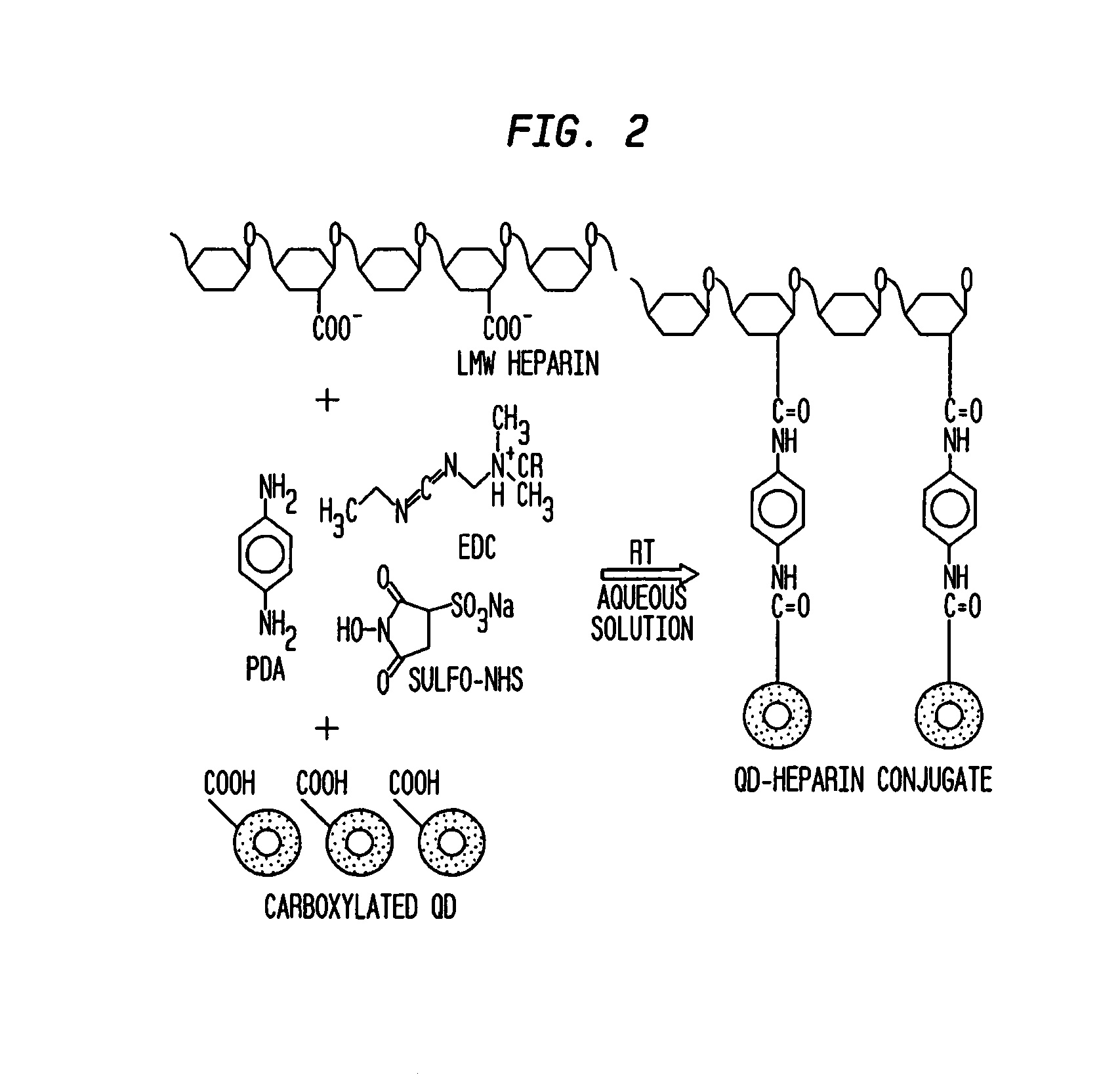
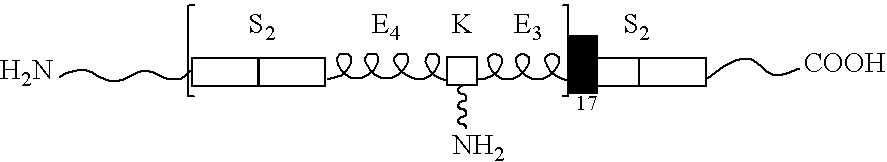
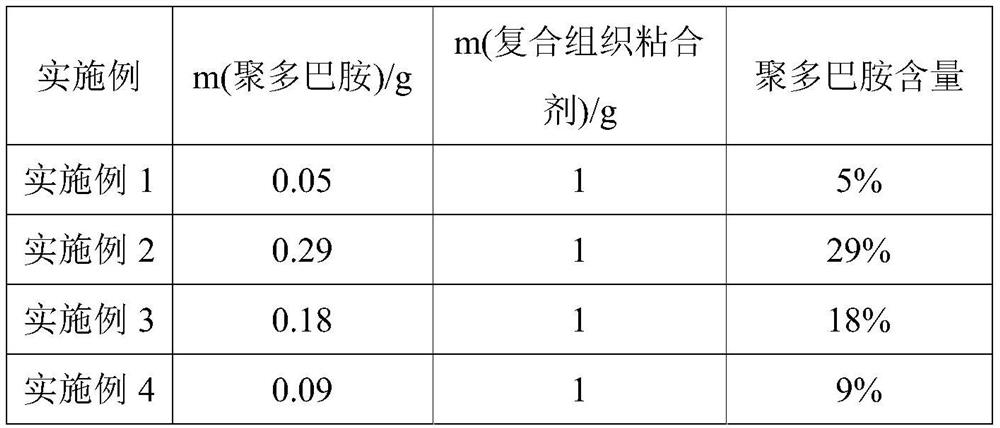
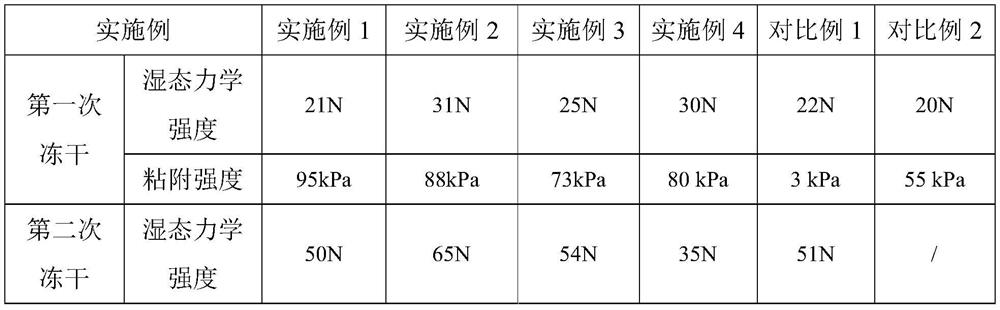
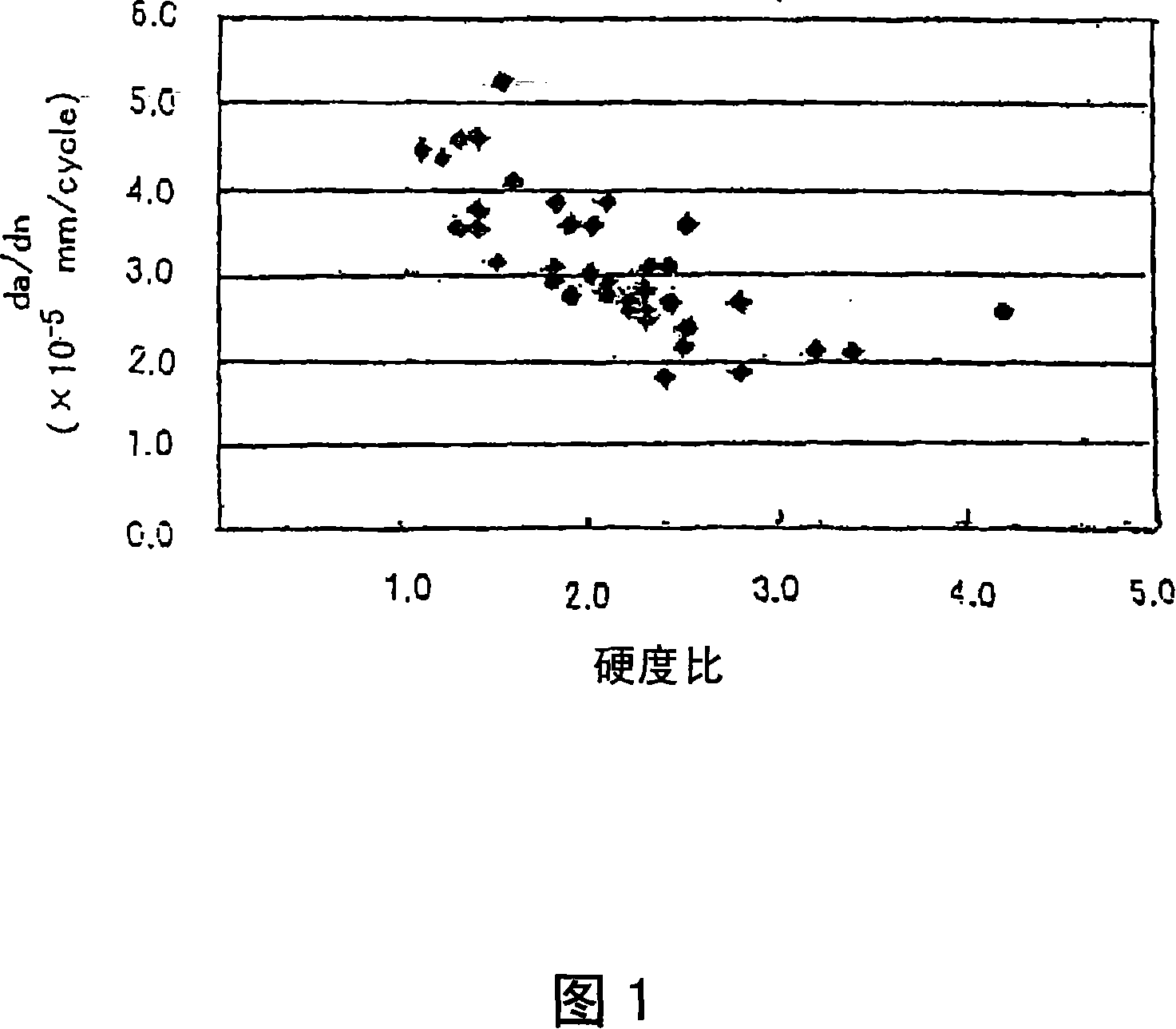
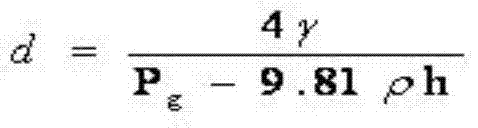
Patents
Literature
99 results about "Composite tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A composite tissue allograft (CTA) is a construct made up skin, muscle, tendon, nerves, bone and blood vessels from another human being that potentially can be transplanted to an appropriate recipient.
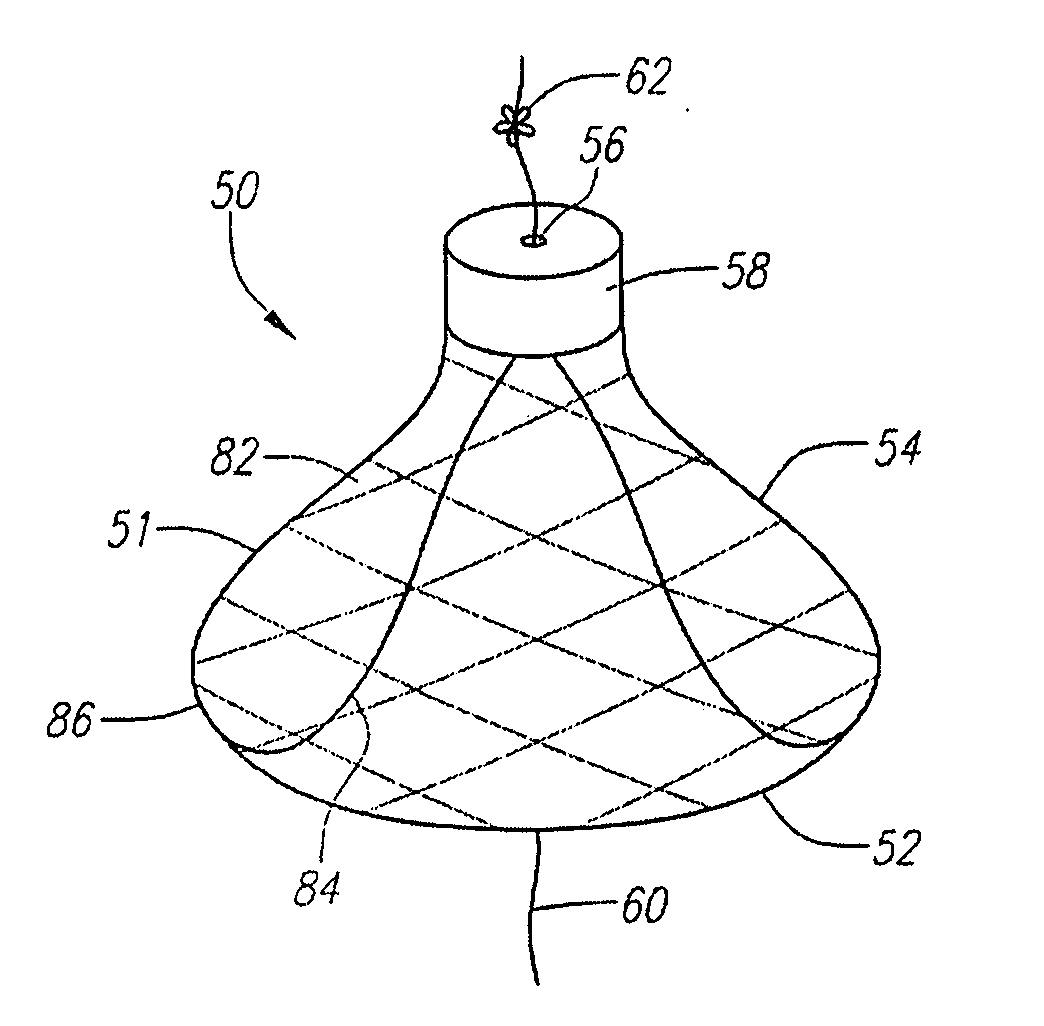
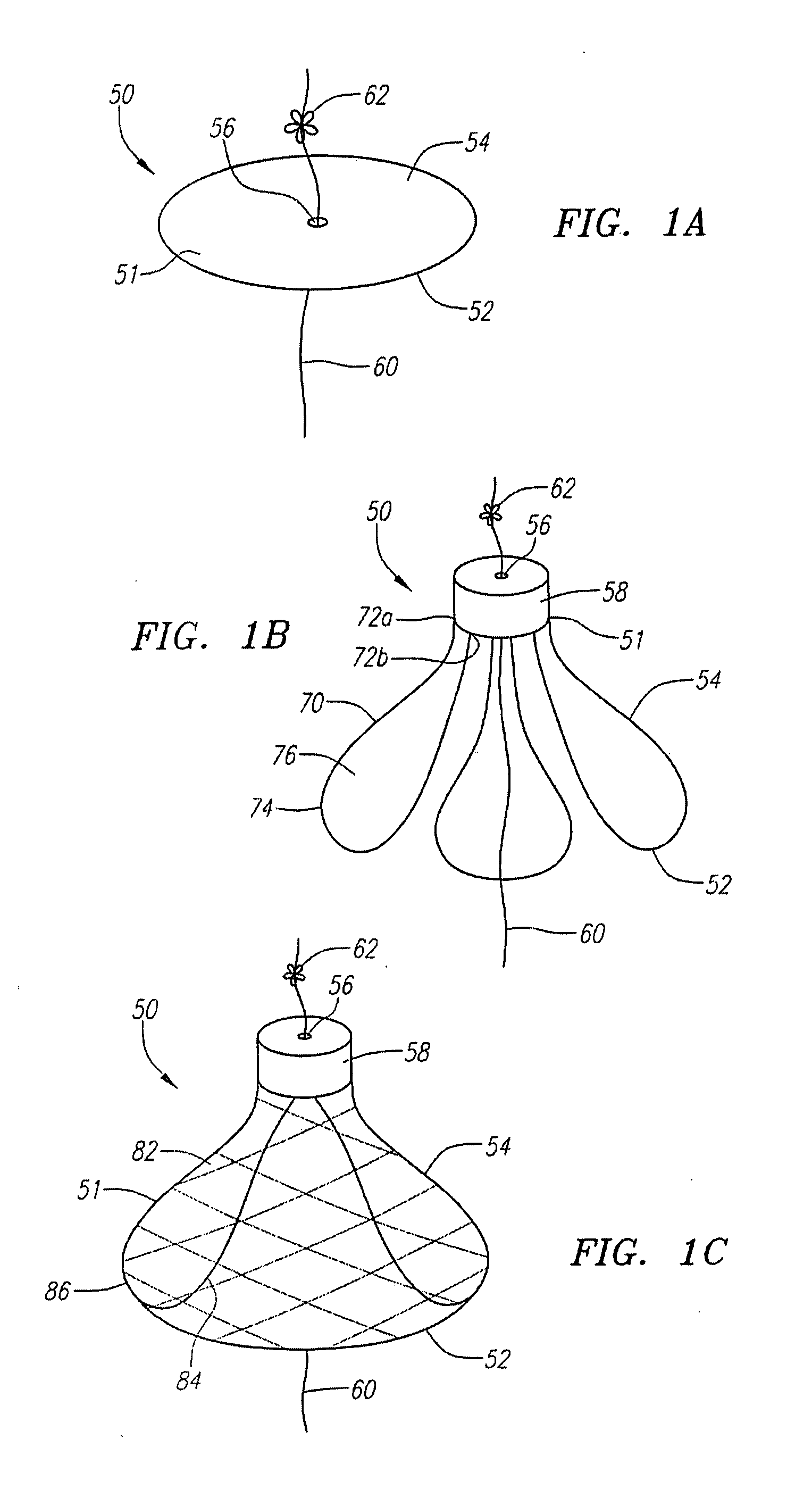
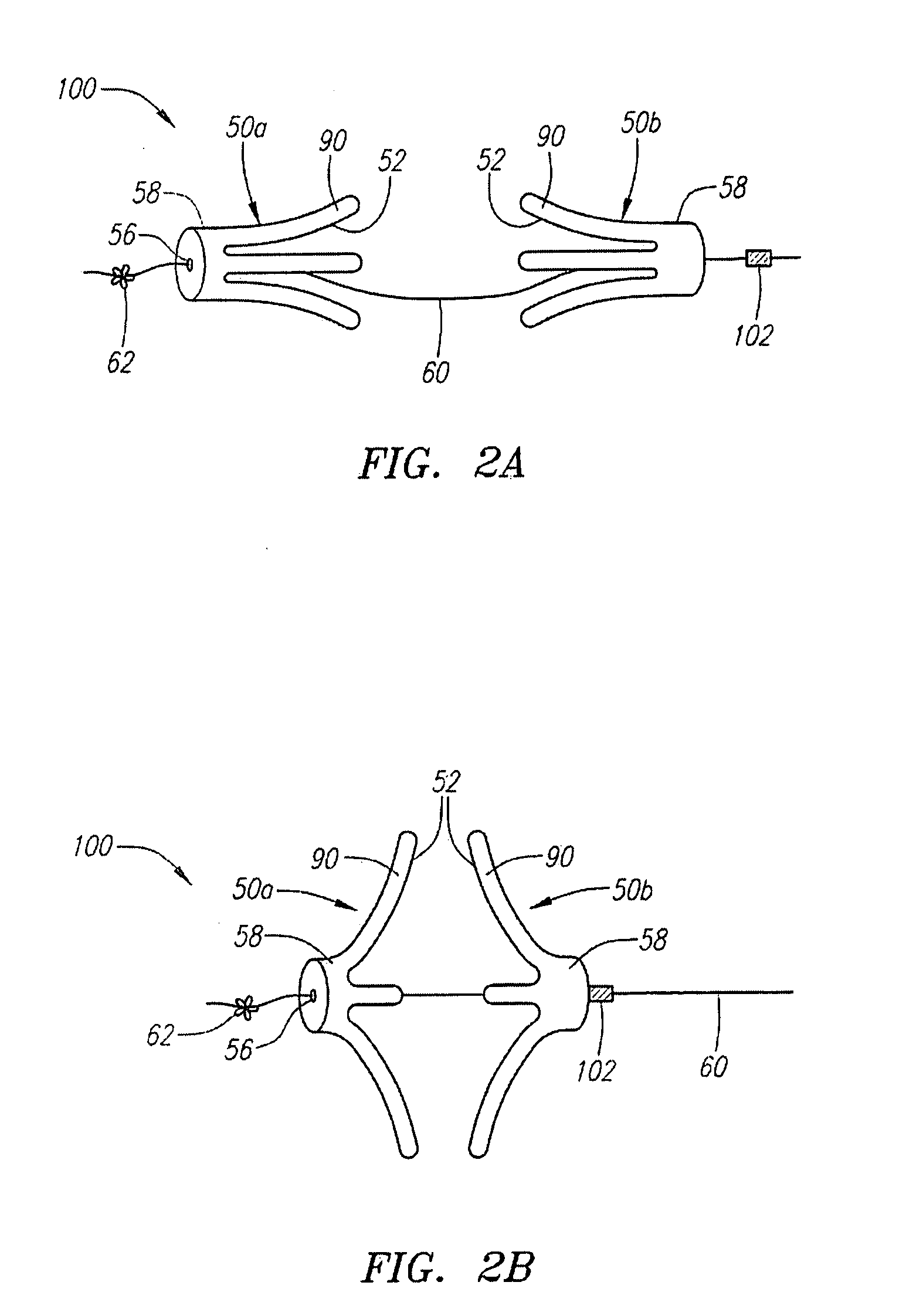
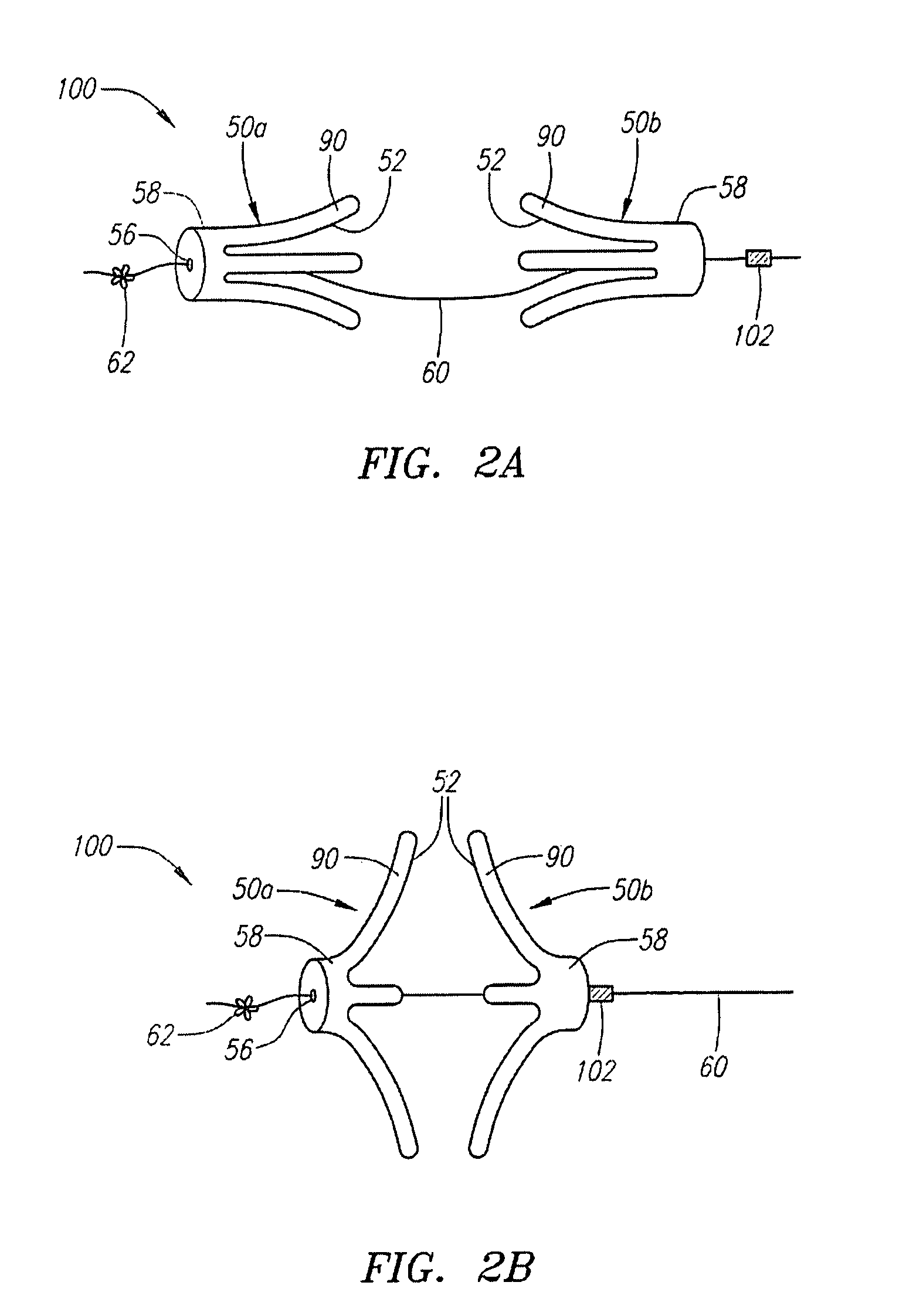
Low profile tissue anchors, tissue anchor systems, and methods for their delivery and use
ActiveUS20080009888A1Facilitate and promote tissue healingFacilitate and promote and reconfigurationSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesBiomedical engineeringComposite tissue
Tissue anchors include a flat, broad, and large contact surface for engagement with a portion of tissue. Several embodiments of composite tissue anchors include a support element and an overlay element. Tissue anchor assemblies include two or more tissue anchors, a connector, and a cinching mechanism. In some embodiments, the tissue anchors included in the tissue anchor assemblies are of different types, sizes, and / or shapes.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Synovial fluid barrier
InactiveUS20060178743A1Improve regenerative healingImprove responseSuture equipmentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSynovial jointsSacroiliac joint
A composite tissue formed in situ is provided. The composite tissue includes a synovial joint tissue; and a barrier material adhered thereto for sealing the synovial joint tissue against synovial fluid. Also provided is a method for regenerating synovial joint tissue in situ by excluding synovial fluid therefrom. The method includes providing a synovial joint tissue having a defect; and placing a barrier material in intimate contact with the defect for sealing the defect against synovial fluid. The barrier material includes a curable protein copolymer. The method further includes curing the protein copolymer in situ. The barrier material can include a crosslinked network, or a self gelled network of repeating elastin-like and fibroin-like polymer chains.
Owner:SPINEWAVE
Production of tissue engineered digits and limbs
ActiveUS20060257377A1Enhance tissue maturationImprove functionalityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBone formingTissue construct
The invention pertains to methods of producing artificial composite tissue constructs that permit coordinated motion. Biocompatable structural matrices having sufficient rigidity to provide structural support for cartilage-forming cells and bone-forming cells are used. Biocompatable flexible matrices seeded with muscle cells are joined to the structural matrices to produce artificial composite tissue constructs that are capable of coordinated motion.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Composite tissue adhesive
InactiveUS6939364B1Precise temperature controlShorten treatment timeSurgical instrument detailsSurgical veterinaryThermal energyHigh concentration
Consistent with the present invention, tissue adhesive compositions and an associated laser exposure system are provided for bonding or sealing biological tissues. The compositions are comprised of chemically derivatized soluble collagen which is formulated to concentrations ranging from 300 mg / ml (30%) to 800 mg / ml (80%) collagen protein. In particular, Type I collagen, for example, is first prepared by extraction from bovine or porcine hide and purified. The collagen preparations are then chemically derivatized with sulfhydryl reagents to improve cohesive strength and with secondary derivatizing agents, such as carboxyl groups, to improve the adhesive strength of the solder to the tissue. The compositions are then formed into viscous solutions, gels or solid films, which when exposed to energy generated from an infrared laser, for example, undergo thermally induced phase transitions. Solid or semi-solid protein compositions become less viscous enabling the high concentration protein to penetrate the interstices of treated biological tissue or to fill voids in tissue. As thermal energy is released into the surrounding environment, the protein compositions again become solid or semi-solid, adhering to the treated tissue or tissue space.
Owner:CONVERSION ENERGY ENTERPRISES
Preparation method of an in situ pore-forming self-setting calcium phosphate composite tissue engineering scaffold
The invention discloses a making method of composite tissue engineering rack of original poring self-solidifying calcium phosphate, which comprises the following steps: placing porous rack of calcium phosphate cement into drier to dry; immersing porous rack into macromolecular solution; extracting into vacuum for 0.5-6h; injecting macromolecular material into the pore of porous rack of calcium phosphate cement; drying the surface of porous rack through filter paper; pre-freezing under -60- -4 deg.c for 1-48h; drying the frozen material to do multiple injections until the pore is filled with cement; obtaining the product.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Water-repellent anti-contamination hygroscopic perspiratory composite tissue knitted fabric and production method thereof
ActiveCN102031622AGood water repellency and antifouling functionGood moisture wicking functionWeft knittingBleaching apparatusYarnNatural fiber
The invention relates to a water-repellent anti-contamination hygroscopic perspiratory composite tissue knitted fabric produced in knitting industry and a production method thereof. An outer coil of the knitted fabric is made of yarn treated by water-repellent anti-contamination technology; a coil at a middle connection layer is made of natural fiber yarn with good hygroscopic and water absorbent performance; an inner coil is made of hygroscopic fiber yarn, and the hygroscopic fiber yarn is treated by hydrophilicity, has a microcellular structure and is in a deformed cross section; the fabric tissue is double-rib double-layer composite tissue, and is knitted on a 2+2 needle track double-surface circular knitting machine; and the knitted fabric is subjected to preforming, degreasing and cleaning, softening, dewatering, expanding, drying, forming and the like. The outer layer of the provided knitted fabric has excellent water-repellent anti-contamination function, and the inner layer has excellent hygroscopic perspiratory function; the knitted fabric has soft hand feel, good permeability and elasticity and antistatic performance, and is widely applied to sportswear, summer clothing, work clothes of hotels and oil field, regimentals and the like; three-tissue structure of the knitted fabric is formed by one-step knitting so that the production technology has easiness in control and the product quality is reliable.
Owner:ANHUI HAOBO INT UNDERWEAR +1
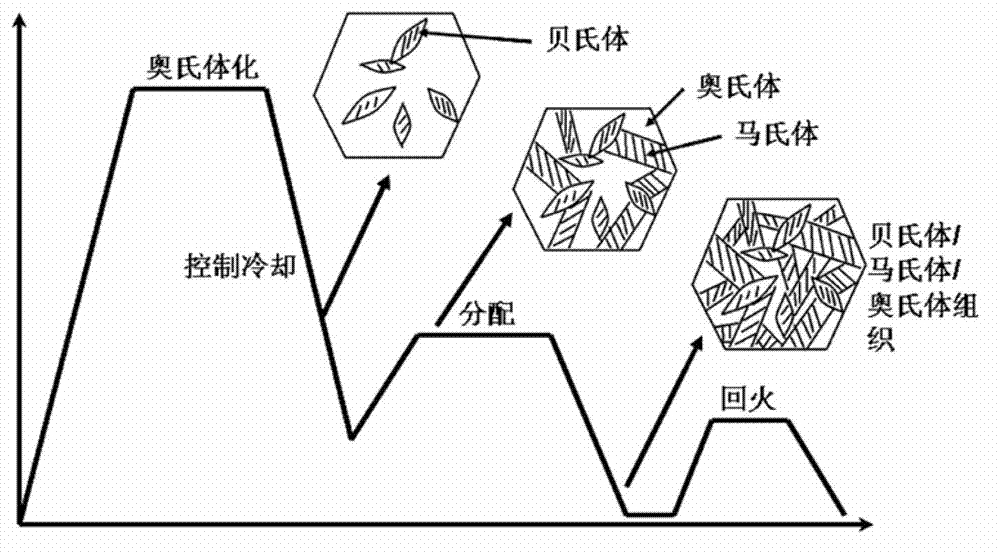
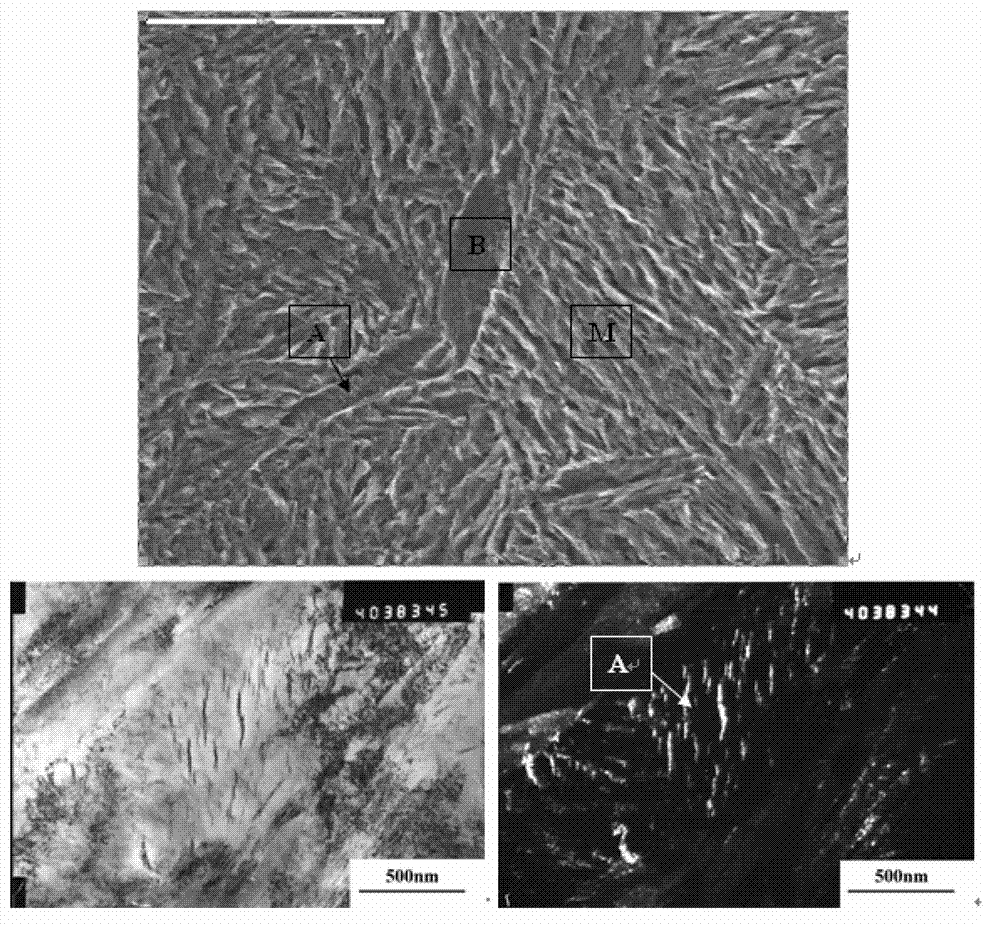
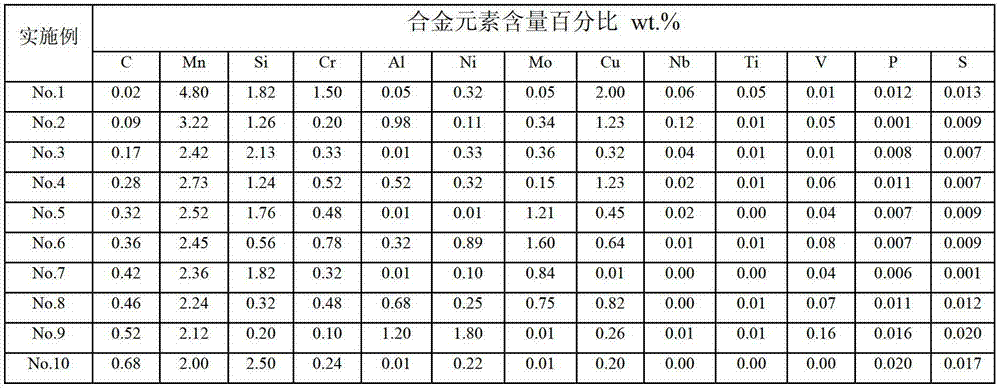
Preparation method of bainite/martensite/austenite composite high-strength steel
InactiveCN103243275AImprove stabilityOvercome the disadvantage of high costHeat treatment process controlSmelting processThick wall
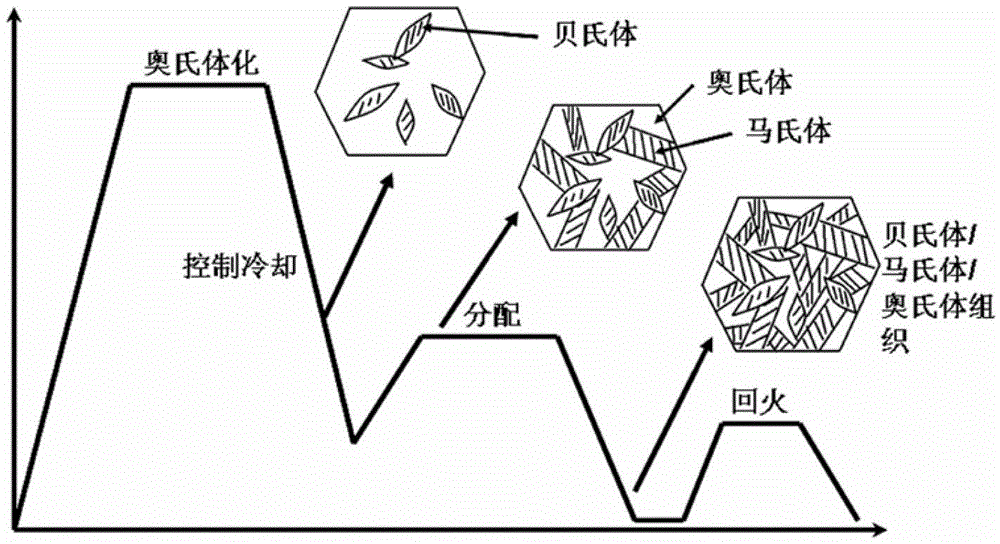
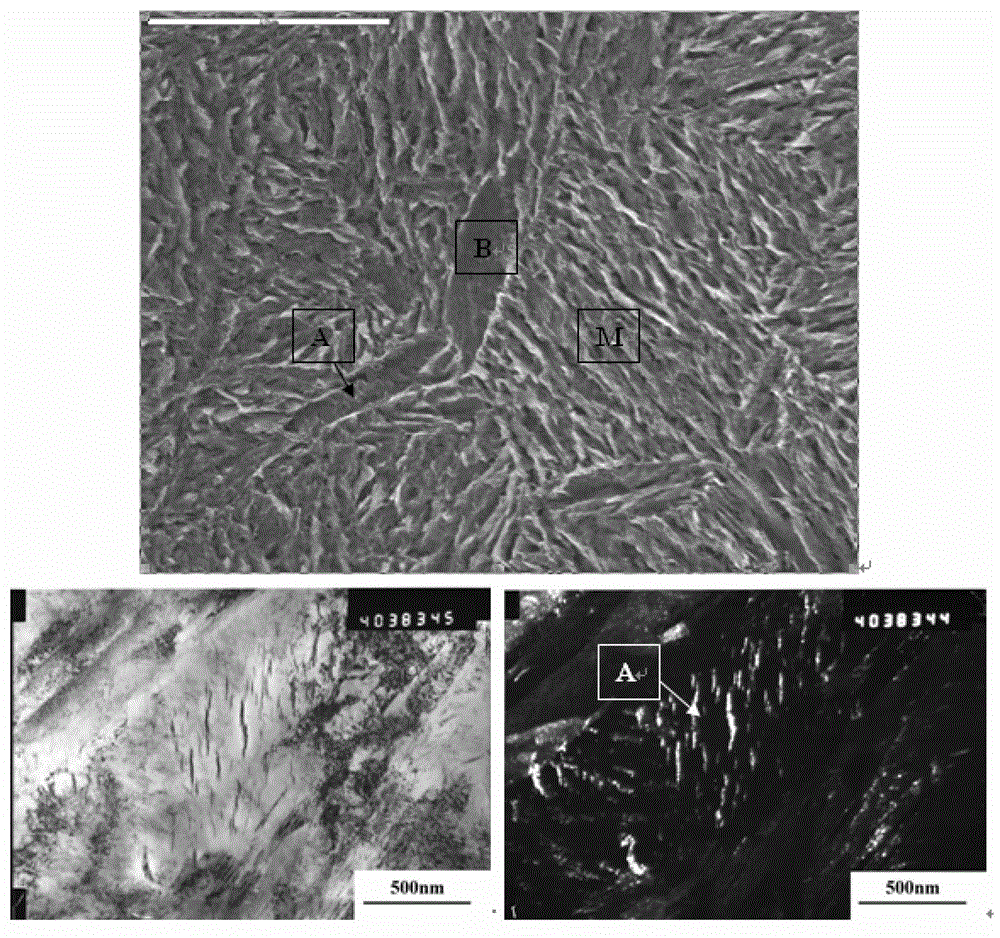
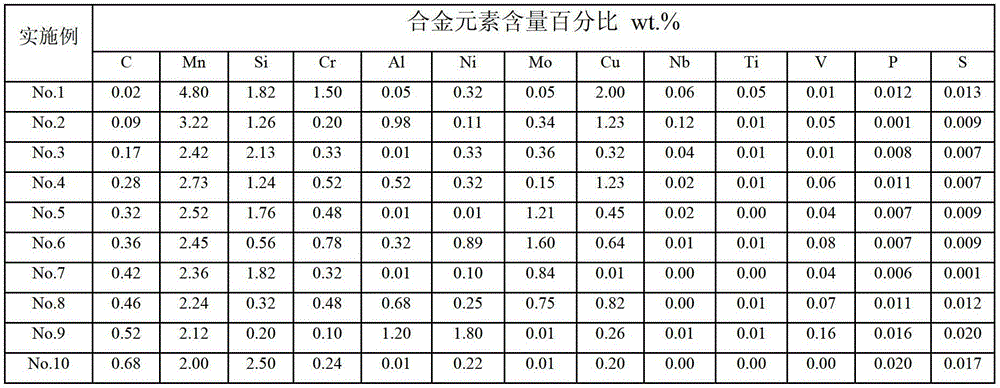
The invention discloses a preparation method of bainite / martensite / austenite composite high-strength steel, belonging to the field of low-alloy high-strength steel. According to the composite high-strength steel, C, Mn, Si and Cr are used as main alloy elements, Al, Ni, Mo, Cu, Nb, Ti, V and the like are added, and the balance is Fe. The preparation method comprises the following steps: smelting, casting, forging or rolling to prepare rails, thick-wall pipes, large-section bars or thick pipes and the like by adopting a conventional steel-smelting process; carrying out austenitizing; controlling cooling by adopting different cooling media to obtain a part of bainite tissue in the cooling process; instantly carrying out distribution treatment and low-temperature tempering treatment so as to finally obtain a bainite / martensite / austenite composite tissue which is good in strong plasticity and toughness coordination, wherein the distribution time is 30-360 minutes. For a component which is large in size and easy to crack in quenching, the bainite / martensite / austenite composite high-strength steel has wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Light Activated Composite Tissue Adhesives
InactiveUS20110125187A1Facilitate cross-linkingImprove cohesive strengthOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesComposite filmWavelength
Owner:CONVERSION ENERGY ENTERPRISES
Method for preparing organic and inorganic nanometer composite organization engineering stent material by using thermal phase separation
ActiveCN1792379AHigh strengthImprove hydrophilicitySurgeryPharmaceutical containersFreeze-dryingPolymer solution
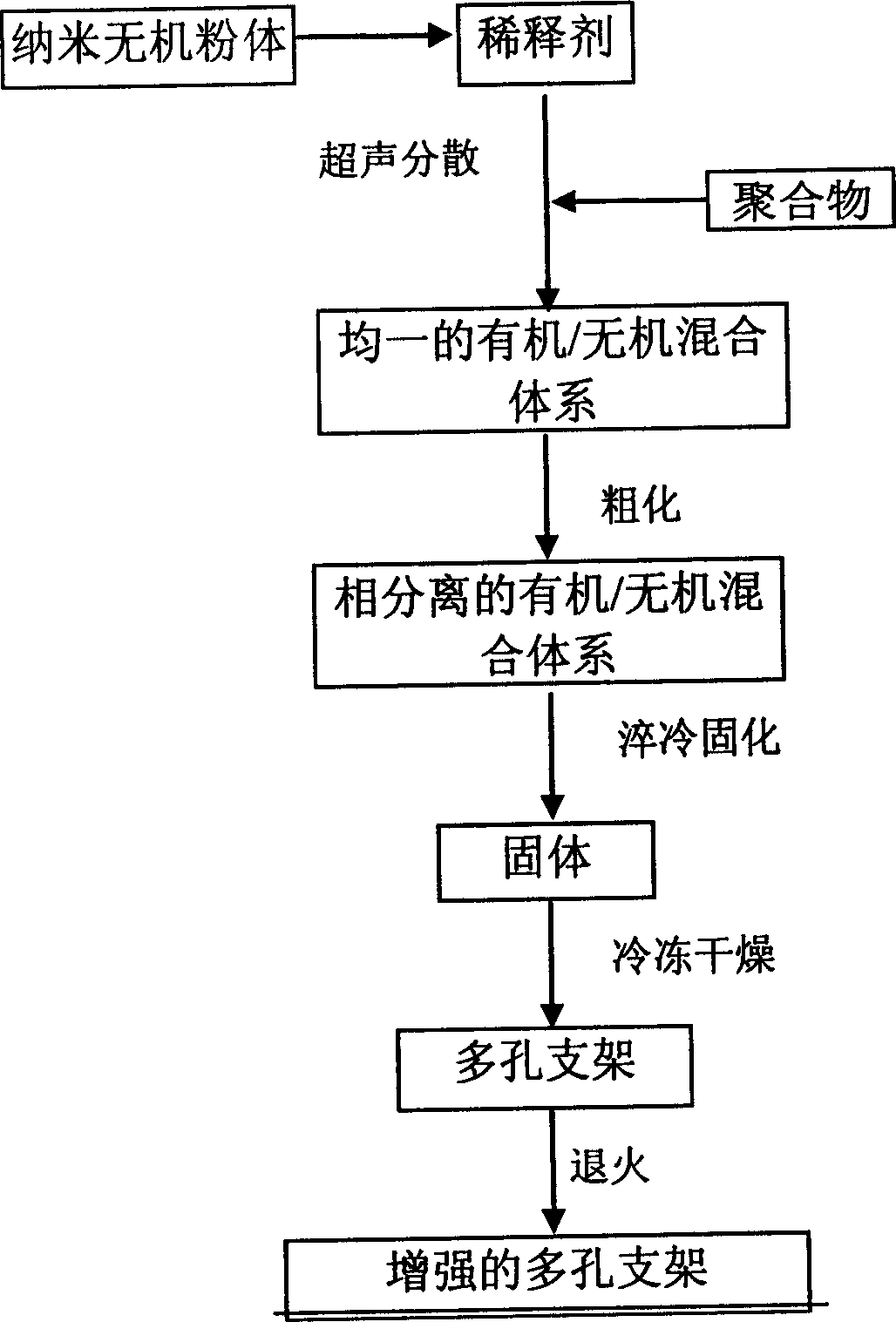
A method for preparing the composite organic-inorganic nano material used for tissue engineering scaffold by thermal phase separation includes such steps as ultrasonic dispersing of inorganic nano-particles in polymer solution to obtain a uniform mixture system, lowering temp, coarsening the mixture system for a certain time while generating phase separation, freeze drying to remove solvent, to obtain porous scaffold, and annealing for improving its strength.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Production of tissue engineered digits and limbs
ActiveUS8728463B2Increase vascularisationEncourages recruitmentBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBone formingComposite tissue
The invention pertains to methods of producing artificial composite tissue constructs that permit coordinated motion. Biocompatable structural matrices having sufficient rigidity to provide structural support for cartilage-forming cells and bone-forming cells are used. Biocompatable flexible matrices seeded with muscle cells are joined to the structural matrices to produce artificial composite tissue constructs that are capable of coordinated motion.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
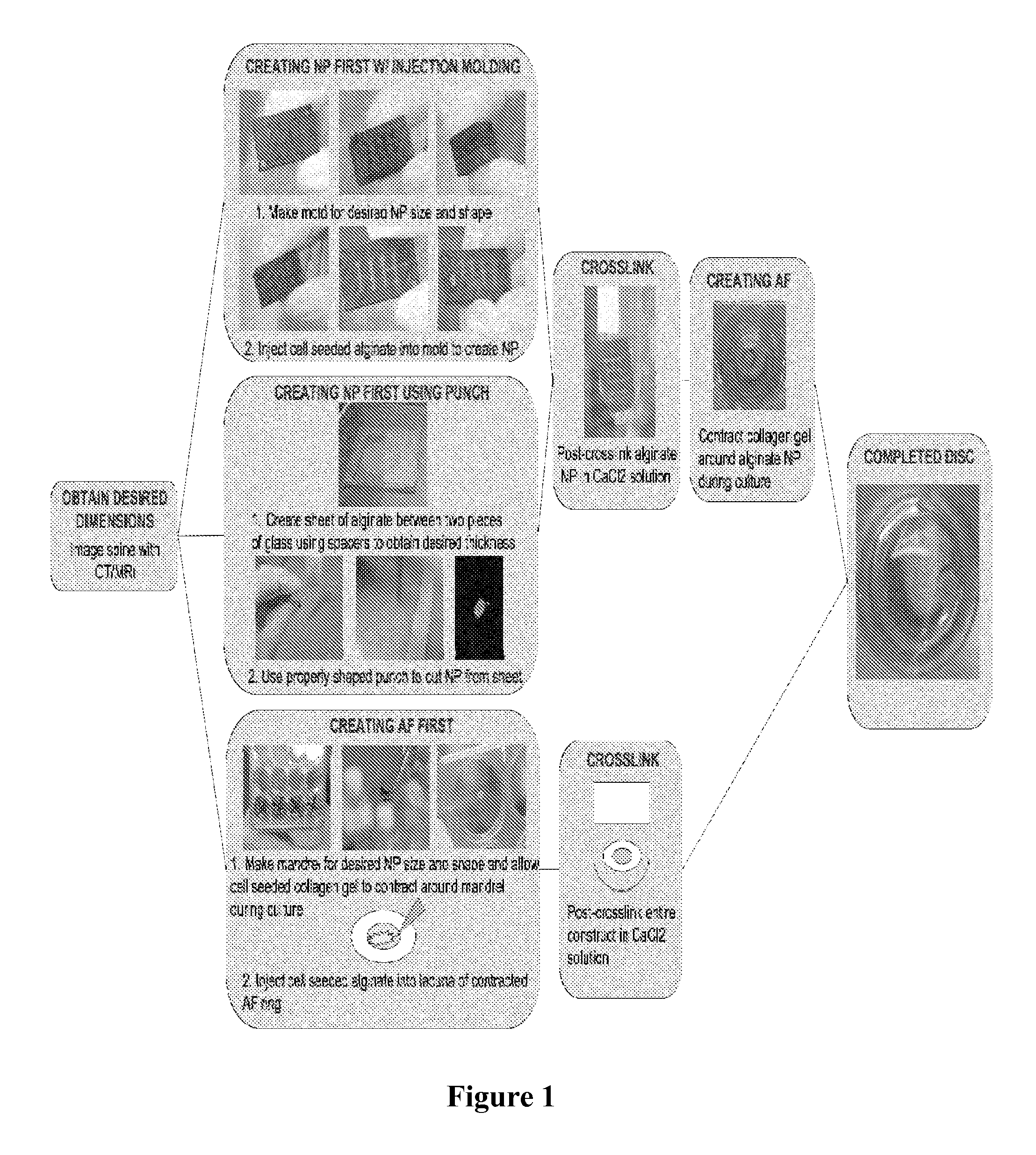
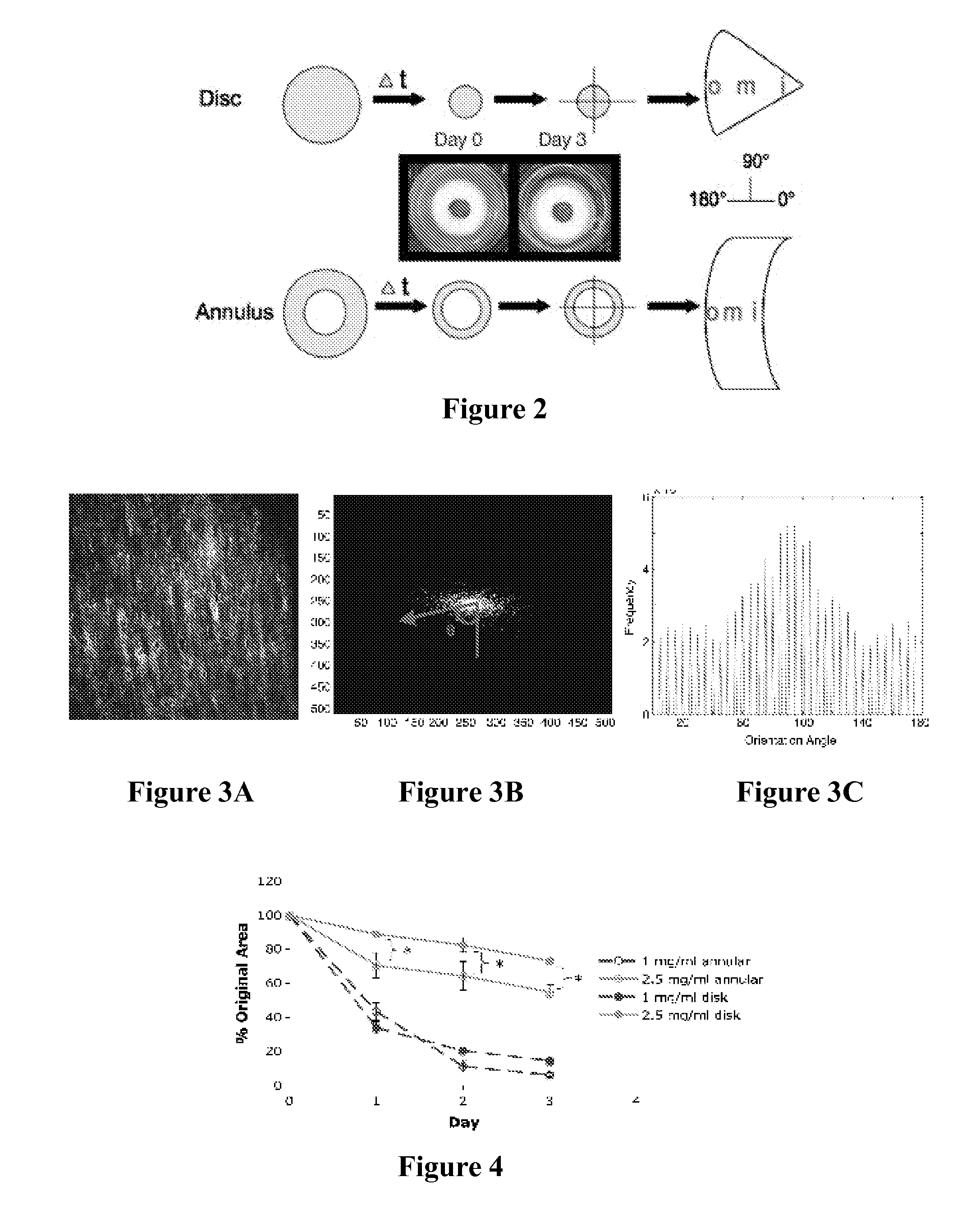
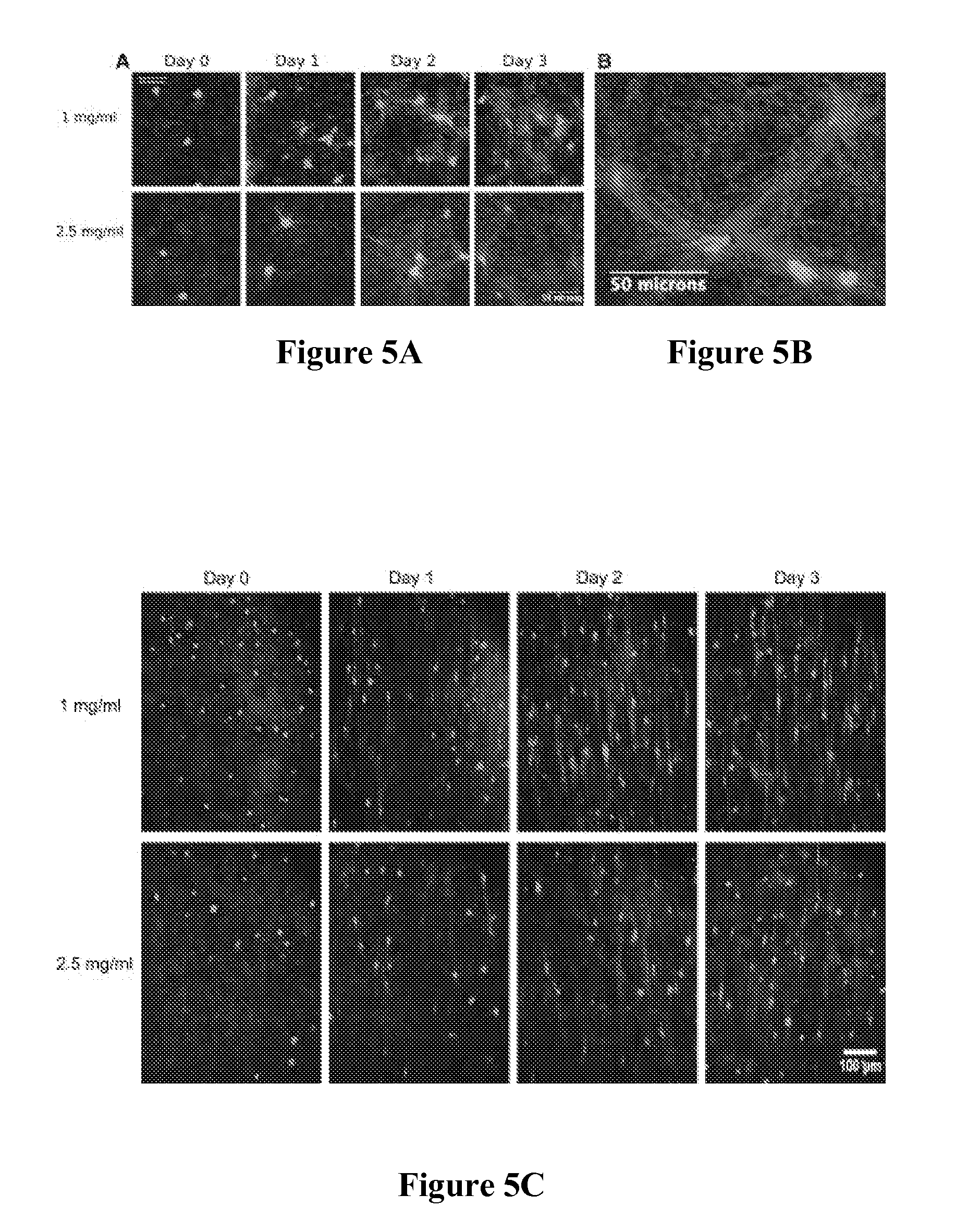
Composite tissue-engineered intervertebral disc with self-assembled annular alignment
ActiveUS9044335B2Remarkable ability to restore functionUnknown materialsSpinal implantsFiberIntervertebral disc
The present invention relates to a tissue-engineered intervertebral disc (IVD) suitable for total disc replacement in a mammal and methods of fabrication. The IVD comprises a nucleus pulposus structure comprising a first population of living cells that secrete a hydrophilic protein and an annulus fibrosis structure surrounding and in contact with the nucleus pulposus structure, the annulus fibrosis structure comprising a second population of living cells and type I collagen. The collagen fibrils in the annulus fibrosis structure are circumferentially aligned around the nucleus pulposus region due to cell-mediated contraction in the annulus fibrosis structure. Also disclosed are methods of fabricating tissue-engineered intervertebral discs.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Low profile tissue anchors, tissue anchor systems, and methods for their delivery and use
ActiveUS8870916B2Improve gripIncreased resistance to pull-throughSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesBiomedical engineeringComposite tissue
Tissue anchors include a flat, broad, and large contact surface for engagement with a portion of tissue. Several embodiments of composite tissue anchors include a support element and an overlay element. Tissue anchor assemblies include two or more tissue anchors, a connector, and a cinching mechanism. In some embodiments, the tissue anchors included in the tissue anchor assemblies are of different types, sizes, and / or shapes.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Composite tissue repairing sheet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105435309AImprove repair effectGood mechanical propertiesTissue regenerationProsthesisSpinningElectrospinning
The invention discloses a composite tissue repairing sheet and a preparation method thereof. The composite tissue repairing sheet comprises an electrostatic spinning film layer, a bonding layer and a woven mesh layer; the electrostatic spinning film layer is prepared from a material A, the bonding layer is prepared from a material B through electrostatic spinning, and the hot melting temperature of the material B is lower than the hot melting temperature of the material A; and the bonding layer is disposed between the electrostatic spinning film layer and the woven mesh layer, and the bonding layer is heated and melt through hot press, and thus the electrostatic spinning film layer is bonded with the woven mesh layer. The prepared composite tissue repairing sheet possesses good mechanical properties of a woven mesh and the three-dimensional porous structure and the soft characteristic of the electrostatic spinning film, facilitates to promote rapid growth of cell in the sheet, and possesses relatively good fusion property with hyperplastic tissue.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Preparation method of nano apatite crystal composite tissue engineering support material
A composite tissue-engineered porous scaffold material is prepared from the nano-class hydroxy phosphorite particles, medical polyamide and foaming agent through proportionally mixing, heating to fuse it, injection moulding under 30-50 MPa to form porous scaffold, and removing the surficial layer to open the pores. Its advantage is high mechanical performance.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Tissue engineered bone-cartilage complex tissue graft and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a tissue engineered bone-cartilage composite tissue transplant and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the tissue engineering field. The method comprises the following steps: seed cells are implanted on a scaffold material and cultured in vitro to form the tissue engineered bone-cartilage composite tissue transplant; the seed cells are osteogenic stem cells; the scaffold material comprises an osteogenic part and a chondroblast part, and the osteogenic part is added with an osteoblast induction factor and modified by a type-I collagen in a preparation process; and the chondroblast part is added with a chondroblast induction factor and modified by a type-II collagen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are successfully induced into osteocytes and chondrocytes, and bone tissues and cartilage tissues are formed after the obtained transplant is transplanted in vivo. Satisfactory effect is obtained from the tissue engineered bone-cartilage composite tissue which is constructed by the transplant.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Composite active bone cement containing sustained release drug-loading nanoparticles and preparation method of bone cement
ActiveCN104288833AGood slow releaseReduce the burst effectSurgical adhesivesProsthesisCalcium biphosphateSustained release drug
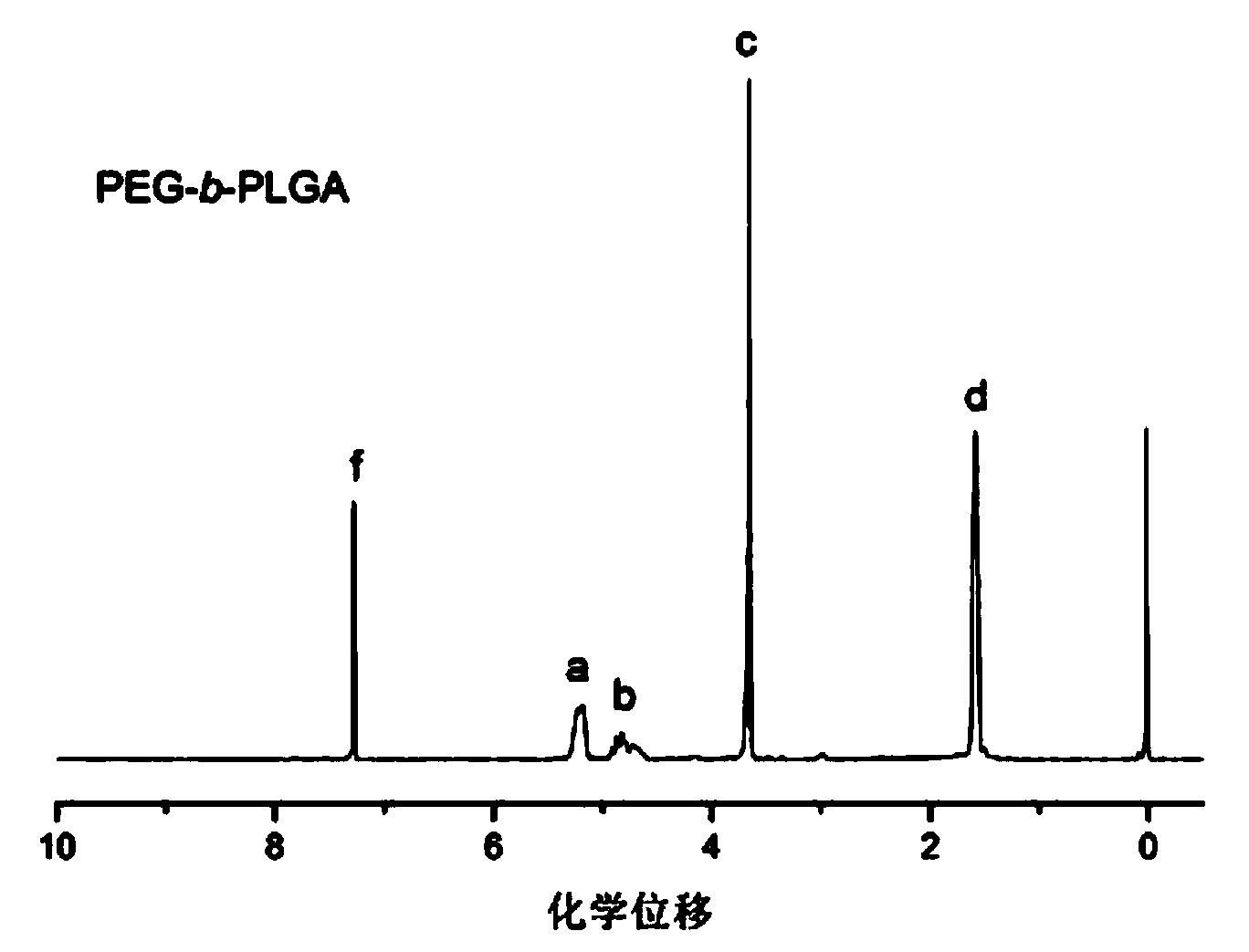
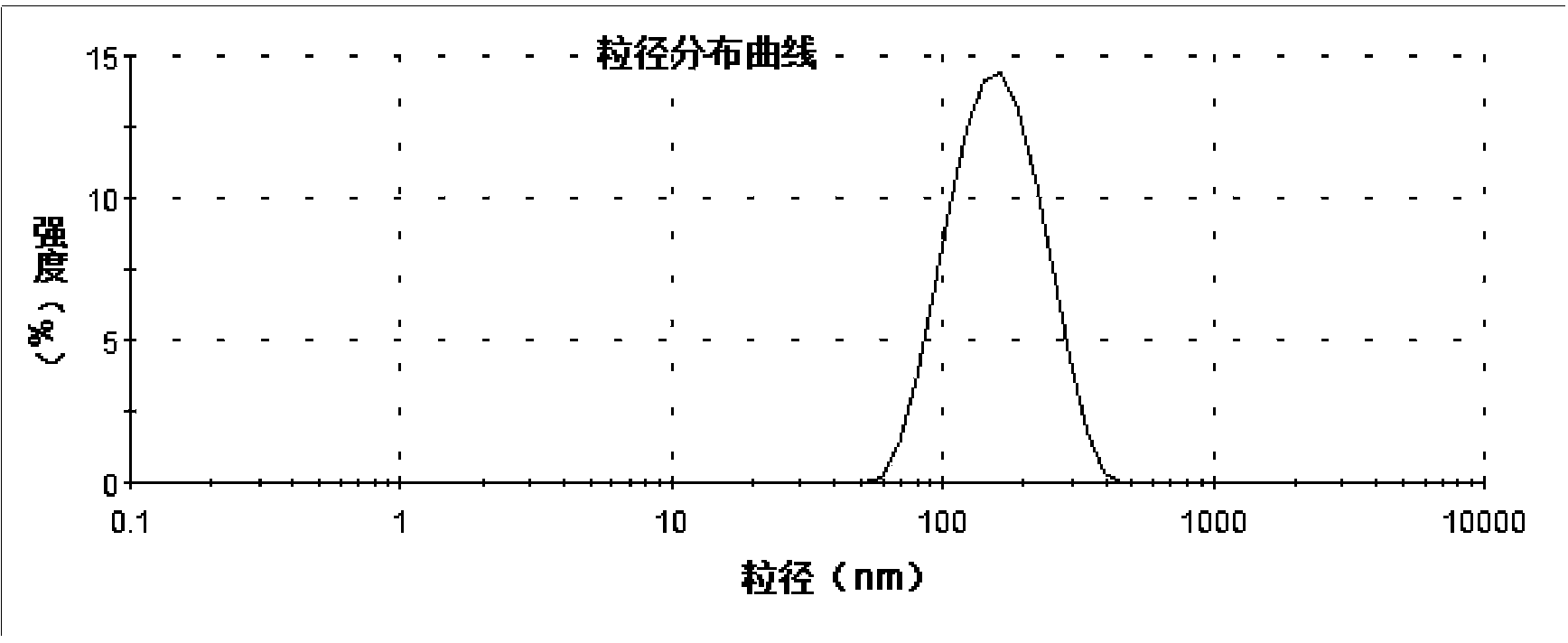
The invention discloses composite active bone cement containing sustained release drug-loading nanoparticles. The composite active bone cement comprises sustained release drug-loading nanoparticles and calcium phosphate bone cement, wherein the sustained release drug-loading nanoparticles comprise PEG-b-PLGA polymer drug carriers and hydrophobic medicines. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the composite active bone cement containing sustained release drug-loading nanoparticles. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking polyethylene glycol PEG as an initiator, carrying out a ring opening polymerization reaction, thereby obtaining a high-molecular polymer PEG-b-PLGA to serve as a drug carrier; preparing the drug-loading nanoparticles through a solvent volatilization method; and mixing the drug-loading nanoparticles with calcium phosphate bone cement powder, curing and forming, thereby obtaining the composite active bone cement. After the composite active bone cement provided by the invention is implanted into a patient, an eruption effect of the medicine can be reasonably reduced, slow release of the loaded medicines and long-term stabilization of the vertebral body of the patient are facilitated, and the composite active bone cement can serve as a composite tissue engineering scaffold for integrating bone repair and treatment.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Composite tissue repair patch and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106693059ANot easy to layerImprove mechanical propertiesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationPorosityBreaking strength
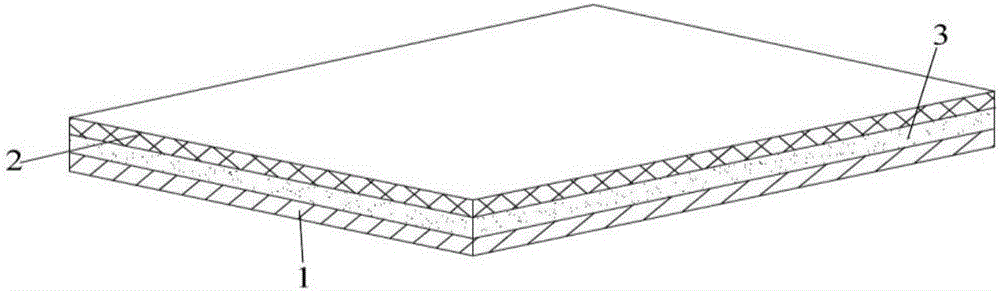
The invention relates to a composite tissue repair patch and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite tissue repair patch comprises a nanofiber membrane, a woven mesh and an adhesive material, wherein the adhesive material is located between the nanofiber membrane and the woven mesh; the adhesive material contains hydrophilic substances, the nanofiber membrane and the woven mesh are bonded through the adhesive material, and the adhesive material is embedded into pores of the nanofiber membrane and the woven mesh; the peel strength between the nanofiber membrane and the woven mesh is 20-75 cN / mm; the breaking strength of the composite tissue repair patch is 8-12.5 Mpa; preferably, the breaking elongation of the composite tissue repair patch is 20%-250%; more preferably, the porosity of the composite tissue repair patch is 50%-90%. The composite tissue repair patch is not likely to be layered and has the good mechanical property and soft characteristic.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Composite tissue corrugated paper board as well as production process and production equipment thereof
InactiveCN103568438AIncrease the weight typeImprove technical indicatorsMechanical working/deformationPaper/cardboard layered productsGramPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a composite tissue corrugated paper board. The composite tissue corrugated paper board comprises an inner layer, a core layer and an outer layer, wherein the inner layer is positioned at the inner side of the core layer; the outer layer is positioned at the outer side of the core layer; the inner layer is a backing paper; the core layer is a corrugated paper; the outer layer is compounded by two layers of tissues. The invention further discloses production equipment and process of the composite tissue corrugated paper board, wherein the production equipment comprises a backing paper tube, a core paper tube, a first tissue tube, a second tissue tube, a paper pulling windlass, an upper forging windlass, a lower forging windlass, a first single tile cementing device, a second single tile cementing device, a tissue cementing device and a heating board; a backing paper preheater is arranged behind the backing paper tube; a pressure windlass is arranged behind the backing paper preheater; a core paper preheater is arranged behind the core paper tube. The composite tissue corrugated paper board of the invention adopts tissues with different gram weights to process composite tissues, and uses corrugated papers and backing papers to obtain corrugated paper boards with various gram weights, so that the client demands can be satisfied. Moreover, the technical index of the composite tissue corrugated paper board is higher than the theoretical value, so that the quality requirements are met.
Owner:苏州正隆纸业有限公司
Loaded drug sustained release composite tissue repairing material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a loaded drug sustained release composite tissue repairing material and a preparation method thereof. The repairing material comprises a material having a three dimensional structure, porosity, and permeability, a drug or a drug loading medium. The repairing material can sustained release loaded drugs. Moreover, the release curve is controllable. The tissue compatibility and host-material immune reaction type of the repairing material are not changed. The repairing material is biocompatible, nontoxic, and harmless. The biological functions and special functions of the repairing material are enhanced, and the clinical application prospect is good.
Owner:EXCELLENCE MEDICAL TECH SUZHOU CO LTD +2
Production of tissue engineered digits and limbs
ActiveUS20140371869A1Increase vascularisationEncourages recruitmentPeptide/protein ingredientsBone implantBone formingBiology
The invention pertains to methods of producing artificial composite tissue constructs that permit coordinated motion. Biocompatable structural matrices having sufficient rigidity to provide structural support for cartilage-forming cells and bone-forming cells are used. Biocompatable flexible matrices seeded with muscle cells are joined to the structural matrices to produce artificial composite tissue constructs that are capable of coordinated motion.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Preparation method of precursor of composite tissues and organs with multichannel multilayer cell structure
InactiveCN102631710AImprove mechanical propertiesGood biocompatibilityProsthesisMatrix solutionCell layer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a precursor of composite tissues and organs with a multichannel multilayer cell structure. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: one or more cell matrix solution and synthetic macromolecule solution are prepared, the synthetic macromolecule solution is injected into a main mold to form the lower surface of a support, and then the one or more cell matrix solution is injected into an assembling mold in a layered manner to form a plurality of cell matrix layers through crosslinking; and an inner mold is removed, the synthetic macromolecule solution is injected into the outer surface and the surrounding gap of the cell matrix layers to form an outer support, and the assembling mold is removed. The preparation method can be used for forming a complex multichannel three-dimensional structure combining different cell matrix materials containing uniform internal channels with a case of the synthetic macromolecule support, and overcomes the defects of tissue engineering that when cells are induced and cultured in the three-dimensional support, the needed time is long, the type of the cells is single, the distribution of the cells is nonuniform, the cells closed in a cell layer which exceeds a certain thickness are not easy to survive, nutrient channels do not exist, the layering differentiation on the stem cells is difficult to realize, the limitation on the appearance of the support is strong, and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Synovial fluid barrier
InactiveUS7825083B2Improve responseImprove regenerative healingSuture equipmentsPeptide/protein ingredientsJoint synovialSurgery
Owner:SPINEWAVE
Composite tissue adhesive as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112791227AAccelerates hydration swelling effectFast dryingSurgical adhesivesBandagesPolymer scienceCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a composite tissue adhesive as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite tissue adhesive comprises a three-dimensional porous matrix and an adhesion enhancing factor adsorbed on the surface of the matrix, wherein the three-dimensional porous matrix is obtained by freeze-drying composite hydrogel of GelMA and polyacrylic acid grafted with N-hydroxysuccinimide, and the adhesion enhancing factor is polydopamine. The composite tissue adhesive disclosed by the invention has a porous structure and can absorb liquid for wetting a wound surface, and polyacrylic acid is provided with carboxylic acid groups with negative charges, so the hydration expansion effect of the tissue adhesive can be accelerated, a tissue surface drying speed can be accelerated, and the composite tissue adhesive has a liquid absorption amount of 500% or above; and the composite tissue adhesive provided by the invention has two components which can be bonded with amino groups on wound tissues, and the adhesion strength of the composite tissue adhesive with wet wound tissues can reach 180 kPa or above.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Steel plate with excellent inhibition of welding heat affected section and manufacturing method of the same
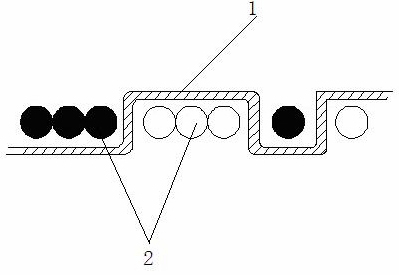
InactiveCN101153372AExcellent resistance to fatigue crack growthPrevent toughness from deterioratingComposite tissueDiamond
A steep contains at least one of the C: 0.03-0.18%, Si: 0.02-0.5%, Mn: 0.9-2.0%, N:0.003-0.01%, REM:0.001-0.1% and Ca: 0.0003-0.02%, and Zr: 0.001-0.05%, satisfying P: less than 0.02%, S: less than 0.015%, and Al: less than 0.01%. When measuring the composition of the oxide compounds contained in the steel as the single oxide compound for mass conversion, the total amount of the REM oxide compound and the CaO is more than 5%, the ZrO2 is more than 5%, and the compound is a composite tissue constituted by soft character and hard character, and the ratio (Hv1 / Hv2) of the diamond pyramid hardness Hv1 of the hard character and the Hv2 of soft character is 1.5-5.0, and the equivalent circle diameter of the grain diameter of the soft character is less than 20 mum.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
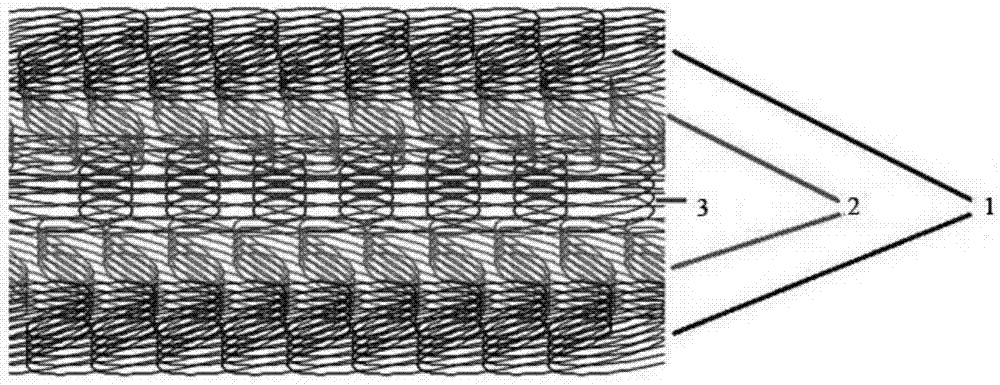
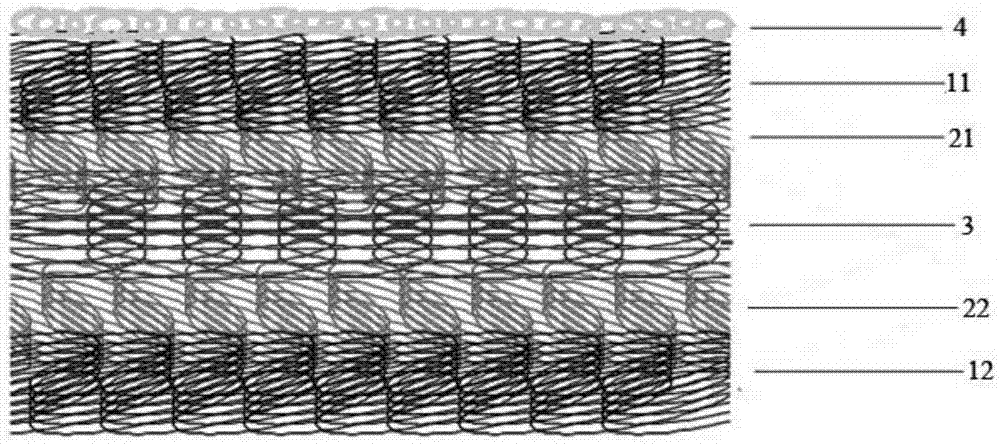
Filtering cloth woven from monofilaments and multifilaments
InactiveCN102199831AImprove permeabilityExtended service lifeWoven fabricsFiltration separationYarnEngineering
The invention discloses filtering cloth woven from monofilaments and multifilaments, relating to the field of industrial filtering cloth. Monofilaments and multifilaments are interwoven, the multifilaments completely float on the surface of the entire cloth so as to play a favorable interception role, when materials enter to the interior of the cloth, a favorable filtering effect can be achieved because the interior of the cloth are completely the nomofilaments which have favorable permeability, and thus, the service life of the filter cloth is prolonged. In addition, the design method can be used for fully exerting the strong force effect of the two yarns, the requirement on the industry for high load bearing of the filter cloth is met, 3 / 11 / 3 composite tissues are adopted and have long floating line yarns, so that a smooth surface effect is achieved, and thus, cake discharging after filtering is facilitated and no material is stuck to the filter cloth.
Owner:DALIAN HUALONG FILTER CLOTH
Preparation method of bainite/martensite/austenite composite high-strength steel
InactiveCN103243275BImprove stabilityOvercome the disadvantage of high costHeat treatment process controlSmelting processThick wall
The invention discloses a preparation method of bainite / martensite / austenite composite high-strength steel, belonging to the field of low-alloy high-strength steel. According to the composite high-strength steel, C, Mn, Si and Cr are used as main alloy elements, Al, Ni, Mo, Cu, Nb, Ti, V and the like are added, and the balance is Fe. The preparation method comprises the following steps: smelting, casting, forging or rolling to prepare rails, thick-wall pipes, large-section bars or thick pipes and the like by adopting a conventional steel-smelting process; carrying out austenitizing; controlling cooling by adopting different cooling media to obtain a part of bainite tissue in the cooling process; instantly carrying out distribution treatment and low-temperature tempering treatment so as to finally obtain a bainite / martensite / austenite composite tissue which is good in strong plasticity and toughness coordination, wherein the distribution time is 30-360 minutes. For a component which is large in size and easy to crack in quenching, the bainite / martensite / austenite composite high-strength steel has wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Light activated composite tissue adhesives
InactiveUS9006182B2Facilitate cross-linkingImprove cohesive strengthOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesForeign matterLesion
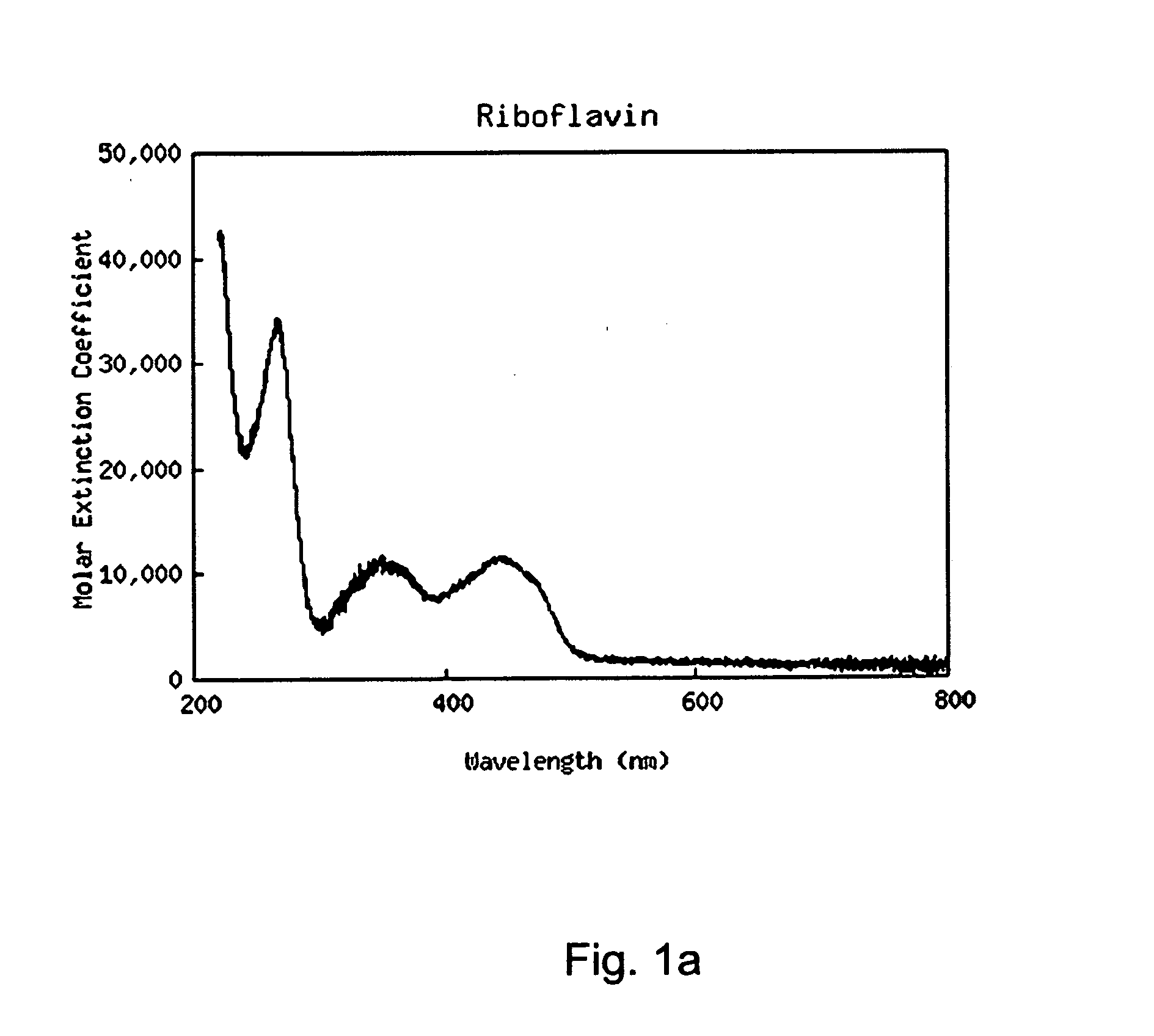
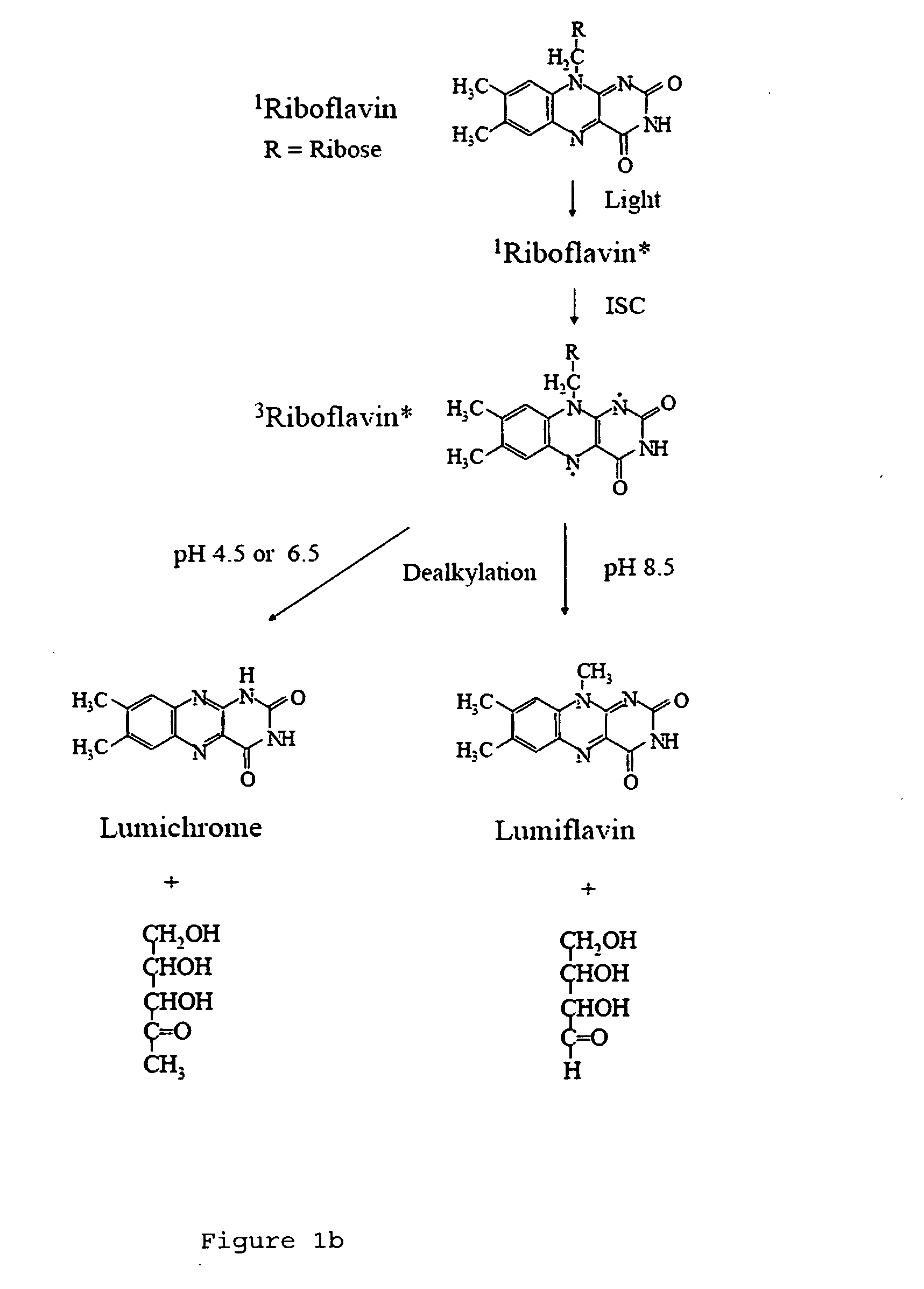
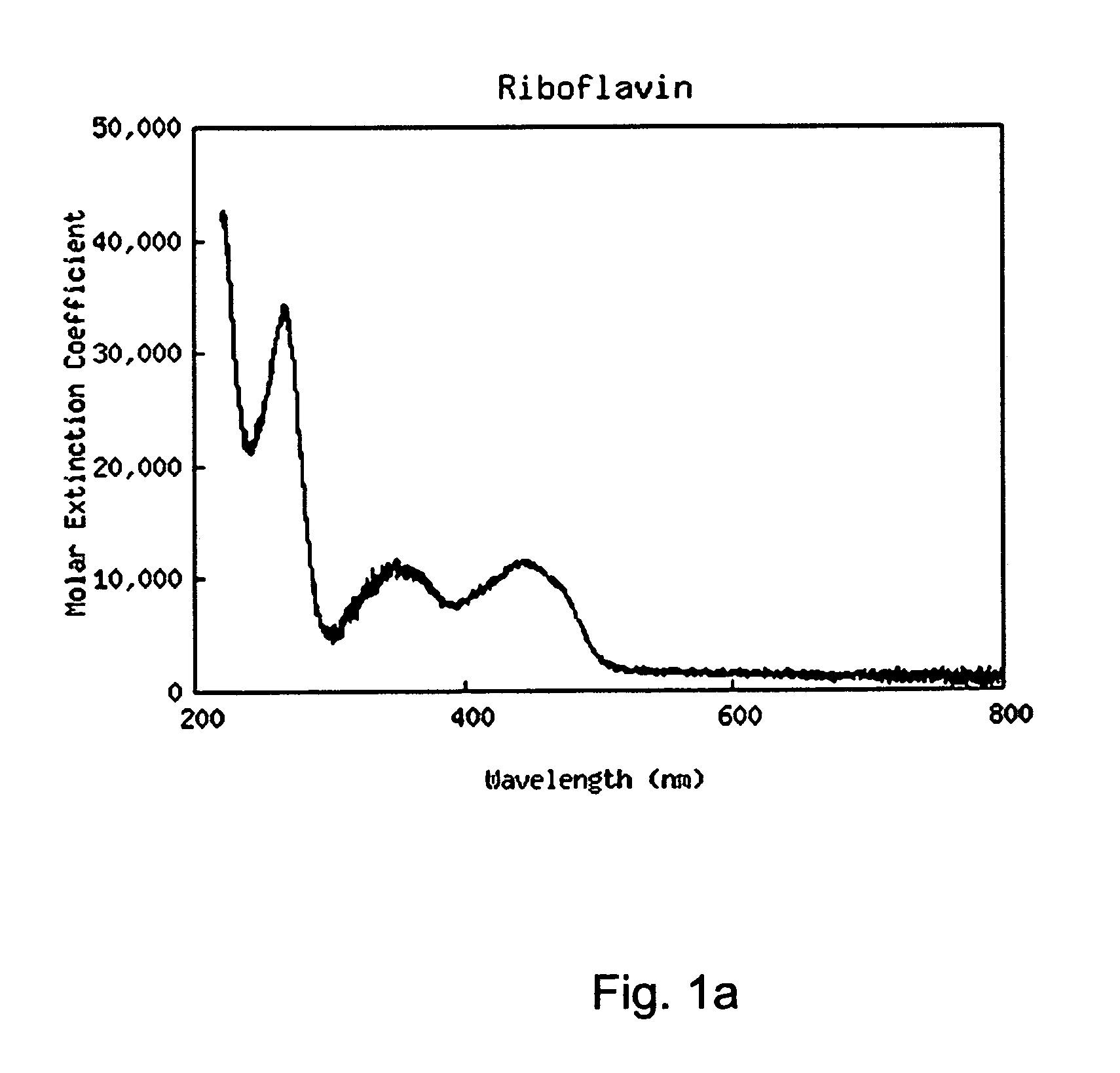
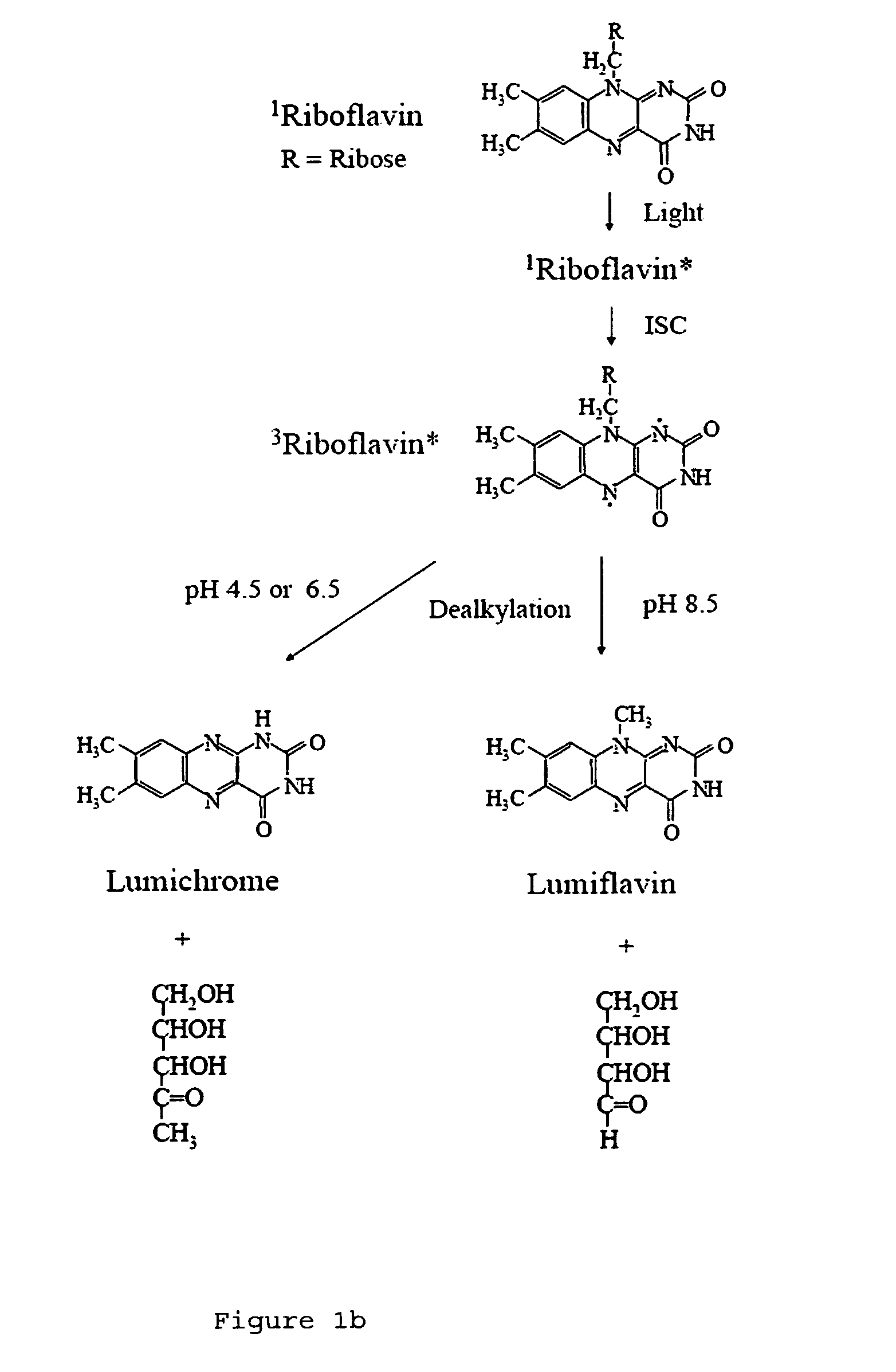
A light activated collagen-flavin composite layer incorporating riboflavin is applied as treatment for infected lesions. These composites have also been found to be strong tissue adheives that are effective in closing and sealing wounds, fixation of grafts / implants and anastomoses. Advantages include speed of closure, reduced infection due to the elimination of foreign matter, evidence of accelerated wound healing and the ease of use in complex surgery, especially when watertight seals, limited access or small repair size are important factors. The riboflavin in the collagen layer is exposed to light (e.g., light having a wavelength between 360-375 nm or 440-480 nm), decomposing the riboflavin to form reactive oxygen species (ROS). Strong crosslinks between the collagen composite and tissue results. In addition, similar exposures eradicate pathogens in the wound.
Owner:CONVERSION ENERGY ENTERPRISES
Composite tissue engineering skin containing live cells and preparation method for composite tissue engineering skin
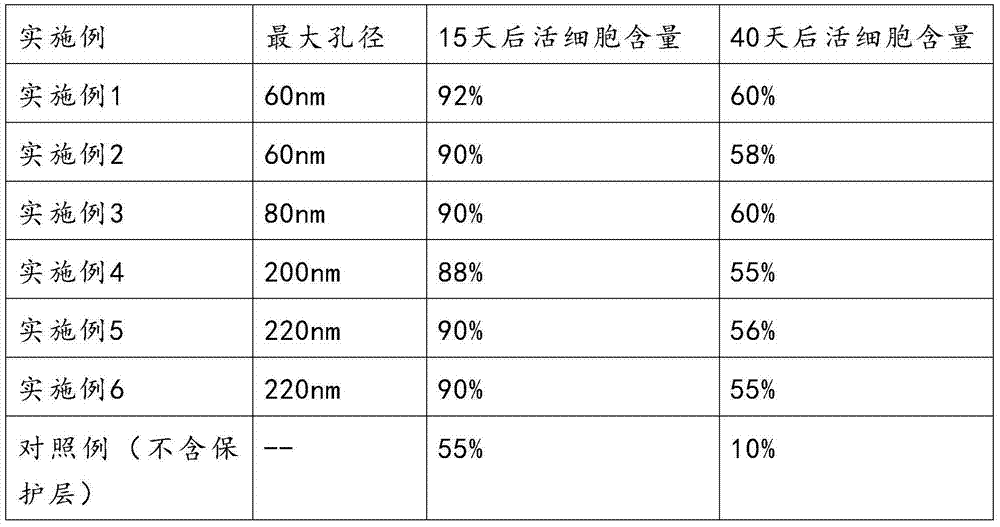
The invention relates to the biological field, and in particular relates to composite tissue engineering skin containing live cells and a preparation method for the composite tissue engineering skin. The composite tissue engineering skin not only contains live cells, but also contains a degradable polymer material protective layer, so that the composite tissue engineering skin is reinforced in isolating capacity, the cost is reduced and the quality guarantee period is prolonged. The defects that the tissue engineering skin containing live cells in the prior art is high in cost, short in quality guarantee period and poor in isolating capacity are overcome. According to the embodiment of the invention, the composite tissue engineering skin containing live cells provided by the invention comprises a corium layer and a degradable polymer material protective layer, wherein the corium layer comprises liver humanized fibroblast or mesenchymal stem cells which are differentiated towards the fibroblast.
Owner:陕西艾尔肤组织工程有限公司
Method for constructing composite tissue engineering skins
ActiveCN106620855AIdeal three-dimensional network structureMeet the requirements of morphologyProsthesisFiberReticular formation
The invention discloses a method for constructing composite tissue engineering skins. The method includes that human epidermal stem cells are used as seed cells, sheep accellular dermal matrixes are used as scaffold carriers, and the composite tissue engineering skins can be constructed by means of in-vitro culture by the aid of gas-liquid interface separation processes. The method has the advantages that the composite tissue engineering skins constructed by the aid of the method have perfect three-dimensional netted structures, and accordingly growth of cells and formation of new collagen fibers can be promoted; the composite tissue engineering skins are short in construction time and complete in histological structure and are similar to natural skins, and morphology requirements on tissue engineering skins can be met.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Method for improving mechanical properties of steel plate through thermal forming-subcritical quenching-partitioning technology
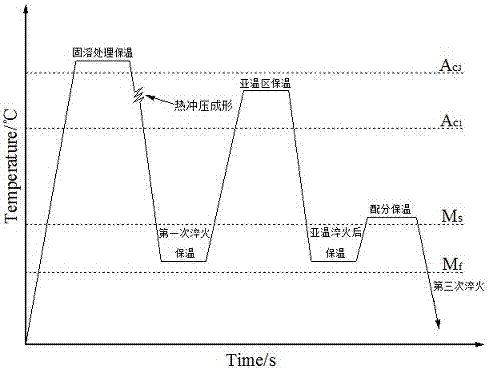
The invention relates to a method for improving the mechanical properties of a steel plate through a thermal forming-subcritical quenching-partitioning technology. According to the method for improving the mechanical properties of the steel plate through the thermal forming-subcritical quenching-partitioning technology, the steel plate is heated to a temperature over Ac3 at a certain rate, and the temperature is kept for a certain time; the steel plate is transferred into a stamping die for hot stamping forming and quenching treatment, the steel plate is quenched to a temperature (QT1) between Ms and Mf, and the temperature is kept for a certain time; the steel plate is reheated to a temperature between Ac1 and Ac3, and the temperature is slightly lower than Ac3 and kept for a certain time; then, the steel plate is rapidly quenched to a temperature (QT2) between Ms and Mf, and the temperature is kept for a certain time; then, the steel plate is reheated to a temperature slightly higher than the Ms, and the temperature is kept; and finally, the steel plate is quenched to the indoor temperature. By the adoption of the method for improving the mechanical properties of the steel plate through the thermal forming-subcritical quenching-partitioning technology, the new thermal forming-subcritical quenching-partitioning technology is formed through combination of a subcritical quenching capable of achieving ultra-fine treatment and toughening of composite tissue, a hot stamping forming technology and a quenching-partitioning technology, and the treated hypoeutectoid steel is multi-phase tissue provided with martensite, granular ferrite, retained austenite and M / A islands and has excellent mechanical properties. Besides, by the adoption of the thermal forming- subcritical quenching-partitioning technology, the production cost of products is low, and the performance and cost ratio is high.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com