Patents
Literature
877results about "Alignment for track following on tapes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
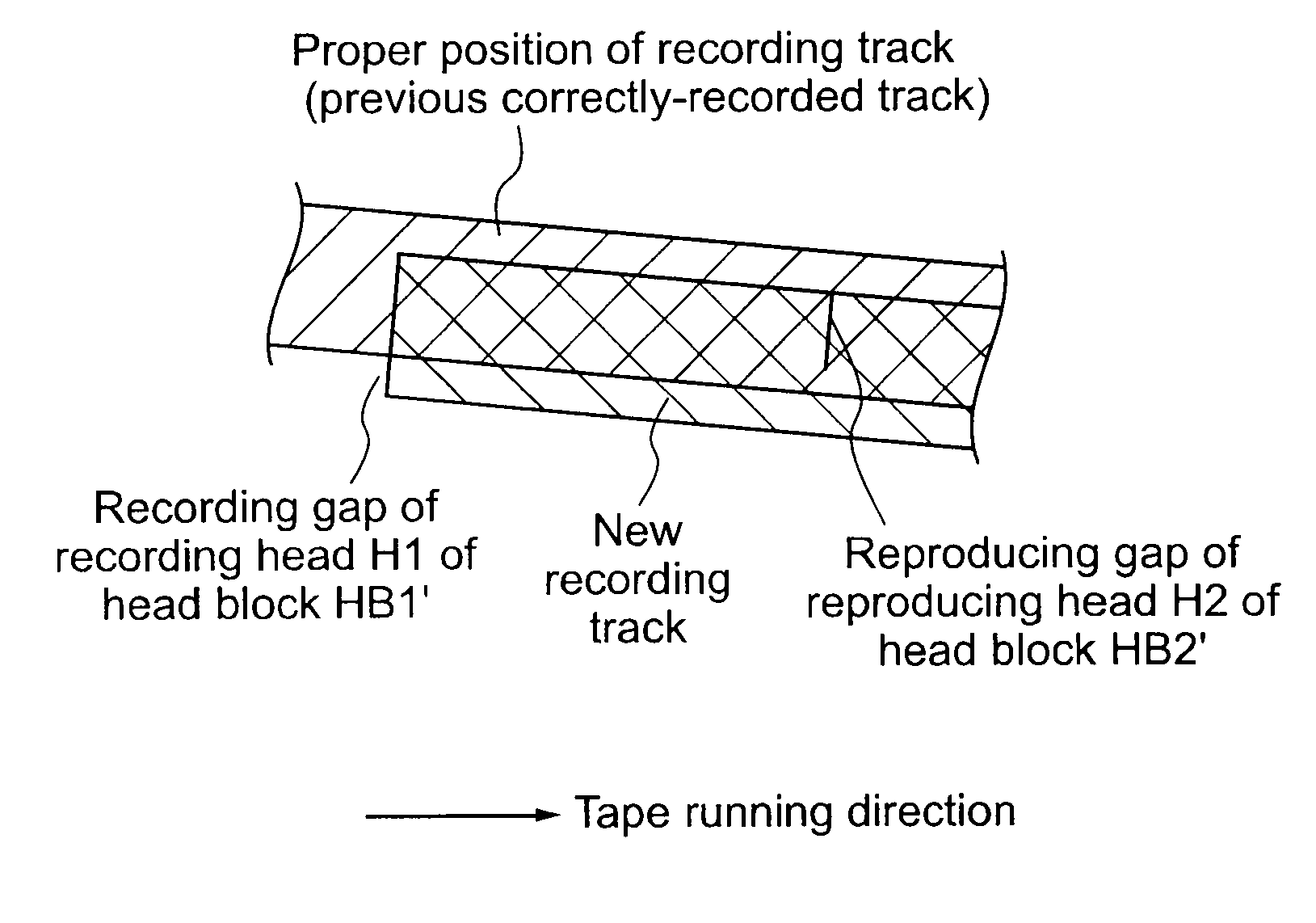
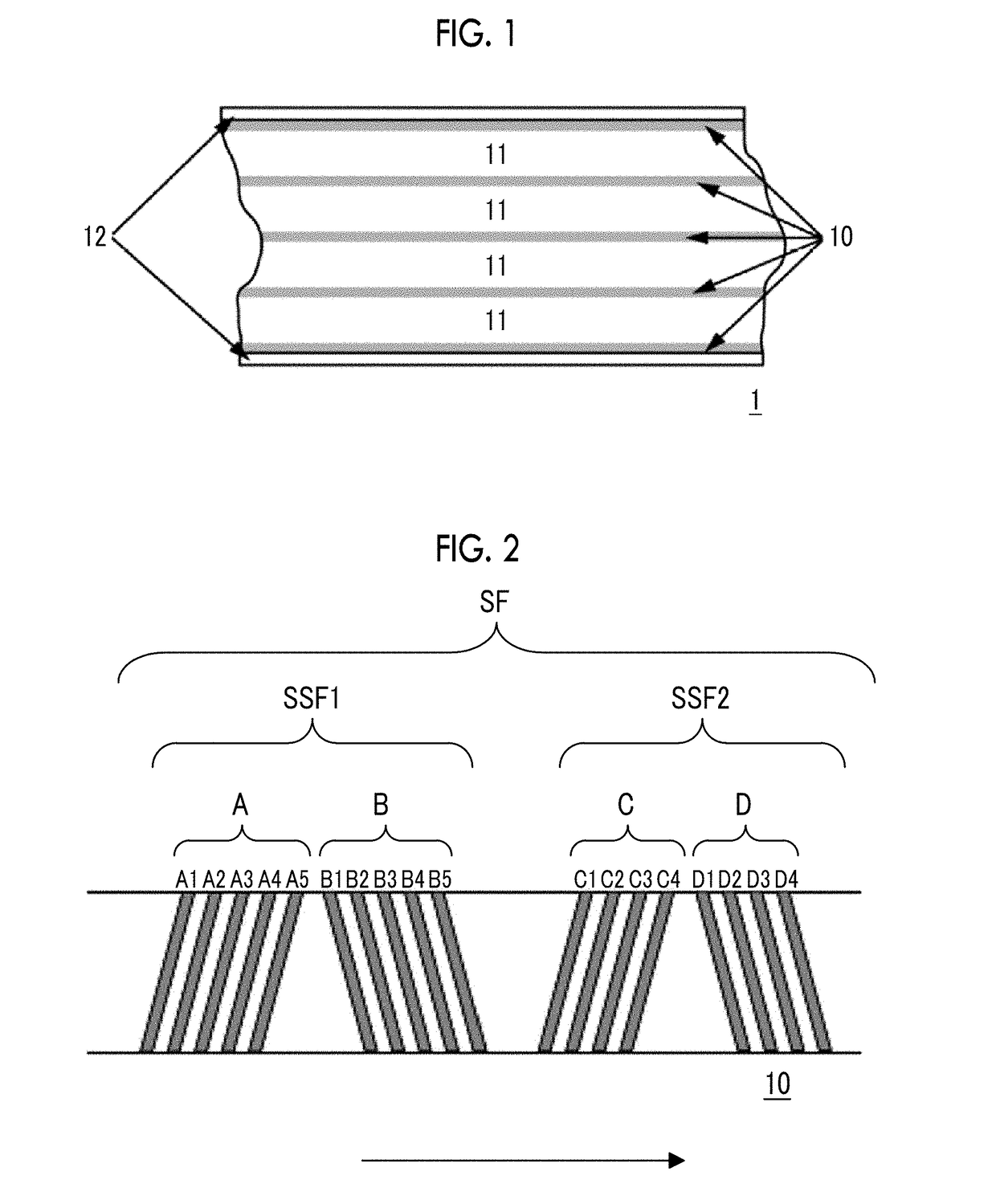
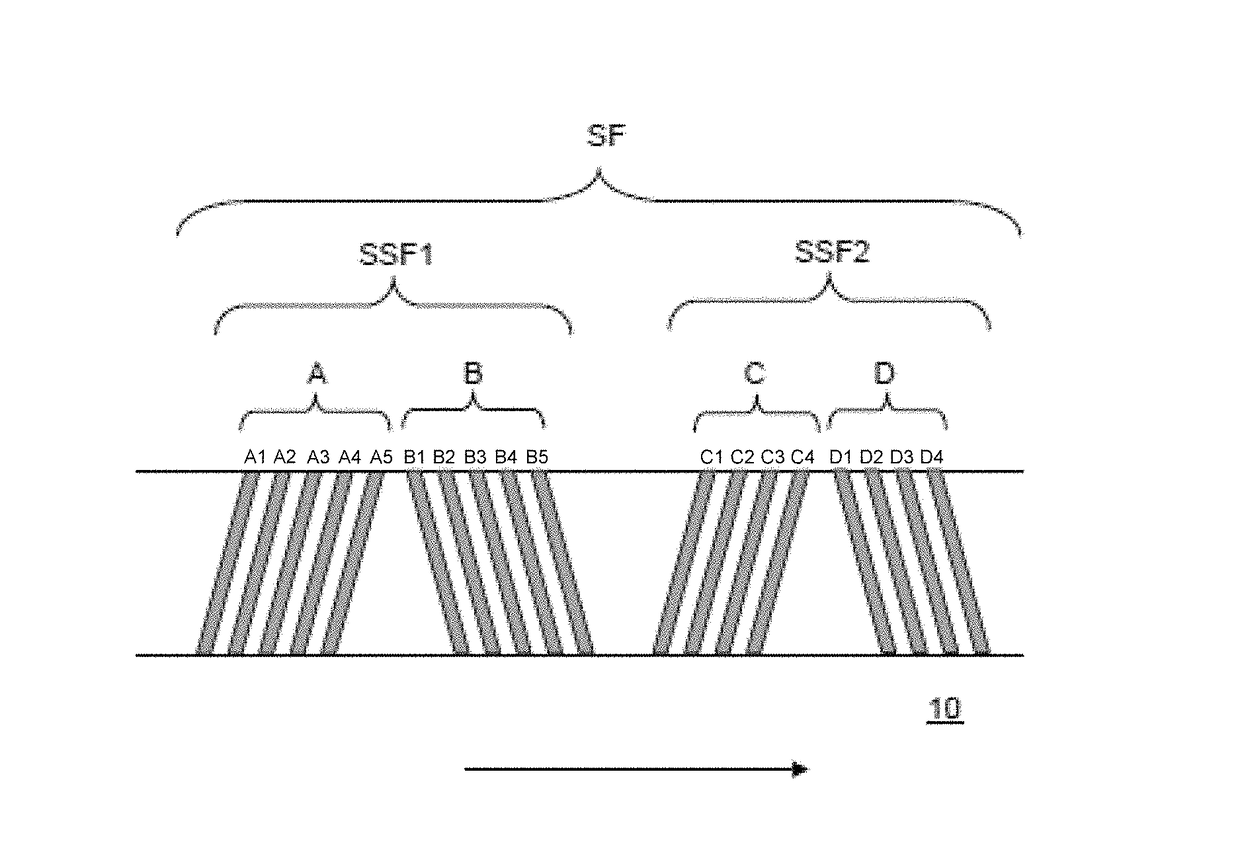
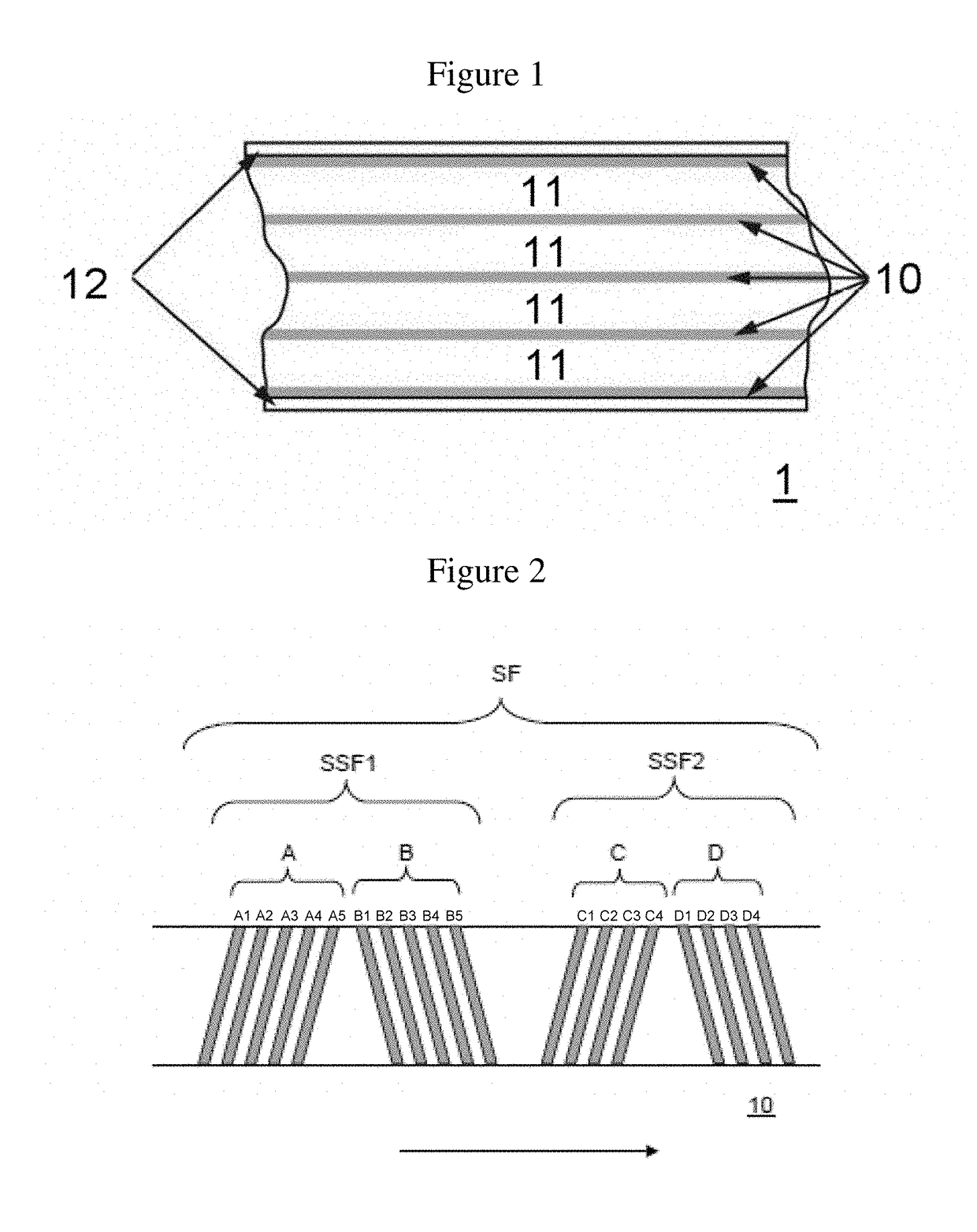
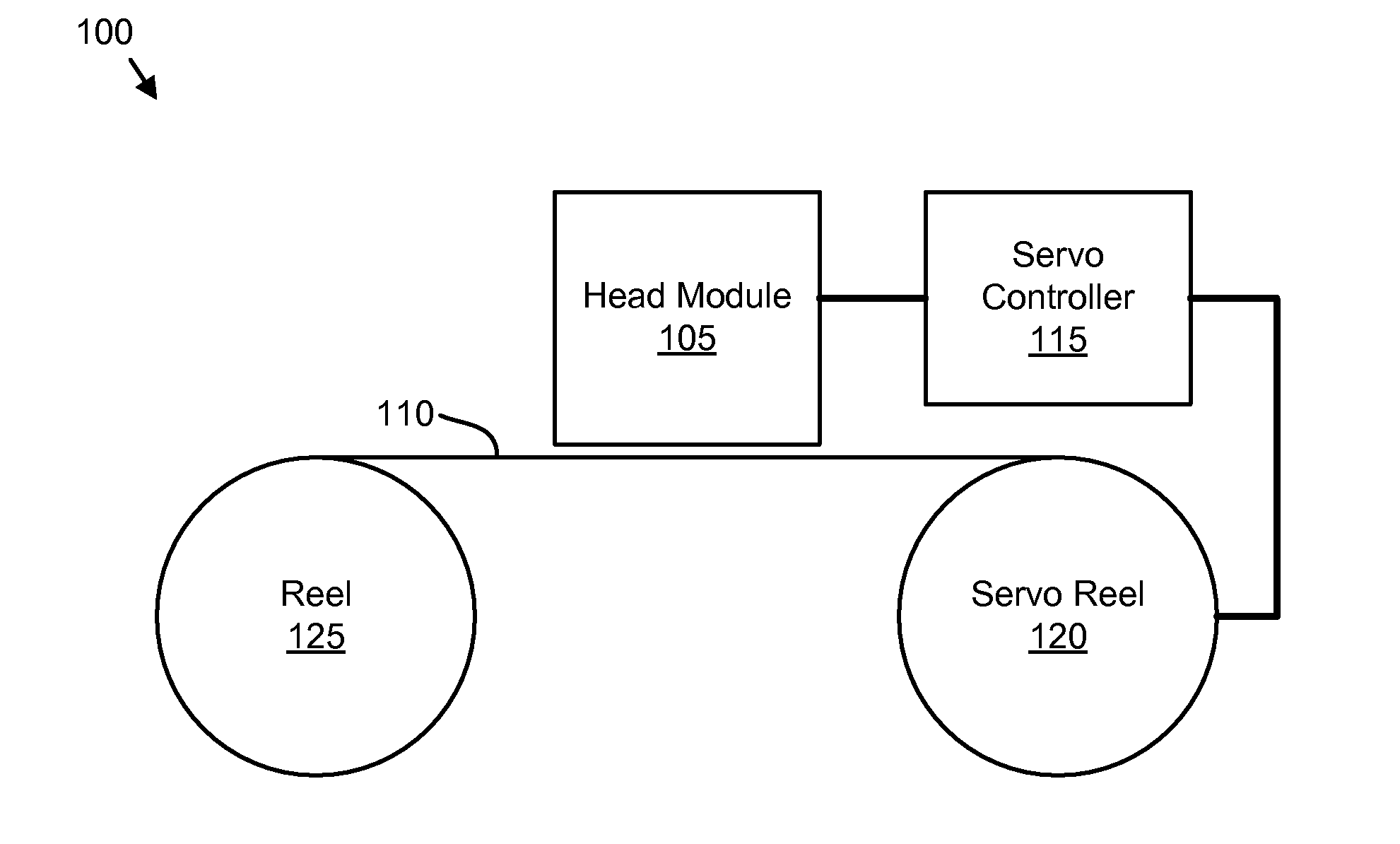
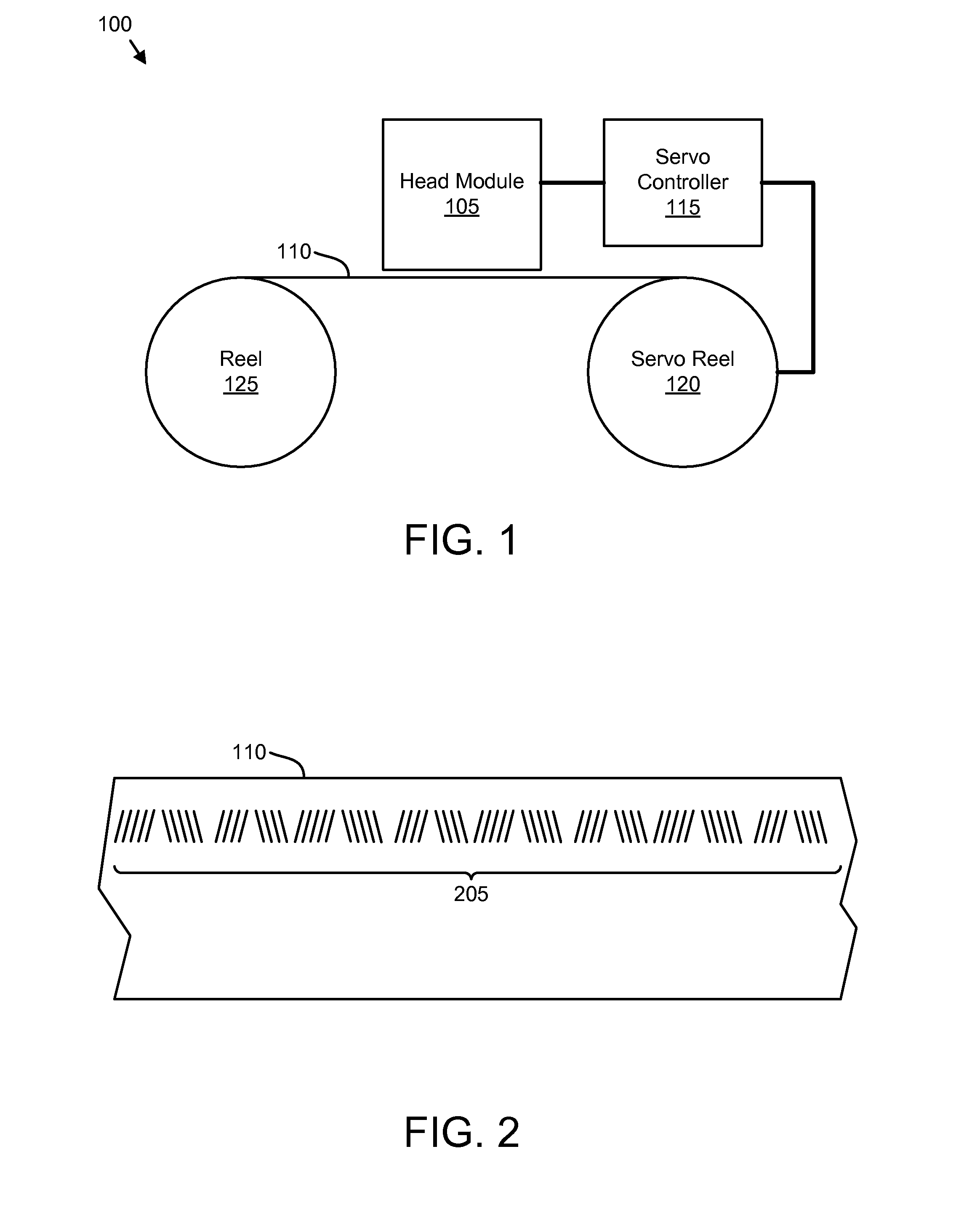
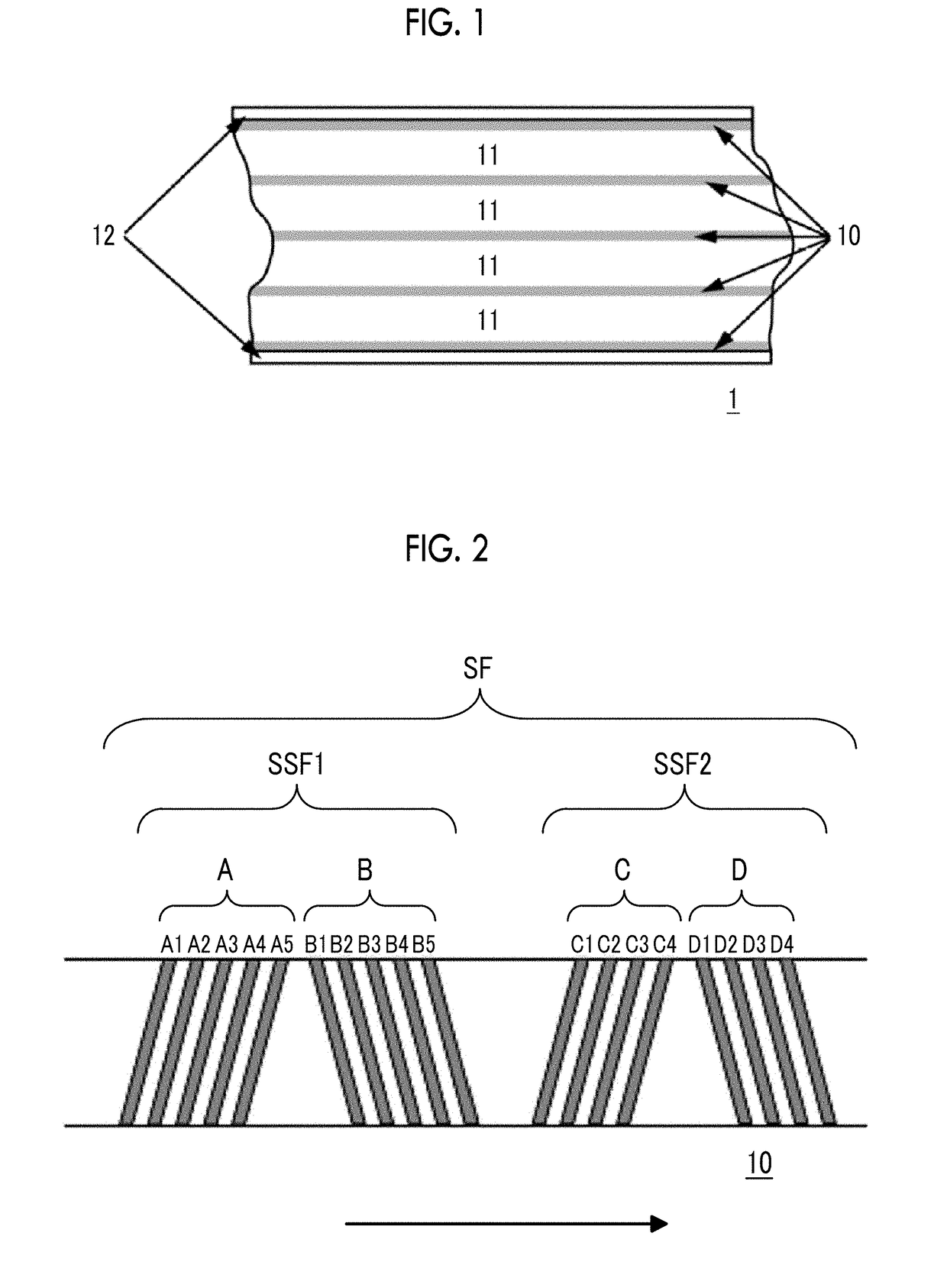
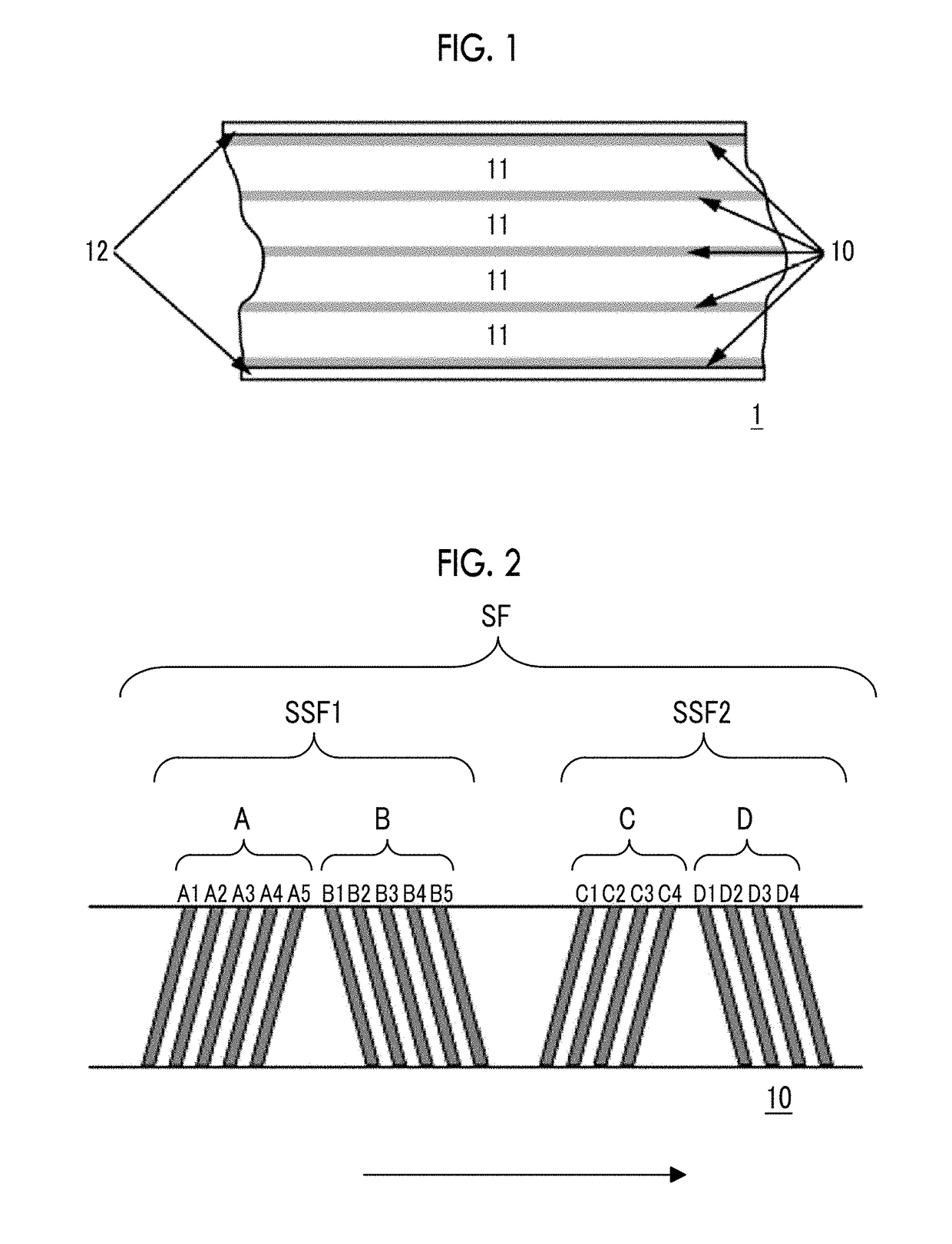
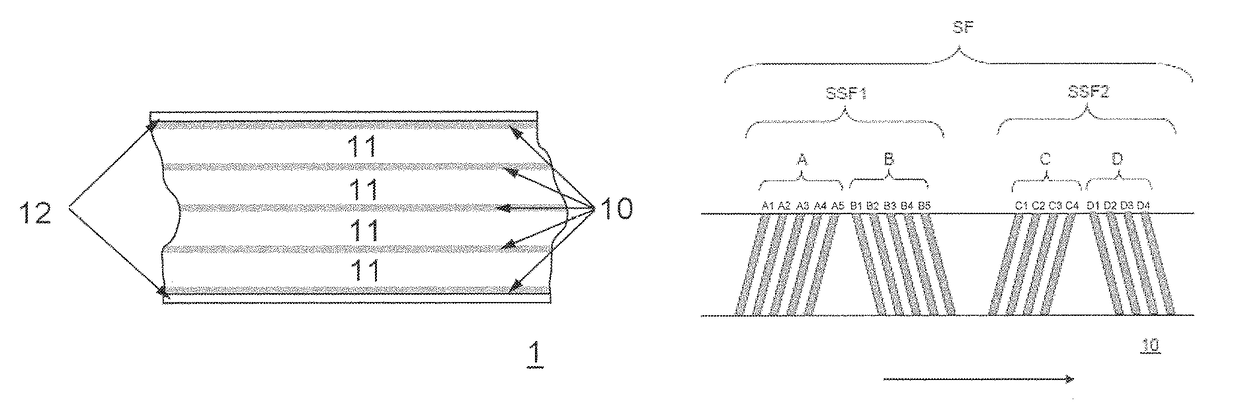
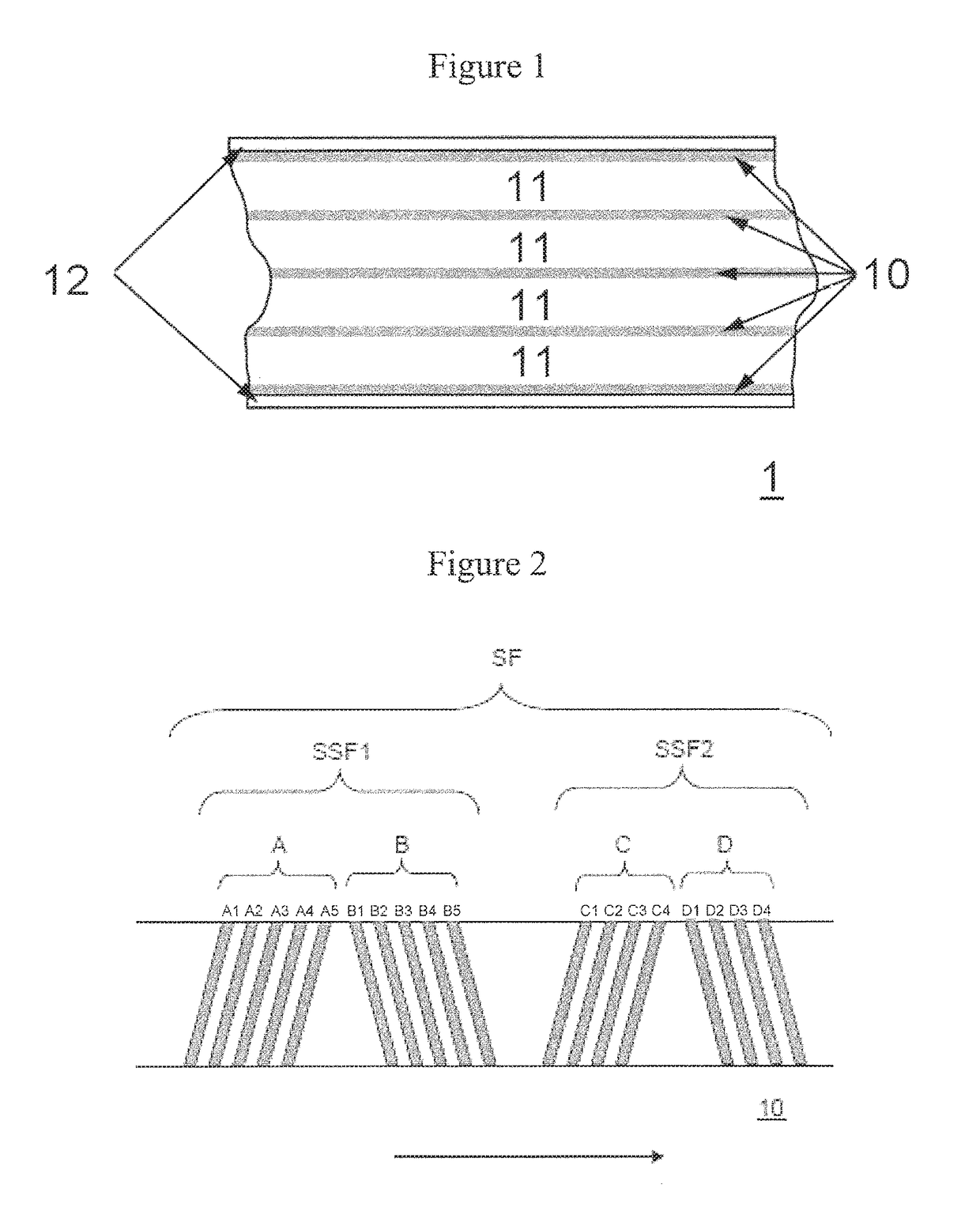
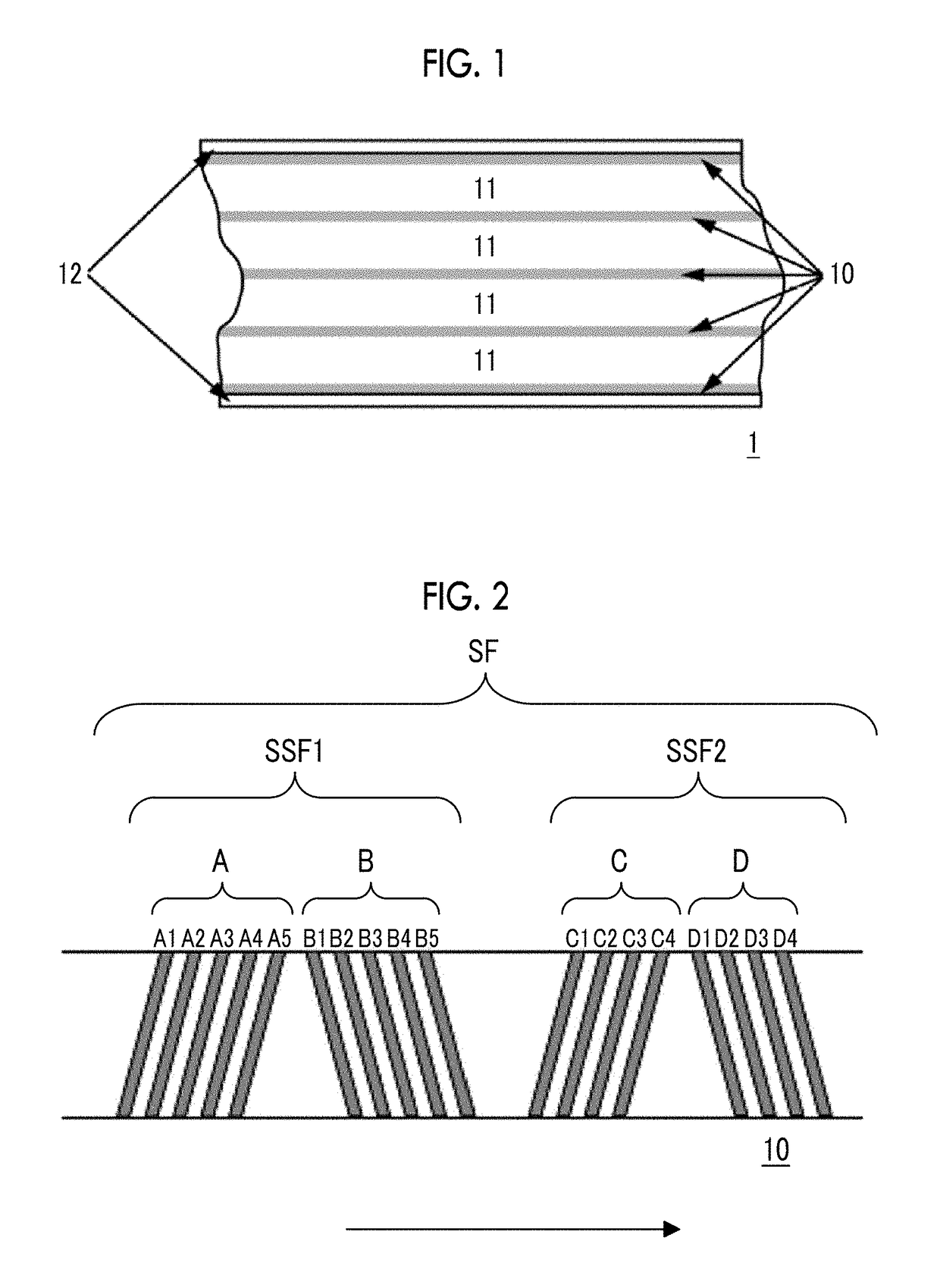
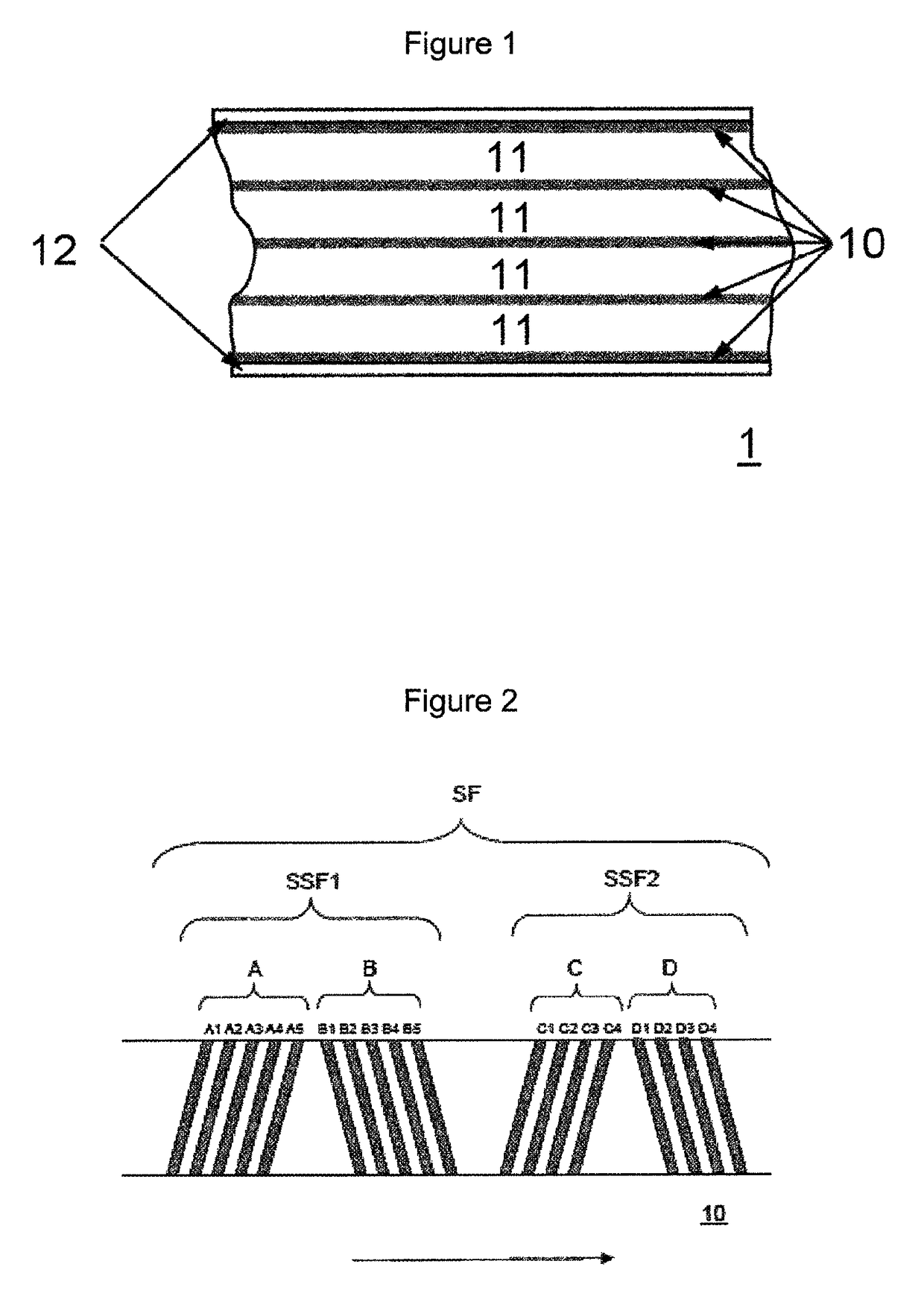
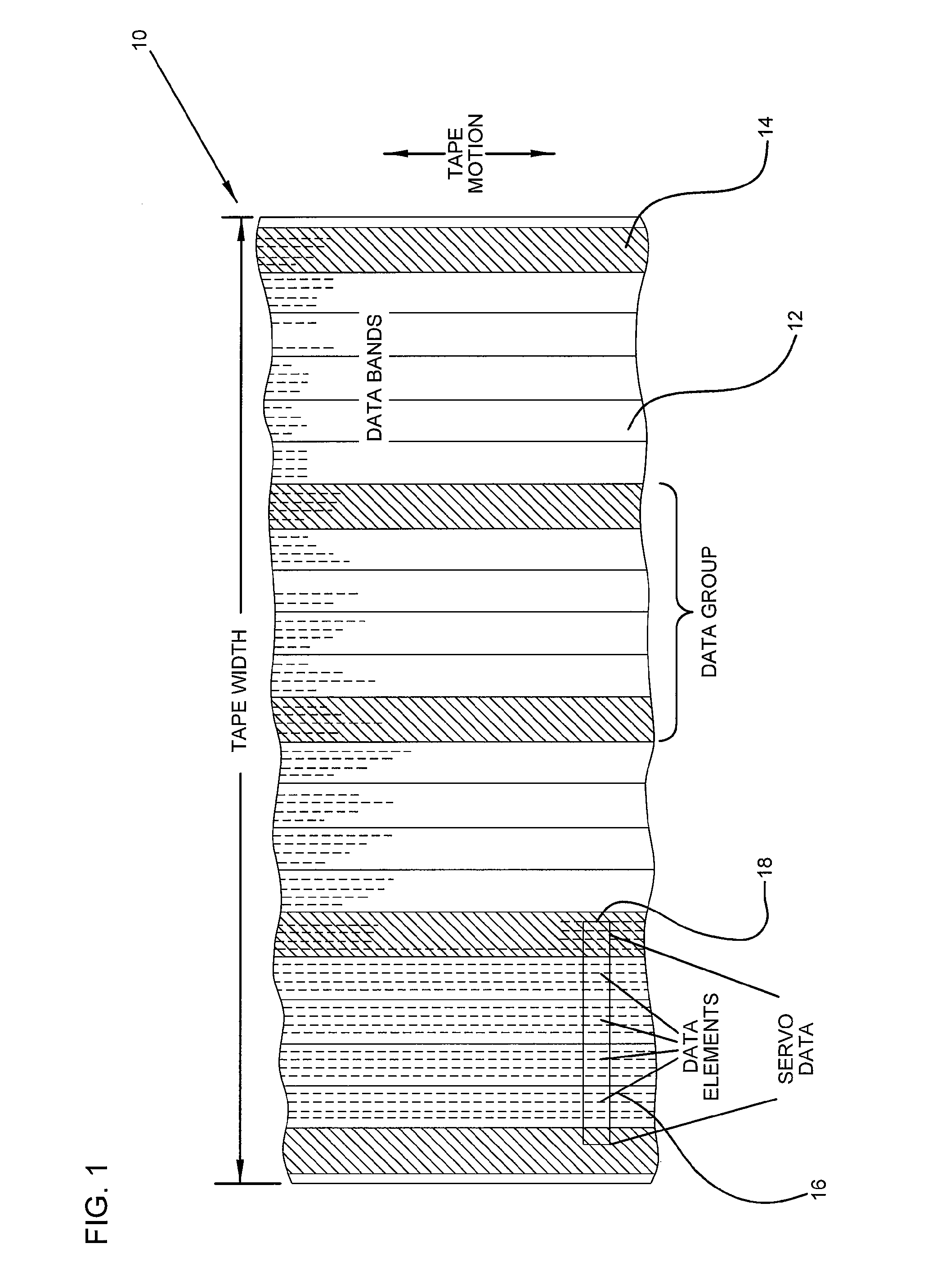
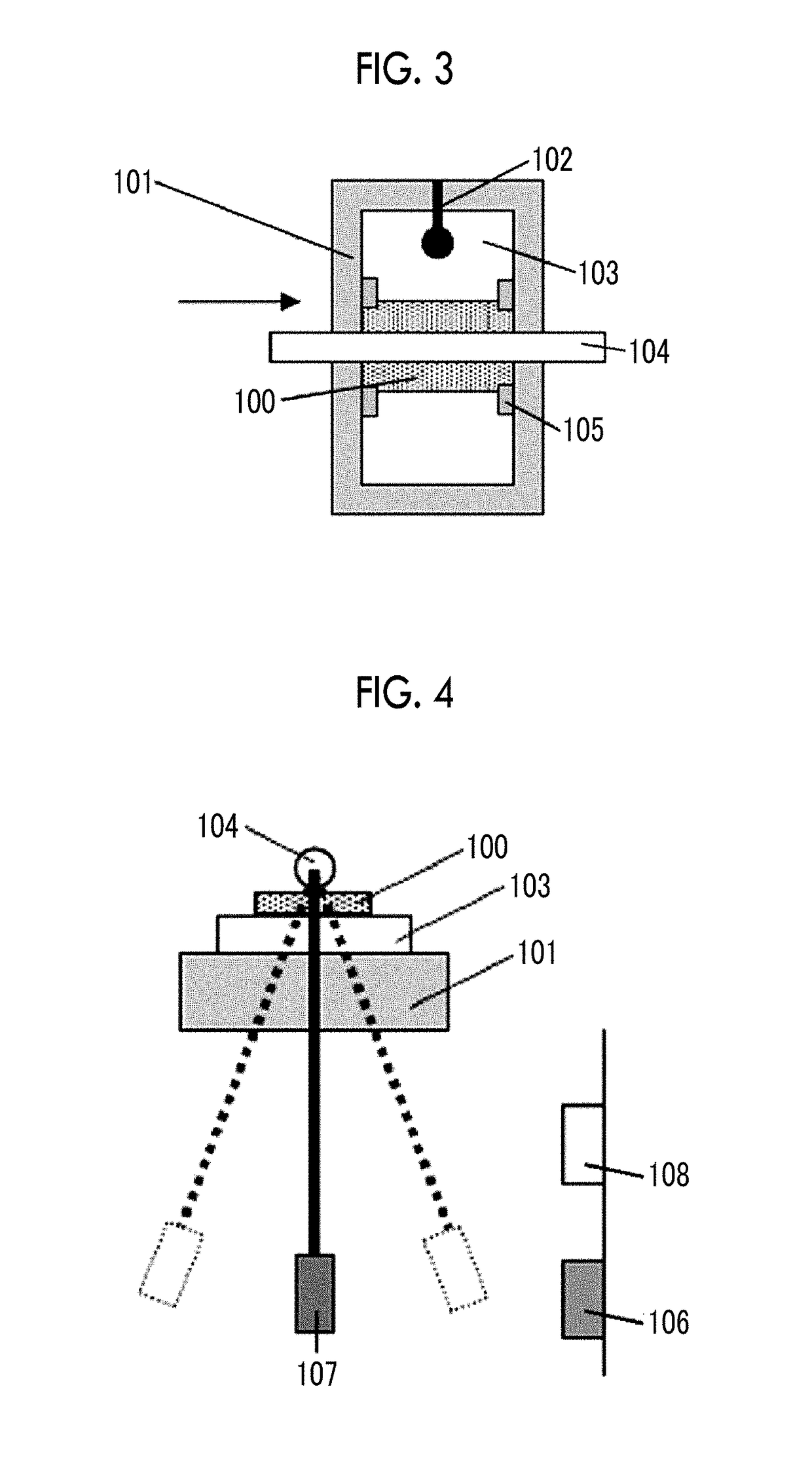
High density timing based servo format for use with tilted transducer arrays
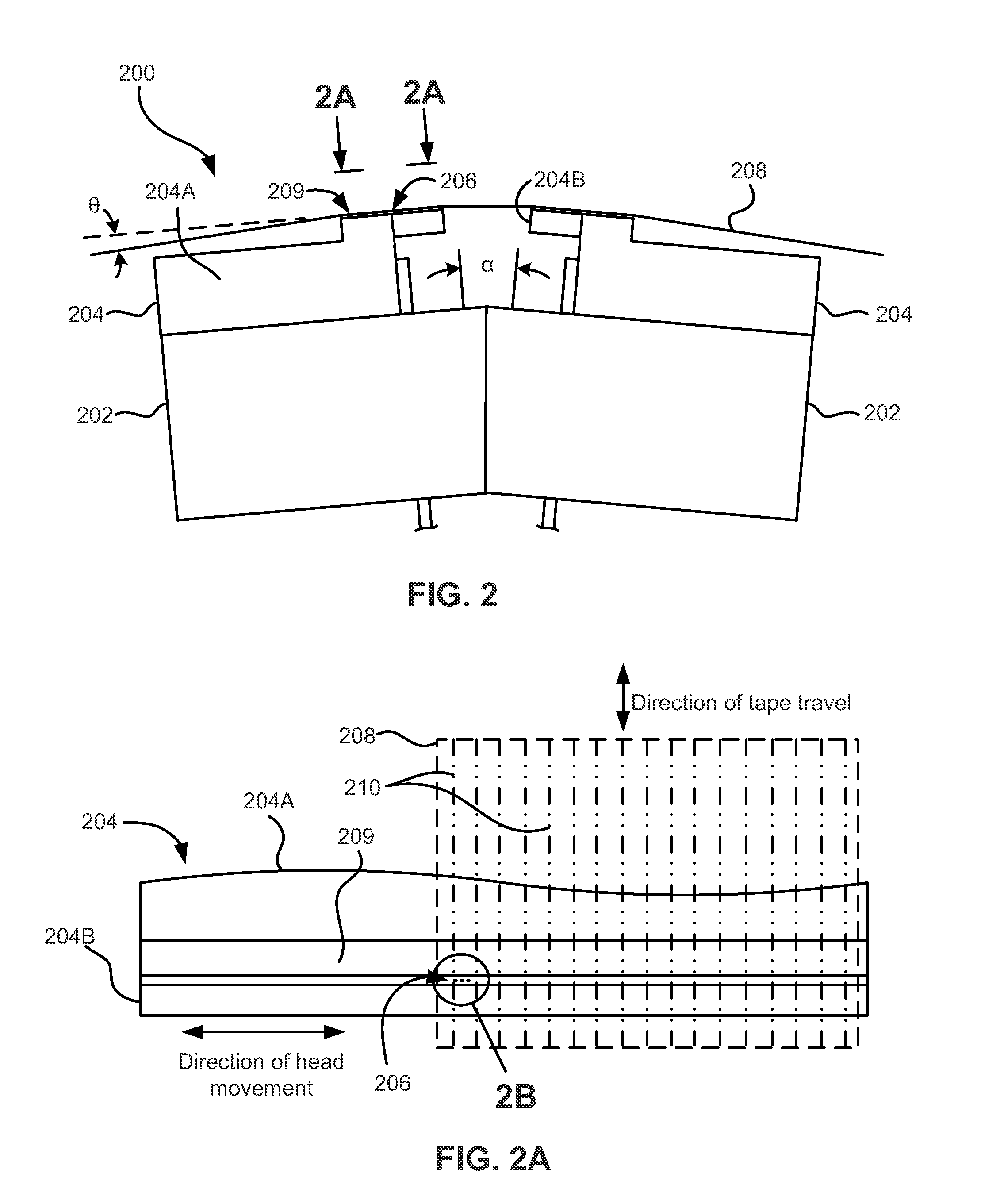
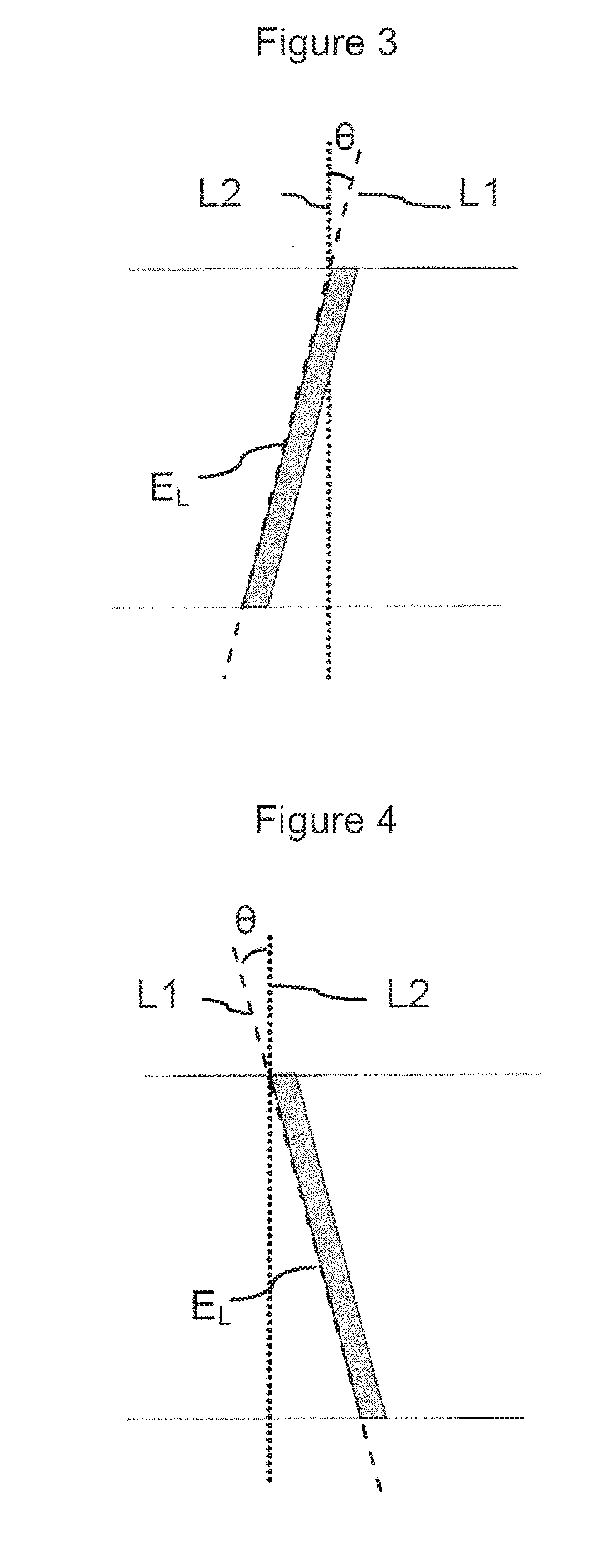
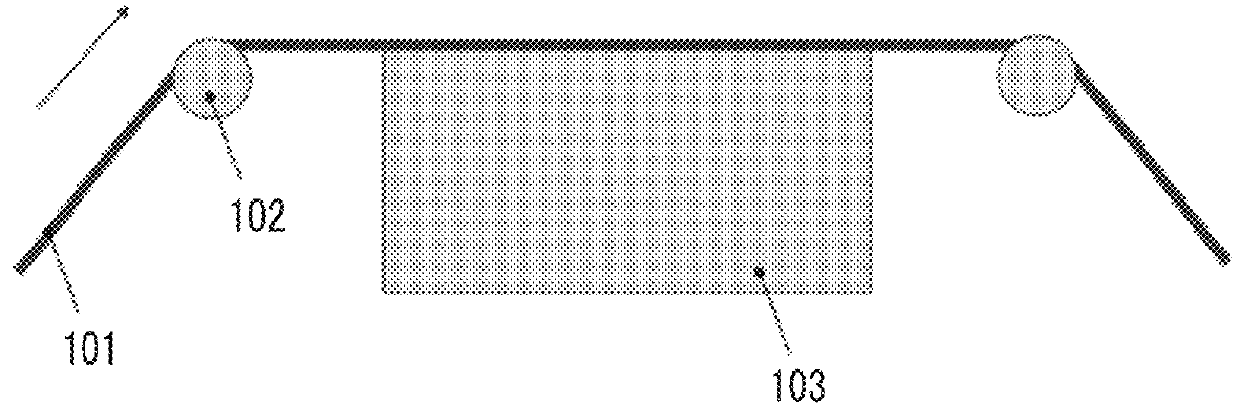
A product, according to one embodiment, includes a magnetic recording tape having opposite ends, a longitudinal axis of the magnetic recording tape being defined between the ends. The magnetic recording tape has at least one servo track, the at least one servo track having a plurality of first magnetic bars and a plurality of third magnetic bars oriented to form chevron-like patterns with the first magnetic bars. The first magnetic bars each have a longitudinal axis oriented at a first angle between 2 and 88 degrees from the longitudinal axis of the magnetic recording tape. The third magnetic bars each have a longitudinal axis oriented at a second angle between 2 and 88 degrees from the longitudinal axis of the magnetic recording tape, the second angle having a different numerical absolute value than the first angle.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
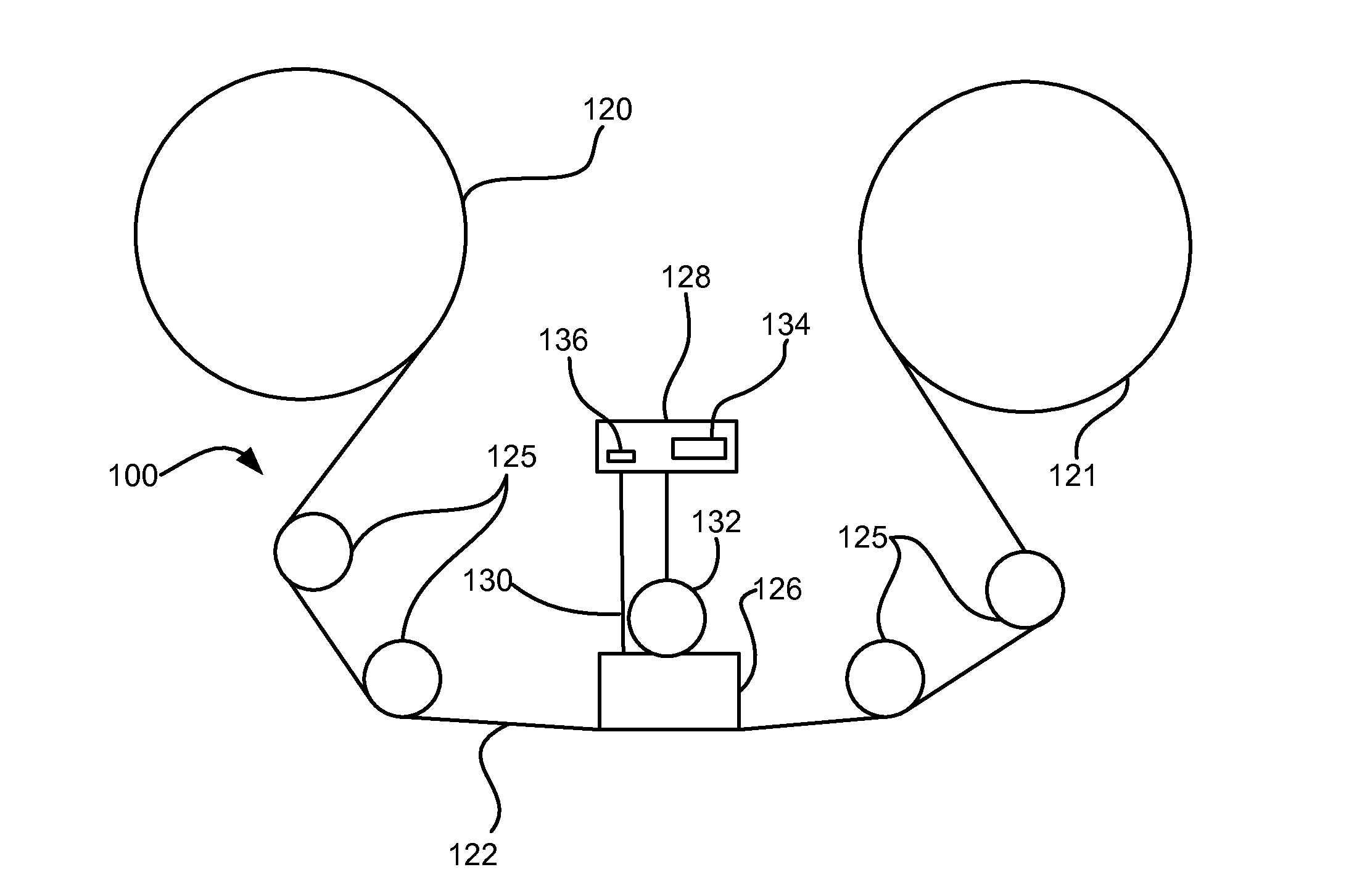
Systems and method for forming a servo pattern on a magnetic tape
InactiveUS7153366B1Maintain alignmentLiquid surface applicatorsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeEngineering
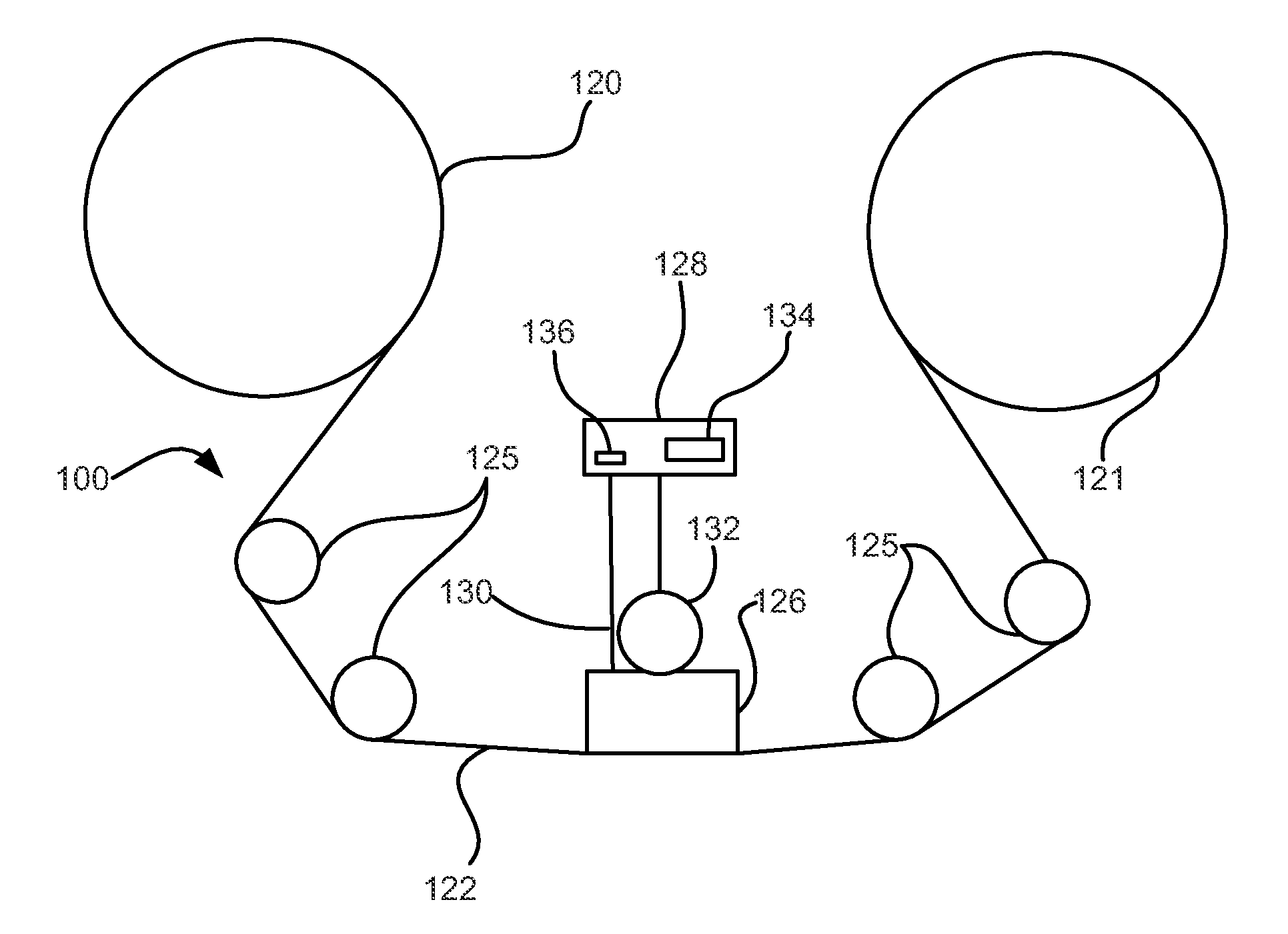
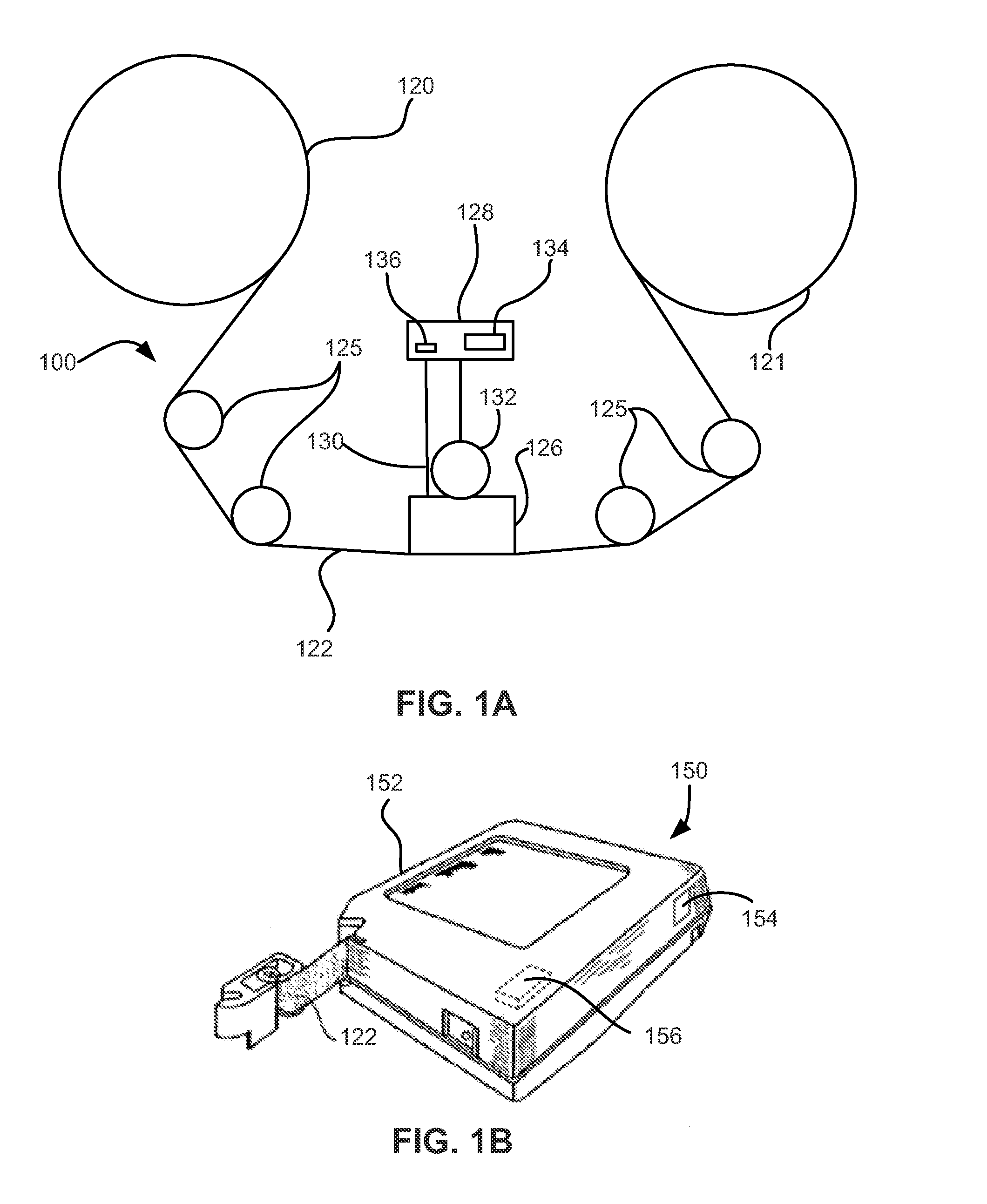
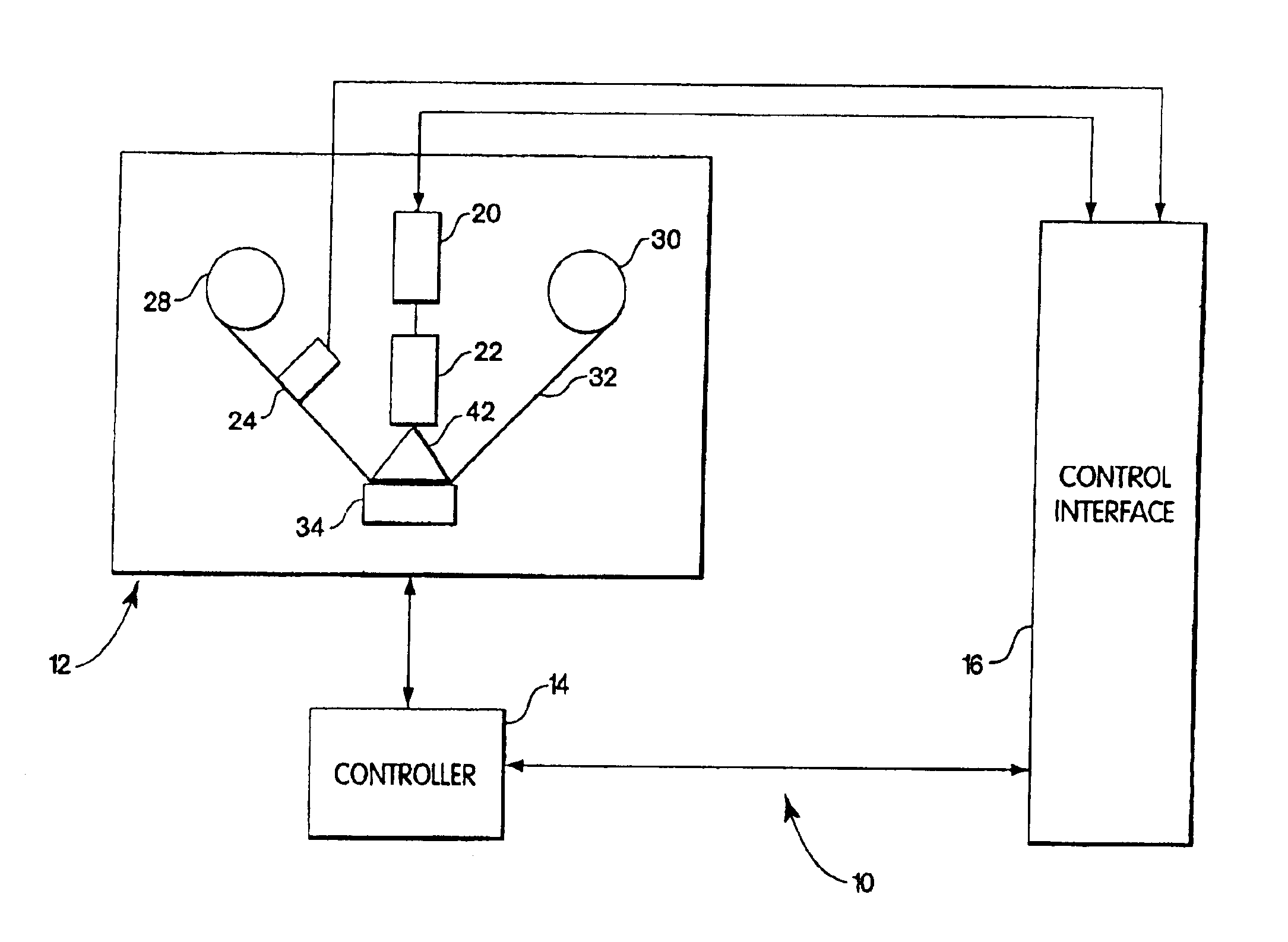
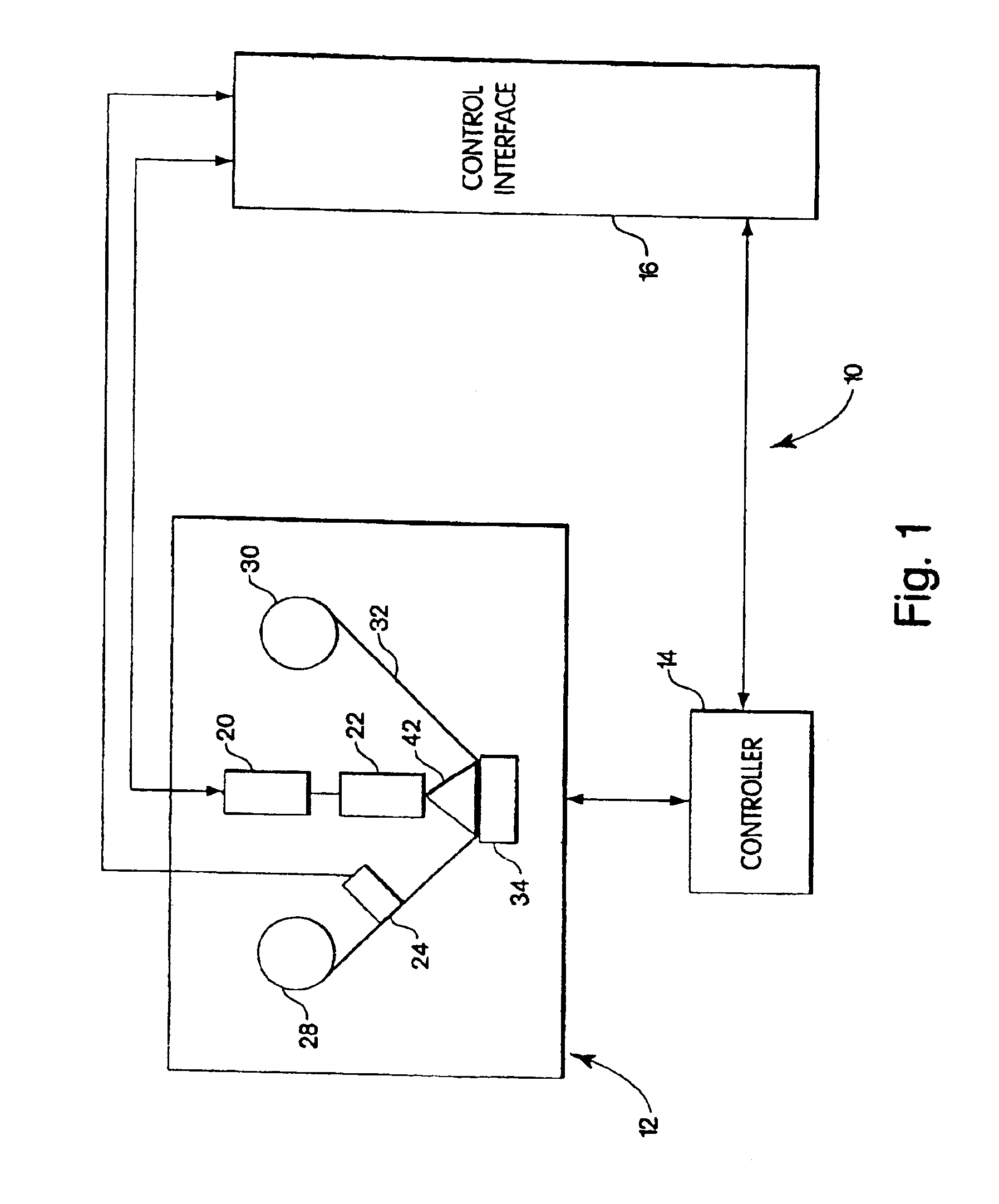
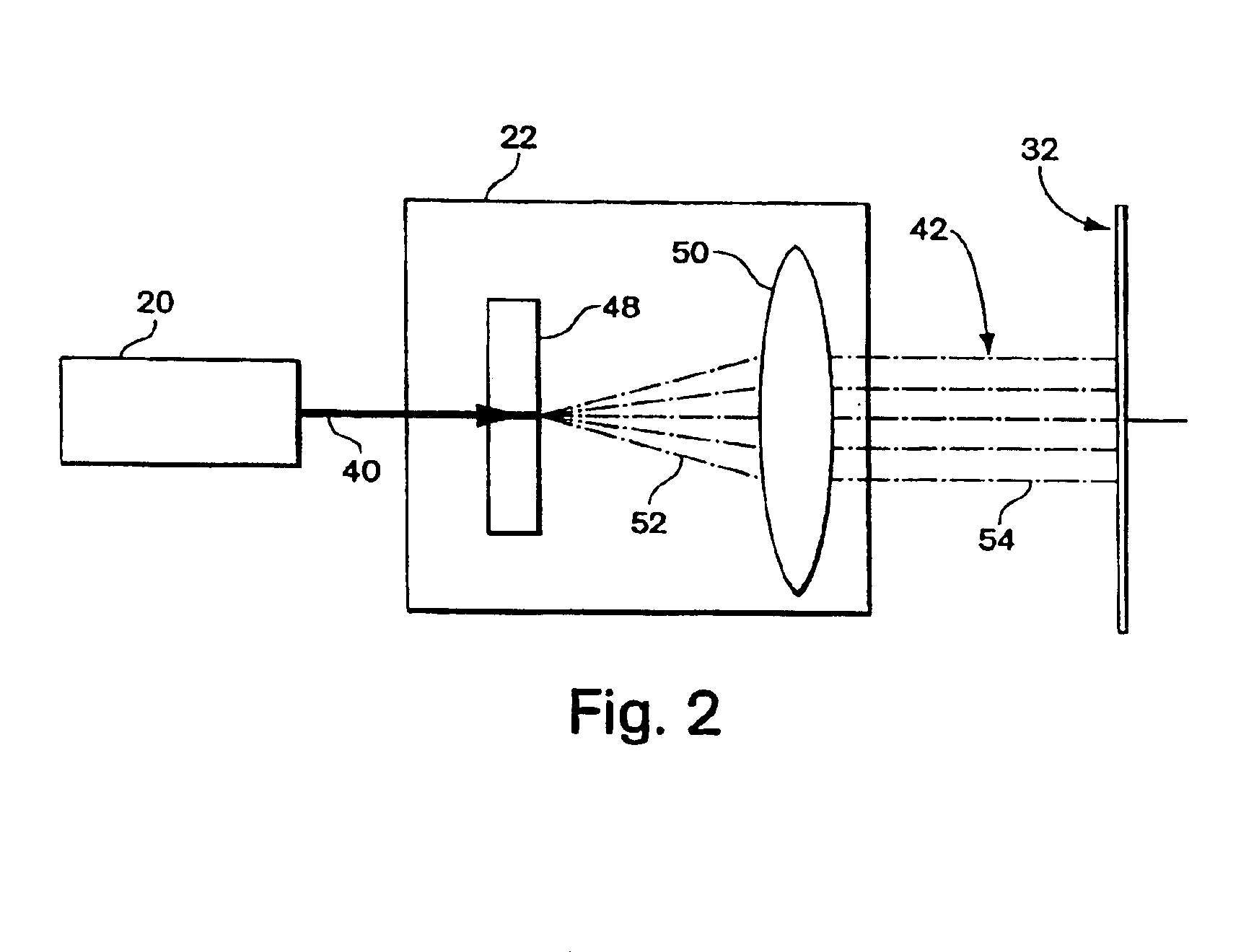
The systems, methods and products of the invention include systems and methods for manufacturing servo tracks on a magnetic tape. In one aspect, the invention includes systems for manufacturing magnetic tapes having servo tracks thereon wherein the servo tracks are optically detectable and are capable of being processed by a servo control system for maintaining alignment of a magnetic recording head with the data tracks on the recording side of the magnetic tape. In one practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the non-recording side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the non- recording side of the magnetic tape. In another practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the magnetic side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the magnetic side of the magnetic tape. Such engraved patterns can act as optical servo tracks for maintaining alignment of the recording head with the data tracks on the magnetic tape.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170186460A1Increase capacityEnhance head positioningAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tension forceMagnetic force microscope
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the coercive force measured in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 167 kA / m, a timing-based servo pattern is present on the magnetic layer, and the edge shape specified by observing the timing-based servo pattern with a magnetic force microscope is a shape in which the difference between the value of the 99.9% cumulative distribution function of the width of misalignment from the ideal shape in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and the value L0.1 of the 0.1% cumulative distribution function, L99.9-L0.1, is less than or equal to 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for forming a servo pattern on a magnetic tape
InactiveUS7029726B1Maintain alignmentTrack finding/aligningRadiation applicationsMagnetic tapeControl theory
The systems, methods and products of the invention include systems and methods for manufacturing servo tracks on a magnetic tape. In one aspect, the invention includes systems for manufacturing magnetic tapes having servo tracks thereon wherein the servo tracks are optically detectable and are capable of being processed by a servo control system for maintaining alignment of a magnetic recording head with the data tracks on the recording side of the magnetic tape. In one practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the non-recording side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the non-recording side of the magnetic tape. In another practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the magnetic side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the magnetic side of the magnetic tape. Such engraved patterns can act as optical servo tracks for maintaining alignment of the recording head with the data tracks on the magnetic tape.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
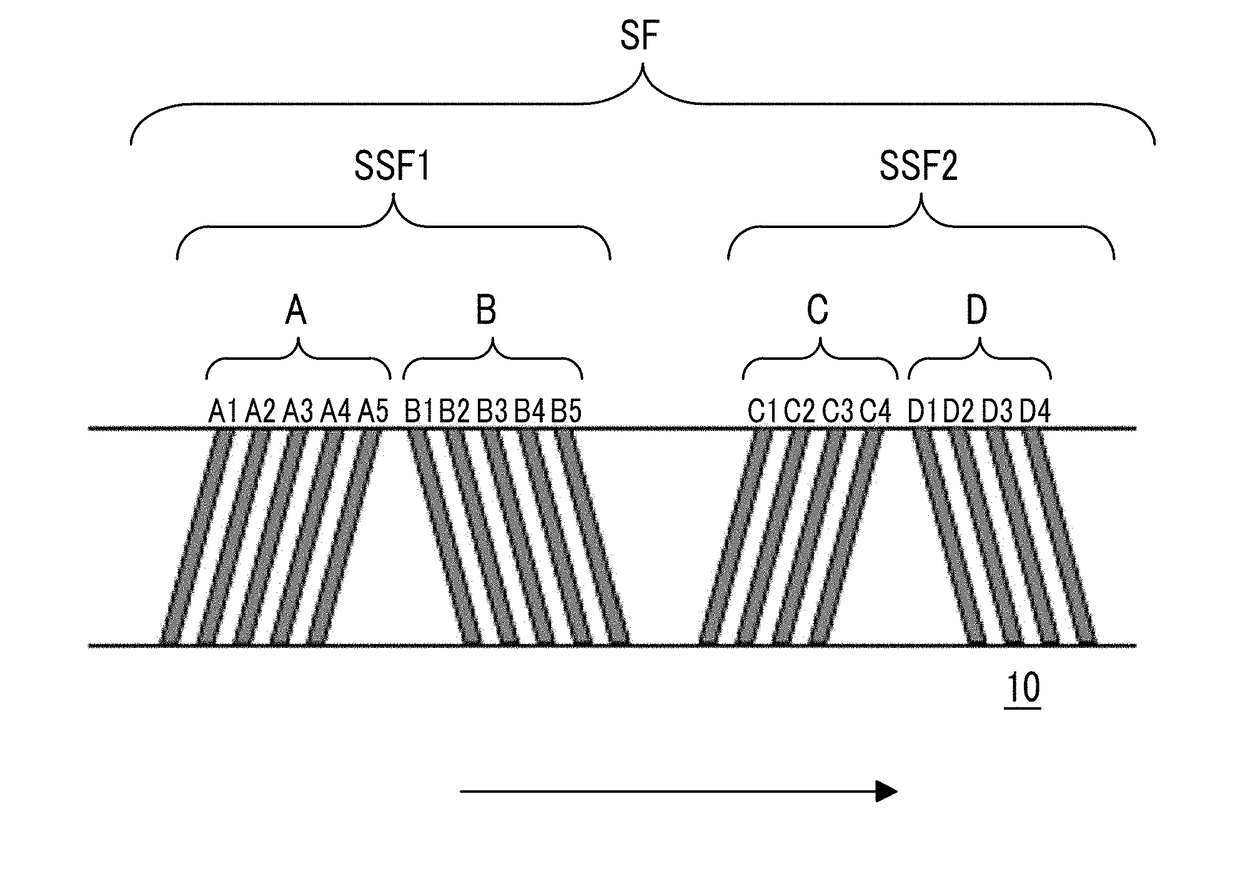
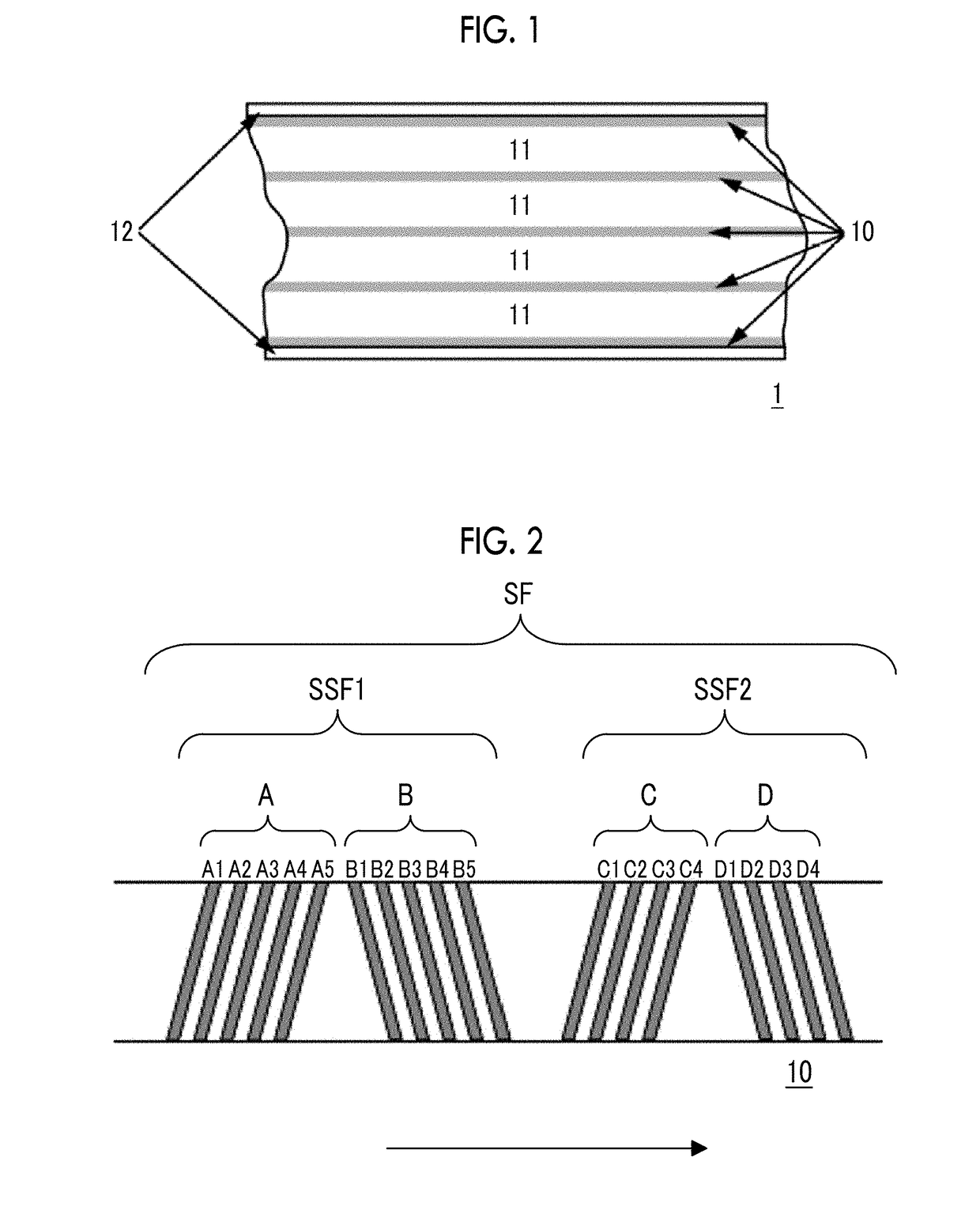
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape apparatus, servo pattern recording apparatus, magnetic tape producing method, and magnetic tape recording method
ActiveUS20090161249A1Accurate recordSuppress crosstalkAlignment for track following on tapesTape carriersMagnetic tapeControl theory
Provided is a magnetic tape that includes a data band, including servo patterns, data, and a guard space. The servo patterns is formed along a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape with an interval provided between each of the servo patterns, each of the servo patterns formed across a full width of the data band. The data is disposed between the servo patterns. The guard space is disposed between each of the servo patterns and the data.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170372740A1Improve accuracyAccurate informationBase layers for recording layersAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeFull width at half maximum
Provided is a magnetic tape in which the total thickness is equal to or smaller than 5.30 μm, the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, a magnetic layer surface Ra is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, the magnetic layer includes fatty acid ester, a full width at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the magnetic layer before performing vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 7.0 nm, a full width at half maximum of spacing distribution measured after performing the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 7.0 nm, and a difference between a spacing measured after performing the vacuum heating and a spacing measured before performing the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 8.0 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS9837116B2Increase the number ofIncrease recording capacityAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS10074393B2Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tension force
The magnetic tape includes a magnetic layer having ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume equal to or smaller than 1,600 nm3, and an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern specified by a magnetic force microscope observation is a shape in which a difference (l99.9−l0.1) between a value l99.9 of a cumulative frequency function of 99.9% of a position deviation width from an ideal shape in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and a value l0.1 of the cumulative frequency function of 0.1% thereof is equal to or smaller than 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
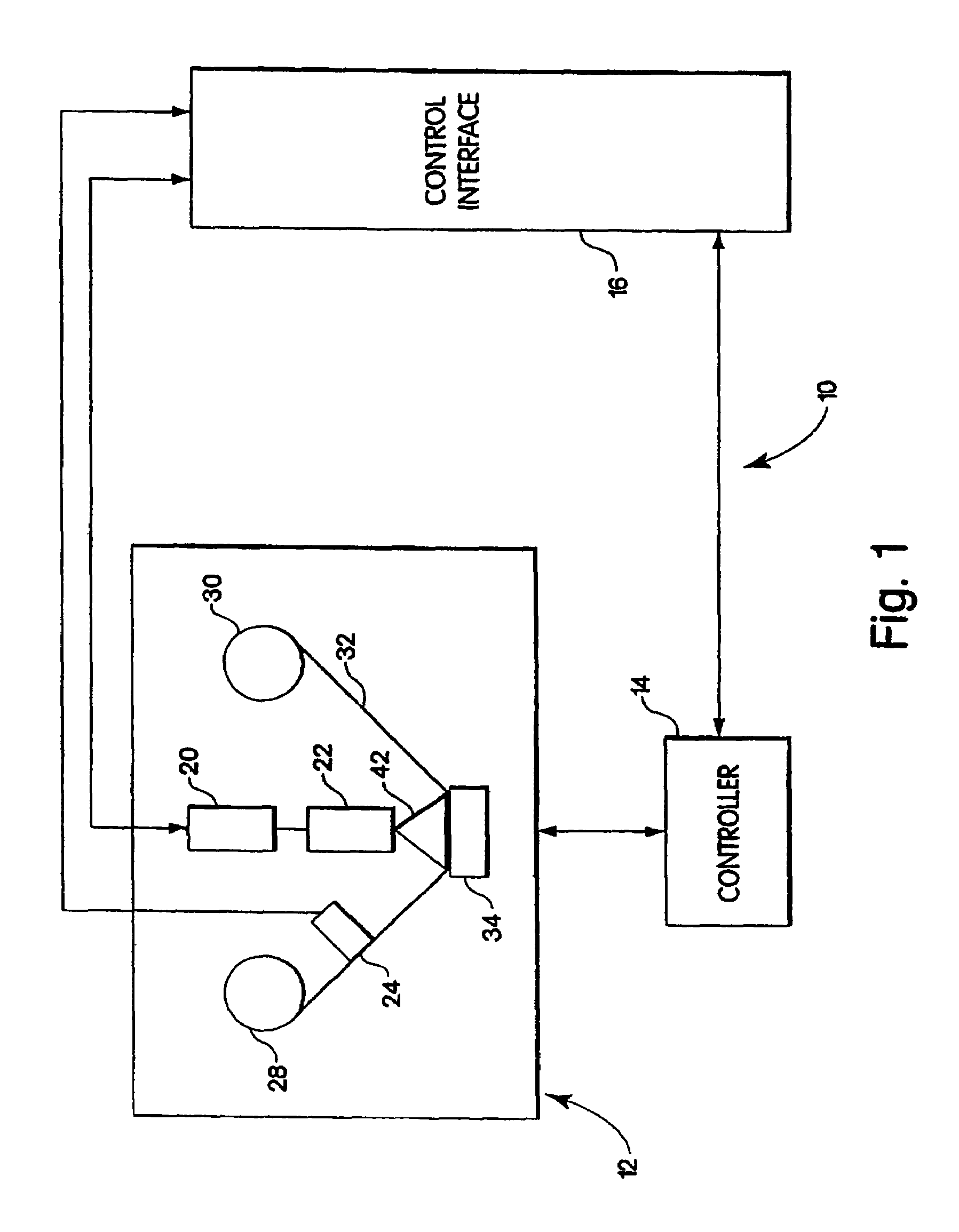
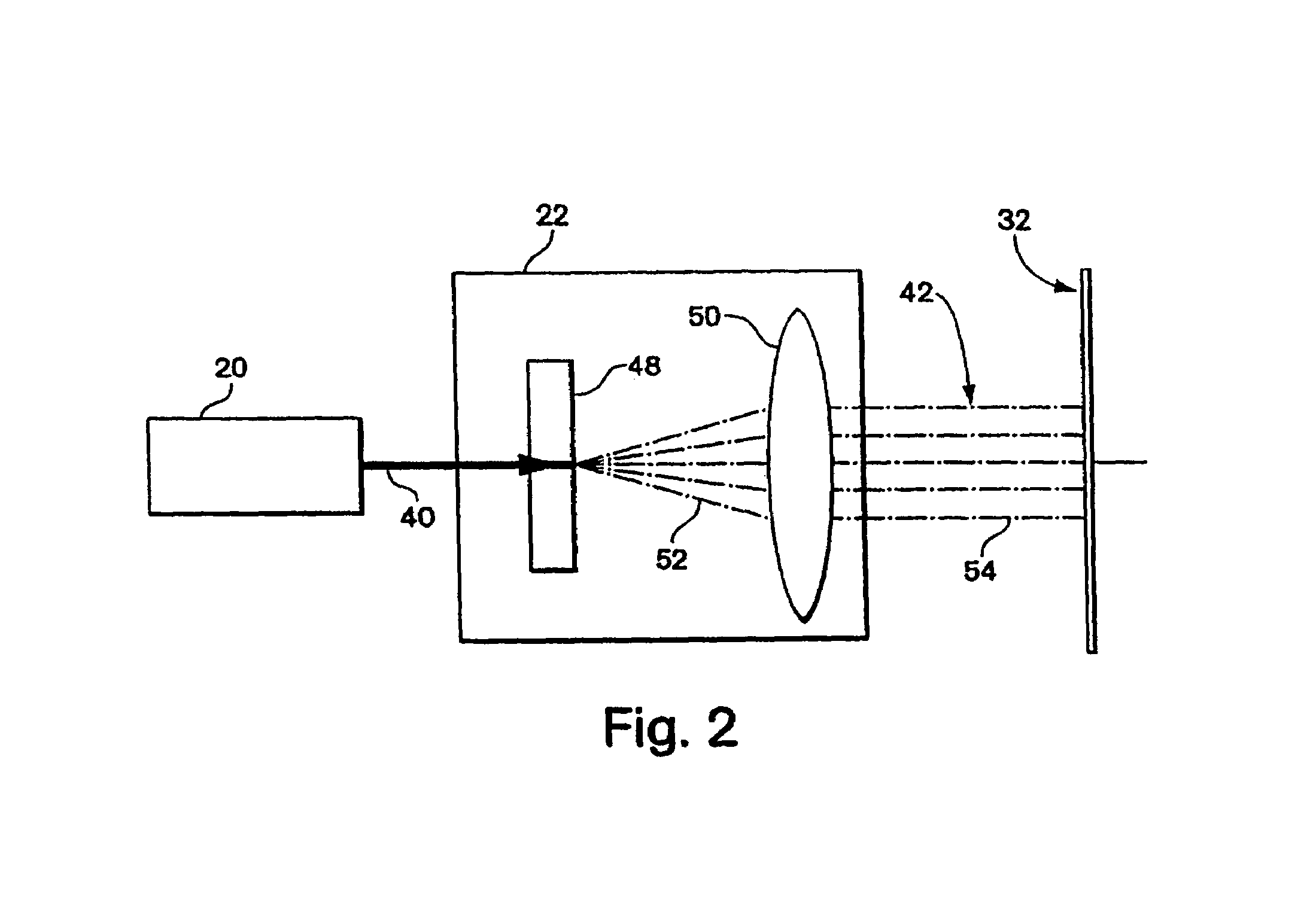
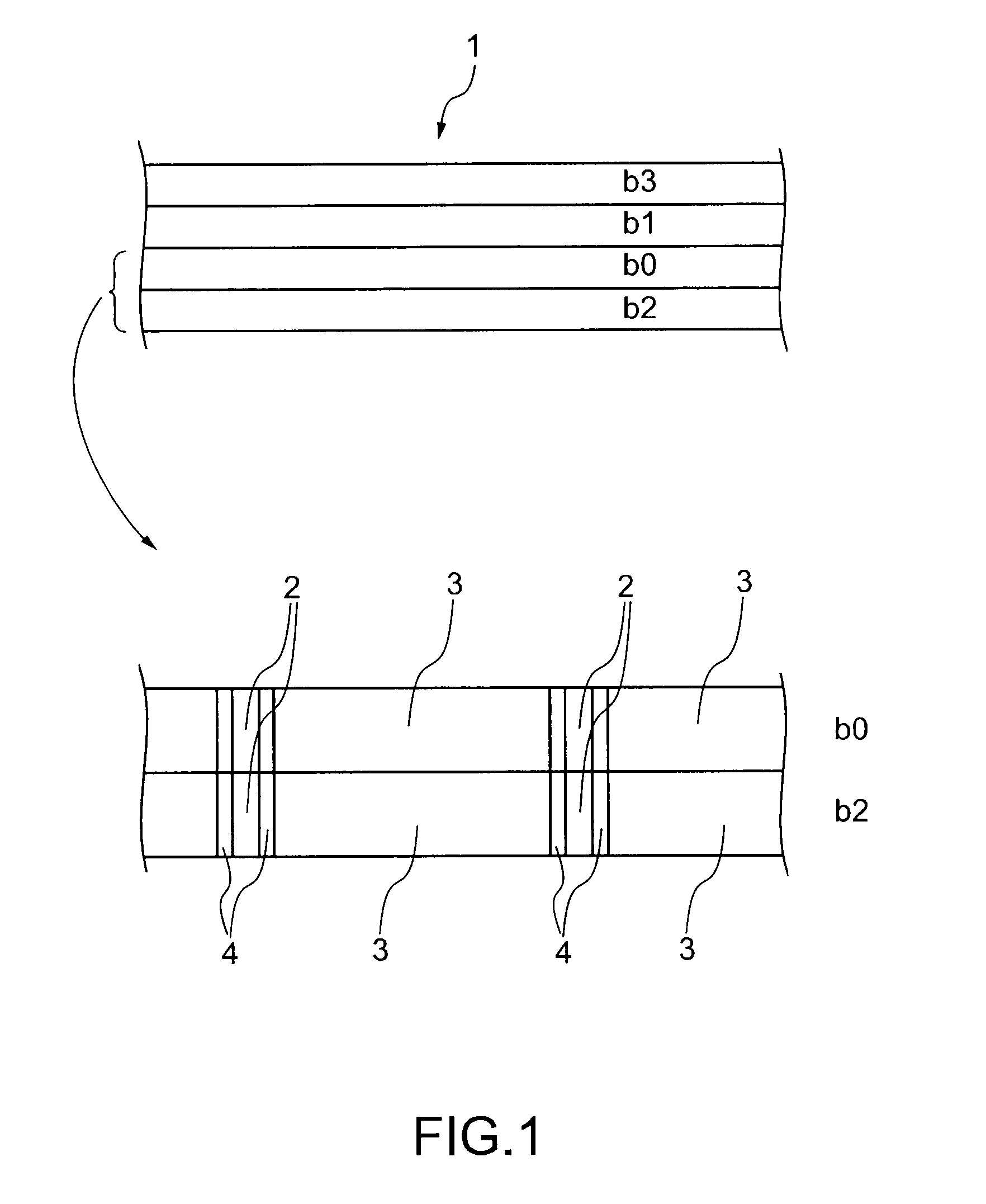
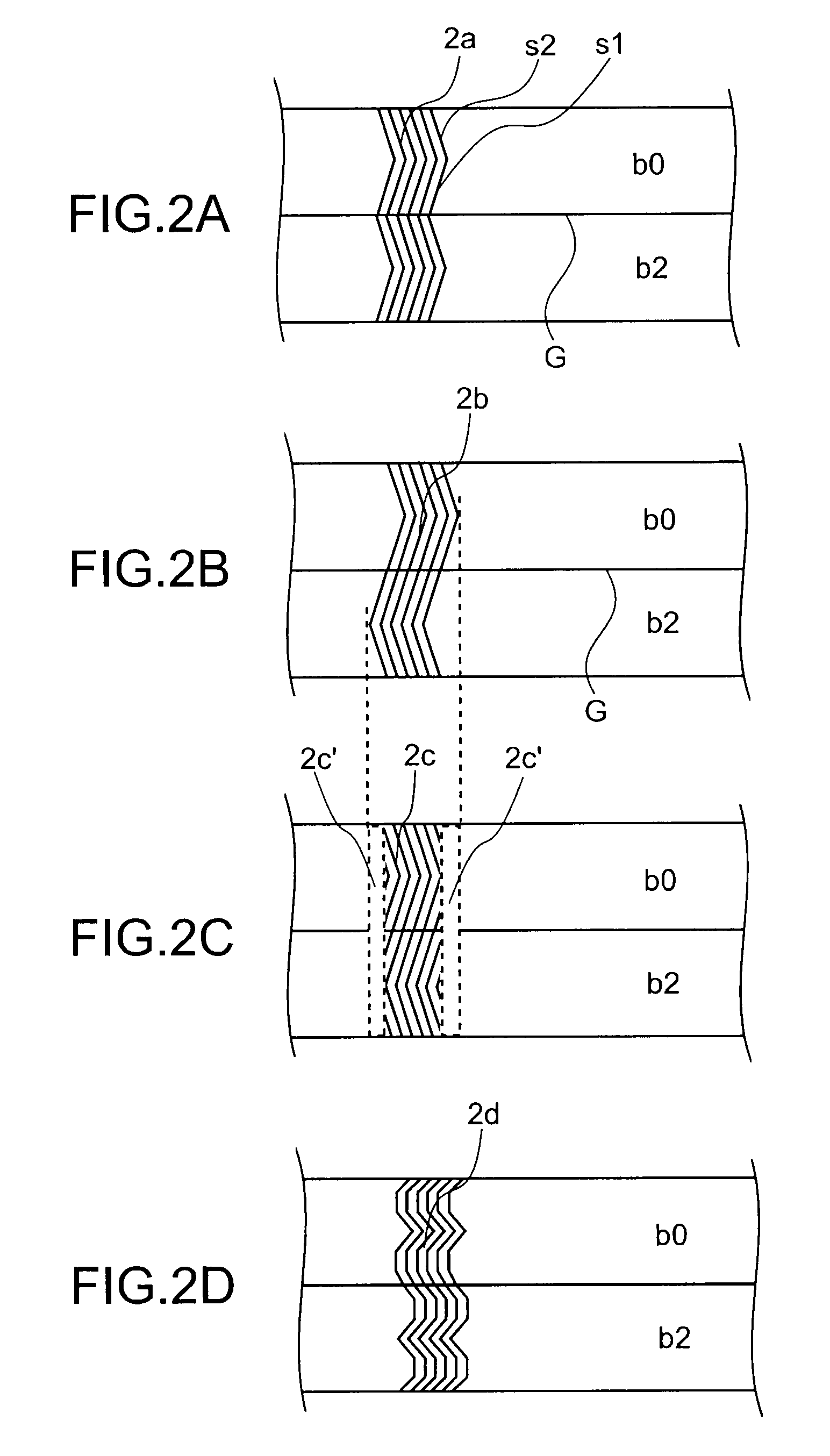
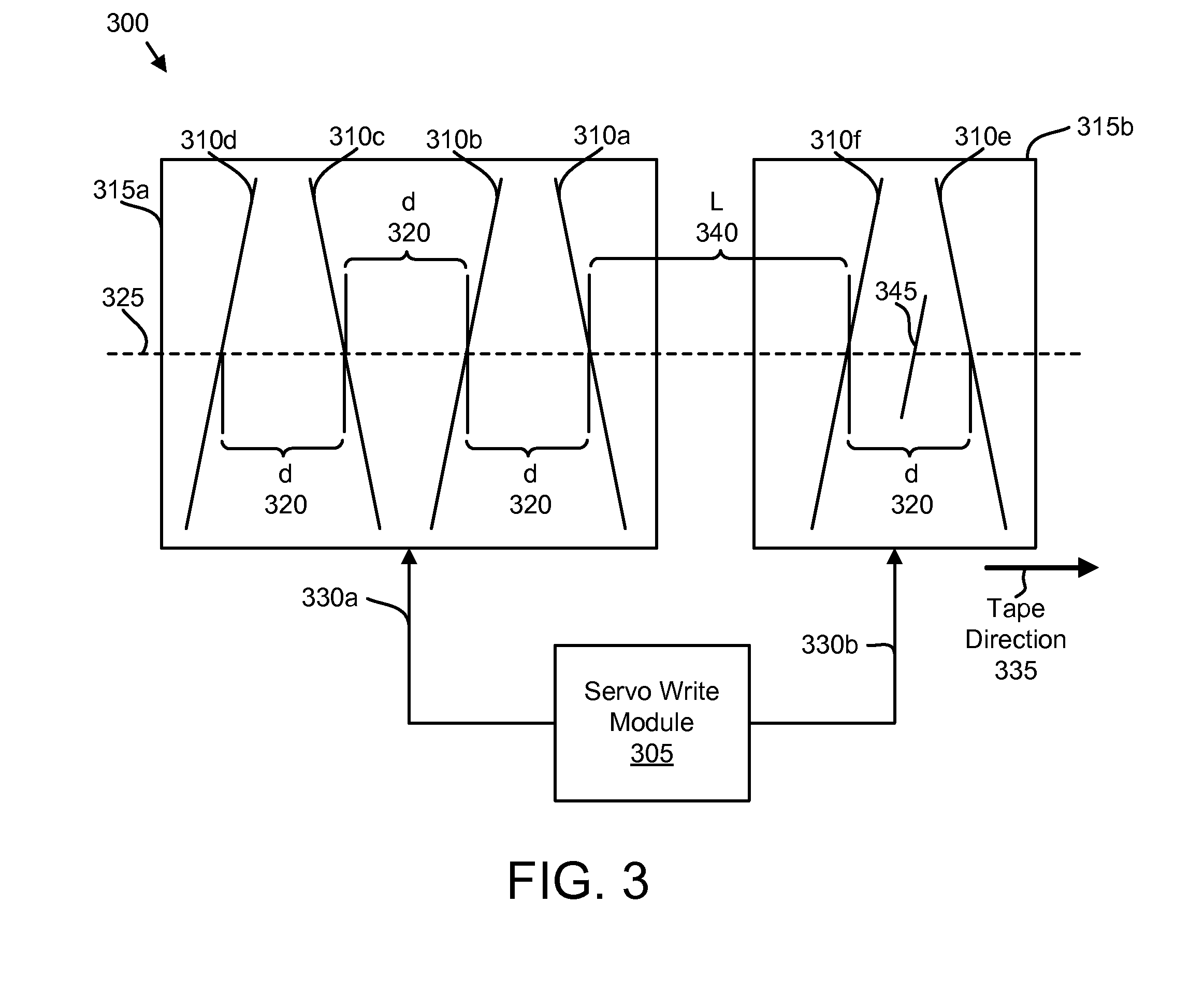
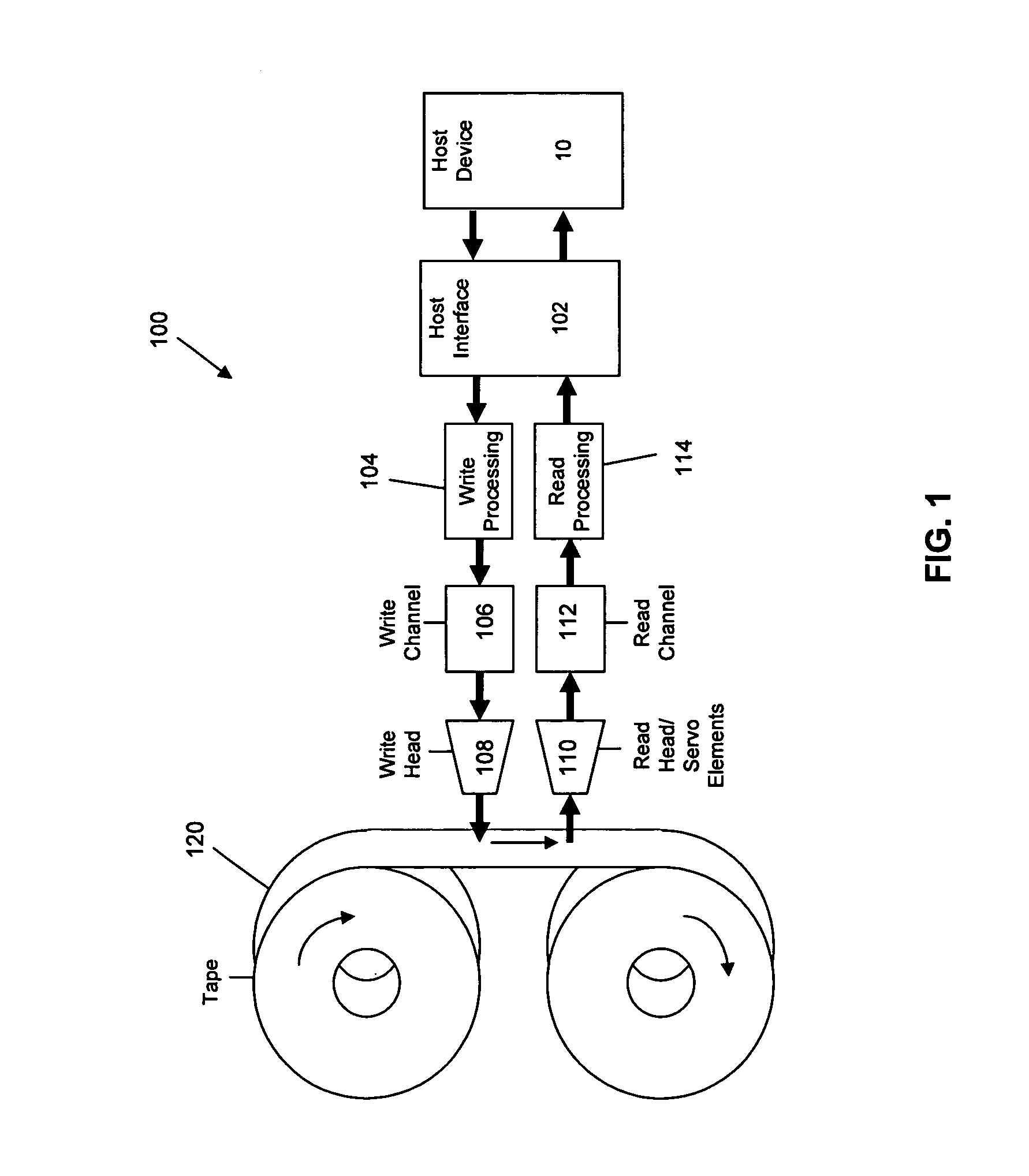
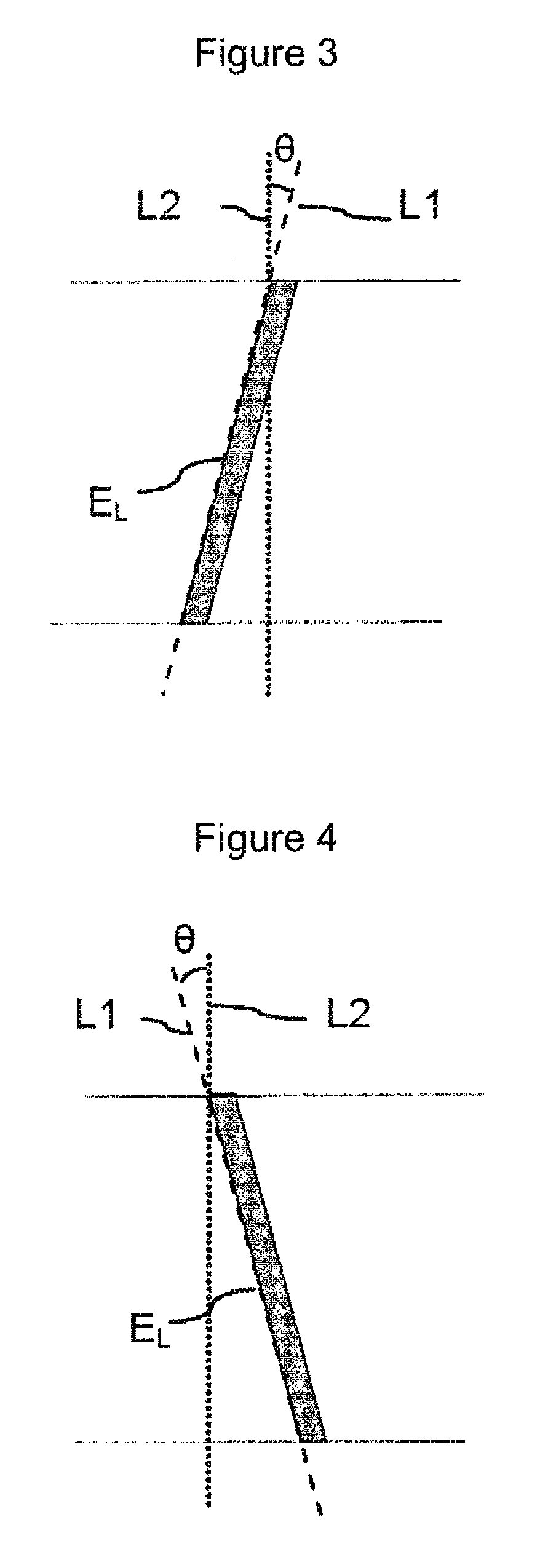
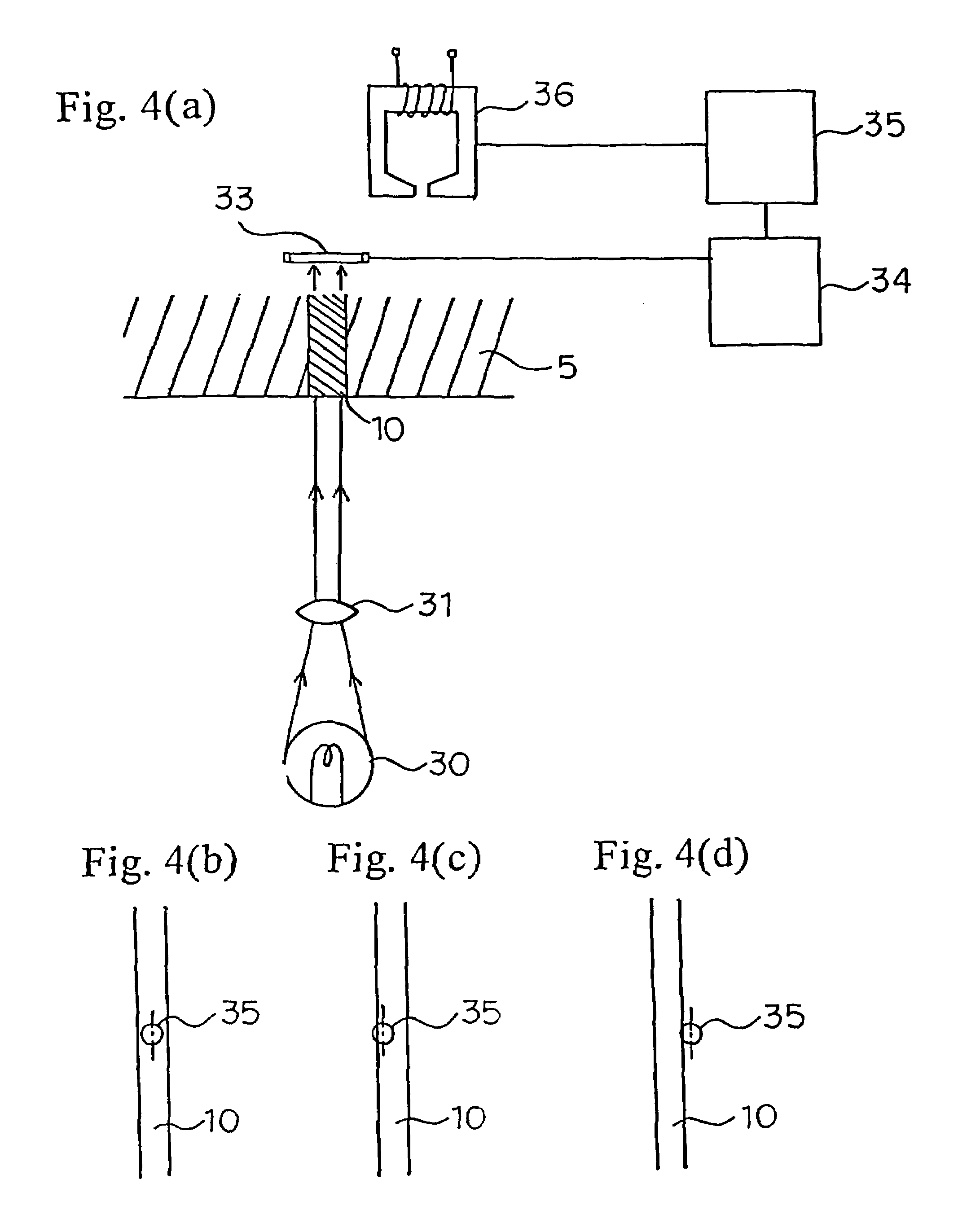
Apparatus, system, and method for timing based servo tape formating
InactiveUS20080174897A1Reduce readReduce write errorDriving/moving recording headsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeComputer science
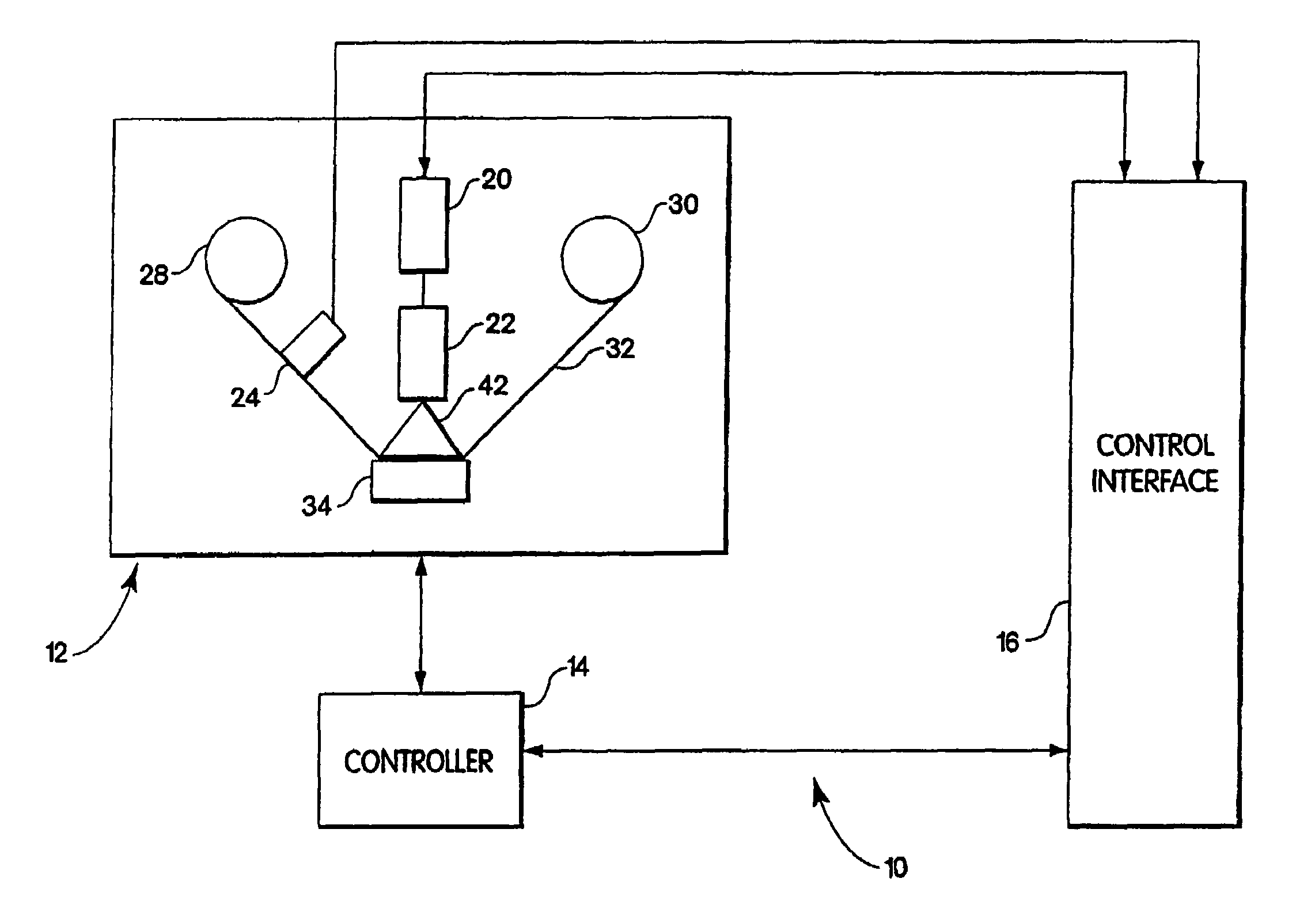
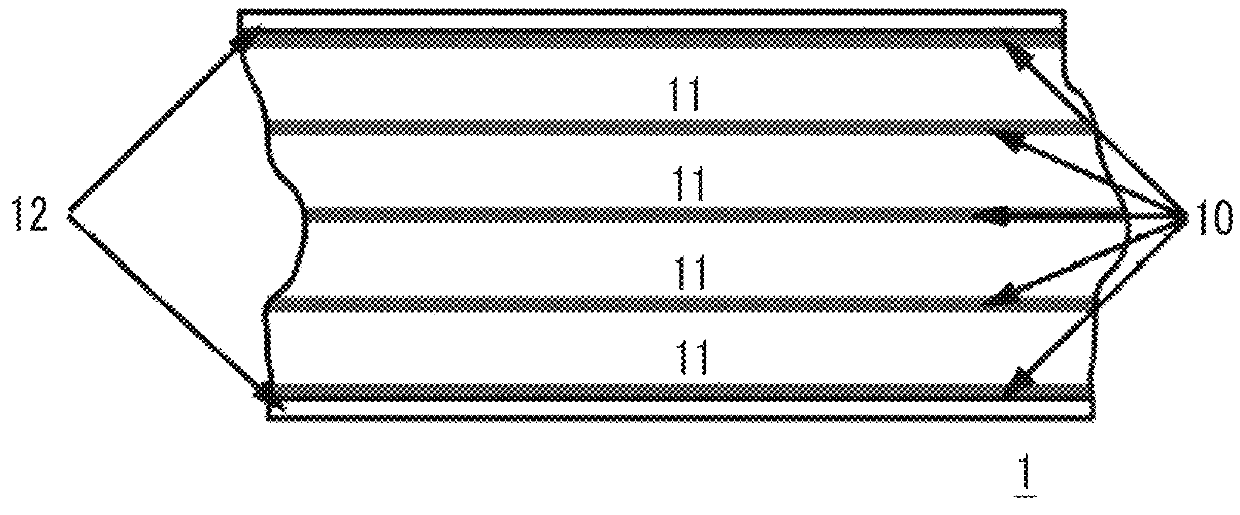
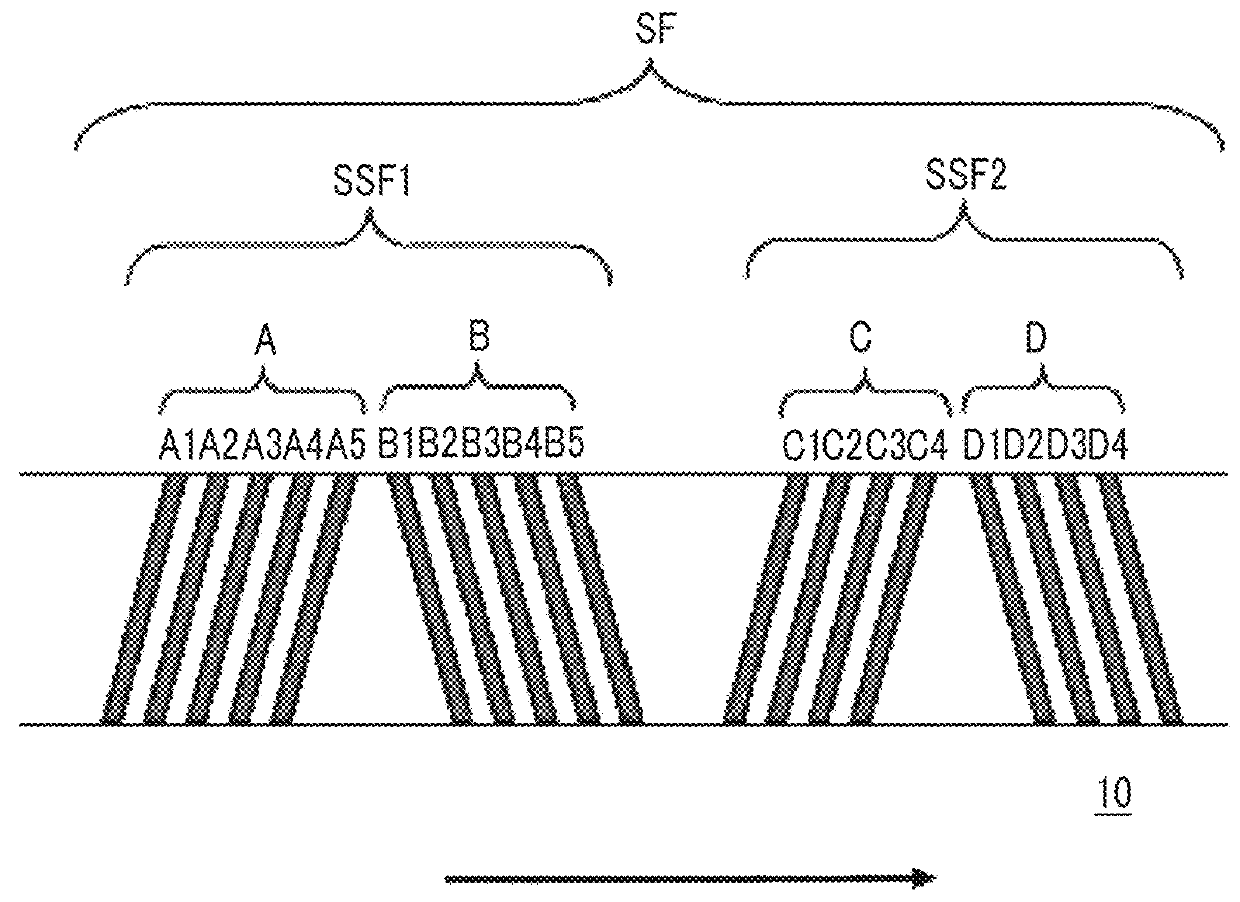
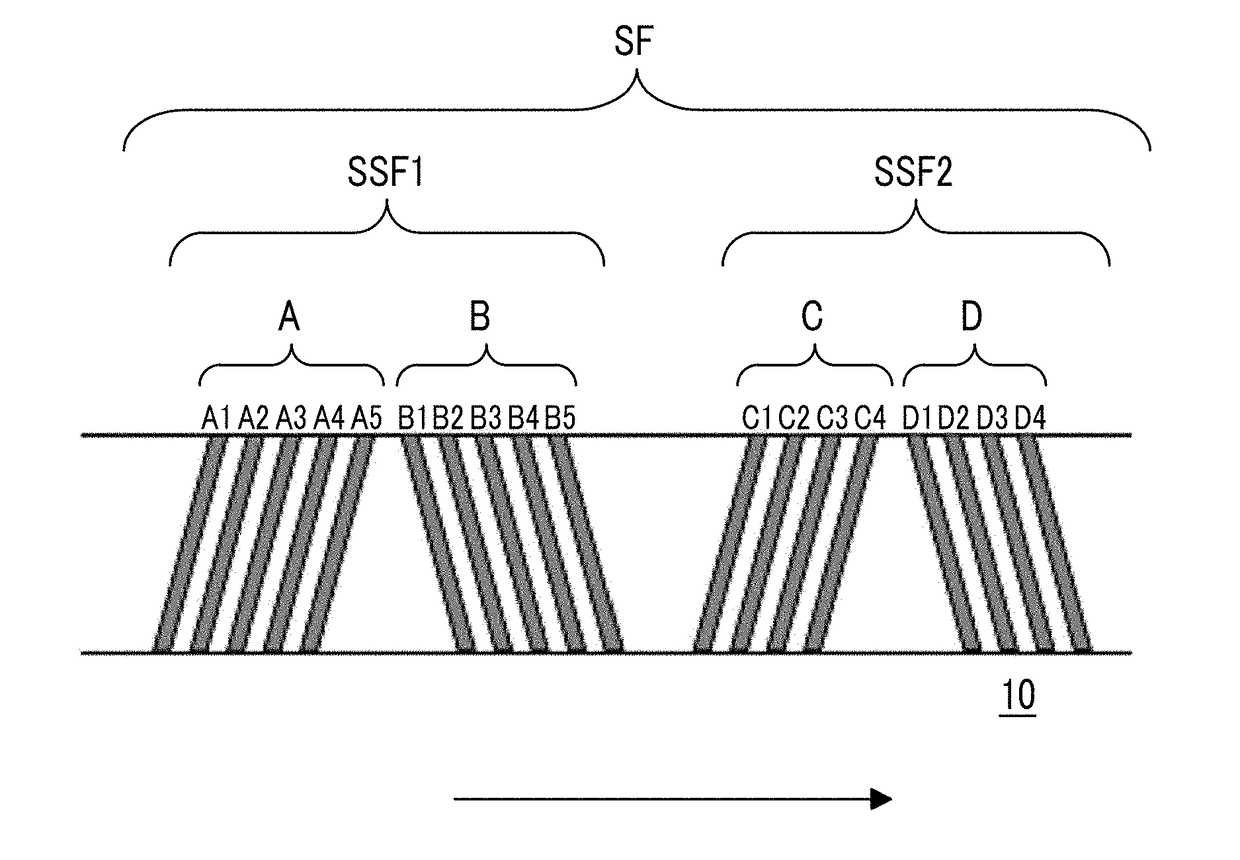
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for formatting a timing-based servo pattern on a magnetic tape. A first write head concurrently writes a base number of stripes to a plurality of first stripe patterns with a first and third element and writes the base number of stripes to a plurality of second stripe patterns with a second and fourth element of a first write head in response to at least one first write signal. A second write head concurrently writes an incremental number of stripes to a specified first stripe pattern to form a first incremental stripe pattern with a fifth write element and writes the incremental number of stripes to a specified second stripe pattern to form a second incremental stripe pattern with a sixth write element.
Owner:IBM CORP
Measurement and correction of magnetic writer offset error
ActiveUS20160260449A1Reduced readback error rateImprove read performanceAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageComputer scienceComputer program
A method, according to one embodiment, includes writing a plurality of shingled tracks using an array of writers, determining first and second positions of an array of readers relative to the shingled tracks, the first and second positions being above and / or beyond track edges of the shingled tracks, repositioning the array of readers to various locations between the first and second positions and reading data from the shingled tracks, determining a read offset point where read performance is about the highest during the reading performed when repositioning the array of readers between the first and second positions, and computing, using the read offset point, data describing a lateral writing position to use during writing such that shingled tracks are written in a location specified by a format. Other systems, methods, and computer program products are described in additional embodiments.
Owner:IBM CORP
Robust metric computation of longitudinal position (LPOS) data symbol detection
InactiveUS8576510B2Driving/moving recording headsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeEngineering
In one embodiment, a tape drive system includes a magnetic head having a servo sensor for sensing a defined servo track of a magnetic tape and configured to read servo pulses from servo bursts of the servo track while the magnetic tape is moving past the magnetic head with the servo bursts representing an encoded data symbol, an analog-to-digital converter configured to provide a sequence of samples of the readback servo signal, a digital correlator configured to compute a correlation signal between the sequence and a reference waveform, a timing reference module configured to provide a reference timing model having interpolation instants to the digital correlator, a correlation interpolator configured to interpolate the correlation signal at the interpolation instants and compute a longitudinal position (LPOS) detection metric, and an LPOS detector configured to decode the encoded data symbol of the servo bursts using the computed LPOS detection metric.
Owner:IBM CORP
Magnetic tape device, magnetic reproducing method, and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS10134433B2Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeX-ray
Provided is a magnetic tape device in which a magnetic tape transportation speed is equal to or lower than 18 m / sec, Ra measured regarding a surface of a magnetic layer of a magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a C-H derived C concentration calculated from a C-H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %, and ΔSFD (=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C.) in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 0.50, with the SFD25° C. being SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of 25° C., and the SFD−190° C. being SFD measured at a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Robust metric computation of longitudinal position (LPOS) data symbol detection
InactiveUS20130088794A1Driving/moving recording headsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeControl theory
In one embodiment, a tape drive system includes a magnetic head having a servo sensor for sensing a defined servo track of a magnetic tape and configured to read servo pulses from servo bursts of the servo track while the magnetic tape is moving past the magnetic head with the servo bursts representing an encoded data symbol, an analog-to-digital converter configured to provide a sequence of samples of the readback servo signal, a digital correlator configured to compute a correlation signal between the sequence and a reference waveform, a timing reference module configured to provide a reference timing model having interpolation instants to the digital correlator, a correlation interpolator configured to interpolate the correlation signal at the interpolation instants and compute a longitudinal position (LPOS) detection metric, and an LPOS detector configured to decode the encoded data symbol of the servo bursts using the computed LPOS detection metric.
Owner:IBM CORP
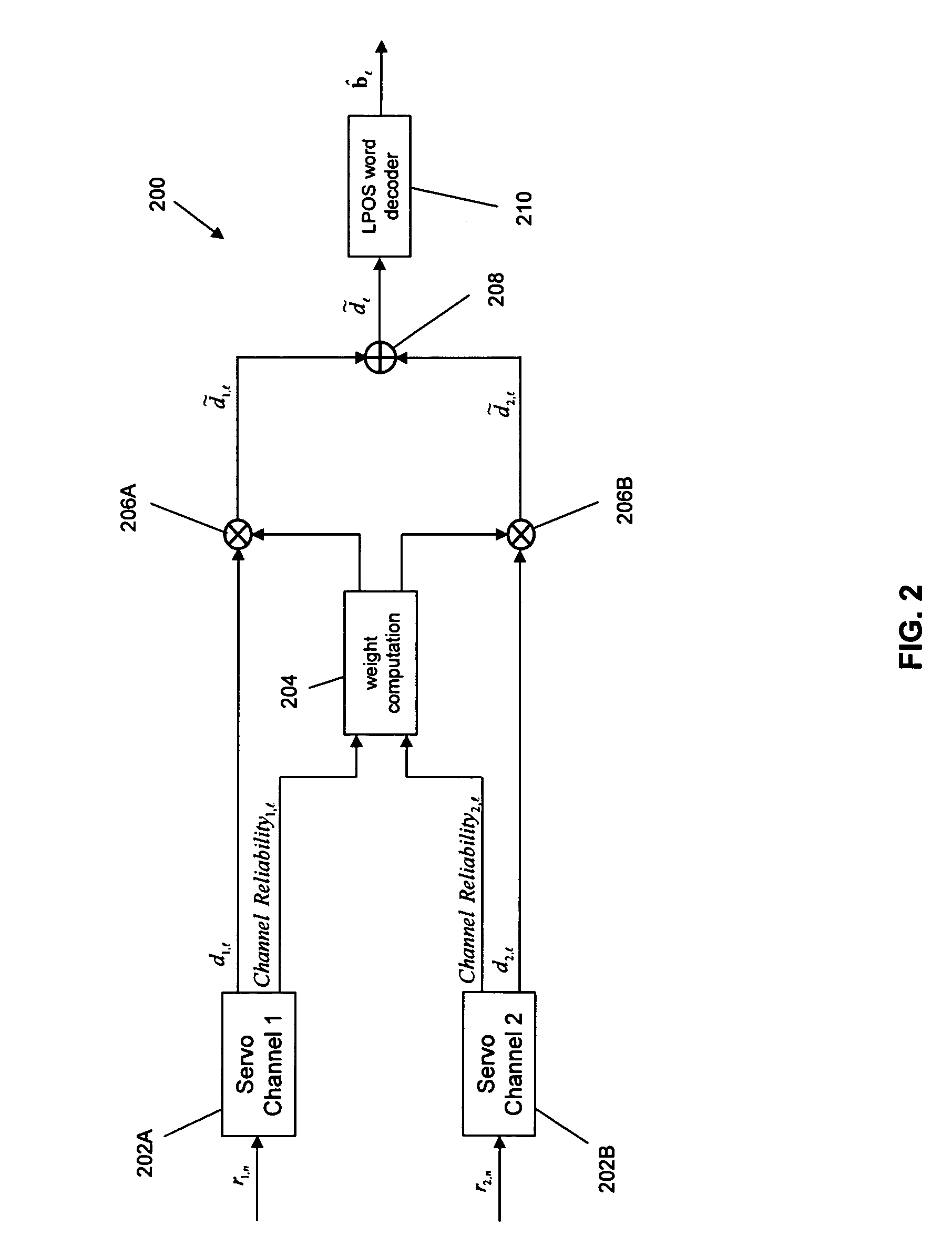
Combining information from parallel servo channels
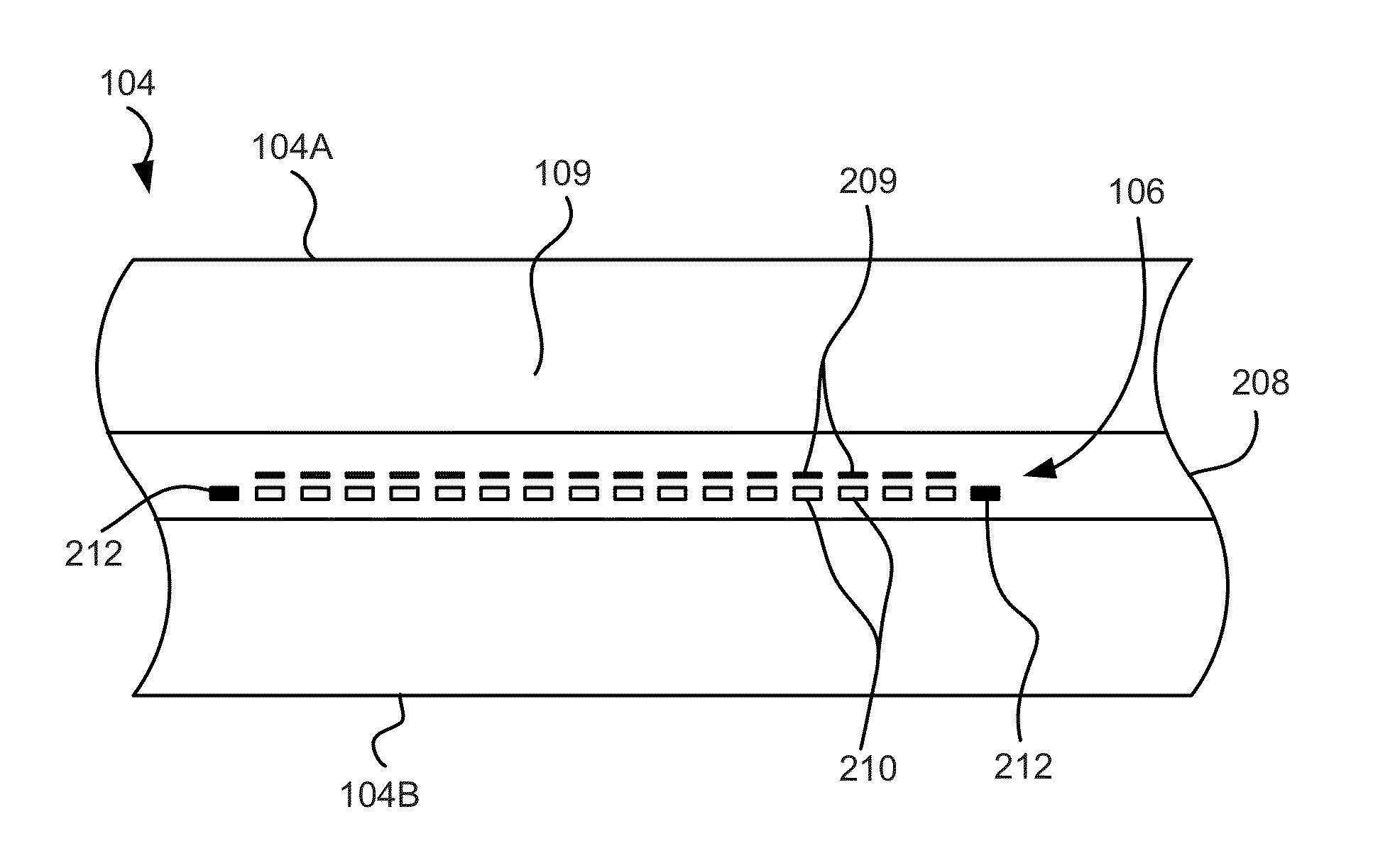
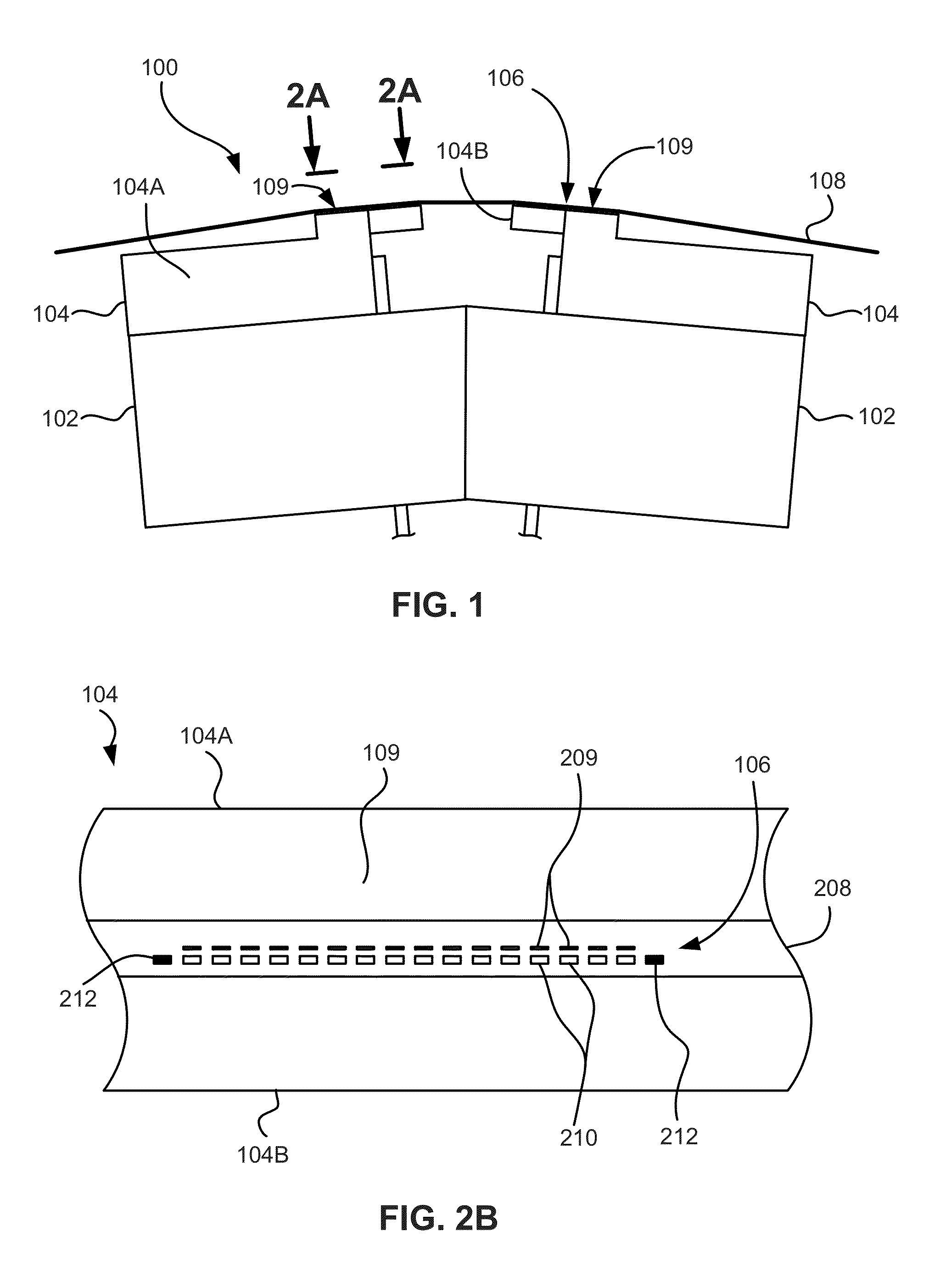
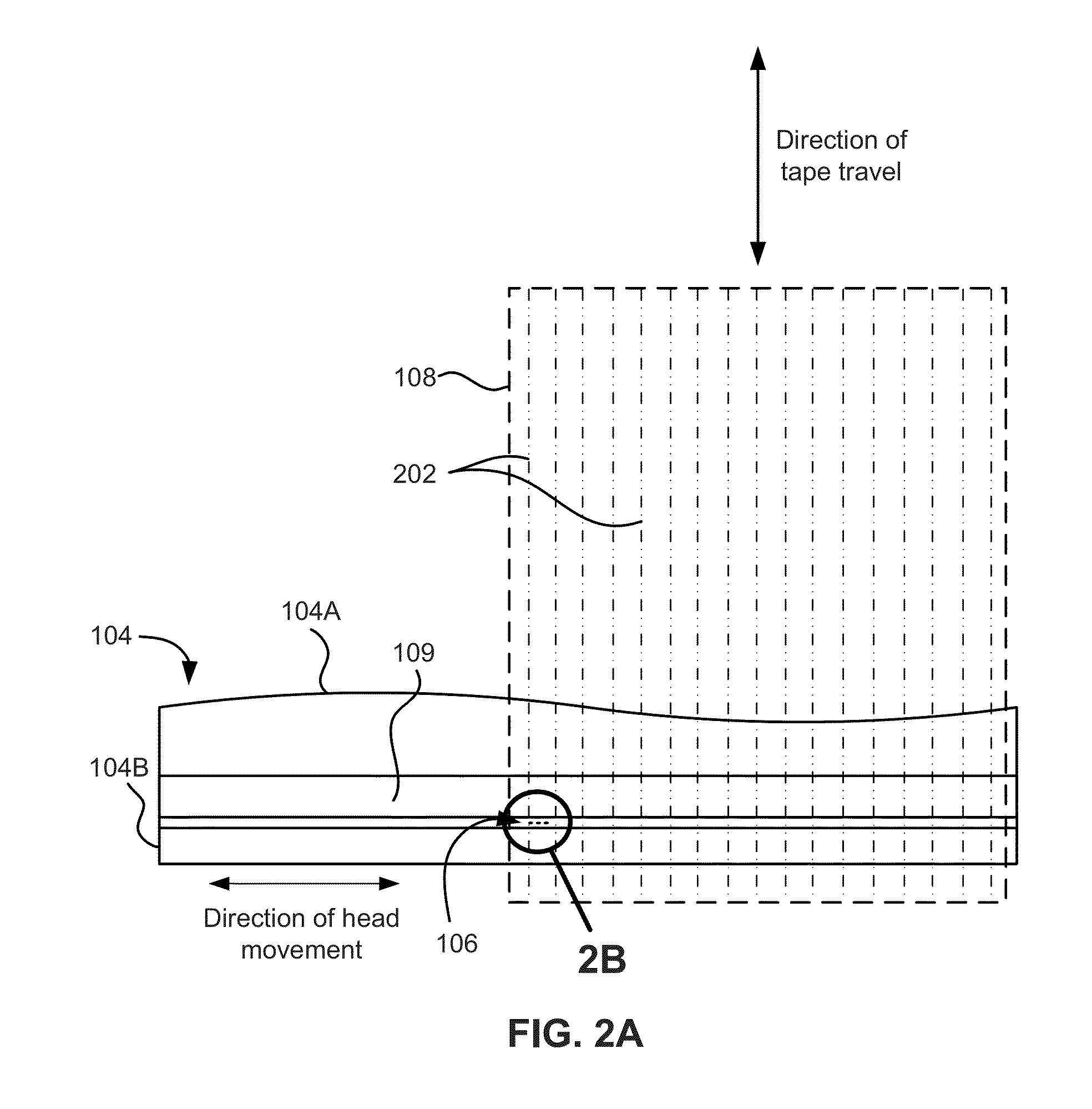
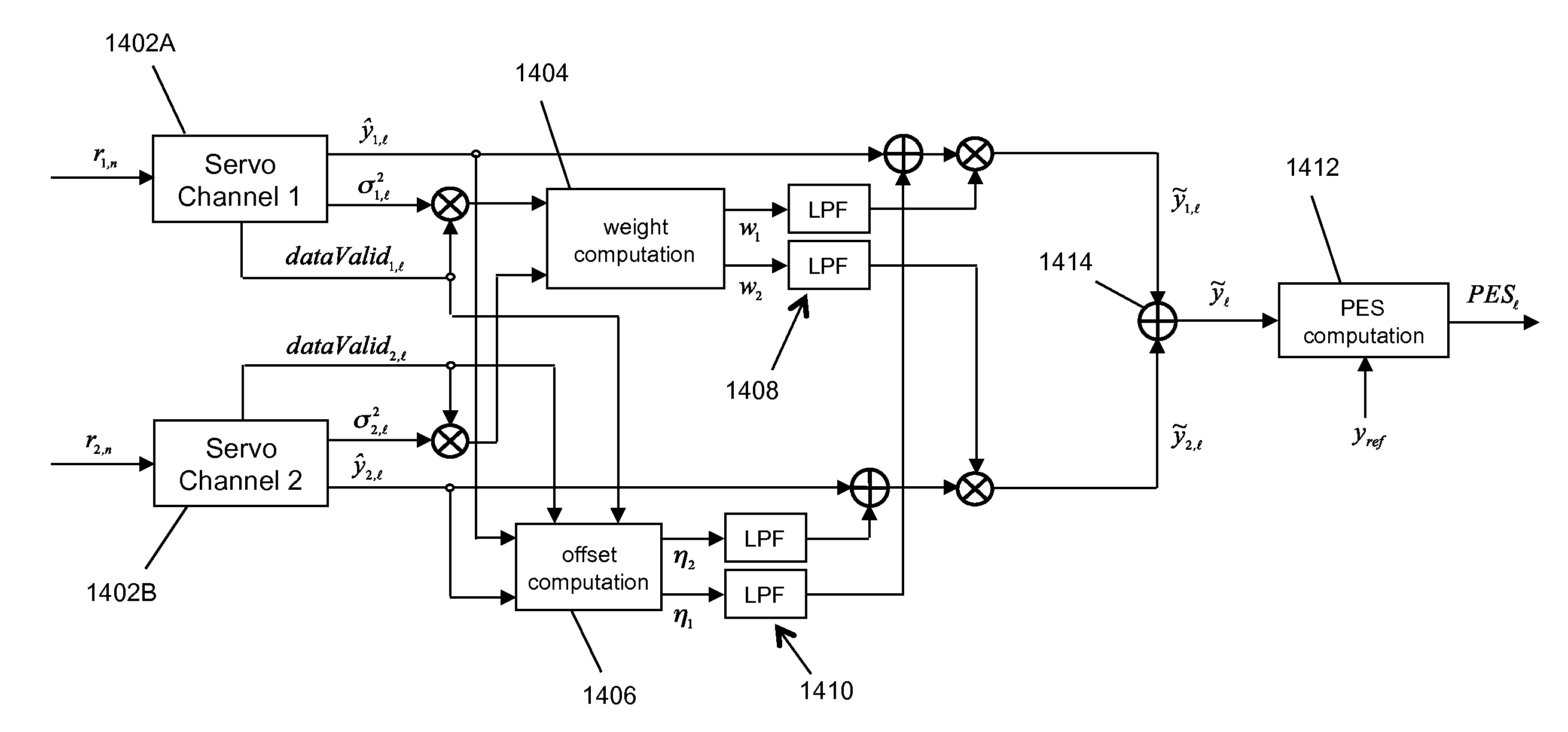
InactiveUS7839599B2Driving/moving recording headsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeEngineering
A weighted combining scheme exploits information from two servo channels operating in parallel. A timing-based servo module comprises two synchronous servo channels coupled respectively to receive two digital servo signals read from a data tape. Both channels have outputs for an unweighted parameter estimate and for a measure of the channel reliability. A weight computation module provides first and second weight signals using the measures of channel reliability from the servo channels. An offset computation module provides first and second offset terms which are summed with the unweighted parameter estimates. Multiplying nodes receive the unweighted parameter estimates and the weight signals and outputs offset weighted parameter estimates. A summing node receives the offset weighted parameter estimates and outputs a combined offset weighted parameter estimate to a servomechanism.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
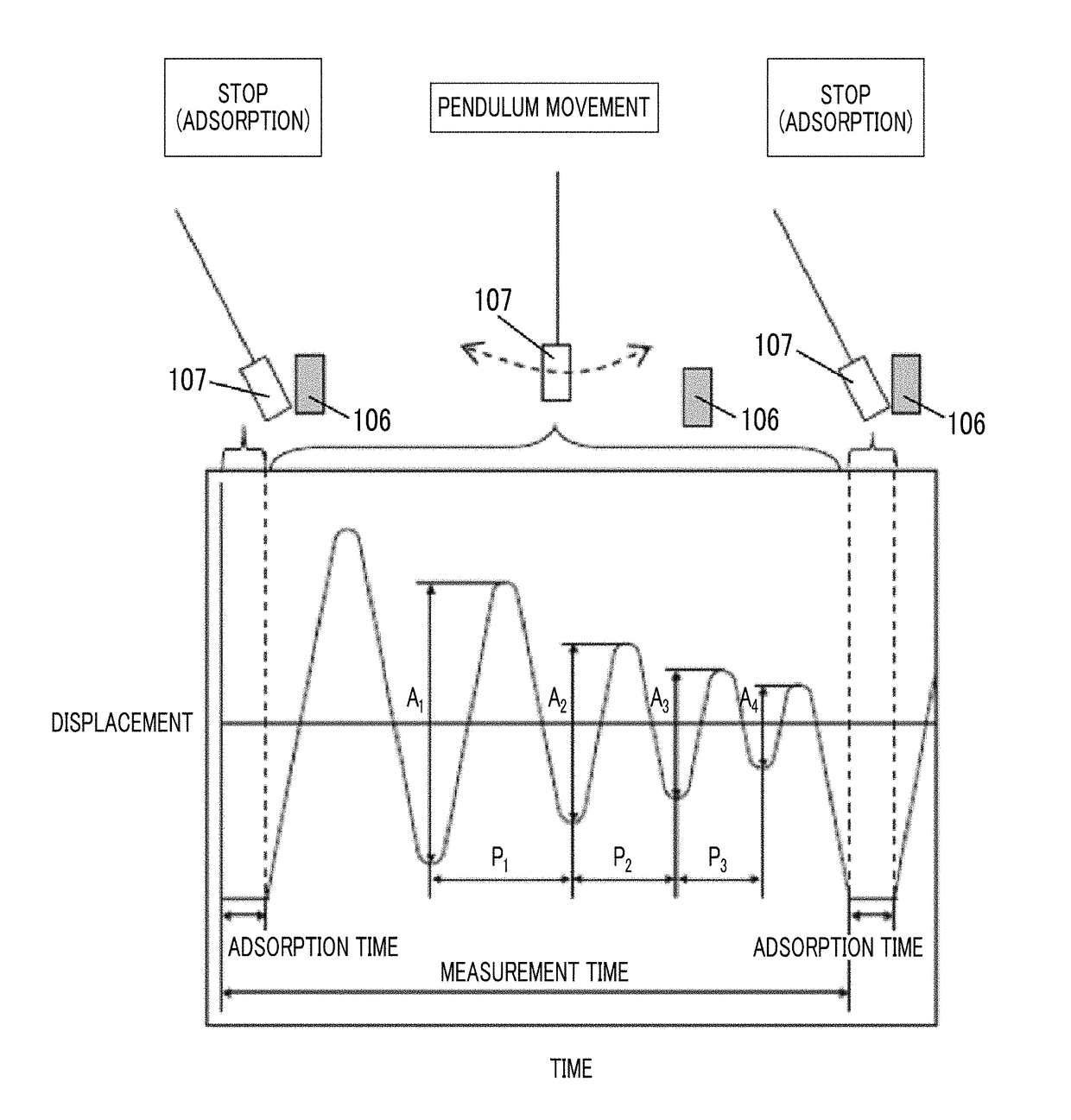
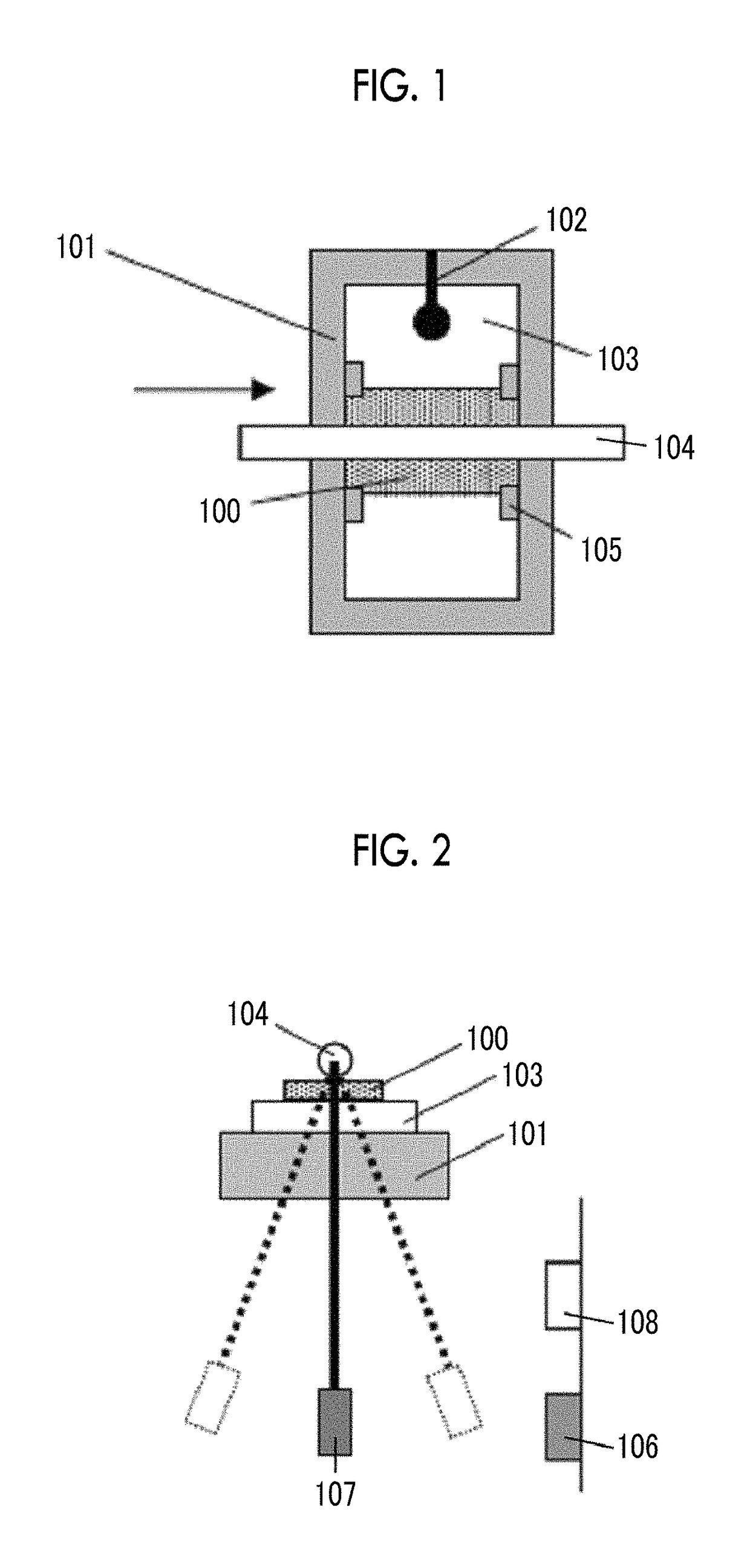
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS9972351B1Avoid it happening againImprove accuracyAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeEngineering
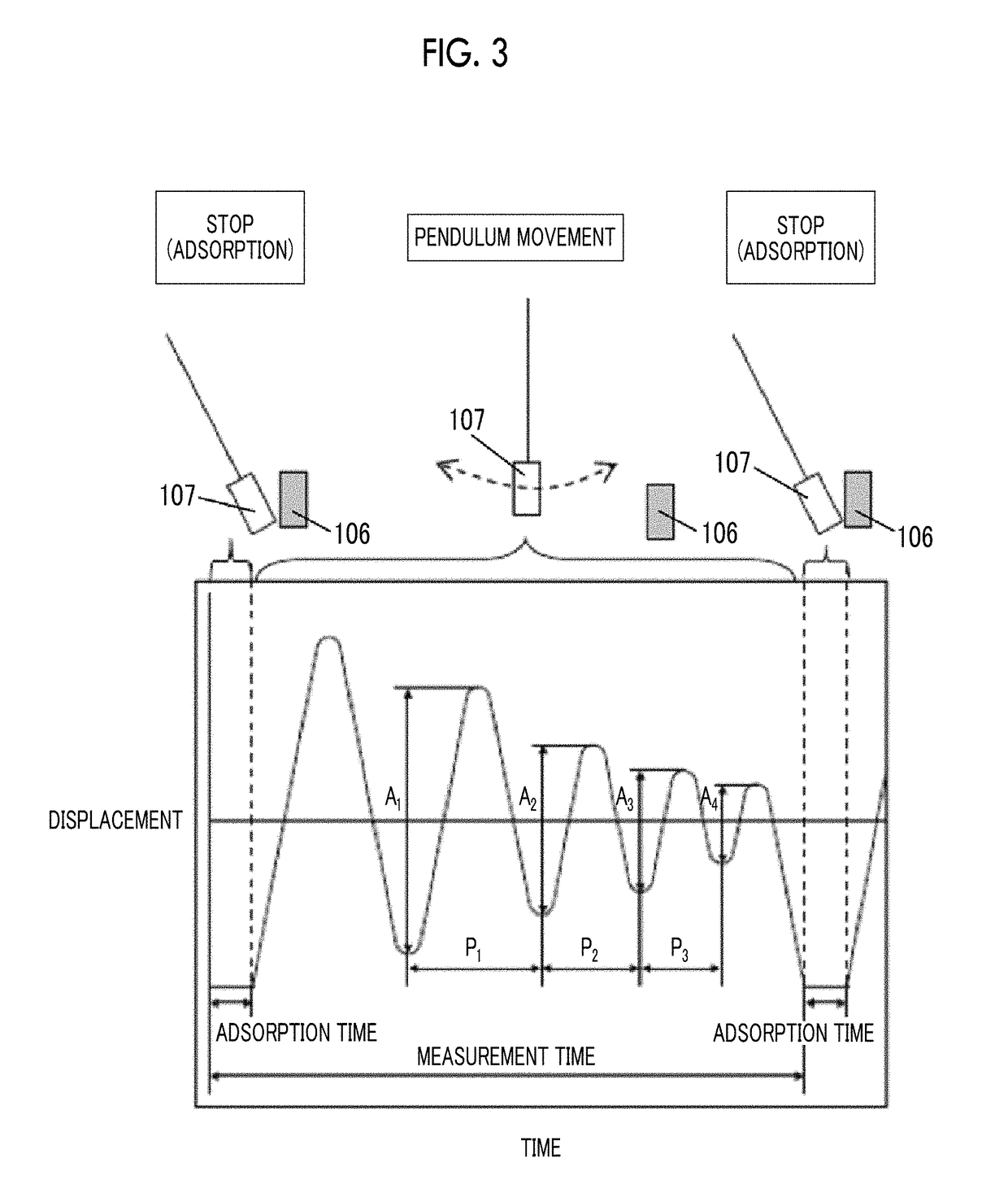
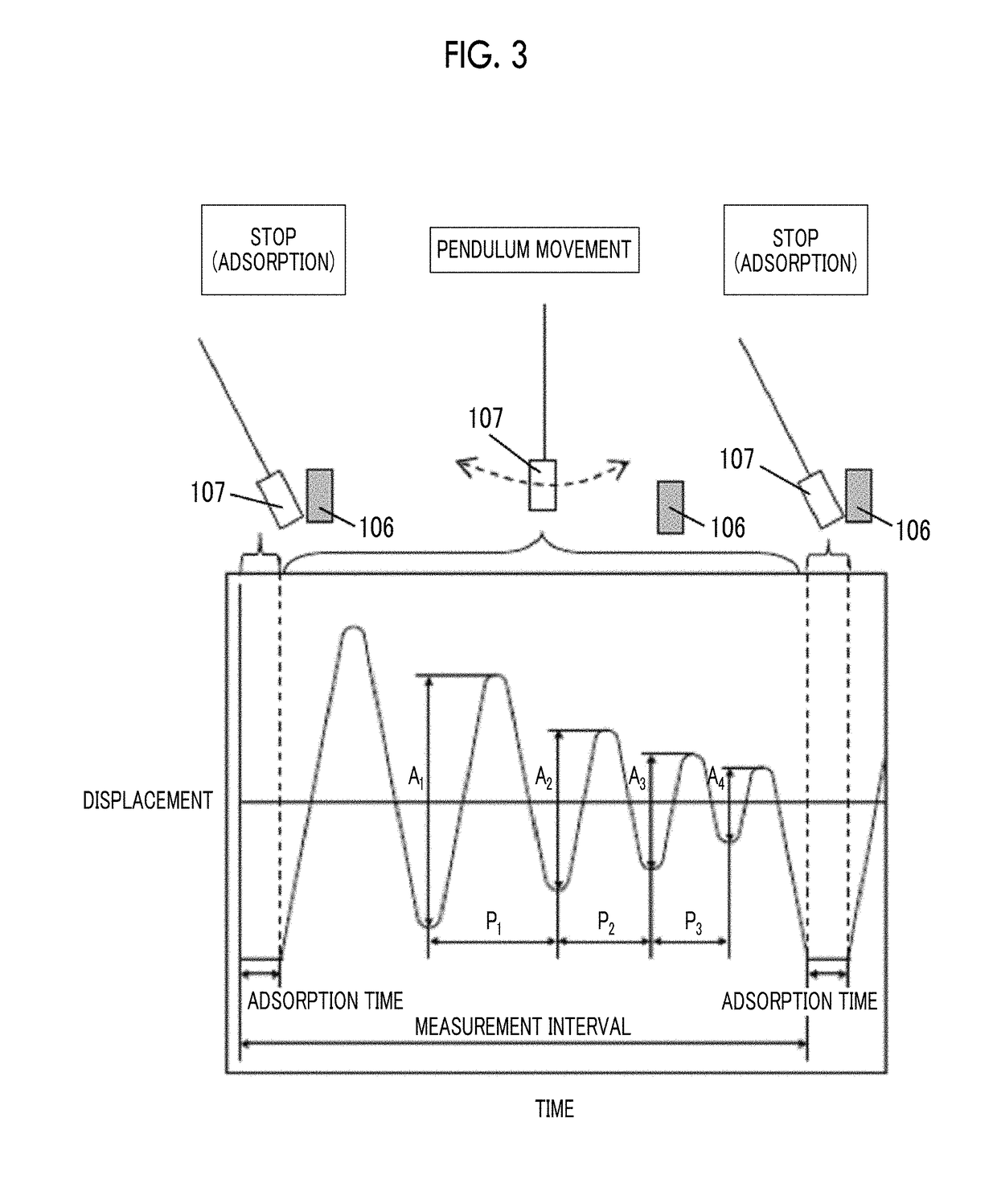
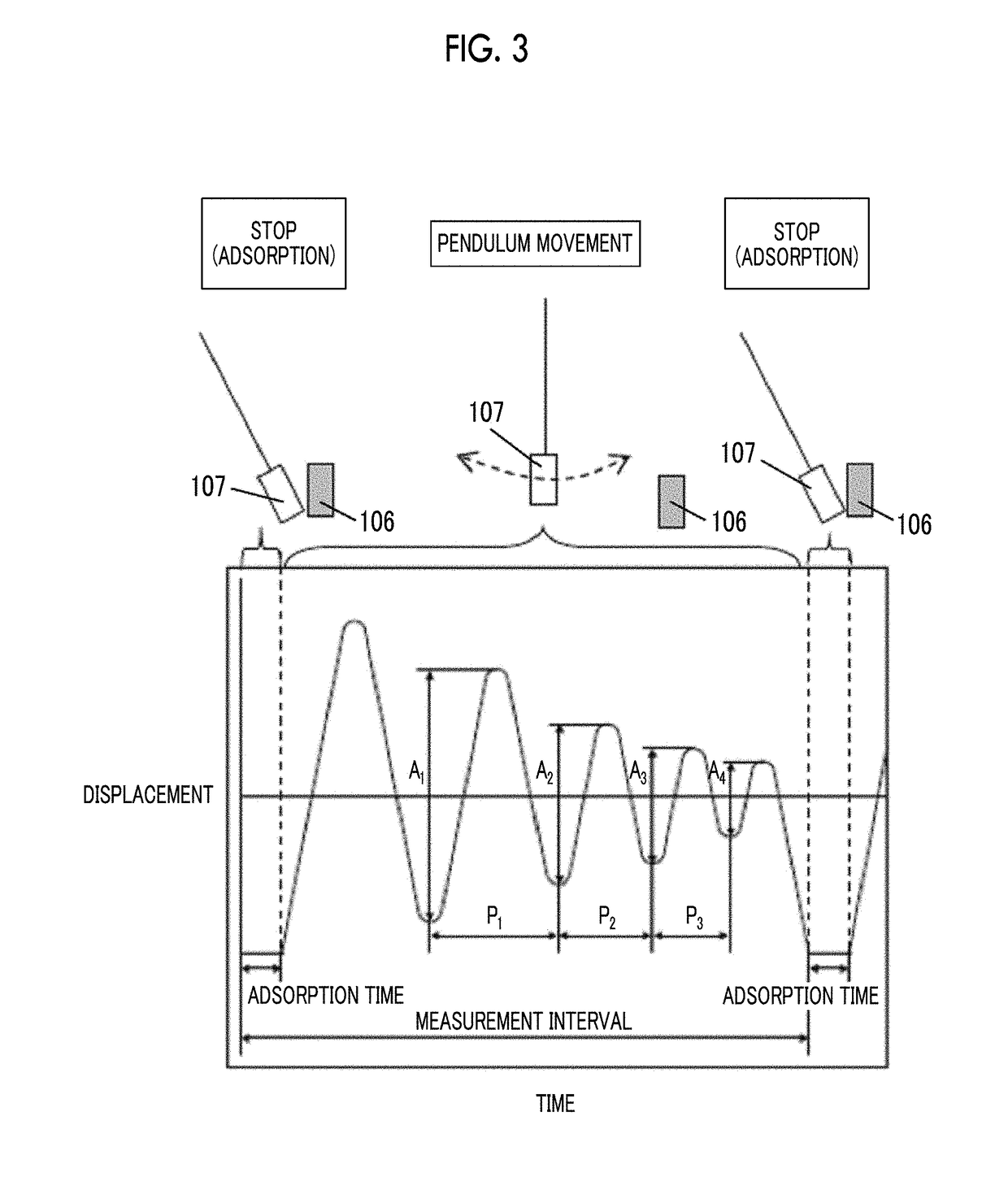
The magnetic tape device including: a magnetic tape; and a servo head, in which the servo head is a magnetic head including a tunnel magnetoresistance effect type element as a servo pattern reading element, the magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, the magnetic layer includes a servo pattern, and logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20180374507A1Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesIn planeMagnetic force microscope
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume equal to or smaller than 1,600 nm3, an XRD intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, and an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern specified by magnetic force microscope observation is a shape in which a difference (L99.9−L0.1) is equal to or smaller than 180 nm, and a magnetic tape device including the magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
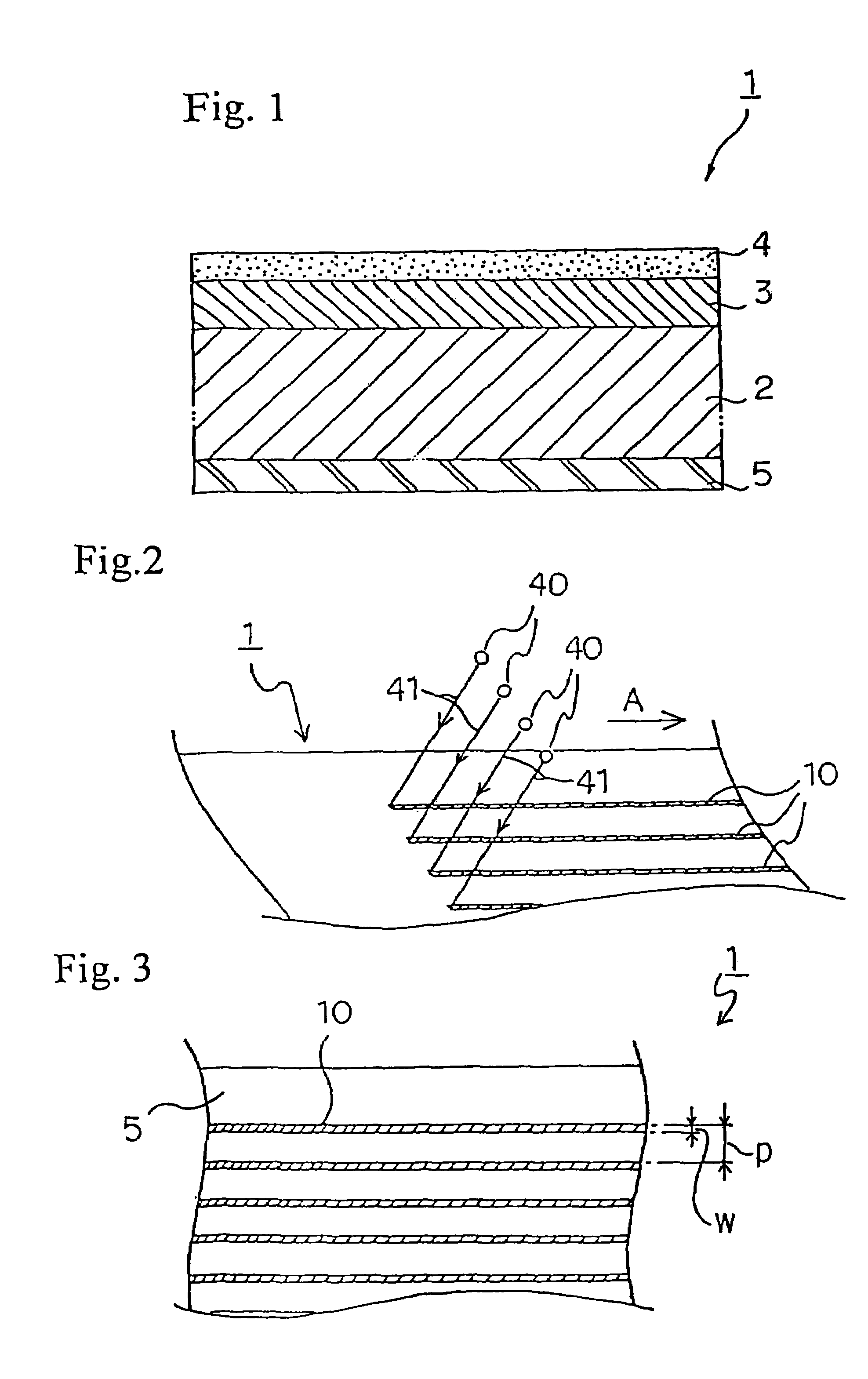
Magnetic tape and maufacturing method thereof, and servo writer and servo write method
ActiveUS20050057838A1Driving/moving recording headsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeMagnetization
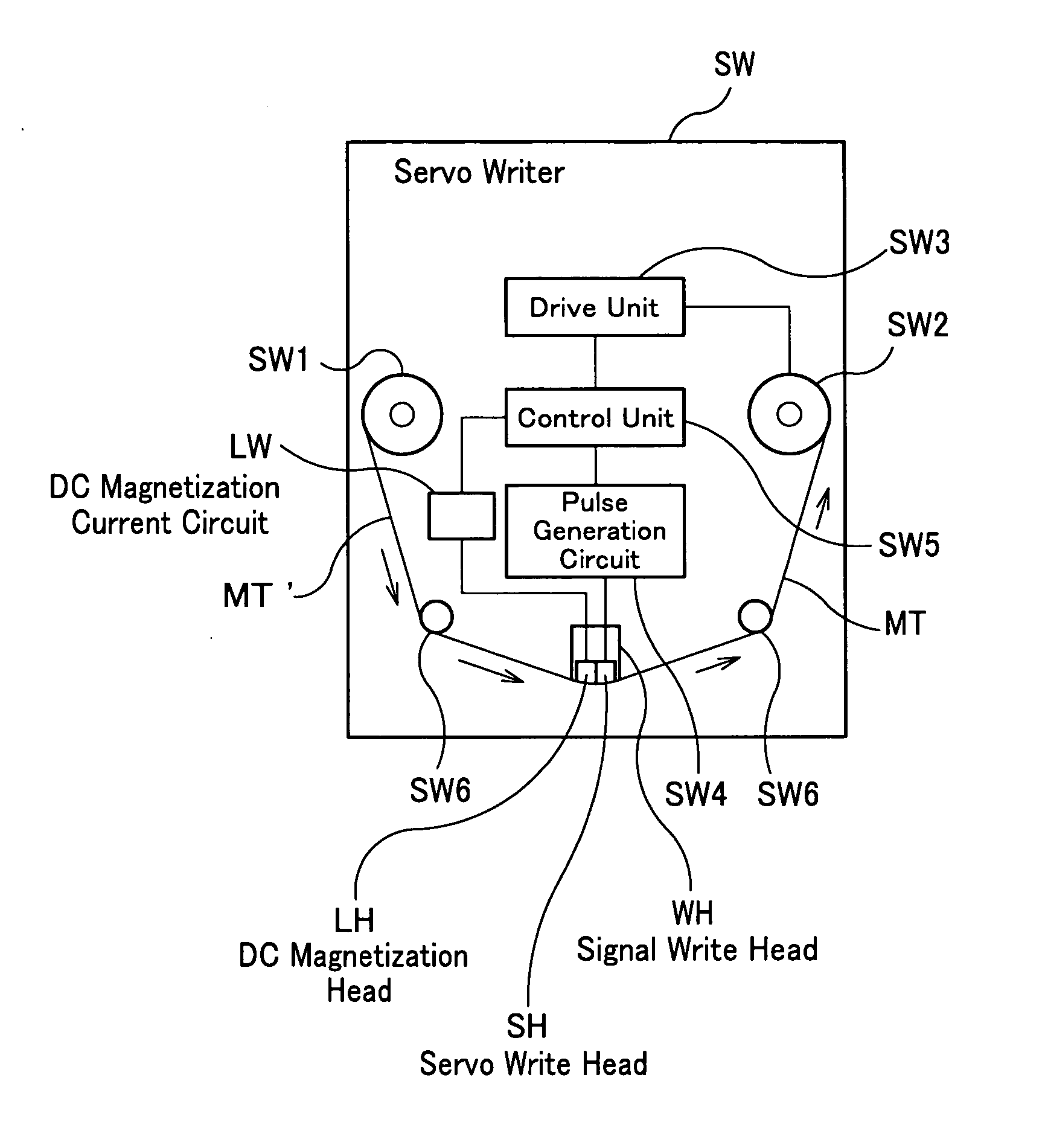
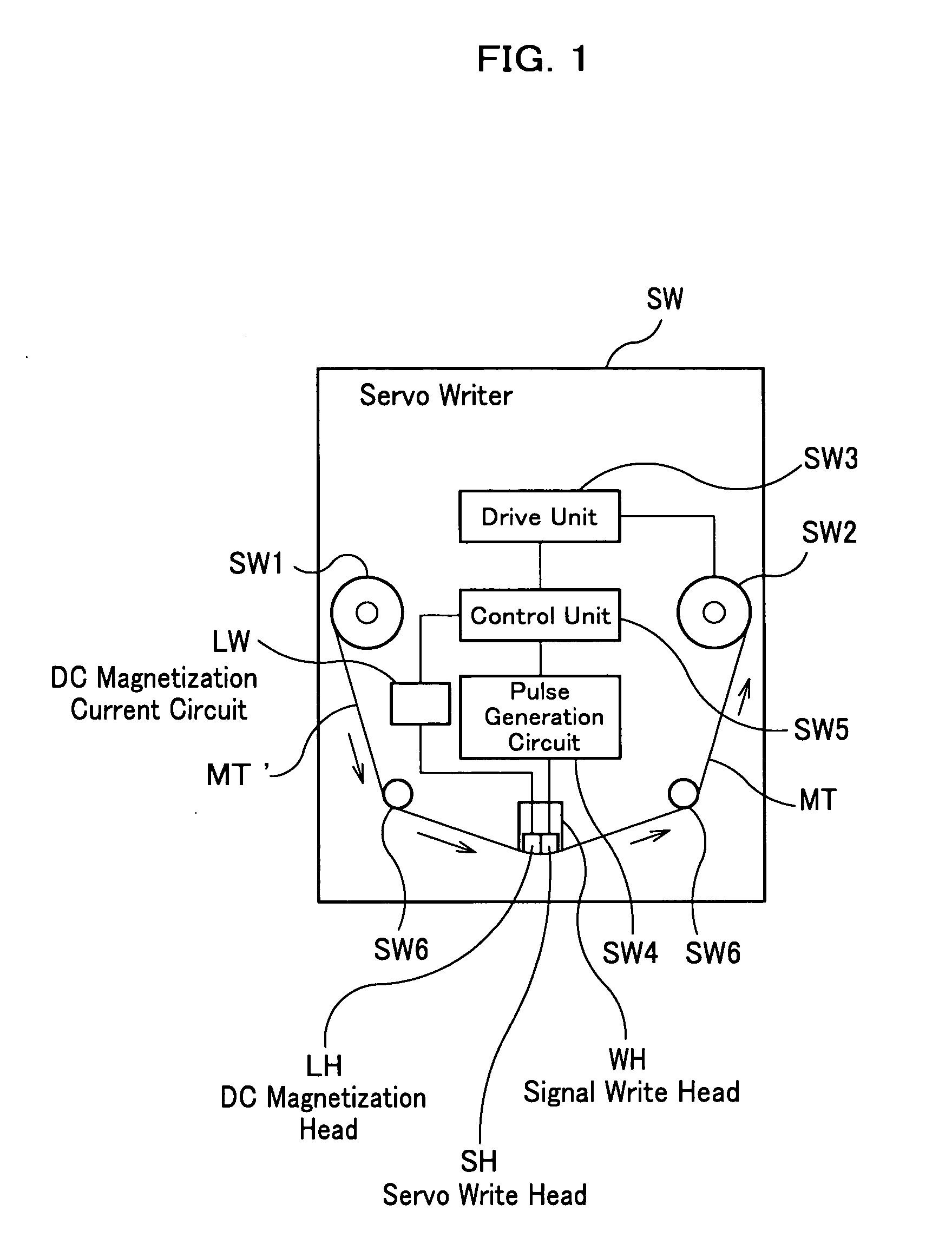
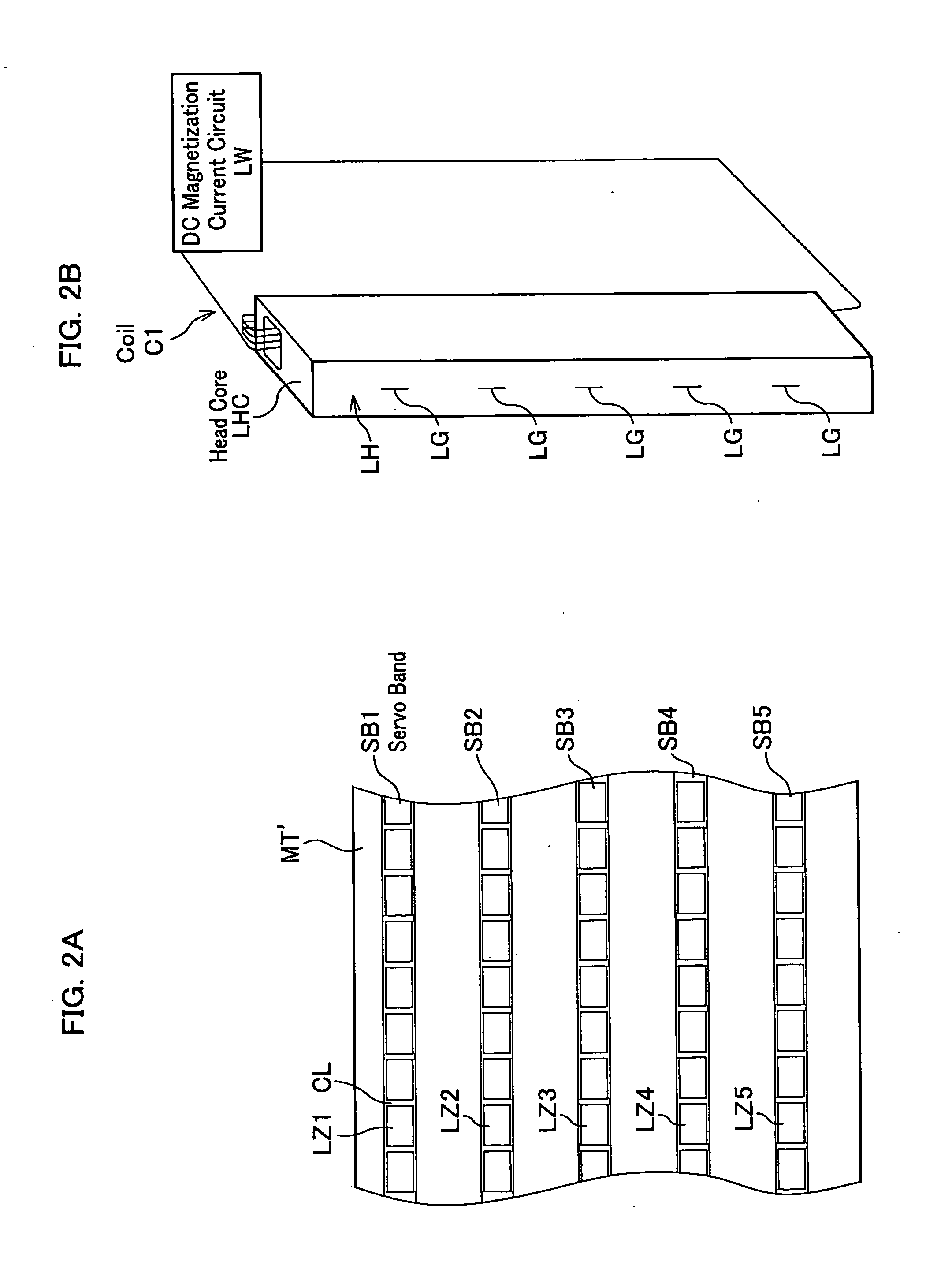
A magnetic tape of the present invention comprises a plurality of servo bands and servo signals for performing tracking-control of a magnetic head, wherein the servo signals are recorded on the servo bands, wherein a DC magnetization region magnetized in one direction by direct current is arranged along longitudinal directions of the magnetic tape on the servo bands, wherein each of the servo signals is magnetized in a reverse direction for the one direction of a DC magnetization and is recorded within the DC magnetization region, and wherein any of a relative ratio and relative difference of DC magnetization intensity in the DC magnetization region and recording magnetization intensity of each of the servo signals differs for each of the servo bands.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170372744A1Restrain output decreaseImprove accuracyBase layers for recording layersAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeFull width at half maximum
Provided is a magnetic tape in which the total thickness of a non-magnetic layer and a magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.60 μm, the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, the magnetic layer includes fatty acid ester, a full width at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the magnetic layer before performing vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 7.0 nm, a full width at half maximum of spacing distribution measured after performing the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 7.0 nm, and a difference between a spacing measured after performing the vacuum heating and a spacing measured before performing the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 8.0 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS9779772B1High precisionAccurate informationAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein a timing based servo pattern is present on the magnetic layer, the centerline average surface roughness Ra that is measured on the surface of the magnetic layer is less than or equal to 1.8 nm, and the coefficient of friction that is measured on the base portion of the surface of the magnetic layer is less than or equal to 0.35.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS10008230B1Improve accuracyExact reproductionProtective coatings for layersFilamentary/web record carriersMagnetic tapeFull width at half maximum
The magnetic tape device includes: a magnetic tape; and a servo head, in which the servo head is a TMR head, the magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder, a binding agent, and fatty acid ester on the non-magnetic support, the magnetic layer includes a servo pattern, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding a surface of the magnetic layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 7.0 nm, and a difference between a spacing measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the magnetic layer after performing the vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape and a spacing measured before performing the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 9.0 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170372742A1Restrain output decreaseImprove accuracyBase layers for recording layersAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeElectron microscope
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; a non-magnetic layer including non-magnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic layer, in which the total thickness of the non-magnetic layer and the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.60 μm, the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, the magnetic layer includes an abrasive, and a tilt cos η of the ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder with respect to a surface of the magnetic layer acquired by cross section observation performed by using a scanning transmission electron microscope is 0.85 to 1.00.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS20180240481A1Lower the resistance valueAvoid it happening againAlignment for track following on tapesTape carriersX-rayEngineering
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head as a servo head; and a magnetic tape which includes a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder and a binding agent, and including a servo pattern, an XRD intensity ratio (Int(110) / Int(114)) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170372736A1Improve surface smoothnessDefect signalAlignment for track following on tapesTape carriersMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic support, in which the total thickness of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 5.30 μm, the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, the magnetic layer includes an abrasive, and a tilt cos θ of the ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder with respect to a surface of the magnetic layer acquired by cross section observation performed by using a scanning transmission electron microscope is 0.85 to 1.00.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape with specific servo pattern edge shape and magnetic tape device using same
ActiveUS9773519B2Accurate informationImprove positionAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tension forceMagnetic force microscope
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the coercive force measured in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 167 kA / m, a timing-based servo pattern is present on the magnetic layer, and the edge shape specified by observing the timing-based servo pattern with a magnetic force microscope is a shape in which the difference between the value L99.9 of the 99.9% cumulative distribution function of the width of misalignment from the ideal shape in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and the value L0.1 of the 0.1% cumulative distribution function, L99.9−L0.1, is less than or equal to 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180240478A1Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head as a reproducing head; and a magnetic tape which includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, an XRD intensity ratio (Int(110) / Int(114)) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170358318A1Improve surface smoothnessImproved head positioning accuracyAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeX-ray
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic layer including non-magnetic powder and a binder on a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic layer, in which the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, one or more components selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide are at least included in the magnetic layer, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 45 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170355022A1Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape includes a magnetic layer having ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume equal to or smaller than 1,600 nm3, and an edge shape of the timing-based servo pattern specified by a magnetic force microscope observation is a shape in which a difference (l99.9−l0.1) between a value l99.9 of a cumulative frequency function of 99.9% of a position deviation width from an ideal shape in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and a value l0.1 of the cumulative frequency function of 0.1% thereof is equal to or smaller than 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
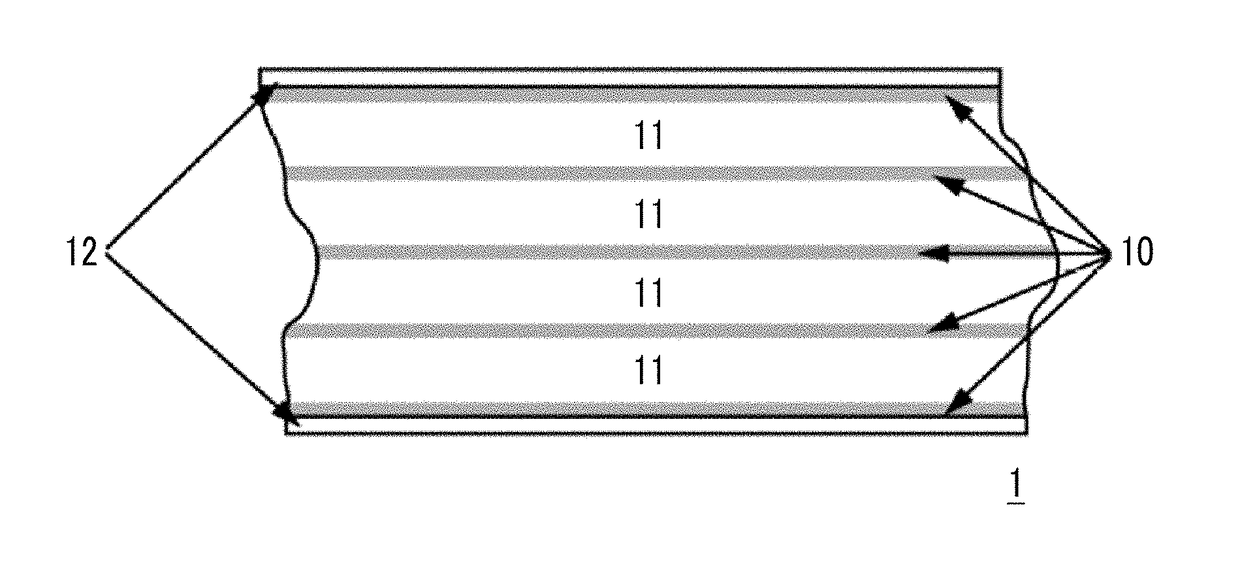
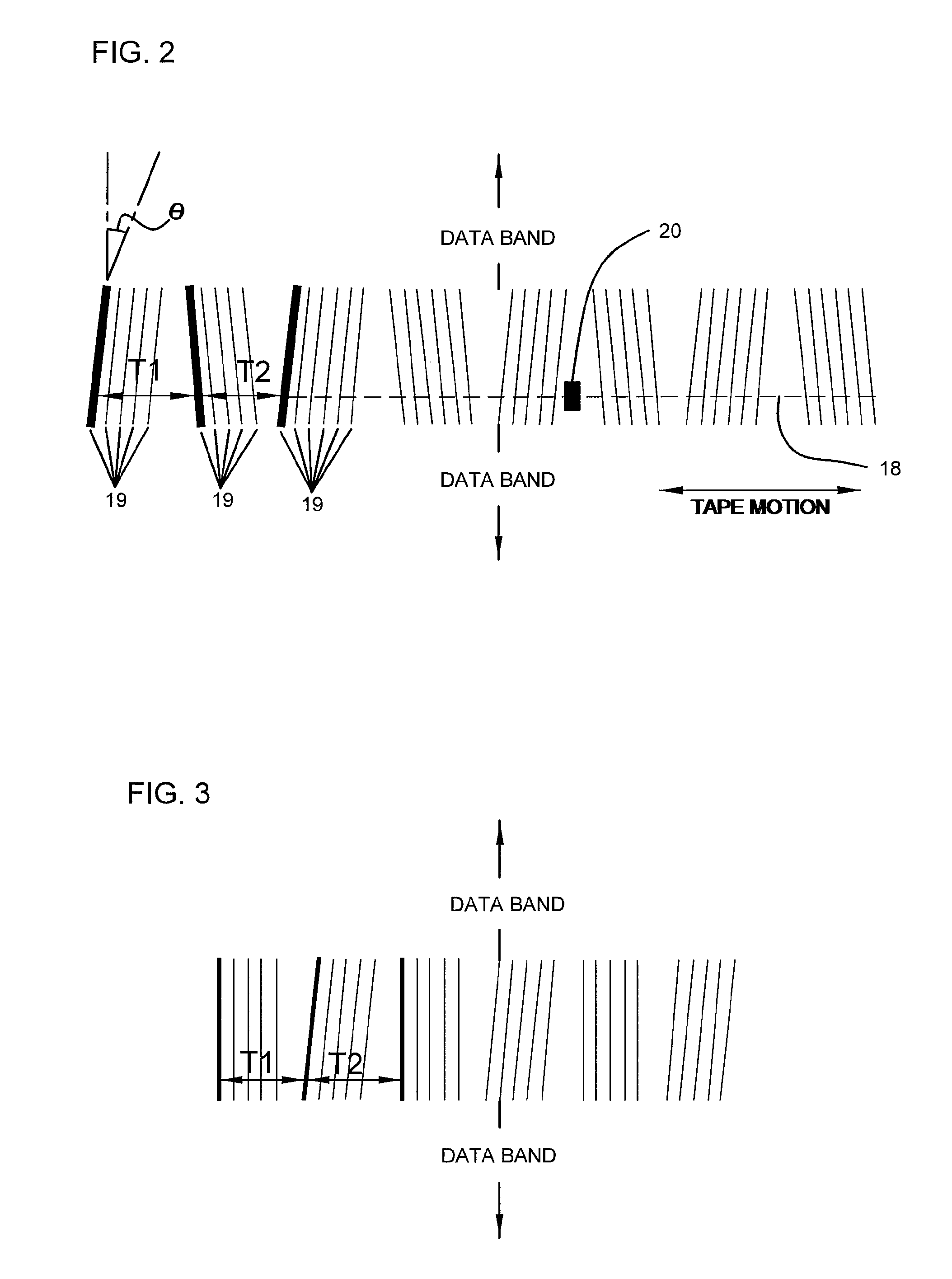
Stepped time based servo pattern and head
InactiveUS7511907B2Driving/moving recording headsManufacturing heads with multiple gapsGraphicsMagnetic tape
The present invention relates to apparatuses and methods used in manufacturing magnetic tape. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method of writing a servo pattern on magnetic tape so as to minimize errors in the servo pattern, the heads used to write such servo data, and the magnetic tape manufactured with such heads. Errors in the servo pattern may be minimized by synthesizing the slanted transitions in a time based servo pattern using servo write gaps that are perpendicular to the tape motion. In so minimizing errors, distortion in the reading and / or writing of the data tracks can be prevented.
Owner:ADVANCED RES
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170372727A1Restrain output decreaseImprove accuracyAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; a non-magnetic layer including non-magnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic layer, in which the total thickness of the non-magnetic layer and the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.60 μm, the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, and logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape
InactiveUS7255908B2Without reducing data areaReduce areaLayered productsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeOxygen
A magnetic tape (1) characterized by having a backcoating layer (5) which comprises a binder and fine particles having been dispersed in the binder and being capable of irreversibly changing in color on oxidation reaction, and has a sufficient number of microvoids of sufficient size to supply sufficient oxygen to cause the oxidation reaction.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com