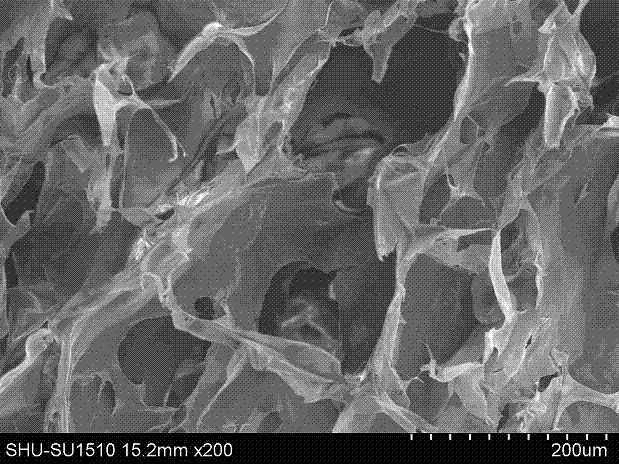
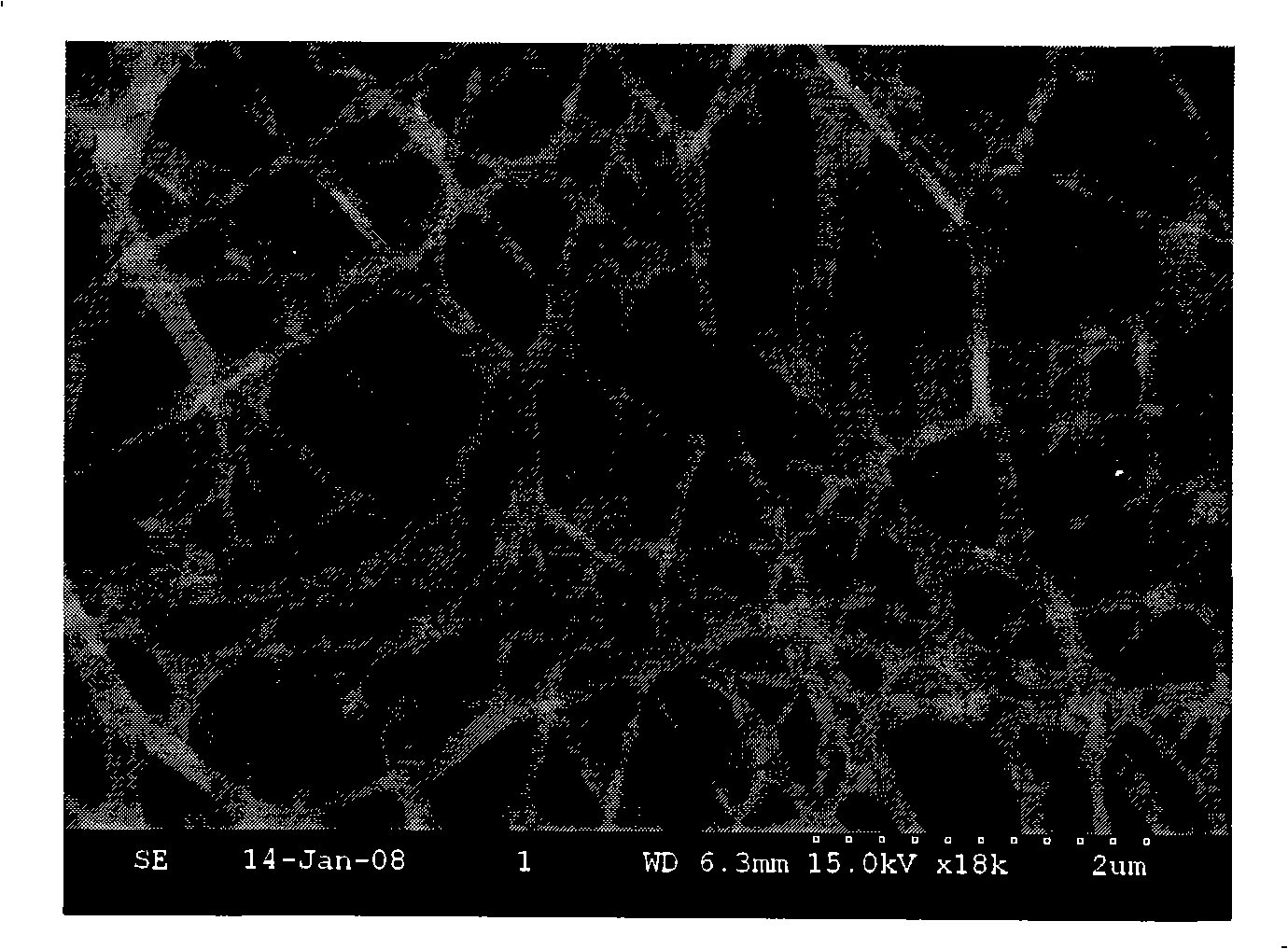
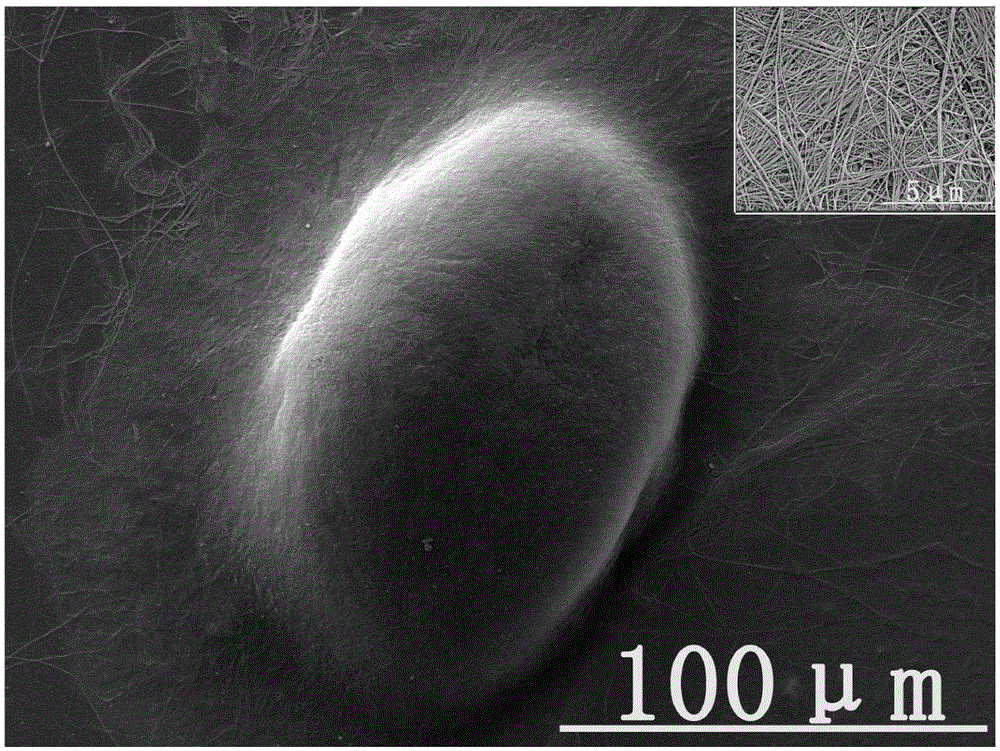
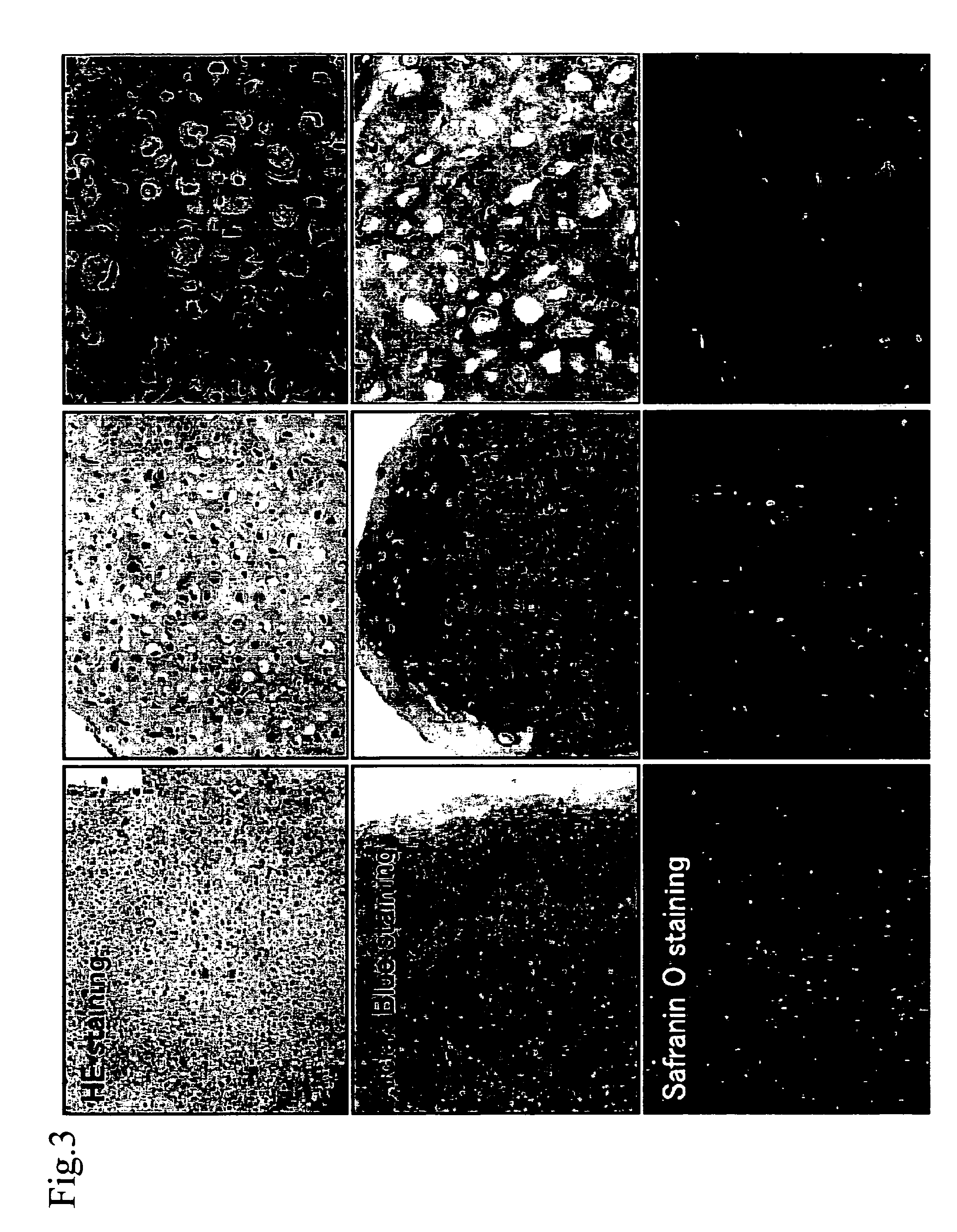
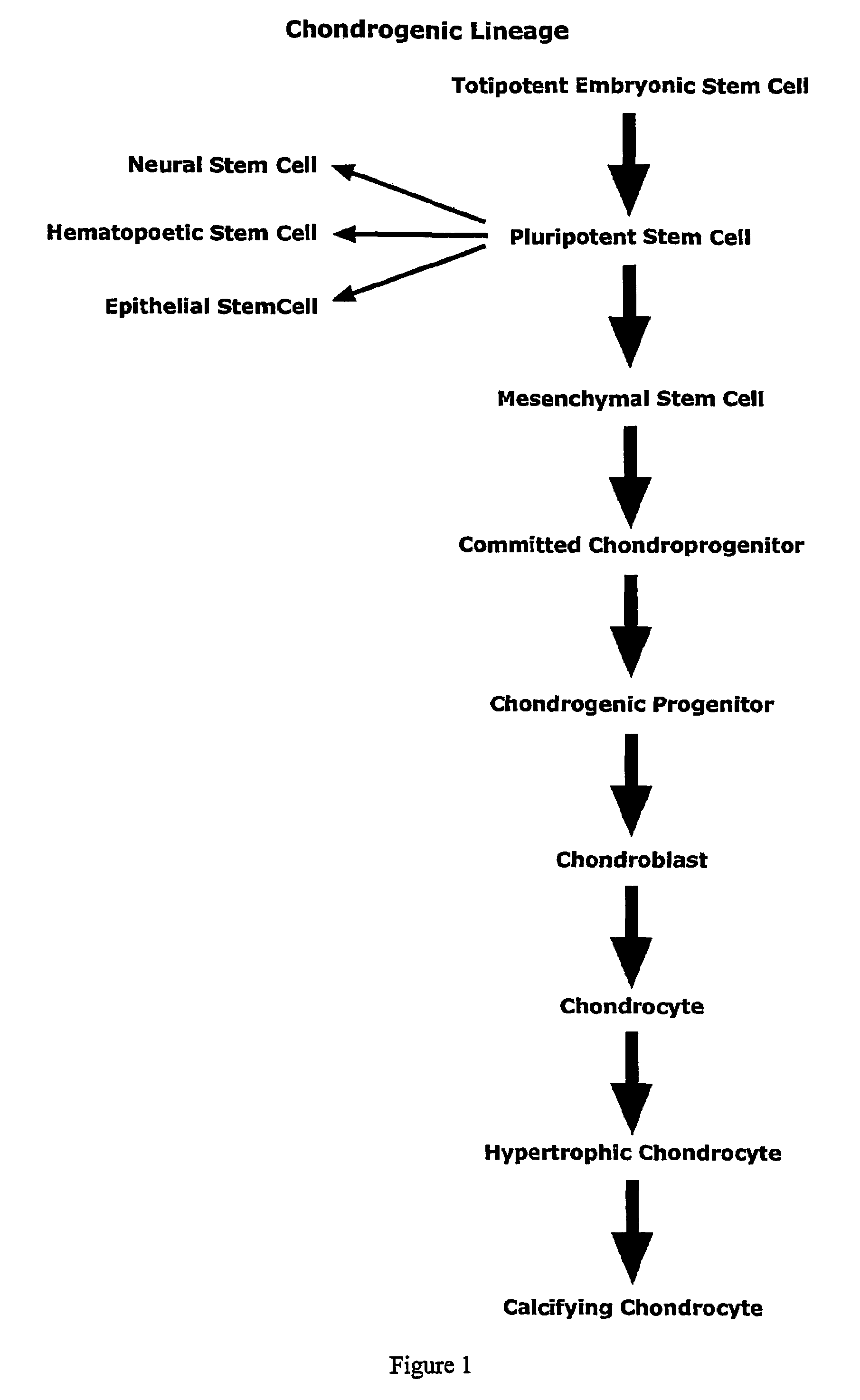
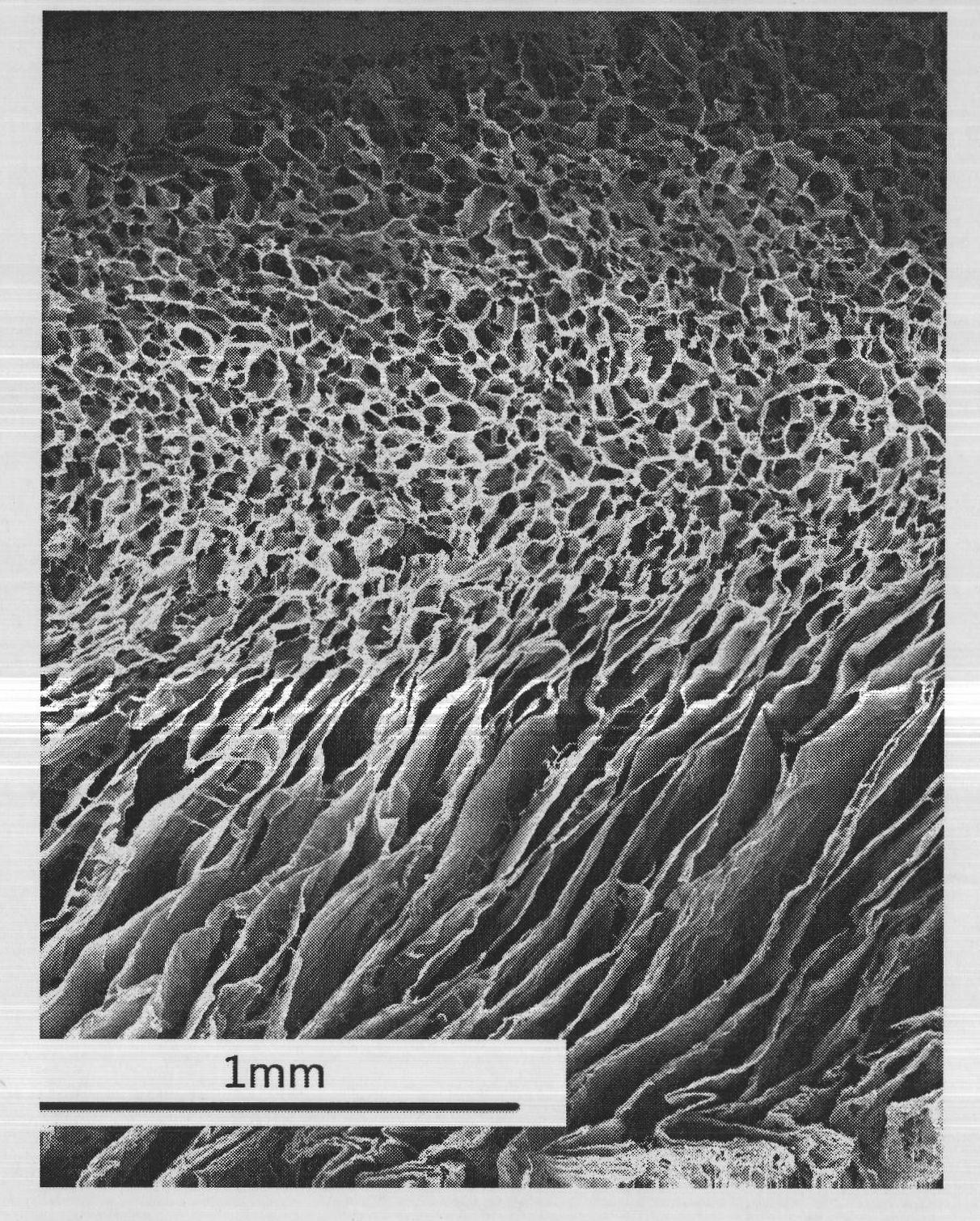
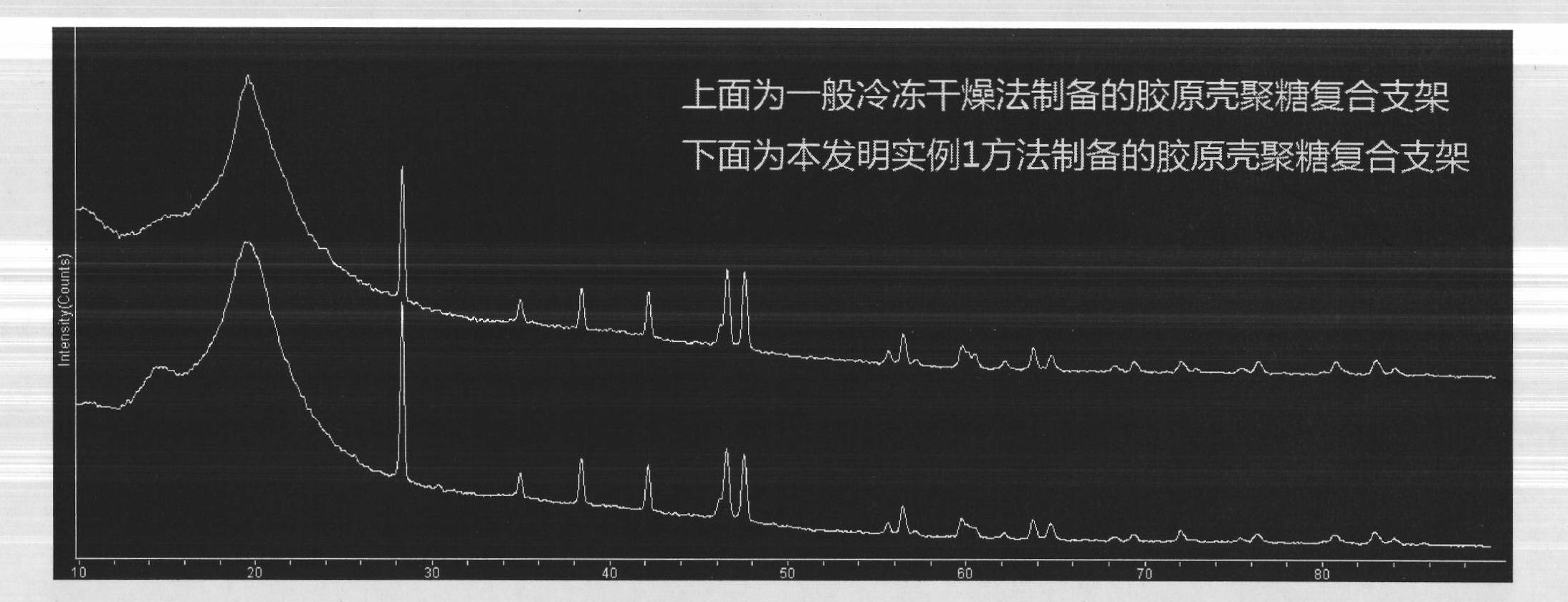
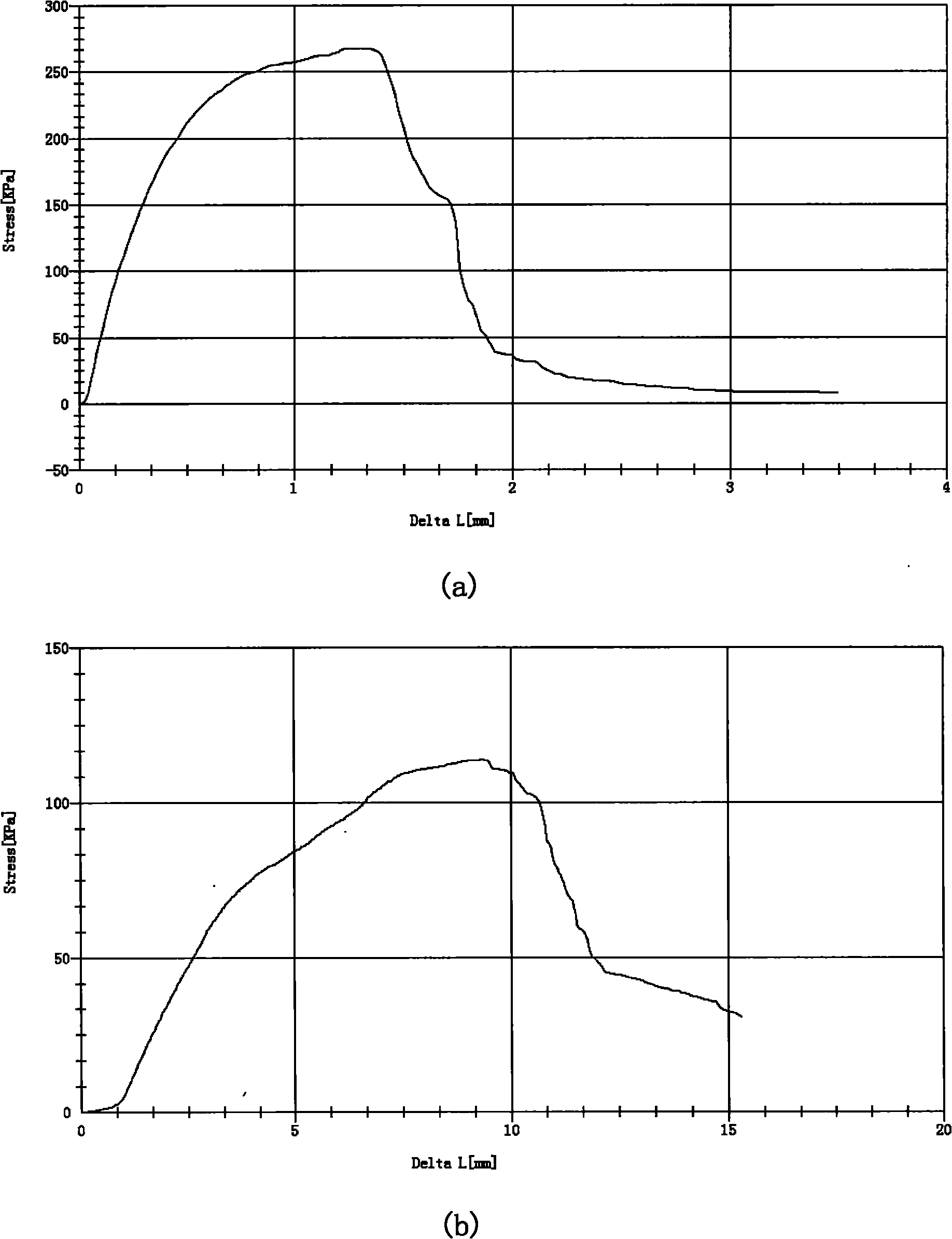
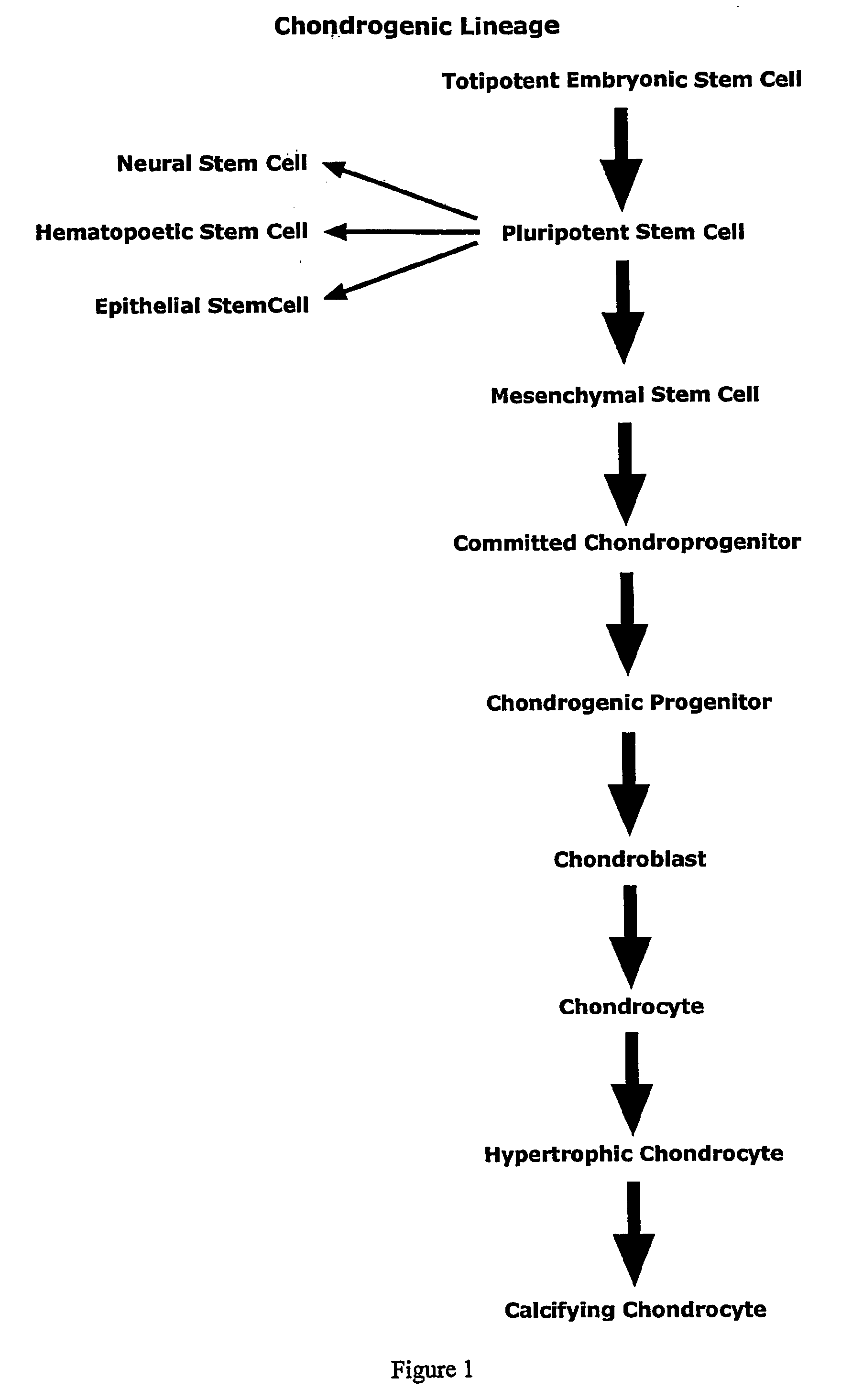
Patents
Literature
125 results about "Cartilage tissue engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioactive, resorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering
InactiveUS20050118236A1High porosityImprove manufacturabilityBiocideSynthetic resin layered productsPorosityFiber
Flexible, bioactive glass meshes and scaffolds made therefrom are provided. The meshes comprise interwoven bioactive glass fibers that can be coated with resorbable polymers. Meshes can also be woven from glass fibers and resorbable polymers. Scaffolds can be constructed by a plurality of meshes, which can have varying porosities to create porosity gradients in the scaffold. Methods of making scaffolds are provided which can comprise pulling bioactive glass fibers, winding the fibers, forming the fibers into bundles, coating the fibers with a resorbable polymer, and creating a biaxial weave with the bundles. Soft tissue engineering methods are also provided for creating scaffolds for incubating cells such as fibroblasts and chondroblasts. Meshes and scaffolds are suitable for tissue engineering, such as bone tissue engineering and cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:GENTIS
Composite material for porous material and gel use thereof
InactiveCN1644221AImprove stabilityGood adhesionProsthesisCalcium biphosphateAlpha-tricalcium phosphate
A composition of porous material and gel for preparing artificial bone is prepared from collagen and porous material chosen from alpha-tricalcium phosphate / hydroxy apatite, beta-tricalcium phosphate / hydroxy apatite-coral, calcium phosphate / hydroxy apatite, calcium carbonatel tricalcium phosphate, etc.
Owner:徐小良
Preparation method for nanofiber porous scaffold having compression elasticity in wet state
The invention relates to a preparation method for a nanofiber porous scaffold having compression elasticity in a wet state. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving gelatin and polylactic acid in a solvent so as to obtain a mixed solution, and carrying out electrostatic spinning so as to obtain a nanofiber membrane; feeding the nanofiber membrane into tertiary butanol, smashing, freezing and freeze-drying so as to obtain a non-crosslinked freeze-dried scaffold; immersing the non-crosslinked freeze-dried scaffold into cross-linking liquid, washing, soaking in deionized water, freezing and freeze-drying so as to obtain the nanofiber porous scaffold. The nanofiber porous scaffold prepared through the preparation method has degradability, biocompatibility and relatively high porosity, and has a certain compression resistance at the wet state, can quickly stop bleeding, is beneficial to cell adhesion, cell proliferation and tissue regeneration, and can be applicable to hemostatic materials, cartilage tissue engineering, skin tissue engineering and other fields.
Owner:诺一迈尔(苏州)生命科技有限公司
Hydroswellable, Segmented, Aliphatic Polyurethanes and Polyurethane Ureas
InactiveUS20090233887A1Increase volumeRestoring the function of diseased or defective articulating jointsBiocideImpression capsPolyethylene glycolSegmented polyurethane
Hydroswellable, absorbable and non-absorbable, aliphatic, segmented polyurethanes and polyurethane-urea capable of swelling in the biological environment with associated increase in volume of at least 3 percent have more than one type of segments, including those derived from polyethylene glycol and the molecular chains are structurally tailored to allow the use of corresponding formulations and medical devices as carriers for bioactive agents, rheological modifiers of cyanoacrylate-based tissue adhesives, as protective devices for repairing defective or diseased components of articulating joints and their cartilage, and scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:POLY MED
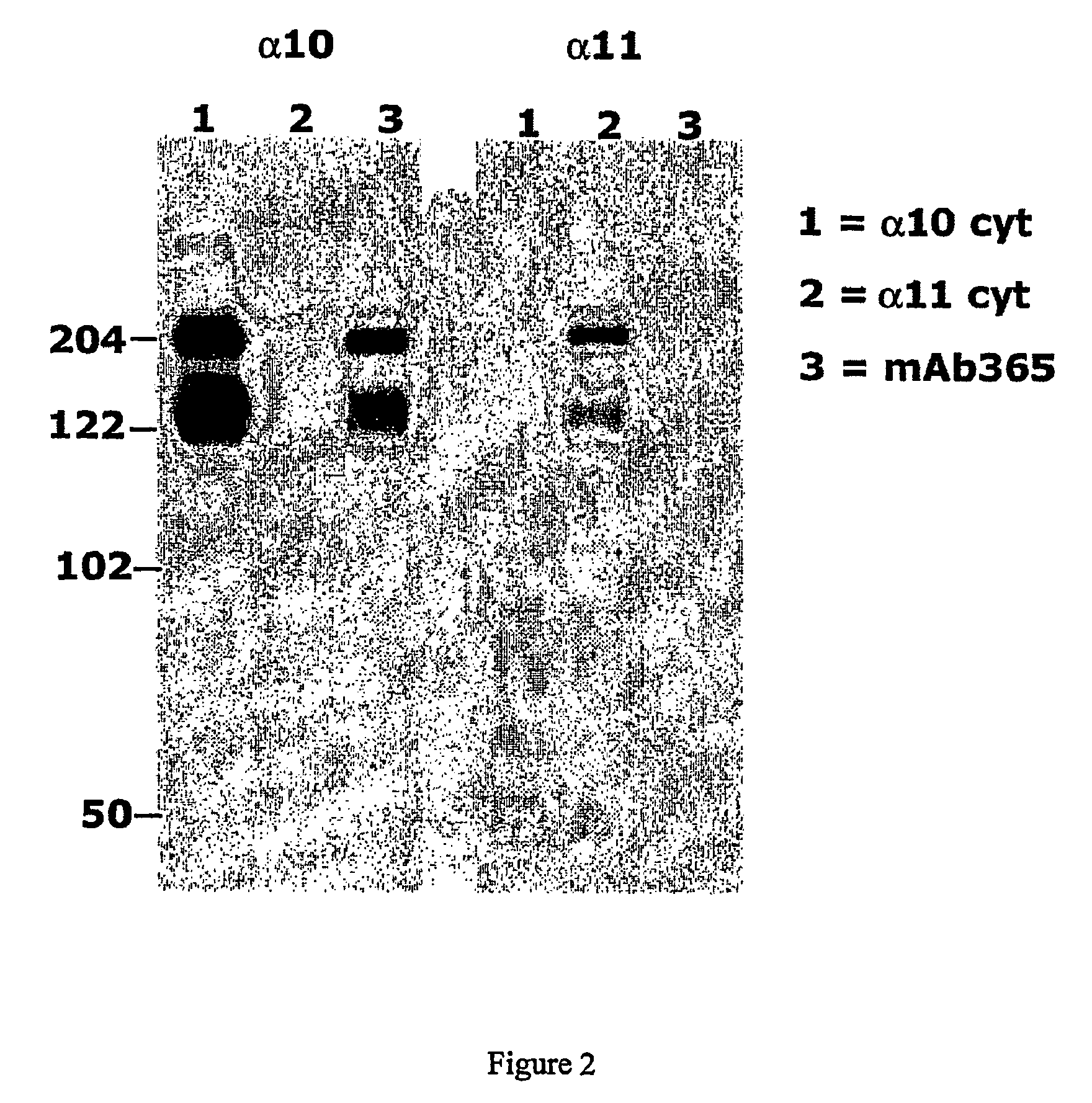
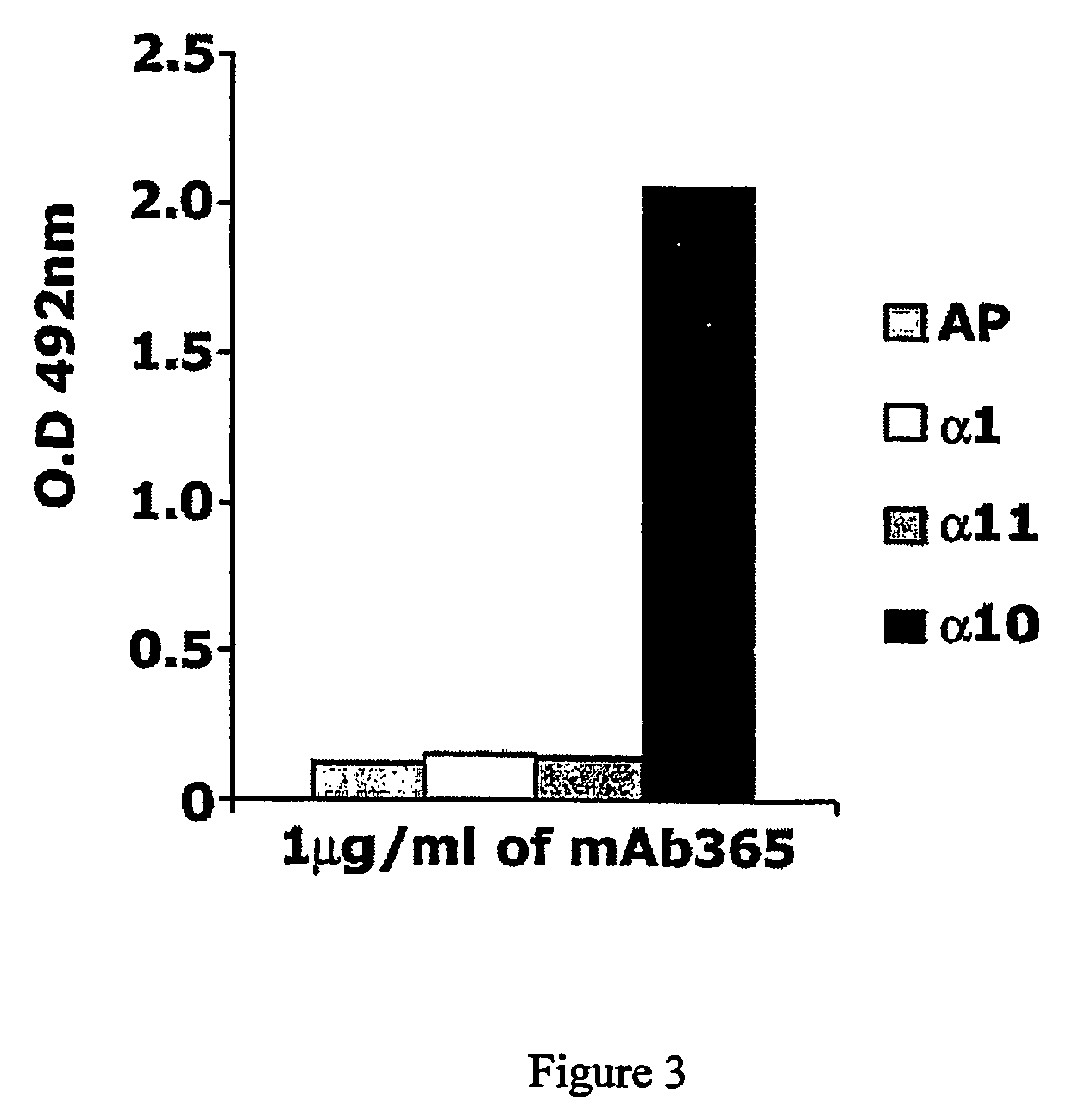
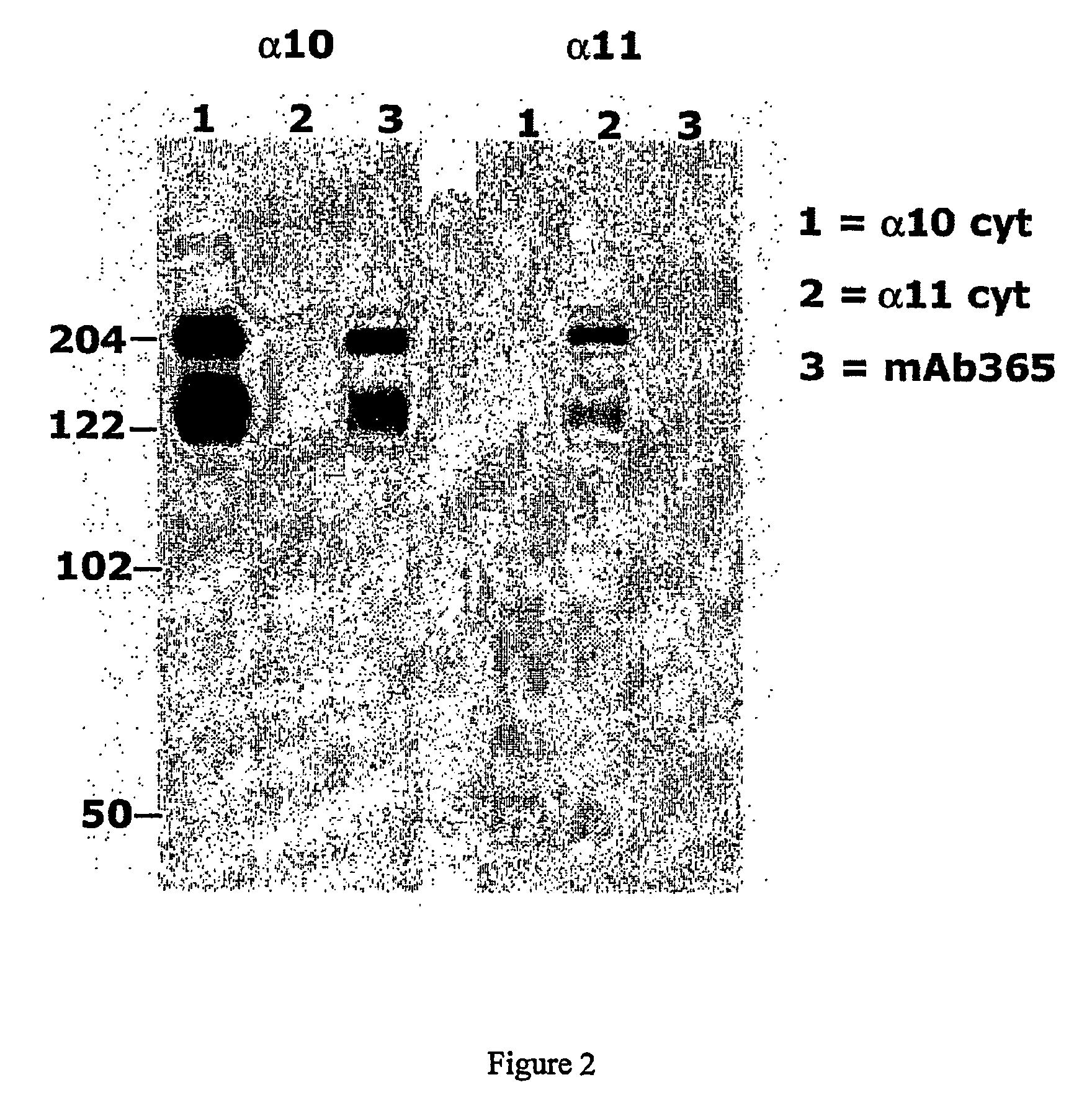
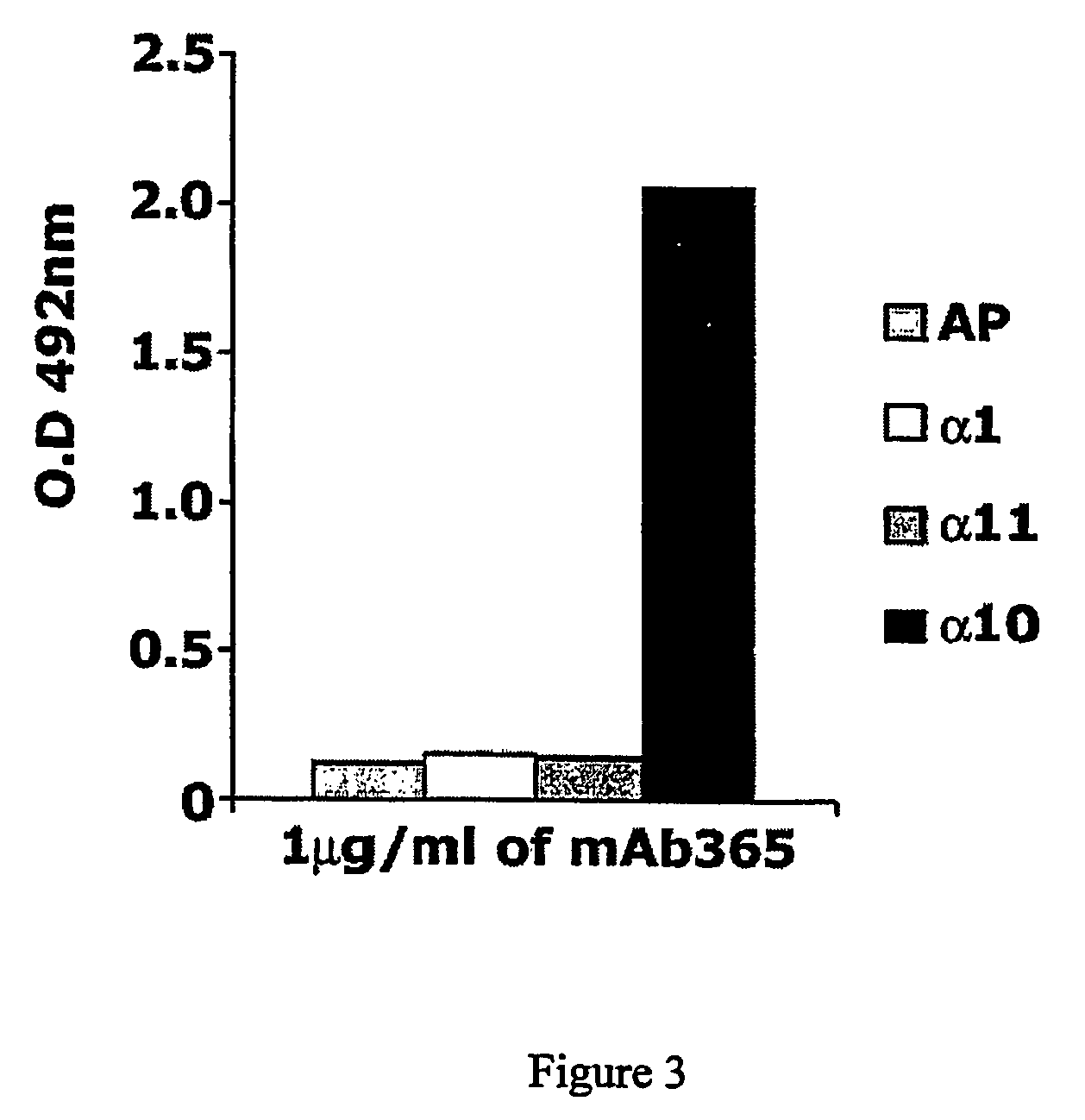
Monoclonal antibody capable of binding integrin alpha 10 beta 1
The present invention provides a monoclonal antibody or a fragment thereof binding to the extracellular I-domain of integrin alpha10beta1 and a hybridoma cell line deposited at the Deutsche Sammlung von Microorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH under the accession number DSM ACC2583. Furthermore, the present invention also provides a monoclonal antibody or a fragment thereof binding to the extracellular I-domain of integrin alpha10beta1 produced by the hybridoma cell line deposited. Method and uses of the antibody or a fragment thereof in identifying and selecting cells of a chondrogenic nature for treatment purposes, in particular for the identification and isolation of chondrocytes, mesenchymal progenitor cells and embryonic stem cells for tissue engineering of cartilage, or for identifying diagnostic and therapeutic tools in studying the biological role and the structural / functional relationships of the integrin alpha10beta1 with its various extracellular matrix ligands are also included.
Owner:XINTELA AB
Cartilage tissue engineering repair bracket and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103877616AHigh mechanical strengthImprove induction abilityCoatingsProsthesisBone Marrow Stromal CellCartilage repair
The invention discloses a cartilage tissue engineering repair bracket and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the cartilage tissue repair field. The bracket comprises natural high polymer water-gel and decalcified bone matrix which is coupled with affinitive peptides of mesenchymal stem cells on surface; the affinitive peptides of the mesenchymal stem cells are coupled on the surface of the decalcified bone matrix to obtain the cartilage tissue engineering repair bracket with special mesenchymal stem cell affinity. By being placed in a cartilage defective region, the cartilage tissue engineering repair bracket can collect a plurality of BMSC (bone marrow stromal cells); and in the bracket, under mating effect of the natural high polymer water-gel and the decalcified bone matrix, the BMSC can be retained in the cartilage defective region for a long time, so that the cartilage repair has a longer curative effect period. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the bracket, wherein the natural high polymer water-gel aqueous liquor is injected in the decalcified bone matrix which is coupled with affinitive peptides of mesenchymal stem cells on surface to carry out gelation reaction to obtain the bracket with higher mechanical strength and inducibility. The method is simple and high in practicability.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Cartilage tissue engineering scaffold material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103638562AControl mechanical propertiesControl degradabilityProsthesisSide chainBone tissue engineering
The invention discloses a cartilage tissue engineering scaffold material and a preparation method thereof. The scaffold material is a three-dimensional porous structure formed by using sodium alginate and chitosan as a base material, and enabling the carboxyl on a side chain of the sodium alginate activated by activation cross-linking agent to react with amino group of chitosan, wherein molar ratio of the sodium alginate carboxyl to the chitosan amino group is (3:7)-(7:3), and the final product only contains two components, sodium alginate and chitosan. The three-dimensional porous scaffold provided by the invention has good biocompatibility, and is suitable for the cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Three-dimensional porous tissue engineering bracket material, preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to three-dimensional porous engineering support material, comprising poly butylene succinate PBS and polycaprolactone PCL, wherein, the weight proportion is that the poly butylene succinate is 90 to 10 shares and the polycaprolactone is 10 to 90 shares. The invention also relates the preparation of the material, which is characterized in that the pore-foaming agent is arranged in a mold evenly and then the PBS / PLC blending chloroform solution is poured in; the support rudiment is put in a hood for 24 hours before immersing deionized water for 2 to 4 days; the PBS / PLC support material can be obtained after drying in vacuum. The invention relates to application of the material also, which mains that the material can be used as supports of bone or cartilage tissue engineered cells for repairing and restructuring the bone or cartilage tissue organ. The support material has the advantages of even inner hole structure and good communication between the holes, namely the hold diameter is between 10 to 500Mum and the porosity is between 70 to 91 percent, as well as the advantages of steady structure and easy preparation technology.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Tissue engineering scaffold material for repairing cartilage defects and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101979105AEasy to prepareFor long-term storageProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingCartilage tissue engineering
The invention discloses a tissue engineering scaffold material for repairing cartilage defects and a preparation method thereof. The tissue engineering scaffold material is prepared by the following steps of: cleaning the spongy bone at the shoulder blade of a fresh pig; cutting the spongy bone into small blocks with diameter of between 5 and 10mm and thickness of between 3 and 5mm; degreasing, decalcifying and deproteinizing; immersing with alcohol for 30 minutes; and air-drying, wherein the decalcifying time is 6 hours. The prepared demineralized spongy bone matrix (DSBM) has the characteristics of relatively simple and convenient preparation method, and capacity of being obtained on a large scale, can be stored for a long time at a low temperature and is economic and cheap. The material can be prepared into different shapes and sizes according to the shapes of the defects to be repaired, so the material is convenient to apply. The DSBM remains a natural netlike gap structural system of the pig spongy bone, has high cellular compatibility, biocompatibility and degradability and is a very good cartilage tissue engineering scaffold material.
Owner:昆明医学院第一附属医院
Cartilage tissue engineering rack and its application
The present invention provides one kind of double layer cartilage tissue engineering rack comprising one compact layer and one loose layer communicated each other. The rack has excellent biological performance, sufficient cell tissue holding space, certain blocking effect and capacity to allow nutritious matters to pass through freely. It is used in repairing human body's cartilage tissue and constructing extracorporeal cartilage tissue. It is made through preparing solution of different concentrations with acid extracted collagen, freeze drying to obtain collagen sponge, flattening, injecting collagen solution of different concentration, and drying for the second time to obtain the double layer cartilage tissue engineering rack. The rack has the pore size controlled through controlling the concentration of the solution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Three-dimensional stephanoporate organization engineering bracket material, fibre cementing method preparing same and applications thereof
InactiveCN101249277AAdjust the micropore sizeRegulates biodegradation rateBone implantPorosityRoom temperature
The invention relates to a three-dimensional porous tissue engineering stent material, a fiber-gluing preparation method thereof and the application thereof, The material comprises poly butylene succinate and polycaprolactone; the weight portion is: poly butylene succinate 90 to 10 parts, polycaprolactone 10 to 90 parts; preparation: 1) mixing poly butylene succinate and polycaprolactone to obtain fiber by melt spinning; 2) cutting fiber and filling the fiber into a module, the fiber being arranged in an even structure; 3) putting the mould into a vacuum oven with 50 to 90 DEG C and keeping for 5 minutes to 1 hour, demoulding at room temperature and drying in vacuum after cooling, and obtaining three-dimensional tissue engineering stent material; 4) sterilizing and packing the three-dimensional porous tissue engineering stent material; The material has the application of being used as bone or cartilage tissue engineering cytoskeleton for repairing and rebuilding of bone or cartilage tissue organ. The tissue engineering stent material has evenly structured, internal pores that communicate with each other. The aperture of the pores is 10 to 500 Mum, and the porosity changes between 70 to 91 percent, so that the systematic structure of the stent is stable and easy to produce.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Cartilage tissue engineering bracket and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a cartilage tissue engineering bracket and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of cartilage repair. Components of the bracket comprise natural high polymer water-gel and decalcified bone matrix. By combining the natural high polymer water-gel with the decalcified bone matrix, the bracket not only has plasticity, adhesion and injection of the water-gel, but also has various advantages brought by the natural biological bracket material; and moreover, the decalcified bone matrix can provide a collagenous fiber net rack, and provides higher mechanical strength and inducibility for the prepared bracket, and further promotes adhesion, multiplication and differentiation of the cells. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the cartilage tissue engineering bracket, which comprises steps of injecting prepared natural high polymer water-gel liquor in the decalcified bone matrix, so that the natural high polymer water-gel is completely infiltrated into gaps of the decalcified bone matrix, and carrying out gelatinization reaction at a preset temperature to obtain the cartilage tissue engineering bracket with higher mechanical strength and higher inducibility. The method is simple, easy to operate and high in practicability.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Polycaprolactone/polyethyleneglycol tissue engineering bracket material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a polycaprolactone / polyethyleneglycol tissue engineering stent material and a preparation method thereof. The components of the material include: polycaprolactone and polyethylenelycol with the proportion of 100 to 0 to 40 to 60. The preparation method includes: (1) the polycaprolactone and the polyethylenelycol with a certain proportion are dissolved in cosolvent to obtain uniform transparent solution; (2) the solution is spun into a fiber felt of nano / secondary micron grade by the technique of electrostatic spinning; (3) a vacuum oven is vacuumed to remove the residual solvent of the fiber felt; (4) the fiber felt is took out, and is overlapped and filled in the mold with a specific shape; (5) the mold is put in the vacuum oven and is took out to be cooled for the UV sterilization after being heated at the constant temperature near the blend melting temperature. The stent material system of the invention has the advantages of stable structure, uniform structure of internal holes and is mutually communicated with holes and can be used as a cartilage tissue engineering cell stent.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Hyaluronic acid supramolecular hydrogel for three-dimensional culture of chondrocytes, and preparation and application of hyaluronic acid supramolecular hydrogel
ActiveCN111892719AImprove repair effectEvenly dispersedSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture supports/coatingFunctional monomerCartilage repair
The invention belongs to the technical field of regenerative medical materials, and discloses hyaluronic acid supramolecular hydrogel for three-dimensional culture of chondrocytes, and preparation andapplication of the hyaluronic acid supramolecular hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: with water as a reaction medium, carrying out a copolymerization reaction on methacrylic anhydride modified hyaluronic acid, a double-bond functionalized ureido pyrimidinone functional monomer and 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl methacrylate under the action of an initiating system, and carrying out subsequent treatment to obtain the hyaluronic acid supramolecular hydrogel. The hydrogel is used in the field of cartilage tissue engineering, and is used for three-dimensional culture of chondrocytes and preparation of cartilage repair materials. The hydrogel disclosed by the invention has sol-gel conversion and self-repairing properties, uniform dispersion of the chondrocytes can be easily realizedby sol at a low temperature, and the sol can undergo phase change to form gel after being conveyed to a cartilage injury part, so in-situ fixation of the chondrocytes is realized; and the formation of a dynamic three-dimensional microenvironment of the hydrogel is beneficial for the maintenance of chondrocyte functions and the secretion of cartilage characteristic matrixes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Tissue engineering cartilage composite scaffold and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105288737AGood biocompatibilityGood biomechanical strengthProsthesisCartilage cellsCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention belongs to the field of cartilage tissue engineering. The invention discloses a tissue engineering cartilage composite scaffold, which is constructed based on an extracellular matrix-derived cartilage micro-tissue, and a preparation method of the composite scaffold. Specifically, a cartilage extracellular matrix-derived micro-carrier is prepared from fresh cartilage through such processes as wet pulverization, sieving, decellularizing and the like; and the prepared micro-carrier can be used as a seed cell amplification vector. By virtue of a bioreactor, cartilage cells are rapidly amplified by the micro-carrier and the phenotype of the cartilage cells is kept; and meanwhile, the induced differentiation of stem cells towards the cartilage is also promoted and the cartilage micro-tissue is formed. By filling the cartilage micro-tissue in pores of a three-dimensional porous scaffold which is good in mechanical performance, the tissue engineering cartilage composite scaffold is constructed. The composite scaffold is good in mechanical performance, rich in natural cartilage extracellular matrix components and conducive to the induced differentiation of the stem cells towards the cartilage, and the composite scaffold is capable of providing a good microenvironment for the growth of seed cells and is expected to accelerate the in vivo construction speed of the tissue engineering cartilage.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
Method for preparing double-layer bionic cartilage tissue engineering scaffold
InactiveCN101810885AThe overall thickness is thinGood mechanical propertiesProsthesisCartilage injuryCartilage cells
The invention discloses a method for preparing a double-layer bionic cartilage tissue engineering scaffold, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a substrate; secondly, preparing the double-layer bionic cartilage tissue engineering scaffold on the surface of the substrate; and finally, soaking the double-layer bionic cartilage scaffold on the surface of the substrate by usingsolution of NaOH, and peeling the double-layer bionic cartilage scaffold from the substrate. The method has simple operation and high stability; the prepared double-layer bionic cartilage scaffold has a thin thickness and good mechanical properties and is favorable for clinical application; the scaffold is molded integrally; a vertical hole is tightly connected with a round hole to avoid the problem of breaking away from each other; the structure of the scaffold is similar to a natural cartilage structure and is hopeful to better maintain the phenotype of cartilage cells and improve the repairing effect on cartilage injuries; and the cartilage scaffold can be directly combined with a substrate comprising polylactic acid (PLA) / bone powder to form a bone cartilage scaffold used for repairing bone cartilage simultaneous colobomata, and a cartilage layer part still has a double-layer structure.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of silk fibroin-poly(hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate) composite fiber membrane
InactiveCN102102278AGood biocompatibilityGood mechanical propertiesFilament/thread formingConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsPorosityFiber
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silk fibroin-poly(hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate) composite fiber membrane, which comprises the steps of: mixing a prepared silk fibroin solution with a poly(hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate) solution to prepare a spinning solution, and conducting electrostatic spinning and aftertreatment. Based on the electrostatic spinning method, the composite fiber membrane is prepared, and the fiber membrane has good biocompatibility of the silk fibroin and the excellent mechanical performance of the poly(hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate) simultaneously, is more applicable to the biomedical field, and is expected to be used as a material for engineering of skin, nerves and cartilaginous tissues. The prepared composite fiber membrane has higher porosity, good mechanical performance, good air permeability and moisture permeability and large liquid absorption amount, can be degraded in human body and can promote tissue repair; and the preparation method has simple process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Monoclonal antibody capable of binding integrin alpha 10 beta 1
The present invention provides a monoclonal antibody or a fragment thereof binding to the extracellular I-domain of integrin alpha10beta1 and a hybridoma cell line deposited at the Deutsche Sammlung von Microorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH under the accession number DSM ACC2583. Furthermore, the present invention also provides a monoclonal antibody or a fragment thereof binding to the extracellular I-domain of integrin alpha10beta1 produced by the hybridoma cell line deposited. Method and uses of the antibody or a fragment thereof in identifying and selecting cells of a chondrogenic nature for treatment purposes, in particular for the identification and isolation of chondrocytes, mesenchymal progenitor cells and embryonic stem cells for tissue engineering of cartilage, or for identifying diagnostic and therapeutic tools in studying the biological role and the structural / functional relationships of the integrin alpha10beta1 with its various extracellular matrix ligands are also included.
Owner:XINTELA AB
Application of electrical stimulation for functional tissue engineering in vitro and in vivo
InactiveUS8367410B2Highly integratedImprove functionalityMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processExcitable cellIt integration
The present invention provides new methods for the in vitro preparation of bioartificial tissue equivalents and their enhanced integration after implantation in vivo. These methods include submitting a tissue construct to a biomimetic electrical stimulation during cultivation in vitro to improve its structural and functional properties, and / or in vivo, after implantation of the construct, to enhance its integration with host tissue and increase cell survival and functionality. The inventive methods are particularly useful for the production of bioartificial equivalents and / or the repair and replacement of native tissues that contain electrically excitable cells and are subject to electrical stimulation in vivo, such as, for example, cardiac muscle tissue, striated skeletal muscle tissue, smooth muscle tissue, bone, vasculature, and nerve tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for three-dimensional cartilage tissue engineering using bone marrow cells in tissue engineering bone marrow cells in simulated microgravity environment
This invention provides a method for three-dimensional cartilage tissue engineering by culturing bone marrow cells in a simulated microgravity environment that is realized by a bioreactor such as an RWV.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Cartilage tissue engineering scaffold composite material
The present invention uses L-lactic acid polymer whose molecular weight is 80000-200000 and calcium polyphosphate fibre whose mean length is 5-15 mm and adopts dissolving casting granule leaching process to obtain the invented skeleton material capable of being transplanted in the body. As compared with tissue engineering scaffold material of existent technology said invented product possesses high voidage, good biological degradable property and physical mechanical property, and possesses three-D communication, micropore and reticular microstructure, so that it can completely meet the basic requirements for tissue engineering.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA +1
Cartilage tissue engineering scaffold and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a cartilage tissue engineering scaffold and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of cartilage repair. The cartilage tissue engineering scaffold comprises a chitosan hydrogel outer skeleton and at least one decalcified cortical bone matrix microsphere coated in the chitosan hydrogel outer skeleton and with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell affinity peptide modified on the surface, wherein diameter of each decalcified cortical bone matrix microsphere is 500-800 micrometers. The cartilage tissue engineering scaffold has high rheological property, easiness in plasticizing, biomechanical strength and performance of specifically gathering bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, thereby being suitable for cartilage defect areas different in shape, lasting in effect and capable of acquiring more differentiated cartilage cells, has high cartilage tissue repair ability and is convenient for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Preparation technology of biphasic bone and cartilage tissue engineering scaffold material
InactiveCN102872480AUniform pore size distributionGood biocompatibilityProsthesisFreeze-dryingRefrigerated temperature
The invention discloses a preparation technology of biphasic bone and cartilage tissue engineering scaffold material. Firstly chitosan and collagen powder are added into acetate solution and laid in a refrigerator to be preserved; then PLA solution is prepared, and bone dust is put into the PLA solution and is uniformly mixed and stirred; then prepared PLA / bone dust solution is injected into a die to be prefrozen; then collagen / chitosan solution is added into the prefrozen die to be prefrozen, and a scaffold sample is obtained after freeze drying; and finally the bone and cartilage biphasic scaffold conducted to freeze drying is taken out from the die. The preparation technology ensures that a bone layer scaffold has the hardness and the strength approximate to that of natural bone tissue, is not only beneficial to the repair of cartilage tissue, but also convenient for clinically operating and fixing the scaffold; and meanwhile, a cartilage layer scaffold is provided with a multilayer structure containing perpendicular pore canals, is convenient for guiding cells on the scaffold to grow at a state close to that of a natural cartilage laminated structure, and improves the injury repair effect of cartilage.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of silk fibroin and chitosan three-dimensional scaffold material
InactiveCN105521522AMeet the requirements of physical and chemical propertiesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationBone tissue engineeringThree dimensional scaffolds
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silk fibroin / chitosan three-dimensional scaffold material, and belongs to the field of the preparation of a cartilage tissue engineering scaffold material. The invention provides a method for preparing the three-dimensional scaffold material from silk fibroin and chitosan. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing the silk fibroin; and then, mixing and processing the silk fibroin and the chitosan, so that the silk fibroin / chitosan three-dimensional scaffold material is obtained. The silk fibroin / chitosan three-dimensional scaffold material prepared by the method conforms to the requirements on the physicochemical properties of the cartilage tissue engineering scaffold material; and the scaffold material is expected to become a relatively ideal scaffold material for cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:SHAANXI YUHANG ELECTRONICS
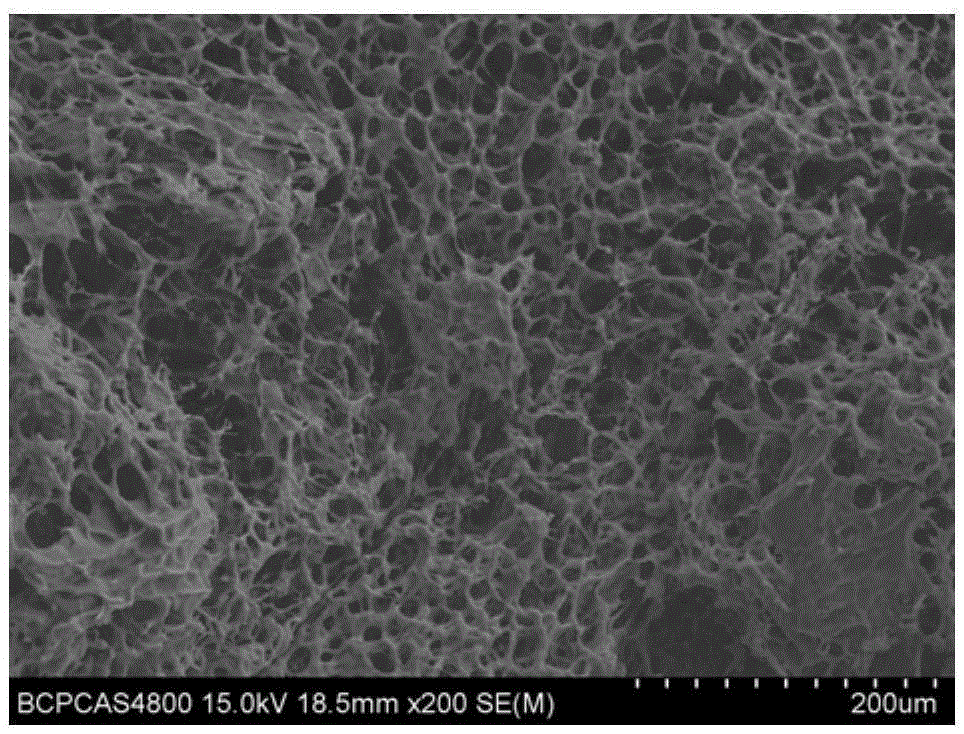
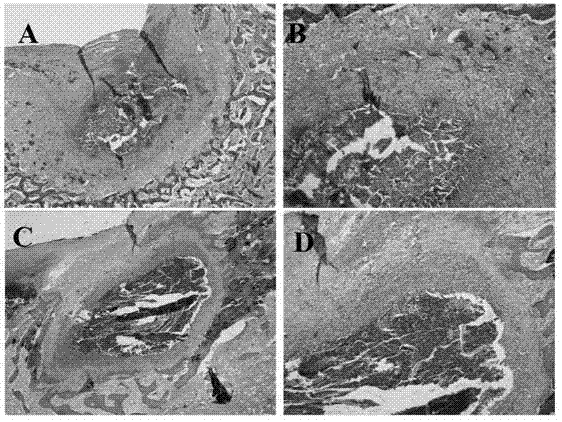
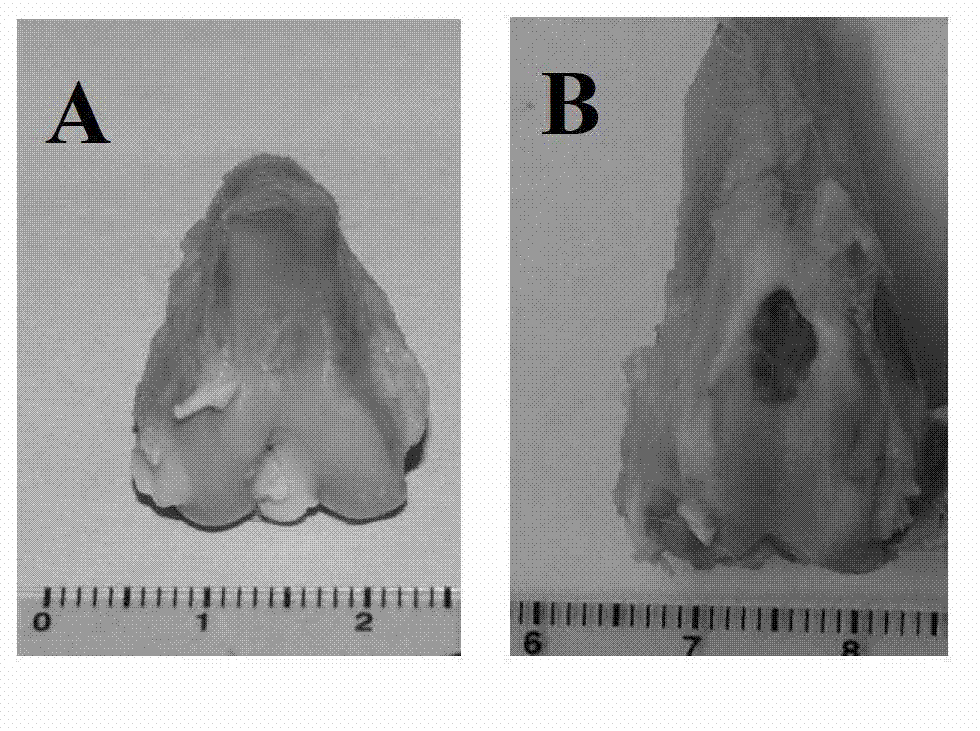
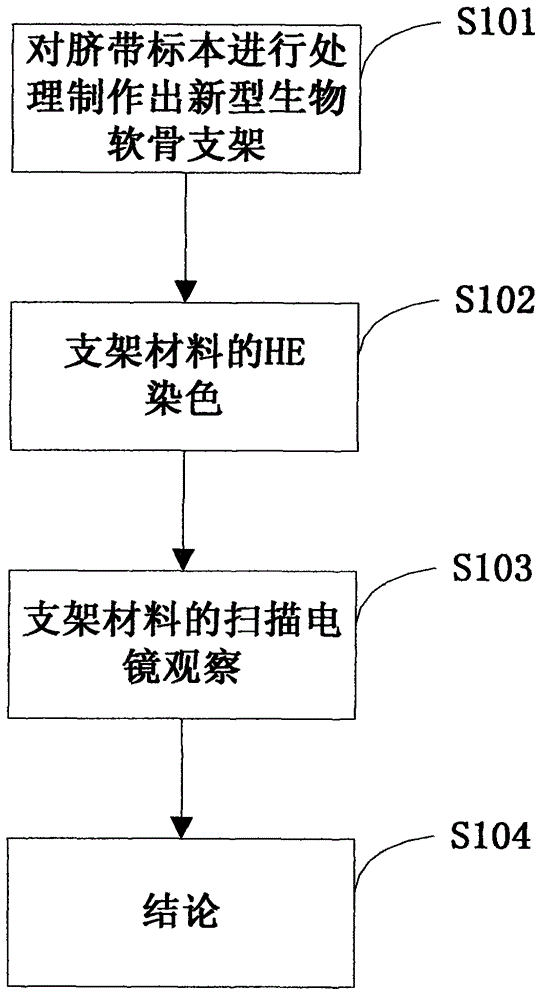
Method for manufacturing novel biological cartilage support by using umbilical cord Wharton jelly
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a novel biological cartilage support by using umbilical cord Wharton jelly. The method comprises the following steps of: treating an umbilical cord specimen to manufacture a novel biological cartilage support; performing paraffin embedding on a support material, slicing, performing H ematine (HE) dyeing, and observing a porous structure of the material under a light microscope; slicing the manufactured three-dimensional porous support into slices of 50 micrometers, spraying platinum on the surfaces of the slices, observing under a scanning electron microscope, shooting a scanned photograph by selecting appropriate multiples, and observing the appearance of the composite support material; and performing cell-free treatment on the umbilical cord Wharton jelly by combining a physical method and a chemical method, forming by using a freeze-drying method to manufacture the three-dimensional porous sponge-shaped support, wherein cells are removed completely, and a collagen structure is not damaged. According to the method, the umbilical cord Wharton jelly is subjected to the cell-free treatment by combining the physical method and the chemical method, and is formed by a freeze-drying method to manufacture the three-dimensional porous sponge-shaped support successfully, the cells are removed completely, and the collagen structure is not damaged, so that the three-dimensional porous sponge-shaped support is suitable to be used as a support carrier in cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:吴鸿
Separation culture method for cartilage stem cells
InactiveCN102399745AStrong expansion abilityPrecise definitionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsFibroblastCell separation
The invention provides a separation culture method for cartilage stem cells. In the method, the cartilage stem cells are screened from cartilage tissue cells; fibroblast-like cells maintained under the culturing condition of a specific culture medium have the capabilities of differentiating bones, cartilages and fat; and compared with adult cells, the cartilage stem cells have good amplification capabilities, and can pass on for over 15 generations without changing the original characteristics after being obtained from a primary generation. In the method, the cartilage stem cells are obtained by screening and purifying under a specific culturing condition, so that the content of the cartilage stem cells is over 95 percent. A technology disclosed by the invention contributes to harvesting cartilage tissue specific stem cells, and can be applied to bone and cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods and reagents for tissue engineering of cartilage in vitro
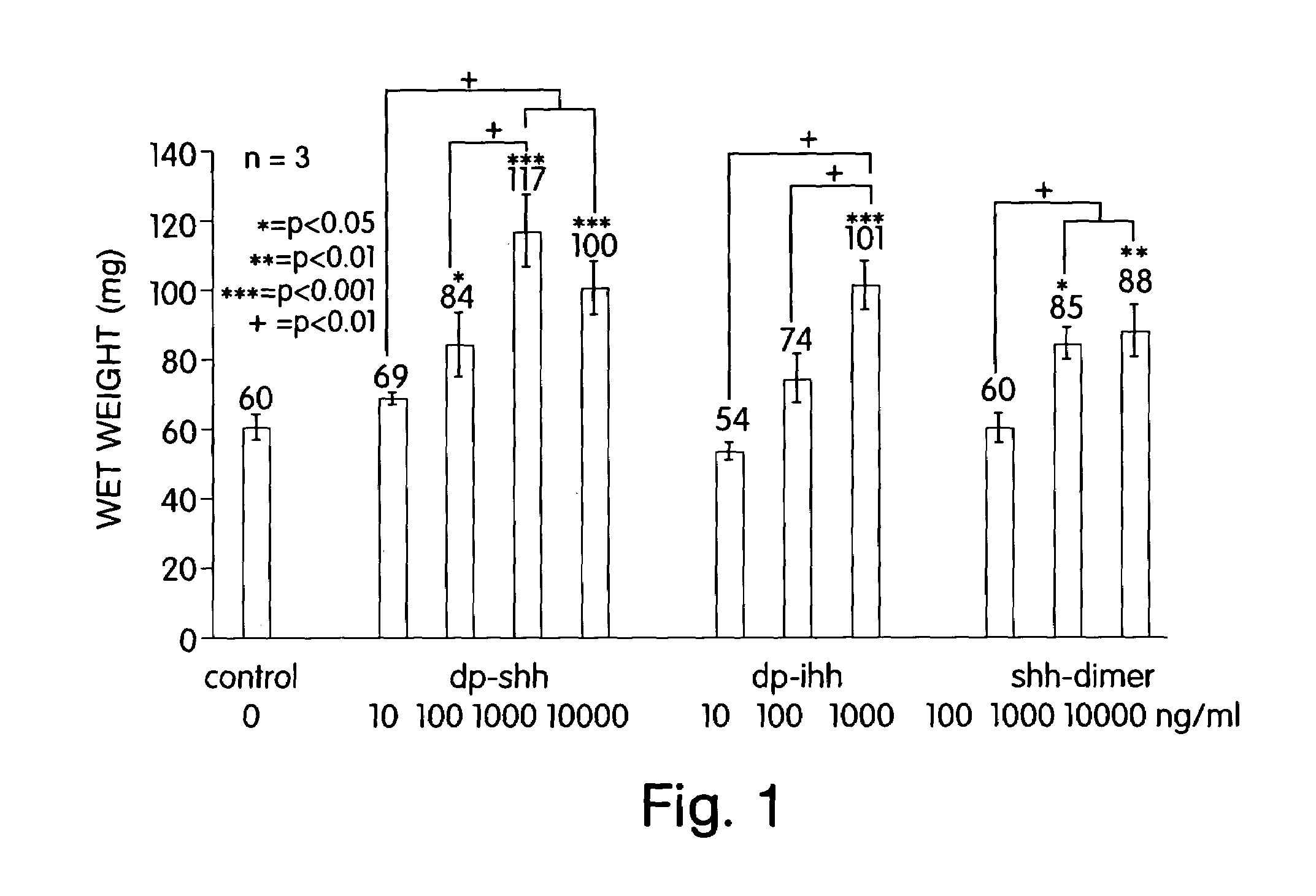
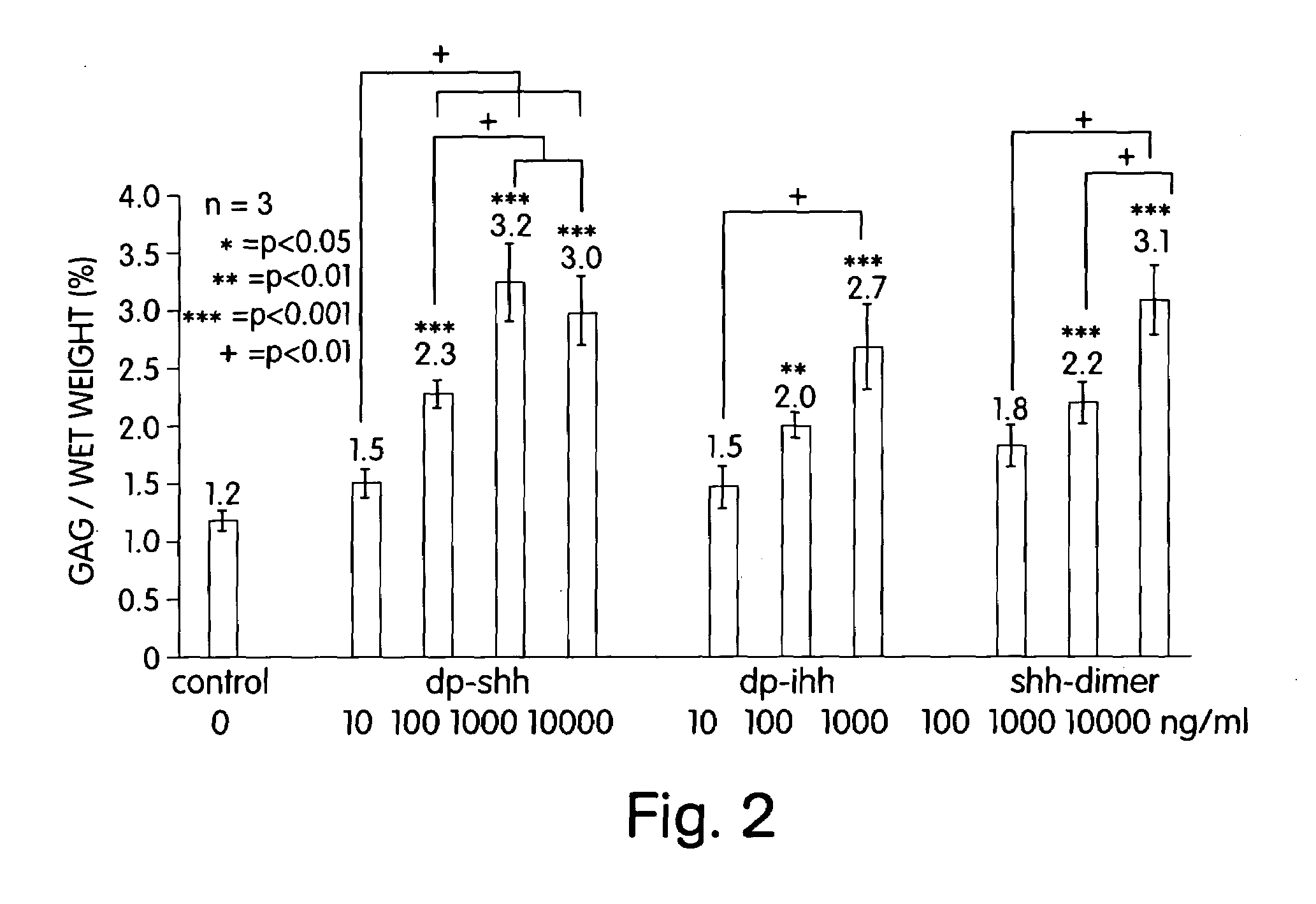
The present invention makes available an optimal concentration of a hedgehog polypeptide for modulating growth and / or cartilage production by chondrocytes. The present invention allows for improvements in the culturing of chondrocytes to develop cartilaginous tissue ex vivo suitable for implantation to replace damaged or deteriorated cartilage in a patient.
Owner:CURIS INC
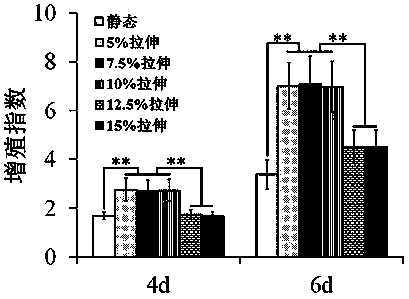
Mechanical environment culture method for improving proliferation activity of chondrocytes and maintaining phenotype of chondrocytes
InactiveCN109182257AIncrease proliferative activityImprove proliferative abilityCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCultured cellProliferation activity
The invention discloses a mechanical environment culture method for improving the proliferation activity of chondrocytes and maintaining phenotype of chondrocytes. The invention comprises the following steps: step 1, carrying out separation, culture and identification of chondrocytes; 2, inoculating the chondrocytes into a culture apparatus, loading the chondrocytes during the culture process, andculturing the chondrocyte in a mechanical environment so that the chondrocytes are mechanically stimulated. Under culture in mechanical environment, the proliferation of chondrocytes is improved, andco-cultured cells is promoted to have a good cartilage phenotype, which can quickly and effectively provide excellent seed cells for cartilage tissue engineering, and solve the clinical and practicalneeds of tissue engineering cartilage seed cells.
Owner:WEIFANG MEDICAL UNIV
Growth-factor-chitosan-microsphere loaded DBM support joint cartilage repairing material
InactiveCN104056304AEasy to prepareConvenient natural mesh void structure systemProsthesisShoulder bonesMicrosphere
The invention discloses a growth-factor-chitosan-microsphere loaded DBM support joint cartilage repairing material. A method for preparing the growth-factor-chitosan-microsphere loaded DBM support joint cartilage repairing material includes the following steps: (1) preparing a DBM: adopting a fresh pig shoulder blade, removing the periosteum, the cartilage and the soft tissues, taking the cancellous bone of the shoulder blade, preparing the cancellous bone to be in a cake shape, carrying out repeated stirring and washing with flowing water to remove the marrow, the bloodiness and the surface grease, and after washing is carried out through the tap water, placing the cancellous bone into an environment at -80 DEG C for storage for three days to carry out proper processing; (2) preparing chitosan sustained release microspheres; (3) preparing wrapping growth factor microspheres, and calculating the encapsulation efficiency and the drug loading capacity; (4) preparing a growth-factor-chitosan-sustained-release-microsphere loaded DBM composite, and measuring amido bond connection after cross bonding is carried out a DBM support and the microspheres through EDC with the infrared ray method. The growth-factor-chitosan-microsphere loaded DBM support joint cartilage repairing material has the good cellular and biology compatibility and the good degradability, and is a good cartilage tissue engineering support material.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF KUNMING MEDICAL UNIV
Three-dimension porous tissue engineering carrier material and preparation and application
InactiveCN101147812AGood 3D through-hole structureUniform heat conductionProsthesisPorosityMicrometer
The present invention relates to a three-dimensional porous tissue engineering carrier material, its preparation and application. Said three-dimensional porous tissue engineering carrier material includes three-dimensional porous structure, its internal porous structure is uniform, three-dimensional through degree is above 90%, pore size is 50-500 micrometer and porosity is 65-90%. Its preparation method includes the following steps: using polyhydroxybutyrate valerate (PHBV) and polycaprolactone (PCL) as raw material, mixing them, melting and spinning to obtain fibre whose diameter is 10-500 micrometer, cutting said fibre to make said fibres have identical length, making said fibres be uniformly arranged and filled into a mould, sealing said mould for 5min-1n at 50-80deg.C, demoulding, sterilizing and packaging so as to obtain the invented product. Said product can be used for repairing or reconstructing some tissue organs.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com