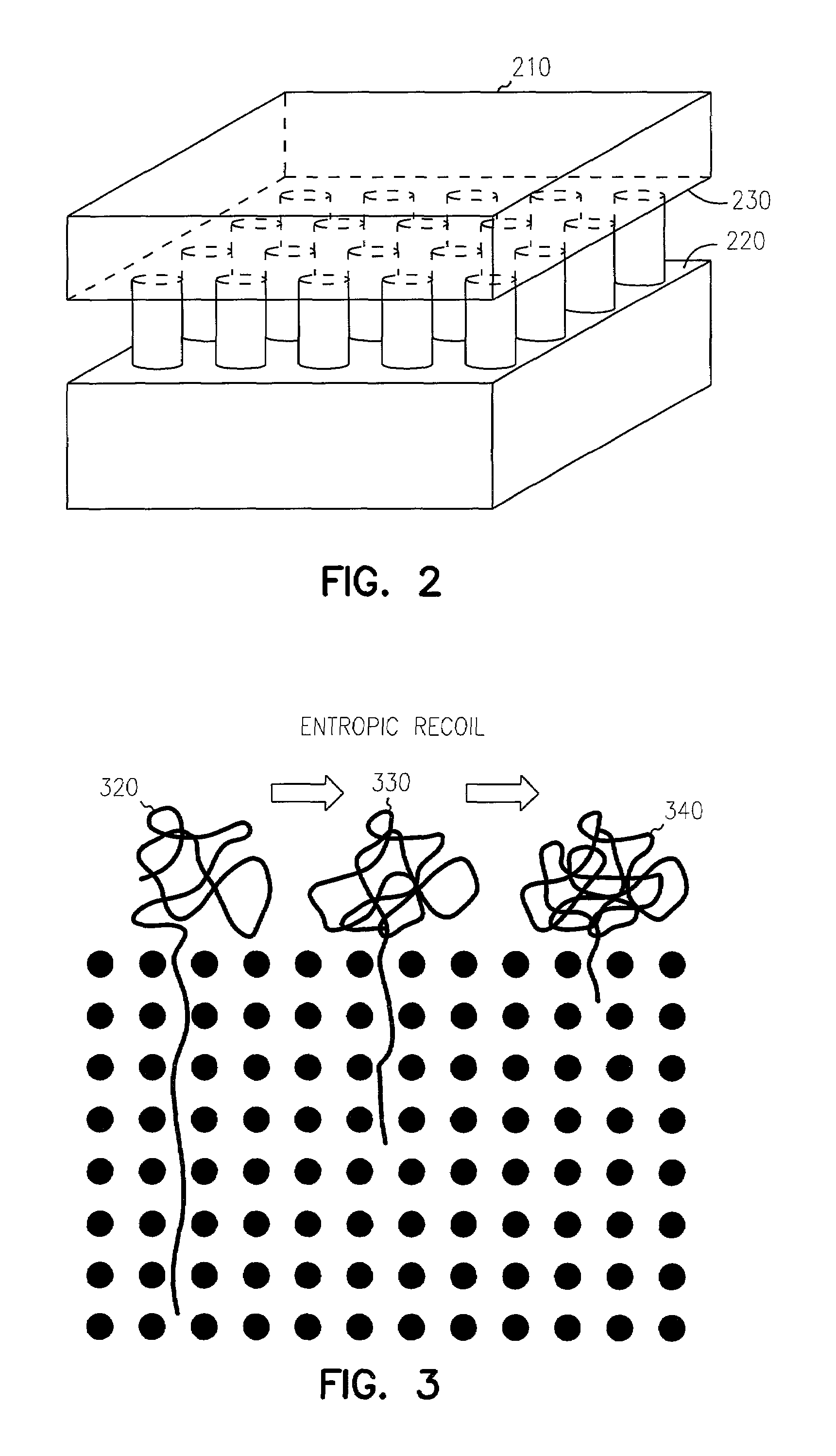
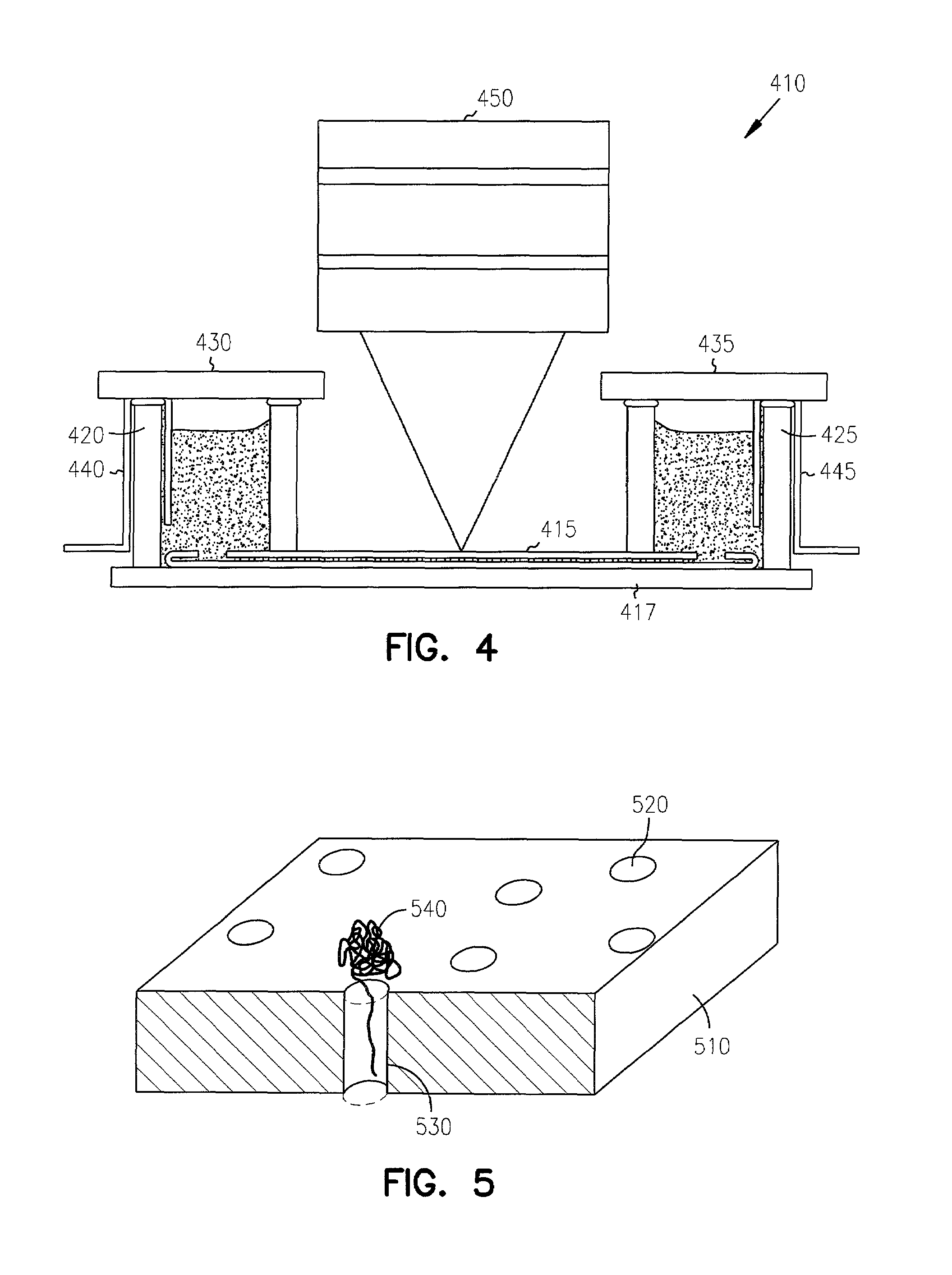
ActiveUS7316769B2Reduce entropyLong to extractElectrolysis componentsComponent separationChemistrySemiconductor
Separation of long molecules by length is obtained by forcing such molecules to traverse a boundary between a low free-energy region and a high free-energy region. In one embodiment, the high free-energy region is a dense pillar region or other structure formed on a semiconductor substrate. One or more membranes are used in further embodiments. The low free-energy region is a larger chamber formed adjacent the high free-energy region. A recoil phase allows longer molecules not fully driven into the high free-energy region to recoil into the low free-energy region. In a further variation, the high free-energy region is a membrane having nanoscale holes.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
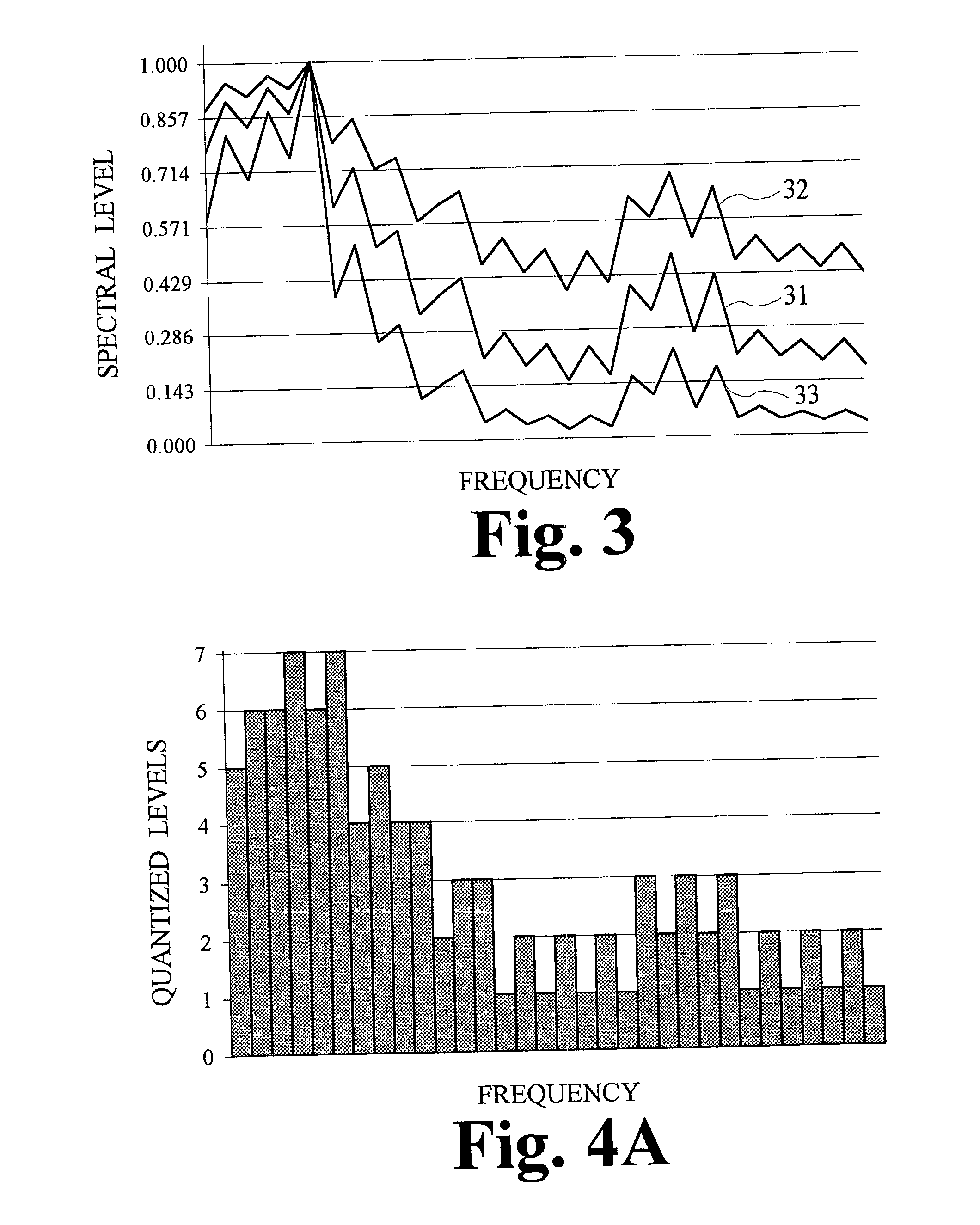
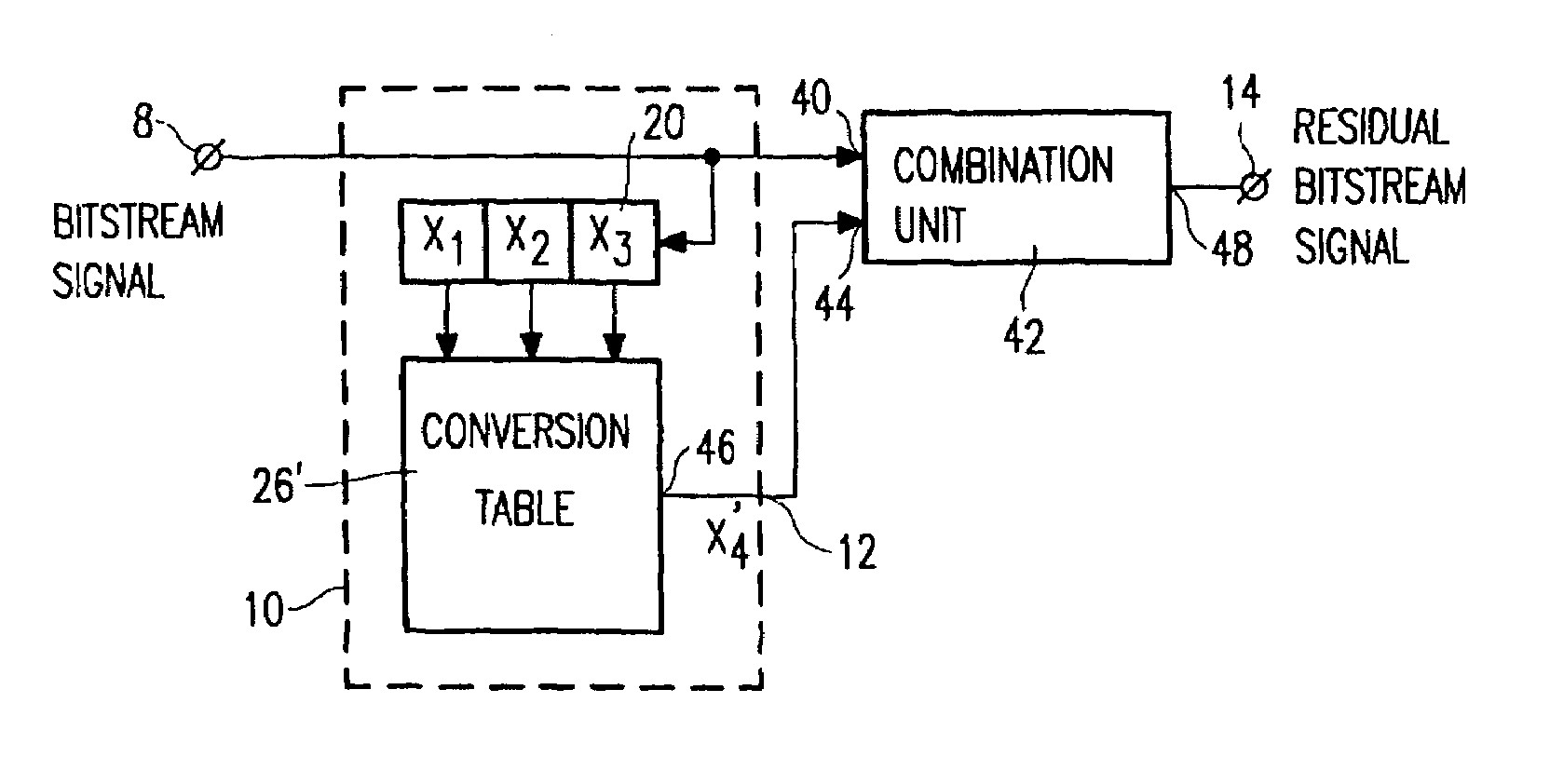
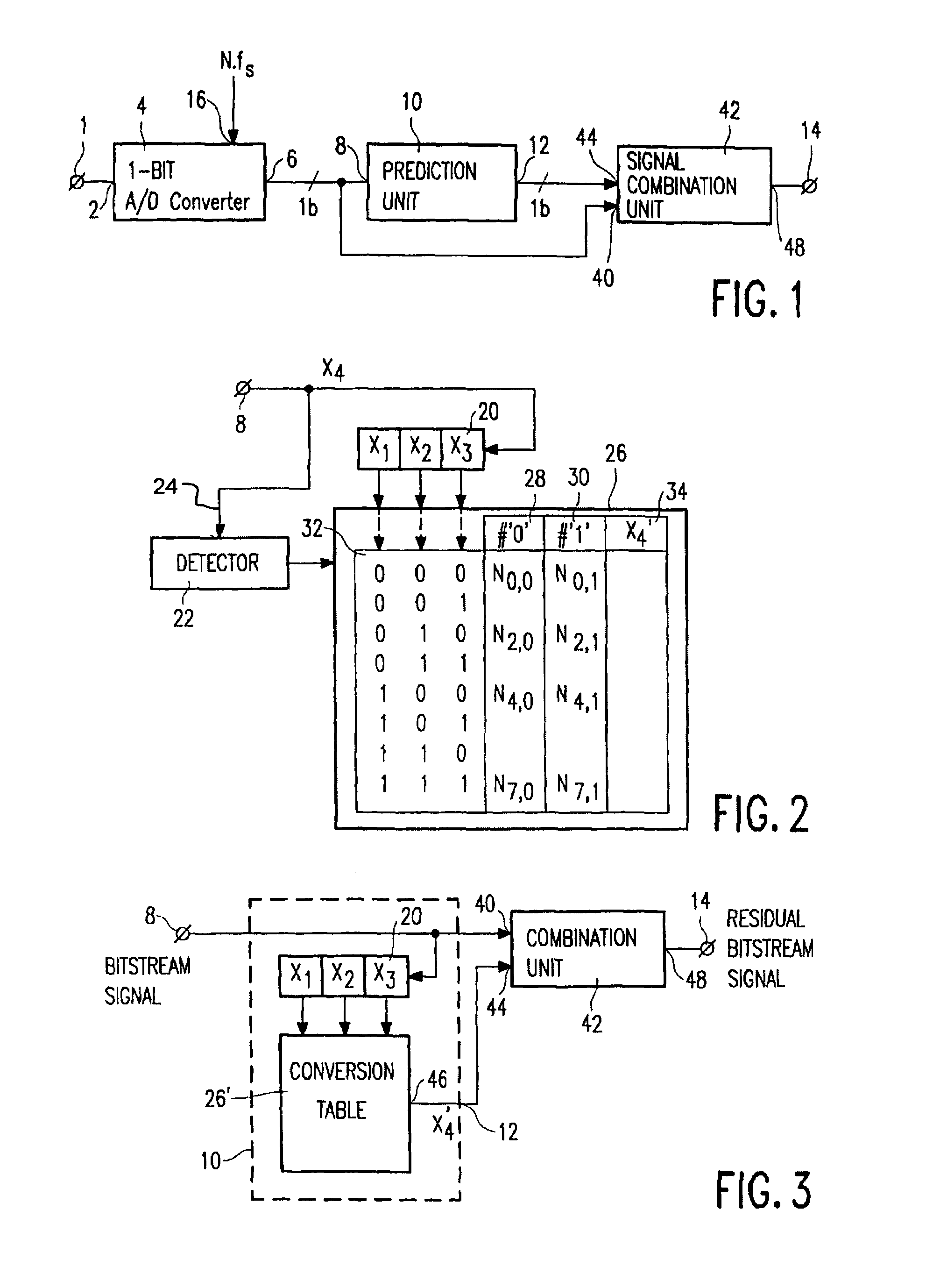
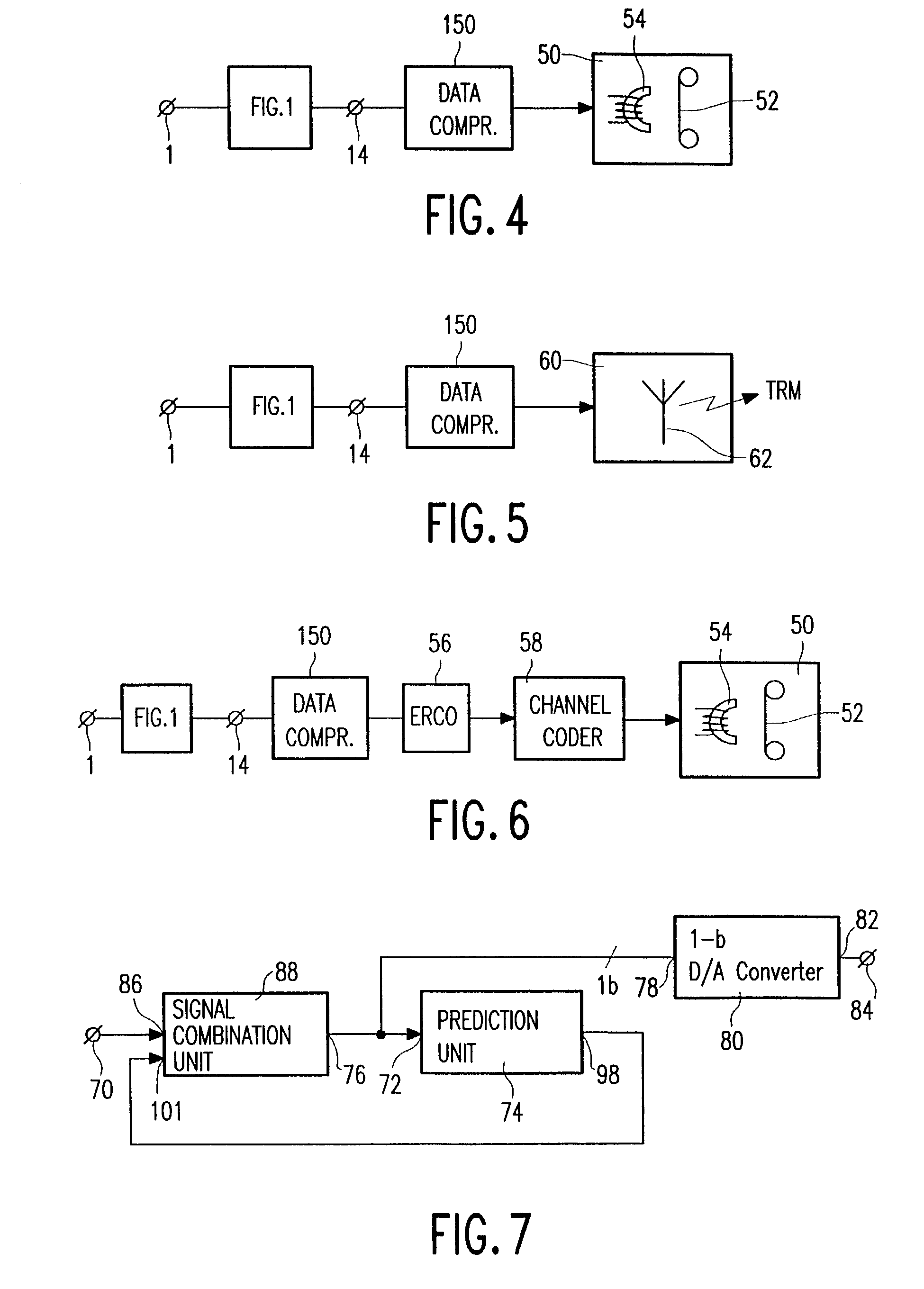
Bitstream data reduction coding by applying prediction
InactiveUS7107212B2Increase of lossless compression performanceConsiderable effectElectric signal transmission systemsRecord information storageComputer scienceAudio signal
A data processing apparatus for data processing an audio signal includes an input terminal (1) for receiving the audio signal, a 1-bit A / D converter (4) for A / D converting the audio signal to for a bitstream signal, a prediction unit (10) for carrying out a prediction step on the bitstream signal to form a predicted bitstream signal, a signal combination unit (42) for combining the bitstream signal and the predicted bitstream signal to form a residue bitstream signal, and an output terminal (14) for supplying the residual bitstream signal.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
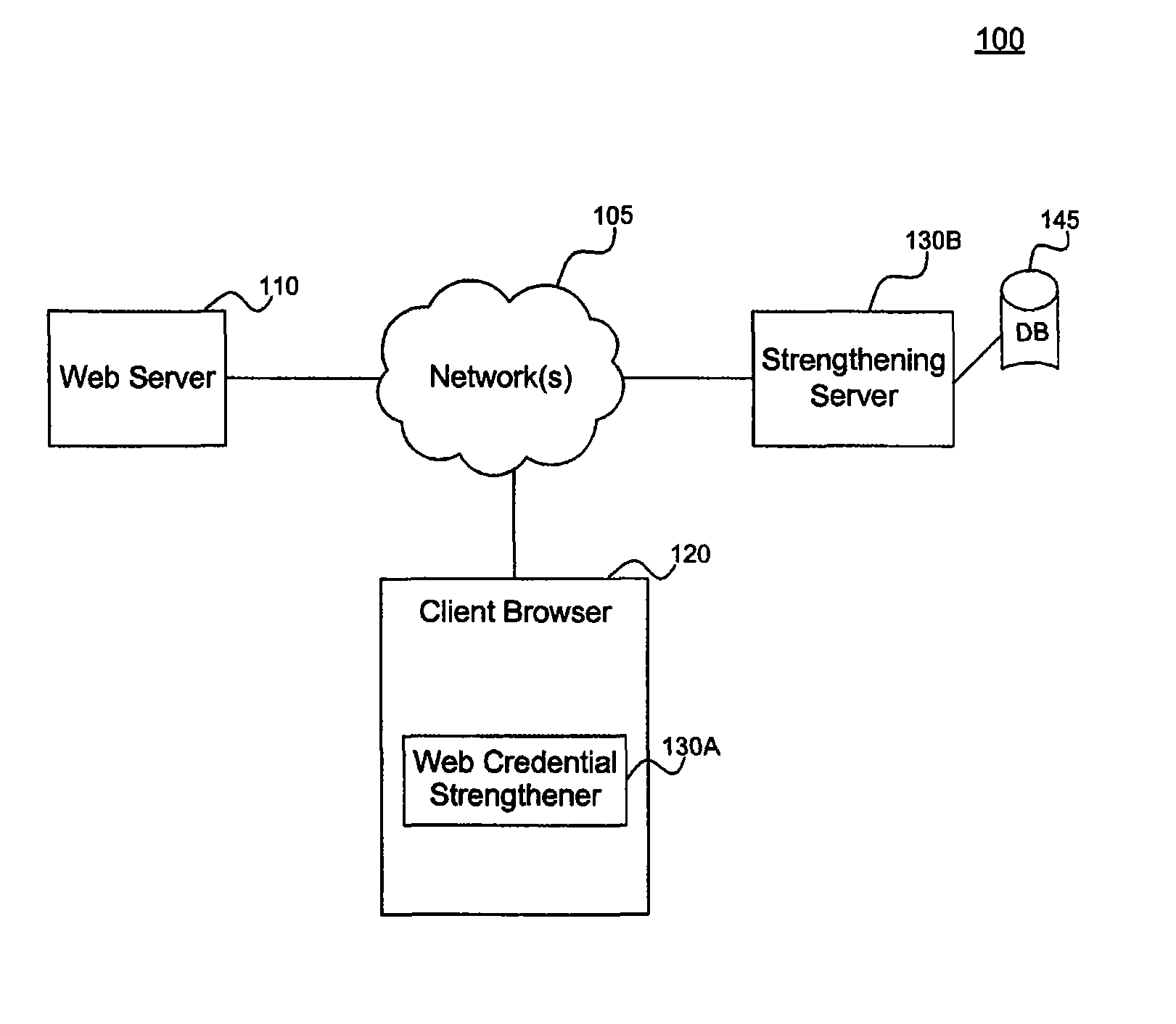
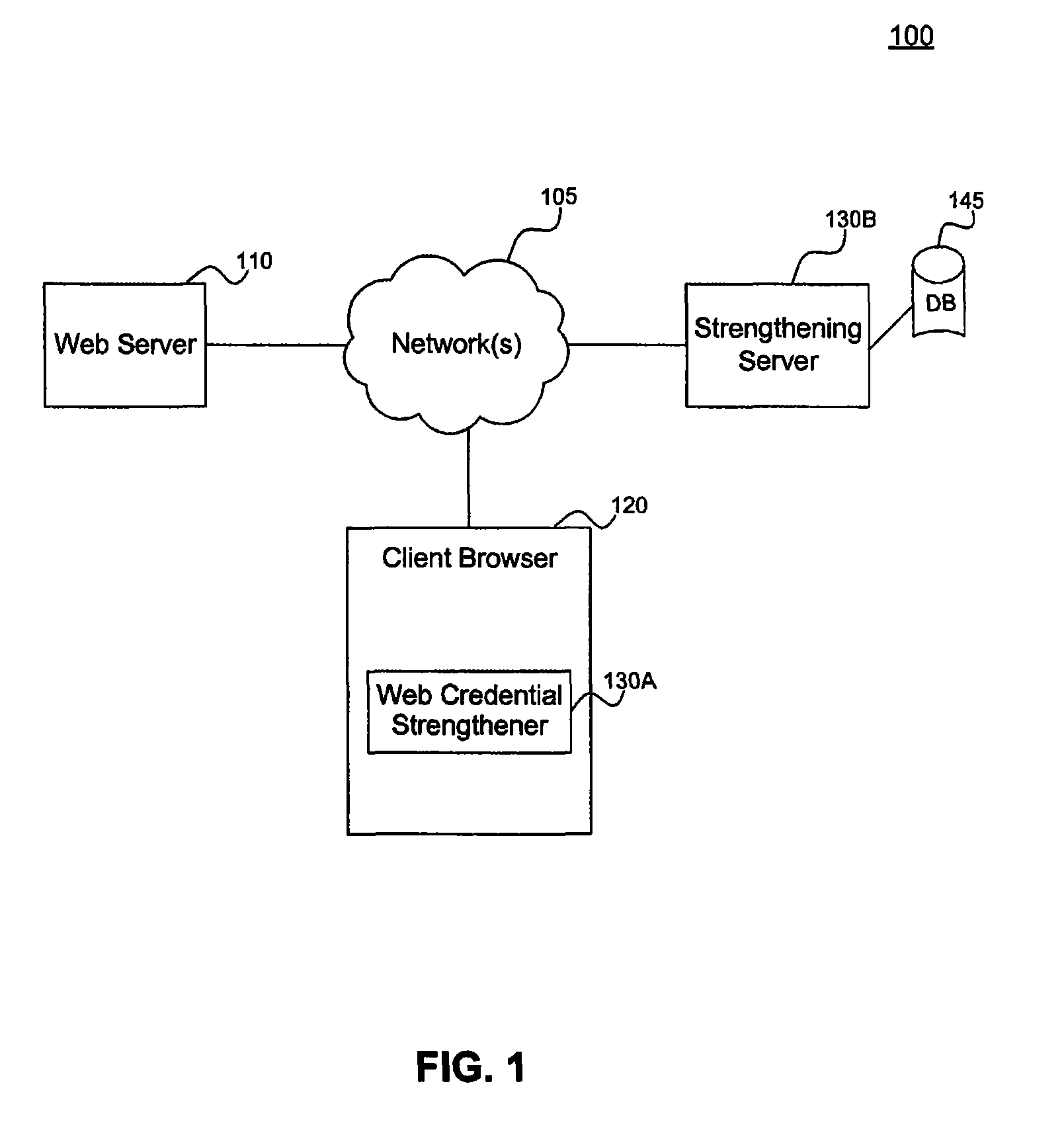
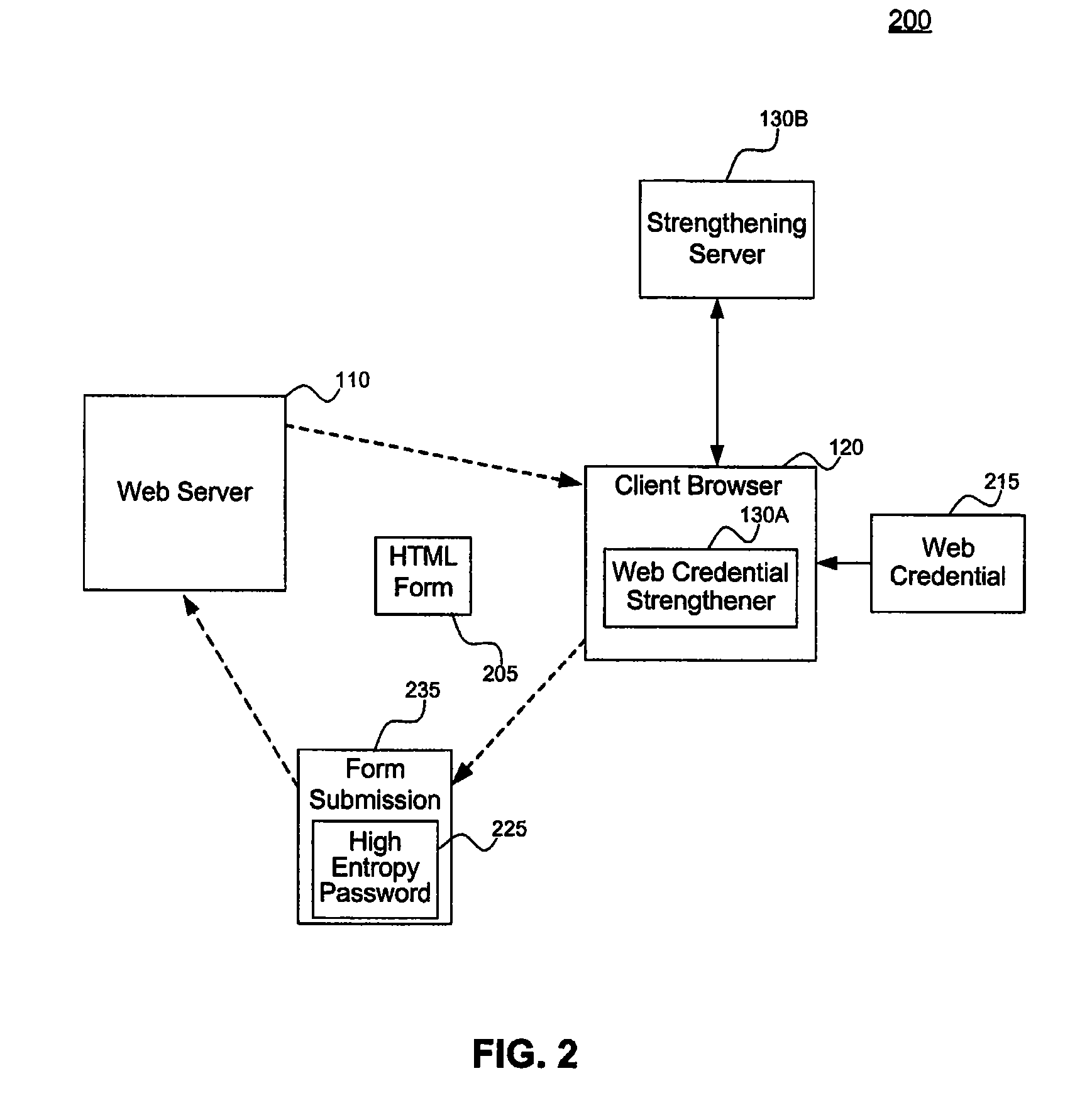
Systems and methods for strengthening web credentials
InactiveUS8381272B1Reduce the amount of informationDamage and harmDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsWeb serviceClient-side
The present invention relates to systems and methods for securing web-based transactions. A system for securing web-based transactions includes a credential strengthener coupled to a client browser. The client browser communicates with a web server in a web-transaction. The credential strengthener converts a web credential entered by a user at the client browser to a higher entropy web credential associated with the user. The client browser then returns the higher entropy web credential for further use in the web transaction. A method for securing a web-based transaction includes steps of converting a web credential entered by a user at a client browser to a higher entropy web credential associated with the user, and returning the higher entropy web credential to the web server to continue the web transaction.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for motion vector field encoding
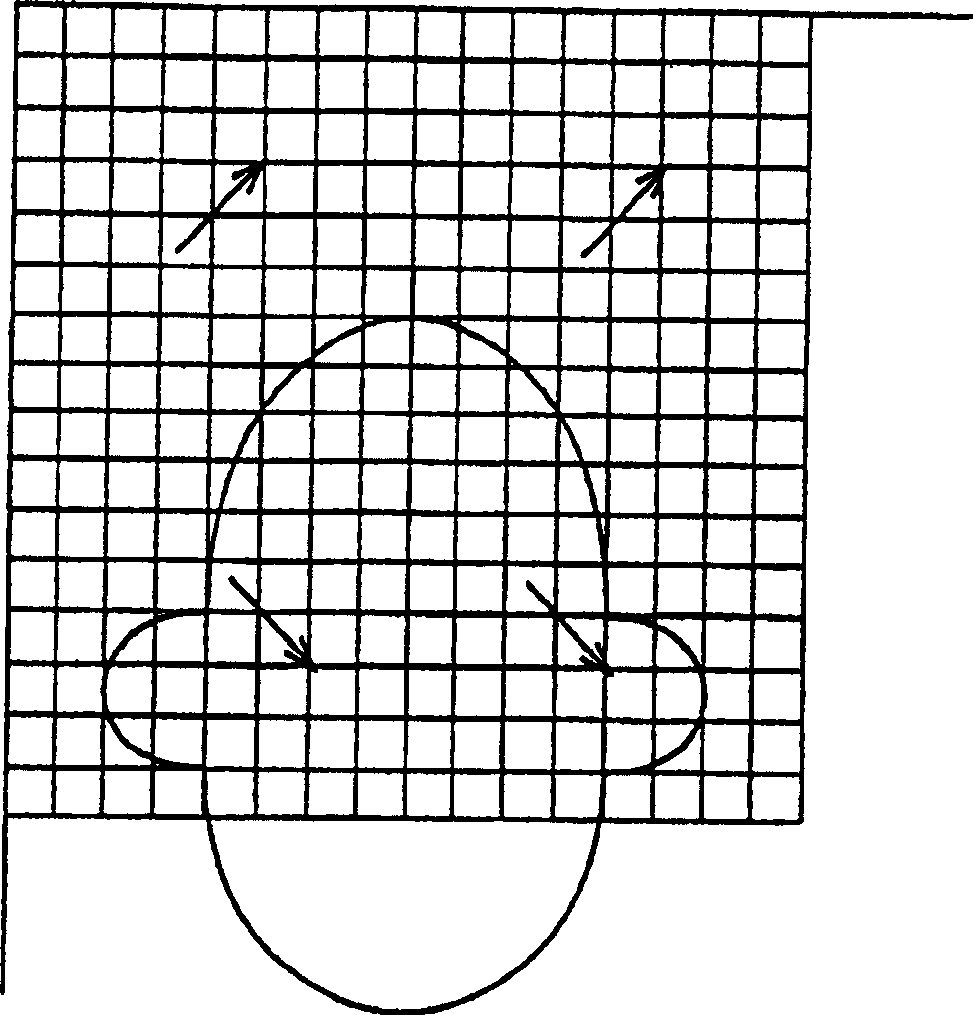
InactiveCN1717050AImprove visual qualityReduce the number of human factorsPulse modulation television signal transmissionCode conversionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A method of processing data relating to an image in a sequence of digitized images comprises deriving a motion vector field for the image and smoothing the motion vector field by replacing a given motion vector by a new motion vector derived using averaging based on adjoining motion vectors, the method further comprising identifying where motion discontinuities occur in the image and omitting a motion vector or vectors from the averaging if they are separated from the given motion vector by a motion discontinuity.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
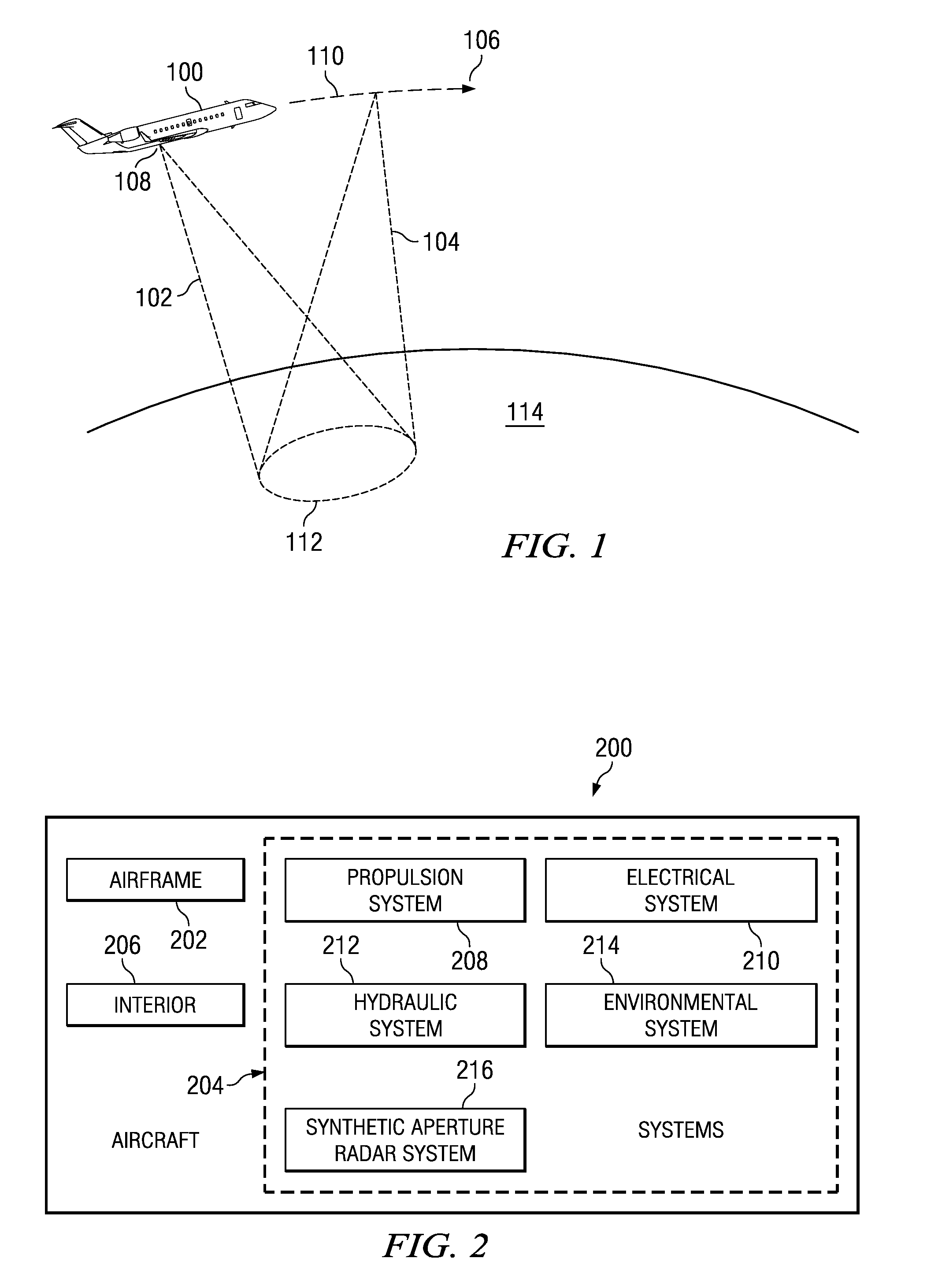
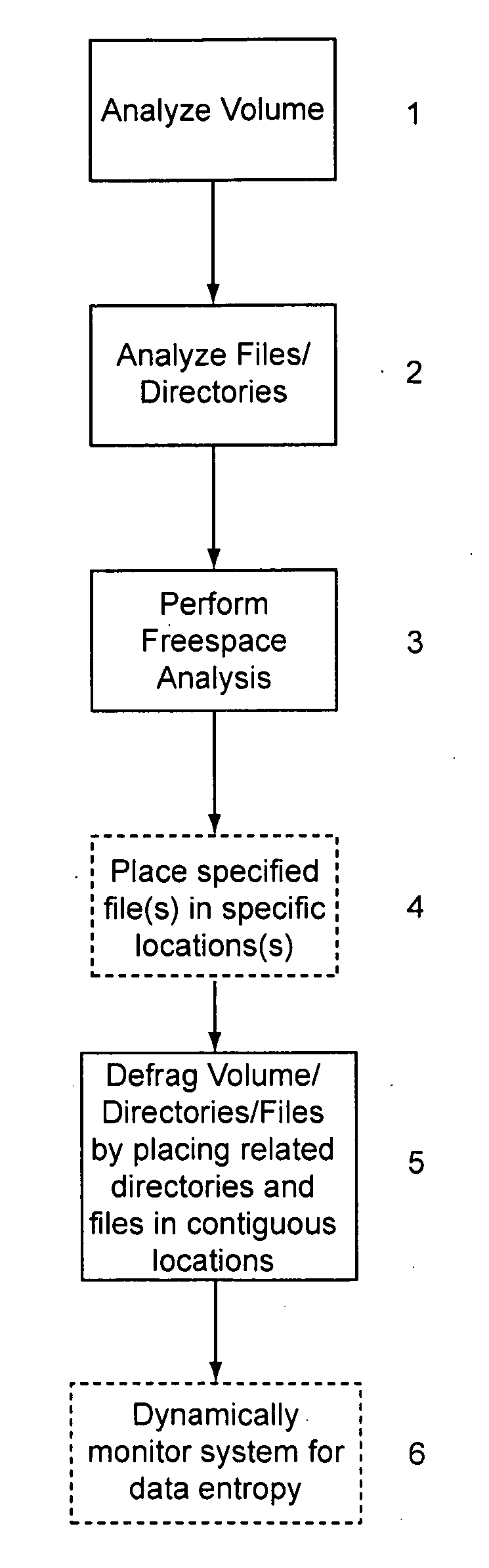
Autofocus for minimum entropy through multi-dimensional optimization
Owner:THE BOEING CO
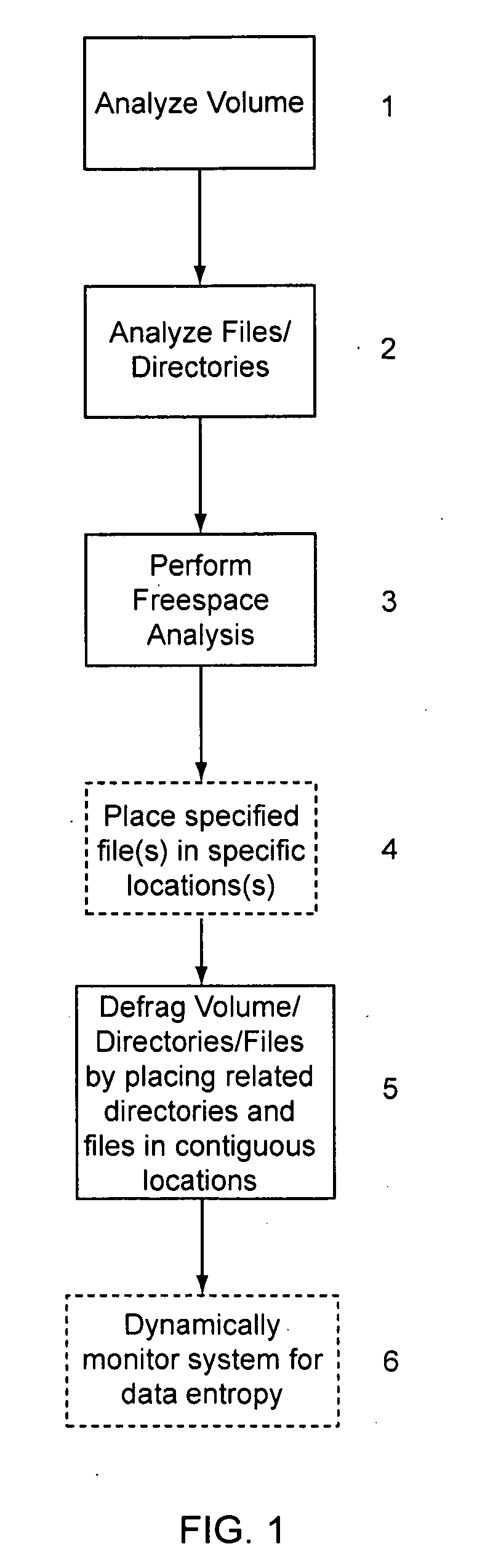
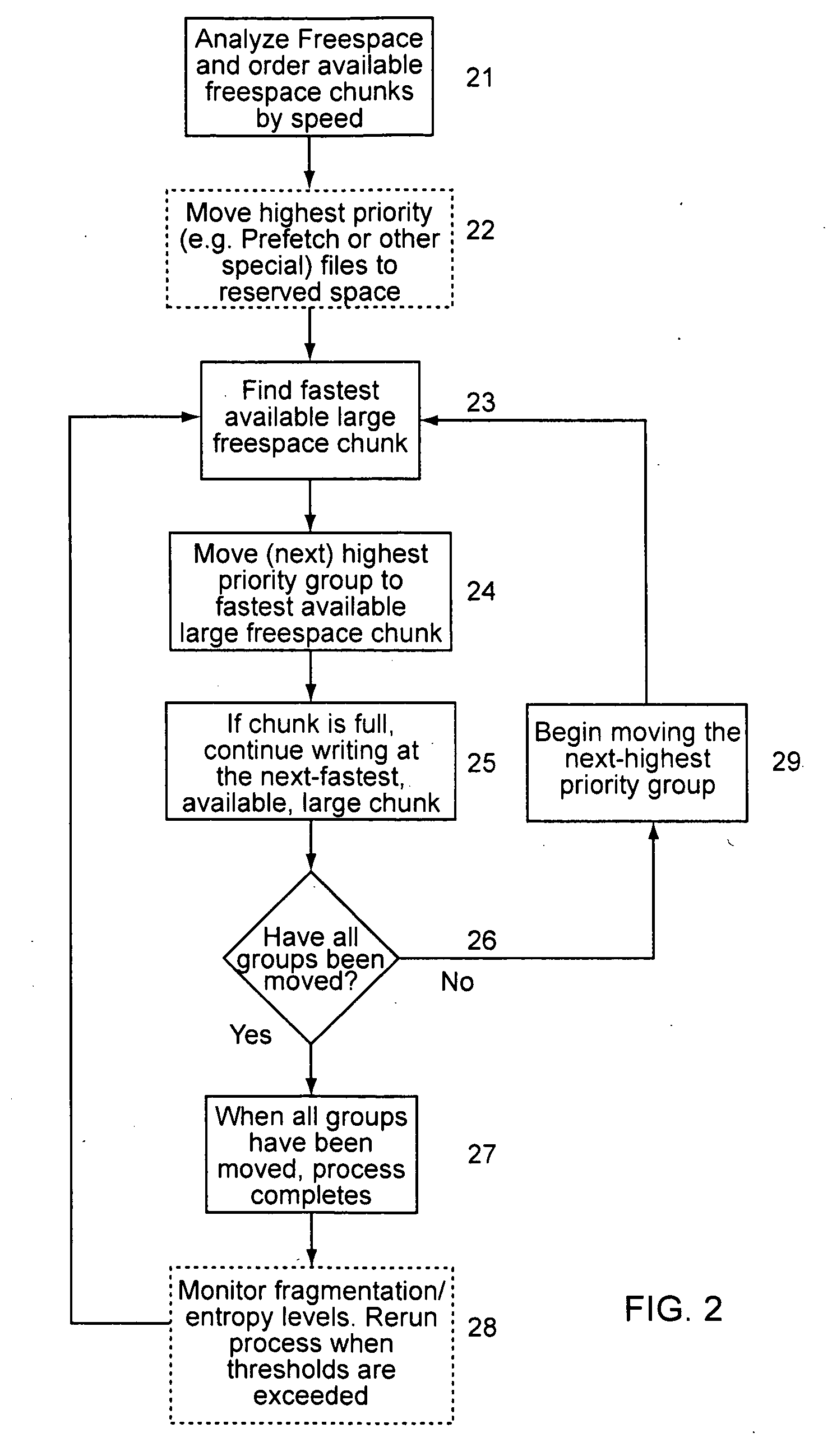
System and method for efficient data storage
InactiveUS20120047189A1Reduce entropyReduce amount of timeDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsHard disc driveData entity
A system and method for efficient data storage, which reduces data entropy of data on a data storage device. The technique organizes related data entities (such as files on a hard drive) in close physical proximity and in a predictive or ordered sequence, to reduce the amount of time and effort (mechanical, computational, or otherwise) a storage / retrieval device needs to expend locating each data entity as it processes a sequence of requests. For example, the data may be organized and stored according to a file directory index structure, whereby data and free space fragmentation is also reduced.
Owner:IOLO TECHNOLOGIES
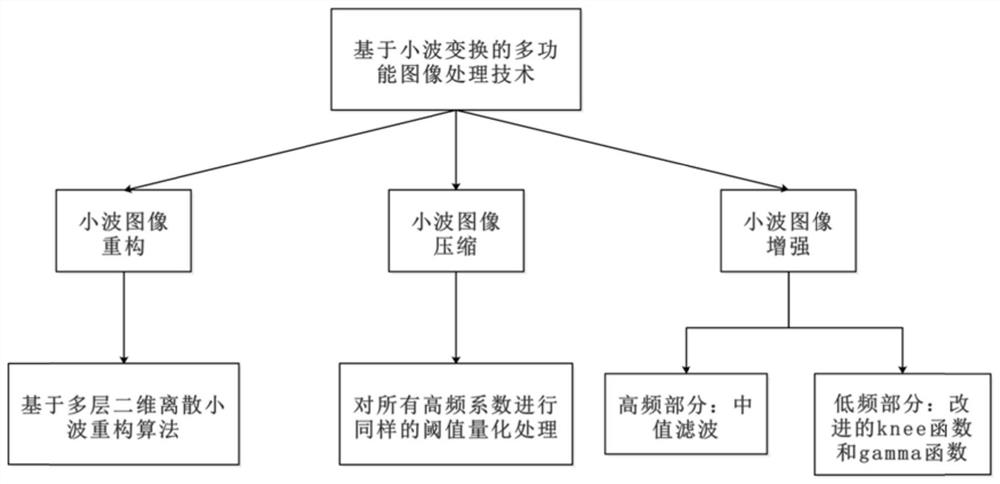
Multifunctional image processing method based on wavelet transform
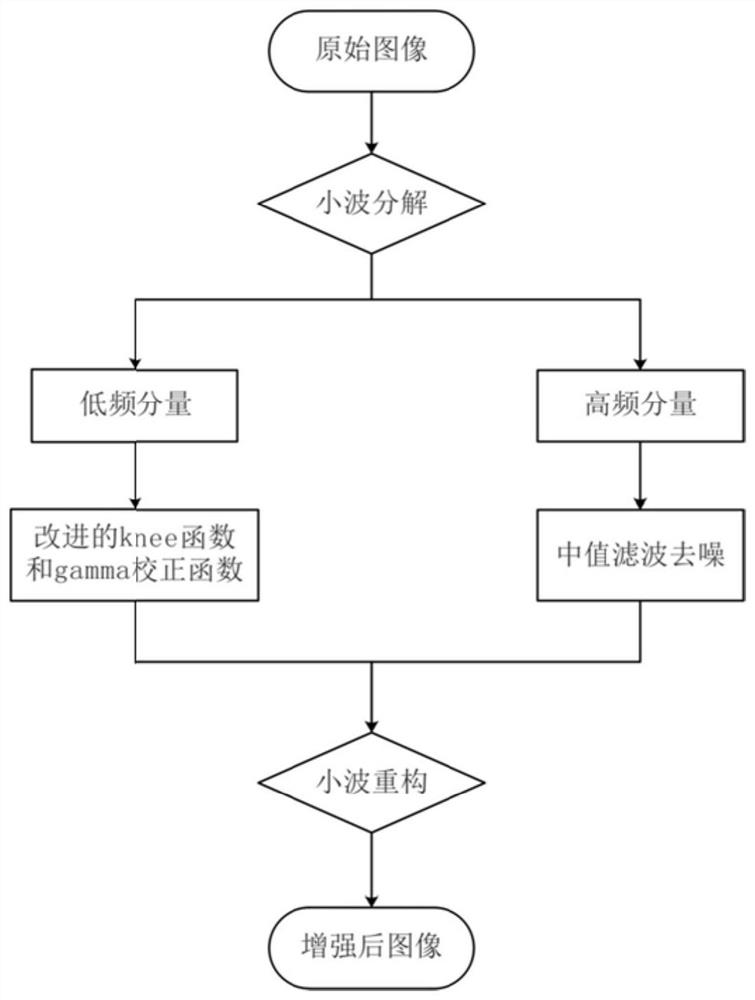
PendingCN111798396AReduce entropyCharacterize non-stationarityImage enhancementImage analysisQuantization (image processing)Time domain
The invention provides a multifunctional image processing method based on wavelet transform. The multifunctional image processing method comprises the following steps: step 1, reading an original image; 2, decomposing the original image into a high-frequency part and a low-frequency part by wavelet transform; 3, for the high-frequency part of the image, performing threshold quantization processingon all high-frequency coefficients, and then performing median filtering to complete compression of the high-frequency part and image enhancement; 4, for the low-frequency part of the image, enhancing a low-frequency coefficient by adopting an improved function; and step 5, reconstructing the processed high-frequency part and the processed low-frequency part by using wavelet inverse transformation to obtain a reconstructed image. According to the method, wavelet transformation is adopted to process the image, so that the entropy after signal transformation is reduced, the non-stationarity ofthe signal can be well described, and feature extraction and protection are facilitated. According to the method, wavelet transform is adopted, so that denoising is more facilitated in a wavelet domain than in a time domain, and different wavelet functions can be selected according to different application requirements to obtain an optimal processing effect.
Owner:CHINA INFOMRAITON CONSULTING & DESIGNING INST CO LTD
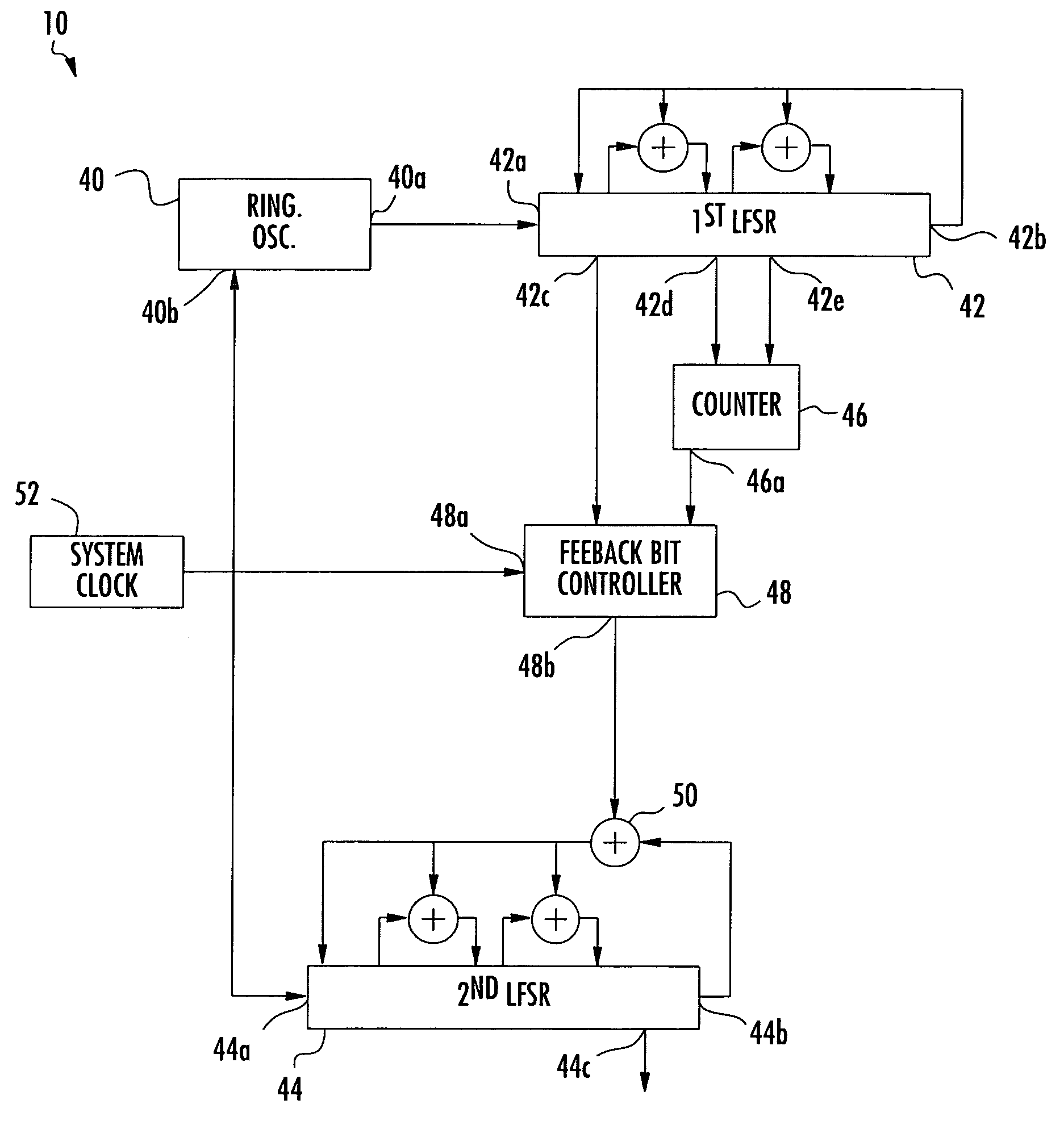
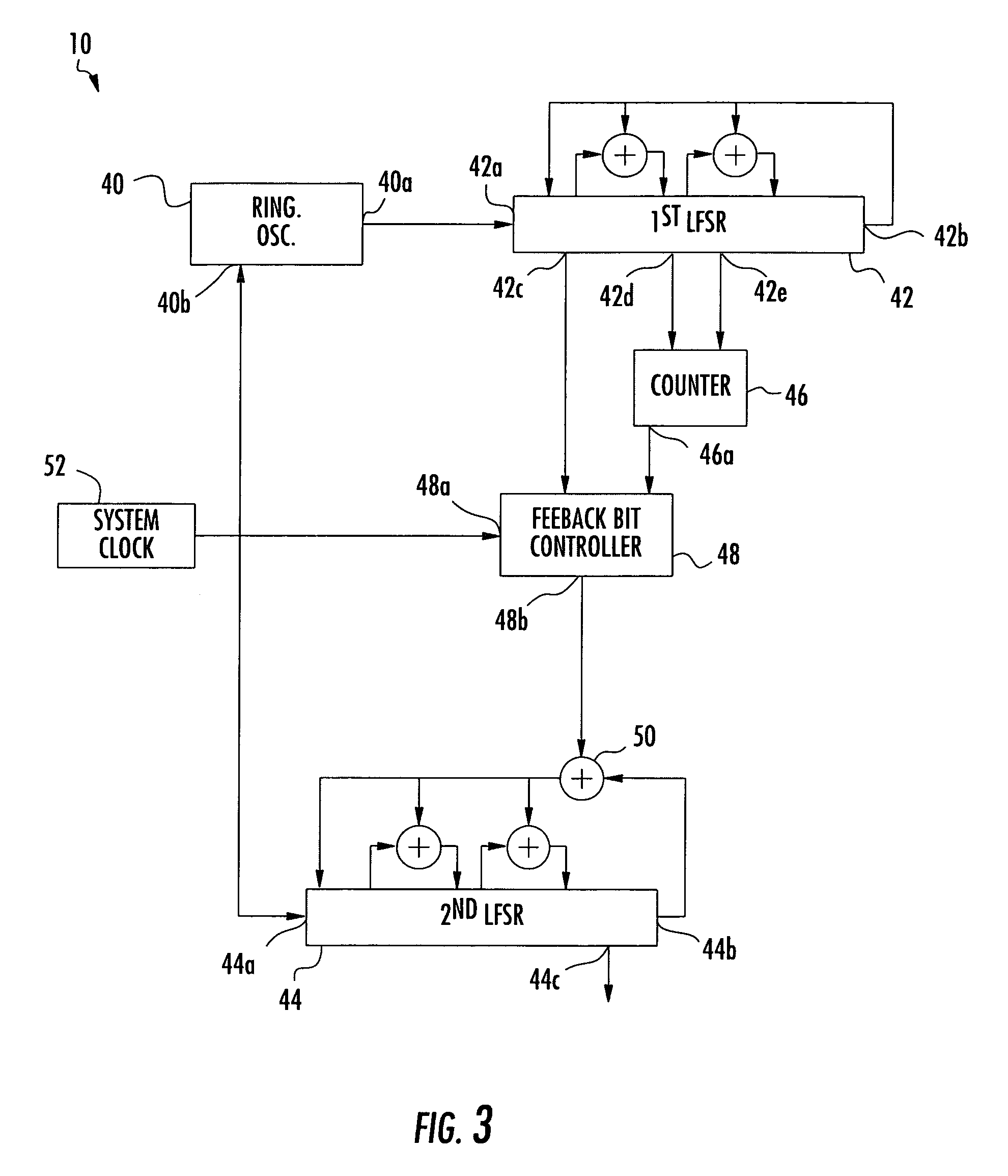
Random number source and associated methods
ActiveUS7293054B2Increase entropyReduce entropyRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationPhase noiseComputer science
A random number source includes a ring oscillator generating an internal clock signal having random phase noise, and a first linear feedback shift register connected to the ring oscillator. A counter is connected to a first tap of the first linear feedback shift register for generating a count signal. A feedback bit controller is connected to a second tap of the first linear feedback shift register for generating a random feedback bit for a time based upon the count signal. A second linear feedback shift register is connected to the feedback bit controller for generating a random number based upon the random feedback bit.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
Systems including electromechanical polymer sensors and actuators
ActiveUS9053617B2Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureTactile signalling systemsInput/output processes for data processingTransducerEngineering
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
EMP actuators for deformable surface and keyboard application
ActiveUS9170650B2Reduce entropyReduce the temperatureInput/output for user-computer interactionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionTouch SensesDisplay device
A localized multimodal haptic system includes one or more electromechanical polymer (EMP) transducers, each including an EMP layer, such as an electrostrictive polymer active layer. In some applications the EMP transducer may perform an actuator function or a sensor function, or both. The EMP polymer layer has a first surface and a second surface on which one or more electrodes are provided. The EMP layer of the EMP actuator may be 5 microns thick or less. The EMP transducers may provide local haptic response to a local a stimulus. In one application, a touch sensor may be associated with each EMP transducer, such that the haptic event at the touch sensor may be responded to by activating only the associated EMP transducer. Furthermore, the EMP transducer may act as its own touch sensor. A variety of haptic responses may be made available. The EMP transducers may be used in various other applications, such as providing complex surface morphology, keyboard, braille display, and audio speakers.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
Gapless screw rotor device
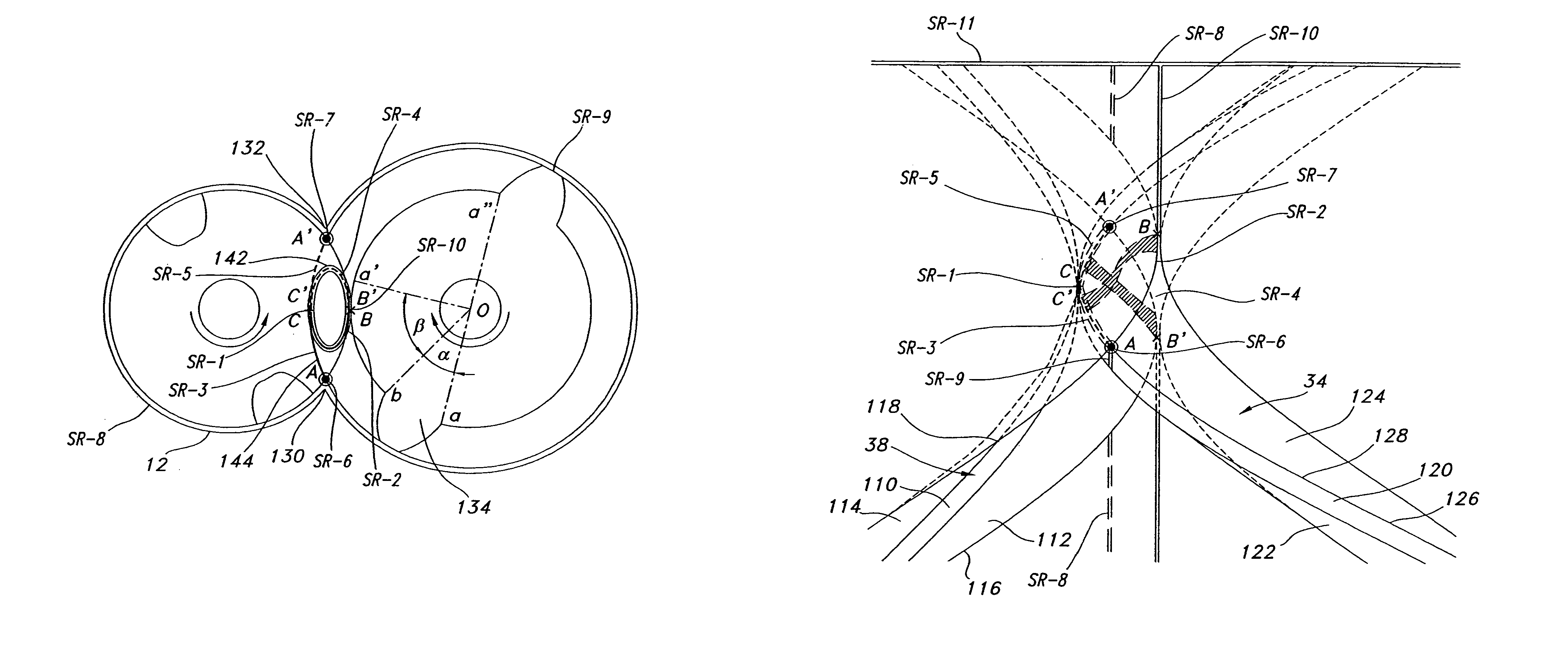
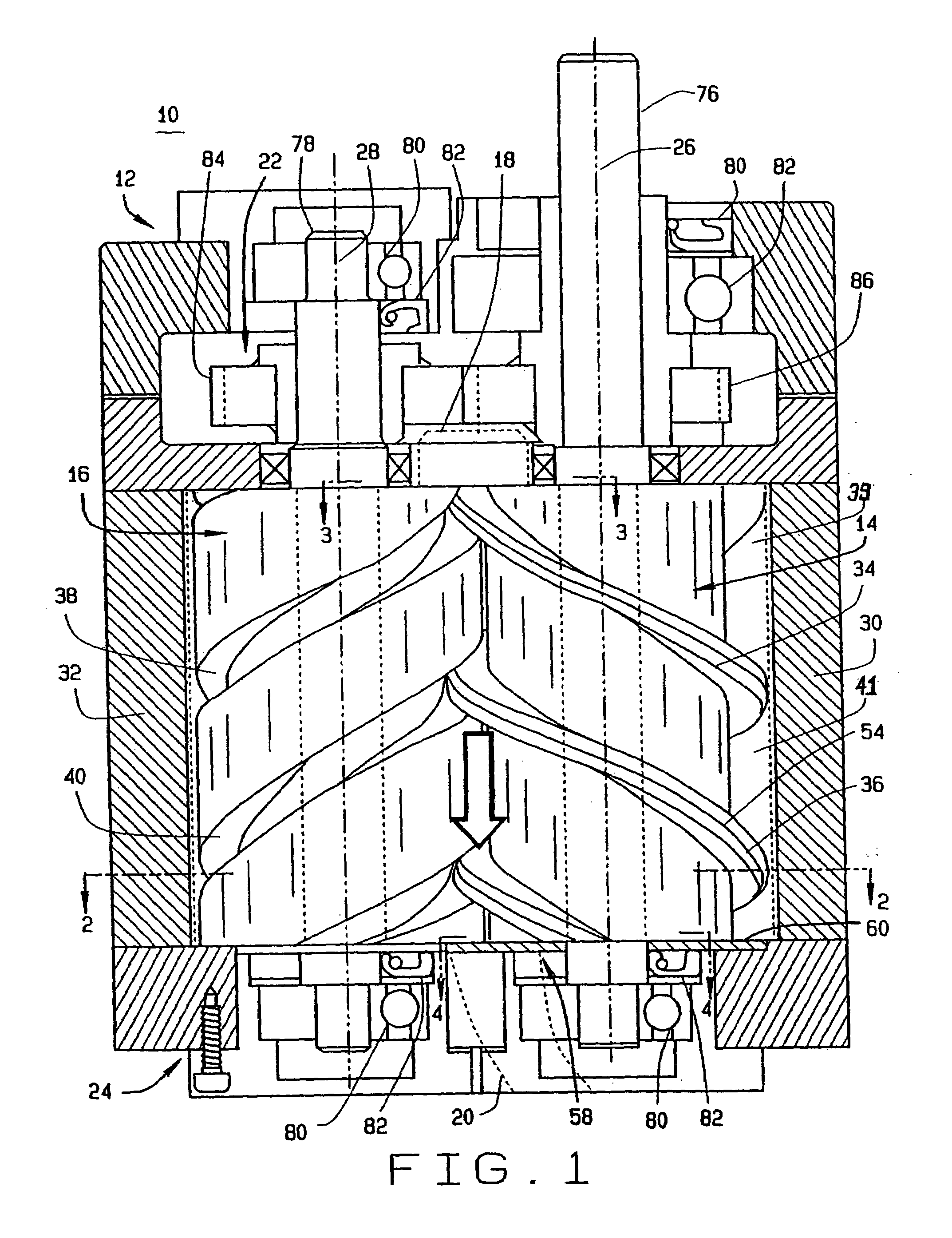
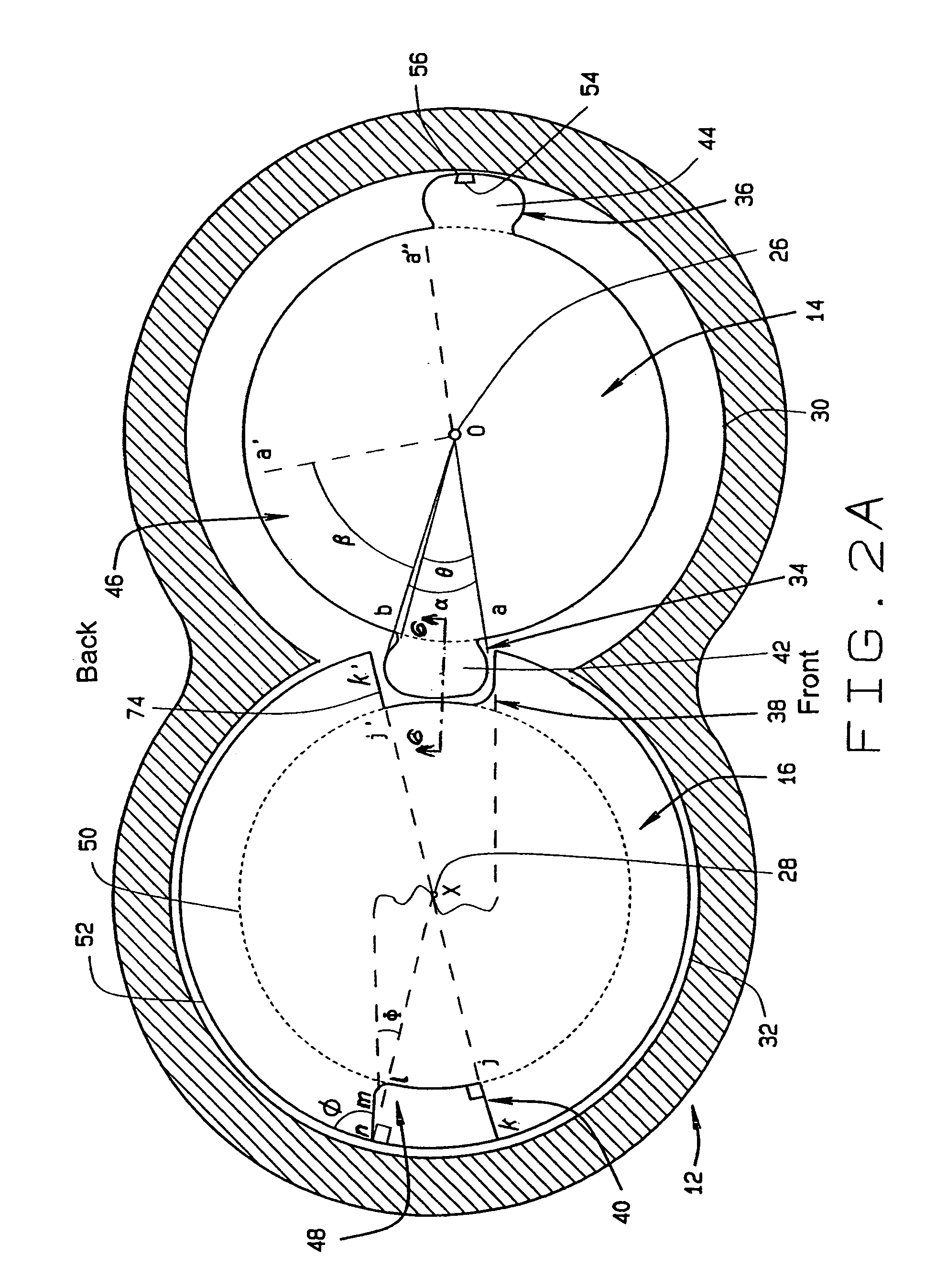
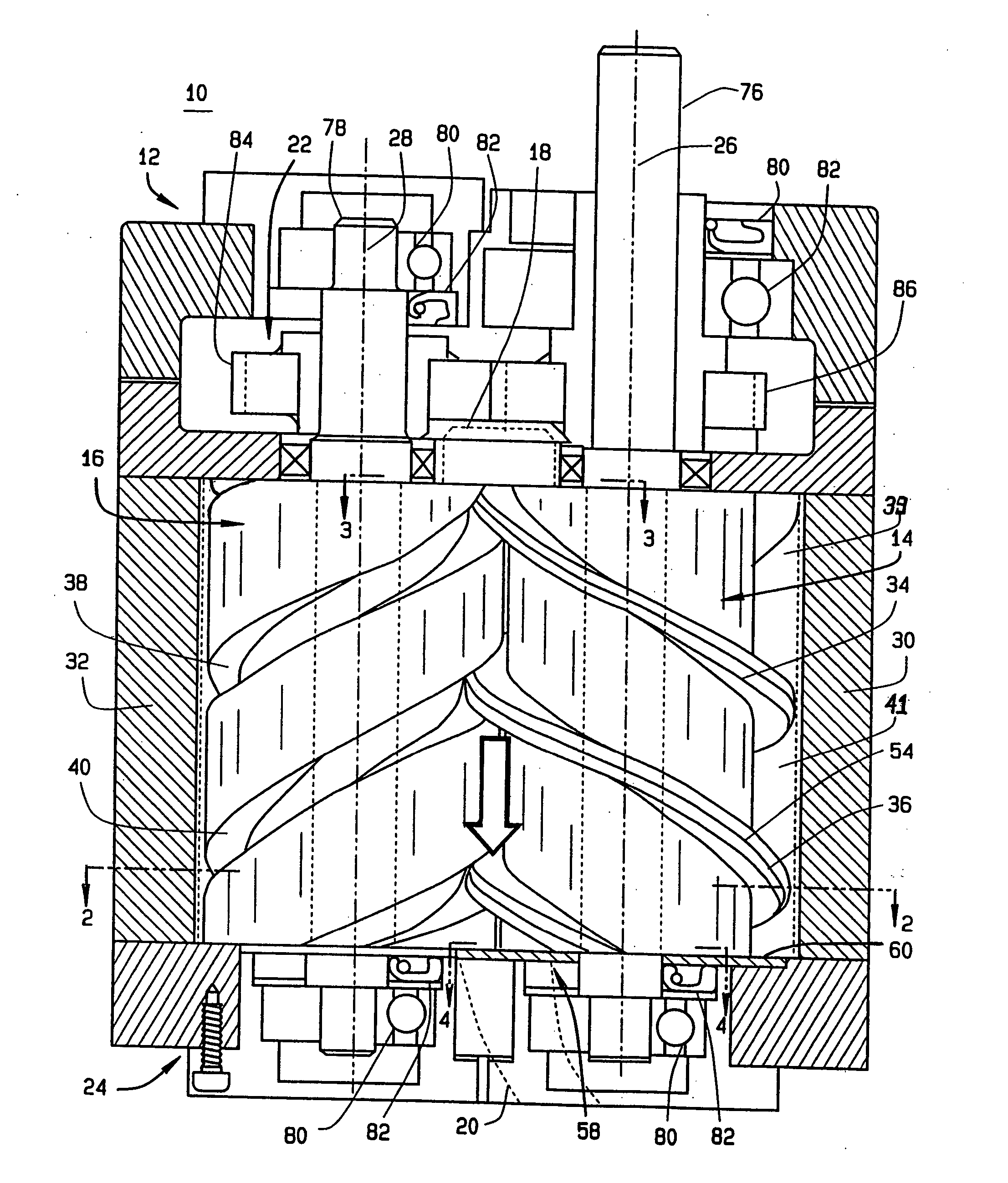
InactiveUS7008201B2Maximize thermodynamic efficiency and volumetric efficiencyReduce manufacturing costOscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsScrew threadHelix
A screw rotor device has a housing with an inlet port and an outlet port, a male rotor with helical threads, and a female rotor with helical grooves. The helical threads and helical grooves are designed to eliminate the blow hole leak pathway for multiple-pitch screw rotor devices as well as single-pitch screw rotor devices. The male rotor has a pair of helical threads with a phase-offset aspect, and the female rotor has a corresponding pair of helical grooves. The female rotor counter-rotates with respect to the male rotor and each of the helical grooves respectively intermeshes in phase with each of the helical threads. The phase-offset aspect of the helical threads is formed by a pair of teeth bounding a toothless sector.
Owner:IMPERIAL RES
Gapless screw rotor device
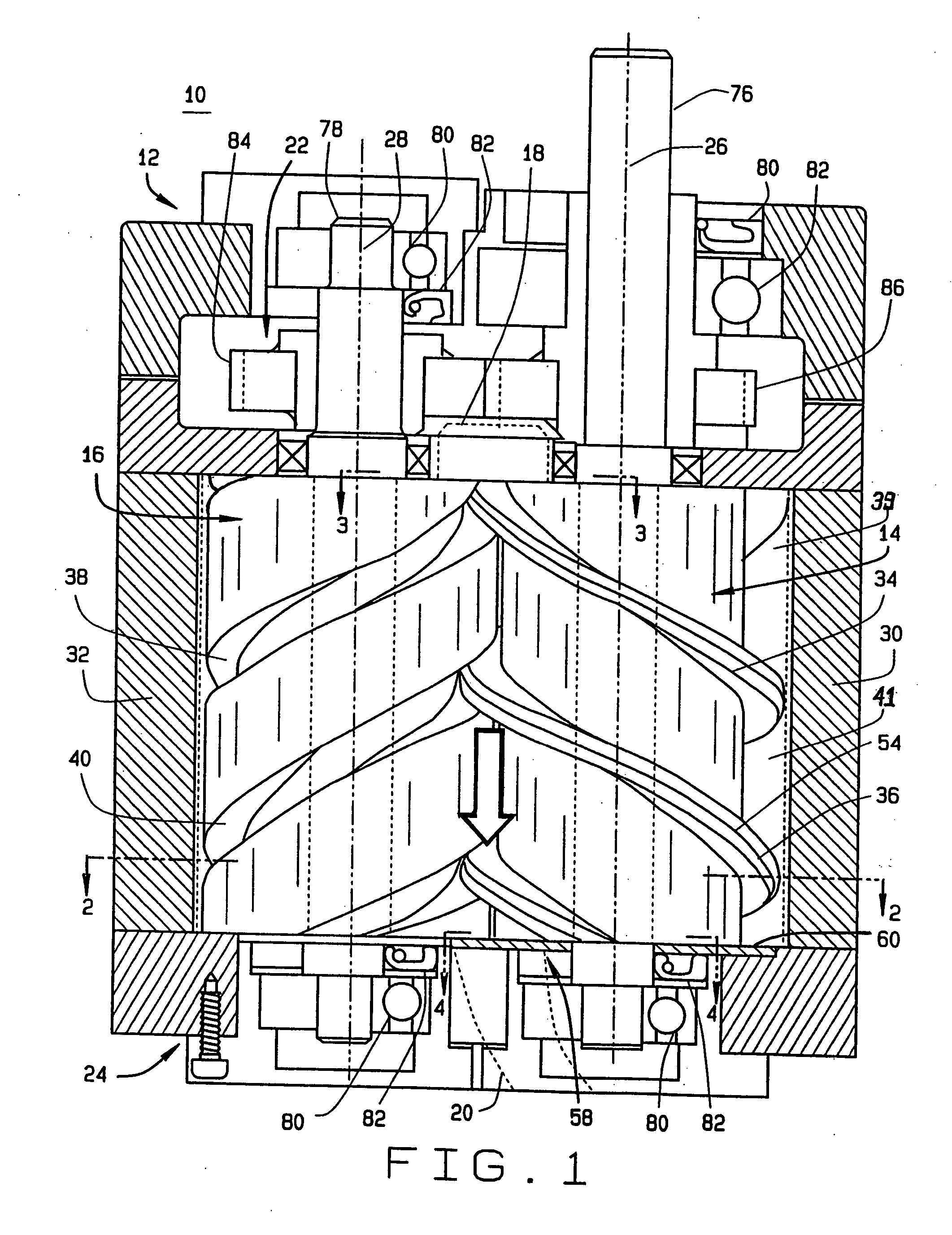
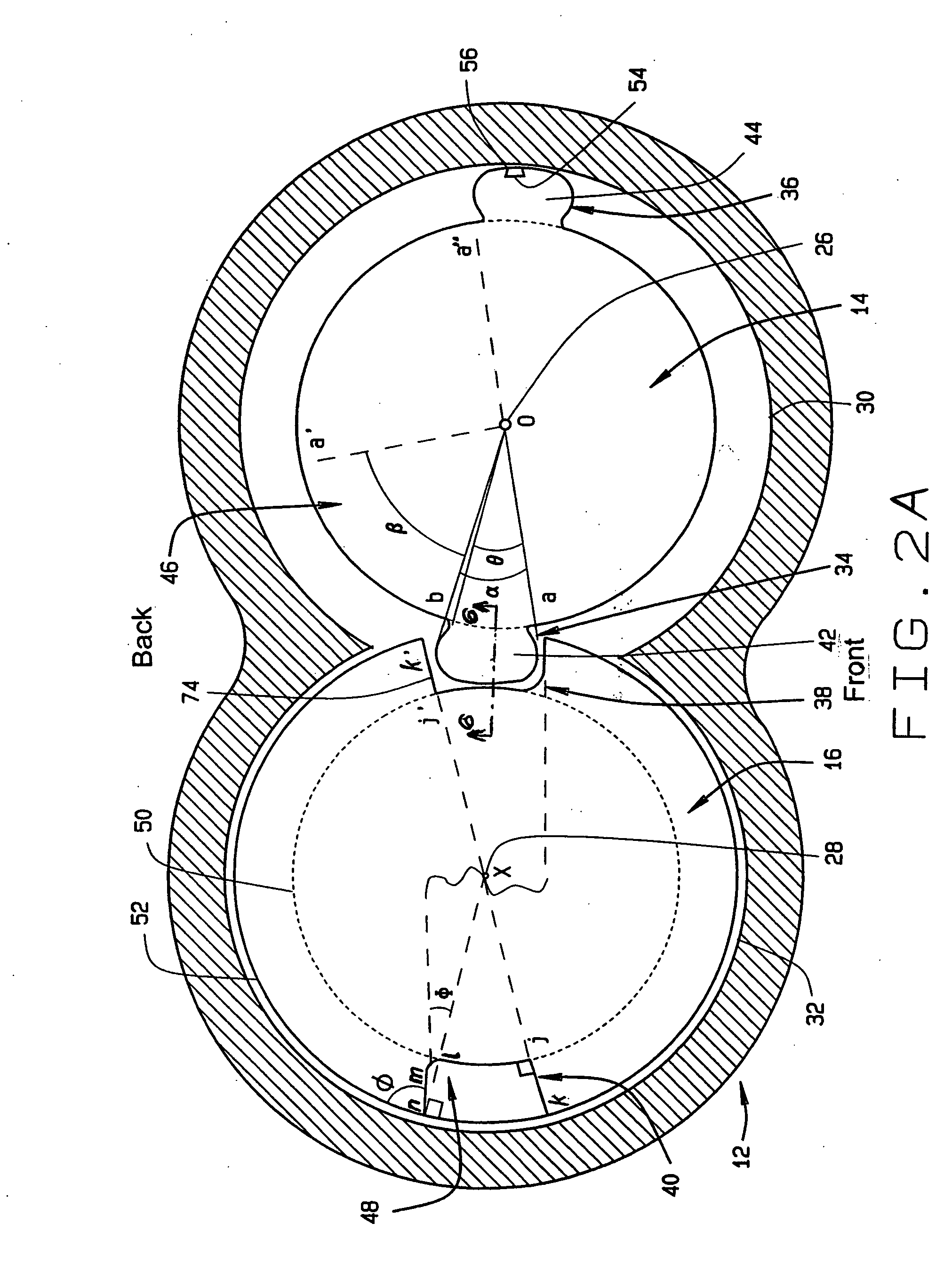
InactiveUS20050129561A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce gapOscillating piston enginesSealing arrangement for pumpsEngineeringScrew thread
A screw rotor device has a housing with an inlet port and an outlet port, a male rotor with helical threads, and a female rotor with helical grooves. The helical threads and helical grooves are designed to eliminate the blow hole leak pathway for multiple-pitch screw rotor devices as well as single-pitch screw rotor devices. The male rotor has a pair of helical threads with a phase-offset aspect, and the female rotor has a corresponding pair of helical grooves. The female rotor counter-rotates with respect to the male rotor and each of the helical grooves respectively intermeshes in phase with each of the helical threads. The phase-offset aspect of the helical threads is formed by a pair of teeth bounding a toothless sector.
Owner:IMPERIAL RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com