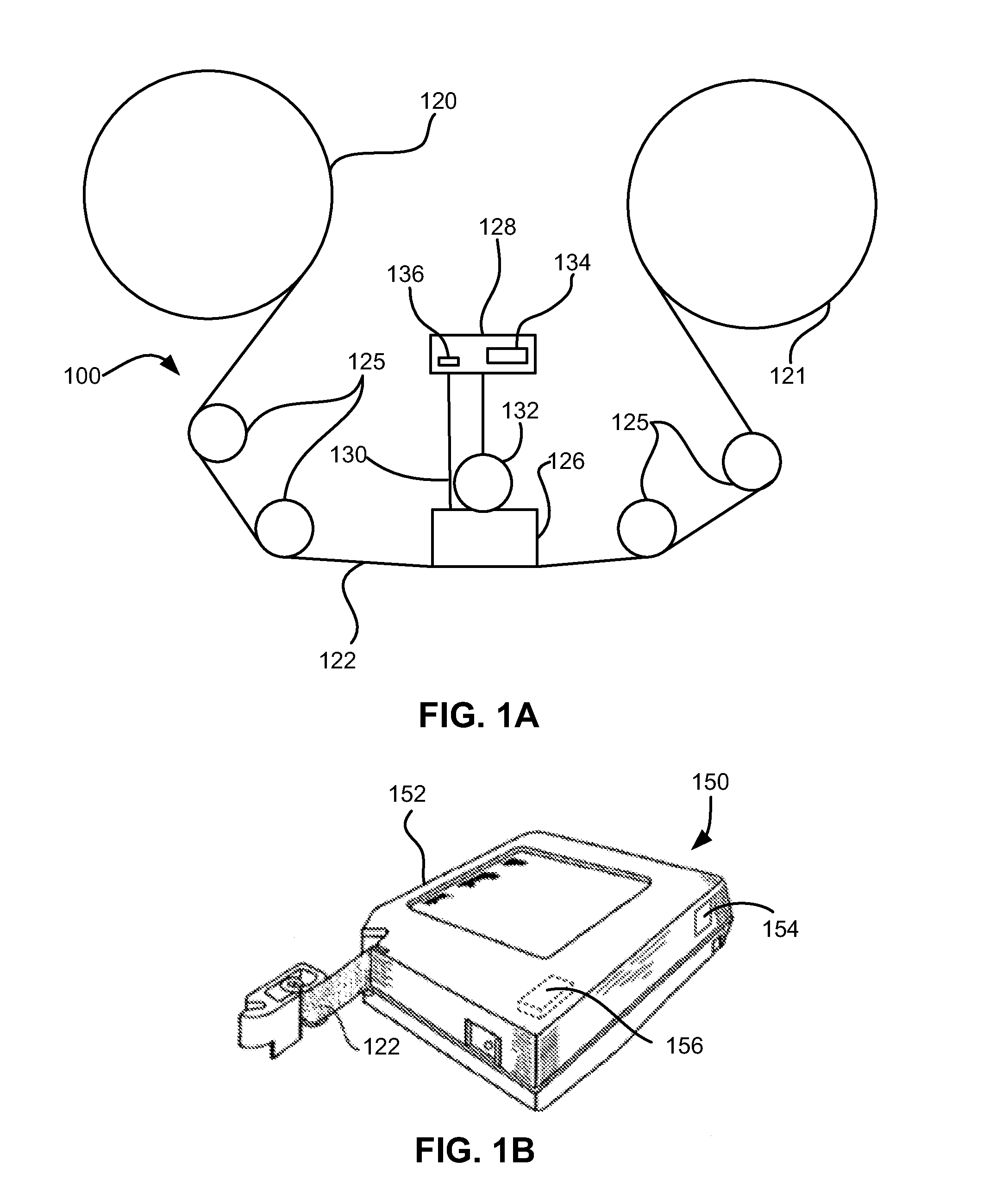
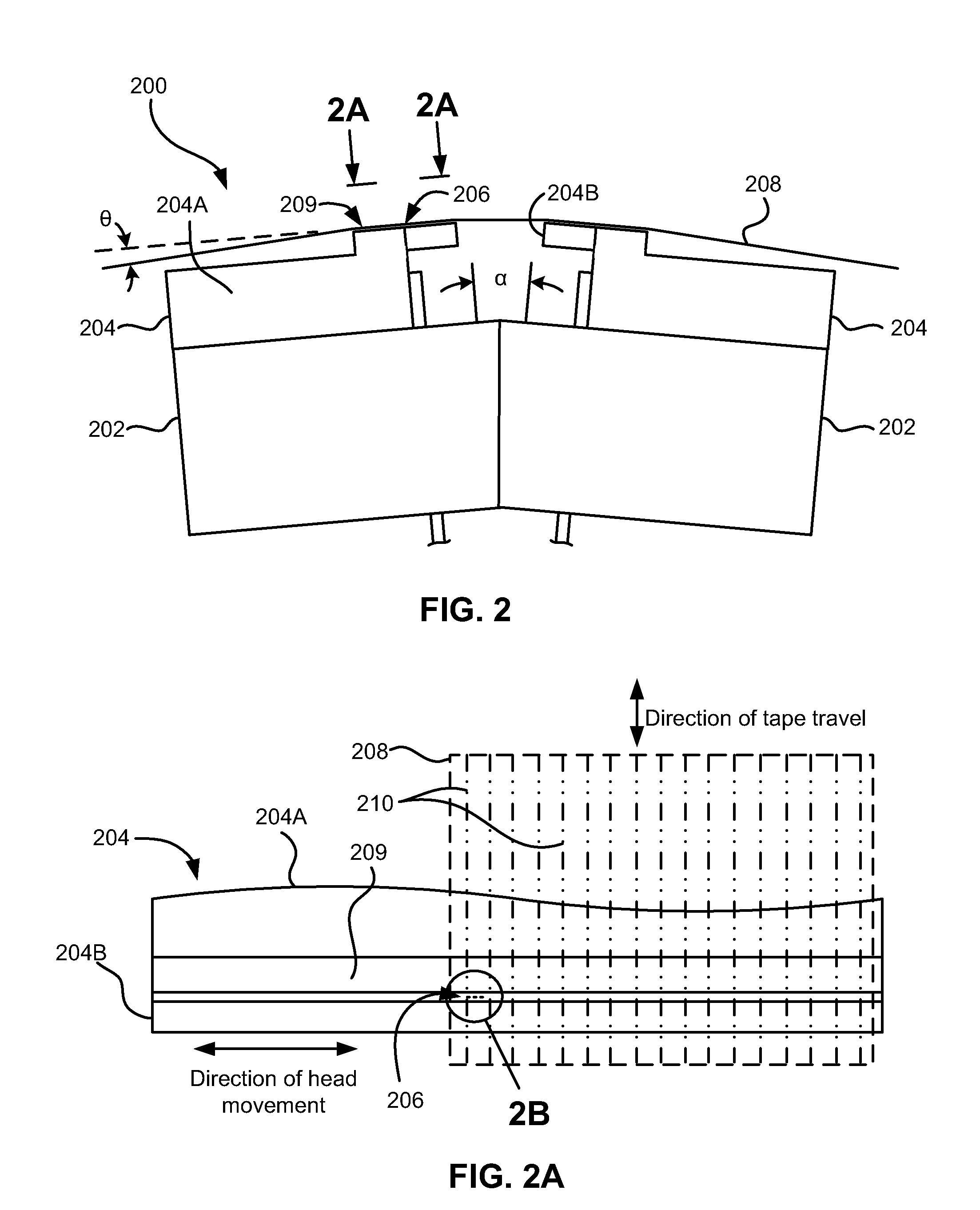
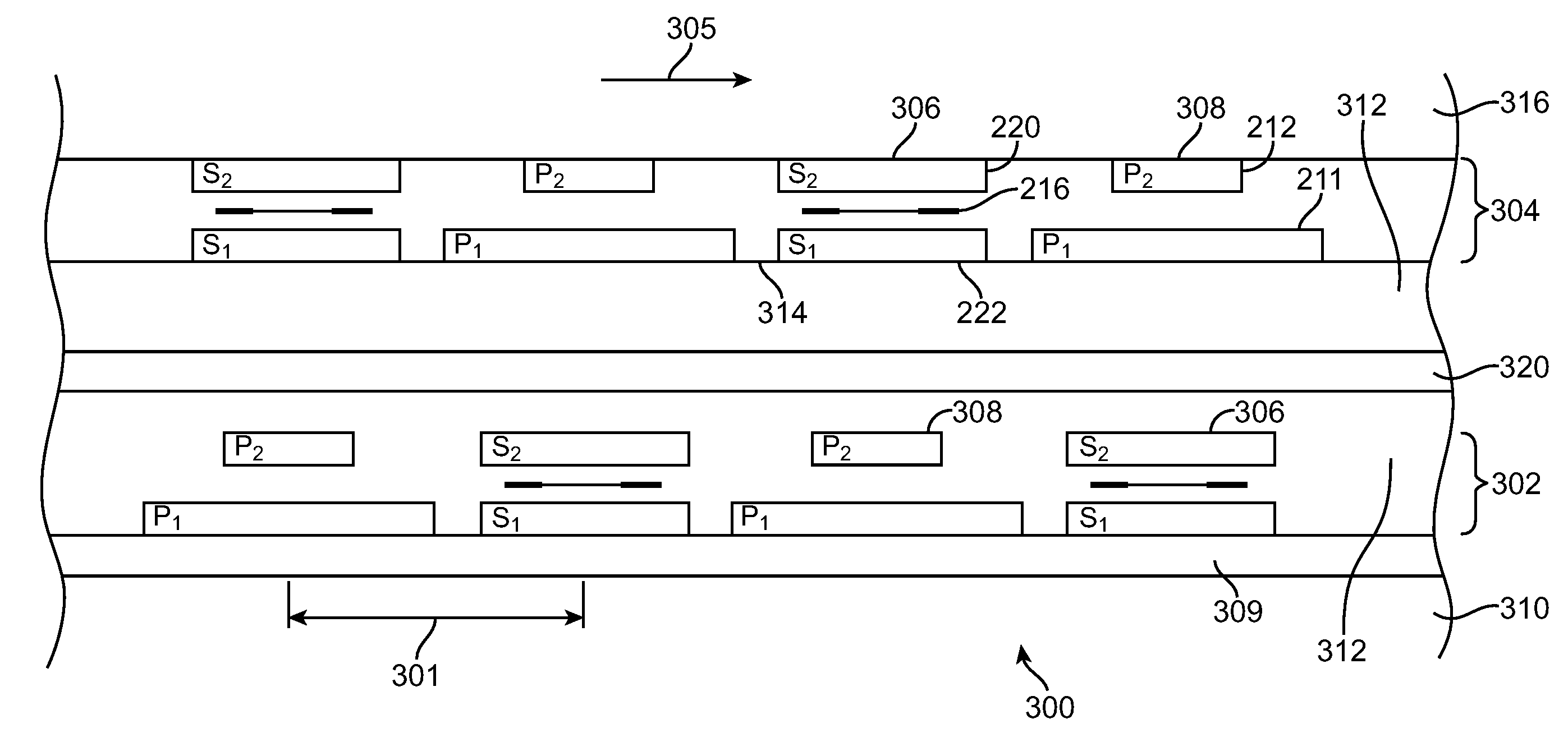
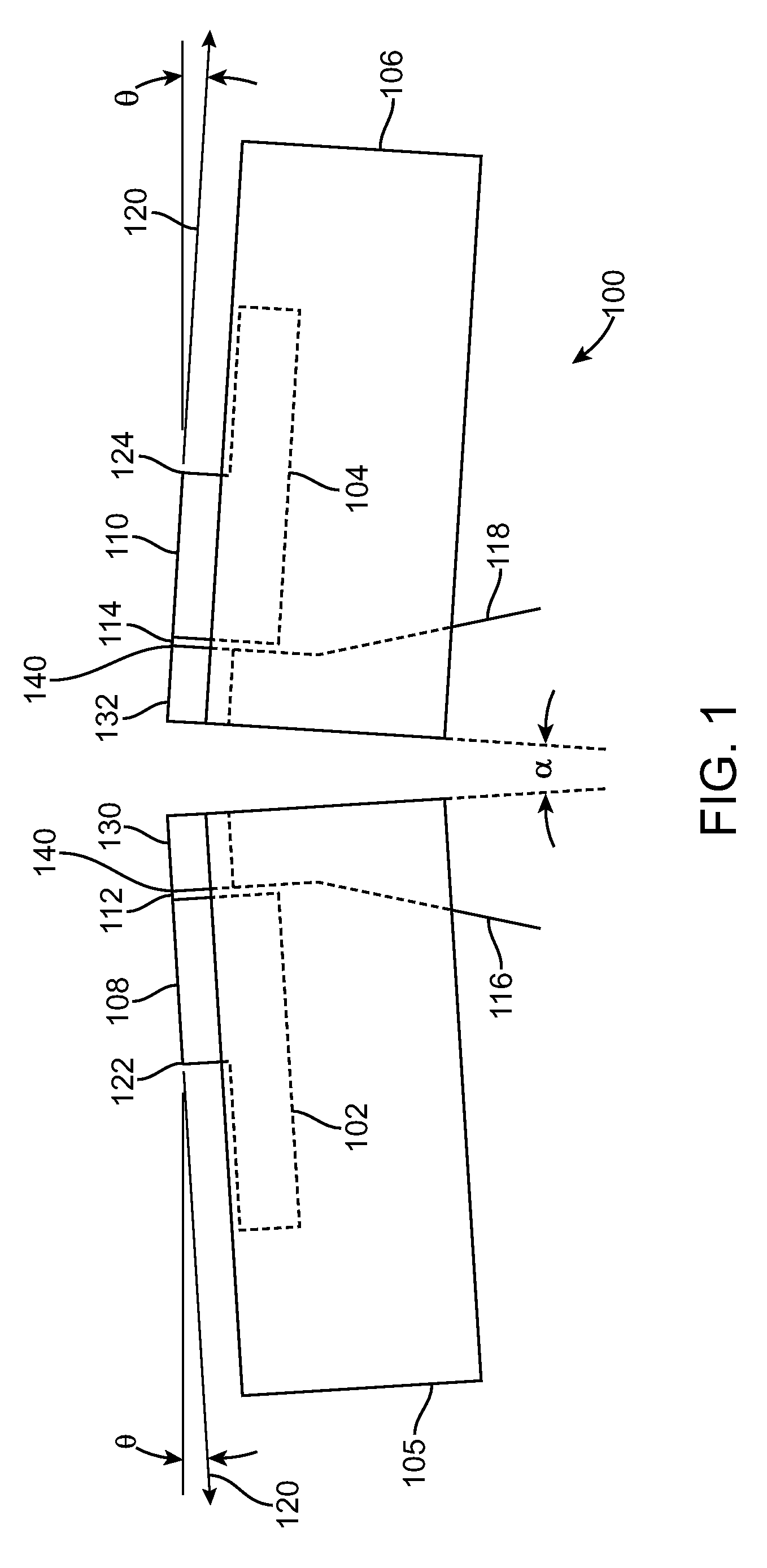
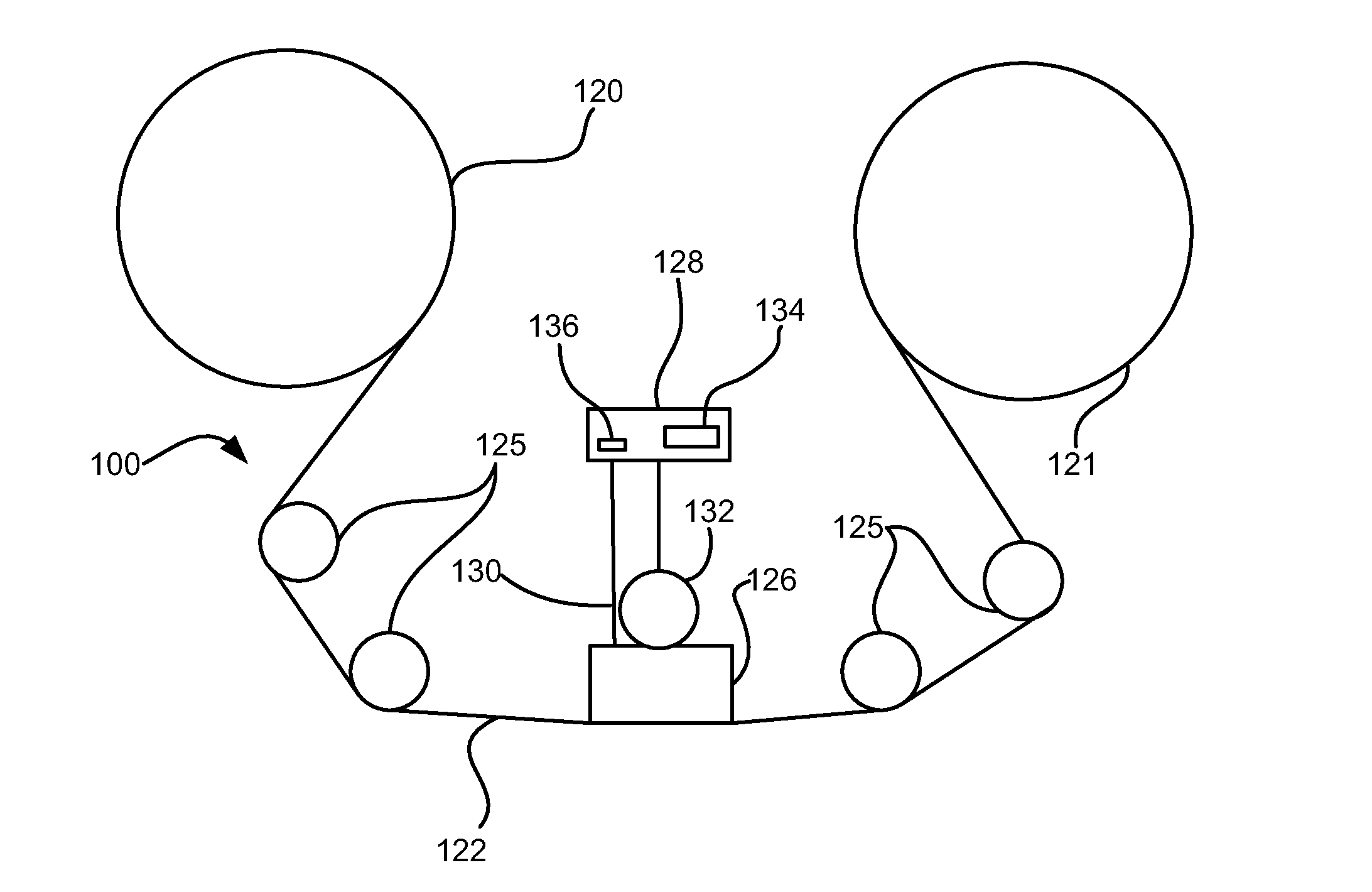
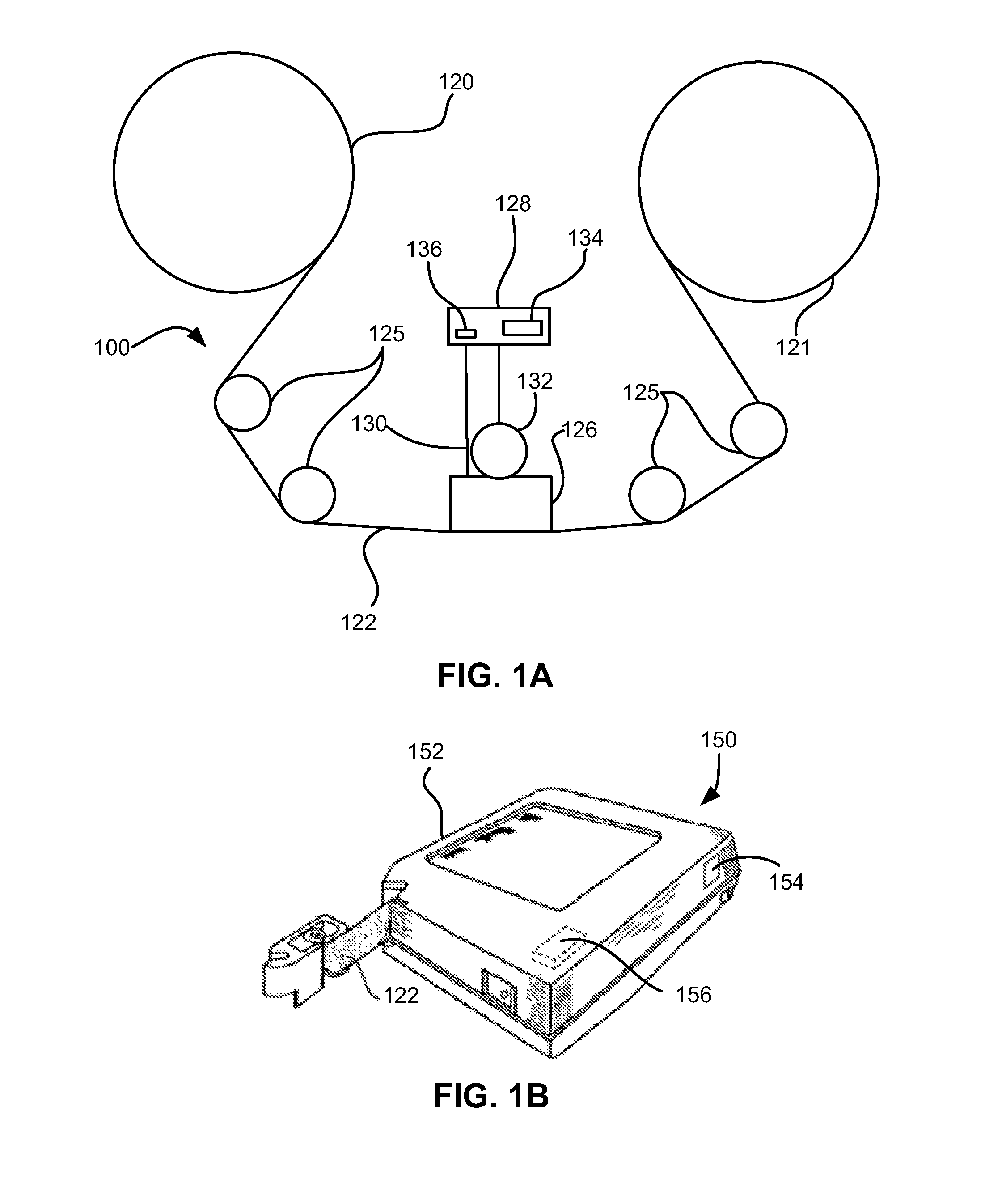
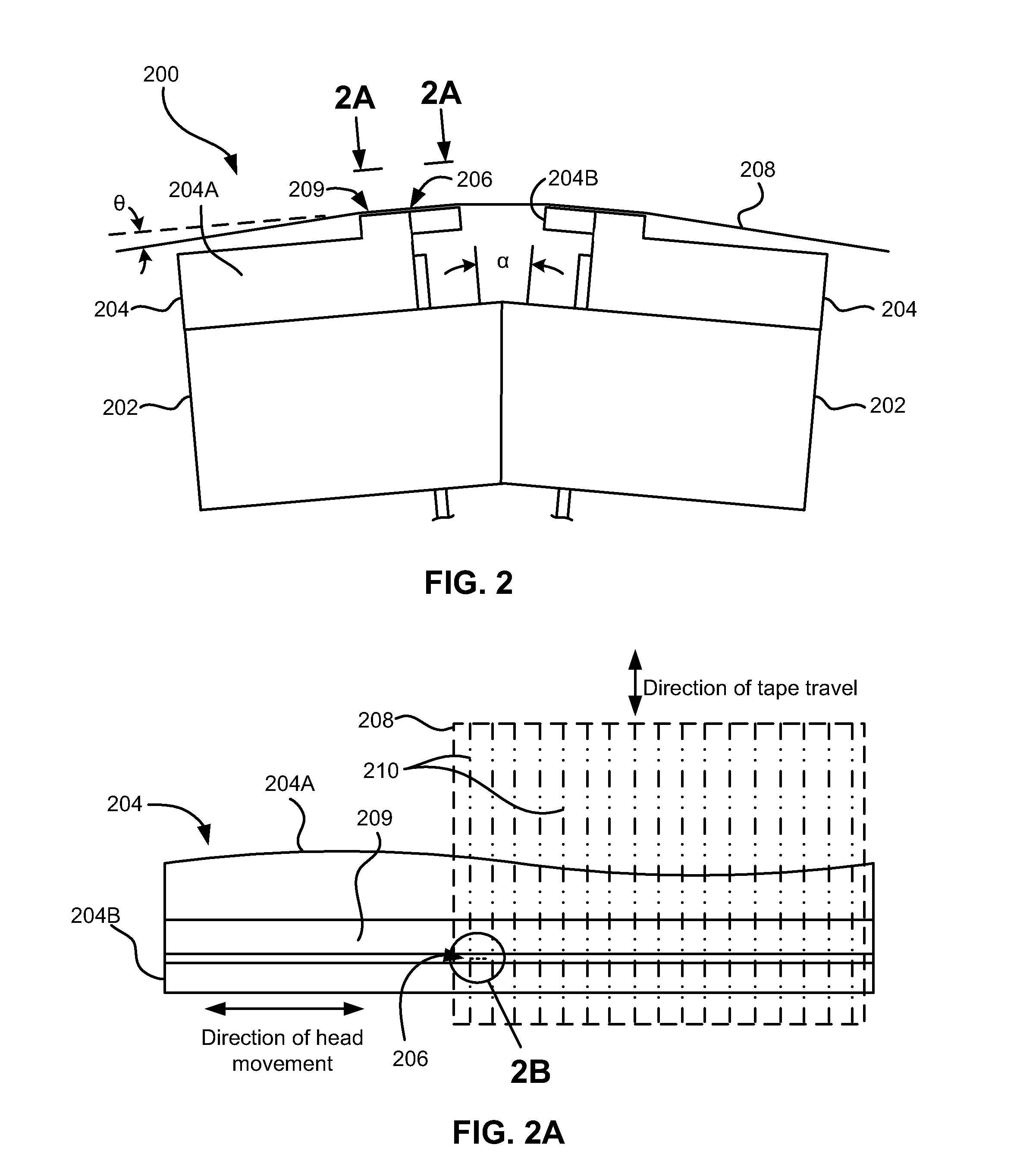
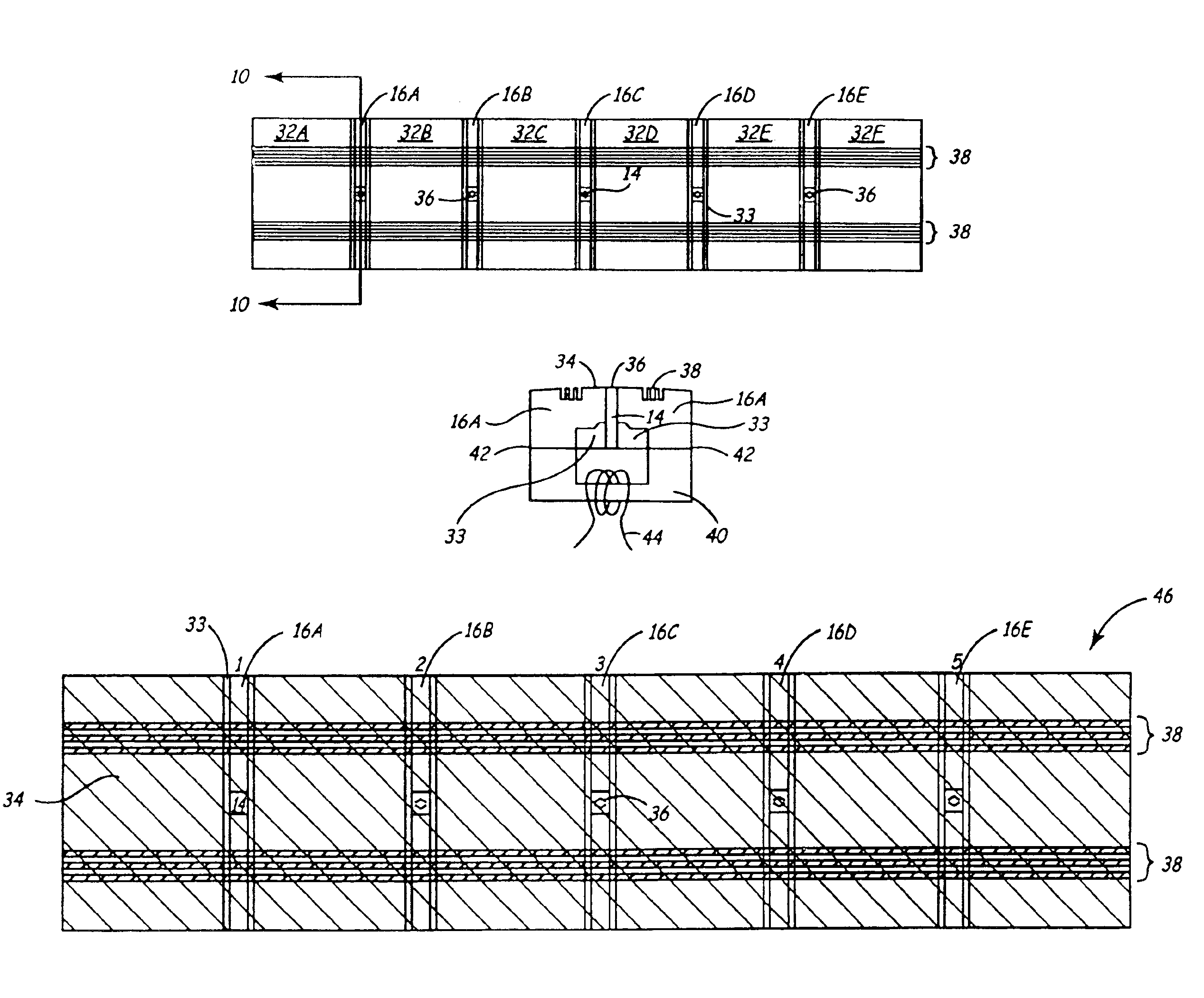
Patents
Literature
157results about "Heads relative to moving tape" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
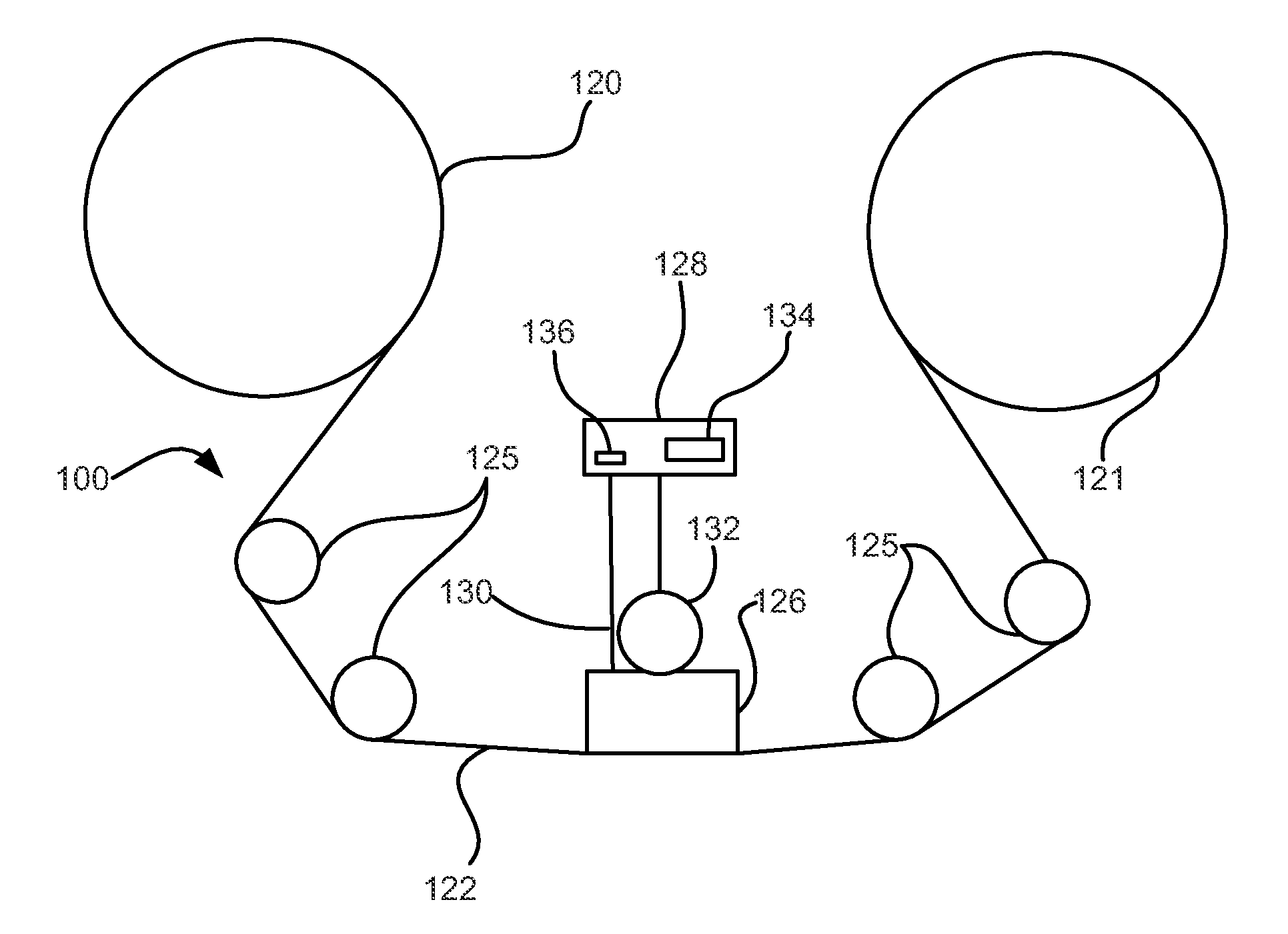
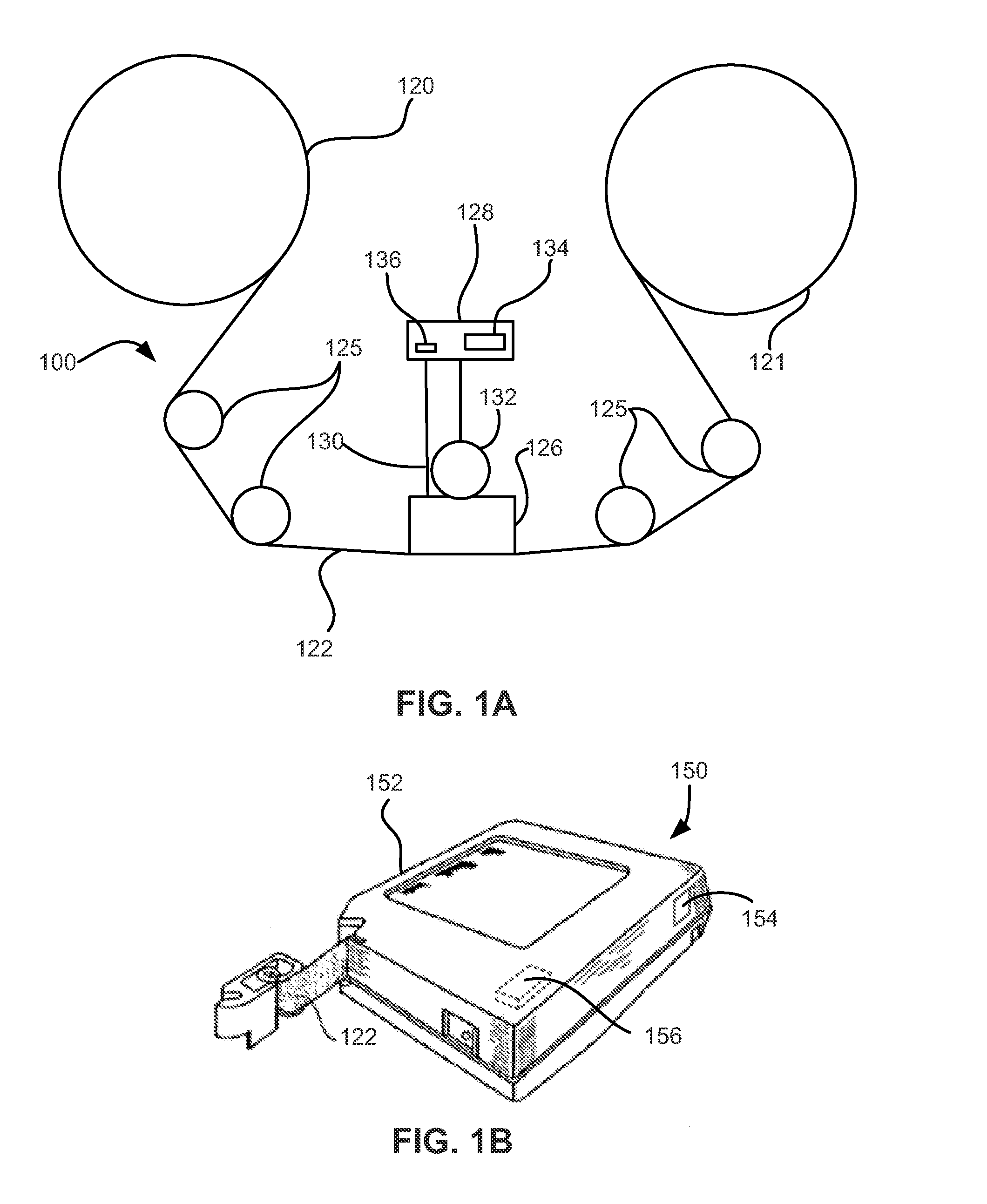
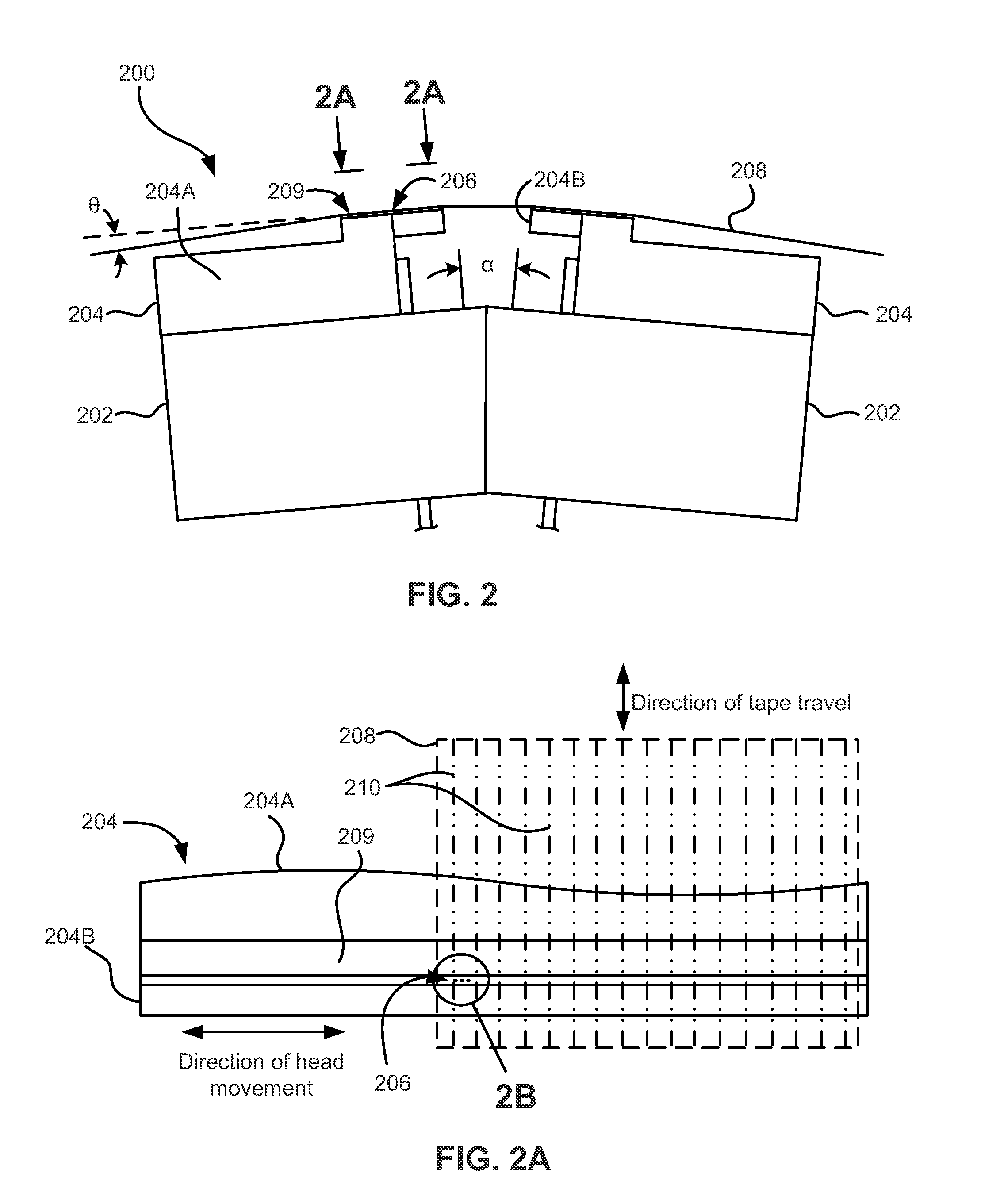
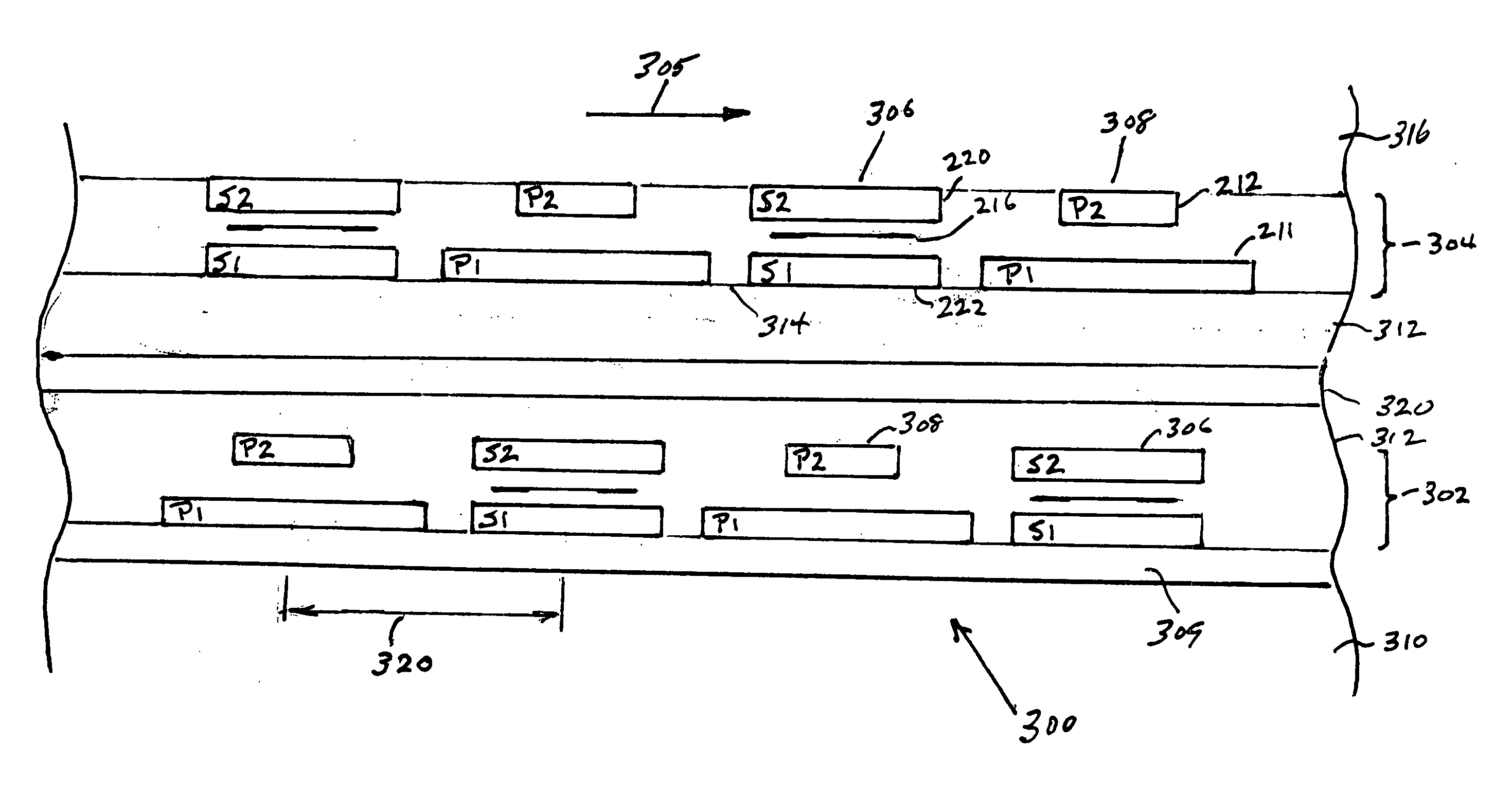
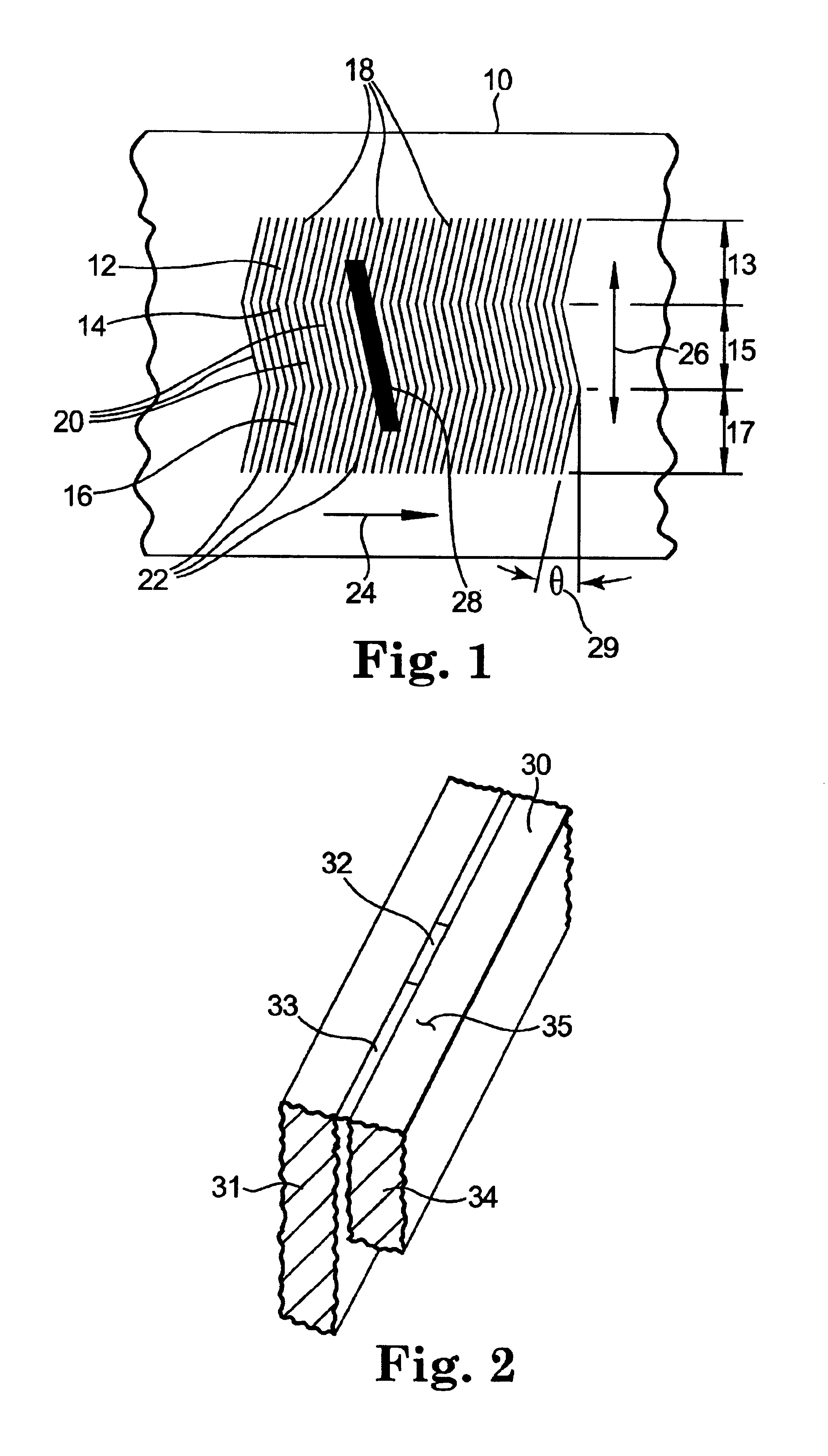
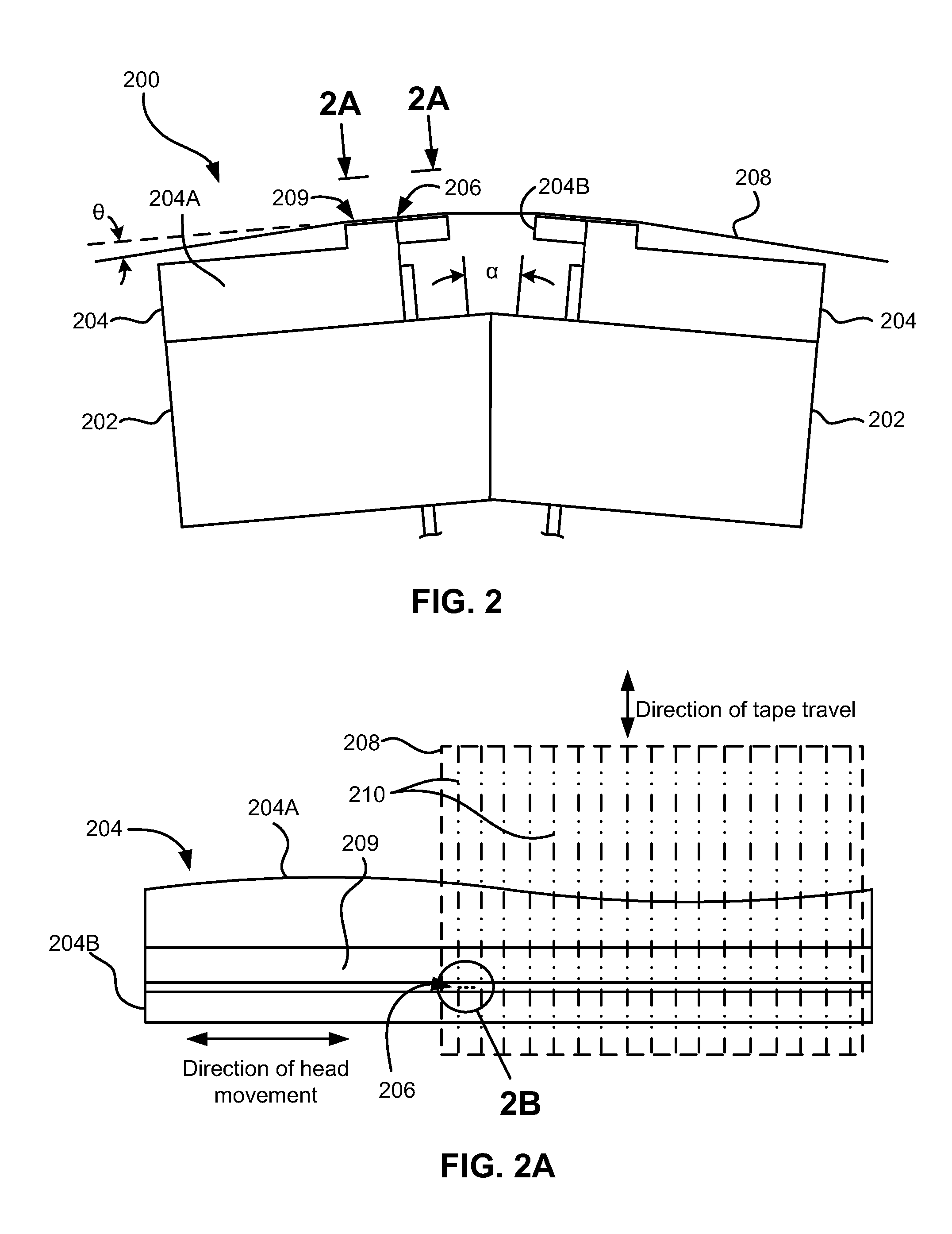
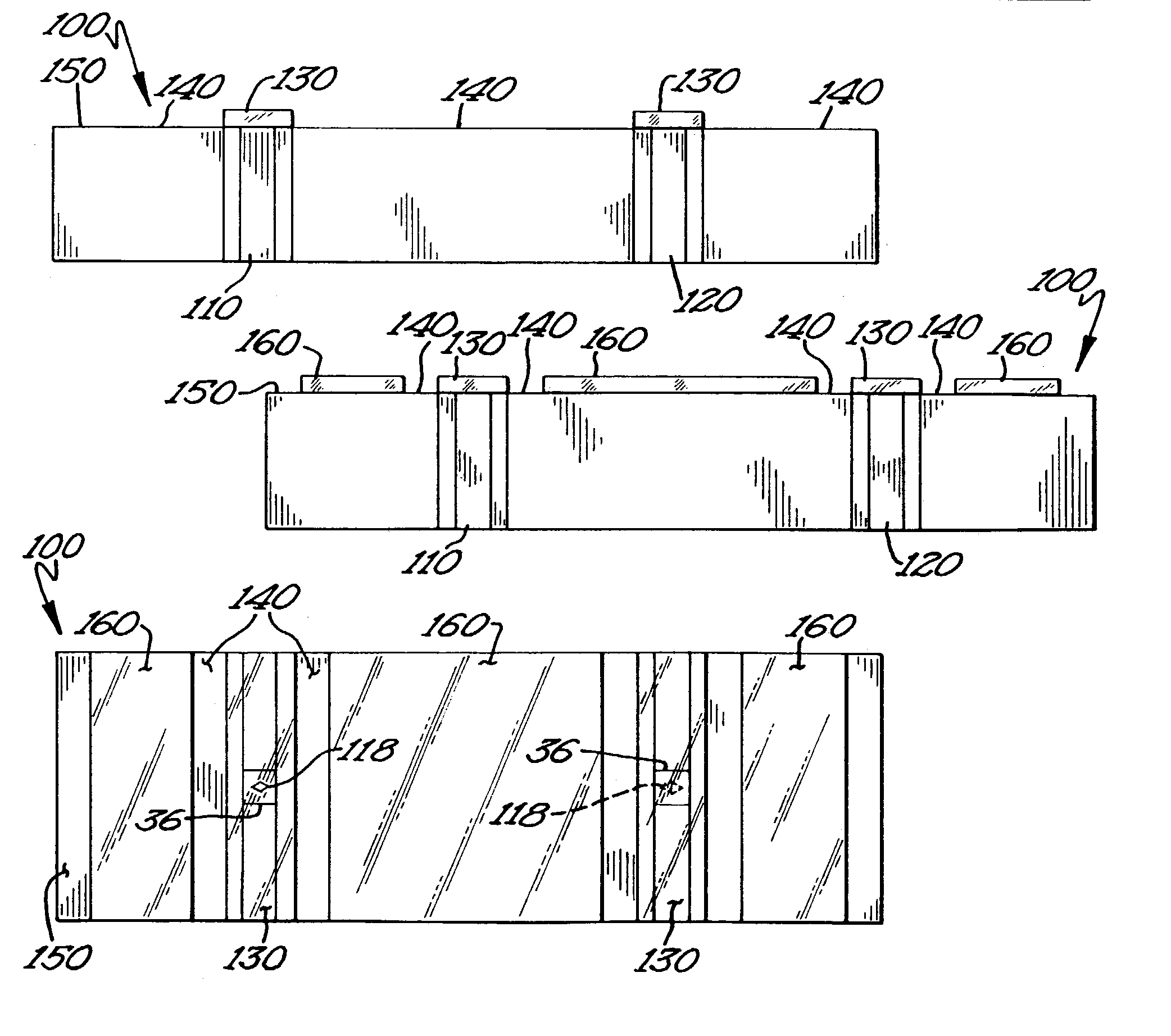
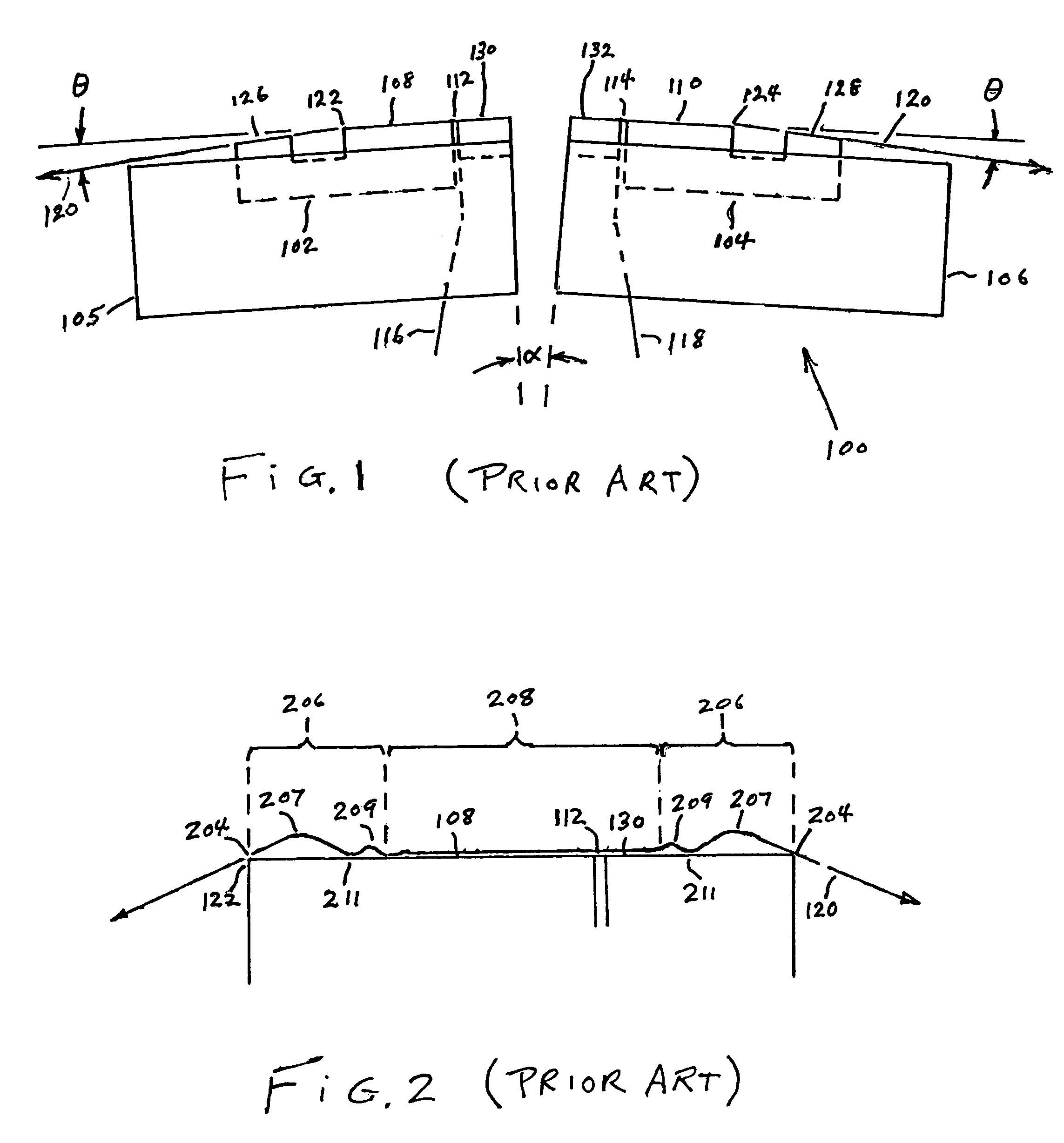
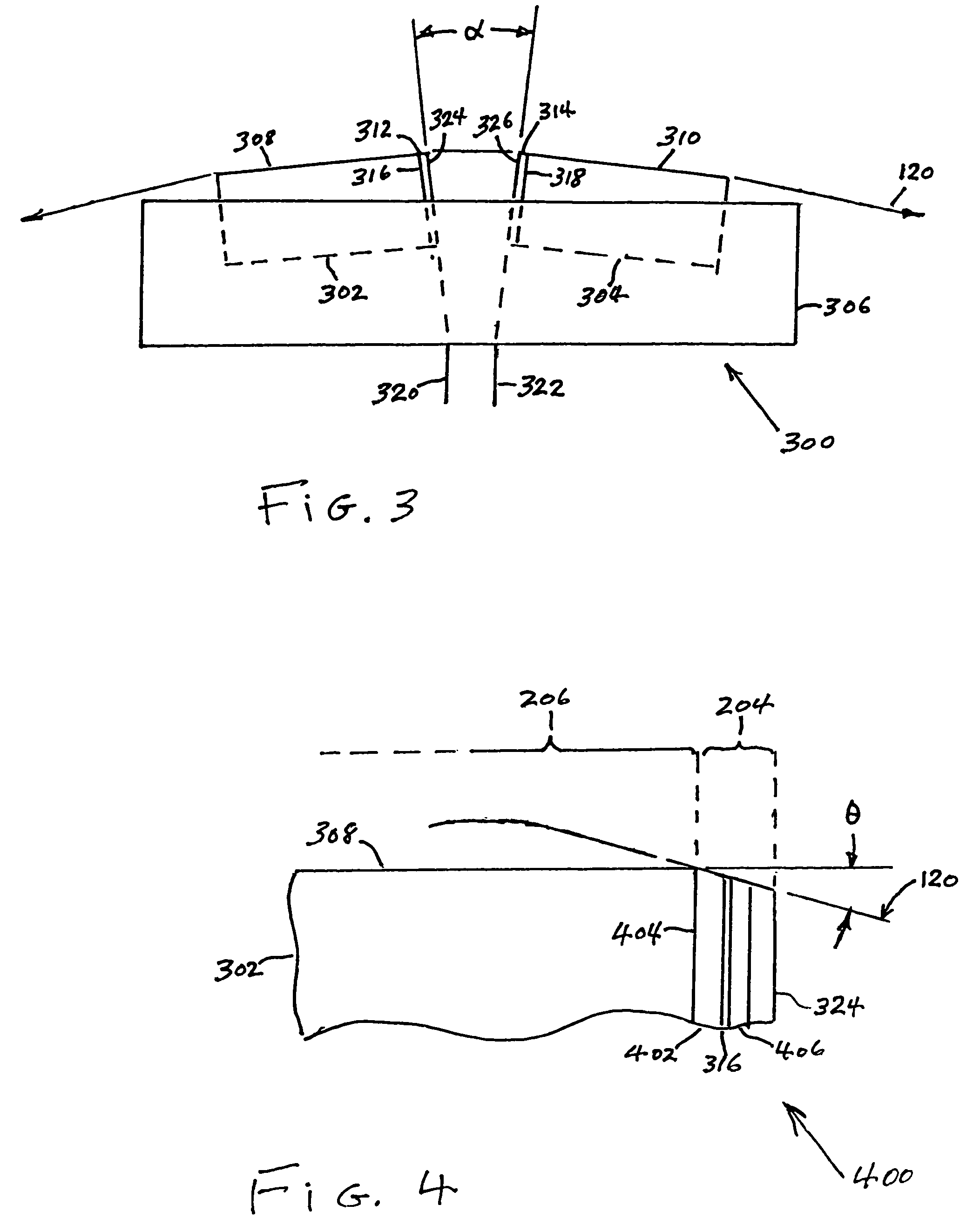
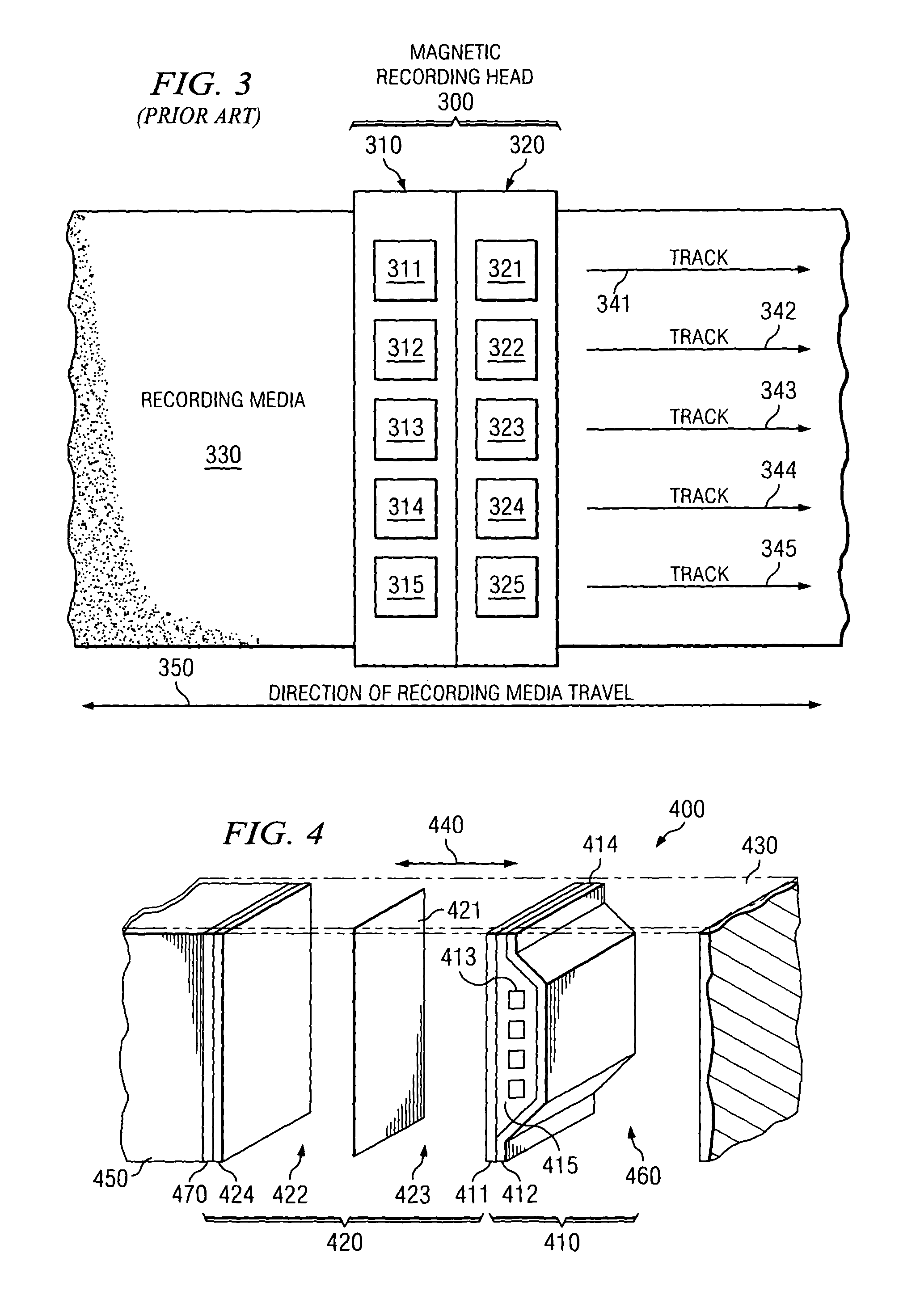
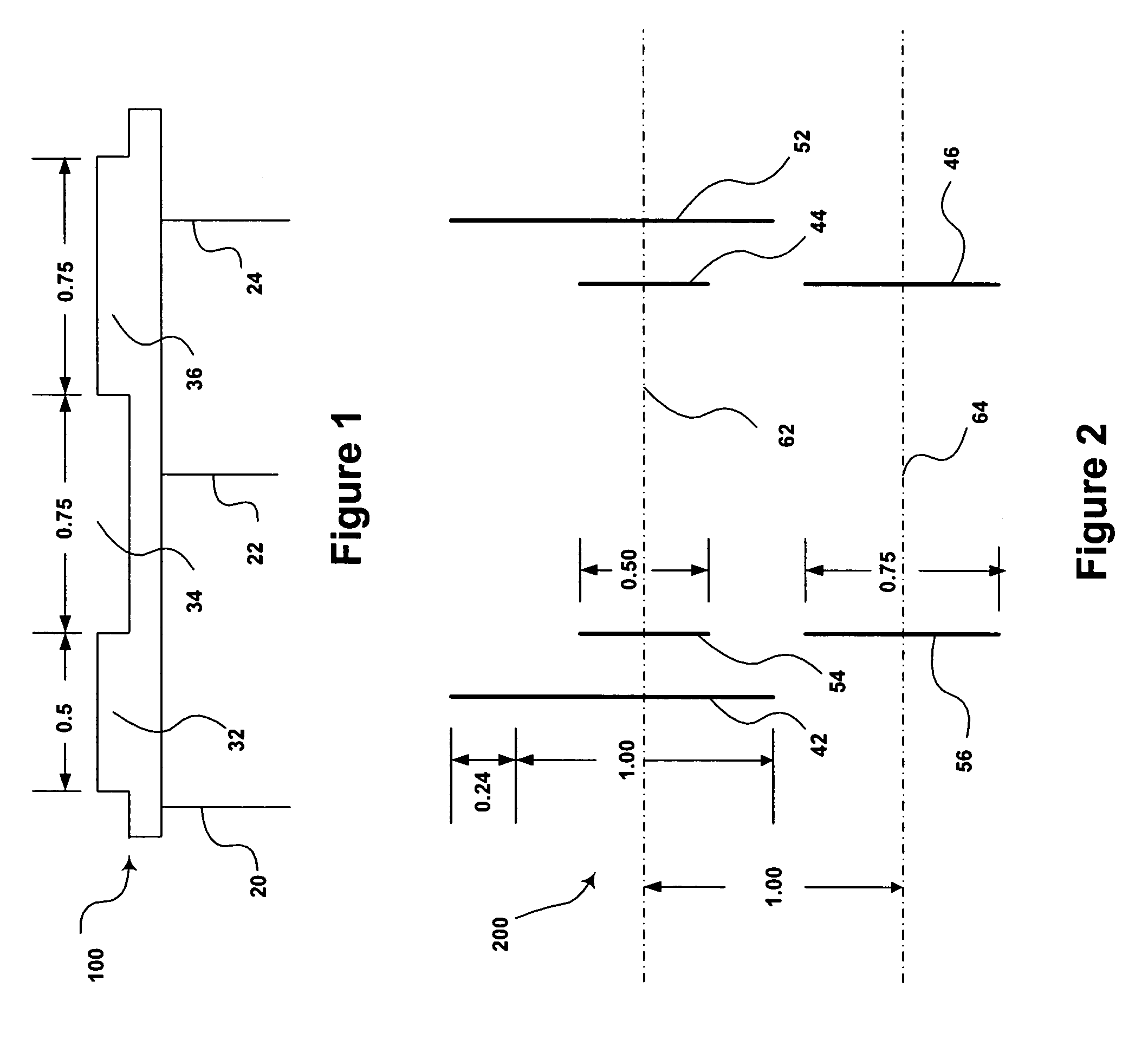
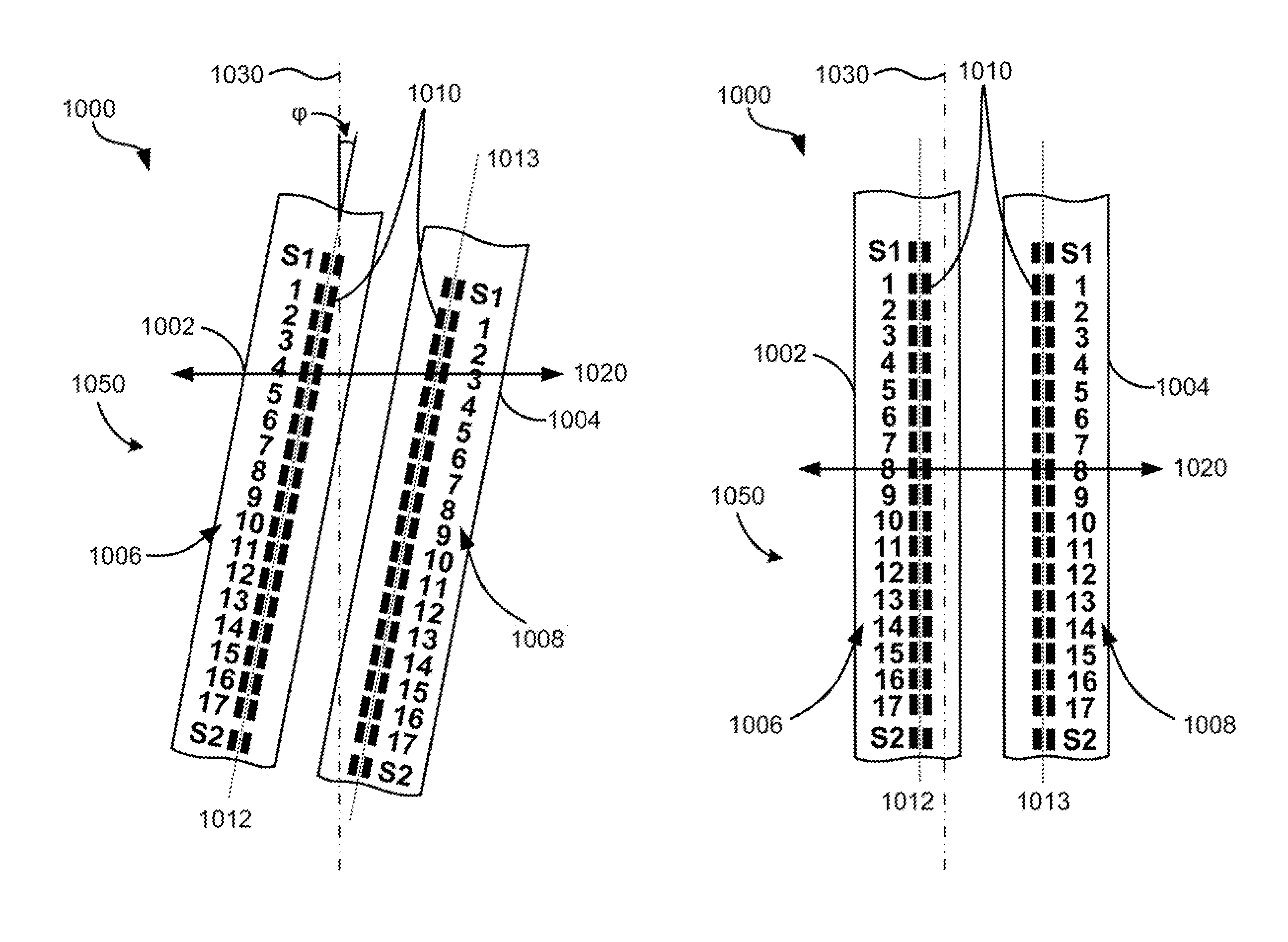
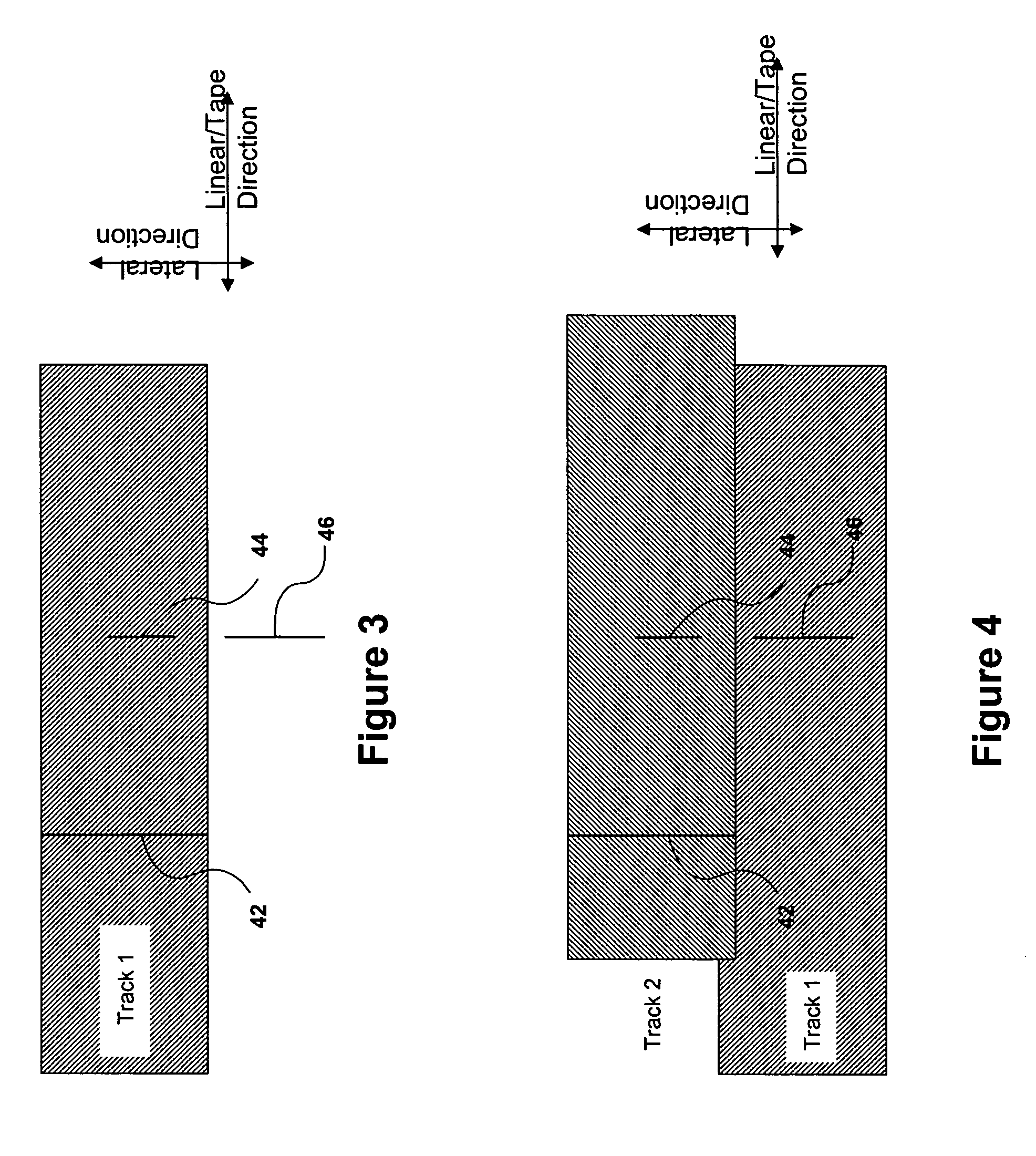
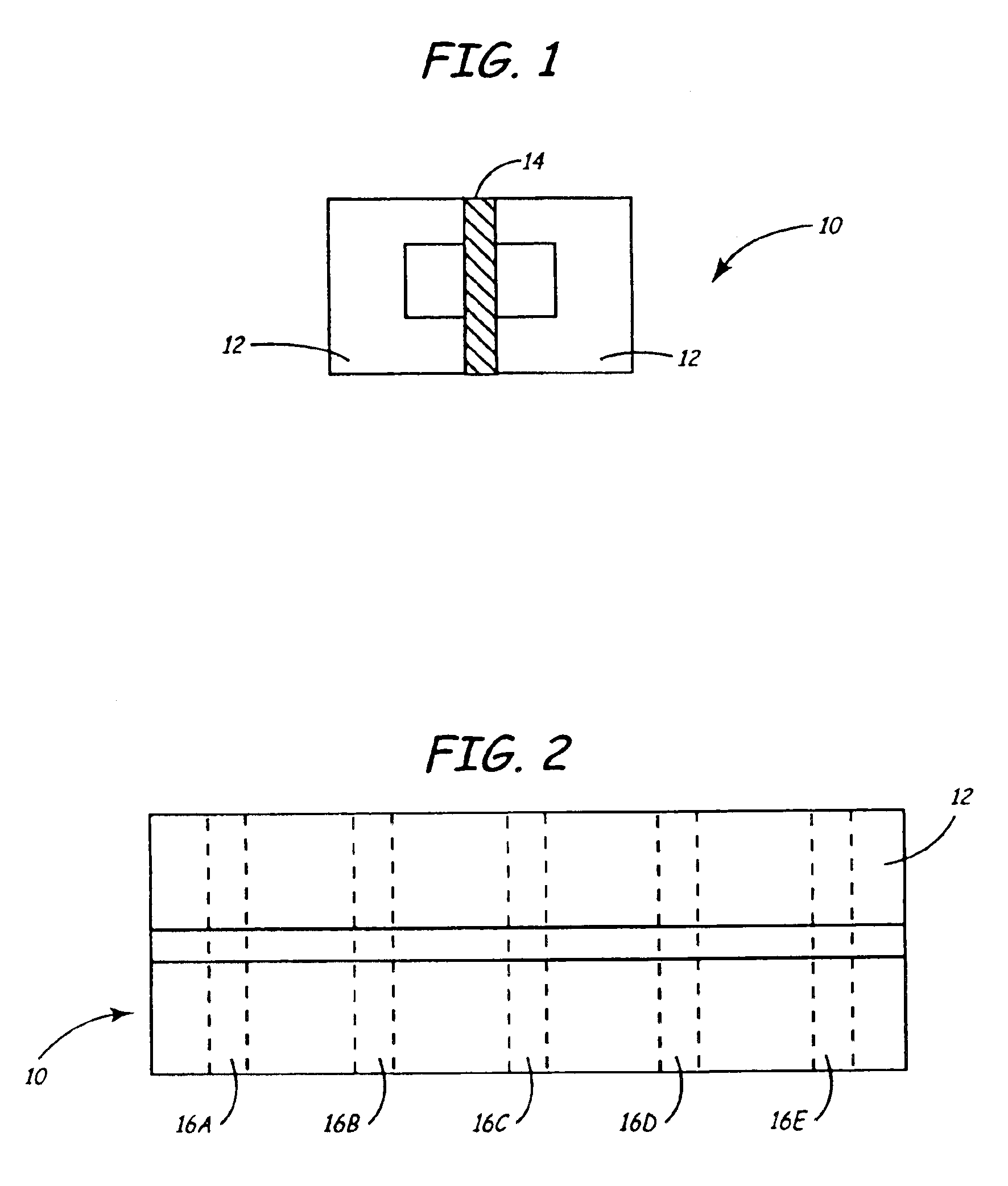
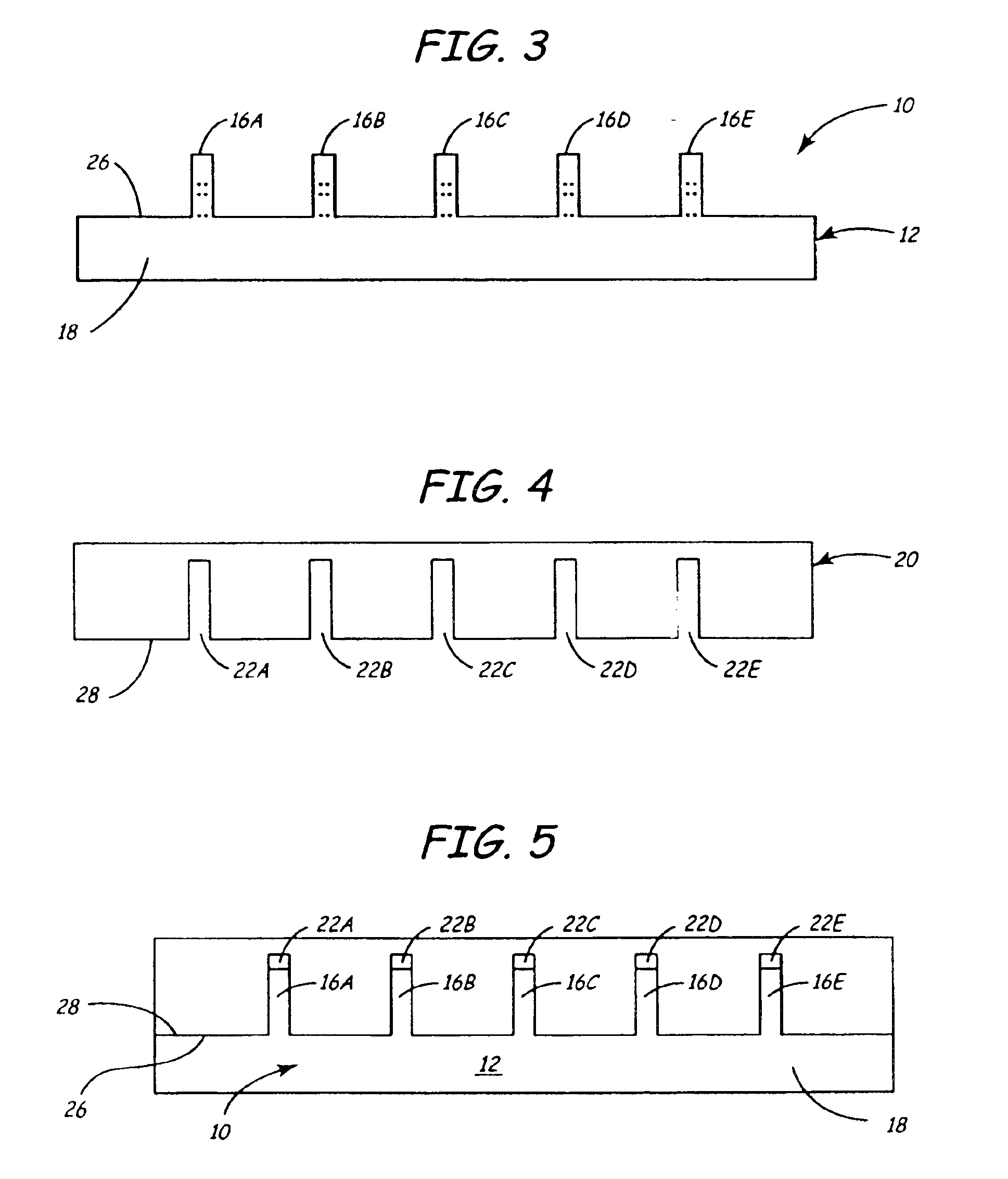
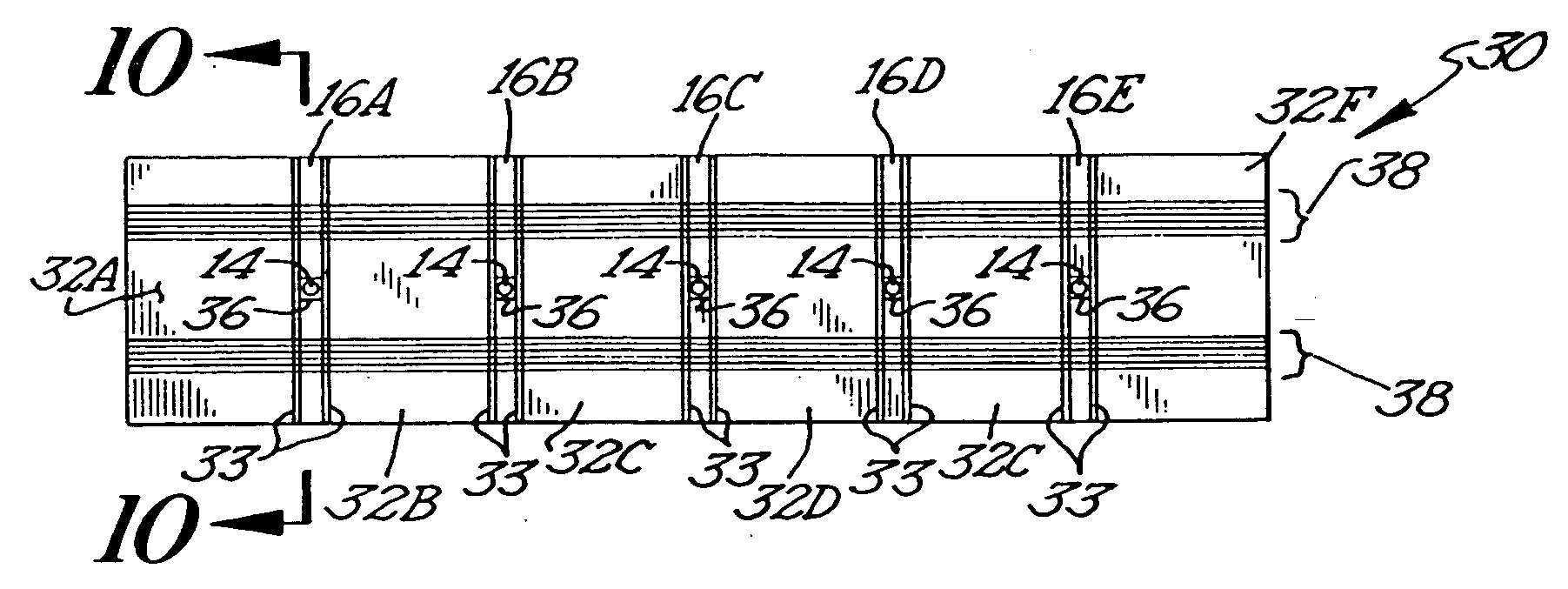
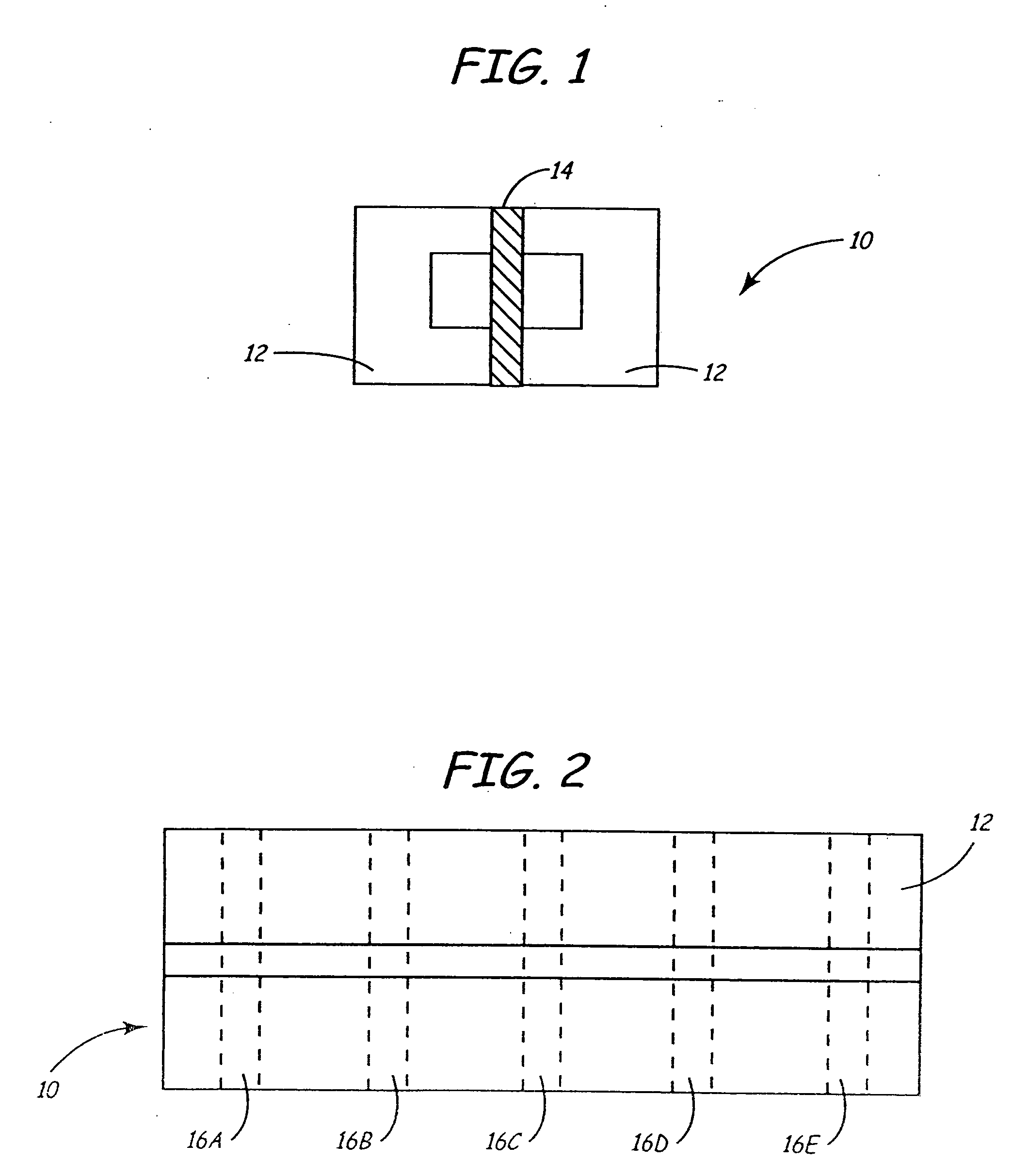
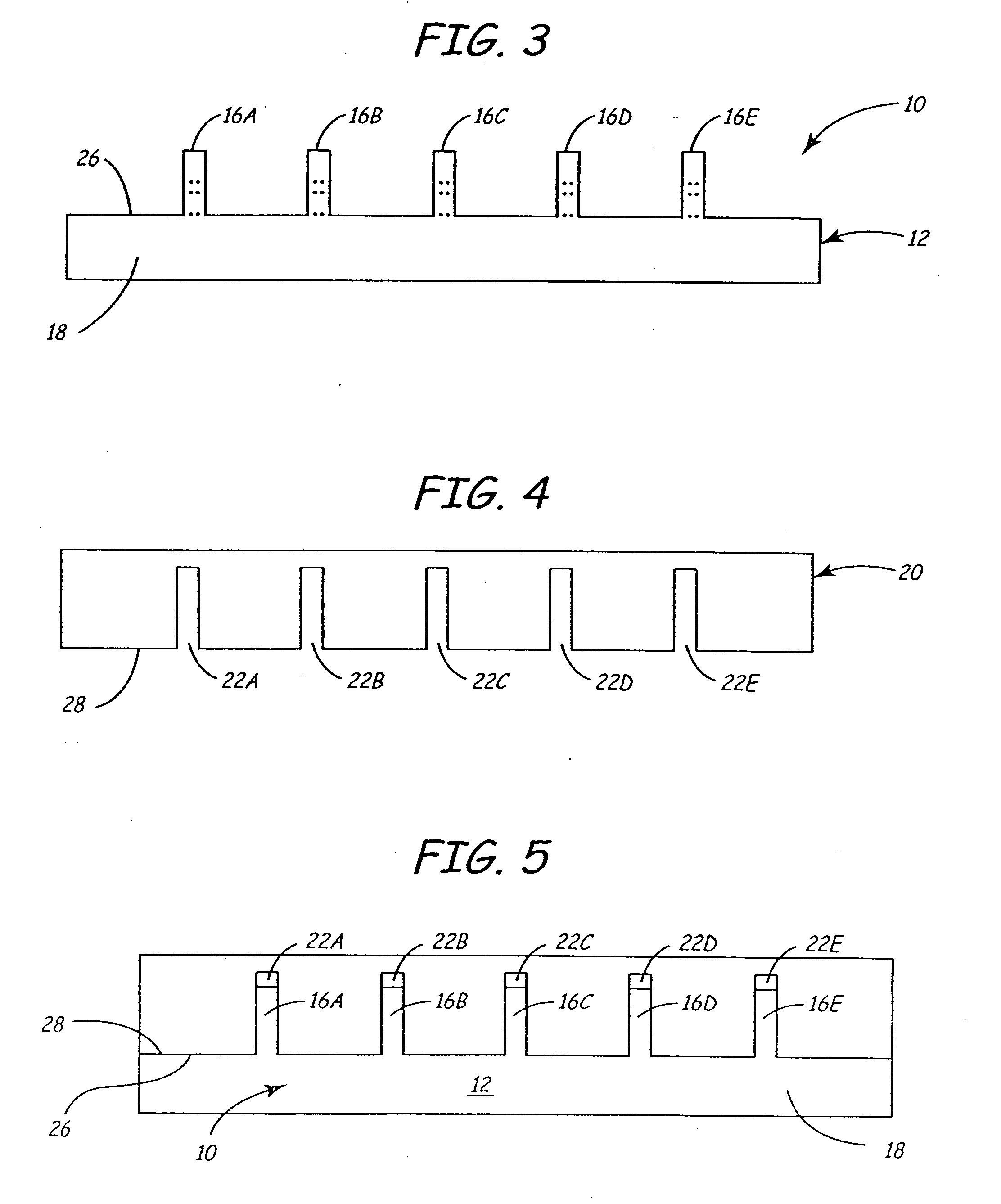
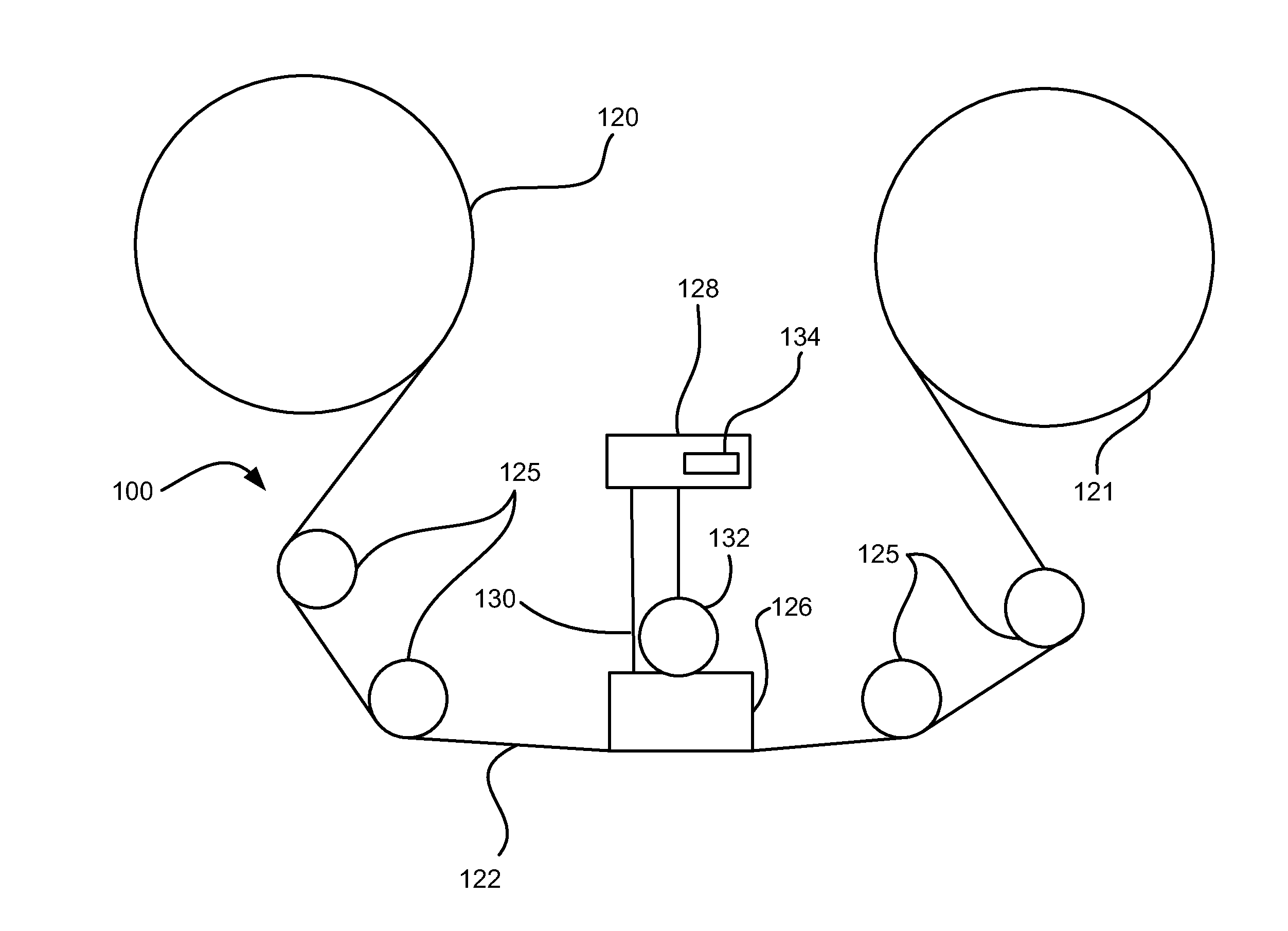
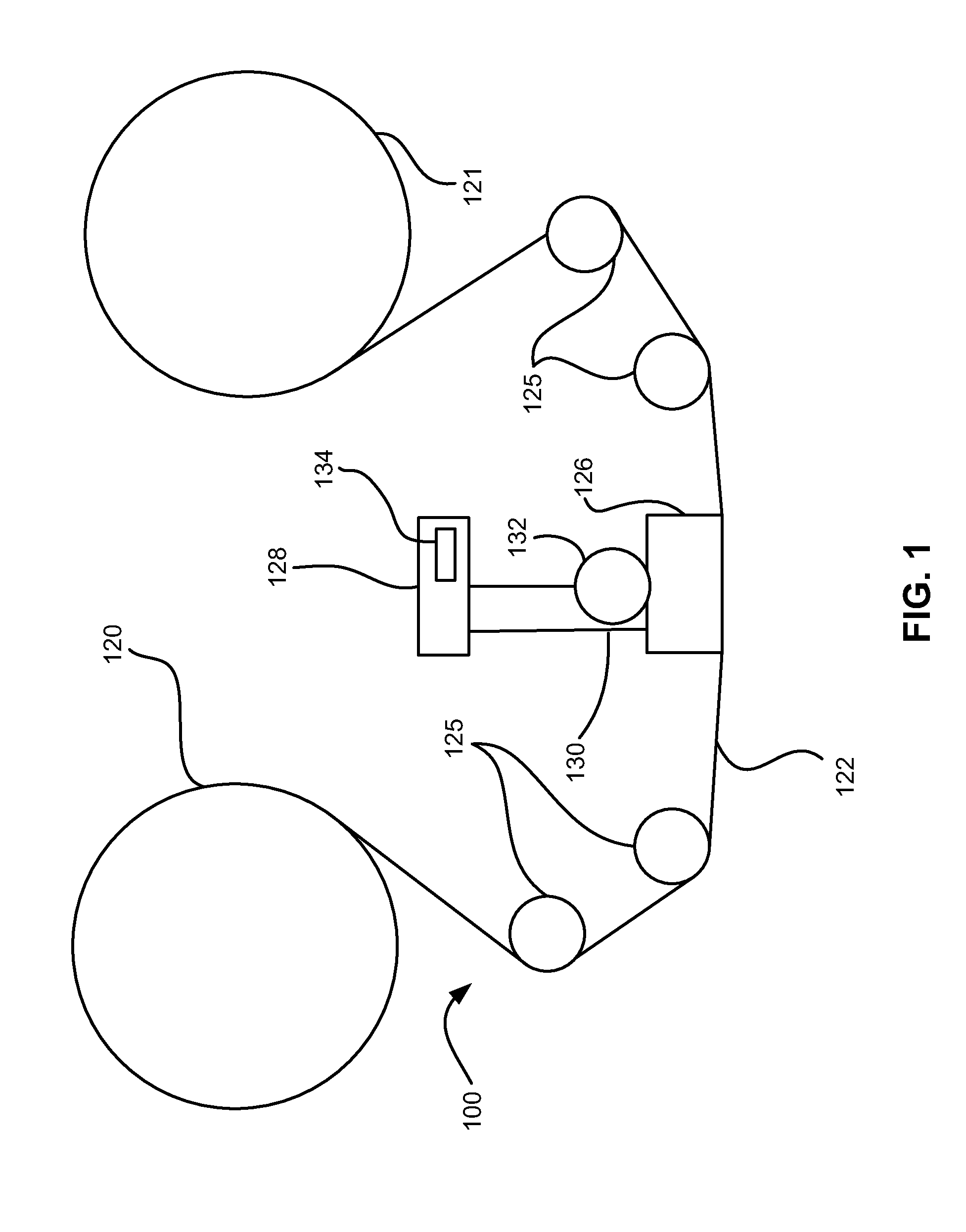
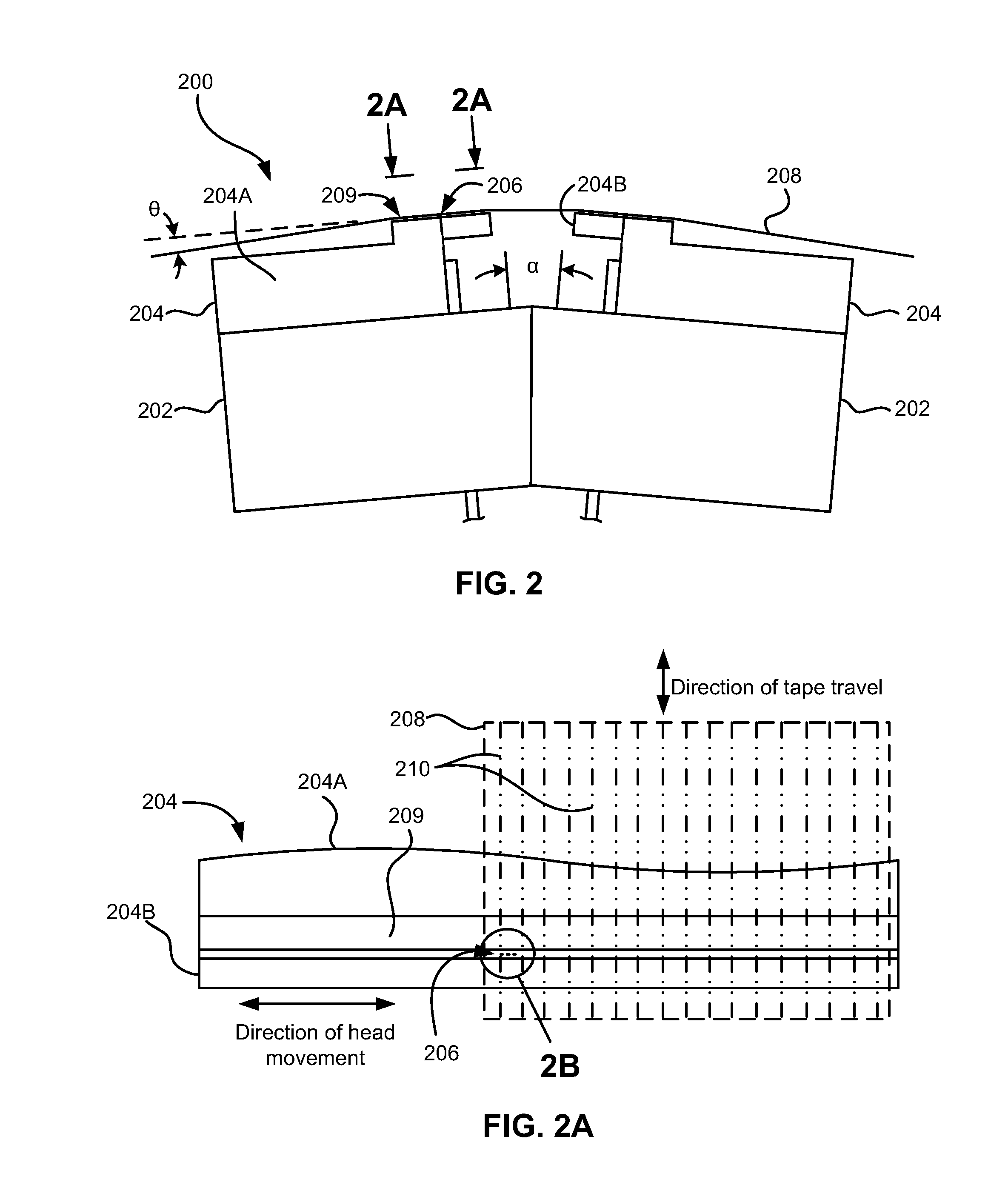
High density timing based servo format for use with tilted transducer arrays
A product, according to one embodiment, includes a magnetic recording tape having opposite ends, a longitudinal axis of the magnetic recording tape being defined between the ends. The magnetic recording tape has at least one servo track, the at least one servo track having a plurality of first magnetic bars and a plurality of third magnetic bars oriented to form chevron-like patterns with the first magnetic bars. The first magnetic bars each have a longitudinal axis oriented at a first angle between 2 and 88 degrees from the longitudinal axis of the magnetic recording tape. The third magnetic bars each have a longitudinal axis oriented at a second angle between 2 and 88 degrees from the longitudinal axis of the magnetic recording tape, the second angle having a different numerical absolute value than the first angle.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
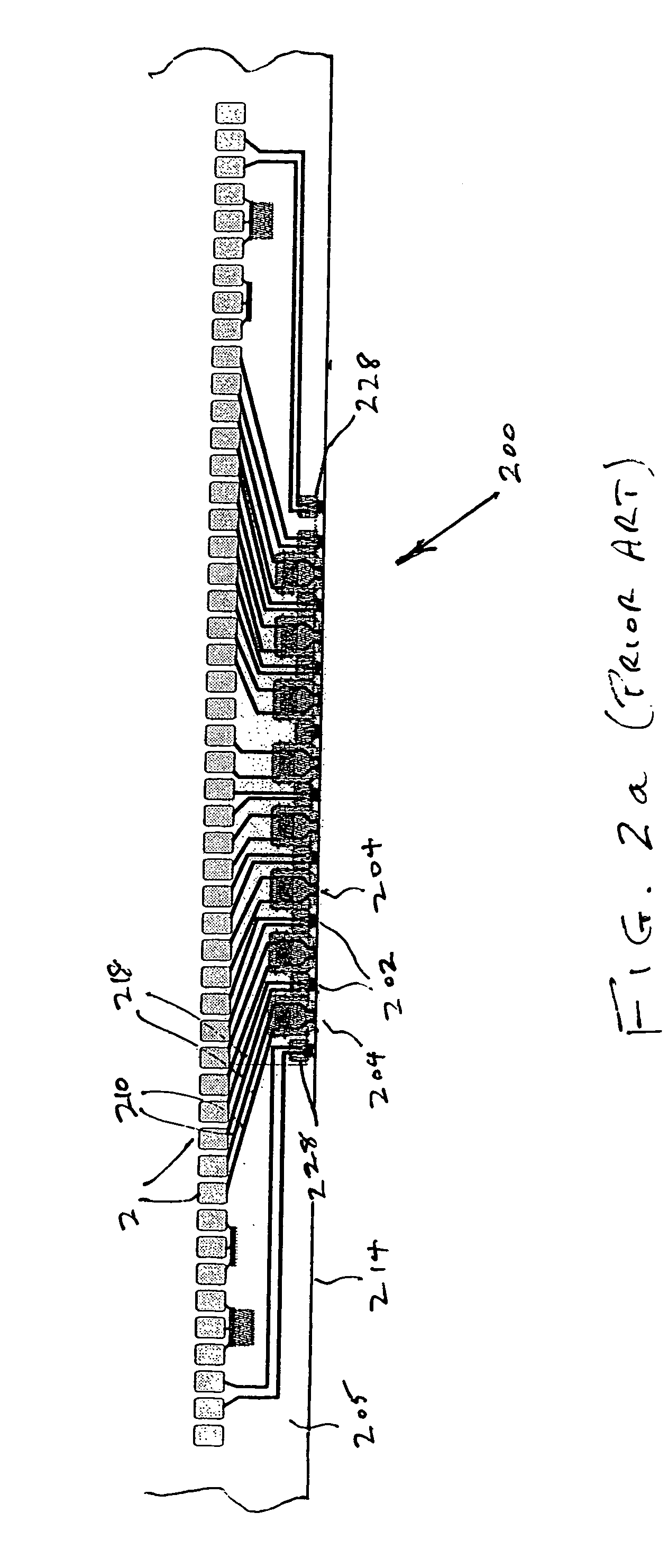
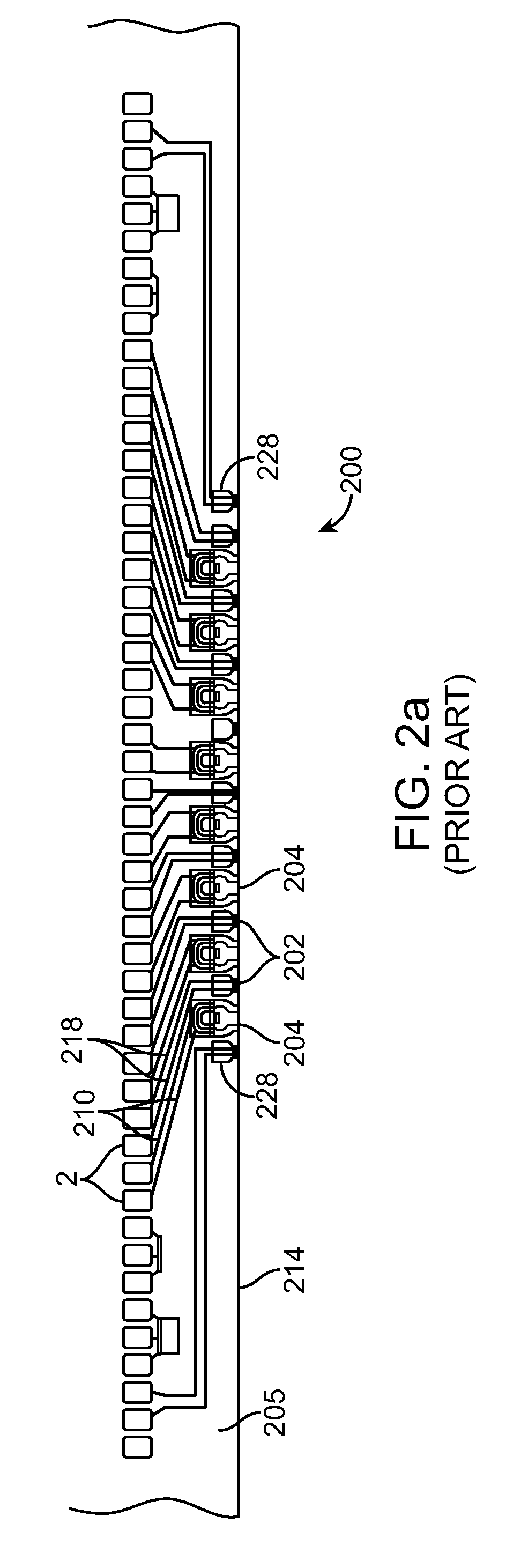
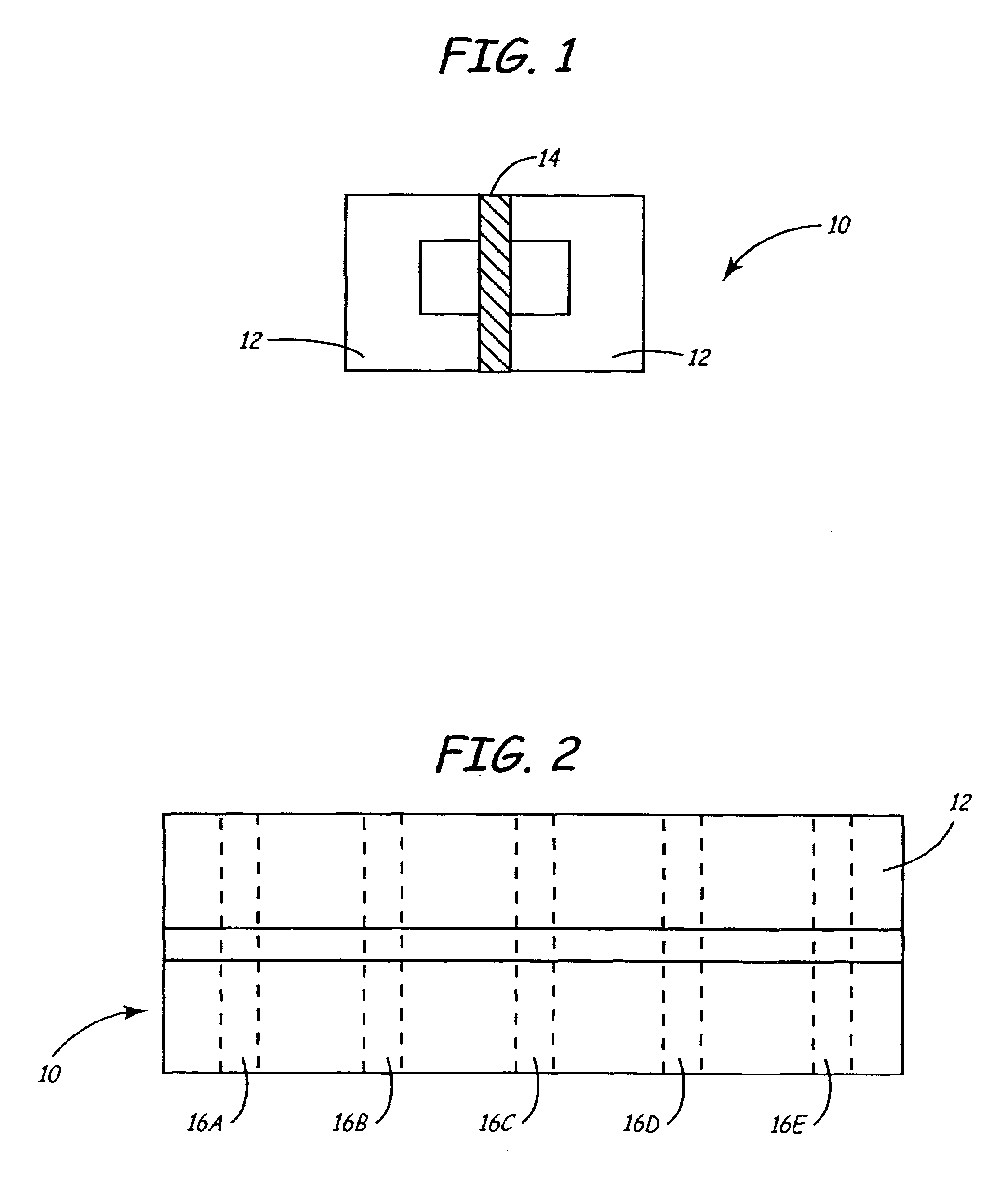
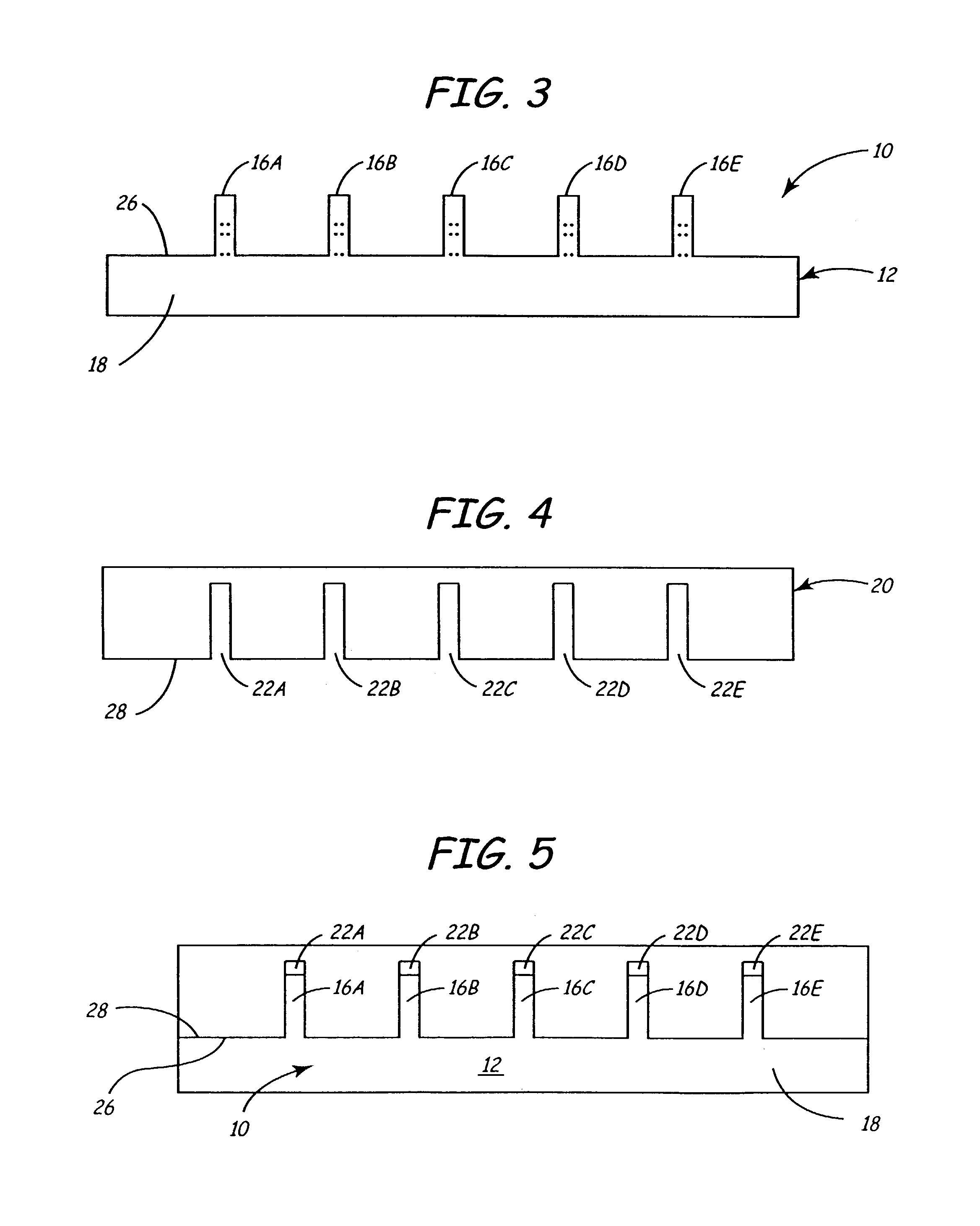
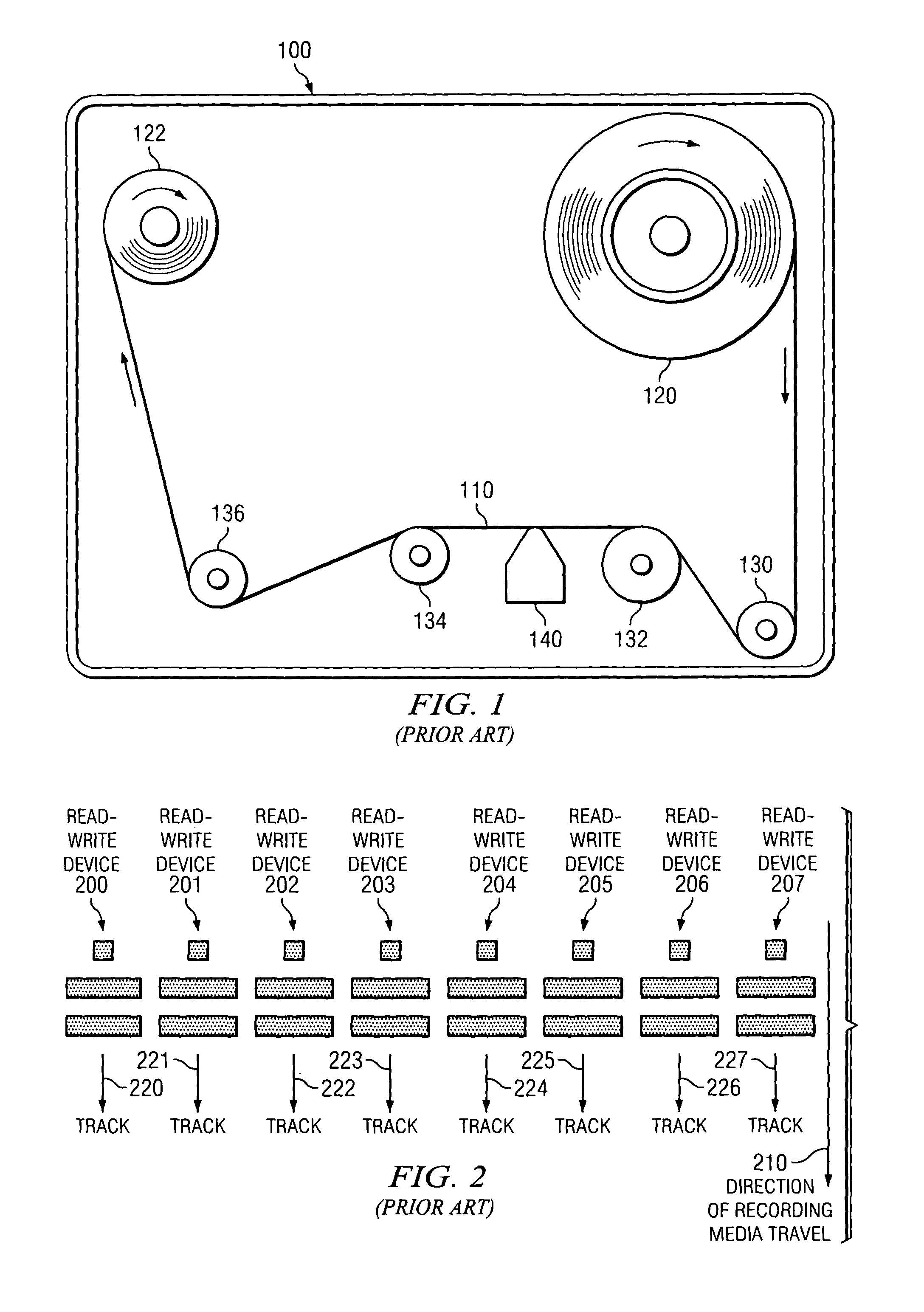
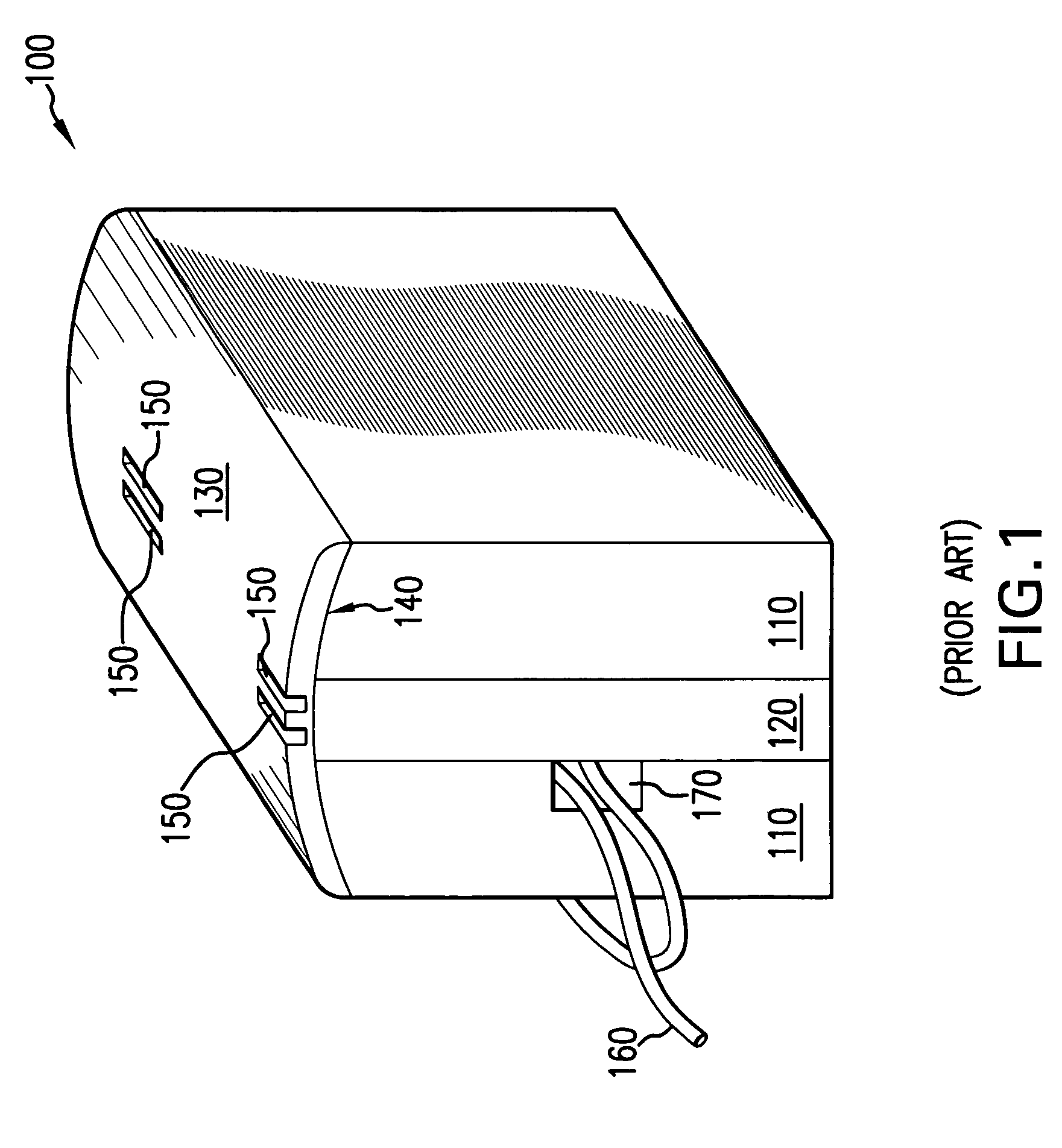
Tape recording head with multiple planes of transducer arrays
InactiveUS20060039082A1Manufacturing heads with multiple gapsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsLinear motionMagnetic tape
A tape recording head is provided comprising a multiple plane transducer row having a plurality of planes of transducer arrays fabricated on a substrate and which may be staggered or offset relative to one another in a direction perpendicular to the direction of linear motion of the recording tape over the recording head. The multiple plane recording head provides a significant advantage over a head having a single transducer plane by allowing simultaneous reading (or writing) of data tracks on a magnetic recording tape that are more closely spaced apart with respect to one another than the spacing of the read (or write) transducers in a single plane.
Owner:IBM CORP
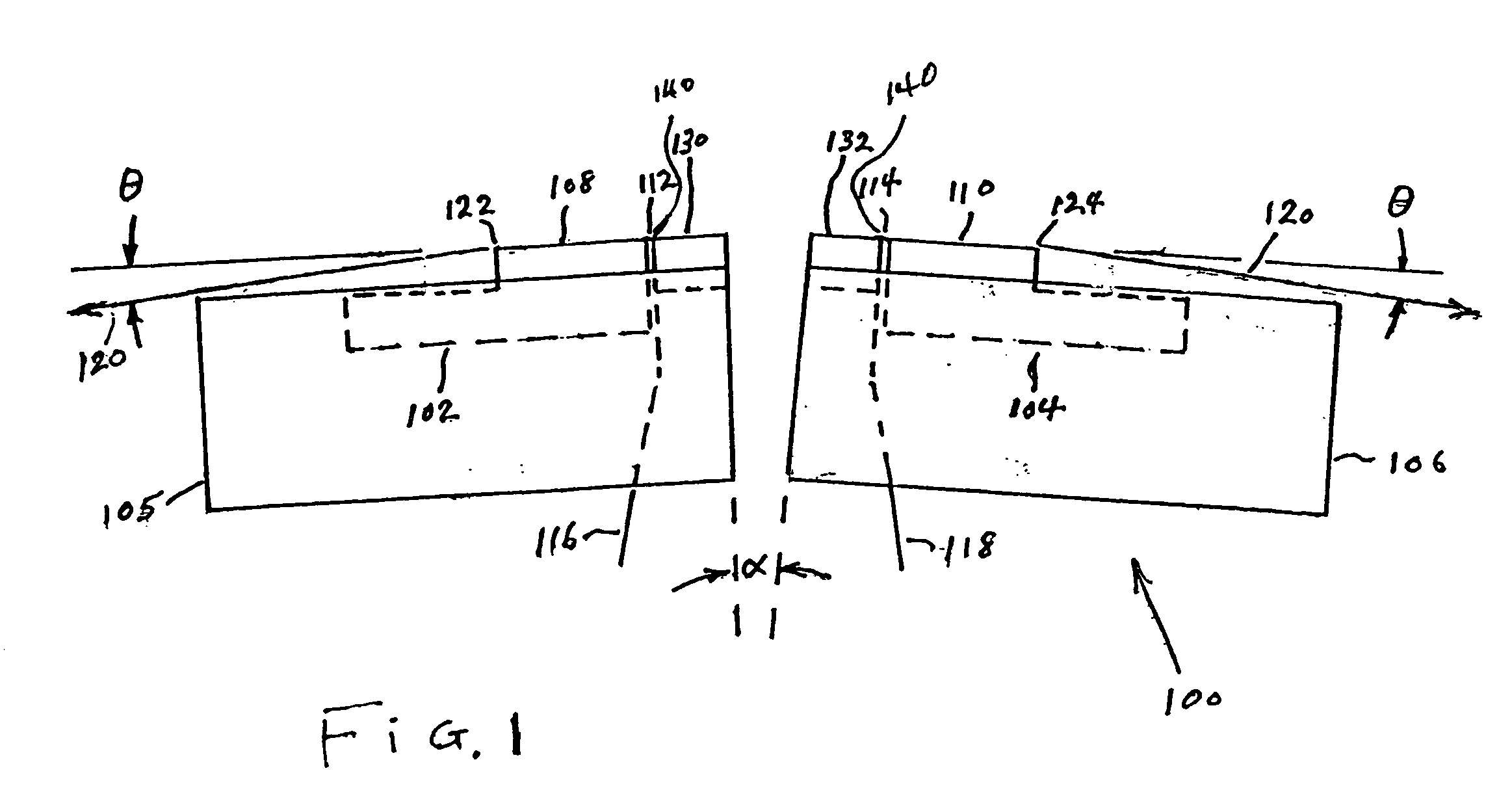
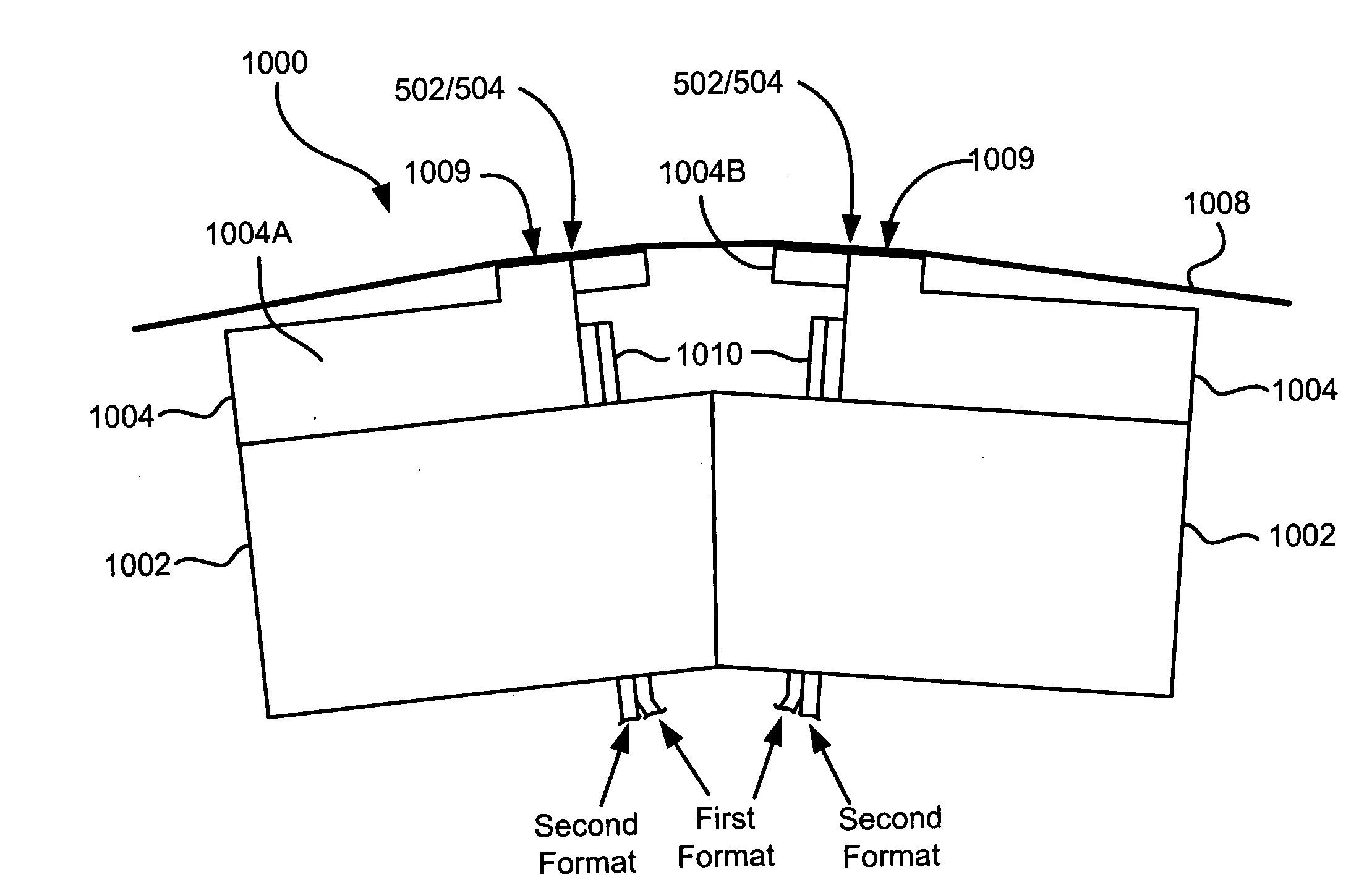
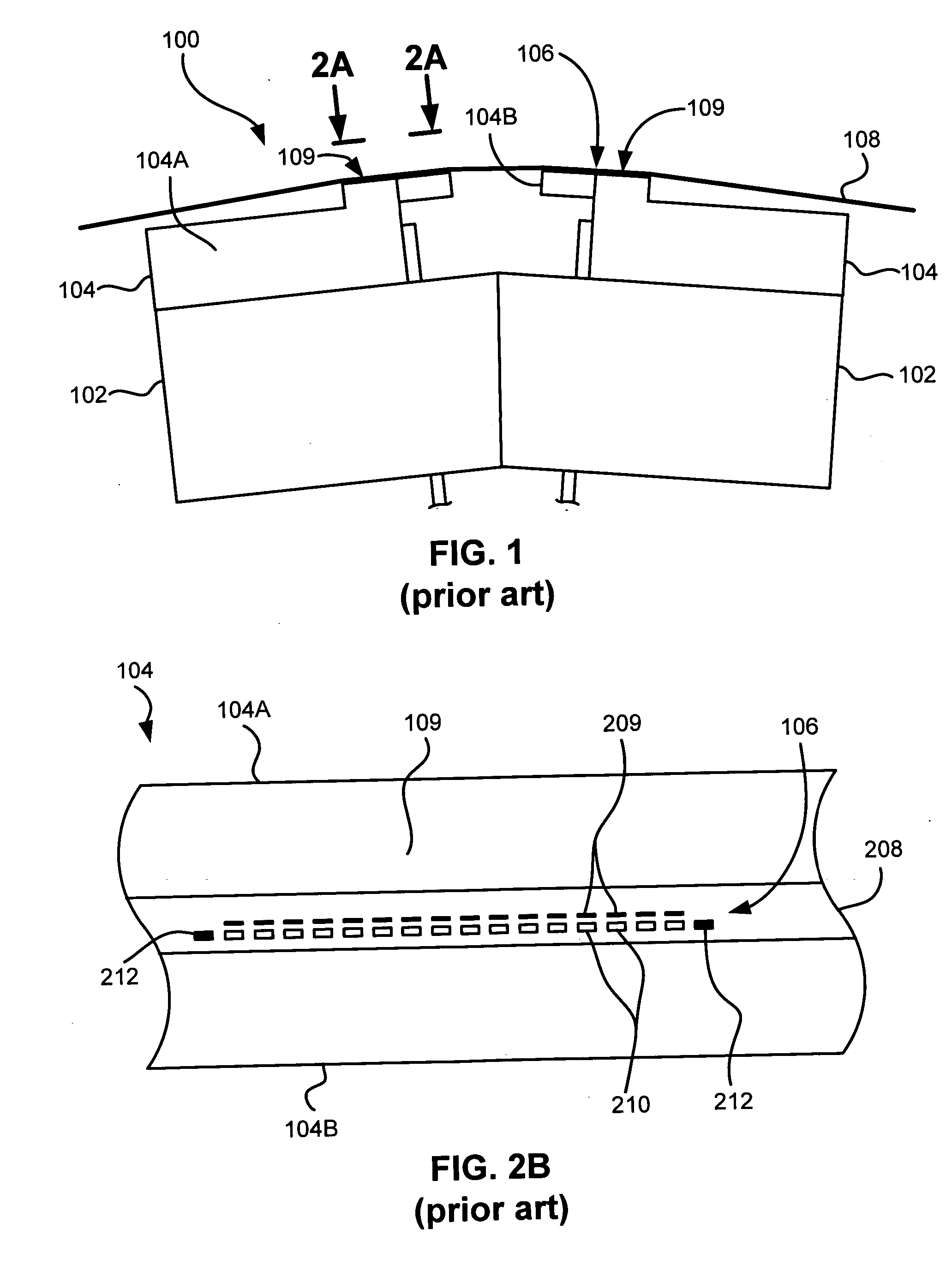
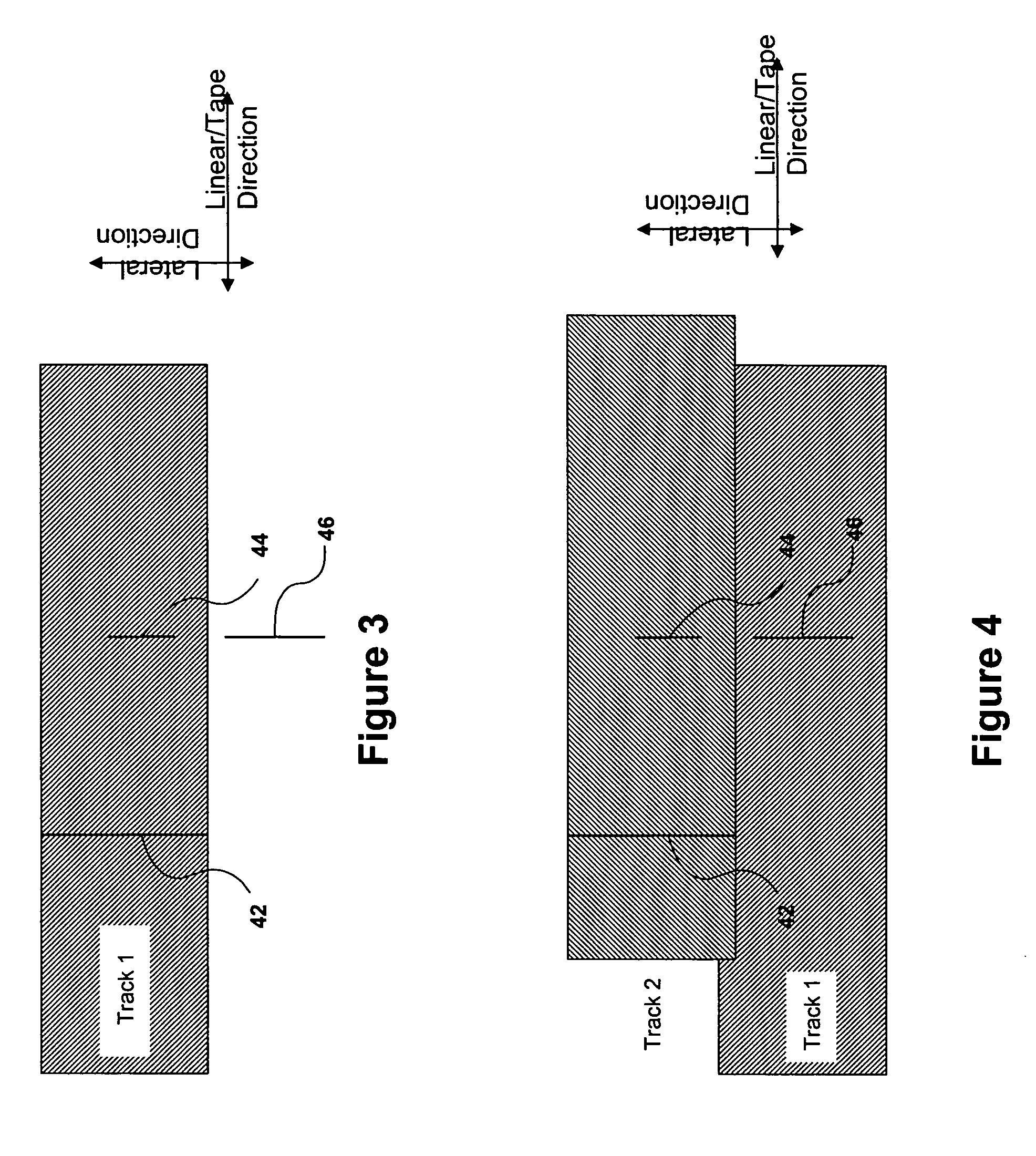
Multi-format magnetic head
A magnetic head includes a first array of elements associated with a first data format and a second array of elements associated with a second data format, the elements being selected from a group consisting of readers, writers, and combinations thereof. The first and second arrays of elements are adjacent each other in a direction transverse to a direction of travel of a magnetic medium over the head.
Owner:IBM CORP
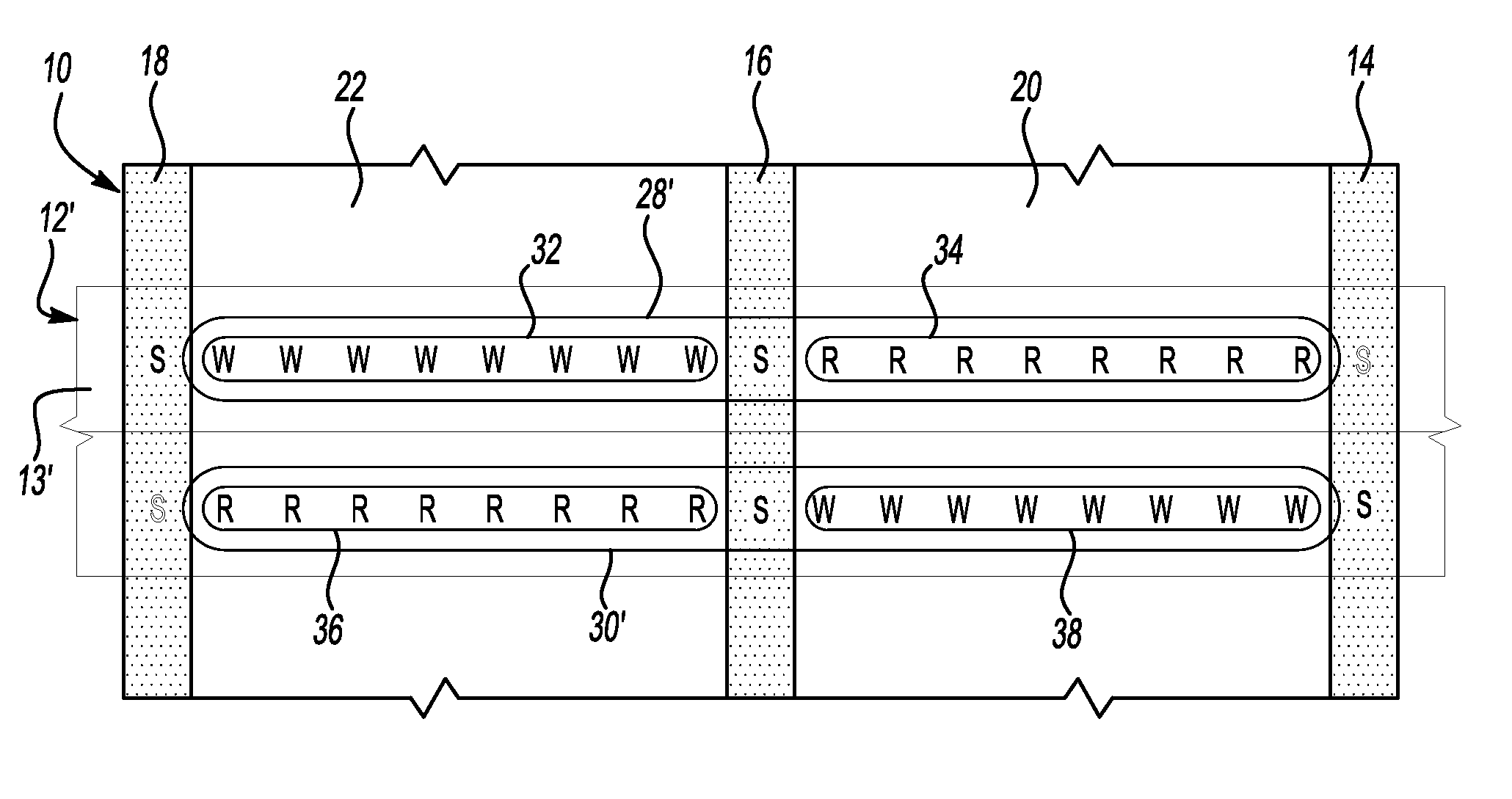
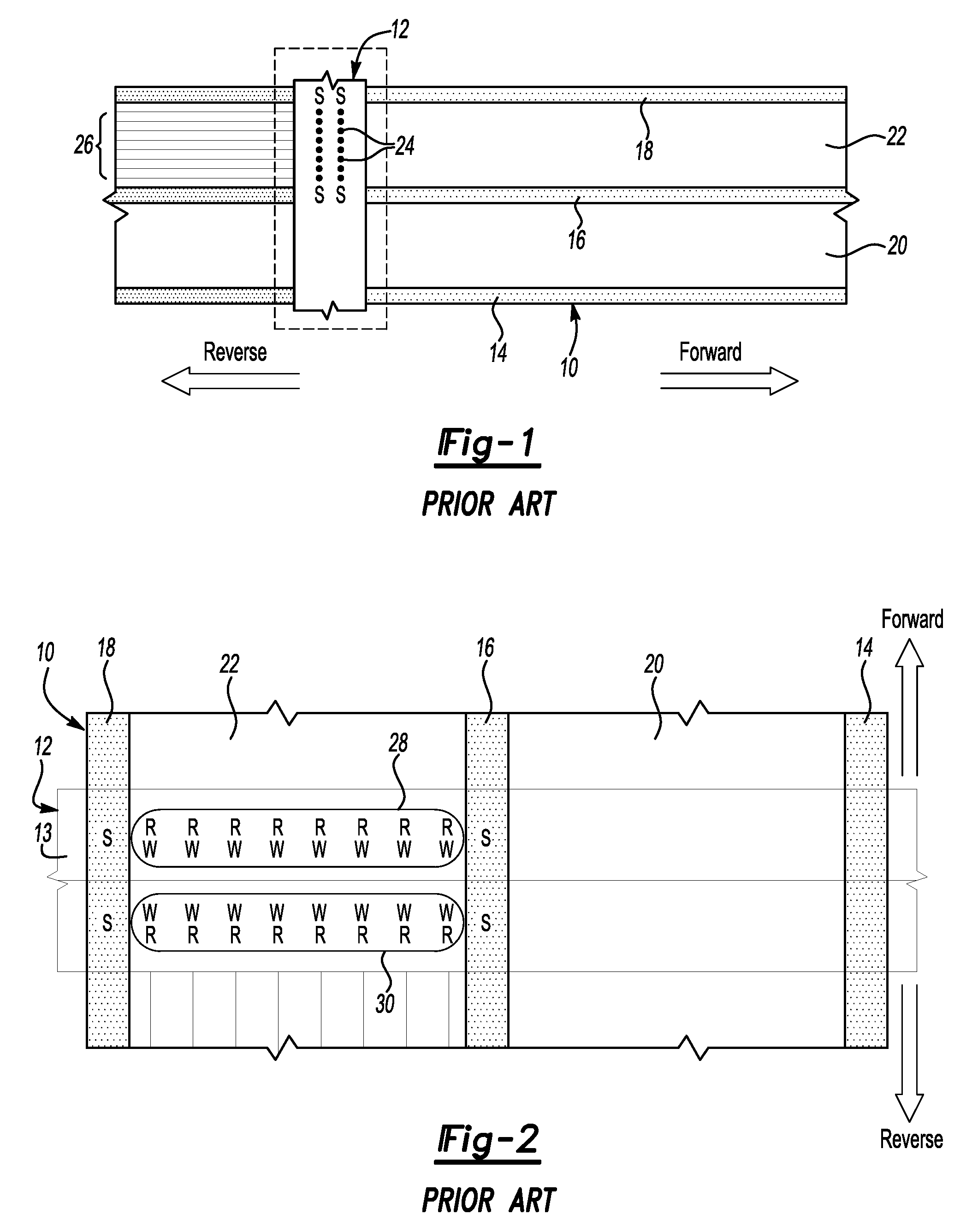
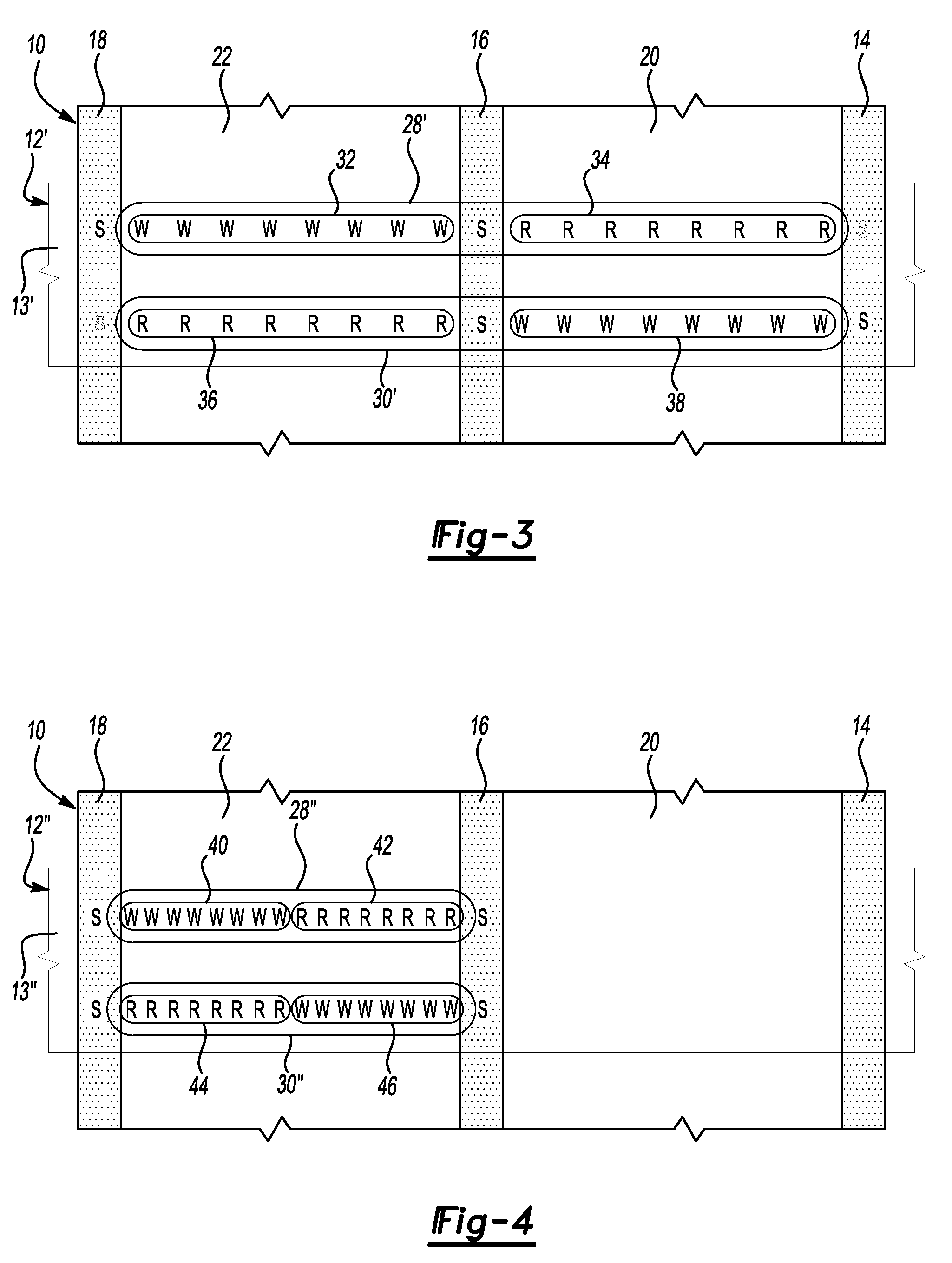
Hybrid servopositioning systems
InactiveUS6873487B2Driving/moving recording headsHeads using thin filmsData recordingComputer science
Servopositioning systems, methods, formats, and data recording media used in association with the same, employing both time-based and amplitude-based transverse tracking servo bands in the same or different locations on the medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
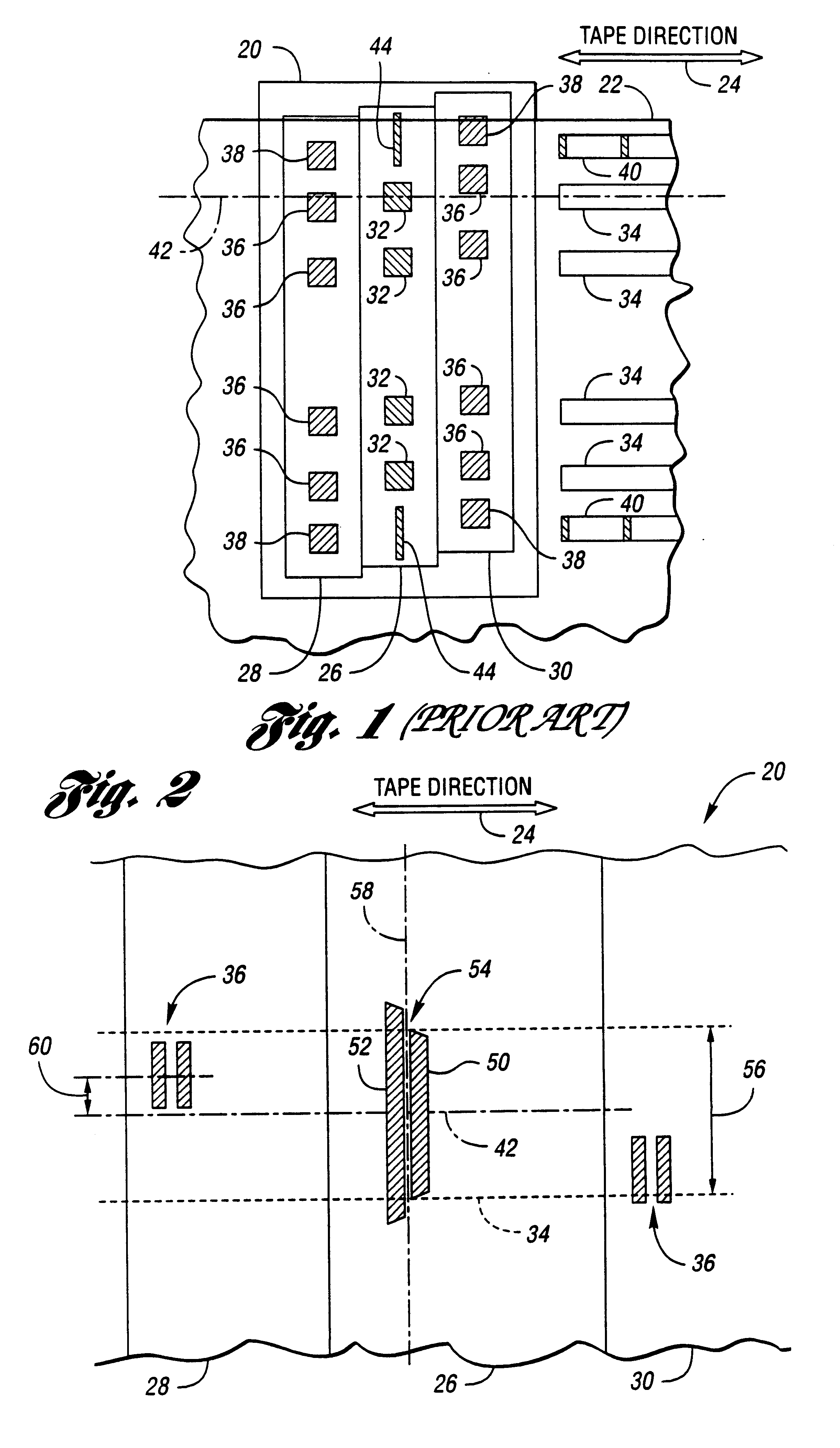
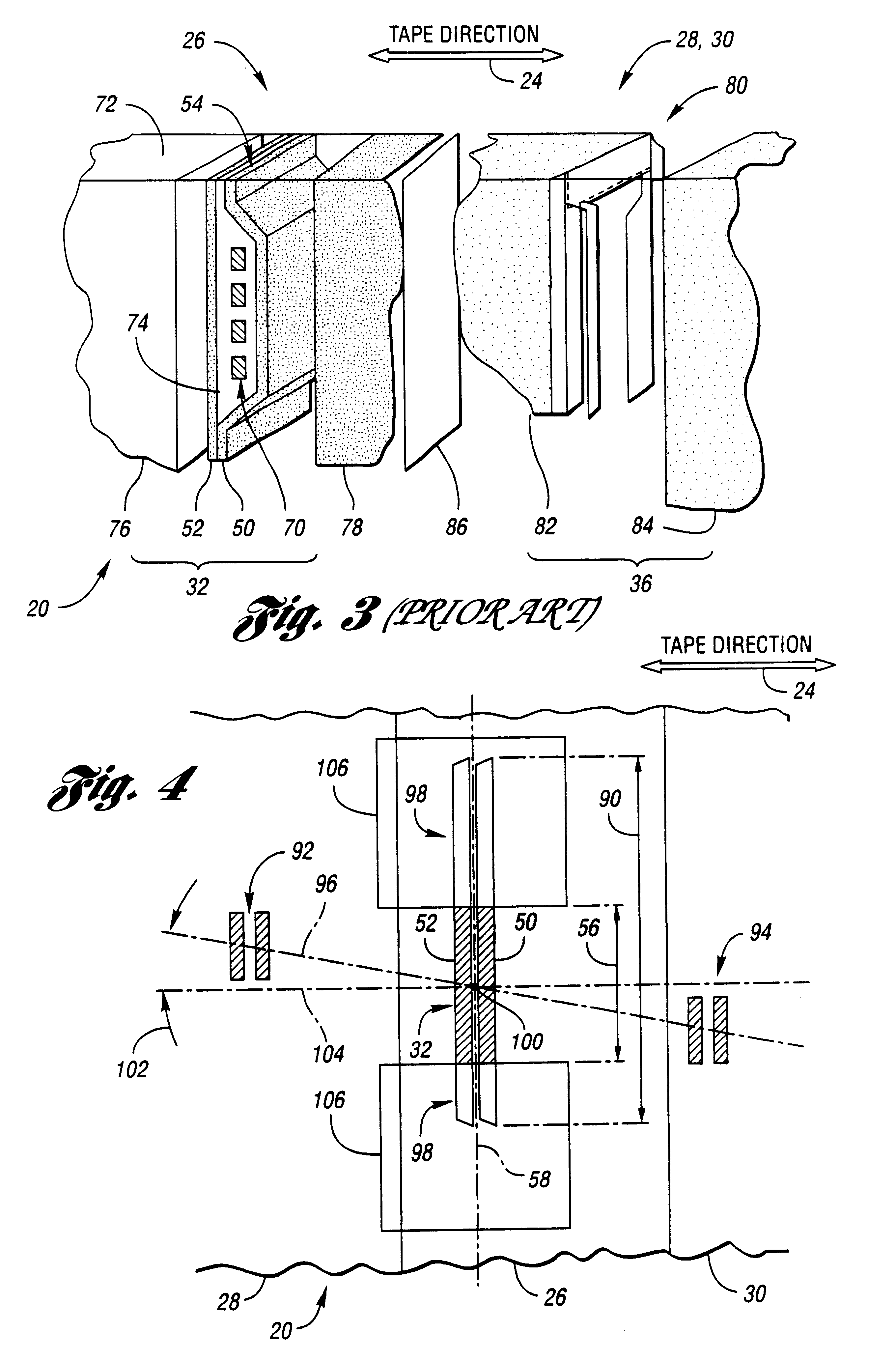
Apparatus and method for the control and positioning of magnetic recording heads in an azimuth recording system
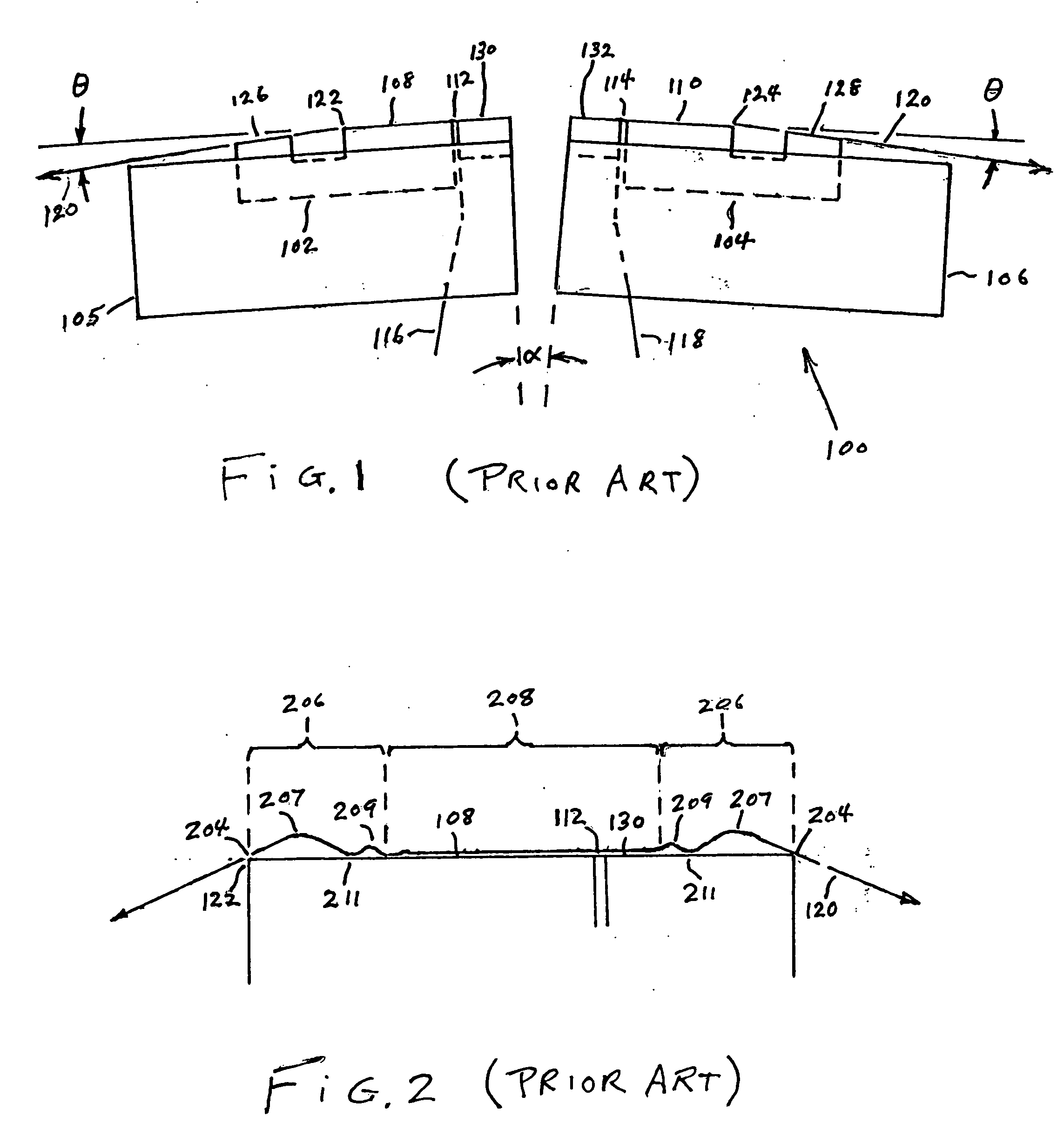
InactiveUS6088184AImprove recording densityImproved azimuthal recordingDriving/moving recording headsFilamentary/web record carriersMagnetic tapeRecording density
A magnetic recording apparatus and method for the azimuthal recording of data to and from data storage tracks contained on digital linear tape. The magnetic recording apparatus includes a magnetic data recording head assembly. A magnetic recording head is centrally located within the magnetic data recording head assembly. The magnetic data recording head assembly includes a control device coupled to a left servo sensor, wherein the left sensor is located to the left of and external to the magnetic recording head. The magnetic recording apparatus additionally includes a control device coupled to a right servo sensor, wherein the right servo sensor is located to the right of and external to the magnetic recording head. The left and right servo sensors assist the magnetic recording head to tilt and rotate at a predetermined angle with respect to a particular data storage track contained on a digital linear tape, during a recording operation, thereby increasing recording density and providing improved azimuthal recording.
Owner:IBM CORP
Large angle azimuth recording and head configurations
InactiveUS6947247B2Increasing overall tape data storage densitySuppress and eliminate adjacent track signalManufacture head surfaceDriving/moving recording headsComputer hardwareAzimuth
Large angle azimuth recording methods and devices. In one aspect of the invention methods of recording one or data tracks having data transitions oriented at a large azimuth angle are provided. In another aspect of the invention methods of reading a data track having data transitions oriented at a large azimuth angle are provided. Such methods include steps of suppressing a side track signal. In other aspects of the invention, head modules and devices for writing and / or reading large azimuth angle data tracks are provided.
Owner:ADVANCED RES
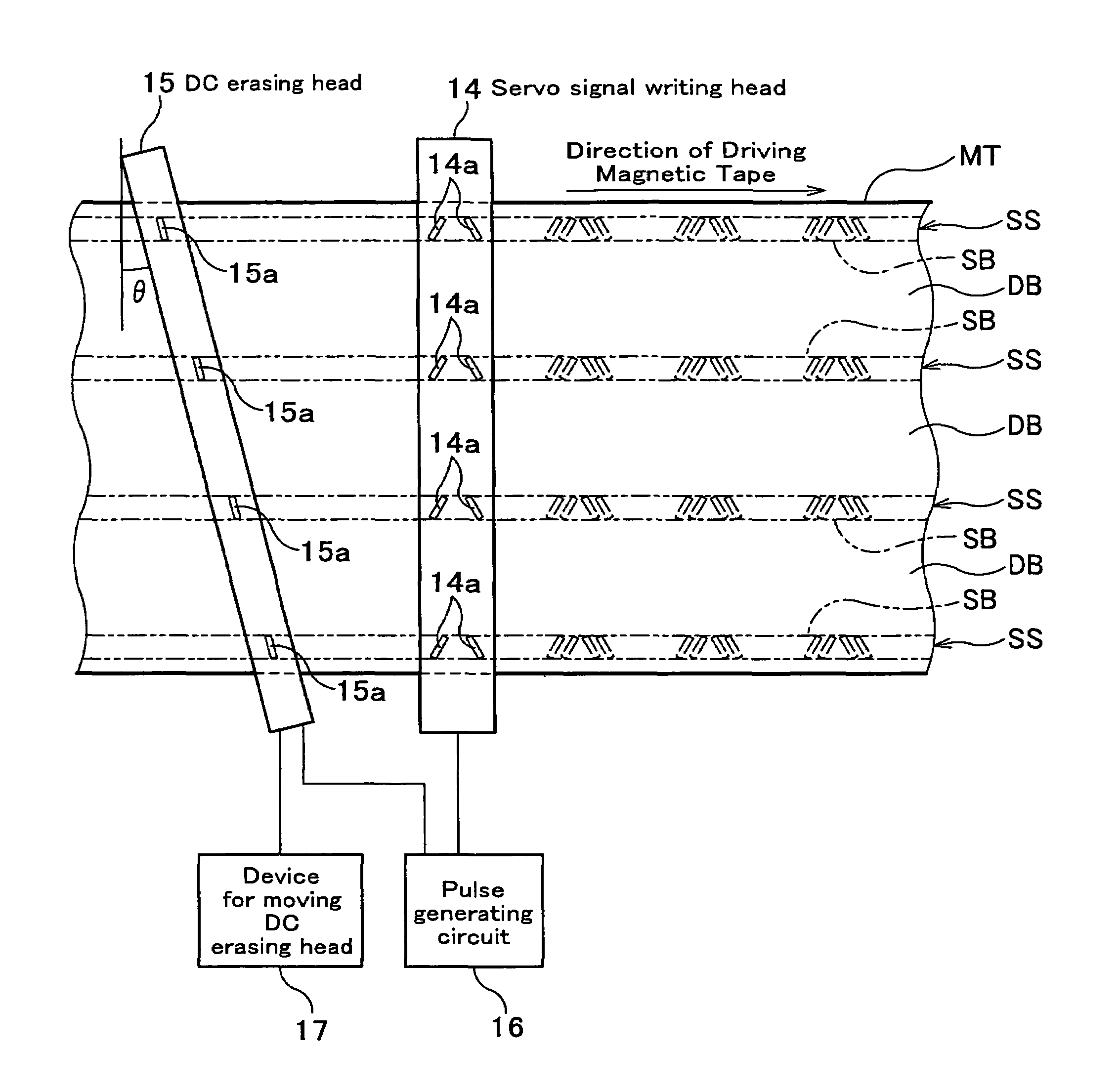
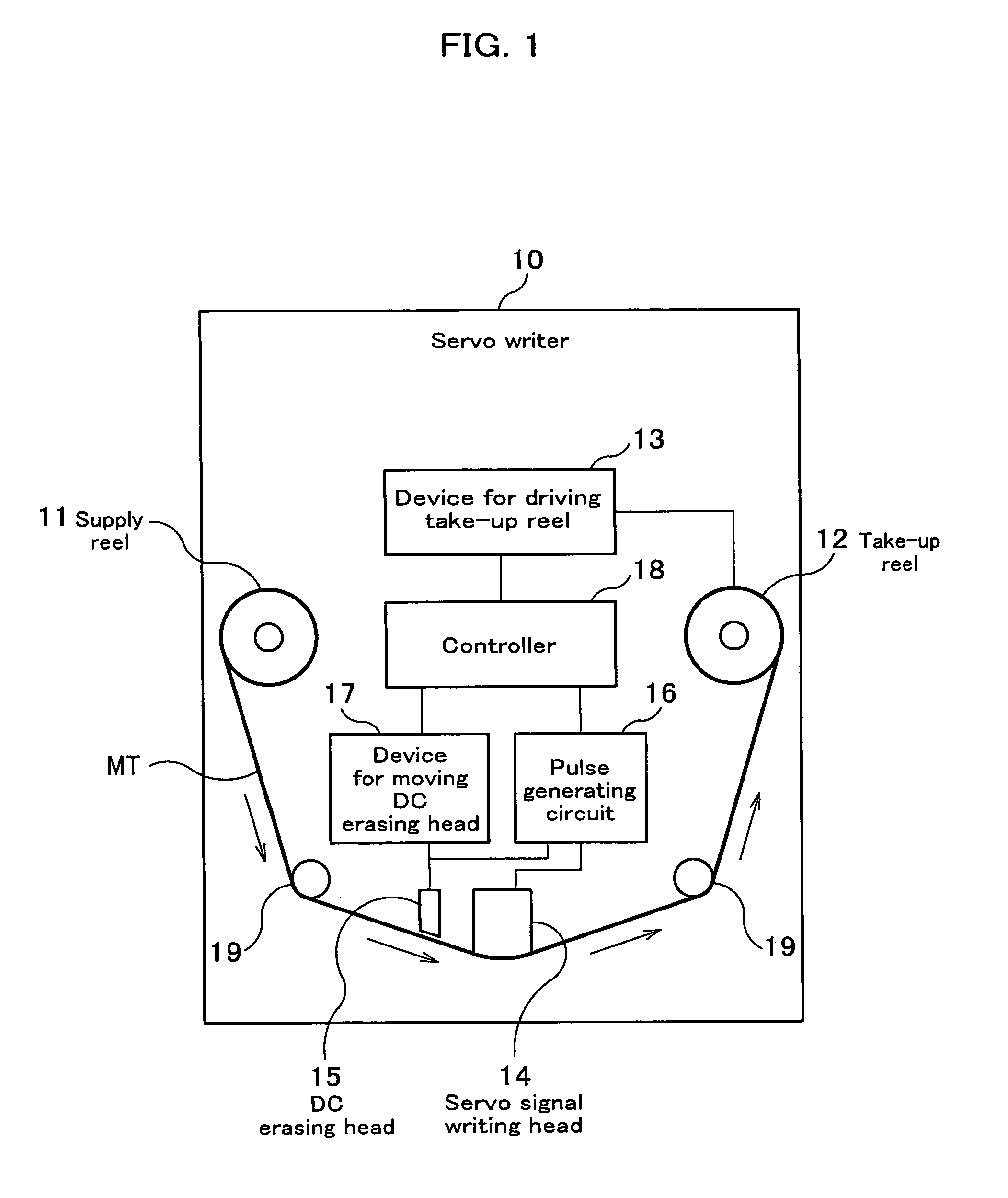
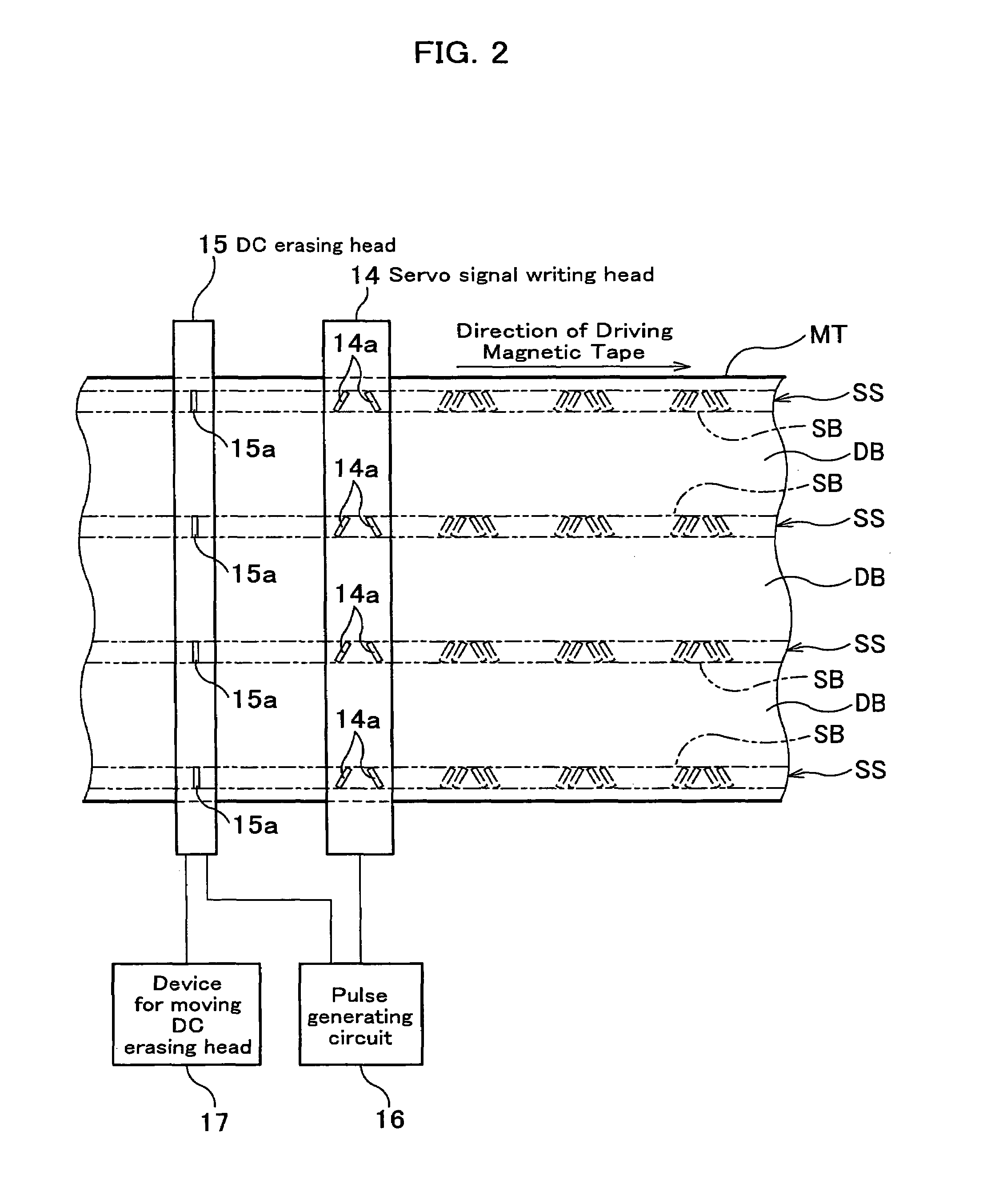
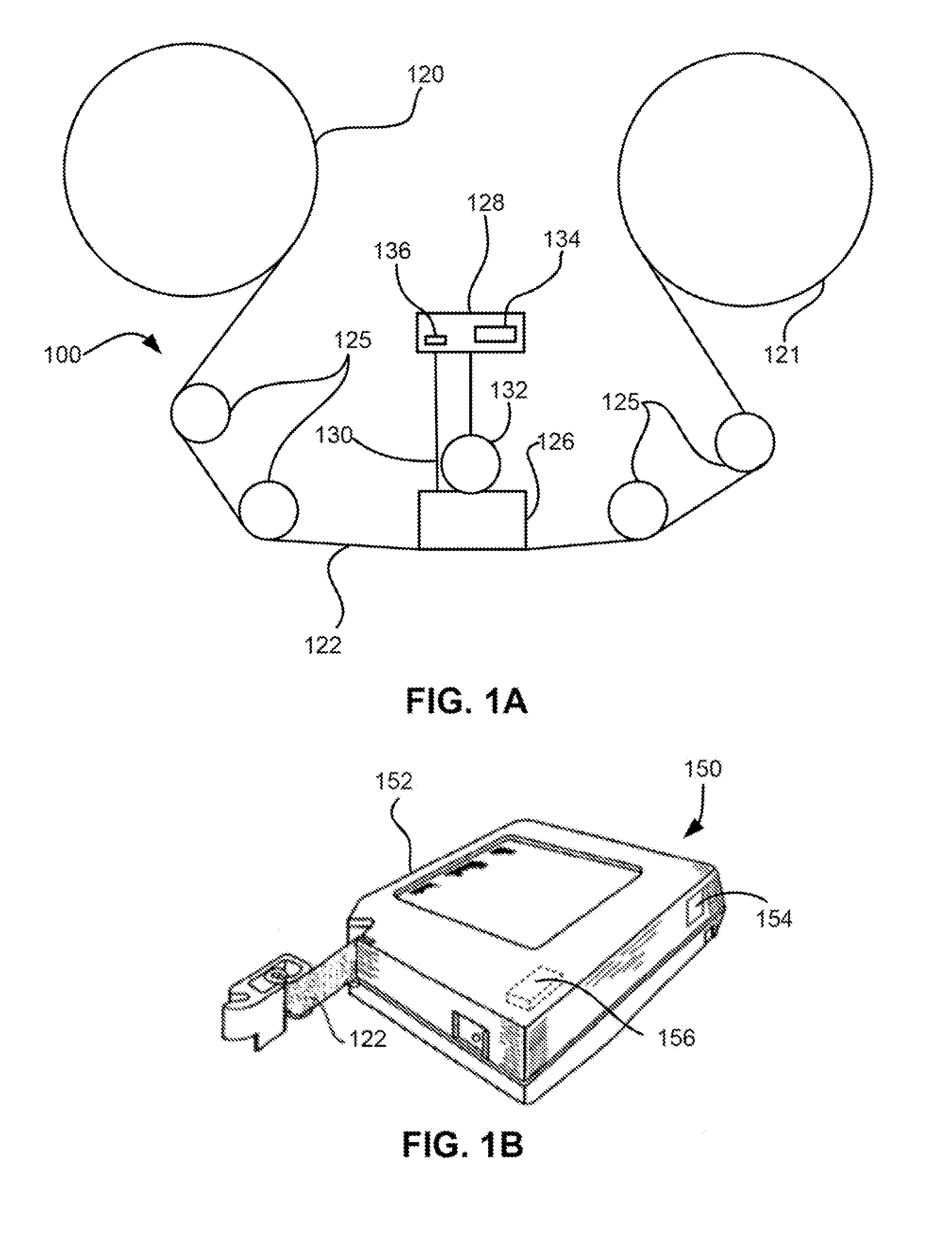
Servo writer and servo writing process
InactiveUS7142388B2Alignment for track following on tapesVacuum evaporation coatingSignal onMagnetic tape
A servo writer according to the present invention is a servo writer which writes a servo signal on a servo band of a magnetic tape. It comprises a magnetic tape driving system in which a magnetic tape supplied from a supply reel is taken up by a take-up reel to drive the magnetic tape; a DC erasing head which is slidably in contact with said driving tape and which DC-magnetizes said servo band with imparting an azimuth relative to said servo band; and a servo signal writing head provided on a downstream of said DC erasing head in the driving direction of the magnetic tape, which is slidably in contact with said driving tape and which magnetizes the servo band by a magnetizing force having a component with a reverse magnetizing force relative to the magnetizing force of the DC erasing head in the lengthwise direction of the magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Magnetic tape, magnetic tape cartridge, and magnetic tape apparatus
ActiveUS20200035262A1Magnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeRefractive index
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which an absolute value ΔN of a difference between a refractive index Nxy measured regarding an in-plane direction of the magnetic layer and a refractive index Nz measured regarding a thickness direction of the magnetic layer is 0.25 to 0.40, and a coefficient of friction measured regarding a base portion of a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.30, a magnetic tape cartridge and a magnetic tape apparatus including this magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
High track density magnetic recording head
ActiveUS7130152B1High track densityMade preciselyManufacturing heads with multiple gapsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsTrack densityMagnetic media
Closer spacing of elements for writing multiple tracks onto a magnetic media increases the areal density of stored information. A thin film multiple track recording head includes recording gaps in a plane parallel with the head substrate. This configuration allows for flexible placement of the elements within the head, improved control of recording gap geometry, and alternating azimuth gap angles.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
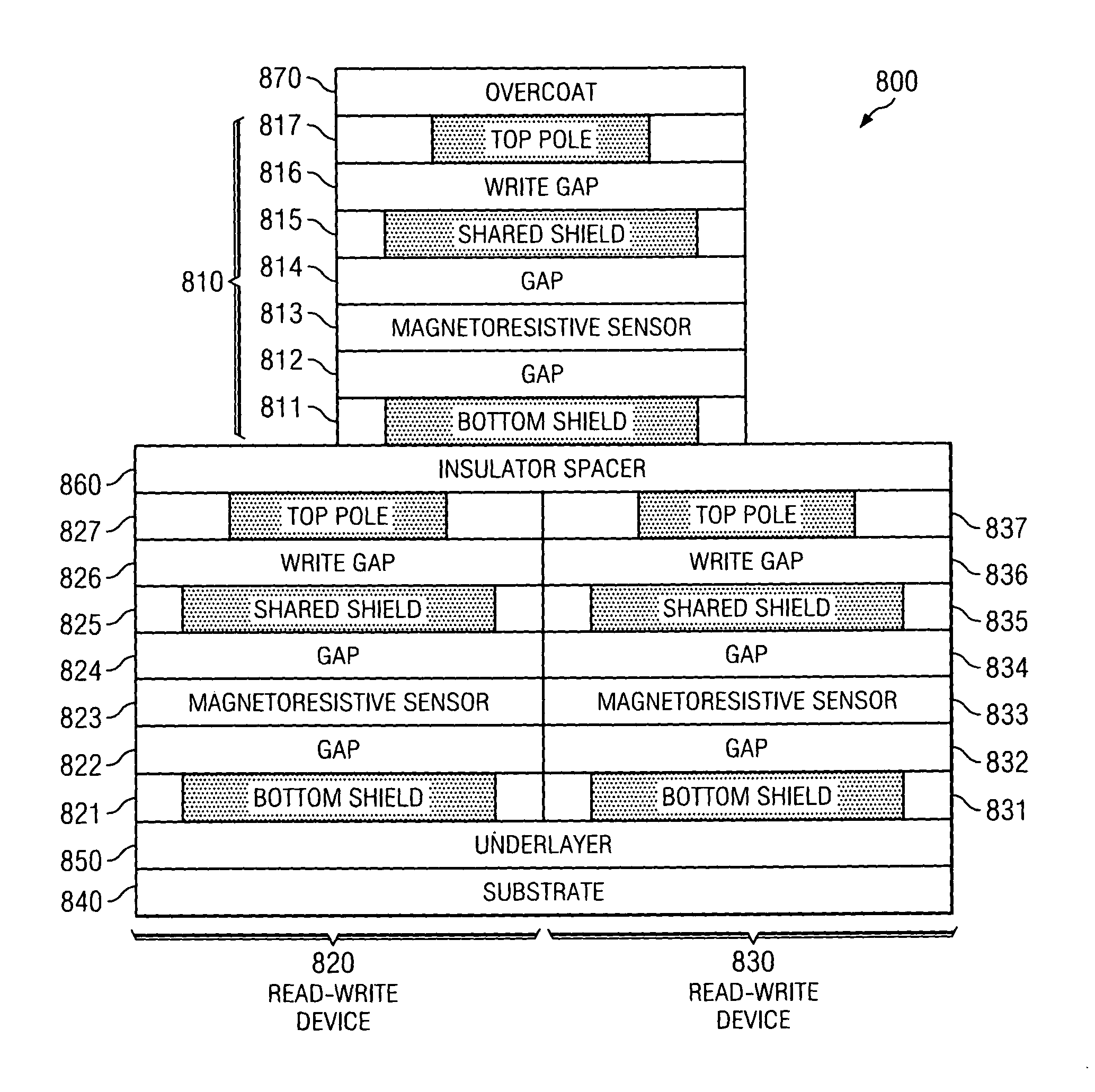
Magnetic recording head having protected reader sensors and near zero recessed write poles
InactiveUS20140063646A1Manufacture head surfaceDriving/moving recording headsComputer hardwareMagnetic poles
A magnetic head according to one embodiment includes a module, the module having both read and write transducers positioned towards a media facing side of the module, wherein the read and write transducers are selected from a group consisting of piggyback read-write transducers, merged read-write transducers, interleaved read and write transducers, and an array of write transducers flanked by servo read transducers; wherein the write transducers include write poles having media facing sides with negative, zero or near-zero recession from a plane extending along the media facing side of a substrate of the module; wherein the read transducers each have at least one shield, wherein a media facing side of the at least one shield is more recessed from the plane than the write poles.
Owner:IBM CORP
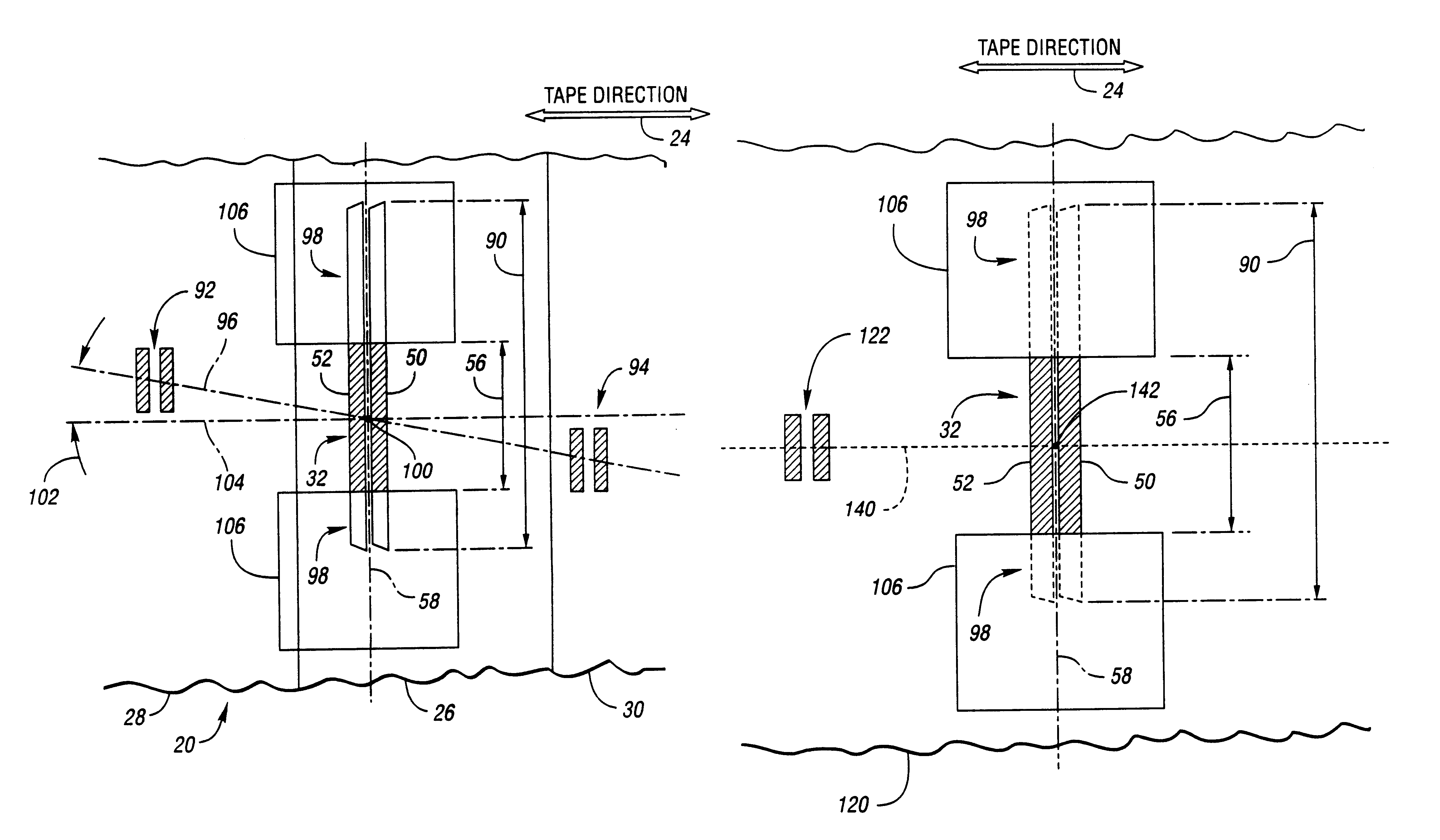
Quasi-statically oriented, bi-directional tape recording head
InactiveUS20140327983A1Driving/moving recording headsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsSensor arrayMagnetic tape
Owner:IBM CORP
Tape recording head with multiple planes of transducer arrays
InactiveUS7551393B2Manufacturing heads with multiple gapsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsLinear motionMagnetic tape
A tape recording head is provided comprising a multiple plane transducer row having a plurality of planes of transducer arrays fabricated on a substrate and which may be staggered or offset relative to one another in a direction perpendicular to the direction of linear motion of the recording tape over the recording head. The multiple plane recording head provides a significant advantage over a head having a single transducer plane by allowing simultaneous reading (or writing) of data tracks on a magnetic recording tape that are more closely spaced apart with respect to one another than the spacing of the read (or write) transducers in a single plane.
Owner:IBM CORP
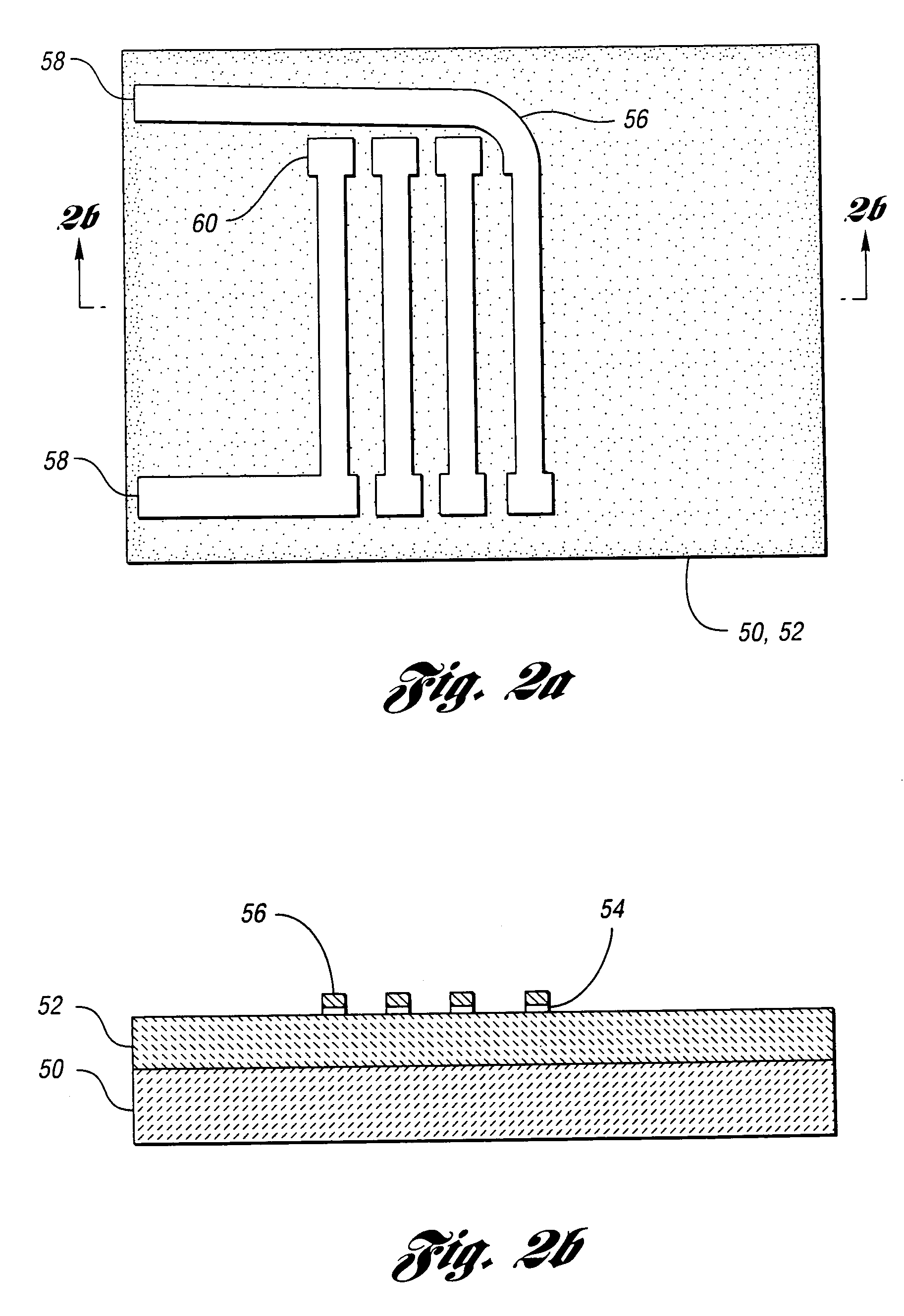
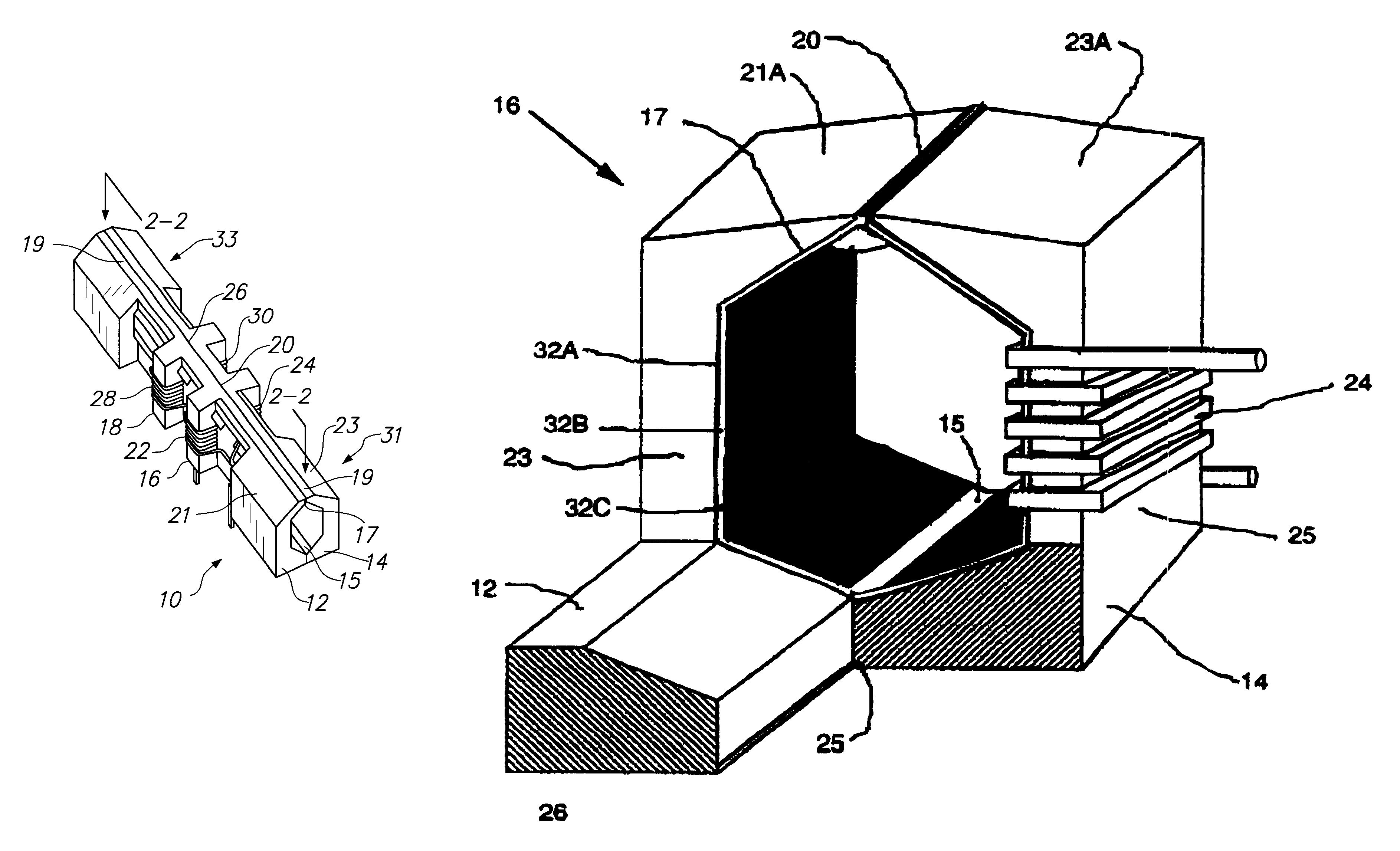
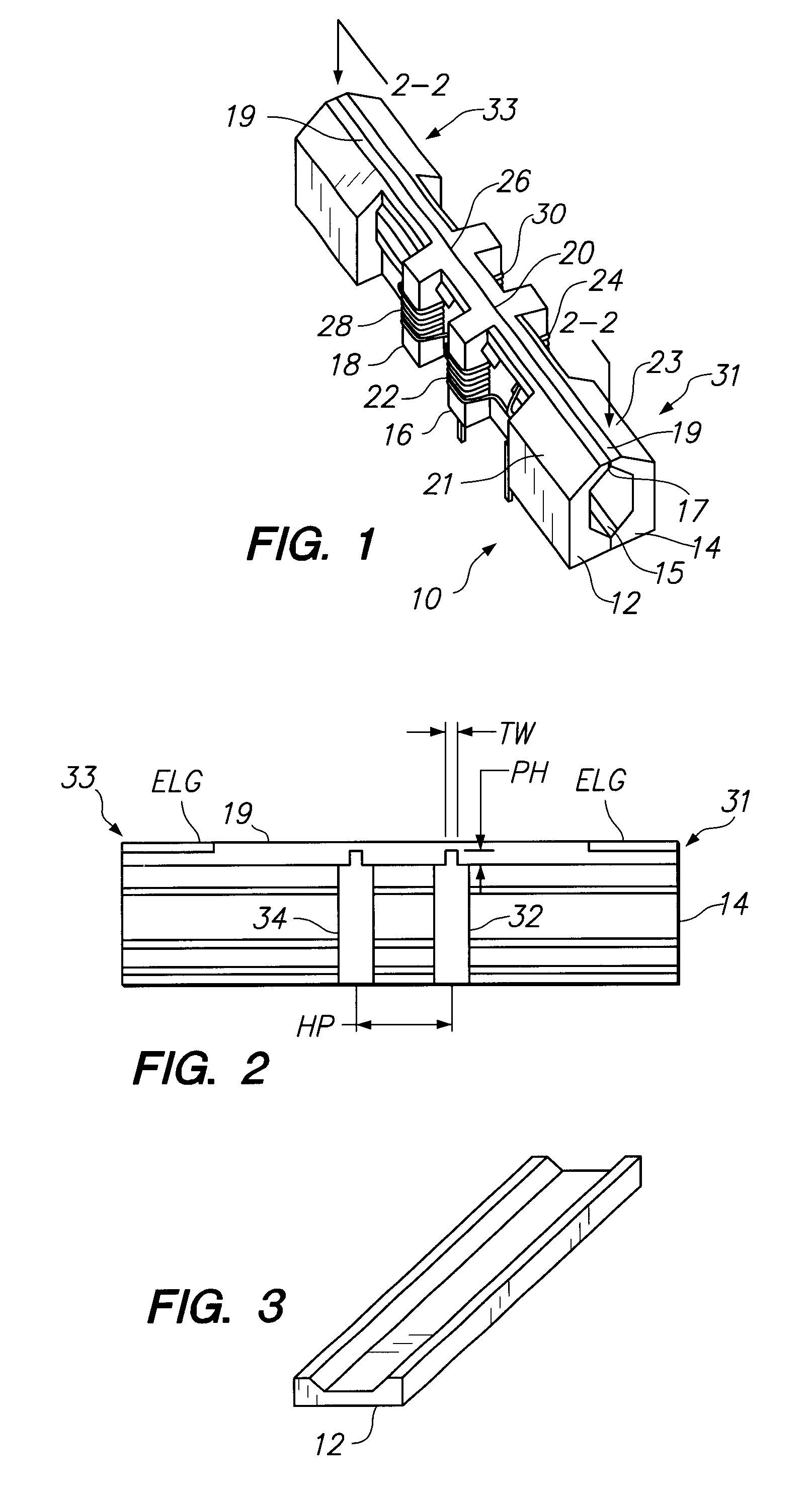
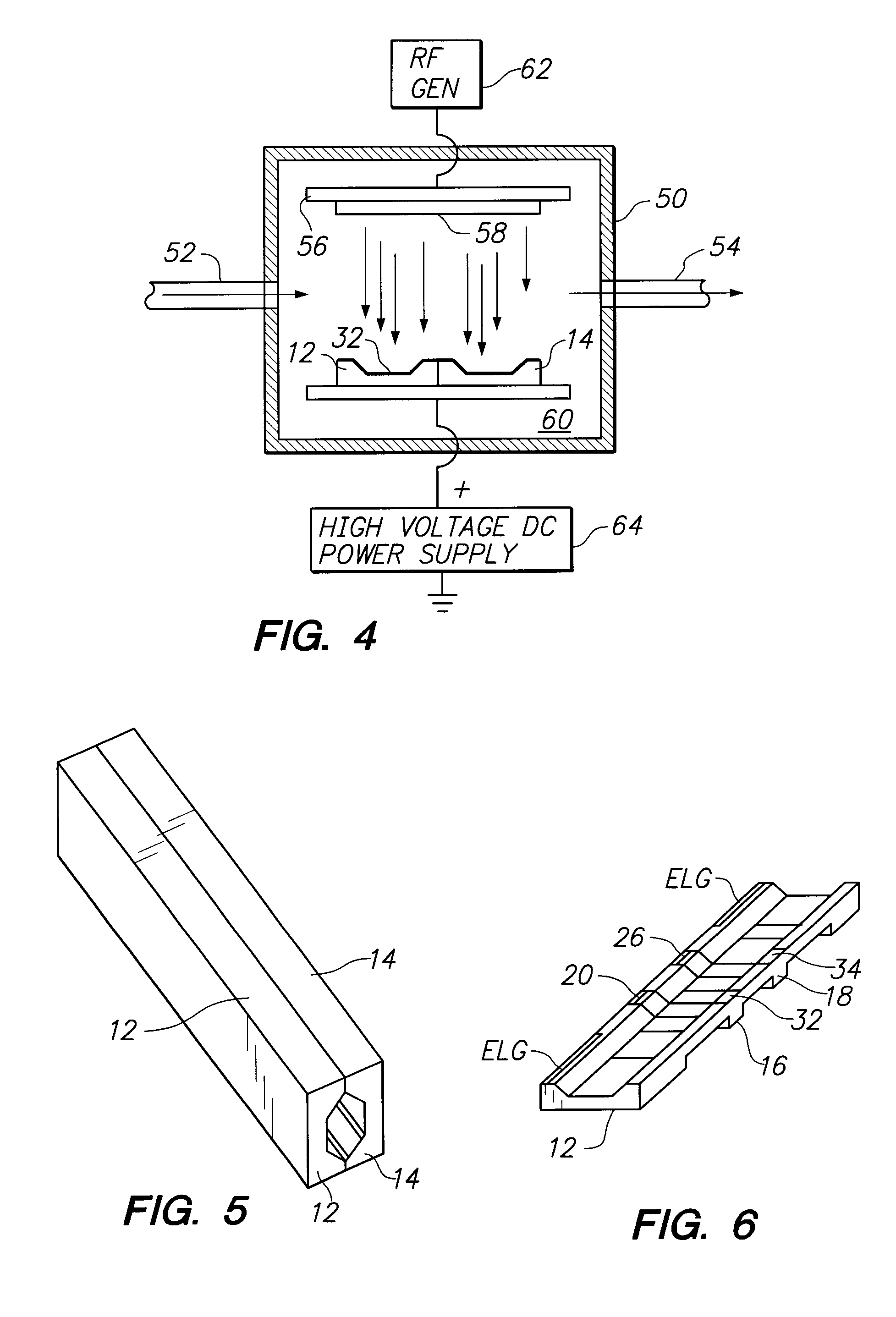
Self-aligned metal film core multi-channel recording head for tape drives
InactiveUS6288870B1Improve high frequency performanceManufacture head surfaceManufacturing heads with multiple gapsMagnetic transducersEngineering
A self-aligned multi-channel tape head structure has a non-magnetic ceramic substrate defining an interior longitudinal channel and a plurality of head regions. At least one head leg at each region defines lateral openings to the interior longitudinal channel. Each head region has a thin-film metal magnetic core deposited on an inside wall surface of the ceramic substrate and a magnetic gap in a longitudinal face of the ceramic substrate. A coil of wire is wound around each head leg to provide a magnetic transducer head at each head region.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Wear pads for timing-based surface film servo heads
InactiveUS6989960B2Avoid negative effectsQuick wearElectrical transducersManufacture head surfaceEngineeringBearing surface
A thin film magnetic recording head is provided with a tape bearing surface that has magnetically isolated channels while still providing a maximum continuous surface area with which to engage the media. This can be accomplished by providing spaces in the magnetically permeable thin film that are large enough to prevent cross-talk between the channels, but small enough to prevent significant interference with the moving media. Alternatively, magnetically impermeable thin film spacers can be provided to magnetically isolate each of the channels. The spacers are generally even with the magnetically permeable thin film so as to provide a continuous media-bearing surface.
Owner:ADVANCED RES
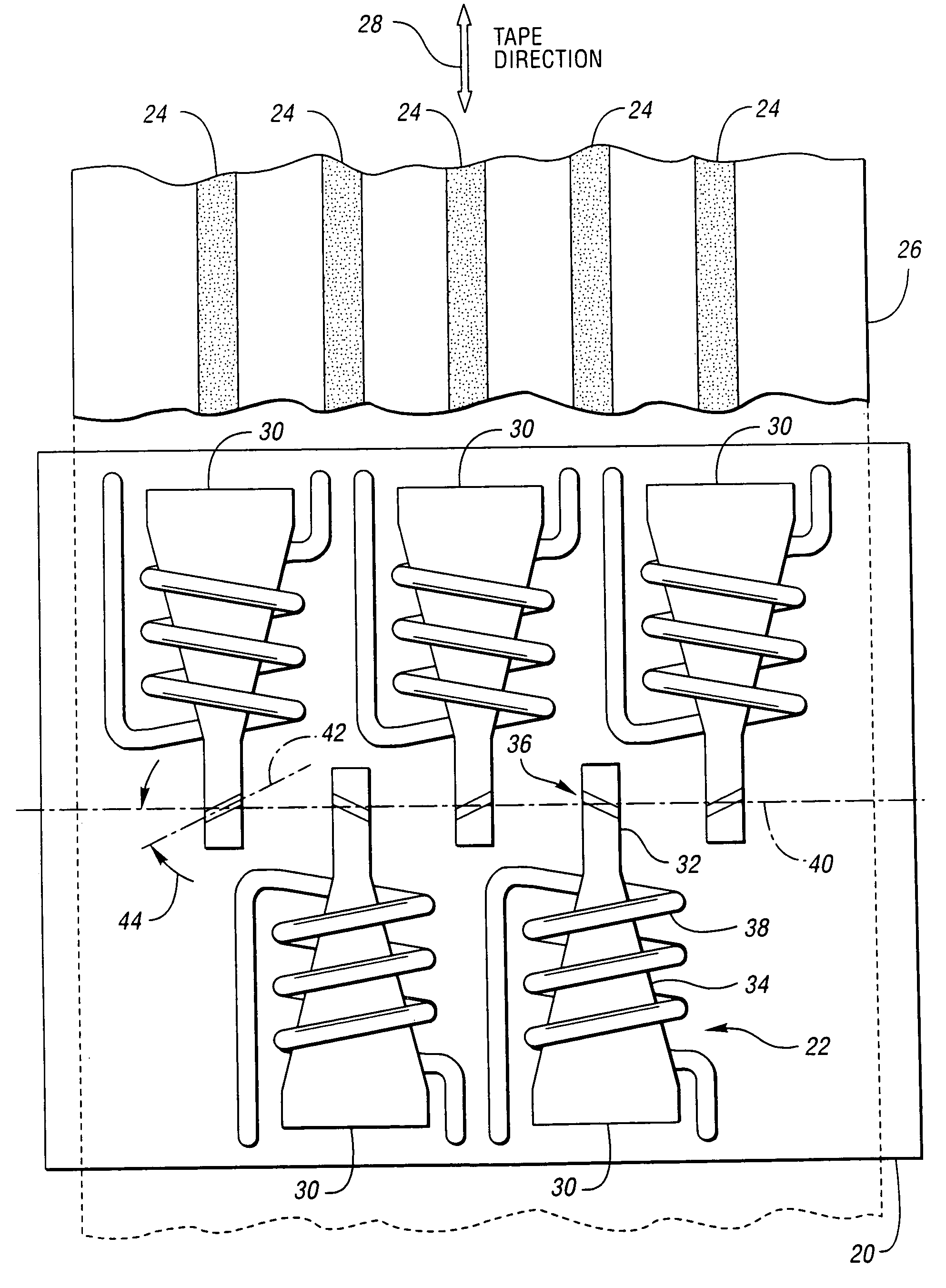
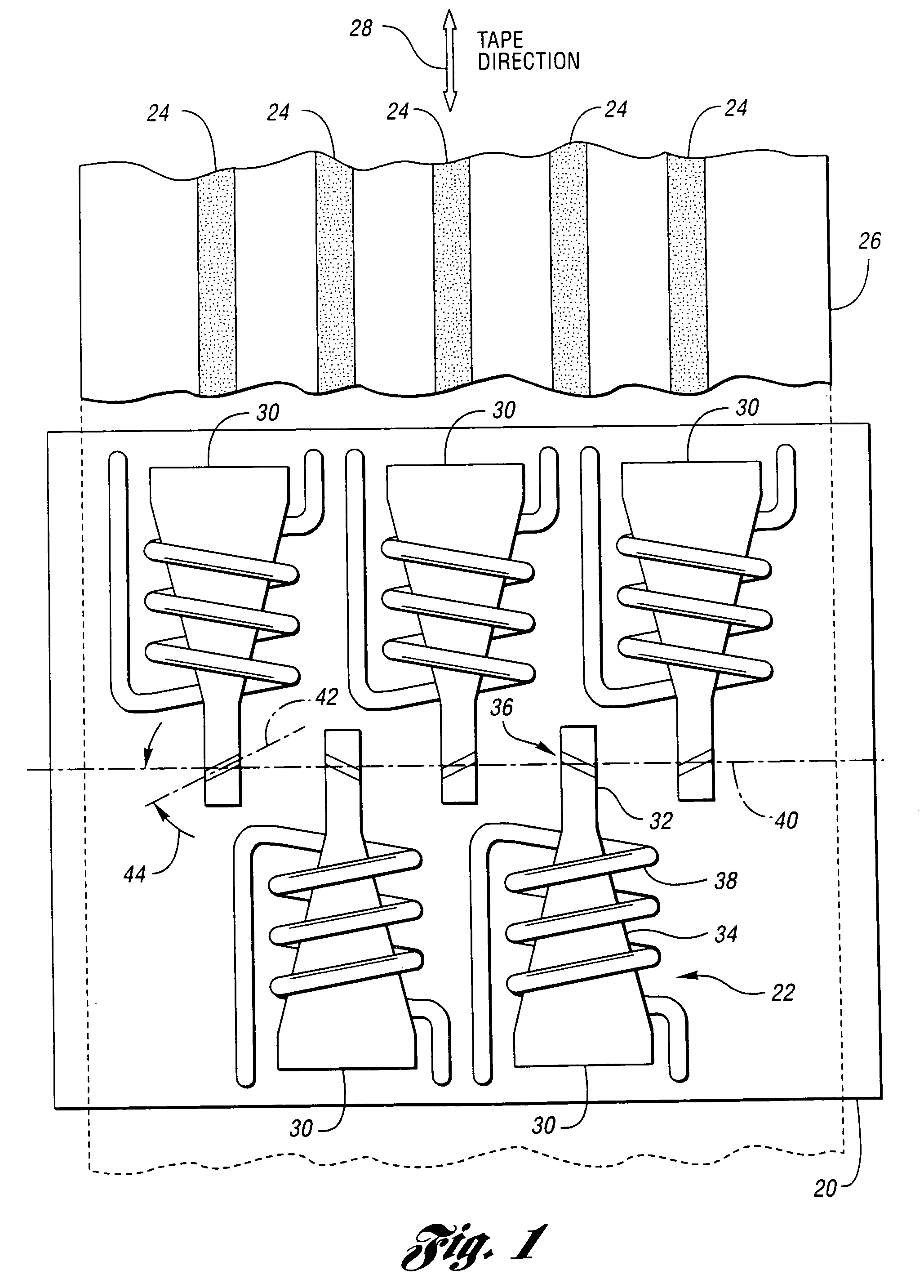
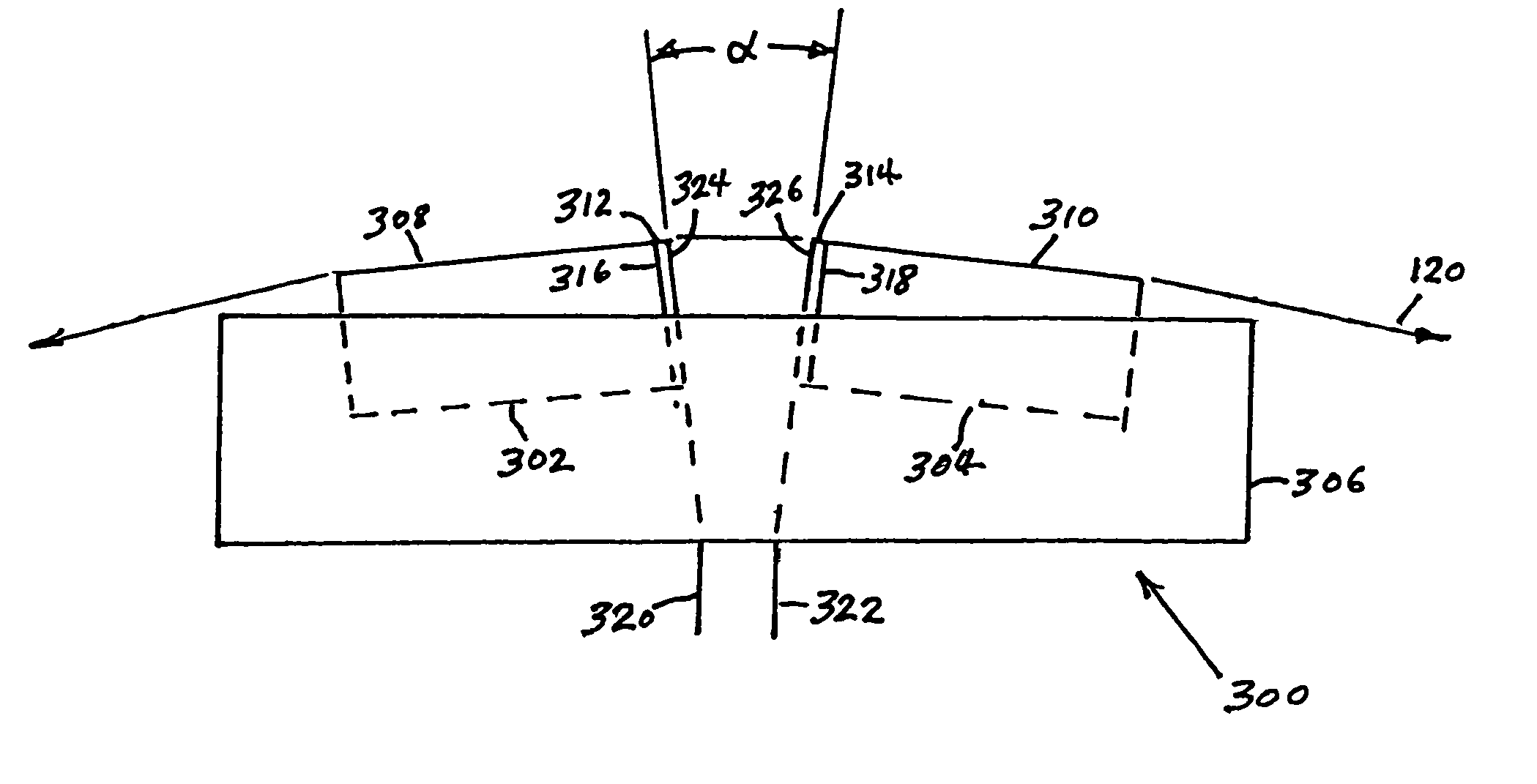
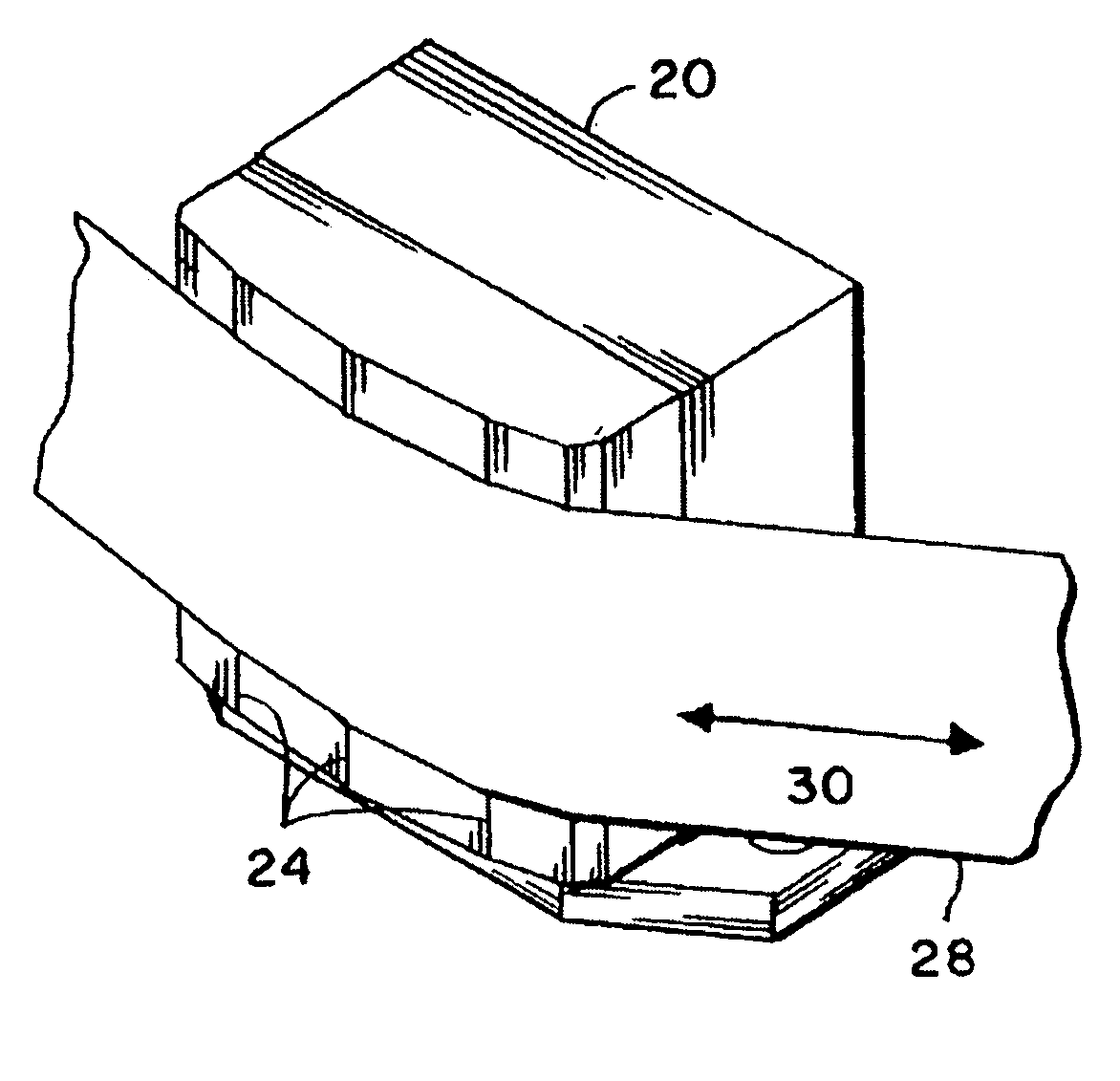
Compression zone recording head
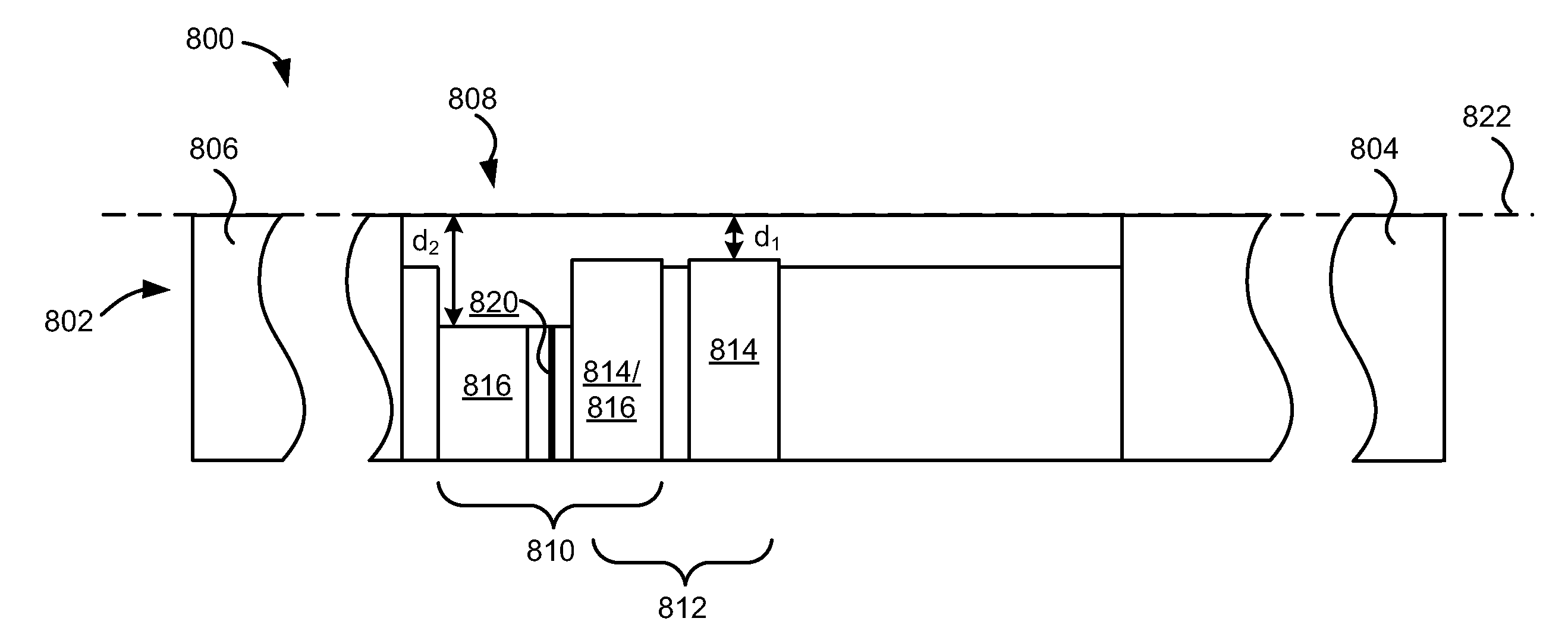
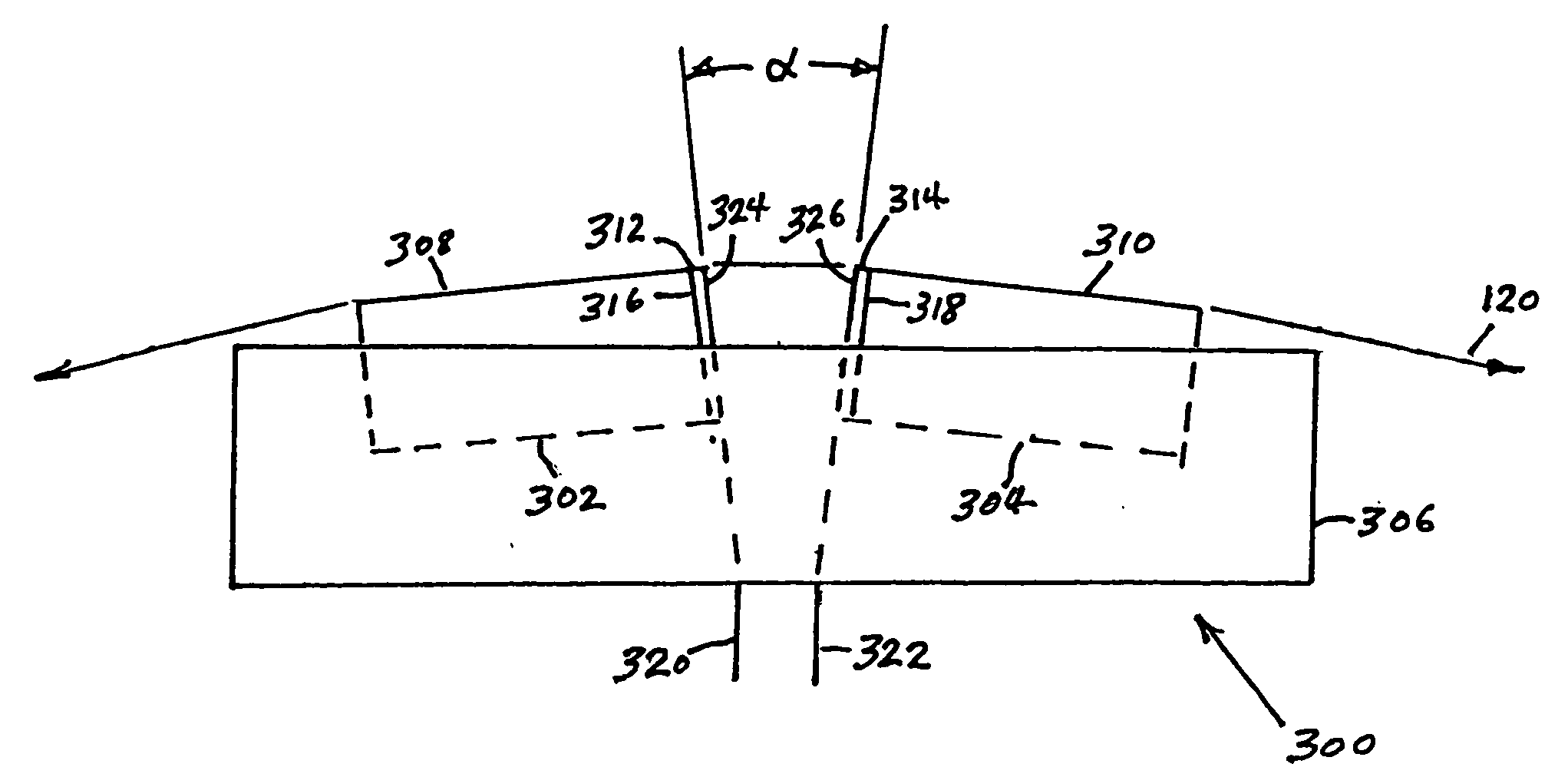
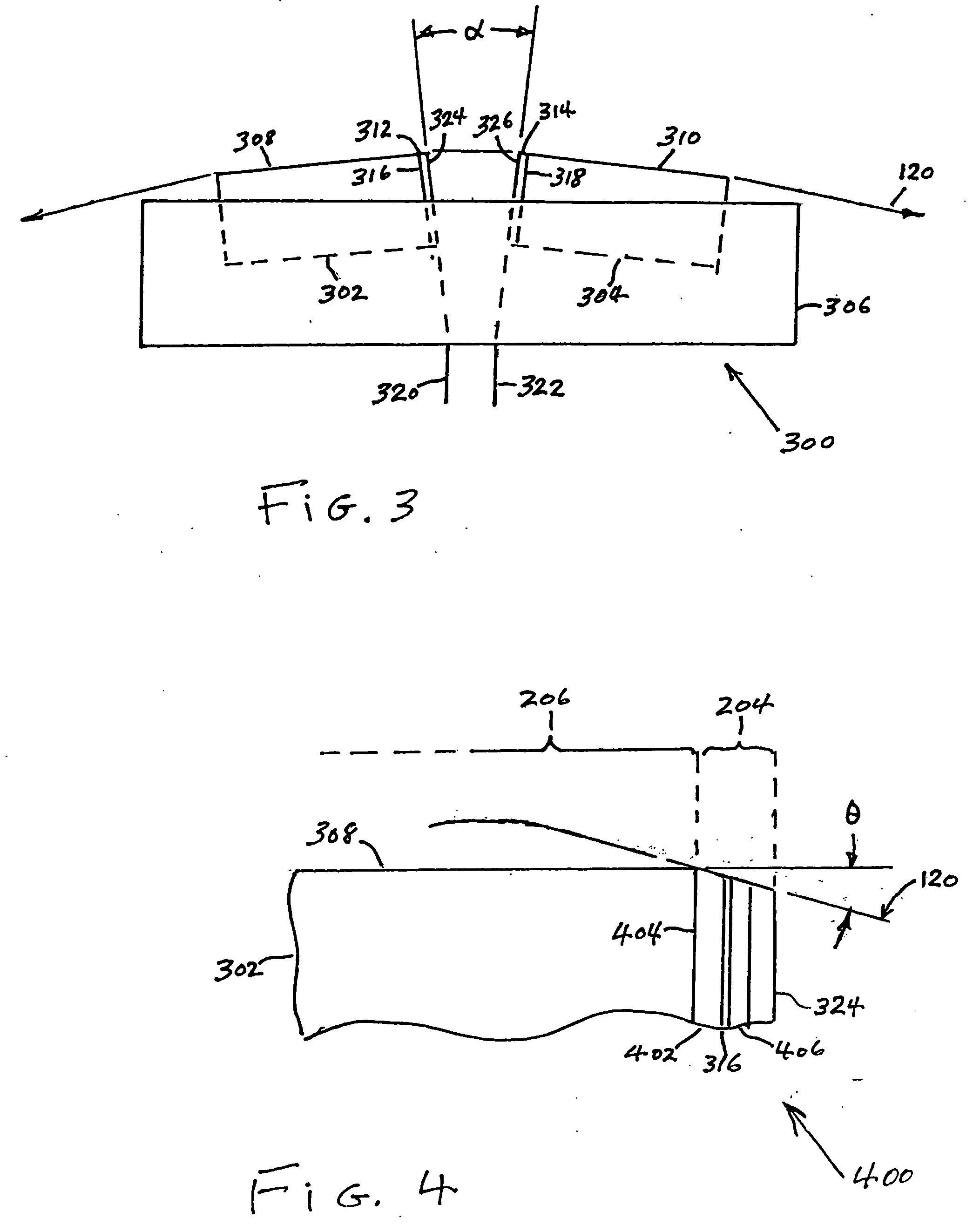
InactiveUS7248438B2Reduce manufacturing costFlying lowRecord information storageHeads relative to moving tapeTransducerSputter deposition
A compression zone recording head is provided having the recording tape in contact or near contact with the recording read / write transducer elements in a compression zone of the tape passing over a transducing surface. The compression zone recording head comprises a flat or shallow contour head having a thin, hard, preferably conducting closure to provide wear protection to the transducers. In one embodiment of the invention, the transducers are located in a compression zone region where the recording tape contacts an edge of the transducing surface at a controlled wrap angle. In another embodiment, the transducers are located in a canopy zone region of the transducing surface due to bending of the tape due to the overwrap. The protective closure is preferably made of sputter deposited Al—Fe—Si, or alternatively of a deposited or bonded layer of Al—Fe—Si, Al—O—Ti—C, Zr—O—Ti, Si—N, Si—C or Zr—O.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Multi-level, multi-track magnetic recording head
ActiveUS7751148B1Manufacturing heads with multiple gapsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsEngineeringRecording media
In at least one embodiment, a magnetic recording head comprising first and second linear levels of magnetic recording devices is provided. Each device in the first linear level is aligned adjacently in a row and is spaced apart from another device in the first linear level. The first linear level is perpendicular to a comparative direction of a recording media travel. The second linear level of magnetic recording devices being connected to the first linear level of magnetic recording devices. Each device in the second linear level is aligned adjacently in a row and is spaced apart from another device in the second linear level. Each device in the second linear level is aligned with an insulating gap between the each device in the first linear level.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Highly aligned thin film tape head
InactiveUS6496329B2Improved tape head element alignmentEasy alignmentManufacturing heads with multiple gapsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsComputer hardwareData density
Reducing alignment errors between a read element and corresponding write elements permits narrower data tracks and, hence, greater data density on magnetic tape. A method for manufacturing a thin film tape head having multiple write elements and at least one read element corresponding to each write element is provided. Excess material is trimmed from each write element to align the write element with corresponding read elements. The excess material may be track trimmed using a focused ion beam.
Owner:STORAGE TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Compression zone recording head
InactiveUS20050128640A1Low flying heightReduce manufacturing costRecord information storageHeads relative to moving tapeTransducerSputter deposition
A compression zone recording head is provided having the recording tape in contact or near contact with the recording read / write transducer elements in a compression zone of the tape passing over a transducing surface. The compression zone recording head comprises a flat or shallow contour head having a thin, hard, preferably conducting closure to provide wear protection to the transducers. In one embodiment of the invention, the transducers are located in a compression zone region where the recording tape contacts an edge of the transducing surface at a controlled wrap angle. In another embodiment, the transducers are located in a canopy zone region of the transducing surface due to bending of the tape due to the overwrap. The protective closure is preferably made of sputter deposited Al—Fe—Si, or alternatively of a deposited or bonded layer of Al—Fe—Si, Al—O—Ti—C, Zr—O—Ti, Si—N, Si—C or Zr—O.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and systems for magnetic recording
InactiveUS7116514B2Manufacturing heads with multiple gapsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic storageTransducer
According to one aspect, methods and systems for determining the position of a recording head using existing data structures on magnetic storage media are provided. In one example, a recording head writes data to an active track on a magnetic storage tape, the recording head including a write element and a read element in a known spatial relationship, wherein the read element is configured to access at least a portion of a reference track when the write element is accessing the active track. A controller determines a relative position of the transducer element to the reference track and repositions the recording head to write data to the active track. The read element may be a backward channel reader or dedicated read element of the recording head for reading reference tracks during read and / or write operations.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
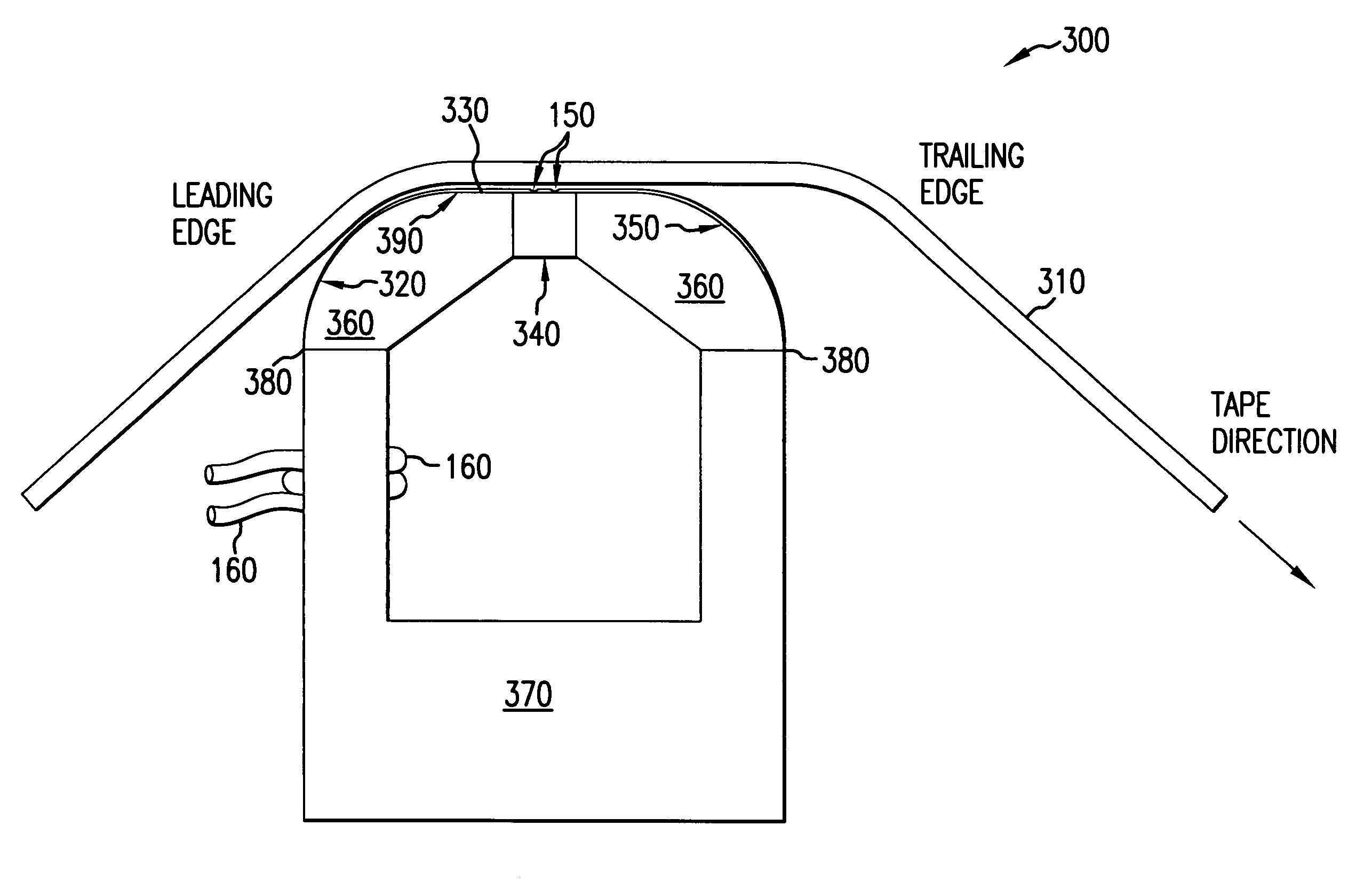
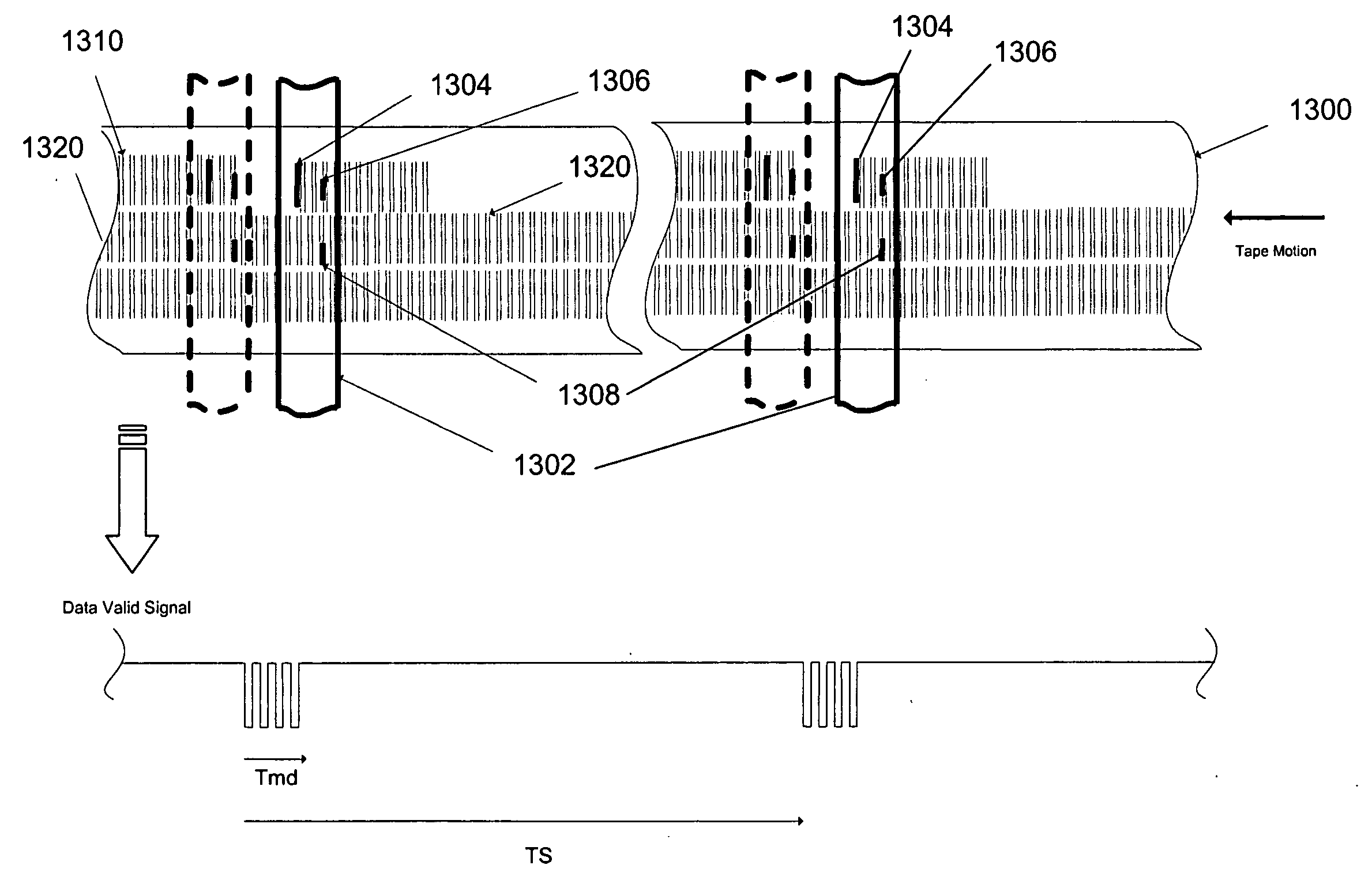
Servo write method for magnetic tape
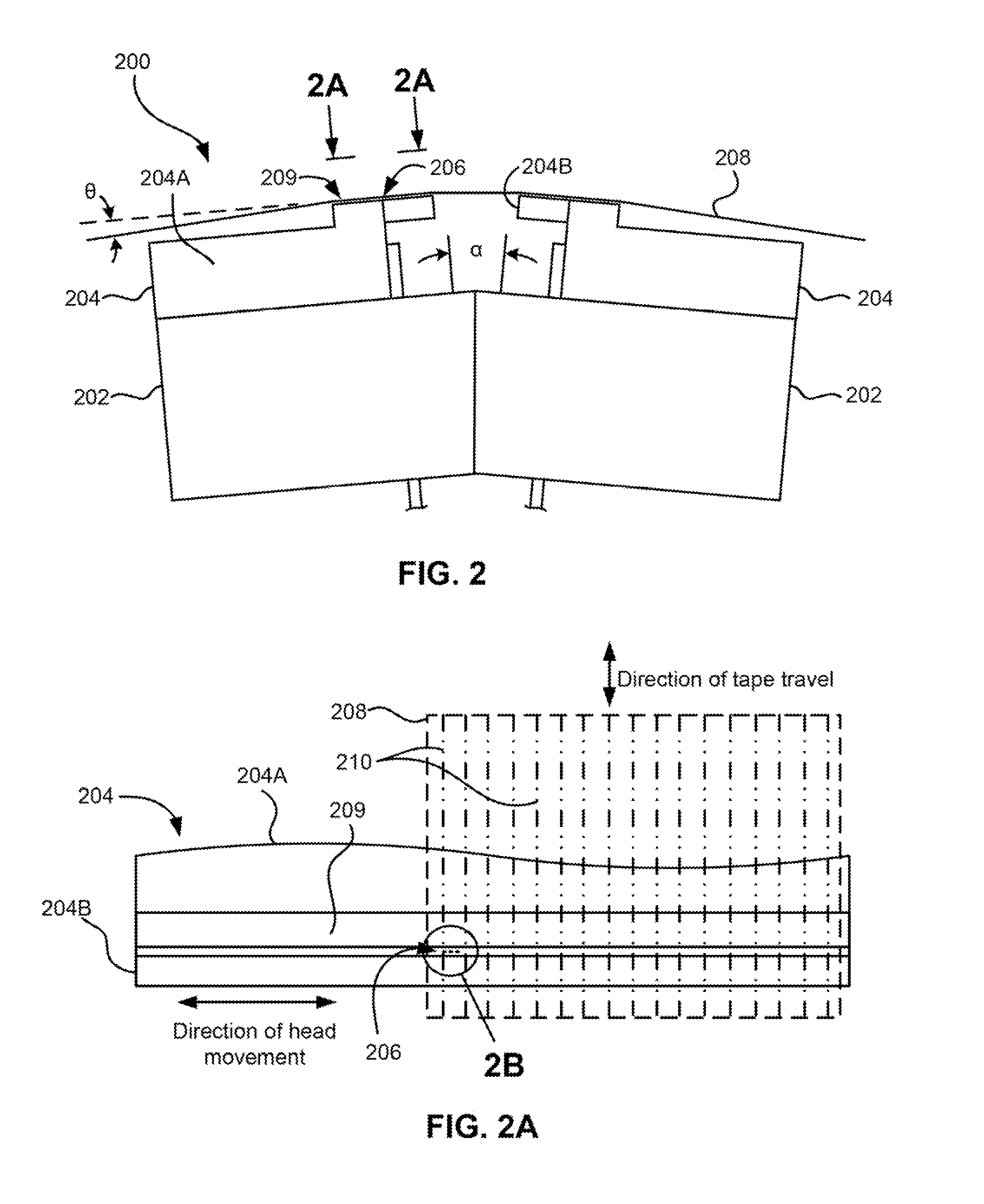
InactiveUS7206167B2Improve production efficiencyReduce wearManufacture head surfaceAlignment for track following on tapesBatch processingSemiconductor materials
A batch fabrication technique is described that increases the manufacturing efficiency of servo write heads and also improves servo pattern definition for fine features, while reducing tape and head wear. Multiple heads are fabricated as a batch from one or more ferrite wafers. A nominally flat, large wafer surface and a contour suitable for uniform photoresist application and planar photolithography permit fine servo pattern definition. A rounded leading edge on the head creates an air bearing to reduce wear of the tape and of the head. Moreover, any head wear occurs at the leading edge rather than in the region of the head where the servo pattern is formed. The servo write head may have a substantially planar head surface. A leading edge is disposed adjacent to the head surface such that the tape contacts the leading edge before passing over the head surface. The leading edge is rounded to form an air bearing between the head surface and the tape. A rounded trailing edge may be disposed adjacent to the head surface such that the tape passes over the trailing edge after passing over the head surface. The head may be formed from an upper ferrite wafer having a non-magnetic spacer. Non-magnetic material is photolithographically defined to produce gaps above the spacer. The non-magnetic material may be photoresist, semiconductor materials, glass, metal or the like. The material may even be removed later to leave air gaps. The non-magnetic material forms a region where the field loops out to intersect the passing tape, thereby transferring a magnetic pattern to tape. Additionally, a lower ferrite wafer may be mated to the upper ferrite wafer to complete a magnetic circuit around the gaps. The upper or lower ferrite wafer may have a channel through which an inductive winding passes. Multiple heads may be formed through batch processing of the upper and lower ferrite wafers.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
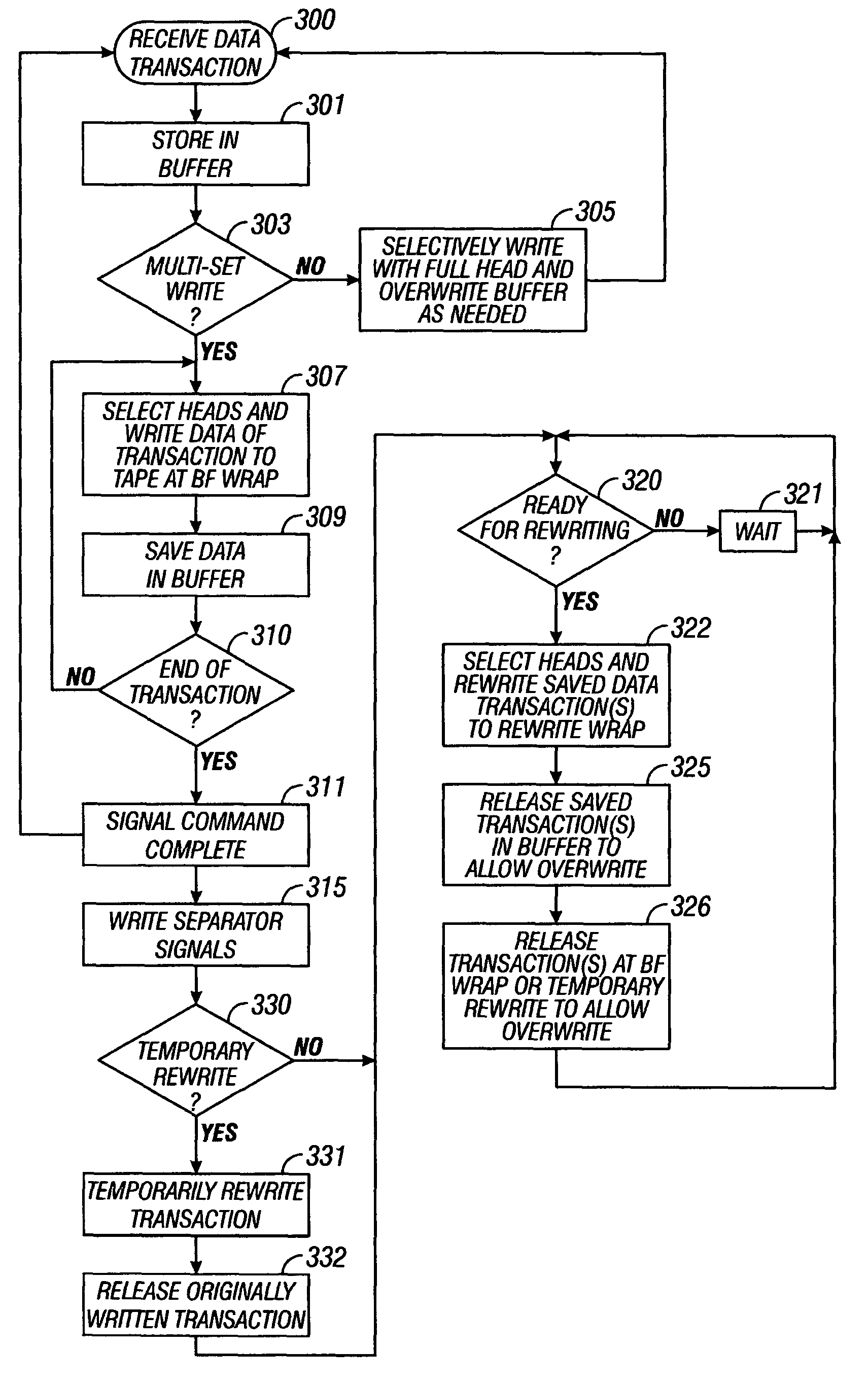
Storing data to magnetic tape both to one set of tracks and in the same operation rewritten to another set of tracks
InactiveUS6970311B2Input/output to record carriersData buffering arrangementsMagnetic tapeComputer science
A recording system of a magnetic tape drive is operated to cause one separate set of write heads to write data discontinuously to magnetic tape as received, and to save the data, and, during the same operation, to cause another separate set of write heads to rewrite data to magnetic tape in a continuous arrangement. The writing may be in parallel and simultaneous. Thus, during the same operation, and at the same time, the separate sets of the plurality of write heads, temporarily write the received data to magnetic tape so that the sender can erase its copy, and rewrite the saved data to the magnetic tape in a permanent arrangement, without waiting to complete first writing received data, to complete subsequently rewriting the data, and repeating.
Owner:IBM CORP
Backward compatible head for quasi-static tilted reading and/or recording
InactiveUS9007712B1Record information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsMagnetic mediaTransducer
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
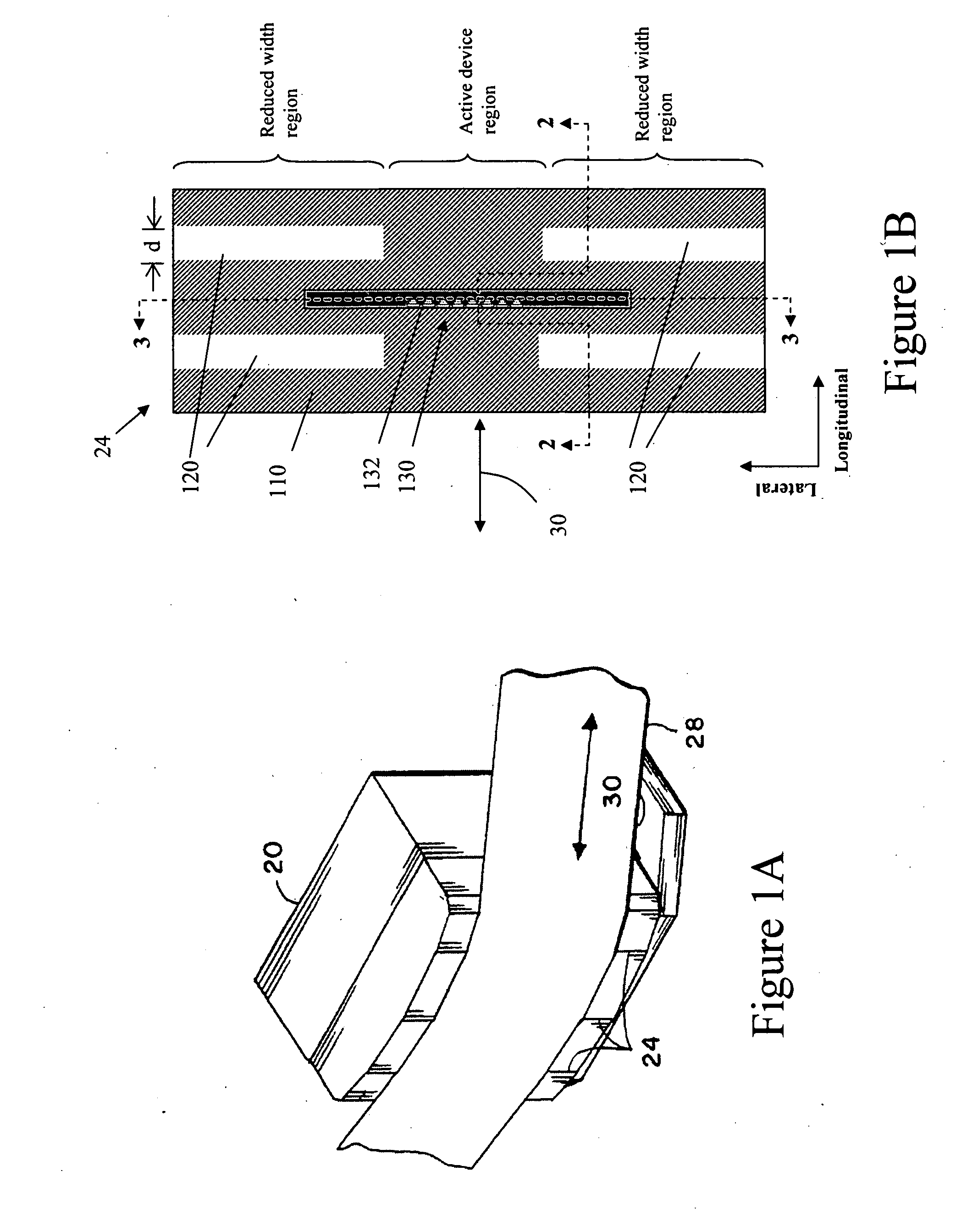
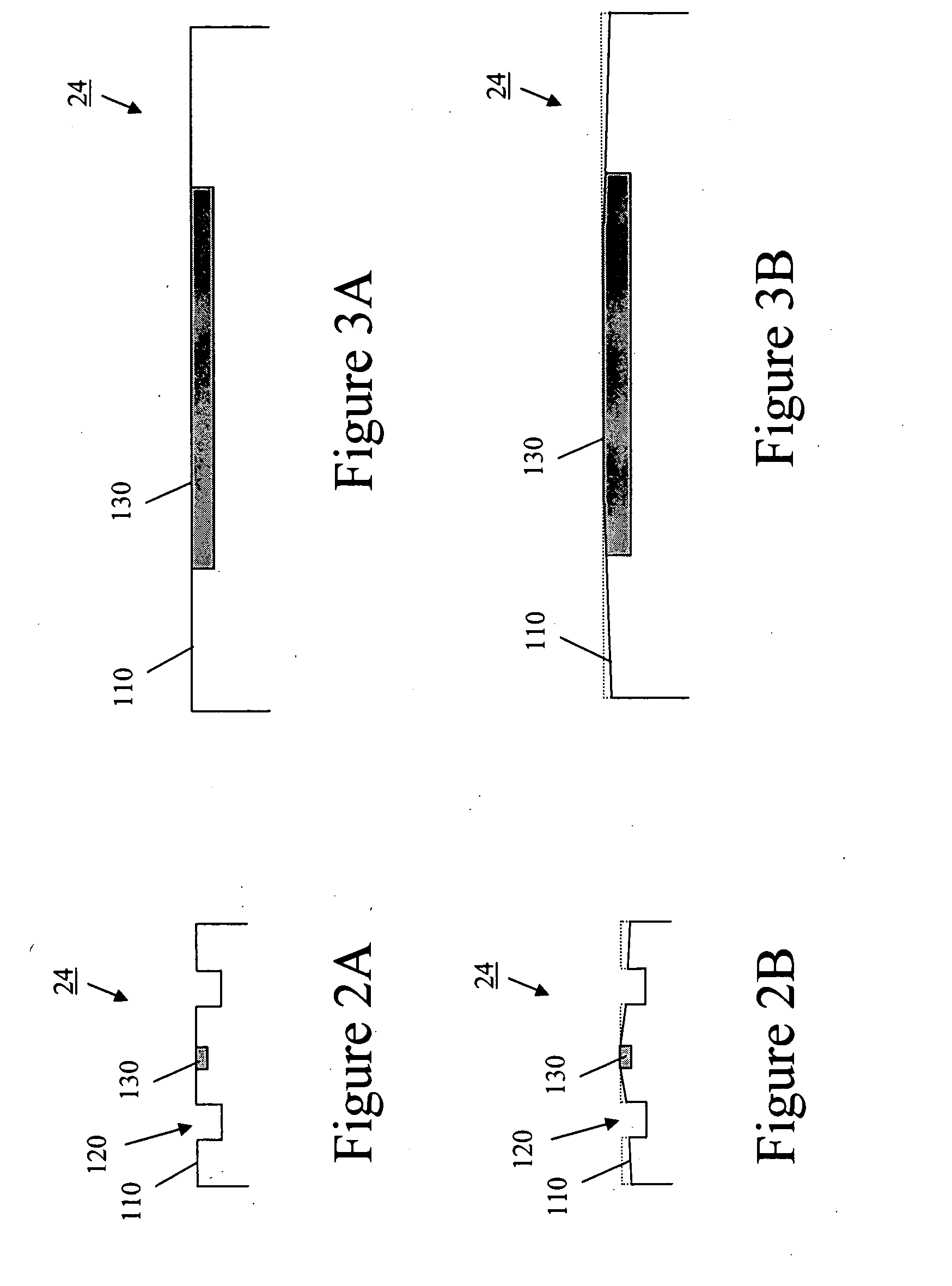
Read/write head having varying wear regions and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20070183091A1Longitudinal width can be reducedManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageTransducerBiomedical engineering
An exemplary magnetic head structure and method of manufacture is described. In one example, the method includes forming a support surface having a longitudinal width associated with at least one data transducer and a reduced longitudinal width region offset along a lateral direction from the at least one data transducer. The method further includes lapping the support surface such that the at least one data transducer is raised or elevated relative to at least a portion of the support surface. In one example, the at least one data transducer is raised relative to laterally offset portions of the support surface, and in one example, to laterally offset portions positioned between adjacent data transducers.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Methods and systems for magnetic recording
InactiveUS20050083600A1Manufacturing heads with multiple gapsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic storageTransducer
According to one aspect, methods and systems for determining the position of a recording head using existing data structures on magnetic storage media are provided. In one example, a recording head writes data to an active track on a magnetic storage tape, the recording head including a write element and a read element in a known spatial relationship, wherein the read element is configured to access at least a portion of a reference track when the write element is accessing the active track. A controller determines a relative position of the transducer element to the reference track and repositions the recording head to write data to the active track. The read element may be a backward channel reader or dedicated read element of the recording head for reading reference tracks during read and / or write operations.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Multi-format magnetic head
A magnetic head includes a first array of elements associated with a first data format and a second array of elements associated with a second data format, the elements being selected from a group consisting of readers, writers, and combinations thereof. The first and second arrays of elements are adjacent each other in a direction transverse to a direction of travel of a magnetic medium over the head.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Quasi-statically oriented head for recording non-legacy formats
InactiveUS20140334033A1Stable separationAlignment for track following on tapesTape carriersComputer hardwareMagnetic tape
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Low inductance, ferrite sub-gap substrate structure for surface film magnetic recording heads
InactiveUS6894869B2Avoid passingReduce reluctanceManufacture head surfaceManufacturing heads with multiple gapsMetallurgyLow inductance
A thin film magnetic recording head is fabricated by forming a substrate from opposing ferrite blocks which have a ceramic member bonded between them. This structure is then diced to form a plurality of columns, wherein each column has a ferrite / ceramic combination. Each column represents a single channel in the completed head. A block of ceramic is then cut to match the columned structure and the two are bonded together. The bonded structure is then cut or ground until a head is formed, having ceramic disposed between each channel. A ferrite back-gap is then added to each channel, minimizing the reluctance of the flux path. The thin film is patterned on the head to optimize various channel configurations.
Owner:ADVANCED RES
Wear pads for timing-based surface film servo heads
InactiveUS20060061906A1Improve linearityEliminate magnetic flux leakageManufacture head surfaceManufacturing heads with multiple gapsEngineeringBearing surface
Owner:ADVANCED RES
Tape head layout having offset read and write element arrays
ActiveUS8045290B2Driving/moving recording headsManufacturing heads with multiple gapsComputer hardwareComputer science
A tape head assembly for writing data to and reading data from a tape includes a tape head member having an engagement surface that is configured to engage the tape as the tape moves past the tape head member. A plurality of arrays of interactive elements are supported on the engagement surface. Each array is longitudinally offset from each other array. Each individual array includes a read group having only read elements and a write group having only write elements. Each read group is laterally offset from each write group within each array.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Magnetic recording head having protected reader sensors and near zero recession writer poles
InactiveUS20140063645A1Manufacture head surfaceDriving/moving recording headsMechanical engineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A magnetic head according to one embodiment includes a module, the module having first and second transducers of different transducer types positioned towards a media facing side of the module, wherein the different transducer types are selected from a group consisting of data reader transducers, servo reader transducers, write transducers, piggyback read-write transducers and merged read-write transducers; a first protection structure for protecting the first transducer; and wherein the second transducer has either no protection or is protected by a second protection structure that is different than the first protection structure.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com