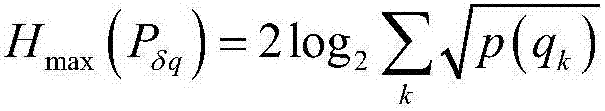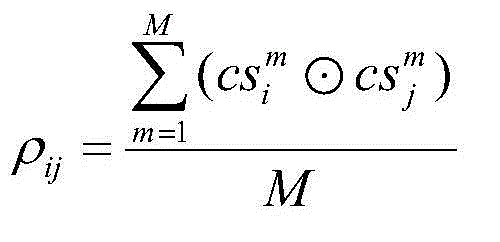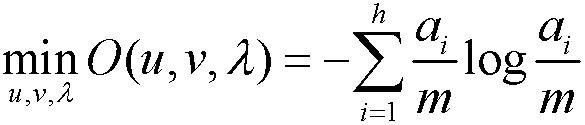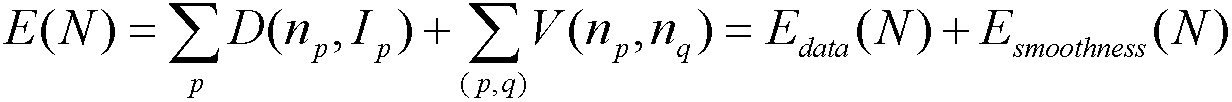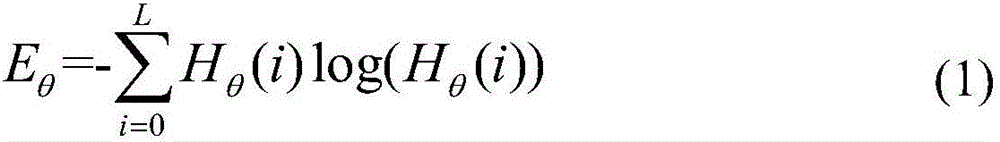Patents
Literature
91 results about "Minimum entropy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Efficient simulation system of quantum algorithm gates on classical computer based on fast algorithm
InactiveUS20060224547A1Effective simulationReduce in quantityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsFast algorithmMinimum entropy
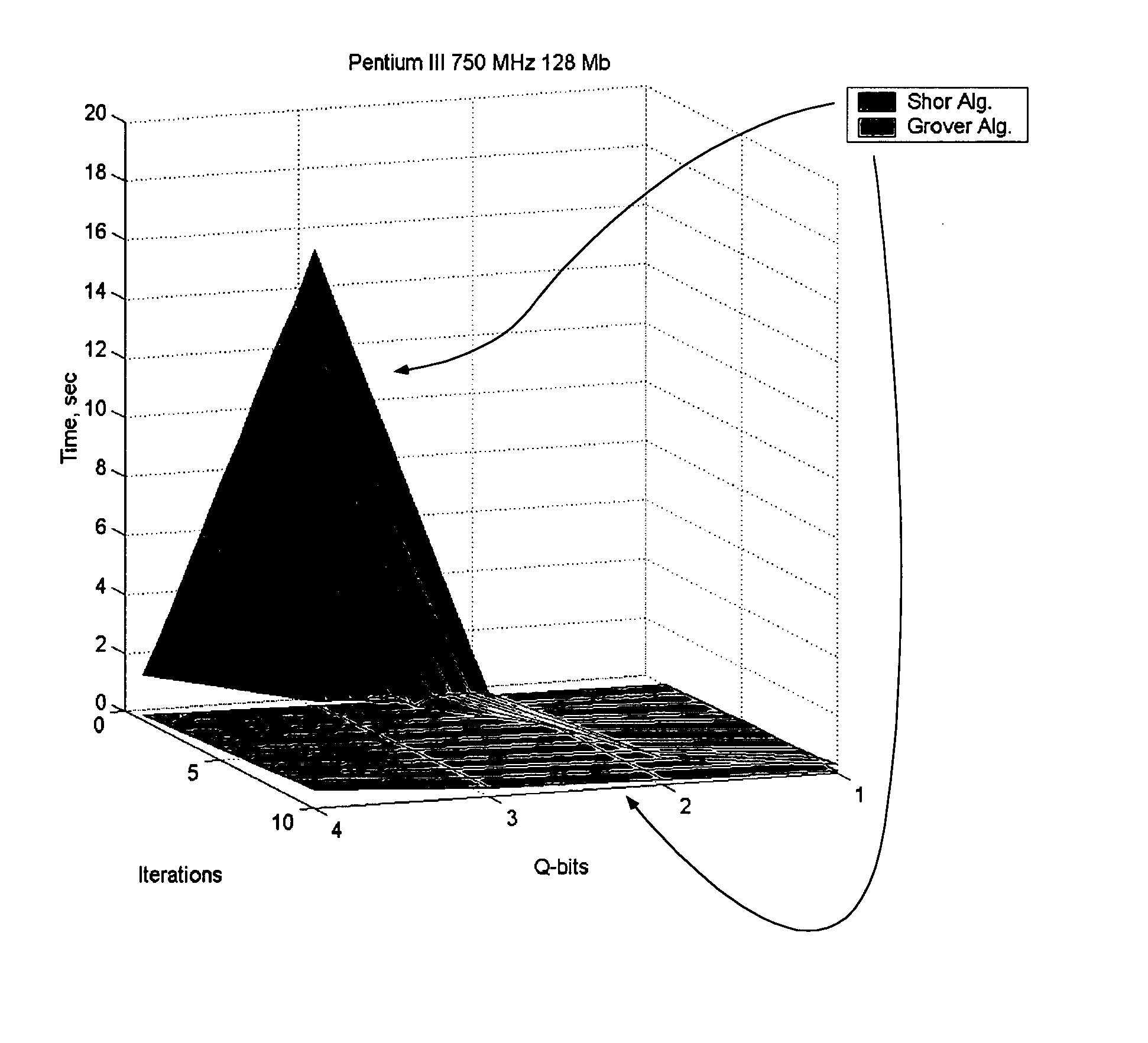
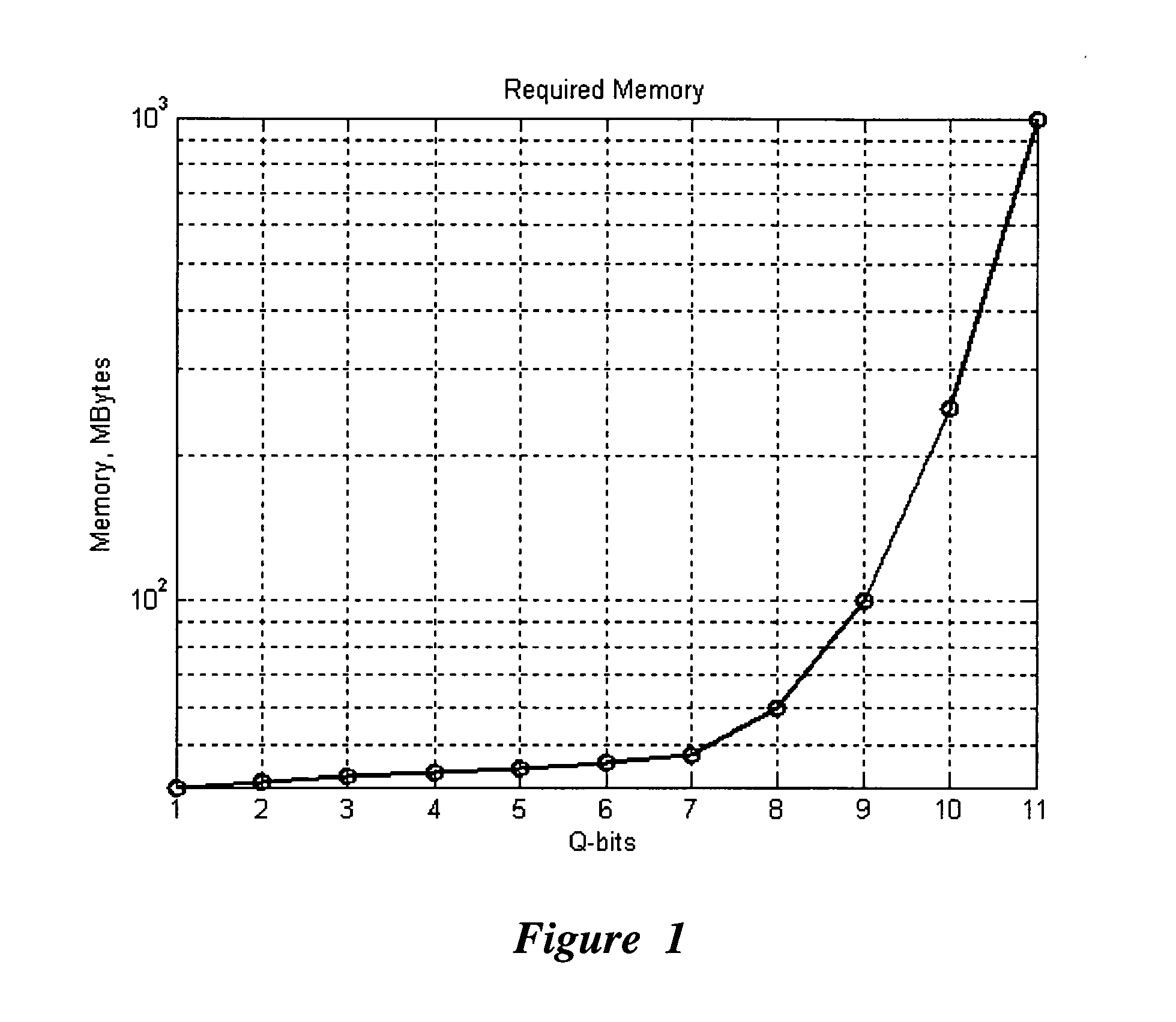
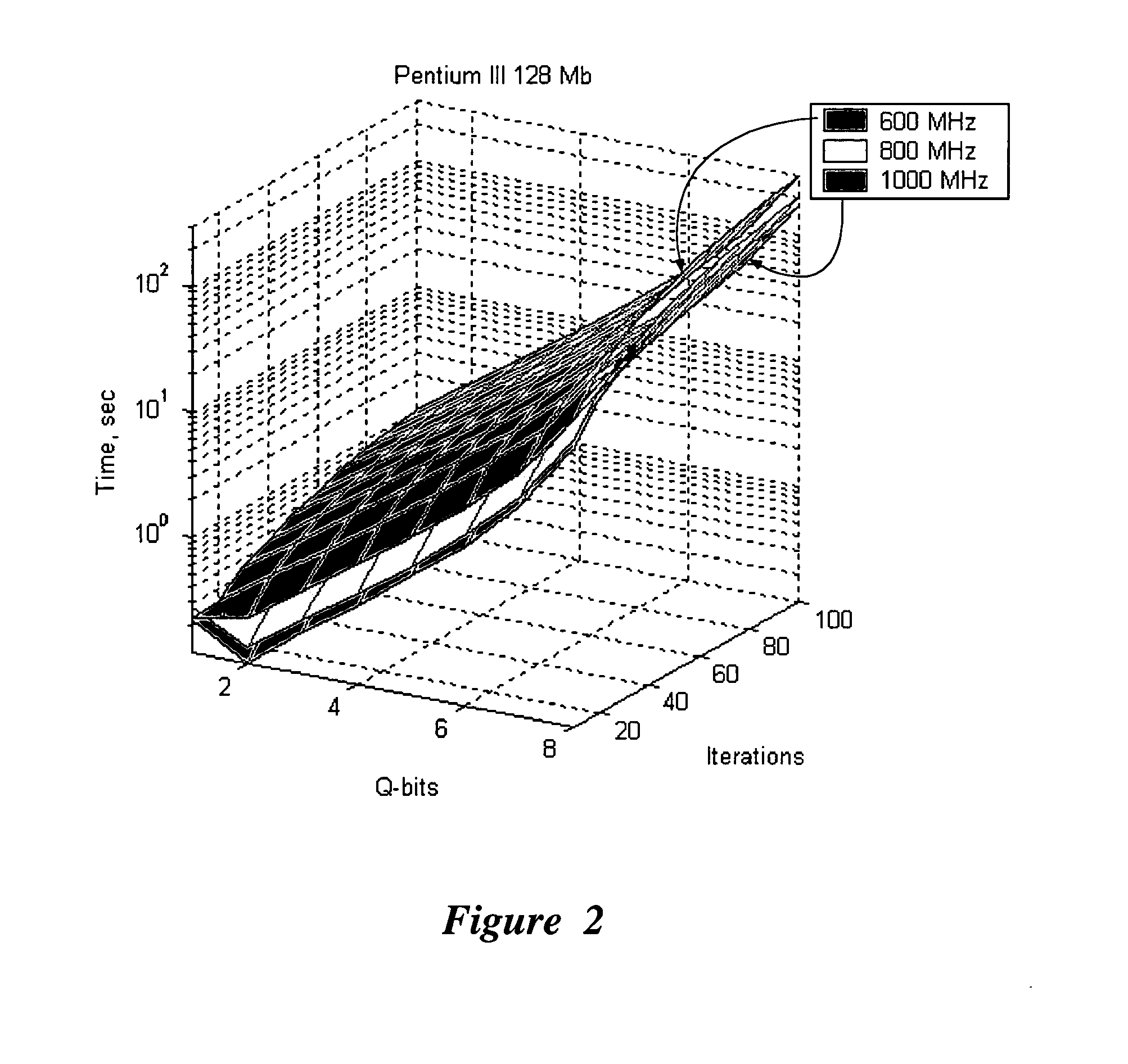
An efficient simulation system of quantum algorithm gates for classical computers with a Von Neumann architecture is described. In one embodiment, a Quantum Algorithm is solved using an algorithmic-based approach, wherein matrix elements of the quantum gate are calculated on demand. In one embodiment, a problem-oriented approach to implementing Grover's algorithm is provided with a termination condition determined by observation of Shannon minimum entropy. In one embodiment, a Quantum Control Algorithm is solved by using a reduced number of quantum operations.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
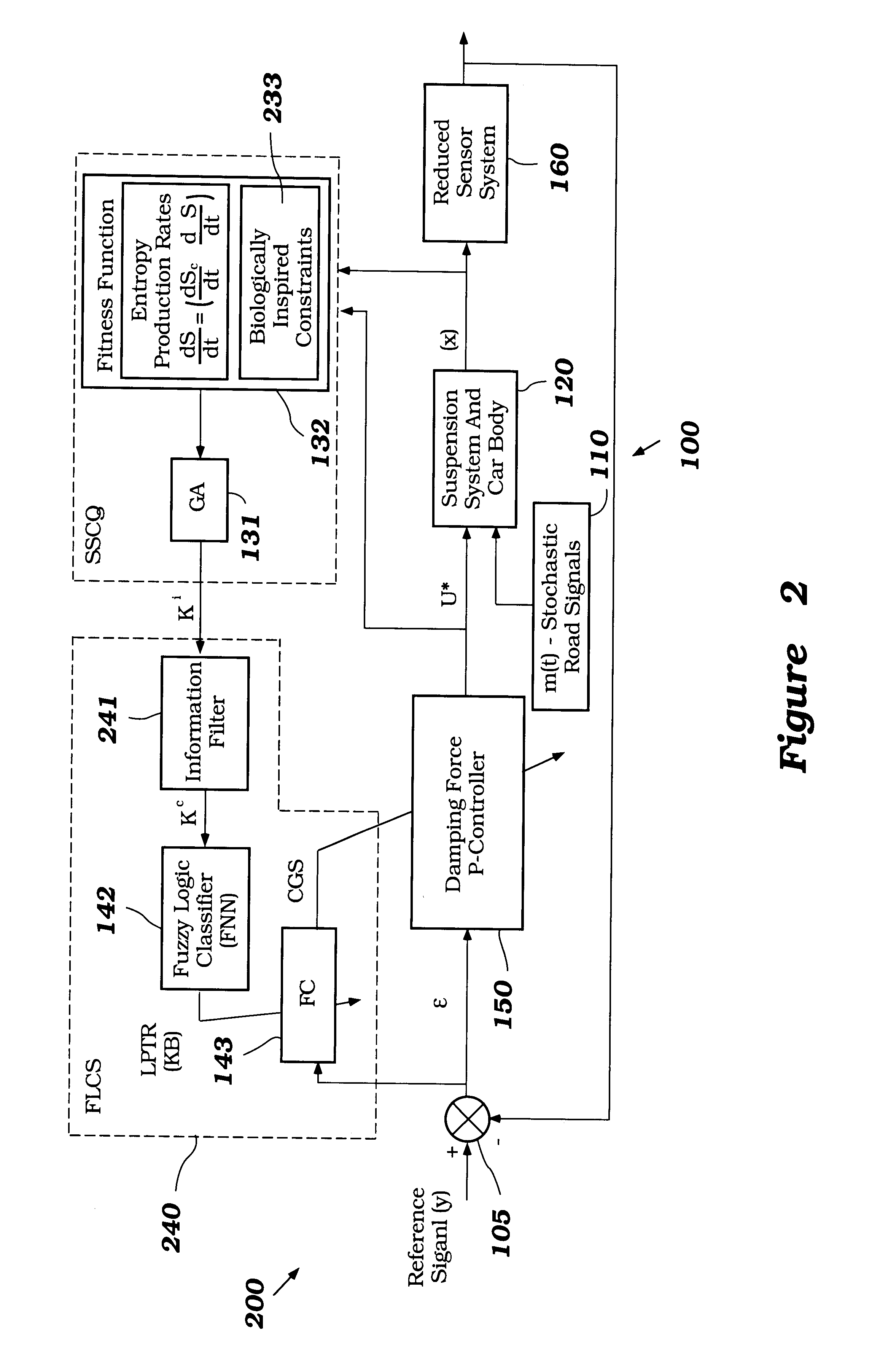
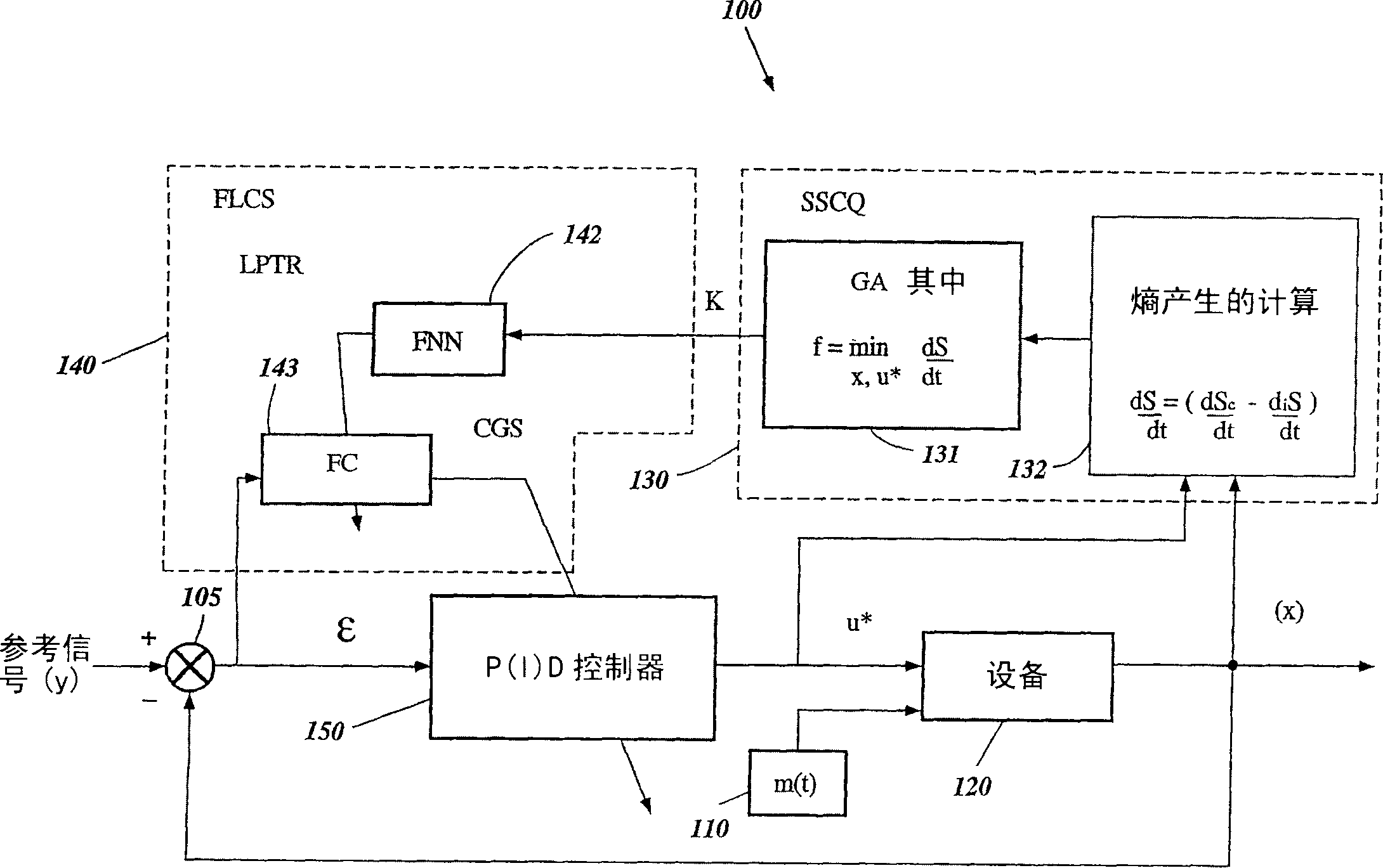
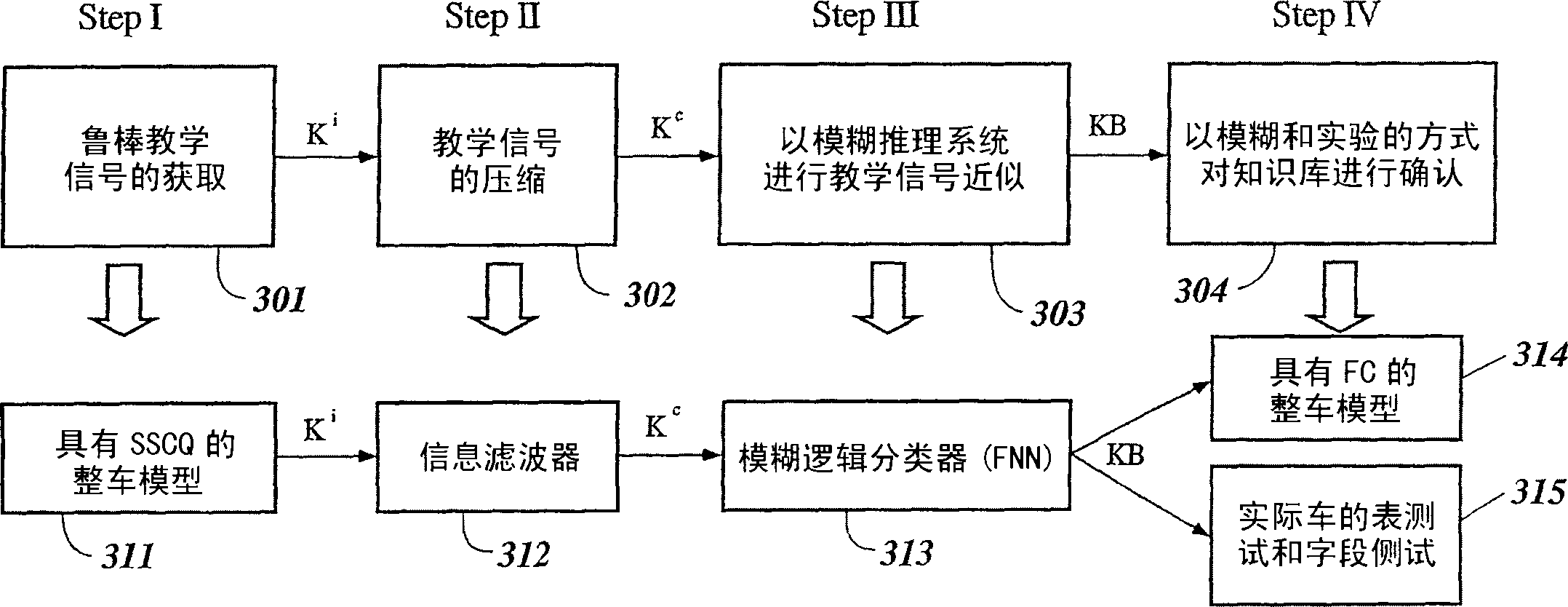
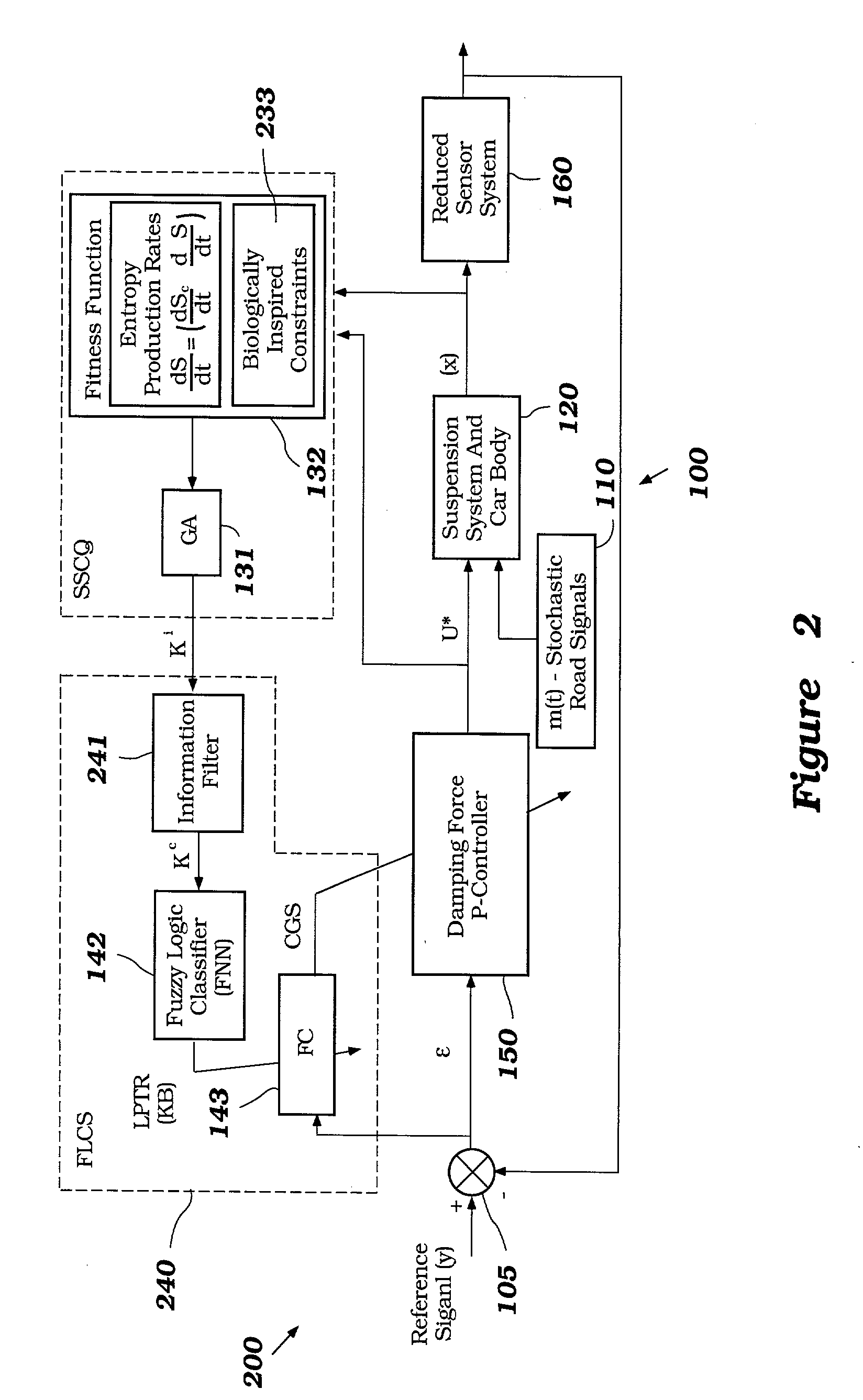
System and method for nonlinear dynamic control based on soft computing with discrete constraints
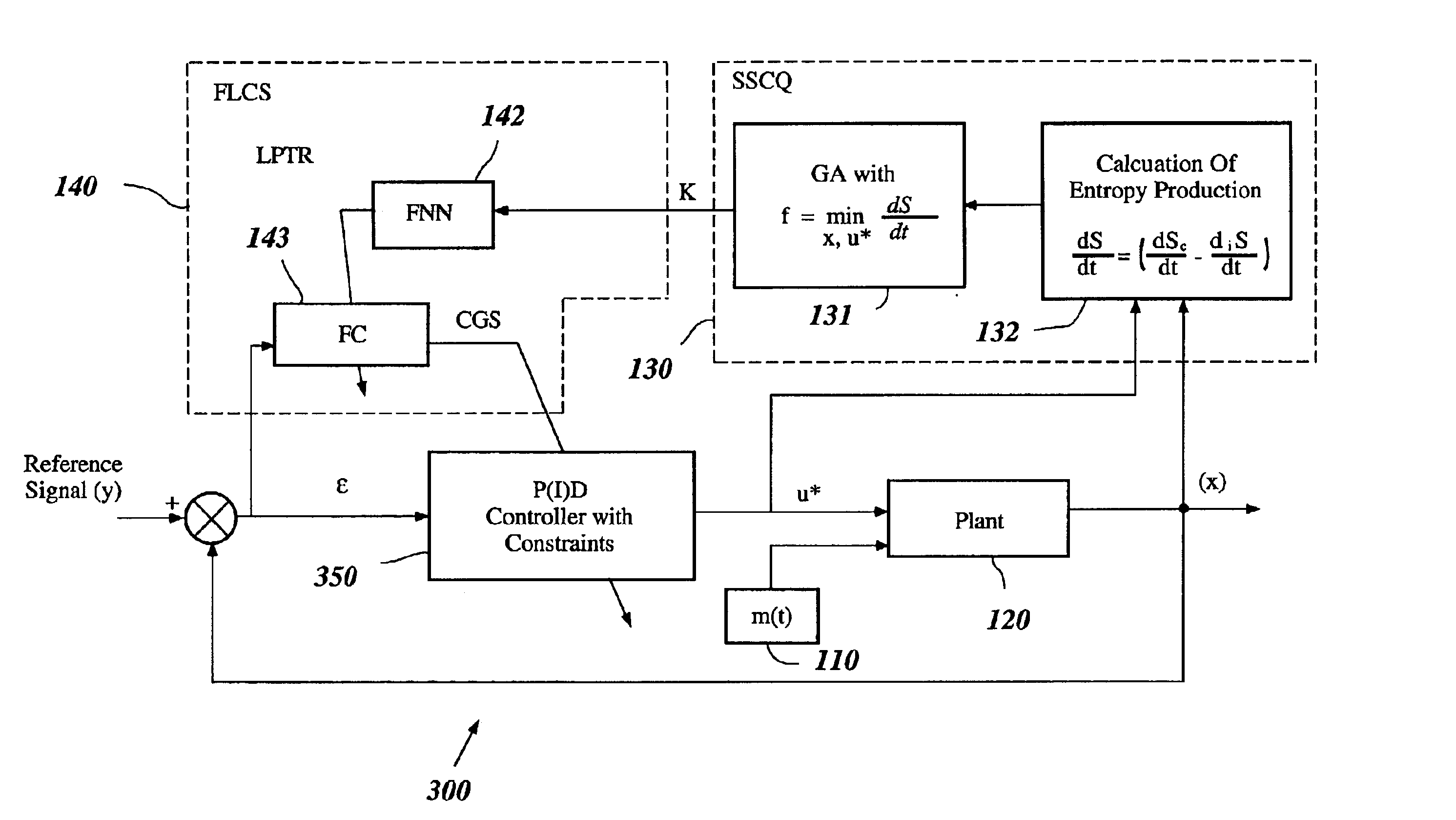
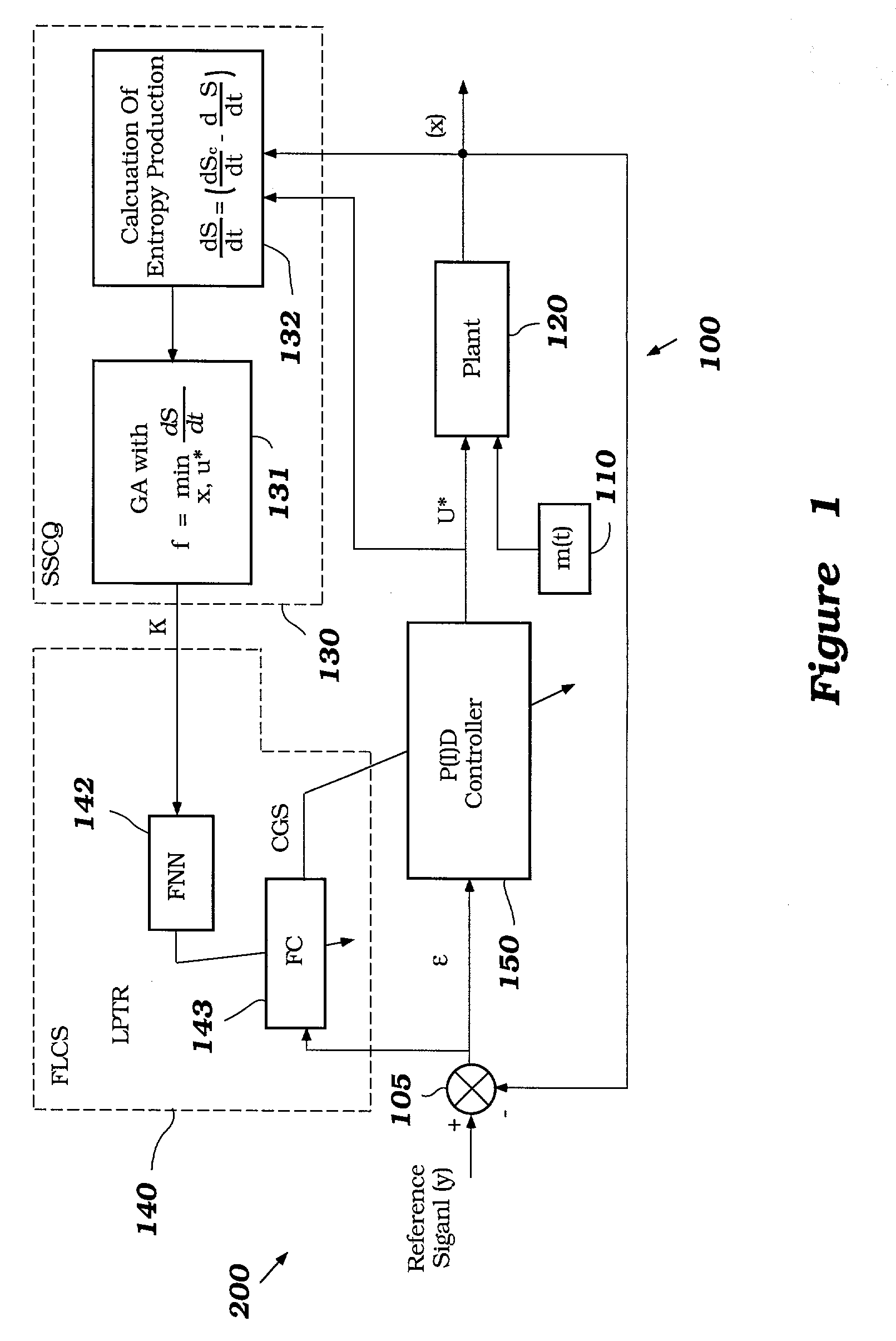
InactiveUS6950712B2Minimizes entropyMaximizes sensor information contentDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesNon linear dynamicMinimum entropy
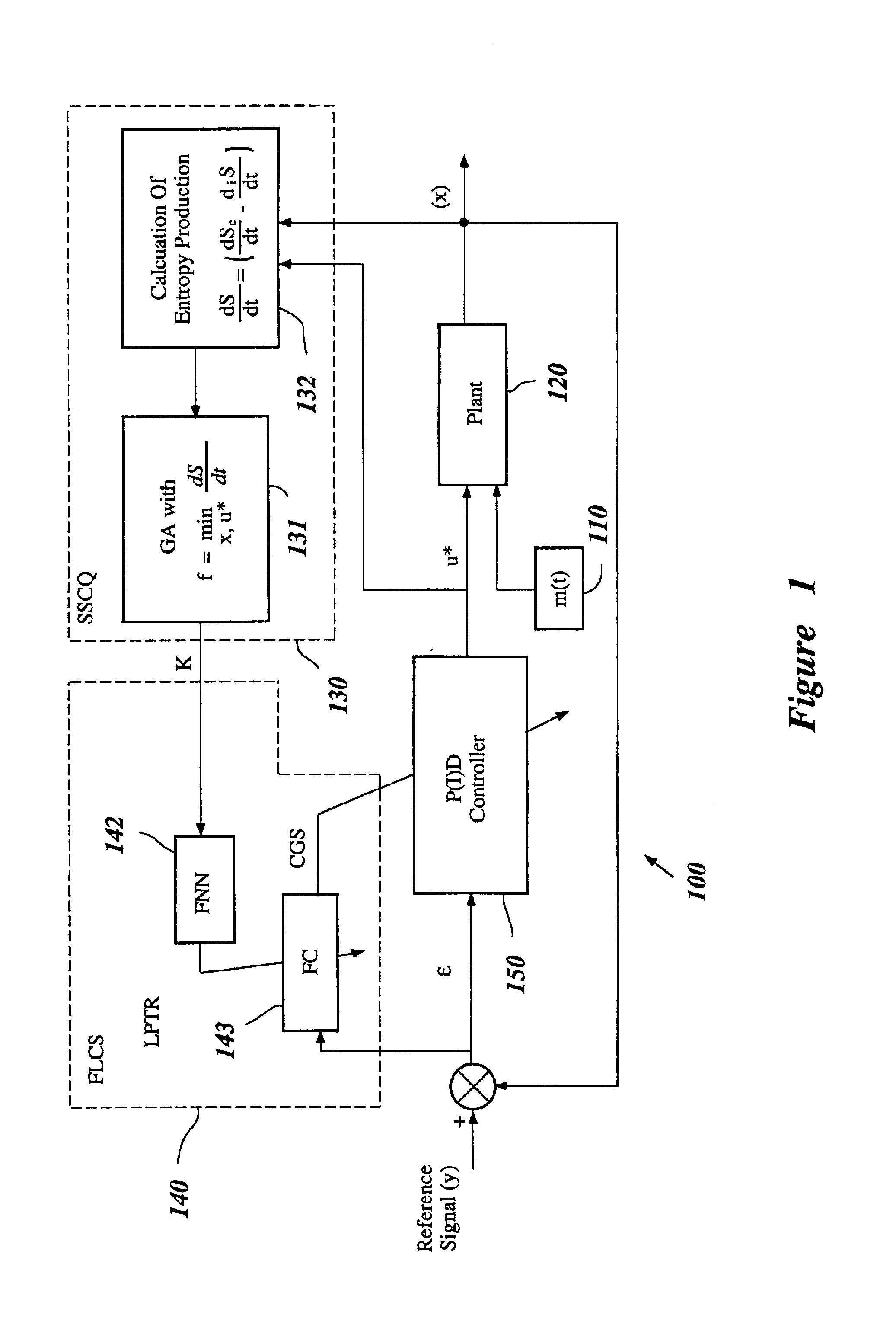
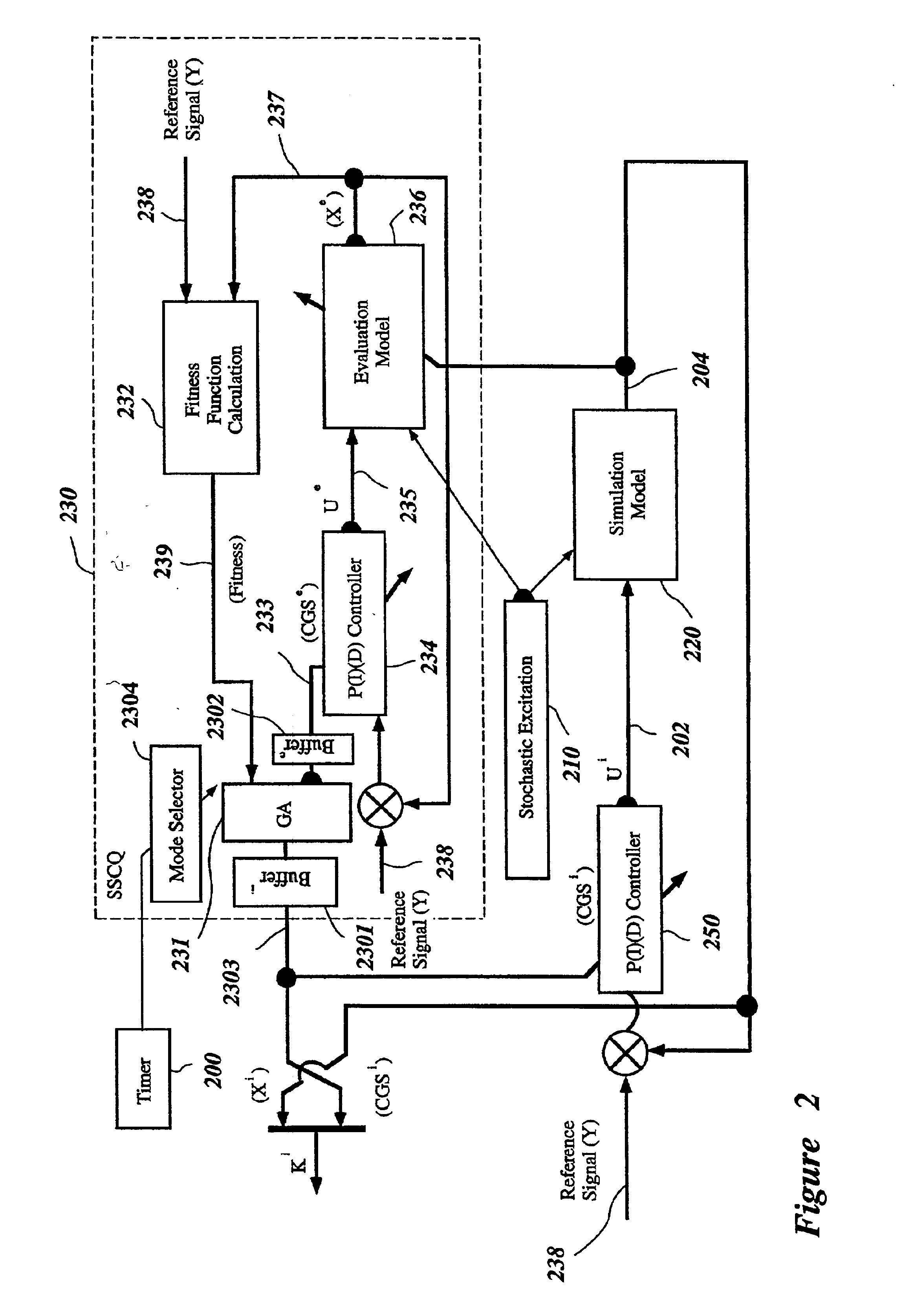
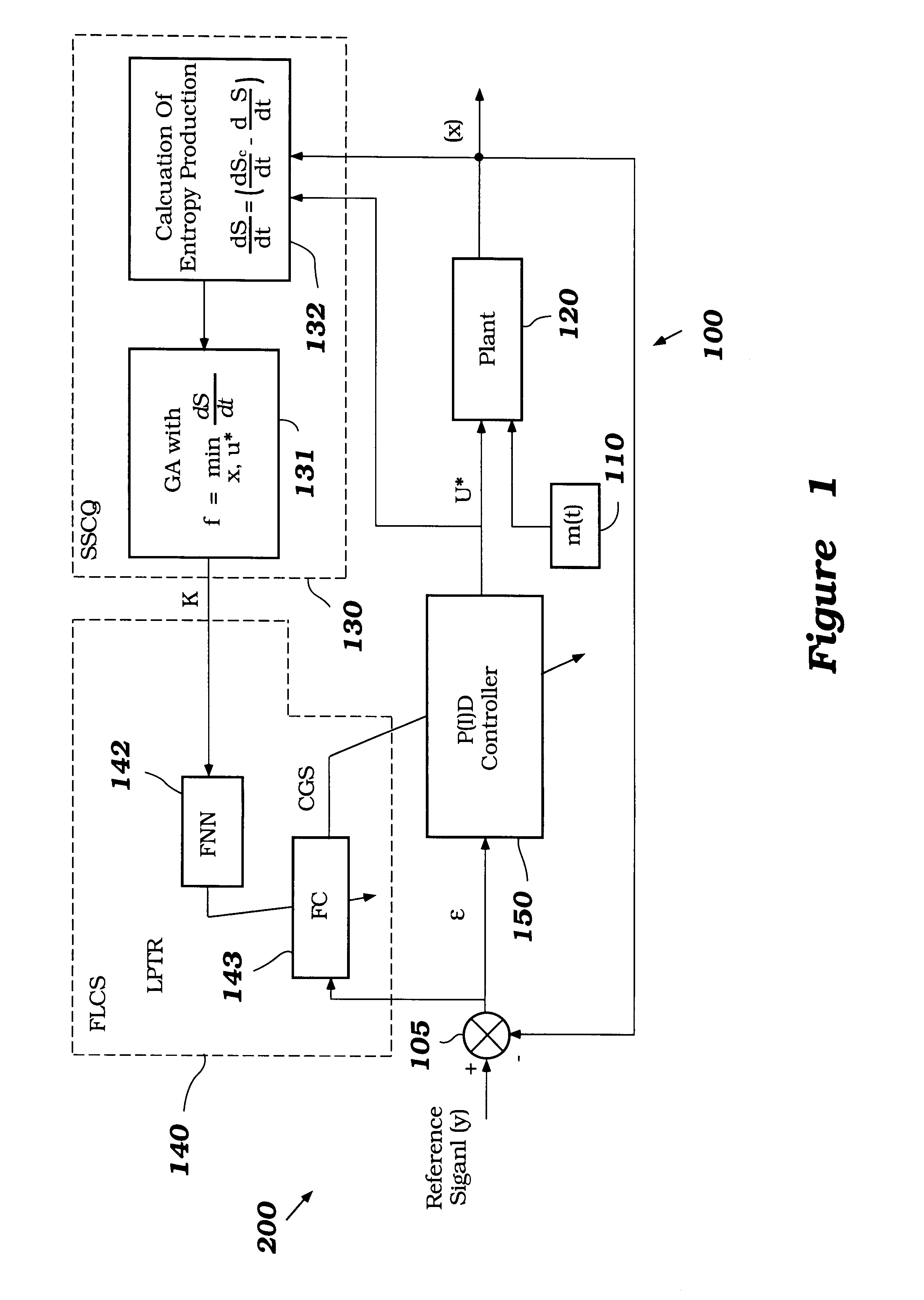
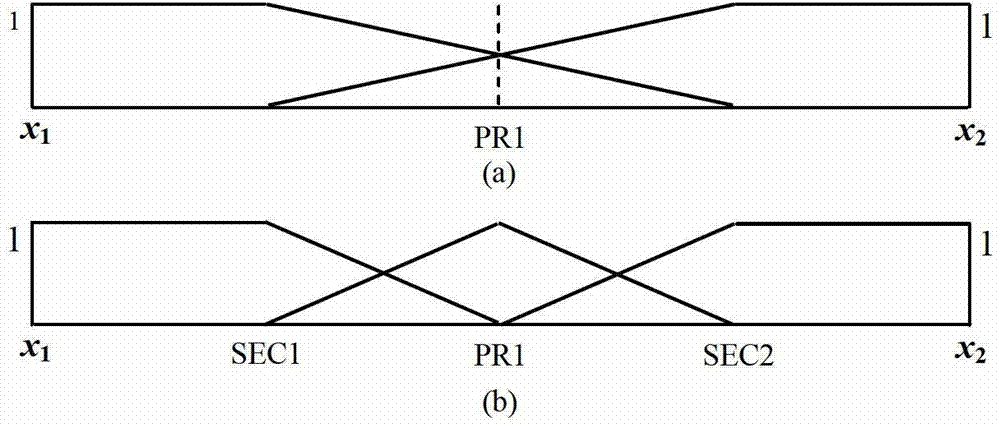
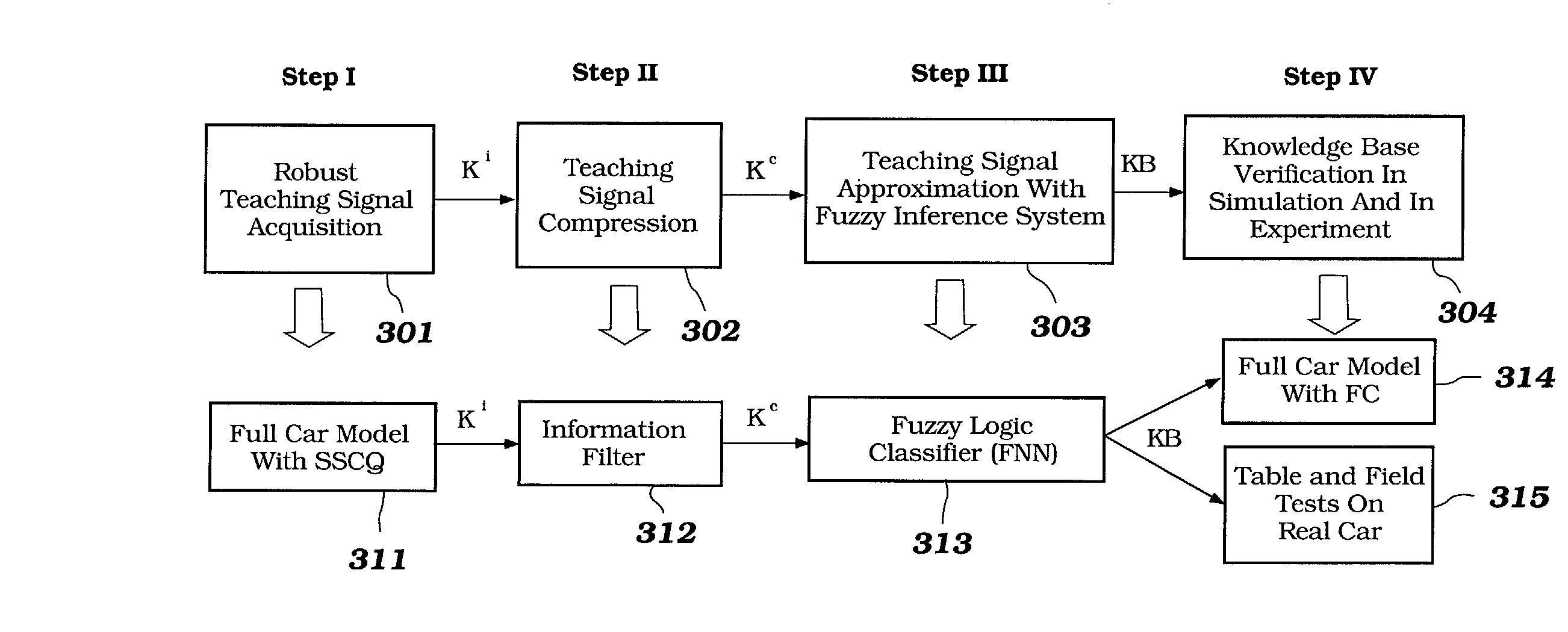
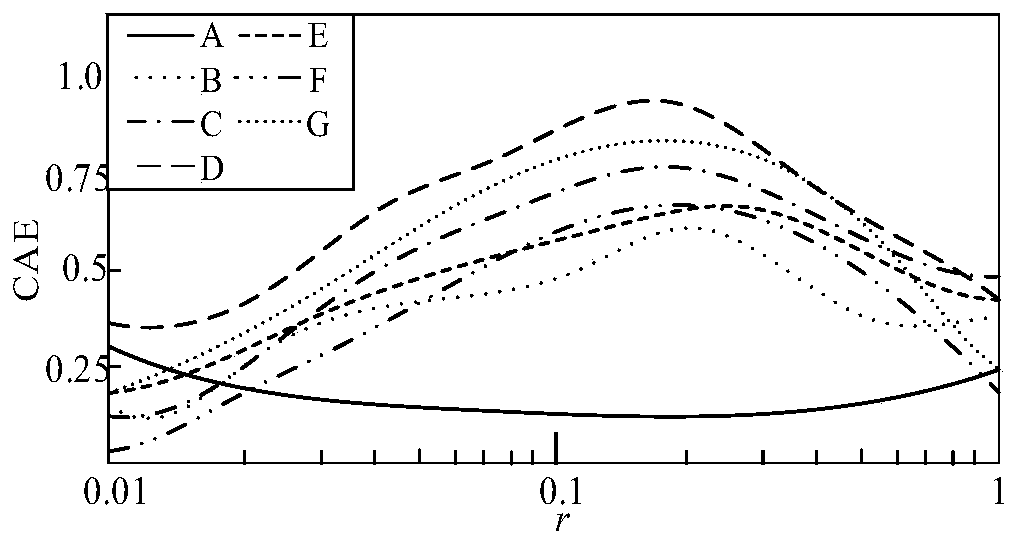
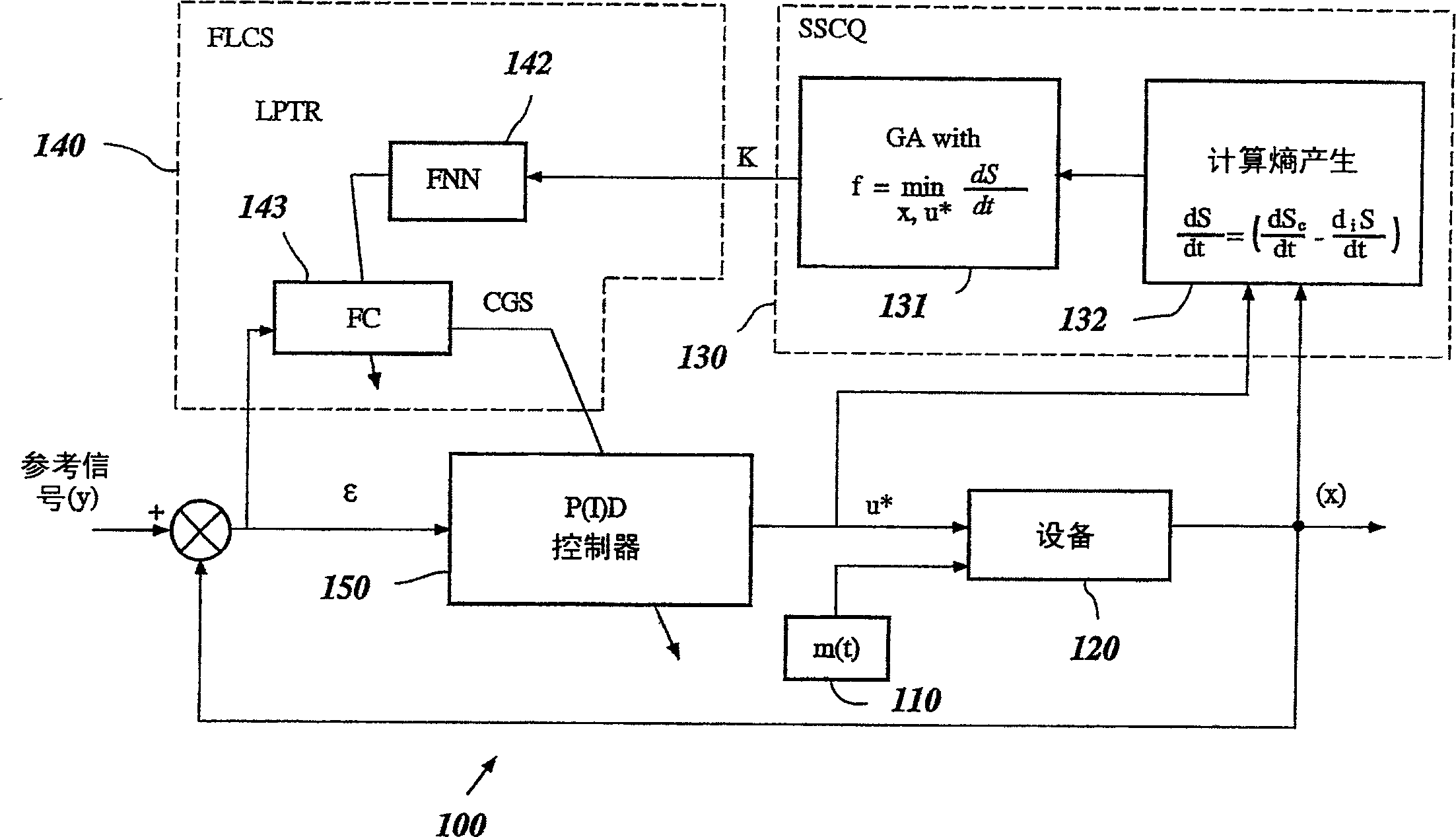
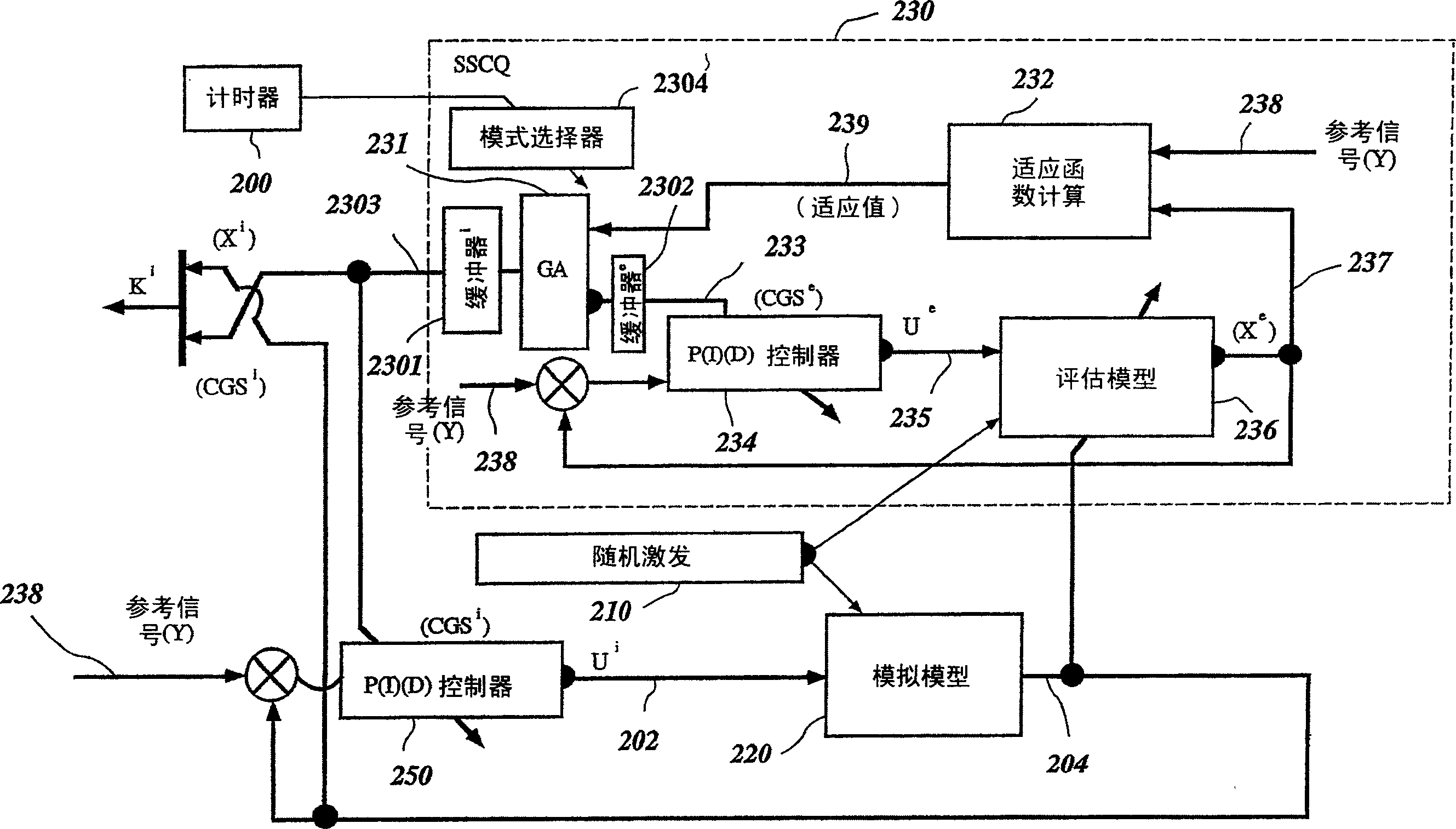
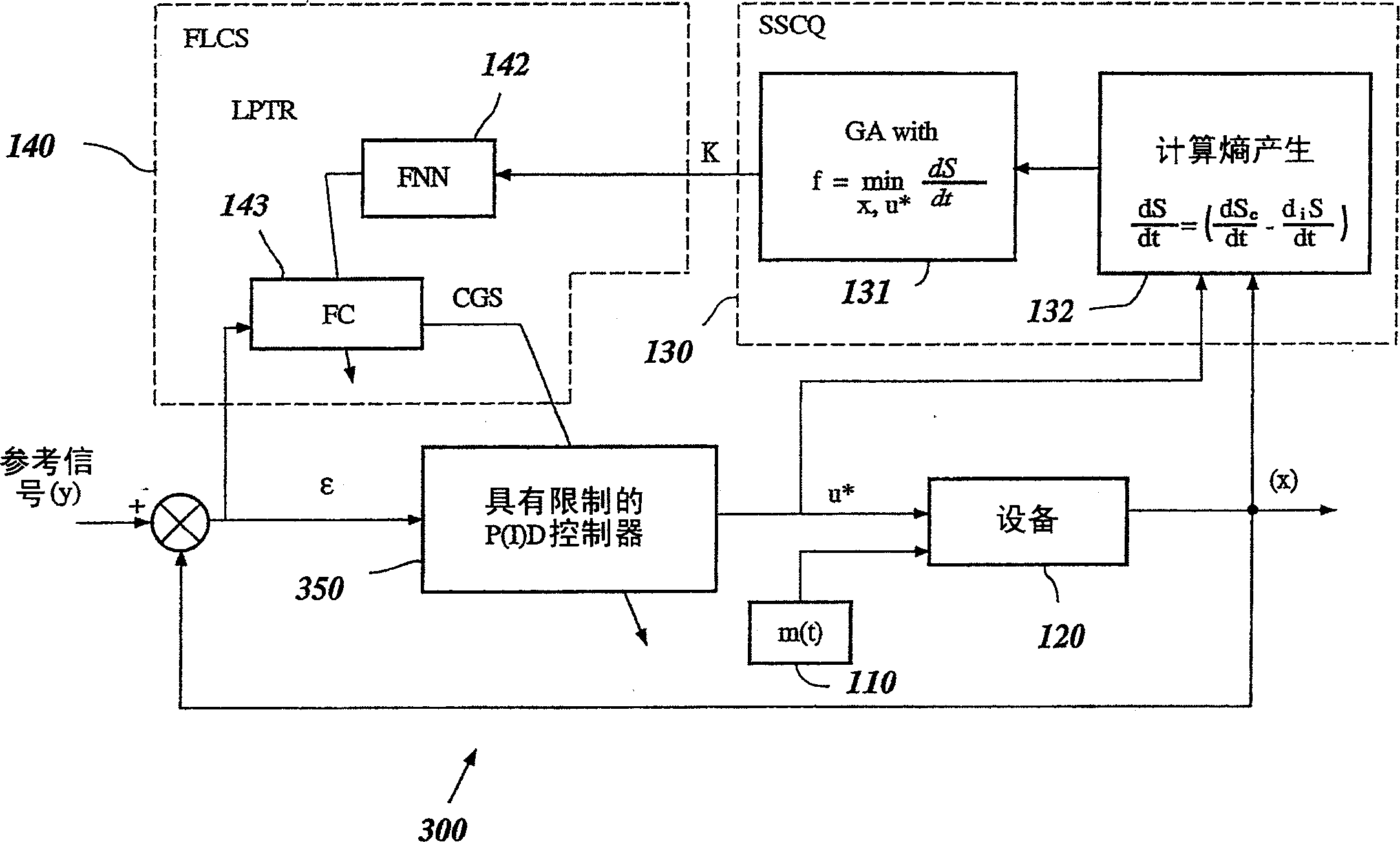
A control system using a genetic analyzer based on discrete constraints is described. In one embodiment, a genetic algorithm with step-coded chromosomes is used to develop a teaching signal that provides good control qualities for a controller with discrete constraints, such as, for example, a step-constrained controller. In one embodiment, the control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy. In one embodiment, the genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal for a fuzzy logic classifier system that develops a knowledge base. The teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from the knowledge base. The control system can be used to control complex plants described by nonlinear, unstable, dissipative models. In one embodiment, the step-constrained control system is configured to control stepping motors.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
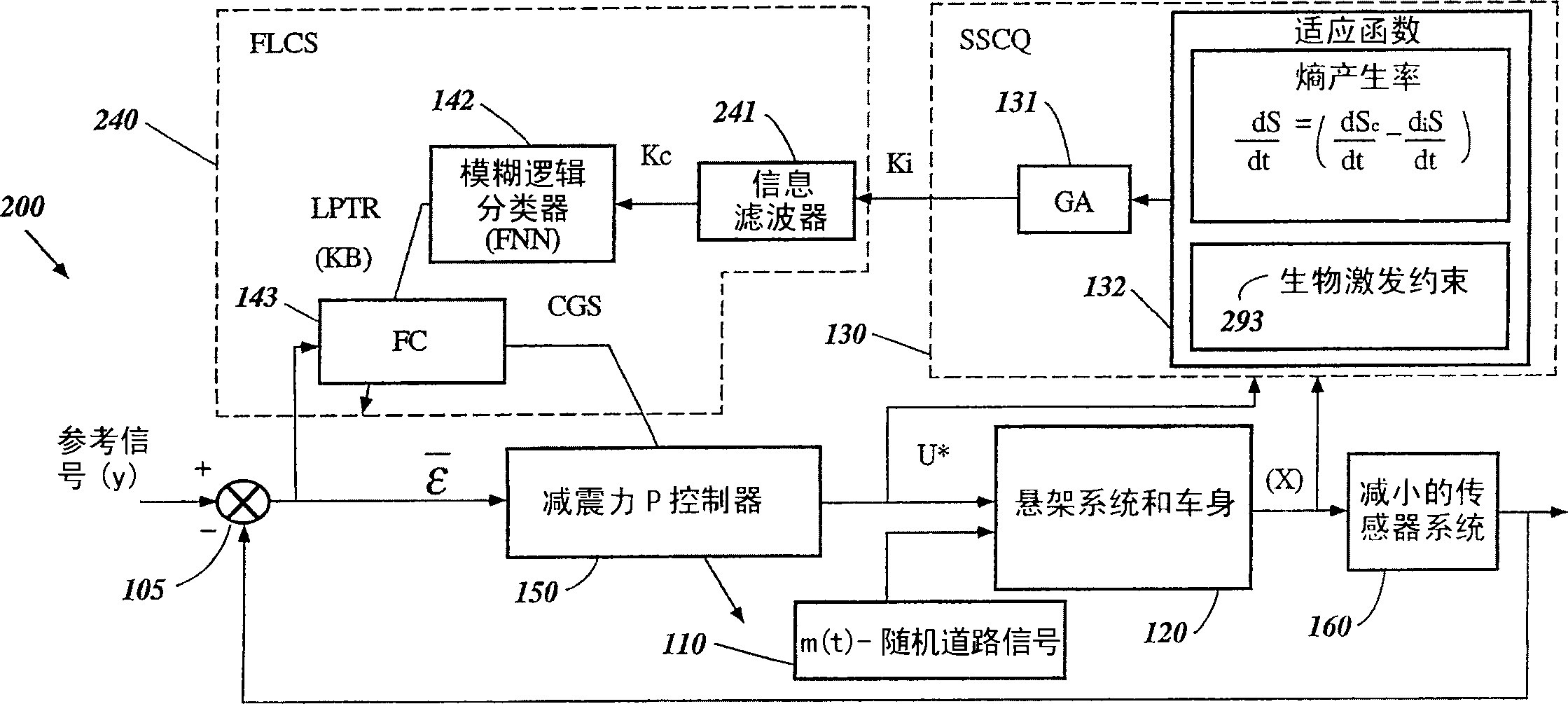
Intelligent mechatronic control suspension system based on soft computing
InactiveUS6701236B2Maximises informationLightweight productionSpringsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemFuzzy control system
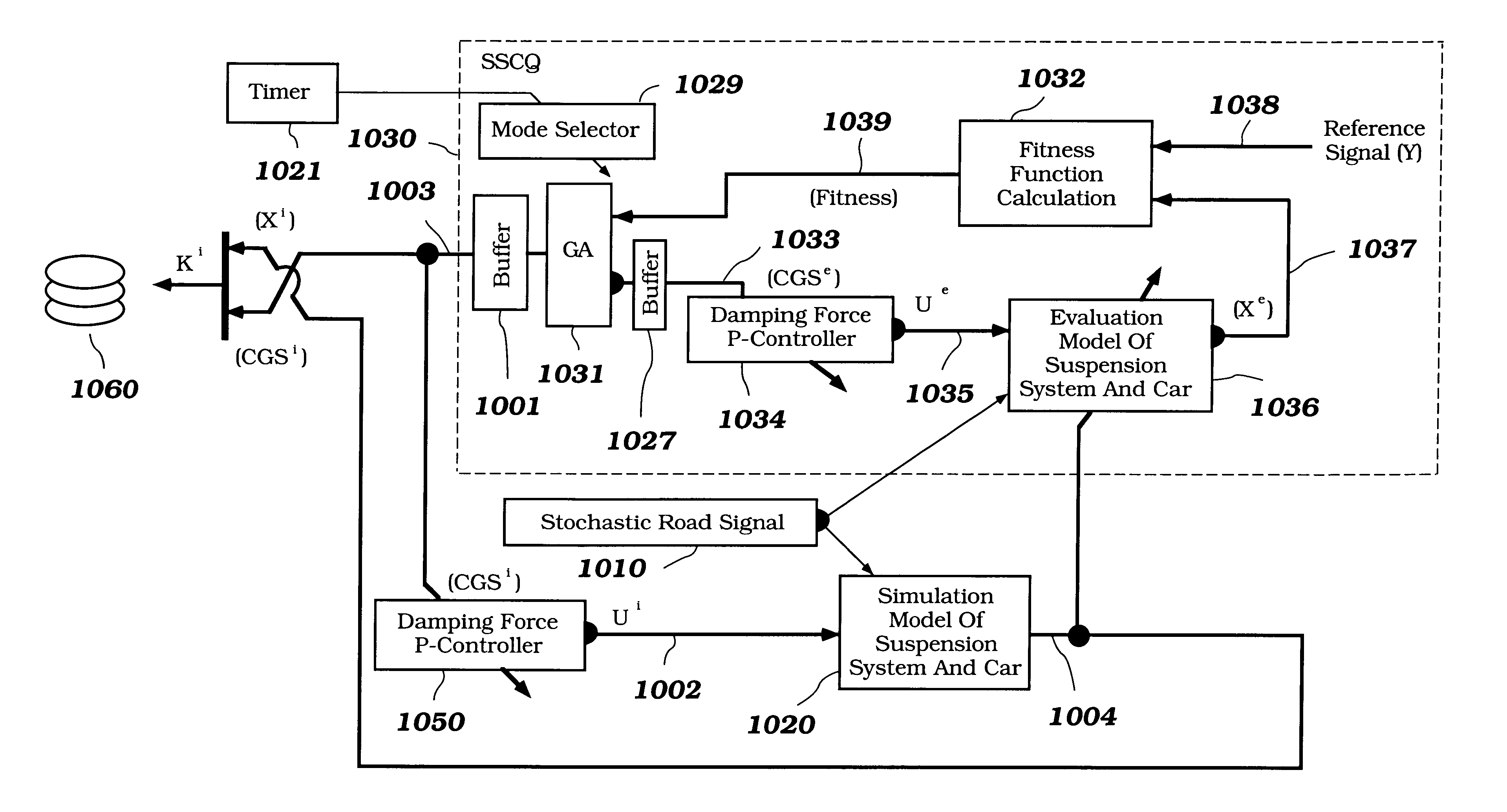
A control system for optimizing a shock absorber having a non-linear kinetic characteristic is described. The control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy and biologically inspired constraints relating to mechanical constraints and / or rider comfort, driveability, etc. In one embodiment, a genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal. An information filter is used to filter the teaching signal to produce a compressed teaching signal. The compressed teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from a knowledge base. In one embodiment, the control system includes a learning system, such as a neural network that is trained by the compressed training signal. The learning system is used to create a knowledge base for use by an online fuzzy controller. The online fuzzy controller is used to program a linear controller.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Intelligent mechatronic control suspension system based on quantum soft computing
InactiveCN1672171AGood precisionImprove reliabilityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsQuantum search algorithmMinimum entropy
A control system for optimizing a shock absorber having a non-linear kinetic characteristic is described. The control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy and biologically inspired constraints relating to mechanical constraints and / or rider comfort, driveability, etc. In one embodiment, a genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal. The teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from a knowledge base. A learning system is used to create the knowledge base for use by the online fuzzy controller. In one embodiment, the learning system uses a quantum search algorithm to search a number of solution spaces to obtain information for the knowledge base. The online fuzzy controller is used to program a linear controller.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Travel time index entropy traffic circulation evaluation method
ActiveCN103413263AAccurate evaluationAccurate measurementData processing applicationsRoad vehicles traffic controlLower limitRoad networks
The invention discloses a travel time index entropy traffic circulation evaluation method which comprises the following steps of a, calculating the free stream speed of each road section in a road network according to historical speed data provided by road network vehicle detection equipment, b, calculating the travel time index of each road section, c, calculating cut-off positions of the travel time indexes according to a quantile method or road capacity, d, calculating discrete probability distribution of the travel time indexes of a probe vehicle, e, calculating the entropy of the travel time indexes, f, calculating the highest possible value of the entropy as the upper limit of a dynamic range through the maximum entropy theorem, g, using the minimum entropy value Hmin of the travel time indexes as the lower limit of the dynamic range of the entropy of the travel time indexes, and h, carrying out normalization processing between the upper limit and the lower limit of the dynamic range of the entropy to obtain a road network traffic circulation evaluation value. The travel time index entropy traffic circulation evaluation method is a scientific characterization method of traffic circulation states, and measurement of traffic jam severity degree is achieved from the aspects of system confusion and randomness and uncertainty of travel time.
Owner:北京交通发展研究院
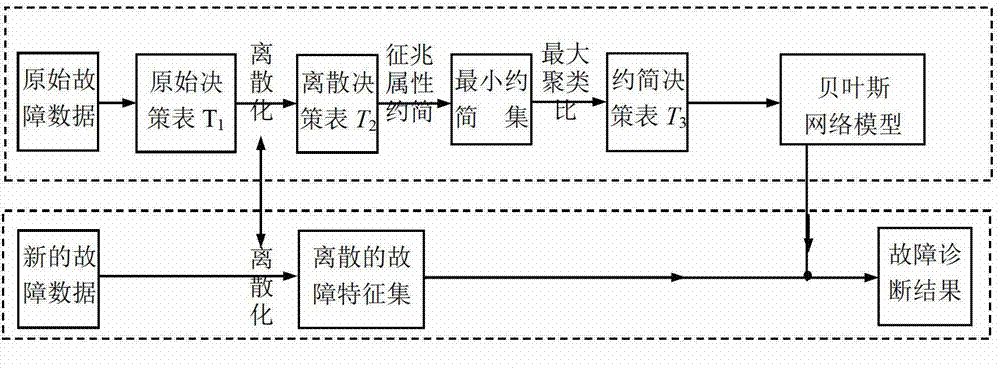
Intelligent fault diagnosis method based on rough Bayesian network classifier
InactiveCN102879677AOvercome rigidityOvercoming the Weakness of Critical MisjudgmentElectrical testingInference methodsCurse of dimensionalityMinimum entropy
The invention provides an intelligent fault diagnosis method based on a rough Bayesian network classifier, which comprises the following steps: using standard fault feature data as a fault diagnosis condition attribute set, using a standard fault mode as a fault diagnosis decision attribute set, and adopting a rough set principle to construct an original fault diagnosis information table T1; adopting the minimum entropy method to carry out discrete processing on various continuous fault diagnosis condition attribute values in the T1, so as to form a discretization fault diagnosis information table T2; using a rough set discernable matrix and a nuclear theory to carry out attribute reduction and optimal feature selection on the T2, so as to form a reduction fault diagnosis information table T3; and using the T3 to establish the Bayesian network classifier, so as to realize efficient and quick intelligent fault diagnosis. The intelligent fault diagnosis method avoids the 'curse of dimensionality' problem existed in a Bayesian network diagnostic method, overcomes weaknesses of rigid reasoning and critical misjudgment in a rough set diagnostic method, and greatly improves the efficiency and accuracy of fault diagnosis.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Intelligent mechatronic control suspension system based on soft computing
A control system for optimizing a shock absorber having a non-linear kinetic characteristic is described. The control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy and biologically inspired constraints relating to mechanical constraints and / or rider comfort, driveability, etc. In one embodiment, a genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal. An information filter is used to filter the teaching signal to produce a compressed teaching signal. The compressed teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from a knowledge base. In one embodiment, the control system includes a learning system, such as a neural network that is trained by the compressed training signal. The learning system is used to create a knowledge base for use by an online fuzzy controller. The online fuzzy controller is used to program a linear controller.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
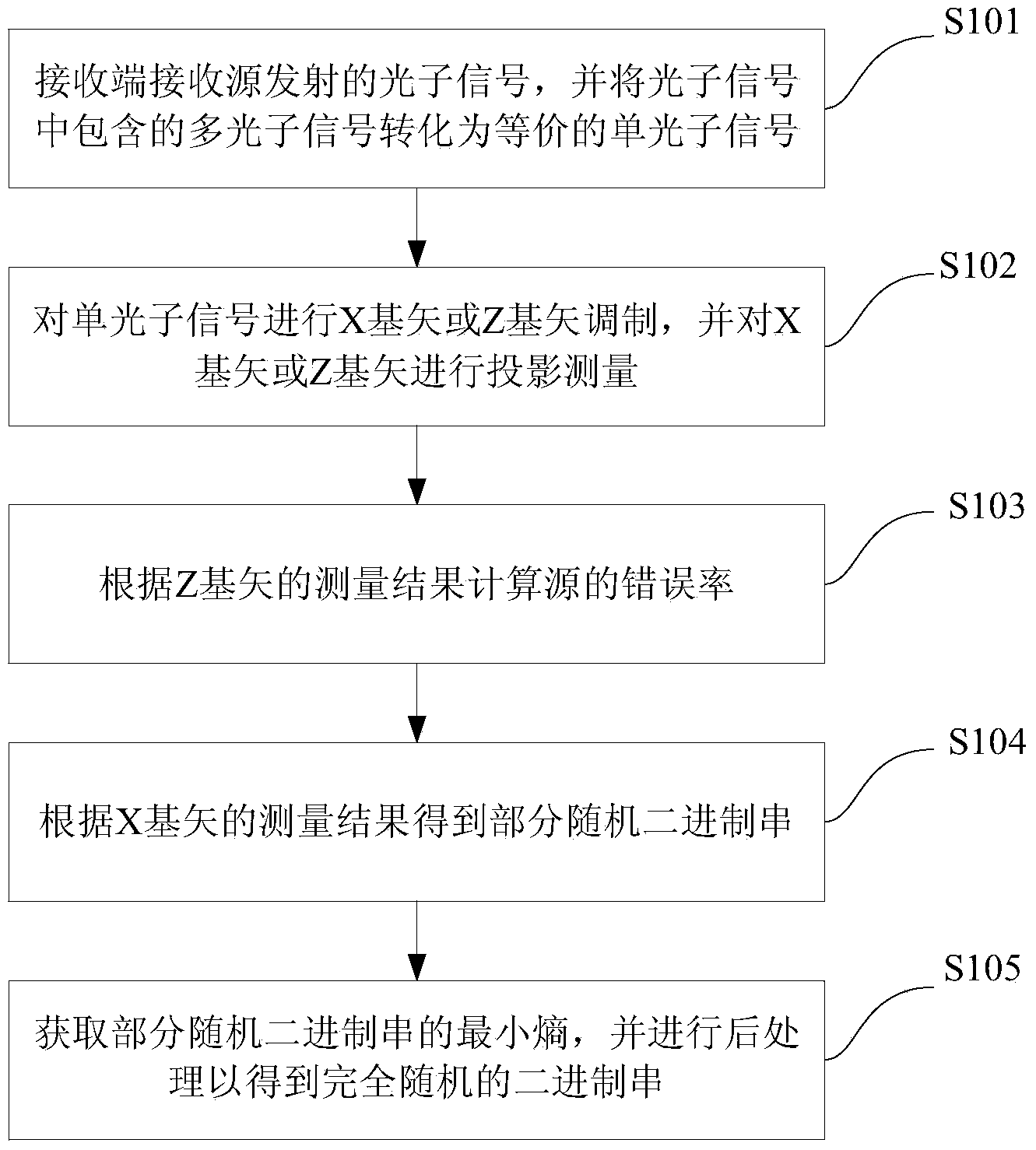
Source irrelevant quantum random number generation method and device
ActiveCN104238996AGuaranteed correctnessChannel loss toleranceRandom number generatorsMinimum entropyBinary strings
The invention provides a source irrelevant quantum random number generation method, which comprises the following steps: receiving a photon signal emitted via a source by a receiving end, and converting a multiphoton signal contained in the photon signal into an equivalent single-photon signal; carrying out X basis vector or Z basis vector modulation on the single-photon signal, and carrying out projection measurement on an X basis vector or Z basis vector; according to the measurement result of the Z basis vector, calculating an error rate; according to the measurement result of the X basis vector, obtaining parts of random binary string; obtaining the minimum entropy of the parts of random binary string, and carrying out aftertreatment to obtain a completely random binary string. The method disclosed by the invention does not need to depend on source hypothesis, a true random number guaranteed by quantum mechanics can be generated, and the method can tolerate high channel loss, and has high practical value. The invention also provides a source irrelevant quantum random number generation device.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Measuring method of bi-static forward-looking and squinting synthetic aperture radar Doppler center frequency
ActiveCN101937077AImprove assay efficiencyImprove efficiencyWave based measurement systemsTime domainSynthetic aperture radar
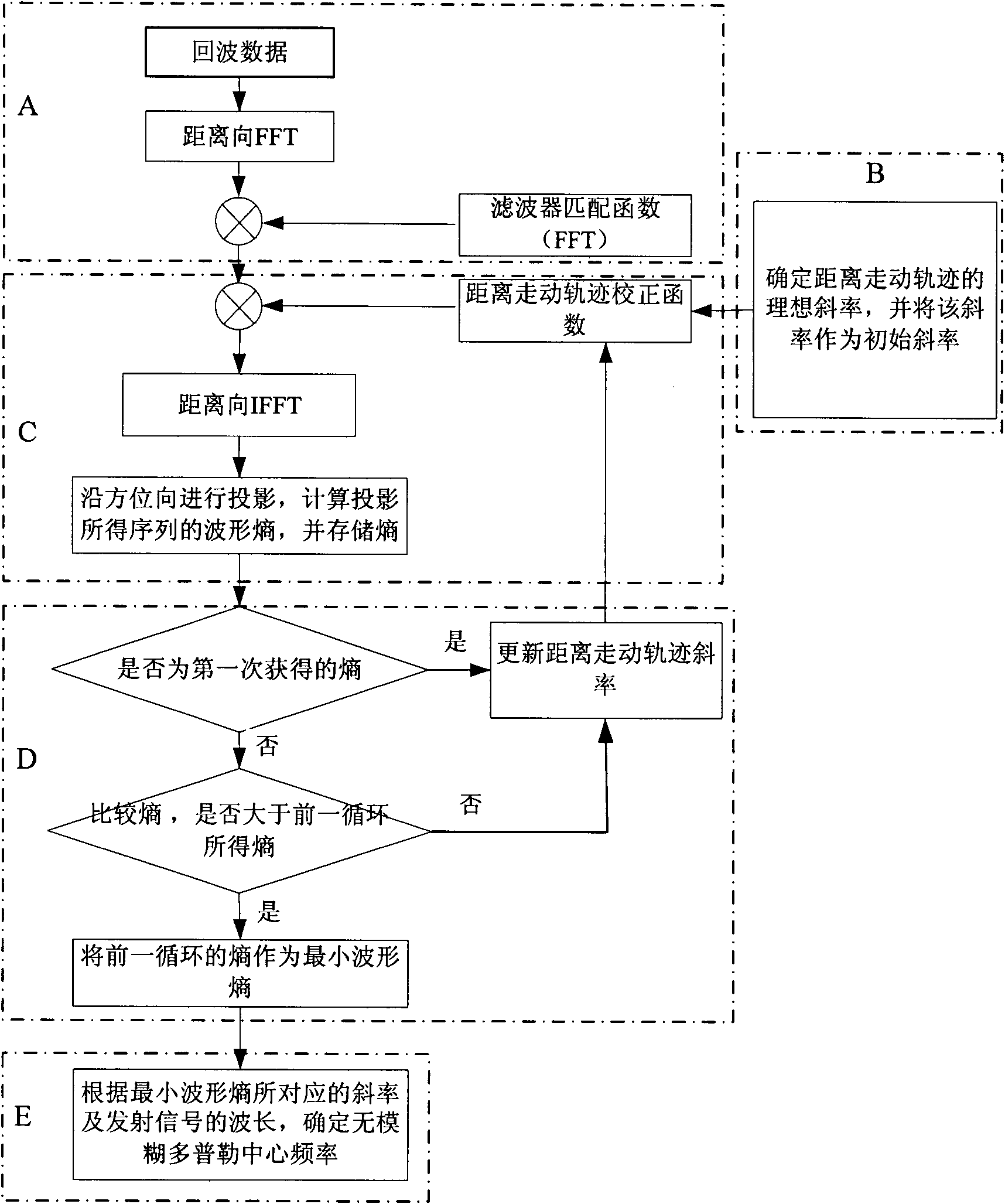
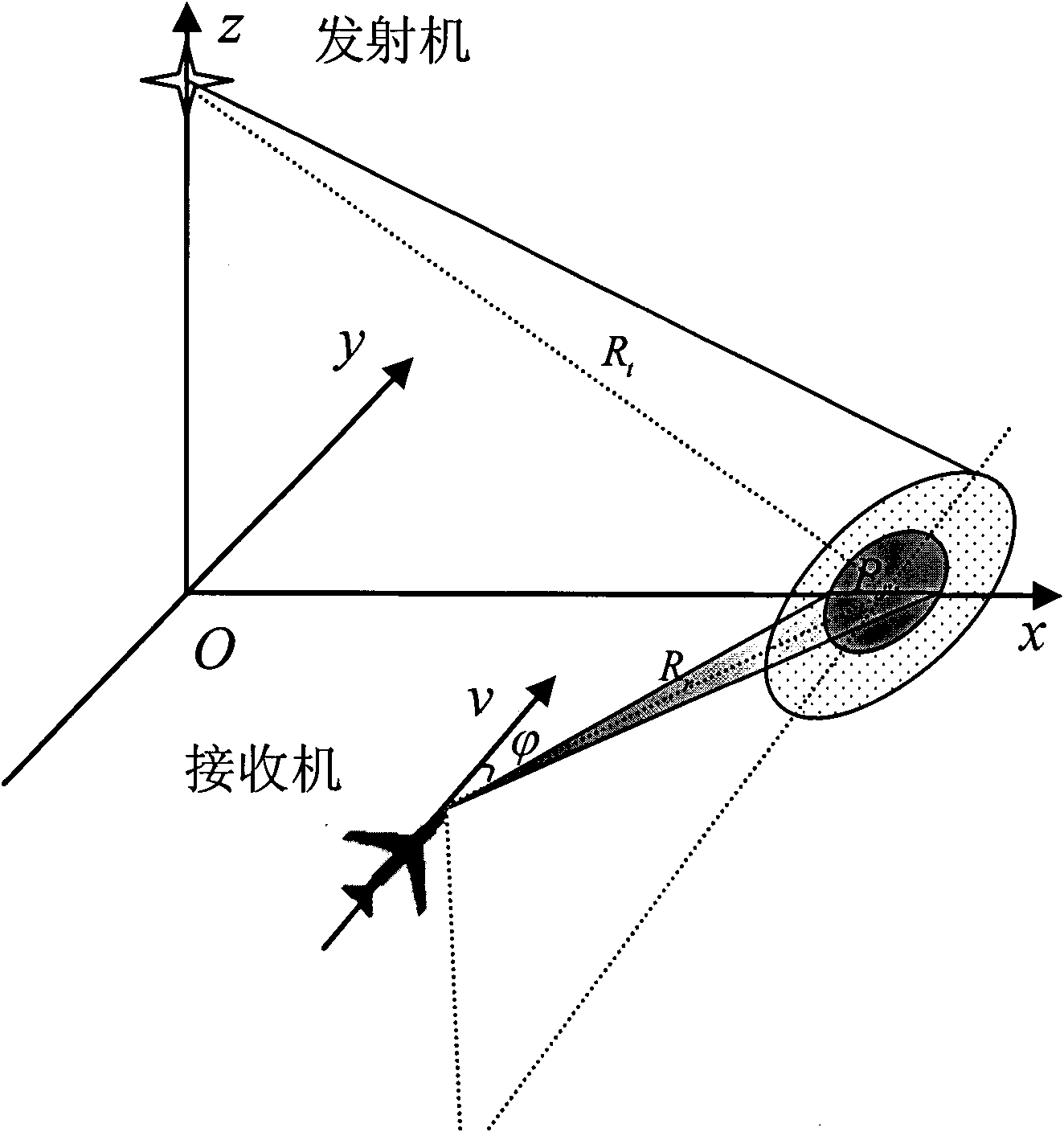
The invention belongs to a measuring method of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) non-fuzzy Doppler center frequency, comprising: compressing range direction pulse; obtaining initial slope; converting a frequency domain and a time domain; obtaining the waveform entropy of a sequence; determining the minimum waveform entropy; and determining the non-fuzzy Doppler center frequency. The invention utilizes the geometrical characteristics of the synthetic aperture radar echo on range time and azimuth time domains and the self information of a mobile platform to repeatedly correct range ambulating trajectory so as to determine the minimum entropy, thus measuring whether the trajectory is well corrected or not; the slop ratio of the corresponding trajectory to the wavelength of an emitted signal is used for obtaining the non-fuzzy Doppler center frequency; and the measured frequency is improved by more than 5 times compared with Laden conversion. Thus, on the aspect of bi-static forward-looking and squinting synthetic aperture radar (SAR) Doppler center frequency, the invention has the characteristics of simple and accurate measurement, short processing time, high efficiency, strong instantaneity and capability of providing accurate and reliable data for subsequent high-precision imaging and motion compensation.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Rapid sparse aperture ISAR self-focusing and imaging method based on ADMM
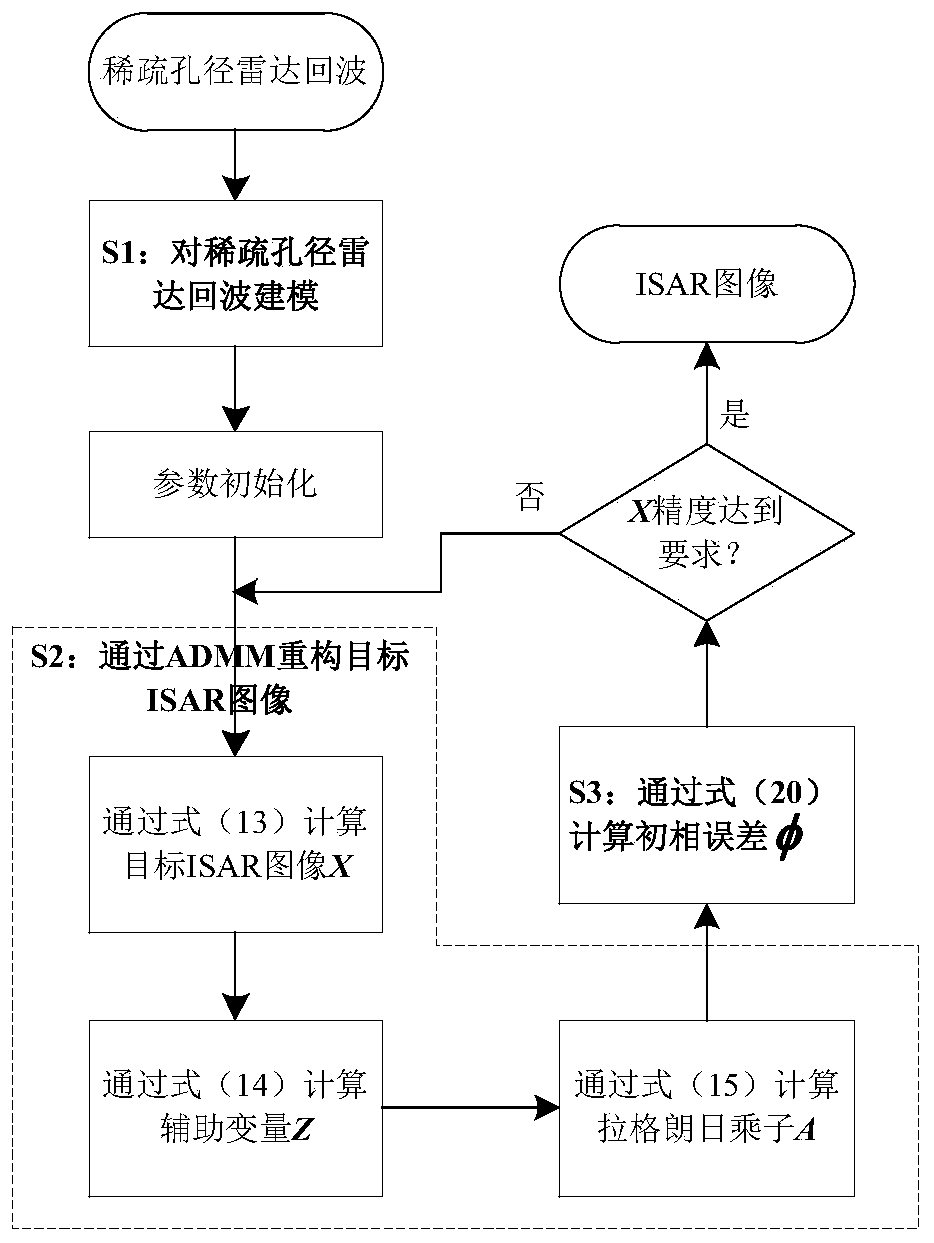
ActiveCN110275166AAchieving self-focusImprove resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Minimum entropy
The invention belongs to the radar signal processing field and especially relates to a rapid sparse aperture ISAR self-focusing and imaging method based on ADMM. The method comprises the following steps of S1, modeling a sparse aperture radar echo; S2, reconstructing a target ISAR image X through the ADMM; and S3, estimating an initial phase error phi through a minimum entropy criterion. The method has advantages that the initial phase error can be effectively estimated from the sparse aperture radar echo so as to realize ISAR self-focusing, and sidelobe and grating lobe influences introduced by undersampling can be effectively eliminated so as to obtain a high resolution ISAR image; robustness is high, and ISAR self-focusing and imaging can still be realized under a low signal to noise ratio condition; operation efficiency is high, the method can be applied to a real-time ISAR imaging system, and the method has an important engineering application value.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
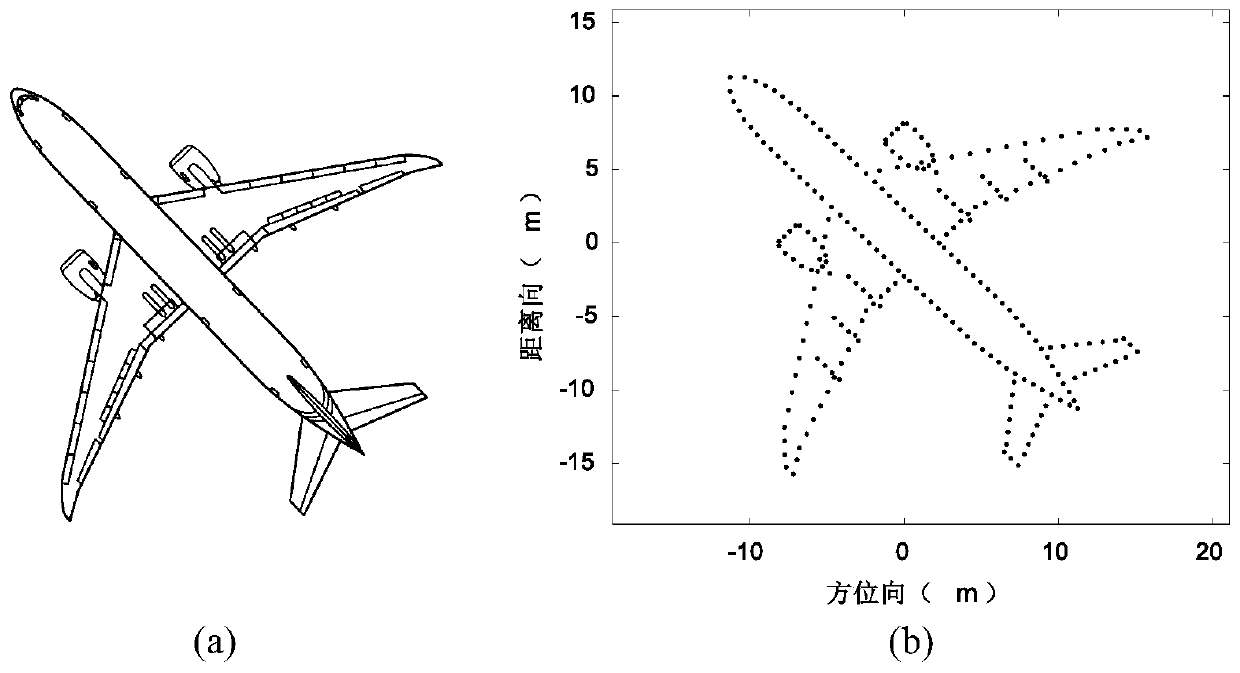
Autofocus for minimum entropy through multi-dimensional optimization
Owner:THE BOEING CO
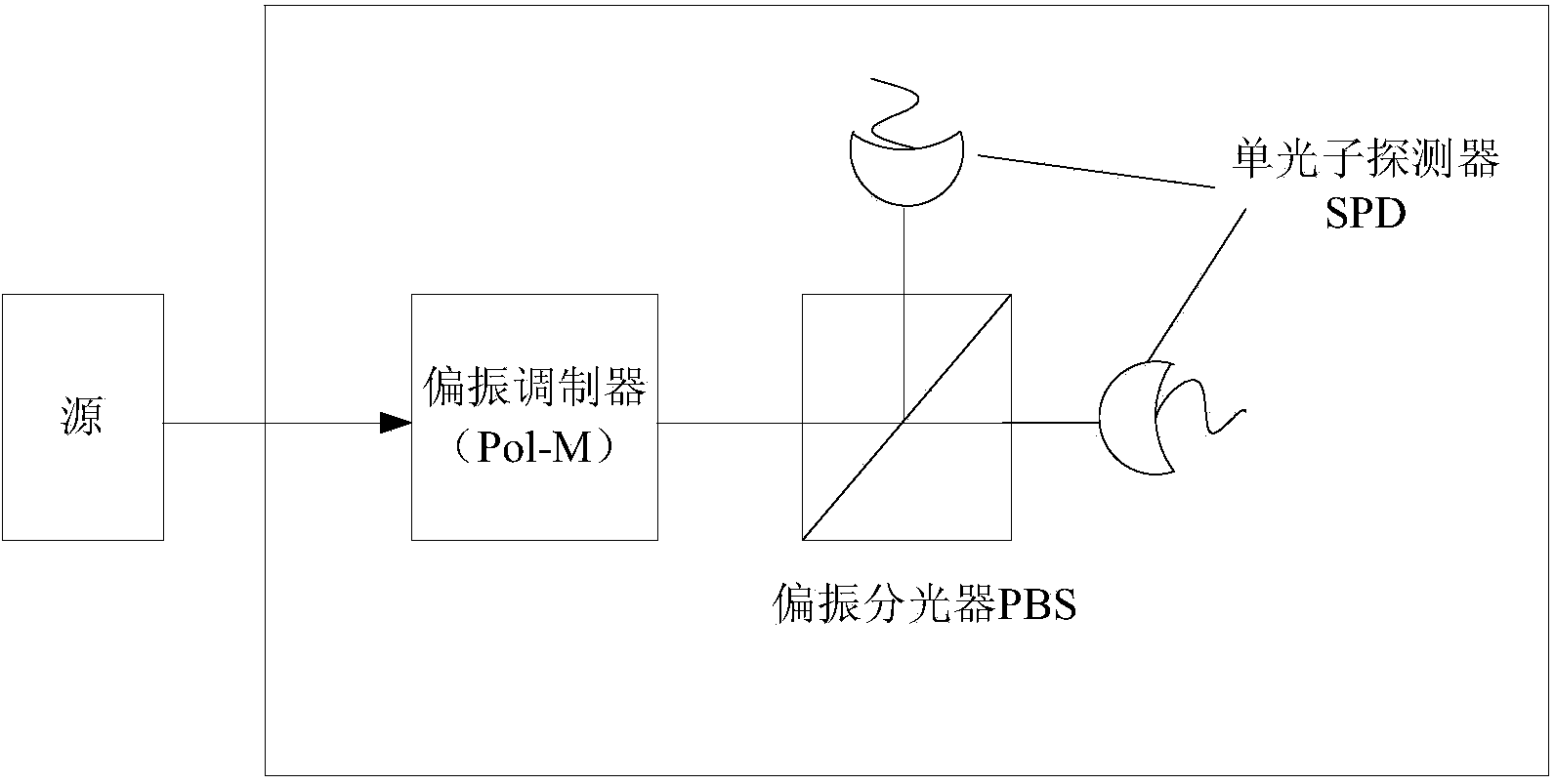
Method and device for optics based quantum random number generation
ActiveCN107066236ASmall sizeLow costQuantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic sensorMinimum entropy
The invention provides a method and a device for optics based quantum random number generation. A method and device for generating random numbers based on an optical process of quantum nature. According to one exemplary aspect, the method includes randomly emitting photons from a light source and absorbing the emitted photons by a photon sensor having a plurality of pixels. Furthermore, respective minimum entropy levels can be calculated for each of the pixels of the photon sensor and a randomness extractor can be associated with each of pixels based on the calculated minimum entropy level of that pixel. After this calibration, the method and device generates a number of high-entropy bits used for generating a random number.
Owner:ID量子技术公司
Verifiable and secure privacy amplification method based on quantum key distribution
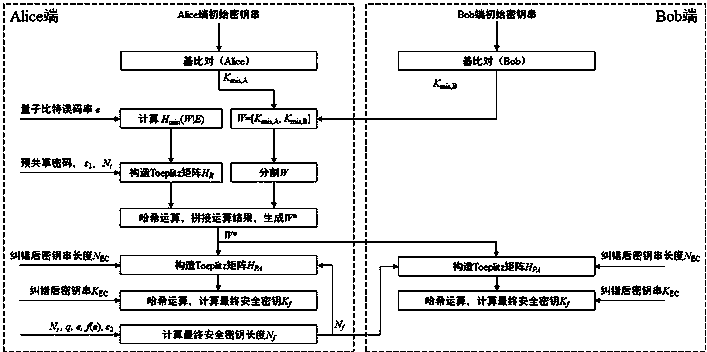
ActiveCN108599934AMeet security needsEasy to implementKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobLower limit
The invention discloses a verifiable and secure privacy amplification method based on quantum key distribution. The method comprises the steps of S1, generating an initial random number string W, respectively generating random number strings K<mis,A> and K<mis,B> by two communication parties (Alice and Bob) in a base comparison process of quantum key distribution, and combining the two random number strings into a random number string W=[<Kmis,A>, K<mis,B>] by the Alice; S2, verifying randomness, after an error correction phase of the quantum key distribution is finished, estimating the minimum entropy lower limit of the W relative to an attacker Eve, wherein H<min>(W|E) is greater than or equal to 1-H<2>(e); S3, calculating a final secure key length N<f>; S4, extracting a perfect random string W*, through adoption of a partial pre-shared secure key of the two communication parties, constructing a Toeplitz matrix H<R>, and extracting the perfect random number string W* from the W according to the H<R>; S5, negotiating a universal hash function H<PA> through a public channel according to the W*; and S6, respectively carrying out hash operation on error corrected key strings by the two communication parties according to the H<PA>, and generating a final secure key. The method has the advantages of verifiability, security, easy realization and simplification of quantum key distribution system design and realization.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on short-time Hilbert transform
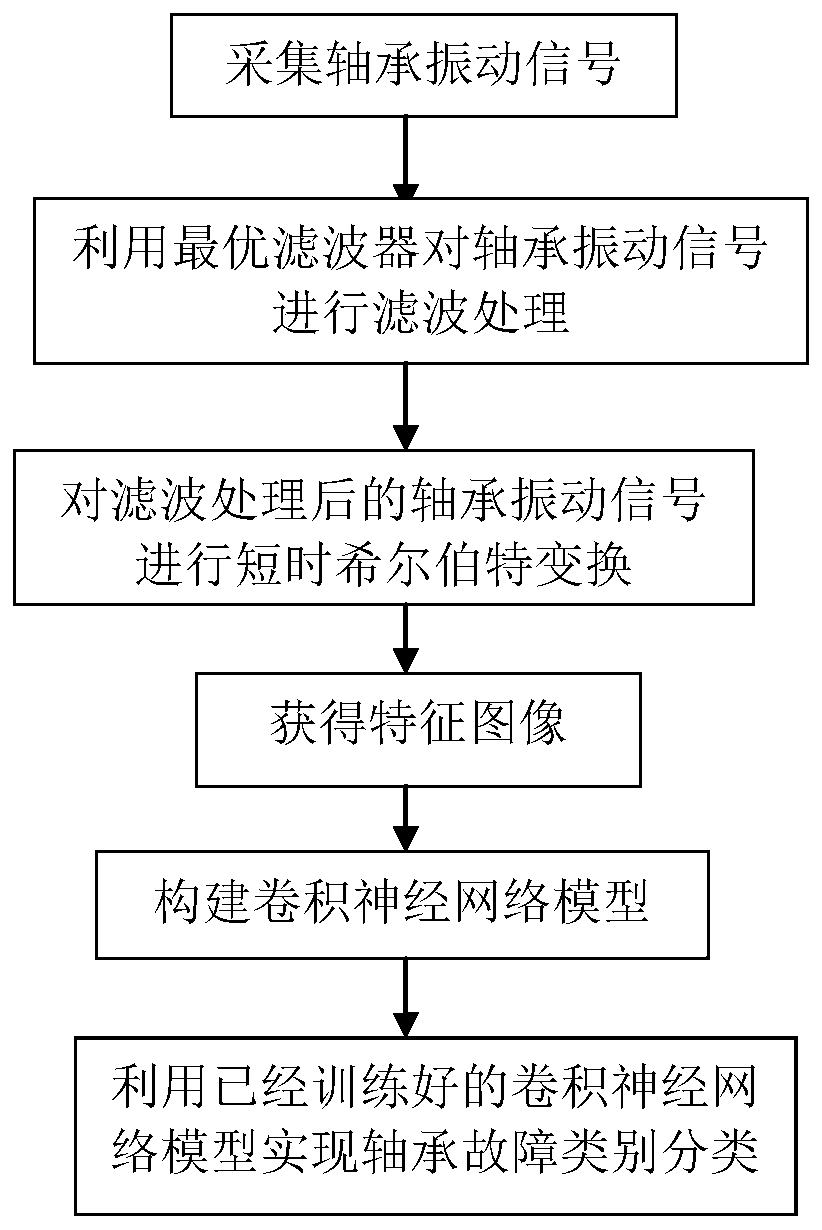
ActiveCN111238814AEfficient extractionPreserve vibration signal characteristicsMachine part testingNeural architecturesMinimum entropyEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of bearing fault detection, and discloses a rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on short-time Hilbert transform, and the method comprises the steps: A) collecting a bearing vibration signal, and designing an optimal filter through employing minimum entropy deconvolution; B) carrying out filtering processing on the bearing vibration signal by using the optimal filter; C) performing short-time Hilbert transform on the filtered bearing vibration signal to obtain a feature image; D) constructing a convolutional neural network model; and E) utilizing the trained convolutional neural network model to realize bearing fault category classification. The minimum entropy deconvolution is utilized to carry out filtering processing on the collectedsignals, and then the short-time Hilbert transform method is utilized to acquire the feature images so that the vibration signal features can be retained to the maximum extent, the classification of the bearing fault types and the fault severity is realized through the convolutional neural network and the accuracy of fault classification is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU ANMAISHENG INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
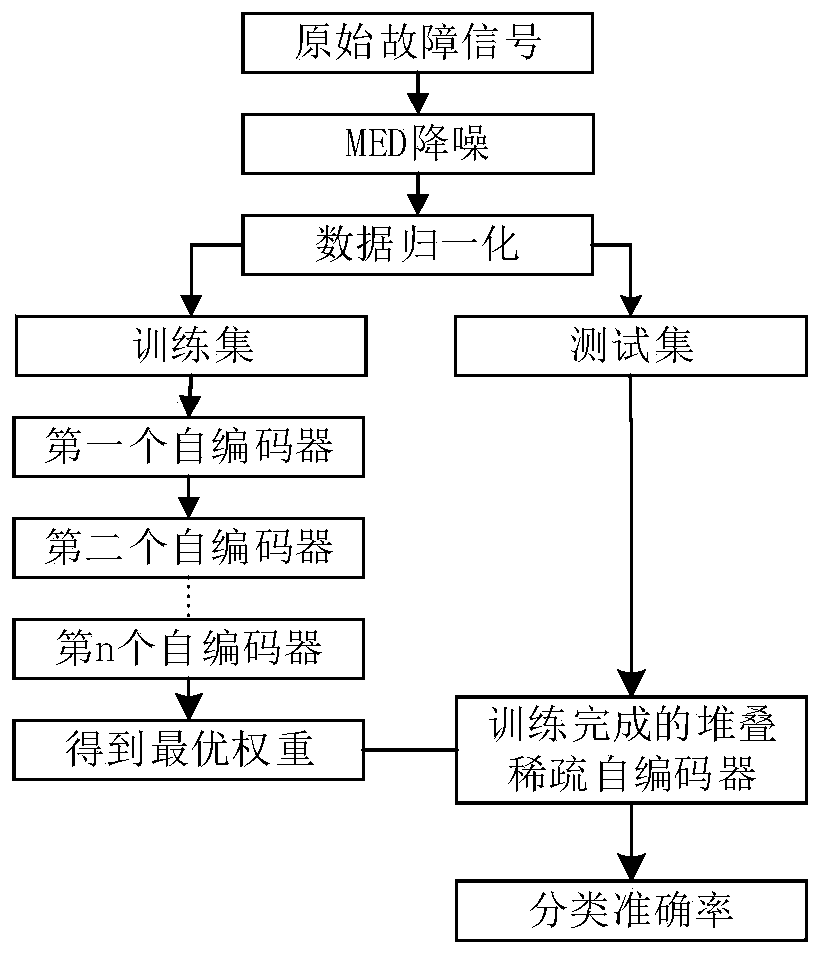
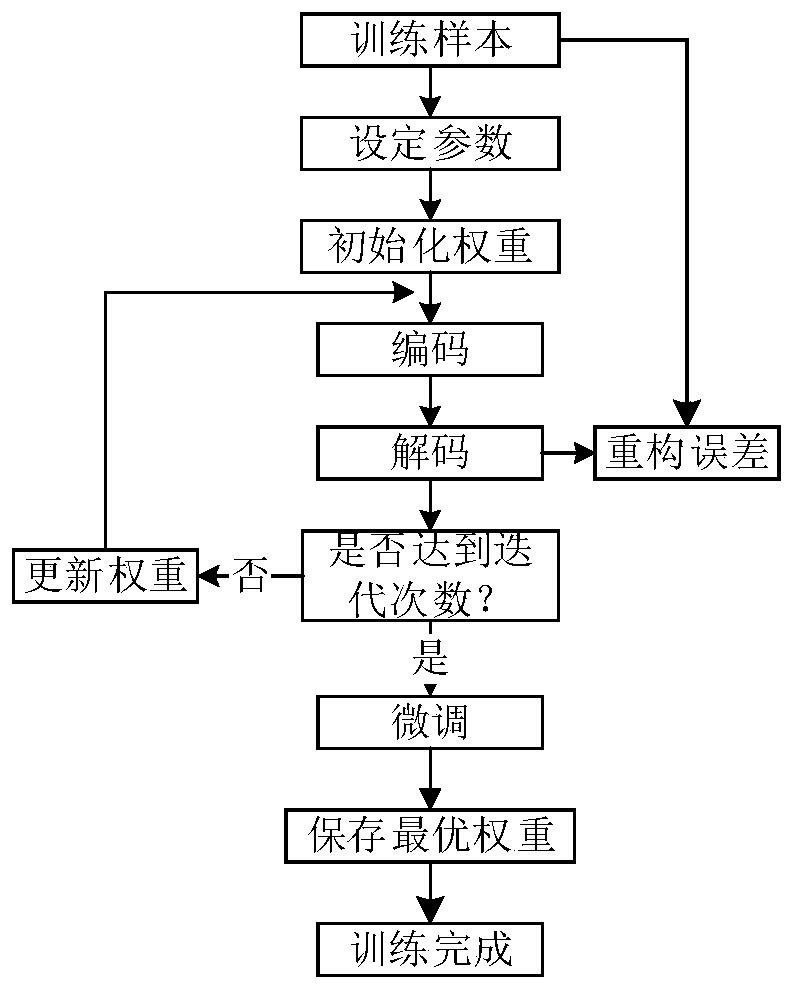
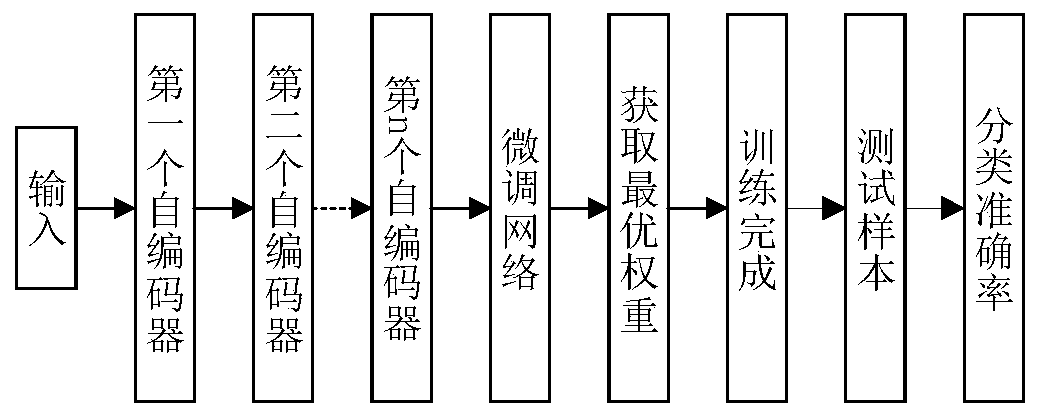
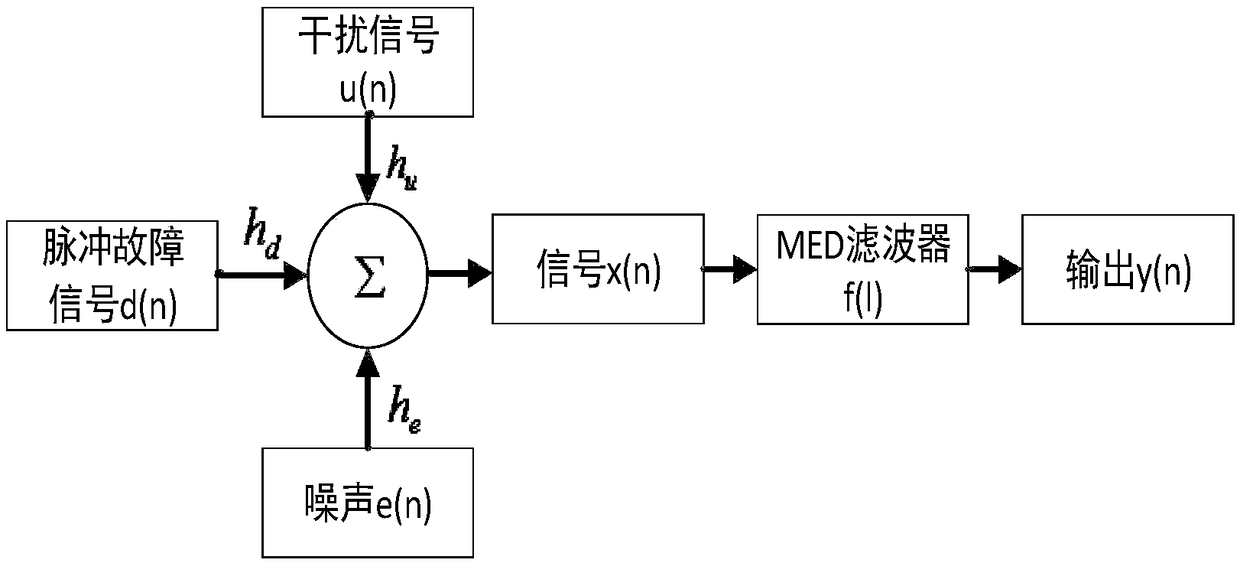
Fault diagnosis method based on minimum entropy deconvolution and stacked sparse auto-encoder
PendingCN110991424AOvercoming the problem of high noise making accurate diagnosis difficultHigh fault identificationMachine part testingCharacter and pattern recognitionTest sampleMinimum entropy
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis method based on minimum entropy deconvolution and a stacked sparse auto-encoder, which belongs to the technical field of fault diagnosis. The method comprisesthe following specific steps of: acquiring an original fault vibration signal of a to-be-diagnosed object, performing minimum entropy deconvolution processing on the original fault vibration signal,dividing the fault samples into a plurality of training samples and test samples, training the multi-fault classifier based on the stacked sparse auto-encoder by adopting a plurality of training samples, classifying the test samples by adopting the trained multi-fault classifier, and identifying the working state and the fault type of the fault object according to the classification result. The fault diagnosis method provided by the invention has high innovativeness, and compared with a traditional intelligent diagnosis algorithm, the fault diagnosis method provided by the invention has high recognition degree in a fault recognition process.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for fault diagnosis of wind turbine bear
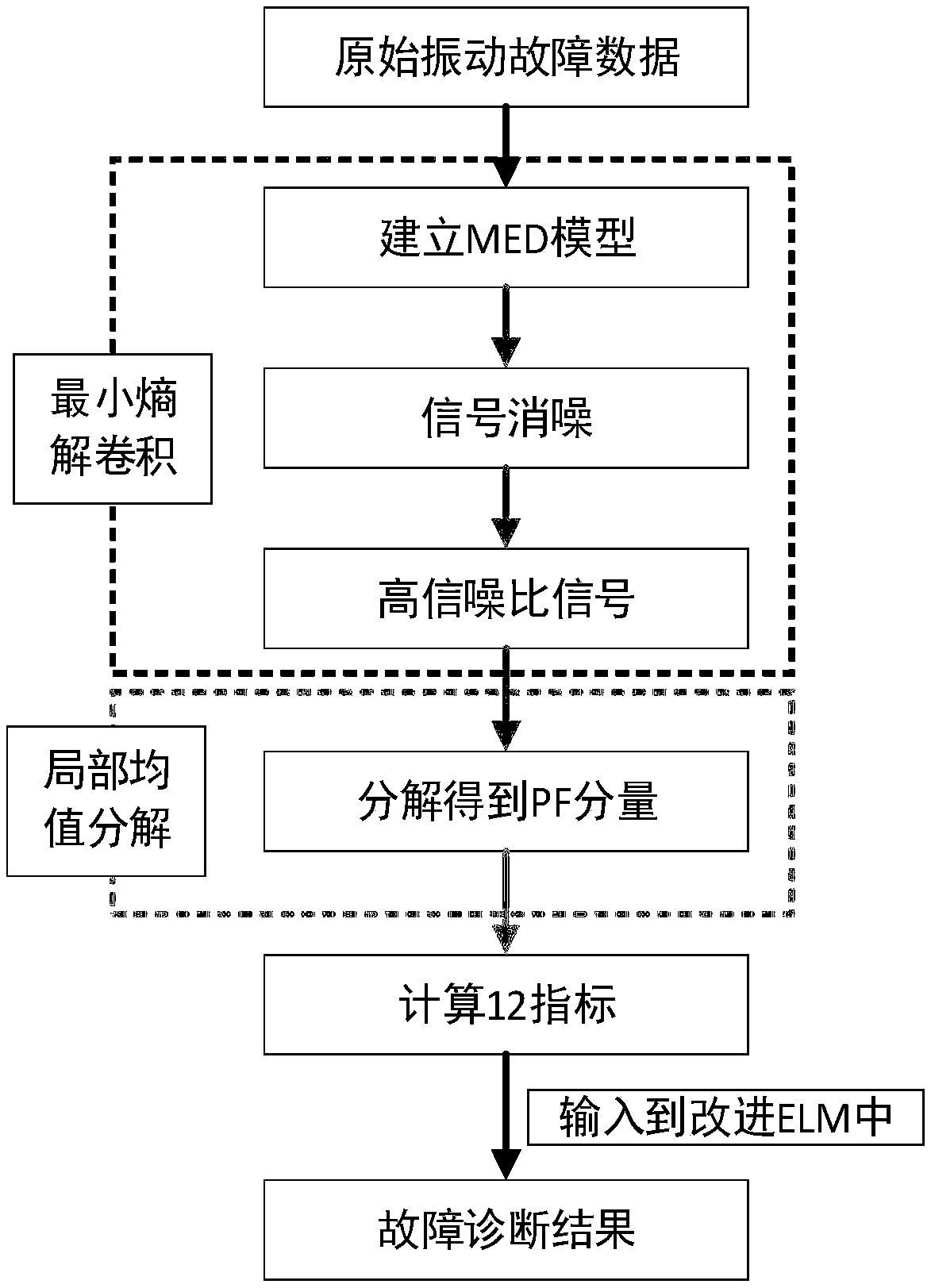
ActiveCN109033719AObvious fault featuresImprove signal-to-noise ratioGeometric CADMachine bearings testingLearning machineDecomposition
The invention discloses a wind turbine bearing fault diagnosis method. Firstly, an optimal filter is designed by using the principle of minimum entropy, and the impulse impact in the signal is highlighted. Secondly, the fault signal is decomposed by local mean decomposition, and the PF component which is highly correlated with the original signal is extracted to compute the parameter index, and then the feature vector set is formed. Finally, a fault classification model of wind turbine bearing based on improved extreme learning machine is established, and the set of eigenvectors is inputted into the improved extreme learning machine to diagnose the fault. As the method of the invention utilizes the minimum entropy deconvolution to effectively improve the signal-to-noise ratio, the fault characteristics of the wind turbine bear are obvious; on the other hand, the complete time-frequency distribution of the original signal is obtained by using the local mean decomposition method, and thefault types of the wind turbine bearing can be directly detected from the fault model of the improved limit learning machine.
Owner:温州大学苍南研究院
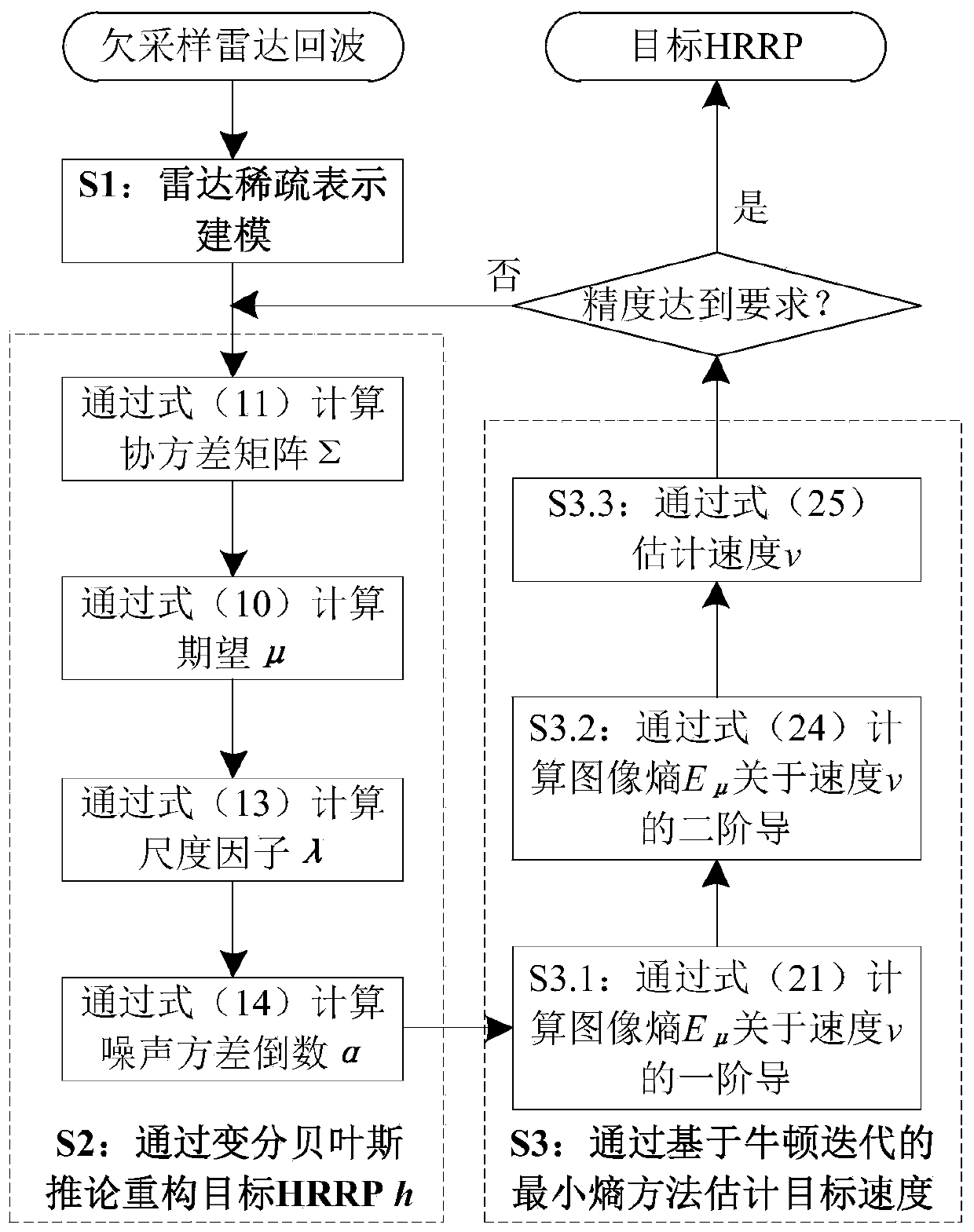
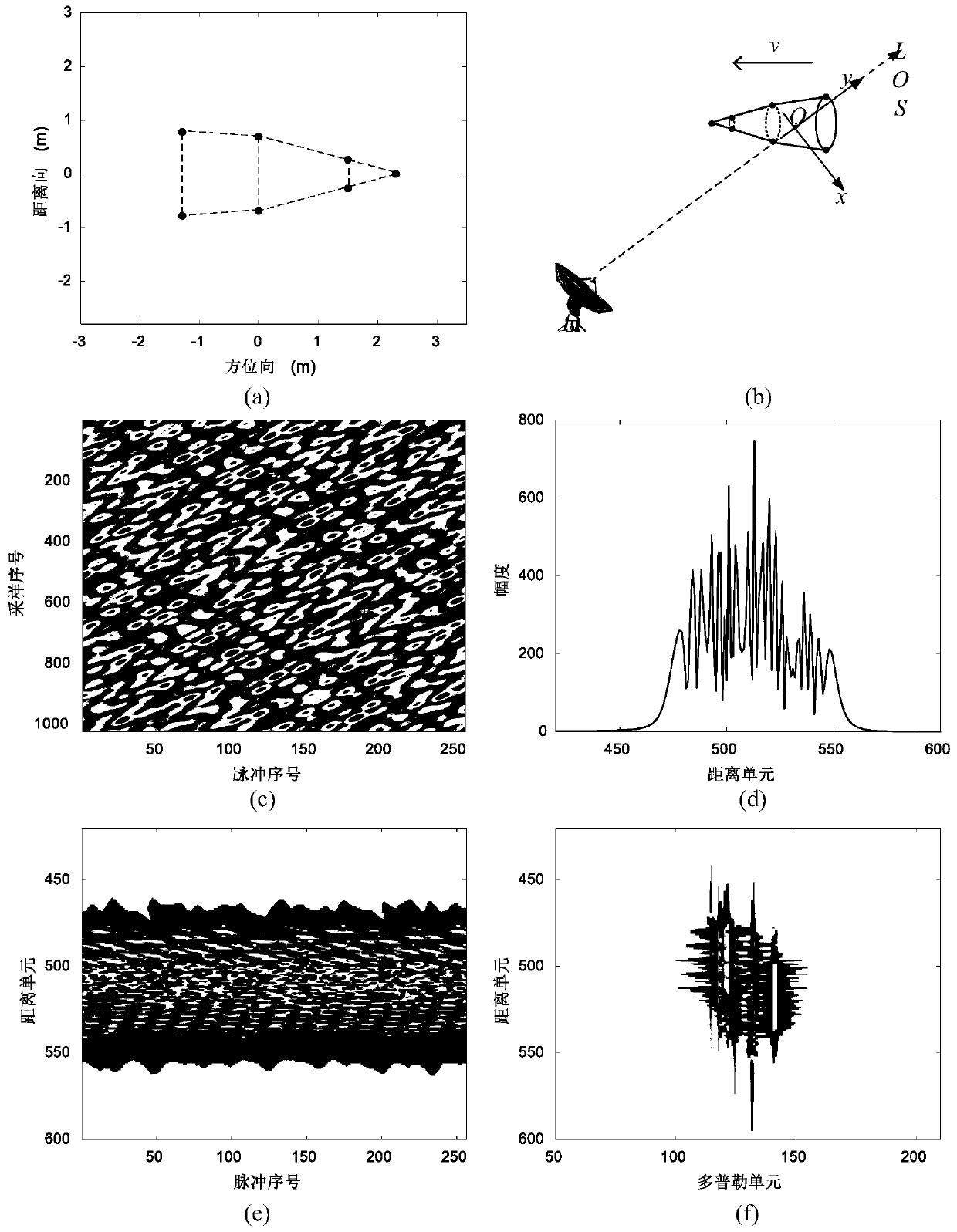
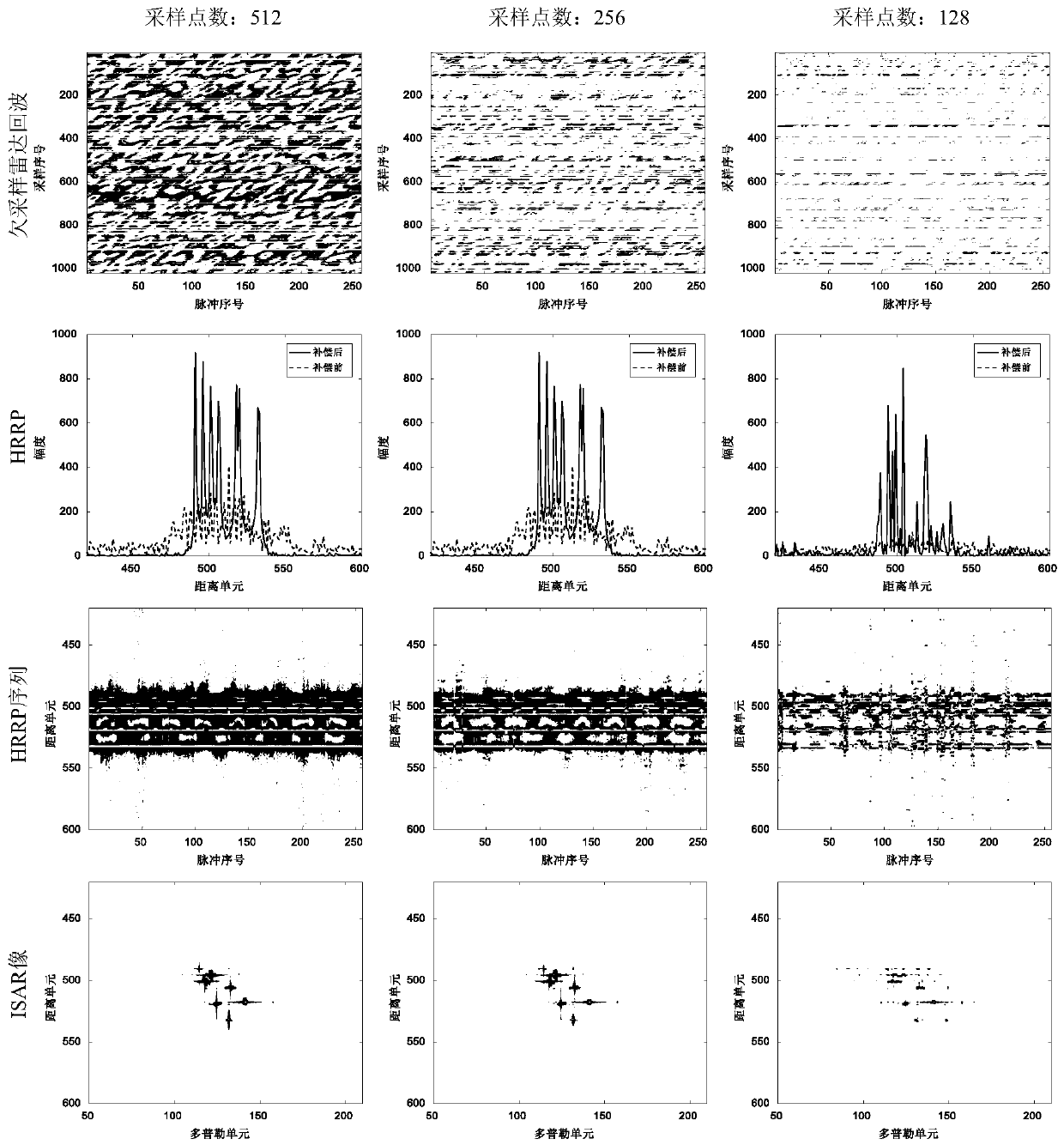
Variational Bayesian inference-based high-speed target HRPP reconstruction method
ActiveCN110068805AHigh resolutionFocusWave based measurement systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Algorithm
The invention belongs to the field of radar signal processing, and relates to a variational Bayesian inference-based high-speed target HRPP reconstruction method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, carrying out sparse representation modeling on a target undersampled echo; S2, reconstructing a target HRPP through a variational Bayesian inference; and S3, estimating a target speed on through a newton iteration-based minimum entropy method: S3.1, calculating a first derivative, about the target speed, of an image entropy, S3.2, calculating second derivative, about the target speed, of the image entropy, and S3.3, estimating the target speed through a newton iterative. Through the method, high-speed moving target HRRP reconstruction under undersampling condition can be realized, target speeds can be effectively estimated from undersampled echoes under the condition of radar echo undersampling caused by the factors such as low signal to noise ratio, strong interference and thelike, and high-order phase errors imported by the target speeds can be compensated, so that distortions such as widening, defocusing and the like of target HRRPs are corrected, the target HRRPs with good focusing effect and high resolution are obtained, and an important engineering application value is provided for radar target recognition.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
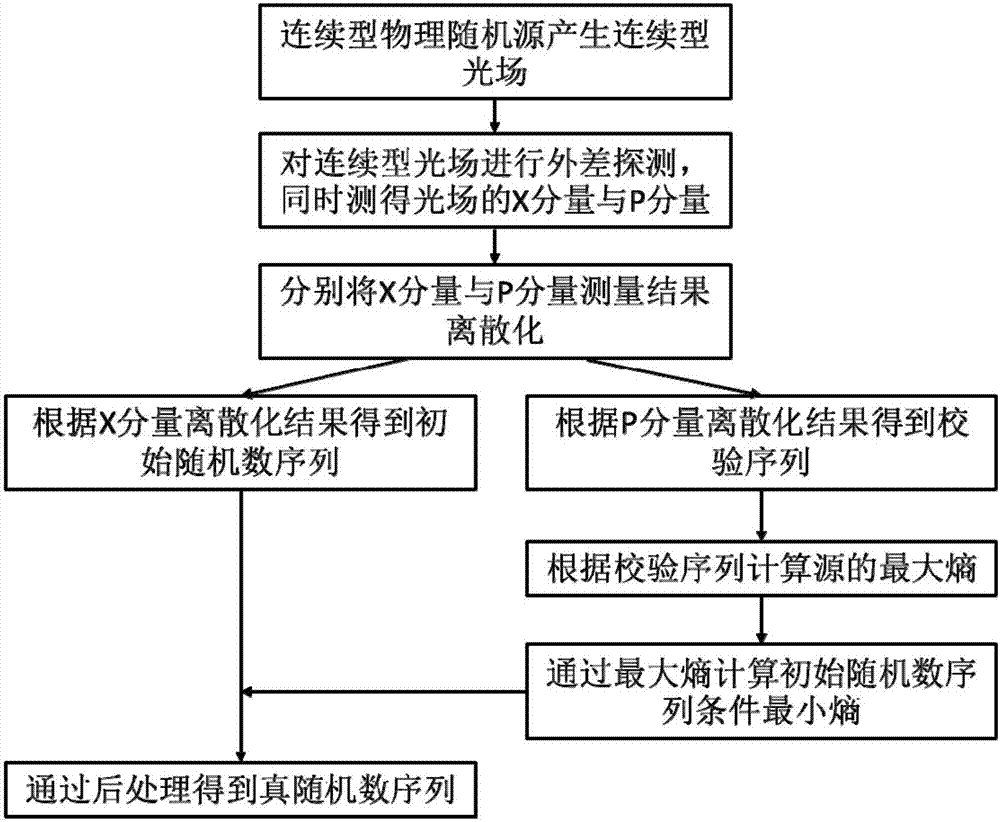
Generation method and device for source independent continuous quantum random number
InactiveCN107368282ARealize measurementGuaranteed randomnessRandom number generatorsContinuous lightContinuous measurement
The invention puts forward a generation method and device for a source independent continuous quantum random number. The method comprises the following steps that: a continuous physical random source generates a continuous light field; the continuous light field is subjected to heterodyne detection, and meanwhile, two non-commutative mechanical quantities of the light field are measured, wherein the two non-commutative mechanical quantities are a component X (regular coordinate) and a component P (regular momentum); the continuous measurement results of the two mechanical quantities are discretized to independently obtain an initial random sequence under one component and a checking sequence under the other component; according to the checking sequence, the maximum entropy of a continuous random source is calculated; and through an entropy uncertainty principle and a maximum entropy calculation result, the conditional minimum entropy of the initial random sequence is obtained, and a completely random binary system true random sequence is obtained through postprocessing. By use of the method, additional random number does not need to be provided, the method does not depend on a hypothesis for sources, a "trusted" part in the physical random source can be effectively extracted, and the quantum random number is generated.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Fast estimation method for non-uniform rotating target motion parameter
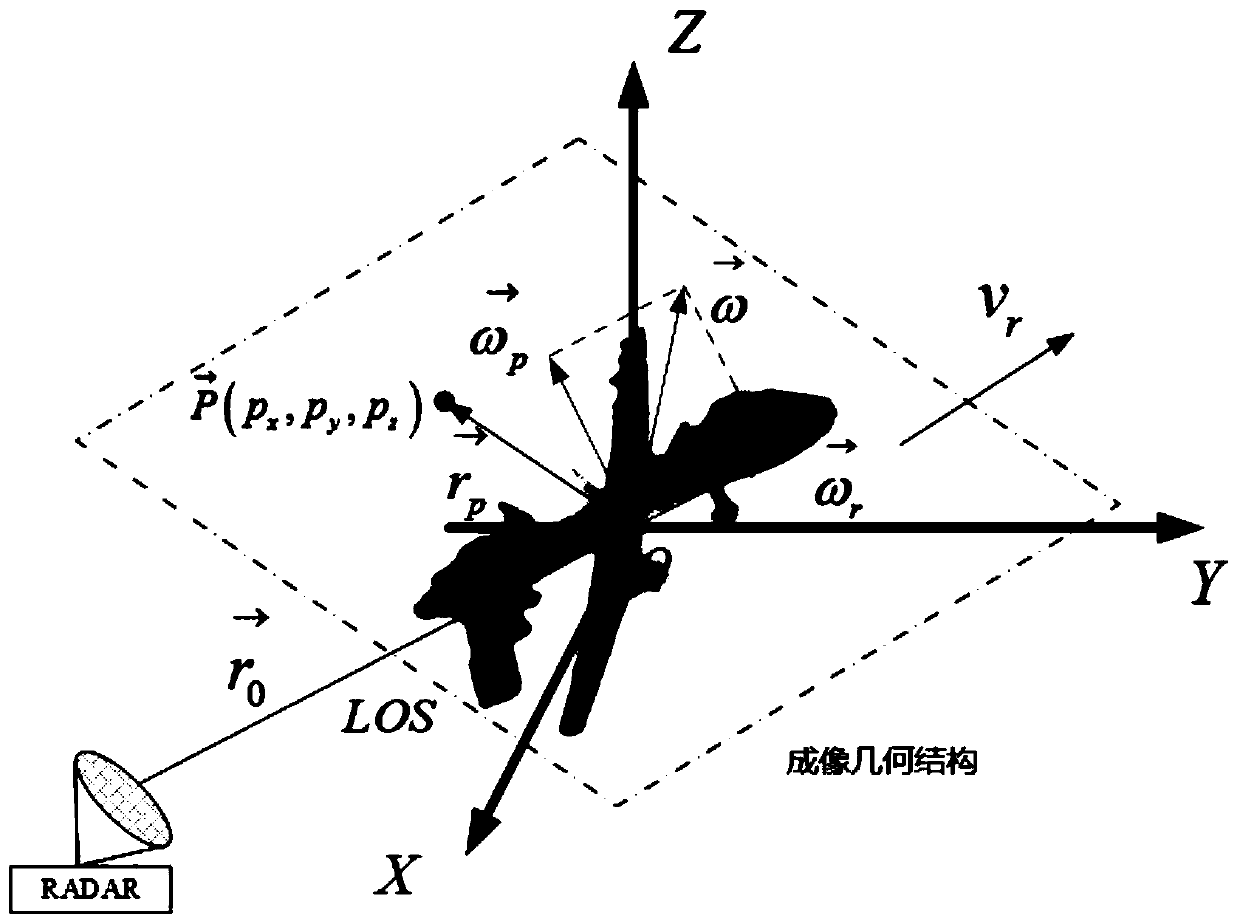
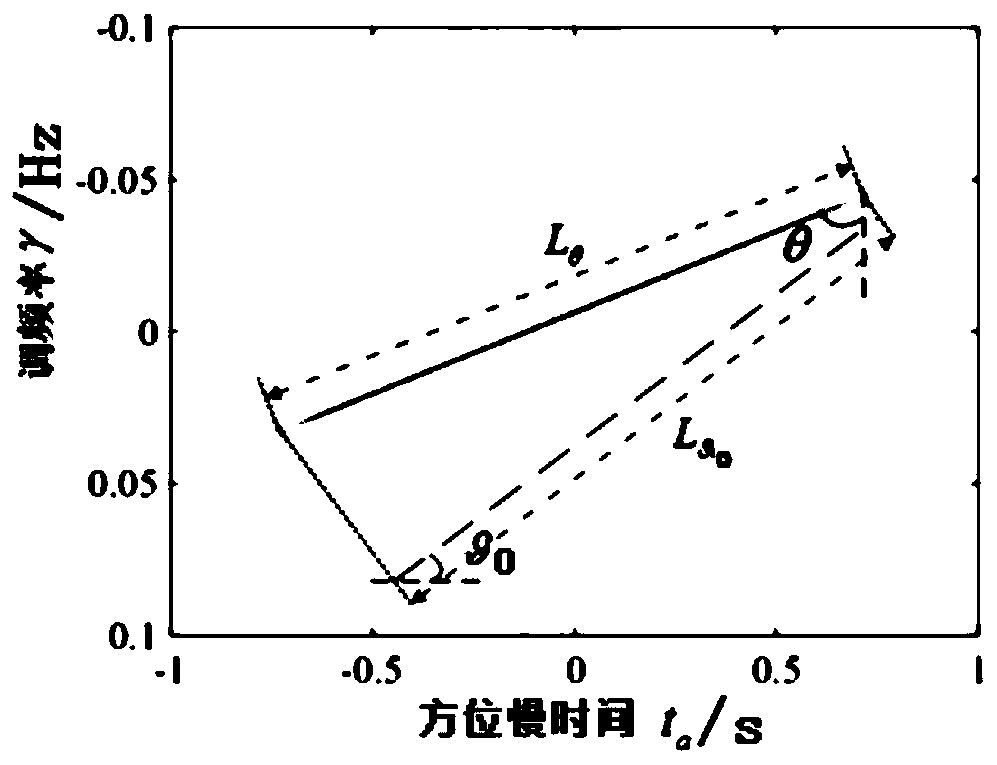
PendingCN110146886AHigh precisionImprove robustnessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmImaging quality
The invention discloses a fast estimation method for a non-uniform rotating target motion parameter. The method comprises specific steps: an echo signal in a single distance unit is modeled into a QFMsignal; a correlation function is constructed, the QFM signal is converted to a time-chirp distribution plane, and minimum entropy criterion-based weighted least squares Radon transform is adopted toestimate secondary chirp; the estimation accuracy and the robustness of the algorithm in a low signal-to-noise ratio environment are improved effectively at the same time; TFD-based weighted least squares Radon transform is adopted to estimate linear chirp, and through filtering, cross-term interference is eliminated; and according to the geometric information in a distance-Doppler domain, the center frequency is directly estimated. The calculation amount of the target motion parameter estimation process can be significantly reduced, the influences of transmission errors on estimation of eachmotion parameter are effectively avoided, and the final target parameter estimation precision and the ISAR imaging quality are ensured.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
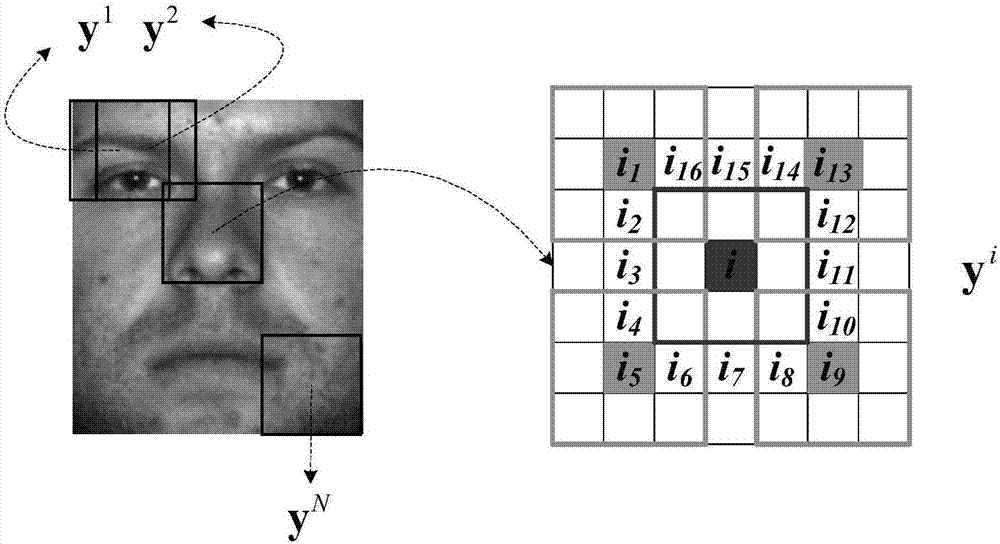
Single-sample face recognition method based on sparse probability distribution and multi-stage category screening
InactiveCN106951819ASolve the problem of entropy minimizationAccurate classification basisCharacter and pattern recognitionSingle sampleEffective solution
The invention discloses a single-sample face recognition method based on sparse probability distribution and multi-stage category screening, comprising the following steps: first, a face image is divided into blocks and the blocks are divided into sub blocks, wherein it is assumed that the different sub blocks in the same block are different samples belonging to the same category, and thus, the problem that many sub-space learning methods and sparse representation methods cannot work or the performance decline under the condition of a single sample is solved; then, each block of the face image is recognized, and the category probability distribution of the face is obtained by means of voting; and finally, irrelevant categories are excluded iteratively using a multi-stage category screening structure based on the idea of minimum entropy, and an ideal face recognition classification effect is achieved. The method has good robustness to expressions, illumination change and occlusion, and has high recognition accuracy. Thus, a simple and effective solution to the single-sample face recognition problem is provided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
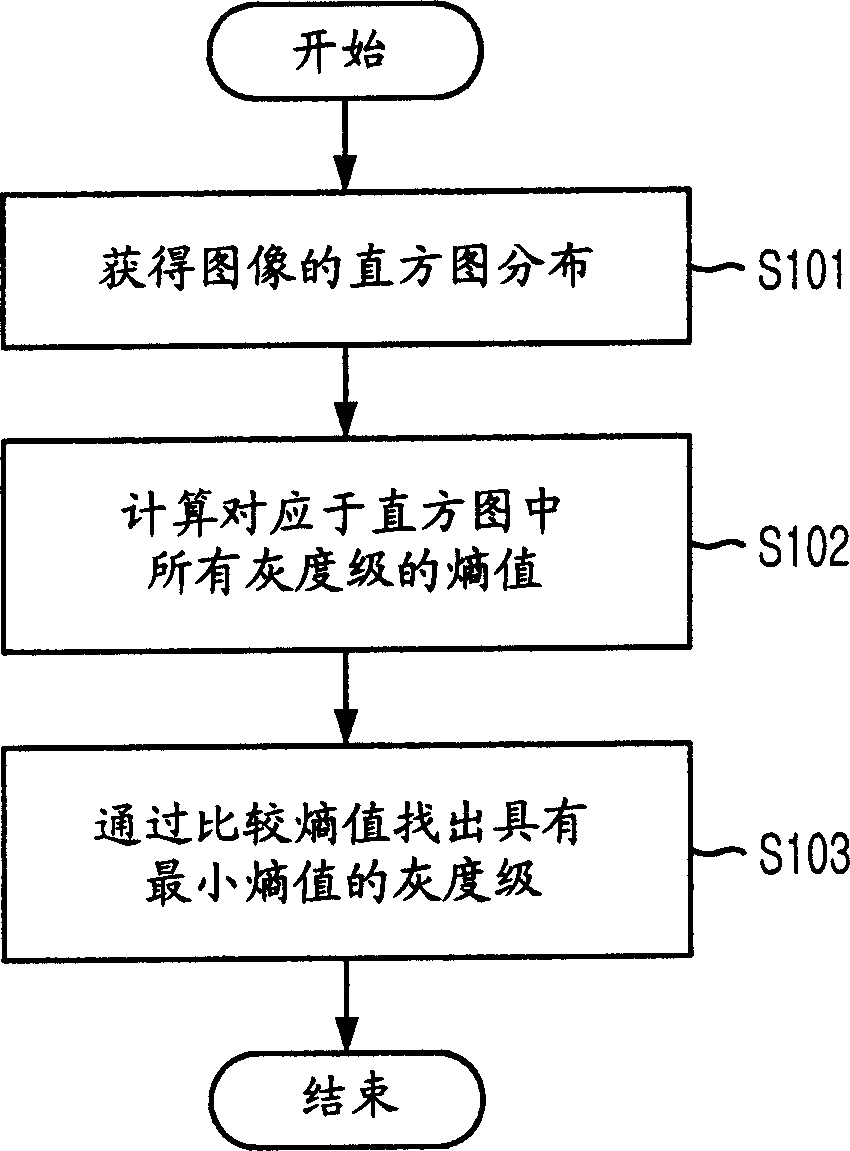
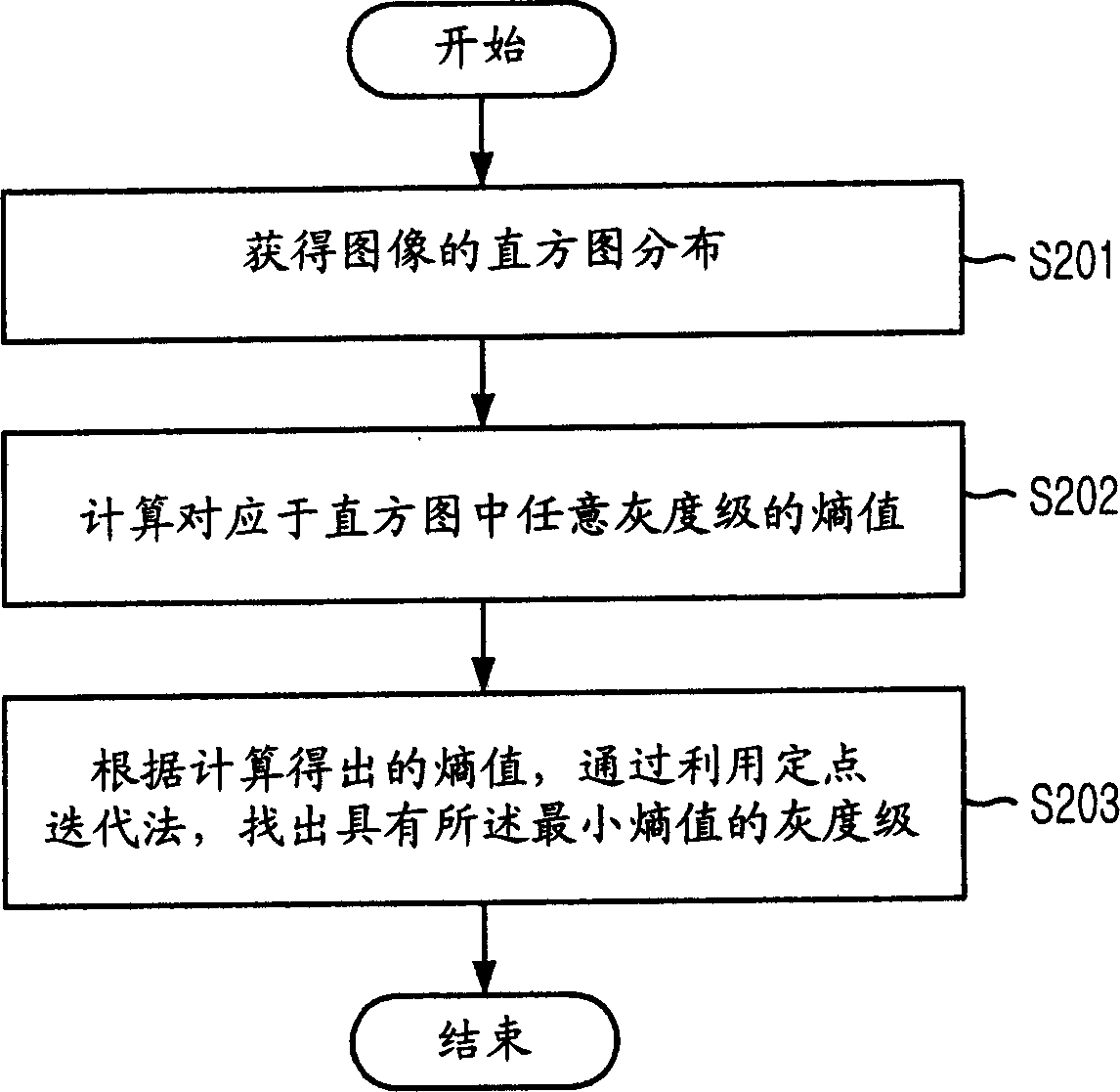
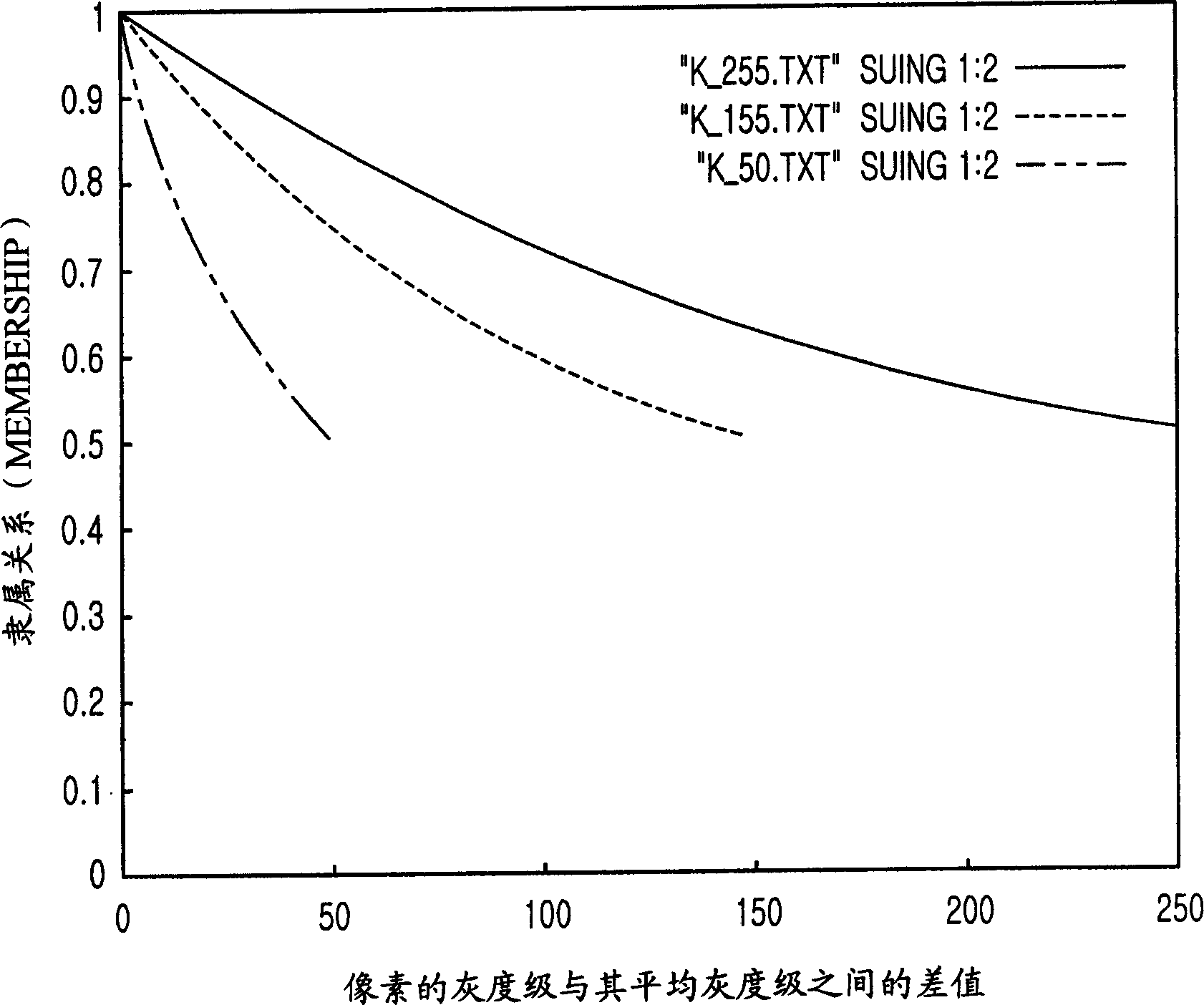
Method for looking up optinum threshold from image separation
A method for finding the optimal threshold for image segmentation in image recognition is disclosed. The method includes the steps of: a) gaining histogram distribution of an image; b) computing entropy values corresponding to gray levels in the histogram; and c) gaining a minimum entropy value corresponding to the gray level as the threshold value by using a fixed point iteration FPI based on the computed entropy values. The invention is capable of finding out an optimal threshold in a short time by applying a fast analytical approach method based on an FPI(Fixed Point Iteration) method together with a division termination condition for an image having multi-threshold through analysis for an entropy feature of the image.
Owner:PANTECH CO LTD
Remote sensing image building detection and classification method based on global optimization decision
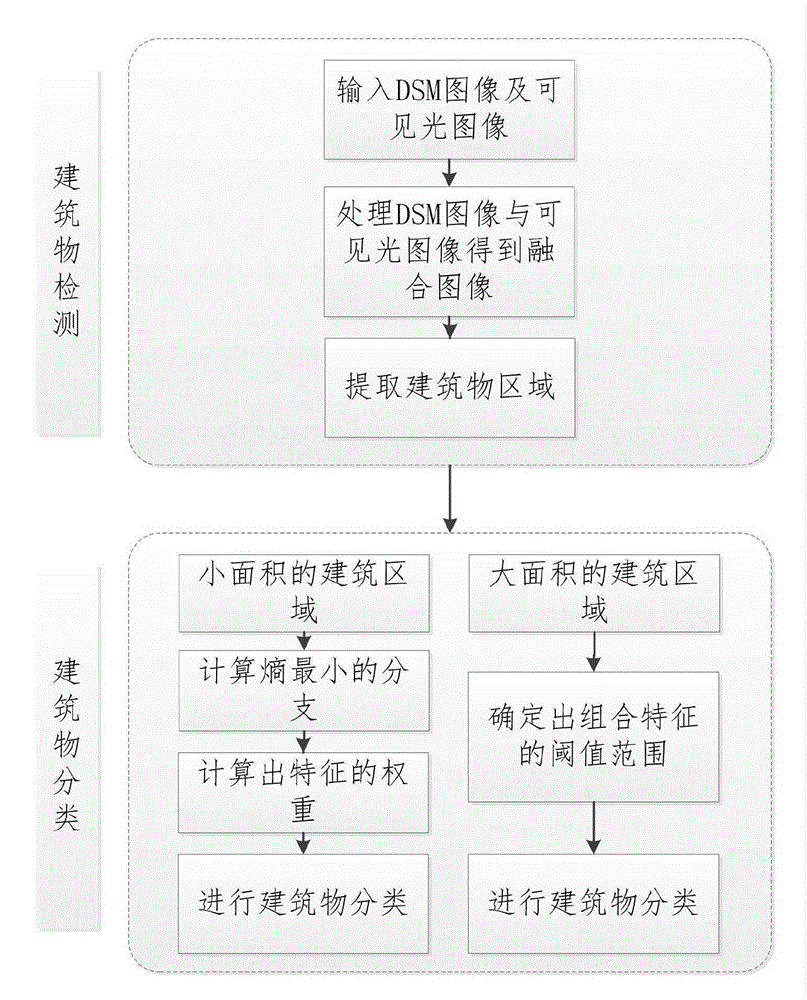
ActiveCN105184308AAccurate detection and classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionRadarMinimum entropy
A remote sensing image building detection and classification method comprises the following steps: acquiring DSM drawing data and visible light drawing data derived from an airborne radar laser; converting the size of the DSM drawing and performing the binarization of the DSM drawing; filtering the interference of the image edge, and merging the DSM drawing and the visible light drawing together; separating big and small white areas of the merged image, classifying the big areas through employing combination features, and deciding the features of the building classification of the small areas through employing the global optimization; classifying buildings according to preset threshold values of each feature, and calculating a branch having a minimum entropy; calculating a building area having a maximum purity in the branch; obtaining each feature weight through combining with the data, the maximal characteristic of the weight being this grade classification feature; and determining the sequence of the characteristics in order to realize the remote sensing image building detection and classification process. The remote sensing image building detection and classification method based on a global optimization decision may be used for the remote sensing image building detection and classification, has an important significance in the accurate detection and classification of the remote sensing image buildings, and has a broad market prospect and application value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Voltage sag source identification method based on mutual approximation entropy
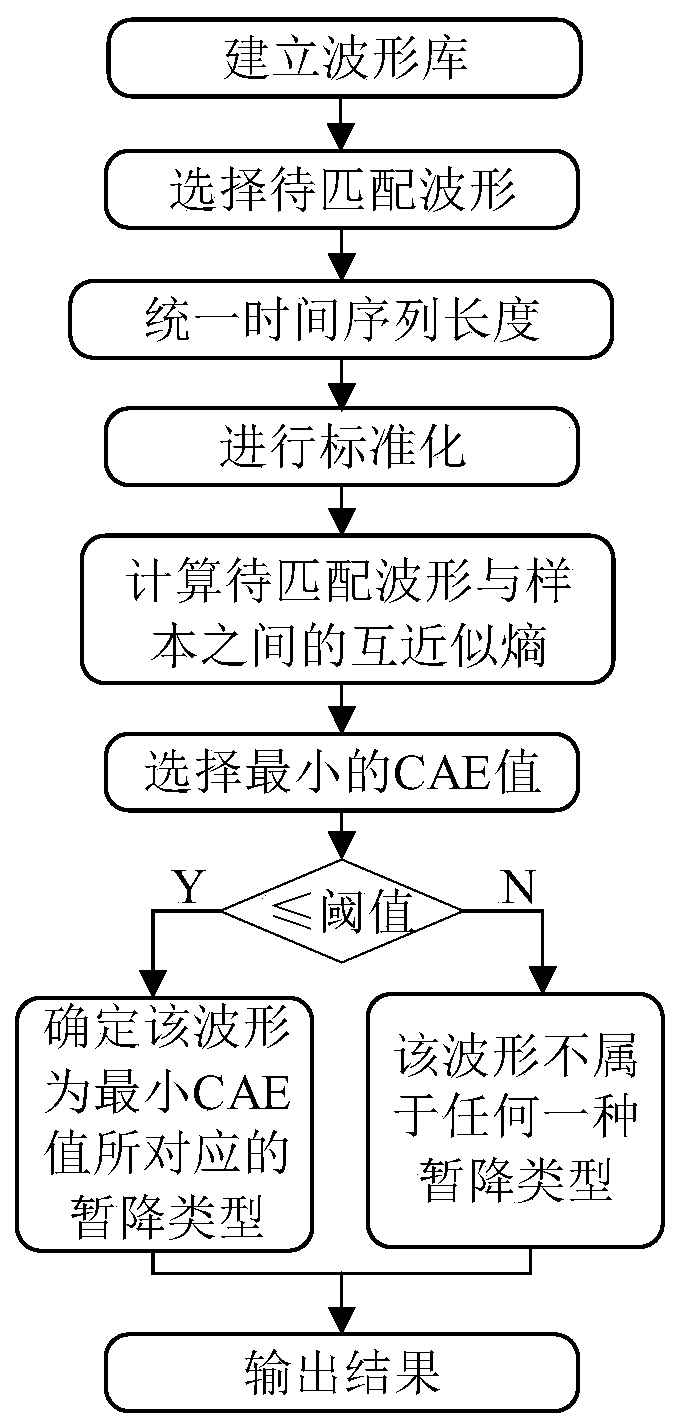
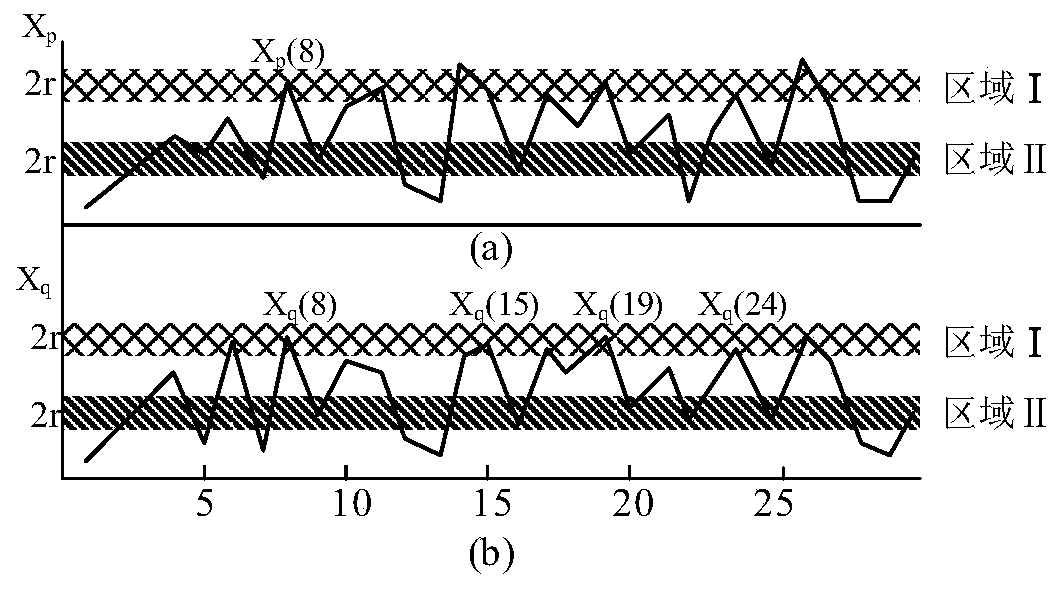
ActiveCN109828184AReduced characteristicsReduce the problem that relies heavily on the accuracy of feature extractionFault locationSource typeMinimum entropy
The invention discloses a voltage sag source identification method based on mutual approximation entropy. The method comprises the steps of: (1) establishing a sample waveform library; (2) performingdata preprocessing; (3) calculating mutual approximate entropy values of a waveform to be matched and the sample waveform, and retaining the minimum entropy value therein and the information of the corresponding sample; and (4) performing sag source type identification: determining whether the minimum entropy value is in a threshold range or not, if not, determining that a pending result is reliable, namely, the waveform to be matched being the sag source type, or else, determining that the waveform to be matched does not belong to any one sag source type in the waveform library. The voltage sag source identification method has high accuracy at the aspect of actually measured waveform identification of the voltage sag source, is short in the required sampling window and simple and easy toimplement the algorithm, help engineers with correct determination of the voltage sag source types and the generation reasons to a certain extent to provide targeted theoretical guidance for treatmentof the voltage sag source problem, and has great application value and prospects.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System and method for nonlinear dynamic control based on soft computing with discrete constraints
InactiveCN1672103ABiological modelsSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum entropyNon linear dynamic
A control system using a genetic analyzer based on discrete constraints is described. In one embodiment, a genetic algorithm with step-coded chromosomes is used to develop a teaching signal that provides good control qualities for a controller with discrete constraints, such as, for example, a step-constrained controller. In one embodiment, the control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy. In one embodiment, the genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal for a fuzzy logic classifier system that develops a knowledge base. The teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from the knowledge base. The control system can be used to control complex plants described by nonlinear, unstable, dissipative models. In one embodiment, the step-constrained control system is configured to control stepping motors.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
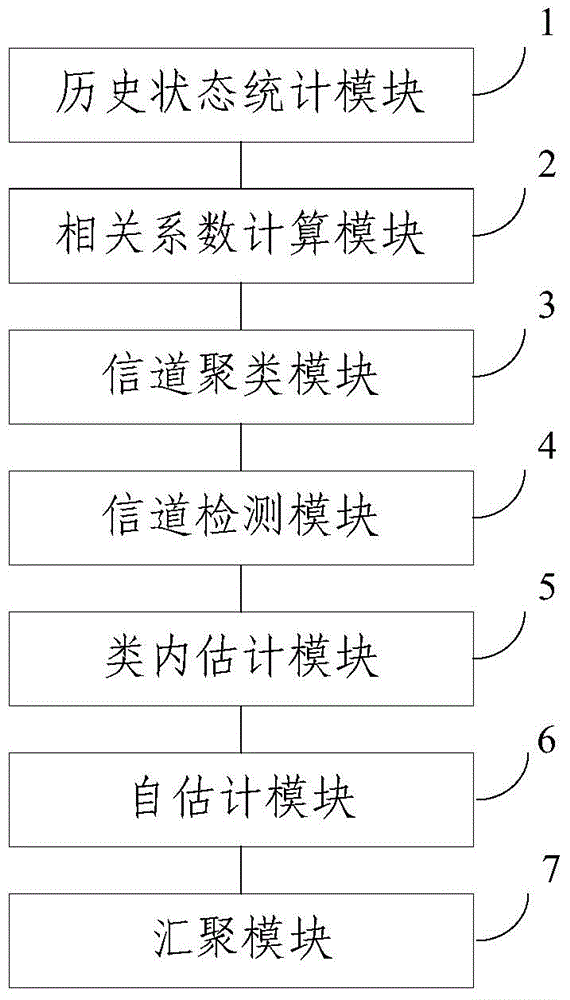
Frequency spectrum perception method and apparatus based on channel cluster
ActiveCN103957537AReduce the numberShorten the timeError preventionHigh level techniquesMinimum entropyEstimation result
The invention relates to a frequency spectrum perception method and apparatus based on a channel cluster. The method comprises: according to historical detection data, counting the historical occupation state of each channel; according to the historical occupation state of each channel, respectively calculating a correlation coefficient between any two channels; according to the correlation coefficient, utilizing a channel cluster algorithm perform clustering on the channels, and generating a predetermined number of types; respectively selecting one detection channel from each type, and detecting the occupation states of the detection channels; according to the occupation states of the detection channels, performing occupation state intra-type estimation on other channels beside the detection channel in each type by use of an intra-type estimation algorithm; and according to the historical occupation states of each channel, performing occupation state self-estimation on other channels beside the detection channel in each type; and unifying two estimation results through a minimum entropy aggregation method. By using the method and apparatus provided by the invention, the quantity of the channels needing detection is substantially reduced, and enormous time and energy are saved for a frequency spectrum perception process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
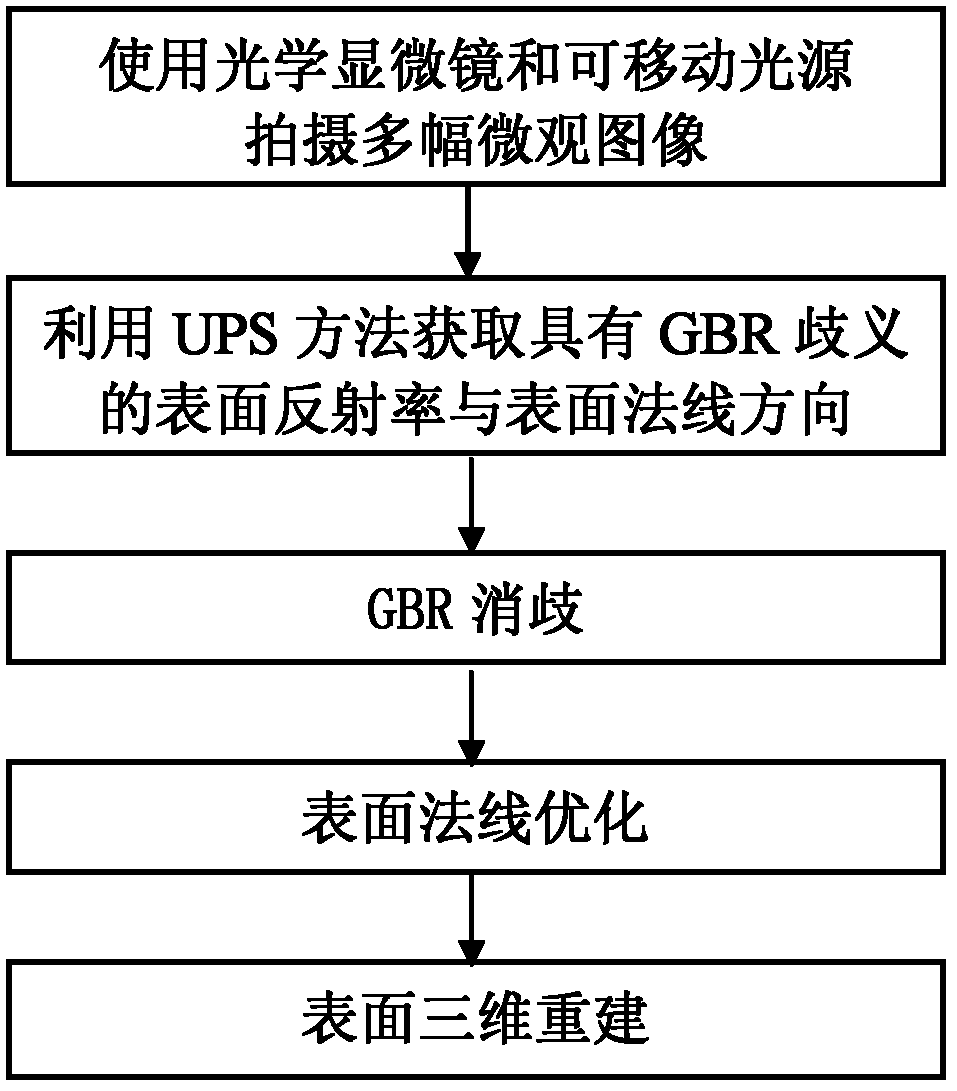
Three-dimensional measurement method for microstructure based on optical microscope and variable illumination
The invention discloses a three-dimensional measurement method for a microstructure based on an optical microscope and variable illumination. According to the method, a three-dimensional morphology of the surface of the microstructure is re-established according to multiple microscopic images shot by the optical microscope in different illumination directions of a fixed viewpoint. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining a surface albedo and a normal direction with GBR (guaranteed bit rate) ambiguity by adopting a UPS (ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy) method and surface integrable restrain; then obtaining the surface albedo or the normal direction without ambiguity based on a GBR disambiguity method with minimum entropy; in order to reduce the influence of noise, further optimizing the normal direction of the surface by utilizing a graph cutting method in a model of a Markov random field; and finally, re-establishing the three-dimensional morphology of the surface of the microstructure by adopting an integration method according to the normal direction of the surface.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Entropy method for range alignment for integration of target returns
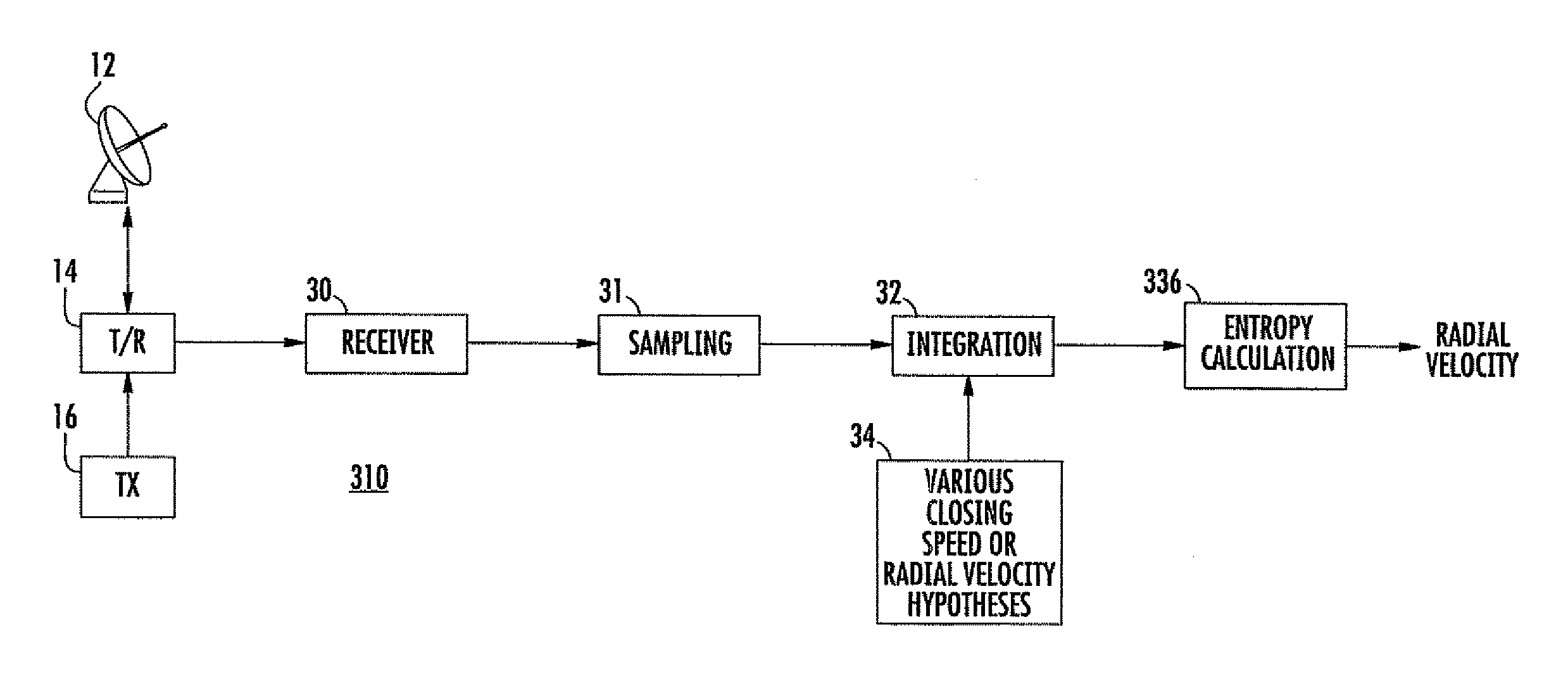
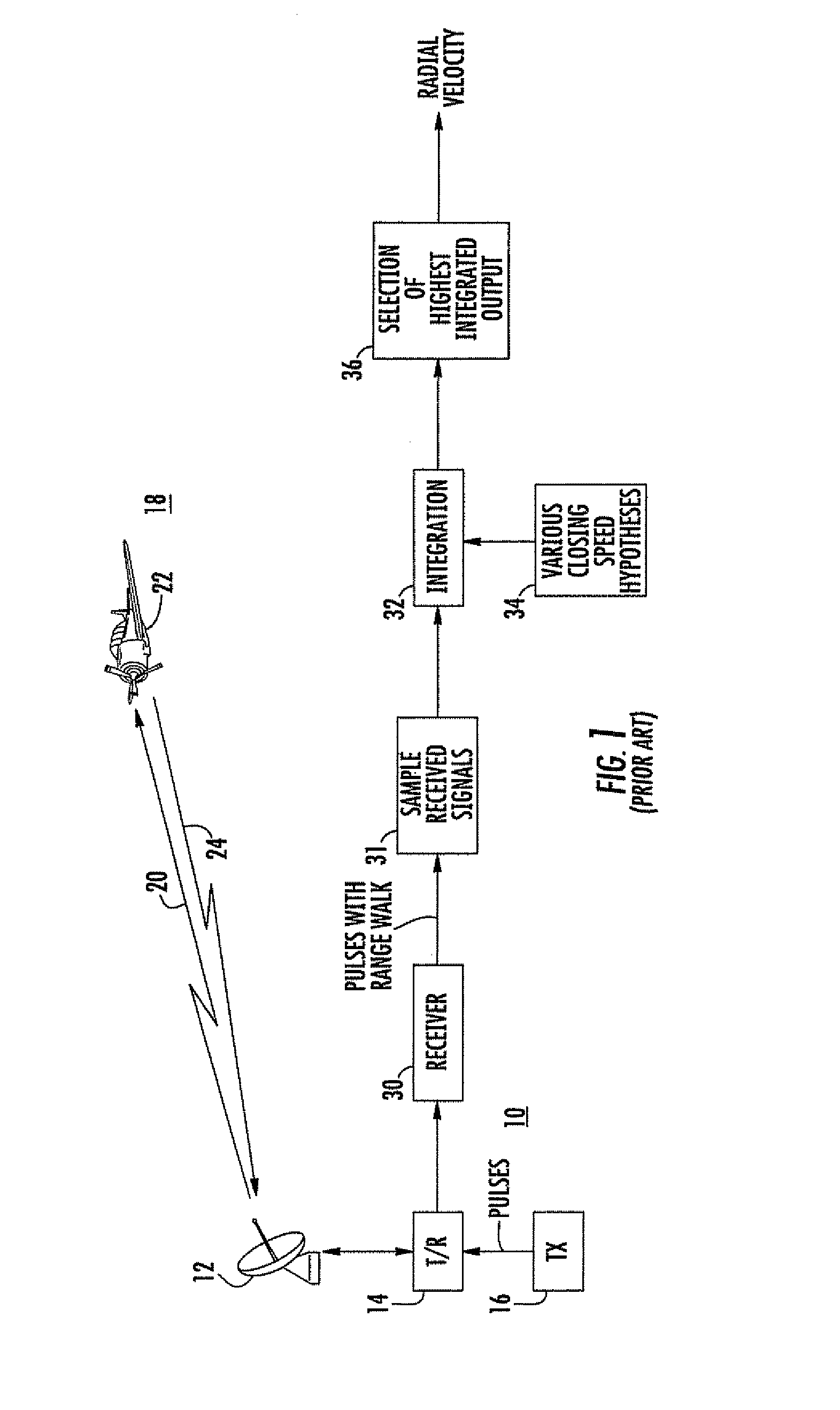
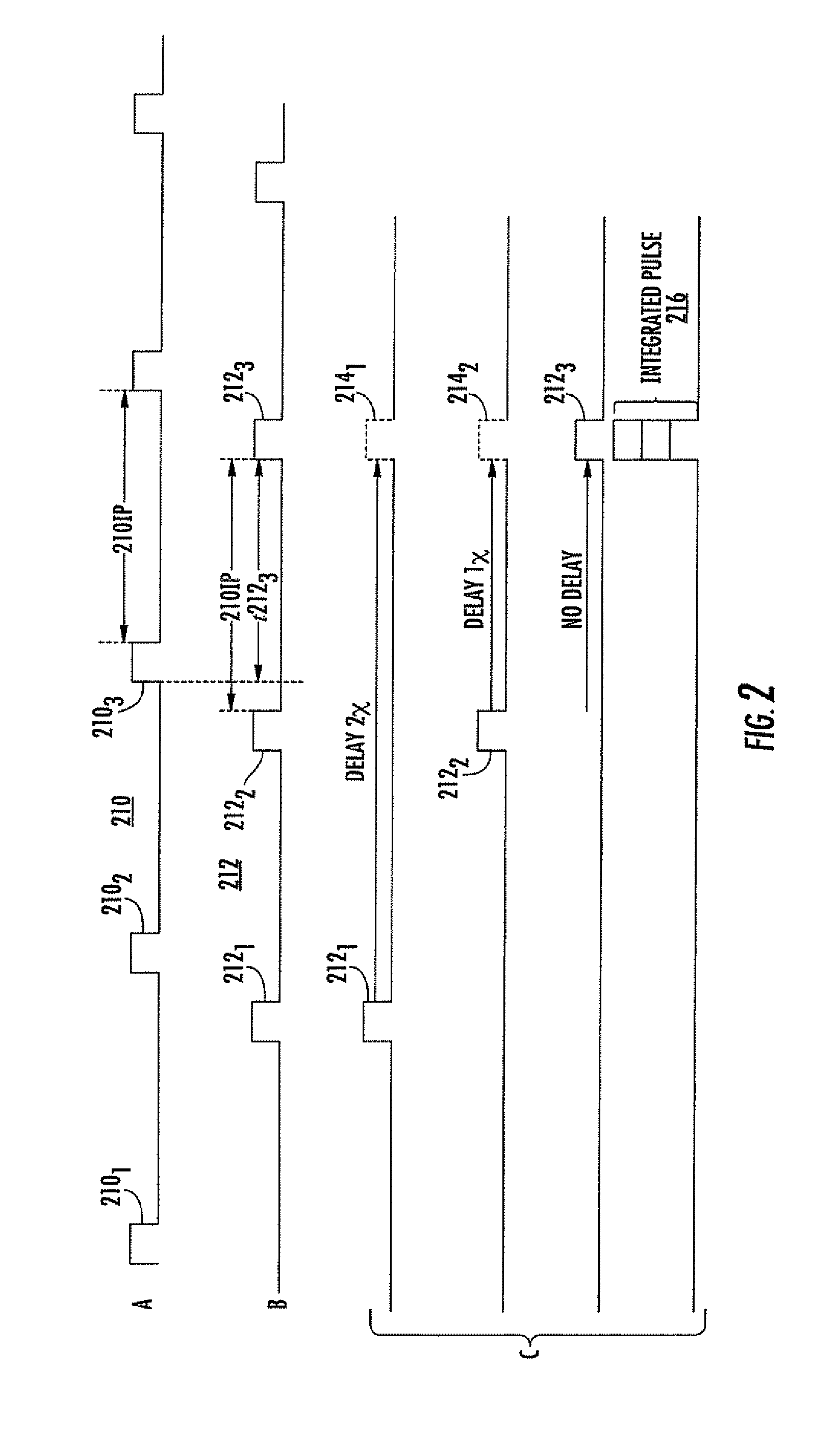
The proper timing or alignment for coherent or noncoherent integration of radar pulses returned from a potentially moving target is determined by determining the entropy associated with sets of range samples based on a plurality of different velocity hypotheses. That set associated with the minimum entropy is deemed to be the correct velocity hypothesis, and integration is then performed using the velocity hypothesis so determined.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
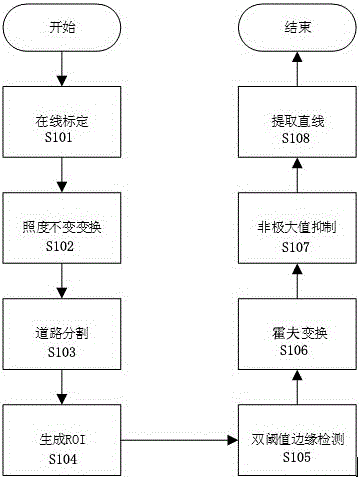
Fast lane line detection method
InactiveCN106326850AImprove adaptabilityImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionIlluminanceMinimum entropy
The invention relates to a fast lane line detection method, comprising steps of performing unchanged-illuminance conversion on an inputted image, determining an unchanged-illuminance conversion parameter through an online calibration method based on a minimum entropy, using the determined unchanged-illuminance conversion parameter to divide a road in order to determine a boundary, performing double threshold value edge detection based on a determined boundary, performing estimation on a parameter space based on a result of a double-threshold value edge detection and detecting a line based on an estimated parameter space distribution condition. The fast lane line detection method can help to realize fast lane line detection in a robustness manner.
Owner:NINGBO ONSIGHT CO LTD
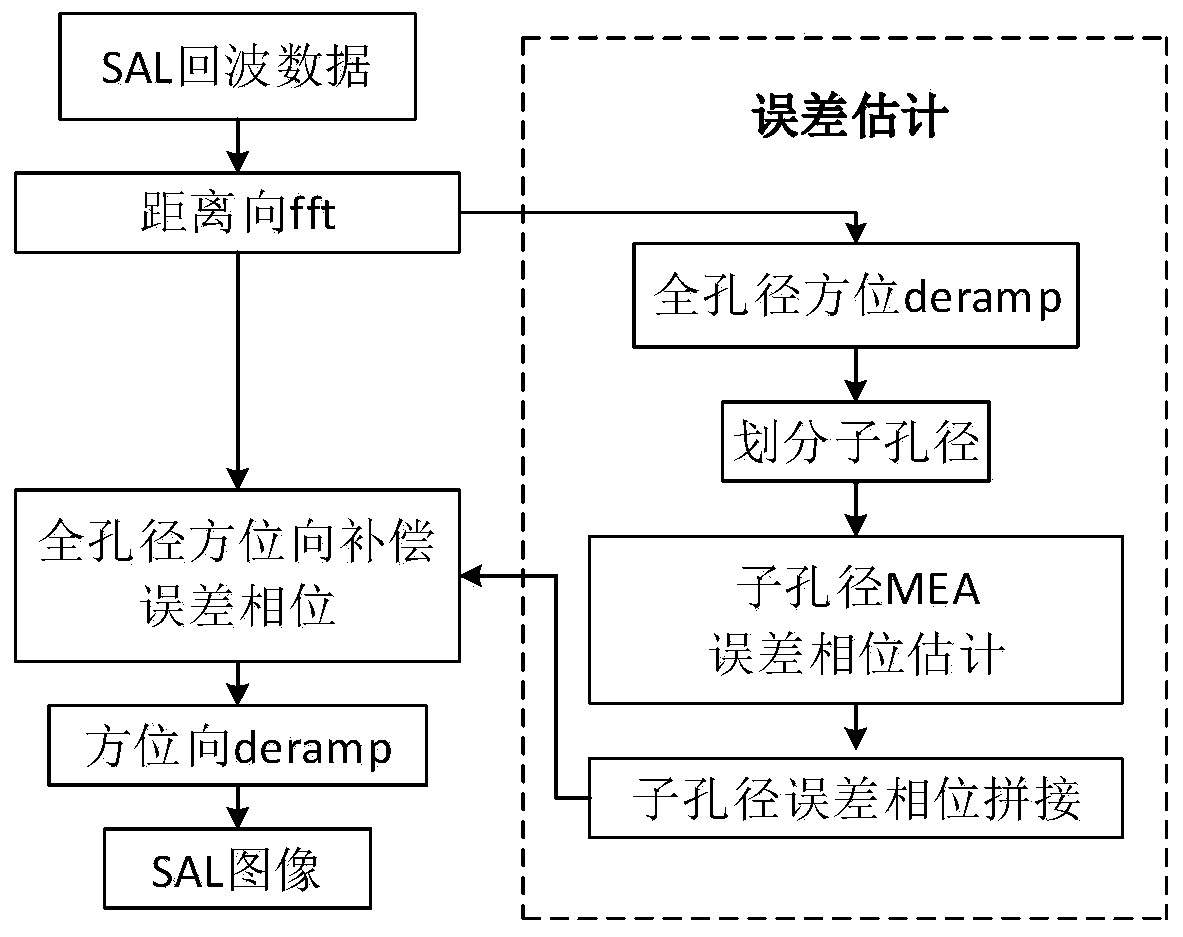
SAL (synthetic aperture ladar) full-aperture imaging method based on MEA (minimum entropy autofocus) and deramp
ActiveCN110095787AHigh resolutionImprove robustnessElectromagnetic wave reradiationSynthetic aperture sonarImaging quality
The invention discloses an SAL (synthetic aperture ladar) full-aperture imaging method based on MEA (minimum entropy autofocus) and deramp. With the method adopted, the problem of large movement errorbrought to echoes by the vibration of a carrying aircraft is solved. The method includes the following steps that: echo data signals are collected; range-direction pulse compression is performed on the received data; azimuth-direction deramp operation is performed on the range-direction pulse compressed data, so that the azimuth-direction focusing phase of the range-direction pulse compressed data can be compensated; a data block is divided into sub-apertures, phase error estimation is performed on sub-aperture data; sub-aperture phase errors are spliced, so that a full-aperture phase error is obtained; azimuth-direction phase error compensation is performed on the whole range-direction pulse compressed data; azimuth-direction derramp is carried out, the azimuth-direction pulse compression of the whole data of an SAL is achieved, the full-aperture imaging of the SAL is completed, and a high-resolution image is obtained. According to the method, sub-aperture division is performed on the data through a full-aperture imaging method; sub-aperture error phases are extracted through the MEA, all the error phases are spliced; overall phase compensation is performed on full-aperture data;and therefore, the utilization rate of original data is improved, estimated errors are more accurate, compensation is more effective, and the resolution of the imaging of the synthetic aperture laserradar is effectively improved. When the method is used for compensating high-order phase errors in the imaging of the synthetic aperture laser radar, a higher signal-to-noise ratio can be obtained, and the image resolution and image quality of the SAL can be improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Ground penetrating radar wave velocity estimation method based on diffraction, imaging and minimum entropy technology
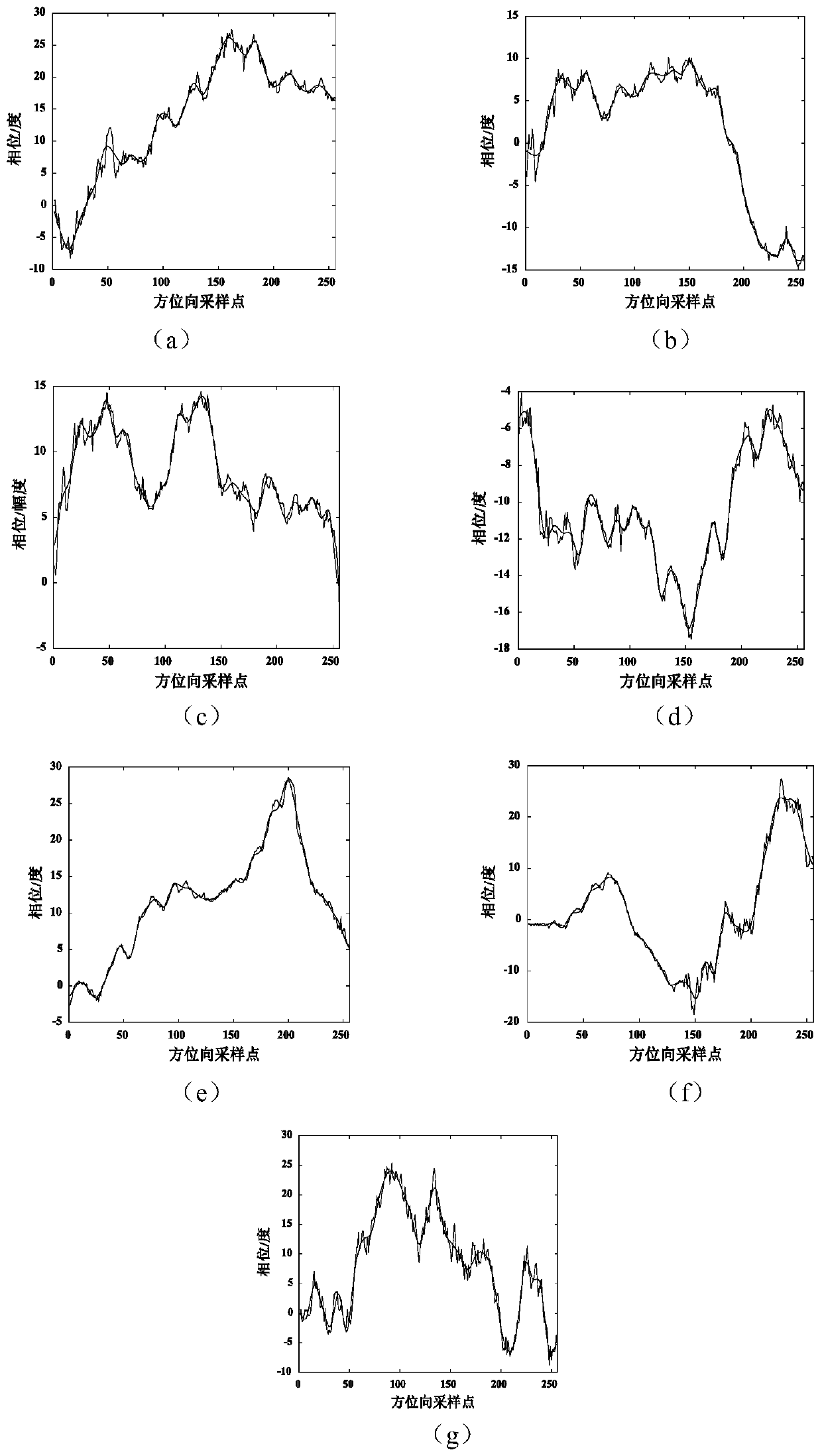
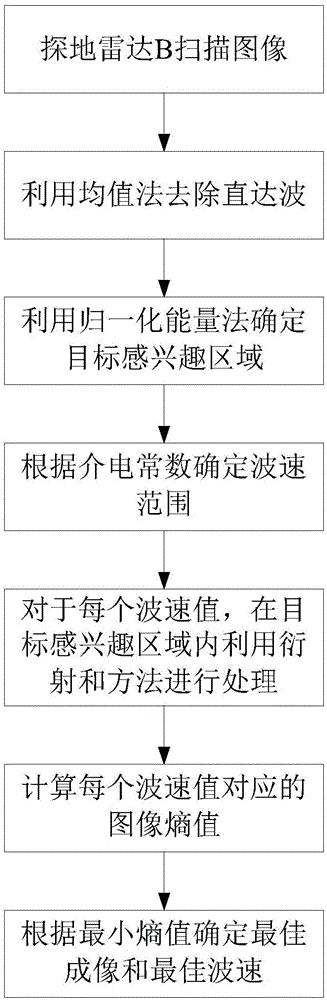
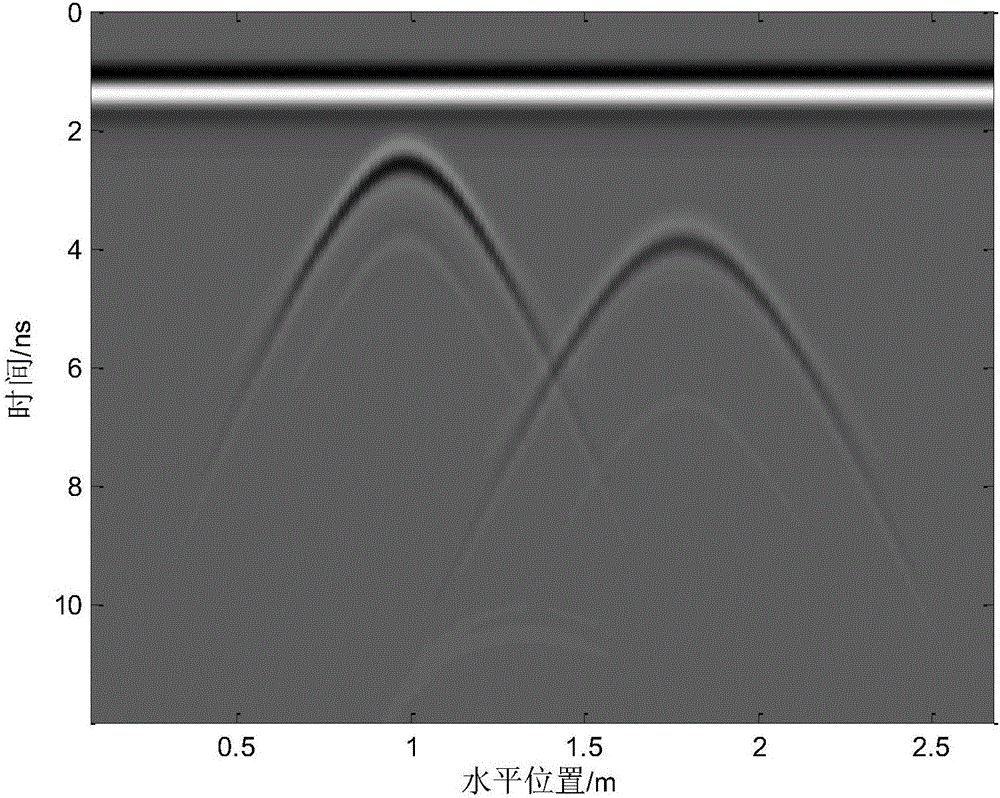
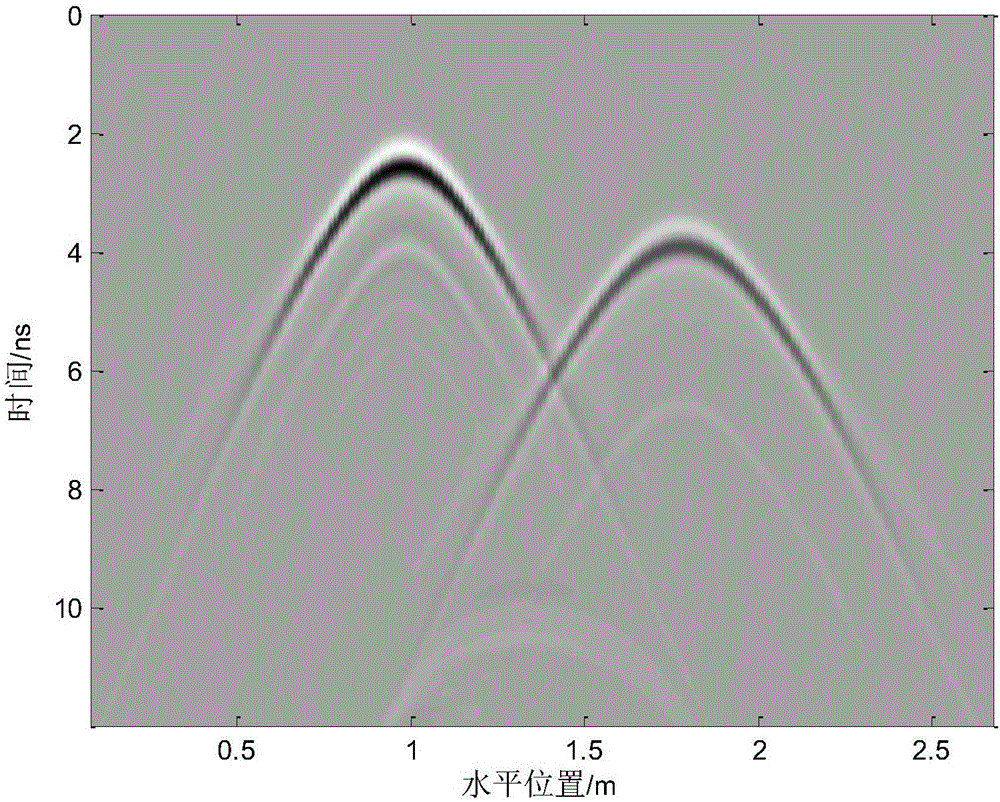
ActiveCN106443674AReduce the amount of search calculationReduce the amount of accumulated calculationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEstimation methodsMinimum entropy
The invention discloses a ground penetrating radar wave velocity estimation method based on diffraction, imaging and a minimum entropy technology. The method comprises the steps that a mean method is used to remove the direct wave component of an image; the normalized energy of the image in a two-dimensional direction is calculated, and an appropriate threshold is selected to determine a target interest region; the wave velocity range is determined according to the dielectric constant of a medium; for each wave velocity value, diffraction and the method are used to carry out synthetic aperture imaging on the image according to a target hyperbolic feature in the target interest region, and the entropy of the processed image is calculated; and finally the image corresponding to the minimum entropy is selected as the optimum imaging, and the corresponding wave velocity is the optimum wave velocity. According to the invention, the complexity of diffraction and processing is reduced by selecting the target interest region and setting a cumulative point horizontal position range; the image entropy is used to automatically determine the optimum imaging and the optimum velocity; the calculation amount is effectively reduced under the condition that the target information is completely kept; and the method has the advantages of simple calculation, high robustness and high estimation accuracy, and is suitable for engineering applications.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com