Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Reduce reluctance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
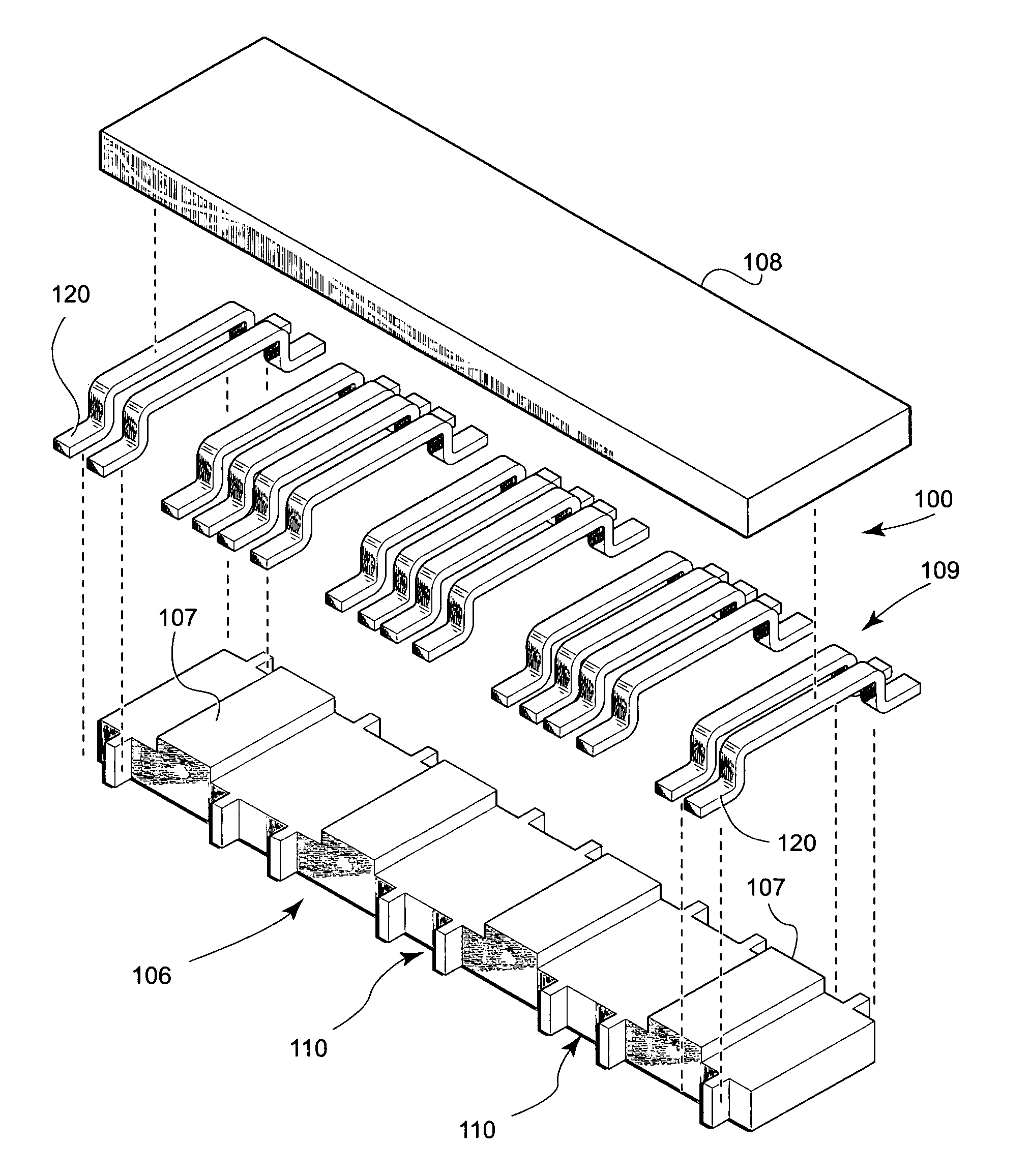
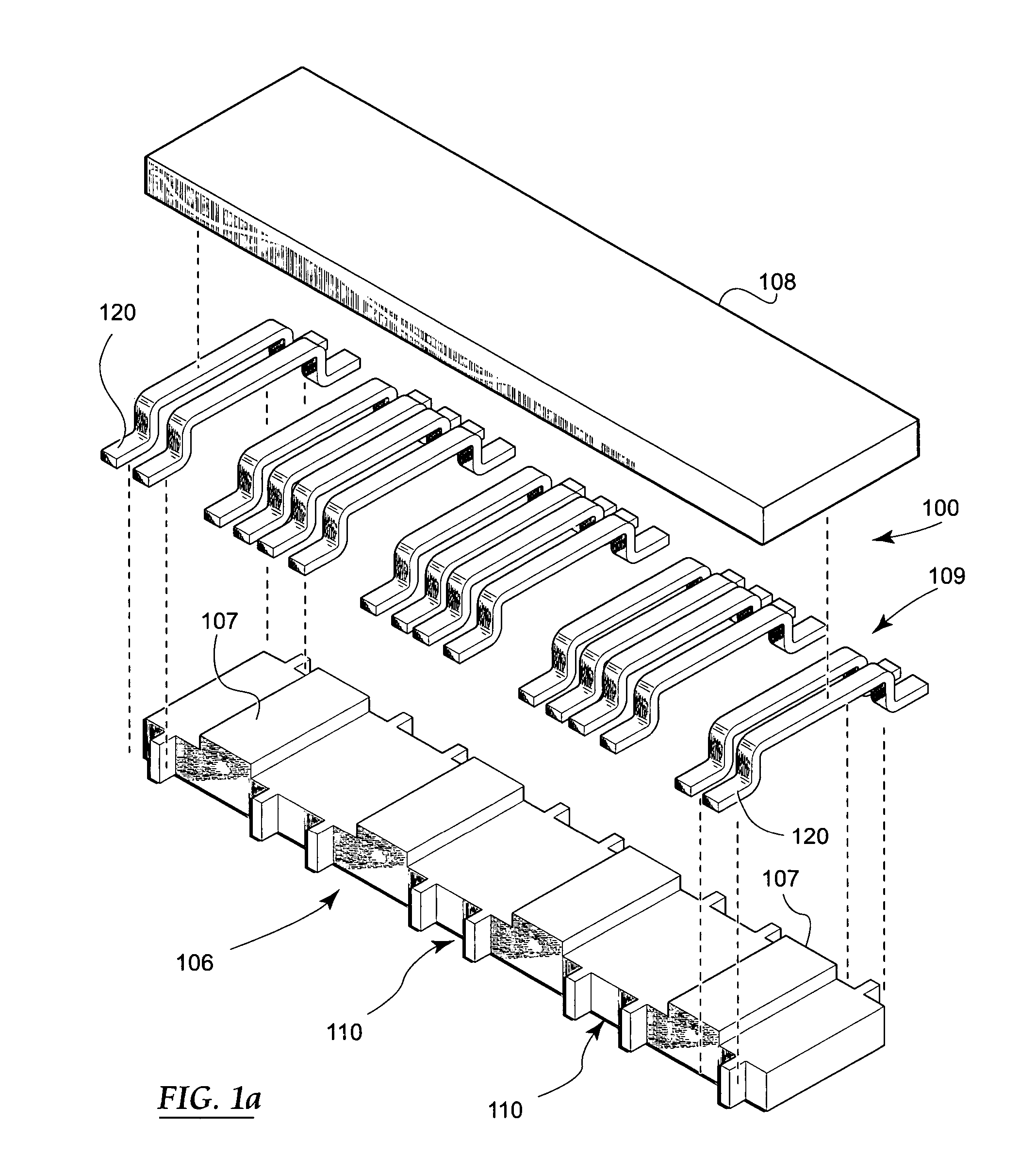
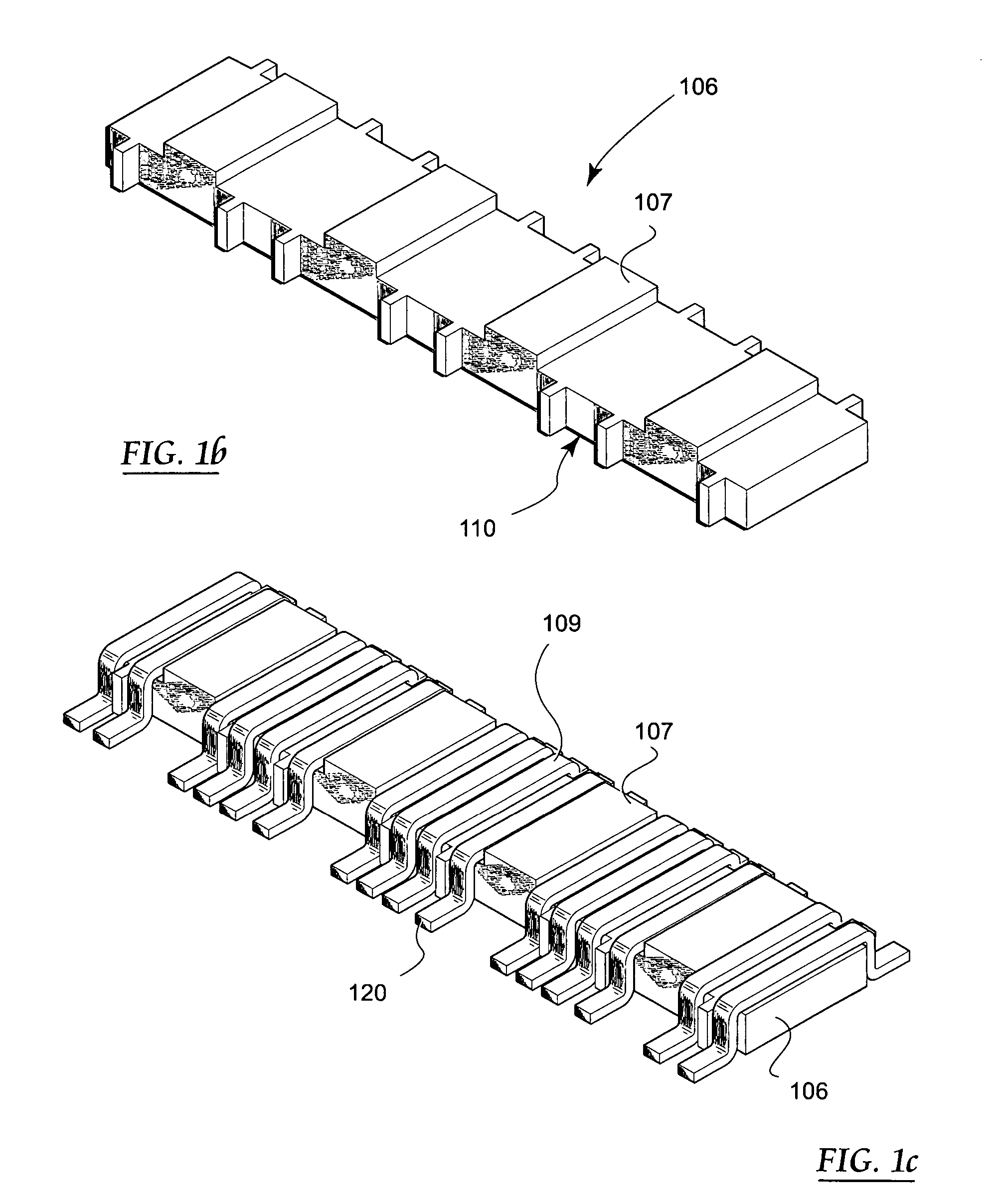
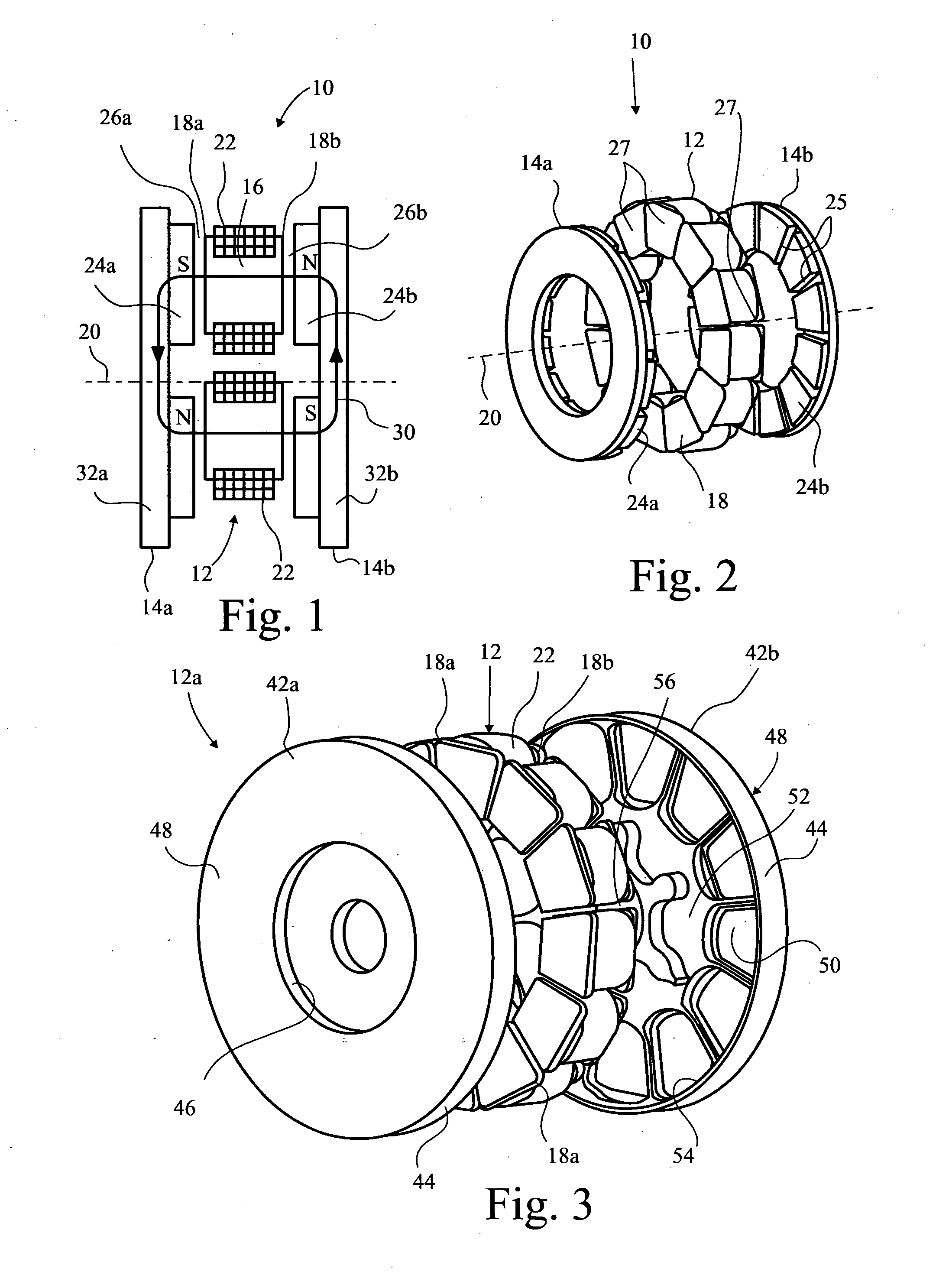
Precision inductive devices and methods
ActiveUS20060145800A1Mitigation of flux leakage effectImprove balanceTransformers/inductances casingsPrinted inductancesEngineeringInductor
A low cost, low profile, small size and high performance inductive device for use in, e.g., electronic circuits. In one exemplary embodiment, the device includes a ferrite core comprising multiple inductors and optimized for electrical and magnetic performance. Improvements in performance are obtained by, inter alia, control of the properties of the gap region(s) as well as placement of the windings relative to the gap. The magnetic path properties of the inductors at the ends of the device are also optionally controllable so as to provide precise matching of inductances. Optionally, the device is also self-leaded, thereby simplifying its installation and mating to a parent device (e.g., PCB). Methods for manufacturing and utilizing the device are also disclosed.
Owner:PULSE ELECTRONICS
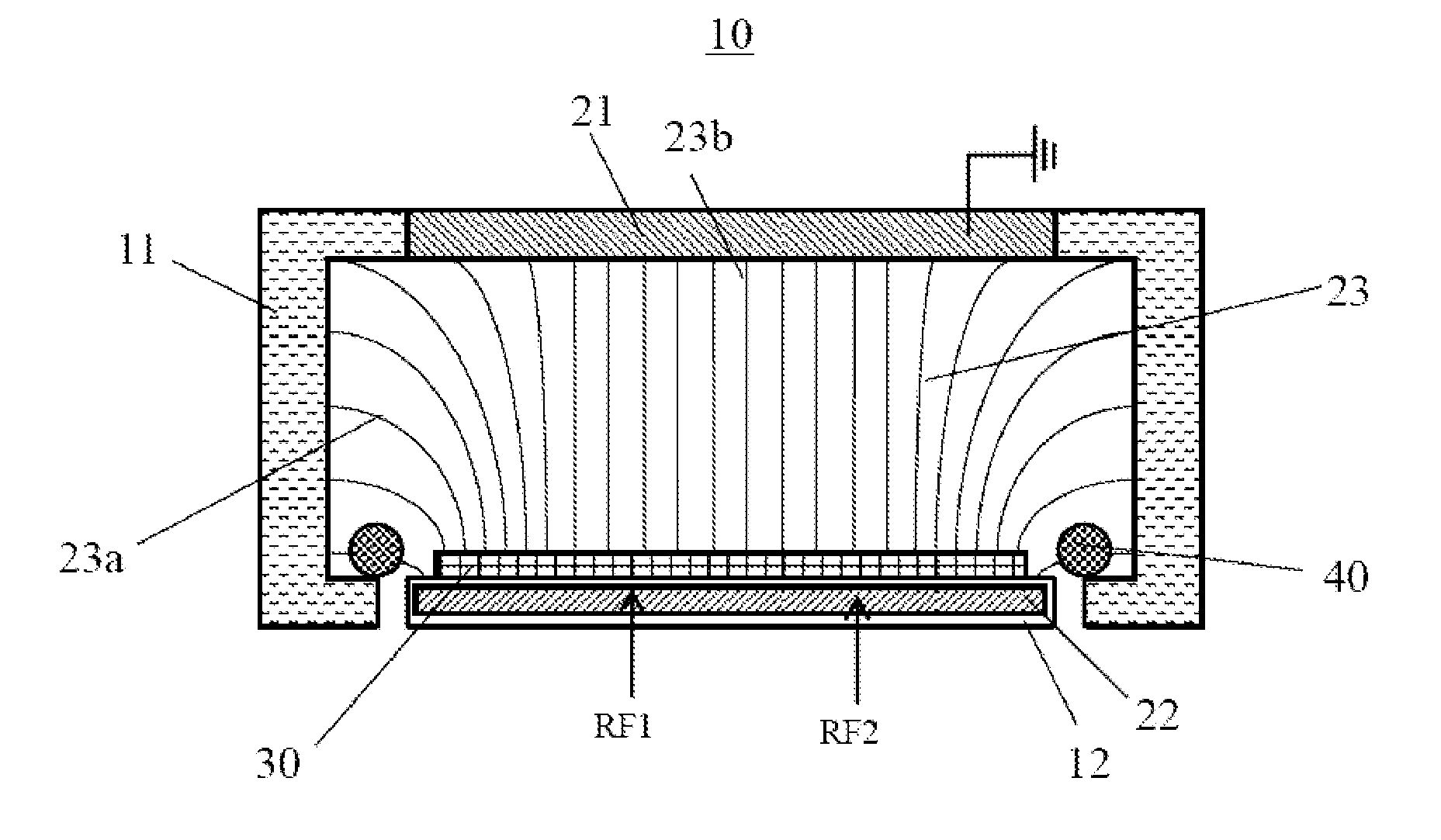
Capacitive-coupled plasma processing apparatus and method for processing substrate
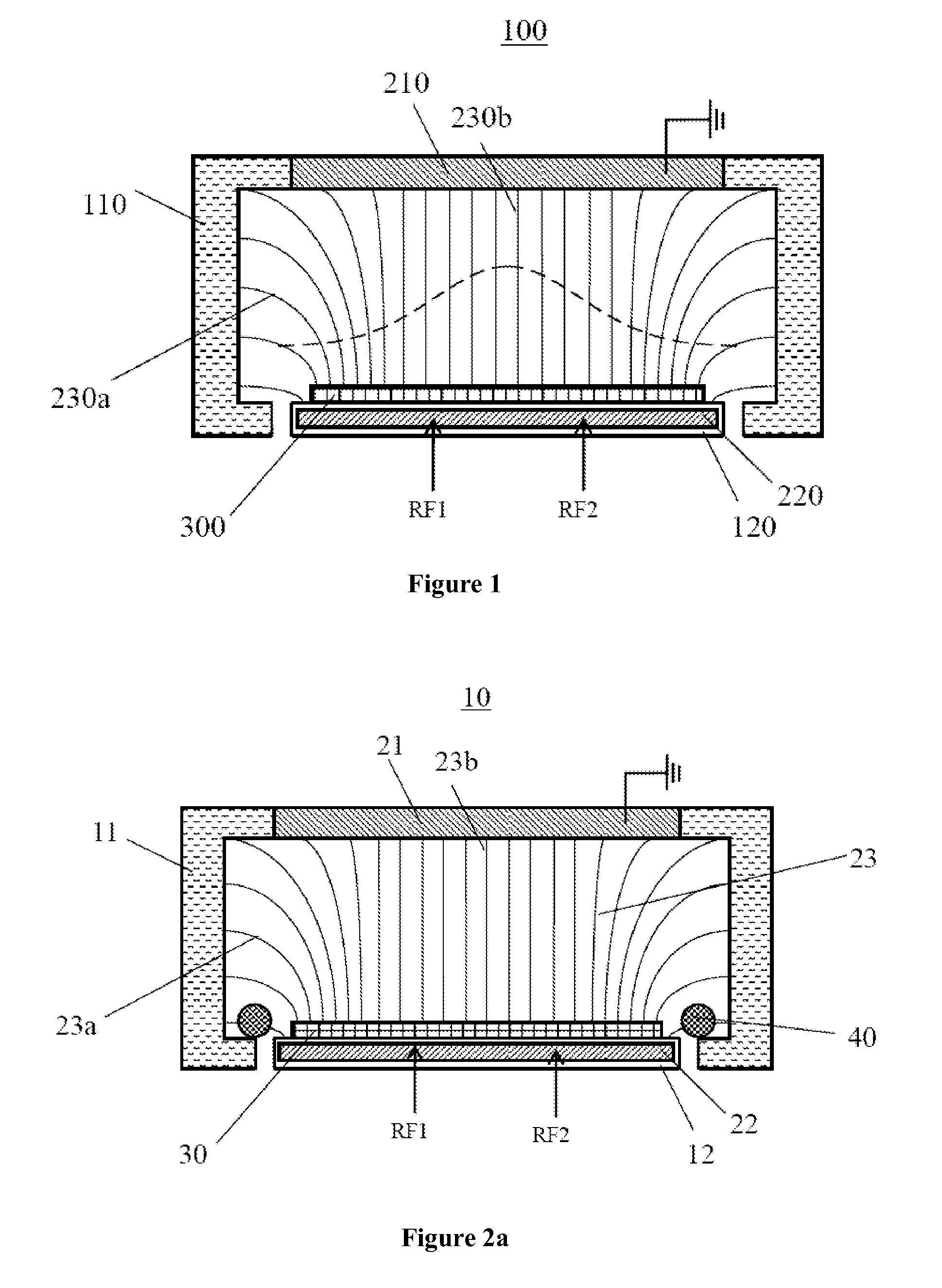
ActiveUS20130032574A1Adjust electric field strengthIncrease the electric field strengthElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceHigh pressure
The present invention relates to a capacitive-coupled plasma processing apparatus, wherein an electric field regulating element, i.e., an “electric field lens”, is arranged in the reaction chamber to generate a regenerated electric field in a direction opposite to that of the original radio frequency electric field in the reaction chamber, so that the non-uniformity of etching rate on the surface of the substrate of the plasma incurred by the original radio frequency electric field is decreased; and the electric field regulating element, i.e., the “electric field lens”, further decreases the equivalent quality factor Q value of the reaction chamber, expands the radio frequency band, and prevents high-voltage electric arcing. The present invention further provides a method for processing the substrate using the processing apparatus.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FAB EQUIP INC CHINA
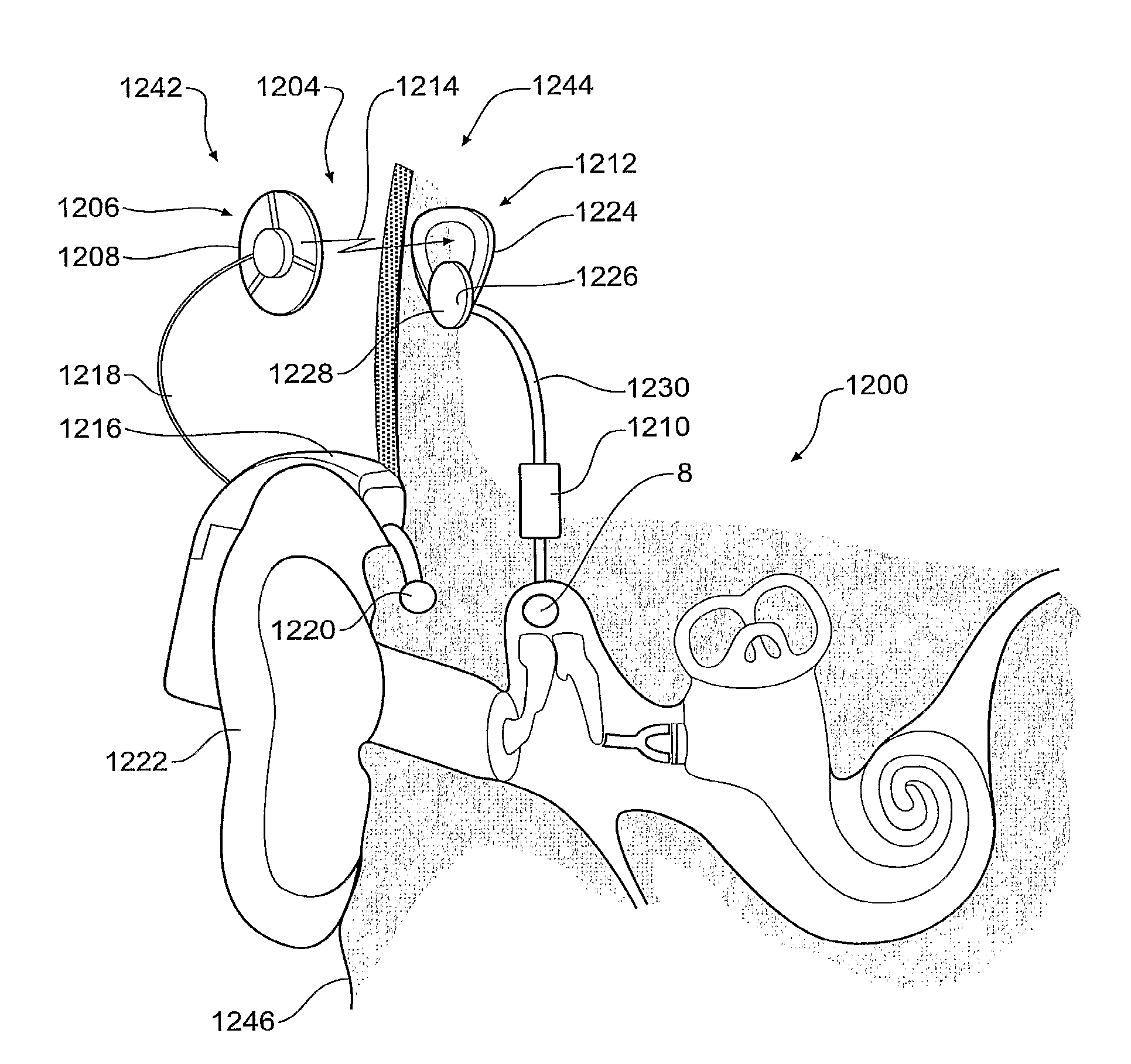
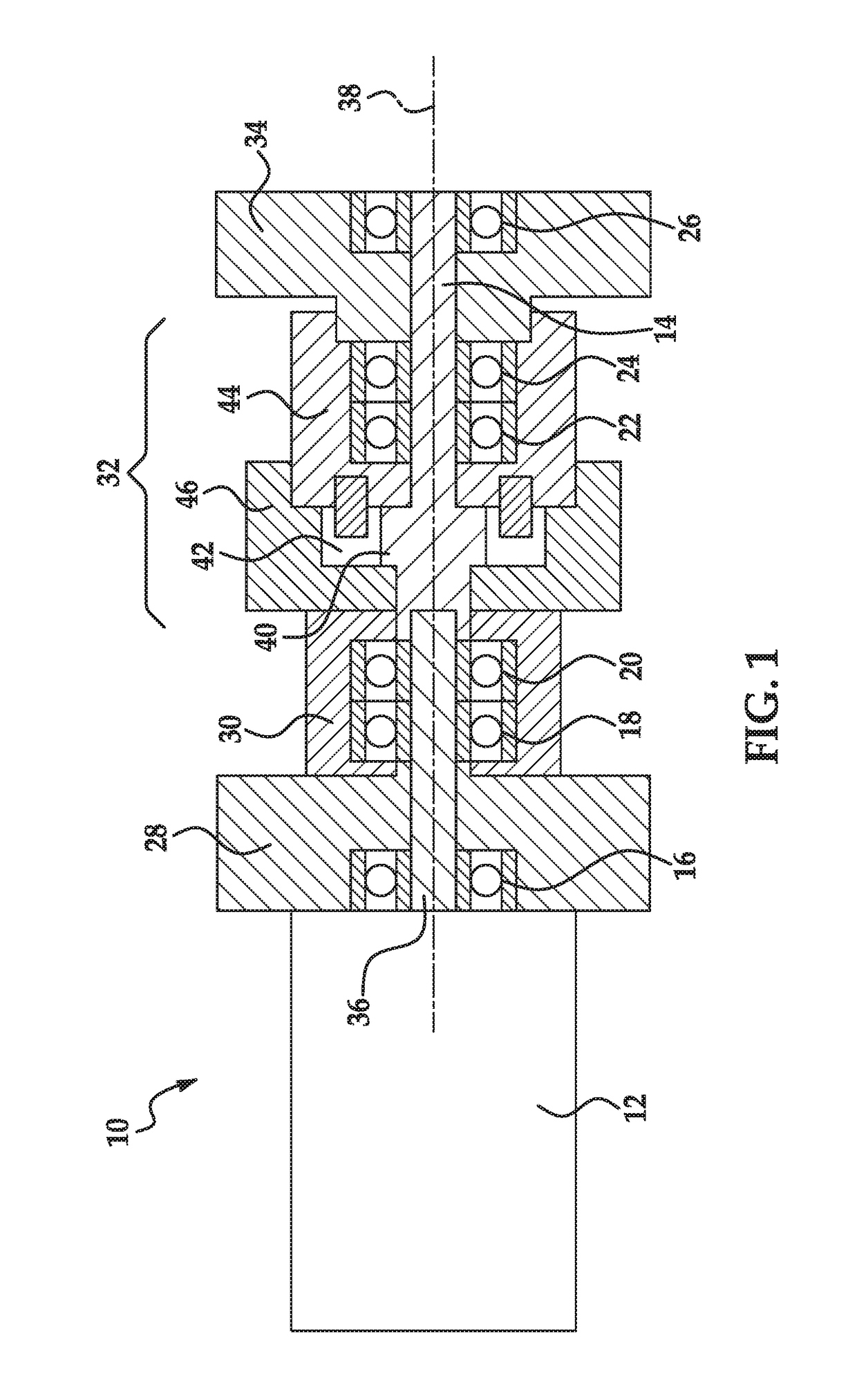
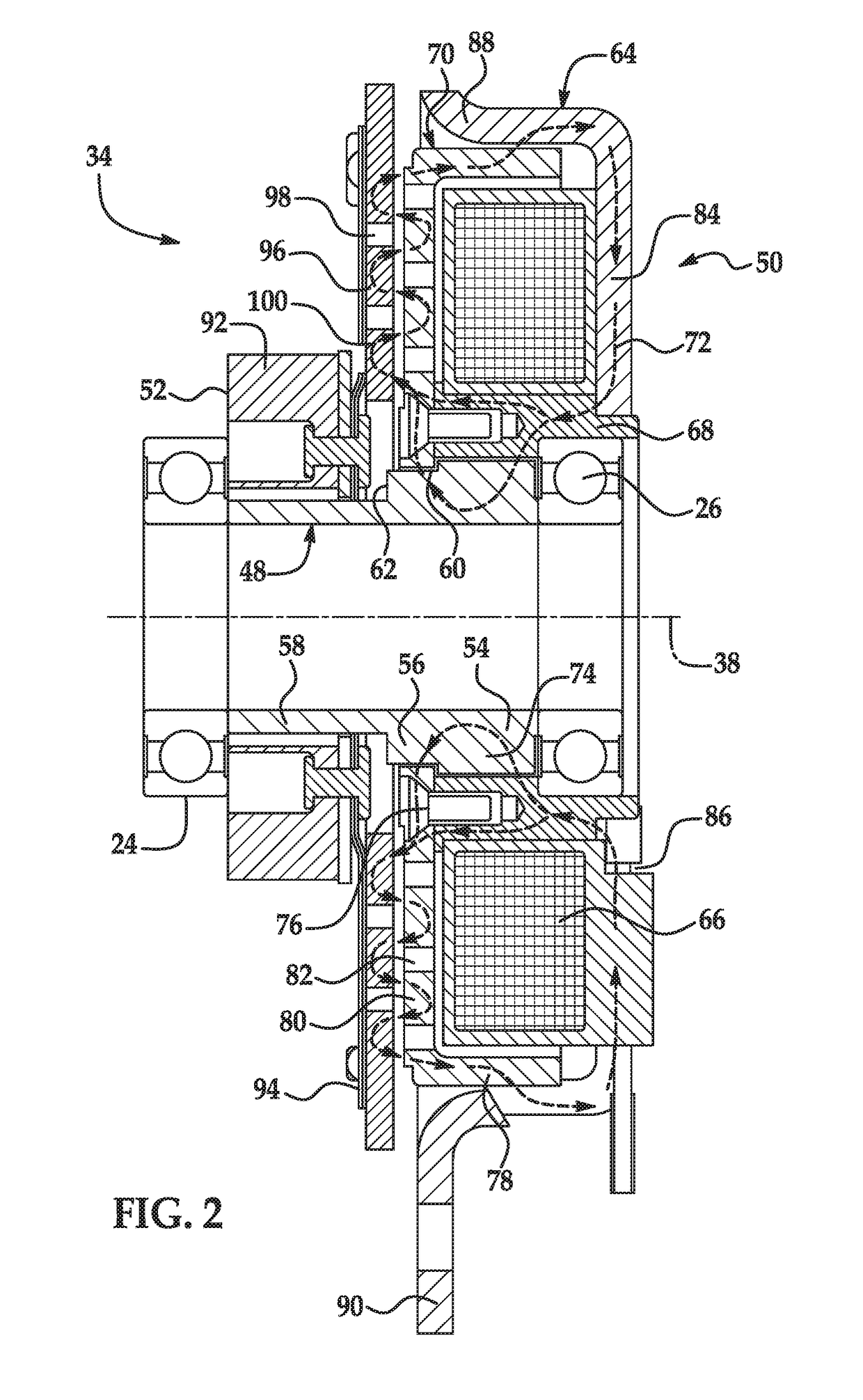
Implantable actuator for hearing aid application
InactiveUS20140163309A1Reduce reluctanceEar implantsHearing aids mounting/interconnectionProsthesisHearing aid
An electromechanical actuator for an implantable hearing aid device including a mechanical output structure that has a first portion and a second portion, wherein the first portion is a mechanical attachment structure to attach a stapes prosthesis, and wherein the second portion is a wire-like member coupling the mechanical attachment structure to a magnetically permeable armature shaft assembly.
Owner:BERNHARD HANS +9
Magnetorheological suspensions damping device for automobile suspension system
InactiveCN1603651AReduce power consumptionSmall currentSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetorheological fluidEngineering
The invention involving a magnetorheological fluid damping device for automobile suspension system.The magnetic field generator of this damping device consists of permanent magnet and electromagnetic coil.On the top of the damping device,there are guide apparatus and damping regulator,the function of which is that to ensure the damping channel is uniform annular duct and to meet the high-damp requirement in the restoration process and low-damp requirement in the compression process of damper seperately.The current in the electromagnetic coil designs of bi-directional and this controls the magnetic field intersity of the damping channel,decreases the excitation current of the electromagnetic coil,reduces energy consumption and decreases damper fever.On the non-controlling conditions,this damping device has the equivalent characteristics of the traditional shock absorber and can instead the passive shock absorber,after equiping corresponding current controller,this device can regulate the damping characteristics of suspension system,which improves the automobile driving safety and ride comfort.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Electromagnetic exciter and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20090096299A1Reduce the number of partsEasy to assembleManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMechanical vibrations separationElectromagnetStator
A thin electromagnetic exciter has a flat casing including a casing body (2) and a cover (3), a stator (10) including an electromagnet having a coil wound around a yoke, and an oscillator (20) including a bar-shaped permanent magnet and a weight integrally attached thereto. The stator and the oscillator are disposed adjacently over a bottom wall portion (2c) of the casing body. The stator is secured to the casing body. The oscillator is vibratably supported relative to the casing body through resilient support members.
Owner:CITIZEN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multistage variable reluctance motor/generator
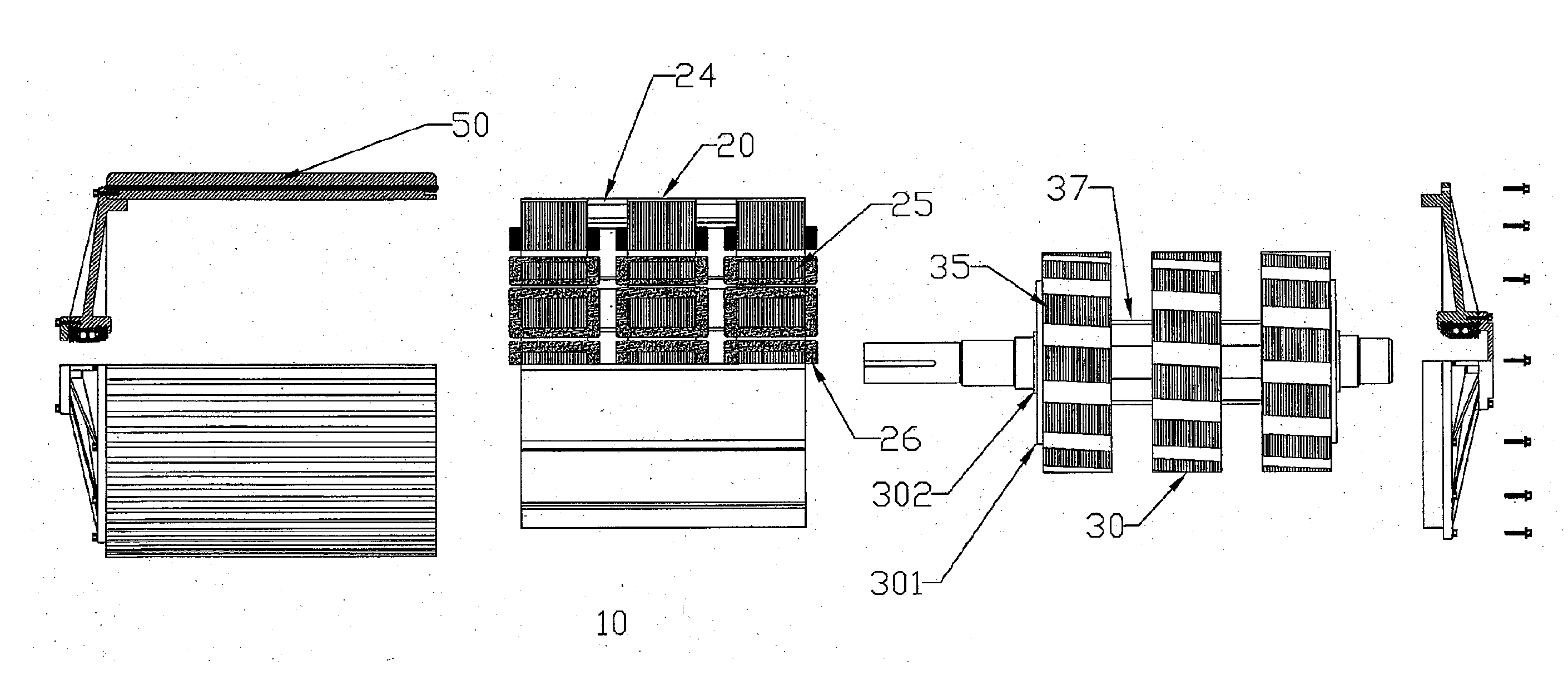
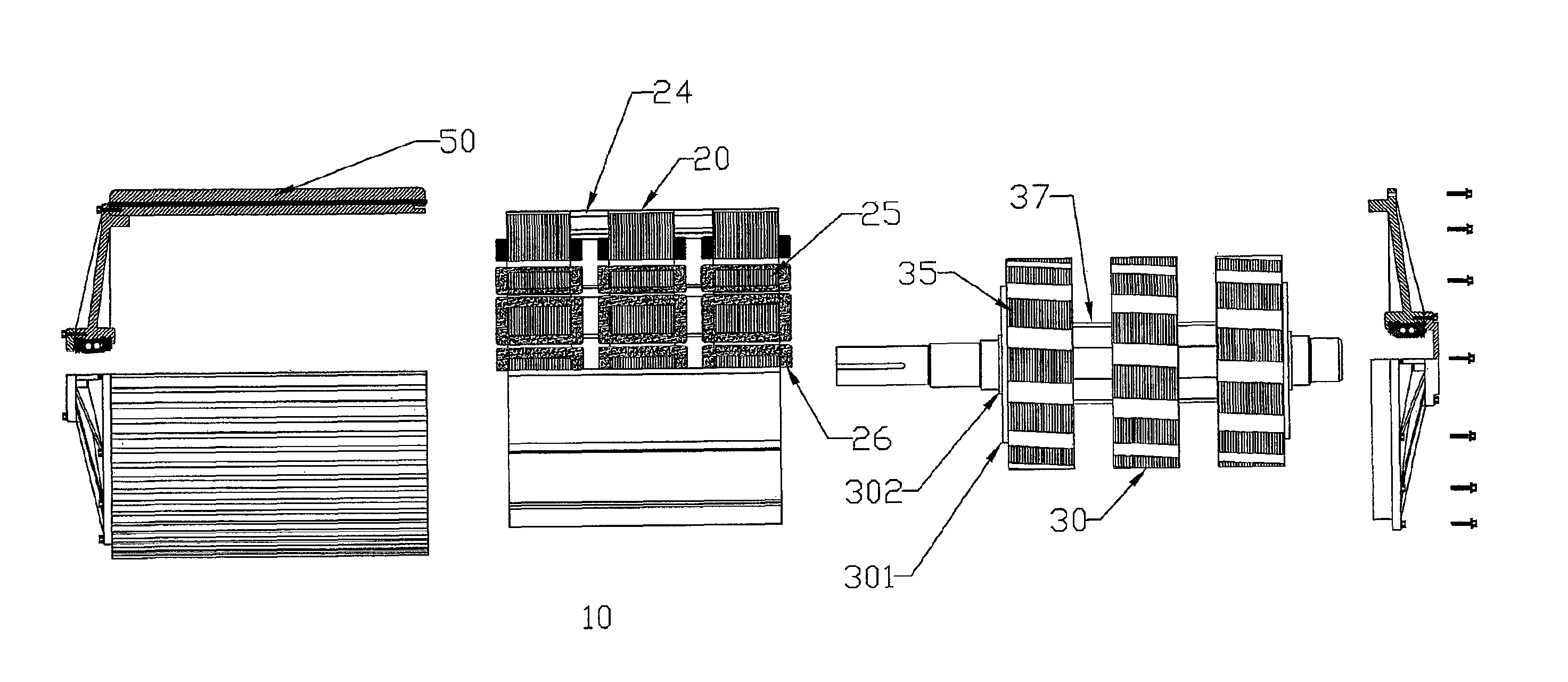
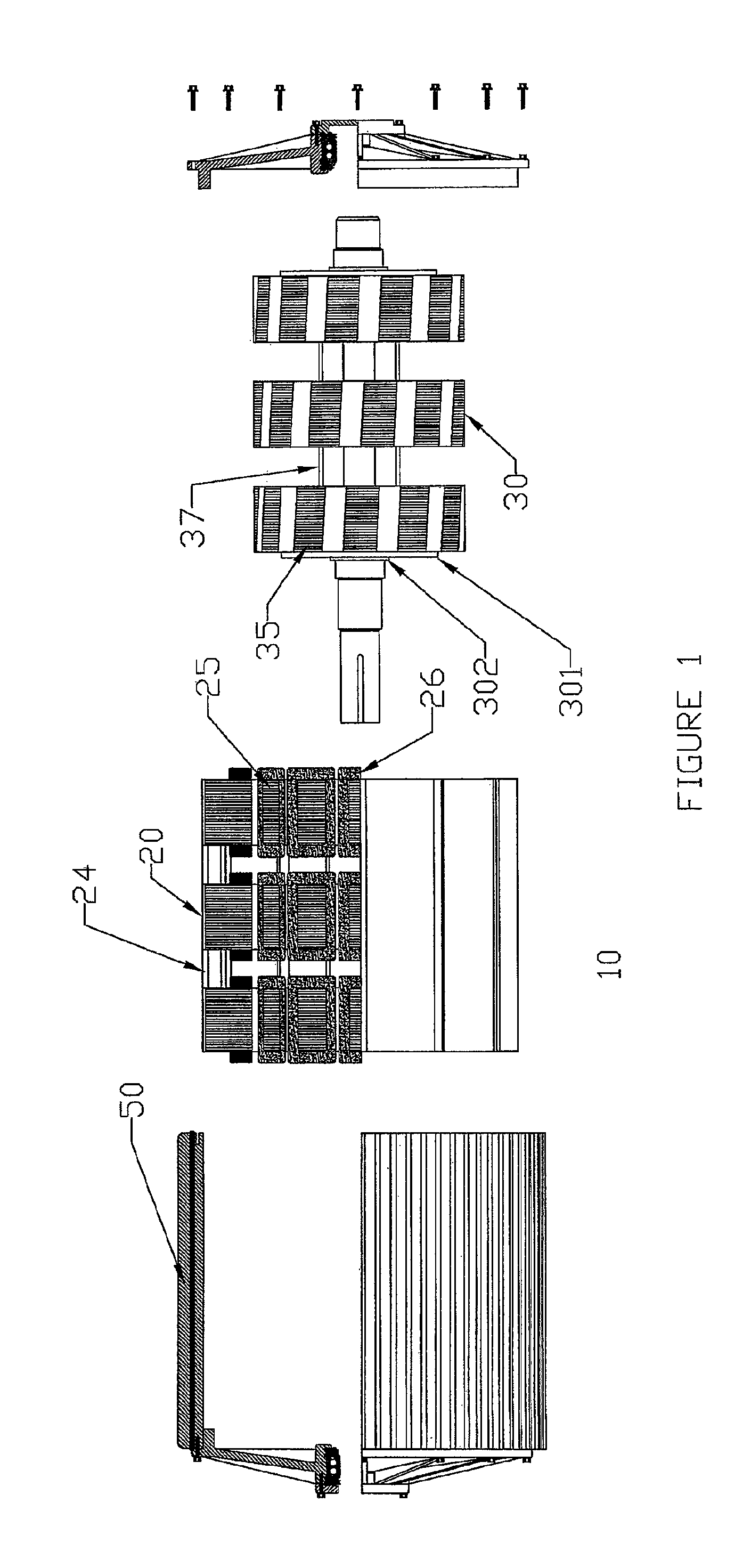
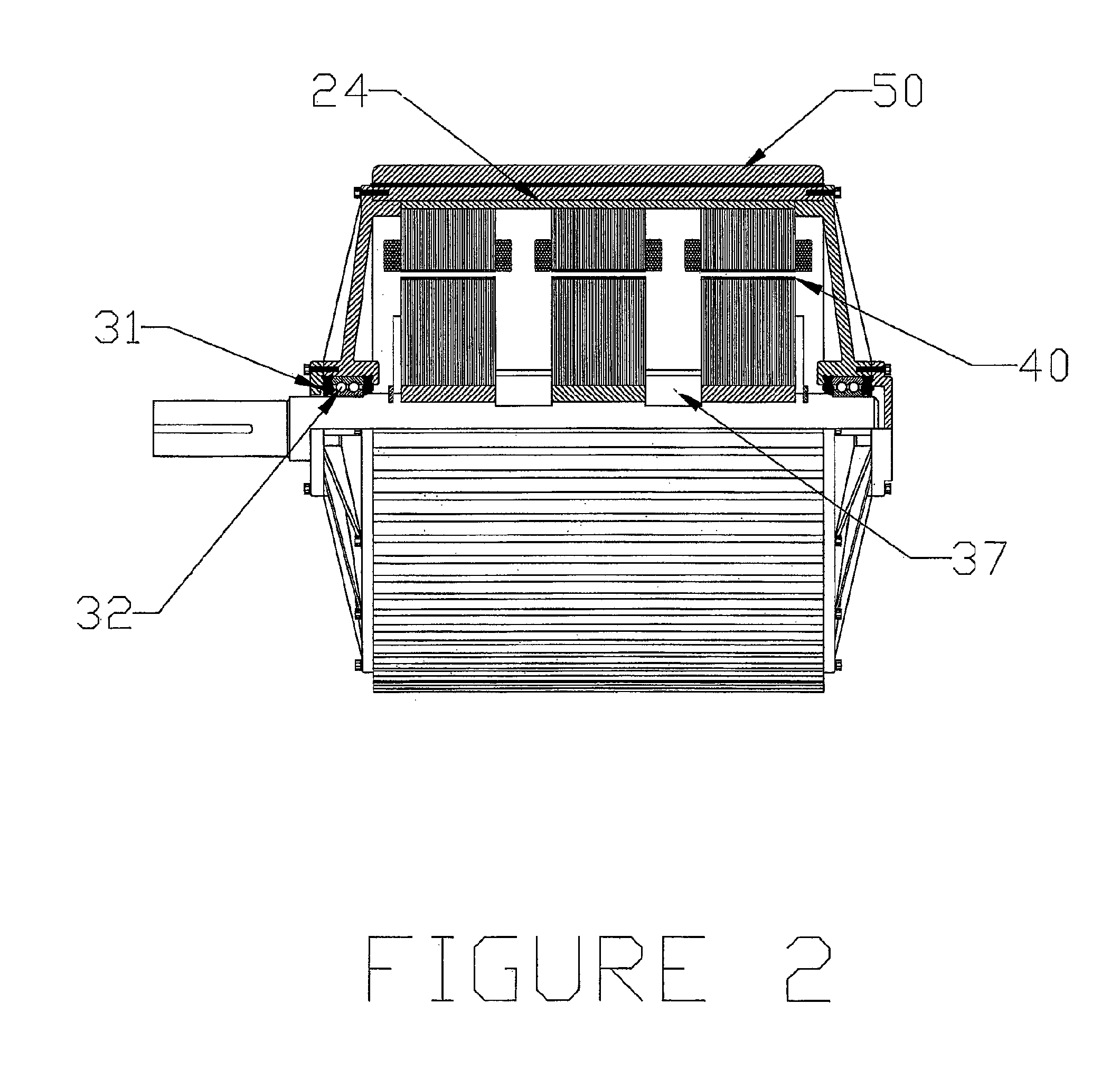
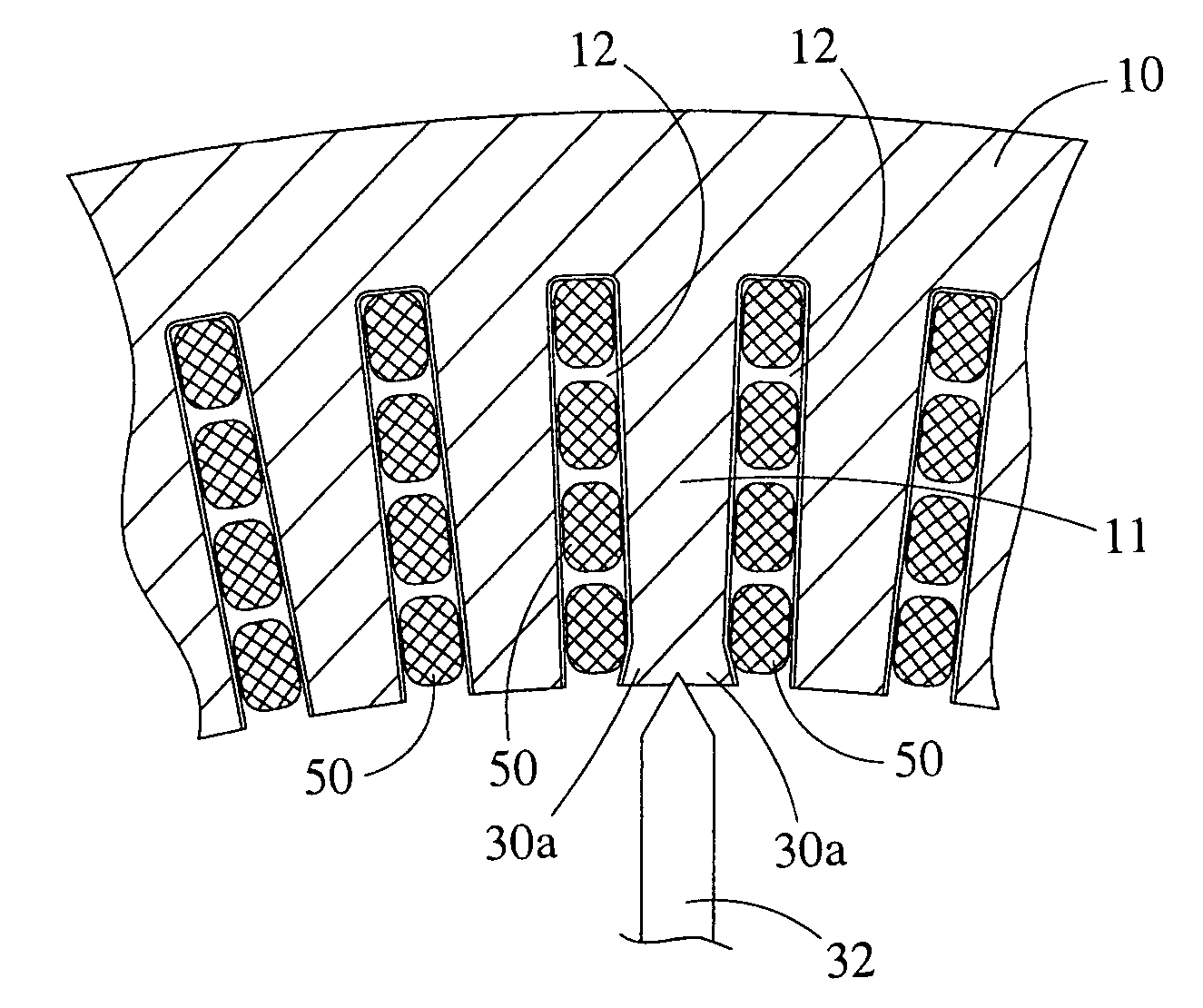
ActiveUS20100156205A1Reduce complexityImprove rendering capabilitiesSynchronous generatorsAC motor controlCopper lossMagnetic flux
A compact, rugged, variable reluctance, variable speed, electric motor capable of producing high torque at high electrical energy conversion efficiencies is provided. The present invention provides for a multi-stage motor design having a number of discreet rotor and stator elements on a common shaft. This configuration provides for the simplest of magnetic structures and produces a powerful magnetic flux modelling design technique that is used to further optimize the motor design and subsequent control logic. Thermal mapping of the magnetic mass provides for advanced cooling techniques that are used to ensure long in-service life in the most extreme of industrial applications. The electric motor inherently provides low vibration thereby greatly reducing noise; low turn to turn voltage potentials thereby eliminating costly phase to phase shorting potential; efficient motor operation through the reduction in switching and copper losses in both the machine and its control system.
Owner:SUNCO INVESTMENTS
Electric machine- modular
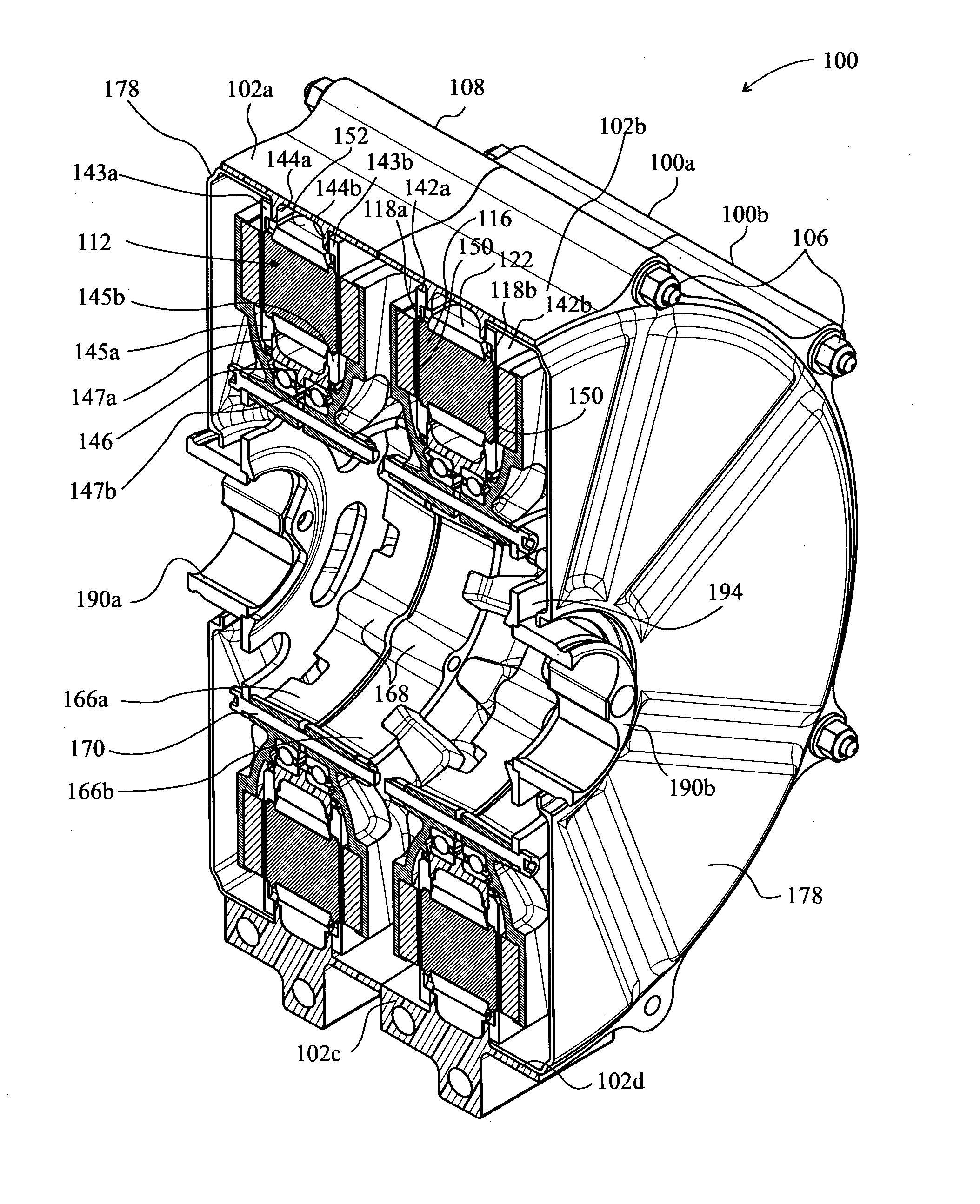
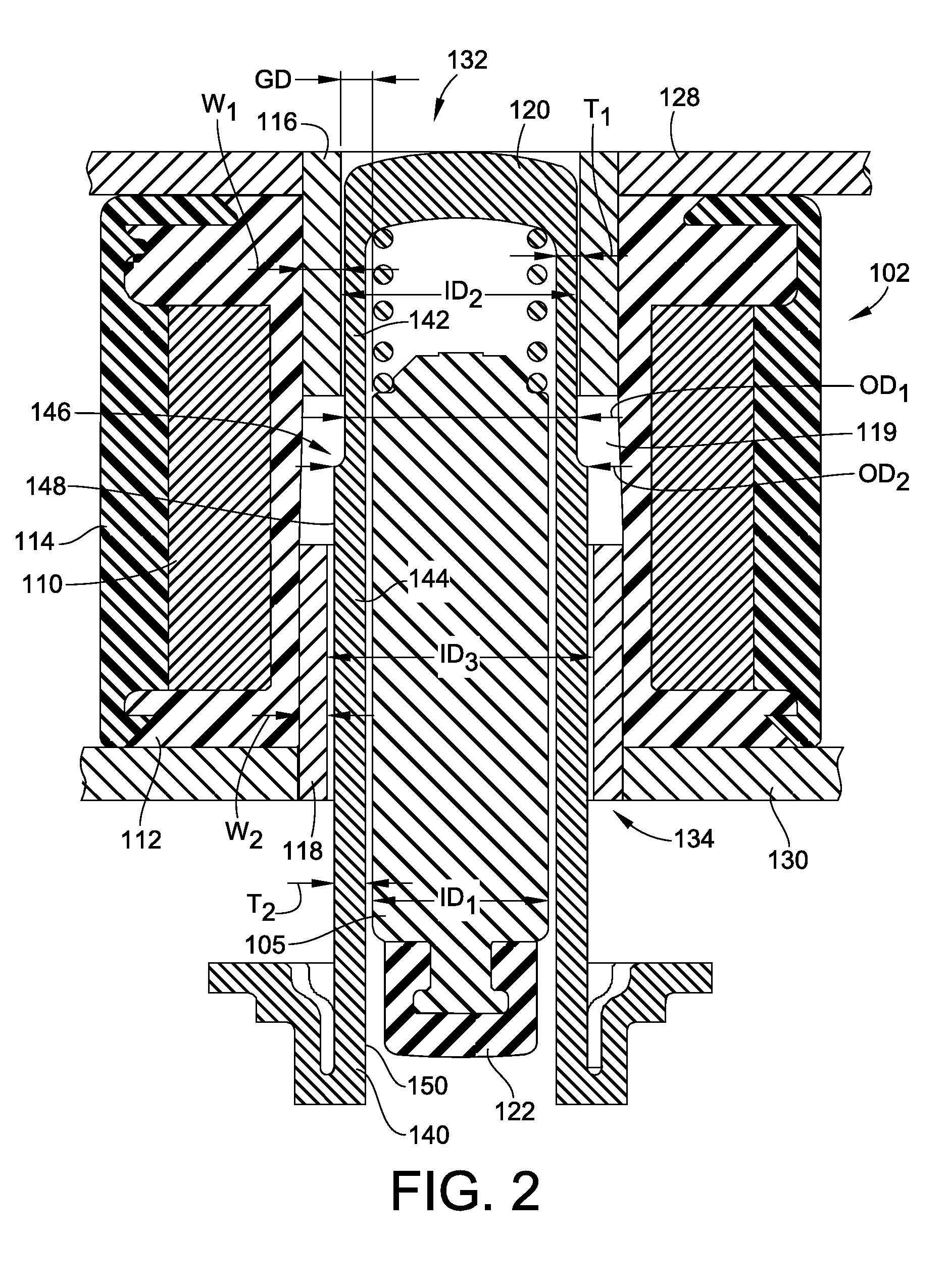
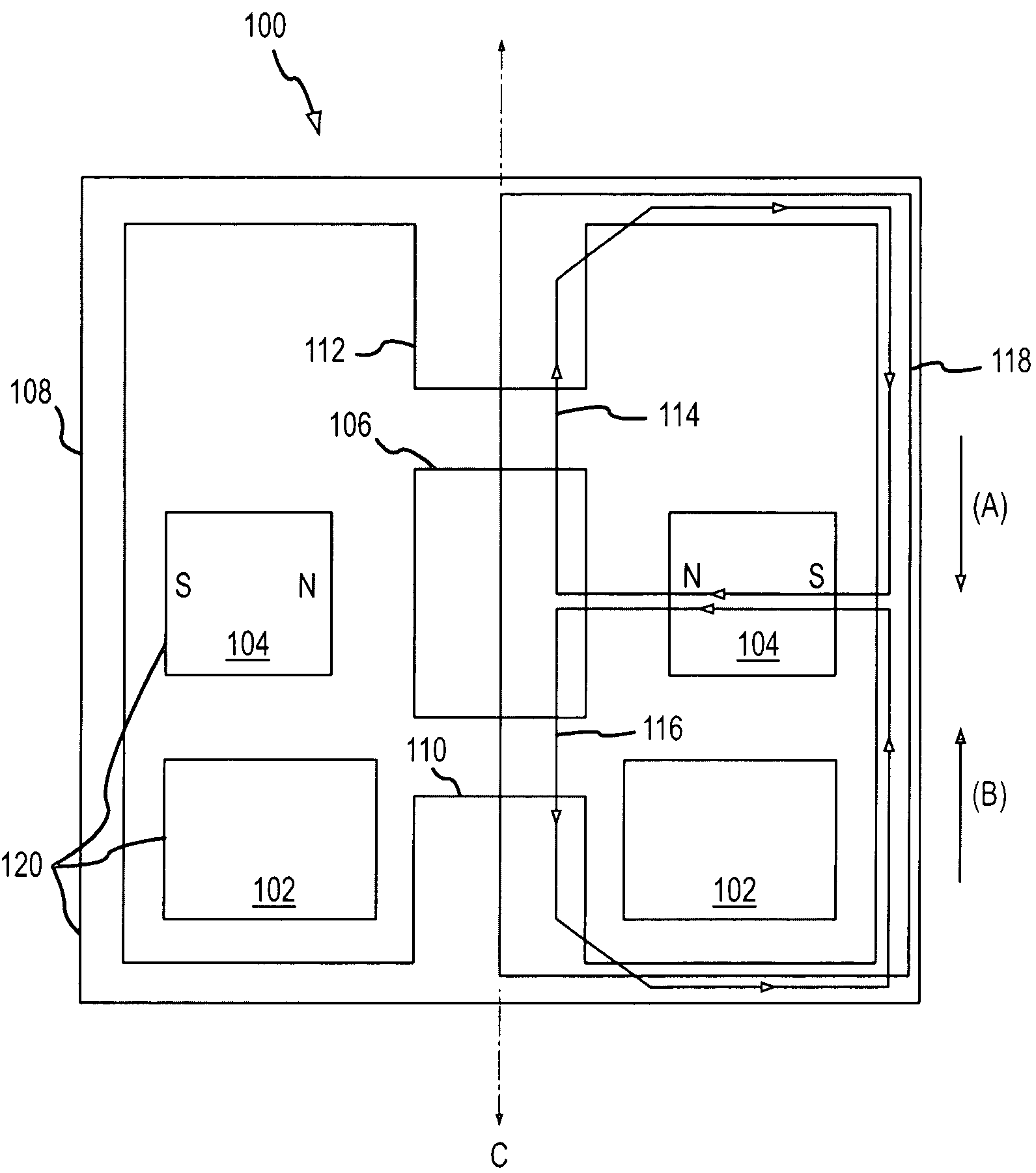
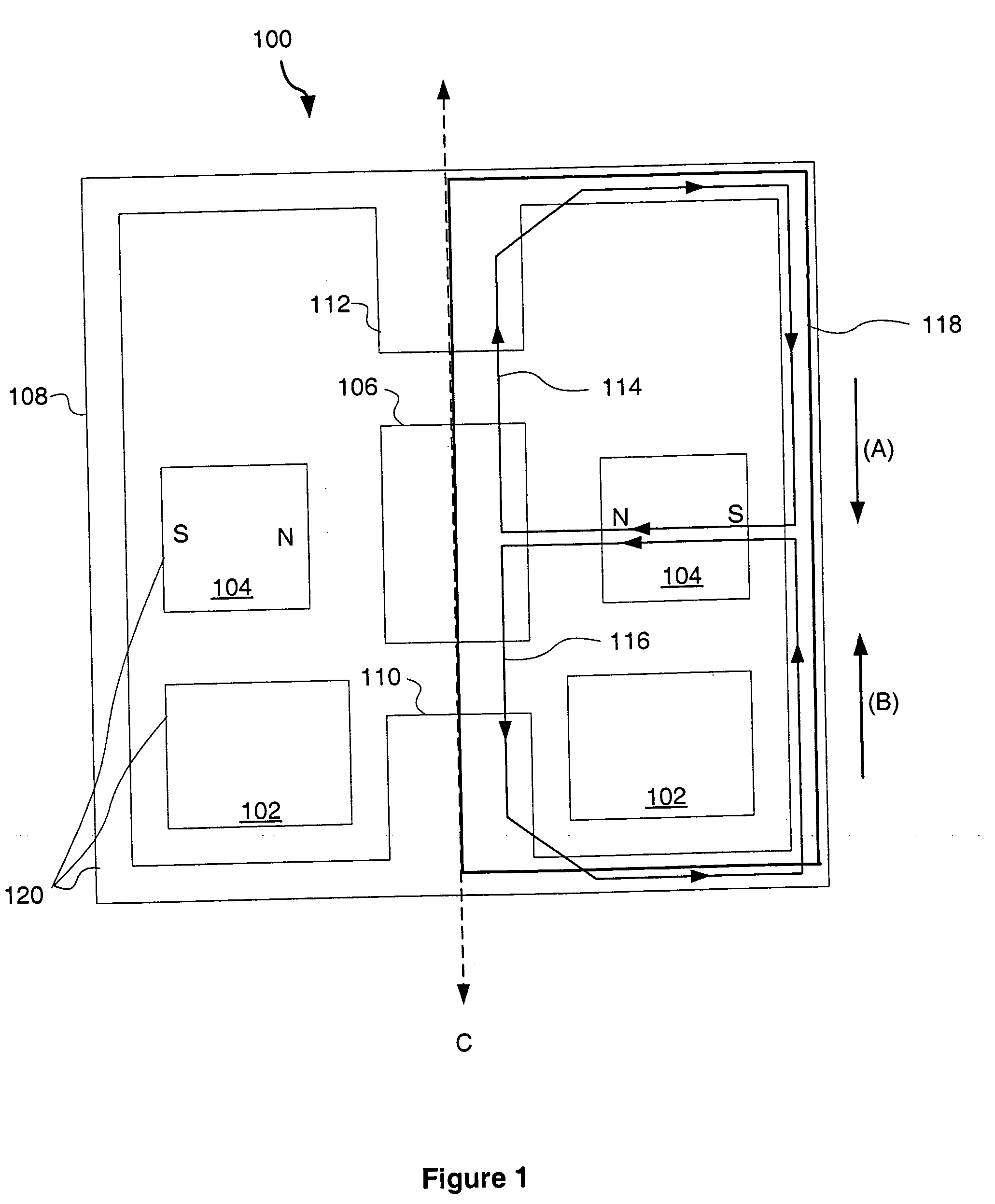
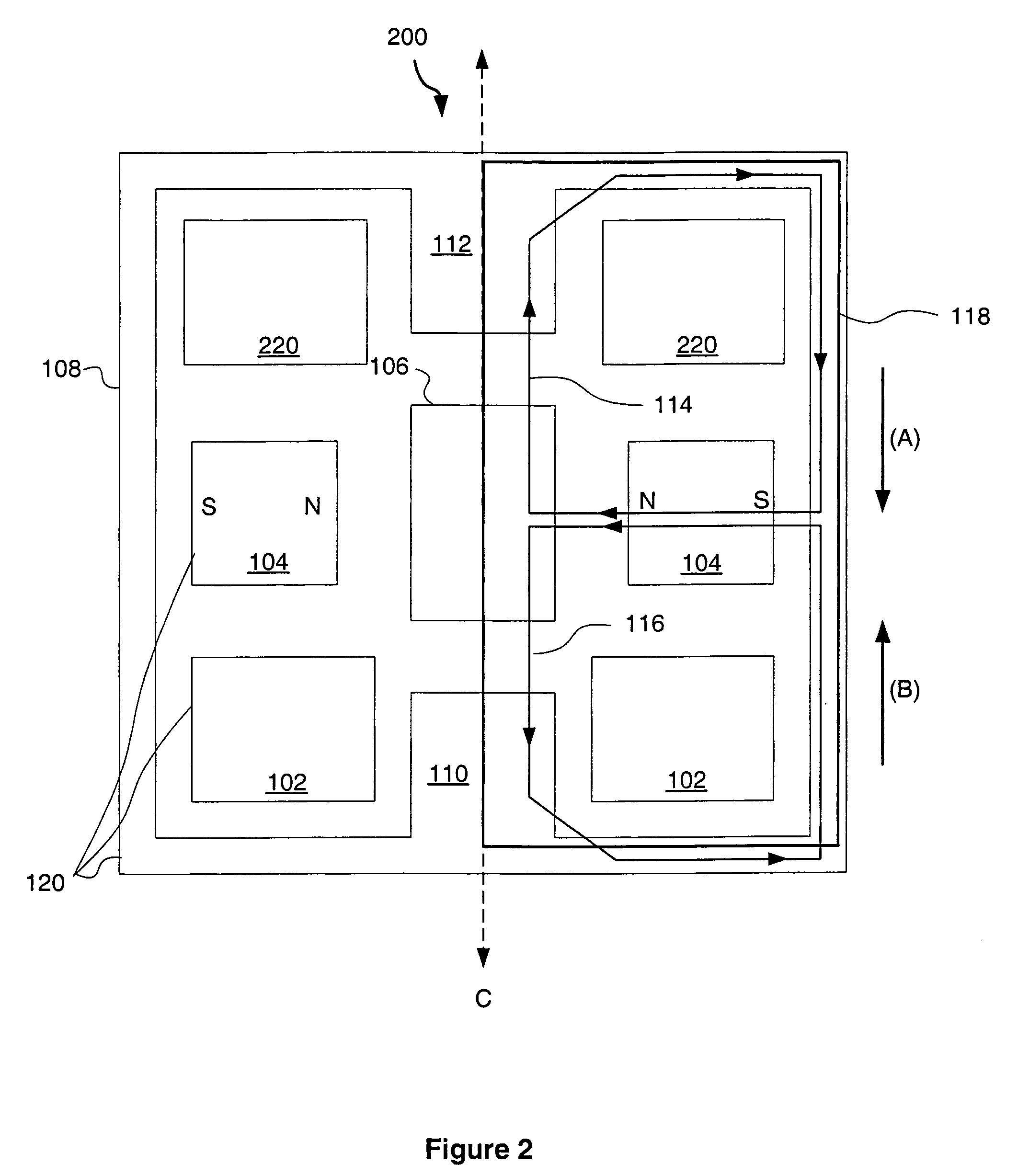
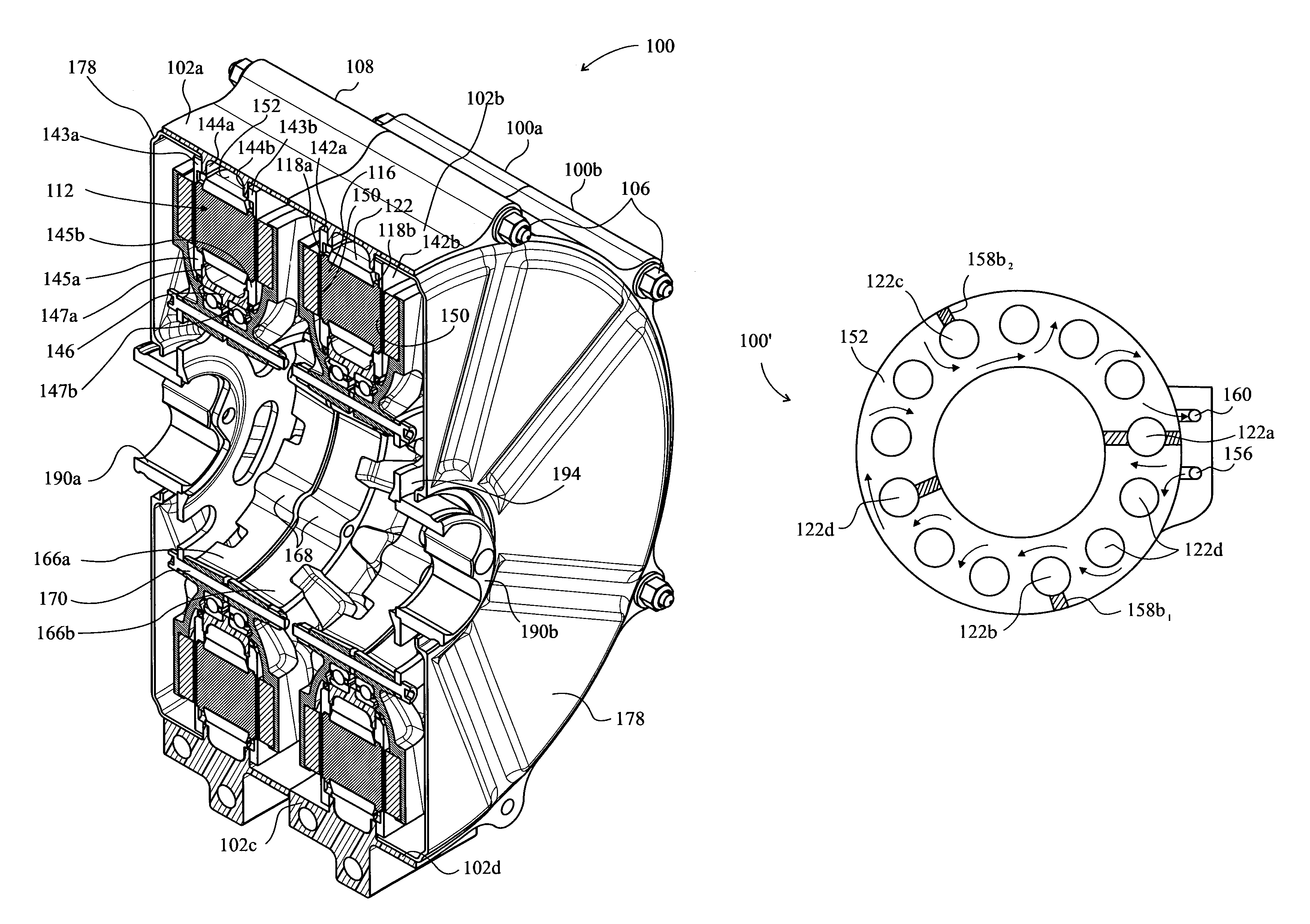
ActiveUS20110309726A1Gap minimizationReluctance of the overall magnetic circuit for the coils and magnets is reducedMagnetic circuit rotating partsMechanical energy handlingElectric machineStator coil
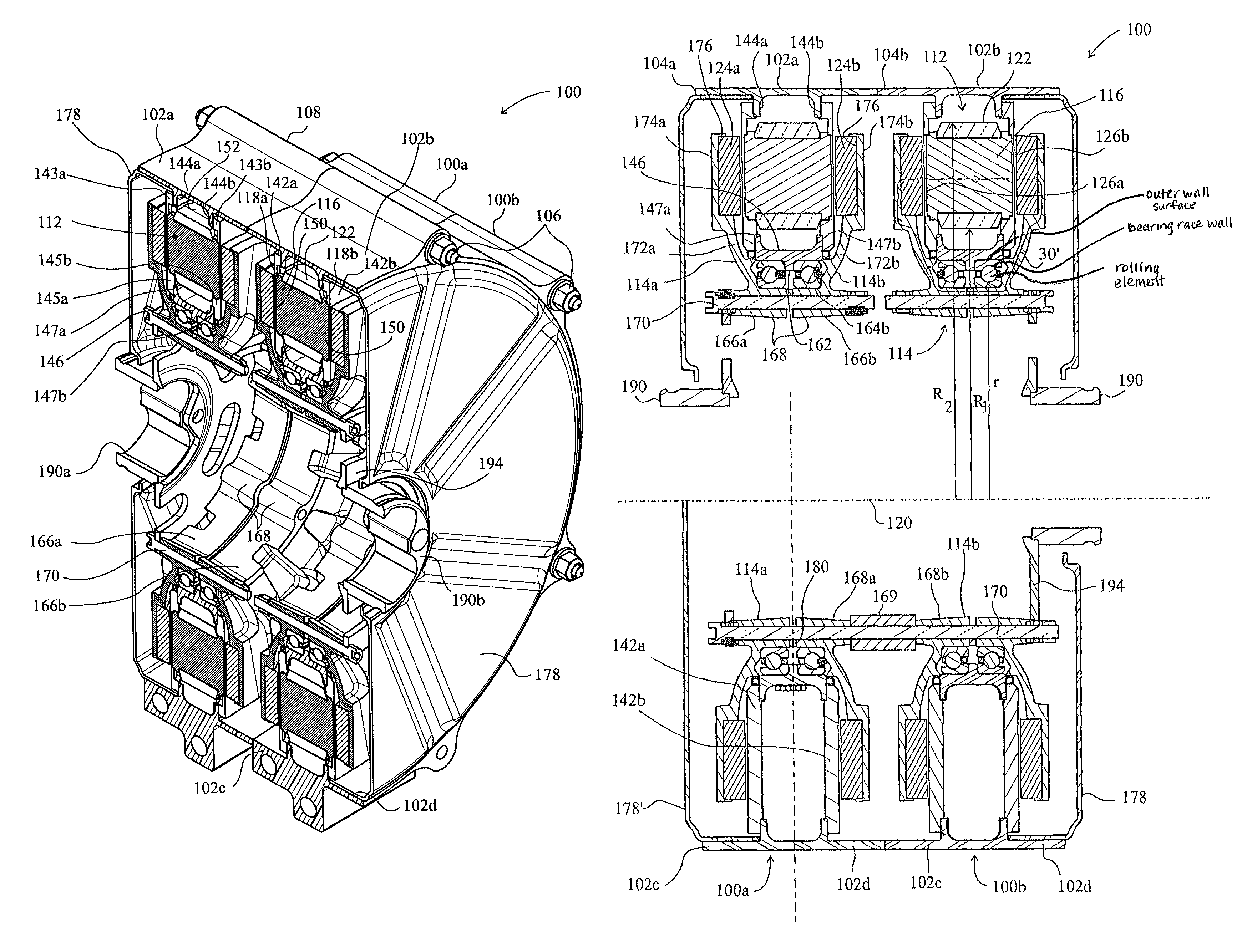
An electric machine (100) comprises a stator (112) and a rotor (114a, b) mounted for rotation about a rotor axis (120) with respect to the stator. Permanent magnets (124a, b) are carried by the rotor. The rotor has an output (190). The stator has coils (122) wound on stator bars (116) for interaction with the magnets. The rotor has two stages (114a,b) arranged one at either end of the stator bars, with two air gaps (126a,b) between the ends of the bars and the rotor stages. An annular housing (102, 142a, b, 146) retains and mounts the stator. A bearing (164a, b) is between the rotor and stator, the rotor being hollow around said rotor axis. There are two significant magnetic flux paths (30,30′) of the motor. The first passes between adjacent coils in a circuit on a substantially circumferential plane with respect to the axis (120). A second path 30′ is in an axial plane, passing around the bearing. The stator coils are spaced around the rotor axis and approach the rotor axis no closer than a first, stator radius (R1) of the stator. The bearing comprises rolling elements rolling on a surface of the rotor that is no closer to the rotor axis than a second, rotor radius (r), which rotor radius is between 60% and 90% of the stator radius.
Owner:YASA LIMITED
Slotted NMR antenna cover
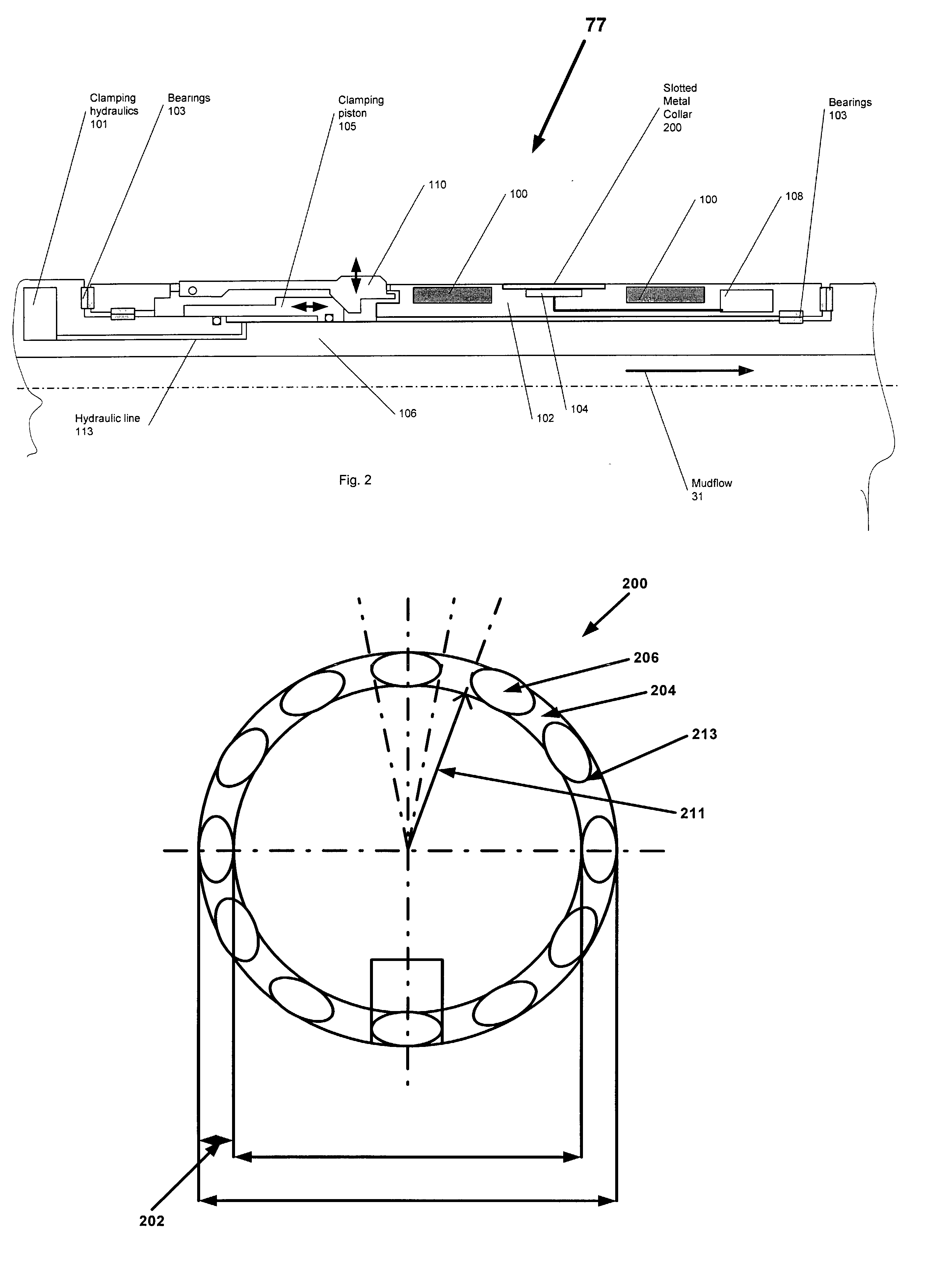
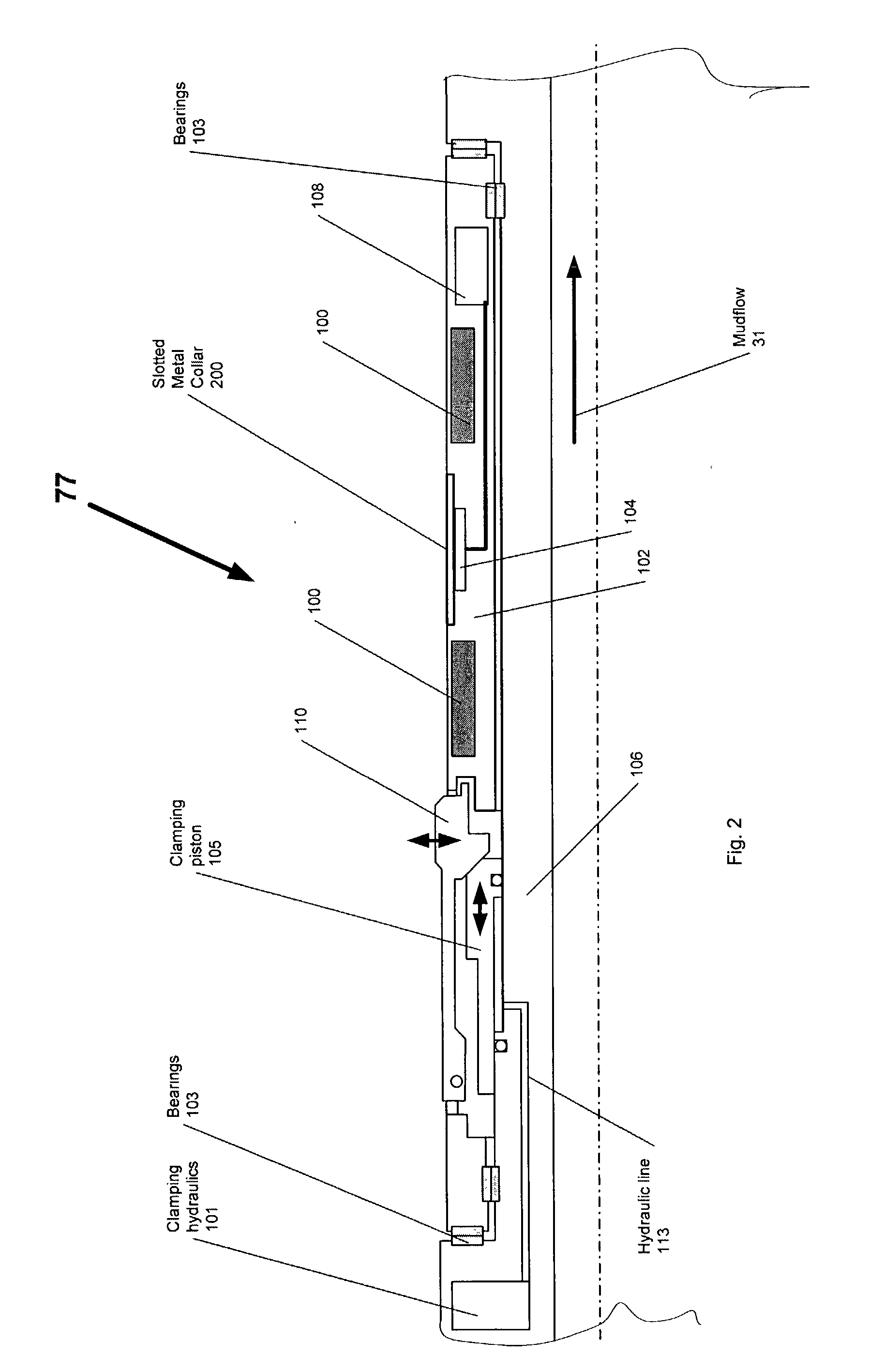
InactiveUS6838876B2Improve antenna efficiencyReduce power consumptionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMRBeam patternConductive materials
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for an NMR antenna with slotted metal cover
InactiveUS20030155915A1Improve antenna efficiencyReduce transmissionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMRBeam patternConductive materials
A slotted NMR antenna cover for improved mechanical ruggedness during transmission and reception of NMR signals in a down hole environment during either MWD or wire line operations. A NMR slotted antenna cover is provided comprising an elongated tubular structure with longitudinal gaps or slots filled with a RF transmissive or non-conductive material. The slots can befilled at the slot ends with soft magnetic material to improve efficiency of the antenna. The slots are radial concave to reduce eddy currents induced by alternating magnetic flux entering and leaving the slots surrounding the antenna. In another embodiment, the antenna cover is RF transmissive on only a portion of the antenna, via slots or transmissive material, so that the antenna cover can be used to allow RF transmission from the antenna in a side looking or beam pattern restricted mode only.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
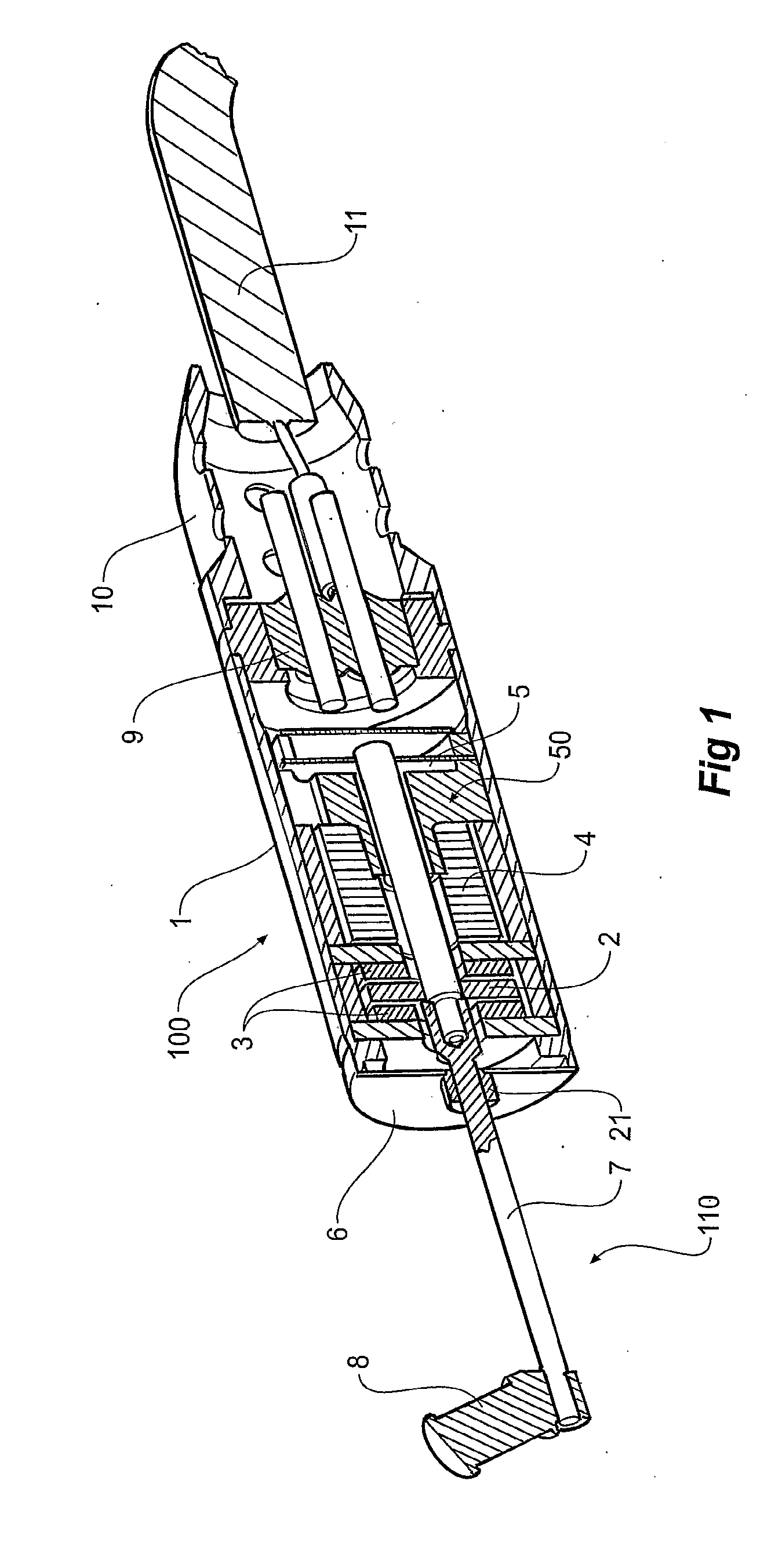
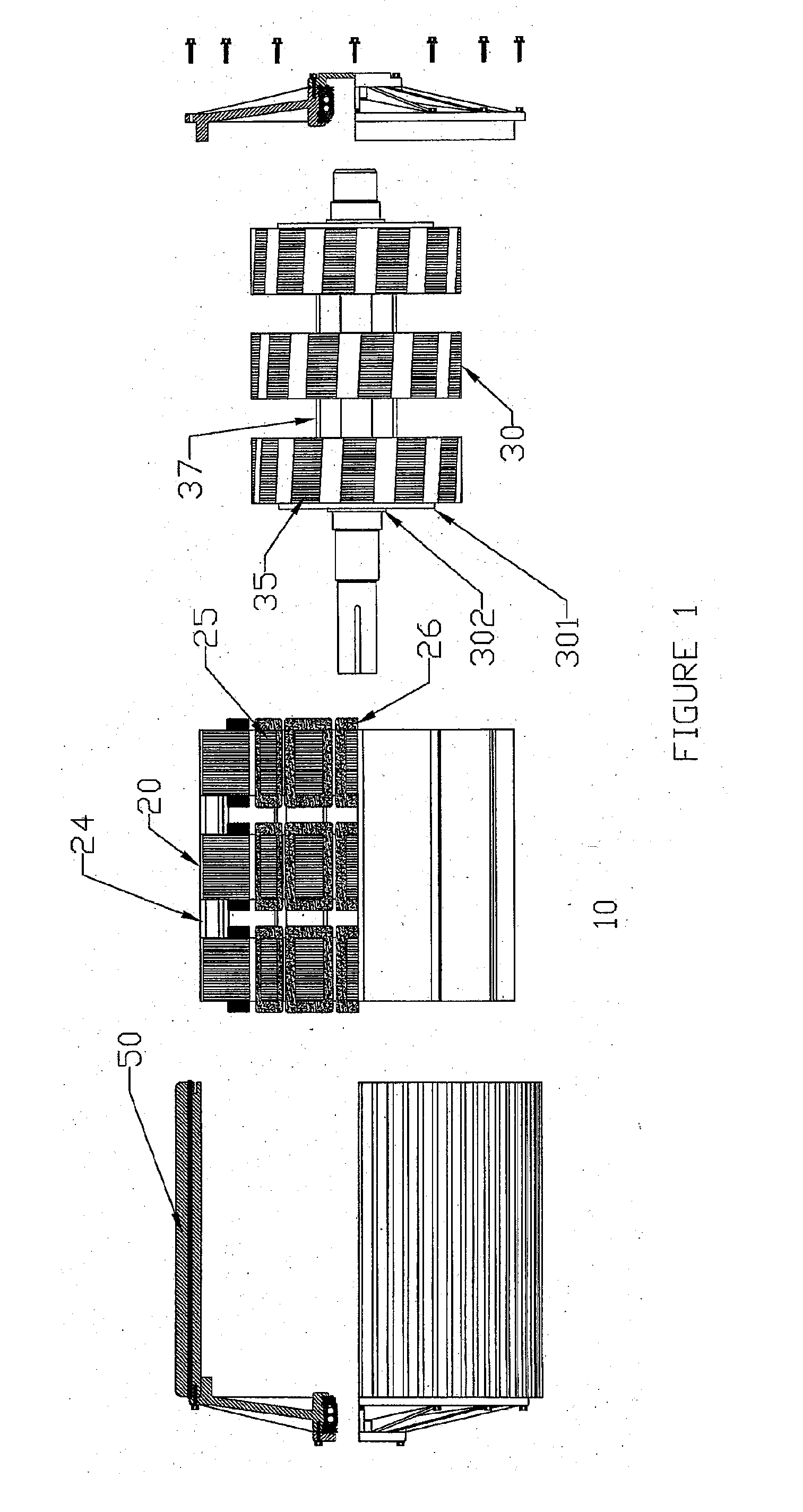
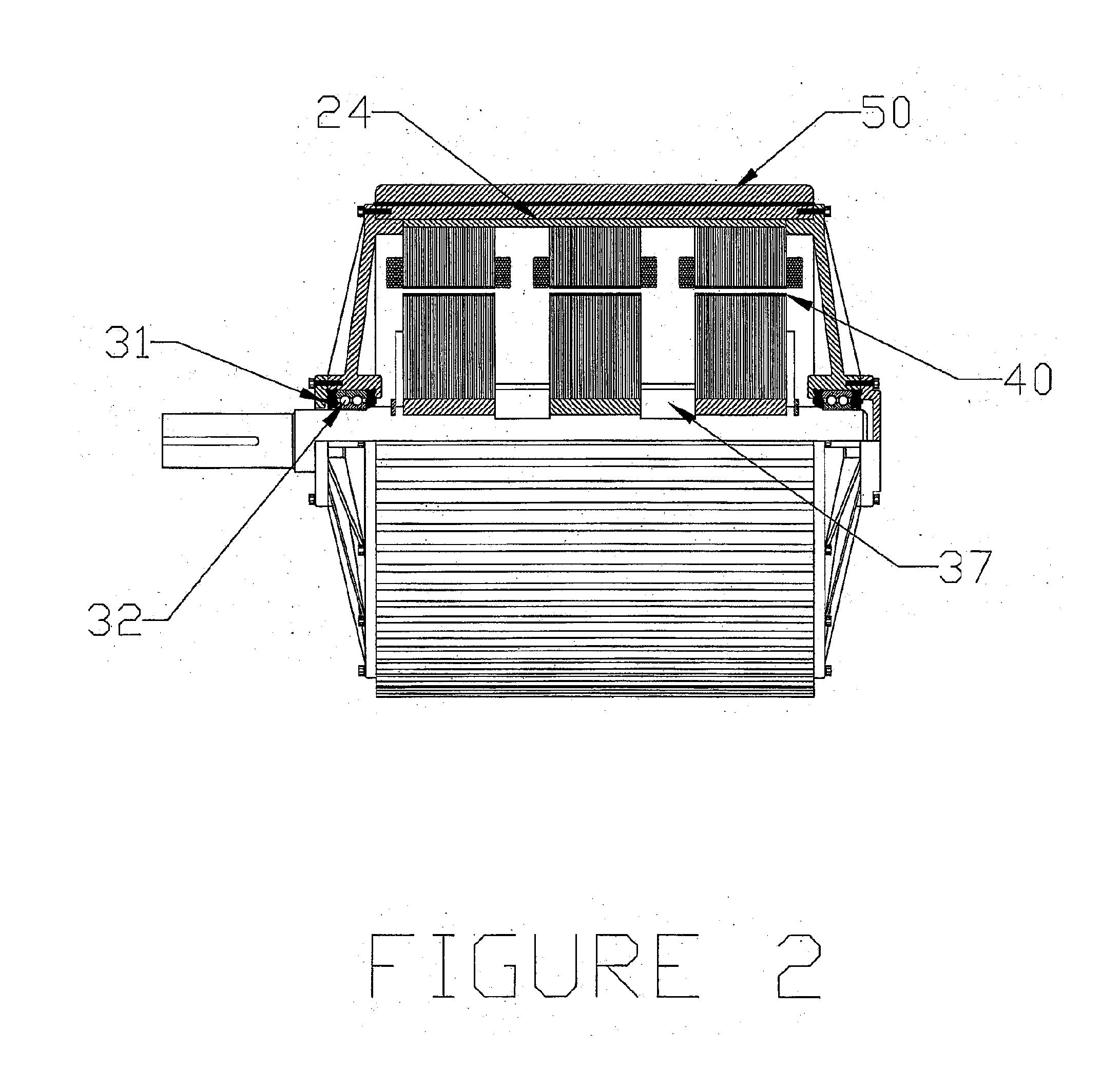
Low inductance, ferrite sub-gap substrate structure for surface film magnetic recording heads
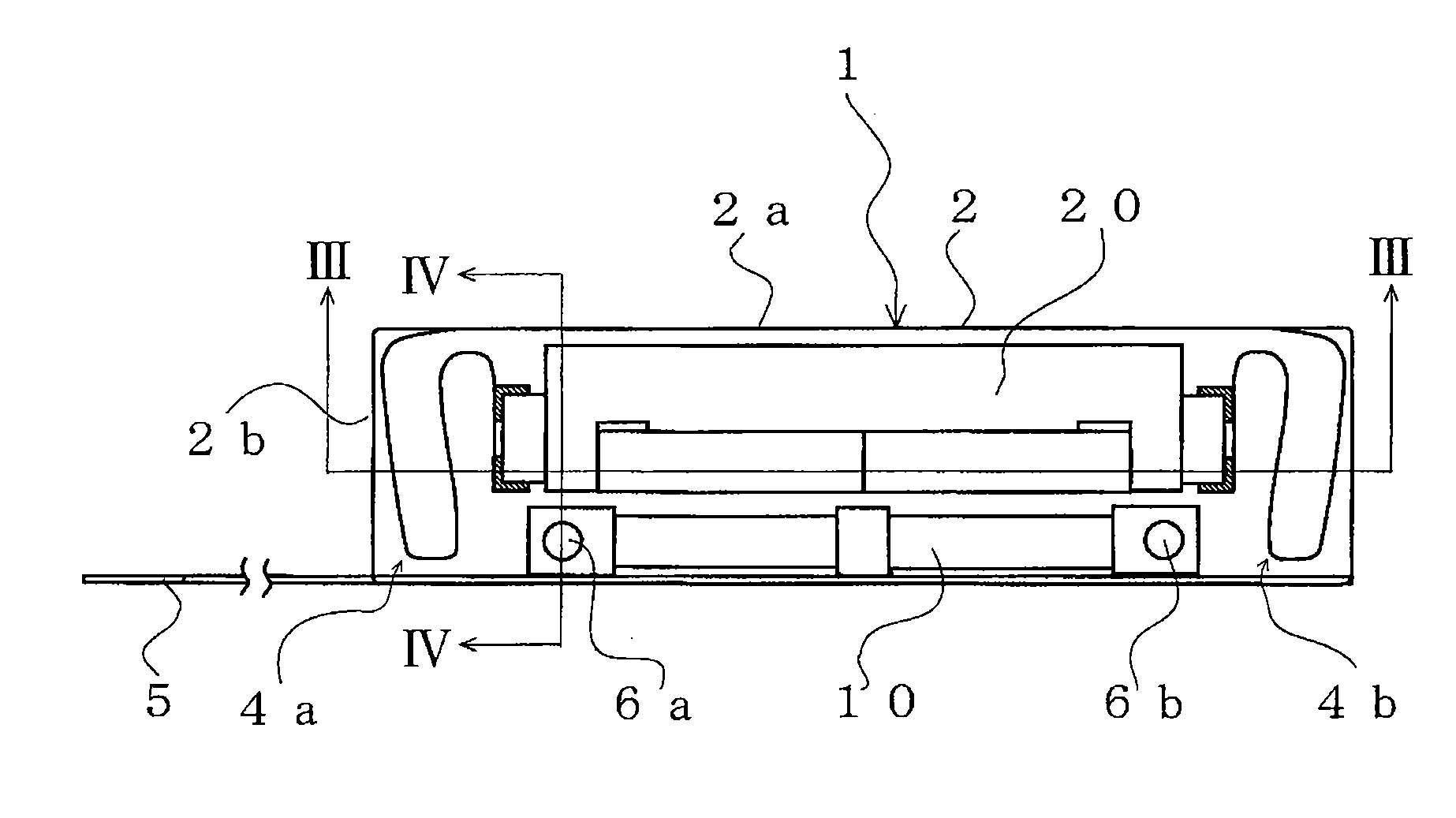
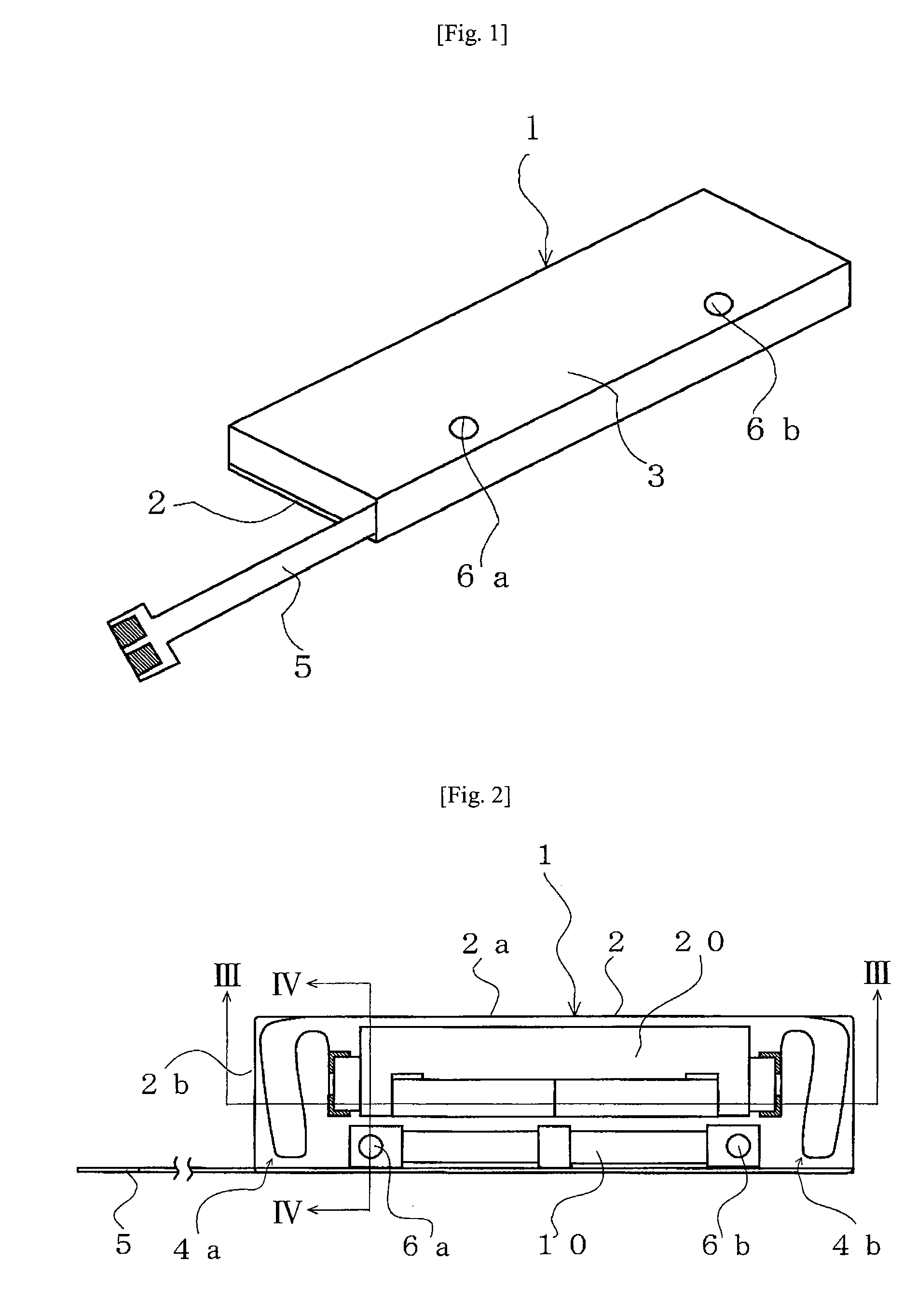
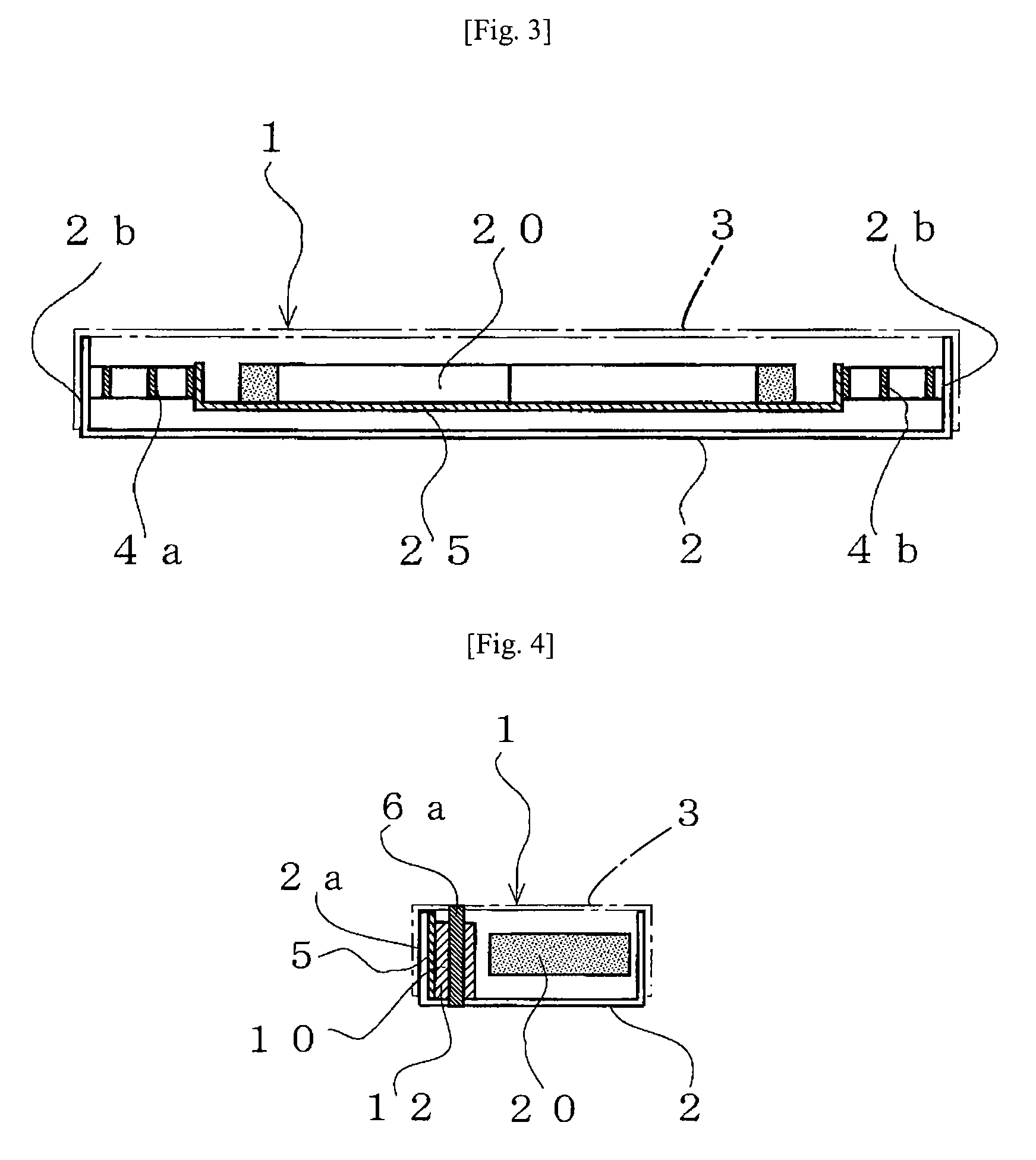
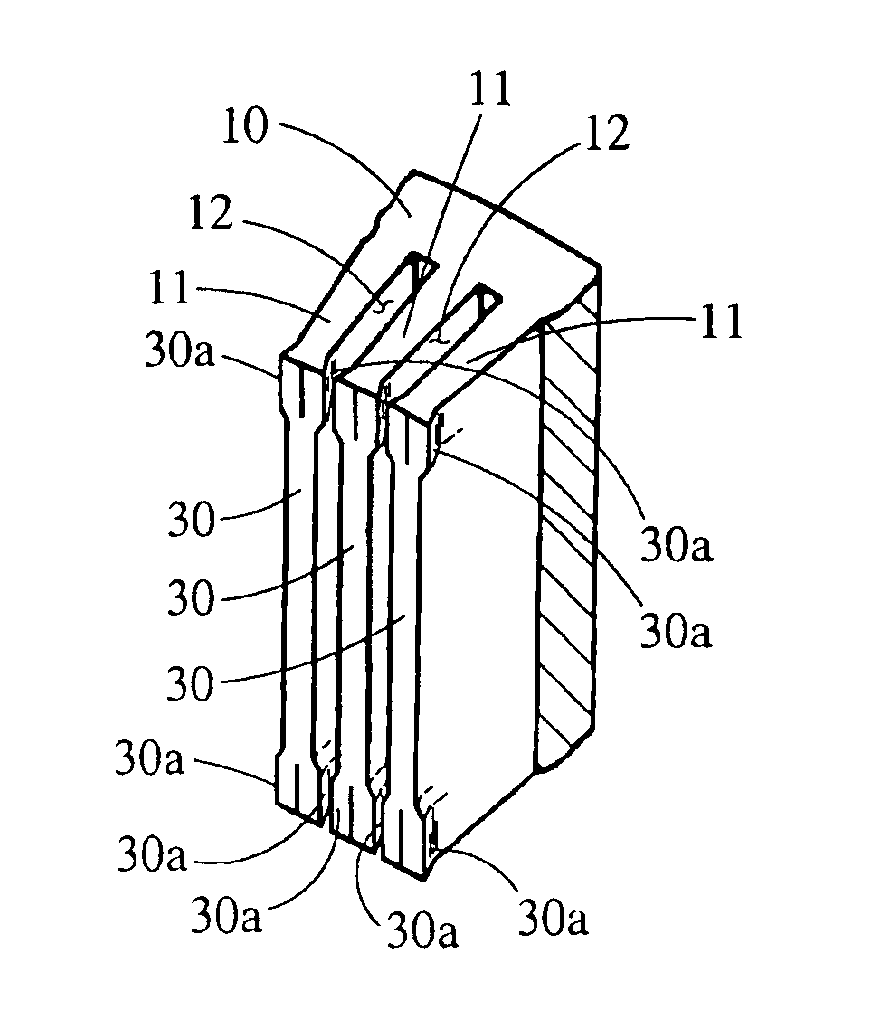
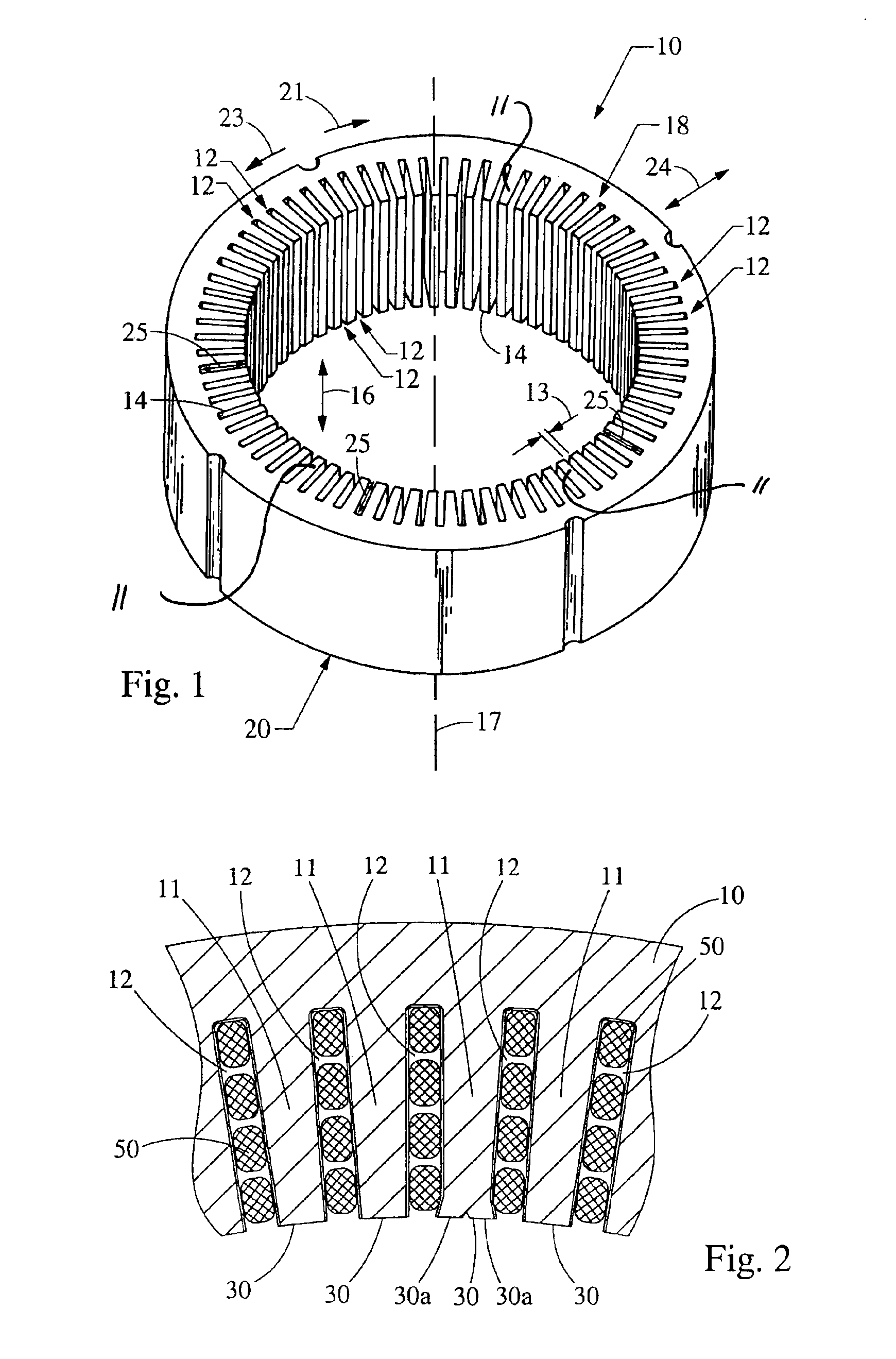
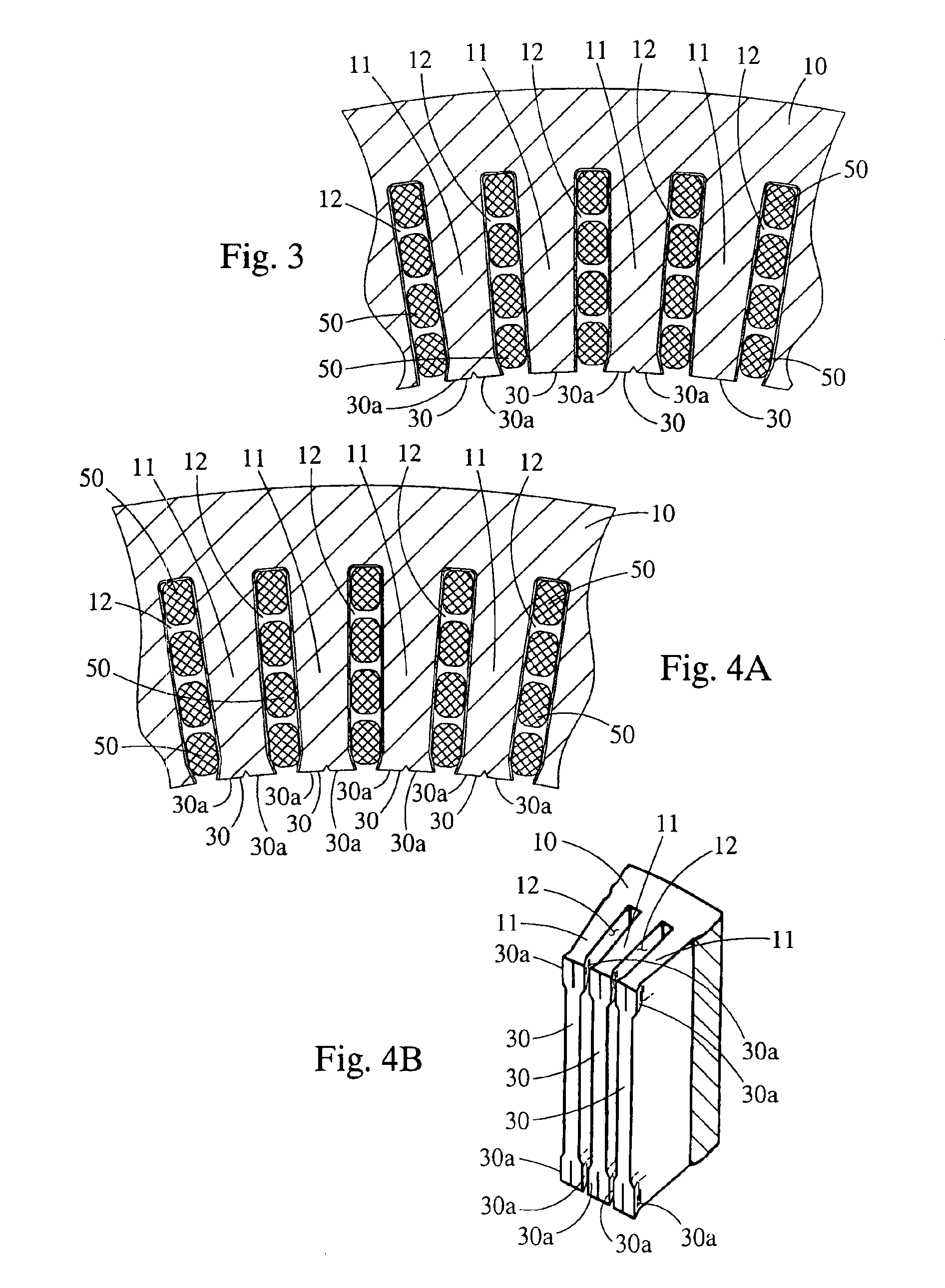
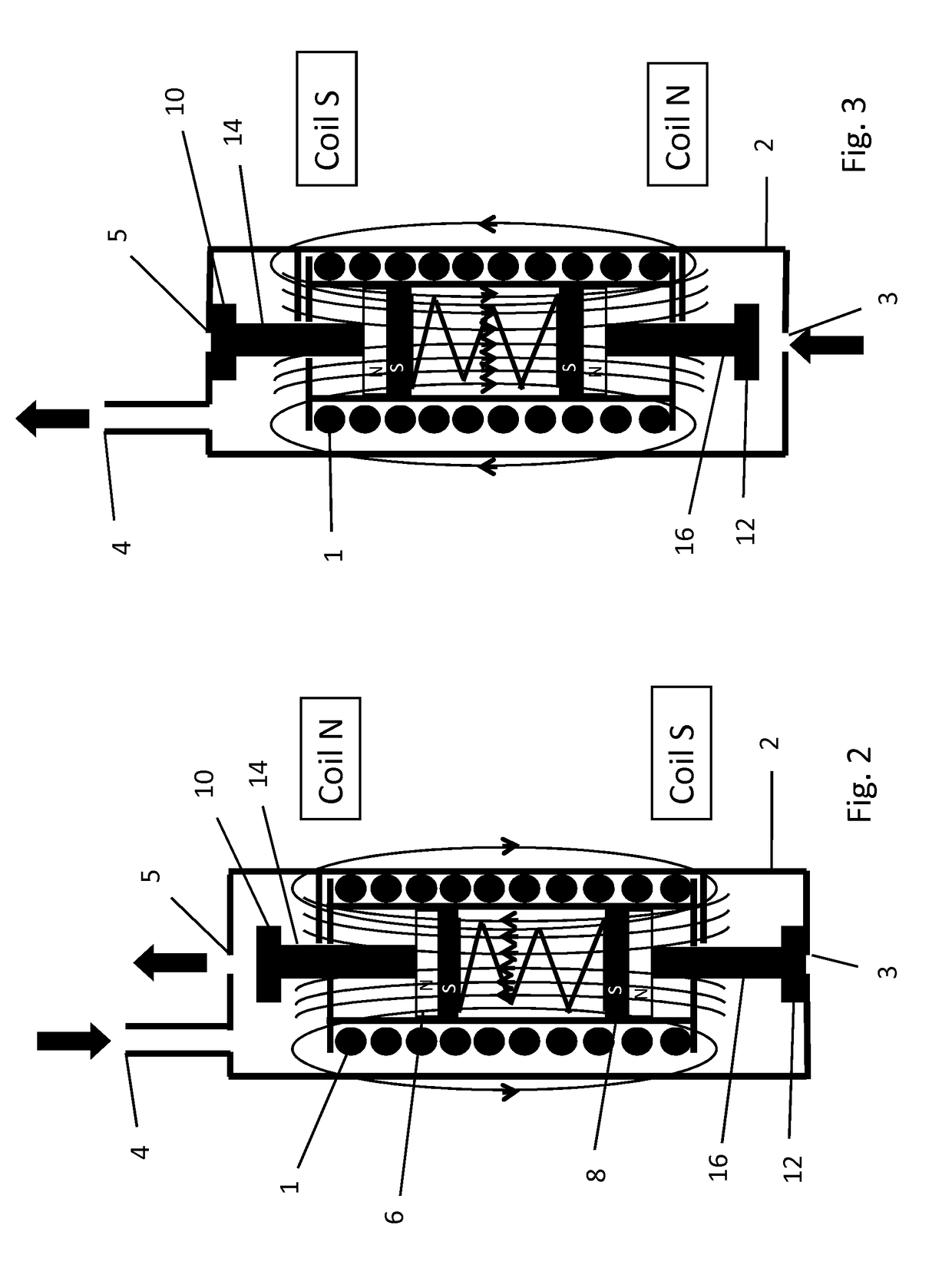
InactiveUS6894869B2Avoid passingReduce reluctanceManufacture head surfaceManufacturing heads with multiple gapsMetallurgyLow inductance
A thin film magnetic recording head is fabricated by forming a substrate from opposing ferrite blocks which have a ceramic member bonded between them. This structure is then diced to form a plurality of columns, wherein each column has a ferrite / ceramic combination. Each column represents a single channel in the completed head. A block of ceramic is then cut to match the columned structure and the two are bonded together. The bonded structure is then cut or ground until a head is formed, having ceramic disposed between each channel. A ferrite back-gap is then added to each channel, minimizing the reluctance of the flux path. The thin film is patterned on the head to optimize various channel configurations.
Owner:ADVANCED RES
Solenoid for a Direct Acting Valve Having Stepped Guide Tube
InactiveUS20120153199A1Reduce material costsImprove magnetic circuit efficiencyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetsConductor CoilCopper
A solenoid for a direct acting solenoid valve having reduced copper in a coil thereof is provided. The solenoid utilizes a stepped profile for a guide tube thereof, which reduces reluctance in the magnetic circuit such that a coil with less copper windings can be used. A direct acting solenoid valve utilizing such a reduced copper solenoid is also provided.
Owner:ROBERTSHAW CONTROLS CO
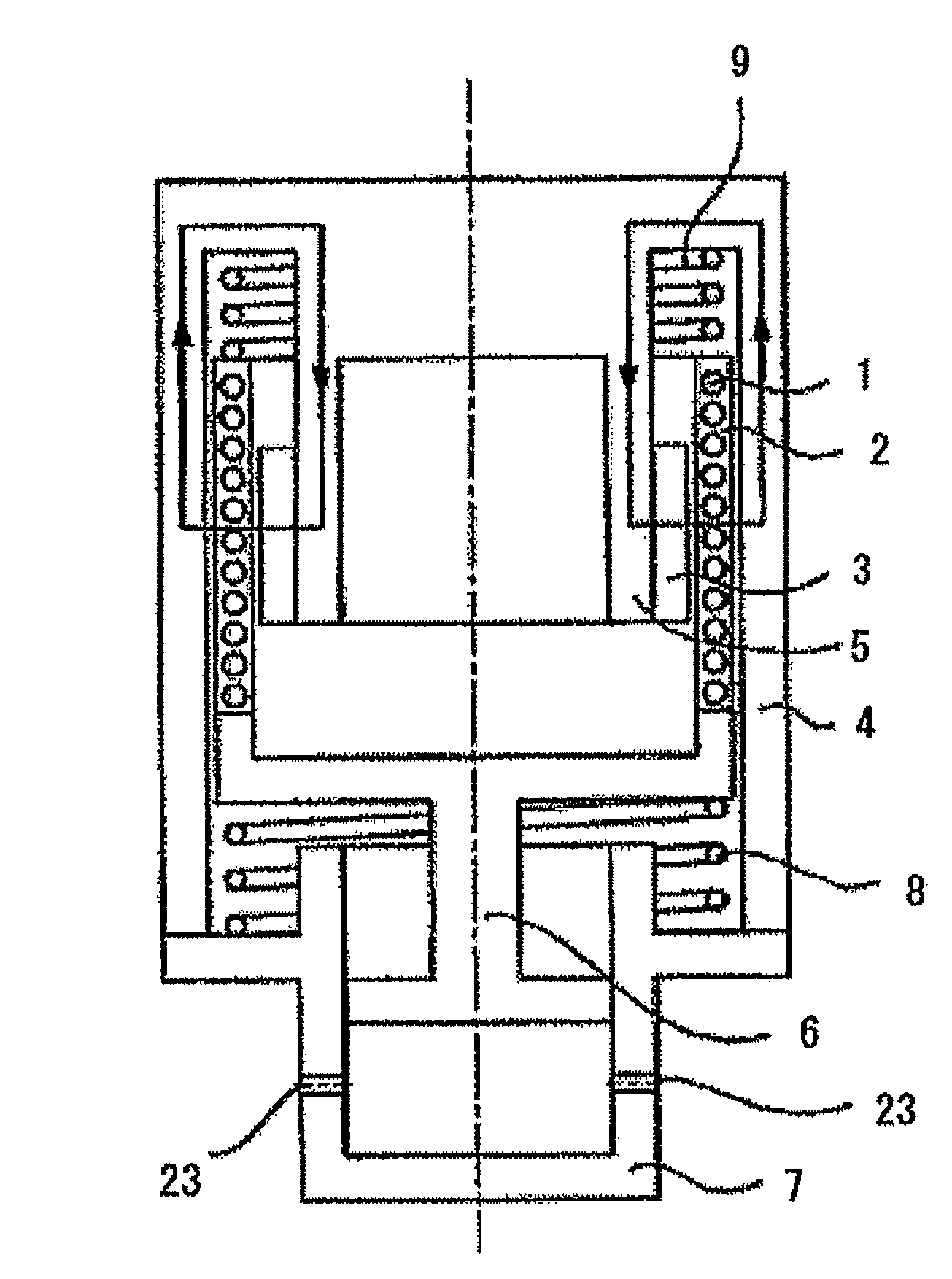
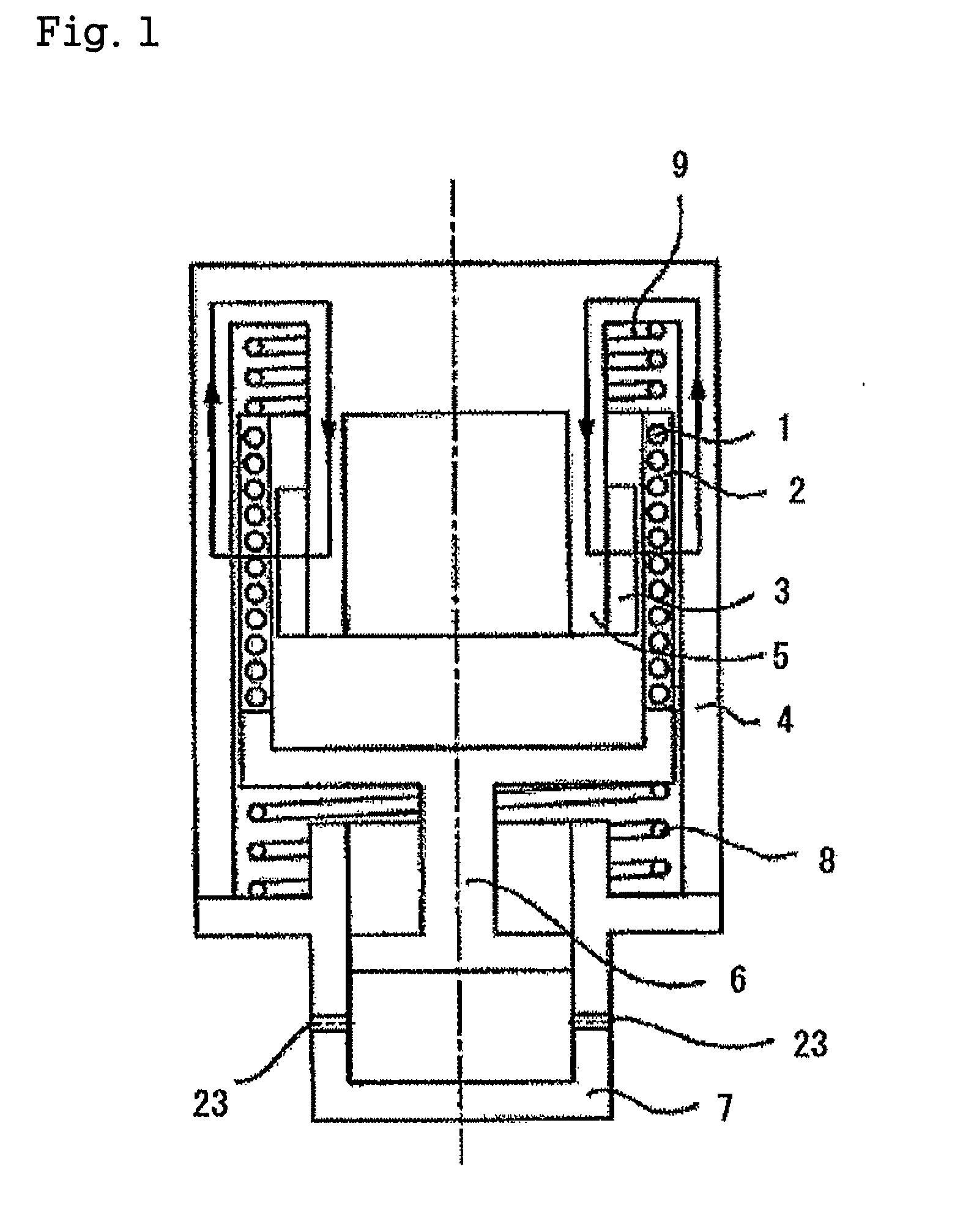
Linear motor, linear dynamo, reciprocation-type compressor driving system that is powered by linear motor, and charge system that uses linear dynamo
InactiveUS20130313838A1Reduce gapReduce reluctanceMachines/enginesMechanical energy handlingPhysicsDynamo
The disclosed is a linear motor which comprises an armature part including a coil, a field magnet part including a permanent magnet or an electromagnet, and a yoke part, in which the armature part is distributed in the field magnet part to excite the coil in the armature part, and which gives either the armature part or the field magnet part a rectilinear motion, wherein the armature part has a molded body in which the coil is covered with a magnetic substance, or has a structure in which a wall is formed on at least one of the internal circumference and the outer circumference of the coil with a magnetic cylindrical body.
Owner:NIPPON PISTONRING CO LTD
Multistage variable reluctance motor/generator
ActiveUS8138652B2Optimize arrangement and construction and performance and cooling and controlOptimize design elementSynchronous generatorsAC motor controlMotor designHigh torque
A compact, rugged, variable reluctance, variable speed, electric motor capable of producing high torque at high electrical energy conversion efficiencies is provided. The present invention provides for a multi-stage motor design having a number of discreet rotor and stator elements on a common shaft. This configuration provides for the simplest of magnetic structures and produces a powerful magnetic flux modelling design technique that is used to further optimize the motor design and subsequent control logic. Thermal mapping of the magnetic mass provides for advanced cooling techniques that are used to ensure long in-service life in the most extreme of industrial applications. The electric motor inherently provides low vibration thereby greatly reducing noise; low turn to turn voltage potentials thereby eliminating costly phase to phase shorting potential; efficient motor operation through the reduction in switching and copper losses in both the machine and its control system.
Owner:SUNCO INVESTMENTS
Stator of a rotary electric machine having staked core teeth
InactiveUS20050062359A1Eliminates potentialReduce reluctanceMagnetic circuitSynchronous machinesElectrical and Electronics engineeringConductor Coil
A stator of a rotary electric machine having secured core slot insulators includes a multi-phase stator winding, having a plurality of slot segments that are adapted to be radially inserted into a plurality of circumferentially spaced axially-extending core slots in a surface of a cylindrically-shaped stator core. The stator winding includes the plurality of slot segments alternately connected at the first and second ends of the stator core by a plurality of end loop segments to form the winding. At least one of the core teeth includes a distal end that is staked such that the distal end of the at least one core tooth is flared outward circumferentially to secure the stator winding within the core slots.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Mounting bracket for a security device
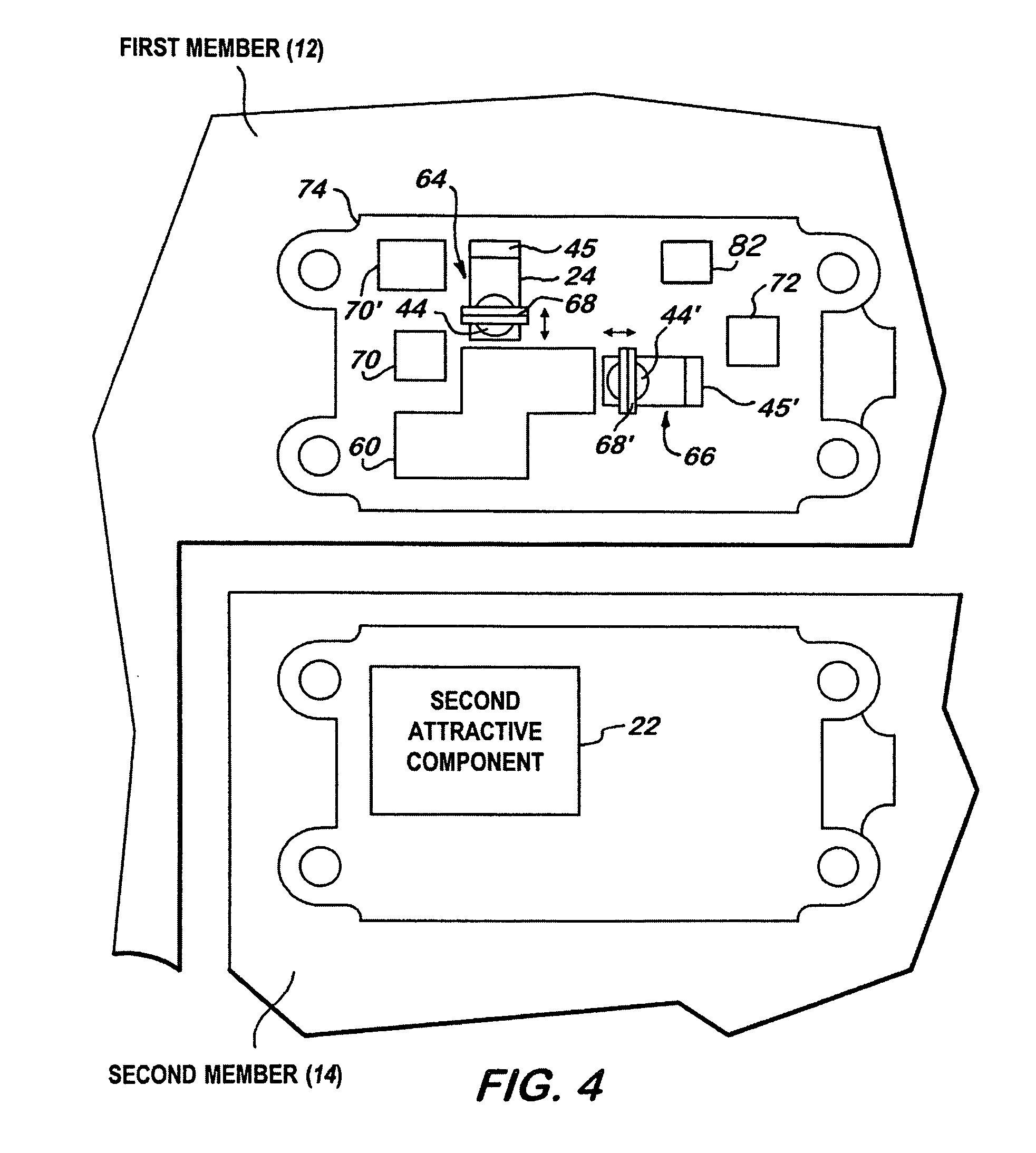
InactiveUS7187259B1DistanceIncrease distanceContact mechanismsPermanent magnet contact switchesRelative motionMagnetic switching
A universal magnetic switching assembly for detecting relative movement between first and second members, the universal switching assembly mounted on a bracket that may be used to adjust the positioning of the magnetic components relative to each other on opposing members to maintain the operational gap between the opposing magnetic components.
Owner:HARCO LAB
Valve actuator
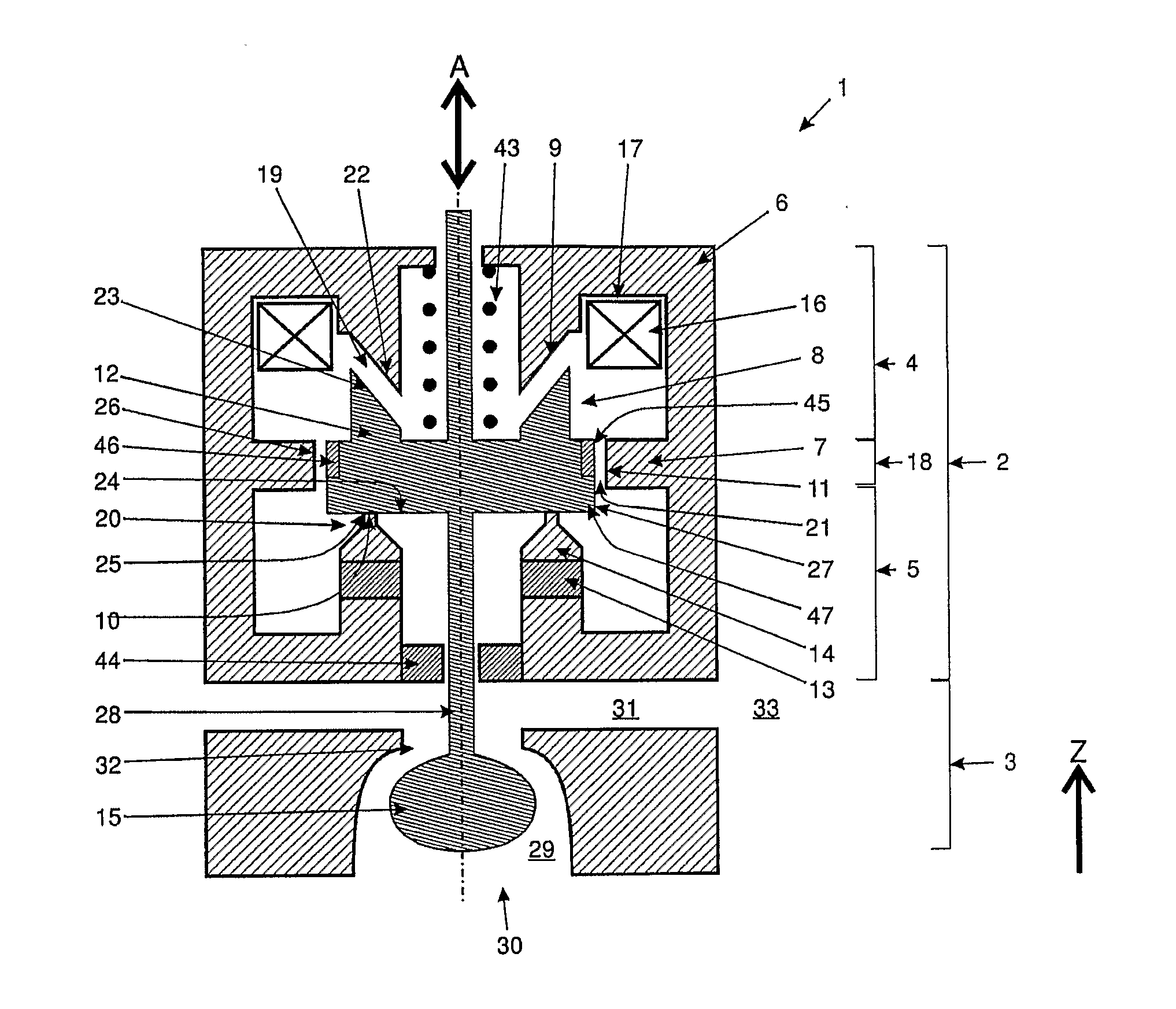
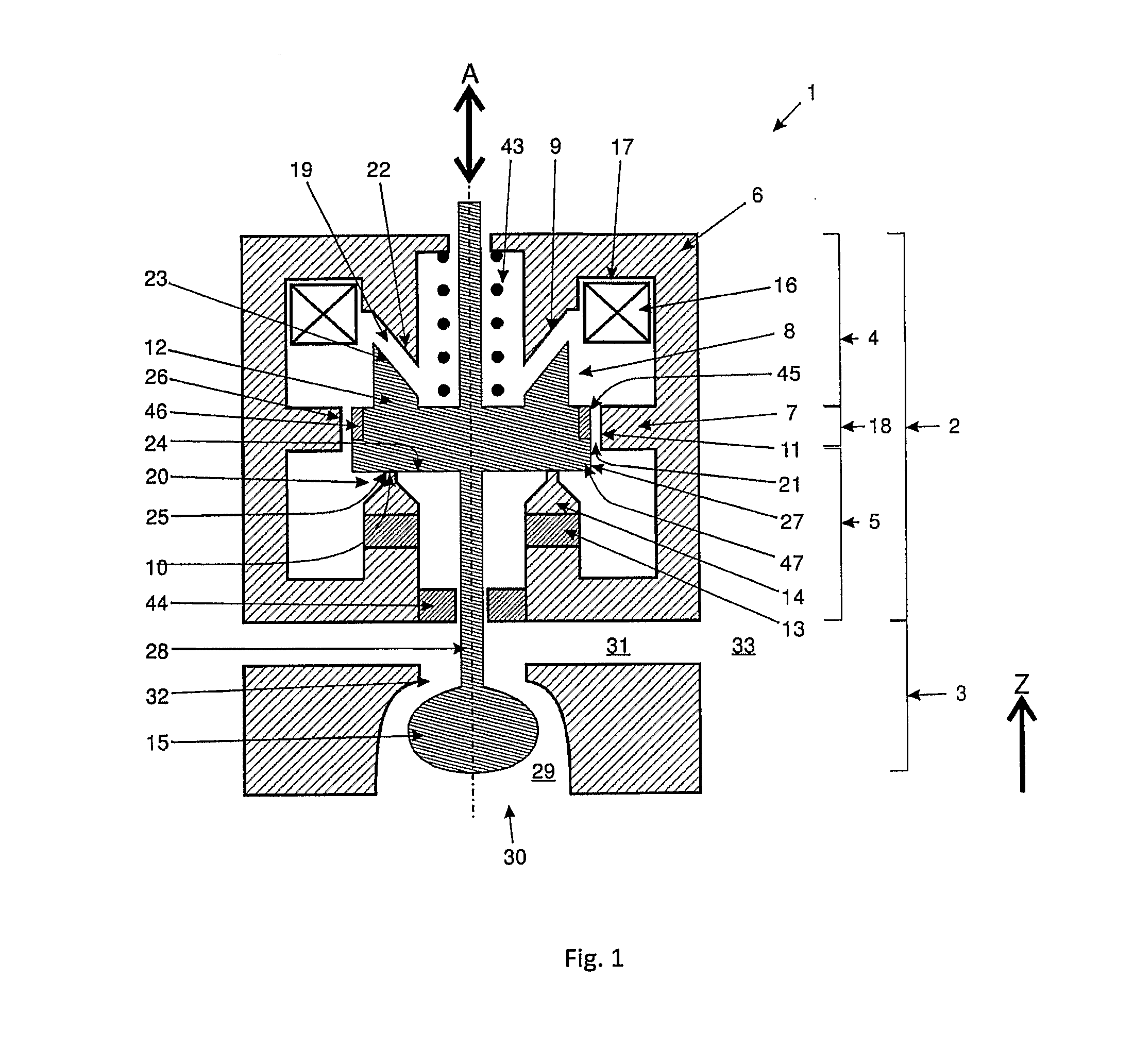
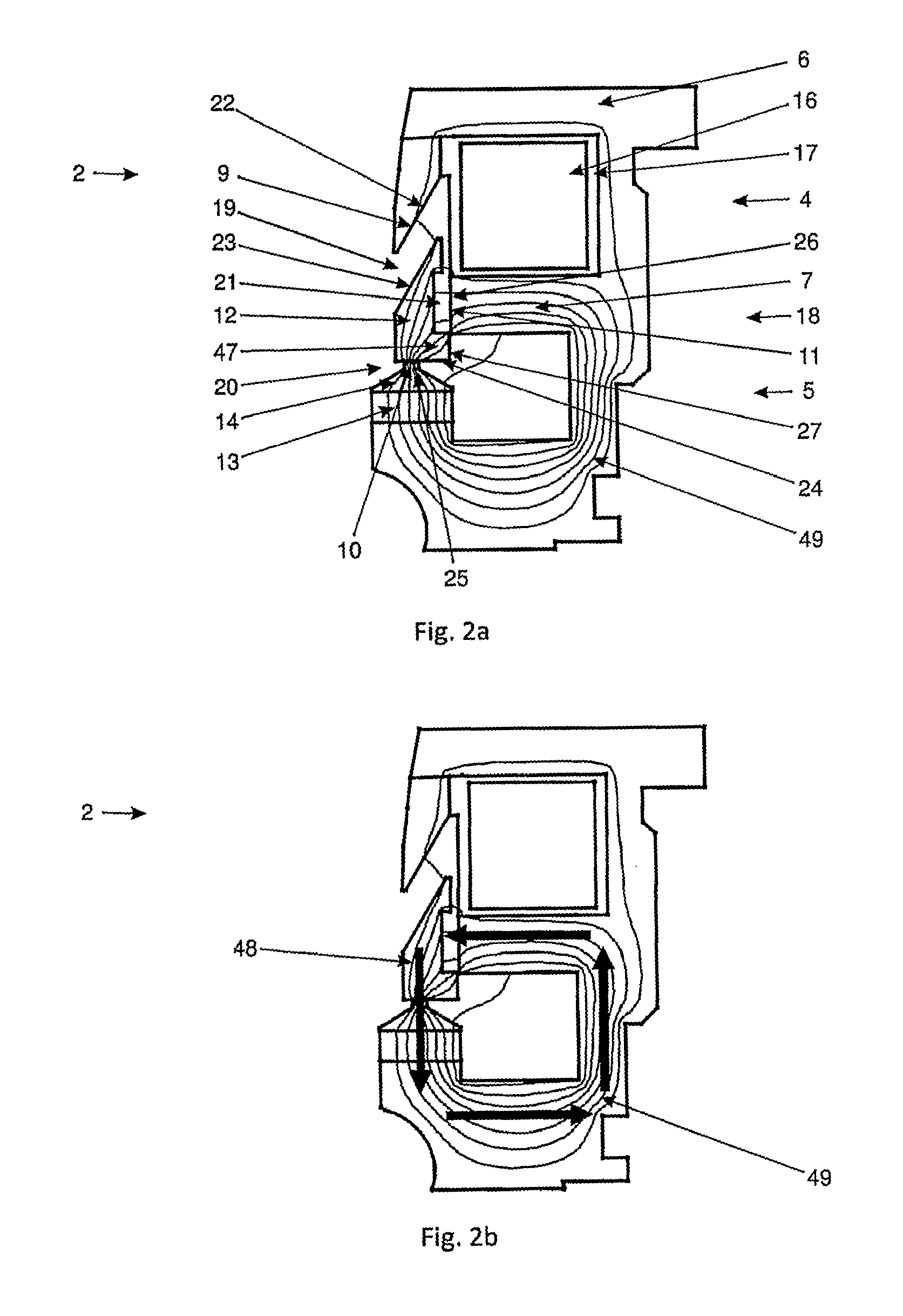
ActiveUS20110253918A1Effectively cancellingAccurate timingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPump controlValve actuatorEngineering
The invention relates to a valve actuator (2), comprising a magnetic core (6) with an interspace (8) and at least one bifurcating branch (7), at least one variable magnetic field generating device (16), at least one permanent magnetic field generating device (13) and at least one movable magnetic component (12), wherein the bifurcating branch (7) defines a first region (4) and a second region (5) of said magnetic core (6). Said movable magnetic component (12) is movably arranged within said interspace (8) of said magnetic core (6) in such a way that a first gap (19) is formed between a first surface (23) of said movable magnetic component (12) and a first surface (22) of said interspace (8) of said magnetic core (6), a second gap (20) is formed between a second surface (24) of said movable magnetic component (12) and a second surface (25) of said interspace (8) of said magnetic core (6), and a third gap (21) is formed between a third surface (27) of said movable magnetic component (12) and a third surface (26) of said bifurcating branch (7) of said magnetic core (6). At least one of said variable magnetic field generating devices (48, 49) is associated with said first region (4) of said magnetic core (6) and at least one of said permanent magnetic field generating devices (13) is associated with said second region (5) of said magnetic core (6). Said valve actuator (2) is designed and arranged in a way that a magnetic flux, generated by at least one at least one of said variable magnetic field generating devices (16) is able to exert a force on said at least one movable magnetic component (12) and is able to cancel the magnetic flux (48, 49), generated by at least one of said permanent magnetic field generating devices (13). At least one magnetic flux limiting means (7, 12) is provided, whose magnetic flux limit can be reached or exceeded.
Owner:ARTEMIS INTELLIGENT POWER +1
Stator of a rotary electric machine having stacked core teeth
InactiveUS6949857B2Raise the potentialMinimizing chanceWindingsMagnetic circuitElectric machineEngineering
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Variable reluctance motor
ActiveUS7166069B2Improve operating characteristicsGood curative effectSynchronous generatorsSynchronous motorsLinear relationshipReluctance motor
A variable reluctance motor is provided having a linear relationship between an input current and an output force. According to one aspect of the invention, the motor comprises a stator, an armature, and at least one magnetic member to provide a biasing force on the armature. According to this characterization, the motor also includes a drive coil to generate an electromagnetic field in response to a current input. The electromagnetic field, in turn, moves the armature relative to the stator during motor operation.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Low inductance, ferrite sub-gap substrate structure for surface film magnetic recording heads
InactiveUS20050275968A1Avoid passingReduce reluctanceManufacture head surfaceManufacture unitary devices of plural headsMagnetic reluctanceOptoelectronics
Owner:DUGAS MATTHEW P
Mounting bracket for a security device
InactiveUS20070035370A1Misalignment problemReduce magnetic field strengthContact mechanismsPermanent magnet contact switchesEngineeringRelative motion
A universal magnetic switching assembly for detecting relative movement between first and second members, the universal switching assembly mounted on a bracket that may be used to adjust the positioning of the magnetic components relative to each other on opposing members to maintain the operational gap between the opposing magnetic components.
Owner:HARCO LAB
Permanent magnet bearing with large bearing capacity and damping performance
InactiveCN102003462AIncrease magnetic inductionReduce Flux LeakageBearingsMagnetic bearingEngineering
The invention relates to a permanent magnet bearing with large bearing capacity and damping performance. A bearing stator is arranged at the upper part of an axial air gap, a stator soft magnetic ring (1) is provided with an annular groove, and a stator inner insulating magnetic ring (13), a carrying permanent magnet inner ring (4), a stator carrying bearing limit ring (3), a stator carrying permanent magnet outer ring (2), a stator damping permanent ring (5) and a stator outer insulating ring (6) are arranged in the annular groove from the inner circle to the outer circle; a bearing rotor is arranged at the lower part of the axial air gap and is provided with another annular groove, and a rotor inner insulating magnetic ring (11), a rotor damping permanent magnet ring (12), a rotor bearing permanent magnet inner ring (10), a rotor carrying bearing limit ring (9), a rotor carrying permanent magnet outer ring (8) and a rotor outer insulating ring (7) are arranged in the annular groove from the inner circle to the outer circle. When the rotor vibrates in horizontal direction, the permanent magnet bearing with the structure can provide eddy current damping to help the rotor to pass the critical rotating speed successfully; in addition, an eddy current damper and the permanent magnet bearing are integrated into a whole, thereby achieving compact structure and saving space.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Variable reluctance motor
ActiveUS20050225180A1Improve operating characteristicsGood curative effectSynchronous generatorsSynchronous motorsElectric machineLinear relationship
A variable reluctance motor is provided having a linear relationship between an input current and an output force. According to one aspect of the invention, the motor comprises a stator, an armature, and at least one magnetic member to provide a biasing force on the armature. According to this characterization, the motor also includes a drive coil to generate an electromagnetic field in response to a current input. The electromagnetic field, in turn, moves the armature relative to the stator during motor operation.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Cooled electric machine
ActiveUS9496776B2Gap minimizationImprove rigidityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineEngineering
Owner:YASA LIMITED
Electrochemical Ion Exchange Treatment of Fluids
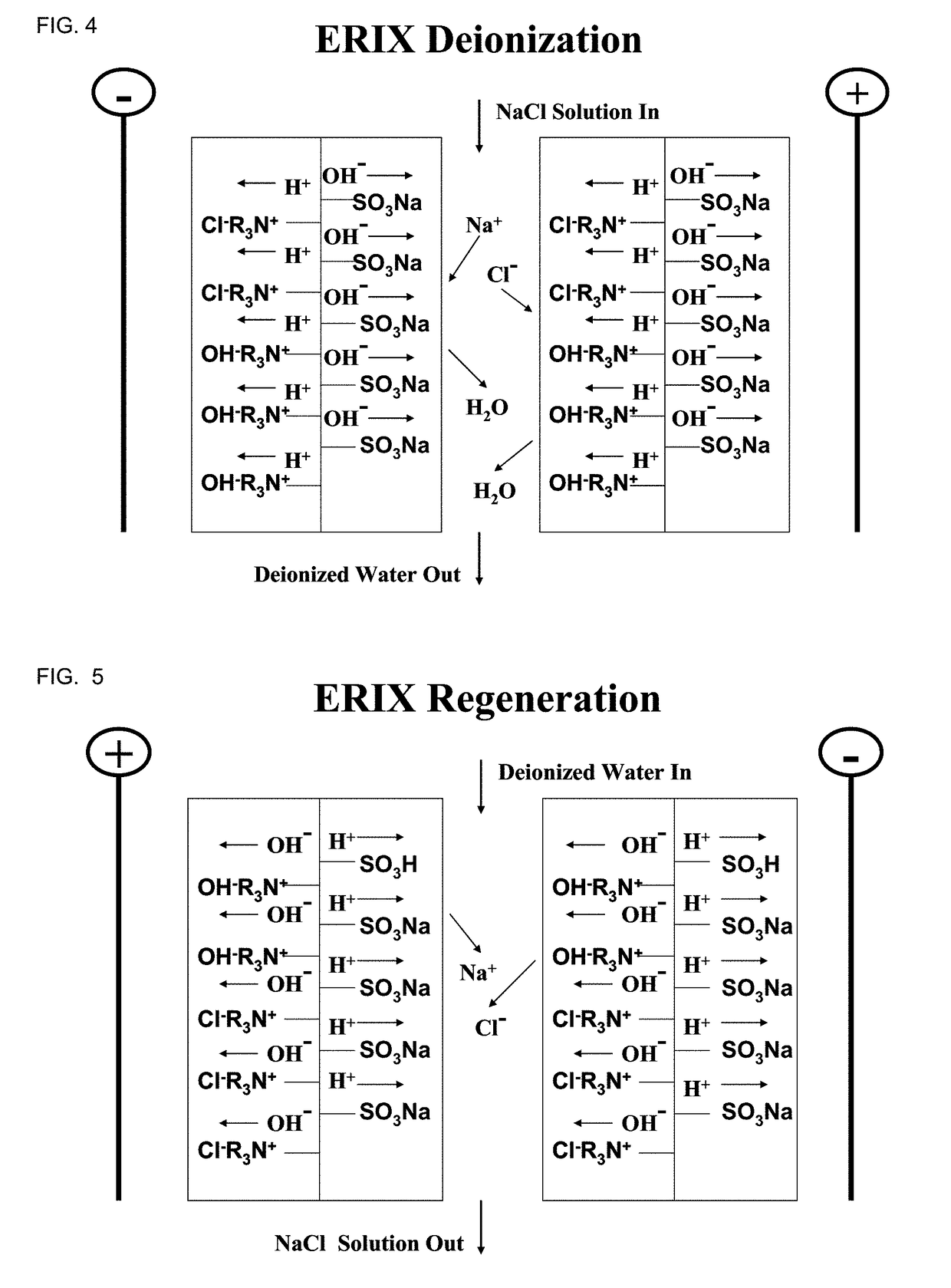
ActiveUS20180354820A1Reduce reluctanceIon-exchange process apparatusMembranesIon-exchange membranesElectrical battery
A fluid treatment apparatus is constructed from at least one electrochemical cell including a bipolar ion exchange membrane and having a single output orifice to deliver treated fluid. The apparatus may employ a power supply transformer featuring a magnetic dispersion bridge to regulate the magnetic flux to secondary coils, thereby limiting the current delivered to the load and protecting the apparatus from over-current damage. The cell includes a membrane assembly which incorporates both the inner and outer electrodes to provide repeatable assembly and service, as well as reliable performance. The apparatus will provide continuous fluid treatment when designed with at least two stages, each stage including at least one cell, in which one stage is treating influent solution and another stage is regenerating. A method to operate these apparatus includes the steps of deionizing influent solution without interruption, halting deionization water flow and removing power from the deionization cells, flushing the liquid between membrane layers to the drain outlet, initiating regeneration power, and initiating regeneration flow.
Owner:ERIX SOLUTIONS CORP
Electric machine-modular
ActiveUS9318938B2Reluctance of the overall magnetic circuit for the coils and magnets is reducedReduce reluctanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineStator coil
An electric machine (100) comprises a stator (112) and a rotor (114a, b) mounted for rotation about a rotor axis (120) with respect to the stator. Permanent magnets (124a, b) are carried by the rotor. The rotor has an output (190). The stator has coils (122) wound on stator bars (116) for interaction with the magnets. The rotor has two stages (114a,b) arranged one at either end of the stator bars, with two air gaps (126a,b) between the ends of the bars and the rotor stages. An annular housing (102, 142a, b, 146) retains and mounts the stator. A bearing (164a, b) is between the rotor and stator, the rotor being hollow around said rotor axis. There are two significant magnetic flux paths (30,30′) of the motor. The first passes between adjacent coils in a circuit on a substantially circumferential plane with respect to the axis (120). A second path 30′ is in an axial plane, passing around the bearing. The stator coils are spaced around the rotor axis and approach the rotor axis no closer than a first, stator radius (R1) of the stator. The bearing comprises rolling elements rolling on a surface of the rotor that is no closer to the rotor axis than a second, rotor radius (r), which rotor radius is between 60% and 90% of the stator radius.
Owner:YASA LIMITED
Core cap for loudspeaker
ActiveUS20060182305A1Reducing ability to carryReduce capacityTransducer detailsNuclear engineeringLoudspeaker
A core cap or top plate for use with loudspeakers that includes offset adhesive control grooves on the opposite faces of the disk-like core cap is disclosed. The grooves are offset from one another by a distance that makes the smallest dimension between any feature of the grooves about the same as the nominal thickness of the core cap. The core cap increases the magnetic flux capacity over prior art core cap designs, while maintaining features advantageous to error-proof the orientation of the core cap in the loudspeaker.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Solenoid valve
ActiveUS20170146150A1Lose weightMore compactVehicle seatsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSolenoid valveEngineering
The present relation is directed to solenoid valve comprising an input port including a spring biased input sealing tip, a first and second output port. The second output port including an output sealing tip, and a solenoid coil arrangement for generating magnetic fields which result in a force either on the input sealing tip or the output sealing tip. Wherein the solenoid valve arrangement consists of a single solenoid coil, that includes a permanent magnet movable in a first and second axial direction by a magnetic field. The permanent magnet being connected to the input sealing tip and to the output sealing tip such that movement of the permanent magnet in the first direction pulls the input sealing tip to open the input port and movement of the permanent magnet in the opposite direction pulls the output sealing tip to open the second output port.
Owner:LEAR CORP
Planar coil and support for actuator of fluid mover
ActiveUS20150316046A1Enhanced magnetic forceReduce vibrationFlexible member pumpsDynamo-electric machinesPower flowEngineering
A fluid mover includes a chamber with one or more outlet openings, first and / or second fluidic diaphragm(s) having a portion movable in the chamber to cause fluid to move at the outlet opening, and a coil assembly magnetically coupled to the fluidic diaphragm to move the movable portion of the fluidic diaphragm(s) in response to a current in the coil. The coil assembly includes a coil with an opening, and a plug may be positioned in the opening and / or a support may be positioned around a periphery of the coil. The plug and / or the support may have a magnetic permeability greater than one and be arranged so magnetic field lines created by the coil pass through the plug and / or support. The coil, plug and / or support may define a flat surface, e.g., such that a uniform gap is present between the diaphragm(s) and the coil, plug and / or support.
Owner:AAVID THERMALLOY LLV
Linear motor with electromagnetically actuated spring mover
ActiveUS9685847B2Reduce reluctancePumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesResonanceMagnetic reluctance
Reluctance-based resonant linear motors and methods of operation are provided. An example linear motor includes a spring having a plurality of coils. The linear motor includes a stator coaxially surrounding at least a portion of the spring. The stator includes a plurality of teeth. The linear motor includes a plurality of windings respectively positioned within a plurality of winding cavities respectively formed by the plurality of teeth. The application of electrical energy to the plurality of windings generates a magnetic field that flows through one or more of the coils of the spring. The flow of the magnetic field through the one or more coils of the spring causes the spring to actuate towards a compressed position. An example method includes periodically applying electrical energy to the plurality of windings such that the spring oscillates at a resonance frequency associated with the linear motor.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Electromagnetic brake for a power transmission assembly
ActiveUS9874254B2Reduce reluctanceIncrease magnetic attractionMagnetically actuated clutchesBrake actuating mechanismsRotational axisElectrical conductor
An electromagnetic brake includes a hub disposed about a shaft and configured for rotation with the shaft about a rotational axis. An electromagnet assembly is fixed against rotation about the axis and includes a housing defining axially extending, radially spaced inner and outer poles and a brake plate extending radially therebetween. A conductor is disposed between the poles on one side of the brake plate. An armature is disposed on the other side of the brake plate and coupled to a body driven by the shaft. The electromagnet assembly, armature and hub form an electromagnetic circuit when the conductor is energized urging the armature towards the brake plate. A portion of the magnetic flux in the circuit travels radially inwardly across a first radial air gap from the inner pole to the hub and then radially outwardly across a second radial air gap from the hub to the brake plate.
Owner:WARNER ELECTRIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com