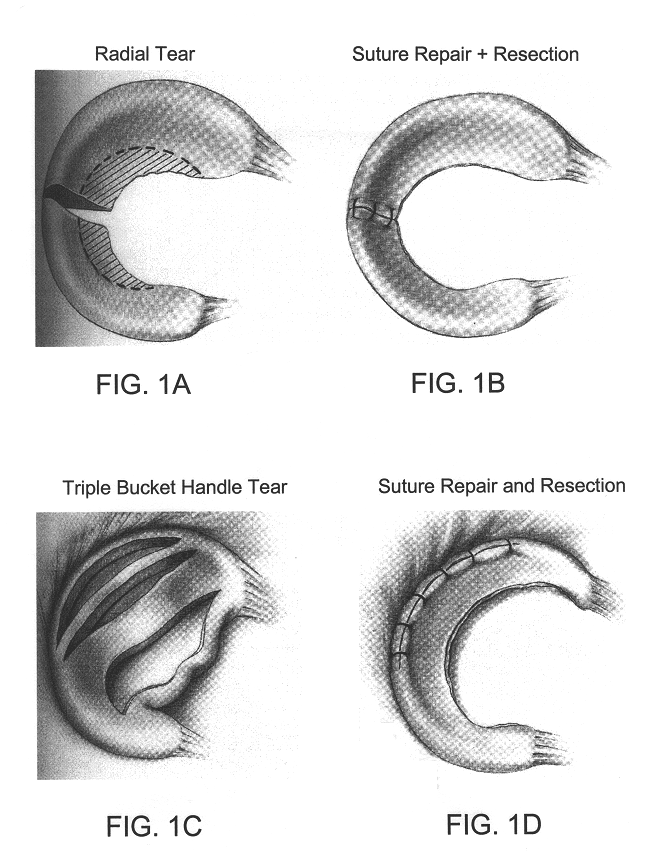
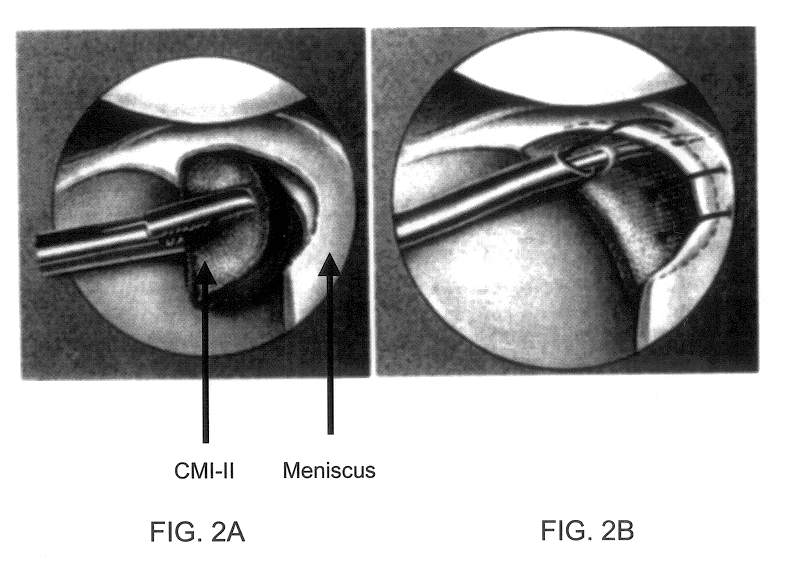
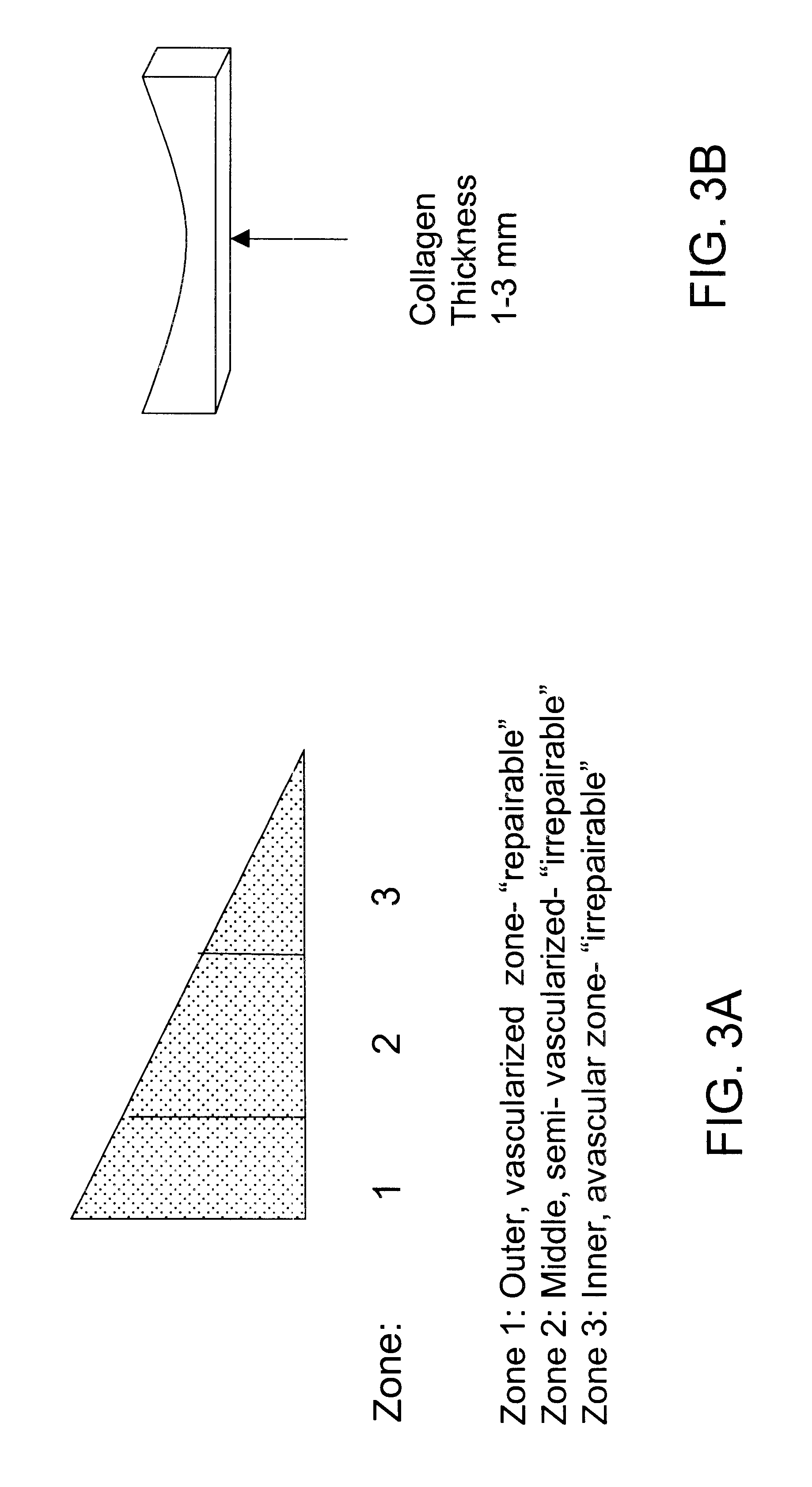
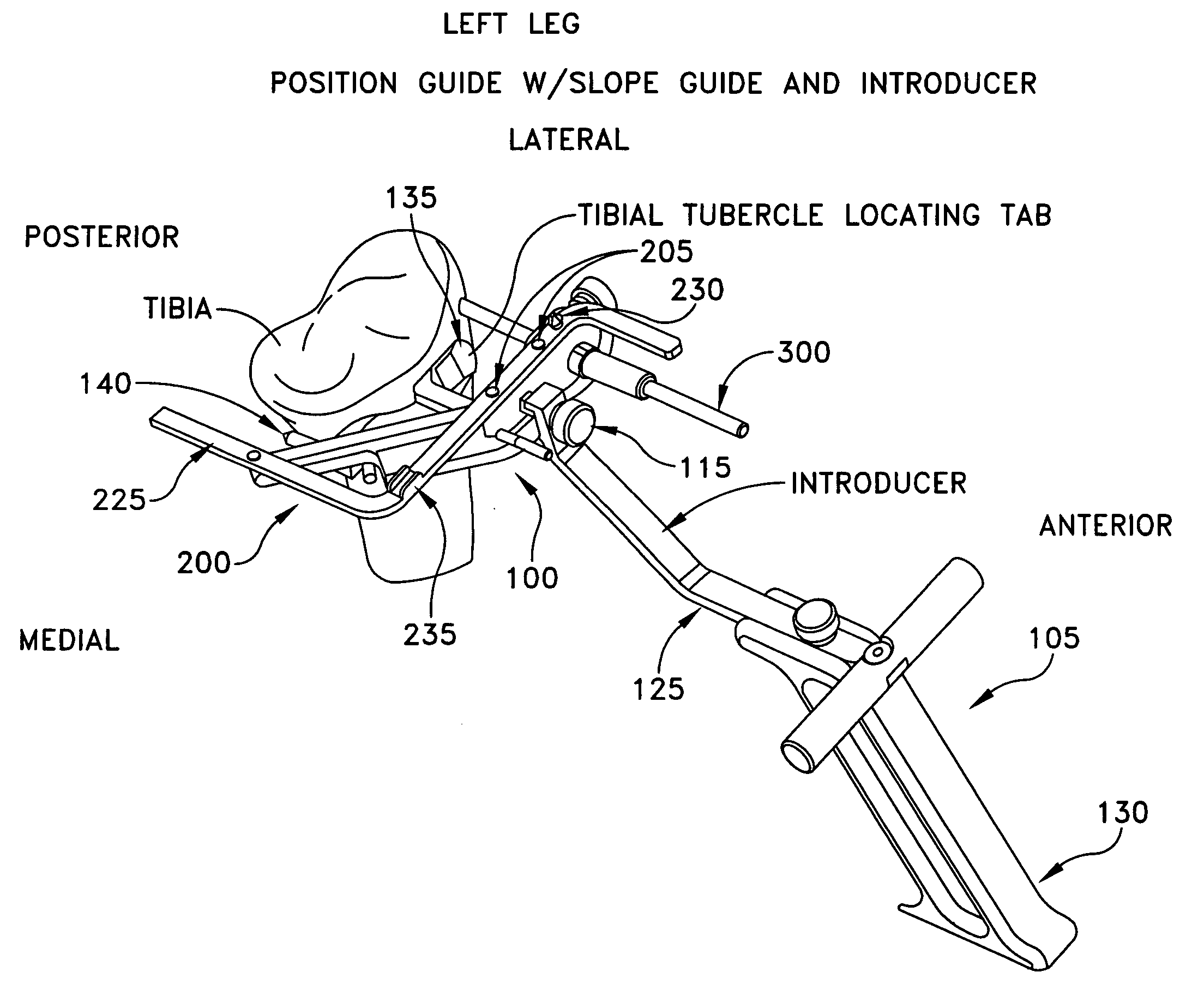
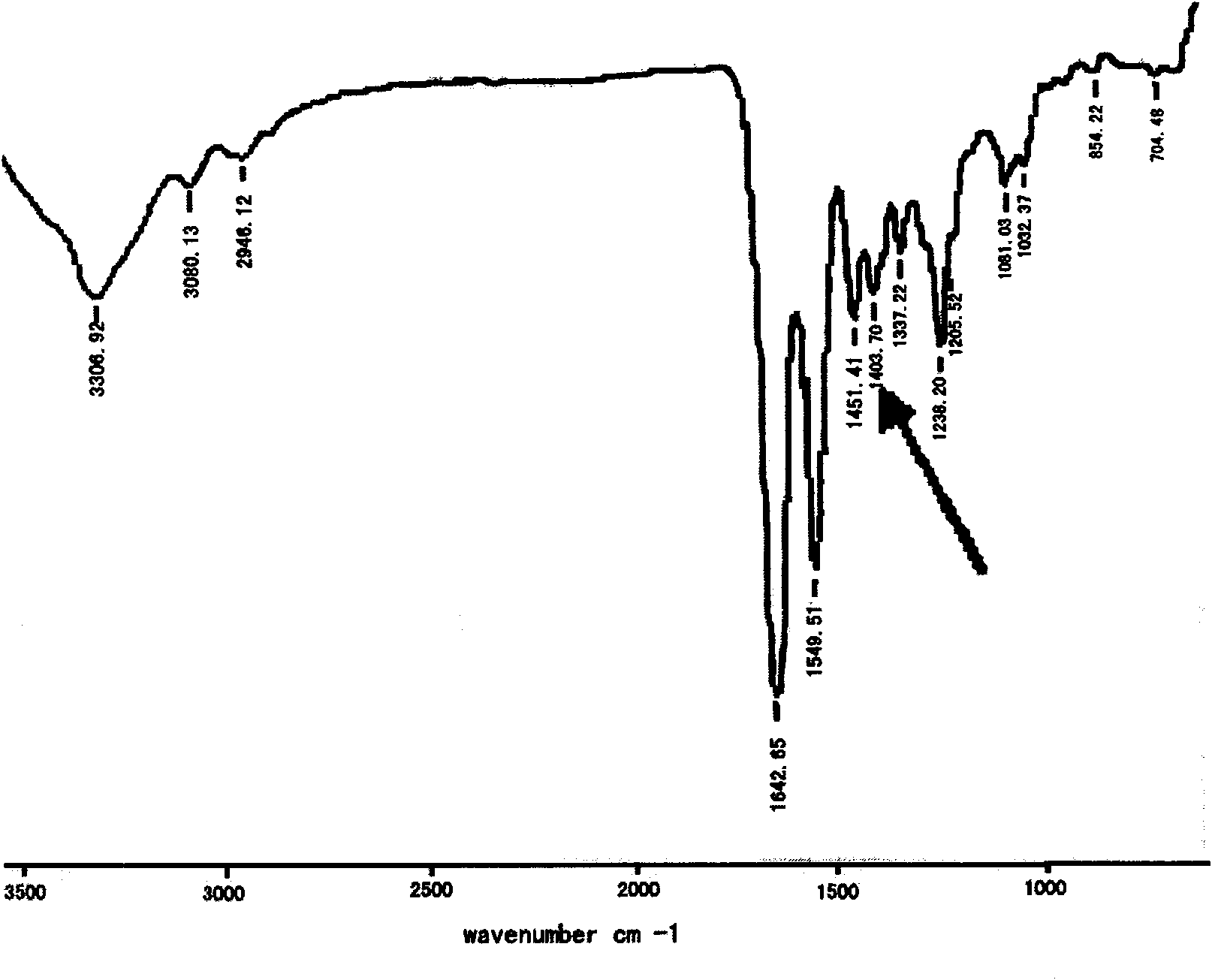
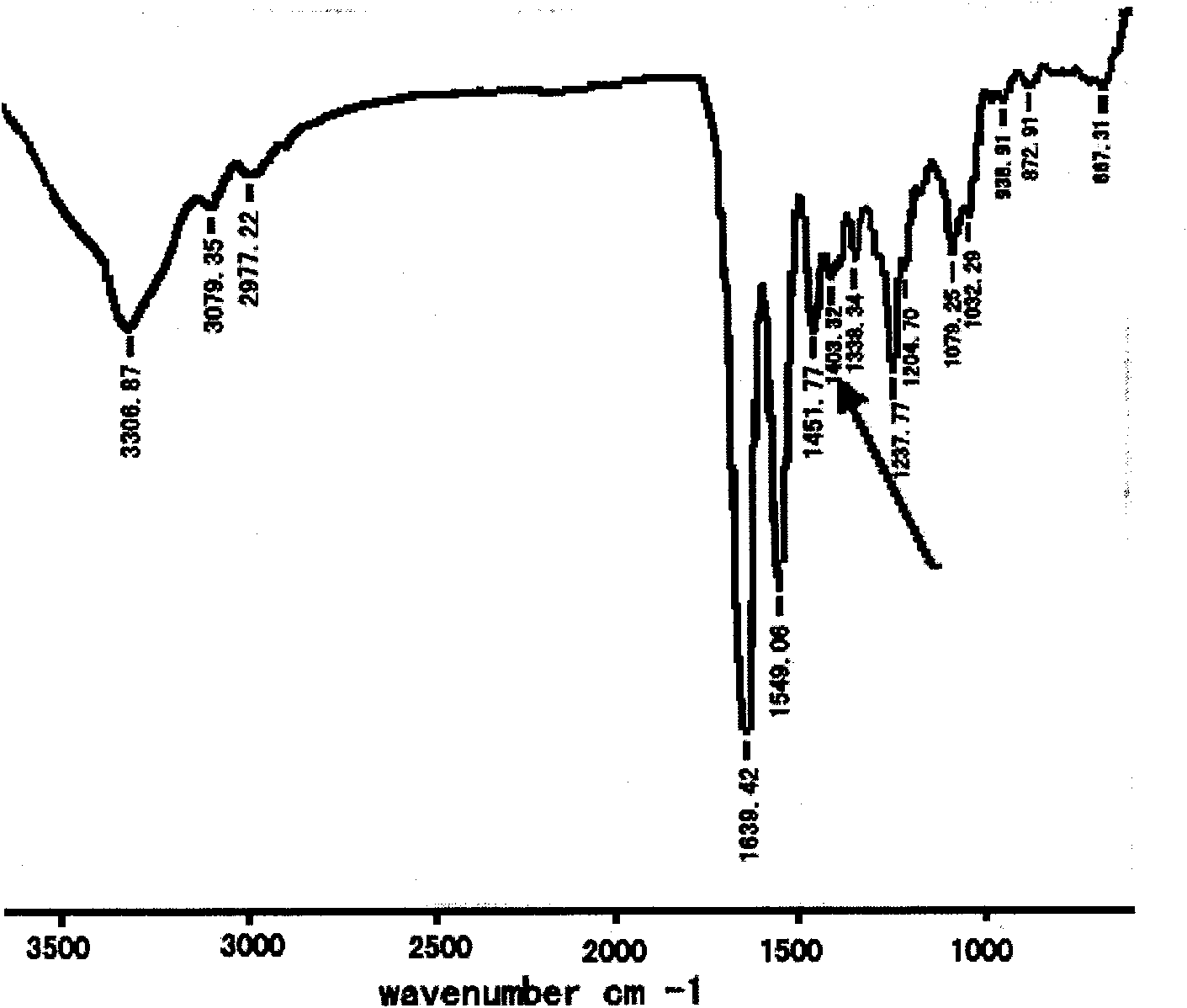
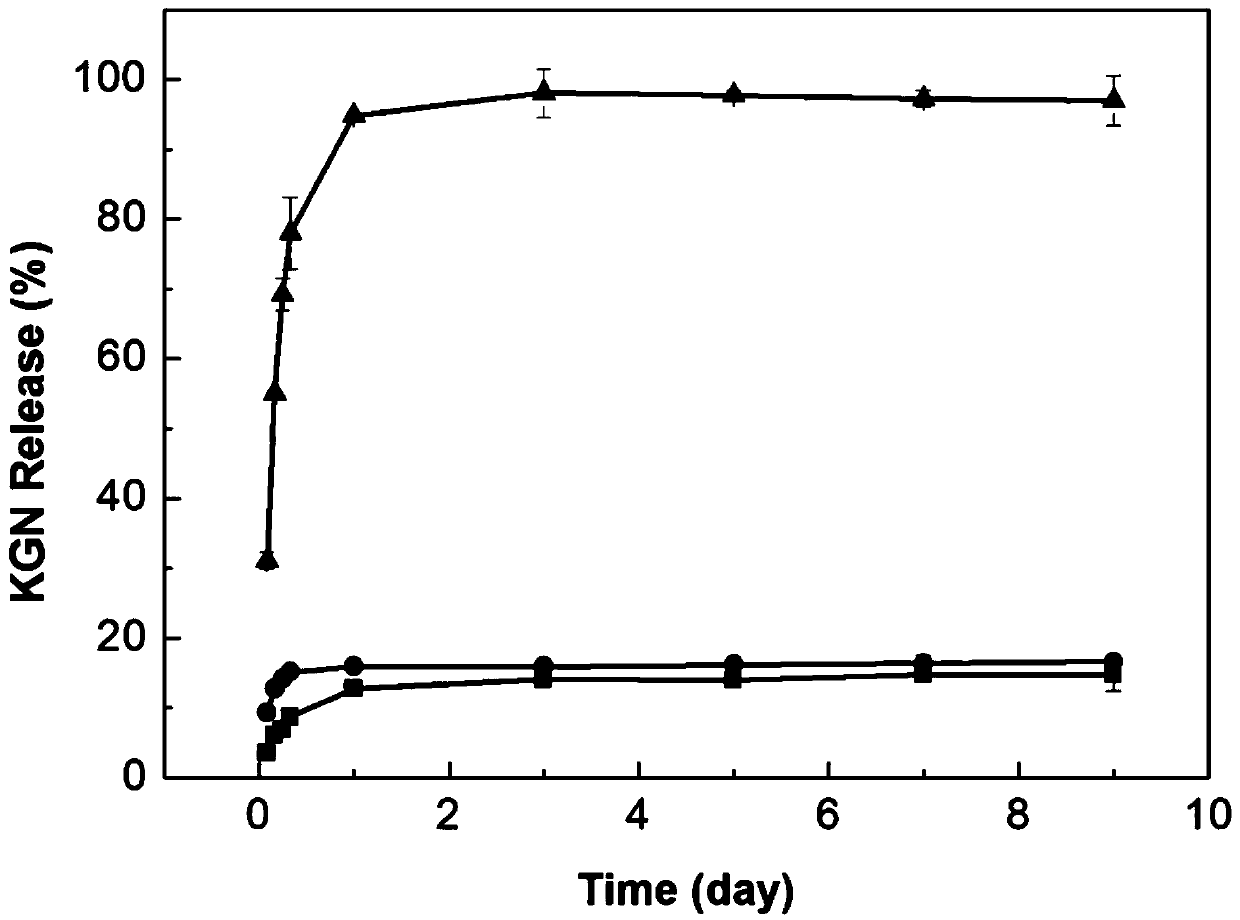
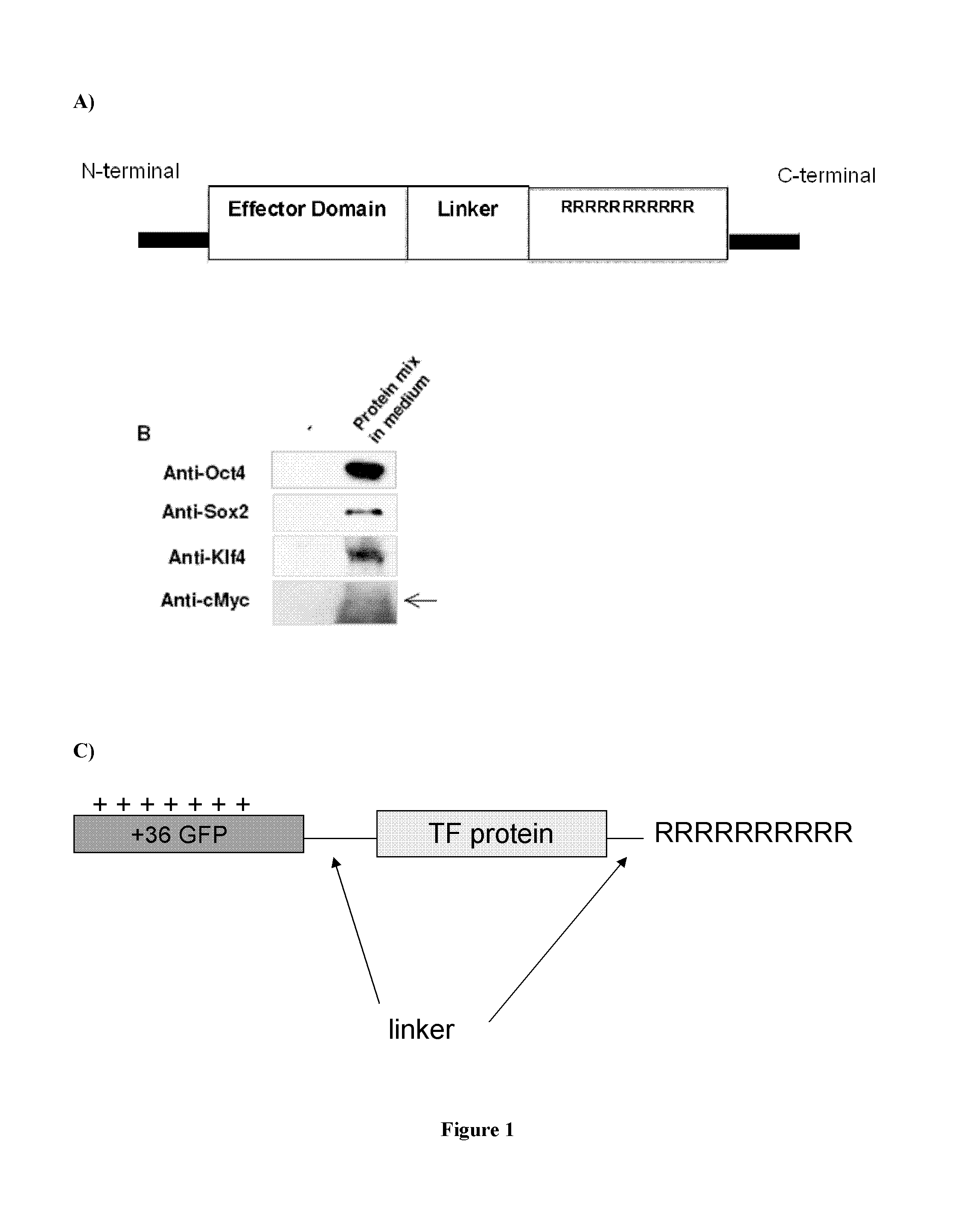
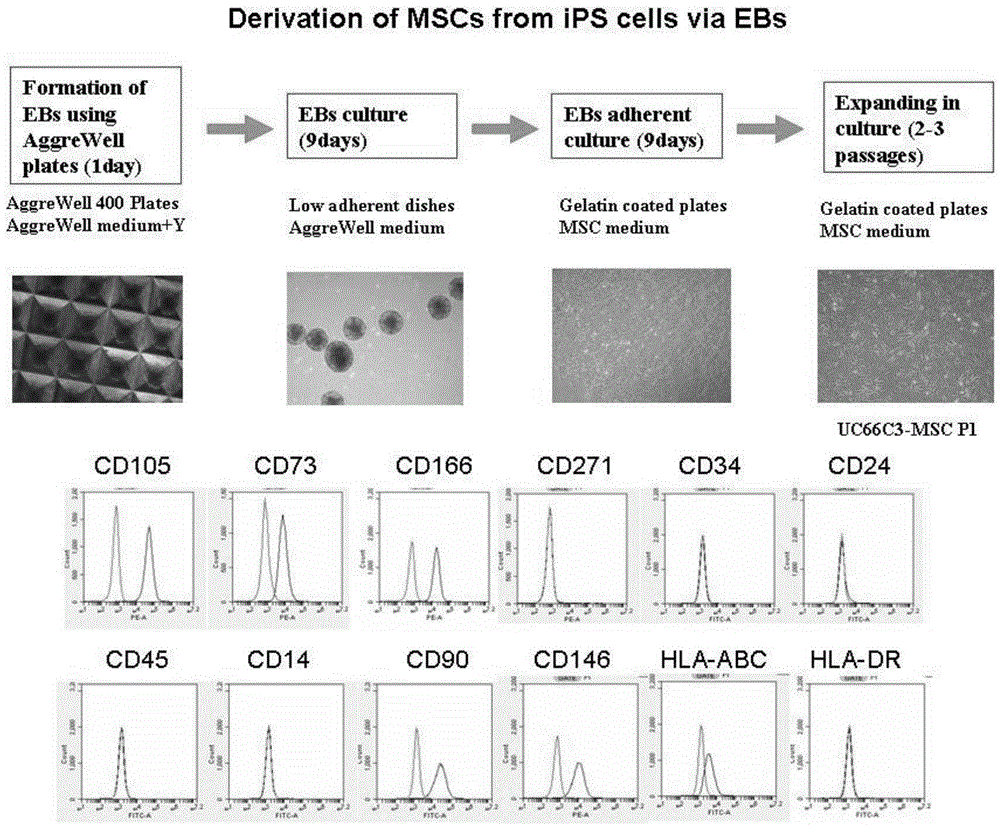
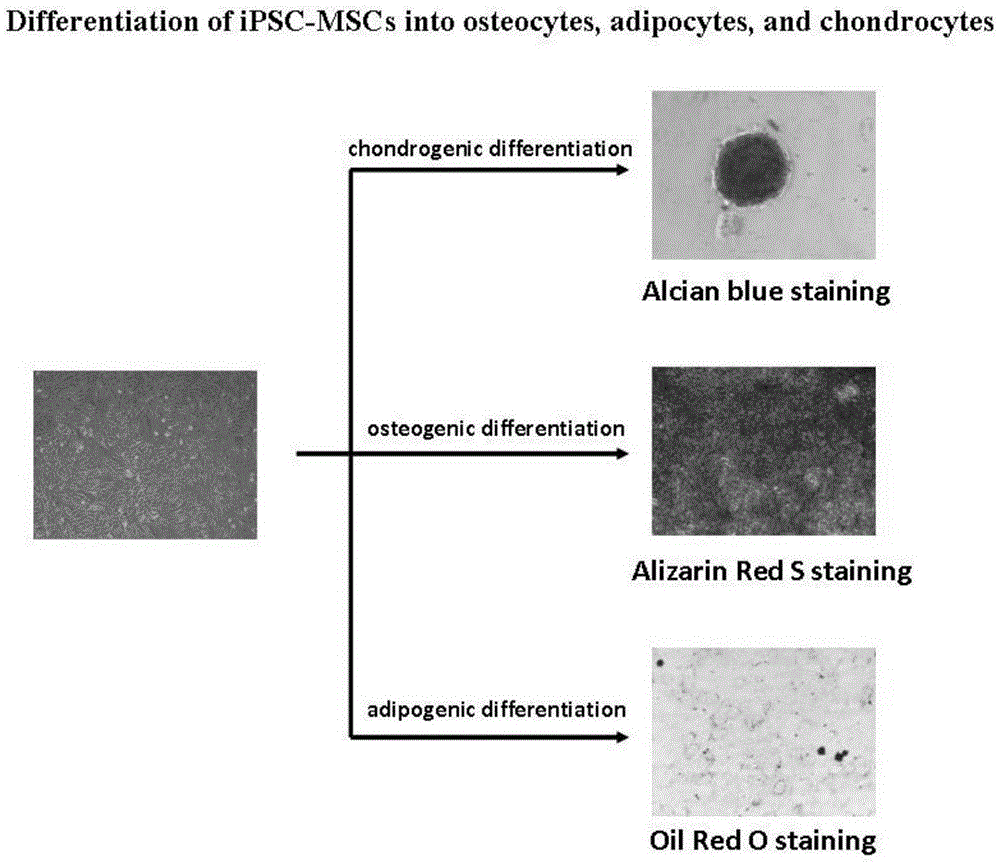
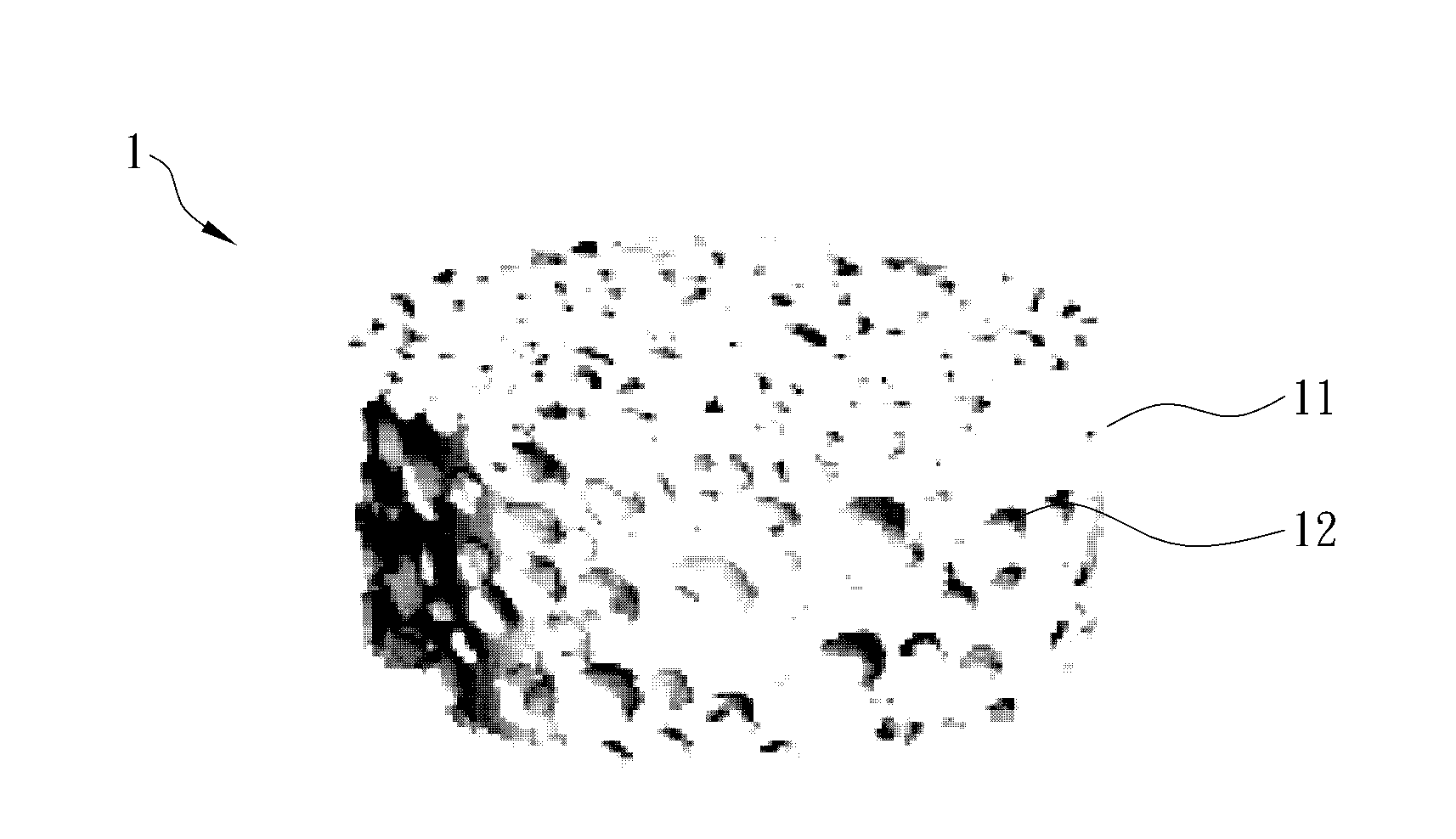Patents
Literature
145 results about "Repair cartilage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cartilage can degrade over time if you're not careful. Cartilage damage occurs for various reasons. Growth or repair of cartilage, however, has limited potential. If a joint is burdened by improper alignment, excessive weight, excessive activity, overuse, or injury, articular cartilage can wear away.
Compositions for regeneration and repair of cartilage lesions
InactiveUS6511958B1Increase ratingsImprove repair qualitySuture equipmentsPowder deliveryMedicineCartilage lesion
Disclosed is a cartilage repair product that induces both cell ingrowth into a bioresorbable material and cell differentiation into cartilage tissue. Such a product is useful for regenerating and / or repairing both vascular and avascular cartilage lesions, particularly articular cartilage lesions, and even more particularly mensical tissue lesions, including tears as well as segmental defects. Also disclosed is a method of regenerating and repairing cartilage lesions using such a product.
Owner:ZIMMER ORTHOBIOLOGICS
Method and apparatus for reconstructing a ligament and/or repairing cartilage, and for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
A method for reconstructing a knee ligament and for performing a tibial osteotomy on the knee in a single procedure, the method comprising:forming a bone tunnel through the tibia at a location appropriate for the ligament reconstruction, disposing a graft ligament in the bone tunnel, and securing the graft ligament in the bone tunnel, and forming a wedge-like opening in the bone at a location appropriate for the tibial osteotomy, positioning an osteotomy implant in the wedge-like opening in the bone, and securing the osteotomy implant in the wedge-like opening in the bone;wherein the osteotomy implant is secured in the wedge-like opening in the bone with a fastener which extends through the implant and into the bone tunnel.
Owner:ARTHREX
Method and apparatus for reconstructing a ligament and/or repairing cartilage, and for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
A method for reconstructing a knee ligament and for performing a tibial osteotomy on the knee in a single procedure, the method comprising:forming a bone tunnel through the tibia at a location appropriate for the ligament reconstruction, disposing a graft ligament in the bone tunnel, and securing the graft ligament in the bone tunnel, and forming a wedge-like opening in the bone at a location appropriate for the tibial osteotomy, positioning an osteotomy implant in the wedge-like opening in the bone, and securing the osteotomy implant in the wedge-like opening in the bone;wherein the osteotomy implant is secured in the wedge-like opening in the bone with a fastener which extends through the implant and into the bone tunnel.
Owner:ARTHREX
Osteogenic devices and methods of use thereof for repair of endochondral bone and osteochondral defects
InactiveUS7041641B2Avoid undesirable formationOvercome problemsPowder deliveryImpression capsRepair tissueNon union
Disclosed herein are improved osteogenic devices and methods of use thereof for repair of bone and cartilage defects. The devices and methods promote accelerated formation of repair tissue with enhanced stability using less osteogenic protein than devices in the art. Defects susceptible to repair with the instant invention include, but are not limited to: critical size defects, non-critical size defects, non-union fractures, fractures, osteochondral defects, subchondral defects, and defects resulting from degenerative diseases such as osteochondritis dessicans.
Owner:MARIEL THERAPEUTICS
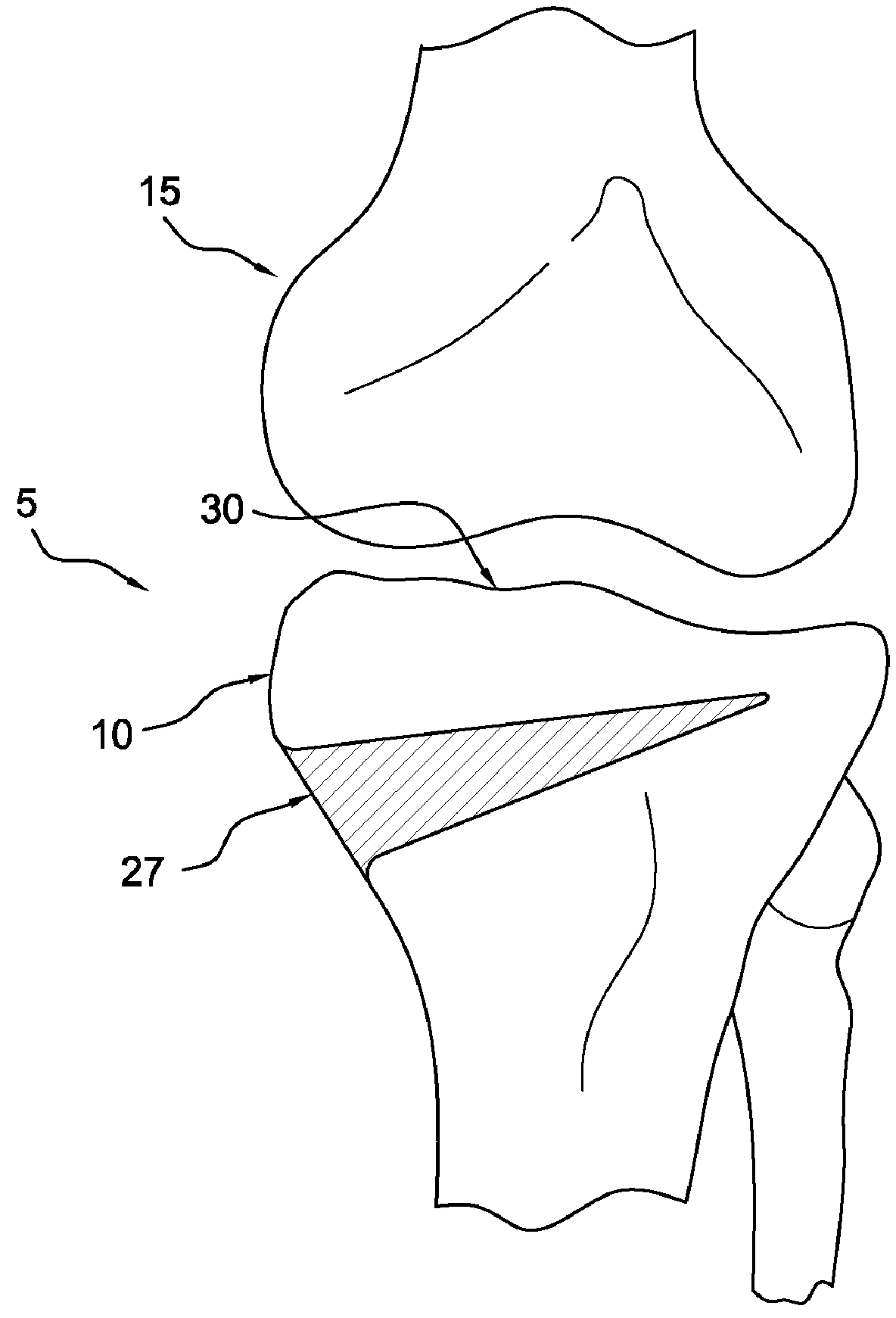
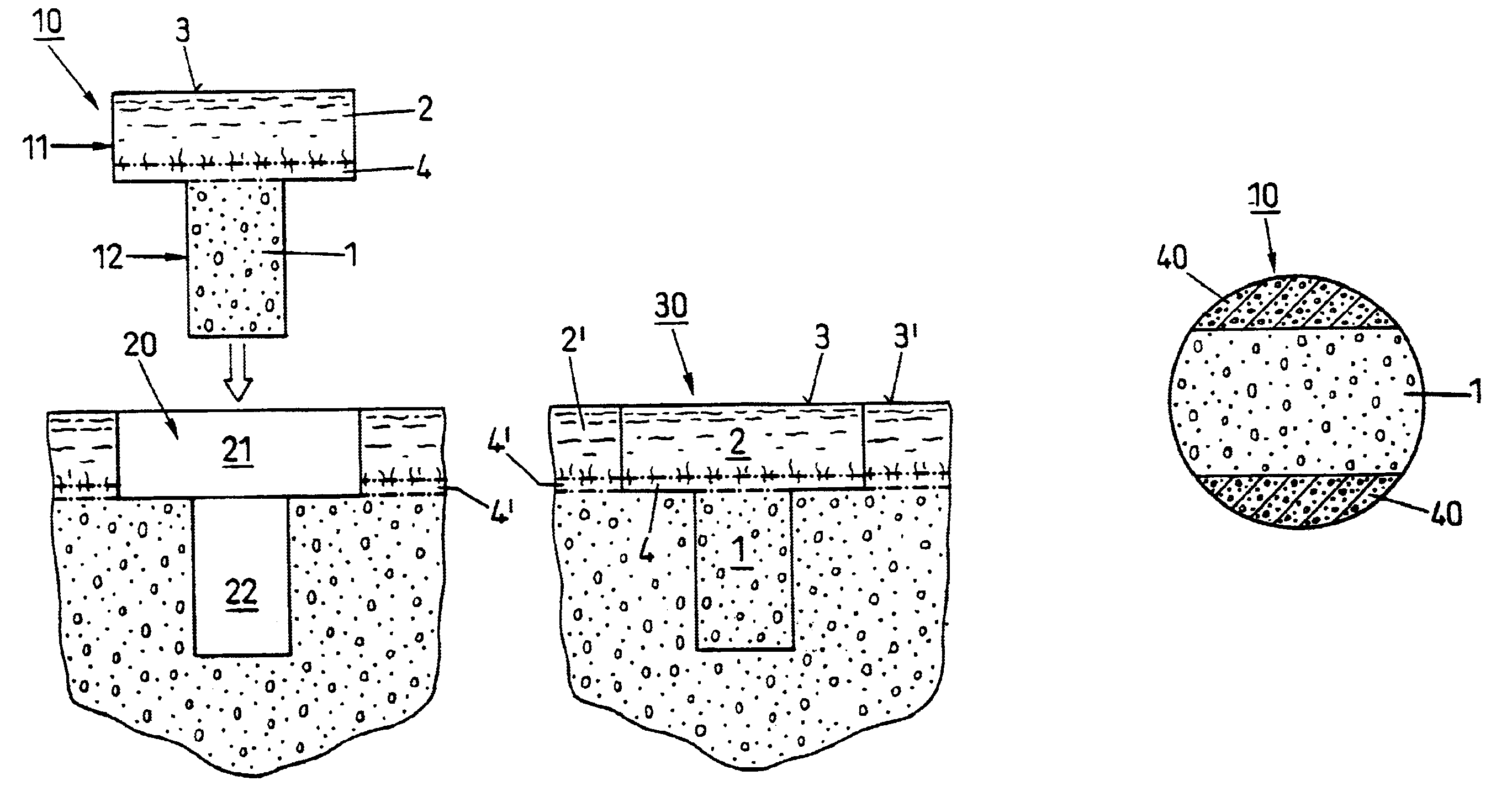
Preparation for repairing cartilage defects or cartilage/bone defects in human or animal joints
InactiveUS6858042B2Reduce absorptionResistant to resorptionBone implantJoint implantsRepair tissueCyst
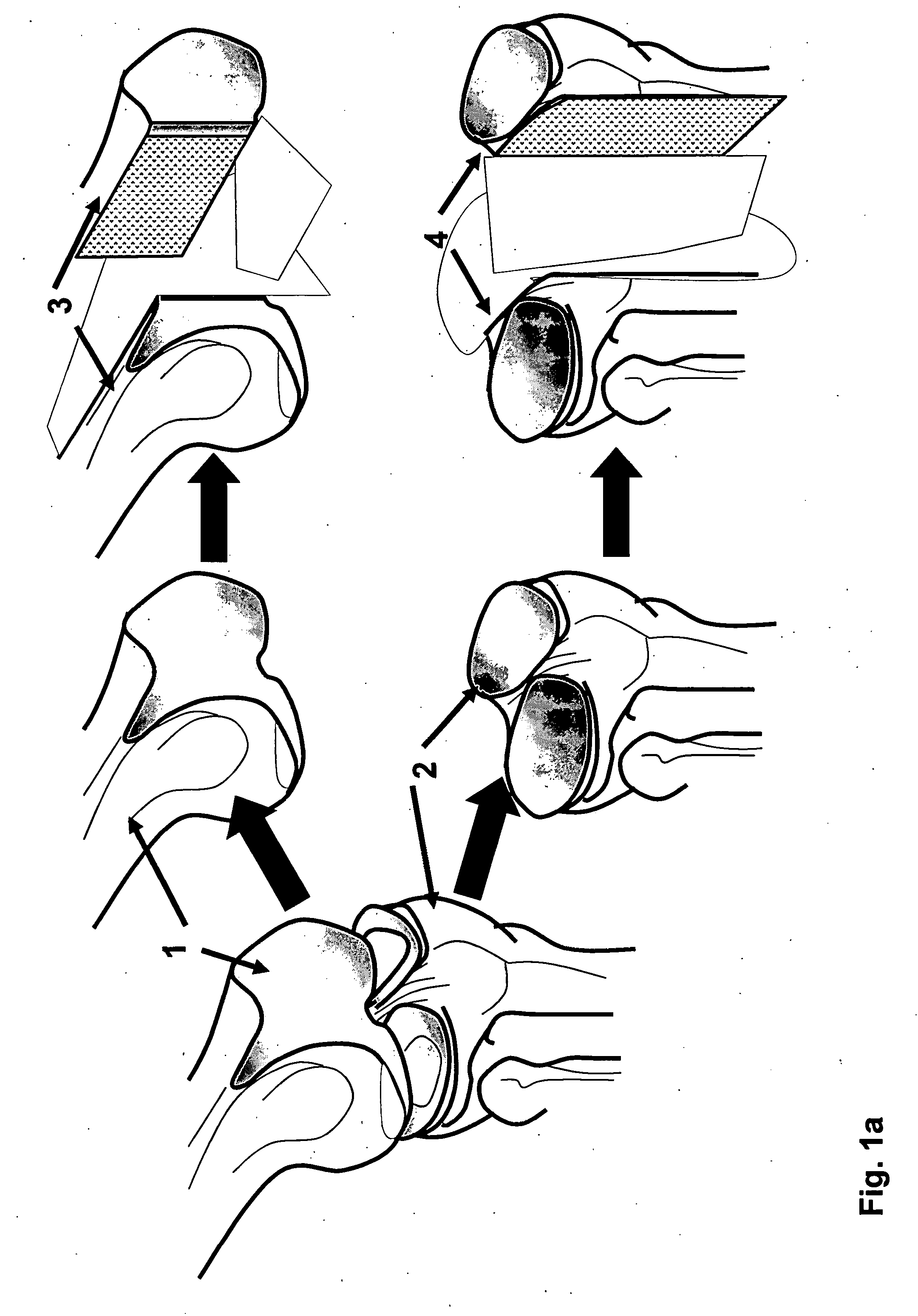
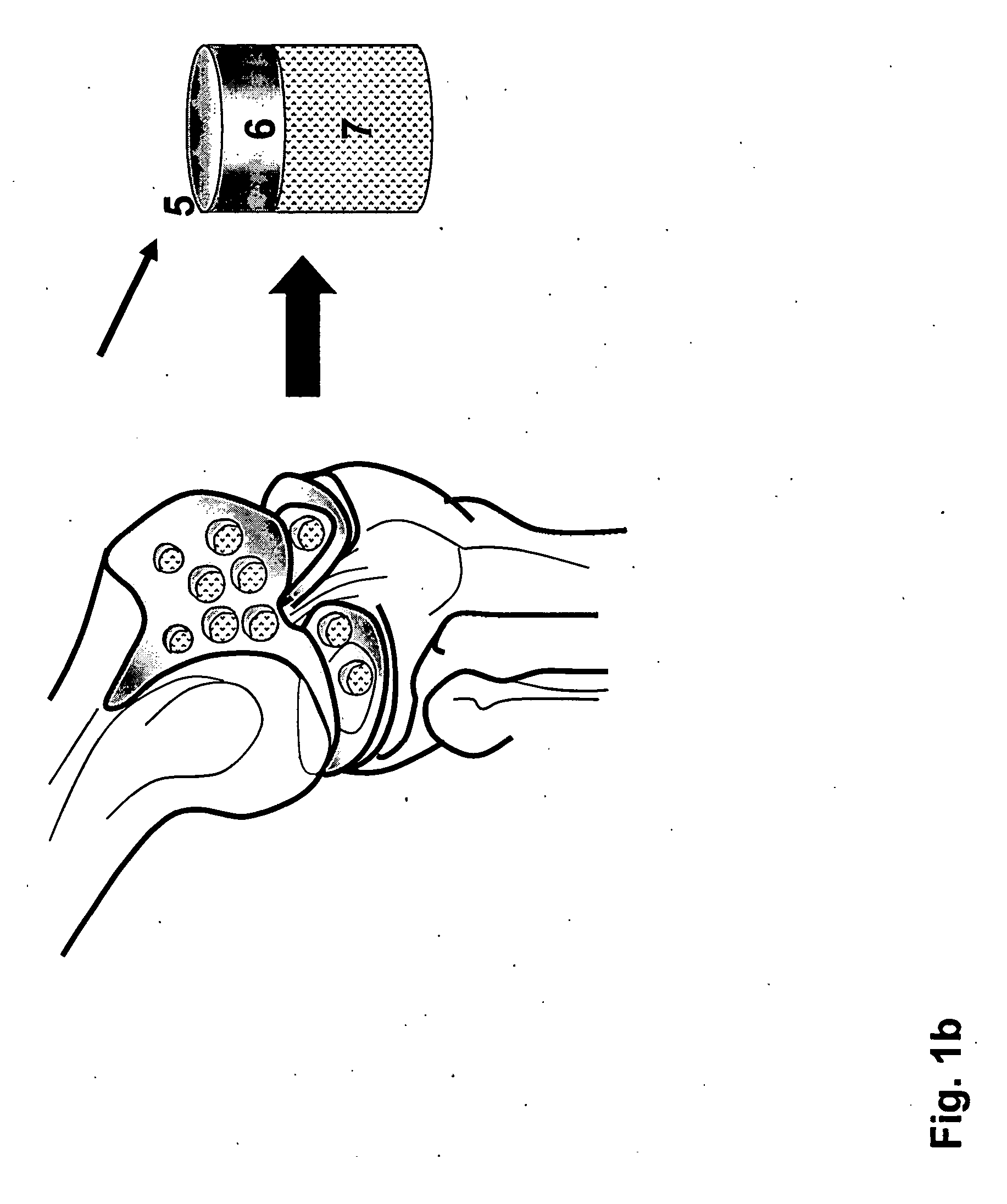
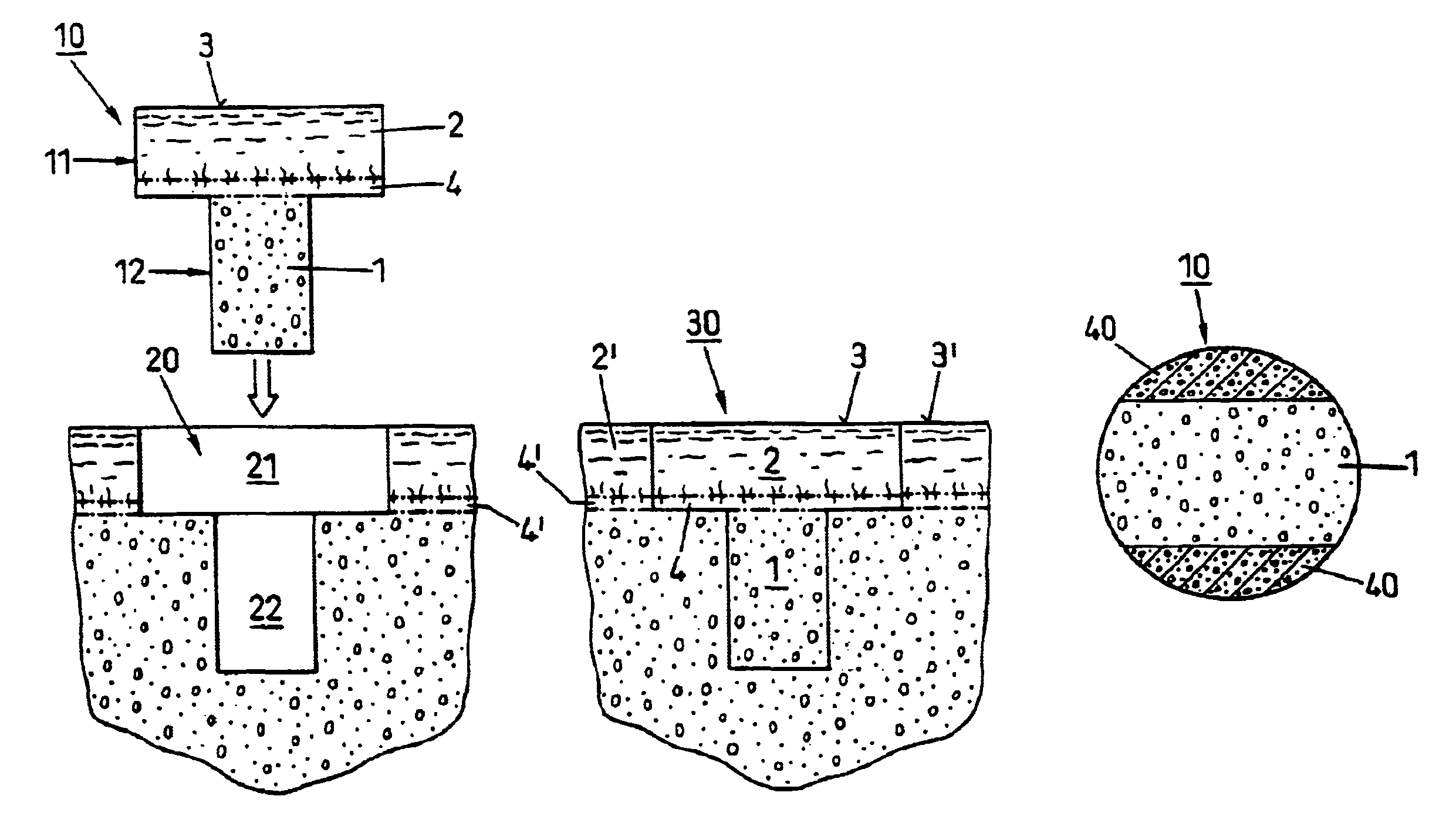
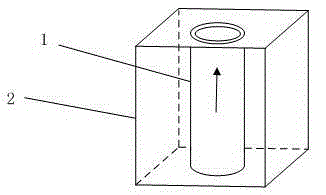
Repairs of cartilage defects or of cartilage / bone defects in human or animal joints with the help of devices including a bone part (1), a cartilage layer (2) and a subchondral bone plate (4) or an imitation of such a plate in the transition region between the cartilage layer (2) and the bone part (1). After implantation, the bone part (4) is resorbed and is replaced by reparative tissue only after being essentially totally resorbed. In a critical phase of the healing process, a mechanically inferior cyst is located in the place of the implanted bone part (1). In order to prevent the cartilage layer (2) from sinking into the cyst space during this critical phase of the healing process the device has a top part (11) and a bottom part (12), wherein the top part (11) consists essentially of the cartilage layer (2) and the subchondral bone plate (4) and the bottom part (12) corresponds essentially to the bone part (1) and wherein the top part (11) parallel to the subchondral bone plate (4) has a larger diameter than the bottom part (12). After implantation in a suitable opening or bore (20), the cartilage layer (2) and the subchondral bone plate (4) are supported not only on the bone part (1) but also on native bone tissue having a loading capacity not changing during the healing process. Therefore, the implanted cartilage layer cannot sink during the healing process.
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
Means for cartilage repair
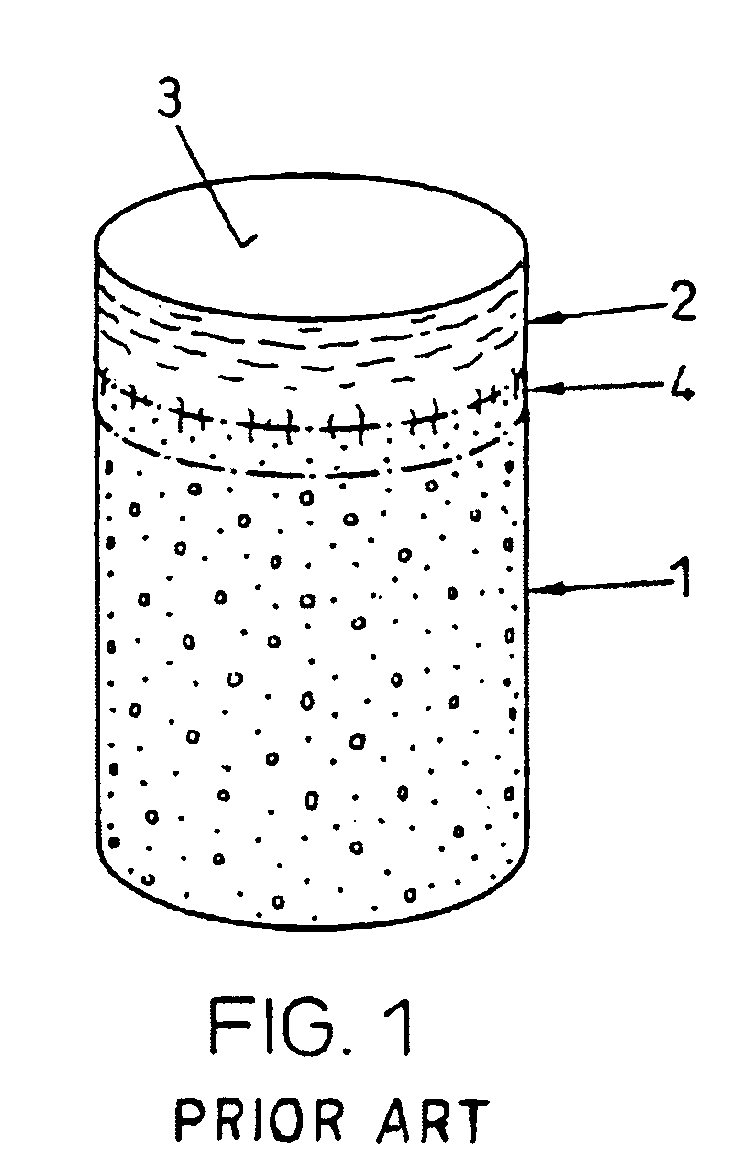
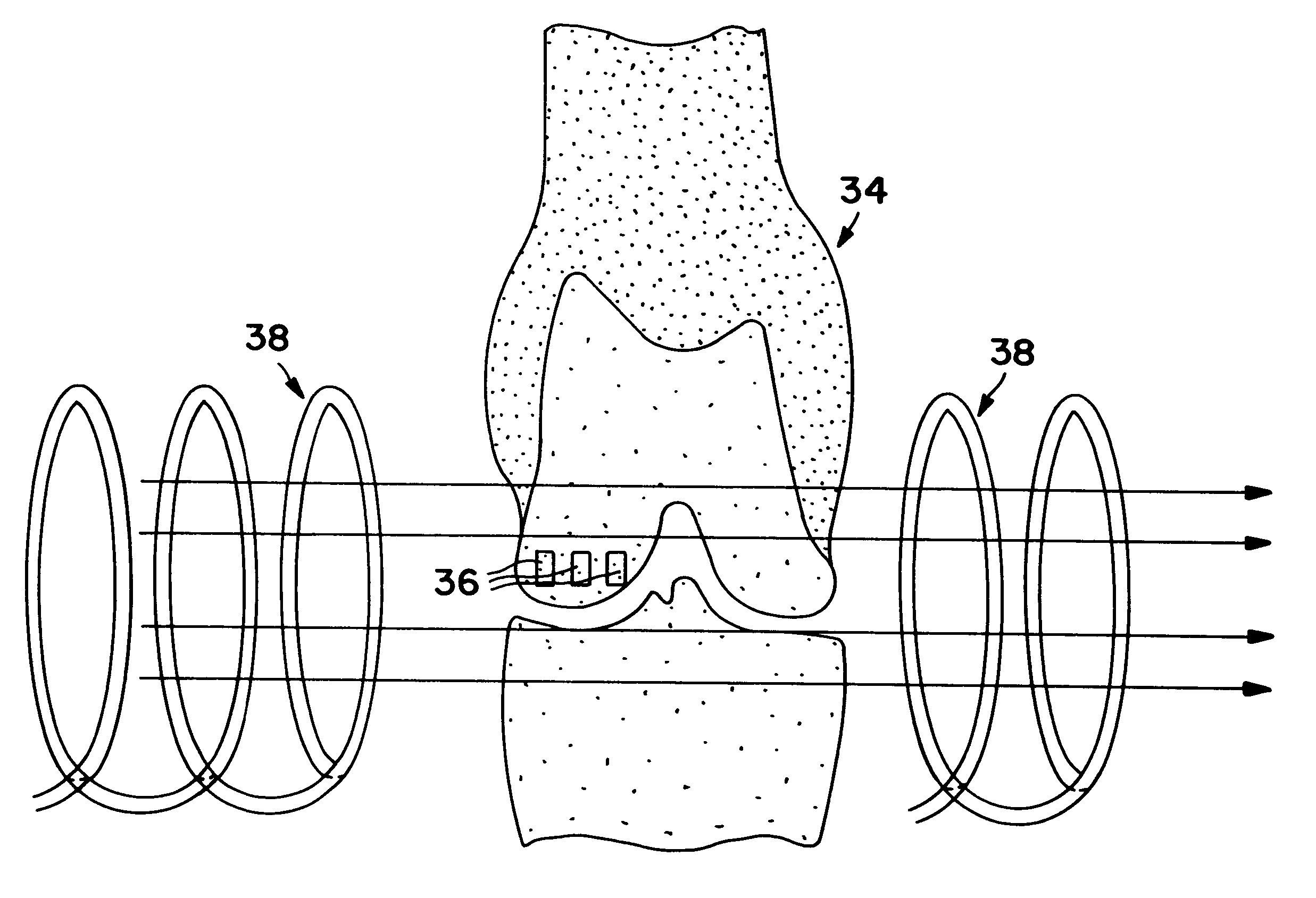
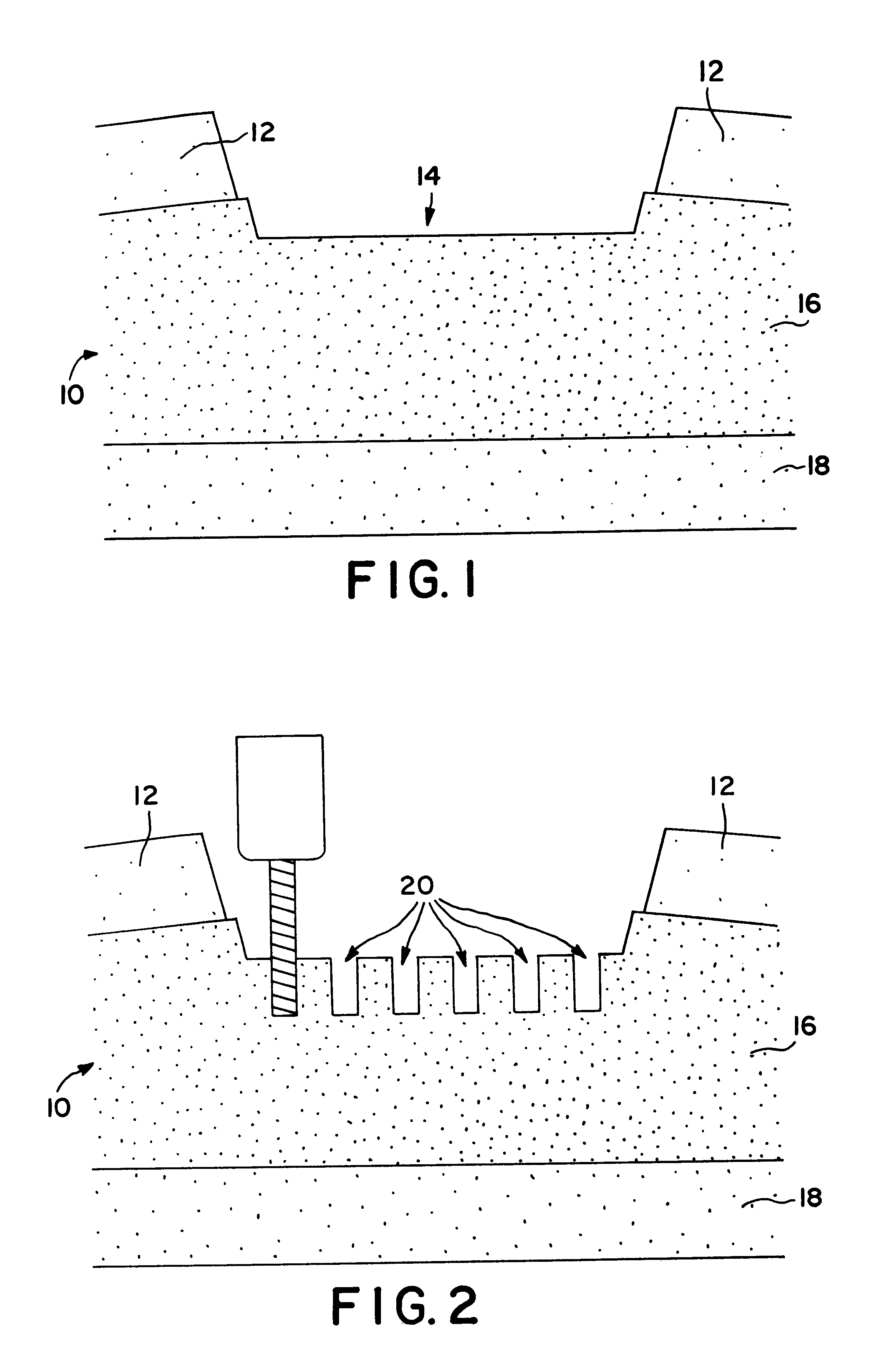
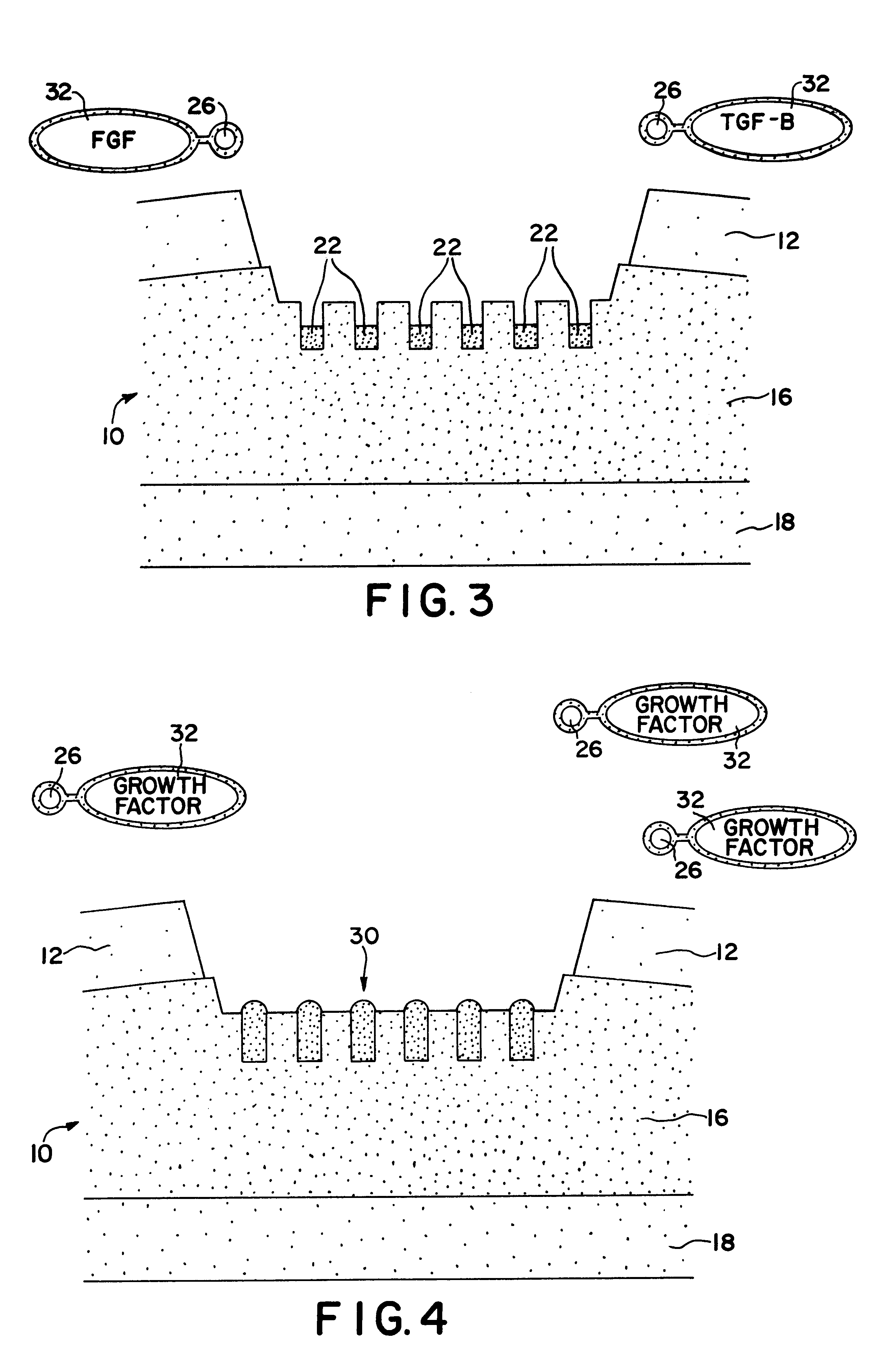
InactiveUS6179871B1Minimize extraneous effectEvenly spacedPowder deliveryElectrotherapyChondral defectGrowth promoting
A method for repairing a defect in cartilage, comprising the provision of apertures in the cartilage by drilling holes at the base of the cartilage defect, which holes may enter the mesenchymal depot, introducing a porous scaffold material containing a plurality of magnetic particles into the apertures, and subsequently and sequentially injecting magnetically-tagged cartilage growth promoting materials such as various growth factors or chondrocytes into the area of the defect. The magnetically tagged growth promoting material is then drawn into the apertures by magnetic attraction of the magnetic particles contained in the porous scaffold material, either by virtue of the particles being permanently magnetic, or by the imposition of an external magnetic field. The present application claims the biodegradable porous scaffold material containing the plurality of magnetic particles.
Owner:HALPERN ALAN A
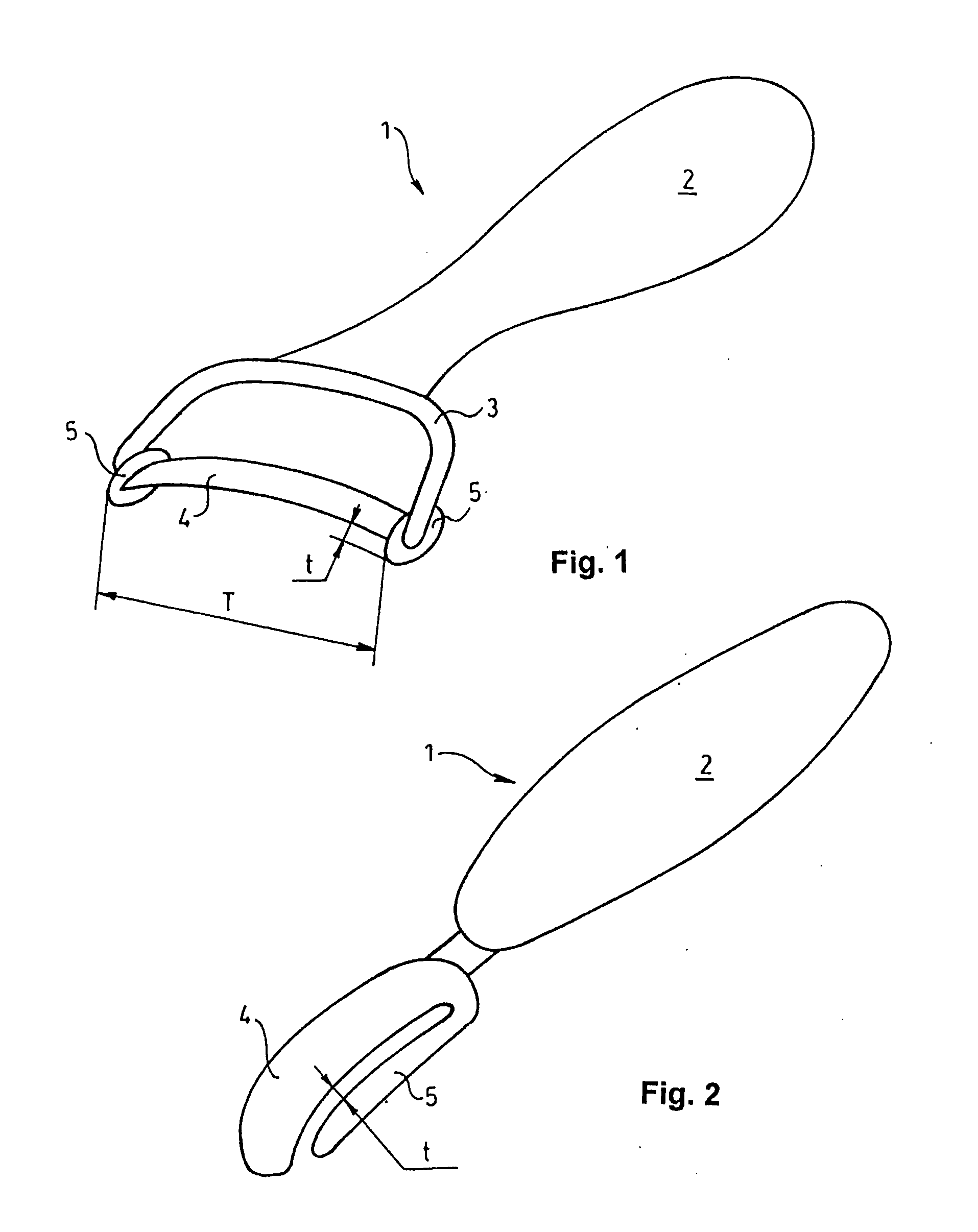
Articular cartilage, device and method for repairing cartilage defects
InactiveUS20100211173A1Easy to useSimple structureSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisYarnCartilage cells
The articular cartilage according to the invention is made of pure cartilage and is provided with incisions (12) on the surface facing the bone. The cartilage cells are preferably seeded on the surface provided with incisions (12). The method for producing the articular cartilage comprises the step of collecting cartilage from joints, wherein pure cartilage is collected without bone, and incisions are made on the surface of the cartilage intended to face the bone. It is preferably fresh frozen until use. The device for harvesting articular cartilage, comprises handle and cutting blade, wherein the cutting blade (4) is curvilinear and is provided with spacer elements (5), meanwhile the device for producing incisions in articular cartilages comprises handle (2) and a bridge (3) connected to said handle (2) and being provided with one or more cutting blade(s) (4). During the method for applying the articular cartilage the articular cartilage is fixed by thin surgical yarn stitches, by fibrin glue or by small anchors (FIG. 8).
Owner:PECSI TUDOMANYEGYETEM
Osteogenic devices and methods of use thereof for repair of endochondral bone and osteochondral defects
InactiveUS20060177475A1Restore an osteochondral or a chondral defectInhibition formationImpression capsPeptide/protein ingredientsRepair tissueOsteogenic proteins
Disclosed herein are improved osteogenic devices and methods of use thereof for repair of bone and cartilage defects. The devices and methods promote accelerated formation of repair tissue with enhanced stability using less osteogenic protein than devices in the art. Defects susceptible to repair with the instant invention include, but are not limited to: critical size defects, non-critical size defects, non-union fractures, fractures, osteochondral defects, subchondral defects, and defects resulting from degenerative diseases such as osteochondritis dessicans.
Owner:MARIEL THERAPEUTICS
A gradient laminated composite supporting frame material based on bionic structures and its preparation method
The invention relates to a kind of laminated gradient composite scaffold material based on the bionic structure and its preparation method. The said material has three or more layers of porous structure, comprising of hyaluronic acid, PLGA, PLA, collagen II and nano-hydroxyapatite (nano-HA) , beta- tricalcium phosphate ( beta-TCP). The upper layer is made by collagen II / hyaluronic acid or PLGA and PLA imitating the cartilage layer. With the counterfeit the calcified cartilage layer in the middle, it is one layer or multi- sublayer, made by nano-HA or beta-TCP with collagen II / hyaluronic acid or PLGA and PLA; the bottom is made of nano-HA or beta-TCP with collagen II or PLGA and PLA. From top to bottom, the content of inorganic material increases in its layers, about 0 to 60 mass percent of layers. The aperture of the scaffold material is 50 to 450 micron, with 70 to 93 percent porosity. The scaffold material made by this invention has an adjustable degradation rate, good mechanical and biocompatible properties, can adapt to culture with cartilage bone cells and compound with growth factor and small molecular or peptides, it can be used to repair cartilage simultaneously.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cartilage cell epimatrix three-dimensional porous sponge stent for tissue engineering and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101496913AFacilitate in vitro constructionPromotes regeneration in the bodyBone implantCartilage cellsCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a three-dimensional porous cartilage extracellular matrix sponge scaffold made of natural cartilage, which can compound cells further to construct tissue engineered cartilage, and can be used for clinically repairing cartilage defects. In the invention, conditions which can fully perform cell extraction and form a porous scaffold matrix are provided by processing cartilage into cartilage microfilaments, and then the cell extraction and solidification and / or strengthening treatment are performed to obtain the three-dimensional porous cartilage extracellular matrix sponge scaffold which is completely decellurized. The antigenicity and cell components are removed in the natural cartilage, and an extracellular matrix component of the cartilage is retained to obtain the scaffold with appropriate pore diameter and porosity, suitable degradation rate, good biocompatibility and certain biomechanical strength. The scaffold has the advantages of broad material sources, low cost, simple and feasible preparation technology, and good repetitiveness; and the scaffold can be widely applied in the field of tissue engineering and has good clinical application prospect.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
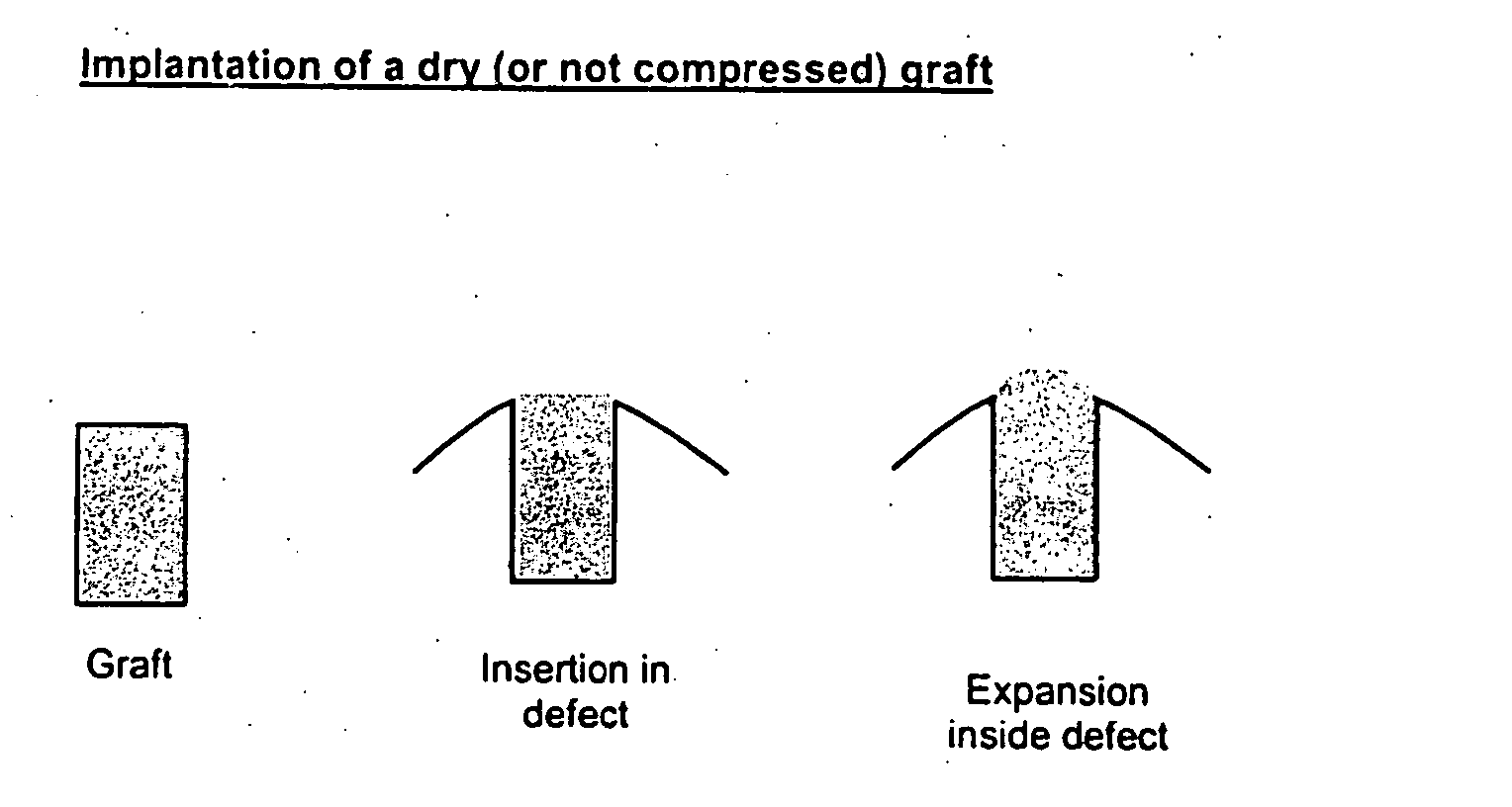
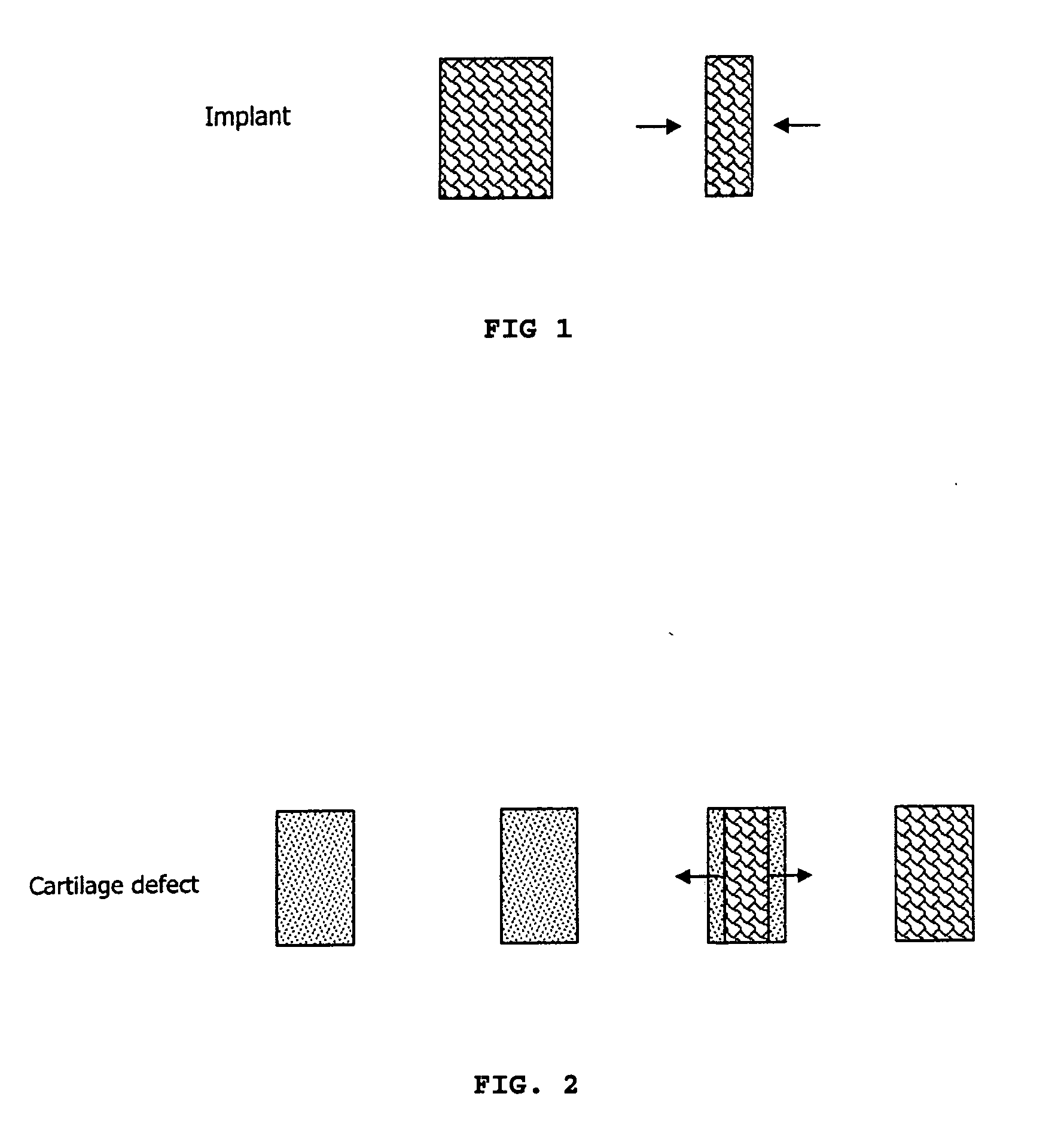
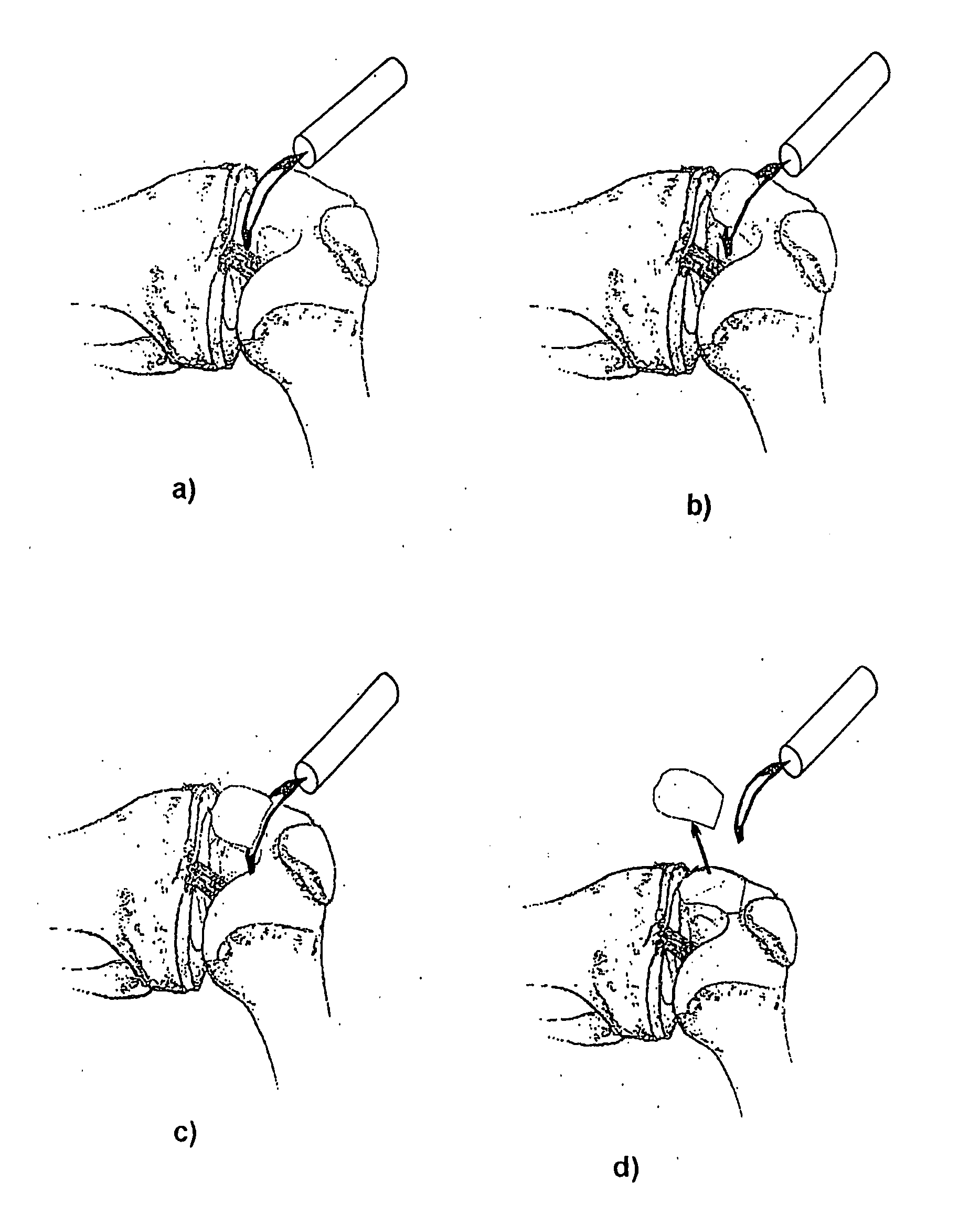
Implantation of Cartilage
ActiveUS20130030528A1Restrict subsequent apoptosisMaintain compatibilityBone implantSurgeryChondral defectBiomedical engineering
The invention is directed towards a process for implanting a cartilage graft into a cartilage defect and sealing the implanted cartilage graft with recipient tissue. The invention is also directed towards a process for repairing a cartilage defect and implanting a cartilage graft into a human or animal. The invention is further directed toward a repaired cartilage defect.
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Dual-layer composite scaffold for repairing cartilage of tissue engineered bone and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103877614AGood biocompatibilityGood bone conductionProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingComposite scaffold
The invention discloses a double-layer composite scaffold for repairing cartilage in a tissue-engineered bone. The scaffold comprises a cartilage layer and a subchondral layer, wherein the cartilage layer and the subchondral layer are combined into a whole through photopolymerisable modified hyaluronic acid gel, wherein the cartilage layer is made from transformed chondrocyte-loaded photopolymerisable modified hyaluronic acid gel, and the subchondral layer is made of a porous bio-glass scaffold. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the double-layer composite scaffold for repairing cartilage in a tissue-engineered bone, which comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the transformed chondrocyte-loaded photopolymerisable modified hyaluronic acid gel and in-vitro induced transformed chondrocyte cells, and forming mixed gel through ultraviolet polymerization; putting the porous bio-glass scaffold on the mixed gel, adding the photopolymerisable modified hyaluronic acid gel, and performing light-crosslinking to obtain the double-layer composite scaffold for repairing cartilage in the tissue-engineered bone. The double-layer composite scaffold has excellent biocompatibility and can be degraded, and the preparation method is simple.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Tissue engineering scaffold material for repairing cartilage defects and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101979105AEasy to prepareFor long-term storageProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingCartilage tissue engineering
The invention discloses a tissue engineering scaffold material for repairing cartilage defects and a preparation method thereof. The tissue engineering scaffold material is prepared by the following steps of: cleaning the spongy bone at the shoulder blade of a fresh pig; cutting the spongy bone into small blocks with diameter of between 5 and 10mm and thickness of between 3 and 5mm; degreasing, decalcifying and deproteinizing; immersing with alcohol for 30 minutes; and air-drying, wherein the decalcifying time is 6 hours. The prepared demineralized spongy bone matrix (DSBM) has the characteristics of relatively simple and convenient preparation method, and capacity of being obtained on a large scale, can be stored for a long time at a low temperature and is economic and cheap. The material can be prepared into different shapes and sizes according to the shapes of the defects to be repaired, so the material is convenient to apply. The DSBM remains a natural netlike gap structural system of the pig spongy bone, has high cellular compatibility, biocompatibility and degradability and is a very good cartilage tissue engineering scaffold material.
Owner:昆明医学院第一附属医院
Surgical grafts for repairing chondral defects
An implant containing a collagen matrix embedded with chondrocyte-like cells, its use in repairing a chondral defect, and a method of preparing the implant.
Owner:KARTIGEN BIOMEDICINE INC
Implant for repairing a cartilage defect
InactiveUS20070265705A1Effective and reliable treatmentBone implantLigamentsBiomedical engineeringSynovial space
The present invention relates to an implant for repairing a cartilage defect comprising a first layer and a second layer. The first layer comprises a membrane-like structure and the second layer comprises a sponge-like structure with directional and / or interconnected pores. The first layer is facing the synovial space and the second layer is located towards bone.
Owner:TETEC TISSUE ENG TECH
Cartilage derived collagen sponge scaffold and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101890184AQuality is easy to controlEasy to useProsthesisCartilage cellsBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cartilage derived collagen sponge scaffold and a collagen sponge scaffold prepared by the method. The method comprises the following steps of crushing, removing cells, removing telopeptide, dissolving and crosslinking, and the obtained collagen sponge scaffold has good biocompatibility and extremely low antigenicity; and a homogenized sponge scaffold can be prepared from cartilages of a plurality of individuals from the conspecific animals, has controllable pore diameter and porosity, can provide appropriate growth and propagation environment for cartilage cells and bone mesenchymal stem cells, particularly has good effect of repairing cartilage defect parts, and is more favorable for standardized production and clinical use.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Peptide for repairing cartilage and/or treating osteoarthritis
ActiveCN106749606AOvercome stabilityOvercome the shortcoming of short half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticCartilage repairIn vivo
The invention discloses a peptide (called BM23 peptide) which comprises 23 amino acids. The peptide derives from a BMP-2 amino acid sequence and is formed by mutation and modification. Compared with BMP-2, the peptide has remarkably improved stability and in-vivo effect duration, has activity for promoting differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into cartilage cells and promoting cartilage cell proliferation, and can be used for repairing cartilage and / or treating osteoarthritis.
Owner:LINK HEALTH GRP
Composition for repairing cartilage tissue and method for making the same
InactiveUS20130344114A1Reduce the burden onRelieve painBiocideSkeletal disorderProgenitorCell biology
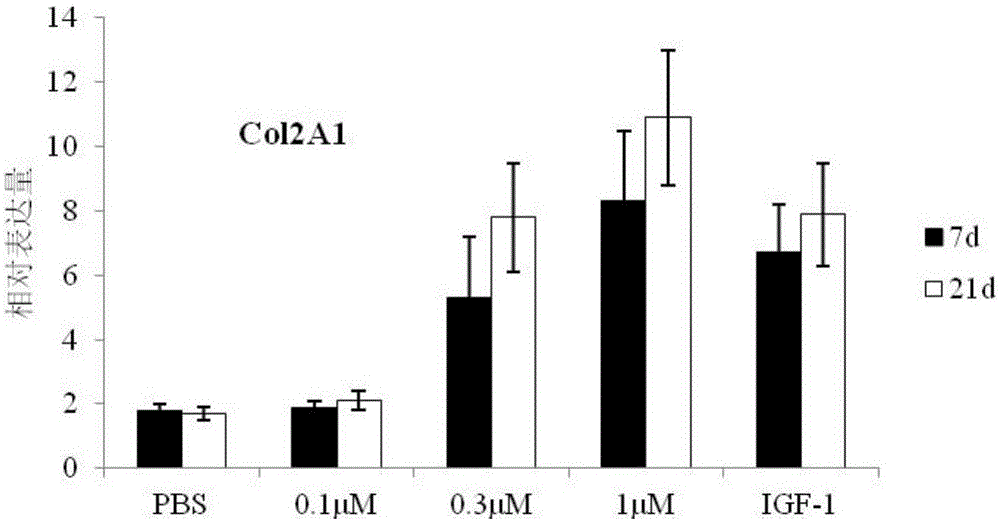
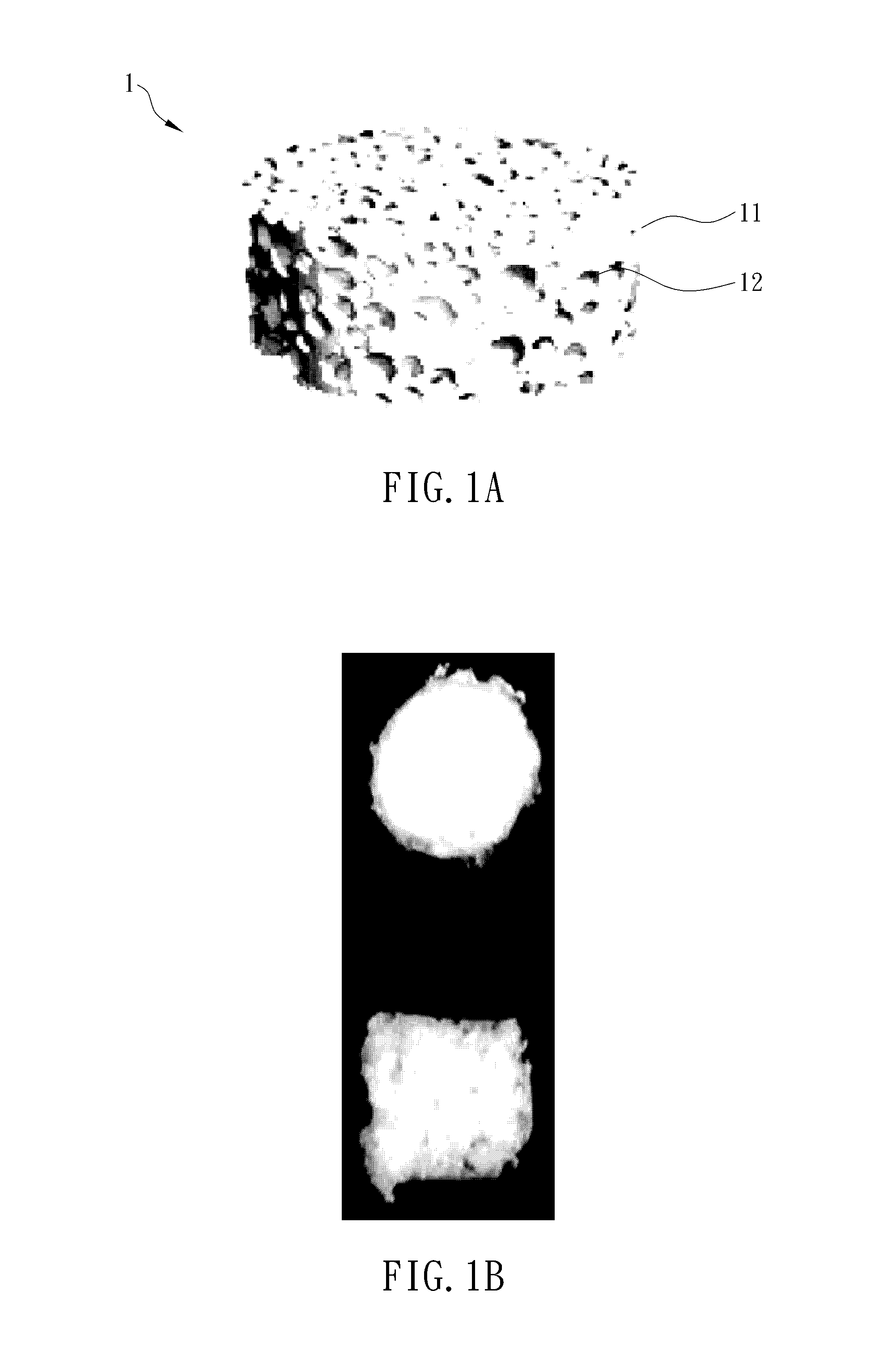
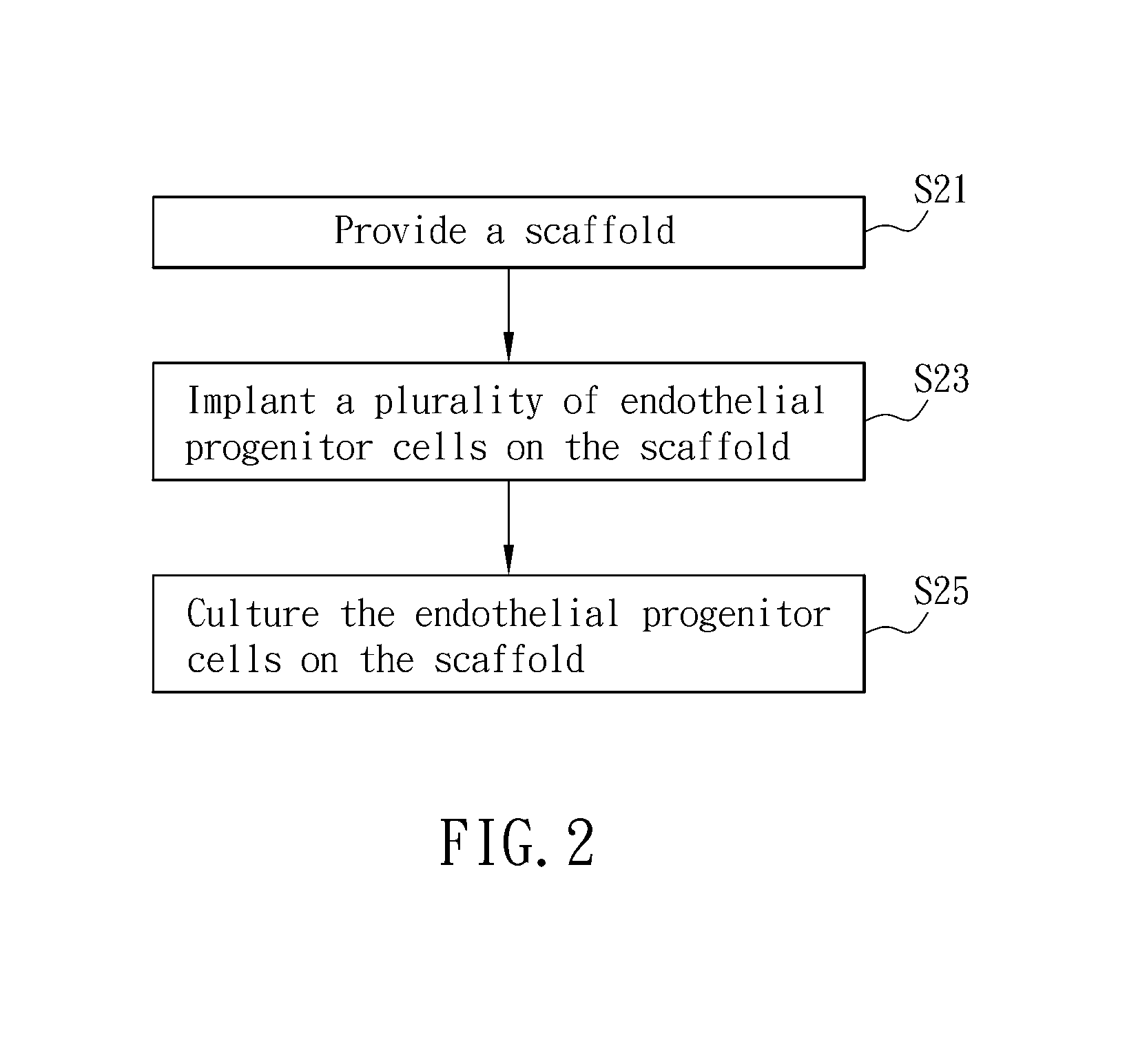
A composition for repairing cartilage tissues includes a scaffold and a plurality of endothelial progenitor cells. The endothelial progenitor cells adhere on the scaffold. A method of making the composition for repairing cartilage tissue is also disclosed. This is advantageous for safely and quickly repairing cartilage tissues by using the composition and the manufacturing method thereof.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
II type collagen hyaloplasm acid compound sponge bracket and use thereof
ActiveCN101862475BAppropriate mechanical strengthReduce manufacturing costProsthesisControlled releaseCross-link
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, in particular to a bionic II type collagen hyaloplasm acid compound sponge bracket for repairing cartilage in tissue engineering. The preparation method of the II type collagen hyaloplasm acid compound sponge bracket comprises the following steps of: extracting high-purity II type collagen solution; concentrating the II type collagen solution by means of a polyethylene glycol concentration method; gradually mixing hyaloplasm acid solution with the high-purity II type collagen solution by means of a partial homogenate method; and crosslinking the concentrated II type collagen hyaloplasm acid compound sponge with EDC and NHS dual cross-linking agent to obtain the II type collagen hyaloplasm acid compound sponge bracket. The II type collagenhyaloplasm acid compound sponge bracket can be taken as a tissue engineering implant, a cell culturing bracket material or medicine controlled release and the like for the prevention and the cure of the repair of the cartilage injury.
Owner:广州市红十字会医院
Preparation method of composite drug-loaded delivery material based on hydrogel and liposome
The invention relates to a preparation method of a composite drug-loaded delivery material based on a hydrogel and liposome, which belongs to the technical field of biomaterials, and aims to solve thetechnical problem of fast release of the hydrogel as a scaffold material for repairing cartilage defects. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1. dissolving the lipid and a drug in acontainer in an organic solvent, after fully dissolving, removing the organic solvent by rotary evaporation, forming a liposome film on the surface of the container, adding a buffer solution, and fully shaking the material to make the liposome film for hydration shedding to obtain a liposome solution; and 2. thoroughly mixing the liposome solution and a polyethylene glycol solution, adding a chitosan solution or a chitosan derivative solution, and obtaining the composite drug-loaded delivery material based on the hydrogel and the liposome after standing. The liposome of the present inventioncan be loaded with the drug to achieve long-term slow release, and can be used as a carrier delivery system for the drug; and the drug and the liposome have synergism to achieve long-term slow releaseof the drug loaded on a stent material.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Methods and compositions for repairing cartilage
InactiveUS7416889B2Optimizes chondrogenic activityShorten the timeBiocideCulture processTissue repairMammal
Owner:RHODE ISLAND HOSPITAL
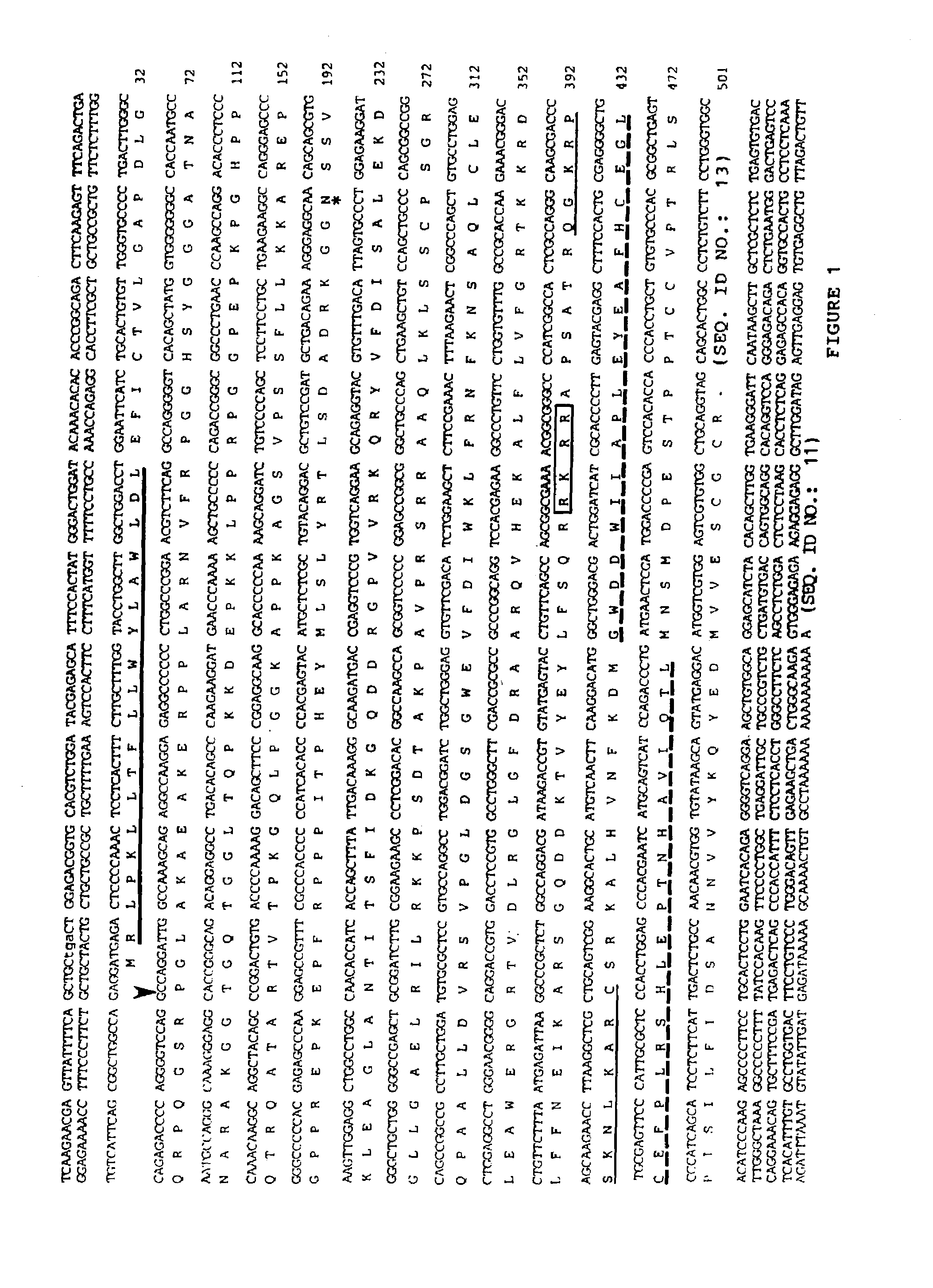
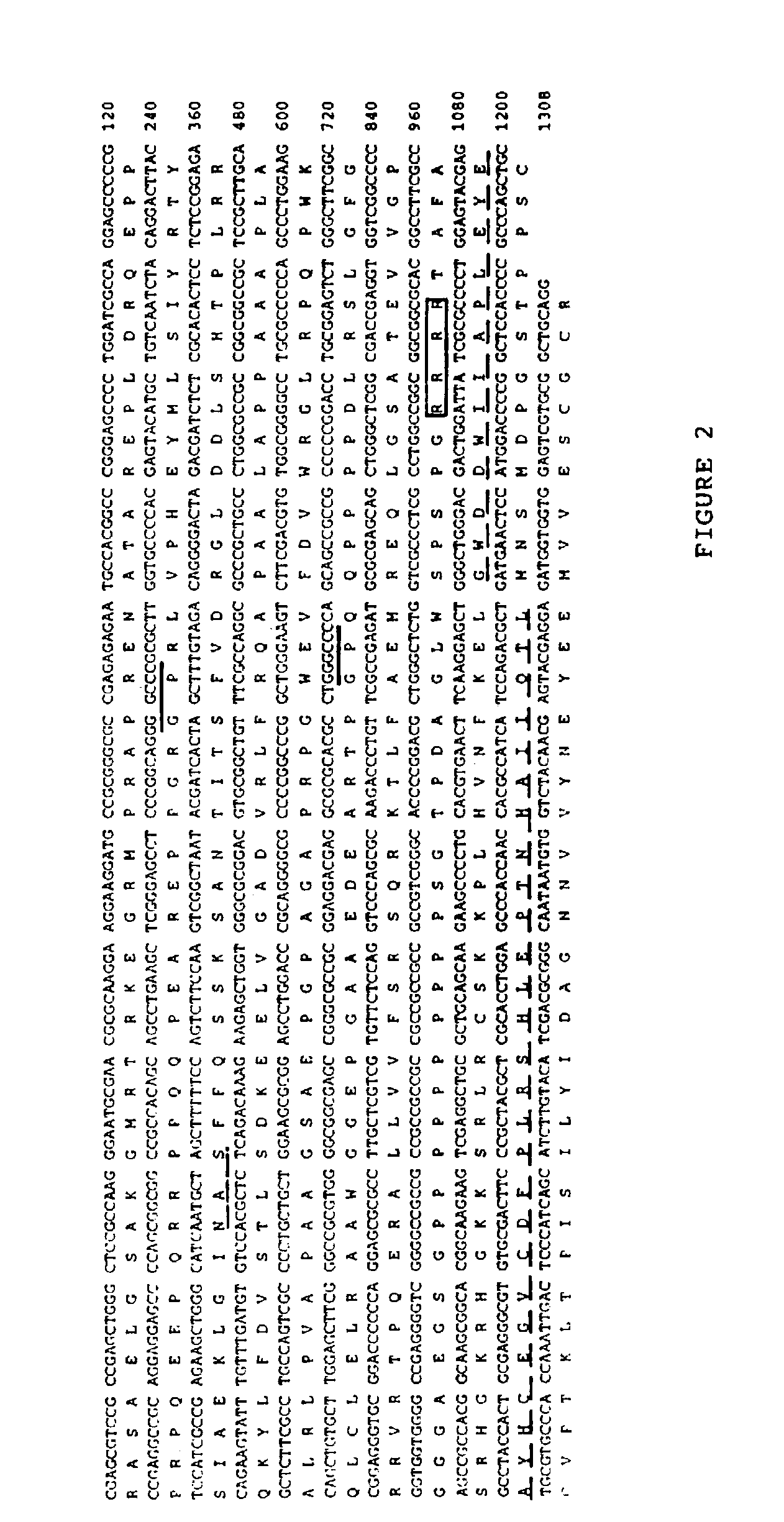
Cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins
Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins (CDMP-1 and CDMP-2) from human and bovine cartilage extracts. These proteins exhibit chondrogenic activity and can be used to repair cartilage defects in a mammal.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Preparation for repairing cartilage defects or cartilage/bone defects in human or animal joints
InactiveUSRE43714E1Reduce absorptionResistant to resorptionBone implantJoint implantsMetatarsal bone partRepair tissue
Repairs of cartilage defects or of cartilage / bone defects in human or animal joints with the help of devices including a bone part (1), a cartilage layer (2) and a subchondral bone plate (4) or an imitation of such a plate in the transition region between the cartilage layer (2) and the bone part (1). After implantation, the bone part (4) is resorbed and is replaced by reparative tissue only after being essentially totally resorbed. In a critical phase of the healing process, a mechanically inferior cyst is located in the place of the implanted bone part (1). In order to prevent the cartilage layer (2) from sinking into the cyst space during this critical phase of the healing process the device has a top part (11). and a bottom part (12), wherein the top part (11) consists essentially of the cartilage layer (2) and the subchondral bone plate (4) and the bottom part (12) corresponds essentially to the bone part (1) and wherein the top part (11) parallel to the subchondral bone plate (4) has a larger diameter than the bottom part (12). After implantation in a suitable opening or bore (20), the cartilage layer (2) and the subchondral bone plate (4) are supported not only on the bone part (1) but also on native bone tissue having a loading capacity not changing during the healing process. Therefore, the implanted cartilage layer cannot sink during the healing process.
Owner:ZIMMER ORTHOBIOLOGICS
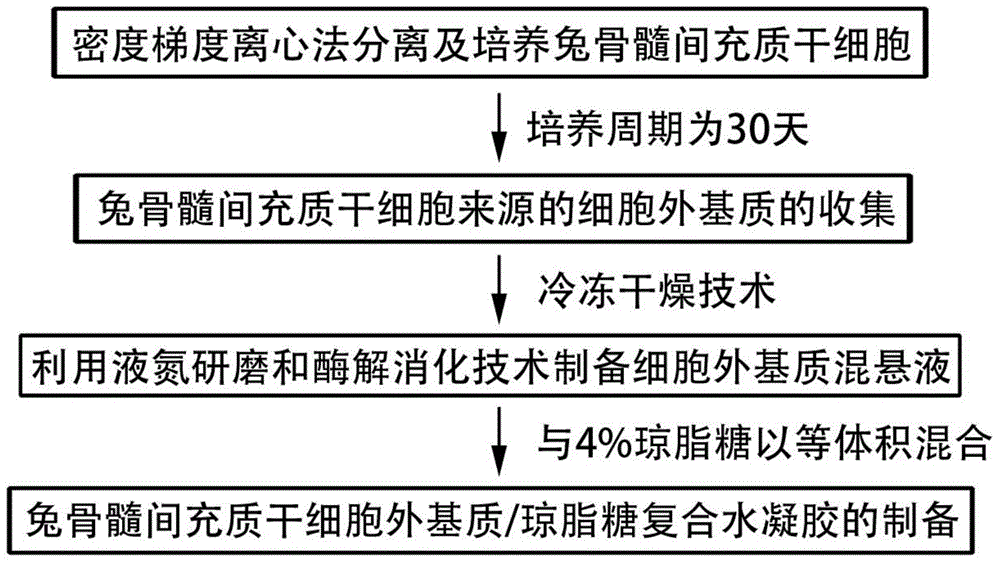
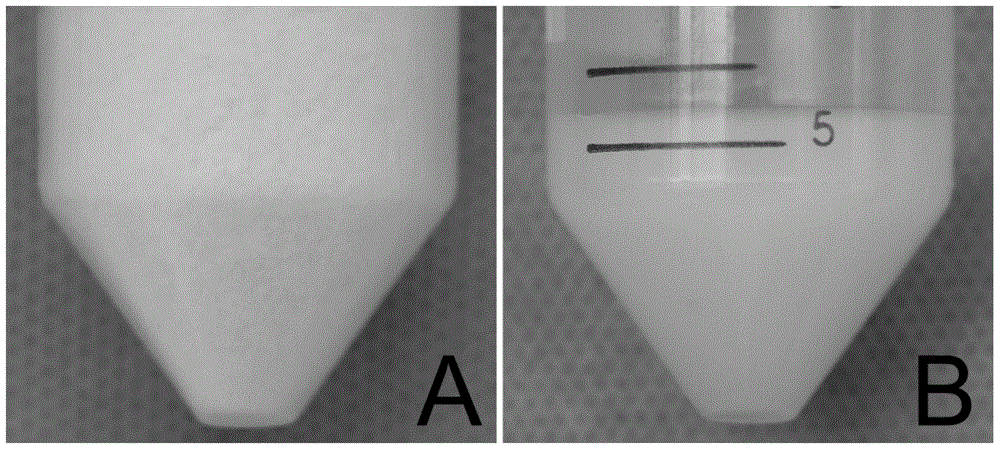
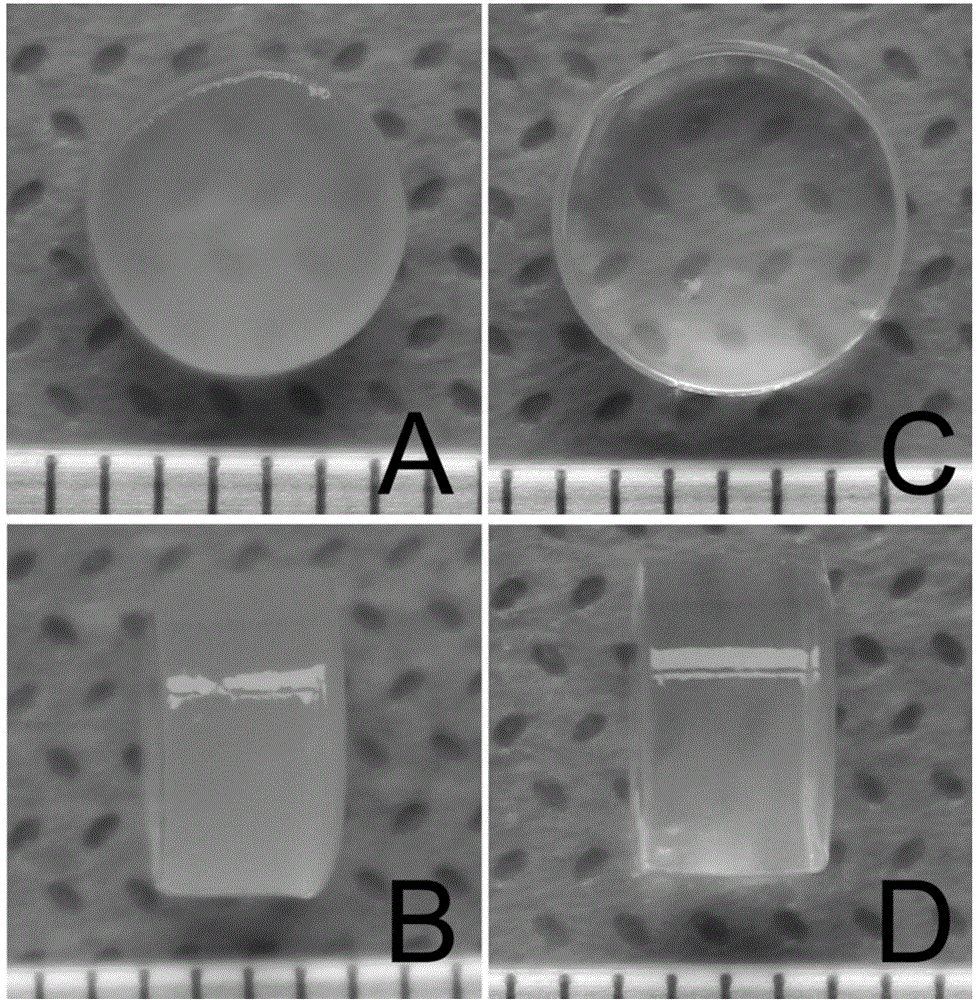
Injectable mesenchymal stem cell extracellular matrix/agarose composite hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104307046AImprove adhesionImprove plasticitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisEnzymatic digestionCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses injectable mesenchymal stem cell extracellular matrix / agarose composite hydrogel as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: culturing mesenchymal stem cells of a rabbit in vitro with monolayer high density, collecting a secreted extracellular matrix of the mesenchymal stem cells, and acquiring an extracellular matrix suspension by utilizing freeze drying, grinding under liquid nitrogen and an enzymatic digestion technology; and then fully and uniformly mixing the extracellular matrix suspension and agarose with same volume to prepare the mesenchymal stem cell extracellular matrix / agarose composite hydrogel material. The injectable mesenchymal stem cell extracellular matrix / agarose composite hydrogel can be injected into cartilage defect parts in arbitrary shapes by virtue of a simple injection mode and has good adhesion integration capability with peripheral host tissues,is sufficient in cell source, avoids potential risks caused by xenogenic resource materials, and is convenient to repair cartilage defects in arbitrary shapes to reach purpose of good integration with the peripheral host tissues.
Owner:南京医科大学附属南京医院
Compositions and methods for re-programming cells without genetic modification for repairing cartilage damage
InactiveUS20140289882A1Increased collagen typeType of reductionPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderDiseaseReprogramming
The present inventions are directed to compositions and methods regarding the reprogramming of other cells (such as embryonic stem cells (ESCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), MSCs, fibroblasts, hematopoietic stem cells, endothelian stem cells, adipocytes, chondrocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts and endothelial cells) into chondrogenic cells without introducing exogenous genes to the samples. In particular, the present inventions are directed to transducible materials that are capable of transducing into the biological samples but are not genes or causing genetic modifications. The present inventions also are directed to methods of reprogramming the path of biological samples or treating diseases using the tranducible compositions thereof.
Owner:VIVOSCRIPT
Cartilage extracellular matrix and silk fibroin composite orientation cartilage support and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105251052AFix performance issuesStructural solutionAnimals/human peptidesProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a cartilage extracellular matrix and silk fibroin composite orientation cartilage support and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the biological tissue engineering technology. According to the cartilage extracellular matrix and silk fibroin composite orientation cartilage support and the preparation method of the cartilage support, cartilage extracellular matrixes are prepared through articular cartilage of people, pigs, cows or sheep, silk fibroin is prepared through mulberry silk, after the cartilage extracellular matrixes and the silk fibroin are evenly mixed according to a specific proportion, directed crystallization is performed under a certain temperature, ultraviolet cross linking is firstly performed after freezing and drying, and then cross linking of carbodiimide and N-hydroxysuccinimide or glutaraldehyde and genipin is performed so that the cartilage extracellular matrix and silk fibroin composite orientation cartilage support can be prepared. Due to the design, biocompatibility is good, and immunological rejective reaction is avoided; a composition structure and mechanical properties are similar to those of cartilage extracellular matrixes of people; material sources are wide, cost is low, the preparation technology is simple, the cartilage extracellular matrix and silk fibroin composite orientation cartilage support can be used for constructing tissue engineering cartilage and repairing cartilage degradation, and clinical application prospects are good.
Owner:TIANJIN HOSPITAL
Preparation method of biological 3D printing composite ink for repairing cartilage defects
InactiveCN112295015APromote growthMeet the needs of tissue engineering repairAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regeneration3d printCartilage cells
The invention discloses a preparation method of biological 3D printing composite ink for repairing cartilage defects, and relates to the technical field of biological 3D printing. The preparation method of the biological 3D printing composite ink for repairing the cartilage defects comprises the following steps: obtaining fresh transparent articular facet cartilage or costal cartilage from animals, removing cartilage cells by adopting physical, chemical and biological methods, and carrying out sterilizing and freeze-drying; carrying out grinding under the condition of low temperature with liquid nitrogen so as to obtain extracellular matrix powder; and then, uniformly mixing the extracellular matrix powder with a mixed material according to a certain ratio, adding deionized water, and allowing dispersing and dissolving so as to form a uniform and stable suspension, namely a target product. The preparation method of the biological 3D printing composite ink for repairing the cartilage defects provided by the invention has the following beneficial effects: the obtained extracellular matrix powder can be combined with different materials so as to satisfy biological 3D printing composite ink meeting different requirements; and moreover, the ink can be rapidly crosslinked and cured, and is relatively low in cytotoxicity, relatively high in biocompatibility and capable of being co-printed with stem cells so as to meet tissue engineering repair requirements. Thus, the ink has relatively good clinical application prospects and values.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY +1
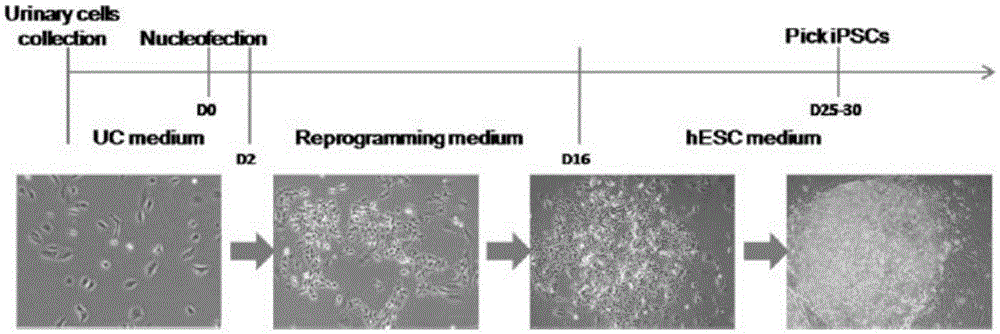
Method for constructing cartilage tissues by aid of human urine cells
The invention provides a method for preparing cartilage tissues from artificial in-vitro sources by the aid of human urine cells in an in-vitro manner. The method includes steps of (1), a), reprogramming the human urine cells to generate induced pluripotent stem cells and directionally differentiating the induced pluripotent stem cells to obtain mesenchymal stem cells, or b), carrying out transdifferentiation to generate the mesenchymal stem cells; (2), cultivating the mesenchymal stem cells obtained at the step (1) in cartilage induced differentiation media to obtain the cartilage tissues from the artificial in-vitro sources. The method has the advantages that the cartilage tissues are constructed in the in-vitro manner and can be used for replacing damaged or lesion tissue cells, so that the purpose of repairing cartilage can be achieved, and the effective method is provided for constructing the cartilage tissues in the in-vitro manner and has huge application value.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation of composite hydrogel tissue engineer cartilage repairing scaffold with biological activity
ActiveCN103143058AImprove biological activityIdeal three-dimensional porous structureProsthesisPolyvinyl alcoholBacterial strain
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite hydrogel tissue engineer cartilage repairing scaffold with biological activity. The preparation method comprises the steps of: preparing a paraffin model of the cartilage repairing scaffold; by taking the paraffin model as a template, selecting and fermenting-cultivating a bacterial strain capable of secreting bacterial cellulose; removing paraffin from a fermentation product, and purifying, dewatering and immersing the fermentation product, thus obtaining a bacterial cellulose hydrogel cartilage repairing scaffold containing 30-50% of CaC12 aqueous solution by weight; dissolving polyvinyl alcohol in an Na2HPO4 aqueous solution, thus obtaining a mixed solution A; enabling the mixed solution A to enter the bacterial cellulose hydrogel cartilage repairing scaffold by virtue of an immersion method to obtain a product; freezing-unfreezing the obtained product for multiple times, and irradiating the product by gamma rays, thus obtaining the composite hydrogel tissue engineer cartilage repairing scaffold with biological activity. Composite hydrogel prepared by the method has an appropriate appearance, a porous structure, an excellent mechanical property and excellent biological activity and can be used as a tissue engineer scaffold material for repairing cartilage tissue.
Owner:钟春燕
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com