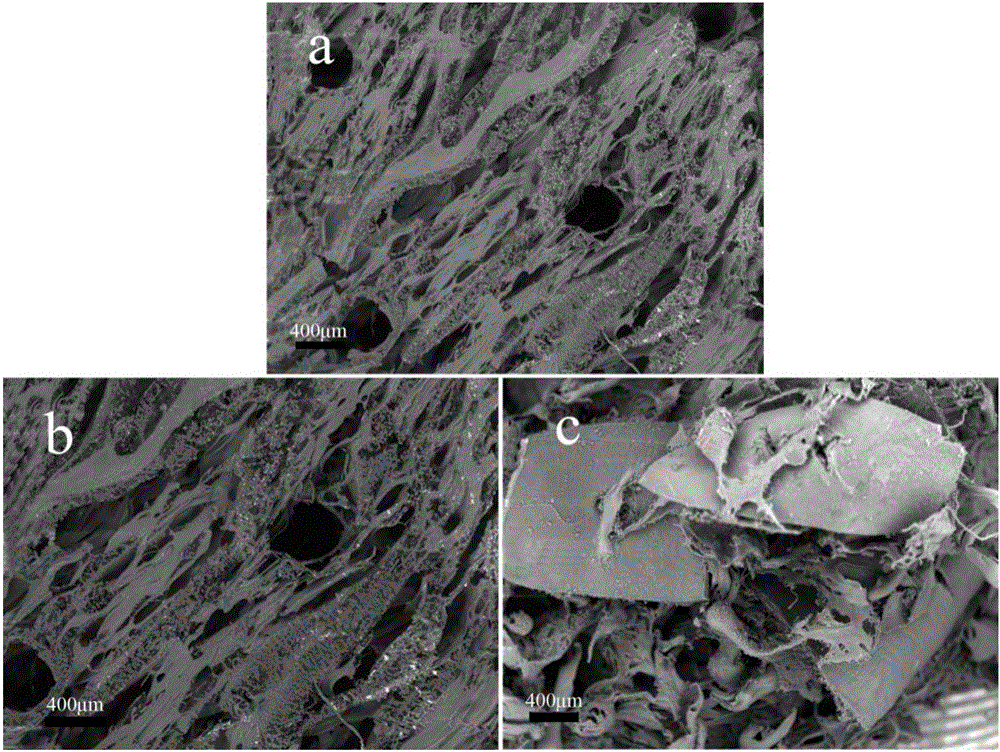
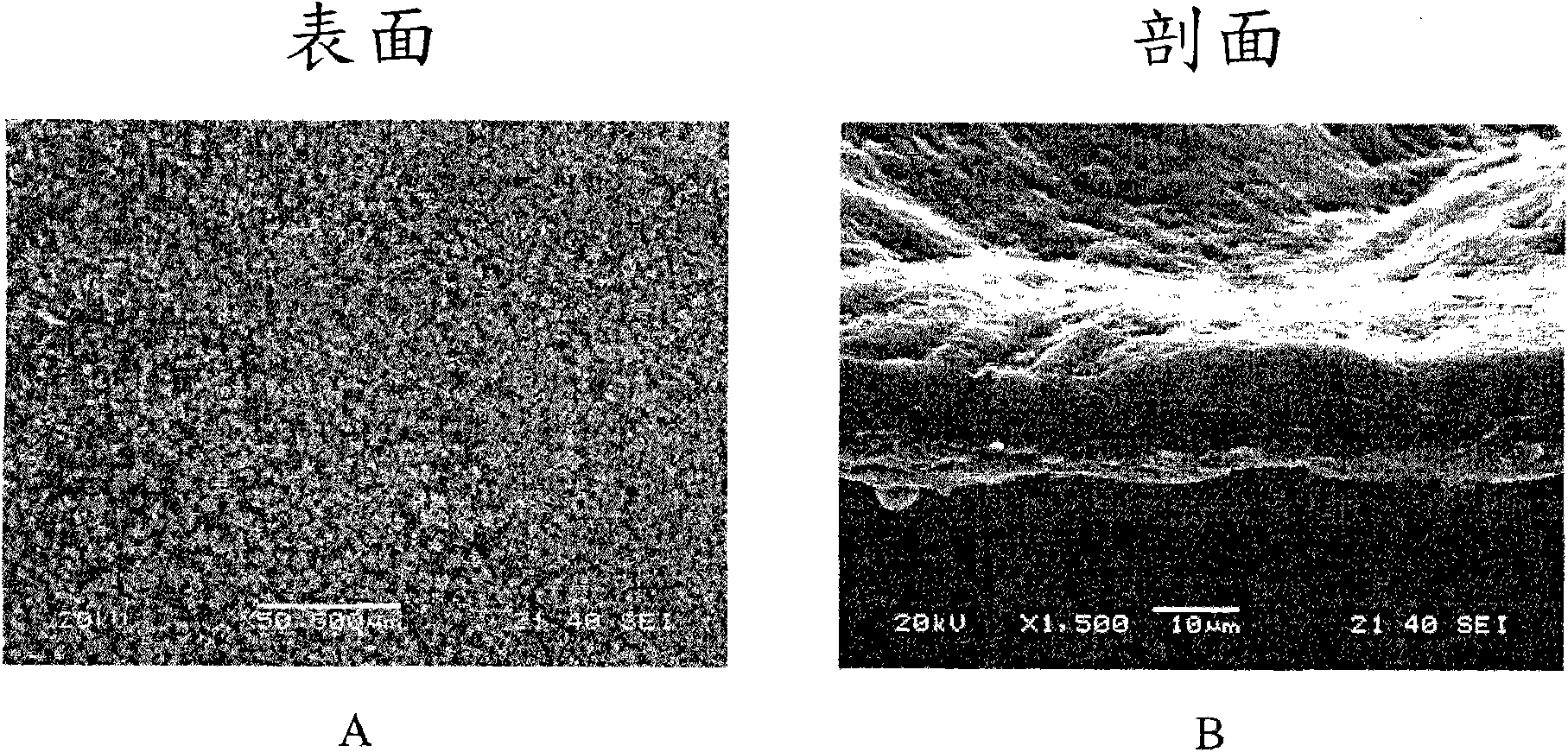
Patents
Literature
414 results about "Decellularization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Decellularization (also spelt decellularisation in British English) is the process used in biomedical engineering to isolate the extracellular matrix (ECM) of a tissue from its inhabiting cells, leaving an ECM scaffold of the original tissue, which can be used in artificial organ and tissue regeneration. Organ and tissue transplantation treat a variety of medical problems, ranging from end organ failure to cosmetic surgery. One of the greatest limitations to organ transplantation derives from organ rejection caused by antibodies of the transplant recipient reacting to donor antigens on cell surfaces within the donor organ. Because of unfavorable immune responses, transplant patients suffer a lifetime taking immunosuppressing medication. Stephen F. Badylak pioneered the process of decellularization at the McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. This process creates a natural biomaterial to act as a scaffold for cell growth, differentiation and tissue development. By recellularizing an ECM scaffold with a patient’s own cells, the adverse immune response is eliminated. Nowadays, commercially available ECM scaffolds are available for a wide variety of tissue engineering. Using peracetic acid to decellularize ECM scaffolds have been found to be false and only disinfects the tissue.
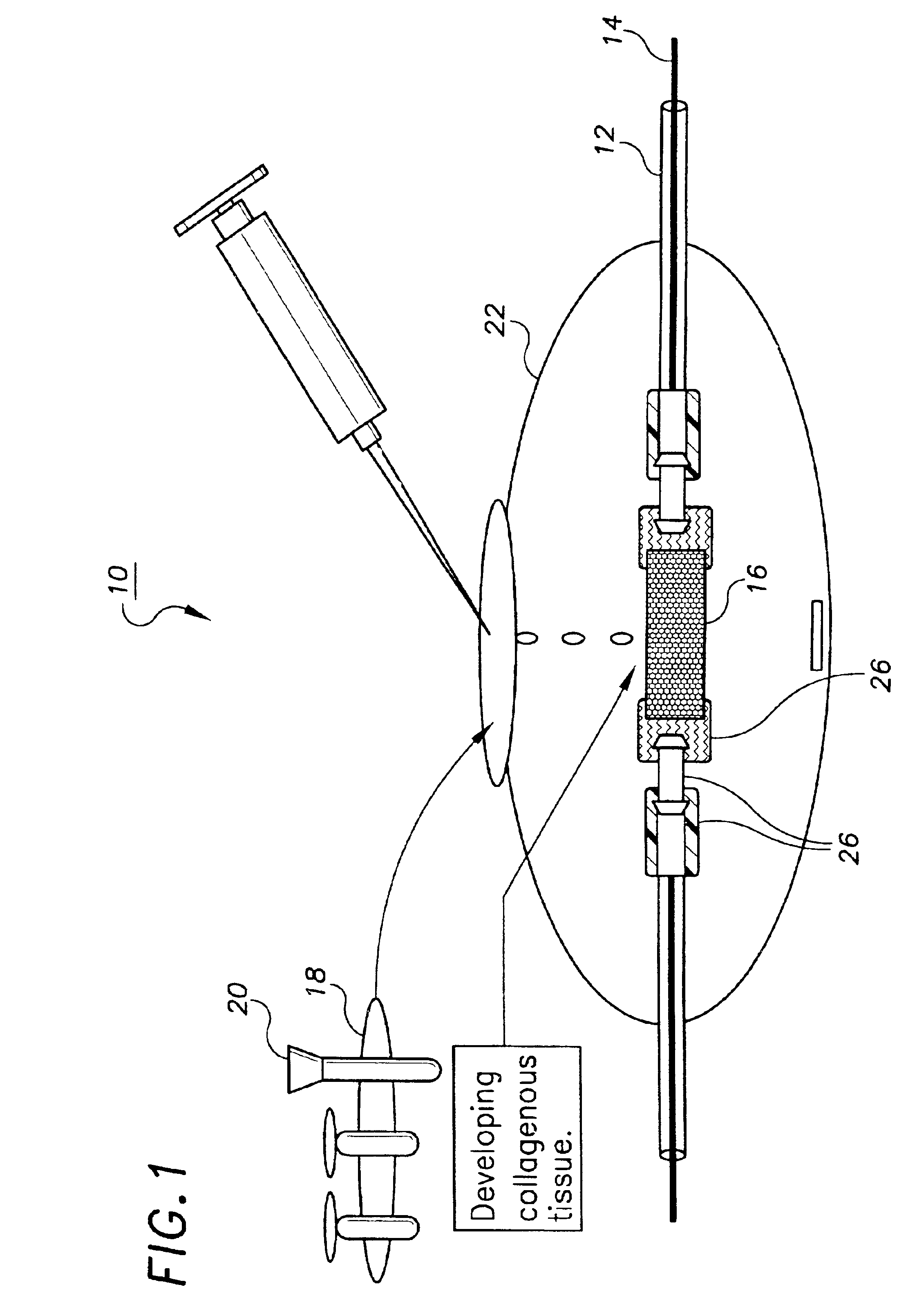
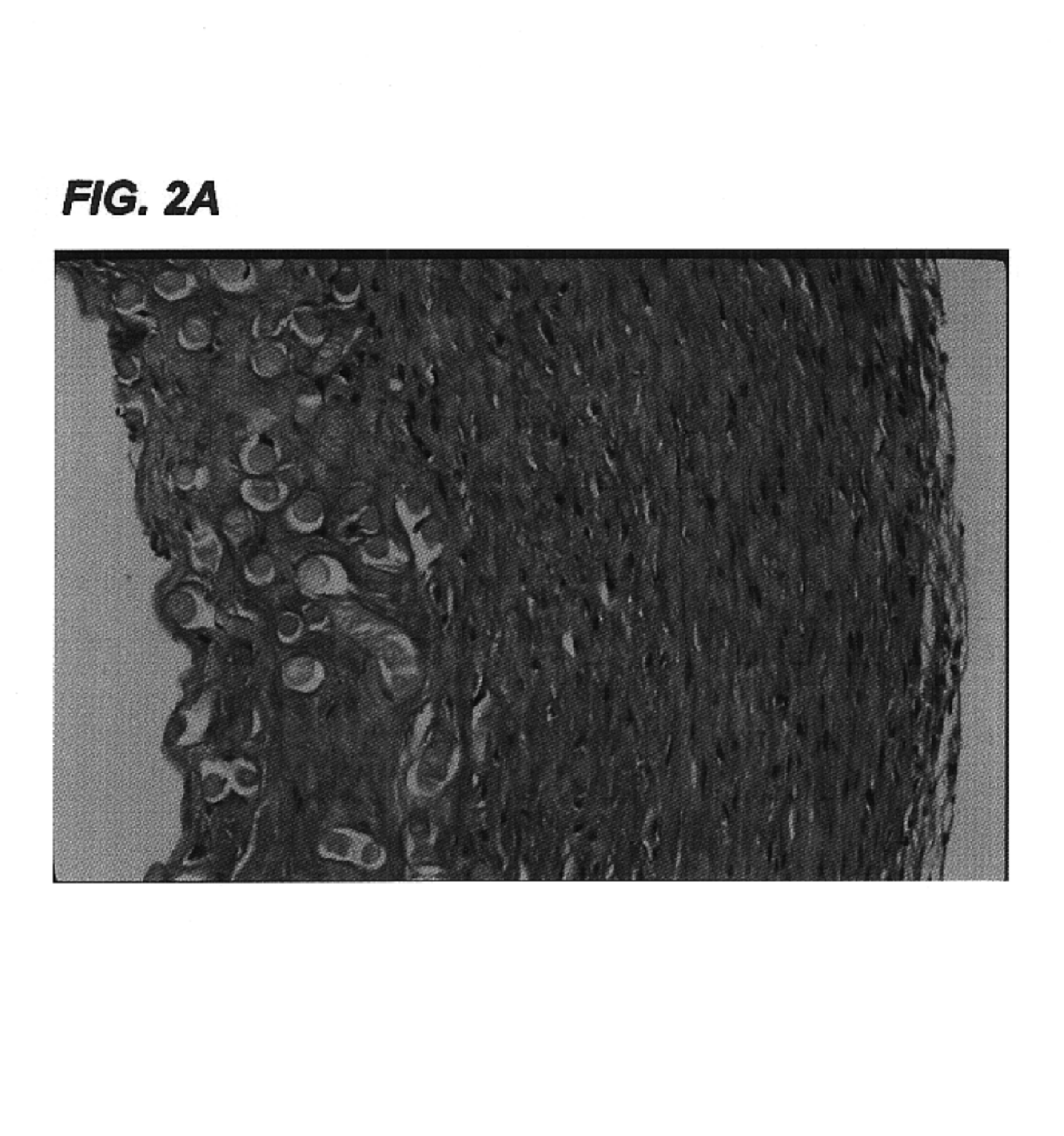
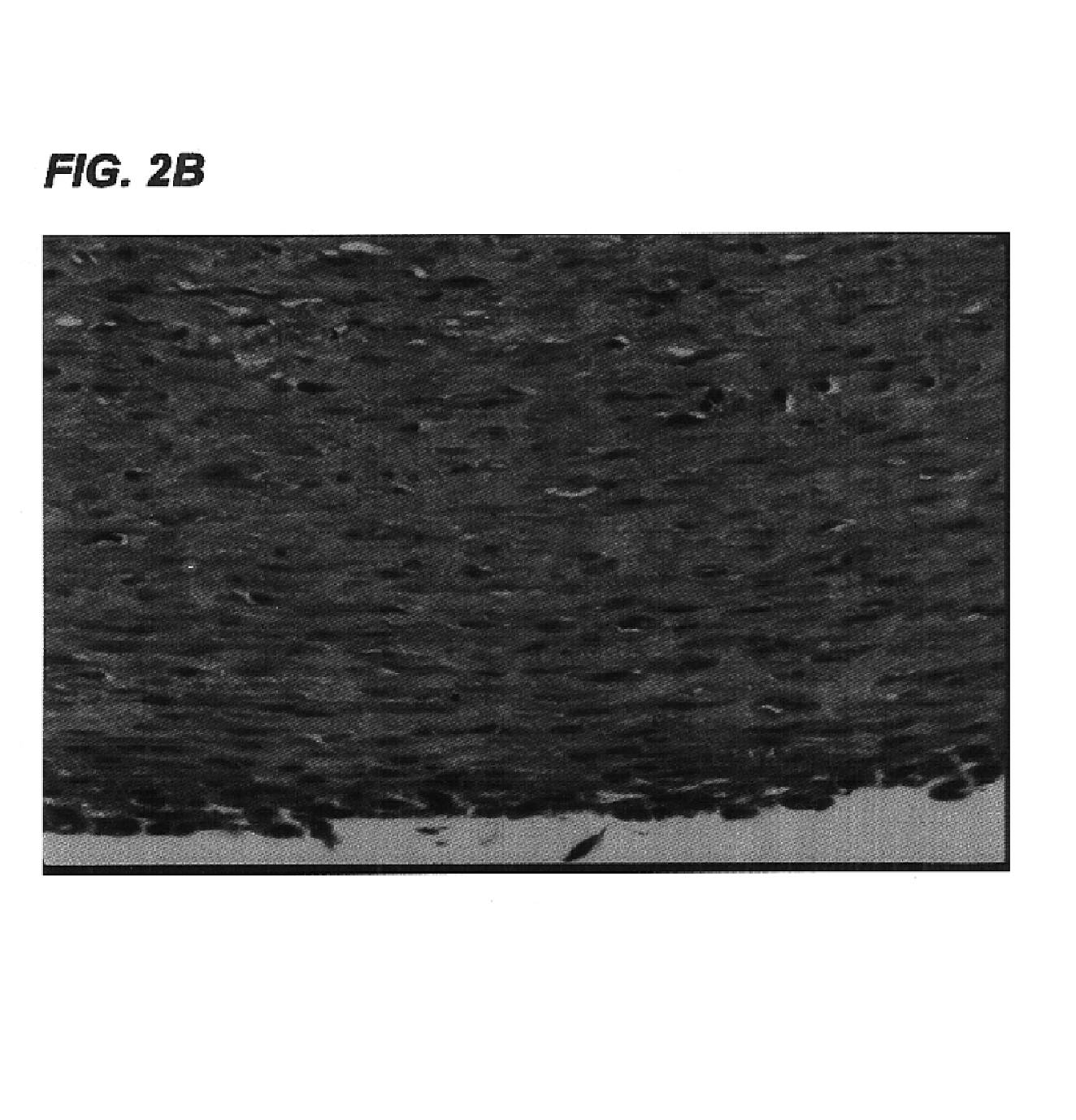
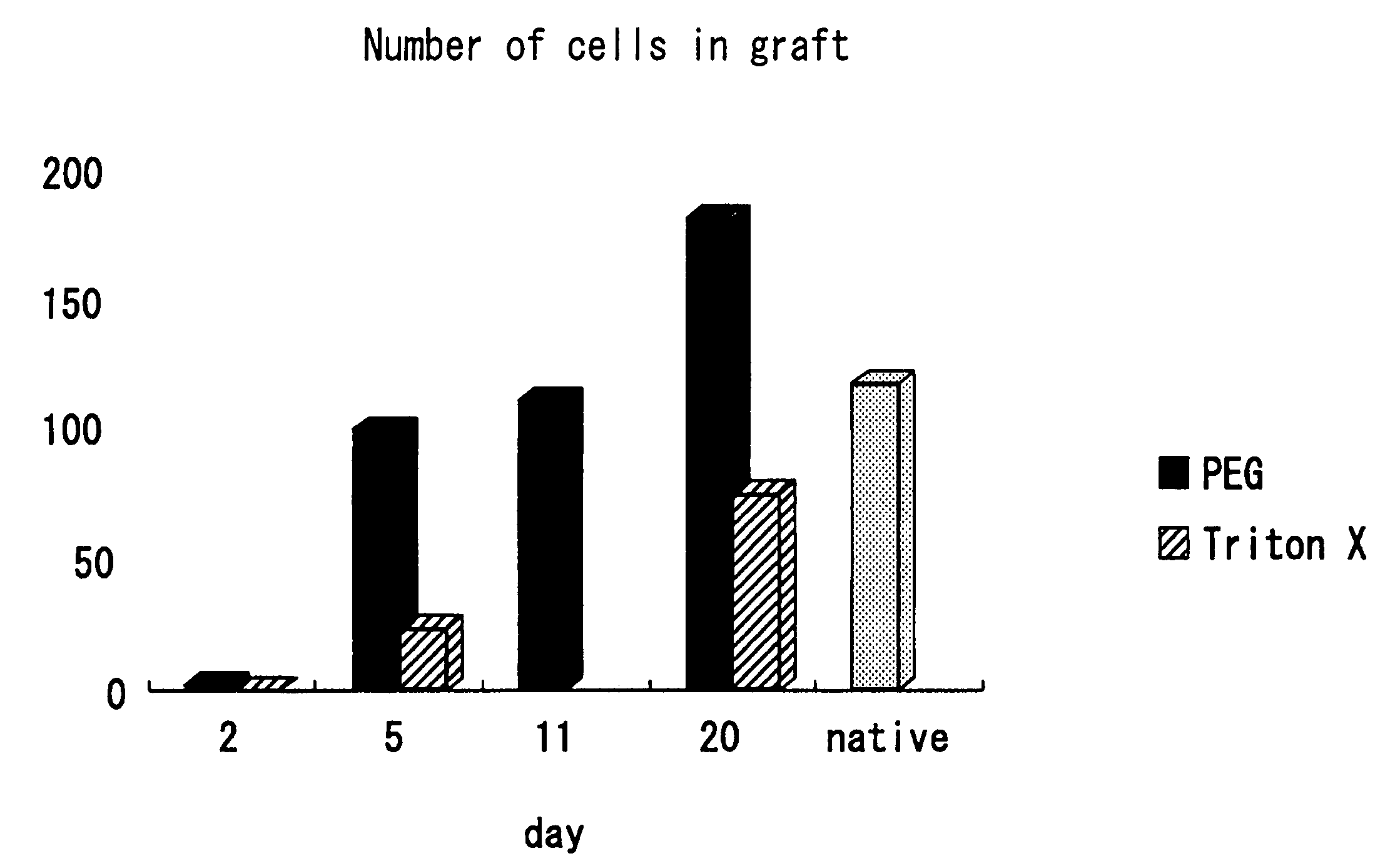
Decellularized tissue engineered constructs and tissues
InactiveUS6962814B2Low immunogenicityReduction in immuneBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth phaseCell-Extracellular Matrix
New methods for producing tissue engineered constructs and engineered native tissues are disclosed. The methods include producing a tissue engineered construct by growing cells in vitro on a substrate and then decellularizing the construct to produce a decellularized construct consisting largely of extracellular matrix components. The construct can be used immediately or stored until needed. The decellularized construct can be used for further tissue engineering, which may include seeding the construct with cells obtained from the intended recipient of the construct. During any of the growth phases required for production of the construct, the developing construct may be subjected to various tissue engineering steps such as application of mechanical stimuli including pulsatile forces. The methods also include producing an engineered native tissue by harvesting tissue from an animal or human, performing one or more tissue engineering steps on the tissue, and subjecting the tissue to decellularization. The decellularized, engineered native tissue may then be subjected to further tissue engineering steps.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Decellularized tissue
InactiveUS20050256588A1Minimal damageGuaranteed maximum utilizationArtificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsCalcificationDecellularization
An objective of the present invention is to overcome a problem that there is an inverse relationship between the decellularization rate and the strength of tissue. This problem was solved by immersing tissue in a solution containing a non-micellar amphipathic molecule (e.g., a 1,2-epoxide polymer). Thus, the present invention provides decellularized tissue, in which the cell survival rate of the tissue is less than a level at which calcification or an immune reaction is elicited in an organism and the tissue damage rate of the tissue is suppressed to a level which permits clinical applications. Tissue prepared by the above-described treatment preferably retains a certain level of tissue strength. Further, the tissue of the present invention has an effect of performing cell replacement.
Owner:CARDIO +1
Acellular soft tissue-derived matrices and methods for preparing same
InactiveUS20150037436A1Mammal material medical ingredientsTissue regenerationTissue repairAcellular matrix
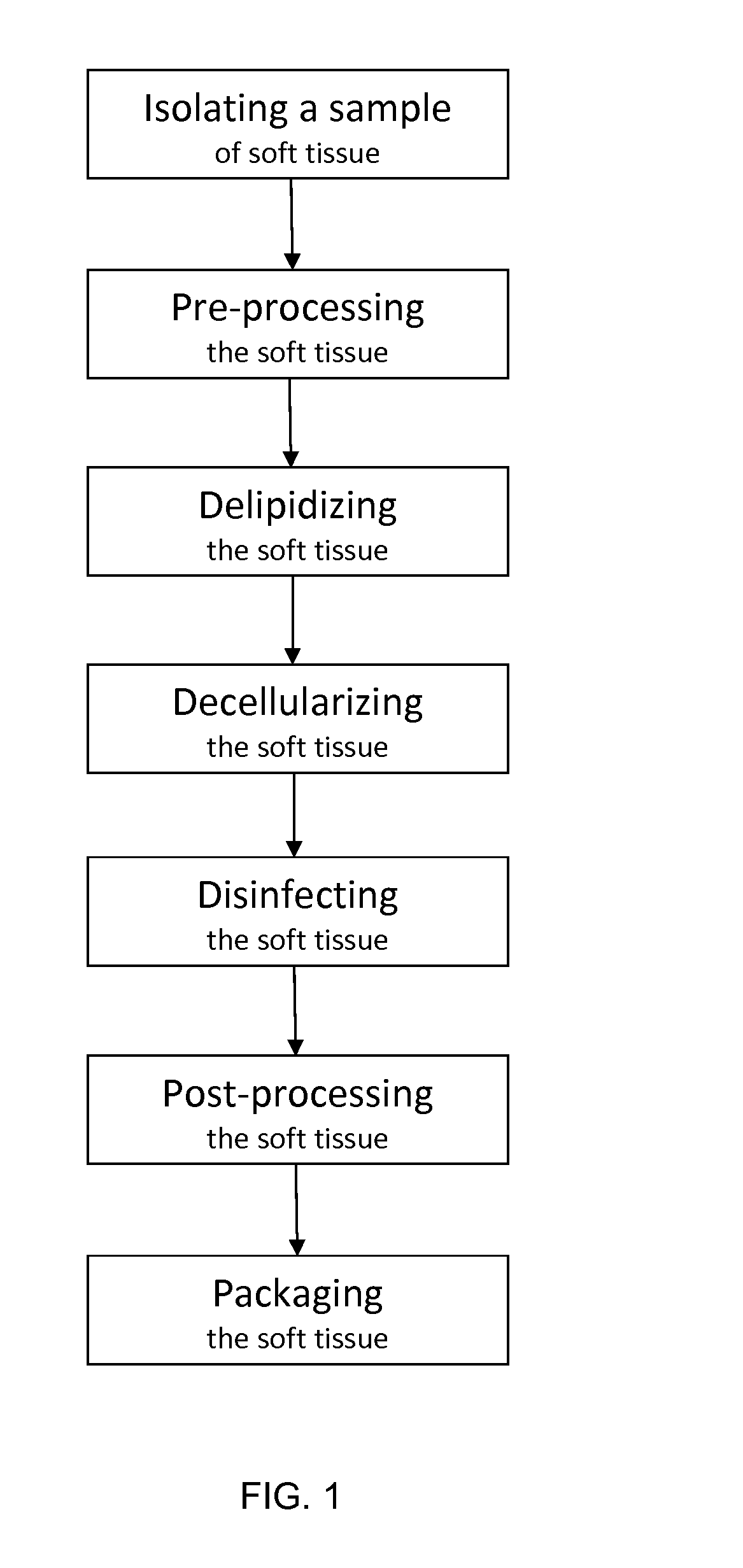
An acellular soft tissue-derived matrix includes a collagenous tissue that has been delipidated and decellularized. Adipose tissue is among the soft tissues suitable for manufacturing an acellular soft tissue-derived matrix. Exogenous tissuegenic cells and other biologically-active factors may be added to the acellular matrix. The acellular matrix may be provided as particles, a slurry, a paste, a gel, or in some other form. The acellular matrix may be provided as a three-dimensional scaffold that has been reconstituted from particles of the three-dimensional tissue. The three-dimensional scaffold may have the shape of an anatomical feature and serve as a template for tissue repair or replacement. A method of making an acellular soft tissue-derived matrix includes steps of removing lipid from the soft tissue by solvent extraction and chemical decellularization of the soft tissue.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Method of Preparing Isolated Cell-Free Skin, Cell-Free Dermal Matrix, Method of Producing the Same and Composite Cultured Skin with The Use of the Cell-Free Dermal Matrix
InactiveUS20070269791A1Easy to peelNot cause any damageDead animal preservationProsthesisFreeze thawingCell free
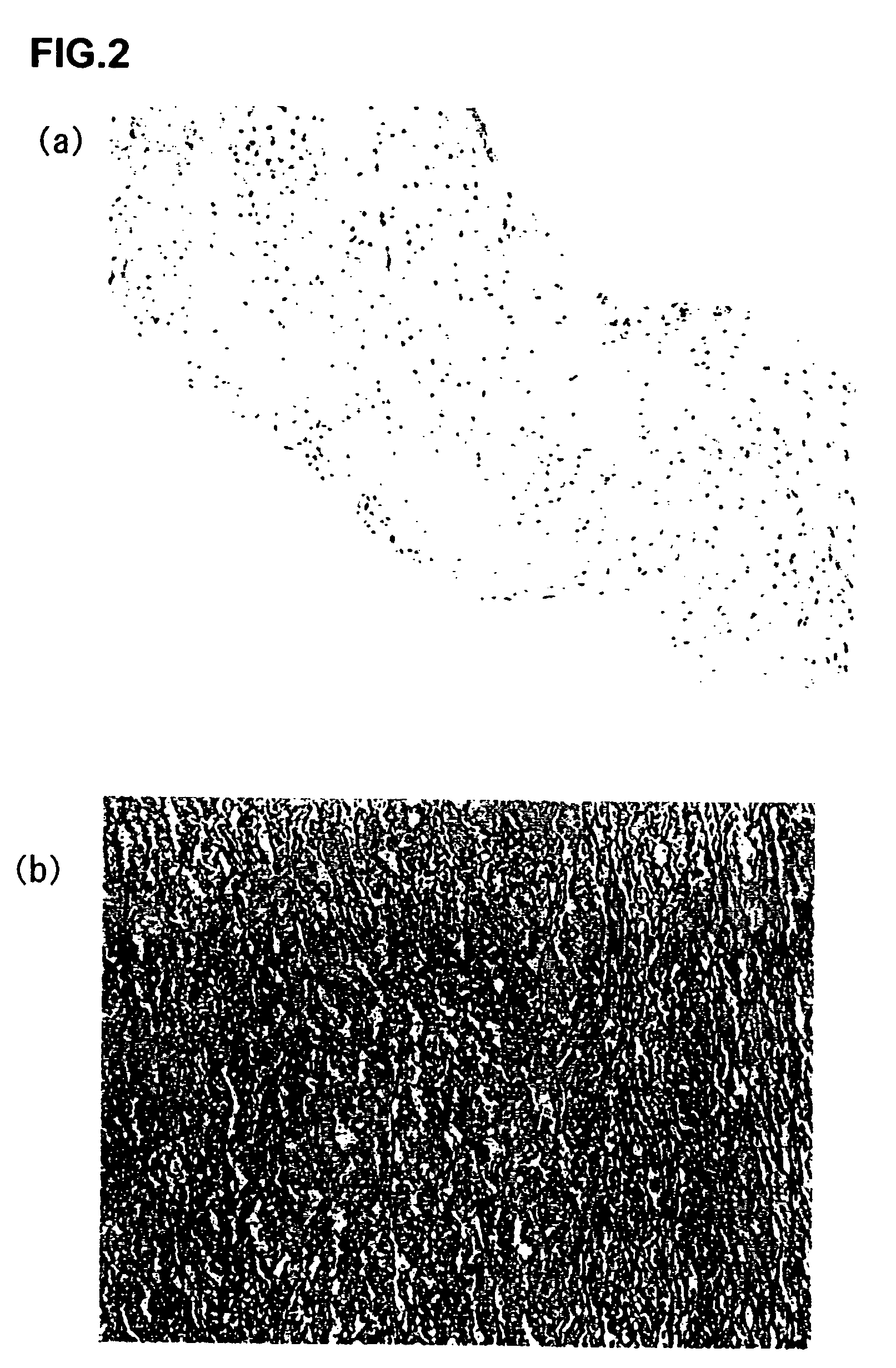
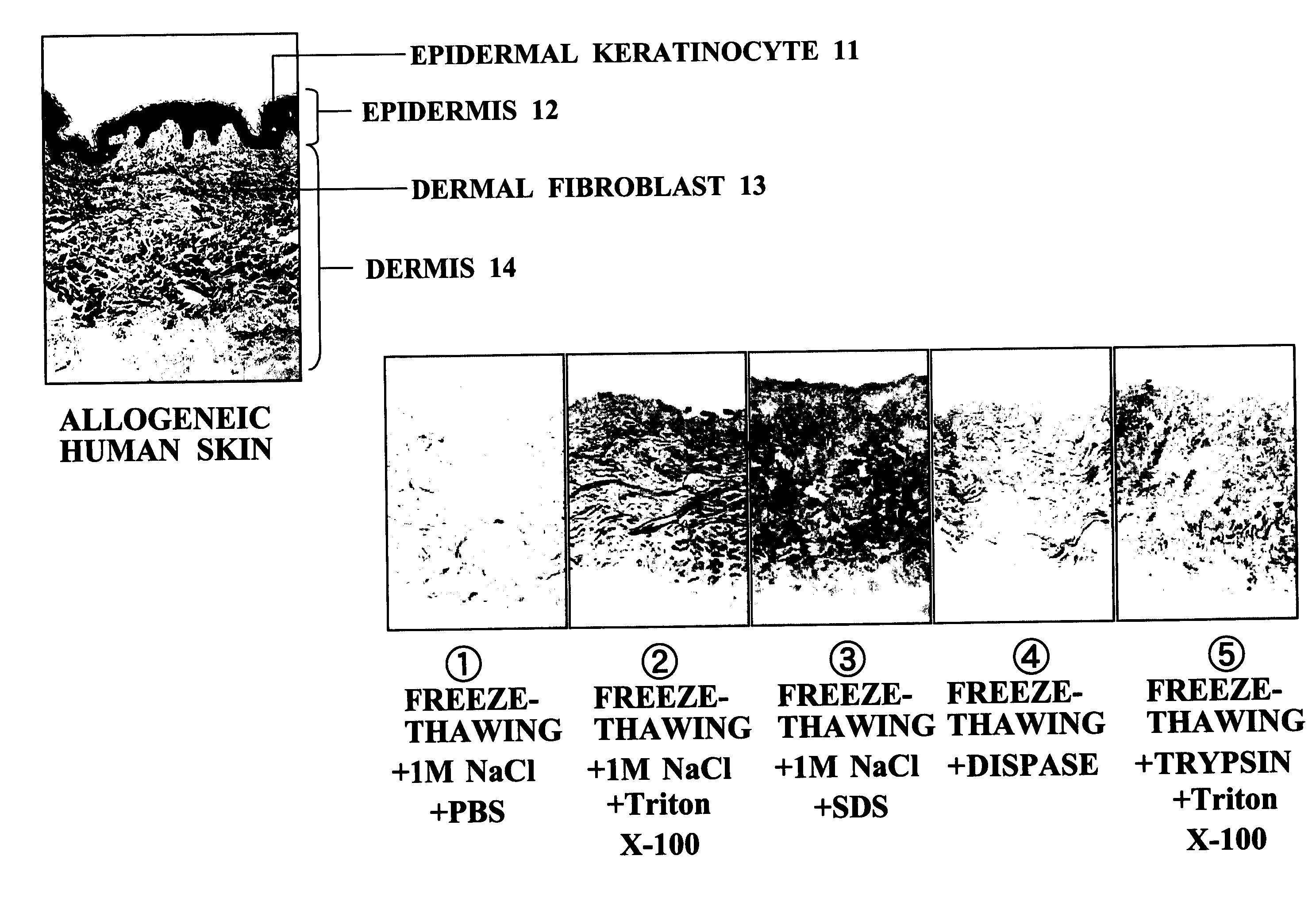
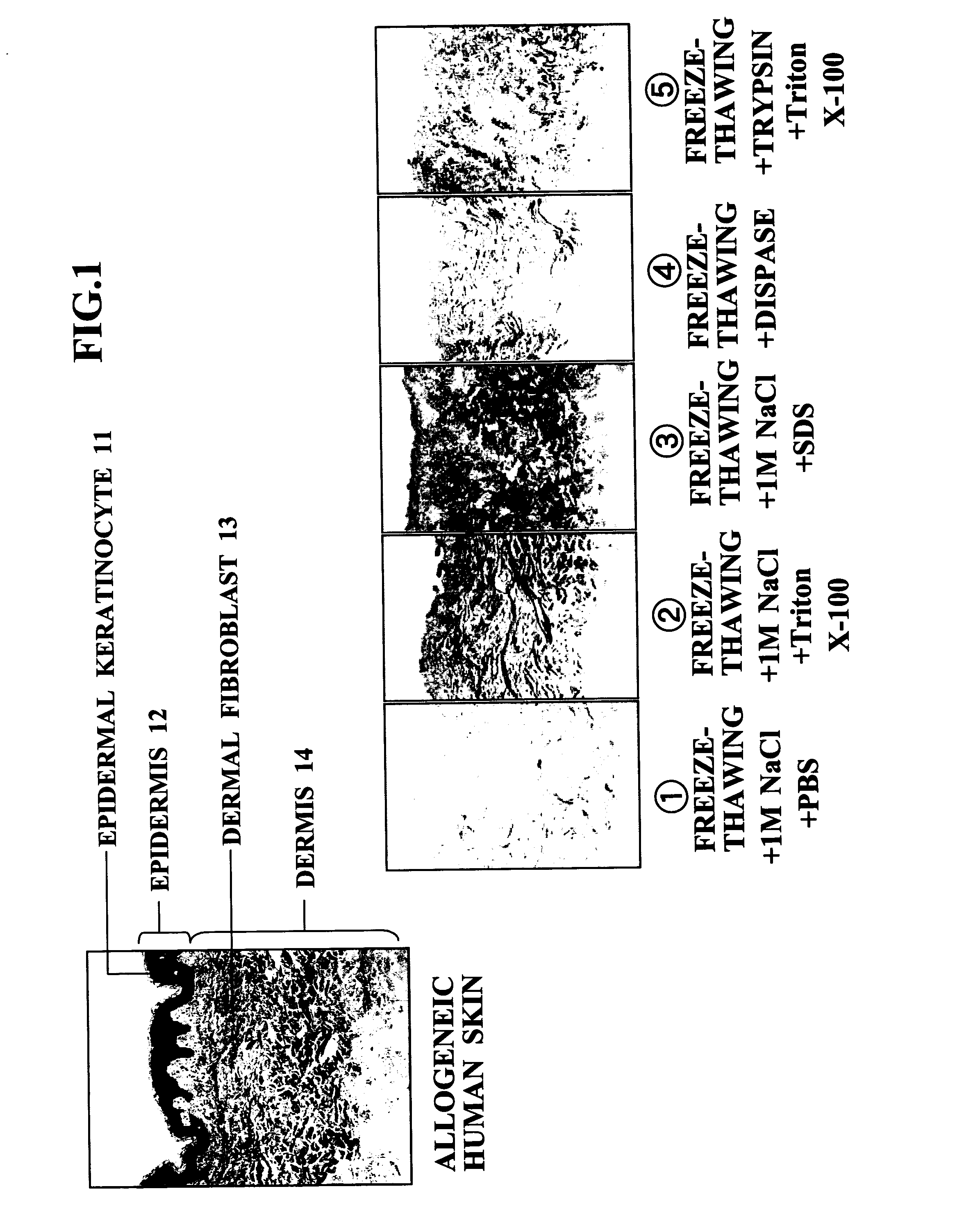
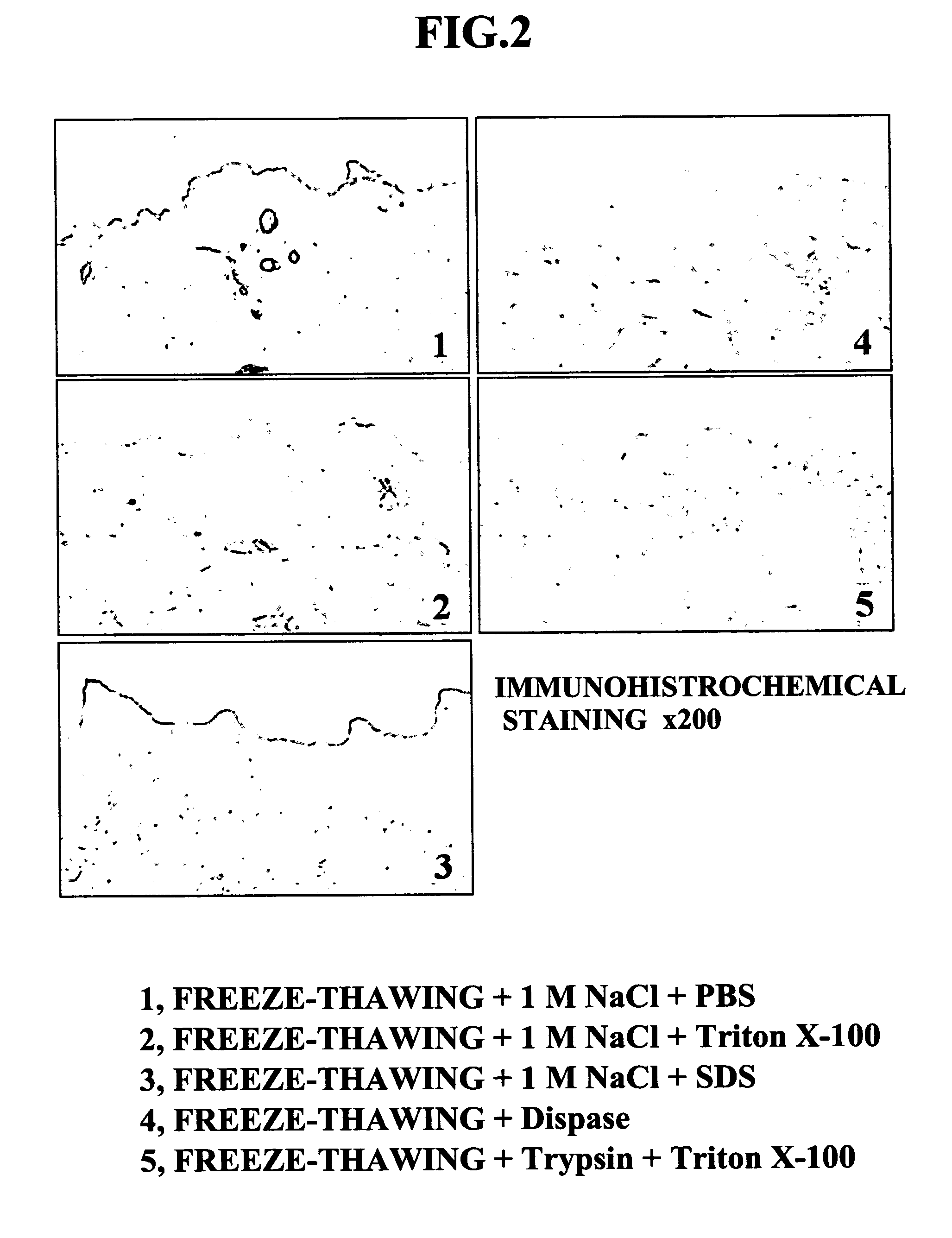
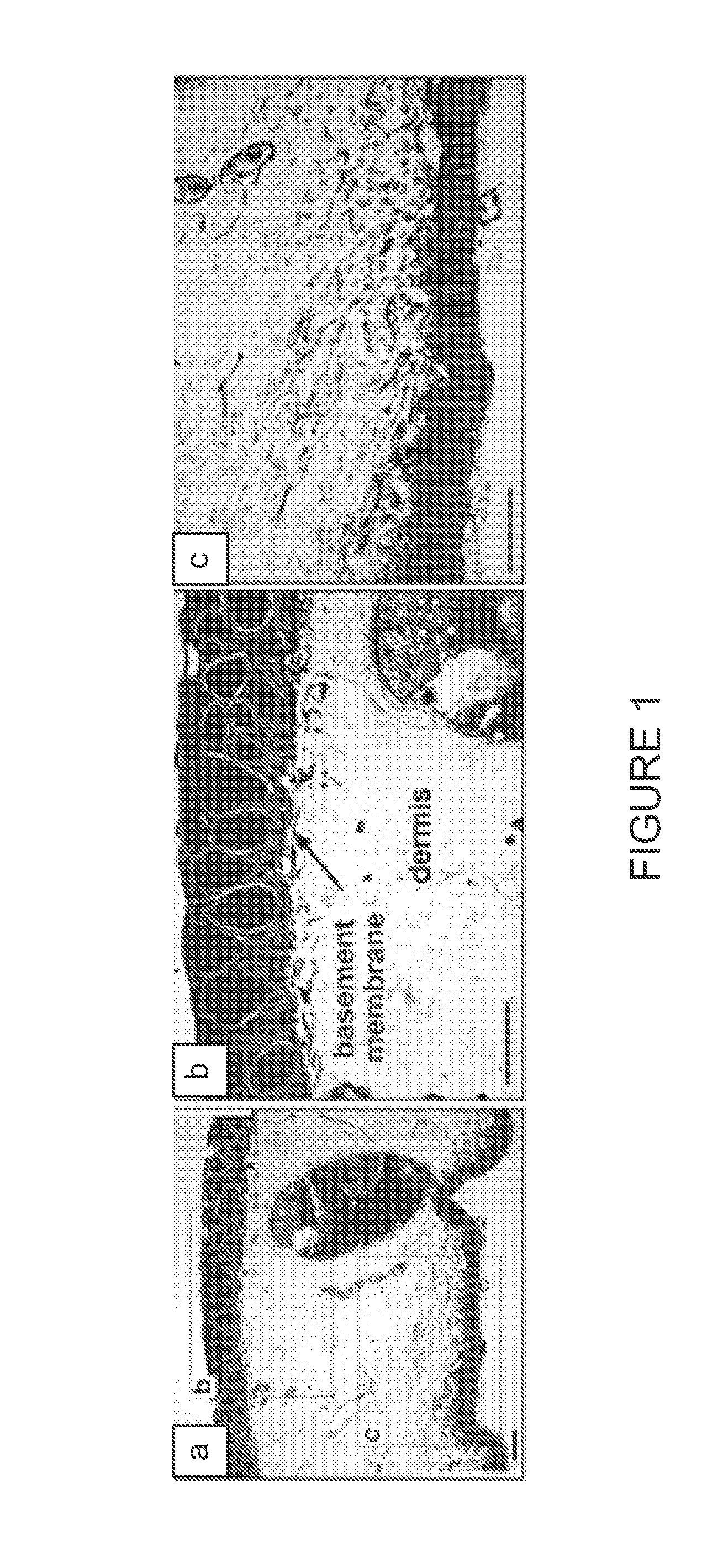
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for producing an ADM suitable as a scaffold for a cultured skin, that is, a separation and decellularization method that enables various types of extracellular matrixes such as a basement membrane to be preserved, allows the epidermal layer to be peeled off easily, and does not cause any damage to the dermal matrix. The present invention relates to a skin separation and decellularization method comprising a step of freeze thawing harvested skin and then separating the skin into epidermis and dermis by a treatment with hypertonic saline, and a step of washing the separated dermis.
Owner:YOSHIHIRO TAKAMI
Decellularized Tissue and Method of Preparing the Same
InactiveUS20070244568A1Improve efficiencyGood effectMammal material medical ingredientsProsthesisUltravioletSolvent
Decellularization of tissue by means of an amphipathic solvent a well-established practice. However, situations exist where the provision of enhanced decellularization is preferred. There is a demand for treating methods for coping with such situations. Thus, it is intended to provide a method for enhancing decellularization. The method comprises not only the immersing of a tissue in a solution containing an amphiphilic molecule in non-micellar form (for example, 1,2-epoxide polymer) but also performing a radical reaction (for example, treatment selected from the group consisting of exposure to gamma-ray irradiation, ultraviolet irradiation, a free radical supply source, ultrasonication, electron beam irradiation, and X-ray irradiation).
Owner:CARDIO +1
Compositions and Methods for Tissue Repair with Extracellular Matrices
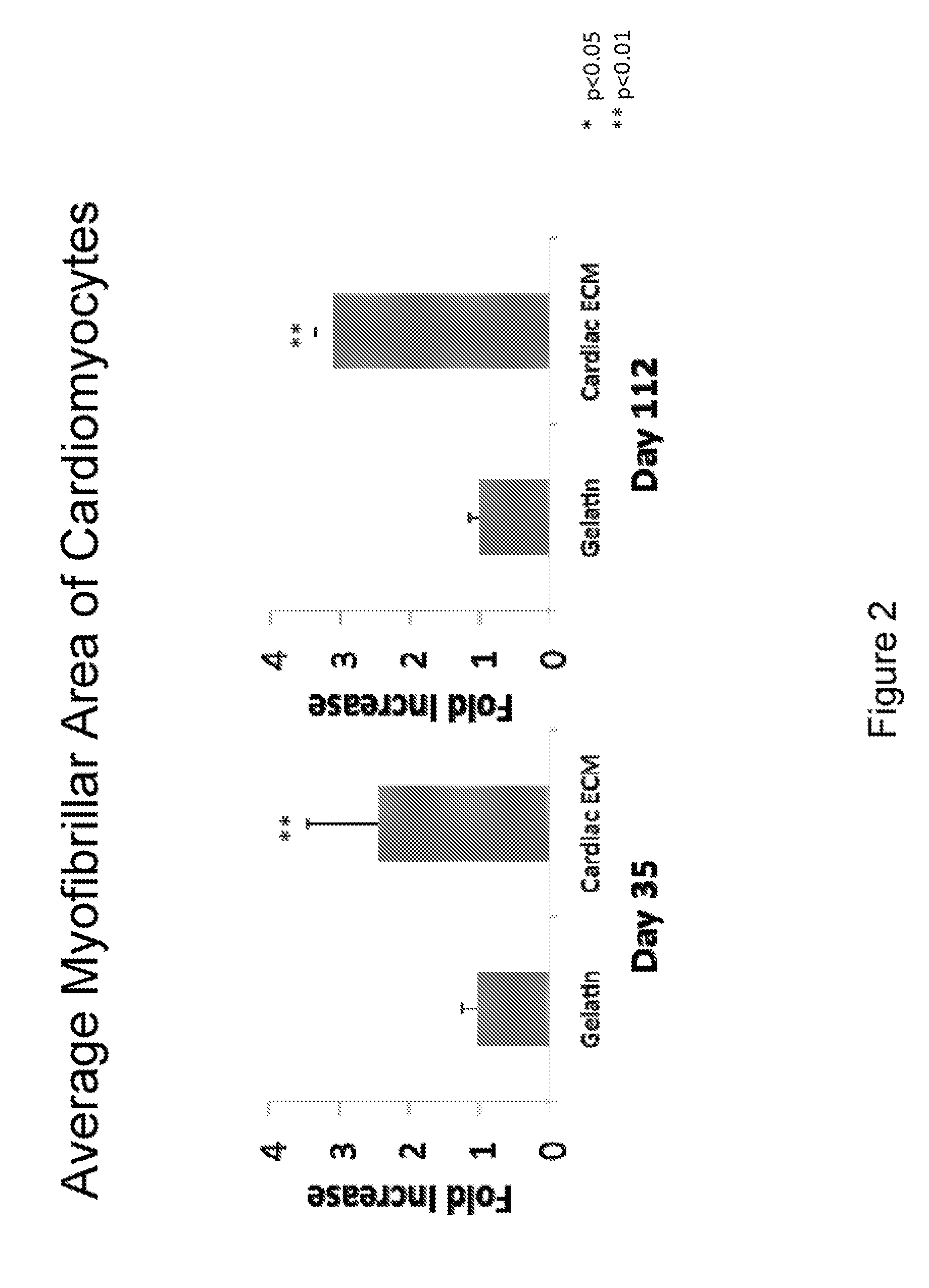
Described herein are compositions comprising decellularized cardiac extracellular matrix and therapeutic uses thereof. Methods for treating, repairing or regenerating defective, diseased, damaged or ischemic cells, tissues or organs in a subject, preferably a human, using a decellularized cardiac extracellular matrix of the invention are provided. Methods of preparing cardiomyocyte culture surfaces and culturing cells with absorbed decellularized cardiac extracellular matrix are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Chemical treatment for removing cellular and nuclear material from naturally occurring extracellular matrix-based biomaterials
A method is provided for sequential decellularization of an isolated tissue using solubilizing solutions comprising at least one oxidizing agent that removes all cellular and nuclear materials from the tissue while substantially maintaining the biological and, mechanical properties, and the biochemical properties of the resulting extracellular matrix.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Acellular cornea or acellular corneal stroma, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101985051ARetain toughnessLow immunogenicityProsthesisFreeze thawingVaccine Immunogenicity
The invention discloses acellular cornea or acellular corneal stroma, a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) obtaining fresh animal full-thickness cornea or corneal stroma; (2) removing corneal epithelium, corneal endothelium and stroma cells, namely 1, soaking the full-thickness cornea or the corneal stroma in pure water at room temperature; 2, placing the soaked full-thickness cornea or corneal stroma into enzyme solution, digesting with oscillating, and washing with balanced salt solution with oscillating; and 3, repeating freeze-thaw processes of the full-thickness cornea or the corneal stroma for 4 to 8 times and washing with balanced salt solution with oscillating to obtain the acellular cornea or the acellular corneal stroma; (3) dehydrating; and (4) sterilizing and storing. In the method, the decellularization processing time of the cornea is short; the influence on the structure and the physiological property of the cornea is small; and the processed cornea has very low immunogenicity which is similar to the property of natural cornea. The acellular cornea or the acellular corneal stroma can be applied to artificial cornea construction of tissue engineering and also can serve as a medical material applied to corneal transplantation and refraction surgery.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
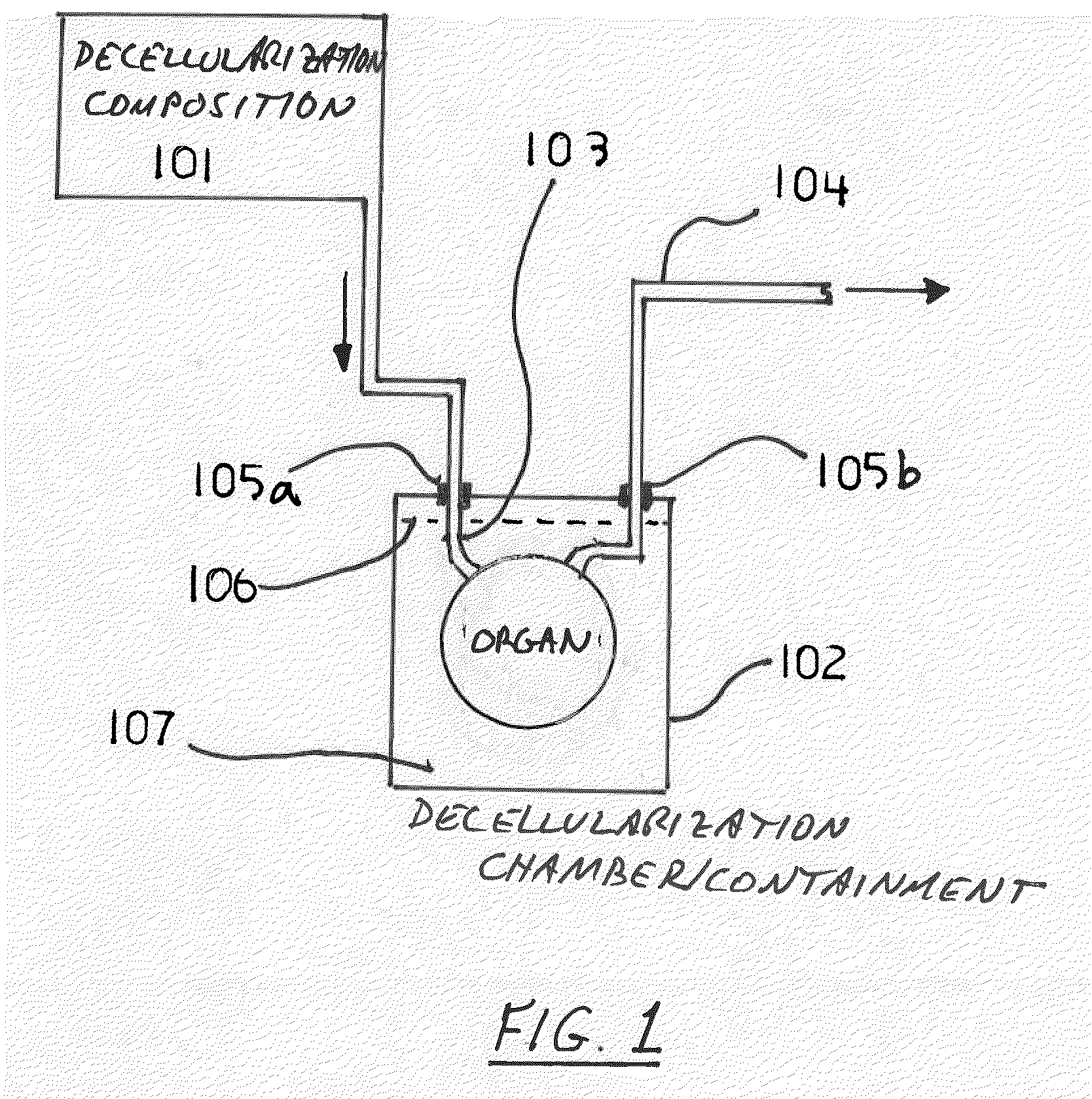
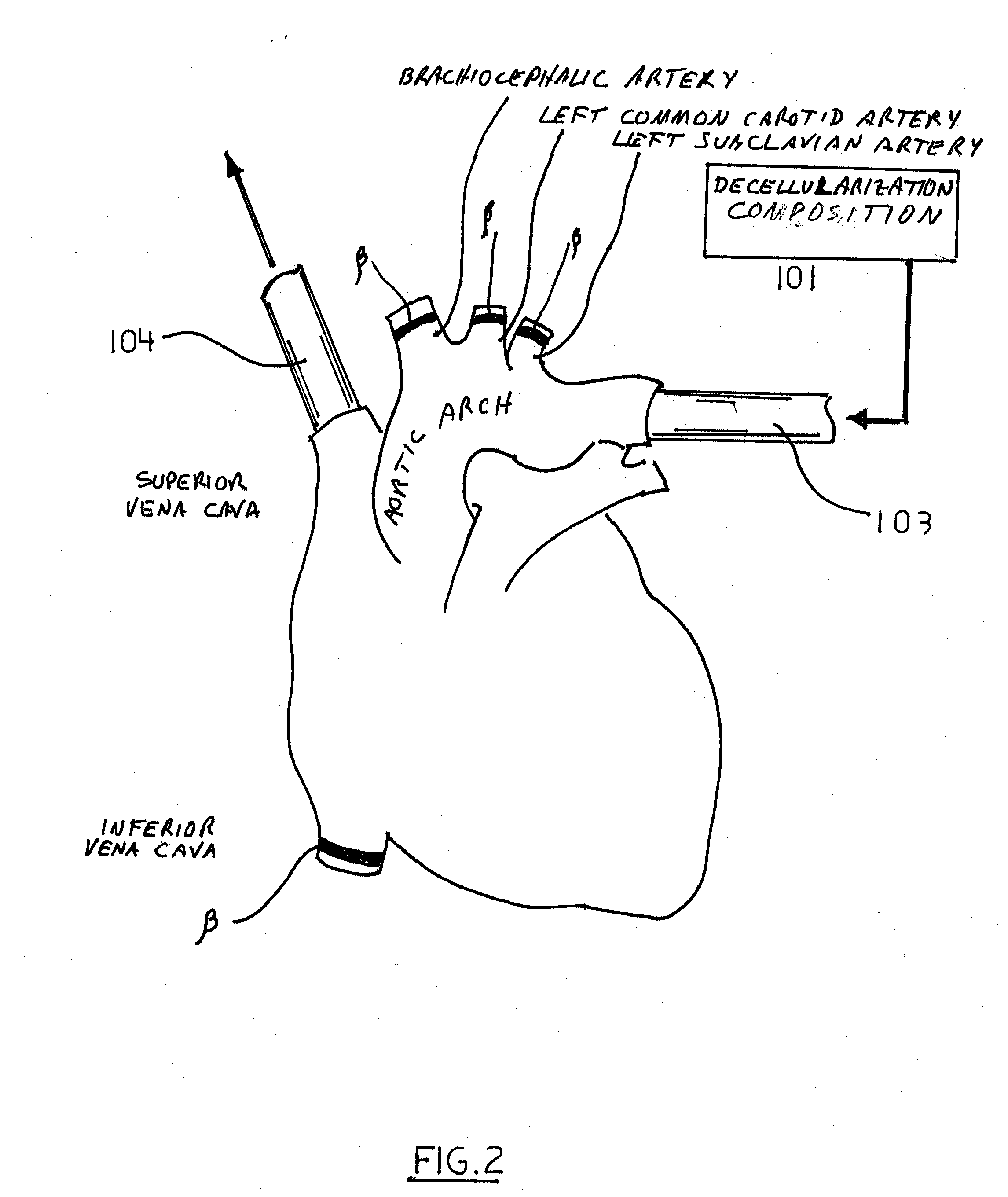
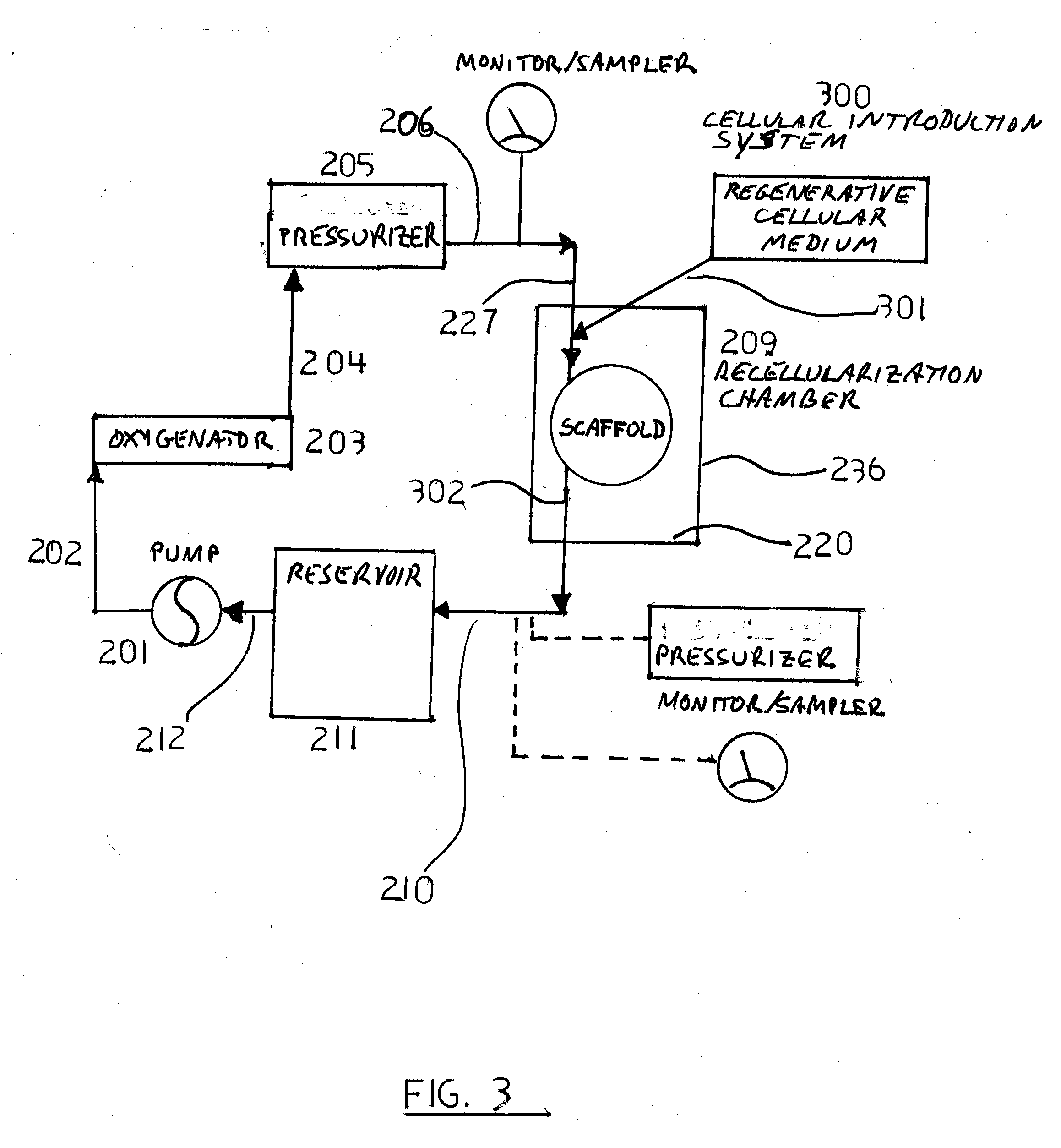
Decellularization and recellularization apparatuses and systems containing the same
InactiveUS20100093066A1Reduce and minimize residencyDead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixMedicine
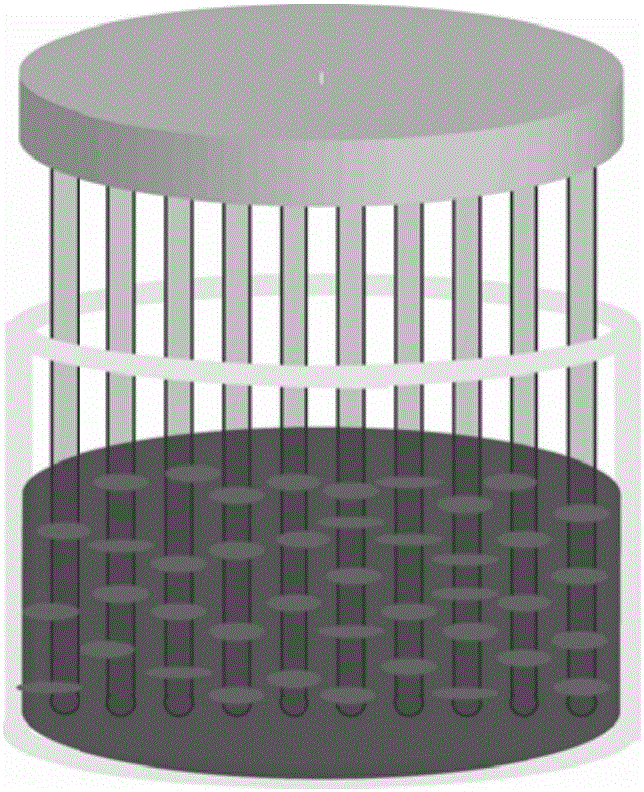
The invention described herein provides systems and apparatuses for an initial preparation of an organ or tissue scaffold comprising an extracellular matrix, and subsequent recellularization of the scaffold to ultimately form a resultant artificial organ or tissue incorporating the natural and original extracellular matrix. The techniques and equipment of the invention collectively minimize scaffold collapse, compression or physical damage to the organ as well as afford the advantages of significant maintenance of the initial natural structural and biochemical attributes of the organ or tissue. The invention is particularly useful in organ and tissue transplantation and repair.
Owner:MIROMATRIX MEDICAL
Decellularization and recellularization of organs and tissues
ActiveCN101272815APharmaceutical delivery mechanismMammal material medical ingredientsDecellularizationSolid organ
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Method for preparing animal derived implantable medical biomaterial
The invention provides a method for preparing an animal derived implantable medical biomaterial. The method comprises the following steps of: pretreatment, separation and primary cleaning of an animal tissue material; virus inactivation; decellularization; sodium chloride treatment; formation; packing and sterilization. According to the animal derived decellularized extracellular cell matrix (ECM) material prepared by using the method, animal derived cell components and DNA components are completely removed, meanwhile, the components and the three-dimensional structure of the natural ECM are completely kept, active growth factors for promoting tissue regeneration can be induced, residues of endotoxin, organic solvent and toxic solvent are avoided, and products with different sizes, thicknesses and mechanical strengths can be formed according to different indications.
Owner:BEIJING BIOSIS HEALING BIOLOGICAL TECH
Ply tissue engineering corneal frame and manufacturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN101947144AThe production process is simple and reliableShorten the timeEye implantsDiseaseFiber
The invention discloses a ply tissue engineering corneal frame and a manufacturing method and an application thereof, relating to a ply tissue engineering corneal frame of the biomedicine. Compared with the existing materials, the invention provides a ply tissue engineering corneal frame and a manufacturing method and an application thereof, which has abundant resources, high transparency, good biocompatibility, thorough decellularization and strong safety, and the performance approaches to that of a fresh cornea, so that the ply tissue engineering corneal frame can be accepted by majority of patients and applied clinically for a long term. The ply tissue engineering corneal frame is an animal derived decellularized ply corneal stroma sheet and does not contain cellular constituents; collagenous fibers are tidily arranged, and gaps are regular; corneal light transmittance is 80-95%, and tensile strength is 2-5N / mm<2>. The ply tissue engineering corneal frame can be served as the substitute for various donor materials for corneal transplantation and can be used for treating a series of diseases of corneal trauma and chemical burn, corneal tumor and a series of hyperplastic diseases, a series of diseases of corneal neovascularisation and scar, corneal immune diseases, a series of diseases caused by corneal transplantation exclusive reaction and other keratopathy.
Owner:XIAMEN DAKAI BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for preparing human body or animal accellular tissues
ActiveCN103191466AReasonable formulaReduce procurement costsTissue cultureAbsorbent padsHuman bodyCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a method for preparing human body or animal accellular tissues. According to the method, the decellularized tissue obtained by treating human or animal tissues, such as skin, pleuroperitoneal membrane, esophagus mucous membrane, small intestine mucous membrane, pericardium, vessel, nervus, cardiac valves, bone, cartilage, muscle tendon, and the like through processes of inactivation of virus, derosination, decellularization, and the like is an acellular three-dimensional network structure tissue, and extracellular matrix components are kept. The tissue prepared by the method can be used as an implantable repair material for a human body and also can be used as a support material of tissue engineering cell culture. The skin, the pleuroperitoneal membrane, the esophagus mucous membrane, the small intestine mucous membrane, the pericardium, and the like also can be used as a wound covering material.
Owner:上海优越生物医学科技有限公司
Decellularization cornea preparation method
The invention relates to a decellularization cornea preparation method, which adopts steps of corneal epithelium layer removing, ultraviolet cross-linking, viral inactivation, decellularization treatment, gradient dehydration, radiation protection and sterilization. According to the present invention, the prepared decellularization cornea has characteristics of complete antigen removing, no excitation of host acquired immunity reaction, good biocompatibility, low damage on nature corneal stroma, maintaining of structure characteristics of the nature corneal, and maintaining of effective components of the nature corneal so as to provide physical and chemical properties similar to the nature corneal; and after the prepared decellularization cornea is transplanted, animal experiment results show that characteristics of transparent transplanted cornea, no scar formation, no melting generation and no neovascularization are provided, the transplanted cornea and the recipient bed are completely integrated after transplanting a month, the transplanted cornea is subjected to complete epithelization after three months, corneal stroma cells migrate toward the decellularization cornea graft so as to prove that the tissue just takes place slow reconstruction, and the transplanted cornea after 6 months does not show significant difference in histology and appearance detection compared with the nature cornea.
Owner:SHAANXI BIO REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
Bio-derivative tendon repair material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101496912AMaintain the three-dimensional structure of spacePromote ingrowthLigamentsMusclesDepolymerizationFreeze-drying
The invention provides a repair material for biological derivative tendon. The material takes homogeneous or heterogeneous tendon as a raw material and is formed through disinfection, degreasing, deproteinization, decellularization, freeze drying, depolymerization, devillication recombination and secondary disinfection. A method for preparing a tendon scaffold material comprises the following steps that: on one hand, a periphery structure of a tendon tissue is destructed through treatment processes of removing soft tissues, the disinfecting, the degreasing and the decellularization, and the repellency of a transplantation receipt to the tendon is reduced; on the other hand, a basic mechanism, partial enzyme activity of the tendon tissue and the continuity of the tendon tissue are further maintained through a freeze drying process so as to provide a good scaffold structure for the revascularization and cell tissue of the tendon.
Owner:北京科健生物技术有限公司
Scaffolds of umbilical cord decellularized Wharton jelly for tissue engineering and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102198292AControllable fine structureModerate degradation rateProsthesisFine structureEnzymatic digestion
The invention discloses scaffolds of umbilical cord decellularized Wharton jelly for tissue engineering and a preparation method thereof. Umbilical cords are employed as the raw material and their outer membranes and vascular tissues are peeled off. And the rest part of the umbilical cords is subjected to hypotonic freeze-thaw, mechanical pulverization, differential centrifugation, enzymatic digestion for decellularization. Then the umbilical cord Wharton jelly is collected and injected into a mold. After freeze drying and crosslinking, multiple three dimensional porous sponge scaffolds and composite scaffolds can be obtained. The method of the invention has the advantages of wide material source, low cost, simple technology. And the prepared scaffolds are characterized by controllable fine structure, appropriate degradation rate, good biocompatibility, and biomechanical strength, which are in favor of cell adhesion and the uniform distribution of seed cells within the scaffolds, as well as seed cell multiplication, migration and growth. Thus, the scaffolds of umbilical cord decellularized Wharton jelly in the invention can be widely applied in the tissue engineering field such ascartilage, bone, skin and nerve, with a favorable clinical application prospect.
Owner:卢世璧
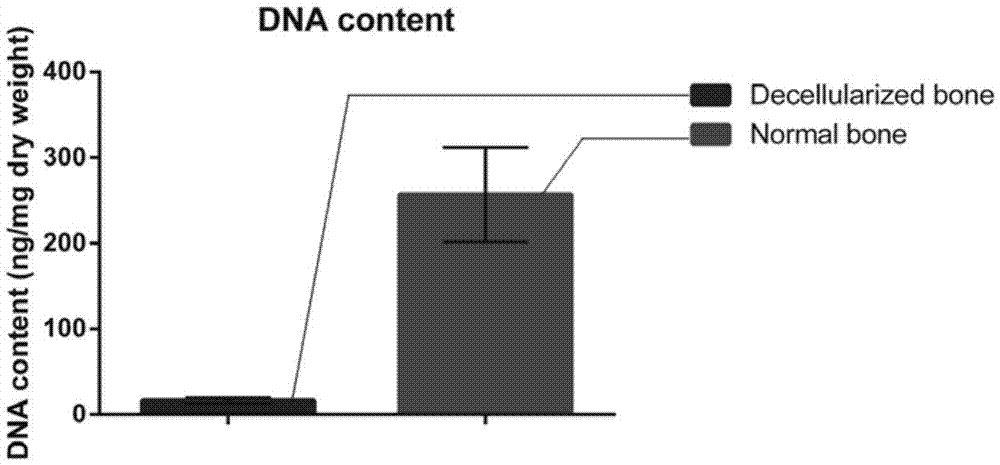
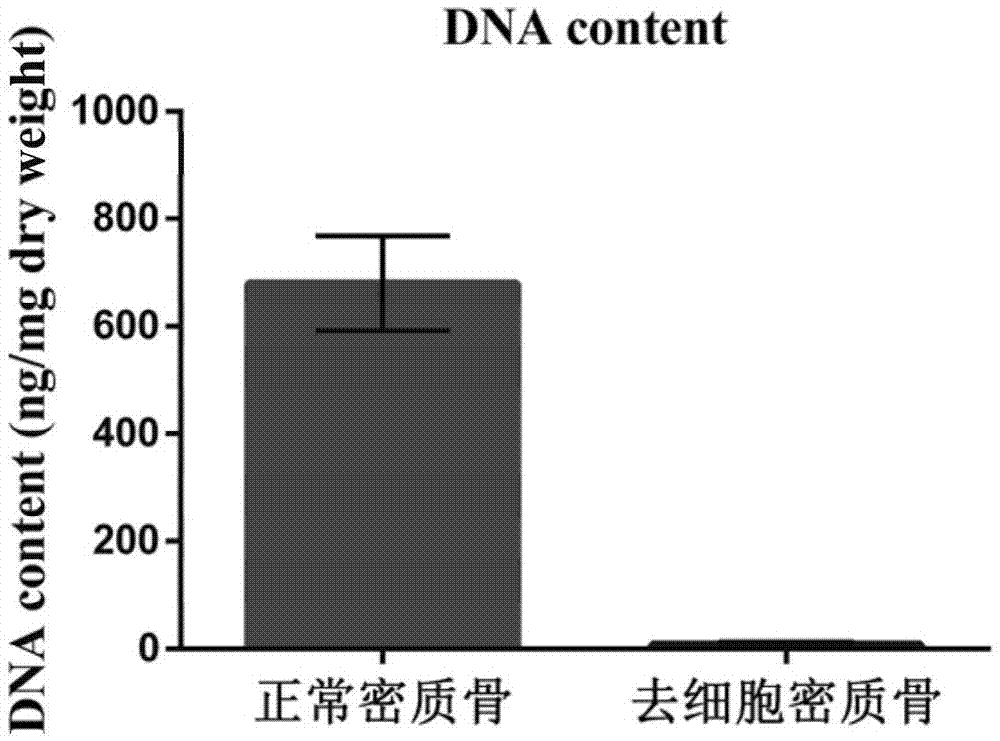
Natural-tissue-derived decellularized and decalcified bone material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105435307AImprove biological activityImprove manufacturing speedProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a natural-tissue-derived decellularized and decalcified bone material. According to the method, any bone tissue of a mammal is treated with a protease inhibitor-containing normal saline buffer, an organic solvent, Tirton X-containing PBS (phosphate buffer saline), SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfonate)-containing PBS, pancreatin-containing PBS, deoxyribonuclease-containing PBS, an EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) isotonic solution and ultrasonic waves, and the decellularized and decalcified bone material is obtained. Cancellous bones and cortical bones can be decellularized completely and simultaneously, the conditions are mild, damage to an ECM (extracellular matrix) is avoided, rapidness and stability are realized, and the obtained decellularized and decalcified bone material has the advantages of good biocompatibility, high plasticity, high biomechanical strength and the like and can be used for clinically repairing bone regeneration and repair disorder such as bone defects, nonunion and the like caused by various causes.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Biological tissue matrix material, and preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN107007886AImprove processing efficiencyHigh bonding strengthTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberCell-Extracellular Matrix
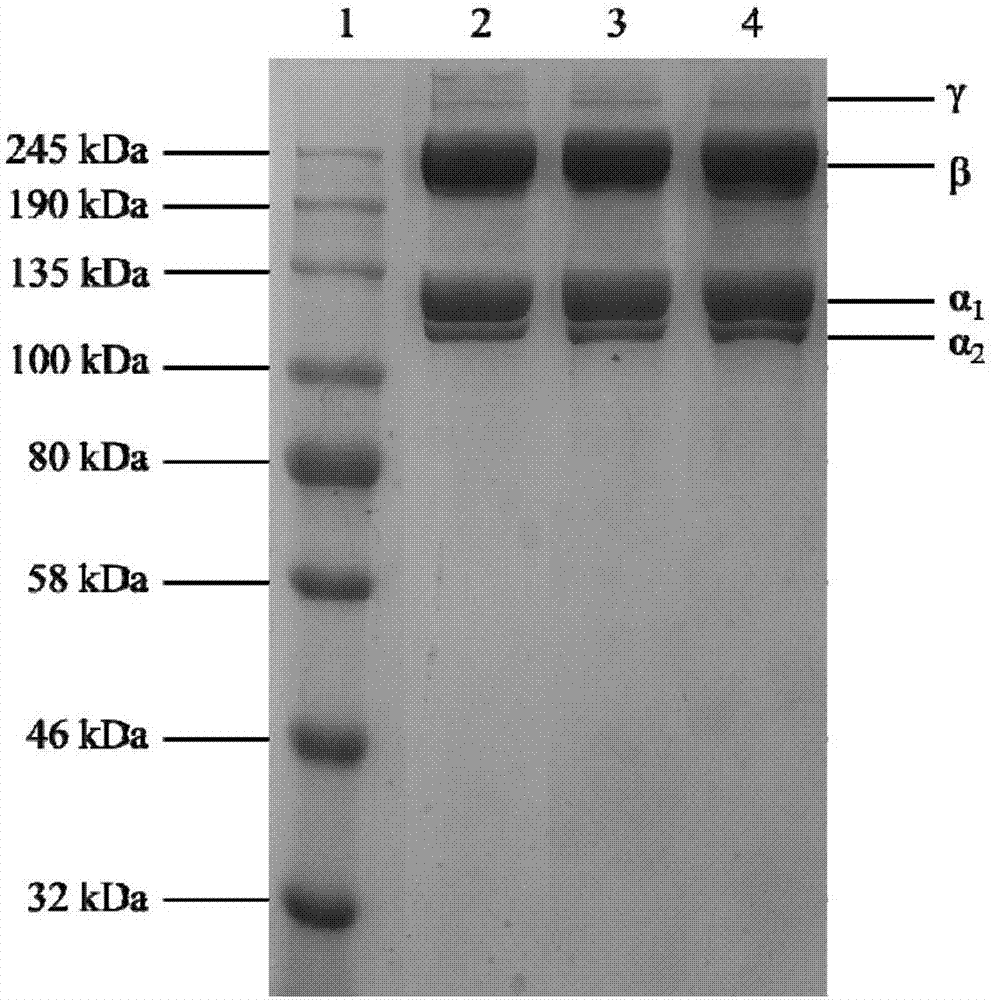
The invention provides a biological tissue matrix material, and a preparation method and a purpose thereof. The biological tissue matrix material is characterized by comprising an extracellular matrix, wherein the extracellular matrix comprises collagenous fiber, growth factors and fibronectin. The biological tissue matrix material is prepared from small intestinal submucosa matrix materials. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps that decellularization is performed: decellularized liquid contains trypsin and PBS solution, and also contains EDTA, EDTA-2Na or EDTA-4Na; the decellularized liquid is used for treatment in multi-frequency ultrasonic environment for decellularization; the dual-frequency ultrasound at least contains two ultrasonic frequencies with different frequencies. The decellularization process technology is improved; the DNA residual quantity of the obtained product is lower; the immunogenicity is lower; the anti-infection capability is higher; the restoration capability is higher.
Owner:BEIJING BIOSIS HEALING BIOLOGICAL TECH
Vascularization support for tissue engineering and construction method of vascularization support
InactiveCN106075582AShorten the timeRealize "multi-directional" growthTissue regenerationProsthesisBiological bodyAcellular matrix
The invention belongs to the field of tissue engineering, and discloses a vascularization support for tissue engineering and a construction method of the vascularization support. The construction method includes (1), pre-treating an acellular matrix to remove impurities possibly introduced in decellularization and storage processes; (2), producing an acellular matrix / composite material compound support according to a tissue engineering support forming method; (3), post-treating the acellular matrix / composite material compound support obtained in the step (2), and removing residual substances in the production process to obtain the vascularization support for tissue engineering. The construction method has the advantages that the method is based on basic principles in organism vascularization processes and is conformity to migration and multiplication features of endothelial cells, microenvironments for organism vascularization are simulated to the greatest extent, the cellular matrix / composite material compound support is construed to develop advantages of both the acellular matrix and a composite material, and the support product capable of meeting tissue engineering vascularization requirements is constructed.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Decellularized adipose tissue
This invention provides a method for decellularizing adipose tissue, comprising subjecting the adipose tissue to one or more incubations in an enzymatic digestion solution containing one or more enzymes, and one or more solvent extractions, wherein decellularized adipose tissue comprising an extracellular matrix with well-preserved three-dimensional structure is obtained. The invention also provides a decellularized adipose tissue comprising an extracellular matrix with well-preserved three-dimensional architecture, and bioscaffolds. microcarrier beads, and coatings comprising the decellularized adipose tissue.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Method for preparing a cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane
InactiveCN101563450ASkeletal disorderCell culture supports/coatingHigh concentrationCell-Extracellular Matrix
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane, more particularly, to a method for preparing a chondrocyte-derived ECM membrane, the method comprising the steps of forming a suitable thickness of ECM membrane by culturing chondrocytes derived from animal cartilage at a high concentration in vitro, and drying it after decellularization process. The cell-derived ECM membrane scaffold according to the present invention is composed of extracellular matrix secreted by chondrocytes so that the membrane has excellent biocompatibility as well as an immune-previlage effect specific to cartilage. Since the membrane also has a suitable compressive strength, it can be used to replace periosteum for cartilage regeneration or artificial collagen membrane and used as dura mater transplant material, a natural ECM membrane for treating skin loss, materials for cell transplantation and a growth factor delivery vehicle.
Owner:REGENPRIME
Method For Producing An Acellular Dermal Matrix, And Acellular Dermal Matrix Produced By Same
ActiveUS20120329034A1Improve stabilityMinimize changesVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsSucroseCuticle
The present invention relates to a method for producing an acellular dermal matrix, and to an acellular dermal matrix produced by same, and more particularly, to a method for producing an acellular dermal matrix, in which sucrose is added to base ingredients consisting of glycerol, propylene glycol, and a base solvent or solution so as to produce a cryoprotectant, the solution is injected into the skin below the epidermis and dermis from which cells have been removed, and freeze-drying is then performed.
Owner:CG BIO CO LTD
Compound tissue engineering scaffold containing PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) strengthening net, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a scaffold material for tissue engineering construction and a preparation method thereof, and particularly relates to a compound tissue engineering scaffold containing a PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) strengthening net, and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound tissue engineering scaffold containing a PLGA strengthening net comprises a porous scaffold having good biocompatibility and a PLGA strengthening net, wherein the PLGA strengthening net is formed by weaving PLGA fibers, and the PLGA strengthening net is tightly combined with the porous scaffold. The compound tissue engineering scaffold containing a PLGA strengthening net has mechanical property similar to that of the acellular dermal matrix, and is more beneficial to the maintenance of three-dimensional porous structures of the scaffold, thereby being more beneficial to the ingrowth of cells, blood vessels and tissues; and because of the good biocompatibility of collagen, chitosan and other naturally-derived macromolecules, the biological performance of the compound scaffold is maintained, thereby being beneficial to the adhesion, propagation and secretion of cells. Thus, the compound tissue engineering scaffold is a good renewable material applicable to the construction of tissues and organs of tissue engineering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dura graft, preparation method and applications in dural damage repair thereof
The invention provides a dura graft and a preparation method thereof. The dura graft is prepared from an acellular dermal matrix. The acellular dermal matrix is obtained from allogenic skin by crosslinking treatment, digestion treatment with a protease solution, decellularization with a hypertonic saline solution containing a surfactant, DNA degradation, amino acid nutrition treatment and freeze drying. The invention also provides applications of the dura graft in preparing repair materials used in the treatment of dural damage. The acellular dermal matrix is obtained from human skin tissue and undergoes physicochemical and biochemical treatment, so that all the components that may cause immunological rejection are removed. A fibrous stereoscopic scaffold structure of the original tissue is completely reserved, and new vessels and fibroblasts rapidly grow in the dura graft after implantation. Therefore, the dura graft has good clinical effects.
Owner:BEIJING JAYYALIFE BIOTECH CO LTD
Acellular dermal matrix and preparing method of acellular dermal matrix
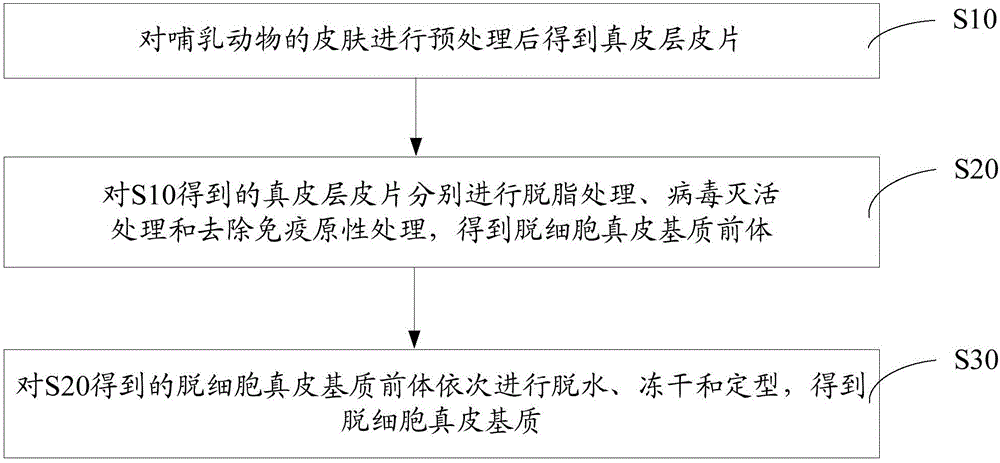
The invention discloses an acellular dermal matrix and a preparing method of the acellular dermal matrix. The preparing method of the acellular dermal matrix comprises the following steps of: performing pre-processing on the skin of a mammal to obtain a skin corium flap; respectively performing degreasing processing, virus inactivation processing and immunogenicity removal processing on the skin corium flap to obtain an acellular dermal matrix precursor (the immunogenicity removal processing operation comprises the step of alternately soaking the skin corium flap into a prolease solution and a surfactant solution); and sequentially performing dewatering, freeze-drying and shaping on the acellular dermal matrix precursor to obtain the acellular dermal matrix. The preparing method of the acellular dermal matrix has the advantages that the skin corium flap is alternately soaked in the prolease solution and the surfactant solution, so that the immunogenicity of the acellular dermal matrix can be reduced to the maximum degree; the normal collagen structure of the acellular dermal matrix is also remained; the prepared acellular dermal matrix has the proper degradation speed, good biocompatibility and good bone induction capability.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDO BIOMATERIALS
Microenvironment construction method for three dimensional culture of cells and application
ActiveCN110272860ABeneficial technical effectPromote proliferationArtificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
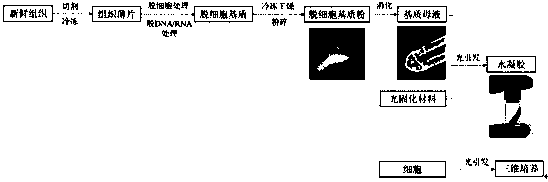
The invention discloses a microenvironment construction method for three dimensional culture of cells based on a specificity extracellular matrix and an application. A specificity extracellular matrix extraction method, the specificity extracellular matrix and a photocuring material are combined to prepare hydrogel, and the invention relates to an application of the hydrogel to in vitro three dimensional culture and particularly an organ chip technique. According to the technical scheme, in accordance with tissue or organs of different density, surfactants having different decellularization capacity are selected, through combination of the manner that enzyme treatment is selected and an ammonia solution is used as a solvent, particularly-compact tissue or organs are treated, and the preferred combination of the enzyme and surfactants comprises Trypsin and a Triton X-100 solution, and the solvent is a 0.05%-0.5% ammonia solution. The extracellular matrix and a light-initiating colloid-forming material are compounded for preparing the hydrogel so as to construct cell culture microenvironment. The method has the advantages of being high in colloid-forming speed, simple in colloid-forming condition, controllable in hydrogel mechanical property and the like.
Owner:江苏艾玮得生物科技有限公司
Tissue-engineered skin containing blood vessels and hair follicle structures based on 3D printing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108525021ASimple structureIncrease elasticityAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationMicrosphereVascular endothelium
The invention relates to tissue-engineered skin containing blood vessels and hair follicle structures based on 3D printing and a preparation method thereof. The tissue-engineered skin is composed of an epidermal layer, an acellular dermal scaffold and a dermis layer, wherein in the epidermal layer, epidermal stem cells are used seed cells, the seed cells are printed on the upper surface of the acellular dermal scaffold through a 3D printer after being compounded with a hydrogel carrier to differentiate and form a normal epidermal structure, in the dermis layer, mesenchymal stem cells, vascularendothelial cells, dermal papilla cells and adipose-derived stem cells are used as seed cells, the seed cells and a hydrogel carrier are compounded, through the 3D printer, gelatin slow-release micropheres compounded with cytokines are printed on the lower surface of the acellular dermal scaffold, and meanwhile, the hydrogel compound of the seed cells is printed in the gelatin slow-release micropheres to form a dermis structure with a three-dimensional spatial structure.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Compound multilayer medical dressing of aquatic biological source crosslinking collagen
ActiveCN107233613AWide variety of sourcesIncrease profitConnective tissue peptidesSurgical adhesivesFreeze-dryingCollagen sponge
The invention discloses an aquatic biological source medical collagen with high purity and activity, and is capable of solving the problems of a natural collagen dressing that the mechanical strength is bad, the degradation resistance ability is weak and the wound is easily infected by microorganisms. An acid extraction method and a method of removing telopeptide by pepsase are used for extracting the collagen, the extraction ratio is improved by the ultrahigh pressure treatment and a tissue mashing method, and through a series of purification operations, such as decellularization, protein elimination, degreasing, repeated salting out, dialysis, degerming, decoloration and heat source removal, the medical collagen with the high purity and activity is prepared. A netlike collagen sponge with uniform pores is prepared by a vacuum freeze-drying technology, and the collagen sponge is modified by a physical crosslinking and chemical crosslinking mode so as to prepare the inner layer, and is compounded with a chitosan outer layer film and a medical non-woven fabric base cloth layer, finally a compound multilayer medical dressing finished product is obtained by Co-60 sterilization.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Biological amnion and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103520780AEasy to prepareWide variety of sourcesLayered productsSurgeryFreeze-dryingDrug biological activity
The invention relates to a biological amnion and a preparation method thereof. The biological amnion has three layers including a slow release layer, an amnion layer and a collagen layer from top to bottom, wherein the slow release layer consists of collagen and biological active factors, the amnion layer consists of an amnion subjected to decellularization treatment, and the collagen layer is formed by freeze-drying and compounding collagen. The biological amnion is prepared through the steps of raw material pretreatment, virus inactivation, decellularization treatm. The biological amnion prepared by the invention has the characteristics of an effect of slowly releasing the active factors, low antigenicity on removing epithelial cells, convenience in product operation, difficulty in curling, good adhesiveness with surrounding tissues, difficulty in sliding and the like. Meanwhile, by using a process for performing the decellularization treatment on the amnion, disclosed by the invention, a natural compact collagen structure in the amnion can be effectively retained, the biological amnion can fully achieve a physical barrier effect after being applied to tenorrhaphy, and an animal experiment proves that the biological amnion can effectively achieve an effect of preventing tissue adhesion.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Decellularized biomaterial from non-mammalian tissue
ActiveUS20150352257A1Lower immune responseReduce inflammationPeptide/protein ingredientsEpidermal cells/skin cellsCellular componentFunctional integrity
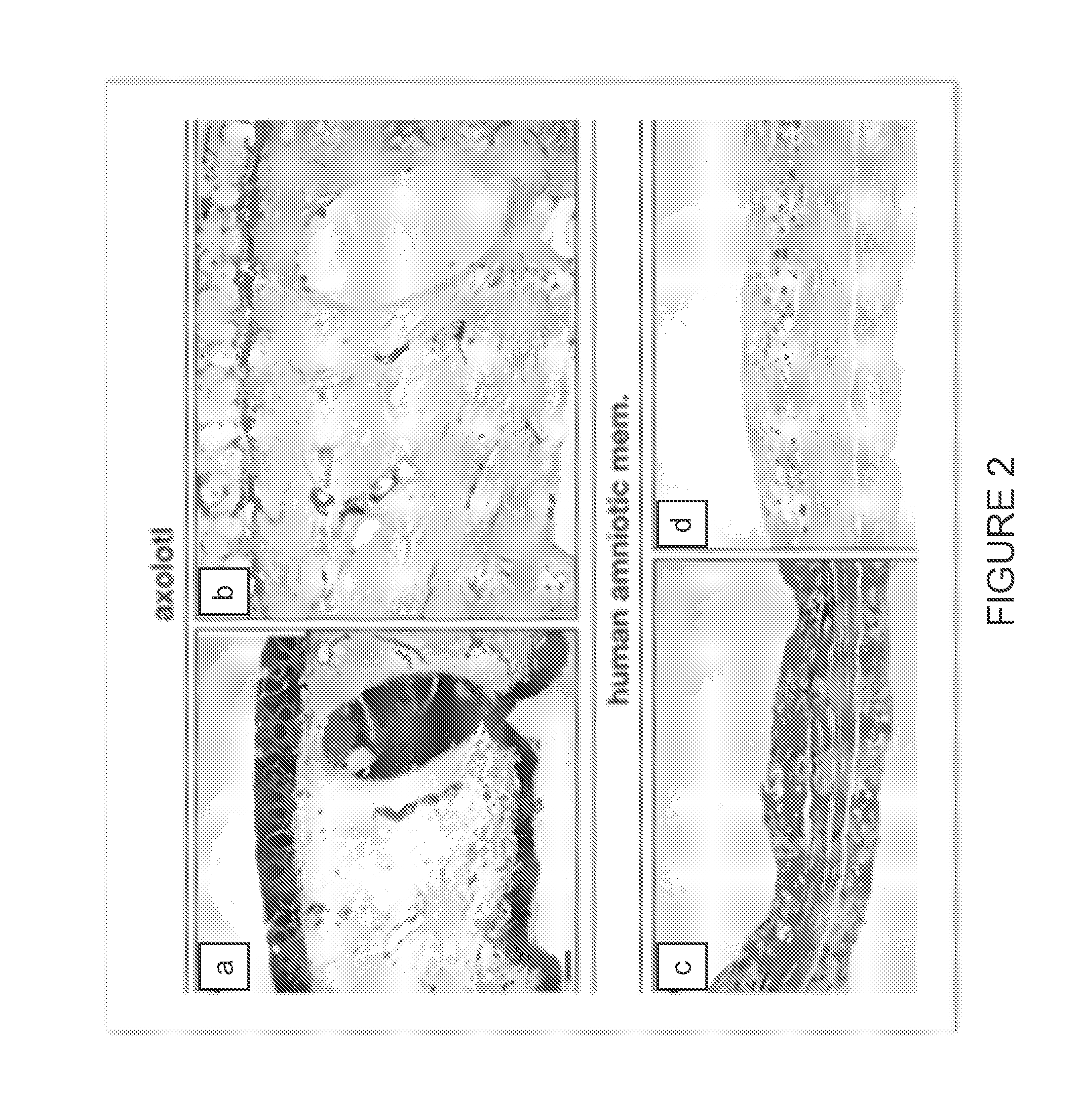
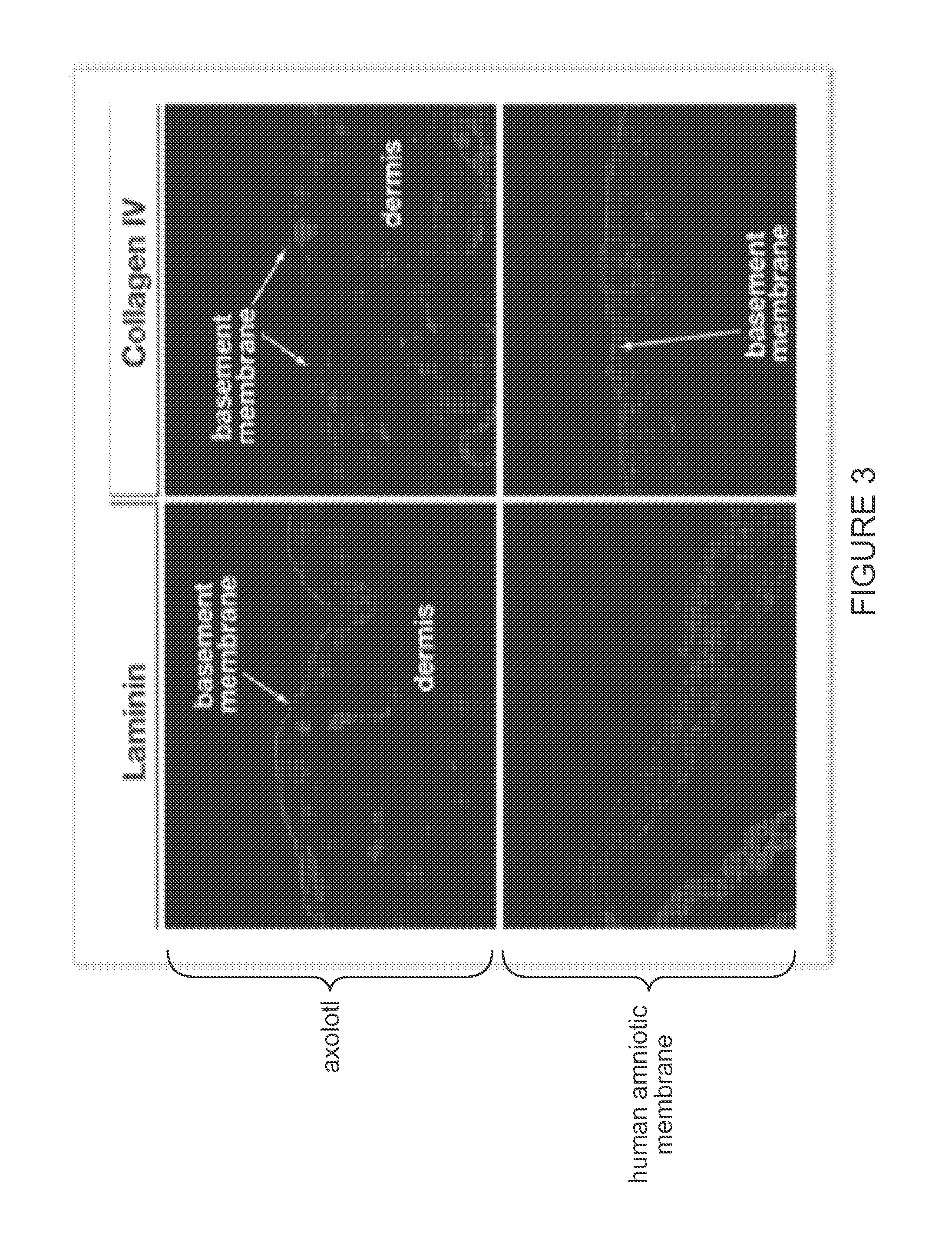
The growth factor profile, connective tissue matrix constituents, and immunoprivileged status of urodele extracellular matrix (ECM) and accompanying cutaneous tissue, plus the presence of antimicrobial peptides there, render urodele-derived tissue an ideal source for biological scaffolds for xenotransplantation. In particular, a biological scaffold biomaterial can be obtained by a process that entails (A) obtaining a tissue sample from a urodele, where the tissue comprises ECM, inclusive of the basement membrane, and (B) subjecting the tissue sample to a decellularization process that maintains the structural and functional integrity of the extracellular matrix, by virtue of retaining its fibrous and non-fibrous proteins, glycoaminoglycans (GAGs) and proteoglycans, while removing sufficient cellular components of the sample to reduce or eliminate antigenicity and immunogenicity for xenograft purposes. The resultant urodele-derived biomaterial can be used to enhance restoration of skin homeostasis, to reduce the severity, duration and associated damage caused by post-surgical inflammation, and to promote progression of natural healing and regeneration processes. In addition, the biomaterial promotes the formation of remodeled tissue that is comparable in quality, function, and compliance to undamaged human tissue.
Owner:NEXTGEN BIOLOGICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com