Patents
Literature
995results about "Animal undercarriages" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sensor assemblies
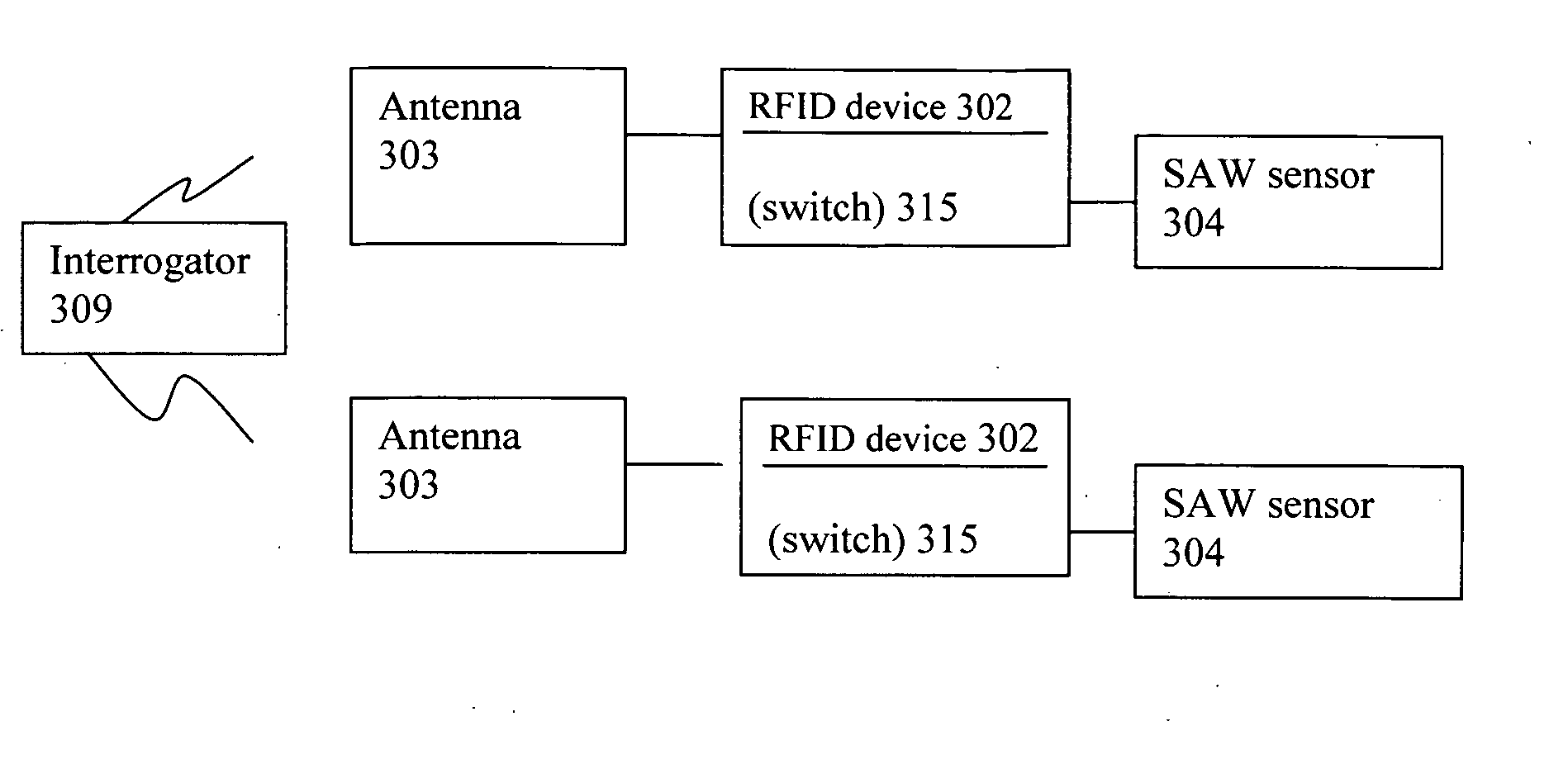
InactiveUS20060025897A1Low costPrecise positioningVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRadio frequency signalPhysical quantity
Sensor assembly capable of obtaining and providing a measurement of a physical quantity, e.g., measurement of temperature and / or pressure of a vehicular tire, includes an antenna capable of receiving a radio frequency signal, a radio frequency identification (RFID) device coupled to the antenna, a sensor coupled to the RFID device arranged to generate a measurement of the physical quantity or quantities, and a switch coupled to the RFID device and arranged to connect or disconnect the sensor from a circuit with the antenna dependent on whether the antenna receives a particular signal associated with the RFID device. When the antenna receives the particular signal associated with the RFID device, the RFID device causes the switch to close and connect the sensor in the circuit with the antenna to enable the measurement generated by the sensor to be directed to and transmitted by the antenna.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
Method and apparatus for improving vehicle operator performance
ActiveUS7565230B2Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDriver/operatorEngineering
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
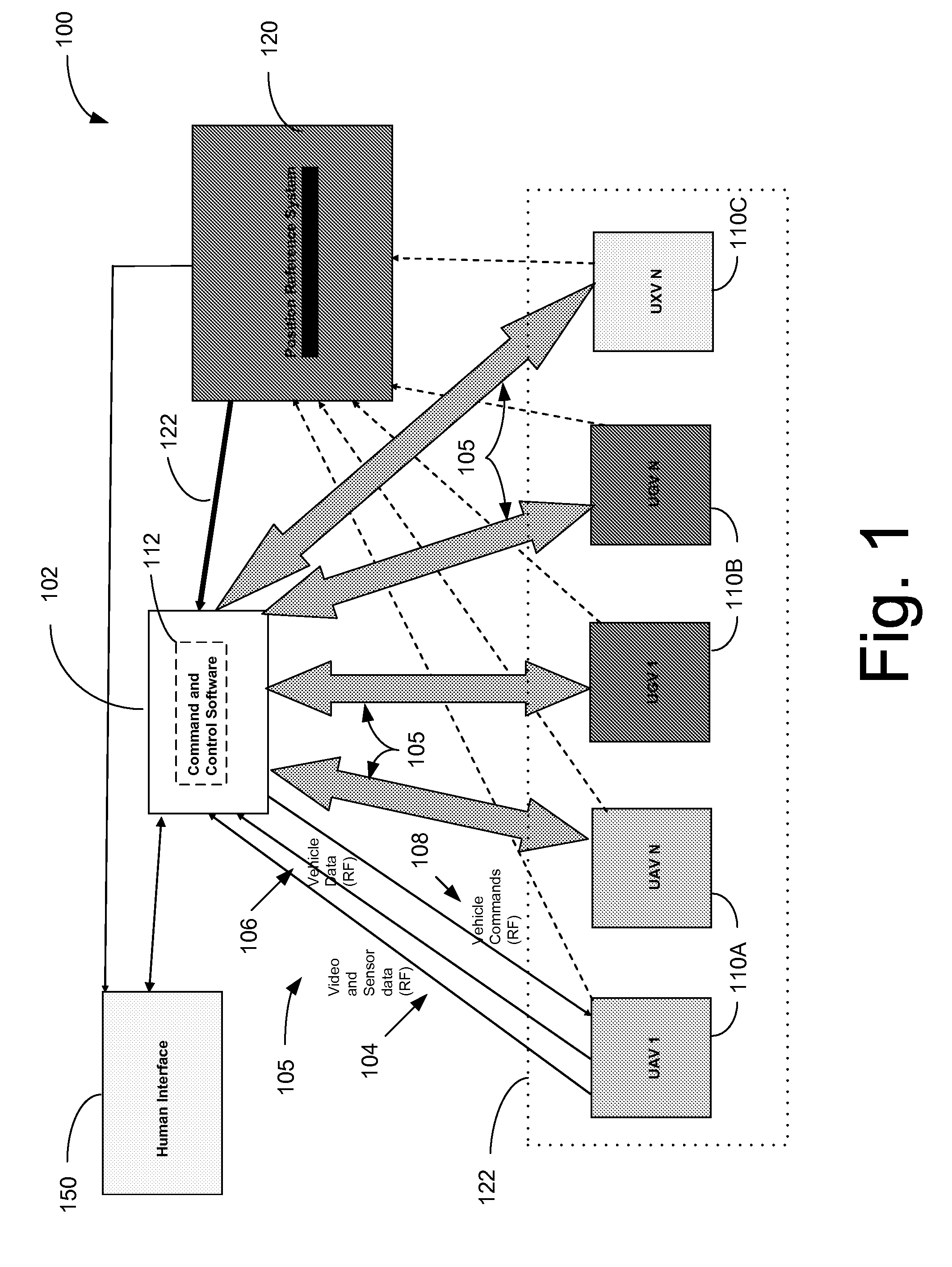
Real-time geographic information system and method
InactiveUS20070027591A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlUser inputDisplay device
An information system for dynamic distribution of location-related information between users with different perspective views includes a number of user units each including a viewing arrangement defining a viewing direction and a registration subsystem for deriving a mapping between the current perspective view and a shared location reference. The user units also include a data management system and a wireless communication arrangement. At least one of the user units further includes a user input interface for designating a viewed location within the current perspective view for association with location-related information to generate a new location-related information entry for sharing with others of the plurality of user units. At least one other of the user units further includes a display device associated with the viewing arrangement for displaying location-related information correctly positioned in the context of the current perspective view.
Owner:RAFAEL ADVANCED DEFENSE SYSTEMS
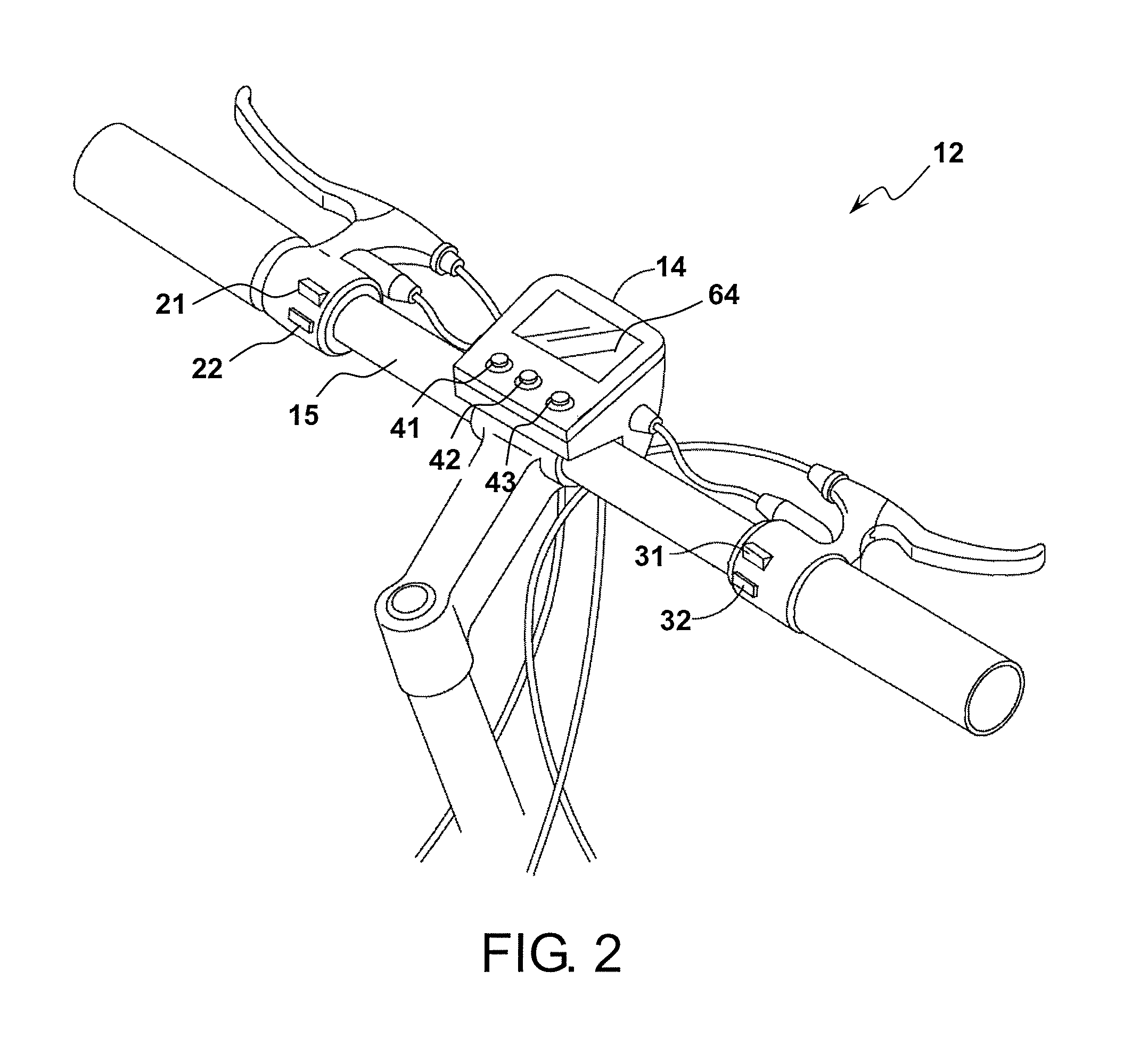
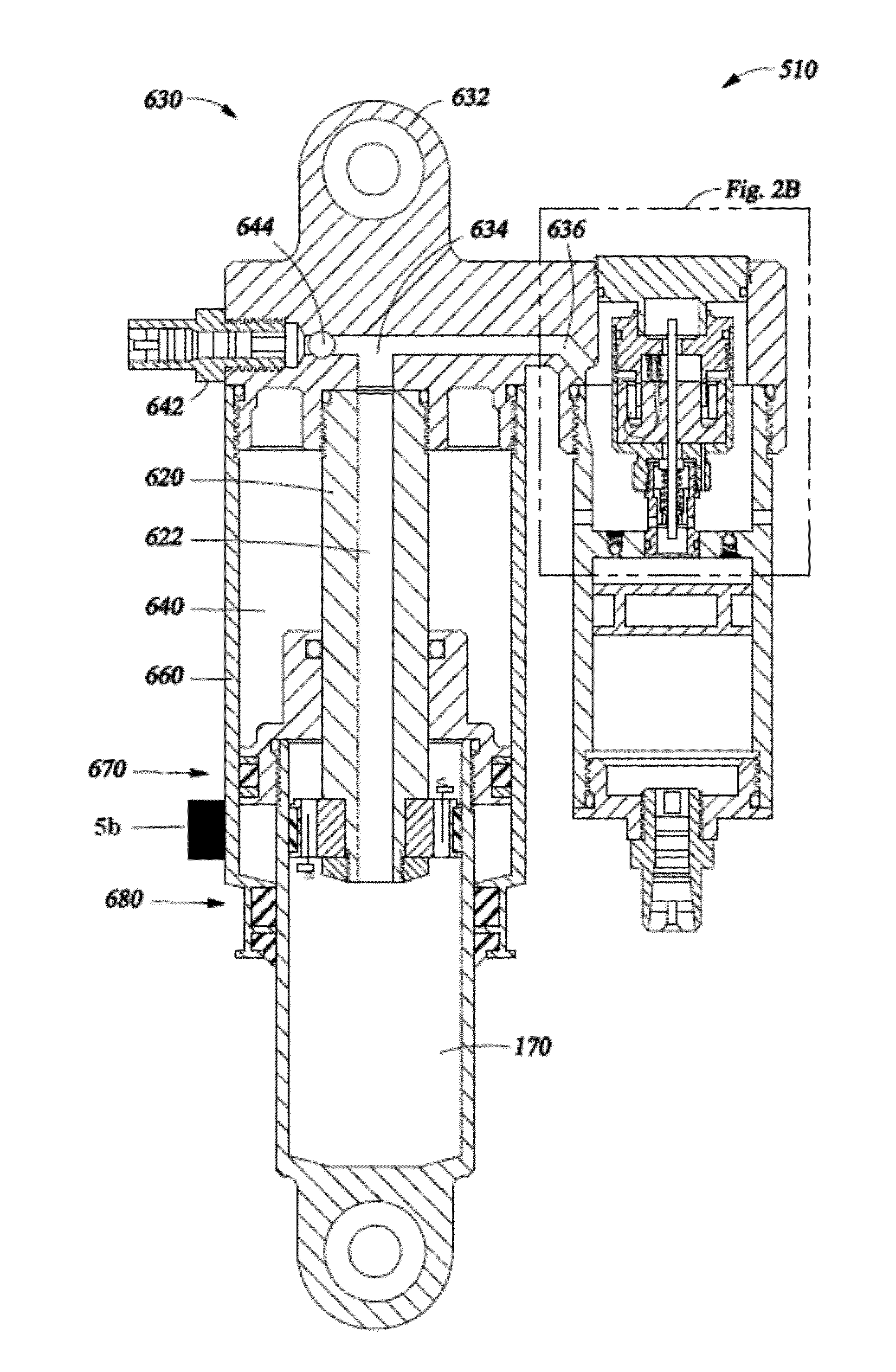
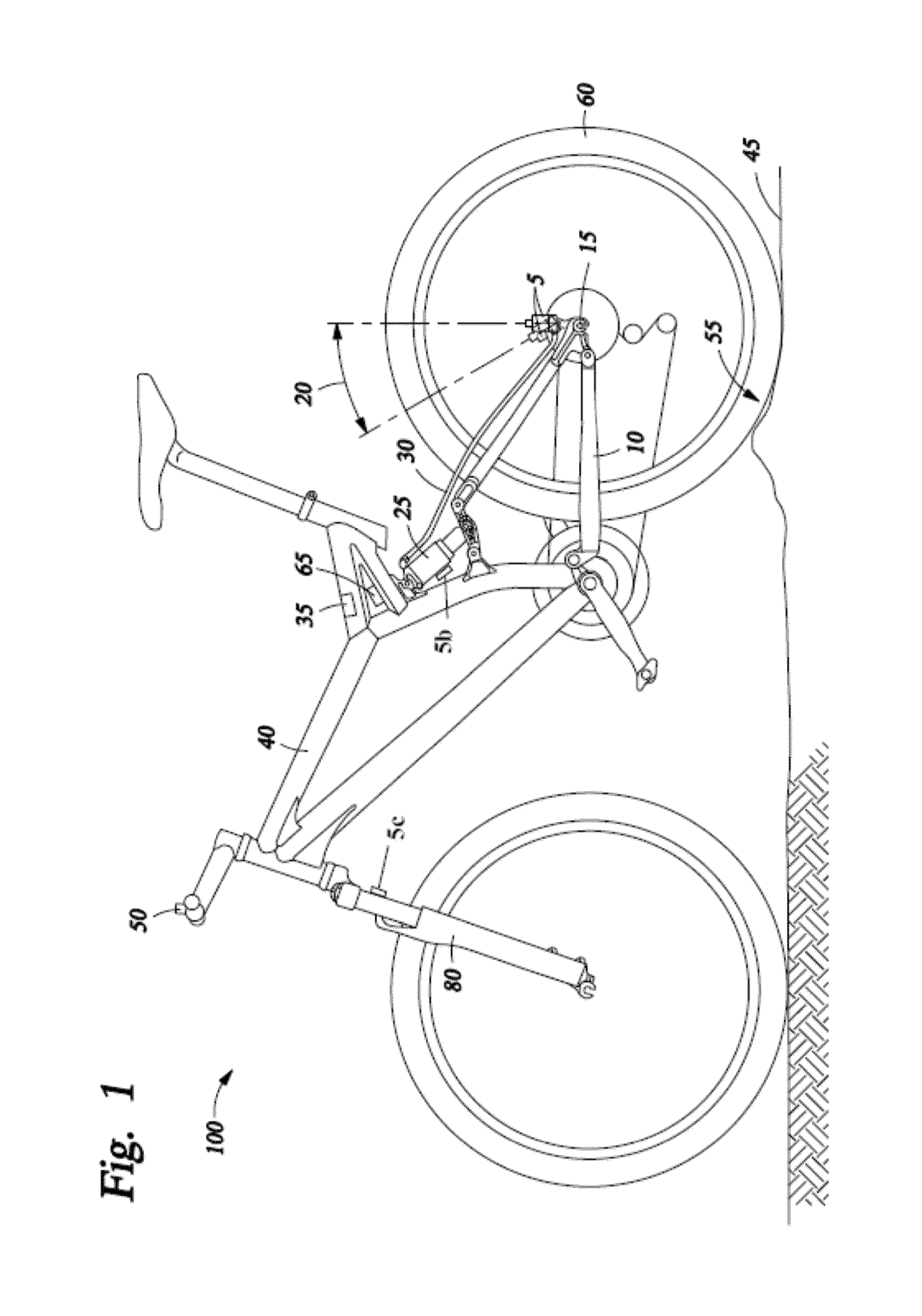
Bicycle user interface system and method of operation thereof
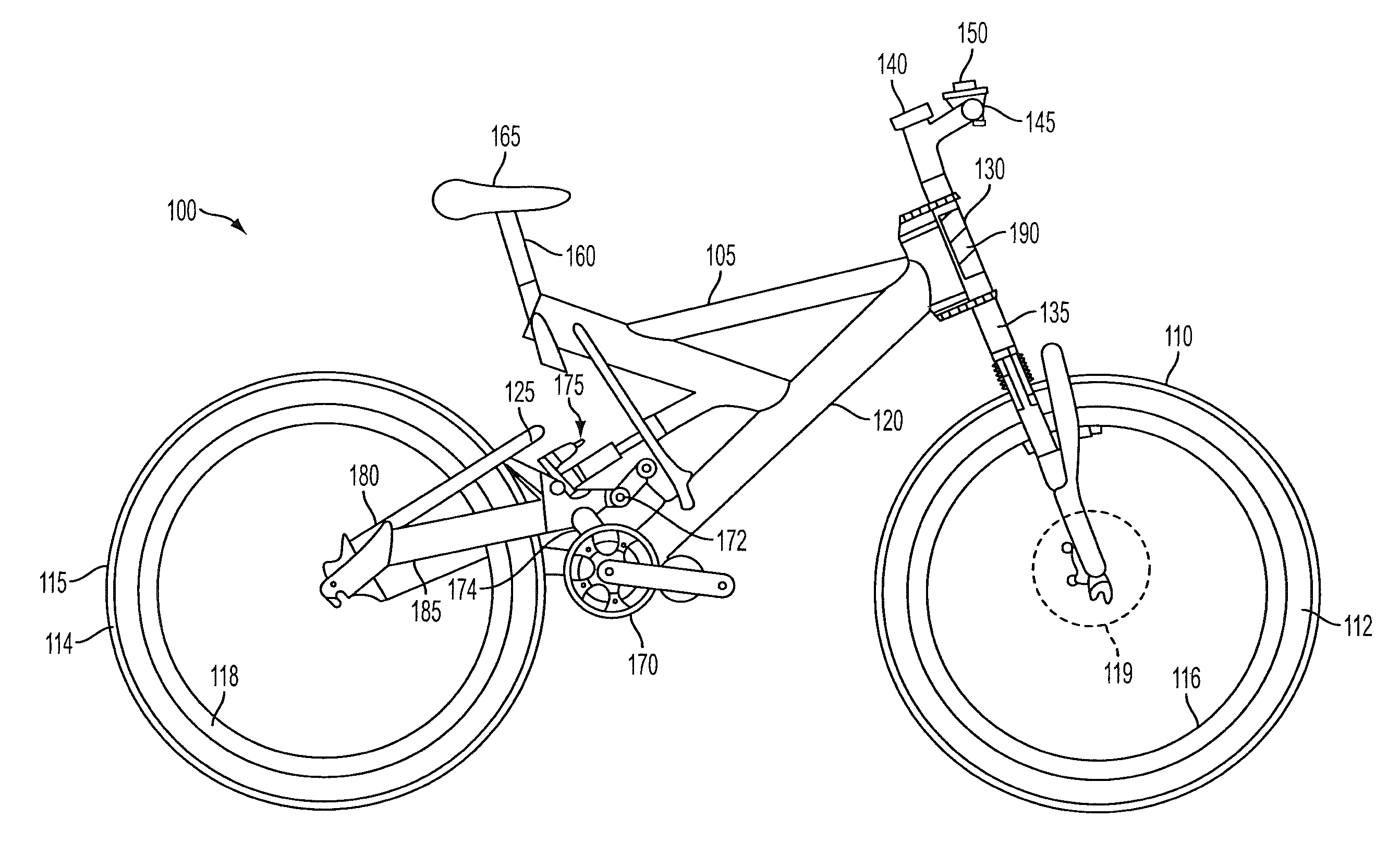
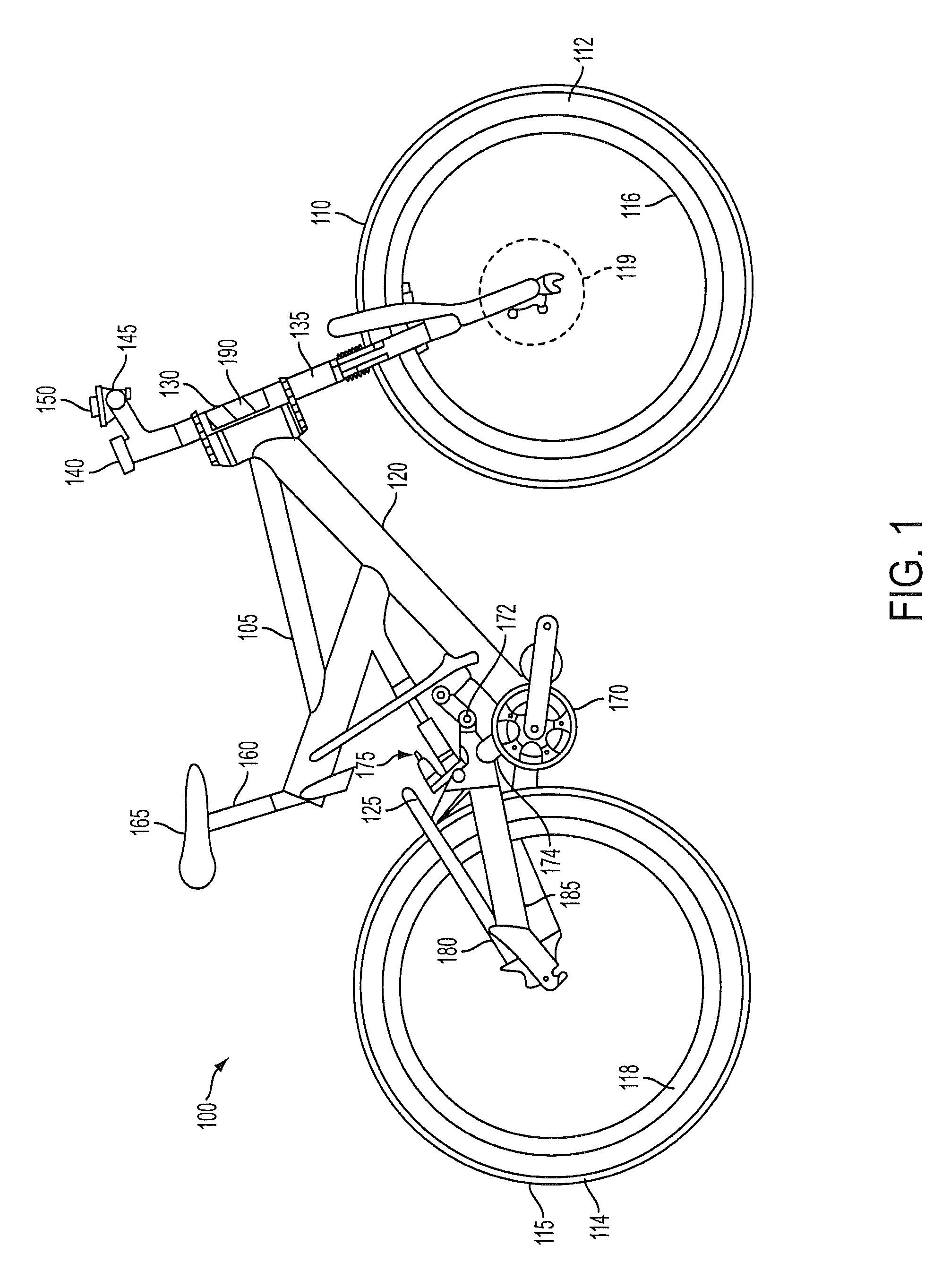
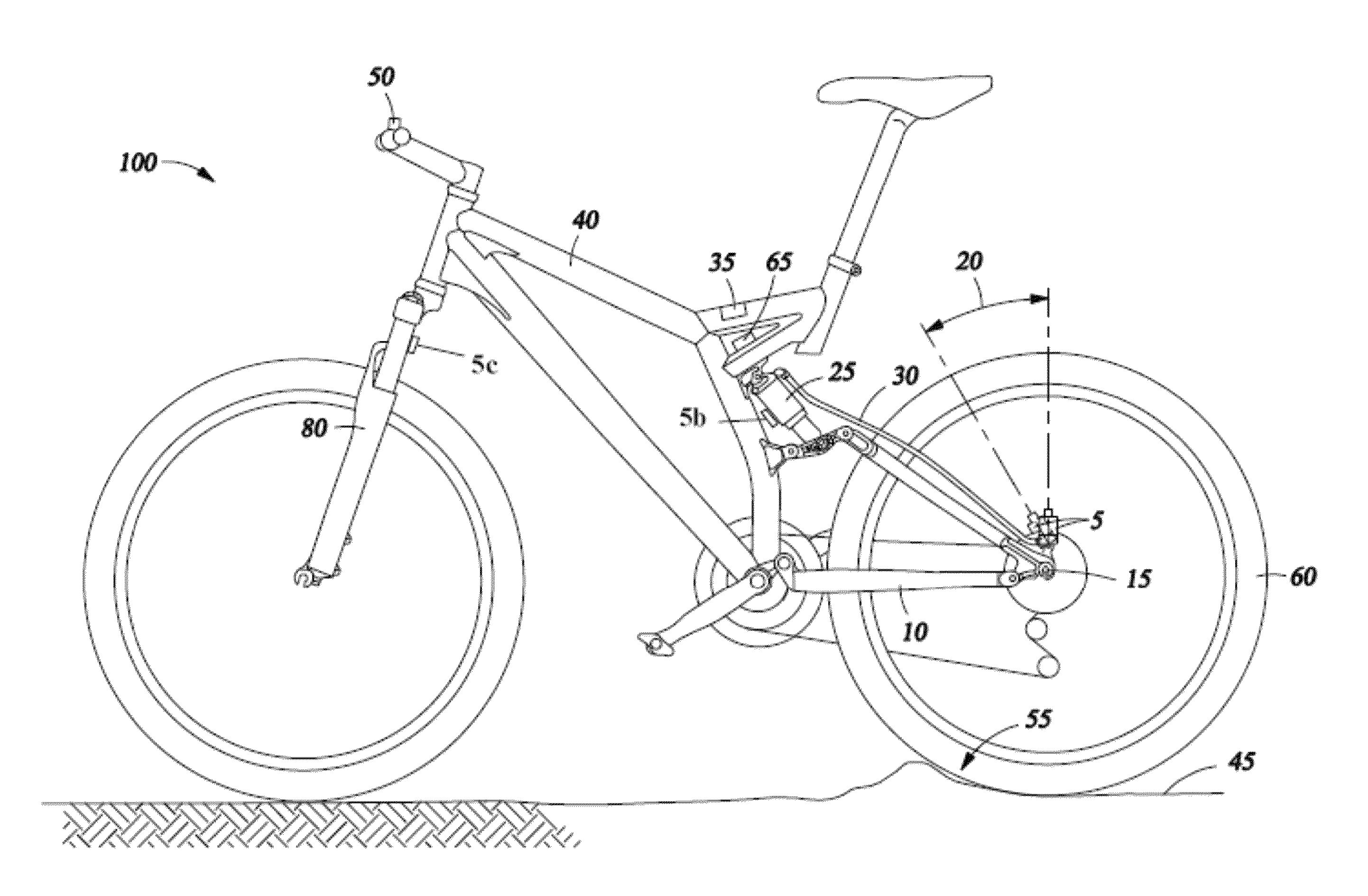
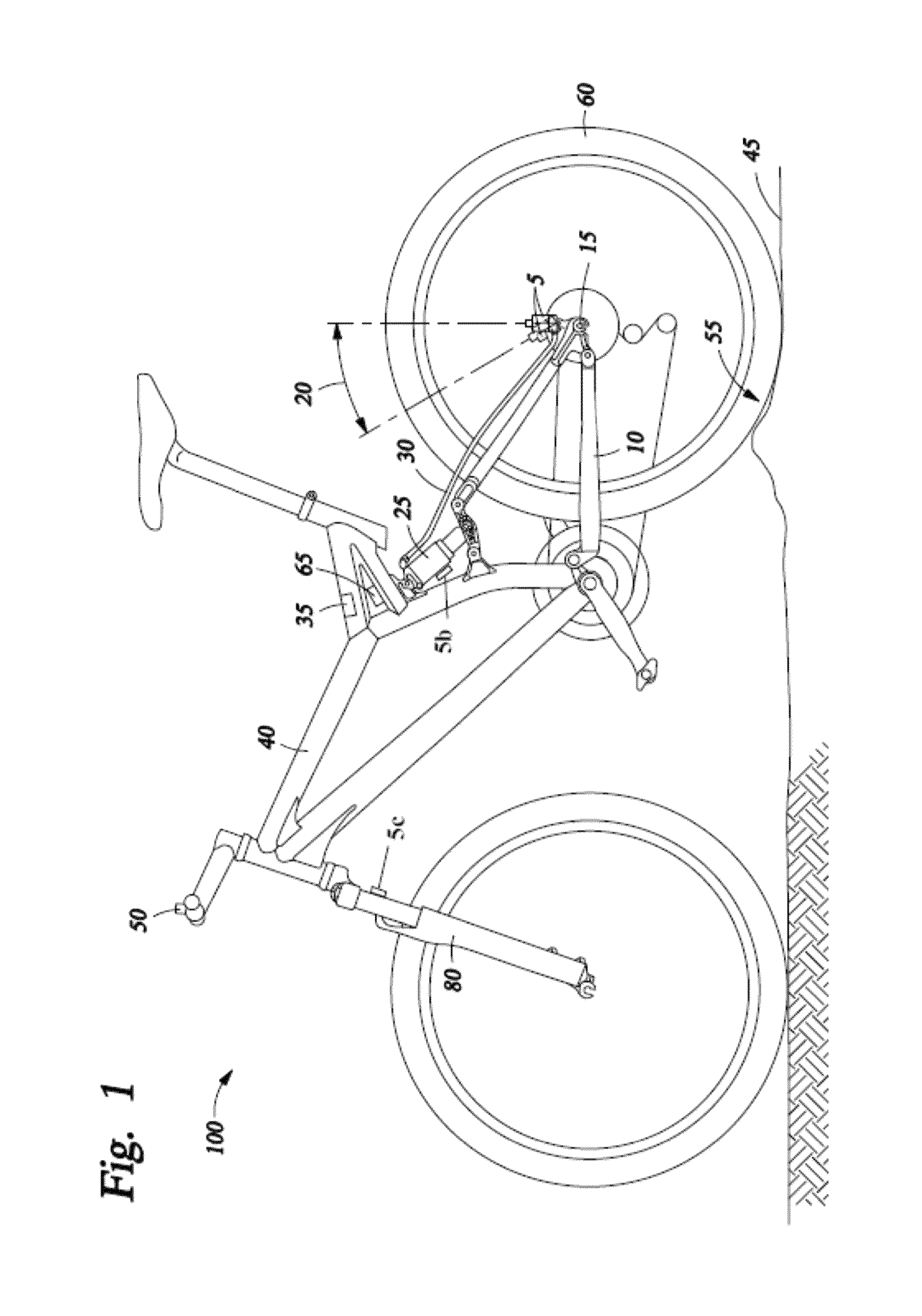
A bicycle is disclosed having a control system with a user interface and an active suspension system. The control system includes a one or more sensors arranged to measure and transmit a signal indicative of the terrain over which the bicycle is being ridden. The active suspension system includes a valve box that is fluidly coupled to each chamber of the lower cylinder. An orifice in the valve box is changed in size in response to a signal from a sensor associated with the front wheel that changes the response of the suspension system due to changing terrain conditions. The user interface includes a selection device mounted to the handlebars that allows the user to change parameters of the active suspension system during operation of the bicycle.
Owner:CANNONDALE BICYCLE CORPORATION
Vehicle systems control for improving stability
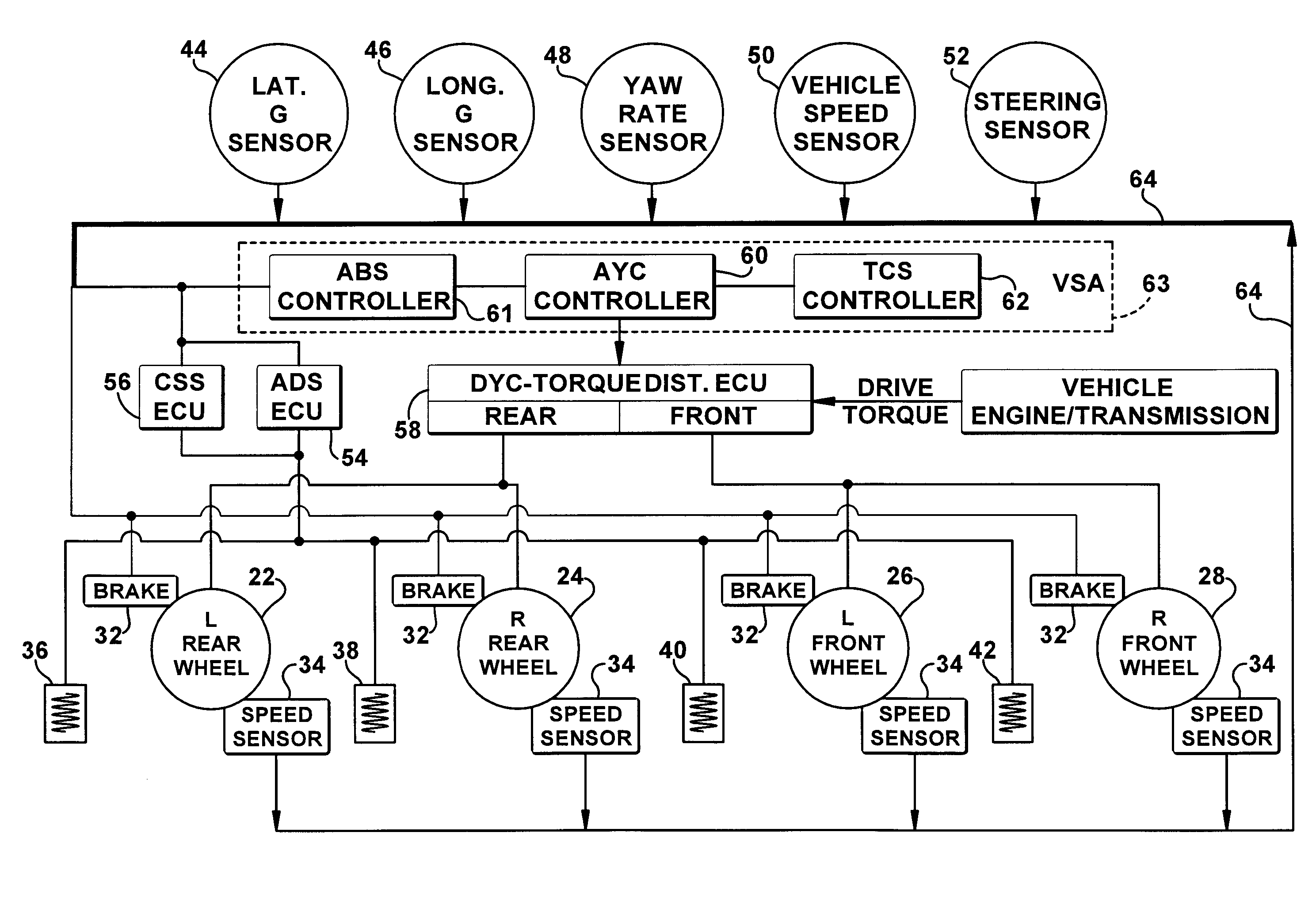
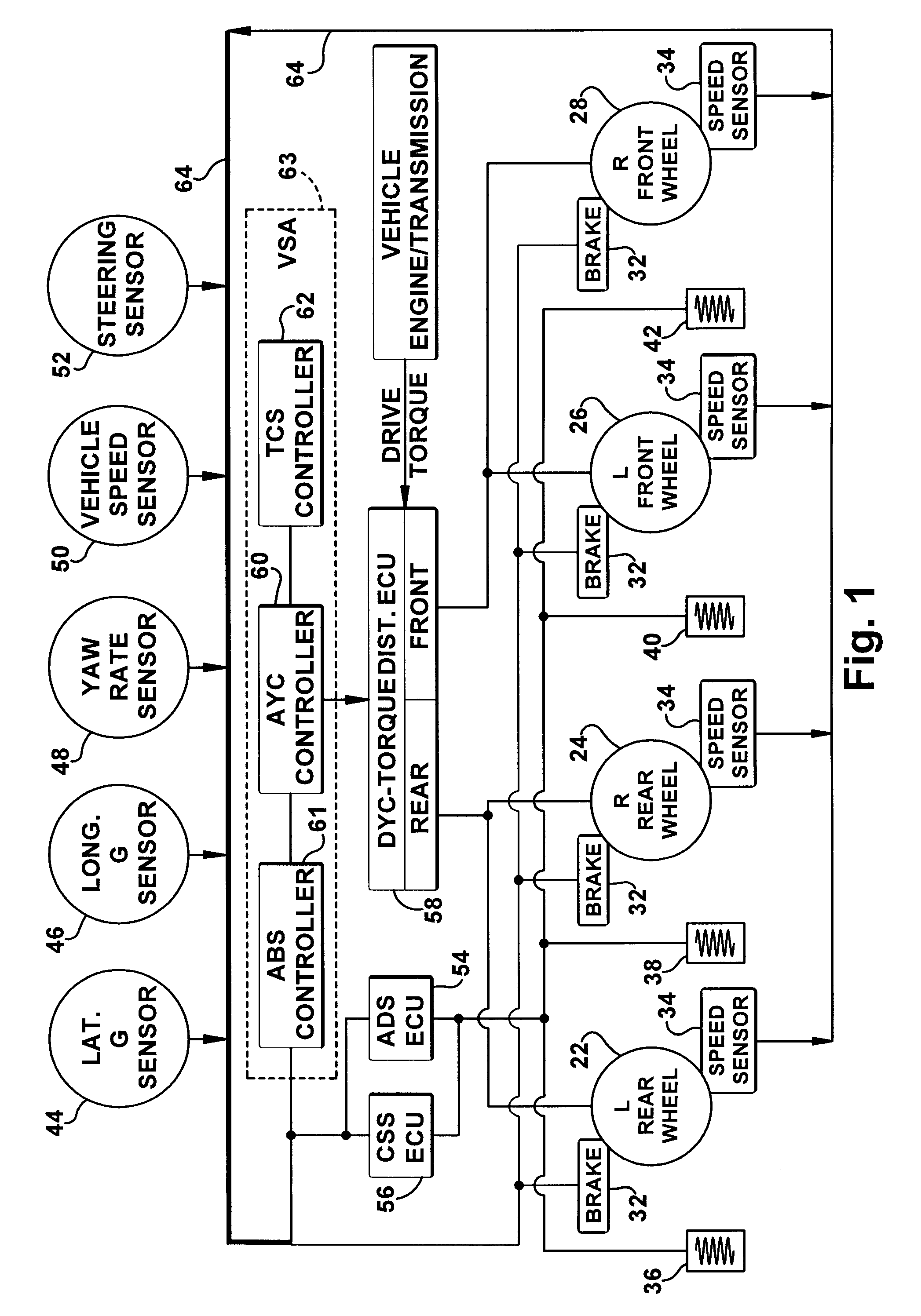
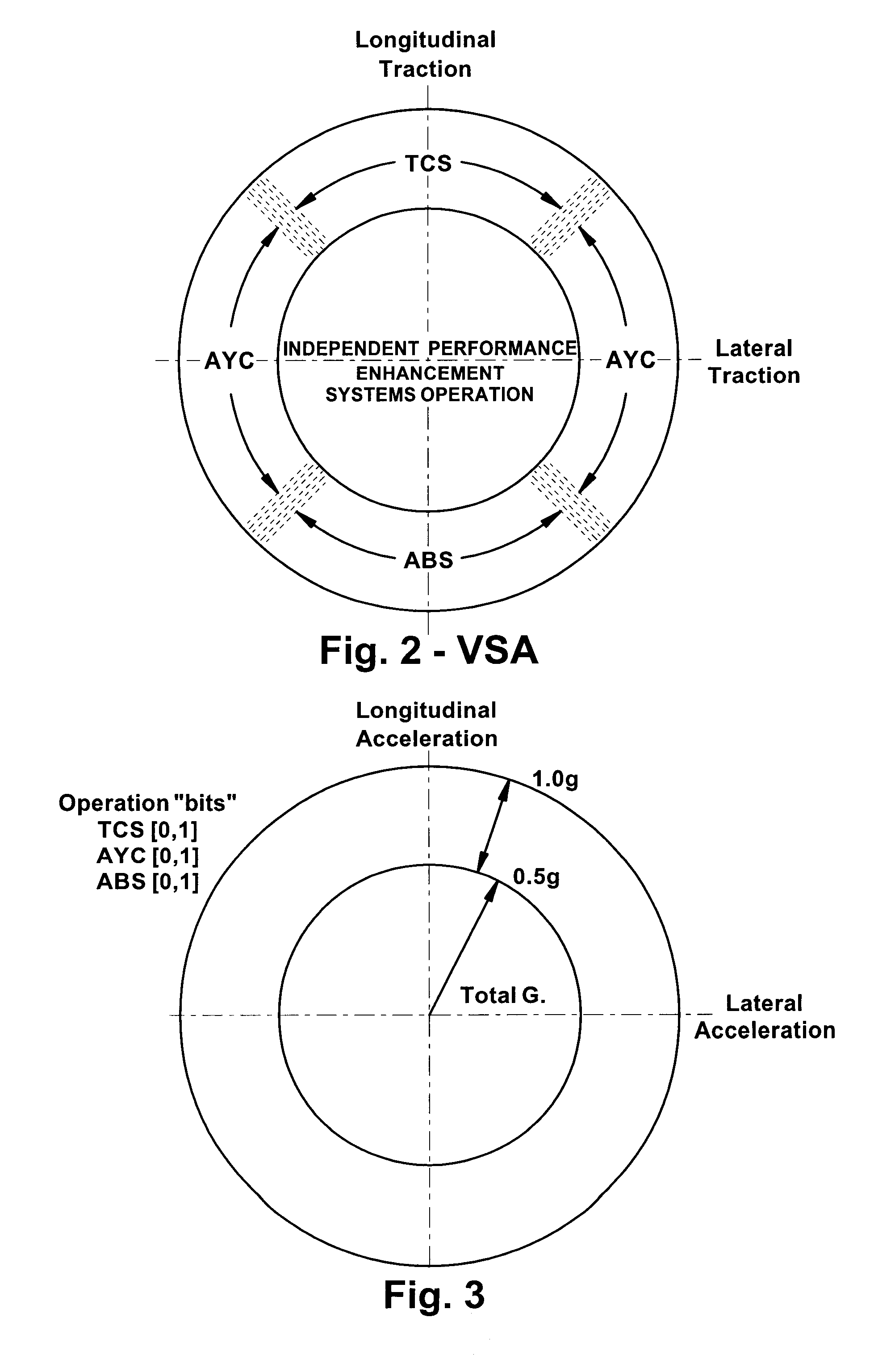
InactiveUS20080183353A1Improve vehicle stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemTraction control system
Improved methods of controlling the stability of a vehicle are provided via the cooperative operation of vehicle stability control systems such as an Active Yaw Control system, Antilock Braking System, and Traction Control System. These methods use recognition of road surface information including the road friction coefficient (mu), wheel slippage, and yaw deviations. The methods then modify the settings of the active damping system and / or the distribution of drive torque, as necessary, to increase / reduce damping in the suspension and shift torque application at the wheels, thus preventing a significant shift of load in the vehicle and / or improving vehicle drivability and comfort. The adjustments of the active damping system or torque distribution temporarily override any characteristics that were pre-selected by the driver.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
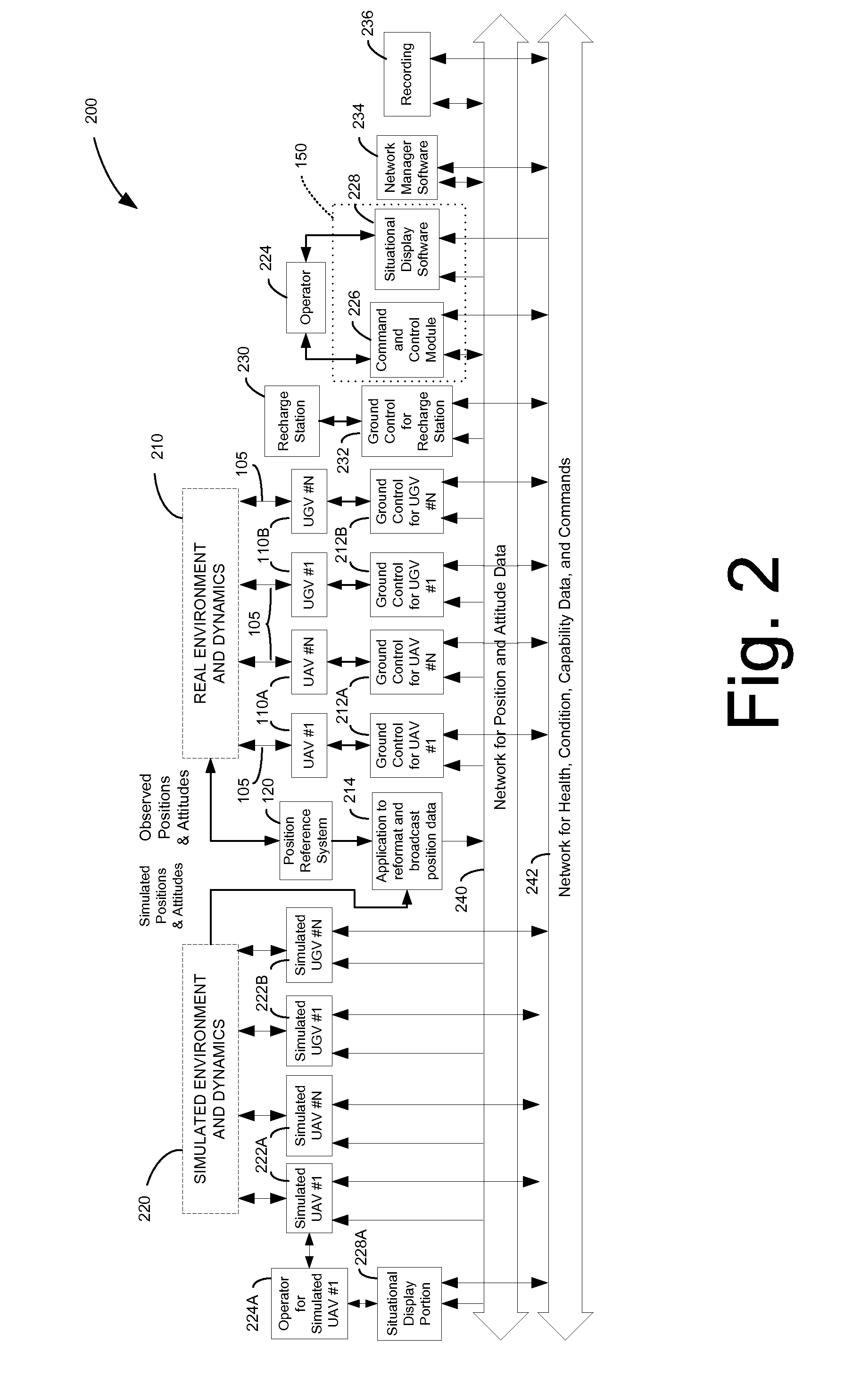
Autonomous Vehicle Rapid Development Testbed Systems and Methods
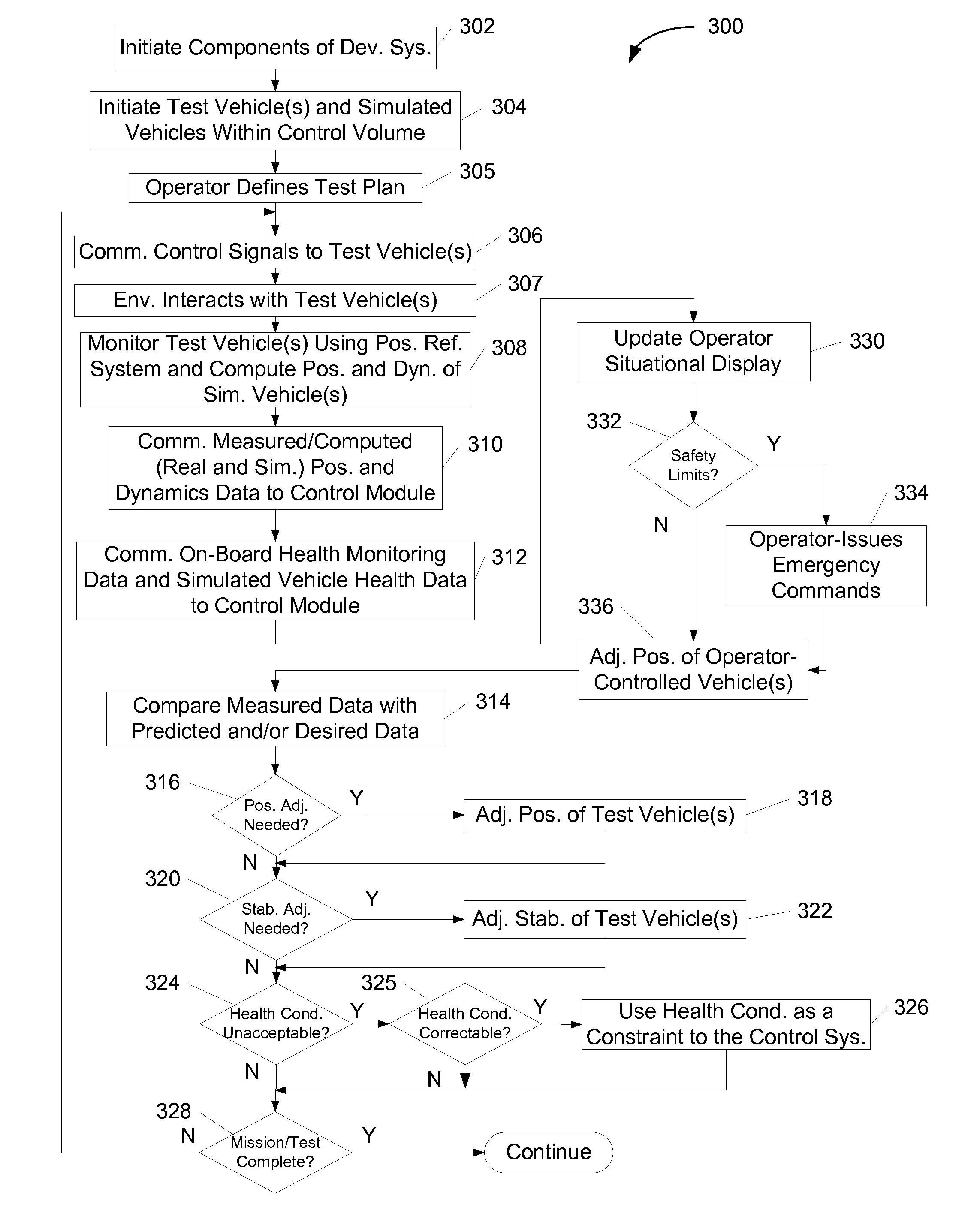
ActiveUS20080033684A1Easy to detectRapid development and testingVehicle testingDigital data processing detailsCommand and controlControl signal
Systems and methods for development testing of vehicles and components are disclosed. In one embodiment, a system includes a position reference system and a command and control architecture. The position reference system is configured to repetitively measure one or more position and motion characteristics of one or more vehicles operating within a control volume. The command and control architecture is configured to receive the repetitively measured characteristics from the position reference system, and to determine corresponding control signals based thereon. The control signals are then transmitted to the one or more vehicles to control at least one of position, movement, and stabilization of the one or more vehicles in a closed-loop feedback manner. The system may further include a health monitoring component configured to monitor health conditions of the one or more vehicles, the control signals being determined at least in part on the health conditions.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
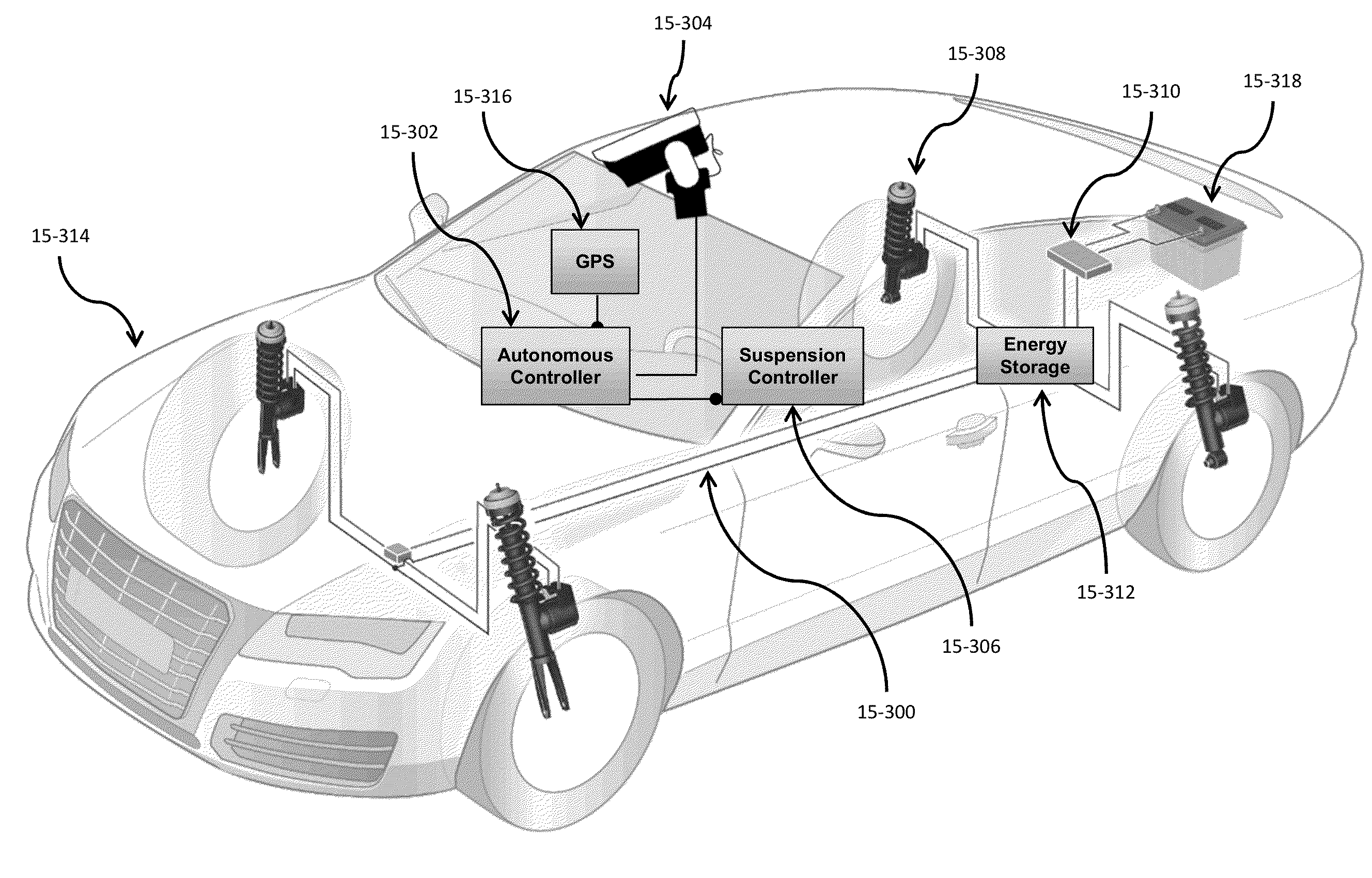
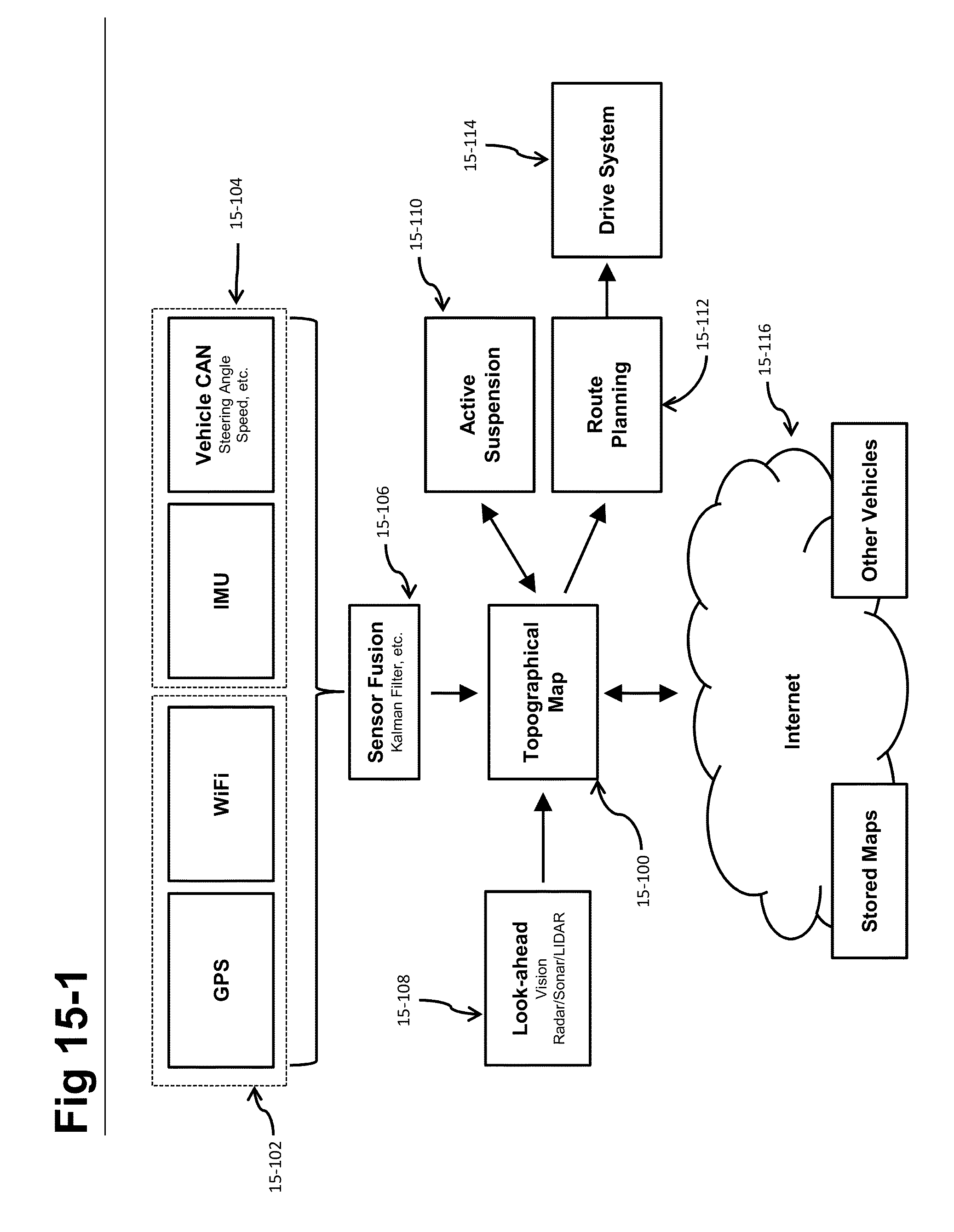
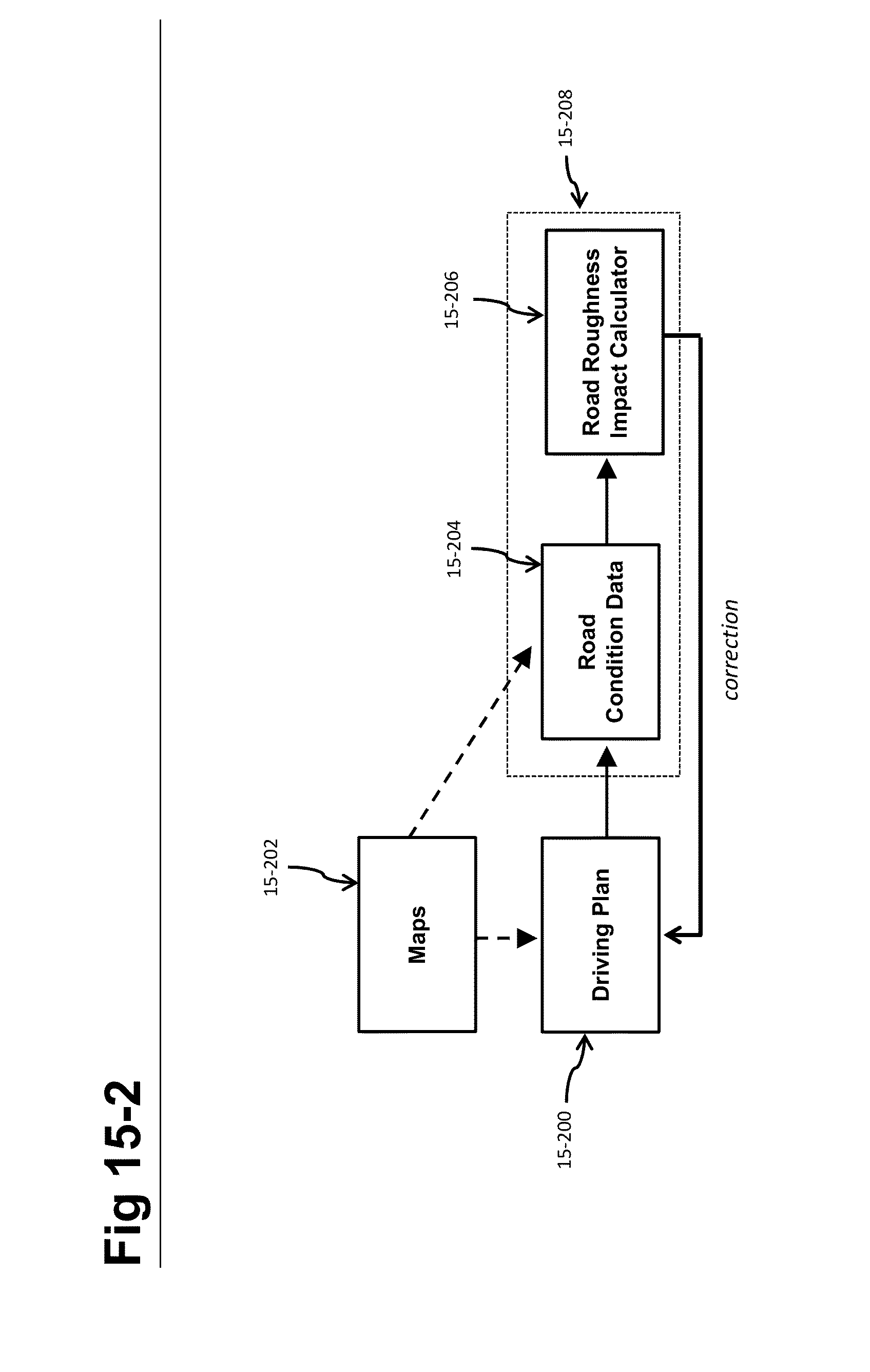
Self-driving vehicle with integrated active suspension
InactiveUS20140297116A1Improve ride comfort performanceActive suspension technologiesDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesRoad surfaceEngineering
A self-driving vehicle with an integrated fully-active suspension system. The fully-active suspension utilizes data from one or more sensors used for autonomous driving (e.g. vision, LIDAR, GPS) in order to anticipate road conditions in advance. The system builds a topographical map of the road surface. Suspension and road data is delivered back to the vehicle in order to change autonomous driving behavior including route planning. Energy storage is regulated based on a planned route. Forward and lateral acceleration feel is mitigated through active pitch and tilt compensation. The fully-active suspension pushes and pulls the suspension in three or more operational quadrants in order to deliver superior ride comfort, handling, and / safety of the vehicle.
Owner:CLEARMOTION INC
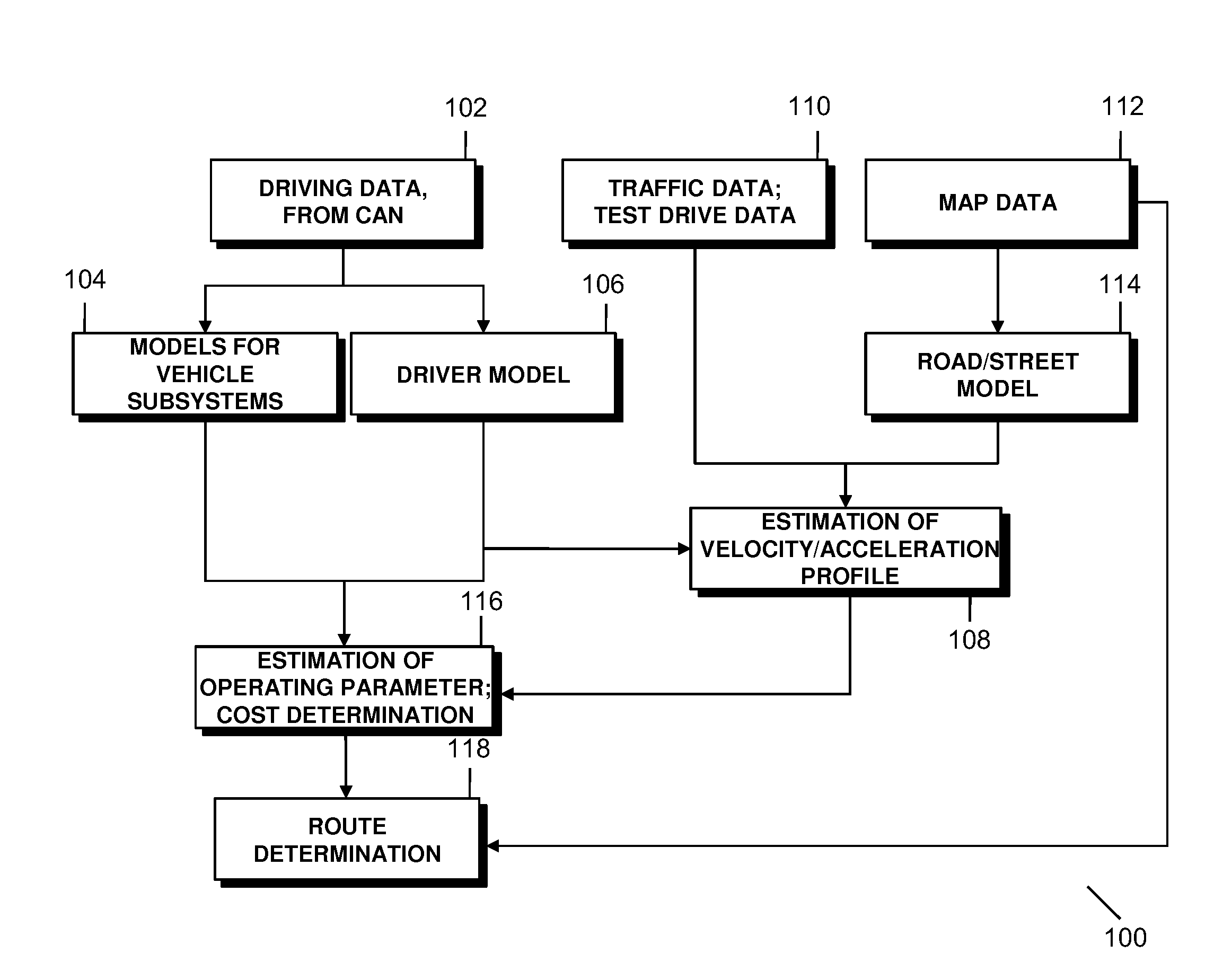
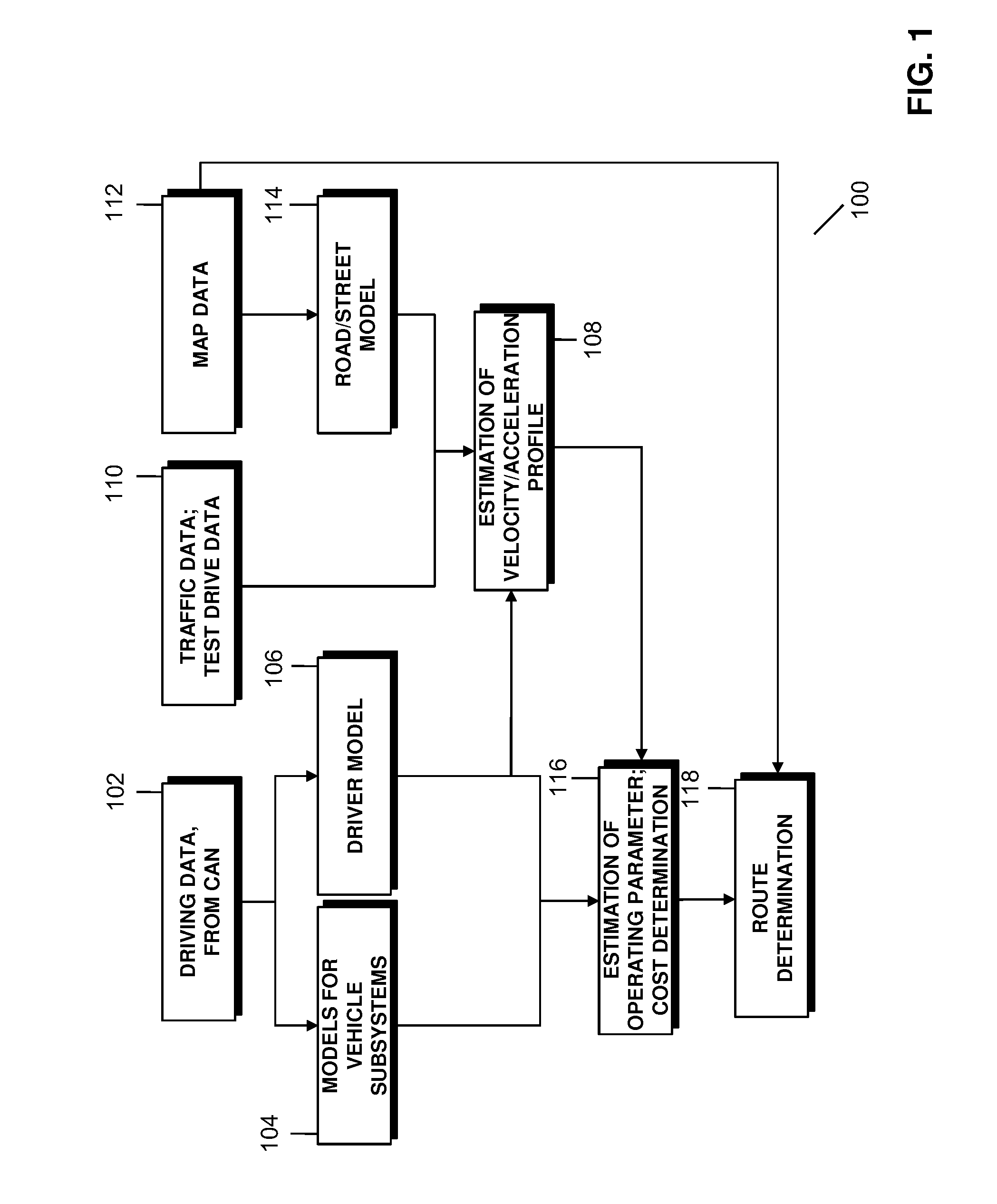
Method of estimating a propulsion-related operating parameter
ActiveUS20110040438A1Maximize precisionVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesNavigation systemAutomotive engineering
A method is provided for estimating a propulsion-related operating parameter of a vehicle for a road segment, and for determining routes based on the estimate. The method may be employed, for example, in a vehicle navigation system. In one example method, at least one operating parameter of the vehicle is estimated for the road segment based on information corresponding to the road segment. The propulsion-related operating parameter is estimated for the road segment using the at least one estimated operating parameter and at least one vehicle specific parameter. The at least one vehicle specific parameter is determined by acquiring driving data to determine a plurality of vehicle operating parameters while the vehicle is in operation. At least two of the determined vehicle operating parameters are used in a predetermined relationship that includes the at least one vehicle specific parameter. The at least one vehicle specific parameter is then determined from the driving data for the at least two vehicle operating parameters and the relationship.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
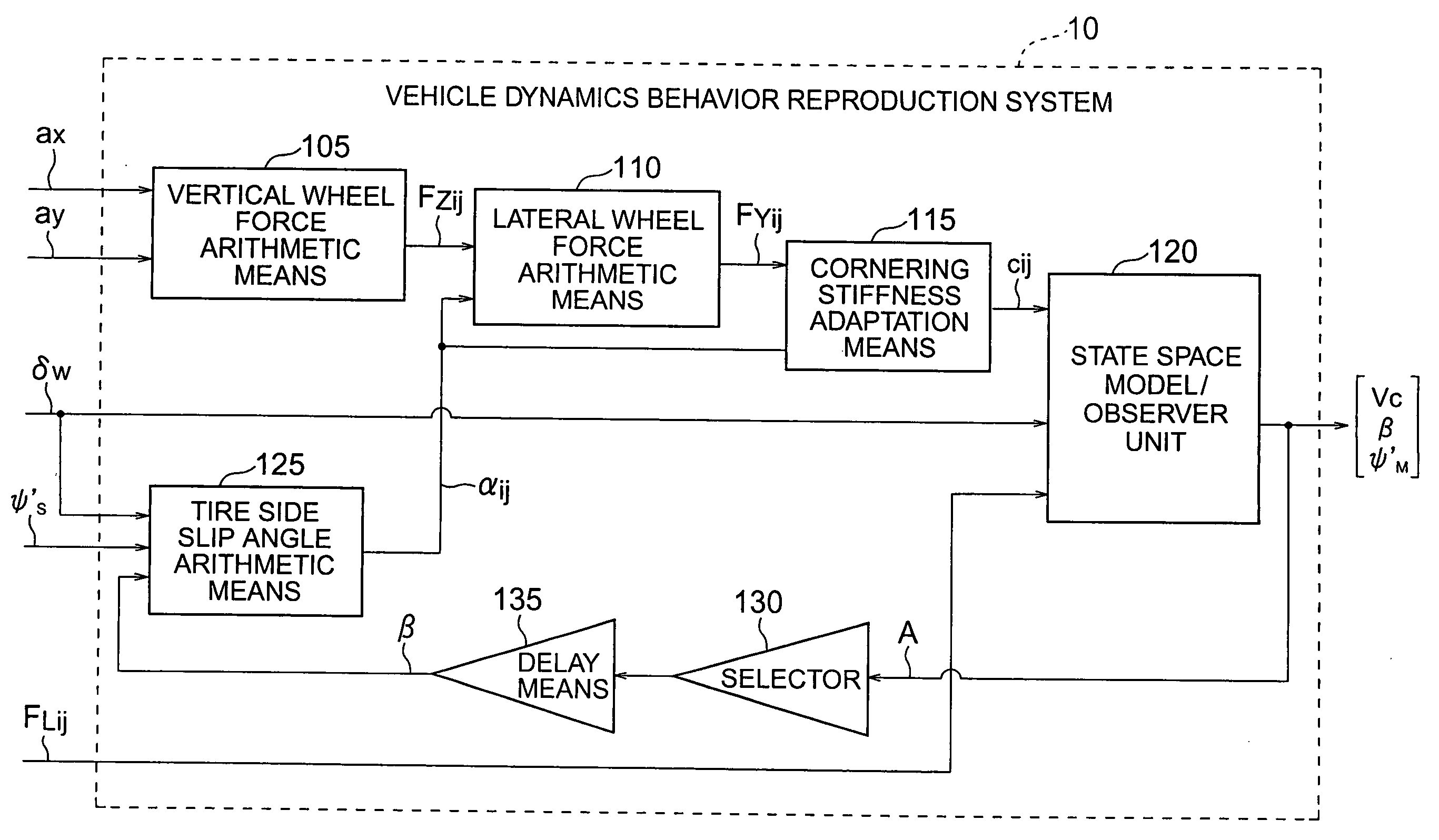
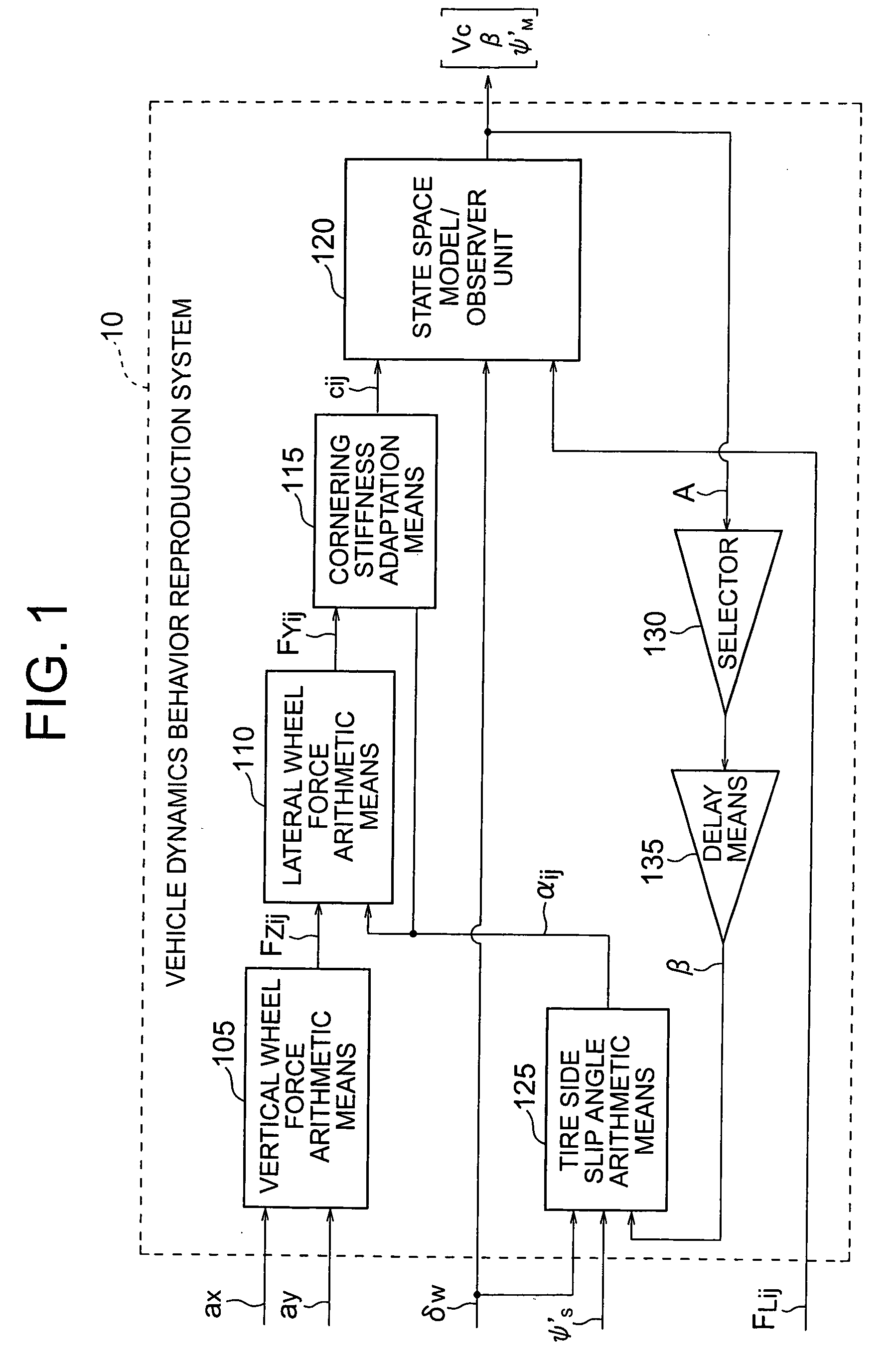
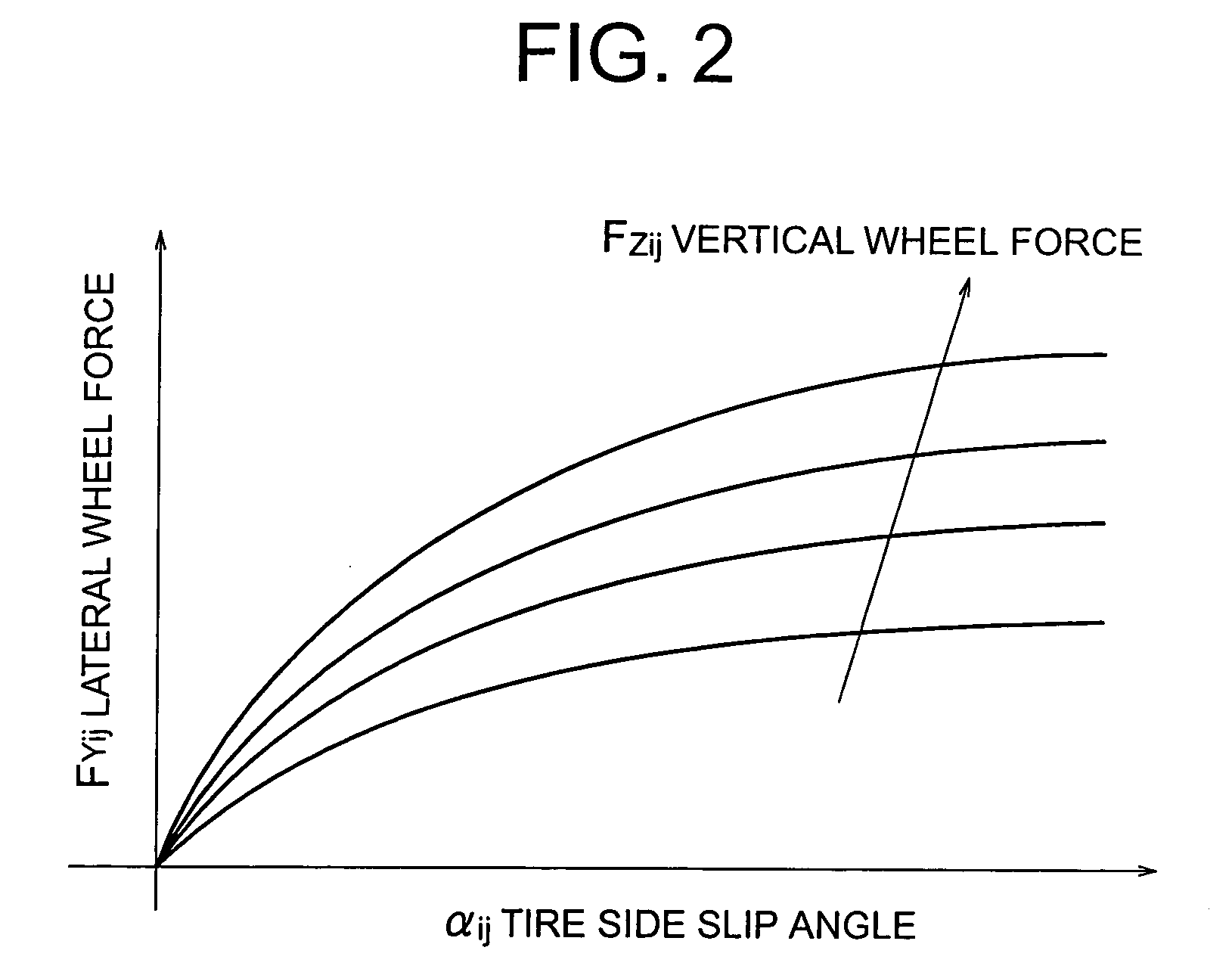
Vehicle dynamics behavior reproduction system
InactiveUS20050154513A1Increase the scope of applicationEasy to solveDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesVehicle dynamicsNonlinear approximation
A vehicle dynamics behavior reproduction system capable of describing accurately behavior of a motor vehicle in a lateral direction even for nonlinear driving situation includes a vertical wheel force arithmetic means (105), a lateral wheel force arithmetic means (110), a cornering stiffness adaptation means (115), a state space model / observer unit (120), a selector (130), a delay means (135), and a tire side slip angle arithmetic means (125). Vertical wheel forces (FZij) and tire side slip angles (αij) are determined by using sensor information and estimated values while lateral wheel forces (FYij) are determined in accordance with a relatively simple nonlinear approximation equation. The lateral wheel force (FYij) and the tire side slip angle (αij) provide bases for adaptation of cornering stiffnesses at individual wheels. Vehicle motion is accurately described to a marginal stability by using adapted cornering stiffnesses (Cij) and other information.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
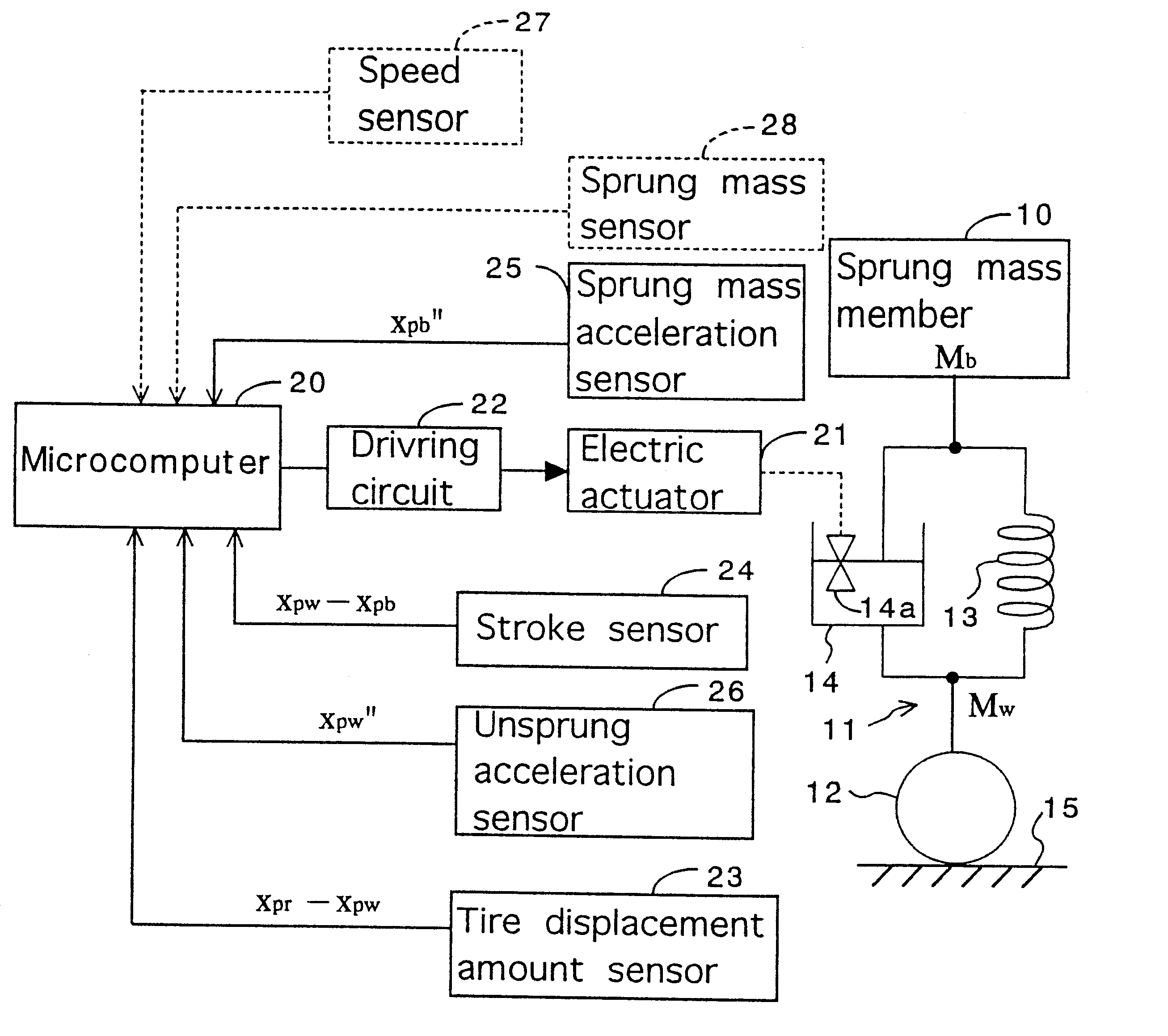
Control system for resilient support mechanism such as vehicle suspension mechanism
InactiveUS6314353B1Continuous changeEnhance running stability and comfortDigital data processing detailsNon-rotating vibration suppressionDamping factorRelative displacement
A control system for a resilient support mechanism such as a suspension mechanism of a wheeled vehicle including a damper disposed between an unsprung mass member and a sprung mass member of the vehicle, wherein a damping coefficient of the damper is divided into a linear portion and a nonlinear portion, and wherein the nonlinear portion of the damping coefficient is defined as a control input u and applied with a frequency weight Wu(s), while a vertical velocity of the sprung mass member, a relative velocity of the sprung mass member to the unsprung mass member and a vertical acceleration of the sprung mass member are defined as an evaluation output zp and applied with a frequency weight Ws(s). In the control system, a nonlinear Hinfin control theory is applied to a generalized plant to obtain a positive definite symmetric solution P and to calculate a target damping force based on the positive definite symmetric solution P and a state amount such as the vertical velocity of the sprung mass member, a relative displacement of the sprung mass member to the unsprung mass member or the like.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
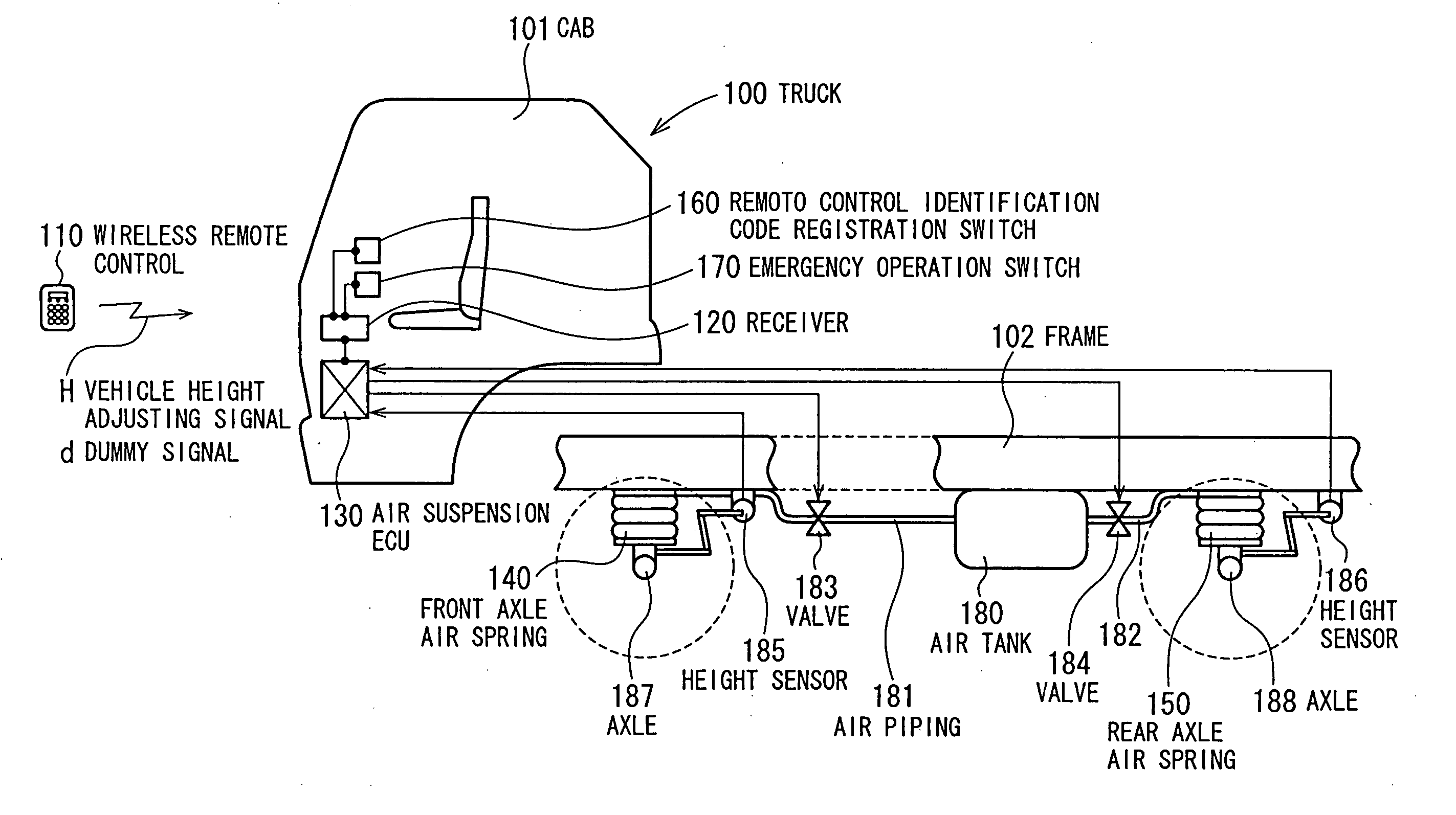
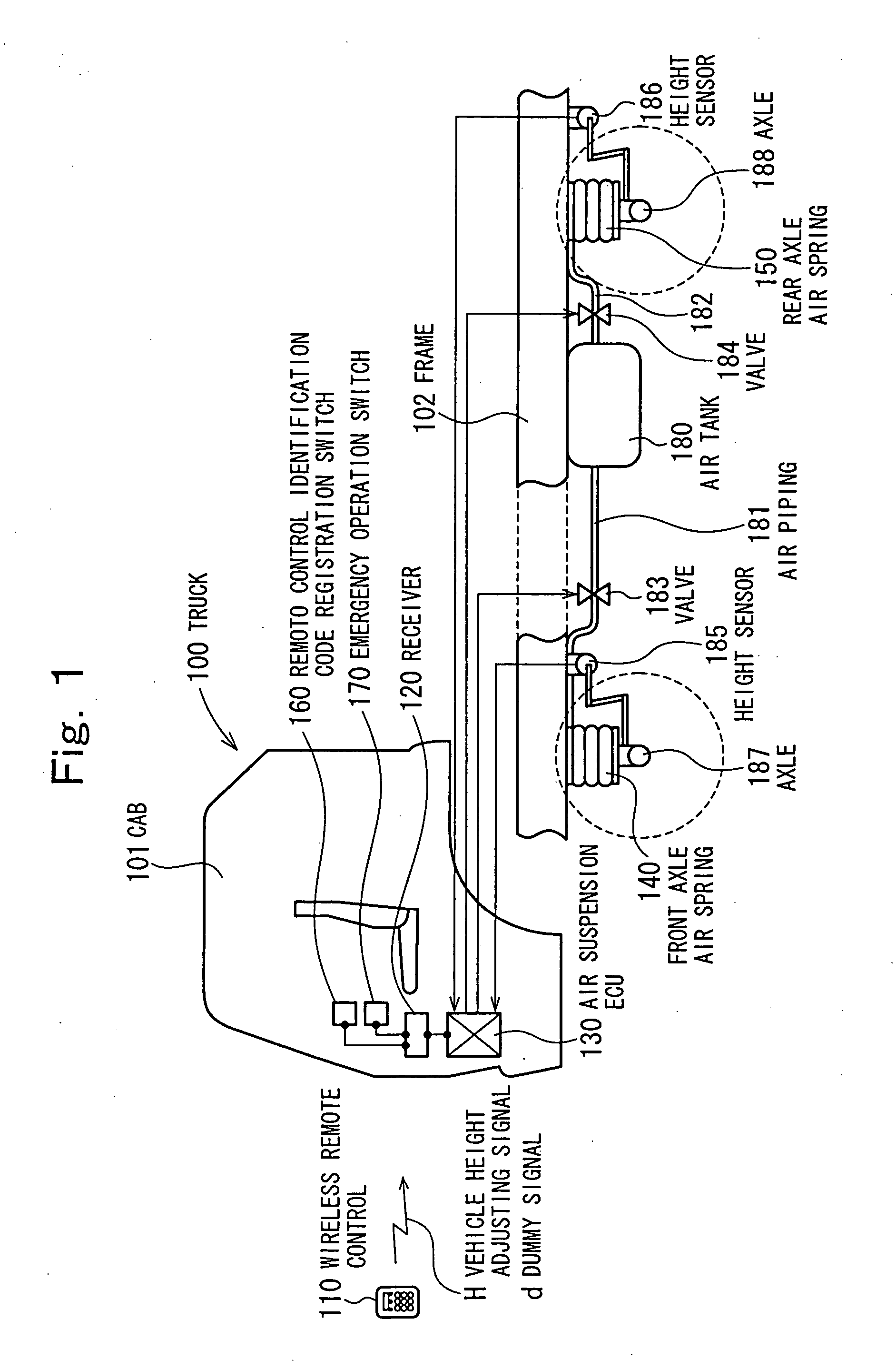
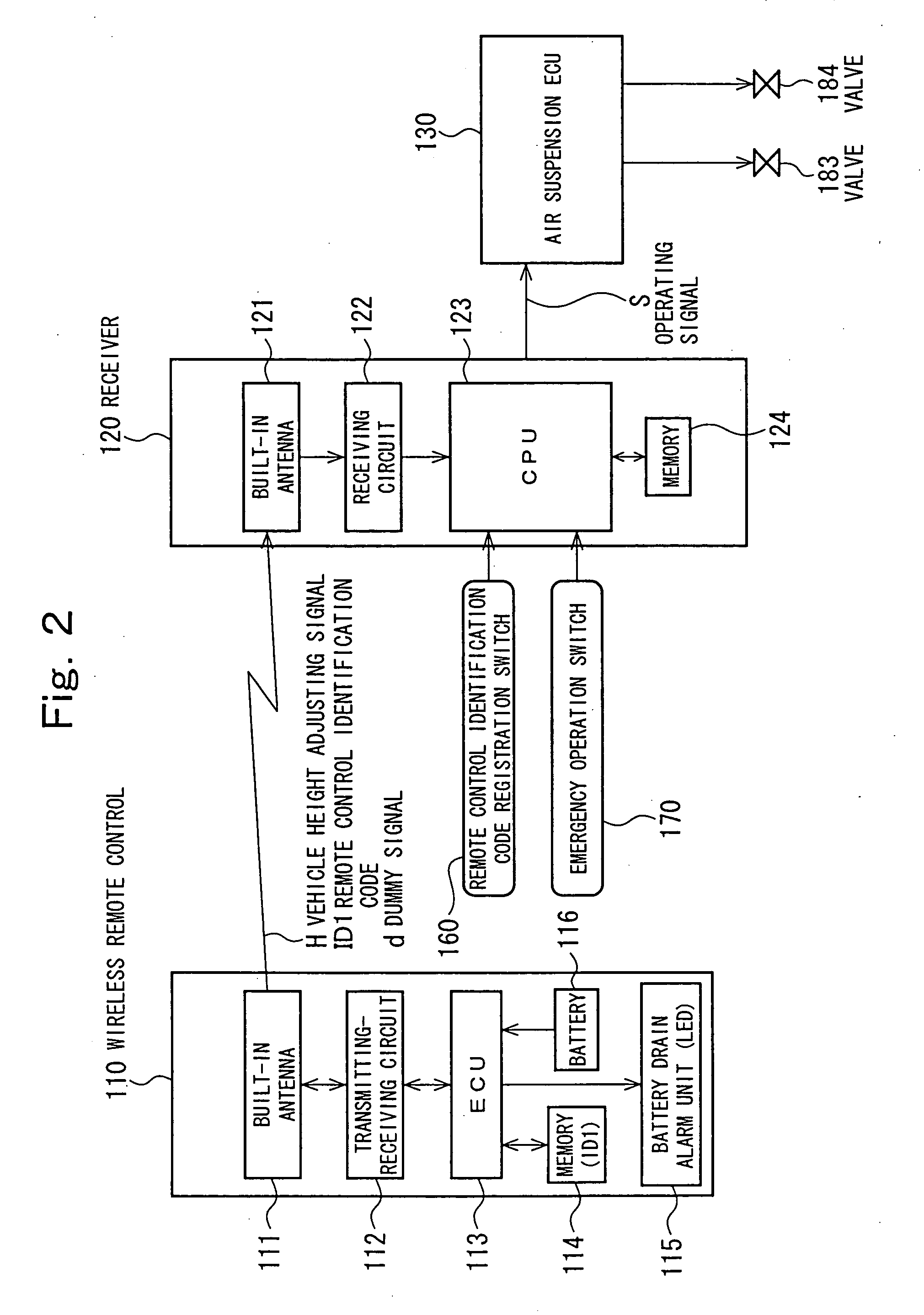
Vehicle height adjusting apparatus
InactiveUS20050110229A1Improve efficiencyReduce riskDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesRemote controlAir spring
To improve operability for vehicle height adjustment, while ensuring safety, in a vehicle such as a truck, a wireless remote control radio-transmits a vehicle height adjusting signal tagged with a remote control identification code. The remote control identification code is preregistered in a receiver, which, upon receipt of the vehicle height adjusting signal tagged with the remote control identification code, takes in the vehicle height adjusting signal. According to information contained in the received vehicle height adjusting signal, an air suspension ECU controls supply and discharge of compressed air for air springs to adjust the vehicle height. When an emergency operation switch is operated, the vehicle height adjusting signal from the wireless remote control is disabled, and vehicle height adjustment is preferentially made based on a switching signal from the emergency operation switch.
Owner:MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
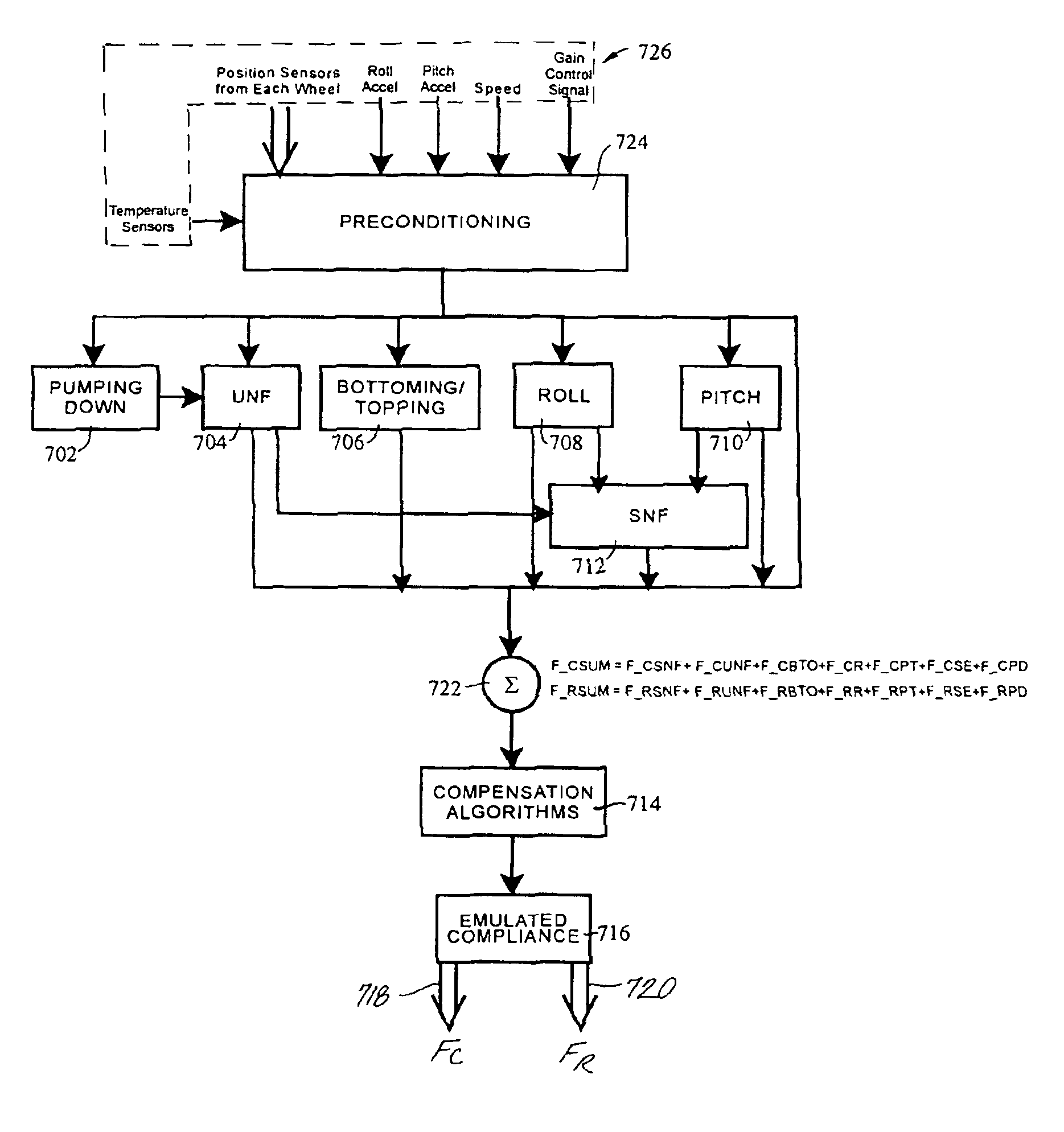
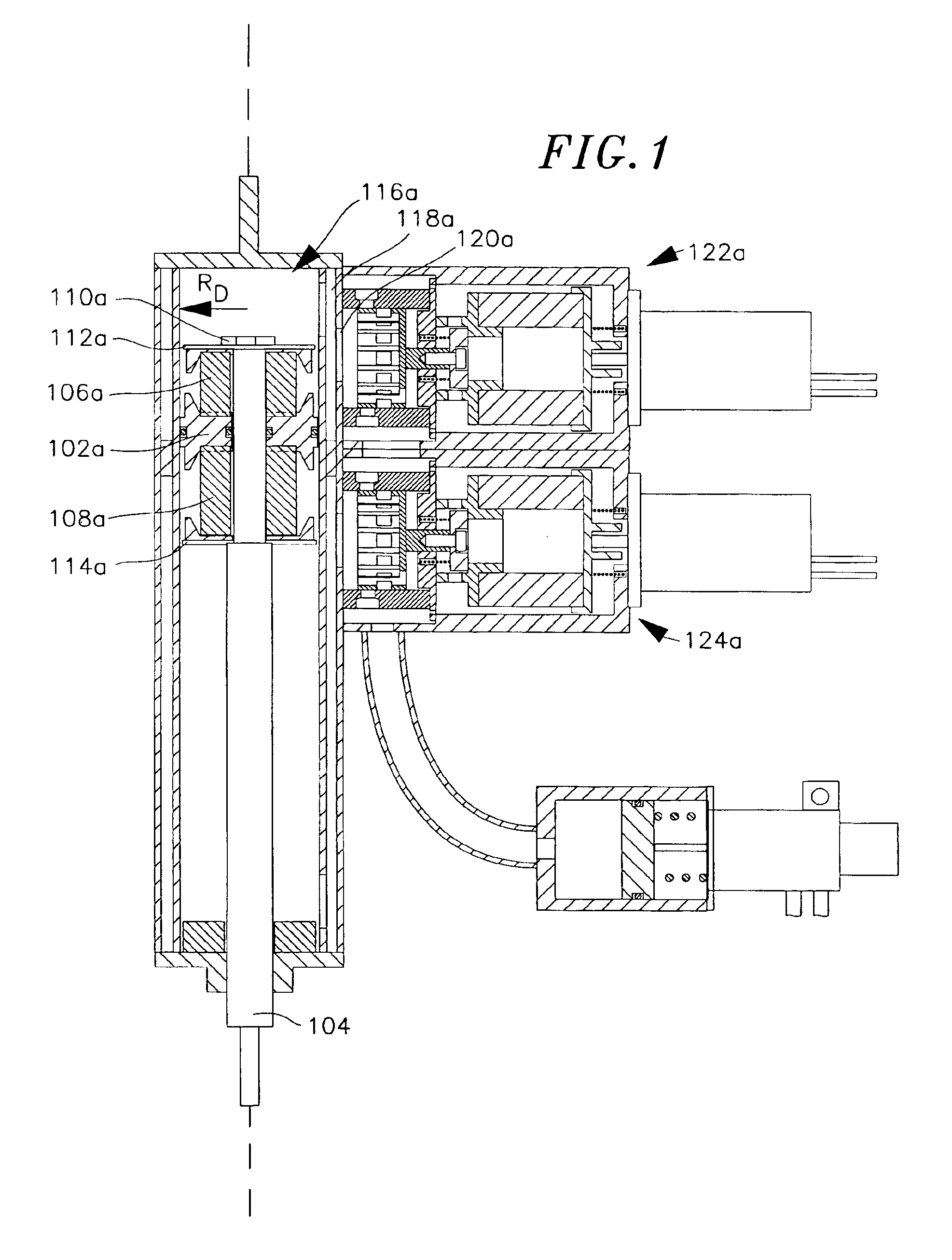
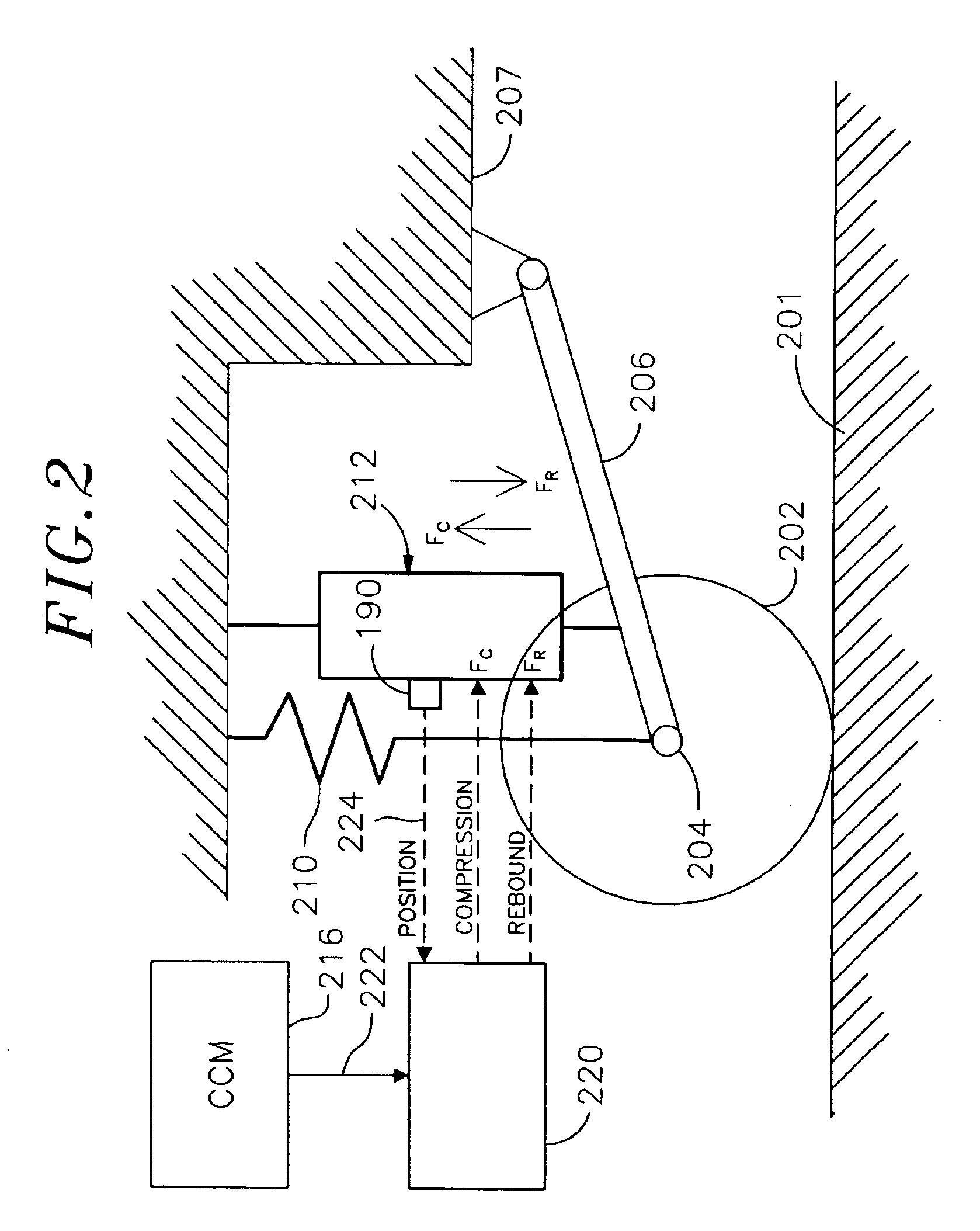
Enhanced computer optimized adaptive suspension system and method
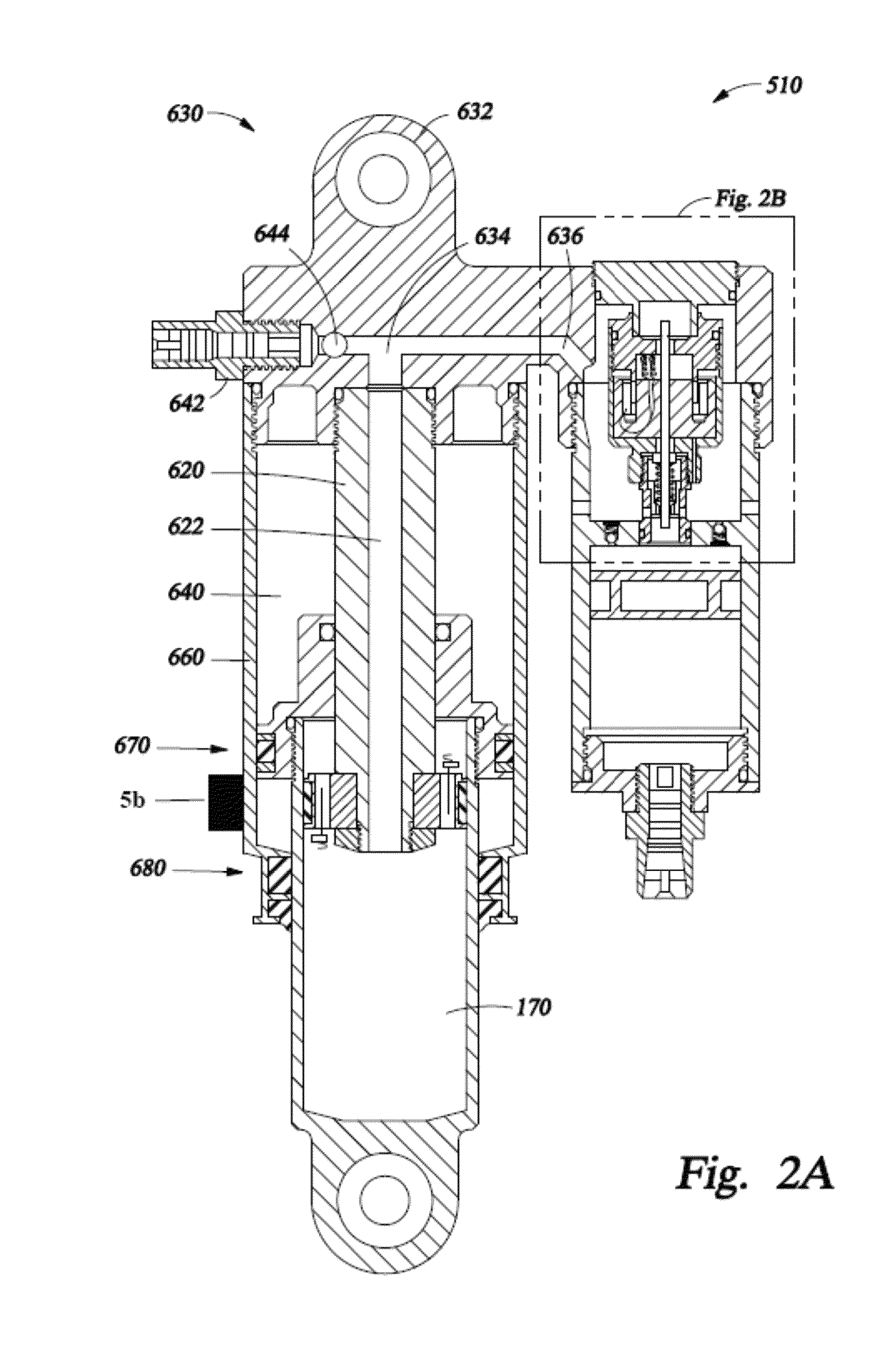
InactiveUS7076351B2Minimizing body motionIncrease fluid pressureAuxillary drivesFunctional valve typesComputer optimizationControl signal
A system and method for controlling a damping system. The system has at least two dampers for damping between sprung and unsprung masses in the compression and rebound directions. Sensors generate signals based on position and other parameters of motion representative of the displacement between the sprung and unsprung masses. The process determines the appropriate compression and rebound forces to be applied at the wheels. A regulator responds to at least one of the independent compression and rebound control signals for adjusting, respectively, at least one of compression and rebound resisting forces of the dampers between the masses. Compliance for the dampers is emulated with software to produce the desired compliance forces. The distributed controller includes a processor that is responsive to signals representative of the position signals for forming the compression and rebound control signals for the regulator as a function of motion between the masses or a motion of a vehicle in which the dampers are located. The system has the capability of locking the suspension when parked.
Owner:WICKA JOHN D +1
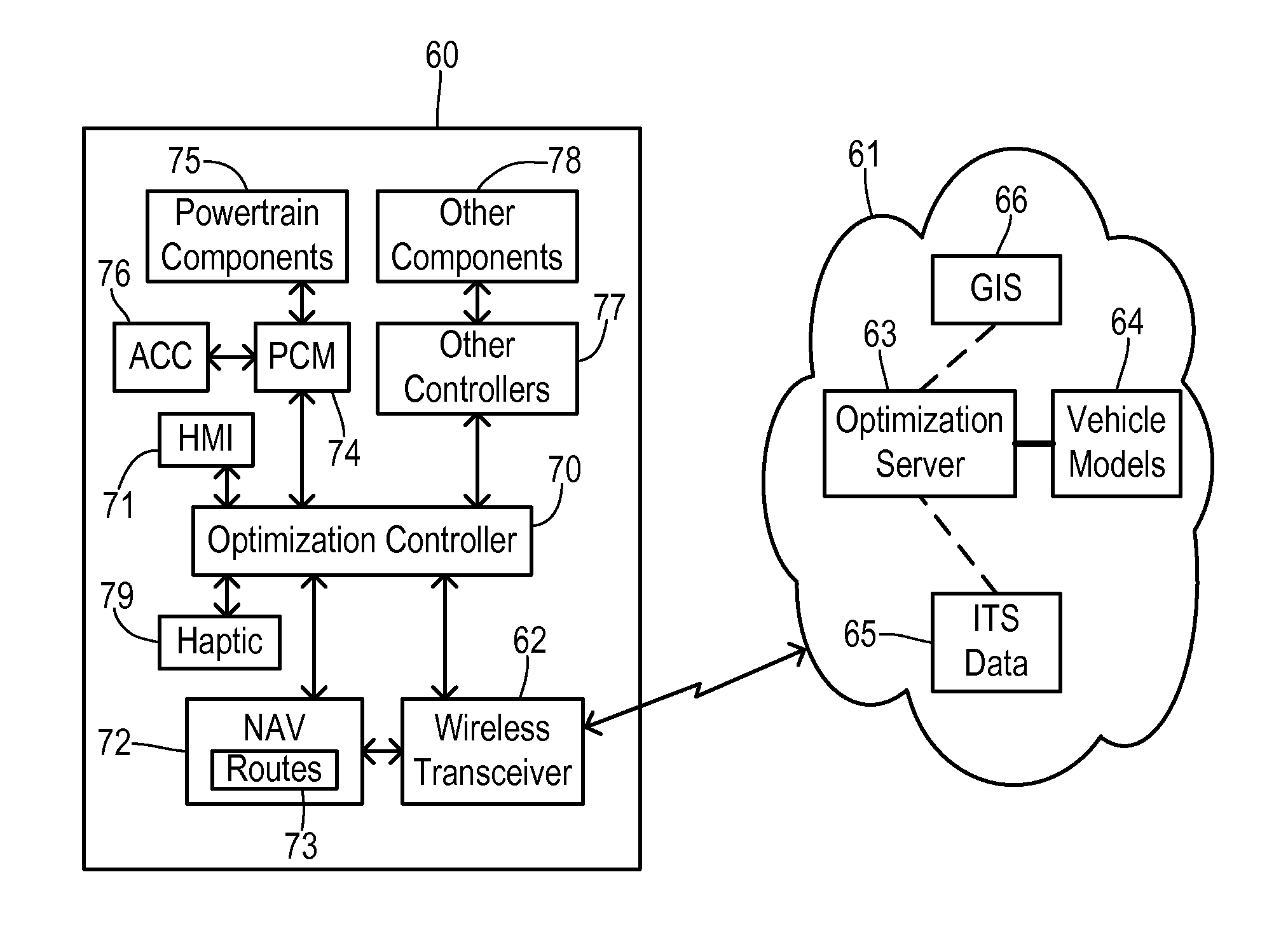
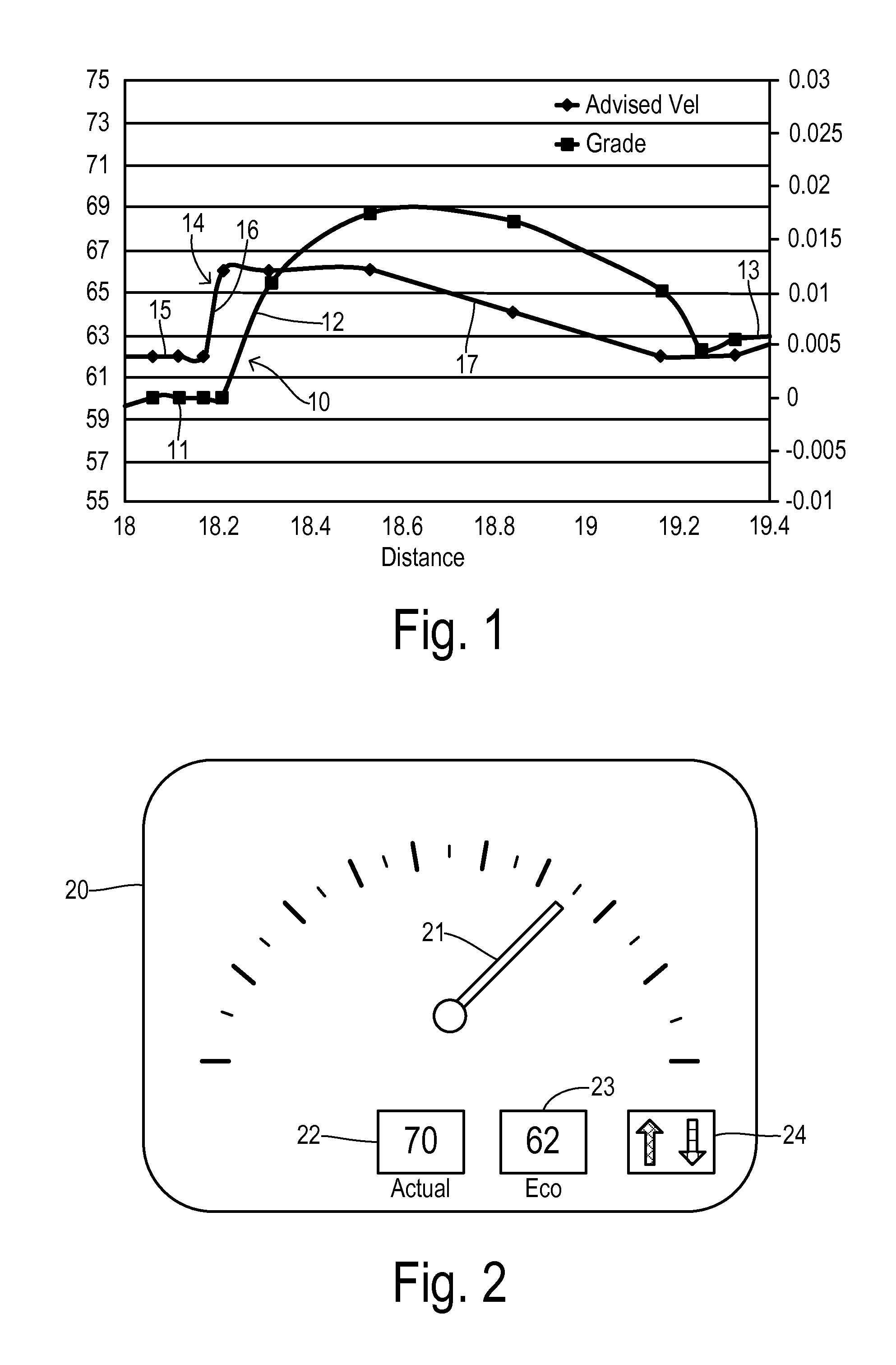
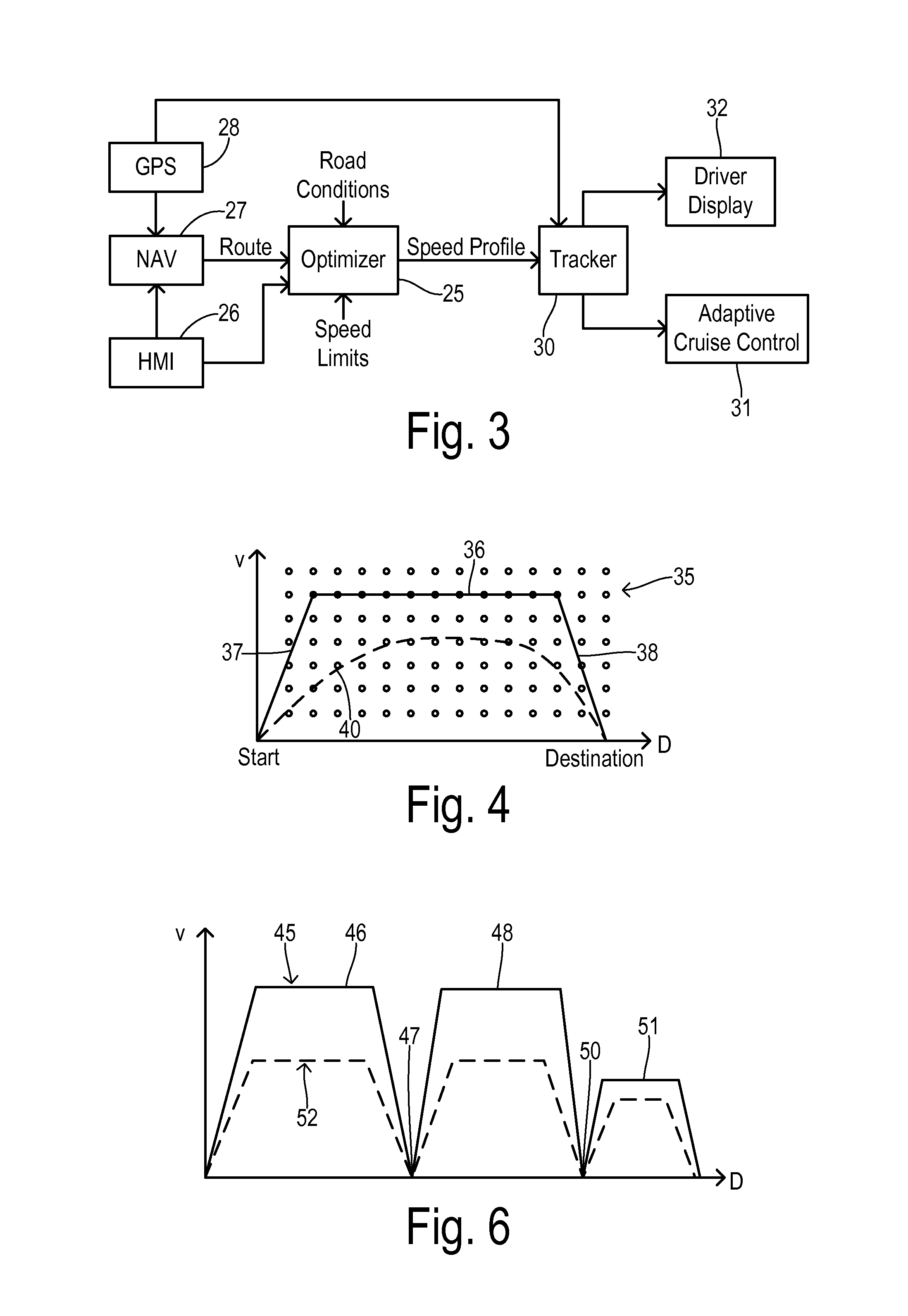
Route navigation with optimal speed profile
ActiveUS20140277835A1Reduce energy consumptionImprove carrying capacityInstruments for road network navigationVehicle fittingsEngineeringEnergy expenditure
Energy consumption of a vehicle is optimized while traveling a route assembled of road segments between a first position and a destination. A speed profile generator is located at least partially off of the vehicle and uses an energy consumption model of the vehicle together with road grade data corresponding to the route to calculate an optimal speed profile. The speed profile specifies target speeds for respective locations on the route for traversing the route with an optimized energy consumption. The speed profile generator compares energy consumption for a plurality of feasible speed profile trajectories between a maximum trajectory and a minimum trajectory in order to identify the optimal speed profile. A speed updater is responsive to a current position of the vehicle and the optimal speed profile to initiate the target speed for the current position.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
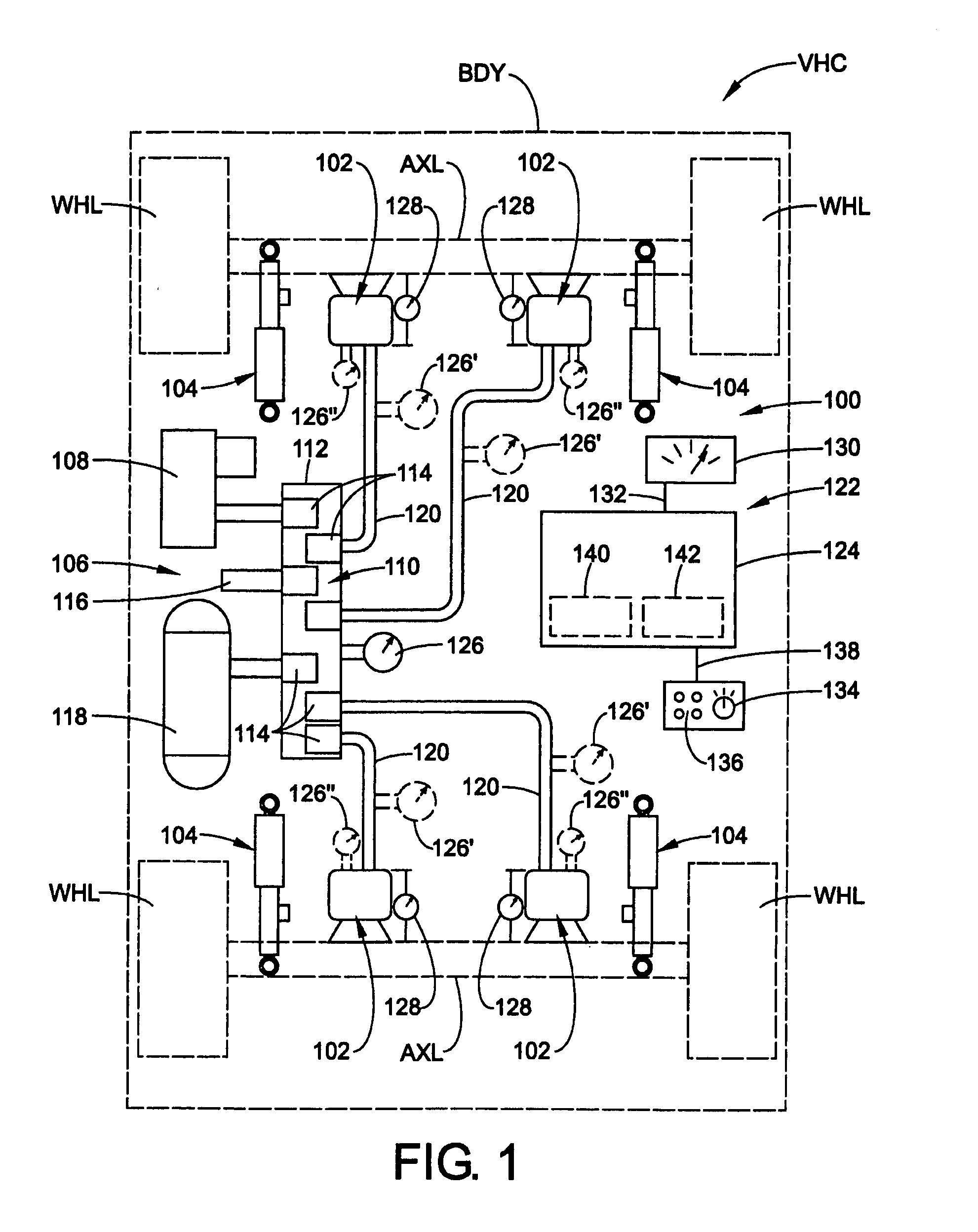
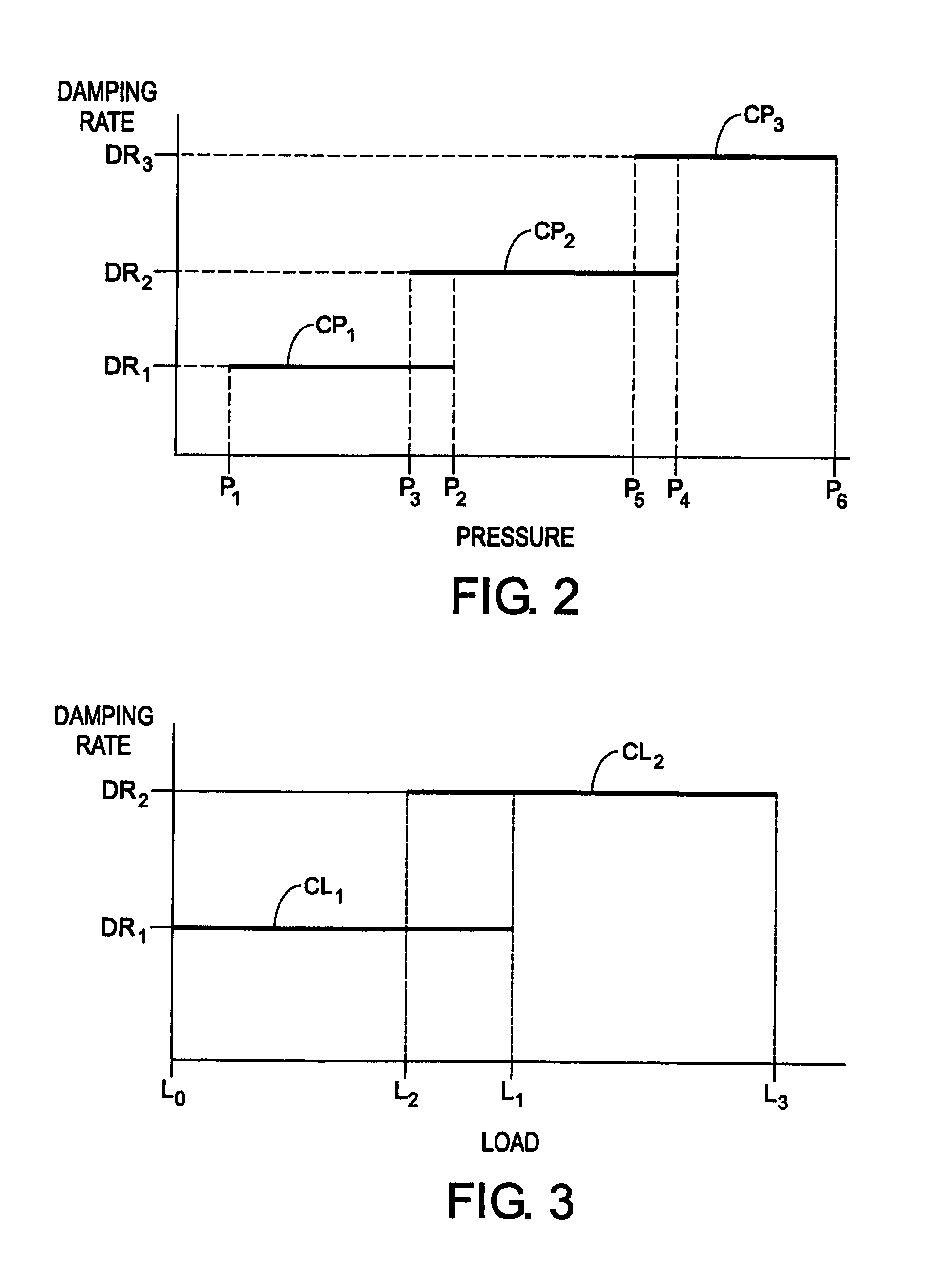
Vehicle suspension system and method
A control system is operatively associated with a suspension system of a vehicle. The associated suspension system includes an associated fluid spring operating at an associated fluid pressure and an associated variable-rate damper having an associated electronically-variable damping rate. The control system includes a pressure sensor operative to generate a pressure sensor signal indicative of the associated fluid pressure of the associated fluid spring, and a controller in communication with the pressure sensor and the associated variable-rate damper. The controller is operative to receive the pressure sensor signal and generate a damper adjustment signal based at least partially on the pressure sensor signal for adjusting the associated electronically-variable damping rate of the associated variable-rate damper. A vehicle suspension system includes such a control system, and a method of controlling a suspension system of a vehicle is also included.
Owner:DRIVERIGHT HLDG
Vibration control apparatus for automotive vehicle
InactiveUS20050049761A1Accurate compensationRapid responseInternal combustion piston enginesNon-rotating vibration suppressionMobile vehicleResidual vibration
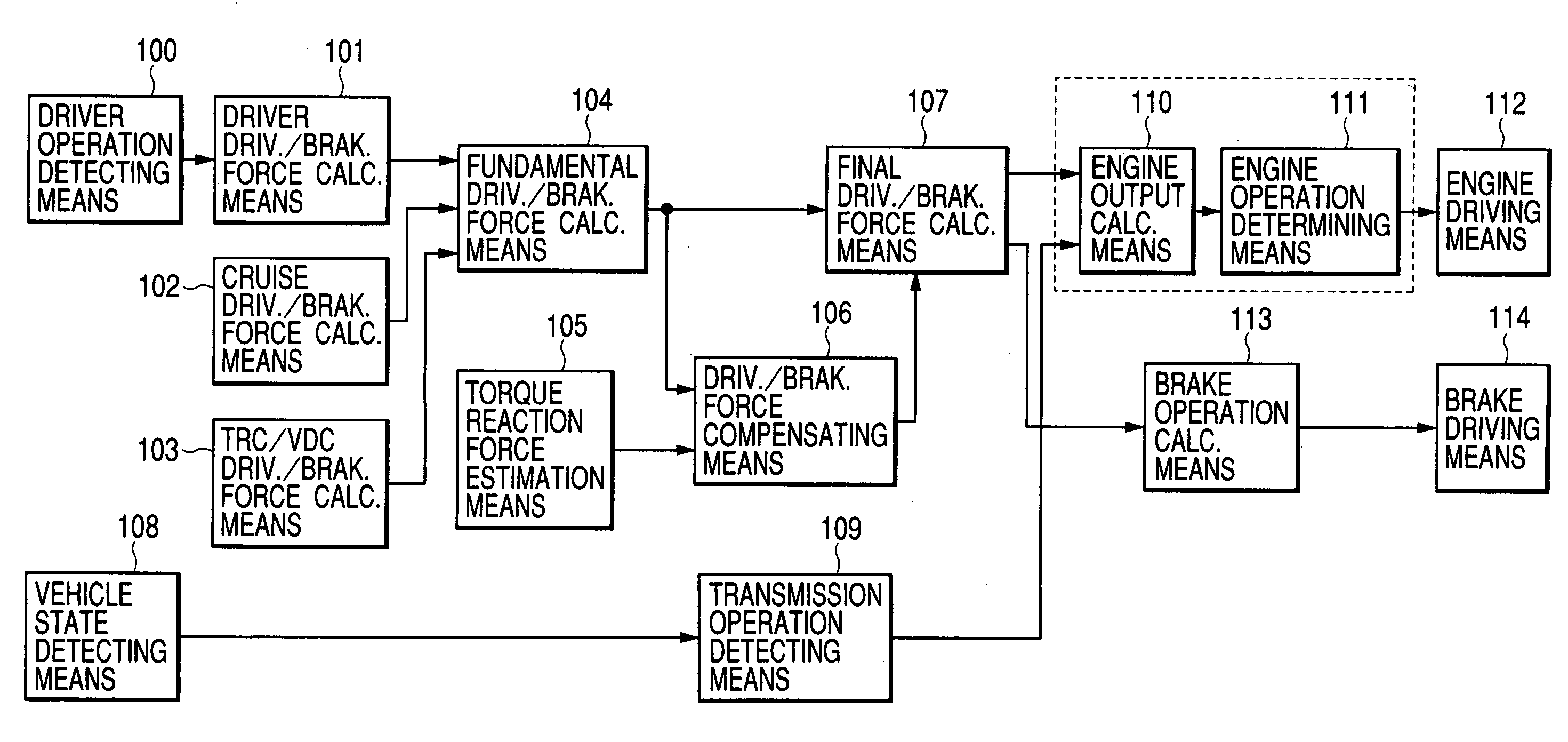
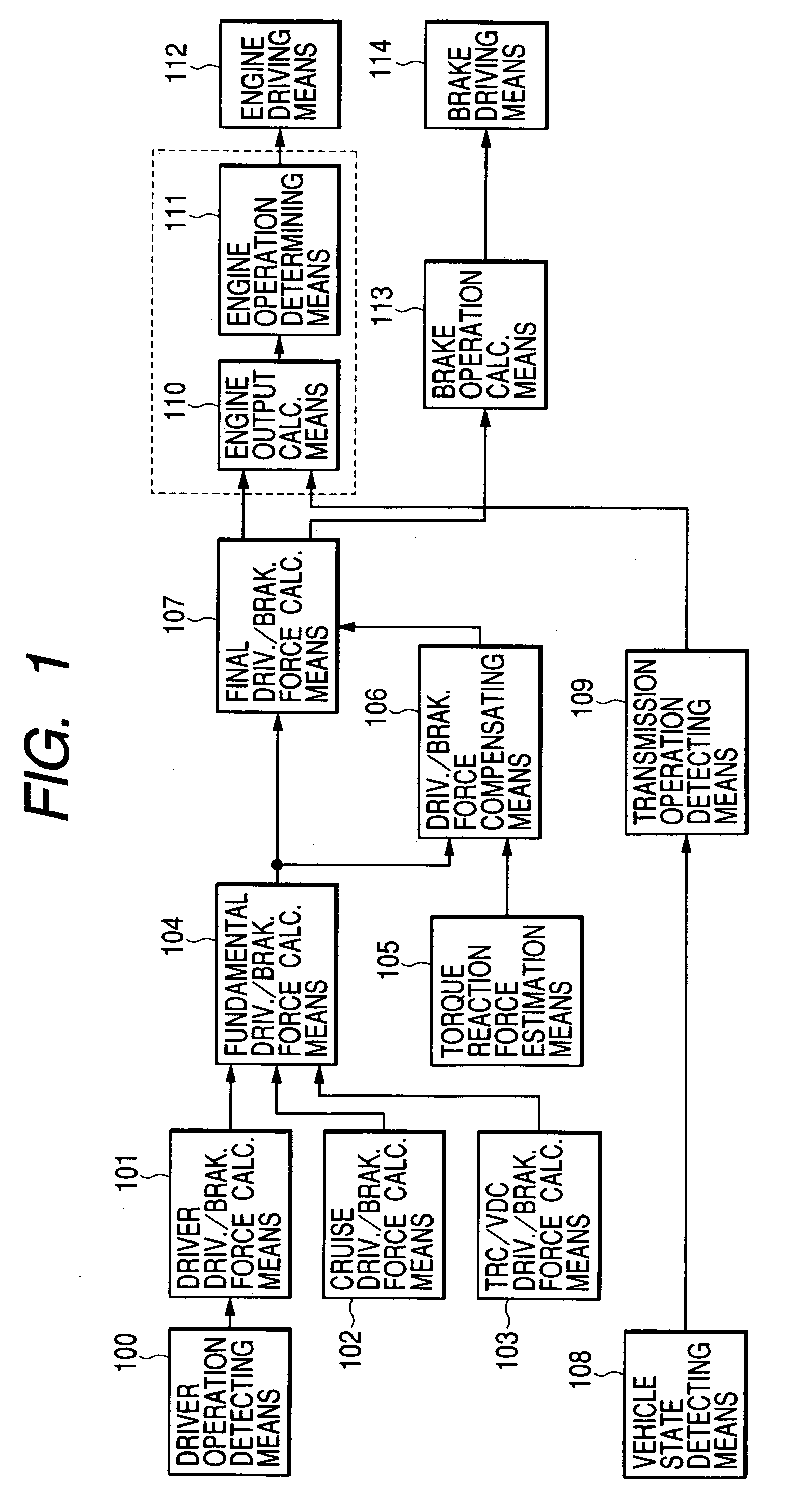
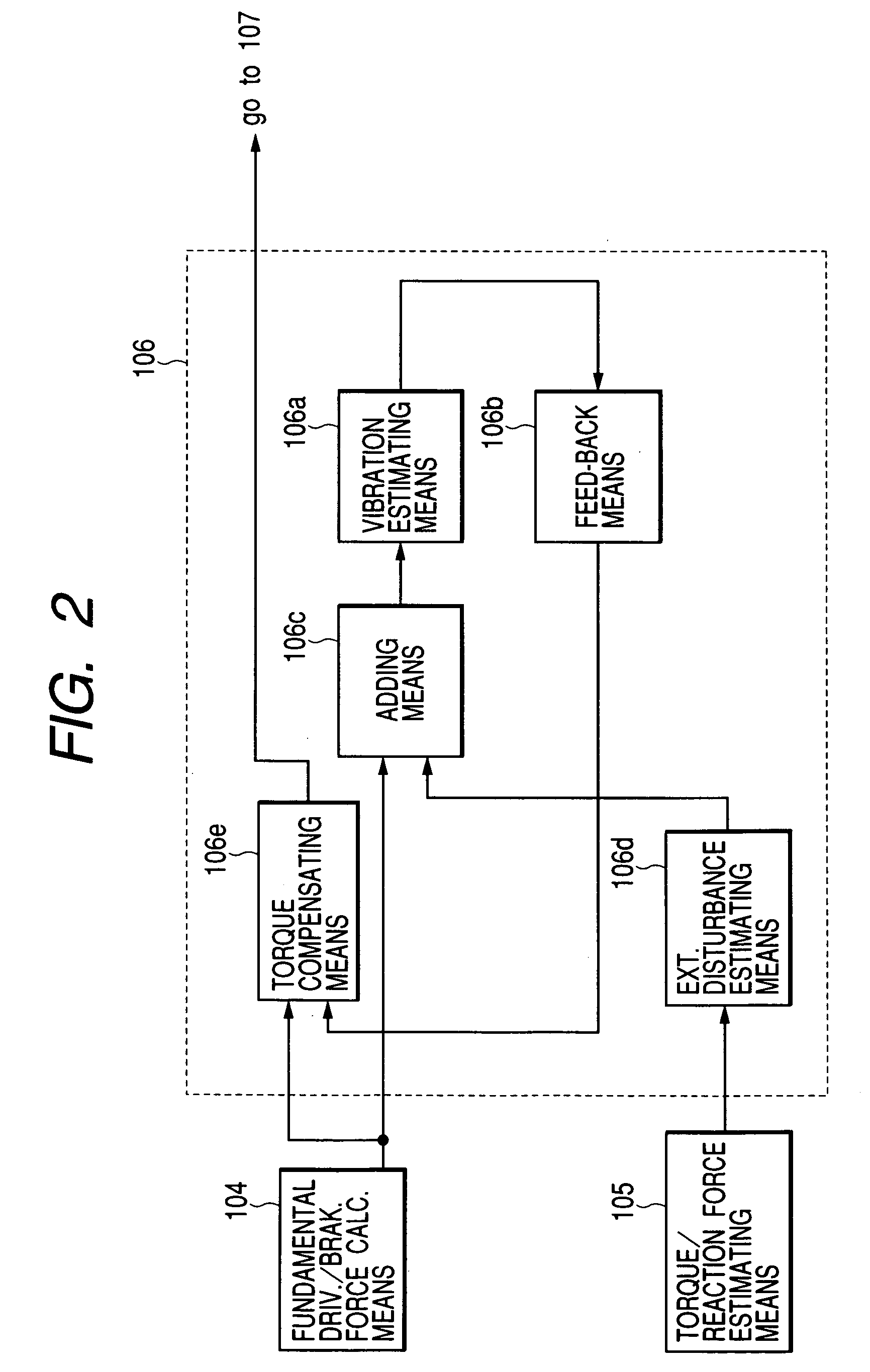
An object of the present invention is to execute an optimum control of vibrations due to a driver's operation of an accelerator pedal, steering wheel and brake pedal. The operation instructions are inputted into a vibration calculating means (kinetic model) comprising a vehicle body model, suspension model and tire model. Conventional kinetic model controlled the suspension in order to suppress the vehicle body vibration. However, in the kinetic model of the present invention, the tire vibration due to a change in the engine output is first absorbed by the suspension, whereby a residual vibration which was not be absorbed yet by the suspension is transferred to the vehicle body. The operation inputs are compensated by the three feed-back loops between the outputs of the above-mentioned three portions and input of the tire portion, giving the highest priority on the vehicle body model.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Bicycle distributed computing arrangement and method of operation
A bicycle is disclosed having a control system with a user interface and an active suspension system. The control system includes a one or more sensors arranged to measure and transmit a signal indicative of the terrain over which the bicycle is being ridden. The active suspension system includes a valve box that is fluidly coupled to each chamber of the lower cylinder. An orifice in the valve box is changed in size in response to a signal from a sensor associated with the front wheel that changes the response of the suspension system due to changing terrain conditions. The user interface includes a selection device mounted to the handlebars that allows the user to change parameters of the active suspension system during operation of the bicycle.
Owner:CANNONDALE BICYCLE CORPORATION
Adaptive Active Suspension System With Road Preview
ActiveUS20140195112A1Deleterious effectAnimal undercarriagesAxle suspensionsControl theorySelf adaptive
A method for controlling an active suspension includes steps of determining a dimension of a road abnormality ahead of the vehicle and comparing the dimension with a vehicle dimension. Responsive to the comparison, the abnormality is classified as one type of a plurality of predetermined types. Responsive to a height dimension of the abnormality, the abnormality is further classified as having one of a small, medium, or large severity. The suspension is controlled responsive to the type and severity.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Vehicle Control System With Advanced Tire Monitoring
ActiveUS20080243334A1Improve vehicle rideImprove handlingDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesVehicle dynamicsControl system
A control system (11) for a vehicle (10) includes vehicle dynamics sensors (35-47) providing a vehicle dynamics signal. Tire monitoring system sensors (20) in each wheel generate tire signals including temperature, pressure and acceleration data. A controller (26) communicates with the tire monitoring system sensors (20) and at least one vehicle dynamics sensor, and generates a roadway surface condition estimation value as a function of the multi-axis acceleration data of the tire signals. The roadway surface condition estimation value is transmitted to a suspension control system (33) to adjust the vevhicle suspension characteristics in response to the roadway surface condition estimation value.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Methods and apparatus for suspension set up
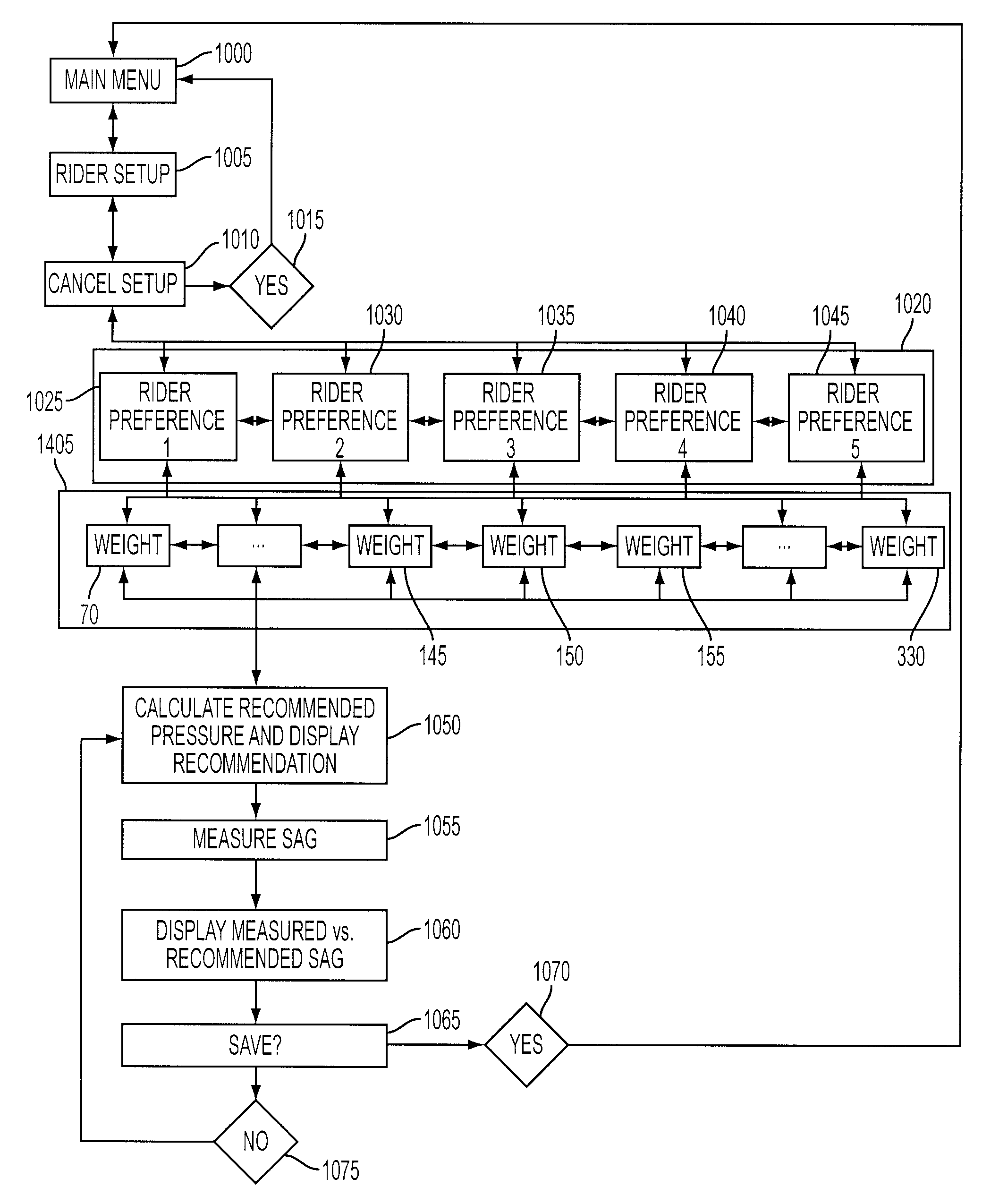
ActiveUS8838335B2Enjoyable experience for the riderAccurate settingImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringDigital image
A method and apparatus are disclosed that assist a user in performing proper setup of a vehicle suspension. A user may utilize a device equipped with an image sensor to assist the user in proper setup of a vehicle suspension. The device executes an application that prompts the user for input and instructs the user to perform a number of steps for adjusting the suspension components. In one embodiment, the application does not communicate with sensors on the vehicle. In another embodiment, the application may communicate with various sensors located on the vehicle to provide feedback to the device during the setup routine. In one embodiment, the device may analyze a digital image of a suspension component to provide feedback about a physical characteristic of the component.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
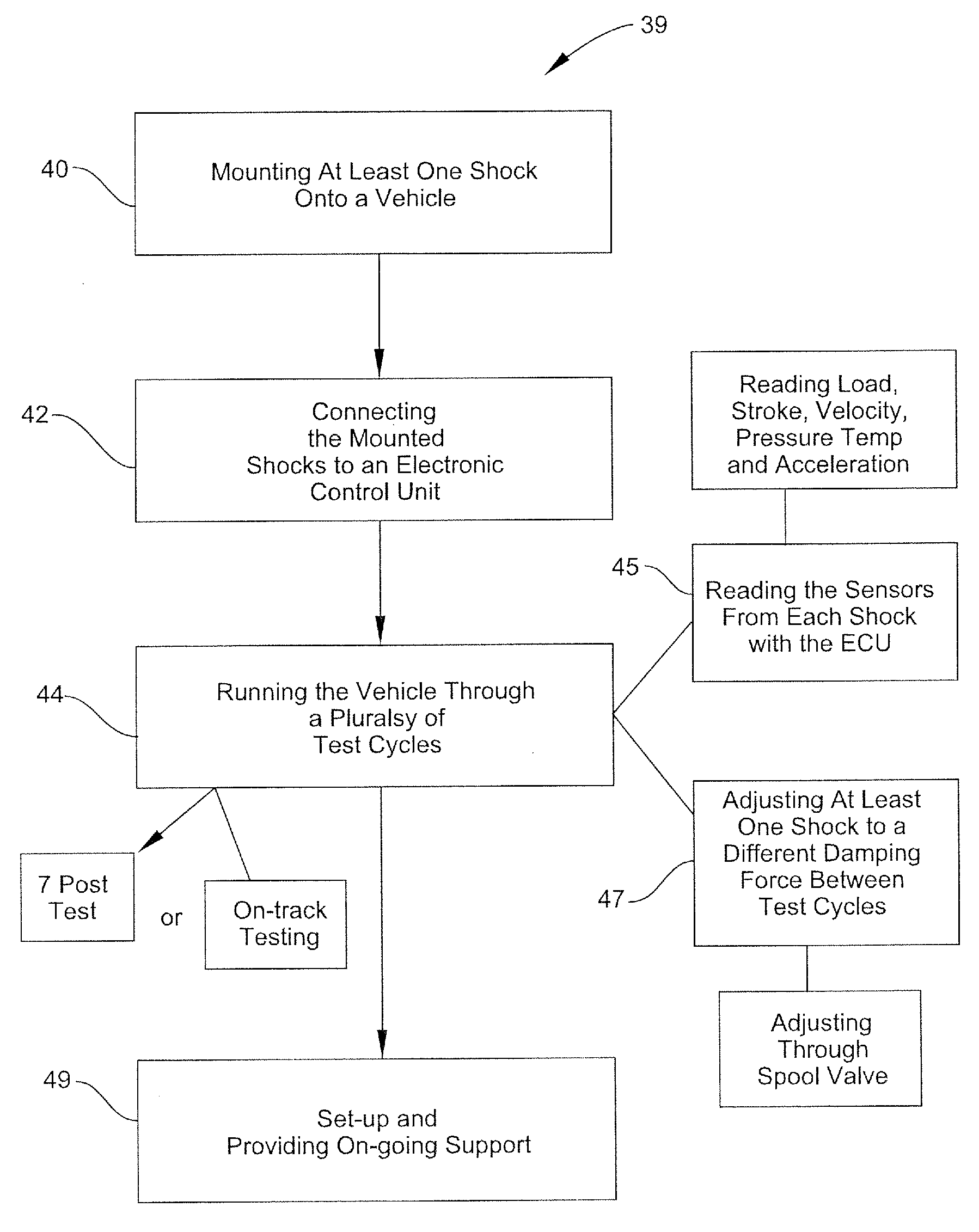
Method, system, and device for optimizing a vehicle's suspension
A method, system, and device for optimizing a vehicle's suspension includes: mounting at least one modified passive shock with a plurality of sensors onto a vehicle, where the shock is adjustable for a plurality of damping forces; connecting the shock to an electronic control unit being for adjusting the damping forces of the shock and reading the plurality of sensors; and running the vehicle through a plurality of test cycles where the electronic control unit reading the plurality of sensors during each test cycle and adjusting the shock to a different damping force between each test cycle, where the adjusted shock emulating the damping forces of multiple standard passive shocks.
Owner:ARNOTT T&P HLDG LLC
Methods and apparatuses for operating a data processing system
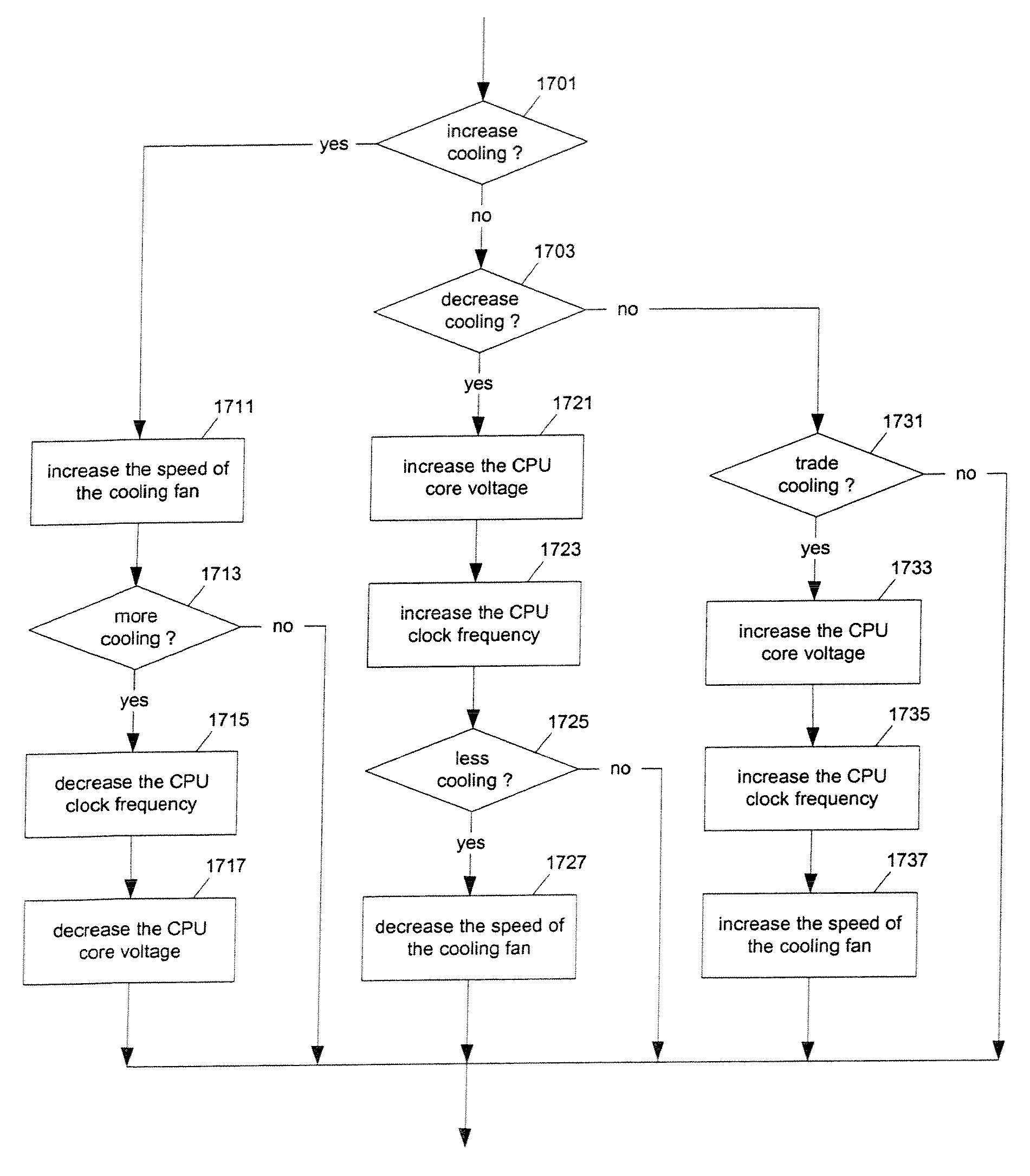
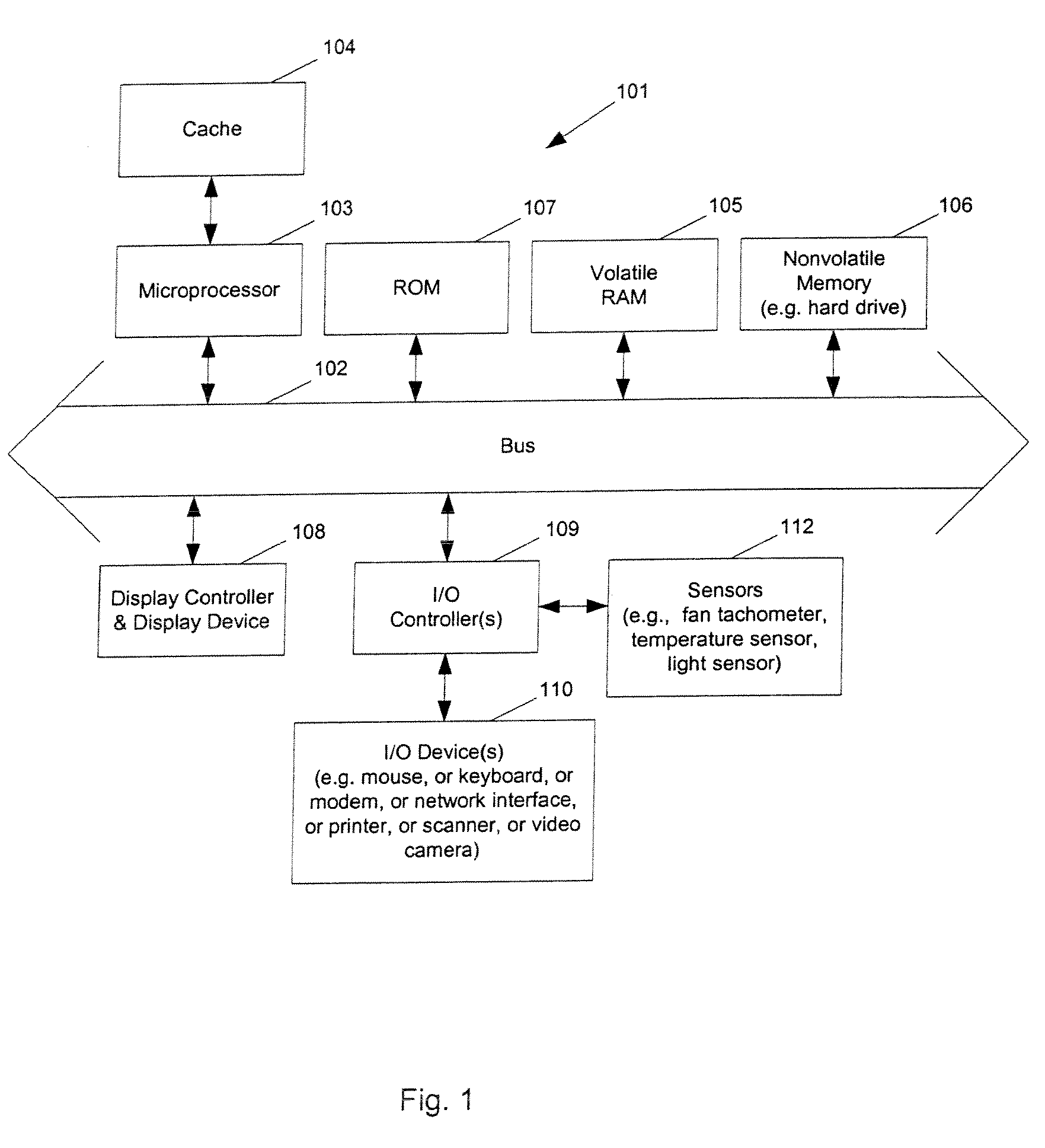
ActiveUS20100117579A1Balance performanceShorten speedDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlHard disc driveThermistor
Methods and apparatuses to manage working states of a data processing system. At least one embodiment of the present invention includes a data processing system with one or more sensors (e.g., physical sensors such as tachometer and thermistors, and logical sensors such as CPU load) for fine grain control of one or more components (e.g., processor, fan, hard drive, optical drive) of the system for working conditions that balance various goals (e.g., user preferences, performance, power consumption, thermal constraints, acoustic noise). In one example, the clock frequency and core voltage for a processor are actively managed to balance performance and power consumption (heat generation) without a significant latency. In one example, the speed of a cooling fan is actively managed to balance cooling effort and noise (and / or power consumption).
Owner:APPLE INC
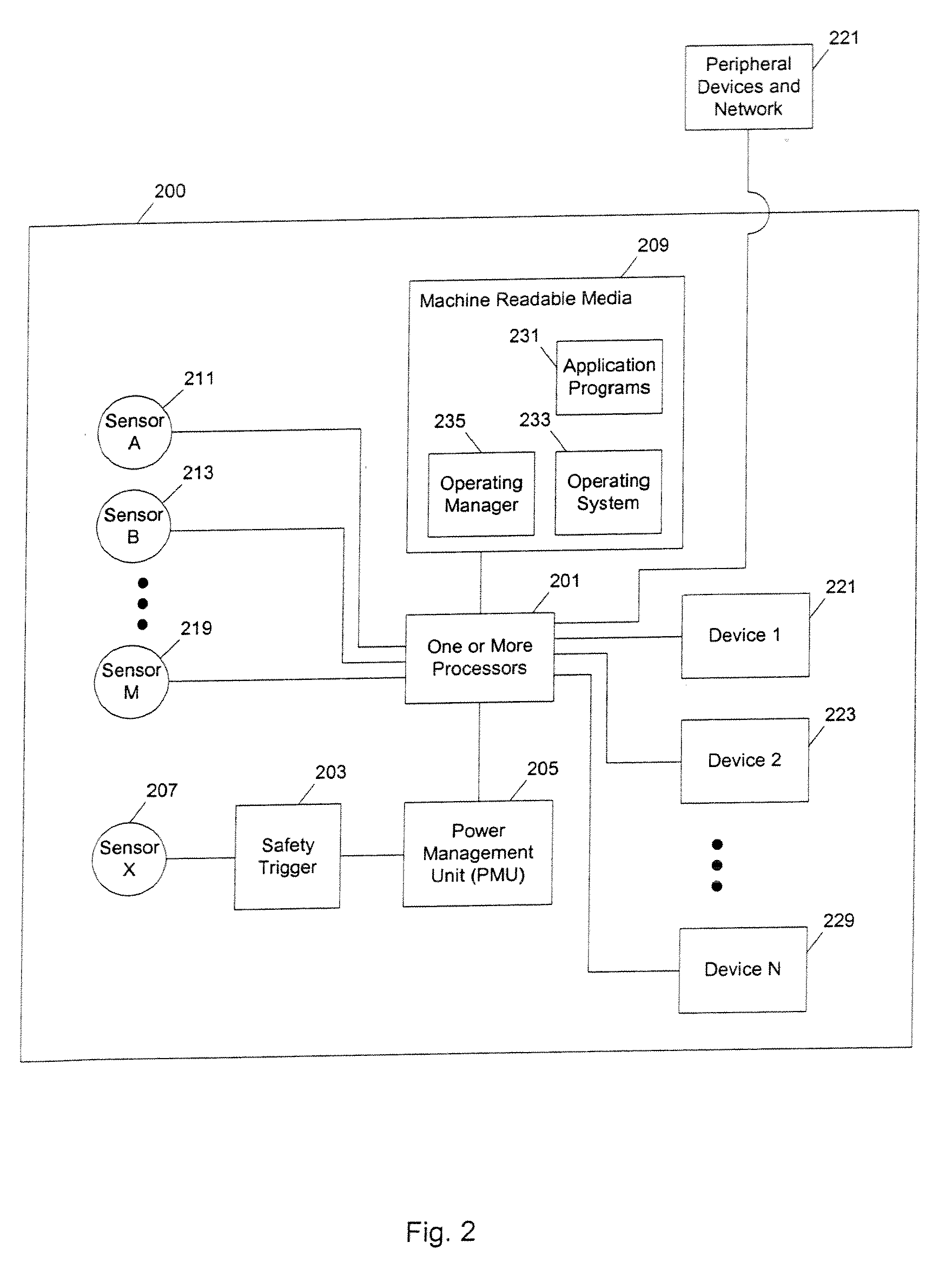
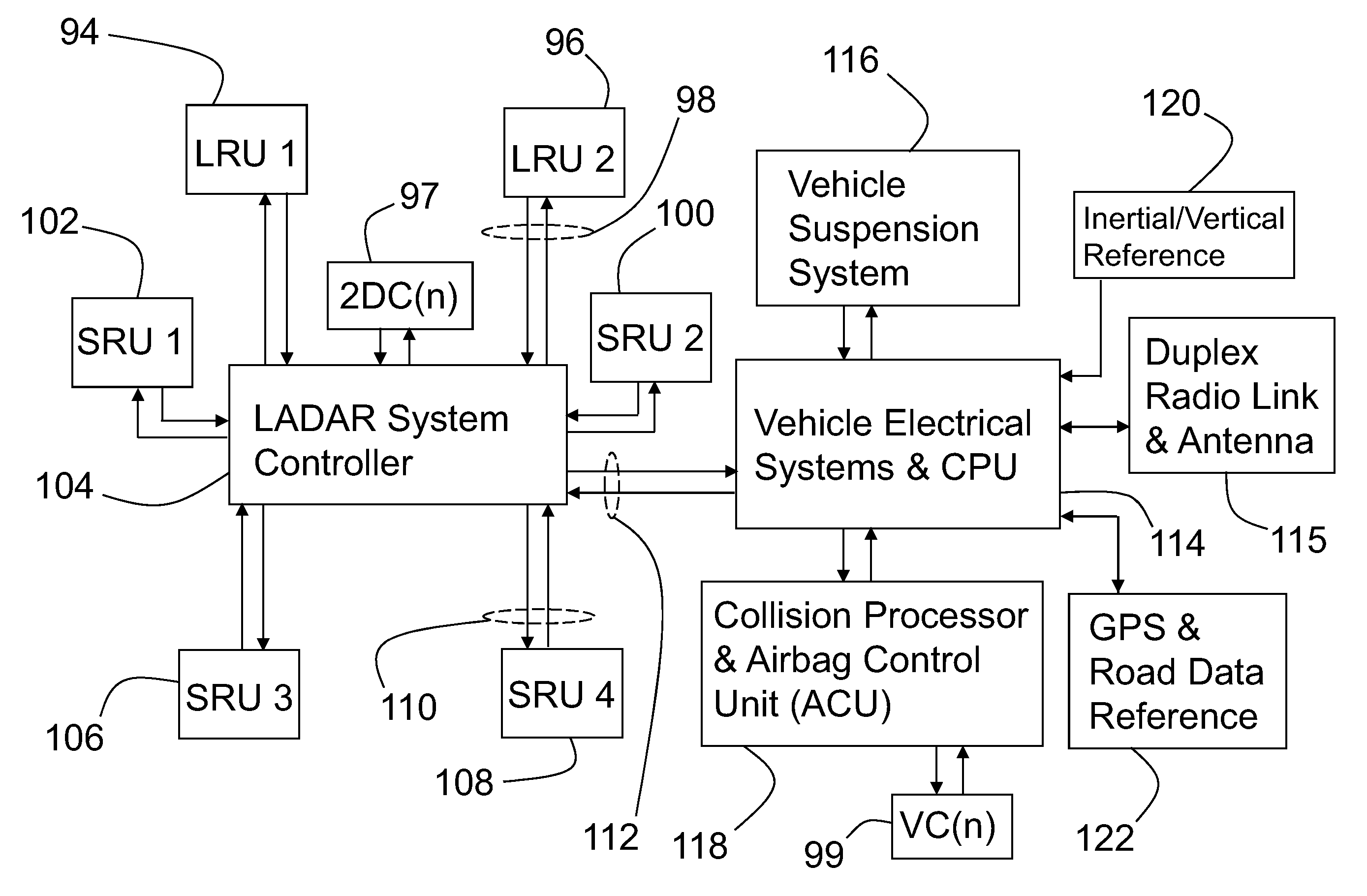
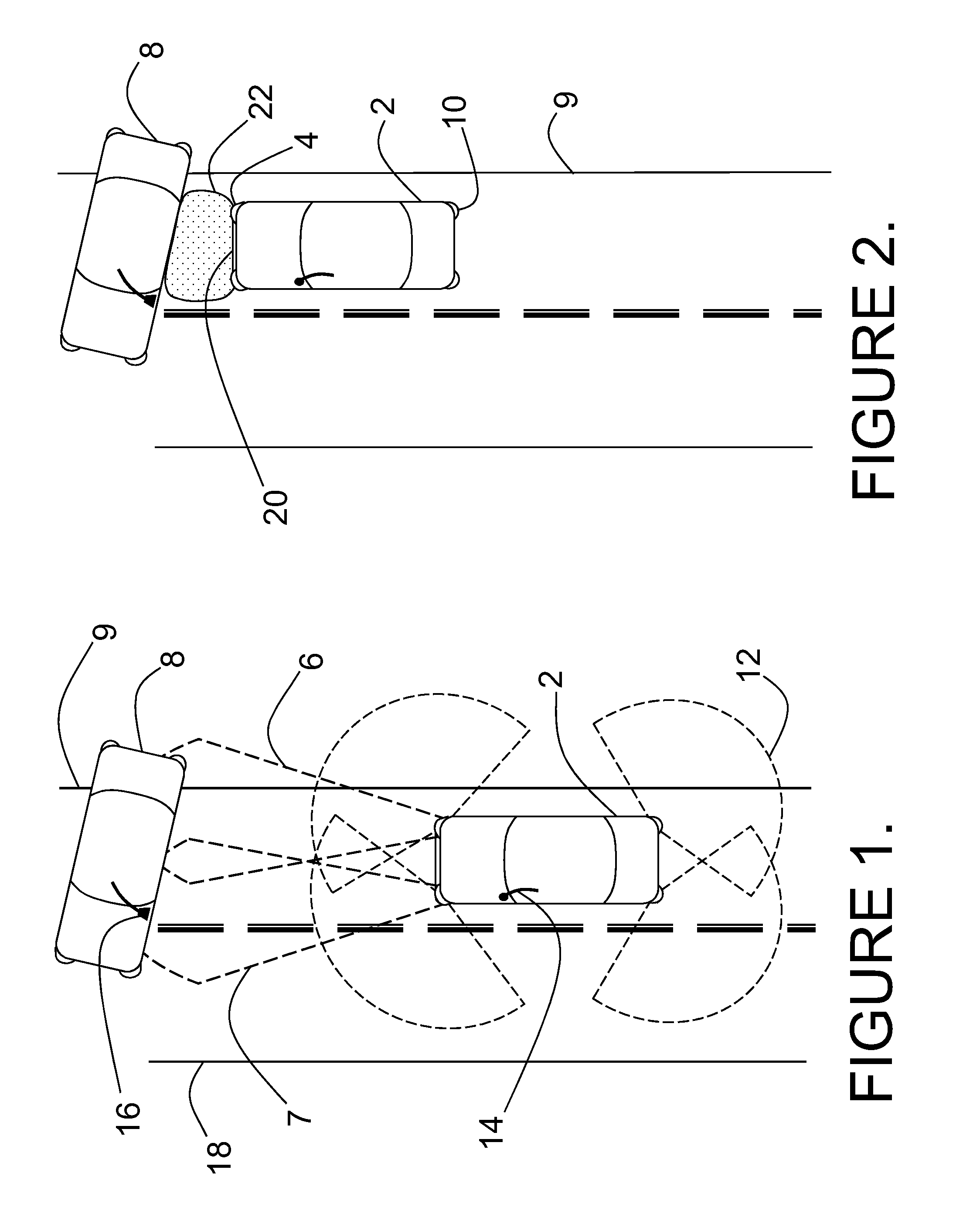
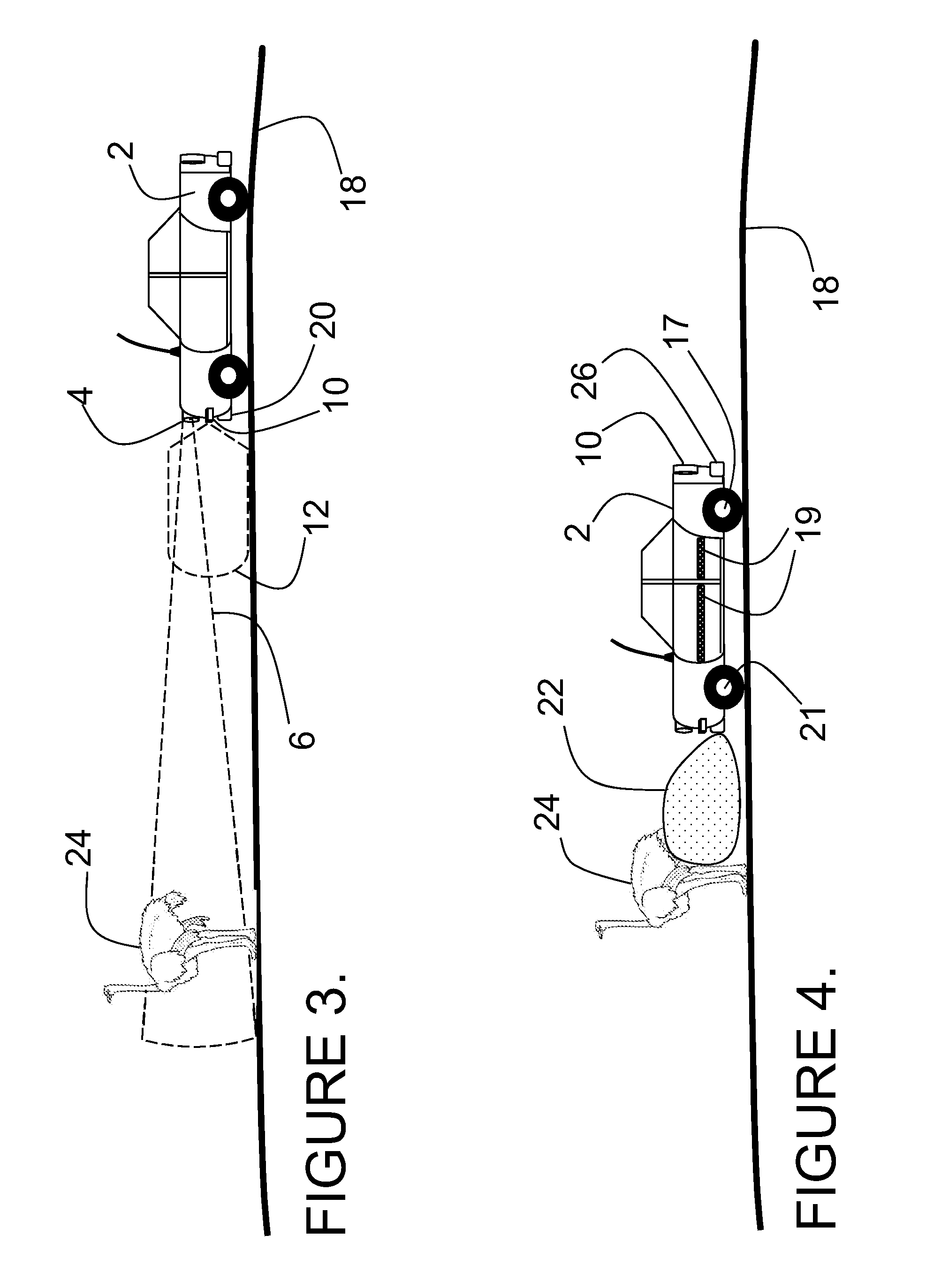
Ladar enabled impact mitigation system
ActiveUS20150202939A1Reduce harmReduce severityRoad vehicles traffic controlDigital data processing detailsImpact mitigationEngineering
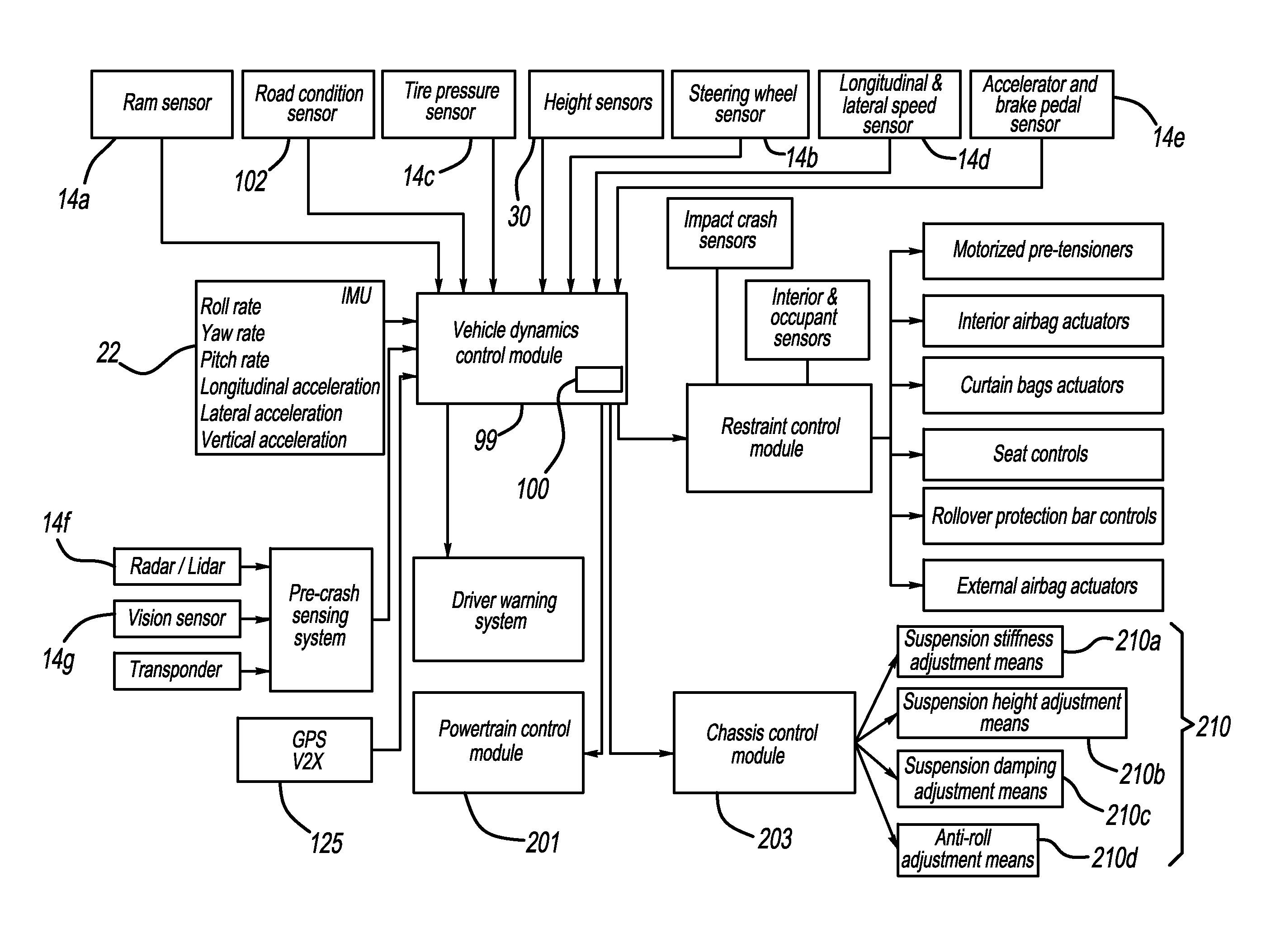
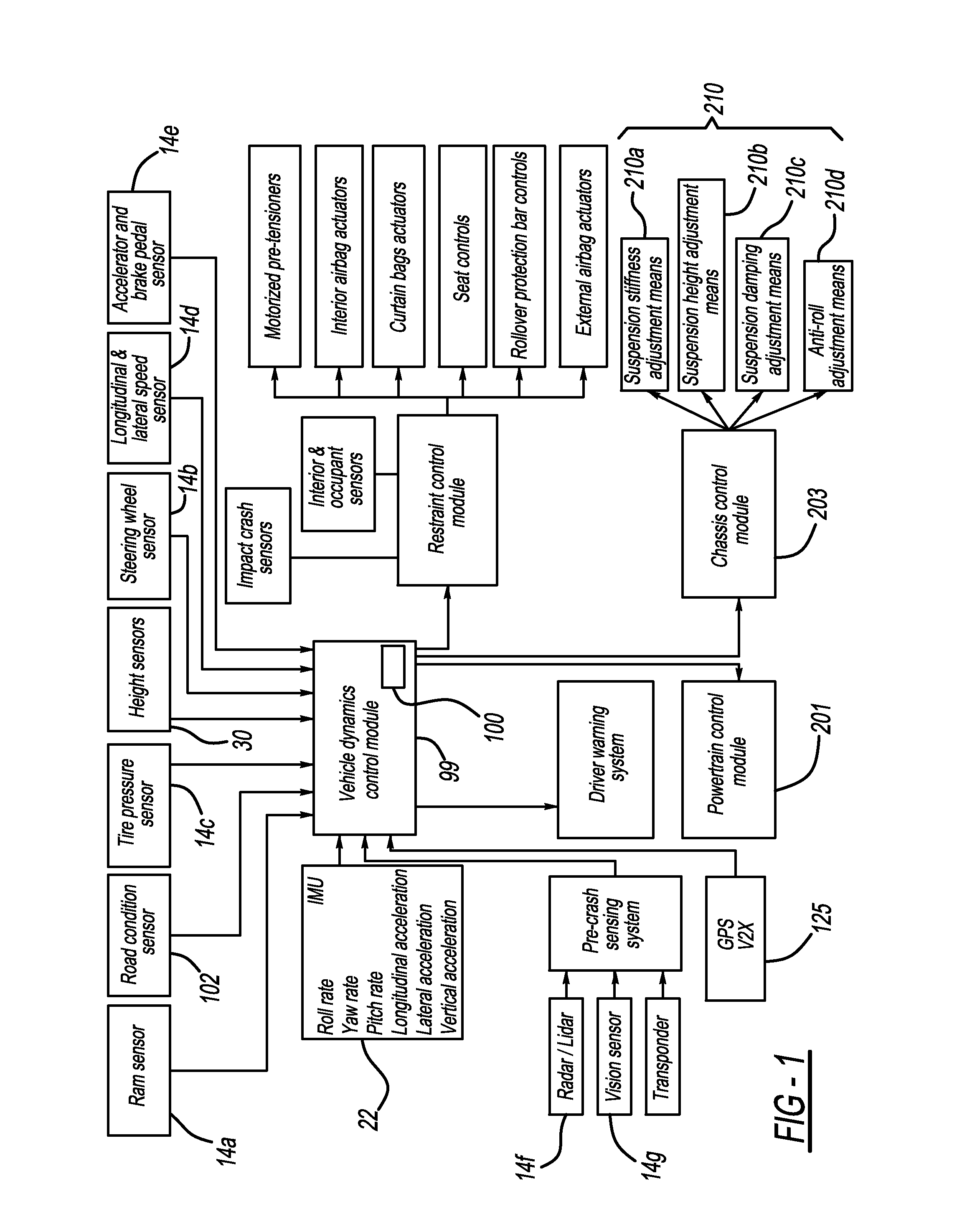
A collision mitigation system is proposed which makes use of forward mounted long range ladar sensors and short range ladar sensors mounted in auxiliary lamps to identify obstacles and to predict unavoidable collisions therewith, and a duplex radio link in communication with secondary vehicles, and a number of external airbags deployable under the control of an airbag control unit, to reduce the forces of impact on the host vehicle, secondary vehicles, and bipeds and quadrupeds wandering into the roadway. A suspension modification system makes use of headlight mounted long range ladar sensors and short range ladar sensors mounted in auxiliary lamps to characterize the road surface, identify road hazards, and make adaptations to a number of active suspension components, each with the ability to absorb shock, elevate or lower the vehicle, and adjust the spring rate of the individual wheel suspensions.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
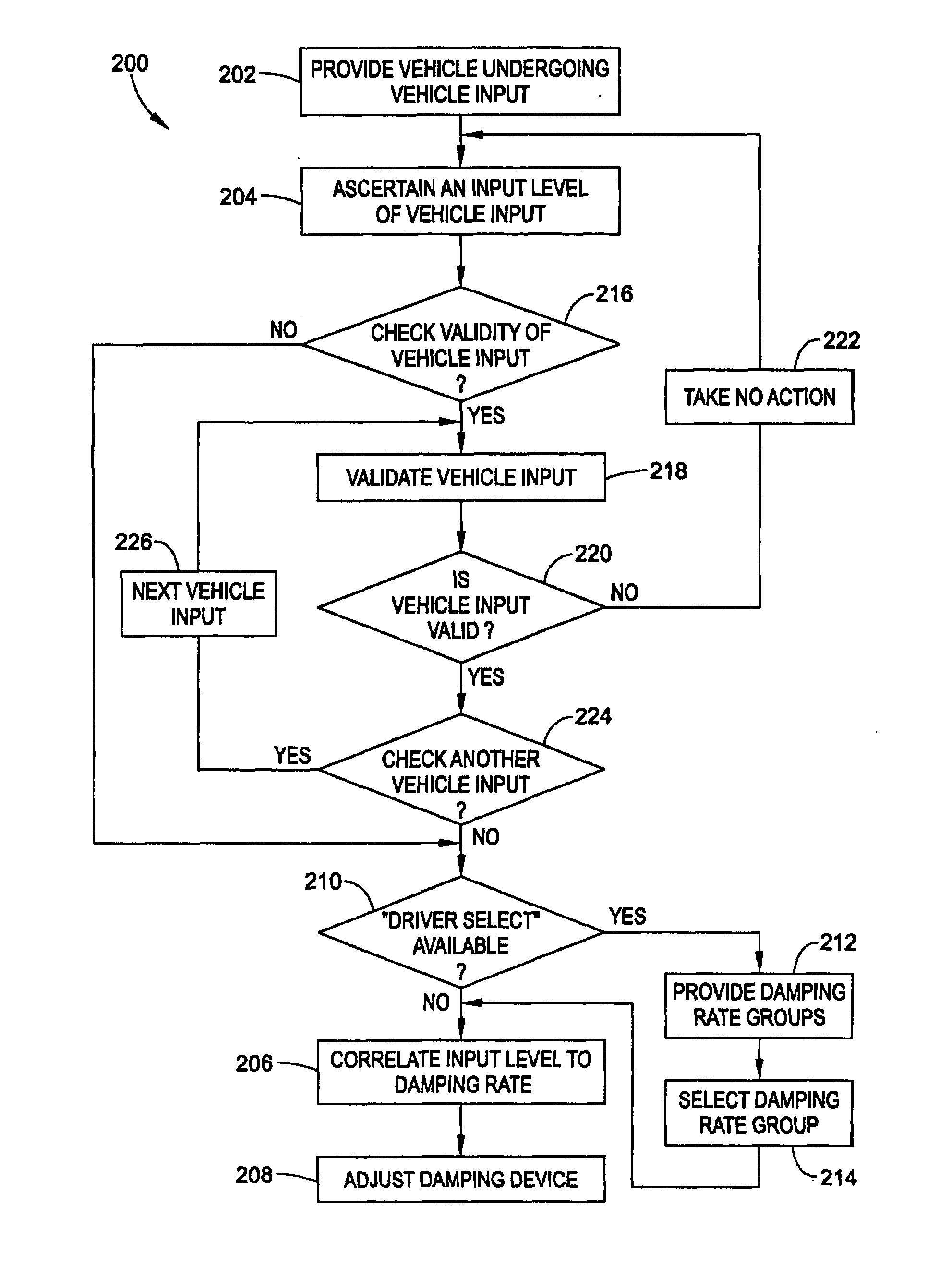
Method and apparatus for controlling damping of a vehicle suspension
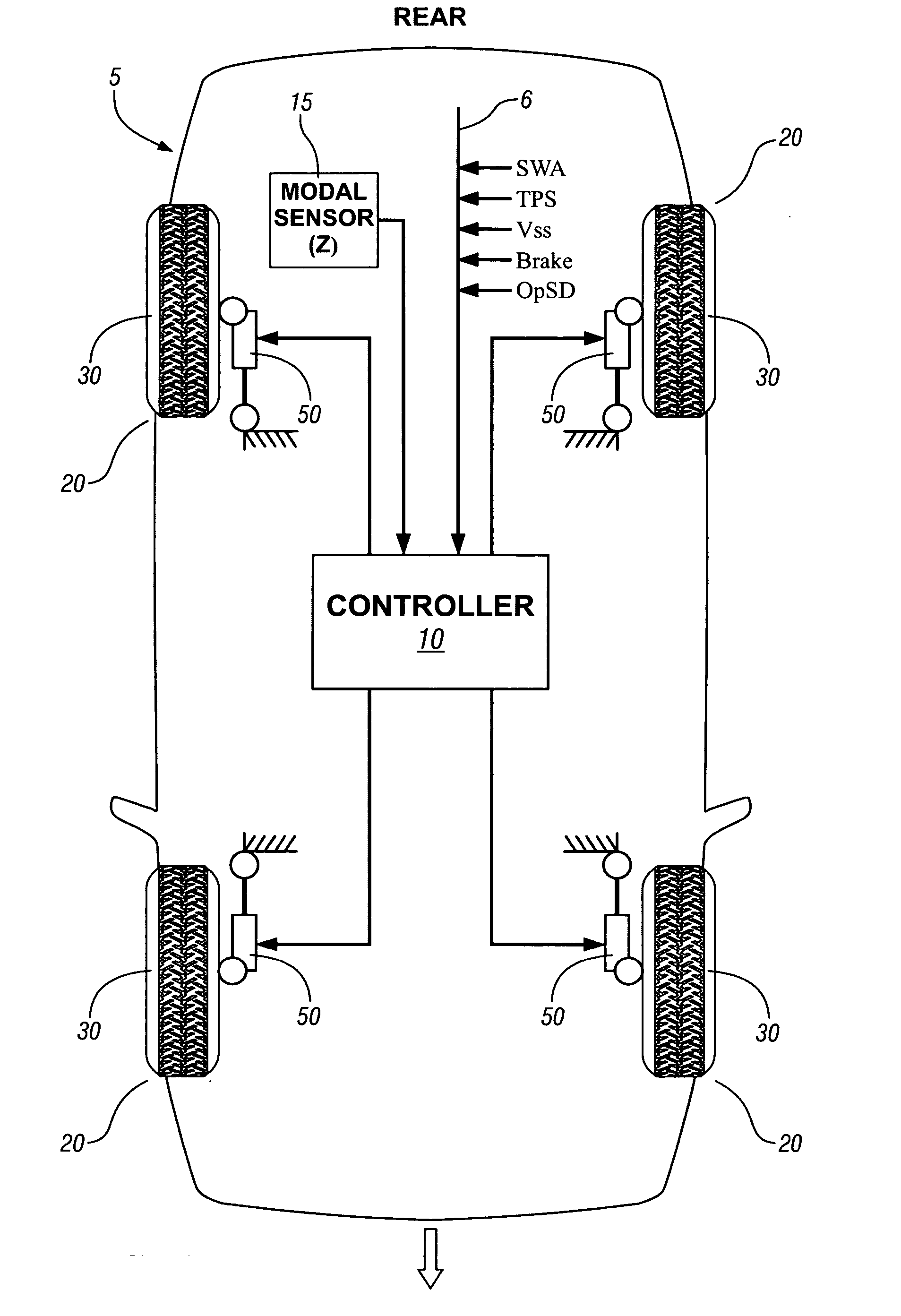
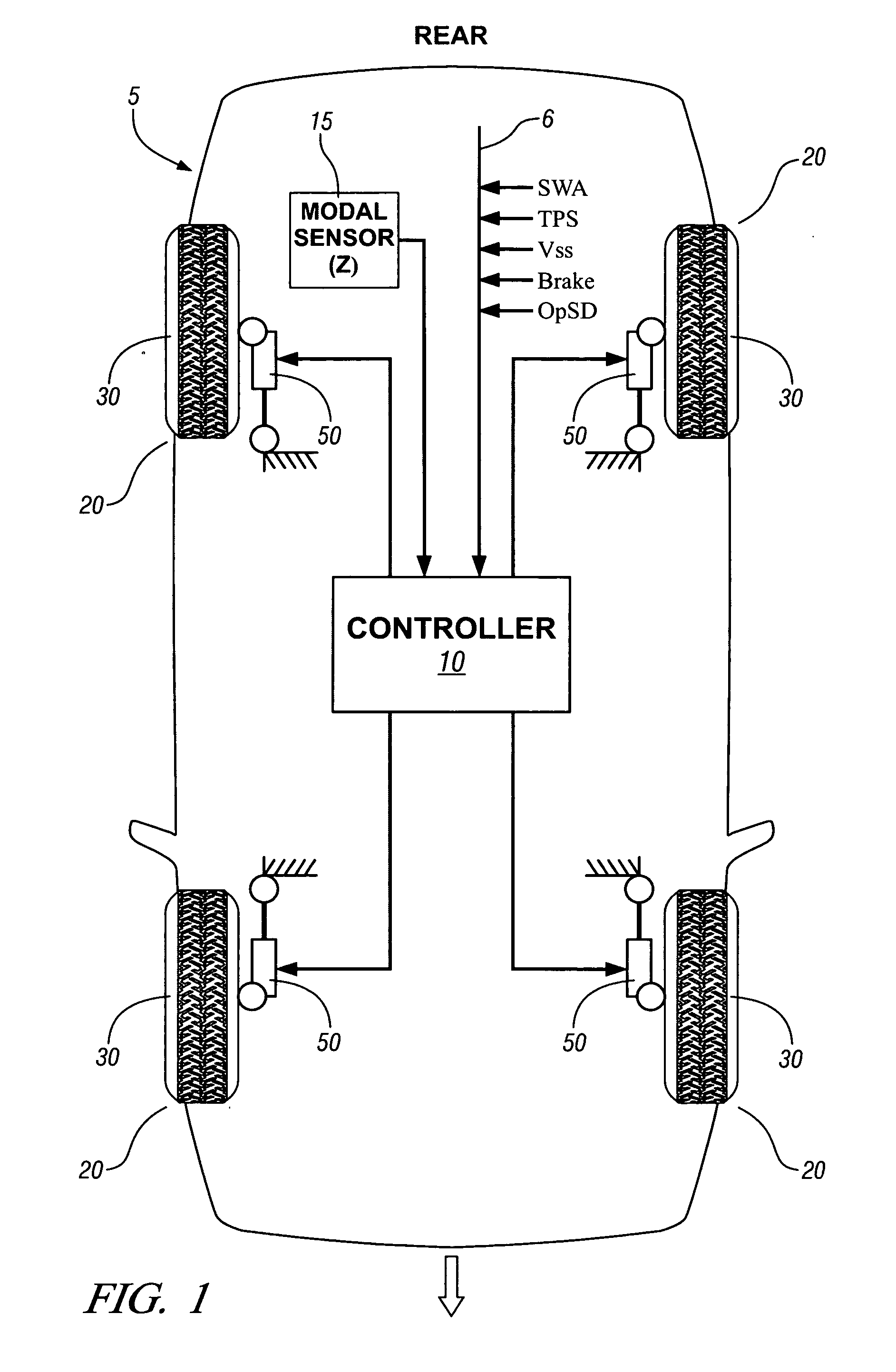
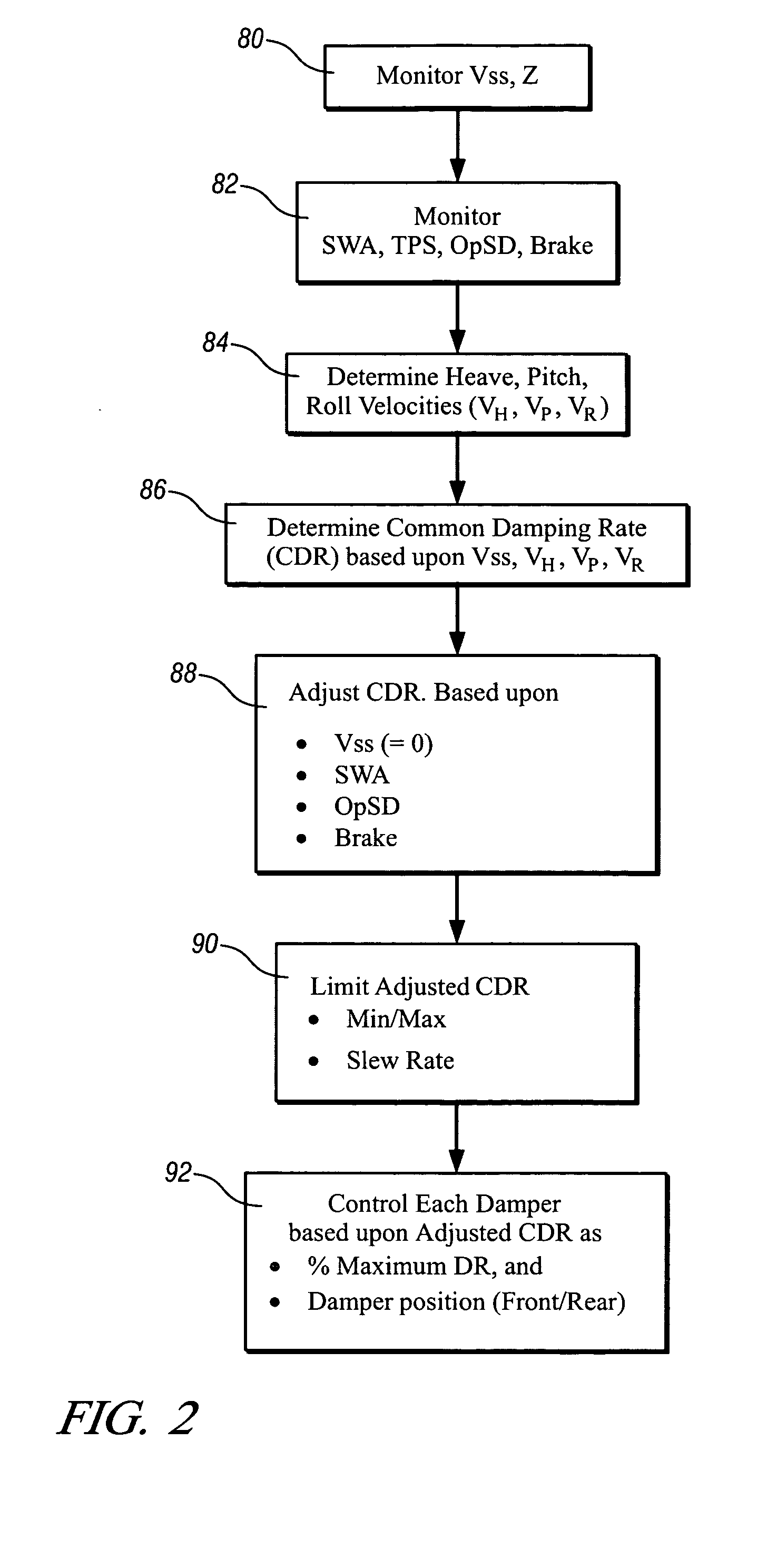
ActiveUS20070088475A1Less-high-frequency contentAvoid controlDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesSemi activeAccelerometer
A method and algorithm for semi-active suspension damper control is described. The algorithm controls the damper setting to limit vehicle body movement in terms of body modal velocities of heave, roll and pitch. The main input, body movement, is measured with accelerometers. The control output comprises a request in percent of damper control range. Vehicle speed-dependent minimum and maximum limits are applied. The method includes monitoring vehicle speed and a modal sensing system. A common damping rate for the dampers is determined based upon parameters for speed, heave, pitch, and roll. Each damper is controlled based upon the common damping rate adjusted based upon a location of each of the controllable suspension dampers. The output comprises a single signal, translated to a front and rear setting. The purpose is to always have a balanced setting of the four dampers.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
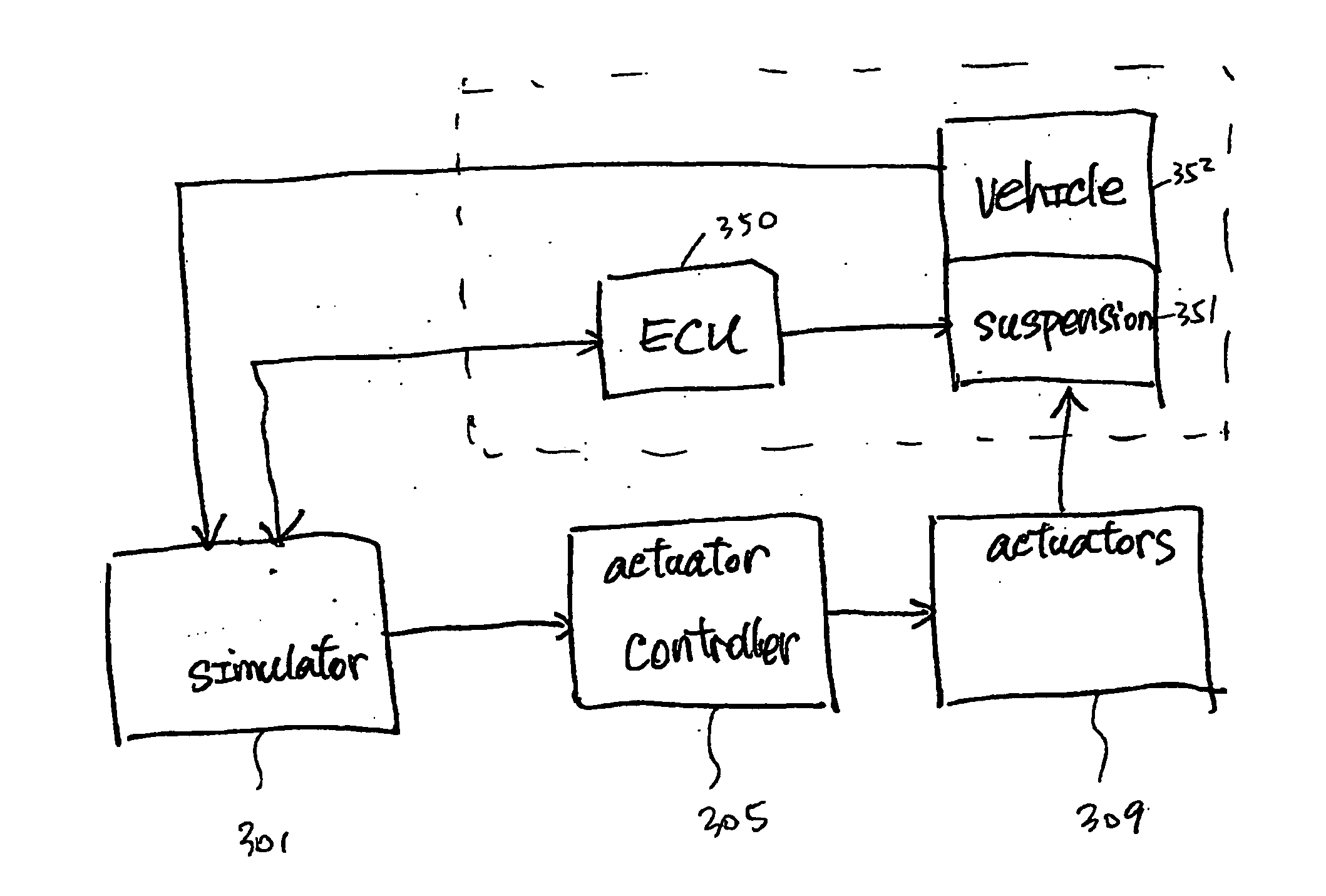
Dynamic vehicle suspension system testing and simulation
InactiveUS20070260372A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsSystem testingIntegration testing
A dynamic vehicle tester providing integrated testing and simulation for determining characteristics of a unit under test. Changes occurred on the unit under test are dynamically obtained, considered and incorporated in generating test conditions to be applied to the unit under test. In particular, testing of a vehicle suspension system may be accomplished.
Owner:MTS SYSTEMS CORPORATION
Bicycle suspension control apparatus
A bicycle suspension control apparatus is basically provided with a power supply sensor and a controller. The power supply sensor detects a power level of a power supply being supplied from the power supply to electrically adjustable front and rear suspensions. The controller is configured to selectively change at least one electrically adjustable suspension parameter of each of the front and rear suspensions. The controller receives a power level signal from the power supply sensor. The controller prohibits changing the electrically adjustable suspension parameter of the rear suspension upon the power supply sensor detecting the power level of the power supply being below a first prescribed power level. The controller permits changing the electrically adjustable suspension parameter of the front suspension upon the power supply sensor detecting the power level of the power supply being below the first prescribed power level.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
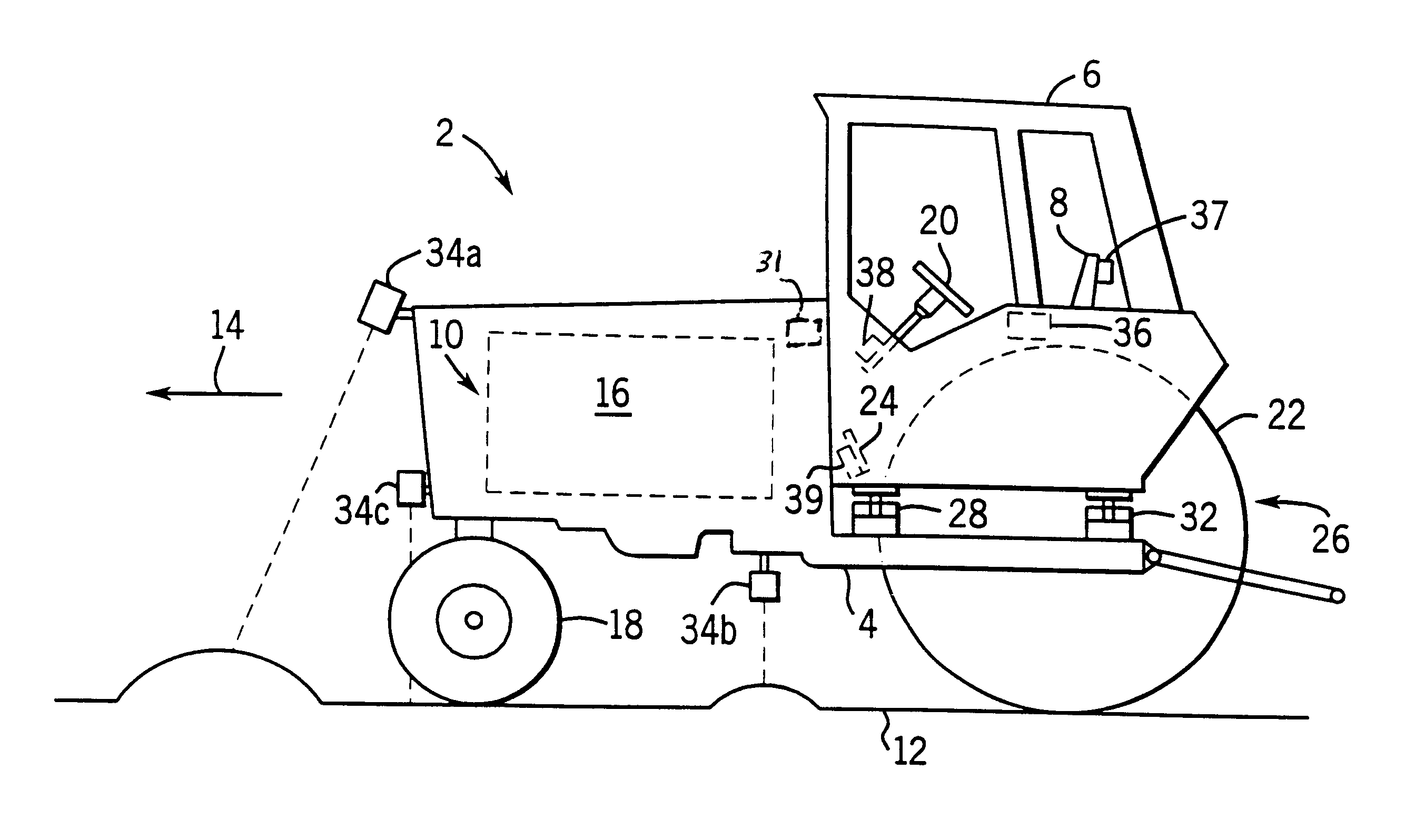
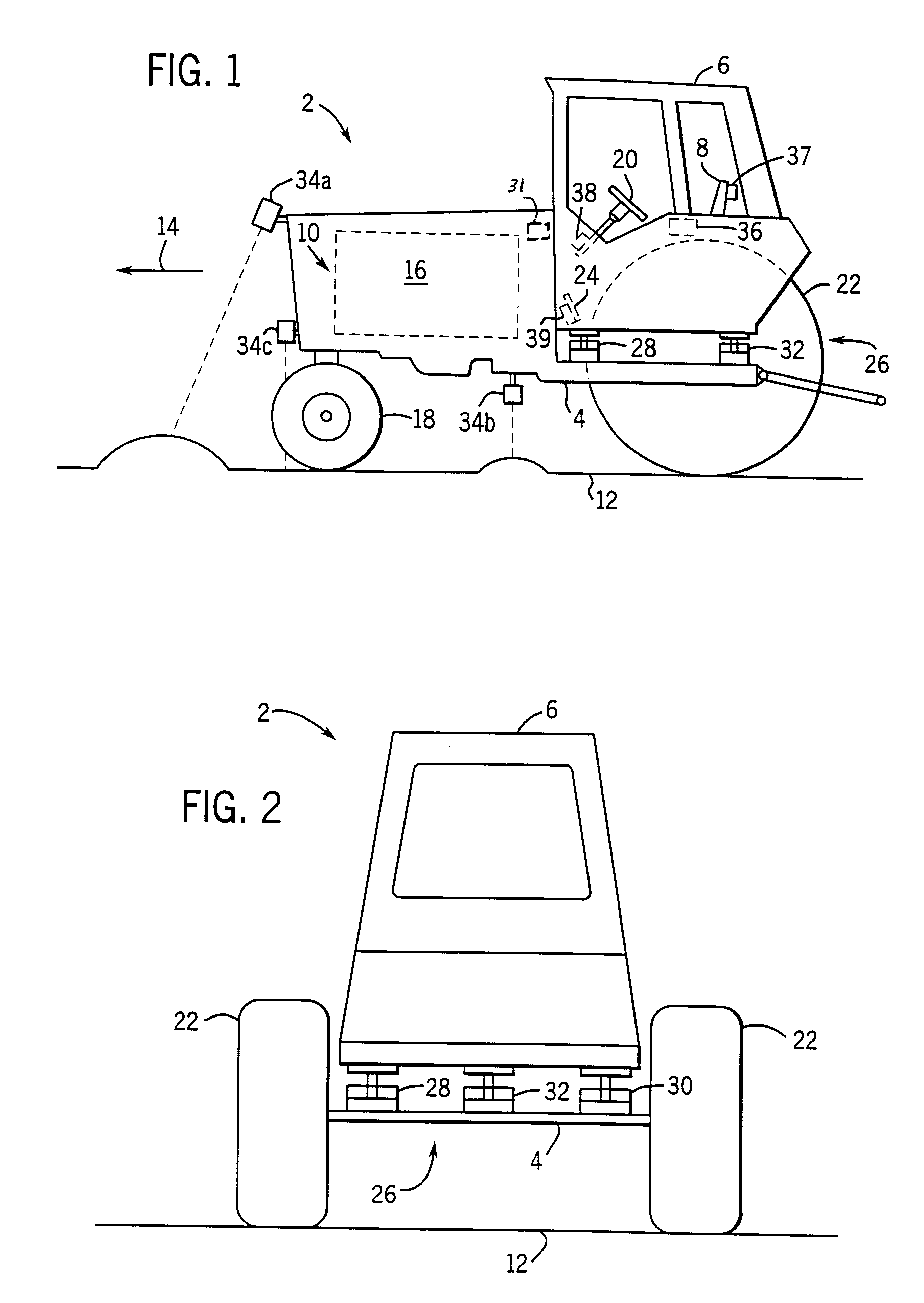
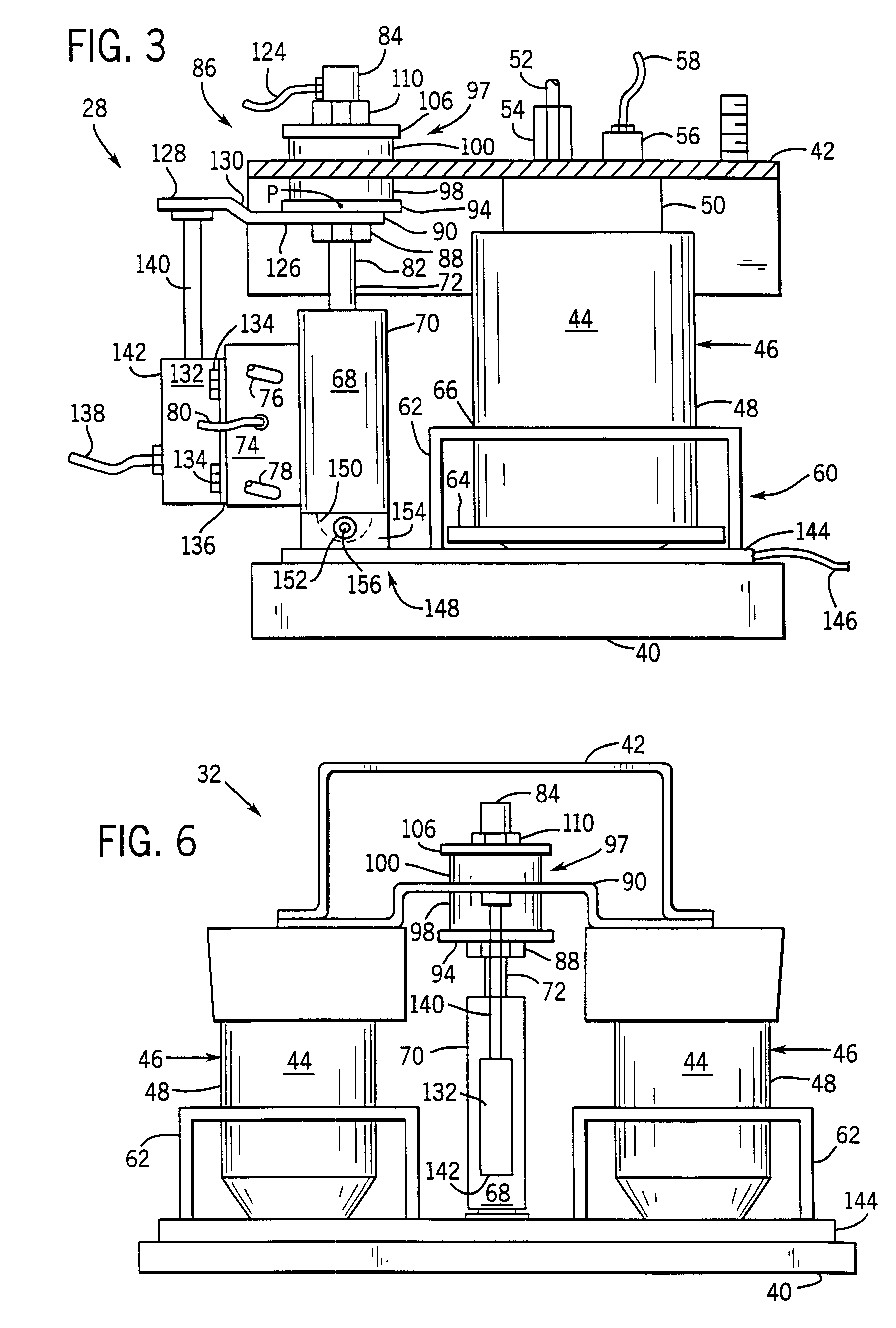
Apparatus for facilitating reduction of vibration in a work vehicle having an active CAB suspension system
InactiveUS6898501B2Reduce vibrationEar treatmentAnalogue computers for trafficEngineeringSignal processing
An apparatus and method for determining when a component of a work vehicle experiences vibration above a predetermined threshold, and responding to the vibration so that the vibration is reduced below the predetermined threshold. The apparatus, which is in a work vehicle that includes a chassis, an operator's cab and an active cab suspension system, includes a sensor that is configured to sense a quantity representative of the vibration experienced by the component of the work vehicle and to develop a first signal indicative of that quantity. The apparatus also includes a signal processor that is coupled to the sensor and is configured to develop, in response to the first signal, a second signal indicative of whether the vibration experienced by the component is above the predetermined threshold. The apparatus further includes a device that is coupled to the signal processor and, in response to the second signal, is either configured to provide an indication or configured to take an action to reduce the vibration below the predetermined threshold when the vibration is above the predetermined threshold.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC +1
Device for warning drivers of automobiles of excessive speed of turning around a curve
InactiveUS6873253B2Low costGuaranteed uptimeVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringRoad surface
An autonomous device for warning drivers of automobiles of excessive speed of turning around a curve. The device is compact with both the sensing means and alarm audio and / or visual signal producing means. The sensing means comprises two, alternatively activated and differentially calibrated by means of a proposed calibration device, pair of mercury switches, each pair comprising two oppositely inclined mercury switches for monitoring right and left turns of the vehicle, wherein the first pair is adapted for use in conditions of dry road surface by calibration at a predetermined value of inclination and a second pair is adapted for use in conditions of wet road surface by calibration at a different predetermined value of inclination.
Owner:VEZIRIS SPYROS
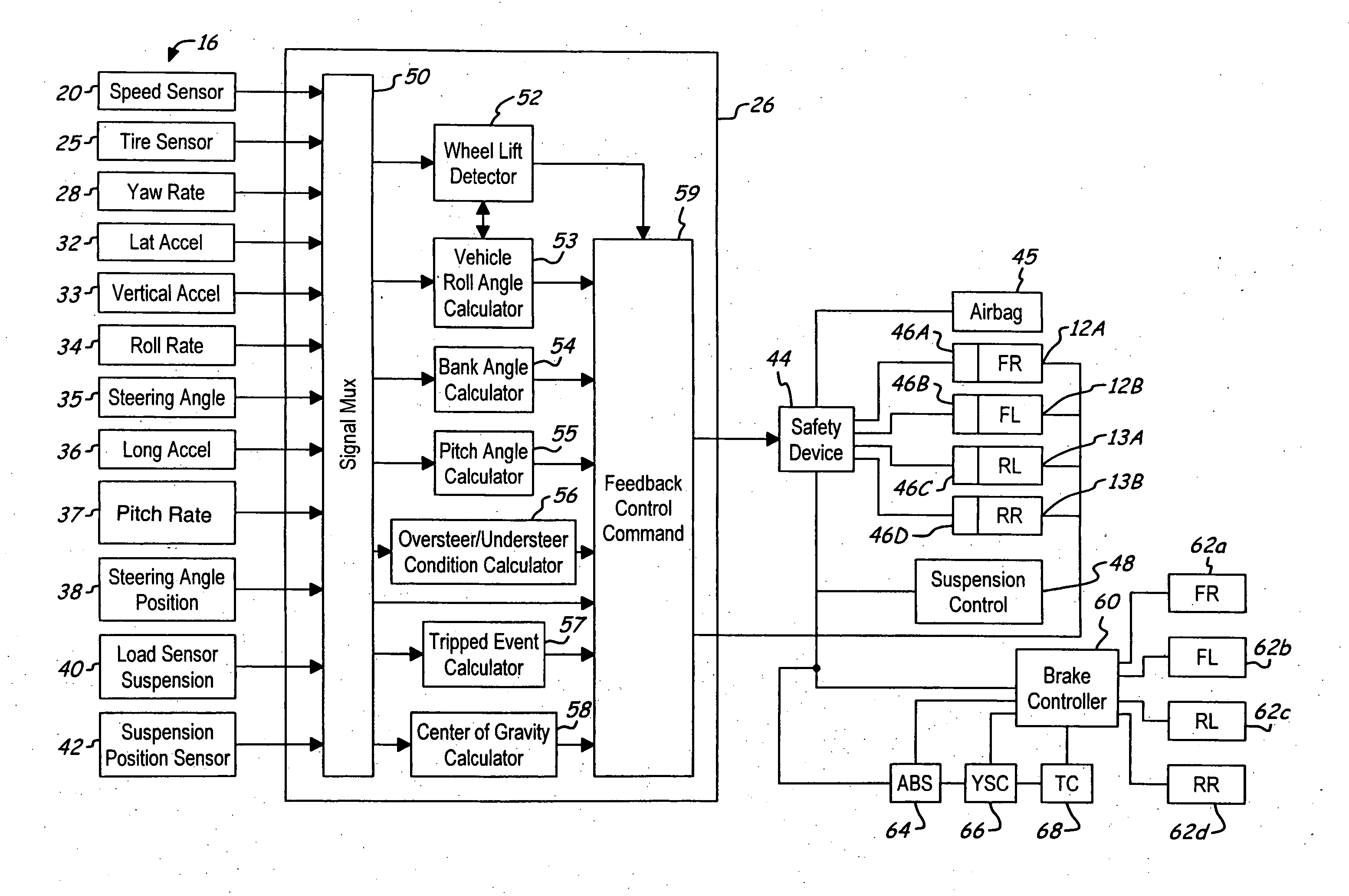
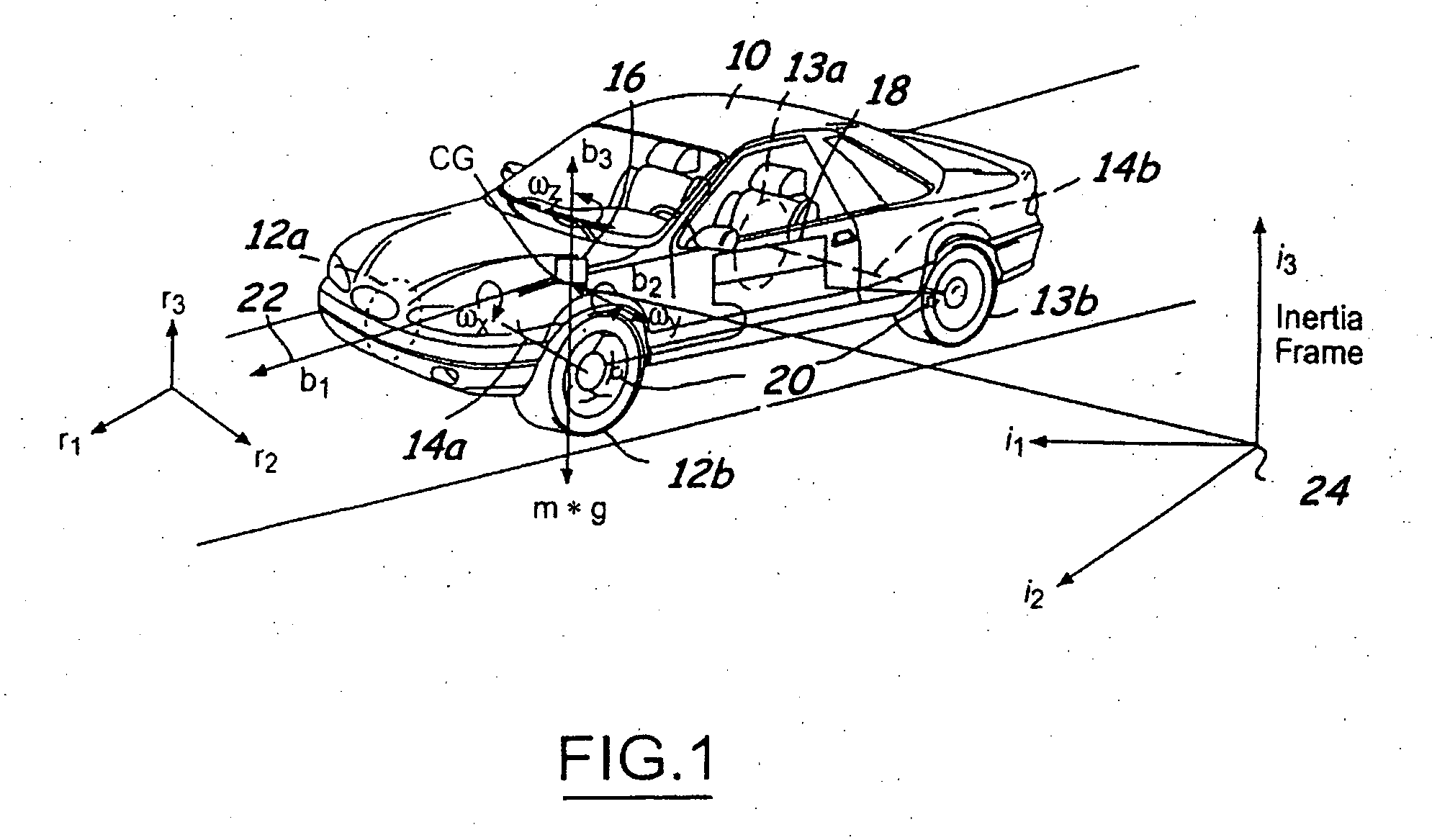
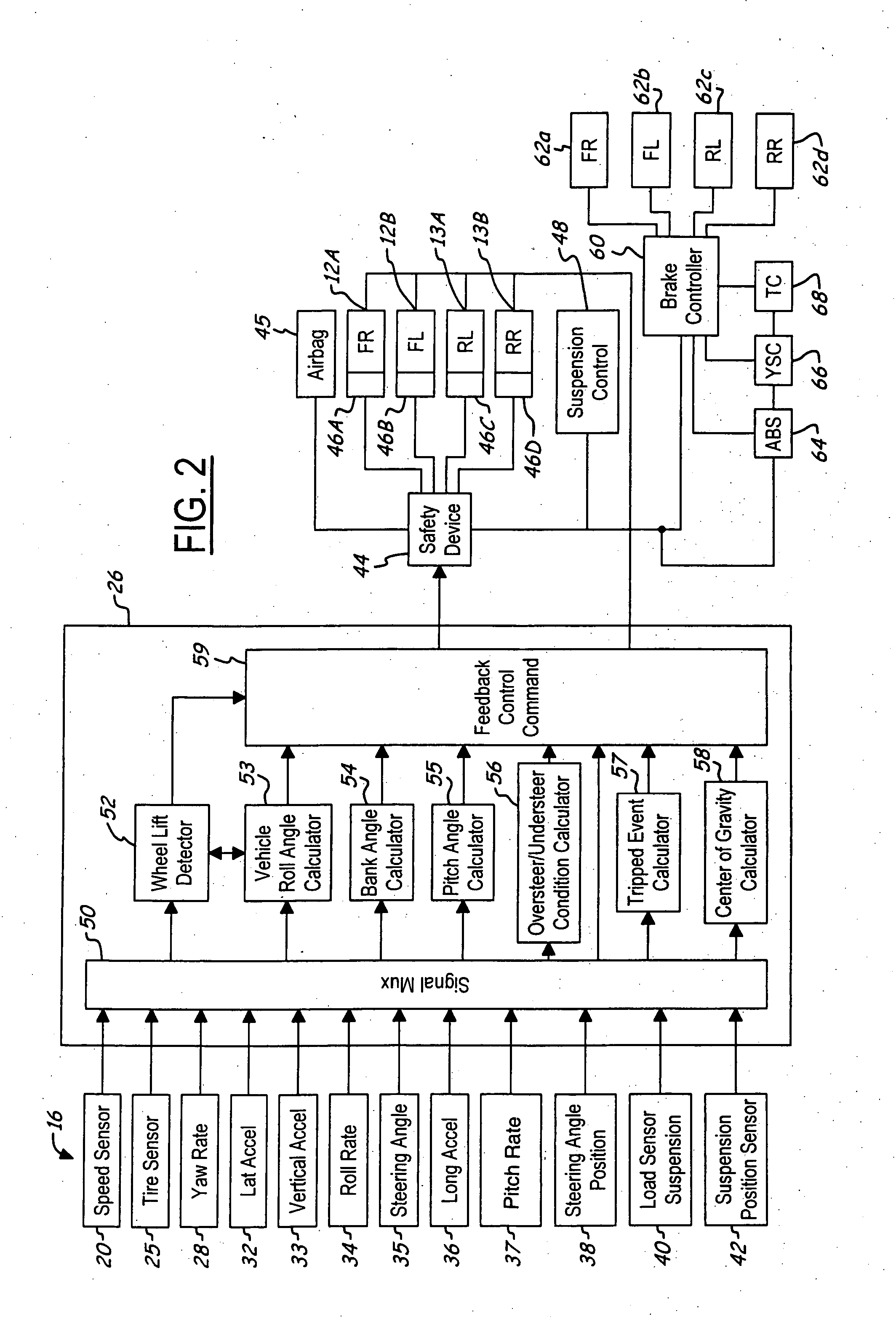
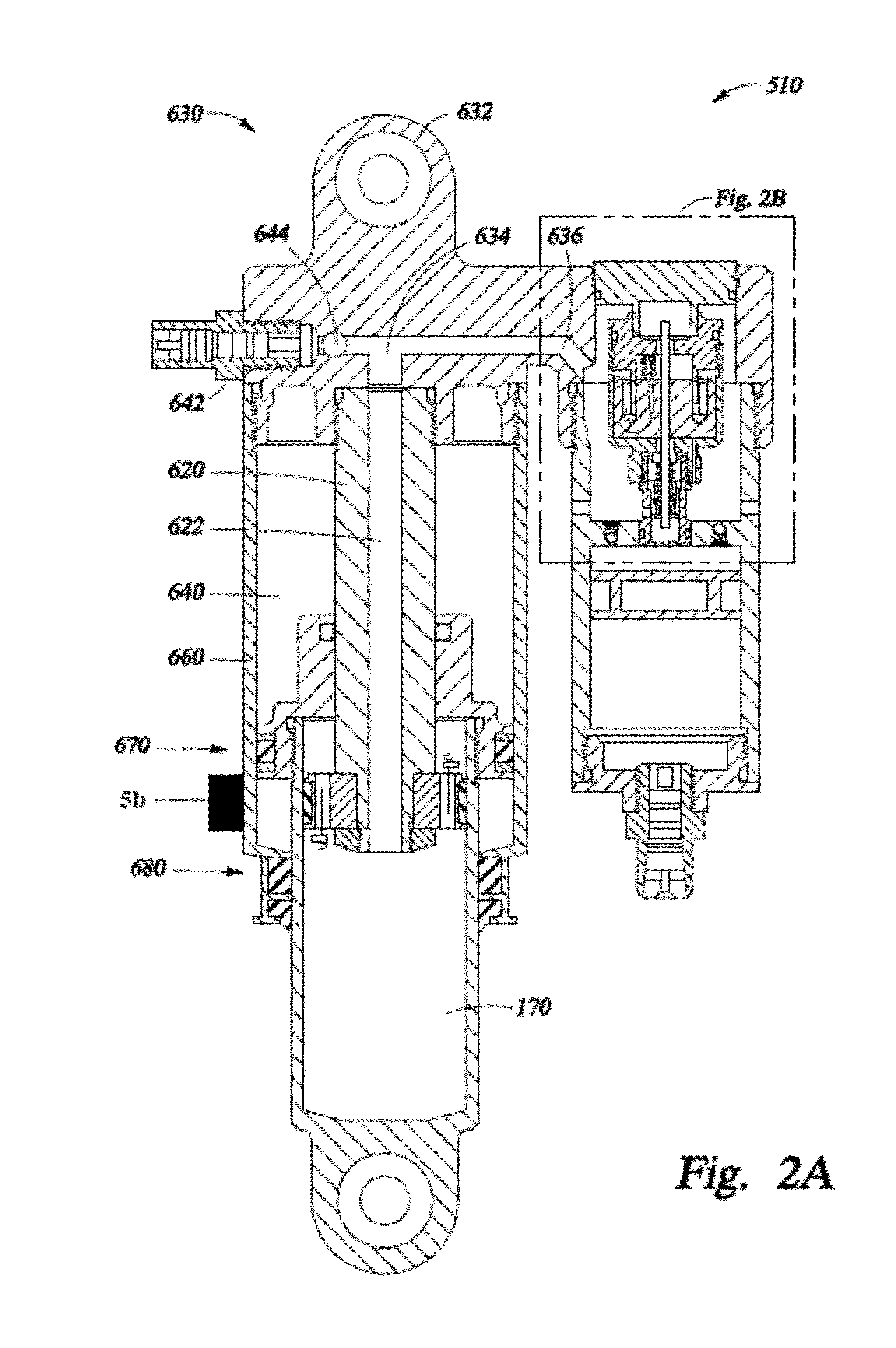
System and method for controlling a safety system of a vehicle in response to conditions sensed by tire sensors related applications
InactiveUS20050033486A1Low costDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemForce sensor
A control system for a vehicle (10) is described for use in conjunction with the safety system (44) of the vehicle (10). A tire sensor or plurality of tire sensors generates tire force signals. The tire force signals may include lateral tire forces, longitudinal (or torque) tire forces, and normal tire forces. Based upon the tire force signals, a safety system (44) may be activated. The tire force sensors may be used to monitor various conditions including but not limited to sensing a roll condition, wheel lift detection, a trip event, oversteering and understeering conditions, pitch angle, bank angle, roll angle, and the position of the center of gravity of the vehicle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Methods and apparatus for suspension set up
ActiveUS20130144489A1Accurate settingEnjoyable experience for the riderImage enhancementImage analysisUser inputEngineering
A method and apparatus are disclosed that assist a user in performing proper setup of a vehicle suspension. A user may utilize a device equipped with an image sensor to assist the user in proper setup of a vehicle suspension. The device executes an application that prompts the user for input and instructs the user to perform a number of steps for adjusting the suspension components. In one embodiment, the application does not communicate with sensors on the vehicle. In another embodiment, the application may communicate with various sensors located on the vehicle to provide feedback to the device during the setup routine. In one embodiment, the device may analyze a digital image of a suspension component to provide feedback about a physical characteristic of the component.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
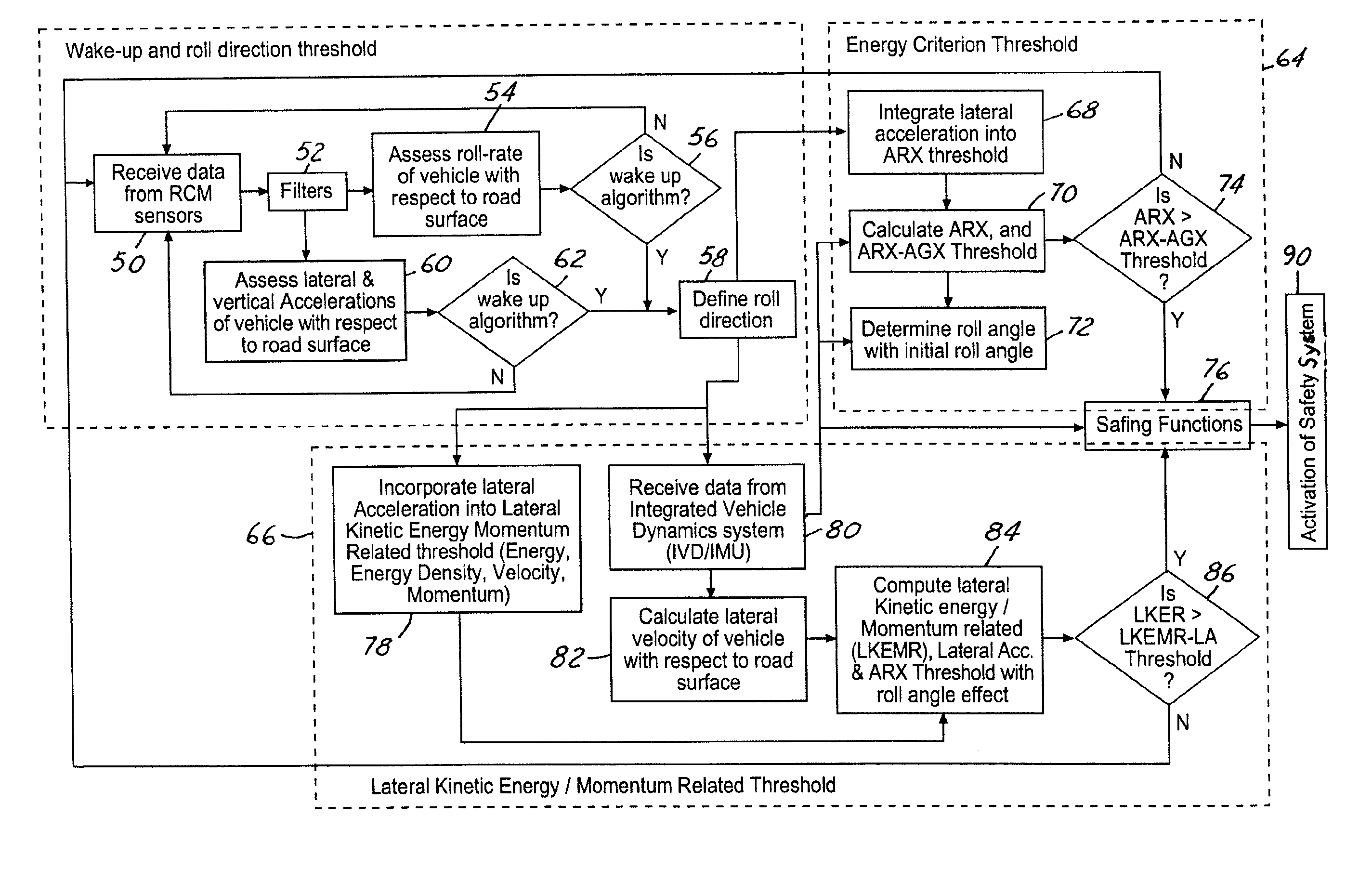
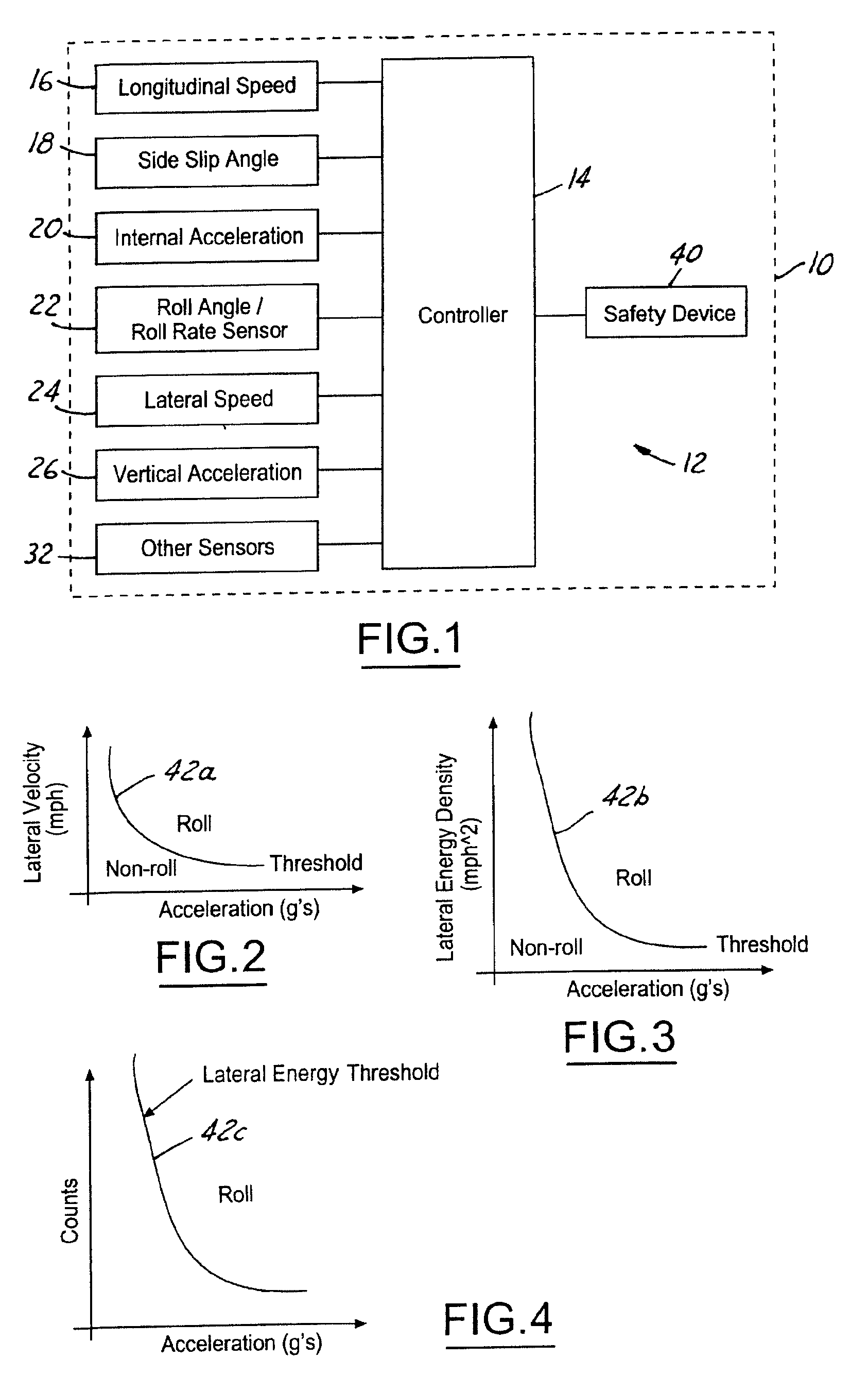
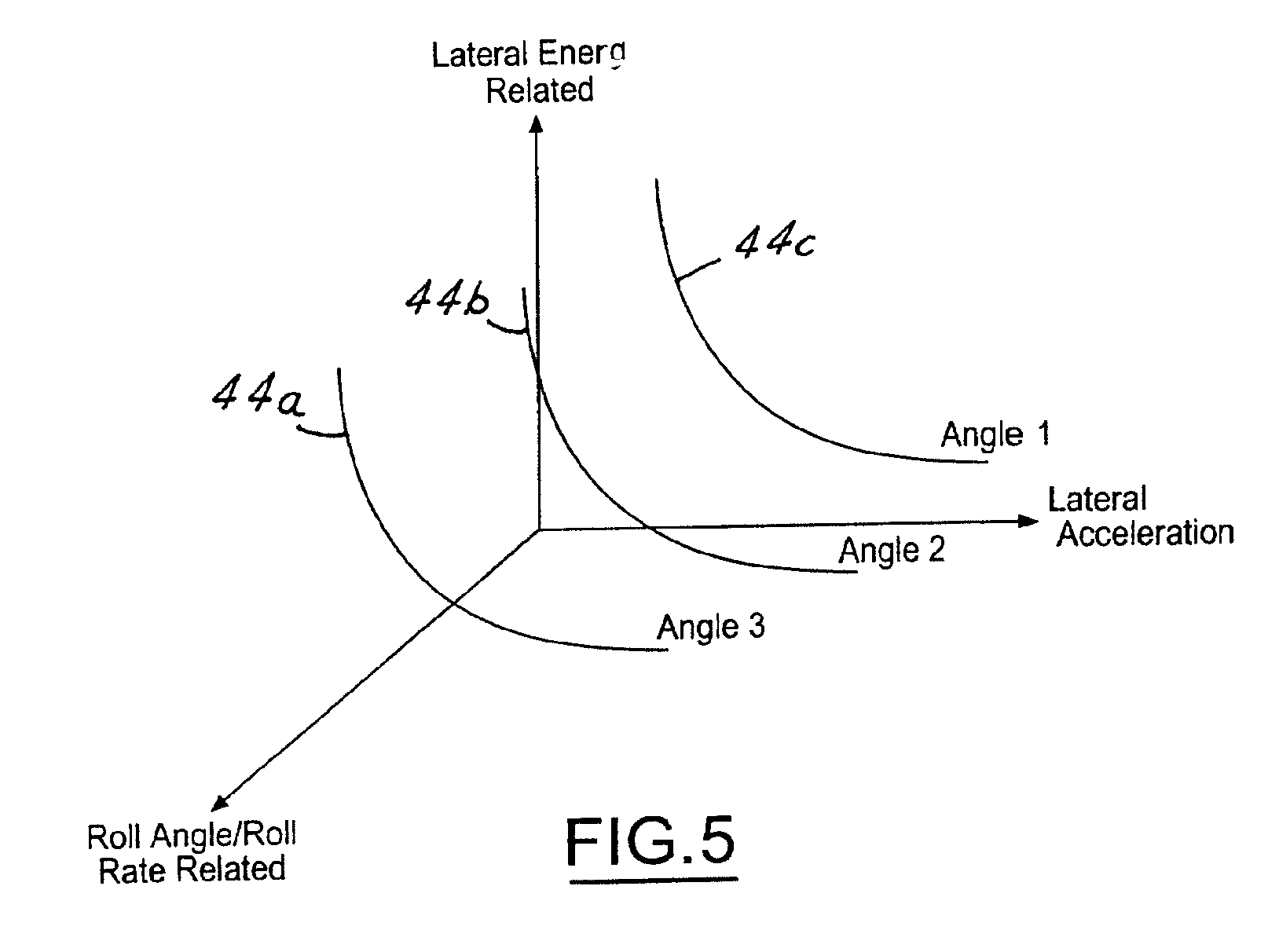
Kinetic energy density rollover detective sensing algorithm
ActiveUS6856868B1Improved rollover detectionEasy to detectHand manipulated computer devicesAnalogue computers for trafficMobile vehicleRollover
A rollover detection system (12) for an automotive vehicle (10) includes a controller (14) that is hooked to various types of sensors. The sensors may include a lateral acceleration sensor and another sensor or combination of sensors that gives an indication to another lateral condition of the vehicle. The controller determines a roll condition in response to comparing the lateral acceleration and the lateral condition other than lateral acceleration to a threshold. When the conditions are above the threshold then a roll condition is indicated. When a roll condition is indicated a safety device (40) may be controlled to prevent rollover and / or deploy a safety device.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com