Patents
Literature
654results about How to "Accurate compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Assured archival and retrieval system for digital intellectual property
ActiveUS7856414B2Economy of scaleImprove integrityFinanceDigital data processing detailsIntellectual propertyDigital rights management
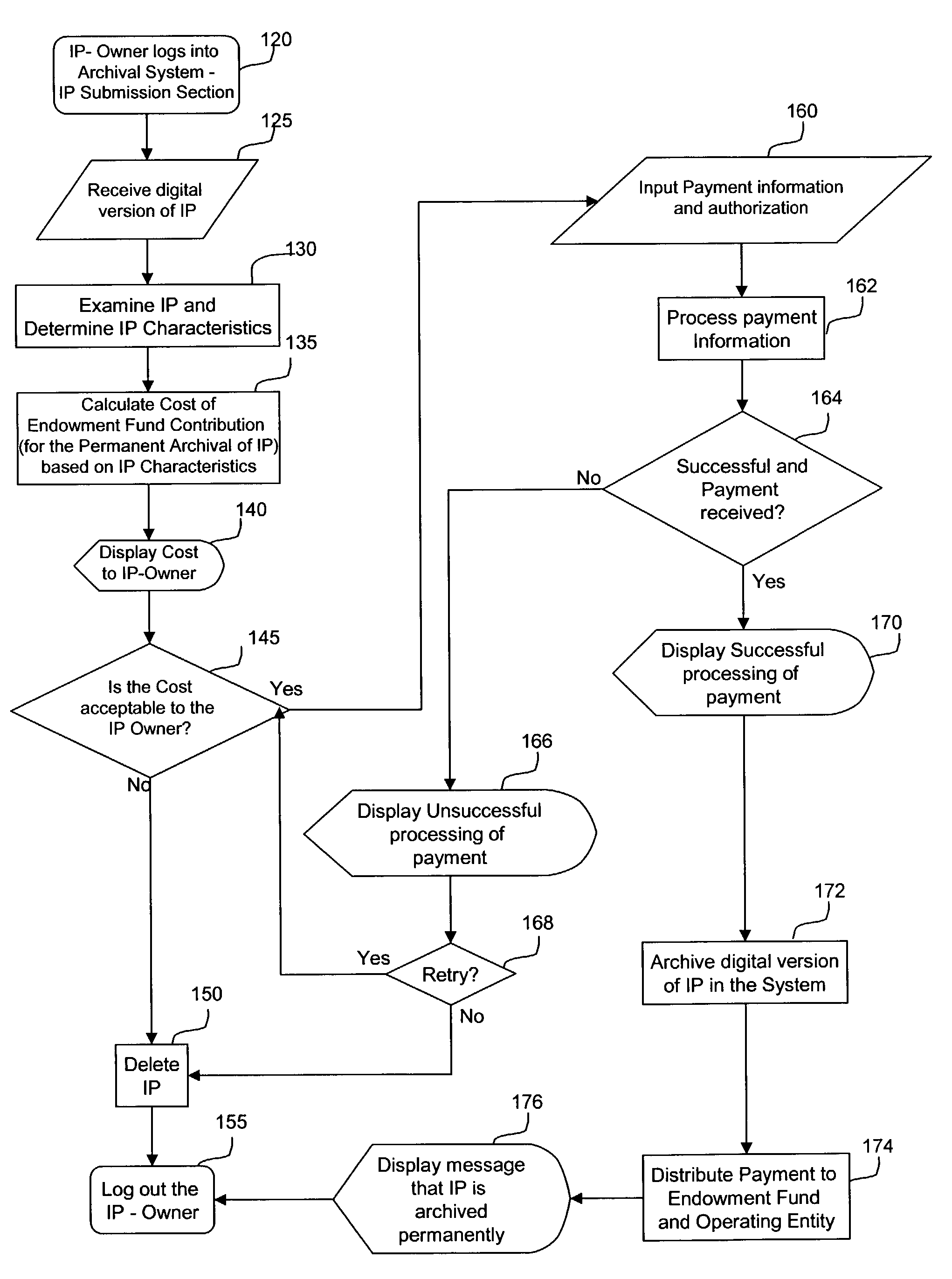
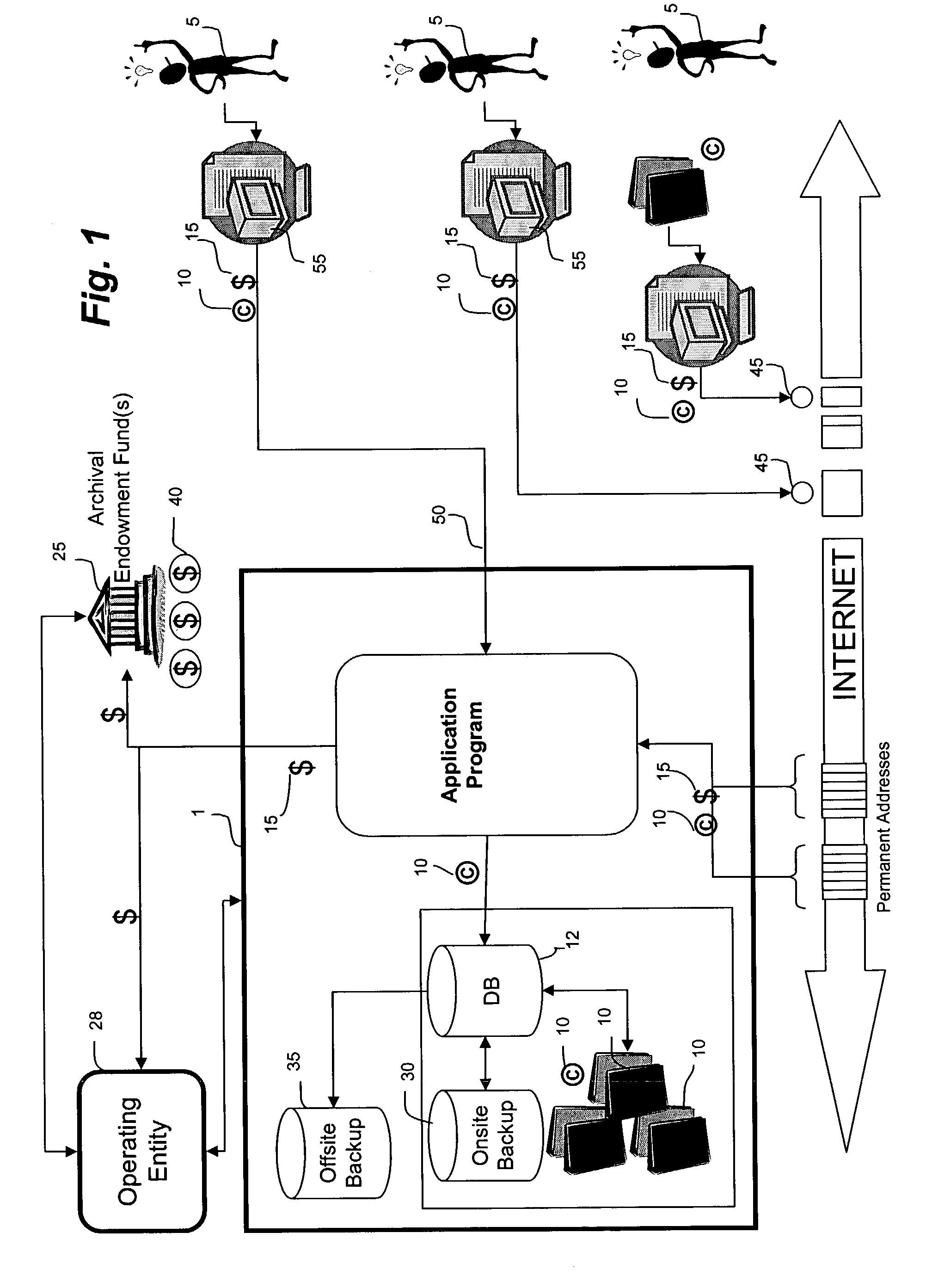
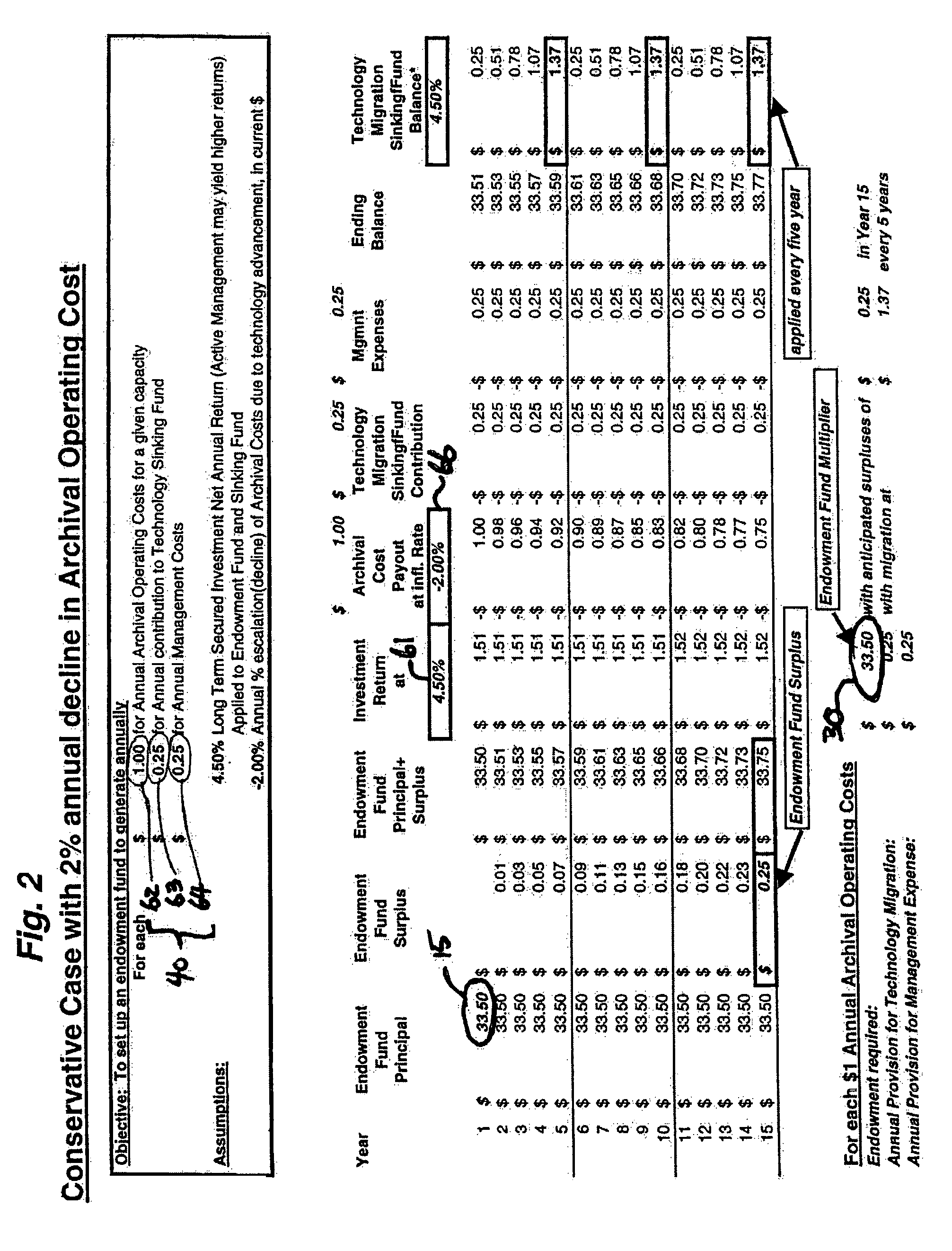
A system and method of use for permanently archiving intellectual properties (IP) in a digital archival system. An owner contributes each IP with an initial financial contribution including a discrete archival endowment which is sufficient to fund archival of the IP for an assured archival period. A plurality of discrete archival endowments can be pooled into one or more archival endowment funds, jointly managed for the maintenance of each archived IP. The endowment funds can be managed by a trustee separate from the management of the digital archive. Retrieval can be funded through retrieval fees or an endowment maintained separate from the archival endowment fund. Digital rights management can remunerate owners and revenue tracking can capitalize the value of each IP. Access to the archive system is preferably through a variety of membership options including owners, users, and partners.
Owner:ZEE CHRISTOPHER
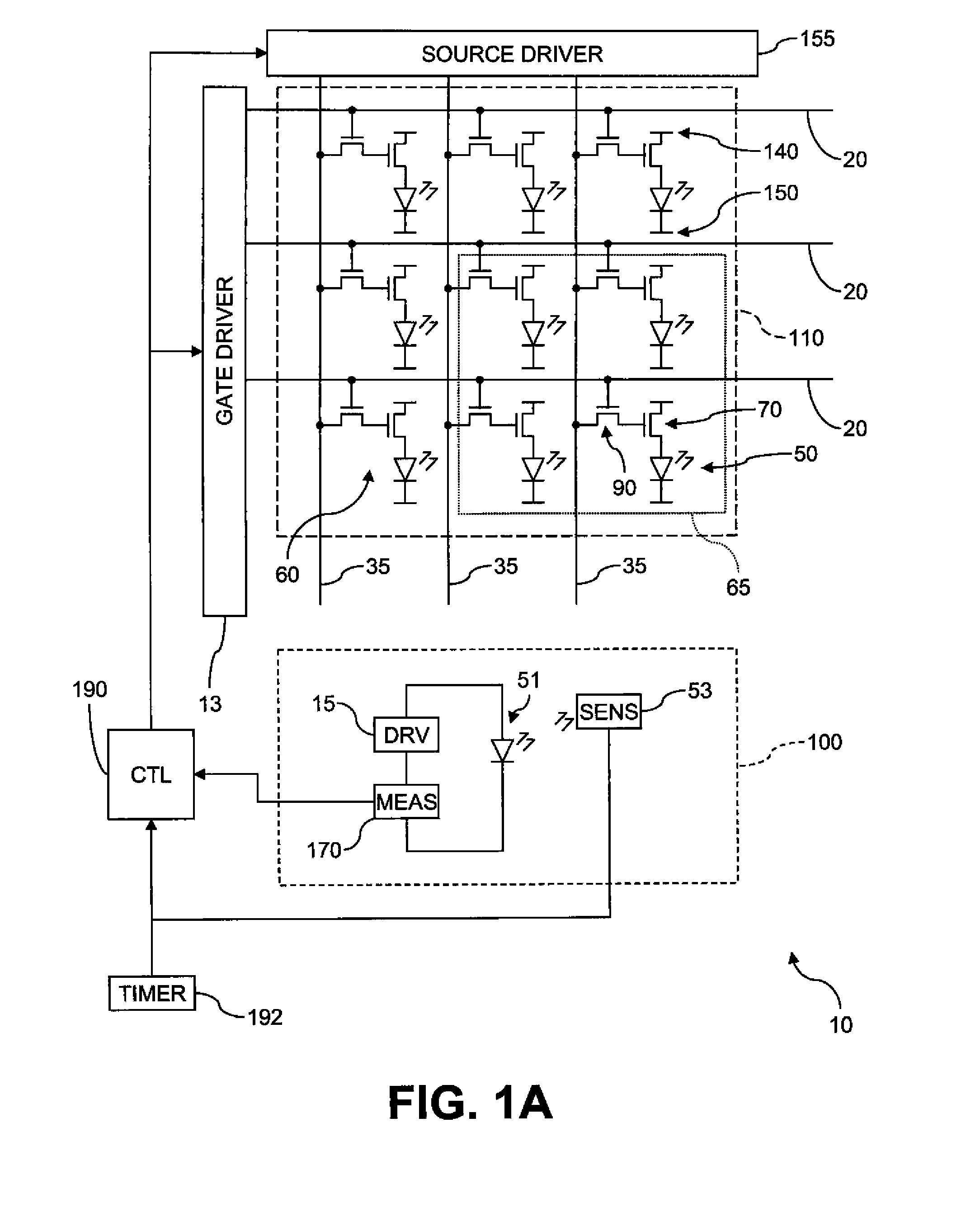
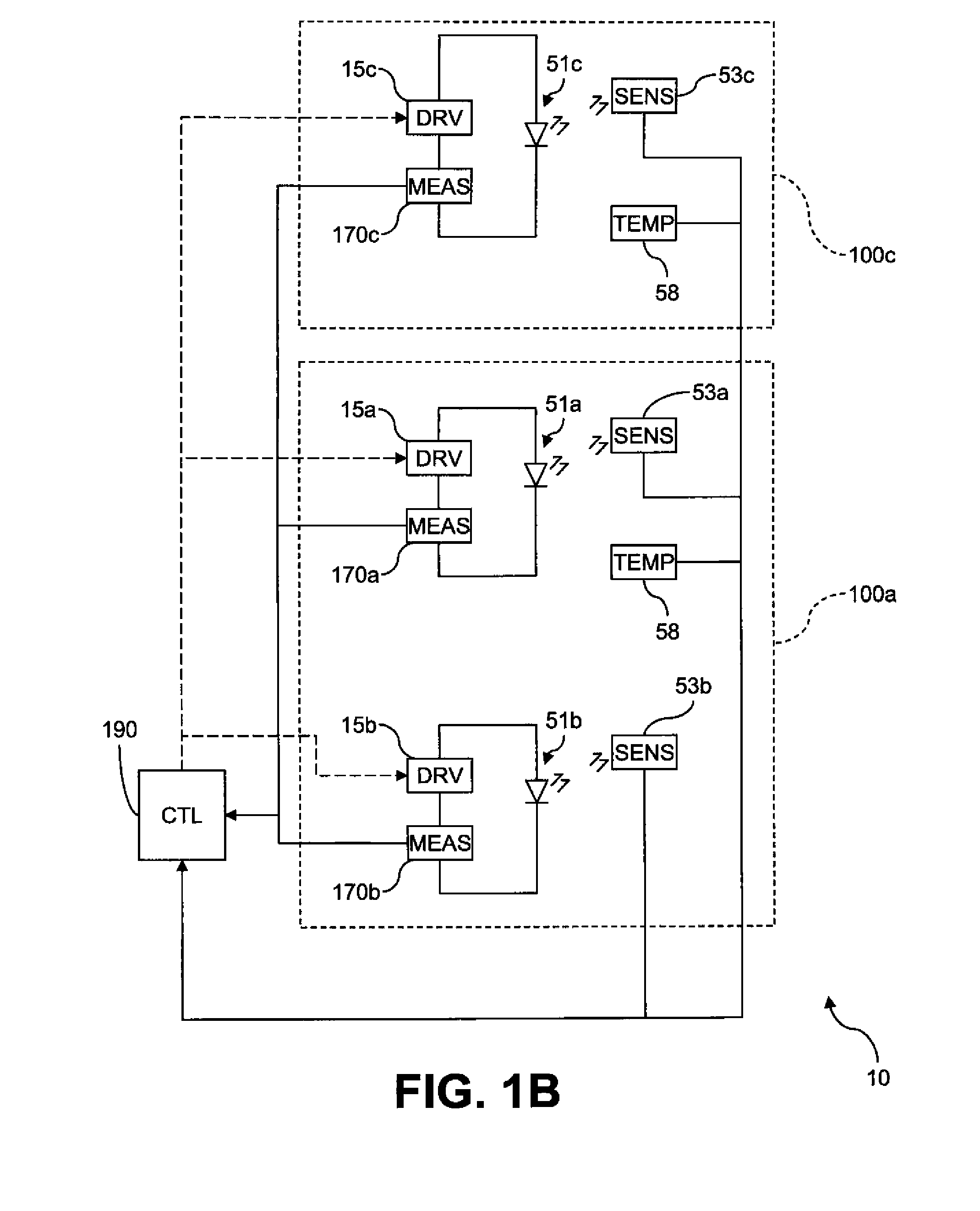
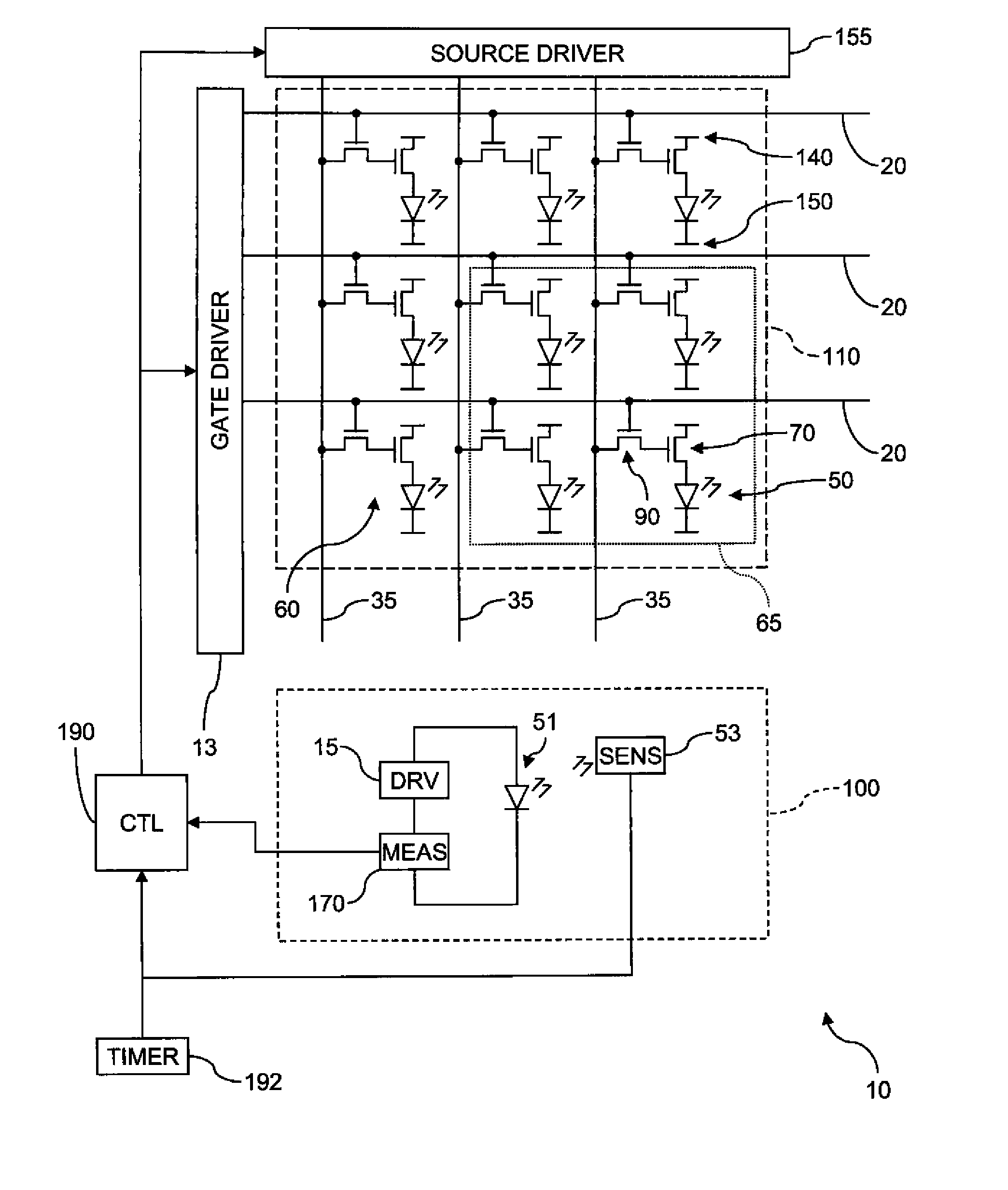
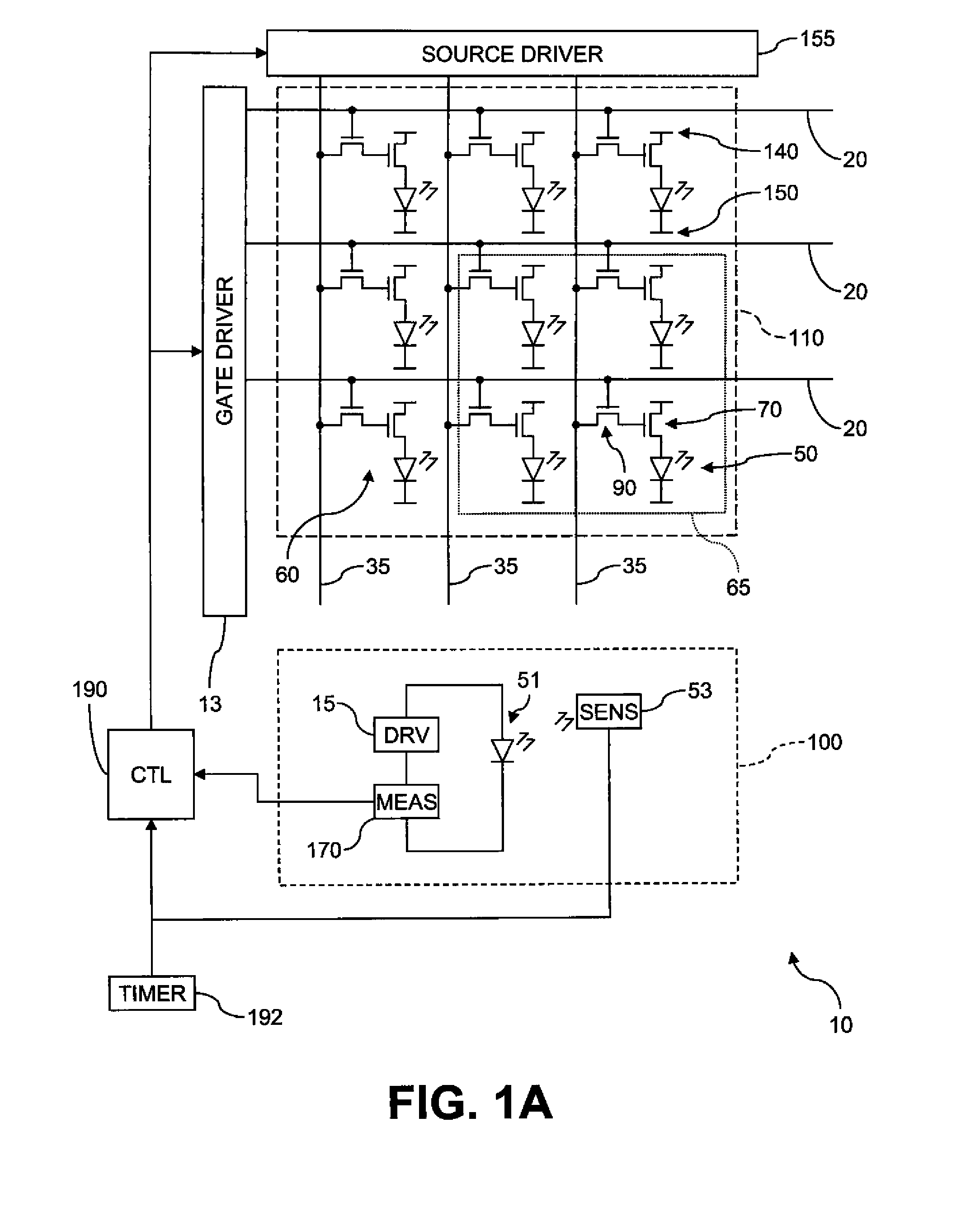
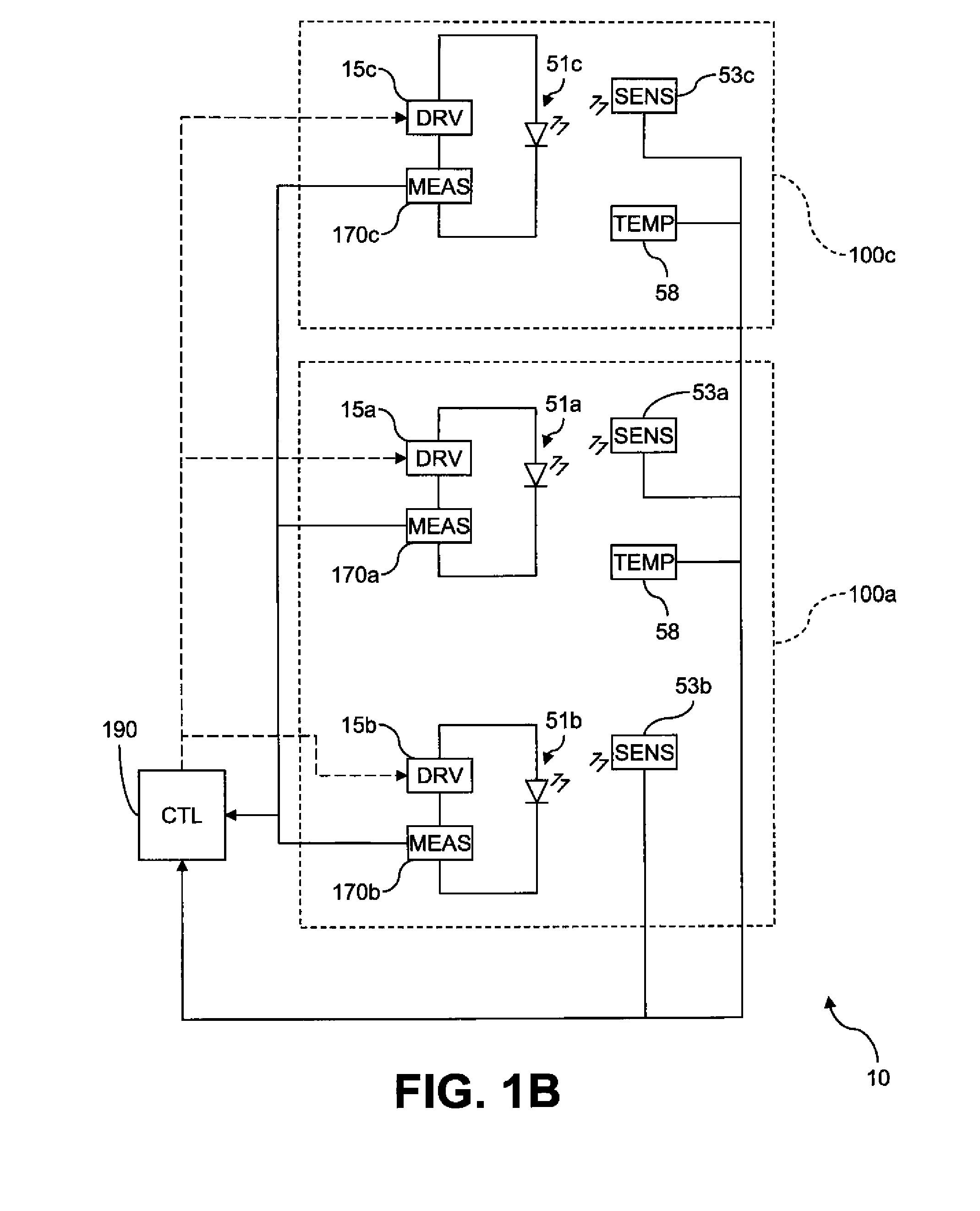
Electroluminescent device aging compensation with reference subpixels
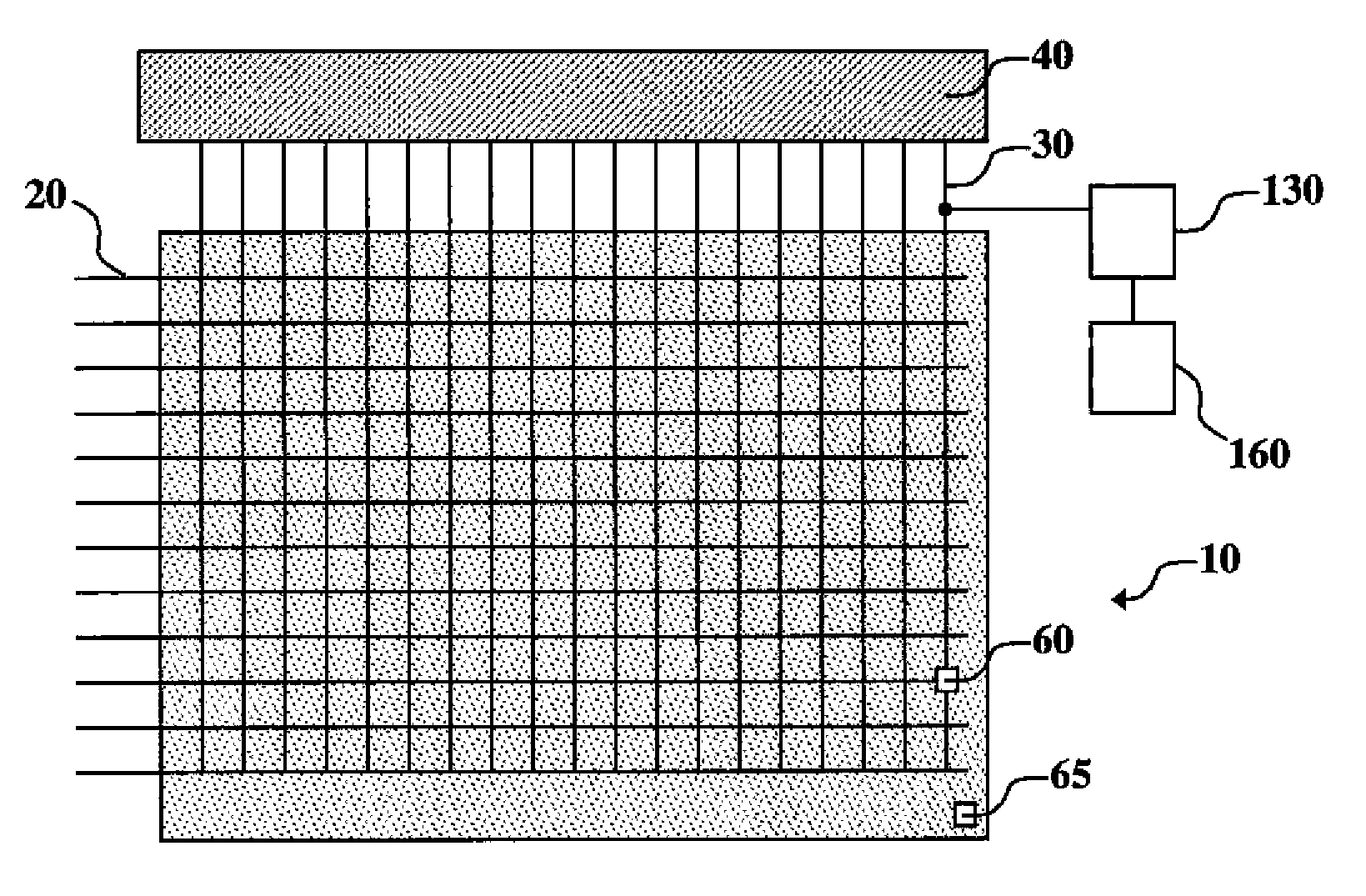
ActiveUS20110074750A1Accurate agingIncrease the aperture ratioCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriver circuitElectricity
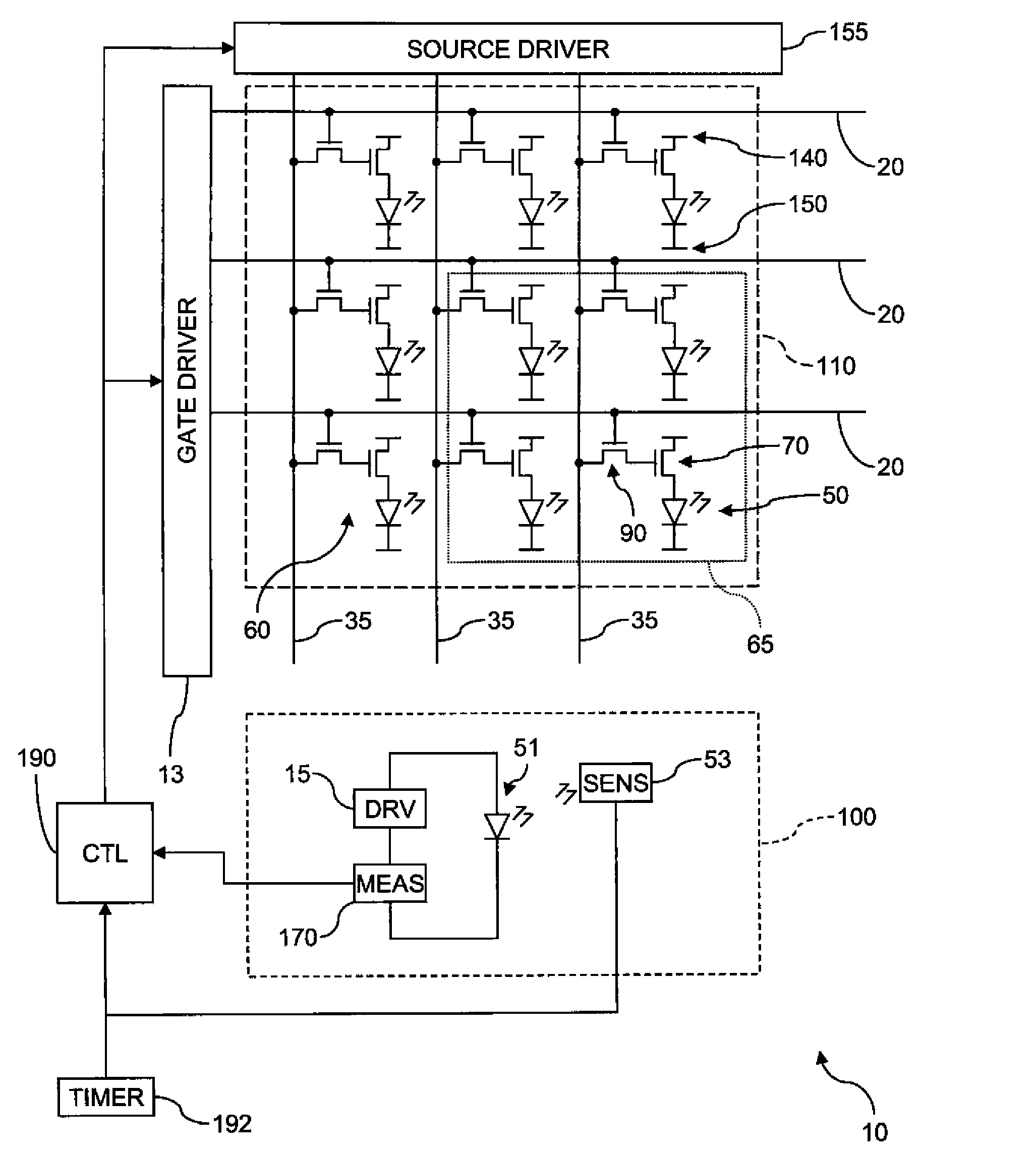
An electroluminescent (EL) device including an illumination area having one or more primary EL emitters; a reference area having a reference EL emitter; a reference driver circuit for causing the reference EL emitter to emit light while the EL device is active; a sensor for detecting light emitted by the reference EL emitter; and a measurement unit for detecting an aging-related electrical parameter of the reference EL emitter while it is emitting light. The device further includes a controller for receiving an input signal for each primary EL emitter in the illumination area, forming a corrected input signal from each input signal using the detected light and the aging-related electrical parameter, and applying the corrected input signals to the respective primary EL emitters in the illumination area.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
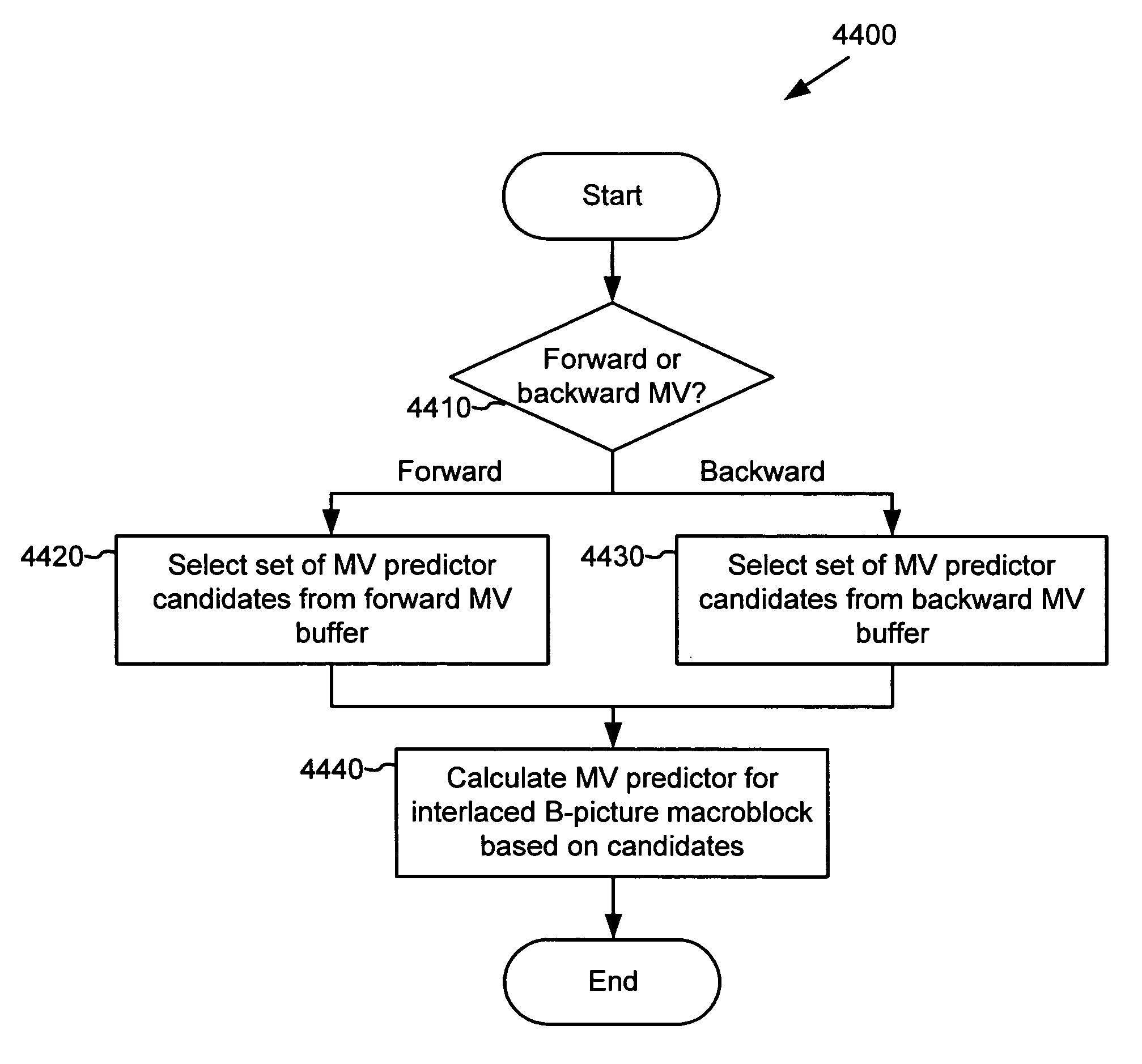
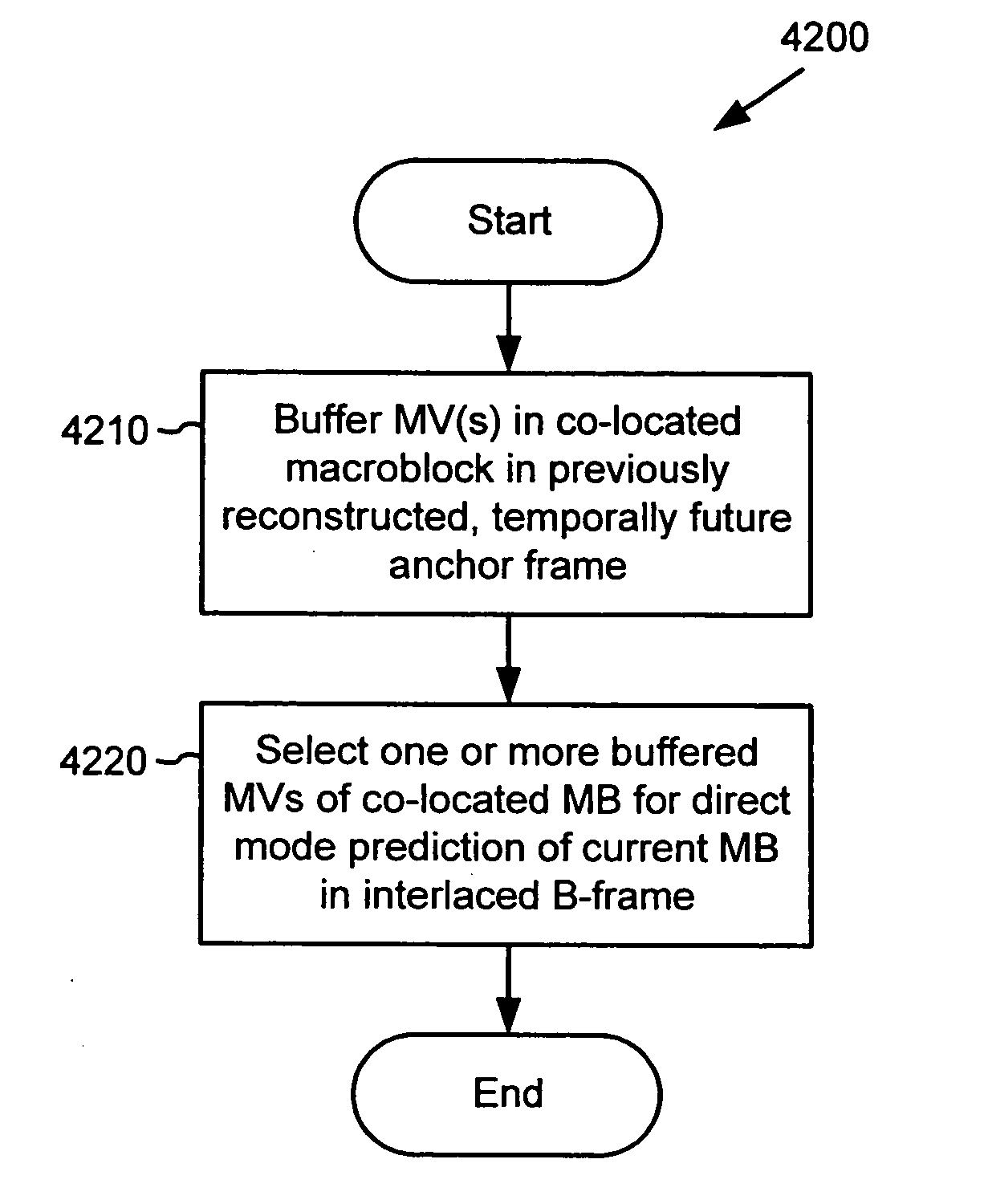
Advanced bi-directional predictive coding of interlaced video
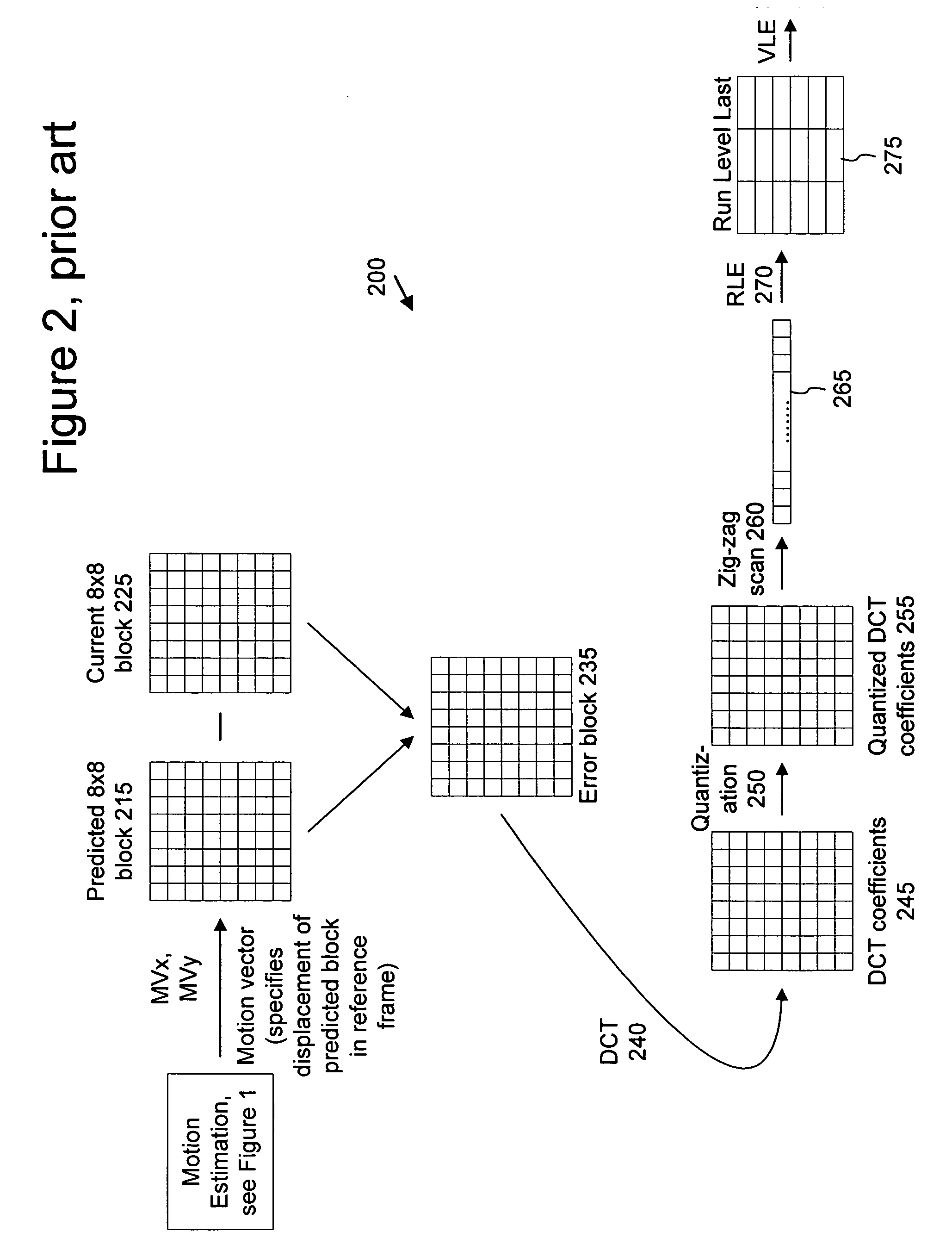
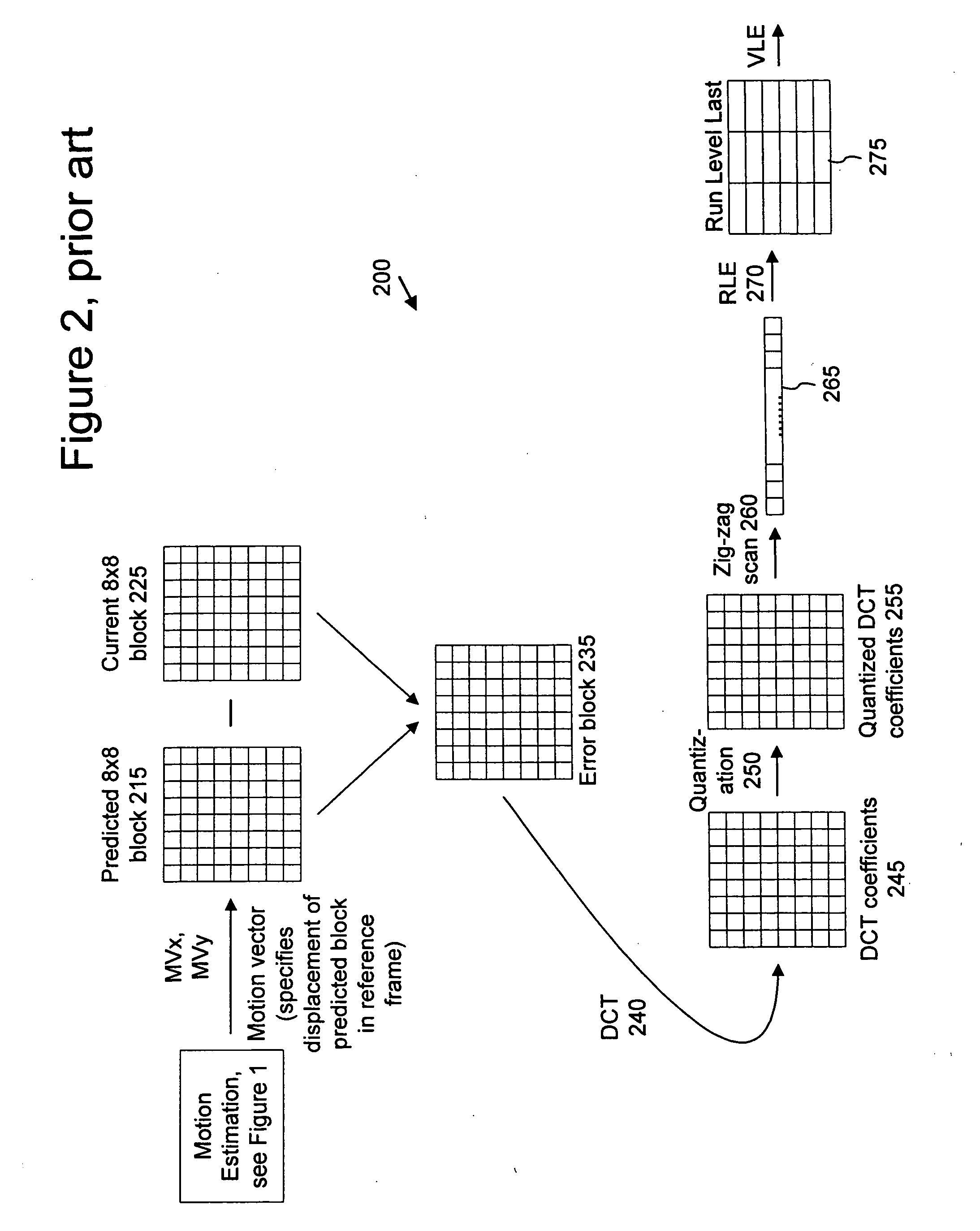
ActiveUS20050053292A1Accurate compensationReduce encoding overheadPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionInterlaced videoMotion vector
For interlaced B-fields or interlaced B-frames, forward motion vectors are predicted by an encoder / decoder using forward motion vectors from a forward motion vector buffer, and backward motion vectors are predicted using backward motion vectors from a backward motion vector buffer. The resulting motion vectors are added to the corresponding buffer. Holes in motion vector buffers can be filled in with estimated motion vector values. An encoder / decoder switches prediction modes between fields in a field-coded macroblock of an interlaced B-frame. For interlaced B-frames and interlaced B-fields, an encoder / decoder computes direct mode motion vectors. For interlaced B-fields or interlaced B-frames, an encoder / decoder uses 4 MV coding. An encoder / decoder uses “self-referencing” B-frames. An encoder sends binary information indicating whether a prediction mode is forward or not-forward for one or more macroblocks in an interlaced B-field. An encoder / decoder uses intra-coded B-fields [“BI-fields”].
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Electroluminescent device aging compensation with reference subpixels
ActiveUS8339386B2Accurate agingAccurate compensationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriver circuitElectricity
An electroluminescent (EL) device including an illumination area having one or more primary EL emitters; a reference area having a reference EL emitter; a reference driver circuit for causing the reference EL emitter to emit light while the EL device is active; a sensor for detecting light emitted by the reference EL emitter; and a measurement unit for detecting an aging-related electrical parameter of the reference EL emitter while it is emitting light. The device further includes a controller for receiving an input signal for each primary EL emitter in the illumination area, forming a corrected input signal from each input signal using the detected light and the aging-related electrical parameter, and applying the corrected input signals to the respective primary EL emitters in the illumination area.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
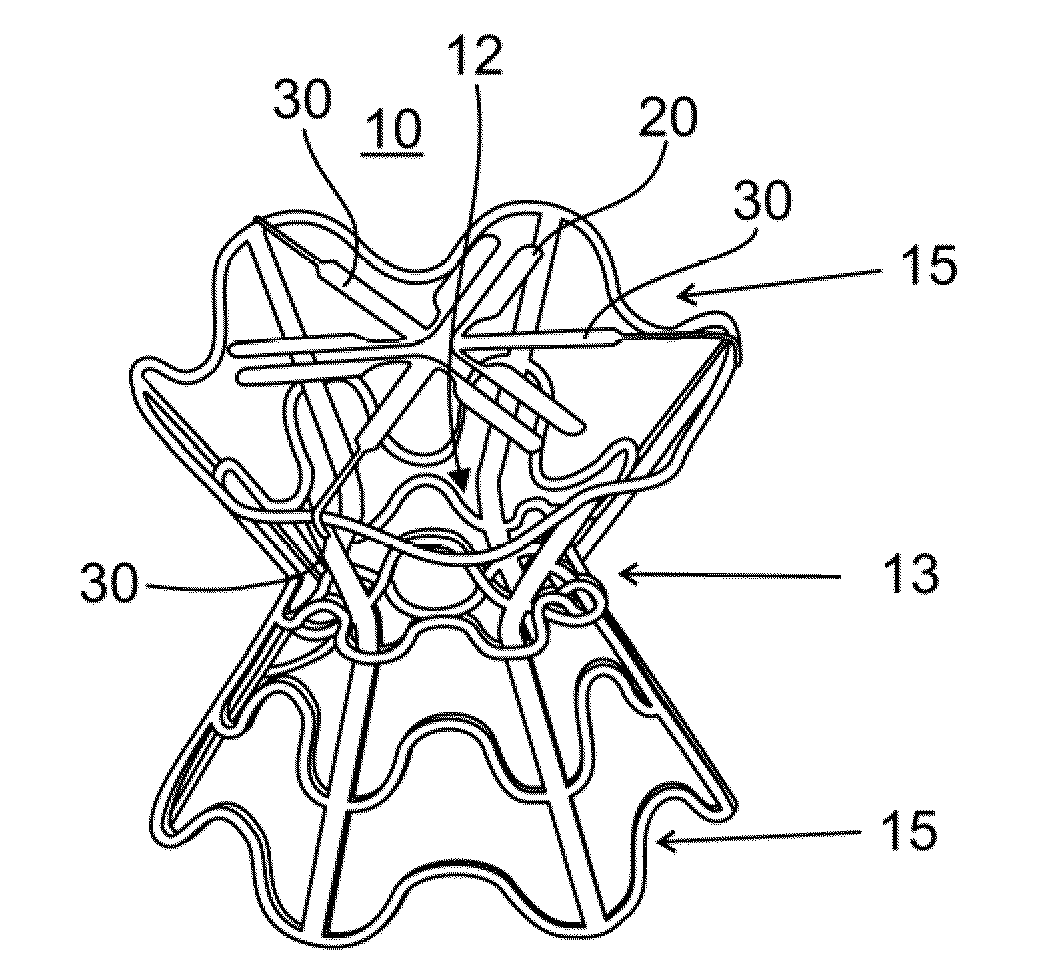
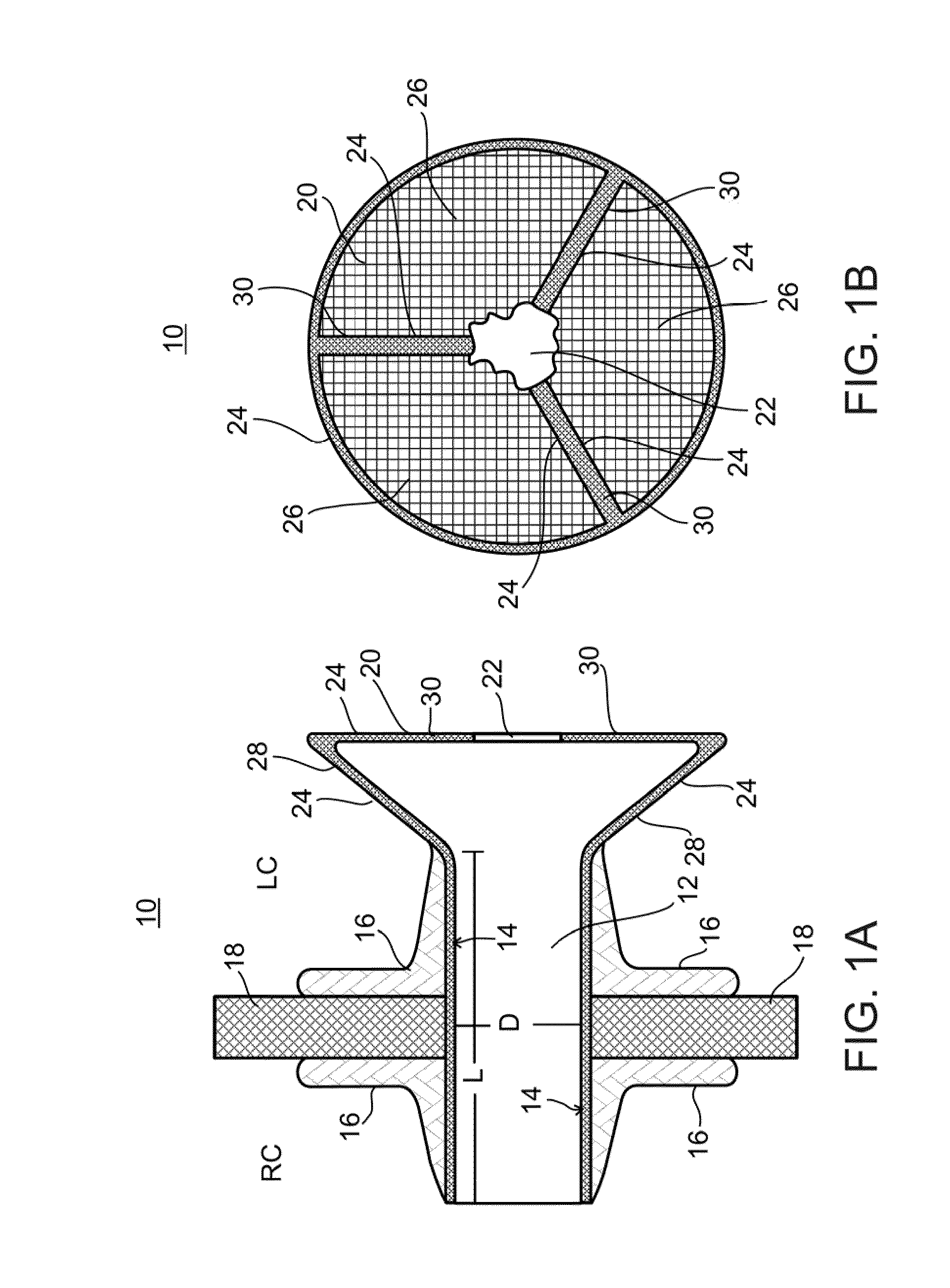
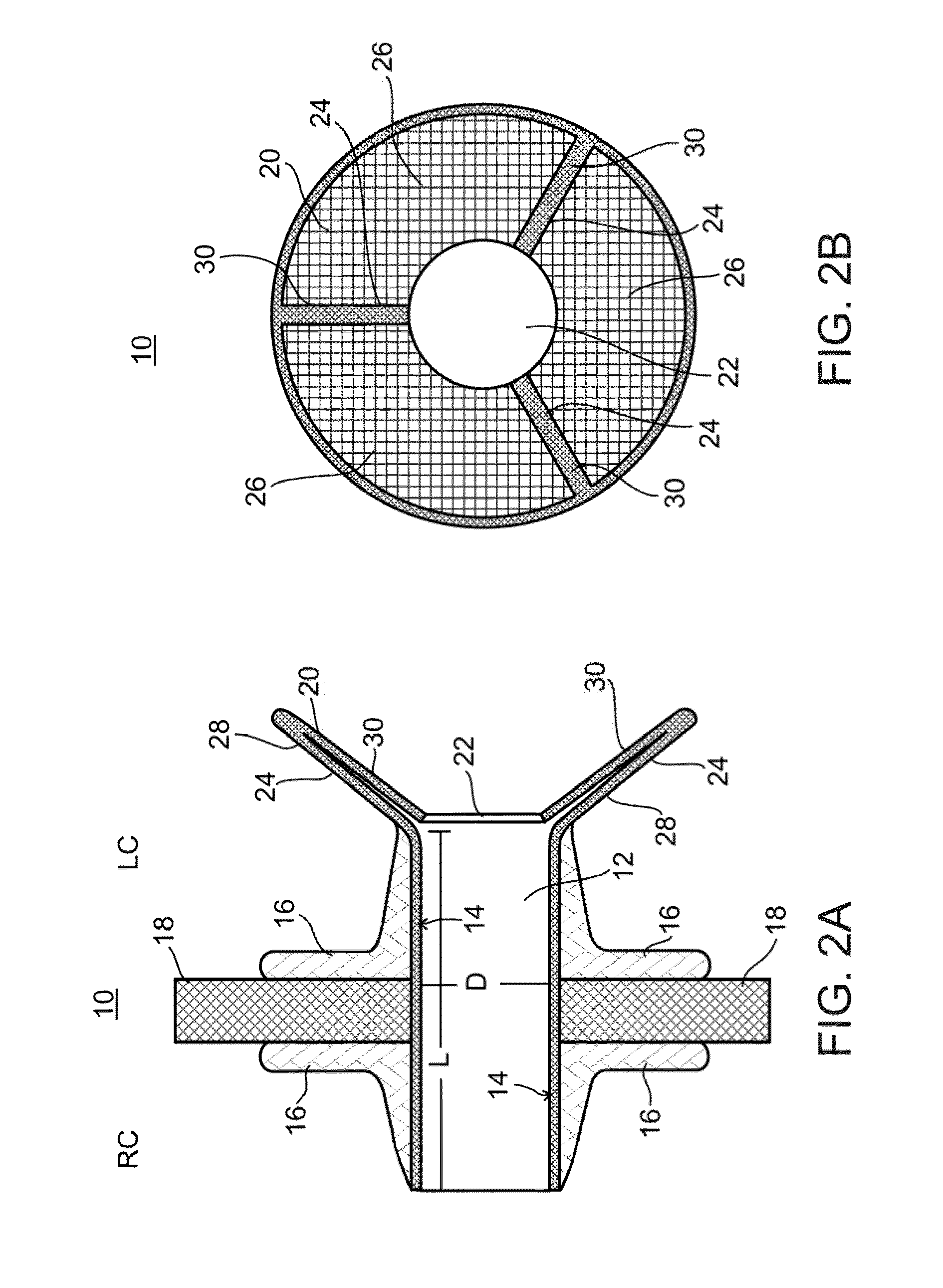
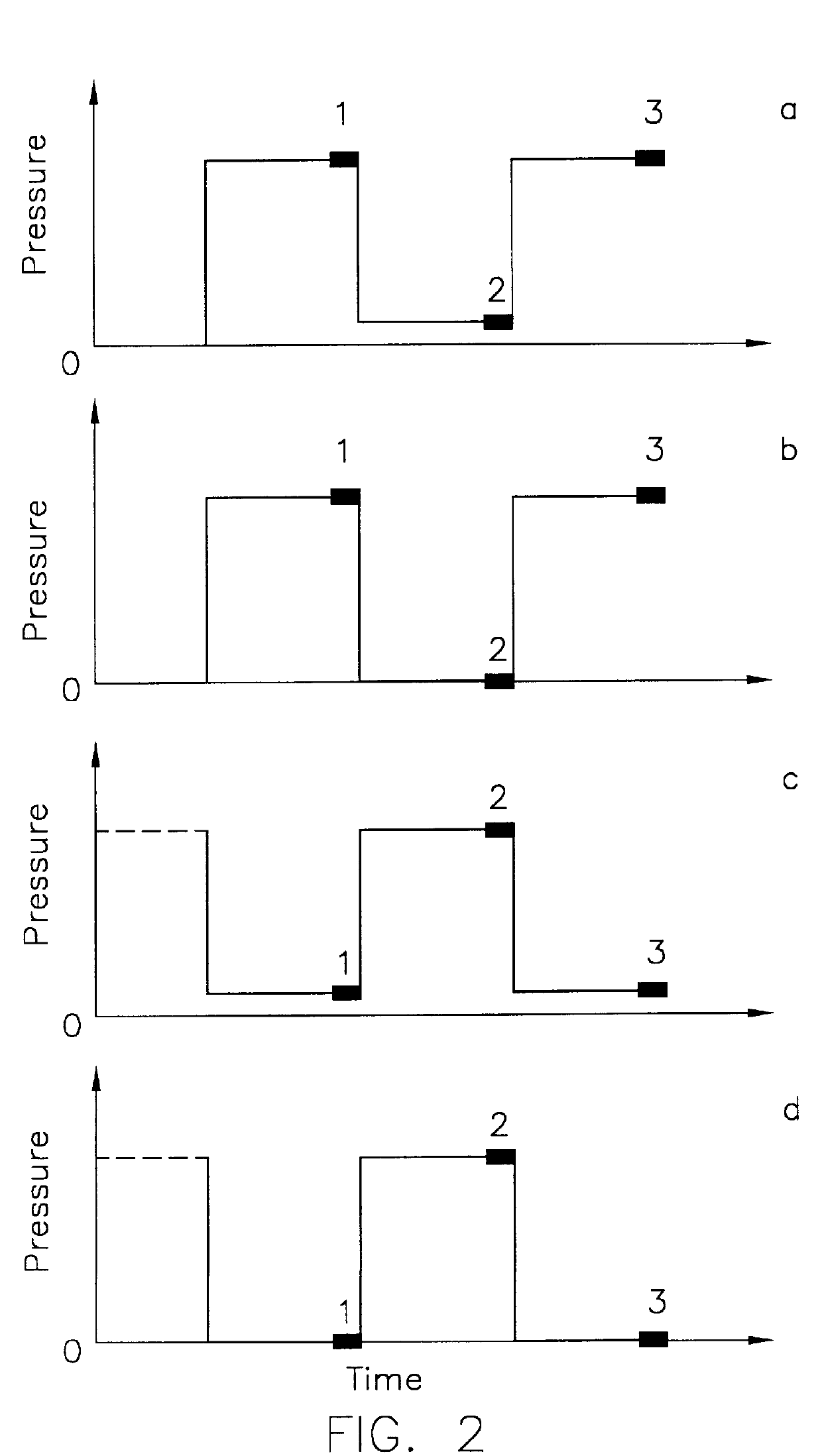
Device and method for regulating pressure in a heart chamber
A device for regulating blood pressure in a heart chamber is provided. The device includes a shunt positionable within a septum of the heart. The shunt is designed for enabling blood flow between a left heart chamber and a right heart chamber, wherein the flow rate capacity of the device is mostly a function of pressure in the left heart chamber.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
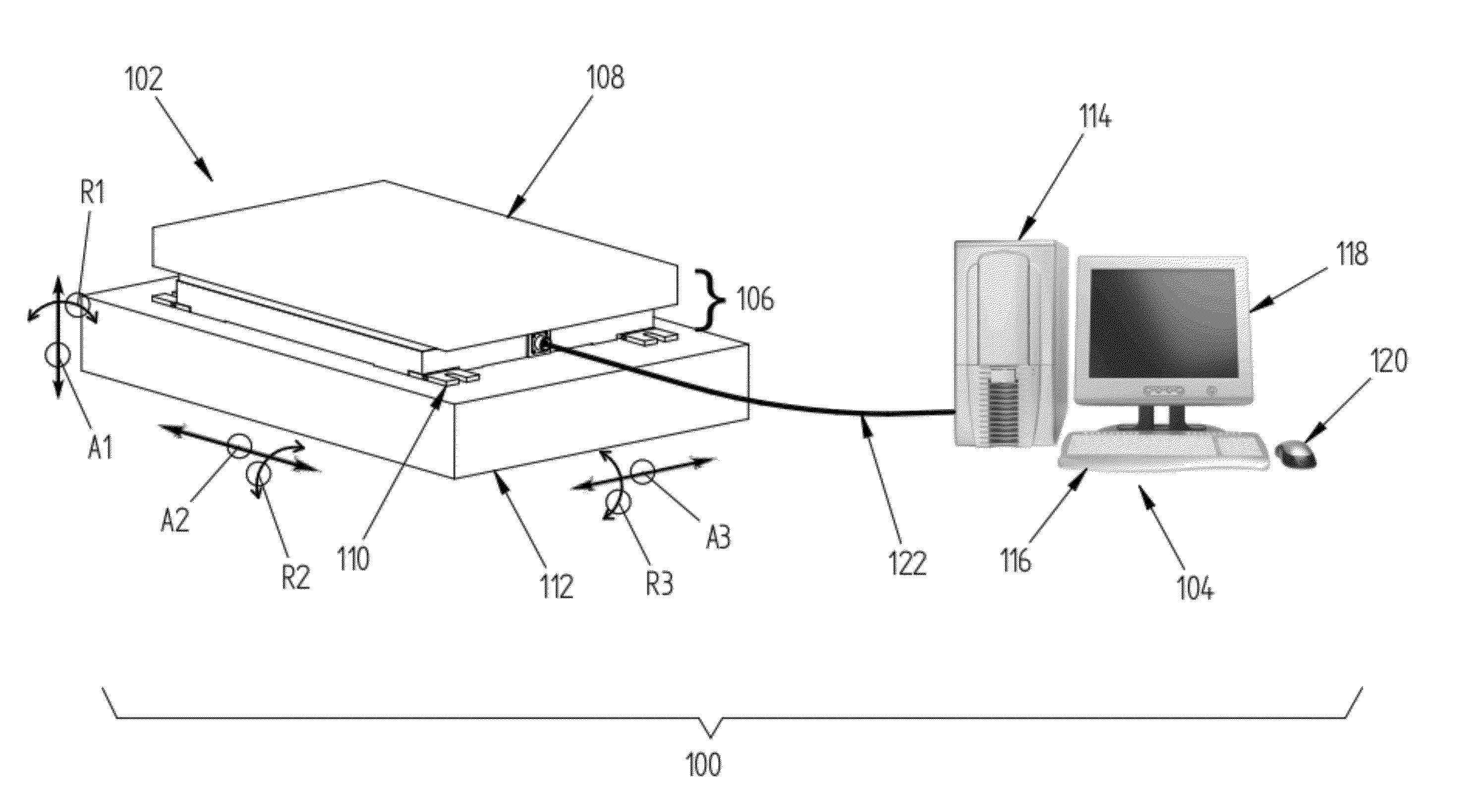
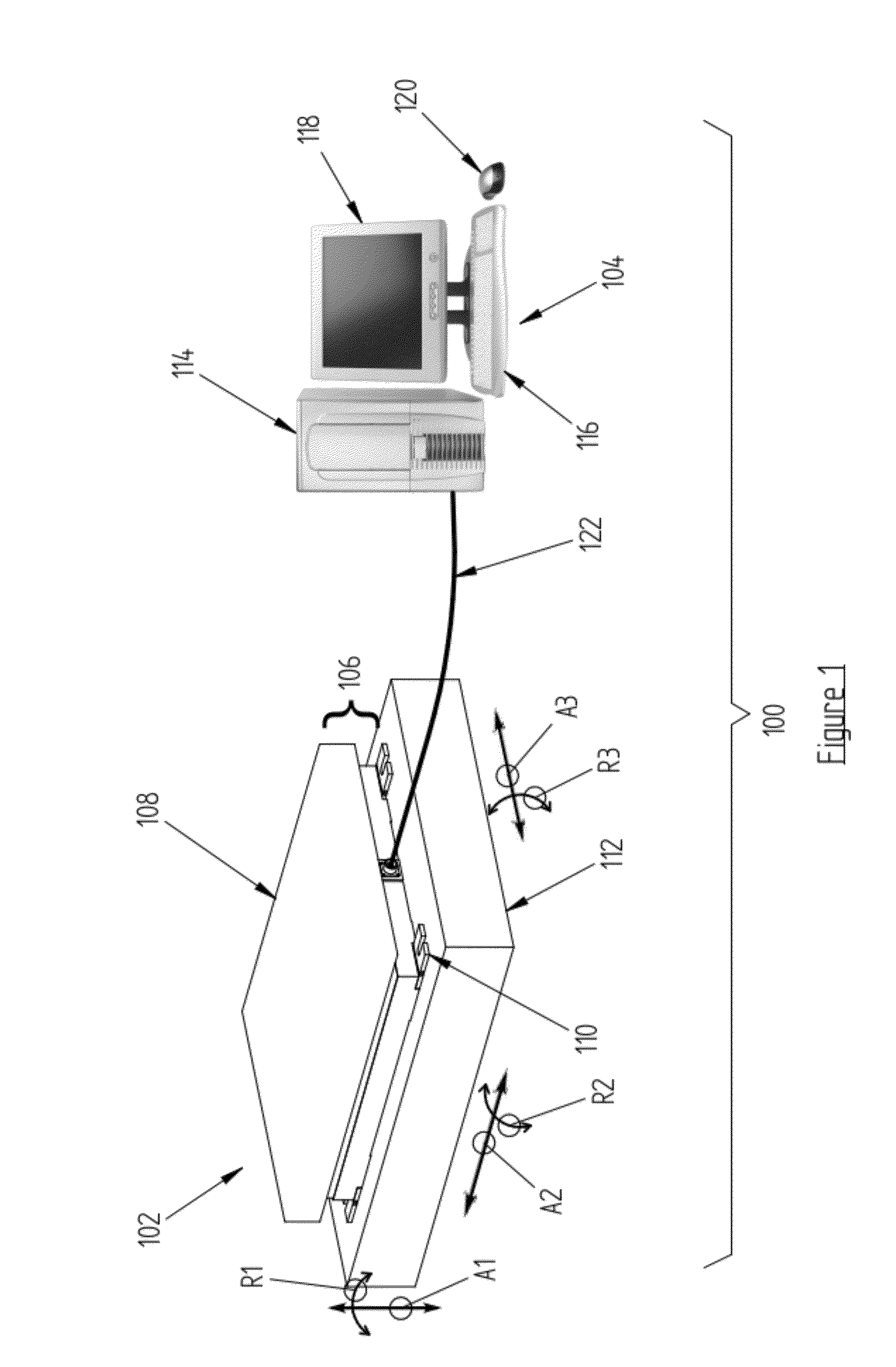
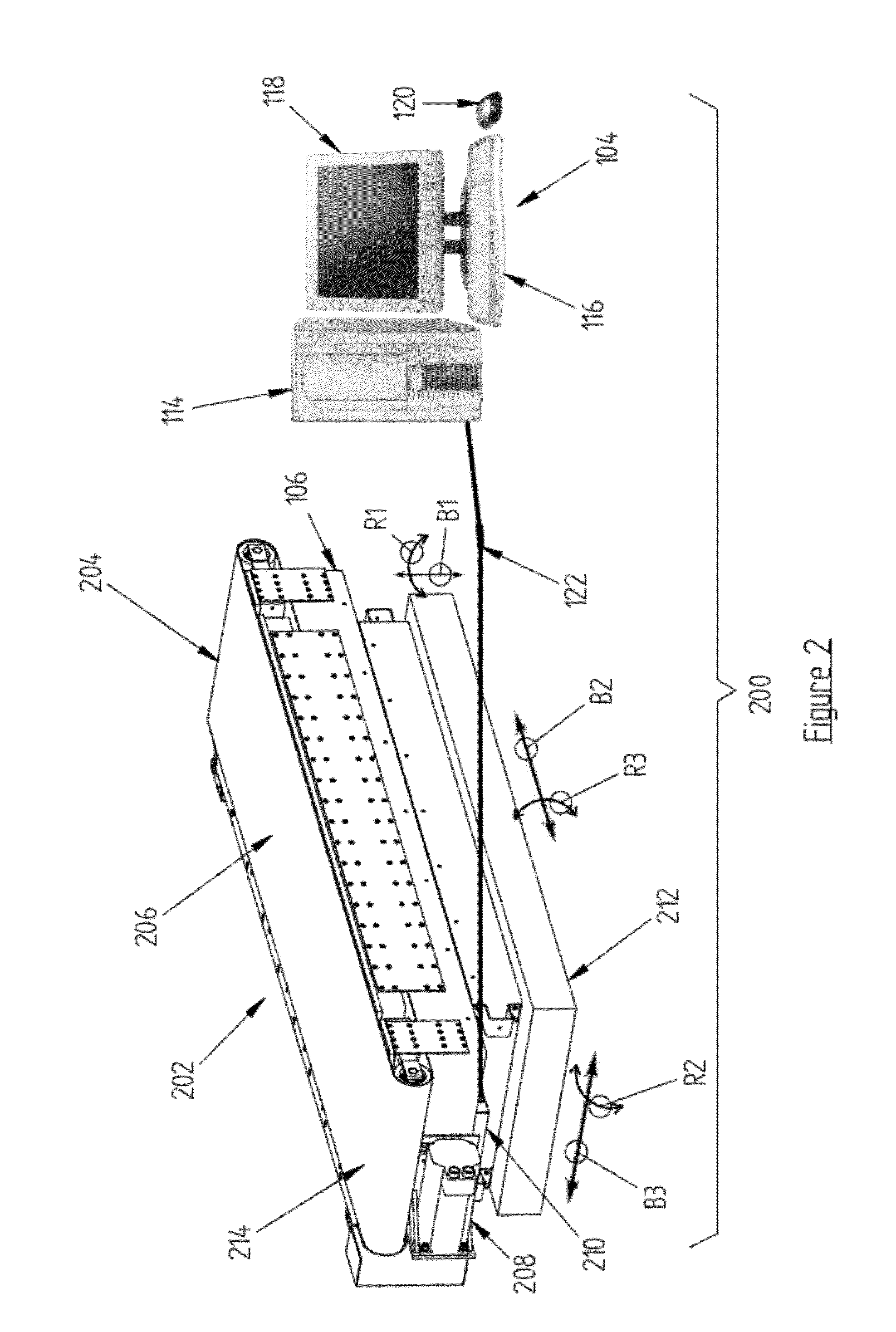
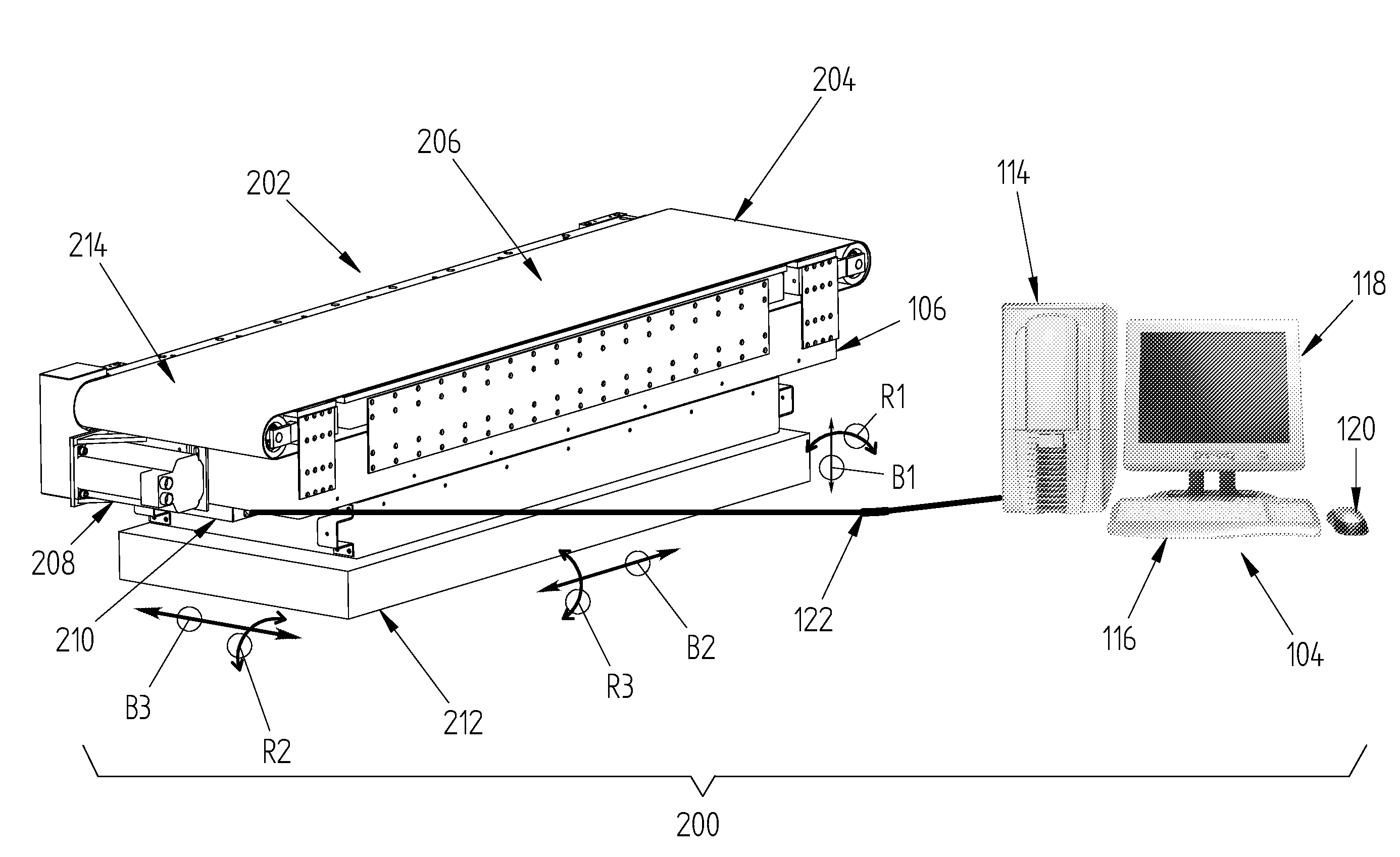
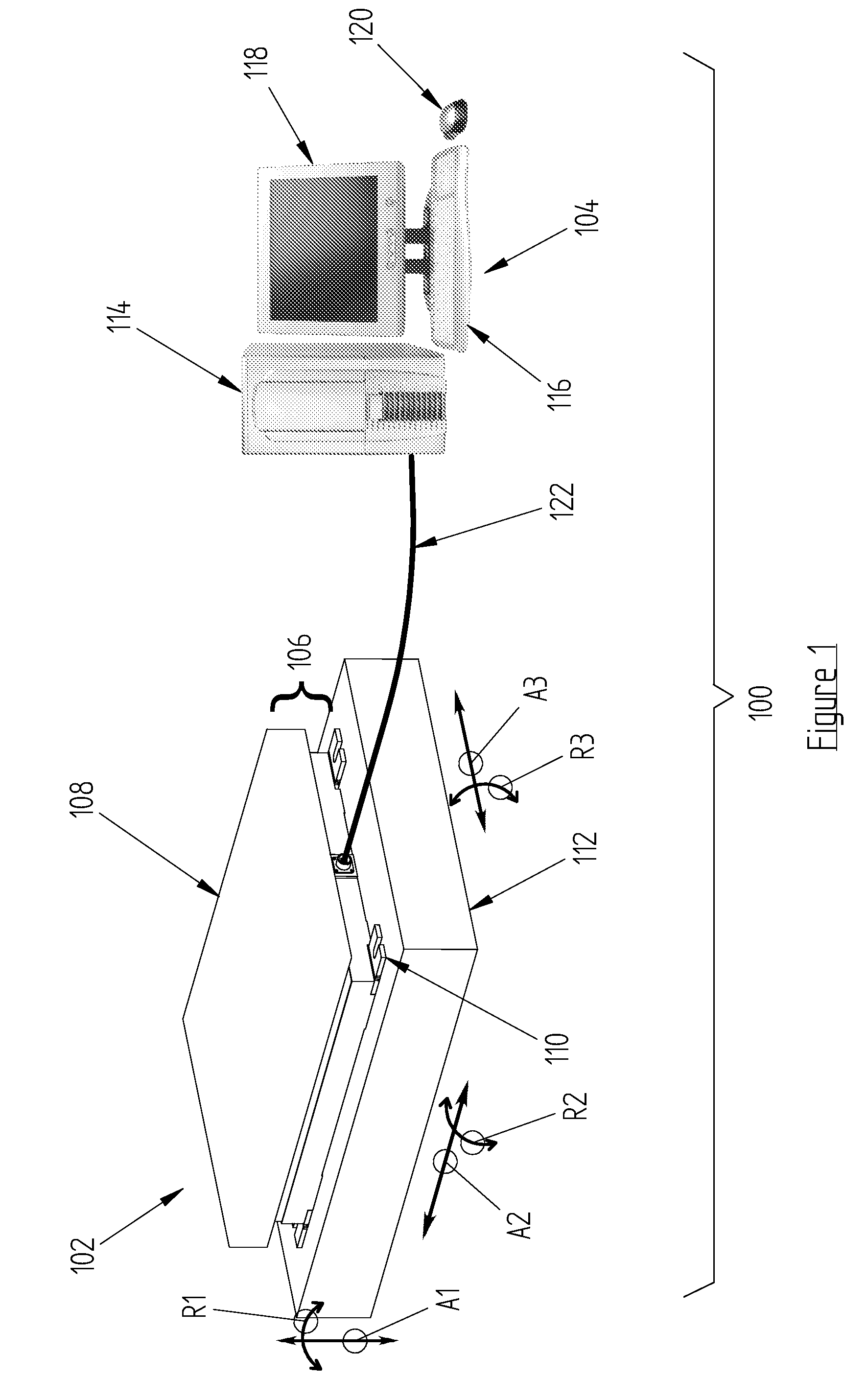
Force and/or motion measurement system having inertial compensation and method thereof
ActiveUS8315823B2Accurate compensationAccurately determineForce measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurement deviceSeries compensation
According to one aspect of the invention, a force measurement system includes a force measurement assembly, a motion base configured to displace the force measurement assembly, and an inertial compensation system configured to determine the inertial forces and / or moments resulting from the displacement of the force measurement assembly by the motion base. According to another aspect of the invention, a method for accurately determining the forces and / or moments applied to a surface of a force measurement device by a subject disposed thereon is disclosed, which includes the step of determining, by using an inertial compensation system, the inertial forces and / or moments resulting from the displacement of a force measurement assembly by a motion base. According to still another aspect of the invention, a force and / or motion measurement system having inertial compensation includes a motion acquisition system having a plurality of motion sensing devices configured to capture a subject's movement.
Owner:BERTEC
Force and/or Motion Measurement System Having Inertial Compensation and Method Thereof
ActiveUS20120266648A1Accurate compensationAccurately determineForce measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurement deviceEngineering
According to one aspect of the invention, a force measurement system includes a force measurement assembly, a motion base configured to displace the force measurement assembly, and an inertial compensation system configured to determine the inertial forces and / or moments resulting from the displacement of the force measurement assembly by the motion base. According to another aspect of the invention, a method for accurately determining the forces and / or moments applied to a surface of a force measurement device by a subject disposed thereon is disclosed, which includes the step of determining, by using an inertial compensation system, the inertial forces and / or moments resulting from the displacement of a force measurement assembly by a motion base. According to still another aspect of the invention, a force and / or motion measurement system having inertial compensation includes a motion acquisition system having a plurality of motion sensing devices configured to capture a subject's movement.
Owner:BERTEC
Force Measurement System Having Inertial Compensation
ActiveUS20120271565A1Accurate force measurementAccurate compensationForce measurementInertial sensorsAccelerometerAngular velocity
A force measurement system having inertial compensation includes a force measurement assembly with at least one accelerometer configured to measure the acceleration thereof. According to one aspect of the invention, the force measurement system additionally includes at least one angular velocity sensor configured to measure the angular velocity of the force measurement assembly. According to another aspect of the invention, the force measurement system additionally includes a data processing device with a computer-readable medium loaded thereon that is configured to execute a calibration procedure for determining the inertial parameters of the force measurement assembly by utilizing the measured acceleration of the force measurement assembly while the force measurement assembly is subjected to a plurality of applied linear and / or rotational motion profiles. According to still another aspect of the invention, the at least one accelerometer is disposed on the force transducer.
Owner:BERTEC
Method and an apparatus for monitoring and controlling flows
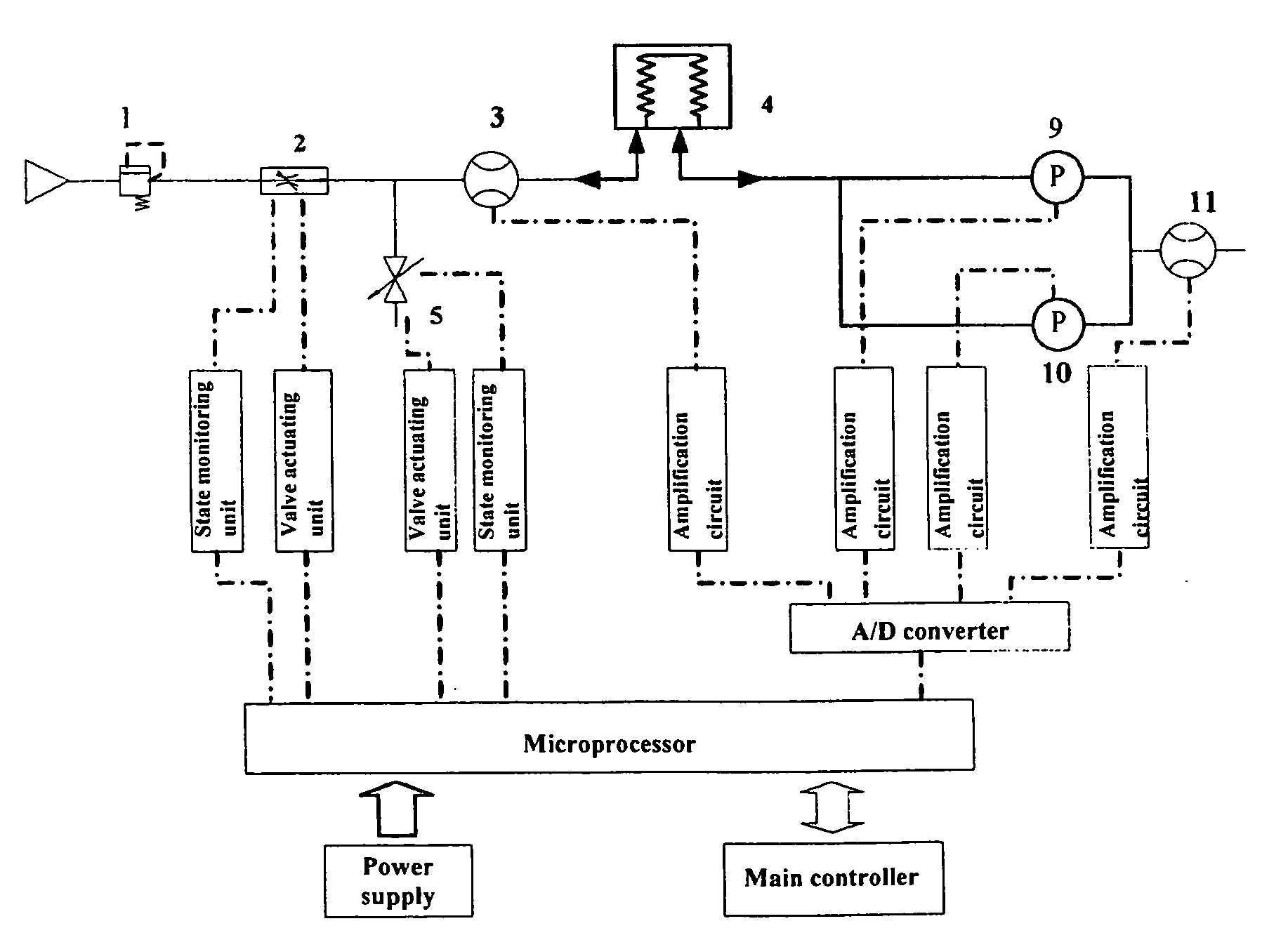
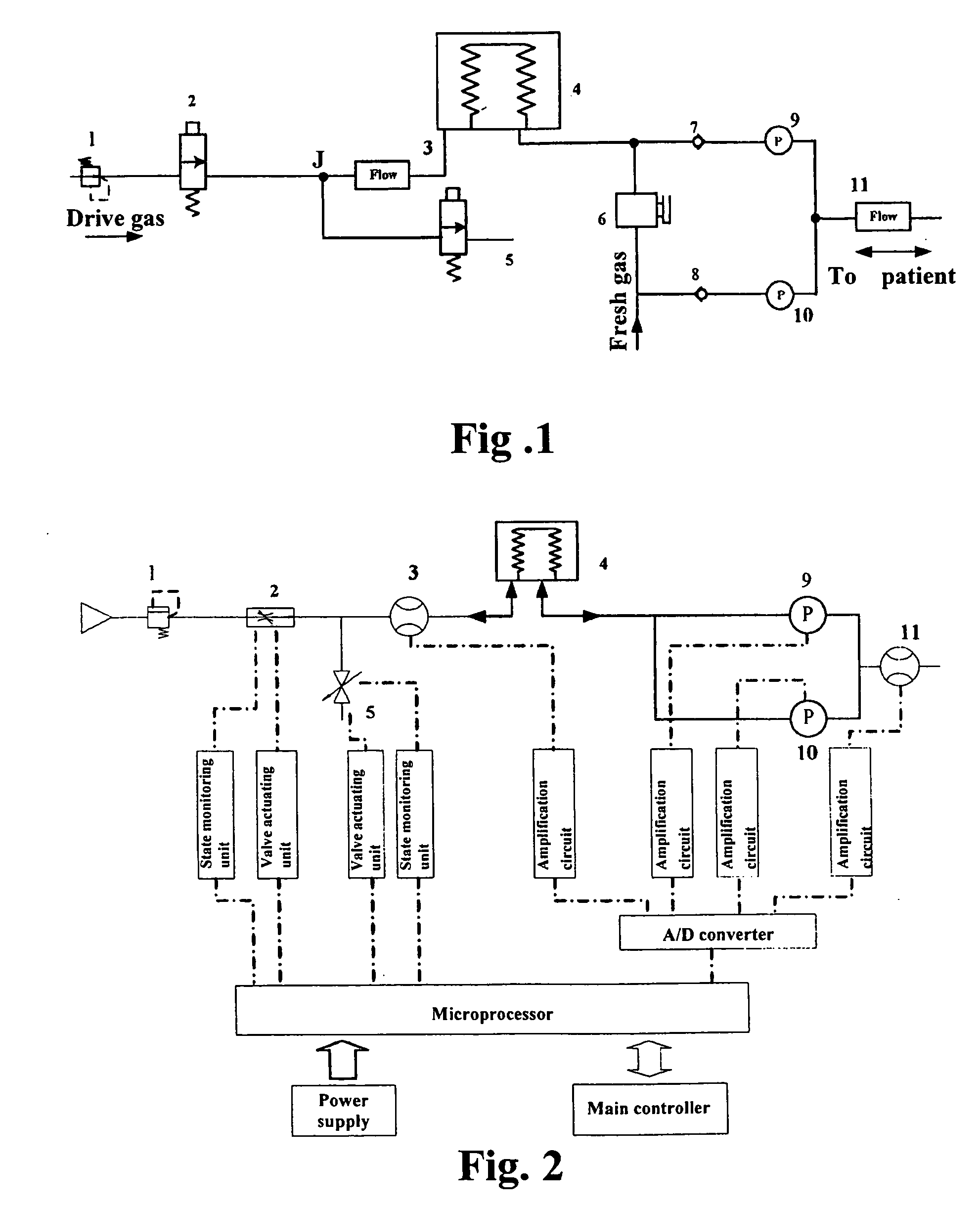
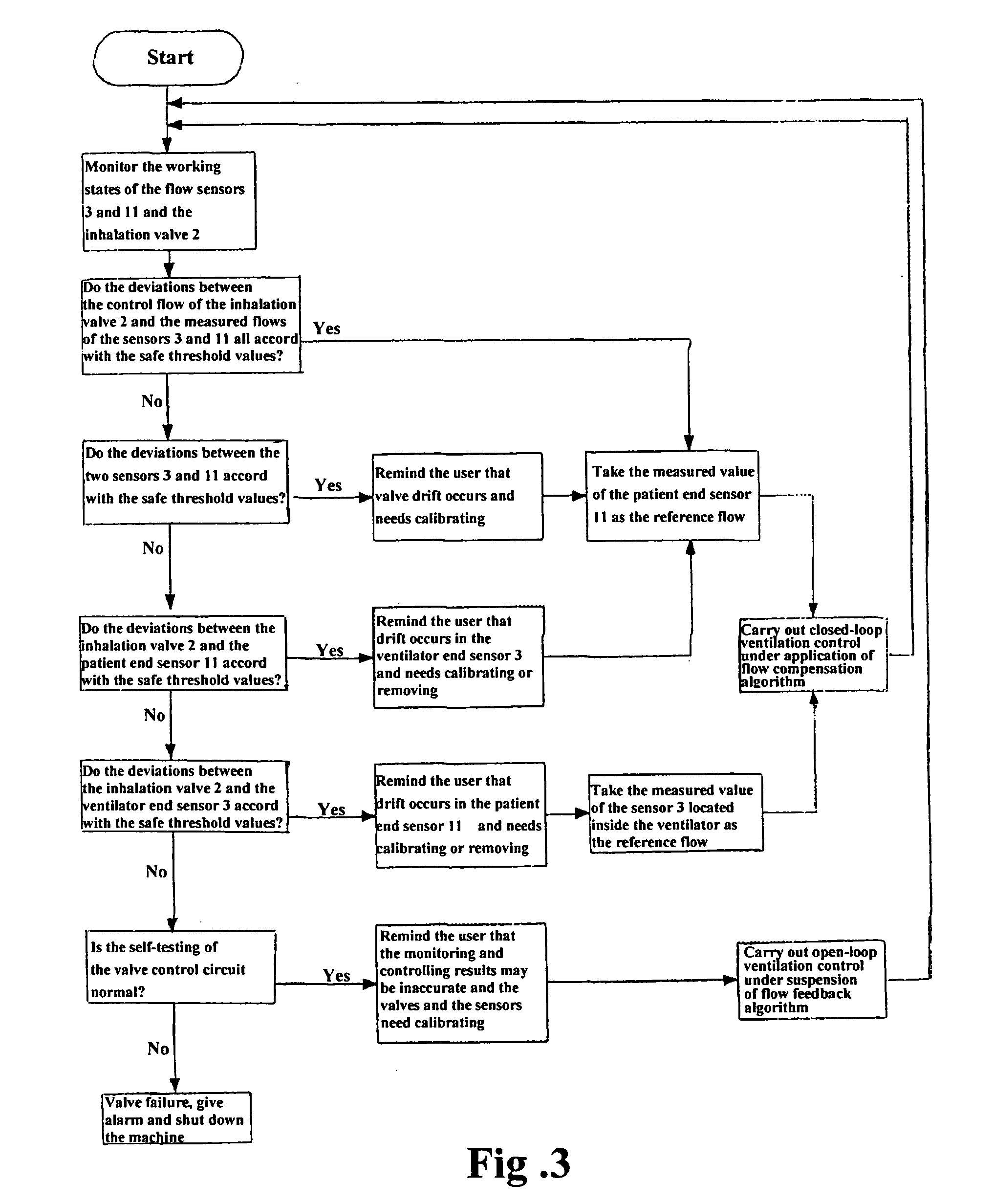
ActiveUS20070163579A1Accurate flow monitoringEasy to controlRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExpired gasVALVE PORT
A method and an apparatus for monitoring and controlling flows in medical equipment including an anesthetic machine and a ventilator for influencing a patient's respiratory system are disclosed. The apparatus comprises a microprocessor and an airway system comprising drive gas conduits provided with an inhalation valve (2) and an exhalation valve (5) for gas discharging as well as a ventilator end flow sensor (3) for measuring the introduced or discharged drive gas flow through the valves. The airway system also comprises patient end breathing tubing in which a patient end flow sensor (11) for measuring the patient's inspired and expired gas flow is provided. By comparing the measured values of the two flow sensors against the characteristic curve of the inhalation valve (2), the microprocessor can judge the operation states and accuracy of the respective flow sensors and the inhalation valve (2).
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
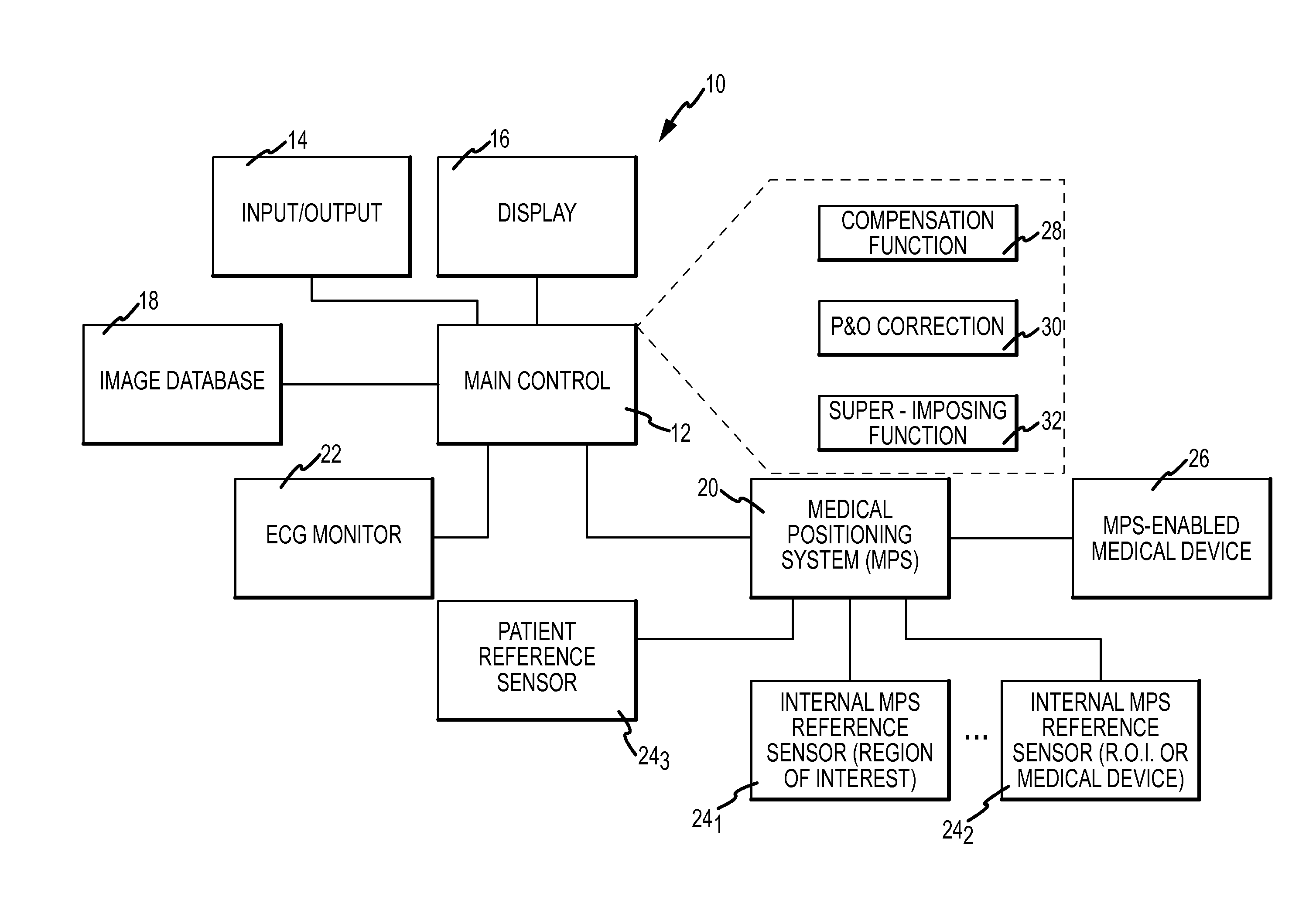
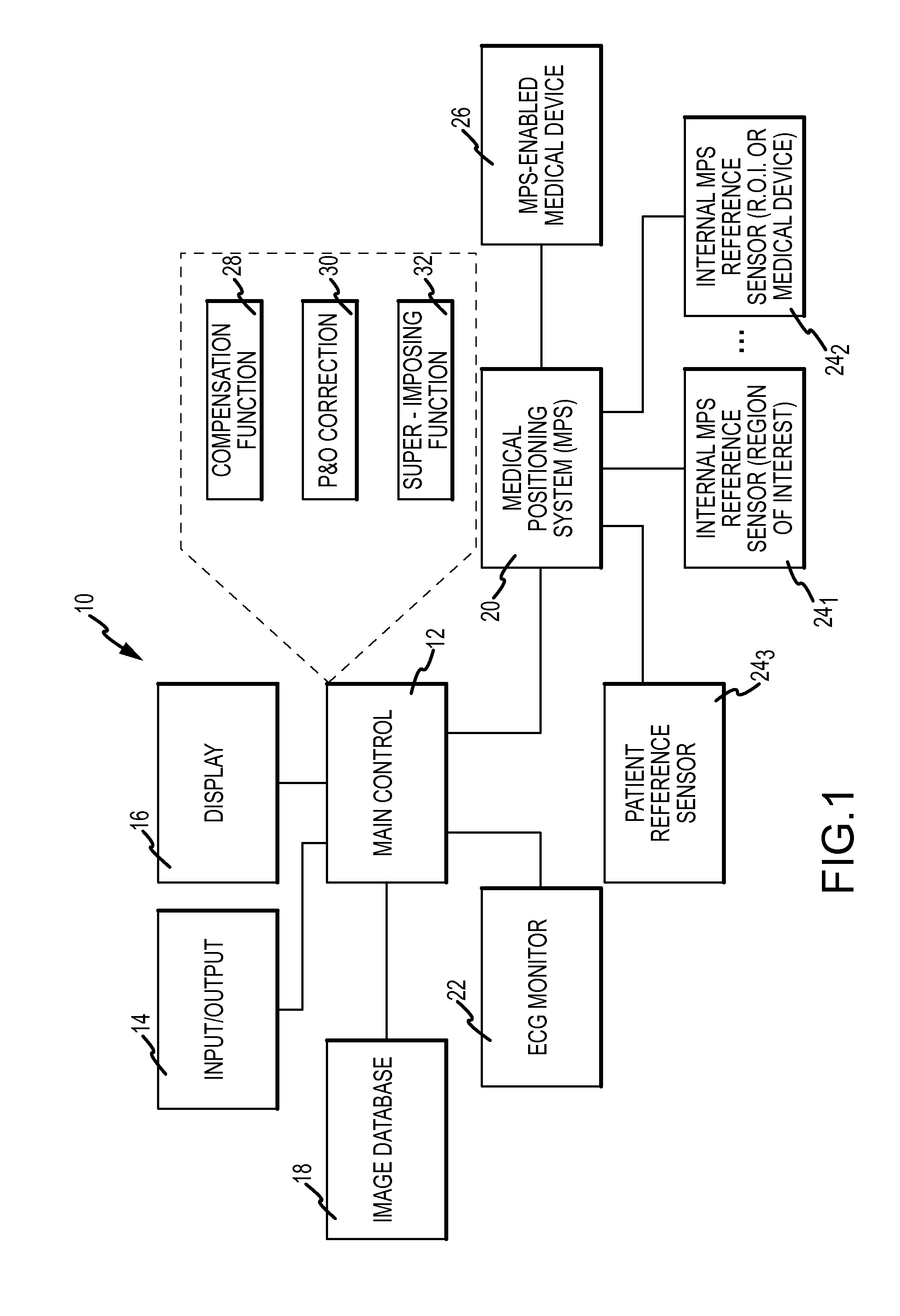
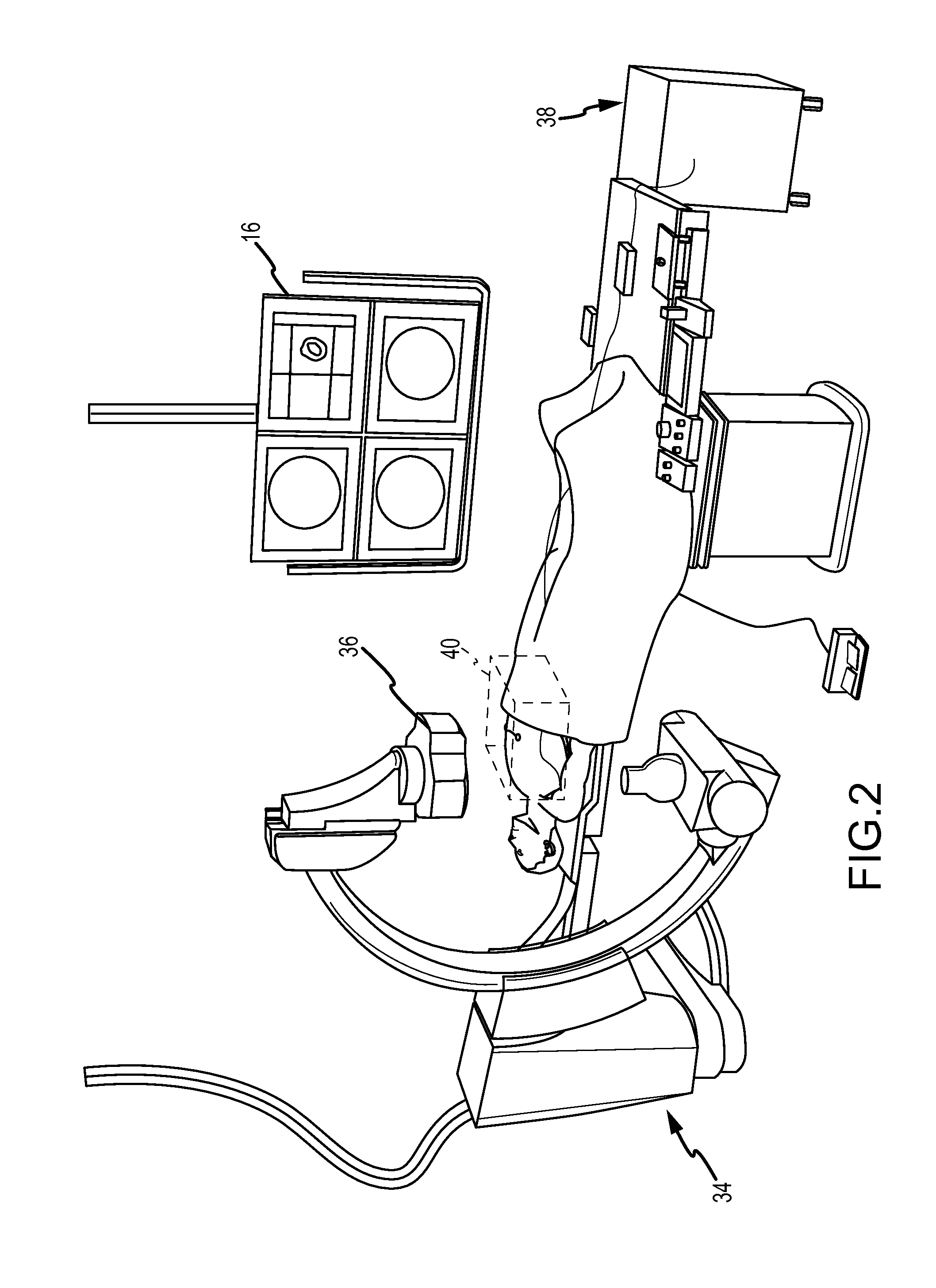
Compensation of motion in a moving organ using an internal position reference sensor
ActiveUS20110158488A1Reduce motion errorsAccurate compensationImage enhancementImage analysisMedical deviceComputer science
An apparatus for displaying a moving region of interest located within a body includes a positioning system to determine a position and orientation (P&O) of a medical device as well as to track, using an internal position reference sensor, the motion of the region of interest over time. A compensation function block generates a motion compensation function based on the motion of the region of interest, which is configured to compensate for the motion of the region of interest between a first time, for example a time at which an image was acquired and a second time, for example a time at which a P&O of the device was measured. The measured P&O is corrected using the compensation function. A representation of the medical device is superimposed on the image in accordance with the corrected P&O.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Force measurement system having inertial compensation
ActiveUS8315822B2Accurate compensationAccurate force measurementForce measurementInertial sensorsAccelerometerAngular velocity
A force measurement system having inertial compensation includes a force measurement assembly with at least one accelerometer configured to measure the acceleration thereof. According to one aspect of the invention, the force measurement system additionally includes at least one angular velocity sensor configured to measure the angular velocity of the force measurement assembly. According to another aspect of the invention, the force measurement system additionally includes a data processing device with a computer-readable medium loaded thereon that is configured to execute a calibration procedure for determining the inertial parameters of the force measurement assembly by utilizing the measured acceleration of the force measurement assembly while the force measurement assembly is subjected to a plurality of applied linear and / or rotational motion profiles. According to still another aspect of the invention, the at least one accelerometer is disposed on the force transducer.
Owner:BERTEC
Device and method for regulating pressure in a heart chamber
A device for regulating blood pressure in a heart chamber is provided. The device includes a shunt positionable within a septum of the heart. The shunt is designed for enabling blood flow between a left heart chamber and a right heart chamber, wherein the flow rate capacity of the device is mostly a function of pressure in the left heart chamber.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
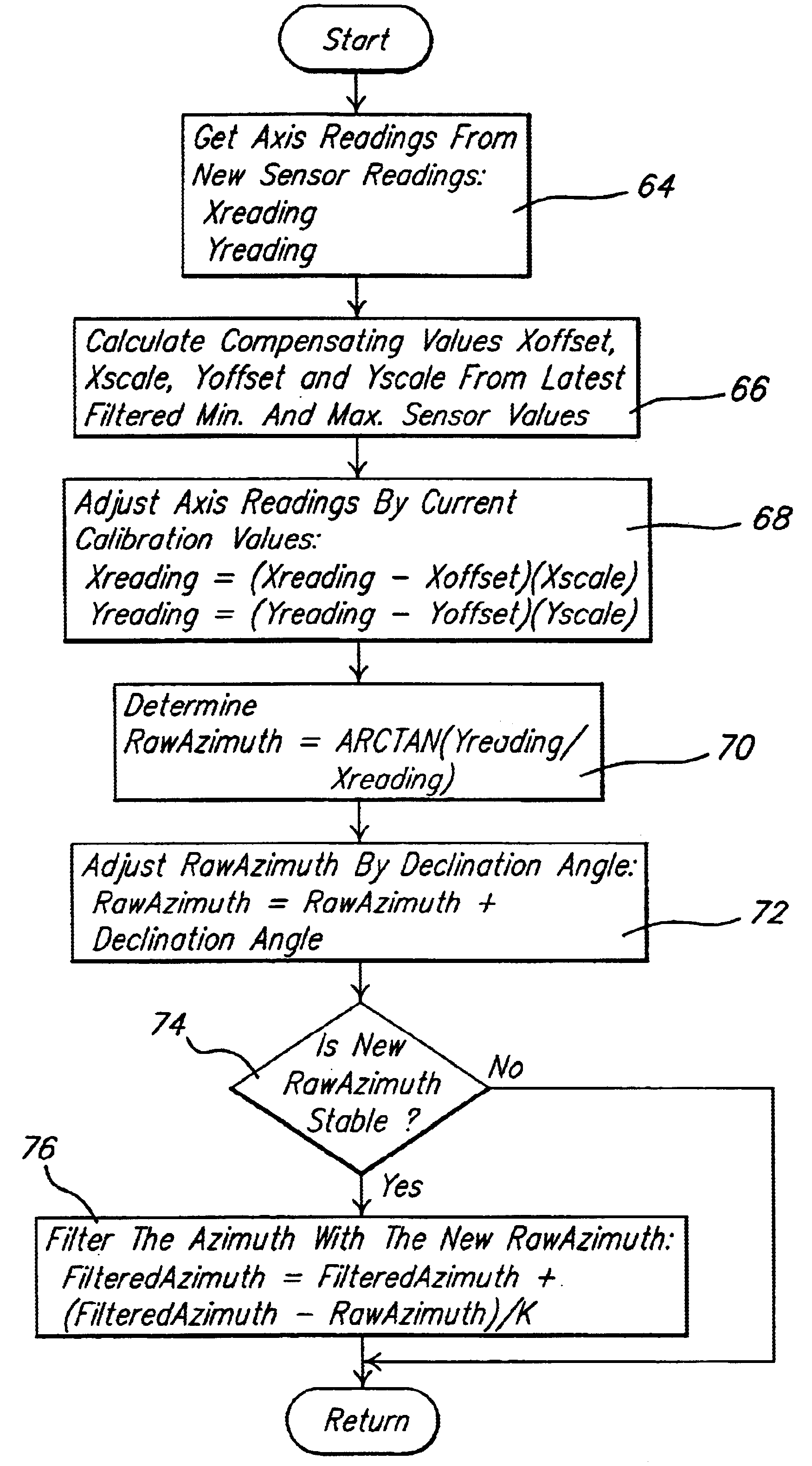
Method of automatic continuous calibration for an electronic compass
InactiveUS6651003B2Accurate compensationAdaptableInstruments for road network navigationTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesComputer visionArtificial intelligence
Owner:INNOVATIVE DESIGN SOLUTIONS
Feedback control method for a heliostat
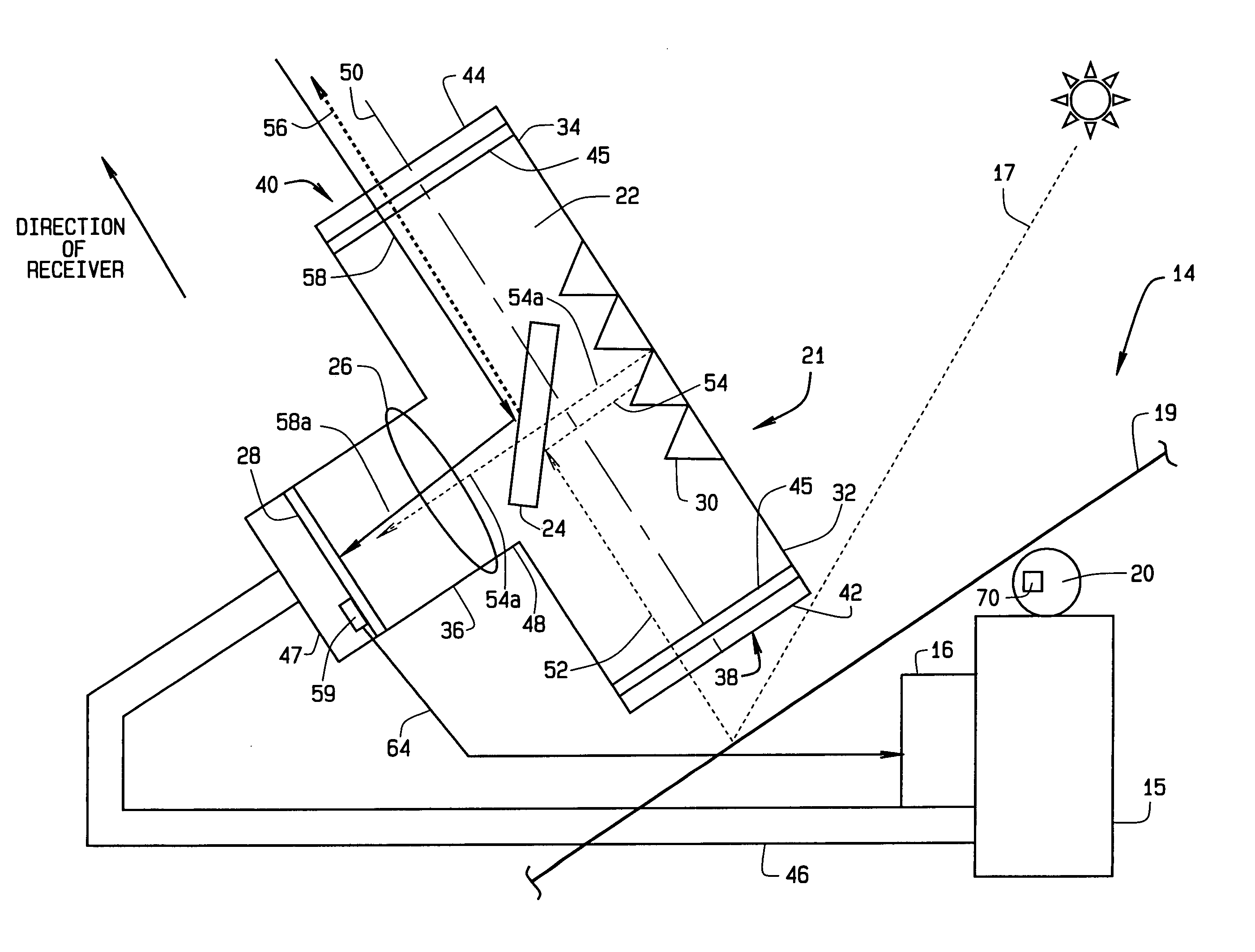
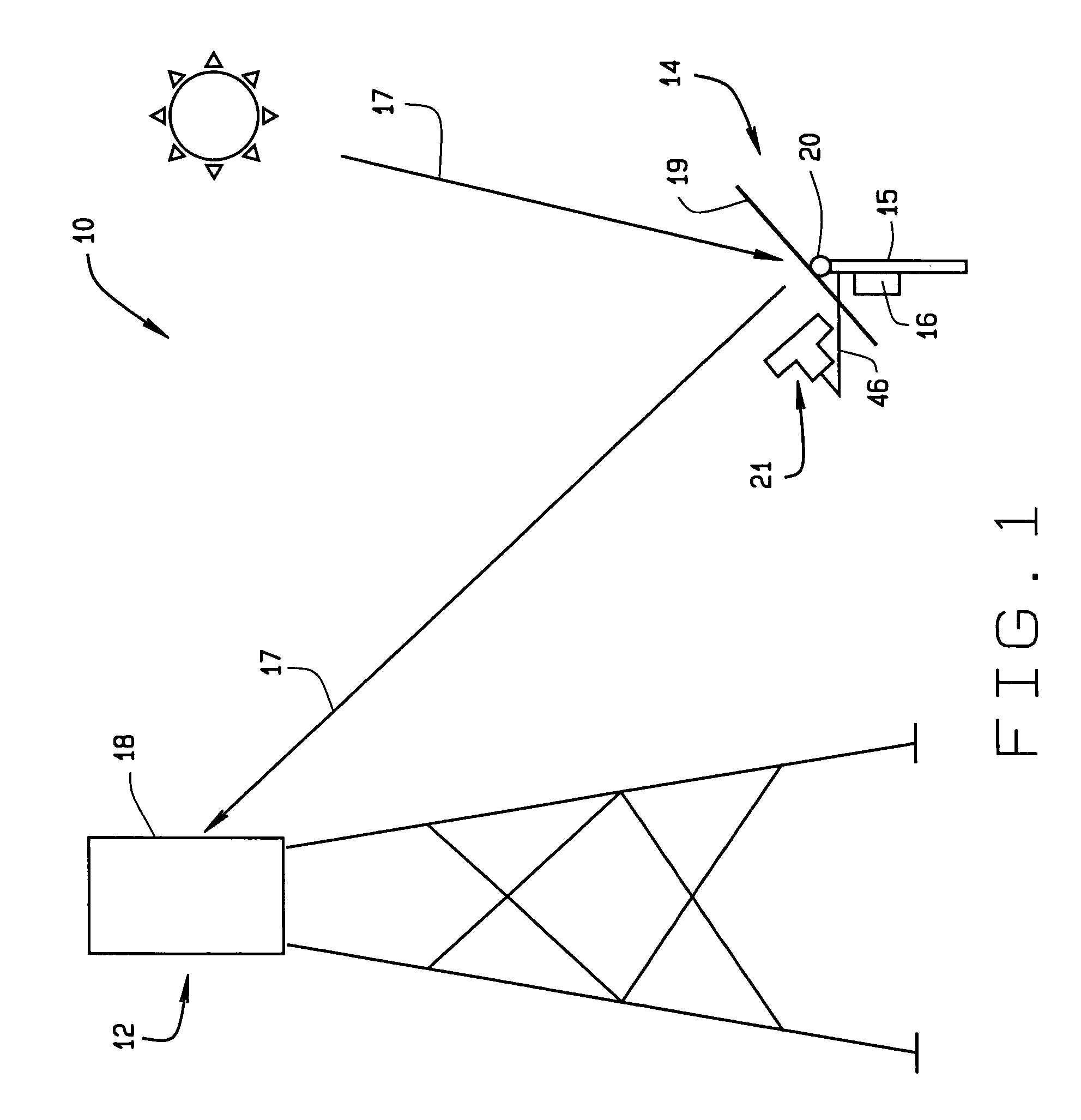
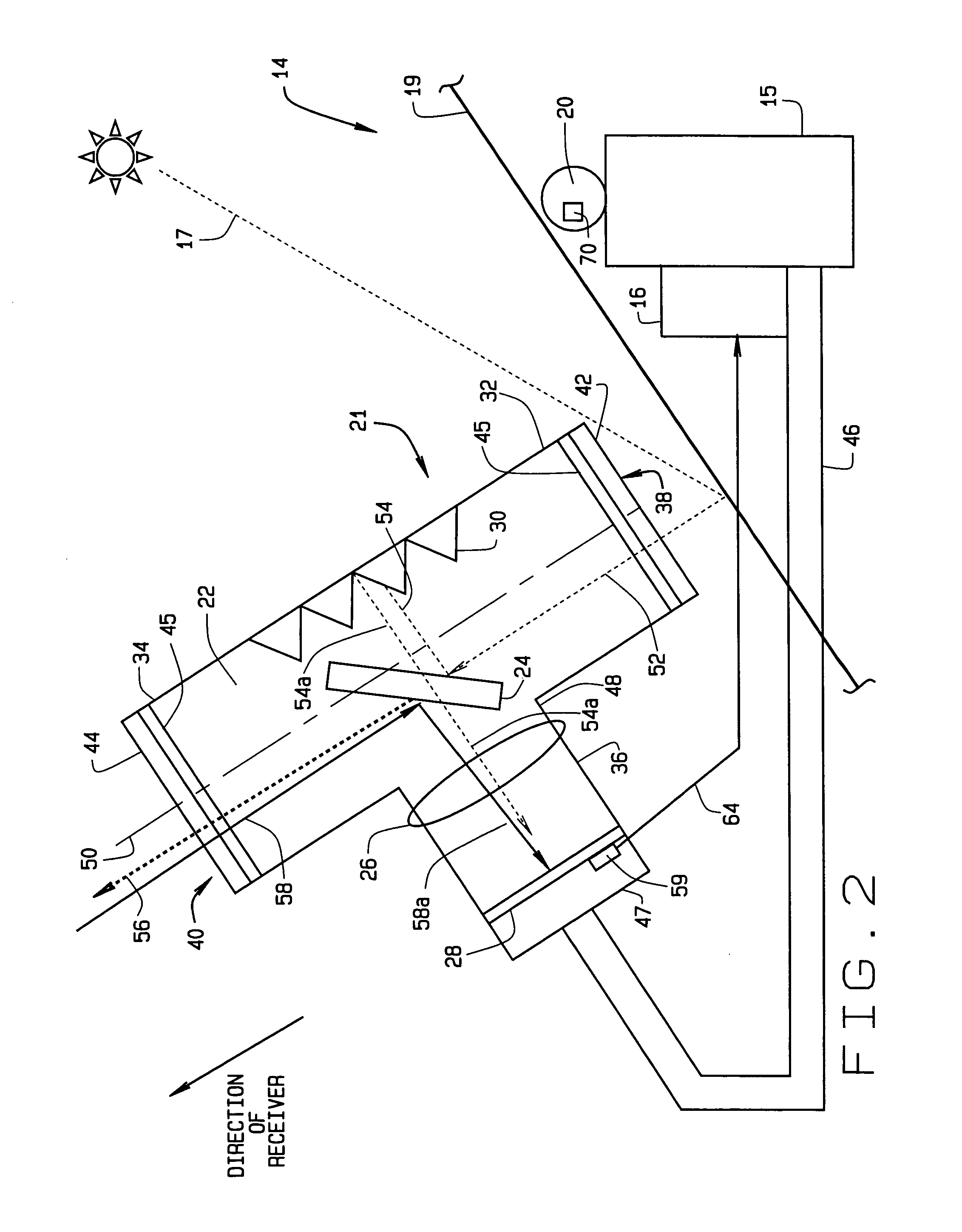
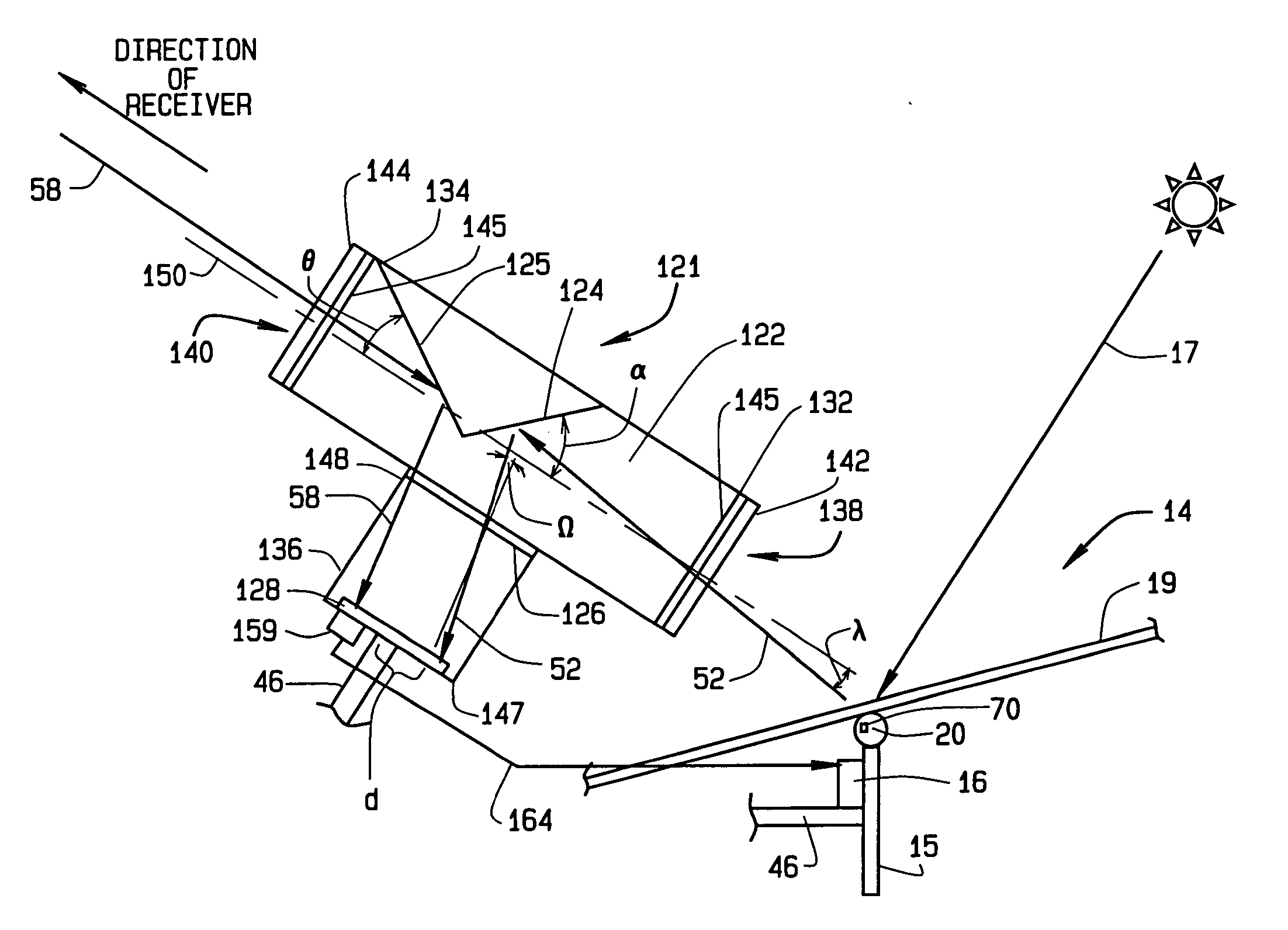
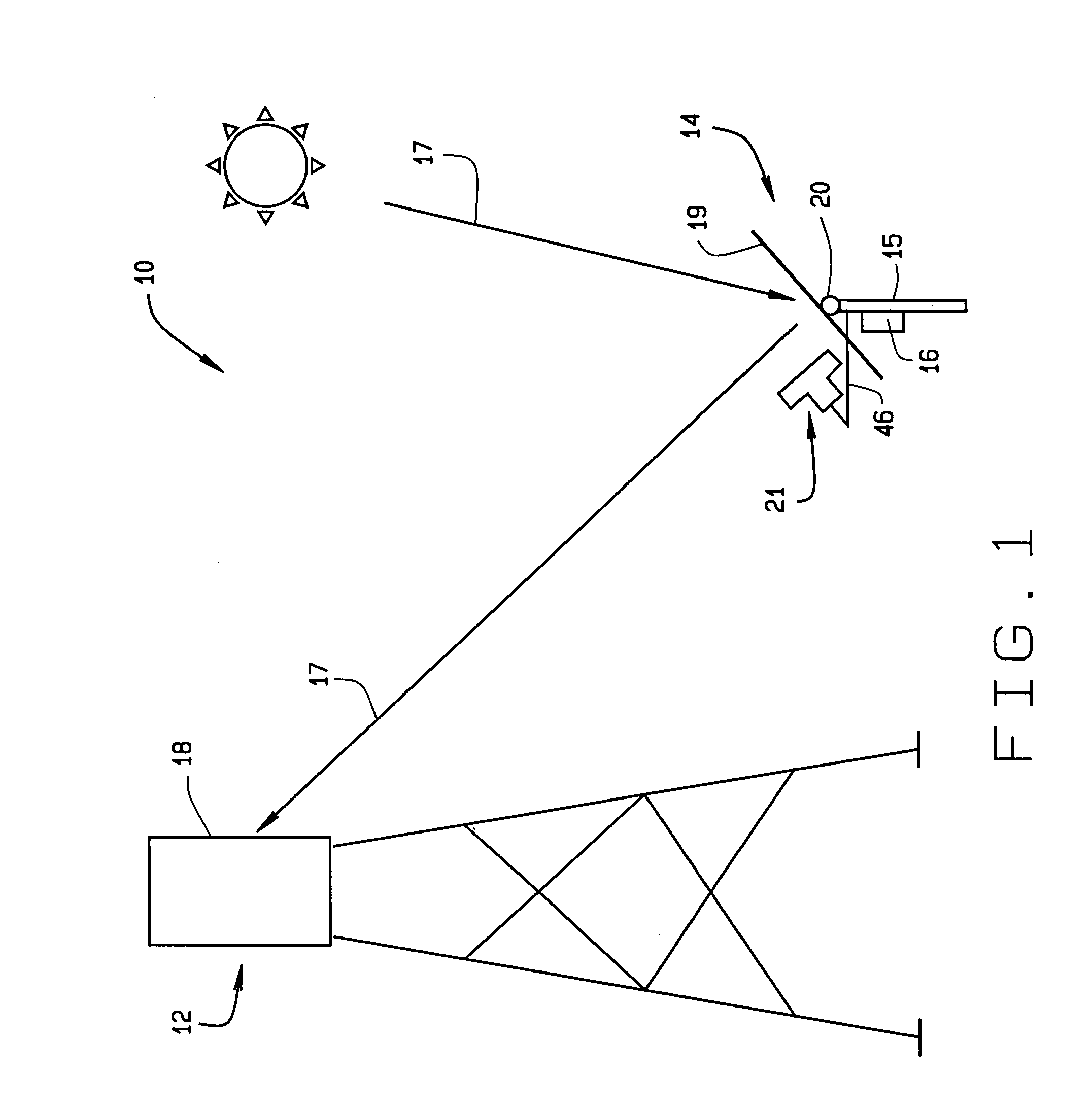
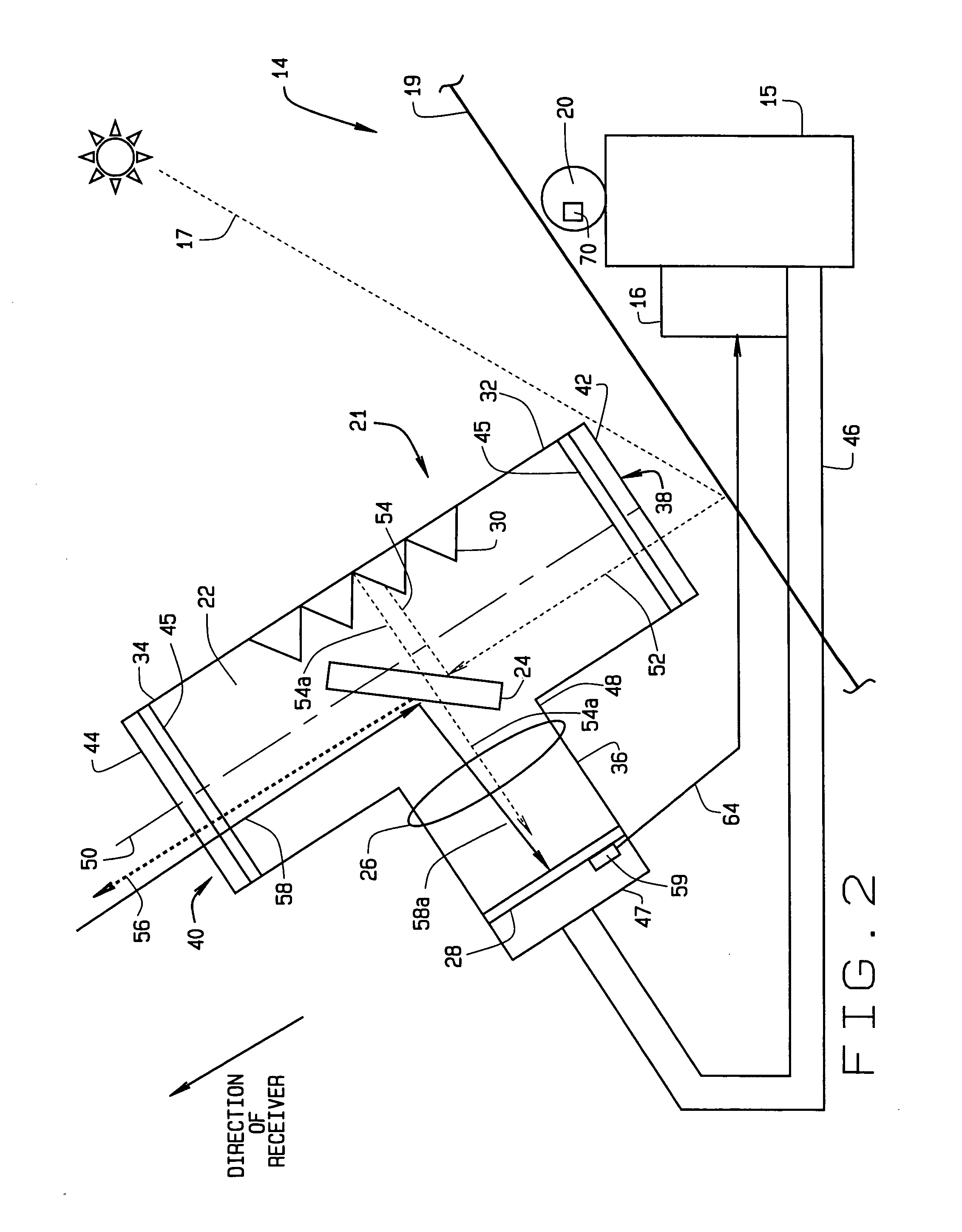
InactiveUS7207327B2Accurately reflectImprove pointing accuracySolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueHeliostatEngineering
An instrument for a solar energy system including a receiver and a heliostat to reflect solar energy on to the receiver. The instrument includes a first element adapted to form an image of the sun, a second element adapted to form an image of the receiver, and a detector. The detector is positioned to receive each of the images and a comparator is adapted to detect a distance between the images. The comparator generates an error correction signal based on the distance between the images. The error correction signal is received by a controller that controls the operation of a postioner that adjusts the position of the heliostat accordingly.
Owner:SOLARRESERVE TECH +1
Unit circuit, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
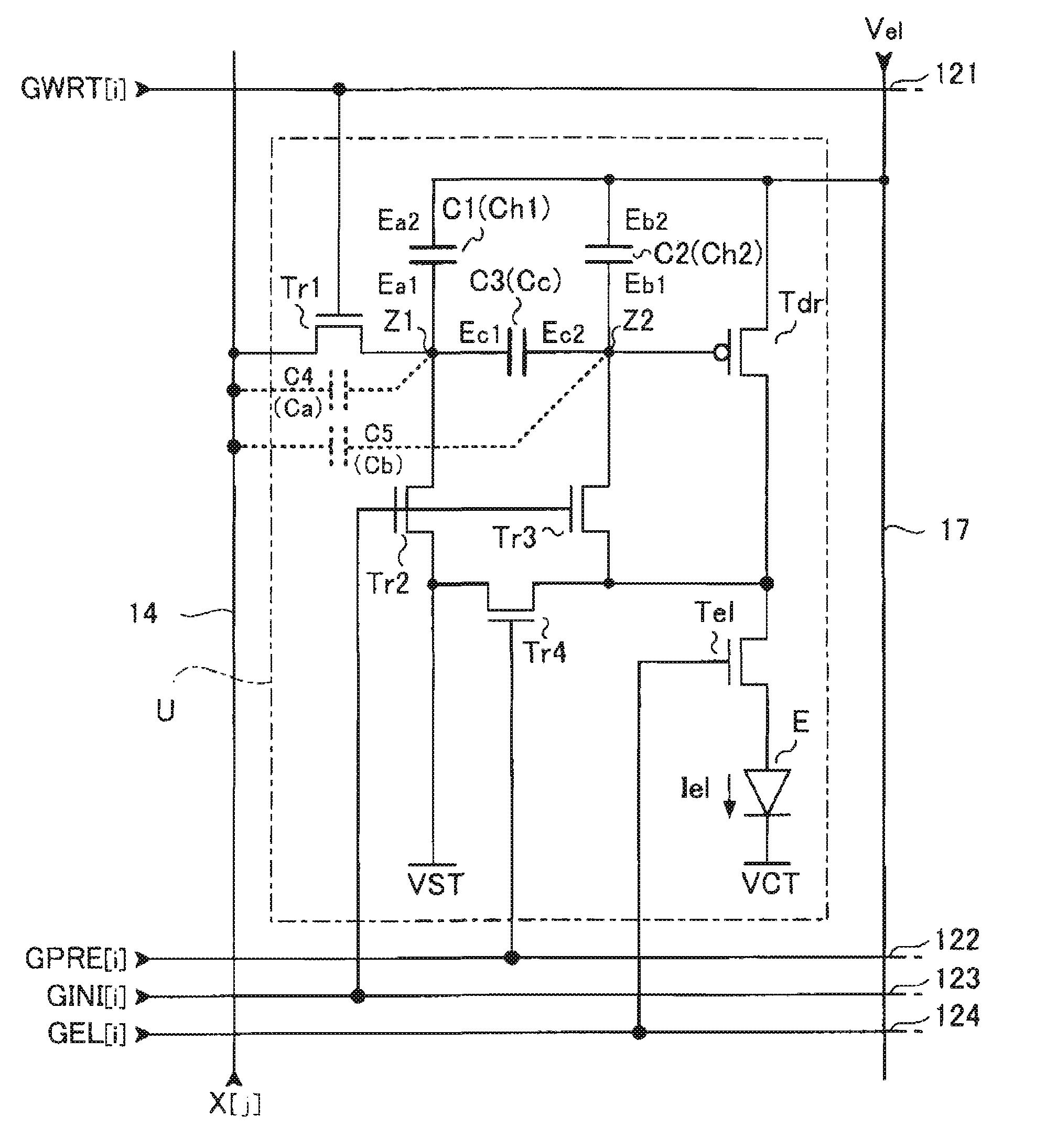
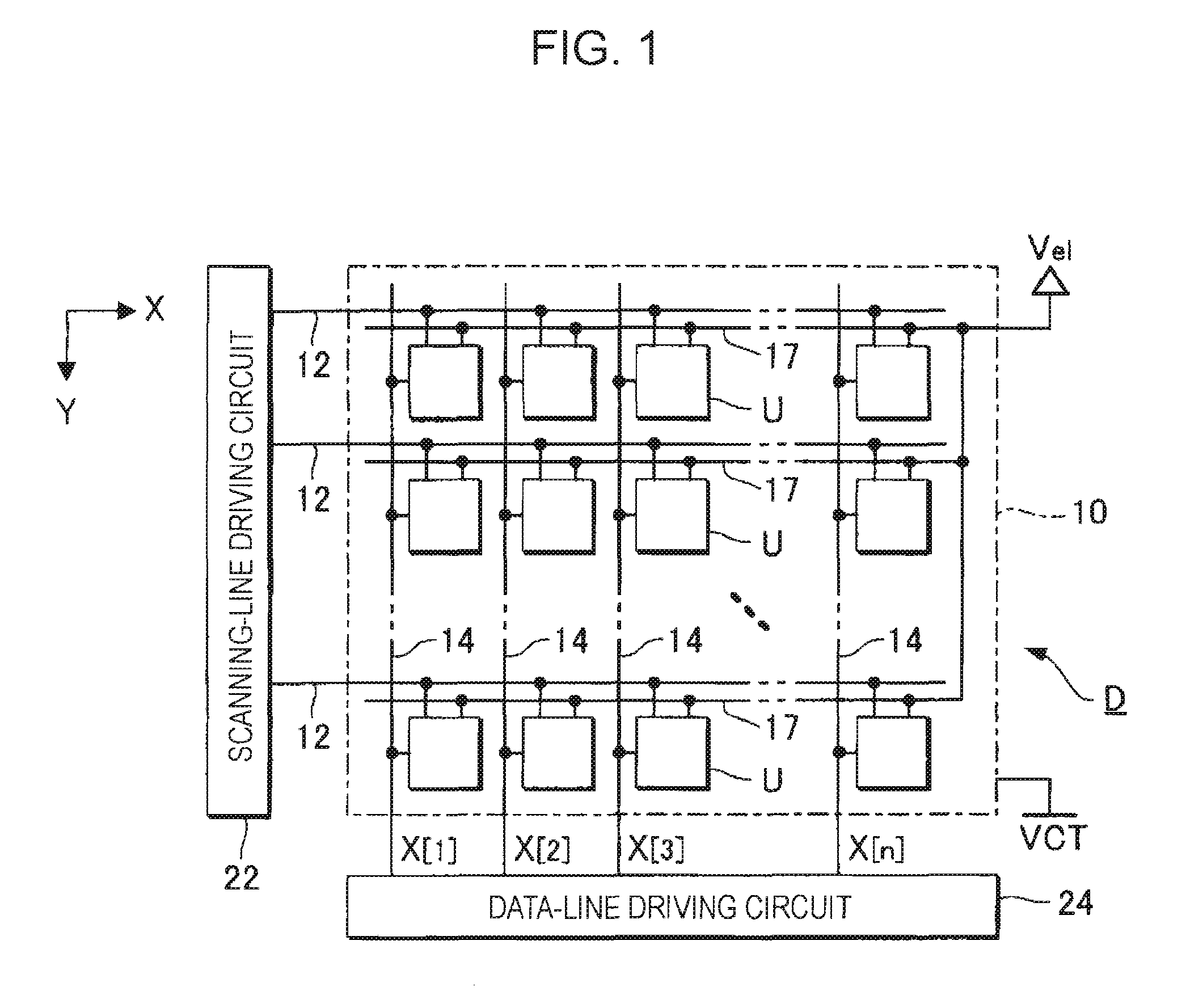
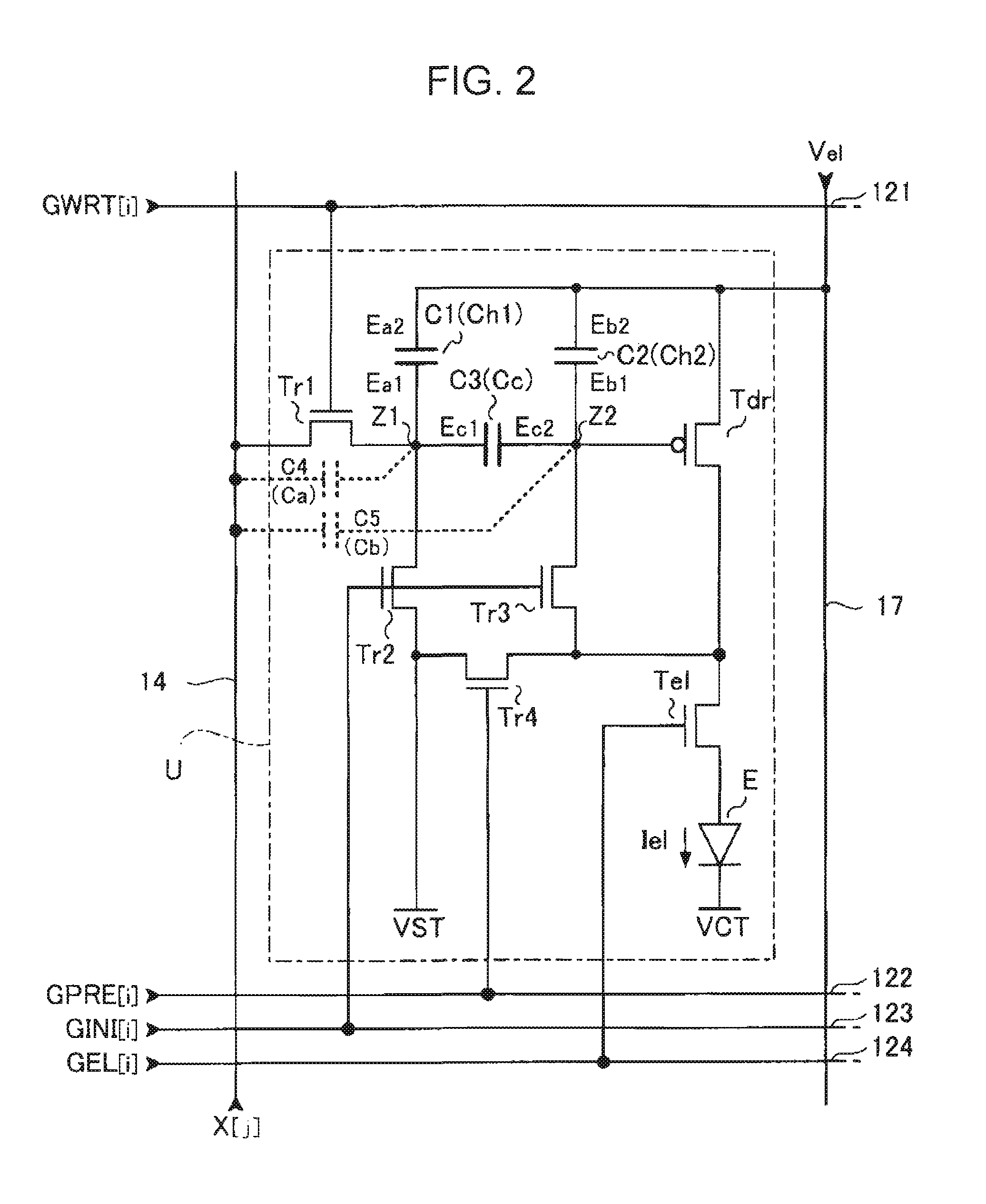
ActiveUS20070273619A1Accurately compensate variationAccurate compensationElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceElectricity
A unit circuit includes an electro-optical element, a first capacitive element, a second capacitive element, a third capacitive element, a drive transistor, a first switching element, an initialization unit, and a compensation unit. The electro-optical element emits an amount of light in accordance with a magnitude of a drive current. The first capacitive element includes a first electrode and a second electrode, the first electrode is electrically connected to a first node, and the second electrode is capable of receiving a fixed potential. The second capacitive element includes a third electrode and a fourth electrode, the third electrode is electrically connected to a second node, and the fourth electrode is capable of receiving a fixed potential. The third capacitive element includes a fifth electrode and a sixth electrode, the fifth electrode is electrically connected to the first node, and the sixth electrode is electrically connected to the second node. The drive transistor includes a gate, a source, and a drain and outputs the drive current in a driving period. The gate thereof is electrically connected to the second node. In a data writing period, the first switching element is in an on state and supplies to the first node a data potential supplied via a data line. The initialization unit causes the third capacitive element to discharge charges stored therein in an initialization period. The compensation unit electrically connects the source and the drain of the drive transistor together in a compensation period.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
Display device and method for driving the same
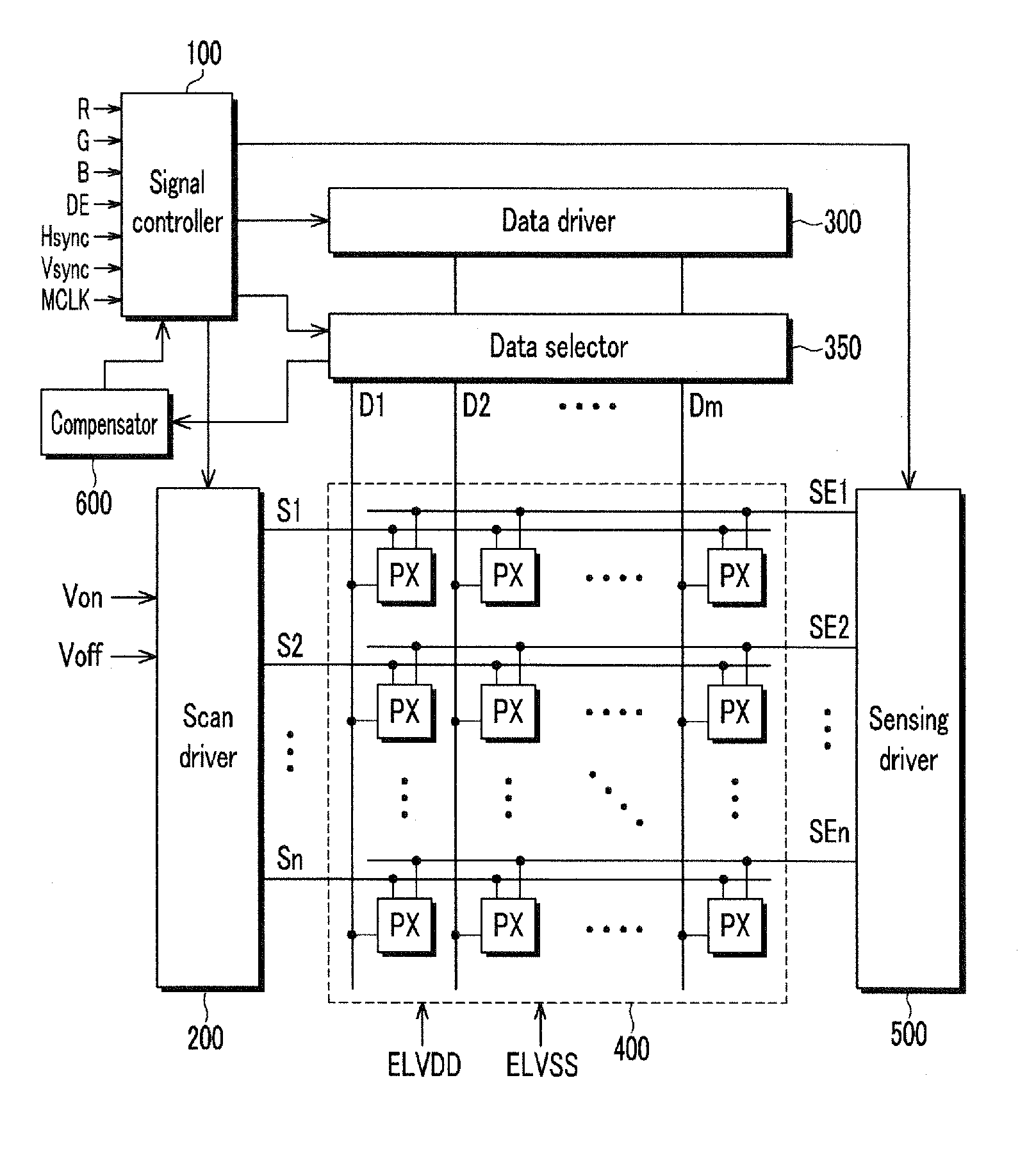
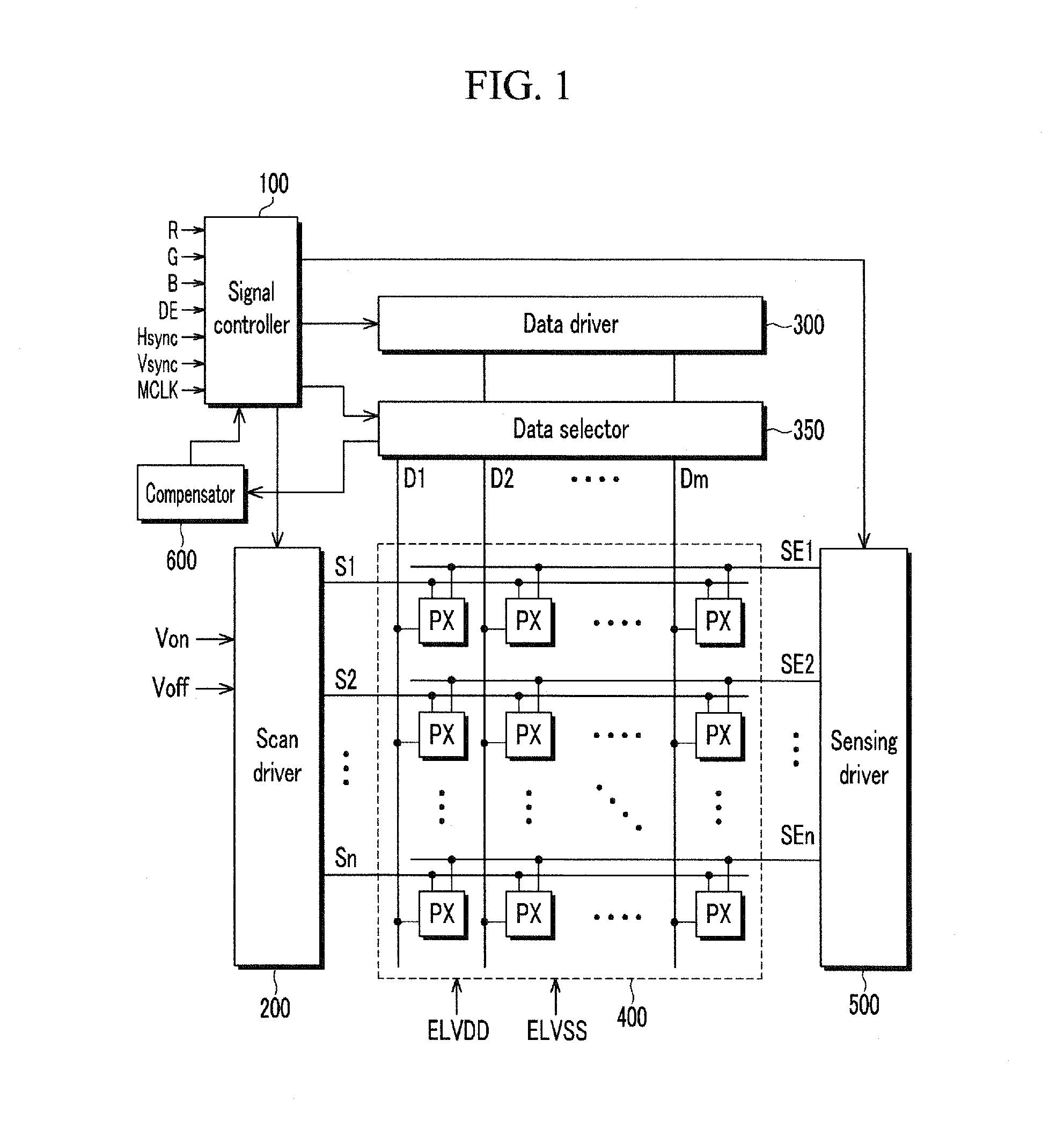
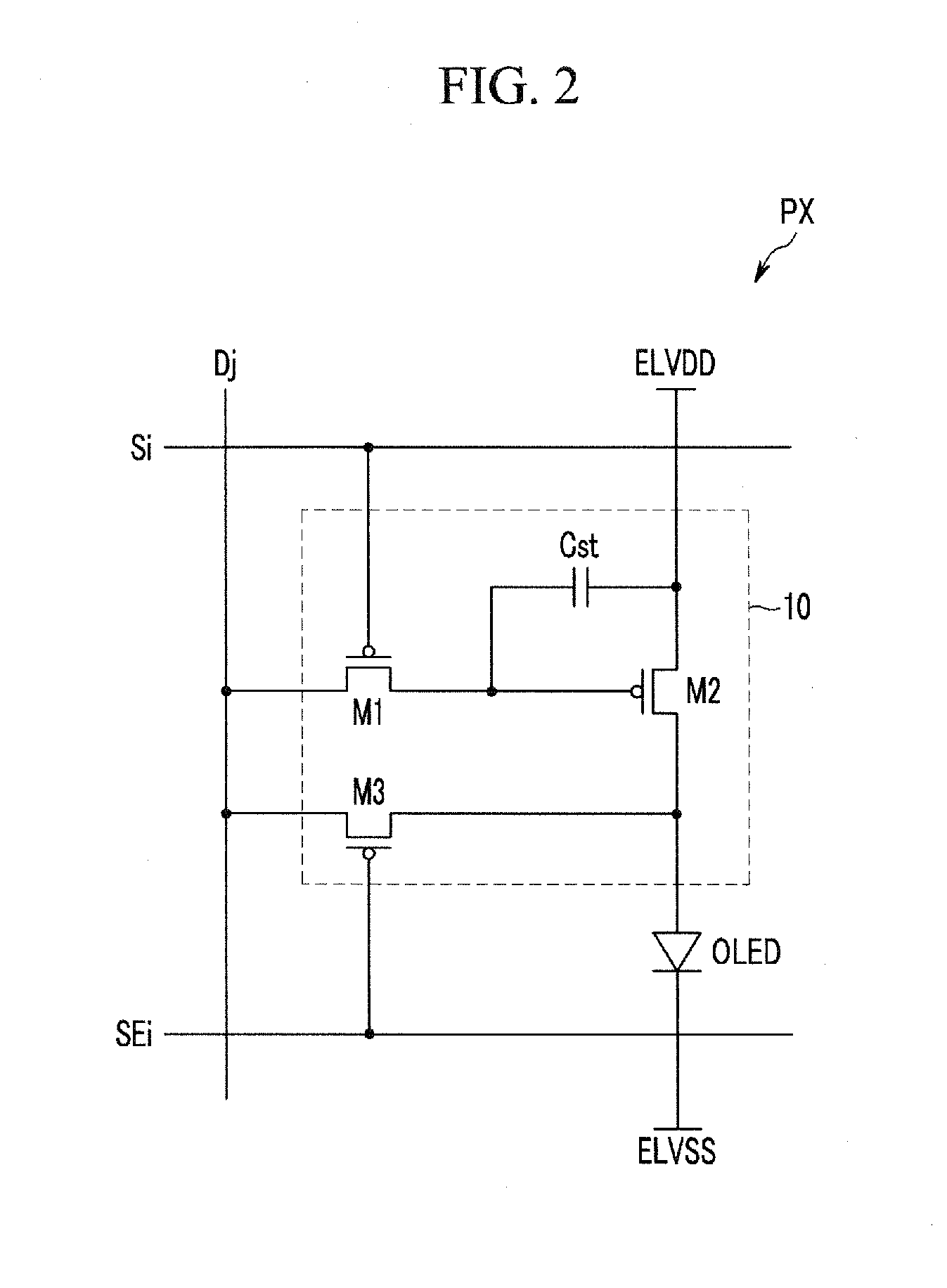
ActiveUS20110254871A1Accurately measure variation in characteristic of driving transistorAccurate compensationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
A display device includes a plurality of pixels, each of said plurality of pixels includes a driving transistor and a light emitting diode, a compensator to receive first and second pixel currents generated by the plurality of pixels according to first and second data voltages respectively applied to the plurality of pixels, the compensator to calculate an image data compensation amount to compensate for variations in characteristics of the driving transistor of each of said plurality of pixels and a data selector to transmit the first and second data voltages to the plurality of pixels and to transmit the first and second pixel currents to the compensator, the compensator to measure the first and second pixel currents generated as a result of the first and second data voltages corresponding to different gray scale levels and to calculate an actual threshold voltage and mobility of the driving transistor of each of the pixels, the compensator including a measurement resistor, the compensator to control a resistance value of the measurement resistor, the measurement resistor to convert the first pixel current corresponding to the first data voltage into a first measured voltage and the second pixel current corresponding to the second data voltage into a second measured voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
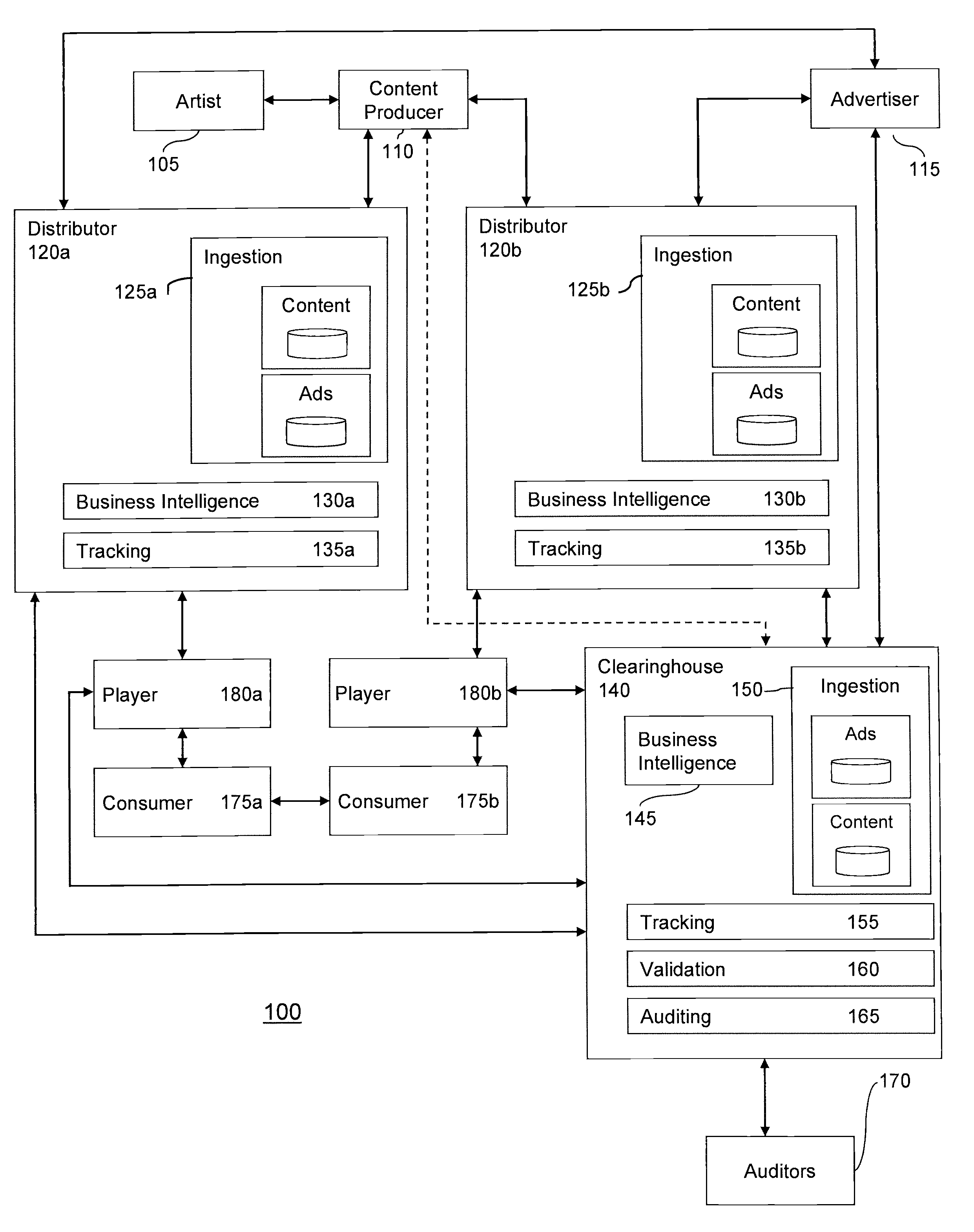
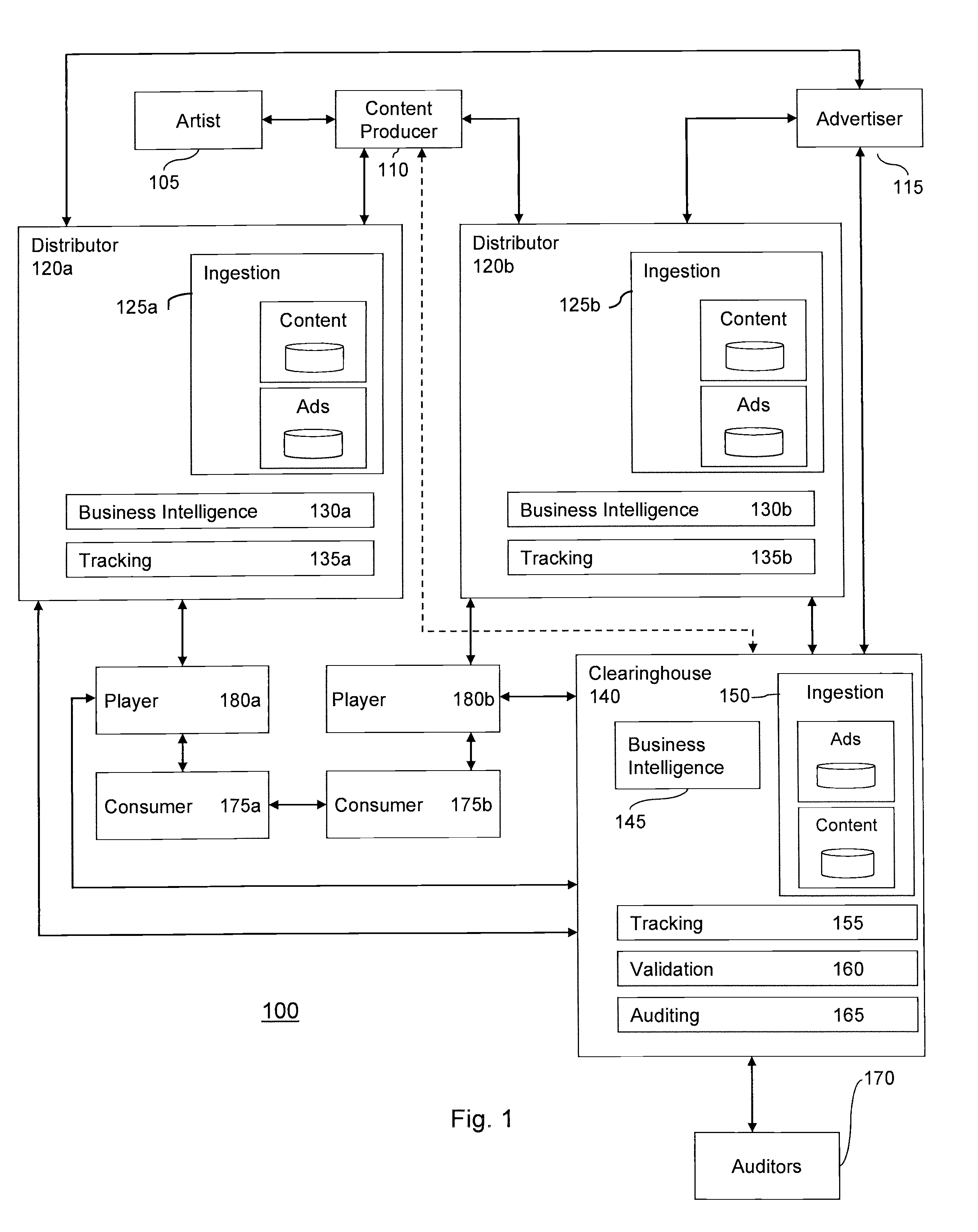
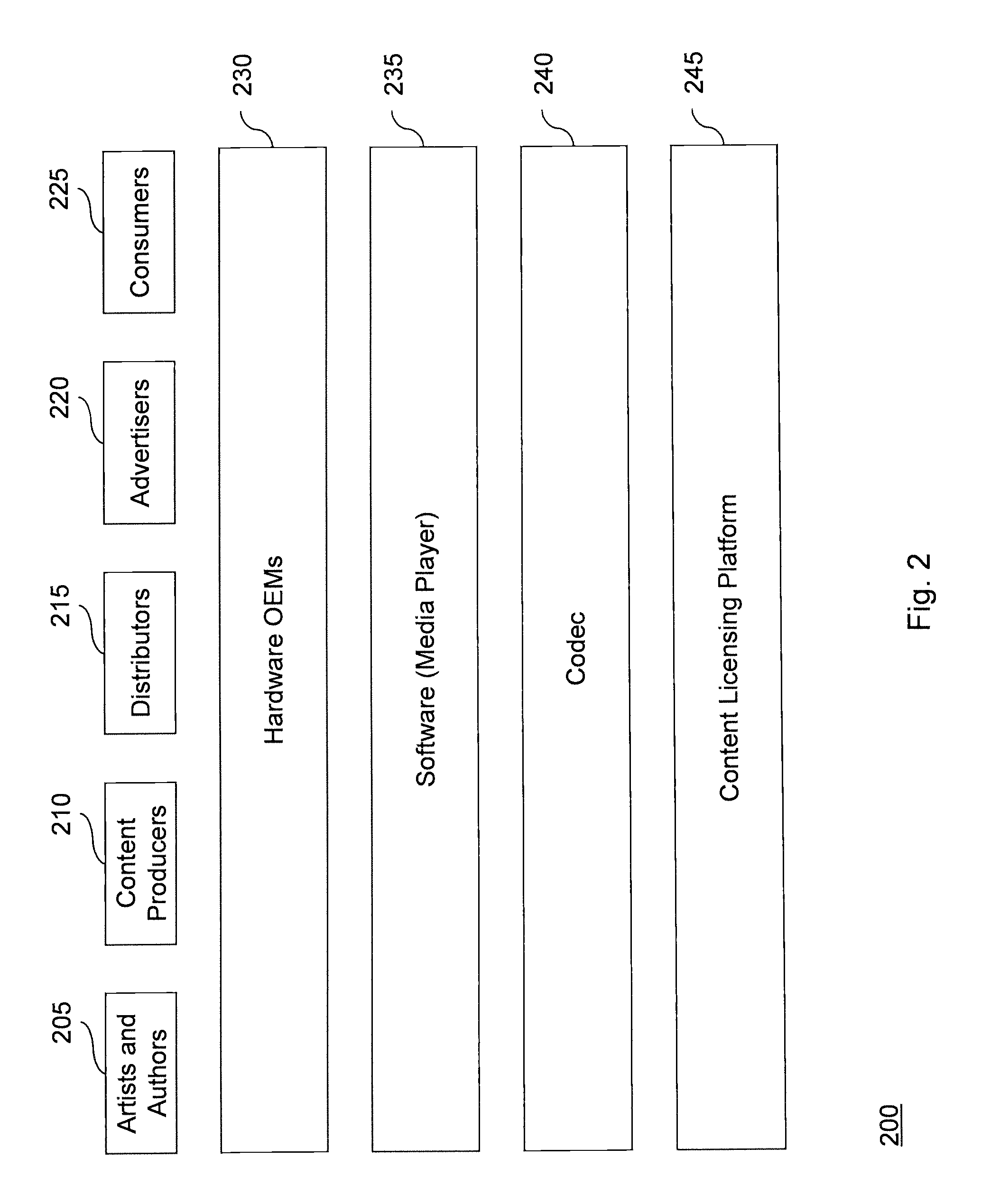
System and method for managing content consumption using a content licensing platform
InactiveUS20080133311A1Maximizing content asset transaction valueDrawback can be addressedAdvertisementsOffice automationInvoiceContent management system
A centralized content management system is provided. The system may balance interests among content creators, content owners, advertisers, consumers, and / or others in a content transaction chain. Media, advertising, or other types of content may have a content licensing platform embedded therein. The platform may enable a centralized clearinghouse to automatically monitor consumption of various types of content. Accordingly, the clearinghouse may use the monitored information to pay owners of consumed media content, invoice sponsors of consumed advertising content, build consumer profiles, or other things. Furthermore, content asset transaction value may be maximized throughout the chain, as content creators may establish prices for their content, advertisers may compete for ad-insertion, and consumers may establish a desired price for content using a variable pricing scheme.
Owner:TEXTALIVE MEDIA TECH
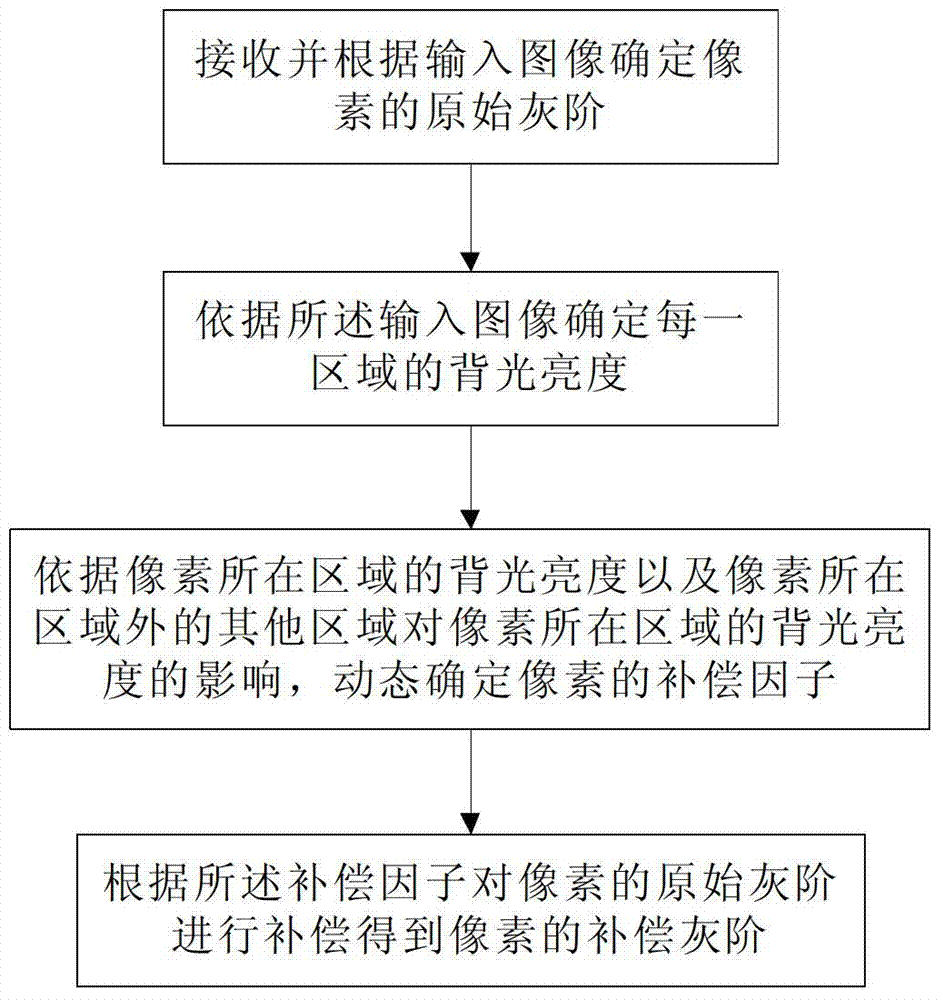
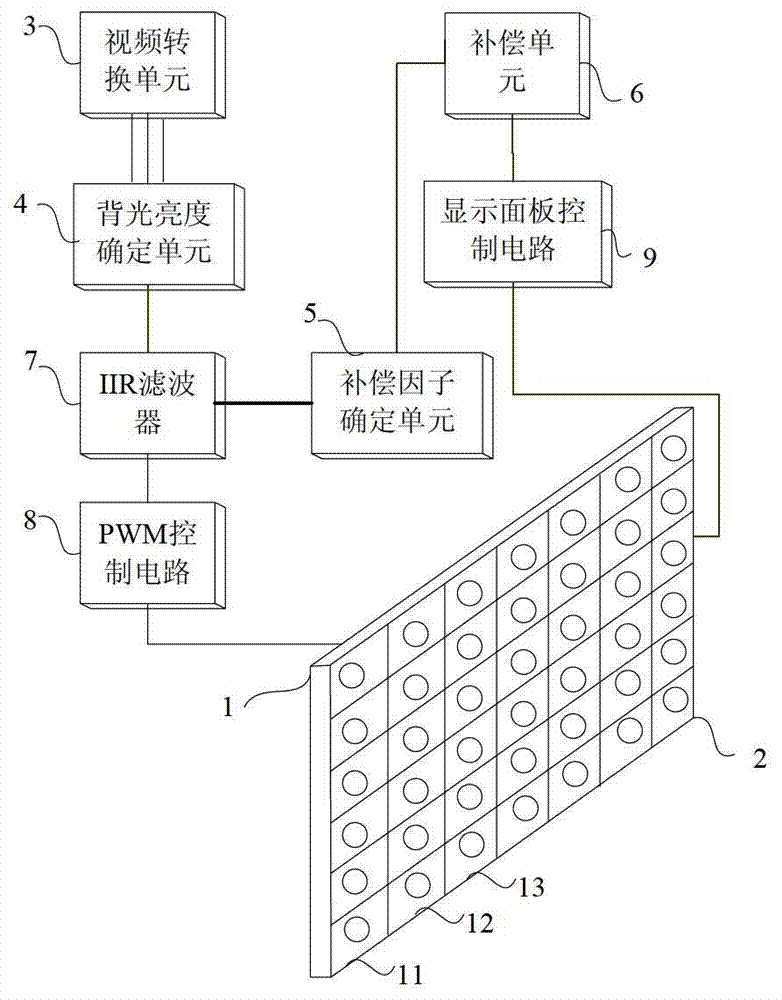
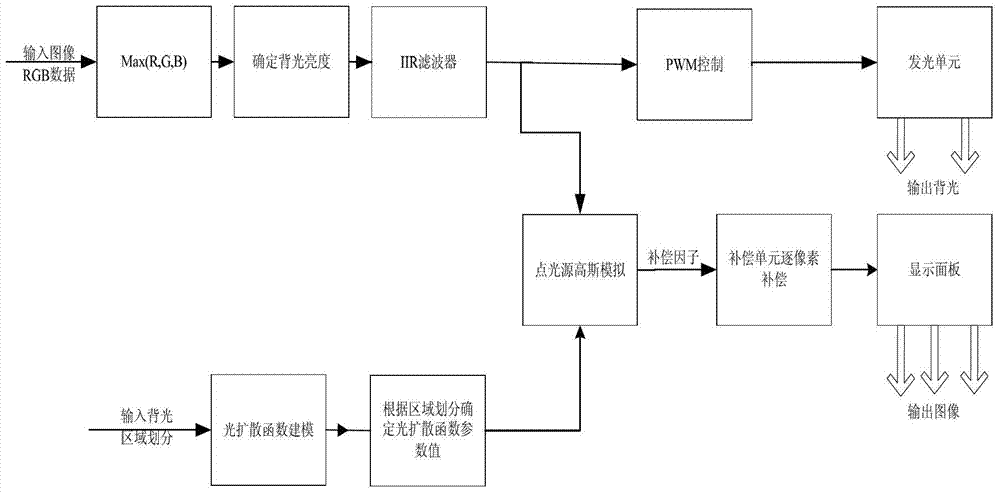
Direct type backlight luminance compensation method and display device
ActiveCN103295553AImprove the display effectSmall distortionStatic indicating devicesElectric light circuit arrangementDisplay deviceComputer science
The invention discloses a direct type backlight luminance compensation method and a display device, and is designed for solving the problems that image distortion is large after luminance compensation in the existing direct type backlight luminance compensation methods. The direct type backlight luminance compensation method includes: receiving and confirming original gray scale of pixel (i,j) according to input images; confirming backlight brightness of each area according to the input images; dynamically confirming compensating factors fcom (i,j) according to backlight brightness in pixel (i,j) area and influence on backlight brightness from other areas outside the pixel (i,j) area to the pixel (i,j) area; compensating original gray scale of pixel (i,j) according to the compensating factors fcom (i,j) to acquire compensating gray scale of pixel (i,j), wherein, i is taken as line number of pixel, and j is taken as column number of pixel. The direct type backlight luminance compensation method and the display device have the advantages that image distortion is small, data volume is small and the like after luminance compensation.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Four motion vector coding and decoding in bi-directionally predicted interlaced pictures
ActiveUS20050053298A1Accurate compensationReduce encoding overheadPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMotion vectorComputer science
For interlaced B-fields or interlaced B-frames, an encoder / decoder uses 4MV coding. For example, 4MV is used in one-direction prediction modes (forward or backward modes), but not in other available prediction modes (e.g., direct, interpolated). Using 4MV allows more accurate motion compensation for interlaced B-fields and interlaced B-frames; limiting 4MV to forward and backward modes reduces coding overhead and avoids decoding complexity associated with combining 4MV with modes such as direct and interpolated.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Compensating for effects of variations in gas refractivity in interferometers
InactiveUS6842256B2Rapid and accurate compensationCompensated rapidly and accuratelyPhase-affecting property measurementsInterferometersRefractive indexAcoustics
Methods and system for compensating for effects of changes and variations of gas refractivity in a measurement and / or reference beam path of an interferometer are disclosed.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
Mobile communication terminal module and mobile communication terminal
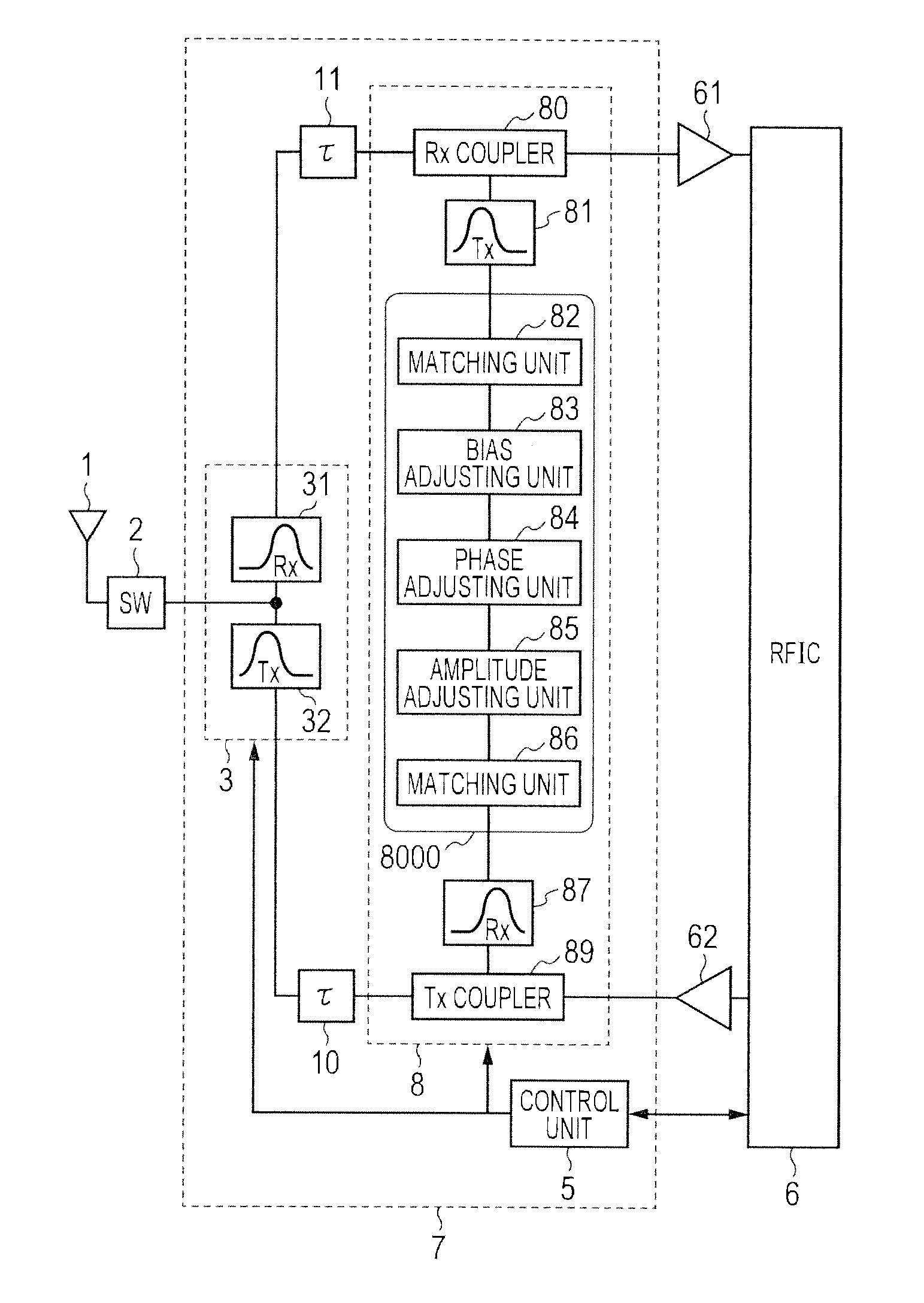
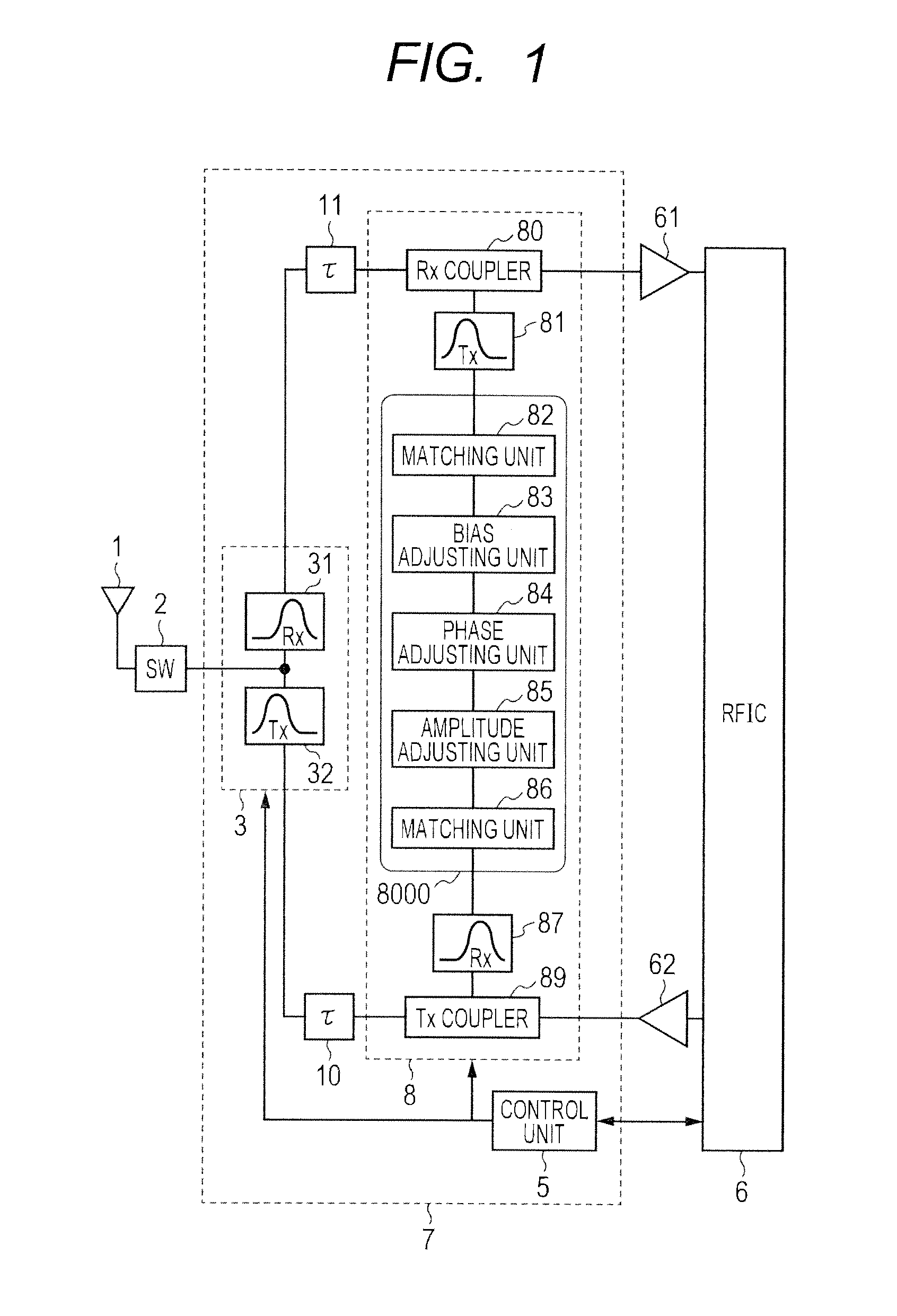
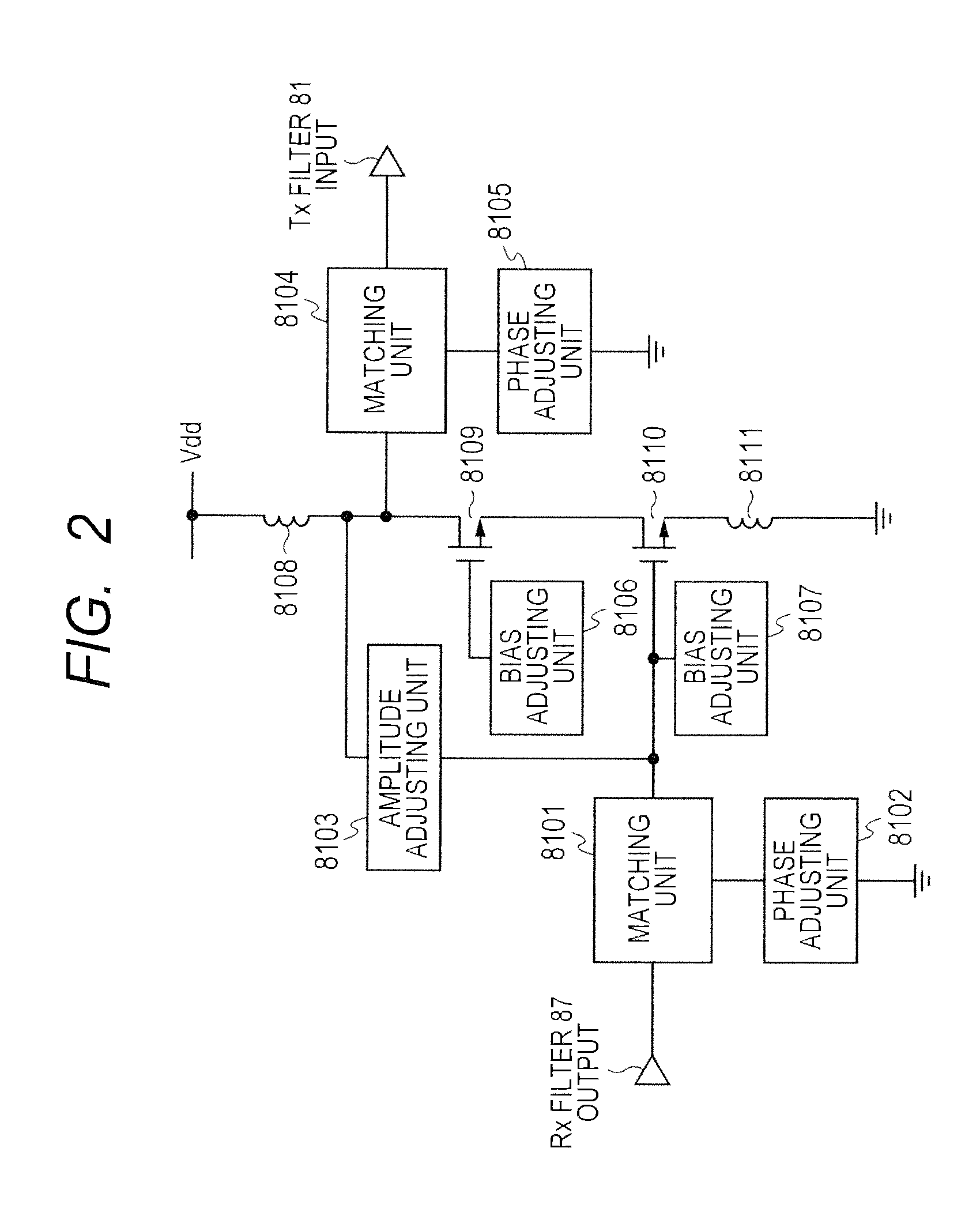
InactiveUS20130242809A1Speed up calibrationHigh precision compensationTransmitters monitoringRadio transmissionNarrow rangeStopband
In a tunable duplexer combining a tunable filter with a canceler, calibration for optimizing passband characteristics and stop band characteristics is accelerated, and the deterioration of performance due to variations is highly accurately compensated. The tunable filter is calibrated to acquire isolation characteristics, and then coarse calibration and fine calibration are performed on the canceler. In coarse calibration, the use band of the tunable filter is set to a suppression band, and the isolation characteristics of the canceler are acquired. An amplitude, a phase, and a bias voltage are adjusted based on a result of comparison with the acquired isolation characteristics of the tunable filter for determining an approximate convergence. Fine calibration is further performed, and the optimum point is determined in a narrow range near the convergence.
Owner:HITACHI MEDIA ELECTORONICS CO LTD
Battery connecting plate, and attachment structure of the same
ActiveUS7077704B2Easily and accurately mountedSize toleranceVehicle connectorsElectric discharge tubesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:YAZAKI CORP +1
Apparatus for measuring the flow rate due to a leak in a pressurized pipe system
InactiveUS6082182AConducive to separationReduce effectDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateLiquid temperatureEngineering
Owner:VISTA RES INC
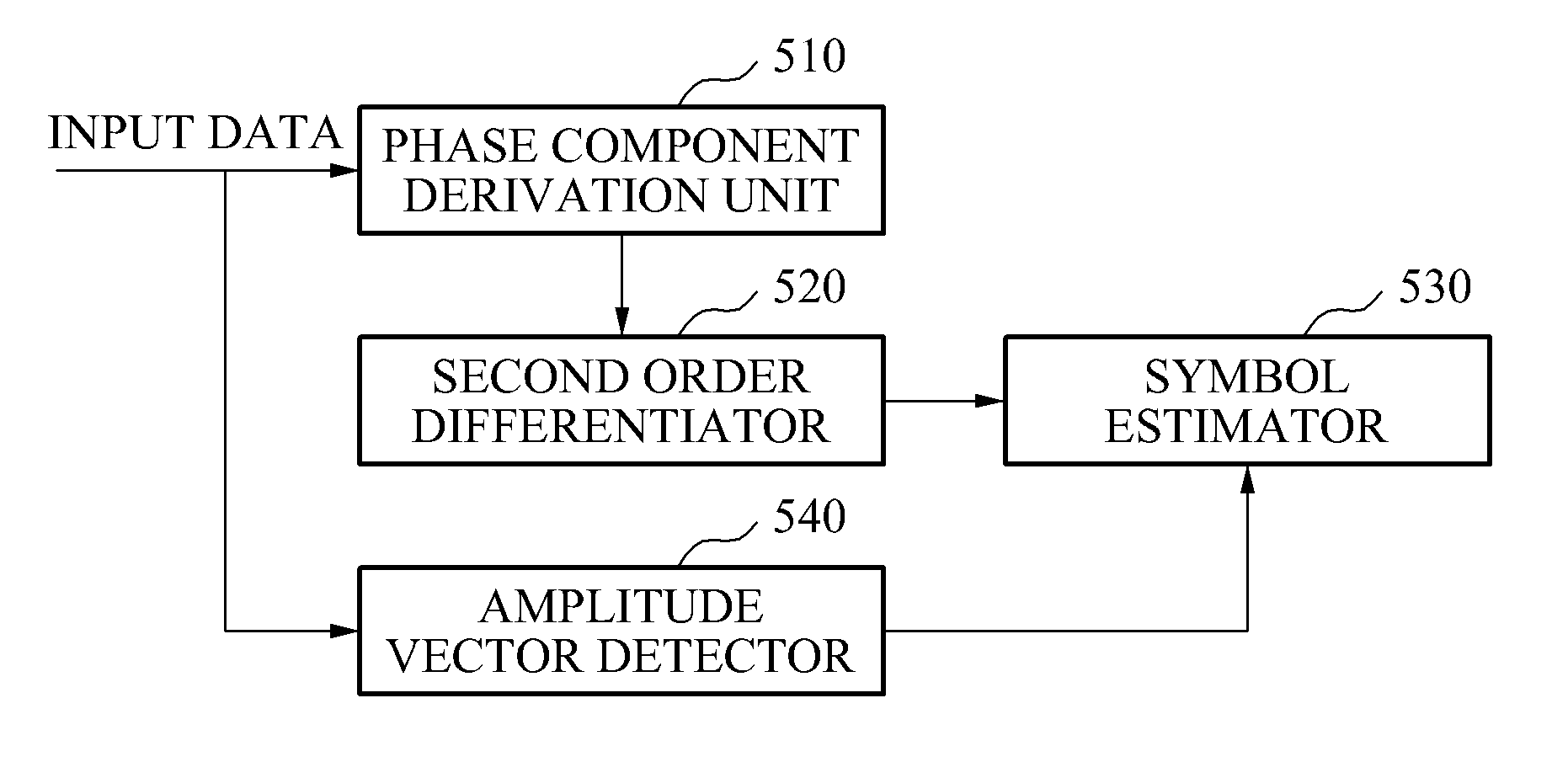
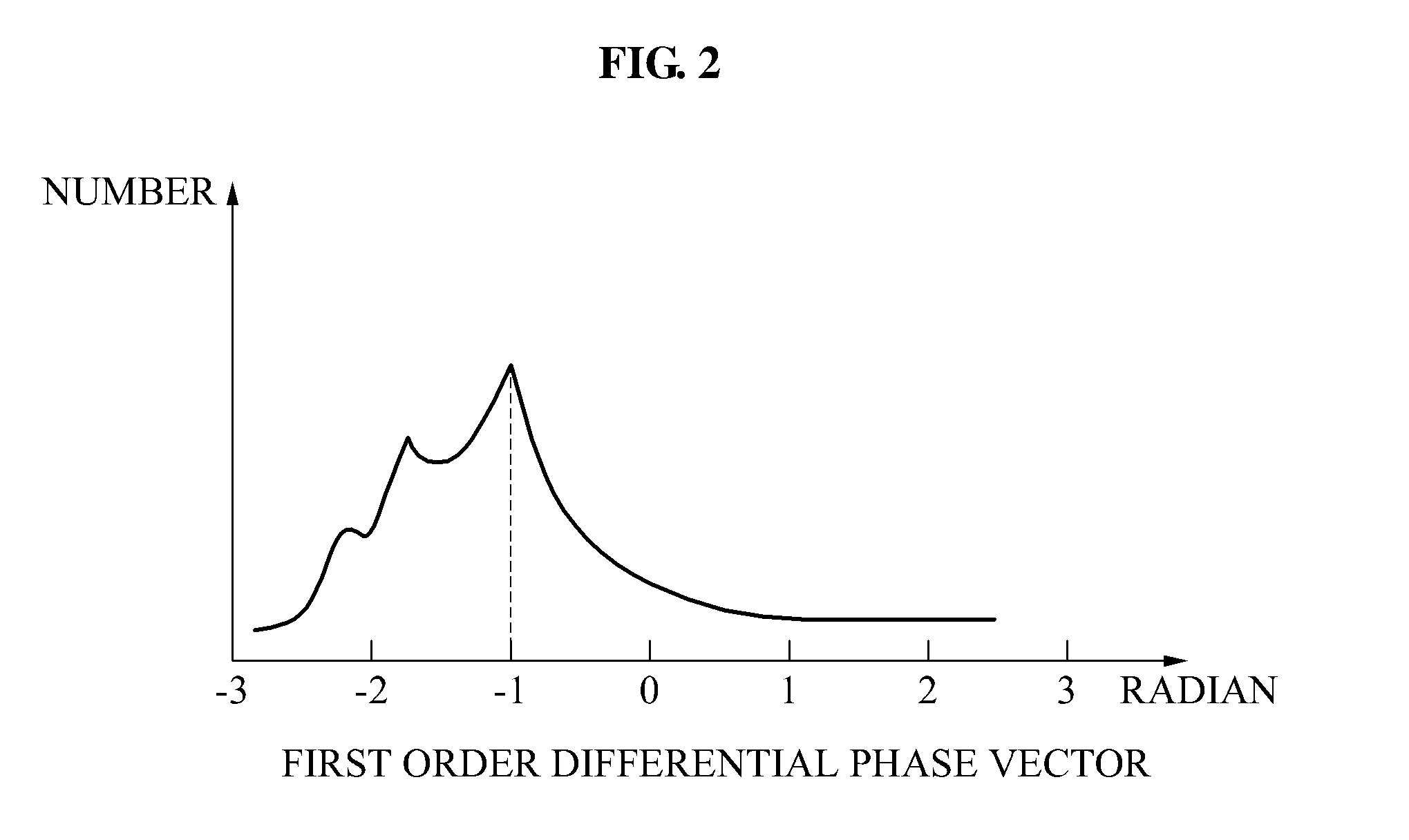
Device and method of estimating symbol using second order differential phase vector
ActiveUS20110150064A1Low complex metricAccurate compensationModulation type identificationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDifferential phaseComputer science
Provided is a method of estimating a symbol. The method may include deriving phase components of input data, applying a second order differentiation to the phase components to obtain a second order differential phase vector, and estimating symbols corresponding to the input data using the second order differential phase vector.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
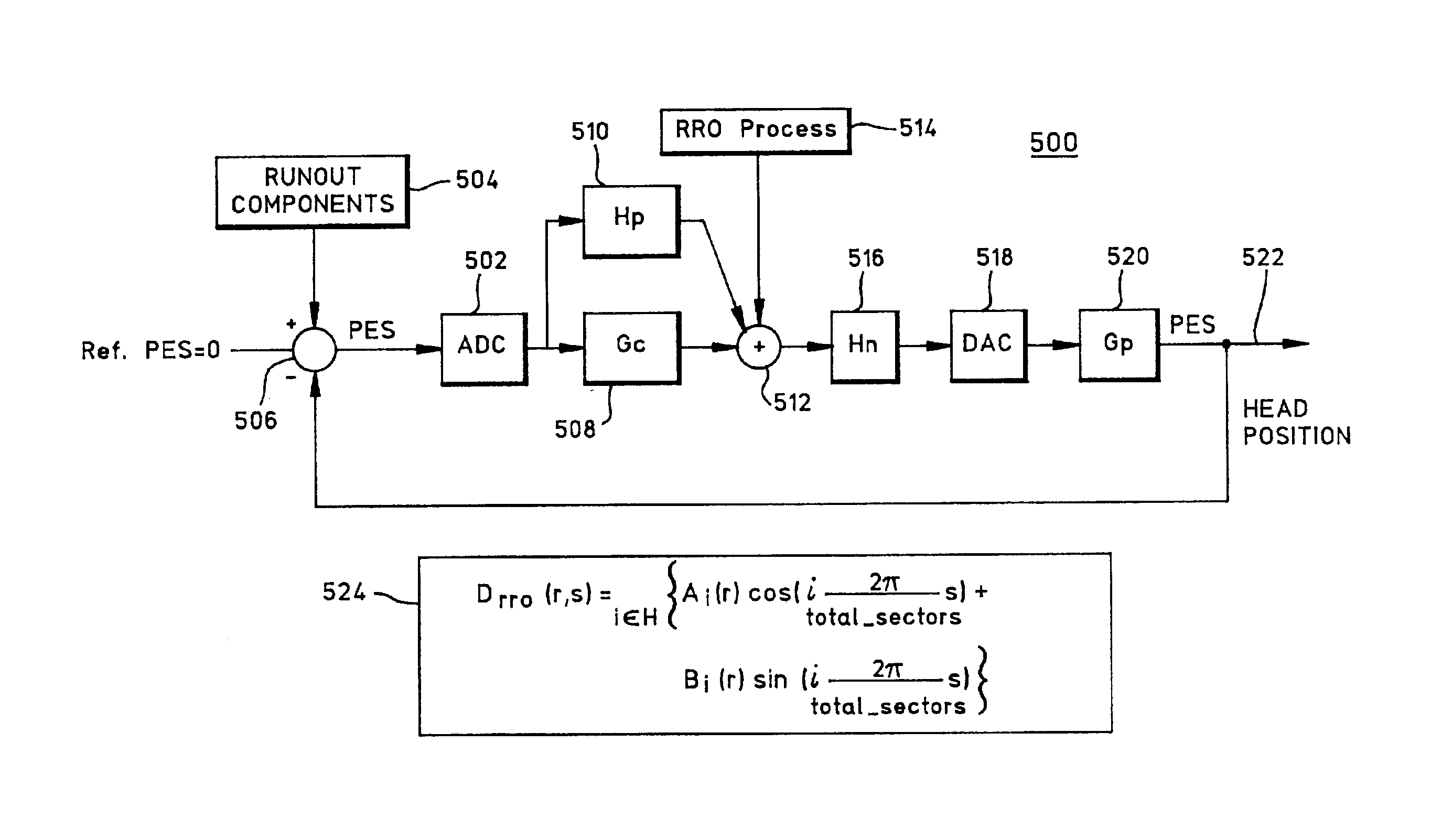
Repeatable runout (RRO) compensation methods and apparatus for data storage devices
InactiveUS6937424B2Reducing RRO errorAccurate compensationTrack finding/aligningAlignment for track following on tapesLeast squaresHarmonic
In one illustrative example, a method for use in reducing Repeatable Run Out (RRO) error in a data storage device involves obtaining an RRO measurement for each track of a limited number of N disk tracks; characterizing the RRO measurement for each track with real and imaginary values by performing a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) calculation on each RRO measurement; performing a least-squares fit on all of the real values to identify a first set of (n+1) coefficients of an nth-order polynomial function which is a function of disk track r and representable in the form Ai(r)=anrn+a(n−1)r(n−1)+ . . . +a1r+a0; and performing a least-squares fit on all of the imaginary values to identify a second set of (n+1) coefficients of an nth-order polynomial function which is a function of disk track r and representable in the form Bi(r)=bnrn+b(n−1)r(n−1)+ . . . +b1r+b0. RRO compensation is performed based on the relation DRRO(r, s)=Σi for all H {Ai(r)cos(i(s2π / total_sectors))+Bi(r)sin(i(s2π / total_sectors))} where DRRO is the estimated RRO error; r is a track number; s is a sector number at track number r; i is an RRO harmonic number; H is a set of harmonics to be compensated; and total_sectors is a total number of sectors along track number r. Advantageously, RRO variations across the disk can be accurately compensated for with use of a small amount of memory.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Feedback control method for a heliostat
InactiveUS20050274376A1Accurately reflectImprove pointing accuracySolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueHeliostatEngineering
An instrument for a solar energy system including a receiver and a heliostat to reflect solar energy on to the receiver. The instrument includes a first element adapted to form an image of the sun, a second element adapted to form an image of the receiver, and a detector. The detector is positioned to receive each of the images and a comparator is adapted to detect a distance between the images. The comparator generates an error correction signal based on the distance between the images. The error correction signal is received by a controller that controls the operation of a postioner that adjusts the position of the heliostat accordingly.
Owner:SOLARRESERVE TECH +1
Optical disk drive having a tilt compensator
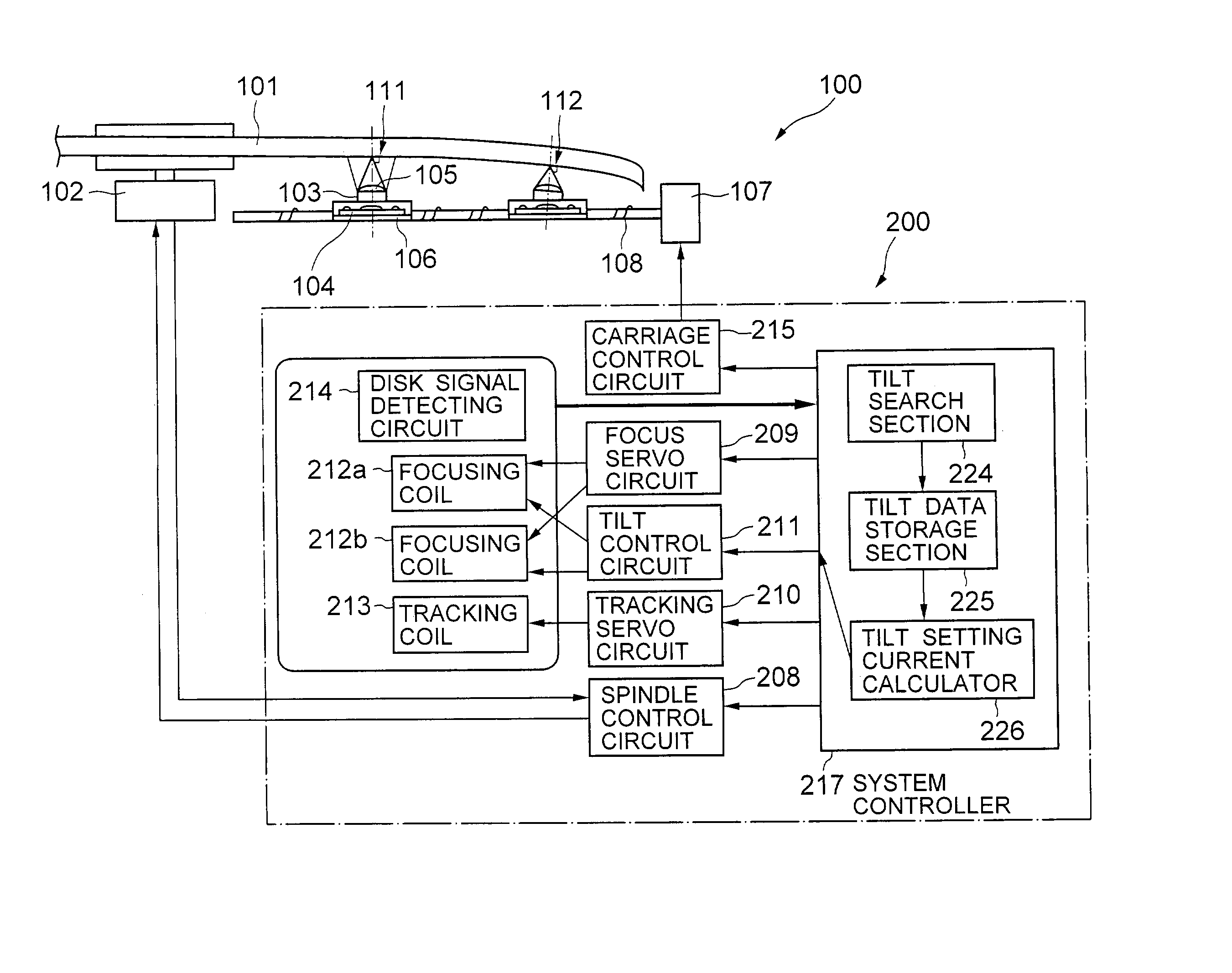
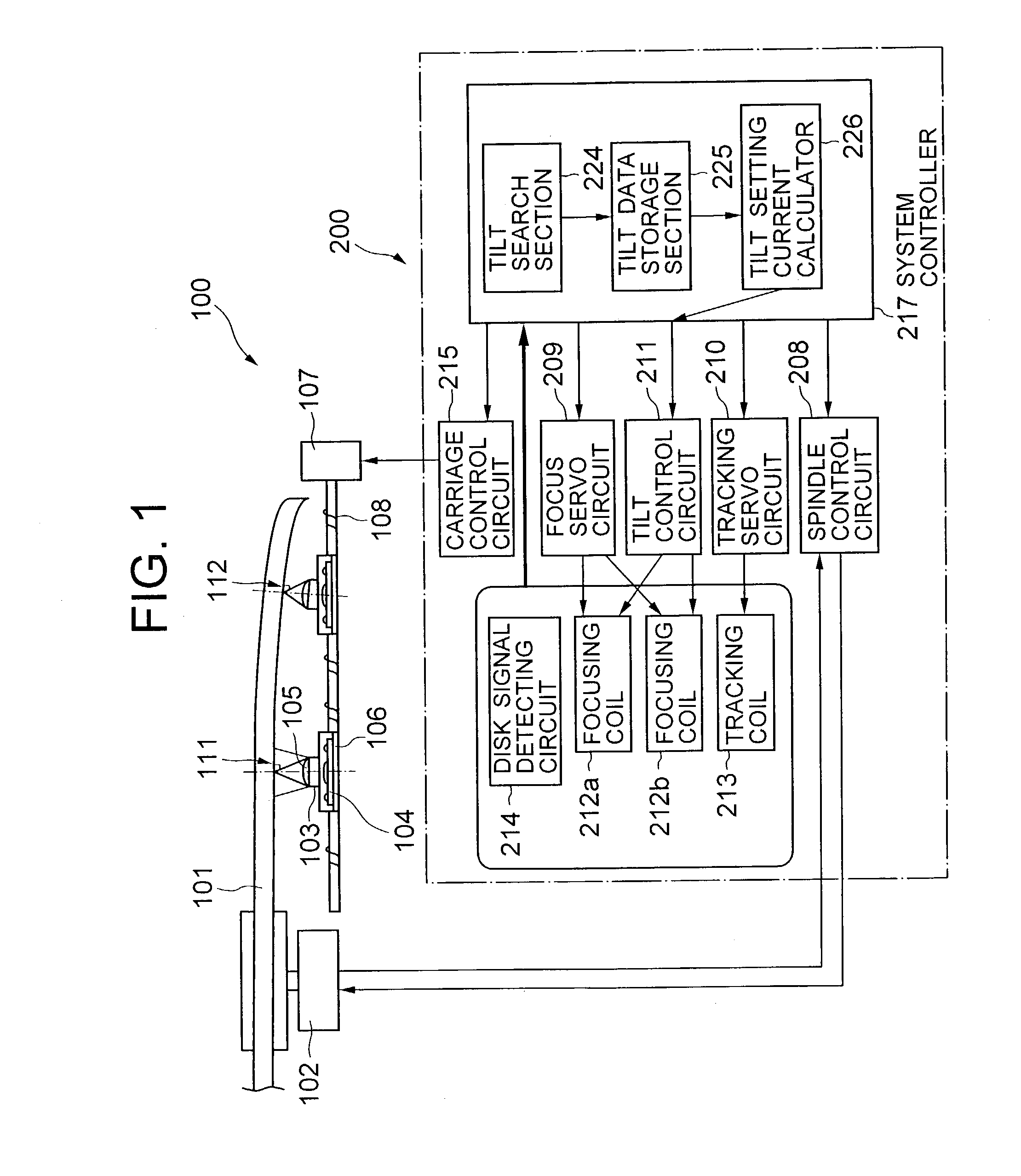
InactiveUS20030179665A1Accurate compensationCombination recordingRecord information storageRadial positionOptical disc drive
A tilt compensator in an optical disk drive detects an optimum tilt setting of the objective lens with respect to a reference plane of the optical head, which allows the optical head to obtain an optimum characteristic of a disk signal at a specified radial position of an optical disk. The optimum tilt setting is corrected at a desired track of the optical disk by using a difference between a first tilt angle of the reference plane with respect to the optical disk measured at the specified radial position and a second tilt angle of the reference plane measured at a desire track of the optical disk. The disk signal is a RF signal, a jitter of the encoded RF signal, a tracking error signal or a wobble signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
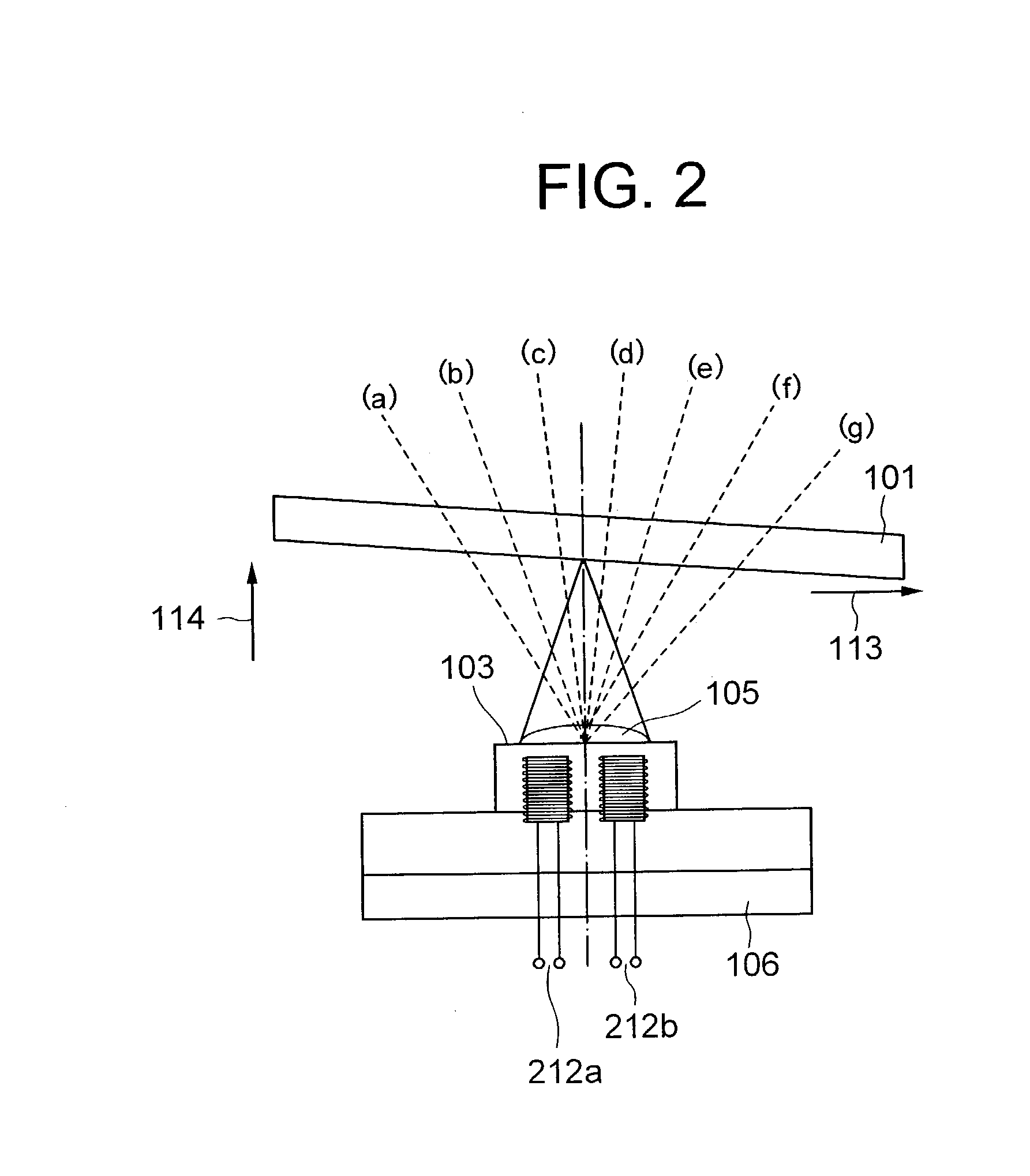
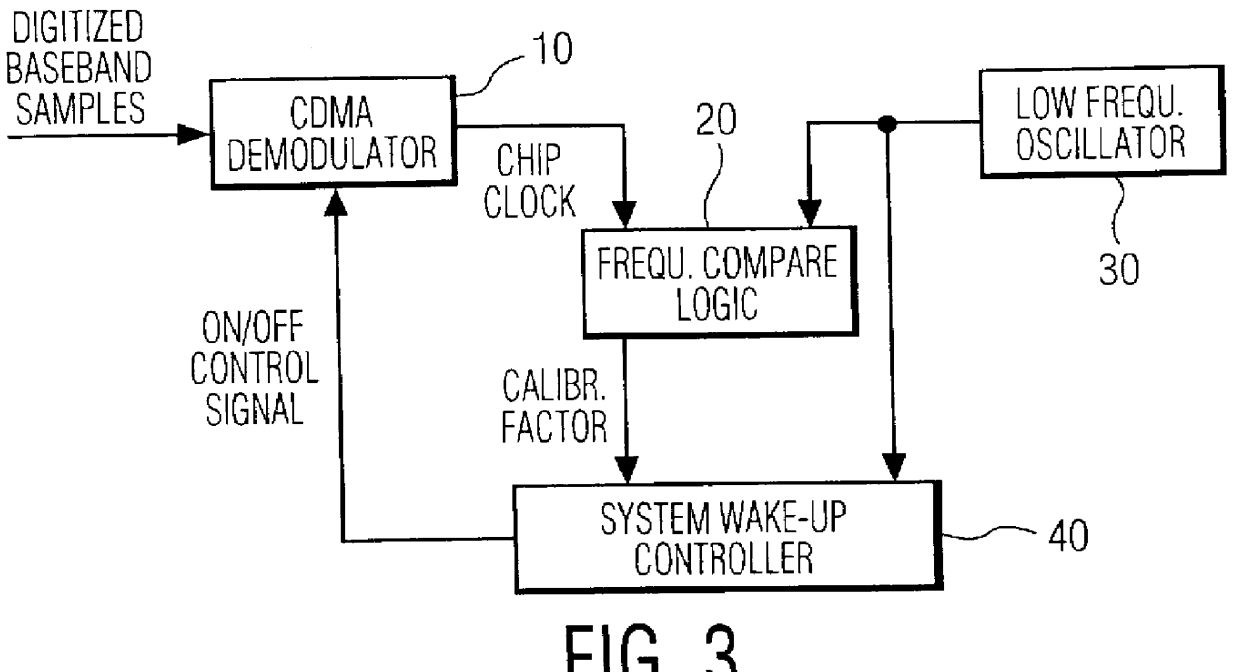
Circuit for synchronizing CDMA mobile phones
InactiveUS6028855AAccurately reacquireReduce power consumptionPower managementSynchronisation arrangementNetwork clockEngineering
A frequency calibration circuit for use in a spread spectrum receiver. The receiver includes circuitry for receiving a spread spectrum signal from a base station and for recovering a network clock signal therefrom, a low frequency oscillator for producing an oscillator clock signal, and a frequency comparator that takes as inputs the network clock signal and the oscillator clock signal and produces a calibration factor based on the difference between the clock signals. A controller coupled to the low frequency oscillator amd the frequency comparator utilizes the calibration factor together with the low frequency oscillator clock signal to output a accurate and precision timed signal thereby being able to accurately require the timing of the paging channel.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Digital-drive electroluminescent display with aging compensation
ActiveUS20100156766A1Simple voltage measurement circuitryAccurate compensationStatic indicating devicesElectricityCurrent source
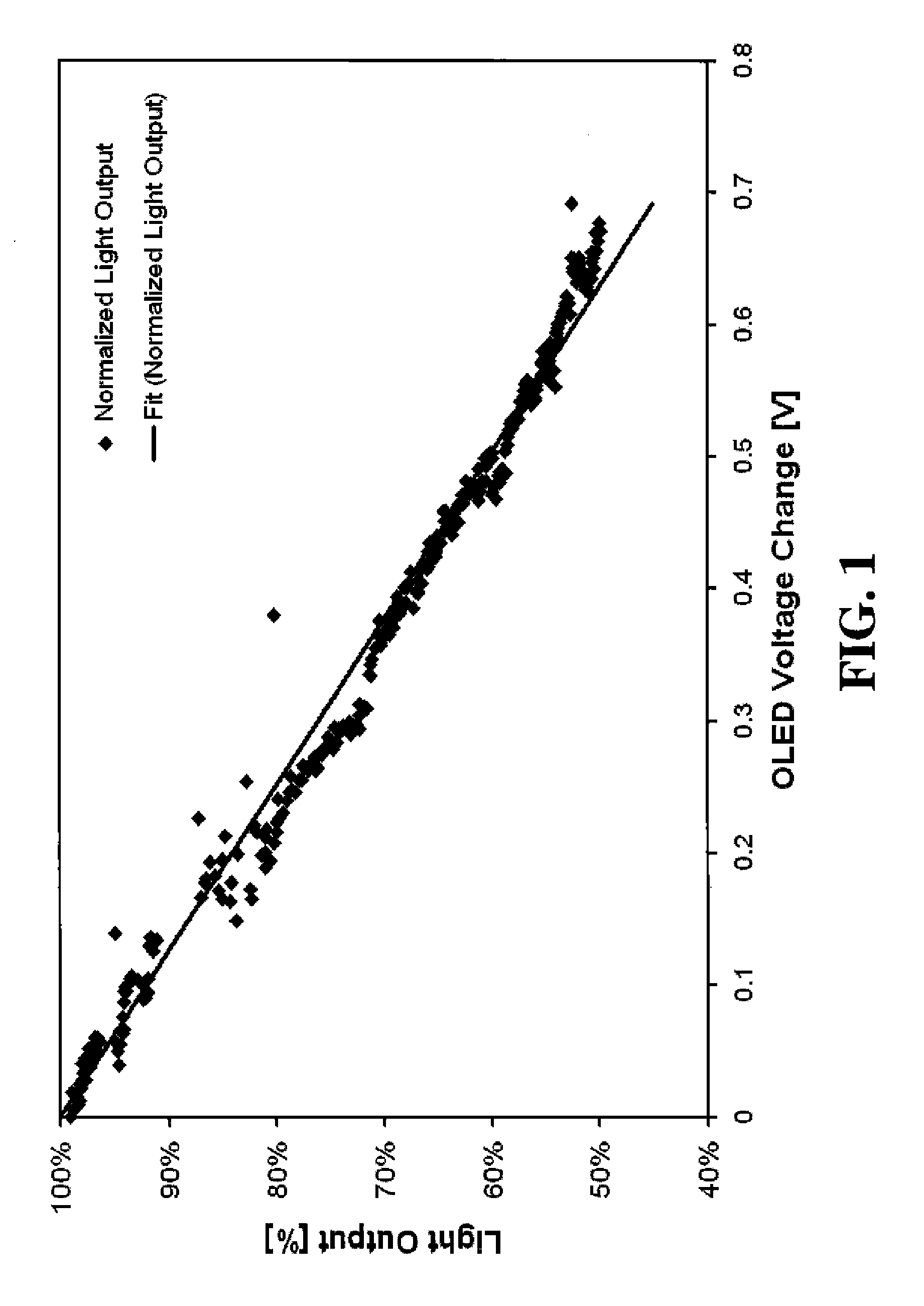
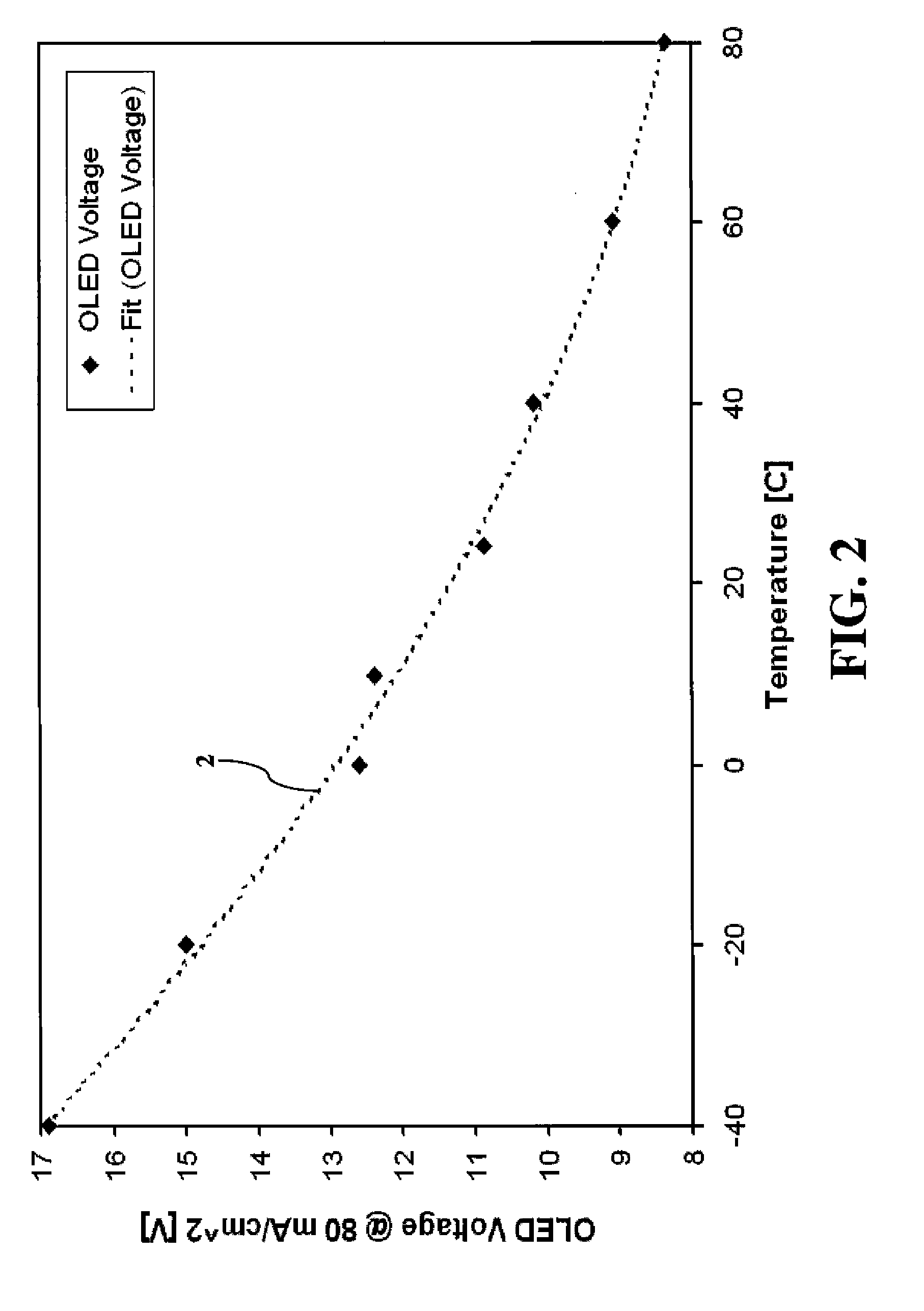
An electroluminescent (EL) subpixel driven by a digital-drive scheme has a readout transistor driven by a current source when the drive transistor is non-conducting. This produces an emitter-voltage signal from which an aging signal representing the efficiency of the EL emitter can be computed. The aging signal is used to determine the loss in current of the subpixel when active, and an input signal is adjusted to provide increased on-time to compensate for voltage rise and efficiency loss of the EL emitter. Variations due to temperature can also be compensated for.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Signal transmitter
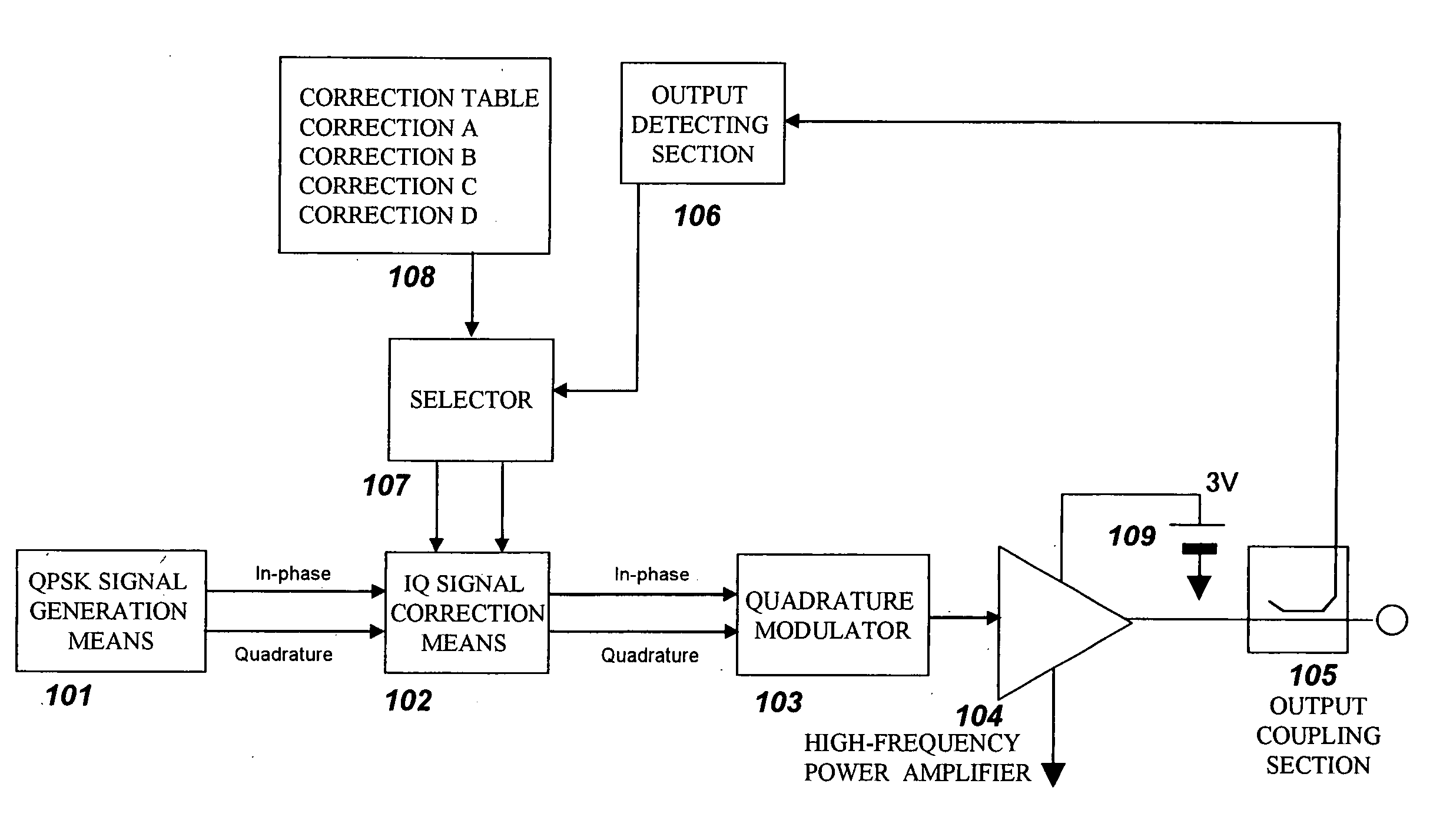
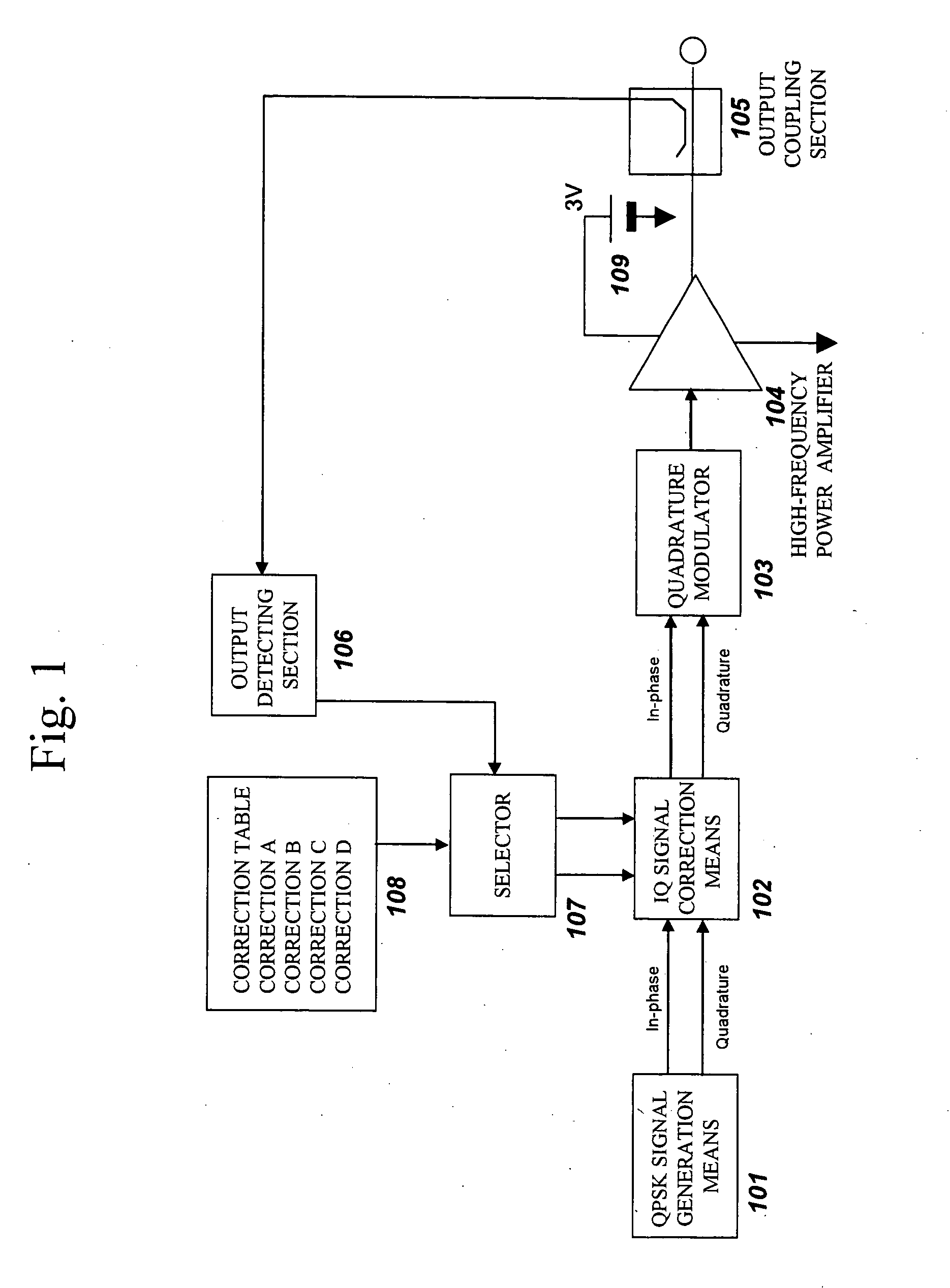
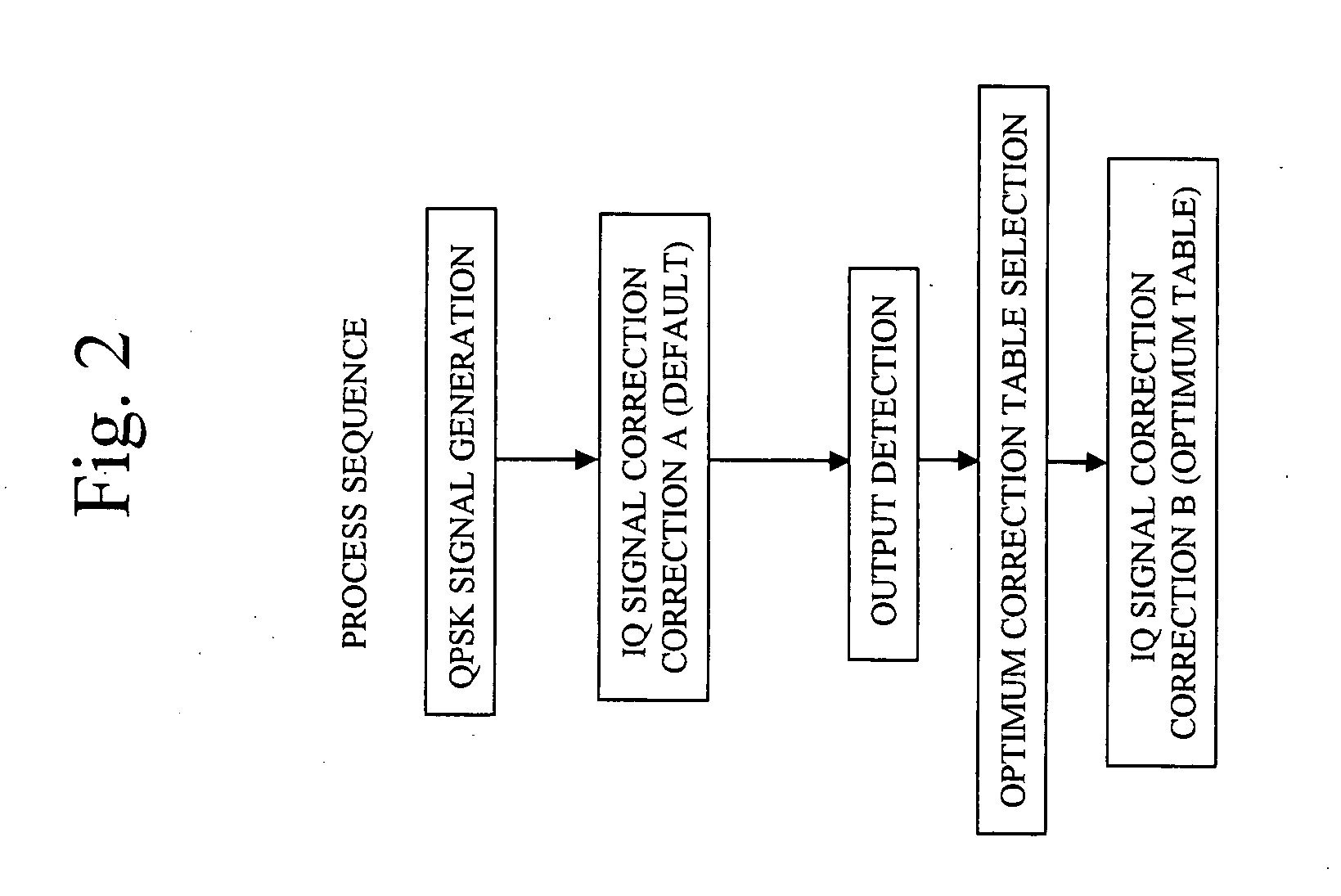
InactiveUS20050118965A1Compensate for thermal characteristics of a radio frequency power amplifier efficiently and correctlyAccurate detectionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierFrequency spectrum
An amplitude component and a phase component among modulating signals are supplied into a radio frequency wave input terminal and a power supply terminal of a radio frequency power amplifier, respectively, and an original modulated wave is obtained from an output of the radio frequency power amplifier. The output of the radio frequency power amplifier is detected by an output detecting section, correction data to a detection voltage closest to the detection voltage among correction datatables which have been measured in various temperature environments and stored in advance are selected by a selector, and correction of an amplitude component and a phase component is performed by phase-amplitude correction means. Thereby enabling EER operation without spectrum degradation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com