Preparation method of biological 3D printing composite ink for repairing cartilage defects
A 3D printing and cartilage technology, applied in the field of biological 3D printing, can solve the problems of natural three-dimensional microenvironment that cannot simulate cell growth, cell adhesion, unsatisfactory directional differentiation, and difficulty in accurate imitation, and achieve good clinical application prospects and value, rapid cross-linking and curing, and high biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1. The present invention provides a technical solution: a method for preparing a bio-3D printing composite ink for repairing cartilage defects, comprising the following steps:
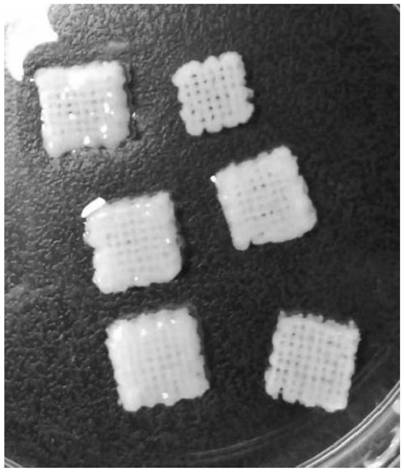
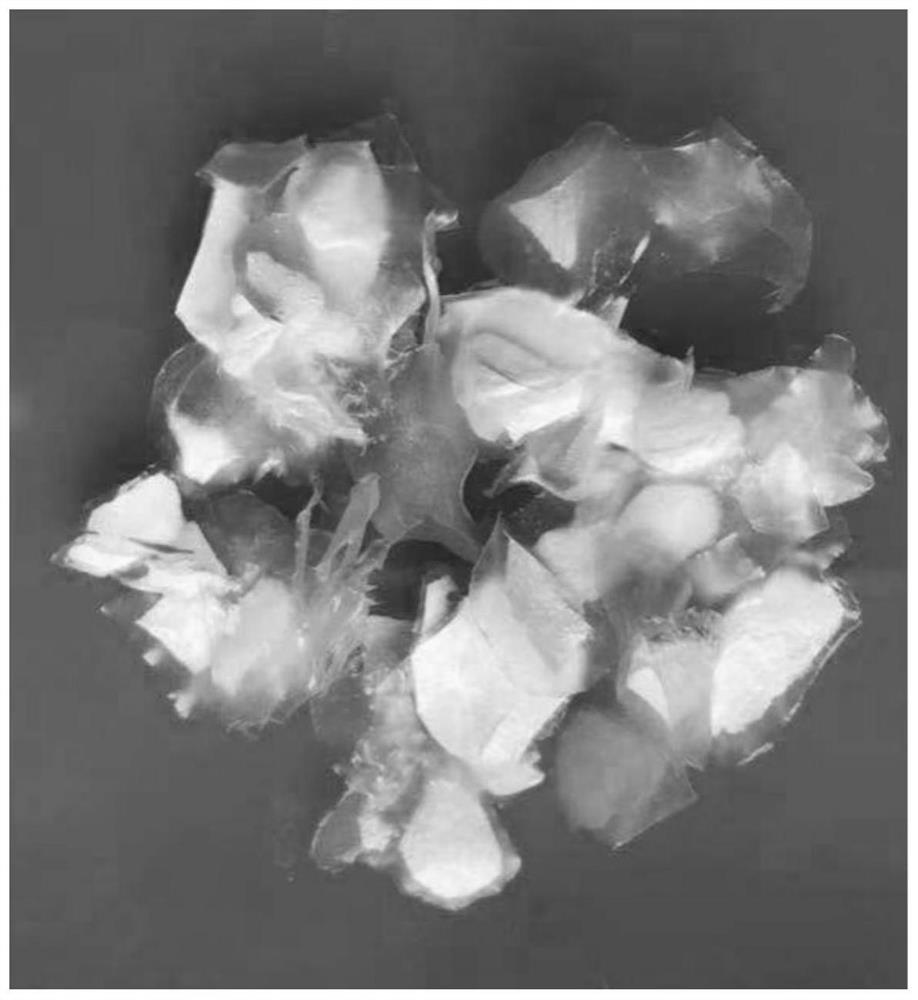
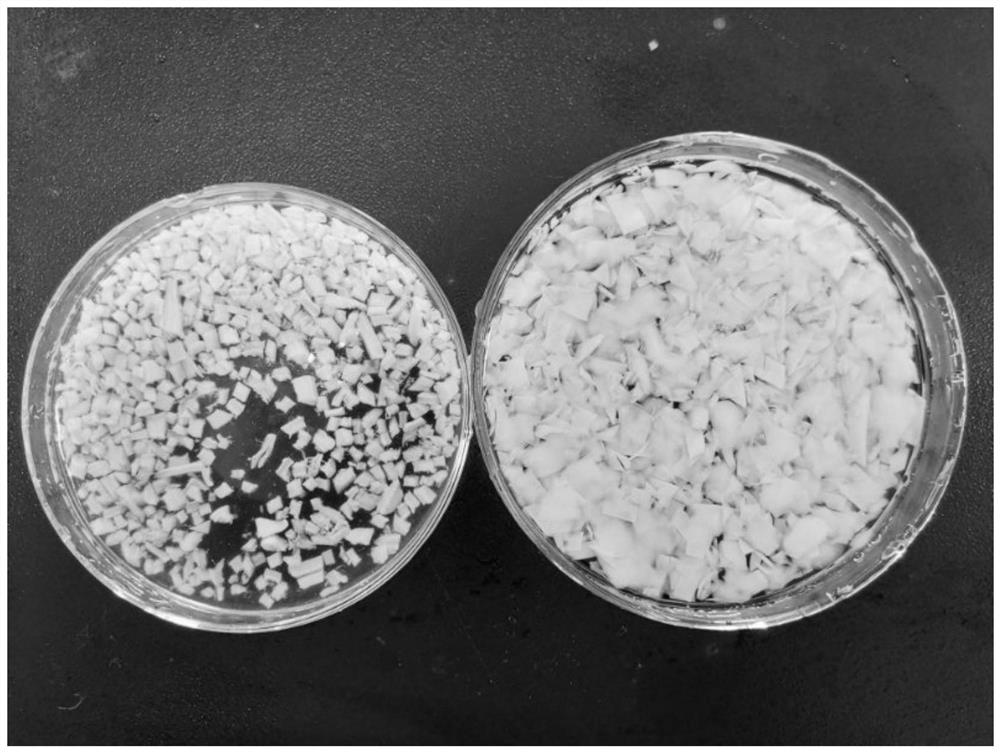
[0033] S1. Preparation of cartilage granules: take the fresh articular surface hyaline cartilage or costal cartilage of animals, cut off the hyaline cartilage from the articular surface with a sharp scalpel blade to obtain cartilage slices, and then cut the cartilage slices into granules with a particle size of 1-2mm 3 (Such as figure 1 shown);
[0034] S2. Decellularization treatment: Soak cartilage particles in hypotonic Tris-HCl buffer, the concentration of hypotonic Tris-HCl buffer is 10mM, PH=8, and then cycle freeze-thaw at -80°C ~ 37°C 6 cycles; then digest with 0.25% trypsin at 37°C for 24 hours, and replace the trypsin solution every 4 hours; then wash away the trypsin with hypertonic Tris-HCl buffer solution, The permeated Tris-HCl buffer solution is composed of NaCl 1.5M...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2. The present invention provides a technical solution: a method for preparing a bio-3D printing composite ink for repairing cartilage defects, comprising the following steps:
[0042] S1. Preparation of cartilage granules: take the fresh articular surface hyaline cartilage or costal cartilage of animals, cut off the hyaline cartilage from the articular surface with a sharp scalpel blade to obtain cartilage slices, and then cut the cartilage slices into granules with a particle size of 1-2mm 3 (Such as figure 1 shown);
[0043] S2. Decellularization treatment: Soak cartilage particles in hypotonic Tris-HCl buffer, the concentration of hypotonic Tris-HCl buffer is 10mM, PH=8, and then cycle freeze-thaw at -80°C ~ 37°C 6 cycles; then digest with 0.25% trypsin at 37°C for 24 hours, and replace the trypsin solution every 4 hours; then wash away the trypsin with hypertonic Tris-HCl buffer solution, The permeated Tris-HCl buffer solution is composed of NaCl 1.5M...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3. The present invention provides a technical solution: a method for preparing a bio-3D printing composite ink for repairing cartilage defects, comprising the following steps:
[0051] S1. Preparation of cartilage granules: take the fresh articular surface hyaline cartilage or costal cartilage of animals, cut off the hyaline cartilage from the articular surface with a sharp scalpel blade to obtain cartilage slices, and then cut the cartilage slices into granules with a particle size of 1-2mm 3 (Such as figure 1 shown);
[0052] S2. Decellularization treatment: Soak cartilage particles in hypotonic Tris-HCl buffer, the concentration of hypotonic Tris-HCl buffer is 10mM, PH=8, and then cycle freeze-thaw at -80°C ~ 37°C 6 cycles; then digest with 0.25% trypsin at 37°C for 24 hours, and replace the trypsin solution every 4 hours; then wash away the trypsin with hypertonic Tris-HCl buffer solution, The permeated Tris-HCl buffer solution is composed of NaCl 1.5M...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com