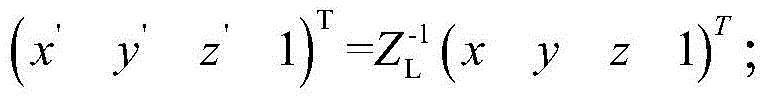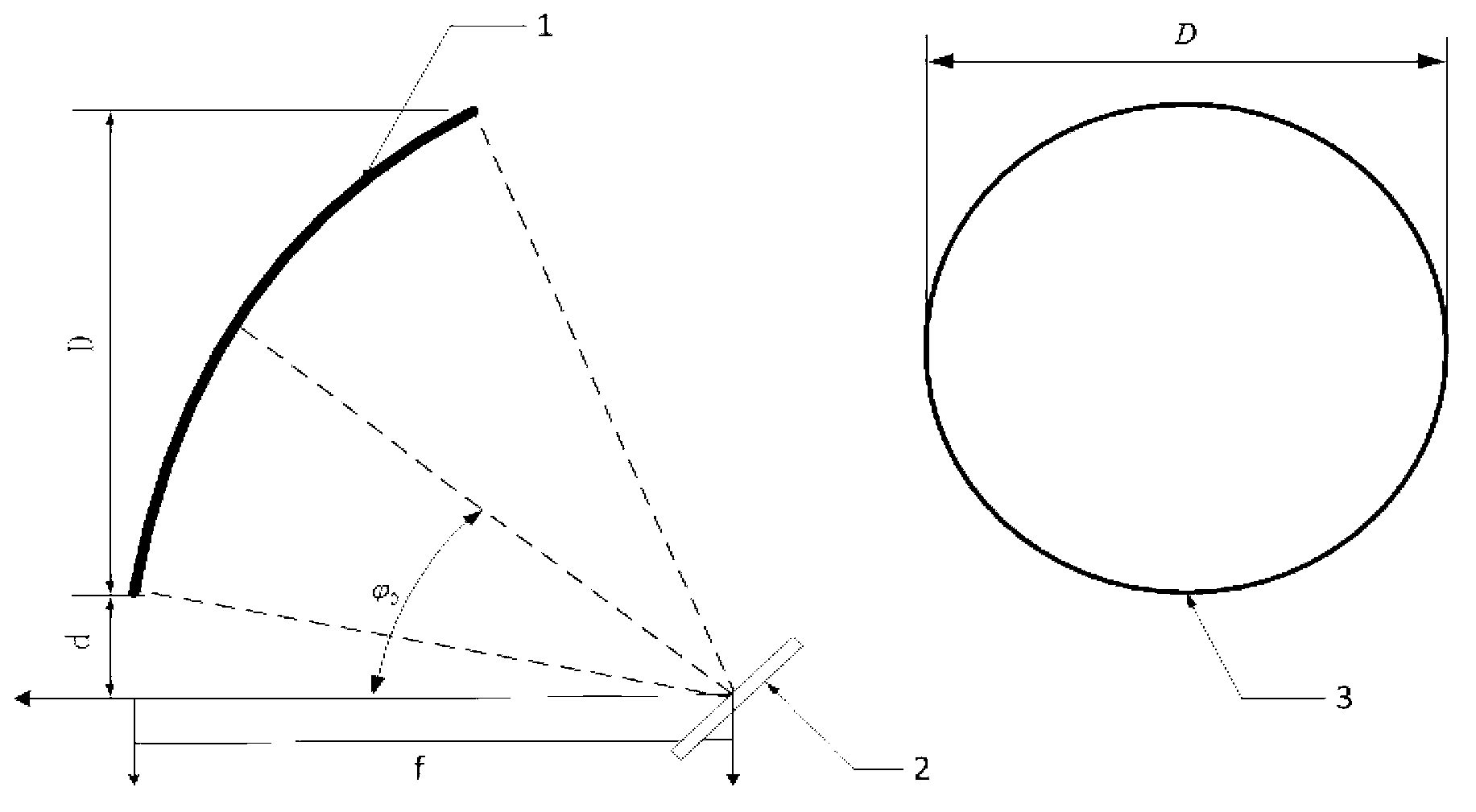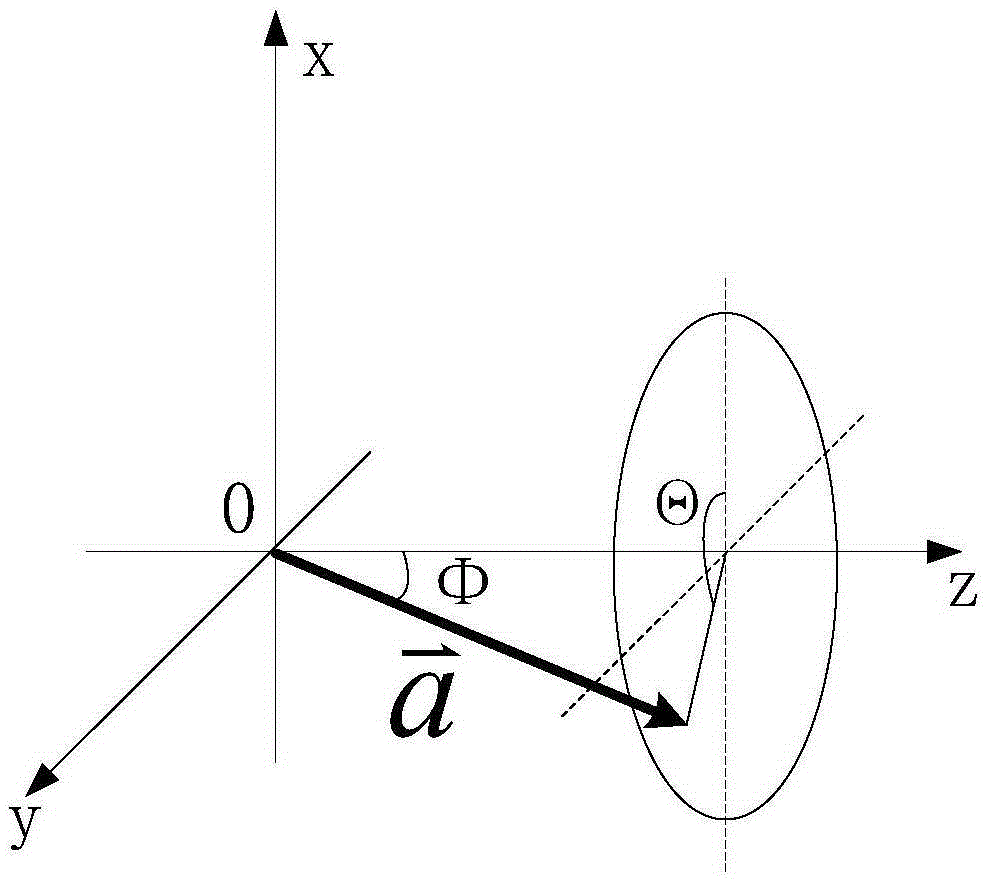Patents
Literature
210results about How to "Improve pointing accuracy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
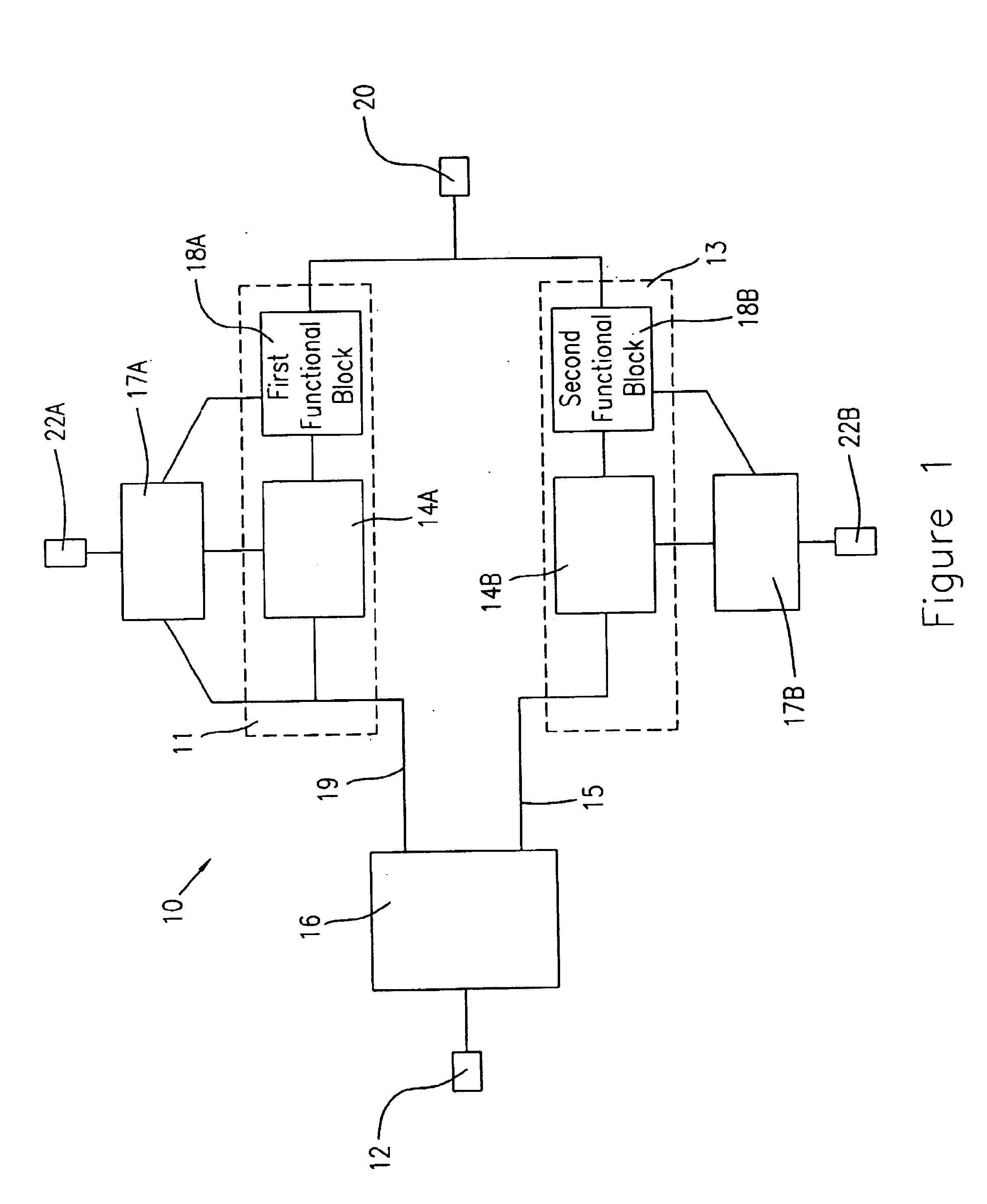
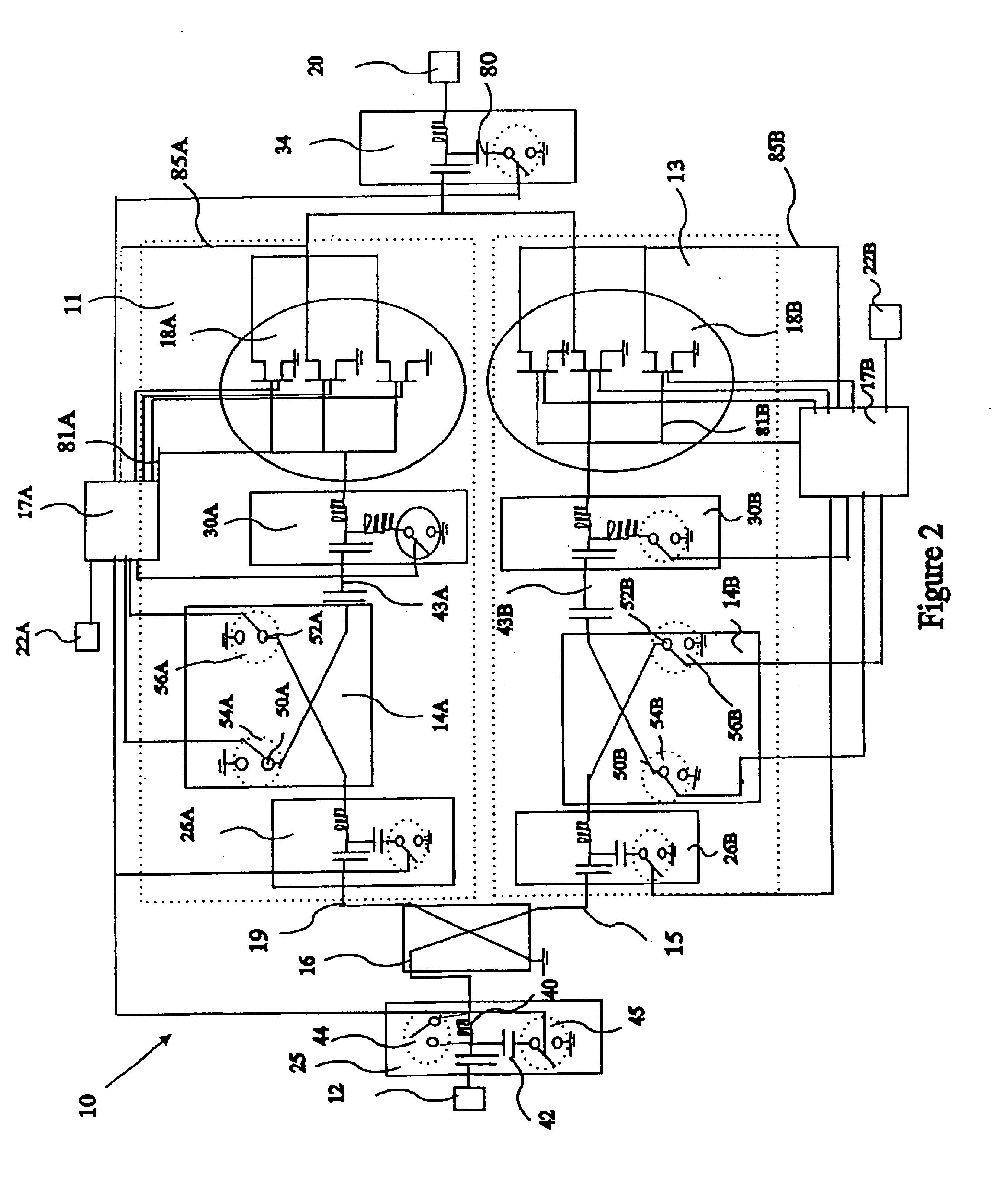
Feedback control method for a heliostat
InactiveUS7207327B2Accurately reflectImprove pointing accuracySolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueHeliostatEngineering
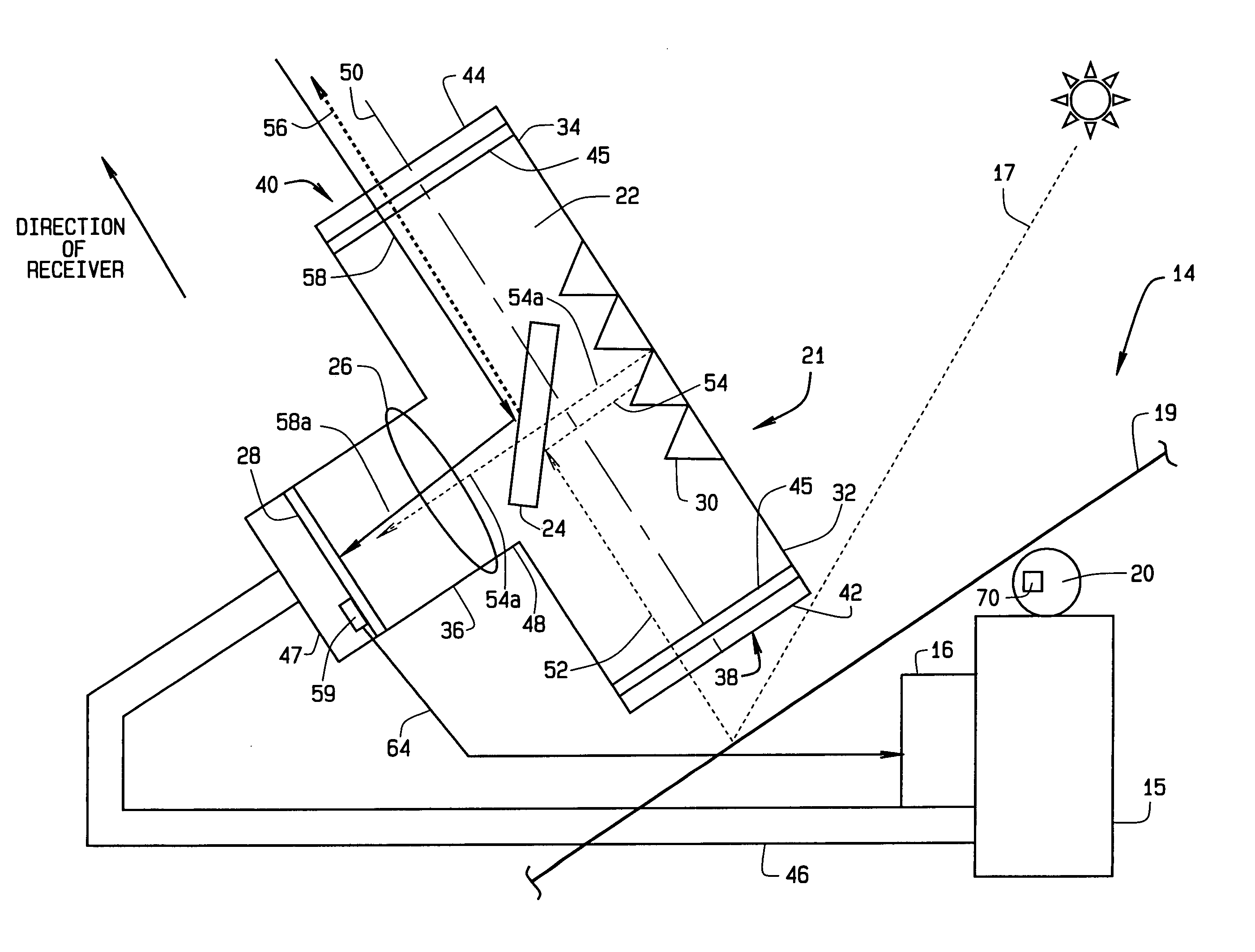
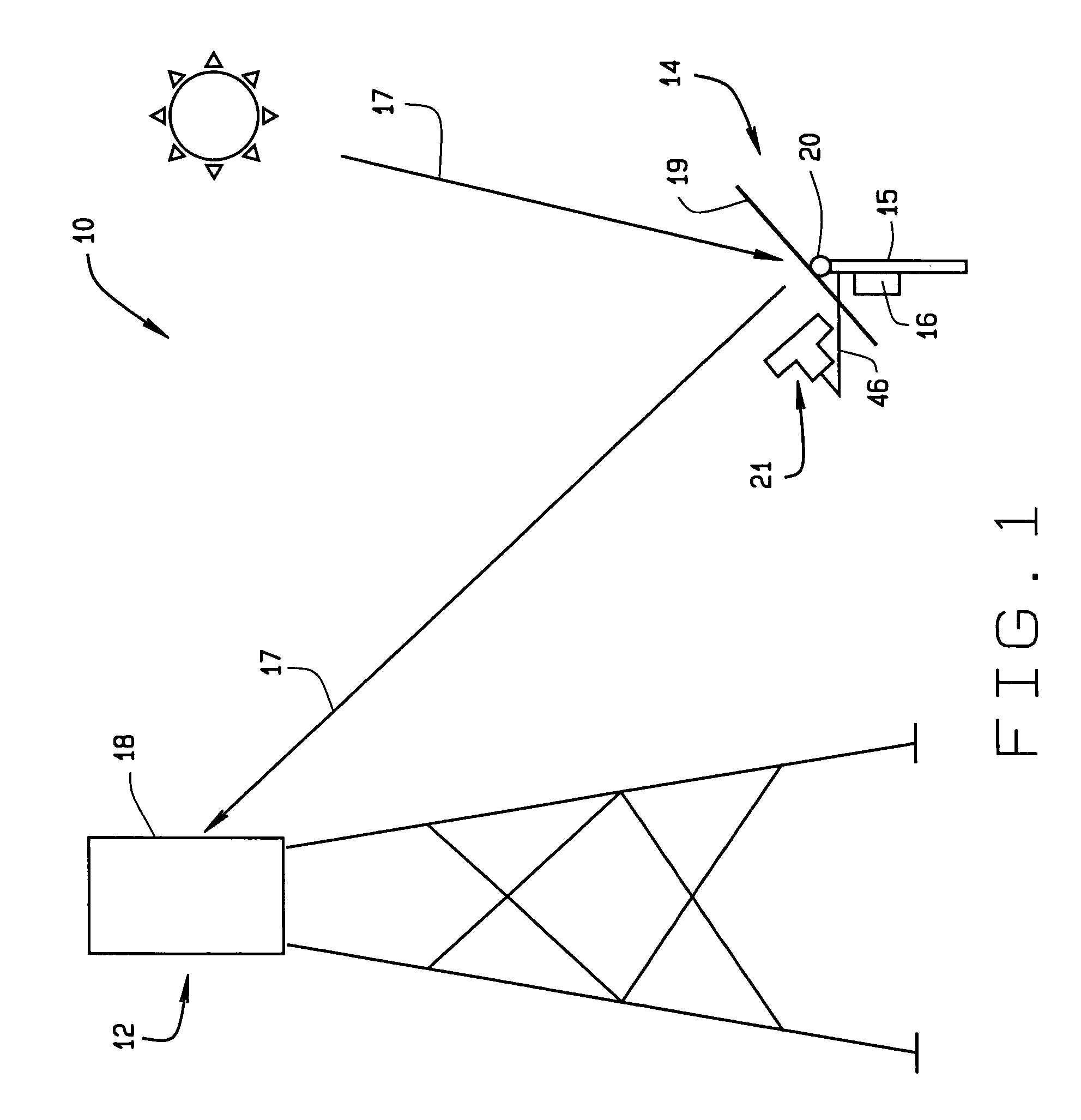
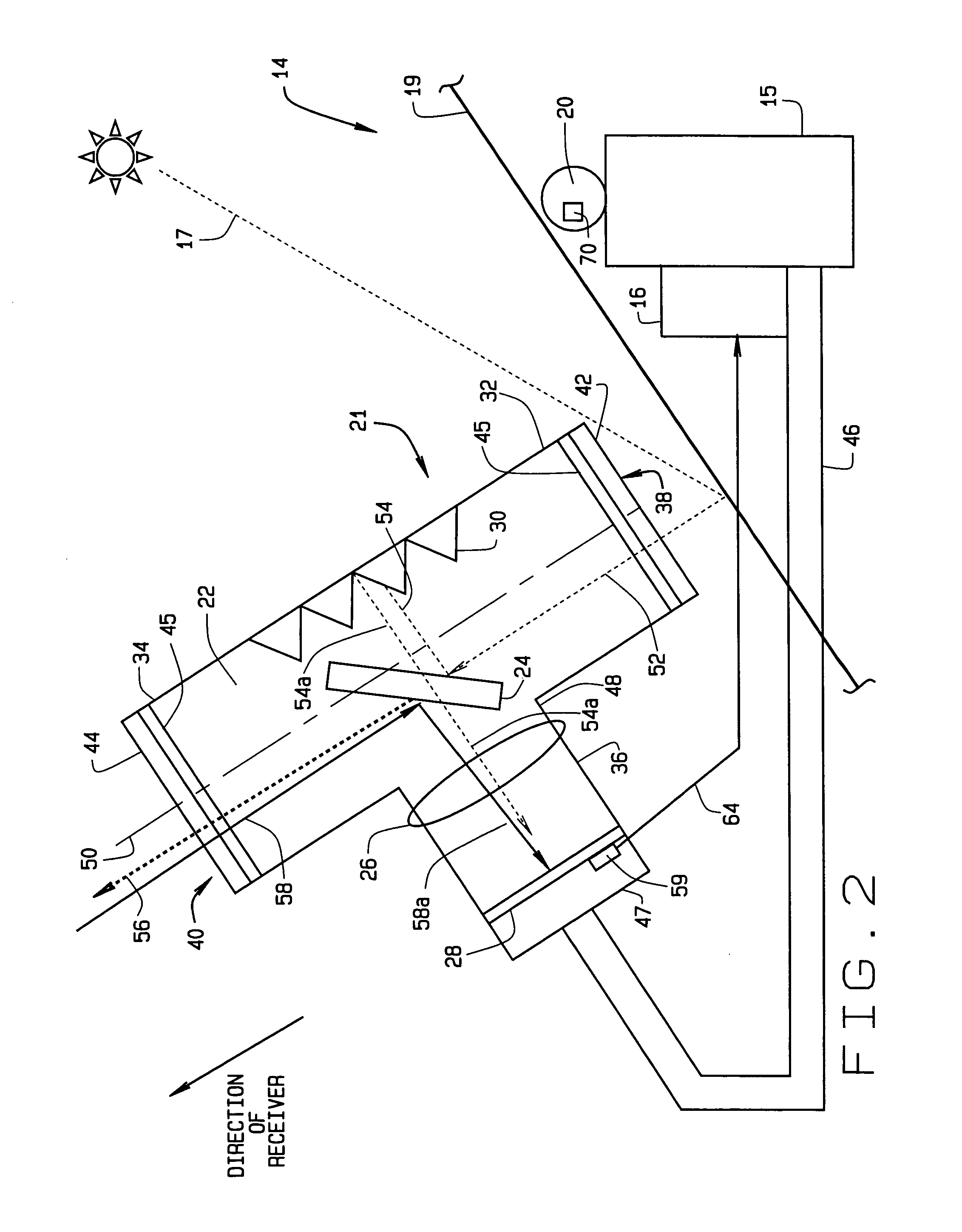
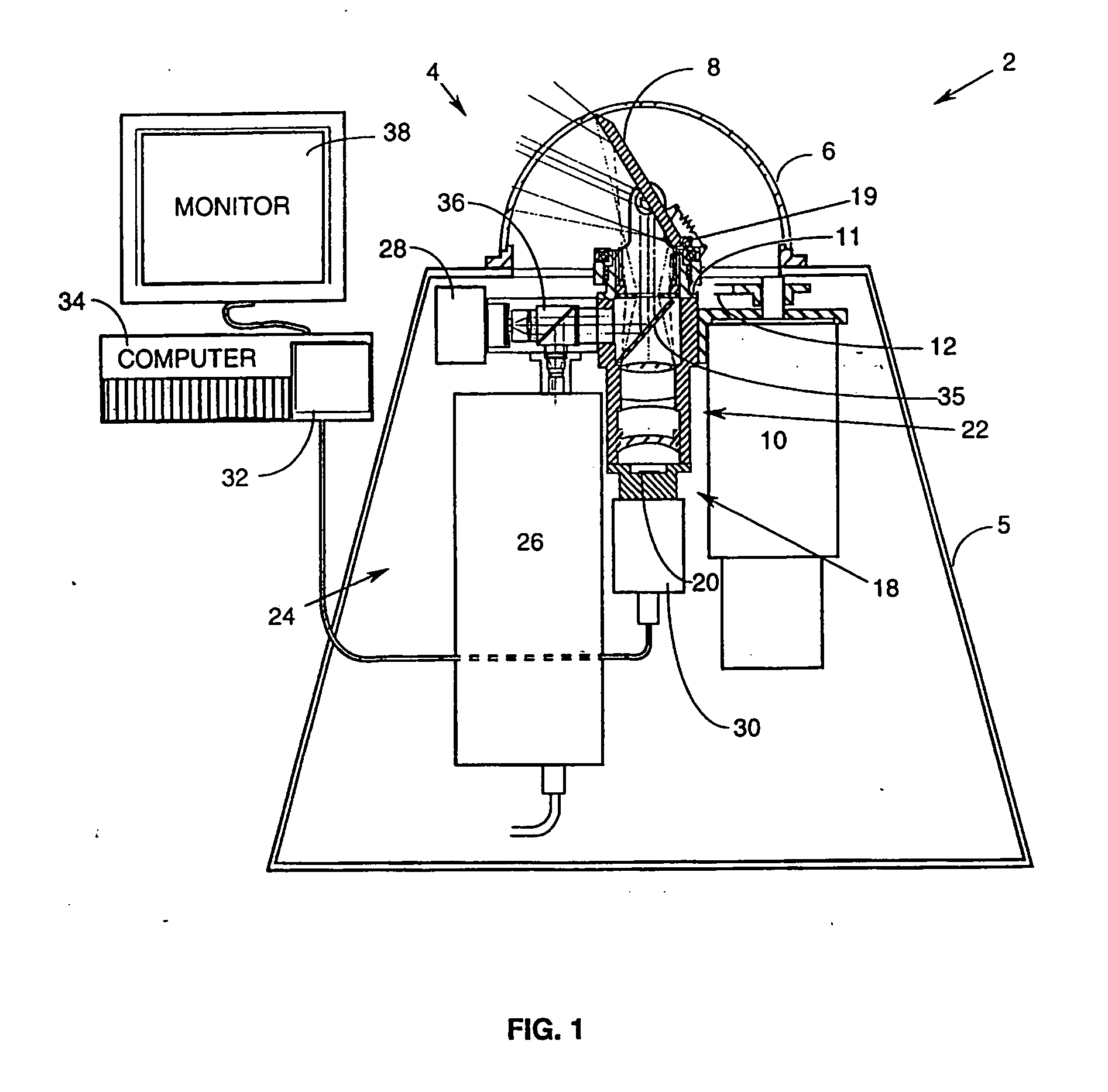
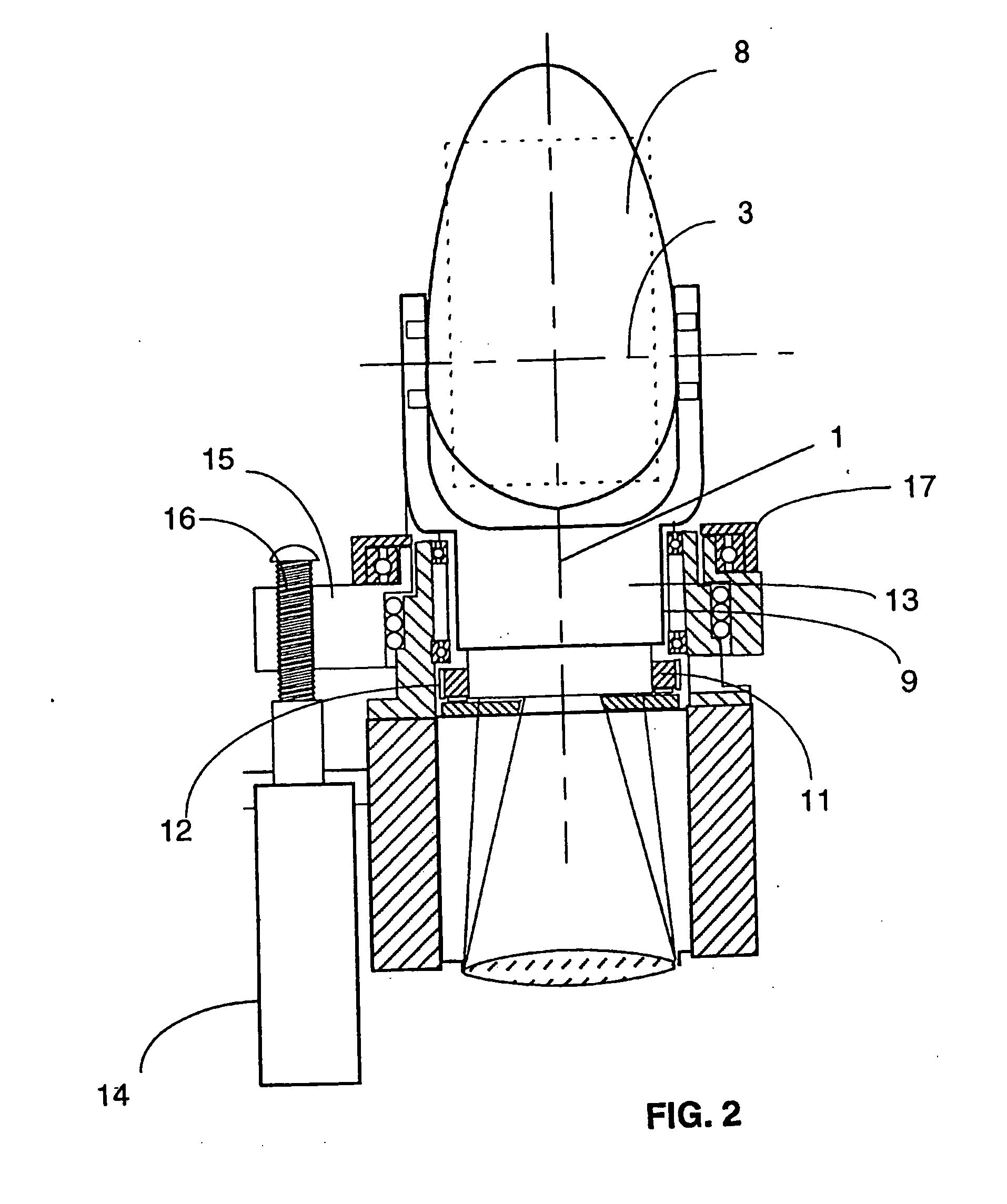
An instrument for a solar energy system including a receiver and a heliostat to reflect solar energy on to the receiver. The instrument includes a first element adapted to form an image of the sun, a second element adapted to form an image of the receiver, and a detector. The detector is positioned to receive each of the images and a comparator is adapted to detect a distance between the images. The comparator generates an error correction signal based on the distance between the images. The error correction signal is received by a controller that controls the operation of a postioner that adjusts the position of the heliostat accordingly.
Owner:SOLARRESERVE TECH +1
Target acquisition and tracking system
InactiveUS20090260511A1Accurate informationImprove effective detection rateWeapon control systemsAiming meansBack projectionEngineering
A projectile tracking system for acquiring and precisely tracking a projectile in flight in order to reveal the source from which the projectile was fired. The source is revealed by the back projection of a 3-dimensional track file. In preferred embodiments the system is installed on a vehicle, such as an un-manned blimp or other aircraft, road vehicle or ship, for locating and destroying small arms fire directed at the vehicle. A kill system may also be included on the vehicle to destroy the source of the projectile.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
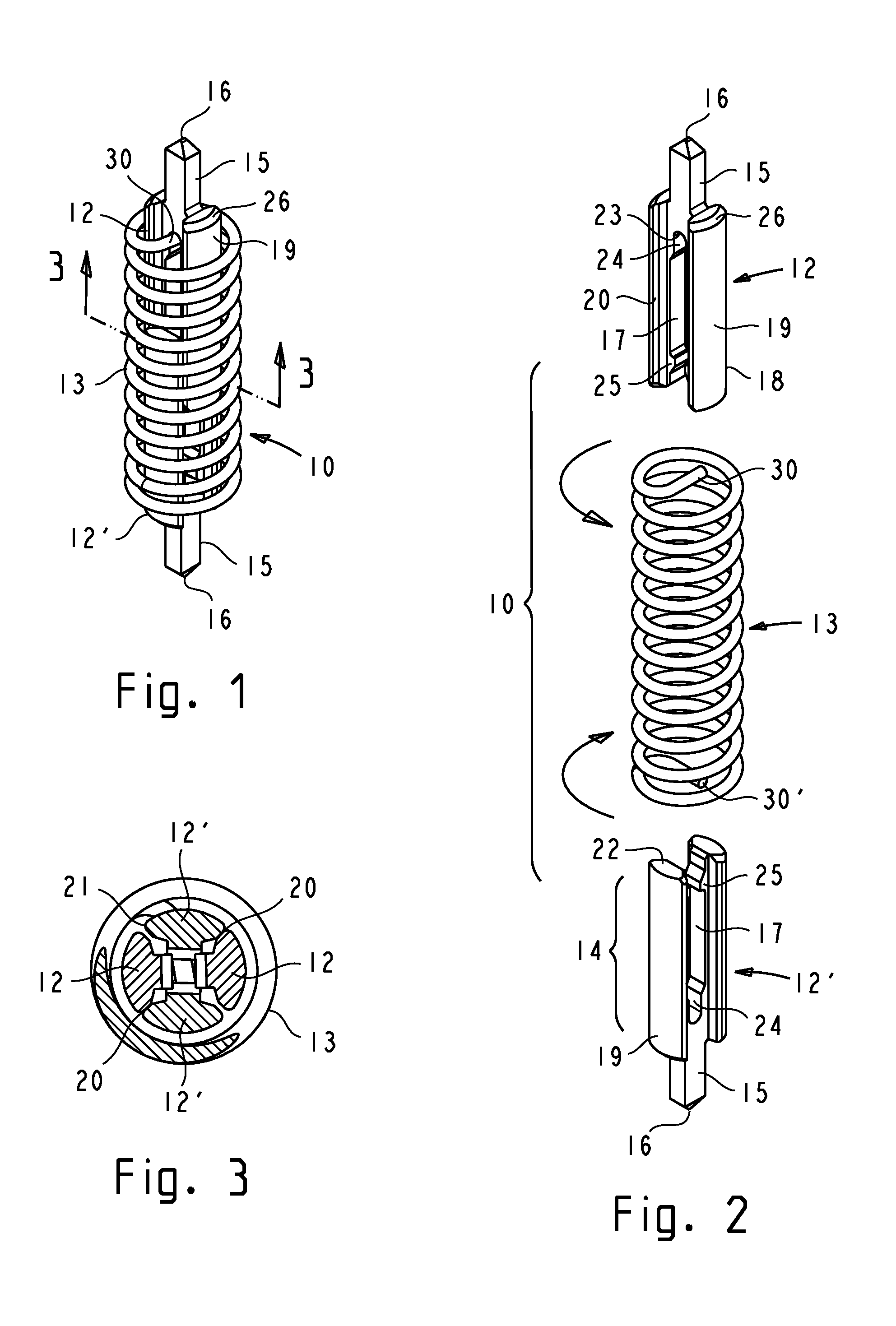
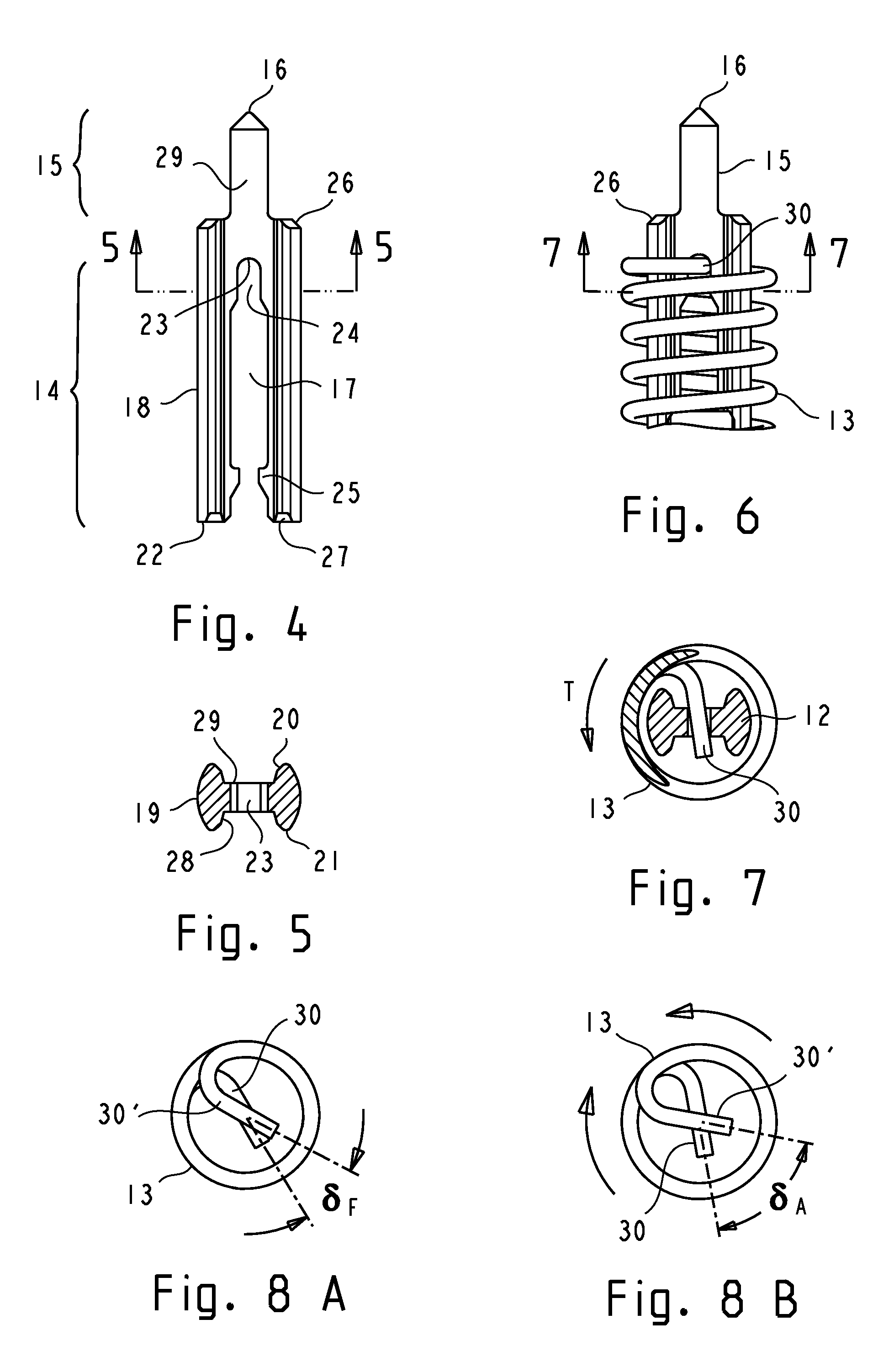
Low inductance contact probe with conductively coupled plungers
InactiveUS8373430B1Electrical effect is reducedPrevent rotationContact member manufacturingElectrical measurement instrument detailsAxial displacementCoupling
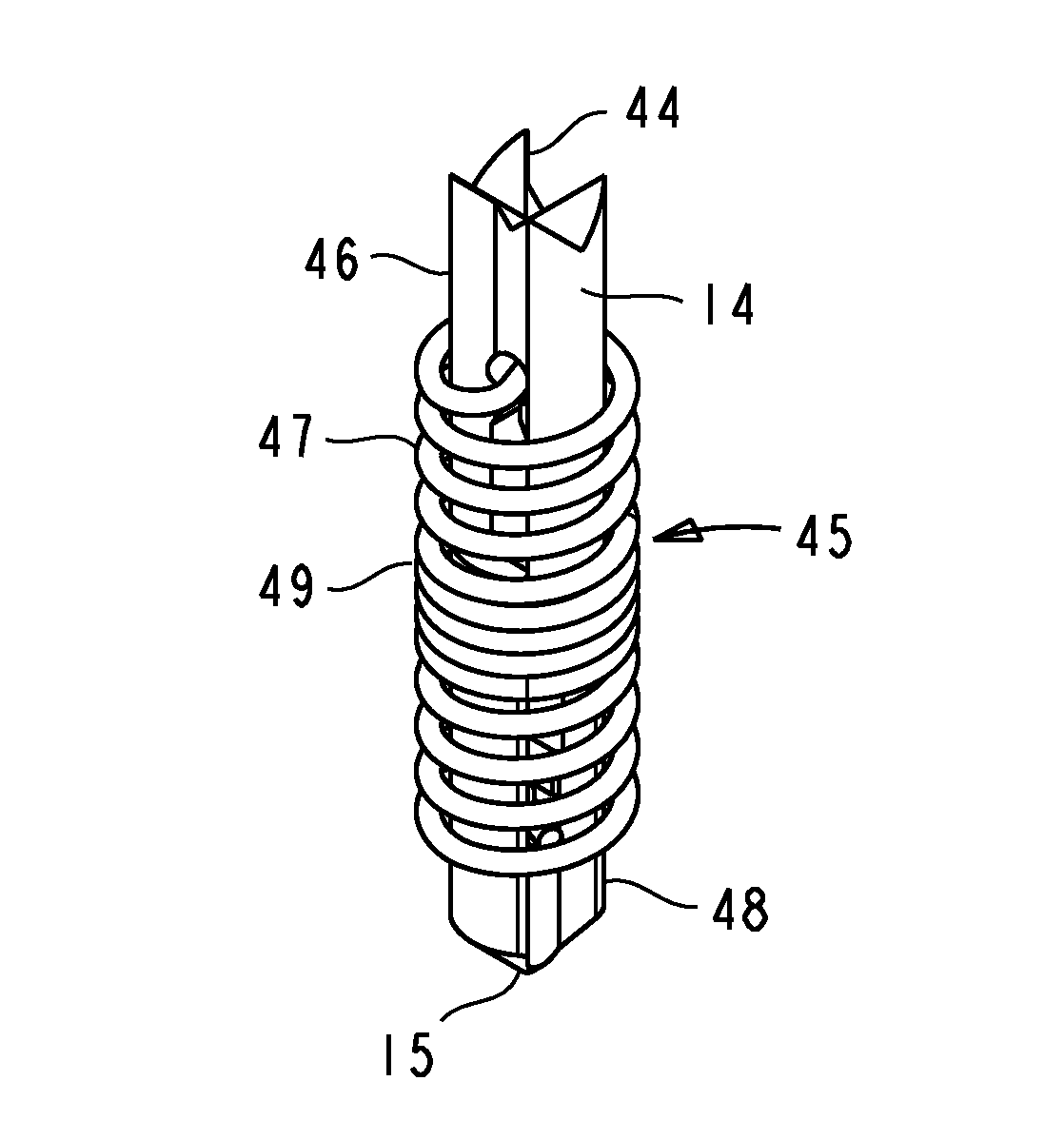
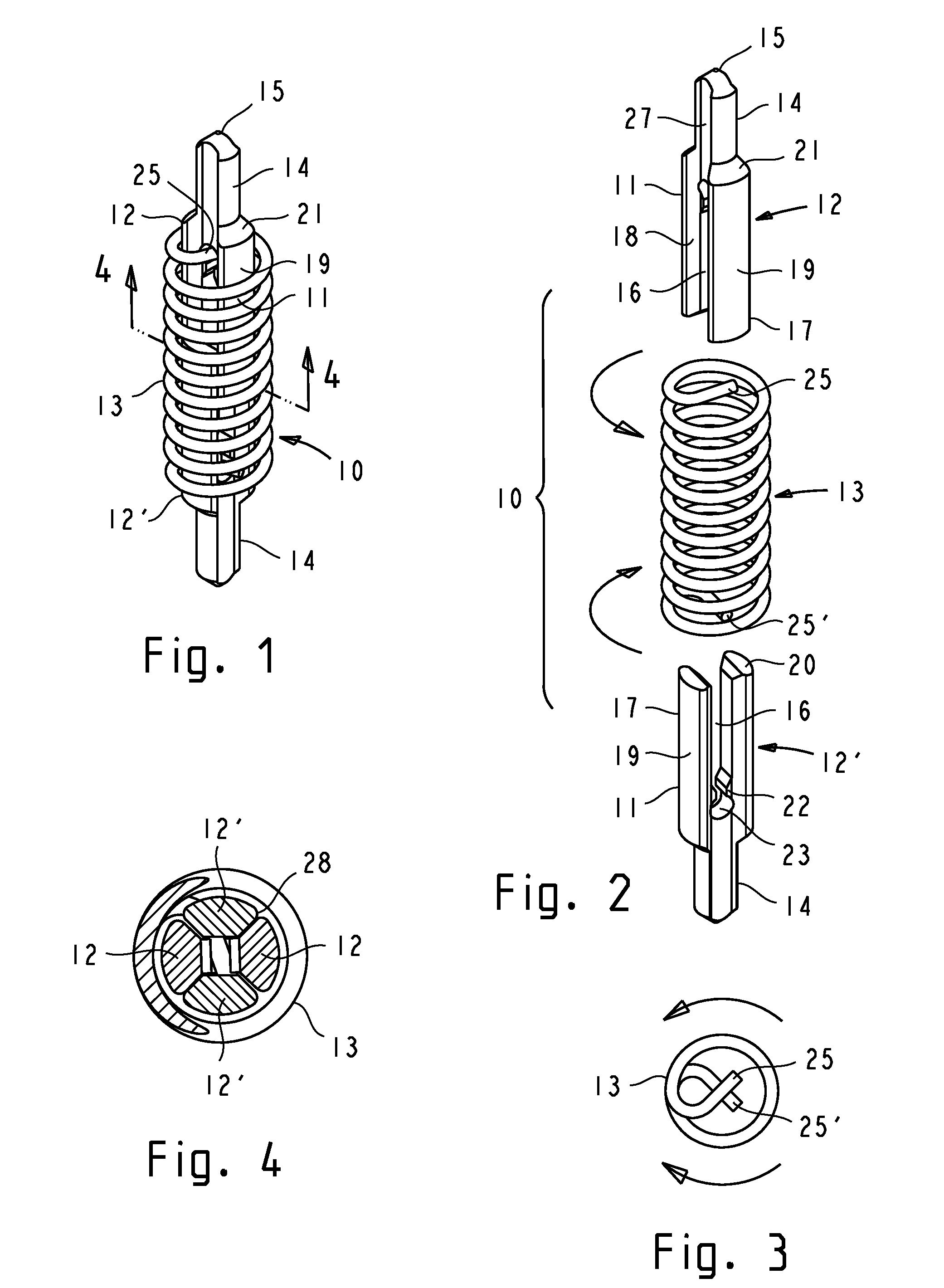
A low inductance contact probe comprises conductively coupled plungers. The plungers have coupling means which enable them to be slidably and non-rotatably engaged. A coil spring is attached to the plungers in a manner that prevents rotation of the spring's ends. The spring provides an axial plunger bias, and a torsional bias for conductive coupling between the plungers. The torsional bias is generated by an axial displacement of the spring and by twisting the spring a predetermined angle prior to attachment to the plungers. Torsion-induced contact forces between the plungers assure a direct conductive path through the plungers. The torsional bias further enables a positive attachment of the spring to the plungers. Plungers with hermaphroditic coupling means can be fabricated from a drawn profiled stock by stamping or machining. Essential plunger coupling features can be prefabricated in a drawn profiled stock with a high degree of dimensional accuracy and reproducibility.
Owner:SOCHOR JERZY ROMAN
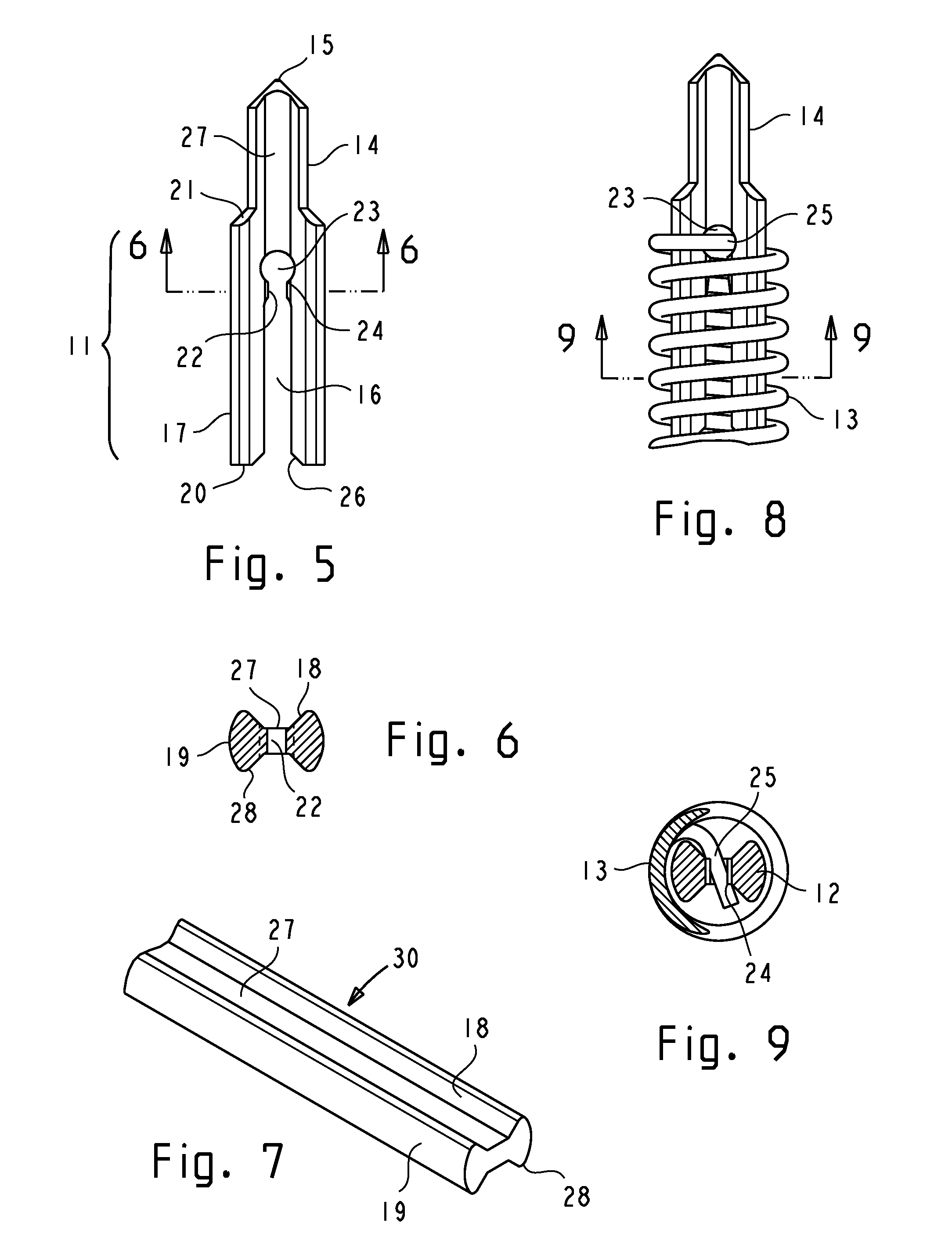
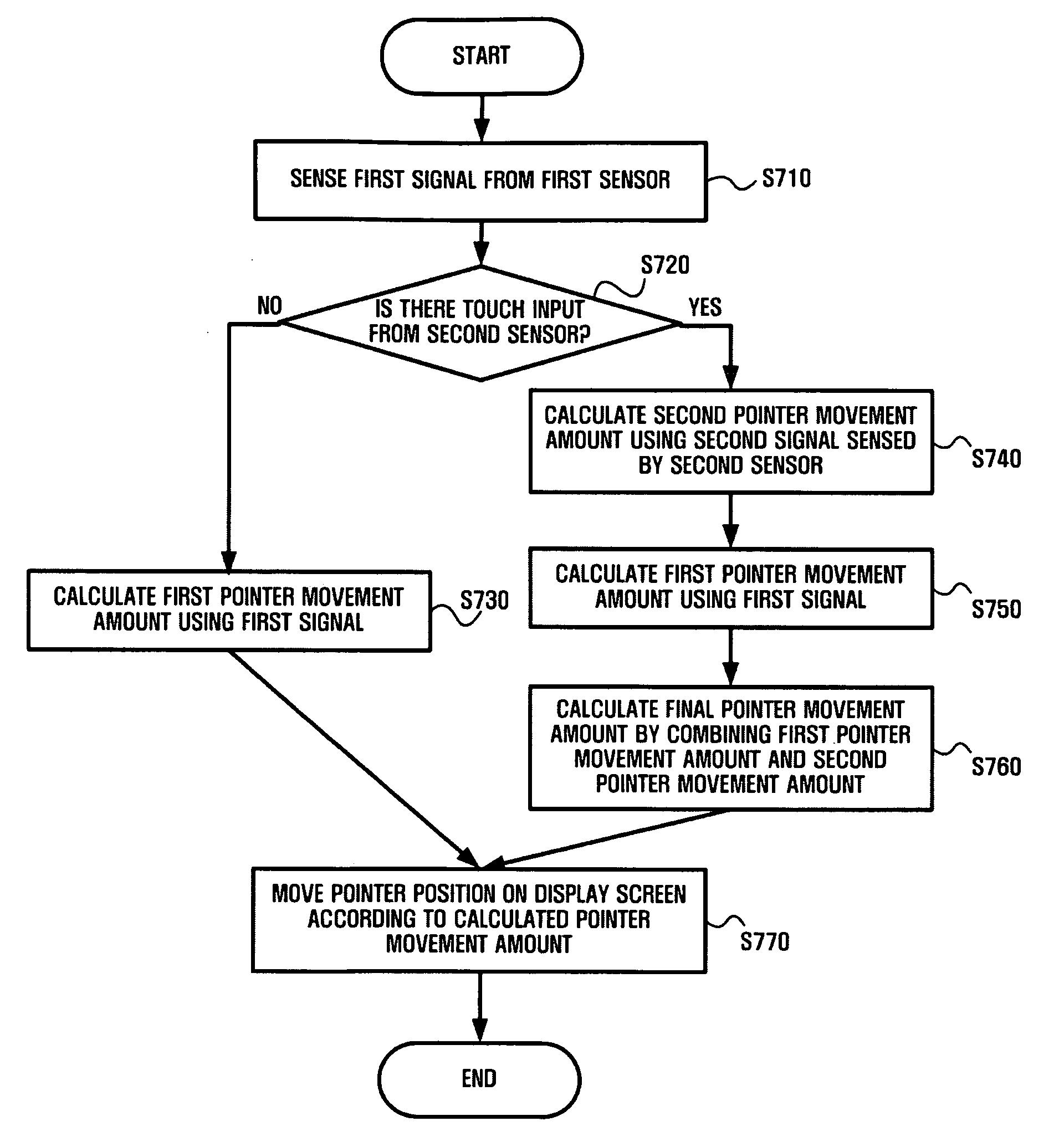
Dual pointing device and method based on 3-D motion and touch sensors
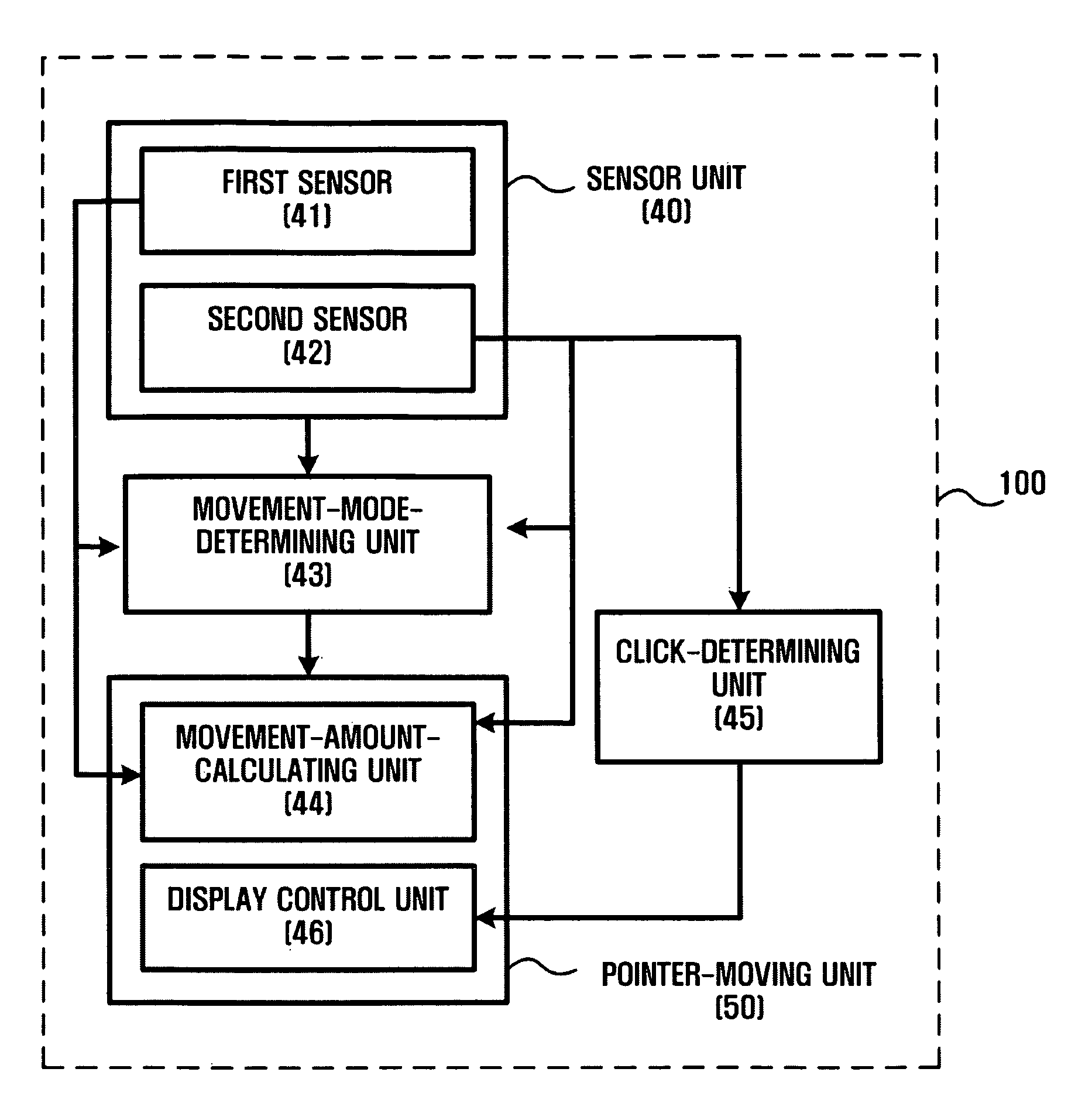
InactiveUS20090153500A1Improve pointing accuracyPointing accuratelyCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPointing deviceComputer science
A dual pointing device and method based on 3-D motion and touch sensors are provided. The dual pointing device includes a sensor including a first sensor sensing a motion in a space and a second sensor sensing a touch input, a movement-mode-determining unit determining a movement mode type using signals of the first and second sensors, and a pointer-moving unit moving a pointer on a display screen using at least one of the signals of the first sensor and the second sensor according to the determined movement mode type.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
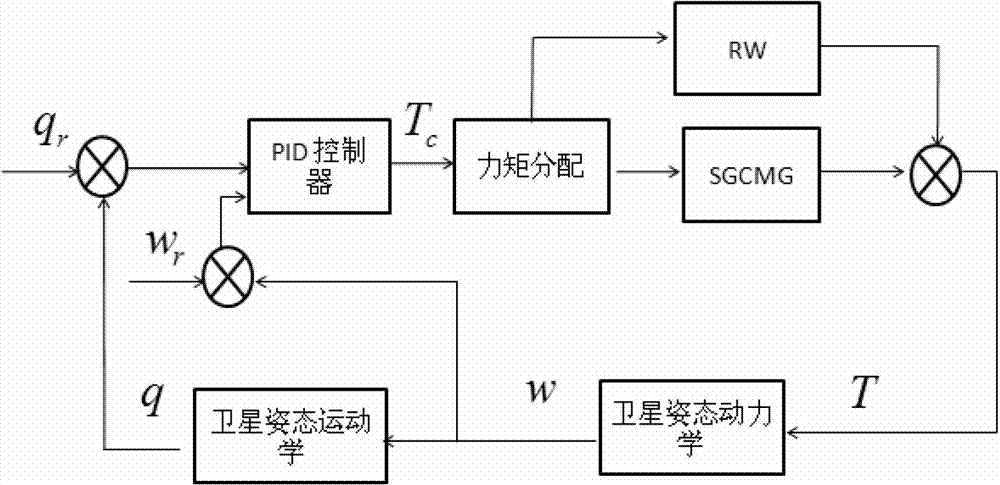
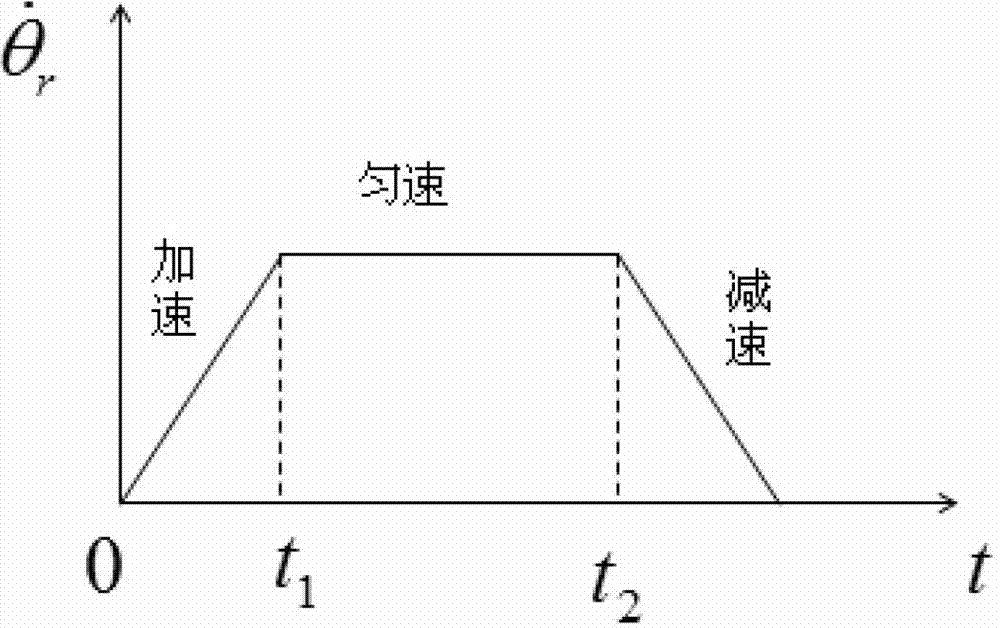
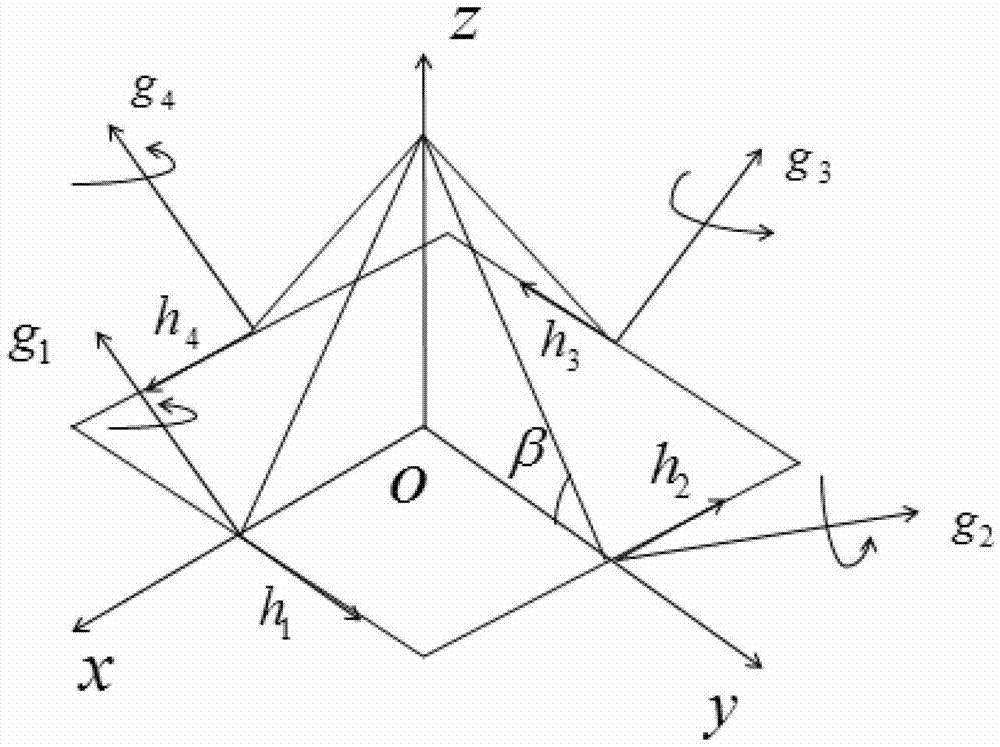
Spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver method based on single gimbal control moment gyro (SGCMG) and reaction wheel (RW)
ActiveCN103092208AHigh precisionReduce maneuvering timeAttitude controlAdaptive controlEngineeringFlywheel
The invention discloses a spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver method based on a single gimbal control moment gyro (SGCMG) and a reaction wheel (RW) and relates to a spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver method which is used for achieving spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver. According to the method, a control moment gyro (CMG) and the RW are used as a combination executing mechanism to achieve the spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver. Angular speed of winding around an Euler main shaft is divided into three sections. Needed controlling torque is generated through the CMG in an accelerating section and a braking section. After a constant speed section and the braking section are finished, a compensate torque generated by the RW is adopted to guarantee that the angular speed is kept near a steady state value so that the spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver is achieved. The method is suitable for the attitude maneuver condition that a spacecraft is provided with the CMG and the RW so that rapid maneuver of the spacecraft is achieved and attitude directing in high accuracy and stability are guaranteed. The method is suitable for maneuver control of the spacecraft.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Electronically programmable multimode circuit
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Missile protection system for vehicles
InactiveUS20060283317A1Improve effective detection rateImprove pointing accuracyAircraft componentsAiming meansBack projectionEngineering
A projectile tracking system for acquiring and precisely tracking a projectile in flight in order to reveal the source from which the projectile was fired. The source is revealed by the back projection of a 3-dimensional track file. In preferred embodiments the system is installed on a vehicle, such as an un-manned blimp or other aircraft, road vehicle or ship, for locating and destroying small arms fire directed at the vehicle. A kill system may also be included on the vehicle to destroy the source of the projectile.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Embedded satellite configuration
InactiveCN106742063AReduce feature sizeReduce the inertia of the whole starCosmonautic power supply systemsArtificial satellitesSpace environmentSolar cell
The invention provides an embedded satellite configuration. The embedded satellite configuration comprises a platform cabin, a loading cabin, a docking locking-unlocking mechanism, a non-contact magnetic suspension direct force control mechanism and a solar cell array. The platform cabin is in a hollow annular structure; the loading cabin is arranged in the platform cabin; the docking locking-unlocking mechanism and the non-contact magnetic suspension direct force control mechanism are arranged between the platform cabin and the loading cabin respectively; the solar cell array is arranged on the side of the platform cabin. Ultrahigh-precision ultrahigh-stability control requirements of satellites are met, quality characteristics and agile mobility performances of the satellites are improved, a loading space environment is improved, and influences of platform disturbance and thermal cycling on satellite loading are reduced. According to a design conception of non-contact split design and centralized control, the embedded satellite configuration has advantages of structural configuration compactness, high control precision, high environmental adaptability, low development risk, short cycle and simplicity and feasibility in integration and final assembly.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
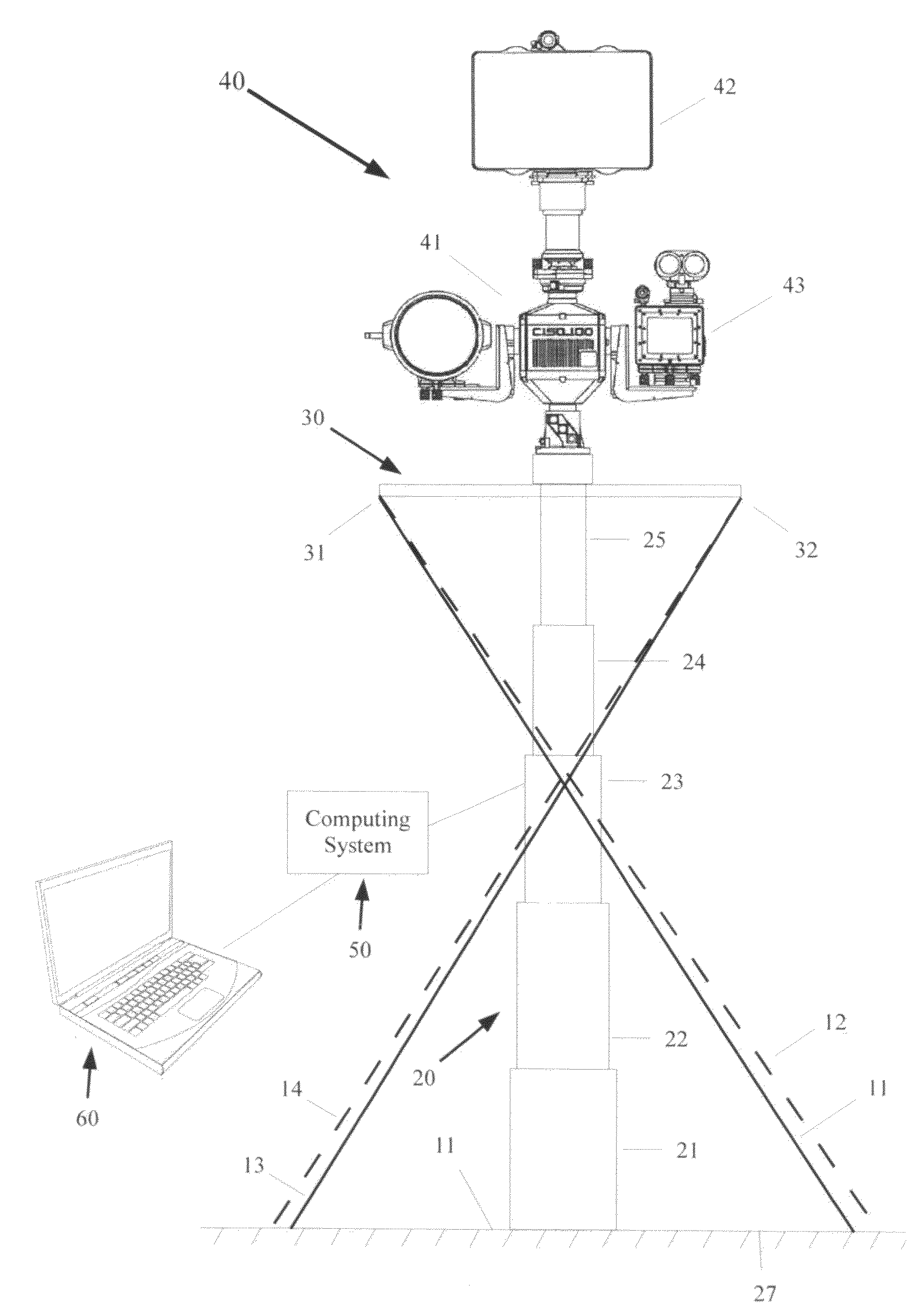
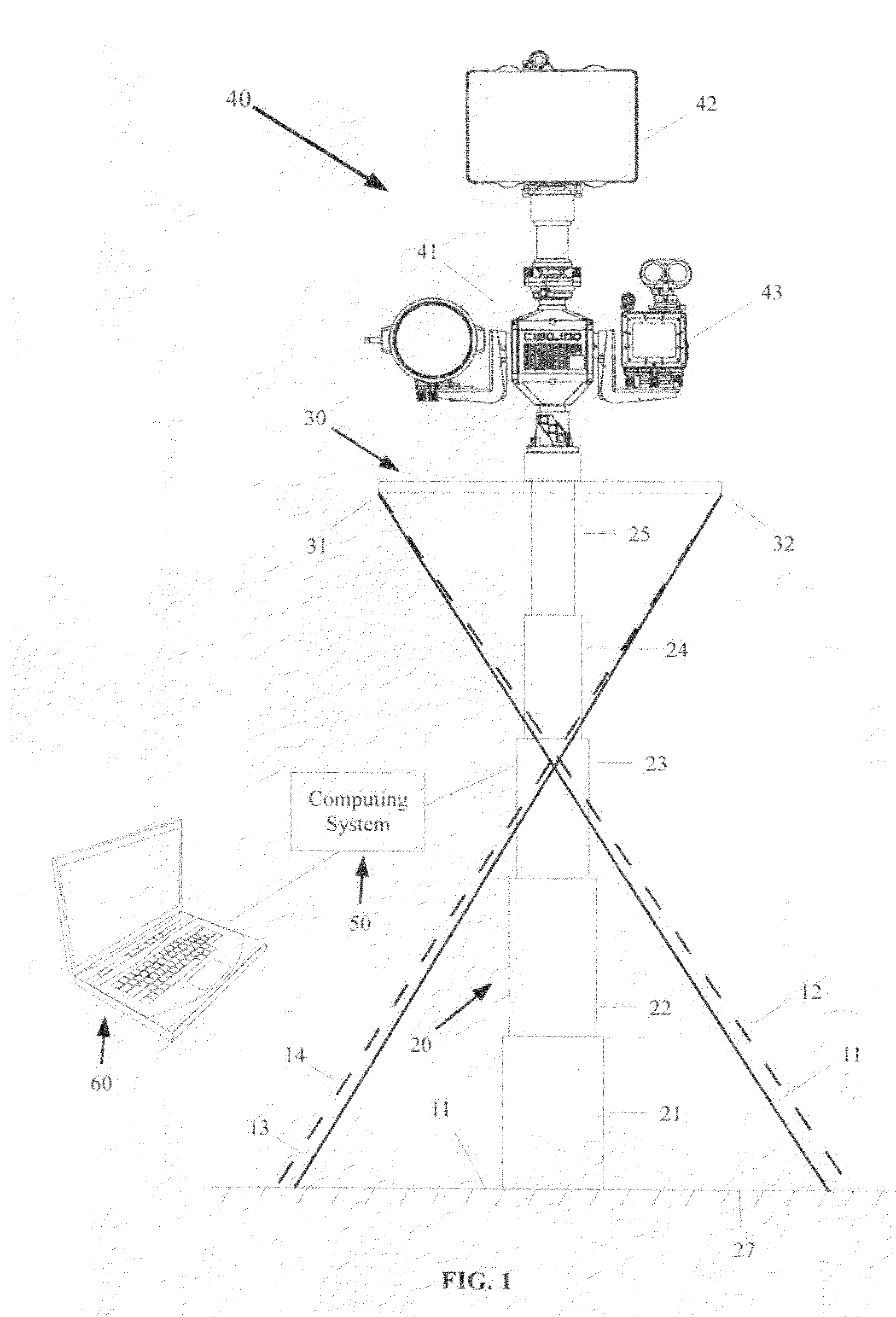
Mechanical stabilization and automated positional corrections for stationary or mobile surveillance systems
InactiveUS20110007157A1Cost-effective and accurateImprove efficiencyAntenna supports/mountingsSurveying instrumentsRadarMechanical stability
A system for providing mechanical stabilization with automated corrections for stationary or mobile surveillance platforms comprises: a telescoping mast that supports a sensor package containing a camera, surveillance radar, a pan tilt unit, and a tilt sensor with a precision compass. Stabilization involves hardware and software enhancements to conventional surveillance systems. Mast stabilization is achieved by a mechanical guy-wire arrangement which provides for both anti-twist and anti-sway support of the mast upper end through a crisscrossed guy wire arrangement. Eight different software algorithms contribute to stability and highly accurate and rapid slewing of the surveillance equipment. A mast tilt calibration algorithm in combination with a calibration sensor package provides for automatic electronic leveling of the camera with dwells at predetermined pan angles. A mast stability measurement algorithm assesses mechanical stability of the mast by comparing measured mass tilt versus pan characteristics to an ideal curve for a perfectly stabile mast.
Owner:TELEPHONICS
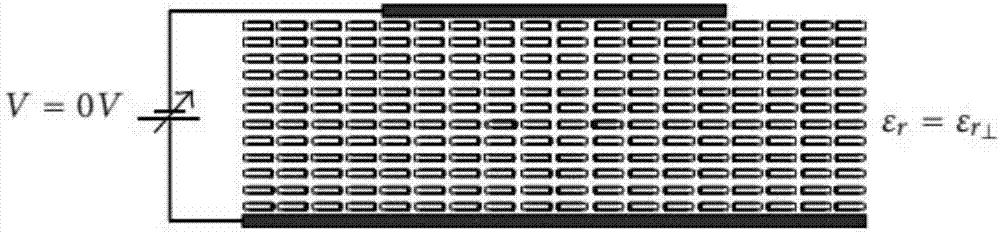
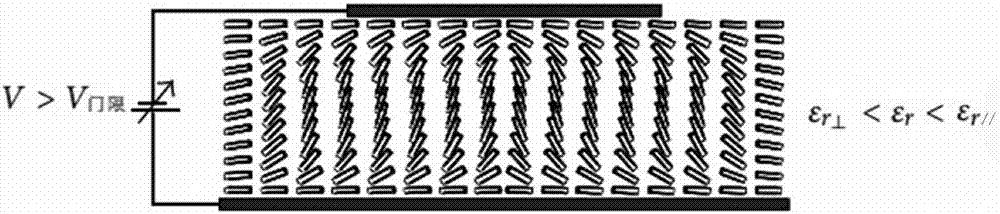
Phased array antenna based on meta-material electromagnetic characteristics
ActiveCN107275805AHigh gainReduce sidelobe levelParticular array feeding systemsAntennas earthing switches associationMicrostrip patch antennaAntenna gain
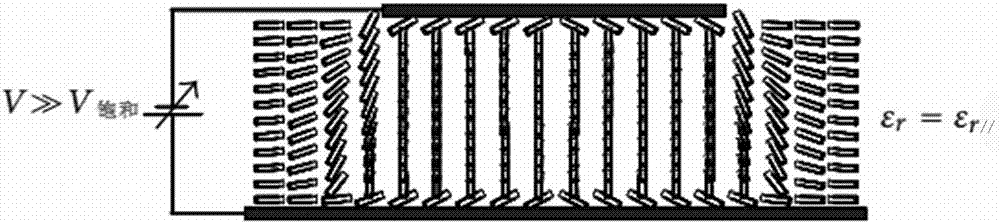
The invention mainly belongs to the technical field of microwaves and millimeter waves and particularly relates to a phased array antenna based on meta-material electromagnetic characteristics. The phased array antenna comprises a microstrip patch antenna unit and a feed device. The microstrip patch antenna unit comprises a positive electrode, a dielectric substrate and a negative electrode. The microstrip patch antenna unit adopts a metamaterial as the dielectric substrate. By applying a bias voltage to the metamaterial dielectric substrate and changing the dielectric constant [Epsilon]r of the metamaterial dielectric substrate, a microstrip patch unit to which the bias voltage is applied is enabled in a resonant condition. A microstrip patch unit to which the bias voltage is not applied is not in the resonant condition, to achieve sparsification of the phased array antenna unit. The phased array antenna unit of the present invention controls the excitation phase of the activated radiation unit more precisely so as to improve the pointing accuracy of the main beam of the antenna, increase the antenna gain, reduce the antenna side lobe level, expand the antenna beam scanning range and extend the working bandwidth of the antenna.
Owner:BEIJING HUAMETA TECH CO LTD
Contact probe with conductively coupled plungers
InactiveUS8547128B1Electrical effect is reducedPrevent rotationElectrical measurement instrument detailsCoupling device detailsCouplingCoil spring
A contact probe comprises conductively coupled plungers and a coil spring. The plungers have coupling means which enable them to be slidably and non-rotatably engaged. The spring is attached to the plungers in a manner that prevents rotation of the spring's ends. A desired magnitude of torsional bias is generated by twisting the spring a predetermined angle prior to attachment of the spring to the plungers. An additional torsional bias is generated by the tendency of the spring to twist when the spring is axially displaced. The resultant torsional bias rotatably biases the coupling means of the plungers against each other, generating contact forces for a direct conductive coupling between the plungers. The plungers are self-latching or are retentively attached to the spring using the torsional bias of the spring. Plungers with hermaphroditic coupling means can be fabricated from a sheet metal or a profiled stock by stamping or machining.
Owner:SOCHOR JERZY ROMAN
Antenna autotrack control system for precision spot beam pointing control
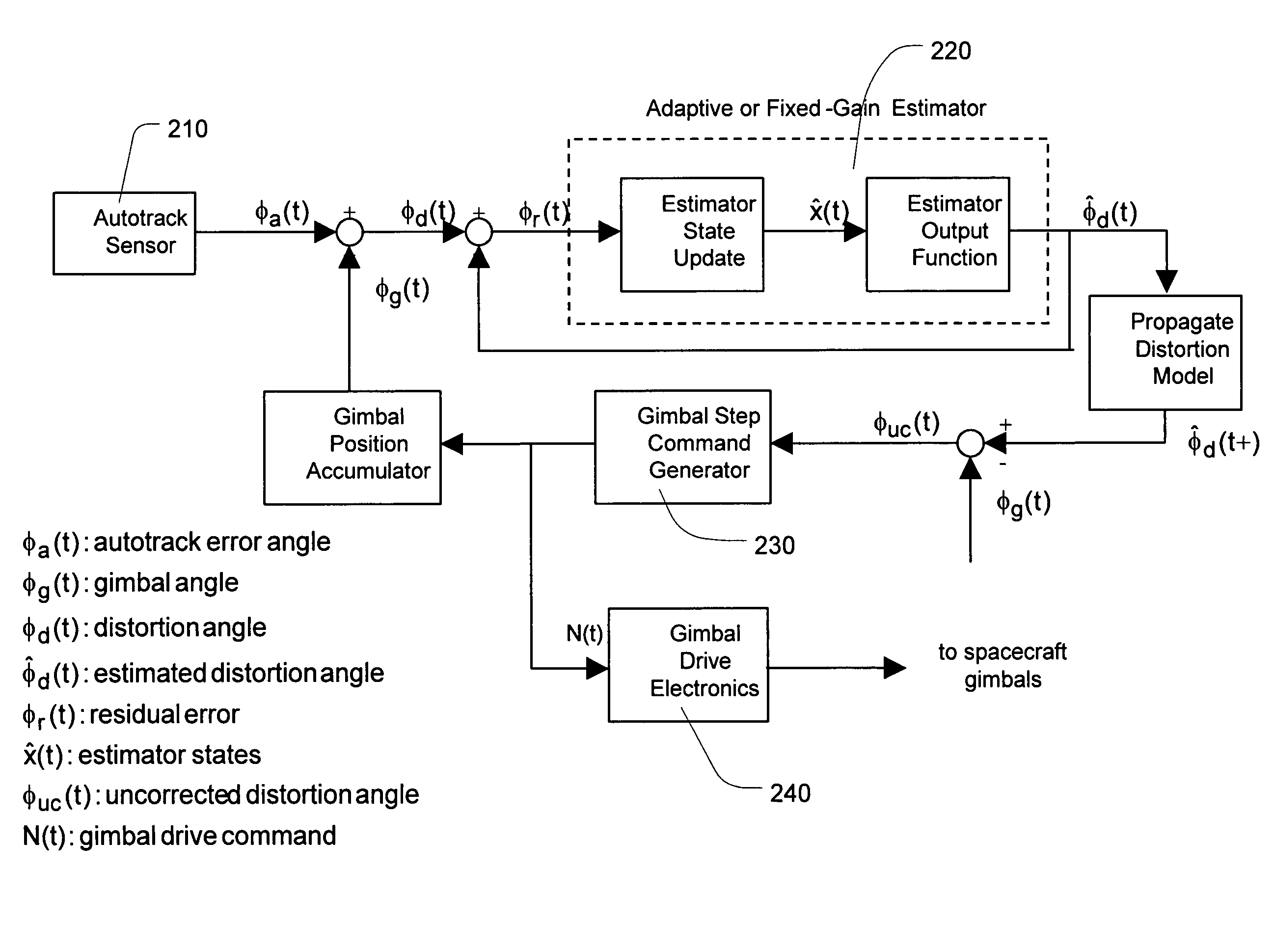
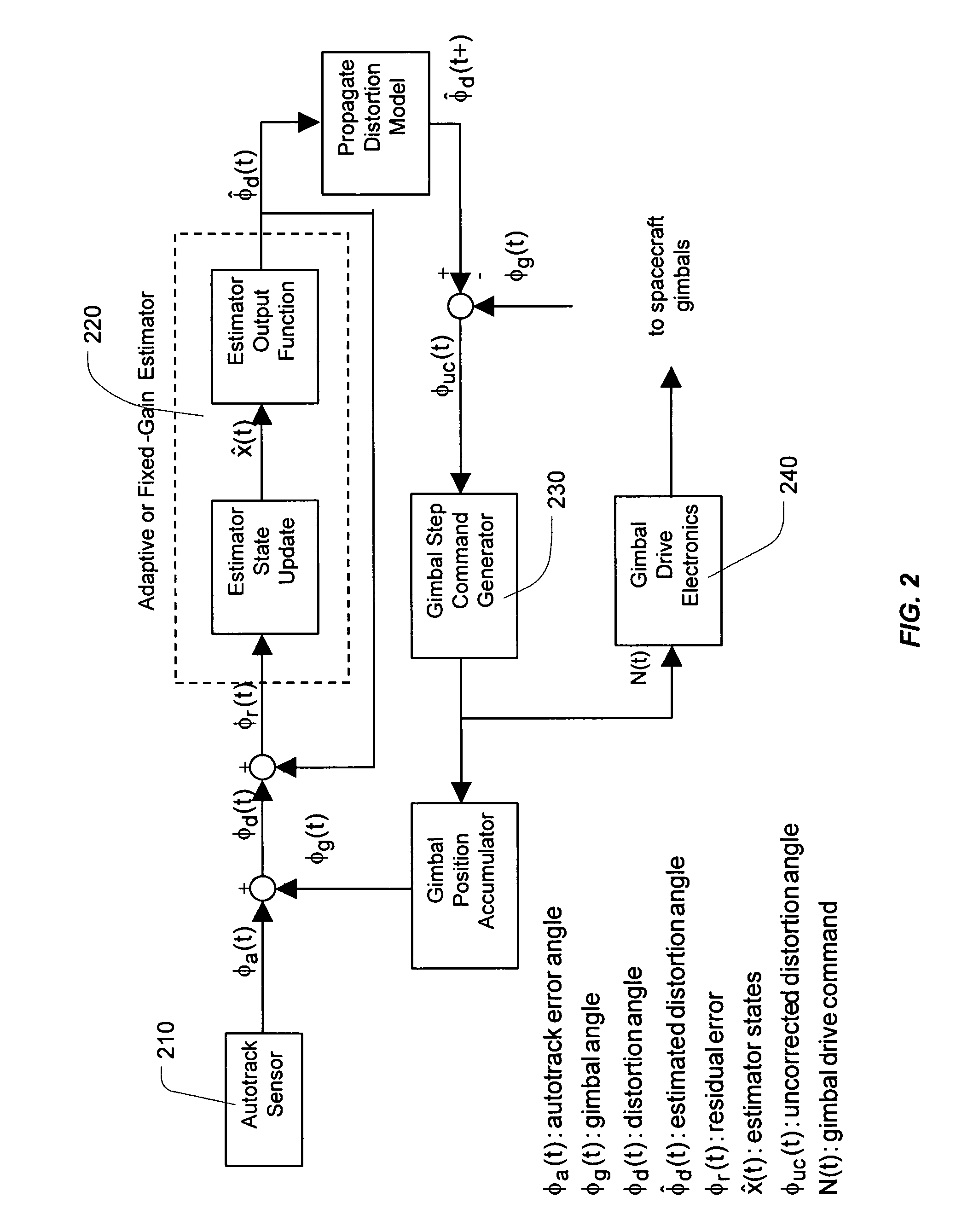
ActiveUS7663542B1Improve performancePreventing excessive gimbal steppingAntenna detailsControl systemLearning models
The present invention provides a system and a method for improving spacecraft antenna pointing accuracy utilizing feedforward estimation. The present invention takes advantage of the fact that spacecraft antenna pointing error has periodic behavior with a period of 24 hours. Thus, unlike the prior art feedback systems which blindly correct antenna pointing error continuously reacting only to presently sensed error, the present invention takes an intelligent approach and learns the periodic behavior of spacecraft antenna pointing error. Then, an estimate of antenna pointing error at a particular time going forward is predicted based on the learned model of the periodic behavior of the antenna pointing error. The predicted estimate is then used to correct or cancel out the antenna pointing error at a particular time in the future. The result is more accurate correction of spacecraft antenna pointing error by more than a factor of two.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Electronically programmable multimode circuit
An electronically programmable multimode circuit is described. More particularly, the present invention is an electronically programmable multimode circuit that includes a first path and a second path wherein a mode and a signal directional flow direction is controlled through the selective biasing of the first path and the second path. A multimode circuit is produced that contains modes such as a phase shifter mode, an IQ modulation mode, an amplifier mode, a mixer mode, and a multiplier mode.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
High-precision imaging attitude pointing control method based on agile satellite
ActiveCN110174899AReduce correctionImprove smoothnessNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansSkyOptical axis
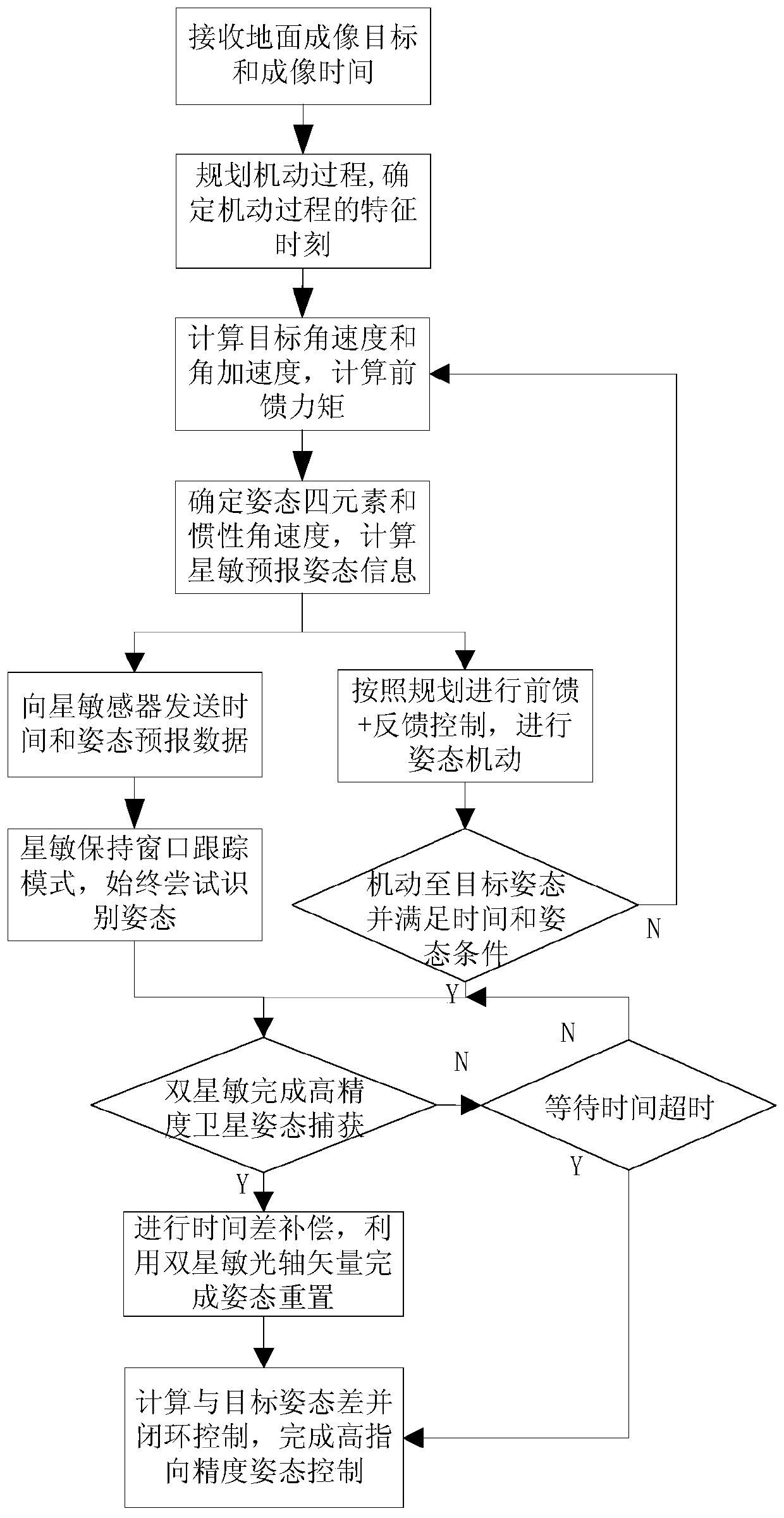
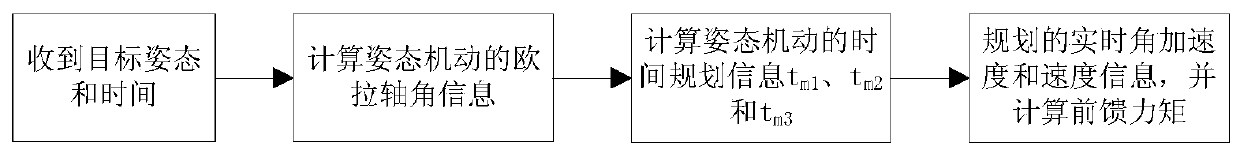
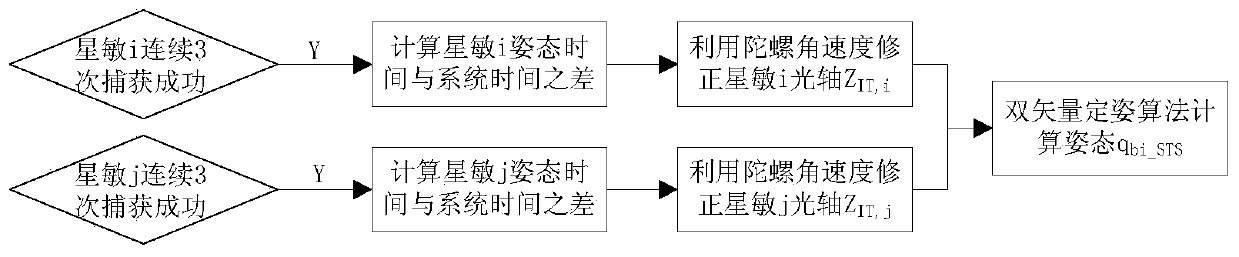
A high-precision imaging attitude pointing control method based on the agile satellite is provided. The method comprises that: an attitude maneuvering process is planned according to the specified ground imaging target and time; in the maneuvering process, the attitude prediction information and the corresponding time are calculated and transmitted to a star sensor according to a fixed frequency;the star sensor predicts the sky window according to the time and attitude data, and keeps trying to extract the attitude in a window tracking mode; the satellite moves to the vicinity of the target and gradually decelerates, the star sensor captures the satellite attitude information quickly in a high-precision manner, and the system uses double star-sensitive optical axis vectors to compete attitude reset; and finally, closed-loop correction is performed by using the difference between the reset attitude and the target attitude to complete the high-precision attitude pointing control. According to the method provided by the present invention, the star-sensitive high-precision attitude information available only at small angular velocities is fully used to compensate for the influence ofgyro measurement information with nonlinear and drift variation characteristics on imaging pointing precision.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Azimuth-pitch movement two-shaft seat rack
ActiveCN106125770ASimple structureEasy to operateStands/trestlesControl using feedbackConnection typeRadar
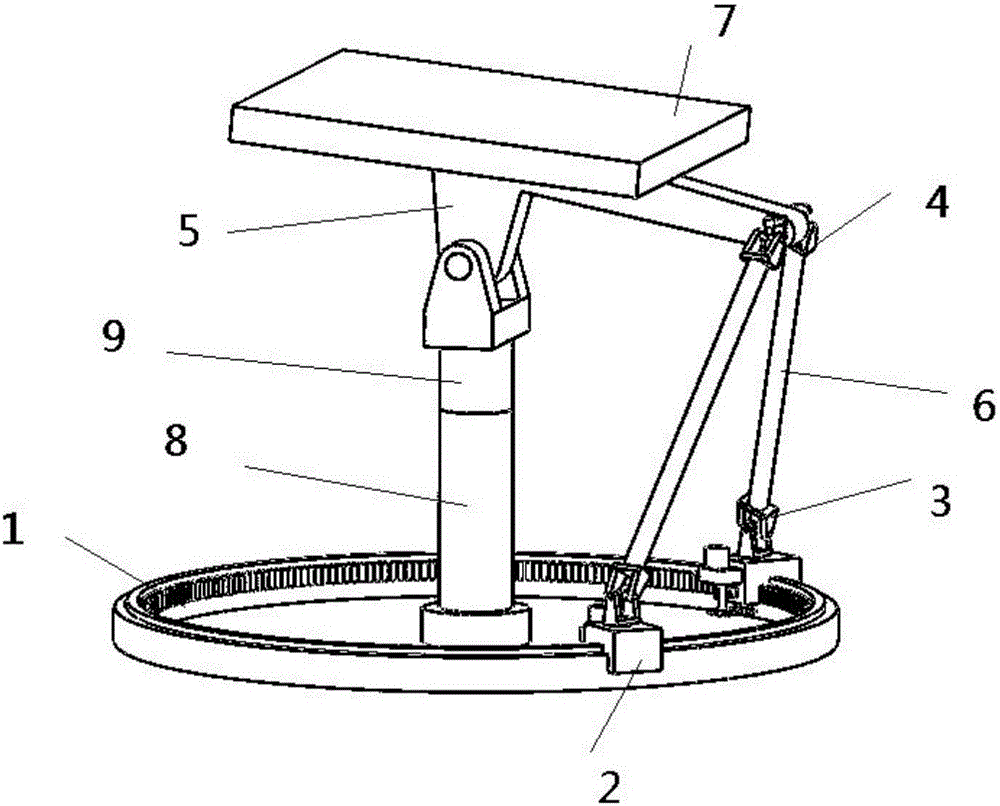
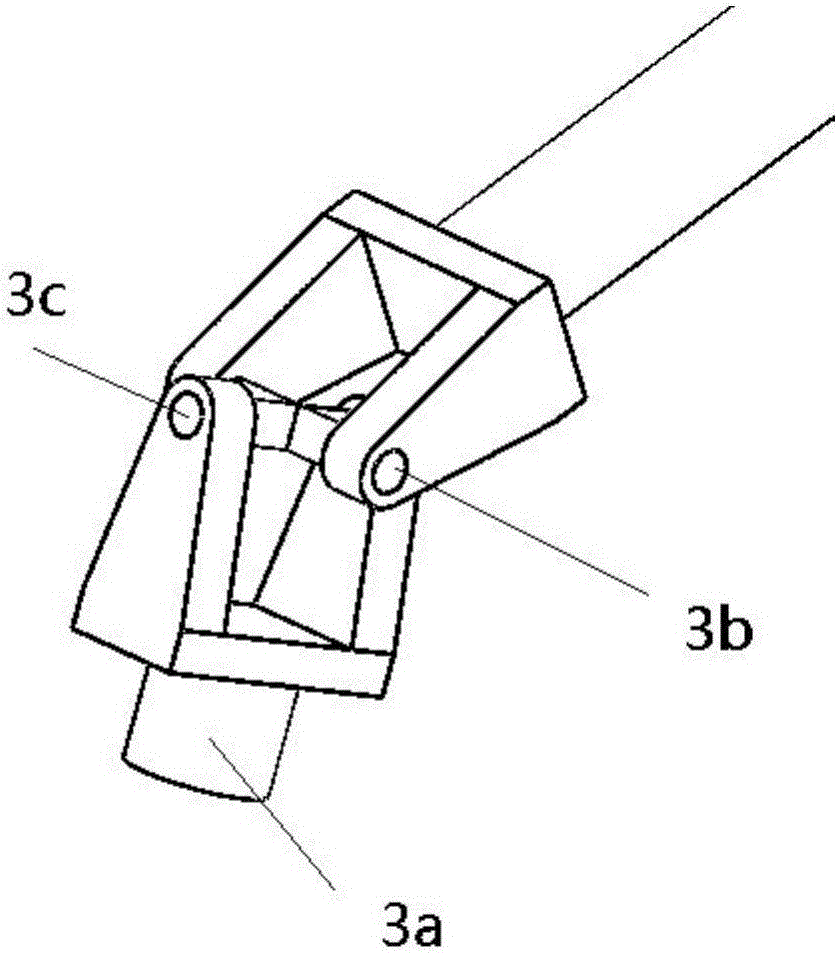
The invention discloses an azimuth-pitch movement two-shaft seat rack which is provided with a circular rail. The vertical axis of a vertical column is at the center of the circular rail, and the vertical column is connected to a rotation platform through the first rotation pair with a horizontal axis and is connected to a rack or ground through a second rotation pair with a vertical axis. The upper ends of two connection rods are connected to the rotation platform through hookjoints, and a sliding mechanism and the lower end of the connection rod are connected by using a composite hinge with three degrees of rotation freedom. According to the azimuth-pitch movement two-shaft seat rack, 0-degree to 90-degree pitch movement and -180-degree to 180-degree azimuth movement can be realized, external equipment can be a radar antenna, an astronomy radio camera, a camera, a sunlight reflector, and a solar energy sailboard. The structure is simple, the operation is convenient, and the problems of a heavy structure, a large driving power, and driving joint error accumulation of a traditional series connection type azimuth-pitch seat frame for large-scale apparatus equipment with a large quality are solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for determining wheel-track type reflector antenna pointing error
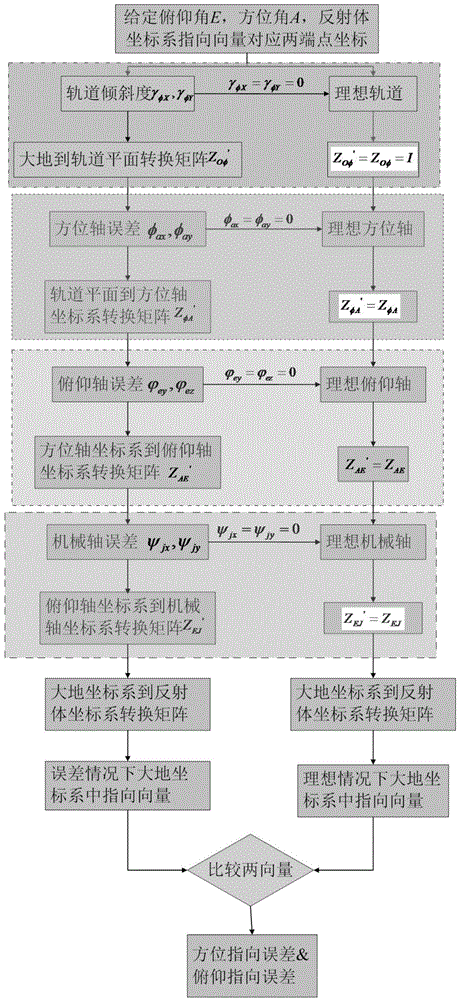
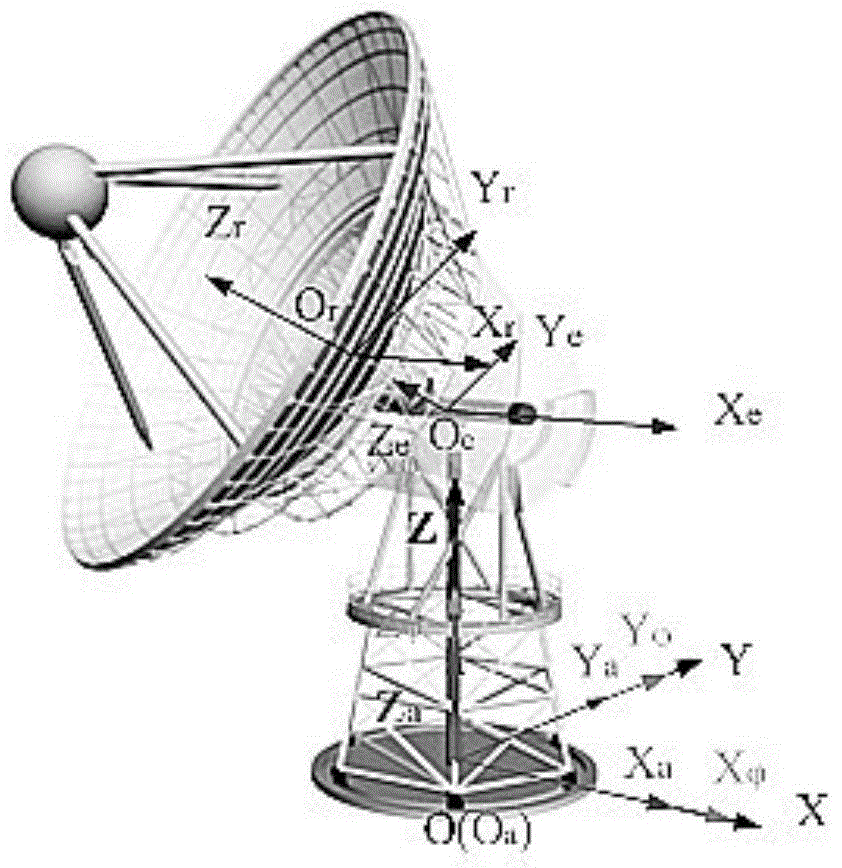
InactiveCN104931008AAccurate determination of pointing errorImprove pointing accuracyAngle measurementSystem errorAzimuth
The invention discloses a method for determining a wheel-track type reflector antenna pointing error. The problems that an existing analysis method cannot give complete consideration to factors of out-of-level tracks, non-plumb azimuth axes, non-vertical pitch axes, non-vertical pitch azimuth axes and non-vertical mechanical axes and pitch axes, and the relationship between a comprehensive axial system error and the antenna pointing error cannot be built are solved. The method includes the implementation steps that according to wheel-track type reflector antenna model parameters, a conversion matrix of a geodetic coordinate system to a reflector coordinate system under the ideal condition, namely the axial-system-error-free condition is built, and the pointing vector quantity under the ideal condition is obtained; then according to the axial system error distribution condition, a conversion matrix under the condition that the error exists is built, and the pointing vector quantity at the time is obtained; the azimuth and pitching pointing errors are accordingly obtained. According to the method, the influences of the comprehensive axial system error on the antenna pointing error are systematically considered, a foundation is laid to designing a follow-up high-pointing-accuracy antenna, and the development period is shortened.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
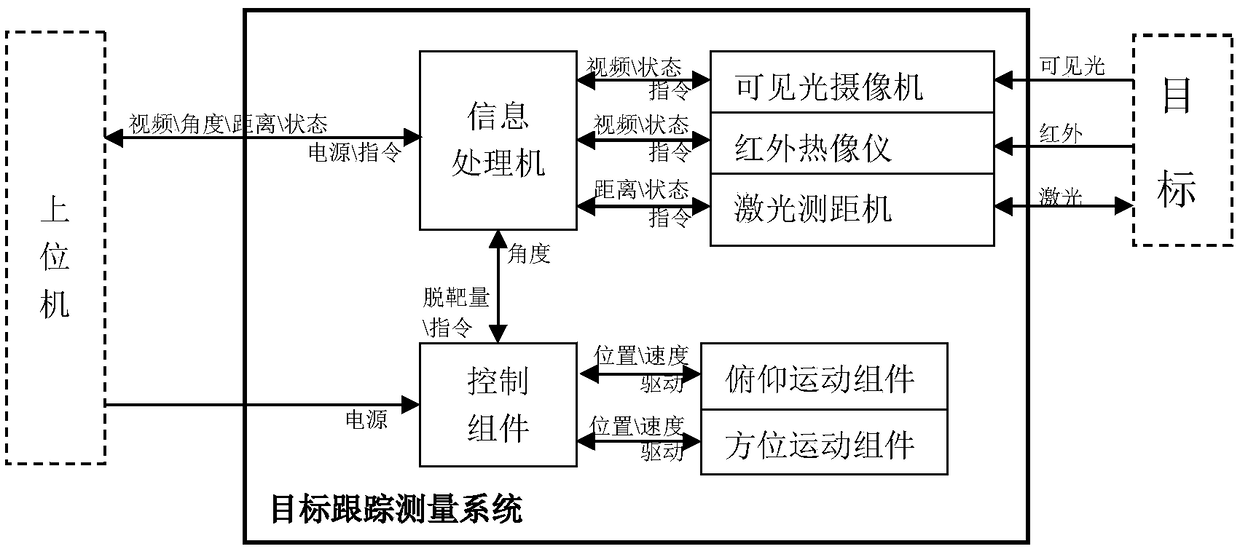
Multi-source target tracking measurement system and tracking method based on active vision
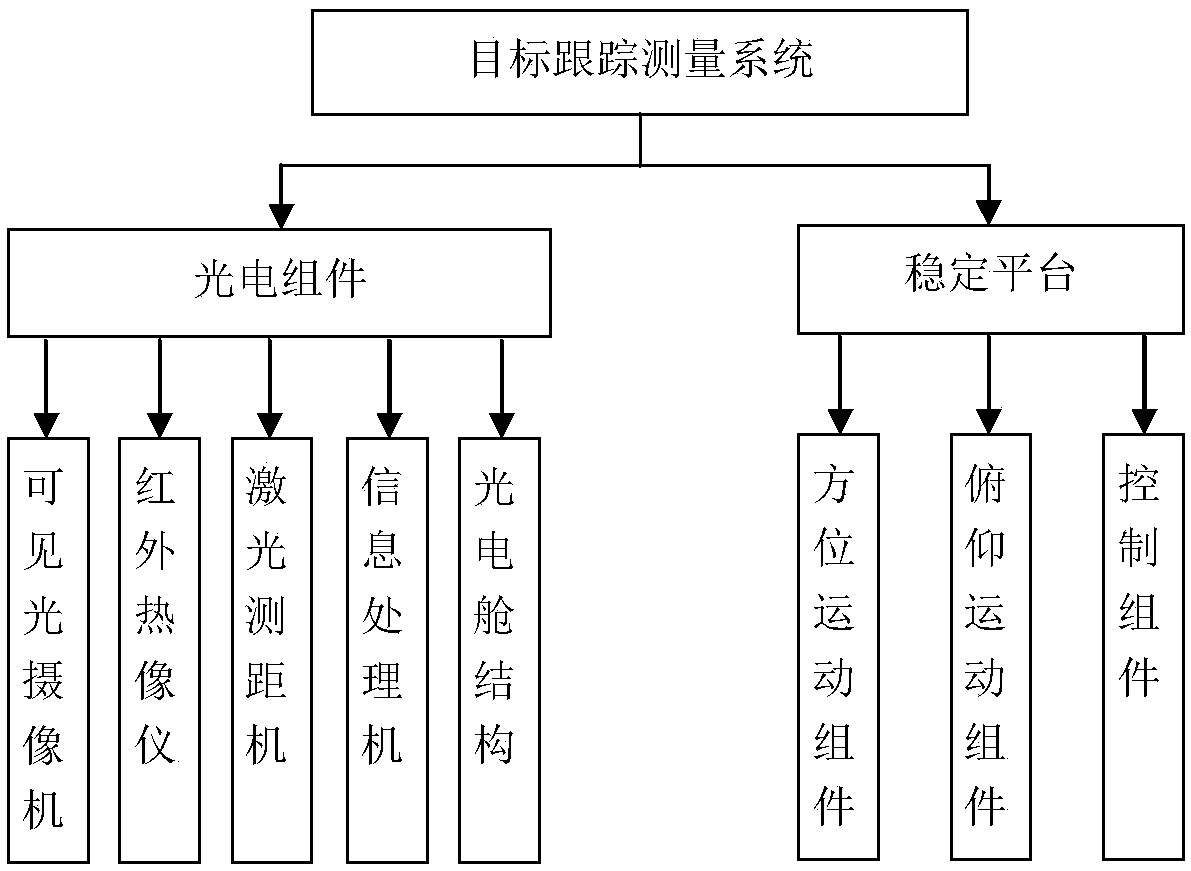
InactiveCN109212545ARealization of tracking measurementExpand the field of viewRadiation pyrometryElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingImaging processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and relates to a multi-source target tracking measurement system and tracking method based on active vision. The system comprises a photoelectric assembly and a stable platform, wherein the photoelectric assembly is composed of a visible light camera, an infrared thermal imager, a laser range finder, an information processor and a photoelectric cabin structure; the visible light camera, the infrared thermal imager, the laser range finder and the information processor are all installed inside the photoelectric cabin structure; the stable platform consists of an orientation motion assembly, a pitching motion assembly and a control assembly; and the control assembly receives an instruction sent by the information processor, andcontrols the orientation motion assembly and the pitching motion assembly to enable visual axes to stably point to a target. The invention further provides the multi-source target tracking method based on the active vision. The orientation motion assembly and the pitching motion assembly are driven to rotate according to the control instruction, so that the visual axis of the visible light cameraand the visual axis of the infrared thermal imager point to the target, and the target is always kept in the center of a shot image.
Owner:CHANGSHA CHAOCHUANG ELECTRONICS TECH
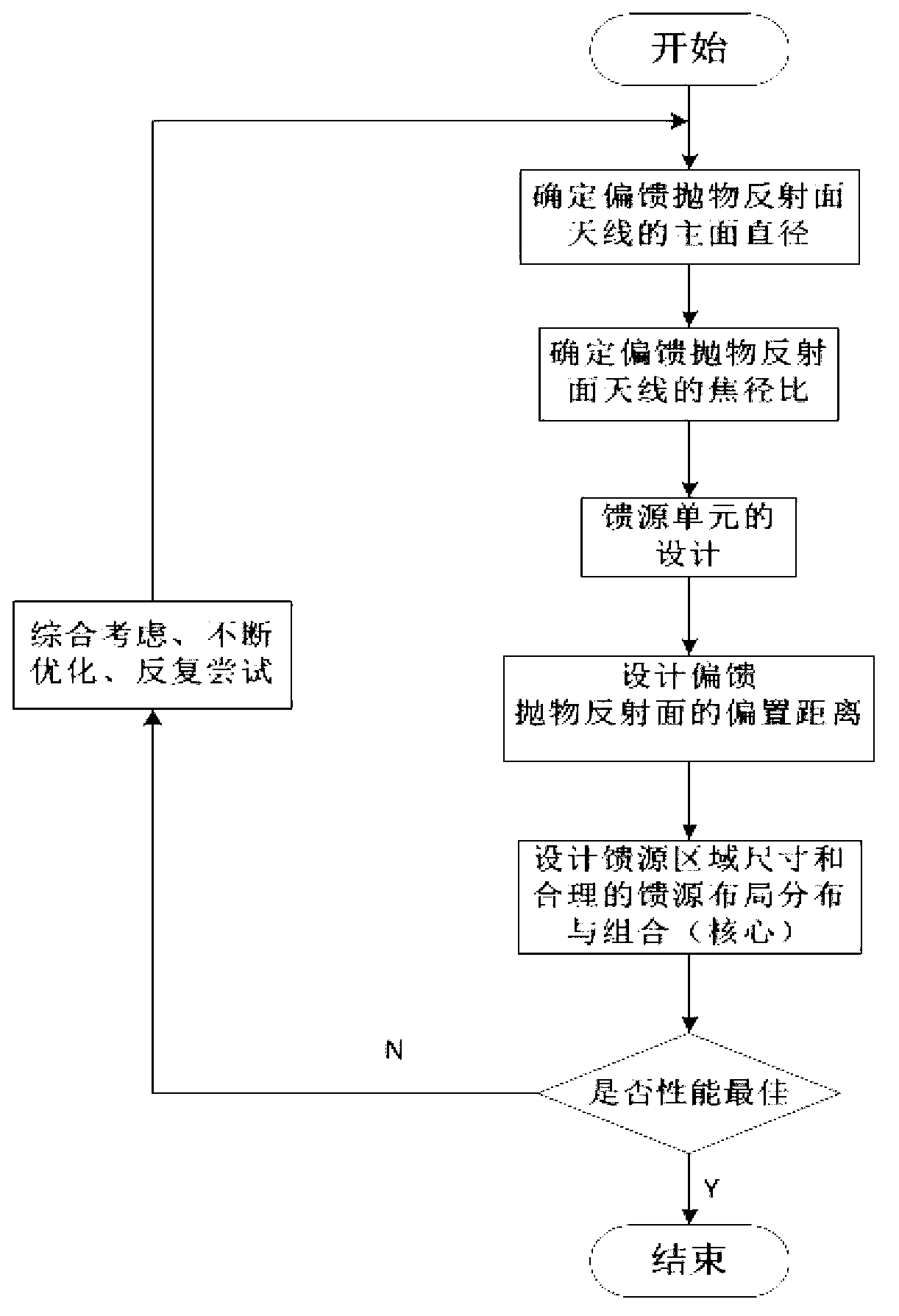
Method for designing partial-feed paraboloid multi-beam antenna feed array
The invention discloses a method for designing partial-feed paraboloid multi-beam antenna feed array and is applicable to a satellite communication system. A reflection-side multi-beam antenna adopts a primary feed utilizing a feed array as paraboloid. The principle of forming multiple beams includes beams of the paraboloid antenna are deviated by means of transverse focus offset of the feed. According to the structural size of the integral antenna system and design procedure of feed array arrangement, a novel feed array layout is provided. The number of generable spot beams is twice times of practical feed number, all beams are tightly arranged, appointed spatial angle can be uniformly covered, and each spot beam has electrical characteristics of good gain uniformity, low minor lobe level, small beam width, high pointing accuracy and the like. The method for designing partial-feed paraboloid multi-beam antenna feed array is directly used for satellite-borne equipment or ground control communication station and has wide potential application and typical application value in the satellite communication system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Dual pointing device and method based on 3-D motion and touch sensors
InactiveUS8049737B2Improve pointing accuracyCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPointing deviceComputer science
A dual pointing device and method based on 3-D motion and touch sensors are provided. The dual pointing device includes a sensor including a first sensor sensing a motion in a space and a second sensor sensing a touch input, a movement-mode-determining unit determining a movement mode type using signals of the first and second sensors, and a pointer-moving unit moving a pointer on a display screen using at least one of the signals of the first sensor and the second sensor according to the determined movement mode type.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
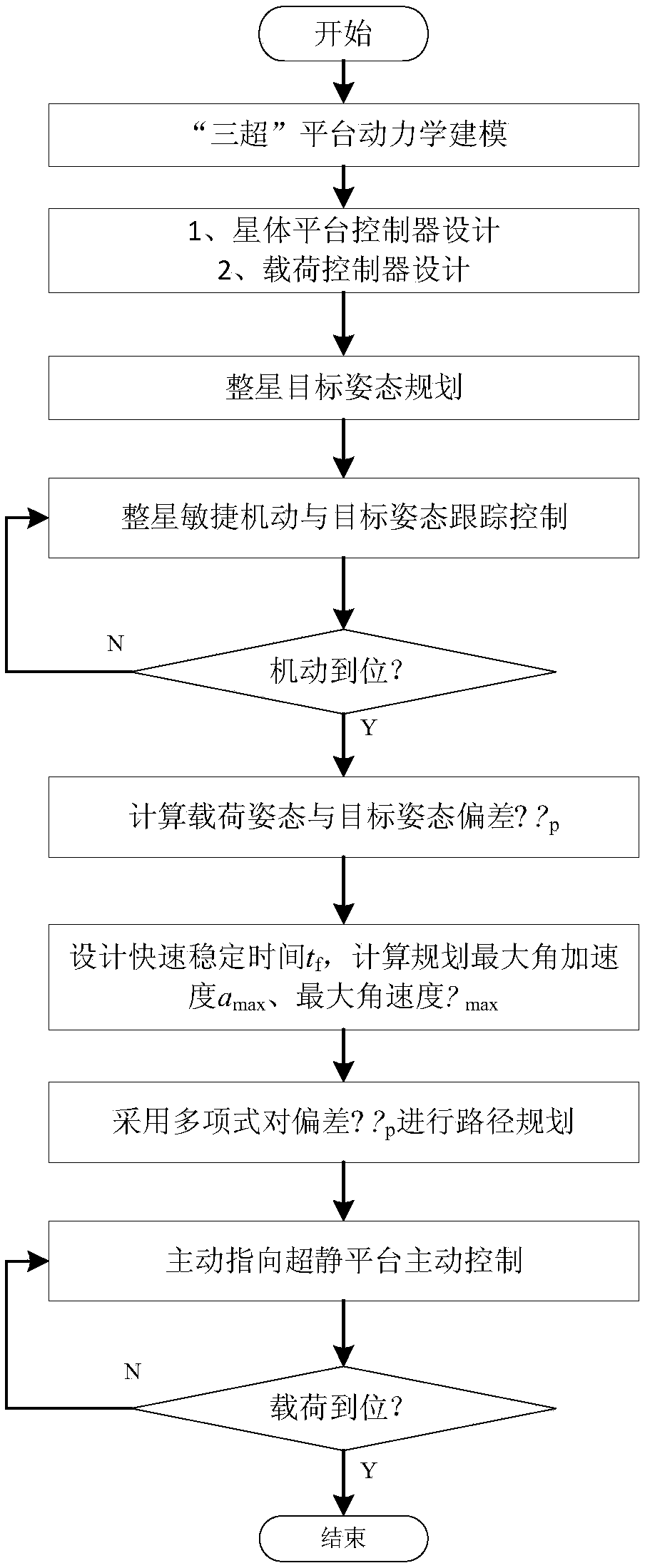
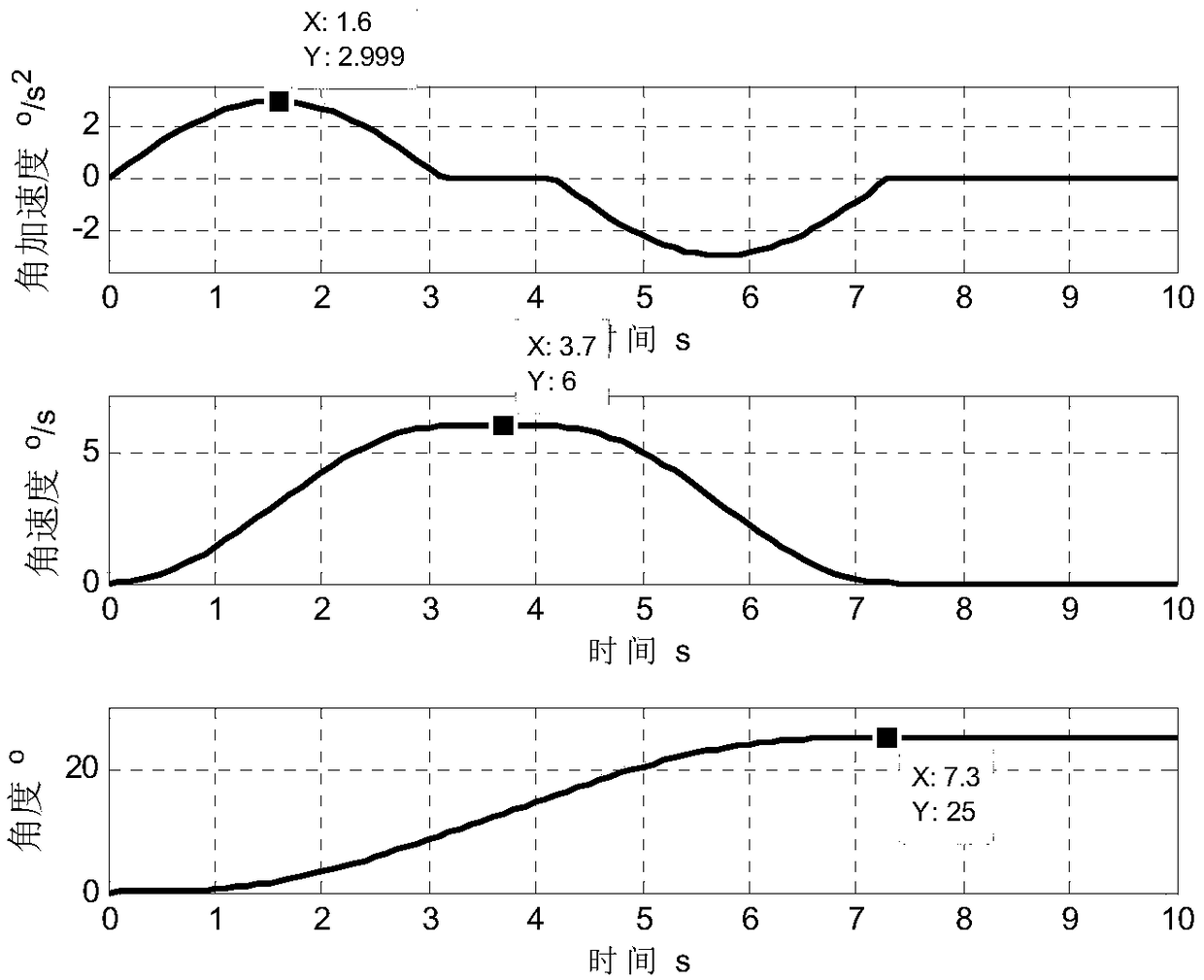
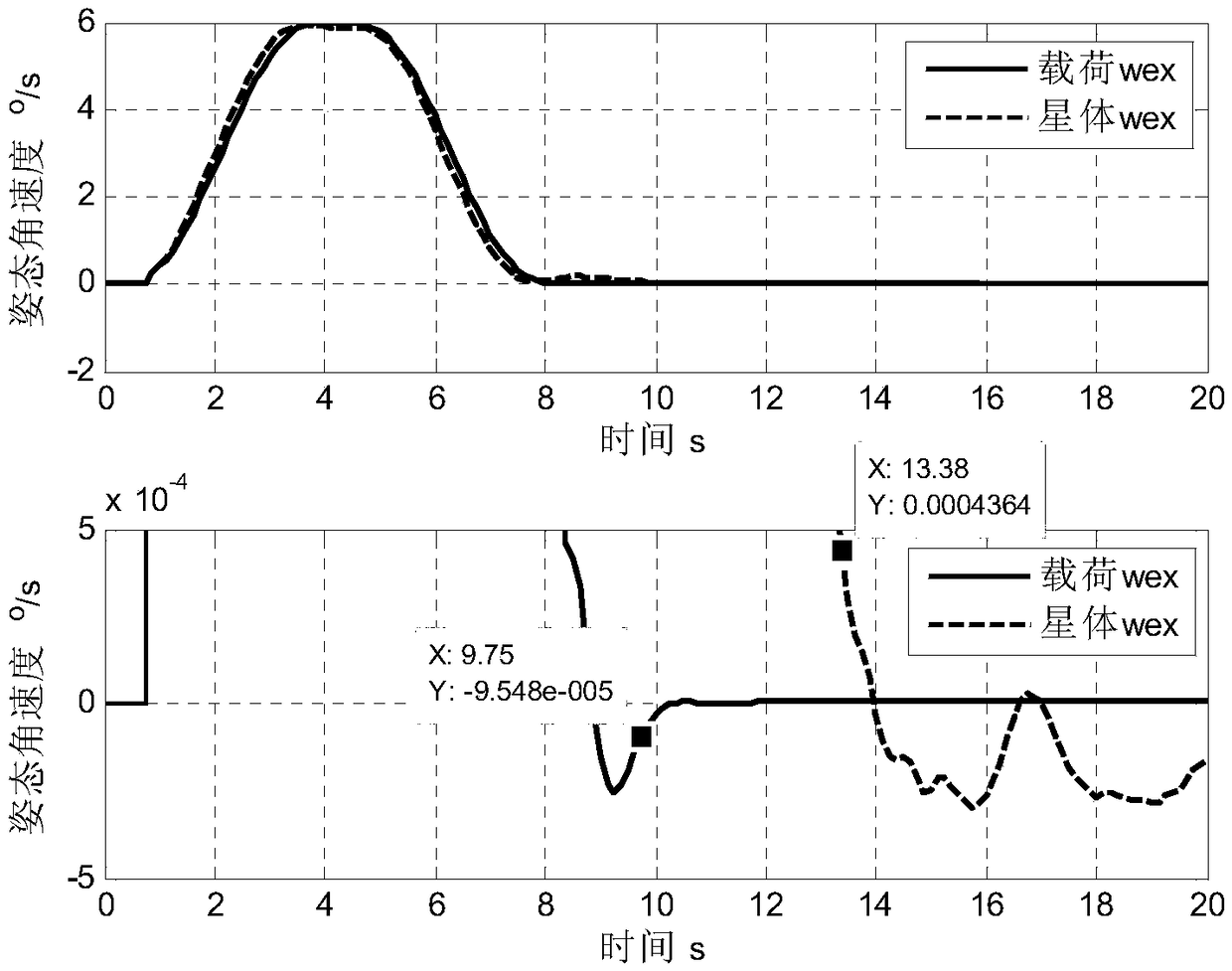
Agile maneuvering and fast stable control method of three-super platform
ActiveCN108646775AEasy loadingImprove pointing accuracyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsAttitude controlImage resolution
The invention provides an agile maneuvering and fast stable control method of a three-super platform, and is applied to the field of very high resolution ratio earth observation, space-aeronautics moving target agile tracking and the like with load agile maneuvering and fast stable demands. The designed three-super platform comprises astral first-level attitude control and active pointing ultra quiet platform second-level control. During large-angle fast maneuvering, active attitude control is carried out on astral first level to achieve 6 (degrees per second) of agile maneuvering, and an active pointing ultra quiet platform performs passive vibration isolation control. When the astral first-level attitude is maneuvering in place and a loaded attitude error is in a control range of the active pointing ultra quiet platform, a polynomial planning method is adopted to perform smooth transition on loaded deviation attitude delta theta p after maneuvering in place, and the active pointing ultra quiet platform second-level control is carried out to achieve fast and stable loading. The simulation result shows that load fast stable time is superior to 2.5 seconds, and the stable time of anastral platform is 6 seconds.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
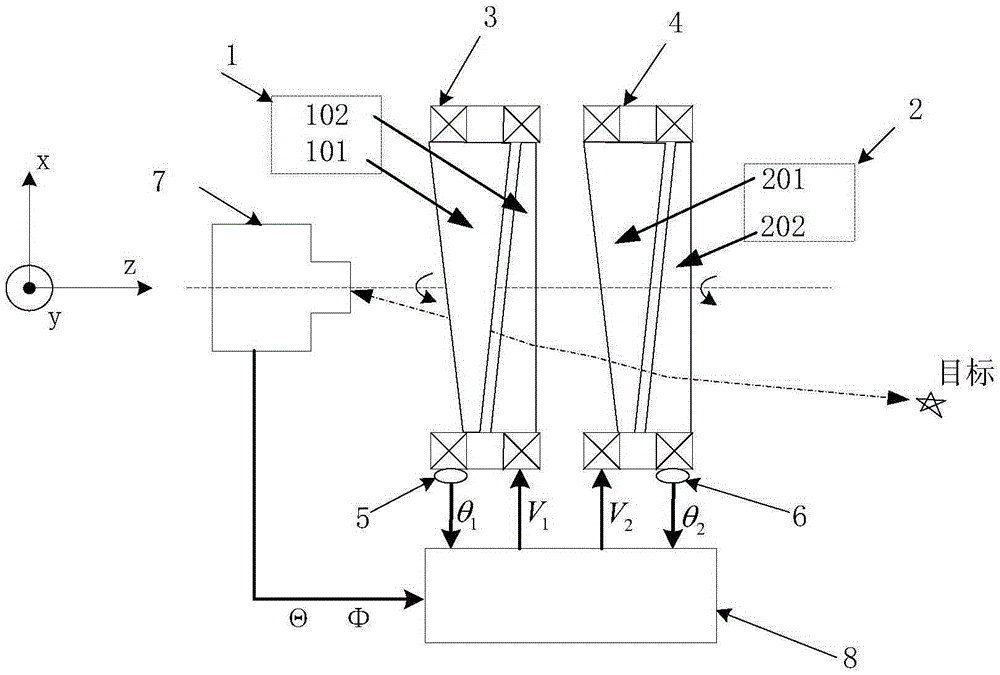
Method for improving pointing precision of achromatic rotating prism group
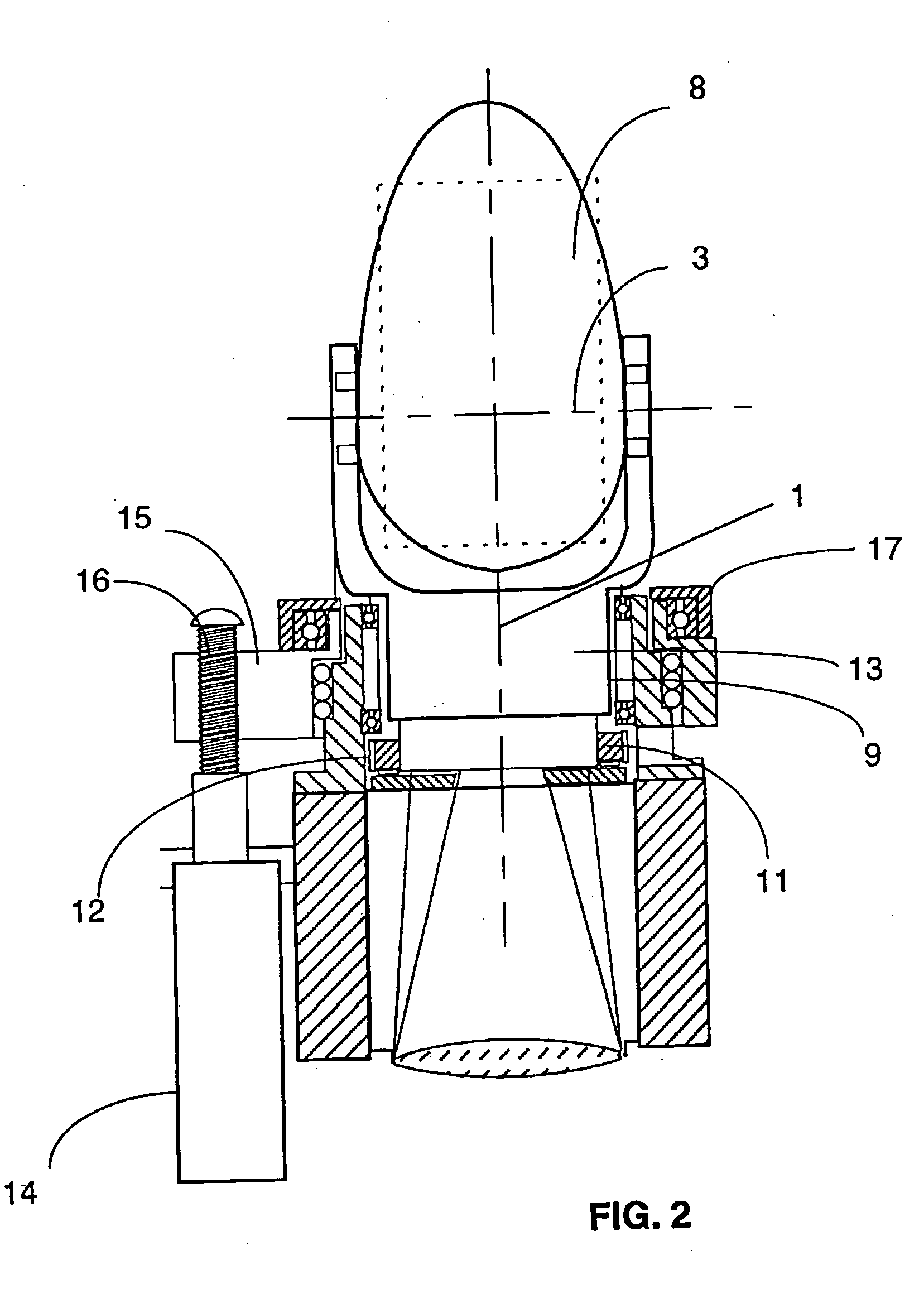
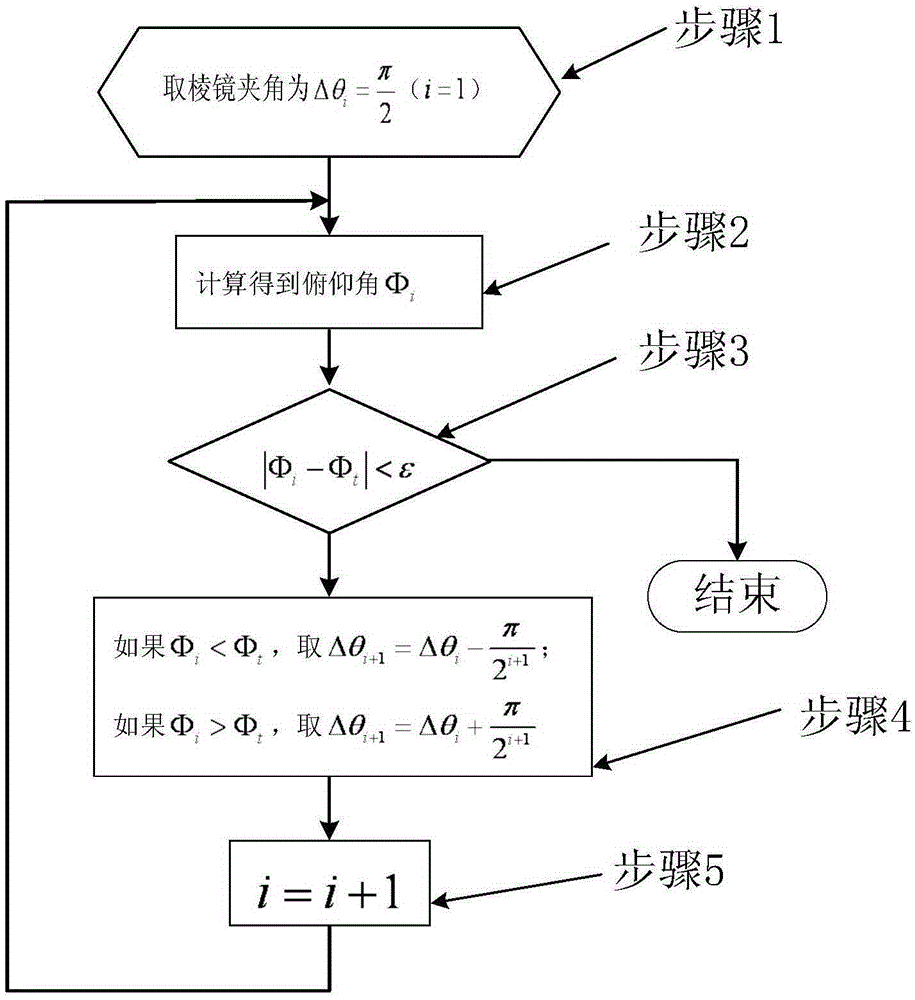
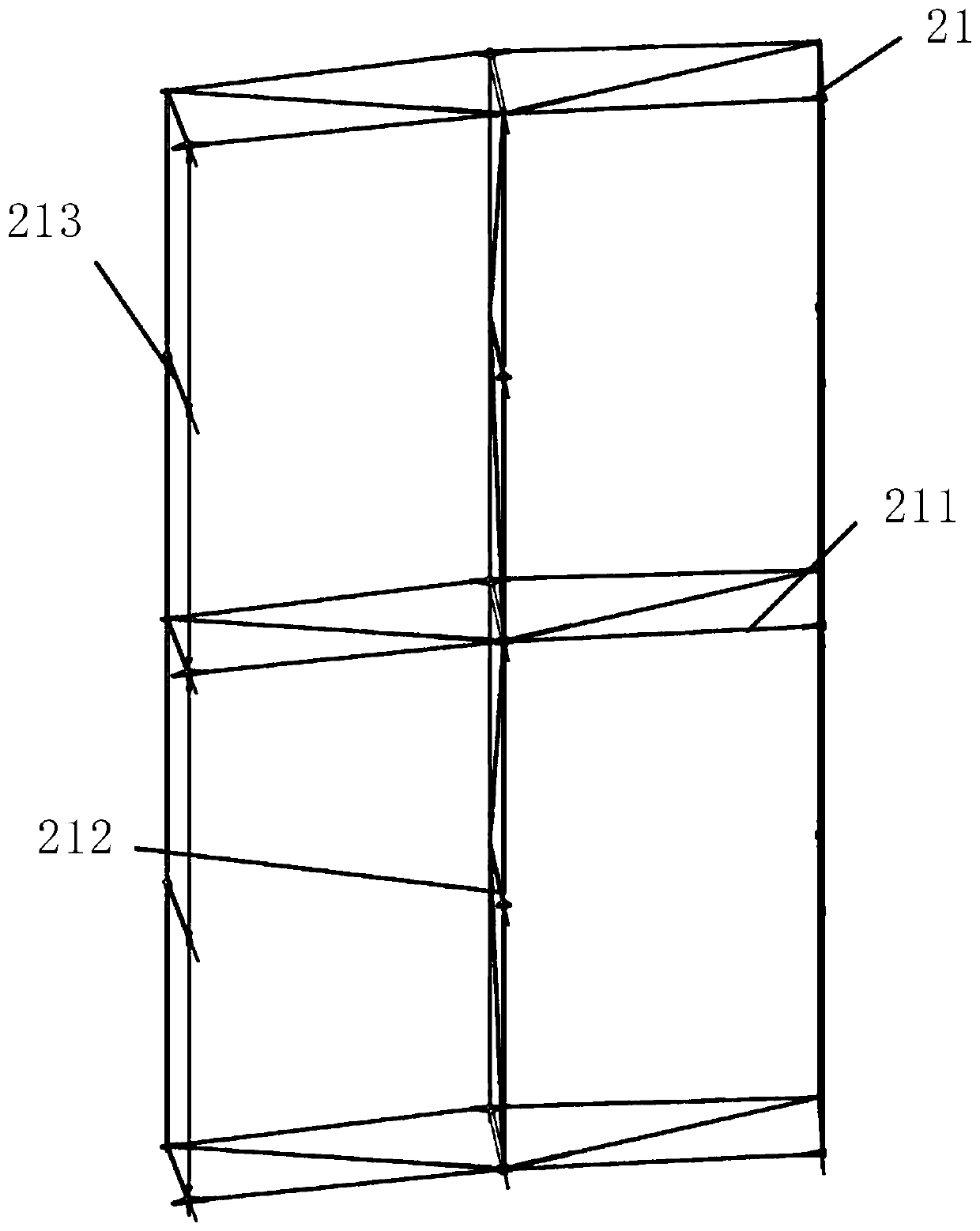
ActiveCN105353781ASolve the problem of precise pointingFix pointing errorControl using feedbackObservational errorLight beam
The invention provides a method for improving the pointing precision of an achromatic rotating prism group. The achromatic rotating prism group comprises a first prism group (1), a second prism group (2), a first motor (3), a second motor (4), a first position sensor (5), a second position sensor (6), a detector (7) and a controller (8). The first prism group (1) is composed of a first prism (101) and a second prism (102). The second prism group (2) is composed of a third prism (201) and a fourth prism (202). The method comprises the steps that firstly, a mathematic model of the achromatic rotating prism group is established, and a precise resolving algorithm is provided to complete light beam high-precision pointing in theory; and secondly, prism group parameters are optimized through an optimization algorithm, the influences of machining, installation and measuring errors are reduced, and the practical pointing precision of the system is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Satellite-borne deployable mesh antenna
ActiveCN109818151AHigh precisionLightweight structureCollapsable antennas meansAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesMicrowaveThermal deformation
The invention discloses a satellite-borne deployable mesh antenna. The satellite-borne deployable mesh antenna comprises an antenna reflecting surface extending arm (1), an antenna reflecting surfacedeployable supporting assembly (2) and a cable net structure (3). The antenna reflecting surface extending arm adopts a carbon fiber composite material hollow round rod design, so that the weight of the extending arm and the in-orbit thermal deformation of the extending arm are reduced, and the antenna pointing accuracy is ensured. The antenna reflecting surface deployable supporting assembly (2)is composed of module units, can be increased or decreased according to the aperture requirement of the antenna reflecting surface, and is high in expandability. The cable net structure is designed ina multi-layer cable net mode, ground adjustment of the profile precision of the reflecting surface is achieved, and the requirement of microwave antenna detection for the profile precision of the reflecting surface is met. According to the invention, factors such as antenna emission folding and in-orbit unfolding, antenna reflecting surface function and performance testing and antenna reflectingsurface profile precision adjusting are comprehensively considered for design, and the requirement of satellite in-orbit ground detection can be met.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
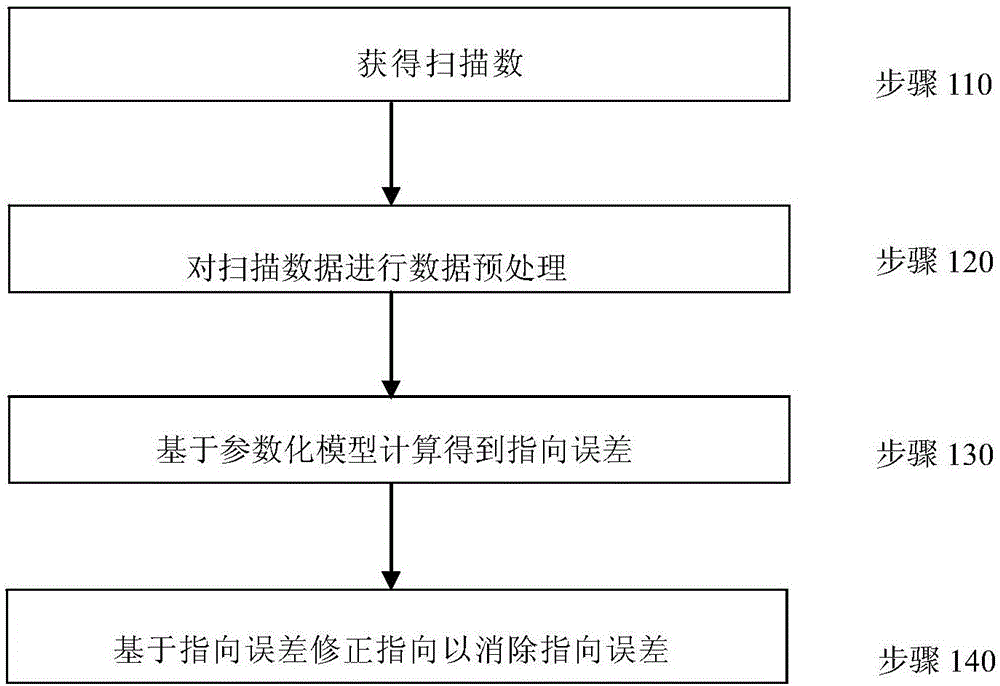
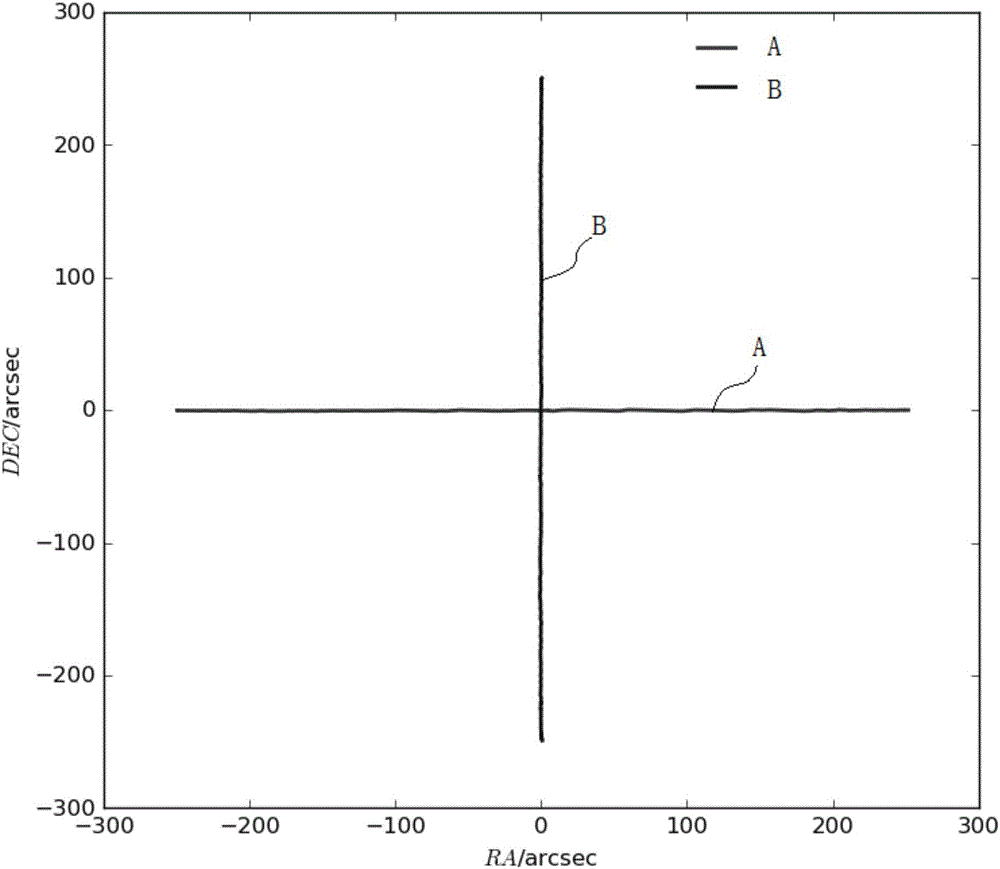
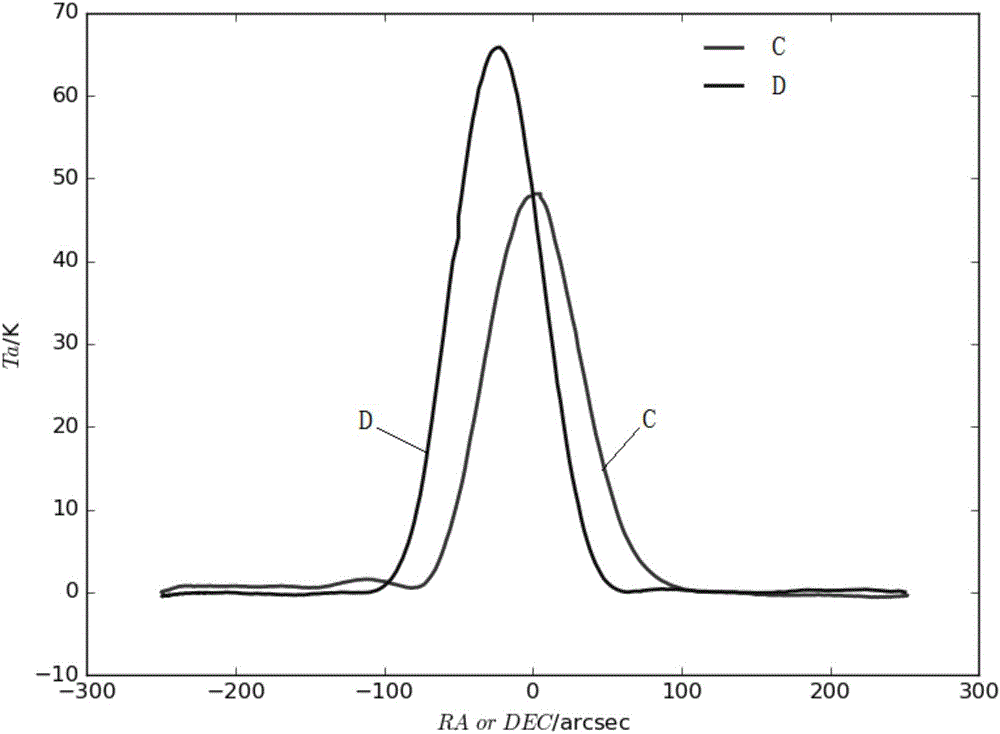
Real-time correction method for pointing direction of radio telescope
ActiveCN106200697AEliminate pointing errorsImprove pointing accuracyControl using feedbackAntennasHigh elevationRadio telescope
The invention discloses a real-time correction method for the pointing direction of a radio telescope. The method includes the following steps that the radio telescope is controlled to carry out at least one time of scanning on a radio source in the right ascensison direction and the declination direction respectively to obtain right ascensison scanning data and declination scanning data; based on a linear function and a Gaussian function, a parameterized model for describing the right ascensison scanning data and the declination scanning data is established, and parameters for describing pointing errors are contained in the parameterized model; the right ascensison scanning data and the declination scanning data are substituted into the parameterized model, pointing errors in the right ascensison direction and the declination direction are acquired through a fitting algorithm, and pointing errors of the orientation and the pitching direction are acquired through coordinate conversion; the pointing direction of the radio telescope is controlled to be corrected based on the pointing errors to eliminate the pointing errors. The real-time correction method for the pointing direction of the radio telescope can be used for real-time correction of the pointing direction of the radio telescope to eliminate the pointing errors in real time, and meanwhile can solve the problem that the orientation operating speed is too high in the high-elevation scanning process under the orientation and a pitching coordinate system.
Owner:SHANGHAI ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Eccentric mechanism of dynamic pointing type rotary guiding well-drilling tool
ActiveCN106677703AExtended service lifeImprove reliabilityDirectional drillingWell drillingEngineering
The invention discloses an eccentric mechanism of a dynamic pointing type rotary guiding well-drilling tool. An external eccentric ring frameless direct-driving motor encoder is connected with an external eccentric ring flange, the external eccentric ring flange is connected with an external eccentric ring frameless direct-driving motor, and an external eccentric ring frameless direct-driving motor rotor is connected with an external eccentric ring; the outer wall of the external eccentric ring is matched with an external eccentric ring holding bearing, the outer wall of the external eccentric ring holding bearing is matched with the inner wall of a rotary outer sleeve, and the inner wall of the external eccentric ring is matched with the outer walls of an internal eccentric ring fitted bearing and an external eccentric ring fitted bearing; the inner walls of the internal eccentric ring fitted bearing and the external eccentric ring fitted bearing are matched with the outer wall of an internal eccentric ring, and the inner wall of the internal eccentric ring is matched with the outer wall of the internal eccentric ring fitted bearing; and an internal eccentric ring frameless direct-driving motor rotor is connected with an internal eccentric flange, and the internal eccentric flange is connected with an internal eccentric ring frameless direct-driving motor encoder. Control of the eccentric mechanism over the internal eccentric ring and the external eccentric ring is achieved mainly by controlling frameless direct-driving motors, so that tool guiding is achieved, and accurate control of well track is achieved.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
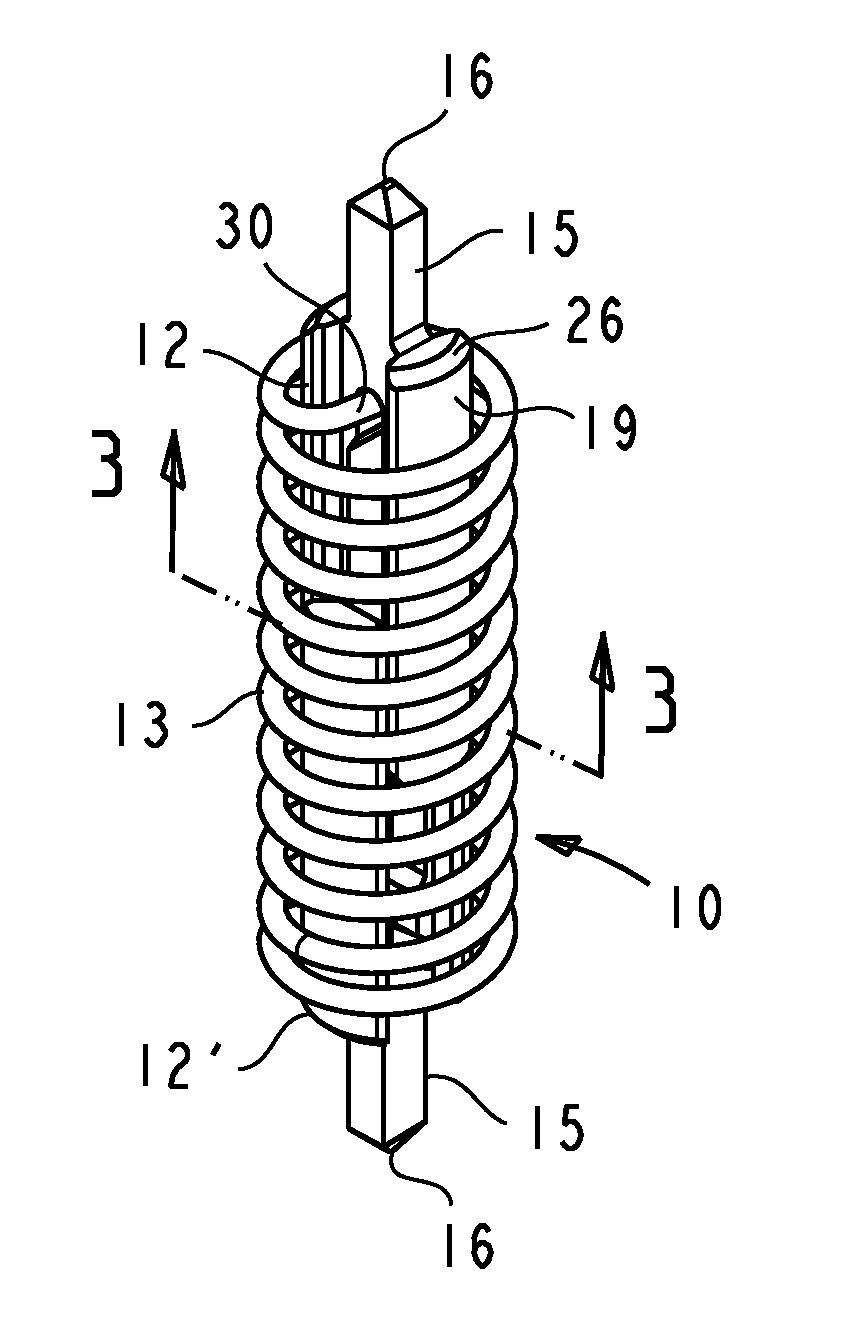
Probe with contact ring
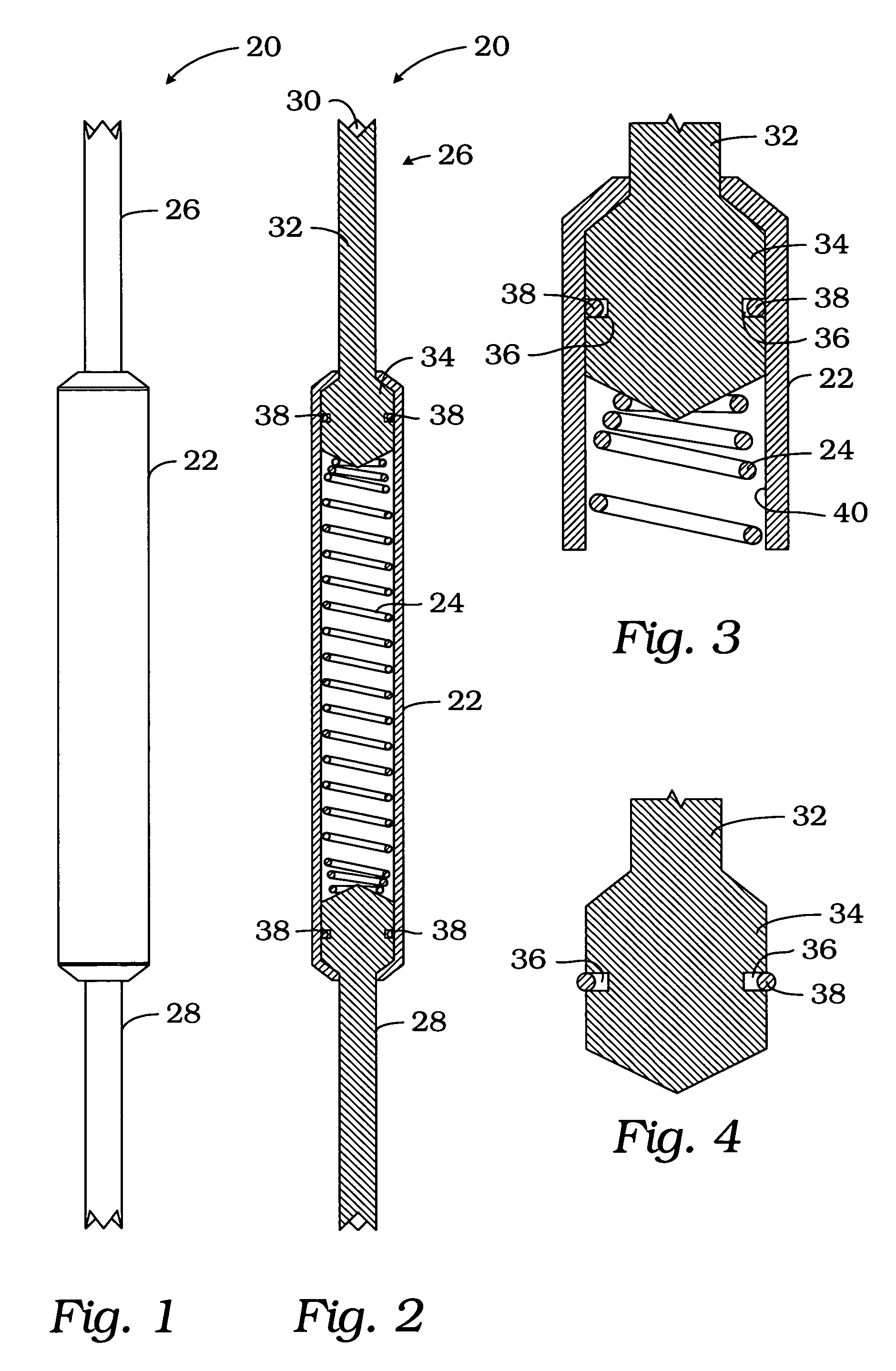
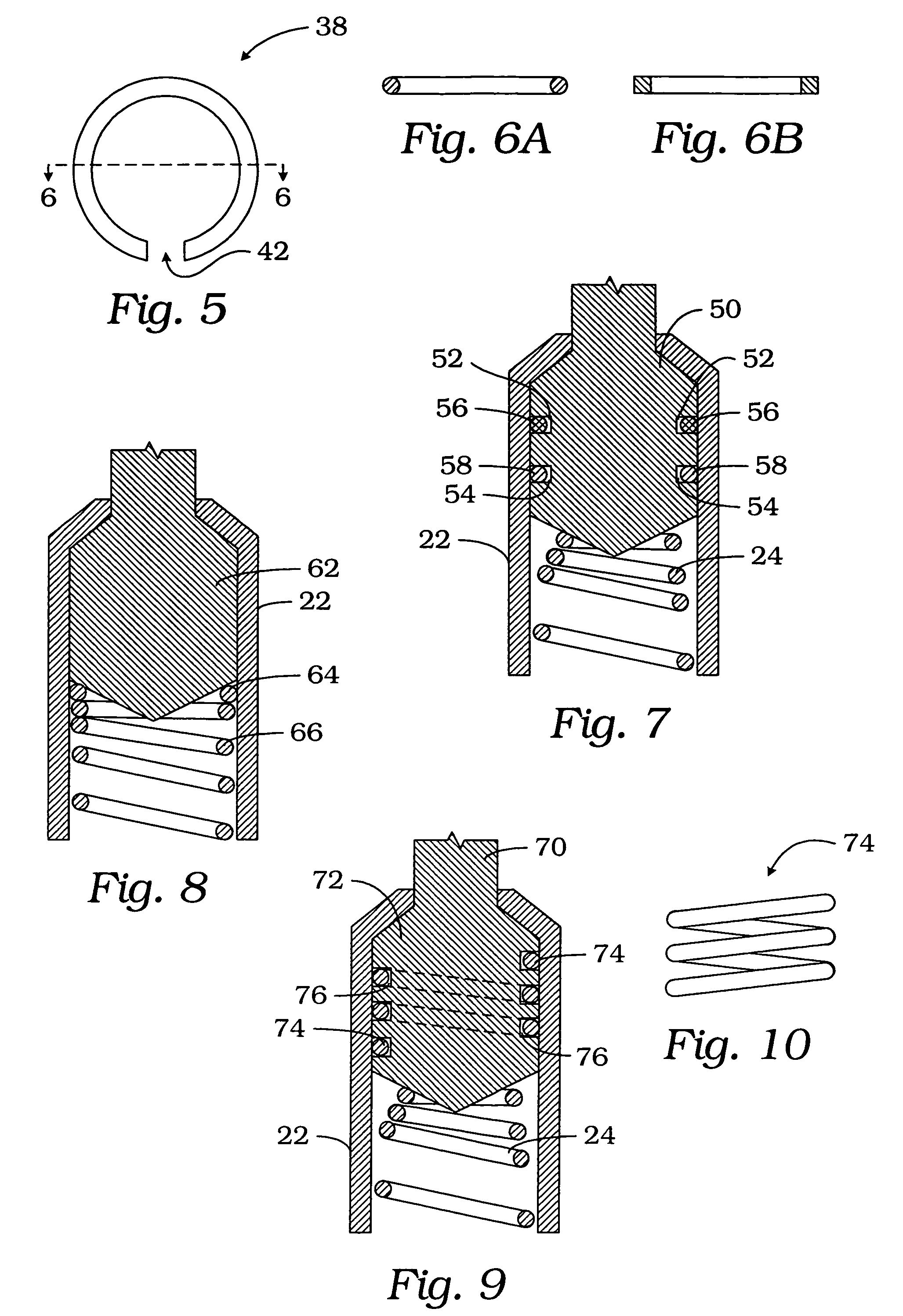
ActiveUS7362118B2Improve pointing accuracyElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingEngineeringElectrical contacts
Owner:SMITHS INTERCONNECT AMERICAS INC
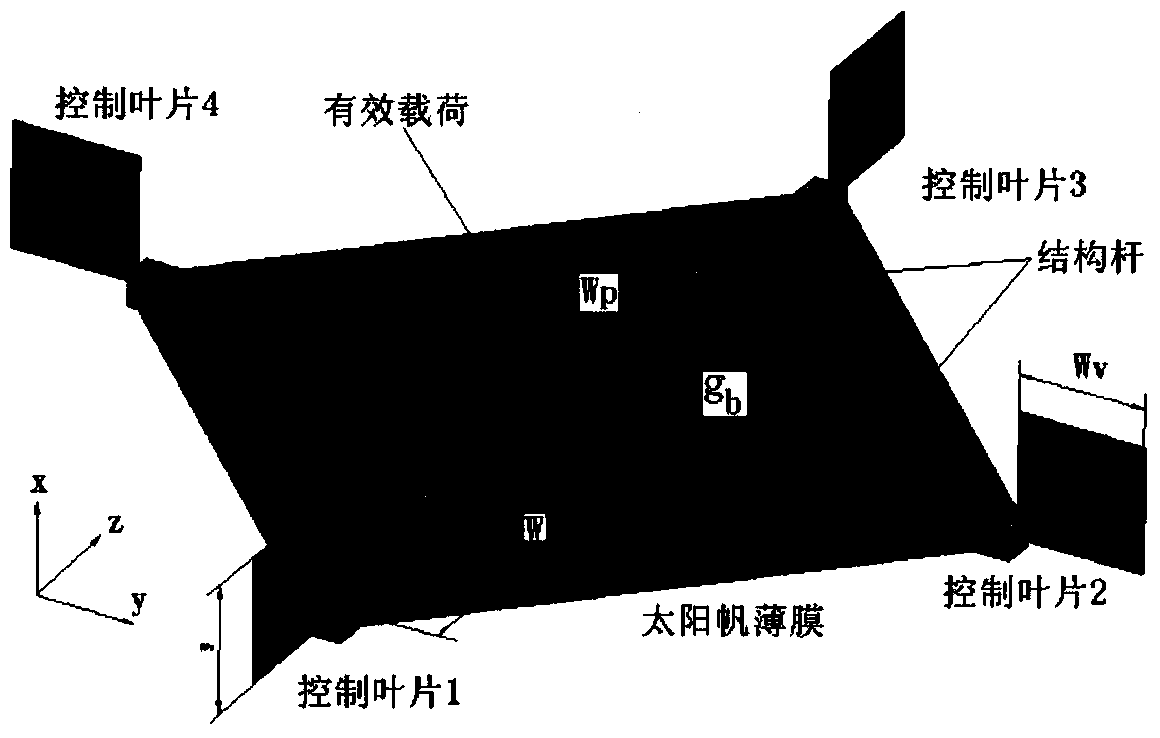
Sliding block executing mechanism used for attitude control over solar sail spacecraft
ActiveCN104002994AEase of technical implementationAbundant resourcesSpacecraft guiding apparatusDrive wheelAttitude control
The invention provides a sliding block executing mechanism used for attitude control over a solar sail spacecraft. The sliding block executing mechanism comprises a central box, a pre-tightening regulating unit, a control unit, a driving wheel unit, a driven wheel unit and an adjustable auxiliary driven wheel unit; a telescopic arm penetrates through a hole in the center of a front panel and a hole in the center of a rear panel of the central box; the pre-tightening regulating unit comprises a pre-tightening screw and a pre-tightening nut, and the pre-tightening screw penetrates through an upper panel of the central box; the control motor is driven by obtaining electric energy from a solar battery; the driving wheel unit comprises two protruding idler wheels which are connected with a motor shaft of the control motor through connection shafts, and the outer walls of the two protruding idler wheels make tight contact with the periphery of a stretching arm; two protruding idler wheels of the driven wheel unit penetrates through a rotary shaft and are arranged between two polytetrafluoroethylene sliding rings, the outer walls of the two protruding idler wheels make tight contact with the periphery of the stretching arm, and the rotary shaft is fixed to a support of a lower panel of the central box; the adjustable auxiliary driven wheel unit comprises four protruding idler wheels and four triangular supports, and the triangular supports are regulated so that the outer walls of the protruding idler wheels can make tight contact with the periphery of the stretching arm.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Attitude tracking control method for satellite earth scanning
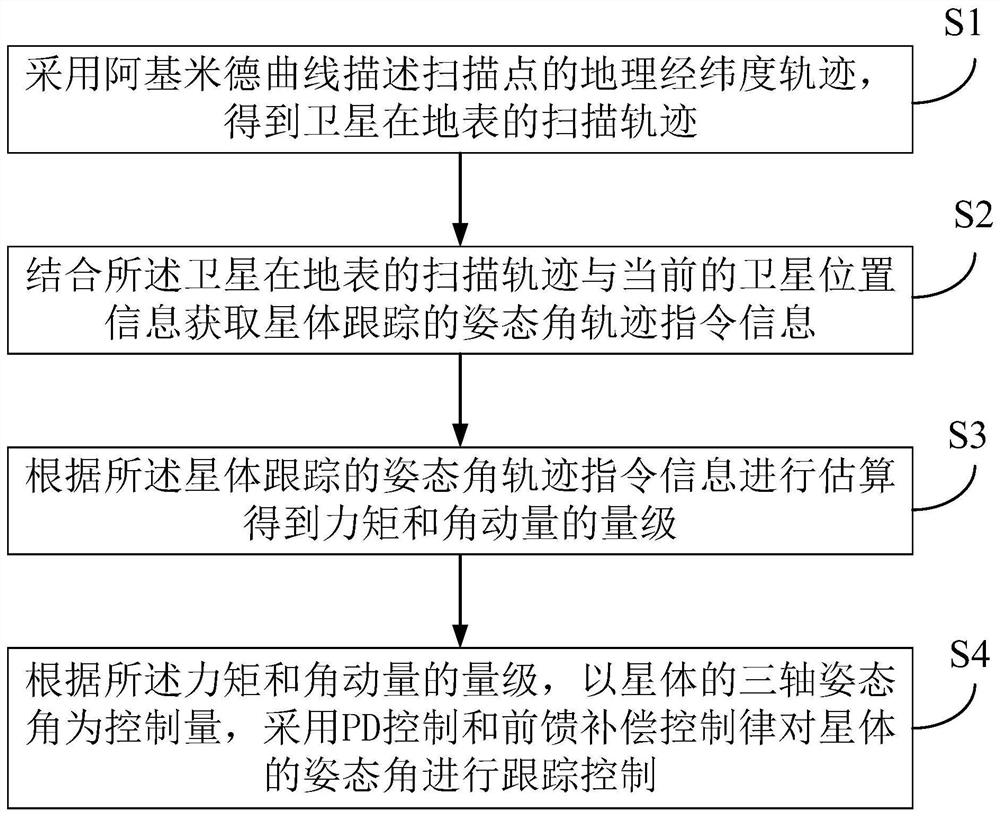
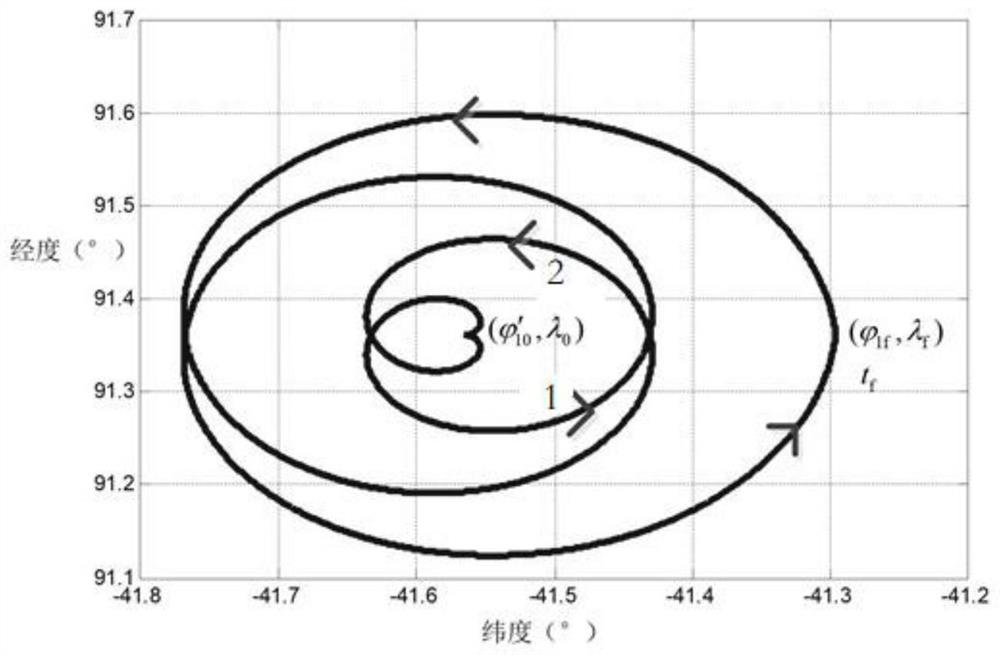
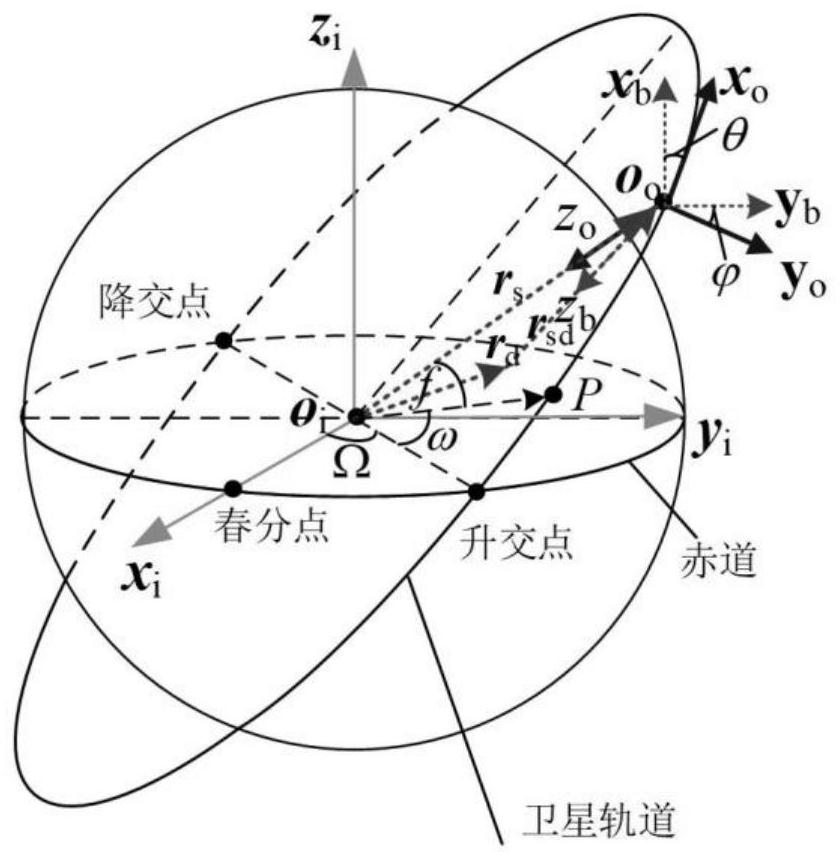
PendingCN111897357ASimplified descriptionAvoid the trajectory planning processAttitude controlSatellite trackingLongitude
The invention discloses an attitude tracking control method for satellite earth scanning. The method comprises the steps of describing a geographic longitude and latitude track of a scanning point byadopting an Archimedes curve to obtain a scanning track of a satellite on the earth surface; combining the scanning trajectory of the satellite on the earth surface with the current satellite positioninformation to obtain attitude angle trajectory instruction information of satellite tracking; estimating the magnitudes of moment and angular momentum according to the attitude angle trajectory instruction information tracked by the satellite; and according to the magnitudes of the moment and the angular momentum, taking the three-axis attitude angle of the satellite as a controlled variable, and performing tracking control on the attitude angle of the satellite by adopting PD control and feedforward compensation control laws. According to the invention, the function of scanning the earth surface according to a specific track through maneuvering of satellite attitudes is realized, so that the structure of the satellite is simpler, the size and weight of the satellite can be effectively reduced, and the reliability of the system is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
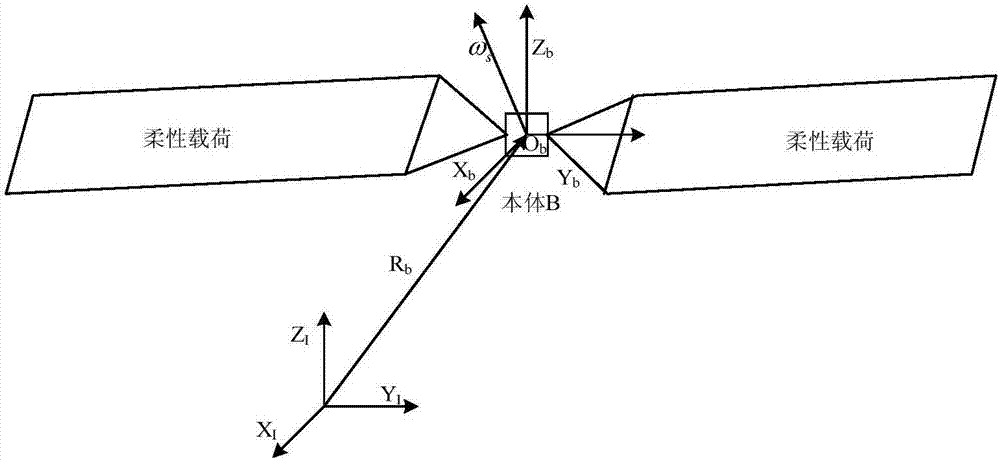
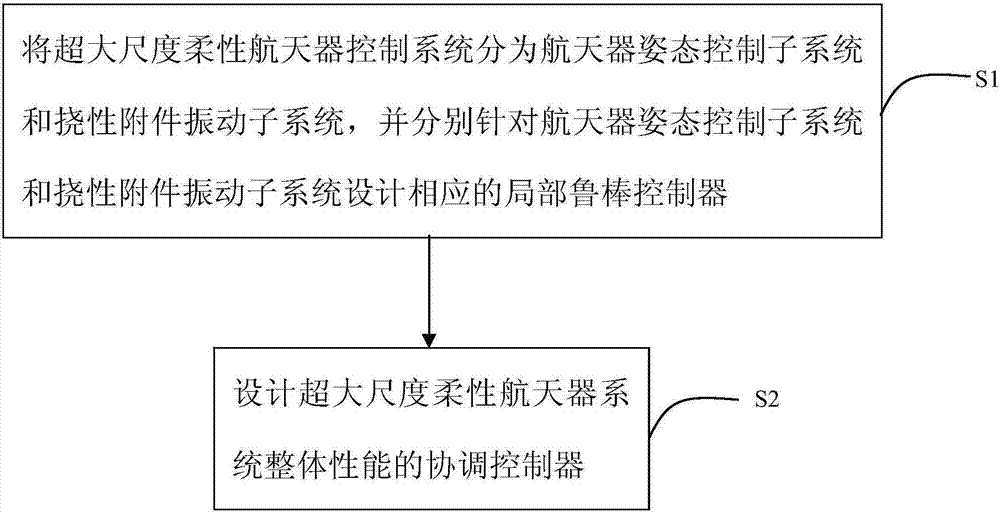
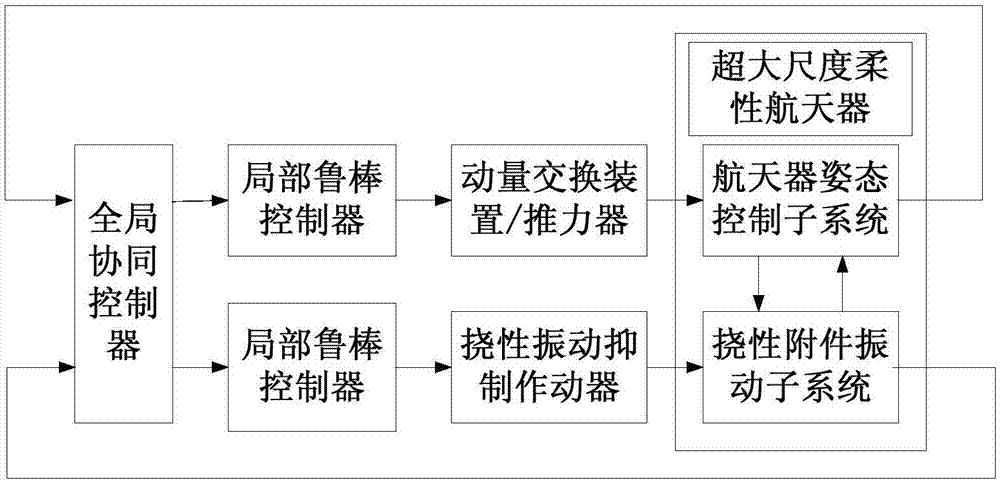
Super-size flexible spacecraft dispersion cooperative control method
ActiveCN107015567AHigh deformation control precisionImprove pointing accuracyAttitude controlDispersion stabilitySpacecraft attitude control
The invention discloses a super-size flexible spacecraft dispersion cooperative control method, and aims to achieve high stability and vibration inhibition control on a super-size flexible spacecraft. The method comprises the following steps: S1, dividing a super-size flexible spacecraft control system into a spacecraft posture control subsystem and a flexible attachment vibration subsystem, and designing corresponding partial robust controllers for the spacecraft posture control subsystem and the flexible attachment vibration subsystem respectively; and S2, designing a coordinate controller for overall properties of the super-size flexible spacecraft control system. The method has the advantages that according to the dynamic characteristics of the super-size flexible spacecraft, a dispersion cooperative control method is adopted, a partial structure is stably controlled through dispersion stability, overall high-precision performance indexes are achieved through the cooperative controller, high appointing precision and stability of postures and deformation control precision of a flexible component are achieved, and the method is widely applied to high-precision high-stability appointing control on a large-size flexible structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
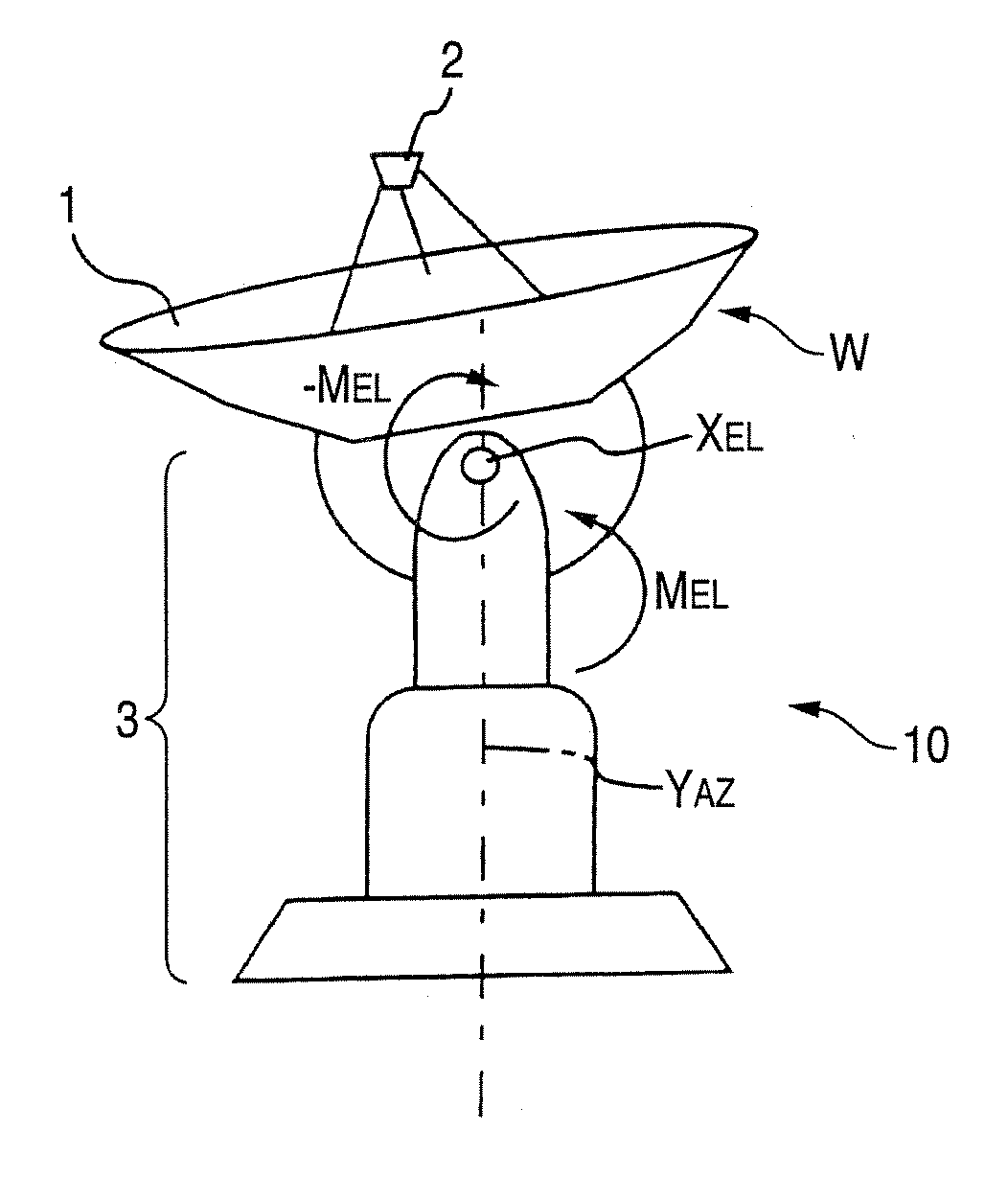
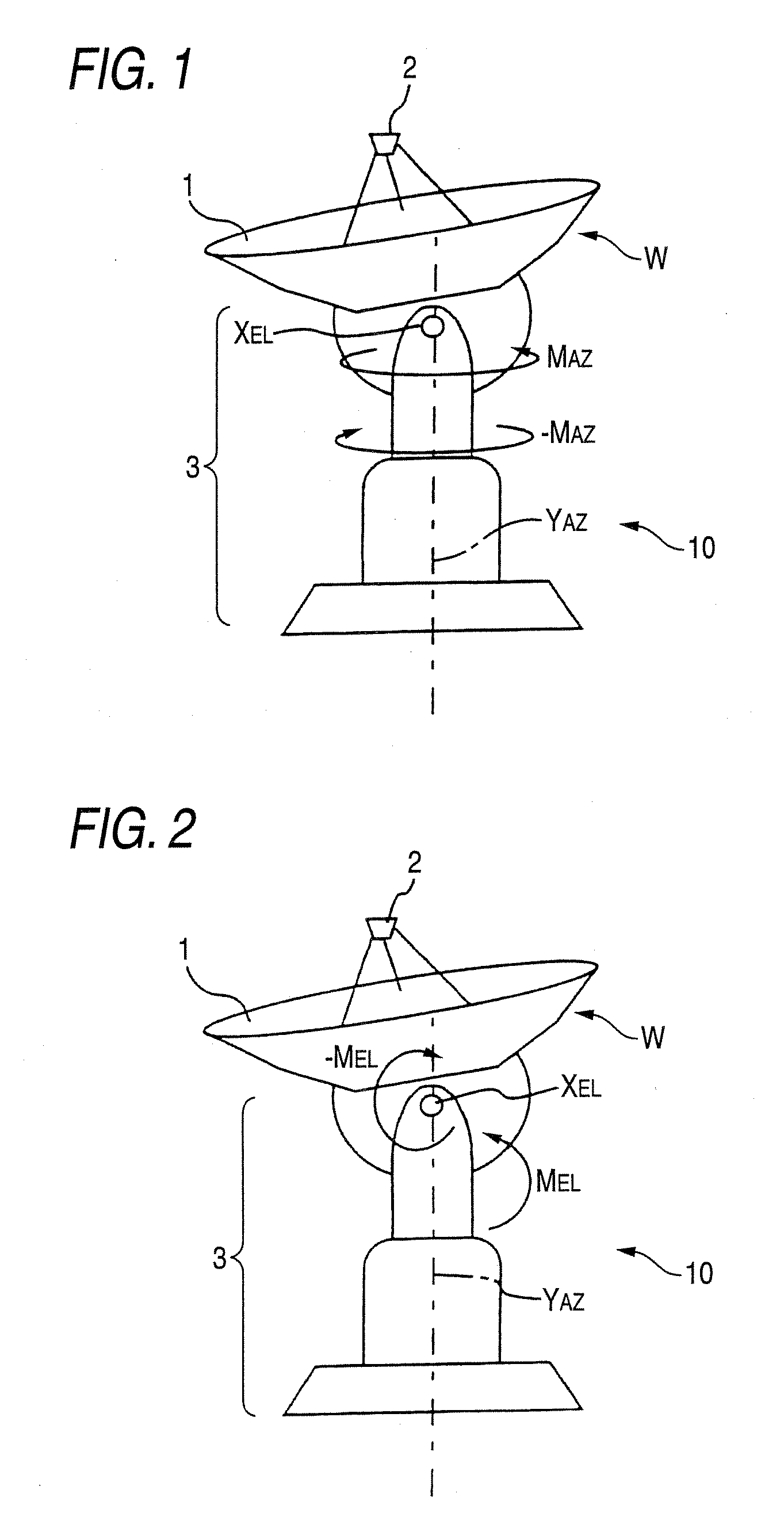
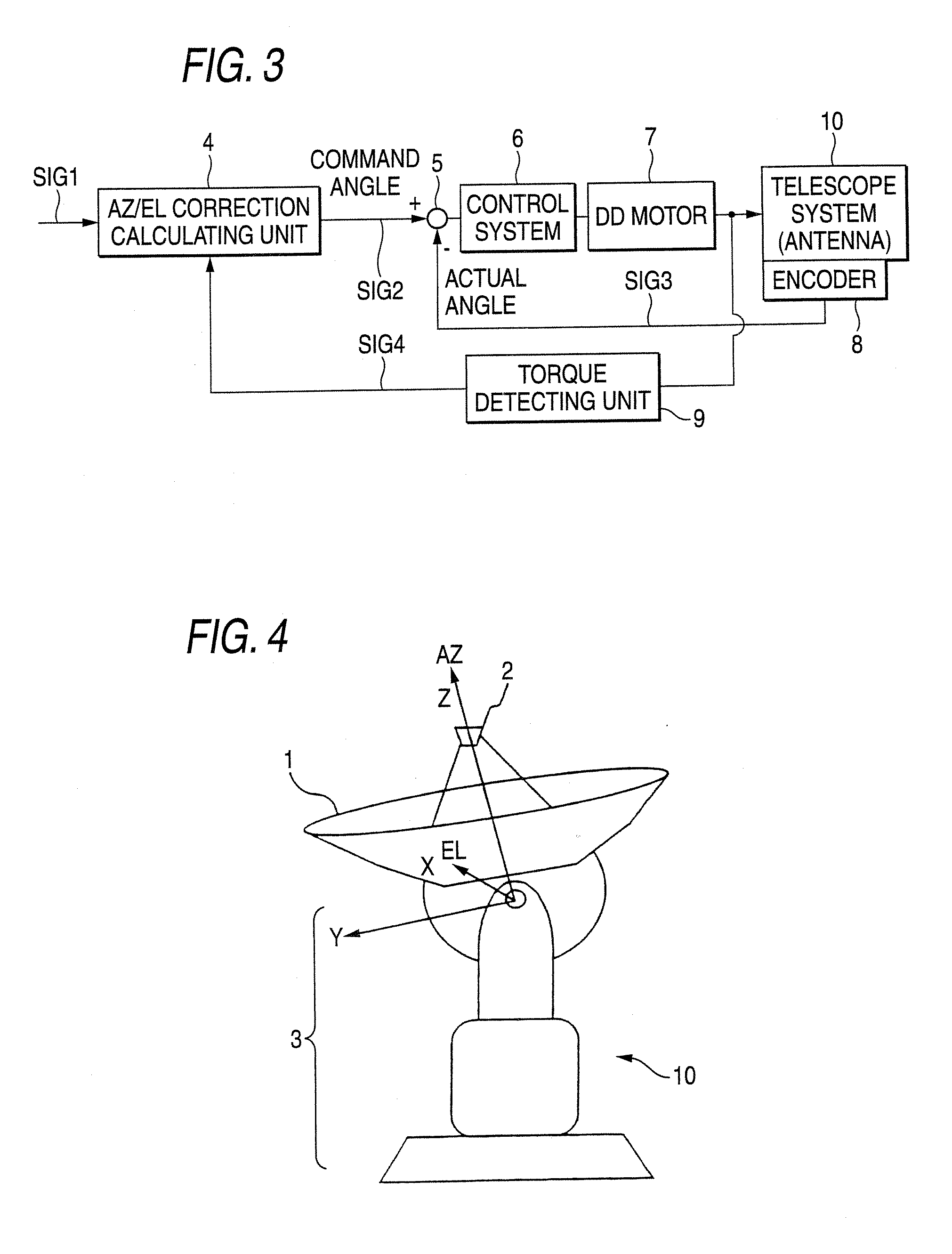
Telescope system
InactiveUS20070097004A1Improve directivityImprove pointing accuracyVibration dampingWind-induced force reductionControl theoryTelescope
There is provided a telescope system including: a main reflector unit; a pedestal unit that bears the main reflector unit to be rotatable around AZ and EL axes; and a motor that drives the main reflector unit. The telescope system corrects deformation of the main reflector unit and the pedestal unit due to the wind force to improve pointing accuracy of the mina mirror unit and the pedestal unit. The telescope system detects motor torques on the AZ axis and the EL axis, predicts deformation of a telescope due to the wind force from torque signals of the motor torques and a pointing error due to the deformation and feeds back the deformation and the pointing error to AZ and EL command values to perform correction of the pointing error.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
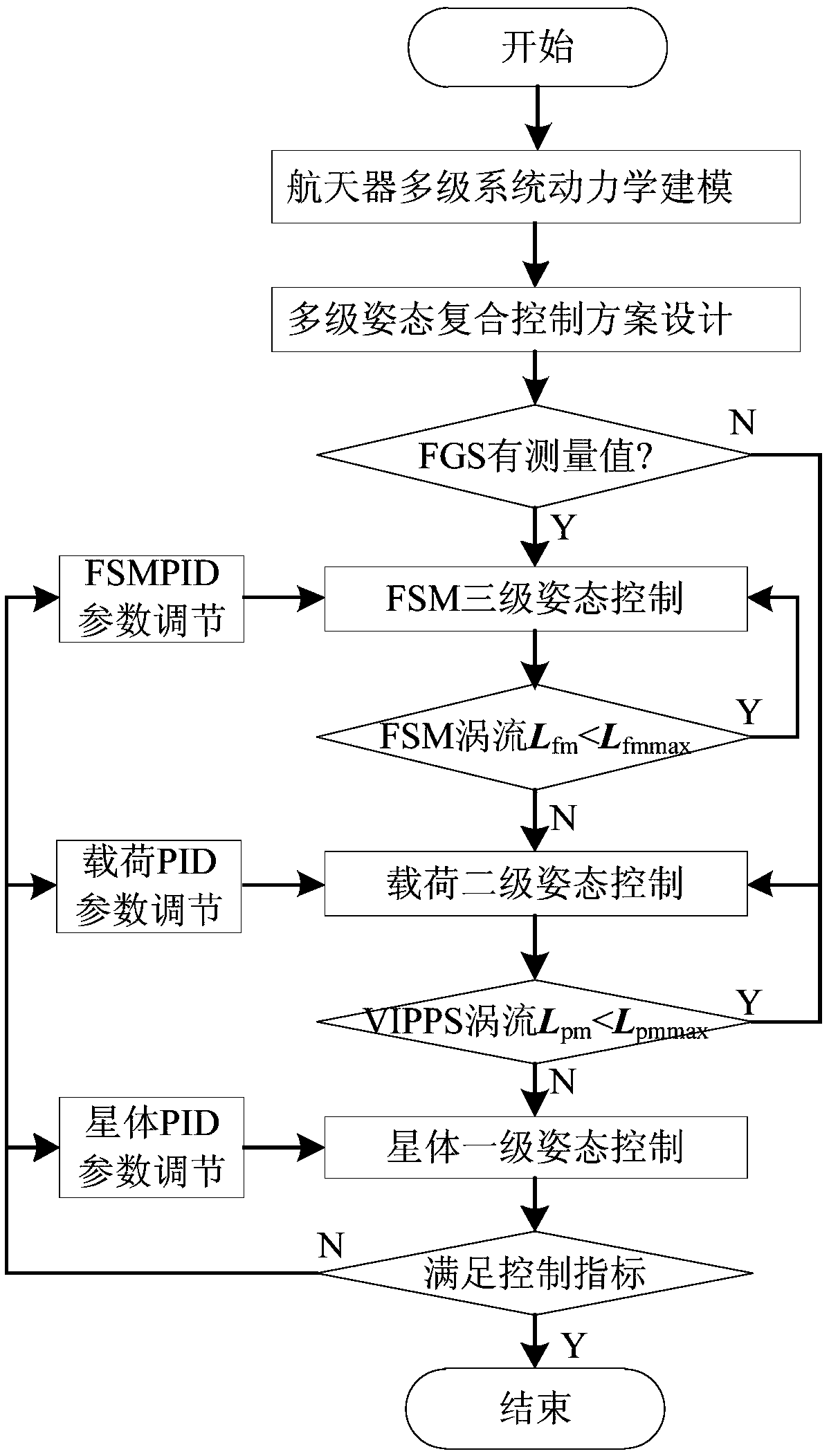
Coarse and fine layered, fast and slow combined and active and passive integrated multi-level composite control method for spacecraft
ActiveCN109002047AImprove load stability indexReduce the stability indexCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsThree levelGyroscope
The invention relates to a coarse and fine layered, fast and slow combined and active and passive integrated multi-level composite control method for a spacecraft. A layered control idea in a star-load-fast reflection mirror three-level system includes the following steps: 1) fast reflection mirror third-level control: adopting a guiding star sensor as a measuring component, adopting a fast reflection mirror actuator as an executing mechanism, and adopting a PID controller to realize the ultra-high-precision pointing control of a rolling-pitching axis of a fast reflection mirror; 2) load secondary control: adopting a load star sensor, a micrometer gyroscope and an FSM eddy current as the measuring components, adopting an active pointing ultra-static platform (VIPPS) actuator as the executing mechanism, and adopting the PID controller to realize the high-precision pointing control of the load; and 3) star first-level control: adopting a gyroscope, the load star sensor and a VIPPS eddy current as the measuring components, adopting a momentum wheel as the executing mechanism, and adopting the PID controller to realize the coarse pointing control of the star.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com