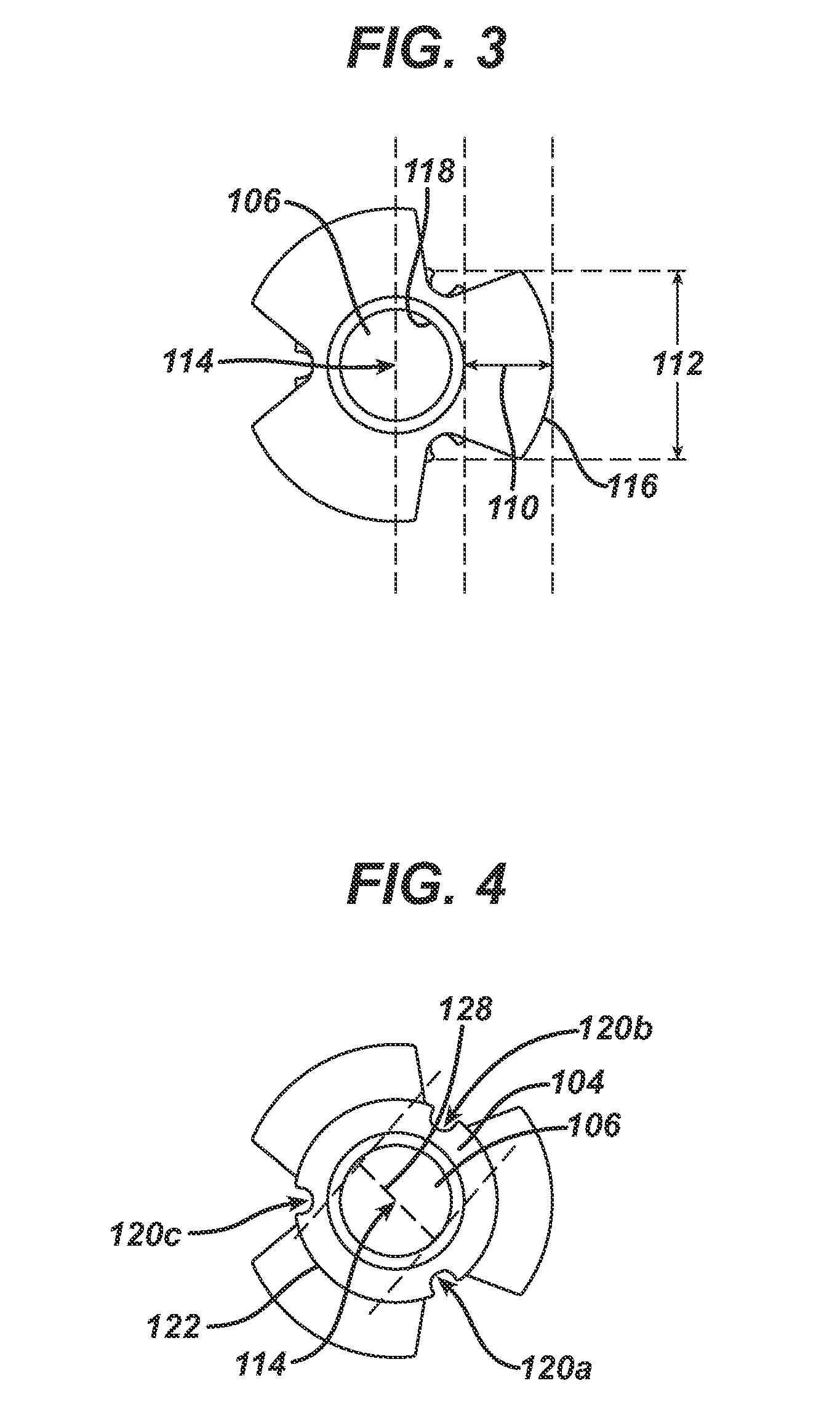
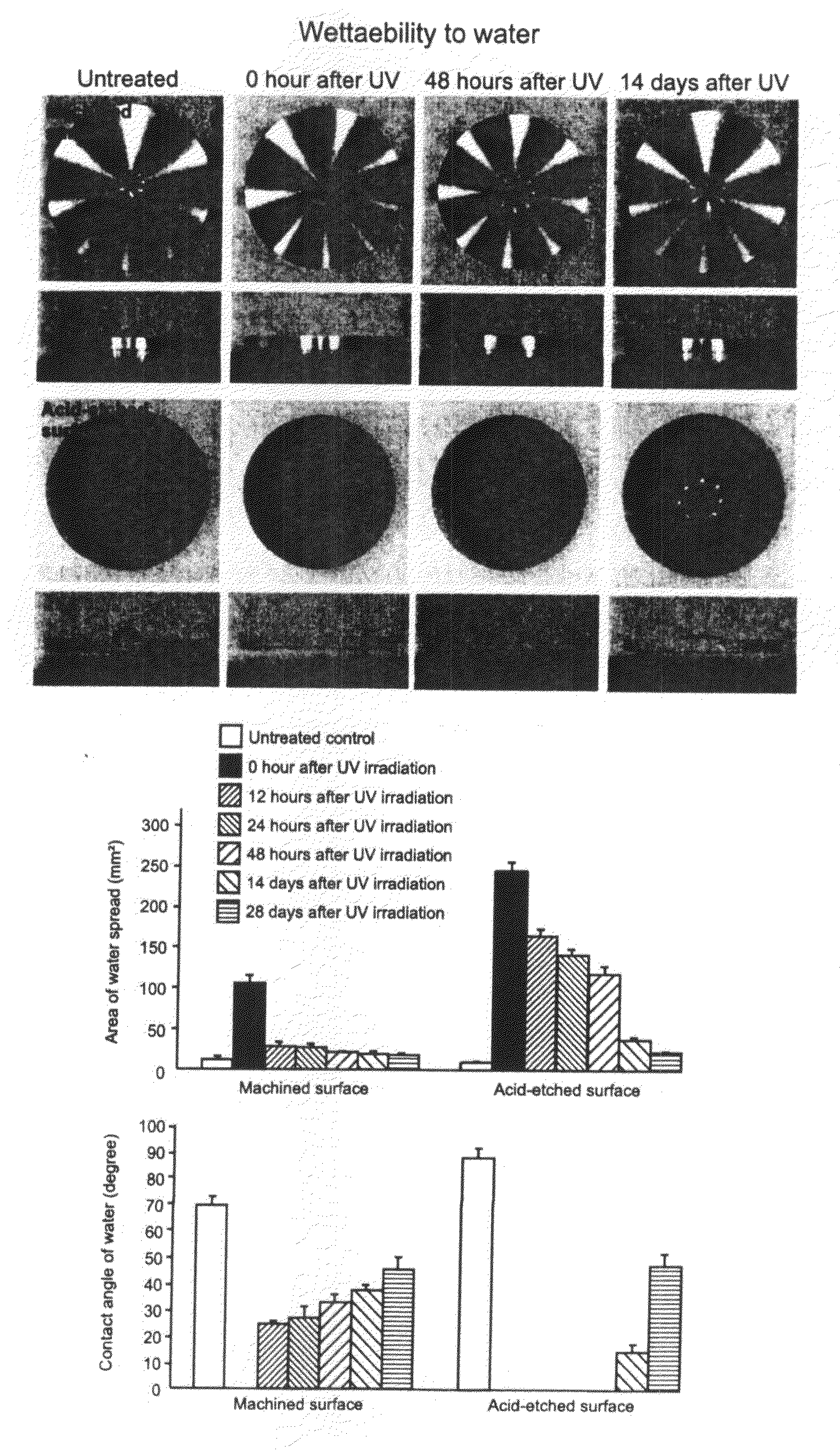
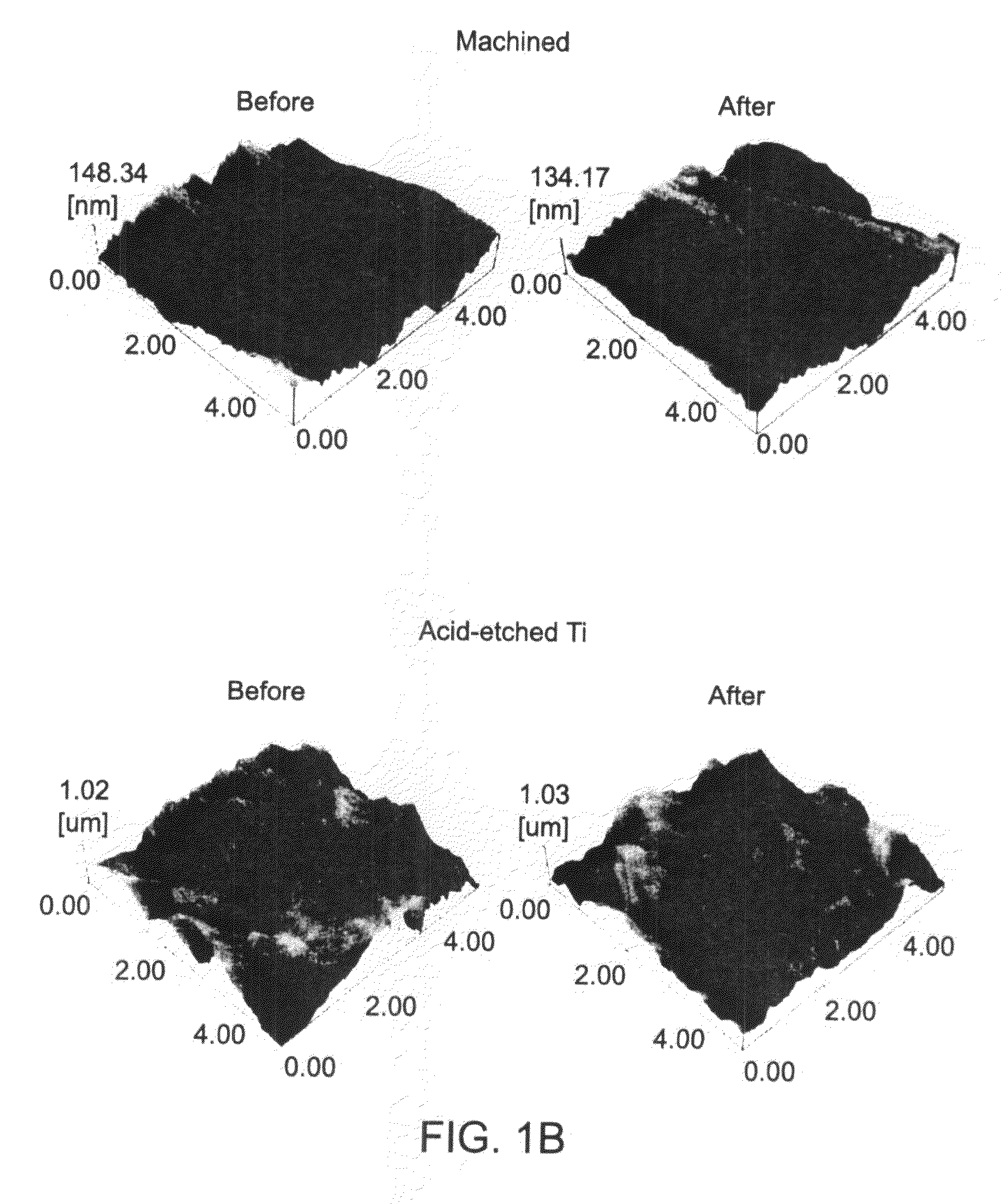
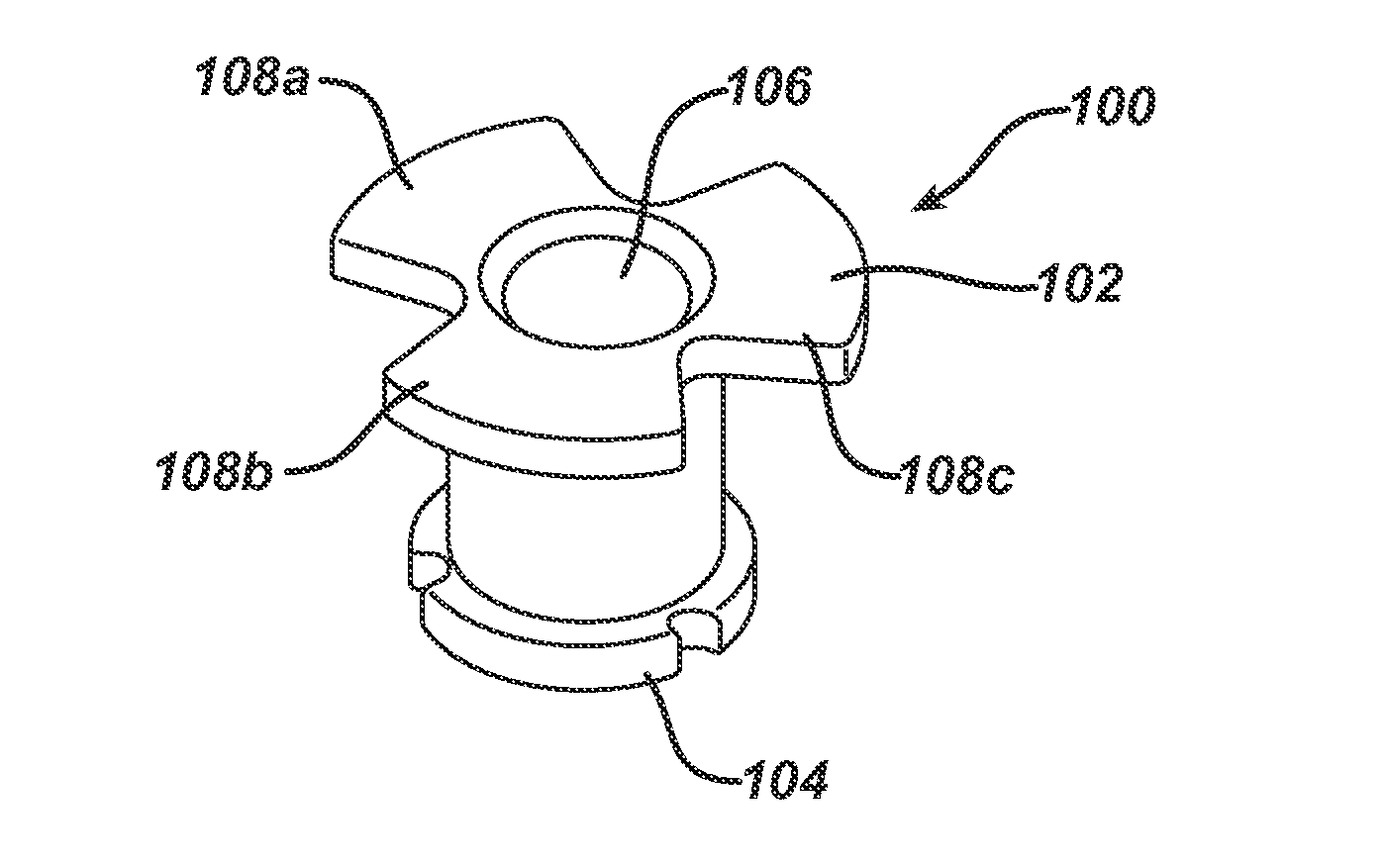
Patents
Literature
240results about "Ear implants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
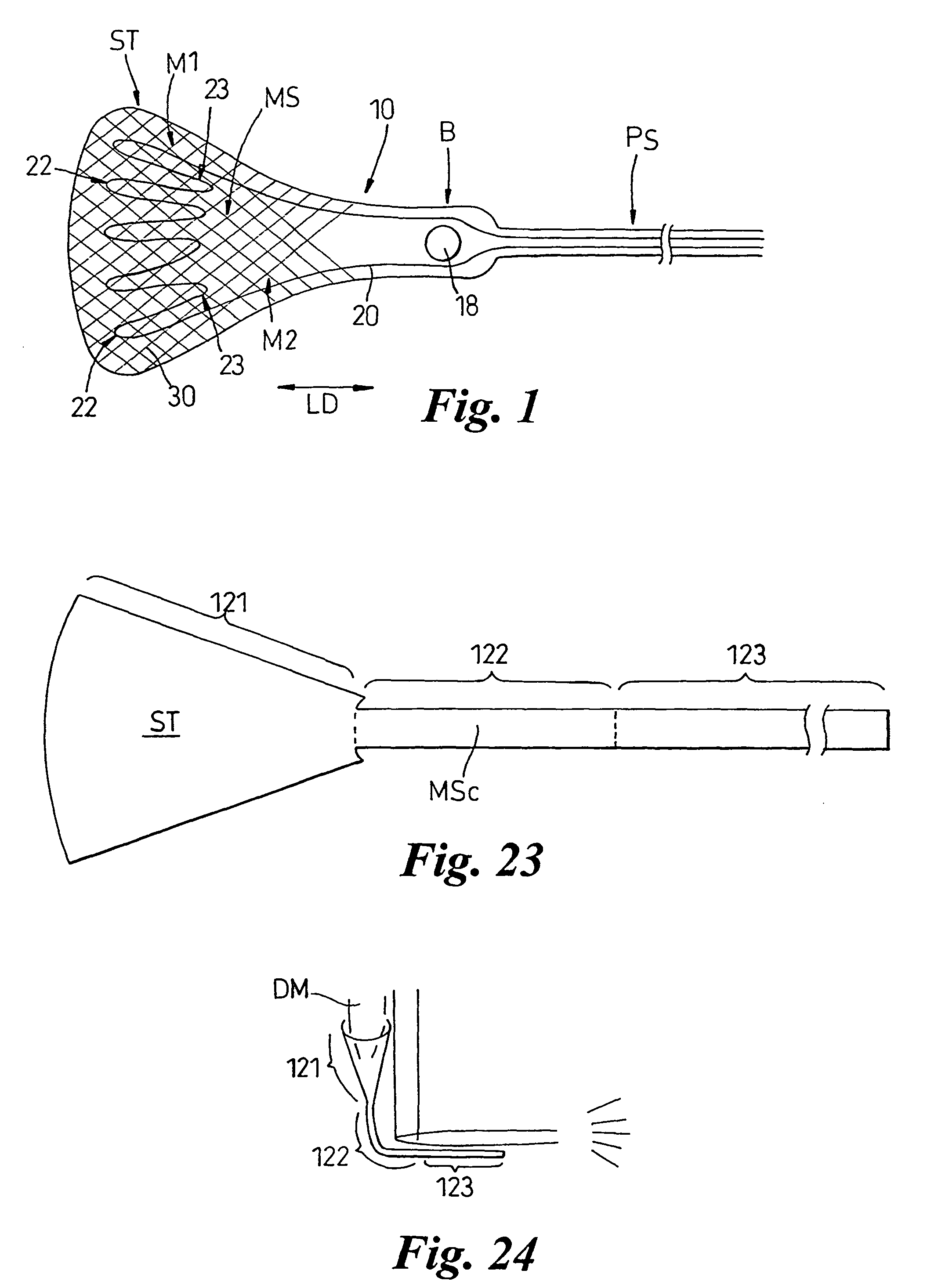
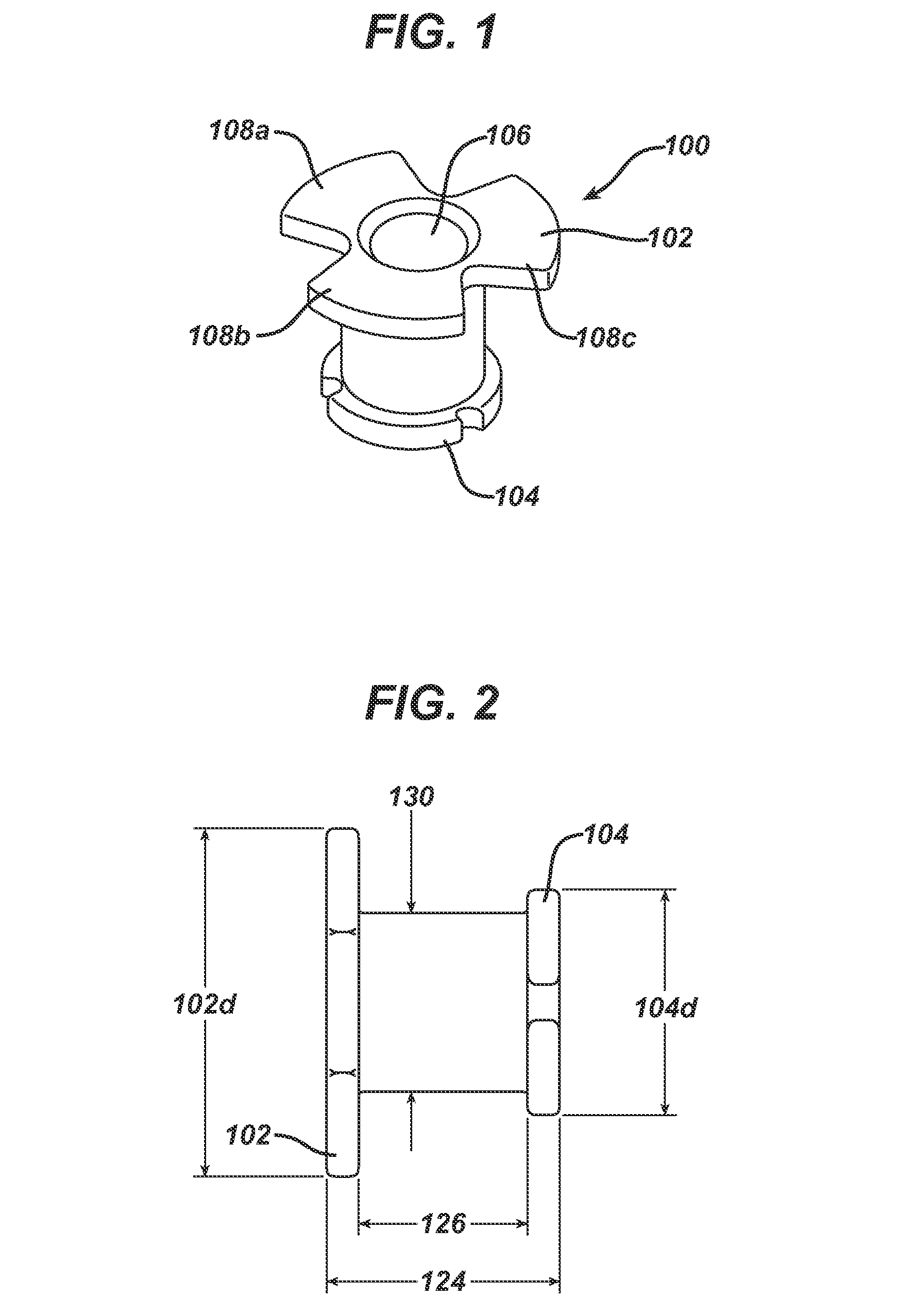
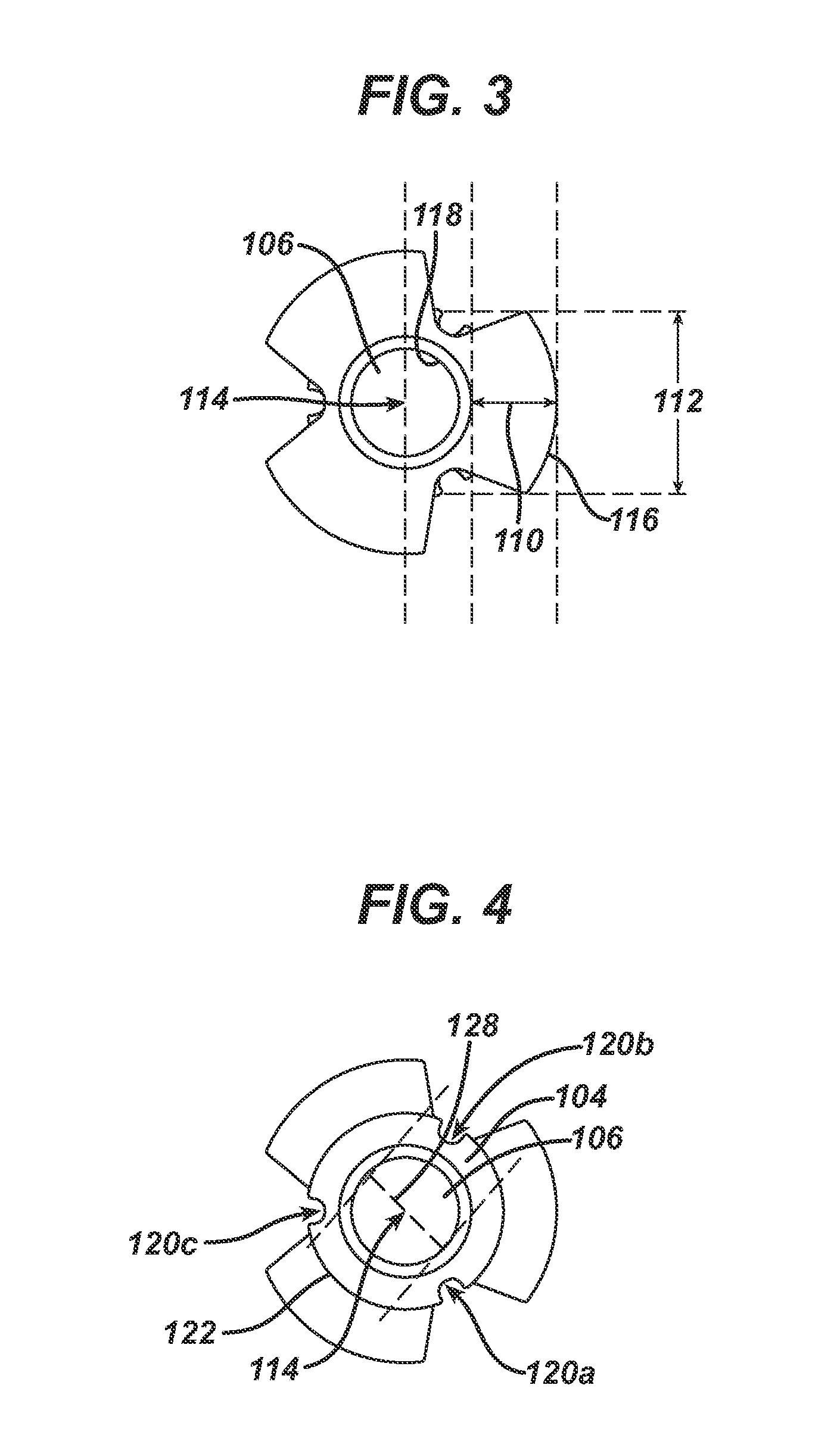
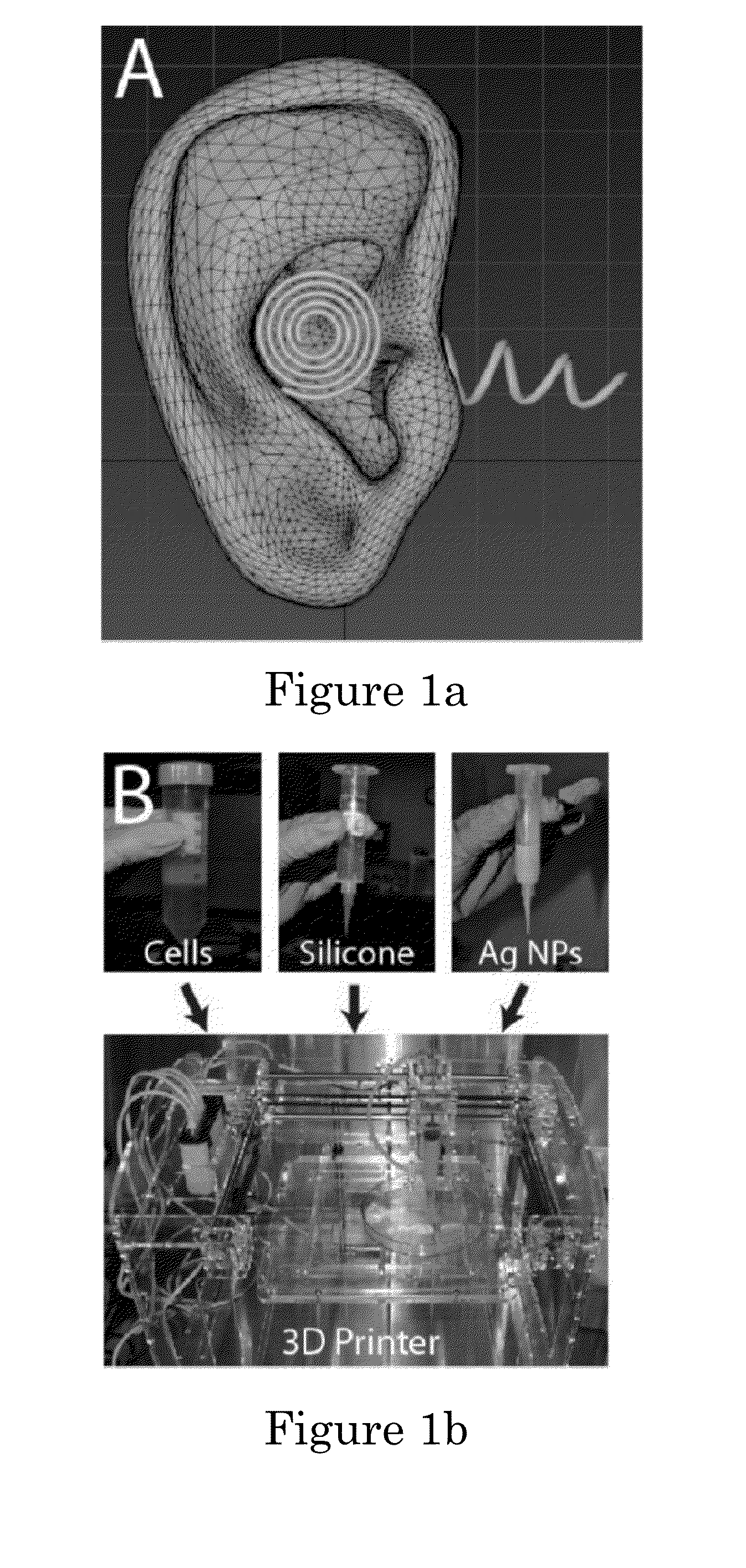
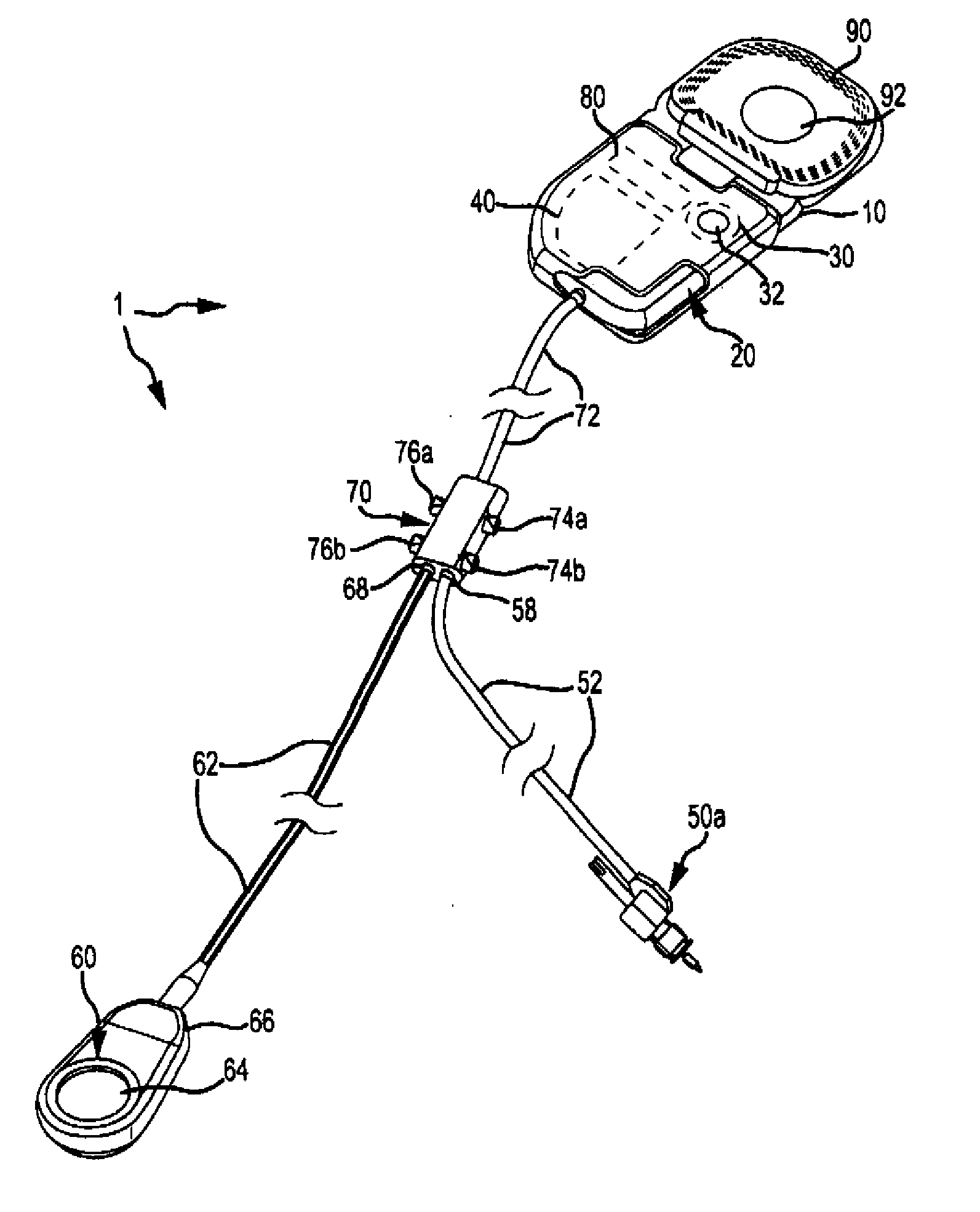
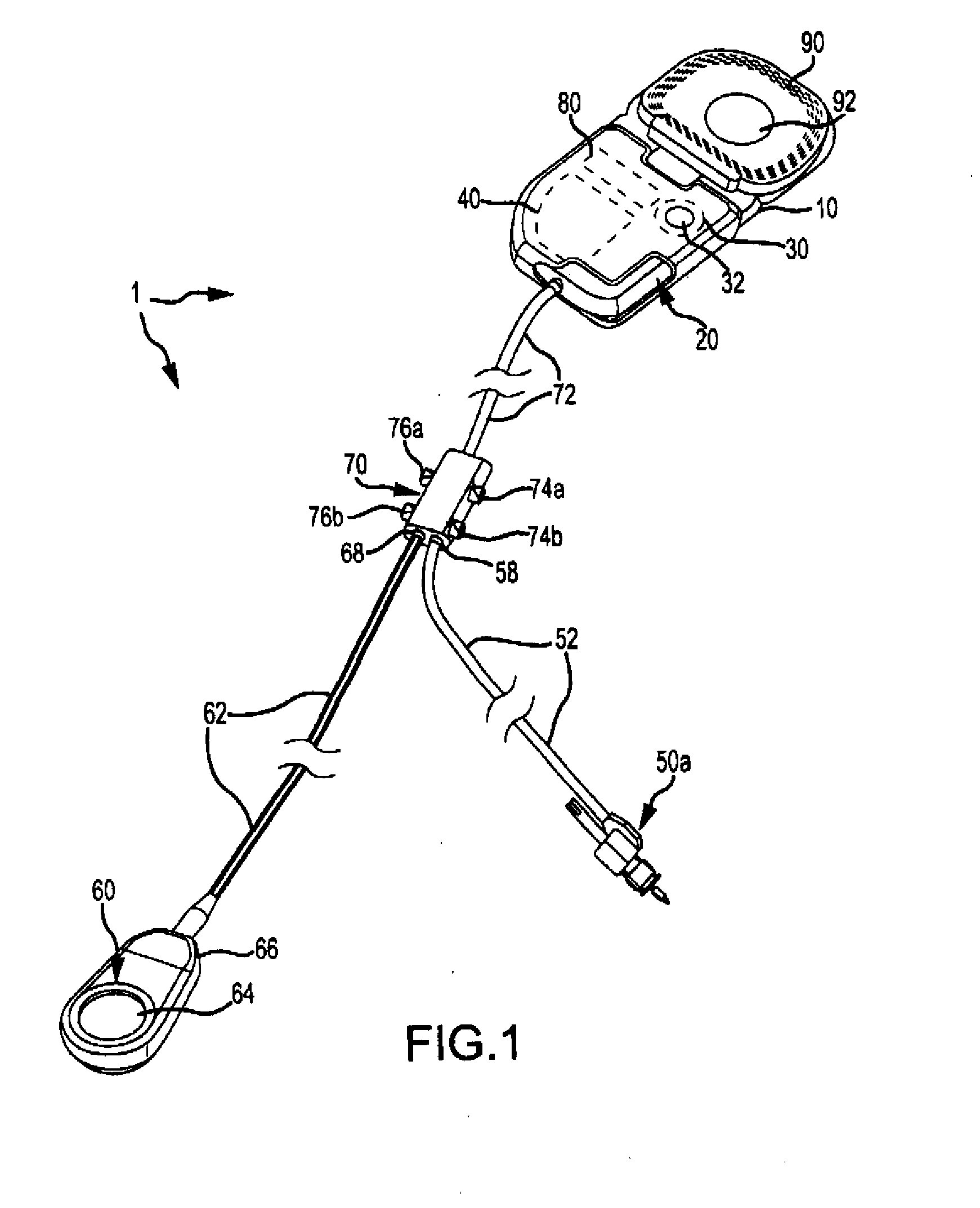
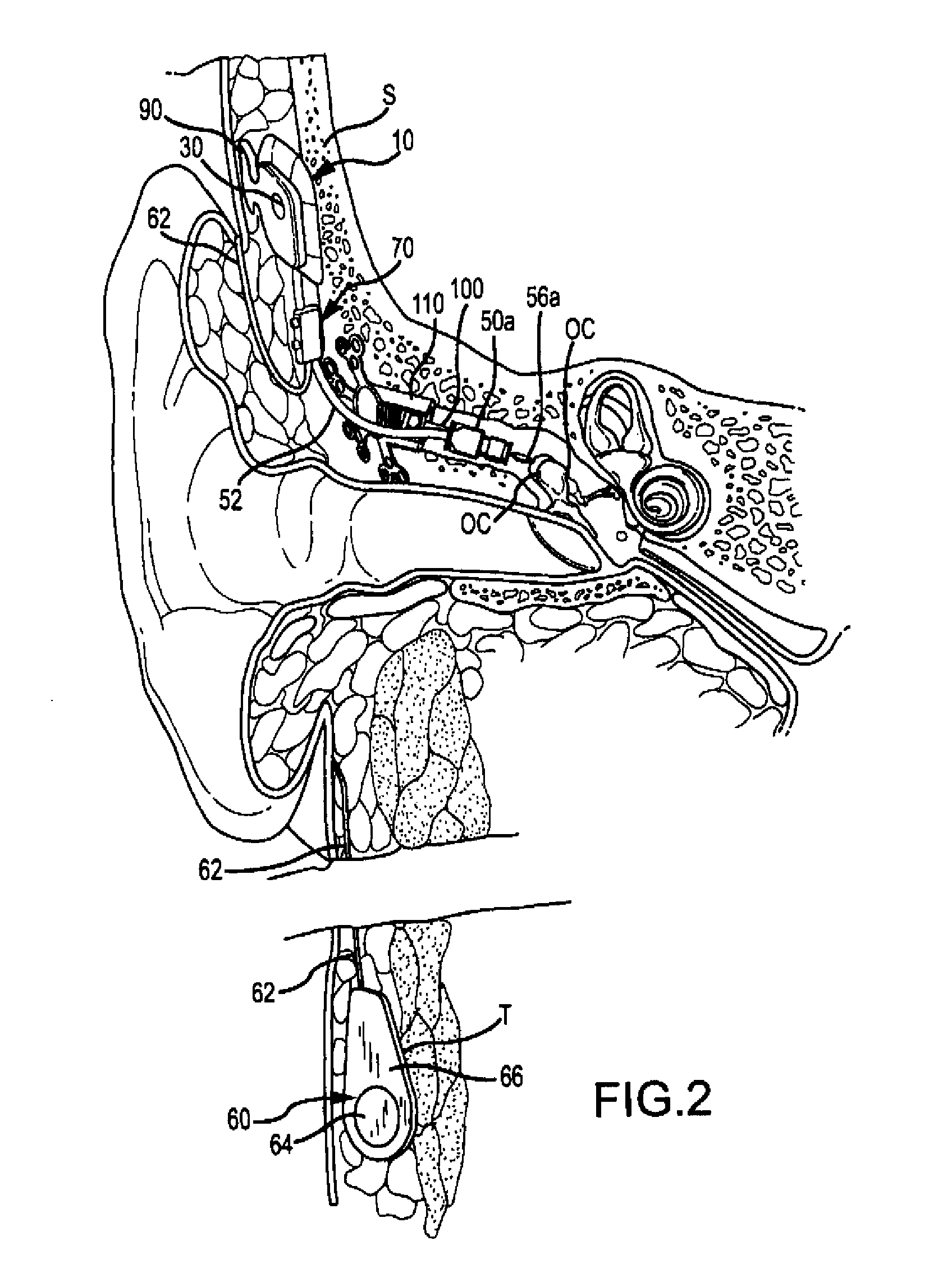
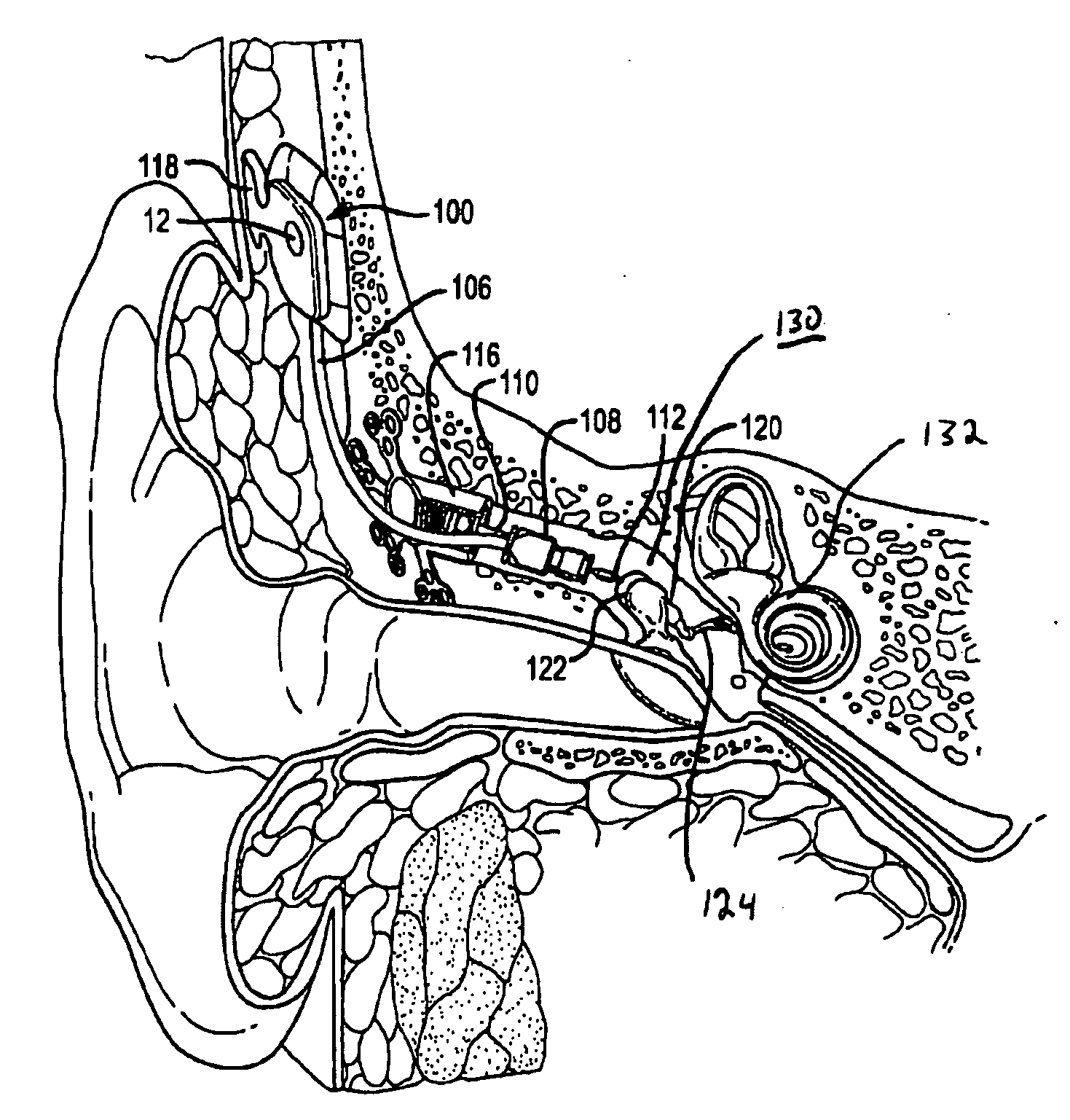
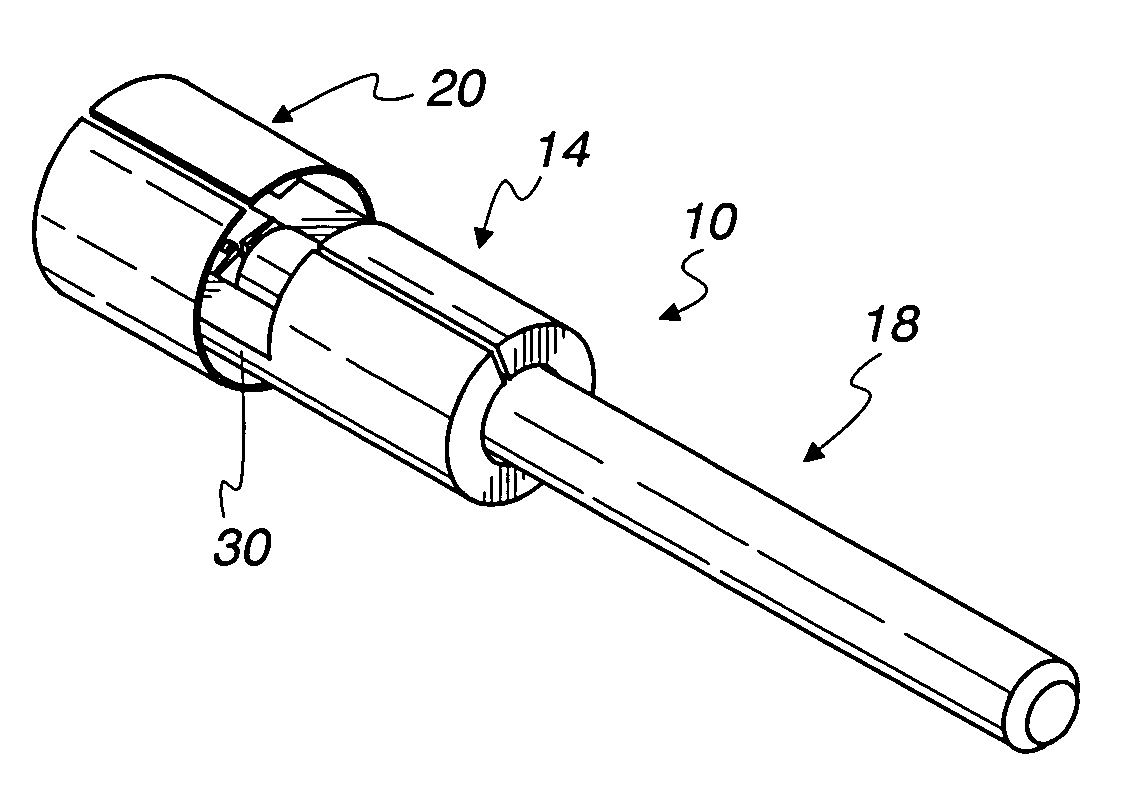
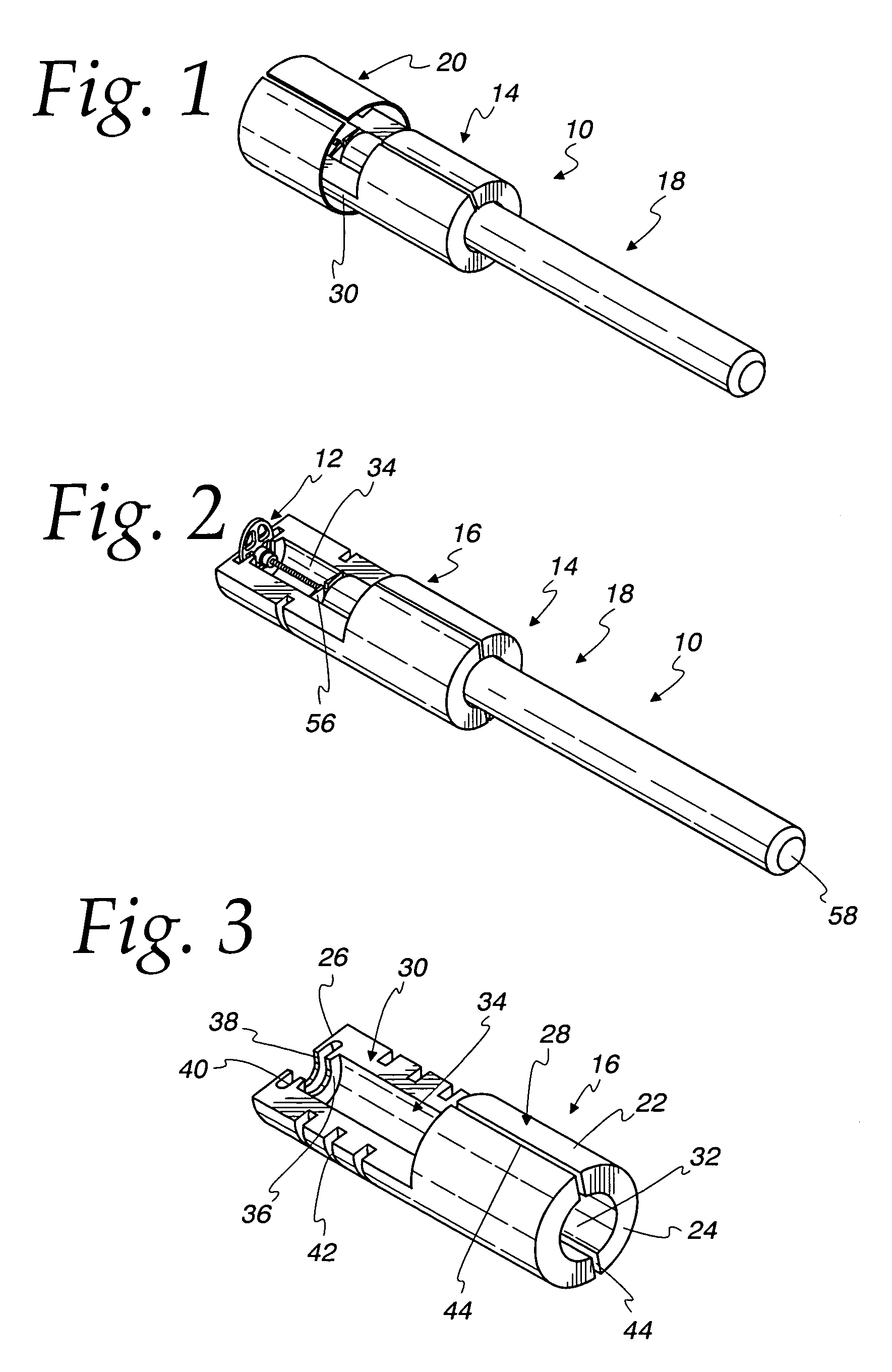
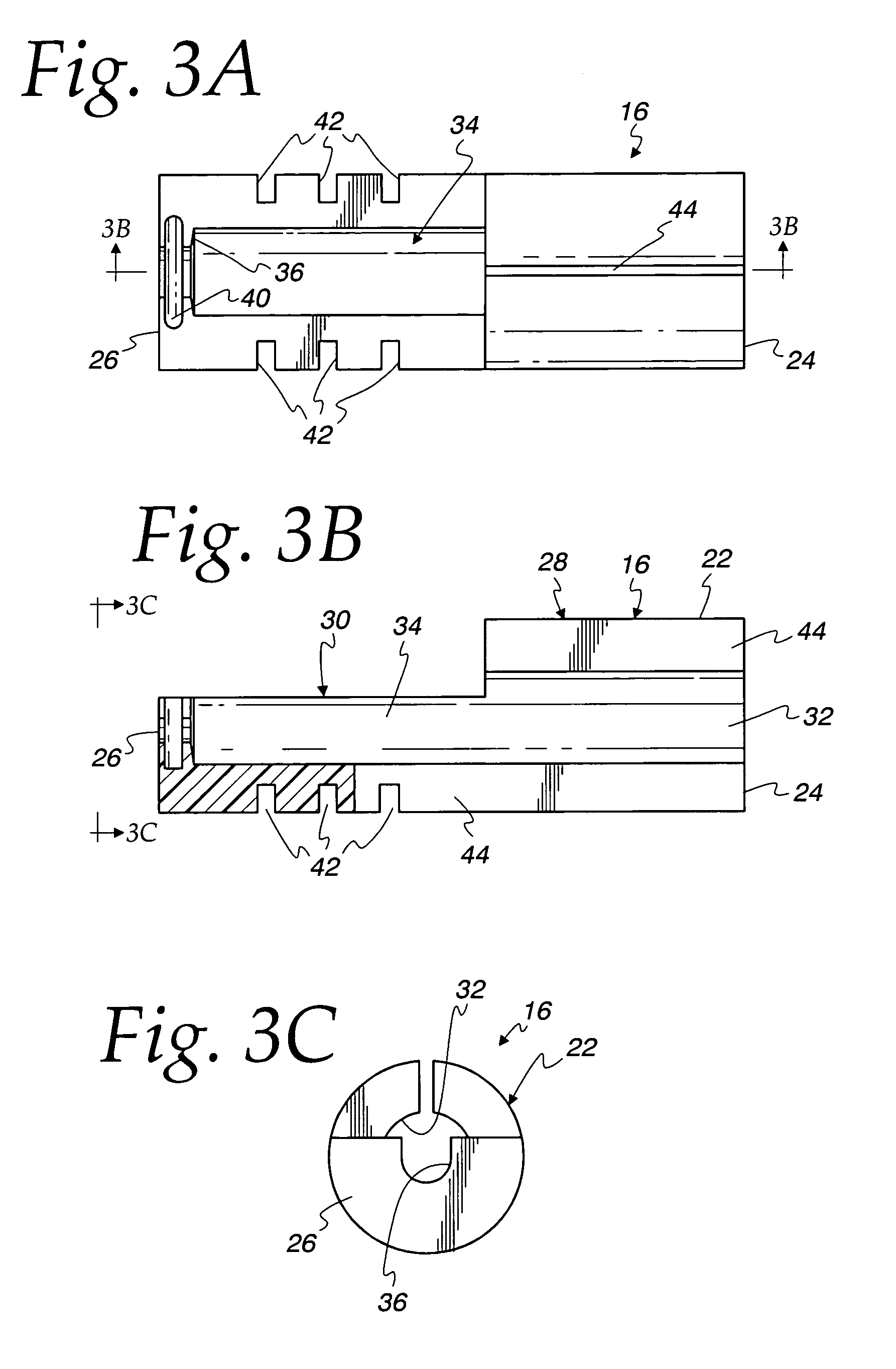
Direct tympanic drive via a floating filament assembly
InactiveUS6940989B1Efficient couplingFrictionCompletely in canal hearing aidsEar treatmentAir coreEngineering
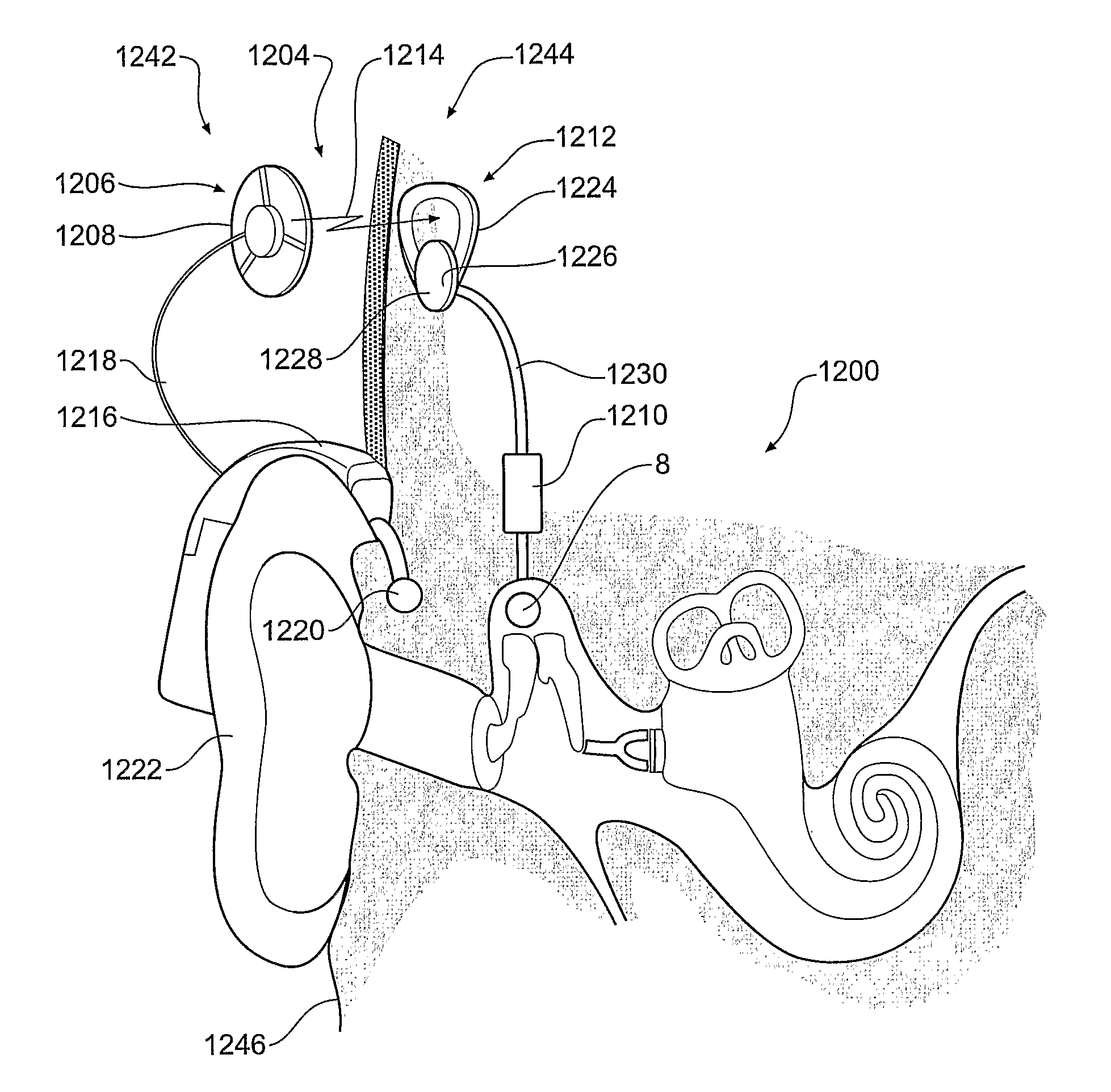
A canal hearing device has a subminiature filament assembly which vibrates and directly drives the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and imparts audible mechanical vibrations thereto. The filament assembly is partially supported by the tympanic membrane via capillary adhesion thereto and is dynamically coupled to a stationary vibration force element position at a distance from the tympanic membrane within the ear canal. The elongated filament assembly is freely movable within an operable range and is essentially floating with respect to the vibration force element. In a preferred embodiment, the vibrational filament assembly comprises a magnetic section which is insertable into the air-core of an electromagnetic coil. The filament assembly is coupled to the tympanic membrane via an articulated tympanic contact coupler.
Owner:INSOUND MEDICAL INC
Repair of tympanic membrane using placenta derived collagen biofabric
The present invention provides a method of repairing a tympanic membrane deformity, such as a tympanic membrane perforation, commonly referred to as tympanoplasty or myringoplasty, using a collagen biofabric. The collagen biofabric is preferably laminated. The invention further provides kits comprising one or more pieces of collagen biofabric, for example laminated collagen biofabric, for the repair of a tympanic membrane.
Owner:ANTHROGENESIS CORP
Implantable actuator for hearing aid application
InactiveUS20140163309A1Reduce reluctanceEar implantsHearing aids mounting/interconnectionProsthesisHearing aid
An electromechanical actuator for an implantable hearing aid device including a mechanical output structure that has a first portion and a second portion, wherein the first portion is a mechanical attachment structure to attach a stapes prosthesis, and wherein the second portion is a wire-like member coupling the mechanical attachment structure to a magnetically permeable armature shaft assembly.
Owner:BERNHARD HANS +9
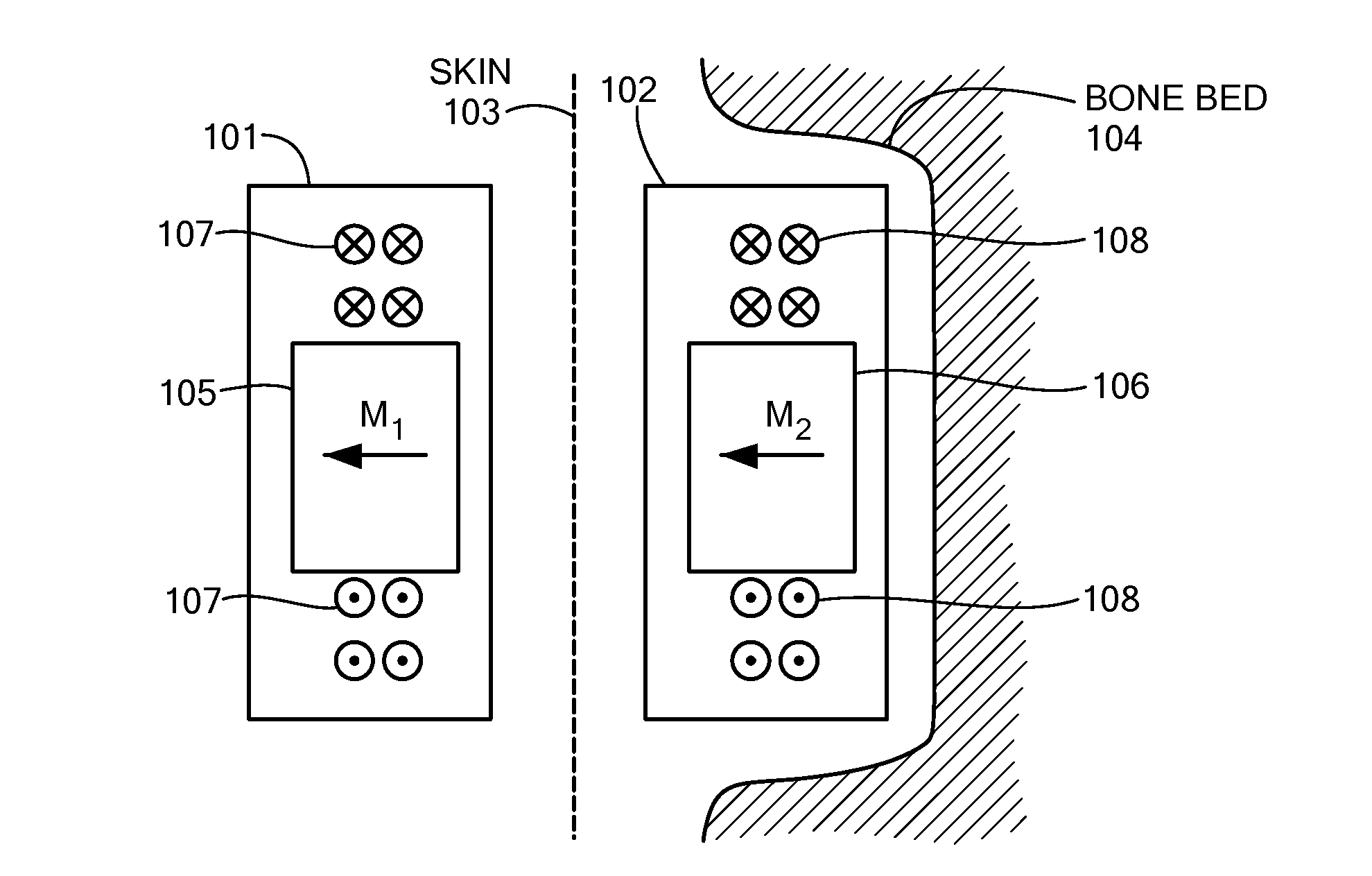
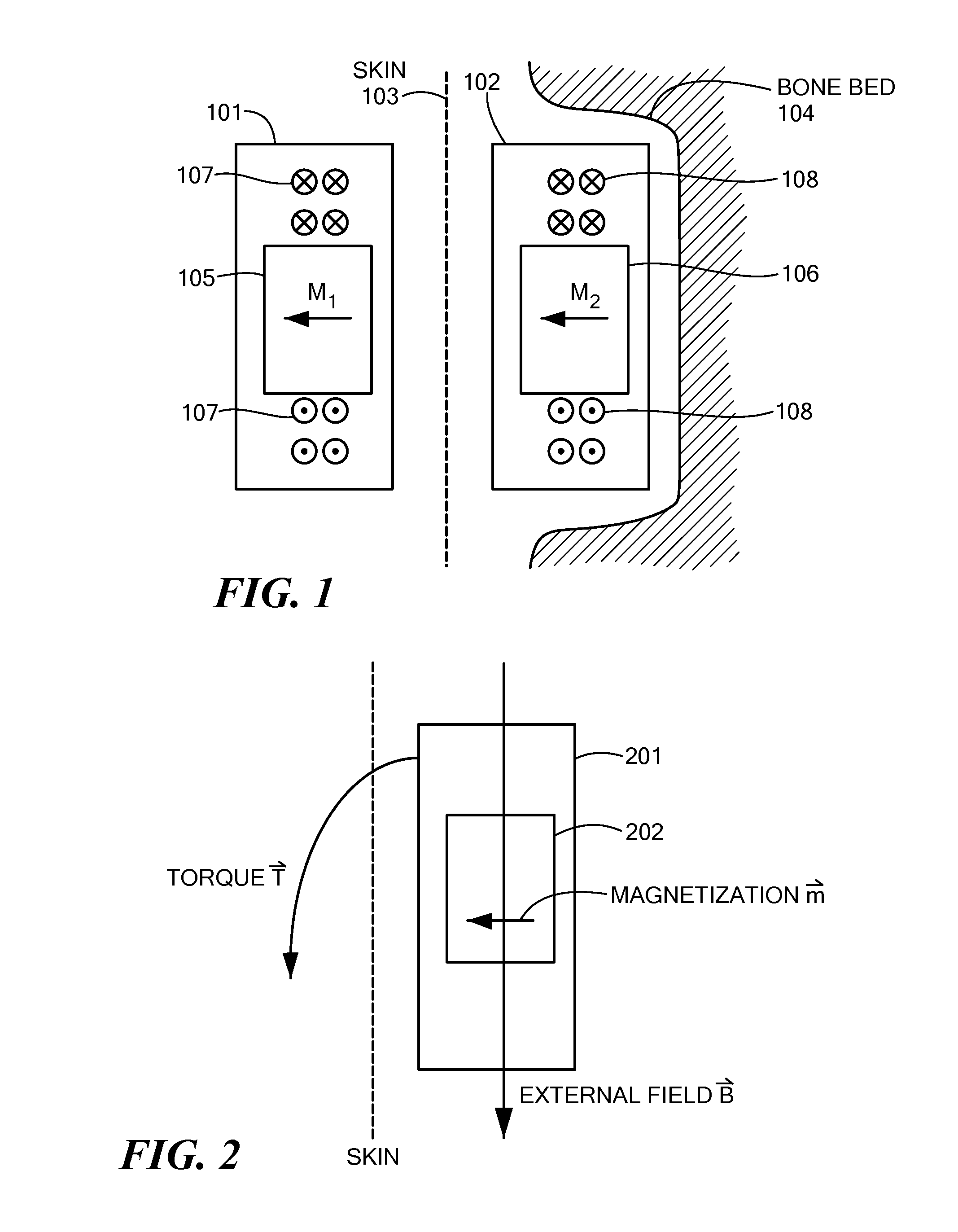
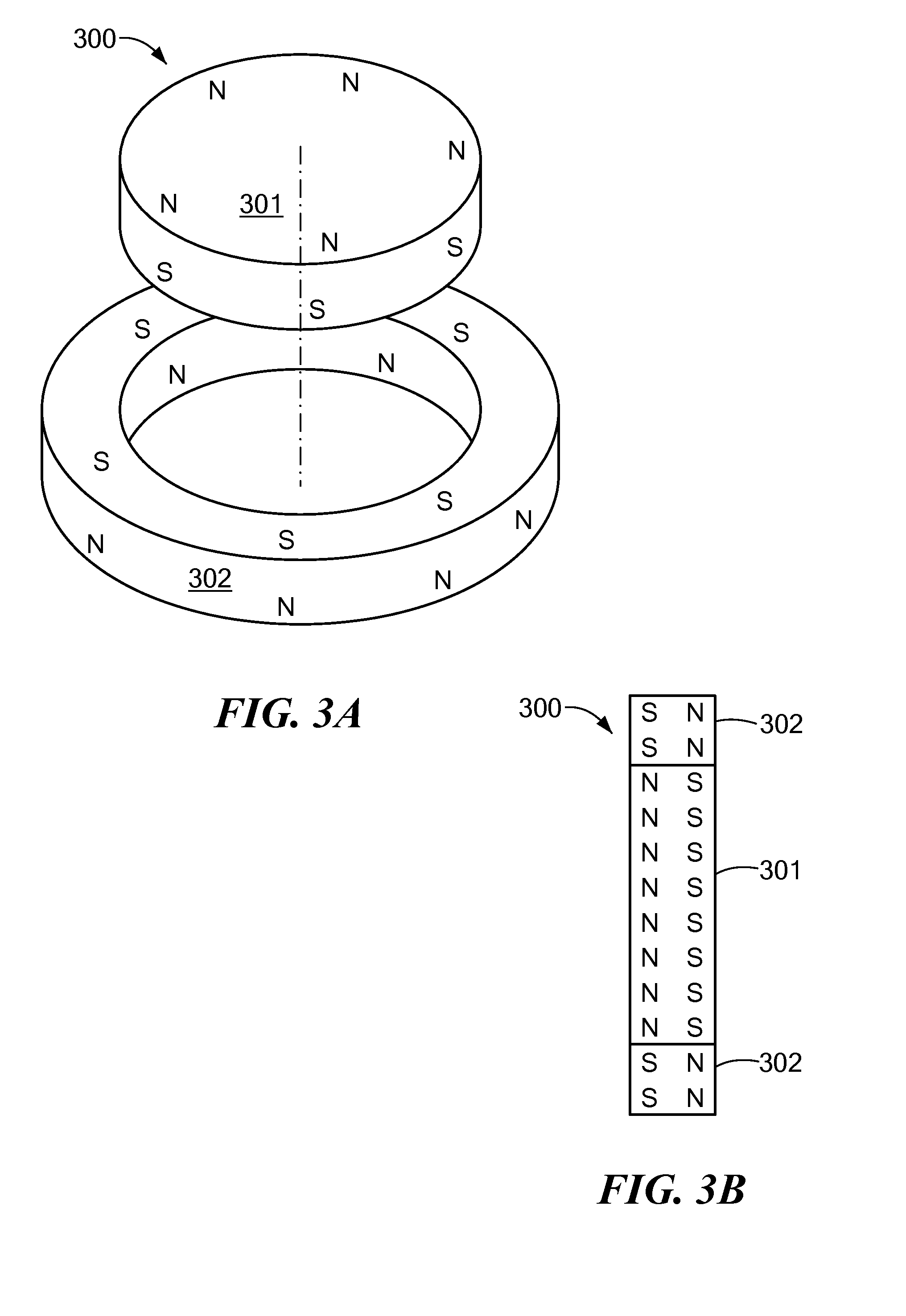
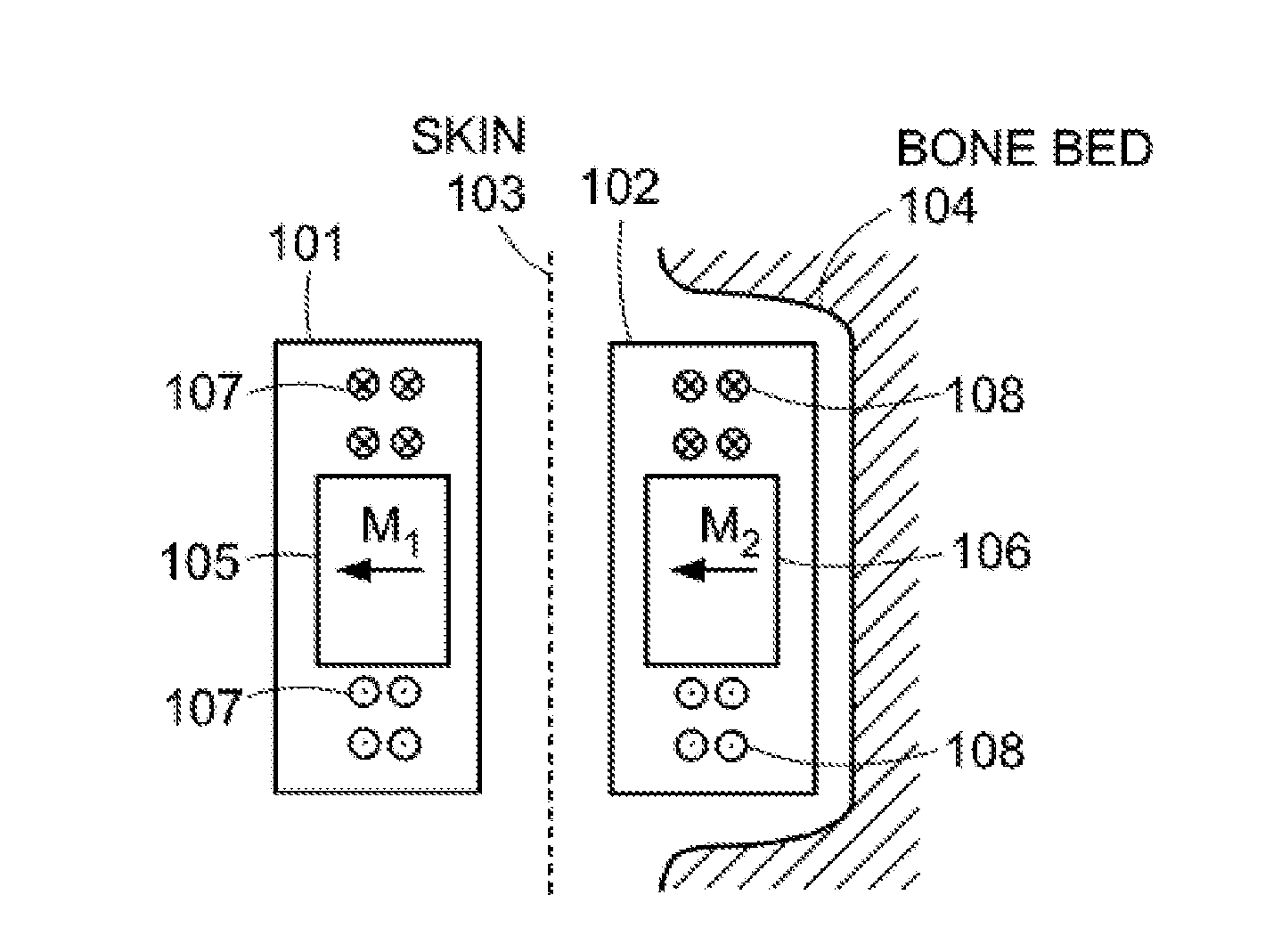
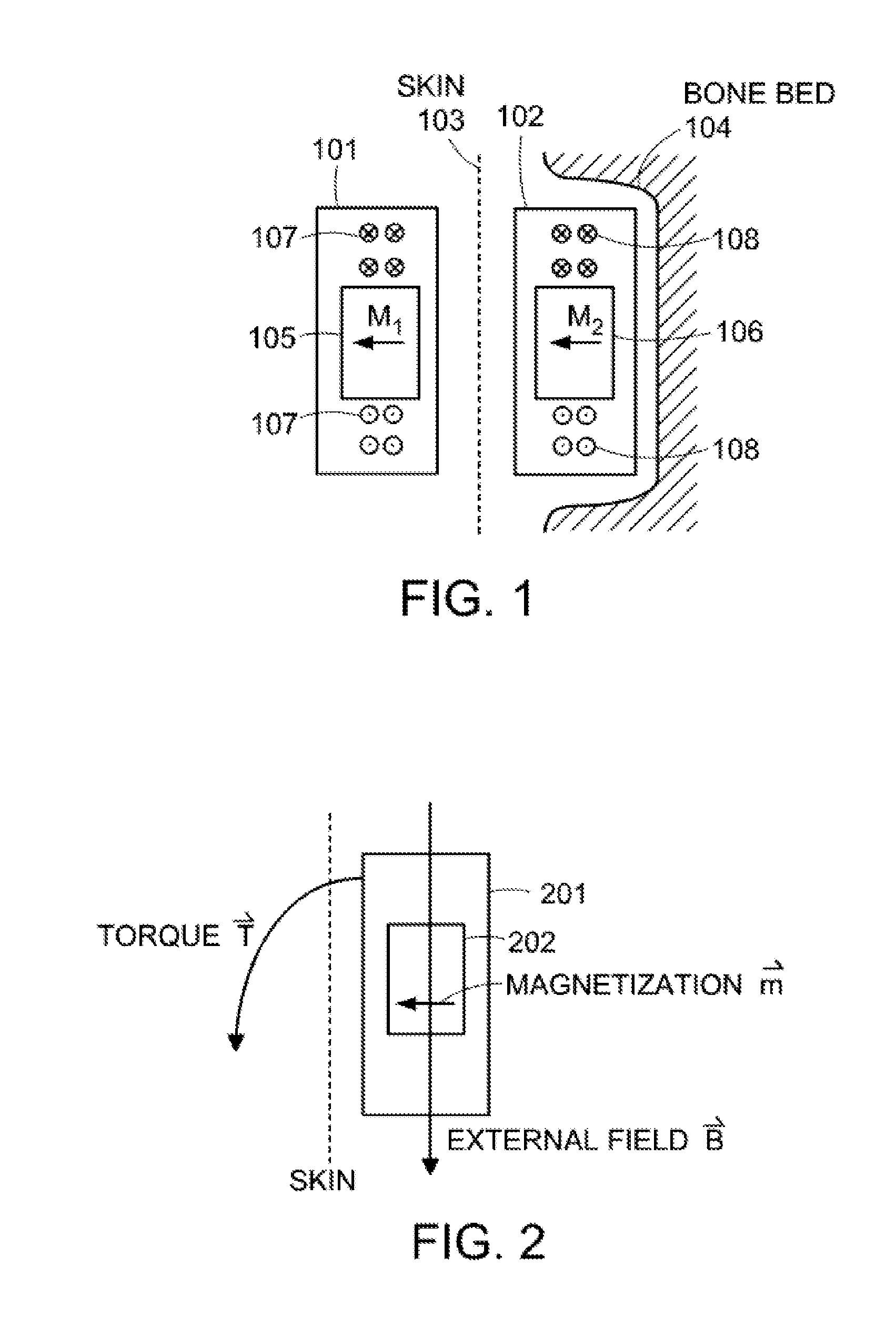
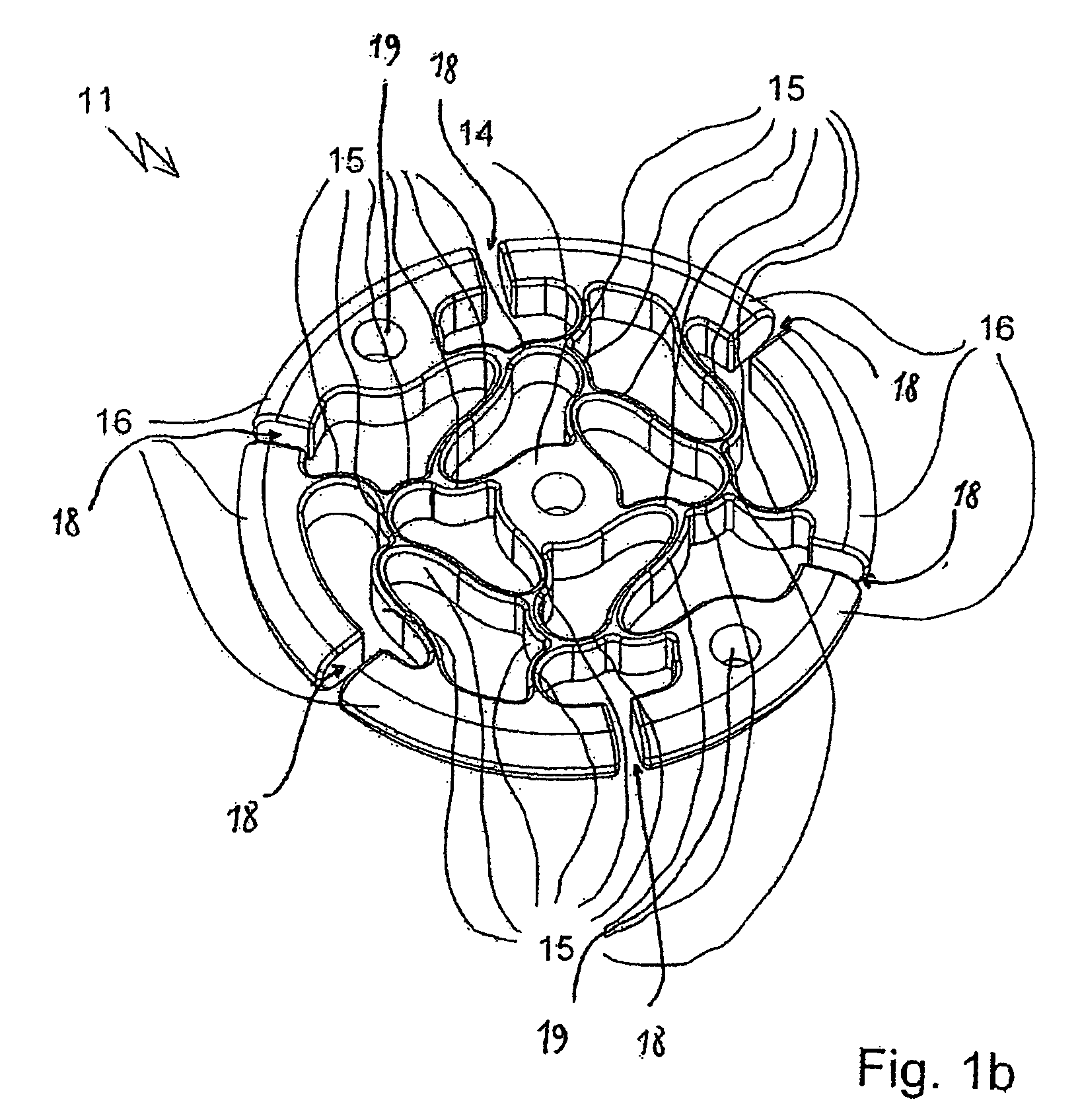
Magnetic Attachment Arrangement for Implantable Device
A magnet arrangement is described for use in implantable devices. An implantable housing contains a portion of an implantable electronic system. A cylindrical implant magnet arrangement within the housing includes multiple adjacent magnetic sections wherein at least two of the magnetic sections have opposing magnetic orientations in opposite magnetic directions. There may also be a similar external housing having a corresponding magnet arrangement.
Owner:VIBRANT MED EL HEARING TECH
Implantable Actuator For Hearing Aid Applications
InactiveUS20080188707A1Reduce reluctanceMinimize air gapHearing aids mounting/interconnectionEar implantsIncusSudden sensorineural hearing loss
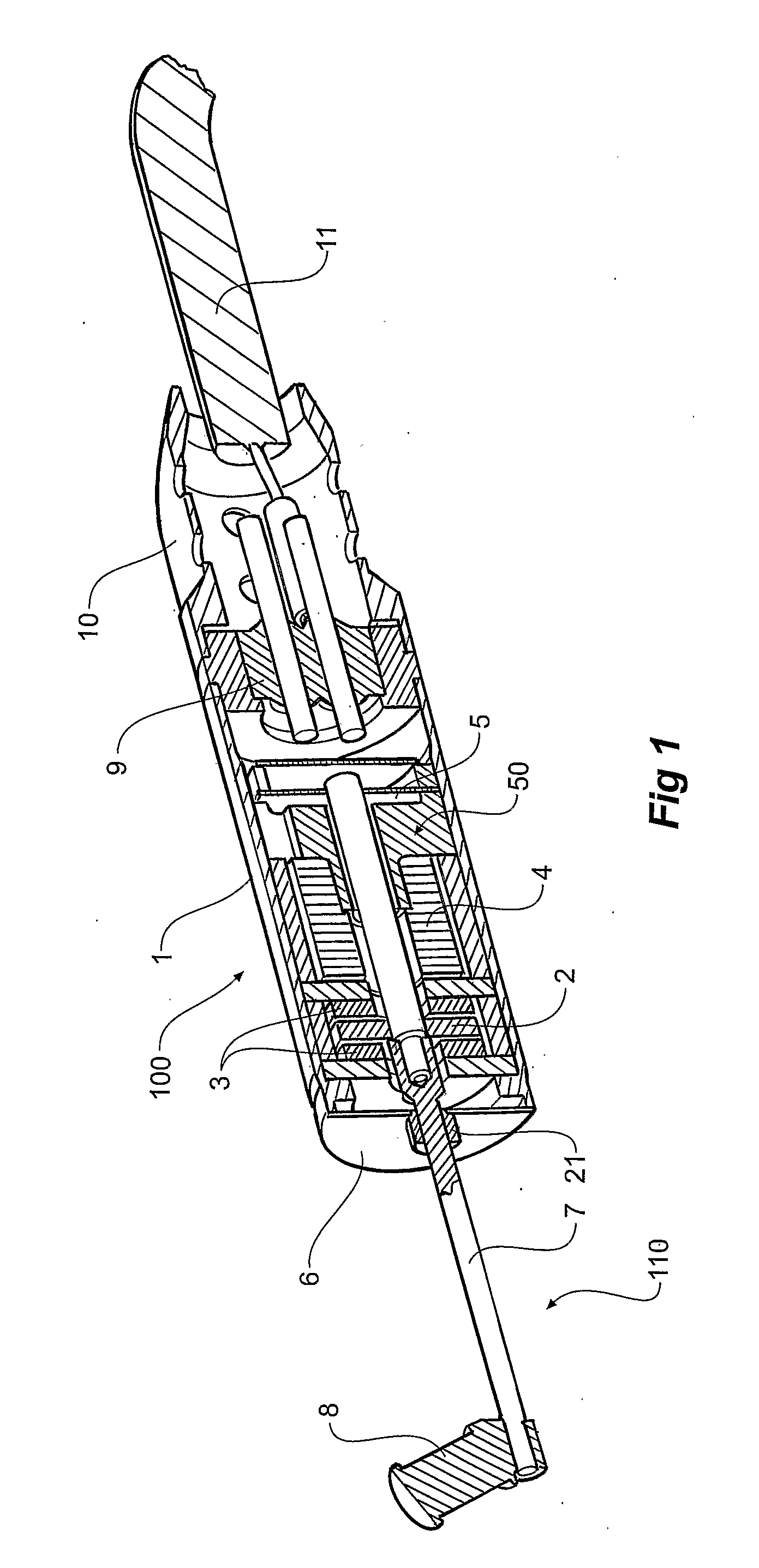
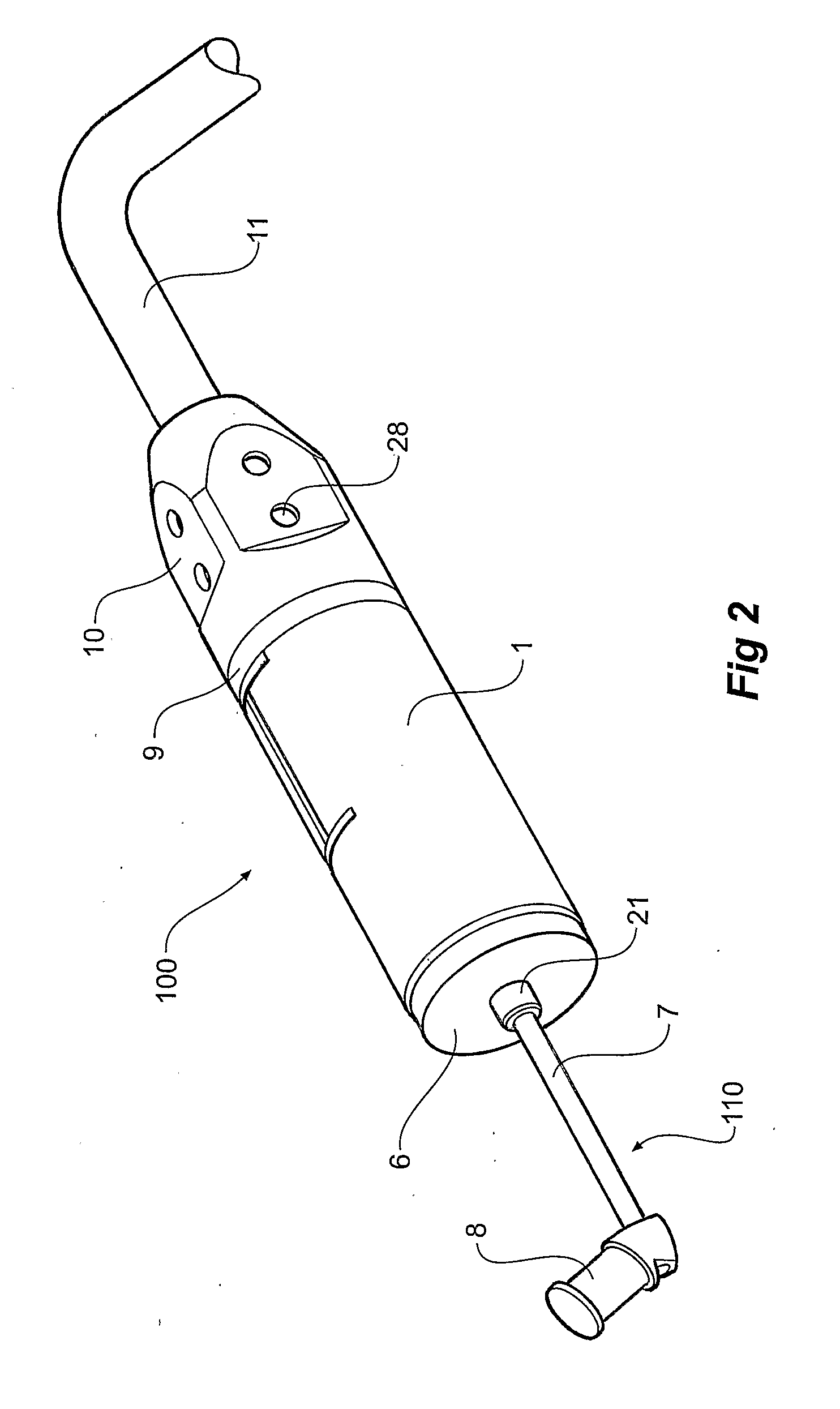
An electromechanical actuator (100) suitable, for example, in hearing aid applications is disclosed. Certain embodiments of the actuator comprise a hermetic titanium housing (1), a mechanical output structure (110) emulating the long process of incus (8), and means for efficiently generating movement in the audible frequency range. The electromechanical actuator (100) may be configured to be coupled to the inner ear fluids via a conventional stapes prosthesis. The implantable actuator (100), which may be considered to be operably equivalent to a loudspeaker of a conventional hearing aid, may bypass the outer and the middle ear in order to directly drive the inner ear fluids. As such, embodiments of the electromechanical actuator of the present invention may be used to remedy any source of conductive hearing loss. Additionally, certain embodiments of the electromechanical actuator may be configured to provide sufficiently high output levels to treat severe sensorineural hearing loss while being sufficiently small to completely fit into a human mastoid.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
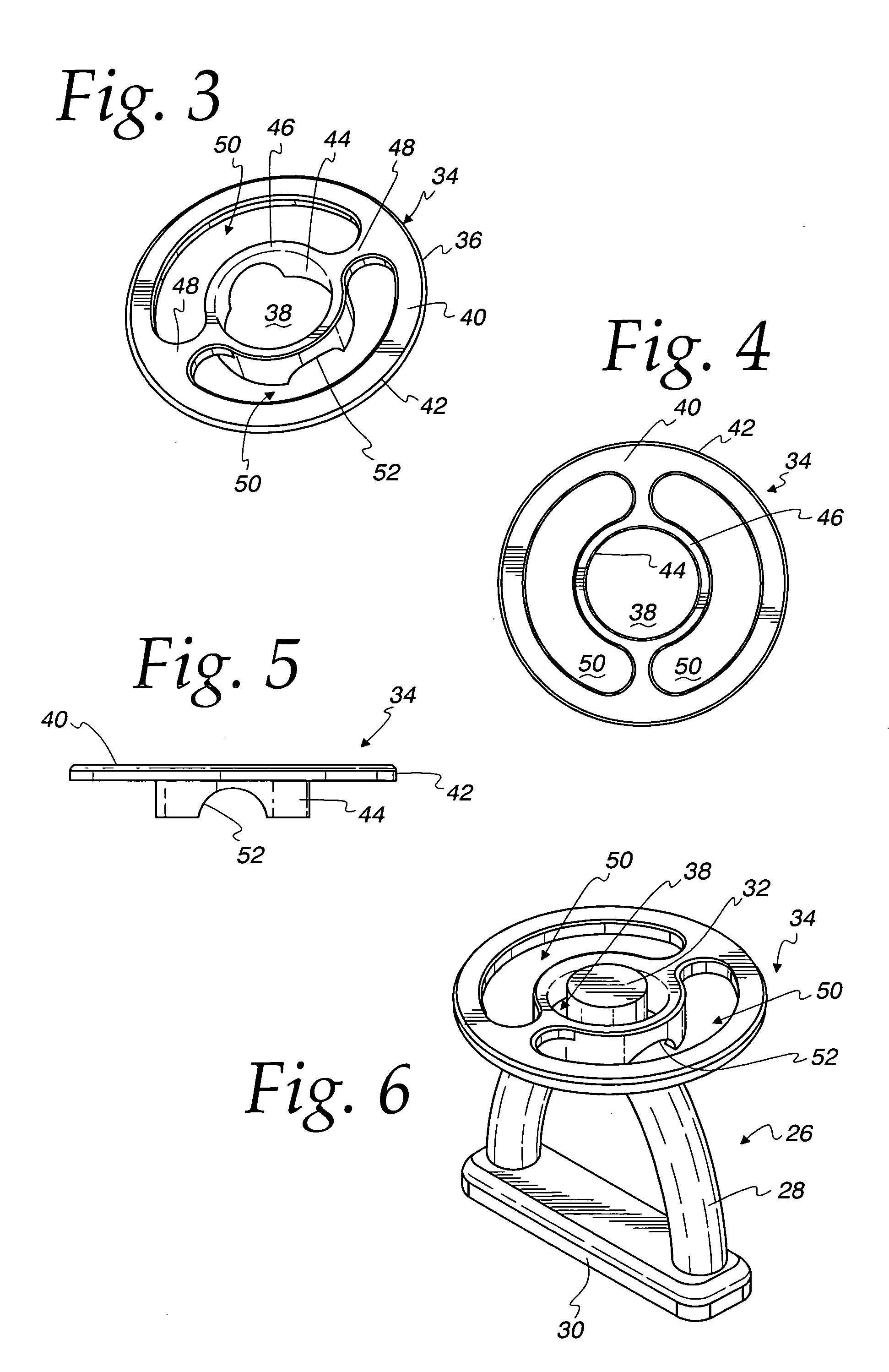
Textile prosthesis
InactiveUS7338531B2Less structural distortionConvenient to accommodateInternal osteosythesisLigamentsYarnProsthesis
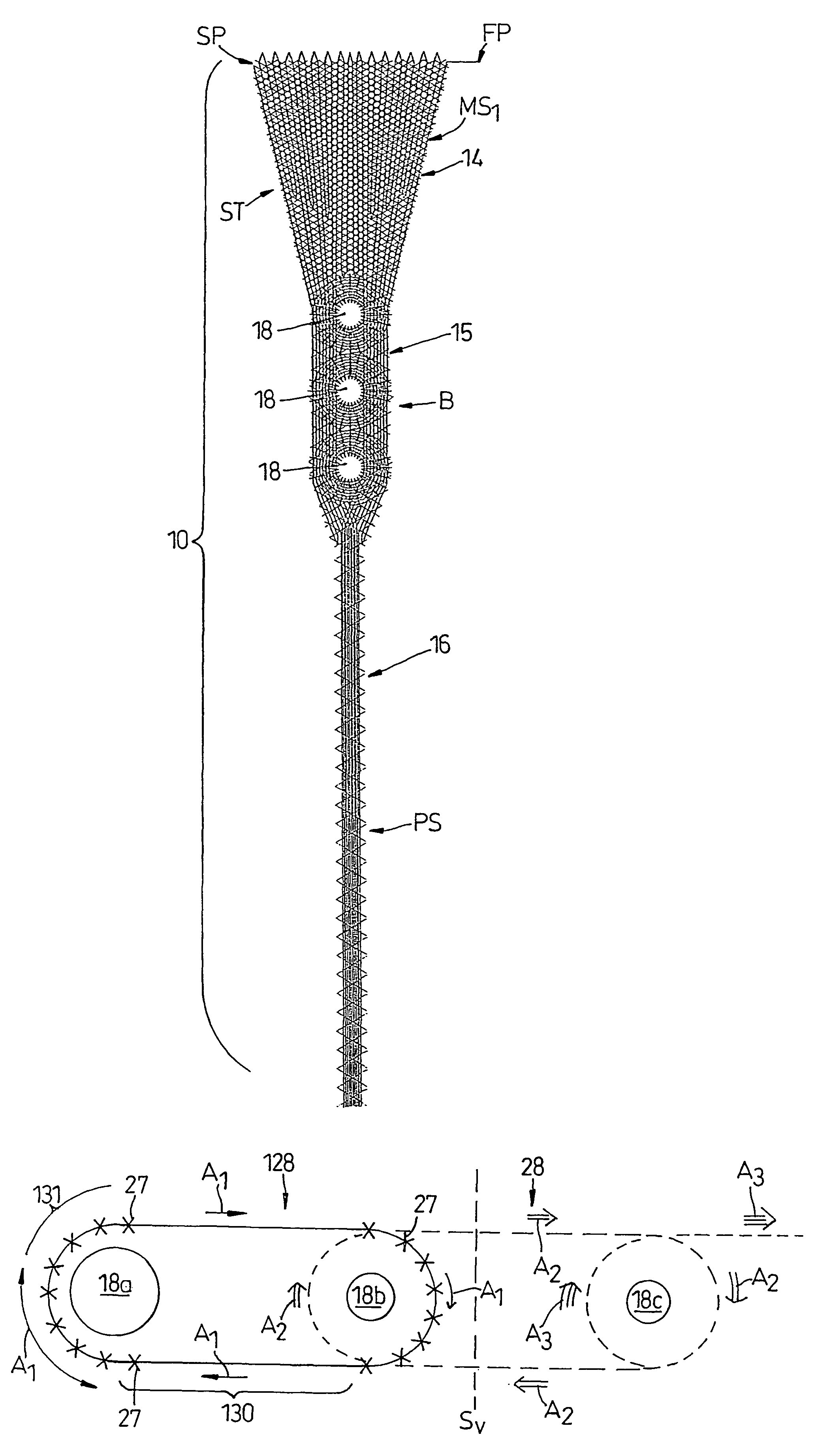
A textile prosthesis comprising a unitary body of predetermined shape having structural integrity, the body including at least one anchorage body portion for attachment to an anatomical body part, the body being composed of a combination of binding yarns and tensile load bearing filaments, the binding yarns being located at least in the or in each of said anchorage body portions and being interconnected to one another by sewn stitches, the tensile load bearing filaments being located inbetween said stitches so as to be constrained to extend through said unitary body along predetermined pathways extending in one or more predetermined directions so as to render the body resistance to stretch when a tensile load is applied in said one or more predetermined directions.
Owner:ELLIS DEV +1
Implant device
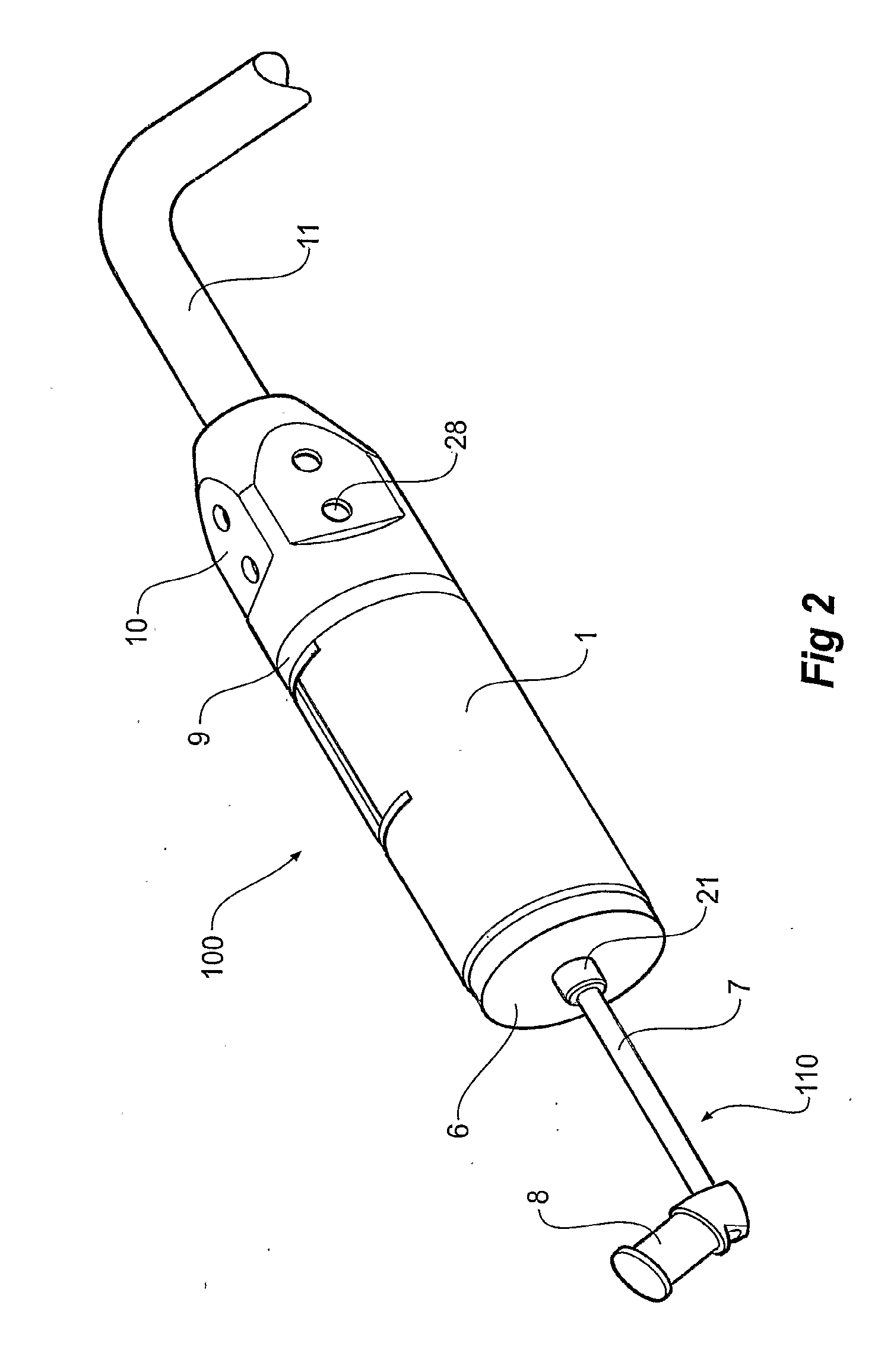
ActiveUS7409070B2Incorrect tightening torqueReduce riskSuture equipmentsDental implantsBone-anchored hearing aidBone tissue
An implant device for bone anchored hearing aids of the type that include a screw-shaped anchoring element for anchorage in the bone tissue, an abutment sleeve for skin penetration and arranged to be connected to the fixture with a screw connection and a tool for installing the implant into the bone tissue. The fixture and the abutment sleeve are made as a pre-mounted unit that unit is arranged to be installed in one step by means of the tool, which is arranged to cooperate with a tool engaging portion on the abutment sleeve. This arrangement requires fewer pieces to handle for the surgeon during the installation, which means that the surgical procedure can be carried out in a simpler and predetermined way, at the same time as the advantages inherent in a two-piece implant device are maintained.
Owner:COCHLEAR BONE ANCHORED SOLUTIONS
Length-variable auditory ossicle prosthesis
An auditory ossicle prosthesis with a first and a second securing element for mechanical securement in the middle ear as well as a connecting element, which is rigidly connected to the securing elements and connects them to each other and has a receiving part and a push-in part that can be pushed into a receiving opening of the same, the connecting element being designed so as to be variable in length in the axial direction between the receiving part and the push-in part, and it being possible for the receiving part and the push-in part to be clamped in a desired relative coaxial pushed-in position, characterized in that the clamping force FK between the receiving part and the push-in part in the clamped state is at least 10 times, preferably approximately 100 times, greater than the maximum external forces naturally occurring in the middle ear in the region of the ossicles. In this way it is possible in a simple manner for a desired, defined length of the prosthesis to be established even before it is clamped in between the two securing points, and for this length to be maintained exactly with a lasting effect even after completion of the operation, for example after the insertion of a second securing element, formed as a piston, through a perforated stirrup footplate.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
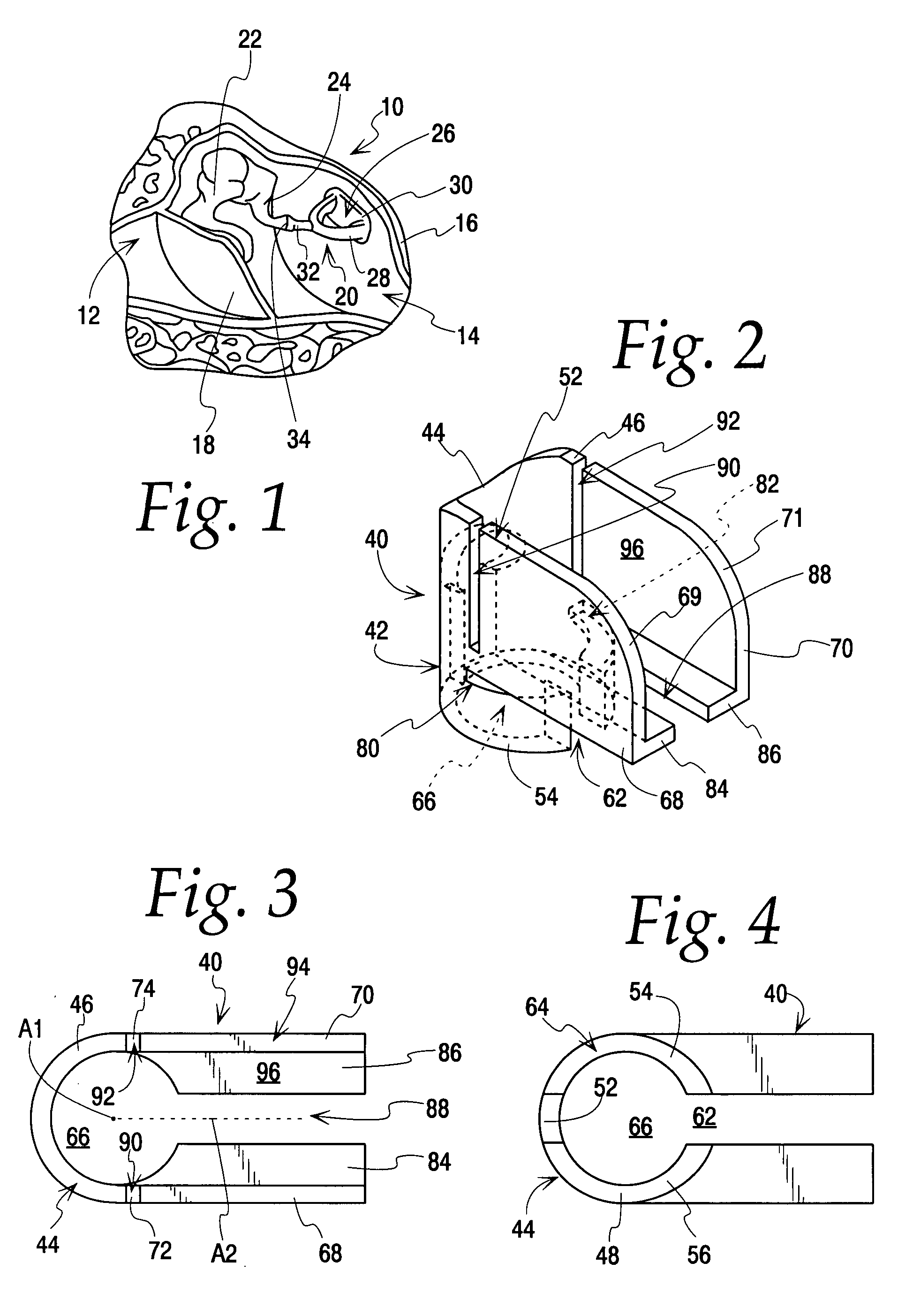
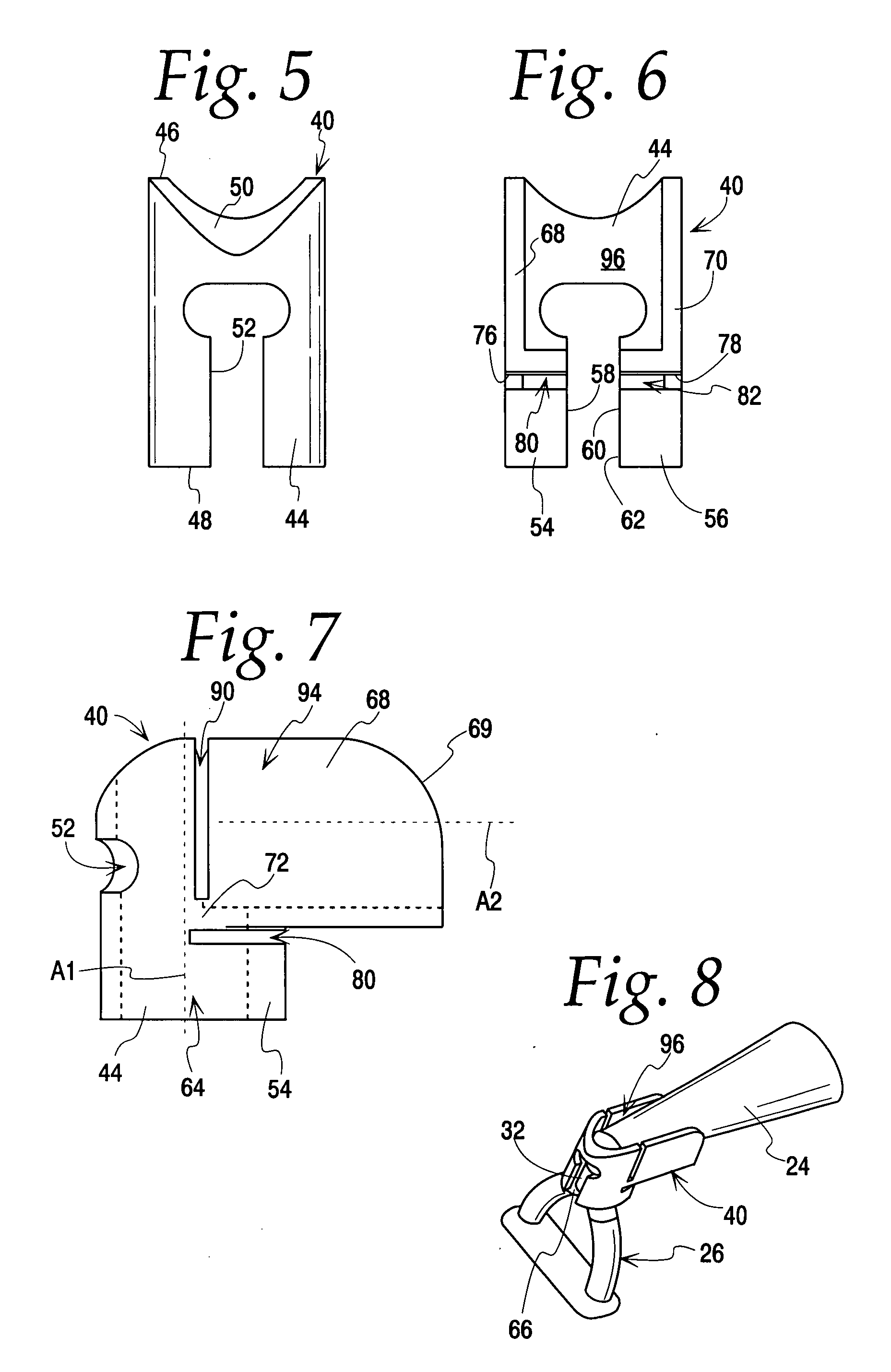
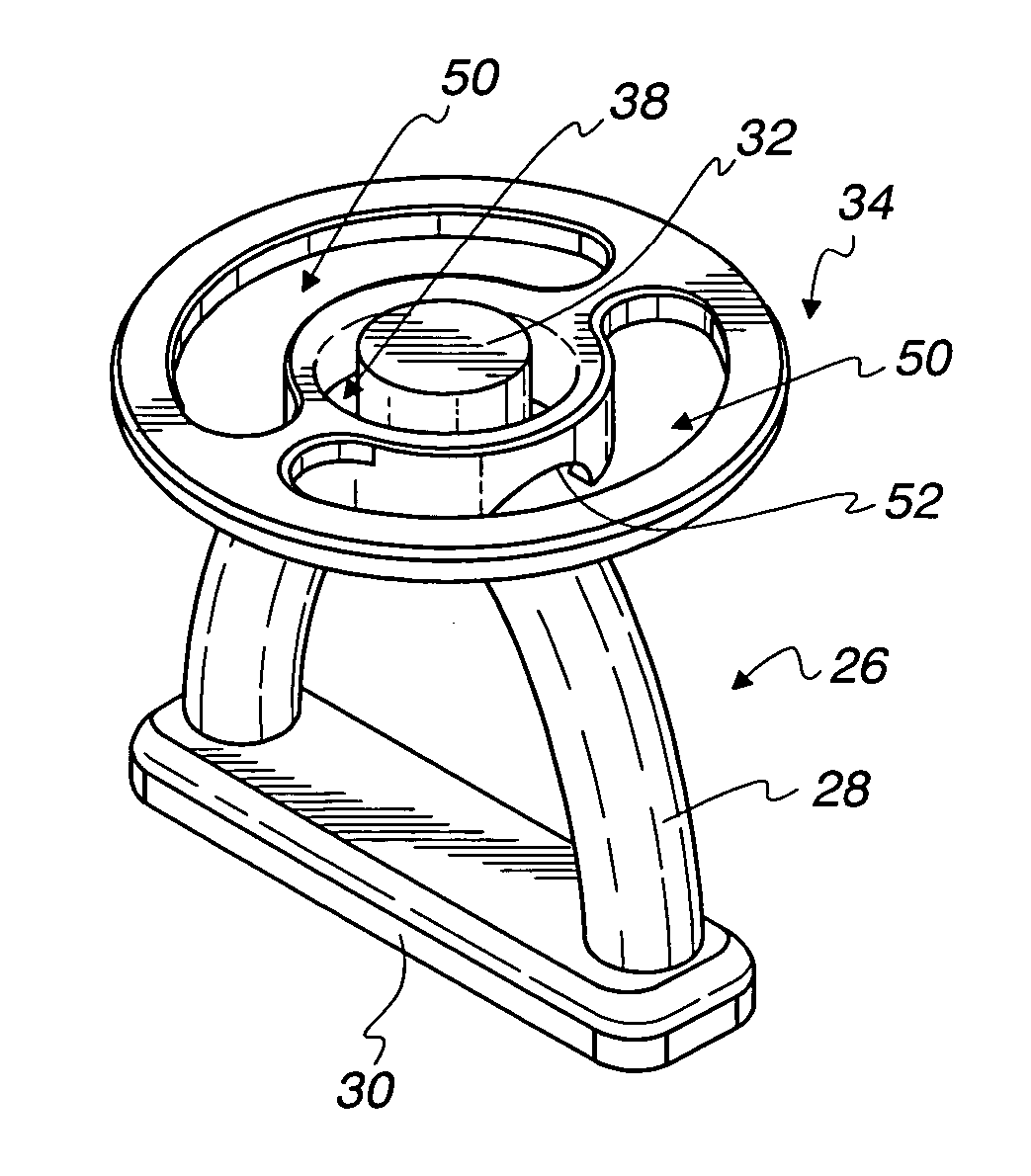
Tympanic membrane pressure equalization tube
The invention is a tympanic membrane pressure equalization tube. The tube has a distal end and a proximal end and a tube lumen. A medial flange is located at the distal end of the tube and has 2 or more retention elements and a space between each retention element. A lateral flange is located at the proximal end of the tube. The outside diameter of the medial flange is greater than the outside diameter of the lateral flange and the diameter of the medial flange is between about 2.0 and 5.0 mm and the diameter of the lateral flange is between about 1.75 mm and 4.0 mm.
Owner:TUSKER MEDICAL
Medical Implants
InactiveUS20090283701A1Relieve symptomsIncrease surface areaDental implantsNanotechBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tympanic Membrane Pressure Equalization Tube
The invention is a tympanic membrane pressure equalization tube. The tube has a distal end and a proximal end and a tube lumen. A medial flange is located at the distal end of the tube and has 2 or more retention elements and a space between each retention element. A lateral flange is located at the proximal end of the tube. The outside diameter of the medial flange is greater than the outside diameter of the lateral flange and the diameter of the medial flange is between about 2.0 and 5.0 mm and the diameter of the lateral flange is between about 1.75 mm and 4.0 mm.
Owner:TUSKER MEDICAL
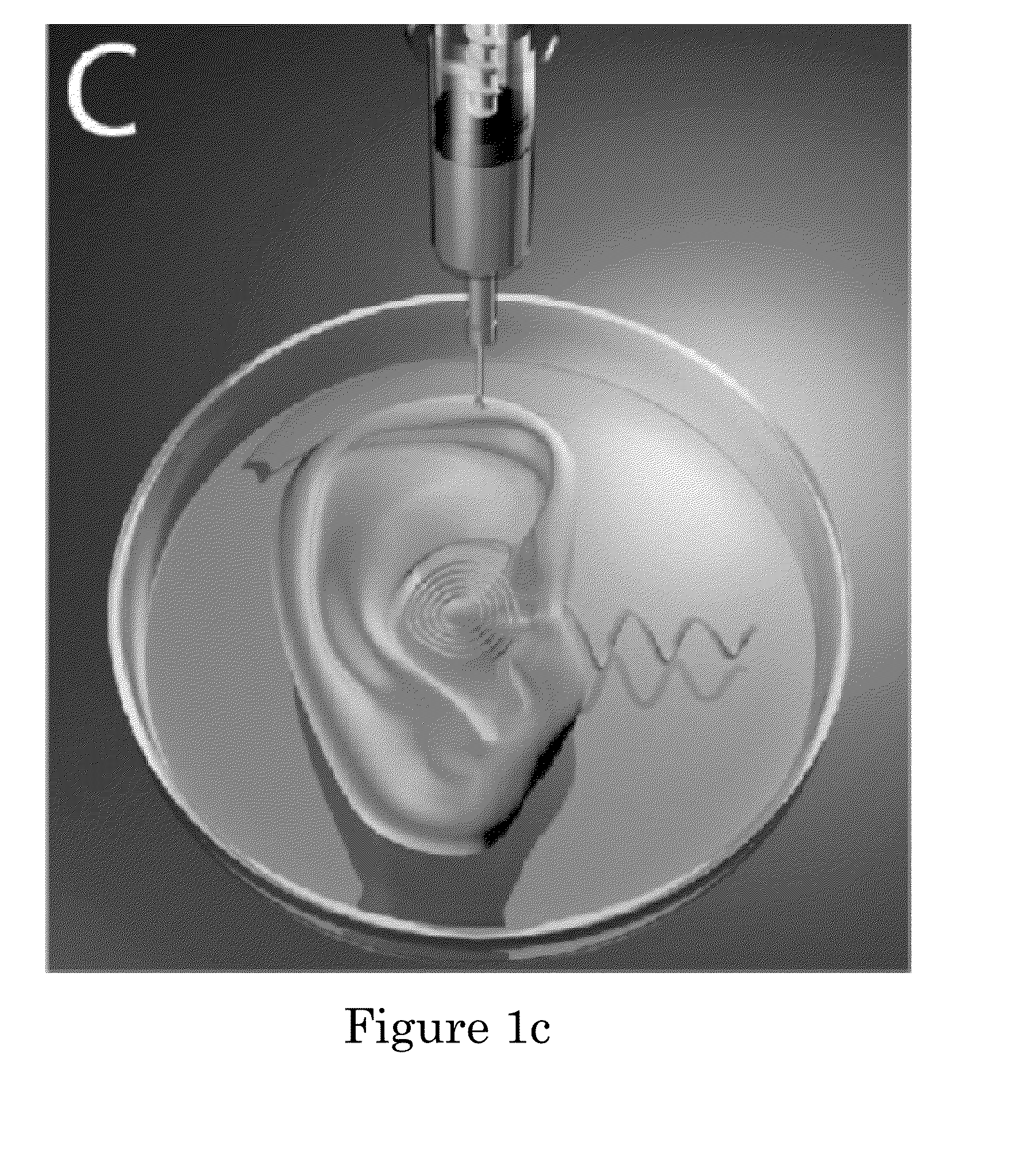
Multi-functional hybrid devices/structures using 3D printing
A bioelectronic device and method of making is disclosed. The device includes a scaffold formed via 3D printing. The device also includes a biologic and an electronic device formed via 3D printing, the biologic and electronic device being interweaved with or coupled to the scaffold. The electronic component may e.g., include at least one of hard conductors, soft conductors, insulators and semiconductors. The scaffold may be formed of at least one of synthetic polymers and natural biological polymers. The biologic may include at least one of animal cells, plant cells, cellular organelles, proteins and DNA (including RNA).
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Ossicle prosthesis with sensitive top plate
ActiveUS20080234817A1Increase flexibilityIncrease variabilityWound clampsEar implantsProsthesisPost operative
An ossicle prosthesis includes, at one end, a first fastening element designed as a top plate for mechanical connection with the tympanic membrane, and, at the other end, a second fastening element for mechanical connection with a component or parts of a component of the ossicular chain or with the inner ear, and a connecting element that connects the two fastening elements with each other in a sound-conducting manner; the top plate includes a radially outward annular region, a radially inward attachment region for mechanically attaching the top plate to the connecting element, and several segment elements for radially connecting the annular region with the attachment region, characterized by the fact that the segment elements are geometrically designed such that they locally emulate any localized medial motions made by the tympanic membrane, but they do not transmit the motion to distant regions of the top plate. As a result, a high level of post-operative flexibility and variability of the prosthesis, and higher-quality sound conduction through the prosthesis may be attained in a technically simple, uncomplicated, and cost-favorable manner.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Surface treatment for implants
The present invention provides a wear-resistant titanium alloy orthopedic device. Also provided is a method of forming a wear-resistant titanium alloy orthopedic device by deeply diffusing oxygen into the titanium alloy device. A method of hardening a device formed of titanium by deeply diffusing oxygen into the titanium alloy device is provided.
Owner:AESCULAP II
Middle ear prosthesis
A middle ear prosthesis comprises a body of deformable material capable of retaining different shapes. The body comprises a slotted wall defining a cavity for receiving a bone of the middle ear. The wall is deformable proximate slots in the wall between an open position for receiving the bone and a closed position wherein the body is reshaped to grasp the bone.
Owner:CLARITY
Myringopexy type titanium prosthesis
A middle ear prosthesis comprises a one piece disk shaped prosthesis including a generally circular malleable body including a bore. The body engages a tympanic membrane and the bore receives a head of a stapes when implanted in a middle ear. More particularly, the middle ear prosthesis comprises a body comprising an annular head, a collar, and a plurality of radially extending members connecting the head to the collar. The head engages a tympanic membrane and the collar receives a head of a stapes when implanted in a middle ear.
Owner:CLARITY
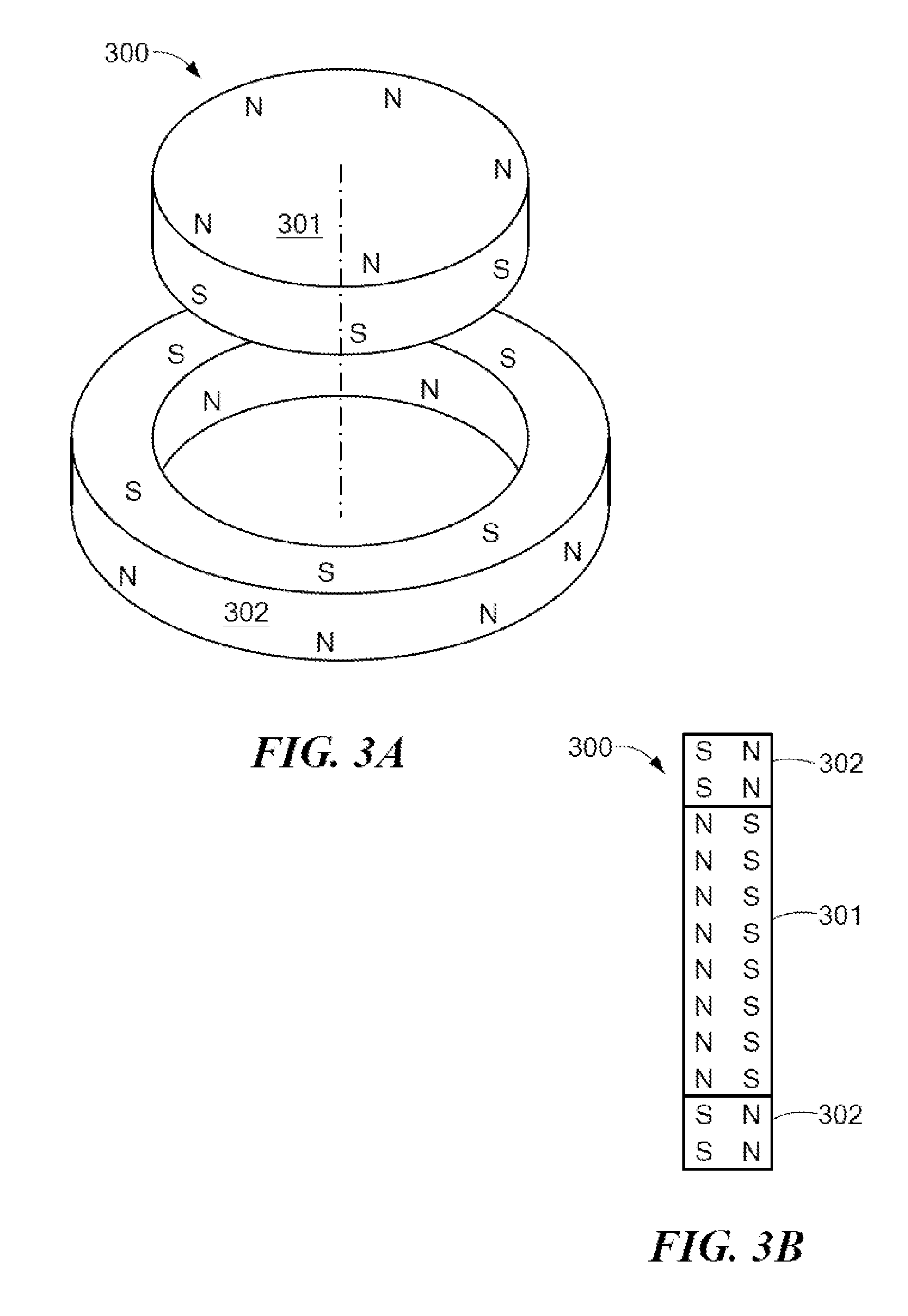
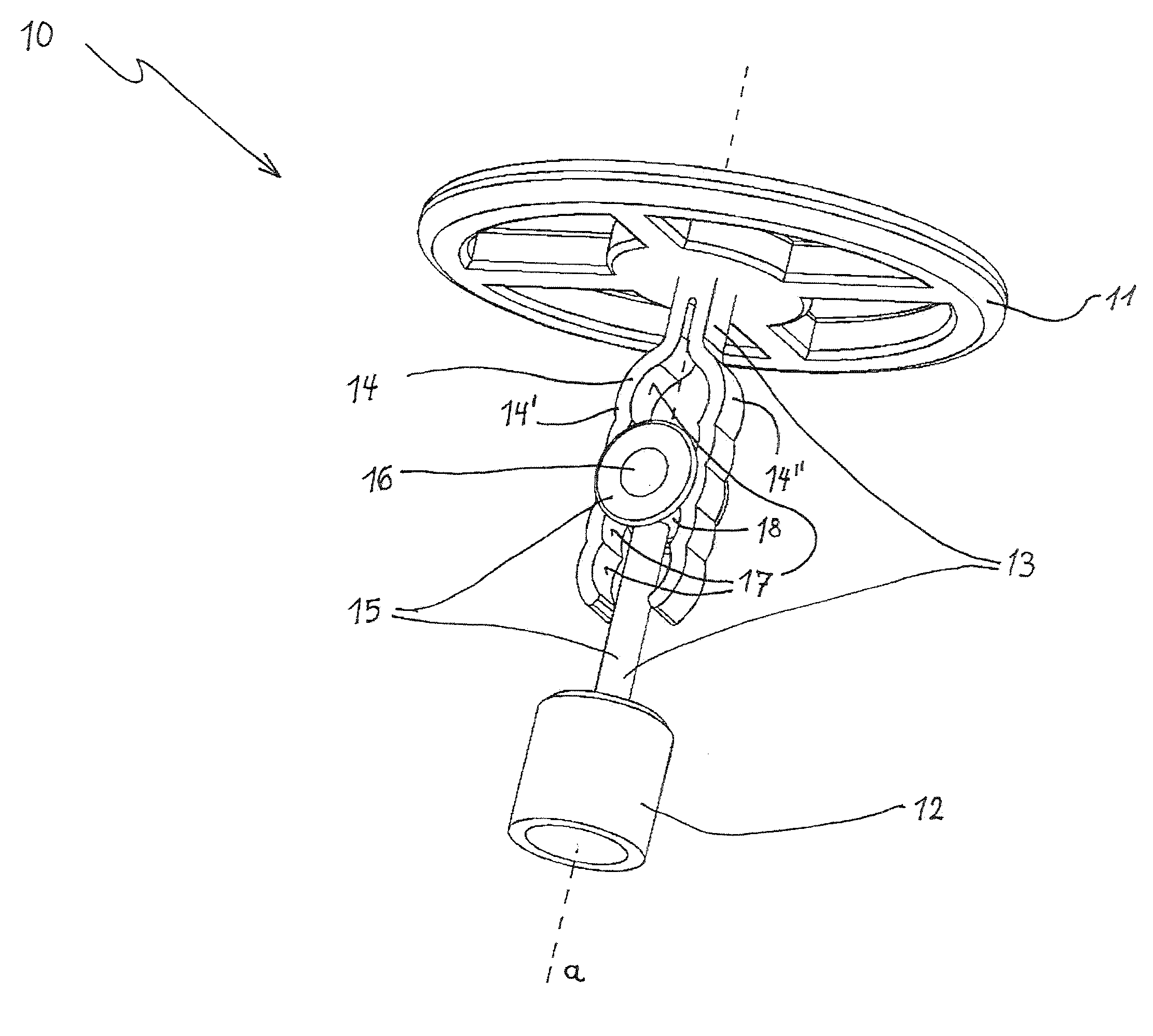
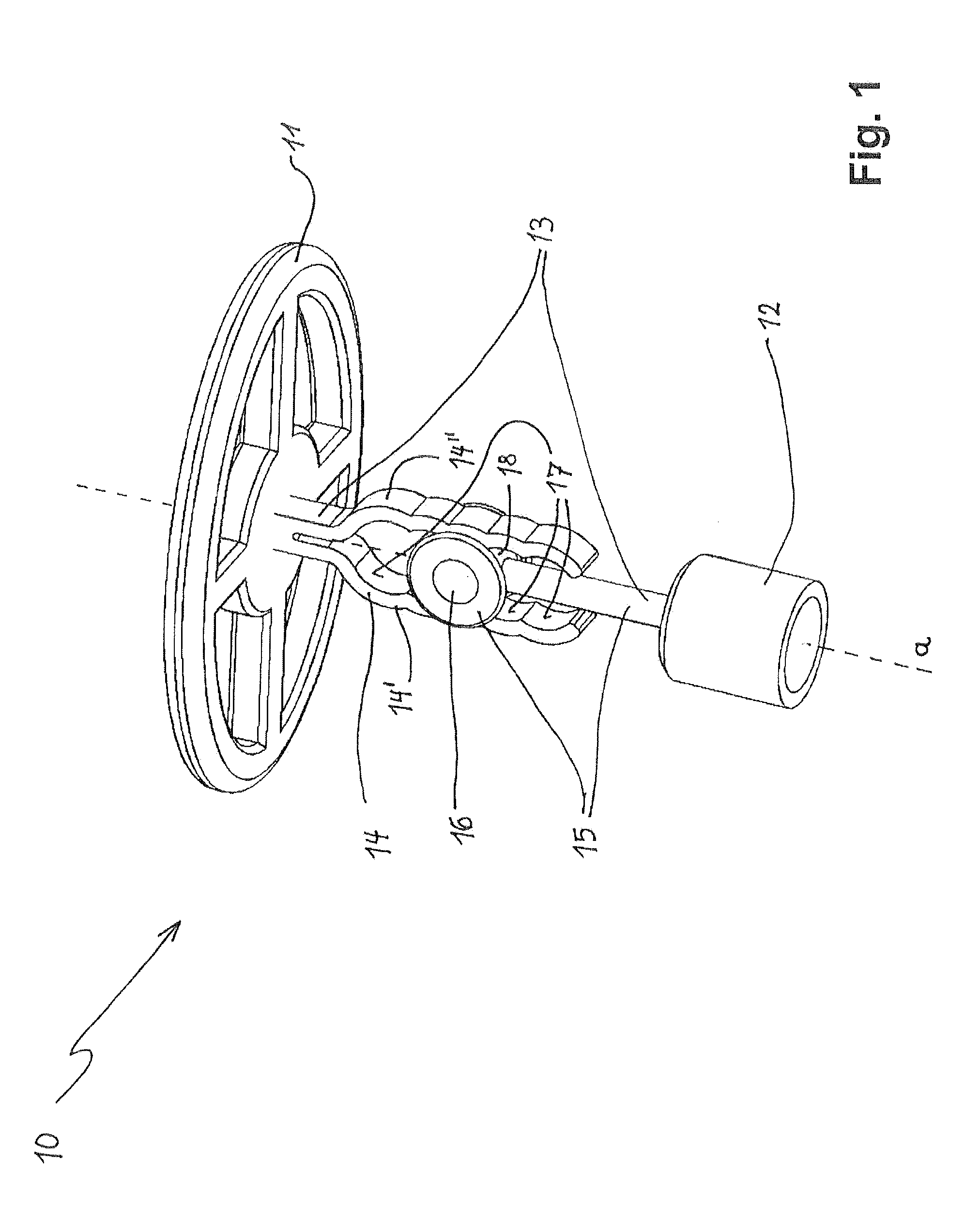
Magnetic Attachment System for Implantable Device
A magnet arrangement is described for use with hearing implant systems. An external device for use with an implant system has an external device housing that contains external elements of a hearing implant system. A cylindrical external magnet arrangement within the housing has multiple magnetic sections lying in a common plane, including an inner center disc having an inner magnetic orientation in an inner magnetic direction, and an outer radial ring having an outer magnetic orientation in an outer magnetic direction opposite to the inner magnetic direction.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Implantable auditory stimulation system and method with offset implanted microphones
InactiveUS20100317913A1Improve utilizationPromotes its utilizationElectrotherapySignal processingMicrophone signalAuditory stimulation
An improved implantable auditory stimulation system includes two or more implanted microphones for transcutaneous detection of acoustic signals. Each of the implanted microphones provides an output signal. The microphone output signals may be combinatively utilized by an implanted processor to generate a signal for driving an implanted auditory stimulation device. The implanted microphones may be located at offset subcutaneous locations and / or may be provided with different design sensitivities, wherein combinative processing of the microphone output signals may yield an improved drive signal. In one embodiment, the microphone signal may be processed for beamforming and / or directionality purposes.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
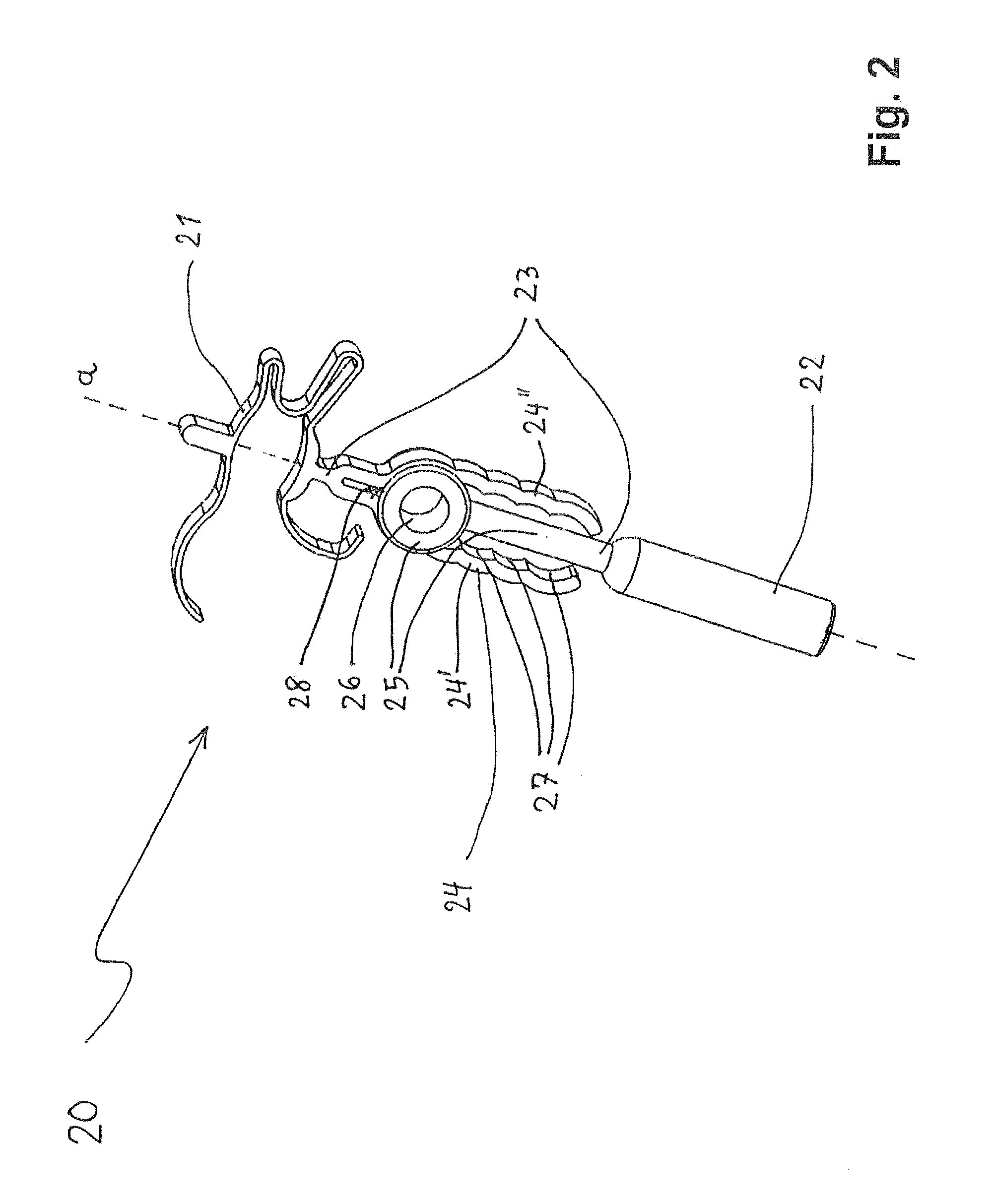
Spanning connector for implantable hearing instrument
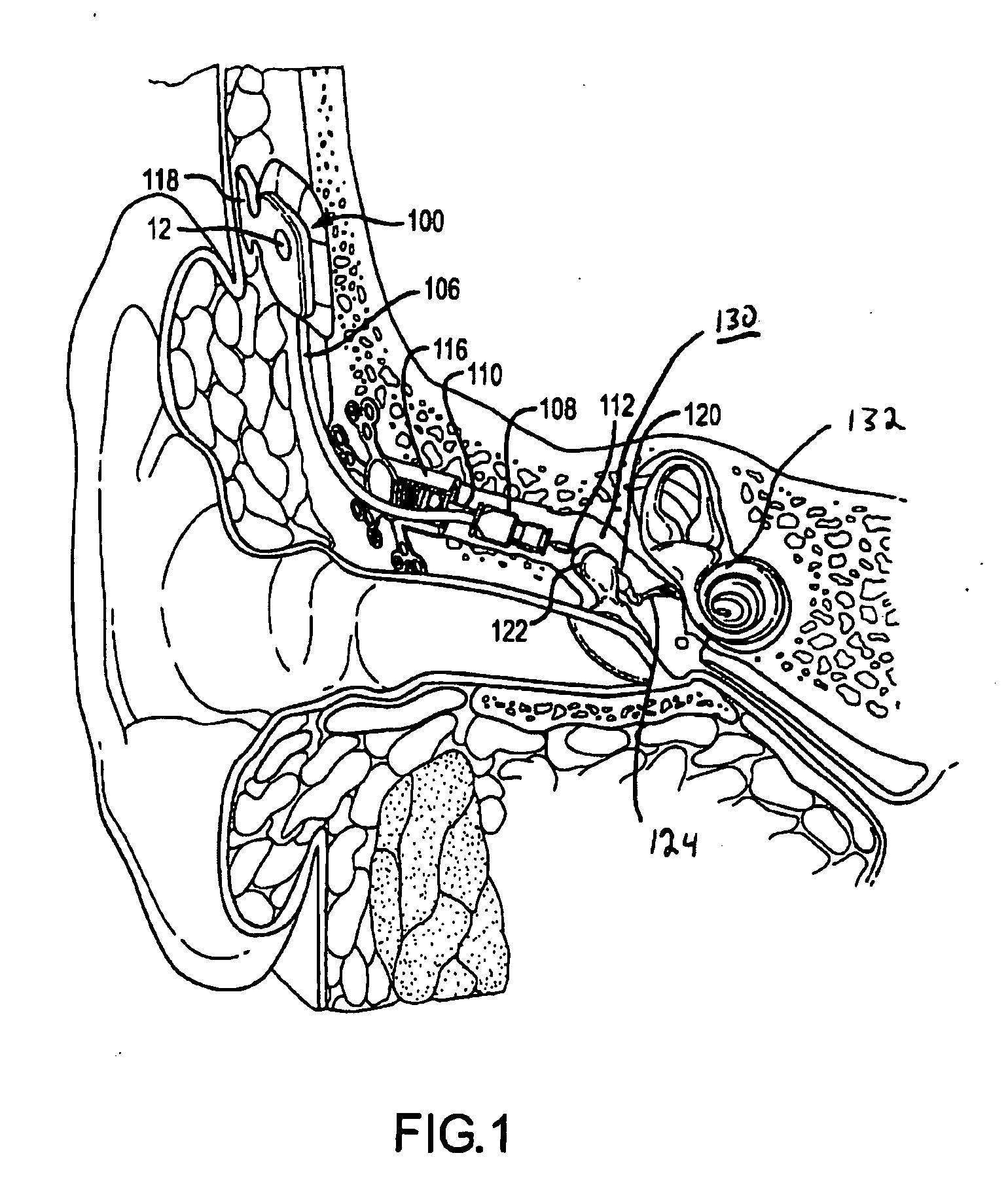
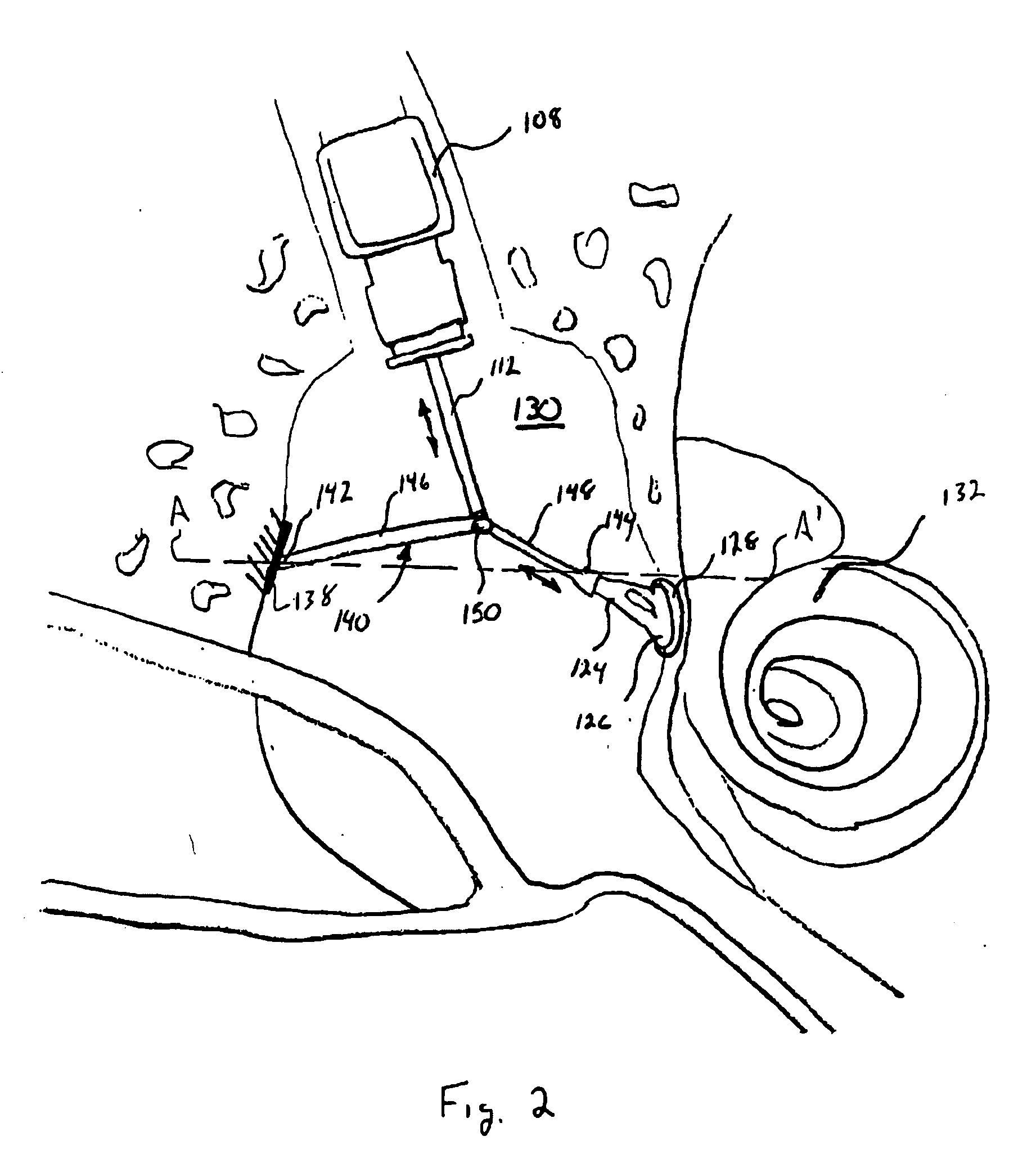
ActiveUS20090124849A1Closely alignedEffectively transmit vibratory signalDiagnosticsSurgeryHearing transducerTympanic cavity
Provided herein are various connectors that allow for translating the axial movement of an implantable hearing transducer 108 from a first direction to a second direction. In various arrangements, these connectors form a spanning connector 200 that extend across a portion of a tympanic cavity of a patient. One end 202 of the connector 200 may be affixed to the tympanic cavity, and a second end 204 may engage an auditory component. In such an arrangement, a vibratory actuator 112 may engage the connector 200 between the first and second ends 22, 204. Such an arrangement may provide improved alignment of actuator movement with a direction of movement of an auditory component.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Artificial eardrum using silk protein and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20100286774A1Easy to useGood biocompatibilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAlginic acid
Provided is an artificial eardrum using silk protein and a method of fabricating the same. The artificial eardrum is fabricated in the form of a silk membrane by desalinating and drying silk protein (or silk fibroin) or a silk protein complex solution obtained after removal of sericin from a silkworm cocoon or silk fiber. Thus, regeneration of an eardrum perforated due to disease or a sudden accident is stimulated, a boundary of the regenerated eardrum is clean and biocompatibility and transparency are increased. In addition, the artificial eardrum may be fabricated using the silk protein or silk protein complex solution obtained from a silkworm cocoon alone or mixed with collagen, alginic acid, PEG or pluronic 127.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND HALLYM UNIV +1
Ossicular prosthesis adjusting device
An ossicular prosthesis delivery system having an ossicular prosthesis including an enlarged head and a shaft axially, moveably mounted to the head to adjust shaft length. An elongate main body having an operating portion, including a cylindrical through bore, connected to an adjusting portion, including a generally semi-cylindrical upwardly opening channel coaxial with the bore. An end wall at a distal end of the adjusting portion includes a through passage coaxial with the channel and an upwardly opening cavity. An elongate cylindrical plunger has a claw at one end. The plunger is received in the bore with the claw in the channel and an opposite end extending outwardly of the operating portion. The ossicular prosthesis' shaft is positioned in the channel with the head received in the cavity and the plunger is rotatable in the bore to capture the shaft and is reciprocally moveable in the bore to adjust shaft length of the ossicular prosthesis.
Owner:CLARITY
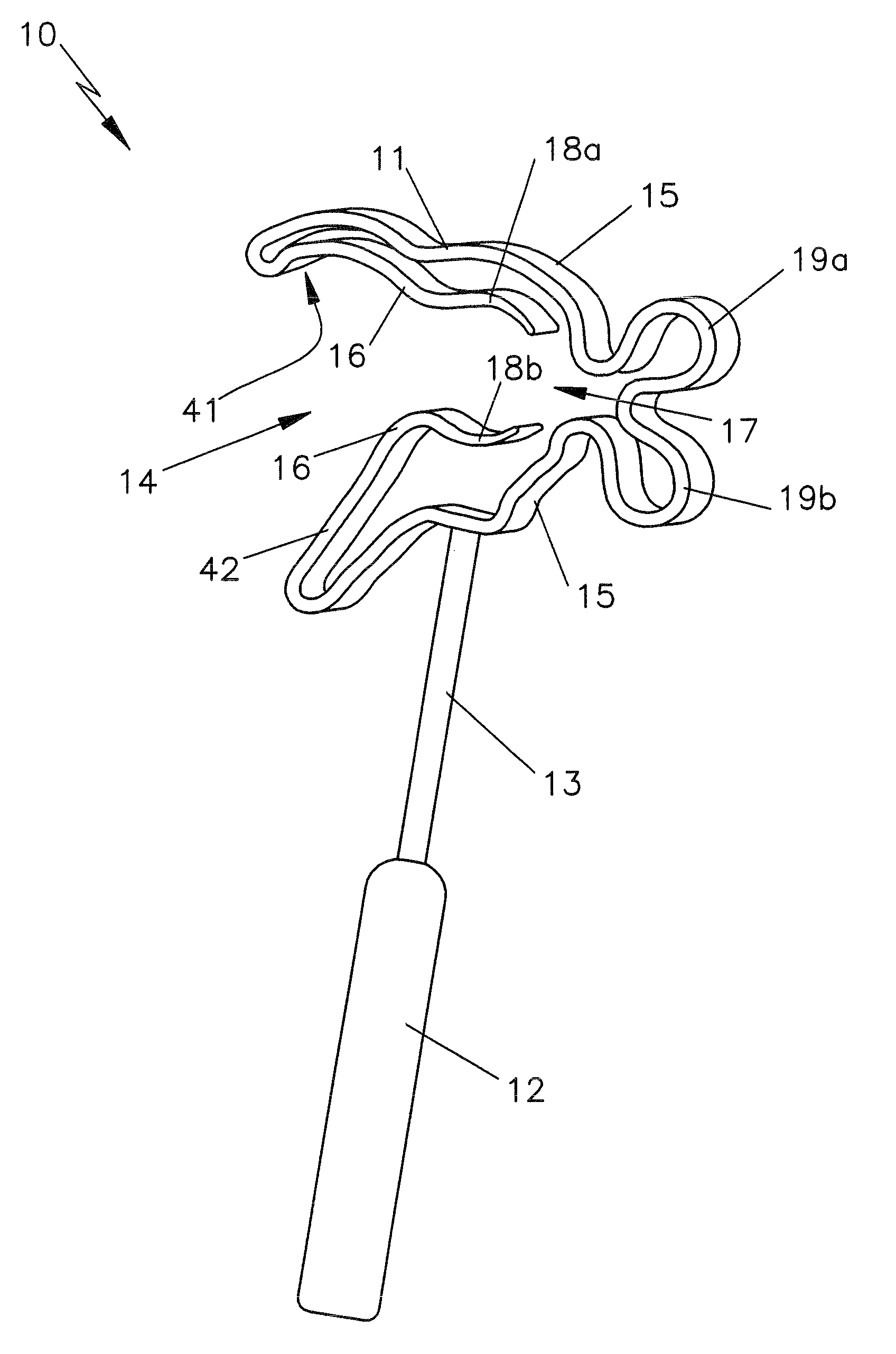
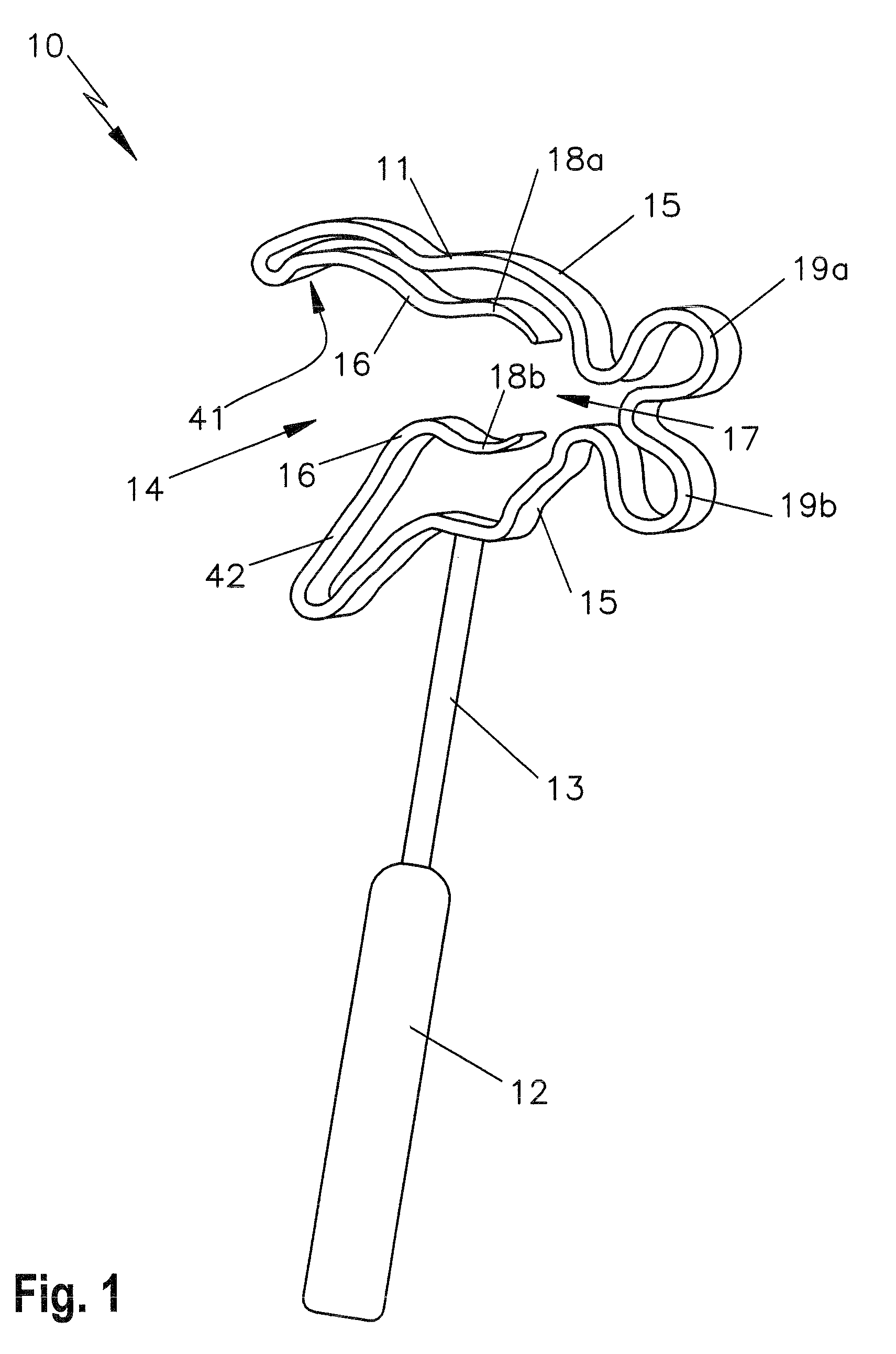
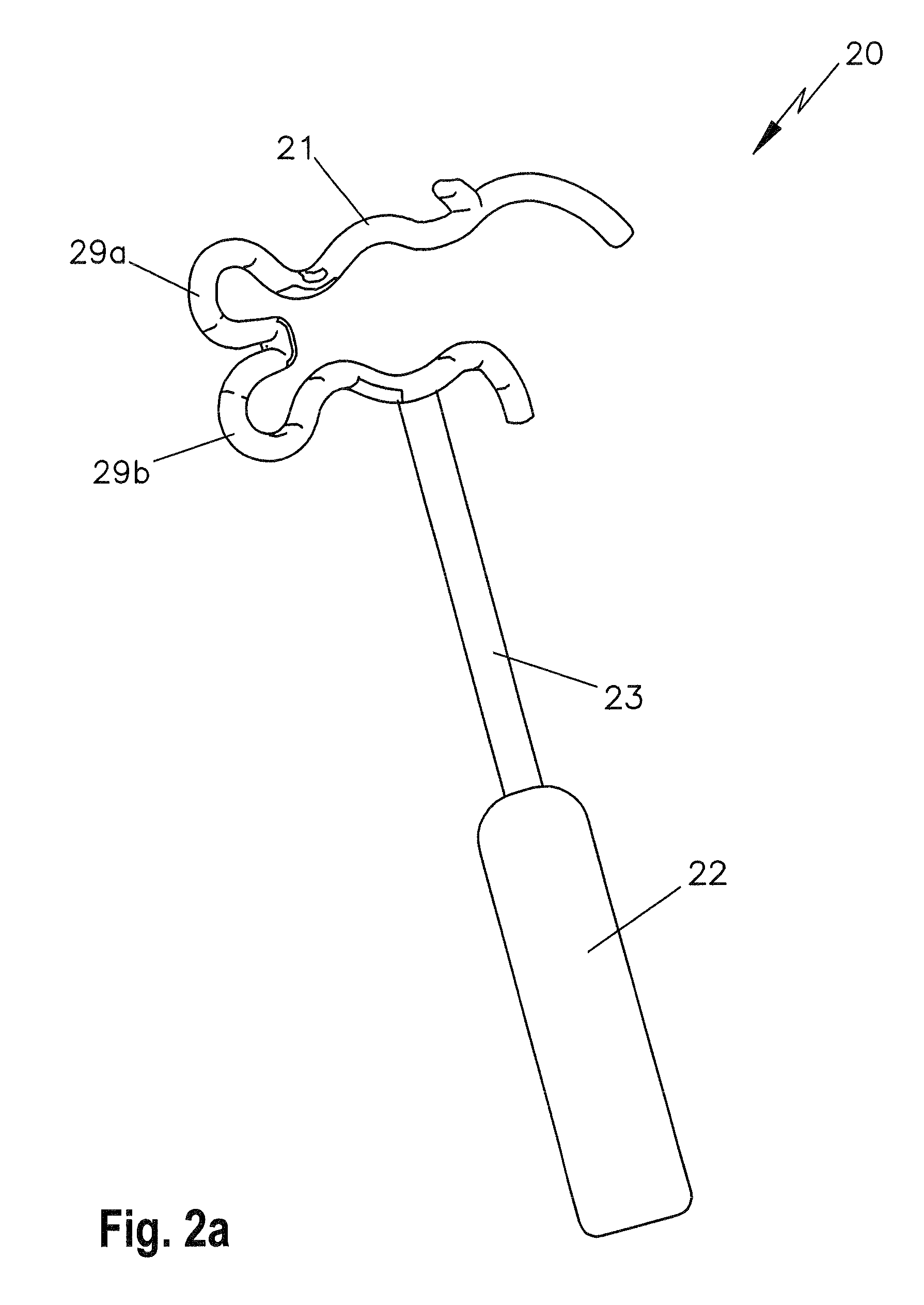
Ossicle prosthesis
An ossicle prosthesis (10), which replaces or spans at least one member of the human ossicle chain; the ossicle prosthesis (10) has a securing element embodied as a first elastic clip (11), for mechanical connection with a member of the ossicle chain, the securing element is open towards the outside on one side, with an outer opening (14) for receiving the ossicle member. The securing element form-lockingly embraces the ossicle member with two regions which are joined together on their ends located diametrically opposite the outer opening (14) via a portion extending at a spacing from the ossicle member. The portion connecting the two regions has at least two circular recesses (19a, 19b), which are curved outward in a circular arc from the member of the ossicle chain.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Artificial eardrum using silk protein and method of fabricating the same
Provided are an artificial eardrum using silk protein and a method of fabricating the same. The artificial eardrum is fabricated in the form of a silk membrane by desalinating and drying silk protein (or silk fibroin) or a silk protein complex solution obtained after removal of sericin from a silkworm cocoon or silk fiber. Thus, regeneration of an eardrum perforated due to disease or a sudden accident is stimulated, a boundary of the regenerated eardrum is clean and biocompatibility and transparency are increased. In addition, the artificial eardrum may be fabricated using the silk protein or silk protein complex solution obtained from a silkworm cocoon alone or mixed with collagen, alginic acid, PEG or pluronic 127.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND HALLYM UNIV +1
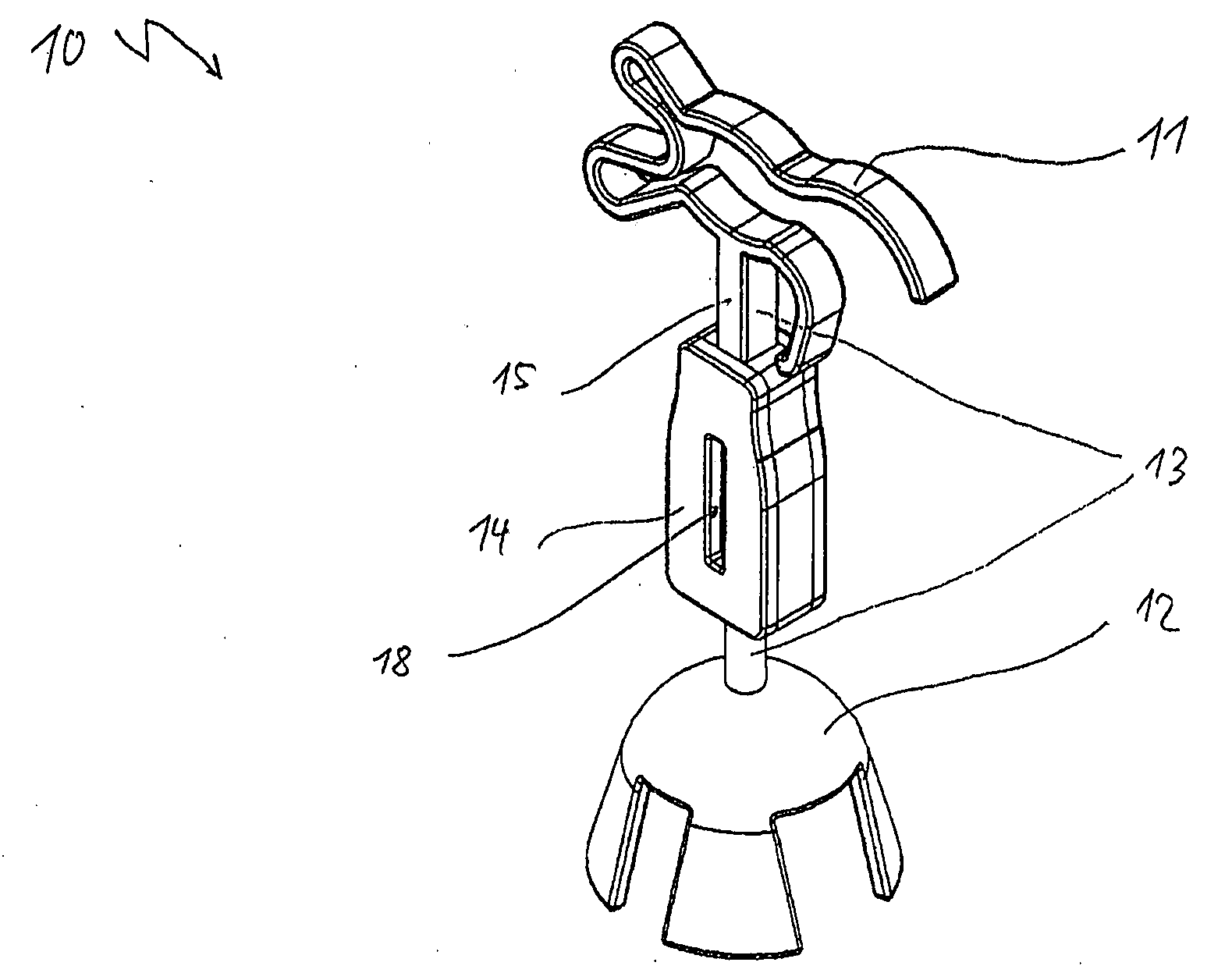
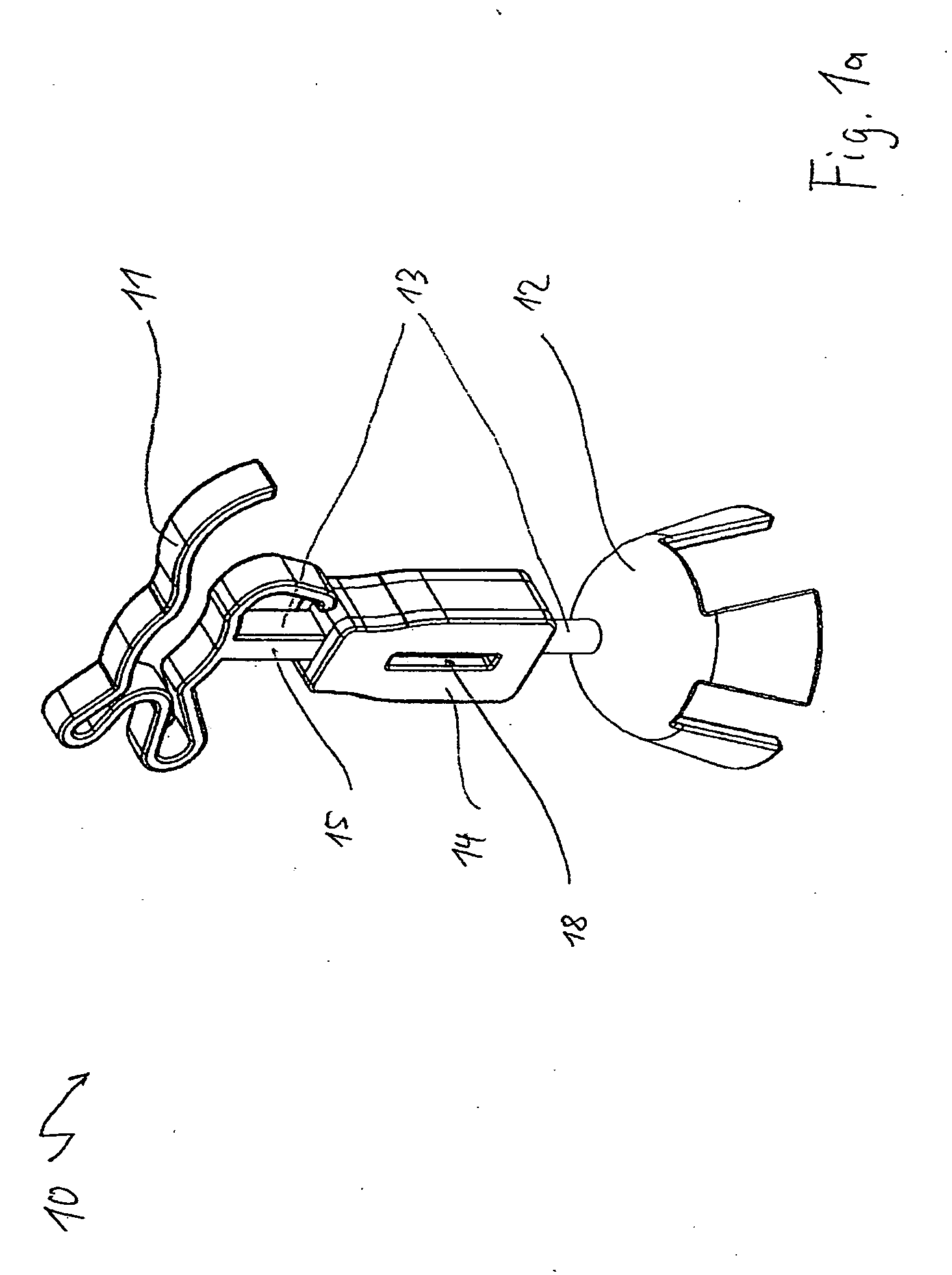
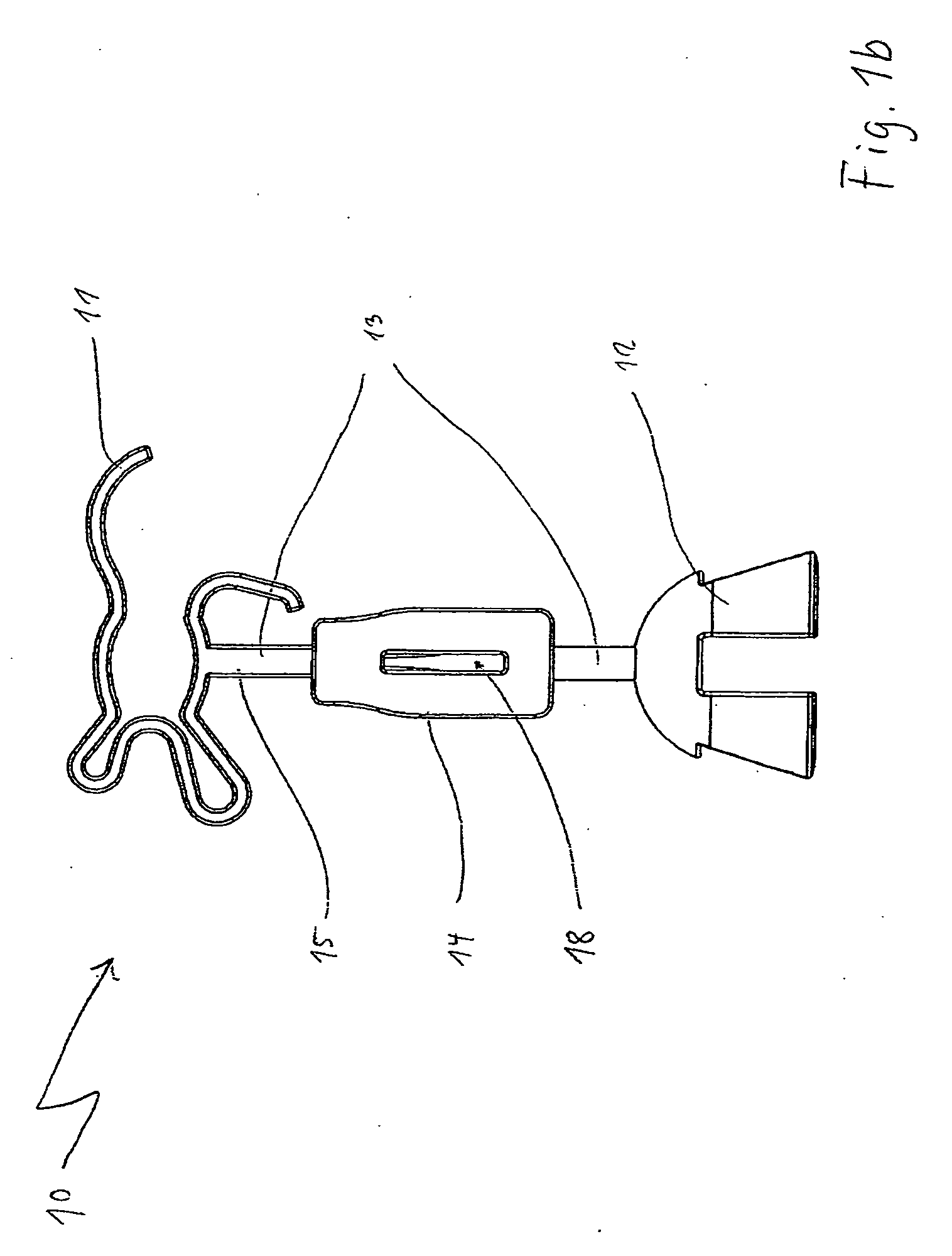
Auditory ossicle prosthesis with variable coupling surfaces
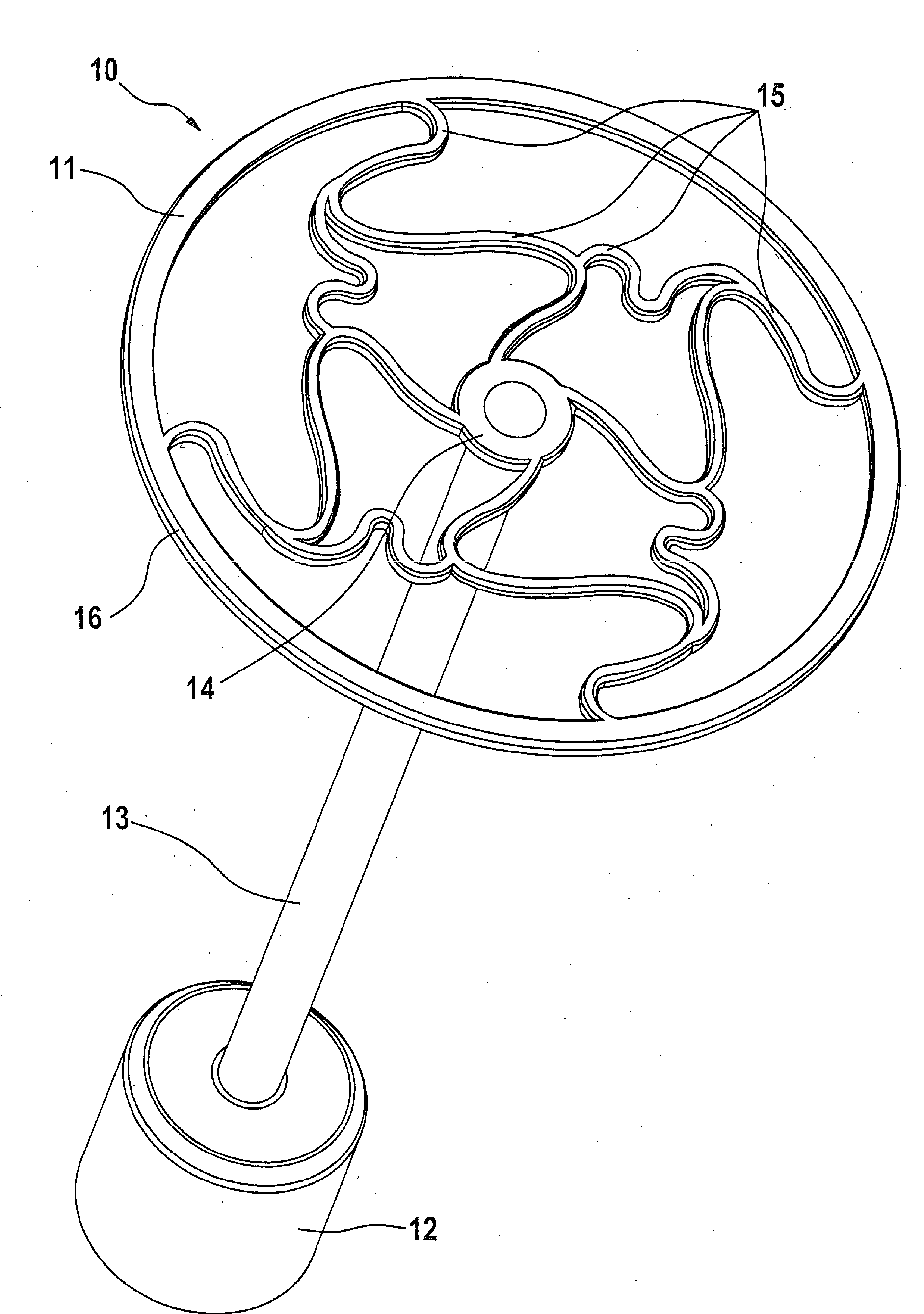
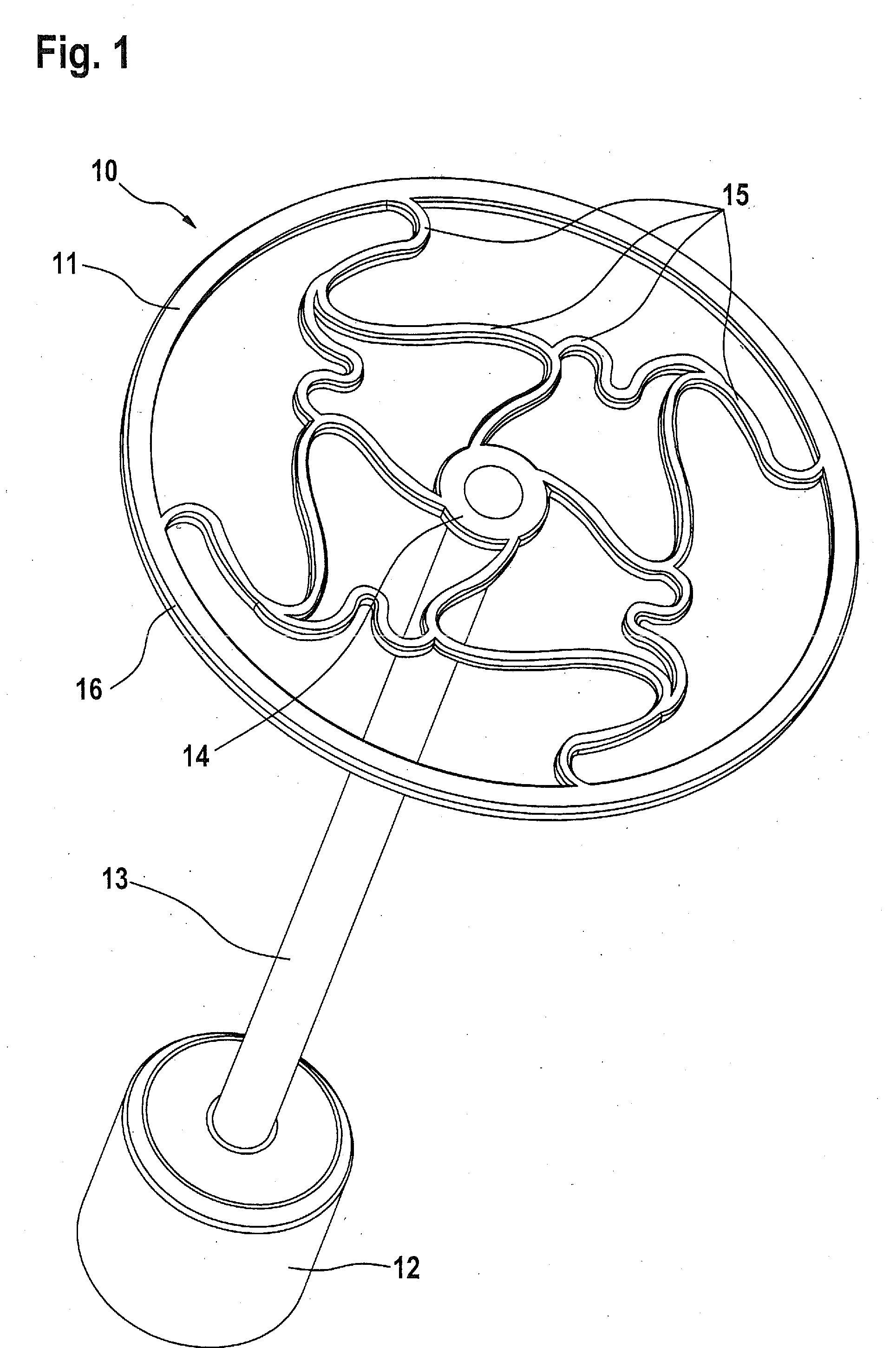
An auditory ossicle prosthesis (10) which comprises, at one end, a plate-shaped first securing element (11) for bearing on the tympanic membrane or on the footplate of the stirrup, and, at the other end, a second securing element (12) for mechanical connection to the ossicular chain or to the inner ear, and also a connection element (13) that connects the two securing elements so as to conduct sound, wherein the first securing element has a radially inner coupling area (14) for coupling the first securing element to the connection element, and also a plurality of web elements (15) for radial connection of the coupling area to radially outer portions (16) of the first securing element, is characterized in that the coupling area, the web elements and the radially outer portions are of such a geometric configuration, and their material so chosen, that a plastic deformation is effected by stretching or pushing together in the plane of the plate of the first securing element, by means of which plastic deformation the external diameter of the first securing element is permanently increased or reduced. This means that the number of different prostheses to be kept ready during an operation can be reduced to a single standard prosthesis, without losing the possibility of optimal adaptation of the prosthesis to the specific case of use.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
Variable-length passive ossicular prosthesis
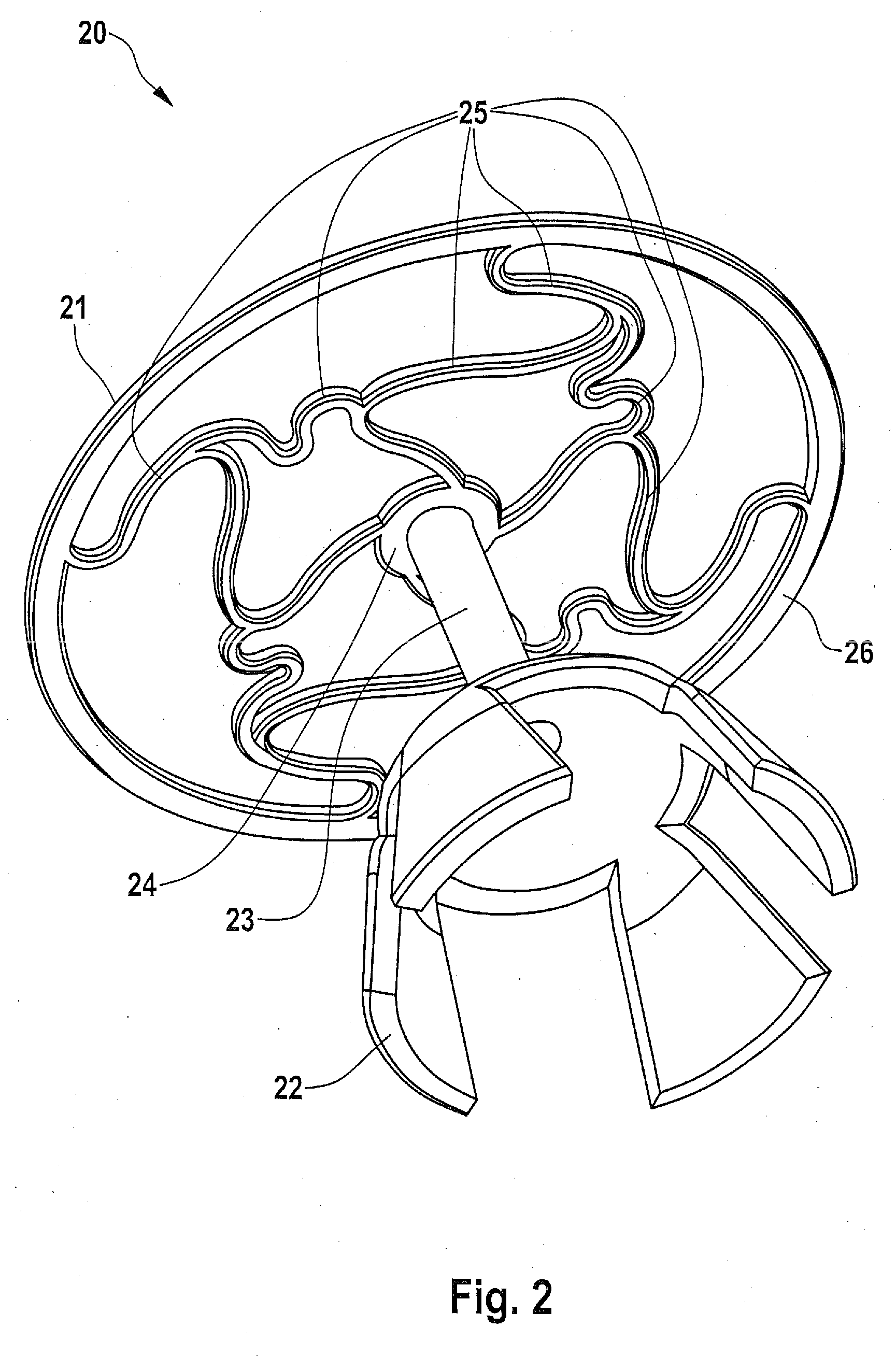
ActiveUS20140094910A1Avoid reactionPrecise and reproducibleEar implantsEngineeringTympanic Membranes
A passive ossicular prosthesis includes a first and second fastening element for connection to the tympanic membrane. A connecting element connects the fastening elements in a sound-conducting manner. The connecting element includes a receiving part and an insertion part. The insertion part is inserted into a receiving opening of the receiving part. The receiving part encloses an end section of the insertion part in the manner of a clamp by way of two opposing, parallel legs disposed parallel to a shank axis of the connecting element. The legs have catch devices that fix the enclosed end section discrete spatial positions relative to the shank axis.
Owner:HEINZ KURZ MEDIZINTECHN
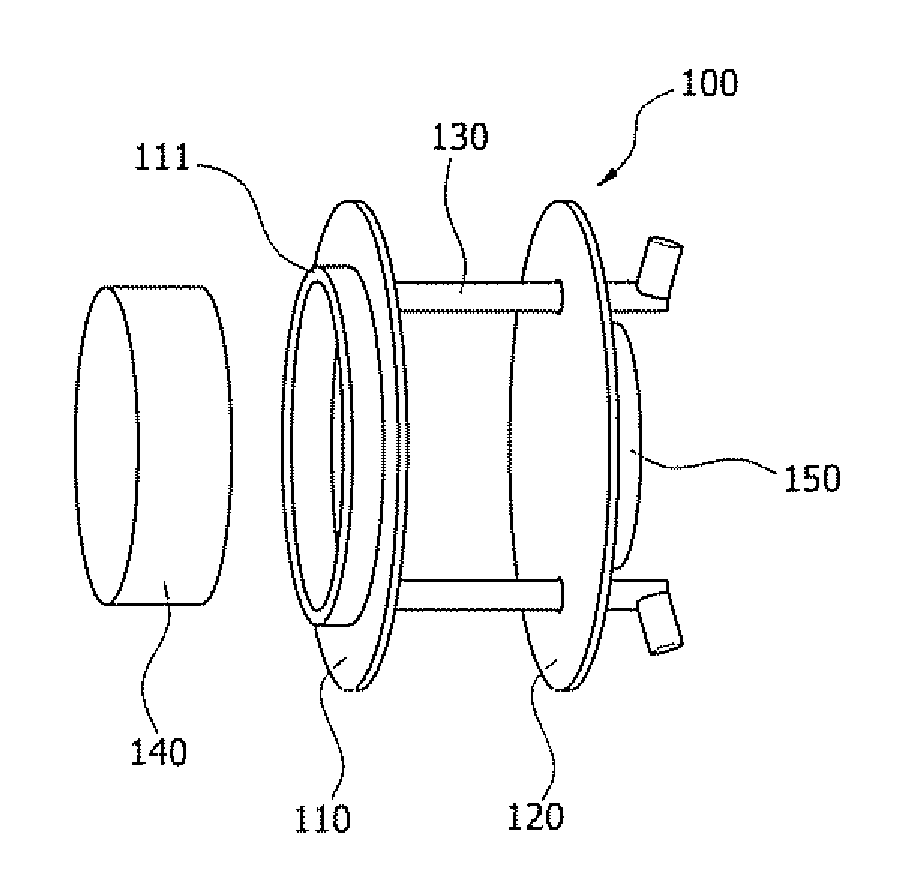
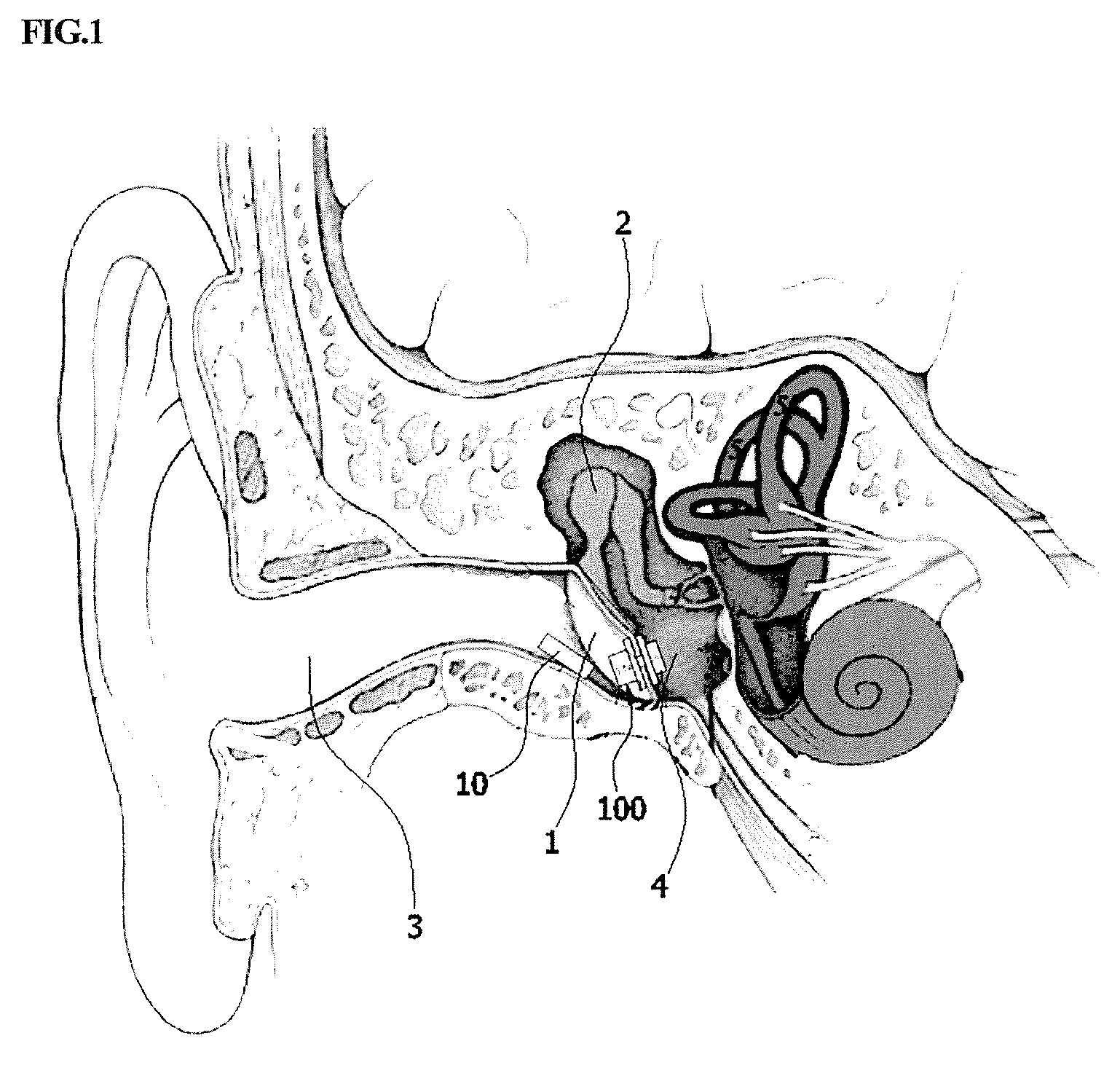
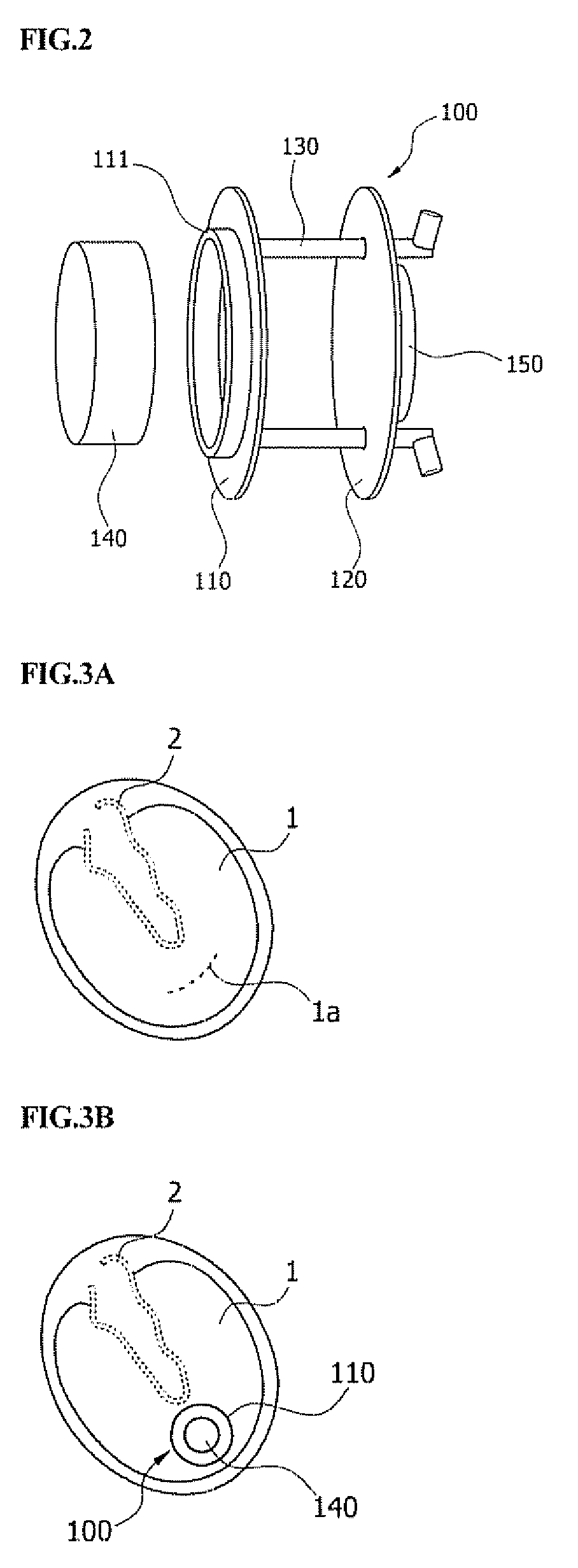
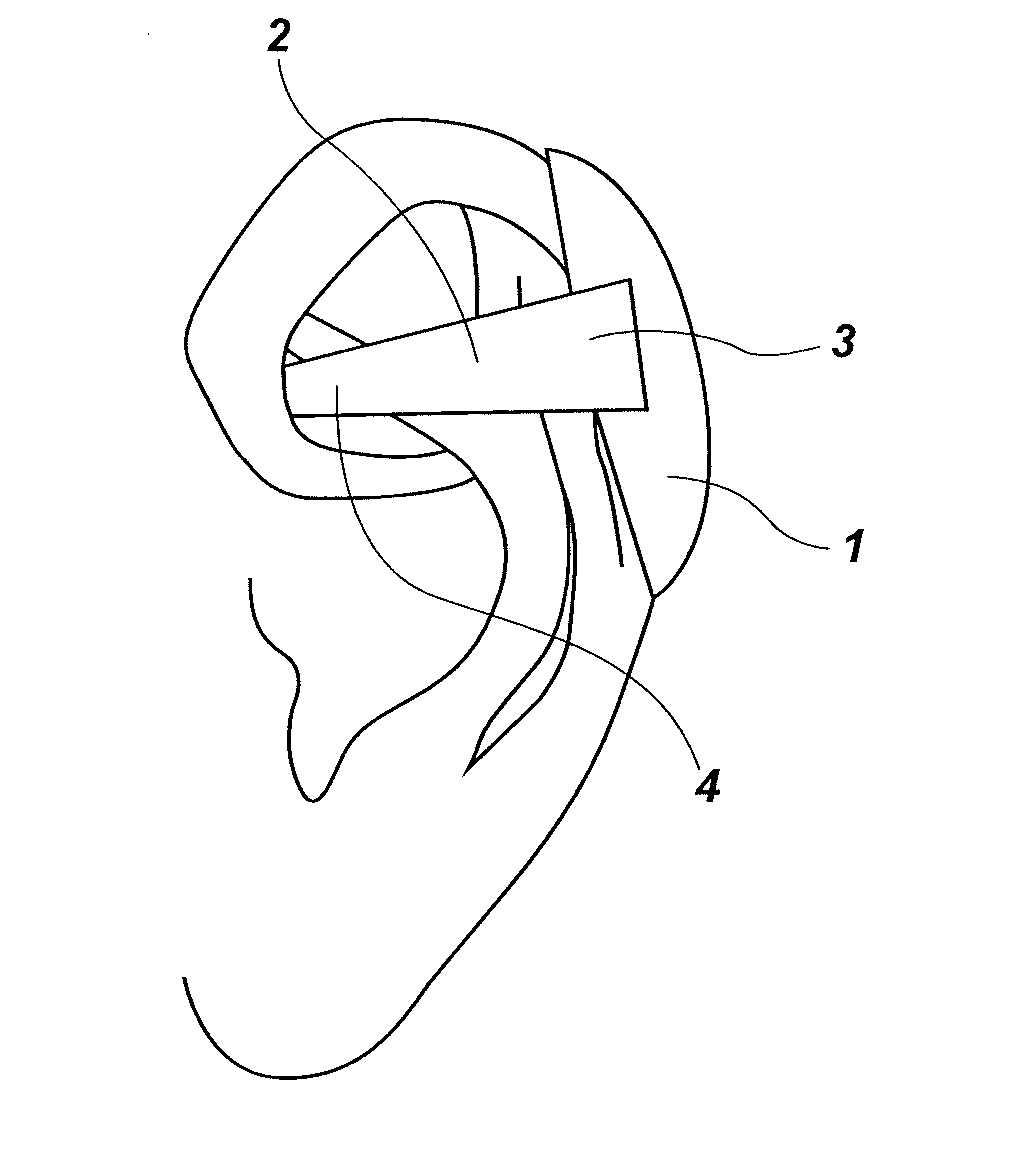
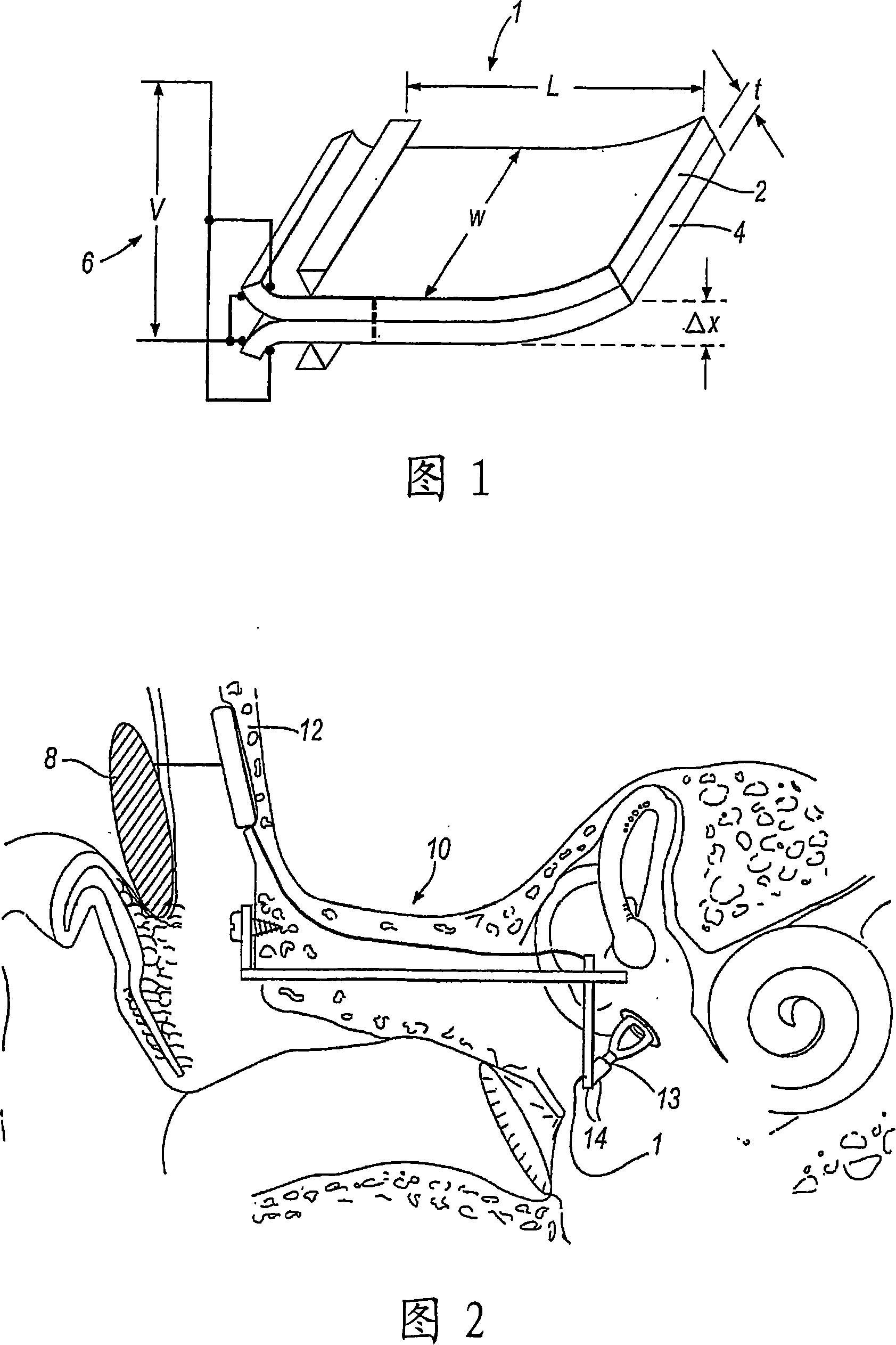
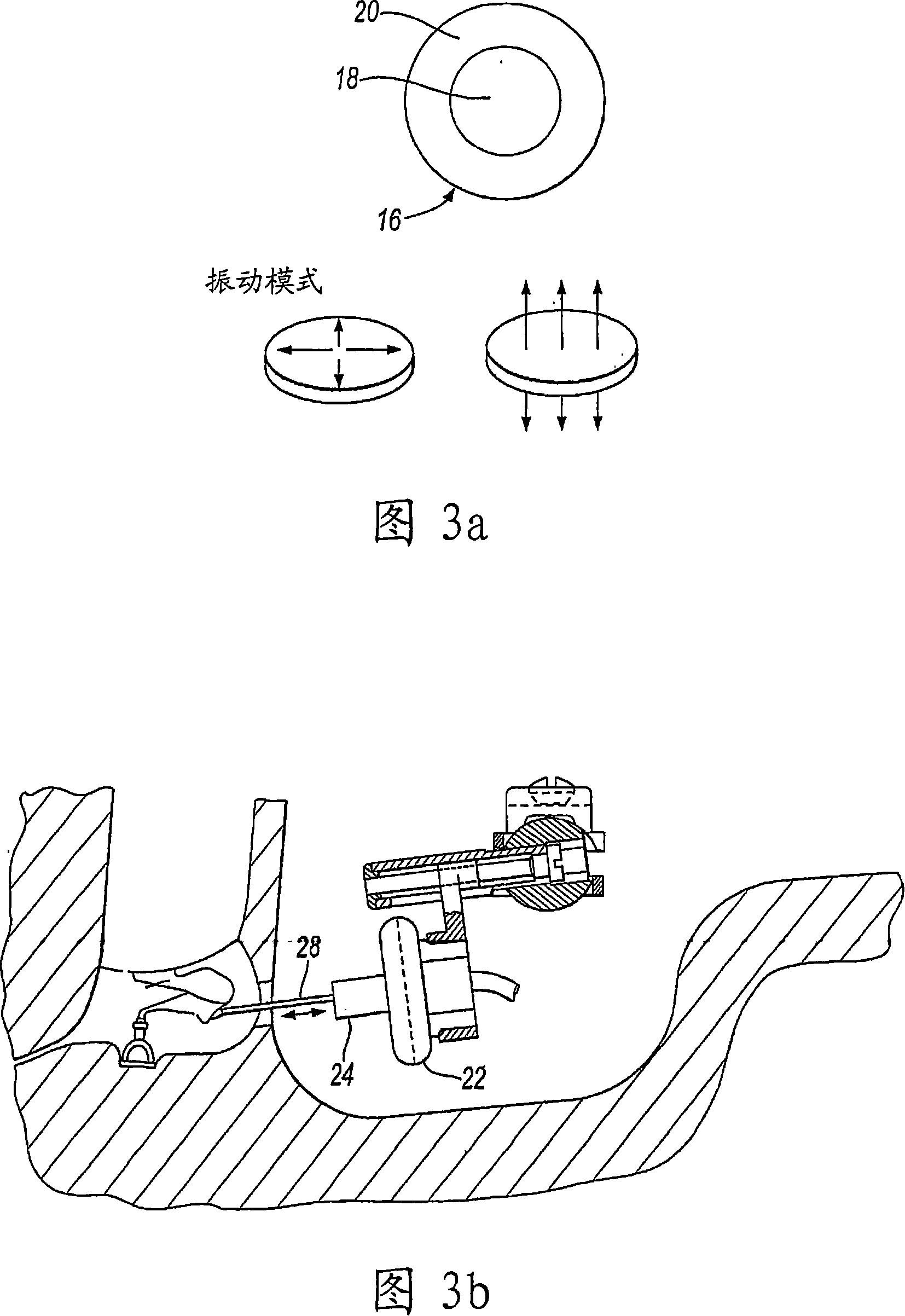
Transtympanic vibration device for implantable hearing aid and apparatus for installing the same
InactiveUS8211174B2Easily install vibration deviceImprove adhesionElectrotherapyDeaf-aid setsEngineeringHearing aid
A transtympanic vibration device for an implantable healing aid, suitable for being vibrated by magnetic flux transmitted from an outside and transferring vibration to a tympanic membrane. The device includes an outer plate having one surface on which a detachable magnet is detachably arranged; an inner plate sandwiching the tympanic membrane in cooperation with the outer plate and having a on which a fixed magnet is arranged; and at least one connection member connecting the outer plate and the inner plate with each other in such a manner that a distance between the outer plate and the inner plate can be adjusted.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND DANKOOK UNIV +1
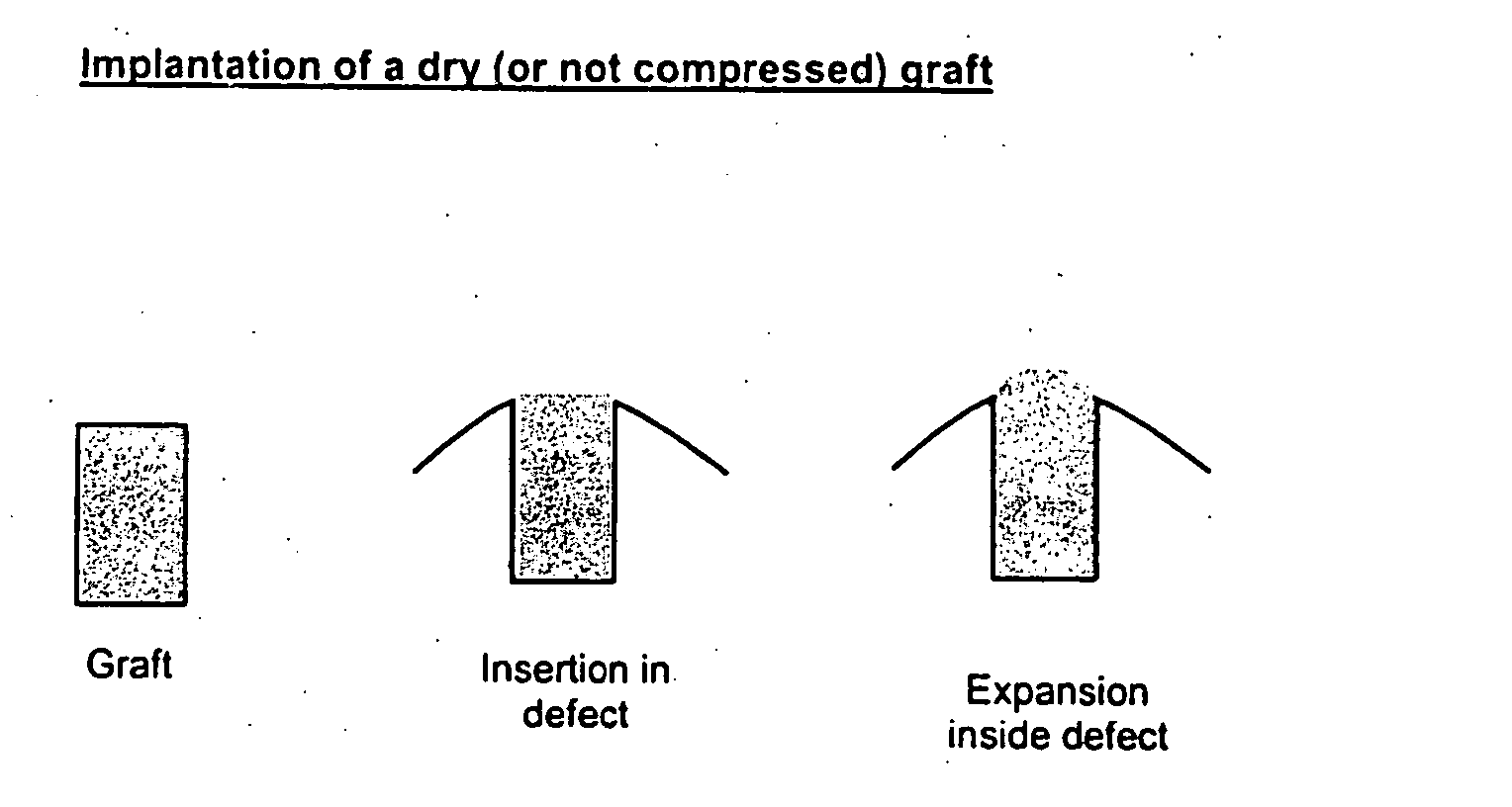
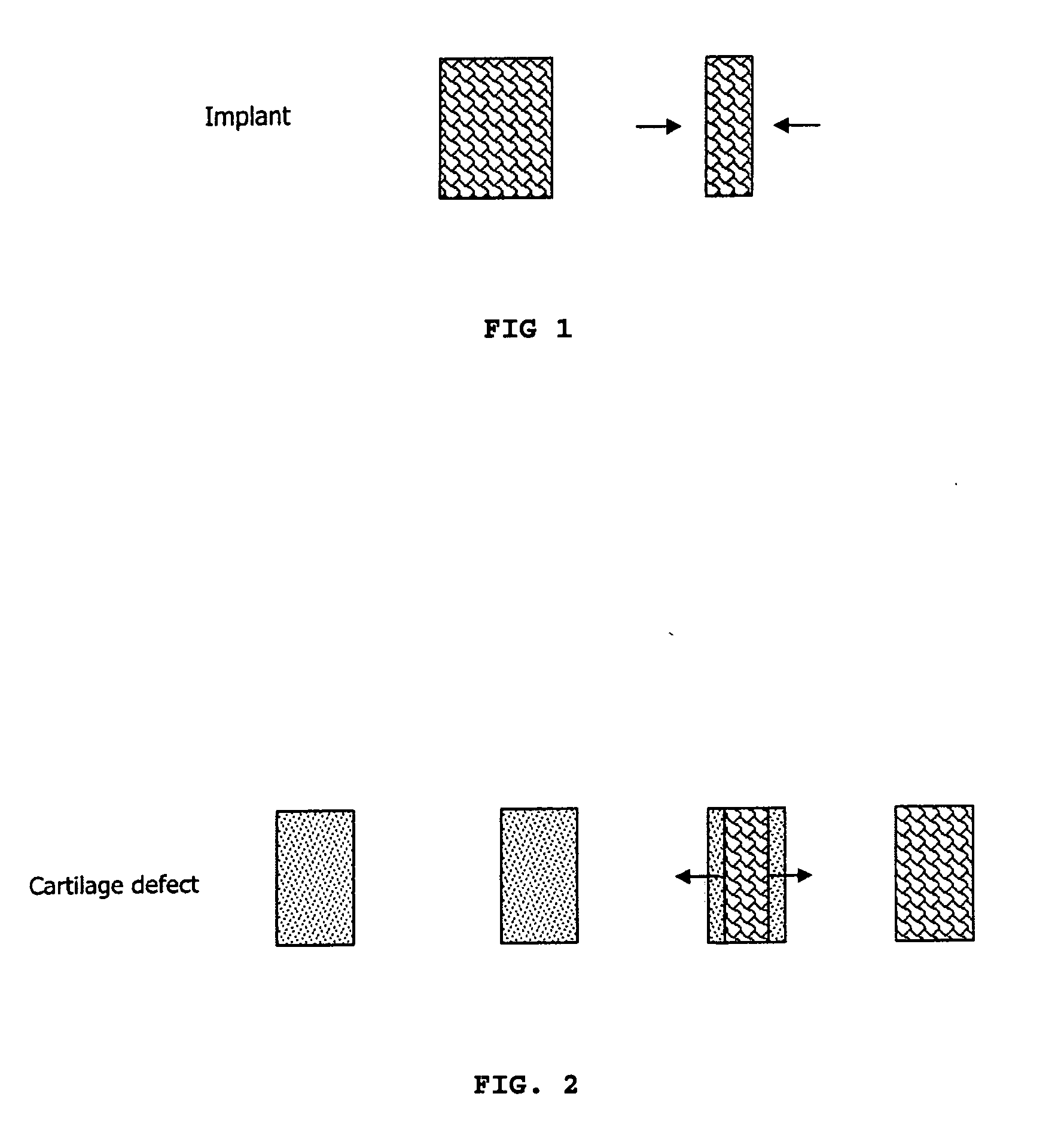
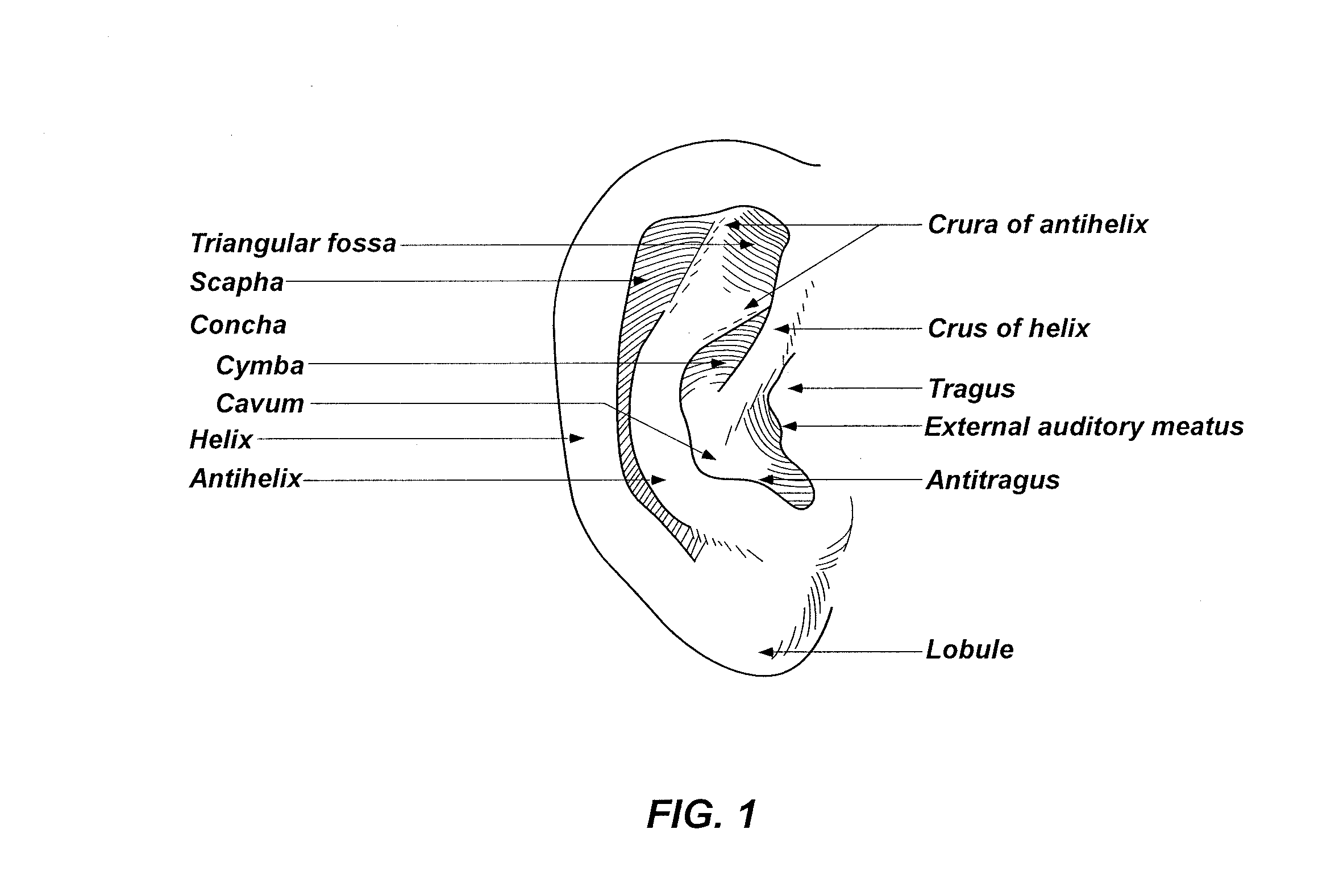
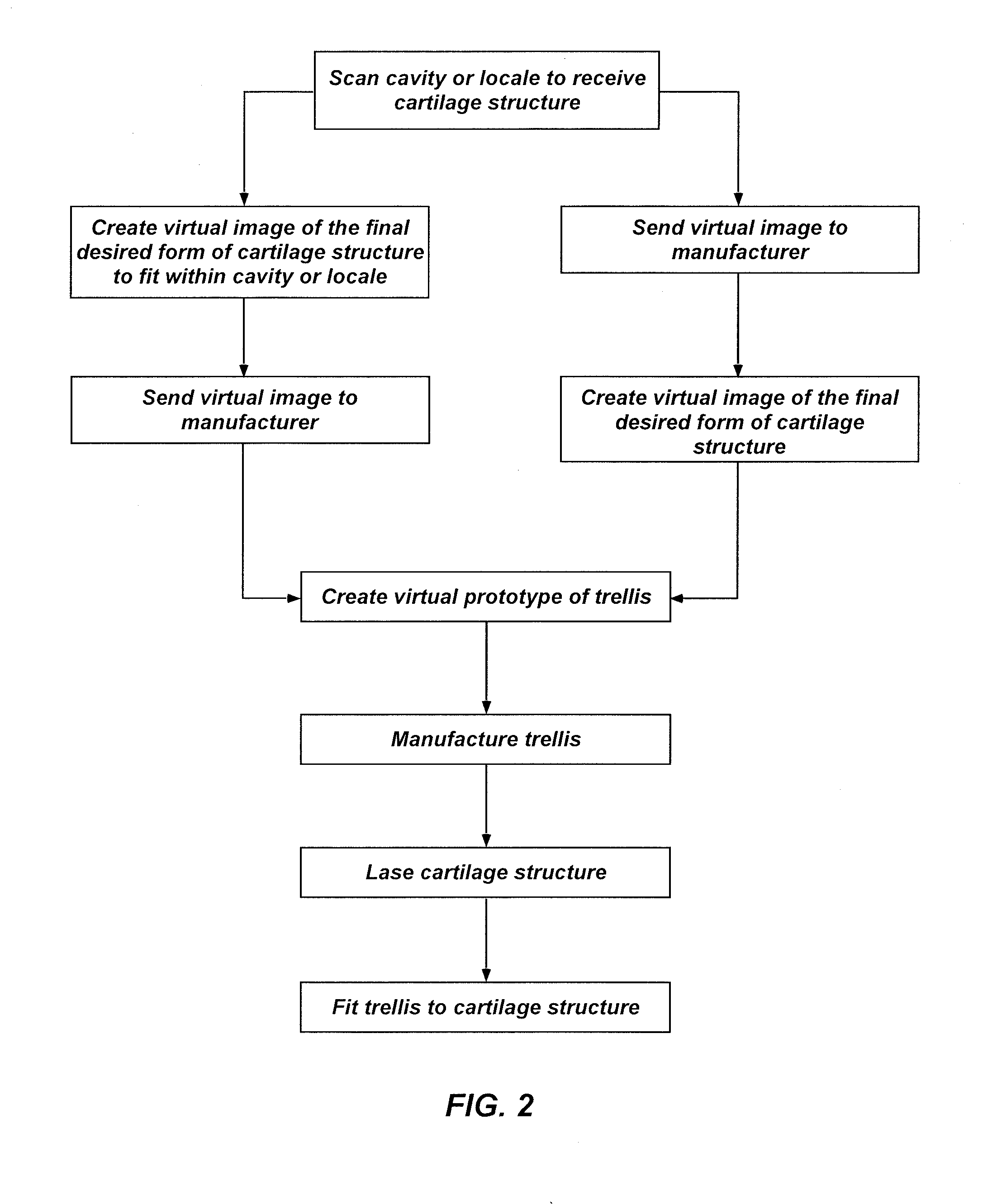
Devices and methods for reshaping cartilage structures
InactiveUS20140188158A1Wide applicabilityLess painfulAdditive manufacturing apparatusEar treatmentComputer scienceVirtual prototyping
Owner:CHONDROCYTE
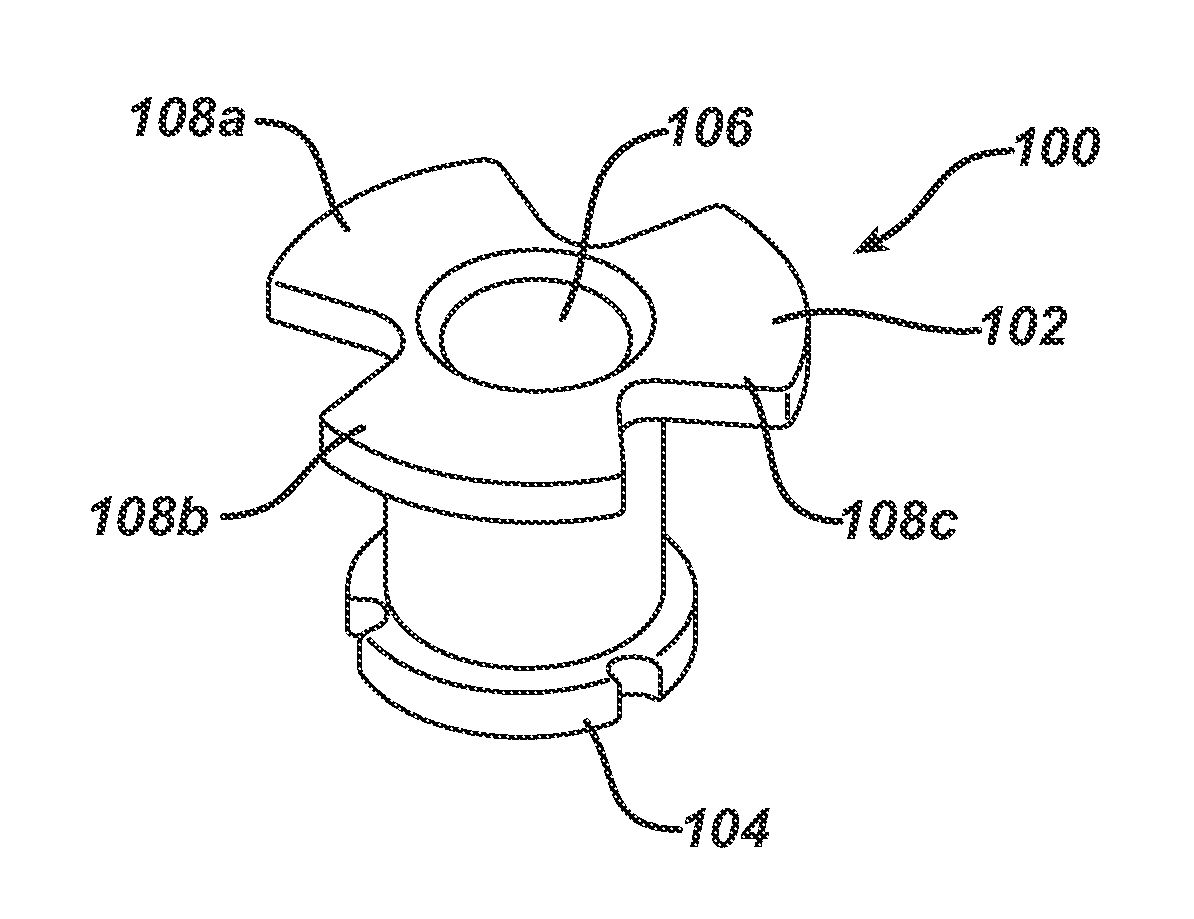
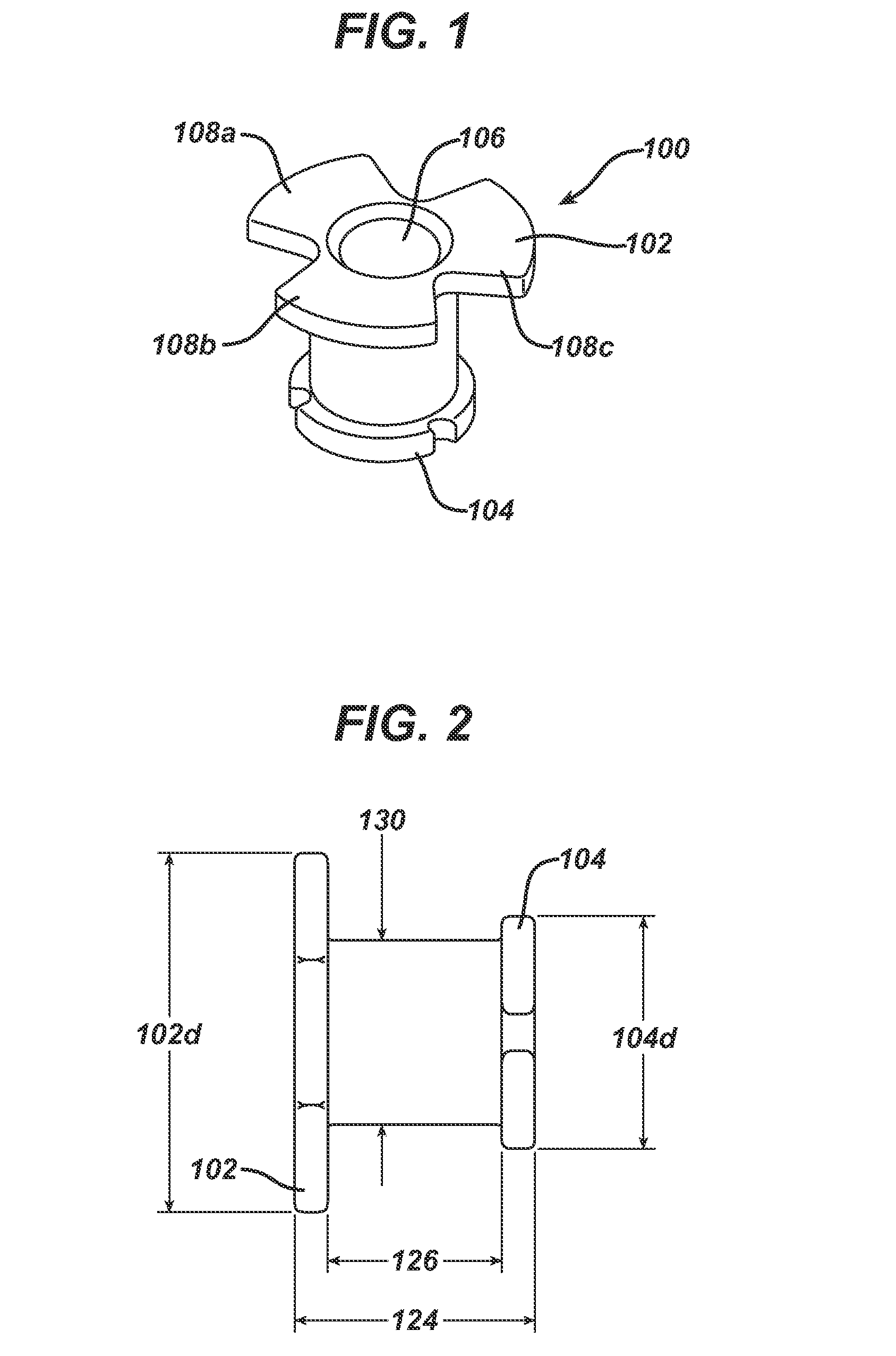
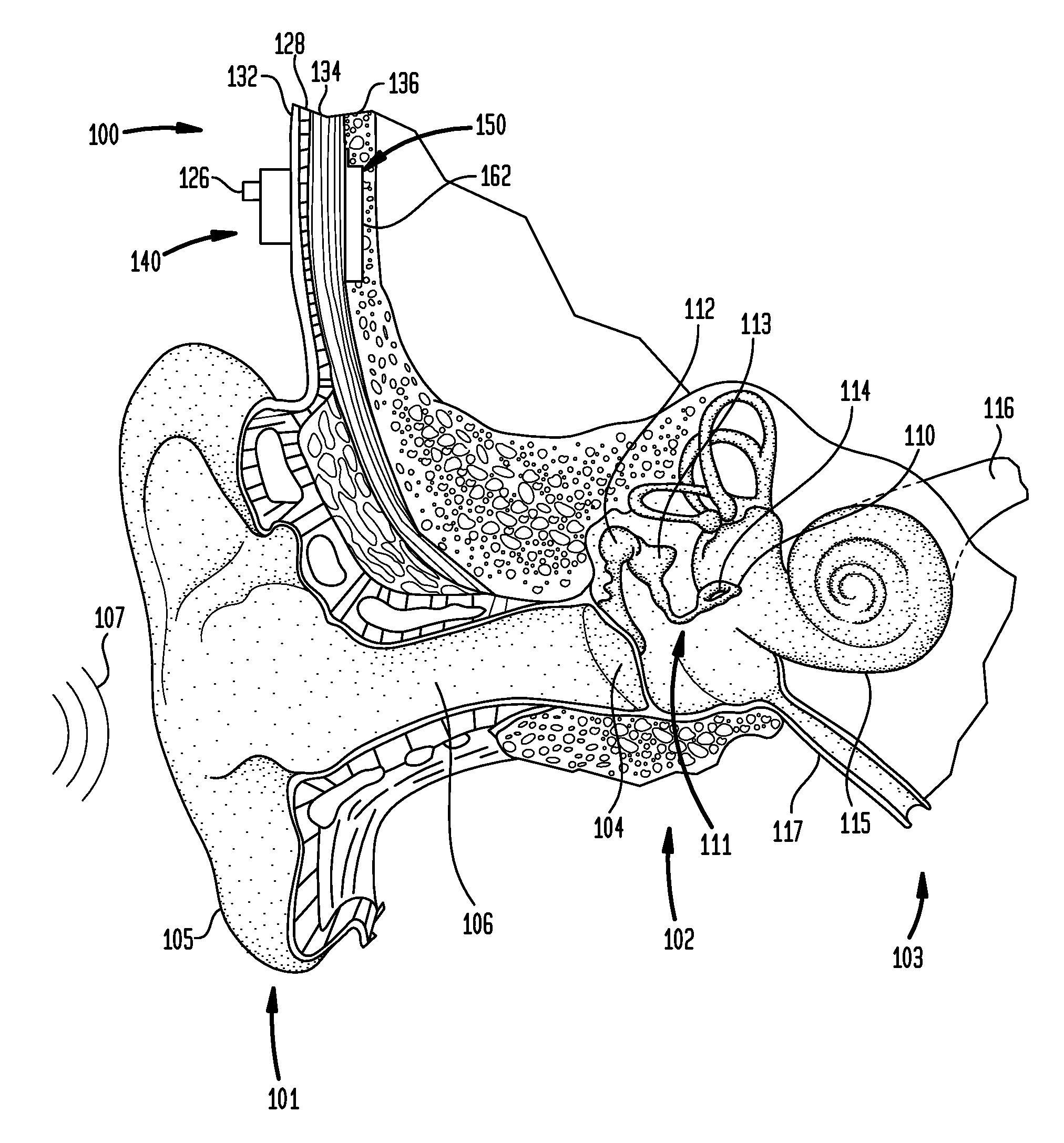
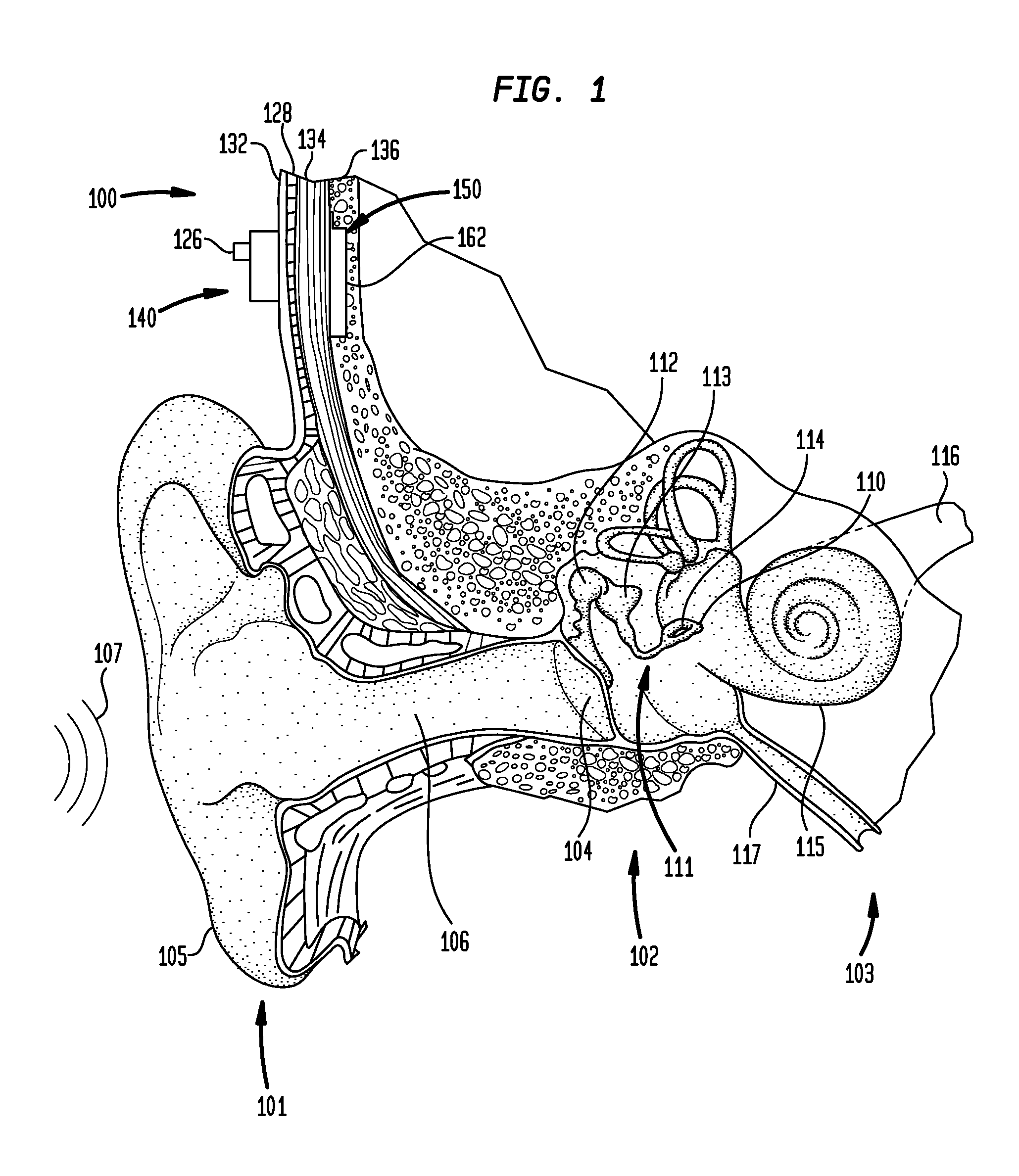
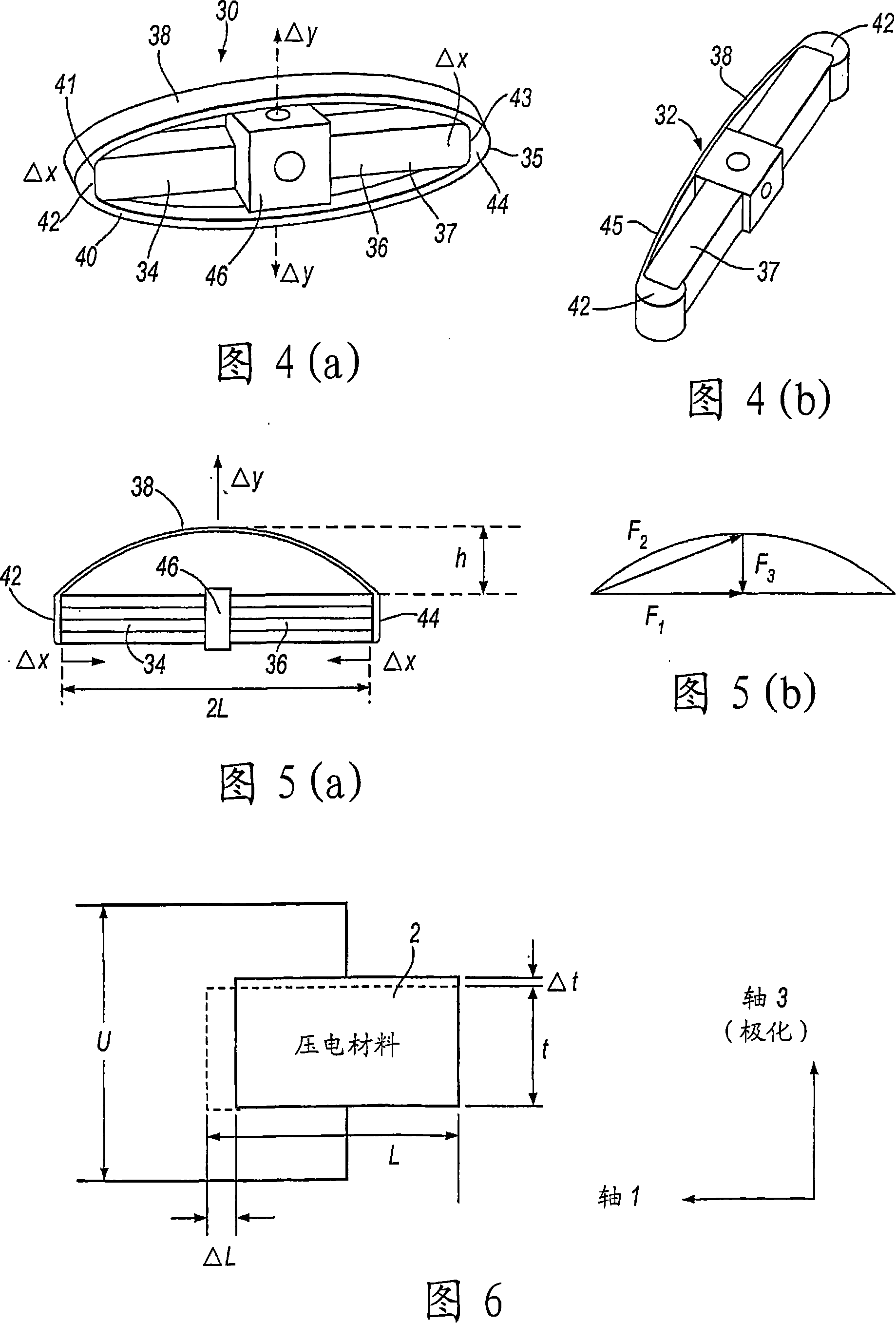
Hearing implant
ActiveCN101128172AImprove structural integrityAvoid destructionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesEar treatmentAudio power amplifierMiddle ear
The present invention concerns an actuator for an implantable hearing aid for implantation into the human middle ear. The actuator comprises a substantially elongate piezoelectric component (34, 36) having first and second operating end faces (41, 43), said end faces extending substantially at right angles to the longitudinal axis of the piezoelectric component. Also there is provided a frame component comprising at least one flextensional amplifier element (32), the flextensional amplifier element being integral with and connecting first and second frame end portions (42, 44), the first and second frame end portions also extending substantially at right angles to longitudinal axis of the piezoelectric component when fitted thereto, whereby the first and second end portions are in contact with the piezoelectric component end faces.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com