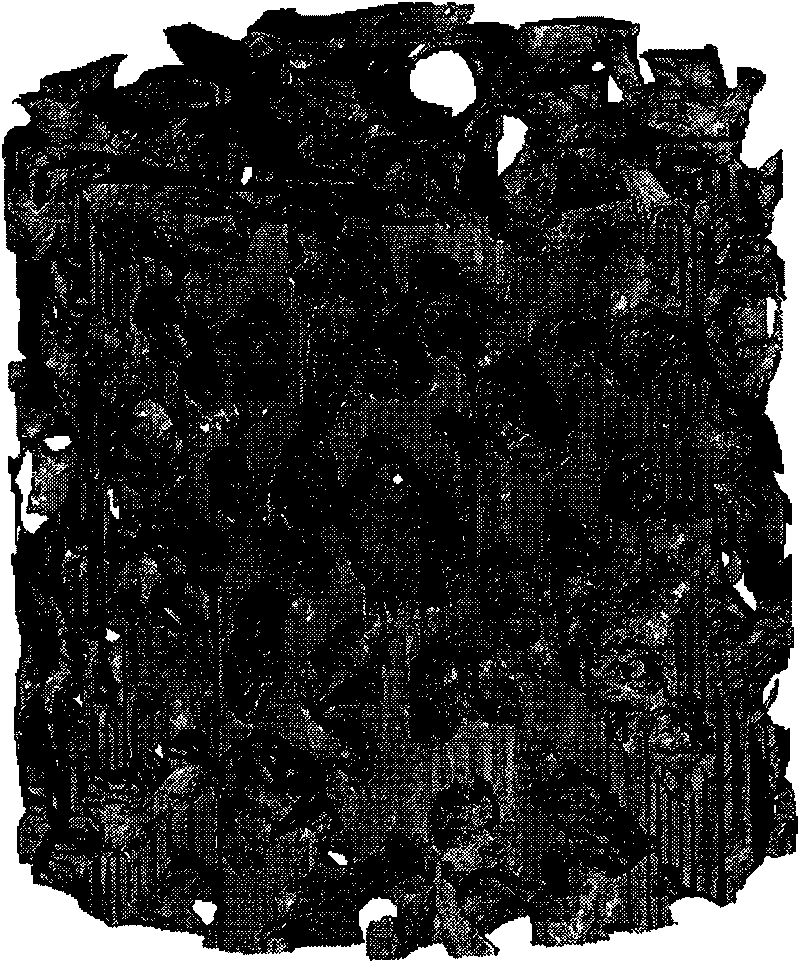Patents
Literature
63 results about "Spongy bone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spongy bone is found on the inside of some bones, and it is surrounded by the stronger, more protective compact bone. Cancellous bone tissue is found at the end of long bones, at joints, and in the vertebrae, the bones of the spinal column. Cancellous bone makes up a larger portion of the bone than the external compact bone tissue.
Intersomatic setting and fusion system
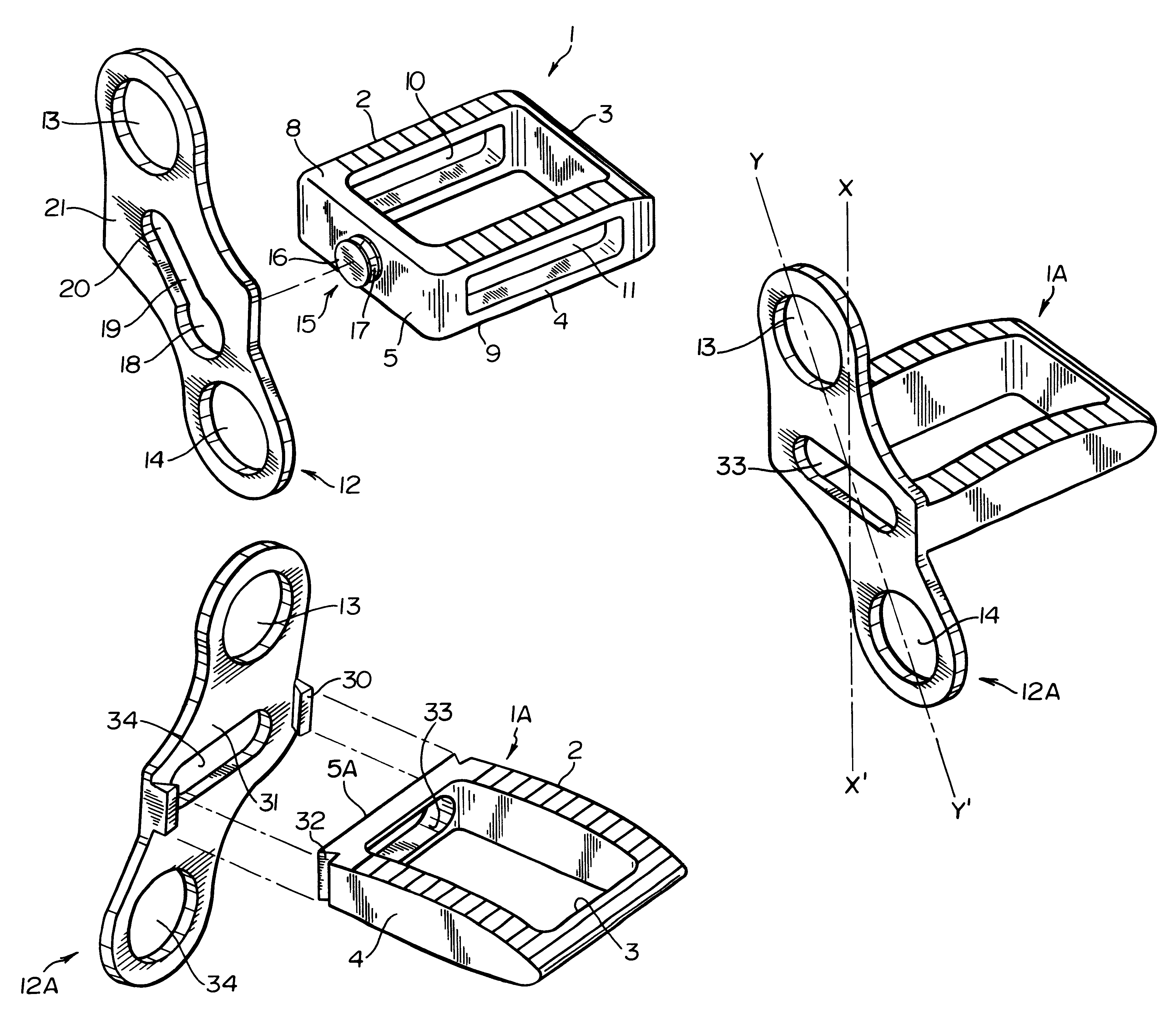
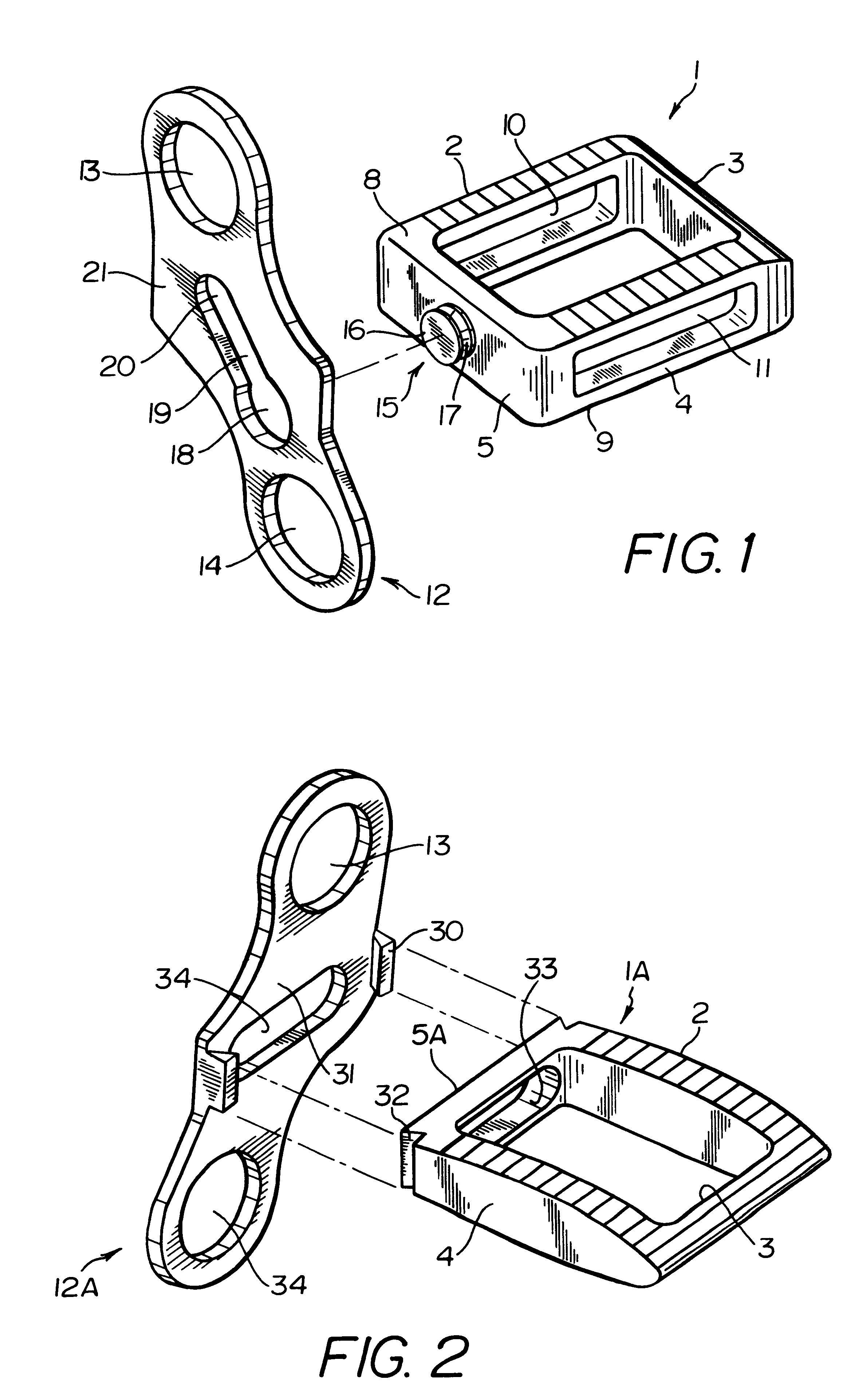
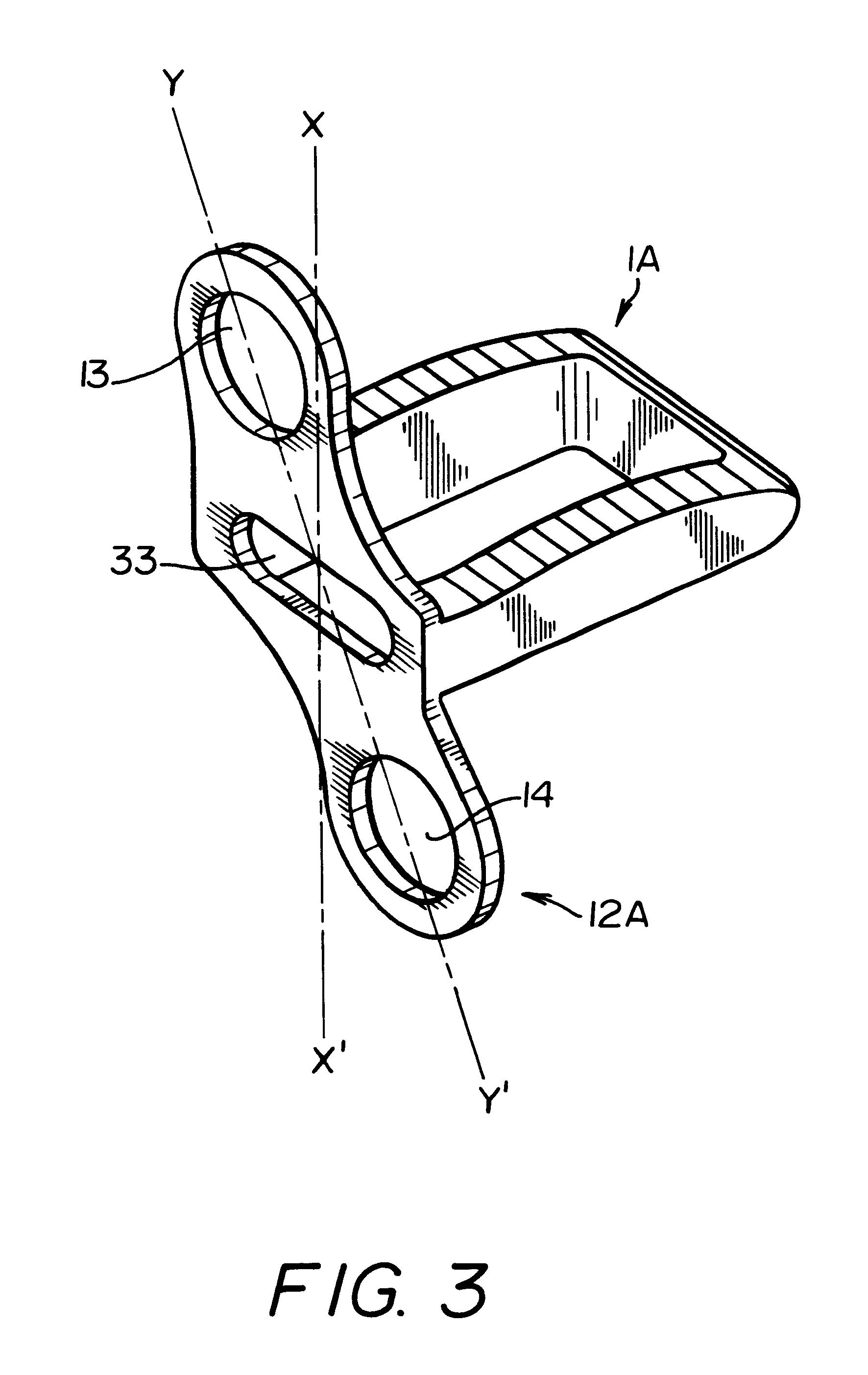
A system for intersomatic fusion and setting of vertebrae. The system includes at least one open internal cage arranged for receiving spongy bone or bone substitute and is designed to be interposed between two vertebrae during diskectomy. The cage (1) includes on its anterior face (5) an external element forming a plate (12) extending in a plane substantially perpendicular to the insertion plane of the cage (1), and has at each of its ends an anchor device (13,14) adapted for anchoring to at least two adjacent vertebrae to be secured to each other by the cage (1). The system can be separated into two parts, the cage and the plate.
Owner:SCIENTX
Pore network model (PNM)-based bionic bone scaffold designing method
InactiveCN102087676APromote differentiationImprove liquidityBone implantSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork modelImaging data
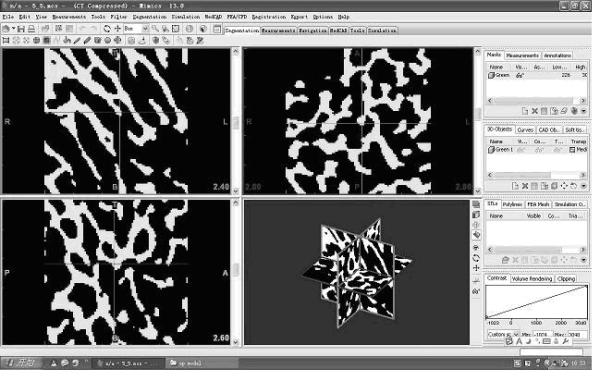
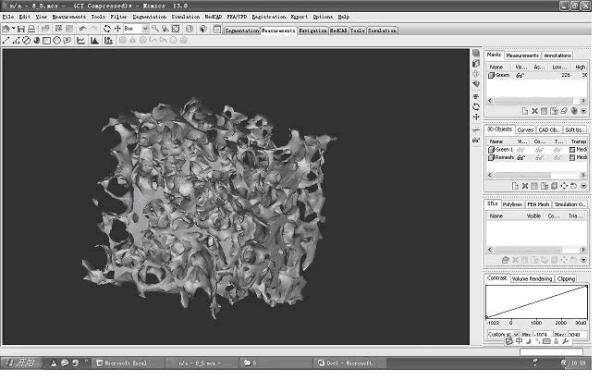
The invention relates to a pore network model (PNM)-based bionic bone scaffold constructing method. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a cross section image of microscopic three-dimensional micropore structural information and three-dimensional space position density information of a human bone by a micro computed tomography (Micro-CT) technology; performing threshold value processing to acquire binarized image data; extracting a spongy bone part, and measuring by using Mimics software to acquire porosity, penetration rate, aperture and the like; programming PNM bone scaffold parameters according to a PNM principle by using the acquired bone overall dimension data and internal size data; acquiring a generating program of the bone scaffold by using a programming tool C++ and OPENGRIP language programming; generating a three-dimensional model of the PNM bionic bone scaffold by using a Unigraphics (UG) secondary development platform; and finally leading the PNM bionic bone scaffold into the Mimics software to verify the parameters, such as the aperture, the penetration rate and the like of the PNM bionic bone scaffold. The bone scaffold well imitates a natural bone, and has high performance similar to that of the natural bone; and a good porous structure and the high penetration rate are favorable for differentiation and flowing of bone derived cells.
Owner:上海蓝衍生物科技有限公司
Dental implant fixture
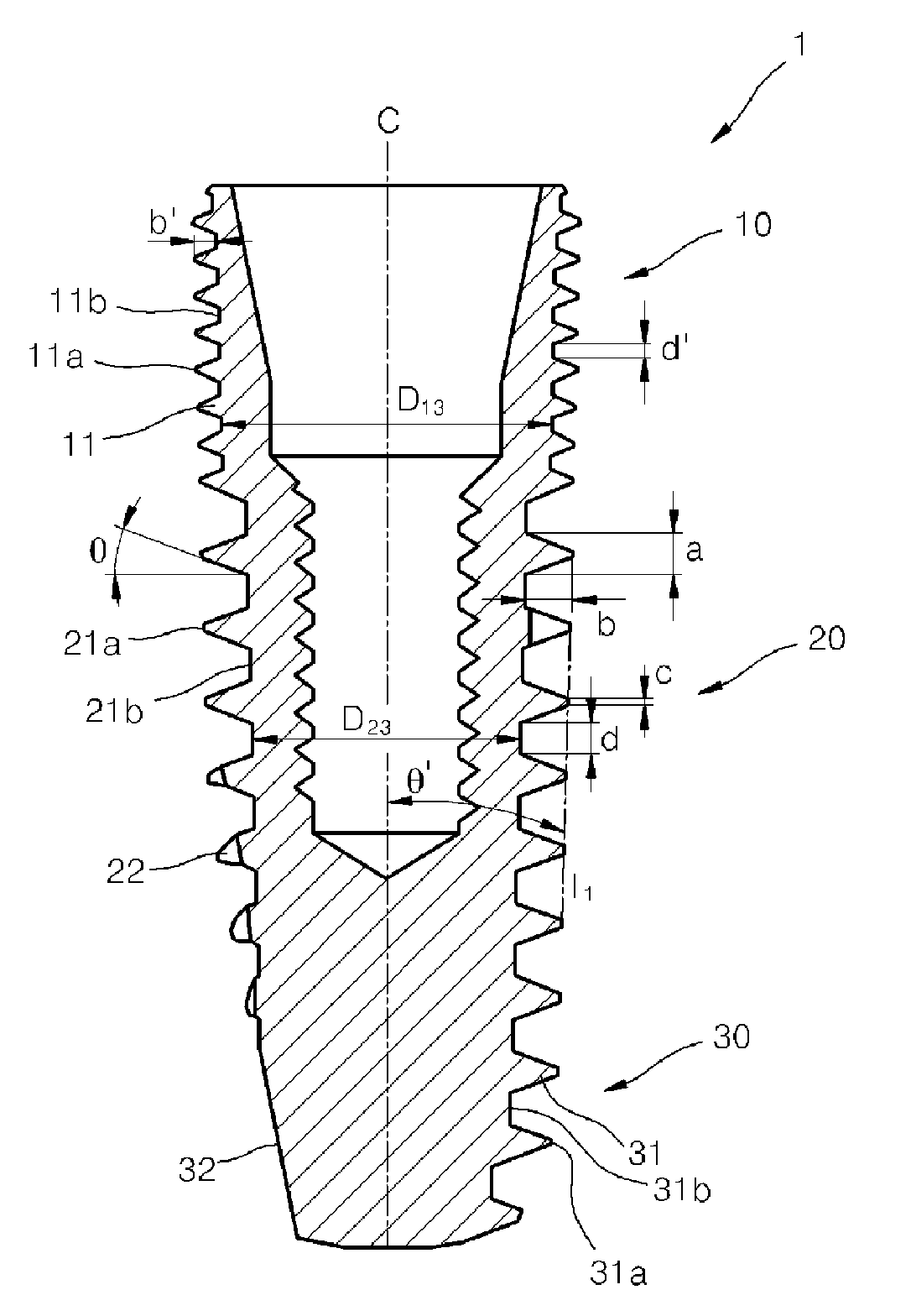
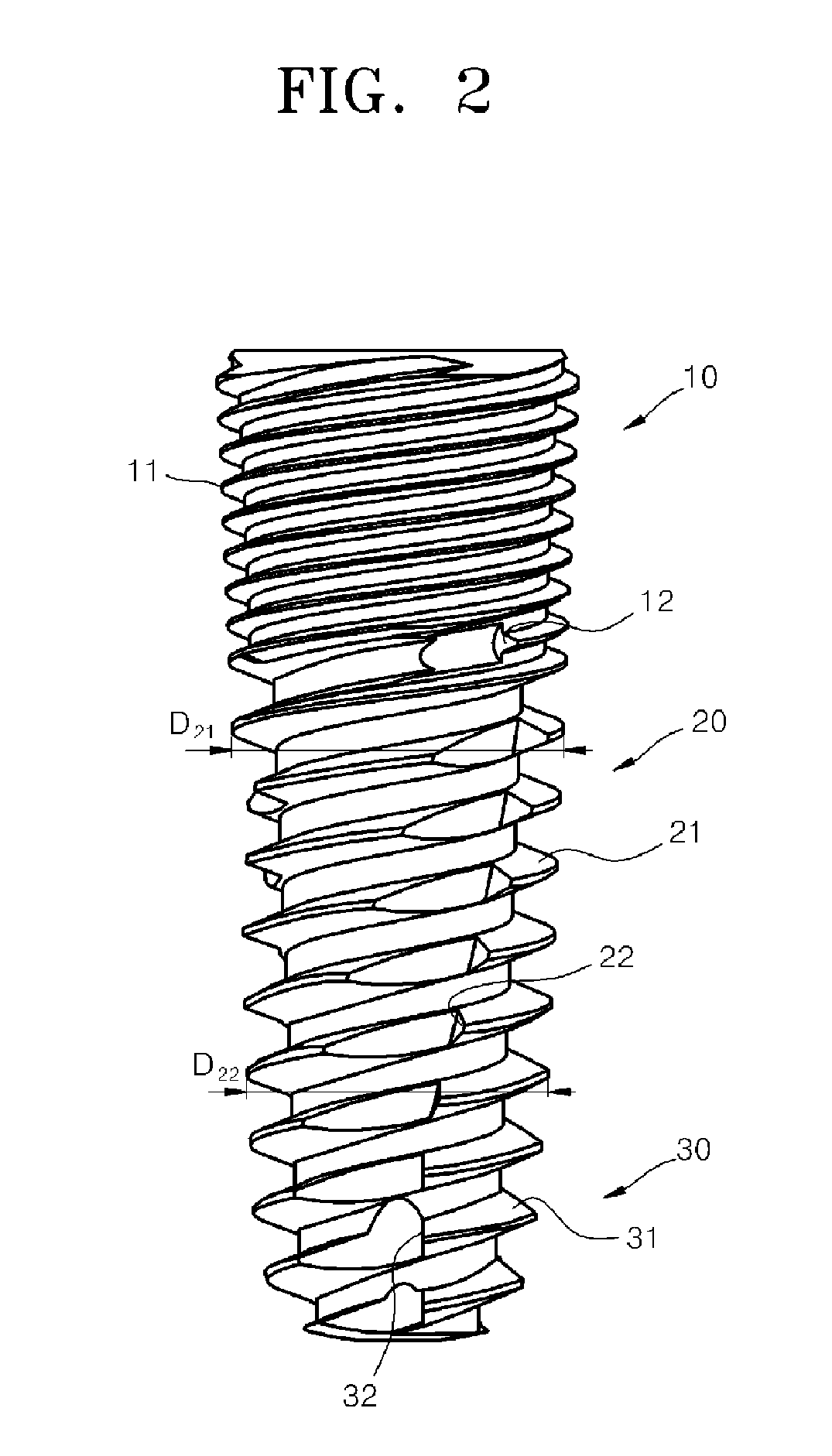
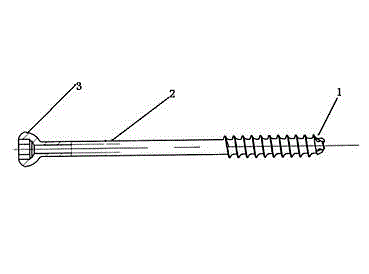
The present invention relates to a dental implant fixture, and more particularly, to a dental implant fixture which rotates about a central axis thereof, and thus is inserted into a bone tissue constituted by a cortical bone and a spongy bone to form an artificial tooth root, wherein the dental implant fixture includes a first portion, a second portion, and a third portion. The first portion is inserted into the cortical bone and has an outer surface with a first screw thread whereon first vertices and first valleys are alternately arranged. The second portion is disposed beneath the first portion and inserted into the spongy bone, has an outer surface with a second screw thread whereon second vertices and second valleys are alternately arranged. The distance between the adjacent second vertices of the second screw thread is larger than the distance between the adjacent first vertices of the first screw thread. The third portion is disposed beneath the second portion, and has an outer surface with a third screw thread whereon third vertices and third valleys are alternately arranged, and a first cutting part which is hollowed such that the first cutting part is closer to the central axis than the third valleys. The lower outer diameter of the second screw thread is smaller than the upper outer diameter of the second screw thread.
Owner:OSSTEMIMPLANT CO LTD
Bone tissue filling material
InactiveCN1511595ALow priceGood biocompatibilitySurgeryProsthesisSpinal columnBiocompatibility Testing
The present invention provides a kind of bone tissue filling material. Spongy bone of ox is first treated to become inorganic matter, soaked in sodium pyrophosphate solution, dried and high temperature calcined to produce calcined bone tissue filling material. The filling material is soaked in suspension of zinc chloride, dried and high temperature calcined to obtain the zinc-containing calcined porous bone tissue filling material. The porous bone tissue filling material has low cost, good biocompatibility, homogeneous and communicated pores, certain mechanical strength, capacity of promoting bone growth and other features, and is suitable for filling bone deficiency, spinal column fusion and cell rack in bone tissue engineering, etc.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Bone filling cement
ActiveUS20100228358A1Impart stiffnessReduce stiffnessCosmetic preparationsImpression capsInjectable boneGlycerol
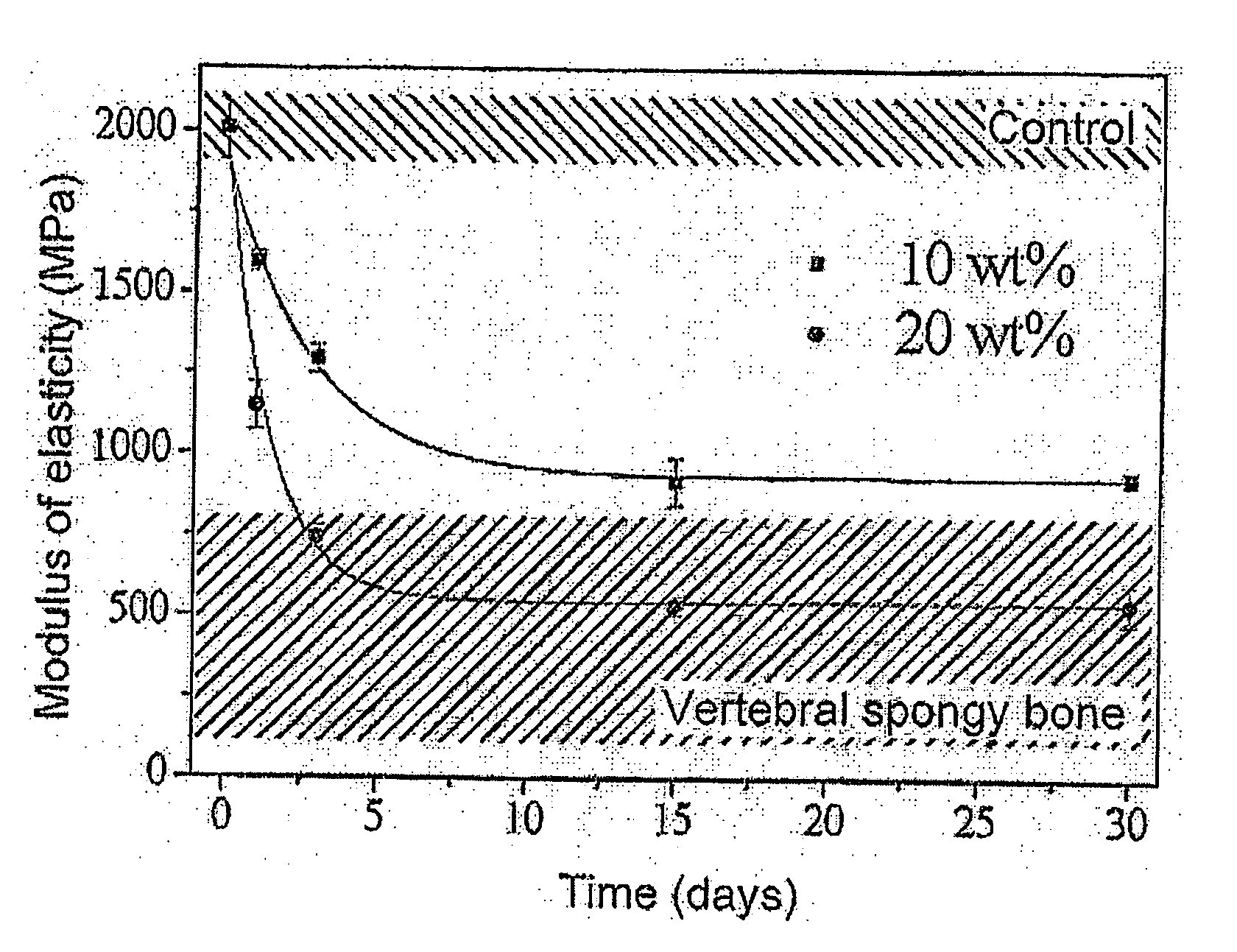
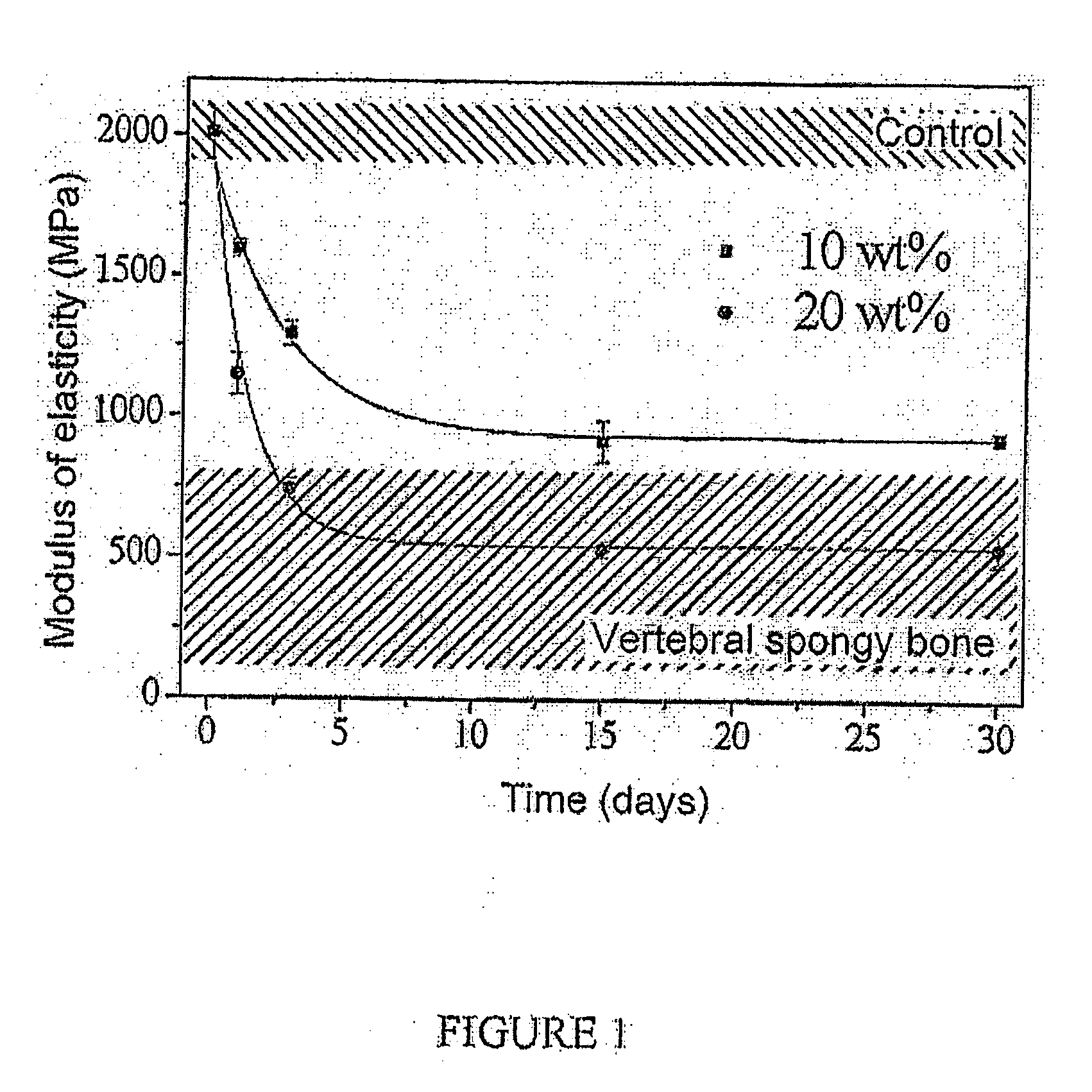
The present invention relates to an injectable bone cement for filling bones with mechanical properties equivalent to those of vertebral spongy bone comprising 70 to 99 wt. % of an acrylic polymer combined with an inorganic type radiopaque compound and 1 to 30 wt. % of calibrated hydrophilic flexible solid particles, said calibrated hydrophilic flexible solid particles being chosen from gelatin, poly(glycerol sebacate) or a mixture thereof.A bone cement according to the invention is particularly intended for vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty or cementoplasty.
Owner:TEKNIMED SAS
Extract and mechanical properties measurement method of bone trabecula and measurement mechanism
InactiveCN101158679AAvoid damageSubsequent measurement results are authentic and reliableUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisMeasurement deviceBiomechanics
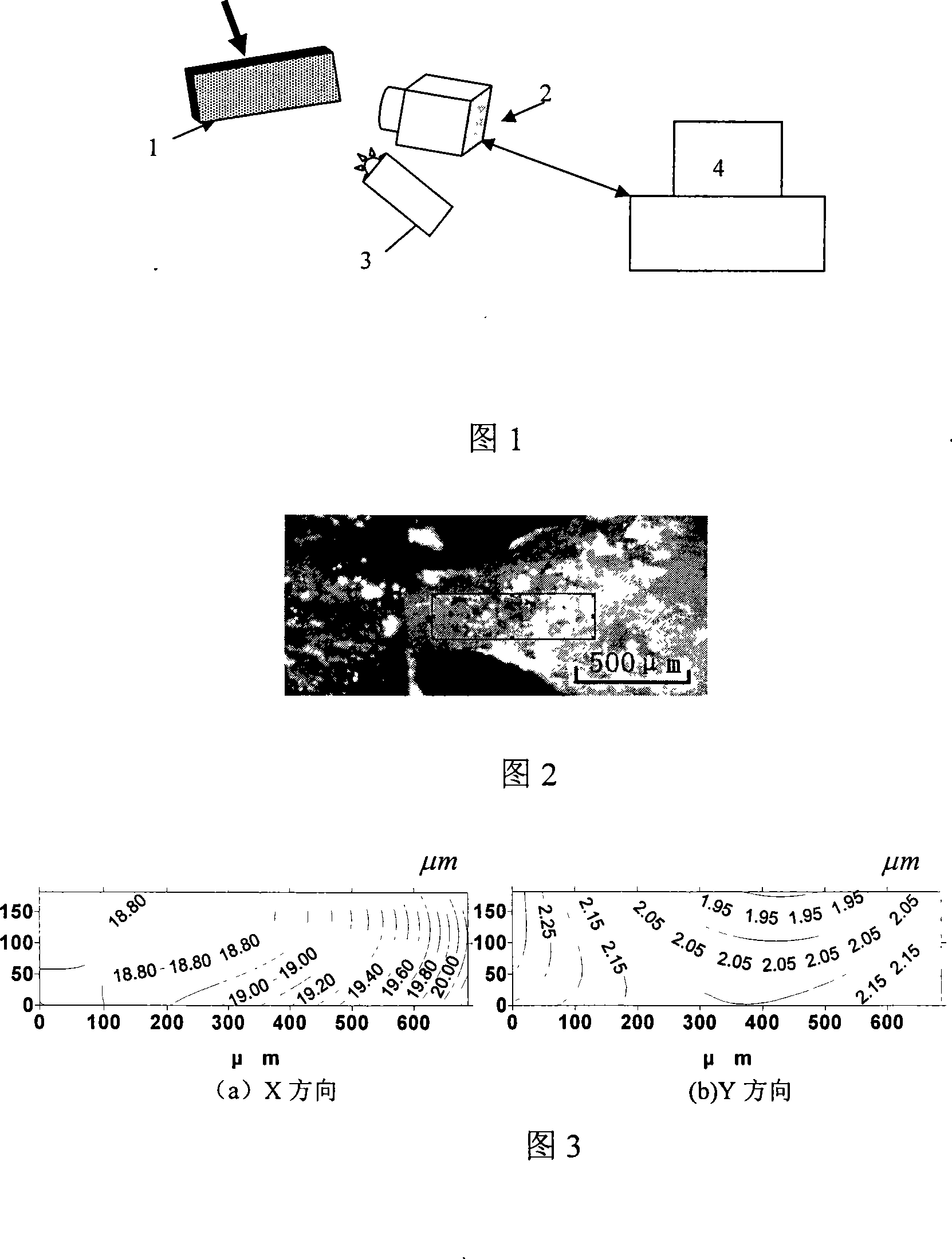
The invention relates to an extracting of a bone trabecula and a test method and a device of mechanical property, which belongs to the biological mechanics experiment technical field. The method comprises: 1. the bone is cut into a plurality of small blocks at the length of the bone trabecula; 2. the marrow in the middle of each small spongy bone block is rejected clearly and the spongy bone structure is only left; 3. a small spongy bone block which has an intact bone trabecula is chosen and the bone trabecula around the intact bone trabecula is cut away; 4. the bone trabecula is stretched and compressed at the direction paralleled with a loading force, and the two ends of the bone trabecula are fixed; 5. the CCD camera is aimed to the bone trabecula so as to lead the picture of the bone trabecula in the CCD to be clear; 6. the displacement of the stretching or compressing of the bone trabecula is controlled; 7. the picture and the load of the bone trabecula in each time quantum are recorded synchronously; 8. the displacement field and the strain field of each load is worked out according to DSCM; namely the poisson ratio of the material and the strain curve of the strain of the bone trabecula can be obtained. The invention can minimize the damage greatly, and lead a plurality of mechanical property parameters to be more correct.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Tissue engineering scaffold material for repairing cartilage defects and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101979105AEasy to prepareFor long-term storageProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingCartilage tissue engineering
The invention discloses a tissue engineering scaffold material for repairing cartilage defects and a preparation method thereof. The tissue engineering scaffold material is prepared by the following steps of: cleaning the spongy bone at the shoulder blade of a fresh pig; cutting the spongy bone into small blocks with diameter of between 5 and 10mm and thickness of between 3 and 5mm; degreasing, decalcifying and deproteinizing; immersing with alcohol for 30 minutes; and air-drying, wherein the decalcifying time is 6 hours. The prepared demineralized spongy bone matrix (DSBM) has the characteristics of relatively simple and convenient preparation method, and capacity of being obtained on a large scale, can be stored for a long time at a low temperature and is economic and cheap. The material can be prepared into different shapes and sizes according to the shapes of the defects to be repaired, so the material is convenient to apply. The DSBM remains a natural netlike gap structural system of the pig spongy bone, has high cellular compatibility, biocompatibility and degradability and is a very good cartilage tissue engineering scaffold material.
Owner:昆明医学院第一附属医院
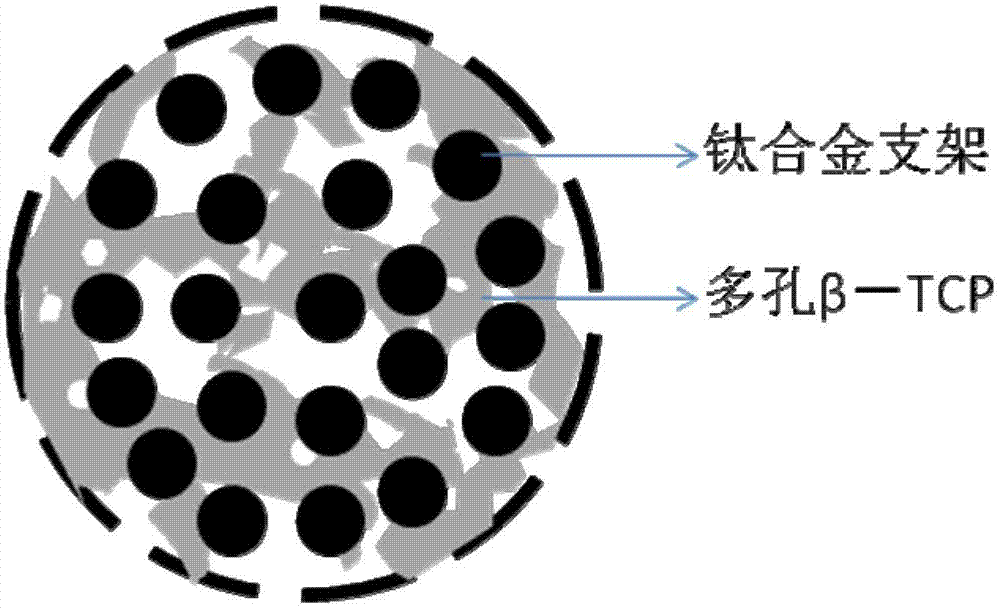
Compound porous beta-TCP (tertiary calcium phosphate) titanium alloy human astragal support bar and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102764888AGood bone conductionAppropriate degradation rateAnkle jointsJoint implantsOsseointegrationPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a compound porous beta-TCP (tertiary calcium phosphate) titanium alloy human astragal support bar and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps: firstly, inputting model data into an electronic beam melting device according to design requirements to prepare the needed porous titanium alloy human astragal support bar; and secondly, mixing powdery beta-TCP with hydrogen peroxide and polyvinyl alcohol solution into pasty slurry, pouring the pasty slurry into pores of a titanium alloy support after sufficiently and uniformly stirring the pasty slurry, removing excess water by an evaporation method, and performing rubber discharging and sintering to obtain the compound biological ceramic porous beta-TCP titanium alloy human astragal support bar. The porous titanium alloy human astragal support bar prepared by the preparation method has an elastic modulus similar to that of a human bone tissue, the compressive strength of the support bar is higher than that of a spongy bone and slightly lower than a cortical bone, the support bar can provide effective biomechanical support in an astragal after being implanted into the astragal by the aid of a regular pore structure and internally compounded porous beta-TCP components with fine osteoinductive activity, and the support bar has an excellent osseointegration capacity.
Owner:维度(西安)生物医疗科技有限公司
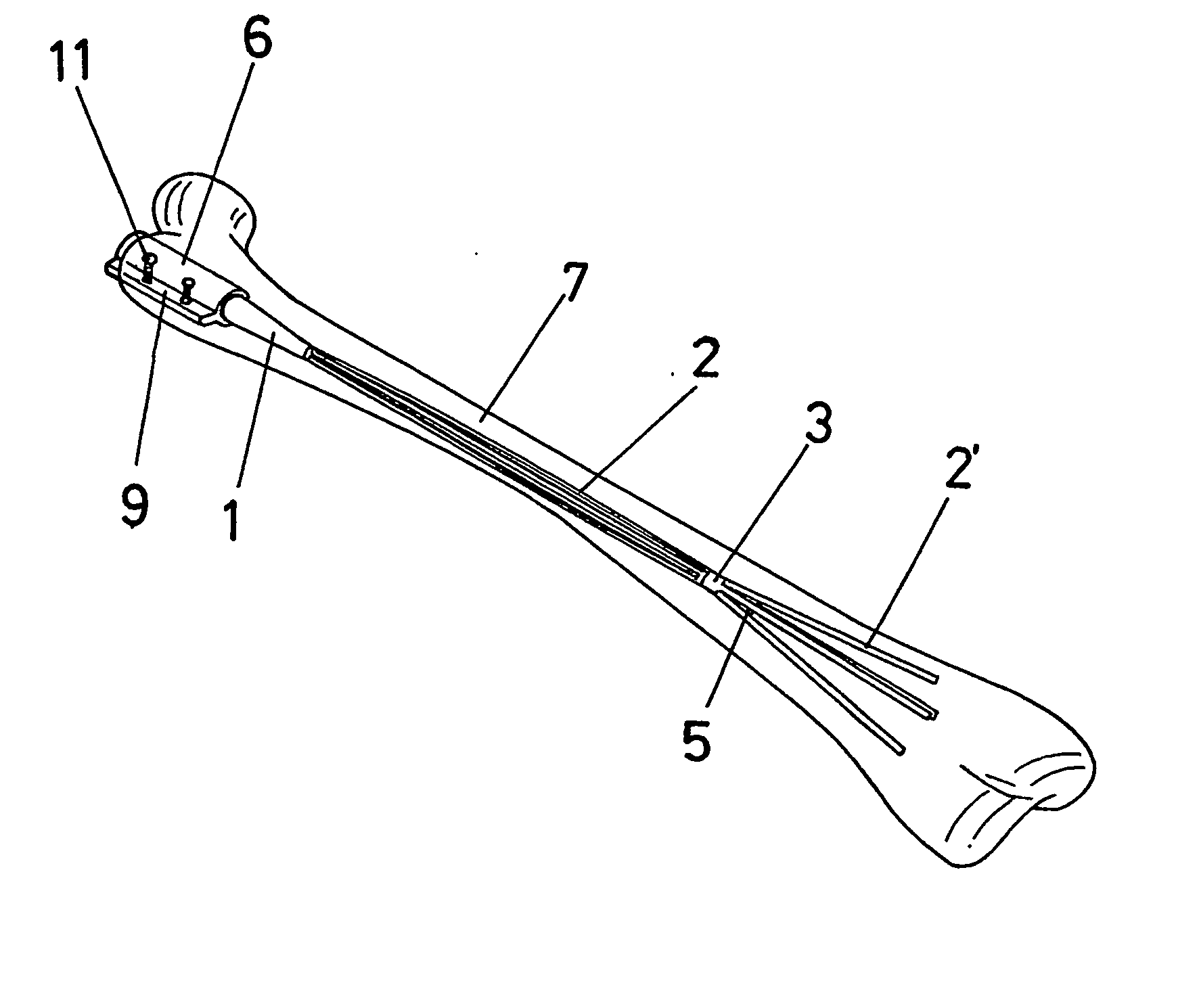
Intramedullary Nail
InactiveUS20070250062A1Easy to implantLess damageInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBone tissueIliac screw
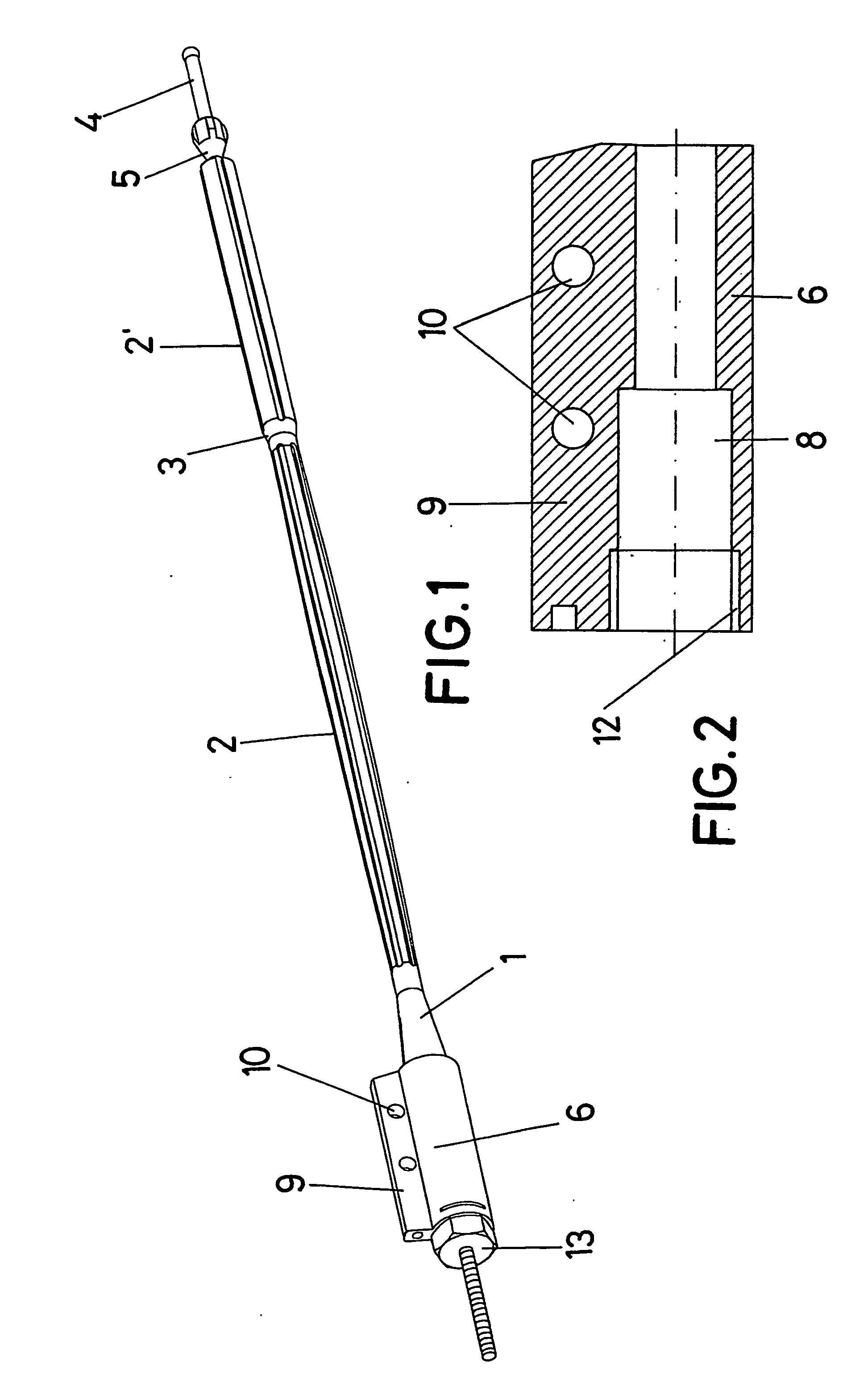
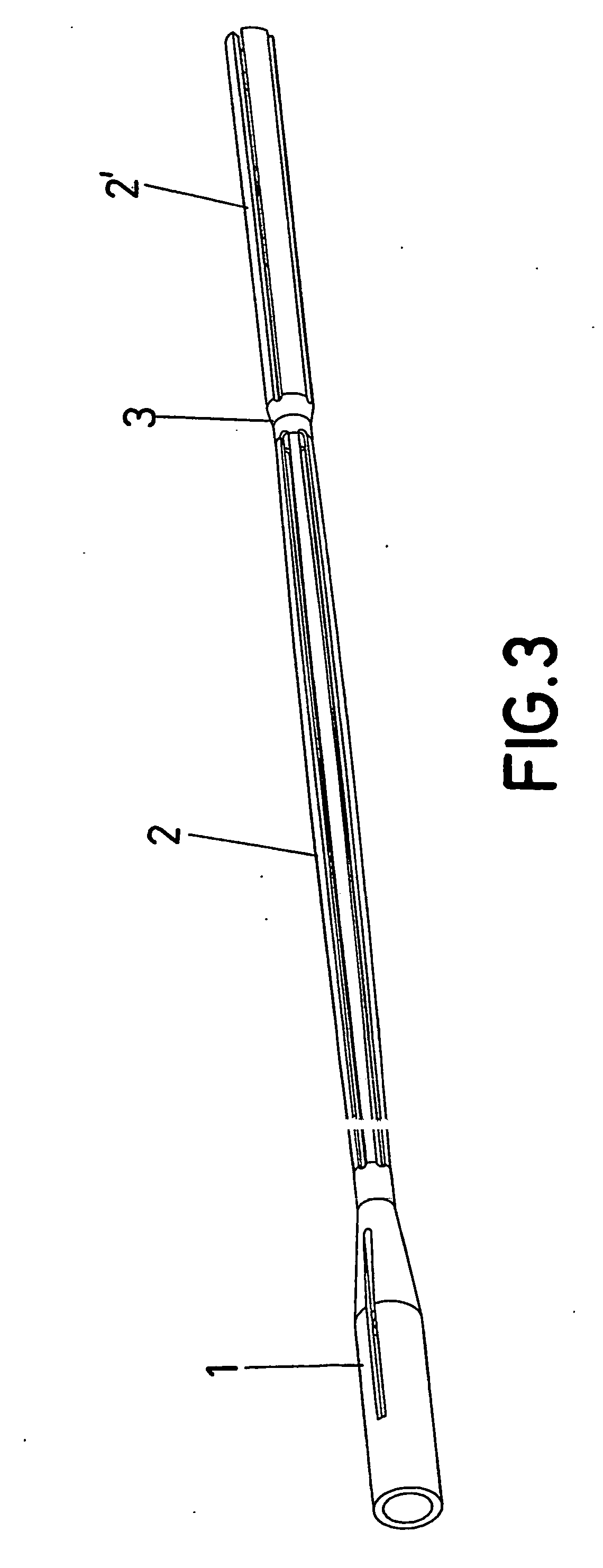
The invention relates to an intramedullary nail. More specifically, the invention relates to a structure which combines a tubular nail (1-2-3-2′), a probe (4) which can move axially inside the tubular nail and a bone-fixing support (6), such as to form a head (1) on said nail, from which a plurality of thin rods (2) extend integrally. The rods are distributed over a considerably-long imaginary cylindrical surface having a reduced diameter and meet at a node A(3), beyond which they extend into segments (2′)j having an independent free end. According to the invention, a projecting part (5) of the probe (4) acts on the aforementioned segments (2′) when the probe is moved towards the head (1), in order to produce the radial deformation of the rods (2′) such as to enable same to penetrate the spongy bone tissue. When the protrusion (5) reaches the node (3) of the nail, said node (3) moves towards the head (1), thereby causing the radial expansion of the above-mentioned segment (2) of the rods. In this way, the rods adapt to the inner wall of the bone, exerting an elastic tension for improved fixing, said fixing necessitating only the screws that are used to stabilise the support (6) to which the head (1) of the nail is subsequently fixed internally.
Owner:ARA PINILLA JAVIER +2
Integrated three-layer composite scaffold for repairing joint cartilages, and production method thereof
InactiveCN107485731AImprove structural stabilityStrong bonding between layersAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantCross-linkBinding force
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Injectable active bone repair material
The invention relates to an injectable active bone repair material. The material has good liquidity, can reach a bone defect part through injection and quickly solidify the defect part, and can obviously promote the healing of bone trauma along with gradual release of rear bone growth factors so as to shorten the healing period. Main components of the injectable active bone repair material consist of multiple calcium salts such as phosphoric acid calcium salt, calcium sulfate, calcium carbonate and the like, stowage factor microspheres and solidifying conditioner. The injectable active bone repair material has good injectability and collapse resistance. The solidifying time is 15 to 30 minutes, the temperature rise is not over 45 DEG C during solidifying, and the material does not cause adverse effect on tissues of an implanted part. After solidifying for half an hour, the material reaches the strength of spongy bone. All the components of the material are medicinal raw materials approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration, and can meet the safety of clinical use.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDO BIOMATERIALS
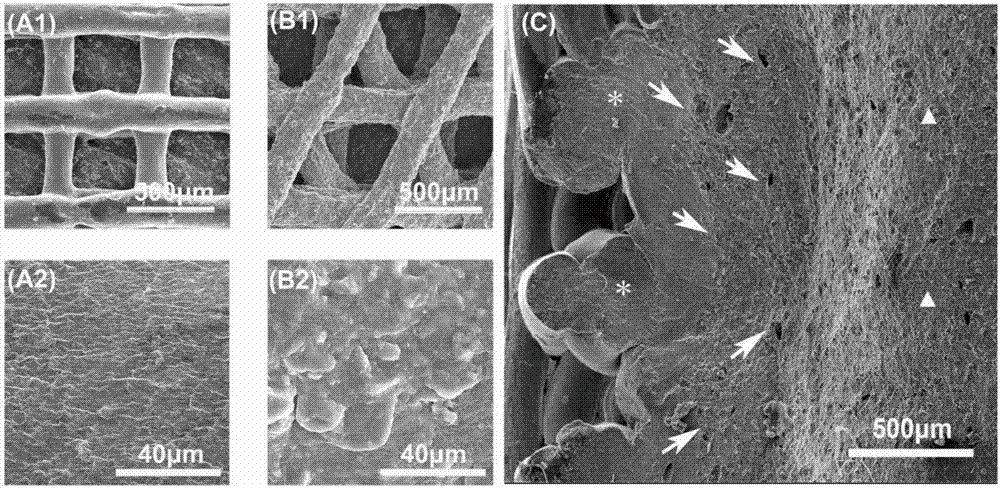
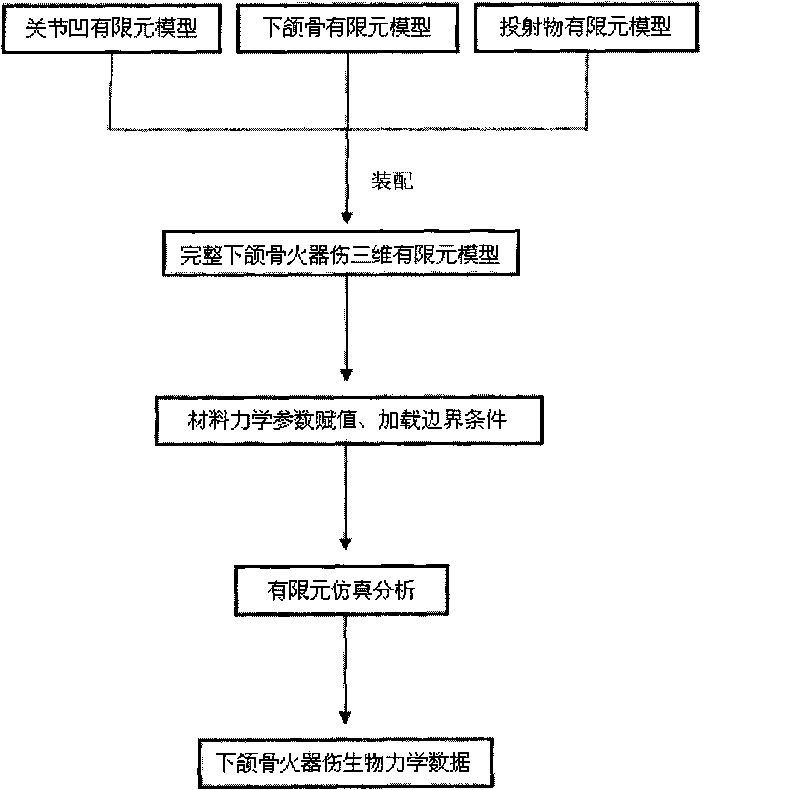
Mandible firearm wound simulation method
InactiveCN101706844AImprove calculation accuracyReduce modeling timeSpecial data processing applications3D modellingArticular surfacesVirtual field
The invention discloses a mandible firearm wound simulation method which comprises the steps of respectively building tetrahedron-hexahedron combined three-dimensional finite element models of temporal-mandibular joint concave articular surface, mandible and dejectile; then respectively conducting material assignment and assembling on the spongy bone, cortical bone and dejectile of the mandible, thus obtaining a complete mandible firearm wound mechanical model; determining model boundary conditions and loading different penetration speeds and conducting finite element analysis, thus obtaining the stress, strain and deformation fracture situation of all the parts of the mandible when suffering from penetration of dejectiles with different speed. The method can make up the defects of the current animal model when studying mandible firearm wound, provides biomechanics basis for studying mandible firearm wound, and is used for mandible firearm wound mechanism research, mandible firearm wound lethal effect evaluation, maxillofacial region protective equipment design and evaluation, mandible firearm wound medical evaluation and virtual field reconstruction.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
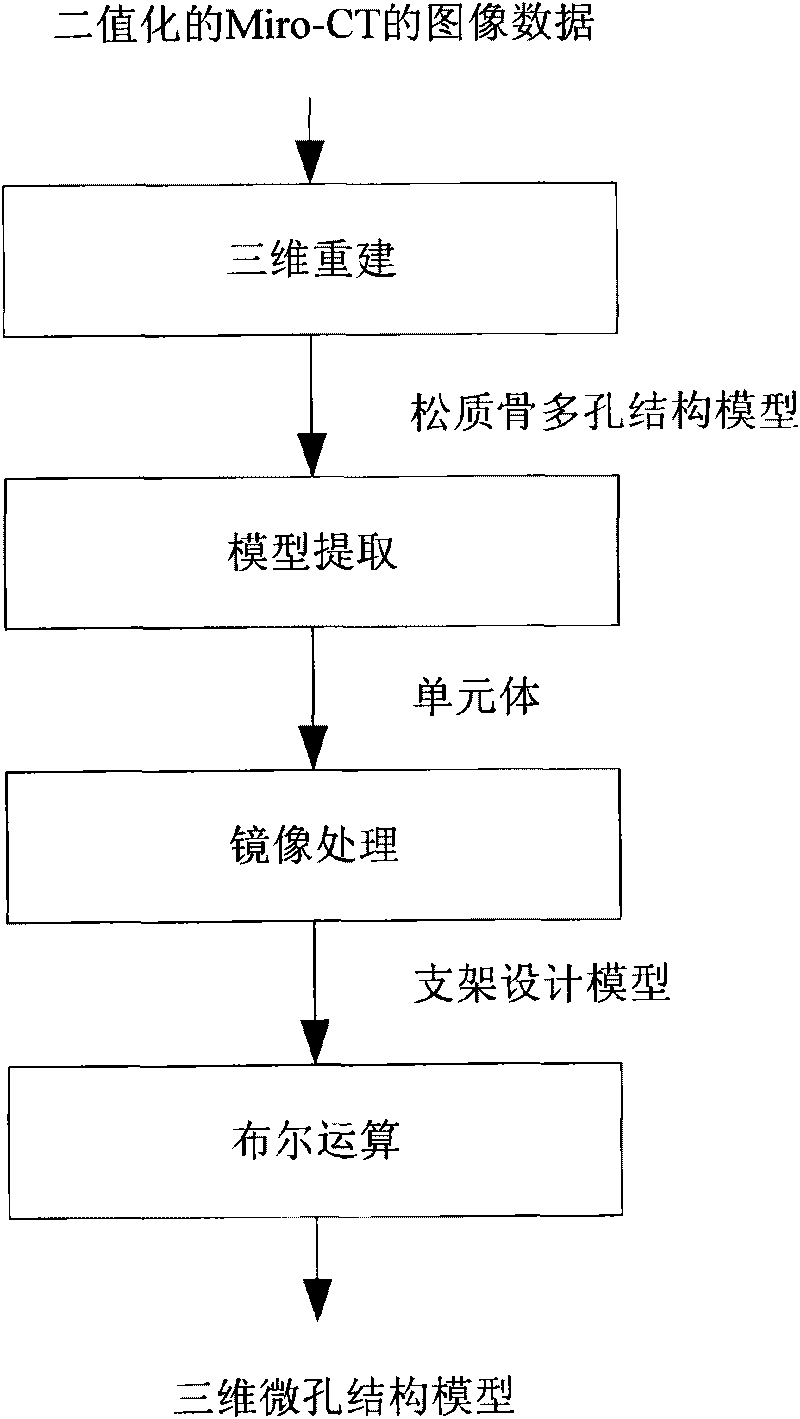
Method for constructing porosity-controlled bionic scaffold
InactiveCN101980214AFast modelingReduce difficultyBone implantSpecial data processing applicationsCell adhesionData reconstruction
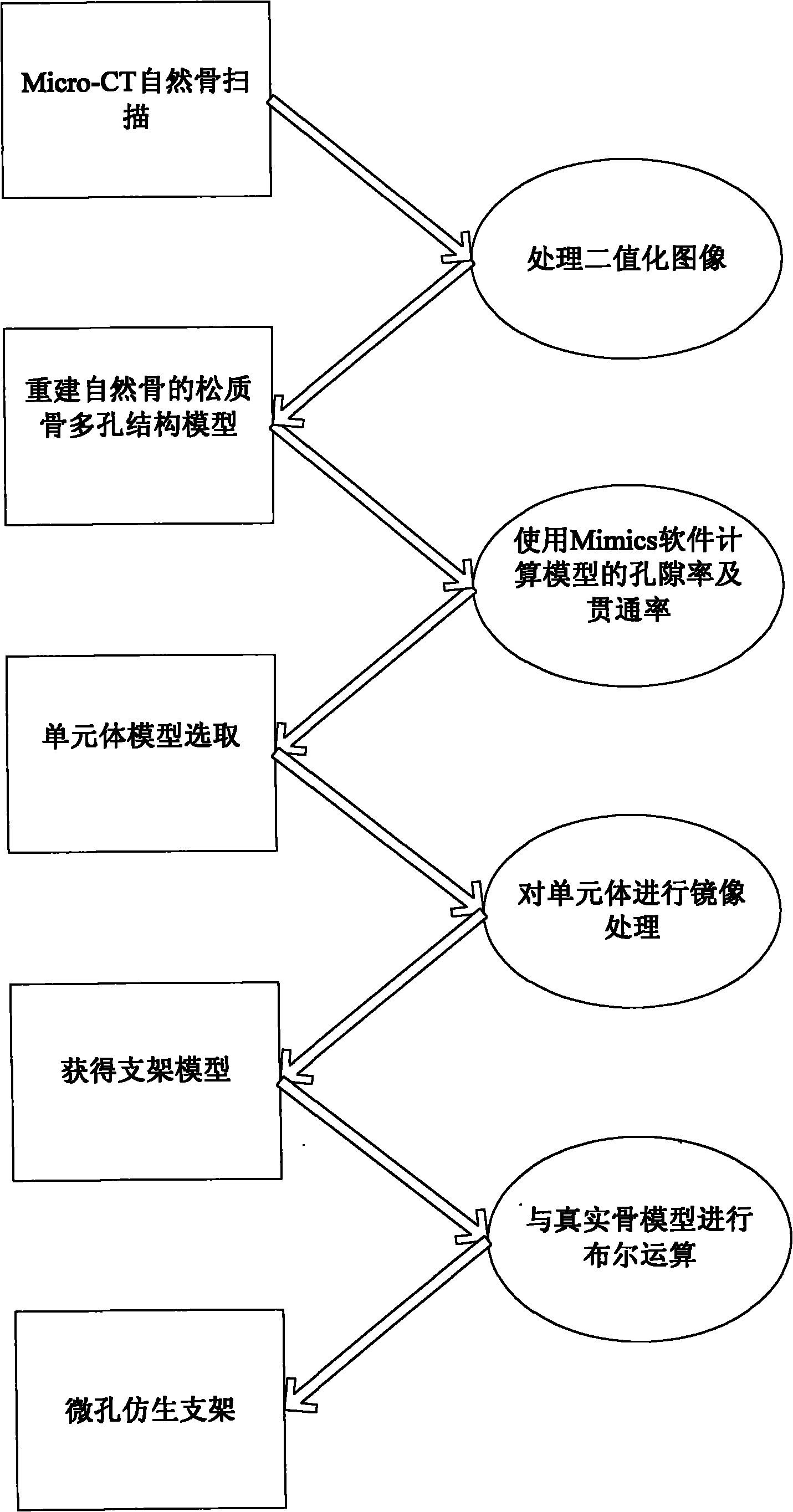
The invention relates to a method for constructing a porosity-controlled bionic scaffold, which comprises the following steps of: scanning the entire natural bone by using Micro-CT technology, extracting spongy bone data and reconstructing a porous structure model of a spongy bone; measuring the porosity of the spongy bone model by using Mimics; then constructing a unit body with a proper porous structure according to the porosity; processing the unit body by using an image to obtain a three-dimensional porous structure model; and finally, performing Boolean intersection operation on the three-dimensional porous structure model and a damaged bone model so as to construct a porous structure model of the bionic scaffold, which is matched with the damaged part. In the method, the porosity corresponding to the natural bone can be obtained in the process of reconstructing and measuring, the characteristics of the natural bone can be better simulated in construction, and cell adhesion, crawling and bone replacement are more convenient. The bone scaffold constructed by the method has the same outline as real bone, which better contributes to implantation of the scaffold. A parameterized construction method can adjust different porosity characteristics of different natural bones and makes scaffold construction convenient. A construction method for obtaining the unit body by processing a unit body image solves the problem of porosity communication in a microstructure.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
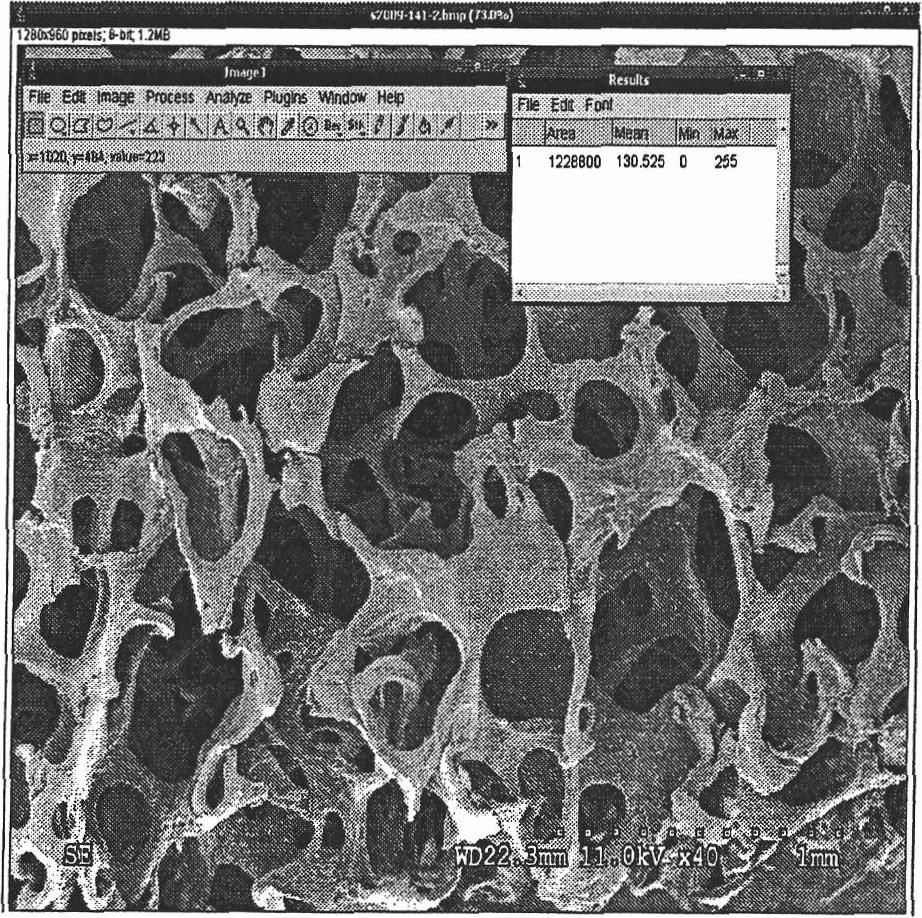
Ultrasonic frequency spectrum offset parameter imaging method used for characterization of spongy bone microstructure
InactiveCN101658434AIncrease reflectionOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesFrequency spectrumSonification
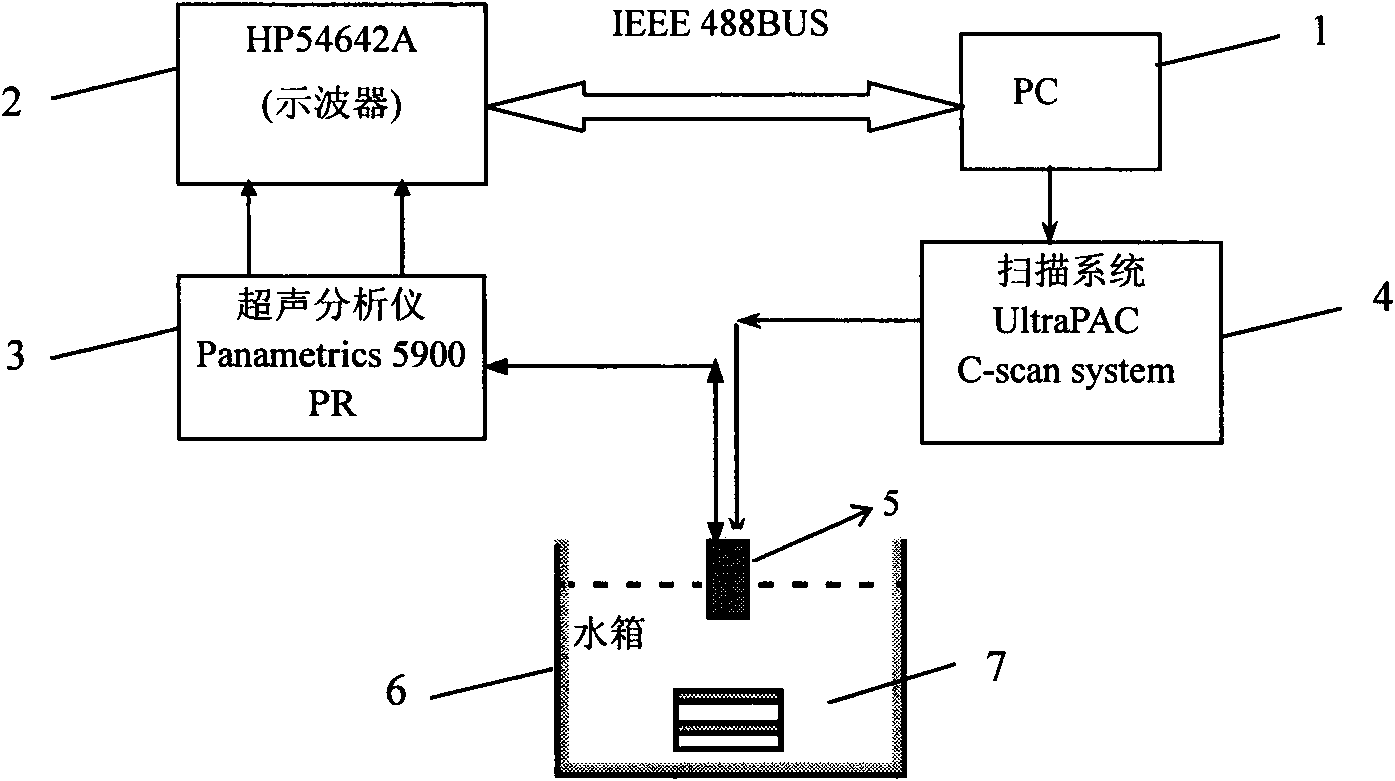
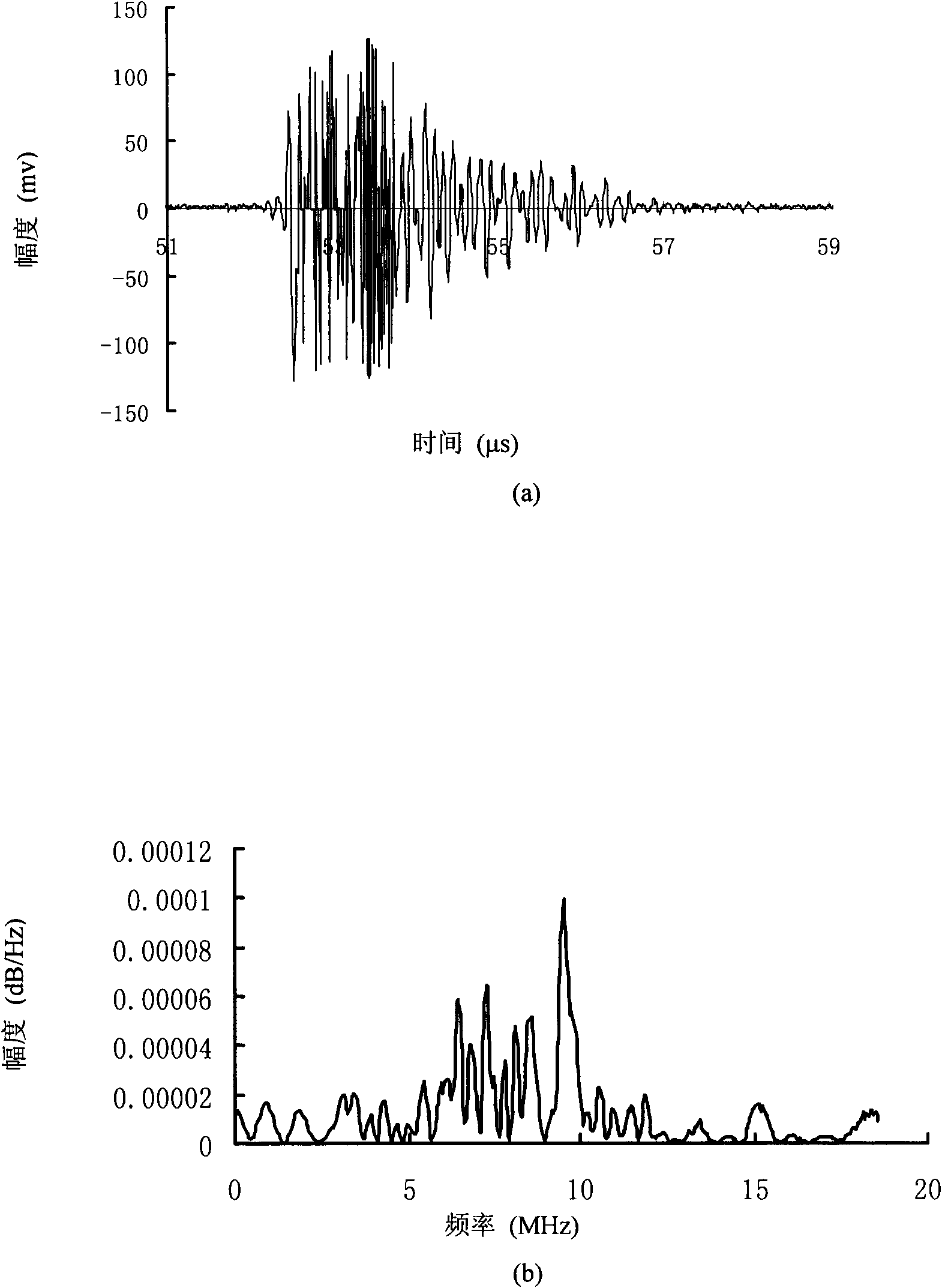
The invention belongs to the ultrasonic mechanical technical field, and particularly relates to an ultrasonic frequency spectrum offset parameter imaging method used for characterization of a spongy bone microstructure. The method comprises the following steps: scanning a spongy bone to be detected with a single high-frequency ultrasonic probe, and vertically emitting an ultrasonic pulse wave to the spongy bone at each scanning position; receiving an ultrasonic backscattering signal by the same probe when ultrasonic wave transmission is affected by the spongy bone microstructure; respectivelyperforming signal processing on the received signal at each scanning position, and extracting the frequency spectrum offset parameters of the received signal and the transmit signal to obtain an ultrasonic frequency spectrum offset parameter matrix corresponding to a scanning area; and mapping the parameter matrix into an ultrasonic frequency spectrum offset parameter image, and proportionally setting pixel values and parameter values. The method for ultrasonic imaging on the spongy bone with the frequency spectrum offset parameters of the backscattering signal is firstly proposed in the invention, and the method can help better reflect spongy bone microstructure characteristics compared with the traditional spongy bone ultrasonic imaging method based on a transmission method.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for constructing microporous structure of bionic support
InactiveCN101719172AReduce difficultyProcessing speedBone implantSpecial data processing applicationsMicro structureCell adhesion
The invention relates to a method for constructing a microporous structure of a bionic support, which comprises the following steps: performing overall scanning of a natural bone by using Micro-CT technology to extract data of a spongy bone and reconstructing the spongy bone to obtain a model of the microporous structure of the spongy bone; extracting a model of a unit body from the model of the spongy bone; obtaining a model of a three-dimensional microporous structure by mirroring; and finally, performing Boolean intersection operation with the model of the three-dimensional microporous structure and a model of a damaged bone to obtain a model of the microporous structure of the bionic support matched with a damaged part. According to the design method, the amount of processed data is reduced in a reconstruction process. The design method of obtaining a large model by mirroring the unit body solves the problem of local fault in the micro structure. According to design requirements, the model of the microporous structure, which is obtained by mirroring, may have an infinite size. The microporous structure of the obtained model of the bionic support is similar to the structure of a real bone, which is more favorable for cell adhesion, cell climbing and osteogenic replacement. The bone support designed by the method has the same profile as the real bone and thus can be implanted more conveniently.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Calcium phosphate/bioactive glass bone repair bracket and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109133971APromotes hydrationShorten the setting timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramicwareHydration reactionBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a calcium phosphate / bioactive glass bone repair bracket and a preparation method thereof. According to the calcium phosphate / bioactive glass bone repair bracket disclosed by the invention, calcium phosphate bone cement and bioactive glass are used as raw materials, a 3D printing technique is used, and the calcium phosphate / bioactive glass bone repair bracket having communicating macropores is obtained. The bioactive glass can promote a hydration reaction of bone cement, and shorten the coagulation time; besides, the solidified bracket releases Ca ions, P ions and Si ions through quick dissolution of bioglass, so that the degradation properties of the bracket are improved, and more stable chemical bonds and higher biological activity are provided. The bracket is modified through gelatin, so that the mechanical strength of the bracket can be effectively improved. The prepared bone repair bracket disclosed by the invention has communicating macropores, the mechanical strength of the bone repair bracket meets demands of spongy bones, and the bone repair bracket has excellent biocompatibility, can effectively promote regeneration of bone tissues, and has a favorable application prospect in the field of bone tissue repair.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RAINHOME PHARM&TECH CO LTD
Renewable green environment-friendly material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103495375AWide variety of sourcesLow priceOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionEnvironmental resistancePorosity
The invention provides a renewable green environment-friendly material and a preparation method and application thereof. The renewable green environment-friendly material is prepared by calcining an animal bone at a temperature of 500 to 650 DEG C to remove organic components so as to form a porous structure and then taking out a sintered product for air cooling. The environment-friendly material comprises a porous compact bone with porosity of 42 to 51.5% and a porous spongy bone with porosity of 75 to 85% obtained after calcination of the animal bone, and the main component of the material is hydroxylapatite with a crystal grain size of 100 to 300 nm. The environment-friendly material is applicable to treatment of heavy metal ions in wastewater. In use, the environment-friendly material is put into wastewater for treatment of the wastewater. The environment-friendly material has the advantages of strong renewability, greenness, energy conservation and environment friendliness; the preparation method is simple, needs low cost, is suitable for industrial production, can fully utilize the resource of waste animal bones and reduces environmental pollution; the material has a high heavy metal ion adsorption rate, as high as more than 90.1%, so the material has wide application prospects.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
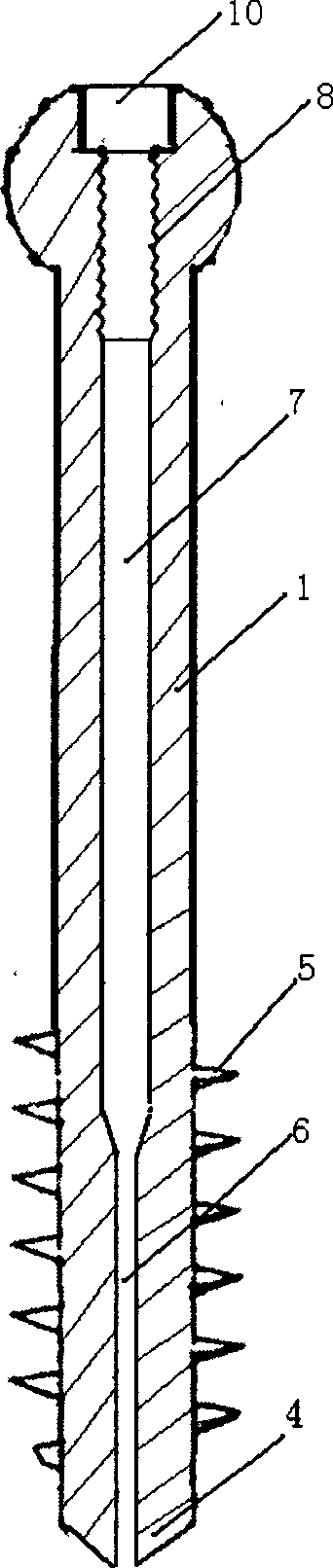
Expanding type spongy bone hollow screw
The expanding bolt for use in spongy bone includes one outer screw a one inner screw. The outer screw in integral structure has one tip end, one outer thread section, one spherical end and one inside hole including one front section of small diameter and one back section with inner threads. The front part of the outer screw is cut to form two or four expansion slots. The inner screw matched with the inner treads of the outer screw has one conic tip, threads and socket head for screwing in. There is also one tip steel pin matching the front section of the outer screw. The present invention is for inner fixing of fracture and has high stability and reliability.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Stem cells and devices for bone regeneration
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Proximal thighbone internal fixation system with minimal invasion
InactiveCN101716093AReasonable designCompact structureInternal osteosythesisBone CortexCortical bone
The invention discloses a proximal femur internal fixation system with minimal invasion, relating to an internal fixation system used for proximal femur comminuted fracture, femoral neck fracture, subtrochanteric fracture and femur backbone fracture. The internal fixation system comprises an internal fixation steel plate, an internal fixation bolt and a locking device, wherein the internal fixation steel plate adopts a dynamic hip screw steel plate or a proximal femur internal steel plate, the dynamic hip screw steel plate is composed of a head part and the rod part, and the proximal femur internal steel plate is composed of a head part and a rod part; the locking device comprises a rotary pin, a sliding pin, a spring and a locking disc; the internal fixation bolt comprises a combined tension force bolt or a combined hollow bolt, a hollow bolt, a spongy bone bolt, a cortical bone bolt and a locking bolt, wherein the combined tension force bolt is composed of a connecting sleeve, a connecting bush and a tension force bolt; the combined hollow bolt is composed of a hollow bolt and a bolt sleeve. The internal fixation steel plate and the internal fixation bolt are connected and fixed by the locking device, which can simplify operation steps, shorten operation time and leave small cut.
Owner:KANGHUI MEDICAL INNOVATION
Device for providing spongy bone with bone substitute and/or bone reinforcing material, bone substitute and/or bone reinforcing material and method
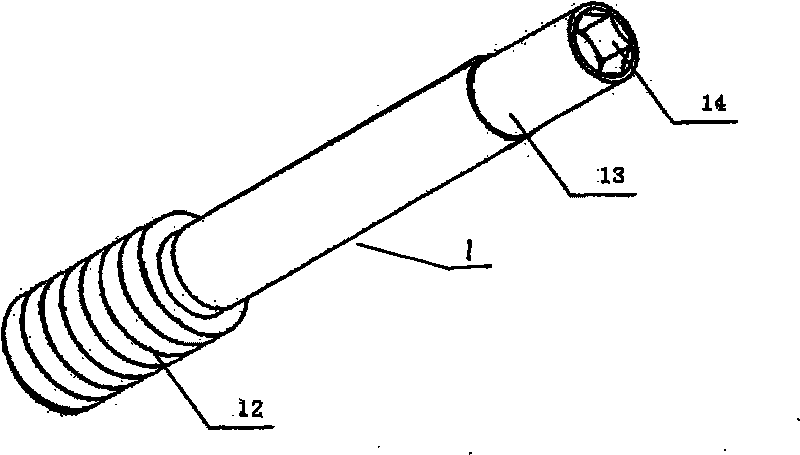
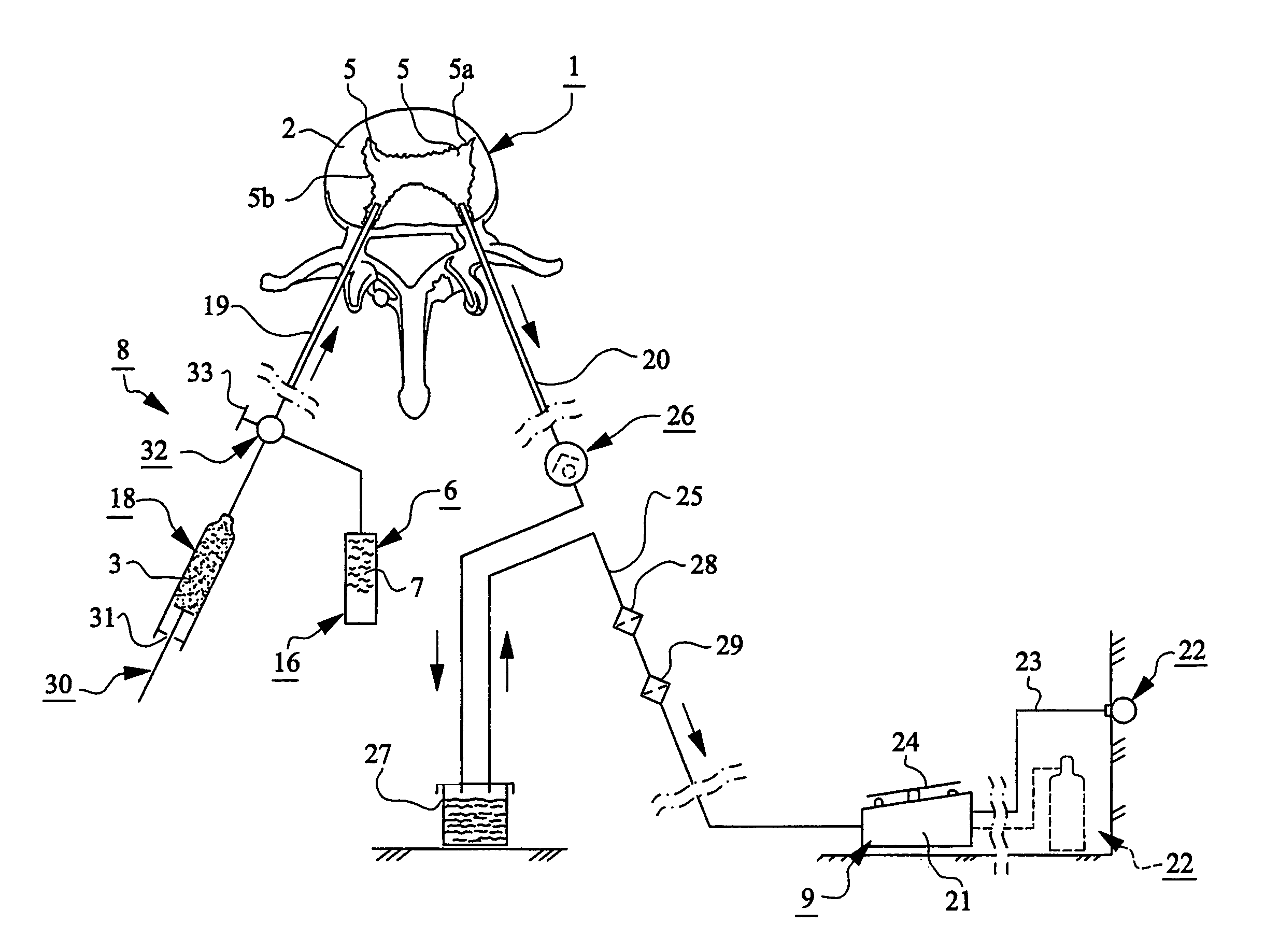
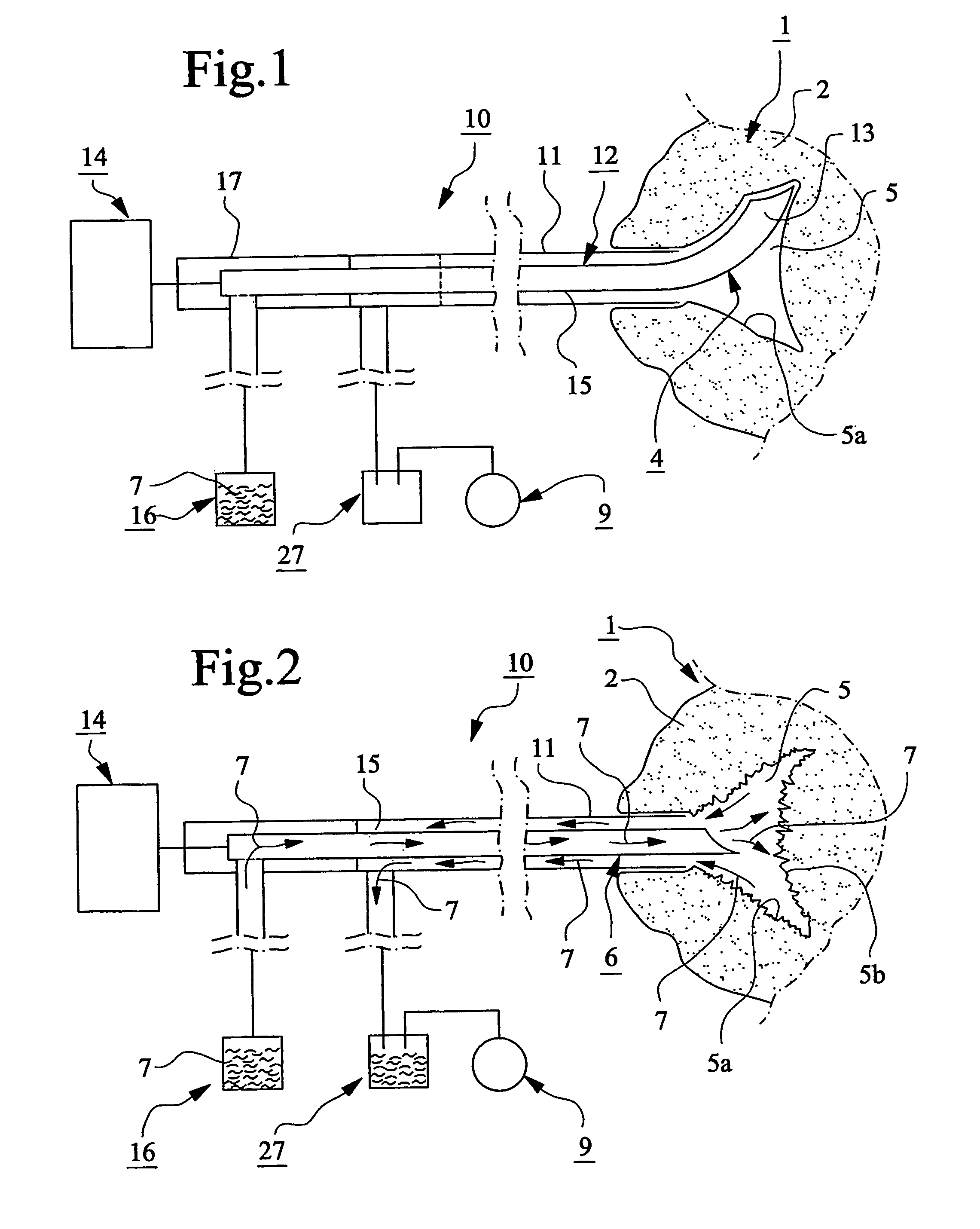
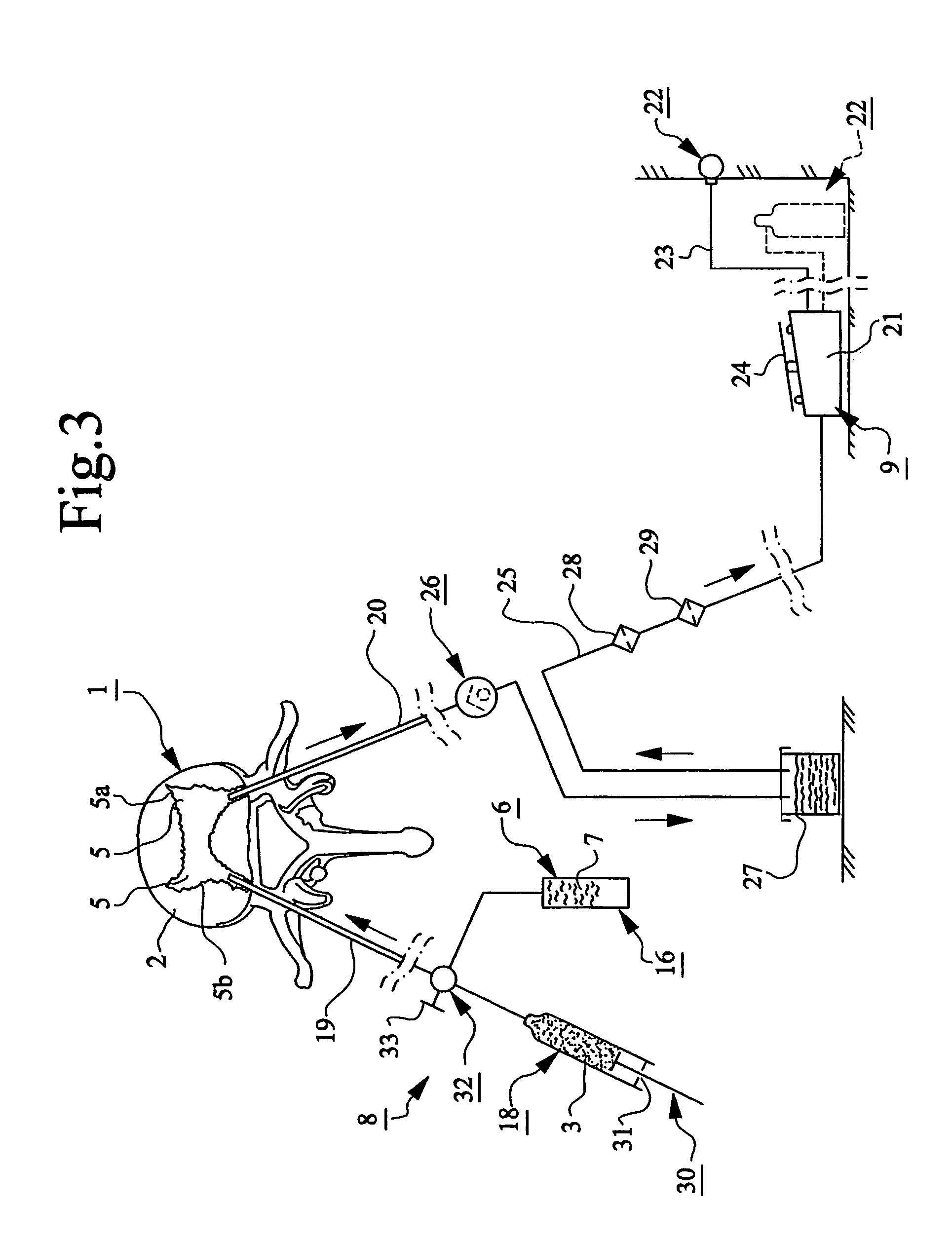
The present invention relates to a device for providing spongy bone with bone substitute and / or bone reinforcing material, wherein at least one perforating device (4) is provided for making at least one hole (5) in the spongy bone (1) and wherein at least one flushing or rinsing device (6) is provided for flushing or rinsing the hole (5) with a rinsing agent (7). At least one vacuum source (9) is provided for generating a vacuum in the hole (5) in the spongy bone (1) for sucking and / or facilitating insertion or feeding of the bone substitute and / or bone reinforcing material (3) into said spongy bone (1). The invention also relates to bone substitute and / or bone reinforcing material and methods in connection with the invention.
Owner:TEG HLDG
Bionic structure monolithic catalyst preparing method based on 3D printing technology
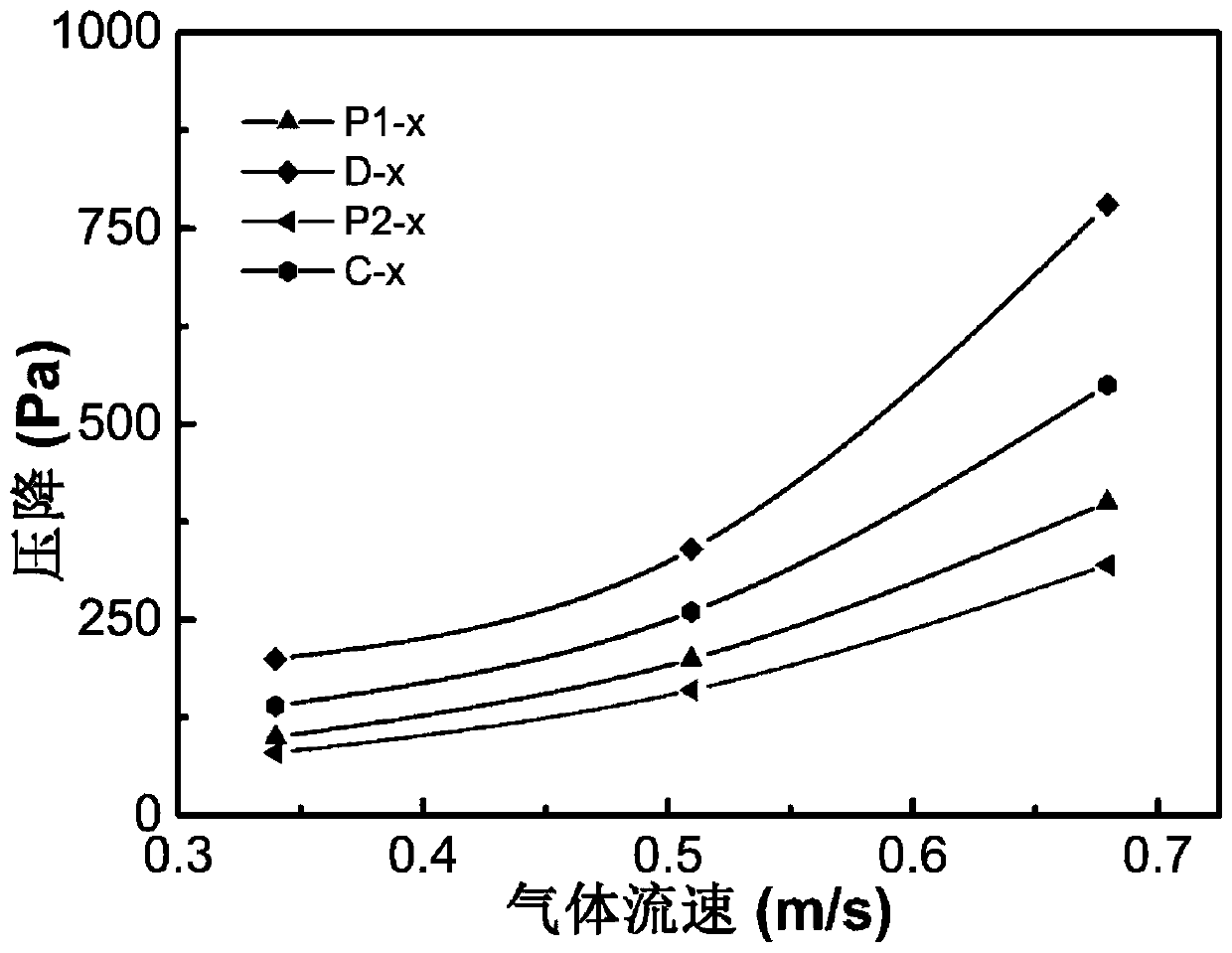
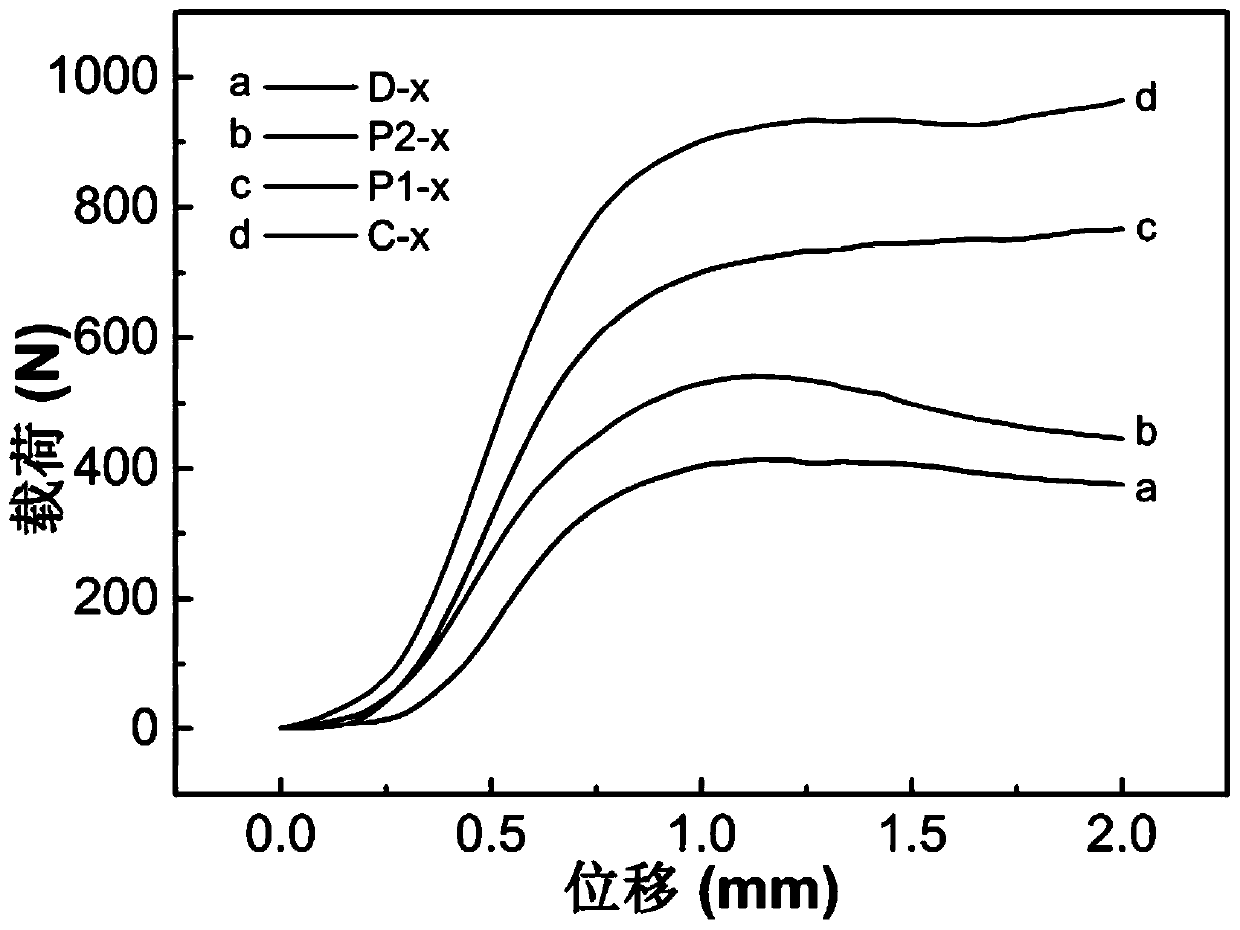
ActiveCN110901046AIncrease contactImprove conversion rateAdditive manufacturing apparatusCatalyst activation/preparation3d printPtru catalyst
The invention provides a bionic structure monolithic catalyst preparing method based on the 3D printing technology and relates to preparation of catalysts. The bionic structure monolithic catalyst preparing method based on the 3D printing technology comprises the following steps that (1), a piece of spongy bone is cut off from the end of animal bone, steeped in trichloro ethylene to remove greaseand subjected to ultrasonic treatment, and a porous spongy bone sample is obtained; (2), the spongy bone sample obtained in the step (1) is subjected to Micro-CT scanning, and a series of Micro-CT images of the spongy bone sample are obtained, reconstruction is carried out on the Micro-CT images, and a three-dimensional digital model of the spongy bone sample is obtained; and (3), the 3D printingtechnology is adopted for carrying out 3D printing on the three-dimensional digital model obtained in the step (2), and a bionic structure monolithic catalyst is obtained. The bionic structure monolithic catalyst has excellent mechanical performance, the pressure drop occurring when gas passes through the catalyst can be effectively reduced, energy consumption can be reduced, and the bionic structure monolithic catalyst can be widely applied to the fields such as catalytic reactions.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Dental implant fixture
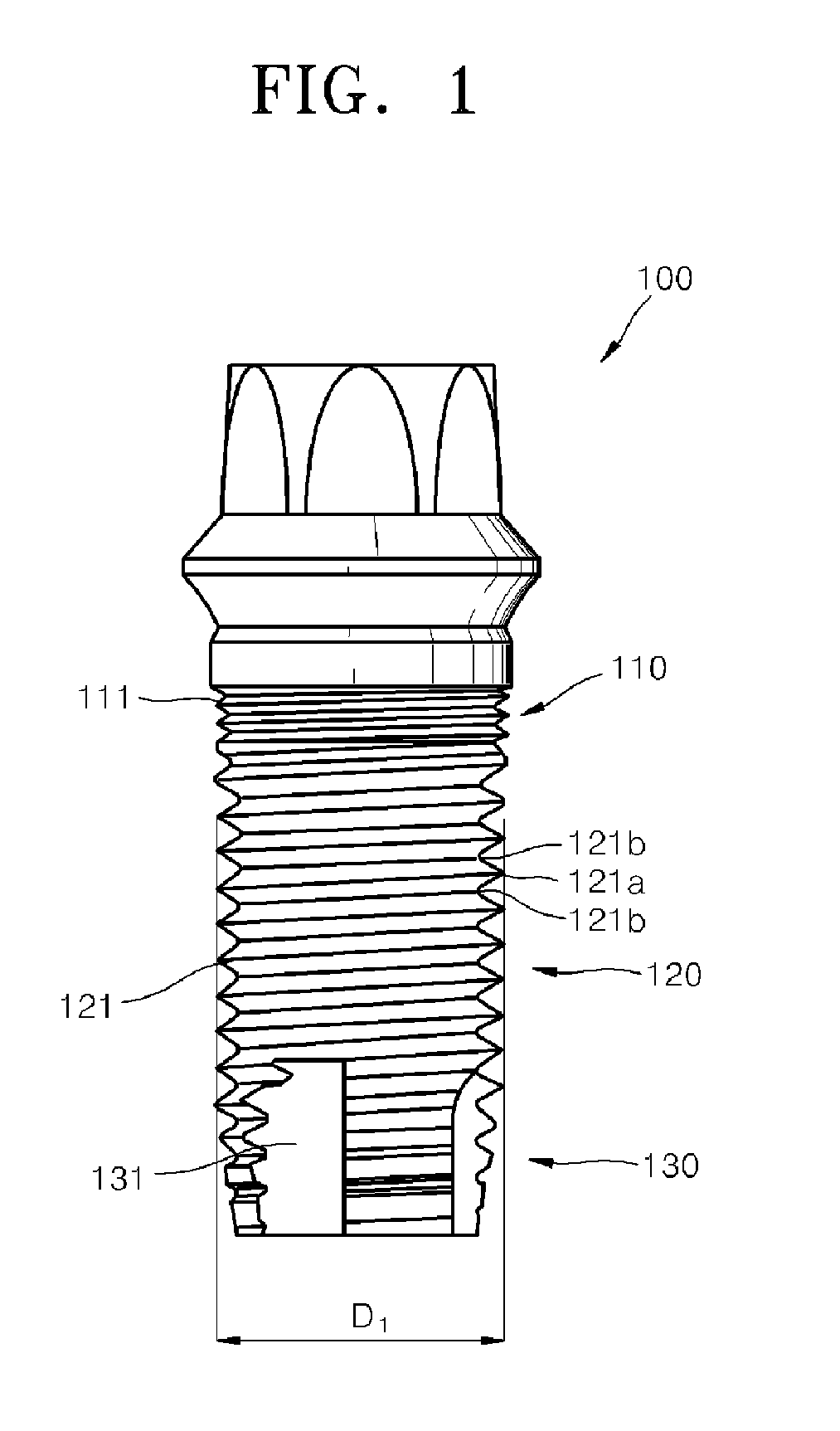
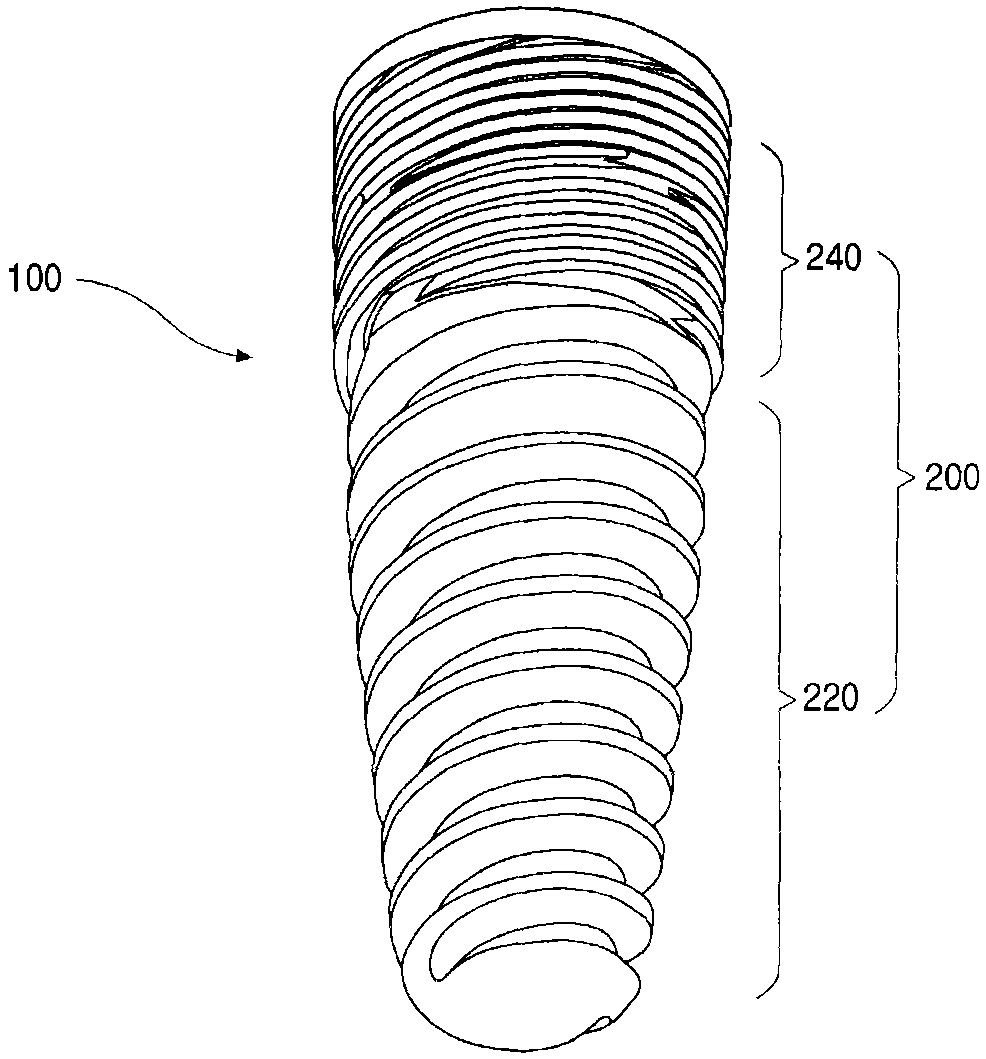
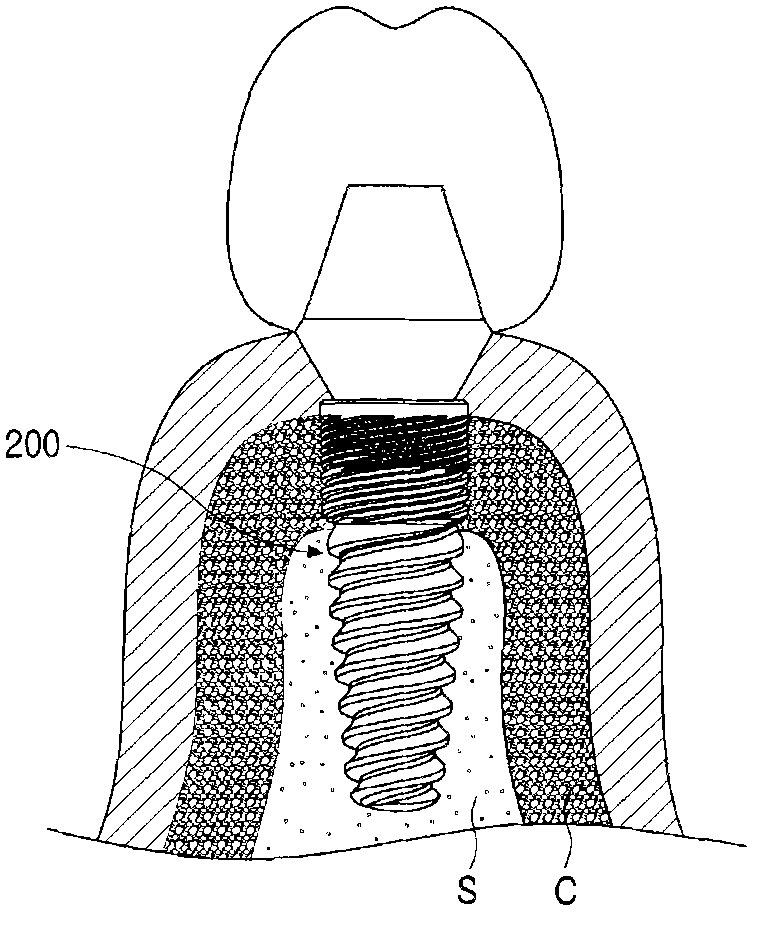
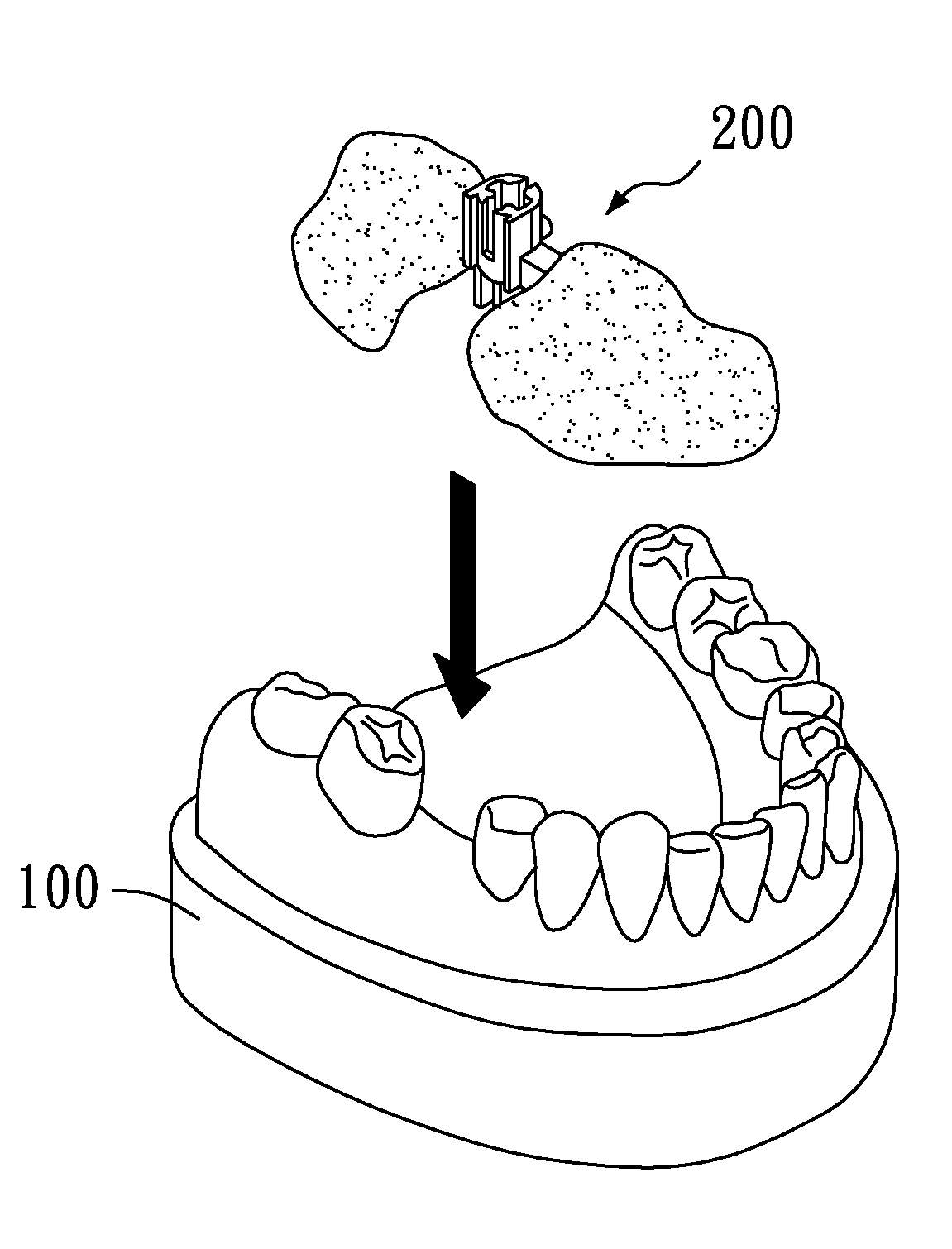
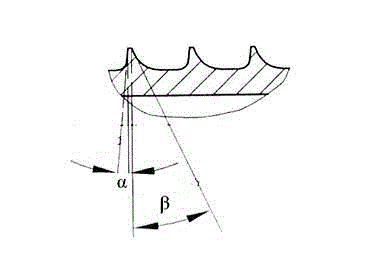
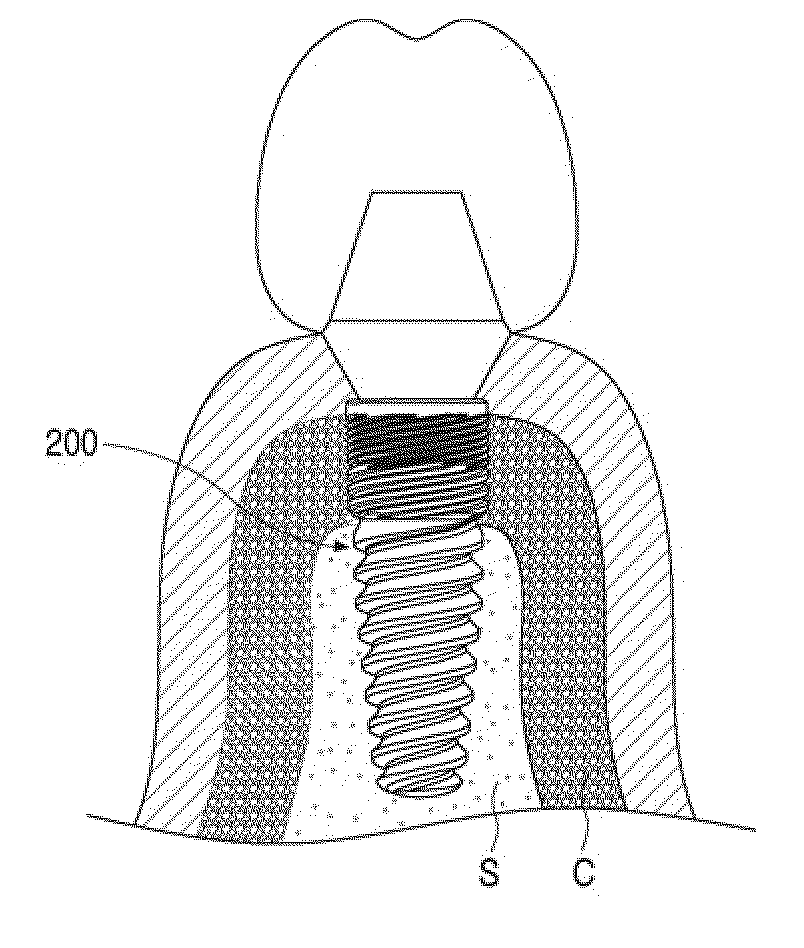
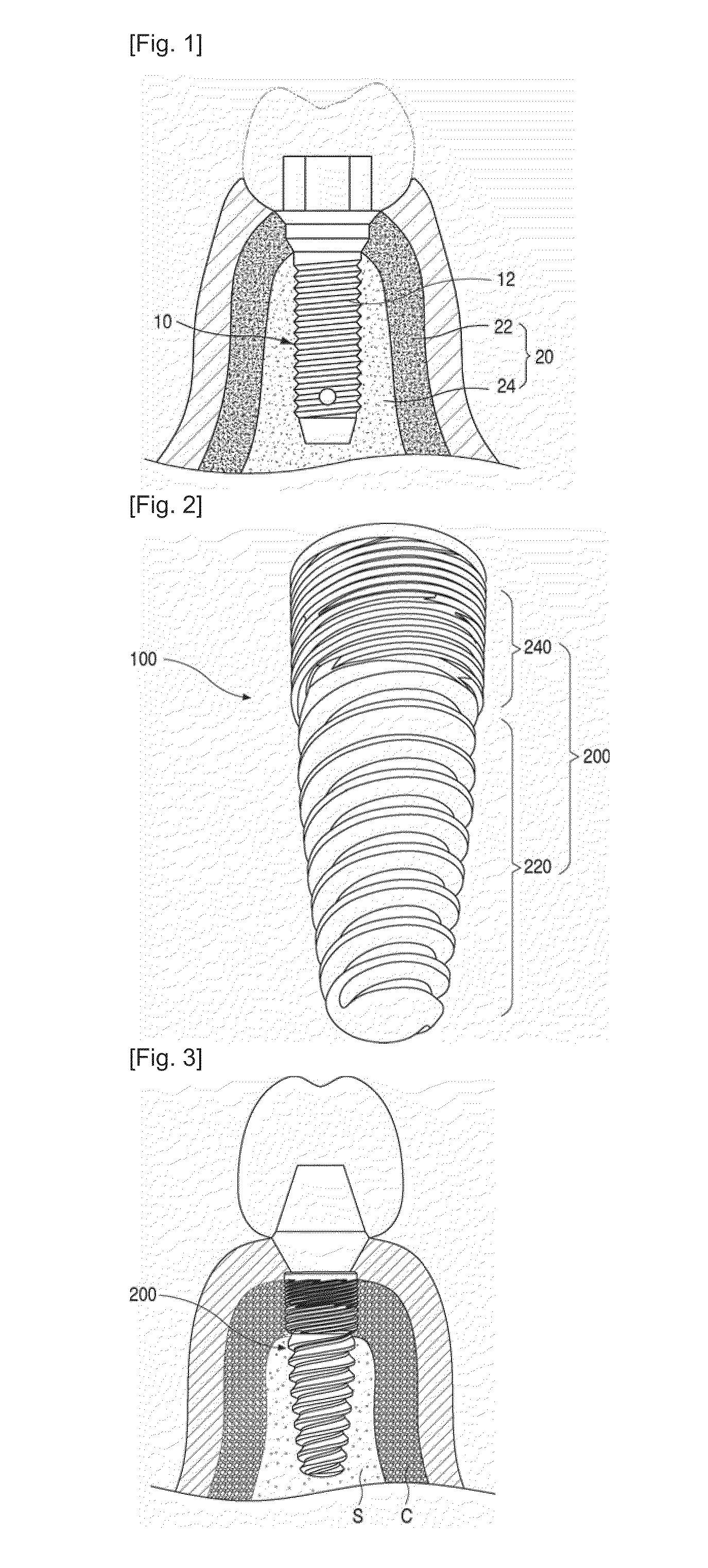
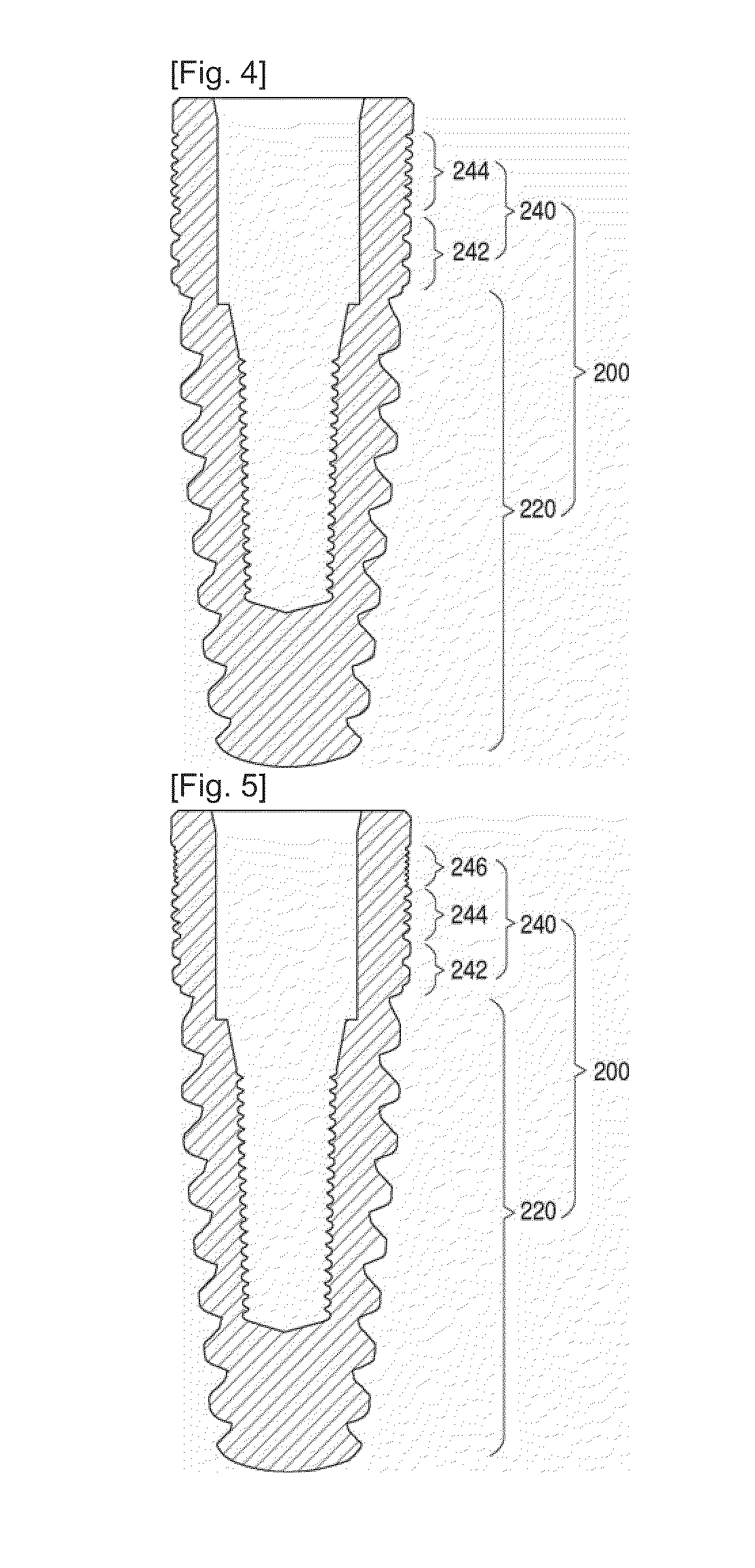
Provided is a dental implant fixture with 3 or more ridged portions having mutually different pitches to distribute load uniformly across osseous tissue. The pitches of the ridged portions (200) progressively decrease in one direction. The ridged portions (200) include a larger ridged portion (220) that contacts spongy bone with low bone density, and a smaller ridged portion (240) that contacts cortical bone with high bone density. The smaller ridged portion (240) is provided with 2 or more threaded regions with respectively different pitches. With this configuration, bone decay and bone damage can be prevented, and synostosis can be improved.
Owner:柯泰克股份有限公司
Pill for treating cold bone paralysis
InactiveCN101342289AAchieve antibody recoveryEliminate lesionsInanimate material medical ingredientsSkeletal disorderLiver and kidneyAnkylosing spondylitis
The present invention relates to a Chinese patent medicine which is prepared in the form of capsules and used for treating a plurality of types of proplapse of lumbar intervertebral disc, spinal stenosis, regressive changes, hyperplasia of all parts of bones, ankylosing spondylitis, and a plurality of types of rheumatism. The formula comprises snow lotus on the great icy mountain, holly, Japanese teasel fried in salt, roasted Chinese ephedra, and other types of Chinese medicine. The Chinese patent medicine has the functions of eliminating the pathological changes caused by various factors, strongly compensating the deficiency of liver and kidney, resulting in the physiological changes of bones from the pathological changes, absorbing and rehabilitating the spongy bone and the compact bone, and realizing the recovery of bone diseases. The therapy not only has rapid effects, but is also suitable for patients which can not be cured in various types of treatment. Moreover, the Chinese patent medicine has proven to have no case of relapse.
Owner:刘晓兵 +1
Planning and guiding method and excavation guiding device for correctly implanting artificial tooth root at predetermined site
A planning and guiding method and excavation guiding device correctly implant an artificial tooth root at a predetermined site, perform various excavation processes on a cortical bone section and a spongy bone section by stage-based guidance, and guide eccentric excavation of the cortical bone section and concentric excavation of the spongy bone section according to a bone pattern, such that the artificial tooth root thus implanted is not only positioned at a planned ideal site but also manifests appropriate initial stability.
Owner:LIU EN HENG
Half-thread spongy bone hollow screw
The invention relates to a half-thread spongy bone hollow screw which comprises a nail head (1), a nail rod (2) and a nail tail (3). The hollow screw has a total length of 35 to 140mm; the nail rod (2) is a titanium alloy nail body; a through hole with a diameter of 2.2mm is formed in the nail rod (2); and the nail rod (2) comprises a threaded section at the front end and an unthreaded section at the tail end. The half-thread spongy bone hollow screw disclosed by the invention has a simple structure and is simple and convenient to use.
Owner:唐佩福 +2
Improved bone biospy device
A bone biopsy device is disclosed, comprising an outer cannula provided with a mouth with a cutting edge to section a frustule of spongy bone, a plate mounted slidably within the cannula and providedwith a semi-cylindrical portion at its distal end, and a stylet mounted slidably within the plate and provided with a pointed tip which protrudes from the mouth of the cannula to pierce the compact part of the bone. The mouth of the cannula has on its inside a narrowing and the semi-cylindrical part of the plate has at its distal end at least one pair of opposed lunettes / anchorages adapted to bend, with respect to a horizontal plane, towards the interior of the semi-cylindrical portion when they encounter the narrowing of the mouth, so as to occlude the lumen of the plate and clasp the base ofthe sectioned frustule and allow extraction of the frustule by means of the plate whilst the cannula is kept at the operating site, allowing aspiration of marrow after the frustule has been removed.
Owner:罗伯托赞贝利
Dental Implant Fixture
InactiveUS20110076642A1Avoid damageReduce spacingDental implantsFastening prosthesisLow bone densityBone Cortex
Provided is a dental implant fixture with 3 or more ridged portions having mutually different pitches to distribute load uniformly across osseous tissue. The pitches of the ridged portions (200) progressively decrease in one direction. The ridged portions (200) include a larger ridged portion (220) that contacts spongy bone with low bone density, and a smaller ridged portion (240) that contacts cortical bone with high bone density. The smaller ridged portion (240) is provided with 2 or more threaded regions with respectively different pitches. With this configuration, bone decay and bone damage can be prevented, and synostosis can be improved.
Owner:COTEC CORP
Children type tumor joint prosthesis reserving femur neck and knee joint surface
InactiveCN111789702APreserve bone growth functionImprove stabilityJoint implantsFemoral headsEngineeringFEMORAL CONDYLE
The invention provides a children type tumor joint prosthesis reserving a femur neck and a knee joint surface. The children type tumor joint prosthesis reserving a femur neck and a knee joint surfacecomprises a backbone extension segment, wherein a femur near end prosthesis and a femur far end prosthesis are respectively assembled and connected to two ends of the backbone extension segment; porous structure grooves having bone trabecula are formed in the junction surface of the femur near end prosthesis and a femur and the junction surface of the femur far end prosthesis and femur condyle; afemur outside steel plate is in dismountable connection to the outer side of the femur far end prosthesis; and a femur near end central pulling force nail and femur near end assistant nail are connected with the femur near end prosthesis and the femur, and locking nails and spongy bone pulling force nails are connected with the femur far end prosthesis and the femur condyle. The prosthesis is connected with metaphyseal dysplasia tissue of a femur upper segment and a femur far end, and the bone growth function of a child patient is reserved. The situation that the skeleton growth of a postoperative child patient is not limited by the steel plate can be guaranteed, after the prosthesis and bone tissue form reliable biological fixation, the femur outside steel plate can be demounted, and theincreased spongy bone pulling force nails crossed inside and outside can further improve the stability and the reliability of the prosthesis.
Owner:BEIJING LIDAKANG TECH
Spongy bone for pets for eating and preparation method of spongy bone
The invention relates to a spongy bone and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a spongy bone for pets for eating and a preparation method of the spongy bone. According to the technical scheme, the spongy bone for pets for eating is characterized by comprising the following raw materials: wheat gluten, corn starch, chicken or / and beef, meat and bone meal, edible glycerinum, edible gelatin, yeast powder, edible essence, DL-alanine, salt, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, potassium chloride, an antioxidant, vitamin and mineral substances. According to the technical scheme, the preparation method comprises the following procedures: 1 dissolving; 2 activating the yeast powder; 3 mixing evenly; 4 mixing slurry; 5 fermenting and toughening; 6 processing and molding; 7 foaming; and 8 drying. Through the effects of the schemes, the novel spongy bone for pets for eating and the preparation method of the spongy bone are provided; the novel spongy bone is abundant in nutrient and low in cost, and is capable of well controlling the hardness of the product.
Owner:上海懿丰宠物用品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com