Tissue engineering cartilage composite scaffold and preparation method thereof
A composite scaffold and tissue engineering technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of cell loss, long recovery period, extracellular matrix loss, etc., to promote chondrogenic differentiation, good biocompatibility, good mechanics the effect of strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: Preparation of cartilage extracellular matrix-derived microcarriers
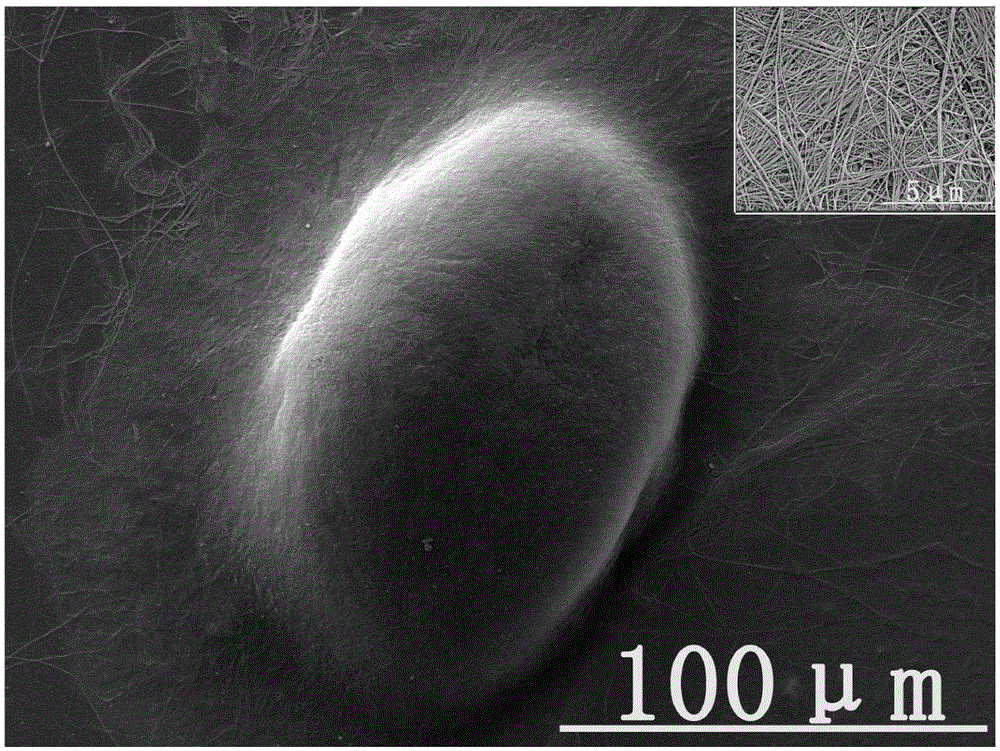
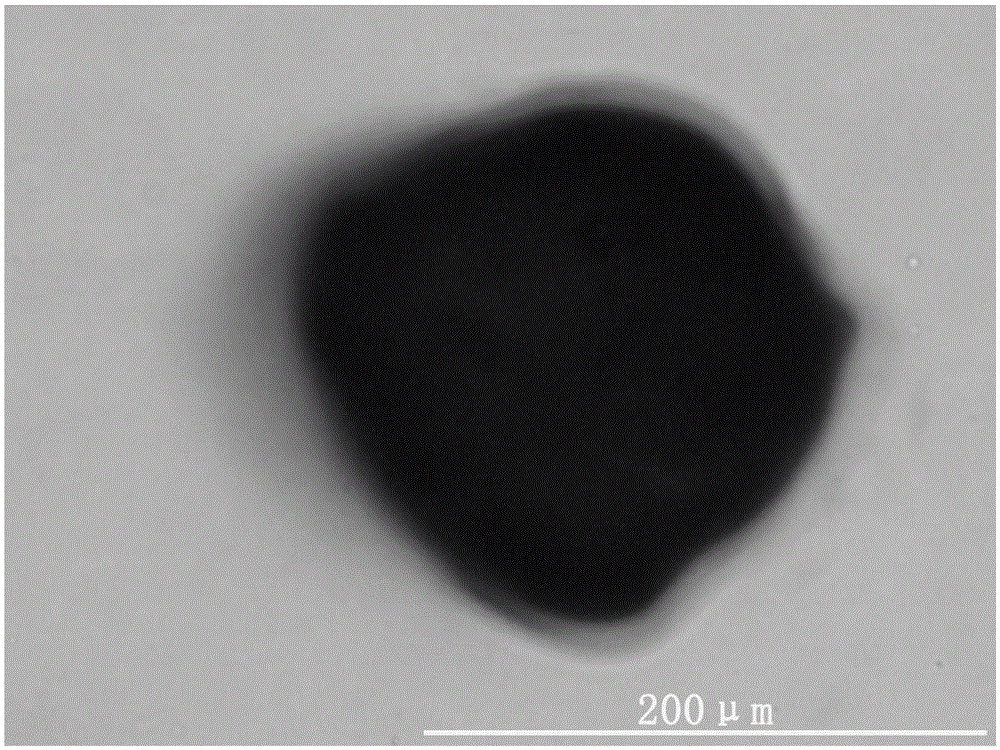
[0046] 500 g of the obtained fresh porcine articular cartilage was rinsed repeatedly with sterile physiological saline, mixed with a certain amount of sterile three-distilled water, and placed in a pulverizer for pulverization. Pass through stainless steel sieves with sieve diameters of 100 μm and 500 μm respectively to obtain cartilage extracellular matrix-derived microparticles with a diameter of 100 μm-500 μm. Add 1% SDS solution at 4°C, place in a shaker, and keep shaking for 8 hours. After washing away the remaining SDS solution with sterile three-distilled water, add the microparticles to 5ml DNAse (50U / mL) and RNase (1U / mL) solution, shake on a shaker at 37°C for 4 hours, remove cellular components. The decellularized cartilage extracellular matrix-derived microparticles are thoroughly washed to remove residual decellularized fluid. After packaging, place it at 25kGyC O 60 Radia...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Cartilage extracellular matrix-derived microcarriers with a diameter of 100 μm-500 μm were prepared according to the method in Example 1.
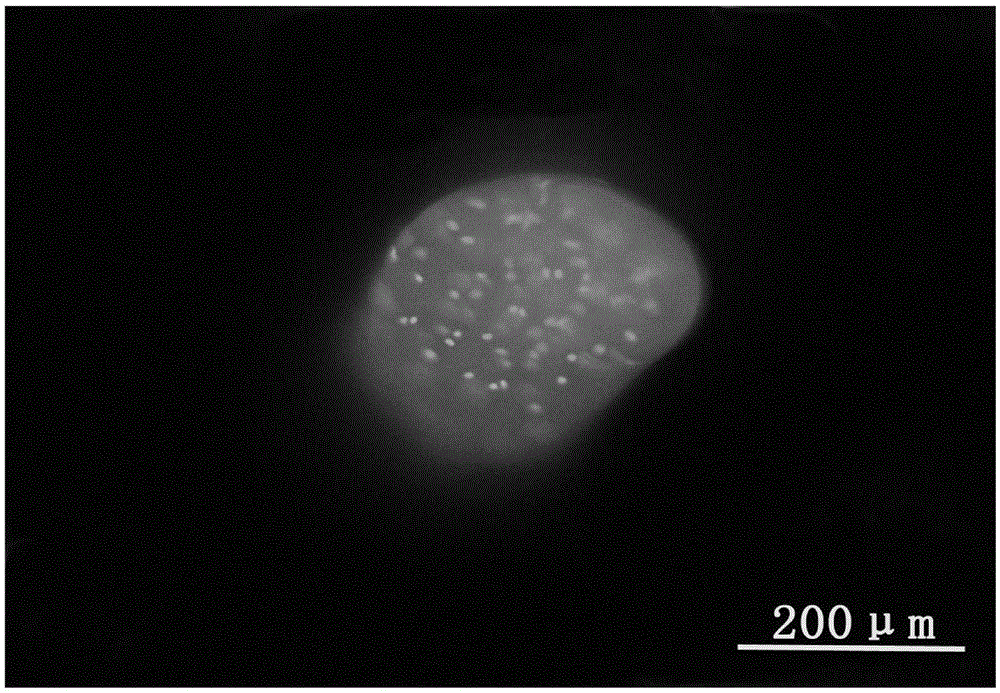
[0055] 100mg cartilage extracellular matrix-derived microcarriers and 50ml containing 1 × 10 6 The DMEM cell suspension of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells was mixed and placed in the reaction chamber of a rotary three-dimensional bioreactor (Rotary Cell Culture Systems, RCCS-D) for co-cultivation. In order to facilitate the attachment of cells to the microparticles, the rotation speed of the bioreactor was set at 30 rpm, with 1 minute per rotation and 30 minutes of rest. After 24 hours, the rotation speed was set to 80rpm and the rotation was continued. Bioreactor placed at 37 °C 5% CO 2 condition. The medium was changed every 2-3 days.
[0056] The 3D printed PLGA porous scaffold with a pore diameter of about 600 μm was placed in a petri dish and immersed in a 1.8% (w / v) sodium alginate solution. The chondrocyte extrace...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Cartilage extracellular matrix-derived microcarriers with a diameter of 100 μm-500 μm were prepared according to the method in Example 1.
[0059] 100mg cartilage extracellular matrix-derived microcarriers and 50ml containing 8 × 10 6 The DMEM cell suspension of rat chondrocytes was mixed and placed in the reaction chamber of a rotary three-dimensional bioreactor (Rotary Cell Culture Systems, RCCS-D) for co-cultivation. In order to facilitate the attachment of cells to the microparticles, the rotational speed of the bioreactor was set at 50 rpm, with 1 minute per revolution and 30 minutes of rest. After 24 hours, the rotation speed was set to 100rpm and the rotation was continued. Bioreactor placed at 37 °C 5% CO 2 condition. The medium was changed every 2-3 days.
[0060] A porous demineralized bone matrix scaffold with a pore diameter of about 2000 μm was placed in a culture dish and immersed in a 2.4% (w / v) fibrinogen solution. The chondrocyte extracellular matr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com