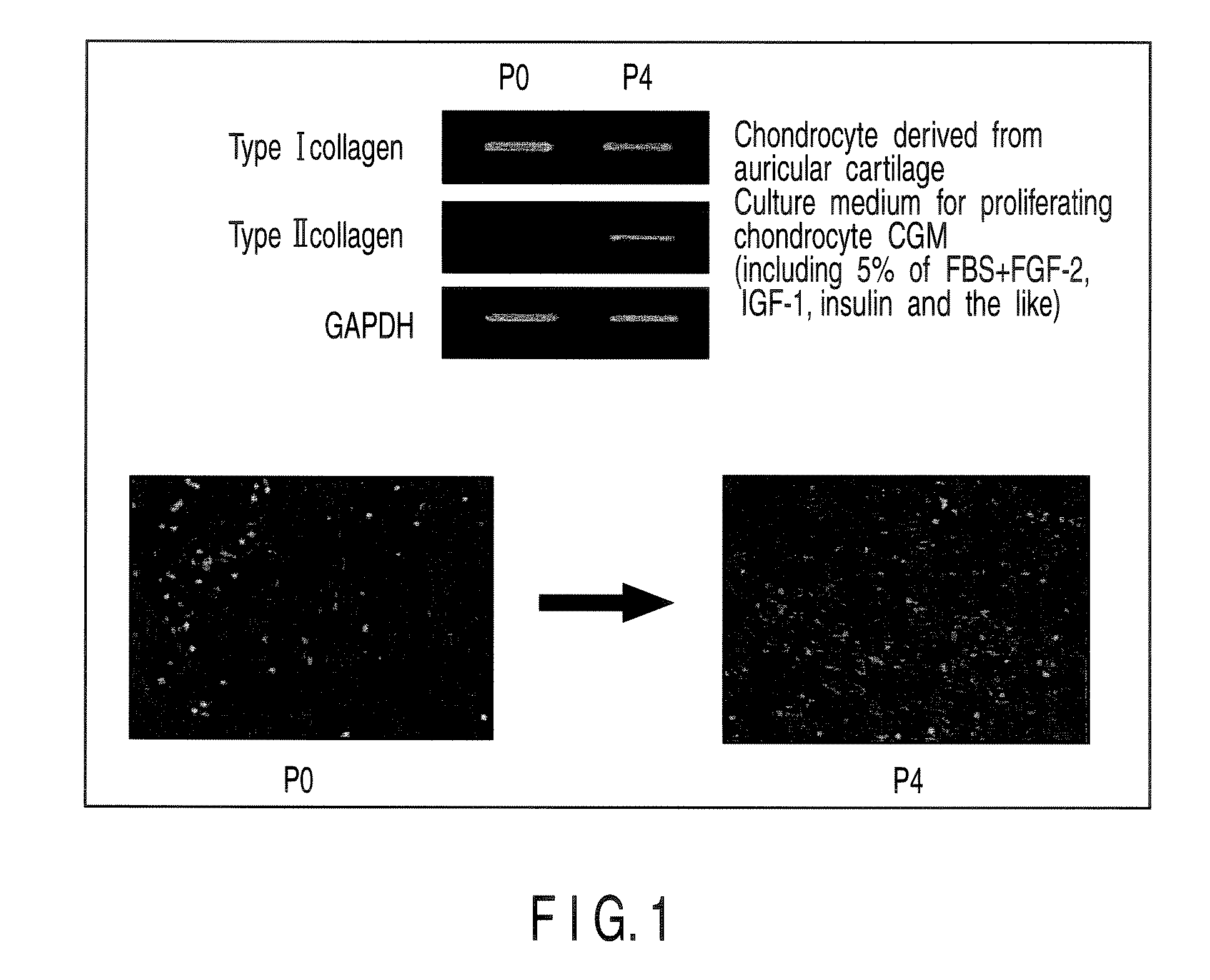
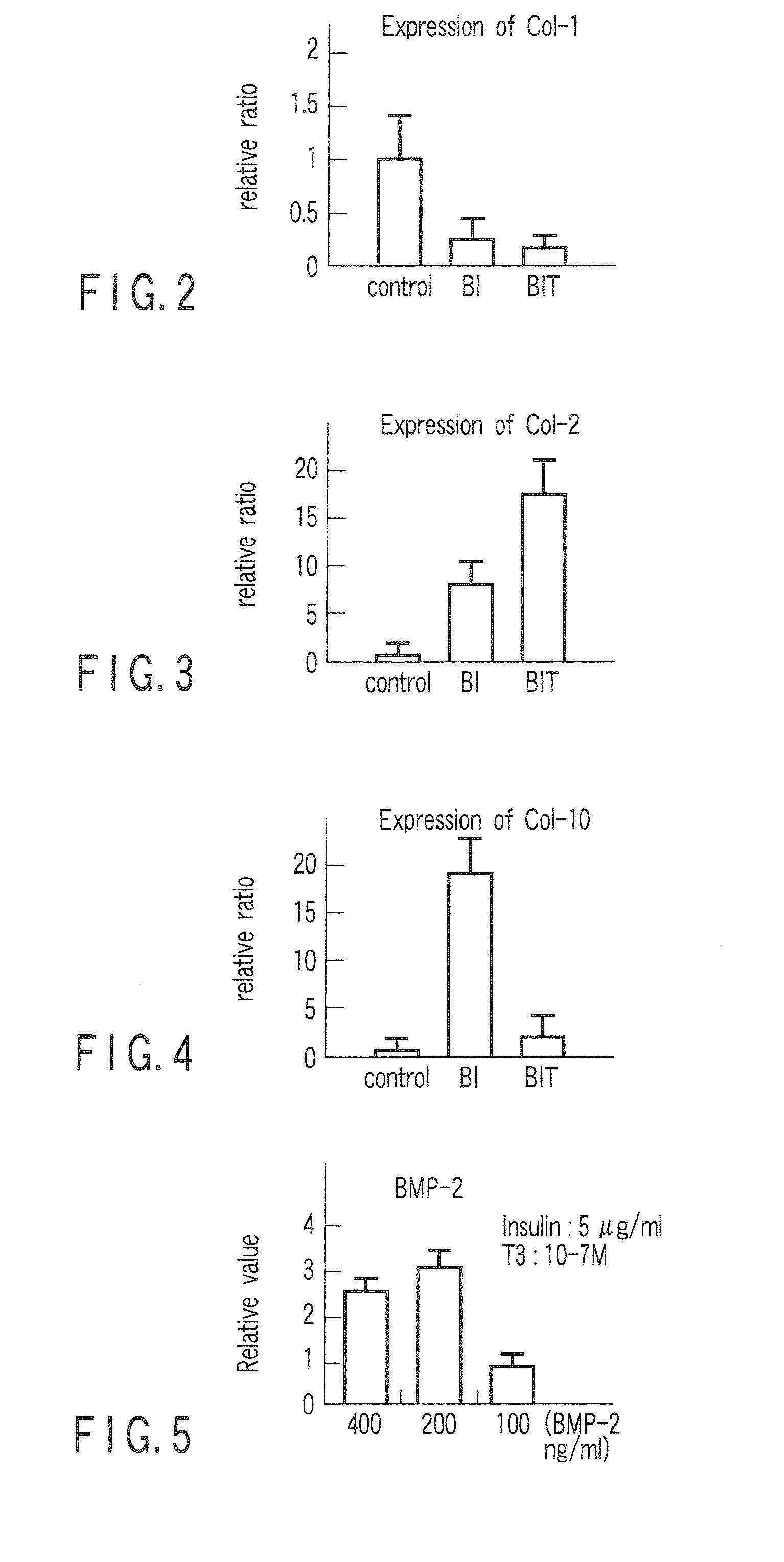
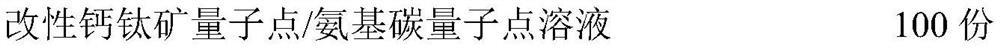Patents
Literature
66 results about "Chondroblast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chondroblasts, or perichondrial cells, is the name given to mesenchymal progenitor cells in situ which, from endochondral ossification, will form chondrocytes in the growing cartilage matrix. Another name for them is subchondral cortico-spongious progenitors. They have euchromatic nuclei and stain by basic dyes. These cells are extremely important in Chondrogenesis due to their role in forming both the Chondrocytes and cartilage matrix which will eventually form cartilage. Use of the term is technically inaccurate since mesenchymal progenitors can also technically differentiate into osteoblasts or fat. Chondroblasts are called Chondrocytes when they embed themselves in the cartilage matrix, consisting of proteoglycan and collagen fibers, until they lie in the matrix lacunae. Once they embed themselves into the cartilage matrix, they grow the cartilage matrix by growing more cartilage extracellular matrix rather than by dividing further.
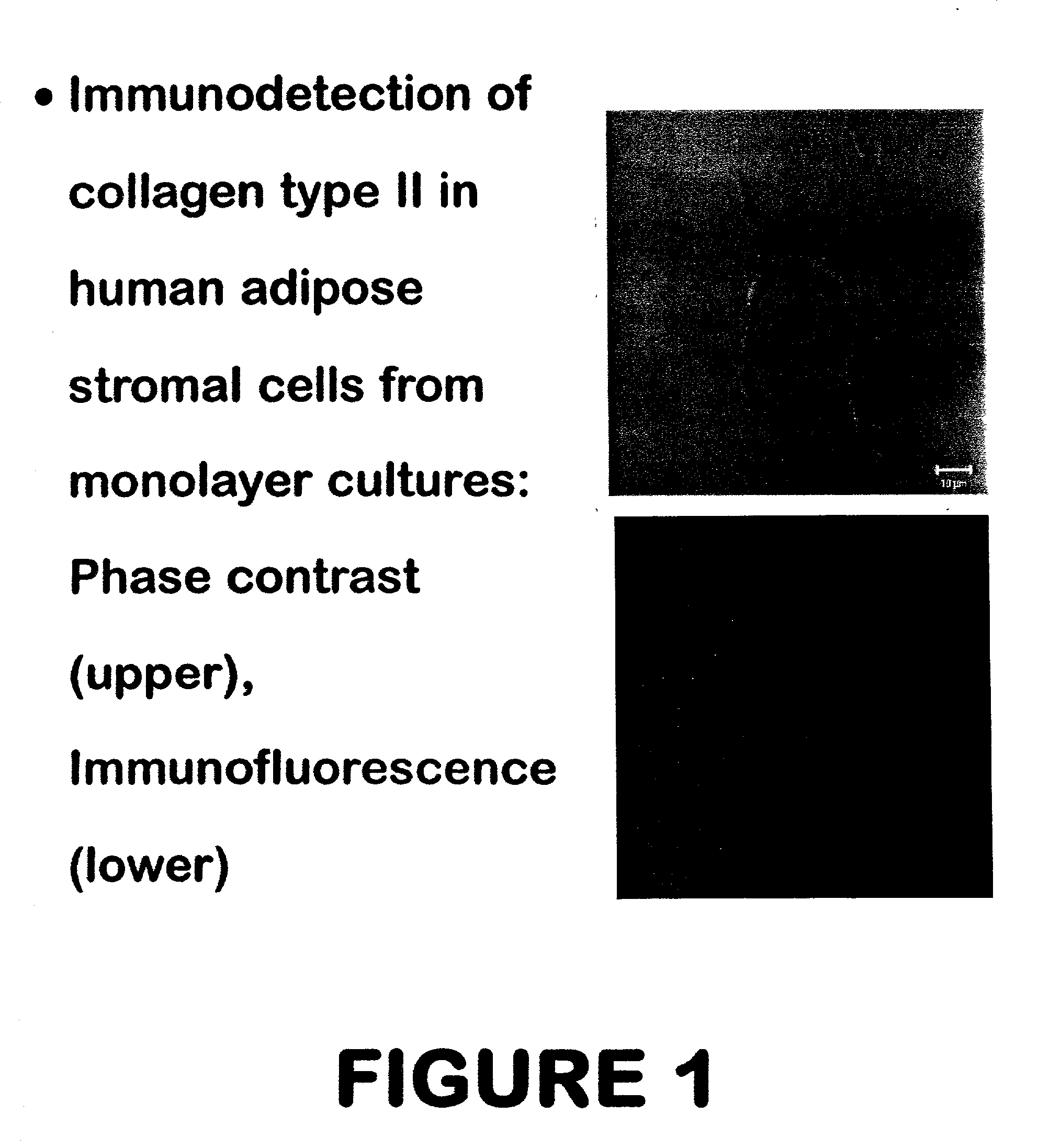
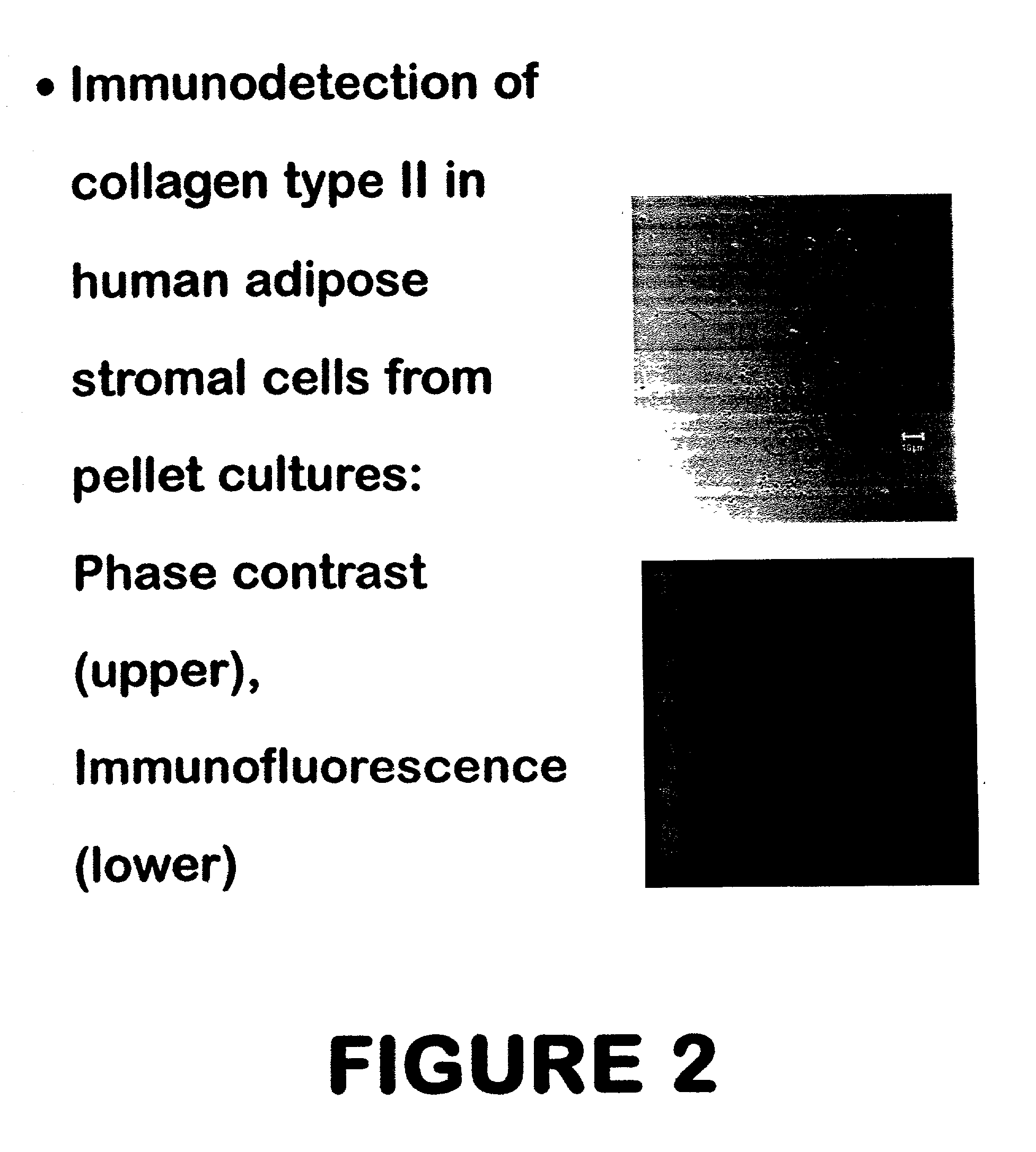
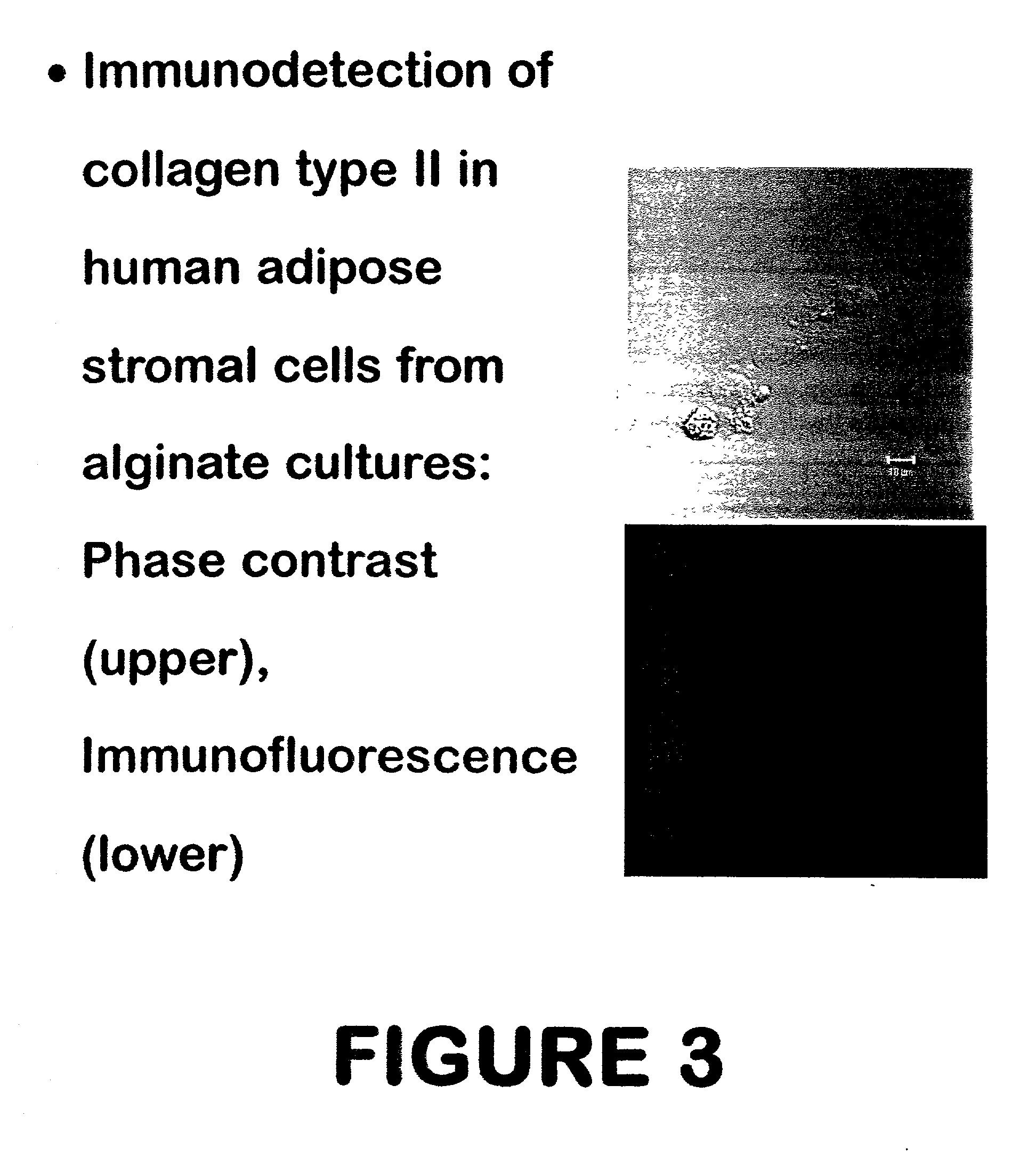
Use of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells for chondrocyte differentiation and cartilage repair
Methods and compositions for directing adipose-derived stromal cells cultivated in vitro to differentiate into cells of the chondrocyte lineage are disclosed. The invention further provides a variety of chondroinductive agents which can be used singly or in combination with other nutrient components to induce chondrogenesis in adipose-derived stromal cells either in cultivating monolayers or in a biocompatible lattice or matrix in a three-dimensional configuration. Use of the differentiated chondrocytes for the therapeutic treatment of a number of human conditions and diseases including repair of cartilage in vivo is disclosed.
Owner:COGNATE BIOSERVICES
Bioactive, resorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering
InactiveUS20050118236A1High porosityImprove manufacturabilityBiocideSynthetic resin layered productsPorosityFiber
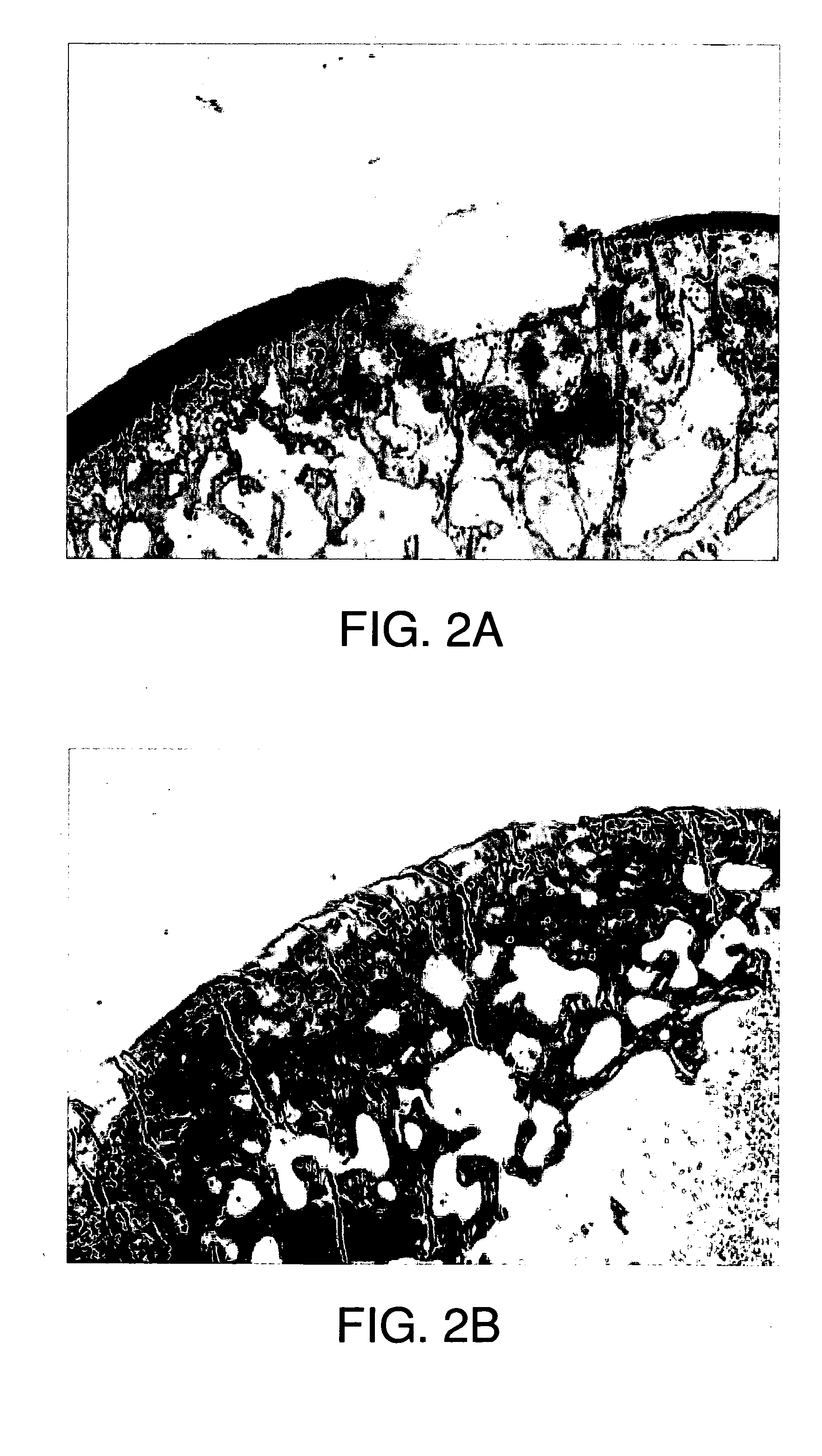
Flexible, bioactive glass meshes and scaffolds made therefrom are provided. The meshes comprise interwoven bioactive glass fibers that can be coated with resorbable polymers. Meshes can also be woven from glass fibers and resorbable polymers. Scaffolds can be constructed by a plurality of meshes, which can have varying porosities to create porosity gradients in the scaffold. Methods of making scaffolds are provided which can comprise pulling bioactive glass fibers, winding the fibers, forming the fibers into bundles, coating the fibers with a resorbable polymer, and creating a biaxial weave with the bundles. Soft tissue engineering methods are also provided for creating scaffolds for incubating cells such as fibroblasts and chondroblasts. Meshes and scaffolds are suitable for tissue engineering, such as bone tissue engineering and cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:GENTIS
Graft collar and scaffold apparatuses for musculoskeletal tissue engineering and related methods
This application describes apparatuses and methods for musculoskeletal tissue engineering. Specifically, graft collar and scaffold apparatuses are provided for promoting fixation of musculoskeletal soft tissue to bone.This application provides for graft collars comprising biopolymer mesh and / or polymer-fiber mesh for fixing tendon to bone. In one aspect, the graft collar comprises more than one region, wherein the regions can comprise different materials configured to promote integration of and the regeneration of the interfacial region between tendon and bone.This application also provides for scaffold apparatuses and methods for fixing musculoskeletal soft tissue to bone. The scaffold apparatus is multiphasic, preferably triphasic, and each phase is configured promote growth and proliferation of a different cell and its associated tissue. In one aspect, the scaffold apparatus is triphasic, with phases comprising materials to promote growth and proliferation of fibroblasts, chondroblasts, and osteoblasts. In addition, an apparatus comprising two portions, each of said portion being the scaffold apparatus described above is provided, wherein each of said portion encases one end of a soft tissue graft. Further, a triphasic interference screw is provided.This application further provides apparatuses and methods for inducing formation of fibrocartilage comprising wrapping a graft collar with polymer-fiber mesh configured to apply compression to the graft collar. In another aspect, the polymer-fiber is applied directly to the graft to apply compression to the graft.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods and compositions for repair of cartilage using an in vivo bioreactor
Methods and compositions for the biological repair of cartilage using a hybrid construct combining both an inert structure and living core are described. The inert structure is intended to act not only as a delivery system to feed and grow a living, core component, but also as an inducer of cell differentiation. The inert structure comprises concentric internal and external and inflatable / expandable balloon-like bio-polymers. The living core comprises the cell-matrix construct comprised of HDFs, for example, seeded in a scaffold. The method comprises surgically removing a damaged cartilage from a patient and inserting the hybrid construct into the cavity generated after the foregoing surgical intervention. The balloons of the inert structure are successively inflated within the target area, such as a joint, for example. Also disclosed herein are methods for growing and differentiating human fibroblasts into chondrocyte-like cells via mechanical strain.
Owner:SPINALCYTE
Vitro repair of bone and/or cartilage defects
The present invention relates to methods and materials for in vivo repair of cartilage or bone and cartilage defects in mammals. The invention relates to membranes carrying a composition comprising at least one stimulation molecule, which is capable of inducing signal transduction in chondroblasts / chondrocytes and / or osteoblasts / osteocytes. Furthermore the invention relates to a method for the preparation of chondroblasts / chondrocytes and / or osteoblasts / osteocytes suspensions.
Owner:INTERFACE BIOTECH
Complex support body for regenerating bone-cartilage, method for manufacturing thereof, and composition for treating bone and cartilage related diseases comprising same as active ingredient
ActiveUS20140012393A1Regenerate bone and cartilageBone implantTissue regenerationDiseaseCartilage cells
The present invention relates to a complex support body for regenerating bone-cartilage, a method for manufacturing thereof, and a composition for treating bone and cartilage related diseases comprising the same as an active ingredient, and more particularly, to a complex support body for regenerating bone-cartilage, which comprises a bone regeneration layer consisting of a biodegradable polymer and a biocompatible ceramic, and a cartilage regeneration layer, which is coupled to the bone regeneration layer and in which cells that can be differentiated into cartilages cells are fixed; a method for manufacturing thereof; and a composition for treating bone and cartilage related diseases comprising the same as an active ingredient. The complex support body of the present invention for regenerating bone-cartilage is manufactured as a three-dimensional support body, which is similar to a living tissue, according to a bioplotting method, and exerts the effect of regeneration into a bone tissue and a cartilage tissue, respectively, depending on materials encountered in the environment where the complex support body for regenerating bone-cartilage is used.
Owner:INJE UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Method for cell implantation
An endoscopic method for treating cartilage or bone defects in an animal, said method comprising the steps of: I) identifying the position of the defect, ii) applying cells selected from the group consisting of chondrocytes, chondroblasts, osteocytes and osteoblasts and combinations thereof into the cartilage or bone defect. In particular, the invention relates to a method for arthroscopic or endoscopic implantation of homologous or autologous cells into a defect of an animal body, the method comprising a step of I) arthroscopic or endoscopic application of a fluid to a cavity or surface containing the defect, and the steps of ii) application of the cells to the defect substantially simultaneously with a support material, the application being performed at the defect covered by the fluid, iii) mixing of the cells and the supporting material, iv) solidification of the supporting material so that the defect is covered by a mixture of cells and support material without any significant amount of fluid, and v) optionally, removal of the fluid from the cavity or surface by drainage or suction.
Owner:INTERFACE BIOTECH
Method for 3D cultivating and inducing stem cell of mesenchyme of bone marrow and chondroblast
InactiveCN1563364AAvoid damageReduce degradationTissue cultureOn/in organic carrierMesenchymeMicrocarrier
A method for preparing chondroblast of bone marrow mesogalia stem cell with three dimensional cultivation and induction includes steps of placing bone marrow mesogalia stem cell into suspending culture device preset with culture medium and microcarrier for suspending cultivation; cloning abovesaid stem cells with agitation, adding induction culture medium of chondroblast in culture meidum containing harvested cytodex3 microcrrier and abovesaid stem cells gromn on it; and carrying out induction for chondroblast assembly from abovesaid stem cells.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tissue engineered bone-cartilage complex tissue graft and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a tissue engineered bone-cartilage composite tissue transplant and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the tissue engineering field. The method comprises the following steps: seed cells are implanted on a scaffold material and cultured in vitro to form the tissue engineered bone-cartilage composite tissue transplant; the seed cells are osteogenic stem cells; the scaffold material comprises an osteogenic part and a chondroblast part, and the osteogenic part is added with an osteoblast induction factor and modified by a type-I collagen in a preparation process; and the chondroblast part is added with a chondroblast induction factor and modified by a type-II collagen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are successfully induced into osteocytes and chondrocytes, and bone tissues and cartilage tissues are formed after the obtained transplant is transplanted in vivo. Satisfactory effect is obtained from the tissue engineered bone-cartilage composite tissue which is constructed by the transplant.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing individual porous thyroid cartilage support
ActiveCN103656760ASurgical needs to ensure personalized defect repairImprove adsorption capacitySpecial data processing applicationsProsthesisData acquisitionHydroxylapatite
The invention discloses a method for preparing an individual porous thyroid cartilage support. The method comprises the following steps: performing data acquisition on a living body by using high-precision medical CT, partitioning a thyroid cartilage area by using a partitioning algorithm, and exporting the data in a text format; performing in-vitro isolated point removal, noise reduction, surface smoothing and reverse three-dimensional modeling on the acquired data in reverse engineering software; performing rapid mold design by using industrial CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software UG-NX, and preparing a rapid mold through rapid molding; preparing foam slurry which takes hydroxylapatite particles as a filling matrix by using a gel foaming method, injecting the slurry into the rapid mold, and initiating an in-situ curing reaction so as to finish preparation of a cartilage support blank; demolding and drying the support blank, and performing high-temperature sintering, thereby obtaining the individual porous thyroid cartilage support. After the support is implanted into the body of a patient, the surrounding cartilage metrocyte and growth factors can be effectively absorbed, a metabolism channel is provided for growth of the cartilage metrocyte, and the cartilage metrocyte grows into individual bones.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Isolated culture and identification method of porcine adipose-derived stem cells
InactiveCN105602896AStrong proliferative abilityGood proliferative abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAntigenStem Cell Isolation
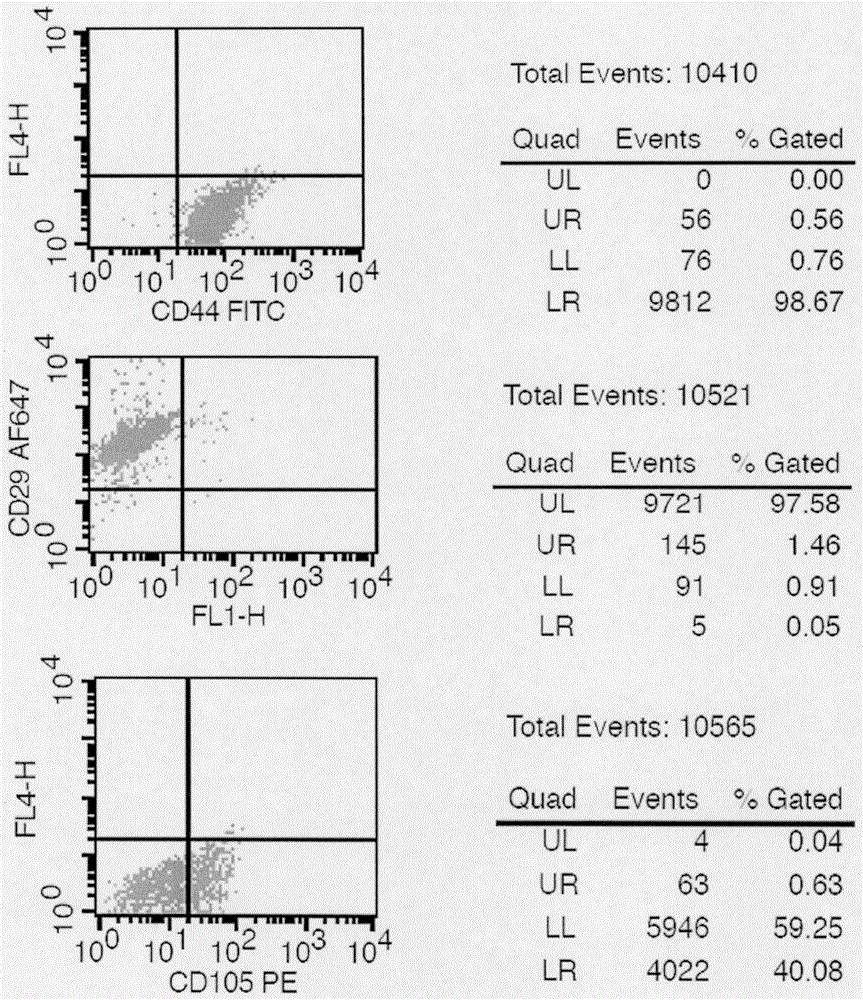
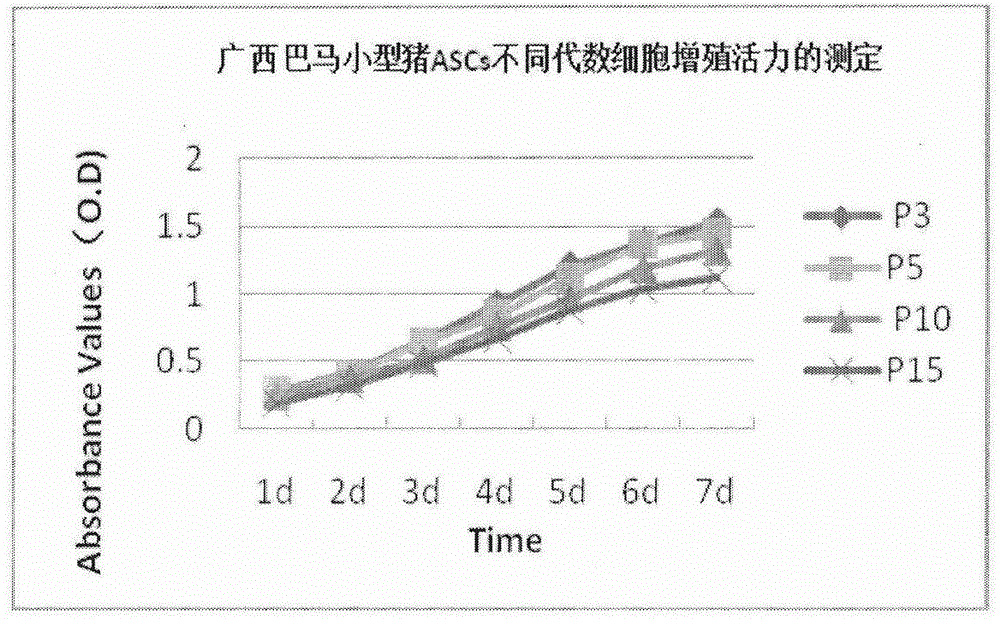
The invention discloses an isolated culture and identification method of porcine adipose-derived stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: 1) isolated culture and purification of adipose-derived stem cells; and 2) subculturing of adipose-derived stem cells. The adipose-derived stem cells obtained by the method disclosed by the invention have good genetic stability, and the genetic stability is still kept after the adipose-derived stem cells are continuously cultured in vitro to the 15th generation; with good dryness, the adipose-derived stem cells still have the surface antigen characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells after cultured in vitro to the 18th generation; and with good multi-directional differentiation property, the adipose-derived stem cells have the ability of differentiating into osteoblasts, chondroblasts and lipoblasts.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Bone defect repair material based on modified perovskite quantum dots/amino carbon quantum dots and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112618788AStimulate proliferation and regenerationHigh fluorescence quantum efficiencyTissue regenerationProsthesisPhosphoric acidAcyl group
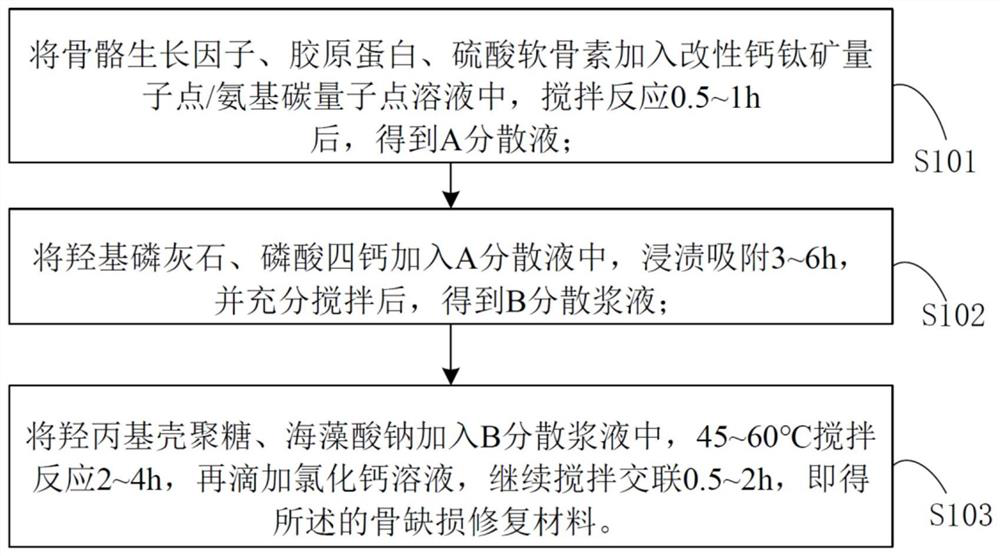
The invention discloses a bone defect repair material based on modified perovskite quantum dots and a preparation method of the bone defect repair material. The bone defect repair material comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 20-30% of hydroxyapatite, 10-20% of octacalcium phosphate, 0.5-2% of bone morphogenetic protein, 1-5% of collagen, 0.5-2% of chondroitin sulfate, 3-5% of carboxymethyl chitosan and the balance of a modified perovskite quantum dot solution. The modified perovskite quantum dot / amino carbon quantum dot solution is prepared from the following reaction raw materials in parts by mass: 0.5 to 1.5 parts of perovskite quantum dots, 8 to 16 parts of dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl ethanolamine, 3 to 7 parts of acidic amino acid, 1 to 3 parts of reduced glutathione, 0.5 to 1 part of EDC.HCl, 20 to 30 parts of chloroform and 100 parts of deionized water. Perovskite quantum dots and amino carbon quantum dots are introduced into the bone defect repair material for the first time, stem cell transfection is mediated by quantum dot and stem cell behavior changes are monitored by utilizing a fluorescence microscopy imaging technology; meanwhile, the stem cells are induced to differentiate towards osteoblasts and chondroblasts, and proliferation and regeneration of the osteoblasts are stimulated.
Owner:蚌埠泰鑫材料技术有限公司
Preparation, induced differentiation and application of self-assembled mesenchymal stem cell aggregate
InactiveCN104962517APromote differentiationFacilitate communicationSkeletal disorderSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHigh densityArticular cartilage
The invention discloses preparation, induced differentiation and application of a self-assembled mesenchymal stem cell aggregate. The mesenchymal stem cell aggregate is prepared through the following steps of (1), coating a porous culture plate by using aquogel under aseptic conditions; (2), carrying out amplification cultivation on mesenchymal stem cells to obtain the third generation; and (3), preparing cell suspension from the third generation of mesenchymal stem cells by using aggregate forming induced liquid, adding the cell suspension into each pore of the coated porous culture plate so that the number of cells in each pore is 1*10<5> to 1*10<6>, changing the aggregate every day to form induced liquid for one time, and putting the porous culture plate in a cell culture box to culture so as to form the mesenchymal stem cell aggregate with the diameter of 500-600mu m. According to the invention, high-density three-dimensional culture of mesenchymal stem cells can be realized without a bracket material; the uniformity of chondroblast induced mesenchymal stem cells is increased; and the mesenchymal stem cell aggregate can be directly used for repairing articular cartilage defects.
Owner:广东佰鸿干细胞再生医学有限公司
Biosynthetic cartilaginous matrix and methods for their production
An isolated, acellular biosynthetic cartilaginous matrix substantially devoid of synthetic biodegradable scaffold structure is provided. Through a method with the steps of a) contacting in vitro a population of chondrogenic cells with a synthetic biodegradable scaffold; b) culturing in vitro for a period of time said chondrogenic cells within said synthetic biodegradable scaffold so that the chondrogenic cells produce a biosynthetic cartilaginous matrix; c) substantially removing any antigen derived from said chondrogenic cells a matrix suitable of implantation into a living individual mammal, such as a human being is obtained.
Owner:COLOPLAST AS +1
Tissue- engineered cartilage graftimplant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103495208AImprove adhesionPromote vascularizationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisCartilage cellsBiomechanics
The invention relates to a tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of induced differentiation carried out on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) by utilizing a bioactive inducing factor to form a cartilage cell chondroblast composite scaffold material and so as to construct a tissue tissue-engineered cartilage by utilizing a biological activity inducing factor in biomedicine tissue engineering. The tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant is prepared by adopting the method comprising the following steps: (1) preparing a Nano-HA / PLLA (hyaluronic aciddroxyapatite / poly left L-lactic acid) cartilage scaffold material; (2) carrying out coculture on BMSCs and the Nano-HA / PLLA cartilage scaffold material, and carrying out induced differentiation on BMSCs to form cartilage cells by adopting a cartilage formation inducing solution, so that the tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant is obtained. The tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant improves flexibility and biodegradability of the cartilage scaffold material, improves biomechanical property and is more beneficial to adhesion, growth and vascularization of bone cells; an animal experiment proves that the tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant has a good cartilage defect repairing function.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
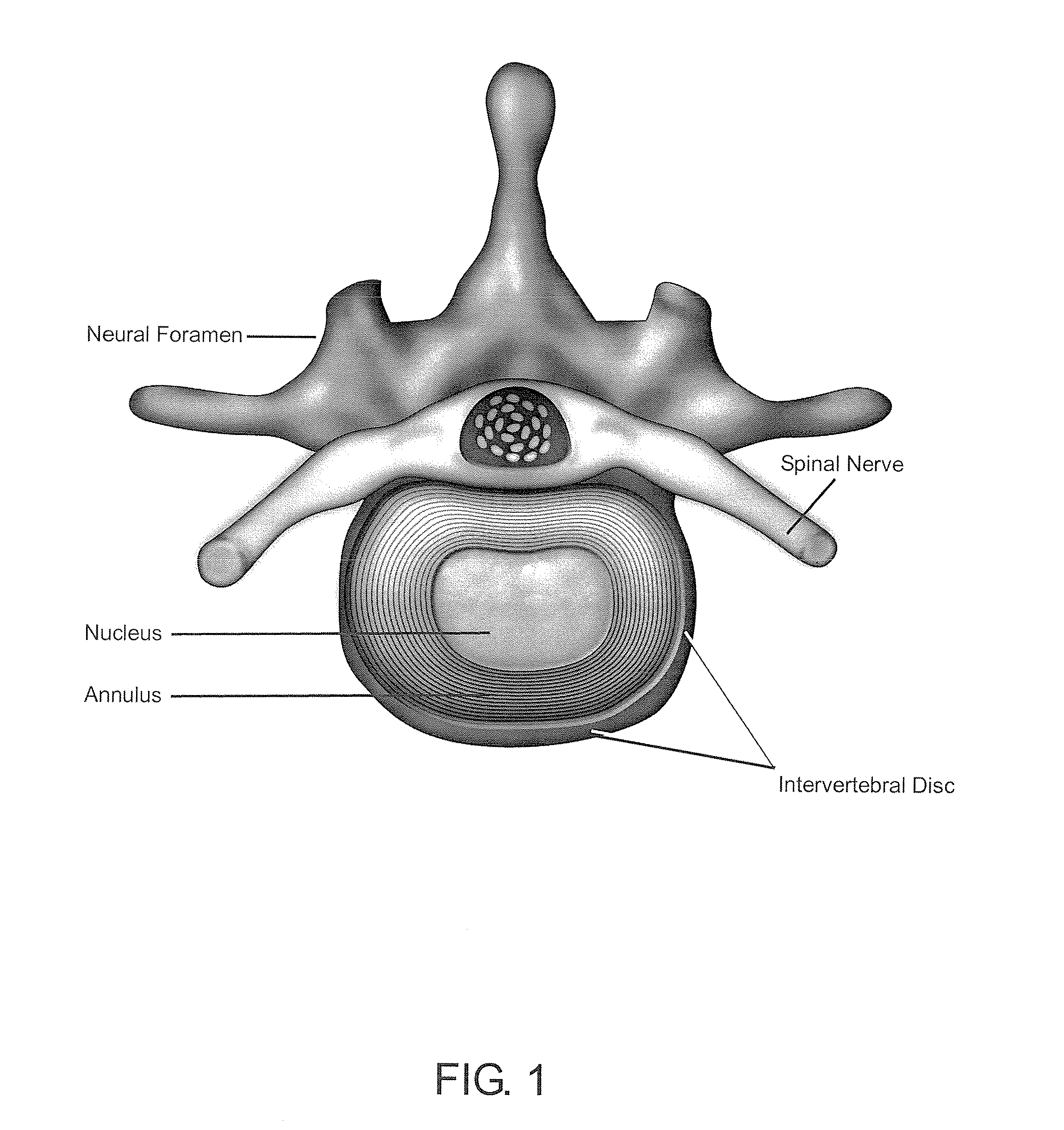
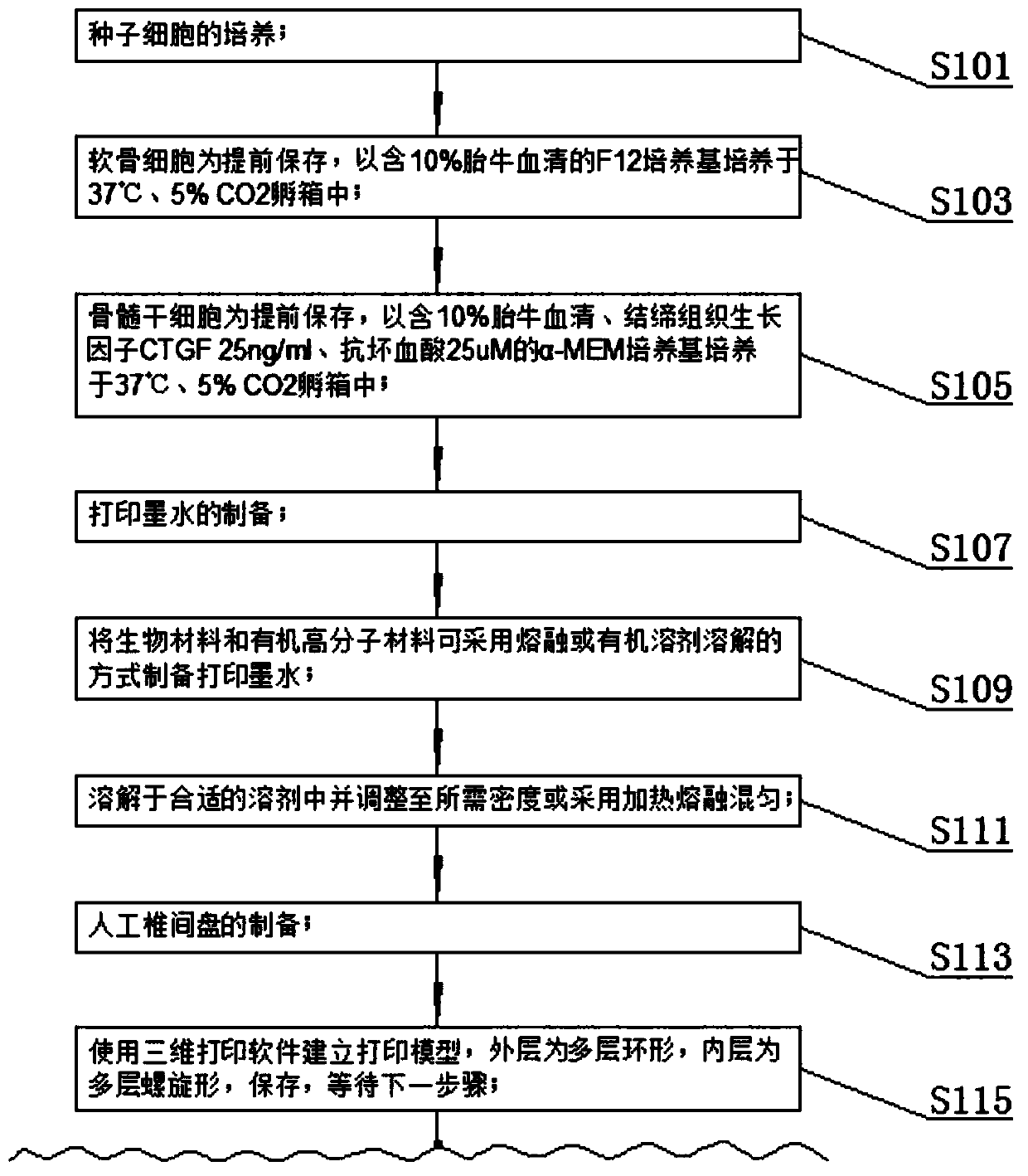
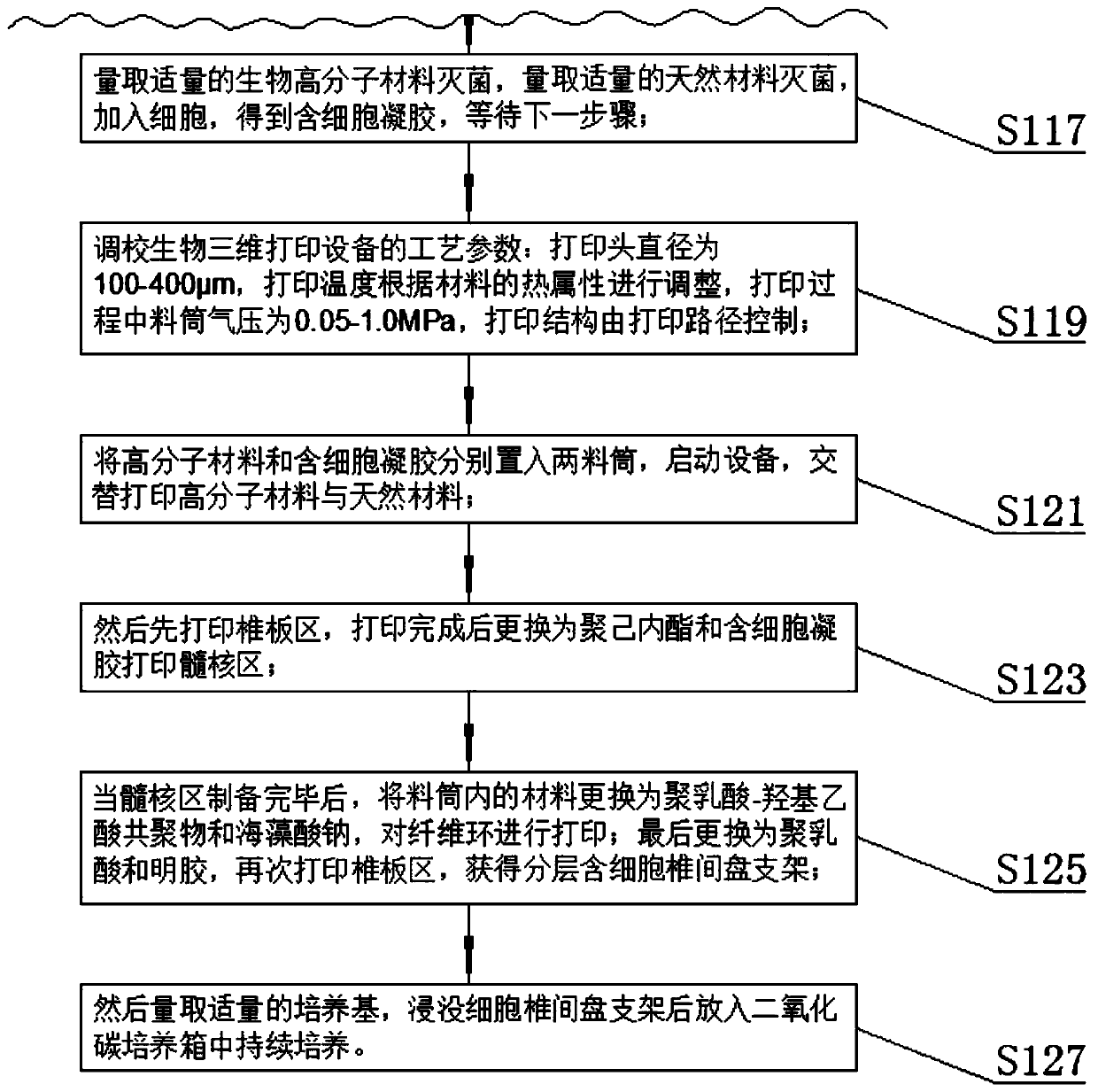
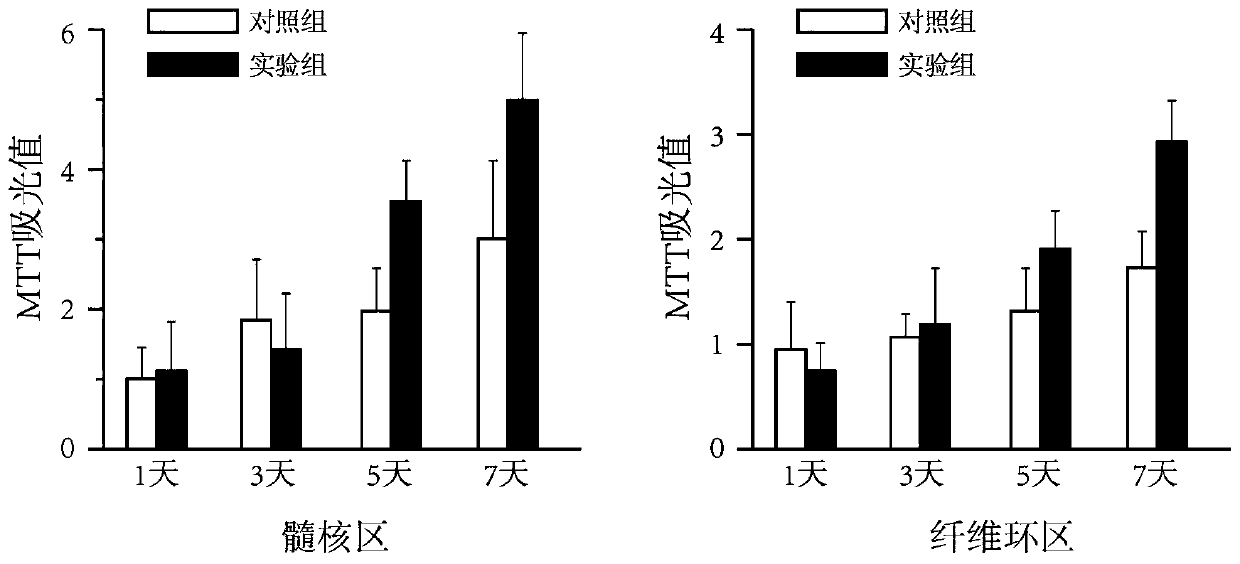
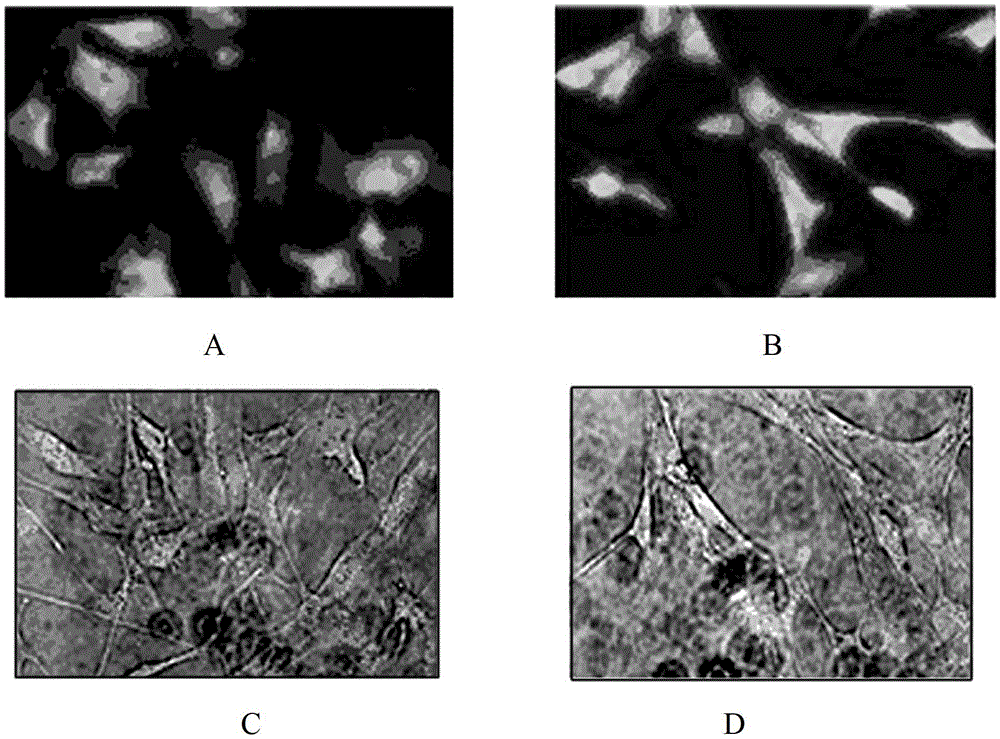
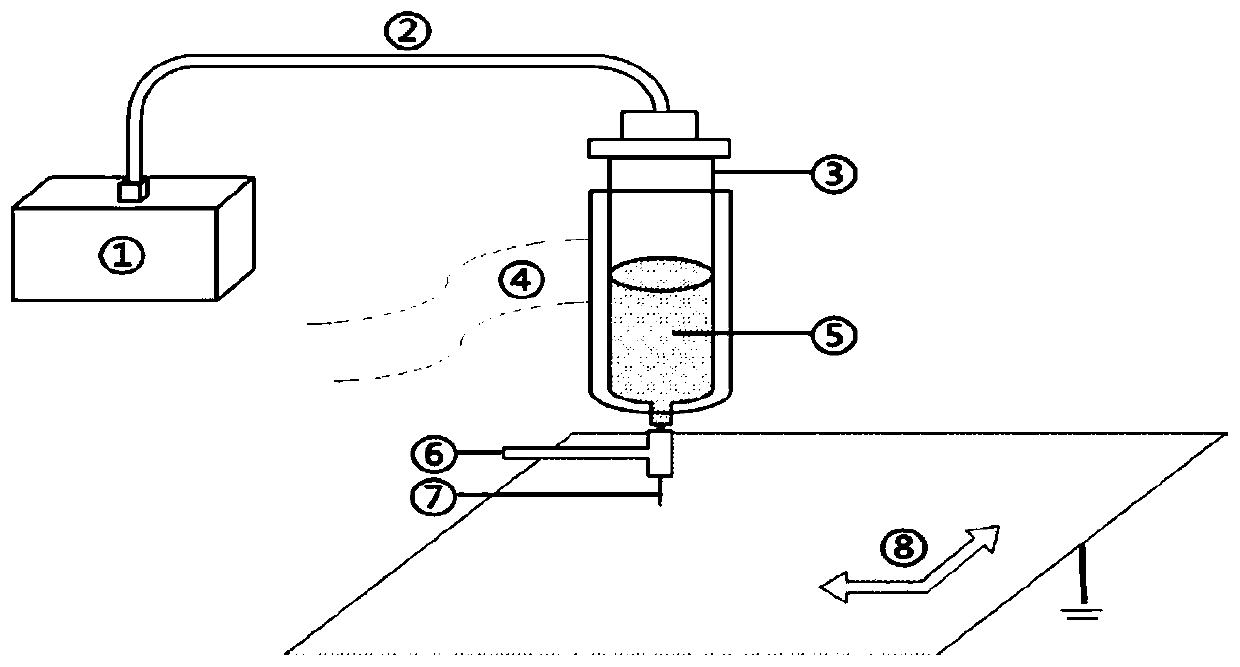
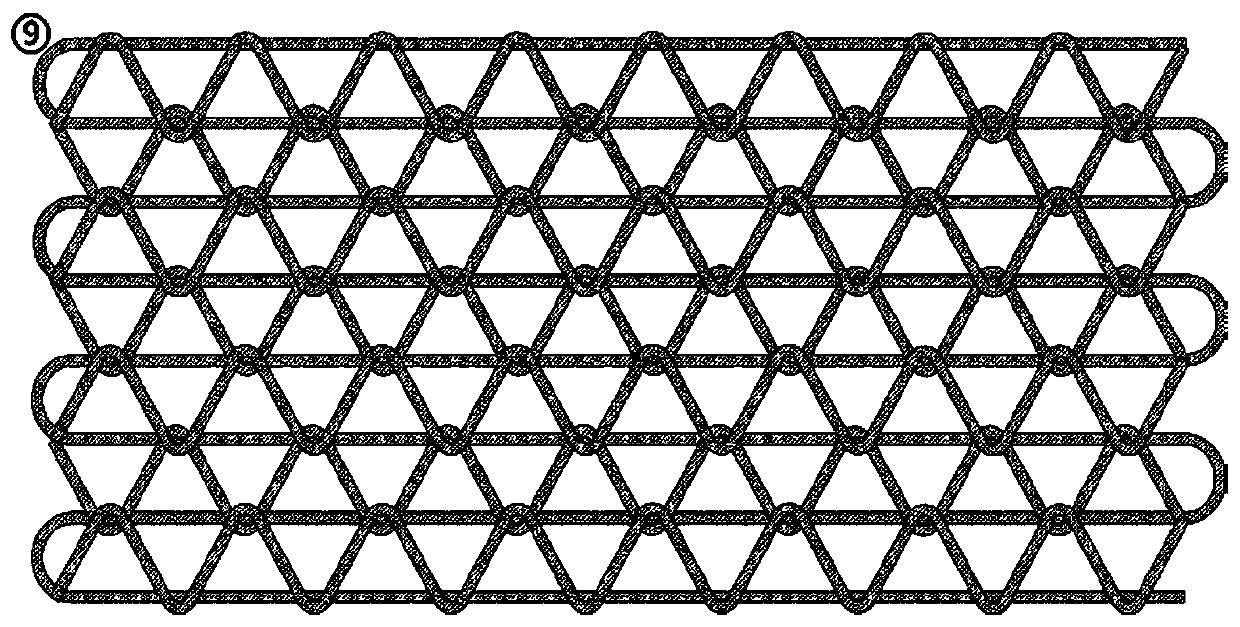
Electrostatic arch wire three-dimensional printed artificial intervertebral disc bracket and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110464875AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh precisionAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisPorosityArch wires
The invention discloses an electrostatic arch wire three-dimensional printed artificial intervertebral disc bracket and a preparation method thereof. The electrostatic arch wire three-dimensional printed artificial intervertebral disc bracket is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 10-16 parts of chondrocyte, 3-6 parts of fetal calf serum, 8-10 parts of bone marrow stem cells, 7-9 parts of connective tissue growth factors, 5-6 parts of ascorbic acid, 7-9 parts of a biological material, 7-9 parts of an organic macromolecule material and 7-9 parts of a biological macromolecule material. The electrostatic arch wire three-dimensional printed artificial intervertebral disc bracket has the beneficial effects that properties such as a controllable porosity, a large specificsurface area, good biocompatibility and good mechanical properties achieved by printing wires which are mutually interwoven are achieved, according to demands, printing route parameters are designed,an artificial bionic intervertebral disc which is high in structure precision and controllable in mechanical property and meanwhile carries a great number of seed cells for multiplication repairing can be obtained, micro environments around the intervertebral disc can be rapidly established, and functions of the intervertebral disc can be recovered.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for inducing synovium mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated to chondrocytes by in-vitro lentivirus mediated BMP-2 (Bone Morphogenetic Protein) genes
InactiveCN103146755AThe production process is complicatedReduce outputFermentationGenetic engineeringStem Cell IsolationLentivirus
The invention relates to a method for inducing synovium mesenchymal stem cells (SMSCs) to be differentiated to chondrocytes by in-vitro lentivirus mediated BMP-2 (Bone Morphogenetic Protein) genes. The method comprises the following steps of: separating and culturing synovium mesenchymal stem cells; constructing a recombinant plasmid pFUGW-oBMP-2; preparing morbus virosus of transfected lentivirus; and transfecting synovium mesenchymal stem cells by the morbus virosus of transfected lentivirus, wherein in the step of preparing morbus virosus of transfected lentivirus, the transfected lentivirus is jointly formed by the recombinant plasmid pFUGW-oBMP-2 and a packaging plasmid; and in the step of transfecting synovium mesenchymal stem cells by the morbus virosus of transfected lentivirus, synovium mesenchymal stem cells over third generation is taken to be mixed with the morbus virosus of transfected lentivirus, and then added into incomplete chondroblast inducing culture liquid to induce so as to obtain chondrocytes. SMSCs transfected by the transfected lentivirus provided by the invention are safe enough and can be spontaneously differentiated to cartilage in vitro.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Cell culture solution for enhancing cartilage differentiation induction, method and application
PendingCN111826343APromote growthPromote proliferationCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsChondroblast differentiationPlatelet lysate
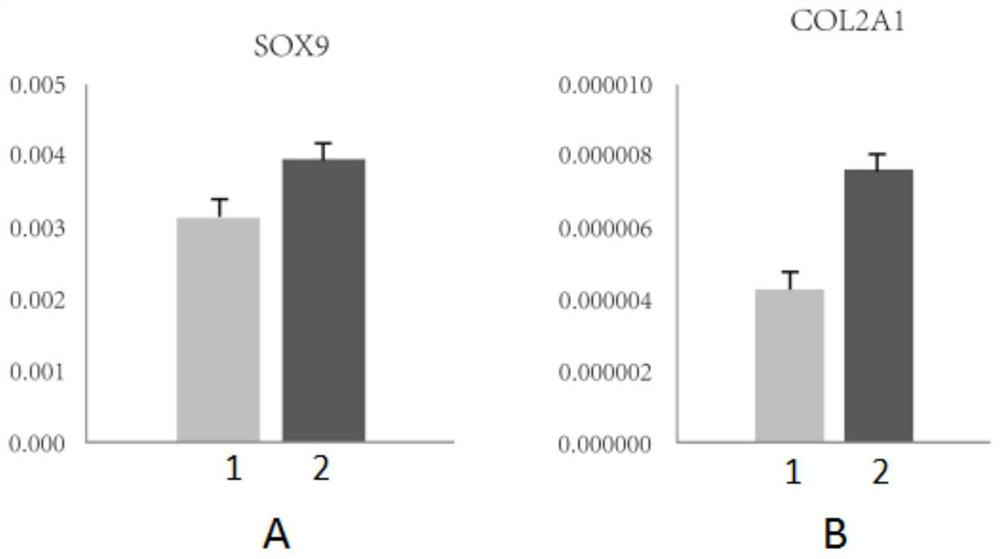
The invention discloses a cell culture solution for enhancing cartilage differentiation induction, a method and an application. A blood platelet lysate is extracted and prepared from clinically wasteplacental blood, so that the source is wide, and the cost is low. Mesenchymal stem cells obtained by the method can stably grow in an adherent manner, characteristics are similar to those of cells obtained by a conventional culture method, and the cells are in a typical fusiform vortex shape under a microscope; and compared with the conventional culture method, the method has the advantages that expression of cartilage differentiation marker genes SOX9 and COL2A1 in the cells can be effectively activated, the number and strength of formed cartilages after in-vitro induction are obviously improved, and the higher chondroblast differentiation capacity is shown.
Owner:北京中卫医正科技有限公司
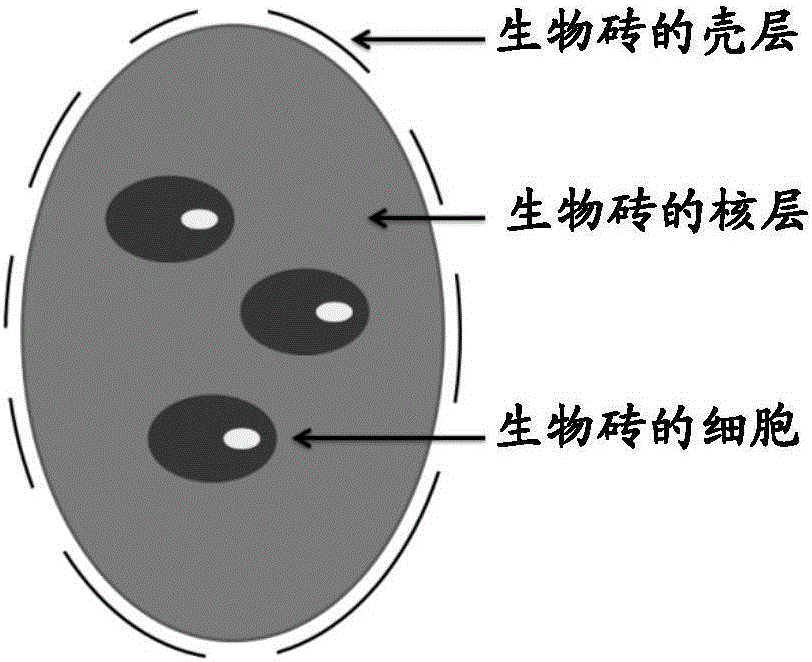
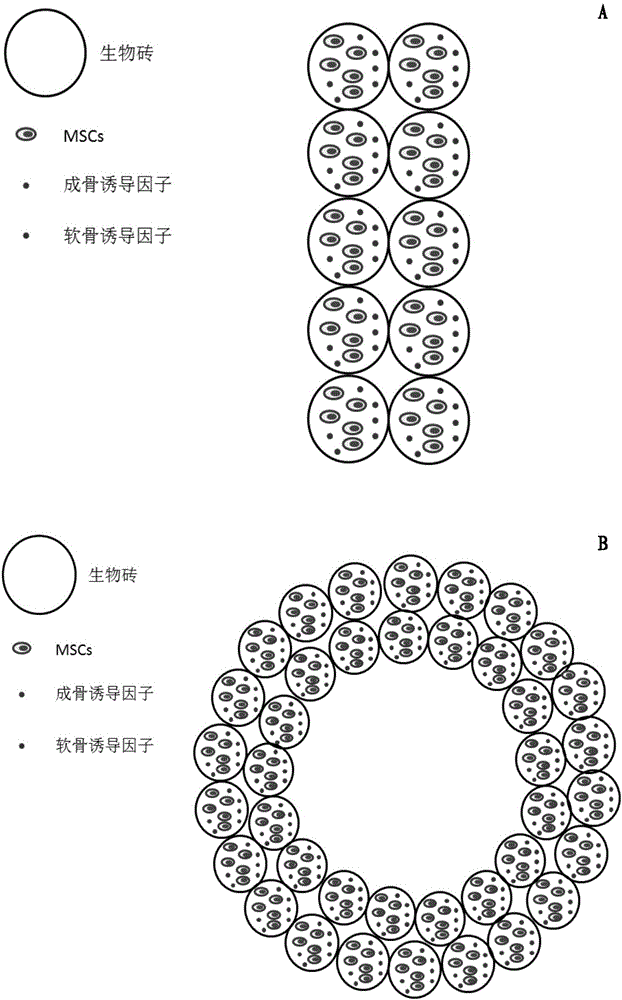
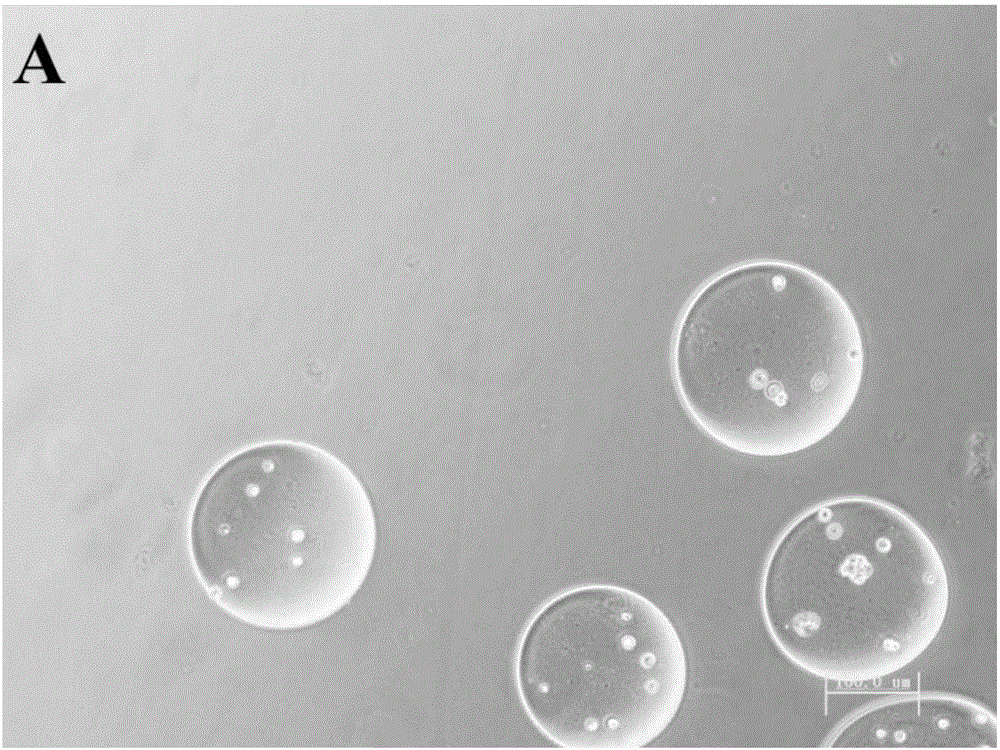
Biobricks containing mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) and application thereof
ActiveCN106039407AGood size controlControllable numberCompounds screening/testingSkeletal disorderEngineeringComposite structure
Owner:SICHUAN REVOTEK CO LTD
Method of inducing fibroblasts into chondrocyte like cells
InactiveCN107267448AImprove securityExperiment operation is simpleCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTransdifferentiationFibroblast
The invention relates to a method for inducing fibroblasts into chondrocyte like cells, and belongs to the field of cell biology and regenerative medicine. The method aims at the general problems that carrier mediation and transgenic operation are needed, requirements on experimental facilities and technical level are relatively high, the security of produced chondrocytes is relatively poor and the like in methods for transdifferentiation of the fibroblasts into the chondrocytes in the prior art, and uses fish oocyte extract for inducing reprogramming of the fibroblasts into the chondrocyte like cells. The chondrocyte like cells are obtained only by use of the fish oocyte extract for inducing and use of a chondroblast induction medium for directional inducing culture without introduction of exogenous genes, so that experimental operation is relatively simple, and the obtained chondrocyte like cells are better in security, and have a broad application prospect in the field of cartilage tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Owner:中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九二〇医院
Method for converting in-vitro activated adipose-derived stem cells into chondroblasts
InactiveCN111518751AReduce rejectionKeep aliveCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPancreatic hormoneTransferrin
The invention discloses a method for converting in-vitro activated adipose-derived stem cells into chondroblasts. The method comprises the following steps of preparing a DMEM culture medium, wherein the DMEM culture medium is prepared from 1% of fetal calf serum, 10 ng / ml of TGF-beta, 100 ng / ml of BMP-6, 6.25 mu g / ml of insulin, 0.1 mu mol / L of dexamethasone, 6.25 mu g / ml of transferrin and 50 mumol / L of ascorbyl phosphate; culturing the adipose-derived stem cells formed into micelles in the DMEM culture medium; and injecting the adipose-derived stem cells cultured for 7-9 days into an articular cavity and converting the adipose-derived stem cells into chondroblasts. The method has the advantages of time saving, simple process control and low rejection of the generated chondroblasts.
Owner:GUANGDONG XIANKANGDA BIOTECH CO LTD
Tissue engineering trachea implant and construction method and use
InactiveCN101322859ACreate preparation modeAchieve permanent functional reconstructionCatheterTubular organ implantsIn vivoBiological materials
The invention provides a trachea implant in tissue engineering. Chondroblast is combined with degradable biomaterial and then cultured and constructed jointly in vitro and in vivo, and has the blood supply connection with cultured tissues in vivo. The trachea implant in tissue engineering of the invention can effectively repair the segmental defect of the trachea. The invention further provides a construction method and a use method thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI TISSUE ENG LIFE SCI
Method for inducing production of chondroblast from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN108753700AIncrease success rateA lot of cellsCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMicroparticleCytokine
The invention belongs to the field of stem cells and discloses a method and medium for production of chondroblast from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. The medium comprises a cytokine bFGF. Themethod utilizes gelatin microparticles as scaffold materials and a three-dimensional culture method to induce production of chondroblast from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells based on the medium.The method has good induction effects and a high success rate and can acquire a lot of cells.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Adhesive cartilage implant
InactiveUS20100166822A1Reduce the temperatureBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsCulture cellBone implant
A method of producing a cartilage implant which may include coating a substrate with a thermo-sensitive polymer, seeding the polymer with a cell suspension comprising cells that may differentiate into chrondocyte-like cells, wherein the seeding may be conducted at a first temperature, culturing the cell suspension at an increased temperature, whereby cells in the suspension may adhere to the polymer and differentiate into chrondrocyte-like cells, which may form a cartilagenous implant, and decreasing the temperature of the polymer which may allow detachment of the implant from the polymer. The present invention may also include an implant based on this method. The invention may further include a cartilage implant for use in a patient in need thereof, which may include a random three-dimensional configuration of differentiated cells, which may have a natural adhesion surface on at least a portion of the outer surface of the three-dimensional configuration.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Method for inducing differentiation of adipose derived stem cells into chondrocyte
ActiveCN111454901APromote proliferationImprove the efficiency of induced differentiationCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCalcium alginateGene expression
The invention provides a method for inducing differentiation of adipose derived stem cells into chondrocyte. The method comprises the steps of preparing adipose derived stem cell-sodium alginate suspension, preparing adipose derived stem cell-calcium alginate microbeads, and performing induced culture. According to the method for inducing differentiation of adipose derived stem cells into chondrocyte, an incomplete cartilage forming induced culture solution containing PRP and transforming growth factor-beta superfamily members (TGF-[beta]1, IGF-1 and BMP-6) is utilized, and PRP and transforming growth factor-beta superfamily members are in united use, so that synergistic reactions are achieved, Sox-9 gene expression can be raised, differentiation of induced adipose derived stem cells intohypertrophy phenotypes is restrained, cell proliferation is promoted, and induced differentiation efficiency is improved. The proliferation vitality of the chondrocyte obtained through induced differentiation for 13-15 days by the method disclosed by the invention is 3.4 times of that of a control group A, 2.2 times of that of an experimental group B, and 1.95 times of that of an experimental group C.
Owner:SHANDONG XINRUI BIOTECH CO LTD
Redifferentiation medium for making dedifferentiated chondrocyte to be redifferentiated into chondrocyte
InactiveUS20070134793A1Efficient productionReadily and efficientlyCulture processSkeletal disorderCell biologyChondrocyte
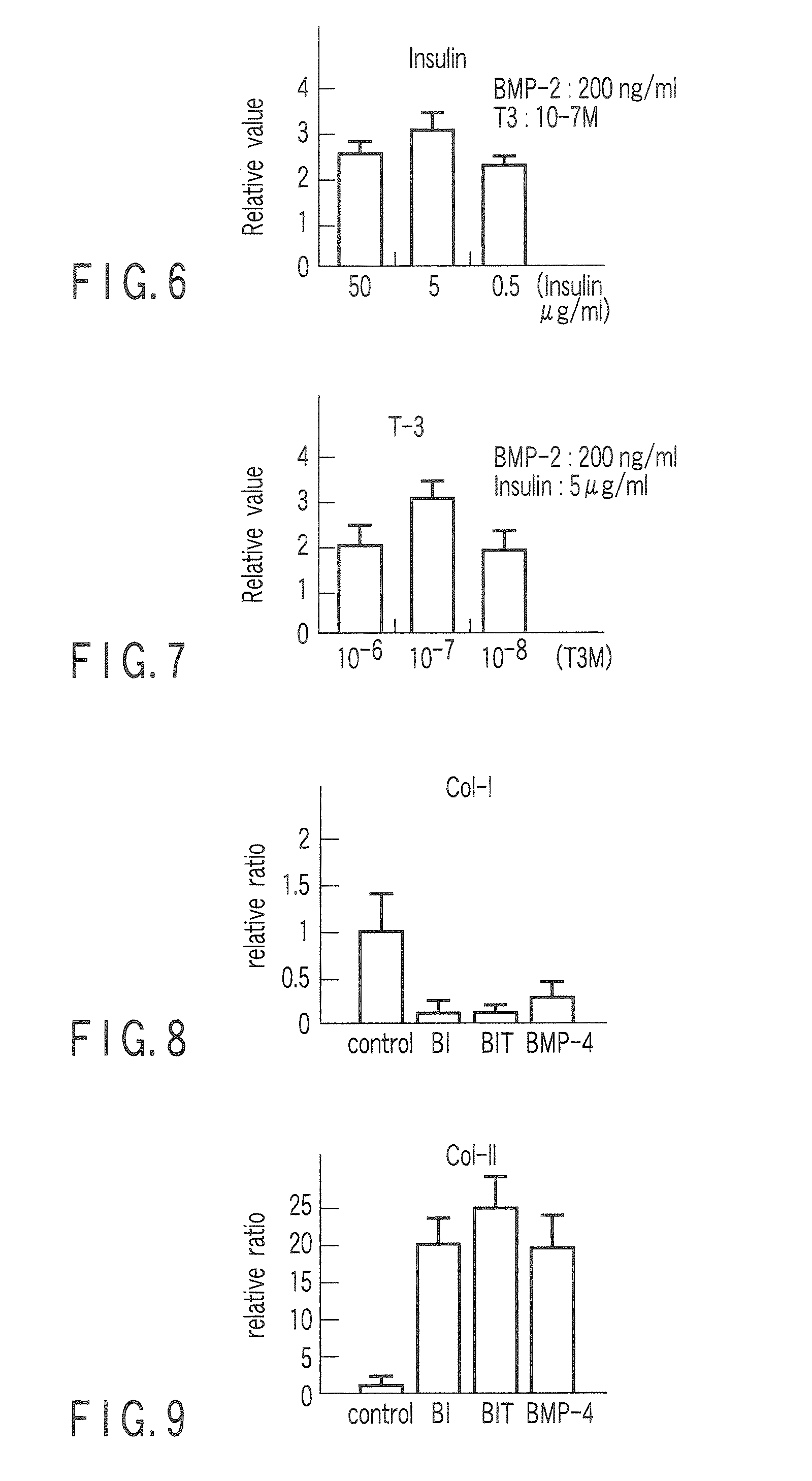
The object of the invention is to provide a redifferention medium and a redifferention method for making dedifferentiated chondrocyte to be redifferentiated into original chondrocyte, the dedifferentiated chondrocyte having attenuated cartilage characteristics due to dedifferentiation during in vitro culture. Accordingly, the invention provides a redifferention medium which is used for redifferentiating the dedifferentiated chondrocyte into the original chondrocyte, and contains insulin and at least one selected from BMP-2 and analogues thereof. The invention also provides a method for redifferentiating the dedifferentiated chondrocyte into the chondrocyte by culturing the dedifferentiated chondrocyte using the redifferentiation medium. The redifferentiation medium preferably further contains T3.
Owner:FUJISOFT +1
Processing method of tissue engineered implant
ActiveCN101332312ANo damageBest physiological performanceProsthesisShort termsBiomedical engineering
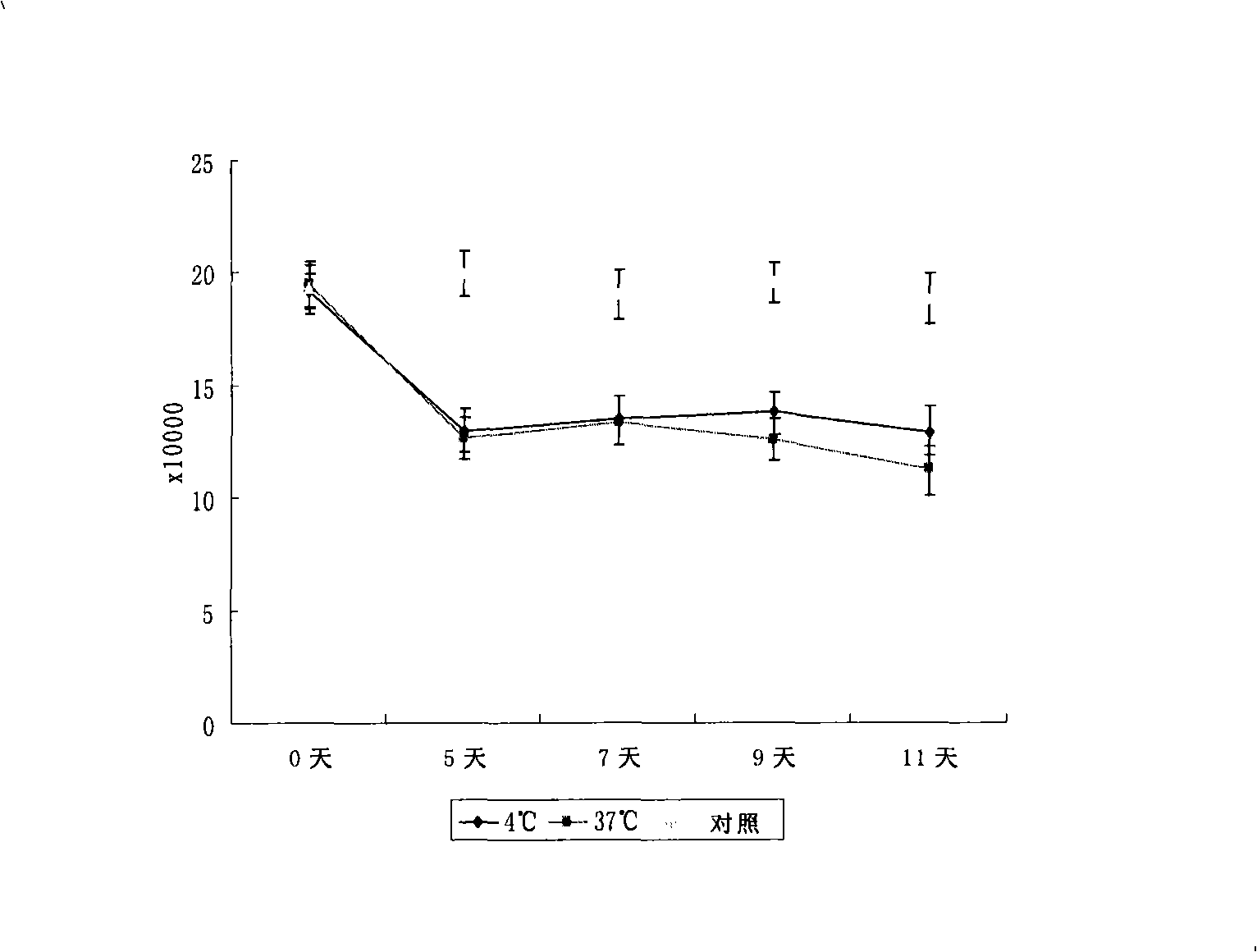
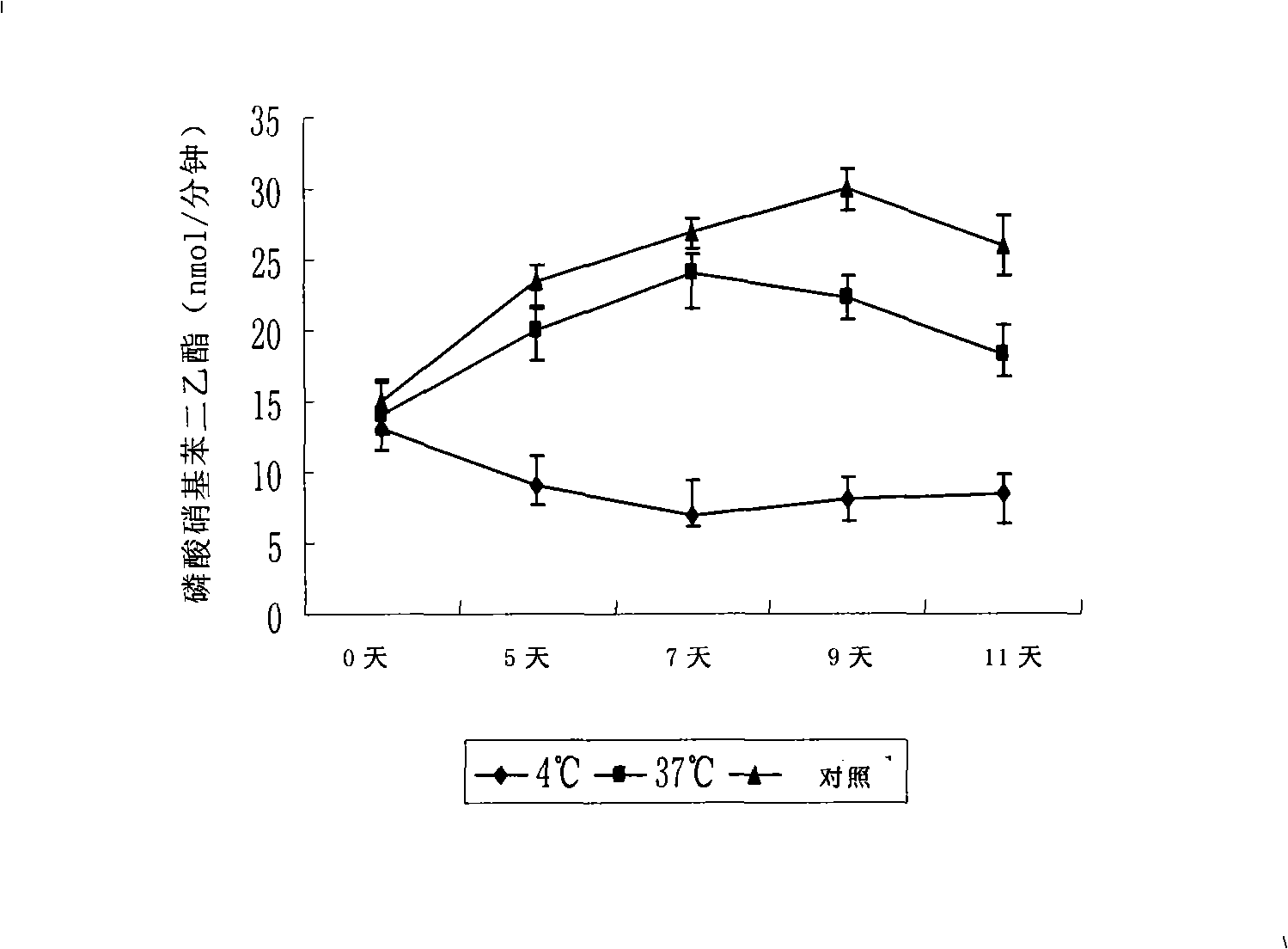
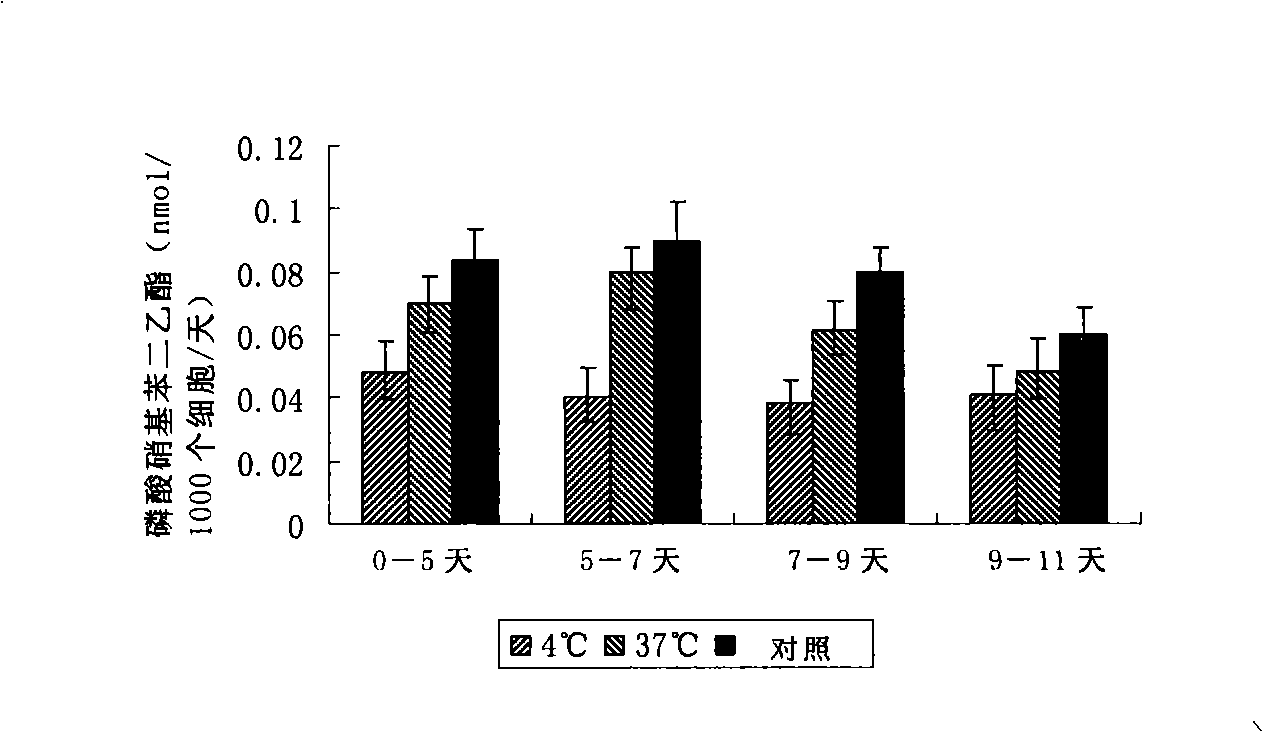
The invention discloses a disposal method for a tissue-engineered graft, comprising the following steps: (a) placing a bone graft or a cartilage graft and osteogenesis induced liquid or chondroblast induced liquid in a container for 2 hours to 14 days under 37 plus or minus 2 DEG C; (b) taking out of the bone graft or the cartilage graft from the container as the preparation material for transplant operation. The method can preserve the graft in a short term but brings no damage to the graft and keep good physical performance while the cost is low and the operation is easy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TISSUE ENG LIFE SCI
Method for constructing cartilage patch stent based on polycaprolactone electrostatic spinning 3D printing and device thereof
InactiveCN110859993AGood biomechanical propertiesGood biocompatibilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationCartilage cellsCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a method for constructing a cartilage patch stent based on polycaprolactone electrostatic spinning 3D printing and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) designing an individualized 3D model of a stent according to characteristic parameters of the stent based on individual characteristics; (2) by utilizing an electrostatic spinning 3D printing technology and taking polycaprolactone as a raw material, printing the cartilage patch stent according to the individualized 3D model; (3) inducing the cartilage cells to be planted on the cartilage patchstent, amplifying the cartilage cells on the stent, secreting extracellular matrixes, and forming a cartilage cell-extracellular matrix-support complex. According to the preparation method, polycaprolactone is taken as the raw material, a technical means of combining electrostatic spinning and 3D printing is employed so as to construct the cartilage patch, and the prepared cartilage patch is widerin application range and excellent in biomechanical property.
Owner:SHANGHAI PULMONARY HOSPITAL
Preparation method and application of polymer coating for long-term in-vitro culture of human fat stem cells
ActiveCN106635977AGood optical clarityGood biocompatibilityCulture processCell culture supports/coatingOptical transparencyBiocompatibility Testing
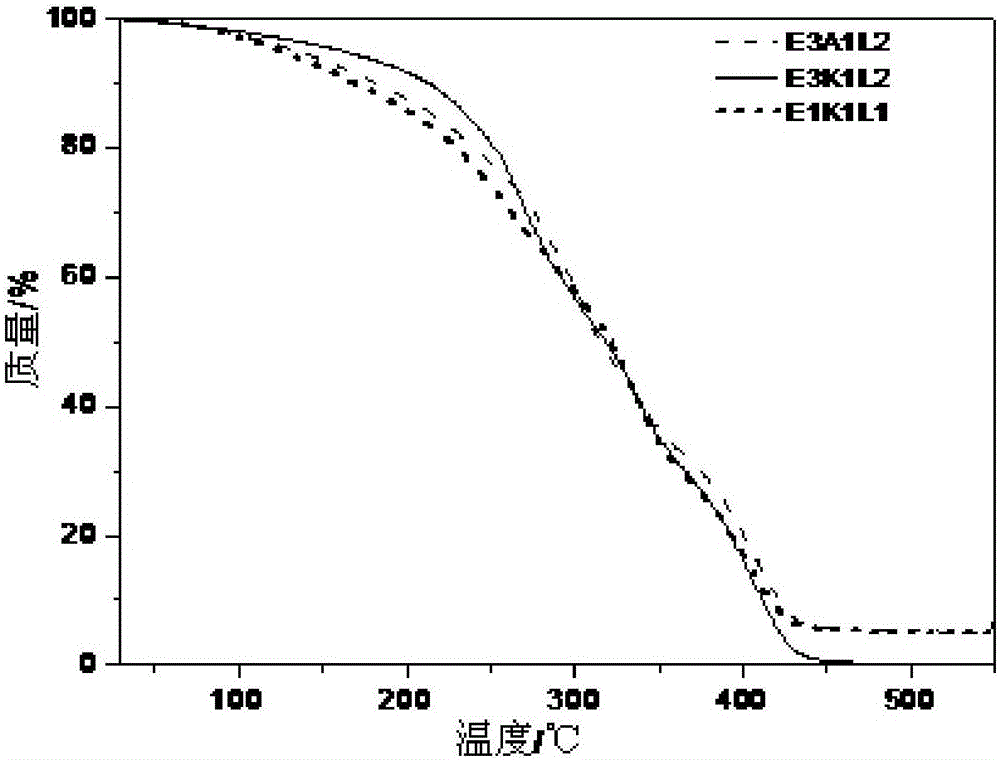
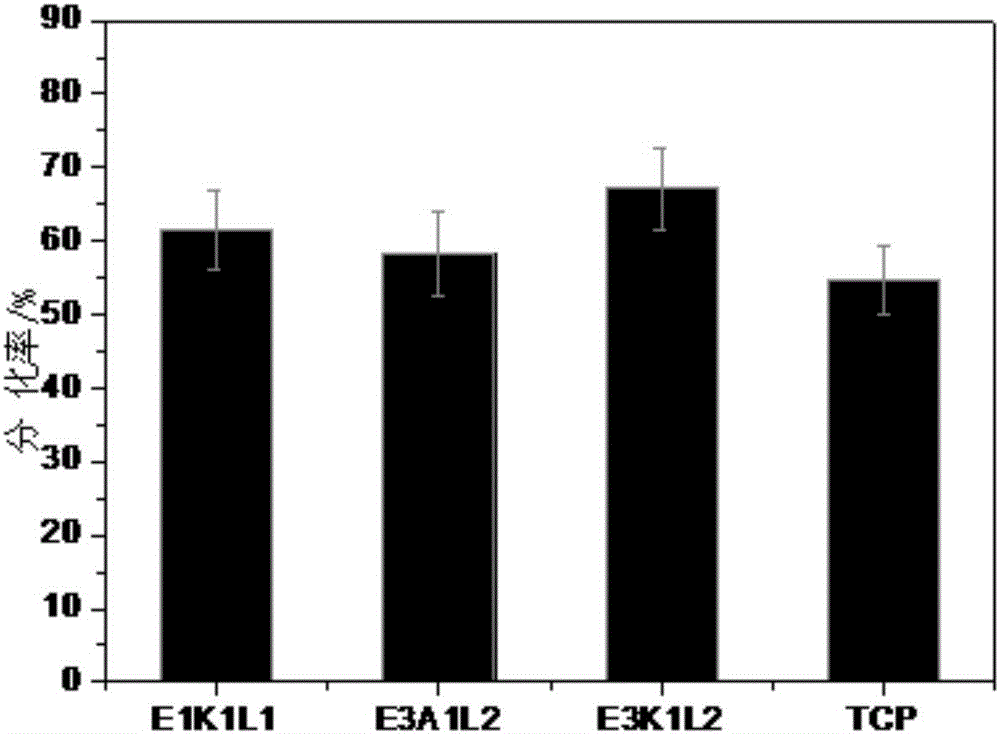
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of polymer coating for long-term in-vitro culture of human fat stem cells; the preparation method comprises: treating a cover glass, preparing the polymer coating, carrying out long-term culture of human fat stem cells on the polymer coating, inducing differentiation of the human fat stem cells to lipoblasts, osteoblasts and chondroblasts, and carrying out characterizing three types of induced adult cells by staining; monomers include hydroxyethyl methylacrylate A, methacryloyloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride solution E, cyclohexyl methacrylate L, and 2-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate K; the polymer coating is from EK1L1, E3K1L2 or E3A1L2, wherein the numbers refer to the mass ratios of the monomers. The preparation method and application of the polymer coating for long-term in-vitro culture of human fat stem cells have the advantages that the polymer coating based on acrylate / acrylamide has good optical clarity and biocompatibility, benefiting cell culture and observation; the polymer coating can promote the growth of human fat stem cells to maintain their reproducibility, and may also maintain stem cell characteristics of the human fat stem cells.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
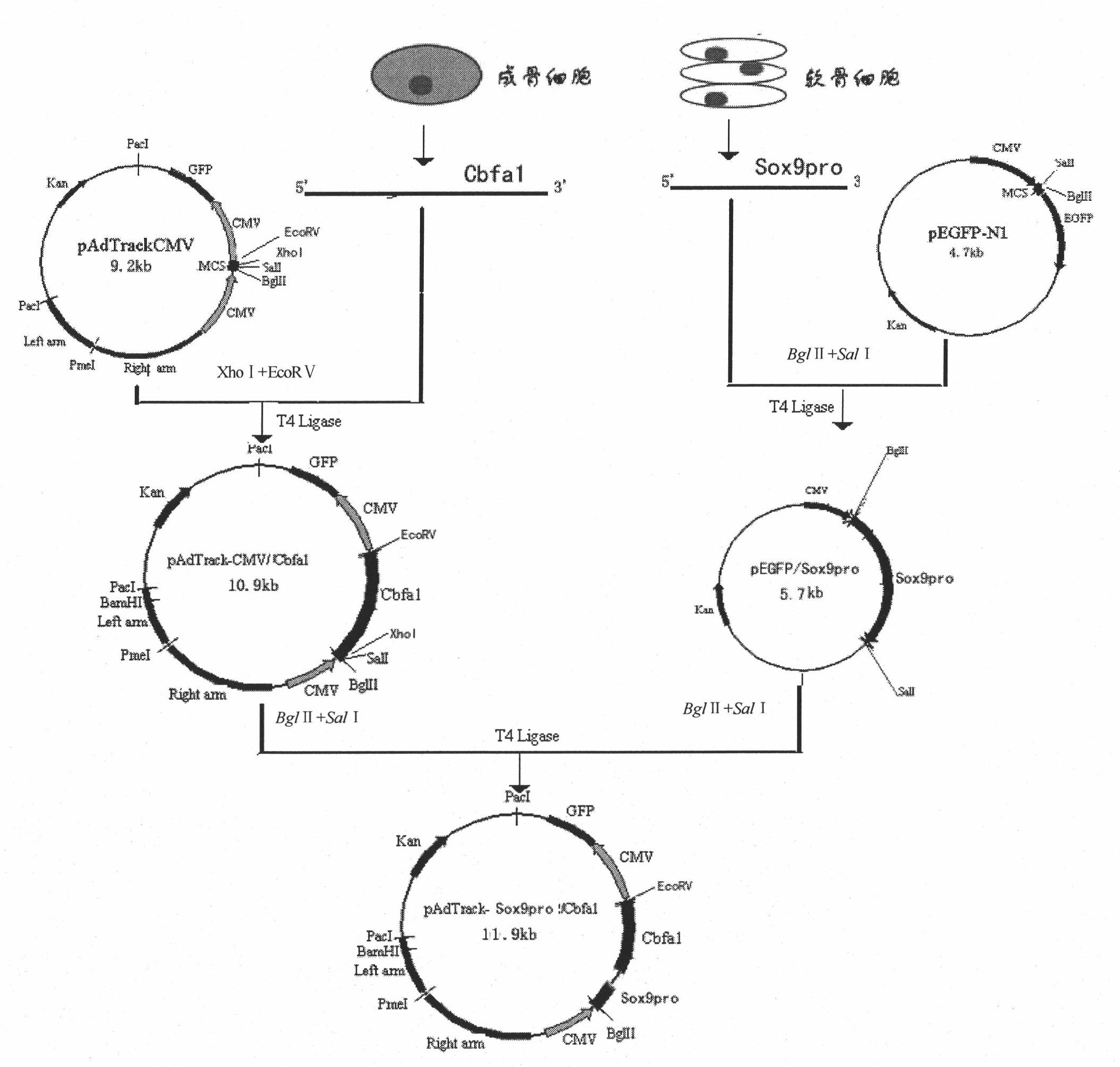
Core-binding factor alpha1 gene recombinant virus for specifically promoting cartilage differentiation, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101979520AEasy to prepareLow costViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationCartilage cellsCore binding factor
The invention discloses a core-binding factor alpha1 (Cbfa1) gene recombinant virus for specially promoting cartilage differentiation, a preparation method and application thereof. The recombinant virus contains one Cbfa1 gene expression box regulated and controlled by a Sox9 gene promoter; the preparation method comprises the following steps of clone of Cbfa1 gene full-length cDNA and construction of Cbfa1 gene recombinant adenovirus shuttle plasmid, clone of Sox9 gene promoter fragment and construction of the Sox9 gene promoter recombinant expression carrier, construction of Cbfa1 gene recombinant adenovirus carrier regulated and controlled by the Sox9 gene promoter, package, amplification and purification of the Cbfa1 gene recombinant adenovirus regulated and controlled by the Sox9 gene promoter and the like. The recombinant virus can be used for preparing seed cells for directionally inducing chondroblast differentiation and can efficiently and specifically ensure that the mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into chondroblast on the premise of differentiating into osteogenesis / cartilage cells.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com